GhassemBasir Missile unveiled by Iran

- 08 May 2025
In News:
Iran has recently introduced a new solid-fuel medium-range ballistic missile (MRBM) named GhassemBasir.
About the GhassemBasir Missile
The missile is designed to engage targets at distances exceeding 1,200 kilometers, enhancing Iran’s strategic strike capabilities.
Key Features:
- Size and Weight: The missile measures approximately 11 meters in length and weighs around 7 tons.
- Advanced Materials: Its airframe is reportedly constructed using carbon fiber composite materials, which reduce structural weight and lower its radar signature.
- Warhead: The missile carries a warhead estimated to weigh about 500 kilograms.
- Propulsion: Powered by a solid-fuel system, the missile benefits from quicker launch readiness and improved storage stability compared to liquid-fuel missiles.
- Speed: Capable of reaching speeds up to Mach 12.
- Guidance System: Equipped with a thermal imaging sensor that enables the missile to detect and home in on targets by sensing heat signatures during the final flight phase.
- Maneuverable Reentry Vehicle (MaRV): The missile features a MaRV that separates from the booster, reducing aerodynamic drag, decreasing radar detectability, and enhancing ballistic performance.
- Mobility: It can be launched from mobile transporter-erector-launchers (TELs), including vehicles resembling civilian trucks, increasing its operational flexibility and survivability.
Alcatraz Island
- 08 May 2025
In News:
The President of the United States has recently instructed his administration to undertake a project to rebuild and expand Alcatraz, the notorious prison that has been closed for over six decades. This historic site is located on a remote island off the coast of San Francisco, California.
About Alcatraz Island
Alcatraz Island, often referred to as “The Rock,” is a small rocky island situated in San Francisco Bay, California, covering approximately 22 acres (9 hectares).
Historical Overview
- 1849: The island was sold to the U.S. government.
- 1854: Alcatraz became home to the first lighthouse on California’s coast.
- 1859: The first permanent army troops were stationed on the island.
- 1861: Alcatraz was converted into a military prison.
- 1907: It was officially designated as the Pacific Branch of the U.S. Military Prison.
- 1933: The U.S. Army vacated the island.
- 1934–1963: Alcatraz functioned as a federal prison, housing some of America’s most dangerous criminals.
Prison Details
The prison had a capacity to hold over 330 inmates in cells measuring approximately 10 feet by 4.5 feet (3 meters by 1.5 meters). However, the actual number of prisoners rarely exceeded 260 at any given time. Known as the most secure and inescapable prison in the United States, Alcatraz was famous for its isolation and strict security measures. Although a few inmates attempted to escape, the harsh currents of San Francisco Bay made survival unlikely.
Closure and Current Status
Due to the high costs of upkeep, the prison was officially closed in March 1963. In 1972, Alcatraz was incorporated into the newly established Golden Gate National Recreation Area and was opened to the public. Today, it remains a popular tourist destination, attracting visitors from around the world.
Organization of Islamic Cooperation (OIC)

- 08 May 2025
About the OIC
The Organization of Islamic Cooperation (OIC) is the world’s second-largest intergovernmental organization after the United Nations, comprising 57 member states across four continents. It was established on September 25, 1969, following the historic summit held in Rabat, Morocco, which was convened in response to the arson attack on the Al-Aqsa Mosque in occupied Jerusalem.
Objectives and Purpose
The OIC’s primary goals are to:
- Preserve and promote Islamic values.
- Safeguard the national sovereignty and independence of its member states.
- Contribute to international peace and security.
- Serve as the collective voice of the Muslim world, protecting their interests across economic, social, and political spheres.
Structure and Headquarters
- The OIC’s headquarters is located in Jeddah, Saudi Arabia.
- Its official languages are Arabic, English, and French.
Membership
Notable member countries include Afghanistan, Bahrain, Bangladesh, Egypt, Indonesia, Iran, Iraq, Jordan, Kuwait, Lebanon, Libya, Malaysia, Maldives, Morocco, Niger, Oman, Pakistan, the Palestinian Authority, Qatar, Saudi Arabia, Sudan, Turkey, Uganda, United Arab Emirates, and Yemen, among others.
Principal Organs of the OIC
- Islamic Summit Conference (ISC):The highest authority of the OIC, meeting every three years to set the organization’s policies and strategic direction.
- Council of Foreign Ministers (CFM):Convening annually, the CFM reviews and oversees the implementation of decisions made by the Islamic Summit.
