Noctilucent Clouds
- 17 Jul 2025
In News:
Recently, rare noctilucent clouds were sighted over parts of Scotland, drawing attention due to their unique shimmering appearance in the night sky. These occurrences are significant in the context of climate studies and upper atmospheric science.
What are Noctilucent Clouds?
- Definition: Noctilucent clouds (NLCs), also known as polar mesospheric clouds, are high-altitude ice crystal clouds that appear thin, wispy, and glow with a blue or silvery hue after sunset.
- Etymology: The term “noctilucent” is derived from Latin—"nocto" (night) and "lucent" (shining)—meaning "night shining."
Atmospheric Location
- These are the highest clouds in Earth’s atmosphere, found in the mesosphere, around 76–85 km above the Earth's surface.
- In contrast, most other cloud types form in the troposphere, the lowest atmospheric layer.
Seasonal and Geographical Occurrence
- Seasonality:
- Northern Hemisphere: Visible from late May to early August, peaking during June and July.
- Southern Hemisphere: Much rarer; may appear from late November to early February, most commonly in December and January.
- Latitude Range: Typically occur between 45° and 80° latitude, both north and south of the equator.
- Visibility Conditions:
- Seen only during summer months, shortly after sunset or just before sunrise.
- The Sun remains just below the horizon, illuminating these high clouds from below, creating a glowing effect while the lower atmosphere is in darkness.
Formation Mechanism
- Composition: Made up of tiny ice crystals.
- Temperature Conditions: The mesosphere becomes extremely cold during summer, enabling the formation of ice on fine particles.
- Sources of Dust Nuclei:
- Natural: Micrometeorites, volcanic dust.
- Anthropogenic: Rocket exhaust particles and other upper-atmospheric pollutants.
- Optical Phenomenon: These ice crystals reflect sunlight even when the lower atmosphere is dark, giving them their luminous appearance.
Significance
- Serve as indicators of mesospheric conditions, especially temperature and humidity.
- Their increasing frequency and intensity in recent decades may be linked to climate change and human activities, including space exploration.
- Valuable for understanding upper atmospheric dynamics, particularly in the context of atmospheric chemistry and space weather.
Discovery of Penico
- 09 Jul 2025
In News:
Archaeologists have recently uncovered a significant archaeological site in northern Peru—an ancient city named Penico, estimated to be around 3,500 years old. The discovery sheds new light on early urban development, trade networks, and cultural evolution in pre-Inca South America.
Location and Time Period
- Geographic Location: Penico is located in the Barranca Province of northern Peru, approximately 200 km north of Lima, the capital.
- Altitude: The site is situated on a hillside terrace, around 600 metres above sea level.
- Estimated Age: The city is believed to have been founded between 1800 BCE and 1500 BCE, roughly during the same period as early civilizations in Egypt, Sumeria, and the Indus Valley.
Key Features of the Site
Urban and Architectural Highlights:
- The city is laid out around a central circular plaza, encircled by at least 18 identified stone-and-mud structures.
- Structures include:
- Ceremonial temples
- Residential complexes
- Public gathering areas with sculpted wall reliefs
Notable Artifacts:
- Clay figurines depicting human and animal forms
- Pututus (conch shell trumpets), traditionally used for long-distance communication
- Beaded necklaces and ceremonial artifacts crafted from shells and stones
Cultural and Historical Significance
Strategic Importance:
- Penico’s elevated location likely served both practical and symbolic purposes—protecting against natural disasters such as floods or landslides, while also enhancing the visibility and monumentality of its structures.
- The city’s placement made it a vital trading nexus, linking communities across the Pacific coast, Andean highlands, and the Amazon basin.
Link to the Caral Civilization:
- Penico is situated near the ancient city of Caral, considered the oldest known civilization in the Americas (dating back to 3000 BCE in the Supe Valley).
- Researchers suggest that Penico represents a cultural continuation or evolution of the Caral society, which declined due to climatic disruptions.
- The discovery of Penico offers valuable insight into how civilizations adapted and transitioned post-Caral, particularly in terms of urban planning, trade, and ceremonial practices.
Comparative Civilizational Context:
- Despite emerging in geographic isolation, Penico developed contemporaneously with Bronze Age civilizations of Mesopotamia, the Nile Valley, and South Asia, showcasing parallel patterns in complex societal development.
