Northern Pintail Duck

- 26 Feb 2025
In News:
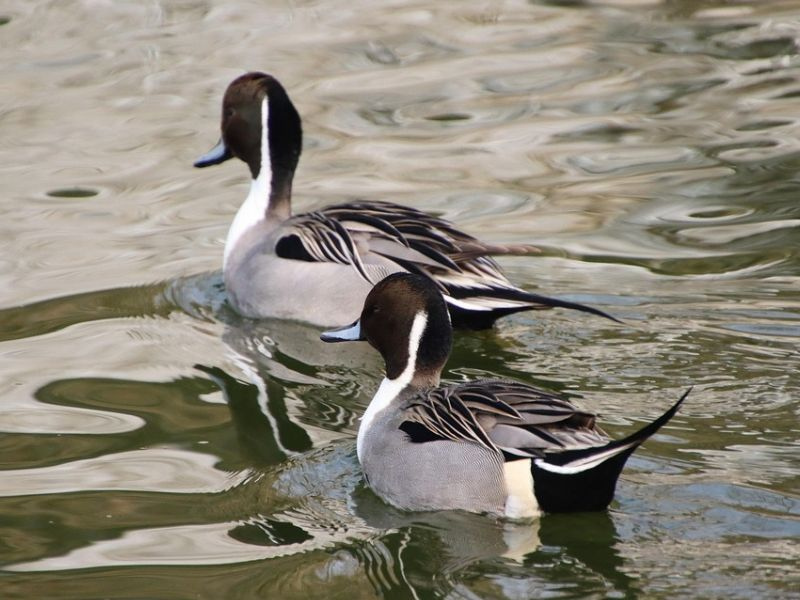
A flock of Northern Pintail ducks was recently sighted at an unprecedented altitude of 13,500 feet in Tawang, Arunachal Pradesh—far above their typical wintering habitats. This rare event has sparked interest in their migration behavior and adaptability to high altitudes.
About Northern Pintail Duck
- Scientific Name:Anas acuta
- Type: Migratory waterfowl known for elegance and long-range migration
- Common Nickname: Northern nomads
Distribution & Migration
- Found across every continent except Antarctica
- Breed in northern regions of Europe, Asia, and North America
- Migrate southward in winter to regions including the Indian subcontinent
- Typically observed in low-lying wetlands; rarely at high altitudes
- Do not breed or reside south of the equator
- Seen in the high-altitude region of Arunachal Pradesh during winter, raising questions about changing migration patterns and climate adaptability
Key Features
- Size: Around 60 cm in length, over 1 kg in weight
- Wingspan: Up to 91 cm
- Speed: Capable of flying at 48 miles per hour due to aerodynamic build
- Male Appearance: Buff-gray body, chocolate-brown head, broad white stripe on chest, black back patterns
- Female Appearance: Mottled brown body, lighter chest and neck
Conservation Status
- Listed as “Least Concern” under the IUCN Red List
- Despite being widespread, their migratory nature warrants regular monitoring to track habitat changes and population health
African-Asian Rural Development Organization (AARDO)

- 26 Feb 2025
In News:
The 21st AARDO Conference recently concluded in New Delhi, reaffirming the commitment to community-led rural development, local knowledge sharing, and South-South cooperation.
About AARDO
- Full Form: African-Asian Rural Development Organization
- Nature: Intergovernmental, autonomous organization
- Established:March 31, 1962
- Headquarters:New Delhi, India
- Origin:
- Conceptualized at the 1955 East Asian Rural Reconstruction Conference (Tokyo)
- Formalized after the 1961 Afro-Asian Conference on Rural Reconstruction (New Delhi)
- Permanent HQ established in 1966 in India
Membership
- Full Members:32 countries from Asia and Africa (e.g., India, Bangladesh, Egypt, Zambia, Malaysia)
- Associate Members:3 entities (e.g., Korea Rural Community Corporation, Agricultural Bank of Sudan)
- Eligibility: Open to Afro-Asian countries that are full or associate members of the UN or its specialized agencies focused on rural development
Observer Status with International Organizations
AARDO has observer status with:
- FAO – Food and Agriculture Organization
- IFAD – International Fund for Agricultural Development
- UNDP – United Nations Development Programme
- UNESCO – United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization
- UNCTAD – United Nations Conference on Trade and Development
Objectives & Aims
- South-South Cooperation: Enhance technical and economic collaboration in rural development between Asia and Africa
- Sustainable Rural Development: Promote poverty alleviation, food security, and climate-resilient agriculture
- Capacity Building & Knowledge Sharing: Encourage exchange of best practices, innovations, and research
Functions
- Policy & Dialogue Platform: Facilitates discussions among member countries on rural development strategies
- Training & Capacity Building: Organizes international, regional, and national training programs to strengthen rural institutions
- Research & Action Studies: Initiates and disseminates research on shared challenges in agriculture and rural livelihoods
- Pilot Projects: Offers technical and financial assistance for pilot projects to serve as replicable models
- International Collaboration: Partners with UN agencies, regional bodies, and NGOs for integrated rural development
- Data Sharing: Provides members with disaggregated statistics and information for informed decision-making
Soliga Tribe and Tiger Conservation

- 26 Feb 2025
In News:
In the 119th edition of Mann Ki Baat, Prime Minister Narendra Modi lauded the Soliga tribe of the BiligiriRanganathaswamy Temple (BRT) Tiger Reserve in Karnataka for their significant role in tiger conservation and sustainable forest practices.
Who are the Soligas?
- Location: Indigenous, forest-dwelling tribe residing primarily in Chamarajanagar district, Karnataka, and parts of Tamil Nadu, especially around Biligiri Rangana Hills and Male Mahadeshwara Hills.
- Meaning of the Name: "Soliga" translates to “children of bamboo”, symbolizing their deep ecological ties.
- Language: They speak Sholaga (a Dravidian language), along with Kannada and Tamil.
- Lifestyle:Soligas live in bamboo-and-mud huts, practice shifting cultivation, and depend on non-timber forest produce (NTFP) for sustenance.
- Diet & Livelihood:Honey is a staple in their diet; they extensively forage and harvest forest produce like amla, gooseberries, and medicinal herbs, leaving a portion for wildlife—a reflection of their conservation ethos.
Religious and Cultural Practices:
- Soligasworship wildlife, especially the tiger, locally called “DoddaNayi” (Great Dog). They have even built temples dedicated to tigers.
- Their belief system includes Hindu customs, animism, and naturism, highlighting their spiritual connection with nature.
- They produce eco-friendly artifacts like ‘jottai’ (leaf cups), showcasing sustainable craftsmanship.
Recognition of Forest Rights:
- In 2011, Soligas became the first tribal community in India to receive legal recognition of their forest rights within a tiger reserve, under the Forest Rights Act (FRA).
- This ruling allowed them to reside within the BRT Tiger Reserve and sustainably collect forest produce without displacing wildlife.
Role in Tiger Conservation:
- Soligas’ traditional knowledge of forest ecology helps them coexist peacefully with wildlife, minimizing human-animal conflict.
- They assist the Forest Department in fire prevention, wildlife tracking, and ecological management.
- Their cultural practices ensure minimal disturbance to wildlife. For instance, during harvest, they intentionally leave 25–33% of the produce in the forest for animals.
BiligiriRanganathaswamy Temple (BRT) Tiger Reserve:
- Location: Chamarajanagar district, Karnataka; lies at the confluence of the Western and Eastern Ghats, forming a critical wildlife corridor.
- Ecosystem: Rich in biodiversity with forest types including:
- Southern Tropical Evergreen
- Semi-Evergreen
- Moist Deciduous
- Flora:Axlewood, Rosewood, Terminalia spp., Indian Gooseberry, Ceylon Oak, Golden Shower Tree.
- Fauna: Tigers, Wild Dogs, Sloth Bears, Sambars, Bison, and endangered species like the Icthyophisghytinosus (Caecilian).
- Cultural Site: Named after Lord Rangaswamy, the reserve houses the Biligiri Temple atop mist-covered hills.
USD-INR Buy/Sell Swap Auction

- 26 Feb 2025
In News:
The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) has announced its largest-ever USD-INR Buy/Sell Swap Auction worth $10 billionfor a tenor of three years. This strategic move is aimed at addressing the persistent liquidity deficit in the banking system and stabilizing the Rupee-Dollar exchange rate.
What is a USD-INR Buy/Sell Swap Auction?
A Dollar/Rupee Buy-Sell Swap Auction is a foreign exchange (forex) tool used by RBI to manage domestic liquidity and curb currency volatility. It is a two-leg transaction:
- First Leg (Buy Phase):Banks sell US dollars to the RBI and receive rupee liquidity.
- Reverse Leg (Sell Phase):RBI sells back the same amount of US dollars to banks at a future date (here, after 3 years), along with a swap premium.
Key Features of the February 2025 Swap Auction:
- Auction Size: USD 10 billion
- Tenor: 3 years (long-term)
- Rupee Liquidity Injected: Approx. ?86,000 crore
- Auction Date: 28 February 2025
- Spot Settlement Date: 4 March 2025
- Far-leg Settlement Date: 6 March 2028
- Reference Rate: Based on FBIL (Financial Benchmarks India Pvt Ltd) benchmark
Objectives and Benefits:
- Liquidity Management:
- Addresses durable liquidity needs; helps ease banking system deficit (estimated at ?1.7 lakh crore).
- Supports credit flow to businesses, aiding economic growth.
- Exchange Rate Stability:
- Reduces volatility in the USD/INR rate (expected to stabilize around ?86.30).
- Mitigates pressure from foreign fund outflows.
- Efficient Forex Reserve Utilization:
- Uses RBI’s reserves productively to manage monetary conditions.
- Enhances Policy Transmission:
- Aligns money market interest rates with RBI’s monetary policy stance.
- Supports Inflation Control:
- Infuses liquidity without directly adding to inflationary pressures.
Challenges and Limitations:
- Impact on Forex Reserves:Large-scale swaps temporarily tie up reserves.
- Global Dependencies:Effectiveness may be affected by global interest rate differentials, capital flows, and external shocks.
- Market Speculation Risks:Poor timing or execution could trigger speculative activity in the forex market.
- Temporary Measure:Swap auctions offer short- to medium-term relief; structural reforms are needed for long-term liquidity management.
Bharat Tech Triumph Program (TTP)
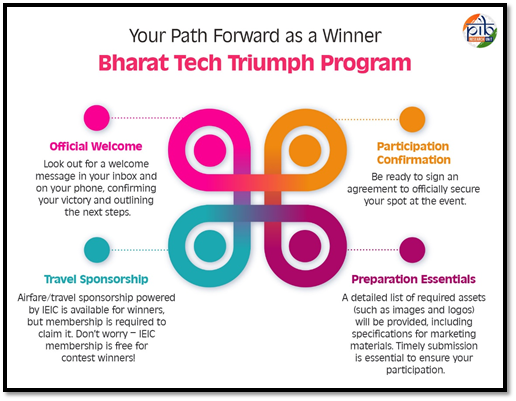
- 26 Feb 2025
In News:
Launched under the Create in India Challenge Season 1, the Bharat Tech Triumph Program (TTP) is a flagship initiative aimed at promoting India’s gaming and interactive entertainment ecosystem on the global stage.
Key Highlights
- Launch Year: 2025
- Ministry Involved: Ministry of Information and Broadcasting (MIB)
- Organizing Partner: Interactive Entertainment and Innovation Council (IEIC)
Objectives:
- Identify and showcase Indian gaming talent internationally.
- Support the growth of the gaming, animation, visual effects, and immersive technology (AR/VR/Metaverse) sectors.
- Boost the 'Create in India' initiative in the media and entertainment domain.
- Enable Indian developers and startups to create globally competitive digital products.
Program Features:
- Eligibility:
Open to developers, studios, startups, and tech companies with working prototypes in:- Game development
- Esports
- Business solutions for gaming ecosystem
- Selection Process:
- Game Submission
- Expert Evaluation – Based on product, pitch, and team viability
- Final Showcase – Winners selected by a jury
Global Exposure Platforms:
- Game Developers Conference (GDC) 2025
- Location: San Francisco
- Dates: March 17–21, 2025
- World Audio Visual Entertainment Summit (WAVES) 2025
- Location: Mumbai
- Dates: May 1–4, 2025
- Venue: Jio World Convention Centre &Jio World Gardens
- Focus Areas: Broadcasting, AVGC-XR, Digital Media, Innovation, and Films
Relevance of WAVES Summit:
- WAVES acts as a global convergence point for the Media & Entertainment (M&E) sector.
- AVGC-XR (Animation, Visual Effects, Gaming, Comics + AR/VR/Metaverse) is a central pillar, aligning with TTP’s goals.
Significance for India:
- Positions India as a global hub for innovation in digital entertainment.
- Supports Atmanirbhar Bharat in the tech and creative economy sectors.
- Encourages cross-border collaborations and export of Indian intellectual property in the gaming domain.
Quality of Public Expenditure (QPE) Index
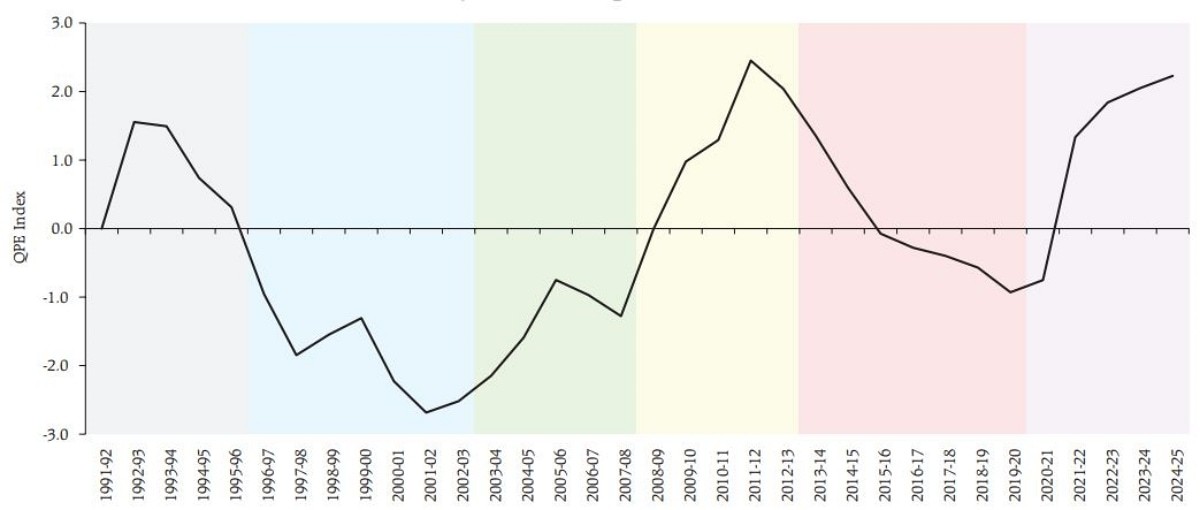
- 25 Feb 2025
In News:
The Quality of Public Expenditure (QPE) Index, developed by the Reserve Bank of India (RBI), measures how efficiently public funds are allocated and utilized by the Central and State governments. Unlike traditional fiscal measures that focus on total expenditure, the QPE Index assesses the composition and developmental impact of government spending, emphasizing long-term economic growth and social development.
Key Components of the QPE Index
Indicator What it Measures Significance
Capital Outlay to GDP Ratio - Share of GDP spent on physical infrastructure - Higher ratio = better quality of expenditure
Revenue Expenditure to Capital Outlay Ratio - Relative spending on salaries, pensions vs. asset creation - Lower ratio = better efficiency
Development Expenditure to GDP Ratio - Spending on education, healthcare, R&D, infrastructure - Higher ratio = enhanced productivity
Development Expenditure as % of Total Expenditure - Proportion of total expenditure directed to development sectors - Higher share = improved allocation
Interest Payments to Total Expenditure Ratio - Financial burden from past borrowings - Lower ratio = better fiscal health
Evolution of Public Expenditure (1991–2025)
- 1991–1997(Early liberalization):
- Slight improvement at Centre; states faced fiscal pressure.
- Public investment declined due to focus on fiscal deficit reduction.
- 1997–2003:Decline in QPE due to Fifth Pay Commission, rising interest burden, dominance of revenue expenditure.
- 2003–2008(FRBM Era):
- Fiscal Responsibility and Budget Management (FRBM) Act, 2003 improved fiscal discipline.
- States gained from higher tax devolution; capital spending rose.
- Growth momentum sustained until the 2008 Global Financial Crisis (GFC).
- 2008–2013(GFC response):
- Stimulus spending initially boosted development but later widened fiscal deficits.
- Spending quality eroded over time.
- 2013–2019(GST & 14th Finance Commission):
- 14th Finance Commission (2015) increased states' tax share to 42%, improving state-level development spending.
- GST rollout (2017) benefited states more than Centre initially, stressing Centre’s finances.
- 2019–2025(COVID-19 & Recovery):
- Pandemic-induced fiscal stimulus reduced QPE temporarily.
- Post-pandemic recovery led by record capital expenditure boosted infrastructure, improving QPE.
- By FY 2024–25, India's QPE reached its highest level since 1991 reforms.
Recent Trends in Public Expenditure (as per Economic Survey 2024–25 & Budget 2025–26)
- Capital expenditure (Capex) rose 8.2% YoY.
- Revenue expenditure (primarily by states) increased 12% YoY.
- FY 2025–26 Budget allocated ?11.21 lakh crore for Capex (3.1% of GDP).
- Capex to GDP ratio increased from 1.5% in 2000 to 2.5% in 2023.
- Revenue expenditure to Capex ratio improved from 8:1 in 2000 to 5:1 in 2023.
- Development expenditure rose from 6% to 8% of GDP between 2000–2023.
- Interest payments declined from 25% to 20% of total expenditure in the same period.
Why Quality of Public Expenditure Matters
- Governments use citizens’ money (via taxes or borrowing). Efficient use ensures better socio-economic outcomes.
- High QPE means greater focus on productive investment over populist spending (freebies, subsidies).
- Better QPE leads to:
- Higher GDP growth (average 6.5% annually since 2000).
- Improved infrastructure and service delivery.
- Enhanced social indicators like literacy (77.7% in 2023) and life expectancy (70 years).
Challenges Affecting Public Expenditure Quality
- Persistent revenue deficits (3.3% of GDP in 2023) limit fiscal space for Capex.
- Rising populism: Loan waivers, cash handouts, free electricity.
- Welfare scheme inefficiencies: Leakages in MGNREGA, PDS.
- Debt servicing: High interest payments constrain spending.
- Inter-state disparities: Unequal fiscal capacity hampers balanced development.
Way Forward
- Boost Capex to over 3% of GDP to enhance infrastructure-led growth.
- Rationalize subsidies via Direct Benefit Transfers (DBT).
- Strengthen fiscal federalism through equitable devolution and performance-based grants.
- Leverage technology for transparent and outcome-based expenditure tracking.
- Reform FRBM Act:
- Focus on debt-to-GDP targets.
- Introduce flexibility in deficit norms during crises.
Biotechnology and Bioeconomy in North East India

- 25 Feb 2025
In News:
The North Eastern Region (NER) of India, endowed with rich biodiversity, cultural heritage, and indigenous knowledge, is undergoing a transformation through biotechnology-led initiatives. The Department of Biotechnology (DBT) under the Ministry of Science and Technology is spearheading this change to harness the region’s biological resources for inclusive and sustainable development.
Biotechnology: Definition and Types
Biotechnology involves the use of biological systems or organisms to develop products and technologies that improve healthcare, agriculture, industry, and the environment.
Types of Biotechnology:
- Medical Biotechnology – Vaccines, gene therapy, diagnostics.
- Agricultural Biotechnology – Pest-resistant crops, high-yield seeds, and sustainable agriculture.
- Industrial Biotechnology – Biofuels, biodegradable plastics, enzyme-based processes.
- Environmental Biotechnology – Waste treatment, pollution control, and bioremediation.
Why North East India is Ideal for Biotech Development
- Biodiversity Hotspot: Home to 8,000+ plant species, including 850+ medicinal plants and agro-climatic diversity.
- Indigenous Knowledge: Rich traditional practices in herbal medicine and organic farming.
- Agri-Biotech Potential: Ideal for medicinal crops, essential oils, and organic produce.
- Industrial Opportunity: Scope for biofuel production, value-added food processing, and pharmaceutical industries.
Key DBT Programmes and Initiatives in the North East
- DBT North Eastern Programme
- Since 2010, 10% of DBT’s annual budget is dedicated to NER.
- Focus: R&D, education, infrastructure, entrepreneurship, and employment generation in biotechnology.
- Twinning R&D Programme (2010–11)
- Promotes collaborative biotech research between NER and national institutes.
- Over 65 institutional partnerships, supporting 650+ projects and benefiting ~2,500 researchers/students.
- Biotech Hubs Network (Since 2011)
- 126 Biotech Hubs established across universities and colleges.
- Phase II supports 54 hubs for focused research on local issues.
- BLiSS (Biotech Labs in Senior Secondary Schools): Started in 2014 to introduce biotechnology at the school level.
- Visiting Research Professorship (VRP) Programme:Launched in 2015 to utilize the expertise of top scientists for NER biotechnology development.
- Chemical Ecology Programme (2015): Collaborative training by NCBS, UAS, and IISc for Ph.D. scholars in the field of chemical ecology.
- Genomics Training Programme (2016):Conducted by DBT-NIBMG, Kalyani, for biomedical researchers in the region.
Agri-Biotech and Livelihood-Oriented Initiatives
- DBT-NECAB (Phase III): Enhancing biotech applications in agriculture.
- Citrus Research: Disease-free scion material of Khasi mandarin and sweet orange developed at IHT, Assam.
- Medicinal Crop Cultivation: 64.1 acres under Curcuma caesia and lemongrass cultivation; 649 farmers trained.
- Essential Oil Distillation: Facility set up in Mudoi village, Arunachal Pradesh, for revenue support.
- Value-Addition in Wild Fruits: Docynia indica (Assam apple) processed into products like jam, pickles, and candy.
Technology-Driven Achievements
- Bacterial Blight-Resistant Rice (Patkai): Developed by Assam Agricultural University; notified by CVRC.
- Brucellosis Detection Kit: Lateral Flow Assay (LFA) to detect anti-Brucella antibodies in livestock.
- Pig Disease Diagnosis Expert System (PDDES): Mobile app for livestock disease detection and management (available on Google Play Store).
Challenges in NER’s Biotech Growth
- Limited infrastructure for biotech R&D and production.
- High cost of commercial biotech projects.
- Shortage of trained professionals in advanced biotech fields.
- Vulnerability to climate change and poor connectivity with markets.
Way Forward
- Strengthen Infrastructure: Develop biotech parks, R&D centers, and incubators.
- Skill Development: Train local youth, researchers, and farmers.
- Public-Private Partnerships: Foster industrial collaboration for startups and innovation.
- Eco-friendly Technologies: Promote sustainable and low-impact biotech industries.
- Digital Integration: Use AI and data analytics for agricultural and healthcare biotech solutions.
Northern White Rhino
- 25 Feb 2025
In News:
The Northern White Rhino (NWR) is on the brink of extinction, with only two females—Najin and Fatu—remaining at the Ol Pejeta Conservancy in Kenya. However, a breakthrough in In-Vitro Fertilization (IVF) has rekindled hope for reviving this subspecies, with 36 lab-created embryos ready for implantation. This effort is part of an international project named BioRescue.
About the White Rhino
- Scientific Name: Ceratotherium simum
- Common Name: Square-lipped rhinoceros (due to broad upper lip)
- Subspecies:
- Northern White Rhino (Ceratotherium simum cottoni)
- Southern White Rhino (Ceratotherium simum simum)
- Habitat:
- Southern White Rhino: South Africa, Namibia, Zimbabwe, Kenya
- Northern White Rhino: Historically central and eastern Africa; now only in captivity
- IUCN Status:
- White Rhino (overall): Near Threatened
- Northern White Rhino: Critically Endangered
- Southern White Rhino: Near Threatened
Biological Features
- Second-largest land mammal after elephants
- Square upper lip adapted for grazing on short grasses
- Two horns, with the front horn being larger
- No actual color difference between black and white rhinos
Social & Dietary Behavior
- Diet: Pure herbivores; feed almost exclusively on short grasses
- Behavior:
- Semi-social and territorial
- Males mark territories with dung
- SWRs form larger social herds; NWRs were found in smaller groups
Threats to Survival
- Poaching for horns
- Habitat loss due to human encroachment
- Civil unrest, particularly in their native range
- Low genetic diversity, especially critical in the NWR
- Climate change, affecting habitat and water sources
Conservation Through Reproductive Technology
BioRescue Initiative
- An international scientific effort launched in 2015 to save the NWR using advanced reproductive technologies.
- Uses frozen sperm from deceased males and eggs from Najin and Fatu to create embryos in the lab.
- 36 embryos have been successfully created and are stored for future implantation.
IVF and Surrogacy
- First-ever rhino pregnancy via lab-made embryo announced recently.
- Southern white rhinos are used as surrogate mothers due to genetic similarity and higher population.
- IVF and embryo transfers are the only options since the last male NWR, Sudan, died in 2018, and both remaining females are non-reproductive due to age and health.
Challenges & Concerns
- Limited gene pool restricts genetic variability.
- Loss of unique traits if crossbred with southern white rhinos.
- Behavioral imprinting: IVF calves must learn from remaining NWR females before they pass away.
- Ethical and ecological concerns: Critics argue conservation must also address root causes like poaching, habitat destruction, and lack of genetic diversity, not just focus on “test-tube” solutions.
Indian Rhinoceros
- Scientific Name: Rhinoceros unicornis (Greater One-Horned Rhino)
- IUCN Status: Vulnerable
- Habitat: Indian subcontinent (Assam, West Bengal, UP, Nepal)
- It is distinct from African rhinos, both genetically and ecologically.
Electronic Personnel License (EPL) for Pilots
- 25 Feb 2025
In News:
India has launched the Electronic Personnel License (EPL) for pilots, becoming the second country globally, after China, to implement this advanced digital licensing system.
What is EPL?
- Electronic Personnel License (EPL) is a digital version of pilot licenses, replacing the traditional physical cards.
- Pilots can securely access their EPL via the eGCA Mobile Application developed by the Directorate General of Civil Aviation (DGCA).
- It ensures real-time verification, enhancing efficiency, transparency, and security in licensing procedures.
Significance of EPL
- Aligns with:
- Digital India and Ease of Doing Business initiatives.
- ICAO’s Amendment 178 to Annex 1 on Personnel Licensing, promoting digital transformation.
- Enhances:
- Safety and efficiency in civil aviation operations.
- Environmental sustainability by reducing the use of plastic and paper.
- Global employability of Indian pilots through instant international credential verification.
Implementation & Governance
- Ministry: Ministry of Civil Aviation, Government of India.
- Executing Agency: Directorate General of Civil Aviation (DGCA).
- EPL implementation positions India as a leader in aviation innovation and modern governance.
International Civil Aviation Organization (ICAO):
- Established: 1947 under the Chicago Convention (1944).
- Headquarters: Montreal, Canada.
- Nature: A specialized intergovernmental agency affiliated with the United Nations (UN).
- Functions:
- Sets standards and regulations for aviation safety, security, efficiency, and environmental performance.
- Promotes peaceful and efficient international air transport.
- Facilitates global cooperation and market liberalization in aviation.
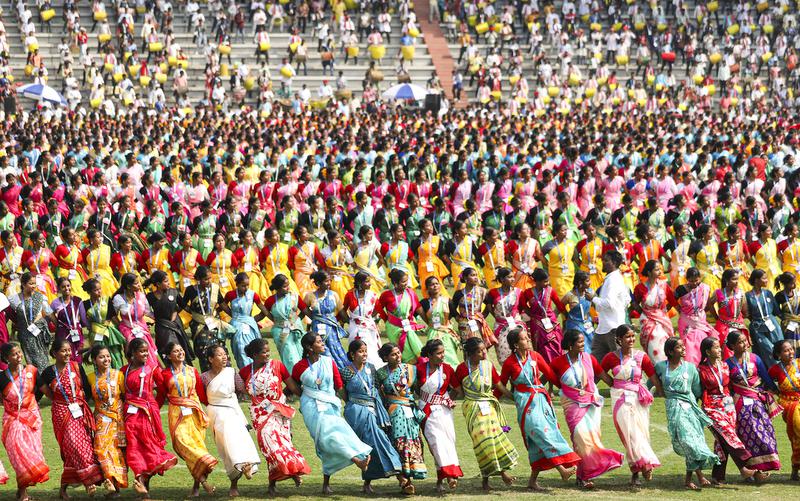
Jhumoir Binandini (Jhumur) Dance

- 25 Feb 2025
In News:
The Prime Minister of India is set to attend the Jhumoir Binandini (Mega Jhumoir) 2025, a grand cultural event featuring around 8,600 performers showcasing the traditional Jhumur dance. This event highlights the rich cultural contributions of the tea tribe community of Assam.
About Jhumoir (Jhumur) Dance
- Jhumur, also known as Jhumoir, is a traditional folk dance performed predominantly by the Adivasi tea tribes of Assam.
- It is typically showcased during the harvest season, as well as on occasions like weddings and community festivals.
- The dance was introduced to Assam by the tea garden workers, who originally migrated from regions like Jharkhand, Odisha, Chhattisgarh, and West Bengal in the 19th century under British colonial rule.
Cultural Origins and Community
- The dance traces its roots to the Sadan ethnolinguistic group from the Chotanagpur plateau (present-day Jharkhand).
- The tea tribe community is a multi-ethnic group comprising descendants of migrant tea garden laborers.
- These communities have significantly shaped Assam’s socio-cultural landscape.
Performance Style and Attire
- Jhumur is performed in a circular formation, with dancers often holding each other's waists.
- The performance features rhythmic footwork, swaying movements, and energetic music.
- Women typically wear colorful sarees, often in red and white, while men dress in dhotis and kurtas.
- The musical accompaniment includes traditional instruments like the Madal, Dhol, Dhak, Taal (cymbals), and Flute.
Themes and Social Significance
- Jhumur songs blend liveliness with social commentary, often highlighting the struggles, exploitation, and migration experiences of the tea plantation workers.
- Major tea garden festivals where Jhumur is performed include Tushu Puja and Karam Puja, both celebrating the harvest.
- The dance fosters community bonding, promotes cultural pride, and represents Assam’s syncretic cultural heritage.
- It stands as a symbol of inclusivity, unity, and the resilience of the tea tribe community.
Dr. Purnima Devi Barman

- 24 Feb 2025
In News:
Indian wildlife biologist Dr. Purnima Devi Barman has been named among TIME Magazine’s Women of the Year 2025, recognizing her as one of 13 global leaders working toward a more equitable and sustainable world. She is the only Indian woman on the list.
Key Contributions:
- Known for her pioneering conservation work with the greater adjutant stork (locally called Hargila), once critically endangered and culturally stigmatized in Assam.
- Founded the Hargila Army, a women-led grassroots movement focused on protecting the stork’s habitat and changing negative local perceptions.
- Her model uniquely blends wildlife conservation with women’s empowerment, engaging thousands of rural women in ecological and livelihood activities.
Impact:
- Due to her efforts, the greater adjutant stork’s population in Assam has significantly recovered, leading to its status being upgraded from “endangered” to “near threatened” by IUCN.
- The Hargila Army, with over 10,000 members, participates in bird rescue, awareness campaigns, tree planting, and embroidery-based income generation.
- Her approach has become a global model for community-based conservation.
Background:
- Hails from the Kamrup region of Assam.
- Holds a Master’s degree in Zoology from Gauhati University.
- Inspired by her early life near the Brahmaputra and her grandmother’s teachings on biodiversity.
Awards & Recognition:
- Nari Shakti Puraskar (2017) – India’s highest civilian award for women.
- UN Champions of the Earth Award (2022) – For entrepreneurial vision in conservation.
- Whitley Gold Award (2017, 2024) – Often called the "Green Oscar".
Other Roles:
- Director of Women in Nature Network (YNN) – India chapter.
- Member of IUCN’s Stork, Ibis, and Spoonbill Specialist Group.
About TIME Magazine:
- Founded in 1923, USA.
- Known for its global recognitions like Person of the Year and Women of the Year.
- Now operates as a multimedia platform covering politics, science, and culture.
Microsoft’s Majorana 1 Quantum Chip
- 24 Feb 2025
In News:
Microsoft has unveiled Majorana 1, a new quantum chip that marks a significant advancement in quantum computing, suggesting that scalable quantum systems could be achieved in years rather than decades.
What is Majorana 1?
- It is the world’s first quantum chip built on a topological architecture, using Majorana fermions, exotic subatomic particles that are both particles and antiparticles.
- The chip is designed to be more stable and error-resistant than current quantum technologies developed by competitors like Google and IBM.
Core Technology & Innovation:
- Material Composition: Made from indium arsenide (a semiconductor) and aluminum (a superconductor).
- Topological Superconductivity: When cooled near absolute zero and exposed to magnetic fields, it enables the formation of Majorana Zero Modes, which serve as building blocks for stable qubits.
- Topoconductor Architecture: A new class of materials creating a topological state, offering enhanced fault tolerance.
Quantum Advantage:
- Qubit Efficiency: Majorana 1 reduces the number of physical qubits needed to generate logical (error-corrected) qubits.
- Error-Resistance: Its design addresses two major quantum computing limitations — qubit instability (decoherence) and high error rates.
- Scalability Potential: The chip includes eight topological qubits, with future potential to scale up to a million-qubit system.
Why This Matters:
- Improved Reliability: Lower error rates enhance the practical applicability of quantum systems.
- Accelerated Development: Brings the world closer to realizing commercially viable quantum computers.
- Wide Applications: Potential use in drug discovery, material science, clean energy solutions, and more.
- AI Integration: May combine with artificial intelligence to tackle global challenges like microplastic degradation.
Quantum Computing in Brief:
- Quantum Computers use qubits and properties like superposition and entanglement to perform highly complex calculations.
- Major Challenges: Qubit instability and error correction.
- Significance: Quantum computing could revolutionize fields by solving problems beyond the reach of classical computers.
Technology Adoption Fund (TAF)

- 24 Feb 2025
In News:
IN-SPACe, India’s space sector regulator under the Department of Space, has launched the Technology Adoption Fund (TAF) to accelerate the commercialization of indigenous space technologies.
About TAF:
- Objective: To bridge the gap between early-stage innovation and market-ready space solutions developed by Indian startups, MSMEs, and industries.
- Goal: Reduce dependence on imported technologies and strengthen India's position in the global space sector.
Key Features:
- Financial Support:
- Startups/MSMEs: Up to 60% of project cost.
- Larger industries: Up to 40%.
- Funding cap: ?25 crore per project.
- Eligibility: Open to all non-government entities (NGEs) with commercially viable space innovations.
- Support Provided:
- Partial funding for development and commercialization.
- Technical mentoring and guidance.
- Focus Areas: Launch vehicles, satellites, space-based applications, and related services.
- Outcomes Expected:
- Development of new space products.
- Intellectual property generation.
- Enhanced production capabilities.
- Economic growth and job creation.
About IN-SPACe:
- Established: 2020
- Ministry: Department of Space
- Location: Ahmedabad, Gujarat
- Role: Single-window agency promoting private participation in India's space ecosystem.
- Functions:
- Authorizes and monitors private sector space activities.
- Facilitates access to ISRO infrastructure.
- Collaborates with academia, industry, and research bodies.
Significance:
- Encourages private innovation in space tech.
- Aligns with the larger vision of making India a hub for space entrepreneurship.
- Strengthens India’s self-reliance and competitiveness in global space technology.
Remission and the Supreme Court’s 2025 Ruling

- 24 Feb 2025
In News:
Recently, the Supreme Court directed states with remission policies to consider the premature release of prisoners even if they don’t apply for remission beforehand.
What is Remission?
- Remission refers to the reduction of a convict's sentence by the government before the term is completed. It does not nullify the conviction, but shortens imprisonment.
- It is governed by:
- Section 473 of BNSS, 2023 (earlier Section 432 of CrPC, 1973) – empowers state governments to grant remission.
- Articles 72 and 161 of the Constitution – empower the President and Governors respectively to remit sentences.
- Section 475 of BNSS (earlier Section 433A CrPC) – restricts remission for life convicts found guilty of offences punishable by death until 14 years of imprisonment are completed.
Background: SC’s Suo Motu Intervention
- The Supreme Court in 2025, in the suomotu case In Re: Policy Strategy for Grant of Bail, altered the interpretation of remission rules to address prison overcrowding.
- The Court held that states must consider remission for eligible convicts even without a formal application, if a remission policy exists.
Shift in Judicial Interpretation
- Earlier rulings (Sangeet v. Haryana and Mohinder Singh v. Punjab, 2013) required a convict's application for remission.
- The 2025 judgment acknowledges that many state prison manuals already mandate prison authorities to initiate remission review.
- It recognized that failing to consider remission proactively could lead to arbitrary discrimination, violating Article 14 (Right to Equality).
Key Guidelines Issued by the Supreme Court
- Suo motu Remission:States must automatically assess eligibility under remission policies—no application needed.
- Mandatory Remission Policy:States without existing remission policies must formulate a comprehensive one within two months.
- Conditions for Remission Must Be:
- Reasonable, non-oppressive, and clearly defined.
- Based on factors like motive, criminal background, and public safety.
- Aimed at rehabilitation and prevention of recurrence.
- Safeguards Against Arbitrary Cancellation:
- Minor breaches shouldn’t lead to automatic cancellation.
- Notice and hearing must be given before cancellation.
- Transparency:
- Legal aid bodies must monitor remission cases.
- States to maintain real-time digital data on remission.
Significance and Implications
- The ruling helps streamline remission processes and could contribute to decongesting Indian prisons, which are heavily overcrowded.
- It ensures uniformity and fairness in the exercise of executive powers related to sentencing.
- Reinforces constitutional values of equality and procedural fairness for prisoners.
Note:
- Remission ≠ Pardon: Remission reduces sentence, doesn’t erase conviction.
- Articles 72 & 161: Concern constitutional remission powers (President & Governor).
- BNSS Sections 473 & 475: Replace CrPC Sections 432 & 433A, relevant for state remission powers.
- Suo motu action by SC: Taken to address systemic prison overcrowding.
- Article 14 invoked: To ensure equitable treatment of eligible prisoners.
Brazil Joins OPEC+
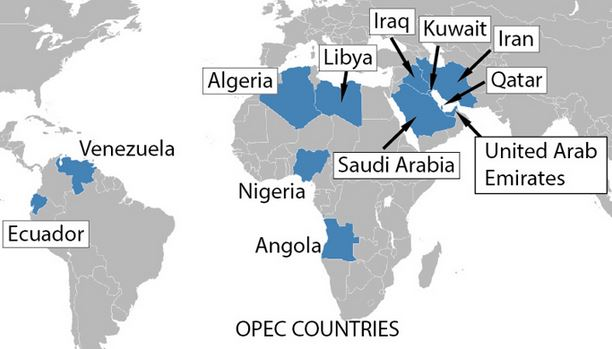
- 24 Feb 2025
Brazil Joins OPEC+
Source: Times of India
In News:
In February 2025, Brazil officially joined OPEC+, a coalition of oil-producing nations. This development comes ahead of Brazil hosting COP30, the annual UN climate summit.
About OPEC and OPEC+
- OPEC (Organization of the Petroleum Exporting Countries):
- A permanent intergovernmental organization established in 1960 at the Baghdad Conference.
- Aims to coordinate and unify petroleum policies to ensure stable prices and regular supply.
- Headquartered in Vienna, Austria.
- Current members include Saudi Arabia, Iran, Iraq, UAE, Nigeria, Libya, Algeria, and others.
- OPEC+ Formation:
- Created in 2016 to stabilize oil markets, particularly in response to rising U.S. shale oil production.
- Includes 12 OPEC members plus 11 non-OPEC countries like Russia, Kazakhstan, Mexico, and now Brazil (2025).
- Functions as a forum for strategic discussions but not all members are bound by production quotas.
Brazil’s Role and Strategic Significance
- Oil Production Status:
- Seventh-largest oil producer globally, with around 4.3 million barrels/day.
- In 2024, crude oil became Brazil’s top export, overtaking soybeans.
- OPEC+ Membership:
- Brazil joins the Charter of Cooperation but retains autonomy in production decisions.
- It seeks to influence global oil policy while protecting its energy interests.
- Balancing Act:
- While focusing on oil revenue for economic growth and energy transition funding, Brazil also pursues renewable energy through agencies like IRENA.
- This dual approach reflects an attempt to align development with environmental commitments.
Environmental Concerns and Criticism
- Brazil’s decision to expand oil exploration—especially near sensitive ecosystems like the Amazon—has drawn criticism.
- Environmentalists argue it contradicts climate goals, particularly as Brazil prepares to host COP30.
Note:
- OPEC+ is not a formal organization but a strategic alliance.
- Brazil is part of OPEC+ but is not bound by production quotas.
- OPEC’s headquarters is in Vienna, Austria (Austria is not an OPEC member).
- India is not a member of OPEC or OPEC+.
Ali Ai Ligang Festival and the Mising Tribe

- 23 Feb 2025
In News:
The Mising tribe, Assam’s largest tribal community, celebrated Ali Ai Ligang in Shankarpur, Jorhat, on the first Wednesday of the Fagun month.
About the Mising Tribe
- Region: Indigenous tribe from Northeast India; primarily reside in Upper Assam and parts of Arunachal Pradesh, with some presence in South Tibet (China).
- Population: As per Census 2011, there are 6,80,424 Mising people in Assam.
- Ethnolinguistic Group: Belong to the Tani group, speak Tibeto-Burmese languages.
- Referred as: Called “Lhobhas” (southerners) by Tibetans.
- Unique Feature: Known as the only riparian tribe of Northeast India, with livelihoods closely linked to rivers like the Brahmaputra.
- Habitat: Construct stilt houses known as Chang Ghar to withstand seasonal floods.
Cultural and Religious Practices
- Religion: Practice Donyi-Poloism – worship of the Sun (Donyi) and the Moon (Polo) as supreme deities.
- Traditional Economy:
- Traditionally practiced Jhum (slash and burn) cultivation.
- Now settled cultivators skilled in wet paddy cultivation.
- Engage in fishing, weaving, and vegetable farming.
- Women are proficient in weaving traditional Mising textiles.
Ali Ai Ligang Festival
- Main Festival of the Mising community.
- Timing: Celebrated in February, on the first Wednesday of Fagun month (as per the Assamese calendar).
- Name Meaning:
- Ali – edible root
- Ai – seed
- Ligang – sowing
Signifies the beginning of the agricultural cycle – first sowing of seeds and roots.
Significance and Rituals
- Purpose: Marks the start of cultivation, invokes blessings from Donyi-Polo to protect crops from pests and natural calamities.
- Community Importance: Strengthens communal ties and preserves agrarian traditions.
- Ritual Practices:
- Morung Okum (Morung Ghar) – youth dormitory where offerings like Apong (rice beer), dry meat, and fish are made.
- Gumrag Dance – performed by men and women to signify joy, unity, and prosperity.
- Feast and Dress – Traditional Mising delicacies are prepared, and people wear colorful ethnic attire.
Modern Celebrations
- Originally village-based, now also celebrated in urban centers like Jorhat.
- Includes stage performances, cultural competitions, and large community gatherings.
- In Jorhat, it has been celebrated for the past 40 years, organized annually by Mising Agom Kebang (Mising apex literary and cultural body).
SWARBICA Executive Body Meeting 2025

- 23 Feb 2025
In News:
- The Executive Body Meeting of the South and West Asian Regional Branch of the International Council on Archives (SWARBICA) was held on 20–21 February 2025 at the India International Centre, New Delhi.
- It was inaugurated by Union Minister for Culture and Tourism, Gajendra Singh Shekhawat, and hosted by the National Archives of India.
- This is the second time India has hosted the SWARBICA meeting, the last being in Colombo, Sri Lanka, in 2017.
Key Highlights
- The event marked the first SWARBICA Executive Meeting in eight years.
- Participating nations included Nepal, Bhutan, Bangladesh, and Sri Lanka.
- Pakistan joined the meeting virtually, while Iran could not attend due to visa-related issues.
- The meeting provided a platform for regional cooperation in archival development, emphasizing shared cultural and religious heritage.
Agenda and Focus Areas
- Digital Preservation & Archives Digitization:
- Arun Singhal, Director General of the National Archives of India (NAI) and Treasurer of SWARBICA, presented NAI’s ongoing efforts in the digitization of archival records.
- Emphasis was placed on training programs, technical exchange, and conservation practices.
- AI in Digital Archiving:
- Aseminar titled "Using AI for Digital Preservation in Archives" was organized.
- Experts from India, Bangladesh, Nepal, Sri Lanka, and SAMHiTA (India International Centre) discussed the potential of artificial intelligence in archival science.
About SWARBICA
- It functions as a regional arm of the International Council on Archives (ICA), fostering collaboration among archival institutions in South and West Asia.
- Established: The idea was proposed in 1973 at an ICA meeting in Brussels and officially launched on 11th December 1976 at Vigyan Bhawan, New Delhi.
- SWARBICA promotes professional networking, training, resource sharing, and advancement in archival practices among member countries.
Significance for India
- Reflects India’s leadership in regional cultural cooperation.
- Aligns with national goals of digital governance, knowledge preservation, and heritage conservation.
- Strengthens India's cultural diplomacy in South and West Asia.
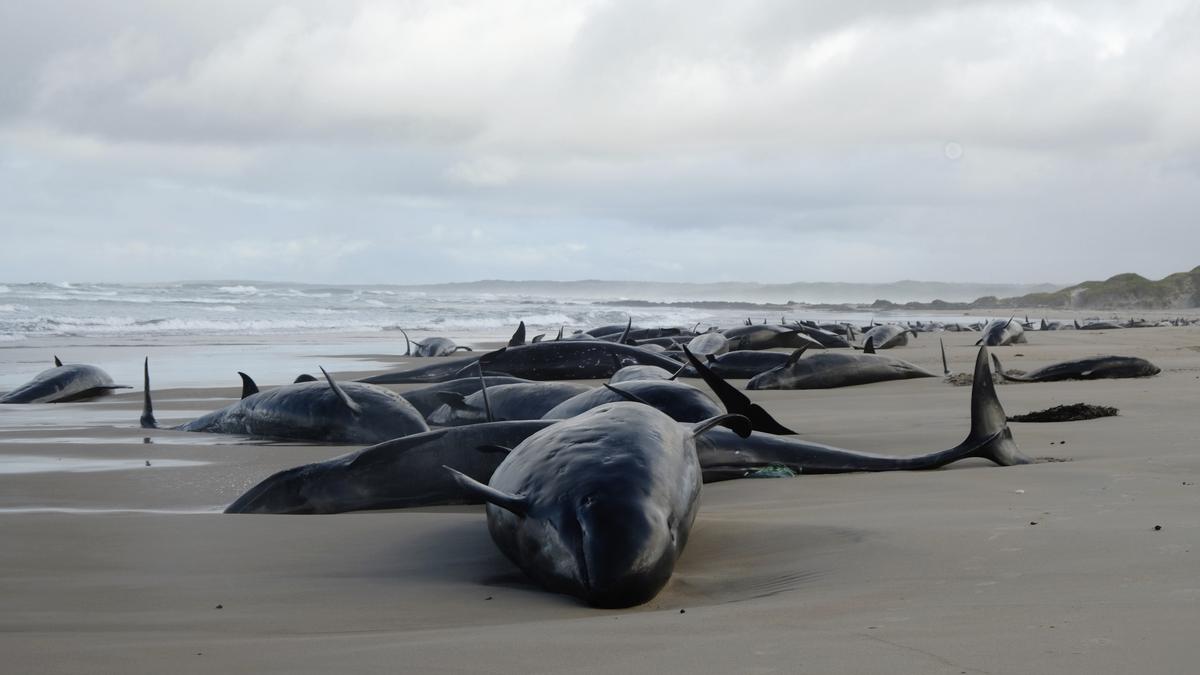
Mass Stranding of False Killer Whales in Tasmania

- 23 Feb 2025
In News:
Recently, over 150 false killer whales were found stranded on a remote beach near Arthur River on the northwest coast of Tasmania, Australia. The incident is one of several mass strandings reported in the region in recent years.
The event echoes earlier mass strandings:
- In 2022, 230 pilot whales stranded at Macquarie Harbor.
- In 2020, 470 long-finned pilot whales were stranded at the same site—the largest mass stranding in Australian history.
Possible Causes of Whale Strandings
Although the precise cause remains uncertain, potential factors include:
- Disorientation from loud underwater noises (e.g., naval exercises, seismic surveys)
- Illness, old age, injury
- Fleeing predators
- Severe weather events
- Geomagnetic anomalies
About False Killer Whales
- False killer whales (Pseudorca crassidens) are not true killer whales but belong to the Delphinidae family, which also includes dolphins and pilot whales.
- They are large, social cetaceans, often found in warm, deep oceanic waters.
- These whales are highly vocal and social, forming strong social bonds within pods.
- Like other cetaceans, they rely on echolocation (underwater sound) for communication, hunting, and navigation.
About Killer Whales (Orcas)
- Although not involved in the stranding, killer whales (Orcinus orca) are relevant as close relatives within the same family (Delphinidae).
- Known for their distinct black and white markings, orcas are the largest members of the dolphin family.
- They are globally distributed in both open oceans and coastal waters.
- Killer whales live in stable matrilineal pods and use complex vocalizations.
Conservation Status
- The IUCN Red List classifies false killer whales and killer whales as Data Deficient, indicating that there is insufficient information to assess their risk of extinction.
WEST Tokamak Reactor

- 23 Feb 2025
In News:
The WEST Tokamak reactor in southern France has set a new world record by sustaining a nuclear fusion plasma for 1,337 seconds (22 minutes and 17 seconds), surpassing the previous record of 1,066 seconds held by China’s EAST reactor by 25%. This achievement is a major milestone in the global quest for clean, limitless energy through nuclear fusion.
About Nuclear Fusion
- Nuclear Fusion is the process of combining two light atomic nuclei (typically deuterium and tritium) to form a heavier nucleus, releasing vast amounts of energy.
- The mass defect (loss of mass) in the fusion process converts into energy, as per Einstein’s equation E=mc2E = mc^2E=mc2.
- This reaction occurs in the plasma state—a hot, ionized gas consisting of free electrons and atomic nuclei.
How Tokamak Reactors Work
- A Tokamak is a doughnut-shaped (toroidal) magnetic confinement device that replicates the Sun’s fusion process.
- It uses superconducting magnetic coils to confine and heat the plasma to temperatures exceeding 50 million°C, about three times hotter than the Sun's core.
- Fusion reactors inject external power (WEST used 2 MW) to maintain the plasma and prevent it from touching reactor walls.
WEST Reactor: Key Highlights
- Operated by the French Alternative Energies and Atomic Energy Commission (CEA).
- Aims to simulate long-duration, high-temperature plasma conditions.
- Reached a plasma state sustained for over 22 minutes at 50 million°C.
- Contributes critical insights and validation to the ongoing ITER project, the world’s largest nuclear fusion experiment also based in southern France.
Significance of the Achievement
To make fusion viable for electricity generation, three key conditions must be met:
- High temperature – to overcome electrostatic repulsion between nuclei.
- Sustained confinement time – achieved by WEST.
- Sufficient plasma density – to ensure high collision rates.
Maintaining plasma for extended durations is crucial for transitioning from experimental reactors to commercial fusion energy systems.
Advantages of Nuclear Fusion
- High Energy Output: Produces 4x more energy per kg of fuel than fission, and nearly 4 million times more than fossil fuels.
- Environmentally Clean: Emits no greenhouse gases or long-lived radioactive waste. Only byproducts are inert helium and neutrons.
- Abundant Fuel Supply: Fusion uses deuterium (from seawater) and tritium, eliminating the need for uranium mining.
- Inherent Safety: Fusion reactions are inherently safe as they cannot trigger uncontrolled chain reactions, unlike fission.
Fusion vs. Fission: A Comparison
Aspect Nuclear Fusion Nuclear Fission
Process Combines light nuclei Splits heavy nuclei
Fuel Deuterium and Tritium Uranium or Plutonium
Energy Output Extremely high Moderate
Waste Minimal and short-lived Long-lived radioactive waste
Emissions No greenhouse gases Potential radiation hazards
Safety No risk of meltdown Risk of runaway reactions/meltdowns
Global Perspective
- Over 200 tokamaks are operational globally.
- The ITER project is set to become the centerpiece of global fusion research.
- Recent breakthroughs like those at WEST provide a technical roadmap for future commercial reactors.
Nvidia's Evo 2

- 23 Feb 2025
In News:
Nvidia, in collaboration with the Arc Institute and Stanford University, has launched Evo 2 — the world’s largest publicly available AI model for genomic data — aiming to revolutionize genetic research and biomedical innovation.
About Evo 2
- Type: Foundation AI model for genomics.
- Function: Understands and designs genetic code across all domains of life.
- Scale: Trained on ~9 trillion nucleotides from 128,000+ organisms, including bacteria, plants, animals, and humans.
- Platform: Built using 2,000 Nvidia H100 processors on Amazon Cloud, through the NVIDIA DGX Cloud platform.
- Access: Freely available on Nvidia’s BioNeMo research platform.
Key Features
- Accuracy in Mutation Detection:Accurately identified 90% of harmful mutations in BRCA1 — a gene linked to breast cancer.
- Speed and Efficiency:Enables rapid pattern recognition in vast genomic datasets — research that would otherwise take years.
- Collaborative Development:Created by Nvidia in partnership with Arc Institute (nonprofit research body founded in 2021 with $650 million funding) and Stanford University.
Applications
- Healthcare & Medicine:
- Predicts form and function of proteins.
- Identifies gene mutations and their impact.
- Facilitates precision medicine and gene therapy development.
- Agricultural Biotechnology:
- Aids in designing climate-resilient crops.
- Industrial & Environmental Science:
- Assists in creating enzymes to break down pollutants.
- Supports development of new bio-materials.
Significance for India & Global Science
- Accelerates biomolecular research and biotech innovation.
- Contributes to scientific self-reliance and the bioeconomy.
- Enhances capability in combating diseases like cancer and improving food security.
Meta’s Project Waterworth
- 22 Feb 2025
In News:
Meta has launched Project Waterworth, its most ambitious subsea cable initiative to date, aimed at enhancing global digital connectivity. The project involves the deployment of AI-driven subsea cable infrastructure, with India being a key beneficiary.
Key Features:
- Massive Scale:A multi-billion dollar, multi-year global initiative, the project will lay over 50,000 km of undersea cables, connecting five continents, including India, the USA, Brazil, South Africa, and others.
- AI Integration:The project leverages advanced machine learning models to predict and mitigate network disruptions, ensuring greater resilience and reliability of global internet infrastructure.
- Deep Water Deployment:The cable will operate at depths reaching 7,000 meters, using enhanced burial techniques in high-risk areas to prevent damage from ship anchors and other maritime hazards.
- Digital Backbone:Subsea cables like those in Project Waterworth currently carry over 95% of global internet traffic, forming the backbone of international digital communication, video streaming, e-commerce, and cloud-based AI services.
Strategic Relevance for India:
- India’s Digital Push:The project supports India’s growing digital economy by ensuring faster, more reliable internet connectivity and fostering digital inclusion and innovation.
- AI and Infrastructure Synergy:With AI-driven maintenance and deployment, the initiative complements India's vision of becoming a global hub for AI, data centers, and digital services.
- Economic and Strategic Benefits:Enhanced connectivity is expected to boost economic cooperation, cross-border trade, and participation in global digital platforms.
India–Qatar Strategic Partnership

- 22 Feb 2025
In News:
In February 2025, His Highness Sheikh Tamim bin Hamad Al-Thani, Amir of Qatar, paid a State Visit to India, during which India and Qatar elevated their bilateral relations to a Strategic Partnership.
Major Outcomes of the 2025 Summit
- Strategic Partnership Agreement:Formalized multifaceted cooperation across sectors—trade, investment, energy, security, technology, and people-to-people ties.
- Trade and Economic Engagement:
- Target set to double bilateral trade to $30 billion by 2030 (from $14 billion in FY 2023–24).
- Joint Commission on Trade and Commerce established to monitor economic ties.
- Qatar Investment Authority (QIA) pledged $10 billion in Indian infrastructure, green energy, and startups.
- Revised Double Taxation Avoidance Agreement signed.
- Energy Cooperation:
- A landmark 20-year LNG supply deal (2028–2048) between QatarEnergy and Petronet LNG.
- Collaboration in renewable energy including green hydrogen, solar energy, and AI-based efficiency solutions.
- Investment and Digital Integration:
- QIA to open an office in India; Qatar National Bank to set up presence in GIFT City.
- India’s UPI system operationalized in Qatar's POS infrastructure; nationwide rollout planned.
- Technology and Innovation:
- Cooperation in AI, semiconductors, IoT, robotics and digital governance.
- Indian startups to participate in Web Summits in Doha (2024–25).
People-to-People and Cultural Ties
- Over 830,000 Indians reside in Qatar, forming the largest expatriate community.
- MoUs signed on youth, sports, education, archives, and cultural cooperation.
- Agreement to celebrate India-Qatar Year of Culture, Friendship and Sports.
Security and Counter-Terrorism
- Strong condemnation of terrorism in all forms, including cross-border terrorism.
- Commitment to enhanced cooperation in intelligence sharing, cybercrime, anti-money laundering, and countering transnational crimes.
- Emphasis on regular meetings of the Joint Committee on Security and Law Enforcement.
Labour and Health Cooperation
- Agreement to hold regular Joint Working Group on Labour and Employment to address expatriate welfare and mobility.
- Collaboration in the health sector, including pharma exports, device registration, and pandemic response mechanisms.
Geopolitical and Multilateral Cooperation
- Exchange of views on Middle East stability, UN reforms, and India-GCC engagement.
- Appreciation for Qatar’s Chairmanship of the India-GCC Strategic Dialogue (Sept 2024).
- Agreement on UN Security Council reform and advancing SDG goals through multilateralism.
Challenges Ahead
- Trade Imbalance: Imports of LNG/LPG ($12B) far exceed exports (<$2B).
- Labour Rights Concerns: Working conditions of Indian laborers in Qatar remain under scrutiny.
- Legal and Judicial Issues: Over 600 Indians in Qatari jails; need for agreement on transfer of sentenced persons.
- Geopolitical Complexities: Qatar’s involvement in West Asian diplomacy presents nuanced challenges.
- Naval Veterans Case: Pending resolution affects diplomatic sentiment.
Way Forward
- Boost Indian exports in pharmaceuticals, IT, engineering goods.
- Expedite India-Qatar Bilateral Investment Treaty (BIT) to streamline FDI.
- Expand collaboration in green hydrogen, carbon capture, and energy diversification.
- Strengthen ministerial-level engagements, labor welfare frameworks, and regional security dialogue.
NAKSHA Programme
- 22 Feb 2025
In News:
The Union Ministry of Rural Development has launched a pilot project titled NAKSHA(National Geospatial Knowledge-based Land Survey of Urban Habitations) in 152 Urban Local Bodies (ULBs) across 26 States and 3 Union Territories, with the inauguration taking place in Raisen, Madhya Pradesh.
Key Highlights:
Objective of NAKSHA
The NAKSHA initiative aims to:
- Create and update urban land records for accurate, reliable documentation of property ownership.
- Empower citizens by improving ease of access to land records.
- Facilitate urban planning and reduce land-related disputes.
- Promote transparency, efficiency, and sustainable development through an IT-based system.
Key Features
- Technical Partner: The Survey of India will carry out aerial surveys and provide orthorectified imagery via third-party vendors.
- Implementation Partners:
- Madhya Pradesh State Electronics Development Corporation (MPSEDC) will develop a web-based GIS platform.
- National Informatics Centre Services Inc. (NICSI) will provide data storage facilities.
- Execution at State Level: States and UTs will conduct field surveys and ground truthing, leading to the final publication of urban and semi-urban land records.
Kaveri 2.0 Cyberattack

- 22 Feb 2025
In News:
In January–February 2025, Karnataka's property registration portal, Kaveri 2.0, faced major disruptions due to a Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attack, severely affecting property registrations and revenue generation. The portal, launched in 2023, is a key component of the state's e-governance infrastructure.
What is a DDoS Attack?
A Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attack aims to disrupt a server, service, or network by flooding it with excessive traffic, rendering it inaccessible to legitimate users.
How it works:
- Botnet Formation: Hackers compromise multiple devices using malware, turning them into bots.
- Traffic Overload: These bots generate huge volumes of fake traffic directed at the target system.
- Service Disruption: The targeted service slows down or crashes, affecting user access.
Types of DDoS Attacks:
- Bandwidth Saturation – Exhausting the target's internet capacity.
- Protocol Exploitation – Abusing vulnerabilities in network protocols.
- Application Targeting – Crashing specific applications or services.
Kaveri 2.0 Case: AI-Based DDoS Attack
- The Stamps and Registration Department (SRD) of Karnataka confirmed that the portal was targeted using AI tools that generated over 20 lakh fake search queries per day—far beyond its capacity of 2.5 lakh.
- These queries mainly targeted services like Encumbrance Certificate (EC) searches, causing widespread slowdown and outages.
- On February 1, only 556 property registrations occurred, compared to the usual 8,000–9,000 daily, with revenue dipping to ?15.18 crore from an average of over ?62 crore.
- After mitigation, services were restored by February 7, returning to normal levels of 7,225 registrations and ?62.59 crore in revenue.
Impact of DDoS Attacks on Public Services
- Operational Disruption: Essential citizen services are halted, creating public inconvenience.
- Financial Loss: Delayed transactions and reduced revenue, as seen in the Kaveri 2.0 case.
- Reputational Damage: Public trust in digital governance platforms may erode.
- Cybersecurity Risks: DDoS attacks can mask more sophisticated intrusions.
Preventive Measures
- Traffic Filtering: Using AI tools to detect and block abnormal traffic.
- Rate Limiting: Restricting the number of queries per user/IP.
- Bot Detection: Implementing CAPTCHAs and behavior analysis.
- Robust Authentication: Enhancing security for administrative access.
- Incident Response Teams: Dedicated cybersecurity units to respond to threats promptly.
Chief Election Commissioner Appointment

- 22 Feb 2025
In News:
Gyanesh Kumar has been appointed as the new Chief Election Commissioner (CEC) of India, becoming the first to be selected under the new legislative framework — The Chief Election Commissioner and Other Election Commissioners Act, 2023. He succeeds Rajiv Kumar. Simultaneously, Dr. Vivek Joshi, former Haryana Chief Secretary, was appointed as an Election Commissioner.
Constitutional Basis
- Article 324 of the Indian Constitution provides for the Election Commission of India (ECI), consisting of the CEC and such other Election Commissioners as the President may determine.
- It vests the superintendence, direction, and control of elections in the ECI for conducting elections to Parliament, State Legislatures, and for the offices of the President and Vice President.
Earlier Appointment Process
- Governed by convention and the Election Commission (Conditions of Service of Election Commissioners and Transaction of Business) Act, 1991.
- The CEC was appointed by the President on the advice of the Prime Minister, with no formal selection mechanism defined in law.
New Appointment Process (2023 Act)
The Chief Election Commissioner and Other Election Commissioners Act, 2023 introduced a formal selection process:
- Selection Committee:
- Prime Minister (Chairperson)
- A Union Cabinet Minister (nominated by the PM)
- Leader of Opposition (or largest opposition party leader) in the Lok Sabha
- Search Committee:
- Headed by the Cabinet Secretary, this body shortlists eligible candidates.
- Eligibility Criteria:
- Must be a person of integrity
- Must have experience in election management
- Must be or have been a Secretary (or equivalent) to the Government of India
Service Conditions (As per 2023 Act)
- Salary & Status: Equivalent to that of a Cabinet Secretary (earlier: Supreme Court judge).
- Tenure: 6 years or till the age of 65, whichever is earlier.
- Reappointment: Not permitted.
Removal Process
- CEC: Can only be removed in the same manner and on the same grounds as a Supreme Court judge (i.e., by Parliament through impeachment).
- Election Commissioners: Can only be removed on the recommendation of the CEC.
Functions & Powers of CEC
- Conducts elections to the Lok Sabha, Rajya Sabha, State Assemblies, and offices of the President & Vice President.
- Regulates political parties and election funding.
- Enforces the Model Code of Conduct (MCC).
- Maintains and updates electoral rolls and supervises the voter registration process.
- Has the authority to disqualify candidates and cancel elections in case of serious irregularities.
- Advises the President and Governors on election-related matters.
Judicial Context & Controversy
- In the Anoop Baranwal vs Union of India case, the Supreme Court ruled that the independence of the ECI must be preserved and directed that a law be enacted to define the appointment process.
- Until such legislation was passed, the Court had prescribed a selection committee comprising:
- The Prime Minister
- The Leader of Opposition in the Lok Sabha
- The Chief Justice of India (CJI)
- However, the 2023 Act excluded the CJI, replacing the judiciary with another executive appointee, raising concerns about executive dominance.
- Multiple petitions challenging the constitutionality of the Act are pending before the Supreme Court.
Pradhan Mantri Annadata Aay Sanrakshan Abhiyan (PM-AASHA)

- 21 Feb 2025
In News:
Context:
The Government of India has approved the continuation of the PM-AASHA Scheme till 2025–26, aligning with the 15th Finance Commission cycle, to strengthen farmer income security and achieve self-sufficiency in pulses production.
Overview of PM-AASHA Scheme
- Launched by: Ministry of Agriculture & Farmers’ Welfare
- Objective: To ensure remunerative prices to farmers and stabilize market prices of key crops.
- Type: Umbrella scheme combining various price support mechanisms.
Key Components
- Price Support Scheme (PSS)
- Procurement of pulses, oilseeds, and copra at Minimum Support Prices (MSP) through NAFED and NCCF.
- Covers 25% of national production, except for 100% procurement of Tur, Urad, and Masur during 2024–25 and extended for the next four years.
- Procurement is done from pre-registered farmers through State-level agencies.
- Price Deficiency Payment Scheme (PDPS)
- Farmers receive direct payments for the shortfall between the MSP and market price.
- Covers 40% of oilseed production for a duration of four months.
- Price Stabilization Fund (PSF)
- Maintains buffer stocks of pulses and onions.
- Aims to stabilize prices, prevent hoarding, and ensure affordable supply for consumers.
- Market Intervention Scheme (MIS)
- Provides price support for perishable horticultural crops.
- Covers 25% of production with direct financial transfers to farmers, not physical procurement.
Recent Developments (2025)
- Procurement Commitment:The Union Government announced 100% procurement of Tur (Arhar), Urad, and Masur under PSS for 2024–25, extended for four years, to reduce import dependence and promote self-sufficiency.
- Tur Procurement Approval:Union Agriculture Minister Shivraj Singh Chouhan approved procurement of 13.22 Lakh Metric Tonnes (LMT) of Tur for Kharif 2024–25 in 9 states:
Andhra Pradesh, Chhattisgarh, Gujarat, Haryana, Karnataka, Madhya Pradesh, Maharashtra, Telangana, and Uttar Pradesh. - Procurement Progress(as of 15 Feb 2025):
- 0.15 LMT of Tur procured from Andhra Pradesh, Karnataka, Maharashtra, and Telangana.
- 12,006 farmers have benefited so far.
- Procurement in remaining states will commence shortly.
- Central procurement is conducted by NAFED and NCCF.
UNESCO’s “Imagine a World with More Women in Science” Campaign

- 21 Feb 2025
In News:
On February 11, 2025, to mark the 10th anniversary of the International Day of Women and Girls in Science, UNESCO, with support from Canada’s International Development Centre (IDRC), launched the global campaign titled “Imagine a World with More Women in Science.”
Campaign Highlights
- Objective: Promote gender equality in science and innovation by encouraging the active participation and leadership of women in STEMM (Science, Technology, Engineering, Mathematics, and Medicine).
- Social Media Drive: The campaign uses the hashtag #EveryVoiceInScience to amplify diverse voices and encourage global engagement.
- Focus: Emphasizes the real-world impact of gender disparities in science, including missed innovations, biased artificial intelligence, and inequitable scientific opportunities.
Background
- The UN General Assembly (UNGA) declared February 11 as the International Day of Women and Girls in Science in 2015 to foster female participation in scientific research and innovation globally.
Current Status of Women in Science
Global Trends
- Representation: Women comprise only one-third of the global scientific workforce.
- Leadership Gap: Merely 10% of STEM leadership positions are held by women.
India-Specific Data
- STEMM Enrolment: Women account for 43% of enrolment in STEMM disciplines.
- Women Scientists: Only 18.6% of scientists in India are women.
- R&D Projects: About 25% of R&D projects are led by women researchers.
Challenges Faced by Women in Science
Challenge Description
Restrictive Social Norms Traditional gender roles hinder women’s
scientific pursuits.
Lack of Role Models Few visible female leaders discourage young women from
aspiring to scientific careers.
Workplace Inequality Gender biases, hostile work environments, and lack of inclusive
policies create barriers.
Educational Gaps Gender-biased teaching content and insufficient support systems
limit girls’ access to science education.
Recommended Measures
Dismantle Gender Stereotypes
- Remove gender biases from teaching and learning materials.
- Include contributions of female scientists in textbooks with visuals.
- Promote equitable representation of women in boards, panels, and decision-making bodies.
Enhance Visibility of Women Role Models
- Highlight discoveries by female scientists.
- Increase media and curriculum exposure to successful women in science.
Open Educational Pathways
- Promote inclusive teaching practices and gender-neutral curricula.
- Encourage CSR (Corporate Social Responsibility) initiatives to support girls in science education.
Create Inclusive Work Environments
- Enforce policies for diversity, equity, and inclusion.
- Take strong action against gender-based violence, including sexism and harassment in the workplace.
- Advance women into leadership roles in scientific institutions.
mRNA-Based Cancer Vaccine
- 21 Feb 2025
In News:
Russia has announced the development of an mRNA-based personalized cancer vaccine, expected to be available free of cost to patients by early 2025. It is being developed under the Russian Ministry of Health, with pre-clinical trials showing promising results in suppressing tumour growth and metastasis.
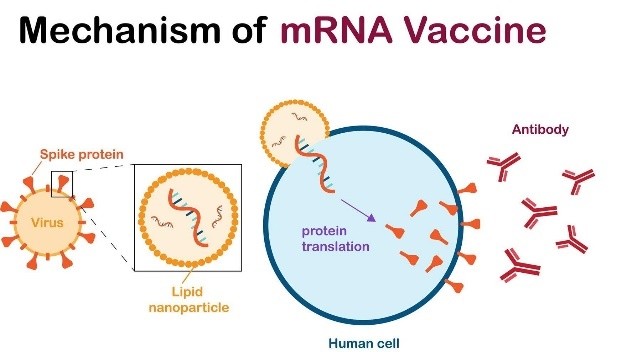
What is an mRNA-Based Cancer Vaccine?
- mRNA (Messenger RNA) vaccines deliver genetic instructions to the body’s cells to produce antigens—proteins that trigger an immune response.
- In the case of cancer, these vaccines train the immune system to recognize and destroy tumor-specific antigens, thereby attacking cancer cells.
- Unlike conventional vaccines, these are therapeutic, not preventive, and are used in existing cancer patients.
How Does It Work?
- The vaccine prompts the body to produce proteins that mimic tumor markers.
- These markers stimulate the immune system to target and destroy cancer cells.
- The treatment is personalized, with the mRNA sequence tailored to match the unique antigens of a patient’s tumour, enhancing precision and efficacy.
- It can potentially target multiple antigens simultaneously, unlike standard mRNA vaccines such as those for COVID-19.
Advantages Over Conventional Therapies
- Selective Action: Targets only cancer cells, minimizing damage to healthy tissue.
- Fewer Side Effects: Compared to chemotherapy, the side effects are significantly reduced.
- Customizable: Can be adapted to target various cancers through tumor-specific markers.
- Boosts Immunity: Enhances the body’s natural defense mechanisms for long-term protection.
mRNA Technology – Core Concepts
- mRNA is a single-stranded RNA transcribed from DNA.
- It delivers genetic instructions to ribosomes (protein factories) in cells to produce specific proteins.
- In mRNA vaccines, this mechanism is harnessed to make the body generate target antigens, which the immune system learns to combat.
India and mRNA Vaccines
- India has approved two mRNA COVID-19 vaccines developed by Gennova Biopharmaceuticals with DBT-BIRAC support:
- GEMCOVAC-OM(Omicron-specific)
- GEMCOVAC-19
- Features include needle-free delivery and thermostability, marking India’s entry into mRNA-based immunotherapy platforms.
Cautions and Limitations
- Not Preventive: These are not preventive like HPV or Hepatitis B vaccines, which protect against cancers linked to viruses.
- Limited Data: Russian vaccine data is not yet publicly available; clinical validation is pending.
- Not Universally Effective: Immunotherapy may not work for all types or stages of cancer.
- Time-Consuming Trials: New treatments must undergo phased trials, often spanning years, before general approval.
AI-Powered Surveillance in Similipal Tiger Reserve
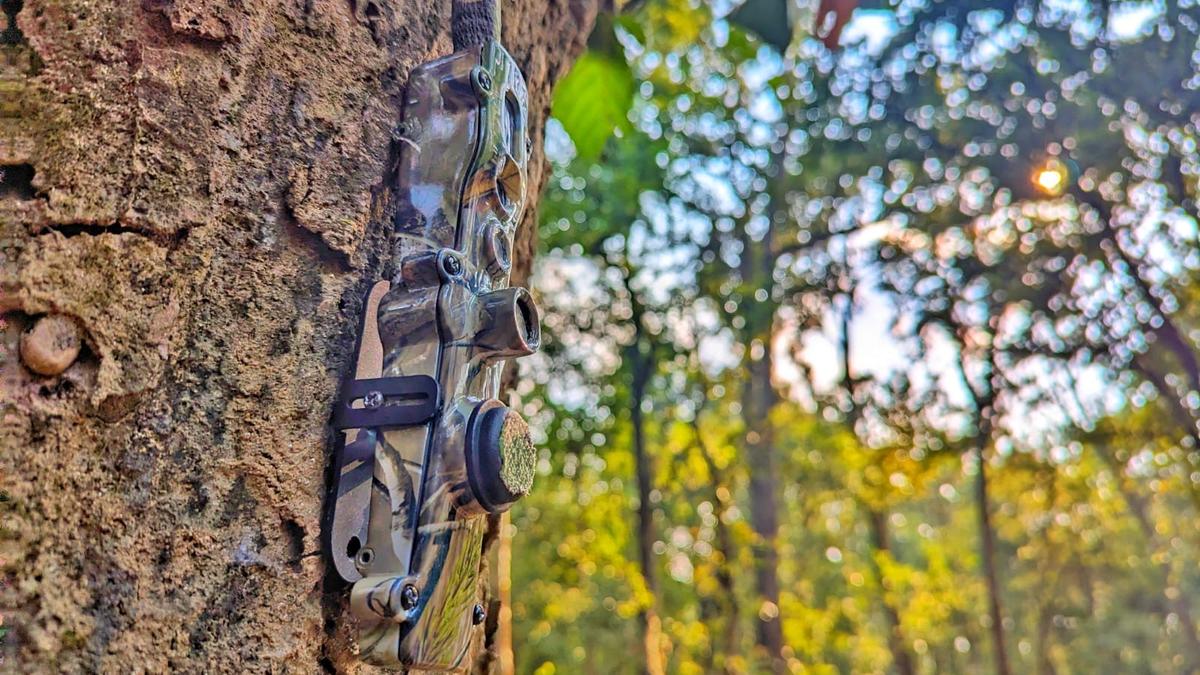

- 21 Feb 2025
In News:
The Similipal Tiger Reserve in Odisha has seen a significant drop in poaching activities following the deployment of TrailGuard AI-enabled surveillance cameras. These advanced systems are helping protect both forest personnel and wildlife by providing real-time alerts and enhancing enforcement actions.
About TrailGuard AI System
- Developed by: Nightjar Technologies, Gurgaon.
- Design:
- Two-part system: a pen-sized camera unit and a notepad-sized battery/communication unit connected via a 2-metre cable.
- Camouflaged and compact, reducing chances of being detected or stolen.
- Operation:
- Operates in low-power mode by default, switches to high-power mode upon sensing movement.
- Uses on-device AI inference to identify object classes (e.g., humans, animals, vehicles).
- Sends alerts via cellular network within 30–40 seconds to a central control room.
- Battery life: 6 months to 1 year.
- Cost: ?50,000–53,000 per unit.
Impact and Achievements
- Installed: 100–150 AI-enabled cameras in Similipal.
- In 10 months, led to:
- 96 poachers arrested
- 86+ country-made guns seized
- 40+ arrests in December 2024 alone
- Enabled quick house raids and identifications using photographic evidence.
- Enabled one conviction within six months, with more expected.
Integrated Enforcement System
- Real-time alerts displayed on a central control room screen.
- Information shared swiftly via WhatsApp groups and VHF radio.
- Ground teams rely on human intelligence sources (including undercover staff) to identify suspects.
- Raids and arrests are executed only after 100% identity confirmation, ensuring due process.
Advantages of the System
- Enhances forest ranger safety.
- Enables targeted and proactive patrolling.
- Effective in challenging terrains with minimal maintenance.
- Also used to monitor wildlife, including profiling of tuskers.
- Functions as an anti-poaching as well as human-wildlife conflict mitigation tool.
Wider Adoption and Future Plans
- Apart from Similipal, TrailGuard AI has been deployed at:
- Kanha Tiger Reserve, Madhya Pradesh (20 cameras)
- Dudhwa National Park, Uttar Pradesh (10 cameras)
- Total: Active in 14+ sites across five states
- Planned expansion to other protected areas in Odisha.
Community Sensitivity and Tribal Engagement
- Similipal is surrounded by tribal communities, where hunting has traditional roots.
- Increased surveillance has caused concerns over restricted forest access for collecting firewood and non-timber forest products.
- The forest department is:
- Holding awareness meetings in local languages.
- Exploring safe and non-intrusive access solutions for villagers.
- Ensuring that enforcement doesn’t indiscriminately impact local livelihoods.
Conservation Significance
- Demonstrates the fusion of technology with conservation.
- Aligns with India’s broader environmental goals under:
- Project Tiger
- National Wildlife Action Plan
- Digital India initiatives in conservation.
Exercise Komodo

- 21 Feb 2025
In News:
The Indian Navy's platforms—INS Shardul, an amphibious warfare ship, and the P-8I Long Range Maritime Surveillance Aircraft—participated in the International Fleet Review (IFR) 2025 and the 5th edition of the Multilateral Naval Exercise Komodo held in Bali, Indonesia, from 15 to 22 February 2025.
International Fleet Review (IFR) 2025
- IFR 2025 is a prestigious multinational naval event reviewed by the President of Indonesia.
- Participating nations showcased naval assets including warships, helicopters, and maritime aircraft.
- The Indian Navy took part in:
- International Maritime Security Symposium
- Tactical floor games
- City parade
- Coral and mangrove plantation
- Beach cleaning activities
- Baby turtle release, promoting environmental and maritime sustainability.
Exercise Komodo 2025
- Initiated in 2014, Exercise Komodo is a non-combat multilateral naval exercise hosted by the Indonesian Navy.
- The 2025 edition had the theme: "Maritime Partnership for Peace and Stability".
- Objectives:
- Promote maritime cooperation
- Enhance interoperability
- Foster regional security cooperation
- Key Features:
- Participation from 39 countries
- Involvement of 34 foreign and 18 Indonesian Navy warships
- Included:
- Naval exercises
- Officer exchange forums
- Bilateral naval meetings
- Defense exhibition
- Cultural parades
Strategic Context and Bilateral Engagements
- The participation builds upon the Indian Navy’s involvement in the La Pérouse exercises in Indonesia (January 2025) involving INS Mumbai and a P-8I aircraft.
- It coincided with the visit of Admiral Muhammad Ali, Chief of Staff of the Indonesian Navy, to India during the Republic Day 2025, accompanying President Prabowo Subianto as the Chief Guest.
Significance for India
- The participation reaffirms India’s commitment to SAGAR (Security and Growth for All in the Region).
- It strengthens India-Indonesia defense ties and underscores India's proactive role in regional maritime diplomacy and environmental stewardship.
Gravehawk Hybrid Air Defense System

- 20 Feb 2025
In News:
The Gravehawk is a newly developed mobile surface-to-air missile (SAM) system, introduced by the United Kingdom in collaboration with Denmark, to bolster Ukraine's defenses against Russian aerial threats. This innovative hybrid system exemplifies the modern trend in NATO of repurposing existing missile technology to build flexible, cost-effective, and rapidly deployable air defense platforms.
Overview and Development
- The Gravehawk system is designed to counter short-range aerial threats such as drones, cruise missiles, and low-flying aircraft.
- It combines Western and Soviet-era missile technologies, providing Ukraine with a unique edge in a contested aerial environment.
- The United Kingdom, in partnership with Denmark, is actively delivering these systems to Ukraine, with 15 additional units expected in the coming months.
- The cost per system is approximately USD 1.25 million, with Denmark covering 50% of the expense.
Key Features and Technical Capabilities
- Missiles Used: The system utilizes infrared-guided missiles including the AIM-132 ASRAAM (Advanced Short Range Air-to-Air Missile) and the Soviet-origin R-73 (AA-11 Archer).
- Guidance System: Both missiles employ passive infrared (IR) seekers, allowing them to track heat signatures of targets without emitting radar signals, thereby reducing vulnerability to electronic warfare (EW) detection.
- Speed and Range: Missiles can reach speeds of up to Mach 2.5 and engage targets at distances of approximately 12 miles (about 19 km).
- R-73 Specifics: Originally developed for close-range dogfights, the R-73 is highly maneuverable, capable of tracking targets up to 40 km ahead and 300 meters behind, with off-boresight targeting up to 40 degrees.
- Mobility: Mounted on all-terrain Drops vehicles, the system offers rapid ground mobility and deployment flexibility.
- Containerized Launch Platform: Housed in ISO-standard shipping containers, the system’s roof rolls back to expose two missile rails—repurposed from Soviet-era fighters like the Sukhoi Su-27.
- Crew and Operation: Operated by a five-member crew, the system incorporates electro-optical and infrared targeting cameras, enabling remote operation and safe standoff missile launches.
Strategic Relevance for Ukraine
- Ukraine’s acquisition of the Gravehawk system marks a significant advancement in its air defense capabilities, particularly in the face of persistent Russian air and missile attacks.
- It enhances short-range interception capacity, allows for quick reaction deployment, and reduces dependence on continuous NATO resupplies. Additionally, the system’s use of widely available R-73 missiles ensures operational sustainability.
- The Gravehawk is part of a broader effort to field "hybrid systems", where older missile stocks are integrated into modern platforms.
- Other such initiatives include FrankenSAM programs developed by the U.S. and UK, where systems like ASRAAM have been adapted to ground-based launchers.
- Ukraine has also employed R-73 missiles on drone boats and unmanned surface vessels to target Russian air assets, showcasing the multi-domain applicability of these munitions.
Prime Minister’s Yoga Awards 2025

- 20 Feb 2025
In News:
The Ministry of Ayush has officially opened nominations for the Prime Minister’s Yoga Awards 2025, which will be conferred on the occasion of the International Day of Yoga (IDY) 2025. These prestigious awards aim to honour individuals and organizations that have made exceptional and sustained contributions to the promotion and development of Yoga at both national and international levels.
Background and Objective
Instituted by the Government of India and endorsed by the Hon’ble Prime Minister, the awards recognize Yoga’s vital role in:
- Health promotion
- Disease prevention
- Management of lifestyle-related disorders
The initiative reflects the government’s broader vision to acknowledge and encourage meaningful contributions in advancing Yoga as a holistic system of well-being and preventive healthcare.
Award Categories and Benefits
The awards will be presented in the following four categories:
- National Individual
- National Organization
- International Individual
- International Organization
Each awardee will receive:
- A Trophy
- A Certificate of Recognition
- A Cash Prize of ?25 lakh
Eligibility Criteria
- Individual applicants must be 40 years or older.
- They should possess a minimum of 20 years of committed work in promoting Yoga.
- Organizations must have a proven track record in the field of Yoga development and outreach.
Applicants or nominees can apply for only one category (either National or International) in a given year. Applications can be submitted directly by individuals/entities or through nominations made by recognized Yoga institutions.
Application and Submission Process
- Nominations and applications are to be submitted through the MyGov platform:
https://innovateindia.mygov.in/pm-yoga-awards-2025/ - The link is also accessible on the Ministry of Ayush website and those of its autonomous bodies.
- The deadline for submission is March 31, 2025.
Selection Procedure
The award process involves two key stages:
- A Screening Committee formed by the Ministry of Ayush will evaluate all entries and recommend a maximum of 50 nominations per category.
- These shortlisted names will be reviewed by a high-level Evaluation Jury comprising eminent personalities from diverse fields, which will serve as the final decision-making body.
Significance of the Initiative
The Prime Minister’s Yoga Awards not only celebrate excellence in Yoga but also further the objectives of initiatives like Fit India Movement, Ayushman Bharat, and the mainstreaming of traditional Indian wellness systems.
The awards are a key element of the Ministry of Ayush’s broader mandate to integrate traditional systems such as Ayurveda, Yoga & Naturopathy, Unani, Siddha, Sowa-Rigpa, and Homeopathy into the healthcare ecosystem of India.
India–U.S. Underwater Domain Awareness Cooperation