- General Secretariat:The executive branch responsible for executing the resolutions of the ISC and CFM.
Additionally, the OIC has established various ministerial-level committees—some chaired by heads of state—to coordinate cooperation among member countries in political, economic, cultural, social, spiritual, and scientific fields.
Partnerships and Global Engagement
The OIC collaborates closely with international organizations, including all specialized agencies of the United Nations, as well as governments and civil society organizations (CSOs). These partnerships help address concerns affecting its member states and the global Muslim community.
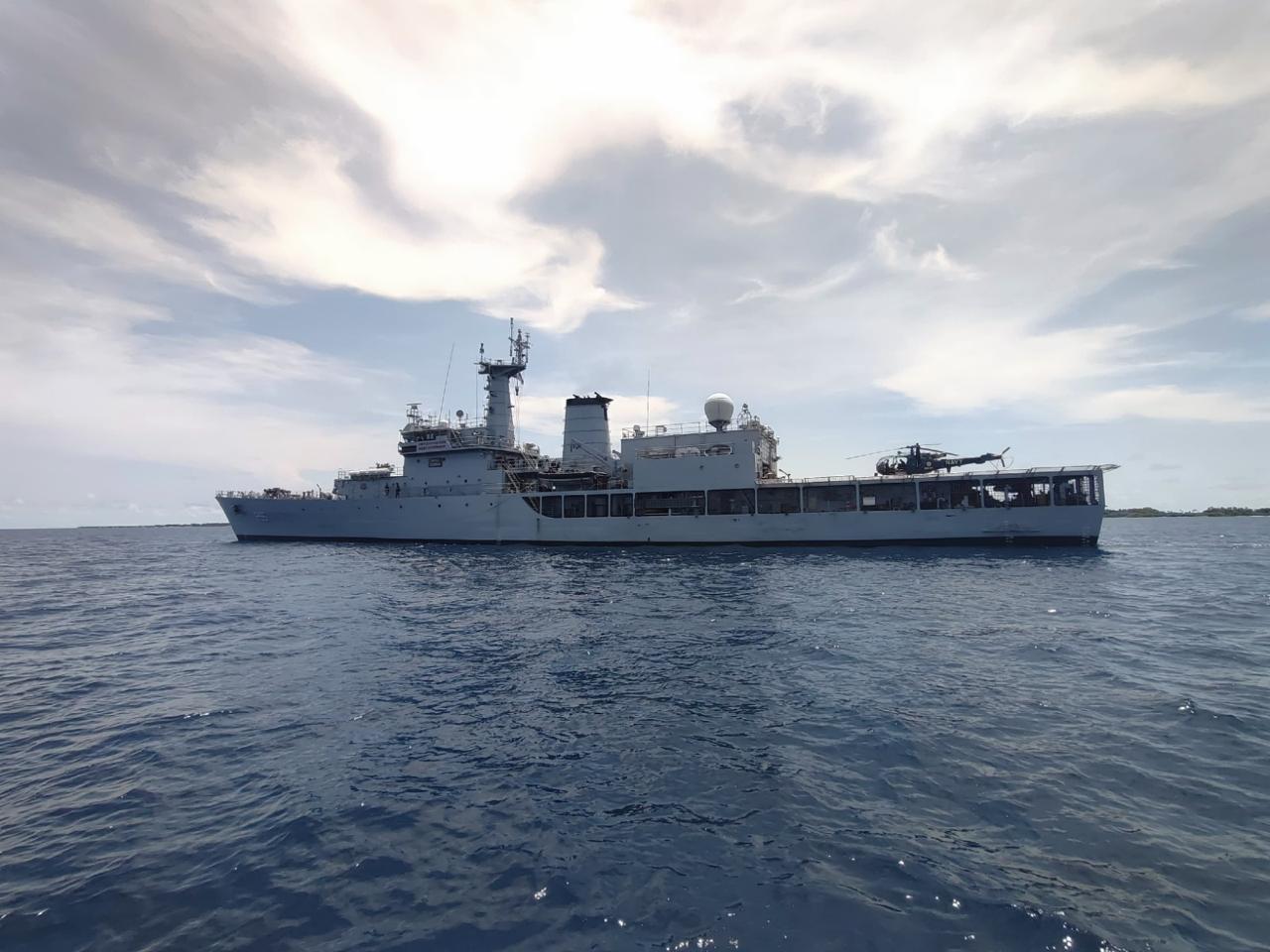
INS Sharda

- 08 May 2025
In News:
The Indian Navy’s offshore patrol vessel, INS Sharda, has reached Maafilaafushi Atoll in the Maldives to participate in its first-ever Humanitarian Assistance and Disaster Relief (HADR) exercise, scheduled from May 4 to May 10, 2025.
