Viksit Bharat–Guarantee for Rozgar and Ajeevika Mission (Gramin) Bill, 2025 (VB-G RaM G)

- 18 Dec 2025
In News:
The Union Government has introduced the Viksit Bharat–Guarantee for Rozgar and Ajeevika Mission (Gramin) Bill, 2025 (VB-G RaM G) in the Lok Sabha to replace the Mahatma Gandhi National Rural Employment Guarantee Act (MGNREGA), 2005.
It marks a structural shift in India’s rural wage employment framework in line with the Viksit Bharat @2047 vision.
What is VB-G RaM G?
It is a proposed statutory rural wage employment guarantee law that:
- Assures 125 days of wage employment per rural household per financial year (earlier 100 days under MGNREGA)
- Focuses on durable, productivity-enhancing rural assets
- Integrates employment generation with infrastructure creation, livelihoods, and climate resilience
Core Objectives
- Move from distress-relief employment to development-linked employment
- Ensure convergence of rural schemes
- Create durable and climate-resilient assets
- Improve transparency, digital monitoring, and accountability
Key Features of the Bill
1. Enhanced Employment Guarantee
- Increased from 100 to 125 days
- About 25% higher income potential for rural households
2. Four Priority Work Categories
Works are restricted to:
- Water security (water harvesting, irrigation, conservation)
- Core rural infrastructure (roads, connectivity)
- Livelihood infrastructure (storage, markets, productive assets)
- Climate-resilience works (flood control, drought mitigation, soil conservation)
All works will be mapped into a proposed Viksit Bharat National Rural Infrastructure Stack.
3. Shift to Normative Funding
- Moves from demand-driven (MGNREGA model) to budget-based normative allocation
- Funds distributed to States using objective parameters
- Unemployment allowance still payable if work is not provided
4. Funding Pattern (Centrally Sponsored Scheme)
- 60:40 – Centre : States (most States)
- 90:10 – North-Eastern & Himalayan States
- 100% Central funding – UTs without legislature
5. Digital Governance & Transparency
Mandatory provisions include:
- Biometric attendance
- Aadhaar-linked wage payments
- Geo-tagging of assets
- AI-based fraud detection
- Real-time MIS dashboards
- Weekly public disclosure meetings at Gram Panchayat level
- Strengthened social audits
6. Agricultural Season Safeguard
- States can declare up to 60 days (aggregate) when works will pause during peak sowing/harvesting
- Aims to:
- Ensure farm labour availability
- Prevent wage inflation in agriculture
7. Decentralised Planning
- Works planned through Viksit Gram Panchayat Plans (VGPPs)
- Spatial planning integration with PM Gati Shakti
- Plans aggregated from Gram Panchayat → Block → District → State
8. Institutional Mechanism
- Central & State Gramin Rozgar Guarantee Councils
- States must notify their operational scheme within 6 months of enactment
Why Replace MGNREGA? (Government’s Rationale)
- Rural poverty decline: From 25.7% (2011-12) to ~5% (2023-24)
- Need to shift from relief works to productive infrastructure
- Asset quality issues under MGNREGA
- Reported misappropriation (~?193 crore in 2024-25)
- Only a small % of households completed 100 days post-pandemic
- Rising need for climate-resilient rural infrastructure
Major Differences from MGNREGA
|
Feature |
MGNREGA |
VB-G RaM G (Proposed) |
|
Nature |
Demand-driven legal right |
Normative, budget-linked guarantee |
|
Workdays |
100 |
125 |
|
Work scope |
Broad categories |
4 focused priority sectors |
|
Funding |
Mostly Centre-funded wages |
60:40 cost sharing (most states) |
|
Technology |
Supportive |
Mandatory & codified |
|
Planning |
Gram Sabha-based |
VGPP + national infrastructure stack |
Global Cooling Watch 2025 Report
- 15 Nov 2025
In News:
United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP) released the Global Cooling Watch 2025 report at COP30 in Belém, Brazil, projecting that global cooling demand may triple by 2050 under current trends, resulting in a major rise in emissions and power system stress.
About Global Cooling Watch 2025 Report
- Nature: UNEP’s second global assessment on cooling and its environmental, economic, and equity dimensions.
- Purpose:
- Assess global cooling trends and future projections
- Present a Sustainable Cooling Pathway for near-zero emissions
- Support the Global Cooling Pledge framework
Key Findings and Trends
1. Rising Cooling Demand
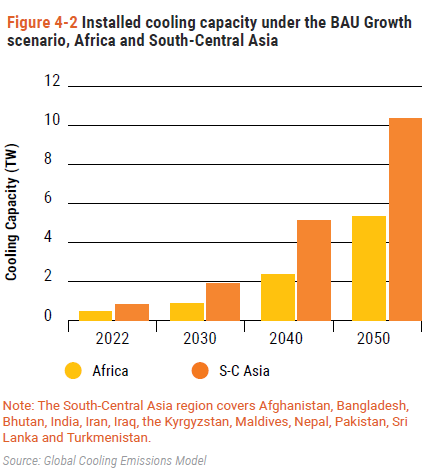
- Cooling capacity expected to increase 2.6 times (from 22 TW to 58 TW) by 2050.
- Driven by urban expansion, rising incomes, and worsening heatwaves.
2. Emission Expansion
- Cooling-related emissions may reach 10.5 billion tonnes CO?e by 2050.
- Nearly double 2022 levels without stringent policy measures.
3. Developing Country Surge
- Cooling demand in Article 5 (developing) countries projected to grow fourfold, deepening infrastructure disparities.
4. Escalating Power Consumption
- Global cooling electricity use may rise from 5,000 TWh (2022) to 18,000 TWh (2050).
- Significant implications for peak load management, especially in tropical regions.
5. Heat Inequality
- Over 2 billion people lack access to affordable, efficient cooling systems.
- Heightened vulnerability to extreme heat stress.
6. Passive Cooling Potential
- Passive measures (reflective roofs, ventilation design, urban greening) can reduce indoor temperatures by up to 8°C.
- Potential to cut energy consumption by 15-55%.
7. Refrigerant Transition
- Switching from HFCs to low-GWP refrigerants may avert up to 0.4°C of warming this century.
8. Global Cooling Pledge Progress
- 72 countries + 80 organizations have joined.
- Target: 68% reduction in cooling-sector emissions by 2050.
Successes Highlighted
- Strengthened international cooperation via the Global Cooling Pledge.
- Wider adoption of passive cooling in building policies.
- Technological improvements boosting efficiency by around 50%.
- Enhanced private sector involvement in sustainable cooling solutions.
- Tiered access initiatives improving cooling equity.
Limitations and Challenges
- Persistent inequality in access to cooling in tropical developing nations.
- Global funding currently covers less than 20% of adaptation and resilience needs.
- Fragmented policy coordination across sectors.
- Delays in HFC phase-down and inadequate refrigerant disposal.
- Continued dependence on fossil-fuel-based electricity.
UNEP Recommendations
- Implement a Sustainable Cooling Pathway combining:
- Passive cooling design
- High-efficiency cooling appliances
- Rapid integration of renewable energy
- Strengthen Kigali Amendment implementation and ensure full refrigerant lifecycle recovery.
- Increase green finance through concessional loans, PPP models, and climate bonds.
- Make passive cooling standards mandatory in building codes and urban planning.
- Provide targeted subsidies and access programs for heat-vulnerable populations.
Special Intensive Revision 2025

- 01 Nov 2025
In News:
The Election Commission of India (ECI) has initiated the Special Intensive Revision (SIR) 2025, a large-scale verification exercise aimed at ensuring that India’s electoral rolls remain accurate, inclusive, and up-to-date. Covering twelve States and Union Territories, this marks the most comprehensive revision of voter records in nearly two decades.
Purpose and Objectives
The SIR 2025 is designed to:
- Authenticate voter data to eliminate duplication and ineligible entries.
- Verify citizenship and age to ensure that only eligible Indian citizens remain on the rolls.
- Update demographic information such as addresses and photographs.
- Enhance transparency in the voter registration process and strengthen public trust in electoral institutions.
Through this exercise, the ECI seeks to uphold the Representation of the People Act, 1950, which mandates a clean and credible electoral register as the foundation of free and fair elections.
Implementation and Process
The revision process is being carried out by the Election Commission under the supervision of the Chief Election Commissioner and coordinated at the State and district levels through Chief Electoral Officers (CEOs), District Magistrates (DMs), and Electoral Registration Officers (EROs).
Key stages of the exercise include:
- Enumeration and Data Collection: Field officials known as Booth Level Officers (BLOs) visit households to distribute and collect pre-filled forms containing existing voter details.
Voters may also submit or verify their information online via the ECI’s voter portal. - Verification through Historical Records: Citizens are encouraged to confirm their or a family member’s presence in electoral rolls from earlier intensive revisions (2002–2005). This helps maintain continuity in the voter database and authenticate older registrations.
- Document-Based Scrutiny: In cases where a voter cannot trace prior records, documents proving identity, residence, age, and citizenship are reviewed. This ensures compliance with the Citizenship Act, 1955, particularly for voters born after 1987.
- Draft and Final Roll Publication: Following field verification, draft rolls are published for public inspection and correction. After resolving claims and objections, the final electoral rolls are released, forming the official list for upcoming elections.
Significance of the SIR 2025
- Reviving Electoral Accuracy: This is the first full-scale revision of voter rolls in nearly twenty years, addressing issues like outdated entries, migration, and data mismatches.
- Citizenship Assurance: The verification framework ensures that only legitimate Indian citizens exercise voting rights, strengthening electoral credibility.
- Technological Modernisation: Integration with digital platforms such as the ECI voter portal enhances accessibility and reduces manual errors.
- Transparency and Accountability: The participation of political party representatives as Booth Level Agents (BLAs) provides an additional layer of oversight.
- Foundation for Free and Fair Elections: A verified, inclusive, and error-free voter list is critical to maintaining the integrity of democratic processes and protecting voter rights.
Angikaar 2025 Campaign
- 12 Sep 2025
In News:
The Ministry of Housing and Urban Affairs (MoHUA) has launched Angikaar 2025, a nationwide outreach campaign under the Pradhan Mantri Awas Yojana – Urban 2.0 (PMAY-U 2.0). The initiative seeks to bridge last-mile implementation gaps, accelerate housing delivery, and ensure that welfare benefits reach vulnerable urban families.
Objectives of Angikaar 2025
- Awareness Generation: Create widespread awareness of PMAY-U 2.0 across urban India.
- Housing Delivery: Fast-track verification of applications and completion of sanctioned houses.
- Beneficiary Support: Facilitate access to financial assistance, credit-linked support, and convergence with other welfare schemes.
- Inclusion: Prioritise housing needs of Special Focus Groups identified under PMAY-U 2.0.
Key Features
- Coverage: Over 5,000 Urban Local Bodies (ULBs) across India.
- Activities: Door-to-door campaigns, awareness drives, loan melas, cultural events, and anchor events under PM Awas Mela – Shehri.
- Convergence: Linkage with schemes such as the Credit Risk Guarantee Fund Trust for Low Income Housing (CRGFTLIH) and PM Surya Ghar: Muft Bijli Yojana.
PMAY-U Progress So Far
- Sanctioned Houses: 120 lakh.
- Completed & Delivered: 94.11 lakh pucca houses.
- Pending: Angikaar 2025 will focus on expediting completion of remaining sanctioned houses.
- Future Target under PMAY-U 2.0: Provide financial support (up to ?2.5 lakh per family) to an additional one crore urban families for constructing or purchasing pucca houses.
Significance
- Last-Mile Outreach: Brings government schemes closer to beneficiaries through direct engagement.
- Community Mobilisation: Promotes Jan Bhagidari (people’s participation) via awareness camps and cultural events.
- Holistic Development: Integrates housing with access to electricity, financial inclusion, and basic services.
- Housing for All: Reaffirms the government’s commitment to inclusive and sustainable urban development.
India–Singapore Comprehensive Strategic Partnership (CSP): 2025 Roadmap
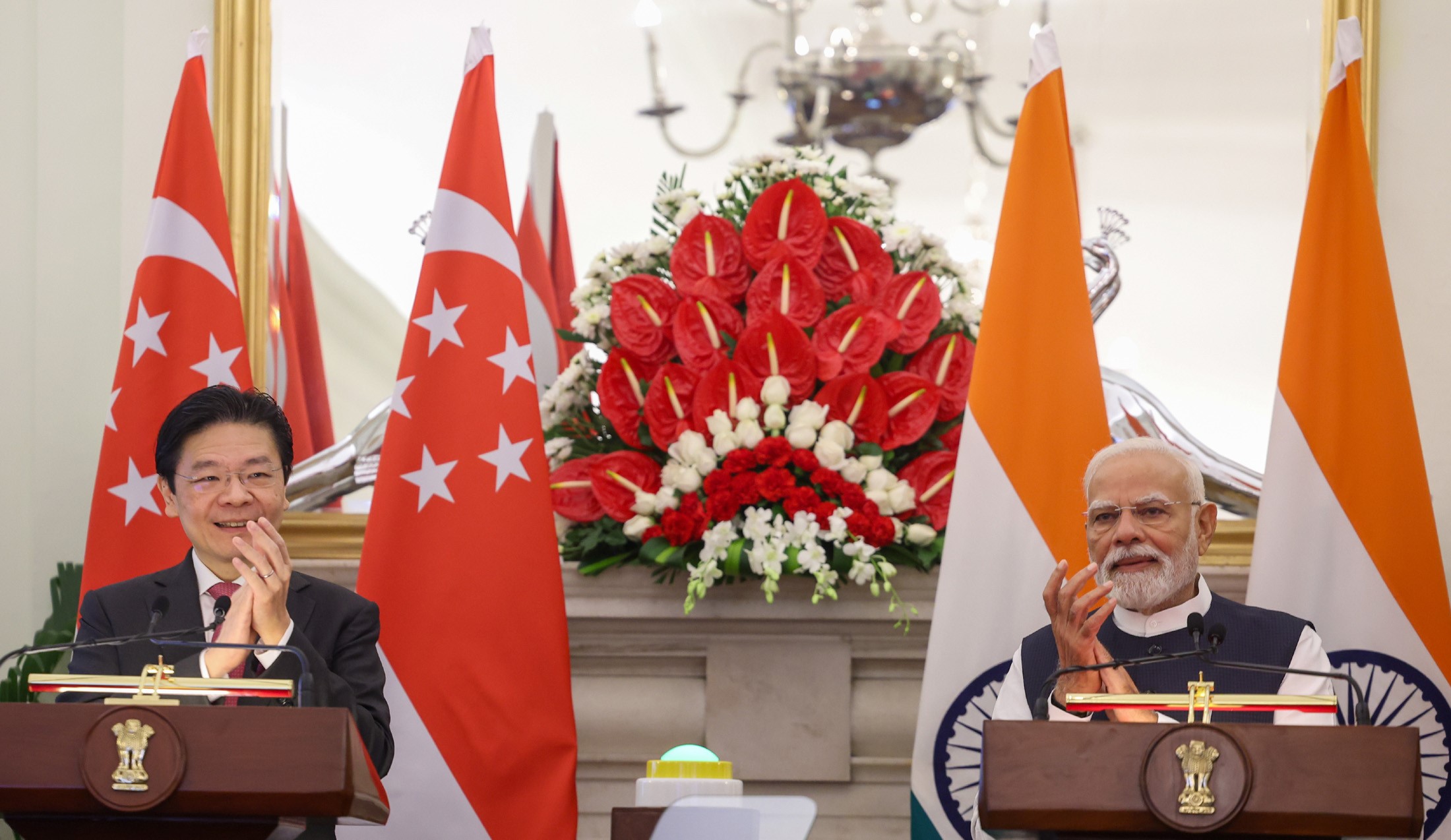

- 10 Sep 2025
In News:
The visit of Singapore Prime Minister Lawrence Wong to India in September 2025 marked 60 years of diplomatic relations and culminated in the adoption of a forward-looking Comprehensive Strategic Partnership (CSP) Roadmap. This elevates bilateral ties beyond trade to encompass technology, security, sustainability, and people-centric cooperation, reinforcing Singapore’s role as a vital partner in India’s Act East Policy and Indo-Pacific vision.
What is CSP?
- The Comprehensive Strategic Partnership (CSP) is the highest level of bilateral engagement between India and Singapore.
- It was elevated from a Strategic Partnership in 2015, and deepened further in 2025 through the adoption of a roadmap across eight key sectors.
Eight-Pillar Cooperation Framework
- Economic Cooperation
- Review of Comprehensive Economic Cooperation Agreement (CECA) and ASEAN-India Trade in Goods Agreement (AITIGA) in 2025.
- Partnership in semiconductors: Singapore produces 10% of global semiconductors and 20% of semiconductor equipment—key to India’s domestic chip manufacturing ambitions.
- Cooperation in industrial parks, sustainable manufacturing, capital market connectivity (NSE-IFSC-SGX GIFT Connect), and space collaboration.
- Skills Development
- Establishment of the National Centre of Excellence for Advanced Manufacturing in Chennai.
- Joint efforts in Technical and Vocational Education and Training (TVET), skill certification, train-the-trainers programmes, and nursing skill cooperation (expansion of the Singapore–Assam model).
- Digitalisation
- Expansion of UPI–PayNow linkage for seamless cross-border payments.
- Collaboration in fintech, cybersecurity, AI applications (healthcare, agriculture), start-up ecosystems, and adoption of TradeTrust for e-Bills of Lading in trade documentation.
- Sustainability & Green Growth
- Cooperation in green hydrogen, ammonia, and civil nuclear energy.
- Joint climate initiatives under Article 6.2 of the Paris Agreement.
- Collaboration in the International Solar Alliance (ISA) and Global Biofuels Alliance.
- Partnership in food security, agricultural exports, and water management.
- Connectivity
- Establishment of an India–Singapore Green and Digital Shipping Corridor linking major Indian ports with Singapore.
- Knowledge-sharing in aviation (air services agreement, sustainable aviation fuel, MRO collaboration).
- Healthcare & Medicine
- MoU on Health and Medicine: digital health, maternal and child health, disease surveillance, and medical R&D.
- Nursing cooperation and skills training to enhance employability in Singapore.
- People-to-People & Cultural Exchanges
- Student and professional exchanges, parliamentary engagement, think tank linkages, and public service training.
- Promotion of cultural heritage and maritime history collaborations.
- Defence& Security
- Enhanced military cooperation through SIMBEX 2025 and other tri-service exercises.
- Collaboration on defence technology (AI, automation, unmanned systems, quantum computing).
- Maritime security including submarine rescue cooperation and regional patrols.
- Strengthened counter-terrorism efforts via FATF and other multilateral mechanisms.
- Singapore acknowledged India’s interest in the Malacca Straits Patrol (MSP); India’s Andaman & Nicobar Command enhances regional maritime domain awareness.
Strategic Significance
- Positions Singapore as India’s gateway to Southeast Asia and the broader Indo-Pacific.
- Enhances regional security architecture aligned with ASEAN principles.
- Demonstrates how middle powers can address global uncertainties through technology partnerships, defence collaboration, and sustainable growth initiatives.
State of Food Security and Nutrition in the World (SOFI) 2025 Report

- 30 Jul 2025
In News:
Hunger affected up to 720 million people worldwide in 2024 — around 8.2 per cent of the global population, while 2.3 billion people in the world were estimated to have been moderately or severely food insecure, according to the ‘State of Food and Nutrition in the World’ (SOFI) 2025.
Key Highlights:
- Released by: Jointly published by FAO, IFAD, UNICEF, WFP, and WHO.
- Purpose:
- Annual global assessment to monitor progress on Sustainable Development Goal (SDG) 2:
- Target 2.1: End hunger and ensure access to safe, nutritious food.
- Target 2.2: End all forms of malnutrition.
Key Global Findings (2024 Data)
- Chronic Hunger:
- 720 million people (approx. 8.2% of global population) suffered from chronic hunger in 2024.
- Although lower than 8.5% (2023) and 8.7% (2022), it remains above pre-pandemic (2015) levels.
- 96 million more people are hungry now than in 2015.
- Food Insecurity:
- 2.3 billion people were moderately or severely food insecure in 2024.
- This is 335 million more than in 2019 (pre-COVID) and 683 million more than in 2015.
- Regional Distribution:
- Asia: 323 million undernourished (highest in absolute numbers).
- Africa: 307 million (highest prevalence, over 20% of population).
- Latin America & Caribbean: 34 million.
- Trends & Progress:
- Modest improvements in Southeast Asia, Southern Asia, and South America.
- Worsening hunger in parts of Africa and Western Asia due to conflict and climate stress.
Projections for 2030
- By 2030, 512 million people (6% of global population) may remain chronically undernourished.
- A decline of only 65 million since 2015, far short of the Zero Hunger target.
- 60% of these undernourished people are projected to be in Africa, with 17.6% prevalence.
India-Specific Insights
- Nutritional Affordability:
- 6% of Indians cannot afford a healthy diet despite food surplus.
- Urban areas show improvement due to post-pandemic income recovery.
- Rural areas face continued hardship due to PDS inefficiencies and price volatility.
- Child Malnutrition:
- High rates of stunting and wasting persist.
- Micronutrient deficiencies (hidden hunger) are common due to cereal-heavy diets lacking diversity.
- Policy Recommendations:
- Strengthen inclusion of millets, pulses, and fortified foods in public nutrition schemes.
- Address regional and demographic disparities through targeted interventions.
Major Drivers of Food Insecurity
- Post-COVID Aftermath: Reversed a decade of gains in global food security.
- Climate Events: Floods, droughts, and heatwaves have disrupted food systems.
- Conflicts & Wars: Ongoing wars (e.g. Ukraine) have triggered food price inflation and supply disruptions.
- Inflation:
- Since 2020, food price inflation has outpaced general inflation globally.
- Disproportionately affects low-income and vulnerable populations.
SOFI 2025: Recommendations
- Protect vulnerable populations via targeted fiscal support.
- Align macroeconomic policies to stabilize food markets.
- Invest in resilient agrifood systems and nutrition-sensitive agriculture.
- Strengthen food and nutrition data systems for informed policymaking.
- Promote dietary diversity and nutrition education.
SDG Context & Governance
- SDG 2 (Zero Hunger) is among the 17 UN Sustainable Development Goals adopted in 2015.
- These are non-binding, but serve as guiding principles for national policy and international cooperation.
- The SOFI report tracks progress annually against Targets 2.1 & 2.2.
- With only 5 years left to 2030, the current pace is inadequate for achieving global food and nutrition targets.
Global Gender Gap Report 2025
- 14 Jun 2025
In News:
The 19th edition of Global Gender Gap Report 2025 was released by World Economic Forum (WEF).
Key Highlights:
Countries Covered: 148
Global Parity Status:
- Overall Gender Gap Closed: 68.8%
- Estimated Time to Full Parity: 123 years (at current pace)
Assessment Criteria (Four Dimensions):
- Economic Participation and Opportunity
- Educational Attainment
- Health and Survival
- Political Empowerment
The index uses a parity score (0–100%) to quantify gender equality, where 100% indicates full parity.
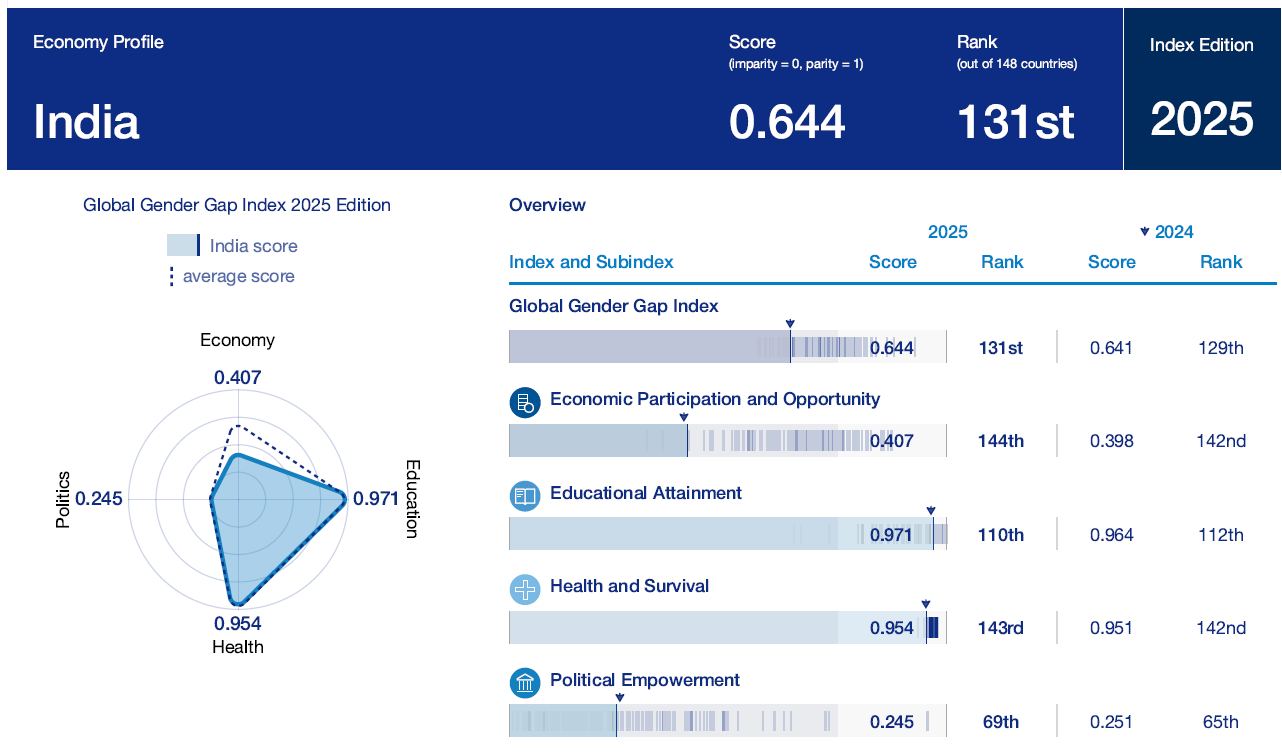
India’s Performance (Rank: 131/148)
- Parity Score: 64.1%
- South Asia Rank: Among the lowest; only Maldives (138) and Pakistan (148) rank below
- India’s 2024 Rank: 129 (slipped 2 positions in 2025)
Domain-wise Performance:
- Economic Participation and Opportunity
- Improved: Score increased by 0.9 percentage points to 40.7%
- Earned Income Parity: Rose from 28.6% to 29.9%
- Labour Force Participation: Stagnant at 45.9%
- Insight: Despite income parity gains, the gap in actual earnings and participation remains wide.
- Educational Attainment
- Near Parity Achieved: 97.1%
- Driven by rising female literacy and higher tertiary enrolment
- Challenge: Translating education into workforce participation remains limited.
- Health and Survival
- Marginal Gains: Improved parity in sex ratio at birth and healthy life expectancy
- However, overall life expectancy declined for both genders, muting the parity effect.
- Political Empowerment
- Significant Decline:
- Women MPs fell from 14.7% to 13.8%
- Women ministers dropped from 6.5% to 5.6%
- Trend: Continued decline from the 2019 peak of 30% female political representation
- Significant Decline:
South Asia and Global Comparison
- Bangladesh: Best performer in South Asia, ranked 24th globally (up by 75 positions)
- Other Neighbours:
- Bhutan (119),
- Nepal (125),
- Sri Lanka (130),
- Maldives (138),
- Pakistan (148 – last)
- Global Top 5 Countries:
- Iceland (Top for 16th year in a row)
- Finland
- Norway
- United Kingdom
- New Zealand
Key Global Insights
- Women in Workforce: 41.2% of global workforce
- Leadership Representation: Only 28.8% of leadership roles are held by women
- Despite post-pandemic recovery in gender parity, leadership gaps and decision-making roles remain major bottlenecks.
Implications for India
- The report underscores that gender parity is not just a social imperative, but also crucial for inclusive and resilient economic growth.
- India’s sluggish progress in political empowerment and gender wage gap highlight the need for institutional reforms, affirmative actions, and gender-sensitive policies in governance, employment, and leadership.
INS Arnala
- 08 Jun 2025
In News:
The Indian Navy is set to commission 'Arnala', the first warship under the Anti-Submarine Warfare Shallow Water Craft (ASW-SWC) series at the Naval Dockyard in Visakhapatnam. The commissioning will be presided over by Chief of Defence Staff, General Anil Chauhan.
About INS Arnala
- Type: First in the series of 16 Anti-Submarine Warfare Shallow Water Crafts (ASW-SWC)
- Builder:
- Primary: Garden Reach Shipbuilders & Engineers (GRSE), Kolkata
- Partner: L&T Shipbuilders
- Delivery Date: May 8, 2025
- Indigenous Content: Over 80%
- Partners Involved:
- BEL, L&T, Mahindra Defence, MEIL
- 55+ MSMEs involved in the supply chain
Capabilities & Features
- Length: 77 meters
- Displacement: 1,490+ tonnes
- Propulsion: Diesel engine-waterjet system (a first for a warship of this size in India)
- Roles:
- Anti-submarine operations in coastal/shallow waters
- Subsurface surveillance
- Search and Rescue (SAR)
- Low-intensity maritime operations
Significance
- Aatmanirbhar Bharat Milestone: Highlights indigenous shipbuilding and defence manufacturing capabilities
- Boost to Coastal Defence: Enhances the Navy’s reach in shallow and strategic coastal zones
- Employment & Industrial Growth: Significant MSME and domestic defence industry involvement
Heritage & Symbolism
- Name Origin: Inspired by Arnala Fort, near Vasai, Maharashtra
- Built by the Marathas in 1737 under Chimaji Appa
- Historically guarded the Vaitarna River mouth and northern Konkan coast
- Design Symbolism:
- Armoured hull reflects the resilient walls of Arnala Fort
- Advanced sensors and weapons echo the fort’s cannons
- Crest:
- Stylised auger shell – precision, strength, vigilance
- Motto: Arnave Shauryam — “Valour in the Ocean”
Rediscovery of Losgna Genus in India
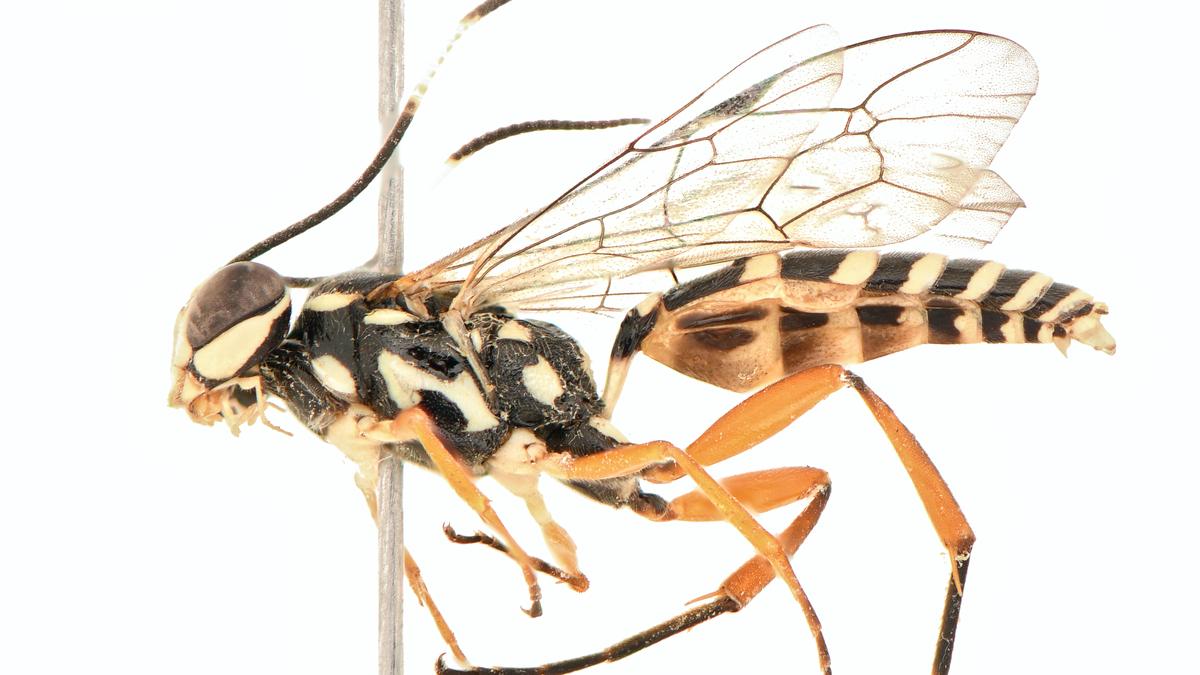

- 08 Jun 2025
In News:
At a time when habitat loss and climate change threaten countless species, the discovery of a new species of parasitic wasp - named ‘Losgna Occidentalis’ from Chandigarh has drawn attention to the unexplored richness of India’s biodiversity.
Location of Discovery
- Place: Chandigarh, Union Territory of India
- Habitat: Urban dry scrub forest
- Time: Winter of 2023–24
- Significance: First formal description of any insect species from Chandigarh
Species Description
- Name: Losgna occidentalis
- Genus: Losgna (Ichneumonidae family – Parasitic wasps)
- Group Role: Parasitic wasps known for laying eggs inside/on arthropod hosts
- Ecological Role: Pollinators and biological control agents (important in ecosystems)
Historical Context
- Losgna genus was last recorded in India in 1965, in Heinrich’s monograph
- No Indian records or specimens existed post-1965 in any institution
- Only known specimens (of other Losgna species) are preserved in:
- Natural History Museum, London
- The Hope Collection, Oxford University
- Zoologische Staatssammlung München, Germany
Naming Rationale
- "Occidentalis" (Latin for "Western")
- Signifies the westernmost known range of the genus
- Earlier Losgna records were only from:
- Northeast India
- Southeast Asia (tropical forests)
- Published in Zootaxa (peer-reviewed journal for animal taxonomy)
Importance & Implications
- Rediscovery highlights India’s hidden and threatened biodiversity
- Emphasizes the critical role of taxonomy in conservation
- Shows potential for citizen-led discoveries and backyard biodiversity
- Demonstrates the need for:
- Responsible specimen collection
- International scientific collaboration
- Support for underfunded taxonomy sectors
Discovery of 800-Year-Old Pandya-Era Shiva Temple
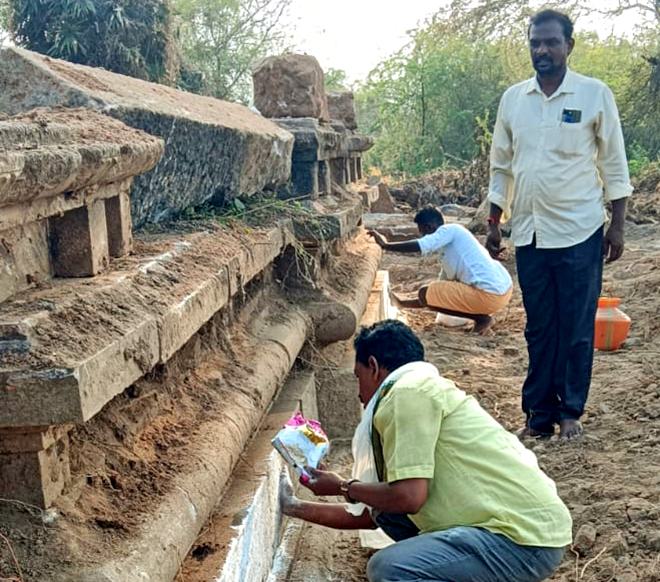

- 08 Jun 2025
In News:
An 800-year-old Shiva temple of the later Pandya period has been unearthed at Udampatti, a village in Melur taluk, Madurai district, Tamil Nadu.
Key Highlights:
- Discovery: Foundation of a later Pandya period Shiva temple (dated to 1217–1218 CE) unearthed accidentally by children.
Architectural Insights:
- Only the stone base of the temple (north and south sides) survives.
- Identified as a Shaivite temple using foundation engravings and reference to Silpa Sastram.
Inscriptions & Historical Significance:
- Inscriptions deciphered by C. Santhalingam (Pandya Nadu Centre for Historical Research).
- Temple identified as Thennavanisvaram, located in ancient Attur (present-day Udampatti).
- “Thennavan” was a Pandya royal title, suggesting direct patronage.
Key Inscriptions (1217–18 CE):
- A sale deed records the transfer of a waterbody named Nagankudi along with wet/dry land.
- Seller: Alagaperumal, chieftain of Kalavalinadu
- Buyer: Nambi Perambala Kuthan alias Kangeyan
- Sale amount: 64 kasu (coins)
- Tax revenue from the land assigned to the temple for daily expenses, indicating its financial independence.
Archaeological Relevance:
- Confirms ancient village name (Attur), showcasing socio-economic practices during the Later Pandya period.
- Highlights temple economy, land-water rights, and administrative structures.
Pandya Dynasty
- One of the Three Crowned Tamil Dynasties (alongside Cholas and Cheras).
- Capital: Initially Korkai, later Madurai.
- Early Pandyas active since 4th century BCE; Later Pandyas (1216–1345 CE) saw a golden age under Maravarman Sundara Pandyan.
- Controlled parts of Sri Lanka, Telugu regions, and had trade links with Rome & Southeast Asia.
- Symbol: Fish
Cultural Contributions:
- Patronage of Sangam literature, Shaivism, Vaishnavism, Jainism.
- Temples: Meenakshi Temple (Madurai), Nellaiappar Temple (Tirunelveli).
- Promoted Tamil arts, Bharatanatyam, and education.
Decline:
- Succumbed to Chola, Hoysala conflicts and Delhi Sultanate invasions.
- Madurai Sultanate (1335) and later Madurai Nayak dynasty (1529) succeeded their rule.
National e-Vidhan Application (NeVA)

- 08 Jun 2025
In News:
Union Minister of State Dr. L. Murugan will inaugurate the National e-Vidhan Application (NeVA) for the Puducherry Legislative Assembly.
What is NeVA?
- Full Form: National e-Vidhan Application
- Launched by: Ministry of Parliamentary Affairs (MoPA)
- Aim: Make legislative functioning paperless across all 37 State/UT legislatures under the idea of “One Nation – One Application.”
Key Features:
- Unified digital platform for legislative work
- Enables real-time document access, online notices, and session management
- Integrates AI/ML-based real-time translation (via partnership with BHASHINI, MeitY)
- Promotes transparency, efficiency, and environmental sustainability
Funding & Implementation:
- Approved by: Public Investment Board (PIB) on 15 January 2020
- Budget: ?673.94 crore
- Model: Centrally Sponsored Scheme (CSS)
Significance:
- Digital transformation of legislative processes
- Creation of a central data repository
- Enhanced inter-legislature connectivity
- Boosts Digital India and Good Governance goals
Indian Giant Flying Squirrel
- 13 Apr 2025
In News:
A rare sighting of the Indian Giant Flying Squirrel (Petauristaphilippensis) has been reported in Ranikhet, a hill station in Uttarakhand, highlighting the ecological richness of the region.
About Indian Giant Flying Squirrel
Feature Description
Scientific Name Petauristaphilippensis
Size Body length: 30–45 cm; Tail length: up to 60 cm
Appearance Rufous coat, grey underparts, large eyes, and a gliding membrane from wrist
to ankle
Locomotion Glides up to 60 meters between trees using patagium (gliding membrane)
Habitat and Distribution
- Found in tropical and subtropical forests across central and southern India
- Inhabits evergreen, semi-evergreen, and deciduous forests, especially near forest edges
- Recent sighting in Uttarakhand indicates possible range expansion or overlooked presence
Ecological Role
- Diet: Fruits, nuts, leaves, and bark
- Acts as a seed disperser, supporting forest regeneration
- Considered a keystone species due to its ecological significance
Behavioural Traits
- Nocturnal and arboreal
- Emits alarm calls upon detecting predators like owls
- Active at night, gliding from tree to tree in search of food
Conservation Status
Category Status
IUCN Red List (Global) Least Concern
IUCN Status (India) Near Threatened (due to habitat loss)
Wildlife Protection Act, 1972 Schedule II
Threats
- Habitat loss and fragmentation
- Deforestation and degradation of forest corridors
- Increasing human encroachment in forested landscapes
EnviStats India 2025
- 06 Jun 2025
In News:
India's annual mean temperature rise up from 25.05°C in 2001 to 25.74°C in 2024, Electricity generation from renewable sources increased more than three times in 10 years.
- Released by: Ministry of Statistics and Programme Implementation (MoSPI) on June 5, 2025, on the occasion of World Environment Day
- Framework Used: UN's Framework for the Development of Environment Statistics (FDES 2013)
Key Highlights:
Climate Trends
- Annual Mean Temperature rose from 25.05°C (2001) to 25.74°C (2024).
- 2024 recorded as India’s hottest year since 1901; also, globally the hottest year in 175 years.
- Annual Minimum and Maximum Temperatures (2021–24):
- Minimum: 19.32°C → 20.24°C
- Maximum: 30.78°C → 31.25°C
Rainfall Patterns
- Rainfall shows seasonal concentration between June–September, with signs of shifting patterns such as late onset or extended rains into October.
- No clear long-term trend, reflecting erratic monsoonal behaviour.
Energy Generation
Thermal & Renewable Power (2013–14 to 2023–24)
- Thermal: 7.92 lakh GWh → 13.26 lakh GWh
- Renewable: 65,520 GWh → 2.25 lakh GWh, over 3x increase in renewable energy output in a decade.
Biodiversity and Faunal Statistics
Faunal Diversity
- Global Faunal Species: 16,73,627
- India's Share: 1,04,561 species
- Habitat-specific Species in India:
- Soil Ecosystem: 22,404
- Freshwater Ecosystem: 9,436
- Mangrove System: 5,023
- Estuarine Ecosystem: 3,383
- Marine Fauna (India): 20,613 out of global 2,47,605
Fisheries Production
Inland vs. Marine Fish (2013–14 to 2023–24)
- Inland Fish Production: 61 lakh tonnes → 139 lakh tonnes
- Marine Fish Production: 34 lakh tonnes → 45 lakh tonnes
Public Expenditure (2021–22)
- Environment Sustainability Sector: ?2,433 crore (highest among sectors)
- Conservation of Natural Resources: Increasing trend
- Agro-Forestry: Lowest allocation
New Data indicators introduced
- Ramsar sites
- Access to sanitation
- Transport infrastructure
- Electricity access
Poshan Pakhwada 2025 and Palna Scheme
- 10 Apr 2025
In News:
The Ministry of Women and Child Development (MoWCD) is spearheading a dual approach to address malnutrition and childcare challenges in India through two flagship initiatives—Poshan Pakhwada 2025 and the Palna Scheme under Mission Shakti.
Poshan Pakhwada 2025
- 7th edition observed from April 8–22, 2025, under Poshan Abhiyaan.
- Focuses on four key themes:
- Nutrition in the first 1,000 days (conception to age two).
- Promotion of the Poshan Tracker digital platform.
- Community-based Management of Acute Malnutrition (CMAM).
- Encouraging a healthy lifestyle to reduce childhood obesity.
- Poshan Tracker App (AI-enabled; launched in 2021):
- Registers all Anganwadi Centres (AWCs).
- Enables real-time monitoring of beneficiaries, meal distribution, and health data.
- Allows family self-registration via web.
- CMAM protocol (introduced in 2023): Empowers Anganwadi workers to detect and manage malnutrition at the grassroots.
- Special focus on tribal and remote areas, promoting awareness on breastfeeding, balanced diets, and early stimulation.
- Campaign supported by 18 partner ministries, with outreach via village camps, home visits, and awareness drives.
Palna Scheme under Mission Shakti
- Centrally sponsored scheme launched in 2022, succeeding the National Crèche Scheme.
- Operates under the Samarthya sub-scheme of Mission Shakti.
- Aims to provide quality crèche services for children aged 6 months to 6 years, especially for working mothers.
Key Features:
- Implemented by: Ministry of Women and Child Development (MoWCD).
- Funding Ratio:
- 60:40 (Centre: State),
- 90:10 for NE and special category states.
- Two crèche models:
- Standalone Crèches near homes/workplaces.
- Anganwadi-cum-Crèches (AWCCs) integrated within Anganwadi Centres.
- Facilities Provided:
- Nutritional meals, growth monitoring, immunization.
- Early stimulation and pre-school education.
- Support for continued breastfeeding.
- Crèche Capacity: Each unit supports up to 25 children.
- As of March 2025:
- 11,395 AWCCs approved across 34 States/UTs; 1,761 operational, catering to ~28,783 children.
- 1,284 Standalone Crèches operational with ~23,368 children enrolled.
- 17,000 new AWCCs planned for 2024–25.
- Legal Backing: Mandated in workplaces with 50+ employees under the Maternity Benefit Act (amended).
Significance for India
Together, Poshan Pakhwada and Palna contribute to achieving SDG 2 (Zero Hunger) and SDG 3 (Good Health and Well-being) by ensuring a lifecycle approach to nutrition and holistic early childhood care. They reflect the government's commitment to digital governance, gender empowerment, and inclusive development.
Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO)

- 08 Apr 2025
In News:
The Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) has launched two major global initiatives to advance inclusive and sustainable agrifood systems:
- “Four Betters Courses” Initiative – To revolutionize agrifood systems education
- “Commit to Grow Equality” Initiative – To bridge the gender gap in agrifood sectors
1. Four Betters Courses Initiative
- Launched: October 2024 during the World Food Forum
- Objective: To integrate FAO’s expertise into global agrifood systems education through partnerships with universities and academic networks.
- Alignment: Anchored in the FAO Strategic Framework 2022–2031
Core Philosophy – The “Four Betters” Approach:
- Better Production – Promote efficient, inclusive, and resilient food systems
- Better Nutrition – Ensure access to safe, nutritious, and affordable diets
- Better Environment – Address climate change and protect ecosystems
- Better Life – Improve rural livelihoods and reduce inequalities
- Delivery Platform: Implemented through the FAO eLearning Academy, which provides over 600 multilingual, certified courses.
2. Commit to Grow Equality (CGE) Initiative
- Launched: 2024 on the platform of the United Nations General Assembly (UNGA)
- Objective: To narrow the gender gap in agrifood systems and enhance women’s empowerment, especially in rural areas.
Key Highlights:
- Aims to benefit over 54 million women worldwide
- Mobilizes $1 billion in investments toward gender-responsive agrifood initiatives
- Provides strategic tools for tracking gender equality outcomes in public and private sectors
- Promotes gender-aligned national agricultural policies
- Facilitates evidence-based policymaking and fosters collaboration across governments, NGOs, and the private sector
Pradhan Mantri MUDRA Yojana (PMMY)

- 08 Apr 2025
In News:
The Pradhan Mantri MUDRA Yojana (PMMY), a flagship initiative aimed at providing financial support to unfunded micro and small enterprises, has completed 10 years since its launch in 2015.
Overview of PMMY
- Objective: To offer collateral-free institutional credit to non-corporate, non-farm micro and small enterprises.
- Loan Limit: Up to ?20 lakh without any collateral.
- Implementing Institutions (MLIs):
- Scheduled Commercial Banks
- Regional Rural Banks (RRBs)
- Non-Banking Financial Companies (NBFCs)
- Micro Finance Institutions (MFIs)
Categories of MUDRA Loans
Loan Category Loan Amount Range
Shishu Up to ?50,000
Kishor ?50,000 to ?5 lakh
Tarun ?5 lakh to ?10 lakh
Tarun Plus ?10 lakh to ?20 lakh
Key Achievements (2015–2025)
- Boost to Entrepreneurship: PMMY has sanctioned over 52 crore loans amounting to ?32.61 lakh crore, catalyzing a grassroots entrepreneurship revolution.
- MSME Sector Financing: Lending to MSMEs increased significantly:
- From ?8.51 lakh crore in FY14
- To ?27.25 lakh crore in FY24
- Projected to exceed ?30 lakh crore in FY25
- Women Empowerment: 68% of Mudra beneficiaries are women, highlighting the scheme’s impact in fostering women-led enterprises.
- Social Inclusion:
- 50% of loan accounts are held by SC, ST, and OBC entrepreneurs.
- 11% of beneficiaries belong to minority communities, showcasing PMMY’s contribution to inclusive growth.
Woolly Flying Squirrel
- 08 Apr 2025
In News:
The Wildlife Wing of the Himachal Pradesh Forest Department (HPFD) has recently documented the first-ever photographic evidence of the Woolly Flying Squirrel in Miyar Valley, located in the Lahaul and Spiti district. This marks a significant discovery, as the species is extremely elusive and rarely sighted.
About Woolly Flying Squirrel
- Common Name: Woolly Flying Squirrel / Western Woolly Flying Squirrel
- Scientific Name: Eupetaurus cinereus
- Taxonomy: The only known species under the genus Eupetaurus
- Conservation Status: Listed as Endangered on the IUCN Red List
Habitat and Distribution
- Endemism: Confined to the northwestern Himalayas
- Countries Found: Northern Pakistan and northwestern India
- Habitat Type: Inhabits a narrow elevational range within dry coniferous forests, typically in fragmented habitats
- Historical Records:
- Rediscovered in 1994, nearly 70 years after it was presumed extinct
- Since then, reported from Sai Valley, Gorabad, and Balti Gali in northern Pakistan
Key Characteristics
- Equipped with patagium (elastic skin membrane) that connects the forelimbs and hind limbs, enabling gliding—typical of flying squirrels
- Fur: Dense, straight, and silky
- Dorsal side: Blue-gray
- Ventral side: Pale gray
- Throat and ears: Covered in creamy white hairs
- Feet soles: Dense black fur, except for bare pinkish-brown toe pads
World Health Day 2025
- 08 Apr 2025
In News:
World Health Day, observed annually on 7 April, highlights pressing global health issues and mobilises action to improve public health outcomes.
- Established by: World Health Organization (WHO)
- First celebrated: 1950
Overview and Significance
World Health Day is commemorated to mark the founding of the WHO in 1948. It serves to raise awareness about global health issues and mobilize efforts to improve public health outcomes.
The 2025 theme, Healthy Beginnings, Hopeful Futures, emphasizes maternal and newborn health, calling for coordinated efforts to eliminate preventable deaths and support long-term well-being of women and children.
This year’s observance launches a year-long global campaign aimed at:
- Promoting safe pregnancies and institutional deliveries
- Supporting maternal nutrition and postnatal care
- Encouraging healthcare equity for women and newborns
India’s Progress in Maternal and Child Health
India has made significant strides through initiatives under the Ministry of Health and Family Welfare, particularly via Ayushman Bharat and the National Health Mission (NHM).
Key Health Indicators (India vs Global, 1990–2020)
Indicator India Reduction (%) Global Reduction (%)
Maternal Mortality Ratio 83% 42%
Neonatal Mortality Rate 65% 51%
Infant Mortality Rate 69% 55%
Under-5 Mortality Rate 75% 58%
Recent National Data:
- MMR reduced from 130 (2014–16) to 97 (2018–20) per 1,00,000 live births
- IMR dropped from 39 (2014) to 28 (2020)
- NMR reduced from 26 (2014) to 20 (2020)
- U5MR declined from 45 (2014) to 32 (2020)
Major Initiatives for Maternal and Child Health
- Maternal Death Surveillance and Response (MDSR): Tracks maternal deaths and implements corrective measures.
- Mother and Child Protection (MCP) Card: Educates women on nutrition, rest, and health entitlements.
- Reproductive and Child Health (RCH) Portal: Tracks maternal and child health services.
- Anaemia Mukt Bharat: Focuses on anaemia reduction under POSHAN Abhiyan.
- Birth Waiting Homes: Ensures institutional deliveries in remote areas.
- VHSNDs and Outreach Camps: Deliver maternal and child services in rural and tribal areas.
Healthcare Access and Infrastructure
- Ayushman Arogya Mandirs (HWCs): 1.76 lakh active centers
- 107.10 crore screenings for hypertension
- 94.56 crore screenings for diabetes
- 5.06 crore wellness sessions (e.g., yoga) conducted
- 17,000+ health facilities certified under National Quality Assurance Standards (NQAS)
Digital Health Ecosystem
- Ayushman Bharat Digital Mission (ABDM):
- 76+ crore ABHA IDs
- 5.95 lakh verified healthcare professionals
- 52+ crore linked health records
- U-WIN Platform:
- 7.90 crore beneficiaries
- 1.32 crore vaccination sessions
- 29.22 crore vaccine doses administered
- eSanjeevani Telemedicine:
- Over 36 crore consultations
- World's largest primary telehealth platform
- 130+ specialities, 131,793 spokes, and 17,051 hubs
Disease Elimination Success
- The WHO World Malaria Report 2024 highlights India’s major strides in malaria elimination, with a 69% drop in cases and 68% reduction in deaths between 2017 and 2023.
- Contributing just 0.8% of global cases in 2023, India’s exit from WHO's High Burden to High Impact (HBHI) group in 2024 marks a significant public health achievement.
- The Government of India has eliminated Trachoma as a public health problem in 2024, a feat recognised by the WHO.
- The Government of India’s proactive Measles-Rubella vaccination drive, strong surveillance, and public awareness efforts have greatly improved public health.
- According to WHO’s Global TB Report, India has made strong progress in tuberculosis control.
- Under the National Tuberculosis Elimination Programme (NTEP), TB incidence fell by 17.7%, from 237 to 195 cases per lakh population between 2015 and 2023.
- TB-related deaths also declined from 28 to 22 per lakh.
- Notably, missing TB cases dropped by 83%, from 15 lakh in 2015 to 2.5 lakh in 2023.
- As of 6th April, 2025, the Pradhan Mantri TB Mukt Bharat Abhiyaan, launched in September 2022, has registered over 2.5 lakh Ni-kshay Mitra volunteers supporting over 15 lakh TB patients. This initiative has further been expanded to include family members of TB patients.
- Kala-azar Elimination: India has successfully achieved Kala-azar elimination as of October 2024, with 100% of endemic blocks reaching the target of less than one case per 10,000 population by the end of 2023.
INS Varsha
- 08 Apr 2025
In News:
India is set to operationalise INS Varsha, its first dedicated base for nuclear-powered submarines, by 2026. Located near Rambilli, about 50 km south of Visakhapatnam, Andhra Pradesh, this high-security facility is part of the classified Project Varsha, aimed at strengthening India’s maritime and nuclear deterrence capabilities in the Bay of Bengal and Indian Ocean Region (IOR).
Key Features:
- Strategic Location: Near deep waters of the Bay of Bengal, facilitating stealthy submarine movement and minimizing detection.
- Infrastructure:
- Underground pens and tunnel systems to conceal and protect nuclear submarines.
- Inner and outer harbour facilities; inner harbour completed, work ongoing on breakwaters and jetties.
- 20 sq. km area, capacity to house at least 10–12 nuclear submarines.
- Stealth Capabilities: Similar to China’s Hainan base, it offers satellite-evasion advantages, crucial for the survivability of SSBNs (nuclear-powered ballistic missile submarines).
- Support Facilities: Proximity to BARC Atchutapuram for nuclear infrastructure, enabling swift integration and maintenance of strategic assets.
- Geopolitical Role: Counters Chinese dual-use naval infrastructure at Hambantota (Sri Lanka) and BNS Sheikh Hasina (Bangladesh).
Strategic Significance:
- Enhances second-strike capability, vital for nuclear deterrence under India's nuclear triad.
- Enables undetected deterrent patrols by SSBNs, ensuring survivability in case of counterforce attacks.
- Facilitates rapid access to key chokepoints, especially the Strait of Malacca.
India’s Expanding Nuclear Submarine Fleet
INS Aridhaman – Third SSBN:
- Scheduled for commissioning in 2025.
- 7,000-tonne displacement, more capable than predecessors INS Arihant and INS Arighat.
- Equipped with K-4 Submarine-Launched Ballistic Missiles (SLBMs) with a range of 3,500 km.
- Built under the Advanced Technology Vessel (ATV) project by Shipbuilding Centre, Visakhapatnam, with BARC and DRDO support.
- Designed for long-duration deterrent patrols in deep sea.
Future Developments:
- India launched its fourth SSBN in November 2024, with ~75% indigenous content.
- Plans underway for even larger SSBNs and the construction of six nuclear-powered attack submarines (SSNs), starting with two approved 9,800-tonne SSNs for conventional strike and escort roles.
Related Naval Expansion – Project Seabird (Karwar Base):
- Located on the western coast, expanding to accommodate 50 warships and submarines, plus 40 auxiliary vessels.
- Will include a dual-use air station, new dockyard, and multiple dry berths.
Ayush Suraksha Portal

- 31 May 2025
In News:
The Ayush Suraksha Portal was launched in May 2025 by the Union Minister of State (Independent Charge) for Ayush, in compliance with the Supreme Court's directive. The portal marks a major step in enhancing regulatory oversight, public safety, and pharmacovigilance within the Ayush sector.
Objective
The portal aims to:
- Monitor and act on misleading advertisements.
- Track and respond to adverse drug reactions (ADRs).
- Promote transparency, accountability, and public participation in the regulation of traditional medicine systems.
Key Features
- Centralised digital platform for real-time reporting and analysis of misleading advertisements and ADRs.
- Accessible to the general public, healthcare professionals, and regulatory authorities.
- Ensures direct citizen participation by allowing users to report issues and track action taken.
- Developed with technical support from the Central Council for Research in Siddha (CCRS).
- Integrated with the National Pharmacovigilance Program for Ayush.
Institutional Integration
The portal coordinates with multiple regulatory and enforcement bodies:
- Ayush vertical under CDSCO
- Ministry of Information & Broadcasting (MoI&B)
- Central Consumer Protection Authority (CCPA)
- National Commission for Indian System of Medicine (NCISM)
- National Commission for Homoeopathy (NCH)
- Pharmacy Council of India (PCI)
- Food Safety and Standards Authority of India (FSSAI)
- State Licensing Authorities (SLAs)
Significance
- Meets the Supreme Court’s deadline ahead of time, reinforcing legal compliance.
- Enables real-time regulatory action, inter-state coordination, and data-driven governance.
- Enhances public trust and safety in the use of traditional medicines.
- Reflects the Ministry of Ayush’s commitment to evidence-based practices and responsible governance.
National Florence Nightingale Award 2025
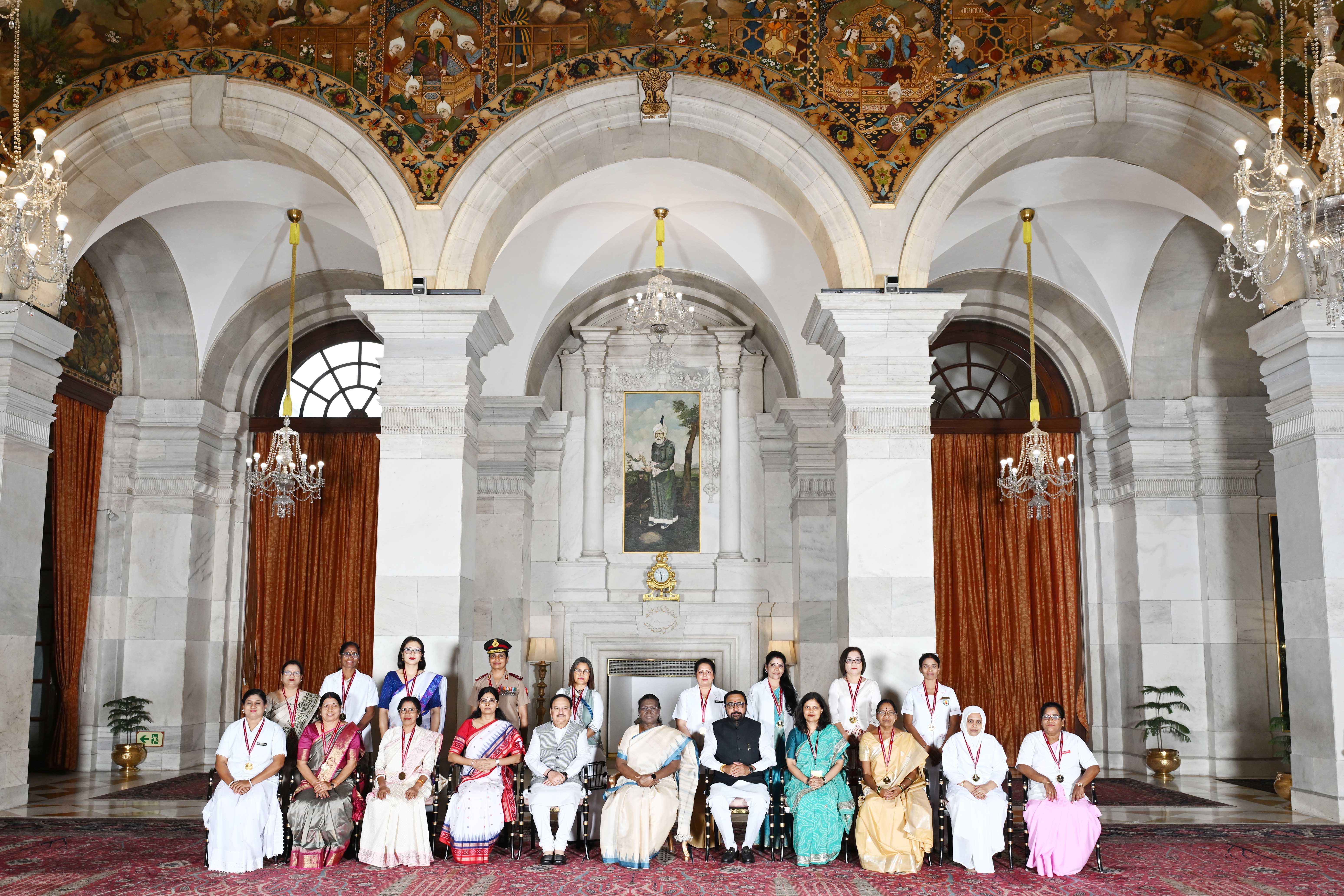

- 31 May 2025
In News:
The President of India recently conferred the National Florence Nightingale Awards 2025 to exemplary nursing professionals in a formal ceremony held at Rashtrapati Bhavan.
About the National Florence Nightingale Awards
- Established: 1973
- Administered by: Ministry of Health and Family Welfare, Government of India
- Purpose: To honour exceptional contributions of nursing personnel across India in recognition of their meritorious service to society.
The award is open to nurses working in government, private, and voluntary healthcare settings, including hospitals, community health centres, educational institutions, and administrative roles.
Award Components
- Certificate of Merit
- Cash Prize: ?1,00,000
- Medal of Honour
About Florence Nightingale
- Florence Nightingale (1820–1910) was a pioneering English nurse, social reformer, and statistician, widely considered the founder of modern nursing.
- She gained recognition during the Crimean War for organizing the care of wounded soldiers in Constantinople (now Istanbul).
She also revolutionized nursing education by establishing the Nightingale School of Nursing at St. Thomas’ Hospital, London, the first institution based on scientific nursing principles.
Swachh Survekshan Grameen (SSG) 2025

- 31 May 2025
In News:
The Union Minister of Jal Shakti recently launched Swachh Survekshan Grameen (SSG) 2025, India’s largest rural sanitation survey, conducted by the Department of Drinking Water and Sanitation (DDWS) under the Ministry of Jal Shakti.
Objective and Scope:
SSG 2025 is designed to evaluate the impact and sustainability of rural sanitation outcomes achieved under the Swachh Bharat Mission – Gramin (SBM-G) Phase II, particularly focusing on the Open Defecation Free (ODF) Plus Model.
- The survey aims to rank all States, Union Territories, and Districts based on both quantitative and qualitative sanitation indicators.
- 21,000 villages across 761 districts in 34 States/UTs will be covered.
Key Assessment Components:
The evaluation follows a structured framework with four major components:
- Service-Level Progress (SLP): Based on data from district self-assessments and verification of ODF Plus Model villages.
- Direct Observation of Sanitation Status: Field-based observations in sampled villages, households, and public places such as schools and Common Service Centers (CSCs).
- Infrastructure Functionality Check: Includes assessment of:
- Plastic Waste Management Units (PWMUs)
- Faecal Sludge Management (FSM) plants
- GOBARdhan plants
- Swachhata Green Leaf Rating (SGLR) sites
- Citizen Feedback: Collected through a dedicated mobile application and direct interviews, ensuring community participation and transparency.
Key Innovations in SSG 2025:
- Geo-fencing for data authenticity and integrity.
- Emphasis on Jan Bhagidari (public participation) to sustain and validate sanitation achievements.
- Engagement of an independent agency for unbiased survey implementation.
- Launch of Swachhata Chronicles Volume III and a compendium of best practices from States to promote knowledge sharing.
Significance:
- Reinforces India’s commitment to sustainable sanitation and rural development.
- Encourages evidence-based policy interventions and fosters competitive federalism.
- Highlights sanitation as a continuous developmental journey, not a one-time target.
Pedicularis rajeshiana
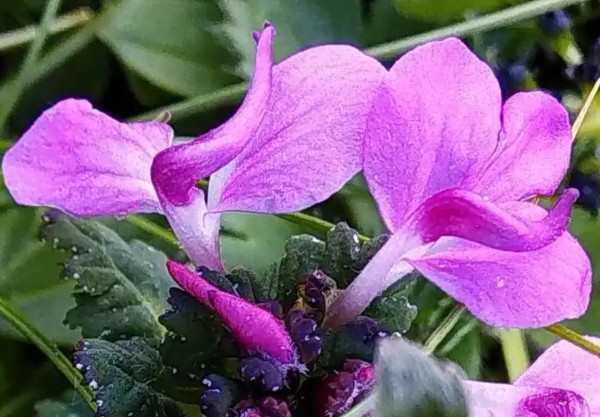

- 30 May 2025
In News:
Researchers from the Botanical Survey of India (BSI), under the Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change (MoEF&CC), have discovered a new plant species — Pedicularis rajeshiana — in the high-altitude regions of Rohtang Pass, Himachal Pradesh.
Key Facts:
Taxonomy and Classification
- Scientific Name: Pedicularis rajeshiana
- Family: Orobanchaceae
- Common Group: Louseworts (Hemiparasitic plants – partially dependent on host plants for nutrients, but also photosynthetic)
- Named by: Botanist Dr. Arti Garg, formerly of BSI Prayagraj, now with BSI Dehradun
- Publication: Officially recorded in the international journal Phytotaxa (Mongolia)
Habitat and Discovery
- Location: Rohtang Pass, Pir Panjal range, Western Himalayas
- Altitude: ~4,390 metres (14,400 feet)
- Habitat: Shaded rocky slopes in scattered patches
- Discovery Project: "Flora of India" initiative by MoEF&CC and BSI
Unique Botanical Characteristics
- Size: Smaller than related species like P. porrecta and P. heydei
- Floral Features:
- Deeply cut lower labium (lip)
- Stamens positioned at three distinct levels inside the flower
- Rare pollen morphology with croton-like surface texture
- Two flowers observed with twin galea (hood-like structures) — a first in the genus, possibly an evolutionary trait to enhance pollination
Ecological Significance
- Endemicity: Many Pedicularis species are habitat-specific and endemic to certain Himalayan regions
- India's Diversity: Home to 83 known species of Pedicularis, with 36 in the western Himalayas
- Conservation Value: The specificity of habitat and rarity suggest potential threat status; conservation is crucial.
India’s First Gene-Edited Sheep

- 30 May 2025
In News:
Sher-e-Kashmir University of Agricultural Sciences and Technology (SKUAST-Kashmir) has successfully developed India’s first gene-edited sheep, marking a significant breakthrough in the field of animal biotechnology.
Key Highlights:
- Institution Involved: Sher-e-Kashmir University of Agricultural Sciences and Technology (SKUAST), Srinagar.
- Technology Used:
- CRISPR-Cas9 gene editing — a precision genome editing tool that won the 2020 Nobel Prize in Chemistry.
- Gene editing was conducted without insertion of foreign DNA, thus the sheep is non-transgenic and differs from traditional GMOs.
- Gene Targeted: The myostatin gene, which regulates muscle growth, was edited to enhance muscle mass.
- Result: Muscle mass increased by 30%, a trait absent in Indian sheep breeds but seen in select European breeds like the Texel.
- Significance:
- Improved meat yield and quality in sheep.
- Potential for disease-resistant and higher-reproduction-rate livestock in the future.
- Supports India’s evolving biotech policy by promoting non-transgenic, gene-edited organisms that are more likely to receive regulatory acceptance.
- Aligns with goals of sustainability and food security by enhancing productivity per animal.
- Regulatory & Safety Aspects:
- Research adhered to international biosafety protocols.
- Sponsored by the Indian Council of Agricultural Research (ICAR).
- Legacy & Research Background:
- Developed after 4 years of dedicated research.
- Led by Prof. Riaz Ahmad Shah, also known for creating India’s first cloned Pashmina goat, Noori, in 2012, and contributing to the world’s first cloned buffalo at NDRI, Karnal.
Implications for the Future:
- Opens doors for precision breeding in livestock to boost India’s animal husbandry sector.
- Strengthens India’s position in advanced genomic research and supports the vision of Atmanirbhar Bharat in biotechnology.
- Awaits comprehensive regulatory framework for gene-edited animals, currently under government consideration.
WMO Climate Forecast 2025–2029
- 30 May 2025
In News:
The World Meteorological Organization (WMO) has released its latest decadal climate forecast (2025–2029), warning of a continued trend of record-breaking global temperatures. This projection raises serious concerns about climate risks, sustainable development, and international climate commitments under the Paris Agreement.
Key Projections:
- Annual Global Temperature Rise: Each year from 2025–2029 is projected to be 1.2°C to 1.9°C above pre-industrial levels (1850–1900).
- Record Heat Likelihood:
- 80% chance that at least one year will surpass 2024, currently the warmest year on record.
- 86% probability that one year will exceed the 1.5°C threshold.
- Five-Year Mean Warming: 70% chance that the 2025–2029 average will be above 1.5°C, a sharp rise from 47% (2024–2028) and 32% (2023–2027).
Note: The Paris Agreement’s 1.5°C limit refers to long-term (20-year) averages, but short-term overshoots are now increasingly probable.
Regional and Thematic Insights:
1. Arctic Amplification: Arctic winters (Nov–Mar) are projected to be 2.4°C warmer than the 1991–2020 average—3.5× faster than the global rate.
2. Sea Ice Decline: Continued sea ice reduction is expected in the Barents Sea, Bering Sea, and Sea of Okhotsk, impacting marine biodiversity and indigenous livelihoods.
3. Precipitation Variability:
- Wetter-than-average conditions likely in:
- Sahel region
- Northern Europe
- Alaska and Northern Siberia
- Drier conditions expected over:
- Amazon Basin
- Parts of South Asia
South Asia may witness generally wet years, though seasonal variability will persist.
Impact and Implications:
- Extreme Weather Events: Increased warming will fuel more intense heatwaves, extreme rainfall, droughts, and floods, stressing both urban systems and agriculture.
- Cryosphere and Ocean Changes:
- Accelerated glacier and sea ice melt will raise sea levels.
- Ocean heating contributes to acidification and marine biodiversity loss.
- Threat to Sustainable Development: Progress on SDGs, particularly food security, water availability, and health, is at risk in vulnerable regions.
Way Forward:
- Revise NDCs at COP30: Strengthen and align Nationally Determined Contributions (NDCs) with the 1.5°C goal.
- Accelerate Clean Energy Transition: Promote renewables, energy efficiency, and net-zero strategies to reduce GHG emissions.
- Adaptation and Resilience: Invest in climate-resilient infrastructure and early warning systems.
- Climate Monitoring & Forecasting: Enhance WMO-led regional forecasts and risk assessment tools.
- Preserve Natural Carbon Sinks: Protect forests, wetlands, and oceans to mitigate atmospheric CO?.
Menstrual Hygiene in India: Insights from the 2025 Survey

- 29 May 2025
In News:
Menstrual Hygiene Day, observed annually on May 28, raises awareness about safe menstrual practices and their role in ensuring health, dignity, and equality for women and girls. Ahead of the day, the everteen Menstrual Hygiene Survey 2025 has highlighted growing concerns around misinformation, stigma, and access to menstrual products in India.
Key Findings from the Survey:
- Social Media & Misinformation:
- 71.6% of women find social media informative on menstruation.
- However, only 11.5% trust it during emergencies.
- 1 in 4 women reported that misinformation online negatively affected their menstrual health.
- Examples of Misinformation:
- Harmful remedies such as applying menstrual blood for skincare, or drinking coffee/lemonade for cramps.
- Myths like avoiding exercise, temple visits, or not washing hair during periods.
- Misleading claims linking light flow to infertility or tampon use to anatomical changes.
- Menstrual Pain & Remedies:
- 82.7% of respondents experience menstrual pain.
- Only 14.2% use painkillers; 41.5% use no remedy at all.
- Cramps roll-ons used by just 5.5%.
- Menstrual Products Usage:
- 87.8% use sanitary pads (most common).
- Disposable period panties (5.7%) are more popular than menstrual cups (4.7%) or tampons (1.6%).
- 35.4% purchase menstrual products online citing convenience and discounts.
- A significant number of offline buyers report discomfort at physical stores.
- Online Discourse:
- 34% of women shared personal menstrual experiences online.
- Yet, 37.6% feared privacy breaches and 11.4% feared social judgment.
Menstrual Hygiene: Broader Context
- Definition: Safe and hygienic management of menstruation, including the use of clean products, proper disposal, access to sanitation, and health education.
- Global Concern: According to UNICEF, 500 million women globally lack access to adequate menstrual hygiene facilities.
Challenges in India:
- Digital Myths & Stigma: Despite digital access, online spaces are rife with misinformation and taboo-laden content.
- Access Inequality: Significant urban-rural divide in menstrual health services, infrastructure, and product availability.
- Awareness Gaps: Cultural silence and lack of comprehensive health education still persist.
Policy Interventions & Governance:
- Relevant Government Initiatives:
- SUVIDHA Scheme: Affordable biodegradable sanitary napkins at Jan Aushadhi Kendras.
- Swachh Bharat Mission: Incorporates Menstrual Hygiene Management (MHM) into sanitation programs.
- Global Frameworks: Sustainable Development Goal (SDG) 6 – Right to clean water and sanitation, encompassing menstrual hygiene.
Modified Interest Subvention Scheme (MISS) – FY 2025–26
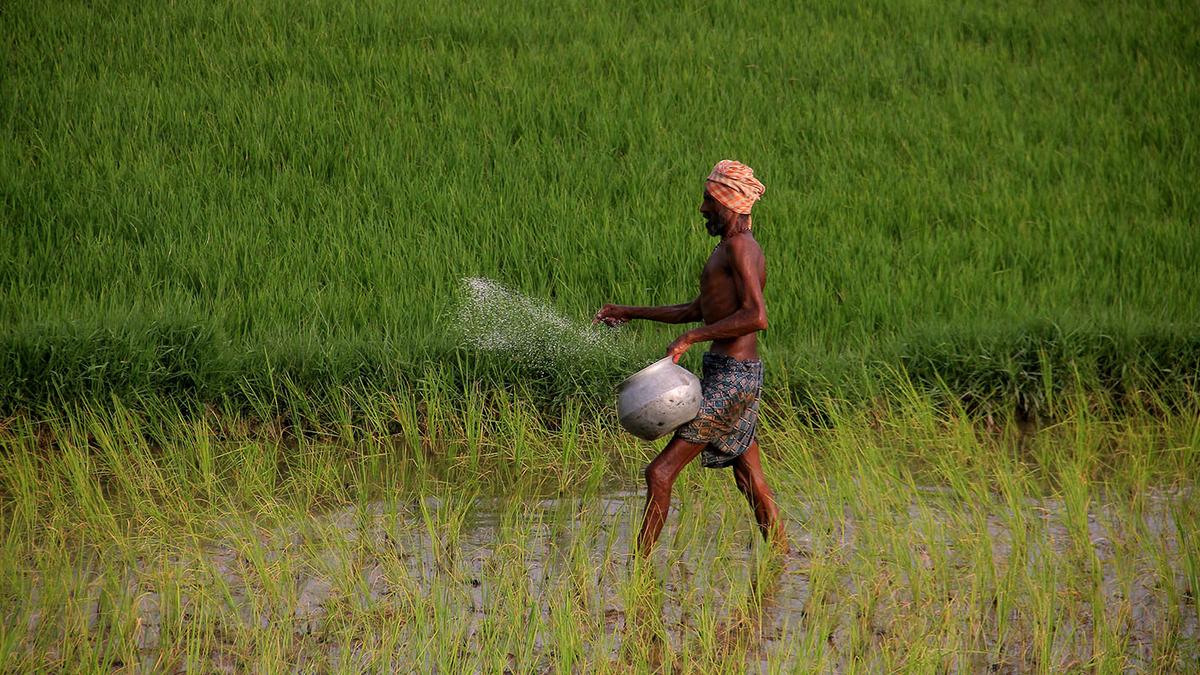

