National Mission on Edible Oils (NMEO)
- 13 Dec 2025
In News:
The Government of India is implementing the National Mission on Edible Oils (NMEO) through two components -NMEO–Oil Palm (NMEO-OP) and NMEO–Oilseeds (NMEO-OS), to reduce India’s heavy dependence on edible oil imports. In 2023–24, imports met about 56% of domestic edible oil demand.
NMEO – Oil Palm (NMEO-OP)
- About:Launched in 2021 as a Centrally Sponsored Scheme, NMEO-OP aims to expand oil palm cultivation and increase domestic Crude Palm Oil (CPO) production.
- Financial Outlay: ?11,040 crore
- Key Features
- Viability Price (VP): Price assurance mechanism to protect farmers from fluctuations in global CPO prices
- Higher Subsidies: Assistance for planting material increased significantly (up to ?29,000/ha) along with maintenance support
- Rejuvenation Aid: ?250 per plant for replacing old palms
- Regional Focus: Special emphasis on North-East India and traditional states like Andhra Pradesh and Telangana
- Targets
- Area Expansion: 6.5 lakh hectares under oil palm by 2025–26
- Production:
- 11.2 lakh tonnes CPO by 2025–26
- 28 lakh tonnes CPO by 2029–30
- Consumption Benchmark: Maintain edible oil consumption at 19 kg/person/year till 2025–26
- Progress
- 2.5 lakh hectares added under NMEO-OP (as of Nov 2025)
- Total oil palm area reached 6.2 lakh hectares
- CPO production rose from 1.91 lakh tonnes (2014–15) to 3.8 lakh tonnes (2024–25)
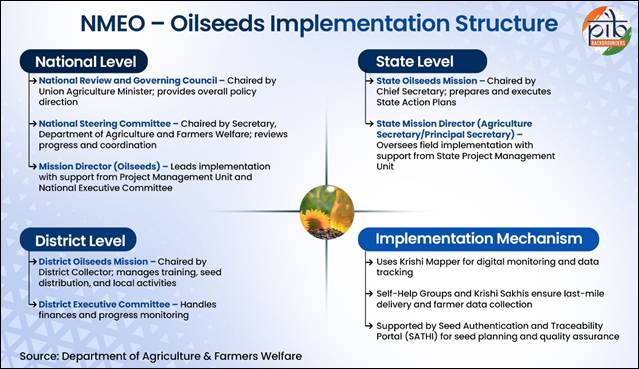
NMEO – Oilseeds (NMEO-OS)
- About:Approved in 2024 for the period 2024–25 to 2030–31, NMEO-OS focuses on achieving self-sufficiency in edible oils by boosting production of major oilseed crops.
- Coverage: Targets 9 major oilseed crops including:Mustard, Groundnut, Soybean, Sunflower, Sesame, Safflower, Niger, Castor, and Linseed
- Also promotes oils from secondary sources such as cottonseed, rice bran, coconut, and tree-borne oilseeds (neem, jatropha, karanja, mahua, simarouba).
Key Objectives
- Bridge yield gaps via improved seeds and technologies
- Expand area using fallow lands and intercropping
- Strengthen seed systems and market access
- Promote value addition and higher farmer returns
Targets
- Increase oilseed area from 29 million ha (2022–23) to 33 million ha (2030–31)
- Raise oilseed production from 39 million tonnes to 69.7 million tonnes
- Add 40 lakh hectares through crop diversification and fallow land use
Combined Impact of NMEO
Together, NMEO-OP and NMEO-OS aim to produce 25.45 million tonnes of edible oil by 2030–31, meeting about 72% of India’s domestic demand.