Strengthening Regional Maritime Cooperation and Disaster Preparedness
This exercise is a key part of India’s strategic efforts to enhance regional maritime cooperation and bolster disaster readiness within the Indian Ocean Region (IOR). It underscores India’s steadfast commitment to its “Neighbourhood First” Policy, which recognizes the Maldives as a close maritime neighbour with deep strategic and cultural ties.
Aligning with the MAHASAGAR Vision
The HADR exercise supports the recently unveiled MAHASAGAR vision—Mutual and Holistic Advancement for Security and Growth Across Regions—introduced by the Prime Minister during the Mauritius visit. MAHASAGAR reaffirms India’s role as a net security provider and first responder in the Indian Ocean, building on the earlier SAGAR doctrine (Security and Growth for All in the Region). Both frameworks emphasize inclusive security, regional cooperation, and disaster resilience.
Objectives of the HADR Exercise
According to the Indian Navy, the exercise aims to:
- Enhance interoperability between the Indian Navy and the Maldives National Defence Force (MNDF).
- Conduct joint drills focusing on Search and Rescue (SAR), disaster response coordination, logistical support, and medical aid.
- Facilitate training programs for capacity building among personnel.
- Engage with local communities to raise awareness and strengthen disaster preparedness.
This maiden HADR exercise by INS Sharda marks a significant step toward deepening India-Maldives maritime collaboration and regional disaster management capabilities.
Metal-Free Catalyst for Hydrogen Fuel Production
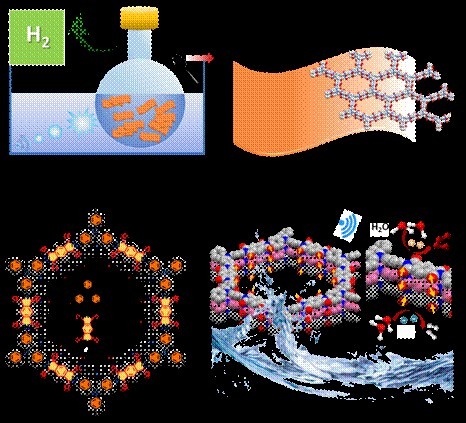
- 08 May 2025
In News:
In a significant breakthrough for clean energy technology, Indian scientists have engineered a metal-free catalyst capable of generating hydrogen fuel by harnessing mechanical energy. This innovation marks a major step forward in sustainable hydrogen production, aligning closely with India’s National Green Hydrogen Mission and its goal to lead in green energy solutions.
What is the Metal-Free Catalyst?
The catalyst is a specially designed donor-acceptor covalent organic framework (COF) that functions as a piezocatalyst without relying on any metal components. It can efficiently split water molecules to produce hydrogen gas (H?) when subjected to mechanical forces such as vibrations or pressure.
Development and Collaboration
This pioneering catalyst was developed at the Jawaharlal Nehru Centre for Advanced Scientific Research (JNCASR) in Bengaluru, under the leadership of Professor Tapas K. Maji. The project was carried out in collaboration with the Indian Institute of Science Education and Research (IISER) Pune and Wroc?aw University of Science and Technology in Poland.
Key Features of the Catalyst
- Metal-Free Composition: Made entirely from organic molecules, specifically TAPA (donor) and PDA (acceptor), connected through stable imide bonds.
- Ferrielectric Ordering (FiE): This internal property creates strong electric fields within the material, driving the catalytic water-splitting process.
- Porous, Sponge-like Structure: Enhances water permeability and promotes efficient separation of charges generated during the reaction.
- Mechanically Activated: The catalyst produces electron-hole pairs when exposed to mechanical pressure, enabling effective hydrogen generation.
Significance and Impact
- Environmentally Friendly: Eliminates the need for expensive and potentially harmful metal-based catalysts by using sustainable organic materials.
- Energy-Efficient: Utilizes ambient mechanical energy sources, such as vibrations or applied pressure, to power hydrogen production.
- Supports India’s Clean Energy Goals: Advances the objectives of the National Green Hydrogen Mission, strengthening India’s position in global clean energy innovation and reducing dependence on fossil fuels.
- Scalable and Cost-Effective: Offers a practical and affordable alternative to conventional metal-based hydrogen production technologies, making it suitable for widespread adoption.