- 29 May 2025
In News:
The Union Cabinet has approved the continuation of the Interest Subvention (IS) component under the Modified Interest Subvention Scheme (MISS) for the financial year 2025–26, retaining the existing structure and interest rates.
About the Scheme:
- Type: Central Sector Scheme
- Objective: To provide short-term agricultural credit to farmers at affordable interest rates through Kisan Credit Cards (KCC).
Key Features:
- Loan Coverage:
- Short-term crop loans up to ?3 lakh per farmer through KCC.
- For loans exclusively for animal husbandry or fisheries, the benefit applies up to ?2 lakh.
- Interest Rates:
- Base interest rate: 7%
- 1.5% interest subvention to lending institutions
- 3% Prompt Repayment Incentive (PRI) for timely repayment
- Effective interest rate for prompt payers: 4%
- Implementing & Monitoring Agencies:
- Reserve Bank of India (RBI)
- National Bank for Agriculture and Rural Development (NABARD)
- Operated via Public Sector Banks, Regional Rural Banks, Cooperative Banks, and Private Banks in rural/semi-urban areas.
Recent Updates and Rationale:
- No structural changes have been introduced in the scheme for FY 2025–26.
- The scheme continues amidst rising lending costs, with stable repo rates and MCLR trends.
- It ensures credit access for small and marginal farmers, critical for financial inclusion and agricultural productivity.
Impact on Agricultural Credit:
- KCC Accounts: Over 7.75 crore active accounts across India.
- Institutional Credit Growth:
- Disbursement via KCC increased from ?4.26 lakh crore (2014) to ?10.05 lakh crore (Dec 2024).
- Total agricultural credit rose from ?7.3 lakh crore (FY 2013–14) to ?25.49 lakh crore (FY 2023–24).
- Digital Reform: Kisan Rin Portal (KRP) launched in August 2023 has improved transparency and efficiency in claim processing.
Significance:
- Helps ensure timely and affordable institutional credit to the farming sector.
- Supports the government's goal of doubling farmers’ income.
- Strengthens the rural credit delivery system and promotes inclusive growth in agriculture.
Madden-Julian Oscillation (MJO)
- 29 May 2025
In News:
In 2025, the early onset of the southwest monsoon in Kerala (May 24) and Mumbai (May 26—the earliest on record) was significantly influenced by the Madden-Julian Oscillation (MJO), as reported by the India Meteorological Department (IMD).
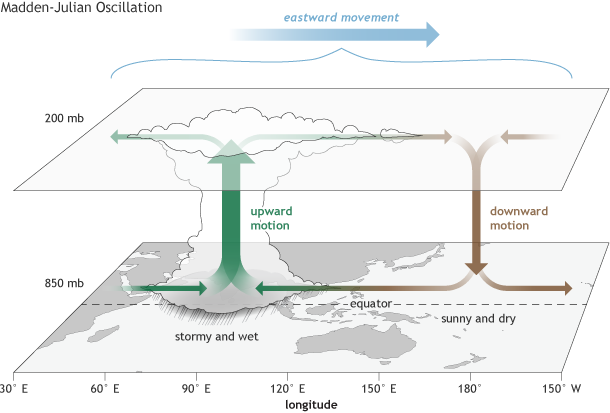
What is the MJO?
- The Madden-Julian Oscillation (MJO) is a large-scale atmospheric phenomenon observed in the tropical belt (30°N to 30°S).
- It is an eastward-moving disturbance involving winds, clouds, pressure, and rainfall that circles the globe every 30 to 60 days (occasionally up to 90 days).
- Identified in 1971 by Roland Madden and Paul Julian, it differs from ENSO (El Niño–Southern Oscillation) in being intra-seasonal and transient.
Phases of MJO:
- Enhanced Convective Phase:
- Associated with increased cloudiness, low pressure, and above-normal rainfall.
- Characterized by rising air and moisture convergence.
- Suppressed Convective Phase:
- Brings clearer skies and reduced rainfall due to subsiding dry air.
- These phases shift eastward and influence weather globally, including India.
Formation and Movement:
- Triggered by surface wind convergence that causes upward motion, cloud formation, and upper-level wind divergence.
- Travels at 4–8 m/s, completing a global circuit roughly every 30–60 days.
MJO’s Impact on Indian Monsoon:
- MJO in active phase over the Indian Ocean can:
- Trigger early monsoon onset, as seen in 2024 and 2025.
- Enhance cyclogenesis and monsoon depressions.
- Improve intra-seasonal rainfall variability.
- May 2025 Event:
- The MJO was in Phase 4 with amplitude >1, indicating strong activity conducive to rainfall.
- This condition, along with favorable local and oceanic factors, supported early monsoon advancement in India.
Global Influence of MJO:
- Cyclone Modulation: Alters frequency and intensity of tropical cyclones.
- Weather Extremes: Affects jet streams, triggering cold surges, heatwaves, or floods in mid-latitudes (e.g., U.S., Europe, Australia).
- Interaction with ENSO: While not always directly linked, MJO can amplify or be influenced by El Niño conditions.
Dark Patterns and India’s Regulatory Response
- 29 May 2025
In News:
The Ministry of Consumer Affairs, Food, and Public Distribution has initiated a robust crackdown on Dark Patterns—deceptive design practices used on digital platforms to manipulate consumer behavior. A recent high-level stakeholder meeting in Delhi, chaired by Union Minister Prahlad Joshi, brought together representatives from major e-commerce platforms like Amazon, Flipkart, Zomato, and Ola, along with consumer organizations and law institutions, to address the growing concern.
What are Dark Patterns?
Dark Patterns are user interface designs that intentionally mislead or coerce consumers into making decisions they would not have otherwise made. These manipulative tactics exploit psychological principles and cognitive biases to serve the commercial interests of platforms—often at the cost of consumer autonomy.
Types of Dark Patterns Identified by the Government:
The Department of Consumer Affairs has officially recognized 13 types of dark patterns in its November 2023 guidelines. Prominent among them are:
- False Urgency: Creating artificial time pressure (e.g., “Only 1 seat left!”).
- Basket Sneaking: Adding items to the cart without user consent.
- Confirm Shaming: Using guilt-driven language to influence decisions.
- Subscription Trap: Making subscription easy but cancellation difficult.
- Interface Interference: Hiding crucial information or options.
- Bait and Switch: Advertising one offer and switching to another.
- Hidden Costs: Revealing extra charges only at checkout.
- Forced Action: Making users complete unrelated tasks to proceed.
- Disguised Ads, Trick Questions, Nagging, SAAS Billing Abuse, and Rogue Malware Links are other examples.
These practices have been found across multiple digital sectors including e-commerce, travel, OTT platforms, edtech, online banking, and quick commerce.
Consumer Impact and Rising Complaints:
The National Consumer Helpline has witnessed a significant increase in grievances related to dark patterns. Platforms are accused of eroding consumer trust, causing financial harm, breaching privacy, and distorting fair market practices.
According to LocalCircles, based on a survey conducted across 392 districts with feedback from 2.30 lakh consumers, the worst offenders include edtech, airline, and taxi app services. Notably, companies like Uber and Rapido were recently issued notices by the Central Consumer Protection Authority (CCPA) for coercing users into paying tips in advance.
Regulatory Measures in India:
- Consumer Protection Act, 2019: While it prohibits unfair trade practices, it lacks explicit provisions targeting dark patterns, making enforcement challenging.
- 2023 Guidelines on Dark Patterns: Released by the Department of Consumer Affairs, these guidelines define deceptive interfaces as violations of consumer rights and misleading advertisements.
- Self-Audit Mandate: E-commerce companies have been instructed to conduct internal audits and eliminate dark patterns from their platforms.
- Proposed Joint Working Group: A mechanism is being considered to increase industry awareness and enforce compliance.
- Voluntary and Legal Enforcement: The government has urged digital firms to integrate the guidelines into internal policies and consumer grievance redressal systems.
Jinchuanloong niedu
- 28 May 2025
In News:
A newly discovered genus and species of sauropod dinosaur, Jinchuanloong niedu, has been identified from fossil remains found in the Xinhe Formation near Jinchang city in Gansu Province, northwestern China. This discovery adds to the growing diversity of early-diverging sauropods from the Middle Jurassic period, dating back approximately 165 million years.
About Jinchuanloong niedu
- Jinchuanloong niedu belongs to the group Eusauropoda, which comprises early-diverging, strictly herbivorous, long-necked, quadrupedal dinosaurs.
- The fossil specimen includes a nearly complete skull with mandible, five cervical vertebrae, and 29 articulated caudal vertebrae.
- The skull measures approximately 31 cm in length and 12.5 cm in height. Notably, complete skulls are rare in non-neosauropod eusauropods due to their fragile nature.
- The skull is well-preserved, although slightly deformed due to compression. Most cranial sutures remain distinctly visible, aiding paleontological study.
Paleontological Significance
- This species is the earliest sauropod identified from Gansu Province, enriching the diversity of known early-diverging sauropods in East Asia.
- The discovery contributes valuable insights into sauropod evolution in northwest China, particularly during the Middle Jurassic.
- The presence of Jinchuanloong niedu helps trace lineage continuity in the aftermath of a global warming event during the late Early Jurassic, which led to the extinction of other sauropod groups, leaving only eusauropods.
Eusauropoda and Sauropod Evolution
- Sauropods, which existed from the Early Jurassic to the Late Cretaceous, were the largest land animals to have ever lived and were found on all continents.
- Characterized by massive size, long necks and tails, and a herbivorous diet, sauropods include both neosauropods and non-neosauropods.
- During the Middle and Late Jurassic, non-neosauropod eusauropods like Shunosaurus, Omeisaurus, and Mamenchisaurus-like taxa became dominant.
Kumbakonam Vetrilai (Betel Leaf)
- 28 May 2025
In News:
Kumbakonam Vetrilai, a traditional betel (paan) leaf variety cultivated in Tamil Nadu, was recently granted the Geographical Indication (GI) tag by the Government of India. This recognition was published in the Government Gazette in November 2024 and officially announced in April 2025, taking Tamil Nadu’s total GI products to 62.
Geographical and Agricultural Context
Kumbakonam Vetrilai is predominantly grown in the Cauvery river basin in Thanjavur district, covering areas like Kumbakonam, Ayyampettai, Swamimalai, Rajagiri, Thiruvaiyaru, and Papanasam. The region's fertile soil gives the leaves a distinct taste and aroma.
The oblong, heart-shaped leaves, ranging from dark to light green, are known for their pungent flavour and are a staple in South Asian households, used primarily in preparing paan—a post-meal chew with cultural and ceremonial value.
Cultivation and Harvest
The cultivation cycle begins with planting during March–May and August–October. Banana suckers are commonly used to provide shade for the vines. The first leaves, called kolundhu vetrilai, appear 20–25 days after planting.
- Maaruvethalai (1st year harvest): Yields larger leaves with a shelf life of 6–7 days and fetches premium market prices.
- Kelavethalai and Kattavethalai (2nd and 3rd year harvests): Smaller leaves with reduced yield.
The cultivation is labour- and capital-intensive, with most farmers operating on less than one acre. Adverse weather, soil issues, and labour shortages frequently impact profitability.
Cultural and Medicinal Value
Apart from its ritual and culinary use, betel leaf is valued for medicinal properties. Rich in antioxidants and chavicol (an anti-inflammatory compound), it aids digestion and is believed to help manage oxidative stress and diabetes-related conditions.
Economic and Export Potential
The leaves are sold at Rs. 80–180 per 100 leaves and are also exported. However, only about 10 out of 100 days are considered profitable due to market and climatic fluctuations.
GI Tag Benefits and Challenges
The GI tag:
- Confirms the authenticity and regional uniqueness of Kumbakonam Vetrilai.
- Helps curb misuse of the name and ensures only genuine, high-quality products are marketed.
- Boosts export potential and preserves agro-cultural heritage.
Despite this recognition, many farmers and sellers remain unaware of the GI tag. As per Sanjai Gandhi, the IP attorney behind the GI application, there's a pressing need for awareness, capacity-building, and marketing support to help stakeholders leverage the tag effectively.
Efforts are underway through outreach programs and school and college awareness initiatives. This GI tag is also notable as Thanjavur’s first agricultural GI recognition, adding to the region’s rich cultural profile.
National Apprenticeship Promotion and Training Schemes

- 28 May 2025
In News:
Recently, the 38th Meeting of the Central Apprenticeship Council (CAC), chaired by the Minister of State (Independent Charge) for the Ministry of Skill Development and Entrepreneurship (MSDE), recommended a 36% increase in stipends under two key skilling initiatives—National Apprenticeship Promotion Scheme (NAPS) and National Apprenticeship Training Scheme (NATS). This move aims to enhance apprenticeship attractiveness, reduce dropout rates, and improve youth employability across India.
About NAPS (Launched: 19 August 2016)
- Objective: To build industry-relevant skilled manpower by promoting on-the-job training and bridging the gap between education and employment.
- Administered by: Ministry of Skill Development and Entrepreneurship (MSDE).
- Key Features:
- Provides financial support to establishments for engaging apprentices.
- Encourages MSME participation and focuses on aspirational districts and the North-East.
- Offers partial stipend reimbursement under the Apprentices Act, 1961.
- Apprentices receive a certificate from NAPS, enhancing employability.
- Over 43.47 lakh apprentices engaged across 36 States/UTs till May 2025.
- Female participation reached 20%, with efforts to boost inclusion.
About NATS
- Target Group: Graduates, Diploma holders, and Vocational certificate holders.
- Provisions:
- Offers 6–12 months of practical, hands-on training.
- Employers receive 50% stipend reimbursement.
- Apprentices are issued a Government of India Certificate of Proficiency, valid across employment exchanges.
- FY 2024–25 Stats: Over 5.23 lakh apprentices enrolled.
Key Reforms Recommended by CAC (2025)
- Stipend Enhancement:
- Proposed increase from ?5,000–?9,000 to ?6,800–?12,300.
- To be adjusted biennially based on Consumer Price Index (CPI).
- Inclusive Skilling Framework:
- Definition of “Person with Benchmark Disability” to be added under the Apprenticeship Rules.
- Trades must indicate suitability for PwBDs with reserved training slots.
- Curricular Integration:
- Push for Degree Apprenticeships and Apprenticeship Embedded Degree Programmes (AEDP).
- Definitions added for "Institution", "UGC", and "Contractual Staff".
- Flexible Training Modes: Employers may provide Basic and Practical Training through online, virtual, or blended modes, adhering to standard curricula.
- Decentralized Administration: Proposal to establish Regional Boards to improve scheme outreach and governance.
- Sectoral Expansion:
- Adoption of NIC Code 2008 to replace outdated 1987 list.
- Brings emerging sectors like IT, software, telecom, biotech, and renewable energy under apprenticeship coverage.
- Operational Improvements:
- Align CTS (Craftsmen Training Scheme) courses with apprenticeship notification timelines.
- Consideration of location-based stipend rationalization based on cost of living.
- Proposal for insurance coverage for apprentices during contract periods.
Governance and Stakeholder Involvement
The Central Apprenticeship Council includes representatives from:
- Ministries: Education, Labour, MSME, Railways, Textiles.
- Industry: BHEL, Indian Oil, Tata, Maruti, Reliance.
- Institutions: NSDC, UGC, AICTE.
- State advisors and domain experts from labour and education fields.
Semi-Transparent Perovskite Solar Cell Technology
- 28 May 2025
In News:
Researchers at IIT Bombay have developed an advanced semi-transparent perovskite solar cell (PSC) layered over a traditional silicon solar cell. This results in a 4-terminal (4T) tandem solar cell that significantly boosts power conversion efficiency (PCE) to ~30%, compared to the current average of ~20% in conventional solar panels.
Key Features and Technology
- Structure: Tandem architecture using a bottom silicon sub-cell and a top layer of indigenously developed halide perovskite semiconductor.
- Material Efficiency: Halide perovskite is one of the most efficient light-absorbing materials and can be locally produced using available chemical resources.
- Cost & Efficiency Gains:
- Potential to reduce solar power cost to ?1/kWh, down from ?2.5–4/kWh.
- Offers 25–30% more efficiency compared to standard solar panels.
- Stability Improvements: Previously, PSCs degraded quickly. The new configuration extends lifespan up to 10 years, enhancing durability under heat and low-light conditions.
Strategic Significance for India
- Indigenous Manufacturing: Reduces dependence on imported raw materials, especially those dominated by China.
- Commercialization Plan:
- Maharashtra government and MAHAGENCO exploring large-scale implementation.
- ART-PV India Pvt. Ltd., a start-up from IIT Bombay's SINE, aims to deliver a commercial wafer-size solution by December 2027 using indigenous equipment.
- Applications:
- Rooftop solar installations
- Building-integrated photovoltaics (BIPV)
- Vehicle-integrated photovoltaics (VIPV)
Clean Energy Linkage: IIT Bombay is also working with the Maharashtra government to develop green hydrogen solutions. The PSC’s high open-circuit voltage makes it suitable for solar-to-hydrogen (STH) applications, offering performance comparable to costly compound semiconductors but at lower cost and with locally accessible materials.
Alicella gigantea
- 27 May 2025
In News:
Rare giant shrimp is more widespread than previously believed; new findings reveal.
About the Species:
- Alicella gigantea is a giant deep-sea amphipod crustacean, growing up to 34 cm in length, making it one of the largest known amphipods.
- Amphipods are shrimp-like organisms; over 10,000 species are known globally, inhabiting a wide range of aquatic environments.
Habitat and Depth Range:
- Inhabits the abyssal (3,000–6,000 m) and hadal zones (>6,000 m) of the ocean.
- Notable sightings include:
- A 28 cm specimen observed at 5,304 m in the North Pacific.
- Captures from 6,746 m depth in the Murray Fracture Zone (North Pacific).
Global Distribution:
- Contrary to earlier beliefs, A. gigantea is not rare but is among the most widely distributed deep-sea species.
- Recent analysis compiled 195 records from 75 locations across the Pacific, Atlantic, and Indian Oceans, covering 15 different seafloor features.
- Found in 59% of the world’s oceans.
- The Pacific Ocean is its most significant habitat, with 75% of the seafloor in its suitable depth range.
Genetic Insights:
- Genetic analyses (16S, COI, 28S genes) show low genetic divergence across populations.
- This suggests A. gigantea represents a single, globally distributed species with strong genetic conservation.
- A shared haplotype network across regions indicates minimal genetic differentiation, supporting global connectivity among populations.
Conservation and Research Significance:
- Despite its wide range, A. gigantea remains poorly understood, particularly in terms of population size, ecology, and evolutionary history.
- Only seven studies have sequenced its DNA to date.
- The findings are a significant step toward understanding deep-sea biodiversity, biogeography, and conservation priorities in abyssal ecosystems.
RBI Dividend Transfer to Government (FY 2024–25)

- 27 May 2025
In News:
- The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) has approved a record dividend transfer of ?2.69 lakh crore to the Government of India for FY 2024–25.
- This amount is 27% higher than the ?2.10 lakh crore transferred in the previous year (2023–24).
- The transfer follows the Revised Economic Capital Framework (ECF), approved on May 15, 2025.
What is a Dividend in Public Finance?
- A dividend is the non-tax revenue received by the government as the sole shareholder of the RBI.
- It helps bridge the fiscal deficit.
- RBI dividend distribution is governed by the Reserve Bank of India Act, 1934.
- Unlike corporate dividends that require shareholder approval, RBI transfers are governed by policy mechanisms set by the Central Board.
Economic Capital Framework (ECF) and Risk Buffer
- The Contingent Risk Buffer (CRB) has been raised to 7.5% of the RBI’s balance sheet for FY 2024–25.
- Earlier CRB levels:
- 5.5% (2018–22)
- 6% (2022–23)
- 6.5% (2023–24)
- The CRB helps ensure the RBI maintains sufficient capital to absorb financial shocks.
Reasons for Higher Surplus in 2024–25
- Robust foreign exchange (forex) sales, especially in January 2025, with RBI being the top seller among Asian central banks.
- Increased interest income from government securities and foreign investments.
- Gains from forex transactions during high market volatility.
- Forex reserves had peaked at $704 billion in September 2024, from which large volumes of dollars were sold to stabilise the rupee.
Implications for the Union Budget 2025–26
- The Budget had projected ?2.56 lakh crore as dividend income from RBI and PSUs; the actual RBI dividend itself exceeds this estimate.
- Experts expect the fiscal deficit to reduce by 20 basis points (bps) from the budgeted 4.4% to ~4.2% of GDP.
- The surplus provides a non-tax revenue cushion, helping offset shortfalls in tax or disinvestment receipts and manage additional spending.
Expert Views
- Surplus driven by prudent RBI policy, forex gains, and high interest income. CRB increase reduced the possible surplus, otherwise it could have exceeded ?3.5 lakh crore.
- The surplus equals 0.4–0.5 trillion (?40,000–?50,000 crore) or 11–14 bps of GDP, offering fiscal flexibility.
- Market expected ?3 lakh crore; disappointment due to higher risk buffer provisioning.
Sagarmatha Sambaad 2025

- 27 May 2025
In News:
Union Environment Minister Shri Bhupender Yadav represented India at the 1st Sagarmatha Sambaad in Kathmandu, Nepal, a high-level biennial global dialogue convened under the theme “Climate Change, Mountains, and the Future of Humanity.”
The forum, held during the International Year of Glaciers’ Preservation 2025, focused on mountain ecosystems, climate resilience, and transboundary conservation.
India’s Key Proposals and Commitments
Reaffirmed India’s climate leadership and proposed a five-point call for global action to protect mountain ecosystems:
- Enhanced Scientific Cooperation: Promote joint research on cryospheric changes, biodiversity, and hydrological cycles.
- Building Climate Resilience: Develop early warning systems for Glacial Lake Outburst Floods (GLOFs) and invest in climate-resilient infrastructure in mountainous areas.
- Empowering Mountain Communities: Center policies on local welfare, integrate traditional ecological knowledge, and promote green livelihoods such as eco-tourism.
- Providing Green Finance: Ensure adequate and predictable climate finance for adaptation and mitigation in mountain nations, in line with the Paris Agreement.
- Recognizing Mountain Perspectives: Integrate mountain-specific issues into global climate negotiations and sustainable development agendas.
India’s Initiatives and Regional Cooperation
India highlighted the ecological value of the Himalayas and called for enhanced transboundary conservation among Himalayan nations under the International Big Cats Alliance. This alliance promotes joint protection of species like snow leopards, tigers, and leopards.
- Under Project Snow Leopard, India conducted its first comprehensive snow leopard assessment (2019–2023), recording 718 snow leopards, comprising 10–15% of the global population.
Significance of the Himalayan Ecosystem
- Hydrological Role: The Himalayas are the "Water Towers of Asia", feeding rivers like the Ganga, Brahmaputra, and Indus, and supplying around 1.2 trillion cubic meters of freshwater annually.
- Ecological Richness: A biodiversity hotspot, home to over 10,000 vascular plant species, 979 bird species, and 300 mammals such as the red panda and Himalayan tahr.
- Cultural Importance: Sacred in Hinduism and Buddhism, the Himalayas house pilgrimage sites like Kedarnath, Badrinath, and Mount Kailash.
- Economic Value: Support tourism, agriculture, forestry, and renewable energy. States like Uttarakhand, Assam, and West Bengal derive over 10% of state GDP from tourism.
The Lohit Basin project in Arunachal Pradesh (13,000 MW) exemplifies hydropower potential. - Climate Regulation: The range blocks cold Central Asian winds and influences monsoon patterns, ensuring rainfall for agriculture. Himalayan forests are major carbon sinks, mitigating global warming.
Key Challenges in the Himalayan Region
- Climate Disasters: Rising temperatures and glacier melt cause avalanches, landslides, and cloudbursts. E.g., 2025 Uttarakhand avalanche; 2023 Sikkim GLOF.
- Unsustainable Development: Slope cutting, deforestation, and seismic vulnerability threaten settlements (e.g., Joshimath subsidence linked to infrastructure projects).
- Glacier Retreat:
- Gangotri glacier has retreated over 850 meters in 25 years.
- Hindu Kush glaciers may lose 75% of volume by 2100.
- Biodiversity Loss: Invasive species and habitat loss displace native flora and fauna; 90% of endemic species in Sikkim Himalayas displaced.
- Unregulated Tourism: Littering and plastic waste—92.7% of Himalayan waste is plastic, 72% non-recyclable (2022 audit).
Recommendations for Sustainable Development
- Eco-sensitive Infrastructure: Mandatory Environmental Impact Assessments (EIAs), bioengineering, and electric mobility in high-altitude towns.
- Regulated Tourism: Introduce carrying capacity limits, permit-based entry, and promote low-impact tourism models.
- Glacier Monitoring & Water Management: Use remote sensing and GIS for glacier health; adopt ice stupas, rainwater harvesting, and efficient irrigation.
- Afforestation & Forest Conservation: Launch community-driven forestry projects (e.g., Van Andolan in Uttarakhand) to restore degraded ecosystems.
- Climate Adaptation Strategies: Expand early warning systems for GLOFs; promote climate-resilient crops and agricultural practices.
- Sustainable Livelihoods: Encourage organic farming, herbal industries, and eco-handicrafts to diversify mountain economies.
Bharat Seva Kendra (BSK)

- 27 May 2025
In News:
The Chamber of Commerce and Industry of India (CCI India) has highlighted the role of Bharat Seva Kendra (BSK) in enhancing last-mile service delivery and addressing the urban-rural service gap.
About Bharat Seva Kendra (BSK):
- Launched by: Chamber of Commerce and Industry of India (CCI India).
- Objective: To provide essential government services and welfare benefits directly to rural citizens.
- Nature: A grassroots, nationwide service delivery initiative focused on creating self-reliant rural communities.
Key Features:
- Single-window access to schemes in sectors like healthcare, education, employment, agriculture, financial inclusion, and digital empowerment.
- Digital Inclusion: Modern infrastructure and digital literacy programs to help villagers use e-governance tools effectively.
- Human Network: Backed by a large cadre of 2.5 lakh sarpanches and 6.5 lakh BSK Sarthis, who act as facilitators between government schemes and rural beneficiaries.
- Goal: Reduce bureaucratic delays, enhance transparency, and ensure timely access to welfare schemes.
CCI India’s Role:
- Type: A national-level autonomous business body.
- Functions: Policy advocacy, business facilitation, and supporting domestic and foreign investment.
- Engagement: Represents diverse industries and collaborates with stakeholders including policymakers, industry, and civil society.
Significance for Governance:
- Promotes last-mile delivery of public services.
- Acts as a catalyst for rural digital transformation and inclusive development.
- Enhances administrative efficiency and citizen empowerment in rural India.
Turtle Conservation in Assam’s Temple Ponds

- 26 May 2025
In News:
On World Turtle Day (May 23, 2025), Assam’s Nagshankar Temple was officially declared a model temple for turtle conservation, highlighting the ecological role of temple ponds in preserving India’s turtle biodiversity.
Key Highlights
Nagshankar Temple – A Model for Turtle Conservation
- Location: Sootea town, Biswanath district, ~70 km from Tezpur, Assam.
- Established: Believed to be built in the 4th century AD by King Nagashankar of the Nagakha dynasty.
- Religious Importance: Dedicated to Lord Shiva, but turtles are revered as incarnations of Lord Vishnu.
- Ecological Value: Functions as a micro-wildlife sanctuary — home to 250–300 turtles, along with peacocks, pythons, and deer.
Turtle Conservation Initiatives
Species Conserved:
- Black Softshell Turtle (Nilssonia nigricans) – Critically Endangered
- Indian Softshell Turtle (Nilssonia gangetica)
- Malayan Softshell Turtle
These species thrive in the temple pond, which is fed by the Brahmaputra River basin, offering a suitable natural habitat.
Community & Scientific Collaboration:
- Key Stakeholders:
- Nagshankar Temple Committee
- Turtle Survival Alliance (TSA) India
- Help Earth (NGO)
- Kaziranga National Park & Tiger Reserve
- Assam Forest Department
- Conservation Methods:
- Artificial egg incubation and wild release of hatchlings.
- Dried-fish diet introduced for temple turtles, replacing harmful offerings (e.g., biscuits, puffed rice).
- Capacity-building workshops for forest staff and students to aid in turtle surveys.
Result: 486 hatchlings of the black softshell turtle have been released into the wild from the Nagshankar Temple pond.
Statewide Turtle Conservation Model
- Assam houses ~25 temple ponds actively involved in turtle conservation.
- Notable site: Hayagriva Madhav Temple in Hajo (Kamrup district).
- State Zoo in Guwahati has a dedicated breeding facility (established 2010) for the Assam Roofed Turtle (Pangshura sylhetensis, "Asomi Dura").
Google’s AI Matryoshka Strategy
- 26 May 2025
In News:
At its 2025 I/O Developer Conference, Google unveiled AI Matryoshka, a multi-layered artificial intelligence (AI) ecosystem powered by its latest Gemini 2.5 models. This marks a fundamental restructuring of Google’s platforms around AI, affecting users, developers, and enterprises.
What is AI Matryoshka?
- Concept: Named after the Russian nesting dolls, AI Matryoshka is a layered AI architecture where each outer application or interface draws intelligence from a core AI “brain.”
- Objective: To embed AI deeply and uniformly across Google’s services, enabling agentic, intelligent, and autonomous interactions.
Core AI Models: Gemini 2.5
- Gemini 2.5 Pro:
- Advanced reasoning and mathematics capabilities.
- Achieved high scores on USAMO 2025 (a premier U.S. math olympiad).
- Features a mode called Deep Think for complex problem-solving.
- Gemini 2.5 Flash:
- A more efficient, lightweight model using 20–30% fewer tokens.
- Supports natural audio output and multi-speaker TTS in 24 languages.
- Set to become the default model in Gemini applications.
Foundational Hardware: Ironwood TPUs
- Ironwood (7th Gen TPUs):
- Delivers 42.5 exaFLOPS of compute power per pod.
- Offers 10x performance boost over previous TPUs.
- Supports large-scale training and deployment of generative AI models.
Generative Media Models
- Imagen 4: Advanced image generation.
- Veo 3: High-quality video generation.
- Lyria 2: Music creation using AI.
- Copyright Tools:
- SynthID (watermarking) and SynthID Detector (verification) aim to address copyright concerns over the training data.
Developer Ecosystem
- Gemini API & Vertex AI:
- Model Context Protocol (MCP): Enables agent-to-agent communication.
- Thinking Budgets: Let developers allocate compute resources wisely.
- Project Mariner: Tool for automating complex tasks.
- Thought Summaries: Improves transparency of AI decisions.
- Coding Agent – Jules:
- Beta launched globally.
- Integrates with code repositories to write tests, build features, and fix bugs using Gemini 2.5 Pro.
User-Centric Features
- Search Integration (AI Mode):
- Rolls out first in the U.S. with Deep Search generating cited, multimodal answers.
- Offers virtual shopping try-ons and agentic checkout, raising privacy and data security concerns.
- Gemini App:
- Available on Android and iOS with Live and image generation features.
- Deep Research allows analysis of private documents and images, necessitating strong data protection protocols.
- Integrated into Chrome (for Pro and Ultra users) for webpage summarization.
- Canvas Feature: A creative workspace for interactive infographics, quizzes, and audio content in 45 languages.
Subscription Tiers and Privacy Concerns
- Google AI Ultra Tier:
- Offers premium access to advanced capabilities, including video generation with native audio.
- Raises questions about "privacy premium" – whether better AI safety features will be available only to paying users.
India’s Coastline Redefined
- 26 May 2025
In News:
The Ministry of Home Affairs, in its 2023–24 annual report (Dec 2024), announced a significant update to India’s coastline length — revised from 7,516.6 km to 11,098.8 km. This change was not due to any new territorial acquisition or geological activity but resulted from improved measurement techniques, reflecting the "coastline paradox" in geography.
What Is the Coastline Paradox?
The coastline paradox, first explained by British mathematician Lewis Fry Richardson and later expanded by Benoît Mandelbrot, shows that the length of a coastline increases with finer measurement scales. This is because coastlines, like fractals, reveal more detail (creeks, estuaries, inlets) the more closely they are examined.
- Using large-scale maps (e.g., 1:4,500,000), previous estimates missed finer details.
- Modern tools allow capturing every tidal creek, sandbar, and estuarine curve, dramatically increasing measured length.
Measurement Methodology (2024 Update)
Aspect Details
Agencies Involved National Hydrographic Office (NHO), Survey of India
Previous Map Scale 1:4,500,000 (1970s)
New Map Scale 1:250,000 (electronic navigation charts)
Key Technologies GIS, LIDAR-GPS, satellite altimetry, drone imaging
Reference Line Used Highwater Line (based on 2011 data)
Mapped Features Included Tidal creeks, sandbars, estuaries, low-tide islands
Review Frequency Every 10 years from 2024–25
Geographical and Strategic Overview
- India’s New Coastline Length: 11,098.8 km
- No New Land Added: No change in land boundaries or annexation.
- Coastal States & UTs: 11 coastal States + 2 UTs (Andaman & Nicobar Islands, Lakshadweep)
- State with Longest Coastline: Gujarat (~1,600 km)
Why This Matters
1. Maritime Security
- Longer coast = More area to monitor and protect.
- Post-26/11, India enhanced coastal surveillance (radar grid, coastal police).
- Navy and Coast Guard deployment strategies need updates.
2. Disaster Management
- Accurate coastline data helps in cyclone, tsunami early warning systems (e.g., Odisha).
- Supports better Coastal Regulation Zone (CRZ) mapping.
3. Economic and Strategic Planning
- Affects Exclusive Economic Zone (EEZ) and fishing rights.
- Informs infrastructure development: ports, shipping, Sagarmala, tourism.
- Boosts India’s aspirations in the Blue Economy.
Schistura densiclava
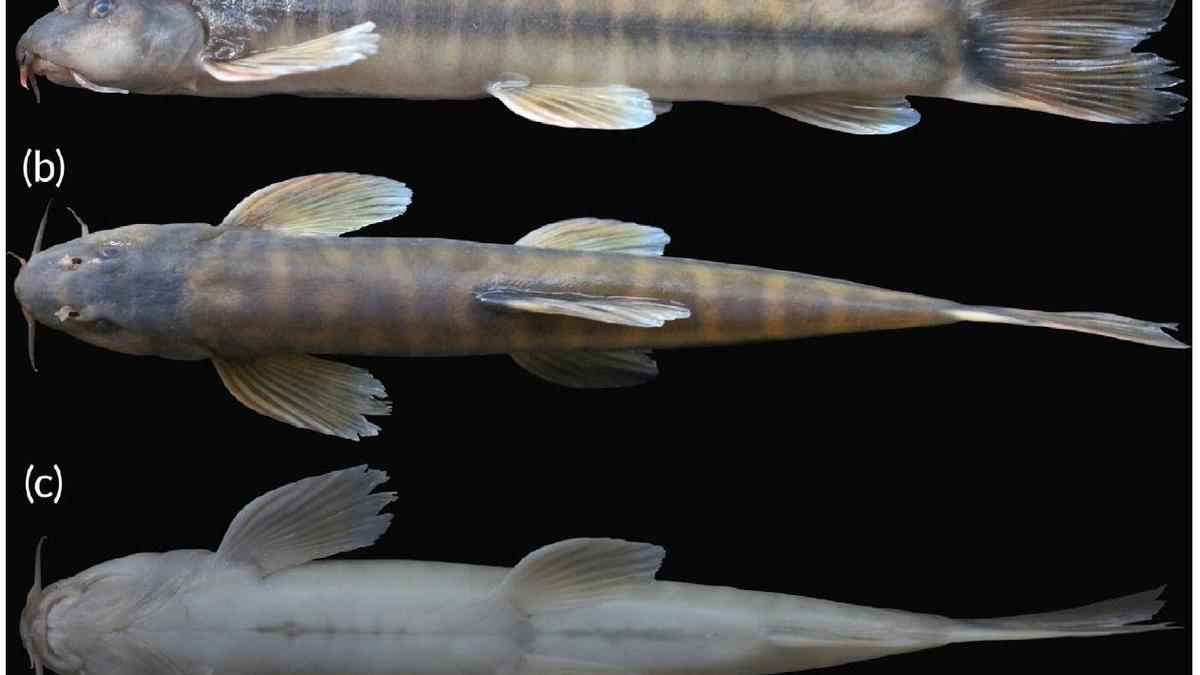

- 26 May 2025
In News:
A newly discovered species of cave-dwelling loach, Schistura densiclava, has been recorded from the Krem Mawjymbuin cave in the East Khasi Hills district of Meghalaya, India. This species becomes the sixth known cave-dwelling fish from the state, emphasizing Meghalaya’s rich subterranean biodiversity.
Taxonomy and Classification
- Family: Nemacheilidae (bottom-dwelling freshwater fishes)
- Type: Troglophile — adapted to live in caves but can survive and reproduce in surface (epigean) waters.
- Distinct Feature: Unlike typical cave fishes, S. densiclava retains pigmentation and functional eyes, indicating adaptability to both subterranean and overground aquatic environments.
Habitat and Environment
- Found 60 meters inside the Krem Mawjymbuin, a limestone cave with a surveyed length of 1.6 km and an altitude of 206 meters.
- The species inhabits a cool, fast-flowing stream with a temperature of 18°C and low oxygen levels.
- The cave is ecologically sensitive and was previously in the news due to a local ban on worship at a Shivalinga-like formation within it.
Morphological Characteristics
- Coloration: Pale yellow-green body with 14–20 greyish to faint black vertical bars.
- Named densiclava due to the thick dark stripe near the dorsal fin ("densiclava" = Latin for "thick stripe").
- Sexual Dimorphism:
- Males: Slimmer with irregular patterns and puffier cheeks.
- Females: Sturdier with more consistent markings.
Scientific Significance
- Genetic testing confirmed Schistura densiclava as a distinct and previously unrecorded species.
- Its endemic distribution, limited to a single cave system, marks it as a species of high conservation concern.
- The discovery was published in the Journal of Fish Biology by a team led by Kangkan Sarma from Gauhati University, along with other Indian ichthyologists.
Tamil Nadu’s Space Industrial Policy and IN-SPACe
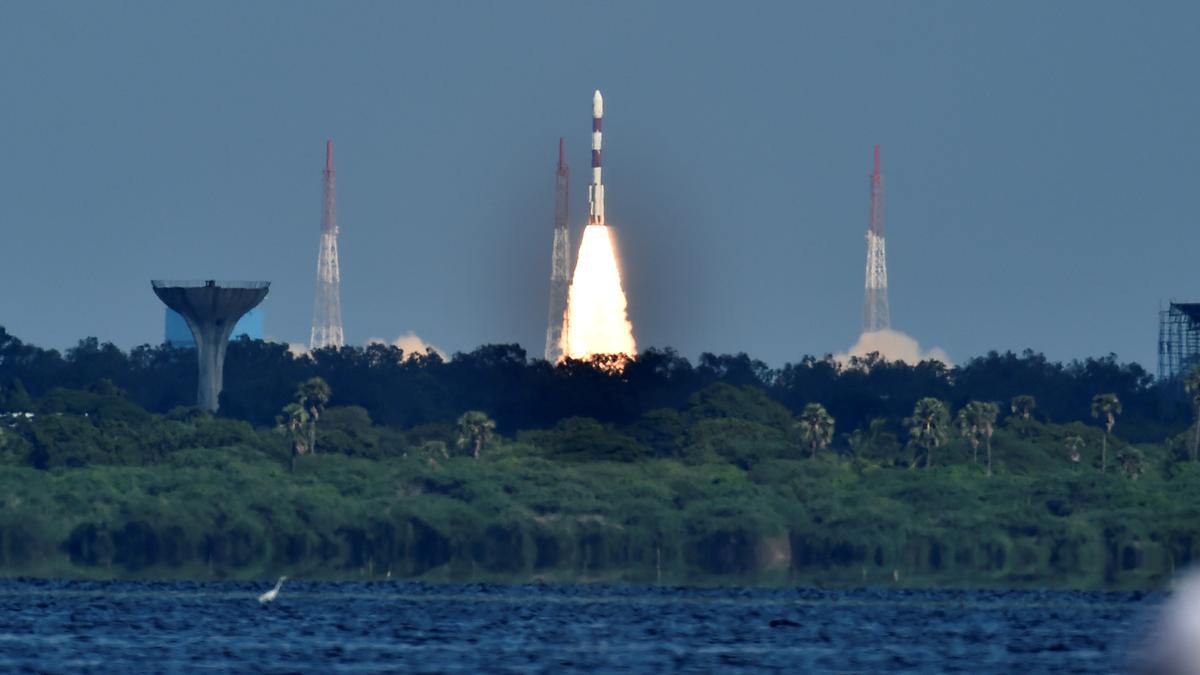

- 26 May 2025
In News:
Recently, the Tamil Nadu Cabinet approved its Space Industrial Policy, becoming the third state after Karnataka and Gujarat to adopt a dedicated strategy to stimulate investments and innovation in the space sector. This move aligns with the national framework set by the Indian Space Policy 2023 and supports India's growing space economy.
IN-SPACe and its Role:
- IN-SPACe (Indian National Space Promotion and Authorisation Centre) is an autonomous, single-window agency under the Department of Space (DoS).
- Created as part of India’s space sector reforms, it promotes and authorises the participation of Non-Governmental Entities (NGEs) in space activities.
- Functions include:
- Supporting private entities in the development of launch vehicles, satellites, and space-based services.
- Facilitating access to ISRO infrastructure and co-development initiatives.
- Providing support for research, innovation, and educational collaboration.
- Headquartered at Bopal, Ahmedabad, it serves as the bridge between ISRO and private sector stakeholders.
- IN-SPACe encouraged Tamil Nadu to formulate the Space Industrial Policy to promote the state’s role in India’s space mission.
Tamil Nadu’s Strategic Space Assets:
- ISRO Propulsion Complex (IPRC), Mahendragiri (Tirunelveli): Engaged in testing cryogenic engines, liquid propulsion systems, and R&D activities.
- Second Spaceport at Kulasekarapattinam (Thoothukudi): Enhances satellite launch capacity, especially for small satellites and polar launches.
- Presence of space-tech startups in areas like:
- Reusable launch vehicles
- In-space manufacturing
- In-orbit refuelling
- Satellite data analytics
- Space Technology Incubation Centre (STIC) at NIT Trichy supports southern-region ISRO projects and academia-industry collaboration.
- Over 250 ISRO vendors operate in the state, creating a robust supply chain ecosystem.
Objectives of Tamil Nadu's Space Industrial Policy:
- Target investment: ?10,000 crore over the next 5 years.
- Employment generation: Estimated 10,000 direct and indirect jobs.
- Strengthens Tamil Nadu’s capabilities in:
- Electronics and precision manufacturing
- Strategic electronics and space-grade components
- Promotes integration of space technologies in governance (e.g., disaster management, fisheries, agriculture, health, transport).
Policy Incentives:
- Payroll subsidy for companies engaged in R&D or setting up Global Capability Centres.
- Space Bays: Select regions will be designated to offer structured incentive packages for investments below ?300 crore.
- Industrial housing incentive: 10% subsidy (capped at ?10 crore) for building residential facilities in space industrial parks.
- Green initiatives: 25% capital subsidy (capped at ?5 crore) for environmentally sustainable developments.
Institutional Support:
- TIDCO (Tamil Nadu Industrial Development Corporation) signed an MoU with IN-SPACe to facilitate:
- Manufacturing activities
- Strategic collaborations with private companies
- R&D and design-based projects in the space domain
Khelo India Youth Games 2025

- 06 May 2025
In News:
- Prime Minister Narendra Modi virtually inaugurated the 7th edition of the Khelo India Youth Games (KIYG) on May 4, 2025, marking Bihar’s first time hosting a national-level multi-sport event.
- The event will be held across five cities in Bihar: Patna, Rajgir, Gaya, Bhagalpur, and Begusarai from May 4–15, 2025.
About Khelo India Youth Games (KIYG)
Feature Details
Launch Year 2018
Nodal Ministry Ministry of Youth Affairs and Sports
Target Group Youth athletes under 17 and 21 years of age
Objective Promote grassroots sports, mass participation, and talent
development for global competition
Host Cities in 2025 Patna, Rajgir, Gaya, Bhagalpur, Begusarai
Total Athletes (2025) Over 6,000 participants
Special Highlights of KIYG 2025
- Medal Events: Competitions held in 27 sporting disciplines.
- New Inclusions:
- Sepaktakraw included as a medal sport for the first time.
- Esports introduced as a demonstration event, reflecting the rise of digital-age sports.
- Support for Athletes: Winners eligible for scholarships under the Khelo India Scheme to pursue professional training.
Significance
- PM Modi emphasized the role of regular tournaments like KIYG in shaping India’s sports ecosystem.
- Cited Vaibhav Suryavanshi, a 14-year-old cricketer who scored a 38-ball century in IPL 2025, as a symbol of emerging youth talent.
- Highlighted that platforms like Khelo India events (youth, para, winter, and senior levels) help identify, nurture and promote talent, building confidence among young athletes.
Previous Editions of KIYG
Edition Host City
1st (2018) New Delhi
2nd (2019) Pune
3rd (2020) Guwahati
4th (2021) Panchkula
5th (2022) Bhopal
6th (2023) Chennai
7th (2025) Bihar (multiple cities)
Global Wind Energy Report 2025
- 05 May 2025
In News:
The Global Wind Energy Council (GWEC), in its Global Wind Report 2025, has warned that current global wind energy growth is insufficient to meet the targets aligned with the Paris Agreement and net-zero emissions by 2050. As per the report, at current trends, only 77% of the wind capacity required by 2030 will be achieved — putting the 1.5°C global warming limit at serious risk.
Global Wind Energy Landscape (as of 2024)
- New Capacity Added: 117 GW (up from 116.6 GW in 2023)
- Total Global Capacity: 1,136 GW
- Leading Countries:
- China: 70% of new installations
- USA, Brazil, India, and Germany followed.
- Emerging Markets: Uzbekistan, Egypt, and Saudi Arabia showed significant growth.
- Regional Progress:
- Africa and Middle East: Onshore wind capacity doubled compared to previous years.
- Offshore Wind: Only 8 GW added (down 26% from 2023), the lowest since 2021.
Key Challenges Identified by GWEC
- Policy Uncertainty: Regulatory delays and instability in key markets.
- Grid Infrastructure Deficits: Underinvestment in transmission and distribution systems.
- Financial Constraints: Inflation, high interest rates, trade protectionism.
- Market Inefficiencies: Weak renewable energy auction systems.
Global Commitments & Urgency
- At COP28 (Dubai), countries pledged to triple renewable energy capacity by 2030.
- To align with this goal, annual wind installations must rise to 320 GW by 2030.
- Failure to scale up urgently risks missing a vital climate mitigation window.
Wind Energy in India – Status and Prospects (as of March 2025)
- Total Installed Capacity: 50.04 GW
- Capacity Added (FY 2024–25): 4.15 GW
- (Up from 3.25 GW in FY 2023–24)
- Global Rank: 4th largest wind power producer (after China, USA, Germany)
- Top States:
- Gujarat
- Tamil Nadu
- Karnataka
- Manufacturing Strength: Domestic wind turbine manufacturing capacity is ~18,000 MW/year.
- Offshore Wind Potential:
- Gujarat: 36 GW
- Tamil Nadu: 35 GW
WAVES 2025 & WAM!
- 01 May 2025
In News:
In line with the vision of “Create in India, Create for the World,” the Ministry of Information & Broadcasting, in partnership with the Media & Entertainment Association of India (MEAI), is hosting WAVES 2025—India’s largest summit for the Media & Entertainment (M&E) sector. A major highlight of this summit is the WAM! (WAVES Anime & Manga Contest)—India’s first national initiative to promote original Indian IPs in anime, manga, webtoons, and cosplay.
What is WAM!?
- Full Form: WAVES Anime & Manga Contest.
- Nature: India’s first national initiative focused on discovering and nurturing original Indian creative intellectual properties (IPs) in:Anime, Manga, Webtoons&Cosplay
- Organisers: Ministry of Information & Broadcasting, in collaboration with MEAI.
- Finale: To be held at WAVES 2025, from May 1–4, 2025, at the Jio World Convention Centre, Mumbai.
- Participants: Finalists from 11 cities selected through regional contests.
Global Support & Incentives
- Crunchyroll, a global anime platform (a joint venture of Sony Pictures Entertainment and Aniplex, Japan), is the Title Sponsor of WAM! 2025.
- It has introduced a Creator Development Grant to support Indian talent and foster global-ready original content.
Grant Details
Category Student (INR) Professional (INR)
Manga 25,000 25,000
Webtoon 25,000 25,000
Anime 50,000 50,000
- Winners of WAM! 2025 will represent India at Anime Japan 2026 in Tokyo—one of the world's leading anime conventions—marking India’s presence on the global animation stage.
About WAVES 2025
- Full Form: World Audio-Visual & Entertainment Summit.
- Objective: Showcase India's capabilities in content creation, technological innovation, and media & entertainment IP development.
- Hosted by: Government of India.
- Venue: Jio World Convention Centre, Mumbai
Key Pillars of WAVES 2025
- AVGC-XR Sector Focus:Animation, Visual Effects, Gaming, Comics&Extended Reality (XR) including AR, VR, and Mixed Reality.
- "Create in India" Challenges (CIC):
- Season 1 witnessed over 1 lakh registrations, including 1,100 international participants.
- 750+ finalists selected through 32 unique creative challenges.
- Thematic Focus Areas:
- Broadcasting, Films, Television, Radio
- Print & Digital Media, Advertising, Social Media Platforms
- Sound & Music
- Generative AI, Augmented Reality (AR), Virtual Reality (VR), Extended Reality (XR)
- Target Audience: Content creators, industry professionals, investors, technology innovators, and global studios.
USCIRF’s 2025 Report

- 30 Mar 2025
In News:
In its 2025 Annual Report, the United States Commission on International Religious Freedom (USCIRF) recommended designating India as a "Country of Particular Concern" (CPC), citing alleged systemic violations of religious freedom.
Key USCIRF Recommendations:
- Label India as a CPC under the International Religious Freedom Act (IRFA), 1998.
- Impose targeted sanctions on Indian institutions, including the Research and Analysis Wing (RAW), and individuals such as Vikash Yadav.
- Review bilateral defence agreements, including drone deals.
- Prioritise religious freedom in diplomatic dialogues with India.
- Reintroduce the Transnational Repression Reporting Act, 2024 to monitor global religious freedom violations.
About USCIRF:
- Established by: U.S. Congress (1998) under IRFA.
- Nature: Independent, bipartisan federal agency.
- Not affiliated with: U.S. State Department (but works in coordination).
- Structure: 9 Commissioners appointed by the U.S. President and Congressional leaders.
- Mandate: Monitor global religious freedom (FoRB), advise U.S. leadership, recommend sanctions, and publish annual reports.
Core Functions:
- Track global trends in freedom of religion or belief.
- Recommend policy actions including CPC designation.
- Advocate for religious prisoners of conscience.
- Maintain a FoRB Victims List and issue thematic reports.
India’s Official Response:
The Ministry of External Affairs (MEA) firmly rejected USCIRF’s report, calling it “biased and politically motivated.”
- MEA Spokesperson Randhir Jaiswal criticized the report for misrepresenting isolated incidents and ignoring India’s multicultural and pluralistic society.
- Highlighted India’s 1.4 billion diverse population, representing all major religions.
- Emphasized that USCIRF’s assessments reflect a deliberate narrative rather than genuine concern for religious rights.
- Asserted that such reports would not affect India’s image as a democratic and tolerant nation.
- Called for USCIRF itself to be recognized as an “entity of concern.”
India to Host FATF Private Sector Collaborative Forum 2025 in Mumbai
- 25 Mar 2025
In News:
- India will host the FATF Private Sector Collaborative Forum (PSCF) 2025 in Mumbai from March 25-27, 2025. This event will focus on global priorities such as payment transparency, financial inclusion, and the digital transformation of financial systems.
- The forum will be a critical platform for addressing the evolving challenges of money laundering and terrorist financing through the use of digital tools and enhanced transparency.
Key Agenda
The discussions at PSCF 2025 will revolve around tackling contemporary financial crimes, including those linked to cryptocurrency-related laundering. Key topics will include:
- Strengthening Anti-Money Laundering (AML) and Counter-Terrorist Financing (CFT) compliance mechanisms.
- Promoting financial inclusion through risk-based supervision of regulated entities.
- Enhancing transparency in beneficial ownership and using digital tools to bolster AML/CFT measures.
- Addressing emerging risks, including terrorist financing and proliferation financing.
The forum will also assess how the private sector can enhance information-sharing practices to address these threats more effectively.
About FATF
The Financial Action Task Force (FATF), established in 1989 during the G7 Summit in Paris, is an intergovernmental body that sets international standards to combat money laundering and terrorist financing. The FATF’s mission is to develop policies, establish guidelines, and promote global cooperation to mitigate the financial risks associated with these crimes.
- Headquarters: Paris, France.
- Membership: FATF has 39 member countries, including major economies such as the United States, India, China, Saudi Arabia, Germany, and theEuropean Union.
- Regional Bodies: In addition to its direct members, FATF affiliates over 180 countries through FATF-Style Regional Bodies (FSRBs) like the Asia Pacific Group (APG) and the Eurasian Group.
- FATF Recommendations are recognized as the global standard for AML/CFT measures.
FATF evaluates countries' efforts to comply with these standards, providing assessments and promoting policy changes to counteract financial crimes. Countries that fail to comply may be placed on the grey list or blacklist.
FATF Grey and Black Lists
Countries that fail to meet FATF standards are placed on one of two lists:
- Black List: Countries known as Non-Cooperative Countries or Territories (NCCTs), which directly support terrorist financing and money laundering. North Korea, Iran, and Myanmar are currently on this list.
- Grey List: Countries considered at risk of supporting financial crimes but not yet fully engaging in those activities. Being on the grey list serves as a warning, with the risk of moving to the blacklist if improvements are not made.
Countries on the blacklist face severe international sanctions, including restrictions on financial aid and economic interactions from organizations like the IMF, World Bank, and Asian Development Bank.
India's Role in FATF
India became a member of FATF in 2010 and has made significant strides in improving its AML/CFT frameworks. In 2024, FATF acknowledged India’s efforts towards anti-money laundering and countering terrorist financing, placing it in the "regular follow-up" category for continued compliance.
The upcoming PSCF 2025 will be a milestone in India’s ongoing commitment to global financial security, as it seeks to enhance international collaboration and discuss innovative ways to address evolving threats in financial crimes.
World Happiness Report 2025
- 23 Mar 2025
In News:
The World Happiness Report (WHR) 2025 was released on 20th March (World Happiness Day) by the Wellbeing Research Centre at the University of Oxford, in collaboration with Gallup and the UN Sustainable Development Solutions Network (UNSDSN).
India’s Performance:
- India’s Rank (2025):118th out of 147 countries (Improved from 126th in 2024).
- Sub-Indicator Performance:
- Donations: 57th
- Volunteering: 10th
- Helping a Stranger: 74th
- Wallet Return Probability:
- 115th (by neighbor)
- 86th (by stranger)
- 93rd (by police)
- Sub-Indicator Performance:
- Happiness Score: Increased from 4.054 (2021–23) to 4.389 (2022–24).
- Rank among Neighbors:
- Nepal: 92nd
- Pakistan: 109th
- Myanmar: 126th
- Sri Lanka: 133rd
- Bangladesh: 134th
Top 10 Happiest Countries (2025):
- Finland (8th consecutive year)
- Denmark
- Iceland
- Sweden
- Israel
- Costa Rica (new entrant)
- Netherlands
- Norway
- Luxembourg
- Mexico(new entrant)
Least Happy Countries (Bottom 5):
- 147th: Afghanistan (4th consecutive year as lowest)
- 146th: Sierra Leone
- 145th: Lebanon
- 144th: Malawi
- 143rd: Zimbabwe
About the Report:
- Purpose: Measures global well-being through life evaluations and promotes policy focus on happiness, mental health, and quality of life over mere economic growth.
- Methodology:
- Based on Gallup World Poll (2022–2024 data).
- Uses Cantril Ladder Scale (0–10) for life evaluation.
- Six Key Indicators:
- GDP per capita
- Healthy life expectancy
- Social support
- Freedom to make life choices
- Generosity
- Perception of corruption
Global Trends in Happiness (2025):
- Nordic Dominance: Finland, Denmark, Iceland, and Sweden occupy top ranks.
- Decline in Western Countries:
- USA: 24th (down from 11th in 2012)
- UK: 23rd (lowest since 2017)
- Rising loneliness and social isolation major causes.
- Israel (5th): Maintained high rank despite ongoing conflict.
- Social Support Decline: 19% of young adults globally report having no one to rely on.
Special Focus: India vs Pakistan – The Paradox
Despite India’s:
- Higher GDP per capita ($2,480.8 vs Pakistan’s $1,365.3),
- Better health indicators (life expectancy: 58.1 vs 56.9),
- Better corruption perception rank (India: 96th, Pakistan: 135th),
India still ranks lower in happiness.
Reason: Low scores in perceived freedom and individual life satisfaction.
World Happiness Day:
- Observed on: 20th March
- Initiated by: Bhutan, which pioneered the concept of Gross National Happiness (GNH).
- Adopted by UNGA: July 2012
- Theme 2025:"Caring and Sharing"
Bongosagar 2025 Naval Exercise
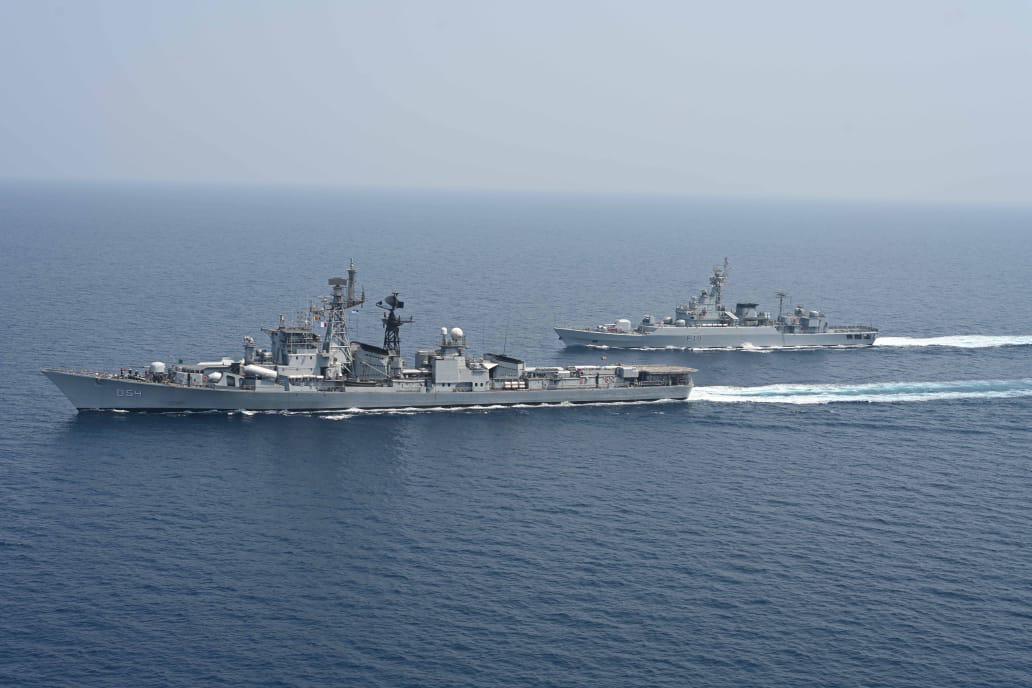

- 16 Mar 2025
In News:
India and Bangladesh conducted the Bongosagar 2025 naval exercise in the Bay of Bengal, aimed at enhancing maritime cooperation, operational interoperability, and regional security. This joint exercise aligns with India's maritime foreign policy doctrine — SAGAR (Security and Growth for All in the Region).
Key Highlights
- Participants:
- Indian Navy: INS Ranvir, a Rajput-class guided missile destroyer, commissioned in 1986.
- Bangladesh Navy: BNS Abu Ubaidah.
- Objectives:
- Strengthen tactical planning, information sharing, and coordinated response capabilities.
- Enhance interoperability for seamless maritime operations.
- Reinforce regional trust and cooperation under the SAGAR framework.
- Exercise Components:
- Surface firing drills
- Tactical manoeuvres
- Underway replenishment
- VBSS (Visit, Board, Search and Seizure) operations
- Cross-deck boarding exercises
- Communication drills
- Professional knowledge quizzes and steam past ceremonies
Strategic Significance
- Supports India’s SAGAR initiative (2015), promoting security and growth in the Indian Ocean region.
- Aligns with the broader MAHASAGAR (2025) vision — Mutual and Holistic Advancement for Security and Growth Across Regions — targeting deeper engagement with the Global South.
- Enhances the ability of both navies to counter maritime threats, uphold freedom of navigation, and ensure regional maritime stability.
India-Bangladesh Defence Cooperation
- Army-level: Exercise Sampriti
- Navy-level: Exercises Bongosagar and Coordinated Patrol (CORPAT)
Remission and the Supreme Court’s 2025 Ruling

- 24 Feb 2025
In News:
Recently, the Supreme Court directed states with remission policies to consider the premature release of prisoners even if they don’t apply for remission beforehand.
What is Remission?
- Remission refers to the reduction of a convict's sentence by the government before the term is completed. It does not nullify the conviction, but shortens imprisonment.
- It is governed by:
- Section 473 of BNSS, 2023 (earlier Section 432 of CrPC, 1973) – empowers state governments to grant remission.
- Articles 72 and 161 of the Constitution – empower the President and Governors respectively to remit sentences.
- Section 475 of BNSS (earlier Section 433A CrPC) – restricts remission for life convicts found guilty of offences punishable by death until 14 years of imprisonment are completed.
Background: SC’s Suo Motu Intervention
- The Supreme Court in 2025, in the suomotu case In Re: Policy Strategy for Grant of Bail, altered the interpretation of remission rules to address prison overcrowding.
- The Court held that states must consider remission for eligible convicts even without a formal application, if a remission policy exists.
Shift in Judicial Interpretation
- Earlier rulings (Sangeet v. Haryana and Mohinder Singh v. Punjab, 2013) required a convict's application for remission.
- The 2025 judgment acknowledges that many state prison manuals already mandate prison authorities to initiate remission review.
- It recognized that failing to consider remission proactively could lead to arbitrary discrimination, violating Article 14 (Right to Equality).
Key Guidelines Issued by the Supreme Court
- Suo motu Remission:States must automatically assess eligibility under remission policies—no application needed.
- Mandatory Remission Policy:States without existing remission policies must formulate a comprehensive one within two months.
- Conditions for Remission Must Be:
- Reasonable, non-oppressive, and clearly defined.
- Based on factors like motive, criminal background, and public safety.
- Aimed at rehabilitation and prevention of recurrence.
- Safeguards Against Arbitrary Cancellation:
- Minor breaches shouldn’t lead to automatic cancellation.
- Notice and hearing must be given before cancellation.
- Transparency:
- Legal aid bodies must monitor remission cases.
- States to maintain real-time digital data on remission.
Significance and Implications
- The ruling helps streamline remission processes and could contribute to decongesting Indian prisons, which are heavily overcrowded.
- It ensures uniformity and fairness in the exercise of executive powers related to sentencing.
- Reinforces constitutional values of equality and procedural fairness for prisoners.
Note:
- Remission ≠ Pardon: Remission reduces sentence, doesn’t erase conviction.
- Articles 72 & 161: Concern constitutional remission powers (President & Governor).
- BNSS Sections 473 & 475: Replace CrPC Sections 432 & 433A, relevant for state remission powers.
- Suo motu action by SC: Taken to address systemic prison overcrowding.
- Article 14 invoked: To ensure equitable treatment of eligible prisoners.
Aero India 2025

- 20 Feb 2025
In News:
Aero India 2025, the 15th edition of Asia's largest biennial airshow, is scheduled to take place from February 10 to 14, 2025, at the Air Force Station, Yelahanka, in Bengaluru, Karnataka.
Organized by the Defence Exhibition Organisation under the Ministry of Defence, with support from HAL, DRDO, and the Indian Air Force, the event showcases India's growing prowess in aerospace, aviation, and defense technologies.
Key Highlights:
Edition: 15th (First held in 1996; originally Avia India in 1993)
Theme: “The Runway to a Billion Opportunities”
Conclave Theme: “BRIDGE – Building Resilience through International Defence and Global Engagement”
Objectives and Significance
- Promote Indigenous Manufacturing: In alignment with ‘Make in India’ and ‘Atmanirbhar Bharat’, the show promotes domestic aerospace and defense production.
- Showcase Technological Advancements: Cutting-edge systems including fighter jets, helicopters, UAVs, and AI-integrated defense solutions will be exhibited.
- Encourage Global Partnerships: Facilitates joint ventures, MoUs, and technology transfers between Indian and foreign defense firms.
- Boost Strategic Diplomacy: A platform for global defense ministers, CEOs, and military leaders to foster bilateral and multilateral defense ties.
- Stimulate Investment: Attracts FDI and international contracts in India’s defense sector.
Key Events
- Live Aerial Displays: Aerobatic performances by combat aircraft, helicopters, and elite teams like Surya Kiran.
- Defense Ministers’ Conclave: Deliberations on enhancing international defense cooperation.
- CEO Roundtable: Industry leaders discuss emerging trends and investment prospects.
- Manthan/iDEX Pavilion: Showcasing start-up innovations in defense and aerospace.
- India Pavilion: A dedicated zone for indigenous defense production and capabilities.
- International Seminar (Feb 8–9): Focused on Futuristic Aerospace Technologies and related R&D challenges.
Strategic Role of Aero India
Aero India plays a pivotal role in:
- Supporting Medium Multi-Role Combat Aircraft (MMRCA) procurements.
- Demonstrating India's readiness as a global defense manufacturing hub.
- Enhancing India’s geopolitical standing by fostering defense diplomacy through multilateral engagement.
Tribal Welfare in Union Budget 2025–26

- 09 Feb 2025
In News:
India is home to over 10.45 crore Scheduled Tribe (ST) individuals, comprising 8.6% of the population. Concentrated largely in remote and underdeveloped regions, ST communities face persistent challenges such as land alienation, limited access to quality education, healthcare deficits, and socio-economic exclusion. The Union Budget 2025–26 signals a paradigm shift in tribal welfare, in line with the vision of Viksit Bharat.
Budgetary Commitment
The total allocation for tribal welfare has risen to ?14,925.81 crore in 2025–26—a 45.79% jump from the previous year and a staggering 231.83% increase from 2014–15 levels. The Ministry of Tribal Affairs has witnessed a consistent rise in budget: from ?7,511.64 crore (2023–24) to ?10,237.33 crore (2024–25), and now ?14,925.81 crore.
Flagship Schemes and Initiatives
- Eklavya Model Residential Schools (EMRS) received ?7,088.60 crore, up from ?4,748 crore, to provide quality residential education to ST students. EMDBS, a pilot initiative in high-density tribal areas, enhances outreach.
- Pradhan Mantri Janjatiya Vikas Mission (PMJVM) saw a sharp rise to ?380.40 crore. It promotes tribal entrepreneurship, sustainable Minor Forest Produce (MFP) use, and value chain development.
- Pradhan Mantri Adi Adarsh Gram Yojana (PMAAGY) was allocated ?335.97 crore (163% increase). It aims to convert tribal-majority villages into model habitations by ensuring convergence of development schemes.
- PM-JANMAN Multi-Purpose Centers (MPCs) received ?300 crore, targeting Particularly Vulnerable Tribal Groups (PVTGs) with essential services and institutional support.
- Dharti Aaba Janjatiya Gram Utkarsh Abhiyan (DAJGUA), launched in 2024, envisions the holistic development of 63,843 tribal villages. With an outlay of ?79,156 crore over five years, it integrates 17 ministries and 25 interventions. The Ministry of Tribal Affairs has allocated ?2,000 crore for 2025–26 alone.
Persistent Challenges
Despite constitutional safeguards (Articles 15(4), 46, 244, 275(1), etc.), tribal communities face significant hurdles:
- Land and Resource Rights: Only 50% of 42.76 lakh Forest Rights Act (FRA) claims have been approved (MoTA, 2022). Displacement from mining and infrastructure projects persists.
- Education: ST literacy stands at 59% (Census 2011) with high dropout rates due to poverty and language gaps.
- Health: Malnutrition, maternal mortality, and diseases like Sickle Cell remain endemic.
- Marginalization: Tribals face economic deprivation, exploitation (bonded labor, trafficking), and erosion of cultural identity.
- Underrepresentation: Despite reserved seats, policy influence remains limited.
The Way Forward
- Land Rights: Effective implementation of FRA and safeguards against forced displacement.
- Education: Expand EMRS/EMDBS and promote bilingual, culturally relevant curricula.
- Health: Improve rural health infrastructure and target tribal-specific diseases.
- Women’s Empowerment: Support SHGs and skill-based livelihood through schemes like Adivasi Mahila Sashaktikaran Yojana.
- Cultural Continuity: Support tribal art, festivals, and language preservation through digital and educational platforms.
- Inclusive Governance: Strengthen Gram Sabhas and tribal representation in policymaking.
Dunki Routes
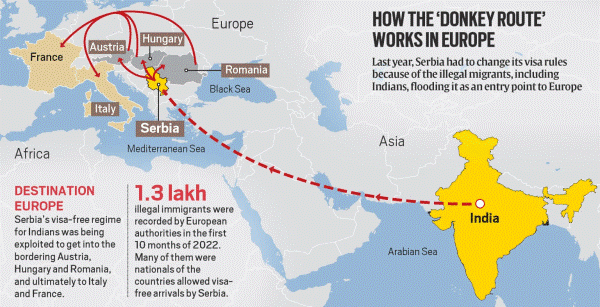
- 09 Feb 2025
In News:
Recently, a US military aircraft carrying 104 deported Indian nationals landed at Amritsar Airport. These deportees had entered the United States through the illegal “Dunki” route, paying between ?30 lakh and ?1 crore to agents and human traffickers.
Since 2009, over 15,000 Indians have been deported from the US for illegal entry, with India now figuring among the top non-Latin American countries in deportation rankings.
What is the ‘Dunki Route’?
- The “Dunki” or “Donkey” route refers to an unauthorised, arduous journey that migrants undertake through multiple countries to reach destinations like the United States, bypassing legal immigration processes.
- Routes often begin in countries with visa-on-arrival access or easy tourist visa policies for Indians:
- Latin America: Ecuador, Bolivia, Guyana, Brazil, Venezuela
- Europe/Central Asia: Azerbaijan, Turkey, Kazakhstan
- Southeast Asia: Malaysia (via Bangkok)
- Migrants often transit through Mexico, Guatemala, or Costa Rica before crossing into the US through illegal land borders.
How the Network Operates:
- Human trafficking syndicates use fake or manipulated visas (e.g., Schengen visas) to move migrants across Europe, Central Asia, and Latin America.
- Indian passport holders are sent to countries with lenient visa regimes, followed by overland or sea routes to US borders.
- Delhi Police (IGI unit) revealed that many migrants travel to Turkey or Kazakhstan and then cross to Russia or Latin America before attempting US entry.
Reasons Behind Illegal Migration:
- Economic Opportunities: Low wages in India drive migration to higher-paying economies.
- Limited Legal Avenues: Long, uncertain visa approval processes discourage legal pathways.
- Cultural Pressures: In communities like the Patels of Gujarat, migration to the US is tied to social prestige, often compelling families to sell land or take loans.
- Success Stories: Stories of successful illegal migrants inspire others to follow suit.
- Thriving Smuggling Rackets: Demand for migration has led to lucrative smuggling networks.
Consequences and Risks:
- Human Cost: Migrants risk robbery, assault, rape, and death, with bodies often unrecovered.
- Economic Loss: Families face financial ruin due to heavy agent fees.
- Legal Repercussions: Deportation, detention, and blacklisting from future visas.
- Geopolitical Sensitivity: Damages bilateral ties with countries like the US and strains consular systems.
Government Response and Policy Measures:
Proposed Legislation:
- India is considering the Overseas Mobility (Facilitation and Welfare) Bill, 2024 to:
- Promote safe, orderly, and regular migration
- Replace the outdated Emigration Act, 1983
- Establish comprehensive mechanisms for migrant protection and regulation
Awareness Campaigns:
- Indian embassies and consulates regularly issue:
- Advisories on fraudulent agents
- Guidance on safe migration
- Lists of registered recruiting agencies
Migration Trends and Global Standing:
- World Migration Report 2024 (IOM):
- India received $111 billion in remittances in 2022 – highest globally
- India is the largest country of origin for international migrants, with large diasporas in the UAE, US, and Saudi Arabia
H-1B Visa: The Legal Face of Indian Migration to the US
- H-1B Program: Allows US employers to hire foreign workers in high-skill occupations requiring at least a bachelor’s degree.
- Duration: Maximum of six years, renewable under certain conditions, or convertible into a Green Card.
- Indian Dominance:
- Indians have accounted for over 70% of all H-1B visa approvals since 2015
- Chinese applicants make up the second-largest group (~12–13%)
Political Challenges:
- Immigration, including H-1B, is a polarising issue in US politics.
- Rising anti-immigration sentiment, especially under administrations like Trump 2.0, affects policy and visa quotas.
Hotspot States and Migration Routes in India:
- Major source states of illegal migrants: Gujarat, Punjab, Haryana
- These regions are hubs for agents who facilitate illegal migration using Dunki routes and exploit aspirational youth.
Ranikhet Disease in India
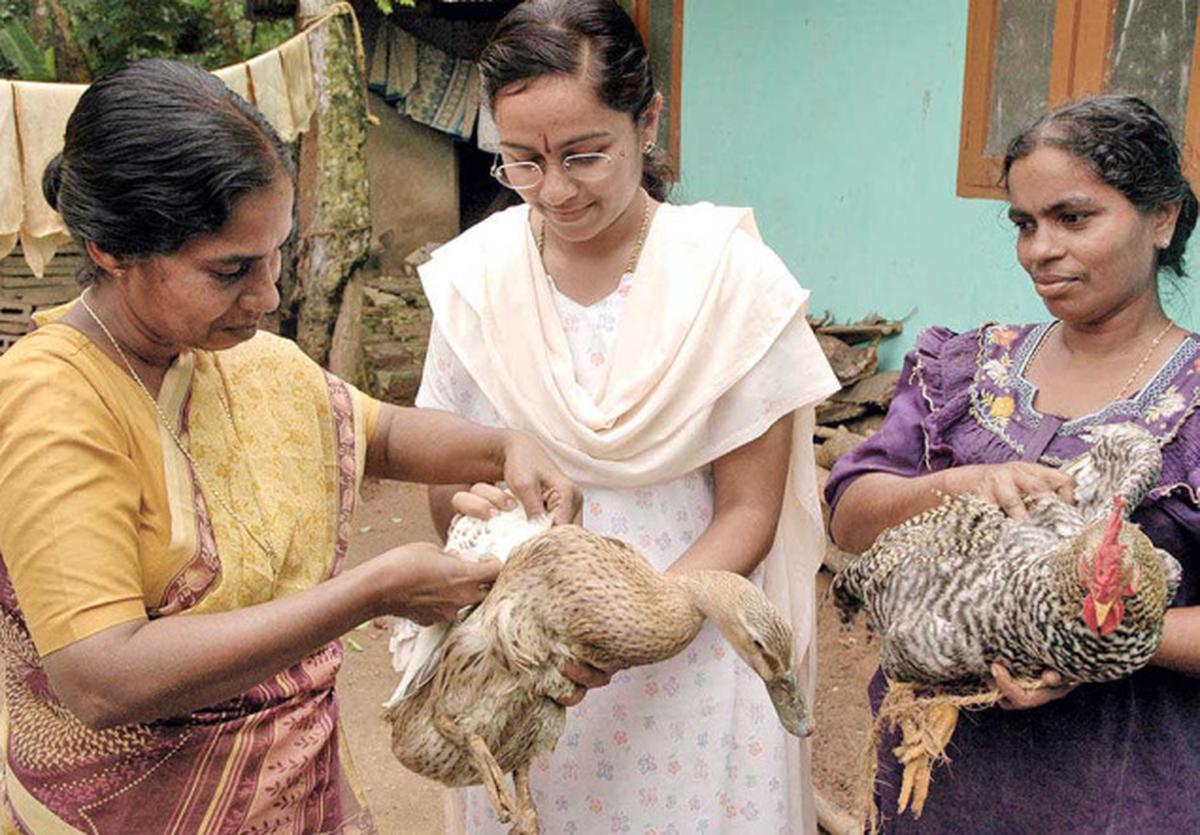

- 09 Feb 2025
In News:
Recent outbreaks of suspected Ranikhet disease (Newcastle Disease) have caused the death of approximately 1.5 lakh chickens in poultry farms across Andhra Pradesh (Eluru, Guntur, Prakasam, and the Godavari districts) and Haryana (Barwala and Raipur Rani in Panchkula). These outbreaks have raised alarms about biosecurity measures, especially in regions that are major poultry producers.
About Ranikhet Disease:
- Also known as: Newcastle Disease (ND)
- Causative Agent: Avian avulavirus 1 (also called Avian Paramyxovirus-1 or APMV-1)
- Affected Species: Primarily chickens, but also turkeys, ducks, pigeons, crows, geese, guinea fowls, partridges, doves, and even hedgehogs (suspected reservoirs).
- Nature of Disease: Highly contagious and fatal viral disease.
- Transmission:
- Direct contact with infected bird secretions (especially feces)
- Contaminated feed, water, equipment, clothing, and environment
- ND virus can survive for weeks in cool environments, increasing risk in winter.
Symptoms and Impact:
- In Birds:
- Respiratory issues: Sneezing, gasping
- Nervous symptoms: Droopiness, loss of coordination
- Digestive symptoms: Diarrhea
- Mortality rate: Ranges from 50% to 100%
- Production impact: Drop in egg production and fertility
- In Humans:
- Mild zoonotic effect, primarily conjunctivitis in people handling infected birds or lab samples.
- Usually self-limiting and non-fatal.
Recent Outbreaks and Investigations:
Andhra Pradesh:
- Approximately 1.5 lakh birds have died across multiple districts.
- Suspected cause: Highly virulent strain of Ranikhet Disease.
Haryana (Barwala–Raipur Rani belt):
- This belt houses around 115 poultry farms and is the second-largest poultry producer in Asia.
- Previously affected by bird flu outbreaks in 2006 and 2014.
- Northern Regional Disease Diagnostic Laboratory (NRDDL), Jalandhar collected 40 new samples from affected farms after being unsatisfied with earlier ones.
- Preliminary suspicion points toward Ranikhet Disease; however, cold wave conditions and the presence of older birds (not replaced due to COVID-19 restrictions) may have also contributed.
- The region falls in the path of migratory birds, whose droppings can spread avian flu viruses, complicating disease identification.
Current Challenges:
- Lack of effective treatment: No curative treatment exists. Management relies on preventive vaccination, biosecurity measures, and good poultry housing practices.
- Diagnostic delays: Require reliable sampling and laboratory testing to confirm the cause.
- Climate sensitivity: Poultry are vulnerable to extreme cold, especially if housing and care are inadequate.
- Pandemic aftershocks: COVID-19 disruptions prevented the routine replacement of older birds, increasing vulnerability.
PRASHAD Scheme