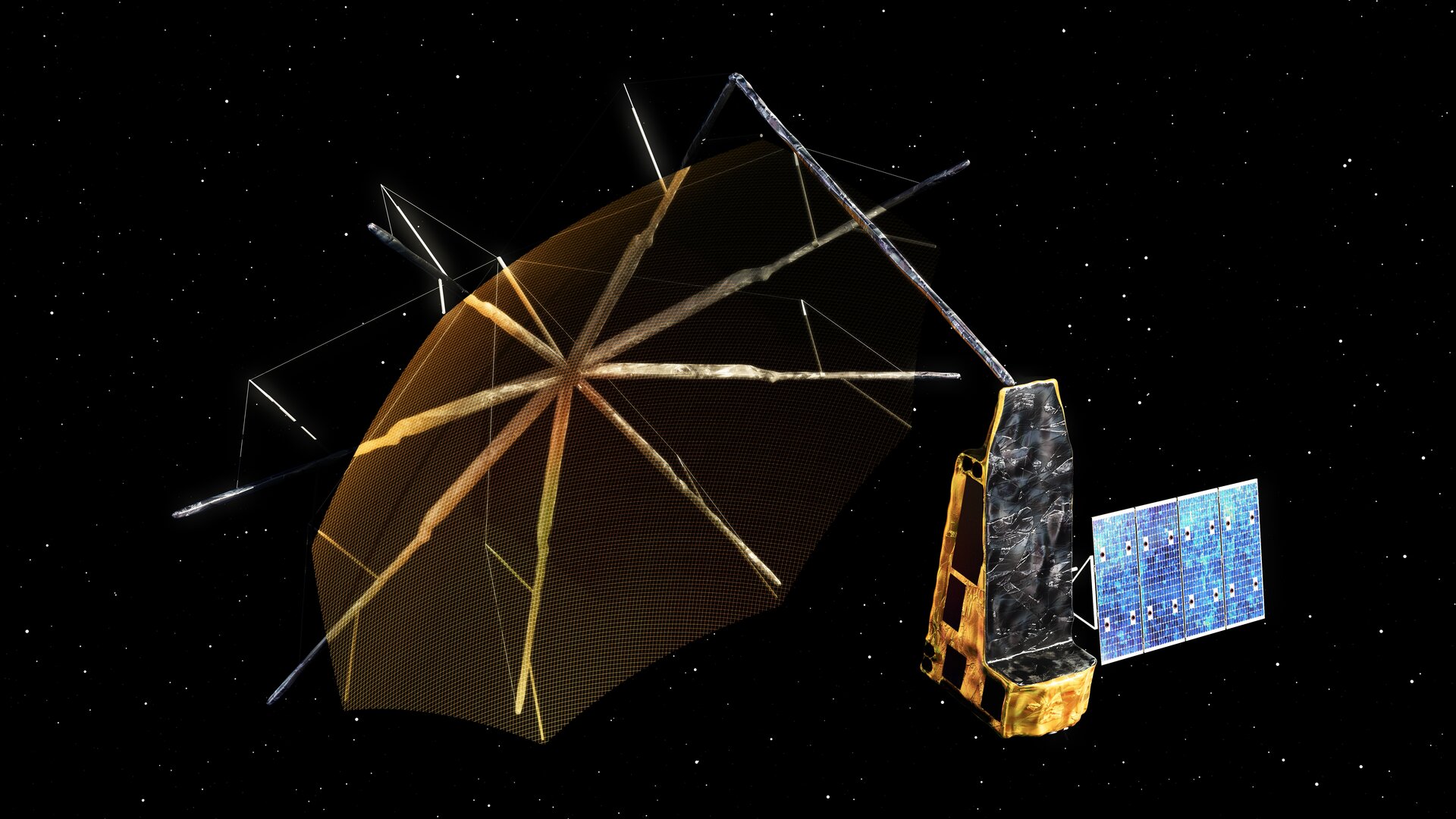
ESA Biomass Satellite Mission

- 09 Apr 2025
In News:
The Biomass Mission is a new Earth observation mission by the European Space Agency (ESA) aimed at enhancing our understanding of the global carbon cycle through accurate forest biomass measurements.
Launch Details:
- Rocket: Vega-C
- Launch Site: Europe’s Spaceport, French Guiana
- Orbit: Sun-Synchronous Orbit (SSO) at an altitude of ~666 km
- Scheduled Launch Date: 29 April 2025 (subject to final checks)
Key Features:
- First satellite to use P-band radar (long-wavelength synthetic aperture radar).
