150 Years of Vande Mataram

- 09 Nov 2025
In News:
India has commenced a year-long national commemoration marking 150 years of Vande Mataram, with an enthusiastic response across the country and abroad. The celebrations were approved by the Union Cabinet on October 1 and formally inaugurated through a grand national event in New Delhi led by the Prime Minister. The President of India and other constitutional authorities have also extended their greetings, underlining the song’s enduring national significance.
About Vande Mataram
- Author: Bankim Chandra Chattopadhyay
- First Appearance: Serialized in the Bengali journal Bangadarshan and later included in the novel Anandamath (1882)
- Language: Blend of Sanskrit and Bengali
- Status: National Song of India (adopted on 24 January 1950)
Vande Mataram is not merely a song but a symbolic invocation of the motherland, embodying India’s cultural, spiritual, and national identity.
Historical Significance
- First sung publicly by Rabindranath Tagore at the 1896 Indian National Congress session in Calcutta
- Became a political slogan during the Swadeshi Movement (first used as a slogan on 7 August 1905)
- Madam Bhikaji Cama unfurled India’s tricolour in Stuttgart (1907) with the words Vande Mataram inscribed on it
- Served as a rallying cry for freedom fighters, inspiring mass participation in the national movement
The song played a critical role in forging a shared emotional and cultural identity during colonial resistance.
Baliyatra Festival

- 09 Nov 2025
In News:
The President of India, Droupadi Murmu, recently extended greetings to the nation, especially to the people of Odisha, on the occasion of the historic Baliyatra festival and Boita Bandana. She described Baliyatra as a symbol of Odisha’s glorious maritime commercial tradition and rich cultural heritage, inspiring citizens to draw strength from the past to build a developed nation.
About Baliyatra Festival
- Location: Cuttack, Odisha
- Time of Celebration: Annually on Kartika Purnima (full moon day of Kartika month)
- Literal Meaning: Bali Jatra means “Voyage to Bali”
The festival marks the day when ancient Kalingan seafaring traders (Sadhabas) set sail for distant lands across the Bay of Bengal.
Historical Significance
Baliyatra commemorates Odisha’s over 2,000-year-old maritime and trade links between ancient Kalinga (present-day Odisha) and regions of South and Southeast Asia, including:
- Bali
- Java
- Sumatra
- Borneo
- Burma (Myanmar)
- Ceylon (Sri Lanka)
These voyages played a vital role in spreading Indian culture, language, religion, art, and trade networks, making Kalinga one of the most prosperous maritime powers of ancient India.
Cultural Practices and Celebrations
- Boita Bandana: Women float small boats (boitas) made of paper, banana leaf, or sholapith, with lighted lamps, on rivers—especially the Mahanadi—to honour the ancient sailors.
- Festivities:
- Large fairs and exhibitions
- Folk dance and music
- Traditional food and craft stalls
- Cultural performances reflecting Odisha’s heritage
The festival celebrates the courage, navigational expertise, and commercial acumen of Kalinga’s sailors.
India’s first 500 km Quantum Key Distribution (QKD) network