- 09 Feb 2025
In News:
The Parliamentary Standing Committee on Transport, Tourism and Culture has raised concerns over delays in the completion of projects under the Spiritual Tourism Circuits and the PRASHAD Scheme.
It has recommended the establishment of a Standard Operating Procedure (SOP) and emphasized obtaining prior clearances to ensure timely execution of future projects.
About PRASHAD Scheme
- Full Form: Pilgrimage Rejuvenation and Spirituality Augmentation Drive.
- Launched: 2014–15 by the Ministry of Tourism, Government of India.
- Objective: To promote, develop, and enhance spiritual tourism infrastructure at important pilgrimage sites across India.
Aims and Objectives:
- Improve infrastructure (roads, water supply, sanitation, waste management).
- Enhance connectivity (road, rail, and air) to pilgrimage destinations.
- Preserve and conserve religious and cultural heritage sites.
- Promote eco-friendly and sustainable tourism practices.
- Increase domestic and international tourist footfall through spiritual tourism.
- Generate local employment through skill development and livelihood programmes.
Funding Model:
- 100% centrally funded for eligible components.
- Also includes voluntary contributions through Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) and Public-Private Partnership (PPP) initiatives.
Implementation Challenges and Parliamentary Findings
Spiritual Tourism Circuits under Swadesh Darshan Scheme:
- Launched to promote thematic tourism circuits, including 23 Spiritual Circuits across India.
- Of these, five circuits remain incomplete, with two key circuits in Kerala—
- Sabarimala–Erumeli–Pampa–Sannidhanam Circuit
- Sivagiri Sree Narayana Guru Ashram Circuit
- Progress Status (as of September 2023):
- Sabarimala Circuit: 76% complete
- Sivagiri Circuit: 51% complete
- Original target completion dates: June 2023 and October 2023, respectively.
Reasons for Delay:
- Lack of timely clearances from Temple Authorities.
- Administrative and coordination issues across agencies.
Committee Recommendations:
- Formulate a clear-cut SOP for the execution of spiritual tourism projects.
- Ensure pre-approval and coordination with all concerned stakeholders before initiating construction.
- Strengthen planning at the Detailed Project Report (DPR) stage to anticipate implementation challenges and avoid delays and cost overruns.
PRASHAD Scheme Performance:
- Out of 45 sanctioned projects, only 21 have been completed as of the latest report.
- The committee noted this performance as unsatisfactory, even accounting for disruptions due to the COVID-19 pandemic.
Stryker Infantry Combat Vehicle

- 09 Feb 2025
In News:
India-U.S. defence cooperation is advancing with the proposed co-production of the Stryker Infantry Combat Vehicle (ICV). This deal represents a significant leap in bilateral defence industrial collaboration and aligns with India's strategic goal of military modernization and indigenisation under the ‘Make in India’ initiative.
About Stryker Infantry Combat Vehicle (ICV):
- Origin: Jointly developed by General Dynamics Land Systems (GDLS) Canada and U.S., it is the first new military vehicle inducted into U.S. Army service since the 1980s.
- Type: Eight-wheeled armoured infantry combat vehicle designed for rapid deployment and battlefield mobility.
- Variants: Includes Infantry Carrier Vehicle (ICV), Mobile Gun System (MGS), reconnaissance vehicle, medical evacuation vehicle, fire support vehicle, and Anti-Tank Guided Missile (ATGM) carrier.
Key Features:
- Mobility: Top speed of ~100 km/h and an operational range of 483 km. Can be airlifted using C-17 and C-130 aircraft (both in IAF’s fleet) or Chinook helicopters, enhancing deployment in remote terrains.
- Firepower: Equipped with a 30 mm cannon and a 105 mm mobile gun.
- Protection: V-hull structure for blast protection; composite armour reinforced with ceramic tiles offers increased survivability against IEDs and small arms.
- Capacity: Operated by a 2-member crew and can transport a 9-member infantry squad.
Operational Evaluation in India:
- High-Altitude Trials: Conducted in Ladakh (13,000–18,000 feet) during September–October 2024. Evaluation reports were shared with Army Headquarters for further review.
- Javelin ATGM Demonstration: Conducted alongside Stryker trials; however, the performance was sub-optimal due to the vintage system used. Repeat trials have been requested by India.
Strategic Importance for India:
- Tactical Advantage: Enhanced mobility and survivability in high-altitude warfare make it suitable for regions like Ladakh and Arunachal Pradesh.
- Border Security: Bolsters India's defence posture along sensitive frontiers with China and Pakistan.
- Force Modernization: Meets the Indian Army’s requirement for ICVs with integrated ATGM capabilities.
- Aatmanirbhar Bharat Push: The proposed model includes initial direct imports followed by large-scale license production in India, potentially by Bharat Earth Movers Limited (BEML).
Defence Diplomacy and Industrial Cooperation:
- The deal is being advanced under the India-U.S. Defence Industrial Cooperation Roadmap, focusing on co-development and co-production.
- In November 2023, Indian Defence Secretary confirmed discussions under this framework.
- The U.S. has reiterated the importance of India enhancing procurement of U.S.-made defence equipment, aiming at a balanced trade partnership.
- The Stryker deal is expected to feature in high-level bilateral dialogues, including the visit of Prime Minister Narendra Modi to Washington DC and during engagements at Aero India.
Challenges and Reservations:
- Some Indian defence officials have flagged concerns, noting that similar ICVs have been developed by Indian private companies.
- Delays in previous U.S. defence exports (e.g., F-404 jet engines for LCA-Mk1A) have also raised caution regarding timelines and reliability.
Fort William Renamed Vijay Durg

- 08 Feb 2025
In News:
In a significant step towards decolonising the Indian Armed Forces and aligning with indigenous historical consciousness, Fort William, the headquarters of the Eastern Command of the Indian Army in Kolkata, has been renamed Vijay Durg. This renaming is part of a broader initiative to remove colonial-era symbols and practices and restore Indian military heritage.
Historical Background of Fort William
- Construction: The original Fort William was constructed in 1696 by the English East India Company. It was later attacked and captured by Siraj-ud-Daulah, the Nawab of Bengal, in 1756.
- The Black Hole Incident: The original fort had an inner bastion used for imprisoning captives, leading to the infamous “Black Hole of Calcutta” narrative.
- Reconstruction: After the Battle of Plassey (1757) and the defeat of Siraj-ud-Daulah, Robert Clive initiated the construction of a new fort, which was completed in 1773 or 1781 (sources differ).
- Naming: It was named Fort William in honour of King William III of England.
Architectural Features
- Design: The fort is octagonal in shape with a massive structure made of brick and mortar.
- Area: Spread across 70.9 acres on the eastern bank of the Hooghly River, it features hundreds of arched windows and lush green surroundings.
- Aesthetics: Its walls are adorned with intricate stonework, reflecting colonial military architecture.
Recent Changes and Renaming
- New Name: Vijay Durg – Inspired by Vijaydurg Fort in Maharashtra, a prominent naval base of the Marathas under Chhatrapati Shivaji Maharaj.
- Other Changes:
- Kitchener House has been renamed Manekshaw House, after Field Marshal Sam Manekshaw.
- St. George’s Gate has been renamed Shivaji Gate.
- Implementation: According to the Defence Public Relations Office in Kolkata, the name change was decided in mid-December 2024, and internal communications have already adopted the new nomenclature, though an official notification is awaited.
Broader De-Colonisation Drive in Indian Defence
The renaming of Fort William is part of a larger movement initiated by the Government of India to eliminate colonial vestiges in the armed forces. Prime Minister Narendra Modi, in a 2022 speech at Kevadia, Gujarat, urged the forces to discard “legacy systems” and move towards “freedom from the mentality of slavery (gulami ki mansikta se mukti)”.
Key Initiatives:
- Indianisation of military music during the Beating Retreat ceremony.
- Adoption of a new naval ensign (2022) inspired by the seal of Chhatrapati Shivaji Maharaj, moving away from British colonial symbols.
- Renaming of military establishments and symbols rooted in colonial heritage.
- Review publication (2024) titled “Colonial Practices and the Armed Forces – A Review”, released at the Joint Commanders’ Conference in Lucknow by Defence Minister Rajnath Singh.
Mount Taranaki

- 08 Feb 2025
In News:
In a significant legal and environmental development, Mount Taranaki—officially now known by its M?ori name Taranaki Maunga—has been granted legal personhood by the government of New Zealand.
This move marks it as the third natural feature in the country to receive such status, following the Te Urewera National Park (2014) and the Whanganui River (2017).
This recognition reflects an increasing global trend toward acknowledging the intrinsic rights of natural entities and respecting the spiritual beliefs of indigenous communities.
About Taranaki Maunga
- Location: Situated in Egmont National Park, North Island, New Zealand.
- Dual Naming: Historically known as Mount Egmont, it is now officially referred to by its indigenous name, Taranaki Maunga, as part of decolonization and cultural revival efforts.
- Elevation: Stands at 8,261 feet, making it the second-highest peak in the North Island of New Zealand.
- Geological Type: It is a stratovolcano (composite cone) with a nearly perfect symmetrical shape—one of the most symmetrical volcanic cones in the world.
- Formation: Formed due to the subduction of the Pacific Plate beneath the Australian Plate. The magma source lies deeper than that of the Taupo Volcanic Zone volcanoes.
- Topography: Surrounded by a circular ring plain formed from lahars (volcanic mudflows) and landslides.
- Status: A snow-capped dormant volcano and culturally revered natural landmark.
- Cultural Significance: The M?ori, indigenous people of New Zealand, regard Taranaki Maunga as a sacred ancestor, embedding it deeply in their oral traditions and spirituality.
Legal Personhood and Its Significance
Granting legal personhood to Taranaki Maunga means it now holds rights, duties, and liabilities akin to a legal human being, and its interests will be represented by appointed guardians—often including indigenous representatives.
This legal framework recognizes:
- The spiritual and cultural relationship that the M?ori have with the mountain.
- The need to protect natural ecosystems not merely for utility but as living entities deserving of rights and dignity.
Comparative Insights: India’s Legal Approach to Natural Entities
India has witnessed similar developments:
- Uttarakhand High Court (2017–18): Granted legal personhood to the Ganga and Yamuna rivers, along with the Gangotri and Yamunotri glaciers. However, the Supreme Court later stayed this ruling.
- Punjab and Haryana High Court (2020): Recognized Sukhna Lake (Chandigarh) as a living entity for environmental protection.
- These decisions stem from the Doctrine of Parens Patriae, which allows the state to act as a guardian for those who cannot protect themselves—extending this protection to natural entities such as rivers, forests, and wildlife.
Iskander-M

- 08 Feb 2025
In News:
In a significant defense development with wide-ranging geopolitical implications, the Russian Federation is preparing to mass-produce the Iskander-M tactical ballistic missile, a new-generation weapon system with enhanced range and destructive capabilities. This move is part of Russia’s broader strategy to upgrade its missile arsenal amid ongoing tensions with NATO, especially in the context of the Ukraine conflict.
Key Features and Strategic Purpose
The 9K720 Iskander-M, developed by the Machine-Building Design Bureau (Kolomna), is a medium-range tactical ballistic missile with an effective range of up to 1,000 kilometers. It is capable of delivering both conventional and nuclear warheads, making it a versatile and high-impact weapon in regional conflict scenarios.
- The missile is precision-targeted and designed to neutralize high-value enemy assets, including NATO’s military infrastructure in Eastern Europe, especially in Ukraine.
- The production of the upgraded missile, unofficially referred to as the Iskander-1000, is expected to begin in full swing by 2025.
- The missile is reported to be highly destructive, with the ability to conduct deep strikes with minimal detection, offering Russia a tactical advantage in asymmetric warfare.
Deployment of Oreshnik Missile Systems in Belarus
In a parallel development, Russia has confirmed the deployment of Oreshnik medium-range ballistic missile systems in Belarus, a strategic ally. This decision follows agreements between the Russian and Belarusian leadership, reinforcing the military integration under their collective defense pact.
- The Oreshnik system, though less publicly detailed than the Iskander, is designed for tactical use and contributes to enhancing Russia’s regional defense shield.
- According to Russian foreign ministry officials, Belarus already hosts a joint Regional Forces Group, non-strategic nuclear weapons, and modern Russian defense systems.
- The positioning of these systems near NATO’s eastern borders heightens tensions with Western powers, particularly the United States, Poland, the Baltic States, and the European Union.
Geopolitical Ramifications
The Iskander-M and Oreshnik missile programs are part of Russia’s strategic doctrine to deter NATO's influence and reassert its military dominance in Eastern Europe. These deployments are:
- Likely to escalate NATO-Russia tensions, increasing the risk of a regional arms race.
- Expected to complicate European security dynamics, especially in Poland, Ukraine, and the Baltic states, which are seen as potential frontlines.
- Raising the prospect of further military escalation in the ongoing Russia-Ukraine conflict.
- Prompting NATO countermeasures, including deployment of missile defense systems and increased troop presence near Eastern borders.
Brucellosis Outbreak in Kerala
- 08 Feb 2025
In News:
An eight-year-old girl, Shasa Fathima, from Kottakkal in Malappuram district, Kerala, recently died after undergoing nearly two months of treatment for brucellosis at the Government Medical College Hospital, Kozhikode. This tragic incident has renewed public health concerns regarding zoonotic infections in India.
What is Brucellosis?
According to the World Health Organization (WHO), brucellosis is a bacterial disease caused by various species of the genus Brucella. The bacteria primarily infect: cattle, swine, goats, sheep & dogs.
Humans typically contract the infection through:
- Direct contact with infected animals or their secretions (blood, placenta, fetus, uterine fluids)
- Ingestion of contaminated animal products, especially unpasteurised milk and cheese
- Inhalation of airborne bacteria (e.g., in lab or farm environments)
Human-to-human transmission is extremely rare, as per WHO guidelines.
Symptoms and Incubation Period
- The disease presents a wide spectrum of symptoms: fever, weakness, weight loss, general discomfort or malaise.
- In many cases, symptoms may be mild or go undiagnosed. The incubation period ranges from one week to two months, most commonly between two to four weeks.
At-Risk Populations
- Brucellosis can affect individuals of all age groups. However, certain occupational groups are at higher risk, including: farmers and dairy workers, butchers, hunters, veterinarians, laboratory personnel. These individuals are often exposed to animal blood and reproductive fluids, which are primary modes of transmission.
Status in Kerala
Kerala has reported sporadic cases of brucellosis in recent years. In 2023, cases emerged from Kollam (July) and Thiruvananthapuram (October). While the disease is not new to the state, fatalities remain rare.
In response, the Department of Animal Husbandry has initiated awareness campaigns for dairy farmers and conducted milk sample testing across cooperative societies to monitor possible sources of infection.
Treatment and Prevention
Treatment typically involves a combination of antibiotics:
- Doxycycline (100 mg, twice daily for 45 days)
- Streptomycin (1 g daily for 15 days)
Effective preventive measures include:
- Vaccination of livestock (cattle, goats, sheep)
- Pasteurisation of milk and dairy products before human consumption
- Public awareness campaigns on the dangers of consuming unpasteurised animal products
- Regulatory policies on the sale of raw milk
Shatavari

- 07 Feb 2025
In News:
The Ministry of Ayush has launched a nationwide campaign titled “Shatavari – For Better Health” to raise public awareness on the health benefits of Asparagus racemosus (commonly known as Shatavari), especially in the context of women’s health and the broader objective of holistic well-being.
About Shatavari (Asparagus racemosus)
- Family: Asparagaceae (formerly Liliaceae)
- Common Names: Satawar, Satamuli
- Ayurvedic Significance: Known as the “Queen of Herbs”, Shatavari is praised in classical Ayurvedic texts like Charak Samhita and Ashtang Hridayam for treating women’s reproductive health disorders.
- Name Meaning: ‘Shatavari’ translates to “acceptable to many”, signifying its diverse benefits.
- Botanical Description: It is a woody climber (1–2 meters tall), with pine-needle-like leaves and small white flowers.
- Habitat and Distribution: Found in tropical climates at low altitudes across Asia, Africa, and Australia.
Medicinal Uses
- The dried roots of Shatavari are used medicinally.
- Acts as a tonic, diuretic, galactagogue (promotes lactation), and has ulcer-healing properties.
- Strengthens mucosal resistance and provides cytoprotection.
- Widely used for addressing female reproductive health issues, immunity enhancement, and promoting overall vitality.
The Campaign: “Shatavari – For Better Health”
- Launched by: Shri Prataprao Jadhav, MoS (Independent Charge), Ministry of Ayush.
- Organized by: National Medicinal Plants Board (NMPB).
- This campaign follows successful species-specific initiatives on Amla, Moringa, Giloe, and Ashwagandha.
- Shatavari is being positioned as a crucial resource in advancing women’s health, supporting the Panch Pran Goals set by the Prime Minister for a Developed India by 2047.
- Focus on achieving holistic well-being and integrating traditional medicine with public health awareness.
Policy and Financial Support
- Under the Central Sector Scheme for Conservation, Development, and Sustainable Management of Medicinal Plants, the Ministry promotes the cultivation and sustainable use of Shatavari.
- Financial assistance of ?18.9 lakhs will be provided to eligible organizations to support awareness and adoption.
National Youth Parliament Scheme (NYPS) 2.0

- 07 Feb 2025
In News:
The Ministry of Parliamentary Affairs has recently provided updates in the Rajya Sabha on the National Youth Parliament Scheme (NYPS) 2.0, emphasizing its role in fostering democratic values, constitutional awareness, and active citizenship among Indian youth.
About NYPS 2.0
Launched by the Ministry of Parliamentary Affairs, NYPS 2.0 aims to strengthen the roots of democracy and enhance understanding of parliamentary practices and government functioning among citizens, especially students.
Objectives
- Instill discipline, tolerance for diverse views, and democratic ethos among youth.
- Educate students about the procedures of Parliament, constitutional values, and functioning of the government.
- Encourage a democratic way of life through civic engagement.
Participation Modes via NYPS 2.0 Web Portal
The dedicated web-portal enables inclusive citizen participation in three formats:
- Institutional Participation:
- Open to all educational institutions.
- Institutions can organize Youth Parliament sittings as per portal guidelines.
- Two sub-categories:
- Kishore Sabha: For students of Class VI to XII.
- Tarun Sabha: For undergraduate and postgraduate students.
- Group Participation: Open to any group of citizens willing to conduct Youth Parliament sittings under defined norms.
- Individual Participation: Citizens can individually engage by taking a quiz on the theme ‘Bhartiya Democracy in Action’.
Training and Educational Resources
To support participants, the portal offers comprehensive e-training material, including:
- Literature on Youth Parliament
- Model Debates, Questions, and List of Business
- Model Scripts
- Video tutorials and other interactive resources
National Policy for Rare Diseases (NPRD) 2021

- 07 Feb 2025
In News:
Patient advocacy groups across India have raised serious concerns over delays in implementing the National Policy for Rare Diseases (NPRD) 2021, which has left many rare disease patients — especially children — in life-threatening situations. They have urged the government for immediate intervention to resume life-saving treatments and release stalled funds under the policy.
Rare Diseases:
- Rare diseases are severe, often genetic, life-threatening disorders that impact a small percentage of the population.
- They disproportionately affect children, with 30% of diagnosed patients not surviving beyond age five without timely treatment.
- Examples include Lysosomal Storage Disorders (LSDs) such as Gaucher, Pompe, Fabry, and MPS I & II.
About NPRD 2021
The Ministry of Health & Family Welfare launched the National Policy for Rare Diseases in March 2021 to streamline the diagnosis, research, and treatment of rare diseases in India.
Key Features of NPRD 2021:
- 63 rare diseases currently included under the policy (as recommended by the Central Technical Committee for Rare Diseases (CTCRD)).
- Categorization of diseases into three groups:
- Group 1: Diseases amenable to one-time curative treatment.
- Group 2: Diseases requiring long-term/lifelong treatment with relatively lower cost.
- Group 3: Diseases requiring very high-cost lifelong therapy where patient selection is critical.
Institutional Support:
- 12 Centres of Excellence (CoEs) identified at premier government hospitals to provide diagnosis and treatment.
- Nidan Kendras established to provide genetic testing and counselling services.
- National Consortium for Research and Development on Therapeutics for Rare Diseases (NCRDTRD) set up to coordinate R&D and promote indigenous drug manufacturing.
- Tax exemptions (on GST and Customs Duty) granted for imported drugs for individual and institutional use.
Financial Provisions:
- Financial assistance of up to ?50 lakh per patient for treatment at CoEs.
- Patients must register at CoEs to receive diagnosis and initiate treatment.
Challenges and Crisis
Despite policy provisions, implementation has been stalled, leading to a healthcare emergency for rare disease patients.
Key Issues Raised:
- Insufficient funding: The ?50 lakh cap is inadequate for chronic and ultra-rare diseases that need lifelong therapy.
- Administrative delays: Fund disbursement to CoEs has been slow, disrupting continuity of treatment.
- Impact on Patients:
- Patients like Alishba Khan, Ashok Kumar, Imran Ghoshi, and Adrija Mudy with Gaucher or MPS I have exhausted their funding.
- Patients who had previously stabilized are now regressing due to interrupted therapy at leading hospitals like AIIMS Delhi, IGICH Bangalore, and IPGMER Kolkata.
Legal Developments:
- On October 4, 2024, the Delhi High Court directed the Ministry of Health and Family Welfare to:
- Release additional funds beyond the ?50 lakh limit.
- Create a ?974 crore National Fund for FY 2024–25 and 2025–26.
- Months later, no concrete action has been taken, further eroding trust in the policy's effectiveness.
Demands by Advocacy Groups
- Sustainable, long-term funding model for lifelong treatment of rare and ultra-rare diseases.
- Immediate fund release to CoEs and simplification of administrative processes.
- Ensure uninterrupted access to essential therapies and expand the scope of financial support.
Dhimsa Dance

- 06 Feb 2025
In News:
In a significant development, tribal families from Neelabandha, a remote hilltop hamlet in Anakapalli district, Andhra Pradesh, received electricity for the first time since Independence. In celebration, they performed the Dhimsa dance, a vibrant expression of tribal culture.
About Dhimsa Dance:
- Origin & Region:
- Dhimsa is a traditional tribal dance predominantly performed in Andhra Pradesh, especially in the tribal belts of the Eastern Ghats.
- Its origin can be traced to the Koraput region (present-day Odisha and bordering Andhra Pradesh), primarily home to the Gond tribe.
- Communities Performing Dhimsa:
- Tribes such as Bagata, Valmiki, Poraja, Khond, Gadaba, Kondadora, Mukadora, and Kotia actively perform this dance.
- Occasions:
- Commonly performed during festivals, weddings, and the hunting festival in April.
- Celebratory, spiritual, and social in nature, symbolizing unity and joy.
- Dance Formation and Movements:
- Performed in circular formations with dancers holding each other's arms.
- Emphasis on synchronized hand and leg movements.
- Troupes usually consist of 20 or more dancers.
- Themes:
- Dhimsa is a narrative dance that expresses tribal mythologies, folktales, cultural mores, economic activities, kinship, and marital life.
- Musical Instruments Used:
- Dappu, Tudumu, Mori, Kidgi, Gilka, and Jodukommulu.
- A combination of percussion and wind instruments drives the rhythm and variation in the dance.
- Varieties:
- There are 12 known types of Dhimsa dances, each varying in pace, rhythm, and purpose.
Rural Electrification of Neelabandha Village:
- Background:
- Neelabandha is located in Arla Panchayat of Rolugunta Mandal in Anakapalli district.
- Consists of four households (approximately 20 individuals) who had been living without electricity since Independence.
- Implementation:
- The electrification was part of the Andhra Pradesh government’s rural development drive to provide basic infrastructure to underdeveloped tribal villages.
- Under the directions of District Collector Vijaya Krishnan, and CMD of APEPDCL, Prithvi Tej, the Eastern Power Distribution Company of Andhra Pradesh (EPDCL) carried out the electrification.
- Challenges Overcome:
- The hamlet lacked motorable roads, making it difficult to transport materials.
- Electricity poles had to be carried manually for over 6 km to reach the village.
- Outcome:
- Free electricity was provided to the villagers, marking a major milestone in tribal welfare.
- In a heartfelt celebration, the villagers performed Dhimsa under electric lights for the first time.
Issues Still Persisting:
- Infrastructure Deficits:
- The village still lacks road connectivity, educational access, and healthcare facilities.
- These gaps hinder children's ability to attend school and access essential services.
- Community Response:
- Local leaders, including CPI(M) district committee member K. Govind, welcomed the electrification but urged the government to address remaining developmental needs.
Makhana Board

- 06 Feb 2025
In News:
In the Union Budget 2025–26, Finance Minister announced the establishment of a Makhana Board in Bihar with a dedicated budget of ?100 crore to boost the production, processing, and export of Makhana (Fox Nuts).
About Makhana (Fox Nuts):
- Botanical Name: Euryale ferox
- Family: Nymphaeaceae (Water lily family)
- Description:
- Makhana is the dried edible seed of the prickly water lily.
- Grown in freshwater bodies across South and East Asia.
- The plant is known for its violet and white flowers and large, round, prickly leaves.
- Due to its black outer covering, Makhana is nicknamed the "Black Diamond."
Nutritional and Medicinal Value:
- Low in fat, rich in carbohydrates, and a good source of protein and minerals.
- Widely used in:
- Traditional medicine
- Health and wellness products
- Culinary preparations such as popped Makhana (‘Lava’)
Major Producing Regions:
- India:
- Bihar produces 90% of India’s total Makhana, especially in the Mithilanchal region.
- Key districts: Darbhanga, Madhubani, Purnea, Katihar, Saharsa, Supaul, Araria, Kishanganj, Sitamarhi.
- The first four districts contribute 80% of Bihar’s Makhana output.
- Bihar produces 90% of India’s total Makhana, especially in the Mithilanchal region.
- Other Indian states: Assam, Manipur, West Bengal, Tripura, Odisha.
- Other countries: Nepal, Bangladesh, China, Japan, Korea.
- GI Tag: Mithila Makhana received the Geographical Indication (GI) tag in 2022.
Climatic Conditions for Cultivation:
- Type: Aquatic crop; grows in stagnant water bodies (ponds, lakes, wetlands).
- Ideal Conditions:
- Water Depth: 4–6 feet
- Temperature: 20°C – 35°C
- Relative Humidity: 50% – 90%
- Annual Rainfall: 100 – 250 cm
About the Makhana Board:
- Allocated Budget: ?100 crore
- Objectives:
- Train farmers in advanced cultivation techniques.
- Support processing and value addition in the Makhana supply chain.
- Facilitate financial aid and access to government schemes.
- Develop export infrastructure and promote branding and marketing.
Makhana under ODOP Scheme:
- Recognized as a One District One Product (ODOP) commodity for Bihar.
- Under ODOP, the Union Government provides subsidies to processors for:
- Infrastructure development
- Branding and marketing
About ODOP Scheme:
- Launched by: Ministry of Food Processing Industries (MoFPI)
- Objective: Promote district-level economic specialization and turn each district into an export hub.
- Origin: First launched in Uttar Pradesh (2018); adopted as a national initiative under the Atmanirbhar Bharat vision.
- Implementation:
- In coordination with the ‘Districts as Export Hubs’ (DEH) initiative.
- Managed by DGFT, Department of Commerce, and DPIIT.
- Significance:
- Encourages rural entrepreneurship, local employment, and global trade linkages.
- Strengthens district economies by scaling up traditional and unique products.
Gyan Bharatam Mission

- 06 Feb 2025
In News:
The Union Budget 2025–26 announced the launch of the Gyan Bharatam Mission, a significant cultural initiative aimed at the survey, documentation, digitization, and conservation of over one crore manuscripts across India.
Key Details:
- A special national mission focusing on India’s manuscript heritage preserved in:
- Academic institutions
- Libraries
- Museums
- Private collections
- Objective:
To document and conserve more than one crore manuscripts, centralize them into a national digital repository, and make them accessible to researchers, students, and institutions globally. - Significance:
- Facilitates knowledge-sharing through digitization.
- Promotes India's traditional knowledge systems.
- Enhances academic and historical research in the Indian knowledge domain.
What is a Manuscript?
- A manuscript is a handwritten composition on materials such as:
- Palm leaf, paper, cloth, bark, or metal.
- Must be at least 75 years old and possess scientific, historical, or aesthetic value.
- Printed texts and lithographs are not considered manuscripts.
- Manuscripts may exist in hundreds of languages and scripts, e.g.:
- Sanskrit manuscripts written in Devanagari, Grantha, Oriya, and other scripts.
- Unlike epigraphs or official records (firmans, revenue documents), manuscripts hold knowledge content, not just historical data.
National Manuscripts Mission (NMM)
- Launched in 2003 under the Ministry of Culture, operated through the Indira Gandhi National Centre for the Arts (IGNCA).
- Mandate: Identify, preserve, and make accessible India's manuscript wealth.
- Revival: The 2025–26 Budget seeks to rejuvenate NMM to implement the Gyan Bharatam Mission effectively.
Budgetary Provisions
- NMM allocation increased from ?3.5 crore to ?60 crore for FY 2025–26.
- Culture Ministry overall allocation:
- ?3,360.96 crore, up from a revised estimate of ?3,260.93 crore.
- Other Key Allocations:
- Archaeological Survey of India (ASI): ?1,278.49 crore
- National Libraries and Archives: ?156.55 crore
- Museums (National Museum, NGMA): ?126.63 crore
- Note: Allocations for centenary events, cultural collaborations have been reduced.
Extra-Long Staple (ELS) Cotton

- 06 Feb 2025
In News:
In the Union Budget 2025–26, the Union Finance Minister announced a five-year Cotton Mission to boost productivity, sustainability, and promotion of Extra-Long Staple (ELS) cotton in India, aiming to reduce import dependency and strengthen the high-end textile sector.
What is Extra-Long Staple (ELS) Cotton?
- Definition: ELS cotton refers to cotton varieties with fibre lengths of 30 mm or more, renowned for their superior softness, strength, durability, and premium quality.
- Botanical Origin: Derived primarily from the species Gossypium barbadense, commonly known as Egyptian or Pima cotton.
Distinguishing Cotton Types by Fibre Length
Type Fibre Length Species Quality Uses Yield per Acre
Short Staple < 25 mm Gossypium hirsutum Coarser Low-cost textiles High
Medium Staple 25–28.6 mm Gossypium hirsutum Moderate Everyday fabrics 10–12 quintals
Extra-Long 30 mm & above Gossypium barbadense Superior Luxury textiles 7–8 quintals
Staple (ELS)
Special Characteristics of ELS Cotton
- Softer & Smoother: Ideal for premium, luxury clothing.
- Stronger & More Durable: Resistant to wear and tear.
- Resistant to Pilling: Maintains smoothness over time.
- Luxurious Finish: Produces fine yarns with a natural sheen.
- Minimal Finishing Required: Retains natural texture and quality.
Global and Indian Production Landscape
- Origin: Native to South America.
- Globally Grown In:
- Egypt, China, Australia, Peru – leading producers.
- In India:
- Cultivated in Atpadi Taluka (Sangli, Maharashtra), around Coimbatore (Tamil Nadu), and in parts of Karnataka and Madhya Pradesh.
- Grown mostly in rain-fed areas with warm climates and fertile soil, aiding fibre quality.
Challenges in ELS Cotton Cultivation in India
- Low Yield: ELS cotton yields 7–8 quintals/acre, significantly lower than medium staple varieties (10–12 quintals/acre).
- Market Linkage Deficit: Farmers struggle to fetch premium prices for ELS cotton due to weak market access and lack of dedicated procurement infrastructure.
- Technological Gaps: Limited access to improved seed varieties, agronomic practices, and technologies like HtBT (Herbicide-tolerant Bt) cotton.
- Import Dependency: India imports 20–25 lakh bales annually, accounting for ~90% of its ELS cotton requirements, to meet demand from the premium textile industry.
Significance of the Five-Year Cotton Mission
- Aimed at:
- Enhancing productivity and sustainability of ELS cotton.
- Reducing import dependence through indigenous development.
- Strengthening high-value textile exports by ensuring reliable ELS supply.
- Supports:
- Farmer income enhancement through value-added cultivation.
- Research and development in ELS cotton seed technology.
- Improved extension services, supply chain development, and market support mechanisms.
Kolleru Lake
- 06 Feb 2025
In News:
The Southern Zonal Bench of the National Green Tribunal (NGT) has recently restrained the Andhra Pradesh government from proceeding with six proposed infrastructure projects in the Kolleru wetland area, citing violations of environmental protocols and lack of statutory clearances.
About Kolleru Lake
- Location: Northeastern Andhra Pradesh, between the Krishna and Godavari river deltas, near Eluru city.
- Type: One of Asia’s largest shallow freshwater lakes, covering an area of 308 sq. km.
- Hydrology:
- Fed by Budameru and Tammileru rivers.
- Drains into the Bay of Bengal via Upputeru river (a tidal water channel).
- Acts as a natural flood-balancing reservoir for the Krishna and Godavari river systems.
- Ecological Importance:
- Declared a Wildlife Sanctuary in 1999 and a Ramsar Site in 2002.
- Designated as an Important Bird Area (IBA) due to the presence of over 50,000 waterfowl annually.
- Lies on the Central Asian Flyway (CAF), a major migratory bird route.
- Key Avian Species:
- Grey Pelican (indicator species), Siberian Cranes, Glossy Ibis, Open-billed Stork, Purple Moorhen, Painted Storks.
Kolleru Bird Sanctuary
- A protected wetland marsh habitat within the Kolleru Lake region.
- Supports diverse aquatic flora and fauna, serving as a crucial ecosystem for migratory and resident bird species.
Infrastructure Projects and Legal Challenges
- The projects were proposed under the entity "A.P. Krishna – Kolleru Salinity Mitigation Projects Corporation Limited" with a total capital outlay of approximately ?2,952 crore.
- The plans included construction of three regulators-cum-roads across the Upputeru river and other barrages, regulators, and sluices, falling within the Coastal Regulation Zone (CRZ).
- The Andhra Pradesh Water Resources Department (WRD) issued G.O. Ms. No. 63 (dated 2nd December 2020) authorizing the project.
Grounds for NGT Intervention
- Key objections included:
- Absence of scientific or ecological studies.
- Lack of consultations with wetland experts, wildlife conservationists, and hydrologists.
- No clearances obtained from:
- Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change (MoEF&CC)
- A.P. Coastal Zone Management Authority (CZMA)
- A.P. Pollution Control Board (PCB)
- National Board for Wildlife (NBWL)
NGT Observations and Ruling
- The tribunal emphasized the need for comprehensive evaluation of ecological and hydrological impacts before proceeding.
- It cited potential threats to the lake’s ecosystem, including:
- Disruption to natural hydrology.
- Loss of biodiversity and eco-sensitive habitats.
- The NGT ruled that the projects should not proceed unless fully compliant with environmental laws and backed by appropriate expert assessments.
- The ruling reinforced India's obligations under the Ramsar Convention and domestic environmental legislation, stressing the urgent need to protect the integrity of the Kolleru ecosystem.
Henipavirus

- 05 Feb 2025
In News:
A henipavirus, specifically the Camp Hill virus, has been detected in North America for the first time. This discovery in northern short-tailed shrews—a small mammal species found commonly in Canada and the U.S.—raises concerns over a potential zoonotic disease outbreak.
About Henipavirus
- Virus Type: Henipaviruses are zoonotic, negative-sense RNA viruses.
- Family: Paramyxoviridae.
- Natural Hosts: Pteropid fruit bats (commonly known as flying foxes).
- Other Hosts: Capable of infecting various mammals, including humans, horses, pigs, and shrews.
Notable Henipaviruses:
- Hendra virus (HeV):
- First identified in Australia.
- Mortality rate: Up to 70%.
- Nipah virus (NiV):
- Found in Southeast Asia, including Malaysia and Bangladesh.
- Case fatality rate ranges from 40% to 75%, depending on surveillance and clinical care.
Symptoms and Disease Progression
- Initial symptoms: Fever, dizziness, headache, and muscle pain (myalgias).
- Advanced symptoms: Respiratory issues, encephalitis (brain inflammation), confusion, abnormal reflexes, seizures, and coma.
- Relapsing encephalitis may occur months or years after apparent recovery.
- Fatality Risk: High, primarily due to encephalitis and multi-organ failure caused by damage to small blood vessels (microinfarction) in organs like the brain, liver, and kidney.
Why are Henipaviruses so dangerous?
- Henipaviruses produce proteins that:
- Suppress the innate immune system.
- Block interferon-stimulated antiviral responses, aiding viral replication.
- Act as virulence factors, allowing widespread infection and severe outcomes.
Modes of Transmission
- Animal-to-human:
- Direct contact with infected animals (e.g., fruit bats, pigs, horses, shrews).
- Consumption of contaminated food or water (e.g., raw date palm sap in Nipah outbreaks).
- Human-to-human: Via bodily fluids, close contact, or respiratory droplets during caregiving.
Treatment and Prevention
- Treatment:
- No specific vaccine or antiviral currently exists.
- Management is symptomatic and supportive (respiratory support, ICU care).
- Prevention:
- Vaccination of horses (in HeV-risk regions like Australia).
- Avoiding contact with fruit bats and sick animals.
- Isolating infected individuals and animals to prevent spread.
India-Maldives Joint Military Exercise ‘Ekuverin’

- 05 Feb 2025
In News:
The 13th edition of Exercise Ekuverin, a bilateral joint military exercise between the Indian Army and the Maldives National Defence Force (MNDF), commenced in the Maldives on February 4, 2025. The exercise continues to reinforce defence and strategic ties between the two nations.
About Exercise Ekuverin
- Name Meaning: “Ekuverin” means ‘Friends’ in Dhivehi, the official language of the Maldives—symbolizing the deep and friendly defence partnership between India and the Maldives.
- First Conducted: The exercise was initiated in 2009 as part of annual bilateral defence cooperation.
- Venue Alternation: It is held alternatively in India and the Maldives every year.
- 2023 Edition: Conducted at Chaubatia, Uttarakhand from June 11 to 24.
- 2025 Edition: Being hosted in the Maldives.
Key Objectives and Features
- Military Interoperability: Enhances coordination and operational synergy between Indian and Maldivian armed forces.
- Counter-Insurgency and Counter-Terrorism (CI/CT): Focuses on joint tactical drills to counter modern asymmetric threats.
- Humanitarian Assistance and Disaster Relief (HADR): Equips forces to respond effectively to natural disasters and humanitarian crises.
- Strengthening IOR Security: Reinforces regional maritime and strategic stability in the Indian Ocean Region (IOR), a key area of India’s strategic interest.
Significance for India-Maldives Relations
- Strategic Partnership: Builds mutual trust and defence preparedness, aligning with India’s “Neighbourhood First” policy.
- Capacity Building: Helps enhance the capability of the MNDF through joint training with a larger and more experienced Indian Army.
- Regional Security Cooperation: Plays a crucial role in maintaining peace, security, and freedom of navigation in the IOR.
India’s Defence Engagement with Southeast Asia
India actively conducts multiple bilateral and multilateral defence exercises with Southeast Asian countries to enhance defence diplomacy and promote a free, open, and secure Indo-Pacific.
Key Defence Exercises with Southeast Asian Nations:
- Garuda Shakti: Special Forces exercise with Indonesia (Nov 2022, Sangga Buana Training Area).
- Mitra Shakti: Annual exercise with Sri Lanka, last held in 2022.
- VINBAX: India-Vietnam bilateral exercise; 3rd edition held in 2022.
- IMBEX: India-Myanmar bilateral exercise (last noted in 2017–18).
- Maitree: Joint annual military exercise with Thailand, conducted since 2006.
- CORPAT: Coordinated Patrols with Indonesia, Thailand, and Malaysia for maritime domain awareness and security.
- AIME 2023: The first ASEAN-India Maritime Exercise, conducted in May 2023, involving navies from India and ASEAN nations (Brunei, Indonesia, Malaysia, Philippines, Singapore, Thailand, Vietnam).
Golden-headed Cisticola

- 05 Feb 2025
In News:
In a remarkable ornithological development, the Golden-headed Cisticola (Cisticola exilis) has been sighted in the Mathikettan Shola National Park, Idukki district, Kerala, marking its first recorded presence in the southern Western Ghats after a significant gap.
The finding underscores the ecological richness of the region and highlights the need for intensified avian research in the Western Ghats.
About Golden-headed Cisticola (Cisticola exilis)
- Also known as the bright-capped cisticola, it is a small warbler belonging to the family Cisticolidae.
- It is an omnivorous bird, feeding primarily on invertebrates such as insects and small slugs, along with grass seeds.
- The species is typically found in grassland habitats within mountain ranges, and has been previously recorded in parts of Karnataka, Tamil Nadu, and northern Kerala, notably in Banasura Hills, Wayanad. However, this is the first confirmed sighting in the southern part of the Palakkad Gap.
Physical features of breeding males include:
- Golden-orange plumage on the head, neck, and chest
- Pinkish beaks
- Black streaks on the back
- A distinctive call that aids identification
Habitat and Distribution
- It is widely distributed across Australia and several Asian countries.
- In India, its presence had been limited to select regions of the Western Ghats, making its recent sighting in Mathikettan Shola both rare and ecologically significant.
Conservation Status
- According to the IUCN Red List, the Golden-headed Cisticola is classified as Least Concern. Despite this, the new finding calls for further research into its habitat preferences and conservation needs within India.
About Mathikettan Shola National Park
Located in the southern part of the Palakkad Gap in the Western Ghats of Kerala, Mathikettan Shola is a vital biodiversity hotspot.
- It comprises evergreen forests, moist deciduous forests, shola grasslands, and semi-evergreen vegetation.
- The park hosts three major streams: Uchillkuthi Puzha, Mathikettan Puzha, and Njandar, which are tributaries of the Panniyar River.
- Its highest point is Kattumala, located at the eastern border adjoining Tamil Nadu.
- The Muthavan tribal community resides near the park’s northeastern boundary, reflecting the intricate human-nature interface in the region.
Scientific and Conservation Importance
The rediscovery has been documented in the journal Malabar Trogon by the Malabar Natural History Society, bringing attention to the importance of long-term monitoring and baseline studies in underexplored ecosystems.
It emphasizes:
- The ecological richness of the Western Ghats, a UNESCO World Heritage site.
- The importance of citizen science, as local birdwatchers played a key role in the finding.
- The need for enhanced habitat protection and ornithological research in grassland ecosystems of high-altitude regions.
RBI Digital Payments Index (DPI)

- 05 Feb 2025
In News:
The Reserve Bank of India’s (RBI) Digital Payments Index (DPI) rose to 465.33 as of September 2024, up from 445.5 in March 2024, indicating a sustained increase in the adoption and penetration of digital payments across India.
About the RBI-DPI
- Launched: January 2021
- Constructed by: Reserve Bank of India
- Purpose: To measure the extent and progress of digitisation of payments in India.
- Base Period: March 2018 (DPI Score = 100)
- Frequency of Publication: Semi-annually (March and September)
Significance of the Index
- Acts as a quantitative tool to monitor India’s progress in achieving a less-cash economy.
- Provides stakeholders, policymakers, and researchers a composite view of digital payment trends.
- Helps identify policy focus areas and gaps in digital infrastructure and adoption.
- Supports the goals of financial inclusion, innovation, and digital public infrastructure.
Recent Trends
- September 2024 DPI Score: 465.33
- March 2024 DPI Score: 445.5
- Implication: Demonstrates continued momentum in digital payment adoption, driven by improved payment infrastructure and payment performance nationwide.
Structure of the RBI-DPI
The index is composed of five broad parameters, each with defined weightages and sub-indicators:
Parameter Weightage Description
1. Payment Enablers 25% Internet/mobile penetration, bank account ownership, Aadhaar usage.
2. Payment Infrastructure – Demand Side 10% Number of debit/credit cards, user demand for digital options.
3. Payment Infrastructure – Supply Side 15% Availability of POS machines, ATMs, bank branches, QR codes.
4. Payment Performance 45% Actual volume and value of digital transactions, currency usage trends.
5. Consumer Centricity 5% Digital payment awareness, fraud prevention, grievance redressal.
Each parameter is further broken down into measurable sub-indicators, offering a comprehensive framework for assessment.
Why RBI-DPI Matters for India
- Digital Transformation: Encourages the shift from cash to digital payments, aligning with the goals of Digital India.
- Policy Impact Assessment: Evaluates the effectiveness of regulatory and policy interventions in the payment ecosystem.
- Infrastructure Development: Reflects the outreach of digital payment infrastructure, aiding targeted investments.
- Financial Inclusion: Helps assess how digital modes are reaching the underserved and unbanked populations.
- Data-Driven Governance: Facilitates evidence-based decision-making in financial sector reforms.
SwaRail SuperApp
- 05 Feb 2025
In News:
The Ministry of Railways has launched a unified mobile application, SwaRail, currently in beta testing as of January 31, 2025.
This initiative aims to streamline access to Indian Railways services and enhance user experience by consolidating various apps into a single digital platform.
Key Highlights
What is SwaRail?
- SwaRail is a SuperApp developed by the Centre for Railway Information Systems (CRIS).
- It serves as a comprehensive, one-stop solution for a wide range of Indian Railways services.
- The app is currently in beta testing and is available on the Google Play Store and Apple App Store.
Objective
- To integrate multiple railway-related services under a unified platform.
- To reduce app clutter and device storage consumption.
- To improve user experience through a seamless and intuitive interface.
Developed By: Centre for Railway Information Systems (CRIS)
- CRIS is an organization under the Ministry of Railways.
- It combines IT expertise with railway operational experience.
- CRIS is responsible for developing and maintaining software for core railway functions.
Services Offered via SwaRail
The SuperApp merges functionalities of multiple existing apps, offering:
- Ticketing Services
- Reserved ticket booking
- Unreserved and platform ticket booking
- Freight & Parcel Enquiries
- Parcel booking status
- Freight services information
- Passenger Enquiries
- Real-time train status
- PNR enquiry (along with associated train details)
- Train schedules
- Onboard Services
- Food ordering while traveling
- Complaint redressal via Rail Madad
Notable Features of the SuperApp
Feature Description
Single Sign-On Access all services using a single set of credentials
Unified App Combines multiple previously separate apps (e.g., IRCTC RailConnect, UTS)
Integrated Interface Displays consolidated data like PNR + train info on the same screen
Easy Onboarding Existing users can log in with RailConnect/UTS credentials
Multiple Login Modes Supports m-PIN, biometric authentication, and OTP-based guest login
Smart Wallet Integration Auto-linking of R-Wallets from UTS App for ticket booking transactions
User-Centric Approach
- The app is being actively tested, and users are encouraged to provide feedback during the beta phase.
- CRIS is monitoring performance and issues for improvement before the final public release.
- The government envisions technological integration to ensure efficient, smarter, and citizen-friendly rail services.
World Wetlands Day 2025

- 04 Feb 2025
In News:
World Wetlands Day is observed every year on 2nd February to commemorate the adoption of the Ramsar Convention on Wetlands in 1971 in Ramsar, Iran.
India has been a signatory to the Convention since 1982 and has actively worked towards the conservation and sustainable management of wetlands—critical ecosystems that serve as biodiversity hotspots, natural flood buffers, and carbon sinks.
Theme 2025: "Protecting Wetlands for Our Common Future"
The 2025 theme emphasizes collaborative efforts to protect wetlands to ensure ecological sustainability, biodiversity preservation, and long-term human well-being. It highlights the need for integrated management and foresight in conservation strategies.
Key Event: Parvati Arga Ramsar Site, Gonda, Uttar Pradesh
The Union Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change (MoEFCC) organized the national-level celebrations of World Wetlands Day 2025 at the Parvati Arga Ramsar Site in Gonda district, Uttar Pradesh.
Significance of the Site
- Comprises two rain-fed oxbow lakes—Parvati and Arga—located in the terai region of the Gangetic plains.
- Supports endangered and critically endangered species like the white-rumped vulture, Indian vulture, and Egyptian vulture.
- Attracts migratory birds such as Eurasian coots, greylag geese, northern pintails, and red-crested pochards.
- Threatened by invasive species, notably the common water hyacinth.
- The nearby Tikri Forest is being developed as an eco-tourism site, and a nature-culture tourism corridor is planned between Ayodhya and Devi Patan.
Cultural and Economic Value
- The area includes heritage sites such as the birthplaces of Maharishi Patanjali and Goswami Tulsidas, enhancing its potential as a religious and cultural tourism hub.
- A MoU between Amazon and ARGA (UP Government initiative) aims to empower women entrepreneurs through digital training and market access under Amazon’s Saheli programme.
India's Wetland Landscape and New Ramsar Sites (2025 Update)
India’s tally of Ramsar Sites has risen to 89, with four new additions:
- Udhwa Lake – Jharkhand (first Ramsar site for the state)
- Theerthangal – Tamil Nadu
- Sakkarakottai – Tamil Nadu
- Khecheopalri – Sikkim (first Ramsar site for the state)
- Tamil Nadu leads with 20 Ramsar Sites, followed by Uttar Pradesh with 10 sites.
- Total area under Ramsar protection in India is now approximately 1.358 million hectares.
Amrit Dharohar Initiative
Launched in June 2023, the Amrit Dharohar initiative promotes conservation and sustainable use of Ramsar Sites over three years. It aligns with Budget 2023–24 announcements and focuses on:
- Species and Habitat Conservation
- Nature Tourism
- Wetlands-based Livelihoods
- Wetlands and Carbon Mitigation
The initiative encourages convergence among central ministries, state authorities, and community stakeholders.
Workshops and Public Engagement
A regional workshop for Northern States was organized on 1st February 2025, with participants from nine states and UTs, highlighting collaborative models in wetland management. The main event also included:
- Exhibitions on eco-friendly products, wetland conservation, and green skills.
- Launch of publications like the Integrated Management Plan for Parvati Arga, Factbook of India’s 85 Ramsar Sites, and Development of Van Taungya Villages.
- Felicitation of painting, quiz, and Nukkad Natak competition winners, promoting grassroots awareness.
Significance of Wetlands in India
Wetlands are water-covered ecosystems, either permanently or seasonally flooded. They:
- Support rich biodiversity, including migratory birds and aquatic species.
- Recharge groundwater and regulate floods.
- Provide livelihoods through fisheries and tourism.
- Act as natural carbon sinks, aiding in climate change mitigation.
Major Threats
- Pollution from industrial and domestic effluents
- Encroachment and urbanization
- Invasive species
Kurdistan Region
- 01 Feb 2025
In News:
India recently dispatched a humanitarian shipment of medical supplies to the Kurdistan Region in Iraq, reflecting its commitment to global cooperation and humanitarian diplomacy.
About the Kurdistan Region
- Geographical Spread: The Kurdistan Region is a culturally and geographically distinct area predominantly inhabited by ethnic Kurds, spread across:
- Northern Iraq (Erbil, Sulaymaniyah, Dohuk, Halabja)
- Eastern Turkey
- Western Iran
- Northern Syria and parts of Armenia
- Capital: Erbil (Iraq)
- Terrain: Dominated by the Zagros and Taurus mountain systems
- Major Rivers: Tigris River and Greater Zab River, crucial for agriculture and settlement
Ethnic and Political Context
- Kurds: An ethnic group of 25–30 million people, mostly Sunni Muslims, with no official nation-state. They seek autonomy or independence through the Kurdish nationalist movement.
- Kurdistan Regional Government (KRG): An autonomous administration in northern Iraq, managing the Kurd-majority areas with limited sovereignty under Iraq’s federal system.
- Geopolitical Significance:
- Rich in oil and natural gas, especially in Iraqi Kurdistan
- Strategically located, controlling key border regions and trade routes
- Kurdish militia (Peshmerga) played a critical role in the fight against ISIS
Ongoing Political Disputes
- Kurdish Independence Movement:
- The 2017 independence referendum in Iraqi Kurdistan was rejected by Baghdad, followed by economic and military backlash.
- Kurds face resistance from Iraq, Turkey, Iran, and Syria, which fear territorial fragmentation.
- Turkey regularly conducts military operations against Kurdish groups, labeling them as threats to national security.
India-Kurdistan Relations
- Diplomatic Presence: India established a Consulate in Erbil in August 2016 to deepen ties with the Kurdistan Region and Iraq.
- Economic and Workforce Engagement:
- Indian companies have participated in trade fairs in Erbil and Sulaymaniyah.
- A growing number of Indian workers are employed in sectors like:
- Steel mills
- Oil companies
- Construction projects
- Indian workers are valued for their skills and reliability in these industries.
Financialisation
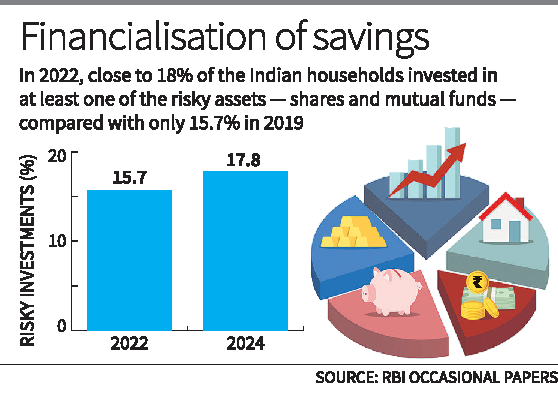
- 01 Feb 2025
In News:
The Economic Survey 2024–25 cautions against the risks of excessive financialisation in India, emphasizing that while finance is a crucial enabler of economic growth, unchecked expansion of the financial sector can pose systemic risks, increase inequality, and divert resources from the real economy.
What is Financialisation?
Financialisation refers to the growing dominance of financial markets, institutions, and motives in shaping economic policies, business decisions, and resource allocation. It involves:
- A shift from productive (real sector) activities like manufacturing to financial activities, including trading, speculation, and asset management.
- Increasing reliance on asset price growth (e.g., stocks, real estate) to stimulate the economy.
- Deep influence of financial motives in corporate governance, economic policies, and household behavior.
Key Drivers of Financialisation in India
- Increased household savings funneled into stock markets.
- Growing retail investor participation in equities and mutual funds.
- Policy and regulation increasingly influenced by financial market considerations.
- Rising public and private sector debt to leverage economic growth.
Risks Highlighted by the Economic Survey
- Real Sector Crowding Out: Over-expansion of the financial sector may compete with the real economy for scarce resources like skilled labour and capital, potentially depriving productive sectors.
- Unsustainable Booms: Rapid financial growth often favours high-collateral, low-productivity investments (e.g., construction) over innovation and manufacturing, creating unsustainable financial booms.
- Complex Financial Products: Proliferation of opaque and complex financial instruments can increase consumer risk exposure and the probability of a financial crisis, as seen during the 2008 global financial meltdown.
- Increased Inequality: Financialisation tends to transfer income from the real sector to the financial sector, worsening income inequality and contributing to wage stagnation.
- Debt Dependency: Over-reliance on financial leverage (debt) increases macro-financial vulnerabilities, especially if credit growth outpaces productive investment.
Global Lessons and Historical Context
- 2008 Global Financial Crisis: Reckless lending and financial engineering, including mortgage-backed securities, led to a global economic collapse. India was impacted indirectly, prompting RBI intervention to stabilise the economy.
- Examples from Ireland & Thailand: Rapid growth of private credit in these countries led to reduced productivity and economic distortions, serving as cautionary tales.
Balanced View on Finance
The Survey recognizes that a well-regulated financial system plays a vital role in:
- Channeling capital to innovative and high-risk ventures.
- Reducing transaction costs and improving price discovery.
- Alleviating poverty and inequality by enabling shock absorption for households and firms.
- Smoothing consumption across economic cycles.
However, the Survey emphasizes that there is a tipping point beyond which financial development becomes counterproductive.
Ultra-Processed Foods (UPFs)

- 01 Feb 2025
In News:
The Economic Survey 2024–25 underscores the adverse impact of Ultra-Processed Foods (UPFs) on public health, particularly among children and youth, and calls for urgent regulatory intervention.
Key Recommendations
- Stringent Front-of-the-Pack Labelling (FOPL): The Survey advocates for clear, enforceable FOPL rules to inform consumers, curb misleading nutrition claims, and restrict aggressive marketing, especially those targeted at children and adolescents.
- Stronger Role for FSSAI: The Food Safety and Standards Authority of India (FSSAI) is advised to:
- Define UPFs clearly in regulation.
- Establish labelling standards.
- Monitor compliance of branded products.
- ‘Health Tax’ Proposal: The Survey proposes higher taxes on UPFs, especially brands engaging in excessive advertising, to act as a deterrent and promote healthier food choices.
- Awareness and Education: It recommends targeted awareness campaigns in schools and colleges, integrated with broader health and lifestyle campaigns, to reduce the rising consumption of UPFs.
Why this matter
- Rising Consumption: According to a 2023 WHO report, India’s UPF consumption grew from $900 million (2006) to over $37.9 billion (2019).
- Long-term National Impact: India's ?2,50,000 crore UPF industry is built on hyper-palatability and is a threat to India’s demographic dividend, productivity, and future economic growth.
Health Risks of UPFs
- Directly linked to:
- Obesity
- Cardiovascular diseases
- Colorectal cancer
- Respiratory and gastrointestinal disorders
- Mental health issues, especially among youth
- Poor dietary intake due to UPFs contributes to micronutrient deficiencies, while synthetic additives may have long-term biological impacts.
What are Ultra-Processed Foods?
UPFs are industrial formulations that undergo extensive processing and typically include:
- Artificial flavours, colours, preservatives, emulsifiers, sweeteners, and other cosmetic additives.
- High sugar, salt, and fat content for taste enhancement.
- Low in essential nutrients such as vitamins, minerals, and fibre.
- Designed for convenience and high palatability, often leading to overconsumption.
Examples of Ultra-Processed Foods
(As per Indian Council of Medical Research - ICMR):
- Commercial bakery items: bread, cakes, biscuits, breakfast cereals
- Snack foods: chips, fries
- Condiments: sauces, jams, mayonnaise
- Dairy & protein products: processed cheese, butter, protein powders, soy chunks, tofu
- Frozen and ready-to-eat foods with additives
- Beverages: energy drinks, health drinks, sweetened fruit juices
- Refined flours of cereals, millets, legumes
- Culinary ingredients containing cosmetic additives like artificial colours or emulsifiers
India adds 4 new Ramsar Sites

- 01 Feb 2025
In News:
The Government of India has added four new Ramsar sites, increasing the total to 89, the highest in Asia and third globally. The newly designated wetlands include:
- Sakkarakottai Bird Sanctuary (Tamil Nadu)
- Therthangal Bird Sanctuary (Tamil Nadu)
- Khecheopalri Wetland (Sikkim)
- Udhwa Lake (Jharkhand)
This marks a significant milestone as Sikkim and Jharkhand have received their first Ramsar recognitions, while Tamil Nadu strengthens its lead with 20 Ramsar sites, the most among Indian states.
About the Ramsar Convention
- Adopted: 1971 in Ramsar, Iran
- Objective: Conservation and wise use of wetlands through local, national, and international cooperation.
- World Wetlands Day: Celebrated on 2nd February to promote awareness.
Key Highlights:
Therthangal Bird Sanctuary – Tamil Nadu
- Notified in 2010; covers 29.29 ha.
- Crucial breeding and foraging site for waterbirds like Spot-billed Pelican, Black-headed Ibis, and Oriental Darter.
- Aids groundwater recharge and climate regulation.
- Part of the Central Asian Flyway.
Sakkarakottai Bird Sanctuary – Tamil Nadu
- Notified in 2012; spans 230.49 ha.
- Located near Gulf of Mannar; significant stopover for migratory birds.
- Hosts endemic species and near-threatened fauna like Lion-tailed Macaque and Giant Squirrel.
Khecheopalri Wetland – Sikkim
- Sacred lake revered by Buddhists and Hindus; called Sho Dzo Sho locally.
- Known as a wish-fulfilling lake.
- Birds prevent leaves from settling on the surface.
- Rich in avifauna: fishing eagles, Brahminy kites.
- Integral to ecotourism and biodiversity conservation.
Udhwa Lake – Jharkhand
- Comprises Pataura Jheel (155 ha) and Brahma Jamalpur Jheel (410 ha).
- First Ramsar site of Jharkhand; near Ganga River.
- Declared a bird sanctuary in 1991; attracts migratory birds from September onwards.
Falls under the Gangetic Plains biogeographic zone.
MSME Trade Enablement and Marketing (TEAM) Initiative

- 31 Jan 2025
In News:
The Ministry of Micro, Small, and Medium Enterprises (MoMSME), in collaboration with the Open Network for Digital Commerce (ONDC), has launched the Trade Enablement and Marketing (TEAM) Initiative. It aims to promote digital commerce among micro and small enterprises (MSEs) in India.
Key Features of TEAM Initiative
- Scheme Under: Raising and Accelerating MSME Productivity (RAMP) Programme
- RAMP is a World Bank-supported Central Sector Scheme implemented from 2022–2027 to enhance market access, technology upgradation, and financial inclusion for MSMEs.
- Objective:
- To empower MSEs through digital commerce integration using ONDC.
- To formalize operations, reduce the cost of doing business, and expand market access.
- To ensure inclusivity with 50% of beneficiaries being women-led enterprises.
- Budget & Duration:
- ?277.35 crore over three years (FY 2024–25 to FY 2026–27).
- Target Beneficiaries:
- 5 lakh MSEs (50% women-led).
- Eligibility: Registered MSEs in manufacturing or service sectors with valid Udyam Registration. Medium enterprises are excluded from most benefits.
- Implementing Agency:
- National Small Industries Corporation (NSIC)
Operational Strategy
- ONDC Integration: MSMEs will be onboarded onto the ONDC network, enabling them to operate digital storefronts with access to interoperable platforms, seamless payment solutions, and logistics services.
- Workshops & Outreach:
- Over 150 workshops will be organized across Tier 2 and Tier 3 cities, especially targeting SC/ST-led and women-led enterprises.
- Workshops will provide training on creating digital catalogues, understanding digital platforms, and maximizing ONDC's benefits.
- Supportive Infrastructure: A dedicated digital portal will offer services including workshop registration, access to finance, grievance redressal, catalogue tools, and account management assistance.
- Financial Assistance: Support to Seller Network Participants for onboarding MSEs and assisting in operational and digital transition needs.
About ONDC:
An initiative of the DPIIT, Ministry of Commerce, ONDC is an open, interoperable network that allows buyers and sellers to transact across multiple digital platforms, aiming to democratize digital commerce and reduce platform monopolies.
National Critical Mineral Mission

- 31 Jan 2025
In News:
The Union Cabinet has launched the National Critical Mineral Mission (NCMM) with a total outlay of ?34,300 crore over seven years, including ?16,300 crore government expenditure and ?18,000 crore investment from PSUs and private players.
Key Highlights:
Objectives of NCMM
- Reduce import dependence on critical minerals vital for clean energy, electronics, defence, and high-tech industries.
- Promote domestic exploration, mining, processing, and recycling of critical minerals.
- Facilitate overseas acquisition of mineral assets.
- Strengthen India’s mineral security and ensure self-reliance (Atmanirbhar Bharat).
Key Features
- Value Chain Coverage: Exploration → Mining → Beneficiation → Processing → Recycling of end-of-life products.
- Fast-track regulatory approvals for mining projects.
- Creation of mineral processing parks and promotion of sustainable extraction technologies.
- Establishing a strategic stockpile of critical minerals.
- Development of a Centre of Excellence on Critical Minerals to support R&D.
- Expansion of PRISM initiative to fund startups and MSMEs in the sector.
- Whole-of-government approach: Collaboration among ministries, PSUs, private sector, and research institutions.
Why Critical Minerals Matter
Critical minerals are essential inputs for:
- Green energy: EV batteries, solar panels, wind turbines.
- Electronics: Semiconductors, fiber optics.
- Defence: Aircraft, missile guidance systems.
- Medical technologies: MRI machines, pacemakers.
India’s clean energy transition and manufacturing competitiveness hinge on a steady and secure supply of these minerals.
India’s Import Dependence
India is dependent on imports, especially from China, for several critical minerals like lithium, cobalt, titanium, graphite, and tellurium. This exposes India to supply chain vulnerabilities amid shifting global geopolitics.
List of 30 Critical Minerals for India
Includes: Lithium, Cobalt, Nickel, Graphite, Rare Earth Elements (REEs), Beryllium, Titanium, Tungsten, Gallium, Indium, Selenium, Cadmium, etc.
Strategic and Legislative Initiatives
- Amendment to MMDR Act (1957) in 2023: Enabled auction of 24 critical mineral blocks.
- OAMDR Act (2002) amendment: Introduced transparent offshore mineral exploration.
- Duty waivers in Union Budget 2024–25: Customs duties removed on key critical minerals to promote domestic processing.
- Exploration by GSI: 368 projects in last 3 years; 227 more planned for FY 2025–26.
- KABIL: Acquired 15,703 ha in Argentina for lithium mining.
Global Context
- Global powers (US, EU, Japan) are pursuing strategies for critical mineral security.
- China dominates refining of lithium, cobalt, and REEs.
- India is part of the Minerals Security Partnership (MSP) to diversify global mineral supply chains.
Significance for India
- Ensures long-term resource security for clean technologies.
- Supports EV and renewable energy manufacturing goals.
- Enhances strategic autonomy in defence and electronics.
- Makes India an attractive hub for foreign investment in green technologies.
Challenges and the Way Forward
- Geopolitical risks in overseas asset acquisition.
- Environmental impacts of large-scale mining.
- Need for strong R&D ecosystem, financial incentives, and public-private partnerships.
- Sustainable mining practices and global collaboration are essential for long-term success.
Contract Farming in India

- 31 Jan 2025
In News:
Contract farming has emerged as a significant model in India's agricultural landscape, especially with its success in processed potato cultivation and the recent rise in French fry exports. As the country transitions from being an importer to a major exporter in sectors like frozen French fries, the contract farming model underpins the structural transformation of Indian agriculture.
Understanding Contract Farming
Contract farming is an agricultural production system where farmers and buyers (agribusinesses, processors, exporters, or retailers) enter into a pre-harvest agreement. This contract outlines key parameters including price, quality, quantity, delivery schedules, and in many cases, input provision and technical assistance.
Types of Contract Farming Arrangements
- Direct Input Provision by the Company: Firms supply seeds, fertilizers, and support services, deducting costs from the final payment to farmers.
- Partnership with Local Input Dealers: A hybrid model balancing company control with third-party services, chosen based on crop complexity, local support availability, and firm capabilities.
Advantages of Contract Farming
- Stable and Enhanced Income: Contracts assure farmers of a fixed price and market access, shielding them from volatile markets. RBI data shows farmers typically receive only 31%–43% of consumer prices; contract farming can significantly improve this share.
- Access to Inputs and Technology: Companies provide high-quality seeds, fertilizers, training, and modern farming practices, leading to improved yields and quality.
- Post-Harvest Efficiency: Streamlined procurement reduces wastage of perishables and post-harvest losses, ensuring efficient supply chain management.
- Credit and Financial Support: Assured incomes help farmers access institutional credit, reducing dependency on informal lenders.
- Food Safety and Export Standards: Training on pesticide use and residue limits ensures compliance with international standards like Maximum Residue Limits (MRLs), boosting export potential.
- Consumer Benefits: Direct procurement reduces intermediaries, enabling competitive pricing and higher quality products.
- Technology Transfer: Farmers benefit from the introduction of new, high-efficiency production techniques.
Concerns and Challenges
- Power Imbalance: Small and marginal farmers often lack bargaining power. This dependency may lead to exploitative contracts or one-sided terms, especially where firms demand investments in crop-specific infrastructure.
- Market Risk and Default: Price volatility can lead to side-selling by farmers or contract breaches by firms when market prices crash.
- Delayed Payments and Inputs: Contractual delays in payment or input delivery can severely affect crop cycles and farmer finances.
- Exclusion of Marginal Farmers: For economies of scale, firms often prefer large landholders, sidelining smallholders.
- Environmental Impact: Monocropping, overuse of water and agrochemicals, and soil degradation threaten long-term sustainability.
- Food Security Trade-offs: A shift to high-value crops under contracts may reduce acreage for food crops, impacting local food security.
- Loss of Autonomy: Farmers may lose control over farming decisions, with firms determining most aspects of cultivation, leading to indirect control over land use.
Case Study: Contract Farming in Potato Sector
India is the second-largest potato producer globally, with Uttar Pradesh, West Bengal, and Bihar as leading states. The Central Potato Research Institute (CPRI), Shimla developed several high-yielding Kufri varieties to support commercial cultivation.
The success of processed potato farming is best illustrated by India’s emergence as an exporter of frozen French fries, driven by contract-based procurement from farmers. However, issues such as the PepsiCo vs. Indian farmers legal dispute over unauthorized cultivation of the FL 2027 variety underline ongoing concerns around intellectual property rights and farmers’ autonomy.
Policy and Legal Framework
- Model APMC Act, 2003: Introduced contract registration, dispute resolution, and exempted market fees while protecting land ownership.
- Model Agricultural Produce and Livestock Contract Farming Act, 2018: Proposed institutional frameworks, insurance provisions, and promotion of Farmer Producer Organizations (FPOs).
- e-NAM Integration: Supports transparent pricing and contract enforcement.
- National Agriculture Policy: Endorses contract farming as a tool for enhancing productivity and rural incomes.
Bharat Sovereign Wealth Fund (BSWF)

- 31 Jan 2025
In News:
India is actively exploring the creation of a Bharat Sovereign Wealth Fund (BSWF) or The Bharat Fund (TBF) to harness the untapped wealth embedded within its public sector ecosystem. This fund aims to unlock and strategically manage dormant capital, estimated at ?40 lakh crore ($450–500 billion), primarily held in equity stakes of around 80 listed public sector enterprises (PSEs) and banks.
What is a Sovereign Wealth Fund (SWF)?
A Sovereign Wealth Fund is a state-owned investment vehicle that manages national savings or surplus revenues—often derived from foreign exchange reserves, natural resource exports, or trade surpluses.
According to the Santiago Principles (2008), SWFs:
- Are owned by the general government (central or sub-national),
- Invest primarily in foreign financial assets, and
- Aim to achieve financial objectives rather than monetary policy.
Types of SWFs include:
- Stabilization Funds: Cushion fiscal shocks from revenue volatility.
- Future Generation Funds: Preserve wealth for long-term national benefit.
- Strategic Development Funds: Support priority sectors and national growth.
- Reserve Investment Funds: Enhance returns on foreign currency reserves.
Examples include:
- Norway’s Government Pension Fund Global ($1.7 trillion),
- China Investment Corporation ($1.35 trillion),
- Abu Dhabi Investment Authority ($993 billion).
India’s SWF Landscape and the BSWF Proposal
India previously explored SWF models in 2007–08 and again in 2010–11. While the National Investment and Infrastructure Fund (NIIF) was launched in 2015, it remains sector-specific and limited in scale. The proposed BSWF envisions a comprehensive and transformational fund akin to global best practices.
Key features of the BSWF proposal:
- Consolidation of government equity in PSEs and PSU banks under a professionally managed umbrella.
- Strategic divestment—e.g., reducing government stake from 51% to 40%—without losing operational control.
- Leveraging this pooled equity to attract global co-investors, potentially unlocking tens or hundreds of billions in foreign capital.
Why India Needs the Bharat SWF
- Wealth Unlocking: Potential monetization of over ?40 lakh crore in dormant government equity assets.
- Fiscal Prudence: Even a modest 2% annual divestment could yield $10+ billion, narrowing the fiscal deficit from 4.9% to ~4.6% of GDP.
- Strategic Sector Investment: Deployment into high-potential sectors—AI, semiconductors, electric vehicles, hydrogen energy, biotechnology—to drive innovation and economic leadership.
- Attracting Global Capital: Enhanced investor confidence, especially from established SWFs like those of Singapore, Norway, and Abu Dhabi, which are already increasing exposure in Indian equities and infrastructure.
- Social Sector Funding: Generate non-debt financial resources for welfare programs and national development missions.
- Soft Power Projection: Fund ventures, disaster relief, and advocacy efforts, strengthening India’s international standing.
Governance and Reform Imperatives
For the BSWF to succeed, it must:
- Be governed by a clear legal and regulatory framework aligned with Santiago Principles.
- Operate independently, with professional asset managers, market-based remuneration, and arm’s length oversight.
- Transition PSEs to function with autonomy and efficiency, reducing bureaucratic delays and enabling innovation.
- Foster joint ventures to turn around non-performing PSEs—among the 1,830 PSEs, around 400 remain non-functional, demanding nearly ?9 lakh crore annually in budgetary support.
Challenges and Concerns
- Macroeconomic Constraints: India faces a current account deficit and substantial fiscal pressures—conditions unlike traditional SWF-rich nations.
- Geopolitical and Market Risks: Global uncertainty and decoupling trends could impact cross-border investment strategies.
- Environmental and Technological Vulnerabilities: Investment risks in carbon-heavy sectors and exposure to data fraud or tech disruptions.
- Institutional Resistance: Political and bureaucratic inertia may delay implementation unless national interest is prioritized.
SWF Investments in India: A Growing Trend
Foreign SWFs are already deepening their footprint in India:
- $6.7 billion in direct investments in 2022 (up from $4.3 billion in 2021).
- Preferred sectors: healthcare, entertainment, renewables, infrastructure.
- Beneficiaries of tax exemptions on direct infrastructure investments via InVITS (Infrastructure Investment Trusts) and AIFs (Alternative Investment Funds), valid for investments made before March 31, 2024.
These incentives have encouraged foreign SWFs to explore establishing physical presence in India’s financial hubs, especially GIFT City, Gandhinagar.
Environment Protection (End-of-Life Vehicles) Rules, 2025
- 31 Jan 2025
In News:
MoEFCC Notifies Rules for End-of-Life Vehicles to Minimize Waste and Pollution.
Key Highlights:
Notified by: Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change (MoEF&CC)
Effective from: April 1, 2025
Legal Basis: Environment Protection Act, 1986
Objective: To promote environmentally sound management of end-of-life vehicles (ELVs), enable recycling and reuse of vehicle components, and reduce resource extraction, pollution, and waste generation.
Key Features of the ELV Rules, 2025
1. Scope and Coverage
- Applicable to all vehicle categories including electric vehicles (EVs), e-rickshaws, and e-carts.
- Exempted vehicles: Agricultural tractors, trailers, combine harvesters, and power tillers.
- Exempted waste types: Batteries, plastics, tyres, used oil, and e-waste (governed under separate waste management rules).
2. Extended Producer Responsibility (EPR)
- Vehicle producers are mandated to meet annual scrapping targets based on the age of vehicles:
- Transport vehicles: 15 years
- Non-transport vehicles: 20 years
- Producers must fulfill their EPR obligations for all vehicles introduced into the domestic market, including those used internally.
- Annual EPR declarations must be submitted to the Central Pollution Control Board (CPCB) by April 30 each year.
- Producers must promote ELV deposition at designated collection centres or Registered Vehicle Scrapping Facilities (RVSFs).
3. Responsibilities of Stakeholders
- Registered Owners & Bulk Consumers: Required to deposit ELVs at designated centres or RVSFs within 180 days of becoming unfit.
- Collection Centres:
- Handle ELVs in an environmentally responsible manner.
- Maintain records and ensure safe storage and transfer to RVSFs.
- Registered Vehicle Scrapping Facilities (RVSFs):
- Undertake depollution, dismantling, segregation, and recycling.
- Ensure environmentally sound disposal of non-recyclables via authorized TSDFs.
- Issue EPR certificates based on the volume of steel processed; valid for 5 years.
4. Monitoring, Compliance, and Penalties
- CPCB and State Pollution Control Boards (SPCBs) are responsible for:
- Registration, inspection, and audit of producers, RVSFs, and bulk consumers.
- Taking action against non-compliance, including suspension or cancellation of registration.
- Levying environmental compensation for violations that cause harm to public health or the environment.
5. Registration & Certification
- Producers register with CPCB; RVSFs and bulk consumers with respective SPCBs.
- Registration certificates are issued within 15 days of application via a centralized online portal.
- EPR certificates are non-transferable and allow adjustment of both current and backlog obligations.
Related Policy and Incentives by MoRTH
The Ministry of Road Transport and Highways (MoRTH) supports the ELV Rules through:
- Vehicle Scrapping Policy: Targets voluntary phasing out of unfit and polluting vehicles.
- Motor Vehicles (Registration and Functions of Vehicle Scrapping Facility) Rules, 2021: Provides operational criteria for RVSFs.
- Central Motor Vehicles (Amendment) Rules, 2021:
- Waiver of registration fee for buyers submitting ELV Certificates of Deposit.
- Concession in motor vehicle tax: 25% for non-transport, 15% for transport vehicles.
Electric Mobility Push
- MoRTH has issued several notifications promoting EVs, including:
- Permit exemptions for battery-operated and ethanol/methanol-fueled vehicles.
- Fee exemptions for registration and renewals.
- Tourist permit benefits for EVs and distinct registration marks for visibility.
PM E-DRIVE Scheme
- Launched by Ministry of Heavy Industries on 29th September 2024 with a ?10,900 crore outlay.
- Aims to support electric 2-wheelers, 3-wheelers, ambulances, trucks, and buses with ?3,679 crore in demand incentives.
- Targets subsidization of over 28 lakh EVs.
F11 Bacteria