- 20 Feb 2025
In News:
India and the United States have deepened their defense partnership by launching the Autonomous Systems Industry Alliance (ASIA), a landmark initiative focused on co-producing Underwater Domain Awareness (UDA) technologies in India.
Understanding Underwater Domain Awareness (UDA)
- UDA refers to the ability to monitor, detect, and evaluate activities beneath the surface of oceans and seas. It plays a vital role in ensuring maritime security, enabling anti-submarine warfare (ASW), managing marine resources, responding to disasters, and protecting the underwater environment.
- In the backdrop of China’s rapid naval expansion and its increasing footprint in the Indian Ocean Region (IOR), enhancing UDA has become imperative for India, both at the bilateral level and as part of the Quad framework (India, U.S., Japan, and Australia).
Strategic Significance and Geopolitical Relevance
The UDA collaboration marks a significant step in Indo-U.S. strategic relations. As the maritime domain becomes increasingly contested, especially in the Indo-Pacific, India’s need for robust submarine detection, surveillance, and underwater intelligence capabilities has become critical. The joint initiative aligns with broader strategic goals such as:
- Enhancing Quad cooperation to maintain a free, open, and secure Indo-Pacific.
- Countering threats arising from Chinese submarine activities and naval assertiveness.
- Enabling shared maritime patrols and airlift capacity for disaster response across the region.
Key Technologies Identified for Co-Production
Several high-end underwater surveillance systems have been identified for co-production or co-development in India under the ASIA framework:
- Sea Picket: An autonomous sonar surveillance platform developed by Thayer Mahan.
- Wave Glider Unmanned Surface Vehicles (USVs): Discussions are underway between Boeing’s Liquid Robotics and Sagar Defence Engineering for the co-production of 60 platforms in India.
- Low-Frequency Active Towed Sonar: Negotiations involve L3 Harris and Bharat Electronics Limited (BEL) for co-development.
- Multistatic Active (MSA) Sonobuoys: A sophisticated submarine-tracking technology, to be co-produced in India by Ultra Maritime and Bharat Dynamics Limited (BDL), with a production line expected by 2027.
- Large-Diameter Autonomous Undersea Vehicles: Produced by Anduril, these offer deep-sea monitoring capabilities.
- Triton Autonomous Underwater and Surface Vehicle: Developed by Ocean Aero, integrates underwater and surface operations.
Existing and Emerging ASW Platforms
India’s anti-submarine warfare capabilities have already been bolstered through U.S. defense acquisitions, including:
- 12 P-8I Poseidon maritime patrol aircraft currently in service.
- 24 MH-60R Multi-Role Helicopters, being inducted to enhance ASW and surveillance.
- 15 MQ-9B Sea Guardian UAVs, part of a 31-unit contract with deliveries beginning from 2029.
- An additional six P-8I aircraft were cleared during the recent bilateral talks.
These platforms significantly improve maritime interoperability among Quad nations and provide India with a strategic edge in underwater operations.
Make-in-India and Technological Sovereignty
The UDA initiative strongly supports India’s Atmanirbhar Bharat vision by fostering indigenous manufacturing of advanced underwater systems. It introduces a first-of-its-kind co-production framework in sensitive defense technologies, thus catalyzing innovation and industrial capability within the Indian defense sector.
The initiative also aims to strengthen logistics, intelligence-sharing, and force mobility between the Indian and U.S. armed forces. Enhanced training, joint operations, and technological exchanges will help sustain forward deployments and enable humanitarian and disaster relief missions across the Indo-Pacific.
Exercise Dharma Guardian 2025

- 20 Feb 2025
In News:
The 6th edition of Exercise Dharma Guardian, a joint annual military exercisealternately hosted in India and Japan since 2018is scheduled from February 25 to March 9, 2025, at Mount Fuji, Japan.
Key Highlights:
Objectives:
- Strengthen Bilateral Defence Relations: Enhances military diplomacy under the India–Japan Special Strategic and Global Partnership.
- Promote Interoperability: Develops joint operational capabilities and tactical synergy in line with UN peacekeeping mandates (Chapter VII).
- Urban and Semi-Desert Warfare: Trains troops in counter-terrorism operations and urban combat scenarios.
- Regional Stability: Supports the Indo-Pacific security architecture and complements Quad defence objectives (India, Japan, US, Australia).
Key Features of Dharma Guardian 2025
- Advanced Tactical Training: Close-quarter battle drills, live-fire exercises, battlefield medical evacuation.
- Joint Counter-Terror Operations: Conducted under UN charter guidelines for multinational cooperation.
- 48-hour Validation Exercise: Simulated real-time combat for assessing operational readiness and coordination.
- ISR and Tactical Mobility Drills: Involves establishing temporary operating bases, ISR (Intelligence, Surveillance, Reconnaissance) grids, mobile vehicle checkpoints, and heliborne insertions.
- House Intervention & Search Operations: Practical training for securing urban areas against militant threats.
- Weapons & Equipment Display: Demonstrates India’s growing defence manufacturing under the Atmanirbhar Bharat initiative.
Mount Fuji – Host Site
- Geographical Significance: Japan’s highest peak at 3,776.24 meters, located 100 km southwest of Tokyo.
- Cultural Importance: Recognized as a UNESCO World Heritage Site (2013) and revered as one of Japan’s “Three Holy Mountains.”
- Training Terrain: Its stratovolcanic landscape provides a realistic backdrop for high-altitude and rugged terrain operations.
Related India-Japan Military Exercises
India and Japan conduct a wide spectrum of bilateral and multilateral defense exercises across all services:
Exercise Name Service Branch Focus Area
Dharma Guardian Army Land-based counter-terror and urban warfare
JIMEX Navy Naval interoperability and maritime security
Malabar (Quad) Navy (Multilateral) Naval drills with US and Australia
Veer Guardian Air Force Air combat tactics and coordination
ShinyuuMaitri Air Force Air mobility and humanitarian operations
Aero India 2025

- 20 Feb 2025
In News:
Aero India 2025, the 15th edition of Asia's largest biennial airshow, is scheduled to take place from February 10 to 14, 2025, at the Air Force Station, Yelahanka, in Bengaluru, Karnataka.
Organized by the Defence Exhibition Organisation under the Ministry of Defence, with support from HAL, DRDO, and the Indian Air Force, the event showcases India's growing prowess in aerospace, aviation, and defense technologies.
Key Highlights:
Edition: 15th (First held in 1996; originally Avia India in 1993)
Theme: “The Runway to a Billion Opportunities”
Conclave Theme: “BRIDGE – Building Resilience through International Defence and Global Engagement”
Objectives and Significance
- Promote Indigenous Manufacturing: In alignment with ‘Make in India’ and ‘Atmanirbhar Bharat’, the show promotes domestic aerospace and defense production.
- Showcase Technological Advancements: Cutting-edge systems including fighter jets, helicopters, UAVs, and AI-integrated defense solutions will be exhibited.
- Encourage Global Partnerships: Facilitates joint ventures, MoUs, and technology transfers between Indian and foreign defense firms.
- Boost Strategic Diplomacy: A platform for global defense ministers, CEOs, and military leaders to foster bilateral and multilateral defense ties.
- Stimulate Investment: Attracts FDI and international contracts in India’s defense sector.
Key Events
- Live Aerial Displays: Aerobatic performances by combat aircraft, helicopters, and elite teams like Surya Kiran.
- Defense Ministers’ Conclave: Deliberations on enhancing international defense cooperation.
- CEO Roundtable: Industry leaders discuss emerging trends and investment prospects.
- Manthan/iDEX Pavilion: Showcasing start-up innovations in defense and aerospace.
- India Pavilion: A dedicated zone for indigenous defense production and capabilities.
- International Seminar (Feb 8–9): Focused on Futuristic Aerospace Technologies and related R&D challenges.
Strategic Role of Aero India
Aero India plays a pivotal role in:
- Supporting Medium Multi-Role Combat Aircraft (MMRCA) procurements.
- Demonstrating India's readiness as a global defense manufacturing hub.
- Enhancing India’s geopolitical standing by fostering defense diplomacy through multilateral engagement.
Climate Risk Index 2025
- 19 Feb 2025
In News:
- The Climate Risk Index (CRI) 2025, published by the international environmental think tank Germanwatch, ranks countries based on their vulnerability to extreme weather events, assessing both human and economic losses due to climate-induced disasters.
- The index, which has been released annually since 2006, covers a 30-year period, evaluating the impact of extreme weather events in terms of economic losses, fatalities, and the number of affected people.
Key Findings:
- Global Impact: From 1993 to 2022, more than 9,400 extreme weather events occurred globally, resulting in 765,000 fatalities and USD 4.2 trillion in economic losses. Heatwaves, droughts, and floods were the leading causes of fatalities and displacement, with heatwaves alone claiming 61,778 lives (83% of fatalities) in 2022. Droughts affected the largest number of people, with 59% of the global population impacted during the past three decades.
- India's Position: India ranks as the 6th most affected country in the world by climate change between 1993 and 2022, suffering significant losses. During this period, the country experienced over 400 extreme weather events, including floods, heatwaves, cyclones, and droughts, causing a loss of USD 180 billion in economic damages and leading to at least 80,000 fatalities (10% of global deaths).
Some notable extreme weather events include:
-
- Cyclones: Gujarat (1998), Odisha (1999), Hudhud (2014), and Amphan (2020).
- Floods: Uttarakhand (2013), Jammu and Kashmir (2014), and Kerala (2018).
- Heatwaves: Intense temperatures exceeding 50°C in 1998, 2002, 2003, and 2015.
Methodology of the Climate Risk Index
The CRI assesses the impact of extreme weather events across three hazard categories:
- Hydrological (floods, landslides),
- Meteorological (storms, cyclones),
- Climatological (heatwaves, droughts).
The six key indicators used for the ranking are:
- Economic loss
- Fatalities
- Affecting population, assessed in both absolute and relative terms.
Climate Risk and Its Implications for India
India’s vulnerability to climate change is highlighted by frequent and intense extreme weather events. The country faces risks from:
- Floods: Regular heavy monsoons lead to significant displacement and damage to infrastructure and agriculture.
- Cyclones: Rising sea levels and warming oceans increase the frequency and intensity of cyclones.
- Heatwaves: India experiences rising temperatures, with heatwaves becoming more intense, contributing to health crises.
- Droughts: A growing concern, affecting agriculture and water resources.
Additionally, the Asia-Pacific Climate Report 2024 projects that India may face a 24.7% GDP loss by 2070 due to climate change impacts, driven by rising sea levels and decreasing labor productivity.
Global Challenges in Climate Change Mitigation
- Historical Responsibility vs. Future Emissions: Developed nations, despite having contributed more to global emissions historically, are pressuring emerging economies like India to take greater responsibility for climate action. This has led to tensions over burden-sharing and the need for climate finance.
- Global Temperature Breach: In 2024, the world breached the 1.5°C threshold for a full year, highlighting the inadequacy of current mitigation efforts. Projections indicate a global temperature increase of 2.6-3.1°C by 2100 if current trends continue.
- Weak Commitments and Insufficient Finance: Many countries have not updated their Nationally Determined Contributions (NDCs), and the USD 300 billion annual funding promised for developing nations is insufficient to meet climate adaptation and mitigation needs.
India's Climate Adaptation Challenges and Suggestions
India faces several climate adaptation challenges, including inadequate infrastructure, insufficient funding, and a lack of robust policy frameworks for disaster risk management. To enhance adaptation efforts, the following measures are suggested:
- Enhanced Climate Finance: Developing countries need greater financial and technical support to manage and adapt to climate-induced losses.
- Strengthening Mitigation Efforts: Nations, including India, must scale up their NDCs to restrict global warming to 1.5°C or lower.
- Accountability of High-Income Countries: Developed nations must expedite mitigation actions and increase financial contributions to support climate-vulnerable countries like India.
National Skill Development Corporation (NSDC)

- 19 Feb 2025
In News:
The National Skill Development Corporation (NSDC) has announced plans to establish 50 Future Skills Centres (FSCs) and 10 NSDC International Academies to enhance skill development and improve workforce readiness in India. This initiative aims to address the country's growing demand for skilled professionals, particularly in emerging technologies and international markets.
About NSDC
- NSDC is a not-for-profit public limited company set up to promote skill development across India.
- It operates under the Ministry of Skill Development & Entrepreneurship (MSDE).
- Established on July 31, 2008, NSDC was founded as a Public-Private Partnership (PPP) under Section 25 of the Companies Act, 1956 (now Section 8 under the 2013 Act).
- The corporation operates with a 49% government stake and 51% private sector participation, ensuring a balanced approach to skill development through public and private sector collaboration.
Key Objectives of NSDC
- Bridging the Skill Gap: NSDC aims to fill the gap between industry requirements and the available workforce by providing industry-relevant training. This enhances workforce employability and supports the growth of the Indian economy.
- Financial Support for Enterprises: NSDC provides funding and concessional loans to enterprises, start-ups, and training organizations to expand their operations and develop a skilled workforce.
- Skilling the Workforce for Emerging Technologies: The corporation focuses on upskilling individuals in emerging technologies to make them market-ready.
Key Functions of NSDC
- Skill Development & Training: NSDC provides vocational training and certification across emerging technologies to align the workforce with current industry needs, ensuring that individuals are equipped with the necessary skills to succeed in the job market.
- Apprenticeship & Job Training: Under the National Apprenticeship Promotion Scheme (NAPS), NSDC trains around 5 million apprentices by disbursing ?100,250 million for skill-based learning, giving them hands-on experience and industry exposure.
- Digital & Remote Skilling: Through the Skill India Digital Hub (SIDH), NSDC offers over 7,100 courses in 23 languages, catering to 30 crore candidates. These online courses provide accessibility to skill development programs across the country, particularly for individuals in remote and rural areas.
- Job & Career Support: NSDC runs JobX, a platform that connects job seekers with potential employers. This platform offers services such as resume building, career coaching, and placement assistance, having already supported 4 million candidates in securing jobs.
New Initiatives by NSDC
To further strengthen India’s skill ecosystem, NSDC is establishing 50 Future Skills Centres (FSCs) and 10 NSDC International Academies. These initiatives will focus on:
- Future Skills Centres: These centers will offer training in emerging fields such as artificial intelligence, data science, cybersecurity, and robotics, ensuring that India's workforce is prepared for future job markets.
- International Academies: The academies will focus on global skill standards and international certifications, enhancing the employability of Indian workers in global markets.
Gulf of Eilat
- 19 Feb 2025
In News:
A new study has revealed that the coral reefs in the Gulf of Eilat (also known as the Gulf of Aqaba) faced a 3,000-year growth shutdown due to global cooling. However, these reefs later recovered naturally from deeper waters, demonstrating resilience in the face of environmental changes.
About the Gulf of Eilat (Gulf of Aqaba)
- Location: The Gulf of Eilat is a northern extension of the Red Sea, positioned east of the Sinai Peninsula and west of the Arabian Peninsula. It is strategically significant and is also known as the Gulf of Aqaba.
- Neighbouring Nations: The Gulf shares its coastline with four countries: Egypt, Israel, Jordan, and Saudi Arabia.
- Geographical Features:
- The Gulf includes important cities like Taba (Egypt), Eilat (Israel), and Aqaba (Jordan), all located at the Gulf’s northernmost point.
- It has a maximum depth of 1,850 meters, making it much deeper than the adjacent Gulf of Suez.
- The Gulf forms the southern end of the Dead Sea Transform, a significant tectonic fault zone, contributing to its unique geological and environmental features.
- Coral Ecosystem: The Gulf of Eilat is home to the world’s northernmost coral reefs. Despite facing various environmental challenges, these reefs have shown remarkable resilience over the years, highlighting their ability to adapt to changing conditions.
Environmental Challenges and Recovery
- The 3,000-year growth shutdown of the coral reefs in the Gulf of Eilat was primarily driven by global cooling. This climatic phenomenon significantly impacted the growth of the reefs, causing a temporary halt in their development. However, the coral ecosystems in the Gulf have since recovered naturally, drawing from deeper waters to rebuild and thrive once again.
- This recovery underscores the resilience of coral ecosystems despite adverse environmental conditions. It also provides valuable insights into how these ecosystems can recover when given the opportunity, even after significant disruptions caused by global climate changes.
Implications for Coral Reef Conservation
- The study's findings emphasize the importance of understanding the adaptive capacity of coral reefs, which are among the most vulnerable ecosystems to climate change.
- The ability of coral reefs in the Gulf of Eilat to recover after a prolonged period of cooling demonstrates that marine ecosystems can endure long-term environmental stress if they are allowed to regenerate naturally.
- This has significant implications for global coral conservation efforts, which must focus on creating conditions that allow reefs to adapt and recover from environmental stresses, including global warming, ocean acidification, and pollution.
- The Gulf of Eilat’s coral reefs provide an important case study for understanding ecological resilience and the potential for natural recovery in marine ecosystems.
NAMASTE Scheme

- 19 Feb 2025
In News:
The National Action for Mechanized Sanitation Ecosystem (NAMASTE) scheme, launched by the Government of India, aims to empower sanitation workers, particularly Sewer and Septic Tank Workers (SSWs), also known as SafaiMitras.
Key Highlights:
- It focuses on ensuring their dignity, safety, and economic empowerment, while promoting the mechanization of sanitation processes.
- The scheme is designed to address the challenges faced by these workers, who are often exposed to hazardous conditions.
Objectives of the NAMASTE Scheme
The primary objectives of the NAMASTE scheme include:
- Formalization of sanitation work and enhancing occupational safety.
- Promotion of mechanized cleaning techniques to reduce manual interventions.
- Providing personal protective equipment (PPE) and other safety devices to workers.
- Ensuring economic and social empowerment of sanitation workers.
Implementing Agencies and Timeline
- The NAMASTE Scheme is implemented by the Ministry of Social Justice and Empowerment (MoSJE) and the Ministry of Housing and Urban Affairs (MoHUA).
- The scheme is executed by the National SafaiKaramcharis Finance and Development Corporation (NSKFDC), under MoSJE.
- The scheme is scheduled for implementation from FY 2023-24 to 2025-26, with a target group comprising sewer workers, septic tank workers, and waste pickers (the latter being added in 2024).
Key Initiatives Under NAMASTE
- Distribution of PPE Kits: Under the scheme, PPE kits are provided to sanitation workers to safeguard them from health hazards, especially while working in unsafe environments like sewer lines and septic tanks. These kits include masks, gloves, goggles, face shields, gowns, and shoe covers.
- Ayushman Health Cards: Ayushman Bharat Pradhan Mantri Jan Arogya Yojana (AB-PMJAY) health cards are distributed to SSWs under the scheme. These cards enable workers to access cashless healthcare at empaneled hospitals, ensuring that sanitation workers receive timely medical attention without financial burden.
- Capacity Building and Training: The scheme promotes capacity building for SSWs through training programs on safety protocols, mechanized cleaning processes, and the use of modern sanitation technologies. This helps improve the efficiency and safety of their work, while also reducing manual handling.
- Promoting Mechanization: To reduce the hazardous practice of manual scavenging, the scheme focuses on providing mechanized equipment to enhance sanitation operations and create safer working conditions for workers.
Surge in Colorectal Diseases in India
- 19 Feb 2025
In News:
In recent years, India has witnessed a marked increase in colorectal diseases, including colorectal cancer, Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD), Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS), and other related disorders. This surge is closely linked to urbanization, dietary transitions, sedentary lifestyles, and improved diagnostic practices.
What are Colorectal Diseases?
Colorectal diseases affect the colon and rectum and encompass a spectrum of conditions:
- Colorectal Cancer: Originates from polyps in the colon or rectum. If untreated, these polyps can turn malignant. The incidence of colorectal cancer is rising rapidly in Indian urban centers, now ranking among the top cancers in cities.
- Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD): A chronic condition involving inflammation of the digestive tract, especially the colon and small intestine. Subtypes include Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis. Once rare in India, IBD is now on the rise due to industrialization, Western diets, and enhanced medical diagnostics.
- Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS): A non-inflammatory, functional bowel disorder marked by abdominal pain, bloating, and altered bowel habits (constipation or diarrhea) without visible bowel damage. IBS is highly prevalent in India.
- Diverticular Disease: Characterized by the formation of small pouches (diverticula) in the colon wall. Inflammation or infection of these pouches leads to complications and discomfort.
- Hemorrhoids and Anal Fissures: Swollen veins or tears in the rectal region, leading to pain, bleeding, and itching—often caused by hard stools or chronic constipation.
Why are these diseases increasing?
- Dietary Shifts: Increased intake of processed foods, red meat, and low-fiber diets (lacking fruits and vegetables) have significantly raised the risk of colorectal cancer and other digestive disorders.
- Physical Inactivity: Sedentary behavior, especially in urban populations, heightens susceptibility to these conditions.
- Rising Obesity: Obesity, closely associated with lifestyle disorders, is a contributing factor for colorectal cancer and IBS.
- Ageing Population: Risk increases with age, and India’s growing elderly demographic intensifies disease burden.
- Genetic and Lifestyle Factors: A family history of colorectal conditions, coupled with habits like smoking and alcohol consumption, further elevate risk levels.
- Gut Microbiota Disruption: Imbalance in gut bacteria and possible infections are emerging as factors in the etiology of IBD; ongoing research aims to establish clearer links.
Common Symptoms
- Persistent changes in bowel habits: constipation, diarrhea, or narrow stools.
- Rectal bleeding: presence of bright red or dark blood in the stool.
- Abdominal pain, bloating, or cramps.
- Unexplained weight loss.
- Chronic fatigue and weakness.
- Sensation of incomplete bowel emptying.
Diagnosis
- Physical Examination and clinical history evaluation.
- Stool Tests for blood, infections, or abnormalities.
- Colonoscopy (gold-standard diagnostic tool) to inspect the colon and collect biopsies.
- Sigmoidoscopy for lower colon and rectum.
- Imaging: CT, MRI, or X-rays to detect abnormalities.
- Blood Tests to assess inflammation and exclude other conditions.
Treatment Modalities
- Medication: Anti-inflammatory drugs (for IBD), antibiotics, pain relief, and symptom-specific treatments.
- Lifestyle Interventions: High-fiber diets (for IBS, diverticulitis), regular physical activity, and stress reduction.
- Surgery: Required in advanced cases of colorectal cancer or severe IBD/diverticular disease.
- Chemotherapy and Radiation Therapy: Used post-operatively or in advanced malignancies.
- Targeted Biological Therapies: Including monoclonal antibodies for immune modulation in IBD.
Mount Etna Eruption 2025

- 18 Feb 2025
In News:
On February 12, 2025, Mount Etna, Europe's tallest and most active volcano, erupted once again, spewing lava flows and dense ash clouds into the atmosphere. The event drew attention not just due to its visual spectacle, but also because of the geological, environmental, and socio-economic implications it carries.
About Mount Etna
- Location: Eastern coast of Sicily, Italy — the largest island in the Mediterranean Sea.
- Type:Active stratovolcano, known for frequent eruptions.
- Height & Size: Highest peak south of the Alps and tallest active volcano in Europe; rises over 3,300 meters and covers 1,190 sq. km with a basal circumference of 140 km.
- Tectonic Setting: Lies above the convergent boundary of the African and Eurasian tectonic plates, making it a hotspot for seismic and volcanic activity.
- Eruption History: Recorded to have erupted over 200 times since 1500 BCE, with persistent volcanic activity.
- UNESCO Recognition: Declared a UNESCO World Heritage Site in 2013 for its exceptional geological features, cultural relevance, and continuous scientific monitoring.
- Decade Volcano Status: Designated a Decade Volcano by the United Nations due to its proximity to densely populated areas, including the city of Catania, and the potential risk it poses, warranting special scientific attention.
Dokra Artwork

- 18 Feb 2025
In News:
During a recent diplomatic visit, Prime Minister Narendra Modi gifted French President Emmanuel Macron and the First Lady symbolic Indian artifacts — a Dokra artwork and a silver hand-engraved mirror — showcasing India’s rich heritage of tribal and fine metal craftsmanship.
Key Highlights:
Dokra Art: A Living Tradition
- Dokra, also known as Dhokra, is a non-ferrous metal casting craft that employs the lost-wax technique, practiced for over 4,000 years.
- It is predominantly practiced by Ojha metalsmiths and DhokraDamar tribes, across Chhattisgarh, Jharkhand, Odisha, West Bengal, and Telangana.
- Notable for its seamless brass sculptures, each Dokra artifact is cast using a single-use clay and wax mould, ensuring that no two pieces are identical.
- Dokra items include figurines, utensils, jewelry, and religious motifs, often reflecting tribal life and nature.
Historical Significance:
- The “Dancing Girl” of Mohenjo-Daro (from the Harappan Civilization) is considered one of the earliest examples of Dokra-style metal casting, underlining its archaeological and civilizational importance.
Craftsmanship Features:
- The casting process takes nearly a month per piece, reflecting the labour-intensive and skilled nature of the art.
- Dokra is globally recognized for its sustainability, aesthetic uniqueness, and its ability to merge function with folklore.
Prime Minister Dhan-Dhaanya Krishi Yojana (PMDKY)

- 18 Feb 2025
In News:
Announced in Union Budget 2025, the Prime Minister Dhan-Dhaanya Krishi Yojana (PMDKY) aims to boost agricultural productivity, sustainability, and rural income in India’s lagging agricultural regions.
Inspired by the Aspirational Districts Programme (ADP), PMDKY targets 100 districts marked by low productivity, moderate cropping intensity, and limited credit access, benefiting approximately 1.7 crore farmers.
Key Highlights:
Objectives:
- Enhancing Agricultural Productivity:Promote scientific techniques and modern farming to improve crop yield and land use efficiency.
- Crop Diversification & Sustainable Practices:Encourage climate-resilient and eco-friendly farming methods, reducing dependence on water-intensive crops.
- Post-Harvest Infrastructure Development:Establish storage and agro-processing units at panchayat and block levels to reduce post-harvest losses (currently ~35-40%).
- Improving Irrigation Efficiency:Support micro-irrigation techniques like drip and sprinkler systems to raise water-use efficiency from the current 38%.
- Expanding Agricultural Credit:Facilitate short- and long-term institutional credit, especially through the Kisan Credit Card (KCC) and agri-fintech models.
Implementation Framework:
- Targeted District Identification:Based on cropping intensity, productivity, and credit penetration, using data from the Ministry of Agriculture, NABARD, and Department of Financial Services.
- Integrated Funding Approach:Leverages existing schemes like RKVY, PMKSY, NFSM, and SMAM through convergence for efficient fund utilization.
- Institutional Mechanism:Multi-tier coordination involving the Centre, States, and District-level authorities for implementation and real-time performance tracking.
- Technology Integration:GIS mapping, AI advisories, blockchain for supply chain transparency, and sensor-based monitoring for precision agriculture.
- Farmer Empowerment:Strengthening Krishi Vigyan Kendras (KVKs) and Farmer Producer Organizations (FPOs) to support knowledge dissemination, skill development, and market access.
Strategic Significance of PMDKY:
- Bridging Regional Disparities:Targets structurally weak districts to ensure balanced regional growth in agriculture.
- Food and Water Security:Supports climate-resilient farming amid rising rainfall variability (+15–20% by 2050) and increasing water scarcity (55% of agriculture is rainfed).
- Boosting Rural Incomes:Aimed at transforming smallholder agriculture, as ~80% of Indian farmers are marginal with an average income of ?1.2 lakh annually.
- Reducing Post-Harvest Losses:Addresses infrastructural bottlenecks causing 35–40% losses, especially in perishables like fruits and vegetables.
India–US TRUST Initiative

- 18 Feb 2025
In News:
India and the United States launched the Transforming Relationship Utilizing Strategic Technology (TRUST) initiative during the Indian Prime Minister’s 2025 visit to the US. This landmark partnership aims to strengthen bilateral cooperation across critical and emerging technology sectors, diversify global supply chains, and reduce dependence on China in strategic industries.
Key Objectives and Scope of the TRUST Initiative
The TRUST initiative is a comprehensive framework focused on:
- Critical Minerals and Advanced Materials
- Establishing resilient supply chains for critical minerals such as lithium, cobalt, and rare earth elements (REEs)—vital for sectors like defense, semiconductors, clean energy, and electric vehicles (EVs).
- Launch of the Strategic Mineral Recovery Programme to recover and process critical minerals from industrial waste.
- Joint R&D and investment under the Minerals Security Partnership (MSP) and Minerals Security Finance Network (MSFN).
- India to scale up exploration, processing, and recycling of critical minerals under the National Critical Minerals Mission (2025–31) with a ?16,300 crore outlay.
- Pharmaceutical Sector Collaboration
- Reducing India’s reliance on China for Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients (APIs) through alternative supply chains and expanded API manufacturing.
- Encouraging investment in Indian pharma production, including facilities in the US.
- Pharma formed 21.9% of India’s $20 billion consumer goods exports to the US in 2023.
- High-Tech and Emerging Technologies
- Joint R&D in semiconductors, AI, quantum computing, space, defense, biotechnology, and energy.
- U.S.-India AI Roadmap to be finalized by 2025, including data center infrastructure, processor access, and AI applications.
- Facilitating innovation through academic, industrial, and government collaboration.
- Technology Transfer and Trade Facilitation
- Easing export controls and restrictions to foster high-tech trade.
- Enabling smoother cross-border technology flows and investment under mechanisms like the CHIPS Act (ITSI Fund).
Associated Initiatives Enhancing TRUST
- iCET (Initiative on Critical and Emerging Technologies) – Launched in 2022, focuses on bilateral cooperation in semiconductors, AI, quantum, and wireless tech with defense applications.
- INDUS-X – Defense innovation initiative involving India’s iDEX and the US Defense Innovation Unit (DIU), emphasizing secure chip designs and green energy.
- CHIPS Act Collaboration – ITSI Fund supports India's semiconductor capacity through funding for R&D and infrastructure.
Strategic Significance
- Reducing China Dependence:China dominates ~70% of global REE production. TRUST helps India and the US build alternative, secure supply chains.
- Boosting Atmanirbhar Bharat:TRUST supports India’s goals under the National Critical Minerals Mission to become self-reliant in key strategic sectors.
- Enhancing Tech and Defense Capability:Ensures timely access to rare materials essential for missiles, radars, fighter jets, AI hardware, and quantum computing.
- Strengthening Pharma and Health Security:Addresses global API shortages and reduces vulnerability in critical drug manufacturing.
- Promoting Clean Energy Transition:Secures supply of minerals like lithium and cobalt essential for battery production and renewable energy tech.
- Fostering Innovation and Investment:Encourages private sector collaboration and US investments in India’s tech, mineral, and pharma sectors.
Current Status of India’s Critical Minerals Ecosystem
- Imports: India is a net importer of most critical minerals; import bill (FY24) stood at approx. ?30,000 crore.
- Exports: India remains a net exporter in rare earths.
- Budgetary Allocation (2025–31):
- ?7,000 crore for exploration.
- ?1,500 crore for recycling incentives.
MITRA Platform

- 18 Feb 2025
ecosystem, the Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI) has launched a new digital platform—MITRA (Mutual Fund Investment Tracing and Retrieval Assistant).
Key Features:
- Objective:MITRA aims to help investors trace, identify, and reclaim inactive or unclaimed mutual fund folios, while ensuring KYC (Know Your Customer) compliance under prevailing regulatory norms.
- Developed by:The platform has been developed at an industry level by the two Qualified Registrar and Transfer Agents (QRTAs) —
- Computer Age Management Services Ltd. (CAMS)
- KFIN Technologies Ltd.
These firms serve as agents of Asset Management Companies (AMCs).
- Hosted by:The platform is hosted jointly by CAMS and KFIN Technologies to serve as a centralized, searchable database for inactive and unclaimed mutual fund folios across the industry.
- Functions:
- Enables investors to search for overlooked investments or investments made in their name by others.
- Facilitates rightful legal claims by heirs or nominees.
- Encourages KYC compliance, thus reducing the number of non-KYC compliant folios.
- Aims to minimize the risks of fraudulent redemptions linked to dormant folios.
- Supports the creation of a transparent financial ecosystem by reducing unclaimed investments.
Definition of Inactive Folio:
- A mutual fund folio is considered inactive when no investor-initiated financial or non-financial transactions have occurred for ten consecutive years, even though the folio holds units.
Institutional Measures:
- Unit Holder Protection Committee (UHPC):SEBI has broadened the role of the UHPC under mutual fund regulations. The committee is now tasked with monitoring inactive folios, unclaimed dividends, and pending redemptions, ensuring proactive steps are taken for investor protection.
- Stakeholder Involvement:SEBI has directed AMCs, RTAs, Registered Investment Advisers (RIAs), the Association of Mutual Funds in India (AMFI), and mutual fund distributors to actively promote awareness regarding MITRA among investors.
FulaniCommunity
- 17 Feb 2025
In News:
The Fulani, one of Africa’s largest and most dispersed ethnic communities, trace their ancestry to the ‘Green Sahara’ period (12,000–5,000 years ago), according to recent genetic and anthropological research. This period, when the Sahara was a fertile, habitable landscape, marks the early development of African pastoralism.
The Fulani population is estimated at 40 million, spread across West and Central Africa, from Senegal and Guinea in the west to Lake Chad in the east. They are particularly concentrated in Nigeria, Mali, Guinea, Senegal, and Niger, and inhabit the Sahel-Savannah belt, straddling arid and semi-arid regions.
Nomadic Lifestyle and Social Structure
Traditionally known for their nomadic pastoralism, the Fulani have maintained a unique socio-cultural identity despite centuries of migration and contact with other African populations. Their society is internally diverse, divided into three main groups:
- Makiyaya: Nomadic herders
- FulaninSoro: Town dwellers
- Bararo: Forest dwellers, with strong ties to ancestral rituals and nature-based belief systems
Fulani communities are largely egalitarian, with a deep emphasis on kinship, family structure, and communal responsibility. Polygamy is widely practiced, and marriage ceremonies are elaborate, often involving intricate rituals and festive celebrations.
Women’s Role and Cultural Expression
Fulani women are recognized for their weaving, artisanal craftsmanship, and particularly their hairstyles, which are often elaborately styled and adorned with beads and cowrie shells—symbols of both identity and aesthetic tradition.
Linguistic and Religious Identity
The Fulani speak Fula (also called Fulfulde or Pulaar), a language belonging to the Atlantic branch of the Niger-Congo language family. Though largely Muslim, many retain spiritual connections with nature-based traditions, particularly among the Bararo groups.
Genetic Heritage and Historical Significance
A recent multinational study led by Uppsala University and Charles University analyzed biological and anthropological data from 460 Fulani individuals across 18 locations in seven African countries. It confirmed a complex genetic history, shaped by:
- Ancient North African ancestry, particularly linked to populations akin to modern-day Berbers of Morocco
- Historical interactions with West, Central, and East African communities
- A shared ancestral genetic component, likely rooted in early pastoral communities of the Green Sahara era
The research underscores that despite their high mobility and limited archaeological footprint, the Fulani have preserved a distinct genetic and cultural identity for millennia.
Fishery Survey of India (FSI)
- 17 Feb 2025
In News:
A landmark deep-sea fishing expedition by the Fishery Survey of India (FSI) has led to the discovery of previously underexploited fishing grounds in the Arabian Sea, offering significant promise for India’s marine resource sustainability, food security, and fishermen’s livelihoods.
Key Highlights of the Expedition
- Conducted by: Fishery Survey of India (FSI), under the Ministry of Fisheries, Animal Husbandry & Dairying
- Supported by: Pradhan Mantri MatsyaSampada Yojana (PMMSY)
- Geographic Scope: Waters between Kollam (Kerala) and Goa, at depths of 300–540 meters
- Location: Approx. 100–120 nautical miles off India’s western coast
- Catch Rate: Average Catch Per Unit Effort (CPUE) recorded at 150–300 kg/hr
- Timing: No significant difference observed in catches between day and night
Marine Biodiversity of the New Grounds
The discovered ecosystem harbors rich and diverse marine life, including:
- Commercially Important Crustaceans:
- Humpback nylon shrimp
- Arabian red shrimp
- Deep sea mud shrimp
- Deepwater spiny lobster
- Deep sea squat lobster
- Cephalopods:
- Opisthoteuthis species
- Octopoteuthissicula
- Diverse Deep-Sea Fishes:
- Froghead eel, Rosy cod, Snake mackerel, Sackfish
- Royal escolar, Bandfishes, Duckbill flathead
- Splendid alfonsino, Myctiophids, Shadow driftfish
- Spinyjawgreeneye, Shortfin neoscopelid, Stargazers
- Elasmobranchs (Cartilaginous Fishes):
- Sicklefin chimaera, Pygmy ribbontail catshark
- Bramble shark, Indian swellshark, Travancore skate
Significance for India’s Fisheries Sector
- Reduces Pressure on Coastal Fisheries: Coastal resources are under stress from overfishing, habitat degradation, and climate change. Deep-sea grounds offer a sustainable alternative.
- Supports Blue Economy Goals: Enhances India’s capacity to sustainably exploit its vast Exclusive Economic Zone (EEZ).
- Economic Benefits: Aligns with the government’s goal of doubling fishermen’s income and generating employment in marine-based livelihoods.
- Scientific Value: Contributes to marine biodiversity documentation and ecosystem-based fisheries management.
14th Asian Fisheries and Aquaculture Forum (14AFAF)

- 17 Feb 2025
In News:
India is set to host the 14th Asian Fisheries and Aquaculture Forum (14AFAF) from February 12–14, 2025, at the ICAR Convention Centre, Pusa Campus, New Delhi.
Key Highlights
- This triennial international event—organized by the Asian Fisheries Society (AFS), Indian Council of Agricultural Research (ICAR), Department of Fisheries (DoF), and AFS Indian Branch (AFSIB)—is themed "Greening the Blue Growth in Asia-Pacific".
- It aims to promote sustainable, inclusive, and innovation-driven development in the fisheries and aquaculture sector.
- Previous Indian Host: India is hosting the AFAF for the second time, the first being the 8th AFAF in Kochi (2007).
- Legacy: AFAF, headquartered in Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, has been a leading platform for fostering global cooperation in fisheries and aquaculture since its inception.
India's Role and Significance
- India ranks second globally in total fish production and aquaculture output, underlining its emerging leadership in the blue economy.
- The forum presents a strategic opportunity to:
- Showcase India’s technological and policy advancements.
- Strengthen international collaborations.
- Promote sustainable, resilient, and globally competitive aquaculture systems.
Forum Structure and Thematic Sessions
The event will feature 20+ technical sessions and keynote presentations by international experts, focusing on priority areas such as:
- Sustainable Fisheries Management:Emphasis on responsible fishing, biodiversity preservation, and efficient resource utilization.
- Climate Change and Fisheries:Addressing climate impacts on aquatic ecosystems and developing adaptive strategies.
- Smart Aquaculture & Technology:Integration of AI, IoT, and blockchain to enhance fish farming efficiency and monitoring.
- Fish Genetics & Biotechnology:Innovations for disease resistance, improved yields, and genetic advancements.
- Post-Harvest and Value Addition:Improving fish quality, market access, and export competitiveness through better processing techniques.
Crocodile Catfish

- 17 Feb 2025
In News:
The recent discovery of the Crocodile Catfish (Bagariussuchus) in the Bahini River near Basistha, Guwahati, Assam, has garnered attention from conservationists and ecologists alike. As one of the largest freshwater catfish species in Asia, its presence in Indian waters raises both scientific interest and ecological concerns.
Taxonomy and Distribution
- Scientific Name: Bagariussuchus
- Family: Sisoridae – the largest family of Asian catfishes, widely distributed across South and Southeast Asia.
- Common Names: Asian Giant River Catfish, Crocodile Goonch Catfish, Giant Devil Catfish
- Geographical Range: Native to countries including India, Nepal, Bangladesh, Myanmar, and Thailand.
Habitat and Morphological Features
- Natural Habitat: Prefers fast-flowing rivers, deep pools, turbulent rapids, and areas with rocky or gravelly substrates.
- Often found among boulders, submerged roots, and debris, thriving in cool, oxygen-rich waters.
- Physical Description:
- Long, cylindrical body with a broad head and wide mouth.
- Typicallydark brown to black, with irregular patches or spots for camouflage.
- Dorsal fin is elongated, stretching along most of the back.
- Size: Can grow up to 1.5 meters in length and weigh over 50 kilograms, though smaller specimens (~70 cm) are also observed.
Behaviour and Ecology
- Feeding Habits: A carnivorous predator, feeding on smaller fish, crustaceans, and aquatic invertebrates.
- Known for its voracious appetite, capable of consuming prey nearly its own size.
- Most active during evening or nighttime, making it a nocturnal feeder.
- Sexual Dimorphism: Males are generally slimmer and may exhibit slightly brighter coloration than females.
Ecological Concerns
- The discovery of the Crocodile Catfish in a non-native region like the Bahini River raises concerns about its invasive potential.
- It can threaten native aquatic biodiversity by preying on indigenous species and disturbing the ecological balance.
- Overfeeding and rapid proliferation can degrade water quality and disrupt food chains.
Conservation Status
- IUCN Red List: Near Threatened (NT): This status reflects concerns about habitat degradation, overfishing, and ecological displacement, which may impact population stability across its range.
India Gas Market Report: Outlook to 2030

- 17 Feb 2025
In News:
The International Energy Agency (IEA), in its report “India Gas Market Report: Outlook to 2030”, has highlighted the transformative potential of natural gas in India’s energy transition.
As India aims to raise the share of natural gas in its primary energy mix from ~6% to 15% by 2030, the report outlines a roadmap for achieving this goal through policy reforms, infrastructure expansion, and market liberalization.
Current Status and Future Outlook
- Demand Growth: India's natural gas consumption is projected to increase by 60%, reaching 103 billion cubic meters (bcm) by 2030. The City Gas Distribution (CGD) sector, which supplies gas to households, transport, and industries, will drive this growth.
- Domestic Production: India produced 35 bcm in 2023, with the Krishna-Godavari deepwater fields contributing a quarter. Production is expected to reach just under 38 bcm by 2030, a modest 8% increase.
- Import Dependency: With domestic supply growth lagging behind demand, LNG imports are expected to more than double, from ~30 bcm in 2023 to around 65 bcm by 2030. India is already the fourth-largest LNG importer globally.
Infrastructure Expansion
India’s natural gas infrastructure has undergone rapid growth:
- Since 2019, the number of CNG stations quadrupled and residential gas connections more than doubled.
- The gas transmission pipeline network expanded by 40%, with another 50% expansion expected by 2030.
- CGD infrastructure is poised for a further boom, supporting increased consumption in urban areas.
Sectoral Trends
- Industry: Heavy industry and manufacturing are expected to add 15 bcm to gas demand by 2030.
- Refining: Gas use in refineries will rise by over 4 bcm as more refineries get connected.
- Transport: Greater CNG adoption, if incentivized, could significantly reduce vehicular emissions.
Challenges Hindering Growth
- Price Distortion: Prices from legacy fields are capped (e.g., USD 6.5–10 per MMBtu), limiting true market-based discovery.
- Monopoly in Transport & Marketing: GAIL’s dominance in both gas marketing and pipeline ownership creates potential conflicts of interest.
- Storage Limitations: India lacks underground gas storage (UGS) and has limited LNG storage capacity, affecting supply security.
- Policy and Regulatory Gaps: Inadequate third-party access and fragmented pricing/taxation systems reduce investor confidence.
Policy Recommendations by IEA
- Gas Pricing Freedom:
- Implement full pricing freedom, in line with Kirit Parekh Committee (2022) recommendations.
- Initially lift ceilings on high-cost deepwater and ultra-deepwater projects.
- Allow producers to sell more output on platforms like the Indian Gas Exchange (IGX).
- Unbundling Supply and Transmission:
- Establish independent gas transmission system operators (TSOs).
- Legally separate marketing from pipeline operations to ensure fair, non-discriminatory access.
- Standardize Gas Sales Agreements (GSAs) and Gas Transmission Agreements (GTAs).
- Infrastructure and Market Development:
- Ensure transparent, regulated third-party access to pipelines.
- Develop strategic gas reserves and expand LNG terminal capacity.
- Improve data transparency on pipeline capacities and tariffs.
- Tax and Regulatory Reforms:
- Harmonize taxes across fuels to create a level playing field.
- Rationalize GST on CNG vehicles and revise import duties on natural gas.
- Offer tax benefits to natural gas similar to electric vehicles to promote adoption.
- Secure Long-Term LNG Contracts:
- With legacy contracts expiring post-2028, proactive procurement is essential to avoid spot market volatility.
Rising Heatwaves in India
- 16 Feb 2025
In News:
India is increasingly facing more frequent, intense, and prolonged heatwaves, posing a significant threat to public health, economic productivity, agricultural stability, andenvironmental sustainability. This trend underscores the broader implications of climate change, particularly for developing economies with large vulnerable populations.
Understanding Heatwaves
A heatwave is defined as a prolonged period of abnormally high temperatures, often accompanied by high humidity. As per the India Meteorological Department (IMD):
- A heatwave is declared when the maximum temperature reaches at least 40°C in plains and 30°C in hilly regions.
- The severity is determined by how much the temperature exceeds the normal.
Impacts of Heatwaves
- Public Health:
- Prolonged heat exposure increases the risk of heatstroke, dehydration, and worsens cardiovascular and respiratory illnesses.
- Vulnerable groups include the elderly, outdoor workers, and those without access to cooling.
- Livelihoods and Employment:
- According to the World Bank, India could lose 34 million jobs by 2030 due to heat-stress-related productivity declines.
- The informal sector and outdoor labourers are especially at risk.
- Agriculture and Food Security:
- Heat stress leads to reduced crop yields, livestock deaths, and increased irrigation demand.
- It threatens the food supply chain and rural incomes.
- Water Scarcity:
- 54% of India’s land is under high to extremely high water stress, as per the World Resources Institute (WRI).
- Heatwaves exacerbate droughts and deplete groundwater sources.
- Environmental Degradation:
- Higher temperatures increase the risk of wildfires, especially in forested and arid zones.
- Ecosystem services and biodiversity are under stress.
- Infrastructure and Energy:
- Rising temperatures lead to increased energy demand for cooling, straining power grids.
- Urban infrastructure suffers due to heat-induced wear and tear.
President’s Rule Imposed in Manipur
- 16 Feb 2025
In News:
On 13th February 2025, President DroupadiMurmu imposed President’s Rule in Manipur under Article 356 of the Constitution, following a report submitted by the State Governor Ajay Kumar Bhalla. The move comes in the wake of a prolonged period of ethnic violence, governance vacuum, and the resignation of Chief Minister N. Biren Singh on 9th February 2025.
Constitutional Provisions:
- Article 356 empowers the President to assume control of a state’s administration if it is determined that the state cannot be governed as per constitutional provisions.
- The Governor’s report or other evidence of breakdown is a prerequisite.
- Under this, the elected state government is dismissed, and the Governor becomes the executive head on behalf of the President.
- The State Legislative Assembly is either dissolved or placed under suspended animation. In Manipur’s case, it is under suspended animation, with its term valid until 2027.
- The proclamation must be approved by both Houses of Parliament within two months, and if extended, it can last up to six months at a time, with a maximum duration of three years.
Crisis Background and Ethnic Conflict
Manipur has witnessed an intense ethnic conflict between the Meitei and Kuki-Zo communities since May 3, 2023. The violence has led to:
- Over 250 people killed, and
- More than 60,000 displaced.
Security concerns and political instability escalated after the Chief Minister’s resignation, with the BJP leadership unable to find a consensus candidate for replacement. The deteriorating law-and-order situation, coupled with governance paralysis, prompted the imposition of President’s Rule.
Security and Migration Concerns
Former CM N. Biren Singh raised alarm over:
- Rising illegal immigration through the 398-km porous border with Myanmar, worsened by the Free Movement Regime (FMR).
- A demographic shift threatening the State’s land, identity, and resources.
- Post-violence governance failure, as state machinery struggled to respond effectively.
He emphasized the need to intensify detection and deportation of illegal immigrants, a concern linked to the root causes of ethnic tension.
Historical Context
- This is not the first time Manipur has come under central rule. The last imposition of President’s Rule in Manipur lasted 277 days, from June 2, 2001 to March 6, 2002.
Devolution Index Report 2024

- 16 Feb 2025
In News:
Recently, the Union Minister of State Prof. S. P. Singh Baghel released the Devolution Index Report at the Indian Institute of Public Administration (IIPA), New Delhi.
Titled “Status of Devolution to Panchayats in States – An Indicative Evidence-Based Ranking 2024”, the report assesses the extent of autonomy and empowerment of Panchayati Raj Institutions (PRIs) across Indian States and UTs.
Context and Constitutional Framework
The initiative is anchored in the vision of Article 243G of the Constitution and the 73rd Constitutional Amendment, which mandates the devolution of powers, authority, and responsibilities to Panchayats over 29 subjects listed in the Eleventh Schedule. It reflects the spirit of grassroots democracy and aims to realize the vision of "Local Self-Government".
Core Objectives and Dimensions of the Index
The Devolution Index provides an evidence-based evaluation of decentralization and self-governance in rural India. It assesses PRIs across six critical dimensions:
- Framework – Legal and institutional setup for decentralization.
- Functions – Scope of responsibilities devolved to Panchayats.
- Finances – Fiscal powers and resource autonomy.
- Functionaries – Availability and control over human resources.
- Capacity Building – Training and skill development mechanisms.
- Accountability – Transparency, audit mechanisms, and citizen participation.
Significance and Policy Implications
- Strengthening Cooperative Federalism: By highlighting inter-state comparisons, the Index fosters competitive federalism in the spirit of collaborative governance.
- Multi-Stakeholder Utility:
- Citizens: Increases transparency in Panchayat functioning and fund utilization.
- Elected Representatives: Offers a data-driven basis for decentralization advocacy.
- Officials & Policymakers: Acts as a policy instrument for reform and targeted capacity building.
- Aligns with National Vision:
- Supports Viksit Bharat goals through ??????????????????????????????? (developed and empowered PRIs).
- Contributes to inclusive rural development and grassroots democratization.
Income-tax Bill, 2025
- 16 Feb 2025
In News:
The Income-tax Bill, 2025, tabled in Parliament on February 13, 2025, seeks to repeal and replace the Income-tax Act, 1961, marking a landmark step in tax law simplification.
It reflects the government's commitment to ease of doing business, legal clarity, and tax compliance, without altering the core tax policy or rate structure.
Guiding Principles
- Textual and structural simplification for better clarity.
- Policy continuity—no major tax policy changes.
- Preservation of existing tax rates for predictability.
Approach and Methodology
- Three-pronged strategy:
- Simplify language and eliminate legalese.
- Remove obsolete, redundant, and repetitive provisions.
- Reorganize the Act for logical and easier navigation.
- Consultative process:
- 20,976 online suggestions received.
- Stakeholder consultations with taxpayers, professionals, and industry bodies.
- International best practices reviewed, notably from Australia and the UK.
Quantitative Simplification
Parameter Income-tax Act, 1961 Income-tax Bill, 2025 Change
Words 5,12,535 2,59,676 ↓ 2,52,859
Chapters 47 23 ↓ 24
Sections 819 536 ↓ 283
Tables 18 57 ↑ 39
Formulae 6 46 ↑ 40
Key Features and Improvements
- Qualitative Enhancements:
- Use of simplified and accessible language.
- Consolidation of amendments to reduce fragmentation.
- Enhanced readability via structured use of tables and formulae.
- Elimination of outdated provisions.
- Introduction of "Tax Year":Defined as the 12-month period beginning April 1, providing better uniformity.
- Crypto as Capital Asset:Virtual Digital Assets (VDAs) such as cryptocurrencies included in the definition of "property", now taxable as capital assets.
- Dispute Resolution Clarity:Improved transparency in Dispute Resolution Panel (DRP) procedures by including points of determination and reasoning—addressing a key criticism of ambiguity in the earlier framework.
- Removal of Obsolete Exemptions:Section 54E, providing capital gain exemptions for transfers before April 1992, has been scrapped.
- Expected Timeline:Once enacted, the Income-tax Act, 2025 is proposed to come into effect from April 1, 2026.
Gangasagar Mela

- 16 Feb 2025
In News:
Recently, several Ministers of the West Bengal government gathered at a conference room on Sagar Island, situated at the mouth of the Bay of Bengal — the southernmost tip of the State — to brief mediapersons on the arrangements for the Gangasagar Mela 2025.
Gangasagar Mela: Overview
- Second-largest human congregation in the world, after the Kumbh Mela.
- Held annually on Makar Sankranti (January 14) at the confluence of River Ganga and Bay of Bengal.
- Pilgrims take a holy dip at the confluence; site houses the Kapil Muni Temple.
- In 2025, the West Bengal government claimed over 1.10 crore pilgrims visited.
Location & Geography
- Sagar Island (Sagardwip/Ganga Sagar):
- Located ~120 km from Kolkata.
- Largest island in the Sundarbans archipelago.
- Population: ~2 lakh (2011 Census).
- Classified under the sand group category.
- Accessed by crossing the Muriganga River via ferry.
Climate Change Impact
- Rising sea levels and erosion are threatening Sagar Island:
- Sea has advanced from 1,500 m to 470 m from the Kapil Muni Temple in ~10 years.
- Tidal surge rises from 4.6 m to 7.6 m during high tides.
- Erosion worsened by:
- Mangrove destruction for construction during mela.
- Flattening of sand dunes and vegetation, removing natural barriers.
Environmental Challenges
- Constructions often violate Coastal Regulation Zone (CRZ) norms (no construction within 500 m of high tide line).
- Beaches have turned muddy, unfit for bathing; pilgrims walk through marshes.
- Concrete embankments, built after removing mangroves, washed away during cyclones.
- Geotextiles used for erosion control are ineffective near the temple due to strong wave action.
Cyclones & Vulnerability
- Recent major cyclones: Yaas (2021), Remal (May 2024), Dana (Oct 2024).
- Local communities frequently displaced; loss of livestock and property reported.
- Rising salinity impacting fish farming and livelihoods.
Socio-Economic Impact
- Youth migration due to lack of job opportunities.
- Local economy disrupted by environmental stress.
- Many locals say the mela offers little direct benefit to them.
Governance and Policy Issues
- West Bengal government spent ~?250 crore in 2024 for mela arrangements.
- Proposed ?4,100 crore World Bank-funded embankment project:
- World Bank: 70% cost; State: 30%.
- Aimed at protecting 52 inhabited islands in Sundarbans.
- Centre-State conflict:
- WB government alleges non-cooperation from the Centre.
- No Central funds provided for the mela, unlike the Kumbh Mela.
- Demand for national mela status for Gangasagar.
Cultural and Political Dimensions
- Religious significance emphasized by Shankaracharya of Puri.
- Soft Hindutva strategy attributed to West Bengal’s ruling party (TMC).
- Political undertones visible in temple construction and event promotion.
UDAN 5.5 – Advancing Last-Mile Air Connectivity
- 15 Feb 2025
In News:
- The Government of India has launched UDAN 5.5, the latest phase of its flagship regional air connectivity scheme UDAN (UdeDesh ka AamNaagrik).
- It aims to enhance last-mile air connectivity in remote, hilly, and island regions using smaller aircraft, helicopters, and seaplanes.
About UDAN Scheme
- Launched: 2016, under the National Civil Aviation Policy (NCAP).
- Nodal Ministry: Ministry of Civil Aviation.
- Purpose: To make air travel affordable, accessible, and widespread, especially in Tier-2 and Tier-3 towns.
Objectives
- Provide affordable air travel to the common citizen.
- Improve air connectivity in unserved and underserved regions.
- Promote regional development and economic integration.
Key Features
- Fare Cap: ?2,500 per hour of flight for 50% of seats (about 500 km distance).
- Viability Gap Funding (VGF):
- Provided to airlines to cover shortfalls between operational cost and revenue.
- Financed via Regional Connectivity Fund (RCF).
- Government Contribution to VGF:
- State Governments: 20%
- Union Territories & North-Eastern Region (NER) States: 10%
- Support Measures: Concessions from Central/State Governments and airport operators.
Special Variants Under UDAN
- Lifeline UDAN: For transporting medical cargo during COVID-19.
- Krishi UDAN: For agricultural produce value realization, especially from NER and tribal districts.
- International UDAN: To connect NER cities like Guwahati and Imphal with international destinations.
UDAN 5.5 – Key Highlights
- Focuses on last-mile connectivity in challenging terrains where traditional aviation is impractical.
- Aircraft Types Allowed:
- Category 1A: < 9 seats
- Category 1: < 20 seats
- Operational Modes:
- Seaplanes: Use of 80 water bodies including waterdromes, ponds, dams.
- Helicopters: Routes mapped from 400 helipads nationwide.
- Small Aircraft: Routes specifically for aircraft under 20-passenger capacity.
- Encourages air taxi and niche aviation operators.
Achievements of UDAN (as of 2024)
- Passenger Impact: Enabled travel for over 1.5 crore passengers.
- Flight Operations: Over 2.8 lakh UDAN flights completed.
- Route Expansion: 619 routes operationalized, including helicopter routes.
- Airport Growth: Number of operational airports doubled from 74 in 2014 to over 157 in 2024.
- Destinations Connected:
- 68 unserved/underserved destinations added: includes 58 airports, 8 heliports, 2 water aerodromes.
Future Scope
- Current Challenges:
- India currently has no active seaplane services.
- Fewer than 20 small aircraft (Category A1) in operation.
- Projected Developments (next 5 years):
- Establishment of 50+ seaplane routes.
- Creation of 20–25 water aerodromes.
- Induction of around 30 new aircraft for regional connectivity.
Einstein Ring Discovered by ESA’s Euclid Telescope
- 15 Feb 2025
In News:
- The European Space Agency’s (ESA) Euclid space telescope has recently discovered a rare Einstein ring around the galaxy NGC 6505, located nearly 590 million light-years from Earth.
- This ring was formed by the light of a distant unnamed galaxy situated 4.42 billion light-years away, distorted and amplified due to gravitational lensing by NGC 6505.
What is an Einstein Ring?
- It is a circular ring of light that appears around a massive celestial object such as a galaxy, dark matter concentration, or cluster of galaxies.
- Caused due to strong gravitational lensing, it occurs when a massive foreground object (gravitational lens) bends and amplifies the light from a background object, resulting in a circular or arc-like appearance.
- The phenomenon only results in a full ring when the observer, lensing object, and background galaxy are almost perfectly aligned.
Theoretical Basis
- Named after Albert Einstein, who in his General Theory of Relativity predicted that massive objects warp space-time, thereby bending the path of light.
- The phenomenon of gravitational lensing, and by extension Einstein rings, was first theoretically anticipated by Einstein and empirically confirmed much later.
Scientific Importance
- Extremely rare phenomena: Occur in less than 1% of galaxies.
- Serve as natural cosmic magnifying lenses that allow scientists to study:
- Dark Matter: Helps trace the invisible distribution of dark matter through gravitational effects.
- Dark Energy: Supports understanding of dark energy’s role in accelerating the universe’s expansion.
- Distant Galaxies: Reveals otherwise invisible galaxies by amplifying their light.
- Universe Expansion: Provides data on how space between galaxies stretches over cosmic time.
Gravitational Lensing: Explained
- Gravitational lensing occurs when a massive body (galaxy, cluster, black hole) creates a gravitational field that bends and magnifies light from objects behind it.
- This leads to multiple outcomes — arcs, double images, or full rings (Einstein rings).
- The lensing object in the recent case is NGC 6505, a galaxy first observed in the 19th century.
Observation and Imaging
- Einstein rings are not visible to the naked eye and require powerful space telescopes like Euclid for detection.
- Euclid captured images showing a bright central galaxy (NGC 6505) with a distinctive, cloudy ring formed by the bent light from the background galaxy.
About the Euclid Space Telescope
- Launched in 2023 by ESA using a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket from Cape Canaveral, Florida.
- Operates from Lagrangian Point 2 (L2), located 1.5 million km from Earth.
- Designed for a six-year mission to study the dark universe.
- Key Objectives:
- Create the largest 3D map of the cosmos.
- Observe billions of galaxies across 10 billion light-years.
- Understand the distribution of dark matter and the influence of dark energy in the early universe.
- Study light emitted from galaxies up to 10 billion years ago to trace cosmic evolution.
Gender Budgeting

- 15 Feb 2025
In News:
The Gender Budget allocation for FY 2025-26 has increased to ?4.49 lakh crore, accounting for 8.86% of the total Union Budget, up from 6.8% in FY 2024-25. This represents a 37.25% increase compared to the ?3.27 lakh crore allocated in the previous year.
Key Highlights:
- Expansion Across Ministries:
- A total of 49 Ministries/Departments and 5 Union Territories (UTs) have reported allocations in the Gender Budget Statement (GBS) for 2025-26, marking the highest participation since the inception of the Gender Budget.
- Twelve new Ministries have been included in the GBS this year, signaling a broader inclusion of gender considerations in sectors such as animal husbandry, biotechnology, water resources, food processing, and railways.
- Gender Budget Allocation Breakdown:
- Part A (100% Women-specific schemes): ?1,05,535.40 crore (23.5% of total GBS).
- Part B (30-99% allocation for women): ?3,26,672 crore (72.75% of total GBS).
- Part C (Below 30% allocation for women): ?16,821.28 crore (3.75% of total GBS).
- Top Ministries reporting high percentages in gender-focused allocations include the Ministry of Women & Child Development (81.79%), Department of Rural Development (65.76%), and Department of Health & Family Welfare (41.10%).
- Focus on Women’s Economic Participation:
- The Union Budget aims to boost women’s participation in economic activities, targeting 70% by 2047.
- Women’s Labour Force Participation Rate (LFPR) rose to 42% in 2023-24 from 33% in 2021-22.
- Efforts to close the gender gap involve increased allocations to programs like Skill India, Deendayal Antyodaya Yojana-National Rural Livelihoods Mission (DAY-NRLM), and PM Vishwakarma, with 52% of the ?1.24 lakh crore allocated for these programs earmarked for women and girls.
- Support for Women Entrepreneurs:
- Women own 20.5% of micro, small, and medium enterprises (MSMEs) in India, employing approximately 27 million people.
- The Budget focuses on empowering women entrepreneurs by advocating for collateral-free loans, alternative credit scoring models, and financial literacy programs.
- Establishing 30 million additional women-owned businesses could generate 150-170 million jobs by 2030, contributing significantly to India's employment needs.
- Gig Economy and Informal Sector:
- The Budget introduces measures to formalize gig workers, 90% of whom are women. By issuing identity cards and registering gig workers on the e-Shram portal, the Budget aims to provide them with access to social security and financial inclusion benefits.
- This addresses the challenges faced by women in the informal sector, including low wages, job insecurity, and lack of maternity benefits.
- Gender Inclusivity in Technology:
- A dedicated ?600 crore allocation under the India AI Mission aims to promote gender inclusivity in the technology sector. This includes the establishment of a Centre of Excellence on Artificial Intelligence (AI) for education and skill development, ensuring women’s participation in high-growth technological fields.
- Gender Budgeting Components:
- Part A: Gender-specific expenditure, directly benefiting women (e.g., BetiBachaoBetiPadhao).
- Part B: Pro-women general expenditure, benefiting both men and women but focusing on women’s advancement (e.g., MGNREGA).
- Part C: Gender-neutral budgets that may require gender-sensitive planning (e.g., Har GharNal project, which reduces women’s time spent fetching water).
- Policy Vision and Challenges:
- The Union Budget for 2025-26 is part of the government’s vision for a "Viksit Bharat" with zero poverty, universal education, 100% skilled labor, and 70% female participation in the workforce by 2047.
- While the Budget lays a strong foundation, addressing persistent challenges like gender pay gaps, occupational segregation, and cultural barriers will require sustained policy interventions, gender-sensitive workplace reforms, and effective implementation of gender-disaggregated data for monitoring outcomes.
Corruption Perceptions Index (CPI) 2024

- 15 Feb 2025
In News:
India ranked 96th out of 180 countries in the Corruption Perceptions Index (CPI) for 2024, with a score of 38, a decline from 39 in 2023 and 40 in 2022. This indicates a worsening perception of corruption within India’s public sector.
Global Context:
- The CPI, compiled annually by Transparency International, is a widely recognized global ranking system that evaluates the perceived levels of corruption in public sectors.
- It uses a scale of 0 to 100, where 0 indicates highly corrupt and 100 signifies very clean.
- The CPI is based on expert assessments and surveys, drawing from at least three data sources out of 13 recognized corruption assessments from organizations like the World Bank and the World Economic Forum.
- Top Ranking Countries: Denmark topped the 2024 CPI, followed by Finland and Singapore, indicating strong governance systems with minimal corruption. These countries are recognized for their effective public sector governance, transparency, and low corruption levels.
- Regional Comparison: Among India’s neighbors, Pakistan ranked 135th, Sri Lanka at 121st, Bangladesh at 149th, and China ranked 76th, performing relatively better than India. The Asia-Pacific region, in general, saw a decline in its average CPI score, dropping by one point to 44.
- Global Trends: The CPI 2024 reveals troubling global trends, with corruption being a persistent issue worldwide. While 32 countries have significantly improved their corruption scores since 2012, 148 countries have either stagnated or worsened in the same period.
- The global average score remains at 43, with more than two-thirds of countries scoring below 50, signaling a widespread corruption problem.
- Corruption’s Impact on Climate Action: One of the significant findings in 2024 is the link between corruption and climate action. Corruption undermines efforts to combat climate change by misappropriating funds meant for emission reduction and climate adaptation projects.
- The report warns that such corruption obstructs effective policies and hinders climate change mitigation, leading to environmental degradation. Furthermore, it highlights that corruption in high-CPI countries often serves the interests of fossil fuel companies, complicating global climate efforts.
- Corruption and Human Rights: The report underscores that corruption not only impedes economic development but also contributes to the erosion of democracy, human rights violations, and instability. Corruption, particularly in the form of misallocation of resources, exacerbates the vulnerability of populations already affected by climate change, poverty, and human rights abuses.
- Financial Hubs and Illicit Funds: Many countries with high CPI scores, despite their lower domestic corruption levels, serve as financial hubs that attract illicit funds stemming from corruption and environmental damage. This "dirty money" exacerbates corruption on a global scale and has far-reaching consequences that extend beyond national borders.
- The Call for Action: Transparency International’s report stresses the need for global cooperation in tackling corruption. It warns that corruption is a major contributor to the rise of authoritarianism and calls for urgent, concrete action to address global corruption. The report emphasizes that combating corruption is crucial for achieving a peaceful, sustainable, and democratic world.
India’s Indigenous Shakti Semiconductor Chip
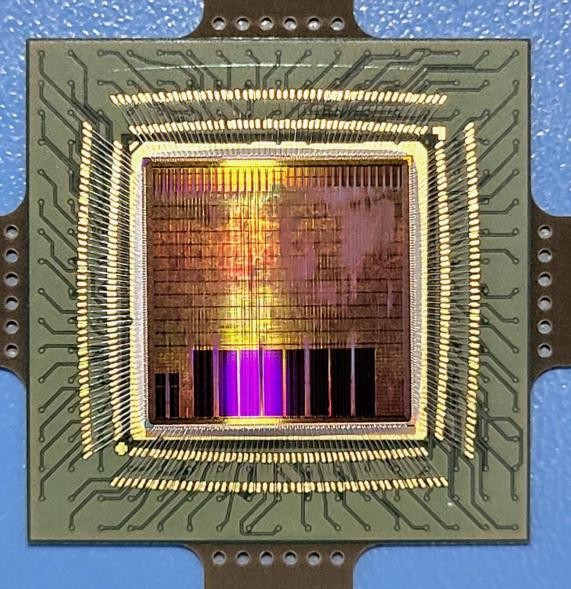
- 15 Feb 2025
In News:
India has achieved a significant milestone in semiconductor technology with the development of the indigenous Shakti semiconductor chip. Developed by the Indian Institute of Technology (IIT) Madras in collaboration with the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) and supported by the Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology (MeitY), the Shakti chip is a crucial component of India’s push for technological self-reliance under the Digital India RISC-V (DIRV) initiative.
Overview of Shakti Semiconductor Chip
- The Shakti chip is an indigenous microprocessor based on the RISC-V open-source Instruction Set Architecture (ISA).
- Its primary objective is to meet the high-performance computing, security, and reliability needs of India’s defense, aerospace, and space industries.
- It was specifically designed to support applications in satellite missions, avionics, embedded systems, and command-and-control operations.
- The chip is the third in the Shakti series, following the earlier RIMO (2018) and MOUSHIK (2020) chips, which served as technology demonstrators.
Key Features:
- Indigenous Development: Fully developed, fabricated, and tested in India, ensuring complete control over the design and manufacturing process.
- RISC-V Architecture: The Shakti chip utilizes the RISC-V open-source architecture, offering flexibility for customization and adaptation to various hardware and application needs.
- Fault Tolerant and Reliable: Designed to endure the harsh conditions of space and defense applications, making it highly reliable for mission-critical functions.
- High-Performance Computing: Supports complex functions like AI-based operations, real-time control systems, and sensor integration, essential for space missions and advanced defense technologies.
- Advanced Security: Aimed at providing robust security measures for critical sectors, including defense and aerospace, ensuring protection against cyber threats.
- Expandable and Scalable: The chip supports multiple boot modes and hybrid memory extensions, allowing for future upgrades and expansions, especially for space exploration.
Applications of the Shakti Chip
- Space Missions: The Shakti chip plays a vital role in powering ISRO's command-and-control systems, satellite avionics, and embedded systems used in various space missions.
- Defense & Aerospace: It enhances India’s strategic autonomy by reducing reliance on foreign semiconductor technology for military-grade electronics.
- IoT & AI Applications: The chip’s high-performance computing capabilities are ideal for smart systems, the Internet of Things (IoT), and AI applications.
- Research and Development: The chip contributes significantly to India’s semiconductor ecosystem, providing a foundation for further R&D in indigenous chip fabrication.
The Digital India RISC-V (DIRV) Initiative
- Launched in April 2022 by MeitY, the DIRV initiative aims to strengthen India’s semiconductor ecosystem by promoting the development of indigenous RISC-V-based microprocessors.
- The initiative emphasizes reducing dependency on foreign semiconductor solutions and fostering self-reliance in the digital sector.
- DIRV also focuses on high-performance computing for emerging technologies such as 5G, AI, and cloud computing. Through collaborations with IITs, ISRO, C-DAC, and private industry partners, the program aims to create a robust ecosystem for scalable microprocessor solutions.
IRIS: A Key Development from Shakti
- One of the most notable outputs of the Shakti chip initiative is the IRIS (Indigenous RISC-V Controller for Space Applications).
- Developed for ISRO’s space missions, the IRIS chip is a high-performance, fault-tolerant, 64-bit processor based on the Shakti microprocessor.
- It has been designed to meet the specific needs of space missions, such as satellite command-and-control systems, by integrating custom modules like watchdog timers and advanced serial buses.
- The IRIS chip also features multiple boot modes and hybrid memory extensions for future scalability and expansion in line with upcoming space missions.
Market Intervention Scheme (MIS)

- 14 Feb 2025
In News:
To enhance the efficacy and wider adoption of MIS, the Government of India revised the guidelines in 2025.
Key Highlights:
- Objective: It aims to provide price support for perishable agricultural and horticultural commodities not covered under the Minimum Support Price (MSP) regime. It prevents distress sales during periods of excessive production and sharp price declines.
- Implementing Authority:The scheme is under the Department of Agriculture & Farmers’ Welfare and is now a component of the PM-AASHA (Pradhan Mantri AnnadataAaySanrakshan Abhiyan) umbrella scheme.
- Eligibility & Activation:
- Implemented on the request of State/UT Governments.
- Triggered when market prices fall by at least 10% compared to the average price of the previous normal year.
- Nature of the Scheme:
- Ad-hoc price support mechanism operational during sudden market crashes.
- Cost-sharing pattern between Centre and States is 50:50, and 75:25 for North-Eastern states.
- Procurement Provisions (Revised 2025):
- Procurement limit increased from 20% to 25% of total production of the crop.
- Direct Benefit Transfer (DBT) mode introduced: States may directly compensate farmers for the price difference between Market Intervention Price (MIP) and actual selling price.
- Physical procurement is optional under the revised scheme.
- Authorized Procurement Agencies:
- Central Nodal Agencies like NAFED (National Agricultural Cooperative Marketing Federation of India) and NCCF (National Cooperative Consumers’ Federation of India).
- Farmer Producer Organizations (FPOs), Farmer Producer Companies (FPCs), and state-nominated agencies can also participate in procurement, storage, and transportation.
- Support for Transportation and Storage:
- Reimbursement of storage and transport costs is provided by Central Nodal Agencies for TOP crops (Tomato, Onion, Potato).
- This provision helps balance regional price disparities between producing and consuming states.
- Significance:
- The revamped MIS strengthens market resilience for perishable crop producers.
- Enhances State participation, reduces post-harvest losses, and ensures remunerative returns through institutional and technological support mechanisms.
SevaBhoj Yojana

- 14 Feb 2025
In News:
Launched in August 2018 by the Ministry of Culture, the SevaBhoj Yojana is a Central Sector Scheme aimed at supporting charitable and religious institutions that provide free food (langar, prasad, bhandara) to the public without discrimination.
Key Highlights:
- The scheme provides reimbursement of the Central Government’s share of Central Goods and Services Tax (CGST) and Integrated Goods and Services Tax (IGST) paid on the purchase of specific raw food items used in preparing meals.
- Objectives of the Scheme
- Reduce the financial burden on charitable/religious institutions engaged in feeding the public.
- Encourage the tradition of community kitchens and public service across diverse religious institutions.
- Promote inclusive religious philanthropy while ensuring transparency and accountability in public spending.
Key Features
Feature Details
Launched By Ministry of Culture, Government of India
Year of Launch August 2018
Target Beneficiaries Temples, Gurudwaras, Mosques, Churches, Ashrams, Monasteries, etc.
Reimbursed Taxes CGST and Central Share of IGST
Scope of Benefit Raw food items used for free food distribution
Coverage Threshold Institutions must serve free food to at least 5000 people/month
Required Duration of Operation Minimum 3 years of continuous food service
Eligibility Criteria
To qualify for the scheme, institutions must:
- Serve free food to a minimum of 5,000 people per month.
- Be in operation for at least three years prior to application.
- Be registered under:
- Section 10 or 12AA of the Income Tax Act, or
- Societies Registration Act, or
- Relevant public trust laws, or
- Statutory religious bodies constituted under law.
- Possess a District Magistrate’s certificate confirming their ongoing food distribution service.
Implementation Mechanism
The scheme ensures transparency and streamlined reimbursement through a digital and multi-tier process:
- Institutions register on the NGO Darpan Portal of NITI Aayog.
- Apply through the Central Sector Monitoring System (CSMS) Portal of the Ministry of Culture.
- Submit relevant documents to the Nodal Central Tax Officer in their State/UT.
- On verification, a Unique Identity Number (UIN) is issued.
- Verified tax claims are forwarded by the concerned GST Authority to the Ministry.
- The Ministry releases the sanctioned amount to the GST Authority, which reimburses the institution.
Governance and Outreach
- The Ministry promotes the scheme through official websites and social media platforms.
- Efforts are made to ensure equitable representation of all religions and communities.
- As of January 2025, several institutions across states have benefited from the scheme, though individual beneficiary counts are not collected.
S?janam

- 14 Feb 2025
In News:
In a significant stride toward sustainable healthcare and waste management, India launched its first indigenous Automated Biomedical Waste Treatment Plant, named S?janam, on April 13, 2025, at AIIMS, New Delhi.
Developed by the CSIR-National Institute for Interdisciplinary Science and Technology (CSIR-NIIST), Thiruvananthapuram, under the Ministry of Science & Technology, this innovative rig marks a paradigm shift in handling biomedical waste, moving away from conventional, polluting incineration techniques.
Why this matter?
India generates approximately 743 tonnes of biomedical waste daily (CPCB, 2023). Safe disposal has been a persistent challenge due to limited infrastructure, high costs, and environmental concerns. The launch of S?janam aligns with the government’s push for “Waste to Wealth” and environmentally responsible healthcare infrastructure, as part of the Atmanirbhar Bharat and Swachh Bharat initiatives.
What is S?janam?
- An automated, eco-friendly biomedical waste treatment rig.
- Designed to disinfect pathogenic waste like blood, urine, sputum, and lab disposables.
- Does not use incinerators, which release toxic emissions such as dioxins and furans.
Key Features & Capacity
Feature Details
Disinfection Process Non-incineration, antimicrobial treatment
Daily Treatment Capacity 400 kg of total biomedical waste
Organic Waste Handling Initially handles 10 kg/day of degradable medical waste
Environmental Safety Neutralizes foul odor; releases pleasant fragrance
Health Safety Minimizes human exposure and risk of contamination
Validation Third-party tested; treated material safer than organic vermicompost
Significance for Public Health and Environment
- Reduces dependency on expensive, energy-intensive incinerators.
- Eco-friendly solution that prevents toxic emissions and groundwater contamination.
- Aligns with Bio-Medical Waste Management Rules, 2016, which mandate safe segregation, treatment, and disposal.
- Enhances India’s capability to respond to health crises (e.g., pandemics), where waste generation spikes.
Strategic Implications
- Promotes indigenous technological innovation under “Make in India.”
- Offers a scalable solution for both urban and rural healthcare setups.
- Contributes to India’s climate commitments by cutting healthcare-related emissions.
NITI Aayog Policy Report on Expanding Quality Higher Education
- 14 Feb 2025
In News:
NITI Aayog released a comprehensive policy report titled ‘Expanding Quality Higher Education through States and State Public Universities (SPUs)’, focusing on the development of higher education institutions, particularly public universities in India.
The report aims to enhance the quality, funding, governance, and employability outcomes within SPUs, which contribute to around 80% of the country's higher education system.
The document, the first of its kind in India, presents a detailed analysis of vital indicators like quality, funding, financing, governance, and employability over the last decade, supported by stakeholder consultations with over 20 states and Union Territories, Vice Chancellors, academicians, and State Higher Education Council Chairs. The report includes nearly 80 policy recommendations, along with 125 performance indicators, aiming to address long-standing challenges within SPUs.
Key Findings from the Report
- Funding:
- Maharashtra leads in funding for higher education, with Bihar and Tamil Nadu following closely behind.
- On the other hand, states like Sikkim, Arunachal Pradesh, and Nagaland have the lowest funding for higher education, highlighting regional disparities.
- University Density:
- The national average university density is 0.8 universities per lakh population. However, states such as Sikkim, with a density of 10.3, and Arunachal Pradesh, Ladakh, Meghalaya, and Uttarakhand have significantly higher densities. In contrast, states like Bihar, Uttar Pradesh, West Bengal, and Maharashtra have lower densities compared to the national average.
- Female Enrolment:
- Kerala, Chhattisgarh, and Himachal Pradesh have achieved higher female enrolment rates than males, which reflects positive gender inclusivity trends in certain regions.
- Challenges:
- Infrastructure deficits, including a lack of quality facilities and resources.
- A shortage of faculty and staff, particularly in advanced fields such as MTech and Ph.D. levels.
- Insufficient investment in research and development (R&D).
- Outdated courses, syllabi, and curricula, which are not aligned with industry needs.
- Financial constraints due to over-reliance on traditional revenue sources like admission fees and state grants.
- Administrative delays in fund sanctioning and the absence of frameworks for securing loans through financial institutions.
Policy Recommendations
The report proposes several reforms to address the aforementioned challenges, with a focus on improving educational quality, securing better funding, enhancing governance, and boosting employability:
- Funding and Investment:
- Increase the combined investment in education to 6% of GDP, as recommended in the National Education Policy (NEP) 2020.
- Increase R&D investment (both public and private) to 2% of GDP, as recommended in the Economic Survey 2017-18.
- Creating Centers of Excellence:
- SPUs should form clusters and focus on addressing local challenges by establishing Centres of Excellence. These centres should focus on region-specific issues to drive academic and practical advancements.
- Governance Reforms:
- Enhance governance structures at SPUs, empowering Vice Chancellors, faculty, and staff through targeted capacity-building initiatives.
- States may consider setting up dedicated finance agencies, similar to the Higher Education Financing Agency (HEFA), to fund infrastructure and research development specifically for SPUs.
- Financial Innovations:
- Develop financial frameworks to increase investment in education, ensuring access to timely funds, and reducing dependency on state grants or admission fees.
- Industry-Academia Collaboration:
- Strengthen the link between academia and industry to ensure that the curricula are relevant and prepare students for the job market. This can be achieved through increased partnerships, internships, and practical learning opportunities.
Pradhan Mantri AnusuchitJaatiAbhyuday Yojana (PM-AJAY)

- 14 Feb 2025
In News:
It is a 100% Centrally Sponsored Scheme initiated by the Ministry of Social Justice and Empowerment. The scheme aims at the socio-economic upliftment of the Scheduled Caste (SC) communities, particularly targeting the reduction of poverty through various initiatives that focus on skill development, infrastructure, and income-generating projects.
Key Highlights:
- Launch and Funding: Launched in 2021, the scheme is fully funded by the central government, though states and Union Territories (UTs) have the option to contribute additional funds from their own resources. PM-AJAY is the consolidation of three pre-existing schemes:
- Pradhan Mantri Adarsh Gram Yojana (PMAGY)
- Special Central Assistance to Scheduled Castes Sub Plan (SCA to SCSP)
- BabuJagjivan Ram Chhatrawas Yojana (BJRCY)
- Objectives of PM-AJAY: The scheme is focused on improving the overall well-being of SC communities by:
- Reducing poverty through income-generating schemes, skill development, and infrastructure projects.
- Promoting social and economic development by improving literacy rates, educational enrolment, and providing better livelihood opportunities.
- Transforming SC-majority villages into model villages with integrated development, enhancing socio-economic indicators like education, healthcare, and financial inclusion.
- Eligibility Criteria
- Scheduled Caste (SC) persons living below the poverty line (BPL) are eligible for benefits.
- For infrastructure development, villages with 50% or more SC population are prioritized for grants.
- Key Components of PM-AJAY: The scheme comprises three core components:
- Adarsh Gram Development (formerly PMAGY): Aims to develop SC-majority villages into model villages with holistic improvements in education, healthcare, infrastructure, and skill development.
- Grants-in-Aid for District/State-Level Projects (formerly SCA to SCSP): Financial assistance is provided for livelihood development projects, including skill development programs and infrastructure projects, to generate sustainable income for SC communities.
- Construction of Hostels in Higher Educational Institutions (formerly BJRCY): Focuses on promoting higher education among SC students by constructing hostels in top-ranked institutions according to the National Institutional Ranking Framework (NIRF). This aims to reduce dropout rates and enhance access to quality education.
Special Provisions under the Grants-in-Aid Component
- 15% of the total grants are exclusively allocated for income-generating schemes for SC women.
- 30% of the grants are allocated for infrastructure development in SC-dominated areas.
- 10% of funds are reserved for skill development programs.
- The scheme encourages the formation of SC women cooperatives for producing and marketing consumer goods and services.
Achievements (2022-23)
- 1,260 villages were declared as Adarsh Gram in the financial year 2023-24 under the Adarsh Gram component.
- Nine new hostels were sanctioned under the Hostel Construction component.
- Perspective plans for seven states were approved under the Grants-in-Aid component.
India introduces HS Code for GI-Tagged Rice Exports