Implementation Support
- Self-Help Groups and Krishi Sakhis act as Community Agriculture Service Providers (CASPs)
- Use of Krishi Mapper digital platform for real-time monitoring
Oilseeds in India — Key Facts
- Oilseeds are India’s second most important crop group after food grains
- Cover 14.3% of gross cropped area
- Provide 12–13% of dietary energy
- Major producing states: Rajasthan (mustard), Madhya Pradesh (soybean), Gujarat, Maharashtra
- Oil palm concentrated in Andhra Pradesh & Telangana, expanding in North-East states
Economic Importance
- Key source of dietary fats and vitamins (A, D, E, K)
- Important cash crops for farmer income
- Contribute ~8% of agricultural exports
- Domestic edible oil production: 12.18 million tonnes (2023–24) vs high demand
Reasons for Import Dependence
- Decline in self-sufficiency after import duty reductions post-WTO reforms
- 76% oilseed area is rainfed, making production climate-vulnerable
- Rising consumption: Rural intake up 83.68%, urban up 48.74% (2004–05 to 2022–23)
Export Promotion Mission

- 13 Dec 2025
In News:
The Government of India has approved the Export Promotion Mission (EPM) to strengthen India’s export ecosystem, with special emphasis on MSMEs, labour-intensive sectors, and low-export-intensity regions.
What is the Export Promotion Mission (EPM)?
The Export Promotion Mission is a unified, digitally driven framework announced in Union Budget 2025–26. It consolidates multiple export-support schemes into one coordinated system to improve efficiency and outcomes.
- Total Outlay: ?25,060 crore
- Duration: FY 2025–26 to FY 2030–31
- Implementing Agency:Directorate General of Foreign Trade (DGFT)
- Anchored through coordination among the Department of Commerce, MSME Ministry, Finance Ministry, Export Promotion Councils, Commodity Boards, financial institutions, industry bodies, and State governments
Two Integrated Sub-Schemes
1. NiryatProtsahan (Financial Support)
Focuses on improving access to affordable trade finance:
- Interest subvention on export credit
- Export factoring and deep-tier financing
- Exporter credit cards for e-commerce
- Collateral support and credit enhancement for MSMEs
2. Niryat Disha (Non-Financial Support)
Enhances export readiness and competitiveness:
- Quality testing, certification, compliance assistance
- Branding, packaging, trade fairs, buyer–seller meets
- Warehousing and logistics support
- Inland transport reimbursement for exporters from remote districts
- District-level export capacity building
Digital Governance
- DGFT operates a paperless digital platform for application, approval, and fund disbursal
- Linked with customs and trade systems for faster processing
- Outcome-based monitoring ensures adaptability to global trade shifts
Sectoral & Regional Focus
EPM prioritizes sectors facing global tariff pressures:
- Textiles
- Leather
- Gems &Jewellery
- Engineering goods
- Marine products
It also targets:
- MSMEs and first-time exporters
- Labour-intensive value chains
- Interior and low-export districts to widen India’s export base
Complementary Financial Support
Credit Guarantee Scheme for Exporters (CGSE)
- Provides 100% government-backed credit guarantee
- Enables additional working capital for exporters, especially MSMEs
- Implemented via National Credit Guarantee Trustee Company
RBI Trade Relief Measures (2025)
The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) introduced steps to ease liquidity stress:
- Moratorium on certain loan repayments
- Extension of export credit tenure up to 450 days
- Relaxation in working-capital norms
- Regulatory forbearance in asset classification
- FEMA relaxation extending export realisation period to 15 months
Expected Outcomes
- Improved access to affordable export finance
- Better quality compliance and global certification
- Stronger international branding of Indian goods
- Growth in exports from non-traditional districts
- Employment generation in manufacturing and logistics
These outcomes support export-led growth, align with Atmanirbhar Bharat, and contribute to the Viksit Bharat @ 2047 vision.