- 30 Jan 2025
In News:
A recent scientific study has identified a bacterial strain, Labrys portucalensis F11 (commonly referred to as F11), capable of degrading per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) — popularly known as “forever chemicals” — by breaking their strong carbon-fluorine (C-F) bonds.
About F11 Bacteria:
- Scientific Name: Labrys portucalensis F11
- Family: Xanthobacteraceae
- Nature: Aerobic and pollutant-resistant bacterium
- Origin: Isolated from industrially contaminated soil in Portugal
- Significance:
- Adapted to thrive in toxic environments
- Uses environmental contaminants as an energy source
- Capable of degrading at least three types of PFAS and certain toxic byproducts
What Are Forever Chemicals (PFAS)?
- Definition: A group of synthetic, man-made chemicals known for their extremely strong C-F bonds, making them persistent and non-biodegradable.
- Why Called 'Forever':
- Resistant to natural breakdown
- Found in air, rainwater, and soil for decades or longer
- Health & Environmental Hazards:
- Linked to cancer, hormonal disorders, immune dysfunction, and environmental toxicity
- Migrate into soil, water, and air during production and use
- Regulation: Certain PFAS are listed under the Stockholm Convention on Persistent Organic Pollutants
Relevance for India and the World:
- Global Impact:
- PFAS are used in a wide range of consumer products such as non-stick cookware, firefighting foams, and food packaging.
- Their persistence poses long-term risks to public health, groundwater contamination, and biodiversity.
- India's Concern:
- Increasing industrialization and waste mismanagement heighten PFAS exposure risks.
- No comprehensive PFAS regulation in place yet; calls for adopting stringent environmental safety norms.
WHO Guidelines on Lower-Sodium Salt Substitutes (LSSS)
- 30 Jan 2025
In News:
Recently, the World Health Organization (WHO) issued new guidelines promoting the use of Lower-Sodium Salt Substitutes (LSSS) to tackle the global burden of hypertension, cardiovascular diseases (CVDs), and stroke, which are largely driven by excessive sodium consumption. This is especially relevant for countries like India, with a high prevalence of high blood pressure and salt consumption.
What Are Lower-Sodium Salt Substitutes (LSSS)?
- LSSS are alternatives to regular table salt, where sodium chloride (NaCl) is partially replaced by potassium chloride (KCl), magnesium sulphate, or calcium chloride.
- They are designed to retain the taste of regular salt while significantly reducing sodium intake and improving heart health.
- LSSS can help lower blood pressure, thanks to the potassium content, which helps balance fluid levels and offset sodium’s harmful effects.
Key WHO Recommendations:
- Daily sodium intake should be restricted to less than 2 grams per day, equivalent to about 5 grams of salt.
- Avoid regular table salt, and replace it, wherever safe, with LSSS for household use.
- LSSS use is not recommended for:
- Pregnant women
- Children
- Individuals with kidney impairments or those requiring low-potassium diets
- The guidelines do not apply to packaged or restaurant foods, which are major contributors to overall sodium intake.
Why Is This Important or India?
- Salt Intake in India: Average salt consumption is 10.4 grams/day, over double the WHO recommendation.
- Hypertension Prevalence: Over 35.5% of India’s population (approx. 315 million people) suffers from hypertension (INDIAB Study).
- CVD Burden: Cardiovascular diseases accounted for 28.1% of all deaths in India (2016) – Global Burden of Disease Study.
- Dietary Impact: Globally, 8 million deaths annually are diet-related, with 1.9 million directly linked to high sodium intake.
Implementation and Policy Measures:
- India’s Response:
- The Food Safety and Standards Authority of India (FSSAI) has initiated sodium reduction policies.
- Edible salt must contain 97% sodium chloride, with anticaking agents limited to 2.2%.
- New labelling norms enforce accurate “low sodium” and “sodium-free” claims.
Public Health and Safety Considerations:
- While LSSS are safe and beneficial for most adults, excess potassium can cause hyperkalemia, especially dangerous for those with kidney disease.
- WHO guidelines aim to maximize benefits and minimize risks by promoting regulated, evidence-based usage.
- Governments, policymakers, and health professionals are urged to integrate LSSS into public health strategies, especially in high-risk populations.
About WHO:
- Established in 1948, the World Health Organization is the UN agency dedicated to promoting global health, preventing disease, and coordinating international health responses.
- It leads efforts for universal health coverage and responds to global health emergencies.
Aroma Mission

- 30 Jan 2025
In News:
The Aroma Mission, also known as the Lavender Revolution, is emerging as a transformative initiative for regions like Jammu & Kashmir and the North East, prioritised under Prime Minister Narendra Modi’s vision for inclusive development.
It aims to harness the untapped potential of India’s biodiverse regions through the scientific cultivation of aromatic crops and production of essential oils, with the dual goals of economic upliftment and sustainable innovation.
Key Objectives and Features:
- Launched By: Ministry of Science & Technology
- Nodal Agency: CSIR-Central Institute of Medicinal and Aromatic Plants (CIMAP), Lucknow
- Started In: Jammu & Kashmir, now extended to the North East
- Known As: Lavender Revolution
- Purpose: Boost India’s aroma industry by promoting the cultivation of high-value aromatic crops and increasing the production of essential oils.
Major Focus Areas:
- Crops Cultivated: Lavender, lemongrass, citronella, palmarosa, vetiver, patchouli, rose, peppermint, and chamomile
- Target Sectors: Cosmetics, aromatherapy, pharmaceuticals, and food flavouring industries
Impact and Achievements:
- Over 5,000 hectares brought under aromatic crop cultivation in the North East.
- Establishment of 39 essential oil distillation units.
- Distribution of 1 lakh agarwood saplings planned to boost the region's share in global aromatic plant trade.
- Expected annual essential oil production: 2,000 tonnes, valued at over ?300 crores.
- Estimated to generate 60 lakh man-days of rural employment.
- Projected increase in farmers’ income by ?60,000–?70,000 per hectare annually.
Institutional Support: IICON – Incubation and Innovation Complex
- Location: CSIR-North East Institute of Science and Technology (CSIR-NEIST), Jorhat, Assam
- Launched By: Dr. Jitendra Singh (Minister of Science & Technology)
- Purpose: Provide technical assistance, advanced facilities, and business incubation support for startups, MSMEs, and SHGs.
- Facilities: Access to 27 cutting-edge technologies for up to two years to help refine production and marketing strategies.
Integrated Development Approach:
The Aroma Mission exemplifies the “whole-of-government” approach, aligning with various flagship programmes such as:
- Start-Up India
- MSME Development
- Doubling Farmers’ Income
- Women Empowerment (e.g., through Rural Women Technology Parks)
- Act East Policy (enhancing North East's connectivity and trade potential)
Over 25 startups and self-help groups have already been empowered through access to facilities and entrepreneurial training at IICON, contributing to local innovation ecosystems.
Strategic Significance:
- Regional Empowerment: Converts underutilised natural resources into economic assets, especially in remote regions like J&K and the North East.
- Environmental Sustainability: Encourages eco-friendly cultivation and reduces pressure on traditional farming.
- Economic Diversification: Supports India’s transition to a bio-economy, with aromatic plant industries offering export potential and rural employment.
- Vision India@2047: Positions the North East as a hub for biotechnology, essential oils, innovation, and trade, aligning with long-term national growth goals.
Olive Ridley Turtles
- 30 Jan 2025
In News:
The Rushikulya river mouth in Odisha is witnessing the anticipated mass nesting of Olive Ridley turtles — a critical event for the survival of this vulnerable marine species. This phenomenon, known as arribada, highlights the ecological significance of India’s coastal biodiversity and the urgent need for marine conservation.
About Olive Ridley Turtles (Lepidochelys olivacea)
- Taxonomy:
- Scientific Name: Lepidochelys olivacea
- Class: Reptilia
- Family: Cheloniidae
- Physical Features: These turtles are the smallest and most abundant of all sea turtle species. They are recognized by their olive or grayish-green heart-shaped carapace. Males and females are similar in size, though females have slightly rounder shells.
- Habitat and Distribution: Olive Ridleys are found in warm, tropical waters of the Pacific, Atlantic, and Indian Oceans, inhabiting both open ocean (pelagic) and coastal waters.
Mass Nesting: The Arribada Phenomenon
- Arribada (Spanish for "arrival") refers to the synchronized mass nesting behavior where thousands of females gather on a single beach to lay eggs.
- Nesting occurs annually between December and March, after long migrations of up to 9,000 km. Each female may lay 90–120 eggs, 1 to 3 times per season.
- Temperature-dependent sex determination influences hatchling sex ratios.
- After nesting, females return to the sea, leaving eggs buried in sand.
Major Nesting Sites in India
- Odisha Coast is the most significant nesting ground in India and globally:
- Gahirmatha Marine Sanctuary: World’s largest mass nesting site.
- Rushikulya River Mouth: Second-largest nesting beach in India.
- Devi River Mouth: Another key nesting site in Odisha.
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands have recently emerged as a new mass nesting area, with over 5,000 nests reported in one season.
Ecological Role and Behavior
- Diet: Omnivorous — they feed on jellyfish, crabs, snails, prawns, molluscs, algae, and small fish.
- Behavior: These turtles undertake long migrations annually between feeding and breeding grounds, spending most of their lives at sea.
Protection Status
- IUCN Red List: Vulnerable
- CITES: Appendix I
- Wildlife (Protection) Act, 1972 (India): Schedule I (highest protection)
Threats to Survival
- Bycatch in Fishing Gear: Accidental entanglement in trawls, gillnets, and longlines.
- Habitat Loss: Coastal development for ports, tourism, and industry disrupts nesting beaches.
- Poaching: Turtles and their eggs are harvested for meat, shell, and leather.
- Pollution: Plastic ingestion and marine debris pose severe health risks.
- Climate Change: Rising sea levels and increased sand temperatures impact nesting and hatchling sex ratios.
Conservation Initiatives
- Operation Olivia: Initiated by the Indian Coast Guard in the 1980s to protect turtles during nesting and prevent illegal fishing.
- Turtle Excluder Devices (TEDs): Mandated by the Odisha government in trawl nets; allow turtles to escape while retaining fish catch.
- Tagging Programs: Use of non-corrosive metal tags to study migration patterns and inform conservation strategies.
Global Investment Trends and India’s FDI Outlook

- 30 Jan 2025
In News:
The Global Investment Trends Monitor Report 2024, released by the United Nations Conference on Trade and Development (UNCTAD), highlights a concerning decline in international project finance and Foreign Direct Investment (FDI), particularly in developing economies. This has significant implications for sustainable development, especially in emerging economies like India.
Key Findings from the UNCTAD Report (2024)
Global FDI Trends:
- Global FDI flows, after adjusting for conduit economies, fell by 8% in 2024, despite a nominal increase to USD 1.4 trillion.
- Developed economies witnessed a 15% drop in FDI (excluding conduit economies like Ireland and Luxembourg), while developing economies saw a 2% decline.
- The decline threatens long-term investment in infrastructure, renewable energy, and other SDG-aligned sectors.
Project Finance and Greenfield Investment:
- International project finance declined by 29% in developed and 23% in developing economies.
- In terms of value, developing economies faced a sharper fall of 33%.
- Key countries like India, China, Brazil, Indonesia, and Mexico reported steeper declines than the global average.
- Greenfield investments fell 6% in developing regions, with Africa and Asia being worst affected.
Sectoral Impacts:
- Investments in SDG-related sectors (e.g., water, sanitation, agrifood systems, and infrastructure) declined by 11%.
- International renewable energy finance fell 16%, with North America (-22%) and developing Asia (-18%) seeing notable contractions.
- Africa was the only region to witness an 8% increase in renewable energy project finance.
India’s FDI Landscape: Trends, Opportunities, and Challenges
Recent Performance:
- Between April 2000 and September 2024, India received over USD 1 trillion in cumulative FDI.
- From 2014 to 2024, India attracted USD 667.4 billion, a 119% increase over the previous decade.
- In 2024, India’s greenfield projects grew, but international project finance fell 23% in number and 33% in value.
Regulatory Framework:
- FDI is regulated under the Foreign Exchange Management Act (FEMA), 1999, administered by DPIIT, Ministry of Commerce and Industry.
- Prohibited sectors: Atomic energy, betting, lotteries, chit funds, tobacco, and real estate (excluding construction development).
Outlook for 2025 and Strategic Opportunities
Global FDI Projections:
- UNCTAD anticipates moderate global FDI growth in 2025.
- Regions like ASEAN, Eastern Europe, and Central America may benefit from supply chain realignments.
- India is projected to see a moderate rise in FDI, aided by:
- Improved financing conditions,
- Mergers and acquisitions,
- Ongoing policy reforms.
Key Growth Sectors:
- High potential in AI, cloud computing, cybersecurity, electric vehicles, and green hydrogen.
- FDI will be influenced by geopolitical dynamics, interest rates, GDP growth, and technological transitions.
FDI in India: Opportunities and Challenges
Opportunities:
- Large consumer base (1.4 billion population) and young workforce (65% under 35).
- Government schemes like Make in India and Atmanirbhar Bharat incentivize foreign investment.
- Strategic location positions India as a gateway to South Asia, the Middle East, and Southeast Asia.
Challenges:
- Regulatory complexity, including retrospective taxation and bureaucratic delays.
- Infrastructure deficits, particularly outside urban hubs.
- Rigid labour laws and inconsistent policy enforcement.
Investor Expectations:
- Technology transfer in priority sectors.
- Employment generation to absorb India’s growing labor force.
- Sustainable investments in line with India’s climate commitments under the National Action Plan on Climate Change.
Asian Waterbird Census 2025

- 29 Jan 2025
In News:
As per the Asian Waterbird Census-2025, a record number of 39,725 birds belonging to 106 species have been sighted in the Coringa Wildlife Sanctuary and adjoining wetlands.
Asian Waterbird Census (AWC): An Overview
- AWC is an annual citizen-science programme that supports the conservation of wetlands and waterbirds across Asia.
- Initiated in 1987 in the Indian subcontinent, it now covers extensive regions of East and Southeast Asia, Japan, Australasia, and parts of the Central Asian and East Asian–Australasian Flyways.
- AWC is the Asian chapter of the global International Waterbird Census (IWC).
- In India, it is coordinated by the Bombay Natural History Society (BNHS) and the Wildlife Institute of India (WII) every January.
About BNHS (Bombay Natural History Society)
- An Indian NGO engaged in biodiversity research and conservation.
- Recognized as a Scientific and Industrial Research Organisation (SIRO) by the Department of Science and Technology.
- Official partner of BirdLife International in India.
Coringa Wildlife Sanctuary (Andhra Pradesh): Census Findings 2025
- The Asian Waterbird Census 2025 recorded a record 39,725 birds representing 106 species in the Coringa Wildlife Sanctuary (CWS) and adjoining Godavari estuary wetlands.
- Of these, nearly 70 species are migratory, using the site as a key winter feeding ground.
Species of Conservation Concern
- Endangered species sighted:
- Indian Skimmer (Rynchops albicollis) – ~450 individuals sighted
- Black-bellied Tern (Sterna acuticauda)
- Great Knot (Calidris tenuirostris)
- Vulnerable species: Common Pochard (Aythya ferina)
- Near Threatened species: 11 species identified
Migratory Pathways and Monitoring
- Migrants such as the Great Knot travel from Russia, Siberia, China, and Mongolia to the Godavari estuary.
- A tagged Great Knot, tracked from Russia, was recorded after a 7,500 km journey, seen in Bhairavapalem mudflat and Etimoga wetland in successive winters (2024 and 2025).
- Data sharing with global avian research groups aids in tracking migratory patterns and supports conservation of endangered species.
Ecological and Ramsar Significance
- The Godavari estuary supports feeding grounds for nearly 90,000 birds, as observed by CWS authorities.
- Avian diversity is a key criterion for Ramsar Site designation, and experts advocate for Coringa Wildlife Sanctuary and its surroundings to be recognized as a wetland of international importance under the Ramsar Convention.
Resumption of Kailash Mansarovar Yatra
- 29 Jan 2025
In News:
After a four-year hiatus due to the COVID-19 pandemic and the 2020 Galwan Valley clash, India and China have agreed to resume the Kailash Mansarovar Yatra in June 2025, along with other confidence-building measures.
This decision aligns with the 75th anniversary of India-China diplomatic relations, symbolizing an attempt to stabilize and recalibrate bilateral ties through people-centric initiatives.
Key Highlights:
Key announcements include:
- Resumption of the Kailash Mansarovar Yatra
- Restoration of direct air services
- Visa issuance for journalists and think tanks
- Hydrological data sharing and cooperation on trans-border rivers
- Enhanced people-to-people exchanges and academic/media dialogues
About the Yatra
- The Yatra involves a pilgrimage to Mount Kailash and Lake Mansarovar in the Tibetan Autonomous Region (Xizang).
- Organised by India’s Ministry of External Affairs between June–September, via two routes:
- Lipulekh Pass (Uttarakhand)
- Nathu La Pass (Sikkim)
- Supported by the state governments of Uttarakhand, Sikkim, and Delhi, and coordinated with the Indo-Tibetan Border Police.
- Open only to Indian citizens with valid passports; no financial subsidy is provided by the Government of India.
Geographical and Religious Significance:
- Mount Kailash, located in the Kailash Range (Transhimalaya), is the source of four major rivers: Sutlej, Brahmaputra, Indus, and Karnali.
- Revered across religions:
- Hindus consider it the abode of Lord Shiva; Mansarovar is one of the 51 Shaktipeeths.
- Buddhists and Tibetans regard it as the ‘Stairway to Heaven’.
- Jains believe Rishabhanatha attained enlightenment here—referred to as Ashtapada.
Diplomatic Interpretations and Differences
- India’s Position: Emphasized a step-by-step, cautious approach focusing on rebuilding trust and resolving contentious issues, particularly the border situation. India sought policy predictability and transparency in trade, and reaffirmed the importance of mutual respect and interests.
- China’s Position: Took a more optimistic and strategic stance, stressing the need to avoid "mutual suspicion" and to advance cooperation based on long-term national interests. It emphasized early action, including the swift resumption of the Yatra and flights.
Ongoing Concerns in Bilateral Relations
- Unresolved Border Disputes:
- Tensions persist along the Line of Actual Control (LAC)—notably in Galwan (2020) and Tawang (2022).
- India and China have made limited progress in resolving issues in Depsang and Demchok.
- Trade Imbalance:
- Bilateral trade in 2023–24 stood at USD 118.4 billion, with India facing a trade deficit of USD 85 billion.
- India raised concerns on market access and non-tariff barriers.
- China-Pakistan Axis:
- The China-Pakistan Economic Corridor (CPEC) runs through Pakistan-occupied Kashmir, violating India’s territorial sovereignty.
- China’s support for Pakistan in multilateral forums remains a thorn in bilateral ties.
- China’s Regional Assertiveness:
- Expanding influence in South Asia and the Indian Ocean through the String of Pearls, strategic presence in Maldives, Sri Lanka, and strong claims in the South China Sea, contribute to regional unease.
Significance of the Current Diplomatic Thaw
- The resumption of the Kailash Mansarovar Yatra reflects a symbolic softening in ties, emphasizing religious diplomacy and people-to-people connection.
- Restoration of direct flights and journalistic presence can aid in reducing mistrust.
- Hydrological cooperation, particularly over the Brahmaputra River, is essential for India’s water security, especially with China constructing mega-dams upstream.
Way Forward
- Rebuild Trust Through Engagement: Maintain diplomatic dialogues via platforms like BRICS, SCO, and G20, while holding to core national interests.
- Resolve Border Disputes: Pursue early finalization of the LAC through confidence-building agreements and military disengagement.
- Diversify Economic Strategy: Reduce dependency on Chinese imports by strengthening domestic manufacturing and regional trade alternatives.
- Enhance Cultural Diplomacy: Use platforms like the Kailash Yatra to foster mutual understanding rooted in shared civilizational values.
- Promote Transparency and Reciprocity: Especially in media, trade, and information sharing, to ensure balanced bilateral engagement.
DeepSeek AI
- 29 Jan 2025
In News:
DeepSeek, a Chinese artificial intelligence (AI) startup based in Hangzhou, has emerged as a major player in the global AI race with the release of its models DeepSeek-V3 and DeepSeek-R1.
These models are designed to rival top-tier Western counterparts such as OpenAI’s GPT-4, Google’s Bard, and Meta’s LLaMA, but at a fraction of the cost.
Key Developments and Technological Edge
- Cost Efficiency: DeepSeek-V3 was trained at a cost of under $6 million, using older Nvidia H800 chips, compared to the estimated $100 million cost of GPT-4. Its subscription fee is significantly lower—$0.50/month versus $20/month for ChatGPT.
- Model Performance:
- DeepSeek-R1, a “reasoning model,” reportedly matches OpenAI’s o1 model in mathematics, coding, and contextual processing, while using fewer resources through incremental reasoning.
- Models use Mixture-of-Experts (MoE) architecture, reinforcement learning, and self-improvement loops, making them more memory-efficient and scalable.
- Advanced Models Released:
- DeepSeek Coder / Coder-V2 (for coding tasks).
- DeepSeek LLM (67B parameters), V2, V3 (671B parameters), and R1-Distill (fine-tuned using synthetic data).
Global Impact and Market Disruption
- App Success & Outages: The DeepSeek AI app topped the U.S. App Store, surpassing ChatGPT. This success triggered large-scale cyberattacks and caused temporary service disruptions.
- Market Reaction: The launch reportedly led to a historic $600 billion drop in Nvidia's market value, highlighting the disruptive potential of cost-efficient AI innovation.
- Geopolitical Ramifications: The rise of DeepSeek is seen as a technological parallel to the 1957 Sputnik moment, which shocked the U.S. and triggered the space race.
DeepSeek has reignited US-China AI rivalry, intensifying great-power competition in frontier technologies.
Strategic Lessons for India
- Bipolar AI Landscape: The U.S. and China dominate AI due to massive investment and infrastructure. Middle powers like India and France face the challenge of staying relevant without matching this scale.
- Doing More with Less: DeepSeek’s success underscores how innovation with limited resources can be effective—providing a model for India to emulate via Small Language Models (SLMs) and cost-efficient AI strategies.
- Sovereign AI & Global Governance:
- India advocates for “Sovereign AI”, balancing independence and strategic alliances, especially with France and the U.S.
- Future cooperation between U.S. and China on AI governance, similar to Cold War-era nuclear agreements, is a possibility.
- India must learn from past exclusions (e.g., nuclear governance) and proactively shape global AI governance frameworks.
- Policy Implications:
- DeepSeek's rise may lead to stricter U.S. chip export restrictions to China.
- It presents both security risks (censorship, pro-China bias) and opportunities (cost-effective models, domestic self-reliance).
Ethical Concerns and Limitations
- Censorship: DeepSeek complies with Chinese state censorship, refusing responses on politically sensitive topics (e.g., Tiananmen Square), raising concerns about bias and lack of transparency.
Security & Privacy: Experts have flagged potential data privacy and AI ethics issues, emphasizing the need for robust global standards and accountability mechanisms.
Indian Squid

- 29 Jan 2025
In News:
Researchers at the Central Marine Fisheries Research Institute (CMFRI), Kochi, have successfully decoded the gene expression pattern of the Indian squid (Uroteuthis duvaucelii), marking a major scientific advancement with wide-ranging implications for neuroscience, environmental studies, and sustainable marine resource management.
About Indian Squid
- Common Name: Indian Calamari
- Scientific Classification: Cephalopod
- Size: Typically 20–30 cm; can grow up to 50 cm
- Appearance: Light pinkish-grey body with two large fins, eight arms, and two longer tentacles used for capturing prey
- Key Abilities:
- Camouflage
- Jet propulsion for rapid movement
- Advanced nervous system
- Problem-solving skills and behavioral intelligence
Habitat & Distribution
- Preferred Habitat: Coastal and open sea regions of the Indian Ocean
- Found at depths ranging from 100 to 500 meters, some even up to 1,500 meters
- Requires high dissolved oxygen levels for respiration
- Geographic Distribution:
- Widely distributed in the Indo-West Pacific
- Found in Indian Ocean, Red Sea, Arabian Sea, from Mozambique to the South China Sea, Philippine Sea, and northward to Taiwan
- Conservation Status: IUCN Red List: Least Concern
Scientific Significance of Genetic Research
- Key Findings:
- Revealed genetic similarities with higher vertebrates like fish and humans, suggesting deep evolutionary links
- Indicates that Indian squid could serve as a model organism to study brain evolution, intelligence, and neurobiological functions
- Potential to inform research in neural circuits, memory, learning, and even neurological diseases
- Findings may also explain squid's adaptive success, such as evading predators and fishing pressures due to high cognitive ability
Institutional Background: CMFRI
- Established: 1947
- Affiliation: Part of the Indian Council of Agricultural Research (ICAR) since 1967
- Headquarters: Kochi, Kerala
- Mandate: Research on sustainable marine fisheries and ecosystem conservation
CMFRI’s Broader Recommendations for Sustainable Marine Management
- Enactment of Sea Fishing Act to regulate fishing beyond territorial waters
- Institutionalization of ecological stock assessments for sustainable exploitation
- Simplification and promotion of open mariculture with focus on environmental sustainability
- Use of AI-based systems to estimate landings and monitor fishing vessels
- Deep-sea resource exploration and alternative fishing methods
- Institutional mechanism for supervising deep-sea fishing
- Strengthening insurance coverage for marine fishers
RBI Payment System Report 2024

- 29 Jan 2025
In News:
The Payment System Report – December 2024 is a bi-annual publication by the Reserve Bank of India (RBI).
It analyses trends in digital and retail payment systems over the last five calendar years (up to CY-2024) and highlights India's transformation into a global leader in payment innovation and inclusion.
Growth in Digital Transactions
- Exponential Growth: Digital payment transactions rose 94 times in volume (from 222 crore in 2013 to 20,787 crore in 2024) and 3.5 times in value (from ?772 lakh crore to ?2,758 lakh crore).
- Recent CAGR (2019–2024):
- Volume: 45.9% CAGR
- Value: 10.2% CAGR
- Retail Digital Payments: From 162 crore transactions in FY13 to 16,416 crore in FY24 — a 100-fold increase in 12 years.
- Digital Payments Index (DPI): Surged from a base of 100 in March 2018 to 445.50 in March 2024, indicating massive digital adoption.
UPI: A Game-Changer
- Launched in 2016 by NPCI, UPI has revolutionized mobile-based payments.
- CAGR (Last 5 Years):
- Volume: 74.03%
- Value: 68.14%
- Monthly Transactions: UPI processes over 16 billion transactions monthly, ranking among the largest globally.
- Inclusive Innovations:
- UPI Lite & UPI Lite X: For offline/small-value payments.
- UPI123Pay: For feature phone users.
- UPI 2.0: Includes auto-debit and recurring payment functionalities.
Credit and Debit Card Trends
- Credit Cards:
- Growth: More than doubled from 5.53 crore (Dec 2019) to 10.80 crore (Dec 2024).
- Debit Cards:
- Stable Usage: Marginal increase from 80.53 crore to 99.09 crore in the same period.
Cross-Border Payment Integration
- RBI is actively enhancing cross-border payments by integrating India's UPI with international Fast Payment Systems (FPSs), addressing high costs, delays, and limited access.
- Key Developments:
- UPI-PayNow Linkage (Feb 2023): India-Singapore real-time cross-border payments.
- UPI-enabled QR Payments: Available in Bhutan, France, Mauritius, Nepal, Singapore, Sri Lanka, UAE.
- Project Nexus:
- A BIS-conceptualized multilateral project.
- Aims to interlink FPSs of India, Malaysia, Philippines, Singapore, and Thailand for seamless retail payments.
Institutional and Legal Framework
- Legal Backbone: Payments and Settlement Systems Act, 2007 (PSS Act) empowers RBI to:
- Regulate, supervise, and license payment system operators.
- Authorize systems like NPCI, card networks, ATM operators, etc.
- Governing Body:
- Board for Regulation and Supervision of Payment and Settlement Systems (BPSS) under RBI.
- Chairperson: RBI Governor; Vice-Chairperson: Deputy Governor (in charge of DPSS).
- Payment Ecosystem Entities:
- RBI-regulated: RTGS, NEFT, Cheques (CTS).
- NPCI-managed: UPI, IMPS, AePS, BBPS, NETC, NACH, Cards.
- Other PSOs: TReDS, PPIs.
Strategic Significance
- Financial Inclusion: Payment systems are critical tools for promoting inclusive growth by ensuring last-mile delivery of services and direct benefit transfers.
- Global Competitiveness: RBI’s regulatory foresight and innovation have placed India among the global frontrunners in digital payments.
Libia Lobo Sardesai

- 28 Jan 2025
In News:
In 2024, at the age of 100, Libia Lobo Sardesai was awarded the Padma Shri for her pivotal role in Goa’s liberation struggle from Portuguese colonial rule.
About Libia Lobo Sardesai
- Born: 25 May 1924, in Portuguese-ruled Goa; raised in Mumbai.
- Profession: Freedom fighter, broadcaster, and Goa’s first Director of Tourism post-liberation.
- Legacy: Symbol of courage and resistance, known as the “voice of Goa’s liberation.”
Role in Goa’s Liberation Movement
- Involvement: Joined the Goan nationalist movement during her college years.
- Underground Radio:
- From 1955 to 1961, Libia, along with her husband Vaman Sardesai and Nicolau Menezes, ran an underground radio station – initially called ‘Q’, later named:
- Goenche Sodvonecho Awaz (Voice of Freedom of Goa) – Konkani
- Voz de Liberdade – Portuguese
- Operated from Amboli (Maharashtra) and Castle Rock (Karnataka) in the Western Ghats.
- Purpose: Counter Portuguese censorship and propaganda; broadcast news, updates, and morale-boosting messages to Goans.
- From 1955 to 1961, Libia, along with her husband Vaman Sardesai and Nicolau Menezes, ran an underground radio station – initially called ‘Q’, later named:
- Final Broadcast:
- On 19 December 1961, Libia flew over Panaji in an IAF plane, announcing Goa’s liberation with the message:
“Rejoice brothers and sisters, Rejoice! Today, after 451 years of alien rule, Goa is free and united with the Motherland.”
Goa Liberation Movement: Background
- Colonial Rule: Goa was under Portuguese rule for over 451 years (from 1510 to 1961).
- Key Phases:
- 1954: India imposed an economic blockade after Portuguese crackdown on satyagrahis.
- August 1955: Mass satyagraha met with violent repression by Portuguese forces.
- Censorship: Portuguese regime enforced total censorship; only official Portuguese narratives were allowed.
- 1961 – Operation Vijay:
- Initiated on 17 December 1961 by the Indian Army under Lt. Gen. J.N. Chaudhuri.
- Portuguese forces surrendered by 19 December 1961, marking Goa’s official liberation.
Notable Leaders of the Movement
- Dr. Ram Manohar Lohia: Sparked initial resistance against Portuguese rule.
- Libia Lobo Sardesai: Voice of the resistance via underground broadcasting.
- Lt. Gen. J.N. Chaudhuri: Led military operations during Operation Vijay.
Significance
- Libia Lobo Sardesai represents the unsung contributions of civil resistance and communication warfare in India’s decolonization.
- Her work sustained nationalist morale, informed citizens under censorship, and shaped the narrative of a liberated Goa.
Aero India 2025
- 28 Jan 2025
In News:
Aero India 2025, the 15th edition of India’s premier aerospace and defence exhibition, is scheduled from February 10–14, 2025, at the Yelahanka Air Force Station, Bengaluru.
Organised by the Ministry of Defence and the Defence Exhibition Organisation (DEO), the event continues to be a vital forum for promoting India's indigenous defence capabilities and fostering international collaboration.
Evolution of Aero India: From Showcase to Strategic Asset
- Inception (1996): Launched as a modest exhibition to attract foreign investments and highlight India’s aerospace potential.
- Growth Phase (2005–2015): Marked by the entry of global giants like Boeing, Airbus, Lockheed Martin, and Dassault Aviation. Indigenous platforms like LCA Tejas began gaining prominence.
- Current Phase (2015–Present): Aligned with ‘Make in India’ and ‘Aatmanirbhar Bharat’, Aero India has become a symbol of India's defence self-reliance and a magnet for global partnerships.
Aero India 2025 Highlights
1. International Participation and Strategic Displays
- Participation from 15+ countries and major OEMs.
- Russia’s Su-57 and USA’s F-35—two of the world’s most advanced 5th-generation fighters—will be showcased together, reflecting India’s growing strategic importance.
- Other prominent platforms: KC-135 Stratotanker, Embraer C-390, and Light Combat Helicopter Prachand.
2. Indigenous Innovation
- Advanced Medium Combat Aircraft (AMCA): India’s 5th-generation stealth fighter, developed by HAL and ADA, will be unveiled.
- Indigenous platforms like LCA Mk2, LUH, HTT-40, ALH, and Naval Twin-Engine Deck-Based Fighter will also be featured.
3. Start-Up Integration via 'Manthan'
- Through the iDEX initiative, Aero India is promoting start-ups working in AI, unmanned systems, cybersecurity, and electronic warfare.
- Start-ups will showcase innovations including jetpack suits, robotics, and defence software tools.
4. Business & Public Engagement
- Business Days: February 10–12, 2025
- Public Days: February 13–14, 2025
- Over 7 lakh visitors expected; the event offers aerial displays, seminars, tech expos, and networking forums.
5. Defence Diplomacy and Deals
- Aero India 2023 had seen over ?80,000 crore worth of MoUs. A similar or higher scale of defence agreements is expected in 2025.
- High-level participation from defence ministers, air chiefs, and CEOs of OEMs, signalling deepening international defence cooperation.
Strategic Significance for India
- Geopolitical Leverage: Participation of both US and Russian defence firms signals India’s strategic autonomy and balanced defence diplomacy.
- Self-Reliance Boost: The event enhances domestic manufacturing by integrating MSMEs, promoting co-development and co-production with foreign partners.
- Global Recognition: Positions India as an emerging aerospace hub in the Indo-Pacific.
- Technological Edge: Demonstrates advancements in stealth technology, avionics, and unmanned systems.
Theme of Aero India 2025: “The Runway to a Billion Opportunities” — highlighting India’s expanding defence manufacturing capabilities and its aim to integrate with the global supply chain.
Uniform Civil Code (UCC) in Uttarakhand

- 28 Jan 2025
In News:
On January 27, 2025, Uttarakhand became the first Indian state to formally implement the Uniform Civil Code (UCC) after Independence. The legislation was passed by the State Assembly on February 7, 2024, and received Presidential assent on March 12, 2024.
Historical Background:
- A five-member expert committee chaired by Justice (Retd.) Ranjana Prakash Desai was constituted to draft the UCC report.
- The committee submitted its report on October 18, 2023.
- Though initially scheduled for implementation by November 9, 2024 (Uttarakhand's Foundation Day), the rollout was delayed due to administrative preparedness and staff training.
Scope and Applicability:
- Applicable to all residents of Uttarakhand, including those in live-in relationships outside the state.
- Scheduled Tribes (as per Article 342) and migrated natives have been exempted to safeguard cultural rights.
Key Provisions of the UCC:
1. Marriage, Divorce & Live-in Relationships
- Legal marriage age: 21 years (men), 18 years (women).
- Mandatory registration of marriages, divorces, and live-in relationships.
- Prohibited practices: Triple talaq, halala, iddat, polygamy, and child marriage.
- Live-in Relationships:
- Mandatory registration for couples aged 21 and above.
- Parental consent required if under 21.
- Termination of live-in relationships requires mutual consent.
- Mandatory reporting of pregnancy within 30 days of childbirth.
- Landlords cannot deny housing to registered live-in couples.
2. Inheritance & Property Rights
- Equal inheritance rights for sons and daughters.
- Children born to live-in couples recognized as legitimate, eligible for inheritance.
3. Wills and Succession
- Wills can be:
- Submitted online.
- Uploaded as handwritten/typed documents.
- Recorded as a 3-minute video.
Digital Infrastructure – UCC Portal (ucc.uk.gov.in):
- Aadhaar-based verification for authenticity.
- AI-based multilingual translation in 22 Indian languages.
- Tatkal service for expedited registrations with a nominal fee.
- Integrated with 13+ departments, including police, civic bodies, and courts.
- Disaster recovery systems and cloud-based architecture ensure secure data management.
- Access to:
- Online registration of marriages, divorces, live-in relationships.
- Upload and registration of wills.
- Grievance redressal and appeal mechanisms.
Administrative Framework:
- Village Panchayat Development Officers appointed as sub-registrars in rural areas.
- Common Service Centres (CSCs) enabled to facilitate registration, especially in remote and mountainous areas.
- Registration applications processed within 15 days, or 3 days in emergencies.
- Appeals must be filed within 30 days of rejection, resolved within 60 days.
Penalties:
- Initial warnings for non-compliance.
- Fines imposed for repeated violations.
Significance:
- The UCC aims to promote gender equality, legal uniformity, and women's empowerment.
- Represents a constitutional vision under Article 44, reinforcing the idea of a common civil law for all citizens.
- Seen as a potential model for other states in India.
Himachal Pradesh: Statehood Day
- 28 Jan 2025
In News:
The Prime Minister greeted the people of Himachal Pradesh (HP) on the occasion of Statehood Day (25th January).
Key Highlights:
Statehood Day: Celebrated annually on 25th January, marking the day Himachal Pradesh attained full statehood in 1971.
Historical Timeline:
- 15 April 1948: Formation of Chief Commissioner’s Province of Himachal Pradesh through the merger of 30 princely hill states.
- 26 January 1950: Became a Part C State with the commencement of the Indian Constitution. (Part C states comprised former Chief Commissioner’s provinces and some princely states.)
- 1 November 1956: Reconstituted as a Union Territory based on the recommendations of the States Reorganisation Commission.
- 1 November 1966: Kangra district and other hilly areas of Punjab merged into Himachal Pradesh, yet it remained a Union Territory.
- 18 December 1970: The State of Himachal Pradesh Act was passed by Parliament.
- 25 January 1971: Himachal Pradesh became the 18th state of the Indian Union.
Jawaharlal Nehru Port Authority

- 28 Jan 2025
In News:
The Jawaharlal Nehru Port Authority (JNPA) in Mumbai is set to become India’s first port to enter top global ports with 10 million TEUs (twenty-foot equivalent units) by 2027.
Overview:
- Location: Navi Mumbai, Maharashtra
- Commissioned: 1989
- Significance: India’s first Landlord Major Port, fully adopting the landlord port model.
Performance & Capacity Expansion:
- In 2024, JNPA handled a record 7.05 million TEUs, operating at over 90% capacity, with an 11% year-on-year growth.
- By 2027, JNPA is projected to become India’s first port to handle 10 million TEUs annually, marking its entry into the global top ports list.
- Current container handling capacity: 7.6 million TEUs
- Projected capacity by 2027: 10.4 million TEUs
Infrastructure Developments:
- Commissioning of Phase II of Bharat Mumbai Container Terminal (BMCT) to add 2.4 million TEUs.
- Upgradation of Nhava Sheva Freeport Terminal expected in 2025.
- Five operational container terminals, including:
- BMCT
- Nhava Sheva International Container Terminal (NSICT)
- Gateway Terminals India Pvt Ltd (GTIPL)
Key Projects & Investments (2024):
- ?2,000 crore worth of capacity enhancement projects launched.
- Solar-powered boat, two indigenously developed 70T tugs, and three fire tenders commissioned for safety and efficiency.
- Agro-processing facility (?284 crore) on 27 acres within port complex to handle 1.2 million tonnes annually – includes processing, sorting, packing, and food safety labs.
- Warehousing and CFS infrastructure (?300 crore investment) to generate 1,20,000 TEUs/year through ambient and temperature-controlled facilities.
Vadhavan Port Project:
- Proposed as India’s 13th major port (under construction).
- MoU with Reliance Industries Ltd: Development of liquid jetty and 50 acres of land under PPP model (investment: ?645 crore; operational by 2030).
- MoU with DBKKVD Dapoli: For integrated agri-horticultural development in Dahanu and Palghar.
- MoU with HUDCO: Funding commitment of ?25,000 crore for port infrastructure under PPP mode.
Strategic Importance:
- JNPA is central to India’s maritime trade, which accounts for 95% of trade by volume and 70% by value.
- Satellite and dry ports at Vadhavan, Jalna, and Wardha to improve hinterland connectivity and trade logistics.
Paraquat Poisoning

- 27 Jan 2025
In News:
- In a landmark ruling, a Thiruvananthapuram court sentenced a 24-year-old woman to death for the murder of her boyfriend by poisoning him with paraquat, a highly toxic herbicide.
- The incident, which occurred in 2022, has brought the spotlight back on paraquat's widespread availability, extreme toxicity, and the lack of regulatory enforcement in India.
What is Paraquat?
- Paraquat, chemically known as paraquat dichloride or methyl viologen, is one of the most widely used herbicides globally.
- It is primarily used for:
- Weed control
- Crop desiccation, especially in crops like cotton before harvest
- Despite its toxicity, India and the United States continue to permit its usage, unlike over 70 countries, including China, Brazil, and the European Union, which have banned it.
WHO Classification
- The World Health Organization (WHO) classifies paraquat as a Category 2 chemical, meaning it is moderately hazardous and irritating to the skin and eyes.
- It has a narrow margin between a safe and lethal dose, making accidental or intentional poisoning common and often fatal.
Routes and Effects of Exposure
- Ingestion is the most common method of poisoning.
- It may also occur through inhalation or skin contact, especially if the exposure is prolonged or the skin is broken.
Symptoms Vary by Dosage and Exposure Time:
Exposure Level Symptoms and Organ Damage
Small Quantity Gradual damage to lungs, liver, kidneys, and heart over days/weeks
Large Quantity Immediate symptoms such as:
- Acute kidney failure
- Liver and heart failure
- Seizures
- Respiratory failure
- Severe abdominal pain
- Bloody diarrhea
- Nausea
- Mouth and throat swelling |
Treatment and Challenges
- No known antidote exists for paraquat poisoning.
- Treatment options include:
- Immunosuppressive therapy
- Charcoal hemoperfusion (a blood-purification technique)
- However, these treatments offer limited efficacy, especially in cases of large-dose ingestion.
Regulatory and Public Health Implications in India
- Despite paraquat’s well-documented toxicity, it remains:
- Legally available in India
- Easily accessible in rural markets
- The lack of regulation increases the risks of:
- Occupational exposure
- Accidental poisoning
- Use in crimes or suicides
Whip System in Indian Parliament

- 27 Jan 2025
In News:
Vice President Jagdeep Dhankhar recently criticized the party whip system, arguing that it curtails the freedom of expression of Members of Parliament (MPs) and enforces servility by mandating strict adherence to the party line. His remarks have sparked a renewed debate on the balance between party discipline and individual autonomy in a parliamentary democracy.
What is a Party Whip?
A whip in parliamentary parlance is both a directive and a designated official of a political party. The directive instructs legislators on voting behavior on specific issues such as bills, motions, or resolutions. The designated whip ensures attendance, adherence, and discipline within the party ranks.
- The term “whip” originated from England’s hunting tradition, where a “whipper-in” kept hounds within the pack.
- The political usage dates back to Edmund Burke in the British Parliament.
- In India, the whip system has been in place since the start of parliamentary governance.
Constitutional and Legal Framework
- The whip system is not mentioned in the Constitution, Rules of Procedure, or any statute, but functions through parliamentary conventions.
- The Anti-Defection Law (52nd Amendment, 1985) enforces the whip by allowing disqualification of MPs/MLAs for defying it, thus preserving political stability and party integrity.
Quorum Requirement: As per Article 100 of the Constitution, quorum in Parliament is one-tenth of the total membership:
- Lok Sabha: 55 members
- Rajya Sabha: 25 members
Types of Whips
- One-Line Whip: Informational—members may abstain.
- Two-Line Whip: Requires presence but does not dictate voting.
- Three-Line Whip: Strictest—mandates attendance and voting as directed.
- Violation can lead to disqualification under the Anti-Defection Law, unless two-thirds of the party members dissent together.
Functions and Significance
- Ensures Attendance: Maintains quorum during critical votes.
- Secures Support: Helps pass or oppose legislation.
- Maintains Discipline: Prevents cross-voting or defection.
- Internal Monitoring: Identifies discontent among MPs and informs party leadership.
- Party Cohesion: Acts as a channel between MPs and party high command.
- Democratic Functioning: Ensures government stability, especially during division voting, where numbers decide the fate of motions like the No-Confidence Motion.
For ruling coalitions, a united stance during such votes is crucial to showcase majority strength.
Chief Whip and Institutional Structure
- The Chief Whip is the most critical functionary in enforcing the whip.
- In the Lok Sabha, the Minister of Parliamentary Affairs usually acts as the government’s chief whip.
- In the Rajya Sabha, it is the Minister of State for Parliamentary Affairs.
- Whips also coordinate which MPs speak, when, and on what issues.
The All-India Whips Conference, held since 1952, allows whips from all parties to discuss coordination strategies and share parliamentary practices.
Criticism and Contemporary Debate
- Critics, including the Vice President, argue that whips limit deliberative democracy, reduce MPs to mere rubber stamps, and suppress individual judgment.
- However, supporters claim that whips are essential to prevent chaos, ensure smooth functioning, and uphold mandated party ideologies, especially in a system where governments often hinge on narrow majorities.
Former Lok Sabha Speaker Sumitra Mahajan defended the whip, stating that MPs elected on a party ticket must uphold the party’s collective ideology and decisions, even if personal disagreement exists.
India’s Journey of Fiscal Consolidation

- 27 Jan 2025
In News:
Fiscal Consolidation refers to the strategic management of government finances aimed at reducing fiscal deficits, controlling public debt, and ensuring macroeconomic stability. India’s recent journey in this regard has been marked by a significant transformation, particularly in the post-2014 era.
Background:
In 2013-14, India was labelled as one of the "Fragile Five", largely due to its ballooning fiscal deficit (touching 5% of GDP in a quarter), high inflation, and weakening currency. This tag underscored the urgency of restoring fiscal health.
Post-2014 Measures:
- FRBM Act Revamp: The government recommitted to the Fiscal Responsibility and Budget Management (FRBM) Act, 2003, revising fiscal targets and focusing on fiscal discipline.
- Deficit Reduction: Fiscal deficit was reduced from 4.5% of GDP in FY 2013-14 to 3.4% in FY 2018-19.
- Revenue Boost: Digitization and broader tax reforms helped increase tax receipts from 10% of GDP (FY 2014-15) to 11.8% (FY 2023-24).
- Capex Focus: Capital expenditure nearly doubled from 1.6% of GDP in FY 2014-15 to 3.2% in FY 2023-24, emphasizing infrastructure over consumption.
Pandemic Impact and Recovery:
- During COVID-19, India’s fiscal deficit soared to 9.2% of GDP (FY 2020-21) due to emergency spending.
- Unlike blanket stimulus in some countries, India opted for targeted support (MSMEs, displaced populations, healthcare) while continuing infrastructure investment.
- This strategy avoided long-term inflationary pressure and built long-term productive capacity.
Structural Reforms:
- Production Linked Incentive (PLI) schemes aimed at reducing import dependence and boosting domestic manufacturing.
- Enhanced export competitiveness due to fiscal prudence and macroeconomic stability.
Current Scenario:
- Fiscal deficit reduced to 5.6% of GDP in FY 2023-24, with a target of 4.9% in FY 2024-25, and further narrowing to 4.5% by FY 2025-26.
- States remain a concern: their deficits exceed the 3% of GSDP limit, averaging 3.2% in FY 2023-24, with rising debt levels and declining capex.
FRBM Act & N.K. Singh Committee:
- FRBM Act (2003) aims to cap the fiscal deficit at 3% of GDP.
- The N.K. Singh Committee (2016) recommended:
- Shift from rigid deficit targets to debt as the primary anchor.
- Set up an autonomous Fiscal Council.
- Flexibility via an “escape clause” (up to 0.5% extra deficit during crises).
- Limit borrowings from RBI to specific emergency conditions.
Significance of Fiscal Consolidation:
- Macroeconomic Stability: Controls inflation and keeps currency stable.
- Investment Magnet: Low deficits improve investor confidence.
- Reduced Debt Burden: Less borrowing means less stress on future generations.
- Efficient Governance: Ensures better resource allocation and economic resilience.
Chronic Pulmonary Aspergillosis (CPA)

- 27 Jan 2025
In News:
A recent study conducted by Assam Medical College and Hospital has revealed a high prevalence of Chronic Pulmonary Aspergillosis (CPA) among tuberculosis (TB) survivors in Assam’s tea garden communities. Published in the PLOS Neglected Tropical Diseases journal, the research underscores a significant public health concern in a region already burdened by TB.
What is Chronic Pulmonary Aspergillosis (CPA)?
- CPA is a severe, life-threatening fungal infection caused by Aspergillus fumigatus, a filamentous fungus commonly found in soil, decaying vegetation, and humid organic matter.
- It predominantly affects individuals with weakened immune systems or pre-existing lung conditions, especially those who have recovered from or are currently battling TB.
- CPA is not contagious and cannot be transmitted from person to person.
Symptoms and Clinical Presentation:
CPA shares many clinical features with TB, making diagnosis challenging:
- Chronic cough
- Haemoptysis (coughing up blood)
- Persistent respiratory symptoms
- Weight loss
- Fatigue
- Shortness of breath
- Wheezing
Key Findings from Assam:
- Study Area: Conducted in Dibrugarh district, covering tea workers and their dependents from four major tea estates.
- Sample Size: 128 patients with prolonged respiratory symptoms (>3 months).
- Prevalence:
- CPA prevalence: 17.18% overall
- Seropositivity in active TB patients: 18.5%
- Seropositivity in post-TB patients: Spiked to 48.9%, indicating a strong link between CPA and previous TB infections.
- Demographic Insights:
- Mean age: 41.9 years
- Higher incidence among middle-aged male workers
- Comparison with Global Trends:
- Assam’s CPA prevalence (60 per 1,00,000) exceeds the global average (42 per 1,00,000)
- Worse than several African nations including Nigeria and the Democratic Republic of Congo (20–50 per 1,00,000)
Contributing Risk Factors in Assam’s Tea Belt:
- High TB burden: 217 per 1,00,000 (National TB Prevalence Survey 2019–2021)
- Poverty and malnutrition
- Kitchen smoke exposure
- Congested living conditions
- Delayed or inadequate TB treatment
Diagnosis and Treatment:
- Diagnosis:
- Serological testing for Aspergillus antibodies
- Radiological imaging to identify fungal growth in lung cavities
- Treatment:
- Antifungal therapy (e.g., itraconazole or voriconazole)
- Surgical removal in severe cases with fungal mass
Public Health Recommendations:
- Routine screening of post-TB patients for CPA in high-risk zones like tea estates
- Awareness campaigns targeting healthcare providers and workers to improve recognition and response
- Education on nutrition, respiratory hygiene, and early symptom detection
- Inclusion of fungal diseases like CPA in broader national TB and occupational health programs
Additional Context: Epidemic Dropsy in Assam’s Tea Belt
- A 2019 study had previously flagged the prevalence of epidemic dropsy, a condition caused by contaminated edible oils with Argemone mexicana oil, adding to the health risks in tea-growing regions.
Unified Pension Scheme (UPS)

- 27 Jan 2025
In News:
The Ministry of Finance has notified the Unified Pension Scheme (UPS) as an option under the National Pension System (NPS) for Central Government employees, effective April 1, 2025. This reform addresses long-standing concerns about the unpredictability of pension returns under the NPS.
Key Highlights:
- Applicability: Applies to Central Government employees currently under the NPS, including those recruited on or after January 1, 2004, who opt for the UPS.
- Objective: To provide guaranteed post-retirement financial security, addressing grievances regarding the market-linked returns of the NPS.
- Regulatory Framework: The scheme will be regulated by the Pension Fund Regulatory and Development Authority (PFRDA), which will issue detailed operational guidelines.
Pension and Benefit Structure
- Guaranteed Monthly Pension:
- 50% of the average basic pay drawn in the last 12 months prior to retirement.
- Requires completion of 25 years of service.
- Those with 10–25 years of service will receive a proportionate pension.
- Dearness Relief (DR): Periodic adjustments based on inflation trends to maintain pension value.
- Family Pension: In case of death, 60% of the employee's pension will be paid to eligible family members.
- Minimum Pension: Assured ?10,000 per month for those completing at least 10 years of service.
- Superannuation Benefits: Includes a lump sum payout and gratuity at retirement.
Contribution Mechanism
- Employee Contribution: 10% of basic pay.
- Government Contribution: 5% of basic pay (subject to revision based on actuarial evaluations).
Background and Policy Evolution
- The Union Cabinet approved the UPS on August 24, 2024, benefiting nearly 2.3 million Central Government employees.
- The move followed demands from staff unions for guaranteed pensions, and political pressure after several states reverted to the Old Pension Scheme (OPS).
- A high-level committee, led by T.V. Somanathan (then Finance Secretary), was formed in April 2023 to review the NPS framework and design an equitable alternative.
ISRO’s NVS-02 Satellite Launch

- 25 Jan 2025
In News:
ISRO successfully launched the NVS-02 satellite aboard GSLV-F15, placing it into a Geosynchronous Transfer Orbit (GTO). This marks ISRO’s 100th mission, reinforcing India’s space and navigation capabilities under the NavIC (Navigation with Indian Constellation) program.
What is NavIC?
- NavIC is India’s indigenous regional satellite navigation system, developed for both civilian and strategic use.
- Offers accurate positioning over India and up to 1,500 km beyond its borders.
- Comparable to GPS (USA), GLONASS (Russia), Galileo (EU), and BeiDou (China).
About NVS-02 Satellite:
Feature Description
Series Second satellite in the next-gen NVS series (after NVS-01 in 2023)
Mission Role Replaces aging IRNSS-1E satellite
Mass 2,250 kg
Power Capacity ~3 kW
Orbit Final orbital slot at 111.75°E in geosynchronous orbit (~36,000 km)
Life Span 12 years
Developed by URSC (U R Rao Satellite Centre), Bengaluru
Technological Advancements:
- Equipped with navigation payloads across L1, L5, and S-bands for enhanced accuracy and broader coverage.
- Features the Rubidium Atomic Frequency Standard (RAFS) – an indigenously developed atomic clock for precision timekeeping.
- Includes C-band ranging payload, similar to NVS-01.
Significance of NVS-02:
- Enhances NavIC’s positioning accuracy for civilian, commercial, and strategic applications:
- Disaster management
- Fleet tracking
- Precision agriculture
- Emergency response
- Mobile navigation
- L1 signal inclusion makes NavIC-compatible with international GNSS systems, improving global device integration.
- Demonstrates India’s technological self-reliance, particularly in atomic clock development.
ISRO’s Launch Vehicles
Vehicle First Flight Notable Use
SLV 1980 Launched Rohini satellite
ASLV 1987 Five-stage solid rocket, retired in 1990s
PSLV 1994 Reliable, used for Mars Orbiter, LEO missions
GSLV 2001 Used for heavier payloads, INSAT/GSAT
GSLV 2014 Heavy-lift, Chandrayaan-2/3, Gaganyaan crew module
Mk III (LVM3)
SSLV 2022 Affordable launches for nano/micro satellites
PKC-ERCP: Rajasthan’s River-Linking Project
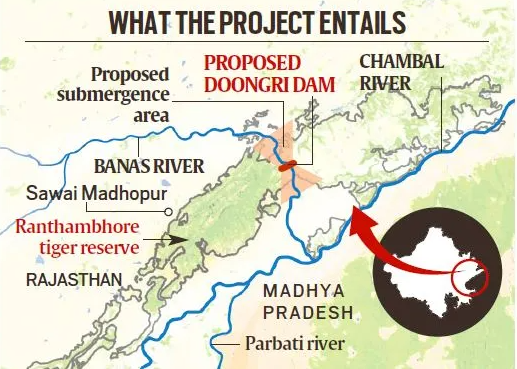
- 25 Jan 2025
In News:
The Parbati-Kalisindh-Chambal-Eastern Rajasthan Canal Project (PKC-ERCP), part of the National Interlinking of Rivers (ILR) programme, aims to address water scarcity in 23 districts of Rajasthan, potentially benefiting 3.45 crore people. However, it has raised serious concerns over its ecological impact, particularly on the Ranthambore Tiger Reserve.
About the PKC-ERCP Project:
Aspect Details
Objective To channel surplus water from the Chambal basin for irrigation, drinking, and industrial use in Rajasthan and Madhya Pradesh
Estimated Cost ?72,000 crore (90% funded by the Central Government)
Water Allocation 4,100 MCM to Rajasthan and 3,000 MCM to Madhya Pradesh
Rivers Involved Chambal, Parbati, Kalisindh, Banas, and tributaries
Major Structure 39 m high, 1.6 km long dam across the Banas River, a Chambal tributary, near Doongri village, ~30 km from Sawai Madhopur
Submergence and Environmental Concerns:
- Total Submergence: ~408.86 sq km in Rajasthan.
- Reservoir Impact: 227 sq km to be submerged under the proposed dam across Banas River.
- Impact on Tiger Reserve:
- 37.03 sq km of the Ranthambore Tiger Reserve (total area: 1,133 sq km) to be submerged.
- This includes parts of Ranthambore National Park (392 sq km) and Keladevi Wildlife Sanctuary (674 sq km).
- May fragment the reserve, disrupting wildlife corridors and tiger movement.
- Ranthambore’s Significance:
- Home to ~57 tigers, it is one of India’s most prominent conservation areas.
- Situated at the Aravalli-Vindhya junction, with rich biodiversity, including leopards, hyenas, sloth bears, and iconic flora like Dhok trees.
- Encompasses the UNESCO-listed Ranthambore Fort and the Great Boundary Fault.
Arguments For the Project:
- Addresses chronic water scarcity in eastern Rajasthan.
- Promotes agricultural productivity, drinking water security, and industrial development.
- Aims to optimize water use by diverting surplus flows.
Arguments Against the Project:
- Biodiversity loss due to habitat submergence and reserve fragmentation.
- Risks to tiger conservation efforts.
- Potential violation of environmental safeguards under the Wildlife Protection Act and Forest Conservation norms.
Long-term ecological costs may outweigh short-term developmental gains.
SEBI’s Sachetisation of Mutual Funds
- 25 Jan 2025
In News:
In January 2025, the Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI) proposed the “sachetisation” of mutual fund investments to promote financial inclusion, especially among low-income and first-time investors.
What is Sachetisation?
- Originating from the FMCG sector (e.g., shampoo sachets), sachetisation refers to offering financial products in small, affordable units, enhancing accessibility and affordability.
- In capital markets, it implies micro-level investment options, particularly through low-ticket SIPs (Systematic Investment Plans).
Objectives:
- Promote financial inclusion and empower economically underserved sections.
- Expand mutual fund penetration to semi-urban and rural areas.
- Encourage long-term savings and wealth creation among new investors.
- Reduce dependency on large institutional or foreign investors by broadening the domestic retail base.
Key Features of SEBI’s Sachet SIP Proposal:
Feature Details
Minimum SIP Amount ?250 per month
Eligibility Only for new mutual fund investors
Investment Limit Up to 3 sachet SIPs across different AMCs
Excluded Schemes Debt funds, sectoral/thematic, small-cap, mid-cap equity funds (due to higher risk)
Commitment Period Encouraged to commit for 5 years (60 SIPs), but premature withdrawal allowed
Payment Modes Only via auto-pay mechanisms such as UPI Autopay and NACH
Cost Incentives AMCs to receive subsidies from SEBI’s Investor Education and Awareness Fund
Distributor Incentive ?500 per investor after completion of 24 monthly SIPs
Significance:
- Democratizes investment access by lowering the entry barrier for mutual funds.
- Encourages behavioral shift towards long-term financial planning and discipline.
- Stabilizes domestic markets by broadening and diversifying the retail investor base.
Supports SEBI’s vision of making capital markets inclusive, tech-enabled, and accessible.
Fiscal Health Index (FHI) 2025

- 25 Jan 2025
In News:
NITI Aayog launched the inaugural Fiscal Health Index (FHI) 2025 on 24 January 2025 in the presence of the 16th Finance Commission Chairman, Dr. Arvind Panagariya. The index evaluates the fiscal performance of 18 major Indian states using FY 2022–23 as the base year.
Key Highlights:
- Objective: To assess, monitor, and improve the fiscal health of Indian states and foster balanced regional development, economic resilience, and fiscal transparency. It aims to support the national goal of Viksit Bharat @2047.
- Developed by:
- NITI Aayog, with data sourced from the Comptroller and Auditor General (CAG).
- Designed as an annual publication to promote informed and targeted state-level policy reforms.
- Evaluation Parameters:
The index comprises five sub-indices that collectively offer a holistic picture of fiscal health:
- Quality of Expenditure – Efficiency in developmental and social sector spending (e.g., health, education).
- Revenue Mobilization – Tax and non-tax revenue generation capacity.
- Fiscal Prudence – Adherence to fiscal deficit targets and sound financial management.
- Debt Index – Absolute level of public debt.
- Debt Sustainability – Debt-to-GSDP ratio and interest burden on revenues.
Key Highlights from FHI 2025:
Top Performing States (Achievers):
Rank State FHI Score Strengths
1. Odisha 67.8 Low fiscal deficit, strong debt management, effective capital expenditure
2. Chhattisgarh 55.2 Revenue growth from mining, fiscal prudence
3. Goa 53.6 High tax efficiency and non-tax revenue
Aspirational States (Facing Challenges):
- Punjab, West Bengal, Kerala, Andhra Pradesh
- Issues: High debt-to-GSDP ratios, revenue deficits, poor revenue mobilization
Sub-Index Insights:
- Revenue Mobilization: Odisha, Goa, and Chhattisgarh excelled; Bihar and West Bengal lagged due to low own-tax revenues.
- Quality of Expenditure: Madhya Pradesh and Chhattisgarh prioritized social sectors; Punjab and Rajasthan underperformed in capital investment.
- Debt Management: Maharashtra and Gujarat maintained robust practices; Punjab and Haryana faced rising interest burdens.
- Debt Sustainability: Odisha and Chhattisgarh displayed strong sustainability; West Bengal and Punjab showed fiscal stress.
- Fiscal Prudence: Odisha and Jharkhand maintained low deficits, enabling better public investment.
Significance for Policy & Governance:
- Encourages healthy interstate competition and promotes cooperative federalism.
- Provides data-driven insights for targeted fiscal reforms.
- Reinforces the need for decentralized and transparent financial governance.
- Offers a benchmark for fiscal performance aligned with national transformation goals.
Recommendations:
- Enhance revenue base via tax reforms and tapping into non-tax sources.
- Boost capital expenditure in infrastructure, health, and education.
- Strengthen debt sustainability frameworks and reporting mechanisms.
- Institutionalize fiscal responsibility through better compliance and accountability.
Sanjay Battlefield Surveillance System

- 25 Jan 2025
In News:
Defence Minister Rajnath Singh recently flagged off Sanjay, an indigenously developed Battlefield Surveillance System (BSS), to be inducted into the Indian Army in phased manner from March to October 2025, designated as the ‘Year of Reforms’ by the Ministry of Defence.
Overview:
- Nature: Automated surveillance system
- Purpose: To integrate real-time data from ground and aerial sensors, enabling swift, informed decision-making in conventional and sub-conventional warfare scenarios.
Key Features:
- Common Surveillance Picture (CSP): Fuses verified sensor data to generate a real-time surveillance image of the battlefield.
- Real-time Integration & Analytics: Processes inputs using advanced analytics to eliminate duplication and enhance situational awareness.
- Secure Networks: Operates over the Indian Army’s Data Network and Satellite Communication Network, ensuring reliable and secure data flow.
- Centralized Web Application: Provides integrated inputs to Command Headquarters and Army HQ through a unified platform, supporting the Indian Army's Decision Support System.
- Indigenous Development: Jointly developed by the Indian Army and Bharat Electronics Limited (BEL) under the Buy (Indian) category, promoting Aatmanirbharta in defense.
Operational Significance:
- Enhances battlefield transparency, situational awareness, and surveillance capabilities along vast and sensitive land borders.
- Functions as a force multiplier in Intelligence, Surveillance & Reconnaissance (ISR) operations.
- Enables network-centric warfare, marking a shift towards data-driven military operations.
Deployment:
- To be inducted into all Brigades, Divisions, and Corps of the Army in three phases (March–October 2025).
Guillain-Barré Syndrome (GBS)
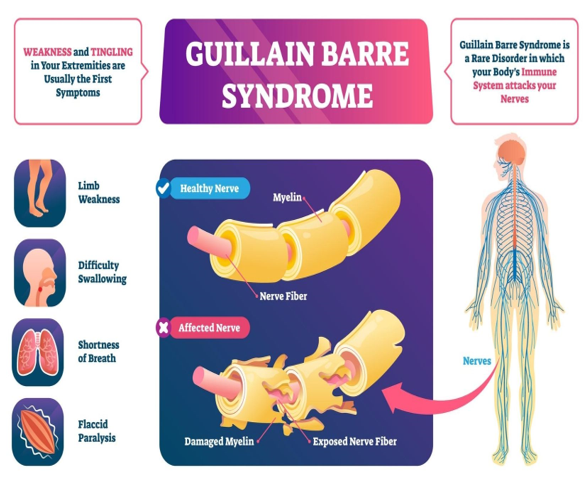
- 24 Jan 2025
In News:
The Pune Health Department has reported a surge in Guillain-Barré Syndrome (GBS) cases, prompting concern due to its severe neurological impact and association with prior infections or immune responses.
What is Guillain-Barré Syndrome?
- Nature of Disorder: A rare autoimmune condition where the body’s immune system attacks the peripheral nervous system, affecting voluntary muscle control and sensory signals (e.g., pain, temperature, and touch).
- Medical Term: Also known as Acute Inflammatory Demyelinating Polyradiculoneuropathy (AIDP).
- System Affected: Peripheral nerves, i.e., nerves outside the brain and spinal cord.
Epidemiology:
- Prevalence: Rare but potentially life-threatening.
- Age Group Affected: Can occur at any age but is most common between 30 to 50 years.
- Non-contagious: GBS is not transmitted from person to person.
Causes and Triggers:
- Exact Cause: Unknown, but usually follows an immune response to:
- Infections: Campylobacter jejuni (foodborne bacteria), Epstein-Barr Virus (EBV), Cytomegalovirus (CMV), respiratory or urinary tract infections.
- Vaccinations: Rarely observed post-immunisation.
- Surgery or trauma: Can act as physical stressors that trigger the syndrome.
Symptoms:
- Initial Signs: Tingling and weakness starting in the legs, progressing upwards.
- Progression:
- Weakness in arms, facial muscles.
- Difficulty walking or balancing.
- In severe cases, respiratory paralysis, requiring ventilator support.
- Onset: Can escalate within hours, days, or weeks.
- Range: Varies from mild muscle weakness to complete paralysis.
Impact:
- Neurological Disruption: Affects communication between the brain and muscles.
- Temporary but Debilitating: Most patients recover over weeks to months, though rehabilitation may be prolonged.
- Critical Care: May require intensive medical and respiratory support in acute stages.
Diagnosis & Treatment:
- No definitive cure, but early intervention improves outcomes.
- Main Treatments:
- Intravenous Immunoglobulin (IVIG):
- Contains healthy antibodies from donated blood.
- Helps suppress the immune attack on nerves.
- Plasmapheresis (Plasma Exchange): Filters harmful antibodies from the blood.
- Supportive Therapy:
- Mechanical ventilation in case of respiratory failure.
- Physiotherapy for muscle recovery and mobility.
Ad Hoc High Court Judges

- 24 Jan 2025
In News:
To address the mounting pendency of criminal cases in several High Courts, the Supreme Court of India has suggested invoking Article 224A of the Constitution, which allows the appointment of retired High Court judges on an ad hoc basis.
Constitutional Provision: Article 224A
- Title: Appointment of Retired Judges at Sittings of High Courts.
- Key Provision: The Chief Justice of a High Court, with the consent of the President, may invite retired judges of the same or other High Courts to act as judges temporarily.
- Status: These judges enjoy the powers, jurisdiction, and privileges of regular High Court judges, but are not deemed permanent judges.
Why the Provision is Being Invoked Now:
- Backlog of Cases: Over 40% vacancy rate in High Courts; huge pendency, especially of criminal cases.
- Delays in Regular Appointments: Slow process of regular judicial appointments prompted the Supreme Court to consider alternative mechanisms.
- Underuse of Article 224A: Only three recorded instances of ad hoc appointments since Independence:
- Justice Suraj Bhan – MP High Court (1972)
- Justice P. Venugopal – Madras High Court (1982–83)
- Justice O.P. Srivastava – Allahabad High Court (2007, Ayodhya case)
Judicial Interpretation – Lok Prahari v. Union of India (2021):
- The Supreme Court laid down guidelines for invoking Article 224A.
- The process must be routed through the SC collegium (CJI + 2 senior-most judges).
- Trigger Point for Appointment:
- High Court vacancies exceed 20% of sanctioned strength (excluding pending proposals).
- More than 10% of pending cases are over 5 years old.
Procedure for Appointment:
- Consent: Retired judge must agree to serve again.
- Initiation: Chief Justice of the High Court forwards the name.
- State and Centre: Proposal routed through State CM → Union Law Ministry.
- SC Collegium: Must review and approve the name.
- Executive Clearance: Law Ministry → PM → President for final approval.
Term & Allowances:
- Duration: Typically 2–3 years, renewable if required.
- Number of Judges: Suggested 2–5 ad hoc judges per High Court.
- Remuneration: Entitled to allowances as per Presidential order.
- Status: Have full judicial powers during tenure.
Concerns & Safeguards:
- Fear of using ad hoc appointments as a substitute for regular appointments.
- Therefore, SC mandates that regular appointment process must be underway before invoking Article 224A.
- Periodic review and panel creation of eligible retired judges recommended.
M23 Armed Group

- 24 Jan 2025
In News:
The March 23 Movement (M23), a rebel group active in eastern Democratic Republic of Congo (DRC), has intensified its insurgency in North Kivu province, capturing key areas like Minova and threatening the provincial capital, Goma.
About M23 Armed Group:
- Full Form: March 23 Movement
- Formation: 2012, by mutineers from the Congolese army protesting a failed 2009 peace deal.
- Base of Operations: Eastern DRC, primarily in North Kivu province.
- Activities: Armed rebellion, territorial control, ethnic conflict, disruption of state authority.
External Support:
- Rwandan Involvement:
- UN Reports (2023): Estimated 3,000–4,000 Rwandan troops operating alongside M23.
- Rwanda alleged to have “de facto control” over M23 operations.
- Kigali denies direct territorial aggression claims.
- International Concerns: The group’s resurgence reflects broader regional instability and transnational military dynamics.
Recent Developments (2024):
- Territorial Gains: Capture of Minova; encroachment on Goma, a strategic and densely populated city.
- Humanitarian Crisis:
- Over 2,30,000 displaced since January 2024.
- Influx of injured civilians in hospitals; risk of further displacement and violence.
- Congolese Military Weakness:
- Internal instability and operational setbacks have contributed to M23’s advances.
- The Congolese army acknowledged a “breakthrough” by M23 with external backing.
Geographical Significance of the Region:
- DRC Capital: Kinshasa
- Strategic Location: Borders 9 countries—Angola, Zambia, Tanzania, Burundi, Rwanda, Uganda, South Sudan, Central African Republic, Republic of Congo.
- Topography:
- Rwenzori & Virunga Mountains: Includes active volcanoes (e.g., Mount Nyiragongo).
- Congo River: Vital for transport, hydroelectric power, and biodiversity.
- Natural Resources:
- Rich in cobalt, coltan, gold, and other rare minerals—critical to the global tech industry.
- The mineral wealth of North Kivu is a major driver of prolonged conflict.
India’s Deep Ocean Mission

- 24 Jan 2025
In News:
India is set to deploy its first human-operated deep-sea submersible as part of the Deep Ocean Mission (DOM), marking a significant leap in the country’s marine research and technological capability.
Key Highlights:
- Submersible Deployment (2024):
- India will operate its first human submersible at a depth of 500 meters this year.
- The goal is to reach a depth of 6,000 meters by 2025.
- The project aligns with the timelines of Gaganyaan, India’s first human space mission—showcasing parallel progress in marine and space technology.
- Indigenous Technology:
- The mission is powered by 100% indigenous technology, underlining India’s growing self-reliance in high-end scientific infrastructure.
About Deep Ocean Mission (DOM):
- Launched: 2021
- Nodal Ministry: Ministry of Earth Sciences (MoES)
- Budget: ?4,077 crore over five years
- Framework: One of nine key missions under PM-STIAC (Prime Minister’s Science, Technology, and Innovation Advisory Council)
Core Objectives:
- Develop deep-sea technologies, including a manned submersible for ocean exploration.
- Explore and harness ocean resources such as: Polymetallic nodules, Hydrothermal sulphides & Rare earth metals
- Study marine biodiversity for sustainable fisheries and conservation.
- Support India’s blue economy through innovation and research.
- Monitor ocean climate change and develop advisory services.
- Promote marine biology and biotechnology via dedicated marine research stations.
- Harvest renewable energy and freshwater from ocean sources.
Key Components and Technologies:
Matsya6000 Submersible:
- India’s first manned deep-sea vehicle.
- Designed to reach 6,000 meters depth.
- Crew Capacity: Three members
- Developed by: National Institute of Ocean Technology (NIOT), Chennai
- Structure: Made of titanium alloy, withstanding 6,000 bar pressure
- Equipped with: Scientific sensors, tools for sampling, viewports, propellers, and acoustic communication systems.
- Combines capabilities of ROVs (Remotely Operated Vehicles) and AUVs (Autonomous Underwater Vehicles).
Varaha Deep-Ocean Mining System:
- Developed by NIOT
- Successfully conducted trials at 5,270 meters
- Key to India’s future in deep-sea mining of critical minerals
Strategic Importance:
- Scientific Advancement: DOM places India among a select group of nations (USA, Russia, China, France, Japan) with human-crewed deep-ocean exploration capacity.
- Economic Potential: Unlocks access to underwater mineral wealth, critical for electronics, defense, and energy sectors.
- Environmental Sustainability: Supports marine biodiversity conservation and promotes sustainable use of oceanic resources.
- Geopolitical Significance: Enhances India’s presence and influence in the Indian Ocean Region (IOR).
- Technological Leap: Strengthens India’s capabilities in underwater robotics, materials engineering, and ocean sciences.
Is Poverty Being Underestimated in India?