- 13 Feb 2025
In News:
India has amended the Customs Tariff Act, 1975, becoming the first country in the world to introduce a Harmonised System (HS) code for Geographical Indication (GI)-tagged rice varieties. This was announced in the Union Budget 2025–26.
Key Features of the Amendment
- HS Code Introduced For:
- 1006-30-11 – GI-tagged parboiled rice
- 1006-30-91 – GI-tagged white rice
- Objective:
- To enable uninterrupted exports of GI rice even during general export restrictions or bans.
- GI rice exports will not require special government notification during such bans.
About Harmonised System (HS) Code
- Full Form: Harmonised System Code
- Developed by: World Customs Organization (WCO)
- Structure: 6-digit global standard; India uses an 8-digit extension for more specific classification.
- Purpose: Classification of traded goods for customs, tariffs, and trade statistics.
- HS Code Hierarchy:
- First 2 digits: Chapter (e.g., “10” for cereals)
- Next 2 digits: Heading (e.g., “06” for rice)
- Last 2 digits: Subheading (e.g., “30” for semi-milled or wholly milled rice)
Impact on GI Rice Exports
- Facilitates global market access for Indian specialty rice varieties.
- Differentiates GI-tagged rice from conventional rice in trade documents.
- Prevents mislabeling and misuse of India’s GI rice identity.
- Allows exports of GI rice even under export bans, without fresh government clearance.
GI-Tagged Rice Varieties in India
- 20 GI-recognized rice varieties, including:Navara, Palakkadan Matta, Pokkali, Wayanad Jeerakasala, etc.
- 20 pending GI applications, including:Seeraga Samba, Jammu & Kashmir Red Rice, Wada Kolam Paddy, etc.
About the World Customs Organization (WCO)
- Established in 1952 as the Customs Co-operation Council; renamed WCO in 1994.
- Headquarters: Brussels, Belgium.
- Membership: 183 customs administrations, including India, covering 98% of global trade.
- Key Functions:
- Maintains and updates the HS Code every 5 years.
- Drives customs modernization through instruments like the Revised Kyoto Convention (RKC).
- Coordinates anti-smuggling, anti-counterfeiting, and trade enforcement efforts.
- Collaborates with global institutions like the WTO and UN to enhance trade efficiency.
Quipu Superstructure

- 13 Feb 2025
In News:
Astronomers have discovered the largest known cosmic structure, named Quipu, in a study led by Hans Bohringer of the Max Planck Institute. The findings are part of efforts to map matter distribution in the universe using redshift data between 0.3 to 0.6, revealing some of the most distant known objects.
Key Features of Quipu:
Attribute Description
Type Superstructure (clusters of galaxy superclusters)
Length ~1.3 billion light-years (Over 13,000 times the Milky Way’s size)
Mass ~200 quadrillion (2 × 10¹?) solar masses
Components ~70 galactic superclusters
Shape Central filament with multiple branching filaments (named after the Incan “Quipu” cord system)
Cosmic Significance:
- Gravitational Lensing (GL): Due to its enormous mass, Quipu bends light from background objects, distorting sky images.
- Cosmic Microwave Background (CMB): Its gravitational field causes fluctuations in the CMB—the relic radiation from the Big Bang.
- Hubble Constant Impact: Quipu and similar structures distort measurements of the Universe’s expansion rate.
Scientific Context:
- Superstructures: Extremely large arrangements of matter including groups of galaxy clusters and superclusters.
- Quipu is hundreds of thousands of times more massive than a single galaxy.
- Discovered at a distance of 425 to 815 million light-years from Earth.
Other Superstructures Identified:
Alongside Quipu, astronomers identified four other massive structures:
- Shapley Supercluster
- Serpens-Corona Borealis Superstructure
- Hercules Supercluster
- Sculptor-Pegasus Superstructure
Together, these five structures:
- Contain ~45% of all galaxy clusters
- Include ~30% of galaxies
- Hold ~25% of the matter in the universe
- Occupy ~13% of the universe’s volume
Future Evolution:
- Scientists consider Quipu a "transient configuration".
- It is expected to break into smaller collapsing units in the future, altering cosmic structures over time.
R-37M Missile

- 13 Feb 2025
In News:
Russia has recently offered the R-37M missile, a state-of-the-art, long-range air-to-air missile, to India. This missile, one of the world’s most advanced, has the potential to transform India's aerial defense capabilities. The offer also comes with the opportunity for India to license the production of this missile domestically. However, the acquisition of such a potent weapon is raising tensions in the region, particularly with Pakistan, China, and Bangladesh, and has broader strategic implications.
Overview of R-37M Missile:
The R-37M, also known by its NATO reporting name AA-13 Axehead, is a hypersonic, long-range air-to-air missile developed by Russia.
It is designed to target high-value assets, such as AWACS (Airborne Warning and Control Systems), tanker aircraft, and other support platforms, beyond visual range (BVR).
Evolved from the R-33 missile, the R-37M significantly enhances air combat capabilities due to its range, speed, and precision.
- Speed and Range: The missile can travel at speeds of up to Mach 6 (approximately 7,400 km/h), enabling it to intercept fast-moving aerial threats. It has an operational range of 300-400 km (160-220 nautical miles), making it one of the longest-reaching air-to-air missiles.
- Weight: The missile weighs 510 kg, with a 60 kg warhead.
- Guidance System: It uses an advanced combination of inertial navigation with mid-course updates, active radar homing, and semi-active radar guidance for the terminal phase.
- Combat Advantage: The R-37M can target beyond visual range, enabling the launching aircraft to engage enemy targets while remaining outside the reach of enemy missiles.
Impact on the Indian Air Force (IAF):
The R-37M missile could replace the current R-77 missile used by India’s Sukhoi Su-30MKI fighter jets. This acquisition will bolster India's air defense by providing enhanced capabilities to intercept aerial threats at greater distances. Additionally, the offer to license the local production of the missile is a significant step toward strengthening India’s defense industry and reducing its dependence on foreign weapon systems. This move can also contribute to India's strategic autonomy in military engagements.
Strategic Implications for Pakistan:
Pakistan’s Air Force (PAF) primarily relies on F-16 fighter jets for its aerial superiority. However, these aircraft are vulnerable to interception beyond the Line of Control (LoC) by the R-37M, which has an engagement range of up to 400 kilometers. This could significantly alter Pakistan's defense posture, as its aircraft would be exposed to threats from Indian aircraft even before crossing the LoC.
Potential Effects on China:
China, which already possesses advanced air-to-air missiles such as the PL-15 and PL-21, will closely monitor India’s acquisition of the R-37M missile. While China is not directly threatened by the missile due to its own advanced defense systems, India’s missile capabilities could alter the balance of air superiority in the region. The acquisition could prompt China to accelerate the development of counter-hypersonic technologies, potentially altering the trajectory of military developments in the region.
Impact on Bangladesh:
Bangladesh, which shares friendly relations with India, could find itself caught in the strategic competition between India and Pakistan, despite its own military capabilities not directly challenging India. The regional military dynamics, influenced by India’s acquisition of advanced weapons like the R-37M, may push Bangladesh to enhance its defense capabilities, either through regional alliances or by procuring advanced defense technologies.
India-Russia Defense Relations:
India’s defense cooperation with Russia has been longstanding and substantial. Between 2015 and 2020, India’s defense imports from Russia were valued at approximately $10 billion, making Russia one of India’s largest defense suppliers. Around 70% of India's defense equipment is of Russian origin. Key joint defense projects include:
- BrahMos Missile: A joint venture to develop a supersonic cruise missile.
- S-400 Triumph: A $5.4 billion deal for five S-400 air defense systems.
- AK-203 Assault Rifles: A project for the local manufacturing of over 700,000 rifles.
- Military Exercises: India and Russia conduct joint military exercises, such as the INDRA (focused on counter-terrorism) and AVIAINDRA (aerial exercises between the Indian Air Force and Russian Aerospace Forces).
Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension (PAH)

- 13 Feb 2025
In News:
- Natco Pharma, a Hyderabad-based generic drug manufacturer, has received final approval from the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (USFDA) for its generic version of Bosentan tablets for oral suspension (32mg).
- This drug, a generic version of Actelion Pharmaceuticals’ Tracleer, is used to treat Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension (PAH), a condition characterized by high blood pressure in the lungs.
- The approval comes after Natco's successful submission of an abbreviated new drug application (ANDA), which was jointly developed with its marketing partner, Lupin Pharmaceuticals, Inc.
- Natco believes that it holds the sole first-to-file status for the product, which qualifies it for a 180-day exclusivity period upon launch. The exclusivity period would allow Natco to be the only supplier of the generic product in the U.S. market for a limited time, which could offer significant market share before generic competition arrives.
- Bosentan, the active ingredient in Tracleer, is prescribed for patients suffering from PAH, a progressive condition that raises the blood pressure in the lungs and causes strain on the heart.
- The treatment helps to improve pulmonary vascular resistance and is indicated for patients aged three years and above, including those with idiopathic or congenital PAH. The product is expected to improve exercise capacity and overall quality of life for these patients.
- In the U.S., Bosentan 32mg oral suspension generated an estimated $11 million in sales for the 12 months ending September 2024.
Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension (PAH) Overview
- It is a specific type of pulmonary hypertension in which the small arteries in the lungs become thickened and narrowed. This results in obstructed blood flow and increased pressure in the pulmonary arteries, which makes the heart work harder to pump blood through the lungs.
- The exact cause of PAH remains unclear, though it is believed to result from injury to the cells lining the blood vessels in the lungs, leading to long-term vascular disease.
- PAH can develop in association with several medical conditions, including congenital heart disease, liver disease, HIV, and autoimmune diseases like scleroderma and lupus. It can also be triggered by past or current drug use, such as the abuse of methamphetamine or the use of certain diet pills.
Symptoms of PAH include:
- Shortness of breath that worsens over time
- Fatigue and dizziness
- Chest pain
- Cyanosis (blue fingers or lips)
- Fainting episodes
While there are treatment options available for PAH, including medications that help manage the symptoms and slow disease progression, there is currently no known cure. PAH remains a significant area of concern in pulmonary healthcare, and the introduction of generic Bosentan by Natco Pharma offers a more affordable treatment option for patients in the U.S.
Exercise Cyclone 2025

- 13 Feb 2025
In News:
- The third edition of the India-Egypt Joint Special Forces Exercise CYCLONE is being conducted from February 10–23, 2025 at the Mahajan Field Firing Range, Rajasthan.
- The previous edition (2nd) was held in Egypt in January 2024, and the first edition was conducted in India in 2023.
About Exercise CYCLONE
- It is a bilateral joint special forces military exercise between India and Egypt.
- Annual exercise, held alternatively in India and Egypt.
- The 2025 edition is focused on:
- Counter-terrorism operations
- High-intensity combat training
- Survival techniques in desert/semi-desert terrain
- Tactical drills and real-world combat scenarios
- Motto of the exercise: “Together we train, together we excel.”
Objectives
- Enhance military-to-military cooperation.
- Strengthen interoperability and joint operational capabilities.
- Exchange of special warfare tactics and combat strategies.
- Operate under frameworks aligned with Chapter VII of the UN Charter (pertaining to threats to peace, breaches of peace, and acts of aggression).
Strategic Importance
- The exercise reflects deepening India-Egypt defence cooperation.
- Aimed at enhancing readiness for evolving security challenges in the region.
- Enables both forces to operate together in simulated combat situations, improving coordination and adaptability.
India-Egypt Relations: Defence and Beyond
- Strategic Partnership established in 2023, covering:
- Political, defence, security, energy, and economic cooperation.
- Bilateral Trade Agreement (1978): Based on Most Favored Nation (MFN) clause.
- India is one of Egypt’s key trading partners in Africa.
Restructured National Bamboo Mission (NBM)

- 12 Feb 2025
In News:
The National Bamboo Mission (NBM) was initially launched in 2006 under the Ministry of Agriculture & Farmers Welfare to promote bamboo-based development. Between 2014–2016, it was subsumed under the Mission for Integrated Development of Horticulture (MIDH).
In 2018-19, it was restructured under the National Mission for Sustainable Agriculture (NMSA) as a Centrally Sponsored Scheme (CSS) to revamp bamboo cultivation, processing, and value chain integration.
A key reform was the 2017 amendment to the Indian Forest Act, 1927, which removed bamboo grown outside forests from the definition of “tree.” This de-regulated its felling and transit, boosting private bamboo farming and easing trade.
Objectives
- Increase the availability of quality planting materials and expand area under bamboo cultivation, especially in non-forest land.
- Promote post-harvest management, primary treatment, seasoning, and preservation technologies.
- Develop market infrastructure, incubation centers, and tools & equipment for value addition.
- Encourage value-added product development, skill development, and entrepreneurship.
- Reduce import dependency on bamboo and bamboo-based products.
Funding Pattern
- General States: 60% Central and 40% State funding.
- Northeastern & Hilly States: 90% Central and 10% State.
- Union Territories, BTSGs & National Level Agencies: 100% Central funding.
Implementation Framework
- Implemented through the State Nodal Departments, nominated by respective State/UT governments.
- Notable example: Bareilly Bamboo Cluster operational in Shahjahanpur district, Uttar Pradesh, since 2019-20, with activities like nursery establishment, bamboo plantation, skill development, and bamboo product demonstration.
Bamboo – Ecological & Economic Significance
- Botanical Classification: Grass (Family: Poaceae, Subfamily: Bambusoideae), ~115 genera and ~1,400 species globally.
- Native to tropical, subtropical, and mild temperate zones, with highest concentration in East and Southeast Asia.
Properties & Applications:
- Carbon Sequestration: Produces 35% more oxygen than comparable vegetation; acts as a natural carbon sink.
- Climate Adaptability: Thrives in degraded lands; prevents soil erosion; vital for land restoration.
- Alternative Energy Source: Among the fastest-growing plants (up to 90 cm/day); can substitute fossil fuels.
- Food & Medicine: Bamboo shoots are consumed in Northeast India; roots and parts used in traditional medicine.
- Livelihood Support: Flexible harvest cycles provide year-round income for farmers.
Bamboo Production Status in India
- 18,000+ inventoried grids reported bamboo presence between 2016–17 to 2019–20.
- Estimated total bamboo culms: 53,336 million.
- 35.19% increase in bamboo culms from ISFR 2019 to ISFR 2021 (an increase of 13,882 million culms).
Restructured Skill India Programme (2022–2026)

- 12 Feb 2025
In News:
The Union Cabinet has approved the continuation and restructuring of the Skill India Programme (SIP) till March 2026, with a financial outlay of ?8,800 crore.
The revamped programme consolidates three flagship schemes under a composite Central Sector Scheme—Pradhan Mantri Kaushal Vikas Yojana 4.0 (PMKVY 4.0), Pradhan Mantri National Apprenticeship Promotion Scheme (PM-NAPS), and Jan ShikshanSansthan (JSS)—with the aim to build a skilled, future-ready workforce.
Objectives and Vision
- Strengthen workforce development through industry-aligned, technology-enabled, and demand-driven skill training.
- Enhance global competitiveness, promote international mobility, and align with India's economic priorities such as Atmanirbhar Bharat, Make in India, and Digital India.
- Enable lifelong learning, skilling, reskilling, and upskilling through inclusive, flexible, and community-based training.
Beneficiaries and Coverage
- Over 2.27 crore individuals have benefited so far.
- Targeted age groups vary across schemes:
- PMKVY 4.0: 15–59 years
- PM-NAPS: 14–35 years
- JSS: 15–45 years
- Emphasis on marginalized sections, women, rural youth, aspirational districts, and the North-East Region.
Key Components of the Restructured Programme
1. Pradhan Mantri Kaushal Vikas Yojana 4.0 (PMKVY 4.0)
- Offers NSQF-aligned training via:
- Short-Term Training (STT)
- Special Projects (SP)
- Recognition of Prior Learning (RPL)
- Introduces 400+ new courses in emerging fields:
- Artificial Intelligence (AI), 5G, Cybersecurity, Green Hydrogen, Drone Technology.
- Establishment of Skill Hubs in premier institutions (IITs, NITs, JNVs, KendriyaVidyalayas, etc.).
- Focus on international mobility:
- Mobility Partnership Agreements (MMPAs), joint certifications, and language proficiency training.
- Blended learning models with digital delivery and regional language content.
- Integration with schemes such as PM Vishwakarma, PM Surya GharMuft Bijli Yojana, National Green Hydrogen Mission, and NAL JAL Mitra.
- Adoption of an Ease of Doing Business framework to reduce compliance burdens.
2. Pradhan Mantri National Apprenticeship Promotion Scheme (PM-NAPS)
- Promotes earn-while-you-learn through industry-specific apprenticeships.
- Government support of 25% stipend (up to ?1,500/month per apprentice) via Direct Benefit Transfer (DBT).
- Focus on both traditional and emerging sectors like AI, robotics, blockchain, green energy, and Industry 4.0.
- Encourages participation of MSMEs and enterprises in underserved regions.
3. Jan ShikshanSansthan (JSS) Scheme
- Community-based skilling for economically disadvantaged, rural youth, and women.
- Offers low-cost, flexible, doorstep training for both self-employment and wage-based livelihoods.
- Linked with initiatives such as PM JANMAN, ULLAS, and financial literacy campaigns.
- Also promotes awareness in health, hygiene, gender equality, and education.
Certification and Digital Integration
- All certifications are aligned with the National Skills Qualification Framework (NSQF).
- Integrated with DigiLocker and the National Credit Framework (NCrF), ensuring:
- Formal recognition of skills.
- Horizontal and vertical mobility in education and employment.
- Micro-credential courses (7.5 to 30 hours) and National Occupational Standards (NoS)-based training introduced.
Supporting Schemes and Initiatives
- SANKALP(Skill Acquisition and Knowledge Awareness for Livelihood Promotion).
- TEJAS (Skilling for international placement).
- Model Skill Loan Scheme.
Significance of Skill India Programme
- Demographic Dividend: With over 65% of India’s population below 35, the programme is pivotal in transforming potential into productivity.
- Employment & Entrepreneurship: Reduces unemployment through structured training, apprenticeships, and encourages skill-based startups.
- Global Workforce Readiness: Aligns with international standards, enabling Indian workers to access global job markets.
- Technological Preparedness: Equips the youth with skills in futuristic technologies.
- Inclusive Growth: Ensures urban-rural and gender-based equity in skilling access.
- Economic Impact: Supports India's manufacturing, IT, and services sectors, driving GDP growth.
India Achieves 100 GW Solar Power Capacity

- 12 Feb 2025
In News:
India has officially surpassed 100 GW of installed solar power capacity as of January 31, 2025, marking a historic milestone in its clean energy journey. This achievement strengthens India’s position as a global leader in renewable energy and signifies major progress toward its ambitious target of 500 GW non-fossil fuel capacity by 2030, as outlined by Prime Minister Narendra Modi.
Union Minister of New and Renewable Energy, highlighted this milestone as a testament to India’s energy self-reliance, driven by key initiatives such as solar parks, rooftop solar schemes, and domestic solar manufacturing.
Growth Trajectory and Achievements
- Installed Capacity Growth:
- From 2.82 GW in 2014 to 100.33 GW in 2025 – a growth of 3450% over a decade.
- Solar energy now accounts for 47% of India’s total installed renewable energy capacity.
- Capacity Pipeline:
- 84.10 GW of solar under implementation.
- 47.49 GW under tendering.
- Including hybrid and RTC renewable projects, India has 296.59 GW of solar and hybrid projects in total.
- Record Additions in 2024:
- 24.5 GW solar capacity added, more than double from 2023.
- 18.5 GW utility-scale installations – a 2.8 times increase from 2023.
- 4.59 GW of rooftop solar added, a 53% increase over 2023.
- Top States in utility-scale solar growth:Rajasthan, Gujarat, Tamil Nadu, Maharashtra, and Madhya Pradesh.
Solar Manufacturing Boom
- Solar module production capacity has grown from 2 GW (2014) to 60 GW (2024).
- With continued policy support, India is targeting 100 GW of manufacturing capacity by 2030.
- This shift makes India a global hub for solar technology and reduces reliance on imports.
Major Government Initiatives Driving Solar Growth
- National Solar Mission (NSM) (2010):Set long-term targets, with 280 GW of solar capacity by 2030 under its ambit.
- PM SuryaGharMuft Bijli Yojana (2024):
- A game-changing rooftop solar scheme aiming to empower households with free, clean electricity.
- Nearly 9 lakh rooftop installations as of early 2025.
- PM-KUSUM Scheme:Promotes solar irrigation pumps and supports farmers with grid-connected solar systems.
- Solar Parks Scheme:Facilitates development of large-scale solar clusters in states to boost capacity.
- Production-Linked Incentive (PLI) Scheme:Incentivizes domestic manufacturing of solar PV modules.
- Net Metering Policy:Allows consumers to generate and export surplus solar power to the grid.
- International Solar Alliance (ISA):India-led global initiative fostering solar energy cooperation among solar-rich countries.
Benefits of Solar Energy for India
- Energy Security: Reduces dependence on fossil fuel imports.
- Environmental Gains: Cuts GHG emissions and combats climate change.
- Economic Boost: Millions of jobs created across installation, manufacturing, and maintenance.
- Affordability: Declining PV costs make solar a cost-effective energy source.
- Rural Electrification: Powers remote and off-grid regions, improving livelihoods.
Challenges and the Way Forward
- Land Acquisition: Scarcity of land hinders large-scale solar deployment.
- Grid Integration: Intermittency of solar power stresses the existing power grid.
- Finance & Investment: Scaling up infrastructure and storage requires sustained capital inflow.
- Storage Solutions: Affordable battery storage is essential for reliability and round-the-clock supply.
Cayman Islands
- 12 Feb 2025
In News:
A magnitude 7.6 earthquake recently struck the Caribbean Sea southwest of the Cayman Islands, as reported by the U.S. Geological Survey. While no tsunami warning was issued, tremors were felt across the region, and assessments of damage are ongoing.
Geographical and Geopolitical Overview
- The Cayman Islands is a British Overseas Territory located in the western Caribbean Sea, south of Cuba and northwest of Jamaica.
- It comprises three islands:
- Grand Cayman (largest and most populous)
- Cayman Brac
- Little Cayman
- The islands are part of the Cayman Ridge, an underwater mountain range, with the islands themselves being the emergent peaks of this ridgeline.
- Area: Only 264 sq. km
- Capital: George Town, located on Grand Cayman
- Official Language: English
- Currency: Cayman Islands Dollar (KYD)
- Ethnic Composition:
- Afro-European: 40%
- African: 20%
- European: 20%
- Other: 20%
Seismic and Climatic Features
- The islands are near the Cayman Trench, a deep subduction zone formed by the interaction between the North American and Caribbean Plates.
- Although major earthquakes are rare, the region is seismically active, and moderate to high seismic events are possible, such as the recent 7.6 magnitude quake.
- Climate: Tropical marine with a distinct wet and dry season; vulnerable to hurricanes, especially during the Atlantic hurricane season (June–November).
Ecological Significance
- Known for crystal-clear waters, coral reefs, and white sand beaches, the Cayman Islands are a global hub for marine biodiversity.
- Key ecological features include:
- Coral reefs, seagrass beds, and mangroves
- Famous dive sites like the Great Blue Hole and Bloody Bay Wall
- Terrestrial biodiversity is limited due to the islands’ small limestone-based land area, but they are home to endemic species such as the Grand Cayman Blue Iguana, which has recovered from critical endangerment through conservation efforts.
Economic Importance: A Global Financial Hub
- The Cayman Islands is renowned as a major offshore financial center and global tax haven.
- Zero taxation: No corporate, income, or capital gains tax
- Home to:
- Offshore banks
- Hedge funds
- Multinational corporations
- The islands offer a favorable regulatory environment and strict financial confidentiality laws, although they now comply with international transparency norms.
TROPEX-25

- 12 Feb 2025
In News:
The Indian Navy’s biennial TROPEX-25is currently underway in the Indian Ocean Region (IOR) from January to March 2025.
It is the Indian Navy’s largest maritime exercise, aimed at testing combat readiness and integrated warfighting capabilities across all domains.
About TROPEX
- Full Form: Theatre Level Operational Readiness Exercise (TROPEX)
- Frequency: Biennial (every two years)
- Lead Agency: Indian Navy
- Participants:
- Indian Navy (all operational units)
- Indian Army (IA)
- Indian Air Force (IAF)
- Indian Coast Guard (ICG)
Purpose and Strategic Objectives
TROPEX-25 aims to:
- Validate core warfighting skills of the Indian Navy.
- Ensure a synchronised, integrated response across services to defend India’s maritime interests.
- Simulate real-time operations in a contested maritime environment, including conventional, asymmetric, and hybrid threats.
- Enhance jointness, interoperability, and combat synergy among the three armed forces and the Coast Guard.
Duration and Operational Scope
- Timeline: January to March 2025 (Three months)
- Location: Various sectors across the Indian Ocean Region (IOR)
- Phases:
- Harbour Phase: Planning and coordination activities.
- Sea Phase: Execution of complex naval and joint operations.
- Joint Work-Up Phase: Includes cyber and electronic warfare, and live weapon firings.
- AMPHEX (Amphibious Exercise): Integrated amphibious operations.
Key Features
- Integrated Combat Operations: Real-time execution of multi-domain missions
- Cyber and Electronic Warfare: Tactical simulations of modern non-kinetic threats
- Live Weapon Firings: Enhancing target precision and battle readiness
- Inter-Service Jointness: High-level coordination across the Navy, Army, Air Force, and Coast Guard
- Maritime Domain Awareness: Surveillance and security operations over vast maritime stretches
Strategic Significance
- Reinforces India’s commitment to safeguarding maritime sovereignty and strategic interests in the Indian Ocean.
- Enhances forward-deployment strategies, logistics, and sustained operations far from the mainland.
- Demonstrates India’s ability to operate “Anytime, Anywhere, Anyhow” in support of national security.
Prime Minister’s 15-Point Programme for Minorities
- 11 Feb 2025
In News:
The Prime Minister’s New 15 Point Programme for welfare of Minorities is a programme which covers various schemes/initiatives of the participating Ministries/Departments with an aim to ensure that the underprivileged and weaker sections of six centrally notified minority communities have equal opportunities for availing the various Government welfare Schemes and contribute to the overall socio-economic development of the Country.
Key Highlights:
The programme has the following broad objectives:
- Enhancing opportunities for education
- Ensuring an equitable share for minorities in economic activities and employment, through existing and new schemes, enhanced credit support for self-employment, and recruitment to State and Central Government jobs
- Improving the conditions of living of minorities by ensuring an appropriate share for them in infrastructure development schemes
- Prevention and control of communal disharmony and violence.
The schemes of the Ministry of Minority Affairs covered under the Prime Minister’s 15 Point Programme are exclusively meant for notified minorities. However, 15% of the outlays and targets, to the extent possible, of schemes/initiatives implemented by other participating Ministries/Departments are earmarked for notified minorities.
The welfare schemes, including initiatives for education and skill development of minorities, being implemented by Ministry of Minority Affairs and other participating ministries under the programme, are as under:
- Pre-Matric Scholarship Scheme
- Post-Matric Scholarship Scheme
- Merit-cum- Means based Scholarship Scheme
- National Minorities Development Finance Corporation (NMDFC) Loan Schemes
- Samagra Shiksha Abhiyaan (M/o Education)
- DeenDayalAntyodaya Yojana (DAY-NRLM)- (M/o Rural Development)
- DeenDayal Upadhyay – GraminKaushalya Yojana (M/o Rural Development)
- Pradhan Mantri Awaas Yojana (M/o Rural Development)
- DeenDayalAntyodaya Yojana - National Urban Livelihoods Mission (M/o Housing & Urban Affairs)
- Priority Sector Lending by Banks (Department of Financial Services)
- Pradhan Mantri Mudra Yojana (Department of Financial Services)
- POSHAN Abhiyaan (Ministry of Women & Child Development)
- National Health Mission (Department of Health & Family Welfare)
- Ayushman Bharat (Department of Health & Family Welfare)
- National Rural Drinking Water Programme (Jal Jeevan Mission), (Department of Drinking Water & Sanitation)
The Schemes are being implemented by the respective Ministries/Departments under the saturation approach of Government. Under the saturation approach of the Government many of the components have achieved mainstreaming.
SwavalambiniProgramme

- 11 Feb 2025
In News:
The SwavalambiniProgramme, launched by the Ministry of Skill Development and Entrepreneurship (MSDE) in collaboration with NITI Aayog, is a pioneering initiative aimed at empowering women in the Northeast.
This programme targets female students in select Higher Education Institutions (HEIs) in Assam, Meghalaya, and Mizoram, providing them with an entrepreneurial mindset, essential resources, and ongoing mentorship to ensure their success in entrepreneurial ventures.
Programme Structure and Implementation
The programme follows a structured, stage-wise entrepreneurial process to guide participants through the various phases of business creation, from awareness to development, mentorship, and funding. It includes the following key components:
- Entrepreneurship Awareness Programme (EAP): Introduces 600 female students to entrepreneurship as a viable career option. The programme involves a 2-day session covering foundational entrepreneurial concepts and opportunities.
- Women Entrepreneurship Development Programme (EDP): This intensive 40-hour training is offered to 300 selected students, covering crucial aspects of business, including:
- Business training and skilling
- Access to finance and market linkages
- Compliance and legal support
- Networking opportunities
- Mentorship: After completing the training, participants receive six months of mentorship to help them translate their ideas into sustainable business ventures.
- Faculty Development Programme (FDP): A 5-day FDP will upskill faculty members in HEIs, enabling them to effectively mentor students in entrepreneurship. The training focuses on industry insights, business incubation strategies, and coaching techniques.
- Award to Rewards Initiative: Successful ventures will be recognized and awarded, inspiring others and fostering a culture of women-led enterprises.
Expected Outcomes and Impact
- The SwavalambiniProgramme aims to promote entrepreneurship among women, with an expectation that 10% of EDP trainees will successfully launch their businesses.
- It strives to establish a clear framework for nurturing and scaling women-led enterprises in India.
- The initiative contributes to economic transformation by making entrepreneurship a viable career path for women, particularly in the Northeast, a region brimming with untapped entrepreneurial potential.
Alignment with National Policies
The SwavalambiniProgramme aligns with several national initiatives and policies aimed at promoting women entrepreneurship:
- National Education Policy (NEP) 2020: The programme complements the NEP’s vision by integrating skill development, industry collaboration, and entrepreneurship-driven education within HEIs.
- Women Entrepreneurship Schemes: It strengthens existing initiatives like Start-Up India, Stand-Up India, PM Mudra Yojana, and the Women Entrepreneurship Platform, providing financial and mentorship support to emerging women entrepreneurs.
- Union Budget 2025: The ?10,000 crore start-up fund and the extension of the 100% tax exemption on start-up profits for five years in the Union Budget 2025 offer crucial financial backing for women-led enterprises.
Launch and Regional Focus
The programme was officially launched across nine colleges and universities in the Northeast, including Gauhati University, North-Eastern Hill University (NEHU), Mizoram University, and others.
National Commission for SafaiKaramcharis (NCSK)

- 11 Feb 2025
In News:
The Union Cabinet, on February 7, 2025, approved the extension of the tenure of the National Commission for SafaiKaramcharis (NCSK) for three years beyond March 31, 2025, i.e., up to March 31, 2028.
The move is aimed at sustaining efforts to eradicate manual scavenging, improve the welfare of sanitation workers, and achieve zero fatalities in hazardous cleaning activities. The extension involves a financial outlay of ?50.91 crore.
Background and Legal Status
- Constitution: NCSK was established in August 1994 under the National Commission for SafaiKaramcharis Act, 1993 as a statutory body.
- Post-2004 Status: The statutory Act lapsed in 2004, and since then, NCSK has functioned as a non-statutory body under the Ministry of Social Justice and Empowerment, with periodic extensions.
- Current Demand: The current Chairperson, M. Venkatesan, has welcomed the extension but stressed the need for granting statutory status to the commission to enhance its authority and effectiveness.
Mandate and Functions
As per Government Notification and MS Act, 2013:
- Policy Recommendations:Recommend specific programmes of action to eliminate inequalities in the status, facilities, and opportunities of SafaiKaramcharis.
- Monitoring and Evaluation:
- Study and evaluate implementation of welfare schemes and programmes.
- Monitor working conditions, including health, safety, and wages of sanitation workers.
- Grievance Redressal:
- Investigate specific complaints and take suomotu cognizance of non-implementation of policies or schemes related to SafaiKaramcharis.
- Report to governments on issues affecting SafaiKaramcharis.
- Role under the Prohibition of Employment as Manual Scavengers and their Rehabilitation Act, 2013:
- Monitor the implementation of the Act.
- Enquire into violations, and convey findings with recommendations to authorities.
- Advise the Centre and States on effective implementation.
- Take suomotu notice of non-compliance.
- Data Collection:
- NCSK remains the only national body tracking sewer and septic tank deaths.
Significance of the Extension
- Aims to improve working conditions in the sanitation sector.
- Supports the socio-economic upliftment of one of the most marginalized communities in India.
- Enhances implementation of manual scavenging prohibition laws.
- Facilitates rehabilitation and dignity for sanitation workers.
- Aligns with the broader vision of inclusive development and social justice.
Pinaka Multiple Rocket Launch System (MRLS)

- 11 Feb 2025
In News:
In a significant step towards modernizing India's artillery capabilities, the Union Ministry of Defence signed contracts worth ?10,147 crore on February 6, 2025, for the procurement of advanced ammunition for the Pinaka Multiple Rocket Launch System (MRLS).
These agreements were concluded with Economic Explosives Limited (EEL) and Munitions India Limited (MIL) for the acquisition of Area Denial Munition (ADM) Type-1 and High Explosive Pre-Fragmented (HEPF)-Mk-1 (enhanced) rockets, respectively.
Pinaka MRLS: An Overview
- Type: All-weather, battle-proven, indirect fire Artillery Weapon System.
- Developer: Armament Research and Development Establishment (ARDE) of DRDO.
- Combat History: First used effectively during the Kargil War, neutralising enemy positions on mountain tops.
- Mobility: Mounted on Tatra trucks, providing high mobility and quick deployment.
- Payload & Firing Capacity:
- Each launcher: 12 rockets.
- Each battery: 6 launchers = 72 rockets.
- Capable of delivering a full salvo in 44 seconds.
- Range:
- Initial range: 60–75 km.
- Guided Pinaka (Pinaka-G) extends range to 75 km, with future plans to extend up to 120 km and eventually 300 km.
- Precision: The guided version uses INS/GPS navigation, allowing high accuracy against critical and time-sensitive targets.
- Warhead Types: High-explosive and submunitions, suitable for a wide variety of targets.
New Ammunition Contracts: Enhancing Lethality
The contracts include the procurement of:
- ADM Type-1: Equipped with specialised warheads designed to disperse sub-munitions over wide areas. These are effective in targeting mechanised formations, vehicles, and personnel, thereby denying area access to the enemy. These are similar to Dual Purpose Improved Conventional Munitions (DPICM).
- HEPF-Mk-1 (Enhanced): An advanced variant of the currently used HEPF rockets with extended range and improved lethality, capable of deep precision strikes in enemy territory.
In addition, a contract was signed with Bharat Electronics Limited (BEL) for upgrades to the Shakti software, which supports artillery operations.
Operational & Strategic Significance
- The upgraded Pinaka system will be the mainstay of long-range rocket artillery in the Indian Army.
- Four Pinaka regiments are already operational, with six more on order.
- The system’s development and expansion are a testament to India’s defenceindigenisation drive.
- The DRDO successfully completed flight tests of the guided Pinaka rocket with a range of 75 km, doubling its earlier reach. Future versions aim for up to 120 km and 300 km range.
Employment and MSME Impact
Besides enhancing strategic deterrence, the ?10,147 crore investment is expected to:
- Generate direct and indirect employment, particularly in the defence manufacturing ecosystem.
- Promote the Indian MSME sector, which contributes components and subsystems for the rockets and launchers.
- Support the vision of Atmanirbhar Bharat by reducing dependency on imported artillery systems.
Pong Dam Lake Wildlife Sanctuary
- 11 Feb 2025
In News:
Pong Dam Lake Wildlife Sanctuary, located in the Kangra district of Himachal Pradesh, has witnessed a record-breaking influx of migratory birds in 2025, according to the latest annual bird census conducted on February 1, 2025.
The sanctuary, a designated Ramsar Site (since 2002) and a Wetland of National Importance (1994), recorded a total of 1,53,719 birds across 97 species, indicating a sharp rise in avifaunal population and reaffirming its ecological significance.
Key Highlights from the 2025 Census
- Migratory birds recorded: 1,44,371 individuals from 55 species.
- Total bird count: 1,53,719 birds from 97 species.
- Increase from 2024: 83,555 more birds.
- Bar-headed Goose population: 90,959 (up from 37,501 in 2024) — highest ever recorded since the census began in 2004.
Other dominant waterfowl included:
- Eurasian Coots – 10,785
- Common Pochards – 9,692
- Common Teals – 8,497
- Northern Pintails – 8,053
Lesser-spotted species included the Greater and Lesser White-fronted Goose, Red Crested Pochard, and Northern Lapwing.
Reasons Behind the Surge
- Experts attribute the significant increase in bird numbers to a decline in the water level of Pong Dam Lake, which exposed additional lakebed areas, creating new feeding grounds. This has made the sanctuary increasingly attractive to birds migrating from Tibet, Central Asia, Russia, Siberia, and the Trans-Himalayan region.
Survey and Conservation Collaboration
- The census was conducted by over 100 participants, including officials from the Himachal Pradesh Forest Department, experts from the Bombay Natural History Society, Wildlife Institute of India, and local birdwatchers. The sanctuary was divided into 25 zones for comprehensive coverage.
- To further conservation efforts, a new Interpretation Centre was inaugurated on January 18, 2025, aimed at promoting awareness about the wetland's role in sustaining biodiversity and supporting migratory birds.
Ecological and Geographical Profile
Pong Dam Lake (Maharana Pratap Sagar)
- Type: Manmade reservoir formed by construction of Pong Dam on the Beas River.
- Location: Wetland zone of the Shivalik hills, Kangra district, Himachal Pradesh.
- Area: Approx. 307 sq. km — among the largest man-made wetlands in northern India.
- Importance: Key stopover on the Trans-Himalayan flyway for migratory birds.
Flora
- Vegetation types: Submerged aquatic vegetation, grasslands, forests.
- Dominant species:Eucalyptus, Acacia, Shisham.
Fauna
- Avifauna: Over 220 bird species recorded; 54 waterfowl species.
- Notable birds: Bar-headed Geese, Pintails, Pochards, Coots, Grebes, Cormorants, Herons, Storks, Grey Partridge, Peafowl.
- Mammals: Sambar, Barking Deer, Nilgai, Wild Boar, Clawless Otter, Leopard.
Rhododendron wattii

- 10 Feb 2025
In News:
A recent study has highlighted the alarming decline of the rare Rhododendron wattii, a species endemic to Nagaland and Manipur, especially in the Dzukou Valley, Nagaland. The species is now on the brink of extinction due to severe threats to its survival, raising serious conservation concerns.
Botanical Profile
- Taxonomy and Discovery:
- First collected by Sir George Watt during his 1882–85 survey in the Japfu Hill range, Nagaland.
- Belongs to the Rhododendron genus, which has over 1,000 species worldwide.
- India hosts 132 taxa, of which 129 are found in the northeastern region.
- Growth and Habitat:
- Grows as a small tree or shrub in the temperate biome.
- Attains a maximum height of 25 feet.
- Endemic to Manipur and Nagaland, predominantly in the Dzukou Valley at ~2,600 metres altitude.
- Phenological Features:
- Evergreen plant with year-round leaf renewal.
- Flowering: Late February to April.
- Fruiting:April to December.
- Produces trusses of 18–25 pink flowers with dark flecks and purplish basal blotches.
- Pollinated by the Fire-tailed Sunbird (Aethopygaignicauda) and bumble bees.
Conservation Concerns:
- Conservation Status:
- Listed as Vulnerable by the IUCN Red List due to:
- Severe population fragmentation.
- Area of occupancy less than 500 sq. km.
- Botanists at the Botanical Survey of India consider it Critically Endangered in its natural habitat.
- Listed as Vulnerable by the IUCN Red List due to:
- Threats to Survival:
- Poor seedling survivability despite abundant seed production.
- Anthropogenic pressures such as:
- Deforestation
- Habitat destruction
- Use of trees for firewood by local communities.
- Wildfires: A major fire incident in 2020–21 severely impacted the Dzukou Valley.
- The lone surviving Rhododendron wattii tree was recorded far from human trails during a recent field study.
Recent Study Highlights:
- Conducted by Imtilila Jing and S.K. Chaturvedi of Nagaland University.
- Published in the Journal of Threatened Taxa.
- Found only one living tree in the surveyed area of 27 sq. km of Dzukou Valley.
- The last previously reported tree in Nagaland (2012–13) was cut down.
Additional Botanical Development in the Region:
While the situation of Rhododendron wattii is grim, the region also witnessed a positive botanical development:
- Discovery of Phalaenopsis wilsonii, a new orchid species in Manipur’s Senapati district.
- Identified by researchers from the Institute of Bioresources and Sustainable Development (IBSD), Imphal.
- It is the ninth species of the Phalaenopsis genus recorded in Manipur.
GREAT Scheme

- 10 Feb 2025
In News:
The Grant for Research & Entrepreneurship across Aspiring Innovators in Technical Textiles (GREAT) scheme, launched in August 2023 under the National Technical Textiles Mission (NTTM), aims to promote startup-led innovation and entrepreneurship in the rapidly growing sector of technical textiles in India.
As of February 2025, the government has approved four startups under the scheme, providing them with financial assistance to develop commercially viable innovations.
About the GREAT Scheme:
- Objective: To encourage young innovators, scientists, and startups in the technical textiles domain to convert ideas into market-ready products or functional prototypes.
- Implementation: Operated by the Ministry of Textiles under the R&D and Innovation Component of the NTTM.
- Financial Support:
- Grants of up to Rs.50 lakh for a period of up to 18 months.
- 10% upfront contribution from startups (e.g., ?5 lakh for a ?50 lakh grant).
- No royalty or equity required by the government.
- Approved Projects: Focus areas include Medical Textiles, Industrial Textiles, and Protective Textiles.
Complementary Initiatives under NTTM:
Academic and Skill Development:
- Education Institutes:
- ?6.5 crore approved for 3 academic institutes, including IIT Indore and NIT Patna, to introduce new courses in Geotextiles, Sports Textiles, Protective Textiles, and more.
- Skill Training:
- 12 Skill Development Courses launched across application areas such as Medical, Agricultural, Mobile, and Protective Textiles.
- Developed by leading Textile Research Associations: SITRA, NITRA, and SASMIRA.
- Aim to train stakeholders across the technical textile value chain.
National Technical Textiles Mission (NTTM): An Overview
- Launched: 2020
- Nodal Ministry: Ministry of Textiles
- Total Outlay: ?1,480 crore
- Mission Goals:
- Make India a global leader in technical textiles.
- Expand the market size to $40–50 billion with 15–20% annual growth.
- Increase domestic penetration and usage of high-performance technical textiles.
Four Key Components:
- Research, Innovation, and Development
- Promotion and Market Development
- Export Promotion
- Education, Training, and Skill Development
- Sectoral Focus:Agro-textiles, Geotextiles, Medical Textiles, Industrial Textiles, Mobile Textiles, Home Textiles, Sports Textiles, Protective Textiles, and others.
- Policy Support:Includes integration with PLI schemes, PM MITRA Parks, and formulation of quality control regulations to strengthen manufacturing capabilities.
Significance for India’s Development:
- Encourages Atmanirbhar Bharat through self-reliant manufacturing and innovation.
- Strengthens India's competitiveness in high-end technical textiles for defense, healthcare, agriculture, infrastructure, and disaster response.
- Bridges the gap between lab-level R&D and market-ready products, especially by supporting startups in early innovation stages.
Grameen Credit Score

- 10 Feb 2025
In News:
The Union Budget 2025–26 introduced the Grameen Credit Score (GCS) framework as a targeted initiative to enhance access to formal credit for Self-Help Groups (SHGs) and the rural population. It reflects the government’s commitment to financial inclusion, rural empowerment, and inclusive development.
What is the Grameen Credit Score?
- The Grameen Credit Score is a rural-specific credit evaluation framework being developed by Public Sector Banks.
- It aims to formalize the credit behavior and transaction history of SHG members and rural individuals, especially women entrepreneurs, and integrate them into India’s central credit ecosystem.
- Unlike conventional credit scores (like CIBIL or CRIF Highmark), GCS is tailored to assess creditworthiness based on local financial behavior, such as SHG repayment records, informal lending history, and community participation.
Key Features and Objectives:
- Improved Credit Assessment:
- Bridges the gap in the current credit bureau systems, which often overlook rural borrowers and SHG members.
- Uses digital records and behavioral insights to provide a customized and accurate credit profile.
- Financial Inclusion:
- Targets women-led SHGs to provide better access to loans, credit cards, and microfinance products.
- Encourages rural borrowers to understand and monitor credit scores, EMIs, and repayment cycles.
- Customized Financial Products:
- Linked with the introduction of custom credit cards for micro-enterprises with credit limits of up to ?5 lakh.
- Facilitates product innovation for grassroots entrepreneurs in agriculture, MSMEs, and allied sectors.
- Support for Broader Rural Ecosystems:
- Integrated with initiatives like the SVAMITVA Scheme for property records digitization.
- Complements reforms like the transformation of India Post into a rural logistics backbone and support for cooperative sectors via the NCDC.
- Economic Empowerment:
- By expanding credit access and improving repayment discipline, GCS is expected to:
- Boost rural entrepreneurship
- Strengthen economic resilience of rural households
- Support the long-term development of the rural economy
- By expanding credit access and improving repayment discipline, GCS is expected to:
Impact on Rural Development and SHGs:
- Empowers rural women through financial independence and enterprise development.
- Enhances formal credit linkage of SHGs, reducing reliance on informal moneylenders.
- Promotes financial literacy and long-term economic stability in villages.
- Aims to be a catalyst for poverty alleviation and inclusive growth.
Gaia Black Holes

- 10 Feb 2025
In News:
The European Space Agency’s Gaia mission, launched in 2013, continues to redefine our understanding of the Milky Way by detecting celestial phenomena through precise astrometry.
One of its most significant contributions has been the discovery of dormant stellar-mass black holes that are not associated with X-ray emissions—previously the main detection method. These discoveries represent a paradigm shift in black hole detection and open new avenues for astrophysical research.
Gaia BH Series: Discovery and Significance
Gaia BH1
- Discovery Year: 2022
- Location: ~1,560 light years from Earth in the Ophiuchus constellation
- Significance:
- Closest known black hole to Earth
- Detected via a yellow star orbiting a dark mass, whose high orbital velocity implied the presence of a black hole nearly nine times the mass of the Sun
- Validated using data from LAMOST (China) and Magellan Clay Telescope (Chile)
Gaia BH2
- Discovery Year: 2023
- Location: ~3,800 light years away in the Centaurus constellation
- Mass: Around nine solar masses
- Observation Method: Tracked motion of a luminous star orbiting an unseen massive companion
Gaia BH3 – A Landmark Discovery
- Discovery Year: 2024
- Distance from Earth: ~1,926 light years (~2,000 light years), making it the second closest black hole
- Location:Aquila constellation, in the Milky Way’s outer regions
- Mass: ~33 times the mass of the Sun, making it the largest known stellar-mass black hole in the Milky Way
- Orbital Partner: A yellow giant star orbiting every 11.6 years, with an average separation similar to the Sun-Uranus distance
- Special Traits:
- It is a dormant or passive black hole, not actively accreting matter
- Lacks X-ray emissions, suggesting a scarcity of surrounding material
- Its companion star’s chemical composition indicates ancient origins, hinting that such massive black holes were formed early in the universe
Scientific Implications:
- Detection Technique Innovation:Gaia uses astrometric mapping to track the apparent motion of stars across the sky. When a star appears to orbit "empty space," astronomers infer the presence of a massive object—typically a black hole—using Kepler’s laws and the Doppler effect.
- Redefining Black Hole Census:Most black holes were previously detected through X-ray emissions. Gaia has revealed non-emitting black holes, indicating a possibly larger hidden black hole population in our galaxy.
- Historical Linkage:Black holes with masses above 30 solar masses were previously only observed through gravitational waves (LIGO/VIRGO, 2015). Gaia BH3 now provides a local, observable counterpart.
India-Japan Steel Dialogue

- 10 Feb 2025
In News:
The 3rd India-Japan Steel Dialogue was held on February 4, 2025, at Vigyan Bhavan, New Delhi, as part of the institutional mechanism under the Memorandum of Cooperation (MoC) signed between the two nations in December 2020. The dialogue was co-chaired by senior officials from India’s Ministry of Steel and Japan’s Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry (METI).
Key Highlights and Strategic Focus Areas:
- Bilateral Steel Cooperation:The dialogue served as a platform to deepen cooperation in areas such as technology exchange, workplace safety, product diversification, and capacity building. Both nations reviewed progress under existing initiatives and reaffirmed commitment to long-term collaboration in the steel sector.
- Ease of Doing Business & Investment Support:India reiterated its commitment to facilitating ease of doing business for Japanese companies, while Japan assured continued technological and financial support for investments in advanced steel technologies in India.
- Sustainable Steel Production:India showcased recent initiatives like the Green Steel Report and the Taxonomy of Green Steel, underlining efforts to align steel production with sustainability goals and climate commitments.
- Demographic & Market Advantages:The Indian delegation highlighted the growing domestic demand driven by infrastructure investments, and the potential of India’s demographic dividend to attract foreign investment in the steel sector.
- Global Regulatory Issues – EU CBAM:Both sides discussed the European Union’s Carbon Border Adjustment Mechanism (EU CBAM), which seeks to impose carbon pricing on imports in sectors such as iron and steel, aluminum, cement, fertilizers, electricity, and hydrogen.
- CBAM Phase Timeline:
- Transitional Phase: 2023–2025 (reporting obligations)
- Full Implementation: From 2026 (financial obligations imposed)
- CBAM Phase Timeline:
Relevance:
CBAM has major implications for international steel trade, necessitating cleaner production methods and greater transparency in carbon emissions data.
Tribal Welfare in Union Budget 2025–26

- 09 Feb 2025
In News:
India is home to over 10.45 crore Scheduled Tribe (ST) individuals, comprising 8.6% of the population. Concentrated largely in remote and underdeveloped regions, ST communities face persistent challenges such as land alienation, limited access to quality education, healthcare deficits, and socio-economic exclusion. The Union Budget 2025–26 signals a paradigm shift in tribal welfare, in line with the vision of Viksit Bharat.
Budgetary Commitment
The total allocation for tribal welfare has risen to ?14,925.81 crore in 2025–26—a 45.79% jump from the previous year and a staggering 231.83% increase from 2014–15 levels. The Ministry of Tribal Affairs has witnessed a consistent rise in budget: from ?7,511.64 crore (2023–24) to ?10,237.33 crore (2024–25), and now ?14,925.81 crore.
Flagship Schemes and Initiatives
- Eklavya Model Residential Schools (EMRS) received ?7,088.60 crore, up from ?4,748 crore, to provide quality residential education to ST students. EMDBS, a pilot initiative in high-density tribal areas, enhances outreach.
- Pradhan Mantri Janjatiya Vikas Mission (PMJVM) saw a sharp rise to ?380.40 crore. It promotes tribal entrepreneurship, sustainable Minor Forest Produce (MFP) use, and value chain development.
- Pradhan Mantri Adi Adarsh Gram Yojana (PMAAGY) was allocated ?335.97 crore (163% increase). It aims to convert tribal-majority villages into model habitations by ensuring convergence of development schemes.
- PM-JANMAN Multi-Purpose Centers (MPCs) received ?300 crore, targeting Particularly Vulnerable Tribal Groups (PVTGs) with essential services and institutional support.
- Dharti Aaba Janjatiya Gram Utkarsh Abhiyan (DAJGUA), launched in 2024, envisions the holistic development of 63,843 tribal villages. With an outlay of ?79,156 crore over five years, it integrates 17 ministries and 25 interventions. The Ministry of Tribal Affairs has allocated ?2,000 crore for 2025–26 alone.
Persistent Challenges
Despite constitutional safeguards (Articles 15(4), 46, 244, 275(1), etc.), tribal communities face significant hurdles:
- Land and Resource Rights: Only 50% of 42.76 lakh Forest Rights Act (FRA) claims have been approved (MoTA, 2022). Displacement from mining and infrastructure projects persists.
- Education: ST literacy stands at 59% (Census 2011) with high dropout rates due to poverty and language gaps.
- Health: Malnutrition, maternal mortality, and diseases like Sickle Cell remain endemic.
- Marginalization: Tribals face economic deprivation, exploitation (bonded labor, trafficking), and erosion of cultural identity.
- Underrepresentation: Despite reserved seats, policy influence remains limited.
The Way Forward
- Land Rights: Effective implementation of FRA and safeguards against forced displacement.
- Education: Expand EMRS/EMDBS and promote bilingual, culturally relevant curricula.
- Health: Improve rural health infrastructure and target tribal-specific diseases.
- Women’s Empowerment: Support SHGs and skill-based livelihood through schemes like Adivasi Mahila Sashaktikaran Yojana.
- Cultural Continuity: Support tribal art, festivals, and language preservation through digital and educational platforms.
- Inclusive Governance: Strengthen Gram Sabhas and tribal representation in policymaking.
Dunki Routes
- 09 Feb 2025
In News:
Recently, a US military aircraft carrying 104 deported Indian nationals landed at Amritsar Airport. These deportees had entered the United States through the illegal “Dunki” route, paying between ?30 lakh and ?1 crore to agents and human traffickers.
Since 2009, over 15,000 Indians have been deported from the US for illegal entry, with India now figuring among the top non-Latin American countries in deportation rankings.
What is the ‘Dunki Route’?
- The “Dunki” or “Donkey” route refers to an unauthorised, arduous journey that migrants undertake through multiple countries to reach destinations like the United States, bypassing legal immigration processes.
- Routes often begin in countries with visa-on-arrival access or easy tourist visa policies for Indians:
- Latin America: Ecuador, Bolivia, Guyana, Brazil, Venezuela
- Europe/Central Asia: Azerbaijan, Turkey, Kazakhstan
- Southeast Asia: Malaysia (via Bangkok)
- Migrants often transit through Mexico, Guatemala, or Costa Rica before crossing into the US through illegal land borders.
How the Network Operates:
- Human trafficking syndicates use fake or manipulated visas (e.g., Schengen visas) to move migrants across Europe, Central Asia, and Latin America.
- Indian passport holders are sent to countries with lenient visa regimes, followed by overland or sea routes to US borders.
- Delhi Police (IGI unit) revealed that many migrants travel to Turkey or Kazakhstan and then cross to Russia or Latin America before attempting US entry.
Reasons Behind Illegal Migration:
- Economic Opportunities: Low wages in India drive migration to higher-paying economies.
- Limited Legal Avenues: Long, uncertain visa approval processes discourage legal pathways.
- Cultural Pressures: In communities like the Patels of Gujarat, migration to the US is tied to social prestige, often compelling families to sell land or take loans.
- Success Stories: Stories of successful illegal migrants inspire others to follow suit.
- Thriving Smuggling Rackets: Demand for migration has led to lucrative smuggling networks.
Consequences and Risks:
- Human Cost: Migrants risk robbery, assault, rape, and death, with bodies often unrecovered.
- Economic Loss: Families face financial ruin due to heavy agent fees.
- Legal Repercussions: Deportation, detention, and blacklisting from future visas.
- Geopolitical Sensitivity: Damages bilateral ties with countries like the US and strains consular systems.
Government Response and Policy Measures:
Proposed Legislation:
- India is considering the Overseas Mobility (Facilitation and Welfare) Bill, 2024 to:
- Promote safe, orderly, and regular migration
- Replace the outdated Emigration Act, 1983
- Establish comprehensive mechanisms for migrant protection and regulation
Awareness Campaigns:
- Indian embassies and consulates regularly issue:
- Advisories on fraudulent agents
- Guidance on safe migration
- Lists of registered recruiting agencies
Migration Trends and Global Standing:
- World Migration Report 2024 (IOM):
- India received $111 billion in remittances in 2022 – highest globally
- India is the largest country of origin for international migrants, with large diasporas in the UAE, US, and Saudi Arabia
H-1B Visa: The Legal Face of Indian Migration to the US
- H-1B Program: Allows US employers to hire foreign workers in high-skill occupations requiring at least a bachelor’s degree.
- Duration: Maximum of six years, renewable under certain conditions, or convertible into a Green Card.
- Indian Dominance:
- Indians have accounted for over 70% of all H-1B visa approvals since 2015
- Chinese applicants make up the second-largest group (~12–13%)
Political Challenges:
- Immigration, including H-1B, is a polarising issue in US politics.
- Rising anti-immigration sentiment, especially under administrations like Trump 2.0, affects policy and visa quotas.
Hotspot States and Migration Routes in India:
- Major source states of illegal migrants: Gujarat, Punjab, Haryana
- These regions are hubs for agents who facilitate illegal migration using Dunki routes and exploit aspirational youth.
Ranikhet Disease in India

- 09 Feb 2025
In News:
Recent outbreaks of suspected Ranikhet disease (Newcastle Disease) have caused the death of approximately 1.5 lakh chickens in poultry farms across Andhra Pradesh (Eluru, Guntur, Prakasam, and the Godavari districts) and Haryana (Barwala and Raipur Rani in Panchkula). These outbreaks have raised alarms about biosecurity measures, especially in regions that are major poultry producers.
About Ranikhet Disease:
- Also known as: Newcastle Disease (ND)
- Causative Agent: Avian avulavirus 1 (also called Avian Paramyxovirus-1 or APMV-1)
- Affected Species: Primarily chickens, but also turkeys, ducks, pigeons, crows, geese, guinea fowls, partridges, doves, and even hedgehogs (suspected reservoirs).
- Nature of Disease: Highly contagious and fatal viral disease.
- Transmission:
- Direct contact with infected bird secretions (especially feces)
- Contaminated feed, water, equipment, clothing, and environment
- ND virus can survive for weeks in cool environments, increasing risk in winter.
Symptoms and Impact:
- In Birds:
- Respiratory issues: Sneezing, gasping
- Nervous symptoms: Droopiness, loss of coordination
- Digestive symptoms: Diarrhea
- Mortality rate: Ranges from 50% to 100%
- Production impact: Drop in egg production and fertility
- In Humans:
- Mild zoonotic effect, primarily conjunctivitis in people handling infected birds or lab samples.
- Usually self-limiting and non-fatal.
Recent Outbreaks and Investigations:
Andhra Pradesh:
- Approximately 1.5 lakh birds have died across multiple districts.
- Suspected cause: Highly virulent strain of Ranikhet Disease.
Haryana (Barwala–Raipur Rani belt):
- This belt houses around 115 poultry farms and is the second-largest poultry producer in Asia.
- Previously affected by bird flu outbreaks in 2006 and 2014.
- Northern Regional Disease Diagnostic Laboratory (NRDDL), Jalandhar collected 40 new samples from affected farms after being unsatisfied with earlier ones.
- Preliminary suspicion points toward Ranikhet Disease; however, cold wave conditions and the presence of older birds (not replaced due to COVID-19 restrictions) may have also contributed.
- The region falls in the path of migratory birds, whose droppings can spread avian flu viruses, complicating disease identification.
Current Challenges:
- Lack of effective treatment: No curative treatment exists. Management relies on preventive vaccination, biosecurity measures, and good poultry housing practices.
- Diagnostic delays: Require reliable sampling and laboratory testing to confirm the cause.
- Climate sensitivity: Poultry are vulnerable to extreme cold, especially if housing and care are inadequate.
- Pandemic aftershocks: COVID-19 disruptions prevented the routine replacement of older birds, increasing vulnerability.
PRASHAD Scheme

- 09 Feb 2025
In News:
The Parliamentary Standing Committee on Transport, Tourism and Culture has raised concerns over delays in the completion of projects under the Spiritual Tourism Circuits and the PRASHAD Scheme.
It has recommended the establishment of a Standard Operating Procedure (SOP) and emphasized obtaining prior clearances to ensure timely execution of future projects.
About PRASHAD Scheme
- Full Form: Pilgrimage Rejuvenation and Spirituality Augmentation Drive.
- Launched: 2014–15 by the Ministry of Tourism, Government of India.
- Objective: To promote, develop, and enhance spiritual tourism infrastructure at important pilgrimage sites across India.
Aims and Objectives:
- Improve infrastructure (roads, water supply, sanitation, waste management).
- Enhance connectivity (road, rail, and air) to pilgrimage destinations.
- Preserve and conserve religious and cultural heritage sites.
- Promote eco-friendly and sustainable tourism practices.
- Increase domestic and international tourist footfall through spiritual tourism.
- Generate local employment through skill development and livelihood programmes.
Funding Model:
- 100% centrally funded for eligible components.
- Also includes voluntary contributions through Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) and Public-Private Partnership (PPP) initiatives.
Implementation Challenges and Parliamentary Findings
Spiritual Tourism Circuits under Swadesh Darshan Scheme:
- Launched to promote thematic tourism circuits, including 23 Spiritual Circuits across India.
- Of these, five circuits remain incomplete, with two key circuits in Kerala—
- Sabarimala–Erumeli–Pampa–Sannidhanam Circuit
- Sivagiri Sree Narayana Guru Ashram Circuit
- Progress Status (as of September 2023):
- Sabarimala Circuit: 76% complete
- Sivagiri Circuit: 51% complete
- Original target completion dates: June 2023 and October 2023, respectively.
Reasons for Delay:
- Lack of timely clearances from Temple Authorities.
- Administrative and coordination issues across agencies.
Committee Recommendations:
- Formulate a clear-cut SOP for the execution of spiritual tourism projects.
- Ensure pre-approval and coordination with all concerned stakeholders before initiating construction.
- Strengthen planning at the Detailed Project Report (DPR) stage to anticipate implementation challenges and avoid delays and cost overruns.
PRASHAD Scheme Performance:
- Out of 45 sanctioned projects, only 21 have been completed as of the latest report.
- The committee noted this performance as unsatisfactory, even accounting for disruptions due to the COVID-19 pandemic.
Stryker Infantry Combat Vehicle

- 09 Feb 2025
In News:
India-U.S. defence cooperation is advancing with the proposed co-production of the Stryker Infantry Combat Vehicle (ICV). This deal represents a significant leap in bilateral defence industrial collaboration and aligns with India's strategic goal of military modernization and indigenisation under the ‘Make in India’ initiative.
About Stryker Infantry Combat Vehicle (ICV):
- Origin: Jointly developed by General Dynamics Land Systems (GDLS) Canada and U.S., it is the first new military vehicle inducted into U.S. Army service since the 1980s.
- Type: Eight-wheeled armoured infantry combat vehicle designed for rapid deployment and battlefield mobility.
- Variants: Includes Infantry Carrier Vehicle (ICV), Mobile Gun System (MGS), reconnaissance vehicle, medical evacuation vehicle, fire support vehicle, and Anti-Tank Guided Missile (ATGM) carrier.
Key Features:
- Mobility: Top speed of ~100 km/h and an operational range of 483 km. Can be airlifted using C-17 and C-130 aircraft (both in IAF’s fleet) or Chinook helicopters, enhancing deployment in remote terrains.
- Firepower: Equipped with a 30 mm cannon and a 105 mm mobile gun.
- Protection: V-hull structure for blast protection; composite armour reinforced with ceramic tiles offers increased survivability against IEDs and small arms.
- Capacity: Operated by a 2-member crew and can transport a 9-member infantry squad.
Operational Evaluation in India:
- High-Altitude Trials: Conducted in Ladakh (13,000–18,000 feet) during September–October 2024. Evaluation reports were shared with Army Headquarters for further review.
- Javelin ATGM Demonstration: Conducted alongside Stryker trials; however, the performance was sub-optimal due to the vintage system used. Repeat trials have been requested by India.
Strategic Importance for India:
- Tactical Advantage: Enhanced mobility and survivability in high-altitude warfare make it suitable for regions like Ladakh and Arunachal Pradesh.
- Border Security: Bolsters India's defence posture along sensitive frontiers with China and Pakistan.
- Force Modernization: Meets the Indian Army’s requirement for ICVs with integrated ATGM capabilities.
- Aatmanirbhar Bharat Push: The proposed model includes initial direct imports followed by large-scale license production in India, potentially by Bharat Earth Movers Limited (BEML).
Defence Diplomacy and Industrial Cooperation:
- The deal is being advanced under the India-U.S. Defence Industrial Cooperation Roadmap, focusing on co-development and co-production.
- In November 2023, Indian Defence Secretary confirmed discussions under this framework.
- The U.S. has reiterated the importance of India enhancing procurement of U.S.-made defence equipment, aiming at a balanced trade partnership.
- The Stryker deal is expected to feature in high-level bilateral dialogues, including the visit of Prime Minister Narendra Modi to Washington DC and during engagements at Aero India.
Challenges and Reservations:
- Some Indian defence officials have flagged concerns, noting that similar ICVs have been developed by Indian private companies.
- Delays in previous U.S. defence exports (e.g., F-404 jet engines for LCA-Mk1A) have also raised caution regarding timelines and reliability.
Fort William Renamed Vijay Durg

- 08 Feb 2025
In News:
In a significant step towards decolonising the Indian Armed Forces and aligning with indigenous historical consciousness, Fort William, the headquarters of the Eastern Command of the Indian Army in Kolkata, has been renamed Vijay Durg. This renaming is part of a broader initiative to remove colonial-era symbols and practices and restore Indian military heritage.
Historical Background of Fort William
- Construction: The original Fort William was constructed in 1696 by the English East India Company. It was later attacked and captured by Siraj-ud-Daulah, the Nawab of Bengal, in 1756.
- The Black Hole Incident: The original fort had an inner bastion used for imprisoning captives, leading to the infamous “Black Hole of Calcutta” narrative.
- Reconstruction: After the Battle of Plassey (1757) and the defeat of Siraj-ud-Daulah, Robert Clive initiated the construction of a new fort, which was completed in 1773 or 1781 (sources differ).
- Naming: It was named Fort William in honour of King William III of England.
Architectural Features
- Design: The fort is octagonal in shape with a massive structure made of brick and mortar.
- Area: Spread across 70.9 acres on the eastern bank of the Hooghly River, it features hundreds of arched windows and lush green surroundings.
- Aesthetics: Its walls are adorned with intricate stonework, reflecting colonial military architecture.
Recent Changes and Renaming
- New Name: Vijay Durg – Inspired by Vijaydurg Fort in Maharashtra, a prominent naval base of the Marathas under Chhatrapati Shivaji Maharaj.
- Other Changes:
- Kitchener House has been renamed Manekshaw House, after Field Marshal Sam Manekshaw.
- St. George’s Gate has been renamed Shivaji Gate.
- Implementation: According to the Defence Public Relations Office in Kolkata, the name change was decided in mid-December 2024, and internal communications have already adopted the new nomenclature, though an official notification is awaited.
Broader De-Colonisation Drive in Indian Defence
The renaming of Fort William is part of a larger movement initiated by the Government of India to eliminate colonial vestiges in the armed forces. Prime Minister Narendra Modi, in a 2022 speech at Kevadia, Gujarat, urged the forces to discard “legacy systems” and move towards “freedom from the mentality of slavery (gulami ki mansikta se mukti)”.
Key Initiatives:
- Indianisation of military music during the Beating Retreat ceremony.
- Adoption of a new naval ensign (2022) inspired by the seal of Chhatrapati Shivaji Maharaj, moving away from British colonial symbols.
- Renaming of military establishments and symbols rooted in colonial heritage.
- Review publication (2024) titled “Colonial Practices and the Armed Forces – A Review”, released at the Joint Commanders’ Conference in Lucknow by Defence Minister Rajnath Singh.
Mount Taranaki

- 08 Feb 2025
In News:
In a significant legal and environmental development, Mount Taranaki—officially now known by its M?ori name Taranaki Maunga—has been granted legal personhood by the government of New Zealand.
This move marks it as the third natural feature in the country to receive such status, following the Te Urewera National Park (2014) and the Whanganui River (2017).
This recognition reflects an increasing global trend toward acknowledging the intrinsic rights of natural entities and respecting the spiritual beliefs of indigenous communities.
About Taranaki Maunga
- Location: Situated in Egmont National Park, North Island, New Zealand.
- Dual Naming: Historically known as Mount Egmont, it is now officially referred to by its indigenous name, Taranaki Maunga, as part of decolonization and cultural revival efforts.
- Elevation: Stands at 8,261 feet, making it the second-highest peak in the North Island of New Zealand.
- Geological Type: It is a stratovolcano (composite cone) with a nearly perfect symmetrical shape—one of the most symmetrical volcanic cones in the world.
- Formation: Formed due to the subduction of the Pacific Plate beneath the Australian Plate. The magma source lies deeper than that of the Taupo Volcanic Zone volcanoes.
- Topography: Surrounded by a circular ring plain formed from lahars (volcanic mudflows) and landslides.
- Status: A snow-capped dormant volcano and culturally revered natural landmark.
- Cultural Significance: The M?ori, indigenous people of New Zealand, regard Taranaki Maunga as a sacred ancestor, embedding it deeply in their oral traditions and spirituality.
Legal Personhood and Its Significance
Granting legal personhood to Taranaki Maunga means it now holds rights, duties, and liabilities akin to a legal human being, and its interests will be represented by appointed guardians—often including indigenous representatives.
This legal framework recognizes:
- The spiritual and cultural relationship that the M?ori have with the mountain.
- The need to protect natural ecosystems not merely for utility but as living entities deserving of rights and dignity.
Comparative Insights: India’s Legal Approach to Natural Entities
India has witnessed similar developments:
- Uttarakhand High Court (2017–18): Granted legal personhood to the Ganga and Yamuna rivers, along with the Gangotri and Yamunotri glaciers. However, the Supreme Court later stayed this ruling.
- Punjab and Haryana High Court (2020): Recognized Sukhna Lake (Chandigarh) as a living entity for environmental protection.
- These decisions stem from the Doctrine of Parens Patriae, which allows the state to act as a guardian for those who cannot protect themselves—extending this protection to natural entities such as rivers, forests, and wildlife.
Iskander-M

- 08 Feb 2025
In News:
In a significant defense development with wide-ranging geopolitical implications, the Russian Federation is preparing to mass-produce the Iskander-M tactical ballistic missile, a new-generation weapon system with enhanced range and destructive capabilities. This move is part of Russia’s broader strategy to upgrade its missile arsenal amid ongoing tensions with NATO, especially in the context of the Ukraine conflict.
Key Features and Strategic Purpose
The 9K720 Iskander-M, developed by the Machine-Building Design Bureau (Kolomna), is a medium-range tactical ballistic missile with an effective range of up to 1,000 kilometers. It is capable of delivering both conventional and nuclear warheads, making it a versatile and high-impact weapon in regional conflict scenarios.
- The missile is precision-targeted and designed to neutralize high-value enemy assets, including NATO’s military infrastructure in Eastern Europe, especially in Ukraine.
- The production of the upgraded missile, unofficially referred to as the Iskander-1000, is expected to begin in full swing by 2025.
- The missile is reported to be highly destructive, with the ability to conduct deep strikes with minimal detection, offering Russia a tactical advantage in asymmetric warfare.
Deployment of Oreshnik Missile Systems in Belarus
In a parallel development, Russia has confirmed the deployment of Oreshnik medium-range ballistic missile systems in Belarus, a strategic ally. This decision follows agreements between the Russian and Belarusian leadership, reinforcing the military integration under their collective defense pact.
- The Oreshnik system, though less publicly detailed than the Iskander, is designed for tactical use and contributes to enhancing Russia’s regional defense shield.
- According to Russian foreign ministry officials, Belarus already hosts a joint Regional Forces Group, non-strategic nuclear weapons, and modern Russian defense systems.
- The positioning of these systems near NATO’s eastern borders heightens tensions with Western powers, particularly the United States, Poland, the Baltic States, and the European Union.
Geopolitical Ramifications
The Iskander-M and Oreshnik missile programs are part of Russia’s strategic doctrine to deter NATO's influence and reassert its military dominance in Eastern Europe. These deployments are:
- Likely to escalate NATO-Russia tensions, increasing the risk of a regional arms race.
- Expected to complicate European security dynamics, especially in Poland, Ukraine, and the Baltic states, which are seen as potential frontlines.
- Raising the prospect of further military escalation in the ongoing Russia-Ukraine conflict.
- Prompting NATO countermeasures, including deployment of missile defense systems and increased troop presence near Eastern borders.
Brucellosis Outbreak in Kerala
- 08 Feb 2025
In News:
An eight-year-old girl, Shasa Fathima, from Kottakkal in Malappuram district, Kerala, recently died after undergoing nearly two months of treatment for brucellosis at the Government Medical College Hospital, Kozhikode. This tragic incident has renewed public health concerns regarding zoonotic infections in India.
What is Brucellosis?
According to the World Health Organization (WHO), brucellosis is a bacterial disease caused by various species of the genus Brucella. The bacteria primarily infect: cattle, swine, goats, sheep & dogs.
Humans typically contract the infection through:
- Direct contact with infected animals or their secretions (blood, placenta, fetus, uterine fluids)
- Ingestion of contaminated animal products, especially unpasteurised milk and cheese
- Inhalation of airborne bacteria (e.g., in lab or farm environments)
Human-to-human transmission is extremely rare, as per WHO guidelines.
Symptoms and Incubation Period
- The disease presents a wide spectrum of symptoms: fever, weakness, weight loss, general discomfort or malaise.
- In many cases, symptoms may be mild or go undiagnosed. The incubation period ranges from one week to two months, most commonly between two to four weeks.
At-Risk Populations
- Brucellosis can affect individuals of all age groups. However, certain occupational groups are at higher risk, including: farmers and dairy workers, butchers, hunters, veterinarians, laboratory personnel. These individuals are often exposed to animal blood and reproductive fluids, which are primary modes of transmission.
Status in Kerala
Kerala has reported sporadic cases of brucellosis in recent years. In 2023, cases emerged from Kollam (July) and Thiruvananthapuram (October). While the disease is not new to the state, fatalities remain rare.
In response, the Department of Animal Husbandry has initiated awareness campaigns for dairy farmers and conducted milk sample testing across cooperative societies to monitor possible sources of infection.
Treatment and Prevention
Treatment typically involves a combination of antibiotics:
- Doxycycline (100 mg, twice daily for 45 days)
- Streptomycin (1 g daily for 15 days)
Effective preventive measures include:
- Vaccination of livestock (cattle, goats, sheep)
- Pasteurisation of milk and dairy products before human consumption
- Public awareness campaigns on the dangers of consuming unpasteurised animal products
- Regulatory policies on the sale of raw milk
Bryospilus Bharaticus

- 08 Feb 2025
In News:
A new species of water flea, Bryospilus (Indobryospilus) bharaticus n. sp., was recently discovered from moss growth on the walls of the Korigad Fort near Pune, Maharashtra.
This marks the first recorded discovery of the genus Bryospilus in Tropical Asia, underscoring the ecological uniqueness of the Western Ghats, a UNESCO World Heritage biodiversity hotspot.
Taxonomic and Morphological Highlights
- It belongs to the genus Bryospilus, a group of tiny crustaceans known as water fleas, which typically inhabit rivers, ponds, and pools.
- The species displays adaptations for semi-terrestrial life, notably using its antennae with large spines for crawling through thick, debris-laden water films on moss surfaces.
- It lacks a main eye—an evolutionary adaptation to low-light habitats where color vision is unnecessary for foraging.
Ecological and Evolutionary Significance
- The genus Bryospilus includes species found in semi-terrestrial habitats in rainforests of West Africa, South and Central America, and New Zealand, making this Indian discovery a significant biogeographical addition.
- The organism’s relatives are typically found in littoral (vegetated) zones of water bodies, whereas some occur in open waters.
- The researchers suggest that ancestors of this species existed on the Indian subcontinent prior to the breakup of Gondwanaland, around 200 million years ago, hinting at Bryospilus bharaticus as a potential Gondwanan relict species.
- Each known Bryospilus species has been isolated to a specific former Gondwanan continent, reinforcing the evolutionary legacy of this find.
Research and Conservation Implications
- The discovery was part of an ongoing survey of underexplored crustacean taxa in the Western Ghats, led by Sameer Padhye and Kan Van Damme, and published in the Journal of Crustacean Biology (Oxford Academic, Sept 2024).
- The species was found in pristine, undisturbed moss habitats on Deccan Plateau hill forts, highlighting the importance of conserving such microhabitats.
- Zooplankton like water fleas are highly sensitive to environmental changes and serve as bioindicators of ecological health. The presence of B. bharaticus indicates low human disturbance in its habitat.
- The authors warn that air pollution and habitat disturbance could threaten these fragile ecosystems and stress the urgency of habitat protection, especially for organisms invisible to the naked eye.
Shatavari

- 07 Feb 2025
In News:
The Ministry of Ayush has launched a nationwide campaign titled “Shatavari – For Better Health” to raise public awareness on the health benefits of Asparagus racemosus (commonly known as Shatavari), especially in the context of women’s health and the broader objective of holistic well-being.
About Shatavari (Asparagus racemosus)
- Family: Asparagaceae (formerly Liliaceae)
- Common Names: Satawar, Satamuli
- Ayurvedic Significance: Known as the “Queen of Herbs”, Shatavari is praised in classical Ayurvedic texts like Charak Samhita and Ashtang Hridayam for treating women’s reproductive health disorders.
- Name Meaning: ‘Shatavari’ translates to “acceptable to many”, signifying its diverse benefits.
- Botanical Description: It is a woody climber (1–2 meters tall), with pine-needle-like leaves and small white flowers.
- Habitat and Distribution: Found in tropical climates at low altitudes across Asia, Africa, and Australia.
Medicinal Uses
- The dried roots of Shatavari are used medicinally.
- Acts as a tonic, diuretic, galactagogue (promotes lactation), and has ulcer-healing properties.
- Strengthens mucosal resistance and provides cytoprotection.
- Widely used for addressing female reproductive health issues, immunity enhancement, and promoting overall vitality.
The Campaign: “Shatavari – For Better Health”
- Launched by: Shri Prataprao Jadhav, MoS (Independent Charge), Ministry of Ayush.
- Organized by: National Medicinal Plants Board (NMPB).
- This campaign follows successful species-specific initiatives on Amla, Moringa, Giloe, and Ashwagandha.
- Shatavari is being positioned as a crucial resource in advancing women’s health, supporting the Panch Pran Goals set by the Prime Minister for a Developed India by 2047.
- Focus on achieving holistic well-being and integrating traditional medicine with public health awareness.
Policy and Financial Support
- Under the Central Sector Scheme for Conservation, Development, and Sustainable Management of Medicinal Plants, the Ministry promotes the cultivation and sustainable use of Shatavari.
- Financial assistance of ?18.9 lakhs will be provided to eligible organizations to support awareness and adoption.
National Youth Parliament Scheme (NYPS) 2.0

- 07 Feb 2025
In News:
The Ministry of Parliamentary Affairs has recently provided updates in the Rajya Sabha on the National Youth Parliament Scheme (NYPS) 2.0, emphasizing its role in fostering democratic values, constitutional awareness, and active citizenship among Indian youth.
About NYPS 2.0
Launched by the Ministry of Parliamentary Affairs, NYPS 2.0 aims to strengthen the roots of democracy and enhance understanding of parliamentary practices and government functioning among citizens, especially students.
Objectives
- Instill discipline, tolerance for diverse views, and democratic ethos among youth.
- Educate students about the procedures of Parliament, constitutional values, and functioning of the government.
- Encourage a democratic way of life through civic engagement.
Participation Modes via NYPS 2.0 Web Portal
The dedicated web-portal enables inclusive citizen participation in three formats:
- Institutional Participation:
- Open to all educational institutions.
- Institutions can organize Youth Parliament sittings as per portal guidelines.
- Two sub-categories:
- Kishore Sabha: For students of Class VI to XII.
- Tarun Sabha: For undergraduate and postgraduate students.
- Group Participation: Open to any group of citizens willing to conduct Youth Parliament sittings under defined norms.
- Individual Participation: Citizens can individually engage by taking a quiz on the theme ‘Bhartiya Democracy in Action’.
Training and Educational Resources
To support participants, the portal offers comprehensive e-training material, including:
- Literature on Youth Parliament
- Model Debates, Questions, and List of Business
- Model Scripts
- Video tutorials and other interactive resources
National Policy for Rare Diseases (NPRD) 2021

- 07 Feb 2025
In News:
Patient advocacy groups across India have raised serious concerns over delays in implementing the National Policy for Rare Diseases (NPRD) 2021, which has left many rare disease patients — especially children — in life-threatening situations. They have urged the government for immediate intervention to resume life-saving treatments and release stalled funds under the policy.
Rare Diseases:
- Rare diseases are severe, often genetic, life-threatening disorders that impact a small percentage of the population.
- They disproportionately affect children, with 30% of diagnosed patients not surviving beyond age five without timely treatment.
- Examples include Lysosomal Storage Disorders (LSDs) such as Gaucher, Pompe, Fabry, and MPS I & II.
About NPRD 2021
The Ministry of Health & Family Welfare launched the National Policy for Rare Diseases in March 2021 to streamline the diagnosis, research, and treatment of rare diseases in India.
Key Features of NPRD 2021:
- 63 rare diseases currently included under the policy (as recommended by the Central Technical Committee for Rare Diseases (CTCRD)).
- Categorization of diseases into three groups:
- Group 1: Diseases amenable to one-time curative treatment.
- Group 2: Diseases requiring long-term/lifelong treatment with relatively lower cost.
- Group 3: Diseases requiring very high-cost lifelong therapy where patient selection is critical.
Institutional Support:
- 12 Centres of Excellence (CoEs) identified at premier government hospitals to provide diagnosis and treatment.
- Nidan Kendras established to provide genetic testing and counselling services.
- National Consortium for Research and Development on Therapeutics for Rare Diseases (NCRDTRD) set up to coordinate R&D and promote indigenous drug manufacturing.
- Tax exemptions (on GST and Customs Duty) granted for imported drugs for individual and institutional use.
Financial Provisions:
- Financial assistance of up to ?50 lakh per patient for treatment at CoEs.
- Patients must register at CoEs to receive diagnosis and initiate treatment.
Challenges and Crisis
Despite policy provisions, implementation has been stalled, leading to a healthcare emergency for rare disease patients.
Key Issues Raised:
- Insufficient funding: The ?50 lakh cap is inadequate for chronic and ultra-rare diseases that need lifelong therapy.
- Administrative delays: Fund disbursement to CoEs has been slow, disrupting continuity of treatment.
- Impact on Patients:
- Patients like Alishba Khan, Ashok Kumar, Imran Ghoshi, and Adrija Mudy with Gaucher or MPS I have exhausted their funding.
- Patients who had previously stabilized are now regressing due to interrupted therapy at leading hospitals like AIIMS Delhi, IGICH Bangalore, and IPGMER Kolkata.
Legal Developments:
- On October 4, 2024, the Delhi High Court directed the Ministry of Health and Family Welfare to:
- Release additional funds beyond the ?50 lakh limit.
- Create a ?974 crore National Fund for FY 2024–25 and 2025–26.
- Months later, no concrete action has been taken, further eroding trust in the policy's effectiveness.
Demands by Advocacy Groups
- Sustainable, long-term funding model for lifelong treatment of rare and ultra-rare diseases.
- Immediate fund release to CoEs and simplification of administrative processes.
- Ensure uninterrupted access to essential therapies and expand the scope of financial support.
Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA)
- 07 Feb 2025
In News:
Researchers from the Institute of Nano Science and Technology (INST), Mohali, an autonomous institute under the Department of Science and Technology (DST), have developed an innovative “self-actuating” drug delivery system that targets rheumatoid arthritis (RA) by delivering therapeutic agents only when needed. This approach offers a revolutionary alternative to conventional systemic treatments.
About Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA)
- Definition: RA is a chronic autoimmune and inflammatory disease where the body’s immune system mistakenly attacks healthy cells, particularly the joints, causing inflammation and tissue damage.
- Commonly Affected Areas: Hands, wrists, and knees — often multiple joints simultaneously.
- Symptoms:
- Inflammation of joint lining
- Chronic pain and joint deformity
- Unsteadiness or balance issues
- May affect lungs, heart, and eyes
- Cause: The exact cause remains unknown, but it involves an immune response attacking the body’s own tissues.
- Traditional Treatment:
- Involves Disease-Modifying Antirheumatic Drugs (DMARDs) such as methotrexate
- Requires frequent dosing
- May lead to systemic side effects and inefficient drug retention
Breakthrough: Self-Actuating Drug Delivery System
Key Features:
- Targeted Drug Release: Releases medication only in response to biochemical signals in the inflamed synovial environment of RA-affected joints.
- Precision and Safety: Reduces side effects by limiting drug release to flare-ups, minimizing exposure to unaffected areas.
- Main Drug Used: Methotrexate, a widely used anti-rheumatic drug.
Mechanism:
- Microspheres are engineered using polymer-lipid hybrid micro-composites:
- Lipid Component (Soya Lecithin): Ensures high drug encapsulation efficiency.
- Polymer Component (Gelatin): Reacts to Matrix Metalloproteinases (MMPs) — enzymes present during RA inflammation.
- Action:
- Enzymes like MMP-2 and MMP-9 increase during RA flare-ups.
- These enzymes cleave the gelatin, triggering controlled, pulsatile release of methotrexate.
- Outcome in Animal Studies:
- Reduced joint swelling and cartilage damage
- Promoted joint repair
- Improved drug bioavailability and retention in joints
Significance
- Improved Patient Outcomes:
- Long-lasting relief with fewer doses
- Reduced systemic toxicity
- Personalized therapy based on inflammation levels
- Enhanced joint function and slower disease progression
- Research Publication: The findings were published in the journal Biomaterial Advances.
Wider Applications
- Potential Use in:
- Other inflammatory conditions like synovitis and inflammatory bowel disease (IBD)
- Veterinary medicine for arthritis in animals
- Regenerative medicine and personalized drug delivery
Extremely Large Telescope (ELT)
- 07 Feb 2025
In News:
As of early 2025, 60% of the construction of the Extremely Large Telescope (ELT) is complete. The telescope is expected to begin its first scientific observations by the end of 2028.
About ELT
The Extremely Large Telescope (ELT) is poised to become the world’s most powerful ground-based optical and infrared telescope, with revolutionary capabilities to explore the universe.
- Location: Cerro Armazones, Atacama Desert, northern Chile
- Altitude: 3,046 meters above sea level
- Managing Body: European Southern Observatory (ESO)
- Project Cost: Approximately $1.51 billion (around 1.3 billion euros)
- Completion Target: Late 2020s
- Primary Mirror: Diameter of 39 meters (128 feet) — the largest of its kind
- Constructed from 798 hexagonal segments, each 1.5 m across and 5 cm thick
Key Scientific Objectives
- Exoplanet Exploration
- Direct imaging of Earth-like exoplanets in habitable zones of nearby stars
- Analysis of atmospheric biosignatures such as oxygen, water vapor, and methane, aiding the search for extraterrestrial life
- Understanding the Early Universe
- Observation of the first stars and galaxies formed post-Big Bang
- Investigation of dark matter and dark energy, crucial for understanding cosmic expansion and the universe’s fate
- Detailed Study of Stars and Galaxies
- Identification and characterization of individual stars in distant galaxies
- Analysis of the formation, evolution, and structure of galaxies over cosmic time
- Black Holes and Cosmic Structures
- Study of supermassive black holes at galactic centers
- Understanding their role in galaxy dynamics and structure
Why Chile’s Atacama Desert?
- Dry Climate: Very low humidity and cloud cover, ensuring clearer skies
- High Altitude: Thin atmosphere reduces atmospheric interference with incoming light
- Minimal Light Pollution: Remote location offers dark skies critical for deep-space observation
- Dome Structure: Protects sensitive instruments from harsh desert conditions
About the European Southern Observatory (ESO)
- Nature: Leading intergovernmental science and technology organization in the field of astronomy
- Headquarters: Garching, Germany
- Members: 16 countries including Austria, Belgium, Brazil, France, Germany, Italy, Spain, and the United Kingdom
- Facilities in Chile:
- La Silla
- Paranal
- Chajnantor
- Mandate: Design, construction, and operation of advanced ground-based telescopes to promote international collaboration and facilitate path-breaking astronomical research
Dhimsa Dance