- Capable of penetrating dense forest canopies to scan tree trunks, branches, and stems — where most of a tree’s carbon is stored.
- Will generate 3D maps of the world’s tropical forests.
Mission Objectives:
- Measure above-ground forest biomass and forest height.
- Create five global biomass maps over its five-year mission.
- Monitor changes in forests to assess their role in carbon sequestration and climate regulation.
Scientific Importance:
- Forests absorb ~8 billion tonnes of CO? annually and are often referred to as "Earth’s green lungs."
- By analyzing forest carbon storage and changes, the mission will contribute significantly to:
- Monitoring climate change
- Supporting carbon accounting
- Improving air quality assessments
Phases of the Mission:
- Initial Phase: Produces detailed 3D forest maps globally.
- Second Phase: Generates global estimates of forest height and biomass.
Relevance to Climate Action:
- Helps in quantifying carbon uptake and release.
- Supports global climate models and carbon budgeting.
- Aids in policy-making for sustainable forest management.
Mount Marapi Eruption
- 06 Apr 2025
In News:
In May 2025, Mount Marapi, one of Indonesia’s most active volcanoes, erupted, spewing a column of volcanic ash 1.5 km into the sky. The event has once again highlighted the seismic vulnerability of the Pacific Ring of Fire, where tectonic activity frequently triggers volcanic eruptions and earthquakes.
About Mount Marapi
- Location: Situated in the Padang Highlands of western Sumatra, Indonesia.
- Type: A stratovolcano (composite volcano), consisting of successive layers of lava, ash, and pyroclastic material.
- Elevation: Rises to 2,891 meters (9,485 feet) above sea level, making it the highest peak in the region.
- Summit Feature: Contains the Bancah caldera (approx. 1.4 km wide), with multiple overlapping craters.
- Tectonic Setting: Lies on the Pacific Ring of Fire, a highly seismically active zone encircling the Pacific Ocean.
- Notable Eruption: In 1979, a deadly eruption-induced lahar (volcanic mudflow) caused by intense rainfall resulted in 60 fatalities.
Dark Oxygen
- 20 Jan 2025
In News:
Scientists who recently discovered that metal lumps on the dark seabed make oxygen, have announced plans to study the deepest parts of Earth's oceans in order to understand the strange phenomenon.
What is Dark Oxygen?
Dark Oxygen refers to oxygen produced deep under the ocean without sunlight or photosynthesis.
Discovered in July 2024, this challenges the long-standing belief that photosynthesis is the sole natural source of oxygen.
Where was it discovered?
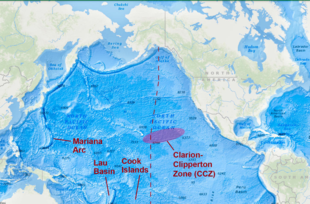
- Location: Clarion-Clipperton Zone (CCZ), 13,100 feet deep in the North Pacific Ocean, between Hawaii and Mexico.
- Zone Significance: Rich in polymetallic nodules containing manganese, iron, cobalt, nickel, copper, and lithium — crucial for green technologies.
Mechanism of Oxygen Production
- Polymetallic nodules on the seafloor generate oxygen via electrochemical reactions.
- These nodules split seawater (H?O) molecules into hydrogen and oxygen, without any light.
- This process is non-biological and independent of photosynthesis.
Why is this Discovery Important?
- Scientific Paradigm Shift: Challenges the idea that photosynthesis is the only natural pathway for oxygen generation.
- Origins of Life: Suggests that oxygen production may have existed before photosynthetic organisms, reshaping theories of early Earth’s evolution.
- Astrobiological Implications: Indicates the possibility of oxygen-rich environments on other planets, even without sunlight — enhancing the search for extraterrestrial life.
- Environmental Tech Potential: Could lead to innovations in renewable energy and carbon-neutral technologies, using metal-based catalysis.
About the Clarion-Clipperton Zone (CCZ)
- Geographic span: Between Hawaii and Mexico in the North Pacific Ocean.
- Resources: Contains vast reserves of critical minerals like manganese, nickel, cobalt — essential for electric vehicles and solar technology.
- A focus area for deep-sea mining and sustainability studies.