- 24 Jan 2025
In News:
The recent 2023-24 Household Consumption Expenditure Survey (HCES) showed a decline in poverty across rural and urban India. However, questions have emerged about whether poverty is being underestimated, due to changes in methodologies, definitions, and data availability.
Evolution of Poverty Measurement in India
- 1970s to 2005: Poverty was defined based on minimum calorie intake; updated every 5 years using NSSO data.
- Tendulkar Committee introduced in response to divergence between NSSO and National Accounts data.
- Post-2011-12: No official poverty estimates or surveys; alternative indices like Multidimensional Poverty Index (MPI) were used.
Current Data Issues
- Different recall periods in surveys (7-day, 30-day, 365-day) create non-comparability.
- Modified Mixed Recall Period (MMRP) introduced in 2017-18 and improved upon in recent years with three household visits, enhancing recall and thus raising reported expenditures.
- Result: Using older poverty lines on newer, higher expenditure data underestimates poverty.
Diverging Poverty Estimates
- Dr. C. Rangarajan (2022-23): Estimated poverty at around 10%.
- Recent factsheet (2023-24) suggests poverty may have declined to single digits.
- A paper using Rangarajan’s methodology on 2022-23 HCES data estimated 25% poverty, but this is debated.
Reasons for Poverty Reduction
- High GDP growth, increased public expenditure, and improved public delivery systems.
- National Food Security Act covers nearly 80 crore people.
- Broadened definition of poverty now includes non-food items and essential services.
- Decline in poverty estimated around 17-18% between 2011-12 and 2023-24.
Rural-Urban Trends
- Consumption gap between rural and urban areas is narrowing.
- Rural consumption patterns becoming more urban-like.
- 2011 Census definitions outdated — many rural areas are peri-urban in character.
Need for Poverty Line Revision
- Lack of consensus and official backing on methodology hinders creation of a new poverty line suited to current data.
- UNDP’s global poverty line is $2.15/day; India’s poverty was 12.9% in 2019 by that metric.
- NITI Aayog’s estimates do not support 25% poverty claim.
Debate on Multidimensional Poverty Index
- India’s MPI (12 indicators) differs from UNDP’s 10-indicator framework.
- Additions like bank accounts and maternal health are India-specific.
- Criticism: Once indicators (e.g., electricity, bank accounts) are met, they remain met — poverty appears to decline permanently, while income vulnerability is not captured.
Estimation and Measurement of India’s Digital Economy – MeitY Report (2025)

- 23 Jan 2025
In News:
Release of Report ‘Estimation and Measurement of India’s Digital Economy’ by Ministry of Electronics & Information Technology.
Key Highlights:
- Released by: Ministry of Electronics & Information Technology (MeitY)
- Prepared by: Indian Council for Research on International Economic Relations (ICRIER)
- Significance: First credible and current estimate of the digital economy using international frameworks (OECD & ADB).
- India is the first developing country to adopt the OECD framework for measuring the digital economy.
Key Findings (2022–23)
Indicator Details
Size ?31.64 lakh crore (~USD 402 billion), 11.74% of national income (GVA)
Employment 14.67 million workers (2.55% of the workforce)
Projected Share by 2029–30 Nearly 20% of GDP (surpassing agriculture & manufacturing)
Structure of India’s Digital Economy
- Digitally Enabling Industries (7.83% of GVA): ICT services, telecom, manufacturing of digital hardware
- New Digital Industries (2%): Big Tech, digital platforms, intermediaries (e.g., e-commerce, ride-sharing)
- Digitalization of Traditional Sectors (2%): BFSI (Banking, Financial Services, Insurance), trade, education
- Insight: Digital transformation is spreading beyond ICT into traditional sectors.
Frameworks Used
Framework Purpose
OECD Estimating core digital and enabling sectors
ADB Input-Output Broader economic impact via inter-industry linkages
India’s Expansion Includes digital share in BFSI, trade, education – not covered under OECD
Key Drivers of India’s Digital Economy
- Widespread mobile use: 1.14 billion subscribers in India
- High internet traffic: 3rd globally, with avg. 16.9 GB/month
- 5G leadership: 2nd largest 5G smartphone market in 2024
- Aadhaar success: 1.3+ billion biometric IDs issued
- Digital payments boom: 1,644 billion transactions in FY24
- ICT service exports: USD 162 billion (2nd highest globally)
- AI leadership: India leads GitHub AI contributions (23%)
- Startup ecosystem: 3rd highest number of unicorns globally
Future Projections (By 2030)
- Digital economy to reach ~20% of national income
- Growth drivers:
- Expansion of digital platforms & intermediaries
- Deepening digitalization in all sectors
- Greater internet & broadband access
Challenges in Measuring Digital Economy
- Difficulty in defining digital sectors due to their integrated nature
- Conventional national accounting systems are inadequate
- Lack of data from:
- Informal sector digitalization
- Smaller platforms and startups
- Digital shifts in healthcare, logistics, etc.
Importance of This Report
- Policy Formulation: Enables targeted strategies for digital growth
- Business Strategy: Helps identify trends, plan investments
- Global Standing: Puts India among early adopters of robust measurement frameworks
Mission SCOT

- 23 Jan 2025
In News:
The Prime Minister of India praised Indian space startup Digantara for the successful launch of Mission SCOT (Space Camera for Object Tracking) — the world’s first commercial SSA satellite, launched via SpaceX’s Transporter-12 rideshare mission.
What is Mission SCOT?
Feature Description
Developer Digantara (Indian space startup), supported by Aditya Birla Ventures & SIDBI
Launched on SpaceX Transporter-12 mission (rideshare platform)
Type First commercial Space Situational Awareness (SSA) satellite
Orbit Sun-Synchronous Orbit – ideal for consistent Earth observation
Function Tracks Resident Space Objects (RSOs) as small as 5 cm in Low Earth Orbit (LEO)
What is Space Situational Awareness (SSA)?
- SSA involves the detection, tracking, cataloging, and prediction of natural and man-made objects in Earth's orbit (like satellites, debris, etc.).
- Ensures safe and sustainable operations by minimizing collision risks.
- Critical due to increasing congestion in LEO, especially with rising numbers of small satellites and mega-constellations.
Key Features of Mission SCOT
Feature Advantage
High Revisit Rate More frequent observations of objects in orbit
Precision Tracking Can track debris ≥ 5 cm in size
All-Weather Monitoring Overcomes limitations of ground-based systems like cloud cover, FoV
Space-based System Unhindered by geography, providing continuous global surveillance
Supports SSA Infrastructure Aids in collision avoidance, space traffic management, and defence preparedness
???????? India’s SSA Ecosystem
Initiative Role
ISRO’s IS4OM Provides Indian Space Situational Assessment Report (ISSAR); enables safe & sustainable space operations
NETRA Project Network for Space Objects Tracking & Analysis – aims to build a dedicated SST (Space Surveillance & Tracking) network using radars & optical telescopes
Multi-Object Tracking Radar Operated at Sriharikota – limited range, being augmented
Collision Avoidance Manoeuvres (CAMs) Regularly performed by ISRO to protect its satellites from debris threats
Global Context: Transporter-12 Rideshare
- A SpaceX program providing low-cost access to space by allowing multiple customers to launch small payloads on a single rocket.
- Enhances global commercial space activity, democratizes space access.
Significance for India
Strategic:
- Strengthens national space defence by enabling indigenous tracking of space threats.
- Reduces reliance on foreign SSA data (e.g., NORAD/US Space Command).
Technological:
- Demonstrates India’s capability in space-based surveillance tech.
- Positions India as a global contributor in the emerging SSA domain.
Economic:
- Boosts private sector space innovation aligned with India’s NewSpace Policy.
- Attracts venture capital and international collaboration.
LID-568
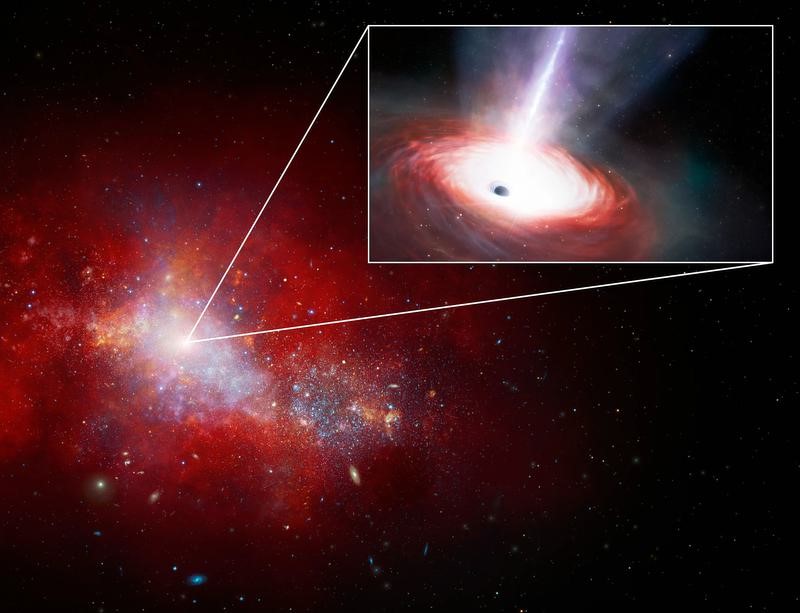
- 23 Jan 2025
In News:
In 2024, an international team of astronomers using NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) and the Chandra X-ray Observatory discovered a low-mass supermassive black hole, LID-568, showing super-Eddington accretion—a rare and extreme feeding process—just 1.5 billion years after the Big Bang.
About LID-568
Feature Description
Type Low-mass supermassive black hole
Age Formed ~1.5 billion years after Big Bang (Universe’s “youth”)
Discovery Observed via Chandra (X-ray) & JWST (infrared)
Location In a distant galaxy with very low star formation
Feeding Rate Accreting at ~40× the Eddington limit (super-Eddington accretion)
Key Concepts
Eddington Limit
- Theoretical upper limit on how fast matter can fall into a black hole before radiation pressure balances gravitational pull.
- Exceeding this limit (super-Eddington) is thought to be unstable and short-lived.
Super-Eddington Accretion
- Observed in LID-568, feeding at 40× Eddington rate.
- Suggests rapid, short bursts of black hole growth, not the slow, steady model previously assumed.
Why is LID-568 Important?
Challenges Current Theories
- Traditional black hole growth models require:
- Long periods (hundreds of millions of years).
- Seed black holes formed from:
- Death of first stars (light seeds: 10–100 solar masses).
- Collapse of primordial gas clouds (heavy seeds: 1,000–100,000 solar masses).
- LID-568 suggests brief, intense growth spurts could create supermassive black holes faster than previously thought.
Impact on Host Galaxy
- Powerful outflows prevent gas accumulation → suppresses star formation.
- Indicates black holes can regulate galaxy evolution, even when young.
Scramjet & Hypersonic Technology
- 23 Jan 2025
In News:
On 21 January 2025, DRDO’s Defence Research & Development Laboratory (DRDL) successfully conducted a 120-second ground test of an indigenously developed Scramjet (Supersonic Combustion Ramjet) engine, marking a major milestone in India’s journey towards hypersonic missile technology.
What is Scramjet Technology?
Definition
A Scramjet is an air-breathing engine that sustains combustion at supersonic speeds—optimized for speeds above Mach 5 (hypersonic range).
Working Principle
- Utilizes vehicle’s forward motion to compress incoming air—no onboard oxidizer needed.
- Injects fuel into the compressed supersonic airflow → ignition → high-speed thrust.
- Operates without moving parts, making it lightweight, efficient, and reliable.
Key Indigenous Innovations
Feature Description
Active-Cooled Combustor Stable combustion achieved at 1.5 km/s airflow, comparable to "keeping a candle lit in a hurricane."
Endothermic Scramjet Fuel First-time development in India; offers cooling + ignition efficiency.
Thermal Barrier Coating (TBC) Jointly developed with DST; withstands temperatures beyond melting point of steel using advanced ceramic coating.
CFD Simulations Used for design optimization and performance validation of flame-holding techniques.
Significance of Scramjet Test
- Stable Combustion: A major challenge in hypersonic propulsion, now successfully demonstrated.
- Hypersonic Missiles:
- Speeds >Mach 5 (~5400 km/h).
- Bypass air defence systems due to speed and maneuverability.
- Enable rapid, high-impact delivery.
- Reusable Launch Vehicles:
- Cuts satellite launch costs via air-breathing propulsion.
- Strategic Edge:
- India joins elite group: USA, Russia, China.
- Strengthens defence deterrence & technological sovereignty.
- Technology Spillover: Advancements in CFD, materials science, flame stabilization, and fuel chemistry.
Global Hypersonic Race
- China (2021): Tested nuclear-capable hypersonic glide vehicle (HGV) that orbited Earth before hitting target.
- USA & Russia: Advanced programs with operational hypersonic systems (e.g., Avangard, Zircon, ARRW).
- India: Now developing indigenous hypersonic missile platform.
Scramjet & Hypersonic Technology

- 23 Jan 2025
In News:
On 21 January 2025, DRDO’s Defence Research & Development Laboratory (DRDL) successfully conducted a 120-second ground test of an indigenously developed Scramjet (Supersonic Combustion Ramjet) engine, marking a major milestone in India’s journey towards hypersonic missile technology.
What is Scramjet Technology?
Definition
A Scramjet is an air-breathing engine that sustains combustion at supersonic speeds—optimized for speeds above Mach 5 (hypersonic range).
Working Principle
- Utilizes vehicle’s forward motion to compress incoming air—no onboard oxidizer needed.
- Injects fuel into the compressed supersonic airflow → ignition → high-speed thrust.
- Operates without moving parts, making it lightweight, efficient, and reliable.
Key Indigenous Innovations
Feature Description
Active-Cooled Combustor Stable combustion achieved at 1.5 km/s airflow, comparable to "keeping a candle lit in a hurricane."
Endothermic Scramjet Fuel First-time development in India; offers cooling + ignition efficiency.
Thermal Barrier Coating (TBC) Jointly developed with DST; withstands temperatures beyond melting point of steel using advanced ceramic coating.
CFD Simulations Used for design optimization and performance validation of flame-holding techniques.
Significance of Scramjet Test
- Stable Combustion: A major challenge in hypersonic propulsion, now successfully demonstrated.
- Hypersonic Missiles:
- Speeds >Mach 5 (~5400 km/h).
- Bypass air defence systems due to speed and maneuverability.
- Enable rapid, high-impact delivery.
- Reusable Launch Vehicles:
- Cuts satellite launch costs via air-breathing propulsion.
- Strategic Edge:
- India joins elite group: USA, Russia, China.
- Strengthens defence deterrence & technological sovereignty.
- Technology Spillover: Advancements in CFD, materials science, flame stabilization, and fuel chemistry.
Global Hypersonic Race
- China (2021): Tested nuclear-capable hypersonic glide vehicle (HGV) that orbited Earth before hitting target.
- USA & Russia: Advanced programs with operational hypersonic systems (e.g., Avangard, Zircon, ARRW).
- India: Now developing indigenous hypersonic missile platform.
10 years of Beti Bachao Beti Padhao (BBBP)

- 23 Jan 2025
In News:
Launched on 22nd January 2015 in Panipat, Haryana, BBBP was initiated in response to the declining Child Sex Ratio (CSR), which stood at 918 girls per 1000 boys (Census 2011). It marked a key step towards gender equality, aiming to curb gender-biased sex-selective elimination and improve the status of the girl child.
Key Highlights:
Core Objectives
- Improve Sex Ratio at Birth (SRB) by two points annually.
- Sustain institutional delivery rate at ≥95%.
- Increase 1st trimester ANC registration and girls' enrollment in secondary education by 1% annually.
- Reduce dropout rates among girls.
- Promote safe menstrual hygiene management (MHM).
Target Groups
- Primary: Young couples, expecting parents, adolescents, households, communities.
- Secondary: Schools, AWCs, health professionals, PRIs, ULBs, NGOs, SHGs, media, and religious leaders.
Implementation Structure
- Type: Centrally Sponsored Scheme (CSS) with 100% Central funding.
- Ministries Involved:
- Women and Child Development
- Health and Family Welfare
- Education
- Financial Assistance (Per District/Year):
- Rs. 40 lakh (SRB ≤918)
- Rs. 30 lakh (SRB 919–952)
- Rs. 20 lakh (SRB >952)
Integration with Mission Shakti (2021–2026)
BBBP now functions under Mission Shakti, which comprises two verticals:
- Sambal (Safety & Security):
- One Stop Centres (OSCs)
- Women Helpline (181)
- Nari Adalat: Alternative dispute resolution
- Samarthya (Empowerment):
- Sakhi Niwas, Palna Creches
- Shakti Sadans (rehabilitation)
- PM Matru Vandana Yojana: Extended support for a second girl child
- SANKALP-HEW: District-level single-window system for all women-centric schemes
Achievements in 10 Years (2015–2025)
- SRB: Improved from 918 (2014-15) to 930 (2023-24)
- Girls’ GER: Rose from 75.5% (2014-15) to 78% (2023-24) in secondary education
- Institutional Deliveries: Increased from 61% to 97.3%
- Kanya Shiksha Pravesh Utsav: Re-enrolled over 1 lakh out-of-school girls
- Economic Empowerment: Integration with skilling initiatives and 70% of PM Mudra loans disbursed to women
- Awareness Campaigns:
- Selfie with Daughter
- Beti Janmotsav
- Yashaswini Bike Expedition
- "Betiyan Bane Kushal" Skill Conference
Sukanya Samriddhi Yojana (SSY) – A Financial Tool for Empowerment
Launched under BBBP, SSY is a small savings scheme to ensure the financial security of girl children.
Key Features
- Eligibility: Indian girl child below 10 years.
- Account: Max 2 per family (exceptions for twins/triplets).
- Deposit Limit: ?250 to ?1.5 lakh/year (15 years).
- Tenure: Account matures 21 years after opening.
- Withdrawals: Up to 50% for higher education after 18 years.
- Tax Benefits: Exempt under Section 80C (EEE status).
Impact
- Over 4.1 crore accounts opened by Nov 2024.
- Promotes long-term savings and financial inclusion.
- Complements BBBP by addressing economic empowerment of girls.
Mission Vatsalya
- Formerly ICPS (2009), then Child Protection Services (2017).
- Merged into Mission Vatsalya in 2021.
- Focuses on:
- Juvenile justice
- Child protection
- Advocacy and rehabilitation
- Ensures “no child is left behind” principle aligned with SDGs.
Pradhan Mantri Matru Vandana Yojana (PMMVY)
- Supports pregnant and lactating mothers:
- ?5,000 in 3 installments + ?1,000 (JSY)
- Now extended to second girl child to promote gender equity.
Targets wage compensation, safe delivery, maternal nutrition, and reduced MMR/IMR.
Mount McKinley

- 22 Jan 2025
In News:
In a controversial move, President Donald Trump (2025) signed an executive order to rename Denali (North America’s highest peak) back to Mount McKinley, and also proposed renaming the Gulf of Mexico to the Gulf of America, citing the need to "honor American greatness."
About Denali / Mount McKinley:
Feature Description
Location Alaska Range, South-Central Alaska, USA
Height 20,310 feet (6,190 meters) – Highest in North America
Geology Giant granite block uplifted by tectonic activity ~60 million years ago
Glaciers Feeds major glaciers: Kahiltna, Muldrow, Peters, Ruth, Traleika
Tectonics Lies along the Denali Fault, a major right-lateral strike-slip fault
National Park Forms the core of Denali National Park and Preserve
Historical Background of the Name:
- Original Name: Denali, meaning “The High One” in the Athabascan language of the Koyukon people.
- 1897: Renamed Mount McKinley by a gold prospector in honor of President William McKinley (1897–1901).
- 1917: Official federal recognition with the creation of Mount McKinley National Park.
- 1980: Park renamed Denali National Park and Preserve; mountain's name remained McKinley federally.
- 2015: Obama administration officially renamed the peak Denali through the U.S. Department of the Interior.
- 2025: Trump issued executive order to revert the name to Mount McKinley, stating McKinley “deserves” the honor.
Rationale Behind Trump’s Renaming Order:
- Claims it honors McKinley’s legacy: economic growth, leadership in Spanish-American War, and tariff reforms.
- Declares Obama’s 2015 decision an “affront” to American heritage.
- Connects the move to his broader theme of “Restoring Names that Honor American Greatness.”
Opposition & Cultural Sensitivity:
- Alaska’s bipartisan leadership, including Senators Lisa Murkowski (R) and Scott Kawasaki (D), oppose the move.
- Indigenous groups maintain that Denali is the rightful and culturally authentic name.
- Critics argue it undermines native heritage and local identity.
Renaming the Gulf of Mexico to “Gulf of America”:
- Also part of Trump’s 2025 executive order.
- Geographic Facts:
- Borders the US, Mexico, and Cuba.
- Crucial to the US energy sector:
- 14% of US crude oil
- 5% of US natural gas
- 48% of refining capacity
- International Validity: The International Hydrographic Organization (IHO) allows local name usage but retains “Gulf of Mexico” in global records.
- Not binding on Mexico or Cuba.
International & Historical Parallels in Naming Disputes:
- Persian Gulf vs. Arabian Gulf (Iran vs. Arab states)
- Sea of Japan vs. East Sea (Japan vs. South Korea)
- South China Sea: Multiple nations claim different names and areas.
About the Denali Fault:
- Major strike-slip fault running through Alaska.
- Responsible for extensive tectonic movement and uplift of Denali.
- Evidence of horizontal displacement (~483 km) over millions of years.
- Marked the final suturing of tectonic plates in North American geological history.
Diamond Imprest Authorization (DIA) Scheme

- 22 Jan 2025
In News:
The Union Government, under the Foreign Trade Policy 2023, has introduced the Diamond Imprest Authorization (DIA) Scheme to enhance India’s competitiveness in the global diamond trade, promote exports, and protect employment, especially in the MSME sector.
Key Highlights:
Objectives:
- Boost value addition and export growth in the diamond sector.
- Support MSME exporters to compete globally.
- Retain India’s position as a global hub for diamond processing and exports.
- Mitigate recent challenges like export decline, job losses, and global demand shifts.
Key Features of the Scheme:
Feature Details
Type of Diamonds Allowed Natural cut and polished diamonds less than ¼ carat (25 cents)
Eligibility Exporters with Two Star Export House status and minimum $15 million annual exports
Export Obligation 10% value addition on imported diamonds
Duty Exemptions Exempts Basic Customs Duty, Anti-dumping Duty, Countervailing Duty, etc.
Effective Date April 1, 2025
Exclusion Lab-Grown Diamonds (LGDs) not covered
Monitoring Agency Gems and Jewellery Export Promotion Council (GJEPC)
Why the Scheme Was Introduced:
Challenges in the Diamond Sector:
- Global: Falling demand in US, Europe, China; rise in lab-grown diamonds.
- Domestic: High unsold inventory, rising operational costs, reduced credit flow, and high corporate tax.
- Employment Impact: Job losses in the diamond cutting and polishing segment.
International Context:
- Inspired by beneficiation policies in diamond-producing countries like Botswana and Namibia, which mandate local value addition.
Significance:
- Enhances India’s role in the global diamond value chain.
- Provides ease of doing business through duty relief.
- Promotes employment generation, especially for diamond assorters and processors.
- Facilitates inclusive growth by supporting MSMEs in a traditionally export-driven industry.
Way Forward:
- Regulate Lab-Grown Diamonds to prevent market distortion.
- Extend export credit period and consider tax exemptions for foreign diamond sellers.
- Ensure technology upgradation and skill training to sustain global leadership.
Closing the Women’s Health Gap
- 22 Jan 2025
In News:
The World Economic Forum (WEF), in collaboration with the McKinsey Health Institute, released the report titled “Blueprint to Close the Women’s Health Gap”, highlighting the economic and social benefits of addressing gender-based health disparities.
Key Insights from the Report:
Economic Potential:
- Closing the women’s health gap could contribute $400 billion to global GDP by 2040.
- Focusing on just three conditions—menopause, PMS, and migraine—could unlock $315 billion in productivity.
Health Disparity:
- Women experience 25% more years of poor health than men.
- Root causes include underrepresentation in research and sex-neutral clinical guidelines.
- Only 10% of trials on major conditions like ischemic heart disease and migraine include sex-disaggregated data.
Key Health Conditions Identified:
Lifespan Conditions:
- Maternal hypertensive disorders
- Postpartum hemorrhage
- Ischemic heart disease
- Cervical cancer
- Breast cancer
Health Span Conditions:
- Endometriosis
- Menopause
- Migraine
- Premenstrual syndrome (PMS)
Addressing these can add 2.5 healthy days per woman per year globally.
Women’s Health Impact Tracking (WHIT):
- A public digital platform by WEF and McKinsey.
- Tracks global health disparities.
- Offers data-driven insights to guide investment and policy decisions, especially for low- and middle-income countries which face 54% of the global women's health burden, yet host only 23% of related clinical trials.
Five Strategic Actions for Stakeholders:
- Count Women – Improve data collection specific to women’s health.
- Study Women – Boost research funding on women-centric health conditions.
- Care for Women – Create tailored clinical guidelines and protocols.
- Include All Women – Ensure equity for marginalized groups.
- Invest in Women – Finance innovative healthcare solutions and service delivery models.
One Nation, One Legislative Platform

- 22 Jan 2025
In News:
- The 85th AIPOC, held in Patna, Bihar, emphasized enhancing the effectiveness of legislative institutions through reforms in decorum, digitization, and public participation.
- A major outcome was the announcement of the One Nation, One Legislative Platform to digitally integrate legislative bodies across India.
All India Presiding Officers’ Conference (AIPOC):
- Established: 1921; first session held in Shimla.
- Role: Apex platform bringing together Presiding Officers of Parliament and State Legislatures.
- Objective: Strengthen democratic institutions by fostering cooperative federalism, legislative accountability, and improved law-making processes.
2025 Conference Highlights:
- Venue: Historic Bihar Legislature Premises, Patna.
- Key Themes:
- Reducing disruptions and maintaining decorum in legislative houses.
- Promoting qualitative debate and discussion.
- Observing the 75th year of the Constitution with participatory democratic celebrations.
- Resolutions Adopted:
- Formulation of internal code of conduct by political parties.
- Nationwide campaigns involving PRIs, urban bodies, students, NGOs, media, and more to celebrate democratic values.
One Nation, One Legislative Platform (ONOLP):
What It Is:
A national mission to create a unified digital ecosystem integrating the Parliament, state legislatures, and local bodies for better legislative coordination and public access.
Key Objectives:
- Real-Time Data Sharing: Seamless, up-to-date legislative information across institutions—proceedings, bills, debates, etc.
- Transparency & Accountability: Open access to deliberations enables citizen oversight and institutional accountability.
- Public Participation: User-friendly access encourages civic engagement in law-making and governance.
- AI & Tech Integration: Use of Artificial Intelligence for data analysis, decision support, and enhanced efficiency.
- Paperless Legislatures: Digitization of records to promote sustainability and reduce bureaucratic delays.
Implementation Support:
- Spearheaded by the Lok Sabha, with Speaker Om Birla announcing its completion by 2025.
- Includes the creation of a central portal for public and institutional use.
Chinar Trees

- 22 Jan 2025
In News:
The J&K Forest Department, in collaboration with the J&K Forest Research Institute (JKFRI), has launched a pioneering conservation initiative to digitally preserve the iconic Chinar trees (Platanus orientalis)—a vital part of Kashmir’s ecological and cultural heritage.
Significance of Chinar Trees:
- Locally known as Boonyi or Boueen, Chinar trees are deeply embedded in Kashmir’s cultural identity.
- These deciduous trees can grow up to 30 meters tall with a girth of 10–15 meters, and can live for over 600 years.
- They are known for their seasonal leaf color transformation—from green in summer to red, amber, and yellow in autumn.
- Notable specimens include Asia’s largest Chinar in Ganderbal and the oldest known Chinar (647 years) in Chattergam, Budgam.
Challenges to Chinar Survival:
- Urban expansion and habitat encroachment.
- Climate change, altering precipitation and temperature patterns.
- Illegal felling and timber exploitation.
- Increased susceptibility to pests and diseases.
Tree Aadhaar & Geo-Tagging Initiative:
- Over 28,500 Chinar trees have been geo-tagged and assigned unique Tree Aadhaar numbers from 2021 to 2023.
- Each tree is fitted with a QR-coded digital plate, enabling real-time access to:
- Tree location, height, girth, canopy dimensions
- Health status, ecological threats, and pest presence
- These plates are spring-mounted metal tags to prevent damage to the trees.
Conservation Goals & Future Plans:
- Digital Protection: Enables proactive monitoring and protection through a centralized database.
- Chinar Atlas: A comprehensive mapping of all Chinar trees in the region.
- Public Access Website: A dedicated digital portal is planned for broader access to Chinar data.
- Risk Assessment: Use of USG-based, non-invasive surveys to identify trees at risk without human interference.
- Emphasis on covering remote and restricted areas in future phases to ensure inclusivity in conservation.
Takers, Not Makers

- 21 Jan 2025
In News:
Report “Takers not makers: The unjust poverty and unearned wealth of colonialism” published by Oxfam.
Key Highlights:
- Released by: Oxfam International at the World Economic Forum 2025
- Core Focus: The report explores historical colonial wealth extraction, especially from India, and connects it to contemporary global inequalities.
Colonial Wealth Drain – India:
- $64.82 trillion extracted from India by Britain (1765–1900), adjusted to today’s value.
- $33.8 trillion (52%) enriched the UK’s richest 10%
- 32% benefited the British middle class
- India's industrial output dropped from 25% in 1750 to 2% in 1900 due to:
- British protectionist policies (especially targeting Asian textiles)
- High taxation, home charges, currency manipulation, and profit repatriation
Conceptual Framework:
- "Drain of Wealth" Theory by Dadabhai Naoroji forms the report’s foundation.
- Colonialism framed as both:
- Historical phenomenon: Loot, repression, forced de-industrialization
- Modern structure (Neo-colonialism): Corporate dominance, digital colonization, and unjust global governance
Neo-Colonial Parallels Today:
- Wages in Global South: 87–95% lower than for same work in Global North
- Multinational corporations:
- Descendants of colonial entities like the East India Company
- Extract resources & exploit labor under unequal terms of trade
- Global institutions like WTO and World Bank perpetuate inequity through imbalanced power dynamics
Ongoing Consequences in Global South:
- Poor public services, education, and healthcare
- Caste, religion, and language divisions institutionalized during colonial rule
- E.g., Only 0.14% of Indian languages used as medium of instruction
- Bengal Famine (1943): Caused by wartime policies & racist attitudes, ~3 million deaths
- Biopiracy cases (e.g., neem) reflect continued exploitation
Wealth Disparity & Inequality:
- Billionaire wealth tripled in growth rate in 2024 (vs. 2023)
- Top 1% own more than 95% of global wealth
- Over 3.5 billion people survive on less than $6.85/day
ILO Global Estimates on International Migrant Workers – 2022

- 21 Jan 2025
In New:
By addressing labour market shortages in host nations and contributing remittances to home countries, International Migrants (IM) continue to make contributions to world economic growth, the fourth edition of ‘Global Estimates on International Migrant Workers’, released by the International Labour Organization (ILO), stated.
Key Findings:
Global Representation:
- International Migrants (IMs) = 4.7% of global labour force - 167.7 million total:
- Employed: 155.6 million
- Unemployed (but seeking work): 12.1 million
- Increase of 30+ million migrant workers since 2013
- Growth rate dropped below 1% annually (2019–2022) due to COVID-19
Gender Composition:
- Male IMs: 61.3% (102.7 million)
- Female IMs: 38.7% (64.9 million)
- Lower female participation attributed to:
- Lower female migration rates globally
- Gender-based barriers in labour markets
- Over-representation in informal and unpaid sectors
Age Distribution:
- Prime working age (25–54 yrs): 74.9%
- Youth (15–24 yrs): 9.3%
- Older adults (55–64 yrs): 12.5%
- Seniors (65+ yrs): 3.4%
Sector-wise Employment:
Sector Share of IMs Notes
Services 68.4% Highest; women dominate (80.7%)
Industry 24.3% On par with non-migrants
Agriculture 7.4% Far lower than non-migrants (24.3%)
Care economy in high-income countries is a major pull for female migrants.
Host Country Distribution:
Region/Income Group % of IMs Notes
High-income countries 68.4% (114 million) Majorly Europe & North America
Upper-middle-income 17.4% (29.2 million)
Arab States 13.3% Declined since 2013
Europe (23.3%) and North America (22.6%) are top destinations. Arab states saw a 3% decline over the decade.
Definition: International Migrants (IMs)
As per the UN: Persons residing in a country different from their place of usual residence for at least one year, regardless of reason or legal status. Includes refugees, asylum seekers, etc.
Role & Contributions of IMs:
- Economic Drivers: Fill labour shortages (healthcare, construction, care work).
- Remittances: Boost home country economies.
- Demographic Support: Help address aging populations in developed nations.
Cultural Exchange: Promote diversity and global connectivity.
Mount Ibu Eruption

- 21 Jan 2025
In News:
Indonesia’s Mount Ibu erupted 1,000 times this month.
Overview:
- Location: Mount Ibu, Halmahera Island, North Maluku province, Indonesia.
- Volcano Type: Stratovolcano (composite volcano) – steep-sided, conical structure formed by successive layers of lava, ash, and pyroclastic material.
- Tectonic Setting: Located on the Pacific Ring of Fire, a major area of subduction zones with high volcanic and seismic activity.
Volcanic Context – Indonesia:
- Pacific Ring of Fire: Indonesia's location makes it one of the most volcanically active regions globally.
- Other Recent Eruptions:
- Mount Lewotobi Laki-Laki (twin-peaked volcano)
- Mount Ruang
- Both have shown heightened activity, triggering mass evacuations.
Indian Coffee Sector
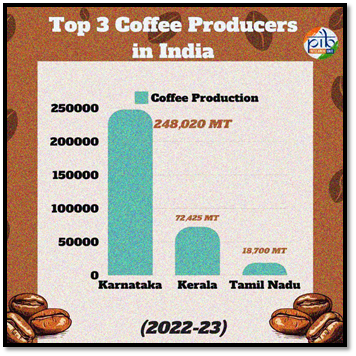
- 21 Jan 2025
In News:
India is now the seventh-largest coffee producer globally with exports reaching $1.29 billion in FY 2023-24, almost double the $719.42 million in 2020-21.
Historical Background
- Origin: Coffee was introduced to India in the 17th century by Baba Budan, a Sufi saint, who brought seven Mocha beans from Yemen and planted them in Baba Budan Giri hills, Karnataka.
- This act laid the foundation for India’s coffee cultivation, which has since evolved into a robust agro-industry.
India’s Global Coffee Status
- 7th largest coffee producer globally (FY 2023–24).
- Exports: Reached $1.29 billion in FY 2023–24, nearly double the $719.42 million in FY 2020–21.
- Major export destinations: Italy, Belgium, Russia.
- Export Share: Over 70% of India's coffee is exported, mostly in unroasted (green bean) form.
Types of Coffee Cultivated
- Arabica: Mild flavor, higher market value.
- Robusta: Strong flavor, more robust; often used in instant coffee.
- India's production: Around 75% is a mix of Arabica and Robusta.
Geographical Distribution
- Major Coffee-Growing Regions:
- Karnataka: Leads with over 70% of national production (~248,020 MT in 2022–23).
- Kerala and Tamil Nadu follow.
- Other contributors: Andhra Pradesh, Odisha, and parts of Northeast India
- Agro-climatic Conditions:
- Altitude: 600–1600 meters
- Temperature: 15°C–28°C
- Rainfall: 150–250 cm annually
- Soil: Well-drained, loamy, rich in humus and minerals
Economic & Environmental Significance
- Coffee is largely grown in the Western and Eastern Ghats, biodiversity-rich zones with shade-grown plantations.
- These plantations:
- Conserve ecology and biodiversity
- Support sustainable agriculture
- Contribute to rural livelihoods
Domestic Trends
- Rising café culture, urbanization, and higher disposable incomes have led to increased coffee consumption.
- Domestic consumption rose from 84,000 tonnes (2012) to 91,000 tonnes (2023).
- Preference for coffee over tea is growing, especially in urban and semi-urban India.
Government Initiatives
- Coffee Board of India initiatives under the Integrated Coffee Development Project (ICDP) aim to:
- Enhance yields
- Expand to non-traditional areas
- Promote sustainable practices
- Araku Valley Model:
- Involves 150,000 tribal families
- 20% increase in production
- Backed by Girijan Co-operative Corporation (GCC) and Integrated Tribal Development Agency (ITDA)
- Aligned with Aatmanirbhar Bharat and rural empowerment
Current Challenges and Future Outlook
- Challenges: Climate change impacts, pest attacks, price volatility in global markets.
- Opportunities:
- Rising global demand for value-added products (roasted & instant coffee)
- Export incentives and improved logistics
- Potential for agri-tourism and organic branding
Entity Locker

- 21 Jan 2025
In News:
The National eGovernance Division (NeGD), under the Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology (MeitY) has developed Entity Locker, a cutting-edge digital platform designed to transform the management and verification of business/organisation documents.
Key Highlights:
What is Entity Locker?
A secure, cloud-based platform that allows real-time access, encrypted storage, and authenticated sharing of business-related documents.
Who can use it?
Large corporations, MSMEs, startups, trusts, societies, and other organizational entities.
- Key Features:
- 10 GB Encrypted Cloud Storage: Ensures secure document management.
- Real-Time Document Access & Verification: Integrated with government databases.
- Consent-Based Sharing: Ensures data privacy during information exchange.
- Digital Signature Authentication: Enables legally valid and secure transactions.
- Aadhaar-Authenticated Role-Based Access: Promotes accountability in document handling.
- Integration with Government Systems: Linked with entities like:
- Ministry of Corporate Affairs (MCA)
- Goods and Services Tax Network (GSTN)
- Directorate General of Foreign Trade (DGFT)
Benefits:
- Reduces administrative burden and document processing time.
- Enhances compliance with statutory and regulatory requirements.
- Enables faster processes like vendor verification, loan applications, and FSSAI compliance.
- Promotes transparency and secure collaboration among stakeholders.
Significance:
Entity Locker is a pivotal component of India’s Digital Public Infrastructure, reflecting the Union Budget 2024–25 vision of promoting digital governance. It supports the broader goals of the Digital India Programme, aiming for a digitally empowered and efficient economy.
ILO World Employment and Social Outlook 2025
- 20 Jan 2025
In News:
The global economy is slowing down, making it harder for labour markets to recover fully since the outbreak of the COVID 19 pandemic, according to the International Labour Organization’s (ILO) report, World Employment and Social Outlook: Trends 2025, released in Geneva
Global Employment Trends
- Unemployment Rate (2024): Remained steady at 5%.
- Youth Unemployment: High at 12.6%, particularly severe in upper-middle-income countries (16%).
- Global Jobs Gap:
- 402 million people want work but are jobless (2024):
- 186 million unemployed
- 137 million temporarily unavailable
- 79 million discouraged workers
- 402 million people want work but are jobless (2024):
- NEET Population (2024):
- 259.1 million globally:
- 173.3 million young women (28.2%)
- 85.8 million young men (13.1%)
- 259.1 million globally:
Economic Growth and Labour Recovery
- Global Growth (2024): 3.2% (↓ from 3.3% in 2023 and 3.6% in 2022)
- Forecast (2025): Similar growth expected, with gradual deceleration ahead.
- Recovery Remains Uneven:
- High-income countries see rise in labour force participation.
- Low-income countries (LICs) face challenges creating decent jobs, with informal work returning to pre-pandemic levels.
- India’s GDP Growth:
- 6.9% in 2024, forecast at 6.4% in 2025
- Driven by monetary easing, domestic demand, and public investment
- Southern Asia: Growth pegged at 6.2% in 2024, 5.8% in 2025, mainly due to India.
- Labour Participation:
- Significant increase in female labour force participation, especially in India.
Key Labour Market Challenges
- Geopolitical Tensions
- Climate Change Costs
- Unresolved Debt Issues
- ~70 countries at risk of debt distress
- Many LICs spend more on debt servicing than on education/health
- Stagnant Real Wages
- Post-pandemic wage recovery mostly in advanced economies
- Vulnerable Jobs in Developing Regions
- Sub-Saharan Africa: 62.6% households live on <USD 3.65/day
- Employment is mainly informal, lacking security
Green and Digital Transitions
- Green Jobs Growth:
- Employment in renewables rose from 13.7 million (2022) to 16.2 million (2023)
- 46% of green energy jobs are in China
- Digital Economy:
- Offers promise, but infrastructure and skills gap limit benefits in many countries.
ILO Recommendations for Social Justice & SDG 2030 Goals
- Boost Productivity & Job Creation: Invest in skills training, education, and infrastructure
- Expand Social Protection: Better access to social security and safe work conditions
- Leverage Private Capital: LICs should channel remittances and diaspora funds into development
- Structural Transformation: Focus on modern services and manufacturing for quality jobs
- Youth Skill Development: Promote education for emerging sectors like green tech and digital economy
- Global Collaboration: Foster inclusive fiscal and monetary policies for equitable recovery
About ILO
- Established: 1919 | UN Agency
- Members: 187 countries
- Headquarters: Geneva, Switzerland
- Unique Tripartite Structure: Brings together governments, employers, and workers to set labour standards and promote decent work for all.
Dark Oxygen
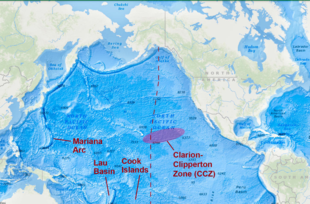
- 20 Jan 2025
In News:
Scientists who recently discovered that metal lumps on the dark seabed make oxygen, have announced plans to study the deepest parts of Earth's oceans in order to understand the strange phenomenon.
What is Dark Oxygen?
Dark Oxygen refers to oxygen produced deep under the ocean without sunlight or photosynthesis.
Discovered in July 2024, this challenges the long-standing belief that photosynthesis is the sole natural source of oxygen.
Where was it discovered?
- Location: Clarion-Clipperton Zone (CCZ), 13,100 feet deep in the North Pacific Ocean, between Hawaii and Mexico.
- Zone Significance: Rich in polymetallic nodules containing manganese, iron, cobalt, nickel, copper, and lithium — crucial for green technologies.
Mechanism of Oxygen Production
- Polymetallic nodules on the seafloor generate oxygen via electrochemical reactions.
- These nodules split seawater (H?O) molecules into hydrogen and oxygen, without any light.
- This process is non-biological and independent of photosynthesis.
Why is this Discovery Important?
- Scientific Paradigm Shift: Challenges the idea that photosynthesis is the only natural pathway for oxygen generation.
- Origins of Life: Suggests that oxygen production may have existed before photosynthetic organisms, reshaping theories of early Earth’s evolution.
- Astrobiological Implications: Indicates the possibility of oxygen-rich environments on other planets, even without sunlight — enhancing the search for extraterrestrial life.
- Environmental Tech Potential: Could lead to innovations in renewable energy and carbon-neutral technologies, using metal-based catalysis.
About the Clarion-Clipperton Zone (CCZ)
- Geographic span: Between Hawaii and Mexico in the North Pacific Ocean.
- Resources: Contains vast reserves of critical minerals like manganese, nickel, cobalt — essential for electric vehicles and solar technology.
- A focus area for deep-sea mining and sustainability studies.
National Panchayat Awards 2024

- 20 Jan 2025
In News:
The President of India conferred the National Panchayat Awards 2024 on 45 outstanding Panchayats for their contributions to inclusive growth, environmental sustainability, and rural development. The event was held on 11th December 2024 (postponed from 24th April due to General Elections).
About the Awards
- Launched to commemorate: 73rd Constitutional Amendment Act, 1992, which gave constitutional status to Panchayats as institutions of local self-governance.
- Usual celebration date: 24th April — observed as National Panchayati Raj Day.
- Revamped in 2022 to align with Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) via Localization of SDGs (LSDGs).
Objectives
- Recognize best practices in rural governance.
- Encourage healthy competition among Panchayats.
- Promote effective implementation of LSDGs and quality service delivery.
Evaluation Structure
- Multi-level assessment: Block → District → State/UT → National level.
- Evaluation based on 9 LSDG themes, including:
- Poverty-Free & Enhanced Livelihoods
- Healthy Panchayat
- Child-Friendly Panchayat
- Water-Sufficient Panchayat
- Clean & Green Panchayat
- Self-Sufficient Infrastructure
- Socially Just & Secured Panchayat
- Panchayat with Good Governance
- Women-Friendly Panchayat
Award Categories
Award Category Focus Area
Deen Dayal Upadhyay Panchayat Satat Vikas Puraskar (DDUPSVP) Top 3 GPs under each LSDG theme
Nanaji Deshmukh Sarvottam Panchayat Satat Vikas Puraskar Top 3 GPs, Block Panchayats & District Panchayats with highest scores across all themes
Gram Urja Swaraj Vishesh Panchayat Puraskar GPs promoting renewable energy adoption
Carbon Neutral Vishesh Panchayat Puraskar GPs achieving net-zero carbon emissions
Panchayat Kshamta Nirmaan Sarvottam Sansthan Puraskar Institutions providing exemplary support to PRIs in implementing LSDGs
Key Highlights of 2024:
- Total Awards: 45 Panchayats
- Women Leadership: 42% of award-winning Panchayats led by women.
- Participation: 1.94 lakh Gram Panchayats competed.
- Prize Money: ?46 crore transferred digitally to awardees.
- Booklet Released: Best Practices of Awardee Panchayats.
- Film Showcased: Highlighting success stories and capacity-building.
State-wise Recognition
- Notable awardees from: Odisha, Tripura, Maharashtra, Uttar Pradesh, Andhra Pradesh, Kerala, Telangana, Assam, etc.
- Tripura & Odisha stood out in total recognitions.
- GPs from Maharashtra, Odisha, and Tripura received special awards for energy and carbon neutrality.
Other Key Initiatives for PRIs
Initiative Purpose
SVAMITVA Scheme (2020) Mapping rural property to provide Record of Rights.
e-Gram Swaraj (e-FMS) Work-based accounting to promote transparency.
mActionSoft Geo-tagging Panchayat assets via GPS-enabled photos.
Citizen Charter Portal “Meri Panchayat Mera Adhikaar” – Service delivery assurance to citizens.
India–Singapore Semiconductor Cooperation

- 20 Jan 2025
In News:
During his 2025 visit to India, Singapore President Tharman Shanmugaratnam announced plans to collaborate with India on semiconductor manufacturing and the creation of a semiconductor ecosystem, marking the 60th anniversary of diplomatic ties between the two nations.
Singapore’s Semiconductor Landscape
- Contribution to Economy: Accounts for ~8% of Singapore’s GDP.
- Global Standing:
- Produces 10% of global semiconductor output.
- 5% of global wafer fabrication capacity.
- 20% of global semiconductor equipment production.
- Comprehensive Ecosystem: End-to-end capabilities from IC design to packaging and testing.
- Infrastructure: Four wafer fabrication parks with advanced facilities.
- Current Limitation: Focused on mature-node chips (28 nm+); lacks high-end logic chip manufacturing (7 nm or below).
India’s Semiconductor Sector
- Market Size (2024): Valued at USD 52 billion; projected to reach USD 103.4 billion by 2030.
- Import Dependency: ~85% of semiconductor needs met through imports.
- Export-Import Gap (2022): USD 5.36 billion (imports) vs. USD 0.52 billion (exports).
India's Advantages:
- Skilled Talent Pool: Large number of STEM graduates.
- Cost Efficiency: Lower manufacturing and operational costs.
- Geopolitical Opportunity: Global supply chain diversification away from China.
Government Initiatives:
- India Semiconductor Mission (ISM)
- Semicon India Programme
- Display & Semiconductor Fab Schemes
- SPECS (Scheme for Promotion of Manufacturing of Electronic Components and Semiconductors)
Foreign Collaborations:
- MoUs with US, Japan, and European Commission.
- Tata–Powerchip (Taiwan) collaboration for a fab in Dholera, Gujarat.
How Singapore Can Support India’s Semiconductor Vision
- Manufacturing Partnerships:
- Collaborations with Singaporean firms for assembly and testing services.
- Access to Singapore's advanced manufacturing technologies.
- Talent Development:
- Academic exchanges in microelectronics and semiconductor engineering.
- Joint research and PhD programs.
- Infrastructure Development:
- Replication of Singapore-style wafer fab parks in India.
- Joint ventures to build specialized semiconductor industrial zones.
- Technology Access & Innovation:
- Transfer of advanced technologies and critical semiconductor materials.
- Collaboration on new-generation tech solutions (e.g., AI chips, advanced computing).
Additional Areas of Bilateral Cooperation
- Digital Economy: Exploring data corridor between GIFT City (India) and Singapore.
- Sustainability: Cooperation on green hydrogen, sustainable aviation fuel, and renewable energy.
Strategic Partnership: Upgraded to Comprehensive Strategic Partnership in 2024.
Internet Governance Internship and Capacity Building (IGICB) Scheme

- 20 Jan 2025
In News:
The National Internet Exchange of India (NIXI) announced the launch of its Internet Governance Internship and Capacity Building Scheme. This program aims to build awareness and develop expertise in internet governance (IG) among Indian citizens.
Key Highlights:
Objective:
To develop awareness and build a skilled pool of professionals in Internet Governance (IG) in India, enabling active Indian participation in global digital policy platforms.
Key Features:
- Internship Format:
- Bi-annual internship with two tracks: 3-month and 6-month durations
- Mentorship by experts from:
- International bodies (e.g., ICANN, APNIC, APTLD)
- Academic institutions and retired officials
- Stipend: ?20,000/month
- Outreach Component: Mandatory awareness programs to be conducted by interns
Focus Areas:
- Engagement with I-Star organizations, such as:
- ICANN (Internet Corporation for Assigned Names and Numbers)
- ISOC (Internet Society)
- IEEE (Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers)
- IETF (Internet Engineering Task Force)
- Exposure to global best practices and policy mechanisms in digital governance
- Capacity building for inclusive participation in emerging internet issues
Significance:
- Promotes digital policy leadership among Indian youth
- Enhances India’s representation in global internet governance dialogues
- Fosters a tech-savvy and policy-aware workforce for digital India initiatives
About NIXI (National Internet Exchange of India):
- Established: 19 June 2003
- Type: Not-for-profit (Section 8 company)
- Parent Ministry: MeitY
- Mandate:
- Enhance internet adoption and digital infrastructure in India
- Key Services:
- Internet Exchange Points (IXPs): Facilitate domestic internet traffic exchange
- .IN Registry: Manage India’s country code top-level domain (.in)
- IRINN: Allocate IPv4 and IPv6 resources within India
Capacity Building & Training: Promote internet-related knowledge and skills
Ratnagiri Buddhist Site

- 19 Jan 2025
In News:
The Archaeological Survey of India (ASI) has resumed excavations at the ancient Buddhist site of Ratnagiri in Odisha’s Jajpur district, unveiling monumental discoveries that underline its rich religious, cultural, and maritime legacy. This renewed effort comes more than 60 years after the site was first excavated between 1958 and 1961.
About Ratnagiri
- Meaning: Ratnagiri translates to “Hill of Jewels.”
- Location: Situated on a hill between the Brahmani and Birupa rivers, northeast of Bhubaneswar.
- Part of the Diamond Triangle: Along with Lalitgiri and Udaygiri, Ratnagiri forms Odisha’s famed “Diamond Triangle” of Buddhist heritage sites.
- Historical Period: Flourished between the 5th and 13th centuries CE, peaking under the Bhauma-Kara dynasty (8th–10th century CE).
- Buddhist School: An important centre for Mahayana and especially Vajrayana (Tantrayana) Buddhism.
- It possibly rivalled Nalanda in prominence as a Buddhist learning centre.
- The monastery complex at Ratnagiri is the only one in India with a curvilinear roof, once housing about 500 monks.
Recent Discoveries by ASI
- Three colossal Buddha heads, each measuring 3–4 feet.
- A massive palm sculpture, 5 feet in size.
- Hundreds of votive stupas, sculptures of Buddhist deities.
- A monolithic elephant statue, 5 feet long and 3.5 feet tall.
- Pottery, inscribed stones, beads, stone pillars, and a brick wall believed to be part of a larger structure.
- Rich ceramic assemblages, which may shed light on the region’s cultural and technological evolution.
These artefacts are estimated to date back to the 8th and 9th centuries CE and are believed to enhance understanding of Buddhism’s evolution in Odisha and its linkages with other cultures.
Buddhism in Odisha & Southeast Asian Links
- Buddhism gained a strong foothold in Odisha after Emperor Ashoka’s conquest of Kalinga (modern-day Odisha) in 261 BCE, a turning point that led him to embrace Buddhism.
- Though Buddha never visited Odisha, the region became instrumental in spreading Buddhism to Southeast Asia, especially during the Bhauma-Kara period.
- The state maintained robust maritime trade and cultural links with regions like Java, Bali, Sumatra, Borneo, Myanmar, and Sri Lanka.
- Baliyatra Festival: A vibrant annual event held in Cuttack, commemorating Odisha’s ancient seafaring ties with Bali and other Southeast Asian regions.
- According to some studies, Chinese monk Hiuen Tsang may have visited Ratnagiri during his travels in India (638–639 CE).
Significance of the Renewed Excavations
- The ASI aims to uncover partially visible structures, complete the site’s mapping, and contextualize the findings within the broader Buddhist history of India and Southeast Asia.
- Researchers hope to discover signs of foreign architectural or cultural influences, further confirming ancient Odisha’s global Buddhist and trade connections.
- The discoveries reaffirm Ratnagiri’s importance as a cornerstone of Buddhist learning and art, potentially on par with other renowned ancient centres like Nalanda and Vikramashila.
Interest Equalisation Scheme (IES)

- 19 Jan 2025
In News:
- Launched in April 2015, the Interest Equalisation Scheme (IES) offers subsidised interest rates on pre- and post-shipment export credit to Indian exporters, particularly MSMEs.
- The Commerce Ministry has sought a Rs 3,000 crore extension of the scheme beyond December 2024, with emphasis on supporting MSME exporters amidst global economic challenges.
Objectives of IES:
- Reduce Cost of Credit: Offers 3% to 5% interest subvention to make export credit affordable.
- Boost Export Competitiveness: Enables Indian exporters, especially MSMEs, to match international pricing.
- Encourage Export Diversification: Supports MSMEs in exploring new markets and products.
- Enhance Financial Inclusion: Promotes access to formal credit systems for small exporters.
Key Features:
- Interest Subsidy:
- 3% for MSME manufacturer exporters.
- 2% for merchant and manufacturer exporters of 410 specified tariff lines.
- Coverage: Initially limited to select products, later extended to all MSME exporters.
- Implementation:
- Managed by the RBI, in coordination with DGFT and authorized banks.
- Subsidy reimbursed to banks offering export credit at reduced rates.
- Banks exceeding Repo Rate + 4% are excluded.
Need for Extension:
- The scheme expired in December 2024, but exporters are demanding continuation due to:
- Rising global inflation and logistics disruptions (e.g., Red Sea crisis).
- Increase in credit duration demands from foreign buyers (120–150 days).
- Decline in export credit availability despite higher demand.
- FIEO reports a drop in outstanding export credit from ?2.27 lakh crore (2023) to ?2.17 lakh crore (2024).
- MSMEs operate on thin margins, and the subvention can make or break deals.
Significance for MSMEs:
- MSMEs contribute ~45% to India’s total exports and often struggle with high borrowing costs and limited financial access.
- Affordable credit via IES allows MSMEs to:
- Remain price competitive.
- Take larger and longer-term orders.
- Invest in product innovation and value addition.
- Improve market diversification and resilience.
Challenges in Accessing Credit:
- Stringent eligibility norms and collateral requirements.
- Complex administrative procedures for availing benefits.
- Limited awareness among small enterprises about the scheme.
- Slow disbursal and inconsistent application by banks.
Policy Implications and the Way Forward:
- A revamped, MSME-focused IES can ensure inclusive growth and boost India’s export-led development.
- Calls for:
- Simplification of procedural norms.
- Higher interest subvention limits or removal of caps (e.g., ?50 lakh per IEC holder).
- Longer validity (multi-year horizon) for predictability and planning.
- Aligns with the broader goals of Atmanirbhar Bharat, Make in India, and achieving $1 trillion in exports by 2030.
Exercise La Perouse 2025
- 19 Jan 2025
In News:
India is participating in the fourth edition of the multinational naval exercise La Perouse, hosted by France in key maritime straits—Malacca, Sunda, and Lombok. The Indian Navy's INS Mumbai, an indigenously built guided-missile destroyer, represents India.
Key Highlights:
- Participating Countries: Navies from India, France, Australia, USA, UK, Indonesia, Malaysia, Singapore, and Canada.
- Objectives:
- Enhance maritime situational awareness.
- Promote tactical interoperability through joint training.
- Conduct surface warfare, anti-air warfare, air defence, and VBSS (Visit, Board, Search and Seizure) operations.
- Strengthen cooperation on maritime surveillance, air operations, and information sharing.
- Significance:
- Demonstrates commitment to a rules-based international order in the Indo-Pacific.
- Reflects India’s vision of SAGAR (Security and Growth for All in the Region).
- Counters increasing presence of Chinese naval forces in the Indo-Pacific.
Strategic Location: Key Straits in Focus
- Strait of Malacca
- Connects: Andaman Sea (Indian Ocean) to South China Sea (Pacific Ocean).
- Geography: Lies between Peninsular Malaysia and Sumatra, near Singapore.
- Significance: One of the world’s busiest trade routes.
- Choke Point: Narrowest part (Philips Channel) is only 2.8 km wide.
- Sunda Strait
- Connects: Java Sea (Pacific) to the Indian Ocean.
- Between: Java and Sumatra (Indonesia).
- Challenges: Volcanic islands (e.g., Krakatoa), shallow depths (20–100 m).
- Importance: Secondary maritime route, strategic in times of congestion in Malacca.
- Lombok Strait
- Connects: Java Sea to the Indian Ocean.
- Between: Bali and Lombok islands.
- Depth: 250–1,300 meters – suitable for large vessels.
- Unique Feature: Part of the Wallace Line, a major ecological boundary.
Sanchar Saathi App

- 19 Jan 2025
In News:
In a landmark move to enhance telecom accessibility, security, and empowerment across India, the Union Minister of Communications launched a suite of citizen-focused initiatives. Key highlights of the event included the launch of the Sanchar Saathi Mobile App, National Broadband Mission (NBM) 2.0 and the inauguration of the Intra Circle Roaming facility at DBN Funded 4G Mobile Sites.
Sanchar Saathi Mobile App
- Launched by: Department of Telecommunications (DoT), Ministry of Communications.
- Platforms: Available on Android and iOS.
- Objective: Strengthen telecom security, empower citizens, and combat telecom fraud.
- Key Features:
- Chakshu (SFC): Report suspected fraud communications (calls/SMS).
- Know Your Mobile Connections: Identify and manage all mobile numbers issued in one’s name.
- Block Lost/Stolen Devices: Swiftly block, trace, and recover lost/stolen mobile phones.
- Verify Handset Genuineness: Confirm the authenticity of mobile handsets before purchase.
Impact so far (via Sanchar Saathi Portal, launched May 2023):
- 2.75 crore fraudulent connections disconnected.
- 25+ lakh lost/stolen devices blocked.
- 12.38 lakh WhatsApp accounts linked to cybercrimes disengaged.
- 11.6 lakh mule bank accounts frozen.
- 90% spoofed international calls blocked within 2 months of new prevention system.
National Broadband Mission (NBM) 2.0
- Launched by: Union Minister of Communications, builds upon NBM 1.0 (2019–2024).
- Part of: National Digital Communications Policy, 2018.
- Aim: Digitally empower citizens and bridge the digital divide to realize the vision of Viksit Bharat by 2047.
Key Targets (by 2030):
- 2.70 lakh villages to be connected with OFC (from ~50,000 now).
- 90% broadband connectivity to anchor institutions (schools, PHCs, Panchayats, Anganwadis).
- Fixed broadband speed: Increase national average from 63.55 Mbps (2024) to 100 Mbps.
- Right of Way (RoW) disposal time: Reduce from 60 days to 30 days.
- Rural internet subscribers: Increase from 45 to 60 per 100 population.
- 30% of mobile towers to be powered by sustainable energy.
- 100% mapping of PSU fiber networks on PM GatiShakti National Master Plan by 2026.
- Enhanced use of “Call Before u Dig (CBuD)” app to protect underground telecom infrastructure.
- Facilitate 5G rollout, and prepare infrastructure for 6G and common telecom ducts in all linear projects.
- Leverage power sector (e.g. Optical Ground Wire - OPGW) for broadband in remote/hilly areas.
Intra Circle Roaming (ICR) at DBN-Funded 4G Sites
- Launched by: Ministry of Communications.
- Implemented under: Digital Bharat Nidhi (DBN), formerly USOF.
- Objective: Allow subscribers of multiple telecom service providers (TSPs) (e.g., BSNL, Airtel, Reliance) to access 4G services from a single DBN-funded tower.
- Impact:
- Eliminates need for duplicate towers.
- Covers 27,000+ towers across 35,400 remote villages.
- Enhances user choice, reduces cost, and ensures efficient infrastructure use.
Nigeria admitted as BRICS Partner Country

- 19 Jan 2025
In News:
- Nigeria has been admitted as the 9th "Partner Country" of the BRICS grouping under Brazil’s presidency in 2025.
- Other BRICS partner countries include Belarus, Bolivia, Cuba, Kazakhstan, Malaysia, Thailand, Uganda, and Uzbekistan.
- A "partner country" in BRICS is allowed to attend summits, ministerial meetings, and participate in joint initiatives, but does not have formal membership or decision-making power.
About Nigeria’s Role
- Nigeria has the 6th largest population globally and the largest in Africa.
- It is the 4th largest economy in Africa, often termed the "Giant of Africa".
- Nigeria plays a significant role in South-South cooperation and reform of global governance structures, aligning with BRICS' strategic objectives.
About BRICS
- Founded: 2009 by Brazil, Russia, India, and China; South Africa joined in 2010.
- New Full Members (as of 2023): Iran, Egypt, Ethiopia, UAE, and Indonesia (effective Jan 2025).
- Membership Invitations: Saudi Arabia has been invited but not yet accepted.
- Applicants: Turkey, Azerbaijan, Malaysia have formally applied.
- Three Pillars of Cooperation:
- Political and Security
- Economic and Financial
- Cultural and People-to-People Exchanges
- Represents ~40% of global population and ~37.3% of global GDP.
India has hosted BRICS Summits in 2012 (4th), 2016 (8th), and 2021 (13th).
Binding DDT-Infused Soil with Biochar
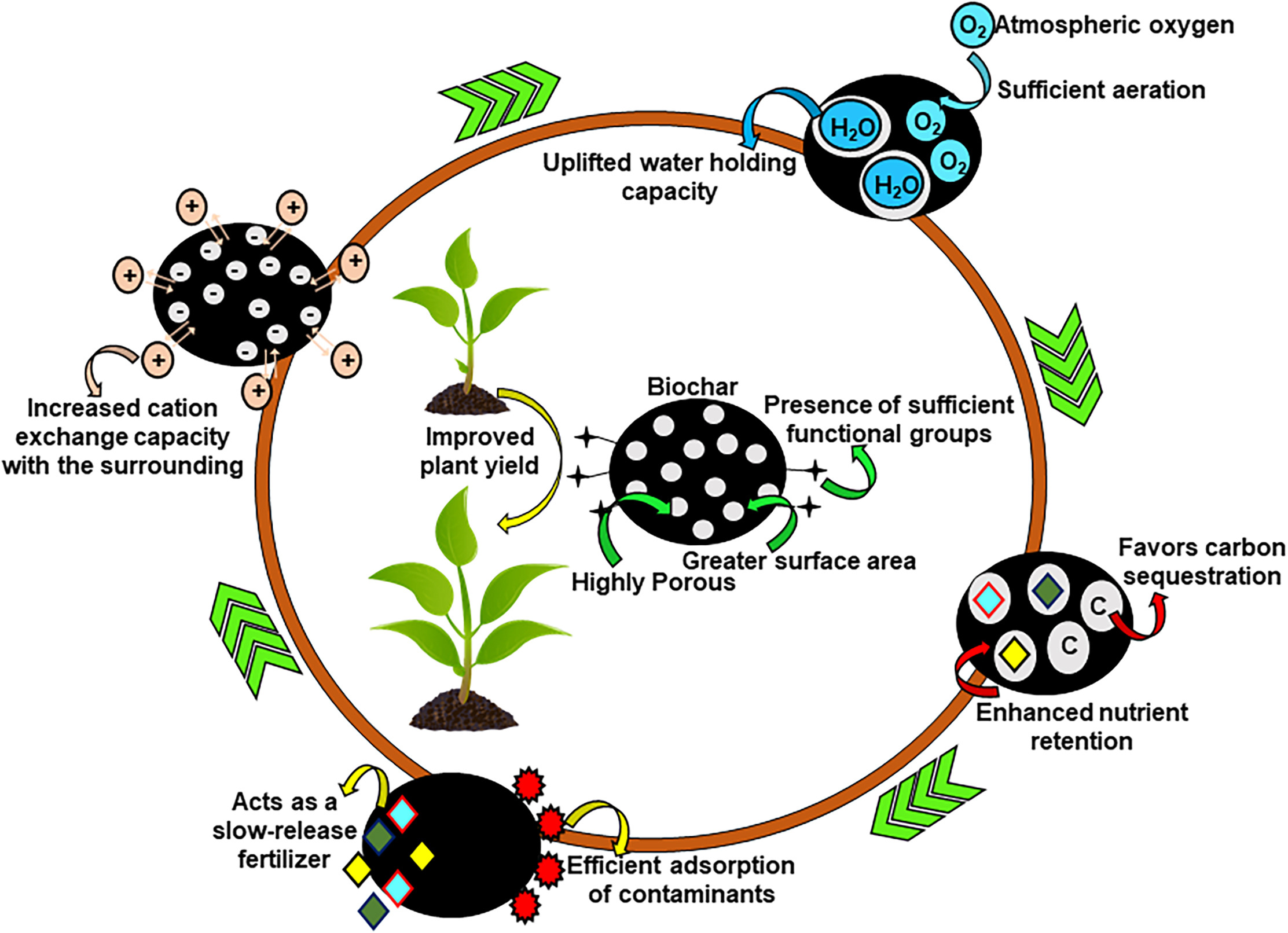
- 18 Jan 2025
In News:
A three-year study was conducted on a 23-hectare DDT-contaminated former tree nursery in southern Sweden. Researchers mixed biochar into sections of the contaminated soil and planted different crops, including pumpkins, legumes, grasses, and willows.
Key findings:
- Reduction of DDT Uptake: The presence of biochar reduced DDT absorption by soil organisms, cutting the toxin uptake by earthworms in half.
- Enhanced Soil Health: Biochar improved soil structure, fertility, and microbial activity.
- Cost-Effective Alternative: Unlike traditional soil removal methods, which are expensive and labor-intensive, biochar treatment offers a sustainable and economical approach.
- Support for Renewable Energy: The method allows for the growth of bioenergy crops such as willow trees, further contributing to environmental benefits.
Implications for Future Agricultural Practices
This breakthrough provides a viable approach to rehabilitate contaminated lands worldwide. Many regions, including India, still grapple with DDT contamination. While India banned agricultural use of DDT in 1972, it continues to be used for disease control under strict regulations. The application of biochar could significantly aid in soil restoration and sustainable land management
About DDT
- Dichlorodiphenyltrichloroethane (DDT) is a synthetic insecticide first introduced in 1939. It was widely used in agriculture and public health initiatives to control vector-borne diseases like malaria.
- However, despite its effectiveness against pests, DDT’s persistence in the environment led to severe ecological and health concerns.
- It degrades slowly, accumulates in fatty tissues, and disrupts ecosystems by affecting soil fertility, harming wildlife, and posing potential human health risks, including endocrine disruption and carcinogenic effects.
Challenges Posed by DDT-Contaminated Soils
The prolonged use of DDT has resulted in extensive soil contamination, making land infertile and unsuitable for cultivation. Conventional methods of decontamination, such as soil excavation and disposal, are expensive and environmentally unsustainable.
Biochar as a Solution
Researchers at Sweden’s Chalmers University of Technology have developed an innovative method to restore DDT-contaminated soils by integrating biochar.
What is Biochar?
Biochar is a charcoal-like material produced by burning organic waste in a controlled oxygen-limited environment (pyrolysis). It is known for its ability to enhance soil quality, bind contaminants, and store carbon for extended periods.
Kuka Rebellion and Namdhari Sect

- 18 Jan 2025
In News:
On January 17, Punjab Chief Minister Bhagwant Mann paid tribute at the Namdhari Shaheed Smarak in Malerkotla to commemorate Kuka Martyrs’ Day. The event marks the execution of 66 Namdhari Sikhs by the British in January 1872.
Kuka Rebellion: An Overview
The Kuka Rebellion was an anti-British movement led by the Namdhari sect in Punjab. It combined religious reform with resistance to colonial rule, reaching its peak in January 1872.
Key Events:
- January 13, 1872: Kukas, led by Hira Singh and Lehna Singh, protested against cow slaughter in Malerkotla.
- January 15, 1872: Clashes occurred between Kukas and government officials. A contingent attacked Malaudh Fort but was repulsed.
- January 17-18, 1872: 66 Kukas were executed by being blown up with cannons under orders of British official John Lambert Cowan.
Reasons Behind the Movement:
- Religious Reform: Opposed meat consumption, alcohol, and social vices.
- Colonial Oppression: Protested against British rule and native collaborators.
- Cow Protection: Strongly opposed cow slaughter, leading to confrontations with British authorities.
Impact and Aftermath:
- Suppression: The British crushed the movement with extreme brutality.
- Exile of Leaders: Satguru Ram Singh and other key leaders were exiled to Rangoon, Burma.
- Legacy of Martyrdom: The sacrifice of young Namdharis like 12-year-old Bishan Singh and Waryam Singh inspired future resistance movements in India.
Who are the Namdharis?
The Namdharis, also called Kukas, are a Sikh sect founded by Satguru Ram Singh in 1857 in Ludhiana. Their distinctive practices include:
- High-pitched recitation of Gurbani (hence the name ‘Kuka’ meaning ‘crying’ or ‘screaming’ in Punjabi).
- Wearing white attire as a sign of mourning for their exiled leader.
- Early adoption of Swadeshi principles, boycotting British goods and services.
Current Status of Namdhari Sect:
- The Namdharis, numbering around 2 lakh in Punjab today, have faced internal divisions since the death of Satguru Jagjit Singh in 2012.
- Two major factions exist:
- One led by Thakur Dilip Singh, headquartered in Sirsa, Haryana.
- Another led by Sangrur Uday Singh, headquartered at Bhaini Sahib, Ludhiana.
- A core belief remains that Satguru Ram Singh is still alive and will return one day.
Significance:
The Kuka Rebellion, though localized, was an important precursor to later national movements against British rule. It showcased the early spirit of resistance, long before organized freedom movements gained momentum in the 20th century.
Global Risks Report 2025
- 18 Jan 2025
In News:
- The World Economic Forum (WEF) has released the 20th edition of the Global Risks Report 2025, outlining the most pressing global risks over short-term (1-2 years) and long-term (10 years) horizons.
- The report, based on the Global Risks Perception Survey (GRPS) 2024-2025, categorizes risks across economic, environmental, geopolitical, societal, and technological domains.
Key Findings of the Report
Short-Term Risks (1-2 Years)
- Misinformation and Disinformation – Undermines trust in governance and institutions, complicating global cooperation.
- Extreme Weather Events – Rising costs and frequency due to climate change.
- State-Based Armed Conflict – Geopolitical tensions, including conflicts such as the Russia-Ukraine war.
Long-Term Risks (10 Years)
- Extreme Weather Events – Ranked as the most significant long-term risk.
- Biodiversity Loss & Ecosystem Collapse – Drastic impact on food security and natural systems.
- Critical Changes to Earth Systems – Irreversible environmental shifts.
Evolving Global Risk Landscape
The risk landscape is shaped by four structural forces:
- Technological Acceleration – Rapid advancements in AI and digital platforms.
- Geostrategic Shifts – Increasing global polarization and armed conflicts.
- Climate Change – Rising environmental hazards.
- Demographic Bifurcation – Aging populations and labor shortages.
Specific Risks and Trends
Environmental Risks
- Pollution: Increasing air, water, and land contamination due to unsustainable production.
- Natural Disasters: Wildfires in the U.S. projected to cause over $200 billion in damages.
- Water Supply Shortages: A major concern for countries like India.
Economic and Trade Risks
- Escalating Trade Protectionism: Increase in tariffs and restrictions (e.g., Make in India, U.S. Inflation Reduction Act).
- Economic Uncertainty: Global inflation projected to decrease to 3.5% by 2025, but trade tensions may reignite financial instability.
- Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) Decline: A 10% drop in 2023 due to trade fragmentation.
Technological Risks
- Misinformation & Disinformation: AI-generated content fuels societal polarization.
- Cybersecurity Threats: AI-driven cyberattacks and algorithmic biases in governance.
- Surveillance & Censorship: Increased digital monitoring with inadequate legal safeguards.
Geopolitical and Societal Risks
- Erosion of Human Rights: Increasing authoritarian surveillance and control.
- Migration & Resource Shortages: Climate-induced migration is a rising global concern.
- Pension Crisis: Aging populations in countries like Japan and Germany threaten economic stability.
India-Specific Risks
- Water Shortages – Critical impact on agriculture and urban development.
- Misinformation & Disinformation – Threatens democratic institutions and governance.
- Pollution (Air, Water, Soil) – Major environmental and health hazard.
- Labor & Talent Shortages – Workforce challenges due to demographic shifts.
- Erosion of Civic Freedoms – Concerns over digital surveillance and censorship.
Policy Recommendations
Global and Domestic Strategies
- Strengthen Multilateral Cooperation: WTO reforms and global trade dispute resolutions.
- Boost Domestic Resilience: Investment in infrastructure, healthcare, and education.
- Combat Pollution: Stricter regulations on air and water pollutants.
- Address Algorithmic Bias: Global standards for AI governance and accountability.
- Ethical Oversight for Biotech: WHO-led regulations for human genome editing.
Long-Term Sustainability Measures
- Flexible Work Policies: Encouraging non-linear career paths.
- Pre-Retirement Health Programs: Improving lifestyle choices to reduce healthcare costs.
- Pension System Reforms: Raising retirement ages and ensuring financial security for retirees.
Global Cybersecurity Outlook 2025
- 18 Jan 2025
In News:
The World Economic Forum (WEF) recently released the Global Cybersecurity Outlook 2025 report. The report examines cybersecurity trends, key challenges, and necessary strategies to enhance global cyber resilience.
About Global Cybersecurity Outlook 2025
Produced in collaboration with Accenture, the report highlights major cybersecurity issues influenced by geopolitical tensions, emerging technologies, supply chain complexities, and cybercrime advancements.
Key Issues Highlighted
- Geopolitical Conflicts:
- Ongoing conflicts, such as the Russia-Ukraine war, have increased cyber vulnerabilities in critical sectors like energy, telecommunications, and nuclear power.
- Nearly 60% of organizations state that geopolitical tensions have impacted their cybersecurity strategies.
- Cybersecurity Readiness:
- Two-thirds of organizations foresee AI impacting cybersecurity, yet only one-third have the tools to assess AI-related risks.
- Smaller organizations face significant challenges in adopting AI-driven security measures.
- Cyber Skills Gap:
- As of 2024, there is a shortage of 4.8 million cybersecurity professionals globally.
- Only 14% of organizations have a skilled workforce to manage current cybersecurity threats.
- Public-sector organizations are notably impacted, with 49% reporting a shortage in cybersecurity talent.
- Supply Chain Interdependencies:
- Over 50% of large organizations identify supply chain complexity as a barrier to cyber resilience.
- Vulnerabilities in third-party software, cyberattacks, and enforcement issues in security standards are key concerns.
- Cybercrime Sophistication:
- Cybercriminals are increasingly leveraging generative AI tools for automated and personalized attacks, including phishing and social engineering.
- In 2024, 42% of organizations experienced phishing and deepfake attacks.
- Regulatory Challenges: 70% of organizations reported that complex cybersecurity regulations cause compliance issues.
Impacts
- Critical Infrastructure:
- Cyberattacks on essential infrastructure, such as water utilities, satellites, and power grids, pose severe risks to public safety.
- Example: A 2024 cyberattack on a U.S. water utility disrupted operations, highlighting vulnerabilities in critical infrastructure systems.
- Biosecurity Risks:
- Advancements in AI, cyberattacks, and genetic engineering create risks for bio-laboratories and research institutions.
- Incidents in South Africa and the UK underscore these threats.
- Economic Disparities: Developed regions like Europe and North America demonstrate stronger cyber resilience compared to emerging economies such as Africa and Latin America.
- Transition Issues to Renewable Energy (RE): The shift to renewable energy introduces new cybersecurity risks, making power grids attractive targets for cybercriminals.
Factors Increasing Cybersecurity Complexity
- Supply Chain Vulnerabilities: Increasingly complex supply chains create risks with limited oversight, enabling cyberattacks to spread across interconnected systems.
- Geopolitical Tensions: Conflicts have driven advanced cyber strategies targeting critical infrastructure.
- AI-Driven Threats: Generative AI enables scalable malware deployment and sophisticated multilingual social engineering attacks.
- Cyber Skills Gap: A growing 8% skills gap leaves two-thirds of organizations unable to meet cybersecurity demands.
- Convergence of Cybercrime and Organized Crime: Rising cyber-enabled fraud has attracted organized crime groups, amplifying social impact.
- Climate-Linked Cyber Risks: Energy grids are increasingly targeted due to their reliance on evolving energy systems.
- Quantum Vulnerabilities: Quantum computing poses risks to public-key encryption, which is essential for securing digital systems.
Way Forward
Strategic Investment:
- Cybersecurity must be viewed as a strategic investment rather than a technical expense.
- Governments are encouraged to modernize legacy systems and upgrade operational technologies to protect critical sectors.
Public-Private Collaboration:
- Collaboration between business and cybersecurity leaders is essential for sharing threat intelligence and enhancing resilience.
- Small and medium enterprises (SMEs) may require government incentives to enhance cybersecurity.
Skills Development: Expanding specialized training programs, certifications, and incentives is crucial to addressing the cybersecurity skills gap.
Focus on Resilience Over Prevention: Nations must prioritize resilience by enhancing response mechanisms, crisis management frameworks, and ensuring continuity of services.
International Cooperation:
- Collaborative efforts through forums like the United Nations (UN) and G20 can strengthen global cybersecurity frameworks.
- Developed nations should assist emerging economies in improving cyber resilience.
Current Framework for Cybersecurity in India
- Legislative Measures:
- Information Technology Act, 2000 (IT Act)
- Digital Personal Data Protection Act, 2023
- Institutional Framework:
- Indian Computer Emergency Response Team (CERT-In)
- National Critical Information Infrastructure Protection Centre (NCIIPC)
- Indian Cyber Crime Coordination Centre (I4C)
- Cyber Swachhta Kendra
- Strategic Initiatives:
- Bharat National Cybersecurity Exercise 2024
- National Cyber Security Policy, 2013
- Sector-Specific Regulations:
- Cybersecurity Framework for SEBI Regulated Entities
- Telecommunications (Critical Telecommunication Infrastructure) Rules, 2024
Rupee Depreciation