- 06 Feb 2025
In News:
In a significant development, tribal families from Neelabandha, a remote hilltop hamlet in Anakapalli district, Andhra Pradesh, received electricity for the first time since Independence. In celebration, they performed the Dhimsa dance, a vibrant expression of tribal culture.
About Dhimsa Dance:
- Origin & Region:
- Dhimsa is a traditional tribal dance predominantly performed in Andhra Pradesh, especially in the tribal belts of the Eastern Ghats.
- Its origin can be traced to the Koraput region (present-day Odisha and bordering Andhra Pradesh), primarily home to the Gond tribe.
- Communities Performing Dhimsa:
- Tribes such as Bagata, Valmiki, Poraja, Khond, Gadaba, Kondadora, Mukadora, and Kotia actively perform this dance.
- Occasions:
- Commonly performed during festivals, weddings, and the hunting festival in April.
- Celebratory, spiritual, and social in nature, symbolizing unity and joy.
- Dance Formation and Movements:
- Performed in circular formations with dancers holding each other's arms.
- Emphasis on synchronized hand and leg movements.
- Troupes usually consist of 20 or more dancers.
- Themes:
- Dhimsa is a narrative dance that expresses tribal mythologies, folktales, cultural mores, economic activities, kinship, and marital life.
- Musical Instruments Used:
- Dappu, Tudumu, Mori, Kidgi, Gilka, and Jodukommulu.
- A combination of percussion and wind instruments drives the rhythm and variation in the dance.
- Varieties:
- There are 12 known types of Dhimsa dances, each varying in pace, rhythm, and purpose.
Rural Electrification of Neelabandha Village:
- Background:
- Neelabandha is located in Arla Panchayat of Rolugunta Mandal in Anakapalli district.
- Consists of four households (approximately 20 individuals) who had been living without electricity since Independence.
- Implementation:
- The electrification was part of the Andhra Pradesh government’s rural development drive to provide basic infrastructure to underdeveloped tribal villages.
- Under the directions of District Collector Vijaya Krishnan, and CMD of APEPDCL, Prithvi Tej, the Eastern Power Distribution Company of Andhra Pradesh (EPDCL) carried out the electrification.
- Challenges Overcome:
- The hamlet lacked motorable roads, making it difficult to transport materials.
- Electricity poles had to be carried manually for over 6 km to reach the village.
- Outcome:
- Free electricity was provided to the villagers, marking a major milestone in tribal welfare.
- In a heartfelt celebration, the villagers performed Dhimsa under electric lights for the first time.
Issues Still Persisting:
- Infrastructure Deficits:
- The village still lacks road connectivity, educational access, and healthcare facilities.
- These gaps hinder children's ability to attend school and access essential services.
- Community Response:
- Local leaders, including CPI(M) district committee member K. Govind, welcomed the electrification but urged the government to address remaining developmental needs.
Makhana Board

- 06 Feb 2025
In News:
In the Union Budget 2025–26, Finance Minister announced the establishment of a Makhana Board in Bihar with a dedicated budget of ?100 crore to boost the production, processing, and export of Makhana (Fox Nuts).
About Makhana (Fox Nuts):
- Botanical Name: Euryale ferox
- Family: Nymphaeaceae (Water lily family)
- Description:
- Makhana is the dried edible seed of the prickly water lily.
- Grown in freshwater bodies across South and East Asia.
- The plant is known for its violet and white flowers and large, round, prickly leaves.
- Due to its black outer covering, Makhana is nicknamed the "Black Diamond."
Nutritional and Medicinal Value:
- Low in fat, rich in carbohydrates, and a good source of protein and minerals.
- Widely used in:
- Traditional medicine
- Health and wellness products
- Culinary preparations such as popped Makhana (‘Lava’)
Major Producing Regions:
- India:
- Bihar produces 90% of India’s total Makhana, especially in the Mithilanchal region.
- Key districts: Darbhanga, Madhubani, Purnea, Katihar, Saharsa, Supaul, Araria, Kishanganj, Sitamarhi.
- The first four districts contribute 80% of Bihar’s Makhana output.
- Bihar produces 90% of India’s total Makhana, especially in the Mithilanchal region.
- Other Indian states: Assam, Manipur, West Bengal, Tripura, Odisha.
- Other countries: Nepal, Bangladesh, China, Japan, Korea.
- GI Tag: Mithila Makhana received the Geographical Indication (GI) tag in 2022.
Climatic Conditions for Cultivation:
- Type: Aquatic crop; grows in stagnant water bodies (ponds, lakes, wetlands).
- Ideal Conditions:
- Water Depth: 4–6 feet
- Temperature: 20°C – 35°C
- Relative Humidity: 50% – 90%
- Annual Rainfall: 100 – 250 cm
About the Makhana Board:
- Allocated Budget: ?100 crore
- Objectives:
- Train farmers in advanced cultivation techniques.
- Support processing and value addition in the Makhana supply chain.
- Facilitate financial aid and access to government schemes.
- Develop export infrastructure and promote branding and marketing.
Makhana under ODOP Scheme:
- Recognized as a One District One Product (ODOP) commodity for Bihar.
- Under ODOP, the Union Government provides subsidies to processors for:
- Infrastructure development
- Branding and marketing
About ODOP Scheme:
- Launched by: Ministry of Food Processing Industries (MoFPI)
- Objective: Promote district-level economic specialization and turn each district into an export hub.
- Origin: First launched in Uttar Pradesh (2018); adopted as a national initiative under the Atmanirbhar Bharat vision.
- Implementation:
- In coordination with the ‘Districts as Export Hubs’ (DEH) initiative.
- Managed by DGFT, Department of Commerce, and DPIIT.
- Significance:
- Encourages rural entrepreneurship, local employment, and global trade linkages.
- Strengthens district economies by scaling up traditional and unique products.
Gyan Bharatam Mission

- 06 Feb 2025
In News:
The Union Budget 2025–26 announced the launch of the Gyan Bharatam Mission, a significant cultural initiative aimed at the survey, documentation, digitization, and conservation of over one crore manuscripts across India.
Key Details:
- A special national mission focusing on India’s manuscript heritage preserved in:
- Academic institutions
- Libraries
- Museums
- Private collections
- Objective:
To document and conserve more than one crore manuscripts, centralize them into a national digital repository, and make them accessible to researchers, students, and institutions globally. - Significance:
- Facilitates knowledge-sharing through digitization.
- Promotes India's traditional knowledge systems.
- Enhances academic and historical research in the Indian knowledge domain.
What is a Manuscript?
- A manuscript is a handwritten composition on materials such as:
- Palm leaf, paper, cloth, bark, or metal.
- Must be at least 75 years old and possess scientific, historical, or aesthetic value.
- Printed texts and lithographs are not considered manuscripts.
- Manuscripts may exist in hundreds of languages and scripts, e.g.:
- Sanskrit manuscripts written in Devanagari, Grantha, Oriya, and other scripts.
- Unlike epigraphs or official records (firmans, revenue documents), manuscripts hold knowledge content, not just historical data.
National Manuscripts Mission (NMM)
- Launched in 2003 under the Ministry of Culture, operated through the Indira Gandhi National Centre for the Arts (IGNCA).
- Mandate: Identify, preserve, and make accessible India's manuscript wealth.
- Revival: The 2025–26 Budget seeks to rejuvenate NMM to implement the Gyan Bharatam Mission effectively.
Budgetary Provisions
- NMM allocation increased from ?3.5 crore to ?60 crore for FY 2025–26.
- Culture Ministry overall allocation:
- ?3,360.96 crore, up from a revised estimate of ?3,260.93 crore.
- Other Key Allocations:
- Archaeological Survey of India (ASI): ?1,278.49 crore
- National Libraries and Archives: ?156.55 crore
- Museums (National Museum, NGMA): ?126.63 crore
- Note: Allocations for centenary events, cultural collaborations have been reduced.
Extra-Long Staple (ELS) Cotton

- 06 Feb 2025
In News:
In the Union Budget 2025–26, the Union Finance Minister announced a five-year Cotton Mission to boost productivity, sustainability, and promotion of Extra-Long Staple (ELS) cotton in India, aiming to reduce import dependency and strengthen the high-end textile sector.
What is Extra-Long Staple (ELS) Cotton?
- Definition: ELS cotton refers to cotton varieties with fibre lengths of 30 mm or more, renowned for their superior softness, strength, durability, and premium quality.
- Botanical Origin: Derived primarily from the species Gossypium barbadense, commonly known as Egyptian or Pima cotton.
Distinguishing Cotton Types by Fibre Length
Type Fibre Length Species Quality Uses Yield per Acre
Short Staple < 25 mm Gossypium hirsutum Coarser Low-cost textiles High
Medium Staple 25–28.6 mm Gossypium hirsutum Moderate Everyday fabrics 10–12 quintals
Extra-Long 30 mm & above Gossypium barbadense Superior Luxury textiles 7–8 quintals
Staple (ELS)
Special Characteristics of ELS Cotton
- Softer & Smoother: Ideal for premium, luxury clothing.
- Stronger & More Durable: Resistant to wear and tear.
- Resistant to Pilling: Maintains smoothness over time.
- Luxurious Finish: Produces fine yarns with a natural sheen.
- Minimal Finishing Required: Retains natural texture and quality.
Global and Indian Production Landscape
- Origin: Native to South America.
- Globally Grown In:
- Egypt, China, Australia, Peru – leading producers.
- In India:
- Cultivated in Atpadi Taluka (Sangli, Maharashtra), around Coimbatore (Tamil Nadu), and in parts of Karnataka and Madhya Pradesh.
- Grown mostly in rain-fed areas with warm climates and fertile soil, aiding fibre quality.
Challenges in ELS Cotton Cultivation in India
- Low Yield: ELS cotton yields 7–8 quintals/acre, significantly lower than medium staple varieties (10–12 quintals/acre).
- Market Linkage Deficit: Farmers struggle to fetch premium prices for ELS cotton due to weak market access and lack of dedicated procurement infrastructure.
- Technological Gaps: Limited access to improved seed varieties, agronomic practices, and technologies like HtBT (Herbicide-tolerant Bt) cotton.
- Import Dependency: India imports 20–25 lakh bales annually, accounting for ~90% of its ELS cotton requirements, to meet demand from the premium textile industry.
Significance of the Five-Year Cotton Mission
- Aimed at:
- Enhancing productivity and sustainability of ELS cotton.
- Reducing import dependence through indigenous development.
- Strengthening high-value textile exports by ensuring reliable ELS supply.
- Supports:
- Farmer income enhancement through value-added cultivation.
- Research and development in ELS cotton seed technology.
- Improved extension services, supply chain development, and market support mechanisms.
Kolleru Lake
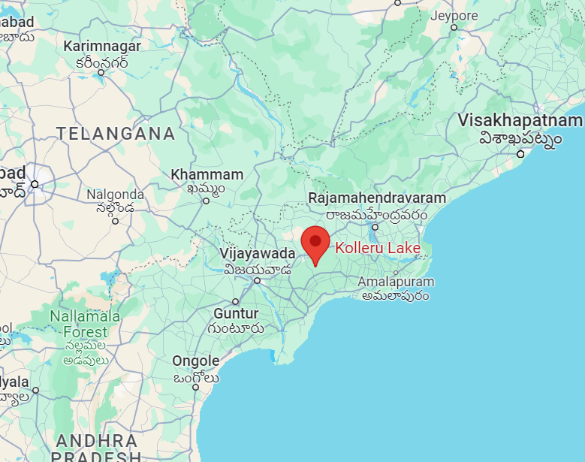
- 06 Feb 2025
In News:
The Southern Zonal Bench of the National Green Tribunal (NGT) has recently restrained the Andhra Pradesh government from proceeding with six proposed infrastructure projects in the Kolleru wetland area, citing violations of environmental protocols and lack of statutory clearances.
About Kolleru Lake
- Location: Northeastern Andhra Pradesh, between the Krishna and Godavari river deltas, near Eluru city.
- Type: One of Asia’s largest shallow freshwater lakes, covering an area of 308 sq. km.
- Hydrology:
- Fed by Budameru and Tammileru rivers.
- Drains into the Bay of Bengal via Upputeru river (a tidal water channel).
- Acts as a natural flood-balancing reservoir for the Krishna and Godavari river systems.
- Ecological Importance:
- Declared a Wildlife Sanctuary in 1999 and a Ramsar Site in 2002.
- Designated as an Important Bird Area (IBA) due to the presence of over 50,000 waterfowl annually.
- Lies on the Central Asian Flyway (CAF), a major migratory bird route.
- Key Avian Species:
- Grey Pelican (indicator species), Siberian Cranes, Glossy Ibis, Open-billed Stork, Purple Moorhen, Painted Storks.
Kolleru Bird Sanctuary
- A protected wetland marsh habitat within the Kolleru Lake region.
- Supports diverse aquatic flora and fauna, serving as a crucial ecosystem for migratory and resident bird species.
Infrastructure Projects and Legal Challenges
- The projects were proposed under the entity "A.P. Krishna – Kolleru Salinity Mitigation Projects Corporation Limited" with a total capital outlay of approximately ?2,952 crore.
- The plans included construction of three regulators-cum-roads across the Upputeru river and other barrages, regulators, and sluices, falling within the Coastal Regulation Zone (CRZ).
- The Andhra Pradesh Water Resources Department (WRD) issued G.O. Ms. No. 63 (dated 2nd December 2020) authorizing the project.
Grounds for NGT Intervention
- Key objections included:
- Absence of scientific or ecological studies.
- Lack of consultations with wetland experts, wildlife conservationists, and hydrologists.
- No clearances obtained from:
- Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change (MoEF&CC)
- A.P. Coastal Zone Management Authority (CZMA)
- A.P. Pollution Control Board (PCB)
- National Board for Wildlife (NBWL)
NGT Observations and Ruling
- The tribunal emphasized the need for comprehensive evaluation of ecological and hydrological impacts before proceeding.
- It cited potential threats to the lake’s ecosystem, including:
- Disruption to natural hydrology.
- Loss of biodiversity and eco-sensitive habitats.
- The NGT ruled that the projects should not proceed unless fully compliant with environmental laws and backed by appropriate expert assessments.
- The ruling reinforced India's obligations under the Ramsar Convention and domestic environmental legislation, stressing the urgent need to protect the integrity of the Kolleru ecosystem.
Henipavirus

- 05 Feb 2025
In News:
A henipavirus, specifically the Camp Hill virus, has been detected in North America for the first time. This discovery in northern short-tailed shrews—a small mammal species found commonly in Canada and the U.S.—raises concerns over a potential zoonotic disease outbreak.
About Henipavirus
- Virus Type: Henipaviruses are zoonotic, negative-sense RNA viruses.
- Family: Paramyxoviridae.
- Natural Hosts: Pteropid fruit bats (commonly known as flying foxes).
- Other Hosts: Capable of infecting various mammals, including humans, horses, pigs, and shrews.
Notable Henipaviruses:
- Hendra virus (HeV):
- First identified in Australia.
- Mortality rate: Up to 70%.
- Nipah virus (NiV):
- Found in Southeast Asia, including Malaysia and Bangladesh.
- Case fatality rate ranges from 40% to 75%, depending on surveillance and clinical care.
Symptoms and Disease Progression
- Initial symptoms: Fever, dizziness, headache, and muscle pain (myalgias).
- Advanced symptoms: Respiratory issues, encephalitis (brain inflammation), confusion, abnormal reflexes, seizures, and coma.
- Relapsing encephalitis may occur months or years after apparent recovery.
- Fatality Risk: High, primarily due to encephalitis and multi-organ failure caused by damage to small blood vessels (microinfarction) in organs like the brain, liver, and kidney.
Why are Henipaviruses so dangerous?
- Henipaviruses produce proteins that:
- Suppress the innate immune system.
- Block interferon-stimulated antiviral responses, aiding viral replication.
- Act as virulence factors, allowing widespread infection and severe outcomes.
Modes of Transmission
- Animal-to-human:
- Direct contact with infected animals (e.g., fruit bats, pigs, horses, shrews).
- Consumption of contaminated food or water (e.g., raw date palm sap in Nipah outbreaks).
- Human-to-human: Via bodily fluids, close contact, or respiratory droplets during caregiving.
Treatment and Prevention
- Treatment:
- No specific vaccine or antiviral currently exists.
- Management is symptomatic and supportive (respiratory support, ICU care).
- Prevention:
- Vaccination of horses (in HeV-risk regions like Australia).
- Avoiding contact with fruit bats and sick animals.
- Isolating infected individuals and animals to prevent spread.
India-Maldives Joint Military Exercise ‘Ekuverin’

- 05 Feb 2025
In News:
The 13th edition of Exercise Ekuverin, a bilateral joint military exercise between the Indian Army and the Maldives National Defence Force (MNDF), commenced in the Maldives on February 4, 2025. The exercise continues to reinforce defence and strategic ties between the two nations.
About Exercise Ekuverin
- Name Meaning: “Ekuverin” means ‘Friends’ in Dhivehi, the official language of the Maldives—symbolizing the deep and friendly defence partnership between India and the Maldives.
- First Conducted: The exercise was initiated in 2009 as part of annual bilateral defence cooperation.
- Venue Alternation: It is held alternatively in India and the Maldives every year.
- 2023 Edition: Conducted at Chaubatia, Uttarakhand from June 11 to 24.
- 2025 Edition: Being hosted in the Maldives.
Key Objectives and Features
- Military Interoperability: Enhances coordination and operational synergy between Indian and Maldivian armed forces.
- Counter-Insurgency and Counter-Terrorism (CI/CT): Focuses on joint tactical drills to counter modern asymmetric threats.
- Humanitarian Assistance and Disaster Relief (HADR): Equips forces to respond effectively to natural disasters and humanitarian crises.
- Strengthening IOR Security: Reinforces regional maritime and strategic stability in the Indian Ocean Region (IOR), a key area of India’s strategic interest.
Significance for India-Maldives Relations
- Strategic Partnership: Builds mutual trust and defence preparedness, aligning with India’s “Neighbourhood First” policy.
- Capacity Building: Helps enhance the capability of the MNDF through joint training with a larger and more experienced Indian Army.
- Regional Security Cooperation: Plays a crucial role in maintaining peace, security, and freedom of navigation in the IOR.
India’s Defence Engagement with Southeast Asia
India actively conducts multiple bilateral and multilateral defence exercises with Southeast Asian countries to enhance defence diplomacy and promote a free, open, and secure Indo-Pacific.
Key Defence Exercises with Southeast Asian Nations:
- Garuda Shakti: Special Forces exercise with Indonesia (Nov 2022, Sangga Buana Training Area).
- Mitra Shakti: Annual exercise with Sri Lanka, last held in 2022.
- VINBAX: India-Vietnam bilateral exercise; 3rd edition held in 2022.
- IMBEX: India-Myanmar bilateral exercise (last noted in 2017–18).
- Maitree: Joint annual military exercise with Thailand, conducted since 2006.
- CORPAT: Coordinated Patrols with Indonesia, Thailand, and Malaysia for maritime domain awareness and security.
- AIME 2023: The first ASEAN-India Maritime Exercise, conducted in May 2023, involving navies from India and ASEAN nations (Brunei, Indonesia, Malaysia, Philippines, Singapore, Thailand, Vietnam).
Golden-headed Cisticola
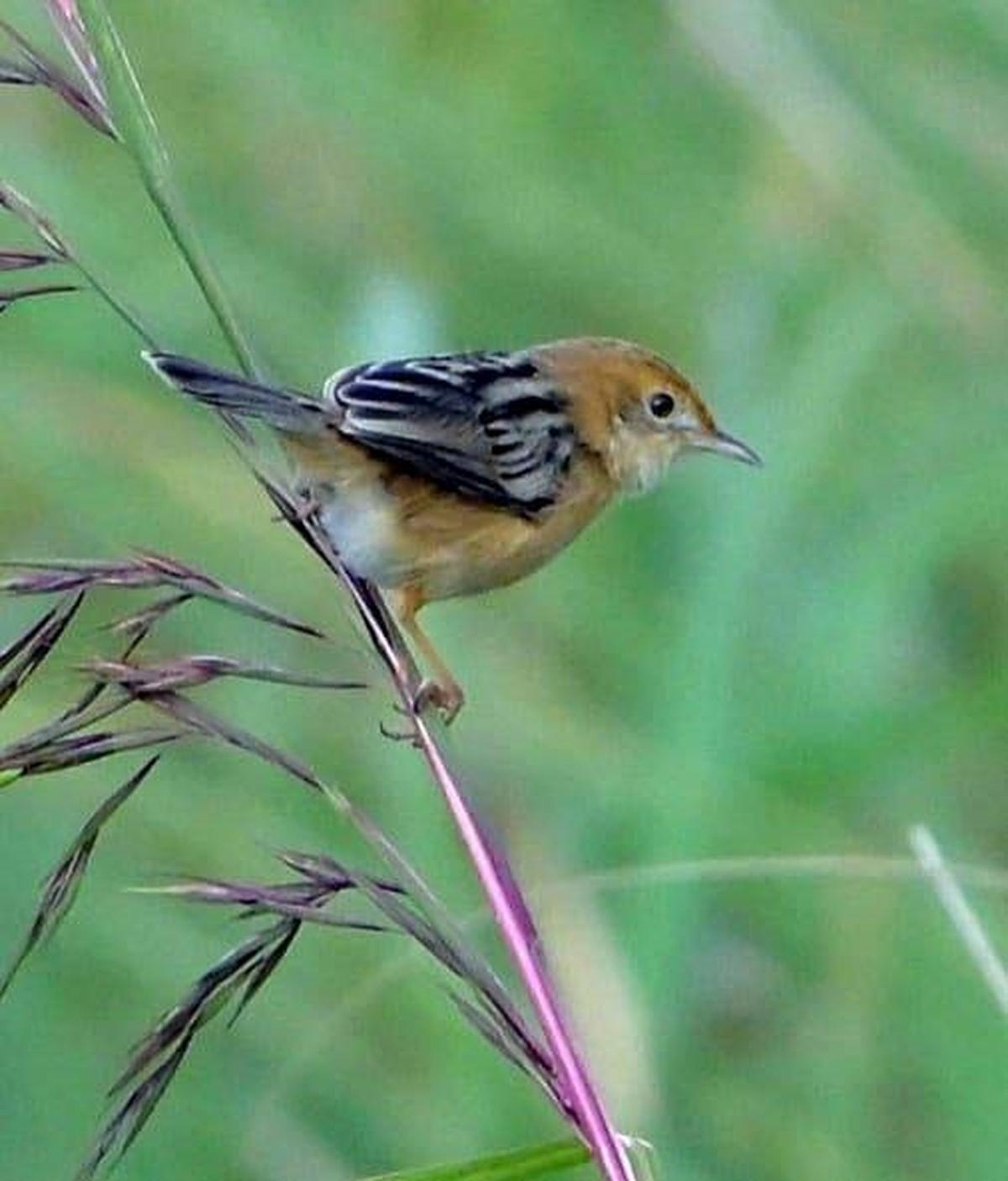

- 05 Feb 2025
In News:
In a remarkable ornithological development, the Golden-headed Cisticola (Cisticola exilis) has been sighted in the Mathikettan Shola National Park, Idukki district, Kerala, marking its first recorded presence in the southern Western Ghats after a significant gap.
The finding underscores the ecological richness of the region and highlights the need for intensified avian research in the Western Ghats.
About Golden-headed Cisticola (Cisticola exilis)
- Also known as the bright-capped cisticola, it is a small warbler belonging to the family Cisticolidae.
- It is an omnivorous bird, feeding primarily on invertebrates such as insects and small slugs, along with grass seeds.
- The species is typically found in grassland habitats within mountain ranges, and has been previously recorded in parts of Karnataka, Tamil Nadu, and northern Kerala, notably in Banasura Hills, Wayanad. However, this is the first confirmed sighting in the southern part of the Palakkad Gap.
Physical features of breeding males include:
- Golden-orange plumage on the head, neck, and chest
- Pinkish beaks
- Black streaks on the back
- A distinctive call that aids identification
Habitat and Distribution
- It is widely distributed across Australia and several Asian countries.
- In India, its presence had been limited to select regions of the Western Ghats, making its recent sighting in Mathikettan Shola both rare and ecologically significant.
Conservation Status
- According to the IUCN Red List, the Golden-headed Cisticola is classified as Least Concern. Despite this, the new finding calls for further research into its habitat preferences and conservation needs within India.
About Mathikettan Shola National Park
Located in the southern part of the Palakkad Gap in the Western Ghats of Kerala, Mathikettan Shola is a vital biodiversity hotspot.
- It comprises evergreen forests, moist deciduous forests, shola grasslands, and semi-evergreen vegetation.
- The park hosts three major streams: Uchillkuthi Puzha, Mathikettan Puzha, and Njandar, which are tributaries of the Panniyar River.
- Its highest point is Kattumala, located at the eastern border adjoining Tamil Nadu.
- The Muthavan tribal community resides near the park’s northeastern boundary, reflecting the intricate human-nature interface in the region.
Scientific and Conservation Importance
The rediscovery has been documented in the journal Malabar Trogon by the Malabar Natural History Society, bringing attention to the importance of long-term monitoring and baseline studies in underexplored ecosystems.
It emphasizes:
- The ecological richness of the Western Ghats, a UNESCO World Heritage site.
- The importance of citizen science, as local birdwatchers played a key role in the finding.
- The need for enhanced habitat protection and ornithological research in grassland ecosystems of high-altitude regions.
RBI Digital Payments Index (DPI)

- 05 Feb 2025
In News:
The Reserve Bank of India’s (RBI) Digital Payments Index (DPI) rose to 465.33 as of September 2024, up from 445.5 in March 2024, indicating a sustained increase in the adoption and penetration of digital payments across India.
About the RBI-DPI
- Launched: January 2021
- Constructed by: Reserve Bank of India
- Purpose: To measure the extent and progress of digitisation of payments in India.
- Base Period: March 2018 (DPI Score = 100)
- Frequency of Publication: Semi-annually (March and September)
Significance of the Index
- Acts as a quantitative tool to monitor India’s progress in achieving a less-cash economy.
- Provides stakeholders, policymakers, and researchers a composite view of digital payment trends.
- Helps identify policy focus areas and gaps in digital infrastructure and adoption.
- Supports the goals of financial inclusion, innovation, and digital public infrastructure.
Recent Trends
- September 2024 DPI Score: 465.33
- March 2024 DPI Score: 445.5
- Implication: Demonstrates continued momentum in digital payment adoption, driven by improved payment infrastructure and payment performance nationwide.
Structure of the RBI-DPI
The index is composed of five broad parameters, each with defined weightages and sub-indicators:
Parameter Weightage Description
1. Payment Enablers 25% Internet/mobile penetration, bank account ownership, Aadhaar usage.
2. Payment Infrastructure – Demand Side 10% Number of debit/credit cards, user demand for digital options.
3. Payment Infrastructure – Supply Side 15% Availability of POS machines, ATMs, bank branches, QR codes.
4. Payment Performance 45% Actual volume and value of digital transactions, currency usage trends.
5. Consumer Centricity 5% Digital payment awareness, fraud prevention, grievance redressal.
Each parameter is further broken down into measurable sub-indicators, offering a comprehensive framework for assessment.
Why RBI-DPI Matters for India
- Digital Transformation: Encourages the shift from cash to digital payments, aligning with the goals of Digital India.
- Policy Impact Assessment: Evaluates the effectiveness of regulatory and policy interventions in the payment ecosystem.
- Infrastructure Development: Reflects the outreach of digital payment infrastructure, aiding targeted investments.
- Financial Inclusion: Helps assess how digital modes are reaching the underserved and unbanked populations.
- Data-Driven Governance: Facilitates evidence-based decision-making in financial sector reforms.
SwaRail SuperApp
- 05 Feb 2025
In News:
The Ministry of Railways has launched a unified mobile application, SwaRail, currently in beta testing as of January 31, 2025.
This initiative aims to streamline access to Indian Railways services and enhance user experience by consolidating various apps into a single digital platform.
Key Highlights
What is SwaRail?
- SwaRail is a SuperApp developed by the Centre for Railway Information Systems (CRIS).
- It serves as a comprehensive, one-stop solution for a wide range of Indian Railways services.
- The app is currently in beta testing and is available on the Google Play Store and Apple App Store.
Objective
- To integrate multiple railway-related services under a unified platform.
- To reduce app clutter and device storage consumption.
- To improve user experience through a seamless and intuitive interface.
Developed By: Centre for Railway Information Systems (CRIS)
- CRIS is an organization under the Ministry of Railways.
- It combines IT expertise with railway operational experience.
- CRIS is responsible for developing and maintaining software for core railway functions.
Services Offered via SwaRail
The SuperApp merges functionalities of multiple existing apps, offering:
- Ticketing Services
- Reserved ticket booking
- Unreserved and platform ticket booking
- Freight & Parcel Enquiries
- Parcel booking status
- Freight services information
- Passenger Enquiries
- Real-time train status
- PNR enquiry (along with associated train details)
- Train schedules
- Onboard Services
- Food ordering while traveling
- Complaint redressal via Rail Madad
Notable Features of the SuperApp
Feature Description
Single Sign-On Access all services using a single set of credentials
Unified App Combines multiple previously separate apps (e.g., IRCTC RailConnect, UTS)
Integrated Interface Displays consolidated data like PNR + train info on the same screen
Easy Onboarding Existing users can log in with RailConnect/UTS credentials
Multiple Login Modes Supports m-PIN, biometric authentication, and OTP-based guest login
Smart Wallet Integration Auto-linking of R-Wallets from UTS App for ticket booking transactions
User-Centric Approach
- The app is being actively tested, and users are encouraged to provide feedback during the beta phase.
- CRIS is monitoring performance and issues for improvement before the final public release.
- The government envisions technological integration to ensure efficient, smarter, and citizen-friendly rail services.
GARBH-INi-DRISHTI

- 04 Feb 2025
In News:
India has made a significant stride in biomedical research and public health with three major developments led by the Translational Health Science and Technology Institute (THSTI) in Faridabad, Haryana.
Key Highlights:
India’s First Ferret Research Facility
- Inaugurated by: Department of Biotechnology (DBT), Ministry of Science & Technology.
- Location: NCR Biotech Science Cluster, Faridabad.
- Purpose: To bolster India's capacity in:
- Vaccine development
- Therapeutic testing
- Research on emerging infectious diseases like influenza, COVID-19, and tuberculosis.
- Significance:
- Strengthens India’s pandemic preparedness.
- Positions India among the select nations with advanced biosafety labs using ferrets—ideal models due to respiratory systems similar to humans.
Launch of GARBH-INi-DRISHTI Data Repository
- Platform: DBT Data Repository and Information Sharing Hub under the GARBH-INi program.
- Dataset Size: Over 12,000 pregnant women, newborns, and postpartum mothers.
- Developed by: THSTI with collaboration from top Indian research institutions and hospitals.
- Features:
- Comprehensive clinical data, medical images, and biospecimens.
- Secure, controlled access promoting ethical research.
- Facilitates predictive tools for preterm birth and maternal health complications.
- Utility:
- Empowers both national and global researchers.
- Informs maternal and neonatal health interventions.
- Supports evidence-based policymaking in public health.
- Program Genesis:
- GARBH-INi (2014): Interdisciplinary initiative to understand preterm birth risks—biological and non-biological.
- Part of: Atal Jai Anusandhan Biotech Mission under the UNaTI initiative.
Technology Transfer Agreement with Industry
- Agreement Between: THSTI and Sundyota Numandis Probioceuticals Pvt. Ltd.
- Technology Transferred:
- Lactobacillus crispatus, a genetically defined synthetic microbial consortium.
- Isolated from reproductive tracts of Indian women enrolled in GARBH-INi.
- Applications:
- Nutraceuticals and probiotics for reproductive health.
- Potential treatments for vaginal infections and urinary tract infections (UTIs).
- Significance:
- Promotes microbiome-based interventions.
- Bridges lab-to-market gap, boosting the biomanufacturing ecosystem.
Strategic Implications for India
- Scientific Diplomacy & Global Standing: With cutting-edge facilities and open data-sharing platforms, India emerges as a key player in global biomedical research.
- Public Health Impact: Supports targeted, data-driven maternal health policies and pandemic response frameworks.
- Innovation Ecosystem: Reflects the convergence of academic research, industry collaboration, and translational science.
World Wetlands Day 2025

- 04 Feb 2025
In News:
World Wetlands Day is observed every year on 2nd February to commemorate the adoption of the Ramsar Convention on Wetlands in 1971 in Ramsar, Iran.
India has been a signatory to the Convention since 1982 and has actively worked towards the conservation and sustainable management of wetlands—critical ecosystems that serve as biodiversity hotspots, natural flood buffers, and carbon sinks.
Theme 2025: "Protecting Wetlands for Our Common Future"
The 2025 theme emphasizes collaborative efforts to protect wetlands to ensure ecological sustainability, biodiversity preservation, and long-term human well-being. It highlights the need for integrated management and foresight in conservation strategies.
Key Event: Parvati Arga Ramsar Site, Gonda, Uttar Pradesh
The Union Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change (MoEFCC) organized the national-level celebrations of World Wetlands Day 2025 at the Parvati Arga Ramsar Site in Gonda district, Uttar Pradesh.
Significance of the Site
- Comprises two rain-fed oxbow lakes—Parvati and Arga—located in the terai region of the Gangetic plains.
- Supports endangered and critically endangered species like the white-rumped vulture, Indian vulture, and Egyptian vulture.
- Attracts migratory birds such as Eurasian coots, greylag geese, northern pintails, and red-crested pochards.
- Threatened by invasive species, notably the common water hyacinth.
- The nearby Tikri Forest is being developed as an eco-tourism site, and a nature-culture tourism corridor is planned between Ayodhya and Devi Patan.
Cultural and Economic Value
- The area includes heritage sites such as the birthplaces of Maharishi Patanjali and Goswami Tulsidas, enhancing its potential as a religious and cultural tourism hub.
- A MoU between Amazon and ARGA (UP Government initiative) aims to empower women entrepreneurs through digital training and market access under Amazon’s Saheli programme.
India's Wetland Landscape and New Ramsar Sites (2025 Update)
India’s tally of Ramsar Sites has risen to 89, with four new additions:
- Udhwa Lake – Jharkhand (first Ramsar site for the state)
- Theerthangal – Tamil Nadu
- Sakkarakottai – Tamil Nadu
- Khecheopalri – Sikkim (first Ramsar site for the state)
- Tamil Nadu leads with 20 Ramsar Sites, followed by Uttar Pradesh with 10 sites.
- Total area under Ramsar protection in India is now approximately 1.358 million hectares.
Amrit Dharohar Initiative
Launched in June 2023, the Amrit Dharohar initiative promotes conservation and sustainable use of Ramsar Sites over three years. It aligns with Budget 2023–24 announcements and focuses on:
- Species and Habitat Conservation
- Nature Tourism
- Wetlands-based Livelihoods
- Wetlands and Carbon Mitigation
The initiative encourages convergence among central ministries, state authorities, and community stakeholders.
Workshops and Public Engagement
A regional workshop for Northern States was organized on 1st February 2025, with participants from nine states and UTs, highlighting collaborative models in wetland management. The main event also included:
- Exhibitions on eco-friendly products, wetland conservation, and green skills.
- Launch of publications like the Integrated Management Plan for Parvati Arga, Factbook of India’s 85 Ramsar Sites, and Development of Van Taungya Villages.
- Felicitation of painting, quiz, and Nukkad Natak competition winners, promoting grassroots awareness.
Significance of Wetlands in India
Wetlands are water-covered ecosystems, either permanently or seasonally flooded. They:
- Support rich biodiversity, including migratory birds and aquatic species.
- Recharge groundwater and regulate floods.
- Provide livelihoods through fisheries and tourism.
- Act as natural carbon sinks, aiding in climate change mitigation.
Major Threats
- Pollution from industrial and domestic effluents
- Encroachment and urbanization
- Invasive species
PM Shram Yogi Maandhan Yojana (PM-SYM)

- 04 Feb 2025
In News:
The Union Budget 2025–26 has accorded the highest-ever allocation of ?32,646 crore to the Ministry of Labour and Employment, representing an 80% increase over the previous year's Revised Estimates.
The enhanced funding reflects the government's strategic focus on employment generation and strengthening social security mechanisms for unorganised workers and gig economy participants.
Key Budgetary Highlights:
1. Employment Generation Scheme:
- ?20,000 crore has been allocated to the new Employment Generation Scheme, double the previous year’s allocation.
- The scheme is aimed at fostering large-scale employment opportunities and skilling across various sectors.
2. Employees’ Pension Scheme:
- Allocation increased by ?300 crore, strengthening retirement security for formal sector workers.
3. PM Shram Yogi Maandhan Yojana (PM-SYM):
- Allocation increased by 37% compared to last year.
- The scheme provides old-age social security to unorganised workers through a voluntary, contributory pension model.
About Pradhan Mantri Shram Yogi Maandhan Yojana (PM-SYM)
Objective:
To provide minimum assured pension and social security to unorganised sector workers, including street vendors, construction workers, agriculture laborers, domestic workers, etc.
Eligibility:
- Indian citizen aged 18–40 years
- Monthly income below ?15,000
- Not a member of EPFO, ESIC, or NPS
Key Features:
- Minimum Assured Pension: ?3,000 per month after 60 years of age.
- Voluntary and Contributory Scheme:
- Contributions made via auto-debit from bank accounts.
- 50:50 matching contribution by the Central Government.
- Pension Fund Management:
- Administered by the Ministry of Labour and Employment.
- Implemented by LIC and CSC e-Governance Services India Ltd.
- LIC acts as the Pension Fund Manager.
Family Pension Provision:
- In case of subscriber's death:
- Spouse receives 50% of the pension amount as family pension.
- If death occurs before 60 years, the spouse may continue contributions or exit the scheme as per norms.
Exit Provisions:
- Exit before 10 years: Subscriber's share with accrued interest is returned.
- Exit after 10 years but before 60 years: Entire contribution with interest returned to the subscriber.
Social Security for Gig Workers
Recognising the gig economy as a critical pillar of India’s modern workforce, the government has taken key steps to enhance their social security:
- e-Shram registration
- Provision of unique identity cards
- Access to healthcare benefits under PM Jan Arogya Yojana
- Expected to benefit around 1 crore gig workers
Iran’s Missile Advancements
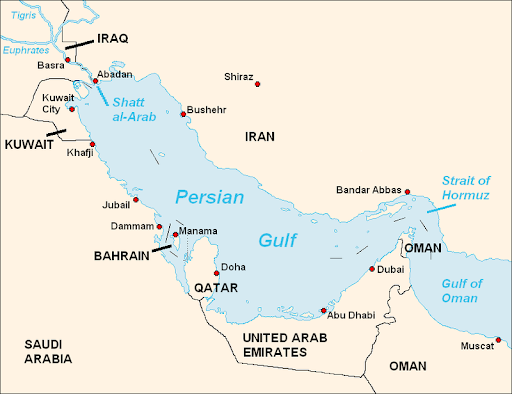
- 04 Feb 2025
In News:
In a significant military development, Iran has successfully test-fired the Ghadr-380, an advanced anti-warship cruise missile with a range of 1,000 kilometers (600 miles).
This capability allows it to target U.S. Navy warships deployed in critical maritime regions like the Persian Gulf and the Sea of Oman. The missile test was launched from an underground missile facility and was broadcast on Iranian state television, underscoring its strategic messaging.
Key Missiles Unveiled by Iran:
1. Ghadr-380 Cruise Missile:
- Type: Anti-warship cruise missile
- Range: Over 1,000 km
- Features:
- Anti-jamming capability
- Quick-launch readiness (operable by one person in less than 5 minutes)
- Launch Details:
- Fired from an underground missile base in central Iran
- Targeted the Sea of Oman
- Specific test timing and warhead specifications were not disclosed
2. Etemad Ballistic Missile:
- Name Meaning: Etemad means "trust" in Persian
- Type: Precision-guided ballistic missile
- Range: 1,700 km (1,056 miles)
- Specifications:
- Length: 16 meters
- Diameter: 1.25 meters
- Equipped with precision-guided warhead
- Built by: Iranian Ministry of Defence
Ballistic vs. Cruise Missiles: Understanding the Distinction
Feature Ballistic Missile Cruise Missile
Propulsion Rocket-propelled at launch; unpowered descent Jet engine-powered throughout flight
Flight Path Arched trajectory (leaves and re-enters atmosphere) Straight, low-altitude flight within atmosphere
Detection Easier to track via radar once launched Difficult to detect due to low-altitude flight
Launch Platforms Ground-based, silo, mobile launchers Ground, air, or sea platforms
Warhead Capability Can carry conventional or nuclear warheads Usually conventional, but may carry nuclear in advanced forms
Iran’s Strategic Missile Doctrine
Underground Missile Facilities:
- Iran maintains extensive underground missile bases, especially in southern Iran near the Strait of Hormuz—a chokepoint for global oil trade.
- Such facilities enhance survivability and rapid response capabilities.
Missile Development Drivers:
- Iran's missile program evolved as a strategic deterrent post the Iran-Iraq War (1980–1988), where both countries used missiles to target civilian areas.
- UN arms embargoes led Iran to focus on domestic development of missile systems, including both cruise and ballistic types.
Capabilities:
- Iran now claims to possess missiles with ranges up to 2,000 kilometers, capable of reaching parts of the Middle East, including Israel.
- The Ghadr-380 and Etemad missiles are examples of technological diversification—from ballistic to precision cruise systems.
Implications for Regional and Global Security
- Deterrence Posture: Iran’s missile advancements strengthen its deterrence, especially amid strained relations with the U.S. and its allies.
- Threat to Maritime Security: The Ghadr-380, with its anti-warship focus, poses a direct threat to U.S. naval assets in the Persian Gulf and adjacent waters.
- Escalation Risks: Enhanced missile capabilities could escalate regional tensions, particularly in flashpoints like the Strait of Hormuz.
- Western Concerns: The U.S. and European nations remain wary of Iran’s dual-track approach involving missile and nuclear program developments.
Shubhanshu Shukla

- 04 Feb 2025
In News:
Group Captain Shubhanshu Shukla of the Indian Air Force (IAF) is set to become the first Indian astronaut to travel to the International Space Station (ISS) on a private mission, marking a significant milestone in India’s space diplomacy and international collaboration in human spaceflight.
Mission Details:
- Mission Name: Axiom Mission 4 (Ax-4)
- Launch Vehicle: SpaceX’s Dragon spacecraft
- Launch Site: Kennedy Space Center, Florida, USA
- Tentative Timeline: Spring 2025
- Duration on ISS: Up to 14 days
- Mission Objectives: Conduct scientific experiments, educational outreach, and commercial activities, in collaboration with NASA and ISRO.
International Collaboration:
- The mission includes astronauts from India, Poland, and Hungary—the first such trilateral collaboration in over four decades.
- Marks the return of human spaceflight for Poland and Hungary after a hiatus of more than 40 years.
- Demonstrates Axiom Space’s emerging role in redefining access to low-Earth orbit and supporting national space programs through private missions.
About Shubhanshu Shukla:
- Born: October 10, 1985, in Lucknow, Uttar Pradesh
- Commissioned into IAF: June 2006, Fighter Wing
- Promoted to Group Captain: March 2024
- Current Role: Astronaut-designate for India’s Gaganyaan human spaceflight mission
- Flight Experience: Over 2,000 hours across multiple aircraft including Su-30 MKI, MiG-21, MiG-29, Jaguar, Hawk, Dornier, and An-32
- Astronaut Training: Trained at Yuri Gagarin Cosmonaut Training Center, Star City, Moscow (1-year program)
Historical Context:
- Rakesh Sharma remains the first Indian to travel to space (1984) aboard Soviet Soyuz T-11, under the Interkosmos program.
- Shukla’s upcoming mission marks a new era of Indian participation in international human space missions, particularly through private partnerships.
National Geospatial Mission
- 03 Feb 2025
In News:
Finance Minister Nirmala Sitharaman announced the launch of a National Geospatial Mission in the Budget 2025-26.
Key Highlights:
Objective: To modernize land records, enhance urban planning, and create a robust geospatial infrastructure to support India’s broader development goals, including sustainable growth, efficient governance, and improved public service delivery.
Key Features of the Mission:
- Modernization of Land Records:
- Digitization and updation of land records using geospatial technology.
- Aim to reduce land disputes and promote efficient and transparent land use.
- Urban and Infrastructure Planning:
- Provides high-resolution geospatial data for informed urban planning.
- Supports better design and execution of infrastructure through integration with the PM Gati Shakti framework.
- Development of National Geospatial Data Infrastructure (NGDI):
- Integrates geospatial data from multiple departments and ministries.
- Enables seamless access and interoperability for users across sectors.
- Open Geospatial Data Policy:
- Encourages private sector participation by allowing access to non-sensitive, high-resolution data.
- Reduces reliance on foreign geospatial data providers.
- Sectoral Impact:
- Agriculture: Precision farming, resource mapping, and yield optimization.
- Disaster Management: Enhances early warning systems and response planning.
- Environmental Monitoring: Facilitates conservation, deforestation tracking, and ecosystem health analysis.
- Transportation: Improves logistics, routing, and infrastructure placement.
- Climate Monitoring: Aids in data-driven climate action and adaptation planning.
- Technological Integration:
- Utilizes emerging technologies such as AI, drones, and quantum computing for spatial data collection and analysis.
- Promotes research and development in geospatial science to drive innovation.
- Support to Private Sector:
- Anticipated growth in demand for services from geospatial startups, drone companies, and mapping enterprises.
- Strengthens India’s indigenous geospatial capability aligned with the booming global geospatial market (projected to reach $1,064 million by 2030).
Significance and Alignment with National Goals:
- Enhances transparency and efficiency in land governance.
- Contributes to sustainable urban development.
- Aligns with Digital India and Atmanirbhar Bharat by reducing data dependency on foreign sources.
- Acts as a foundational enabler for India’s development agenda, particularly in areas of resource management, climate resilience, and national security.
PM Dhan Dhanya Krishi Yojana

- 03 Feb 2025
In News:
- Recently, the Union Government has introduced the PM Dhan Dhanya Krishi Yojana which aims at enhancing agricultural productivity.
- Objective: To boost agricultural productivity, modernize farming practices, and enhance rural prosperity by addressing region-specific challenges in backward agricultural districts.
Key Features:
- Integrated Approach:
- Consolidates multiple existing agricultural schemes under one umbrella for greater synergy and implementation efficiency.
- Draws inspiration from the Aspirational Districts Programme, which has improved socio-economic outcomes in backward regions.
- District-Specific Interventions:
- Focuses on districts with:
- Low crop productivity
- Moderate crop intensity
- Limited institutional credit access
- Implements customized strategies based on the unique challenges of each region.
- Focuses on districts with:
- Core Focus Areas:
- Enhancing farm productivity through modern technology.
- Improving irrigation infrastructure.
- Increasing formal credit availability to reduce dependence on informal moneylenders.
- Promoting crop diversification and sustainable agriculture.
- Strengthening post-harvest infrastructure like storage at Panchayat and block levels.
- Technology-Driven Solutions:
- Encourages adoption of climate-resilient and precision farming.
- Supports digital access to credit and advisory services.
- Financial Inclusion:
- Strengthens linkages with government financial programs, microfinance institutions, and banks.
- Aims to reduce rural indebtedness and promote formal financial participation.
- State and Centre Collaboration: Implementation will involve both central and state governments, ensuring localized solutions with national support.
- Reducing Distress Migration: By improving rural livelihoods and opportunities, the scheme aims to make migration a choice rather than a compulsion.
Onchocerciasis

- 03 Feb 2025
In News:
The World Health Organization (WHO) officially verified Niger as the first country in the African Region and the fifth globally to eliminate onchocerciasis (river blindness) by interrupting the transmission of the parasite Onchocerca volvulus.
What is Onchocerciasis (River Blindness)?
- A parasitic disease caused by the worm Onchocerca volvulus.
- Transmitted by infective blackflies, primarily found in riverine areas.
- Causes severe itching, disfiguring skin conditions, and irreversible blindness.
- It is the second leading infectious cause of blindness globally (after trachoma).
- Predominantly affects rural populations in sub-Saharan Africa, Yemen, and parts of Latin America.
Niger’s Elimination Strategy and Achievements:
Historical Background:
- 1976–1989: Under the WHO Onchocerciasis Control Programme (OCP), Niger used vector control via insecticide spraying, reducing disease transmission.
- 2008–2019: Mass Drug Administration (MDA) with ivermectin and albendazole was carried out, primarily for lymphatic filariasis (LF), but also effectively interrupted onchocerciasis transmission in co-endemic areas.
Assessment and Surveillance:
- 2014: Niger began preliminary assessments following the end of LF MDA.
- Entomological and epidemiological surveys confirmed disease elimination:
- Prevalence dropped from 60% to 0.02%.
- No ongoing transmission of O. volvulus.
Key Contributors to Success:
- Partnerships: Collaborative efforts between the Government of Niger, WHO, Merck Sharpe & Dohme (MSD), and various NGOs.
- Medicine Donation: MSD’s donation of ivermectin.
- Surveillance & Flexibility: Continuous monitoring allowed strategic adaptation.
- Previous Success: Niger was certified free of Guinea-worm disease in 2013.
Global and Regional Significance:
- Niger becomes the fifth country globally to eliminate onchocerciasis:
- Other four countries:
- Colombia (2013)
- Ecuador (2014)
- Mexico (2015)
- Guatemala (2016) (All from the WHO Region of the Americas)
- Other four countries:
- WHO African Region:
- 21 countries have eliminated at least one Neglected Tropical Disease (NTD).
- Onchocerciasis is the second NTD eliminated in Niger after Guinea-worm.
Guneri Inland Mangrove

- 03 Feb 2025
In News:
In 2024, the Gujarat government declared the Inland Mangrove of Guneri, located in Kutch district, as the first Biodiversity Heritage Site (BHS) of the state under the Biological Diversity Act, 2002. The declaration followed a recommendation by the Gujarat Biodiversity Board.
Key Features of Guneri Inland Mangroves:
- Location: Guneri village, Lakhtar tehsil, Kutch district, Gujarat.
- Area: 32.78 hectares.
- Distance from Sea: ~45 km from the Arabian Sea; ~4 km from Kori Creek.
- Nature: Inland (non-coastal) mangrove ecosystem — one of only eight such sites globally and the last remaining in India.
- Terrain: Flat land resembling a forest; no tidal influence or sludge typically seen in coastal mangroves.
- Water Source: Sustained by groundwater retained in limestone deposits; no direct contact with seawater.
Ecological and Geological Significance:
- Possibly originated from:
- Miocene marine transgression, or
- Along the ancient Saraswati River, believed to have flowed in the Great Rann of Kutch around 3000–4000 BCE.
- Limestone formations in western Kutch provide continuous subsurface water flow, enabling survival of this unique mangrove system.
Biodiversity:
- Habitat to:
- 20 migratory bird species
- 25 resident migratory avifaunal species
- Acts as a vital ecosystem for local and seasonal wildlife.
Mangroves in India – 2024 Snapshot:
- As per the “Red List of Mangrove Ecosystems” (May 22, 2024):
- India has 3% of South Asia’s mangrove cover.
- Total mangrove area: 4,975 sq km (0.15% of India's land area).
- Increase: 54 sq km (1.10%) since last assessment.
- State-wise share:
- West Bengal: 42.45% (notably South 24 Parganas & Sundarbans)
- Gujarat: 23.66% (with highest increase: 37 sq km)
- Andaman & Nicobar Islands: 12.39%
Legal Framework:
- Declared under the Biological Diversity Act, 2002, which empowers state governments to notify BHS after consulting local self-government bodies.
- A local Biodiversity Management Committee (BMC), including representatives from self-governance institutions, will oversee protection and conservation.
- This provides a formal structure for site management, previously absent.
Conservation Measures:
- Training programs for local and tribal communities along with forest officials.
- A management plan will be implemented to preserve the unique flora and fauna.
National Bank for Financing Infrastructure and Development (NaBFID)

- 03 Feb 2025
In News:
In the Union Budget 2025, Finance Minister Nirmala Sitharaman announced that the National Bank for Financing Infrastructure and Development (NaBFID) will set up a partial credit enhancement facility to promote corporate bond issuance in the infrastructure sector.
Need for Credit Enhancement:
- Pension and insurance funds in India, as per regulatory norms, can invest only in AA-rated or higher securities.
- Most infrastructure firms issue bonds rated below this threshold (often "A" rated).
- Partial credit enhancement will elevate such bonds to AA ratings, enabling large-scale participation from long-term institutional investors.
Significance:
- Currently, pension and insurance funds prefer government bonds. However, with the government's ongoing fiscal consolidation, sovereign bond issuance is expected to decline.
- This measure provides alternative, long-term investment avenues for these funds.
- Enhances liquidity in the corporate bond market, especially for infrastructure players.
- Helps in reducing infrastructure companies' dependence on banks for funding.
About NaBFID:
- Established: 2021 under The National Bank for Financing Infrastructure and Development Act, 2021.
- Type: Development Finance Institution (DFI).
- Regulator: Reserve Bank of India (RBI) as an All-India Financial Institution (AIFI).
- Purpose: Bridge gaps in long-term, non-recourse infrastructure financing and promote bond and derivatives markets in India.
Development Finance Institutions (DFIs):
- Government-owned or public sector-backed institutions that finance large-scale, long-gestation projects.
- Provide medium (1–5 years) and long-term (>5 years) financing.
- Raise funds via sovereign borrowings, insurance companies, pension funds, and sovereign wealth funds.
- Offer both financial support (loans, guarantees) and technical support (project viability, consultancy).
- Do not accept public deposits.
Benefits of Partial Credit Enhancement:
- Democratizes access to the corporate bond market for sub-AA-rated firms.
- Attracts long-term capital into infrastructure through safer, credit-enhanced instruments.
- Promotes diversification and deepening of India's debt markets.
- Makes infrastructure financing more cost-efficient and sustainable over the long term.
Challenges Ahead:
- Regulatory streamlining is essential.
- Guarantee fees need optimization to ensure cost competitiveness against traditional bank lending.
National Manufacturing Mission

- 02 Feb 2025
In News:
- The National Manufacturing Mission (NMM) has been launched to accelerate India’s transition into a global manufacturing hub.
- This mission is a key component of the Make in India initiative and aims to raise the manufacturing sector’s contribution to GDP from 17% to 25% by 2025.
Scope & Coverage
- Targets small, medium, and large industries across sectors.
- Provides a comprehensive support framework involving policy guidance, execution roadmaps, and governance structures for central ministries and state governments.
Five Core Focus Areas:
- Ease and cost of doing business
- Skilling for future-ready jobs
- Support for a dynamic MSME sector
- Technology availability and innovation
- Enhancement of product quality
Clean Tech Manufacturing Focus
In line with India's sustainable development goals, the mission will promote domestic value addition and build robust manufacturing ecosystems for:
- Solar PV cells
- Electric vehicle (EV) batteries
- Motors and controllers
- Electrolyzers
- Wind turbines
- Very high-voltage transmission equipment
- Grid-scale batteries
Strategic Objective: Reduce reliance on Chinese imports and integrate India into global clean tech supply chains.
MSME Sector Support
- Credit Guarantee Cover for MSMEs increased from ?5 crore to ?10 crore.
- Revised Classification Criteria: Investment and turnover limits enhanced by 2.5x and 2x, respectively.
- Aims to empower MSMEs with greater access to credit and growth incentives.
Sector-Specific Measures
1. Footwear & Leather Sector
- A new Focus Product Scheme will support:
- Design capacity
- Component manufacturing
- Machinery for non-leather and leather footwear
- Expected Impact:
- Employment for 22 lakh persons
- Turnover of ?4 lakh crore
- Exports over ?1.1 lakh crore
2. Toy Manufacturing – National Action Plan for Toys
- Objective: Make India a global hub for innovative and sustainable toys.
- Strategy:
- Develop manufacturing clusters
- Promote skilling and innovation
- Strengthen the ‘Made in India’ brand in the global toy market
3. Food Processing – ‘Purvodaya’ Focus
- Establishment of a National Institute of Food Technology, Entrepreneurship and Management in Bihar.
- Purpose:
- Boost food processing in Eastern India
- Enhance value addition for farmers
- Create employment and entrepreneurial opportunities
Bharatiya Bhasha Pustak Scheme
- 02 Feb 2025
In News:
Announced in the Union Budget 2025–26, the Bharatiya Bhasha Pustak Scheme is a major initiative to provide digital textbooks and learning materials in multiple Indian languages for school and university students.
Key Features:
- Digital Access: Study resources will be made available in digital formats via platforms such as DIKSHA, e-PG Pathshala, and the National Digital Library of India.
- Target Groups: Students in schools, colleges, and universities affiliated with UGC, AICTE, and other regulatory bodies.
- Focus Areas: STEM, social sciences, humanities, and commerce; with a special emphasis on technical education in Indian languages.
- Use of Technology: AI-based tools will support automated translation, voice-assisted learning, and customized content.
- Alignment with NEP 2020: Promotes multilingualism and regional language education, as envisioned in the National Education Policy.
Complementary Initiative – ASMITA (Augmenting Study Materials in Indian Languages)
- Aims to develop 22,000 textbooks in Indian languages over the next five years.
- Jointly led by UGC and the Bharatiya Bhasha Samiti under the Ministry of Education.
- Thirteen nodal universities will coordinate content development, supported by regional institutions.
- SOPs (Standard Operating Procedures) have been developed for translation, writing, editing, review, plagiarism checks, and publication.
Budgetary Allocations and Educational Infrastructure
Highest-Ever Allocation for School Education: ?78,572 crore
- 16.28% rise over revised estimates of 2024–25.
- ?9,503 crore allocated to Kendriya Vidyalaya Sangathan (?776 crore hike).
- Plan to set up 50,000 Atal Tinkering Labs in government schools to foster innovation and scientific thinking.
- BharatNet Project to ensure broadband access in all government secondary schools within three years.
Higher Education Allocation: ?50,077.95 crore
- Covers central universities, IITs, and centrally sponsored schemes.
- Budget for centrally sponsored schemes like PM-USHA and RUSA increased to ?1,815 crore.
- Student financial aid raised to ?2,160 crore.
Boost to IIT Infrastructure:
- Additional infrastructure for five IITs established after 2014, accommodating 6,500 more students.
- Expansion of hostel and academic facilities at IIT Patna.
Artificial Intelligence in Education
- Announcement of a Centre of Excellence in AI for Education with an outlay of ?500 crore.
- Objective: Reduce disparities, improve efficiency, and ensure equitable access to high-quality education using AI technologies.
Microplastics detected in Delhi’s Groundwater

- 02 Feb 2025
In News:
A first-of-its-kind study, commissioned by the Delhi government and conducted by The Energy and Resources Institute (TERI), has revealed the presence of microplastics in groundwater across all 11 districts of Delhi. The interim findings, submitted in November 2024, also reported microplastics in Yamuna River water and soil samples along its banks.
Key Findings:
- Widespread Contamination: Microplastics were found in groundwater samples across Delhi, indicating potential contamination due to leaching from the Yamuna River.
- Additional Contamination: Microplastics were also detected in the Yamuna's water and riverbank soil, suggesting environmental pervasiveness.
- Water Usage Impact: Since Delhi relies on borewells and treated groundwater for drinking and domestic purposes, this contamination raises serious public health concerns.
- No Objection by Authorities: The Delhi government has not disputed the study’s interim findings; further post-monsoon analysis is underway, and a final report is expected later in 2025.
What Are Microplastics?
According to the UN Environment Programme (UNEP):
- Definition: Plastic particles less than 5 mm in size
- Types:
- Primary Microplastics: Manufactured for use in cosmetics (e.g., microbeads) and textiles (e.g., microfibers from clothing, nets)
- Secondary Microplastics: Result from breakdown of larger plastics (e.g., bottles) due to sunlight, abrasion, and ocean waves
Environmental & Health Impacts:
- Persistence: Microplastics are non-biodegradable, mobile, and difficult to eliminate from natural ecosystems.
- Toxicity:
- Can adsorb harmful chemicals, making them more toxic
- Known to bioaccumulate in aquatic food chains
- Human Exposure: Microplastics can enter the human body via:
- Inhalation (air)
- Ingestion (water and seafood)
- Dermal absorption (through skin)
- Health Risks (UNEP Report – From Pollution to Solution, 2021):
- Potential effects on genetics, brain development, respiration, and placental health in newborns
- No global standard exists for safe microplastic limits in drinking water
Ocean Coordination Mechanism (OCM)
- 02 Feb 2025
In News:
Recently, the Intergovernmental Oceanographic Commission of UNESCO (UNESCO-IOC) announced the signature of a Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) enabling the creation of the Ocean Coordination Mechanism (OCM).
What is the Ocean Coordination Mechanism (OCM)?
- It is a collaborative governance initiative aimed at the sustainable management of marine resources in the Caribbean and North Brazil Shelf region.
- Conceived under the 10-year CLME+ Strategic Action Programme (SAP)—endorsed in 2014—it represents a transformative step toward integrated ocean governance.
Key Objectives of OCM:
- Promote sustainable fisheries
- Advance ecosystem restoration and marine spatial planning
- Establish marine protected areas (MPAs)
- Encourage pollution control and blue carbon development
- Foster cross-country and cross-institutional cooperation
It builds on lessons from earlier efforts like the Pacific Islands Regional Ocean Policy (PIROP), aiming to avoid past pitfalls such as vague targets, lack of integration, and funding shortfalls.
Significance of the Caribbean and North Brazil Shelf Region:
- Coral reefs and fisheries contribute ~$610 million annually to local economies
- The North Brazil Shelf is home to over 500 fish species
- Acts as a natural barrier against storms, crucial for climate resilience
Blue Carbon and Climate Action:
The OCM promotes blue carbon projects that utilize coastal ecosystems (like mangroves and seagrasses) for carbon storage, enhancing climate resilience and providing livelihoods to local communities.
Funding Details:
- $15 million from Global Environment Facility (GEF) via the UNDP/GEF PROCARIBE+ Project (2024–2028)
- Additional $126.02 million in co-financing mobilized
- However, the funding is modest compared to initiatives like the Global Fund for Coral Reefs (targeting $3 billion by 2030), raising concerns about OCM's long-term financial sustainability.
Role of IOC-UNESCO:
Established in 1961, the IOC of UNESCO promotes international cooperation in ocean science and policy. Key functions include:
- Marine scientific research (climate, biodiversity, sustainability)
- Tsunami warning systems
- Oceanographic data collection and dissemination
- Leading the UN Ocean Decade (2021–2030) for global marine conservation
Why OCM Matters:
- Addresses the Ocean–Climate–Biodiversity nexus
- Aims to ensure equitable access to marine resources
- Prioritizes local and vulnerable communities
- Integrates traditional knowledge with scientific research for culturally inclusive conservation
Saffron Reedtail Damselfly

- 02 Feb 2025
In News:
For the first time, the Saffron Reedtail Damselfly, a rare and endemic species of the Western Ghats, has been recorded in Karnataka.
This significant discovery was made in Madhugundi village, Chikkamagaluru district, along the Nethravati River. The findings were published in the journal Entomon.
Key Facts:
- Scientific Name: Indosticta deccanensis
- Common Name: Saffron Reedtail
- Family: Platystictidae (commonly known as shadow damselflies)
- Appearance: Slender, delicate body with a characteristic saffron coloration
- Habitat: Prefers slow-moving forest streams surrounded by thick vegetation; requires pristine water quality
Ecological Significance:
- Indicator Species: Highly sensitive to environmental changes and pollution, indicating a healthy, undisturbed ecosystem.
- Biodiversity Implication:
- Previously recorded only in Tamil Nadu and Kerala.
- The first sighting in Karnataka (northern Western Ghats) extends the known range of the species, suggesting it may be more widely distributed than earlier believed.
Conservation Relevance:
- The discovery underscores the ecological richness of the Madhugundi forests, which were severely affected by floods and landslides in 2019.
- Highlights the urgency to protect fragile ecosystems from deforestation, water pollution, and climate change, especially in biodiversity hotspots like the Western Ghats.
About Damselflies (Order: Odonata):
- General Features:
- Predatory, aerial insects
- Slender bodies with net-veined wings
- Fly weakly compared to dragonflies
- Mostly inhabit freshwater habitats
Rusty-Spotted Cat

- 01 Feb 2025
In News:
For the first time, the Rusty-Spotted Cat (Prionailurus rubiginosus) has been spotted in the forests of Purulia district, West Bengal, captured on a camera trap set up by the NGO HEAL during pangolin poaching surveillance. This marks a significant range extension and has excited conservationists and forest officials.
Key Features
- World’s smallest and lightest wild cat: Weighs between 900 grams to 1.5 kg
- Length: Approx. 1.5 feet, with a 1-foot-long tail
- Appearance:
- Fawn-grey coat with rusty red spots on back and flanks
- Short, rounded head with two white facial streaks
- Large eyes with greyish-brown to amber irises – an adaptation to nocturnal behavior
- Short legs, black-soled feet, and an unmarked rusty tail
- Behavior:
- Nocturnal and elusive
- Uses scent marking to establish territory
- Gestation period: 66–70 days
Habitat and Distribution
- Found in dry deciduous and semi-deciduous forests, including:
- Northern & Central India, Western Ghats, Rajasthan, Kachchh, and Peninsular India
- Also present in Sri Lanka and Nepal
- India hosts 80% of the global population
Conservation Status
- IUCN Red List: Near Threatened, due to habitat loss, fragmentation, and human-wildlife conflict
- Wildlife Protection Act, 1972: Schedule I species (highest protection)
Significance of Purulia Sighting
- Located on the eastern edge of the Chota Nagpur Plateau
- Forests are interconnected with neighboring regions like Jharkhand and Odisha
- Notified as reserved forests, not protected forests
- Threats: Hunting by local communities, habitat degradation
Impact of Conservation Efforts
- Post-COVID, the forest ecosystem in Purulia has improved due to reduced human disturbance
- Past sightings of leopards, bears, jackals, and foxes indicate a thriving ecosystem
- HEAL and the Forest Department have launched livestock compensation programs to reduce retaliatory killings of carnivores
Kurdistan Region
- 01 Feb 2025
In News:
India recently dispatched a humanitarian shipment of medical supplies to the Kurdistan Region in Iraq, reflecting its commitment to global cooperation and humanitarian diplomacy.
About the Kurdistan Region
- Geographical Spread: The Kurdistan Region is a culturally and geographically distinct area predominantly inhabited by ethnic Kurds, spread across:
- Northern Iraq (Erbil, Sulaymaniyah, Dohuk, Halabja)
- Eastern Turkey
- Western Iran
- Northern Syria and parts of Armenia
- Capital: Erbil (Iraq)
- Terrain: Dominated by the Zagros and Taurus mountain systems
- Major Rivers: Tigris River and Greater Zab River, crucial for agriculture and settlement
Ethnic and Political Context
- Kurds: An ethnic group of 25–30 million people, mostly Sunni Muslims, with no official nation-state. They seek autonomy or independence through the Kurdish nationalist movement.
- Kurdistan Regional Government (KRG): An autonomous administration in northern Iraq, managing the Kurd-majority areas with limited sovereignty under Iraq’s federal system.
- Geopolitical Significance:
- Rich in oil and natural gas, especially in Iraqi Kurdistan
- Strategically located, controlling key border regions and trade routes
- Kurdish militia (Peshmerga) played a critical role in the fight against ISIS
Ongoing Political Disputes
- Kurdish Independence Movement:
- The 2017 independence referendum in Iraqi Kurdistan was rejected by Baghdad, followed by economic and military backlash.
- Kurds face resistance from Iraq, Turkey, Iran, and Syria, which fear territorial fragmentation.
- Turkey regularly conducts military operations against Kurdish groups, labeling them as threats to national security.
India-Kurdistan Relations
- Diplomatic Presence: India established a Consulate in Erbil in August 2016 to deepen ties with the Kurdistan Region and Iraq.
- Economic and Workforce Engagement:
- Indian companies have participated in trade fairs in Erbil and Sulaymaniyah.
- A growing number of Indian workers are employed in sectors like:
- Steel mills
- Oil companies
- Construction projects
- Indian workers are valued for their skills and reliability in these industries.
Financialisation
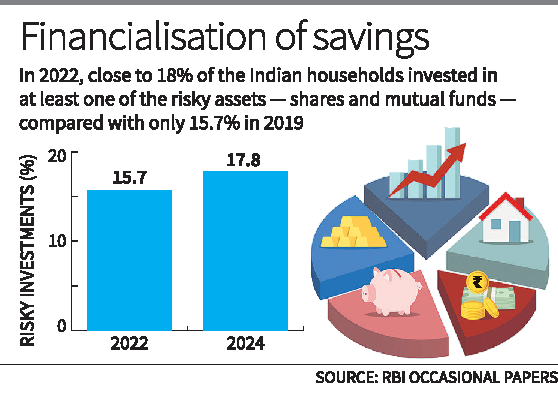
- 01 Feb 2025
In News:
The Economic Survey 2024–25 cautions against the risks of excessive financialisation in India, emphasizing that while finance is a crucial enabler of economic growth, unchecked expansion of the financial sector can pose systemic risks, increase inequality, and divert resources from the real economy.
What is Financialisation?
Financialisation refers to the growing dominance of financial markets, institutions, and motives in shaping economic policies, business decisions, and resource allocation. It involves:
- A shift from productive (real sector) activities like manufacturing to financial activities, including trading, speculation, and asset management.
- Increasing reliance on asset price growth (e.g., stocks, real estate) to stimulate the economy.
- Deep influence of financial motives in corporate governance, economic policies, and household behavior.
Key Drivers of Financialisation in India
- Increased household savings funneled into stock markets.
- Growing retail investor participation in equities and mutual funds.
- Policy and regulation increasingly influenced by financial market considerations.
- Rising public and private sector debt to leverage economic growth.
Risks Highlighted by the Economic Survey
- Real Sector Crowding Out: Over-expansion of the financial sector may compete with the real economy for scarce resources like skilled labour and capital, potentially depriving productive sectors.
- Unsustainable Booms: Rapid financial growth often favours high-collateral, low-productivity investments (e.g., construction) over innovation and manufacturing, creating unsustainable financial booms.
- Complex Financial Products: Proliferation of opaque and complex financial instruments can increase consumer risk exposure and the probability of a financial crisis, as seen during the 2008 global financial meltdown.
- Increased Inequality: Financialisation tends to transfer income from the real sector to the financial sector, worsening income inequality and contributing to wage stagnation.
- Debt Dependency: Over-reliance on financial leverage (debt) increases macro-financial vulnerabilities, especially if credit growth outpaces productive investment.
Global Lessons and Historical Context
- 2008 Global Financial Crisis: Reckless lending and financial engineering, including mortgage-backed securities, led to a global economic collapse. India was impacted indirectly, prompting RBI intervention to stabilise the economy.
- Examples from Ireland & Thailand: Rapid growth of private credit in these countries led to reduced productivity and economic distortions, serving as cautionary tales.
Balanced View on Finance
The Survey recognizes that a well-regulated financial system plays a vital role in:
- Channeling capital to innovative and high-risk ventures.
- Reducing transaction costs and improving price discovery.
- Alleviating poverty and inequality by enabling shock absorption for households and firms.
- Smoothing consumption across economic cycles.
However, the Survey emphasizes that there is a tipping point beyond which financial development becomes counterproductive.
Ultra-Processed Foods (UPFs)

- 01 Feb 2025
In News:
The Economic Survey 2024–25 underscores the adverse impact of Ultra-Processed Foods (UPFs) on public health, particularly among children and youth, and calls for urgent regulatory intervention.
Key Recommendations
- Stringent Front-of-the-Pack Labelling (FOPL): The Survey advocates for clear, enforceable FOPL rules to inform consumers, curb misleading nutrition claims, and restrict aggressive marketing, especially those targeted at children and adolescents.
- Stronger Role for FSSAI: The Food Safety and Standards Authority of India (FSSAI) is advised to:
- Define UPFs clearly in regulation.
- Establish labelling standards.
- Monitor compliance of branded products.
- ‘Health Tax’ Proposal: The Survey proposes higher taxes on UPFs, especially brands engaging in excessive advertising, to act as a deterrent and promote healthier food choices.
- Awareness and Education: It recommends targeted awareness campaigns in schools and colleges, integrated with broader health and lifestyle campaigns, to reduce the rising consumption of UPFs.
Why this matter
- Rising Consumption: According to a 2023 WHO report, India’s UPF consumption grew from $900 million (2006) to over $37.9 billion (2019).
- Long-term National Impact: India's ?2,50,000 crore UPF industry is built on hyper-palatability and is a threat to India’s demographic dividend, productivity, and future economic growth.
Health Risks of UPFs
- Directly linked to:
- Obesity
- Cardiovascular diseases
- Colorectal cancer
- Respiratory and gastrointestinal disorders
- Mental health issues, especially among youth
- Poor dietary intake due to UPFs contributes to micronutrient deficiencies, while synthetic additives may have long-term biological impacts.
What are Ultra-Processed Foods?
UPFs are industrial formulations that undergo extensive processing and typically include:
- Artificial flavours, colours, preservatives, emulsifiers, sweeteners, and other cosmetic additives.
- High sugar, salt, and fat content for taste enhancement.
- Low in essential nutrients such as vitamins, minerals, and fibre.
- Designed for convenience and high palatability, often leading to overconsumption.
Examples of Ultra-Processed Foods
(As per Indian Council of Medical Research - ICMR):
- Commercial bakery items: bread, cakes, biscuits, breakfast cereals
- Snack foods: chips, fries
- Condiments: sauces, jams, mayonnaise
- Dairy & protein products: processed cheese, butter, protein powders, soy chunks, tofu
- Frozen and ready-to-eat foods with additives
- Beverages: energy drinks, health drinks, sweetened fruit juices
- Refined flours of cereals, millets, legumes
- Culinary ingredients containing cosmetic additives like artificial colours or emulsifiers
India adds 4 new Ramsar Sites

- 01 Feb 2025
In News:
The Government of India has added four new Ramsar sites, increasing the total to 89, the highest in Asia and third globally. The newly designated wetlands include:
- Sakkarakottai Bird Sanctuary (Tamil Nadu)
- Therthangal Bird Sanctuary (Tamil Nadu)
- Khecheopalri Wetland (Sikkim)
- Udhwa Lake (Jharkhand)
This marks a significant milestone as Sikkim and Jharkhand have received their first Ramsar recognitions, while Tamil Nadu strengthens its lead with 20 Ramsar sites, the most among Indian states.
About the Ramsar Convention
- Adopted: 1971 in Ramsar, Iran
- Objective: Conservation and wise use of wetlands through local, national, and international cooperation.
- World Wetlands Day: Celebrated on 2nd February to promote awareness.
Key Highlights:
Therthangal Bird Sanctuary – Tamil Nadu
- Notified in 2010; covers 29.29 ha.
- Crucial breeding and foraging site for waterbirds like Spot-billed Pelican, Black-headed Ibis, and Oriental Darter.
- Aids groundwater recharge and climate regulation.
- Part of the Central Asian Flyway.
Sakkarakottai Bird Sanctuary – Tamil Nadu
- Notified in 2012; spans 230.49 ha.
- Located near Gulf of Mannar; significant stopover for migratory birds.
- Hosts endemic species and near-threatened fauna like Lion-tailed Macaque and Giant Squirrel.
Khecheopalri Wetland – Sikkim
- Sacred lake revered by Buddhists and Hindus; called Sho Dzo Sho locally.
- Known as a wish-fulfilling lake.
- Birds prevent leaves from settling on the surface.
- Rich in avifauna: fishing eagles, Brahminy kites.
- Integral to ecotourism and biodiversity conservation.
Udhwa Lake – Jharkhand
- Comprises Pataura Jheel (155 ha) and Brahma Jamalpur Jheel (410 ha).
- First Ramsar site of Jharkhand; near Ganga River.
- Declared a bird sanctuary in 1991; attracts migratory birds from September onwards.
Falls under the Gangetic Plains biogeographic zone.
MSME Trade Enablement and Marketing (TEAM) Initiative

- 31 Jan 2025
In News:
The Ministry of Micro, Small, and Medium Enterprises (MoMSME), in collaboration with the Open Network for Digital Commerce (ONDC), has launched the Trade Enablement and Marketing (TEAM) Initiative. It aims to promote digital commerce among micro and small enterprises (MSEs) in India.
Key Features of TEAM Initiative
- Scheme Under: Raising and Accelerating MSME Productivity (RAMP) Programme
- RAMP is a World Bank-supported Central Sector Scheme implemented from 2022–2027 to enhance market access, technology upgradation, and financial inclusion for MSMEs.
- Objective:
- To empower MSEs through digital commerce integration using ONDC.
- To formalize operations, reduce the cost of doing business, and expand market access.
- To ensure inclusivity with 50% of beneficiaries being women-led enterprises.
- Budget & Duration:
- ?277.35 crore over three years (FY 2024–25 to FY 2026–27).
- Target Beneficiaries:
- 5 lakh MSEs (50% women-led).
- Eligibility: Registered MSEs in manufacturing or service sectors with valid Udyam Registration. Medium enterprises are excluded from most benefits.
- Implementing Agency:
- National Small Industries Corporation (NSIC)
Operational Strategy
- ONDC Integration: MSMEs will be onboarded onto the ONDC network, enabling them to operate digital storefronts with access to interoperable platforms, seamless payment solutions, and logistics services.
- Workshops & Outreach:
- Over 150 workshops will be organized across Tier 2 and Tier 3 cities, especially targeting SC/ST-led and women-led enterprises.
- Workshops will provide training on creating digital catalogues, understanding digital platforms, and maximizing ONDC's benefits.
- Supportive Infrastructure: A dedicated digital portal will offer services including workshop registration, access to finance, grievance redressal, catalogue tools, and account management assistance.
- Financial Assistance: Support to Seller Network Participants for onboarding MSEs and assisting in operational and digital transition needs.
About ONDC:
An initiative of the DPIIT, Ministry of Commerce, ONDC is an open, interoperable network that allows buyers and sellers to transact across multiple digital platforms, aiming to democratize digital commerce and reduce platform monopolies.
National Critical Mineral Mission

- 31 Jan 2025
In News:
The Union Cabinet has launched the National Critical Mineral Mission (NCMM) with a total outlay of ?34,300 crore over seven years, including ?16,300 crore government expenditure and ?18,000 crore investment from PSUs and private players.
Key Highlights:
Objectives of NCMM
- Reduce import dependence on critical minerals vital for clean energy, electronics, defence, and high-tech industries.
- Promote domestic exploration, mining, processing, and recycling of critical minerals.
- Facilitate overseas acquisition of mineral assets.
- Strengthen India’s mineral security and ensure self-reliance (Atmanirbhar Bharat).
Key Features
- Value Chain Coverage: Exploration → Mining → Beneficiation → Processing → Recycling of end-of-life products.
- Fast-track regulatory approvals for mining projects.
- Creation of mineral processing parks and promotion of sustainable extraction technologies.
- Establishing a strategic stockpile of critical minerals.
- Development of a Centre of Excellence on Critical Minerals to support R&D.
- Expansion of PRISM initiative to fund startups and MSMEs in the sector.
- Whole-of-government approach: Collaboration among ministries, PSUs, private sector, and research institutions.
Why Critical Minerals Matter
Critical minerals are essential inputs for:
- Green energy: EV batteries, solar panels, wind turbines.
- Electronics: Semiconductors, fiber optics.
- Defence: Aircraft, missile guidance systems.
- Medical technologies: MRI machines, pacemakers.
India’s clean energy transition and manufacturing competitiveness hinge on a steady and secure supply of these minerals.
India’s Import Dependence
India is dependent on imports, especially from China, for several critical minerals like lithium, cobalt, titanium, graphite, and tellurium. This exposes India to supply chain vulnerabilities amid shifting global geopolitics.
List of 30 Critical Minerals for India
Includes: Lithium, Cobalt, Nickel, Graphite, Rare Earth Elements (REEs), Beryllium, Titanium, Tungsten, Gallium, Indium, Selenium, Cadmium, etc.
Strategic and Legislative Initiatives
- Amendment to MMDR Act (1957) in 2023: Enabled auction of 24 critical mineral blocks.
- OAMDR Act (2002) amendment: Introduced transparent offshore mineral exploration.
- Duty waivers in Union Budget 2024–25: Customs duties removed on key critical minerals to promote domestic processing.
- Exploration by GSI: 368 projects in last 3 years; 227 more planned for FY 2025–26.
- KABIL: Acquired 15,703 ha in Argentina for lithium mining.
Global Context
- Global powers (US, EU, Japan) are pursuing strategies for critical mineral security.
- China dominates refining of lithium, cobalt, and REEs.
- India is part of the Minerals Security Partnership (MSP) to diversify global mineral supply chains.
Significance for India
- Ensures long-term resource security for clean technologies.
- Supports EV and renewable energy manufacturing goals.
- Enhances strategic autonomy in defence and electronics.
- Makes India an attractive hub for foreign investment in green technologies.
Challenges and the Way Forward
- Geopolitical risks in overseas asset acquisition.
- Environmental impacts of large-scale mining.
- Need for strong R&D ecosystem, financial incentives, and public-private partnerships.
- Sustainable mining practices and global collaboration are essential for long-term success.
Contract Farming in India