Status of India’s Exports
- Total exports reached USD 778.21 billion in 2023–24
- Growth of 67% since 2013–14
- Services exports contribute ~44% of total exports
- Major markets include: USA, UAE, Netherlands, China, Singapore, UK, Saudi Arabia, Bangladesh, Germany, Italy
- Export basket shifting from low-value goods to electronics, engineering goods, and advanced manufacturing
Other Major Export Promotion Initiatives
India has also launched multiple initiatives to improve export competitiveness:
- PM Gati Shakti for integrated logistics planning
- National Logistics Policy to reduce logistics cost
- RoDTEP&RoSCTL for tax and duty remission
- PLI Schemes to scale up manufacturing
- TIES Scheme for export infrastructure
- Free Trade Agreements for market access
- Districts as Export Hubs (DEH) initiative
- MSME Lean & ZED schemes for quality improvement
Global Environment Outlook–7 (GEO-7), 2025

- 13 Dec 2025
In News:
The 7th edition of the Global Environment Outlook (GEO-7) was released by the United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP) during its session in Nairobi, warning that the world is far off track in meeting climate and environmental goals.
About Global Environment Outlook (GEO)
- The Global Environment Outlook is UNEP’s flagship assessment of the state of the global environment, future risks, and policy solutions. It provides scientific evidence for international environmental decision-making.
Key Findings of GEO-7
Rising Greenhouse Gas Emissions
- Global GHG emissions have grown ~1.5% annually since 1990
- 2024 recorded temperatures around 1.55°C above pre-industrial levels
- Intensifying heatwaves, floods, droughts, and extreme events
Biodiversity Loss
- 1 million species (out of ~8 million) face extinction
- 20–40% of global land is degraded
- Over 3 billion people are affected by land degradation
Economic Costs of Environmental Damage
- Climate-related disasters cost ~USD 143 billion annually
- Air pollution caused USD 8.1 trillion in health damages in 2019 (≈6% of global GDP)
- 9 million deaths per year linked to pollution
Plastic Pollution Crisis
- About 8 billion tonnes of plastic waste pollute ecosystems
- Toxic chemical exposure leads to ~USD 1.5 trillion annual health losses
Projected Impacts if Current Trends Continue
- Temperature thresholds: Likely to exceed 1.5°C in early 2030s and 2°C by 2040s
- Economic decline: Global GDP may fall 4% by 2050 and 20% by 2100
- Loss of fertile land: Equivalent to losing a country-sized fertile area annually
- Food insecurity: Per capita food availability may drop 3.4% by 2050
- Rising hunger, poverty, displacement, and conflict risks
GEO-7 Recommended Transformative Actions
Economy & Finance
- Move beyond GDP to wealth-based indicators
- Price environmental externalities
- Invest in decarbonization, ecosystem restoration, sustainable agriculture
- USD 8 trillion/year investment needed till 2050
- Could generate USD 20 trillion annual benefits by 2070
Materials & Waste
- Promote circular economy models
- Transparent product design and recycling chains
- Shift from linear consumption to regenerative systems
Energy Transition
- Rapid decarbonization of energy
- Improve energy efficiency
- Secure sustainable critical mineral supply chains
- Reduce air pollution → 9 million premature deaths avoidable by 2050
Food Systems
- Promote sustainable diets
- Reduce food loss and waste
- Improve agricultural efficiency
- Could reduce undernourishment by ~200 million people
Ecosystem Protection
- Scale up ecosystem restoration
- Use Nature-based Solutions (NbS) for adaptation
- Stronger mitigation and biodiversity conservation policies
Collaborative & Integrated Governance
- Solutions must involve governments, private sector, civil society, academia, Indigenous communities
- Policies across sectors must be implemented together, not in isolation
About UNEP
- Established in 1972 after the Stockholm Conference
- Headquarters: Nairobi, Kenya
- Leading global authority on environmental issues
- Major reports include:
- Emissions Gap Report
- Adaptation Gap Report
- Global Environment Outlook
- Frontiers Report
African Penguin
- 13 Dec 2025
In News:
A recent scientific study reported that over 60,000 African penguins died of starvation between 2004 and 2011 after a sharp collapse in sardine stocks off southern Africa. The die-off was particularly severe around Dassen Island and Robben Island.