- 18 Jan 2025
In News:
The Indian rupee has recently experienced sharp devaluation against the US dollar after a period of relative stability. This shift is attributed to several factors, including capital outflows, rising import costs, and RBI’s evolving policy stance.
Understanding Exchange Rate Regimes
Exchange rates are classified into:
- Fixed Exchange Rate: The central bank maintains a constant exchange rate by actively managing reserves.
- Floating Exchange Rate: Market-driven rates with minimal intervention.
- Managed-Floating Exchange Rate: A blend of market forces and central bank intervention.
India has largely pursued a managed-floating exchange rate regime. The RBI has historically responded to excess demand by depreciating the rupee while selling forex reserves and, under excess supply conditions, resisted rupee appreciation to maintain export competitiveness.
Post-COVID Exchange Rate Shift
Between 2022 and November 2024, the RBI temporarily adopted a strategy resembling a fixed exchange rate regime to stabilize the rupee. However, amid rising capital outflows and increased import costs, the RBI recently reverted to its managed-float approach, allowing the rupee to depreciate.
Causes of Rupee Depreciation
- Internal Factors:
- Rising inflation reduced the rupee's real value and increased production costs.
- A widening trade deficit due to higher crude oil imports heightened demand for foreign currency.
- Persistent fiscal imbalances further pressured the rupee.
- Policy ambiguity in the RBI’s stance added market uncertainty.
- External Factors:
- Capital outflows driven by global uncertainties and rising US interest rates.
- Geopolitical tensions (e.g., Russia-Ukraine war) increased India’s import bill.
- The US dollar's strength amid aggressive Federal Reserve rate hikes further weakened the rupee.
Implications of Rupee Devaluation
- Positive Effects:
- Boost to Exports: A weaker rupee makes Indian goods cheaper, enhancing export competitiveness if supported by real exchange rate depreciation.
- Adverse Effects:
- Inflationary Pressures: Higher import costs increase consumer prices.
- Reduced Purchasing Power: Increased costs are often passed on to consumers.
- Foreign Debt Servicing: A depreciated rupee raises debt repayment costs for Indian firms and the government.
- Investor Sentiment: Currency instability diminishes foreign investor confidence, triggering further capital outflows.
Structural Constraints in the Indian Economy
- Divergence between NEER and REER:
- Since the mid-2010s, India's Nominal Effective Exchange Rate (NEER) depreciated while the Real Effective Exchange Rate (REER) appreciated. This divergence undermines export competitiveness, as rising domestic prices offset nominal depreciation benefits.
- Rising Markups:
- Non-financial firms increased their markups on variable costs, contributing to inflation and nullifying the advantages of currency depreciation for exports.
Policy Responses and Recommendations
- RBI Interventions:
- Forex market interventions to manage demand-supply imbalances.
- Interest rate adjustments to attract capital inflows and stabilize the rupee.
- Enhanced forex reserve management to mitigate excessive volatility.
- Fiscal Strategies:
- Reducing Import Dependency: Boost domestic production of high-demand goods like crude oil substitutes.
- Export Incentives: Strengthen export sectors through subsidies, incentives, and improved infrastructure.
- Encouraging Long-Term FDI: Promoting stable investment environments for sustained capital inflows.
- Structural Reforms:
- Policies that enhance domestic production, reduce reliance on volatile foreign portfolio investments (FPIs), and maximize remittances can stabilize the rupee in the long term.
Bharat Ranbhoomi Darshan

- 17 Jan 2025
In News:
The Bharat Ranbhoomi Darshan initiative, launched by Defence Minister coinciding with the 77th Army Day celebrations, is a collaborative effort between the Ministry of Defence and the Ministry of Tourism.
Key Highlights:
- This initiative is designed to promote battlefield and border tourism by providing citizens with access to historically significant battlefields and military sites.
Objectives
- Promote Battlefield and Border Tourism: Encourage citizens and tourists to explore India's military history.
- Enhance Awareness: Educate visitors about India’s historic battles and military valor.
- Socio-Economic Development: Boost infrastructure, connectivity, and local economies in border regions.
Features of Bharat Ranbhoomi Darshan
- Virtual Tours and Interactive Content: The platform offers historical narratives, virtual tours, and interactive multimedia to provide a detailed account of each battlefield.
- Travel Planning Assistance: Visitors can access information regarding permits, travel routes, and accommodations.
- Integration with the Incredible India Campaign: The initiative is part of the government’s broader tourism strategy, ensuring widespread promotion.
- Collaborative Infrastructure Development: The Indian Army is working with local civil authorities to facilitate safe tourism without compromising operational preparedness.
Key Locations Covered
- Galwan Valley (Ladakh): Site of the 2020 India-China clash.
- Doklam: A tri-junction between India, Bhutan, and China.
- Line of Control (LoC) and Line of Actual Control (LAC) Sites:
- Nathu La Pass (Sikkim): Significant in the 1967 Indo-China clashes.
- Longewala (Rajasthan): Site of a key battle during the 1971 Indo-Pak war.
- Other Sites: Locations of the 1962 war with China and various Indo-Pak conflicts.
Significance
- Historical and Patriotic Engagement: Provides citizens firsthand insights into the challenges faced by soldiers in remote, strategic locations.
- Tourism Development in Border Areas: Previously restricted areas now open for visitors, leading to economic benefits for local communities.
- National Security Awareness: Encourages greater appreciation of India's defense forces and their contributions.
Implementation
The first phase of the Bharat Ranbhoomi Darshan project includes key battlefields and border sites across seven major regions. Future phases will expand coverage to additional historical military locations.
Fast Track Immigration FTI-TTP

- 17 Jan 2025
In News:
The Government of India is launching the Fast Track Immigration Trusted Traveller Program (FTI-TTP) to streamline immigration at seven major airports.
Key Highlights:
- The initiative, inaugurated by Union Home Minister Amit Shah, aims to enhance the travel experience for Indian nationals and Overseas Citizen of India (OCI) cardholders.
- This comes seven months after the programme was first introduced at Indira Gandhi International (IGI) Airport, New Delhi. The airports included in this initial phase are: Mumbai, Chennai, Kolkata, Bengaluru, Hyderabad, Cochin and Ahmedabad
Objectives of FTI-TTP
- Provide seamless and secure immigration services.
- Reduce human intervention using automated e-gates.
- Align with the Viksit Bharat@2047 vision for modern infrastructure.
How the Programme Works
The FTI-TTP simplifies immigration with automated e-gates. Travellers must complete a one-time online registration to enroll. The process involves:
- Online Registration: Submit personal details and upload necessary documents via the official portal (https://ftittp.mha.gov.in).
- Biometric Submission: Fingerprints and facial images must be submitted at an airport or Foreigners Regional Registration Office (FRRO).
- Immigration Clearance via E-Gates:
- Passengers scan their boarding passes and passports at e-gates.
- Biometrics are automatically verified.
- Upon authentication, the e-gate opens, granting clearance.
Validity: Registration is valid for five years or until the registered passport expires, whichever comes first.
Who is Eligible?
The first phase of the FTI-TTP is open to:
- Indian nationals.
- OCI cardholders aged between 12 and 70 years.
- Children aged 12-18 can register using their parents’ email/phone number.
- ECR (Emigration Check Required) passport holders are not eligible.
Documents Required for Registration
- Passport-sized photograph (as per Indian passport specifications).
- Scanned copy of passport (front and back pages).
- Proof of current address.
- OCI card details (if applicable).
Key Points to Note
- Registration may take up to a month due to verification by field agencies.
- Applications with incorrect or outdated information may be rejected.
- In case of passport loss or expiry, travellers must reapply and submit fresh biometrics.
- Passports must have at least six months’ validity at the time of applying.
- For support, travellers can reach out via email at india.ftittp-boi@mha.gov.in.
Implementation Phases
The FTI-TTP will be implemented in two phases:
- Phase 1: Covers Indian citizens and OCI cardholders.
- Phase 2: Will extend to foreign travellers.
- The programme will be expanded to 21 major airports across the country.
Comparison with Similar Global Programmes
Several countries have implemented similar fast-track immigration systems:
United States: Global Entry
- Introduced in 2008.
- Offers self-service kiosks for pre-approved travellers.
- Requires background checks and in-person interviews.
United Kingdom: Registered Traveller Service
- Launched in 2015.
- Allows frequent visitors from select countries, including India, to use e-gates.
- Requires visa eligibility or multiple prior visits.
European Union: Smart Borders Initiative
- Implemented in 2016, with full deployment expected by 2024.
- Pre-registers biometric data for faster processing at Schengen Area borders.
Australia: SmartGate
- Started in 2007 for Australian and New Zealand passport holders.
- Uses automated kiosks for identity verification via passport scans and photos.
Saudi Arabia: Smart Travel System
- Launched in 2019.
- Uses automated e-gates for faster immigration clearance.
- Expanding as part of Vision 2030 to improve travel experience, particularly for Hajj pilgrims.
QS World Future Skills Index 2025

- 17 Jan 2025
In News:
The QS World Future Skills Index 2025, released by Quacquarelli Symonds (QS), evaluates countries' readiness to meet the evolving demands of the global job market. It assesses nations based on skill development, education, and economic transformation, highlighting their preparedness for emerging technologies, artificial intelligence (AI), and sustainability.
India’s Performance in the Index:
- Overall Ranking: India is ranked 25th globally, categorizing it as a “Future Skills Contender.”
- Future of Work Category: India ranked 2nd, only behind the United States, reflecting its preparedness for AI, digital, and green jobs.
- Economic Transformation: India scored 58.3, the lowest among the top 30 countries, reflecting challenges in innovation and sustainability.
- Skills Fit: India received a score of 59.1, the weakest among the top 30 nations, indicating a gap between workforce skills and industry requirements.
- Academic Readiness: India’s education system is struggling to keep pace with employer demands, necessitating curriculum reforms and stronger academia-industry collaboration.
Key Findings from the Report:
Strengths:
- Digital Readiness: India has demonstrated strong capabilities in integrating digital talent into the workforce.
- Youth Advantage: A large, young population provides a demographic dividend for sustained economic growth.
- Startup Ecosystem: India’s startup culture and government initiatives support technological advancement and innovation.
Weaknesses:
- Higher Education-Industry Gap: Mismatch between education and employer requirements, particularly in AI, green skills, and entrepreneurship.
- Limited R&D Investment: India’s research and development spending is 0.6% of GDP, far below the global average of 2.7%.
- Low Innovation in Sustainability: India scored 15.6 out of 100, ranking poorly in future-oriented innovation for sustainability.
Challenges and Concerns:
- Skilled Workforce Shortage: The National Skill Development Corporation (NSDC) estimates a 29 million skilled workforce gap in critical sectors such as healthcare, semiconductor manufacturing, and AI.
- Low Employability Rates: Only 25% of management professionals, 20% of engineers, and 10% of graduates meet global employability standards.
- Higher Education Accessibility: Many students face difficulties in accessing quality tertiary education, particularly in skill-intensive fields.
Opportunities for Growth:
- Leverage Demographic Dividend: India can capitalize on its young workforce to dominate skill-based industries while other nations struggle with aging populations.
- Policy Support:
- National Education Policy (NEP) 2020: Focuses on modular education and reskilling initiatives.
- ULLAS Program: Aims to expand lifelong learning and skill development.
- Technological Integration: Advancements in AI and digital learning can help modernize academic curricula and improve job readiness.
Recommendations for Improvement:
- Enhancing Academia-Industry Collaboration: Universities should prioritize problem-solving, entrepreneurship, and creativity to align education with employer needs.
- Increasing R&D Investment: Raising spending on research and development to promote innovation and sustainability.
- Expanding Access to Education: Bridging regional disparities in tertiary education through flexible and modular learning.
- Strengthening Policy Implementation: Ensuring effective execution of skilling programs to reduce the workforce-employability gap.
Eighth Pay Commission

- 17 Jan 2025
In News:
The Union government has approved the constitution of the Eighth Pay Commission, benefiting 50 lakh central government employees and 65 lakh pensioners, including serving and retired defence personnel. The decision, taken ahead of the Delhi Assembly elections, aims to address long-standing demands from trade unions and employee organizations.
Key Features of the 8th Pay Commission
- Early Constitution: Although the Seventh Pay Commission's term ends in 2026, the early establishment of the Eighth Pay Commission ensures timely recommendations and implementation.
- Composition: The commission will have a Chairperson and two members, typically led by a retired Supreme Court judge.
- Terms of Reference (ToR):
- Revision of Pay: Recommend updates to salary structures and allowances.
- Addressing Pay Disparities: Resolve wage differences across various cadres.
- Market Parity: Align pay structures with industry standards.
- Pension and Retirement Benefits: Improve pension schemes and adjust them for inflation.
- Economic Impact Analysis: Assess how salary hikes contribute to economic growth.
- Stakeholder Consultations: Engage with governments and other stakeholders before finalizing recommendations.
Economic Implications of the 8th Pay Commission
- Employee Well-being: Higher wages will enhance the quality of life for government employees.
- Boost to Consumption: Increased salaries are expected to stimulate demand and support economic expansion.
- Ripple Effect on PSUs & States: Many public sector undertakings and state governments follow the central pay commission’s recommendations, potentially leading to wider economic benefits.
- Fiscal Considerations: The implementation of the Seventh Pay Commission in 2016-17 led to an expenditure increase of ?1 lakh crore. A similar rise in 2026-27 could impact fiscal space for capital expenditures.
Challenges and Concerns
- Implementation Delays: Past commissions have taken two years to submit recommendations, which could push implementation beyond 2027.
- Living Wage & Pension Issues: Existing formulas for minimum wage and pension calculations may need revision to reflect rising healthcare, education, and digital access costs.
- Financial Burden on the Exchequer: A significant increase in revenue expenditure could limit the government’s ability to invest in infrastructure and development projects.
Global Economic Prospects (GEP) Report 2025
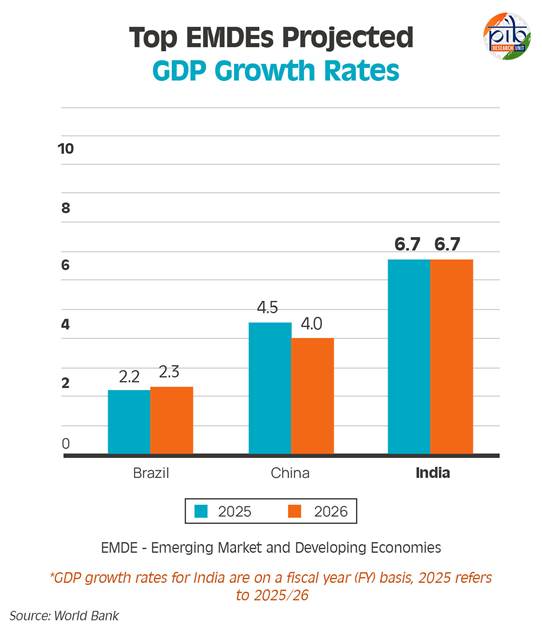
- 17 Jan 2025
In News:
The World Bank has released its Global Economic Prospects (GEP) report for 2025, a flagship biannual publication analyzing trends and projections in the global economy, with a focus on emerging markets and developing economies (EMDEs). The report highlights economic growth forecasts, trade dynamics, and the challenges and opportunities shaping the global economic landscape.
Global Economic Outlook
- The world economy is projected to expand at a steady yet subdued rate of 2.7% in both 2025 and 2026, maintaining the pace of 2024.
- Inflation, which peaked above 8% in recent years, is expected to stabilize at an average rate of 2.7% in 2025 and 2026, aligning with central bank targets.
- Despite growth, the global economy remains 0.4 percentage points below the 2010-2019 average, raising concerns about its ability to tackle poverty effectively.
Challenges and Risks
- Trade Restrictions: New trade restrictions imposed in 2024 were five times higher than the 2010-19 average, contributing to a slowdown in global trade and economic growth.
- Rising Protectionism: Increased fragmentation in global trade policies is limiting exports and hampering economic integration.
- Policy Uncertainty: Adverse policy shifts, sluggish progress in reducing inflation, and weaker performance in major economies pose downside risks to global recovery.
- Debt and Investment Concerns: Developing economies are experiencing sluggish investment growth and high debt levels, exacerbated by climate change-related costs.
Emerging Markets and Developing Economies (EMDEs)
- EMDEs have significantly evolved since 2000, now contributing about 45% of global GDP, compared to 25% at the start of the century.
- The three largest EMDEs—India, China, and Brazil—have accounted for approximately 60% of annual global growth over the past two decades.
- Growth in low- and middle-income developing countries is expected at 4.1% in 2025 and 4% in 2026, with a notable slowdown compared to the early 2000s.
- Low-income countries are projected to rebound to 5.7% in 2025 and 5.9% in 2026, aided by easing conflicts in some regions.
- The world's poorest nations, with annual per capita incomes below USD 1,145, recorded growth of 3.6% in 2024, impacted by conflicts in regions like Gaza and Sudan, alongside lingering effects of COVID-19 and geopolitical tensions.
India-Specific Highlights
- Fastest-Growing Major Economy: India is expected to maintain its position as the world’s fastest-growing major economy, with a projected growth rate of 6.7% in both 2025 and 2026.
- Sectoral Growth: The services sector will remain robust, while manufacturing activity is expected to strengthen.
- Investment Growth: Supported by rising private investment, improved corporate balance sheets, and favorable financing conditions, investment growth in India is expected to remain steady.
- Key Growth Drivers:
- Infrastructure development under the PM GatiShakti National Master Plan.
- Innovation-driven initiatives like Startup India and the Production Linked Incentive (PLI) Scheme.
- Expansion of the digital economy and financial inclusion efforts.
- Rural Demand and Consumption: Growth in rural demand and a recovery in farm production have bolstered consumer spending, although urban consumption remains affected by inflation and slow credit growth.
Human Papillomavirus (HPV)

- 16 Jan 2025
In News:
January is Cervical Cancer Awareness Month, and the focus on this month underscores the critical importance of preventing cervical cancer, a disease responsible for significant mortality among women in India. At the heart of this prevention is the Human Papillomavirus (HPV) vaccine, which is recognized as the most effective measure to prevent cervical cancer and other HPV-related cancers. Despite its potential, the HPV vaccine remains out of reach for many due to its high cost and the need for greater awareness.
HPV and its Impact in India
HPV is responsible for 99.7% of cervical cancers worldwide, making it one of the primary causes of cancer in women. In India, cervical cancer is the third most common cancer among women, accounting for about 6-29% of all cancers in women. As of GLOBOCAN 2020, India alone has 20% of the global burden of cervical cancer, with over 123,000 cases and a 9.1% mortality rate.
Additionally, HPV can lead to several other cancers, including anal, vulvar, vaginal, penile, and throat cancers, making its vaccination vital for overall cancer prevention.
The HPV Vaccine: A Game-Changer
The HPV vaccine is the most effective tool to prevent infections caused by the virus and reduce the incidence of associated cancers. The vaccine works by stimulating the immune system to produce antibodies that neutralize the virus before it can cause damage. There are different types of vaccines authorized in India, including:
- Gardasil (protects against HPV types 6, 11, 16, and 18)
- Cervarix (a bivalent vaccine targeting HPV 16 and 18)
- Cervavac (India's first HPV vaccine, developed by the Serum Institute of India)
The vaccine is recommended for both males and females between 9 and 26 years, with a special focus on children aged 12 to 13 years, as the vaccine is most effective when administered before exposure to the virus. It’s also suitable for people who are immunocompromised or HIV-infected.
Challenges to HPV Vaccination in India
Despite the obvious benefits, the uptake of the HPV vaccine in India faces several barriers:
- High Costs: The price of the vaccine remains prohibitively high. For example:
- Gardasil 9 costs ?10,850 per dose.
- Gardasil 4 is priced between ?2,000 to ?4,000 per dose.
- Cervavac, the Indian-made vaccine, costs around ?2,000 per dose, which is more affordable but still out of reach for many.
- Awareness and Cultural Perceptions: There is a lack of awareness about HPV and its link to cervical cancer. Cultural factors, particularly around reproductive health, can also create reluctance to vaccinate, especially in rural or conservative areas.
- Limited Access: Currently, the vaccine is available through private practitioners and is not part of the National Immunisation Programme (NIP), limiting access to the broader population.
The Way Forward: National Immunisation and Awareness Campaigns
The National Technical Advisory Group on Immunisation (NTAGI) has recommended that the HPV vaccine be included in India’s National Immunisation Programme (NIP). This would enable broader access and affordability, especially for girls aged 9–14 years and ensure that a routine vaccination schedule is implemented at the age of 9 years. Some states like Punjab and Sikkim have already taken steps to introduce the vaccine in their state-level immunization programs.
Additionally, a nationwide HPV vaccination campaign could raise awareness about the vaccine and its benefits, helping to overcome the challenges of cost, safety concerns, and cultural perceptions. Regular cervical cancer screenings (such as Pap smears and HPV tests) should also be encouraged to identify precancerous changes early.
Cabinet Approves Establishment of ‘Third Launch Pad’ at ISRO's Sriharikota Facility

- 16 Jan 2025
In News:
The Union Cabinet, has approved the establishment of a Third Launch Pad (TLP) at the Satish Dhawan Space Centre (SDSC), located at Sriharikota, Andhra Pradesh. This project marks a significant step in enhancing India’s space capabilities and will support the Next Generation Launch Vehicles (NGLV) for ISRO’s evolving space exploration programs.
Key Features of the Third Launch Pad
The TLP will be built with an adaptable design, capable of supporting NGLV and LVM3 vehicles with semi-cryogenic propulsion. The launch pad will also serve as a standby for the Second Launch Pad (SLP) at Sriharikota. This addition will help ISRO meet its growing launch capacity needs, particularly for future human spaceflight missions and space exploration projects. It will facilitate higher launch frequencies, thus boosting the Indian space ecosystem.
Implementation Strategy and Timeline
The Third Launch Pad is planned to be developed within 48 months (4 years), with the total cost pegged at ?3984.86 Crore. The development will involve maximized industry participation and will utilize existing infrastructure at the launch complex. The project will also leverage ISRO’s experience gained from establishing the earlier launch pads.
The Importance of the Third Launch Pad
The TLP is designed to support the Next Generation Launch Vehicles (NGLV), a key part of ISRO’s vision for space exploration. The facility will not only accommodate heavier vehicles but will also ensure standby capacity for the Second Launch Pad (SLP). Its strategic location at Sriharikota ensures several advantages:
- Proximity to the Equator: This offers a substantial increase in payload capacity due to the additional push provided by the Earth's rotation.
- Safety and Accessibility: The site is free from major international maritime or airline routes, ensuring a safe flight path.
- Geographical Advantage: The launch pad is situated on the eastern coast, enabling launches in an easterly direction, maximizing the benefits of Earth’s rotational speed.
Future Plans for Indian Space Exploration
The establishment of the Third Launch Pad is crucial for the expanded vision of India’s space program, particularly in line with the Amrit Kaal period. ISRO aims to achieve ambitious milestones, such as the Bharatiya Antariksh Station (BAS) by 2035 and an Indian Crewed Lunar Landing by 2040. The NGLV will play a pivotal role in these plans, with features like:
- A three-stage vehicle and reusable first stage.
- Semi-cryogenic propulsion, using refined kerosene and liquid oxygen, which will increase payload capacity by three times at 1.5 times the cost of current vehicles.
The Role of Sriharikota in India’s Space Program
Sriharikota, the hub of ISRO’s launch operations, has been integral to India’s space exploration. Currently, the Indian Space Transportation Systems rely on two operational launch pads:
- First Launch Pad (FLP): Established over 30 years ago for PSLV and SSLV missions, FLP continues to support Polar Satellite Launch Vehicle (PSLV) and Small Satellite Launch Vehicle (SSLV) launches.
- Second Launch Pad (SLP): Built primarily for GSLV and LVM3 vehicles, SLP also serves as a standby for PSLV. Over its 20 years of operation, SLP has supported several national missions, including Chandrayaan-3, and is preparing for the Gaganyaan missions.
Does ‘Blood Money’ Have a Legal Standing?

- 16 Jan 2025
In News:
The concept of ‘blood money’ has come under scrutiny recently, especially in the context of the death sentence awarded to Indian nurse Nimisha Priya from Kerala in Yemen. This case, where the focus is on monetary compensation paid to the victim’s family, has sparked renewed discussions on the practice of blood money.
What is ‘Blood Money’?
‘Blood money’ or diya is a term used in Islamic Sharia law and refers to a sum of money that the perpetrator of a crime must pay to the victim or the victim’s family, typically in cases of unintentional murder or homicide. The custom is designed to offer compensation to the family for the loss of income and alleviate their suffering, rather than placing a price on human life. This practice allows the victim’s family to forgive the accused and avoid retribution, called qisas, under the Sharia.
However, even when blood money is paid, the community or state retains the authority to impose a penalty or punishment, which could include imprisonment or other penalties, based on the seriousness of the crime.
How Does Blood Money Figure in Islamic Sharia Law?
In Islamic law, the amount of blood money varies based on several factors such as the victim’s gender, religion, and nationality. The following examples demonstrate the application of blood money in different Islamic countries:
- Saudi Arabia: In Saudi Arabia, blood money is part of traffic regulations, where the perpetrator must pay compensation to the heirs of victims who die in road accidents. While a Sharia court determines the amount of compensation, the police handle the determination of the guilty party. In workplace accidents, a special committee sets the amount. Saudi Arabia has considered reforming its laws to ensure equal compensation for men and women, Muslims and non-Muslims. However, efforts to amend the laws have not yet been fully implemented.
- Iran: In Iran, blood money differs based on the gender and religion of the victim. A woman’s compensation is typically set at half of that of a man’s. While the Supreme Court of Iran upheld a law to equalize compensation for all individuals in 2019, full implementation of the law has yet to be realized.
- Pakistan: Pakistan has incorporated provisions for diya and qisas in its legal system through the Criminal Laws (Amendment) Ordinance, 1991, aligning its practices with those of Islamic law.
- Yemen: In Yemen, parties involved can negotiate compensation, with judicial oversight ensuring fairness.
India’s Stand on ‘Diya’ and Blood Money
India does not include the provision for blood money in its formal legal framework. However, a similar concept exists in the form of plea bargaining, which allows the accused to negotiate with the prosecution in exchange for a reduced sentence or charge. Plea bargaining involves the defendant pleading guilty to a lesser offense in return for a concession, either in terms of the charges or the sentence.
Plea Bargaining in India:
Introduced under the Criminal Law (Amendment) Act, 2005, plea bargaining was added to the Code of Criminal Procedure, 1973. While it bears some resemblance to blood money in that it allows for compensation to the victim, it has significant limitations:
- It can only be applied to crimes punishable by imprisonment of less than seven years.
- It is not applicable to heinous crimes such as murder or rape, or offenses involving women or children under 14.
- The accused must voluntarily agree to plead guilty, with no coercion involved.
While plea bargaining may include compensation under Section 265E of the Code, discussions continue to refine this provision to make it more inclusive, similar to the reforms seen in Islamic countries regarding blood money.
Historical Practices Similar to Blood Money
Throughout history, various cultures have had practices similar to blood money. These include:
- Brehon Law (Ireland): In the 7th century, Brehon law established the concept of Éraic (body price) and Log nEnech (honor price). These were compensation systems that allowed for the amicable resolution of crimes, avoiding capital punishment.
- Galanas (Wales): Galanas in Welsh law determined compensation based on the victim's social status, where a blood fine was required in cases of murder, unless the killing was justified.
- Wergeld (Germany): The Wergeld system in early medieval Germany required compensation for homicide or grave offenses, often in monetary terms.
- Other Medieval States: Several medieval states established a standard payment for the victims’ families in the event of homicide or serious crimes, much like blood money.
Cases of Indians Pardoned with Blood Money
India has witnessed instances where blood money has been invoked for Indian nationals facing death sentences abroad:
- Arjunan Athimuthu (Kuwait, 2019): Arjunan’s death sentence was commuted to life imprisonment after his family paid ?30 lakh in blood money.
- Abdul Rahim (Saudi Arabia): Abdul Rahim, convicted for the murder of a Saudi boy in 2006, was pardoned after ?34 crore in blood money was paid. However, he has not been released from prison yet.
- UAE Cases:
- In 2017, 10 Indians were pardoned after paying 200,000 dirhams as blood money.
In 2009, 17 Indians on death row for the murder of a Pakistani national were pardoned after a blood money amount of nearly ?4 crore was paid.
US AI Hardware Export Restrictions and Impact on India

- 16 Jan 2025
In News:
Days before demitting office, the Joe Biden administration has released an expansive regulatory framework on the export of artificial intelligence (AI) hardware such as graphics processing units (GPUs), which could have far-reaching consequences for India’s AI ambitions.
Three-Tier Framework for AI Hardware Export Restrictions
- Tier 1: Closest US Allies
- Countries: Australia, Belgium, Canada, South Korea, UK, etc.
- No restrictions on computing power deployment.
- Minimal security requirements.
- Impact: Free access to AI technology for these nations.
- Tier 2: Majority of Countries (Including India)
- Countries: India, Brazil, South Africa, etc.
- Restrictions: Limited to importing approximately 50,000 advanced AI chips (around $1 billion) through 2027.
- Potential to Double Cap: If countries sign agreements to uphold strict security standards.
- Impact on India:
- Short-Term: Likely to fulfill current demand for 10,000 GPUs for the IndiaAI Mission.
- Long-Term: Challenges in scaling AI infrastructure, with possible delays in large AI data centers and difficulty acquiring large-scale GPUs.
- Tier 3: Countries of Concern (Restricted Nations)
- Countries: Russia, China, North Korea, Iran, etc.
- No Access to US AI Technology: Nearly total prohibition of AI tech exports.
Special Provisions for India and China
- General Validated End User (GVEU) status for India and China:
- India: Authorisation for civilian and military use, excluding nuclear applications.
- China: Only civilian use permitted under similar conditions.
Why the US Imposed These Restrictions?
- National Security: Prevent adversaries (China, Iran, Russia) from acquiring advanced AI technologies.
- US Technological Leadership: To protect US AI leadership and prevent loss of competitive edge.
- Trusted Ecosystem: Build secure and trusted AI environments for allied nations.
Impact on India
- Short-Term:
- IndiaAI Mission: Current procurement of 10,000 GPUs unlikely to be affected.
- Subsidized GPUs: Available for startups, academia, and researchers.
- Long-Term Concerns:
- Licensing Uncertainties: Possible delays in large-scale AI deployments and AI data centers.
- Impact on Large Firms: Companies like Reliance and Yotta may face challenges scaling up AI compute infrastructure.
- National AI Mission Challenges: Difficulty in acquiring enough GPUs for large-scale AI projects beyond 2027.
- Strategic Leverage: US could use AI export restrictions to negotiate trade deals or tariff adjustments.
Nvidia’s Criticism of the AI Diffusion Rules
- Overreach and Bureaucratic: Nvidia criticized the 200+ page regulatory framework as excessive, secretive, and bureaucratic.
- Harming US Competitiveness: Claims that the rules would hinder US innovation and global leadership, weakening the competitiveness of the US semiconductor and software industries.
- Contrast with Trump’s Approach: Praises the earlier Trump administration for fostering AI growth through industry competition without compromising national security.
Enforcement of the Rules
- Regulatory Control: Managed by the US Bureau of Industry and Security (BIS) under the Department of Commerce.
- Technology Access: Ensures AI chips and models do not reach adversaries or nations posing security risks.
Potential Impact on India’s AI Strategy
- AI Hardware Infrastructure: Challenges in large-scale AI hardware deployment.
- Competitive Disadvantage: Potential delays or downsizing of AI data centers could affect India’s competitiveness in AI technology.
- Strategic Partnerships: India may need to secure General National Validated End User authorizations to ensure uninterrupted access to advanced chips.
- AI Market Growth: India’s AI market projected to grow to $17 billion by 2027, with an annual growth rate of 25%-35%.
Nine Years of Startup India

- 16 Jan 2025
In News:
On January 16, 2025, India marks nine years of Startup India, a transformative journey that began in 2016. Designated as National Startup Day, this occasion celebrates the nation’s strides in fostering a robust and inclusive entrepreneurial ecosystem.
Current Status (as of Jan 2025)
Over 1.59 lakh startups recognized by DPIIT, making India the 3rd largest startup ecosystem globally.
- More than 100 unicorns (startups valued over $1 billion).
- Key hubs: Bengaluru, Hyderabad, Mumbai, Delhi-NCR; growing contribution from smaller cities.
Key Sectors
- Major sectors: Fintech, Edtech, Health-tech, E-commerce.
- Notable companies: Zomato, Nykaa, Ola exemplify India's shift from job seekers to job creators.
Key Milestones (2016–2025)
- Startups grew from around 500 in 2016 to 1.59 lakh in 2025.
- 73,151 startups with at least one-woman director as of 2024, showcasing rise in women entrepreneurship.
- Over 16.6 lakh jobs created by DPIIT-recognized startups by 2024.
Core Features of Startup India
- Ease of Doing Business: Simplified compliance, self-certification, and single-window clearances.
- Tax Benefits: Three-year tax exemptions for eligible startups.
- Funding Support: ?10,000 crore Fund of Funds for Startups (FFS) supports early-stage funding.
- Sector-Specific Policies: Policies focusing on sectors like biotechnology, agriculture, and renewable energy.
Industry-wise Jobs Created
- IT Services: 2.04 lakh jobs.
- Healthcare & Lifesciences: 1.47 lakh jobs.
- Professional & Commercial Services: 94,000 jobs.
- Total direct jobs created: 16.6 lakh (as of Oct 2024).
Flagship Schemes
- Startup India Seed Fund Scheme (SISFS).
- Credit Guarantee Scheme for Startups (CGSS).
- Fund of Funds for Startups (FFS) Scheme.
Other Key Initiatives
- Capacity Building & Handholding: Workshops for regional ecosystems, especially in non-metro cities.
- Outreach & Awareness: Initiatives to facilitate funding, incubation, and mentorship opportunities.
- Ecosystem Development: National-level events like Startup Mahakumbh to bring together key stakeholders.
- International Linkages: India’s G20 Presidency institutionalized Startup20 to enhance global collaborations.
BHASKAR Platform (Launched in Sept 2024)
- Objective: Centralize and streamline interactions within the entrepreneurial ecosystem.
- Key Features:
- Networking: Connects startups, investors, mentors, and government bodies.
- Resources: Provides quick access to essential tools and knowledge for scaling startups.
- Global Outreach: Promotes India as a global innovation hub.
Startup Mahakumbh
- 2024 Edition: Hosted 1,300 exhibitors, 48,000 visitors, and 392 speakers, including unicorn founders and policymakers.
- 2025 Edition (3-5 April, New Delhi): Theme - “Startup India @ 2047 – Unfolding the Bharat Story.”
Ayushman Bharat Pradhan Mantri Jan Arogya Yojana (AB PM-JAY)

- 15 Jan 2025
In News:
Odisha has become the 34th state to implement the Ayushman Bharat Pradhan Mantri Jan Arogya Yojana (AB PM-JAY). The National Health Authority (NHA) of the Union Ministry of Health signed a Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) with the Department of Health and Family Welfare, Government of Odisha to onboard the state under the scheme.
Key Highlights:
- The scheme will be implemented alongside the existing Gopabandhu Jan Arogya Yojana in Odisha.
- It provides health coverage of Rs. 5 lakh per family per annum, with an additional Rs. 5 lakh for women members.
- Approximately 1.03 crore families will be covered under the scheme.
- Shri JP Nadda, Union Health Minister, emphasized that the scheme is the world’s largest and fastest-growing health coverage initiative.
- Shri Mohan Charan Majhi, Chief Minister of Odisha, highlighted that people will now have access to cashless treatment in over 29,000 empaneled hospitals.
About Ayushman Bharat PM-JAY:
- Launched in 2018 under the Ministry of Health & Family Welfare (MoH&FW).
- Targets 12 crore families (~55 crore beneficiaries).
- Provides cashless hospital coverage for secondary and tertiary care.
- Fully funded by the government, with cost-sharing between the Centre and states.
- Covers nearly 2,000 medical procedures, including major surgeries.
Since its inception, over 8.19 crore hospital admissions have been recorded, with ?1.13 lakh crore spent on healthcare for marginalized sections.
Cyclone Dikeledi
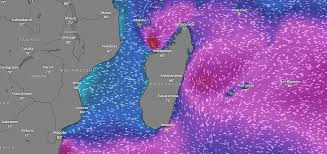
- 15 Jan 2025
Cyclone Dikeledi struck Mayotte, a French overseas territory in the Indian Ocean, located in the Mozambique Channel. The cyclone caused severe flooding and damage, following closely after Cyclone Chido, which had hit the region in December 2024.
About Mayotte:
- Comprises two islands from the Comoros archipelago: Mayotte (Grande Terre) and Pamandzi (Petite Terre).
- It is the poorest region in both France and the European Union.
- Colonized by France in 1843 and annexed along with the Comoros in 1904.
- In a 1974 referendum, while 95% of Comoros opted for independence, 63% of Mayotte voted to remain French.
- While Comoros declared independence in 1975, Mayotte continues to be governed by France.
Cyclone Chido, which struck in December 2024, was recorded as the most severe storm to hit Mayotte in 90 years.
Commissioning of Three Indian Naval Combatants

- 15 Jan 2025
In News:
In a major boost to India’s maritime defense capabilities, three frontline warships—INS Nilgiri, INS Surat, and INS Vaghsheer—were commissioned into the Indian Navy at the Naval Dockyard in Mumbai. This marks a significant step in India's self-reliance in defense manufacturing and strengthens its presence in the Indian Ocean Region (IOR).
INS Nilgiri: Project 17A Stealth Frigate
INS Nilgiri is the lead ship of the Project 17A class, an advanced version of the Shivalik-class frigates, designed for multi-mission capabilities in blue-water operations.
Key Features:
- Advanced stealth technology reducing radar and infrared signatures.
- Equipped with supersonic surface-to-surface missiles, Medium Range Surface-to-Air Missiles (MRSAM), upgraded 76 mm guns, and rapid-fire close-in weapon systems.
- Versatile roles in anti-surface, anti-air, and anti-submarine warfare.
- Constructed using integrated modular design for faster assembly.
- Other ships in this class—Himgiri, Taragiri, Udaygiri, Dunagiri, and Vindhyagiri—are under construction at Mazagon Dock Shipbuilders Limited (MDL) and Garden Reach Shipbuilders and Engineers (GRSE).
INS Surat: Project 15B Stealth Destroyer
INS Surat is the fourth and final guided missile destroyer under Project 15B, following INS Visakhapatnam, INS Mormugao, and INS Imphal. It represents an upgraded version of the Kolkata-class destroyers.
Key Features:
- AI-Enabled Operations: First Indian warship integrated with artificial intelligence solutions for enhanced combat efficiency.
- High-Speed Capability: Can exceed speeds of 30 knots (56 km/h).
- Advanced Armament: Equipped with modern surface-to-air and anti-ship missiles, torpedoes, and sophisticated network-centric warfare sensors.
- Strategic Role: Acts as a high-speed, maneuverable warship with increased strike capability and endurance.
Project 15B was initiated in 2011, with ships named after major Indian cities to symbolize national unity. These destroyers serve as critical assets in naval operations, ensuring dominance in maritime warfare.
INS Vaghsheer: Project 75 Scorpene-Class Submarine
INS Vaghsheer is the sixth and final Kalvari-class submarine built under Project 75, designed for stealth and versatile naval operations.
Key Features:
- Scorpene-Class Design: Developed in collaboration with the French Naval Group.
- Diesel-Electric Propulsion: Silent and highly maneuverable, making it one of the world’s most advanced attack submarines.
- Mission Capabilities: Specializes in anti-surface warfare, anti-submarine warfare, intelligence gathering, and special operations.
- Weapons Systems: Armed with wire-guided torpedoes, anti-ship missiles, and state-of-the-art sonar systems.
The Kalvari-class submarines continue India's legacy of submarine warfare, named after decommissioned Soviet-origin Foxtrot-class submarines post-Independence.
Iran's Capital Relocation

- 15 Jan 2025
In News:
Iran has announced plans to relocate its capital from Tehran to the Makran coastal region due to economic and environmental concerns.
Reasons Behind Relocation
- Overcrowding and Resource Constraints: Tehran, the capital for over 200 years since the Qajar dynasty (1794-1925), faces overpopulation, air pollution, water scarcity, and energy shortages.
- Strategic Importance of Makran: Located in Sistan and Baluchestan Province, Makran’s proximity to the Gulf of Oman enhances its potential for economic development.
- Economic and Maritime Significance: Home to key ports like Chabahar, Makran is vital for Iran’s petroleum reserves and coastal trade.
- Geopolitical Considerations: The development of Makran as an international trade hub could strengthen Iran’s economic ties with Central Asia and the Indian Ocean region.
About Makran
- Geographical Overview: A semi-desert coastal plateau shared by Pakistan and Iran, bordered by the Arabian Sea and the Gulf of Oman.
- Key Ports and Trade Routes: Gwadar (Pakistan) and Chabahar (Iran) serve as critical gateways to the Strait of Hormuz, a global oil supply route.
Alexander’s Invasion and Makran’s Historical Significance
Background of Alexander’s Invasion (327–325 BCE)
- Entry into India: Alexander, King of Macedonia (336-323 BCE), entered India via the Khyber Pass after conquering Kabul.
- Key Battles:
- Battle of Hydaspes (Jhelum): Faced and defeated King Porus, later reinstating him as an ally.
- Retreat at Hyphasis (Beas River): His army, exhausted and wary of the Nanda Empire’s strength, refused to march further east.
The Gedrosian Desert March
- Extreme Hardships: While retreating through the Makran Desert, Alexander lost a third of his army to dehydration, starvation, and exhaustion.
- Comparison with Cyrus the Great: Unlike Cyrus II, who failed to cross the desert, Alexander’s army endured the harsh terrain, albeit with heavy casualties.
Impact of Alexander’s Invasion on India
- Cultural and Trade Exchanges: Facilitated early Indo-Greek interactions and opened key trade routes linking South Asia and Europe.
- Greek Settlements: Established cities like Alexandria (Kabul) and Boukephala (Jhelum), influencing local governance and trade.
- Mauryan Expansion: Weakened regional rulers enabled Chandragupta Maurya to establish the Mauryan Empire.
- Influence on Art and Culture: Indo-Greek fusion led to the Gandhara School of Art, integrating Greek and Indian artistic traditions.
Makaravilakku festival

- 15 Jan 2025
In News:
Kerala police deploy 5,000 personnel at Sabarimala ahead of Makaravilakku festival.
Key Highlights:
- Makaravilakku is a prominent annual Hindu festival held at the Sabarimala Temple in Kerala, dedicated to Lord Ayyappa.
- It marks the celestial event of the Sun entering Capricorn (Makaram Rashi) on Makara Sankranti.
- The festival is a culmination of the 41-day pilgrimage to Sabarimala, celebrated with devotion, discipline, and spiritual purification.
- Sabarimala is one of the largest pilgrimage sites globally, drawing 10-15 million devotees annually.
Location:
- The Sabarimala Temple is located on the Sabarimala hill in Pathanamthitta, Kerala, within the Periyar Tiger Reserve.
- It is surrounded by 18 hills and is located along the banks of the Pamba River.
Key Rituals:
- 41-Day Pilgrimage (Vratham): Devotees observe strict practices like celibacy, fasting, and wearing black or saffron attire to purify the body and soul.
- Makaravilakku (Makara Jyothi): A celestial light appears on Makara Sankranti, believed to be a divine manifestation of Lord Ayyappa.
- Thiruvabharanam Procession: On Makaravilakku day, sacred royal ornaments (Thiruvabharanam) are carried in a procession from the Pandalam Palace to the temple.
- Aarti at Ponnambalamedu: The Makaravilakku light is believed to emanate from camphor lit during the Aarti ritual at Ponnambalamedu, viewed three times from Sabarimala.
Festival Duration:
- The Makaravilakku festival lasts for seven days, starting on Makara Sankranti and concluding with the Guruthi offering, which propitiates the gods of the wilderness.
Significance of Makaravilakku:
- The festival symbolizes the merging of celestial and spiritual energies, highlighting devotion, purity, and self-discipline.
- Devotees chant the mantra "Swamiye Saranam Ayyappa," seeking blessings and protection from Lord Ayyappa.
- The event promotes equality, as all devotees wear simple black or blue attire and carry the sacred bundle, “Irumudi Kettu.”
Cultural and Religious Aspects:
- The festival is an important cultural and religious observance for millions of Hindus.
- Though previously believed to be a supernatural event, Makaravilakku now involves a ritual performed by the Malayaraya tribe, overseen by the Travancore Devaswom Board.
Prohibition on Women:
- The temple traditionally restricts women aged 10-50 from entering. This was challenged in 2018 when the Supreme Court ruled to lift the prohibition, although it remains a contentious issue.
Purulia Observatory

- 14 Jan 2025
In News:
New observatory at remote Purulia district West Bengal is expected to contribute significantly to Astrophysics.
Key Highlights:
Location and Significance:
- Established by: S.N. Bose Centre for Basic Sciences (SNBCBS), an autonomous institute under the Department of Science and Technology (DST), India.
- Location: The observatory is situated at Panchet Hill, in the Garpanchakot area of Purulia district, West Bengal, at an elevation of 600 meters above ground level.
- Longitude Gap: Positioned at a longitude of approximately 86° E, this observatory fills a critical longitudinal gap in global astronomical observation networks. There are very few observatories along this longitude, making it strategically important for observing transient astronomical phenomena that last from minutes to hours.
- Global Impact: This location will allow for unique contributions to global astrophysical research, especially in observing transient events, which require observatories spread across all global longitudes.
Technological and Educational Role:
- The observatory is equipped with a 14-inch telescope for scientific observations.
- It will serve as a training ground for students and researchers, helping them to handle telescopes, record astronomical data, and engage in research.
- The observatory aims to foster national and international collaborations in astronomical research, furthering India’s contributions to the field.
Collaborations and Ecosystem Development:
- MOU with Sidhu Kanu Birsa University: The observatory will be run jointly with Sidhu Kanu Birsa University, sharing resources and responsibilities. The collaboration promises to bring scientific and educational advancements to Purulia, a district traditionally considered backward.
- The establishment of the observatory is expected to boost the local ecosystem, creating a space for scientific engagement and inspiring students in the region.
Research and Contributions:
- The research team, from the Department of Astrophysics at SNBCBS, contributed to the conceptualization, site characterization, and installation of the telescope.
- Their efforts ensure the observatory will be capable of high-quality scientific observations, especially with regard to weather parameters and astronomical seeing conditions.
Future Prospects:
- Scientists emphasized that the observatory will significantly contribute to the global body of knowledge in observational astronomy.
- Also highlighted the potential of the observatory to create a scientific ecosystem in the region.
- The observatory will also serve as a source of inspiration for students in Purulia and provide a much-needed boost to local education in the fields of science and astrophysics.
Konkan Region’s Sada and Biodiversity

- 14 Jan 2025
In News:
A Konkan secret, the flat-top sada is a freshwater paradise.
Key Highlights:
Geography of Sada:
- The Konkan region lies between the Arabian Sea and the Western Ghats.
- Sada refers to flat-topped hills, formed by centuries of erosion, and is a prominent feature in the Ratnagiri district.
- These areas are typically barren except during the monsoon season when they come alive with flora and fauna.
Biodiversity and Ecosystem Services:
- A biodiversity survey between 2022-2024 recorded 459 plant species, with 105 being endemic to the Konkan region.
- The survey also identified 31 species of reptiles, 13 species of amphibians, 169 species of birds, and 41 species of mammals.
- These ecosystems play a vital role in water conservation. The lateritic soil layer atop the Sada acts as a catchment for rainwater, recharging the groundwater and providing freshwater to local communities year-round.
Traditional Land Use and Agriculture:
- Local Farming: During monsoons, the Sada is used by locals for growing traditional crops like rice and millets (e.g., nanchani), using sustainable farming practices without pesticides or chemical fertilizers.
- Water Management: The locals rely on open wells, springs, and perennial streams for freshwater, which are carefully maintained through cultural rituals and community hygiene practices.
Conservation and Cultural Importance:
- The region is home to geoglyphs, ancient artworks estimated to be 10,000 years old, adding to its cultural and historical significance.
- Waterbodies on the Sada serve as habitats for species like the Indian flapshell turtle (Lissemys punctata) and provide water for other wildlife, including leopards, jackals, hyenas, barking deer, and migratory birds.
Environmental Threats:
- Land-use Change: Increasing conversion of open land and croplands into orchards and residential areas, along with various developmental projects, threatens the region's biodiversity.
- Mining: Extraction of laterite stones for construction purposes is another environmental risk.
- Wasteland Classification: The region is often classified as a ‘wasteland’ in the Wasteland Atlas, further complicating conservation efforts.
Israel-Hamas Ceasefire and Hostage Release Deal

- 14 Jan 2025
In News:
Israel and Hamas have agreed on a Gaza ceasefire and hostage release deal after 15 months of war.
Key Highlights:
Ceasefire Agreement Details:
- Location: The deal was brokered in Doha, Qatar.
- Approval Process: The deal must be approved by Israel’s Cabinet to take effect.
- Mediators: The agreement was negotiated by Qatar, Egypt, and the United States, with their involvement ensuring the implementation of the deal.
Phases of the Deal:
- First Phase (42 Days):
- Release of 33 hostages by Hamas, including women, children, and elderly people.
- Hostage Exchange: Hostages will be exchanged for Palestinian prisoners in Israeli jails.
- Gaza Ceasefire and Withdrawal: Israeli forces will gradually withdraw from Central Gaza and move to the borders.
- Return of Displaced Palestinians: Displaced Palestinians will be allowed to return to Northern Gaza.
- Humanitarian Aid: 600 humanitarian aid trucks will be allowed into Gaza daily.
- Second Phase:
- Hostage Release: Negotiations will begin for the release of remaining hostages.
- Full Israeli Troop Withdrawal: Israel will fully withdraw its forces.
- Third Phase:
- Reconstruction of Gaza: Overseen by Egypt, Qatar, and the United Nations.
- Reopening of Border Crossings: For movement in and out of Gaza.
- Return of Hostage Bodies: Return of any bodies of hostages who died.
Background of the Israel-Hamas Conflict:
- Start: On October 7, 2023, Hamas launched an attack on Israel, called Operation Al-Aqsa Flood, causing significant casualties.
- Israeli Response: Israel launched Operation Iron Sword in retaliation.
- Casualties: The conflict resulted in 46,707 Palestinian deaths, mostly civilians, and 1,210 Israeli deaths.
About Gaza Strip:
- Location: A Palestinian enclave on the Mediterranean Sea, bordered by Israel and Egypt.
- Administration: The Gaza Strip is governed by Hamas since 2006.
- Movement Restrictions: Israel controls air space and shoreline, imposing restrictions. Egypt controls one border and also restricts movement.
Gaza Truce Deal:
- Nature: A proposed ceasefire to end the ongoing conflict.
- Primary Parties: Israel and Hamas.
- Supporting Nations: United States, Qatar, and Egypt.
- Significance:
- Aims to stop fighting and address the humanitarian crisis in Gaza.
- Potential to influence regional stability and Israeli politics.
- Marks an important moment in U.S. diplomacy under the Biden administration.
Nag Mark-2

- 14 Jan 2025
In News:
The Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO) successfully conducted field evaluation trials of India's indigenous Anti-Tank Missile - Nag Mark 2 at the Pokhran Field Range in Rajasthan.
Overview of Nag Mk-2:
- Type: Third-generation, fire-and-forget anti-tank guided missile (ATGM).
- Development: Indigenous development by Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO) under the Integrated Guided Missile Development Programme (IGMDP).
- Functionality: Designed to neutralize modern armored threats, including those with Explosive Reactive Armour (ERA), using advanced fire-and-forget technology.
Technological Features:
- Fire-and-Forget Technology: Operators lock onto targets before launch, allowing the missile to autonomously track and engage targets, ensuring precision strikes.
- Lock-on After Launch: The missile can lock onto the target post-launch, providing flexibility in complex battlefield environments.
- Advanced Guidance System: Equipped with Imaging Infrared (IIR) seekers for enhanced accuracy, both during the day and at night.
Performance and Range:
- Effective Range: The missile has a range of 7 to 10 kilometers, a significant improvement over its predecessor, Nag Mk-1, which had a range of only 4 kilometers.
- Test Trials: Successfully destroyed all targets at both maximum and minimum ranges during the field evaluation trials at Pokhran Field Range, Rajasthan.
- Attack Mode: Includes a top-attack capability to target the vulnerable upper surfaces of armored vehicles, enhancing its effectiveness.
Platform and Integration:
- Launch Platform: The missile is launched from the NAMICA (Nag Missile Carrier) Version 2, a tank destroyer vehicle used by the Indian Army to launch anti-tank missiles.
- Versatility: Designed for integration with multiple platforms, enhancing operational flexibility in different combat scenarios.
Strategic and Operational Significance:
- Indigenous Defence Capability: Reduces India's dependence on foreign weapons systems, strengthening self-reliance in defense technology.
- Enhanced Battlefield Readiness: Provides the Indian Army with a cutting-edge weapon to counter modern armored vehicles, improving tactical advantages.
- Operational Effectiveness: The missile’s precision and ability to neutralize targets with minimal collateral damage make it an essential tool in modern warfare.
- Strategic Deterrence: Demonstrates India’s technological advancements in missile systems, signaling strength and deterrence to adversaries.
Bharat Cleantech Manufacturing Platform

- 14 Jan 2025
In News:
Union Minister of Commerce & Industry Shri Piyush Goyal launches Bharat Cleantech Manufacturing Platform.
Bharat Cleantech Manufacturing Platform:
- Objective: Strengthen India's cleantech value chains, especially in solar, wind, hydrogen, and battery storage sectors.
- Platform Features:
- Aims to promote collaboration, co-innovation, and knowledge-sharing among Indian firms.
- Focus on scaling up manufacturing, sharing ideas, technologies, and resources.
- Acts as a financing platform for the cleantech sector.
- Designed to position India as a global leader in sustainability and cleantech innovation.
India's Clean Energy Commitment:
- Target: 500 GW of clean energy capacity by 2030.
- India has been a front-runner in fulfilling its Nationally Determined Contributions (NDCs) under the Paris Agreement and UNFCCC.
- Early Achievement: India achieved its 2022 renewable energy target of 200 GW, 8 years ahead of schedule.
- Largest Interconnected Grid: India boasts the world’s largest interconnected power grid, enhancing its renewable energy distribution capacity.
- Gujarat is a pioneer in solar power adoption in India.
Union Minister Shri Piyush Goyal's Views:
- On Product-Linked Incentives (PLIs):
- PLIs and subsidies are seen as short-term aids; long-term growth of the clean energy sector depends on it becoming self-sustaining.
- Urged Indian firms to innovate and scale up manufacturing within the country.
- On Clean Energy and Sustainability:
- Stressed the importance of innovation and collaboration to achieve sustainability goals.
- India aims to attract international investors by creating a compelling business case for cleantech investments.
- 3S Approach (Speed, Scale, and Skill): Key to implementing India's renewable energy program, emphasizing rapid deployment, large-scale adoption, and skill development in the sector.
Bharat Climate Forum 2025:
- Event Objective: A platform for policymakers, industry leaders, and stakeholders to discuss climate action, clean energy, and India’s role in global climate goals.
- Key Focus Areas:
- Aligning India’s clean energy initiatives with global climate goals (UNFCCC, Paris Agreement).
- Emphasizing India’s early achievements in clean energy adoption.
- Promoting sustainable development and clean energy solutions.
India's Performance in Renewable Energy:
- India’s progress has been commendable in meeting its climate targets and setting up clean energy capacity ahead of schedule.
- The government’s initiatives, led by Prime Minister Narendra Modi, have made solar power affordable and scalable through transparency in auctions, competitive bidding, and speed in project implementation.
World’s First Cryo-Born Baby Corals

- 13 Jan 2025
In News:
World’s First Cryo-Born Baby Corals Successfully Settled on the Great Barrier Reef.
Introduction to Cryo-Born Corals
- Cryo-born corals are created using cryopreservation techniques, which involve freezing coral cells and tissues at very low temperatures.
- The process preserves coral cells by preventing the formation of ice crystals that would otherwise damage them.
- Cryopreservation involves adding cryoprotectants to remove water from cells, enabling their survival during freezing and thawing.
Significance of the Breakthrough
- Climate Change Resilience: The initiative aims to create heat-tolerant corals, which are crucial in combating the impact of rising ocean temperatures due to climate change.
- Selective Breeding Advantage: Cryopreservation allows for controlled breeding and bypasses the limitations of natural coral spawning, which occurs only once a year. This enables multiple reproduction cycles without disturbing wild populations.
The Process of Cryo-Born Coral Production
- Sperm Collection: During coral spawning events, sperm from various coral species is collected and frozen at -196°C using liquid nitrogen, halting metabolic processes.
- Coral Egg Fertilization: Cryopreserved sperm is used to fertilize fresh coral eggs, which are grown in a specialized research facility called the National Sea Simulator.
- Coral Cradles: After growth, the cryo-born corals are carefully transported and settled into specially designed "coral cradles" placed in the Great Barrier Reef, where their growth is monitored during their critical first year.
Importance of Cryo-Born Corals in Reef Restoration
- The primary aim is to introduce millions of heat-tolerant corals annually to restore reefs affected by climate change.
- The Taronga CryoDiversity Bank houses the world’s largest frozen coral sperm collection from 32 coral species, collected annually since 2011, providing a resource for future restoration efforts.
Coral Reefs: An Overview
- Corals are marine invertebrates from the class Anthozoa, phylum Cnidaria.
- Reefs are built by colonies of coral polyps that secrete limestone skeletons and rely on symbiotic algae (zooxanthellae) for nutrition.
- Coral reefs are typically found in shallow, sunlit waters with a temperature range of 16-32°C and depths less than 50 meters.
Global and Indian Coral Conservation Efforts
- India:
- The National Committee on Wetlands, Mangroves, and Coral Reefs (1986) advises on conservation measures.
- The Environment (Protection) Act (1986) prohibits the use of coral and sand in construction.
- Zoological Survey of India (ZSI) uses Biorock technology for coral restoration.
- Global Efforts:
- CITES lists coral species in Appendix II, regulating coral trade.
- The World Heritage Convention designates coral reefs as protected sites.
Global Impact and Future Directions
- The innovative work by Australian scientists opens the door for large-scale restoration efforts by allowing more controlled breeding and genetic diversity, making corals more resilient to climate change.
- This breakthrough could revolutionize coral restoration, scaling up efforts to introduce millions of resilient corals to reefs worldwide, building long-term resilience against climate change.
Sovereign Artificial Intelligence

- 13 Jan 2025
In News:
- The growth of Artificial Intelligence (AI) has been remarkable in recent years. In 2018, a 340-million-parameter AI model was considered large, whereas models like ChatGPT now have 1.8 trillion parameters.
- As part of its ambition to make the digital economy worth USD 1 trillion by 2028, India is focusing on AI sovereignty and investing in semiconductors and AI technologies to achieve this goal.
What is Sovereign AI?
Definition
- Sovereign AI refers to a nation’s ability to develop, control, and deploy AI using its own resources, including infrastructure, data, workforce, and business networks.
- This involves not just developing AI models but also creating infrastructure and nurturing homegrown talent to lead AI advancements within the country.
Key Aspects of Sovereign AI
- National Control: Ensures AI technologies align with a country's laws, regulations, and ethical standards.
- Data Sovereignty: Emphasizes control of data within the country’s borders, protecting privacy, security, and national interests.
- AI in Governance: Generative AI is transforming industries, markets, and governance, with AI-powered tools assisting professionals and governments.
- Ethical Considerations: Countries define security protocols and ethical frameworks to govern the use of AI technologies.
- Strategic Autonomy: Reduces reliance on foreign technologies, encouraging domestic development in AI to achieve strategic independence.
- Economic Competitiveness: AI is crucial for industrial innovation. Without it, nations risk falling behind in the global economy.
Growth and Importance of AI
Evolution of AI Models
- In 2018, a 340-million-parameter model was considered a significant achievement.
- Today, ChatGPT uses 1.8 trillion parameters, and Google’s Gemini uses 1.5 trillion parameters. In comparison, China’s DeepSeek has a model with 240 billion parameters.
- Parameters are the internal variables of AI models, adjusted during training to improve their performance and accuracy.
Strategic Applications
- Sovereign AI plays a pivotal role in critical sectors such as:
- Defense
- Healthcare
- Transportation
- Governance
- It helps redefine industries, boost innovation, and streamline operations across various sectors.
India’s Position in Sovereign AI
AI Infrastructure Development
- Tata Group and Reliance are building AI infrastructure in India, including the development of Large Language Models (LLMs).
- India has allocated USD 1.2 billion for a sovereign AI project under the IndiaAI Mission, which includes creating an AI supercomputer with thousands of chips.
Government Initiatives
- The IndiaAI Mission is designed to boost India’s AI capabilities by building infrastructure, fostering talent, and supporting innovation within the country.
Global AI Compact
- A Global AI Compact has been proposed to ensure equitable access to AI technologies across nations.
- The compact advocates for sharing AI resources globally while promoting cooperation and addressing challenges associated with AI governance.
Pink Fire Retardant

- 13 Jan 2025
In News:
As wildfires continue to rage across Southern California, authorities are deploying pink fire retardant from aircraft to help combat the blazes. Despite its widespread use, concerns over its effectiveness and environmental risks have surfaced in recent years.
What is Pink Fire Retardant?
- Fire retardant is a chemical mixture designed to slow down or extinguish wildfires. The most commonly used product in the U.S. is Phos-Chek, a brand of retardant.
- Phos-Chek primarily contains ammonium phosphate-based slurry (salts like ammonium polyphosphate), which helps the retardant stay longer and resist evaporation, unlike water.
Purpose and Visibility
- Fire retardants are sprayed ahead of fires to coat vegetation, reducing oxygen and preventing flames from spreading.
- Color is added to the fire retardant, often bright pink, to improve visibility. This ensures firefighters can track its spread and create effective fire lines, helping protect lives and property.
Manufacturer
- Perimeter Solutions manufactures Phos-Chek, which is used for aerial fire suppression efforts.
Effectiveness of Pink Fire Retardant
Limited Effectiveness
- The use of fire retardants like Phos-Chek is not always effective across different wildfire conditions.
- Aerial retardants depend on environmental conditions like terrain, slope, and weather for optimal effectiveness.
- Researchers, including Forest Service scientists, suggest that retardant effectiveness is more limited under changing climate conditions.
- Climate change is narrowing the window of opportunity for using aerial retardants, reducing their impact.
Uncertainty in Impact
- The effectiveness of fire retardants is hard to quantify. Multiple firefighting methods are used simultaneously, making it difficult to attribute wildfire suppression success solely to the retardant.
Environmental Concerns of Pink Fire Retardant
Toxicity and Pollution
- Phos-Chek contains toxic metals such as chromium and cadmium, both of which are harmful to humans and the environment.
- Chromium and cadmium are linked to serious health issues, including cancer and liver/kidney diseases.
- Aquatic life is particularly vulnerable to these toxins, as the chemicals can enter waterways, causing extensive damage to ecosystems.
Impact on Rivers and Streams
- The use of pink fire retardant has raised concerns regarding the contamination of rivers and streams.
- A study by the University of Southern California (USC) in 2024 estimated that 850,000 pounds of toxic chemicals have been released into the environment since 2009 due to fire retardant use.
Growing Use and Pollution
- From 2009 to 2021, over 440 million gallons of retardant were applied across U.S. lands.
- During this period, an estimated 400 tons of heavy metals were introduced into the environment, further exacerbating the pollution levels.
Financial and Practical Concerns
High Cost and Inefficiency
- The cost of deploying fire retardant is significant. Aerial firefighting operations require substantial resources, including planes, helicopters, and large quantities of retardant.
- Environmental experts argue that using fire retardant from planes is ineffective and expensive, especially in light of the growing environmental concerns.
India Joins the UN-CEBD

- 13 Jan 2025
In News:
- India has recently joined the United Nations Committee of Experts on Big Data and Data Science for Official Statistics (UN-CEBD), marking a significant step in strengthening its role in global statistical frameworks.
- The inclusion is a result of India's recent membership in the United Nations Statistical Council (UNSC), signaling the nation's growing influence in global data governance.
Key Highlights
- India's Growing Influence: India’s entry into the UN-CEBD highlights its growing stature in the international statistical community, emphasizing its commitment to utilizing big data and data science for informed decision-making.
- Strategic Opportunity: This membership allows India to contribute to shaping global standards in leveraging big data for official statistical purposes, especially in tracking Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs).
What is UN-CEBD?
- UN-CEBD is a specialized body under the United Nations, formed in 2014 to explore the benefits and challenges of using big data and data science to strengthen global statistical systems.
- It was established under the United Nations Statistical Commission (UNSC).
- Members: The committee consists of 31 member states (including India) and 16 international organizations.
Key Objectives
- Monitor SDGs: Use big data to track progress towards achieving the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs).
- Address Data Challenges: Overcome challenges in utilizing non-traditional data sources, such as satellite imagery, Internet of Things (IoT), and private sector data.
- Promote Big Data Use: Encourage practical applications of big data across borders while addressing associated challenges.
Governance and Functions
- Advisory Board: Provides strategic direction, convening four times a year.
- UN Bureau: Manages day-to-day operations.
- Key Functions:
- Strategic Coordination: Vision and direction for utilizing big data in global official statistics.
- Capacity Building: Enhance capabilities through training, technical assistance, and knowledge sharing.
- Public Trust: Establish confidence in using big data for official statistics.
Big Data: Definition and Importance
What is Big Data?
- Big data refers to vast, complex datasets that cannot be processed by traditional data management systems.
- It enables enhanced decision-making and improved processes for policy formulation, product development, and governance.
India's Big Data Initiatives
- National Data & Analytics Platform (NDAP): Facilitates data-driven decision-making.
- Big Data Management Policy: Defines strategies for managing large datasets within government agencies.
- National Data Warehouse on Official Statistics: Centralizes official data for better access and analysis.
The 6Vs of Big Data
- Volume: Large amounts of data.
- Velocity: Speed of data generation and processing.
- Variety: Different types of data.
- Veracity: Accuracy of data.
- Value: Significance of the data.
- Variability: Fluctuations in data.
India’s Role in the UN-CEBD
Contribution to Global Standards
- India's initiatives such as the Data Innovation Lab and the use of satellite imagery and machine learning will be shared with other members, fostering global collaboration in statistical innovations.
- India will contribute to shaping international standards for the use of big data in monitoring SDGs.
Enhancing Statistical Processes
- Modernization of Data: India aims to modernize its statistical processes by incorporating IoT, satellite data, and private-sector data.
- Real-time Insights: Providing policymakers with timely and accurate data to address key socio-economic issues.
- Improving Estimates: Using big data to enhance the accuracy of official statistics, improving governance and policymaking.
Strategic Goals of India's Engagement
- Streamline Statistical Production: Innovation in data collection, processing, and analysis to reduce delays in data availability.
- Improve Decision-Making: Provide real-time, evidence-based insights to policymakers.
- Foster International Collaboration: Share India’s expertise and learn from global best practices to build future-ready statistical systems.
National Youth Day 2025

- 13 Jan 2025
In News:
On January 12, 2025, Prime Minister Shri Narendra Modi participated in the Viksit Bharat Young Leaders Dialogue 2025, an event aimed at empowering India's youth and charting a roadmap for the nation's development. This occasion also coincided with the celebration of National Youth Day, marking the 163rd birth anniversary of Swami Vivekananda, a renowned spiritual leader and social reformer who strongly believed in the transformative potential of India's youth.
Significance of National Youth Day
- Purpose:
- National Youth Day is celebrated to honor Swami Vivekananda's contributions, emphasizing the role of youth in nation-building.
- It promotes empowerment, leadership, and innovation among the youth.
- Year of First Celebration: 1985
- Key Theme (2025): "Arise, Awake, and Realize the Power You Hold"
Key Highlights from the Dialogue
- Goal of the Dialogue:
- Engaging youth in the decision-making process for a developed India by 2047.
- Empowering youth through platforms like quizzes, essay competitions, and thematic presentations.
- Ten Key Themes Discussed:
- Technology & Innovation
- Sustainability
- Women Empowerment
- Manufacturing & Agriculture
- Education and Skill Development
India’s Roadmap for 2047 (Viksit Bharat)
- Vision:
- Economic Power: India is moving toward becoming the third-largest economy.
- Strategic and Cultural Strength: India will have a robust economic, strategic, social, and cultural framework.
- Youth's Role: Innovation in technology, digital economy, space, and manufacturing will drive India’s growth.
- Key Projects and Targets:
- Target: Generating 500 GW of renewable energy by 2030.
- Net Zero Emissions for Railways: Set for 2030.
- Olympics: India aims to host the Olympics in the next decade.
- Space Power: Plans for a space station by 2035.
Viksit Bharat Young Leaders Challenge
- Objective:
- Engage youth in shaping ideas for a developed India.
- The Viksit Bharat Young Leaders Dialogue is part of the Viksit Bharat Challenge.
- Stages of the Challenge:
- Viksit Bharat Quiz: Participation by 30 lakh youth.
- Essay Writing: Over 2 lakh essays on key developmental themes.
- State Rounds: Rigorous in-person competition to identify the top young leaders.
- Participant Categories:
- 1,500 from Viksit Bharat Challenge Track.
- 1,000 from Traditional Track (cultural and science innovation).
- 500 Pathbreakers (leaders in diverse sectors).
Achievements Under Government Benefiting Youth
- Educational Reforms:
- Increase in IITs, IIITs, IIMs, and AIIMS.
- Growth in the number of higher education institutions and their global rankings.
- Economic Growth:
- India's economy has grown to nearly $4 trillion.
- Infrastructure Investments: More than ?11 lakh crore allocated for infrastructure development.
- Employment Opportunities for Youth:
- Mudra Loans: ?23 lakh crore distributed to youth entrepreneurs.
- Startup Ecosystem: India is among the top three in global startups.
- PM Gati Shakti Mission: Facilitating logistics and infrastructure development, creating employment opportunities.
Future Outlook
- Youth as the Future Leaders of India:
- India’s Youth Power: Vital to achieving a developed nation by 2047.
- The Viksit Bharat Young Leaders Dialogue is a platform for youth to voice their opinions and engage with policymakers.
- Role of Youth in India’s Transformation:
- Collective Responsibility: Every citizen's effort is essential for national goals.
- The vision of a Viksit Bharat hinges on the innovative contributions and ownership by young minds.
EmpowHER Biz – Sapno Ki Udaan

- 12 Jan 2025
In News:
The Women Entrepreneurship Platform (WEP) of NITI Aayog, in partnership with New Shop (India’s largest 24/7 convenience retail chain), launched the initiative EmpowHER Biz – Sapno Ki Udaan under the Award to Reward (ATR) program. This program aims to empower women entrepreneurs by providing them with the skills, resources, and mentorship needed to succeed in the organized retail sector. The collaboration seeks to create a robust retail ecosystem that supports women in overcoming barriers such as societal biases, limited access to financing, and a lack of mentorship.
Key Features of the Initiative:
- Target Participants: The program will select 50 women aged 18-35 through an online application process. Women from Delhi NCR, Punjab, Rajasthan, Uttar Pradesh, Haryana, Madhya Pradesh, and Gujarat will be considered.
- Top 20 Participants: The 20 best candidates will receive a 100% waiver on New Shop franchise fees, enabling them to operate their own retail businesses with reduced financial barriers.
- Program Objective: Equip women entrepreneurs with skills such as retail management, digital tools, financial literacy, and business development. Participants will also receive valuable mentorship to help them grow and scale their businesses.
- Focus on Retail: The initiative focuses on empowering women within the organized retail sector, creating a sustainable ecosystem that fosters growth and development for female entrepreneurs.
About Women Entrepreneurship Platform (WEP):
- Incubation & Transition: Established in 2018, WEP was incubated within NITI Aayog and transitioned into a Public-Private Partnership (PPP) in 2022.
- Purpose: WEP aims to empower women entrepreneurs by addressing challenges like information asymmetry and providing essential support in key areas such as:
- Access to Finance
- Market Linkages
- Training & Skilling
- Mentoring & Networking
- Compliance & Legal Assistance
- Business Development Services
- Collaboration: WEP partners with over 30 public and private sector organizations to develop scalable and impactful programs. Since 2023, the Award to Reward initiative offers a framework for stakeholders to create impactful programs for women entrepreneurs.
About New Shop:
- Business Model: New Shop operates over 200 round-the-clock convenience retail stores in high-density areas, including highways and gas stations. The company plans to expand into airports, railway stations, and other mass transit hubs.
- Franchising Vision: By 2030, New Shop aims to empower over 10,000 entrepreneurs in India through its franchising model. The partnership with WEP seeks to help women entrepreneurs access this growth opportunity.
Program Outcomes:
- Mentorship & Training: Participants will be mentored and trained on key aspects such as retail management, business development, and digital tools.
- Franchise Opportunity: Top participants will gain access to New Shop’s franchising ecosystem, providing them a ready-made business opportunity with lower entry barriers.
- Financial Assistance: The program will also provide financial resources to the women, helping them build their businesses with greater ease.
Future of Jobs Report 2025

- 12 Jan 2025
In News:
The World Economic Forum's latest "Future of Jobs Report 2025" has highlighted significant trends and predictions for the global labor market by 2030.
Key Highlights:
Fastest Growing Jobs by 2030
The report identified the following jobs as the fastest-growing by 2030:
- Big Data Specialists
- FinTech Engineers
- AI and Machine Learning Specialists
- Software and Applications Developers
- Security Management Specialists
- Data Warehousing Specialists
- Autonomous and Electric Vehicle Specialists
- UI/UX Designers
- Delivery Drivers
- Internet of Things (IoT) Specialists
Job Disruption and Creation
- 22% of jobs globally will be disrupted by 2030 due to automation and technological advancements.
- 170 million new jobs are expected to be created, resulting in a net increase of 78 million jobs.
- Technological shifts, economic uncertainty, and demographic changes are expected to play significant roles in this transformation.
Skills in High Demand
- AI, Big Data, Cybersecurity: Skills related to artificial intelligence and big data are expected to see an 87% rise, while networks and cybersecurity skills are projected to increase by 70%.
- Creative Thinking, Flexibility: Skills like creative thinking, resilience, flexibility, and agility are also expected to see a significant rise, emphasizing the importance of soft skills in a technology-driven world.
Declining Jobs
The report lists the following positions as expected to decline by 2030:
- Postal Service Clerks
- Bank Tellers
- Data Entry Clerks
- Cashiers and Ticket Clerks
- Telemarketers
- Printing Workers
- Accounting and Bookkeeping Clerks
These roles are being replaced or transformed by automation and AI, which are reshaping traditional job functions.
Technological Advancements
- Digital Access: 60% of employers believe that expanding digital access will be the most transformative trend for businesses.
- AI and Robotics: Employers are investing heavily in AI, robotics, and energy technologies, creating a demand for skilled workers in these sectors.
- Energy Technologies: Jobs related to the green transition, including renewable energy and environmental engineering, will see an uptick as countries strive to meet climate goals.
Key Drivers of Change
- Technological Change: AI, machine learning, and automation will continue to reshape industries.
- Geoeconomic Fragmentation: Geopolitical tensions and economic shifts are prompting businesses to transform their models, leading to a greater demand for cybersecurity and security management roles.
- Aging Populations: The growing demand for healthcare services, especially in high-income economies, will result in more jobs in the care economy (e.g., nursing professionals, social workers).
- Green Transition: The global shift toward clean energy and environmental sustainability will create numerous opportunities for jobs in renewable energy and climate change mitigation.
Implications for India
- AI and Robotics Investment: Indian companies are leading the way in investing in AI, robotics, and autonomous systems.
- Growth Sectors: India’s rapidly developing tech sector will see a rising demand for AI, machine learning, and big data specialists.
- Disruptions in Traditional Jobs: Roles like postal clerks, cashiers, and data entry clerks in India are also expected to face significant reductions due to automation.
Challenges for Employment in India
- Skill Mismatch: There is a significant skill gap, with many workers lacking expertise in emerging fields like AI, cybersecurity, and data science.
- Digital Divide: Urban areas are adapting to new technologies faster than rural areas, which may widen employment disparities.
- Informal Sector: India’s large informal workforce faces challenges in transitioning to technology-driven jobs due to limited access to training and education.
Reskilling and Upskilling
- The WEF report emphasizes that 59% of the global workforce will need reskilling or upskilling by 2030 to remain competitive.
- Workers must adapt to new roles, especially in technology and the green transition, to meet the evolving demands of the job market.
GEAPP and ISA Sign $100 Million Agreement for Solar Projects