- 31 Jan 2025
In News:
Contract farming has emerged as a significant model in India's agricultural landscape, especially with its success in processed potato cultivation and the recent rise in French fry exports. As the country transitions from being an importer to a major exporter in sectors like frozen French fries, the contract farming model underpins the structural transformation of Indian agriculture.
Understanding Contract Farming
Contract farming is an agricultural production system where farmers and buyers (agribusinesses, processors, exporters, or retailers) enter into a pre-harvest agreement. This contract outlines key parameters including price, quality, quantity, delivery schedules, and in many cases, input provision and technical assistance.
Types of Contract Farming Arrangements
- Direct Input Provision by the Company: Firms supply seeds, fertilizers, and support services, deducting costs from the final payment to farmers.
- Partnership with Local Input Dealers: A hybrid model balancing company control with third-party services, chosen based on crop complexity, local support availability, and firm capabilities.
Advantages of Contract Farming
- Stable and Enhanced Income: Contracts assure farmers of a fixed price and market access, shielding them from volatile markets. RBI data shows farmers typically receive only 31%–43% of consumer prices; contract farming can significantly improve this share.
- Access to Inputs and Technology: Companies provide high-quality seeds, fertilizers, training, and modern farming practices, leading to improved yields and quality.
- Post-Harvest Efficiency: Streamlined procurement reduces wastage of perishables and post-harvest losses, ensuring efficient supply chain management.
- Credit and Financial Support: Assured incomes help farmers access institutional credit, reducing dependency on informal lenders.
- Food Safety and Export Standards: Training on pesticide use and residue limits ensures compliance with international standards like Maximum Residue Limits (MRLs), boosting export potential.
- Consumer Benefits: Direct procurement reduces intermediaries, enabling competitive pricing and higher quality products.
- Technology Transfer: Farmers benefit from the introduction of new, high-efficiency production techniques.
Concerns and Challenges
- Power Imbalance: Small and marginal farmers often lack bargaining power. This dependency may lead to exploitative contracts or one-sided terms, especially where firms demand investments in crop-specific infrastructure.
- Market Risk and Default: Price volatility can lead to side-selling by farmers or contract breaches by firms when market prices crash.
- Delayed Payments and Inputs: Contractual delays in payment or input delivery can severely affect crop cycles and farmer finances.
- Exclusion of Marginal Farmers: For economies of scale, firms often prefer large landholders, sidelining smallholders.
- Environmental Impact: Monocropping, overuse of water and agrochemicals, and soil degradation threaten long-term sustainability.
- Food Security Trade-offs: A shift to high-value crops under contracts may reduce acreage for food crops, impacting local food security.
- Loss of Autonomy: Farmers may lose control over farming decisions, with firms determining most aspects of cultivation, leading to indirect control over land use.
Case Study: Contract Farming in Potato Sector
India is the second-largest potato producer globally, with Uttar Pradesh, West Bengal, and Bihar as leading states. The Central Potato Research Institute (CPRI), Shimla developed several high-yielding Kufri varieties to support commercial cultivation.
The success of processed potato farming is best illustrated by India’s emergence as an exporter of frozen French fries, driven by contract-based procurement from farmers. However, issues such as the PepsiCo vs. Indian farmers legal dispute over unauthorized cultivation of the FL 2027 variety underline ongoing concerns around intellectual property rights and farmers’ autonomy.
Policy and Legal Framework
- Model APMC Act, 2003: Introduced contract registration, dispute resolution, and exempted market fees while protecting land ownership.
- Model Agricultural Produce and Livestock Contract Farming Act, 2018: Proposed institutional frameworks, insurance provisions, and promotion of Farmer Producer Organizations (FPOs).
- e-NAM Integration: Supports transparent pricing and contract enforcement.
- National Agriculture Policy: Endorses contract farming as a tool for enhancing productivity and rural incomes.
Bharat Sovereign Wealth Fund (BSWF)

- 31 Jan 2025
In News:
India is actively exploring the creation of a Bharat Sovereign Wealth Fund (BSWF) or The Bharat Fund (TBF) to harness the untapped wealth embedded within its public sector ecosystem. This fund aims to unlock and strategically manage dormant capital, estimated at ?40 lakh crore ($450–500 billion), primarily held in equity stakes of around 80 listed public sector enterprises (PSEs) and banks.
What is a Sovereign Wealth Fund (SWF)?
A Sovereign Wealth Fund is a state-owned investment vehicle that manages national savings or surplus revenues—often derived from foreign exchange reserves, natural resource exports, or trade surpluses.
According to the Santiago Principles (2008), SWFs:
- Are owned by the general government (central or sub-national),
- Invest primarily in foreign financial assets, and
- Aim to achieve financial objectives rather than monetary policy.
Types of SWFs include:
- Stabilization Funds: Cushion fiscal shocks from revenue volatility.
- Future Generation Funds: Preserve wealth for long-term national benefit.
- Strategic Development Funds: Support priority sectors and national growth.
- Reserve Investment Funds: Enhance returns on foreign currency reserves.
Examples include:
- Norway’s Government Pension Fund Global ($1.7 trillion),
- China Investment Corporation ($1.35 trillion),
- Abu Dhabi Investment Authority ($993 billion).
India’s SWF Landscape and the BSWF Proposal
India previously explored SWF models in 2007–08 and again in 2010–11. While the National Investment and Infrastructure Fund (NIIF) was launched in 2015, it remains sector-specific and limited in scale. The proposed BSWF envisions a comprehensive and transformational fund akin to global best practices.
Key features of the BSWF proposal:
- Consolidation of government equity in PSEs and PSU banks under a professionally managed umbrella.
- Strategic divestment—e.g., reducing government stake from 51% to 40%—without losing operational control.
- Leveraging this pooled equity to attract global co-investors, potentially unlocking tens or hundreds of billions in foreign capital.
Why India Needs the Bharat SWF
- Wealth Unlocking: Potential monetization of over ?40 lakh crore in dormant government equity assets.
- Fiscal Prudence: Even a modest 2% annual divestment could yield $10+ billion, narrowing the fiscal deficit from 4.9% to ~4.6% of GDP.
- Strategic Sector Investment: Deployment into high-potential sectors—AI, semiconductors, electric vehicles, hydrogen energy, biotechnology—to drive innovation and economic leadership.
- Attracting Global Capital: Enhanced investor confidence, especially from established SWFs like those of Singapore, Norway, and Abu Dhabi, which are already increasing exposure in Indian equities and infrastructure.
- Social Sector Funding: Generate non-debt financial resources for welfare programs and national development missions.
- Soft Power Projection: Fund ventures, disaster relief, and advocacy efforts, strengthening India’s international standing.
Governance and Reform Imperatives
For the BSWF to succeed, it must:
- Be governed by a clear legal and regulatory framework aligned with Santiago Principles.
- Operate independently, with professional asset managers, market-based remuneration, and arm’s length oversight.
- Transition PSEs to function with autonomy and efficiency, reducing bureaucratic delays and enabling innovation.
- Foster joint ventures to turn around non-performing PSEs—among the 1,830 PSEs, around 400 remain non-functional, demanding nearly ?9 lakh crore annually in budgetary support.
Challenges and Concerns
- Macroeconomic Constraints: India faces a current account deficit and substantial fiscal pressures—conditions unlike traditional SWF-rich nations.
- Geopolitical and Market Risks: Global uncertainty and decoupling trends could impact cross-border investment strategies.
- Environmental and Technological Vulnerabilities: Investment risks in carbon-heavy sectors and exposure to data fraud or tech disruptions.
- Institutional Resistance: Political and bureaucratic inertia may delay implementation unless national interest is prioritized.
SWF Investments in India: A Growing Trend
Foreign SWFs are already deepening their footprint in India:
- $6.7 billion in direct investments in 2022 (up from $4.3 billion in 2021).
- Preferred sectors: healthcare, entertainment, renewables, infrastructure.
- Beneficiaries of tax exemptions on direct infrastructure investments via InVITS (Infrastructure Investment Trusts) and AIFs (Alternative Investment Funds), valid for investments made before March 31, 2024.
These incentives have encouraged foreign SWFs to explore establishing physical presence in India’s financial hubs, especially GIFT City, Gandhinagar.
Environment Protection (End-of-Life Vehicles) Rules, 2025
- 31 Jan 2025
In News:
MoEFCC Notifies Rules for End-of-Life Vehicles to Minimize Waste and Pollution.
Key Highlights:
Notified by: Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change (MoEF&CC)
Effective from: April 1, 2025
Legal Basis: Environment Protection Act, 1986
Objective: To promote environmentally sound management of end-of-life vehicles (ELVs), enable recycling and reuse of vehicle components, and reduce resource extraction, pollution, and waste generation.
Key Features of the ELV Rules, 2025
1. Scope and Coverage
- Applicable to all vehicle categories including electric vehicles (EVs), e-rickshaws, and e-carts.
- Exempted vehicles: Agricultural tractors, trailers, combine harvesters, and power tillers.
- Exempted waste types: Batteries, plastics, tyres, used oil, and e-waste (governed under separate waste management rules).
2. Extended Producer Responsibility (EPR)
- Vehicle producers are mandated to meet annual scrapping targets based on the age of vehicles:
- Transport vehicles: 15 years
- Non-transport vehicles: 20 years
- Producers must fulfill their EPR obligations for all vehicles introduced into the domestic market, including those used internally.
- Annual EPR declarations must be submitted to the Central Pollution Control Board (CPCB) by April 30 each year.
- Producers must promote ELV deposition at designated collection centres or Registered Vehicle Scrapping Facilities (RVSFs).
3. Responsibilities of Stakeholders
- Registered Owners & Bulk Consumers: Required to deposit ELVs at designated centres or RVSFs within 180 days of becoming unfit.
- Collection Centres:
- Handle ELVs in an environmentally responsible manner.
- Maintain records and ensure safe storage and transfer to RVSFs.
- Registered Vehicle Scrapping Facilities (RVSFs):
- Undertake depollution, dismantling, segregation, and recycling.
- Ensure environmentally sound disposal of non-recyclables via authorized TSDFs.
- Issue EPR certificates based on the volume of steel processed; valid for 5 years.
4. Monitoring, Compliance, and Penalties
- CPCB and State Pollution Control Boards (SPCBs) are responsible for:
- Registration, inspection, and audit of producers, RVSFs, and bulk consumers.
- Taking action against non-compliance, including suspension or cancellation of registration.
- Levying environmental compensation for violations that cause harm to public health or the environment.
5. Registration & Certification
- Producers register with CPCB; RVSFs and bulk consumers with respective SPCBs.
- Registration certificates are issued within 15 days of application via a centralized online portal.
- EPR certificates are non-transferable and allow adjustment of both current and backlog obligations.
Related Policy and Incentives by MoRTH
The Ministry of Road Transport and Highways (MoRTH) supports the ELV Rules through:
- Vehicle Scrapping Policy: Targets voluntary phasing out of unfit and polluting vehicles.
- Motor Vehicles (Registration and Functions of Vehicle Scrapping Facility) Rules, 2021: Provides operational criteria for RVSFs.
- Central Motor Vehicles (Amendment) Rules, 2021:
- Waiver of registration fee for buyers submitting ELV Certificates of Deposit.
- Concession in motor vehicle tax: 25% for non-transport, 15% for transport vehicles.
Electric Mobility Push
- MoRTH has issued several notifications promoting EVs, including:
- Permit exemptions for battery-operated and ethanol/methanol-fueled vehicles.
- Fee exemptions for registration and renewals.
- Tourist permit benefits for EVs and distinct registration marks for visibility.
PM E-DRIVE Scheme
- Launched by Ministry of Heavy Industries on 29th September 2024 with a ?10,900 crore outlay.
- Aims to support electric 2-wheelers, 3-wheelers, ambulances, trucks, and buses with ?3,679 crore in demand incentives.
- Targets subsidization of over 28 lakh EVs.
F11 Bacteria

- 30 Jan 2025
In News:
A recent scientific study has identified a bacterial strain, Labrys portucalensis F11 (commonly referred to as F11), capable of degrading per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) — popularly known as “forever chemicals” — by breaking their strong carbon-fluorine (C-F) bonds.
About F11 Bacteria:
- Scientific Name: Labrys portucalensis F11
- Family: Xanthobacteraceae
- Nature: Aerobic and pollutant-resistant bacterium
- Origin: Isolated from industrially contaminated soil in Portugal
- Significance:
- Adapted to thrive in toxic environments
- Uses environmental contaminants as an energy source
- Capable of degrading at least three types of PFAS and certain toxic byproducts
What Are Forever Chemicals (PFAS)?
- Definition: A group of synthetic, man-made chemicals known for their extremely strong C-F bonds, making them persistent and non-biodegradable.
- Why Called 'Forever':
- Resistant to natural breakdown
- Found in air, rainwater, and soil for decades or longer
- Health & Environmental Hazards:
- Linked to cancer, hormonal disorders, immune dysfunction, and environmental toxicity
- Migrate into soil, water, and air during production and use
- Regulation: Certain PFAS are listed under the Stockholm Convention on Persistent Organic Pollutants
Relevance for India and the World:
- Global Impact:
- PFAS are used in a wide range of consumer products such as non-stick cookware, firefighting foams, and food packaging.
- Their persistence poses long-term risks to public health, groundwater contamination, and biodiversity.
- India's Concern:
- Increasing industrialization and waste mismanagement heighten PFAS exposure risks.
- No comprehensive PFAS regulation in place yet; calls for adopting stringent environmental safety norms.
WHO Guidelines on Lower-Sodium Salt Substitutes (LSSS)
- 30 Jan 2025
In News:
Recently, the World Health Organization (WHO) issued new guidelines promoting the use of Lower-Sodium Salt Substitutes (LSSS) to tackle the global burden of hypertension, cardiovascular diseases (CVDs), and stroke, which are largely driven by excessive sodium consumption. This is especially relevant for countries like India, with a high prevalence of high blood pressure and salt consumption.
What Are Lower-Sodium Salt Substitutes (LSSS)?
- LSSS are alternatives to regular table salt, where sodium chloride (NaCl) is partially replaced by potassium chloride (KCl), magnesium sulphate, or calcium chloride.
- They are designed to retain the taste of regular salt while significantly reducing sodium intake and improving heart health.
- LSSS can help lower blood pressure, thanks to the potassium content, which helps balance fluid levels and offset sodium’s harmful effects.
Key WHO Recommendations:
- Daily sodium intake should be restricted to less than 2 grams per day, equivalent to about 5 grams of salt.
- Avoid regular table salt, and replace it, wherever safe, with LSSS for household use.
- LSSS use is not recommended for:
- Pregnant women
- Children
- Individuals with kidney impairments or those requiring low-potassium diets
- The guidelines do not apply to packaged or restaurant foods, which are major contributors to overall sodium intake.
Why Is This Important or India?
- Salt Intake in India: Average salt consumption is 10.4 grams/day, over double the WHO recommendation.
- Hypertension Prevalence: Over 35.5% of India’s population (approx. 315 million people) suffers from hypertension (INDIAB Study).
- CVD Burden: Cardiovascular diseases accounted for 28.1% of all deaths in India (2016) – Global Burden of Disease Study.
- Dietary Impact: Globally, 8 million deaths annually are diet-related, with 1.9 million directly linked to high sodium intake.
Implementation and Policy Measures:
- India’s Response:
- The Food Safety and Standards Authority of India (FSSAI) has initiated sodium reduction policies.
- Edible salt must contain 97% sodium chloride, with anticaking agents limited to 2.2%.
- New labelling norms enforce accurate “low sodium” and “sodium-free” claims.
Public Health and Safety Considerations:
- While LSSS are safe and beneficial for most adults, excess potassium can cause hyperkalemia, especially dangerous for those with kidney disease.
- WHO guidelines aim to maximize benefits and minimize risks by promoting regulated, evidence-based usage.
- Governments, policymakers, and health professionals are urged to integrate LSSS into public health strategies, especially in high-risk populations.
About WHO:
- Established in 1948, the World Health Organization is the UN agency dedicated to promoting global health, preventing disease, and coordinating international health responses.
- It leads efforts for universal health coverage and responds to global health emergencies.
Aroma Mission

- 30 Jan 2025
In News:
The Aroma Mission, also known as the Lavender Revolution, is emerging as a transformative initiative for regions like Jammu & Kashmir and the North East, prioritised under Prime Minister Narendra Modi’s vision for inclusive development.
It aims to harness the untapped potential of India’s biodiverse regions through the scientific cultivation of aromatic crops and production of essential oils, with the dual goals of economic upliftment and sustainable innovation.
Key Objectives and Features:
- Launched By: Ministry of Science & Technology
- Nodal Agency: CSIR-Central Institute of Medicinal and Aromatic Plants (CIMAP), Lucknow
- Started In: Jammu & Kashmir, now extended to the North East
- Known As: Lavender Revolution
- Purpose: Boost India’s aroma industry by promoting the cultivation of high-value aromatic crops and increasing the production of essential oils.
Major Focus Areas:
- Crops Cultivated: Lavender, lemongrass, citronella, palmarosa, vetiver, patchouli, rose, peppermint, and chamomile
- Target Sectors: Cosmetics, aromatherapy, pharmaceuticals, and food flavouring industries
Impact and Achievements:
- Over 5,000 hectares brought under aromatic crop cultivation in the North East.
- Establishment of 39 essential oil distillation units.
- Distribution of 1 lakh agarwood saplings planned to boost the region's share in global aromatic plant trade.
- Expected annual essential oil production: 2,000 tonnes, valued at over ?300 crores.
- Estimated to generate 60 lakh man-days of rural employment.
- Projected increase in farmers’ income by ?60,000–?70,000 per hectare annually.
Institutional Support: IICON – Incubation and Innovation Complex
- Location: CSIR-North East Institute of Science and Technology (CSIR-NEIST), Jorhat, Assam
- Launched By: Dr. Jitendra Singh (Minister of Science & Technology)
- Purpose: Provide technical assistance, advanced facilities, and business incubation support for startups, MSMEs, and SHGs.
- Facilities: Access to 27 cutting-edge technologies for up to two years to help refine production and marketing strategies.
Integrated Development Approach:
The Aroma Mission exemplifies the “whole-of-government” approach, aligning with various flagship programmes such as:
- Start-Up India
- MSME Development
- Doubling Farmers’ Income
- Women Empowerment (e.g., through Rural Women Technology Parks)
- Act East Policy (enhancing North East's connectivity and trade potential)
Over 25 startups and self-help groups have already been empowered through access to facilities and entrepreneurial training at IICON, contributing to local innovation ecosystems.
Strategic Significance:
- Regional Empowerment: Converts underutilised natural resources into economic assets, especially in remote regions like J&K and the North East.
- Environmental Sustainability: Encourages eco-friendly cultivation and reduces pressure on traditional farming.
- Economic Diversification: Supports India’s transition to a bio-economy, with aromatic plant industries offering export potential and rural employment.
- Vision India@2047: Positions the North East as a hub for biotechnology, essential oils, innovation, and trade, aligning with long-term national growth goals.
Olive Ridley Turtles
- 30 Jan 2025
In News:
The Rushikulya river mouth in Odisha is witnessing the anticipated mass nesting of Olive Ridley turtles — a critical event for the survival of this vulnerable marine species. This phenomenon, known as arribada, highlights the ecological significance of India’s coastal biodiversity and the urgent need for marine conservation.
About Olive Ridley Turtles (Lepidochelys olivacea)
- Taxonomy:
- Scientific Name: Lepidochelys olivacea
- Class: Reptilia
- Family: Cheloniidae
- Physical Features: These turtles are the smallest and most abundant of all sea turtle species. They are recognized by their olive or grayish-green heart-shaped carapace. Males and females are similar in size, though females have slightly rounder shells.
- Habitat and Distribution: Olive Ridleys are found in warm, tropical waters of the Pacific, Atlantic, and Indian Oceans, inhabiting both open ocean (pelagic) and coastal waters.
Mass Nesting: The Arribada Phenomenon
- Arribada (Spanish for "arrival") refers to the synchronized mass nesting behavior where thousands of females gather on a single beach to lay eggs.
- Nesting occurs annually between December and March, after long migrations of up to 9,000 km. Each female may lay 90–120 eggs, 1 to 3 times per season.
- Temperature-dependent sex determination influences hatchling sex ratios.
- After nesting, females return to the sea, leaving eggs buried in sand.
Major Nesting Sites in India
- Odisha Coast is the most significant nesting ground in India and globally:
- Gahirmatha Marine Sanctuary: World’s largest mass nesting site.
- Rushikulya River Mouth: Second-largest nesting beach in India.
- Devi River Mouth: Another key nesting site in Odisha.
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands have recently emerged as a new mass nesting area, with over 5,000 nests reported in one season.
Ecological Role and Behavior
- Diet: Omnivorous — they feed on jellyfish, crabs, snails, prawns, molluscs, algae, and small fish.
- Behavior: These turtles undertake long migrations annually between feeding and breeding grounds, spending most of their lives at sea.
Protection Status
- IUCN Red List: Vulnerable
- CITES: Appendix I
- Wildlife (Protection) Act, 1972 (India): Schedule I (highest protection)
Threats to Survival
- Bycatch in Fishing Gear: Accidental entanglement in trawls, gillnets, and longlines.
- Habitat Loss: Coastal development for ports, tourism, and industry disrupts nesting beaches.
- Poaching: Turtles and their eggs are harvested for meat, shell, and leather.
- Pollution: Plastic ingestion and marine debris pose severe health risks.
- Climate Change: Rising sea levels and increased sand temperatures impact nesting and hatchling sex ratios.
Conservation Initiatives
- Operation Olivia: Initiated by the Indian Coast Guard in the 1980s to protect turtles during nesting and prevent illegal fishing.
- Turtle Excluder Devices (TEDs): Mandated by the Odisha government in trawl nets; allow turtles to escape while retaining fish catch.
- Tagging Programs: Use of non-corrosive metal tags to study migration patterns and inform conservation strategies.
Global Investment Trends and India’s FDI Outlook

- 30 Jan 2025
In News:
The Global Investment Trends Monitor Report 2024, released by the United Nations Conference on Trade and Development (UNCTAD), highlights a concerning decline in international project finance and Foreign Direct Investment (FDI), particularly in developing economies. This has significant implications for sustainable development, especially in emerging economies like India.
Key Findings from the UNCTAD Report (2024)
Global FDI Trends:
- Global FDI flows, after adjusting for conduit economies, fell by 8% in 2024, despite a nominal increase to USD 1.4 trillion.
- Developed economies witnessed a 15% drop in FDI (excluding conduit economies like Ireland and Luxembourg), while developing economies saw a 2% decline.
- The decline threatens long-term investment in infrastructure, renewable energy, and other SDG-aligned sectors.
Project Finance and Greenfield Investment:
- International project finance declined by 29% in developed and 23% in developing economies.
- In terms of value, developing economies faced a sharper fall of 33%.
- Key countries like India, China, Brazil, Indonesia, and Mexico reported steeper declines than the global average.
- Greenfield investments fell 6% in developing regions, with Africa and Asia being worst affected.
Sectoral Impacts:
- Investments in SDG-related sectors (e.g., water, sanitation, agrifood systems, and infrastructure) declined by 11%.
- International renewable energy finance fell 16%, with North America (-22%) and developing Asia (-18%) seeing notable contractions.
- Africa was the only region to witness an 8% increase in renewable energy project finance.
India’s FDI Landscape: Trends, Opportunities, and Challenges
Recent Performance:
- Between April 2000 and September 2024, India received over USD 1 trillion in cumulative FDI.
- From 2014 to 2024, India attracted USD 667.4 billion, a 119% increase over the previous decade.
- In 2024, India’s greenfield projects grew, but international project finance fell 23% in number and 33% in value.
Regulatory Framework:
- FDI is regulated under the Foreign Exchange Management Act (FEMA), 1999, administered by DPIIT, Ministry of Commerce and Industry.
- Prohibited sectors: Atomic energy, betting, lotteries, chit funds, tobacco, and real estate (excluding construction development).
Outlook for 2025 and Strategic Opportunities
Global FDI Projections:
- UNCTAD anticipates moderate global FDI growth in 2025.
- Regions like ASEAN, Eastern Europe, and Central America may benefit from supply chain realignments.
- India is projected to see a moderate rise in FDI, aided by:
- Improved financing conditions,
- Mergers and acquisitions,
- Ongoing policy reforms.
Key Growth Sectors:
- High potential in AI, cloud computing, cybersecurity, electric vehicles, and green hydrogen.
- FDI will be influenced by geopolitical dynamics, interest rates, GDP growth, and technological transitions.
FDI in India: Opportunities and Challenges
Opportunities:
- Large consumer base (1.4 billion population) and young workforce (65% under 35).
- Government schemes like Make in India and Atmanirbhar Bharat incentivize foreign investment.
- Strategic location positions India as a gateway to South Asia, the Middle East, and Southeast Asia.
Challenges:
- Regulatory complexity, including retrospective taxation and bureaucratic delays.
- Infrastructure deficits, particularly outside urban hubs.
- Rigid labour laws and inconsistent policy enforcement.
Investor Expectations:
- Technology transfer in priority sectors.
- Employment generation to absorb India’s growing labor force.
- Sustainable investments in line with India’s climate commitments under the National Action Plan on Climate Change.
Asian Waterbird Census 2025

- 29 Jan 2025
In News:
As per the Asian Waterbird Census-2025, a record number of 39,725 birds belonging to 106 species have been sighted in the Coringa Wildlife Sanctuary and adjoining wetlands.
Asian Waterbird Census (AWC): An Overview
- AWC is an annual citizen-science programme that supports the conservation of wetlands and waterbirds across Asia.
- Initiated in 1987 in the Indian subcontinent, it now covers extensive regions of East and Southeast Asia, Japan, Australasia, and parts of the Central Asian and East Asian–Australasian Flyways.
- AWC is the Asian chapter of the global International Waterbird Census (IWC).
- In India, it is coordinated by the Bombay Natural History Society (BNHS) and the Wildlife Institute of India (WII) every January.
About BNHS (Bombay Natural History Society)
- An Indian NGO engaged in biodiversity research and conservation.
- Recognized as a Scientific and Industrial Research Organisation (SIRO) by the Department of Science and Technology.
- Official partner of BirdLife International in India.
Coringa Wildlife Sanctuary (Andhra Pradesh): Census Findings 2025
- The Asian Waterbird Census 2025 recorded a record 39,725 birds representing 106 species in the Coringa Wildlife Sanctuary (CWS) and adjoining Godavari estuary wetlands.
- Of these, nearly 70 species are migratory, using the site as a key winter feeding ground.
Species of Conservation Concern
- Endangered species sighted:
- Indian Skimmer (Rynchops albicollis) – ~450 individuals sighted
- Black-bellied Tern (Sterna acuticauda)
- Great Knot (Calidris tenuirostris)
- Vulnerable species: Common Pochard (Aythya ferina)
- Near Threatened species: 11 species identified
Migratory Pathways and Monitoring
- Migrants such as the Great Knot travel from Russia, Siberia, China, and Mongolia to the Godavari estuary.
- A tagged Great Knot, tracked from Russia, was recorded after a 7,500 km journey, seen in Bhairavapalem mudflat and Etimoga wetland in successive winters (2024 and 2025).
- Data sharing with global avian research groups aids in tracking migratory patterns and supports conservation of endangered species.
Ecological and Ramsar Significance
- The Godavari estuary supports feeding grounds for nearly 90,000 birds, as observed by CWS authorities.
- Avian diversity is a key criterion for Ramsar Site designation, and experts advocate for Coringa Wildlife Sanctuary and its surroundings to be recognized as a wetland of international importance under the Ramsar Convention.
Resumption of Kailash Mansarovar Yatra
- 29 Jan 2025
In News:
After a four-year hiatus due to the COVID-19 pandemic and the 2020 Galwan Valley clash, India and China have agreed to resume the Kailash Mansarovar Yatra in June 2025, along with other confidence-building measures.
This decision aligns with the 75th anniversary of India-China diplomatic relations, symbolizing an attempt to stabilize and recalibrate bilateral ties through people-centric initiatives.
Key Highlights:
Key announcements include:
- Resumption of the Kailash Mansarovar Yatra
- Restoration of direct air services
- Visa issuance for journalists and think tanks
- Hydrological data sharing and cooperation on trans-border rivers
- Enhanced people-to-people exchanges and academic/media dialogues
About the Yatra
- The Yatra involves a pilgrimage to Mount Kailash and Lake Mansarovar in the Tibetan Autonomous Region (Xizang).
- Organised by India’s Ministry of External Affairs between June–September, via two routes:
- Lipulekh Pass (Uttarakhand)
- Nathu La Pass (Sikkim)
- Supported by the state governments of Uttarakhand, Sikkim, and Delhi, and coordinated with the Indo-Tibetan Border Police.
- Open only to Indian citizens with valid passports; no financial subsidy is provided by the Government of India.
Geographical and Religious Significance:
- Mount Kailash, located in the Kailash Range (Transhimalaya), is the source of four major rivers: Sutlej, Brahmaputra, Indus, and Karnali.
- Revered across religions:
- Hindus consider it the abode of Lord Shiva; Mansarovar is one of the 51 Shaktipeeths.
- Buddhists and Tibetans regard it as the ‘Stairway to Heaven’.
- Jains believe Rishabhanatha attained enlightenment here—referred to as Ashtapada.
Diplomatic Interpretations and Differences
- India’s Position: Emphasized a step-by-step, cautious approach focusing on rebuilding trust and resolving contentious issues, particularly the border situation. India sought policy predictability and transparency in trade, and reaffirmed the importance of mutual respect and interests.
- China’s Position: Took a more optimistic and strategic stance, stressing the need to avoid "mutual suspicion" and to advance cooperation based on long-term national interests. It emphasized early action, including the swift resumption of the Yatra and flights.
Ongoing Concerns in Bilateral Relations
- Unresolved Border Disputes:
- Tensions persist along the Line of Actual Control (LAC)—notably in Galwan (2020) and Tawang (2022).
- India and China have made limited progress in resolving issues in Depsang and Demchok.
- Trade Imbalance:
- Bilateral trade in 2023–24 stood at USD 118.4 billion, with India facing a trade deficit of USD 85 billion.
- India raised concerns on market access and non-tariff barriers.
- China-Pakistan Axis:
- The China-Pakistan Economic Corridor (CPEC) runs through Pakistan-occupied Kashmir, violating India’s territorial sovereignty.
- China’s support for Pakistan in multilateral forums remains a thorn in bilateral ties.
- China’s Regional Assertiveness:
- Expanding influence in South Asia and the Indian Ocean through the String of Pearls, strategic presence in Maldives, Sri Lanka, and strong claims in the South China Sea, contribute to regional unease.
Significance of the Current Diplomatic Thaw
- The resumption of the Kailash Mansarovar Yatra reflects a symbolic softening in ties, emphasizing religious diplomacy and people-to-people connection.
- Restoration of direct flights and journalistic presence can aid in reducing mistrust.
- Hydrological cooperation, particularly over the Brahmaputra River, is essential for India’s water security, especially with China constructing mega-dams upstream.
Way Forward
- Rebuild Trust Through Engagement: Maintain diplomatic dialogues via platforms like BRICS, SCO, and G20, while holding to core national interests.
- Resolve Border Disputes: Pursue early finalization of the LAC through confidence-building agreements and military disengagement.
- Diversify Economic Strategy: Reduce dependency on Chinese imports by strengthening domestic manufacturing and regional trade alternatives.
- Enhance Cultural Diplomacy: Use platforms like the Kailash Yatra to foster mutual understanding rooted in shared civilizational values.
- Promote Transparency and Reciprocity: Especially in media, trade, and information sharing, to ensure balanced bilateral engagement.
DeepSeek AI
- 29 Jan 2025
In News:
DeepSeek, a Chinese artificial intelligence (AI) startup based in Hangzhou, has emerged as a major player in the global AI race with the release of its models DeepSeek-V3 and DeepSeek-R1.
These models are designed to rival top-tier Western counterparts such as OpenAI’s GPT-4, Google’s Bard, and Meta’s LLaMA, but at a fraction of the cost.
Key Developments and Technological Edge
- Cost Efficiency: DeepSeek-V3 was trained at a cost of under $6 million, using older Nvidia H800 chips, compared to the estimated $100 million cost of GPT-4. Its subscription fee is significantly lower—$0.50/month versus $20/month for ChatGPT.
- Model Performance:
- DeepSeek-R1, a “reasoning model,” reportedly matches OpenAI’s o1 model in mathematics, coding, and contextual processing, while using fewer resources through incremental reasoning.
- Models use Mixture-of-Experts (MoE) architecture, reinforcement learning, and self-improvement loops, making them more memory-efficient and scalable.
- Advanced Models Released:
- DeepSeek Coder / Coder-V2 (for coding tasks).
- DeepSeek LLM (67B parameters), V2, V3 (671B parameters), and R1-Distill (fine-tuned using synthetic data).
Global Impact and Market Disruption
- App Success & Outages: The DeepSeek AI app topped the U.S. App Store, surpassing ChatGPT. This success triggered large-scale cyberattacks and caused temporary service disruptions.
- Market Reaction: The launch reportedly led to a historic $600 billion drop in Nvidia's market value, highlighting the disruptive potential of cost-efficient AI innovation.
- Geopolitical Ramifications: The rise of DeepSeek is seen as a technological parallel to the 1957 Sputnik moment, which shocked the U.S. and triggered the space race.
DeepSeek has reignited US-China AI rivalry, intensifying great-power competition in frontier technologies.
Strategic Lessons for India
- Bipolar AI Landscape: The U.S. and China dominate AI due to massive investment and infrastructure. Middle powers like India and France face the challenge of staying relevant without matching this scale.
- Doing More with Less: DeepSeek’s success underscores how innovation with limited resources can be effective—providing a model for India to emulate via Small Language Models (SLMs) and cost-efficient AI strategies.
- Sovereign AI & Global Governance:
- India advocates for “Sovereign AI”, balancing independence and strategic alliances, especially with France and the U.S.
- Future cooperation between U.S. and China on AI governance, similar to Cold War-era nuclear agreements, is a possibility.
- India must learn from past exclusions (e.g., nuclear governance) and proactively shape global AI governance frameworks.
- Policy Implications:
- DeepSeek's rise may lead to stricter U.S. chip export restrictions to China.
- It presents both security risks (censorship, pro-China bias) and opportunities (cost-effective models, domestic self-reliance).
Ethical Concerns and Limitations
- Censorship: DeepSeek complies with Chinese state censorship, refusing responses on politically sensitive topics (e.g., Tiananmen Square), raising concerns about bias and lack of transparency.
Security & Privacy: Experts have flagged potential data privacy and AI ethics issues, emphasizing the need for robust global standards and accountability mechanisms.
Indian Squid

- 29 Jan 2025
In News:
Researchers at the Central Marine Fisheries Research Institute (CMFRI), Kochi, have successfully decoded the gene expression pattern of the Indian squid (Uroteuthis duvaucelii), marking a major scientific advancement with wide-ranging implications for neuroscience, environmental studies, and sustainable marine resource management.
About Indian Squid
- Common Name: Indian Calamari
- Scientific Classification: Cephalopod
- Size: Typically 20–30 cm; can grow up to 50 cm
- Appearance: Light pinkish-grey body with two large fins, eight arms, and two longer tentacles used for capturing prey
- Key Abilities:
- Camouflage
- Jet propulsion for rapid movement
- Advanced nervous system
- Problem-solving skills and behavioral intelligence
Habitat & Distribution
- Preferred Habitat: Coastal and open sea regions of the Indian Ocean
- Found at depths ranging from 100 to 500 meters, some even up to 1,500 meters
- Requires high dissolved oxygen levels for respiration
- Geographic Distribution:
- Widely distributed in the Indo-West Pacific
- Found in Indian Ocean, Red Sea, Arabian Sea, from Mozambique to the South China Sea, Philippine Sea, and northward to Taiwan
- Conservation Status: IUCN Red List: Least Concern
Scientific Significance of Genetic Research
- Key Findings:
- Revealed genetic similarities with higher vertebrates like fish and humans, suggesting deep evolutionary links
- Indicates that Indian squid could serve as a model organism to study brain evolution, intelligence, and neurobiological functions
- Potential to inform research in neural circuits, memory, learning, and even neurological diseases
- Findings may also explain squid's adaptive success, such as evading predators and fishing pressures due to high cognitive ability
Institutional Background: CMFRI
- Established: 1947
- Affiliation: Part of the Indian Council of Agricultural Research (ICAR) since 1967
- Headquarters: Kochi, Kerala
- Mandate: Research on sustainable marine fisheries and ecosystem conservation
CMFRI’s Broader Recommendations for Sustainable Marine Management
- Enactment of Sea Fishing Act to regulate fishing beyond territorial waters
- Institutionalization of ecological stock assessments for sustainable exploitation
- Simplification and promotion of open mariculture with focus on environmental sustainability
- Use of AI-based systems to estimate landings and monitor fishing vessels
- Deep-sea resource exploration and alternative fishing methods
- Institutional mechanism for supervising deep-sea fishing
- Strengthening insurance coverage for marine fishers
RBI Payment System Report 2024

- 29 Jan 2025
In News:
The Payment System Report – December 2024 is a bi-annual publication by the Reserve Bank of India (RBI).
It analyses trends in digital and retail payment systems over the last five calendar years (up to CY-2024) and highlights India's transformation into a global leader in payment innovation and inclusion.
Growth in Digital Transactions
- Exponential Growth: Digital payment transactions rose 94 times in volume (from 222 crore in 2013 to 20,787 crore in 2024) and 3.5 times in value (from ?772 lakh crore to ?2,758 lakh crore).
- Recent CAGR (2019–2024):
- Volume: 45.9% CAGR
- Value: 10.2% CAGR
- Retail Digital Payments: From 162 crore transactions in FY13 to 16,416 crore in FY24 — a 100-fold increase in 12 years.
- Digital Payments Index (DPI): Surged from a base of 100 in March 2018 to 445.50 in March 2024, indicating massive digital adoption.
UPI: A Game-Changer
- Launched in 2016 by NPCI, UPI has revolutionized mobile-based payments.
- CAGR (Last 5 Years):
- Volume: 74.03%
- Value: 68.14%
- Monthly Transactions: UPI processes over 16 billion transactions monthly, ranking among the largest globally.
- Inclusive Innovations:
- UPI Lite & UPI Lite X: For offline/small-value payments.
- UPI123Pay: For feature phone users.
- UPI 2.0: Includes auto-debit and recurring payment functionalities.
Credit and Debit Card Trends
- Credit Cards:
- Growth: More than doubled from 5.53 crore (Dec 2019) to 10.80 crore (Dec 2024).
- Debit Cards:
- Stable Usage: Marginal increase from 80.53 crore to 99.09 crore in the same period.
Cross-Border Payment Integration
- RBI is actively enhancing cross-border payments by integrating India's UPI with international Fast Payment Systems (FPSs), addressing high costs, delays, and limited access.
- Key Developments:
- UPI-PayNow Linkage (Feb 2023): India-Singapore real-time cross-border payments.
- UPI-enabled QR Payments: Available in Bhutan, France, Mauritius, Nepal, Singapore, Sri Lanka, UAE.
- Project Nexus:
- A BIS-conceptualized multilateral project.
- Aims to interlink FPSs of India, Malaysia, Philippines, Singapore, and Thailand for seamless retail payments.
Institutional and Legal Framework
- Legal Backbone: Payments and Settlement Systems Act, 2007 (PSS Act) empowers RBI to:
- Regulate, supervise, and license payment system operators.
- Authorize systems like NPCI, card networks, ATM operators, etc.
- Governing Body:
- Board for Regulation and Supervision of Payment and Settlement Systems (BPSS) under RBI.
- Chairperson: RBI Governor; Vice-Chairperson: Deputy Governor (in charge of DPSS).
- Payment Ecosystem Entities:
- RBI-regulated: RTGS, NEFT, Cheques (CTS).
- NPCI-managed: UPI, IMPS, AePS, BBPS, NETC, NACH, Cards.
- Other PSOs: TReDS, PPIs.
Strategic Significance
- Financial Inclusion: Payment systems are critical tools for promoting inclusive growth by ensuring last-mile delivery of services and direct benefit transfers.
- Global Competitiveness: RBI’s regulatory foresight and innovation have placed India among the global frontrunners in digital payments.
Libia Lobo Sardesai

- 28 Jan 2025
In News:
In 2024, at the age of 100, Libia Lobo Sardesai was awarded the Padma Shri for her pivotal role in Goa’s liberation struggle from Portuguese colonial rule.
About Libia Lobo Sardesai
- Born: 25 May 1924, in Portuguese-ruled Goa; raised in Mumbai.
- Profession: Freedom fighter, broadcaster, and Goa’s first Director of Tourism post-liberation.
- Legacy: Symbol of courage and resistance, known as the “voice of Goa’s liberation.”
Role in Goa’s Liberation Movement
- Involvement: Joined the Goan nationalist movement during her college years.
- Underground Radio:
- From 1955 to 1961, Libia, along with her husband Vaman Sardesai and Nicolau Menezes, ran an underground radio station – initially called ‘Q’, later named:
- Goenche Sodvonecho Awaz (Voice of Freedom of Goa) – Konkani
- Voz de Liberdade – Portuguese
- Operated from Amboli (Maharashtra) and Castle Rock (Karnataka) in the Western Ghats.
- Purpose: Counter Portuguese censorship and propaganda; broadcast news, updates, and morale-boosting messages to Goans.
- From 1955 to 1961, Libia, along with her husband Vaman Sardesai and Nicolau Menezes, ran an underground radio station – initially called ‘Q’, later named:
- Final Broadcast:
- On 19 December 1961, Libia flew over Panaji in an IAF plane, announcing Goa’s liberation with the message:
“Rejoice brothers and sisters, Rejoice! Today, after 451 years of alien rule, Goa is free and united with the Motherland.”
Goa Liberation Movement: Background
- Colonial Rule: Goa was under Portuguese rule for over 451 years (from 1510 to 1961).
- Key Phases:
- 1954: India imposed an economic blockade after Portuguese crackdown on satyagrahis.
- August 1955: Mass satyagraha met with violent repression by Portuguese forces.
- Censorship: Portuguese regime enforced total censorship; only official Portuguese narratives were allowed.
- 1961 – Operation Vijay:
- Initiated on 17 December 1961 by the Indian Army under Lt. Gen. J.N. Chaudhuri.
- Portuguese forces surrendered by 19 December 1961, marking Goa’s official liberation.
Notable Leaders of the Movement
- Dr. Ram Manohar Lohia: Sparked initial resistance against Portuguese rule.
- Libia Lobo Sardesai: Voice of the resistance via underground broadcasting.
- Lt. Gen. J.N. Chaudhuri: Led military operations during Operation Vijay.
Significance
- Libia Lobo Sardesai represents the unsung contributions of civil resistance and communication warfare in India’s decolonization.
- Her work sustained nationalist morale, informed citizens under censorship, and shaped the narrative of a liberated Goa.
Aero India 2025
- 28 Jan 2025
In News:
Aero India 2025, the 15th edition of India’s premier aerospace and defence exhibition, is scheduled from February 10–14, 2025, at the Yelahanka Air Force Station, Bengaluru.
Organised by the Ministry of Defence and the Defence Exhibition Organisation (DEO), the event continues to be a vital forum for promoting India's indigenous defence capabilities and fostering international collaboration.
Evolution of Aero India: From Showcase to Strategic Asset
- Inception (1996): Launched as a modest exhibition to attract foreign investments and highlight India’s aerospace potential.
- Growth Phase (2005–2015): Marked by the entry of global giants like Boeing, Airbus, Lockheed Martin, and Dassault Aviation. Indigenous platforms like LCA Tejas began gaining prominence.
- Current Phase (2015–Present): Aligned with ‘Make in India’ and ‘Aatmanirbhar Bharat’, Aero India has become a symbol of India's defence self-reliance and a magnet for global partnerships.
Aero India 2025 Highlights
1. International Participation and Strategic Displays
- Participation from 15+ countries and major OEMs.
- Russia’s Su-57 and USA’s F-35—two of the world’s most advanced 5th-generation fighters—will be showcased together, reflecting India’s growing strategic importance.
- Other prominent platforms: KC-135 Stratotanker, Embraer C-390, and Light Combat Helicopter Prachand.
2. Indigenous Innovation
- Advanced Medium Combat Aircraft (AMCA): India’s 5th-generation stealth fighter, developed by HAL and ADA, will be unveiled.
- Indigenous platforms like LCA Mk2, LUH, HTT-40, ALH, and Naval Twin-Engine Deck-Based Fighter will also be featured.
3. Start-Up Integration via 'Manthan'
- Through the iDEX initiative, Aero India is promoting start-ups working in AI, unmanned systems, cybersecurity, and electronic warfare.
- Start-ups will showcase innovations including jetpack suits, robotics, and defence software tools.
4. Business & Public Engagement
- Business Days: February 10–12, 2025
- Public Days: February 13–14, 2025
- Over 7 lakh visitors expected; the event offers aerial displays, seminars, tech expos, and networking forums.
5. Defence Diplomacy and Deals
- Aero India 2023 had seen over ?80,000 crore worth of MoUs. A similar or higher scale of defence agreements is expected in 2025.
- High-level participation from defence ministers, air chiefs, and CEOs of OEMs, signalling deepening international defence cooperation.
Strategic Significance for India
- Geopolitical Leverage: Participation of both US and Russian defence firms signals India’s strategic autonomy and balanced defence diplomacy.
- Self-Reliance Boost: The event enhances domestic manufacturing by integrating MSMEs, promoting co-development and co-production with foreign partners.
- Global Recognition: Positions India as an emerging aerospace hub in the Indo-Pacific.
- Technological Edge: Demonstrates advancements in stealth technology, avionics, and unmanned systems.
Theme of Aero India 2025: “The Runway to a Billion Opportunities” — highlighting India’s expanding defence manufacturing capabilities and its aim to integrate with the global supply chain.
Uniform Civil Code (UCC) in Uttarakhand

- 28 Jan 2025
In News:
On January 27, 2025, Uttarakhand became the first Indian state to formally implement the Uniform Civil Code (UCC) after Independence. The legislation was passed by the State Assembly on February 7, 2024, and received Presidential assent on March 12, 2024.
Historical Background:
- A five-member expert committee chaired by Justice (Retd.) Ranjana Prakash Desai was constituted to draft the UCC report.
- The committee submitted its report on October 18, 2023.
- Though initially scheduled for implementation by November 9, 2024 (Uttarakhand's Foundation Day), the rollout was delayed due to administrative preparedness and staff training.
Scope and Applicability:
- Applicable to all residents of Uttarakhand, including those in live-in relationships outside the state.
- Scheduled Tribes (as per Article 342) and migrated natives have been exempted to safeguard cultural rights.
Key Provisions of the UCC:
1. Marriage, Divorce & Live-in Relationships
- Legal marriage age: 21 years (men), 18 years (women).
- Mandatory registration of marriages, divorces, and live-in relationships.
- Prohibited practices: Triple talaq, halala, iddat, polygamy, and child marriage.
- Live-in Relationships:
- Mandatory registration for couples aged 21 and above.
- Parental consent required if under 21.
- Termination of live-in relationships requires mutual consent.
- Mandatory reporting of pregnancy within 30 days of childbirth.
- Landlords cannot deny housing to registered live-in couples.
2. Inheritance & Property Rights
- Equal inheritance rights for sons and daughters.
- Children born to live-in couples recognized as legitimate, eligible for inheritance.
3. Wills and Succession
- Wills can be:
- Submitted online.
- Uploaded as handwritten/typed documents.
- Recorded as a 3-minute video.
Digital Infrastructure – UCC Portal (ucc.uk.gov.in):
- Aadhaar-based verification for authenticity.
- AI-based multilingual translation in 22 Indian languages.
- Tatkal service for expedited registrations with a nominal fee.
- Integrated with 13+ departments, including police, civic bodies, and courts.
- Disaster recovery systems and cloud-based architecture ensure secure data management.
- Access to:
- Online registration of marriages, divorces, live-in relationships.
- Upload and registration of wills.
- Grievance redressal and appeal mechanisms.
Administrative Framework:
- Village Panchayat Development Officers appointed as sub-registrars in rural areas.
- Common Service Centres (CSCs) enabled to facilitate registration, especially in remote and mountainous areas.
- Registration applications processed within 15 days, or 3 days in emergencies.
- Appeals must be filed within 30 days of rejection, resolved within 60 days.
Penalties:
- Initial warnings for non-compliance.
- Fines imposed for repeated violations.
Significance:
- The UCC aims to promote gender equality, legal uniformity, and women's empowerment.
- Represents a constitutional vision under Article 44, reinforcing the idea of a common civil law for all citizens.
- Seen as a potential model for other states in India.
Himachal Pradesh: Statehood Day
- 28 Jan 2025
In News:
The Prime Minister greeted the people of Himachal Pradesh (HP) on the occasion of Statehood Day (25th January).
Key Highlights:
Statehood Day: Celebrated annually on 25th January, marking the day Himachal Pradesh attained full statehood in 1971.
Historical Timeline:
- 15 April 1948: Formation of Chief Commissioner’s Province of Himachal Pradesh through the merger of 30 princely hill states.
- 26 January 1950: Became a Part C State with the commencement of the Indian Constitution. (Part C states comprised former Chief Commissioner’s provinces and some princely states.)
- 1 November 1956: Reconstituted as a Union Territory based on the recommendations of the States Reorganisation Commission.
- 1 November 1966: Kangra district and other hilly areas of Punjab merged into Himachal Pradesh, yet it remained a Union Territory.
- 18 December 1970: The State of Himachal Pradesh Act was passed by Parliament.
- 25 January 1971: Himachal Pradesh became the 18th state of the Indian Union.
Jawaharlal Nehru Port Authority

- 28 Jan 2025
In News:
The Jawaharlal Nehru Port Authority (JNPA) in Mumbai is set to become India’s first port to enter top global ports with 10 million TEUs (twenty-foot equivalent units) by 2027.
Overview:
- Location: Navi Mumbai, Maharashtra
- Commissioned: 1989
- Significance: India’s first Landlord Major Port, fully adopting the landlord port model.
Performance & Capacity Expansion:
- In 2024, JNPA handled a record 7.05 million TEUs, operating at over 90% capacity, with an 11% year-on-year growth.
- By 2027, JNPA is projected to become India’s first port to handle 10 million TEUs annually, marking its entry into the global top ports list.
- Current container handling capacity: 7.6 million TEUs
- Projected capacity by 2027: 10.4 million TEUs
Infrastructure Developments:
- Commissioning of Phase II of Bharat Mumbai Container Terminal (BMCT) to add 2.4 million TEUs.
- Upgradation of Nhava Sheva Freeport Terminal expected in 2025.
- Five operational container terminals, including:
- BMCT
- Nhava Sheva International Container Terminal (NSICT)
- Gateway Terminals India Pvt Ltd (GTIPL)
Key Projects & Investments (2024):
- ?2,000 crore worth of capacity enhancement projects launched.
- Solar-powered boat, two indigenously developed 70T tugs, and three fire tenders commissioned for safety and efficiency.
- Agro-processing facility (?284 crore) on 27 acres within port complex to handle 1.2 million tonnes annually – includes processing, sorting, packing, and food safety labs.
- Warehousing and CFS infrastructure (?300 crore investment) to generate 1,20,000 TEUs/year through ambient and temperature-controlled facilities.
Vadhavan Port Project:
- Proposed as India’s 13th major port (under construction).
- MoU with Reliance Industries Ltd: Development of liquid jetty and 50 acres of land under PPP model (investment: ?645 crore; operational by 2030).
- MoU with DBKKVD Dapoli: For integrated agri-horticultural development in Dahanu and Palghar.
- MoU with HUDCO: Funding commitment of ?25,000 crore for port infrastructure under PPP mode.
Strategic Importance:
- JNPA is central to India’s maritime trade, which accounts for 95% of trade by volume and 70% by value.
- Satellite and dry ports at Vadhavan, Jalna, and Wardha to improve hinterland connectivity and trade logistics.
Paraquat Poisoning

- 27 Jan 2025
In News:
- In a landmark ruling, a Thiruvananthapuram court sentenced a 24-year-old woman to death for the murder of her boyfriend by poisoning him with paraquat, a highly toxic herbicide.
- The incident, which occurred in 2022, has brought the spotlight back on paraquat's widespread availability, extreme toxicity, and the lack of regulatory enforcement in India.
What is Paraquat?
- Paraquat, chemically known as paraquat dichloride or methyl viologen, is one of the most widely used herbicides globally.
- It is primarily used for:
- Weed control
- Crop desiccation, especially in crops like cotton before harvest
- Despite its toxicity, India and the United States continue to permit its usage, unlike over 70 countries, including China, Brazil, and the European Union, which have banned it.
WHO Classification
- The World Health Organization (WHO) classifies paraquat as a Category 2 chemical, meaning it is moderately hazardous and irritating to the skin and eyes.
- It has a narrow margin between a safe and lethal dose, making accidental or intentional poisoning common and often fatal.
Routes and Effects of Exposure
- Ingestion is the most common method of poisoning.
- It may also occur through inhalation or skin contact, especially if the exposure is prolonged or the skin is broken.
Symptoms Vary by Dosage and Exposure Time:
Exposure Level Symptoms and Organ Damage
Small Quantity Gradual damage to lungs, liver, kidneys, and heart over days/weeks
Large Quantity Immediate symptoms such as:
- Acute kidney failure
- Liver and heart failure
- Seizures
- Respiratory failure
- Severe abdominal pain
- Bloody diarrhea
- Nausea
- Mouth and throat swelling |
Treatment and Challenges
- No known antidote exists for paraquat poisoning.
- Treatment options include:
- Immunosuppressive therapy
- Charcoal hemoperfusion (a blood-purification technique)
- However, these treatments offer limited efficacy, especially in cases of large-dose ingestion.
Regulatory and Public Health Implications in India
- Despite paraquat’s well-documented toxicity, it remains:
- Legally available in India
- Easily accessible in rural markets
- The lack of regulation increases the risks of:
- Occupational exposure
- Accidental poisoning
- Use in crimes or suicides
Whip System in Indian Parliament

- 27 Jan 2025
In News:
Vice President Jagdeep Dhankhar recently criticized the party whip system, arguing that it curtails the freedom of expression of Members of Parliament (MPs) and enforces servility by mandating strict adherence to the party line. His remarks have sparked a renewed debate on the balance between party discipline and individual autonomy in a parliamentary democracy.
What is a Party Whip?
A whip in parliamentary parlance is both a directive and a designated official of a political party. The directive instructs legislators on voting behavior on specific issues such as bills, motions, or resolutions. The designated whip ensures attendance, adherence, and discipline within the party ranks.
- The term “whip” originated from England’s hunting tradition, where a “whipper-in” kept hounds within the pack.
- The political usage dates back to Edmund Burke in the British Parliament.
- In India, the whip system has been in place since the start of parliamentary governance.
Constitutional and Legal Framework
- The whip system is not mentioned in the Constitution, Rules of Procedure, or any statute, but functions through parliamentary conventions.
- The Anti-Defection Law (52nd Amendment, 1985) enforces the whip by allowing disqualification of MPs/MLAs for defying it, thus preserving political stability and party integrity.
Quorum Requirement: As per Article 100 of the Constitution, quorum in Parliament is one-tenth of the total membership:
- Lok Sabha: 55 members
- Rajya Sabha: 25 members
Types of Whips
- One-Line Whip: Informational—members may abstain.
- Two-Line Whip: Requires presence but does not dictate voting.
- Three-Line Whip: Strictest—mandates attendance and voting as directed.
- Violation can lead to disqualification under the Anti-Defection Law, unless two-thirds of the party members dissent together.
Functions and Significance
- Ensures Attendance: Maintains quorum during critical votes.
- Secures Support: Helps pass or oppose legislation.
- Maintains Discipline: Prevents cross-voting or defection.
- Internal Monitoring: Identifies discontent among MPs and informs party leadership.
- Party Cohesion: Acts as a channel between MPs and party high command.
- Democratic Functioning: Ensures government stability, especially during division voting, where numbers decide the fate of motions like the No-Confidence Motion.
For ruling coalitions, a united stance during such votes is crucial to showcase majority strength.
Chief Whip and Institutional Structure
- The Chief Whip is the most critical functionary in enforcing the whip.
- In the Lok Sabha, the Minister of Parliamentary Affairs usually acts as the government’s chief whip.
- In the Rajya Sabha, it is the Minister of State for Parliamentary Affairs.
- Whips also coordinate which MPs speak, when, and on what issues.
The All-India Whips Conference, held since 1952, allows whips from all parties to discuss coordination strategies and share parliamentary practices.
Criticism and Contemporary Debate
- Critics, including the Vice President, argue that whips limit deliberative democracy, reduce MPs to mere rubber stamps, and suppress individual judgment.
- However, supporters claim that whips are essential to prevent chaos, ensure smooth functioning, and uphold mandated party ideologies, especially in a system where governments often hinge on narrow majorities.
Former Lok Sabha Speaker Sumitra Mahajan defended the whip, stating that MPs elected on a party ticket must uphold the party’s collective ideology and decisions, even if personal disagreement exists.
India’s Journey of Fiscal Consolidation

- 27 Jan 2025
In News:
Fiscal Consolidation refers to the strategic management of government finances aimed at reducing fiscal deficits, controlling public debt, and ensuring macroeconomic stability. India’s recent journey in this regard has been marked by a significant transformation, particularly in the post-2014 era.
Background:
In 2013-14, India was labelled as one of the "Fragile Five", largely due to its ballooning fiscal deficit (touching 5% of GDP in a quarter), high inflation, and weakening currency. This tag underscored the urgency of restoring fiscal health.
Post-2014 Measures:
- FRBM Act Revamp: The government recommitted to the Fiscal Responsibility and Budget Management (FRBM) Act, 2003, revising fiscal targets and focusing on fiscal discipline.
- Deficit Reduction: Fiscal deficit was reduced from 4.5% of GDP in FY 2013-14 to 3.4% in FY 2018-19.
- Revenue Boost: Digitization and broader tax reforms helped increase tax receipts from 10% of GDP (FY 2014-15) to 11.8% (FY 2023-24).
- Capex Focus: Capital expenditure nearly doubled from 1.6% of GDP in FY 2014-15 to 3.2% in FY 2023-24, emphasizing infrastructure over consumption.
Pandemic Impact and Recovery:
- During COVID-19, India’s fiscal deficit soared to 9.2% of GDP (FY 2020-21) due to emergency spending.
- Unlike blanket stimulus in some countries, India opted for targeted support (MSMEs, displaced populations, healthcare) while continuing infrastructure investment.
- This strategy avoided long-term inflationary pressure and built long-term productive capacity.
Structural Reforms:
- Production Linked Incentive (PLI) schemes aimed at reducing import dependence and boosting domestic manufacturing.
- Enhanced export competitiveness due to fiscal prudence and macroeconomic stability.
Current Scenario:
- Fiscal deficit reduced to 5.6% of GDP in FY 2023-24, with a target of 4.9% in FY 2024-25, and further narrowing to 4.5% by FY 2025-26.
- States remain a concern: their deficits exceed the 3% of GSDP limit, averaging 3.2% in FY 2023-24, with rising debt levels and declining capex.
FRBM Act & N.K. Singh Committee:
- FRBM Act (2003) aims to cap the fiscal deficit at 3% of GDP.
- The N.K. Singh Committee (2016) recommended:
- Shift from rigid deficit targets to debt as the primary anchor.
- Set up an autonomous Fiscal Council.
- Flexibility via an “escape clause” (up to 0.5% extra deficit during crises).
- Limit borrowings from RBI to specific emergency conditions.
Significance of Fiscal Consolidation:
- Macroeconomic Stability: Controls inflation and keeps currency stable.
- Investment Magnet: Low deficits improve investor confidence.
- Reduced Debt Burden: Less borrowing means less stress on future generations.
- Efficient Governance: Ensures better resource allocation and economic resilience.
Chronic Pulmonary Aspergillosis (CPA)

- 27 Jan 2025
In News:
A recent study conducted by Assam Medical College and Hospital has revealed a high prevalence of Chronic Pulmonary Aspergillosis (CPA) among tuberculosis (TB) survivors in Assam’s tea garden communities. Published in the PLOS Neglected Tropical Diseases journal, the research underscores a significant public health concern in a region already burdened by TB.
What is Chronic Pulmonary Aspergillosis (CPA)?
- CPA is a severe, life-threatening fungal infection caused by Aspergillus fumigatus, a filamentous fungus commonly found in soil, decaying vegetation, and humid organic matter.
- It predominantly affects individuals with weakened immune systems or pre-existing lung conditions, especially those who have recovered from or are currently battling TB.
- CPA is not contagious and cannot be transmitted from person to person.
Symptoms and Clinical Presentation:
CPA shares many clinical features with TB, making diagnosis challenging:
- Chronic cough
- Haemoptysis (coughing up blood)
- Persistent respiratory symptoms
- Weight loss
- Fatigue
- Shortness of breath
- Wheezing
Key Findings from Assam:
- Study Area: Conducted in Dibrugarh district, covering tea workers and their dependents from four major tea estates.
- Sample Size: 128 patients with prolonged respiratory symptoms (>3 months).
- Prevalence:
- CPA prevalence: 17.18% overall
- Seropositivity in active TB patients: 18.5%
- Seropositivity in post-TB patients: Spiked to 48.9%, indicating a strong link between CPA and previous TB infections.
- Demographic Insights:
- Mean age: 41.9 years
- Higher incidence among middle-aged male workers
- Comparison with Global Trends:
- Assam’s CPA prevalence (60 per 1,00,000) exceeds the global average (42 per 1,00,000)
- Worse than several African nations including Nigeria and the Democratic Republic of Congo (20–50 per 1,00,000)
Contributing Risk Factors in Assam’s Tea Belt:
- High TB burden: 217 per 1,00,000 (National TB Prevalence Survey 2019–2021)
- Poverty and malnutrition
- Kitchen smoke exposure
- Congested living conditions
- Delayed or inadequate TB treatment
Diagnosis and Treatment:
- Diagnosis:
- Serological testing for Aspergillus antibodies
- Radiological imaging to identify fungal growth in lung cavities
- Treatment:
- Antifungal therapy (e.g., itraconazole or voriconazole)
- Surgical removal in severe cases with fungal mass
Public Health Recommendations:
- Routine screening of post-TB patients for CPA in high-risk zones like tea estates
- Awareness campaigns targeting healthcare providers and workers to improve recognition and response
- Education on nutrition, respiratory hygiene, and early symptom detection
- Inclusion of fungal diseases like CPA in broader national TB and occupational health programs
Additional Context: Epidemic Dropsy in Assam’s Tea Belt
- A 2019 study had previously flagged the prevalence of epidemic dropsy, a condition caused by contaminated edible oils with Argemone mexicana oil, adding to the health risks in tea-growing regions.
Unified Pension Scheme (UPS)

- 27 Jan 2025
In News:
The Ministry of Finance has notified the Unified Pension Scheme (UPS) as an option under the National Pension System (NPS) for Central Government employees, effective April 1, 2025. This reform addresses long-standing concerns about the unpredictability of pension returns under the NPS.
Key Highlights:
- Applicability: Applies to Central Government employees currently under the NPS, including those recruited on or after January 1, 2004, who opt for the UPS.
- Objective: To provide guaranteed post-retirement financial security, addressing grievances regarding the market-linked returns of the NPS.
- Regulatory Framework: The scheme will be regulated by the Pension Fund Regulatory and Development Authority (PFRDA), which will issue detailed operational guidelines.
Pension and Benefit Structure
- Guaranteed Monthly Pension:
- 50% of the average basic pay drawn in the last 12 months prior to retirement.
- Requires completion of 25 years of service.
- Those with 10–25 years of service will receive a proportionate pension.
- Dearness Relief (DR): Periodic adjustments based on inflation trends to maintain pension value.
- Family Pension: In case of death, 60% of the employee's pension will be paid to eligible family members.
- Minimum Pension: Assured ?10,000 per month for those completing at least 10 years of service.
- Superannuation Benefits: Includes a lump sum payout and gratuity at retirement.
Contribution Mechanism
- Employee Contribution: 10% of basic pay.
- Government Contribution: 5% of basic pay (subject to revision based on actuarial evaluations).
Background and Policy Evolution
- The Union Cabinet approved the UPS on August 24, 2024, benefiting nearly 2.3 million Central Government employees.
- The move followed demands from staff unions for guaranteed pensions, and political pressure after several states reverted to the Old Pension Scheme (OPS).
- A high-level committee, led by T.V. Somanathan (then Finance Secretary), was formed in April 2023 to review the NPS framework and design an equitable alternative.
ISRO’s NVS-02 Satellite Launch

- 25 Jan 2025
In News:
ISRO successfully launched the NVS-02 satellite aboard GSLV-F15, placing it into a Geosynchronous Transfer Orbit (GTO). This marks ISRO’s 100th mission, reinforcing India’s space and navigation capabilities under the NavIC (Navigation with Indian Constellation) program.
What is NavIC?
- NavIC is India’s indigenous regional satellite navigation system, developed for both civilian and strategic use.
- Offers accurate positioning over India and up to 1,500 km beyond its borders.
- Comparable to GPS (USA), GLONASS (Russia), Galileo (EU), and BeiDou (China).
About NVS-02 Satellite:
Feature Description
Series Second satellite in the next-gen NVS series (after NVS-01 in 2023)
Mission Role Replaces aging IRNSS-1E satellite
Mass 2,250 kg
Power Capacity ~3 kW
Orbit Final orbital slot at 111.75°E in geosynchronous orbit (~36,000 km)
Life Span 12 years
Developed by URSC (U R Rao Satellite Centre), Bengaluru
Technological Advancements:
- Equipped with navigation payloads across L1, L5, and S-bands for enhanced accuracy and broader coverage.
- Features the Rubidium Atomic Frequency Standard (RAFS) – an indigenously developed atomic clock for precision timekeeping.
- Includes C-band ranging payload, similar to NVS-01.
Significance of NVS-02:
- Enhances NavIC’s positioning accuracy for civilian, commercial, and strategic applications:
- Disaster management
- Fleet tracking
- Precision agriculture
- Emergency response
- Mobile navigation
- L1 signal inclusion makes NavIC-compatible with international GNSS systems, improving global device integration.
- Demonstrates India’s technological self-reliance, particularly in atomic clock development.
ISRO’s Launch Vehicles
Vehicle First Flight Notable Use
SLV 1980 Launched Rohini satellite
ASLV 1987 Five-stage solid rocket, retired in 1990s
PSLV 1994 Reliable, used for Mars Orbiter, LEO missions
GSLV 2001 Used for heavier payloads, INSAT/GSAT
GSLV 2014 Heavy-lift, Chandrayaan-2/3, Gaganyaan crew module
Mk III (LVM3)
SSLV 2022 Affordable launches for nano/micro satellites
PKC-ERCP: Rajasthan’s River-Linking Project
- 25 Jan 2025
In News:
The Parbati-Kalisindh-Chambal-Eastern Rajasthan Canal Project (PKC-ERCP), part of the National Interlinking of Rivers (ILR) programme, aims to address water scarcity in 23 districts of Rajasthan, potentially benefiting 3.45 crore people. However, it has raised serious concerns over its ecological impact, particularly on the Ranthambore Tiger Reserve.
About the PKC-ERCP Project:
Aspect Details
Objective To channel surplus water from the Chambal basin for irrigation, drinking, and industrial use in Rajasthan and Madhya Pradesh
Estimated Cost ?72,000 crore (90% funded by the Central Government)
Water Allocation 4,100 MCM to Rajasthan and 3,000 MCM to Madhya Pradesh
Rivers Involved Chambal, Parbati, Kalisindh, Banas, and tributaries
Major Structure 39 m high, 1.6 km long dam across the Banas River, a Chambal tributary, near Doongri village, ~30 km from Sawai Madhopur
Submergence and Environmental Concerns:
- Total Submergence: ~408.86 sq km in Rajasthan.
- Reservoir Impact: 227 sq km to be submerged under the proposed dam across Banas River.
- Impact on Tiger Reserve:
- 37.03 sq km of the Ranthambore Tiger Reserve (total area: 1,133 sq km) to be submerged.
- This includes parts of Ranthambore National Park (392 sq km) and Keladevi Wildlife Sanctuary (674 sq km).
- May fragment the reserve, disrupting wildlife corridors and tiger movement.
- Ranthambore’s Significance:
- Home to ~57 tigers, it is one of India’s most prominent conservation areas.
- Situated at the Aravalli-Vindhya junction, with rich biodiversity, including leopards, hyenas, sloth bears, and iconic flora like Dhok trees.
- Encompasses the UNESCO-listed Ranthambore Fort and the Great Boundary Fault.
Arguments For the Project:
- Addresses chronic water scarcity in eastern Rajasthan.
- Promotes agricultural productivity, drinking water security, and industrial development.
- Aims to optimize water use by diverting surplus flows.
Arguments Against the Project:
- Biodiversity loss due to habitat submergence and reserve fragmentation.
- Risks to tiger conservation efforts.
- Potential violation of environmental safeguards under the Wildlife Protection Act and Forest Conservation norms.
Long-term ecological costs may outweigh short-term developmental gains.
SEBI’s Sachetisation of Mutual Funds
- 25 Jan 2025
In News:
In January 2025, the Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI) proposed the “sachetisation” of mutual fund investments to promote financial inclusion, especially among low-income and first-time investors.
What is Sachetisation?
- Originating from the FMCG sector (e.g., shampoo sachets), sachetisation refers to offering financial products in small, affordable units, enhancing accessibility and affordability.
- In capital markets, it implies micro-level investment options, particularly through low-ticket SIPs (Systematic Investment Plans).
Objectives:
- Promote financial inclusion and empower economically underserved sections.
- Expand mutual fund penetration to semi-urban and rural areas.
- Encourage long-term savings and wealth creation among new investors.
- Reduce dependency on large institutional or foreign investors by broadening the domestic retail base.
Key Features of SEBI’s Sachet SIP Proposal:
Feature Details
Minimum SIP Amount ?250 per month
Eligibility Only for new mutual fund investors
Investment Limit Up to 3 sachet SIPs across different AMCs
Excluded Schemes Debt funds, sectoral/thematic, small-cap, mid-cap equity funds (due to higher risk)
Commitment Period Encouraged to commit for 5 years (60 SIPs), but premature withdrawal allowed
Payment Modes Only via auto-pay mechanisms such as UPI Autopay and NACH
Cost Incentives AMCs to receive subsidies from SEBI’s Investor Education and Awareness Fund
Distributor Incentive ?500 per investor after completion of 24 monthly SIPs
Significance:
- Democratizes investment access by lowering the entry barrier for mutual funds.
- Encourages behavioral shift towards long-term financial planning and discipline.
- Stabilizes domestic markets by broadening and diversifying the retail investor base.
Supports SEBI’s vision of making capital markets inclusive, tech-enabled, and accessible.
Fiscal Health Index (FHI) 2025

- 25 Jan 2025
In News:
NITI Aayog launched the inaugural Fiscal Health Index (FHI) 2025 on 24 January 2025 in the presence of the 16th Finance Commission Chairman, Dr. Arvind Panagariya. The index evaluates the fiscal performance of 18 major Indian states using FY 2022–23 as the base year.
Key Highlights:
- Objective: To assess, monitor, and improve the fiscal health of Indian states and foster balanced regional development, economic resilience, and fiscal transparency. It aims to support the national goal of Viksit Bharat @2047.
- Developed by:
- NITI Aayog, with data sourced from the Comptroller and Auditor General (CAG).
- Designed as an annual publication to promote informed and targeted state-level policy reforms.
- Evaluation Parameters:
The index comprises five sub-indices that collectively offer a holistic picture of fiscal health:
- Quality of Expenditure – Efficiency in developmental and social sector spending (e.g., health, education).
- Revenue Mobilization – Tax and non-tax revenue generation capacity.
- Fiscal Prudence – Adherence to fiscal deficit targets and sound financial management.
- Debt Index – Absolute level of public debt.
- Debt Sustainability – Debt-to-GSDP ratio and interest burden on revenues.
Key Highlights from FHI 2025:
Top Performing States (Achievers):
Rank State FHI Score Strengths
1. Odisha 67.8 Low fiscal deficit, strong debt management, effective capital expenditure
2. Chhattisgarh 55.2 Revenue growth from mining, fiscal prudence
3. Goa 53.6 High tax efficiency and non-tax revenue
Aspirational States (Facing Challenges):
- Punjab, West Bengal, Kerala, Andhra Pradesh
- Issues: High debt-to-GSDP ratios, revenue deficits, poor revenue mobilization
Sub-Index Insights:
- Revenue Mobilization: Odisha, Goa, and Chhattisgarh excelled; Bihar and West Bengal lagged due to low own-tax revenues.
- Quality of Expenditure: Madhya Pradesh and Chhattisgarh prioritized social sectors; Punjab and Rajasthan underperformed in capital investment.
- Debt Management: Maharashtra and Gujarat maintained robust practices; Punjab and Haryana faced rising interest burdens.
- Debt Sustainability: Odisha and Chhattisgarh displayed strong sustainability; West Bengal and Punjab showed fiscal stress.
- Fiscal Prudence: Odisha and Jharkhand maintained low deficits, enabling better public investment.
Significance for Policy & Governance:
- Encourages healthy interstate competition and promotes cooperative federalism.
- Provides data-driven insights for targeted fiscal reforms.
- Reinforces the need for decentralized and transparent financial governance.
- Offers a benchmark for fiscal performance aligned with national transformation goals.
Recommendations:
- Enhance revenue base via tax reforms and tapping into non-tax sources.
- Boost capital expenditure in infrastructure, health, and education.
- Strengthen debt sustainability frameworks and reporting mechanisms.
- Institutionalize fiscal responsibility through better compliance and accountability.
Sanjay Battlefield Surveillance System

- 25 Jan 2025
In News:
Defence Minister Rajnath Singh recently flagged off Sanjay, an indigenously developed Battlefield Surveillance System (BSS), to be inducted into the Indian Army in phased manner from March to October 2025, designated as the ‘Year of Reforms’ by the Ministry of Defence.
Overview:
- Nature: Automated surveillance system
- Purpose: To integrate real-time data from ground and aerial sensors, enabling swift, informed decision-making in conventional and sub-conventional warfare scenarios.
Key Features:
- Common Surveillance Picture (CSP): Fuses verified sensor data to generate a real-time surveillance image of the battlefield.
- Real-time Integration & Analytics: Processes inputs using advanced analytics to eliminate duplication and enhance situational awareness.
- Secure Networks: Operates over the Indian Army’s Data Network and Satellite Communication Network, ensuring reliable and secure data flow.
- Centralized Web Application: Provides integrated inputs to Command Headquarters and Army HQ through a unified platform, supporting the Indian Army's Decision Support System.
- Indigenous Development: Jointly developed by the Indian Army and Bharat Electronics Limited (BEL) under the Buy (Indian) category, promoting Aatmanirbharta in defense.
Operational Significance:
- Enhances battlefield transparency, situational awareness, and surveillance capabilities along vast and sensitive land borders.
- Functions as a force multiplier in Intelligence, Surveillance & Reconnaissance (ISR) operations.
- Enables network-centric warfare, marking a shift towards data-driven military operations.
Deployment:
- To be inducted into all Brigades, Divisions, and Corps of the Army in three phases (March–October 2025).
Guillain-Barré Syndrome (GBS)
- 24 Jan 2025
In News:
The Pune Health Department has reported a surge in Guillain-Barré Syndrome (GBS) cases, prompting concern due to its severe neurological impact and association with prior infections or immune responses.
What is Guillain-Barré Syndrome?
- Nature of Disorder: A rare autoimmune condition where the body’s immune system attacks the peripheral nervous system, affecting voluntary muscle control and sensory signals (e.g., pain, temperature, and touch).
- Medical Term: Also known as Acute Inflammatory Demyelinating Polyradiculoneuropathy (AIDP).
- System Affected: Peripheral nerves, i.e., nerves outside the brain and spinal cord.
Epidemiology:
- Prevalence: Rare but potentially life-threatening.
- Age Group Affected: Can occur at any age but is most common between 30 to 50 years.
- Non-contagious: GBS is not transmitted from person to person.
Causes and Triggers:
- Exact Cause: Unknown, but usually follows an immune response to:
- Infections: Campylobacter jejuni (foodborne bacteria), Epstein-Barr Virus (EBV), Cytomegalovirus (CMV), respiratory or urinary tract infections.
- Vaccinations: Rarely observed post-immunisation.
- Surgery or trauma: Can act as physical stressors that trigger the syndrome.
Symptoms:
- Initial Signs: Tingling and weakness starting in the legs, progressing upwards.
- Progression:
- Weakness in arms, facial muscles.
- Difficulty walking or balancing.
- In severe cases, respiratory paralysis, requiring ventilator support.
- Onset: Can escalate within hours, days, or weeks.
- Range: Varies from mild muscle weakness to complete paralysis.
Impact:
- Neurological Disruption: Affects communication between the brain and muscles.
- Temporary but Debilitating: Most patients recover over weeks to months, though rehabilitation may be prolonged.
- Critical Care: May require intensive medical and respiratory support in acute stages.
Diagnosis & Treatment:
- No definitive cure, but early intervention improves outcomes.
- Main Treatments:
- Intravenous Immunoglobulin (IVIG):
- Contains healthy antibodies from donated blood.
- Helps suppress the immune attack on nerves.
- Plasmapheresis (Plasma Exchange): Filters harmful antibodies from the blood.
- Supportive Therapy:
- Mechanical ventilation in case of respiratory failure.
- Physiotherapy for muscle recovery and mobility.
Ad Hoc High Court Judges

- 24 Jan 2025
In News:
To address the mounting pendency of criminal cases in several High Courts, the Supreme Court of India has suggested invoking Article 224A of the Constitution, which allows the appointment of retired High Court judges on an ad hoc basis.
Constitutional Provision: Article 224A
- Title: Appointment of Retired Judges at Sittings of High Courts.
- Key Provision: The Chief Justice of a High Court, with the consent of the President, may invite retired judges of the same or other High Courts to act as judges temporarily.
- Status: These judges enjoy the powers, jurisdiction, and privileges of regular High Court judges, but are not deemed permanent judges.
Why the Provision is Being Invoked Now:
- Backlog of Cases: Over 40% vacancy rate in High Courts; huge pendency, especially of criminal cases.
- Delays in Regular Appointments: Slow process of regular judicial appointments prompted the Supreme Court to consider alternative mechanisms.
- Underuse of Article 224A: Only three recorded instances of ad hoc appointments since Independence:
- Justice Suraj Bhan – MP High Court (1972)
- Justice P. Venugopal – Madras High Court (1982–83)
- Justice O.P. Srivastava – Allahabad High Court (2007, Ayodhya case)
Judicial Interpretation – Lok Prahari v. Union of India (2021):
- The Supreme Court laid down guidelines for invoking Article 224A.
- The process must be routed through the SC collegium (CJI + 2 senior-most judges).
- Trigger Point for Appointment:
- High Court vacancies exceed 20% of sanctioned strength (excluding pending proposals).
- More than 10% of pending cases are over 5 years old.
Procedure for Appointment:
- Consent: Retired judge must agree to serve again.
- Initiation: Chief Justice of the High Court forwards the name.
- State and Centre: Proposal routed through State CM → Union Law Ministry.
- SC Collegium: Must review and approve the name.
- Executive Clearance: Law Ministry → PM → President for final approval.
Term & Allowances:
- Duration: Typically 2–3 years, renewable if required.
- Number of Judges: Suggested 2–5 ad hoc judges per High Court.
- Remuneration: Entitled to allowances as per Presidential order.
- Status: Have full judicial powers during tenure.
Concerns & Safeguards:
- Fear of using ad hoc appointments as a substitute for regular appointments.
- Therefore, SC mandates that regular appointment process must be underway before invoking Article 224A.
- Periodic review and panel creation of eligible retired judges recommended.
M23 Armed Group

- 24 Jan 2025
In News:
The March 23 Movement (M23), a rebel group active in eastern Democratic Republic of Congo (DRC), has intensified its insurgency in North Kivu province, capturing key areas like Minova and threatening the provincial capital, Goma.
About M23 Armed Group:
- Full Form: March 23 Movement
- Formation: 2012, by mutineers from the Congolese army protesting a failed 2009 peace deal.
- Base of Operations: Eastern DRC, primarily in North Kivu province.
- Activities: Armed rebellion, territorial control, ethnic conflict, disruption of state authority.
External Support:
- Rwandan Involvement:
- UN Reports (2023): Estimated 3,000–4,000 Rwandan troops operating alongside M23.
- Rwanda alleged to have “de facto control” over M23 operations.
- Kigali denies direct territorial aggression claims.
- International Concerns: The group’s resurgence reflects broader regional instability and transnational military dynamics.
Recent Developments (2024):
- Territorial Gains: Capture of Minova; encroachment on Goma, a strategic and densely populated city.
- Humanitarian Crisis:
- Over 2,30,000 displaced since January 2024.
- Influx of injured civilians in hospitals; risk of further displacement and violence.
- Congolese Military Weakness:
- Internal instability and operational setbacks have contributed to M23’s advances.
- The Congolese army acknowledged a “breakthrough” by M23 with external backing.
Geographical Significance of the Region:
- DRC Capital: Kinshasa
- Strategic Location: Borders 9 countries—Angola, Zambia, Tanzania, Burundi, Rwanda, Uganda, South Sudan, Central African Republic, Republic of Congo.
- Topography:
- Rwenzori & Virunga Mountains: Includes active volcanoes (e.g., Mount Nyiragongo).
- Congo River: Vital for transport, hydroelectric power, and biodiversity.
- Natural Resources:
- Rich in cobalt, coltan, gold, and other rare minerals—critical to the global tech industry.
- The mineral wealth of North Kivu is a major driver of prolonged conflict.
India’s Deep Ocean Mission

- 24 Jan 2025
In News:
India is set to deploy its first human-operated deep-sea submersible as part of the Deep Ocean Mission (DOM), marking a significant leap in the country’s marine research and technological capability.
Key Highlights:
- Submersible Deployment (2024):
- India will operate its first human submersible at a depth of 500 meters this year.
- The goal is to reach a depth of 6,000 meters by 2025.
- The project aligns with the timelines of Gaganyaan, India’s first human space mission—showcasing parallel progress in marine and space technology.
- Indigenous Technology:
- The mission is powered by 100% indigenous technology, underlining India’s growing self-reliance in high-end scientific infrastructure.
About Deep Ocean Mission (DOM):
- Launched: 2021
- Nodal Ministry: Ministry of Earth Sciences (MoES)
- Budget: ?4,077 crore over five years
- Framework: One of nine key missions under PM-STIAC (Prime Minister’s Science, Technology, and Innovation Advisory Council)
Core Objectives:
- Develop deep-sea technologies, including a manned submersible for ocean exploration.
- Explore and harness ocean resources such as: Polymetallic nodules, Hydrothermal sulphides & Rare earth metals
- Study marine biodiversity for sustainable fisheries and conservation.
- Support India’s blue economy through innovation and research.
- Monitor ocean climate change and develop advisory services.
- Promote marine biology and biotechnology via dedicated marine research stations.
- Harvest renewable energy and freshwater from ocean sources.
Key Components and Technologies:
Matsya6000 Submersible:
- India’s first manned deep-sea vehicle.
- Designed to reach 6,000 meters depth.
- Crew Capacity: Three members
- Developed by: National Institute of Ocean Technology (NIOT), Chennai
- Structure: Made of titanium alloy, withstanding 6,000 bar pressure
- Equipped with: Scientific sensors, tools for sampling, viewports, propellers, and acoustic communication systems.
- Combines capabilities of ROVs (Remotely Operated Vehicles) and AUVs (Autonomous Underwater Vehicles).
Varaha Deep-Ocean Mining System:
- Developed by NIOT
- Successfully conducted trials at 5,270 meters
- Key to India’s future in deep-sea mining of critical minerals
Strategic Importance:
- Scientific Advancement: DOM places India among a select group of nations (USA, Russia, China, France, Japan) with human-crewed deep-ocean exploration capacity.
- Economic Potential: Unlocks access to underwater mineral wealth, critical for electronics, defense, and energy sectors.
- Environmental Sustainability: Supports marine biodiversity conservation and promotes sustainable use of oceanic resources.
- Geopolitical Significance: Enhances India’s presence and influence in the Indian Ocean Region (IOR).
- Technological Leap: Strengthens India’s capabilities in underwater robotics, materials engineering, and ocean sciences.
Is Poverty Being Underestimated in India?