About the African Penguin
- Common Name: African Penguin
- Scientific Name:Spheniscus demersus
- One of the 18 penguin species globally
- Among the smallest penguins and strong swimmers
- Flightless, adapted to marine life
Distinctive Features
- Black facial mask and unique black chest-spot patterns (like fingerprints)
- Pink glands above the eyes help regulate body temperature (become pinker when hot)
Habitat & Distribution
- Found along the coasts of Namibia and South Africa
- Lives on sandy beaches and rocky shores, unlike Antarctic penguins
- Usually forages within 40 km of the shore
- Comes ashore for breeding, moulting, and resting
Breeding & Life Cycle
- Traditionally breeds in burrows dug into guano, which protect from heat
- Average lifespan: ~20 years in the wild
Annual Moult (Critical Survival Phase)
- Occurs once a year and lasts about 21 days
- Penguins remain on land and cannot enter the sea to feed
- They must build fat reserves before moulting
- During moult, they can lose nearly 50% of body mass
- After moulting, they need reliable food supply to regain strength
What Caused the Mass Starvation?
The study linked penguin deaths to collapse of sardine populations, their primary prey.
Key Findings
- Nearly 62,000 penguins died between 2004–2011
- Sardine stocks fell to ~25% below peak abundance
- Fishing pressure was extremely high, especially west of Cape Agulhas
- Exploitation rates peaked at 80% in 2006
- Large sardine catches occurred close to penguin colonies, reducing food access
Impact on Penguins
- Birds failed to build fat reserves before moult
- Post-moult weakened condition reduced their ability to catch prey
- Increased mortality due to starvation
Role of Climate Change
- Climate change is altering ocean temperatures and currents
- This affects distribution and availability of sardines
- Combined effect of overfishing + climate change intensifies food scarcity
Conservation Status
- Listed as Critically Endangered by the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN)
- Reclassified from Endangered to Critically Endangered in 2024
Conservation Concerns & Measures Needed
- Need for better fisheries management near penguin foraging areas
- Protection of key feeding grounds
- Long-term recovery of sardine biomass
- International conservation efforts under agreements like the African-Eurasian Migratory Waterbirds Agreement
Blue Corner Notice

- 13 Dec 2025
In News:
Recently, INTERPOL issued a Blue Corner Notice to trace the missing owners of a Goa nightclub after a major fire incident. The request from India was processed through the Central Bureau of Investigation (CBI), which is India’s nodal agency for INTERPOL coordination.
What is a Blue Corner Notice?
A Blue Corner Notice (also called an Enquiry Notice) is issued to:
- Collect additional information about a person’s identity
- Establish a person’s location
- Gather details about a person’s activities related to an ongoing criminal investigation
It is generally issued before formal criminal charges are filed.
It enables police forces in different countries to share investigative information.
It is not an arrest warrant
It does not automatically require detention
About INTERPOL
INTERPOL stands for the International Criminal Police Organization. It facilitates cooperation among police forces across countries to tackle transnational crimes such as terrorism, trafficking, cybercrime, financial crimes, and organized crime.
- It has 196 member countries
- India became a member in 1949
- Headquarters is located in Lyon, France
- It is not a United Nations agency, but it has had Permanent Observer status at the UN since 1996
- INTERPOL does not have its own police force; it functions as a coordination and information-sharing platform
Different Types of INTERPOL Notices
- Red Notice – Issued to locate and provisionally arrest a person wanted for prosecution or to serve a sentence.
- Blue Notice – Issued to collect additional information about a person’s identity, location, or activities in relation to a criminal investigation.
- Yellow Notice – Used to help locate missing persons, often minors, or to identify persons unable to identify themselves.
- Black Notice – Issued to seek information about unidentified bodies.
- Green Notice – Warns member countries about individuals with a history of criminal behaviour who may pose a future threat.
- Orange Notice – Warns about an event, person, object, or process posing a serious and imminent threat to public safety.
- Purple Notice – Used to share information on criminal methods, devices, concealment techniques, or modus operandi.
- Silver Notice (Pilot Phase) – Helps identify and trace assets linked to criminal activities.
- INTERPOL–UN Special Notice – Issued for individuals and entities subject to UN Security Council sanctions.