- 09 Nov 2025
In News:
A Bengaluru-based quantum technology startup, QNu Labs Pvt. Ltd., supported by the Department of Science and Technology (DST) under the National Quantum Mission (NQM), has successfully demonstrated India’s first large-scale Quantum Key Distribution (QKD) network spanning over 500 kilometres.
The demonstration was formally announced during the Emerging Science, Technology and Innovation Conclave (ESTIC) 2025.
Institutional and Strategic Support
- Funding Support: I-Hub Quantum Technology Foundation (Technology Innovation Hub under the National Mission on Interdisciplinary Cyber-Physical Systems – NMICPS, hosted at IISER Pune)
- Defence Collaboration: Indian Army (Southern Command) and Corps of Signals
- Model of Collaboration: STRIDE – Synergy of Technology, Research, Industry and Defence Ecosystem
What is Quantum Key Distribution (QKD)?
- Quantum Key Distribution is a quantum-secure communication technology that uses the principles of quantum mechanics to generate and exchange encryption keys between two parties.
- Key principle: Any attempt to intercept or observe quantum information disturbs its state, making eavesdropping immediately detectable, unlike classical encryption methods.
How QKD Works
- Transmits photons (light particles) through optical fibre
- Information is encoded as qubits
- Measurement or cloning by an intruder alters quantum states
- After error correction and privacy amplification, communicating parties obtain a shared secret key
- The key is used for end-to-end encrypted communication
Types of QKD
- Prepare-and-Measure Protocols: Example – BB84 protocol (most widely used)
- Entanglement-Based Protocols: Uses entangled photon pairs for instant intrusion detection
- DV-QKD (Discrete Variable): Photon-based detection
- CV-QKD (Continuous Variable): Uses amplitude and phase of laser light
Key Features of India’s 500 km QKD Network
- Distance: Over 500 km quantum-secure link
- Infrastructure: Deployed on existing optical fibre networks
- Architecture: Multiple trusted nodes to enable long-distance secure key exchange
- Hardware Integration:
- Quantum Suraksha Kavach for high-grade data protection
- QSIP (Quantum Random Number Generator System in Package) for quantum-certified randomness
- Latency & Security: Resistant to both current cyber threats and future quantum computing-based attacks
The test-bed optical fibre network was specially engineered by Southern Command Signals, with selective access provided by the Indian Army in the Rajasthan sector, enabling real-world validation.
Maharashtra Becomes First State to Partner with Starlink
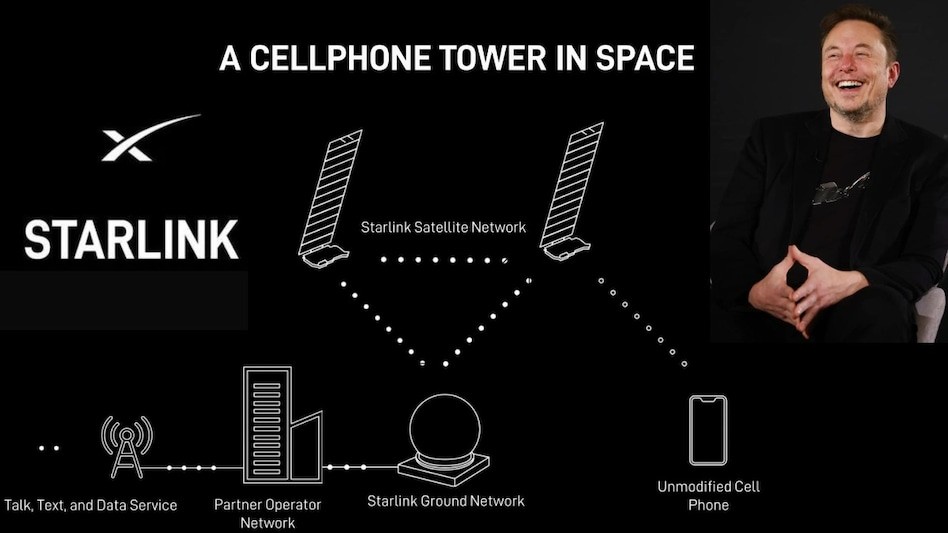
- 09 Nov 2025
In News:
Maharashtra has become the first Indian state to sign a Letter of Intent (LoI) with Starlink Satellite Communications Pvt. Ltd., a subsidiary of SpaceX (USA), to deliver satellite-based broadband internet across government institutions and remote rural areas.
What is Starlink?
Starlink is a satellite-based broadband internet service operated by SpaceX, founded by Elon Musk. It provides high-speed, low-latency internet using a large constellation of Low Earth Orbit (LEO) satellites.
How Starlink Technology Works
- Orbit Type: Low Earth Orbit (LEO) at ~550 km, unlike traditional geostationary satellites at 35,786 km
- Latency: As low as 25 milliseconds, enabling real-time applications
- Inter-Satellite Links (ISLs): Satellites communicate via optical laser links, reducing dependence on ground stations
- Autonomous Collision Avoidance: AI-driven maneuvering systems to avoid space debris
- Compact Flat-Panel Satellites: Optimised for dense launches using Falcon 9 rockets
This architecture ensures stable, fast, and reliable connectivity even in geographically challenging regions.
Objectives of Maharashtra - Starlink Partnership
- Connect remote and underserved areas
- Provide reliable internet to:
- Rural schools (online education)
- Primary health centres (telemedicine)
- Government offices (e-governance)
- Promote digital inclusion and equitable access to public services
- Support Digital India and Good Governance initiatives
Key Features and Advantages
- True global coverage: Network of thousands of LEO satellites
- Low latency & high speed: Suitable for video conferencing, telemedicine, e-learning
- Rural-first approach: Ideal for regions where fibre optics and mobile towers are impractical
- Rapid deployment: Minimal ground infrastructure required
Significance for India
- First-of-its-kind state-level collaboration with a global satellite internet provider
- Sets a policy and implementation precedent for other Indian states
- Strengthens India’s push towards:
- Digital governance
- Inclusive growth
- Technology-driven public service delivery
- Relevant in the context of emergency connectivity, disaster management, and border/tribal areas.
Vedanthangal Bird Sanctuary

- 09 Nov 2025
In News:
Vedanthangal Bird Sanctuary in Tamil Nadu has witnessed the arrival of thousands of migratory birds, marking the beginning of the annual nesting and breeding season. More than 20 migratory bird species have already arrived, leading to increased ecological activity and tourist interest.
Location and Background
- Location: Chengalpattu district, Tamil Nadu
- Distance from Chennai: ~90 km south
- Type: Freshwater wetland and heronry
- Status: One of the oldest protected bird sanctuaries in India
Vedanthangal is a people-protected wetland, with a conservation history spanning centuries. Local communities traditionally protected nesting birds as the manure-rich water (Liquid Guano Effect) from the lake enhanced agricultural productivity in surrounding fields.
Ecological and International Importance
- Recognised as an Important Bird and Biodiversity Area (IBA)
- Lies in the Coromandel Coast biotic province
- Designated as a Ramsar Site in 2022, highlighting its global wetland importance
Avifaunal Diversity (Fauna)
The sanctuary currently hosts over 15,000 birds during peak season.
Early arrivals and breeding species:
- Open-billed stork (already completed breeding with visible chicks)
- Painted stork
- Black-headed ibis
- Eurasian spoonbill
- White ibis
Other prominent species:
- Grey heron, pond heron, night heron
- Little cormorant, darter
- Pelicans, egrets
- Lesser whistling duck, spot-billed duck
- Red-wattled lapwing, little grebe, common moorhen
Vegetation (Flora)
- Barringtonia trees – preferred nesting trees
- Alangium salviflorum
- Acacia nilotica
- Thorn forests and dry evergreen scrub
Forest authorities plan desilting operations and fresh plantation of barringtonia trees during summer when the tank dries, to support long-term nesting habitats.