- 24 Jan 2025
In News:
The recent 2023-24 Household Consumption Expenditure Survey (HCES) showed a decline in poverty across rural and urban India. However, questions have emerged about whether poverty is being underestimated, due to changes in methodologies, definitions, and data availability.
Evolution of Poverty Measurement in India
- 1970s to 2005: Poverty was defined based on minimum calorie intake; updated every 5 years using NSSO data.
- Tendulkar Committee introduced in response to divergence between NSSO and National Accounts data.
- Post-2011-12: No official poverty estimates or surveys; alternative indices like Multidimensional Poverty Index (MPI) were used.
Current Data Issues
- Different recall periods in surveys (7-day, 30-day, 365-day) create non-comparability.
- Modified Mixed Recall Period (MMRP) introduced in 2017-18 and improved upon in recent years with three household visits, enhancing recall and thus raising reported expenditures.
- Result: Using older poverty lines on newer, higher expenditure data underestimates poverty.
Diverging Poverty Estimates
- Dr. C. Rangarajan (2022-23): Estimated poverty at around 10%.
- Recent factsheet (2023-24) suggests poverty may have declined to single digits.
- A paper using Rangarajan’s methodology on 2022-23 HCES data estimated 25% poverty, but this is debated.
Reasons for Poverty Reduction
- High GDP growth, increased public expenditure, and improved public delivery systems.
- National Food Security Act covers nearly 80 crore people.
- Broadened definition of poverty now includes non-food items and essential services.
- Decline in poverty estimated around 17-18% between 2011-12 and 2023-24.
Rural-Urban Trends
- Consumption gap between rural and urban areas is narrowing.
- Rural consumption patterns becoming more urban-like.
- 2011 Census definitions outdated — many rural areas are peri-urban in character.
Need for Poverty Line Revision
- Lack of consensus and official backing on methodology hinders creation of a new poverty line suited to current data.
- UNDP’s global poverty line is $2.15/day; India’s poverty was 12.9% in 2019 by that metric.
- NITI Aayog’s estimates do not support 25% poverty claim.
Debate on Multidimensional Poverty Index
- India’s MPI (12 indicators) differs from UNDP’s 10-indicator framework.
- Additions like bank accounts and maternal health are India-specific.
- Criticism: Once indicators (e.g., electricity, bank accounts) are met, they remain met — poverty appears to decline permanently, while income vulnerability is not captured.
Estimation and Measurement of India’s Digital Economy – MeitY Report (2025)

- 23 Jan 2025
In News:
Release of Report ‘Estimation and Measurement of India’s Digital Economy’ by Ministry of Electronics & Information Technology.
Key Highlights:
- Released by: Ministry of Electronics & Information Technology (MeitY)
- Prepared by: Indian Council for Research on International Economic Relations (ICRIER)
- Significance: First credible and current estimate of the digital economy using international frameworks (OECD & ADB).
- India is the first developing country to adopt the OECD framework for measuring the digital economy.
Key Findings (2022–23)
Indicator Details
Size ?31.64 lakh crore (~USD 402 billion), 11.74% of national income (GVA)
Employment 14.67 million workers (2.55% of the workforce)
Projected Share by 2029–30 Nearly 20% of GDP (surpassing agriculture & manufacturing)
Structure of India’s Digital Economy
- Digitally Enabling Industries (7.83% of GVA): ICT services, telecom, manufacturing of digital hardware
- New Digital Industries (2%): Big Tech, digital platforms, intermediaries (e.g., e-commerce, ride-sharing)
- Digitalization of Traditional Sectors (2%): BFSI (Banking, Financial Services, Insurance), trade, education
- Insight: Digital transformation is spreading beyond ICT into traditional sectors.
Frameworks Used
Framework Purpose
OECD Estimating core digital and enabling sectors
ADB Input-Output Broader economic impact via inter-industry linkages
India’s Expansion Includes digital share in BFSI, trade, education – not covered under OECD
Key Drivers of India’s Digital Economy
- Widespread mobile use: 1.14 billion subscribers in India
- High internet traffic: 3rd globally, with avg. 16.9 GB/month
- 5G leadership: 2nd largest 5G smartphone market in 2024
- Aadhaar success: 1.3+ billion biometric IDs issued
- Digital payments boom: 1,644 billion transactions in FY24
- ICT service exports: USD 162 billion (2nd highest globally)
- AI leadership: India leads GitHub AI contributions (23%)
- Startup ecosystem: 3rd highest number of unicorns globally
Future Projections (By 2030)
- Digital economy to reach ~20% of national income
- Growth drivers:
- Expansion of digital platforms & intermediaries
- Deepening digitalization in all sectors
- Greater internet & broadband access
Challenges in Measuring Digital Economy
- Difficulty in defining digital sectors due to their integrated nature
- Conventional national accounting systems are inadequate
- Lack of data from:
- Informal sector digitalization
- Smaller platforms and startups
- Digital shifts in healthcare, logistics, etc.
Importance of This Report
- Policy Formulation: Enables targeted strategies for digital growth
- Business Strategy: Helps identify trends, plan investments
- Global Standing: Puts India among early adopters of robust measurement frameworks
Mission SCOT

- 23 Jan 2025
In News:
The Prime Minister of India praised Indian space startup Digantara for the successful launch of Mission SCOT (Space Camera for Object Tracking) — the world’s first commercial SSA satellite, launched via SpaceX’s Transporter-12 rideshare mission.
What is Mission SCOT?
Feature Description
Developer Digantara (Indian space startup), supported by Aditya Birla Ventures & SIDBI
Launched on SpaceX Transporter-12 mission (rideshare platform)
Type First commercial Space Situational Awareness (SSA) satellite
Orbit Sun-Synchronous Orbit – ideal for consistent Earth observation
Function Tracks Resident Space Objects (RSOs) as small as 5 cm in Low Earth Orbit (LEO)
What is Space Situational Awareness (SSA)?
- SSA involves the detection, tracking, cataloging, and prediction of natural and man-made objects in Earth's orbit (like satellites, debris, etc.).
- Ensures safe and sustainable operations by minimizing collision risks.
- Critical due to increasing congestion in LEO, especially with rising numbers of small satellites and mega-constellations.
Key Features of Mission SCOT
Feature Advantage
High Revisit Rate More frequent observations of objects in orbit
Precision Tracking Can track debris ≥ 5 cm in size
All-Weather Monitoring Overcomes limitations of ground-based systems like cloud cover, FoV
Space-based System Unhindered by geography, providing continuous global surveillance
Supports SSA Infrastructure Aids in collision avoidance, space traffic management, and defence preparedness
???????? India’s SSA Ecosystem
Initiative Role
ISRO’s IS4OM Provides Indian Space Situational Assessment Report (ISSAR); enables safe & sustainable space operations
NETRA Project Network for Space Objects Tracking & Analysis – aims to build a dedicated SST (Space Surveillance & Tracking) network using radars & optical telescopes
Multi-Object Tracking Radar Operated at Sriharikota – limited range, being augmented
Collision Avoidance Manoeuvres (CAMs) Regularly performed by ISRO to protect its satellites from debris threats
Global Context: Transporter-12 Rideshare
- A SpaceX program providing low-cost access to space by allowing multiple customers to launch small payloads on a single rocket.
- Enhances global commercial space activity, democratizes space access.
Significance for India
Strategic:
- Strengthens national space defence by enabling indigenous tracking of space threats.
- Reduces reliance on foreign SSA data (e.g., NORAD/US Space Command).
Technological:
- Demonstrates India’s capability in space-based surveillance tech.
- Positions India as a global contributor in the emerging SSA domain.
Economic:
- Boosts private sector space innovation aligned with India’s NewSpace Policy.
- Attracts venture capital and international collaboration.
LID-568
- 23 Jan 2025
In News:
In 2024, an international team of astronomers using NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) and the Chandra X-ray Observatory discovered a low-mass supermassive black hole, LID-568, showing super-Eddington accretion—a rare and extreme feeding process—just 1.5 billion years after the Big Bang.
About LID-568
Feature Description
Type Low-mass supermassive black hole
Age Formed ~1.5 billion years after Big Bang (Universe’s “youth”)
Discovery Observed via Chandra (X-ray) & JWST (infrared)
Location In a distant galaxy with very low star formation
Feeding Rate Accreting at ~40× the Eddington limit (super-Eddington accretion)
Key Concepts
Eddington Limit
- Theoretical upper limit on how fast matter can fall into a black hole before radiation pressure balances gravitational pull.
- Exceeding this limit (super-Eddington) is thought to be unstable and short-lived.
Super-Eddington Accretion
- Observed in LID-568, feeding at 40× Eddington rate.
- Suggests rapid, short bursts of black hole growth, not the slow, steady model previously assumed.
Why is LID-568 Important?
Challenges Current Theories
- Traditional black hole growth models require:
- Long periods (hundreds of millions of years).
- Seed black holes formed from:
- Death of first stars (light seeds: 10–100 solar masses).
- Collapse of primordial gas clouds (heavy seeds: 1,000–100,000 solar masses).
- LID-568 suggests brief, intense growth spurts could create supermassive black holes faster than previously thought.
Impact on Host Galaxy
- Powerful outflows prevent gas accumulation → suppresses star formation.
- Indicates black holes can regulate galaxy evolution, even when young.
Scramjet & Hypersonic Technology
- 23 Jan 2025
In News:
On 21 January 2025, DRDO’s Defence Research & Development Laboratory (DRDL) successfully conducted a 120-second ground test of an indigenously developed Scramjet (Supersonic Combustion Ramjet) engine, marking a major milestone in India’s journey towards hypersonic missile technology.
What is Scramjet Technology?
Definition
A Scramjet is an air-breathing engine that sustains combustion at supersonic speeds—optimized for speeds above Mach 5 (hypersonic range).
Working Principle
- Utilizes vehicle’s forward motion to compress incoming air—no onboard oxidizer needed.
- Injects fuel into the compressed supersonic airflow → ignition → high-speed thrust.
- Operates without moving parts, making it lightweight, efficient, and reliable.
Key Indigenous Innovations
Feature Description
Active-Cooled Combustor Stable combustion achieved at 1.5 km/s airflow, comparable to "keeping a candle lit in a hurricane."
Endothermic Scramjet Fuel First-time development in India; offers cooling + ignition efficiency.
Thermal Barrier Coating (TBC) Jointly developed with DST; withstands temperatures beyond melting point of steel using advanced ceramic coating.
CFD Simulations Used for design optimization and performance validation of flame-holding techniques.
Significance of Scramjet Test
- Stable Combustion: A major challenge in hypersonic propulsion, now successfully demonstrated.
- Hypersonic Missiles:
- Speeds >Mach 5 (~5400 km/h).
- Bypass air defence systems due to speed and maneuverability.
- Enable rapid, high-impact delivery.
- Reusable Launch Vehicles:
- Cuts satellite launch costs via air-breathing propulsion.
- Strategic Edge:
- India joins elite group: USA, Russia, China.
- Strengthens defence deterrence & technological sovereignty.
- Technology Spillover: Advancements in CFD, materials science, flame stabilization, and fuel chemistry.
Global Hypersonic Race
- China (2021): Tested nuclear-capable hypersonic glide vehicle (HGV) that orbited Earth before hitting target.
- USA & Russia: Advanced programs with operational hypersonic systems (e.g., Avangard, Zircon, ARRW).
- India: Now developing indigenous hypersonic missile platform.
Scramjet & Hypersonic Technology

- 23 Jan 2025
In News:
On 21 January 2025, DRDO’s Defence Research & Development Laboratory (DRDL) successfully conducted a 120-second ground test of an indigenously developed Scramjet (Supersonic Combustion Ramjet) engine, marking a major milestone in India’s journey towards hypersonic missile technology.
What is Scramjet Technology?
Definition
A Scramjet is an air-breathing engine that sustains combustion at supersonic speeds—optimized for speeds above Mach 5 (hypersonic range).
Working Principle
- Utilizes vehicle’s forward motion to compress incoming air—no onboard oxidizer needed.
- Injects fuel into the compressed supersonic airflow → ignition → high-speed thrust.
- Operates without moving parts, making it lightweight, efficient, and reliable.
Key Indigenous Innovations
Feature Description
Active-Cooled Combustor Stable combustion achieved at 1.5 km/s airflow, comparable to "keeping a candle lit in a hurricane."
Endothermic Scramjet Fuel First-time development in India; offers cooling + ignition efficiency.
Thermal Barrier Coating (TBC) Jointly developed with DST; withstands temperatures beyond melting point of steel using advanced ceramic coating.
CFD Simulations Used for design optimization and performance validation of flame-holding techniques.
Significance of Scramjet Test
- Stable Combustion: A major challenge in hypersonic propulsion, now successfully demonstrated.
- Hypersonic Missiles:
- Speeds >Mach 5 (~5400 km/h).
- Bypass air defence systems due to speed and maneuverability.
- Enable rapid, high-impact delivery.
- Reusable Launch Vehicles:
- Cuts satellite launch costs via air-breathing propulsion.
- Strategic Edge:
- India joins elite group: USA, Russia, China.
- Strengthens defence deterrence & technological sovereignty.
- Technology Spillover: Advancements in CFD, materials science, flame stabilization, and fuel chemistry.
Global Hypersonic Race
- China (2021): Tested nuclear-capable hypersonic glide vehicle (HGV) that orbited Earth before hitting target.
- USA & Russia: Advanced programs with operational hypersonic systems (e.g., Avangard, Zircon, ARRW).
- India: Now developing indigenous hypersonic missile platform.
10 years of Beti Bachao Beti Padhao (BBBP)

- 23 Jan 2025
In News:
Launched on 22nd January 2015 in Panipat, Haryana, BBBP was initiated in response to the declining Child Sex Ratio (CSR), which stood at 918 girls per 1000 boys (Census 2011). It marked a key step towards gender equality, aiming to curb gender-biased sex-selective elimination and improve the status of the girl child.
Key Highlights:
Core Objectives
- Improve Sex Ratio at Birth (SRB) by two points annually.
- Sustain institutional delivery rate at ≥95%.
- Increase 1st trimester ANC registration and girls' enrollment in secondary education by 1% annually.
- Reduce dropout rates among girls.
- Promote safe menstrual hygiene management (MHM).
Target Groups
- Primary: Young couples, expecting parents, adolescents, households, communities.
- Secondary: Schools, AWCs, health professionals, PRIs, ULBs, NGOs, SHGs, media, and religious leaders.
Implementation Structure
- Type: Centrally Sponsored Scheme (CSS) with 100% Central funding.
- Ministries Involved:
- Women and Child Development
- Health and Family Welfare
- Education
- Financial Assistance (Per District/Year):
- Rs. 40 lakh (SRB ≤918)
- Rs. 30 lakh (SRB 919–952)
- Rs. 20 lakh (SRB >952)
Integration with Mission Shakti (2021–2026)
BBBP now functions under Mission Shakti, which comprises two verticals:
- Sambal (Safety & Security):
- One Stop Centres (OSCs)
- Women Helpline (181)
- Nari Adalat: Alternative dispute resolution
- Samarthya (Empowerment):
- Sakhi Niwas, Palna Creches
- Shakti Sadans (rehabilitation)
- PM Matru Vandana Yojana: Extended support for a second girl child
- SANKALP-HEW: District-level single-window system for all women-centric schemes
Achievements in 10 Years (2015–2025)
- SRB: Improved from 918 (2014-15) to 930 (2023-24)
- Girls’ GER: Rose from 75.5% (2014-15) to 78% (2023-24) in secondary education
- Institutional Deliveries: Increased from 61% to 97.3%
- Kanya Shiksha Pravesh Utsav: Re-enrolled over 1 lakh out-of-school girls
- Economic Empowerment: Integration with skilling initiatives and 70% of PM Mudra loans disbursed to women
- Awareness Campaigns:
- Selfie with Daughter
- Beti Janmotsav
- Yashaswini Bike Expedition
- "Betiyan Bane Kushal" Skill Conference
Sukanya Samriddhi Yojana (SSY) – A Financial Tool for Empowerment
Launched under BBBP, SSY is a small savings scheme to ensure the financial security of girl children.
Key Features
- Eligibility: Indian girl child below 10 years.
- Account: Max 2 per family (exceptions for twins/triplets).
- Deposit Limit: ?250 to ?1.5 lakh/year (15 years).
- Tenure: Account matures 21 years after opening.
- Withdrawals: Up to 50% for higher education after 18 years.
- Tax Benefits: Exempt under Section 80C (EEE status).
Impact
- Over 4.1 crore accounts opened by Nov 2024.
- Promotes long-term savings and financial inclusion.
- Complements BBBP by addressing economic empowerment of girls.
Mission Vatsalya
- Formerly ICPS (2009), then Child Protection Services (2017).
- Merged into Mission Vatsalya in 2021.
- Focuses on:
- Juvenile justice
- Child protection
- Advocacy and rehabilitation
- Ensures “no child is left behind” principle aligned with SDGs.
Pradhan Mantri Matru Vandana Yojana (PMMVY)
- Supports pregnant and lactating mothers:
- ?5,000 in 3 installments + ?1,000 (JSY)
- Now extended to second girl child to promote gender equity.
Targets wage compensation, safe delivery, maternal nutrition, and reduced MMR/IMR.
Mount McKinley

- 22 Jan 2025
In News:
In a controversial move, President Donald Trump (2025) signed an executive order to rename Denali (North America’s highest peak) back to Mount McKinley, and also proposed renaming the Gulf of Mexico to the Gulf of America, citing the need to "honor American greatness."
About Denali / Mount McKinley:
Feature Description
Location Alaska Range, South-Central Alaska, USA
Height 20,310 feet (6,190 meters) – Highest in North America
Geology Giant granite block uplifted by tectonic activity ~60 million years ago
Glaciers Feeds major glaciers: Kahiltna, Muldrow, Peters, Ruth, Traleika
Tectonics Lies along the Denali Fault, a major right-lateral strike-slip fault
National Park Forms the core of Denali National Park and Preserve
Historical Background of the Name:
- Original Name: Denali, meaning “The High One” in the Athabascan language of the Koyukon people.
- 1897: Renamed Mount McKinley by a gold prospector in honor of President William McKinley (1897–1901).
- 1917: Official federal recognition with the creation of Mount McKinley National Park.
- 1980: Park renamed Denali National Park and Preserve; mountain's name remained McKinley federally.
- 2015: Obama administration officially renamed the peak Denali through the U.S. Department of the Interior.
- 2025: Trump issued executive order to revert the name to Mount McKinley, stating McKinley “deserves” the honor.
Rationale Behind Trump’s Renaming Order:
- Claims it honors McKinley’s legacy: economic growth, leadership in Spanish-American War, and tariff reforms.
- Declares Obama’s 2015 decision an “affront” to American heritage.
- Connects the move to his broader theme of “Restoring Names that Honor American Greatness.”
Opposition & Cultural Sensitivity:
- Alaska’s bipartisan leadership, including Senators Lisa Murkowski (R) and Scott Kawasaki (D), oppose the move.
- Indigenous groups maintain that Denali is the rightful and culturally authentic name.
- Critics argue it undermines native heritage and local identity.
Renaming the Gulf of Mexico to “Gulf of America”:
- Also part of Trump’s 2025 executive order.
- Geographic Facts:
- Borders the US, Mexico, and Cuba.
- Crucial to the US energy sector:
- 14% of US crude oil
- 5% of US natural gas
- 48% of refining capacity
- International Validity: The International Hydrographic Organization (IHO) allows local name usage but retains “Gulf of Mexico” in global records.
- Not binding on Mexico or Cuba.
International & Historical Parallels in Naming Disputes:
- Persian Gulf vs. Arabian Gulf (Iran vs. Arab states)
- Sea of Japan vs. East Sea (Japan vs. South Korea)
- South China Sea: Multiple nations claim different names and areas.
About the Denali Fault:
- Major strike-slip fault running through Alaska.
- Responsible for extensive tectonic movement and uplift of Denali.
- Evidence of horizontal displacement (~483 km) over millions of years.
- Marked the final suturing of tectonic plates in North American geological history.
Diamond Imprest Authorization (DIA) Scheme

- 22 Jan 2025
In News:
The Union Government, under the Foreign Trade Policy 2023, has introduced the Diamond Imprest Authorization (DIA) Scheme to enhance India’s competitiveness in the global diamond trade, promote exports, and protect employment, especially in the MSME sector.
Key Highlights:
Objectives:
- Boost value addition and export growth in the diamond sector.
- Support MSME exporters to compete globally.
- Retain India’s position as a global hub for diamond processing and exports.
- Mitigate recent challenges like export decline, job losses, and global demand shifts.
Key Features of the Scheme:
Feature Details
Type of Diamonds Allowed Natural cut and polished diamonds less than ¼ carat (25 cents)
Eligibility Exporters with Two Star Export House status and minimum $15 million annual exports
Export Obligation 10% value addition on imported diamonds
Duty Exemptions Exempts Basic Customs Duty, Anti-dumping Duty, Countervailing Duty, etc.
Effective Date April 1, 2025
Exclusion Lab-Grown Diamonds (LGDs) not covered
Monitoring Agency Gems and Jewellery Export Promotion Council (GJEPC)
Why the Scheme Was Introduced:
Challenges in the Diamond Sector:
- Global: Falling demand in US, Europe, China; rise in lab-grown diamonds.
- Domestic: High unsold inventory, rising operational costs, reduced credit flow, and high corporate tax.
- Employment Impact: Job losses in the diamond cutting and polishing segment.
International Context:
- Inspired by beneficiation policies in diamond-producing countries like Botswana and Namibia, which mandate local value addition.
Significance:
- Enhances India’s role in the global diamond value chain.
- Provides ease of doing business through duty relief.
- Promotes employment generation, especially for diamond assorters and processors.
- Facilitates inclusive growth by supporting MSMEs in a traditionally export-driven industry.
Way Forward:
- Regulate Lab-Grown Diamonds to prevent market distortion.
- Extend export credit period and consider tax exemptions for foreign diamond sellers.
- Ensure technology upgradation and skill training to sustain global leadership.
Closing the Women’s Health Gap
- 22 Jan 2025
In News:
The World Economic Forum (WEF), in collaboration with the McKinsey Health Institute, released the report titled “Blueprint to Close the Women’s Health Gap”, highlighting the economic and social benefits of addressing gender-based health disparities.
Key Insights from the Report:
Economic Potential:
- Closing the women’s health gap could contribute $400 billion to global GDP by 2040.
- Focusing on just three conditions—menopause, PMS, and migraine—could unlock $315 billion in productivity.
Health Disparity:
- Women experience 25% more years of poor health than men.
- Root causes include underrepresentation in research and sex-neutral clinical guidelines.
- Only 10% of trials on major conditions like ischemic heart disease and migraine include sex-disaggregated data.
Key Health Conditions Identified:
Lifespan Conditions:
- Maternal hypertensive disorders
- Postpartum hemorrhage
- Ischemic heart disease
- Cervical cancer
- Breast cancer
Health Span Conditions:
- Endometriosis
- Menopause
- Migraine
- Premenstrual syndrome (PMS)
Addressing these can add 2.5 healthy days per woman per year globally.
Women’s Health Impact Tracking (WHIT):
- A public digital platform by WEF and McKinsey.
- Tracks global health disparities.
- Offers data-driven insights to guide investment and policy decisions, especially for low- and middle-income countries which face 54% of the global women's health burden, yet host only 23% of related clinical trials.
Five Strategic Actions for Stakeholders:
- Count Women – Improve data collection specific to women’s health.
- Study Women – Boost research funding on women-centric health conditions.
- Care for Women – Create tailored clinical guidelines and protocols.
- Include All Women – Ensure equity for marginalized groups.
- Invest in Women – Finance innovative healthcare solutions and service delivery models.
One Nation, One Legislative Platform

- 22 Jan 2025
In News:
- The 85th AIPOC, held in Patna, Bihar, emphasized enhancing the effectiveness of legislative institutions through reforms in decorum, digitization, and public participation.
- A major outcome was the announcement of the One Nation, One Legislative Platform to digitally integrate legislative bodies across India.
All India Presiding Officers’ Conference (AIPOC):
- Established: 1921; first session held in Shimla.
- Role: Apex platform bringing together Presiding Officers of Parliament and State Legislatures.
- Objective: Strengthen democratic institutions by fostering cooperative federalism, legislative accountability, and improved law-making processes.
2025 Conference Highlights:
- Venue: Historic Bihar Legislature Premises, Patna.
- Key Themes:
- Reducing disruptions and maintaining decorum in legislative houses.
- Promoting qualitative debate and discussion.
- Observing the 75th year of the Constitution with participatory democratic celebrations.
- Resolutions Adopted:
- Formulation of internal code of conduct by political parties.
- Nationwide campaigns involving PRIs, urban bodies, students, NGOs, media, and more to celebrate democratic values.
One Nation, One Legislative Platform (ONOLP):
What It Is:
A national mission to create a unified digital ecosystem integrating the Parliament, state legislatures, and local bodies for better legislative coordination and public access.
Key Objectives:
- Real-Time Data Sharing: Seamless, up-to-date legislative information across institutions—proceedings, bills, debates, etc.
- Transparency & Accountability: Open access to deliberations enables citizen oversight and institutional accountability.
- Public Participation: User-friendly access encourages civic engagement in law-making and governance.
- AI & Tech Integration: Use of Artificial Intelligence for data analysis, decision support, and enhanced efficiency.
- Paperless Legislatures: Digitization of records to promote sustainability and reduce bureaucratic delays.
Implementation Support:
- Spearheaded by the Lok Sabha, with Speaker Om Birla announcing its completion by 2025.
- Includes the creation of a central portal for public and institutional use.
Chinar Trees

- 22 Jan 2025
In News:
The J&K Forest Department, in collaboration with the J&K Forest Research Institute (JKFRI), has launched a pioneering conservation initiative to digitally preserve the iconic Chinar trees (Platanus orientalis)—a vital part of Kashmir’s ecological and cultural heritage.
Significance of Chinar Trees:
- Locally known as Boonyi or Boueen, Chinar trees are deeply embedded in Kashmir’s cultural identity.
- These deciduous trees can grow up to 30 meters tall with a girth of 10–15 meters, and can live for over 600 years.
- They are known for their seasonal leaf color transformation—from green in summer to red, amber, and yellow in autumn.
- Notable specimens include Asia’s largest Chinar in Ganderbal and the oldest known Chinar (647 years) in Chattergam, Budgam.
Challenges to Chinar Survival:
- Urban expansion and habitat encroachment.
- Climate change, altering precipitation and temperature patterns.
- Illegal felling and timber exploitation.
- Increased susceptibility to pests and diseases.
Tree Aadhaar & Geo-Tagging Initiative:
- Over 28,500 Chinar trees have been geo-tagged and assigned unique Tree Aadhaar numbers from 2021 to 2023.
- Each tree is fitted with a QR-coded digital plate, enabling real-time access to:
- Tree location, height, girth, canopy dimensions
- Health status, ecological threats, and pest presence
- These plates are spring-mounted metal tags to prevent damage to the trees.
Conservation Goals & Future Plans:
- Digital Protection: Enables proactive monitoring and protection through a centralized database.
- Chinar Atlas: A comprehensive mapping of all Chinar trees in the region.
- Public Access Website: A dedicated digital portal is planned for broader access to Chinar data.
- Risk Assessment: Use of USG-based, non-invasive surveys to identify trees at risk without human interference.
- Emphasis on covering remote and restricted areas in future phases to ensure inclusivity in conservation.
Takers, Not Makers

- 21 Jan 2025
In News:
Report “Takers not makers: The unjust poverty and unearned wealth of colonialism” published by Oxfam.
Key Highlights:
- Released by: Oxfam International at the World Economic Forum 2025
- Core Focus: The report explores historical colonial wealth extraction, especially from India, and connects it to contemporary global inequalities.
Colonial Wealth Drain – India:
- $64.82 trillion extracted from India by Britain (1765–1900), adjusted to today’s value.
- $33.8 trillion (52%) enriched the UK’s richest 10%
- 32% benefited the British middle class
- India's industrial output dropped from 25% in 1750 to 2% in 1900 due to:
- British protectionist policies (especially targeting Asian textiles)
- High taxation, home charges, currency manipulation, and profit repatriation
Conceptual Framework:
- "Drain of Wealth" Theory by Dadabhai Naoroji forms the report’s foundation.
- Colonialism framed as both:
- Historical phenomenon: Loot, repression, forced de-industrialization
- Modern structure (Neo-colonialism): Corporate dominance, digital colonization, and unjust global governance
Neo-Colonial Parallels Today:
- Wages in Global South: 87–95% lower than for same work in Global North
- Multinational corporations:
- Descendants of colonial entities like the East India Company
- Extract resources & exploit labor under unequal terms of trade
- Global institutions like WTO and World Bank perpetuate inequity through imbalanced power dynamics
Ongoing Consequences in Global South:
- Poor public services, education, and healthcare
- Caste, religion, and language divisions institutionalized during colonial rule
- E.g., Only 0.14% of Indian languages used as medium of instruction
- Bengal Famine (1943): Caused by wartime policies & racist attitudes, ~3 million deaths
- Biopiracy cases (e.g., neem) reflect continued exploitation
Wealth Disparity & Inequality:
- Billionaire wealth tripled in growth rate in 2024 (vs. 2023)
- Top 1% own more than 95% of global wealth
- Over 3.5 billion people survive on less than $6.85/day
ILO Global Estimates on International Migrant Workers – 2022

- 21 Jan 2025
In New:
By addressing labour market shortages in host nations and contributing remittances to home countries, International Migrants (IM) continue to make contributions to world economic growth, the fourth edition of ‘Global Estimates on International Migrant Workers’, released by the International Labour Organization (ILO), stated.
Key Findings:
Global Representation:
- International Migrants (IMs) = 4.7% of global labour force - 167.7 million total:
- Employed: 155.6 million
- Unemployed (but seeking work): 12.1 million
- Increase of 30+ million migrant workers since 2013
- Growth rate dropped below 1% annually (2019–2022) due to COVID-19
Gender Composition:
- Male IMs: 61.3% (102.7 million)
- Female IMs: 38.7% (64.9 million)
- Lower female participation attributed to:
- Lower female migration rates globally
- Gender-based barriers in labour markets
- Over-representation in informal and unpaid sectors
Age Distribution:
- Prime working age (25–54 yrs): 74.9%
- Youth (15–24 yrs): 9.3%
- Older adults (55–64 yrs): 12.5%
- Seniors (65+ yrs): 3.4%
Sector-wise Employment:
Sector Share of IMs Notes
Services 68.4% Highest; women dominate (80.7%)
Industry 24.3% On par with non-migrants
Agriculture 7.4% Far lower than non-migrants (24.3%)
Care economy in high-income countries is a major pull for female migrants.
Host Country Distribution:
Region/Income Group % of IMs Notes
High-income countries 68.4% (114 million) Majorly Europe & North America
Upper-middle-income 17.4% (29.2 million)
Arab States 13.3% Declined since 2013
Europe (23.3%) and North America (22.6%) are top destinations. Arab states saw a 3% decline over the decade.
Definition: International Migrants (IMs)
As per the UN: Persons residing in a country different from their place of usual residence for at least one year, regardless of reason or legal status. Includes refugees, asylum seekers, etc.
Role & Contributions of IMs:
- Economic Drivers: Fill labour shortages (healthcare, construction, care work).
- Remittances: Boost home country economies.
- Demographic Support: Help address aging populations in developed nations.
Cultural Exchange: Promote diversity and global connectivity.
Mount Ibu Eruption

- 21 Jan 2025
In News:
Indonesia’s Mount Ibu erupted 1,000 times this month.
Overview:
- Location: Mount Ibu, Halmahera Island, North Maluku province, Indonesia.
- Volcano Type: Stratovolcano (composite volcano) – steep-sided, conical structure formed by successive layers of lava, ash, and pyroclastic material.
- Tectonic Setting: Located on the Pacific Ring of Fire, a major area of subduction zones with high volcanic and seismic activity.
Volcanic Context – Indonesia:
- Pacific Ring of Fire: Indonesia's location makes it one of the most volcanically active regions globally.
- Other Recent Eruptions:
- Mount Lewotobi Laki-Laki (twin-peaked volcano)
- Mount Ruang
- Both have shown heightened activity, triggering mass evacuations.
Indian Coffee Sector
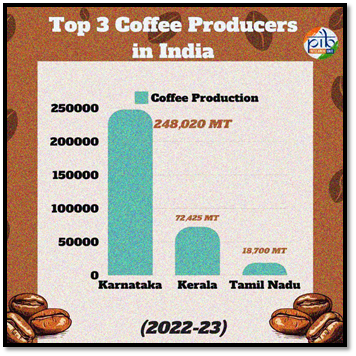
- 21 Jan 2025
In News:
India is now the seventh-largest coffee producer globally with exports reaching $1.29 billion in FY 2023-24, almost double the $719.42 million in 2020-21.
Historical Background
- Origin: Coffee was introduced to India in the 17th century by Baba Budan, a Sufi saint, who brought seven Mocha beans from Yemen and planted them in Baba Budan Giri hills, Karnataka.
- This act laid the foundation for India’s coffee cultivation, which has since evolved into a robust agro-industry.
India’s Global Coffee Status
- 7th largest coffee producer globally (FY 2023–24).
- Exports: Reached $1.29 billion in FY 2023–24, nearly double the $719.42 million in FY 2020–21.
- Major export destinations: Italy, Belgium, Russia.
- Export Share: Over 70% of India's coffee is exported, mostly in unroasted (green bean) form.
Types of Coffee Cultivated
- Arabica: Mild flavor, higher market value.
- Robusta: Strong flavor, more robust; often used in instant coffee.
- India's production: Around 75% is a mix of Arabica and Robusta.
Geographical Distribution
- Major Coffee-Growing Regions:
- Karnataka: Leads with over 70% of national production (~248,020 MT in 2022–23).
- Kerala and Tamil Nadu follow.
- Other contributors: Andhra Pradesh, Odisha, and parts of Northeast India
- Agro-climatic Conditions:
- Altitude: 600–1600 meters
- Temperature: 15°C–28°C
- Rainfall: 150–250 cm annually
- Soil: Well-drained, loamy, rich in humus and minerals
Economic & Environmental Significance
- Coffee is largely grown in the Western and Eastern Ghats, biodiversity-rich zones with shade-grown plantations.
- These plantations:
- Conserve ecology and biodiversity
- Support sustainable agriculture
- Contribute to rural livelihoods
Domestic Trends
- Rising café culture, urbanization, and higher disposable incomes have led to increased coffee consumption.
- Domestic consumption rose from 84,000 tonnes (2012) to 91,000 tonnes (2023).
- Preference for coffee over tea is growing, especially in urban and semi-urban India.
Government Initiatives
- Coffee Board of India initiatives under the Integrated Coffee Development Project (ICDP) aim to:
- Enhance yields
- Expand to non-traditional areas
- Promote sustainable practices
- Araku Valley Model:
- Involves 150,000 tribal families
- 20% increase in production
- Backed by Girijan Co-operative Corporation (GCC) and Integrated Tribal Development Agency (ITDA)
- Aligned with Aatmanirbhar Bharat and rural empowerment
Current Challenges and Future Outlook
- Challenges: Climate change impacts, pest attacks, price volatility in global markets.
- Opportunities:
- Rising global demand for value-added products (roasted & instant coffee)
- Export incentives and improved logistics
- Potential for agri-tourism and organic branding
Entity Locker

- 21 Jan 2025
In News:
The National eGovernance Division (NeGD), under the Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology (MeitY) has developed Entity Locker, a cutting-edge digital platform designed to transform the management and verification of business/organisation documents.
Key Highlights:
What is Entity Locker?
A secure, cloud-based platform that allows real-time access, encrypted storage, and authenticated sharing of business-related documents.
Who can use it?
Large corporations, MSMEs, startups, trusts, societies, and other organizational entities.
- Key Features:
- 10 GB Encrypted Cloud Storage: Ensures secure document management.
- Real-Time Document Access & Verification: Integrated with government databases.
- Consent-Based Sharing: Ensures data privacy during information exchange.
- Digital Signature Authentication: Enables legally valid and secure transactions.
- Aadhaar-Authenticated Role-Based Access: Promotes accountability in document handling.
- Integration with Government Systems: Linked with entities like:
- Ministry of Corporate Affairs (MCA)
- Goods and Services Tax Network (GSTN)
- Directorate General of Foreign Trade (DGFT)
Benefits:
- Reduces administrative burden and document processing time.
- Enhances compliance with statutory and regulatory requirements.
- Enables faster processes like vendor verification, loan applications, and FSSAI compliance.
- Promotes transparency and secure collaboration among stakeholders.
Significance:
Entity Locker is a pivotal component of India’s Digital Public Infrastructure, reflecting the Union Budget 2024–25 vision of promoting digital governance. It supports the broader goals of the Digital India Programme, aiming for a digitally empowered and efficient economy.
ILO World Employment and Social Outlook 2025
- 20 Jan 2025
In News:
The global economy is slowing down, making it harder for labour markets to recover fully since the outbreak of the COVID 19 pandemic, according to the International Labour Organization’s (ILO) report, World Employment and Social Outlook: Trends 2025, released in Geneva
Global Employment Trends
- Unemployment Rate (2024): Remained steady at 5%.
- Youth Unemployment: High at 12.6%, particularly severe in upper-middle-income countries (16%).
- Global Jobs Gap:
- 402 million people want work but are jobless (2024):
- 186 million unemployed
- 137 million temporarily unavailable
- 79 million discouraged workers
- 402 million people want work but are jobless (2024):
- NEET Population (2024):
- 259.1 million globally:
- 173.3 million young women (28.2%)
- 85.8 million young men (13.1%)
- 259.1 million globally:
Economic Growth and Labour Recovery
- Global Growth (2024): 3.2% (↓ from 3.3% in 2023 and 3.6% in 2022)
- Forecast (2025): Similar growth expected, with gradual deceleration ahead.
- Recovery Remains Uneven:
- High-income countries see rise in labour force participation.
- Low-income countries (LICs) face challenges creating decent jobs, with informal work returning to pre-pandemic levels.
- India’s GDP Growth:
- 6.9% in 2024, forecast at 6.4% in 2025
- Driven by monetary easing, domestic demand, and public investment
- Southern Asia: Growth pegged at 6.2% in 2024, 5.8% in 2025, mainly due to India.
- Labour Participation:
- Significant increase in female labour force participation, especially in India.
Key Labour Market Challenges
- Geopolitical Tensions
- Climate Change Costs
- Unresolved Debt Issues
- ~70 countries at risk of debt distress
- Many LICs spend more on debt servicing than on education/health
- Stagnant Real Wages
- Post-pandemic wage recovery mostly in advanced economies
- Vulnerable Jobs in Developing Regions
- Sub-Saharan Africa: 62.6% households live on <USD 3.65/day
- Employment is mainly informal, lacking security
Green and Digital Transitions
- Green Jobs Growth:
- Employment in renewables rose from 13.7 million (2022) to 16.2 million (2023)
- 46% of green energy jobs are in China
- Digital Economy:
- Offers promise, but infrastructure and skills gap limit benefits in many countries.
ILO Recommendations for Social Justice & SDG 2030 Goals
- Boost Productivity & Job Creation: Invest in skills training, education, and infrastructure
- Expand Social Protection: Better access to social security and safe work conditions
- Leverage Private Capital: LICs should channel remittances and diaspora funds into development
- Structural Transformation: Focus on modern services and manufacturing for quality jobs
- Youth Skill Development: Promote education for emerging sectors like green tech and digital economy
- Global Collaboration: Foster inclusive fiscal and monetary policies for equitable recovery
About ILO
- Established: 1919 | UN Agency
- Members: 187 countries
- Headquarters: Geneva, Switzerland
- Unique Tripartite Structure: Brings together governments, employers, and workers to set labour standards and promote decent work for all.
Dark Oxygen
- 20 Jan 2025
In News:
Scientists who recently discovered that metal lumps on the dark seabed make oxygen, have announced plans to study the deepest parts of Earth's oceans in order to understand the strange phenomenon.
What is Dark Oxygen?
Dark Oxygen refers to oxygen produced deep under the ocean without sunlight or photosynthesis.
Discovered in July 2024, this challenges the long-standing belief that photosynthesis is the sole natural source of oxygen.
Where was it discovered?
- Location: Clarion-Clipperton Zone (CCZ), 13,100 feet deep in the North Pacific Ocean, between Hawaii and Mexico.
- Zone Significance: Rich in polymetallic nodules containing manganese, iron, cobalt, nickel, copper, and lithium — crucial for green technologies.
Mechanism of Oxygen Production
- Polymetallic nodules on the seafloor generate oxygen via electrochemical reactions.
- These nodules split seawater (H?O) molecules into hydrogen and oxygen, without any light.
- This process is non-biological and independent of photosynthesis.
Why is this Discovery Important?
- Scientific Paradigm Shift: Challenges the idea that photosynthesis is the only natural pathway for oxygen generation.
- Origins of Life: Suggests that oxygen production may have existed before photosynthetic organisms, reshaping theories of early Earth’s evolution.
- Astrobiological Implications: Indicates the possibility of oxygen-rich environments on other planets, even without sunlight — enhancing the search for extraterrestrial life.
- Environmental Tech Potential: Could lead to innovations in renewable energy and carbon-neutral technologies, using metal-based catalysis.
About the Clarion-Clipperton Zone (CCZ)
- Geographic span: Between Hawaii and Mexico in the North Pacific Ocean.
- Resources: Contains vast reserves of critical minerals like manganese, nickel, cobalt — essential for electric vehicles and solar technology.
- A focus area for deep-sea mining and sustainability studies.
National Panchayat Awards 2024

- 20 Jan 2025
In News:
The President of India conferred the National Panchayat Awards 2024 on 45 outstanding Panchayats for their contributions to inclusive growth, environmental sustainability, and rural development. The event was held on 11th December 2024 (postponed from 24th April due to General Elections).
About the Awards
- Launched to commemorate: 73rd Constitutional Amendment Act, 1992, which gave constitutional status to Panchayats as institutions of local self-governance.
- Usual celebration date: 24th April — observed as National Panchayati Raj Day.
- Revamped in 2022 to align with Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) via Localization of SDGs (LSDGs).
Objectives
- Recognize best practices in rural governance.
- Encourage healthy competition among Panchayats.
- Promote effective implementation of LSDGs and quality service delivery.
Evaluation Structure
- Multi-level assessment: Block → District → State/UT → National level.
- Evaluation based on 9 LSDG themes, including:
- Poverty-Free & Enhanced Livelihoods
- Healthy Panchayat
- Child-Friendly Panchayat
- Water-Sufficient Panchayat
- Clean & Green Panchayat
- Self-Sufficient Infrastructure
- Socially Just & Secured Panchayat
- Panchayat with Good Governance
- Women-Friendly Panchayat
Award Categories
Award Category Focus Area
Deen Dayal Upadhyay Panchayat Satat Vikas Puraskar (DDUPSVP) Top 3 GPs under each LSDG theme
Nanaji Deshmukh Sarvottam Panchayat Satat Vikas Puraskar Top 3 GPs, Block Panchayats & District Panchayats with highest scores across all themes
Gram Urja Swaraj Vishesh Panchayat Puraskar GPs promoting renewable energy adoption
Carbon Neutral Vishesh Panchayat Puraskar GPs achieving net-zero carbon emissions
Panchayat Kshamta Nirmaan Sarvottam Sansthan Puraskar Institutions providing exemplary support to PRIs in implementing LSDGs
Key Highlights of 2024:
- Total Awards: 45 Panchayats
- Women Leadership: 42% of award-winning Panchayats led by women.
- Participation: 1.94 lakh Gram Panchayats competed.
- Prize Money: ?46 crore transferred digitally to awardees.
- Booklet Released: Best Practices of Awardee Panchayats.
- Film Showcased: Highlighting success stories and capacity-building.
State-wise Recognition
- Notable awardees from: Odisha, Tripura, Maharashtra, Uttar Pradesh, Andhra Pradesh, Kerala, Telangana, Assam, etc.
- Tripura & Odisha stood out in total recognitions.
- GPs from Maharashtra, Odisha, and Tripura received special awards for energy and carbon neutrality.
Other Key Initiatives for PRIs
Initiative Purpose
SVAMITVA Scheme (2020) Mapping rural property to provide Record of Rights.
e-Gram Swaraj (e-FMS) Work-based accounting to promote transparency.
mActionSoft Geo-tagging Panchayat assets via GPS-enabled photos.
Citizen Charter Portal “Meri Panchayat Mera Adhikaar” – Service delivery assurance to citizens.
India–Singapore Semiconductor Cooperation

- 20 Jan 2025
In News:
During his 2025 visit to India, Singapore President Tharman Shanmugaratnam announced plans to collaborate with India on semiconductor manufacturing and the creation of a semiconductor ecosystem, marking the 60th anniversary of diplomatic ties between the two nations.
Singapore’s Semiconductor Landscape
- Contribution to Economy: Accounts for ~8% of Singapore’s GDP.
- Global Standing:
- Produces 10% of global semiconductor output.
- 5% of global wafer fabrication capacity.
- 20% of global semiconductor equipment production.
- Comprehensive Ecosystem: End-to-end capabilities from IC design to packaging and testing.
- Infrastructure: Four wafer fabrication parks with advanced facilities.
- Current Limitation: Focused on mature-node chips (28 nm+); lacks high-end logic chip manufacturing (7 nm or below).
India’s Semiconductor Sector
- Market Size (2024): Valued at USD 52 billion; projected to reach USD 103.4 billion by 2030.
- Import Dependency: ~85% of semiconductor needs met through imports.
- Export-Import Gap (2022): USD 5.36 billion (imports) vs. USD 0.52 billion (exports).
India's Advantages:
- Skilled Talent Pool: Large number of STEM graduates.
- Cost Efficiency: Lower manufacturing and operational costs.
- Geopolitical Opportunity: Global supply chain diversification away from China.
Government Initiatives:
- India Semiconductor Mission (ISM)
- Semicon India Programme
- Display & Semiconductor Fab Schemes
- SPECS (Scheme for Promotion of Manufacturing of Electronic Components and Semiconductors)
Foreign Collaborations:
- MoUs with US, Japan, and European Commission.
- Tata–Powerchip (Taiwan) collaboration for a fab in Dholera, Gujarat.
How Singapore Can Support India’s Semiconductor Vision
- Manufacturing Partnerships:
- Collaborations with Singaporean firms for assembly and testing services.
- Access to Singapore's advanced manufacturing technologies.
- Talent Development:
- Academic exchanges in microelectronics and semiconductor engineering.
- Joint research and PhD programs.
- Infrastructure Development:
- Replication of Singapore-style wafer fab parks in India.
- Joint ventures to build specialized semiconductor industrial zones.
- Technology Access & Innovation:
- Transfer of advanced technologies and critical semiconductor materials.
- Collaboration on new-generation tech solutions (e.g., AI chips, advanced computing).
Additional Areas of Bilateral Cooperation
- Digital Economy: Exploring data corridor between GIFT City (India) and Singapore.
- Sustainability: Cooperation on green hydrogen, sustainable aviation fuel, and renewable energy.
Strategic Partnership: Upgraded to Comprehensive Strategic Partnership in 2024.
Internet Governance Internship and Capacity Building (IGICB) Scheme

- 20 Jan 2025
In News:
The National Internet Exchange of India (NIXI) announced the launch of its Internet Governance Internship and Capacity Building Scheme. This program aims to build awareness and develop expertise in internet governance (IG) among Indian citizens.
Key Highlights:
Objective:
To develop awareness and build a skilled pool of professionals in Internet Governance (IG) in India, enabling active Indian participation in global digital policy platforms.
Key Features:
- Internship Format:
- Bi-annual internship with two tracks: 3-month and 6-month durations
- Mentorship by experts from:
- International bodies (e.g., ICANN, APNIC, APTLD)
- Academic institutions and retired officials
- Stipend: ?20,000/month
- Outreach Component: Mandatory awareness programs to be conducted by interns
Focus Areas:
- Engagement with I-Star organizations, such as:
- ICANN (Internet Corporation for Assigned Names and Numbers)
- ISOC (Internet Society)
- IEEE (Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers)
- IETF (Internet Engineering Task Force)
- Exposure to global best practices and policy mechanisms in digital governance
- Capacity building for inclusive participation in emerging internet issues
Significance:
- Promotes digital policy leadership among Indian youth
- Enhances India’s representation in global internet governance dialogues
- Fosters a tech-savvy and policy-aware workforce for digital India initiatives
About NIXI (National Internet Exchange of India):
- Established: 19 June 2003
- Type: Not-for-profit (Section 8 company)
- Parent Ministry: MeitY
- Mandate:
- Enhance internet adoption and digital infrastructure in India
- Key Services:
- Internet Exchange Points (IXPs): Facilitate domestic internet traffic exchange
- .IN Registry: Manage India’s country code top-level domain (.in)
- IRINN: Allocate IPv4 and IPv6 resources within India
Capacity Building & Training: Promote internet-related knowledge and skills
Ratnagiri Buddhist Site

- 19 Jan 2025
In News:
The Archaeological Survey of India (ASI) has resumed excavations at the ancient Buddhist site of Ratnagiri in Odisha’s Jajpur district, unveiling monumental discoveries that underline its rich religious, cultural, and maritime legacy. This renewed effort comes more than 60 years after the site was first excavated between 1958 and 1961.
About Ratnagiri
- Meaning: Ratnagiri translates to “Hill of Jewels.”
- Location: Situated on a hill between the Brahmani and Birupa rivers, northeast of Bhubaneswar.
- Part of the Diamond Triangle: Along with Lalitgiri and Udaygiri, Ratnagiri forms Odisha’s famed “Diamond Triangle” of Buddhist heritage sites.
- Historical Period: Flourished between the 5th and 13th centuries CE, peaking under the Bhauma-Kara dynasty (8th–10th century CE).
- Buddhist School: An important centre for Mahayana and especially Vajrayana (Tantrayana) Buddhism.
- It possibly rivalled Nalanda in prominence as a Buddhist learning centre.
- The monastery complex at Ratnagiri is the only one in India with a curvilinear roof, once housing about 500 monks.
Recent Discoveries by ASI
- Three colossal Buddha heads, each measuring 3–4 feet.
- A massive palm sculpture, 5 feet in size.
- Hundreds of votive stupas, sculptures of Buddhist deities.
- A monolithic elephant statue, 5 feet long and 3.5 feet tall.
- Pottery, inscribed stones, beads, stone pillars, and a brick wall believed to be part of a larger structure.
- Rich ceramic assemblages, which may shed light on the region’s cultural and technological evolution.
These artefacts are estimated to date back to the 8th and 9th centuries CE and are believed to enhance understanding of Buddhism’s evolution in Odisha and its linkages with other cultures.
Buddhism in Odisha & Southeast Asian Links
- Buddhism gained a strong foothold in Odisha after Emperor Ashoka’s conquest of Kalinga (modern-day Odisha) in 261 BCE, a turning point that led him to embrace Buddhism.
- Though Buddha never visited Odisha, the region became instrumental in spreading Buddhism to Southeast Asia, especially during the Bhauma-Kara period.
- The state maintained robust maritime trade and cultural links with regions like Java, Bali, Sumatra, Borneo, Myanmar, and Sri Lanka.
- Baliyatra Festival: A vibrant annual event held in Cuttack, commemorating Odisha’s ancient seafaring ties with Bali and other Southeast Asian regions.
- According to some studies, Chinese monk Hiuen Tsang may have visited Ratnagiri during his travels in India (638–639 CE).
Significance of the Renewed Excavations
- The ASI aims to uncover partially visible structures, complete the site’s mapping, and contextualize the findings within the broader Buddhist history of India and Southeast Asia.
- Researchers hope to discover signs of foreign architectural or cultural influences, further confirming ancient Odisha’s global Buddhist and trade connections.
- The discoveries reaffirm Ratnagiri’s importance as a cornerstone of Buddhist learning and art, potentially on par with other renowned ancient centres like Nalanda and Vikramashila.
Interest Equalisation Scheme (IES)

- 19 Jan 2025
In News:
- Launched in April 2015, the Interest Equalisation Scheme (IES) offers subsidised interest rates on pre- and post-shipment export credit to Indian exporters, particularly MSMEs.
- The Commerce Ministry has sought a Rs 3,000 crore extension of the scheme beyond December 2024, with emphasis on supporting MSME exporters amidst global economic challenges.
Objectives of IES:
- Reduce Cost of Credit: Offers 3% to 5% interest subvention to make export credit affordable.
- Boost Export Competitiveness: Enables Indian exporters, especially MSMEs, to match international pricing.
- Encourage Export Diversification: Supports MSMEs in exploring new markets and products.
- Enhance Financial Inclusion: Promotes access to formal credit systems for small exporters.
Key Features:
- Interest Subsidy:
- 3% for MSME manufacturer exporters.
- 2% for merchant and manufacturer exporters of 410 specified tariff lines.
- Coverage: Initially limited to select products, later extended to all MSME exporters.
- Implementation:
- Managed by the RBI, in coordination with DGFT and authorized banks.
- Subsidy reimbursed to banks offering export credit at reduced rates.
- Banks exceeding Repo Rate + 4% are excluded.
Need for Extension:
- The scheme expired in December 2024, but exporters are demanding continuation due to:
- Rising global inflation and logistics disruptions (e.g., Red Sea crisis).
- Increase in credit duration demands from foreign buyers (120–150 days).
- Decline in export credit availability despite higher demand.
- FIEO reports a drop in outstanding export credit from ?2.27 lakh crore (2023) to ?2.17 lakh crore (2024).
- MSMEs operate on thin margins, and the subvention can make or break deals.
Significance for MSMEs:
- MSMEs contribute ~45% to India’s total exports and often struggle with high borrowing costs and limited financial access.
- Affordable credit via IES allows MSMEs to:
- Remain price competitive.
- Take larger and longer-term orders.
- Invest in product innovation and value addition.
- Improve market diversification and resilience.
Challenges in Accessing Credit:
- Stringent eligibility norms and collateral requirements.
- Complex administrative procedures for availing benefits.
- Limited awareness among small enterprises about the scheme.
- Slow disbursal and inconsistent application by banks.
Policy Implications and the Way Forward:
- A revamped, MSME-focused IES can ensure inclusive growth and boost India’s export-led development.
- Calls for:
- Simplification of procedural norms.
- Higher interest subvention limits or removal of caps (e.g., ?50 lakh per IEC holder).
- Longer validity (multi-year horizon) for predictability and planning.
- Aligns with the broader goals of Atmanirbhar Bharat, Make in India, and achieving $1 trillion in exports by 2030.
Exercise La Perouse 2025
- 19 Jan 2025
In News:
India is participating in the fourth edition of the multinational naval exercise La Perouse, hosted by France in key maritime straits—Malacca, Sunda, and Lombok. The Indian Navy's INS Mumbai, an indigenously built guided-missile destroyer, represents India.
Key Highlights:
- Participating Countries: Navies from India, France, Australia, USA, UK, Indonesia, Malaysia, Singapore, and Canada.
- Objectives:
- Enhance maritime situational awareness.
- Promote tactical interoperability through joint training.
- Conduct surface warfare, anti-air warfare, air defence, and VBSS (Visit, Board, Search and Seizure) operations.
- Strengthen cooperation on maritime surveillance, air operations, and information sharing.
- Significance:
- Demonstrates commitment to a rules-based international order in the Indo-Pacific.
- Reflects India’s vision of SAGAR (Security and Growth for All in the Region).
- Counters increasing presence of Chinese naval forces in the Indo-Pacific.
Strategic Location: Key Straits in Focus
- Strait of Malacca
- Connects: Andaman Sea (Indian Ocean) to South China Sea (Pacific Ocean).
- Geography: Lies between Peninsular Malaysia and Sumatra, near Singapore.
- Significance: One of the world’s busiest trade routes.
- Choke Point: Narrowest part (Philips Channel) is only 2.8 km wide.
- Sunda Strait
- Connects: Java Sea (Pacific) to the Indian Ocean.
- Between: Java and Sumatra (Indonesia).
- Challenges: Volcanic islands (e.g., Krakatoa), shallow depths (20–100 m).
- Importance: Secondary maritime route, strategic in times of congestion in Malacca.
- Lombok Strait
- Connects: Java Sea to the Indian Ocean.
- Between: Bali and Lombok islands.
- Depth: 250–1,300 meters – suitable for large vessels.
- Unique Feature: Part of the Wallace Line, a major ecological boundary.
Sanchar Saathi App

- 19 Jan 2025
In News:
In a landmark move to enhance telecom accessibility, security, and empowerment across India, the Union Minister of Communications launched a suite of citizen-focused initiatives. Key highlights of the event included the launch of the Sanchar Saathi Mobile App, National Broadband Mission (NBM) 2.0 and the inauguration of the Intra Circle Roaming facility at DBN Funded 4G Mobile Sites.
Sanchar Saathi Mobile App
- Launched by: Department of Telecommunications (DoT), Ministry of Communications.
- Platforms: Available on Android and iOS.
- Objective: Strengthen telecom security, empower citizens, and combat telecom fraud.
- Key Features:
- Chakshu (SFC): Report suspected fraud communications (calls/SMS).
- Know Your Mobile Connections: Identify and manage all mobile numbers issued in one’s name.
- Block Lost/Stolen Devices: Swiftly block, trace, and recover lost/stolen mobile phones.
- Verify Handset Genuineness: Confirm the authenticity of mobile handsets before purchase.
Impact so far (via Sanchar Saathi Portal, launched May 2023):
- 2.75 crore fraudulent connections disconnected.
- 25+ lakh lost/stolen devices blocked.
- 12.38 lakh WhatsApp accounts linked to cybercrimes disengaged.
- 11.6 lakh mule bank accounts frozen.
- 90% spoofed international calls blocked within 2 months of new prevention system.
National Broadband Mission (NBM) 2.0
- Launched by: Union Minister of Communications, builds upon NBM 1.0 (2019–2024).
- Part of: National Digital Communications Policy, 2018.
- Aim: Digitally empower citizens and bridge the digital divide to realize the vision of Viksit Bharat by 2047.
Key Targets (by 2030):
- 2.70 lakh villages to be connected with OFC (from ~50,000 now).
- 90% broadband connectivity to anchor institutions (schools, PHCs, Panchayats, Anganwadis).
- Fixed broadband speed: Increase national average from 63.55 Mbps (2024) to 100 Mbps.
- Right of Way (RoW) disposal time: Reduce from 60 days to 30 days.
- Rural internet subscribers: Increase from 45 to 60 per 100 population.
- 30% of mobile towers to be powered by sustainable energy.
- 100% mapping of PSU fiber networks on PM GatiShakti National Master Plan by 2026.
- Enhanced use of “Call Before u Dig (CBuD)” app to protect underground telecom infrastructure.
- Facilitate 5G rollout, and prepare infrastructure for 6G and common telecom ducts in all linear projects.
- Leverage power sector (e.g. Optical Ground Wire - OPGW) for broadband in remote/hilly areas.
Intra Circle Roaming (ICR) at DBN-Funded 4G Sites
- Launched by: Ministry of Communications.
- Implemented under: Digital Bharat Nidhi (DBN), formerly USOF.
- Objective: Allow subscribers of multiple telecom service providers (TSPs) (e.g., BSNL, Airtel, Reliance) to access 4G services from a single DBN-funded tower.
- Impact:
- Eliminates need for duplicate towers.
- Covers 27,000+ towers across 35,400 remote villages.
- Enhances user choice, reduces cost, and ensures efficient infrastructure use.
Nigeria admitted as BRICS Partner Country

- 19 Jan 2025
In News:
- Nigeria has been admitted as the 9th "Partner Country" of the BRICS grouping under Brazil’s presidency in 2025.
- Other BRICS partner countries include Belarus, Bolivia, Cuba, Kazakhstan, Malaysia, Thailand, Uganda, and Uzbekistan.
- A "partner country" in BRICS is allowed to attend summits, ministerial meetings, and participate in joint initiatives, but does not have formal membership or decision-making power.
About Nigeria’s Role
- Nigeria has the 6th largest population globally and the largest in Africa.
- It is the 4th largest economy in Africa, often termed the "Giant of Africa".
- Nigeria plays a significant role in South-South cooperation and reform of global governance structures, aligning with BRICS' strategic objectives.
About BRICS
- Founded: 2009 by Brazil, Russia, India, and China; South Africa joined in 2010.
- New Full Members (as of 2023): Iran, Egypt, Ethiopia, UAE, and Indonesia (effective Jan 2025).
- Membership Invitations: Saudi Arabia has been invited but not yet accepted.
- Applicants: Turkey, Azerbaijan, Malaysia have formally applied.
- Three Pillars of Cooperation:
- Political and Security
- Economic and Financial
- Cultural and People-to-People Exchanges
- Represents ~40% of global population and ~37.3% of global GDP.
India has hosted BRICS Summits in 2012 (4th), 2016 (8th), and 2021 (13th).
Binding DDT-Infused Soil with Biochar
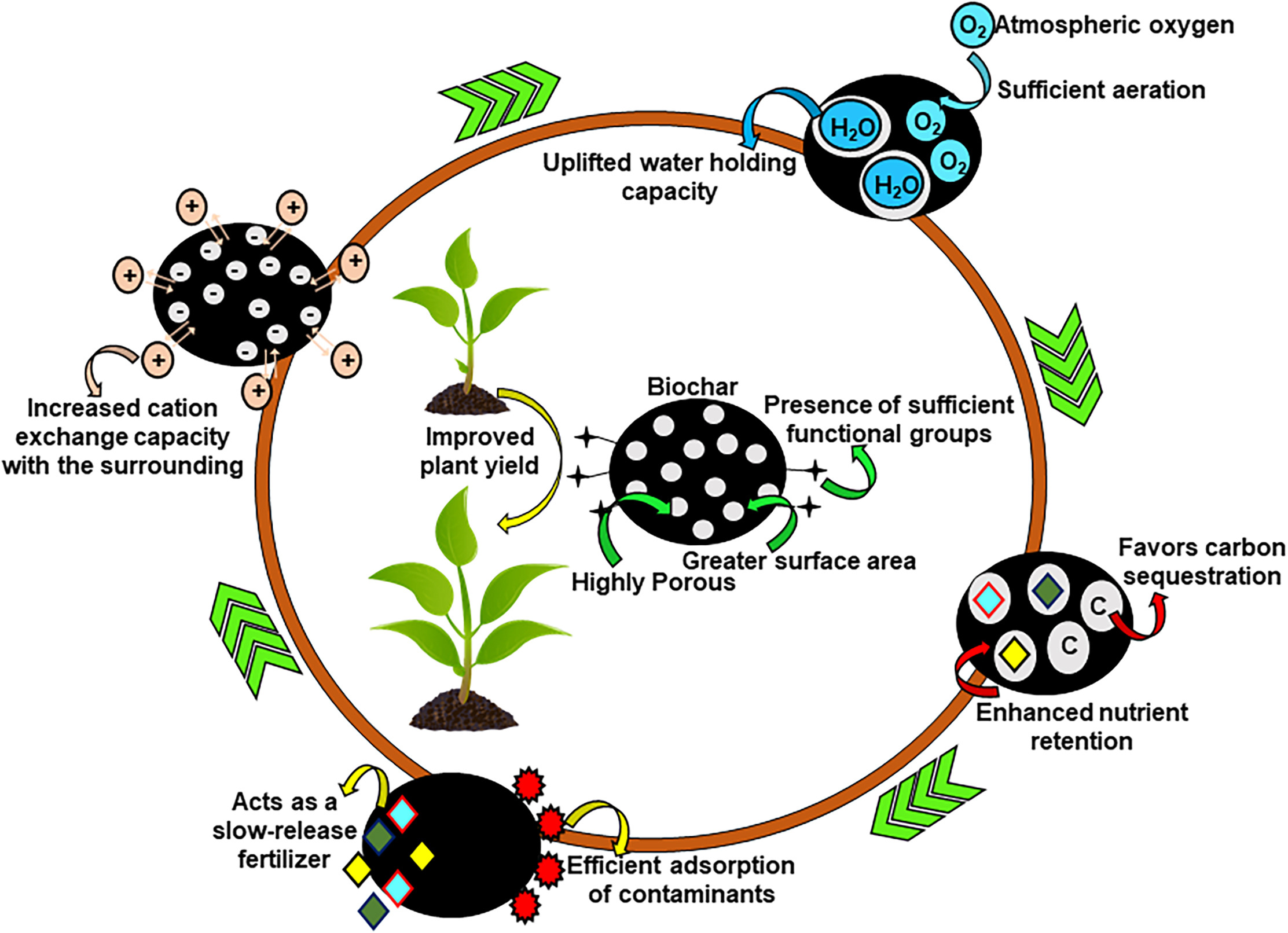
- 18 Jan 2025
In News:
A three-year study was conducted on a 23-hectare DDT-contaminated former tree nursery in southern Sweden. Researchers mixed biochar into sections of the contaminated soil and planted different crops, including pumpkins, legumes, grasses, and willows.
Key findings:
- Reduction of DDT Uptake: The presence of biochar reduced DDT absorption by soil organisms, cutting the toxin uptake by earthworms in half.
- Enhanced Soil Health: Biochar improved soil structure, fertility, and microbial activity.
- Cost-Effective Alternative: Unlike traditional soil removal methods, which are expensive and labor-intensive, biochar treatment offers a sustainable and economical approach.
- Support for Renewable Energy: The method allows for the growth of bioenergy crops such as willow trees, further contributing to environmental benefits.
Implications for Future Agricultural Practices
This breakthrough provides a viable approach to rehabilitate contaminated lands worldwide. Many regions, including India, still grapple with DDT contamination. While India banned agricultural use of DDT in 1972, it continues to be used for disease control under strict regulations. The application of biochar could significantly aid in soil restoration and sustainable land management
About DDT
- Dichlorodiphenyltrichloroethane (DDT) is a synthetic insecticide first introduced in 1939. It was widely used in agriculture and public health initiatives to control vector-borne diseases like malaria.
- However, despite its effectiveness against pests, DDT’s persistence in the environment led to severe ecological and health concerns.
- It degrades slowly, accumulates in fatty tissues, and disrupts ecosystems by affecting soil fertility, harming wildlife, and posing potential human health risks, including endocrine disruption and carcinogenic effects.
Challenges Posed by DDT-Contaminated Soils
The prolonged use of DDT has resulted in extensive soil contamination, making land infertile and unsuitable for cultivation. Conventional methods of decontamination, such as soil excavation and disposal, are expensive and environmentally unsustainable.
Biochar as a Solution
Researchers at Sweden’s Chalmers University of Technology have developed an innovative method to restore DDT-contaminated soils by integrating biochar.
What is Biochar?
Biochar is a charcoal-like material produced by burning organic waste in a controlled oxygen-limited environment (pyrolysis). It is known for its ability to enhance soil quality, bind contaminants, and store carbon for extended periods.
Kuka Rebellion and Namdhari Sect

- 18 Jan 2025
In News:
On January 17, Punjab Chief Minister Bhagwant Mann paid tribute at the Namdhari Shaheed Smarak in Malerkotla to commemorate Kuka Martyrs’ Day. The event marks the execution of 66 Namdhari Sikhs by the British in January 1872.
Kuka Rebellion: An Overview
The Kuka Rebellion was an anti-British movement led by the Namdhari sect in Punjab. It combined religious reform with resistance to colonial rule, reaching its peak in January 1872.
Key Events:
- January 13, 1872: Kukas, led by Hira Singh and Lehna Singh, protested against cow slaughter in Malerkotla.
- January 15, 1872: Clashes occurred between Kukas and government officials. A contingent attacked Malaudh Fort but was repulsed.
- January 17-18, 1872: 66 Kukas were executed by being blown up with cannons under orders of British official John Lambert Cowan.
Reasons Behind the Movement:
- Religious Reform: Opposed meat consumption, alcohol, and social vices.
- Colonial Oppression: Protested against British rule and native collaborators.
- Cow Protection: Strongly opposed cow slaughter, leading to confrontations with British authorities.
Impact and Aftermath:
- Suppression: The British crushed the movement with extreme brutality.
- Exile of Leaders: Satguru Ram Singh and other key leaders were exiled to Rangoon, Burma.
- Legacy of Martyrdom: The sacrifice of young Namdharis like 12-year-old Bishan Singh and Waryam Singh inspired future resistance movements in India.
Who are the Namdharis?
The Namdharis, also called Kukas, are a Sikh sect founded by Satguru Ram Singh in 1857 in Ludhiana. Their distinctive practices include:
- High-pitched recitation of Gurbani (hence the name ‘Kuka’ meaning ‘crying’ or ‘screaming’ in Punjabi).
- Wearing white attire as a sign of mourning for their exiled leader.
- Early adoption of Swadeshi principles, boycotting British goods and services.
Current Status of Namdhari Sect:
- The Namdharis, numbering around 2 lakh in Punjab today, have faced internal divisions since the death of Satguru Jagjit Singh in 2012.
- Two major factions exist:
- One led by Thakur Dilip Singh, headquartered in Sirsa, Haryana.
- Another led by Sangrur Uday Singh, headquartered at Bhaini Sahib, Ludhiana.
- A core belief remains that Satguru Ram Singh is still alive and will return one day.
Significance:
The Kuka Rebellion, though localized, was an important precursor to later national movements against British rule. It showcased the early spirit of resistance, long before organized freedom movements gained momentum in the 20th century.
Global Risks Report 2025
- 18 Jan 2025
In News:
- The World Economic Forum (WEF) has released the 20th edition of the Global Risks Report 2025, outlining the most pressing global risks over short-term (1-2 years) and long-term (10 years) horizons.
- The report, based on the Global Risks Perception Survey (GRPS) 2024-2025, categorizes risks across economic, environmental, geopolitical, societal, and technological domains.
Key Findings of the Report
Short-Term Risks (1-2 Years)
- Misinformation and Disinformation – Undermines trust in governance and institutions, complicating global cooperation.
- Extreme Weather Events – Rising costs and frequency due to climate change.
- State-Based Armed Conflict – Geopolitical tensions, including conflicts such as the Russia-Ukraine war.
Long-Term Risks (10 Years)
- Extreme Weather Events – Ranked as the most significant long-term risk.
- Biodiversity Loss & Ecosystem Collapse – Drastic impact on food security and natural systems.
- Critical Changes to Earth Systems – Irreversible environmental shifts.
Evolving Global Risk Landscape
The risk landscape is shaped by four structural forces:
- Technological Acceleration – Rapid advancements in AI and digital platforms.
- Geostrategic Shifts – Increasing global polarization and armed conflicts.
- Climate Change – Rising environmental hazards.
- Demographic Bifurcation – Aging populations and labor shortages.
Specific Risks and Trends
Environmental Risks
- Pollution: Increasing air, water, and land contamination due to unsustainable production.
- Natural Disasters: Wildfires in the U.S. projected to cause over $200 billion in damages.
- Water Supply Shortages: A major concern for countries like India.
Economic and Trade Risks
- Escalating Trade Protectionism: Increase in tariffs and restrictions (e.g., Make in India, U.S. Inflation Reduction Act).
- Economic Uncertainty: Global inflation projected to decrease to 3.5% by 2025, but trade tensions may reignite financial instability.
- Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) Decline: A 10% drop in 2023 due to trade fragmentation.
Technological Risks
- Misinformation & Disinformation: AI-generated content fuels societal polarization.
- Cybersecurity Threats: AI-driven cyberattacks and algorithmic biases in governance.
- Surveillance & Censorship: Increased digital monitoring with inadequate legal safeguards.
Geopolitical and Societal Risks
- Erosion of Human Rights: Increasing authoritarian surveillance and control.
- Migration & Resource Shortages: Climate-induced migration is a rising global concern.
- Pension Crisis: Aging populations in countries like Japan and Germany threaten economic stability.
India-Specific Risks
- Water Shortages – Critical impact on agriculture and urban development.
- Misinformation & Disinformation – Threatens democratic institutions and governance.
- Pollution (Air, Water, Soil) – Major environmental and health hazard.
- Labor & Talent Shortages – Workforce challenges due to demographic shifts.
- Erosion of Civic Freedoms – Concerns over digital surveillance and censorship.
Policy Recommendations
Global and Domestic Strategies
- Strengthen Multilateral Cooperation: WTO reforms and global trade dispute resolutions.
- Boost Domestic Resilience: Investment in infrastructure, healthcare, and education.
- Combat Pollution: Stricter regulations on air and water pollutants.
- Address Algorithmic Bias: Global standards for AI governance and accountability.
- Ethical Oversight for Biotech: WHO-led regulations for human genome editing.
Long-Term Sustainability Measures
- Flexible Work Policies: Encouraging non-linear career paths.
- Pre-Retirement Health Programs: Improving lifestyle choices to reduce healthcare costs.
- Pension System Reforms: Raising retirement ages and ensuring financial security for retirees.
Global Cybersecurity Outlook 2025
- 18 Jan 2025
In News:
The World Economic Forum (WEF) recently released the Global Cybersecurity Outlook 2025 report. The report examines cybersecurity trends, key challenges, and necessary strategies to enhance global cyber resilience.
About Global Cybersecurity Outlook 2025
Produced in collaboration with Accenture, the report highlights major cybersecurity issues influenced by geopolitical tensions, emerging technologies, supply chain complexities, and cybercrime advancements.
Key Issues Highlighted
- Geopolitical Conflicts:
- Ongoing conflicts, such as the Russia-Ukraine war, have increased cyber vulnerabilities in critical sectors like energy, telecommunications, and nuclear power.
- Nearly 60% of organizations state that geopolitical tensions have impacted their cybersecurity strategies.
- Cybersecurity Readiness:
- Two-thirds of organizations foresee AI impacting cybersecurity, yet only one-third have the tools to assess AI-related risks.
- Smaller organizations face significant challenges in adopting AI-driven security measures.
- Cyber Skills Gap:
- As of 2024, there is a shortage of 4.8 million cybersecurity professionals globally.
- Only 14% of organizations have a skilled workforce to manage current cybersecurity threats.
- Public-sector organizations are notably impacted, with 49% reporting a shortage in cybersecurity talent.
- Supply Chain Interdependencies:
- Over 50% of large organizations identify supply chain complexity as a barrier to cyber resilience.
- Vulnerabilities in third-party software, cyberattacks, and enforcement issues in security standards are key concerns.
- Cybercrime Sophistication:
- Cybercriminals are increasingly leveraging generative AI tools for automated and personalized attacks, including phishing and social engineering.
- In 2024, 42% of organizations experienced phishing and deepfake attacks.
- Regulatory Challenges: 70% of organizations reported that complex cybersecurity regulations cause compliance issues.
Impacts
- Critical Infrastructure:
- Cyberattacks on essential infrastructure, such as water utilities, satellites, and power grids, pose severe risks to public safety.
- Example: A 2024 cyberattack on a U.S. water utility disrupted operations, highlighting vulnerabilities in critical infrastructure systems.
- Biosecurity Risks:
- Advancements in AI, cyberattacks, and genetic engineering create risks for bio-laboratories and research institutions.
- Incidents in South Africa and the UK underscore these threats.
- Economic Disparities: Developed regions like Europe and North America demonstrate stronger cyber resilience compared to emerging economies such as Africa and Latin America.
- Transition Issues to Renewable Energy (RE): The shift to renewable energy introduces new cybersecurity risks, making power grids attractive targets for cybercriminals.
Factors Increasing Cybersecurity Complexity
- Supply Chain Vulnerabilities: Increasingly complex supply chains create risks with limited oversight, enabling cyberattacks to spread across interconnected systems.
- Geopolitical Tensions: Conflicts have driven advanced cyber strategies targeting critical infrastructure.
- AI-Driven Threats: Generative AI enables scalable malware deployment and sophisticated multilingual social engineering attacks.
- Cyber Skills Gap: A growing 8% skills gap leaves two-thirds of organizations unable to meet cybersecurity demands.
- Convergence of Cybercrime and Organized Crime: Rising cyber-enabled fraud has attracted organized crime groups, amplifying social impact.
- Climate-Linked Cyber Risks: Energy grids are increasingly targeted due to their reliance on evolving energy systems.
- Quantum Vulnerabilities: Quantum computing poses risks to public-key encryption, which is essential for securing digital systems.
Way Forward
Strategic Investment:
- Cybersecurity must be viewed as a strategic investment rather than a technical expense.
- Governments are encouraged to modernize legacy systems and upgrade operational technologies to protect critical sectors.
Public-Private Collaboration:
- Collaboration between business and cybersecurity leaders is essential for sharing threat intelligence and enhancing resilience.
- Small and medium enterprises (SMEs) may require government incentives to enhance cybersecurity.
Skills Development: Expanding specialized training programs, certifications, and incentives is crucial to addressing the cybersecurity skills gap.
Focus on Resilience Over Prevention: Nations must prioritize resilience by enhancing response mechanisms, crisis management frameworks, and ensuring continuity of services.
International Cooperation:
- Collaborative efforts through forums like the United Nations (UN) and G20 can strengthen global cybersecurity frameworks.
- Developed nations should assist emerging economies in improving cyber resilience.
Current Framework for Cybersecurity in India
- Legislative Measures:
- Information Technology Act, 2000 (IT Act)
- Digital Personal Data Protection Act, 2023
- Institutional Framework:
- Indian Computer Emergency Response Team (CERT-In)
- National Critical Information Infrastructure Protection Centre (NCIIPC)
- Indian Cyber Crime Coordination Centre (I4C)
- Cyber Swachhta Kendra
- Strategic Initiatives:
- Bharat National Cybersecurity Exercise 2024
- National Cyber Security Policy, 2013
- Sector-Specific Regulations:
- Cybersecurity Framework for SEBI Regulated Entities
- Telecommunications (Critical Telecommunication Infrastructure) Rules, 2024
Rupee Depreciation

- 18 Jan 2025
In News:
The Indian rupee has recently experienced sharp devaluation against the US dollar after a period of relative stability. This shift is attributed to several factors, including capital outflows, rising import costs, and RBI’s evolving policy stance.
Understanding Exchange Rate Regimes
Exchange rates are classified into:
- Fixed Exchange Rate: The central bank maintains a constant exchange rate by actively managing reserves.
- Floating Exchange Rate: Market-driven rates with minimal intervention.
- Managed-Floating Exchange Rate: A blend of market forces and central bank intervention.
India has largely pursued a managed-floating exchange rate regime. The RBI has historically responded to excess demand by depreciating the rupee while selling forex reserves and, under excess supply conditions, resisted rupee appreciation to maintain export competitiveness.
Post-COVID Exchange Rate Shift
Between 2022 and November 2024, the RBI temporarily adopted a strategy resembling a fixed exchange rate regime to stabilize the rupee. However, amid rising capital outflows and increased import costs, the RBI recently reverted to its managed-float approach, allowing the rupee to depreciate.
Causes of Rupee Depreciation
- Internal Factors:
- Rising inflation reduced the rupee's real value and increased production costs.
- A widening trade deficit due to higher crude oil imports heightened demand for foreign currency.
- Persistent fiscal imbalances further pressured the rupee.
- Policy ambiguity in the RBI’s stance added market uncertainty.
- External Factors:
- Capital outflows driven by global uncertainties and rising US interest rates.
- Geopolitical tensions (e.g., Russia-Ukraine war) increased India’s import bill.
- The US dollar's strength amid aggressive Federal Reserve rate hikes further weakened the rupee.
Implications of Rupee Devaluation
- Positive Effects:
- Boost to Exports: A weaker rupee makes Indian goods cheaper, enhancing export competitiveness if supported by real exchange rate depreciation.
- Adverse Effects:
- Inflationary Pressures: Higher import costs increase consumer prices.
- Reduced Purchasing Power: Increased costs are often passed on to consumers.
- Foreign Debt Servicing: A depreciated rupee raises debt repayment costs for Indian firms and the government.
- Investor Sentiment: Currency instability diminishes foreign investor confidence, triggering further capital outflows.
Structural Constraints in the Indian Economy
- Divergence between NEER and REER:
- Since the mid-2010s, India's Nominal Effective Exchange Rate (NEER) depreciated while the Real Effective Exchange Rate (REER) appreciated. This divergence undermines export competitiveness, as rising domestic prices offset nominal depreciation benefits.
- Rising Markups:
- Non-financial firms increased their markups on variable costs, contributing to inflation and nullifying the advantages of currency depreciation for exports.
Policy Responses and Recommendations
- RBI Interventions:
- Forex market interventions to manage demand-supply imbalances.
- Interest rate adjustments to attract capital inflows and stabilize the rupee.
- Enhanced forex reserve management to mitigate excessive volatility.
- Fiscal Strategies:
- Reducing Import Dependency: Boost domestic production of high-demand goods like crude oil substitutes.
- Export Incentives: Strengthen export sectors through subsidies, incentives, and improved infrastructure.
- Encouraging Long-Term FDI: Promoting stable investment environments for sustained capital inflows.
- Structural Reforms:
- Policies that enhance domestic production, reduce reliance on volatile foreign portfolio investments (FPIs), and maximize remittances can stabilize the rupee in the long term.
Bharat Ranbhoomi Darshan

- 17 Jan 2025
In News:
The Bharat Ranbhoomi Darshan initiative, launched by Defence Minister coinciding with the 77th Army Day celebrations, is a collaborative effort between the Ministry of Defence and the Ministry of Tourism.
Key Highlights:
- This initiative is designed to promote battlefield and border tourism by providing citizens with access to historically significant battlefields and military sites.
Objectives
- Promote Battlefield and Border Tourism: Encourage citizens and tourists to explore India's military history.
- Enhance Awareness: Educate visitors about India’s historic battles and military valor.
- Socio-Economic Development: Boost infrastructure, connectivity, and local economies in border regions.
Features of Bharat Ranbhoomi Darshan
- Virtual Tours and Interactive Content: The platform offers historical narratives, virtual tours, and interactive multimedia to provide a detailed account of each battlefield.
- Travel Planning Assistance: Visitors can access information regarding permits, travel routes, and accommodations.
- Integration with the Incredible India Campaign: The initiative is part of the government’s broader tourism strategy, ensuring widespread promotion.
- Collaborative Infrastructure Development: The Indian Army is working with local civil authorities to facilitate safe tourism without compromising operational preparedness.
Key Locations Covered
- Galwan Valley (Ladakh): Site of the 2020 India-China clash.
- Doklam: A tri-junction between India, Bhutan, and China.
- Line of Control (LoC) and Line of Actual Control (LAC) Sites:
- Nathu La Pass (Sikkim): Significant in the 1967 Indo-China clashes.
- Longewala (Rajasthan): Site of a key battle during the 1971 Indo-Pak war.
- Other Sites: Locations of the 1962 war with China and various Indo-Pak conflicts.
Significance
- Historical and Patriotic Engagement: Provides citizens firsthand insights into the challenges faced by soldiers in remote, strategic locations.
- Tourism Development in Border Areas: Previously restricted areas now open for visitors, leading to economic benefits for local communities.
- National Security Awareness: Encourages greater appreciation of India's defense forces and their contributions.
Implementation
The first phase of the Bharat Ranbhoomi Darshan project includes key battlefields and border sites across seven major regions. Future phases will expand coverage to additional historical military locations.
Fast Track Immigration FTI-TTP