- 12 Jan 2025
In News:
The Global Energy Alliance for People and Planet (GEAPP) signed a Multi-Donor Trust Fund (MDTF) agreement with the International Solar Alliance (ISA) to mobilize $100 million for funding high-impact solar energy projects. This collaboration is part of a wider effort to accelerate India's clean energy transition, bridge financing gaps, and enhance the country's energy systems. Along with this agreement, two other key initiatives were announced:
- DUET (Digitalization of Utilities for Energy Transition)
- ENTICE 2.0 (Energy Transitions Innovation Challenge)
These programs aim to address energy transition challenges by fostering scalable, cost-efficient solutions, digitalizing utilities, and supporting innovations for sustainable energy.
Key Features:
- Multi-Donor Trust Fund (MDTF):
- The MDTF aims to raise and deploy $100 million to finance impactful solar energy projects, with ISA driving the strategic direction.
- GEAPP’s Project Management Unit will provide governance, fundraising, and technical expertise to ensure project success.
- The collaboration emphasizes the importance of solar energy in achieving India's clean energy goals.
- DUET (Digitalization of Utilities for Energy Transition):
- Focuses on transforming grid systems by digitalizing grid assets and integrating them with smart sensors.
- Real-time data will help reduce transmission losses and facilitate Battery Energy Storage Systems (BESS) deployment, assisting in the integration of Distributed Renewable Energy (DRE) into the grid.
- ENTICE 2.0 (Energy Transitions Innovation Challenge):
- A platform for identifying and scaling innovative solutions to accelerate the clean energy transition, especially within India's growing startup ecosystem.
- Focuses on supporting investable opportunities for energy transition solutions, building on the earlier success of ENTICE 1.0.
Global Impact of GEAPP:
GEAPP, launched with an initial commitment of $464 million, has already funded 130 projects across 40 countries. These projects have impacted over 50 million people, helping reduce 43 million tons of CO2 emissions. The collaboration with ISA is expected to deepen GEAPP's efforts in mobilizing capital to foster clean energy access and tackle climate change.
India’s Clean Energy Transition:
India has already extended electricity access to over 800 million people, but about 2.5% of households still remain unelectrified. Distributed renewable energy, especially solar energy, will play a pivotal role in reaching these underserved populations. India aims for 47 GW of battery energy storage systems by 2032, which will support grid stability and energy access.
Additional Initiatives and Impact:
- Battery Energy Storage Systems (BESS):
- GEAPP has also supported India’s first commercial standalone BESS project, which will provide 24/7 power to over 12,000 low-income customers.
- The project is set to lower electricity tariffs by 55%, benefiting economically disadvantaged communities.
- Strategic Alliances:
- The partnership with ISA and the strategic initiatives like DUET and ENTICE 2.0 aim to further India’s climate and energy goals, bringing renewable energy solutions to underserved regions, and supporting the country's energy security.
Role of GEAPP and ISA:
- GEAPP works to mobilize financing, provide technical expertise, and ensure effective implementation of renewable energy projects globally.
- ISA focuses on solar energy solutions, and with this agreement, it seeks to enhance the solar energy capacity in its member countries, aligning with climate targets.
About GEAPP:
GEAPP is a multi-stakeholder alliance comprising governments, philanthropy, technology partners, and financial institutions. Its goal is to transition developing economies to clean energy while enhancing economic growth. It aims to:
- Reduce 4 gigatons of carbon emissions.
- Provide clean energy access to 1 billion people.
- Create 150 million new jobs globally.
Twigstats

- 12 Jan 2025
In News:
The tracing of genetic ancestry remains a challenging task due to the statistical similarity among populations across geographical regions. However, recent advances in genetic analysis, particularly the development of the Twigstats tool, are significantly enhancing our ability to reconstruct genetic histories at a very high resolution.
Key Insights from Genetic Research:
- Ancient DNA (aDNA): Prehistoric human ceremonial burials, mass grave mounds, and war graves are rich sources of ancient genetic material, offering key insights into population dynamics. These samples help us understand past migrations, cultural transitions, and the genetic legacy of ancient groups.
- Challenges in Ancestry Tracing:
- Populations often share many genetic similarities, complicating the task of tracing ancestry across regions.
- Ancient DNA samples are typically of lower quality compared to modern samples, limiting the precision of past genetic studies.
- The movement of genes across time and space, through processes like gene flow, adds complexity to the understanding of population ancestry.
Traditional Genetic Techniques:
- Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms (SNPs): Used to identify natural genetic variations, SNP analysis has been central to reconstructing genetic histories. However, it is limited by its reliance on high-quality samples and struggles with closely related groups.
- Haplotypes and Genealogical Trees: By analyzing shared DNA segments (haplotypes) and rare variants, researchers gain a more comprehensive understanding of population structure and ancestry, which can reveal shifts in population over time.
The Emergence of Twigstats:
- What is Twigstats?
- Twigstats is an advanced analytical tool that enhances the precision of ancestry analysis through time-stratified ancestry analysis, a method that allows for a more fine-grained look at genetic data.
- It is designed to address the limitations of traditional methods by integrating SNPs, haplotypes, and rare genetic variants, providing a more holistic view of ancestry.
- The tool is powered by statistical languages R and C++, which help researchers better manage and analyze complex genetic data.
- How It Works: Twigstats builds family trees by analyzing shared genetic mutations, identifying recent mutations that offer a clearer understanding of historical periods and events. It helps trace the evolution of populations and offers insights into their migrations, mixing, and cultural shifts.
Key Features and Impact of Twigstats:
- Time-Stratified Ancestry Analysis: Allows researchers to study how populations evolved over time, with a focus on specific historical periods.
- Enhanced Precision: Reduces statistical errors and enhances the precision of individual-level ancestry reconstruction.
- Higher-Resolution Mapping: Provides high-resolution genetic maps of migration patterns and admixture events across centuries.
Applications of Twigstats:
- Historical Case Studies: The tool has been used to study ancient genomes from Europe, particularly the Iron, Roman, and Viking Ages (500 BC to 1000 AD). It revealed the fine-scale genetic history of populations in regions like northern and central Europe, including the movement of Germanic and Scandinavian peoples.
- Viking Age Insights: Researchers were able to trace the early presence of Scandinavian-like ancestry in regions such as Britain and the Baltic before the traditionally believed start of the Viking Age. This suggests earlier interactions and migrations from Scandinavia, which aligns with historical records of Anglo-Saxon and Viking movements.
- Cultural Transitions: The analysis identified shifts in population genetics corresponding to cultural changes, such as the shift from the Corded Ware culture to the Bronze Age and the influence of the Wielbark culture.
Genetic Methods Used in the Study:
- Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms (SNPs): Commonly used to trace ancestry but requires high-quality samples.
- Haplotypes and Rare Variants: Offer more nuanced insights into population movements by considering combinations of genetic markers inherited together.
- Genealogical Tree Inference: Applied to both ancient and modern genomes, it provides detailed demographic and ancestry information, supporting the reconstruction of high-resolution genetic histories.
Case Study: India’s Genetic History (2009 Study)
- Researchers used SNP analysis to trace the genetic history of India, revealing two major ancestral groups:
- Ancestral North Indians (ANI): Genetically closer to Central Asian, European, and Middle Eastern populations.
- Ancestral South Indians (ASI): A distinct genetic group, showcasing India’s diverse population structure.
India’s First Organic Fisheries Cluster

- 12 Jan 2025
In News:
The Union Minister, Department of Fisheries, Ministry of Fisheries, Animal Husbandry and Dairying Shri Rajiv Ranjan Singh inaugurated and laid the foundation for 50 key projects worth Rs. 50 crores under Pradhan Mantri Matsya Sampada Yojana (PMMSY) covering all North East Region States Except Arunachal Pradesh and Mizoram.
Key Highlights:
- Initiative: India’s first Organic Fisheries Cluster, launched under the Pradhan Mantri Matsya Sampada Yojana (PMMSY). The cluster focuses on sustainable aquaculture, promoting the production of antibiotic, chemical, and pesticide-free organic fish.
- Target Markets: Eco-conscious domestic and global markets.
Sikkim's Role as India’s First Organic State:
- Sikkim's Organic Commitment: Sikkim is the first Indian state to embrace 100% organic farming, covering 75,000 hectares of land.
- Vision: The Organic Fisheries Cluster aligns with Sikkim’s broader goal of promoting organic, sustainable agricultural practices.
Objective of Organic Fisheries Cluster:
- To prevent pollution and protect aquatic ecosystems by using ecologically healthy practices.
- Promotes sustainable fish farming methods, reducing environmental damage.
- Focus on species like amur carp and other carp varieties, aligning with the state’s success in organic farming.
Support from NABARD:
- The National Bank for Agriculture and Rural Development (NABARD) will provide financial and technical assistance.
- Key support includes:
- Infrastructure development.
- Formation of Fisheries-based Farmer Producer Organizations (FFPOs).
- Capacity building of local fishers and farmers.
PMMSY: A Comprehensive Fisheries Development Scheme:
- Investment: ?20,050 crore under PMMSY.
- Objective: To revolutionize India’s fisheries sector by promoting sustainable growth, enhancing fish production, and improving infrastructure.
- Implementation Period: FY 2020-21 to FY 2024-25.
- Key Goals:
- Boosting fish production and exports.
- Enhancing welfare of fishers and farmers.
- Promoting cluster-based development for better efficiency and competitiveness.
Cluster-Based Approach in Fisheries:
- Objective: To bring together geographically connected enterprises to enhance economies of scale.
- Impact: This approach improves financial viability, strengthens the fisheries value chain, and creates new business and livelihood opportunities.
- Types of Clusters: Includes Pearl, Seaweed, Ornamental Fisheries, Cold Water Fisheries, Organic Fisheries, and more.
Fisheries Focus in the North Eastern Region (NER):
- Fisheries Potential: The North Eastern Region (NER) has abundant freshwater resources and is a biodiversity hotspot.
- Growth: Inland fish production in the NER surged from 4.03 lakh tonnes (2014-15) to 6.41 lakh tonnes (2023-24), marking an impressive 5% annual growth.
- Investment in NER: Over ?2,114 crore invested through schemes like Blue Revolution and PMMSY.
- Key Projects:
- 50 projects worth ?50 crore to boost the region’s fisheries infrastructure, generating over 4,500 jobs.
- Projects include hatcheries, cold storage units, aquaculture parks, and fish kiosks.
India’s Global Fisheries Standing:
- India is the second-largest fish producer in the world, contributing 8% to global fish production.
- Top Rankings:
- Second in aquaculture production.
- Leading in shrimp production and exports.
- Third in capture fisheries.
Government Commitments and Schemes:
- Total Investment: Since 2015, the government has committed ?38,572 crore to fisheries development through key schemes like:
- Blue Revolution.
- Fisheries and Aquaculture Infrastructure Development Fund (FIDF).
- PMMSY.
- Pradhan Mantri Matsya Kisan Samridhi Sah-Yojana (PM-MKSSY).
- These initiatives aim to promote sustainable growth, create jobs, and enhance infrastructure in the fisheries sector.
Economic, Environmental, and Social Benefits:
- Economic Impact:
- Higher incomes for fishers and farmers through better production and export.
- Employment generation through infrastructure development.
- Environmental Impact: Reduced pollution and protection of aquatic ecosystems.
- Social Impact: Empowerment of local communities, fostering sustainable livelihoods.
UJALA Scheme

- 10 Jan 2025
In News:
UJALA scheme completes 10 years, saves ?19,153 crore annually
UJALA Scheme (Unnat Jyoti by Affordable LEDs for All)
- Launch Date: 5th January 2015 by PM Narendra Modi
- Objective:
- To promote energy-efficient LED lighting across India
- To reduce energy consumption, lower electricity bills, and decrease carbon emissions
- Implementing Body: Energy Efficiency Services Limited (EESL), Ministry of Power
- Scheme Relevance: Aims to provide affordable LED bulbs, tube lights, and fans to every household
- Global Recognition: World’s largest zero-subsidy domestic lighting scheme
Key Features:
- Affordability: Subsidized LED bulbs (?70-80), reducing the cost of electricity for households
- Energy Efficiency: LEDs consume 90% less energy than incandescent bulbs, 50% less than CFLs
- Environmental Impact: Significant reduction in CO? emissions by avoiding millions of tonnes annually
- Market Transformation: Over 36.87 crore LED bulbs distributed, saving approximately ?19,153 crore on electricity bills each year
- Consumer Benefit:
- On-Bill Financing: LED bulbs available for purchase through deferred payment via electricity bills
- Targeted low-income communities through Self-Help Groups (SHGs)
Achievements:
- Energy Savings: 47.9 billion kWh annually
- Cost Savings: ?19,153 crore saved on electricity bills
- Carbon Emission Reduction: 38.7 million tonnes of CO? avoided per year
- Peak Demand Reduction: 9,586 MW reduction in peak electricity demand
- Street Lighting: Over 1.34 crore LED streetlights installed, saving 9,001 million units annually
Key Initiatives:
- GRAM UJALA Scheme (March 2021): Aimed at rural households, providing LED bulbs at ?10 each
- Street Lighting National Programme (SLNP): Aimed at reducing public lighting costs with energy-efficient streetlights
- Encouraging Domestic Manufacturing: Stimulated local LED production, aligning with the "Make in India" mission
- E-Procurement Transparency: Real-time procurement ensuring price reductions and maintaining quality
Impact on Environment:
- Energy Savings & Carbon Footprint: The scheme significantly reduced the carbon footprint by promoting energy-efficient appliances
- Reduction in Household Consumption: Consumers benefit from reduced energy consumption and lower utility bills
New Method to Improve Nitrogen Use Efficiency (NUE)
- 10 Jan 2025
In News:
A recent breakthrough in agricultural research offers a promising solution to improve Nitrogen Use Efficiency (NUE) in crops, particularly in rice and Arabidopsis, by reducing nitric oxide (NO) levels in plants. This innovative approach provides an environmentally sustainable way to enhance crop yields while minimizing the need for synthetic nitrogen fertilizers, which have significant ecological and economic drawbacks.
Key Findings and Research Overview:
- Reducing NO Levels: The study, conducted by researchers at the National Institute of Plant Genome Research (NIPGR), demonstrated that by reducing nitric oxide (NO) levels in plants, nitrogen uptake could be significantly improved. This leads to a better NUE, a crucial factor for enhancing crop yield sustainably.
- NUE and Its Importance: NUE refers to the efficiency with which plants use nitrogen for biomass production. Improving NUE allows for higher crop yields with less fertilizer input, reducing costs and minimizing nitrogen-related environmental pollution.
- Traditional Approaches and Their Limitations: Current techniques to improve NUE primarily rely on the use of inorganic nitrogen fertilizers. These methods, though effective, have several downsides:
- They involve high operational costs for farmers.
- Excessive fertilizer use contributes to the emission of nitrogen oxides (NOx) and other pollutants.
- The production of these fertilizers also contributes to greenhouse gas emissions.
In contrast, the new study proposes a genetic and pharmacological manipulation of NO levels, offering a sustainable alternative to these traditional, resource-heavy methods.
Study Methodology:
The research team employed both genetic and pharmacological approaches to regulate NO levels in plants:
- Phytoglobin Overexpression: By overexpressing phytoglobin (a natural NO scavenger), the researchers increased the expression of high-affinity nitrate transporters (HATs) like NRT2.1 and NRT2.4. These transporters are essential for efficient nitrogen uptake.
- NO Donor and Scavenger Treatments: Plants were treated with NO donor (SNAP) and NO scavenger (cPTIO) to monitor the effects on NUE.
- Results: The treatment led to more efficient nitrogen uptake, especially under low NO conditions, by enhancing the expression of HATs. This method could increase plant growth and nitrogen utilization without relying on excessive fertilizer use.
Significance and Impact:
This research provides a pathway to enhance crop yield sustainably by addressing one of the most critical challenges in modern agriculture—reducing the reliance on nitrogen fertilizers. By modulating NO levels to regulate nitrogen uptake, this approach offers:
- Reduced need for synthetic fertilizers, lowering farmers' operational costs.
- Minimized environmental impact, including lower nitrogen oxide emissions and less nitrogen runoff.
- Improved nitrogen uptake efficiency, ensuring better crop yields, especially under conditions with limited nitrogen availability.
Broader Implications:
- Global Nitrogen Challenges:
- The overuse of nitrogen fertilizers has been a major driver of nitrogen pollution, leading to issues like eutrophication, biodiversity loss, and climate change.
- According to the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO), excessive nitrogen use has worsened environmental conditions globally, while many regions, particularly in low-income countries, suffer from nitrogen depletion, which reduces crop productivity.
- Health and Environmental Risks:
- Nitrogen pollution contributes to health issues like methemoglobinemia (blue baby syndrome) and various long-term diseases.
- Nitrogen compounds also play a role in greenhouse gas emissions, further exacerbating climate change.
- Future Directions for Sustainable Agriculture:
- This study highlights the need for innovative nitrogen management strategies, integrating both biological and genetic approaches to optimize nitrogen use.
- Research is underway to develop NO scavenging formulations and identify bacteria that could be used in soil to enhance NUE in plants.
- Policy Recommendations:
- Governments should focus on reducing the environmental and health impacts of nitrogen fertilizer production and usage by promoting sustainable farming practices.
- Encouraging biological nitrogen fixation through crops like soybeans and alfalfa, and investing in low-emission fertilizers, can help mitigate nitrogen pollution.
Dr. V. Narayanan Takes Over as ISRO Chairman

- 10 Jan 2025
In News:
Dr. V. Narayanan has been appointed as the new Chairman of ISRO and Secretary of the Department of Space (DoS), effective from January 14, 2025, succeeding Dr. S. Somanath.
Background and Career of Dr. V. Narayanan:
Dr. Narayanan, currently the Director of Liquid Propulsion Systems Centre (LPSC) in Thiruvananthapuram, has been a key figure in ISRO since joining in 1984. With a focus on cryogenic propulsion, he has played an instrumental role in developing critical technologies for ISRO's launch vehicles. Notably, his work has contributed to India becoming the sixth country globally capable of building and operationalizing cryogenic engines.
Dr. Narayanan’s career highlights include:
- Cryogenic Technology: Leading the development of cryogenic engines for LVM3 (India's heaviest launch vehicle) and PSLV, which are central to missions like Chandrayaan and Gaganyaan.
- Chandrayaan-2 & Chandrayaan-3: As part of ISRO’s missions to the moon, his contributions were pivotal in rectifying the propulsion system issues post-Chandrayaan-2's hard landing, leading to the successful soft landing of Chandrayaan-3 in August 2023.
- Gaganyaan Mission: Overseeing the development of the propulsion systems for crew and service modules, critical for India’s ambitious human spaceflight program.
Dr. S. Somanath's Legacy:
Dr. S. Somanath, who served as ISRO Chairman and DoS Secretary spearheaded multiple landmark missions, including:
- Chandrayaan-3, Aditya-L1, and INSAT missions.
- The Small Satellite Launch Vehicle (SSLV), Re-usable Launch Vehicle (RLV-LEX), and Gaganyaan abort missions.
- National Space Policy 2023 and fostering partnerships between ISRO and private ventures.
Dr. Somanath’s tenure significantly elevated India’s space capabilities, with Chandrayaan-3 marking a historic milestone in India’s lunar exploration.
Dr. Narayanan’s Role in Upcoming ISRO Missions:
As ISRO Chairman, Dr. Narayanan will oversee several ambitious space missions, including:
- NVS-02: The launch of India's navigation satellite as part of the IRNSS constellation.
- Unmanned Gaganyaan Mission: Leading the uncrewed G-1 flight, a precursor to India's first human spaceflight.
- Indo-US NISAR Satellite: A significant collaborative launch with NASA for earth observation.
Additionally, high-profile projects such as Chandrayaan-4, India’s own space station, and future missions to Mars and Venus are in the pipeline, although not all may occur during his tenure.
Vision for ISRO Under Dr. Narayanan:
Dr. Narayanan aims to expand India’s presence in space, targeting increased global market share, particularly in the space economy, which currently holds 2% of the global space sector. His leadership will focus on:
- Increasing Satellite Capacity: Expanding India’s satellite fleet, which currently stands at 53, to meet growing demands for communication, navigation, and earth observation.
- Private Sector Involvement: Leveraging space sector reforms and collaborating with private players to drive innovation and meet burgeoning satellite needs.
- Global Collaboration: Strengthening ties with other space agencies, as ISRO continues to build respect on the global stage.
Upcoming Space Missions and ISRO's Agenda for 2025:
Under Dr. Narayanan's leadership, ISRO has a packed agenda for 2025:
- GSLV Mk-II/IRNSS-1K Mission
- Gaganyaan G-1 Mission (uncrewed flight)
- Chandrayaan-4, Bharatiya Antariksha Station, and Venus Orbiter Mission (VOM) preparations.
Dr. Narayanan’s vision aligns with India's broader goals of becoming a dominant player in the global space economy, aspiring to increase its space market share from 2% to 10%.
Indonesia Becomes 10th Member of BRICS
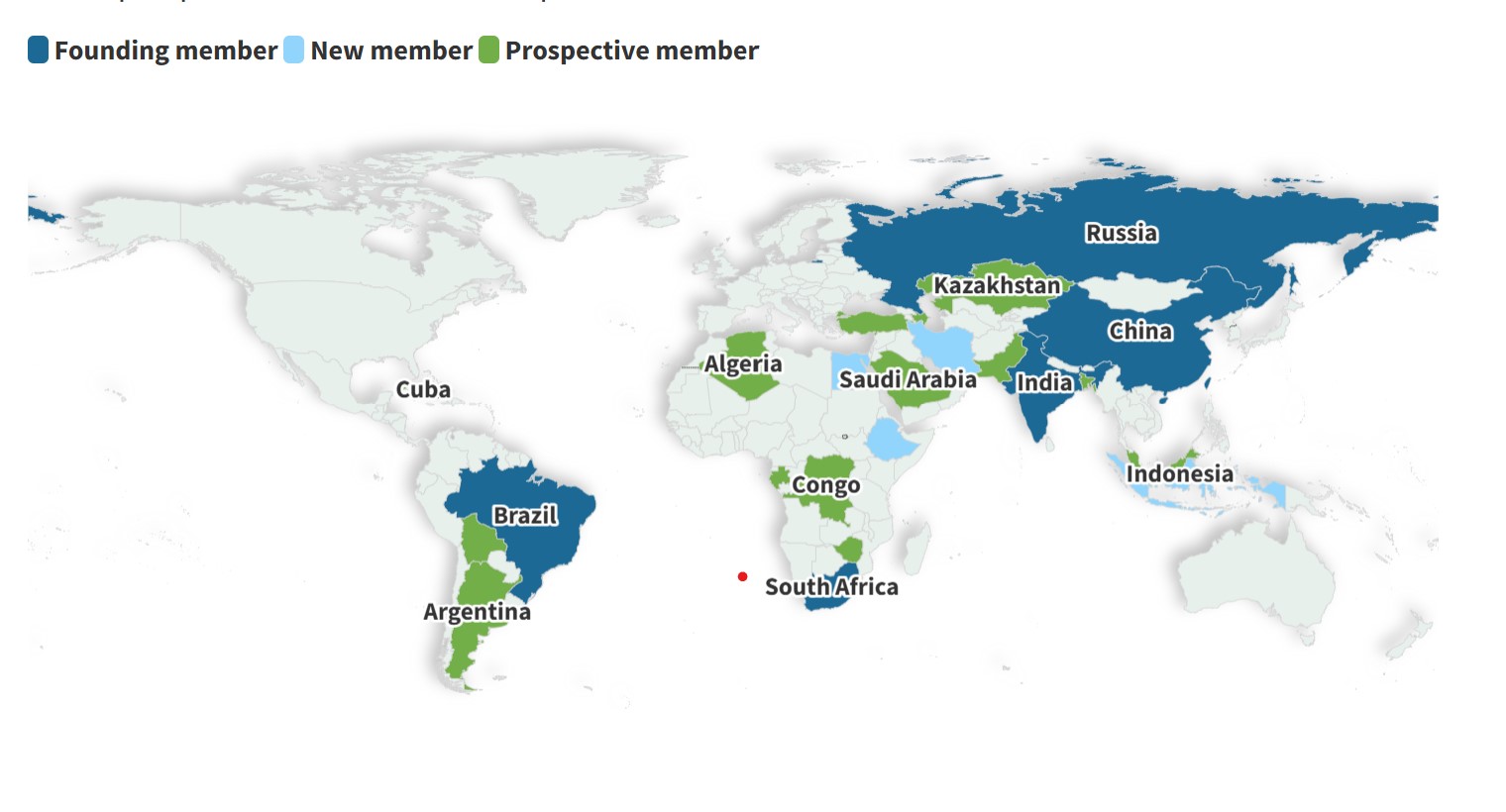
- 10 Jan 2025
In News:
In January 2025, Indonesia officially joined the BRICS group as its 10th member, signaling the expansion of this influential coalition of emerging economies. The addition of Indonesia, a Southeast Asian powerhouse, strengthens BRICS' global position and highlights the group's evolving dynamics.
BRICS Overview:
BRICS (Brazil, Russia, India, China, South Africa) is an informal intergovernmental group that fosters cooperation among major emerging economies. Initially coined as BRIC by economist Jim O'Neill in 2001, the group became BRICS in 2010 with the inclusion of South Africa. The bloc has grown steadily, with Indonesia now joining as its 10th member.
Recent Expansion:
- In 2023, invitations were extended to Saudi Arabia, Iran, UAE, Egypt, Ethiopia, and Argentina.
- By 2024, Iran, Egypt, Ethiopia, and UAE had joined as permanent members.
- Indonesia's membership was finalized in 2025, following its presidential elections and government formation.
Key Objectives of BRICS:
- Economic Growth: Promote trade, investment, and infrastructure development.
- Global Governance Reform: Advocate for equitable representation in global institutions like the UN and IMF.
- Cultural Exchange: Strengthen people-to-people connections and cultural ties.
- South-South Cooperation: Foster collaboration among developing nations.
BRICS Structure and Mechanisms:
- New Development Bank (NDB): Established in 2014, the NDB finances sustainable development projects in BRICS countries.
- Contingent Reserve Arrangement (CRA): A $100 billion safety net for financial crises.
- BRICS Academic Forum: Encourages academic collaboration across member states.
Global Influence and Economic Impact:
- Global Share: BRICS+ represents over 45% of the world’s population and 35% of global GDP (PPP-based).
- Strategic Position: The group acts as a counterbalance to the G7, challenging Western-dominated global financial systems.
- Financial Independence: BRICS aims to reduce dependence on the US dollar by facilitating local currency transactions and exploring a common currency.
- Technology Collaboration: Member countries, such as India and China, collaborate on digital payments and renewable energy technologies.
Indonesia’s Entry into BRICS:
Indonesia, the world’s fourth-most populous nation, strengthens BRICS’ representation in Southeast Asia. The country brings a robust economy and extensive trade networks, boosting the group's negotiating power. Indonesia’s membership was approved during the 2023 BRICS Summit and finalized in January 2025.
- Strategic Importance for Indonesia: The membership aligns with Indonesia's goals to enhance global cooperation, particularly with the Global South. It also reflects Indonesia's growing influence in international trade and geopolitics.
BRICS Challenges:
- Diverse Interests: Differences in economic priorities, such as India's ties with the US and Russia-China’s geopolitical rivalry, complicate consensus-building.
- Geopolitical Tensions: Disputes like the China-India border issue and Russia’s sanctions limit BRICS' ability to present a unified stance.
- Economic Sanctions and Internal Challenges: Countries like Russia face Western sanctions, while domestic issues in Brazil and South Africa divert attention from regional collaboration.
Significance of BRICS’ Expansion:
The expansion of BRICS marks a pivotal shift in global power dynamics, with a focus on South-South cooperation and equitable global governance. Indonesia’s membership further solidifies the group’s influence in Southeast Asia and adds to its efforts to challenge the dominance of Western-led financial institutions.
- Local Currency Use: The group promotes the use of local currencies for trade to reduce reliance on the US dollar.
- Global South Advocacy: BRICS champions the cause of developing nations, ensuring that emerging economies have a voice in global governance.
Recent and Upcoming BRICS Summits:
- 16th BRICS Summit (2024): Held in Kazan, Russia, with a focus on strengthening local currencies and promoting non-dollar transactions.
- 17th BRICS Summit (2025): Scheduled for July 2025 in Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, under the theme "Global South," with an emphasis on payment gateways to facilitate intra-BRICS trade.
Flamingo Festival 2025

- 10 Jan 2025
In News:
The Flamingo Festival 2025 took place at Sullurpeta, in Tirupati district, Andhra Pradesh. It celebrates the arrival of migratory birds, with a focus on flamingos, to the region's key bird habitats, including Pulicat Lake and Nelapattu Bird Sanctuary.
Key Highlights:
- Birdwatching: Over 200 bird species, including flamingos, are expected to flock to the region during this festival.
- Locations: The event spans across five locations:
- Nelapattu Bird Sanctuary
- B.V. Palem (Pulicat Lake)
- Atakanithippa
- Sri City
- Sullurpeta (site for cultural programs and stalls)
- Collaborations: In association with organizations like the Bombay Natural History Society.
- Focus on Local Community: Local residents of the eco-sensitive zone will be prioritized and supported.
Key Facts on Local Wildlife and Significance:
- Pulicat Lake:
- Location: On the Andhra Pradesh-Tamil Nadu border, with 96% of the lake in Andhra Pradesh.
- Significance: The second-largest brackish water lake in India (after Chilika Lake in Odisha).
- Biodiversity: Critical habitat for migratory birds, including flamingos, and home to diverse flora and fauna.
- Economic Importance: Supports local fisheries and provides livelihood to nearby communities.
- Nelapattu Bird Sanctuary:
- Location: 20 km north of Pulicat Lake.
- Ecological Role: Largest breeding site in Southeast Asia for spot-billed pelicans.
- Biodiversity: 189 bird species, including painted storks and glossy ibises.
- Flora and Fauna: Features Barringtonia swamp forests and southern dry evergreen scrub, critical for biodiversity conservation.
- Symbiotic Relationship with Locals: Guano (bird droppings) from pelicans serves as a natural fertilizer for local agriculture, benefiting the farmers.
Flamingo Facts:
- Species: India hosts two flamingo species:
- Greater Flamingo (larger size, pale pink)
- Lesser Flamingo (smaller size, bright pink)
- Behavior: Nomadic and social birds, found in large flocks.
- Coloration: Flamingos' pink color comes from carotenoids in their diet, which are broken down and absorbed into their bodies.
Environmental & Economic Impact: The festival, apart from being a celebration of migratory birds, plays a vital role in:
- Eco-tourism development
- Biodiversity conservation
Local community engagement by highlighting sustainable tourism practices and supporting local livelihoods through eco-friendly initiatives like the Mahatma Gandhi National Rural Employment Guarantee Scheme (MGNREGS).
Bharatpol

- 11 Jan 2025
In News:
Union Home Minister Amit Shah inaugurated the ‘Bharatpol’ portal, which aims to streamline international cooperation for law investigating agencies.
Key Highlights:
Bharatpol is a newly launched portal developed by the Central Bureau of Investigation (CBI) in India to facilitate faster and more efficient international cooperation between Indian law enforcement agencies and Interpol. It was inaugurated by Union Home Minister Amit Shah, to streamline the process of sharing criminal intelligence and coordinating efforts in transnational crimes like cybercrime, human trafficking, drug trafficking, financial fraud, and organized crime.
The portal aims to address the current challenges in international collaboration, which previously relied on slower communication methods such as letters, emails, and faxes, often leading to delays in investigations.
Key Features and Functions of Bharatpol:
- Unified Platform: Bharatpol integrates CBI as the National Central Bureau (NCB-New Delhi) with all Indian law enforcement agencies, from state police forces to higher authorities. This allows better coordination and quicker access to international resources.
- Simplified Request Mechanism: The portal provides a standardized method for frontline police officers to request international assistance from Interpol member countries, using templates for efficiency.
- Rapid Information Dissemination: Bharatpol enables the CBI to quickly share criminal intelligence and other pertinent information with law enforcement agencies across India, helping to tackle international criminal activities in real-time.
- Increase in Utilization of Interpol Notices: The portal makes it easier for Indian law enforcement agencies to issue and manage Red Corner Notices and other Interpol notices, which are essential tools in tracking criminals globally.
- Capacity Building and Training: Bharatpol includes resources for training law enforcement personnel, improving their ability to conduct investigations abroad and seek foreign assistance via Interpol.
How Bharatpol Works:
- Key Modules of Bharatpol:
- Connect: Facilitates the integration of Indian agencies with the Interpol NCB-New Delhi, creating a seamless communication channel.
- INTERPOL Notices: Supports the rapid issuance and processing of Interpol Notices like Red Corner Notices to locate criminals globally.
- References: Enables Indian agencies to seek and offer international assistance for investigations.
- Broadcast: Ensures quick availability of assistance requests from Interpol member countries, facilitating faster responses.
- Resources: Manages document exchanges and training materials to support the capacity-building efforts of law enforcement agencies.
Potential Benefits of Bharatpol:
- Enhanced Coordination: Bharatpol facilitates better collaboration between central, state, and Union Territory agencies, allowing for a more structured and efficient approach to international crime investigations.
- Faster Investigation: Real-time sharing of information and the use of Interpol notices will help in tracking criminals and criminal activities both in India and abroad.
- Simplified Extradition Process: By streamlining international communication, Bharatpol will assist in expediting the extradition of criminals to India for prosecution.
- Support for Transnational Crime Prevention: It will help address growing threats such as cybercrime, human trafficking, and organized crime by improving the ability of Indian law enforcement to collaborate globally.
National Mission on Edible Oils - Oil Palm (NMEO-OP)

- 11 Jan 2025
In News:
- Union Minister Shri Shivraj Singh Chouhan urges states to accelerate efforts under the National Mission on Edible Oils - Oil Palm (NMEO-OP) to enhance domestic production of edible oils and reduce reliance on imports.
Key Facts Regarding the NMEO-OP Scheme:
About the Scheme:
- Objective: Enhance domestic production of crude palm oil (CPO) and reduce India's dependence on edible oil imports.
- Centrally Sponsored Scheme: Focuses on expanding oil palm cultivation in India.
Key Targets:
- Area Expansion: Aim to cover an additional 6.5 lakh hectares by 2025-26, reaching a total of 10 lakh hectares.
- Production Increase: CPO production is targeted to rise from 0.27 lakh tonnes (2019-20) to 11.20 lakh tonnes by 2025-26, and further to 28 lakh tonnes by 2029-30.
- Per-Capita Consumption: Maintain a consumption level of 19 kg/person/annum until 2025-26.
Focus Regions:
- Special Focus: North-Eastern States and Andaman & Nicobar Islands for oil palm cultivation and CPO production.
Key Features:
- Viability Price (VP) Mechanism: Aims to protect farmers from market volatility by providing price assurance. Payments are made through Direct Benefit Transfer (DBT).
- Increased Assistance:
- Assistance for planting material increased from Rs 12,000/ha to Rs 29,000/ha.
- Special assistance of Rs 250 per plant for rejuvenating old gardens.
- Regional Support:
- For North-East and Andaman, an additional 2% of the CPO price is borne by the government to ensure fair payments to farmers.
- Special provisions for half-moon terrace cultivation, bio-fencing, and land clearance for integrated farming.
Oil Palm Cultivation:
- Origin: Native to the tropical rainforests of West Africa, oil palm is a new crop in India with high oil-yielding potential.
- Oil Yield: Oil palm produces five times the yield of traditional oilseeds per hectare.
- Types of Oil Produced:
- Palm Oil: Extracted from the mesocarp (fruit's fleshy part), containing 45-55% oil.
- Palm Kernel Oil: Derived from the kernel, used in lauric oils.
- Major States for Cultivation: Andhra Pradesh, Telangana, Kerala (98% of total production).
- Other Key States: Karnataka, Tamil Nadu, Odisha, Gujarat, Mizoram, Arunachal Pradesh, Assam, Manipur, Nagaland.
India's Oil Palm Potential:
- Cultivated Area: India currently has 3.70 lakh hectares under oil palm cultivation.
- Total Potential Area: Around 28 lakh hectares.
- Imports: India is the world's largest palm oil importer, with imports of 9.2 million tonnes in 2023-24, accounting for 60% of total edible oil imports. The country primarily imports from Indonesia, Malaysia, and Thailand.
Emergency Declared in Trinidad and Tobago
- 11 Jan 2025
In News:
- Trinidad and Tobago declared a state of emergency, in response to a surge in gang violence, which raised the annual death toll to the highest since 2013.
Trinidad and Tobago:
- Location: An island nation in the southern Caribbean, near Venezuela and Guyana.
- Capital: Port of Spain.
- Population: Approximately 1.5 million.
- Ethnic Composition: African (36.3%), Indian (35.4%), Mixed (22.8%), and others.
- Religions: Christianity (64%), Hinduism (18%), Islam (5%), and others.
- Independence: Gained from the UK on August 31, 1962, and became a republic in 1976.
- Member of: Caribbean Community (CARICOM), Commonwealth of Nations, and the United Nations.
- Major Rivers: Ortoire and Caroni.
- Geography:
- Total Land Area: 5,128 sq. km (Trinidad: 4,768 sq. km, Tobago: 300 sq. km).
- Climate: Tropical, with dry and rainy seasons.
- Highest Point: Mount Aripo.
- Natural Resource: Pitch Lake, the world’s largest asphalt reservoir.
- Mountain Range: Northern Range, part of the Andes extension.
Economic and Cultural Significance
- Exports: Major exporter of liquefied natural gas (LNG), methanol, ammonia, and petrochemicals.
- Culture: Known for Carnival, Calypso music, Soca, and the Steelpan (the only musical instrument invented in the 20th century).
- Infrastructure:
- Ports: Port of Spain, Point Lisas, Scarborough.
- Airports: Piarco International Airport (Trinidad) and A.N.R. Robinson International Airport (Tobago).
Engagement with India
- Trinidad and Tobago became the first Caribbean country to adopt India’s UPI platform.
- Both countries granted each other Most Favored Nation (MFN) status in 1997.
- Bilateral trade reached USD 368.96 million in FY 2023-24.
- The Indian diaspora constitutes about 42% of the population.
Past Emergency Declarations:
- 2014: State of emergency declared in response to gang violence.
- 2021: Emergency declared for Covid-19 restrictions.
- 2011: Limited state of emergency for drug-related crimes.
Toda Tribe

- 11 Jan 2025
In News:
- The Toda tribe, one of the oldest Dravidian ethnic groups in the Nilgiris Hills of Tamil Nadu, celebrated their traditional Modhweth festival marking the New Year.
What is the Modhweth Festival?
- About:
- Celebrated annually on the last Sunday of December or the first Sunday of January.
- Held at the Moonpo temple in Muthanadu Mund village, Nilgiri district.
- The Moonpo temple features a unique vertical spire with a thatched roof and a flat stone on top, making it one of the last Toda temples of its kind in the Nilgiris.
- Rituals and Celebrations:
- Prayers are offered to the deity, Thenkish Amman, for good health, rains, and bountiful harvest.
- Participants perform a traditional dance outside the temple.
- Unique Customs:
- Toda youth showcase their strength and masculinity by lifting a greased boulder weighing around 80 kg.
- Women are not part of the celebrations as per traditional customs.
What is the Toda Tribe?
- About:
- A pastoral tribe native to the Nilgiri Hills of Tamil Nadu.
- Classified as a Particularly Vulnerable Tribal Group (PVTG) in Tamil Nadu.
- The Toda language is Dravidian but stands out for its uniqueness among Dravidian languages.
- Significance:
- Toda lands are part of the Nilgiri Biosphere Reserve, a UNESCO International Biosphere Reserve.
- Their territory is also recognized as a UNESCO World Heritage Site.
- Religion and Beliefs:
- Their religious practices are based on a pantheon of gods, with Tökisy (goddess) and Ön (god of the underworld) as central deities.
Nilgiri Biosphere Reserve (NBR)
- About:
- Established in 1986 as India’s first Biosphere Reserve.
- Located across Tamil Nadu, Karnataka, and Kerala.
- India’s first biosphere reserve under UNESCO’s Man and the Biosphere Programme.
- Tribal Groups in NBR:
- Home to several groups such as Adiyan, Aranadan, Kader, Kurichian, Kuruman, and Kurumbas.
- Ecological Significance:
- Represents the confluence of Afro-tropical and Indo-Malayan biotic zones.
- Fauna:
- Home to species like Nilgiri tahr, Nilgiri langur, gaur, Indian elephant, Nilgiri danio (freshwater fish), and Nilgiri barbare.
- Protected Areas in NBR:
- Mudumalai Wildlife Sanctuary, Wayanad Wildlife Sanctuary, Bandipur National Park, Nagarhole National Park, Mukurthi National Park, and Silent Valley.
Z-Morh Tunnel
- 11 Jan 2025
In News:
Recently, Prime Minister Narendra Modi inaugurated the Z-Morh Tunnel at Sonamarg, which has now been renamed the Sonamarg Tunnel.
Key Takeaways:
- A 6.4-km bi-directional tunnel with an approach road of 5.6 km, Z-Morh connects the Sonamarg health resort with Kangan town in the Ganderbal district of central Kashmir.
- The tunnel has acquired its name for the Z-shaped road stretch that was previously at the place where the tunnel is being constructed.
- The Z-Morh project was initiated by the Border Roads Organisation in 2012. Although the BRO awarded the construction contract to Tunnelway Ltd, the project was subsequently taken over by National Highways and Infrastructure Development Corporation Limited (NHIDCL).
Significance
Strategic Importance
- Connectivity: Provides all-weather connectivity from Srinagar to Ladakh, ensuring year-round access.
- Military Significance:
- Critical for rapid deployment of Indian Armed Forces to Ladakh’s border areas, particularly in the context of tensions with Pakistan and China.
- Reduces dependence on air transport, lowering costs and increasing the longevity of the Indian Air Force’s aircraft.
- Adjacent Projects:
- Zojila Tunnel: An even more crucial project connecting Sonamarg to Drass in Ladakh, with an expected completion by December 2026 (extended to 2030). This will bypass the avalanche-prone Zojila Pass.
- Srinagar-Leh Highway: The Z-Morh Tunnel supports the key Srinagar-Leh route, which is important for defence logistics and trade.
Economic Significance
- Tourism:
- Sonamarg, known as the "Meadow of Gold," will benefit from year-round accessibility, boosting tourism.
- Local businesses that rely on seasonal tourist traffic will have consistent revenue flow.
- Trade and Agriculture:
- Reduced travel time and improved road safety will benefit farmers and traders, especially for those transporting goods between Kashmir and Ladakh.
- Facilitates increased investment and economic growth in the region.
Broader Infrastructure Projects in Jammu & Kashmir
Several key infrastructure projects are contributing to regional development:
- Zojila Tunnel
- Cost: ?6,800 crore
- Length: 13 km tunnel, bypassing Zojila Pass.
- Completion: Expected by 2030.
- Strategic Importance: Provides all-weather connectivity to Ladakh.
- Srinagar Semi-Ring Road
- Cost: ?2,919 crore
- Objective: Relieve traffic congestion in five districts, including Srinagar.
- Delay: New completion date is June 2025.
- Hydroelectric Power Projects:
- Ratle HE Project: 850 MW, on Chenab River, Kishtwar district.
- Kwar HE Project: 540 MW, in Kishtwar.
- Pakal Dul HE Project: 1,000 MW, on the Marusudar River, Kishtwar.
- Kiru HE Project: 624 MW, on Chenab River, Kishtwar.
- Strategic Relevance: These projects will enhance energy security and contribute to the region’s power grid.
India’s Recalculated Coastline
- 09 Jan 2025
In News:
India’s coastline has grown significantly over the past five decades, now extending 11,098 km in 2023-24, compared to 7,516 km in 1970. This marks an increase of 47.6% in just over five decades, attributed to a more precise methodology for measuring coastlines.
Key Factors Behind the Growth:
New Methodology for Measuring Coastlines:
- The old methodology used straight-line distances to measure the coastline, a method that didn't capture the complexity of India’s coastlines.
- The updated approach incorporates bays, estuaries, inlets, and other geomorphological features, offering a more accurate and detailed representation of the coastline.
- Advanced technologies like geospatial mapping have been used to ensure greater precision.
State-wise Recalculated Coastline Changes:
- Gujarat:
- Old coastline (1970): 1,214 km
- New coastline (2023-24): 2,340 km
- Growth: The largest absolute increase in coastline, nearly doubling its size.
- West Bengal:
- Old coastline: 157 km
- New coastline: 721 km
- Growth: A dramatic 357% increase, marking the highest percentage rise.
- Tamil Nadu:
- Old coastline: 906 km
- New coastline: 1,068 km
- Growth: Revised length now exceeds Andhra Pradesh’s coastline, which was 1,053 km.
- Puducherry:
- Old coastline: No major shift, but the updated data shows a contraction of 4.9 km (-10.4%), due to erosion and recalculations.
- Kerala:
- Old coastline: Relatively small increase of 30 km (5%), the smallest among the states.
Notable Observations:
- Andhra Pradesh is developing new ports like Ramayapatnam, Krishnapatnam, and Kakinada Gateway, aiming to boost economic growth and employment by leveraging its expanding coastline.
- The recalculated coastline helps in better maritime planning, focusing on port development, tourism, biodiversity conservation, and coastal erosion.
Impact of Coastline Expansion:
- Economic Growth:
- Coastal states, particularly Gujarat and West Bengal, benefit from an expanded coastline that improves maritime trade, port infrastructure, and tourism.
- The expansion supports industrialization, with growing logistics and transportation activities along the coast.
- Environmental Considerations:
- The new data aids biodiversity conservation, helping to track coastal erosion and accretion (land buildup), especially in areas like the West Coast.
- Understanding these changes is essential for disaster preparedness and sustainable coastal management.
- Coastlines of Emergence and Submergence:
- Emerging Coastlines: Land rising due to uplift or falling sea levels, such as along the Tamil Nadu Coast.
- Submerged Coastlines: Land that has sunk or been submerged due to rising sea levels, particularly noticeable along parts of Kerala’s coast.
Geographical Significance of the Expanded Coastline:
- India’s coast touches three major bodies of water: the Bay of Bengal (east), the Indian Ocean (south), and the Arabian Sea (west).
- The expansion reflects more than just geography—accurate coastline data is crucial for policy planning, maritime security, and resource management.
Bhashini Initiative
- 09 Jan 2025
In News:
e-Shram Portal, which aims to provide social security benefits to unorganised workers, has been upgraded with multilingual functionality for all 22 scheduled languages of India. This development, supported by the Bhashini Initiative, ensures that unorganised workers from diverse linguistic backgrounds can access the portal more easily and benefit from government welfare schemes.
About Bhashini Initiative:
- Launched in: July 2022
- Developed by: Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology (MeitY)
- Aim: To eliminate language barriers in accessing digital services by making AI and Natural Language Processing (NLP) tools publicly available.
Key Features:
- Local Language Translation: Bhashini offers AI-powered translation services in 22 scheduled Indian languages to ensure that digital platforms like e-Shram are accessible to everyone in their native languages.
- Open AI and NLP Resources: These tools are made available to Indian MSMEs, startups, and innovators to create a more inclusive digital ecosystem.
- Crowdsourcing Platform (Bhashadaan): A platform for people to contribute to building linguistic datasets through initiatives like Suno India, Likho India, Bolo India, and Dekho India, furthering language diversity in digital services.
- National Digital Public Platform: Aimed at providing universal access to digital content in all Indian languages, facilitating smoother communication across regions.
e-Shram Portal: A One-Stop Solution for Unorganised Workers
- Purpose: The e-Shram portal was created to provide unorganised workers with access to social security benefits and welfare schemes.
Recent Upgrade:
- Multilingual Functionality: The portal has now been upgraded to support 22 scheduled languages, making it more inclusive and user-friendly for workers who speak various regional languages.
- Previous Version: Previously, the portal was only available in English, Hindi, Kannada, and Marathi. The integration of 22 languages is a significant improvement, enabling broader participation.
Importance of the e-Shram Portal for Unorganised Workers:
- Welfare Access: The portal provides access to government schemes designed for the welfare, livelihood, and well-being of unorganised workers, including gig and platform workers and building and construction workers.
- Integration of Social Security Schemes:
- As of now, the portal facilitates access to 12 government schemes, with plans to integrate even more, including state-level programs.
- Future plans include launching a mobile app, a single application form, and the integration of payment gateways for faster disbursement of benefits.
AI-Driven Inclusive Development and Economic Transformation

- 09 Jan 2025
In News:
IndiaAI, under the Digital India Corporation, has partnered with Microsoft to advance AI adoption in India for inclusive development and economic transformation. The collaboration focuses on skilling, innovation, AI safety, and responsible AI development, with a goal of fostering AI innovation across India, particularly in underserved rural and urban areas.
Key Highlights:
- Training 500,000 Individuals by 2026:
- Target Audience: Students, educators, developers, government officials, and women entrepreneurs.
- Goal: Empower these groups with foundational and advanced AI skills for economic opportunities and digital transformation.
- AI Catalysts (Centers of Excellence):
- Establishment of AI hubs in Tier 2 and Tier 3 cities to foster rural AI innovation.
- Objective to equip 100,000 AI innovators and developers through hackathons, community building, and creating an AI marketplace.
- AI Productivity Labs:
- Set up in 20 National Skill Training Institutes (NSTIs) across 10 states.
- Focus on training 20,000 educators and providing AI education to 100,000 students in 200 Industrial Training Institutes (ITIs).
- Support for Startups:
- Microsoft’s Founders Hub program will provide Azure credits, business resources, and mentorship to 1,000 AI startups in India, boosting innovation and growth in the Indian startup ecosystem.
- Development of Indic Language Models:
- Work on creating foundational AI models with support for Indic languages to address India’s linguistic diversity and cultural needs.
- AI Safety Institute:
- Focus on building frameworks, standards, and evaluation metrics for responsible AI development.
- Support for the creation of an AI Safety Institute in India to promote ethical and safe AI practices.
- Infrastructure & Research:
- Microsoft will also focus on enhancing cloud infrastructure and support for AI research through Microsoft Research India.
- AI-driven solutions will be developed for critical sectors like healthcare, education, and agriculture.
Investment and Strategic Goals:
- $3 Billion Investment:
- Microsoft has pledged $3 billion to expand AI and cloud infrastructure in India over the next 2 years. This investment will focus on:
- Building scalable infrastructure for AI applications.
- Enhancing cloud services and AI capabilities.
- Establishing new data centers across India, supporting the AI-first agenda.
- Microsoft has pledged $3 billion to expand AI and cloud infrastructure in India over the next 2 years. This investment will focus on:
- AI Skill Development:
- 10 million people will be trained over the next five years in AI skills, empowering the Indian workforce to adapt to AI technologies, driving job creation and economic growth.
- AI in India’s Economy:
- India aims to become a global leader in AI, with AI-powered solutions contributing to diverse sectors like finance, e-commerce, and manufacturing.
- Focus on economic growth through AI-powered industries and fostering entrepreneurship in underserved communities.
AI Technologies and Applications:
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) involves machines performing tasks that require human intelligence like decision-making, problem-solving, and learning from data.
- Machine Learning (ML): AI systems improve through data without being explicitly programmed.
- Natural Language Processing (NLP): AI systems understand and respond to human language.
- Computer Vision: AI systems analyze and interpret visual information.
- Robotics: AI powers automated tasks through robots in industries like manufacturing and healthcare.
- Cloud Infrastructure enables the scaling of AI systems:
- Cloud Computing provides on-demand access to computing power, essential for AI tasks requiring large amounts of data and processing power.
- Data Centers host AI models and data, and cloud services such as Microsoft Azure will support AI startups and businesses.
Expected Impact and Benefits:
- Inclusive AI Development: Focus on empowering women, students, and rural innovators to bridge the digital divide and promote economic empowerment.
- Startup Ecosystem: The collaboration will foster a robust AI startup ecosystem, promoting innovation and entrepreneurship through AI tools, Azure credits, and mentorship.
- Skill Development & Education: AI-driven skill training initiatives will prepare millions of individuals for the jobs of the future, particularly in the AI-driven economy, and support education reform.
- AI for Critical Sectors: Development of AI-enabled solutions to address challenges in sectors such as healthcare, education, and agriculture, driving social impact and economic growth.
Miyawaki Technique
- 09 Jan 2025
In News:
- Prayagraj Municipal Corporation has successfully transformed over 56,000 square meters of garbage dumps and barren lands into lush green forests using the Miyawaki Technique over the past two years, as part of environmental conservation efforts in preparation for Mahakumbh 2025.
About Miyawaki Technique:
- Origin: Developed by Akira Miyawaki, a Japanese botanist, in the 1970s to create dense and fast-growing forests.
- Key Features:
- Dense Planting: Trees and shrubs are planted close together, often using native species.
- Accelerated Growth: Trees grow 10 times faster than in traditional forests.
- Soil Restoration: Improves soil fertility and promotes natural regeneration.
- Biodiversity Boost: Supports a variety of flora and fauna by mimicking natural ecosystems.
- Significance:
- Urban Reforestation: Converts barren or polluted lands into green spaces.
- Environmental Benefits:
- Reduces air and water pollution.
- Absorbs carbon and helps combat climate change.
- Lowers temperatures by 4-7°C.
- Sustainability: Prevents soil erosion and promotes long-term ecological balance.
Miyawaki Forests in Prayagraj:
- Achievements:
- Over 56,000 square meters of land converted into dense forests using the Miyawaki technique over the last two years.
- The project aims to create oxygen banks in preparation for the Mahakumbh 2025 and enhance air quality for millions of expected visitors.
- Plantations:
- 55,800 square meters of area developed across 10+ locations in Prayagraj.
- Largest plantation: 1.2 lakh trees in Naini industrial area.
- 27,000 trees planted in Baswar after cleaning the city's largest garbage dump.
- Environmental Impact:
- The plantations are helping to reduce dust, dirt, and foul odors, thus improving air quality.
- Temperature regulation: The dense forests can lower temperatures by 4 to 7 degrees Celsius.
- Biodiversity and Soil Fertility: Accelerated growth of trees boosts biodiversity and improves soil fertility.
- Tree Species Planted:
- Mango, Mahua, Neem, Peepal, Tamarind, Arjuna, Teak, Amla.
- Ornamental and medicinal plants like Hibiscus, Kadamba, Gulmohar, etc.
- Other species include Sheesham, Bamboo, Lemon, Drumstick (Sahjan), and Tecoma.
Benefits of Miyawaki Forests:
- Air and Water Pollution Reduction: Trees absorb carbon, purify air, and improve water quality.
- Temperature Control: The forests help in reducing urban heat islands, lowering the temperature during hot months.
- Soil Conservation: The dense forests prevent soil erosion and promote the regeneration of the natural ecosystem.
- Enhanced Biodiversity: The technique supports a rich variety of species, improving ecological balance.
AnemiaPhone

- 09 Jan 2025
In News:
AnemiaPhone, a technology developed by Cornell University researchers to accurately, quickly, and cheaply, assess iron deficiency, has been transferred to the Indian Council of Medical Research (ICMR) for integration into its programmes for anaemia, women’s health, and maternal and child health throughout the country.
Key Highlights:
- Technology Features:
- Portable, Rapid, and Affordable: AnemiaPhone is designed to detect iron deficiency efficiently at low cost.
- Requires a fingerstick (small blood sample).
- Results are available within minutes.
- Wireless: Data uploaded to a clinical database via mobile, tablet, or computer.
- Can be used by healthcare workers to assess iron deficiency on the spot and take action (guidance, triage, referral).
- Working Mechanism:
- A drop of blood is placed on a test strip.
- The reader processes the sample.
- Data is uploaded for immediate diagnosis and action.
- Test results assist in on-the-spot intervention by healthcare workers.
Anaemia and Iron Deficiency:
- Prevalence in India:
- Iron deficiency is a leading cause of anaemia.
- 50%-70% of pregnant women in India suffer from anaemia.
- 59% of women and 47% of children (6-59 months) in India suffer from anaemia (NFHS data).
- Consequences of Anaemia:
- Fatigue, dizziness, organ failure, complications in childbirth, and in severe cases, death.
- Contributes to higher maternal and child mortality rates in India.
- Impact on Health in India:
- India has one of the highest rates of anaemia in the world.
- Iron deficiency is a significant contributor to maternal deaths.
ICMR's Role and Integration into National Programs:
- ICMR and AnemiaPhone:
- The Indian Council of Medical Research (ICMR) has integrated AnemiaPhone into its Anaemia Mukt Bharat (Anaemia-Free India) program.
- The program focuses on eliminating anaemia by 2025 through screening, diagnosis, and treatment in women and children, especially in remote areas.
- Transfer of Technology:
- In November 2024, Cornell University transferred the technology to ICMR for free.
- This collaboration aims to improve health outcomes by sharing innovative health technologies.
Advantages of AnemiaPhone:
- Cost-Effective and Portable:
- Low-cost compared to traditional lab tests.
- Portable and can be used in remote and underserved areas.
- Quick Diagnosis: Results are processed in minutes, allowing healthcare workers to act without delay.
- No Need for Expensive Labs:
- Can be used at primary health centers or in door-to-door health surveys.
- Facilitates healthcare in rural or difficult-to-reach areas.
- Wireless and Easy to Use: The device is user-friendly and does not require extensive training.
Impact on Healthcare System:
- Improvement in Accessibility:
- Helps reduce the need for people to travel long distances for diagnosis, especially in rural areas.
- Ensures early diagnosis and treatment of iron deficiency and anaemia.
- Enhancing Maternal and Child Health: AnemiaPhone will contribute to reducing maternal and child mortality rates linked to anaemia.
Technology Testing and Development:
- Testing in India:
- AnemiaPhone has been tested in India and has shown accurate results in diagnosing iron deficiency.
- Single-use test strips help ensure accuracy and prevent contamination.
Global Health Context:
- Global Prevalence of Anaemia: More than 2 billion people worldwide suffer from anaemia, particularly pregnant women and young children.
- WHO’s Role: The World Health Organization (WHO) identifies anaemia as a major global health issue.
India-Malaysia Cooperation in Critical Minerals and Rare Earth Elements

- 08 Jan 2025
In News:
- On January 7, 2025, during the inaugural India-Malaysia Security Dialogue in New Delhi, both countries agreed to enhance cooperation in critical minerals and rare earth elements (REEs).
- The meeting was co-chaired by India's National Security Adviser, Ajit Doval, and Malaysia’s Director General of the National Security Council, Raja Dato Nushirwan Bin Zainal Abidin.
- The agreement follows the upgrade of bilateral relations to a Comprehensive Strategic Partnership during Malaysian Prime Minister Anwar Ibrahim’s visit to India in August 2024.
- The dialogue also focused on other security aspects such as counter-terrorism, cyber security, and maritime security.
Importance of Critical Minerals and REEs:
-
- Critical Minerals: These are essential for a variety of industries like IT, energy, and defense. They are integral to manufacturing electric vehicle batteries, solar cells, and advanced electronics.
-
- Rare Earth Elements (REEs): Used in high-tech applications such as wind turbines, electric vehicle engines, and high-powered magnets. While their extraction is not rare, it is technically difficult due to their complex nature.
Strategic Relevance:
-
- Global Demand: The global demand for critical minerals is rising, and both countries see it as a strategic necessity to ensure a stable supply of these materials.
- Malaysia's Resources: Malaysia possesses significant deposits of non-rare radioactive earth ores, including essential REEs like Neodymium (Nd), Dysprosium (Dy), and Praseodymium (Pr). These elements are crucial in today’s technological innovations.
- India’s Dependence on Imports: India, which currently imports a substantial portion of its critical minerals, aims to diversify its supply chain by collaborating with Malaysia.
Sustainability and Ecological Accountability:
-
- Both countries recognize the environmental challenges of mining these critical resources. Malaysia aims to adopt responsible mining practices that minimize ecological harm.
- India seeks to ensure a supply chain that aligns with sustainable development goals, balancing economic needs with environmental responsibilities.
Enhancing Supply Chain Resilience:
-
- Diversification of Supply Chain: This partnership aims to reduce India’s dependency on a limited number of countries for critical minerals, enhancing resilience against global supply chain disruptions.
- Collaboration in Extraction and Processing: Both nations are exploring joint ventures in the exploration, extraction, and processing of critical minerals to boost their technological and economic standing globally.
Future Prospects:
-
- The institutionalization of this dialogue through annual meetings is expected to strengthen bilateral cooperation in the critical minerals sector.
- Increased cooperation is likely to enhance economic growth for both countries, aligning them strategically in the global minerals market as demand for these resources continues to soar.
Broader Security Cooperation:
-
- Beyond critical minerals, the India-Malaysia Security Dialogue explored enhanced collaboration in areas like counter-terrorism, cyber security, maritime security, and defense industries.
- This broadening of security cooperation complements the strategic minerals partnership, further solidifying the bilateral ties between the two nations.
Anji Khad Bridge

- 08 Jan 2025
In News:
The Indian Railways has unveiled a monumental engineering achievement with the completion of the Anji Khad Bridge, India’s first cable-stayed rail bridge.
Overview:
- The Anji Khad Bridge is India's first cable-stayed rail bridge, located in Jammu and Kashmir’s Reasi district.
- It is a key part of the Udhampur-Srinagar-Baramulla Rail Link (USBRL) project aimed at enhancing connectivity between Jammu and Kashmir and the rest of India.
- The bridge crosses the Anji River, a tributary of the Chenab River, and is expected to transform regional transport, boost tourism, and promote economic growth.
Key Features:
- Dimensions:
- Total length: 725.5 meters.
- Main Pylon Height: 193 meters from the foundation, standing 331 meters above the riverbed.
- The bridge is designed for train speeds of up to 100 km/h and can withstand wind speeds of up to 213 km/h.
- Structure and Design:
- Asymmetrical cable-stayed design supported by 96 cables with varying lengths (82 to 295 meters).
- The structure includes:
- A 120-meter approach viaduct on the Reasi side.
- A 38-meter approach bridge on the Katra side.
- A 473.25-meter cable-stayed portion crossing the valley.
- A 94.25-meter central embankment linking the main bridge to the approach viaduct.
- Construction Techniques:
- Used advanced construction techniques such as DOKA Jump Form Shuttering, Pump Concreting, and Tower Crane Technique to enhance safety and reduce construction time by 30%.
- A 40-ton tower crane imported from Spain was employed for operations at great heights.
- The project utilized site-specific investigations by IIT Roorkee and IIT Delhi due to the region’s complex geological and seismic conditions.
- Engineering Challenges:
- The bridge had to be constructed in the difficult Himalayan terrain, with fragile geological features such as faults and thrusts.
- Seismic activity in the region required additional precautions in the design and construction process.
- Safety and Monitoring:
- Equipped with an integrated monitoring system that includes multiple sensors to ensure the structural health of the bridge during operation.
Importance and Impact:
- Connectivity: The bridge will significantly improve connectivity between Katra and Reasi, ensuring faster rail travel and linking the Kashmir Valley with the rest of India.
- Tourism and Economic Growth: Expected to boost tourism and economic development by improving access to the region, attracting visitors, and facilitating smoother transportation of goods and services.
- Sustainability: The bridge's design ensures it remains safe under extreme weather conditions, offering long-term reliability for the Indian Railways network.
Collaboration and International Expertise:
- The design and supervision were handled by ITALFERR (Italy), with proof-checking conducted by COWI (UK).
- The project combines Indian engineering codes with Eurocodes, adhering to international standards for structural integrity.
Section 479 of the BNSS 2023

- 08 Jan 2025
In News:
Centre urges states, UTs to ensure undertrial prisoner relief in jails.
Key Highlights:
- Objective: The MHA has urged states and Union Territories (UTs) to implement provisions of Section 479 of the Bharatiya Nagarik Suraksha Sanhita (BNSS) 2023 to provide relief to undertrial prisoners (UTPs) in jails. This initiative aims to address issues such as long detention and overcrowding in prisons.
Key Provisions of Section 479 of BNSS, 2023
- Purpose: To offer relief to undertrial prisoners by mandating their release on bail or bond under specific conditions.
- Key Provisions:
- Subsection (1):
- Release on Bail: UTPs who have served half the maximum sentence for their offense (except offenses punishable by death or life imprisonment) are eligible for release on bail.
- Release on Bond for First-Time Offenders: First-time offenders, who have served one-third of the maximum sentence, are eligible for release on bond by the court.
- Subsection (3):
- Mandatory Application: It is the responsibility of the prison superintendent to apply to the concerned court for the release of eligible prisoners on bail or bond.
- Subsection (1):
- Superintendent’s Role:
- Prison superintendents are mandated to ensure timely applications for bail or bond are filed for eligible UTPs.
Implementation and Reporting
- MHA’s Advisory:
- On January 1, the MHA issued a letter to the Chief Secretaries, Director Generals, and Inspectors General of prisons in all states and UTs to ensure compliance with the provisions of Section 479 of BNSS.
- States and UTs were instructed to report the status of implementation in a prescribed format starting from January 1, 2025.
- Data to be Reported:
- First-Time UTPs: Number of first-time UTPs who have served one-third of their maximum sentence.
- Court Applications: Number of applications for bail filed by jail superintendents.
- Release on Bail: Number of UTPs released on bond or bail after meeting the eligibility criteria.
- Other UTPs: Number of UTPs who have completed half of their sentence, and the number of applications filed for their release.
- MHA’s Campaign:
- Launched on Constitution Day (November 26), this campaign encouraged states and UTs to identify eligible prisoners and file their bail applications, thus helping to reduce overcrowding in prisons and mitigate long-term detention.
Background and Context
- Why Section 479?
- Section 479 aims to reduce the prolonged detention of undertrials, some of whom may have already served significant portions of their maximum sentences. This will not only alleviate overcrowding in prisons but also expedite justice for prisoners who have spent extended periods in jail awaiting trial.
- Earlier MHA Initiatives:
- Prior to this directive, the MHA had issued an advisory on October 16, 2024, encouraging states and UTs to implement Section 479. A special push was also made during Constitution Day to move applications for the release of eligible prisoners.
- Expected Outcome:
- The measures are expected to significantly ease the challenges of overcrowded jails and provide timely relief to undertrials, especially first-time offenders. By enforcing these provisions, the government seeks to improve the judicial process for UTPs and contribute to a more effective and humane criminal justice system.
Sonobuoys

- 08 Jan 2025
In News:
India and the U.S. have announced cooperation on the co-production of U.S. sonobuoys to enhance Undersea Domain Awareness (UDA) for the Indian Navy. This technology is vital for tracking submarines and strengthening defense capabilities, particularly in the Indian Ocean region amidst growing Chinese naval presence.
This partnership is a key step in deepening defense cooperation under the U.S.-India Initiative on Critical and Emerging Technologies (iCET), launched in May 2022, and will contribute to strengthening both countries’ defense industrial bases.
About Sonobuoys
- What They Are:
- Sonobuoys are expendable sonar devices used for anti-submarine warfare and underwater acoustic research.
- Typically, small (13 cm in diameter and 91 cm in length), they are designed for deployment from aircraft or ships to detect submarines in deep waters.
- Working Principles:
- Deployment: Dropped from aircraft or ships, they activate upon water impact.
- Surface Float: Equipped with inflatable floats and radio transmitters to communicate with tracking platforms on the surface.
- Sensors: Hydrophones descend to selected depths, capturing underwater acoustic signals.
- Data Communication: Transmit acoustic data via Very High Frequency (VHF) or Ultra High Frequency (UHF) radios to operators on aircraft or ships.
- Types of Sonobuoys:
- Active Sonobuoys: Emit sound energy and receive echoes, transmitting the data back to operators.
- Passive Sonobuoys: Only listen for underwater sounds from submarines or ships and relay the information back.
- Special Purpose Sonobuoys: Measure environmental data like water temperature and ambient noise.
- Other Applications:
- Beyond anti-submarine warfare, sonobuoys are used for environmental research, including studying marine life such as whales.
Co-production of Sonobuoys: India-U.S. Collaboration
- Manufacturing Agreement:
- Ultra Maritime (U.S.) and Bharat Dynamics Ltd. (BDL) have entered into discussions to co-produce U.S. sonobuoys, in line with India’s "Make in India" initiative.
- The production will follow U.S. Navy standards, with manufacturing split between the U.S. and India.
- The focus will also be on developing bespoke technologies to optimize sonobuoy performance in the unique acoustic environment of the Indian Ocean.
- Interoperability:
- The sonobuoys co-produced in India will be interoperable between U.S. Navy, Indian Navy, and allied aircraft such as P-8, MH-60R, and MQ-9B Sea Guardian.
- This ensures seamless integration and compatibility with naval assets from the U.S., India, Japan, and Australia, especially given the Quad's strategic naval exercises like Malabar.
- Production Location:
- The sonobuoys will be manufactured at BDL's facilities in Visakhapatnam, with a focus on meeting the Indian Navy’s operational demands.
Strategic and Defense Context
- U.S. and Indian Naval Cooperation:
- India has increasingly acquired military platforms from the U.S., such as the P-8I maritime patrol aircraft, MH-60R helicopters, and MQ-9 drones. These assets are also used by other Quad nations like Australia and Japan, highlighting the importance of interoperability and shared defense capabilities in the region.
- Enhanced Maritime Domain Awareness:
- With China’s growing naval presence in the Indian Ocean, the cooperation on sonobuoys aligns with India’s strategic priority of enhancing maritime domain awareness (MDA) and Undersea Domain Awareness (UDA), which are critical for national security.
- Future Plans:
- India has also signed a $3.5 billion contract for 31 MQ-9B drones, enhancing its surveillance capabilities for maritime and other defense applications. Deliveries of these drones will begin in 2029, further boosting India’s defense readiness in the region.
Homo juluensis
- 08 Jan 2025
In News:
A significant discovery in paleoanthropology has unveiled a new species of ancient humans, Homo juluensis. This species, characterized by its unusually large skulls, lived in eastern Asia between 300,000 to 50,000 years ago. The discovery adds to our understanding of human evolution, particularly during the Middle to Late Pleistocene epoch.
Key Characteristics
- Name Origin: Homo juluensis is named after "julu," meaning "big head," reflecting the species' large cranium.
- Geographical Range: This species inhabited regions of eastern Asia, including parts of China, Korea, Japan, and Southeast Asia.
- Fossil Evidence: Fossils have been discovered in Xujiayao and Xuchang (northern and central China), dating from 220,000 to 100,000 years ago.
- Physical Traits:
- Homo juluensis had large braincases, up to 30% larger than modern humans.
- They had thick skulls and facial features reminiscent of both Neanderthals and Denisovans.
- Their dental and jaw features show strong similarities to Neanderthals.
- Cultural Practices:
- They lived in small groups and were hunter-gatherers, hunting wild horses and potentially processing animal hides.
- Their tool-making and survival strategies indicate a complex level of social organization and resource use.
Relationship with Other Ancient Human Species
- Coexistence with Other Species: Homo juluensis coexisted with Neanderthals and Denisovans, potentially interacting and interbreeding with these species.
- Genetic Exchange: Studies suggest hybridization between Neanderthals, Denisovans, and early Homo sapiens played a significant role in shaping the genetic makeup of modern humans, especially in Asia.
- Evolutionary Significance: The species' relationship with other Pleistocene hominins is complex, involving shared ancestry with Homo sapiens, Neanderthals, and Denisovans. The genetic exchange among these populations likely influenced the course of human evolution in eastern Asia.
Neanderthals and Denisovans
- Neanderthals (Homo neanderthalensis):
- Lived between 400,000 to 40,000 years ago, primarily in Europe and parts of Asia.
- Neanderthals contributed significantly to the modern human gene pool, especially among non-African populations.
- Evidence of Neanderthal DNA is present in living humans, indicating past interbreeding with early human species.
- Denisovans:
- Identified through DNA analysis in 2010, based on fossils found in a Siberian cave.
- Closely related to Neanderthals, Denisovans inhabited diverse environments ranging from Siberian mountains to Southeast Asia’s jungles.
- Like Neanderthals, Denisovans interbred with both Homo sapiens and Neanderthals, influencing the genetic structure of modern populations, especially in Asia.
Implications for Human Evolution
- Complex Evolutionary Web:
- The discovery of Homo juluensis highlights the complex web of interrelated ancient human species during the Pleistocene epoch. These species did not live in isolation but likely interacted, competed, and interbred, shaping the evolutionary history of humans in Asia.
- Broader Understanding of Human Development:
- By expanding our knowledge of species like Homo juluensis, we gain a better understanding of the genetic diversity and cultural complexity in ancient human populations. This also provides insights into the environmental and social conditions that shaped early human survival strategies.
- Impact on Modern Genetics:
- The interbreeding between these ancient species has left a lasting imprint on the genetic makeup of modern humans, especially in regions like Asia, where Denisovan genes are still present in the DNA of some populations.
18th Pravasi Bharatiya Divas (PBD)
- 07 Jan 2025
In News:
The 18th Pravasi Bharatiya Divas (PBD) Convention will be held from January 8-10, 2025, in Bhubaneswar, Odisha.
Key Highlights:
- Theme 2025:
- The theme is "Diaspora’s Contribution to a Viksit Bharat", highlighting the vital role of the Indian diaspora in India's development into a prosperous and developed nation.
- Exhibitions:
- The convention will feature four major themed exhibitions:
- Vishwaroop Ram – The Universal Legacy of Ramayana: Showcasing the Ramayana’s influence through traditional and contemporary art forms.
- Diaspora’s Contribution to Technology and Viksit Bharat: Highlighting the global technological impact of the Indian diaspora.
- Spread and Evolution of the Indian Diaspora: Focused on the migration of Indians from Mandvi (Gujarat) to Muscat (Oman).
- Heritage and Culture of Odisha: A look into Odisha’s rich cultural traditions.
- The convention will feature four major themed exhibitions:
- Key Initiatives:
- Pravasi Bharatiya Express: PM Modi will flag off this special tourist train for the diaspora, covering key religious and tourist sites in India under the Pravasi Teertha Darshan Yojana.
- Pravasi Bharatiya Samman Awards (PBSA): Recognizing significant contributions by members of the Indian diaspora in various fields.
About Pravasi Bharatiya Divas (PBD):
- Origins:
- Celebrated on January 9 each year, marking Mahatma Gandhi's return to India from South Africa in 1915, symbolizing the contributions of migrants.
- First held in 2003, the event became biennial in 2015.
- Objectives:
- Recognizes the contributions of the Indian diaspora to India’s growth.
- Fosters engagement between India and its global diaspora.
- Strengthens India’s relations with host countries and promotes understanding of India’s culture and achievements.
Contributions of the Indian Diaspora to a Viksit Bharat:
- Economic Growth:
- The diaspora plays a pivotal role through remittances, investments, and connecting Indian businesses to global markets.
- Example: The development of a thorium-based fuel by a U.S.-based NRI is a significant step toward clean nuclear energy in India.
- Global Trade Linkages:
- Facilitating partnerships, investments, and knowledge exchange to expand India’s trade base and global market presence.
- Supporting Innovation: Diaspora-driven collaborations in emerging markets boost India’s entry into high-growth sectors, enhancing the country's development prospects.
- Cultural Contributions: Indian diaspora members serve as cultural ambassadors, promoting Indian traditions, art, and heritage globally (e.g., Diwali recognized as a public holiday in several U.S. states).
Challenges Faced by the Indian Diaspora:
- Cultural Integration: Struggles with balancing cultural identity and integrating into host societies can lead to alienation.
- Political and Religious Issues: Increasing politicization and religious biases, especially against Hindus and Sikhs, in countries like the USA and Europe.
- Legal and Citizenship Issues: Complicated visa statuses, restrictive immigration laws, and issues like the H-1B visa challenge the diaspora, despite their significant contributions.
- Remittance Challenges: Economic instability, exchange rate fluctuations, and banking hurdles affect the regular flow of remittances to India, impacting families dependent on them.
Government Initiatives for the Diaspora:
- National Pension Scheme for NRIs
- Overseas Citizenship of India (OCI) Card Scheme
- Pravasi Bhartiya Kendra
- Indian Community Welfare Fund (ICWF)
ISRO's Cowpea Seed Germination Experiment in Space
- 07 Jan 2025
In News:
ISRO successfully germinated cowpea seeds (Vigna unguiculata) in microgravity conditions during the PSLV-C60 POEM-4 mission. This experiment, conducted using the Compact Research Module for Orbital Plant Studies (CROPS), marks a significant advancement in space-based agricultural research.
Details of the Experiment:
- Mission Overview:
- The experiment took place aboard the PSLV-C60 POEM-4 mission, which included 24 sophisticated payloads.
- The CROPS payload, developed by the Vikram Sarabhai Space Centre (VSSC), is an automated system designed to study seed germination and plant survival in microgravity environments.
- Methodology:
- Eight cowpea seeds were placed in a controlled, closed-box system, equipped with temperature regulation and advanced monitoring tools.
- The system tracked plant development using high-definition cameras, sensors for oxygen, carbon dioxide, humidity, temperature, and soil moisture levels.
- Significance:
- The cowpea seeds successfully germinated within four days, with leaf development expected soon.
- This breakthrough in space agriculture is vital for the development of sustainable farming techniques in space, especially for long-term space missions and human settlements on other celestial bodies.
Broader Implications:
- Space Agriculture:
- The successful germination of cowpea seeds sets the foundation for growing crops in space, essential for self-sufficient habitats in space.
- This experiment is a significant step towards sustainable space agriculture, reducing the need for Earth-based resources in extraterrestrial environments.
- Future Missions:
- The experiment's success is pivotal for future missions aimed at Moon or Mars exploration, where space-grown crops will be necessary to support human life.
- ISRO’s achievement reinforces its growing expertise in space research and highlights the potential for international collaboration in space exploration and agricultural science.
About Cowpea Seeds:
- Cowpea (also known as lobia in Hindi) is a robust, nutrient-rich legume, ideal for agricultural research due to its adaptability and resilience in varied environments.
- The successful experiment with cowpea seeds holds promise for future extraterrestrial agriculture, ensuring food security for astronauts on long-duration missions.
NCC Republic Day Camp 2025