- 17 Jan 2025
In News:
The Government of India is launching the Fast Track Immigration Trusted Traveller Program (FTI-TTP) to streamline immigration at seven major airports.
Key Highlights:
- The initiative, inaugurated by Union Home Minister Amit Shah, aims to enhance the travel experience for Indian nationals and Overseas Citizen of India (OCI) cardholders.
- This comes seven months after the programme was first introduced at Indira Gandhi International (IGI) Airport, New Delhi. The airports included in this initial phase are: Mumbai, Chennai, Kolkata, Bengaluru, Hyderabad, Cochin and Ahmedabad
Objectives of FTI-TTP
- Provide seamless and secure immigration services.
- Reduce human intervention using automated e-gates.
- Align with the Viksit Bharat@2047 vision for modern infrastructure.
How the Programme Works
The FTI-TTP simplifies immigration with automated e-gates. Travellers must complete a one-time online registration to enroll. The process involves:
- Online Registration: Submit personal details and upload necessary documents via the official portal (https://ftittp.mha.gov.in).
- Biometric Submission: Fingerprints and facial images must be submitted at an airport or Foreigners Regional Registration Office (FRRO).
- Immigration Clearance via E-Gates:
- Passengers scan their boarding passes and passports at e-gates.
- Biometrics are automatically verified.
- Upon authentication, the e-gate opens, granting clearance.
Validity: Registration is valid for five years or until the registered passport expires, whichever comes first.
Who is Eligible?
The first phase of the FTI-TTP is open to:
- Indian nationals.
- OCI cardholders aged between 12 and 70 years.
- Children aged 12-18 can register using their parents’ email/phone number.
- ECR (Emigration Check Required) passport holders are not eligible.
Documents Required for Registration
- Passport-sized photograph (as per Indian passport specifications).
- Scanned copy of passport (front and back pages).
- Proof of current address.
- OCI card details (if applicable).
Key Points to Note
- Registration may take up to a month due to verification by field agencies.
- Applications with incorrect or outdated information may be rejected.
- In case of passport loss or expiry, travellers must reapply and submit fresh biometrics.
- Passports must have at least six months’ validity at the time of applying.
- For support, travellers can reach out via email at india.ftittp-boi@mha.gov.in.
Implementation Phases
The FTI-TTP will be implemented in two phases:
- Phase 1: Covers Indian citizens and OCI cardholders.
- Phase 2: Will extend to foreign travellers.
- The programme will be expanded to 21 major airports across the country.
Comparison with Similar Global Programmes
Several countries have implemented similar fast-track immigration systems:
United States: Global Entry
- Introduced in 2008.
- Offers self-service kiosks for pre-approved travellers.
- Requires background checks and in-person interviews.
United Kingdom: Registered Traveller Service
- Launched in 2015.
- Allows frequent visitors from select countries, including India, to use e-gates.
- Requires visa eligibility or multiple prior visits.
European Union: Smart Borders Initiative
- Implemented in 2016, with full deployment expected by 2024.
- Pre-registers biometric data for faster processing at Schengen Area borders.
Australia: SmartGate
- Started in 2007 for Australian and New Zealand passport holders.
- Uses automated kiosks for identity verification via passport scans and photos.
Saudi Arabia: Smart Travel System
- Launched in 2019.
- Uses automated e-gates for faster immigration clearance.
- Expanding as part of Vision 2030 to improve travel experience, particularly for Hajj pilgrims.
QS World Future Skills Index 2025

- 17 Jan 2025
In News:
The QS World Future Skills Index 2025, released by Quacquarelli Symonds (QS), evaluates countries' readiness to meet the evolving demands of the global job market. It assesses nations based on skill development, education, and economic transformation, highlighting their preparedness for emerging technologies, artificial intelligence (AI), and sustainability.
India’s Performance in the Index:
- Overall Ranking: India is ranked 25th globally, categorizing it as a “Future Skills Contender.”
- Future of Work Category: India ranked 2nd, only behind the United States, reflecting its preparedness for AI, digital, and green jobs.
- Economic Transformation: India scored 58.3, the lowest among the top 30 countries, reflecting challenges in innovation and sustainability.
- Skills Fit: India received a score of 59.1, the weakest among the top 30 nations, indicating a gap between workforce skills and industry requirements.
- Academic Readiness: India’s education system is struggling to keep pace with employer demands, necessitating curriculum reforms and stronger academia-industry collaboration.
Key Findings from the Report:
Strengths:
- Digital Readiness: India has demonstrated strong capabilities in integrating digital talent into the workforce.
- Youth Advantage: A large, young population provides a demographic dividend for sustained economic growth.
- Startup Ecosystem: India’s startup culture and government initiatives support technological advancement and innovation.
Weaknesses:
- Higher Education-Industry Gap: Mismatch between education and employer requirements, particularly in AI, green skills, and entrepreneurship.
- Limited R&D Investment: India’s research and development spending is 0.6% of GDP, far below the global average of 2.7%.
- Low Innovation in Sustainability: India scored 15.6 out of 100, ranking poorly in future-oriented innovation for sustainability.
Challenges and Concerns:
- Skilled Workforce Shortage: The National Skill Development Corporation (NSDC) estimates a 29 million skilled workforce gap in critical sectors such as healthcare, semiconductor manufacturing, and AI.
- Low Employability Rates: Only 25% of management professionals, 20% of engineers, and 10% of graduates meet global employability standards.
- Higher Education Accessibility: Many students face difficulties in accessing quality tertiary education, particularly in skill-intensive fields.
Opportunities for Growth:
- Leverage Demographic Dividend: India can capitalize on its young workforce to dominate skill-based industries while other nations struggle with aging populations.
- Policy Support:
- National Education Policy (NEP) 2020: Focuses on modular education and reskilling initiatives.
- ULLAS Program: Aims to expand lifelong learning and skill development.
- Technological Integration: Advancements in AI and digital learning can help modernize academic curricula and improve job readiness.
Recommendations for Improvement:
- Enhancing Academia-Industry Collaboration: Universities should prioritize problem-solving, entrepreneurship, and creativity to align education with employer needs.
- Increasing R&D Investment: Raising spending on research and development to promote innovation and sustainability.
- Expanding Access to Education: Bridging regional disparities in tertiary education through flexible and modular learning.
- Strengthening Policy Implementation: Ensuring effective execution of skilling programs to reduce the workforce-employability gap.
Eighth Pay Commission

- 17 Jan 2025
In News:
The Union government has approved the constitution of the Eighth Pay Commission, benefiting 50 lakh central government employees and 65 lakh pensioners, including serving and retired defence personnel. The decision, taken ahead of the Delhi Assembly elections, aims to address long-standing demands from trade unions and employee organizations.
Key Features of the 8th Pay Commission
- Early Constitution: Although the Seventh Pay Commission's term ends in 2026, the early establishment of the Eighth Pay Commission ensures timely recommendations and implementation.
- Composition: The commission will have a Chairperson and two members, typically led by a retired Supreme Court judge.
- Terms of Reference (ToR):
- Revision of Pay: Recommend updates to salary structures and allowances.
- Addressing Pay Disparities: Resolve wage differences across various cadres.
- Market Parity: Align pay structures with industry standards.
- Pension and Retirement Benefits: Improve pension schemes and adjust them for inflation.
- Economic Impact Analysis: Assess how salary hikes contribute to economic growth.
- Stakeholder Consultations: Engage with governments and other stakeholders before finalizing recommendations.
Economic Implications of the 8th Pay Commission
- Employee Well-being: Higher wages will enhance the quality of life for government employees.
- Boost to Consumption: Increased salaries are expected to stimulate demand and support economic expansion.
- Ripple Effect on PSUs & States: Many public sector undertakings and state governments follow the central pay commission’s recommendations, potentially leading to wider economic benefits.
- Fiscal Considerations: The implementation of the Seventh Pay Commission in 2016-17 led to an expenditure increase of ?1 lakh crore. A similar rise in 2026-27 could impact fiscal space for capital expenditures.
Challenges and Concerns
- Implementation Delays: Past commissions have taken two years to submit recommendations, which could push implementation beyond 2027.
- Living Wage & Pension Issues: Existing formulas for minimum wage and pension calculations may need revision to reflect rising healthcare, education, and digital access costs.
- Financial Burden on the Exchequer: A significant increase in revenue expenditure could limit the government’s ability to invest in infrastructure and development projects.
Global Economic Prospects (GEP) Report 2025
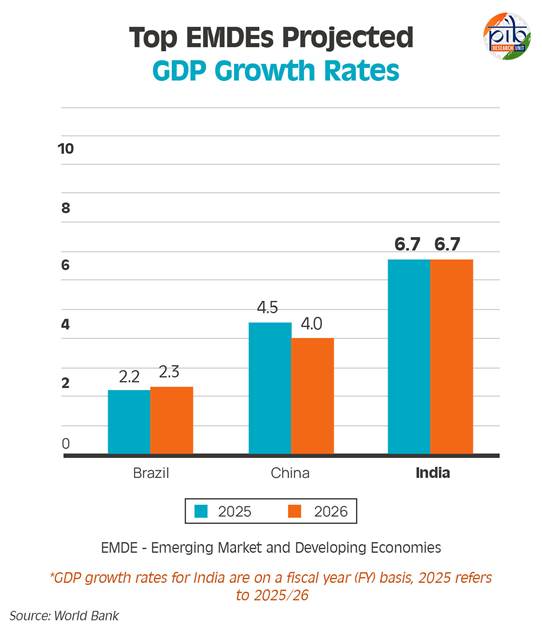
- 17 Jan 2025
In News:
The World Bank has released its Global Economic Prospects (GEP) report for 2025, a flagship biannual publication analyzing trends and projections in the global economy, with a focus on emerging markets and developing economies (EMDEs). The report highlights economic growth forecasts, trade dynamics, and the challenges and opportunities shaping the global economic landscape.
Global Economic Outlook
- The world economy is projected to expand at a steady yet subdued rate of 2.7% in both 2025 and 2026, maintaining the pace of 2024.
- Inflation, which peaked above 8% in recent years, is expected to stabilize at an average rate of 2.7% in 2025 and 2026, aligning with central bank targets.
- Despite growth, the global economy remains 0.4 percentage points below the 2010-2019 average, raising concerns about its ability to tackle poverty effectively.
Challenges and Risks
- Trade Restrictions: New trade restrictions imposed in 2024 were five times higher than the 2010-19 average, contributing to a slowdown in global trade and economic growth.
- Rising Protectionism: Increased fragmentation in global trade policies is limiting exports and hampering economic integration.
- Policy Uncertainty: Adverse policy shifts, sluggish progress in reducing inflation, and weaker performance in major economies pose downside risks to global recovery.
- Debt and Investment Concerns: Developing economies are experiencing sluggish investment growth and high debt levels, exacerbated by climate change-related costs.
Emerging Markets and Developing Economies (EMDEs)
- EMDEs have significantly evolved since 2000, now contributing about 45% of global GDP, compared to 25% at the start of the century.
- The three largest EMDEs—India, China, and Brazil—have accounted for approximately 60% of annual global growth over the past two decades.
- Growth in low- and middle-income developing countries is expected at 4.1% in 2025 and 4% in 2026, with a notable slowdown compared to the early 2000s.
- Low-income countries are projected to rebound to 5.7% in 2025 and 5.9% in 2026, aided by easing conflicts in some regions.
- The world's poorest nations, with annual per capita incomes below USD 1,145, recorded growth of 3.6% in 2024, impacted by conflicts in regions like Gaza and Sudan, alongside lingering effects of COVID-19 and geopolitical tensions.
India-Specific Highlights
- Fastest-Growing Major Economy: India is expected to maintain its position as the world’s fastest-growing major economy, with a projected growth rate of 6.7% in both 2025 and 2026.
- Sectoral Growth: The services sector will remain robust, while manufacturing activity is expected to strengthen.
- Investment Growth: Supported by rising private investment, improved corporate balance sheets, and favorable financing conditions, investment growth in India is expected to remain steady.
- Key Growth Drivers:
- Infrastructure development under the PM GatiShakti National Master Plan.
- Innovation-driven initiatives like Startup India and the Production Linked Incentive (PLI) Scheme.
- Expansion of the digital economy and financial inclusion efforts.
- Rural Demand and Consumption: Growth in rural demand and a recovery in farm production have bolstered consumer spending, although urban consumption remains affected by inflation and slow credit growth.
Human Papillomavirus (HPV)

- 16 Jan 2025
In News:
January is Cervical Cancer Awareness Month, and the focus on this month underscores the critical importance of preventing cervical cancer, a disease responsible for significant mortality among women in India. At the heart of this prevention is the Human Papillomavirus (HPV) vaccine, which is recognized as the most effective measure to prevent cervical cancer and other HPV-related cancers. Despite its potential, the HPV vaccine remains out of reach for many due to its high cost and the need for greater awareness.
HPV and its Impact in India
HPV is responsible for 99.7% of cervical cancers worldwide, making it one of the primary causes of cancer in women. In India, cervical cancer is the third most common cancer among women, accounting for about 6-29% of all cancers in women. As of GLOBOCAN 2020, India alone has 20% of the global burden of cervical cancer, with over 123,000 cases and a 9.1% mortality rate.
Additionally, HPV can lead to several other cancers, including anal, vulvar, vaginal, penile, and throat cancers, making its vaccination vital for overall cancer prevention.
The HPV Vaccine: A Game-Changer
The HPV vaccine is the most effective tool to prevent infections caused by the virus and reduce the incidence of associated cancers. The vaccine works by stimulating the immune system to produce antibodies that neutralize the virus before it can cause damage. There are different types of vaccines authorized in India, including:
- Gardasil (protects against HPV types 6, 11, 16, and 18)
- Cervarix (a bivalent vaccine targeting HPV 16 and 18)
- Cervavac (India's first HPV vaccine, developed by the Serum Institute of India)
The vaccine is recommended for both males and females between 9 and 26 years, with a special focus on children aged 12 to 13 years, as the vaccine is most effective when administered before exposure to the virus. It’s also suitable for people who are immunocompromised or HIV-infected.
Challenges to HPV Vaccination in India
Despite the obvious benefits, the uptake of the HPV vaccine in India faces several barriers:
- High Costs: The price of the vaccine remains prohibitively high. For example:
- Gardasil 9 costs ?10,850 per dose.
- Gardasil 4 is priced between ?2,000 to ?4,000 per dose.
- Cervavac, the Indian-made vaccine, costs around ?2,000 per dose, which is more affordable but still out of reach for many.
- Awareness and Cultural Perceptions: There is a lack of awareness about HPV and its link to cervical cancer. Cultural factors, particularly around reproductive health, can also create reluctance to vaccinate, especially in rural or conservative areas.
- Limited Access: Currently, the vaccine is available through private practitioners and is not part of the National Immunisation Programme (NIP), limiting access to the broader population.
The Way Forward: National Immunisation and Awareness Campaigns
The National Technical Advisory Group on Immunisation (NTAGI) has recommended that the HPV vaccine be included in India’s National Immunisation Programme (NIP). This would enable broader access and affordability, especially for girls aged 9–14 years and ensure that a routine vaccination schedule is implemented at the age of 9 years. Some states like Punjab and Sikkim have already taken steps to introduce the vaccine in their state-level immunization programs.
Additionally, a nationwide HPV vaccination campaign could raise awareness about the vaccine and its benefits, helping to overcome the challenges of cost, safety concerns, and cultural perceptions. Regular cervical cancer screenings (such as Pap smears and HPV tests) should also be encouraged to identify precancerous changes early.
Cabinet Approves Establishment of ‘Third Launch Pad’ at ISRO's Sriharikota Facility

- 16 Jan 2025
In News:
The Union Cabinet, has approved the establishment of a Third Launch Pad (TLP) at the Satish Dhawan Space Centre (SDSC), located at Sriharikota, Andhra Pradesh. This project marks a significant step in enhancing India’s space capabilities and will support the Next Generation Launch Vehicles (NGLV) for ISRO’s evolving space exploration programs.
Key Features of the Third Launch Pad
The TLP will be built with an adaptable design, capable of supporting NGLV and LVM3 vehicles with semi-cryogenic propulsion. The launch pad will also serve as a standby for the Second Launch Pad (SLP) at Sriharikota. This addition will help ISRO meet its growing launch capacity needs, particularly for future human spaceflight missions and space exploration projects. It will facilitate higher launch frequencies, thus boosting the Indian space ecosystem.
Implementation Strategy and Timeline
The Third Launch Pad is planned to be developed within 48 months (4 years), with the total cost pegged at ?3984.86 Crore. The development will involve maximized industry participation and will utilize existing infrastructure at the launch complex. The project will also leverage ISRO’s experience gained from establishing the earlier launch pads.
The Importance of the Third Launch Pad
The TLP is designed to support the Next Generation Launch Vehicles (NGLV), a key part of ISRO’s vision for space exploration. The facility will not only accommodate heavier vehicles but will also ensure standby capacity for the Second Launch Pad (SLP). Its strategic location at Sriharikota ensures several advantages:
- Proximity to the Equator: This offers a substantial increase in payload capacity due to the additional push provided by the Earth's rotation.
- Safety and Accessibility: The site is free from major international maritime or airline routes, ensuring a safe flight path.
- Geographical Advantage: The launch pad is situated on the eastern coast, enabling launches in an easterly direction, maximizing the benefits of Earth’s rotational speed.
Future Plans for Indian Space Exploration
The establishment of the Third Launch Pad is crucial for the expanded vision of India’s space program, particularly in line with the Amrit Kaal period. ISRO aims to achieve ambitious milestones, such as the Bharatiya Antariksh Station (BAS) by 2035 and an Indian Crewed Lunar Landing by 2040. The NGLV will play a pivotal role in these plans, with features like:
- A three-stage vehicle and reusable first stage.
- Semi-cryogenic propulsion, using refined kerosene and liquid oxygen, which will increase payload capacity by three times at 1.5 times the cost of current vehicles.
The Role of Sriharikota in India’s Space Program
Sriharikota, the hub of ISRO’s launch operations, has been integral to India’s space exploration. Currently, the Indian Space Transportation Systems rely on two operational launch pads:
- First Launch Pad (FLP): Established over 30 years ago for PSLV and SSLV missions, FLP continues to support Polar Satellite Launch Vehicle (PSLV) and Small Satellite Launch Vehicle (SSLV) launches.
- Second Launch Pad (SLP): Built primarily for GSLV and LVM3 vehicles, SLP also serves as a standby for PSLV. Over its 20 years of operation, SLP has supported several national missions, including Chandrayaan-3, and is preparing for the Gaganyaan missions.
Does ‘Blood Money’ Have a Legal Standing?

- 16 Jan 2025
In News:
The concept of ‘blood money’ has come under scrutiny recently, especially in the context of the death sentence awarded to Indian nurse Nimisha Priya from Kerala in Yemen. This case, where the focus is on monetary compensation paid to the victim’s family, has sparked renewed discussions on the practice of blood money.
What is ‘Blood Money’?
‘Blood money’ or diya is a term used in Islamic Sharia law and refers to a sum of money that the perpetrator of a crime must pay to the victim or the victim’s family, typically in cases of unintentional murder or homicide. The custom is designed to offer compensation to the family for the loss of income and alleviate their suffering, rather than placing a price on human life. This practice allows the victim’s family to forgive the accused and avoid retribution, called qisas, under the Sharia.
However, even when blood money is paid, the community or state retains the authority to impose a penalty or punishment, which could include imprisonment or other penalties, based on the seriousness of the crime.
How Does Blood Money Figure in Islamic Sharia Law?
In Islamic law, the amount of blood money varies based on several factors such as the victim’s gender, religion, and nationality. The following examples demonstrate the application of blood money in different Islamic countries:
- Saudi Arabia: In Saudi Arabia, blood money is part of traffic regulations, where the perpetrator must pay compensation to the heirs of victims who die in road accidents. While a Sharia court determines the amount of compensation, the police handle the determination of the guilty party. In workplace accidents, a special committee sets the amount. Saudi Arabia has considered reforming its laws to ensure equal compensation for men and women, Muslims and non-Muslims. However, efforts to amend the laws have not yet been fully implemented.
- Iran: In Iran, blood money differs based on the gender and religion of the victim. A woman’s compensation is typically set at half of that of a man’s. While the Supreme Court of Iran upheld a law to equalize compensation for all individuals in 2019, full implementation of the law has yet to be realized.
- Pakistan: Pakistan has incorporated provisions for diya and qisas in its legal system through the Criminal Laws (Amendment) Ordinance, 1991, aligning its practices with those of Islamic law.
- Yemen: In Yemen, parties involved can negotiate compensation, with judicial oversight ensuring fairness.
India’s Stand on ‘Diya’ and Blood Money
India does not include the provision for blood money in its formal legal framework. However, a similar concept exists in the form of plea bargaining, which allows the accused to negotiate with the prosecution in exchange for a reduced sentence or charge. Plea bargaining involves the defendant pleading guilty to a lesser offense in return for a concession, either in terms of the charges or the sentence.
Plea Bargaining in India:
Introduced under the Criminal Law (Amendment) Act, 2005, plea bargaining was added to the Code of Criminal Procedure, 1973. While it bears some resemblance to blood money in that it allows for compensation to the victim, it has significant limitations:
- It can only be applied to crimes punishable by imprisonment of less than seven years.
- It is not applicable to heinous crimes such as murder or rape, or offenses involving women or children under 14.
- The accused must voluntarily agree to plead guilty, with no coercion involved.
While plea bargaining may include compensation under Section 265E of the Code, discussions continue to refine this provision to make it more inclusive, similar to the reforms seen in Islamic countries regarding blood money.
Historical Practices Similar to Blood Money
Throughout history, various cultures have had practices similar to blood money. These include:
- Brehon Law (Ireland): In the 7th century, Brehon law established the concept of Éraic (body price) and Log nEnech (honor price). These were compensation systems that allowed for the amicable resolution of crimes, avoiding capital punishment.
- Galanas (Wales): Galanas in Welsh law determined compensation based on the victim's social status, where a blood fine was required in cases of murder, unless the killing was justified.
- Wergeld (Germany): The Wergeld system in early medieval Germany required compensation for homicide or grave offenses, often in monetary terms.
- Other Medieval States: Several medieval states established a standard payment for the victims’ families in the event of homicide or serious crimes, much like blood money.
Cases of Indians Pardoned with Blood Money
India has witnessed instances where blood money has been invoked for Indian nationals facing death sentences abroad:
- Arjunan Athimuthu (Kuwait, 2019): Arjunan’s death sentence was commuted to life imprisonment after his family paid ?30 lakh in blood money.
- Abdul Rahim (Saudi Arabia): Abdul Rahim, convicted for the murder of a Saudi boy in 2006, was pardoned after ?34 crore in blood money was paid. However, he has not been released from prison yet.
- UAE Cases:
- In 2017, 10 Indians were pardoned after paying 200,000 dirhams as blood money.
In 2009, 17 Indians on death row for the murder of a Pakistani national were pardoned after a blood money amount of nearly ?4 crore was paid.
US AI Hardware Export Restrictions and Impact on India

- 16 Jan 2025
In News:
Days before demitting office, the Joe Biden administration has released an expansive regulatory framework on the export of artificial intelligence (AI) hardware such as graphics processing units (GPUs), which could have far-reaching consequences for India’s AI ambitions.
Three-Tier Framework for AI Hardware Export Restrictions
- Tier 1: Closest US Allies
- Countries: Australia, Belgium, Canada, South Korea, UK, etc.
- No restrictions on computing power deployment.
- Minimal security requirements.
- Impact: Free access to AI technology for these nations.
- Tier 2: Majority of Countries (Including India)
- Countries: India, Brazil, South Africa, etc.
- Restrictions: Limited to importing approximately 50,000 advanced AI chips (around $1 billion) through 2027.
- Potential to Double Cap: If countries sign agreements to uphold strict security standards.
- Impact on India:
- Short-Term: Likely to fulfill current demand for 10,000 GPUs for the IndiaAI Mission.
- Long-Term: Challenges in scaling AI infrastructure, with possible delays in large AI data centers and difficulty acquiring large-scale GPUs.
- Tier 3: Countries of Concern (Restricted Nations)
- Countries: Russia, China, North Korea, Iran, etc.
- No Access to US AI Technology: Nearly total prohibition of AI tech exports.
Special Provisions for India and China
- General Validated End User (GVEU) status for India and China:
- India: Authorisation for civilian and military use, excluding nuclear applications.
- China: Only civilian use permitted under similar conditions.
Why the US Imposed These Restrictions?
- National Security: Prevent adversaries (China, Iran, Russia) from acquiring advanced AI technologies.
- US Technological Leadership: To protect US AI leadership and prevent loss of competitive edge.
- Trusted Ecosystem: Build secure and trusted AI environments for allied nations.
Impact on India
- Short-Term:
- IndiaAI Mission: Current procurement of 10,000 GPUs unlikely to be affected.
- Subsidized GPUs: Available for startups, academia, and researchers.
- Long-Term Concerns:
- Licensing Uncertainties: Possible delays in large-scale AI deployments and AI data centers.
- Impact on Large Firms: Companies like Reliance and Yotta may face challenges scaling up AI compute infrastructure.
- National AI Mission Challenges: Difficulty in acquiring enough GPUs for large-scale AI projects beyond 2027.
- Strategic Leverage: US could use AI export restrictions to negotiate trade deals or tariff adjustments.
Nvidia’s Criticism of the AI Diffusion Rules
- Overreach and Bureaucratic: Nvidia criticized the 200+ page regulatory framework as excessive, secretive, and bureaucratic.
- Harming US Competitiveness: Claims that the rules would hinder US innovation and global leadership, weakening the competitiveness of the US semiconductor and software industries.
- Contrast with Trump’s Approach: Praises the earlier Trump administration for fostering AI growth through industry competition without compromising national security.
Enforcement of the Rules
- Regulatory Control: Managed by the US Bureau of Industry and Security (BIS) under the Department of Commerce.
- Technology Access: Ensures AI chips and models do not reach adversaries or nations posing security risks.
Potential Impact on India’s AI Strategy
- AI Hardware Infrastructure: Challenges in large-scale AI hardware deployment.
- Competitive Disadvantage: Potential delays or downsizing of AI data centers could affect India’s competitiveness in AI technology.
- Strategic Partnerships: India may need to secure General National Validated End User authorizations to ensure uninterrupted access to advanced chips.
- AI Market Growth: India’s AI market projected to grow to $17 billion by 2027, with an annual growth rate of 25%-35%.
Nine Years of Startup India

- 16 Jan 2025
In News:
On January 16, 2025, India marks nine years of Startup India, a transformative journey that began in 2016. Designated as National Startup Day, this occasion celebrates the nation’s strides in fostering a robust and inclusive entrepreneurial ecosystem.
Current Status (as of Jan 2025)
Over 1.59 lakh startups recognized by DPIIT, making India the 3rd largest startup ecosystem globally.
- More than 100 unicorns (startups valued over $1 billion).
- Key hubs: Bengaluru, Hyderabad, Mumbai, Delhi-NCR; growing contribution from smaller cities.
Key Sectors
- Major sectors: Fintech, Edtech, Health-tech, E-commerce.
- Notable companies: Zomato, Nykaa, Ola exemplify India's shift from job seekers to job creators.
Key Milestones (2016–2025)
- Startups grew from around 500 in 2016 to 1.59 lakh in 2025.
- 73,151 startups with at least one-woman director as of 2024, showcasing rise in women entrepreneurship.
- Over 16.6 lakh jobs created by DPIIT-recognized startups by 2024.
Core Features of Startup India
- Ease of Doing Business: Simplified compliance, self-certification, and single-window clearances.
- Tax Benefits: Three-year tax exemptions for eligible startups.
- Funding Support: ?10,000 crore Fund of Funds for Startups (FFS) supports early-stage funding.
- Sector-Specific Policies: Policies focusing on sectors like biotechnology, agriculture, and renewable energy.
Industry-wise Jobs Created
- IT Services: 2.04 lakh jobs.
- Healthcare & Lifesciences: 1.47 lakh jobs.
- Professional & Commercial Services: 94,000 jobs.
- Total direct jobs created: 16.6 lakh (as of Oct 2024).
Flagship Schemes
- Startup India Seed Fund Scheme (SISFS).
- Credit Guarantee Scheme for Startups (CGSS).
- Fund of Funds for Startups (FFS) Scheme.
Other Key Initiatives
- Capacity Building & Handholding: Workshops for regional ecosystems, especially in non-metro cities.
- Outreach & Awareness: Initiatives to facilitate funding, incubation, and mentorship opportunities.
- Ecosystem Development: National-level events like Startup Mahakumbh to bring together key stakeholders.
- International Linkages: India’s G20 Presidency institutionalized Startup20 to enhance global collaborations.
BHASKAR Platform (Launched in Sept 2024)
- Objective: Centralize and streamline interactions within the entrepreneurial ecosystem.
- Key Features:
- Networking: Connects startups, investors, mentors, and government bodies.
- Resources: Provides quick access to essential tools and knowledge for scaling startups.
- Global Outreach: Promotes India as a global innovation hub.
Startup Mahakumbh
- 2024 Edition: Hosted 1,300 exhibitors, 48,000 visitors, and 392 speakers, including unicorn founders and policymakers.
- 2025 Edition (3-5 April, New Delhi): Theme - “Startup India @ 2047 – Unfolding the Bharat Story.”
Ayushman Bharat Pradhan Mantri Jan Arogya Yojana (AB PM-JAY)

- 15 Jan 2025
In News:
Odisha has become the 34th state to implement the Ayushman Bharat Pradhan Mantri Jan Arogya Yojana (AB PM-JAY). The National Health Authority (NHA) of the Union Ministry of Health signed a Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) with the Department of Health and Family Welfare, Government of Odisha to onboard the state under the scheme.
Key Highlights:
- The scheme will be implemented alongside the existing Gopabandhu Jan Arogya Yojana in Odisha.
- It provides health coverage of Rs. 5 lakh per family per annum, with an additional Rs. 5 lakh for women members.
- Approximately 1.03 crore families will be covered under the scheme.
- Shri JP Nadda, Union Health Minister, emphasized that the scheme is the world’s largest and fastest-growing health coverage initiative.
- Shri Mohan Charan Majhi, Chief Minister of Odisha, highlighted that people will now have access to cashless treatment in over 29,000 empaneled hospitals.
About Ayushman Bharat PM-JAY:
- Launched in 2018 under the Ministry of Health & Family Welfare (MoH&FW).
- Targets 12 crore families (~55 crore beneficiaries).
- Provides cashless hospital coverage for secondary and tertiary care.
- Fully funded by the government, with cost-sharing between the Centre and states.
- Covers nearly 2,000 medical procedures, including major surgeries.
Since its inception, over 8.19 crore hospital admissions have been recorded, with ?1.13 lakh crore spent on healthcare for marginalized sections.
Cyclone Dikeledi
- 15 Jan 2025
Cyclone Dikeledi struck Mayotte, a French overseas territory in the Indian Ocean, located in the Mozambique Channel. The cyclone caused severe flooding and damage, following closely after Cyclone Chido, which had hit the region in December 2024.
About Mayotte:
- Comprises two islands from the Comoros archipelago: Mayotte (Grande Terre) and Pamandzi (Petite Terre).
- It is the poorest region in both France and the European Union.
- Colonized by France in 1843 and annexed along with the Comoros in 1904.
- In a 1974 referendum, while 95% of Comoros opted for independence, 63% of Mayotte voted to remain French.
- While Comoros declared independence in 1975, Mayotte continues to be governed by France.
Cyclone Chido, which struck in December 2024, was recorded as the most severe storm to hit Mayotte in 90 years.
Commissioning of Three Indian Naval Combatants

- 15 Jan 2025
In News:
In a major boost to India’s maritime defense capabilities, three frontline warships—INS Nilgiri, INS Surat, and INS Vaghsheer—were commissioned into the Indian Navy at the Naval Dockyard in Mumbai. This marks a significant step in India's self-reliance in defense manufacturing and strengthens its presence in the Indian Ocean Region (IOR).
INS Nilgiri: Project 17A Stealth Frigate
INS Nilgiri is the lead ship of the Project 17A class, an advanced version of the Shivalik-class frigates, designed for multi-mission capabilities in blue-water operations.
Key Features:
- Advanced stealth technology reducing radar and infrared signatures.
- Equipped with supersonic surface-to-surface missiles, Medium Range Surface-to-Air Missiles (MRSAM), upgraded 76 mm guns, and rapid-fire close-in weapon systems.
- Versatile roles in anti-surface, anti-air, and anti-submarine warfare.
- Constructed using integrated modular design for faster assembly.
- Other ships in this class—Himgiri, Taragiri, Udaygiri, Dunagiri, and Vindhyagiri—are under construction at Mazagon Dock Shipbuilders Limited (MDL) and Garden Reach Shipbuilders and Engineers (GRSE).
INS Surat: Project 15B Stealth Destroyer
INS Surat is the fourth and final guided missile destroyer under Project 15B, following INS Visakhapatnam, INS Mormugao, and INS Imphal. It represents an upgraded version of the Kolkata-class destroyers.
Key Features:
- AI-Enabled Operations: First Indian warship integrated with artificial intelligence solutions for enhanced combat efficiency.
- High-Speed Capability: Can exceed speeds of 30 knots (56 km/h).
- Advanced Armament: Equipped with modern surface-to-air and anti-ship missiles, torpedoes, and sophisticated network-centric warfare sensors.
- Strategic Role: Acts as a high-speed, maneuverable warship with increased strike capability and endurance.
Project 15B was initiated in 2011, with ships named after major Indian cities to symbolize national unity. These destroyers serve as critical assets in naval operations, ensuring dominance in maritime warfare.
INS Vaghsheer: Project 75 Scorpene-Class Submarine
INS Vaghsheer is the sixth and final Kalvari-class submarine built under Project 75, designed for stealth and versatile naval operations.
Key Features:
- Scorpene-Class Design: Developed in collaboration with the French Naval Group.
- Diesel-Electric Propulsion: Silent and highly maneuverable, making it one of the world’s most advanced attack submarines.
- Mission Capabilities: Specializes in anti-surface warfare, anti-submarine warfare, intelligence gathering, and special operations.
- Weapons Systems: Armed with wire-guided torpedoes, anti-ship missiles, and state-of-the-art sonar systems.
The Kalvari-class submarines continue India's legacy of submarine warfare, named after decommissioned Soviet-origin Foxtrot-class submarines post-Independence.
Iran's Capital Relocation

- 15 Jan 2025
In News:
Iran has announced plans to relocate its capital from Tehran to the Makran coastal region due to economic and environmental concerns.
Reasons Behind Relocation
- Overcrowding and Resource Constraints: Tehran, the capital for over 200 years since the Qajar dynasty (1794-1925), faces overpopulation, air pollution, water scarcity, and energy shortages.
- Strategic Importance of Makran: Located in Sistan and Baluchestan Province, Makran’s proximity to the Gulf of Oman enhances its potential for economic development.
- Economic and Maritime Significance: Home to key ports like Chabahar, Makran is vital for Iran’s petroleum reserves and coastal trade.
- Geopolitical Considerations: The development of Makran as an international trade hub could strengthen Iran’s economic ties with Central Asia and the Indian Ocean region.
About Makran
- Geographical Overview: A semi-desert coastal plateau shared by Pakistan and Iran, bordered by the Arabian Sea and the Gulf of Oman.
- Key Ports and Trade Routes: Gwadar (Pakistan) and Chabahar (Iran) serve as critical gateways to the Strait of Hormuz, a global oil supply route.
Alexander’s Invasion and Makran’s Historical Significance
Background of Alexander’s Invasion (327–325 BCE)
- Entry into India: Alexander, King of Macedonia (336-323 BCE), entered India via the Khyber Pass after conquering Kabul.
- Key Battles:
- Battle of Hydaspes (Jhelum): Faced and defeated King Porus, later reinstating him as an ally.
- Retreat at Hyphasis (Beas River): His army, exhausted and wary of the Nanda Empire’s strength, refused to march further east.
The Gedrosian Desert March
- Extreme Hardships: While retreating through the Makran Desert, Alexander lost a third of his army to dehydration, starvation, and exhaustion.
- Comparison with Cyrus the Great: Unlike Cyrus II, who failed to cross the desert, Alexander’s army endured the harsh terrain, albeit with heavy casualties.
Impact of Alexander’s Invasion on India
- Cultural and Trade Exchanges: Facilitated early Indo-Greek interactions and opened key trade routes linking South Asia and Europe.
- Greek Settlements: Established cities like Alexandria (Kabul) and Boukephala (Jhelum), influencing local governance and trade.
- Mauryan Expansion: Weakened regional rulers enabled Chandragupta Maurya to establish the Mauryan Empire.
- Influence on Art and Culture: Indo-Greek fusion led to the Gandhara School of Art, integrating Greek and Indian artistic traditions.
Makaravilakku festival

- 15 Jan 2025
In News:
Kerala police deploy 5,000 personnel at Sabarimala ahead of Makaravilakku festival.
Key Highlights:
- Makaravilakku is a prominent annual Hindu festival held at the Sabarimala Temple in Kerala, dedicated to Lord Ayyappa.
- It marks the celestial event of the Sun entering Capricorn (Makaram Rashi) on Makara Sankranti.
- The festival is a culmination of the 41-day pilgrimage to Sabarimala, celebrated with devotion, discipline, and spiritual purification.
- Sabarimala is one of the largest pilgrimage sites globally, drawing 10-15 million devotees annually.
Location:
- The Sabarimala Temple is located on the Sabarimala hill in Pathanamthitta, Kerala, within the Periyar Tiger Reserve.
- It is surrounded by 18 hills and is located along the banks of the Pamba River.
Key Rituals:
- 41-Day Pilgrimage (Vratham): Devotees observe strict practices like celibacy, fasting, and wearing black or saffron attire to purify the body and soul.
- Makaravilakku (Makara Jyothi): A celestial light appears on Makara Sankranti, believed to be a divine manifestation of Lord Ayyappa.
- Thiruvabharanam Procession: On Makaravilakku day, sacred royal ornaments (Thiruvabharanam) are carried in a procession from the Pandalam Palace to the temple.
- Aarti at Ponnambalamedu: The Makaravilakku light is believed to emanate from camphor lit during the Aarti ritual at Ponnambalamedu, viewed three times from Sabarimala.
Festival Duration:
- The Makaravilakku festival lasts for seven days, starting on Makara Sankranti and concluding with the Guruthi offering, which propitiates the gods of the wilderness.
Significance of Makaravilakku:
- The festival symbolizes the merging of celestial and spiritual energies, highlighting devotion, purity, and self-discipline.
- Devotees chant the mantra "Swamiye Saranam Ayyappa," seeking blessings and protection from Lord Ayyappa.
- The event promotes equality, as all devotees wear simple black or blue attire and carry the sacred bundle, “Irumudi Kettu.”
Cultural and Religious Aspects:
- The festival is an important cultural and religious observance for millions of Hindus.
- Though previously believed to be a supernatural event, Makaravilakku now involves a ritual performed by the Malayaraya tribe, overseen by the Travancore Devaswom Board.
Prohibition on Women:
- The temple traditionally restricts women aged 10-50 from entering. This was challenged in 2018 when the Supreme Court ruled to lift the prohibition, although it remains a contentious issue.
Purulia Observatory

- 14 Jan 2025
In News:
New observatory at remote Purulia district West Bengal is expected to contribute significantly to Astrophysics.
Key Highlights:
Location and Significance:
- Established by: S.N. Bose Centre for Basic Sciences (SNBCBS), an autonomous institute under the Department of Science and Technology (DST), India.
- Location: The observatory is situated at Panchet Hill, in the Garpanchakot area of Purulia district, West Bengal, at an elevation of 600 meters above ground level.
- Longitude Gap: Positioned at a longitude of approximately 86° E, this observatory fills a critical longitudinal gap in global astronomical observation networks. There are very few observatories along this longitude, making it strategically important for observing transient astronomical phenomena that last from minutes to hours.
- Global Impact: This location will allow for unique contributions to global astrophysical research, especially in observing transient events, which require observatories spread across all global longitudes.
Technological and Educational Role:
- The observatory is equipped with a 14-inch telescope for scientific observations.
- It will serve as a training ground for students and researchers, helping them to handle telescopes, record astronomical data, and engage in research.
- The observatory aims to foster national and international collaborations in astronomical research, furthering India’s contributions to the field.
Collaborations and Ecosystem Development:
- MOU with Sidhu Kanu Birsa University: The observatory will be run jointly with Sidhu Kanu Birsa University, sharing resources and responsibilities. The collaboration promises to bring scientific and educational advancements to Purulia, a district traditionally considered backward.
- The establishment of the observatory is expected to boost the local ecosystem, creating a space for scientific engagement and inspiring students in the region.
Research and Contributions:
- The research team, from the Department of Astrophysics at SNBCBS, contributed to the conceptualization, site characterization, and installation of the telescope.
- Their efforts ensure the observatory will be capable of high-quality scientific observations, especially with regard to weather parameters and astronomical seeing conditions.
Future Prospects:
- Scientists emphasized that the observatory will significantly contribute to the global body of knowledge in observational astronomy.
- Also highlighted the potential of the observatory to create a scientific ecosystem in the region.
- The observatory will also serve as a source of inspiration for students in Purulia and provide a much-needed boost to local education in the fields of science and astrophysics.
Konkan Region’s Sada and Biodiversity

- 14 Jan 2025
In News:
A Konkan secret, the flat-top sada is a freshwater paradise.
Key Highlights:
Geography of Sada:
- The Konkan region lies between the Arabian Sea and the Western Ghats.
- Sada refers to flat-topped hills, formed by centuries of erosion, and is a prominent feature in the Ratnagiri district.
- These areas are typically barren except during the monsoon season when they come alive with flora and fauna.
Biodiversity and Ecosystem Services:
- A biodiversity survey between 2022-2024 recorded 459 plant species, with 105 being endemic to the Konkan region.
- The survey also identified 31 species of reptiles, 13 species of amphibians, 169 species of birds, and 41 species of mammals.
- These ecosystems play a vital role in water conservation. The lateritic soil layer atop the Sada acts as a catchment for rainwater, recharging the groundwater and providing freshwater to local communities year-round.
Traditional Land Use and Agriculture:
- Local Farming: During monsoons, the Sada is used by locals for growing traditional crops like rice and millets (e.g., nanchani), using sustainable farming practices without pesticides or chemical fertilizers.
- Water Management: The locals rely on open wells, springs, and perennial streams for freshwater, which are carefully maintained through cultural rituals and community hygiene practices.
Conservation and Cultural Importance:
- The region is home to geoglyphs, ancient artworks estimated to be 10,000 years old, adding to its cultural and historical significance.
- Waterbodies on the Sada serve as habitats for species like the Indian flapshell turtle (Lissemys punctata) and provide water for other wildlife, including leopards, jackals, hyenas, barking deer, and migratory birds.
Environmental Threats:
- Land-use Change: Increasing conversion of open land and croplands into orchards and residential areas, along with various developmental projects, threatens the region's biodiversity.
- Mining: Extraction of laterite stones for construction purposes is another environmental risk.
- Wasteland Classification: The region is often classified as a ‘wasteland’ in the Wasteland Atlas, further complicating conservation efforts.
Israel-Hamas Ceasefire and Hostage Release Deal

- 14 Jan 2025
In News:
Israel and Hamas have agreed on a Gaza ceasefire and hostage release deal after 15 months of war.
Key Highlights:
Ceasefire Agreement Details:
- Location: The deal was brokered in Doha, Qatar.
- Approval Process: The deal must be approved by Israel’s Cabinet to take effect.
- Mediators: The agreement was negotiated by Qatar, Egypt, and the United States, with their involvement ensuring the implementation of the deal.
Phases of the Deal:
- First Phase (42 Days):
- Release of 33 hostages by Hamas, including women, children, and elderly people.
- Hostage Exchange: Hostages will be exchanged for Palestinian prisoners in Israeli jails.
- Gaza Ceasefire and Withdrawal: Israeli forces will gradually withdraw from Central Gaza and move to the borders.
- Return of Displaced Palestinians: Displaced Palestinians will be allowed to return to Northern Gaza.
- Humanitarian Aid: 600 humanitarian aid trucks will be allowed into Gaza daily.
- Second Phase:
- Hostage Release: Negotiations will begin for the release of remaining hostages.
- Full Israeli Troop Withdrawal: Israel will fully withdraw its forces.
- Third Phase:
- Reconstruction of Gaza: Overseen by Egypt, Qatar, and the United Nations.
- Reopening of Border Crossings: For movement in and out of Gaza.
- Return of Hostage Bodies: Return of any bodies of hostages who died.
Background of the Israel-Hamas Conflict:
- Start: On October 7, 2023, Hamas launched an attack on Israel, called Operation Al-Aqsa Flood, causing significant casualties.
- Israeli Response: Israel launched Operation Iron Sword in retaliation.
- Casualties: The conflict resulted in 46,707 Palestinian deaths, mostly civilians, and 1,210 Israeli deaths.
About Gaza Strip:
- Location: A Palestinian enclave on the Mediterranean Sea, bordered by Israel and Egypt.
- Administration: The Gaza Strip is governed by Hamas since 2006.
- Movement Restrictions: Israel controls air space and shoreline, imposing restrictions. Egypt controls one border and also restricts movement.
Gaza Truce Deal:
- Nature: A proposed ceasefire to end the ongoing conflict.
- Primary Parties: Israel and Hamas.
- Supporting Nations: United States, Qatar, and Egypt.
- Significance:
- Aims to stop fighting and address the humanitarian crisis in Gaza.
- Potential to influence regional stability and Israeli politics.
- Marks an important moment in U.S. diplomacy under the Biden administration.
Nag Mark-2

- 14 Jan 2025
In News:
The Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO) successfully conducted field evaluation trials of India's indigenous Anti-Tank Missile - Nag Mark 2 at the Pokhran Field Range in Rajasthan.
Overview of Nag Mk-2:
- Type: Third-generation, fire-and-forget anti-tank guided missile (ATGM).
- Development: Indigenous development by Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO) under the Integrated Guided Missile Development Programme (IGMDP).
- Functionality: Designed to neutralize modern armored threats, including those with Explosive Reactive Armour (ERA), using advanced fire-and-forget technology.
Technological Features:
- Fire-and-Forget Technology: Operators lock onto targets before launch, allowing the missile to autonomously track and engage targets, ensuring precision strikes.
- Lock-on After Launch: The missile can lock onto the target post-launch, providing flexibility in complex battlefield environments.
- Advanced Guidance System: Equipped with Imaging Infrared (IIR) seekers for enhanced accuracy, both during the day and at night.
Performance and Range:
- Effective Range: The missile has a range of 7 to 10 kilometers, a significant improvement over its predecessor, Nag Mk-1, which had a range of only 4 kilometers.
- Test Trials: Successfully destroyed all targets at both maximum and minimum ranges during the field evaluation trials at Pokhran Field Range, Rajasthan.
- Attack Mode: Includes a top-attack capability to target the vulnerable upper surfaces of armored vehicles, enhancing its effectiveness.
Platform and Integration:
- Launch Platform: The missile is launched from the NAMICA (Nag Missile Carrier) Version 2, a tank destroyer vehicle used by the Indian Army to launch anti-tank missiles.
- Versatility: Designed for integration with multiple platforms, enhancing operational flexibility in different combat scenarios.
Strategic and Operational Significance:
- Indigenous Defence Capability: Reduces India's dependence on foreign weapons systems, strengthening self-reliance in defense technology.
- Enhanced Battlefield Readiness: Provides the Indian Army with a cutting-edge weapon to counter modern armored vehicles, improving tactical advantages.
- Operational Effectiveness: The missile’s precision and ability to neutralize targets with minimal collateral damage make it an essential tool in modern warfare.
- Strategic Deterrence: Demonstrates India’s technological advancements in missile systems, signaling strength and deterrence to adversaries.
Bharat Cleantech Manufacturing Platform

- 14 Jan 2025
In News:
Union Minister of Commerce & Industry Shri Piyush Goyal launches Bharat Cleantech Manufacturing Platform.
Bharat Cleantech Manufacturing Platform:
- Objective: Strengthen India's cleantech value chains, especially in solar, wind, hydrogen, and battery storage sectors.
- Platform Features:
- Aims to promote collaboration, co-innovation, and knowledge-sharing among Indian firms.
- Focus on scaling up manufacturing, sharing ideas, technologies, and resources.
- Acts as a financing platform for the cleantech sector.
- Designed to position India as a global leader in sustainability and cleantech innovation.
India's Clean Energy Commitment:
- Target: 500 GW of clean energy capacity by 2030.
- India has been a front-runner in fulfilling its Nationally Determined Contributions (NDCs) under the Paris Agreement and UNFCCC.
- Early Achievement: India achieved its 2022 renewable energy target of 200 GW, 8 years ahead of schedule.
- Largest Interconnected Grid: India boasts the world’s largest interconnected power grid, enhancing its renewable energy distribution capacity.
- Gujarat is a pioneer in solar power adoption in India.
Union Minister Shri Piyush Goyal's Views:
- On Product-Linked Incentives (PLIs):
- PLIs and subsidies are seen as short-term aids; long-term growth of the clean energy sector depends on it becoming self-sustaining.
- Urged Indian firms to innovate and scale up manufacturing within the country.
- On Clean Energy and Sustainability:
- Stressed the importance of innovation and collaboration to achieve sustainability goals.
- India aims to attract international investors by creating a compelling business case for cleantech investments.
- 3S Approach (Speed, Scale, and Skill): Key to implementing India's renewable energy program, emphasizing rapid deployment, large-scale adoption, and skill development in the sector.
Bharat Climate Forum 2025:
- Event Objective: A platform for policymakers, industry leaders, and stakeholders to discuss climate action, clean energy, and India’s role in global climate goals.
- Key Focus Areas:
- Aligning India’s clean energy initiatives with global climate goals (UNFCCC, Paris Agreement).
- Emphasizing India’s early achievements in clean energy adoption.
- Promoting sustainable development and clean energy solutions.
India's Performance in Renewable Energy:
- India’s progress has been commendable in meeting its climate targets and setting up clean energy capacity ahead of schedule.
- The government’s initiatives, led by Prime Minister Narendra Modi, have made solar power affordable and scalable through transparency in auctions, competitive bidding, and speed in project implementation.
World’s First Cryo-Born Baby Corals

- 13 Jan 2025
In News:
World’s First Cryo-Born Baby Corals Successfully Settled on the Great Barrier Reef.
Introduction to Cryo-Born Corals
- Cryo-born corals are created using cryopreservation techniques, which involve freezing coral cells and tissues at very low temperatures.
- The process preserves coral cells by preventing the formation of ice crystals that would otherwise damage them.
- Cryopreservation involves adding cryoprotectants to remove water from cells, enabling their survival during freezing and thawing.
Significance of the Breakthrough
- Climate Change Resilience: The initiative aims to create heat-tolerant corals, which are crucial in combating the impact of rising ocean temperatures due to climate change.
- Selective Breeding Advantage: Cryopreservation allows for controlled breeding and bypasses the limitations of natural coral spawning, which occurs only once a year. This enables multiple reproduction cycles without disturbing wild populations.
The Process of Cryo-Born Coral Production
- Sperm Collection: During coral spawning events, sperm from various coral species is collected and frozen at -196°C using liquid nitrogen, halting metabolic processes.
- Coral Egg Fertilization: Cryopreserved sperm is used to fertilize fresh coral eggs, which are grown in a specialized research facility called the National Sea Simulator.
- Coral Cradles: After growth, the cryo-born corals are carefully transported and settled into specially designed "coral cradles" placed in the Great Barrier Reef, where their growth is monitored during their critical first year.
Importance of Cryo-Born Corals in Reef Restoration
- The primary aim is to introduce millions of heat-tolerant corals annually to restore reefs affected by climate change.
- The Taronga CryoDiversity Bank houses the world’s largest frozen coral sperm collection from 32 coral species, collected annually since 2011, providing a resource for future restoration efforts.
Coral Reefs: An Overview
- Corals are marine invertebrates from the class Anthozoa, phylum Cnidaria.
- Reefs are built by colonies of coral polyps that secrete limestone skeletons and rely on symbiotic algae (zooxanthellae) for nutrition.
- Coral reefs are typically found in shallow, sunlit waters with a temperature range of 16-32°C and depths less than 50 meters.
Global and Indian Coral Conservation Efforts
- India:
- The National Committee on Wetlands, Mangroves, and Coral Reefs (1986) advises on conservation measures.
- The Environment (Protection) Act (1986) prohibits the use of coral and sand in construction.
- Zoological Survey of India (ZSI) uses Biorock technology for coral restoration.
- Global Efforts:
- CITES lists coral species in Appendix II, regulating coral trade.
- The World Heritage Convention designates coral reefs as protected sites.
Global Impact and Future Directions
- The innovative work by Australian scientists opens the door for large-scale restoration efforts by allowing more controlled breeding and genetic diversity, making corals more resilient to climate change.
- This breakthrough could revolutionize coral restoration, scaling up efforts to introduce millions of resilient corals to reefs worldwide, building long-term resilience against climate change.
Sovereign Artificial Intelligence

- 13 Jan 2025
In News:
- The growth of Artificial Intelligence (AI) has been remarkable in recent years. In 2018, a 340-million-parameter AI model was considered large, whereas models like ChatGPT now have 1.8 trillion parameters.
- As part of its ambition to make the digital economy worth USD 1 trillion by 2028, India is focusing on AI sovereignty and investing in semiconductors and AI technologies to achieve this goal.
What is Sovereign AI?
Definition
- Sovereign AI refers to a nation’s ability to develop, control, and deploy AI using its own resources, including infrastructure, data, workforce, and business networks.
- This involves not just developing AI models but also creating infrastructure and nurturing homegrown talent to lead AI advancements within the country.
Key Aspects of Sovereign AI
- National Control: Ensures AI technologies align with a country's laws, regulations, and ethical standards.
- Data Sovereignty: Emphasizes control of data within the country’s borders, protecting privacy, security, and national interests.
- AI in Governance: Generative AI is transforming industries, markets, and governance, with AI-powered tools assisting professionals and governments.
- Ethical Considerations: Countries define security protocols and ethical frameworks to govern the use of AI technologies.
- Strategic Autonomy: Reduces reliance on foreign technologies, encouraging domestic development in AI to achieve strategic independence.
- Economic Competitiveness: AI is crucial for industrial innovation. Without it, nations risk falling behind in the global economy.
Growth and Importance of AI
Evolution of AI Models
- In 2018, a 340-million-parameter model was considered a significant achievement.
- Today, ChatGPT uses 1.8 trillion parameters, and Google’s Gemini uses 1.5 trillion parameters. In comparison, China’s DeepSeek has a model with 240 billion parameters.
- Parameters are the internal variables of AI models, adjusted during training to improve their performance and accuracy.
Strategic Applications
- Sovereign AI plays a pivotal role in critical sectors such as:
- Defense
- Healthcare
- Transportation
- Governance
- It helps redefine industries, boost innovation, and streamline operations across various sectors.
India’s Position in Sovereign AI
AI Infrastructure Development
- Tata Group and Reliance are building AI infrastructure in India, including the development of Large Language Models (LLMs).
- India has allocated USD 1.2 billion for a sovereign AI project under the IndiaAI Mission, which includes creating an AI supercomputer with thousands of chips.
Government Initiatives
- The IndiaAI Mission is designed to boost India’s AI capabilities by building infrastructure, fostering talent, and supporting innovation within the country.
Global AI Compact
- A Global AI Compact has been proposed to ensure equitable access to AI technologies across nations.
- The compact advocates for sharing AI resources globally while promoting cooperation and addressing challenges associated with AI governance.
Pink Fire Retardant

- 13 Jan 2025
In News:
As wildfires continue to rage across Southern California, authorities are deploying pink fire retardant from aircraft to help combat the blazes. Despite its widespread use, concerns over its effectiveness and environmental risks have surfaced in recent years.
What is Pink Fire Retardant?
- Fire retardant is a chemical mixture designed to slow down or extinguish wildfires. The most commonly used product in the U.S. is Phos-Chek, a brand of retardant.
- Phos-Chek primarily contains ammonium phosphate-based slurry (salts like ammonium polyphosphate), which helps the retardant stay longer and resist evaporation, unlike water.
Purpose and Visibility
- Fire retardants are sprayed ahead of fires to coat vegetation, reducing oxygen and preventing flames from spreading.
- Color is added to the fire retardant, often bright pink, to improve visibility. This ensures firefighters can track its spread and create effective fire lines, helping protect lives and property.
Manufacturer
- Perimeter Solutions manufactures Phos-Chek, which is used for aerial fire suppression efforts.
Effectiveness of Pink Fire Retardant
Limited Effectiveness
- The use of fire retardants like Phos-Chek is not always effective across different wildfire conditions.
- Aerial retardants depend on environmental conditions like terrain, slope, and weather for optimal effectiveness.
- Researchers, including Forest Service scientists, suggest that retardant effectiveness is more limited under changing climate conditions.
- Climate change is narrowing the window of opportunity for using aerial retardants, reducing their impact.
Uncertainty in Impact
- The effectiveness of fire retardants is hard to quantify. Multiple firefighting methods are used simultaneously, making it difficult to attribute wildfire suppression success solely to the retardant.
Environmental Concerns of Pink Fire Retardant
Toxicity and Pollution
- Phos-Chek contains toxic metals such as chromium and cadmium, both of which are harmful to humans and the environment.
- Chromium and cadmium are linked to serious health issues, including cancer and liver/kidney diseases.
- Aquatic life is particularly vulnerable to these toxins, as the chemicals can enter waterways, causing extensive damage to ecosystems.
Impact on Rivers and Streams
- The use of pink fire retardant has raised concerns regarding the contamination of rivers and streams.
- A study by the University of Southern California (USC) in 2024 estimated that 850,000 pounds of toxic chemicals have been released into the environment since 2009 due to fire retardant use.
Growing Use and Pollution
- From 2009 to 2021, over 440 million gallons of retardant were applied across U.S. lands.
- During this period, an estimated 400 tons of heavy metals were introduced into the environment, further exacerbating the pollution levels.
Financial and Practical Concerns
High Cost and Inefficiency
- The cost of deploying fire retardant is significant. Aerial firefighting operations require substantial resources, including planes, helicopters, and large quantities of retardant.
- Environmental experts argue that using fire retardant from planes is ineffective and expensive, especially in light of the growing environmental concerns.
India Joins the UN-CEBD

- 13 Jan 2025
In News:
- India has recently joined the United Nations Committee of Experts on Big Data and Data Science for Official Statistics (UN-CEBD), marking a significant step in strengthening its role in global statistical frameworks.
- The inclusion is a result of India's recent membership in the United Nations Statistical Council (UNSC), signaling the nation's growing influence in global data governance.
Key Highlights
- India's Growing Influence: India’s entry into the UN-CEBD highlights its growing stature in the international statistical community, emphasizing its commitment to utilizing big data and data science for informed decision-making.
- Strategic Opportunity: This membership allows India to contribute to shaping global standards in leveraging big data for official statistical purposes, especially in tracking Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs).
What is UN-CEBD?
- UN-CEBD is a specialized body under the United Nations, formed in 2014 to explore the benefits and challenges of using big data and data science to strengthen global statistical systems.
- It was established under the United Nations Statistical Commission (UNSC).
- Members: The committee consists of 31 member states (including India) and 16 international organizations.
Key Objectives
- Monitor SDGs: Use big data to track progress towards achieving the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs).
- Address Data Challenges: Overcome challenges in utilizing non-traditional data sources, such as satellite imagery, Internet of Things (IoT), and private sector data.
- Promote Big Data Use: Encourage practical applications of big data across borders while addressing associated challenges.
Governance and Functions
- Advisory Board: Provides strategic direction, convening four times a year.
- UN Bureau: Manages day-to-day operations.
- Key Functions:
- Strategic Coordination: Vision and direction for utilizing big data in global official statistics.
- Capacity Building: Enhance capabilities through training, technical assistance, and knowledge sharing.
- Public Trust: Establish confidence in using big data for official statistics.
Big Data: Definition and Importance
What is Big Data?
- Big data refers to vast, complex datasets that cannot be processed by traditional data management systems.
- It enables enhanced decision-making and improved processes for policy formulation, product development, and governance.
India's Big Data Initiatives
- National Data & Analytics Platform (NDAP): Facilitates data-driven decision-making.
- Big Data Management Policy: Defines strategies for managing large datasets within government agencies.
- National Data Warehouse on Official Statistics: Centralizes official data for better access and analysis.
The 6Vs of Big Data
- Volume: Large amounts of data.
- Velocity: Speed of data generation and processing.
- Variety: Different types of data.
- Veracity: Accuracy of data.
- Value: Significance of the data.
- Variability: Fluctuations in data.
India’s Role in the UN-CEBD
Contribution to Global Standards
- India's initiatives such as the Data Innovation Lab and the use of satellite imagery and machine learning will be shared with other members, fostering global collaboration in statistical innovations.
- India will contribute to shaping international standards for the use of big data in monitoring SDGs.
Enhancing Statistical Processes
- Modernization of Data: India aims to modernize its statistical processes by incorporating IoT, satellite data, and private-sector data.
- Real-time Insights: Providing policymakers with timely and accurate data to address key socio-economic issues.
- Improving Estimates: Using big data to enhance the accuracy of official statistics, improving governance and policymaking.
Strategic Goals of India's Engagement
- Streamline Statistical Production: Innovation in data collection, processing, and analysis to reduce delays in data availability.
- Improve Decision-Making: Provide real-time, evidence-based insights to policymakers.
- Foster International Collaboration: Share India’s expertise and learn from global best practices to build future-ready statistical systems.
National Youth Day 2025

- 13 Jan 2025
In News:
On January 12, 2025, Prime Minister Shri Narendra Modi participated in the Viksit Bharat Young Leaders Dialogue 2025, an event aimed at empowering India's youth and charting a roadmap for the nation's development. This occasion also coincided with the celebration of National Youth Day, marking the 163rd birth anniversary of Swami Vivekananda, a renowned spiritual leader and social reformer who strongly believed in the transformative potential of India's youth.
Significance of National Youth Day
- Purpose:
- National Youth Day is celebrated to honor Swami Vivekananda's contributions, emphasizing the role of youth in nation-building.
- It promotes empowerment, leadership, and innovation among the youth.
- Year of First Celebration: 1985
- Key Theme (2025): "Arise, Awake, and Realize the Power You Hold"
Key Highlights from the Dialogue
- Goal of the Dialogue:
- Engaging youth in the decision-making process for a developed India by 2047.
- Empowering youth through platforms like quizzes, essay competitions, and thematic presentations.
- Ten Key Themes Discussed:
- Technology & Innovation
- Sustainability
- Women Empowerment
- Manufacturing & Agriculture
- Education and Skill Development
India’s Roadmap for 2047 (Viksit Bharat)
- Vision:
- Economic Power: India is moving toward becoming the third-largest economy.
- Strategic and Cultural Strength: India will have a robust economic, strategic, social, and cultural framework.
- Youth's Role: Innovation in technology, digital economy, space, and manufacturing will drive India’s growth.
- Key Projects and Targets:
- Target: Generating 500 GW of renewable energy by 2030.
- Net Zero Emissions for Railways: Set for 2030.
- Olympics: India aims to host the Olympics in the next decade.
- Space Power: Plans for a space station by 2035.
Viksit Bharat Young Leaders Challenge
- Objective:
- Engage youth in shaping ideas for a developed India.
- The Viksit Bharat Young Leaders Dialogue is part of the Viksit Bharat Challenge.
- Stages of the Challenge:
- Viksit Bharat Quiz: Participation by 30 lakh youth.
- Essay Writing: Over 2 lakh essays on key developmental themes.
- State Rounds: Rigorous in-person competition to identify the top young leaders.
- Participant Categories:
- 1,500 from Viksit Bharat Challenge Track.
- 1,000 from Traditional Track (cultural and science innovation).
- 500 Pathbreakers (leaders in diverse sectors).
Achievements Under Government Benefiting Youth
- Educational Reforms:
- Increase in IITs, IIITs, IIMs, and AIIMS.
- Growth in the number of higher education institutions and their global rankings.
- Economic Growth:
- India's economy has grown to nearly $4 trillion.
- Infrastructure Investments: More than ?11 lakh crore allocated for infrastructure development.
- Employment Opportunities for Youth:
- Mudra Loans: ?23 lakh crore distributed to youth entrepreneurs.
- Startup Ecosystem: India is among the top three in global startups.
- PM Gati Shakti Mission: Facilitating logistics and infrastructure development, creating employment opportunities.
Future Outlook
- Youth as the Future Leaders of India:
- India’s Youth Power: Vital to achieving a developed nation by 2047.
- The Viksit Bharat Young Leaders Dialogue is a platform for youth to voice their opinions and engage with policymakers.
- Role of Youth in India’s Transformation:
- Collective Responsibility: Every citizen's effort is essential for national goals.
- The vision of a Viksit Bharat hinges on the innovative contributions and ownership by young minds.
EmpowHER Biz – Sapno Ki Udaan

- 12 Jan 2025
In News:
The Women Entrepreneurship Platform (WEP) of NITI Aayog, in partnership with New Shop (India’s largest 24/7 convenience retail chain), launched the initiative EmpowHER Biz – Sapno Ki Udaan under the Award to Reward (ATR) program. This program aims to empower women entrepreneurs by providing them with the skills, resources, and mentorship needed to succeed in the organized retail sector. The collaboration seeks to create a robust retail ecosystem that supports women in overcoming barriers such as societal biases, limited access to financing, and a lack of mentorship.
Key Features of the Initiative:
- Target Participants: The program will select 50 women aged 18-35 through an online application process. Women from Delhi NCR, Punjab, Rajasthan, Uttar Pradesh, Haryana, Madhya Pradesh, and Gujarat will be considered.
- Top 20 Participants: The 20 best candidates will receive a 100% waiver on New Shop franchise fees, enabling them to operate their own retail businesses with reduced financial barriers.
- Program Objective: Equip women entrepreneurs with skills such as retail management, digital tools, financial literacy, and business development. Participants will also receive valuable mentorship to help them grow and scale their businesses.
- Focus on Retail: The initiative focuses on empowering women within the organized retail sector, creating a sustainable ecosystem that fosters growth and development for female entrepreneurs.
About Women Entrepreneurship Platform (WEP):
- Incubation & Transition: Established in 2018, WEP was incubated within NITI Aayog and transitioned into a Public-Private Partnership (PPP) in 2022.
- Purpose: WEP aims to empower women entrepreneurs by addressing challenges like information asymmetry and providing essential support in key areas such as:
- Access to Finance
- Market Linkages
- Training & Skilling
- Mentoring & Networking
- Compliance & Legal Assistance
- Business Development Services
- Collaboration: WEP partners with over 30 public and private sector organizations to develop scalable and impactful programs. Since 2023, the Award to Reward initiative offers a framework for stakeholders to create impactful programs for women entrepreneurs.
About New Shop:
- Business Model: New Shop operates over 200 round-the-clock convenience retail stores in high-density areas, including highways and gas stations. The company plans to expand into airports, railway stations, and other mass transit hubs.
- Franchising Vision: By 2030, New Shop aims to empower over 10,000 entrepreneurs in India through its franchising model. The partnership with WEP seeks to help women entrepreneurs access this growth opportunity.
Program Outcomes:
- Mentorship & Training: Participants will be mentored and trained on key aspects such as retail management, business development, and digital tools.
- Franchise Opportunity: Top participants will gain access to New Shop’s franchising ecosystem, providing them a ready-made business opportunity with lower entry barriers.
- Financial Assistance: The program will also provide financial resources to the women, helping them build their businesses with greater ease.
Future of Jobs Report 2025

- 12 Jan 2025
In News:
The World Economic Forum's latest "Future of Jobs Report 2025" has highlighted significant trends and predictions for the global labor market by 2030.
Key Highlights:
Fastest Growing Jobs by 2030
The report identified the following jobs as the fastest-growing by 2030:
- Big Data Specialists
- FinTech Engineers
- AI and Machine Learning Specialists
- Software and Applications Developers
- Security Management Specialists
- Data Warehousing Specialists
- Autonomous and Electric Vehicle Specialists
- UI/UX Designers
- Delivery Drivers
- Internet of Things (IoT) Specialists
Job Disruption and Creation
- 22% of jobs globally will be disrupted by 2030 due to automation and technological advancements.
- 170 million new jobs are expected to be created, resulting in a net increase of 78 million jobs.
- Technological shifts, economic uncertainty, and demographic changes are expected to play significant roles in this transformation.
Skills in High Demand
- AI, Big Data, Cybersecurity: Skills related to artificial intelligence and big data are expected to see an 87% rise, while networks and cybersecurity skills are projected to increase by 70%.
- Creative Thinking, Flexibility: Skills like creative thinking, resilience, flexibility, and agility are also expected to see a significant rise, emphasizing the importance of soft skills in a technology-driven world.
Declining Jobs
The report lists the following positions as expected to decline by 2030:
- Postal Service Clerks
- Bank Tellers
- Data Entry Clerks
- Cashiers and Ticket Clerks
- Telemarketers
- Printing Workers
- Accounting and Bookkeeping Clerks
These roles are being replaced or transformed by automation and AI, which are reshaping traditional job functions.
Technological Advancements
- Digital Access: 60% of employers believe that expanding digital access will be the most transformative trend for businesses.
- AI and Robotics: Employers are investing heavily in AI, robotics, and energy technologies, creating a demand for skilled workers in these sectors.
- Energy Technologies: Jobs related to the green transition, including renewable energy and environmental engineering, will see an uptick as countries strive to meet climate goals.
Key Drivers of Change
- Technological Change: AI, machine learning, and automation will continue to reshape industries.
- Geoeconomic Fragmentation: Geopolitical tensions and economic shifts are prompting businesses to transform their models, leading to a greater demand for cybersecurity and security management roles.
- Aging Populations: The growing demand for healthcare services, especially in high-income economies, will result in more jobs in the care economy (e.g., nursing professionals, social workers).
- Green Transition: The global shift toward clean energy and environmental sustainability will create numerous opportunities for jobs in renewable energy and climate change mitigation.
Implications for India
- AI and Robotics Investment: Indian companies are leading the way in investing in AI, robotics, and autonomous systems.
- Growth Sectors: India’s rapidly developing tech sector will see a rising demand for AI, machine learning, and big data specialists.
- Disruptions in Traditional Jobs: Roles like postal clerks, cashiers, and data entry clerks in India are also expected to face significant reductions due to automation.
Challenges for Employment in India
- Skill Mismatch: There is a significant skill gap, with many workers lacking expertise in emerging fields like AI, cybersecurity, and data science.
- Digital Divide: Urban areas are adapting to new technologies faster than rural areas, which may widen employment disparities.
- Informal Sector: India’s large informal workforce faces challenges in transitioning to technology-driven jobs due to limited access to training and education.
Reskilling and Upskilling
- The WEF report emphasizes that 59% of the global workforce will need reskilling or upskilling by 2030 to remain competitive.
- Workers must adapt to new roles, especially in technology and the green transition, to meet the evolving demands of the job market.
GEAPP and ISA Sign $100 Million Agreement for Solar Projects

- 12 Jan 2025
In News:
The Global Energy Alliance for People and Planet (GEAPP) signed a Multi-Donor Trust Fund (MDTF) agreement with the International Solar Alliance (ISA) to mobilize $100 million for funding high-impact solar energy projects. This collaboration is part of a wider effort to accelerate India's clean energy transition, bridge financing gaps, and enhance the country's energy systems. Along with this agreement, two other key initiatives were announced:
- DUET (Digitalization of Utilities for Energy Transition)
- ENTICE 2.0 (Energy Transitions Innovation Challenge)
These programs aim to address energy transition challenges by fostering scalable, cost-efficient solutions, digitalizing utilities, and supporting innovations for sustainable energy.
Key Features:
- Multi-Donor Trust Fund (MDTF):
- The MDTF aims to raise and deploy $100 million to finance impactful solar energy projects, with ISA driving the strategic direction.
- GEAPP’s Project Management Unit will provide governance, fundraising, and technical expertise to ensure project success.
- The collaboration emphasizes the importance of solar energy in achieving India's clean energy goals.
- DUET (Digitalization of Utilities for Energy Transition):
- Focuses on transforming grid systems by digitalizing grid assets and integrating them with smart sensors.
- Real-time data will help reduce transmission losses and facilitate Battery Energy Storage Systems (BESS) deployment, assisting in the integration of Distributed Renewable Energy (DRE) into the grid.
- ENTICE 2.0 (Energy Transitions Innovation Challenge):
- A platform for identifying and scaling innovative solutions to accelerate the clean energy transition, especially within India's growing startup ecosystem.
- Focuses on supporting investable opportunities for energy transition solutions, building on the earlier success of ENTICE 1.0.
Global Impact of GEAPP:
GEAPP, launched with an initial commitment of $464 million, has already funded 130 projects across 40 countries. These projects have impacted over 50 million people, helping reduce 43 million tons of CO2 emissions. The collaboration with ISA is expected to deepen GEAPP's efforts in mobilizing capital to foster clean energy access and tackle climate change.
India’s Clean Energy Transition:
India has already extended electricity access to over 800 million people, but about 2.5% of households still remain unelectrified. Distributed renewable energy, especially solar energy, will play a pivotal role in reaching these underserved populations. India aims for 47 GW of battery energy storage systems by 2032, which will support grid stability and energy access.
Additional Initiatives and Impact:
- Battery Energy Storage Systems (BESS):
- GEAPP has also supported India’s first commercial standalone BESS project, which will provide 24/7 power to over 12,000 low-income customers.
- The project is set to lower electricity tariffs by 55%, benefiting economically disadvantaged communities.
- Strategic Alliances:
- The partnership with ISA and the strategic initiatives like DUET and ENTICE 2.0 aim to further India’s climate and energy goals, bringing renewable energy solutions to underserved regions, and supporting the country's energy security.
Role of GEAPP and ISA:
- GEAPP works to mobilize financing, provide technical expertise, and ensure effective implementation of renewable energy projects globally.
- ISA focuses on solar energy solutions, and with this agreement, it seeks to enhance the solar energy capacity in its member countries, aligning with climate targets.
About GEAPP:
GEAPP is a multi-stakeholder alliance comprising governments, philanthropy, technology partners, and financial institutions. Its goal is to transition developing economies to clean energy while enhancing economic growth. It aims to:
- Reduce 4 gigatons of carbon emissions.
- Provide clean energy access to 1 billion people.
- Create 150 million new jobs globally.
Twigstats

- 12 Jan 2025
In News:
The tracing of genetic ancestry remains a challenging task due to the statistical similarity among populations across geographical regions. However, recent advances in genetic analysis, particularly the development of the Twigstats tool, are significantly enhancing our ability to reconstruct genetic histories at a very high resolution.
Key Insights from Genetic Research:
- Ancient DNA (aDNA): Prehistoric human ceremonial burials, mass grave mounds, and war graves are rich sources of ancient genetic material, offering key insights into population dynamics. These samples help us understand past migrations, cultural transitions, and the genetic legacy of ancient groups.
- Challenges in Ancestry Tracing:
- Populations often share many genetic similarities, complicating the task of tracing ancestry across regions.
- Ancient DNA samples are typically of lower quality compared to modern samples, limiting the precision of past genetic studies.
- The movement of genes across time and space, through processes like gene flow, adds complexity to the understanding of population ancestry.
Traditional Genetic Techniques:
- Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms (SNPs): Used to identify natural genetic variations, SNP analysis has been central to reconstructing genetic histories. However, it is limited by its reliance on high-quality samples and struggles with closely related groups.
- Haplotypes and Genealogical Trees: By analyzing shared DNA segments (haplotypes) and rare variants, researchers gain a more comprehensive understanding of population structure and ancestry, which can reveal shifts in population over time.
The Emergence of Twigstats:
- What is Twigstats?
- Twigstats is an advanced analytical tool that enhances the precision of ancestry analysis through time-stratified ancestry analysis, a method that allows for a more fine-grained look at genetic data.
- It is designed to address the limitations of traditional methods by integrating SNPs, haplotypes, and rare genetic variants, providing a more holistic view of ancestry.
- The tool is powered by statistical languages R and C++, which help researchers better manage and analyze complex genetic data.
- How It Works: Twigstats builds family trees by analyzing shared genetic mutations, identifying recent mutations that offer a clearer understanding of historical periods and events. It helps trace the evolution of populations and offers insights into their migrations, mixing, and cultural shifts.
Key Features and Impact of Twigstats:
- Time-Stratified Ancestry Analysis: Allows researchers to study how populations evolved over time, with a focus on specific historical periods.
- Enhanced Precision: Reduces statistical errors and enhances the precision of individual-level ancestry reconstruction.
- Higher-Resolution Mapping: Provides high-resolution genetic maps of migration patterns and admixture events across centuries.
Applications of Twigstats:
- Historical Case Studies: The tool has been used to study ancient genomes from Europe, particularly the Iron, Roman, and Viking Ages (500 BC to 1000 AD). It revealed the fine-scale genetic history of populations in regions like northern and central Europe, including the movement of Germanic and Scandinavian peoples.
- Viking Age Insights: Researchers were able to trace the early presence of Scandinavian-like ancestry in regions such as Britain and the Baltic before the traditionally believed start of the Viking Age. This suggests earlier interactions and migrations from Scandinavia, which aligns with historical records of Anglo-Saxon and Viking movements.
- Cultural Transitions: The analysis identified shifts in population genetics corresponding to cultural changes, such as the shift from the Corded Ware culture to the Bronze Age and the influence of the Wielbark culture.
Genetic Methods Used in the Study:
- Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms (SNPs): Commonly used to trace ancestry but requires high-quality samples.
- Haplotypes and Rare Variants: Offer more nuanced insights into population movements by considering combinations of genetic markers inherited together.
- Genealogical Tree Inference: Applied to both ancient and modern genomes, it provides detailed demographic and ancestry information, supporting the reconstruction of high-resolution genetic histories.
Case Study: India’s Genetic History (2009 Study)
- Researchers used SNP analysis to trace the genetic history of India, revealing two major ancestral groups:
- Ancestral North Indians (ANI): Genetically closer to Central Asian, European, and Middle Eastern populations.
- Ancestral South Indians (ASI): A distinct genetic group, showcasing India’s diverse population structure.
India’s First Organic Fisheries Cluster

- 12 Jan 2025
In News:
The Union Minister, Department of Fisheries, Ministry of Fisheries, Animal Husbandry and Dairying Shri Rajiv Ranjan Singh inaugurated and laid the foundation for 50 key projects worth Rs. 50 crores under Pradhan Mantri Matsya Sampada Yojana (PMMSY) covering all North East Region States Except Arunachal Pradesh and Mizoram.
Key Highlights:
- Initiative: India’s first Organic Fisheries Cluster, launched under the Pradhan Mantri Matsya Sampada Yojana (PMMSY). The cluster focuses on sustainable aquaculture, promoting the production of antibiotic, chemical, and pesticide-free organic fish.
- Target Markets: Eco-conscious domestic and global markets.
Sikkim's Role as India’s First Organic State:
- Sikkim's Organic Commitment: Sikkim is the first Indian state to embrace 100% organic farming, covering 75,000 hectares of land.
- Vision: The Organic Fisheries Cluster aligns with Sikkim’s broader goal of promoting organic, sustainable agricultural practices.
Objective of Organic Fisheries Cluster:
- To prevent pollution and protect aquatic ecosystems by using ecologically healthy practices.
- Promotes sustainable fish farming methods, reducing environmental damage.
- Focus on species like amur carp and other carp varieties, aligning with the state’s success in organic farming.
Support from NABARD:
- The National Bank for Agriculture and Rural Development (NABARD) will provide financial and technical assistance.
- Key support includes:
- Infrastructure development.
- Formation of Fisheries-based Farmer Producer Organizations (FFPOs).
- Capacity building of local fishers and farmers.
PMMSY: A Comprehensive Fisheries Development Scheme:
- Investment: ?20,050 crore under PMMSY.
- Objective: To revolutionize India’s fisheries sector by promoting sustainable growth, enhancing fish production, and improving infrastructure.
- Implementation Period: FY 2020-21 to FY 2024-25.
- Key Goals:
- Boosting fish production and exports.
- Enhancing welfare of fishers and farmers.
- Promoting cluster-based development for better efficiency and competitiveness.
Cluster-Based Approach in Fisheries:
- Objective: To bring together geographically connected enterprises to enhance economies of scale.
- Impact: This approach improves financial viability, strengthens the fisheries value chain, and creates new business and livelihood opportunities.
- Types of Clusters: Includes Pearl, Seaweed, Ornamental Fisheries, Cold Water Fisheries, Organic Fisheries, and more.
Fisheries Focus in the North Eastern Region (NER):
- Fisheries Potential: The North Eastern Region (NER) has abundant freshwater resources and is a biodiversity hotspot.
- Growth: Inland fish production in the NER surged from 4.03 lakh tonnes (2014-15) to 6.41 lakh tonnes (2023-24), marking an impressive 5% annual growth.
- Investment in NER: Over ?2,114 crore invested through schemes like Blue Revolution and PMMSY.
- Key Projects:
- 50 projects worth ?50 crore to boost the region’s fisheries infrastructure, generating over 4,500 jobs.
- Projects include hatcheries, cold storage units, aquaculture parks, and fish kiosks.
India’s Global Fisheries Standing:
- India is the second-largest fish producer in the world, contributing 8% to global fish production.
- Top Rankings:
- Second in aquaculture production.
- Leading in shrimp production and exports.
- Third in capture fisheries.
Government Commitments and Schemes:
- Total Investment: Since 2015, the government has committed ?38,572 crore to fisheries development through key schemes like:
- Blue Revolution.
- Fisheries and Aquaculture Infrastructure Development Fund (FIDF).
- PMMSY.
- Pradhan Mantri Matsya Kisan Samridhi Sah-Yojana (PM-MKSSY).
- These initiatives aim to promote sustainable growth, create jobs, and enhance infrastructure in the fisheries sector.
Economic, Environmental, and Social Benefits:
- Economic Impact:
- Higher incomes for fishers and farmers through better production and export.
- Employment generation through infrastructure development.
- Environmental Impact: Reduced pollution and protection of aquatic ecosystems.
- Social Impact: Empowerment of local communities, fostering sustainable livelihoods.
UJALA Scheme

- 10 Jan 2025
In News:
UJALA scheme completes 10 years, saves ?19,153 crore annually
UJALA Scheme (Unnat Jyoti by Affordable LEDs for All)
- Launch Date: 5th January 2015 by PM Narendra Modi
- Objective:
- To promote energy-efficient LED lighting across India
- To reduce energy consumption, lower electricity bills, and decrease carbon emissions
- Implementing Body: Energy Efficiency Services Limited (EESL), Ministry of Power
- Scheme Relevance: Aims to provide affordable LED bulbs, tube lights, and fans to every household
- Global Recognition: World’s largest zero-subsidy domestic lighting scheme
Key Features:
- Affordability: Subsidized LED bulbs (?70-80), reducing the cost of electricity for households
- Energy Efficiency: LEDs consume 90% less energy than incandescent bulbs, 50% less than CFLs
- Environmental Impact: Significant reduction in CO? emissions by avoiding millions of tonnes annually
- Market Transformation: Over 36.87 crore LED bulbs distributed, saving approximately ?19,153 crore on electricity bills each year
- Consumer Benefit:
- On-Bill Financing: LED bulbs available for purchase through deferred payment via electricity bills
- Targeted low-income communities through Self-Help Groups (SHGs)
Achievements:
- Energy Savings: 47.9 billion kWh annually
- Cost Savings: ?19,153 crore saved on electricity bills
- Carbon Emission Reduction: 38.7 million tonnes of CO? avoided per year
- Peak Demand Reduction: 9,586 MW reduction in peak electricity demand
- Street Lighting: Over 1.34 crore LED streetlights installed, saving 9,001 million units annually
Key Initiatives:
- GRAM UJALA Scheme (March 2021): Aimed at rural households, providing LED bulbs at ?10 each
- Street Lighting National Programme (SLNP): Aimed at reducing public lighting costs with energy-efficient streetlights
- Encouraging Domestic Manufacturing: Stimulated local LED production, aligning with the "Make in India" mission
- E-Procurement Transparency: Real-time procurement ensuring price reductions and maintaining quality
Impact on Environment:
- Energy Savings & Carbon Footprint: The scheme significantly reduced the carbon footprint by promoting energy-efficient appliances
- Reduction in Household Consumption: Consumers benefit from reduced energy consumption and lower utility bills
New Method to Improve Nitrogen Use Efficiency (NUE)
- 10 Jan 2025
In News:
A recent breakthrough in agricultural research offers a promising solution to improve Nitrogen Use Efficiency (NUE) in crops, particularly in rice and Arabidopsis, by reducing nitric oxide (NO) levels in plants. This innovative approach provides an environmentally sustainable way to enhance crop yields while minimizing the need for synthetic nitrogen fertilizers, which have significant ecological and economic drawbacks.
Key Findings and Research Overview:
- Reducing NO Levels: The study, conducted by researchers at the National Institute of Plant Genome Research (NIPGR), demonstrated that by reducing nitric oxide (NO) levels in plants, nitrogen uptake could be significantly improved. This leads to a better NUE, a crucial factor for enhancing crop yield sustainably.
- NUE and Its Importance: NUE refers to the efficiency with which plants use nitrogen for biomass production. Improving NUE allows for higher crop yields with less fertilizer input, reducing costs and minimizing nitrogen-related environmental pollution.
- Traditional Approaches and Their Limitations: Current techniques to improve NUE primarily rely on the use of inorganic nitrogen fertilizers. These methods, though effective, have several downsides:
- They involve high operational costs for farmers.
- Excessive fertilizer use contributes to the emission of nitrogen oxides (NOx) and other pollutants.
- The production of these fertilizers also contributes to greenhouse gas emissions.
In contrast, the new study proposes a genetic and pharmacological manipulation of NO levels, offering a sustainable alternative to these traditional, resource-heavy methods.
Study Methodology:
The research team employed both genetic and pharmacological approaches to regulate NO levels in plants:
- Phytoglobin Overexpression: By overexpressing phytoglobin (a natural NO scavenger), the researchers increased the expression of high-affinity nitrate transporters (HATs) like NRT2.1 and NRT2.4. These transporters are essential for efficient nitrogen uptake.
- NO Donor and Scavenger Treatments: Plants were treated with NO donor (SNAP) and NO scavenger (cPTIO) to monitor the effects on NUE.
- Results: The treatment led to more efficient nitrogen uptake, especially under low NO conditions, by enhancing the expression of HATs. This method could increase plant growth and nitrogen utilization without relying on excessive fertilizer use.
Significance and Impact:
This research provides a pathway to enhance crop yield sustainably by addressing one of the most critical challenges in modern agriculture—reducing the reliance on nitrogen fertilizers. By modulating NO levels to regulate nitrogen uptake, this approach offers:
- Reduced need for synthetic fertilizers, lowering farmers' operational costs.
- Minimized environmental impact, including lower nitrogen oxide emissions and less nitrogen runoff.
- Improved nitrogen uptake efficiency, ensuring better crop yields, especially under conditions with limited nitrogen availability.
Broader Implications:
- Global Nitrogen Challenges:
- The overuse of nitrogen fertilizers has been a major driver of nitrogen pollution, leading to issues like eutrophication, biodiversity loss, and climate change.
- According to the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO), excessive nitrogen use has worsened environmental conditions globally, while many regions, particularly in low-income countries, suffer from nitrogen depletion, which reduces crop productivity.
- Health and Environmental Risks:
- Nitrogen pollution contributes to health issues like methemoglobinemia (blue baby syndrome) and various long-term diseases.
- Nitrogen compounds also play a role in greenhouse gas emissions, further exacerbating climate change.
- Future Directions for Sustainable Agriculture:
- This study highlights the need for innovative nitrogen management strategies, integrating both biological and genetic approaches to optimize nitrogen use.
- Research is underway to develop NO scavenging formulations and identify bacteria that could be used in soil to enhance NUE in plants.
- Policy Recommendations:
- Governments should focus on reducing the environmental and health impacts of nitrogen fertilizer production and usage by promoting sustainable farming practices.
- Encouraging biological nitrogen fixation through crops like soybeans and alfalfa, and investing in low-emission fertilizers, can help mitigate nitrogen pollution.
Dr. V. Narayanan Takes Over as ISRO Chairman