- 07 Jan 2025
In News:
Vice-President Jagdeep Dhankhar’s Address at NCC Republic Day Camp 2025.
Key Highlights
- PanchPran as the Foundation of India’s Transformation:
- PanchPran (Five Resolutions) were outlined by Vice-President Jagdeep Dhankhar as the guiding principles for India’s future development.
- These principles are fundamental to India’s national progress, ensuring a balanced approach to development and societal transformation.
The Five Principles of PanchPran:
- Social Harmony:
- Aims to strengthen unity by leveraging India’s diverse cultures and traditions as sources of national strength.
- Promotes inclusiveness and national integration.
- Family Enlightenment:
- Emphasizes the importance of families in nurturing patriotic and moral values.
- Acts as a foundation for creating a cohesive, enlightened society that respects traditions.
- Environmental Consciousness:
- Advocates for sustainable development and conservation of nature.
- Focuses on protecting natural resources for future generations.
- Swadeshi (Self-reliance):
- Encourages promoting indigenous products as part of the Atmanirbhar Bharat initiative.
- Strengthens India’s self-reliance by focusing on domestic production and consumption.
- Civic Duties:
- Instills responsibility among citizens to actively contribute to the nation’s growth.
- Encourages participation in community and national development activities.
National Cadet Corps (NCC)
- The National Cadet Corps (NCC) is the youth wing of the Indian Armed Forces, established in 1948.
- It is open to school and college students on a voluntary basis and is a Tri-Services organization, comprising the Army, Navy, and Air Force.
- Purpose and Training:
- Cadets undergo basic military training in small arms and drills.
- Officers and cadets have no obligation for active military service after completing their courses.
- Historical Background:
- Traces its origins back to the ‘University Corps’ formed under the Indian Defence Act of 1917 to address shortages in Army personnel.
- Structure and Leadership:
- The NCC is headed by a Director General (DG), a senior officer with a 3-star rank.
- Its headquarters are located in New Delhi.
Disposal of Toxic Waste from Union Carbide Factory (Bhopal)

- 07 Jan 2025
In News:
The Madhya Pradesh government has begun disposing of the 337 tonnes of toxic waste from the premises of Union Carbide India Limited (UCIL) in Bhopal, 40 years after the gas tragedy.
Key Highlights:
- Packing and Transportation:
- Waste is packed in airtight containers under the supervision of the Central Pollution Control Board (CPCB) and Madhya Pradesh Pollution Control Board (MPPCB).
- 12 specially designed airtight containers are being used for packing, and each container will be loaded onto trucks for transport.
- The waste movement will be escorted with a green corridor of about 250 kilometers.
- Incineration Process:
- The waste will undergo incineration in Pithampur, with residue stored in a two-layer membrane landfill to prevent contamination.
- A trial incineration of 10 tonnes of the waste was done in 2015 with no harmful effects, and results were submitted to the High Court.
Bhopal Gas Tragedy: A Historical Overview
- About the Tragedy:
- In 1984, a chemical leak at the Union Carbide pesticide plant released methyl isocyanate (MIC), leading to one of the worst industrial disasters in history.
- The leak was caused by a failed maintenance attempt and malfunctioning safety systems.
- Immediate effects included respiratory issues, eye problems, and abdominal pain, while long-term effects included chronic lung conditions, genetic abnormalities, and higher infant mortality rates.
- Legal and Government Response:
- In 1985, the Indian government passed the Bhopal Gas Leak Disaster Act to represent victims in legal claims.
- UCIL initially offered USD 5 million, while the Indian government demanded USD 3.3 billion. The case was settled in 1989 for USD 470 million.
- In 2010, seven Indian nationals were convicted for causing death by negligence, but were released on bail.
Hazardous Waste Management in India
- Definition and Types:
- Hazardous waste refers to waste that poses significant risks due to toxicity, reactivity, or corrosiveness.
- Common sources include chemical production, outdated technologies, and wastewater treatment.
- Regulations and Disposal Methods:
- The Environment Protection Act (1986) and the Basel Convention (1992) govern hazardous waste management in India.
- India generates about 7.66 million tonnes of hazardous waste annually, with the majority being landfillable (44.3%) and recyclable (47.2%).
- Disposal methods include incineration, co-processing in cement plants, and material/energy recovery.
- Challenges in Hazardous Waste Management:
- Inadequate treatment technologies, especially in small and medium industries.
- The need for stricter compliance with waste management laws and more efficient remediation of hazardous sites like Bhopal.
Pig-Butchering Scam
- 07 Jan 2025
In News:
In its annual report, the Union Home Ministry has warned the public against getting trapped in organised 'pig-butchering scams'.
Key Highlights:
- What is it?
- The Pig-Butchering Scam is a sophisticated form of cybercrime in which fraudsters deceive victims into investing in fake online trading platforms. The term "pig-butchering" is derived from the analogy of "fattening up" victims before stealing their money, much like preparing a pig for slaughter.
- How it works:
- Initial Contact: Scammers typically reach out to victims through social media platforms, dating apps, or deceptive ads on websites like Google and Facebook.
- Building Trust: Fraudsters create false friendships, using these connections to lure victims into investing in fake online trading apps. Cryptocurrency investments are often involved due to the ambiguity in the crypto market.
- The Scam: Victims are shown fabricated profits to encourage further investment. However, when they try to withdraw their funds, the money is stolen, and they realize the trading platform was fake.
- Features of the Scam:
- Use of fraudulent online trading platforms
- Fabricated blockchain transactions, making fund recovery nearly impossible
- Reliance on victims’ desire for quick financial gains
- Linked to money laundering and cyber slavery in some cases
- Origin of the Scam:
- The scam first appeared in China in 2016, where it was referred to as “sha zhu pan” (translated as "killing pig game").
- It is a form of Ponzi scheme, wherein organized scammers exploit victims by using fake online identities and offering false investment opportunities.
- How Cybercriminals Lure Victims:
- The scammer (host) contacts potential victims via social media, dating apps, or deceptive online advertisements.
- They build trust with the victim, enticing them into exploring online investments and cryptocurrency trading, often capitalizing on the lack of clarity in the crypto space.
- The victim is then persuaded to invest larger amounts in fake trades, believing they are making real profits.
- How the Scam is Executed:
- The scammer uses fake online trading platforms to create the illusion of profit.
- After building the victim’s confidence, the fraudster encourages larger investments.
- When victims try to withdraw their funds, they realize their money is gone, often with blockchain transactions making it nearly impossible to trace or recover the funds.
- Statistics on Cybercrime in India:
- In March 2024, the National Cybercrime Threat Analytical Unit recorded over 37,500 complaints related to cybercrime.
- The highest number of complaints (42%) were associated with WhatsApp (14,746), followed by Telegram (7,651), Instagram (7,152), Facebook (7,051), and YouTube (1,135).
- Union Home Ministry’s Response:
- The MHA has flagged pig-butchering scams as a global phenomenon that could involve large-scale money laundering and cyber slavery.
- The Ministry is collaborating with Google for intelligence sharing to flag suspicious digital lending apps and other forms of fraud.
- The Indian Cyber Crime Coordination Centre is working on capacity building to combat such scams and improve the response to cybercrimes.
Great Nicobar Island Development Project
- 06 Jan 2025
In News:
An international cruise terminal to facilitate a “global” port-led city, “high-end” tourism infrastructure, and a ship-breaking yard are among the new additions to the ?72,000 crore mega-infrastructure project in Great Nicobar Island proposed by the Union Shipping Ministry.
Overview of the Project:
- The Great Nicobar Island Development Project is a ?72,000-crore initiative to transform the southernmost island of India into a hub for defense, logistics, commerce, eco-tourism, and infrastructure development.
- It is being implemented by the Andaman and Nicobar Islands Integrated Development Corporation Ltd (ANIIDCO) over 16,610 hectares of land.
- The project includes multiple components like an International Container Transshipment Terminal (ICTT), an international airport, greenfield cities, a mass rapid transport system, and a free trade zone.
Key Proposed Developments:
- International Container Transshipment Terminal (ICTT): To make Great Nicobar a key player in global maritime trade.
- Greenfield International Airport: To improve connectivity and serve as a strategic airport.
- Greenfield Cities: New urban settlements to support the infrastructure.
- Coastal Mass Rapid Transport System: An advanced transportation network along the coast.
- Free Trade Zone: To facilitate international trade activities.
- International Cruise Terminal (new addition): To attract global tourists and facilitate cruise tourism.
- Ship Breaking Yard (new addition): To establish a facility for ship building and breaking.
Geographical and Ecological Context:
- Great Nicobar Island is the largest island in the Nicobar group, located at the southern tip of India. It is covered in rainforests and hosts diverse species, including endangered ones like the leatherback turtle and the Nicobar megapode.
- The island's ecosystem is rich in biodiversity, with extensive mangroves, coral reefs, and rainforests.
Significance of the Project:
- Geo-strategic Importance: The island’s location near the Malacca Strait offers a strategic maritime advantage, enhancing India’s global maritime presence.
- National Security: With increasing Chinese influence in the region, the project aims to strengthen India's maritime security.
- Economic Growth: The ICTT and other infrastructure will boost economic activities, making the region a vital trade hub.
- Job Creation: The development will lead to numerous job opportunities for locals, especially in sectors like tourism, ports, and transport.
- Tourism Development: With eco-tourism at its core, the project is expected to generate substantial income through tourism, improving the local economy.
- Social Infrastructure: It will lead to improvements in healthcare, education, and digital services through initiatives like telemedicine and tele-education.
Chhattisgarh’s Link between Forest Ecosystem and Green GDP

- 06 Jan 2025
In News:
In a first, the Chhattisgarh state has introduced an innovative plan that connects the ecosystem services of its forests with the Green Gross Domestic Product (Green GDP).
Key Highlights:
Chhattisgarh's Green GDP Initiative:
- First State in India to link forest ecosystem services with Green GDP.
- Forests cover 44% of Chhattisgarh's land area, playing a vital role in climate change mitigation.
- Key forest products (tendu leaves, lac, honey, medicinal plants) contribute significantly to the rural economy.
Green GDP:
- Definition: An adjustment of traditional GDP that accounts for environmental costs like resource depletion and ecosystem degradation.
- Formula:
- Green GDP = Net Domestic Product (NDP) − (Cost of Resource Depletion + Ecosystem Degradation)
- NDP = GDP − Depreciation of Produced Assets.
Importance of Green GDP:
- Traditional GDP overlooks the environmental cost, treating activities like deforestation as economic gains.
- Green GDP adjusts for sustainability, ensuring long-term economic growth aligns with environmental preservation.
Global Context & Initiatives:
- SEEA (System of Environmental-Economic Accounting): Developed by the UN to track economic-environment relationships.
- WAVES: World Bank initiative integrating natural capital into national economic accounts.
- Bhutan’s GNH: Emphasizes ecological sustainability in development.
Benefits of Green GDP for Chhattisgarh:
- Promotes sustainable development by integrating economic and environmental goals.
- Climate Change Mitigation: Forests help absorb CO2, playing a key role in carbon sequestration.
- Biodiversity Conservation: Supports sustainable use of resources, preserving ecosystems.
- Cultural Integration: Acknowledges forests' cultural and spiritual importance to local tribal communities (e.g., sacred groves).
Key Features of the Initiative:
- Valuing Ecosystem Services: Includes clean air (CO? absorption), water conservation, and biodiversity.
- Eco-tourism Promotion: Developing jungle safaris and national parks, boosting local employment.
- Scientific Assessments: Employing experts to quantify forest contributions to the economy.
Challenges of Green GDP Framework:
- Valuation Complexity: Difficult to assign monetary value to non-market environmental benefits like biodiversity.
- Data Gaps: Lack of comprehensive data on environmental degradation and resource usage.
- Implementation: Requires significant changes in accounting systems and policymaking.
- Forest Definition: Plantations like oil palm may be counted as forests, misleading environmental assessments.
- Political Resistance: States may manipulate data to secure funding, prioritizing plantations over natural forests.
- Local Integration: Difficulties in involving local bodies like Panchayats due to literacy and awareness gaps.
Future of Green GDP:
- Sustainable Resource Use: Encourages responsible consumption and production, aligning with SDG 12.
- Climate Action: Contributes to the reduction of fossil fuel reliance and promotes renewable energy, aligning with SDG 13.
- Green Investments: Stimulates green technologies and industries, fostering sustainable economic growth (SDG 8).
LEADS 2024 Report

- 06 Jan 2025
In News:
- Launch of the Logistics Ease Across Different States (LEADS) 2024 report and the Logistics Excellence, Advancement, and Performance Shield (LEAPS) 2024 awards in New Delhi.
Key Highlights:
- Objective of LEADS 2024 Report:
- Evaluate logistics performance across Indian states and union territories.
- Provide actionable insights for logistics reforms to foster competitive federalism.
- Assess logistics infrastructure, services, regulatory environment, and sustainability efforts.
- Performance Evaluation:
Region Achievers Fast Movers Aspirers
Coastal States Gujarat, Karnataka, Maharashtra, Odisha, Tamil Nadu Andhra Pradesh, Goa Kerala, West Bengal
Landlocked States Haryana, Telangana, Uttar Pradesh, Uttarakhand Bihar, Himachal Pradesh, Madhya Pradesh, Punjab, Rajasthan Chhattisgarh, Jharkhand
North-Eastern States Assam, Arunachal Pradesh Meghalaya, Mizoram, Nagaland, Sikkim, Tripura Manipur
Union Territories Chandigarh, Delhi Dadra and Nagar Haveli & Daman and Diu, Jammu and Kashmir, Andaman and Nicobar Islands, Ladakh
Lakshadweep, Puducherry
- Key Remarks:
- Action Plans for Better Logistics: States should develop regional and city-level logistics plans, including for last-mile connectivity, to attract investments.
- Green Logistics: Advocate for sustainable logistics practices to ensure environmentally responsible growth.
- Public-Private Partnerships (PPP): Encourage PPPs to promote multi-modal hubs and streamline logistics infrastructure.
- Technological Integration: Push for the adoption of Artificial Intelligence, Machine Learning, and Data Analytics to enhance efficiency in logistics operations.
- Skill Development & Gender Inclusivity: Focus on workforce inclusivity and skill development to boost sectoral growth. Promote gender diversity in logistics.
- LEAD Framework: Urge logistics sectors to embrace the LEAD framework (Longevity, Efficiency, Accessibility, Digitalisation) for transformation.
- LEAD Framework and Recommendations:
- Longevity, Efficiency, and Effectiveness: Improve long-term logistics strategies.
- Accessibility and Accountability: Ensure better reach and transparent logistics practices.
- Digitalisation: Enhance digital transformation across logistics processes.
- About LEADS:
- Full Form: Logistics Ease Across Different States.
- Launched: 2018 by the Department for Promotion of Industry and Internal Trade (DPIIT), Ministry of Commerce and Industry.
- Purpose: To assess and improve logistics infrastructure and services across Indian states and UTs.
- Methodology: Based on over 7,300 responses from a pan-India survey and inputs from over 750 stakeholder consultations.
- LEAPS 2024 Awards: Recognized excellence in the logistics sector across categories such as air, rail, road, maritime freight service providers, startups, MSMEs, and educational institutions.
- PM GatiShakti Course: Launched a 15-hour online course on “PM GatiShakti Concept for Efficient Infrastructure Planning and National Development”, hosted on iGOT Karmayogi platform and UGC SWAYAM portal.
- Logistics Cost Framework Report: Unveiled a report on the logistics cost framework, aiming to accurately estimate logistics costs in India through a hybrid methodology, incorporating both EXIM and domestic cargo data.
- Significance of LEADS:
- Provides critical insights into logistics performance, helping States and UTs to improve infrastructure, services, and regulatory practices.
- Plays a key role in India's vision of becoming a $32 trillion economy by 2047 by improving logistics efficiency, sustainability, and global competitiveness.
Human Metapneumovirus (HMPV)
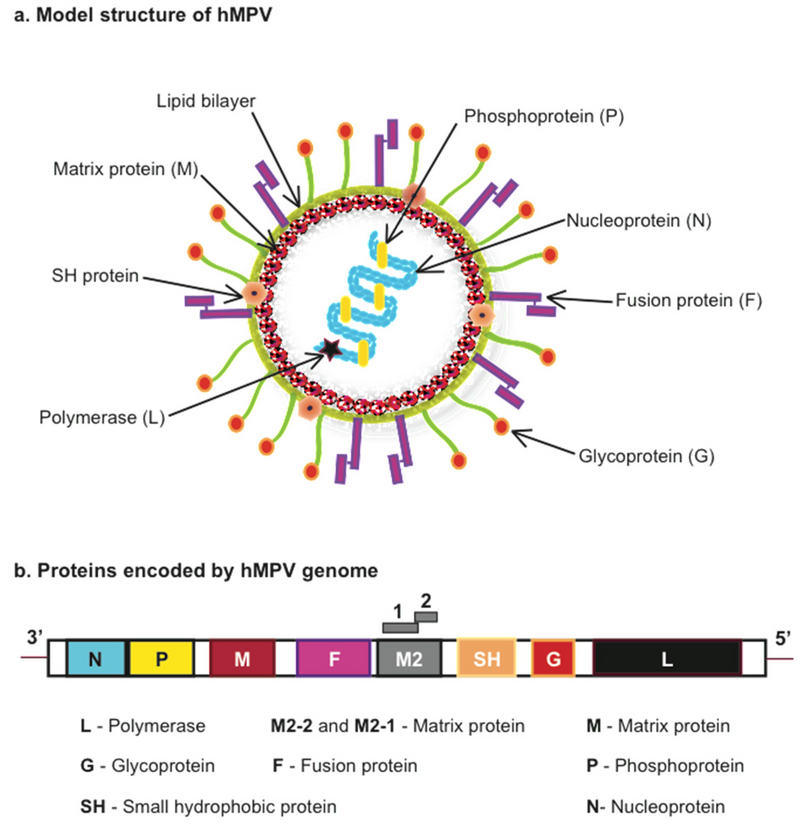
- 06 Jan 2025
In News:
Five years after the COVID pandemic, China is experiencing a surge in HMPV cases, particularly in children under 14 years of age
Key Highlights:
- What is HMPV?
- A respiratory virus from the Pneumoviridae family, discovered in 2001.
- Causes both upper and lower respiratory tract infections, similar to the common cold or flu.
- Origin and Discovery:
- Identified in the Netherlands in 2001 through genomic sequencing of respiratory samples.
- Risk Groups:
- Children under 5 years, especially infants.
- Elderly individuals (65+).
- Immunocompromised persons and those with chronic respiratory conditions (e.g., asthma).
- Symptoms:
- Common: Cough, runny nose, fever, sore throat.
- Severe: Wheezing, shortness of breath, potentially leading to bronchitis or pneumonia.
- Incubation Period: 3-6 days.
- Transmission:
- Spread via droplets from coughing or sneezing.
- Close contact (e.g., handshakes, hugs).
- Contaminated surfaces, touching face after contact.
- Treatment:
- No specific antiviral treatment or vaccine available.
- Symptom management: hydration, rest, OTC medications for fever and congestion.
- Severe cases may require hospitalization (oxygen therapy, IV fluids).
- Diagnosis:
- NAATs (Nucleic Acid Amplification Tests): Detect viral genetic material.
- Antigen-based immunoassays: For severe cases or outbreaks.
- Complications:
- Can lead to bronchiolitis, bronchitis, pneumonia, asthma, or COPD flare-ups.
- Risk of ear infections (otitis media) in some cases.
- Prevention:
- Hygiene: Regular handwashing, covering coughs/sneezes, maintaining personal hygiene.
- Physical Distancing: Avoid close contact, wear masks in crowded settings.
- Caution for Vulnerable Groups: Extra care for individuals with chronic respiratory conditions.
Global Situation:
- China: Experiencing a rise in HMPV cases, particularly among children under 14 years.
- India: No reported cases yet, but monitoring the situation closely.
Key Facts:
- HMPV is a winter virus commonly seen in colder months (winter and early spring).
- Estimated 10%-12% of respiratory illnesses in children are caused by HMPV.
- The virus is part of the Pneumoviridae family, alongside respiratory syncytial virus (RSV), measles, and mumps.
No specific antiviral treatment or vaccine for HMPV; antibiotics are ineffective.
National Sports Awards 2024
- 06 Jan 2025
In News:
The National Sports Awards 2024 were recently announced by the Ministry of Youth Affairs & Sports to celebrate excellence in Indian sports.
Key Highlights:
Major Dhyan Chand Khel Ratna Award
- This is India's highest sporting honor, renamed in 2021 after hockey legend Major Dhyan Chand.
- It’s awarded for exceptional performance in sports over a four-year period.
- 2024 Winners:
- Gukesh D (Chess)
- Harmanpreet Singh (Hockey)
- Praveen Kumar (Para-Athletics)
- Manu Bhaker (Shooting)
- The award includes a cash prize of Rs 25 lakh.
Arjuna Award
- Recognizes outstanding performance in sports over the previous four years and attributes like leadership, discipline, and sportsmanship.
- 2024 Winners: Various athletes across multiple disciplines received this honor.
Arjuna Award (Lifetime)
- Given to retired athletes who have not only excelled during their careers but also contributed to the promotion of sports post-retirement.
- 2024 Winners:
- Shri Sucha Singh (Athletics)
- Shri Murlikant Rajaram Petkar (Para-Swimming)
Dronacharya Award
- Given to coaches who have made a consistent and significant contribution by guiding sportspersons to excel at international events.
- The award includes a bronze statue of Dronacharya, a certificate, and a cash prize.
Maulana Abul Kalam Azad (MAKA) Trophy
- Awarded to the top-performing university in the Khelo India University Games.
- 2024 Winner: Chandigarh University.
Rashtriya Khel Protsahan Puruskar
- Recognizes individuals or organizations for their contribution to the promotion and development of sports.
- 2024 Winner: Physical Education Foundation of India.
These awards were selected by a committee led by Justice (Retd.) V. Ramasubramanian and include eminent sportspersons, journalists, and sports administrators. The winners will receive their awards from the President of India, marking a prestigious moment in Indian sports.
Saint Narahari Tirtha
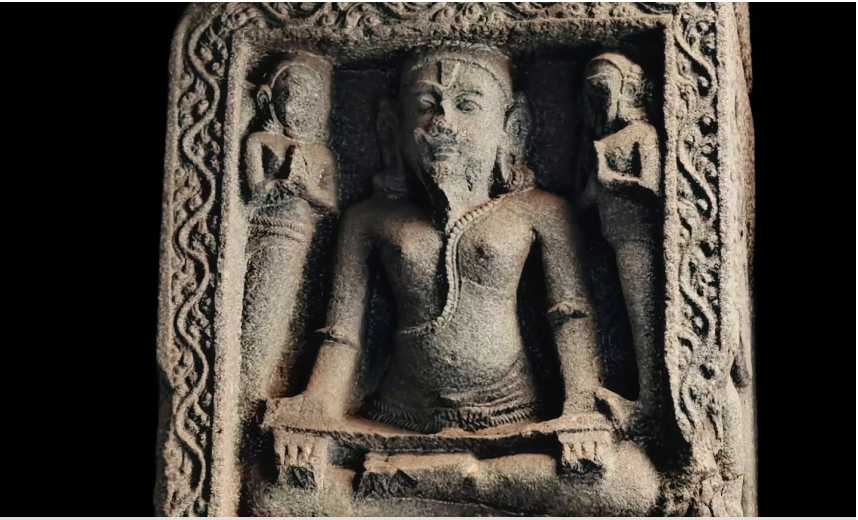

- 05 Jan 2025
In News:
In a remarkable discovery, a member of the Team of Research on Culture and Heritage (TORCH) has hit upon a three-foot idol of the 13th Century saint, Narahari T?rtha recently.
Key Highlights:
Birth and Early Life:
- Born circa 1243 CE in Chikakolu (modern-day Srikakulam, Andhra Pradesh).
- Hailing from an aristocratic family in the Gajapati Empire of Odisha.
Philosophical Influence:
- A prominent disciple of Madhvacharya, the founder of Dvaita philosophy (dualism).
- Narahari Tirtha played a key role in propagating Madhva's Vaishnavism in Eastern India, particularly in the Kalinga region (modern-day Odisha and Andhra Pradesh).
Role in Eastern Ganga Dynasty:
- Served as a minister in the Eastern Ganga Dynasty for over 30 years.
- Guided kings to align their governance with Sanatana Dharma and reformed temple administration.
- His contributions are documented in inscriptions at the Simhachalam and Srikurmam temples.
Religious and Cultural Contributions:
- Played a key role in spreading Vaishnavism and Dvaita philosophy.
- First to compose Devaranamas in Kannada, marking a significant cultural contribution.
- Contributed to the development of Yakshagana Bayalata (a dance-drama) and the classical dance form that evolved into Kuchipudi.
Writings and Intellectual Legacy:
- Authored 15 works, with two surviving texts: Gita Bhasya and Bhavaprakasika.
- His teachings and writings significantly impacted the Madhva tradition and regional literature.
Discovery of the Idol:
- A three-foot idol of Narahari Tirtha was discovered at Simhachalam Temple in Visakhapatnam, Andhra Pradesh.
- The idol depicts Narahari Tirtha holding a script on palm leaves, flanked by devotees.
Contributions to Temple and Education:
- Transformed the Simhachalam Temple into a renowned center for Vaishnavism.
- Played a crucial role in safeguarding sacred idols like Moolarama and Moola Sita for Madhvacharya.
Cultural and Artistic Legacy:
- Promoted regional art forms, helping establish Kuchipudi as a classical dance style in Andhra Pradesh.
- Advocated for Yakshagana Bayalata, a form of dance-drama popular in coastal Karnataka.
Honors and Recognition:
- Bestowed titles such as "Loka Surak?a?a Ati Nipu?a?" and "Yo Avati Kalinga Bhu Sambhav?n" for his contributions to philosophy and governance.
Final Resting Place:
- Narahari Tirtha was consecrated near Chakratirtha at Hampi on the banks of the Tungabhadra River after his death.
- His legacy continues to influence the temple traditions, especially in Puri Jagannath, strengthening the Madhva influence in Odisha.
Year of Artificial Intelligence

- 05 Jan 2025
In News:
The All India Council for Technical Education (AICTE) has declared 2025 as the "Year of Artificial Intelligence" (AI), aiming to empower over 14,000 AICTE-approved colleges and benefit 40 million students. This initiative aligns with the Prime Minister’s vision to make India a global leader in AI and technology.
Key Objectives and Features of the AICTE AI Initiative:
- Positioning India as a Global AI Leader:
- Empowering students with AI skills to drive innovation and lead in the emerging AI-driven economy.
- Preparing India’s workforce for the technological advancements of the future.
- Core Elements of the AICTE AI Initiative:
- AI Affirmation Pledge: Institutions will adopt and display an AI Affirmation Pledge, focusing on innovation, ethics, and education in AI.
- Comprehensive AI Integration:
- Introducing interdisciplinary AI courses and research programs.
- Setting up AI labs in collaboration with industries to meet global standards.
- Promoting ethical AI practices with societal benefits in focus.
- AI Awareness Campaign:
- “AI for All: The Future Begins Here” campaign includes workshops, hackathons, and guest lectures.
- Formation of student-driven AI chapters to foster innovation and research.
- Faculty Development & Industry Partnerships:
- Workshops and certification programs for faculty to improve AI teaching.
- Collaboration with companies like Adobe, CISCO, and IBM for student exposure through internships and mentorships.
- Recognition of Excellence: Institutions excelling in AI integration will be recognized, serving as role models for others.
- Action Plan for Institutions:
- All institutions are required to submit AI Implementation Plans by December 31, 2024. These plans will be evaluated by the AICTE Approval Bureau and exemplary submissions will be highlighted as benchmarks.
- Shaping India as a Global AI Leader:
- AICTE aims to revolutionize India’s education system and enhance its position in the global AI race, focusing on building a self-reliant workforce.
Additional Context on AICTE and its Role:
- AICTE Overview:
- A statutory body and national-level council under the Ministry of Education.
- Established in November 1945 as a national-level apex advisory body for technical education in India.
Government Initiatives to Support AI and Consumer Protection:
- AI and Consumer Protection:
- AI-driven tools launched to enhance consumer protection, such as the National Consumer Helpline, e-MAAP Portal, and Jago Grahak Jago mobile application.
- New guidelines for regulating deceptive marketing in e-commerce to ensure consumer confidence in the digital market.
- Tools like the e-Daakhil Portal for online complaint filing.
Impact:
- This initiative will have a far-reaching impact, involving more than 14,000 institutions and 40 million students nationwide, preparing them for leadership roles in AI and technology, and helping India secure its future in the global AI-driven economy.
Translocation of Tigers from Madhya Pradesh
- 05 Jan 2025
In News:
Madhya Pradesh to translocate 15 Tigers to Rajasthan, Odisha and Chhattisgarh.
Key Highlights of the Translocation:
- Scale of Translocation: Largest relocation of big cats from a single state in India.
- Approval: NTCA has approved the translocation of 15 tigers from Madhya Pradesh to Rajasthan, Chhattisgarh, and Odisha.
- Source Reserves:
- Bandhavgarh, Panna, Kanha, and Pench Tiger Reserves in Madhya Pradesh.
- Distribution Plan:
- Rajasthan: 4 tigresses.
- Chhattisgarh: 2 male tigers and 6 tigresses.
- Odisha: 1 male tiger and 2 tigresses.
- Funding: States receiving tigers will bear all expenses related to translocation.
Objectives of the Translocation:
- Enhance Tiger Conservation: Reintroduce and bolster tiger populations in recipient states.
- Population Management: Relocate tigers to areas with suitable habitats to alleviate territorial disputes in overpopulated reserves.
- Genetic Diversity: Introduce new individuals to isolated tiger groups to prevent inbreeding and support long-term species survival.
About Kanha, Bandhavgarh, and Pench Tiger Reserves:
- Kanha Tiger Reserve:
- Location: Maikal range of the Satpura Mountains.
- Significance: Largest national park in Madhya Pradesh.
- Distinct Feature: First tiger reserve in India with an official mascot, ‘Bhoorsingh the Barasingha’.
- Flora and Fauna: Rich biodiversity with Royal Bengal Tigers, leopards, and the IUCN Vulnerable species, Barasingha.
- Bandhavgarh Tiger Reserve:
- Location: Between Vindhyan and Satpura ranges in Umaria district, Madhya Pradesh.
- Significance: Known for one of the highest densities of Royal Bengal Tigers in India.
- Historical Link: The ancient Bandhavgarh Fort, linked to the legend of Lord Rama and Lakshmana.
- Pench Tiger Reserve:
- Location: Spans Seoni and Chhindwara districts in Madhya Pradesh, extends into Maharashtra.
- Significance: Inspiration for Rudyard Kipling’s The Jungle Book.
- Flora and Fauna: Includes teak, saag, mahua forests; tigers, leopards, wild dogs, and gaur are key species.
Tiger Translocation Project Overview:
- First Project:
- Initiated in 2018, two tigers relocated from Kanha and Bandhavgarh to Satkosia Tiger Reserve in Odisha.
- Main Objectives:
- Reintroduce Tigers: In areas where they have been extirpated or extinct.
- Alleviate Territorial Disputes: Overpopulated reserves need additional tigers to reduce human-animal conflict.
Benefits of Translocation:
- Ecological Balance: Restores predator-prey dynamics in underpopulated reserves.
- Human-Animal Conflict Mitigation: Reduces conflict in overcrowded reserves.
- Rewilding Landscapes: Revives areas where tigers were locally extinct.
Concerns Associated with Translocation:
- Local Community Protests: Villagers fear tigers will pose a threat to their safety.
- Territorial Disputes: New tigers may face conflict with resident tigers.
- Poor Forest Management: Inadequate prey augmentation and habitat management may hinder success.
Madhya Pradesh’s Role in Tiger Conservation:
- Largest Tiger Population: Madhya Pradesh hosts the largest number of tigers in India, with 785 tigers as per NTCA’s 2022 report.
- Tiger Reserves: The state is home to nine tiger reserves, including the newly notified Madhav Tiger Reserve in Shivpuri.
- Translocation Strategy: Madhya Pradesh’s involvement helps reduce local tiger population pressure and contributes to broader conservation efforts across India.
Inter-State Tiger Translocation Goals:
- Reinforcement and Reintroduction: Introduce tigers into areas historically part of their range but from which they have been extirpated or extinct.
- Genetic Diversity: Introduce new tigers to isolated populations to maintain long-term population health.
Thanthai Periyar Memorial

- 05 Jan 2025
In News:
In a significant event for both Kerala and Tamil Nadu, Kerala Chief Minister Pinarayi Vijayan and Tamil Nadu Chief Minister M.K. Stalin are set to reunite at Vaikom, to inaugurate the extensively renovated memorial dedicated to Tamil reformist E.V. Ramasami Naicker, popularly known as Thanthai Periyar. This marks a historic occasion over a year and a half after they jointly inaugurated the centenary celebrations of the Vaikom Satyagraha.
Key Highlights:
Memorial History and Significance:
- Established: January 1994
- Location: 70-cent property near Valiyakavala Junction, Vaikom
- Ownership: Tamil Nadu Government
- Periyar Statue: Installed in 1985 on 84 cents of land provided by Kerala government; remains the centerpiece.
- Historical Neglect: The memorial suffered from years of neglect before the renovation.
Role of Periyar in Vaikom Satyagraha:
- Vaikom Satyagraha (1924–1925):
- First organized movement for the rights of the ‘untouchable’ communities in India.
- Led by prominent leaders like T.K. Madhavan, K.P. Kesava Menon, and K. Kelappan.
- Periyar, alongside his wife Nagamma, joined the movement, seeking access to public roads leading to the Sri Mahadeva Temple in Vaikom.
- Periyar’s Contribution:
- Was imprisoned twice for his participation in the movement.
- Honored with the title Vaikom Veeran for his leadership.
- Impact: The movement played a crucial role in securing social equality for all sections of society.
Periyar’s Legacy:
- Self-Respect Movement: Founded by Periyar to promote social equality and eliminate caste-based discrimination.
- Dravidar Kazhagam: A political and social organization founded by Periyar, advocating for the rights of the Dravidian people.
- Father of the Dravidian Movement: Periyar’s philosophy and activism laid the foundation for the Dravidian political ideology and social reforms in Tamil Nadu.
Rabbit Fever
- 05 Jan 2025
In News:
Tularemia, commonly known as "rabbit fever," is a rare but highly infectious bacterial disease caused by Francisella tularensis. Though uncommon, it can lead to severe health complications if left untreated. Over recent years, cases of tularemia have been on the rise in the United States, drawing attention to the broader environmental and epidemiological factors influencing the disease’s spread.
Rising Incidence of Tularemia
Between 2011 and 2022, the United States saw a 56% increase in the annual average incidence of tularemia infections compared to the previous decade, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Vulnerable populations include children aged 5 to 9, older men, and individuals of American Indian or Alaska Native descent. The increasing number of reported cases highlights the growing concern over this disease, despite its rarity.
Transmission Pathways
Tularemia is primarily transmitted through:
- Direct Contact with Infected Animals: Common carriers include rabbits, hares, and rodents, particularly those infected with Francisella tularensis. This presents a risk for individuals working closely with wildlife, such as hunters.
- Insect Bites: Ticks, especially in regions with high tick populations, and deer flies can spread the disease.
- Contaminated Food or Water: Consuming undercooked meat from infected animals or untreated water can lead to infection.
- Inhalation of Contaminated Dust or Droplets: This is a potential risk in agricultural or laboratory settings and can result in pulmonary tularemia.
Contributing Factors to the Rise in Cases
Several factors contribute to the increasing prevalence of tularemia:
- Climate Change: Rising temperatures are increasing tick activity and extending breeding seasons, allowing the bacteria to spread more easily.
- Habitat Encroachment: Deforestation and increased human interaction with wildlife are amplifying exposure to infected animals.
- Improved Diagnostic Tools: Advances in surveillance and testing methods have made it easier to detect tularemia, leading to more reported cases.
Early Symptoms and Diagnosis
Tularemia symptoms can vary depending on the route of infection. Symptoms typically appear 3 to 5 days post-exposure and may include:
- Sudden high fever (up to 104°F or 40°C)
- Chills, fatigue, and body aches
- Swollen lymph nodes, especially near the site of infection (e.g., under the arms or in the groin)
There are four primary forms of tularemia:
- Ulceroglandular: Characterized by skin ulcers and swollen lymph nodes.
- Glandular: Swollen lymph nodes without ulcers.
- Pneumonic: Lung infection, often resulting from inhalation.
- Typhoidal: A more systemic form, with symptoms like fever and abdominal pain.
Differentiating tularemia from other conditions such as flu, pneumonia, or lymphadenitis is key for diagnosis. A skin ulcer or swollen lymph nodes in individuals with recent exposure to wildlife or ticks is a critical diagnostic clue.
Treatment and Prognosis
Tularemia is treatable with antibiotics. First-line treatment includes streptomycin or gentamicin, while doxycycline or ciprofloxacin may be used for milder cases. Treatment typically lasts 10 to 21 days, and when initiated promptly, the disease has a high recovery rate and minimal complications. However, untreated cases can lead to chronic infections, lung abscesses, pneumonia, or severe sepsis, with mortality rates of 1-2% under treatment. Untreated severe cases can result in mortality rates between 30% and 60%.
Tularemia in India: A Potential Concern?
Tularemia is extremely rare in India, mainly due to the country's differing ecological conditions and limited interaction with the primary reservoirs of Francisella tularensis. However, awareness remains crucial, especially for individuals traveling to endemic regions or working in wildlife settings. Despite its rarity in India, the rising global incidence and changing environmental factors warrant continued vigilance.
Torrijos-Carter Treaties

- 04 Jan 2025
In News:
Recently, Donald Trump threatened to take back the Panama Canal, calling the transfer treaty “foolish”.
Why Trump Called the Panama Canal Transfer 'Foolish'?
- Transit Fees:
- Trump expressed frustration over high transit fees imposed by the Panama Canal Authority (ACP) on U.S. vessels.
- In 2023, due to droughts affecting Lakes Gatun and Alhajuela (which are crucial for canal operations), the ACP reduced crossing slots by 36%, leading to an increase in transit fees for ships.
- Chinese Presence:
- Trump is also concerned about the growing Chinese influence in the Panama Canal region.
- In 2017, Panama became the first Latin American country to sign a Belt and Road Initiative (BRI) agreement with China, increasing Chinese investments.
- Hutchison Ports PPC, a subsidiary of a Hong Kong-based company, operates ports near the canal, raising concerns over China's influence on logistical operations and potential surveillance capabilities.
The Torrijos-Carter Treaties and Canal Transfer:
- Panama Canal Treaty (1977):
- The treaty transferred control of the Panama Canal from the U.S. to Panama by December 31, 1999.
- The U.S. would no longer control the canal, and Panama would assume full responsibility for its operation and defense.
- Permanent Neutrality Treaty (1977):
- Declared the canal to be neutral and open to vessels of all nations.
- U.S. Right to Defense: The U.S. retained the right to defend the neutrality of the canal and had priority passage in case of military emergencies.
Panama’s Response to Trump’s Criticisms:
- Defense of Transit Rates:
- President José Raúl Mulino rejected Trump’s claims, defending the transit fees as being in line with international standards and based on a transparent procedure.
- Sovereignty:
- Mulino emphasized Panama’s sovereignty over the canal, asserting that Panama’s control over the canal was non-negotiable. He categorically denied the presence of Chinese soldiers in the canal, stating that there would never be any.
China’s Response:
- China's Position:
- China's Foreign Ministry responded by emphasizing that the Panama Canal is a neutral passageway, a vital infrastructure for Panama and the global trade system.
- China affirmed its respect for Panama's sovereignty and denied any military presence in the canal area.
Implications and Future:
- Diplomatic Tensions:
- The issue of transit fees and foreign influence, particularly China's presence in the region, is likely to remain a point of diplomatic negotiation.
- Panama is expected to assert its sovereignty and seek international support to prevent any external interference in the canal’s operations.
- U.S. Influence:
- The U.S. might attempt to renegotiate terms related to the Panama Canal's operations, especially concerning transit fees and military rights, although Panama remains firm on maintaining control.
Torrijos-Carter Treaties:
- Significance:
- Panama Canal Treaty and Permanent Neutrality Treaty marked a major shift in U.S.-Latin America relations, ending U.S. control and restoring Panamanian sovereignty.
- The treaties also ensured the neutrality of the canal while maintaining U.S. military access in emergencies.
- Impact:
- The treaties were a symbol of Panama’s regained sovereignty and played a key role in stabilizing relations between the U.S. and Panama, as well as resolving tensions over control of the canal.
Centralized Pension Payments System (CPPS)

- 04 Jan 2025
In News:
- The CPPS aims to enhance pension accessibility and simplify the disbursement process for over 7.85 million pensioners in India.
- Key Benefit: Pensioners can now receive their pension from any bank or branch across India, eliminating the need for physical verifications and providing seamless nationwide pension disbursement.
Key Highlights:
- Key Features:
- No need for physical verification: Pensioners do not have to visit the bank for verification at the time of pension commencement.
- Seamless pension disbursement: Upon release, the pension amount is credited immediately.
- Nationwide access: Pensioners can withdraw their pension from any bank or branch, without needing to transfer Pension Payment Orders (PPO) when relocating or changing banks.
- Significance:
- Eliminates the decentralised pension system, where each regional office maintained separate agreements with a few banks.
- Ensures pension portability, especially for pensioners who move or change banks.
Employees’ Provident Fund Organisation (EPFO):
- Overview:
- EPFO is a statutory body under the Employees' Provident Funds and Miscellaneous Act, 1952, and works under the Ministry of Labour and Employment.
- Structure:
- Administered by a tripartite board called the Central Board of Trustees, consisting of representatives from:
- Government (Central & State)
- Employers
- Employees
- The Central Board of Trustees is chaired by the Union Minister of Labour and Employment.
- Administered by a tripartite board called the Central Board of Trustees, consisting of representatives from:
- Key Schemes Operated by EPFO:
- Employees’ Provident Funds Scheme, 1952 (EPF): A savings scheme for workers.
- Employees’ Pension Scheme, 1995 (EPS): A pension scheme for employees after retirement.
- Employees’ Deposit Linked Insurance Scheme, 1976 (EDLI): Provides life insurance coverage to workers.
- Global Coverage: EPFO is also the nodal agency for implementing Bilateral Social Security Agreements with other countries, offering reciprocal social security benefits to international workers from countries with such agreements.
- Impact: The EPFO schemes cover Indian workers and international workers from countries with which EPFO has signed bilateral agreements.
Key Facts:
- CPPS improves the convenience and accessibility of pension services for millions of pensioners across India by simplifying the pension disbursement process and providing nationwide access without the need for physical verifications.
- EPFO, a statutory body under the Ministry of Labour and Employment, plays a crucial role in managing provident funds, pensions, and insurance schemes for both domestic and international workers, fostering social security across India.
Open Data Kit (ODK) Toolkit

- 04 Jan 2025
In News:
- The Comptroller and Auditor General (CAG) of India has deployed the Open Data Kit (ODK) platform to enhance transparency in government spending and improve accountability in the delivery of government schemes.
- The toolkit is being used for designing, collecting, and managing data relevant to audits.
Key Highlights:
Objective:
- Enhance transparency in public spending.
- Improve accountability in government schemes and projects.
- Collect real-time beneficiary feedback to aid audit planning and identify areas needing additional review.
Key Features:
- End-to-end encryption: Ensures secure data management.
- Integration with CAG’s Operating System (OIOS): Facilitates seamless analysis and management of data.
- Multi-language support: Allows for surveys in multiple languages, making it more accessible to diverse beneficiaries.
- User-friendly interface: Simplifies the design and management of data collection processes for auditors.
Usage and Applications:
- Beneficiary surveys are a key tool for gathering data, helping CAG identify problem areas in government schemes.
- The ODK toolkit was recently deployed in audits of AIIMS institutions in Mangalagiri (Guntur) and Bibinagar (Hyderabad) to assess patient satisfaction and gather evidence for performance reviews.
Working Process:
- Surveys are designed on the ODK platform and deployed to beneficiaries.
- Data is collected in real-time and analyzed using the OIOS system to generate actionable insights for audits.
- Beneficiary feedback is used to evaluate scheme delivery and improve efficiency.
Significance:
- Facilitates data-driven decision-making in audits, ensuring that audits are more transparent and evidence-based.
- Improves the citizen-centric evaluation of government schemes by gathering direct feedback from beneficiaries.
- Enhances the performance review of key institutions like AIIMS, contributing to better service delivery.
- The introduction of the ODK toolkit is part of the CAG’s efforts to use digital tools for better governance and accountability in the public sector. This also aligns with the growing trend of using technology for governance and auditing.
Project VISTAAR

- 04 Jan 2025
In News:
IIT Madras has partnered with the Ministry of Agriculture and Farmers’ Welfare on Project VISTAAR (Virtually Integrated System to Access Agricultural Resources). MoU signed between the Ministry and IIT Madras to integrate information about agricultural start-ups into the VISTAAR platform.
Key Highlights:
Project Objectives:
- Digitalisation of Agricultural Extension: To enhance the efficiency and effectiveness of the agricultural extension system through digital platforms.
- Access to Start-Up Innovations: Provide farmers easy access to over 12,000 start-ups in agriculture and allied sectors, connecting them to technological solutions and innovations.
- Support for Sustainable Agriculture: Focus on making farming more sustainable and climate-resilient by promoting adoption of innovative technologies.
Key Features of VISTAAR:
- Integration of start-up data via IIT Madras' startup information platform and its incubatee, YNOS Venture Engine.
- Advisory services covering:
- Crop production
- Marketing
- Value addition
- Supply chain management
- Information on government schemes for agriculture, allied sectors, and rural development.
- Real-time, contextual, and accurate information to enhance decision-making and improve farming practices.
Significance of the Project:
- The platform will expand the outreach of agricultural extension services, providing support to farmers across India.
- It will ensure farmers access high-quality advisory services that are critical for improving productivity and income.
- Integration of start-up-driven innovations will aid in the adoption of climate-resilient farming practices.
- Timely and accurate information will empower farmers to make informed decisions and improve the efficiency of agricultural processes.
Impact on Farmers:
- Digitalisation will provide farmers with easier access to expert advice and resources, enhancing productivity.
- Improved access to government schemes ensures farmers can avail themselves of financial and technical support for development.
- The project aligns with national objectives of enhancing agriculture’s contribution to India’s economy and ensuring food security.
Air India In-Flight Wi-Fi Connectivity
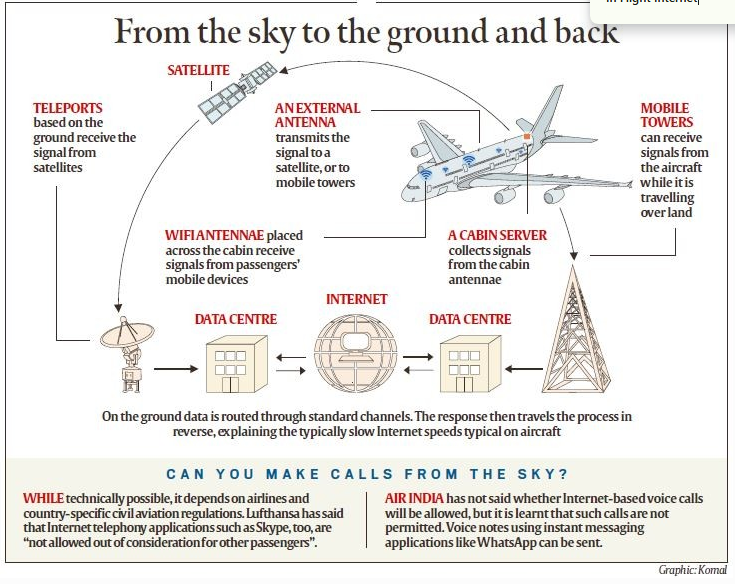
- 04 Jan 2025
In News:
- Tata Group’s Air India launched free Wi-Fi connectivity on select domestic and international flights.
- First Indian airline to offer Internet connectivity on domestic flights.
- The service is free for a limited introductory period on select domestic flights.
- Gradual expansion of Wi-Fi availability to more aircraft in the fleet.
Key Highlights:
Aircraft with Wi-Fi:
- Available on Airbus A350, Boeing 787-9, and select Airbus A321neo aircraft.
- Aircraft equipped with special hardware for Internet connectivity.
- Some aircraft, previously operated by Vistara, now part of Air India after the merger in November.
Technology Partner:
- Vistara’s in-flight Wi-Fi was facilitated by Tata Group’s Nelco, in collaboration with Panasonic Avionics.
- This service is now extended to select Air India domestic flights.
How to Access Wi-Fi:
- Passengers enable Wi-Fi on their devices and connect to the "Air India Wi-Fi" network.
- Redirected to an Air India portal where they enter details (PNR and last name) for access.
Connectivity Technologies:
- Air-to-Ground (ATG) Technology:
- Uses ground-based cellular towers to provide internet.
- Antenna on the aircraft’s belly picks up signals from nearby towers.
- Limited by tower availability, works best over land with dense coverage.
- Satellite-Based Connectivity:
- Uses satellites to provide internet by transmitting signals from ground stations to the aircraft.
- Provides wider coverage, particularly effective over oceans and sparsely populated areas.
In-Flight Wi-Fi Operation:
- Multiple in-cabin antennas collect signals from passengers’ devices.
- Signals are sent to an onboard server.
- For satellite-based systems, signals are transmitted via an antenna to satellites and then relayed to ground stations.
- For ATG systems, signals are sent directly to ground towers.
- In-flight Wi-Fi is slower compared to ground-based internet, though newer technologies are improving speed.
Cost Considerations:
- Airlines incur high initial costs for equipping aircraft with Wi-Fi technology (antennas and hardware).
- Air India is investing in a $400 million retrofit program for its fleet, which could include installing internet connectivity.
- Some airlines install Wi-Fi on new planes, while others retro-fit older models.
Revenue Model:
- Airlines often charge for Wi-Fi after offering a small volume of free internet.
- Some airlines provide free Wi-Fi for loyalty program members or premium passengers (business/first class).
- Air India is offering free Wi-Fi for now, but plans to introduce charges at a later date.
Future Outlook:
- In-flight internet is expected to become a significant source of ancillary revenue.
- Complimentary Wi-Fi for economy class passengers is unlikely in the near-to-medium term due to high costs involved in installation and operation.
Global Context:
- In-flight connectivity is becoming standard on major full-service carriers (FSCs) worldwide.
- Air India's move aligns with global trends, as it aims to be among the world’s leading airlines.
Ramesh Chand Panel
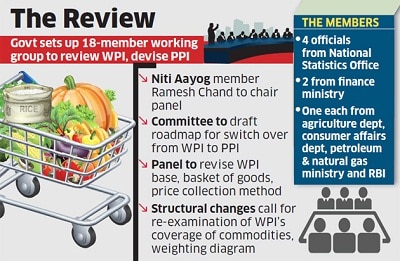
- 03 Jan 2025
In News:
The Government of India has formed an 18-member panel, headed by Ramesh Chand, a member of NITI Aayog, to revise the base year of the Wholesale Price Index (WPI) to 2022-23 from the current base year of 2011-12. The panel will also work on a roadmap for transitioning from WPI to the Producer Price Index (PPI).
Key Highlights:
Role and Mandates of the Panel:
- Revised Commodity Basket: The panel will recommend a new commodity basket for both WPI and PPI, reflecting structural changes in the economy.
- Review of Price Collection System: The panel will evaluate the current system for price collection and propose improvements.
- Computational Methodology: It will determine the computational methodology for both WPI and PPI to ensure accuracy in tracking price changes.
- The panel has been tasked with submitting its final report to the Office of the Economic Adviser at the Department for Promotion of Industry and Internal Trade (DPIT) within 18 months.
Understanding WPI vs. PPI:
- WPI (Wholesale Price Index) tracks the price of goods at the wholesale stage (i.e., goods sold in bulk to businesses), and excludes the service sector.
- Key Characteristics of WPI:
- Does not consider consumer-facing prices.
- Excludes services (about 55% of GDP).
- Can have double-counting bias due to multiple transactions before the final sale.
- Does not account for indirect taxes and may include export/import prices.
- Use: WPI helps in tracking bulk price movements between businesses, but doesn't fully represent consumer price inflation.
- Key Characteristics of WPI:
- PPI (Producer Price Index) tracks prices at various stages of production, considering both goods and services, and measures the average change in prices received by domestic producers.
- Key Characteristics of PPI:
- Excludes indirect taxes (making it more accurate for price movement tracking).
- Includes services, unlike WPI, giving a broader view of price trends across the economy.
- More aligned with international standards (System of National Accounts).
- Reflects prices before consumer consumption, providing a business-oriented perspective of price trends.
- Key Characteristics of PPI:
Why the Transition to PPI?
- The PPI is already used by major economies like the US, China, Germany, and Japan as it provides a more comprehensive measure of inflation from a producer’s perspective.
- It is expected to be a better indicator of inflationary trends in the overall economy, including both goods and services.
Challenges and Roadmap:
- The switch to PPI is complex, and the panel will need to ensure that the transition does not disrupt the current data collection and reporting systems. Both WPI and PPI will run concurrently until PPI stabilizes.
CGWB Report on Groundwater Contamination
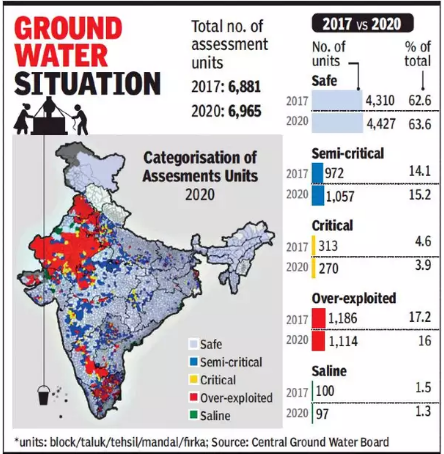
- 03 Jan 2025
In News:
The Central Ground Water Board (CGWB) report on groundwater quality reveals alarming levels of contamination in India's groundwater, with a focus on nitrate, fluoride, arsenic, and uranium. The report highlights the impact of agricultural practices, poor waste management, and urbanisation on water quality.
Key Highlights:
Nitrate Contamination:
- 440 districts in India report excessive nitrate levels in groundwater, with 20% of samples exceeding the permissible nitrate limit of 45 mg/L (WHO and BIS standards).
- High-risk regions: Rajasthan (49%), Karnataka (48%), and Tamil Nadu (37%) are the top states with high nitrate levels. Other affected states include Maharashtra, Telangana, Andhra Pradesh, and Madhya Pradesh.
- Causes: Nitrate contamination is mainly due to excessive use of nitrogen-based fertilizers, over-irrigation, and poor management of animal waste. Urbanisation and improper sewage systems exacerbate the problem.
Other Groundwater Contaminants:
- Fluoride contamination: A significant concern in Rajasthan, Haryana, Karnataka, Andhra Pradesh, and Telangana.
- Arsenic contamination: Elevated arsenic levels found in several states, especially in floodplains of the Ganga and Brahmaputra rivers (West Bengal, Jharkhand, Bihar, Uttar Pradesh, Assam, and Manipur).
- Uranium contamination: 42% of uranium-contaminated samples are from Rajasthan, and 30% from Punjab. Chronic exposure to uranium leads to kidney damage.
Groundwater Extraction and Availability:
- 60.4% of groundwater is being extracted across India.
- 73% of groundwater blocks are classified as in the ‘safe’ zone, an improvement from 67.4% in 2022.
Monsoon Impact:
- Nitrate contamination increases post-monsoon, with 32.66% of samples exceeding safe limits during the rainy season.
Health Implications:
- High nitrate levels, particularly dangerous for infants, can cause blue baby syndrome (methemoglobinemia).
- Long-term exposure to contaminants like fluoride and arsenic can lead to fluorosis and increase the risk of cancers and skin lesions.
Sources of Contamination:
- Agricultural practices: Excessive use of fertilizers, pesticides, and improper irrigation.
- Waste disposal: Leaking septic systems, sewage, and hazardous waste sites contribute to contamination.
- Urbanisation: Increased wastewater and sewage, along with poor waste management, worsen the issue.
Measures to Address Contamination:
- Jal Shakti Abhiyan (JSA) and Atal Bhujal Yojana (ABHY) aim to conserve and manage groundwater resources.
- National Aquifer Mapping and Management Program (NAQUIM) to assess and map aquifer systems.
- Pollution control programs: Under the Water (Prevention & Control) Act, 1974, and initiatives like sewage treatment plants and effluent treatment plants to manage wastewater.
- Public awareness: Campaigns like Swachh Bharat Mission and Catch the Rain educate communities on the importance of groundwater conservation.
Key Statistics:
- 56% of districts in India report groundwater nitrate levels exceeding the safe limit of 45 mg/L.
- Monsoon effects: Post-monsoon data shows a significant increase in contamination levels (32.66% vs. 30.77% pre-monsoon).
National e-Governance Awards (NAeG) Scheme 2025

- 03 Jan 2025
In News:
- The Department of Administrative Reforms & Public Grievances (DARPG) has issued the guidelines for the 28th National e-Governance Awards (NAeG) 2025.
- Nominations for the awards can be submitted online via the official portal: www.nceg.gov.in.
Key Highlights:
- Award Categories: Nominations for the awards can be submitted under the following six categories:
- Government Process Re-engineering: Digital transformation through the use of technology to improve government processes.
- Innovation by Use of AI and New Age Technologies: Fostering citizen-centric services via artificial intelligence and other modern technologies.
- Best e-Gov Practices in Cyber Security: Recognizing excellence in e-Governance practices focused on cybersecurity.
- Grassroot Level Initiatives: Initiatives at the Districts, ULBs (Urban Local Bodies), or Gram Panchayats that deepen service delivery.
- Replication and Scaling Up of Successful Projects: Projects awarded in the past (such as NAeG or Prime Minister’s Awards) that have been successfully replicated or scaled.
- Digital Transformation using Data Analytics: Projects that leverage data analytics on digital platforms for enhancing governance.
- Eligibility: The awards are open to Central Ministries/Departments, State Governments, District Collectors, Research Institutions, and other relevant entities.
- Award Details:
- The NAeG 2025 will feature 16 awards:
- 10 Gold Awards.
- 6 Silver Awards.
- The NAeG 2025 will feature 16 awards:
- Incentives:
- Gold Award winners will receive a Trophy, Certificate, and an incentive of Rs 10 lakh.
- Silver Award winners will receive a Trophy, Certificate, and an incentive of Rs 5 lakh.
- The incentive will be used for further implementation of the awarded projects or bridging resource gaps in public welfare.
- Objective: The goal of the National Awards for e-Governance is to recognize and promote excellence in the implementation of e-Governance initiatives and digital transformation efforts across India.
Tinnitus

- 03 Jan 2025
In News:
Researchers at IIT Bombay have created an affordable device to diagnose and manage tinnitus, a condition involving persistent ringing or buzzing in the ears. The device offers personalized treatment solutions and a comprehensive approach to managing tinnitus.
What is Tinnitus?
- Tinnitus is the perception of sound in the absence of external noise, meaning only the affected individual hears it. It is often caused by underlying conditions such as age-related hearing loss, ear injury, or circulatory system problems.
- It affects over 740 million adults globally, with 120 million experiencing severe symptoms (JAMA Neurology, 2022).
- Common symptoms include sleep disturbances, depression, anxiety, irritability, and significant impacts on mental health and social life.
- Treatment may include: Hearing aids, sound-masking devices, medications, and coping techniques to manage the noise.
Device Features:
- Precise Tinnitus Matching: Identifies the exact nature and frequency of sounds experienced by the patient.
- Customizable Treatment: Provides a tailored, multimodal approach to treatment, ensuring each patient gets a unique experience.
- Tracking Progress: Includes tools to monitor disease progression and patient improvement over time.
Affordability and Accessibility:
- The device is cost-effective, addressing the issue of high costs associated with current tinnitus management solutions.
- This breakthrough is especially beneficial for low-income regions, where access to expensive tinnitus treatment is limited.
Impact on Healthcare:
- The device empowers doctors with precise diagnostic tools, improving the accuracy of diagnosis and the efficacy of treatment.
- It aims to enhance patient quality of life by offering an affordable and accessible solution to tinnitus management.
Funding and Development:
- The project has received funding from Tata Centre for Technology and Design (TCTD), IIT Bombay, and Wadhwani Research Centre for Bioengineering (WRCB).
Significance:
- This development represents a technological advancement in tinnitus care, with the potential to greatly reduce the burden of the condition and improve the well-being of affected individuals worldwide.
Quad 20th Anniversary
- 03 Jan 2025
In News:
Quad Foreign Ministers reaffirmed their commitment to a free, open, and peaceful Indo-Pacific. Marked the 20th anniversary of Quad cooperation, originally formed to respond to the 2004 Indian Ocean earthquake and tsunami.
Key Highlights:
- What is the Quad?
- A strategic forum of the US, Japan, India, and Australia aimed at regional security and economic cooperation in the Indo-Pacific region.
- Founded on shared principles of democracy, human rights, rule of law, and countering China's influence.
- Origins:
- Quad traces its origins to the 2004 Tsunami relief efforts.
- Formed formally in 2007, but Australia withdrew in 2008 due to regional tensions. It rejoined in 2017 following strengthened US-Australia ties.
- Commitment to Regional Security:
- Focus on countering China’s assertive behavior in the Indo-Pacific.
- Ensuring maritime security, countering illegal fishing, promoting infrastructure, and advancing economic cooperation.
- Key Initiatives:
- IPMDA: Real-time monitoring of maritime activities.
- MAITRI: Capacity-building for maritime security.
- Quad Fellowship: Funds graduate-level STEM education in member countries.
- Open RAN: Promoting secure 5G infrastructure.
- Cancer Moonshot: Focus on cervical cancer prevention.
- Military and Naval Cooperation:
- Malabar Exercises: Joint naval drills between India, Japan, the US, and Australia.
- ASEAN and Regional Cooperation:
- Emphasis on ASEAN's central role in the Indo-Pacific region.
- Support for the Pacific Islands Forum and the Indian Ocean Rim Association (IORA).
- Future Developments:
- India to host the next Quad Summit in 2025.
- Continued focus on sustainable regional development, scientific collaboration, and disaster relief efforts.
- Significance of the Quad for India:
- Strategic Importance:
- Provides a platform to counter China's assertive policies, especially in the South China Sea and the "String of Pearls" strategy.
- Aligns with India’s Act East Policy, enhancing ties with East and Southeast Asia.
- Maritime Security: Ensures freedom of navigation and counters illegal activities like piracy and illegal fishing in India’s maritime domain.
- Economic Opportunities:
- Strengthens cooperation on infrastructure projects and trade initiatives, such as the Blue Dot Network.
- Post-COVID, Quad may aid India in attracting manufacturing units shifting from China.
- Scientific and People-to-People Collaboration: Supports STEM education and enhances soft power diplomacy through academic and cultural exchanges.
Rapid Chess Championship

- 02 Jan 2025
In News:
In a monumental achievement, Koneru Humpy from Vijayawada, India, claimed the 2024 FIDE Women’s World Rapid Chess Championship in New York. This victory marks her second World Rapid Chess title, five years after her first win in 2019 in Georgia, making her the first Indian and only the second player after China’s Ju Wenjun to win the title multiple times.
Key Highlights of Humpy’s Victory:
- Final Score: Humpy finished with an impressive 8.5 points from 11 rounds, securing the top spot by defeating Irene Sukandar of Indonesia in the final round.
- Strong Finish: Humpy surged ahead of the other joint leaders to clinch the title, with D. Harika, another Indian chess star, securing 5th place with 8 points.
World Rapid Chess Championship
- The World Rapid Chess Championship is a chess tournament that determines the world's top rapid chess player. The tournament is held annually by FIDE, the International Chess Federation.
- How it works
- The tournament uses a Swiss system, where players are paired with opponents of similar scores in each round.
- Players are not eliminated after losses.
- The player with the highest score at the end of the tournament wins.
- Time controls
- Players are given a set amount of time per move, plus an increment for each move.
- In the World Rapid Championship, players have 15 minutes per move, plus a 10-second increment for each move.
A Historic Year for Indian Chess:
- 2024 has been a remarkable year for Indian chess, with D. Gukesh becoming the youngest-ever World Chess Champion after his victory over Ding Liren (China) at the World Chess Championship in Singapore.
- India also made history by winning both the open and women’s sections at the 2024 Chess Olympiad in Budapest.
H-1B Visa
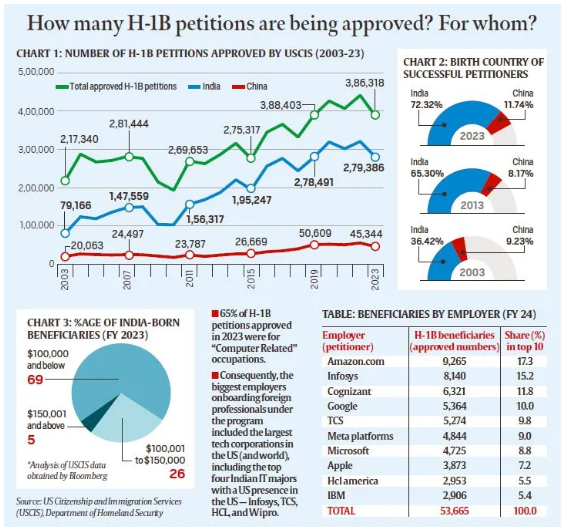
- 02 Jan 2025
In News:
In the weeks leading up to his return as US President, Donald Trump’s supporters are embroiled in a public dispute over skilled immigration and H-1B visas.
What is the H-1B Visa Program?
- Purpose and Overview:
- The H-1B visa is a non-immigrant visa allowing U.S. companies to employ foreign workers in specialized occupations like STEM (Science, Technology, Engineering, Mathematics) and IT, which require at least a bachelor’s degree.
- Introduced in 1990 to help U.S. employers fill positions when there’s a shortage of qualified domestic workers.
- It allows workers to stay in the U.S. for a maximum of six years, with the option to apply for permanent residence (Green Card) or leave for 12 months before reapplying.
- Annual Cap and Exemptions:
- 65,000 new visas are issued annually, with an additional 20,000 for those with a master’s degree or higher from a U.S. university.
- Certain petitions, such as for continuing employment or positions in higher education or nonprofit research, are exempt from the cap.
- Dominance of Indian Beneficiaries:
- Indians are the largest beneficiaries, accounting for over 70% of H-1B visa approvals annually since 2015, with China coming second at around 12-13%.
The Current Controversy
- Trigger for Debate:
- The controversy was sparked by Sriram Krishnan, a Chennai-born tech entrepreneur appointed as Donald Trump’s top AI adviser. His post on X (formerly Twitter) in November 2024, advocating for unlocking skilled immigration, led to backlash within Trump’s anti-immigration base.
- The Political Divide:
- Trump’s supporters, particularly from the MAGA (Make America Great Again) faction, voiced opposition to the H-1B visa program, arguing it undermines American workers and wages.
- This prompted pushback from pro-H-1B advocates like Elon Musk and Vivek Ramaswamy, who argue that the program is crucial for addressing the U.S.'s STEM talent shortages.
- Economic and Political Context:
- Immigration is a polarizing issue in the U.S., with a focus on low-skilled labor migration and its alleged effects on wages and job opportunities for American workers.
- Trump’s stance against low-skilled immigration echoes similar critiques about H-1B workers being employed at lower salaries in tech companies, which some claim depresses wages and reduces job opportunities for U.S. workers.
Criticisms of the H-1B Program
- Abuse of the System:
- Critics argue that companies exploit the H-1B program by hiring foreign workers, especially from India, at lower wages than American employees, particularly in tech industries.
- Elon Musk suggests that the program is “broken” and needs reform, proposing raising the minimum salary for H-1B workers to make it more expensive to hire overseas talent.
- Salary Disparities:
- Data from USCIS (U.S. Citizenship and Immigration Services) shows that 70% of H-1B petitions for Indian professionals in 2023 were for salaries below $100,000, while the median salary for U.S. IT professionals was $104,420.
- Impact on American Jobs:
- Critics argue that companies prefer to hire foreign workers at lower wages to save costs, despite the availability of qualified U.S. talent, thus taking away opportunities for American workers.
Support for the H-1B Program
- Filling the STEM Gap:
- Proponents, including Musk and Ramaswamy, argue that the H-1B visa is essential for filling the STEM skills gap in the U.S., given the global dominance of India and China in STEM fields.
- India and China lead the world in STEM graduates, with 2.55 million and 3.57 million, respectively, compared to the U.S. with 820,000.
- Proponents, including Musk and Ramaswamy, argue that the H-1B visa is essential for filling the STEM skills gap in the U.S., given the global dominance of India and China in STEM fields.
- Economic Benefits:
- The H-1B program helps U.S. companies access top global talent, boosting innovation and economic growth, especially in high-tech industries.
- Tech companies argue that without access to skilled foreign workers, they would struggle to fill critical positions in the technology sector.
Tamil Nadu's First Glass Bridge in Kanyakumari
- 02 Jan 2025
In News:
- The Chief Minister of Tamil Nadu inaugurated India’s first glass bridge over the sea in Kanyakumari, connecting the Thiruvalluvar Statue and the Vivekananda Rock Memorial.
- The bridge provides a safe and scenic walking route between these two iconic landmarks, eliminating the need for ferry trips.
Key Highlights:
- Dimensions and Design
- The bridge is 77 meters long and 10 meters wide, offering uninterrupted views of the sea from a unique vantage point.
- Designed to withstand marine conditions like corrosion and strong winds, ensuring durability and safety for visitors.
- Tourism Investment
- The bridge was built at a cost of ?37 crore, marking a significant investment in tourism infrastructure for Kanyakumari.
- This project aligns with the state’s vision to boost tourism and modernize amenities in the region.
- Significance as a Tourist Attraction
- The bridge is set to become a landmark tourist attraction, enhancing the visitor experience by providing a direct, scenic route between the two monuments.
- It is expected to play a pivotal role in boosting tourist footfall and the local economy.
About Thiruvalluvar Statue
- Location and Design
- The Thiruvalluvar Statue stands on a rock near the Vivekananda Rock Memorial in Kanyakumari.
- It is a symbol of wisdom, officially named the Statue of Wisdom by the Tamil Nadu government.
- Physical Specifications
- The statue stands at a total height of 133 feet (41 meters), with the statue itself measuring 95 feet (29 meters) and the pedestal adding 38 feet (12 meters).
- Weight: The statue weighs approximately 7000 tonnes and is designed in a hollow structure.
About Vivekananda Rock Memorial
- Location and Significance
- Situated on a rock in the Laccadive Sea, around 500 meters from the mainland in Kanyakumari.
- The memorial commemorates Swami Vivekananda, who represented India’s spiritual legacy at the 1893 Parliament of World’s Religions in Chicago.
- Historical and Religious Importance
- The rock is believed to be the site where Swami Vivekananda attained enlightenment.
- It is also associated with goddess Kanyakumari, who is said to have prayed to Lord Shiva on this rock, with an imprint of her feet preserved there.
- Architectural Features
- The memorial incorporates diverse architectural styles, including the Sripada Mandapam and the Vivekananda Mandapam.
- A life-sized bronze statue of Swami Vivekananda is located at the memorial.
- The rock is surrounded by the Bay of Bengal, Indian Ocean, and Arabian Sea, where these three water bodies converge.
Business Ready (B-READY) Report 2024

- 02 Jan 2025
In News:
- The B-READY report, launched by the World Bank in 2024, replaces the Ease of Doing Business (EoDB) index.
- Focus: It evaluates the global business environment to foster inclusive private sector growth, assessing 10 core topics covering a firm's lifecycle, such as business entry, taxation, labor, and international trade.
India’s Potential Challenges
- Business Entry: India faces multiple steps and incomplete digital integration, making it slower compared to benchmarks like Singapore, which achieves one-day registration at minimal cost.
- Labor Regulations: While India has introduced four labor codes, the implementation remains slow and inconsistent, affecting labor flexibility and compliance.
- International Trade: India struggles with customs delays, inconsistent enforcement, and high logistics costs, unlike countries like Germany and Singapore, which promote trade efficiently.
- Business Location: Regulatory delays and inconsistent approvals hinder the establishment of business facilities, affecting investment decisions.
- Public Services Gap: While regulations may be strong, there is often a gap in the provision of public services that support their effective implementation, leading to inefficiencies.
Key Strengths for India
- India is expected to score well in the areas of Quality of Regulations, Effectiveness of Public Services, and Operational Efficiency.
- The country shows promise in promoting digital adoption and aligning with global environmental sustainability practices, though gender-sensitive regulations need more emphasis.
Significance
- The B-READY report serves as an essential benchmark for assessing India's business environment, offering insights into regulatory reforms and operational efficiency.
- Key policy implications for India include the need to:
- Streamline business operations by digitizing registration and regulatory approval processes.
- Improve logistics and trade efficiency by reducing customs delays.
- Address labor market inefficiencies through better implementation of labor codes.
- Invest in public services and promote digital transformation for better compliance and operational ease.
- Focus on sustainability and inclusivity, ensuring gender-sensitive policies and fostering green business practices.
Global Findings from the B-READY Report
- Economies with strong regulatory frameworks and digital tools (e.g., Rwanda, Georgia) show that even countries with varying income levels can achieve high scores.
- High-income countries like Estonia and Singapore still have room for improvement, especially in areas like taxation and dispute resolution.
Comparison of B-READY with Ease of Doing Business (EoDB)
- Scope: B-READY is broader, covering a firm’s lifecycle and social benefits, while EoDB focused mainly on regulatory burdens.
- Indicators: B-READY uses 1,200 indicators from expert consultations and firm-level surveys, offering more comprehensive insights compared to the EoDB's limited metrics.
- Focus on Public Services: Unlike EoDB, which provided limited attention to public services, B-READY explicitly evaluates public service efficiency and operational effectiveness.
Policy Recommendations
- Streamline Business Operations: Inspired by countries like Singapore, India should simplify business registration and reduce delays in customs and regulatory approvals.
- Strengthen Public Services: Focus on improving tax portals, utility access, and dispute resolution systems through digital tools.
- Promote Sustainability: Encourage environmentally sustainable business practices and adopt gender-sensitive regulations to ensure inclusive growth.
- Peer Learning and Global Collaboration: Encourage India to learn from best practices in countries like Singapore and Estonia for effective reforms.
- Tailored Reforms: India must design policies addressing unique local challenges while adhering to global standards.
Stellaria bengalensis

- 02 Jan 2025
In News:
After a plant species of the genus Stellaria (family Caryophyllaceae) was reported from Kerala earlier this year, researchers have identified another member of the same genus at Kalimpong district in West Bengal.
Key Highlights:
Discovery and Identification:
- Published: The discovery was published in Phytotaxa.
- Location: Found in Kalimpong district, West Bengal, at altitudes of 2,245-2,450 metres in the Sangser forest.
- Named: The species is named Stellaria bengalensis after the state of West Bengal.
Taxonomy and Characteristics:
- Family: Caryophyllaceae.
- Type: Annual herb.
- Size: Grows to a height of 8 to 10.5 cm.
- Flowers: White in color, with shorter petals, often included within the sepal, and absence of bracts.
- Seeds: Sharp and pointed.
- Flowering and Fruiting: Occurs from May to September.
Distribution:
- Region: Primarily found in the Himalayan region.
- Similar Species: Stellaria mcclintockiae, identified earlier in Kerala (Nelliyampathy Hills).
- Both species grow in muddy soil slopes and are annuals.
Conservation Status:
- Under IUCN (International Union for Conservation of Nature) criteria, the species is assessed as "data deficient", pending further studies.
- Potential Habitat: There is a possibility of finding more populations in the western Himalayas.
Significance:
- Stellaria bengalensis is the second Stellaria species reported in India in 2025.
- India is home to about 22 Stellaria species, predominantly found in the Himalayan region.
- The discovery adds to biodiversity knowledge in India and underscores the importance of studying plant species in the region.
World Audio Visual & Entertainment Summit (WAVES) 2025

- 30 Dec 2024
In News:
India to Host World Audio Visual & Entertainment Summit (WAVES) 2025.
Key Highlights:
- Purpose: The summit aims to bolster India's media and entertainment (M&E) industry, expand its global influence, and foster innovation and collaboration within the sector.
- Significance: First-ever global summit to cover the entire media and entertainment industry spectrum.
- Objective:
- Foster Dialogue and Trade: WAVES aims to be a premier platform for industry leaders, stakeholders, and innovators to engage in meaningful discussions, explore opportunities, and tackle challenges in the M&E sector.
- Promote India's M&E Industry: Attract trade and investment to India, highlighting its strengths in animation, gaming, entertainment technology, and cinema (both regional and mainstream).
- Focus Areas:
- Industry Advancements: Discussions will revolve around India’s progress in animation, visual effects, gaming, and cinema.
- Global Positioning: Establish India as a global powerhouse in the M&E sector, setting new standards for creativity, innovation, and global influence.
WAVES India - Vision and Mission:
- Vision: Position India as a Global Powerhouse: Enhance India’s standing in the dynamic M&E sector, making it a hub of creativity and innovation worldwide.
- Mission:
- Provide exclusive investment opportunities for global M&E leaders through WAVES.
- Drive India’s Creative Economy through Intellectual Property (IP) Creation for both domestic and international markets.
- Develop M&E Infrastructure: Strengthen industry infrastructure and create a skilled workforce to meet global demands.
- Adapt to New Trends: Embrace emerging technologies and transformations in the M&E landscape.
Expected Outcomes:
- Global Collaboration: Engage global M&E leaders in discussions that provoke ideas and facilitate collaborations.
- Attract Investment: Promote India as a business-friendly investment destination in the M&E sector.
- Skills and Capacity Building: Build capacity in the M&E industry and develop skilled human resources to support international needs.