- 10 Jan 2025
In News:
Dr. V. Narayanan has been appointed as the new Chairman of ISRO and Secretary of the Department of Space (DoS), effective from January 14, 2025, succeeding Dr. S. Somanath.
Background and Career of Dr. V. Narayanan:
Dr. Narayanan, currently the Director of Liquid Propulsion Systems Centre (LPSC) in Thiruvananthapuram, has been a key figure in ISRO since joining in 1984. With a focus on cryogenic propulsion, he has played an instrumental role in developing critical technologies for ISRO's launch vehicles. Notably, his work has contributed to India becoming the sixth country globally capable of building and operationalizing cryogenic engines.
Dr. Narayanan’s career highlights include:
- Cryogenic Technology: Leading the development of cryogenic engines for LVM3 (India's heaviest launch vehicle) and PSLV, which are central to missions like Chandrayaan and Gaganyaan.
- Chandrayaan-2 & Chandrayaan-3: As part of ISRO’s missions to the moon, his contributions were pivotal in rectifying the propulsion system issues post-Chandrayaan-2's hard landing, leading to the successful soft landing of Chandrayaan-3 in August 2023.
- Gaganyaan Mission: Overseeing the development of the propulsion systems for crew and service modules, critical for India’s ambitious human spaceflight program.
Dr. S. Somanath's Legacy:
Dr. S. Somanath, who served as ISRO Chairman and DoS Secretary spearheaded multiple landmark missions, including:
- Chandrayaan-3, Aditya-L1, and INSAT missions.
- The Small Satellite Launch Vehicle (SSLV), Re-usable Launch Vehicle (RLV-LEX), and Gaganyaan abort missions.
- National Space Policy 2023 and fostering partnerships between ISRO and private ventures.
Dr. Somanath’s tenure significantly elevated India’s space capabilities, with Chandrayaan-3 marking a historic milestone in India’s lunar exploration.
Dr. Narayanan’s Role in Upcoming ISRO Missions:
As ISRO Chairman, Dr. Narayanan will oversee several ambitious space missions, including:
- NVS-02: The launch of India's navigation satellite as part of the IRNSS constellation.
- Unmanned Gaganyaan Mission: Leading the uncrewed G-1 flight, a precursor to India's first human spaceflight.
- Indo-US NISAR Satellite: A significant collaborative launch with NASA for earth observation.
Additionally, high-profile projects such as Chandrayaan-4, India’s own space station, and future missions to Mars and Venus are in the pipeline, although not all may occur during his tenure.
Vision for ISRO Under Dr. Narayanan:
Dr. Narayanan aims to expand India’s presence in space, targeting increased global market share, particularly in the space economy, which currently holds 2% of the global space sector. His leadership will focus on:
- Increasing Satellite Capacity: Expanding India’s satellite fleet, which currently stands at 53, to meet growing demands for communication, navigation, and earth observation.
- Private Sector Involvement: Leveraging space sector reforms and collaborating with private players to drive innovation and meet burgeoning satellite needs.
- Global Collaboration: Strengthening ties with other space agencies, as ISRO continues to build respect on the global stage.
Upcoming Space Missions and ISRO's Agenda for 2025:
Under Dr. Narayanan's leadership, ISRO has a packed agenda for 2025:
- GSLV Mk-II/IRNSS-1K Mission
- Gaganyaan G-1 Mission (uncrewed flight)
- Chandrayaan-4, Bharatiya Antariksha Station, and Venus Orbiter Mission (VOM) preparations.
Dr. Narayanan’s vision aligns with India's broader goals of becoming a dominant player in the global space economy, aspiring to increase its space market share from 2% to 10%.
Indonesia Becomes 10th Member of BRICS
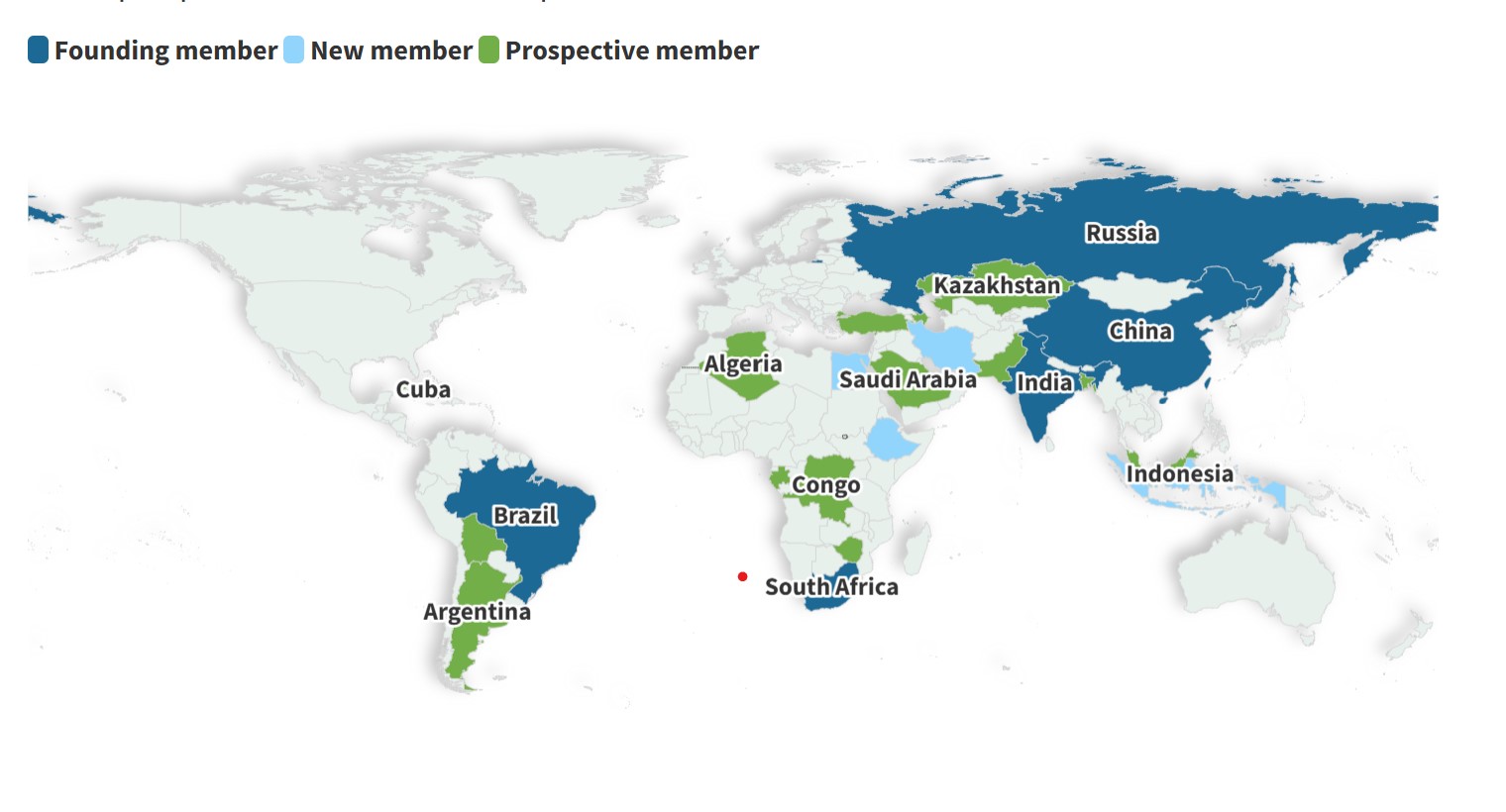
- 10 Jan 2025
In News:
In January 2025, Indonesia officially joined the BRICS group as its 10th member, signaling the expansion of this influential coalition of emerging economies. The addition of Indonesia, a Southeast Asian powerhouse, strengthens BRICS' global position and highlights the group's evolving dynamics.
BRICS Overview:
BRICS (Brazil, Russia, India, China, South Africa) is an informal intergovernmental group that fosters cooperation among major emerging economies. Initially coined as BRIC by economist Jim O'Neill in 2001, the group became BRICS in 2010 with the inclusion of South Africa. The bloc has grown steadily, with Indonesia now joining as its 10th member.
Recent Expansion:
- In 2023, invitations were extended to Saudi Arabia, Iran, UAE, Egypt, Ethiopia, and Argentina.
- By 2024, Iran, Egypt, Ethiopia, and UAE had joined as permanent members.
- Indonesia's membership was finalized in 2025, following its presidential elections and government formation.
Key Objectives of BRICS:
- Economic Growth: Promote trade, investment, and infrastructure development.
- Global Governance Reform: Advocate for equitable representation in global institutions like the UN and IMF.
- Cultural Exchange: Strengthen people-to-people connections and cultural ties.
- South-South Cooperation: Foster collaboration among developing nations.
BRICS Structure and Mechanisms:
- New Development Bank (NDB): Established in 2014, the NDB finances sustainable development projects in BRICS countries.
- Contingent Reserve Arrangement (CRA): A $100 billion safety net for financial crises.
- BRICS Academic Forum: Encourages academic collaboration across member states.
Global Influence and Economic Impact:
- Global Share: BRICS+ represents over 45% of the world’s population and 35% of global GDP (PPP-based).
- Strategic Position: The group acts as a counterbalance to the G7, challenging Western-dominated global financial systems.
- Financial Independence: BRICS aims to reduce dependence on the US dollar by facilitating local currency transactions and exploring a common currency.
- Technology Collaboration: Member countries, such as India and China, collaborate on digital payments and renewable energy technologies.
Indonesia’s Entry into BRICS:
Indonesia, the world’s fourth-most populous nation, strengthens BRICS’ representation in Southeast Asia. The country brings a robust economy and extensive trade networks, boosting the group's negotiating power. Indonesia’s membership was approved during the 2023 BRICS Summit and finalized in January 2025.
- Strategic Importance for Indonesia: The membership aligns with Indonesia's goals to enhance global cooperation, particularly with the Global South. It also reflects Indonesia's growing influence in international trade and geopolitics.
BRICS Challenges:
- Diverse Interests: Differences in economic priorities, such as India's ties with the US and Russia-China’s geopolitical rivalry, complicate consensus-building.
- Geopolitical Tensions: Disputes like the China-India border issue and Russia’s sanctions limit BRICS' ability to present a unified stance.
- Economic Sanctions and Internal Challenges: Countries like Russia face Western sanctions, while domestic issues in Brazil and South Africa divert attention from regional collaboration.
Significance of BRICS’ Expansion:
The expansion of BRICS marks a pivotal shift in global power dynamics, with a focus on South-South cooperation and equitable global governance. Indonesia’s membership further solidifies the group’s influence in Southeast Asia and adds to its efforts to challenge the dominance of Western-led financial institutions.
- Local Currency Use: The group promotes the use of local currencies for trade to reduce reliance on the US dollar.
- Global South Advocacy: BRICS champions the cause of developing nations, ensuring that emerging economies have a voice in global governance.
Recent and Upcoming BRICS Summits:
- 16th BRICS Summit (2024): Held in Kazan, Russia, with a focus on strengthening local currencies and promoting non-dollar transactions.
- 17th BRICS Summit (2025): Scheduled for July 2025 in Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, under the theme "Global South," with an emphasis on payment gateways to facilitate intra-BRICS trade.
Flamingo Festival 2025

- 10 Jan 2025
In News:
The Flamingo Festival 2025 took place at Sullurpeta, in Tirupati district, Andhra Pradesh. It celebrates the arrival of migratory birds, with a focus on flamingos, to the region's key bird habitats, including Pulicat Lake and Nelapattu Bird Sanctuary.
Key Highlights:
- Birdwatching: Over 200 bird species, including flamingos, are expected to flock to the region during this festival.
- Locations: The event spans across five locations:
- Nelapattu Bird Sanctuary
- B.V. Palem (Pulicat Lake)
- Atakanithippa
- Sri City
- Sullurpeta (site for cultural programs and stalls)
- Collaborations: In association with organizations like the Bombay Natural History Society.
- Focus on Local Community: Local residents of the eco-sensitive zone will be prioritized and supported.
Key Facts on Local Wildlife and Significance:
- Pulicat Lake:
- Location: On the Andhra Pradesh-Tamil Nadu border, with 96% of the lake in Andhra Pradesh.
- Significance: The second-largest brackish water lake in India (after Chilika Lake in Odisha).
- Biodiversity: Critical habitat for migratory birds, including flamingos, and home to diverse flora and fauna.
- Economic Importance: Supports local fisheries and provides livelihood to nearby communities.
- Nelapattu Bird Sanctuary:
- Location: 20 km north of Pulicat Lake.
- Ecological Role: Largest breeding site in Southeast Asia for spot-billed pelicans.
- Biodiversity: 189 bird species, including painted storks and glossy ibises.
- Flora and Fauna: Features Barringtonia swamp forests and southern dry evergreen scrub, critical for biodiversity conservation.
- Symbiotic Relationship with Locals: Guano (bird droppings) from pelicans serves as a natural fertilizer for local agriculture, benefiting the farmers.
Flamingo Facts:
- Species: India hosts two flamingo species:
- Greater Flamingo (larger size, pale pink)
- Lesser Flamingo (smaller size, bright pink)
- Behavior: Nomadic and social birds, found in large flocks.
- Coloration: Flamingos' pink color comes from carotenoids in their diet, which are broken down and absorbed into their bodies.
Environmental & Economic Impact: The festival, apart from being a celebration of migratory birds, plays a vital role in:
- Eco-tourism development
- Biodiversity conservation
Local community engagement by highlighting sustainable tourism practices and supporting local livelihoods through eco-friendly initiatives like the Mahatma Gandhi National Rural Employment Guarantee Scheme (MGNREGS).
Bharatpol

- 11 Jan 2025
In News:
Union Home Minister Amit Shah inaugurated the ‘Bharatpol’ portal, which aims to streamline international cooperation for law investigating agencies.
Key Highlights:
Bharatpol is a newly launched portal developed by the Central Bureau of Investigation (CBI) in India to facilitate faster and more efficient international cooperation between Indian law enforcement agencies and Interpol. It was inaugurated by Union Home Minister Amit Shah, to streamline the process of sharing criminal intelligence and coordinating efforts in transnational crimes like cybercrime, human trafficking, drug trafficking, financial fraud, and organized crime.
The portal aims to address the current challenges in international collaboration, which previously relied on slower communication methods such as letters, emails, and faxes, often leading to delays in investigations.
Key Features and Functions of Bharatpol:
- Unified Platform: Bharatpol integrates CBI as the National Central Bureau (NCB-New Delhi) with all Indian law enforcement agencies, from state police forces to higher authorities. This allows better coordination and quicker access to international resources.
- Simplified Request Mechanism: The portal provides a standardized method for frontline police officers to request international assistance from Interpol member countries, using templates for efficiency.
- Rapid Information Dissemination: Bharatpol enables the CBI to quickly share criminal intelligence and other pertinent information with law enforcement agencies across India, helping to tackle international criminal activities in real-time.
- Increase in Utilization of Interpol Notices: The portal makes it easier for Indian law enforcement agencies to issue and manage Red Corner Notices and other Interpol notices, which are essential tools in tracking criminals globally.
- Capacity Building and Training: Bharatpol includes resources for training law enforcement personnel, improving their ability to conduct investigations abroad and seek foreign assistance via Interpol.
How Bharatpol Works:
- Key Modules of Bharatpol:
- Connect: Facilitates the integration of Indian agencies with the Interpol NCB-New Delhi, creating a seamless communication channel.
- INTERPOL Notices: Supports the rapid issuance and processing of Interpol Notices like Red Corner Notices to locate criminals globally.
- References: Enables Indian agencies to seek and offer international assistance for investigations.
- Broadcast: Ensures quick availability of assistance requests from Interpol member countries, facilitating faster responses.
- Resources: Manages document exchanges and training materials to support the capacity-building efforts of law enforcement agencies.
Potential Benefits of Bharatpol:
- Enhanced Coordination: Bharatpol facilitates better collaboration between central, state, and Union Territory agencies, allowing for a more structured and efficient approach to international crime investigations.
- Faster Investigation: Real-time sharing of information and the use of Interpol notices will help in tracking criminals and criminal activities both in India and abroad.
- Simplified Extradition Process: By streamlining international communication, Bharatpol will assist in expediting the extradition of criminals to India for prosecution.
- Support for Transnational Crime Prevention: It will help address growing threats such as cybercrime, human trafficking, and organized crime by improving the ability of Indian law enforcement to collaborate globally.
National Mission on Edible Oils - Oil Palm (NMEO-OP)

- 11 Jan 2025
In News:
- Union Minister Shri Shivraj Singh Chouhan urges states to accelerate efforts under the National Mission on Edible Oils - Oil Palm (NMEO-OP) to enhance domestic production of edible oils and reduce reliance on imports.
Key Facts Regarding the NMEO-OP Scheme:
About the Scheme:
- Objective: Enhance domestic production of crude palm oil (CPO) and reduce India's dependence on edible oil imports.
- Centrally Sponsored Scheme: Focuses on expanding oil palm cultivation in India.
Key Targets:
- Area Expansion: Aim to cover an additional 6.5 lakh hectares by 2025-26, reaching a total of 10 lakh hectares.
- Production Increase: CPO production is targeted to rise from 0.27 lakh tonnes (2019-20) to 11.20 lakh tonnes by 2025-26, and further to 28 lakh tonnes by 2029-30.
- Per-Capita Consumption: Maintain a consumption level of 19 kg/person/annum until 2025-26.
Focus Regions:
- Special Focus: North-Eastern States and Andaman & Nicobar Islands for oil palm cultivation and CPO production.
Key Features:
- Viability Price (VP) Mechanism: Aims to protect farmers from market volatility by providing price assurance. Payments are made through Direct Benefit Transfer (DBT).
- Increased Assistance:
- Assistance for planting material increased from Rs 12,000/ha to Rs 29,000/ha.
- Special assistance of Rs 250 per plant for rejuvenating old gardens.
- Regional Support:
- For North-East and Andaman, an additional 2% of the CPO price is borne by the government to ensure fair payments to farmers.
- Special provisions for half-moon terrace cultivation, bio-fencing, and land clearance for integrated farming.
Oil Palm Cultivation:
- Origin: Native to the tropical rainforests of West Africa, oil palm is a new crop in India with high oil-yielding potential.
- Oil Yield: Oil palm produces five times the yield of traditional oilseeds per hectare.
- Types of Oil Produced:
- Palm Oil: Extracted from the mesocarp (fruit's fleshy part), containing 45-55% oil.
- Palm Kernel Oil: Derived from the kernel, used in lauric oils.
- Major States for Cultivation: Andhra Pradesh, Telangana, Kerala (98% of total production).
- Other Key States: Karnataka, Tamil Nadu, Odisha, Gujarat, Mizoram, Arunachal Pradesh, Assam, Manipur, Nagaland.
India's Oil Palm Potential:
- Cultivated Area: India currently has 3.70 lakh hectares under oil palm cultivation.
- Total Potential Area: Around 28 lakh hectares.
- Imports: India is the world's largest palm oil importer, with imports of 9.2 million tonnes in 2023-24, accounting for 60% of total edible oil imports. The country primarily imports from Indonesia, Malaysia, and Thailand.
Emergency Declared in Trinidad and Tobago
- 11 Jan 2025
In News:
- Trinidad and Tobago declared a state of emergency, in response to a surge in gang violence, which raised the annual death toll to the highest since 2013.
Trinidad and Tobago:
- Location: An island nation in the southern Caribbean, near Venezuela and Guyana.
- Capital: Port of Spain.
- Population: Approximately 1.5 million.
- Ethnic Composition: African (36.3%), Indian (35.4%), Mixed (22.8%), and others.
- Religions: Christianity (64%), Hinduism (18%), Islam (5%), and others.
- Independence: Gained from the UK on August 31, 1962, and became a republic in 1976.
- Member of: Caribbean Community (CARICOM), Commonwealth of Nations, and the United Nations.
- Major Rivers: Ortoire and Caroni.
- Geography:
- Total Land Area: 5,128 sq. km (Trinidad: 4,768 sq. km, Tobago: 300 sq. km).
- Climate: Tropical, with dry and rainy seasons.
- Highest Point: Mount Aripo.
- Natural Resource: Pitch Lake, the world’s largest asphalt reservoir.
- Mountain Range: Northern Range, part of the Andes extension.
Economic and Cultural Significance
- Exports: Major exporter of liquefied natural gas (LNG), methanol, ammonia, and petrochemicals.
- Culture: Known for Carnival, Calypso music, Soca, and the Steelpan (the only musical instrument invented in the 20th century).
- Infrastructure:
- Ports: Port of Spain, Point Lisas, Scarborough.
- Airports: Piarco International Airport (Trinidad) and A.N.R. Robinson International Airport (Tobago).
Engagement with India
- Trinidad and Tobago became the first Caribbean country to adopt India’s UPI platform.
- Both countries granted each other Most Favored Nation (MFN) status in 1997.
- Bilateral trade reached USD 368.96 million in FY 2023-24.
- The Indian diaspora constitutes about 42% of the population.
Past Emergency Declarations:
- 2014: State of emergency declared in response to gang violence.
- 2021: Emergency declared for Covid-19 restrictions.
- 2011: Limited state of emergency for drug-related crimes.
Toda Tribe

- 11 Jan 2025
In News:
- The Toda tribe, one of the oldest Dravidian ethnic groups in the Nilgiris Hills of Tamil Nadu, celebrated their traditional Modhweth festival marking the New Year.
What is the Modhweth Festival?
- About:
- Celebrated annually on the last Sunday of December or the first Sunday of January.
- Held at the Moonpo temple in Muthanadu Mund village, Nilgiri district.
- The Moonpo temple features a unique vertical spire with a thatched roof and a flat stone on top, making it one of the last Toda temples of its kind in the Nilgiris.
- Rituals and Celebrations:
- Prayers are offered to the deity, Thenkish Amman, for good health, rains, and bountiful harvest.
- Participants perform a traditional dance outside the temple.
- Unique Customs:
- Toda youth showcase their strength and masculinity by lifting a greased boulder weighing around 80 kg.
- Women are not part of the celebrations as per traditional customs.
What is the Toda Tribe?
- About:
- A pastoral tribe native to the Nilgiri Hills of Tamil Nadu.
- Classified as a Particularly Vulnerable Tribal Group (PVTG) in Tamil Nadu.
- The Toda language is Dravidian but stands out for its uniqueness among Dravidian languages.
- Significance:
- Toda lands are part of the Nilgiri Biosphere Reserve, a UNESCO International Biosphere Reserve.
- Their territory is also recognized as a UNESCO World Heritage Site.
- Religion and Beliefs:
- Their religious practices are based on a pantheon of gods, with Tökisy (goddess) and Ön (god of the underworld) as central deities.
Nilgiri Biosphere Reserve (NBR)
- About:
- Established in 1986 as India’s first Biosphere Reserve.
- Located across Tamil Nadu, Karnataka, and Kerala.
- India’s first biosphere reserve under UNESCO’s Man and the Biosphere Programme.
- Tribal Groups in NBR:
- Home to several groups such as Adiyan, Aranadan, Kader, Kurichian, Kuruman, and Kurumbas.
- Ecological Significance:
- Represents the confluence of Afro-tropical and Indo-Malayan biotic zones.
- Fauna:
- Home to species like Nilgiri tahr, Nilgiri langur, gaur, Indian elephant, Nilgiri danio (freshwater fish), and Nilgiri barbare.
- Protected Areas in NBR:
- Mudumalai Wildlife Sanctuary, Wayanad Wildlife Sanctuary, Bandipur National Park, Nagarhole National Park, Mukurthi National Park, and Silent Valley.
Z-Morh Tunnel
- 11 Jan 2025
In News:
Recently, Prime Minister Narendra Modi inaugurated the Z-Morh Tunnel at Sonamarg, which has now been renamed the Sonamarg Tunnel.
Key Takeaways:
- A 6.4-km bi-directional tunnel with an approach road of 5.6 km, Z-Morh connects the Sonamarg health resort with Kangan town in the Ganderbal district of central Kashmir.
- The tunnel has acquired its name for the Z-shaped road stretch that was previously at the place where the tunnel is being constructed.
- The Z-Morh project was initiated by the Border Roads Organisation in 2012. Although the BRO awarded the construction contract to Tunnelway Ltd, the project was subsequently taken over by National Highways and Infrastructure Development Corporation Limited (NHIDCL).
Significance
Strategic Importance
- Connectivity: Provides all-weather connectivity from Srinagar to Ladakh, ensuring year-round access.
- Military Significance:
- Critical for rapid deployment of Indian Armed Forces to Ladakh’s border areas, particularly in the context of tensions with Pakistan and China.
- Reduces dependence on air transport, lowering costs and increasing the longevity of the Indian Air Force’s aircraft.
- Adjacent Projects:
- Zojila Tunnel: An even more crucial project connecting Sonamarg to Drass in Ladakh, with an expected completion by December 2026 (extended to 2030). This will bypass the avalanche-prone Zojila Pass.
- Srinagar-Leh Highway: The Z-Morh Tunnel supports the key Srinagar-Leh route, which is important for defence logistics and trade.
Economic Significance
- Tourism:
- Sonamarg, known as the "Meadow of Gold," will benefit from year-round accessibility, boosting tourism.
- Local businesses that rely on seasonal tourist traffic will have consistent revenue flow.
- Trade and Agriculture:
- Reduced travel time and improved road safety will benefit farmers and traders, especially for those transporting goods between Kashmir and Ladakh.
- Facilitates increased investment and economic growth in the region.
Broader Infrastructure Projects in Jammu & Kashmir
Several key infrastructure projects are contributing to regional development:
- Zojila Tunnel
- Cost: ?6,800 crore
- Length: 13 km tunnel, bypassing Zojila Pass.
- Completion: Expected by 2030.
- Strategic Importance: Provides all-weather connectivity to Ladakh.
- Srinagar Semi-Ring Road
- Cost: ?2,919 crore
- Objective: Relieve traffic congestion in five districts, including Srinagar.
- Delay: New completion date is June 2025.
- Hydroelectric Power Projects:
- Ratle HE Project: 850 MW, on Chenab River, Kishtwar district.
- Kwar HE Project: 540 MW, in Kishtwar.
- Pakal Dul HE Project: 1,000 MW, on the Marusudar River, Kishtwar.
- Kiru HE Project: 624 MW, on Chenab River, Kishtwar.
- Strategic Relevance: These projects will enhance energy security and contribute to the region’s power grid.
India’s Recalculated Coastline
- 09 Jan 2025
In News:
India’s coastline has grown significantly over the past five decades, now extending 11,098 km in 2023-24, compared to 7,516 km in 1970. This marks an increase of 47.6% in just over five decades, attributed to a more precise methodology for measuring coastlines.
Key Factors Behind the Growth:
New Methodology for Measuring Coastlines:
- The old methodology used straight-line distances to measure the coastline, a method that didn't capture the complexity of India’s coastlines.
- The updated approach incorporates bays, estuaries, inlets, and other geomorphological features, offering a more accurate and detailed representation of the coastline.
- Advanced technologies like geospatial mapping have been used to ensure greater precision.
State-wise Recalculated Coastline Changes:
- Gujarat:
- Old coastline (1970): 1,214 km
- New coastline (2023-24): 2,340 km
- Growth: The largest absolute increase in coastline, nearly doubling its size.
- West Bengal:
- Old coastline: 157 km
- New coastline: 721 km
- Growth: A dramatic 357% increase, marking the highest percentage rise.
- Tamil Nadu:
- Old coastline: 906 km
- New coastline: 1,068 km
- Growth: Revised length now exceeds Andhra Pradesh’s coastline, which was 1,053 km.
- Puducherry:
- Old coastline: No major shift, but the updated data shows a contraction of 4.9 km (-10.4%), due to erosion and recalculations.
- Kerala:
- Old coastline: Relatively small increase of 30 km (5%), the smallest among the states.
Notable Observations:
- Andhra Pradesh is developing new ports like Ramayapatnam, Krishnapatnam, and Kakinada Gateway, aiming to boost economic growth and employment by leveraging its expanding coastline.
- The recalculated coastline helps in better maritime planning, focusing on port development, tourism, biodiversity conservation, and coastal erosion.
Impact of Coastline Expansion:
- Economic Growth:
- Coastal states, particularly Gujarat and West Bengal, benefit from an expanded coastline that improves maritime trade, port infrastructure, and tourism.
- The expansion supports industrialization, with growing logistics and transportation activities along the coast.
- Environmental Considerations:
- The new data aids biodiversity conservation, helping to track coastal erosion and accretion (land buildup), especially in areas like the West Coast.
- Understanding these changes is essential for disaster preparedness and sustainable coastal management.
- Coastlines of Emergence and Submergence:
- Emerging Coastlines: Land rising due to uplift or falling sea levels, such as along the Tamil Nadu Coast.
- Submerged Coastlines: Land that has sunk or been submerged due to rising sea levels, particularly noticeable along parts of Kerala’s coast.
Geographical Significance of the Expanded Coastline:
- India’s coast touches three major bodies of water: the Bay of Bengal (east), the Indian Ocean (south), and the Arabian Sea (west).
- The expansion reflects more than just geography—accurate coastline data is crucial for policy planning, maritime security, and resource management.
Bhashini Initiative
- 09 Jan 2025
In News:
e-Shram Portal, which aims to provide social security benefits to unorganised workers, has been upgraded with multilingual functionality for all 22 scheduled languages of India. This development, supported by the Bhashini Initiative, ensures that unorganised workers from diverse linguistic backgrounds can access the portal more easily and benefit from government welfare schemes.
About Bhashini Initiative:
- Launched in: July 2022
- Developed by: Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology (MeitY)
- Aim: To eliminate language barriers in accessing digital services by making AI and Natural Language Processing (NLP) tools publicly available.
Key Features:
- Local Language Translation: Bhashini offers AI-powered translation services in 22 scheduled Indian languages to ensure that digital platforms like e-Shram are accessible to everyone in their native languages.
- Open AI and NLP Resources: These tools are made available to Indian MSMEs, startups, and innovators to create a more inclusive digital ecosystem.
- Crowdsourcing Platform (Bhashadaan): A platform for people to contribute to building linguistic datasets through initiatives like Suno India, Likho India, Bolo India, and Dekho India, furthering language diversity in digital services.
- National Digital Public Platform: Aimed at providing universal access to digital content in all Indian languages, facilitating smoother communication across regions.
e-Shram Portal: A One-Stop Solution for Unorganised Workers
- Purpose: The e-Shram portal was created to provide unorganised workers with access to social security benefits and welfare schemes.
Recent Upgrade:
- Multilingual Functionality: The portal has now been upgraded to support 22 scheduled languages, making it more inclusive and user-friendly for workers who speak various regional languages.
- Previous Version: Previously, the portal was only available in English, Hindi, Kannada, and Marathi. The integration of 22 languages is a significant improvement, enabling broader participation.
Importance of the e-Shram Portal for Unorganised Workers:
- Welfare Access: The portal provides access to government schemes designed for the welfare, livelihood, and well-being of unorganised workers, including gig and platform workers and building and construction workers.
- Integration of Social Security Schemes:
- As of now, the portal facilitates access to 12 government schemes, with plans to integrate even more, including state-level programs.
- Future plans include launching a mobile app, a single application form, and the integration of payment gateways for faster disbursement of benefits.
AI-Driven Inclusive Development and Economic Transformation

- 09 Jan 2025
In News:
IndiaAI, under the Digital India Corporation, has partnered with Microsoft to advance AI adoption in India for inclusive development and economic transformation. The collaboration focuses on skilling, innovation, AI safety, and responsible AI development, with a goal of fostering AI innovation across India, particularly in underserved rural and urban areas.
Key Highlights:
- Training 500,000 Individuals by 2026:
- Target Audience: Students, educators, developers, government officials, and women entrepreneurs.
- Goal: Empower these groups with foundational and advanced AI skills for economic opportunities and digital transformation.
- AI Catalysts (Centers of Excellence):
- Establishment of AI hubs in Tier 2 and Tier 3 cities to foster rural AI innovation.
- Objective to equip 100,000 AI innovators and developers through hackathons, community building, and creating an AI marketplace.
- AI Productivity Labs:
- Set up in 20 National Skill Training Institutes (NSTIs) across 10 states.
- Focus on training 20,000 educators and providing AI education to 100,000 students in 200 Industrial Training Institutes (ITIs).
- Support for Startups:
- Microsoft’s Founders Hub program will provide Azure credits, business resources, and mentorship to 1,000 AI startups in India, boosting innovation and growth in the Indian startup ecosystem.
- Development of Indic Language Models:
- Work on creating foundational AI models with support for Indic languages to address India’s linguistic diversity and cultural needs.
- AI Safety Institute:
- Focus on building frameworks, standards, and evaluation metrics for responsible AI development.
- Support for the creation of an AI Safety Institute in India to promote ethical and safe AI practices.
- Infrastructure & Research:
- Microsoft will also focus on enhancing cloud infrastructure and support for AI research through Microsoft Research India.
- AI-driven solutions will be developed for critical sectors like healthcare, education, and agriculture.
Investment and Strategic Goals:
- $3 Billion Investment:
- Microsoft has pledged $3 billion to expand AI and cloud infrastructure in India over the next 2 years. This investment will focus on:
- Building scalable infrastructure for AI applications.
- Enhancing cloud services and AI capabilities.
- Establishing new data centers across India, supporting the AI-first agenda.
- Microsoft has pledged $3 billion to expand AI and cloud infrastructure in India over the next 2 years. This investment will focus on:
- AI Skill Development:
- 10 million people will be trained over the next five years in AI skills, empowering the Indian workforce to adapt to AI technologies, driving job creation and economic growth.
- AI in India’s Economy:
- India aims to become a global leader in AI, with AI-powered solutions contributing to diverse sectors like finance, e-commerce, and manufacturing.
- Focus on economic growth through AI-powered industries and fostering entrepreneurship in underserved communities.
AI Technologies and Applications:
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) involves machines performing tasks that require human intelligence like decision-making, problem-solving, and learning from data.
- Machine Learning (ML): AI systems improve through data without being explicitly programmed.
- Natural Language Processing (NLP): AI systems understand and respond to human language.
- Computer Vision: AI systems analyze and interpret visual information.
- Robotics: AI powers automated tasks through robots in industries like manufacturing and healthcare.
- Cloud Infrastructure enables the scaling of AI systems:
- Cloud Computing provides on-demand access to computing power, essential for AI tasks requiring large amounts of data and processing power.
- Data Centers host AI models and data, and cloud services such as Microsoft Azure will support AI startups and businesses.
Expected Impact and Benefits:
- Inclusive AI Development: Focus on empowering women, students, and rural innovators to bridge the digital divide and promote economic empowerment.
- Startup Ecosystem: The collaboration will foster a robust AI startup ecosystem, promoting innovation and entrepreneurship through AI tools, Azure credits, and mentorship.
- Skill Development & Education: AI-driven skill training initiatives will prepare millions of individuals for the jobs of the future, particularly in the AI-driven economy, and support education reform.
- AI for Critical Sectors: Development of AI-enabled solutions to address challenges in sectors such as healthcare, education, and agriculture, driving social impact and economic growth.
Miyawaki Technique
- 09 Jan 2025
In News:
- Prayagraj Municipal Corporation has successfully transformed over 56,000 square meters of garbage dumps and barren lands into lush green forests using the Miyawaki Technique over the past two years, as part of environmental conservation efforts in preparation for Mahakumbh 2025.
About Miyawaki Technique:
- Origin: Developed by Akira Miyawaki, a Japanese botanist, in the 1970s to create dense and fast-growing forests.
- Key Features:
- Dense Planting: Trees and shrubs are planted close together, often using native species.
- Accelerated Growth: Trees grow 10 times faster than in traditional forests.
- Soil Restoration: Improves soil fertility and promotes natural regeneration.
- Biodiversity Boost: Supports a variety of flora and fauna by mimicking natural ecosystems.
- Significance:
- Urban Reforestation: Converts barren or polluted lands into green spaces.
- Environmental Benefits:
- Reduces air and water pollution.
- Absorbs carbon and helps combat climate change.
- Lowers temperatures by 4-7°C.
- Sustainability: Prevents soil erosion and promotes long-term ecological balance.
Miyawaki Forests in Prayagraj:
- Achievements:
- Over 56,000 square meters of land converted into dense forests using the Miyawaki technique over the last two years.
- The project aims to create oxygen banks in preparation for the Mahakumbh 2025 and enhance air quality for millions of expected visitors.
- Plantations:
- 55,800 square meters of area developed across 10+ locations in Prayagraj.
- Largest plantation: 1.2 lakh trees in Naini industrial area.
- 27,000 trees planted in Baswar after cleaning the city's largest garbage dump.
- Environmental Impact:
- The plantations are helping to reduce dust, dirt, and foul odors, thus improving air quality.
- Temperature regulation: The dense forests can lower temperatures by 4 to 7 degrees Celsius.
- Biodiversity and Soil Fertility: Accelerated growth of trees boosts biodiversity and improves soil fertility.
- Tree Species Planted:
- Mango, Mahua, Neem, Peepal, Tamarind, Arjuna, Teak, Amla.
- Ornamental and medicinal plants like Hibiscus, Kadamba, Gulmohar, etc.
- Other species include Sheesham, Bamboo, Lemon, Drumstick (Sahjan), and Tecoma.
Benefits of Miyawaki Forests:
- Air and Water Pollution Reduction: Trees absorb carbon, purify air, and improve water quality.
- Temperature Control: The forests help in reducing urban heat islands, lowering the temperature during hot months.
- Soil Conservation: The dense forests prevent soil erosion and promote the regeneration of the natural ecosystem.
- Enhanced Biodiversity: The technique supports a rich variety of species, improving ecological balance.
AnemiaPhone

- 09 Jan 2025
In News:
AnemiaPhone, a technology developed by Cornell University researchers to accurately, quickly, and cheaply, assess iron deficiency, has been transferred to the Indian Council of Medical Research (ICMR) for integration into its programmes for anaemia, women’s health, and maternal and child health throughout the country.
Key Highlights:
- Technology Features:
- Portable, Rapid, and Affordable: AnemiaPhone is designed to detect iron deficiency efficiently at low cost.
- Requires a fingerstick (small blood sample).
- Results are available within minutes.
- Wireless: Data uploaded to a clinical database via mobile, tablet, or computer.
- Can be used by healthcare workers to assess iron deficiency on the spot and take action (guidance, triage, referral).
- Working Mechanism:
- A drop of blood is placed on a test strip.
- The reader processes the sample.
- Data is uploaded for immediate diagnosis and action.
- Test results assist in on-the-spot intervention by healthcare workers.
Anaemia and Iron Deficiency:
- Prevalence in India:
- Iron deficiency is a leading cause of anaemia.
- 50%-70% of pregnant women in India suffer from anaemia.
- 59% of women and 47% of children (6-59 months) in India suffer from anaemia (NFHS data).
- Consequences of Anaemia:
- Fatigue, dizziness, organ failure, complications in childbirth, and in severe cases, death.
- Contributes to higher maternal and child mortality rates in India.
- Impact on Health in India:
- India has one of the highest rates of anaemia in the world.
- Iron deficiency is a significant contributor to maternal deaths.
ICMR's Role and Integration into National Programs:
- ICMR and AnemiaPhone:
- The Indian Council of Medical Research (ICMR) has integrated AnemiaPhone into its Anaemia Mukt Bharat (Anaemia-Free India) program.
- The program focuses on eliminating anaemia by 2025 through screening, diagnosis, and treatment in women and children, especially in remote areas.
- Transfer of Technology:
- In November 2024, Cornell University transferred the technology to ICMR for free.
- This collaboration aims to improve health outcomes by sharing innovative health technologies.
Advantages of AnemiaPhone:
- Cost-Effective and Portable:
- Low-cost compared to traditional lab tests.
- Portable and can be used in remote and underserved areas.
- Quick Diagnosis: Results are processed in minutes, allowing healthcare workers to act without delay.
- No Need for Expensive Labs:
- Can be used at primary health centers or in door-to-door health surveys.
- Facilitates healthcare in rural or difficult-to-reach areas.
- Wireless and Easy to Use: The device is user-friendly and does not require extensive training.
Impact on Healthcare System:
- Improvement in Accessibility:
- Helps reduce the need for people to travel long distances for diagnosis, especially in rural areas.
- Ensures early diagnosis and treatment of iron deficiency and anaemia.
- Enhancing Maternal and Child Health: AnemiaPhone will contribute to reducing maternal and child mortality rates linked to anaemia.
Technology Testing and Development:
- Testing in India:
- AnemiaPhone has been tested in India and has shown accurate results in diagnosing iron deficiency.
- Single-use test strips help ensure accuracy and prevent contamination.
Global Health Context:
- Global Prevalence of Anaemia: More than 2 billion people worldwide suffer from anaemia, particularly pregnant women and young children.
- WHO’s Role: The World Health Organization (WHO) identifies anaemia as a major global health issue.
India-Malaysia Cooperation in Critical Minerals and Rare Earth Elements

- 08 Jan 2025
In News:
- On January 7, 2025, during the inaugural India-Malaysia Security Dialogue in New Delhi, both countries agreed to enhance cooperation in critical minerals and rare earth elements (REEs).
- The meeting was co-chaired by India's National Security Adviser, Ajit Doval, and Malaysia’s Director General of the National Security Council, Raja Dato Nushirwan Bin Zainal Abidin.
- The agreement follows the upgrade of bilateral relations to a Comprehensive Strategic Partnership during Malaysian Prime Minister Anwar Ibrahim’s visit to India in August 2024.
- The dialogue also focused on other security aspects such as counter-terrorism, cyber security, and maritime security.
Importance of Critical Minerals and REEs:
-
- Critical Minerals: These are essential for a variety of industries like IT, energy, and defense. They are integral to manufacturing electric vehicle batteries, solar cells, and advanced electronics.
-
- Rare Earth Elements (REEs): Used in high-tech applications such as wind turbines, electric vehicle engines, and high-powered magnets. While their extraction is not rare, it is technically difficult due to their complex nature.
Strategic Relevance:
-
- Global Demand: The global demand for critical minerals is rising, and both countries see it as a strategic necessity to ensure a stable supply of these materials.
- Malaysia's Resources: Malaysia possesses significant deposits of non-rare radioactive earth ores, including essential REEs like Neodymium (Nd), Dysprosium (Dy), and Praseodymium (Pr). These elements are crucial in today’s technological innovations.
- India’s Dependence on Imports: India, which currently imports a substantial portion of its critical minerals, aims to diversify its supply chain by collaborating with Malaysia.
Sustainability and Ecological Accountability:
-
- Both countries recognize the environmental challenges of mining these critical resources. Malaysia aims to adopt responsible mining practices that minimize ecological harm.
- India seeks to ensure a supply chain that aligns with sustainable development goals, balancing economic needs with environmental responsibilities.
Enhancing Supply Chain Resilience:
-
- Diversification of Supply Chain: This partnership aims to reduce India’s dependency on a limited number of countries for critical minerals, enhancing resilience against global supply chain disruptions.
- Collaboration in Extraction and Processing: Both nations are exploring joint ventures in the exploration, extraction, and processing of critical minerals to boost their technological and economic standing globally.
Future Prospects:
-
- The institutionalization of this dialogue through annual meetings is expected to strengthen bilateral cooperation in the critical minerals sector.
- Increased cooperation is likely to enhance economic growth for both countries, aligning them strategically in the global minerals market as demand for these resources continues to soar.
Broader Security Cooperation:
-
- Beyond critical minerals, the India-Malaysia Security Dialogue explored enhanced collaboration in areas like counter-terrorism, cyber security, maritime security, and defense industries.
- This broadening of security cooperation complements the strategic minerals partnership, further solidifying the bilateral ties between the two nations.
Anji Khad Bridge

- 08 Jan 2025
In News:
The Indian Railways has unveiled a monumental engineering achievement with the completion of the Anji Khad Bridge, India’s first cable-stayed rail bridge.
Overview:
- The Anji Khad Bridge is India's first cable-stayed rail bridge, located in Jammu and Kashmir’s Reasi district.
- It is a key part of the Udhampur-Srinagar-Baramulla Rail Link (USBRL) project aimed at enhancing connectivity between Jammu and Kashmir and the rest of India.
- The bridge crosses the Anji River, a tributary of the Chenab River, and is expected to transform regional transport, boost tourism, and promote economic growth.
Key Features:
- Dimensions:
- Total length: 725.5 meters.
- Main Pylon Height: 193 meters from the foundation, standing 331 meters above the riverbed.
- The bridge is designed for train speeds of up to 100 km/h and can withstand wind speeds of up to 213 km/h.
- Structure and Design:
- Asymmetrical cable-stayed design supported by 96 cables with varying lengths (82 to 295 meters).
- The structure includes:
- A 120-meter approach viaduct on the Reasi side.
- A 38-meter approach bridge on the Katra side.
- A 473.25-meter cable-stayed portion crossing the valley.
- A 94.25-meter central embankment linking the main bridge to the approach viaduct.
- Construction Techniques:
- Used advanced construction techniques such as DOKA Jump Form Shuttering, Pump Concreting, and Tower Crane Technique to enhance safety and reduce construction time by 30%.
- A 40-ton tower crane imported from Spain was employed for operations at great heights.
- The project utilized site-specific investigations by IIT Roorkee and IIT Delhi due to the region’s complex geological and seismic conditions.
- Engineering Challenges:
- The bridge had to be constructed in the difficult Himalayan terrain, with fragile geological features such as faults and thrusts.
- Seismic activity in the region required additional precautions in the design and construction process.
- Safety and Monitoring:
- Equipped with an integrated monitoring system that includes multiple sensors to ensure the structural health of the bridge during operation.
Importance and Impact:
- Connectivity: The bridge will significantly improve connectivity between Katra and Reasi, ensuring faster rail travel and linking the Kashmir Valley with the rest of India.
- Tourism and Economic Growth: Expected to boost tourism and economic development by improving access to the region, attracting visitors, and facilitating smoother transportation of goods and services.
- Sustainability: The bridge's design ensures it remains safe under extreme weather conditions, offering long-term reliability for the Indian Railways network.
Collaboration and International Expertise:
- The design and supervision were handled by ITALFERR (Italy), with proof-checking conducted by COWI (UK).
- The project combines Indian engineering codes with Eurocodes, adhering to international standards for structural integrity.
Section 479 of the BNSS 2023

- 08 Jan 2025
In News:
Centre urges states, UTs to ensure undertrial prisoner relief in jails.
Key Highlights:
- Objective: The MHA has urged states and Union Territories (UTs) to implement provisions of Section 479 of the Bharatiya Nagarik Suraksha Sanhita (BNSS) 2023 to provide relief to undertrial prisoners (UTPs) in jails. This initiative aims to address issues such as long detention and overcrowding in prisons.
Key Provisions of Section 479 of BNSS, 2023
- Purpose: To offer relief to undertrial prisoners by mandating their release on bail or bond under specific conditions.
- Key Provisions:
- Subsection (1):
- Release on Bail: UTPs who have served half the maximum sentence for their offense (except offenses punishable by death or life imprisonment) are eligible for release on bail.
- Release on Bond for First-Time Offenders: First-time offenders, who have served one-third of the maximum sentence, are eligible for release on bond by the court.
- Subsection (3):
- Mandatory Application: It is the responsibility of the prison superintendent to apply to the concerned court for the release of eligible prisoners on bail or bond.
- Subsection (1):
- Superintendent’s Role:
- Prison superintendents are mandated to ensure timely applications for bail or bond are filed for eligible UTPs.
Implementation and Reporting
- MHA’s Advisory:
- On January 1, the MHA issued a letter to the Chief Secretaries, Director Generals, and Inspectors General of prisons in all states and UTs to ensure compliance with the provisions of Section 479 of BNSS.
- States and UTs were instructed to report the status of implementation in a prescribed format starting from January 1, 2025.
- Data to be Reported:
- First-Time UTPs: Number of first-time UTPs who have served one-third of their maximum sentence.
- Court Applications: Number of applications for bail filed by jail superintendents.
- Release on Bail: Number of UTPs released on bond or bail after meeting the eligibility criteria.
- Other UTPs: Number of UTPs who have completed half of their sentence, and the number of applications filed for their release.
- MHA’s Campaign:
- Launched on Constitution Day (November 26), this campaign encouraged states and UTs to identify eligible prisoners and file their bail applications, thus helping to reduce overcrowding in prisons and mitigate long-term detention.
Background and Context
- Why Section 479?
- Section 479 aims to reduce the prolonged detention of undertrials, some of whom may have already served significant portions of their maximum sentences. This will not only alleviate overcrowding in prisons but also expedite justice for prisoners who have spent extended periods in jail awaiting trial.
- Earlier MHA Initiatives:
- Prior to this directive, the MHA had issued an advisory on October 16, 2024, encouraging states and UTs to implement Section 479. A special push was also made during Constitution Day to move applications for the release of eligible prisoners.
- Expected Outcome:
- The measures are expected to significantly ease the challenges of overcrowded jails and provide timely relief to undertrials, especially first-time offenders. By enforcing these provisions, the government seeks to improve the judicial process for UTPs and contribute to a more effective and humane criminal justice system.
Sonobuoys

- 08 Jan 2025
In News:
India and the U.S. have announced cooperation on the co-production of U.S. sonobuoys to enhance Undersea Domain Awareness (UDA) for the Indian Navy. This technology is vital for tracking submarines and strengthening defense capabilities, particularly in the Indian Ocean region amidst growing Chinese naval presence.
This partnership is a key step in deepening defense cooperation under the U.S.-India Initiative on Critical and Emerging Technologies (iCET), launched in May 2022, and will contribute to strengthening both countries’ defense industrial bases.
About Sonobuoys
- What They Are:
- Sonobuoys are expendable sonar devices used for anti-submarine warfare and underwater acoustic research.
- Typically, small (13 cm in diameter and 91 cm in length), they are designed for deployment from aircraft or ships to detect submarines in deep waters.
- Working Principles:
- Deployment: Dropped from aircraft or ships, they activate upon water impact.
- Surface Float: Equipped with inflatable floats and radio transmitters to communicate with tracking platforms on the surface.
- Sensors: Hydrophones descend to selected depths, capturing underwater acoustic signals.
- Data Communication: Transmit acoustic data via Very High Frequency (VHF) or Ultra High Frequency (UHF) radios to operators on aircraft or ships.
- Types of Sonobuoys:
- Active Sonobuoys: Emit sound energy and receive echoes, transmitting the data back to operators.
- Passive Sonobuoys: Only listen for underwater sounds from submarines or ships and relay the information back.
- Special Purpose Sonobuoys: Measure environmental data like water temperature and ambient noise.
- Other Applications:
- Beyond anti-submarine warfare, sonobuoys are used for environmental research, including studying marine life such as whales.
Co-production of Sonobuoys: India-U.S. Collaboration
- Manufacturing Agreement:
- Ultra Maritime (U.S.) and Bharat Dynamics Ltd. (BDL) have entered into discussions to co-produce U.S. sonobuoys, in line with India’s "Make in India" initiative.
- The production will follow U.S. Navy standards, with manufacturing split between the U.S. and India.
- The focus will also be on developing bespoke technologies to optimize sonobuoy performance in the unique acoustic environment of the Indian Ocean.
- Interoperability:
- The sonobuoys co-produced in India will be interoperable between U.S. Navy, Indian Navy, and allied aircraft such as P-8, MH-60R, and MQ-9B Sea Guardian.
- This ensures seamless integration and compatibility with naval assets from the U.S., India, Japan, and Australia, especially given the Quad's strategic naval exercises like Malabar.
- Production Location:
- The sonobuoys will be manufactured at BDL's facilities in Visakhapatnam, with a focus on meeting the Indian Navy’s operational demands.
Strategic and Defense Context
- U.S. and Indian Naval Cooperation:
- India has increasingly acquired military platforms from the U.S., such as the P-8I maritime patrol aircraft, MH-60R helicopters, and MQ-9 drones. These assets are also used by other Quad nations like Australia and Japan, highlighting the importance of interoperability and shared defense capabilities in the region.
- Enhanced Maritime Domain Awareness:
- With China’s growing naval presence in the Indian Ocean, the cooperation on sonobuoys aligns with India’s strategic priority of enhancing maritime domain awareness (MDA) and Undersea Domain Awareness (UDA), which are critical for national security.
- Future Plans:
- India has also signed a $3.5 billion contract for 31 MQ-9B drones, enhancing its surveillance capabilities for maritime and other defense applications. Deliveries of these drones will begin in 2029, further boosting India’s defense readiness in the region.
Homo juluensis
- 08 Jan 2025
In News:
A significant discovery in paleoanthropology has unveiled a new species of ancient humans, Homo juluensis. This species, characterized by its unusually large skulls, lived in eastern Asia between 300,000 to 50,000 years ago. The discovery adds to our understanding of human evolution, particularly during the Middle to Late Pleistocene epoch.
Key Characteristics
- Name Origin: Homo juluensis is named after "julu," meaning "big head," reflecting the species' large cranium.
- Geographical Range: This species inhabited regions of eastern Asia, including parts of China, Korea, Japan, and Southeast Asia.
- Fossil Evidence: Fossils have been discovered in Xujiayao and Xuchang (northern and central China), dating from 220,000 to 100,000 years ago.
- Physical Traits:
- Homo juluensis had large braincases, up to 30% larger than modern humans.
- They had thick skulls and facial features reminiscent of both Neanderthals and Denisovans.
- Their dental and jaw features show strong similarities to Neanderthals.
- Cultural Practices:
- They lived in small groups and were hunter-gatherers, hunting wild horses and potentially processing animal hides.
- Their tool-making and survival strategies indicate a complex level of social organization and resource use.
Relationship with Other Ancient Human Species
- Coexistence with Other Species: Homo juluensis coexisted with Neanderthals and Denisovans, potentially interacting and interbreeding with these species.
- Genetic Exchange: Studies suggest hybridization between Neanderthals, Denisovans, and early Homo sapiens played a significant role in shaping the genetic makeup of modern humans, especially in Asia.
- Evolutionary Significance: The species' relationship with other Pleistocene hominins is complex, involving shared ancestry with Homo sapiens, Neanderthals, and Denisovans. The genetic exchange among these populations likely influenced the course of human evolution in eastern Asia.
Neanderthals and Denisovans
- Neanderthals (Homo neanderthalensis):
- Lived between 400,000 to 40,000 years ago, primarily in Europe and parts of Asia.
- Neanderthals contributed significantly to the modern human gene pool, especially among non-African populations.
- Evidence of Neanderthal DNA is present in living humans, indicating past interbreeding with early human species.
- Denisovans:
- Identified through DNA analysis in 2010, based on fossils found in a Siberian cave.
- Closely related to Neanderthals, Denisovans inhabited diverse environments ranging from Siberian mountains to Southeast Asia’s jungles.
- Like Neanderthals, Denisovans interbred with both Homo sapiens and Neanderthals, influencing the genetic structure of modern populations, especially in Asia.
Implications for Human Evolution
- Complex Evolutionary Web:
- The discovery of Homo juluensis highlights the complex web of interrelated ancient human species during the Pleistocene epoch. These species did not live in isolation but likely interacted, competed, and interbred, shaping the evolutionary history of humans in Asia.
- Broader Understanding of Human Development:
- By expanding our knowledge of species like Homo juluensis, we gain a better understanding of the genetic diversity and cultural complexity in ancient human populations. This also provides insights into the environmental and social conditions that shaped early human survival strategies.
- Impact on Modern Genetics:
- The interbreeding between these ancient species has left a lasting imprint on the genetic makeup of modern humans, especially in regions like Asia, where Denisovan genes are still present in the DNA of some populations.
18th Pravasi Bharatiya Divas (PBD)
- 07 Jan 2025
In News:
The 18th Pravasi Bharatiya Divas (PBD) Convention will be held from January 8-10, 2025, in Bhubaneswar, Odisha.
Key Highlights:
- Theme 2025:
- The theme is "Diaspora’s Contribution to a Viksit Bharat", highlighting the vital role of the Indian diaspora in India's development into a prosperous and developed nation.
- Exhibitions:
- The convention will feature four major themed exhibitions:
- Vishwaroop Ram – The Universal Legacy of Ramayana: Showcasing the Ramayana’s influence through traditional and contemporary art forms.
- Diaspora’s Contribution to Technology and Viksit Bharat: Highlighting the global technological impact of the Indian diaspora.
- Spread and Evolution of the Indian Diaspora: Focused on the migration of Indians from Mandvi (Gujarat) to Muscat (Oman).
- Heritage and Culture of Odisha: A look into Odisha’s rich cultural traditions.
- The convention will feature four major themed exhibitions:
- Key Initiatives:
- Pravasi Bharatiya Express: PM Modi will flag off this special tourist train for the diaspora, covering key religious and tourist sites in India under the Pravasi Teertha Darshan Yojana.
- Pravasi Bharatiya Samman Awards (PBSA): Recognizing significant contributions by members of the Indian diaspora in various fields.
About Pravasi Bharatiya Divas (PBD):
- Origins:
- Celebrated on January 9 each year, marking Mahatma Gandhi's return to India from South Africa in 1915, symbolizing the contributions of migrants.
- First held in 2003, the event became biennial in 2015.
- Objectives:
- Recognizes the contributions of the Indian diaspora to India’s growth.
- Fosters engagement between India and its global diaspora.
- Strengthens India’s relations with host countries and promotes understanding of India’s culture and achievements.
Contributions of the Indian Diaspora to a Viksit Bharat:
- Economic Growth:
- The diaspora plays a pivotal role through remittances, investments, and connecting Indian businesses to global markets.
- Example: The development of a thorium-based fuel by a U.S.-based NRI is a significant step toward clean nuclear energy in India.
- Global Trade Linkages:
- Facilitating partnerships, investments, and knowledge exchange to expand India’s trade base and global market presence.
- Supporting Innovation: Diaspora-driven collaborations in emerging markets boost India’s entry into high-growth sectors, enhancing the country's development prospects.
- Cultural Contributions: Indian diaspora members serve as cultural ambassadors, promoting Indian traditions, art, and heritage globally (e.g., Diwali recognized as a public holiday in several U.S. states).
Challenges Faced by the Indian Diaspora:
- Cultural Integration: Struggles with balancing cultural identity and integrating into host societies can lead to alienation.
- Political and Religious Issues: Increasing politicization and religious biases, especially against Hindus and Sikhs, in countries like the USA and Europe.
- Legal and Citizenship Issues: Complicated visa statuses, restrictive immigration laws, and issues like the H-1B visa challenge the diaspora, despite their significant contributions.
- Remittance Challenges: Economic instability, exchange rate fluctuations, and banking hurdles affect the regular flow of remittances to India, impacting families dependent on them.
Government Initiatives for the Diaspora:
- National Pension Scheme for NRIs
- Overseas Citizenship of India (OCI) Card Scheme
- Pravasi Bhartiya Kendra
- Indian Community Welfare Fund (ICWF)
ISRO's Cowpea Seed Germination Experiment in Space
- 07 Jan 2025
In News:
ISRO successfully germinated cowpea seeds (Vigna unguiculata) in microgravity conditions during the PSLV-C60 POEM-4 mission. This experiment, conducted using the Compact Research Module for Orbital Plant Studies (CROPS), marks a significant advancement in space-based agricultural research.
Details of the Experiment:
- Mission Overview:
- The experiment took place aboard the PSLV-C60 POEM-4 mission, which included 24 sophisticated payloads.
- The CROPS payload, developed by the Vikram Sarabhai Space Centre (VSSC), is an automated system designed to study seed germination and plant survival in microgravity environments.
- Methodology:
- Eight cowpea seeds were placed in a controlled, closed-box system, equipped with temperature regulation and advanced monitoring tools.
- The system tracked plant development using high-definition cameras, sensors for oxygen, carbon dioxide, humidity, temperature, and soil moisture levels.
- Significance:
- The cowpea seeds successfully germinated within four days, with leaf development expected soon.
- This breakthrough in space agriculture is vital for the development of sustainable farming techniques in space, especially for long-term space missions and human settlements on other celestial bodies.
Broader Implications:
- Space Agriculture:
- The successful germination of cowpea seeds sets the foundation for growing crops in space, essential for self-sufficient habitats in space.
- This experiment is a significant step towards sustainable space agriculture, reducing the need for Earth-based resources in extraterrestrial environments.
- Future Missions:
- The experiment's success is pivotal for future missions aimed at Moon or Mars exploration, where space-grown crops will be necessary to support human life.
- ISRO’s achievement reinforces its growing expertise in space research and highlights the potential for international collaboration in space exploration and agricultural science.
About Cowpea Seeds:
- Cowpea (also known as lobia in Hindi) is a robust, nutrient-rich legume, ideal for agricultural research due to its adaptability and resilience in varied environments.
- The successful experiment with cowpea seeds holds promise for future extraterrestrial agriculture, ensuring food security for astronauts on long-duration missions.
NCC Republic Day Camp 2025

- 07 Jan 2025
In News:
Vice-President Jagdeep Dhankhar’s Address at NCC Republic Day Camp 2025.
Key Highlights
- PanchPran as the Foundation of India’s Transformation:
- PanchPran (Five Resolutions) were outlined by Vice-President Jagdeep Dhankhar as the guiding principles for India’s future development.
- These principles are fundamental to India’s national progress, ensuring a balanced approach to development and societal transformation.
The Five Principles of PanchPran:
- Social Harmony:
- Aims to strengthen unity by leveraging India’s diverse cultures and traditions as sources of national strength.
- Promotes inclusiveness and national integration.
- Family Enlightenment:
- Emphasizes the importance of families in nurturing patriotic and moral values.
- Acts as a foundation for creating a cohesive, enlightened society that respects traditions.
- Environmental Consciousness:
- Advocates for sustainable development and conservation of nature.
- Focuses on protecting natural resources for future generations.
- Swadeshi (Self-reliance):
- Encourages promoting indigenous products as part of the Atmanirbhar Bharat initiative.
- Strengthens India’s self-reliance by focusing on domestic production and consumption.
- Civic Duties:
- Instills responsibility among citizens to actively contribute to the nation’s growth.
- Encourages participation in community and national development activities.
National Cadet Corps (NCC)
- The National Cadet Corps (NCC) is the youth wing of the Indian Armed Forces, established in 1948.
- It is open to school and college students on a voluntary basis and is a Tri-Services organization, comprising the Army, Navy, and Air Force.
- Purpose and Training:
- Cadets undergo basic military training in small arms and drills.
- Officers and cadets have no obligation for active military service after completing their courses.
- Historical Background:
- Traces its origins back to the ‘University Corps’ formed under the Indian Defence Act of 1917 to address shortages in Army personnel.
- Structure and Leadership:
- The NCC is headed by a Director General (DG), a senior officer with a 3-star rank.
- Its headquarters are located in New Delhi.
Disposal of Toxic Waste from Union Carbide Factory (Bhopal)

- 07 Jan 2025
In News:
The Madhya Pradesh government has begun disposing of the 337 tonnes of toxic waste from the premises of Union Carbide India Limited (UCIL) in Bhopal, 40 years after the gas tragedy.
Key Highlights:
- Packing and Transportation:
- Waste is packed in airtight containers under the supervision of the Central Pollution Control Board (CPCB) and Madhya Pradesh Pollution Control Board (MPPCB).
- 12 specially designed airtight containers are being used for packing, and each container will be loaded onto trucks for transport.
- The waste movement will be escorted with a green corridor of about 250 kilometers.
- Incineration Process:
- The waste will undergo incineration in Pithampur, with residue stored in a two-layer membrane landfill to prevent contamination.
- A trial incineration of 10 tonnes of the waste was done in 2015 with no harmful effects, and results were submitted to the High Court.
Bhopal Gas Tragedy: A Historical Overview
- About the Tragedy:
- In 1984, a chemical leak at the Union Carbide pesticide plant released methyl isocyanate (MIC), leading to one of the worst industrial disasters in history.
- The leak was caused by a failed maintenance attempt and malfunctioning safety systems.
- Immediate effects included respiratory issues, eye problems, and abdominal pain, while long-term effects included chronic lung conditions, genetic abnormalities, and higher infant mortality rates.
- Legal and Government Response:
- In 1985, the Indian government passed the Bhopal Gas Leak Disaster Act to represent victims in legal claims.
- UCIL initially offered USD 5 million, while the Indian government demanded USD 3.3 billion. The case was settled in 1989 for USD 470 million.
- In 2010, seven Indian nationals were convicted for causing death by negligence, but were released on bail.
Hazardous Waste Management in India
- Definition and Types:
- Hazardous waste refers to waste that poses significant risks due to toxicity, reactivity, or corrosiveness.
- Common sources include chemical production, outdated technologies, and wastewater treatment.
- Regulations and Disposal Methods:
- The Environment Protection Act (1986) and the Basel Convention (1992) govern hazardous waste management in India.
- India generates about 7.66 million tonnes of hazardous waste annually, with the majority being landfillable (44.3%) and recyclable (47.2%).
- Disposal methods include incineration, co-processing in cement plants, and material/energy recovery.
- Challenges in Hazardous Waste Management:
- Inadequate treatment technologies, especially in small and medium industries.
- The need for stricter compliance with waste management laws and more efficient remediation of hazardous sites like Bhopal.
Pig-Butchering Scam
- 07 Jan 2025
In News:
In its annual report, the Union Home Ministry has warned the public against getting trapped in organised 'pig-butchering scams'.
Key Highlights:
- What is it?
- The Pig-Butchering Scam is a sophisticated form of cybercrime in which fraudsters deceive victims into investing in fake online trading platforms. The term "pig-butchering" is derived from the analogy of "fattening up" victims before stealing their money, much like preparing a pig for slaughter.
- How it works:
- Initial Contact: Scammers typically reach out to victims through social media platforms, dating apps, or deceptive ads on websites like Google and Facebook.
- Building Trust: Fraudsters create false friendships, using these connections to lure victims into investing in fake online trading apps. Cryptocurrency investments are often involved due to the ambiguity in the crypto market.
- The Scam: Victims are shown fabricated profits to encourage further investment. However, when they try to withdraw their funds, the money is stolen, and they realize the trading platform was fake.
- Features of the Scam:
- Use of fraudulent online trading platforms
- Fabricated blockchain transactions, making fund recovery nearly impossible
- Reliance on victims’ desire for quick financial gains
- Linked to money laundering and cyber slavery in some cases
- Origin of the Scam:
- The scam first appeared in China in 2016, where it was referred to as “sha zhu pan” (translated as "killing pig game").
- It is a form of Ponzi scheme, wherein organized scammers exploit victims by using fake online identities and offering false investment opportunities.
- How Cybercriminals Lure Victims:
- The scammer (host) contacts potential victims via social media, dating apps, or deceptive online advertisements.
- They build trust with the victim, enticing them into exploring online investments and cryptocurrency trading, often capitalizing on the lack of clarity in the crypto space.
- The victim is then persuaded to invest larger amounts in fake trades, believing they are making real profits.
- How the Scam is Executed:
- The scammer uses fake online trading platforms to create the illusion of profit.
- After building the victim’s confidence, the fraudster encourages larger investments.
- When victims try to withdraw their funds, they realize their money is gone, often with blockchain transactions making it nearly impossible to trace or recover the funds.
- Statistics on Cybercrime in India:
- In March 2024, the National Cybercrime Threat Analytical Unit recorded over 37,500 complaints related to cybercrime.
- The highest number of complaints (42%) were associated with WhatsApp (14,746), followed by Telegram (7,651), Instagram (7,152), Facebook (7,051), and YouTube (1,135).
- Union Home Ministry’s Response:
- The MHA has flagged pig-butchering scams as a global phenomenon that could involve large-scale money laundering and cyber slavery.
- The Ministry is collaborating with Google for intelligence sharing to flag suspicious digital lending apps and other forms of fraud.
- The Indian Cyber Crime Coordination Centre is working on capacity building to combat such scams and improve the response to cybercrimes.
Great Nicobar Island Development Project
- 06 Jan 2025
In News:
An international cruise terminal to facilitate a “global” port-led city, “high-end” tourism infrastructure, and a ship-breaking yard are among the new additions to the ?72,000 crore mega-infrastructure project in Great Nicobar Island proposed by the Union Shipping Ministry.
Overview of the Project:
- The Great Nicobar Island Development Project is a ?72,000-crore initiative to transform the southernmost island of India into a hub for defense, logistics, commerce, eco-tourism, and infrastructure development.
- It is being implemented by the Andaman and Nicobar Islands Integrated Development Corporation Ltd (ANIIDCO) over 16,610 hectares of land.
- The project includes multiple components like an International Container Transshipment Terminal (ICTT), an international airport, greenfield cities, a mass rapid transport system, and a free trade zone.
Key Proposed Developments:
- International Container Transshipment Terminal (ICTT): To make Great Nicobar a key player in global maritime trade.
- Greenfield International Airport: To improve connectivity and serve as a strategic airport.
- Greenfield Cities: New urban settlements to support the infrastructure.
- Coastal Mass Rapid Transport System: An advanced transportation network along the coast.
- Free Trade Zone: To facilitate international trade activities.
- International Cruise Terminal (new addition): To attract global tourists and facilitate cruise tourism.
- Ship Breaking Yard (new addition): To establish a facility for ship building and breaking.
Geographical and Ecological Context:
- Great Nicobar Island is the largest island in the Nicobar group, located at the southern tip of India. It is covered in rainforests and hosts diverse species, including endangered ones like the leatherback turtle and the Nicobar megapode.
- The island's ecosystem is rich in biodiversity, with extensive mangroves, coral reefs, and rainforests.
Significance of the Project:
- Geo-strategic Importance: The island’s location near the Malacca Strait offers a strategic maritime advantage, enhancing India’s global maritime presence.
- National Security: With increasing Chinese influence in the region, the project aims to strengthen India's maritime security.
- Economic Growth: The ICTT and other infrastructure will boost economic activities, making the region a vital trade hub.
- Job Creation: The development will lead to numerous job opportunities for locals, especially in sectors like tourism, ports, and transport.
- Tourism Development: With eco-tourism at its core, the project is expected to generate substantial income through tourism, improving the local economy.
- Social Infrastructure: It will lead to improvements in healthcare, education, and digital services through initiatives like telemedicine and tele-education.
Chhattisgarh’s Link between Forest Ecosystem and Green GDP

- 06 Jan 2025
In News:
In a first, the Chhattisgarh state has introduced an innovative plan that connects the ecosystem services of its forests with the Green Gross Domestic Product (Green GDP).
Key Highlights:
Chhattisgarh's Green GDP Initiative:
- First State in India to link forest ecosystem services with Green GDP.
- Forests cover 44% of Chhattisgarh's land area, playing a vital role in climate change mitigation.
- Key forest products (tendu leaves, lac, honey, medicinal plants) contribute significantly to the rural economy.
Green GDP:
- Definition: An adjustment of traditional GDP that accounts for environmental costs like resource depletion and ecosystem degradation.
- Formula:
- Green GDP = Net Domestic Product (NDP) − (Cost of Resource Depletion + Ecosystem Degradation)
- NDP = GDP − Depreciation of Produced Assets.
Importance of Green GDP:
- Traditional GDP overlooks the environmental cost, treating activities like deforestation as economic gains.
- Green GDP adjusts for sustainability, ensuring long-term economic growth aligns with environmental preservation.
Global Context & Initiatives:
- SEEA (System of Environmental-Economic Accounting): Developed by the UN to track economic-environment relationships.
- WAVES: World Bank initiative integrating natural capital into national economic accounts.
- Bhutan’s GNH: Emphasizes ecological sustainability in development.
Benefits of Green GDP for Chhattisgarh:
- Promotes sustainable development by integrating economic and environmental goals.
- Climate Change Mitigation: Forests help absorb CO2, playing a key role in carbon sequestration.
- Biodiversity Conservation: Supports sustainable use of resources, preserving ecosystems.
- Cultural Integration: Acknowledges forests' cultural and spiritual importance to local tribal communities (e.g., sacred groves).
Key Features of the Initiative:
- Valuing Ecosystem Services: Includes clean air (CO? absorption), water conservation, and biodiversity.
- Eco-tourism Promotion: Developing jungle safaris and national parks, boosting local employment.
- Scientific Assessments: Employing experts to quantify forest contributions to the economy.
Challenges of Green GDP Framework:
- Valuation Complexity: Difficult to assign monetary value to non-market environmental benefits like biodiversity.
- Data Gaps: Lack of comprehensive data on environmental degradation and resource usage.
- Implementation: Requires significant changes in accounting systems and policymaking.
- Forest Definition: Plantations like oil palm may be counted as forests, misleading environmental assessments.
- Political Resistance: States may manipulate data to secure funding, prioritizing plantations over natural forests.
- Local Integration: Difficulties in involving local bodies like Panchayats due to literacy and awareness gaps.
Future of Green GDP:
- Sustainable Resource Use: Encourages responsible consumption and production, aligning with SDG 12.
- Climate Action: Contributes to the reduction of fossil fuel reliance and promotes renewable energy, aligning with SDG 13.
- Green Investments: Stimulates green technologies and industries, fostering sustainable economic growth (SDG 8).
LEADS 2024 Report

- 06 Jan 2025
In News:
- Launch of the Logistics Ease Across Different States (LEADS) 2024 report and the Logistics Excellence, Advancement, and Performance Shield (LEAPS) 2024 awards in New Delhi.
Key Highlights:
- Objective of LEADS 2024 Report:
- Evaluate logistics performance across Indian states and union territories.
- Provide actionable insights for logistics reforms to foster competitive federalism.
- Assess logistics infrastructure, services, regulatory environment, and sustainability efforts.
- Performance Evaluation:
Region Achievers Fast Movers Aspirers
Coastal States Gujarat, Karnataka, Maharashtra, Odisha, Tamil Nadu Andhra Pradesh, Goa Kerala, West Bengal
Landlocked States Haryana, Telangana, Uttar Pradesh, Uttarakhand Bihar, Himachal Pradesh, Madhya Pradesh, Punjab, Rajasthan Chhattisgarh, Jharkhand
North-Eastern States Assam, Arunachal Pradesh Meghalaya, Mizoram, Nagaland, Sikkim, Tripura Manipur
Union Territories Chandigarh, Delhi Dadra and Nagar Haveli & Daman and Diu, Jammu and Kashmir, Andaman and Nicobar Islands, Ladakh
Lakshadweep, Puducherry
- Key Remarks:
- Action Plans for Better Logistics: States should develop regional and city-level logistics plans, including for last-mile connectivity, to attract investments.
- Green Logistics: Advocate for sustainable logistics practices to ensure environmentally responsible growth.
- Public-Private Partnerships (PPP): Encourage PPPs to promote multi-modal hubs and streamline logistics infrastructure.
- Technological Integration: Push for the adoption of Artificial Intelligence, Machine Learning, and Data Analytics to enhance efficiency in logistics operations.
- Skill Development & Gender Inclusivity: Focus on workforce inclusivity and skill development to boost sectoral growth. Promote gender diversity in logistics.
- LEAD Framework: Urge logistics sectors to embrace the LEAD framework (Longevity, Efficiency, Accessibility, Digitalisation) for transformation.
- LEAD Framework and Recommendations:
- Longevity, Efficiency, and Effectiveness: Improve long-term logistics strategies.
- Accessibility and Accountability: Ensure better reach and transparent logistics practices.
- Digitalisation: Enhance digital transformation across logistics processes.
- About LEADS:
- Full Form: Logistics Ease Across Different States.
- Launched: 2018 by the Department for Promotion of Industry and Internal Trade (DPIIT), Ministry of Commerce and Industry.
- Purpose: To assess and improve logistics infrastructure and services across Indian states and UTs.
- Methodology: Based on over 7,300 responses from a pan-India survey and inputs from over 750 stakeholder consultations.
- LEAPS 2024 Awards: Recognized excellence in the logistics sector across categories such as air, rail, road, maritime freight service providers, startups, MSMEs, and educational institutions.
- PM GatiShakti Course: Launched a 15-hour online course on “PM GatiShakti Concept for Efficient Infrastructure Planning and National Development”, hosted on iGOT Karmayogi platform and UGC SWAYAM portal.
- Logistics Cost Framework Report: Unveiled a report on the logistics cost framework, aiming to accurately estimate logistics costs in India through a hybrid methodology, incorporating both EXIM and domestic cargo data.
- Significance of LEADS:
- Provides critical insights into logistics performance, helping States and UTs to improve infrastructure, services, and regulatory practices.
- Plays a key role in India's vision of becoming a $32 trillion economy by 2047 by improving logistics efficiency, sustainability, and global competitiveness.
Human Metapneumovirus (HMPV)
- 06 Jan 2025
In News:
Five years after the COVID pandemic, China is experiencing a surge in HMPV cases, particularly in children under 14 years of age
Key Highlights:
- What is HMPV?
- A respiratory virus from the Pneumoviridae family, discovered in 2001.
- Causes both upper and lower respiratory tract infections, similar to the common cold or flu.
- Origin and Discovery:
- Identified in the Netherlands in 2001 through genomic sequencing of respiratory samples.
- Risk Groups:
- Children under 5 years, especially infants.
- Elderly individuals (65+).
- Immunocompromised persons and those with chronic respiratory conditions (e.g., asthma).
- Symptoms:
- Common: Cough, runny nose, fever, sore throat.
- Severe: Wheezing, shortness of breath, potentially leading to bronchitis or pneumonia.
- Incubation Period: 3-6 days.
- Transmission:
- Spread via droplets from coughing or sneezing.
- Close contact (e.g., handshakes, hugs).
- Contaminated surfaces, touching face after contact.
- Treatment:
- No specific antiviral treatment or vaccine available.
- Symptom management: hydration, rest, OTC medications for fever and congestion.
- Severe cases may require hospitalization (oxygen therapy, IV fluids).
- Diagnosis:
- NAATs (Nucleic Acid Amplification Tests): Detect viral genetic material.
- Antigen-based immunoassays: For severe cases or outbreaks.
- Complications:
- Can lead to bronchiolitis, bronchitis, pneumonia, asthma, or COPD flare-ups.
- Risk of ear infections (otitis media) in some cases.
- Prevention:
- Hygiene: Regular handwashing, covering coughs/sneezes, maintaining personal hygiene.
- Physical Distancing: Avoid close contact, wear masks in crowded settings.
- Caution for Vulnerable Groups: Extra care for individuals with chronic respiratory conditions.
Global Situation:
- China: Experiencing a rise in HMPV cases, particularly among children under 14 years.
- India: No reported cases yet, but monitoring the situation closely.
Key Facts:
- HMPV is a winter virus commonly seen in colder months (winter and early spring).
- Estimated 10%-12% of respiratory illnesses in children are caused by HMPV.
- The virus is part of the Pneumoviridae family, alongside respiratory syncytial virus (RSV), measles, and mumps.
No specific antiviral treatment or vaccine for HMPV; antibiotics are ineffective.
National Sports Awards 2024
- 06 Jan 2025
In News:
The National Sports Awards 2024 were recently announced by the Ministry of Youth Affairs & Sports to celebrate excellence in Indian sports.
Key Highlights:
Major Dhyan Chand Khel Ratna Award
- This is India's highest sporting honor, renamed in 2021 after hockey legend Major Dhyan Chand.
- It’s awarded for exceptional performance in sports over a four-year period.
- 2024 Winners:
- Gukesh D (Chess)
- Harmanpreet Singh (Hockey)
- Praveen Kumar (Para-Athletics)
- Manu Bhaker (Shooting)
- The award includes a cash prize of Rs 25 lakh.
Arjuna Award
- Recognizes outstanding performance in sports over the previous four years and attributes like leadership, discipline, and sportsmanship.
- 2024 Winners: Various athletes across multiple disciplines received this honor.
Arjuna Award (Lifetime)
- Given to retired athletes who have not only excelled during their careers but also contributed to the promotion of sports post-retirement.
- 2024 Winners:
- Shri Sucha Singh (Athletics)
- Shri Murlikant Rajaram Petkar (Para-Swimming)
Dronacharya Award
- Given to coaches who have made a consistent and significant contribution by guiding sportspersons to excel at international events.
- The award includes a bronze statue of Dronacharya, a certificate, and a cash prize.
Maulana Abul Kalam Azad (MAKA) Trophy
- Awarded to the top-performing university in the Khelo India University Games.
- 2024 Winner: Chandigarh University.
Rashtriya Khel Protsahan Puruskar
- Recognizes individuals or organizations for their contribution to the promotion and development of sports.
- 2024 Winner: Physical Education Foundation of India.
These awards were selected by a committee led by Justice (Retd.) V. Ramasubramanian and include eminent sportspersons, journalists, and sports administrators. The winners will receive their awards from the President of India, marking a prestigious moment in Indian sports.
Saint Narahari Tirtha

- 05 Jan 2025
In News:
In a remarkable discovery, a member of the Team of Research on Culture and Heritage (TORCH) has hit upon a three-foot idol of the 13th Century saint, Narahari T?rtha recently.
Key Highlights:
Birth and Early Life:
- Born circa 1243 CE in Chikakolu (modern-day Srikakulam, Andhra Pradesh).
- Hailing from an aristocratic family in the Gajapati Empire of Odisha.
Philosophical Influence:
- A prominent disciple of Madhvacharya, the founder of Dvaita philosophy (dualism).
- Narahari Tirtha played a key role in propagating Madhva's Vaishnavism in Eastern India, particularly in the Kalinga region (modern-day Odisha and Andhra Pradesh).
Role in Eastern Ganga Dynasty:
- Served as a minister in the Eastern Ganga Dynasty for over 30 years.
- Guided kings to align their governance with Sanatana Dharma and reformed temple administration.
- His contributions are documented in inscriptions at the Simhachalam and Srikurmam temples.
Religious and Cultural Contributions:
- Played a key role in spreading Vaishnavism and Dvaita philosophy.
- First to compose Devaranamas in Kannada, marking a significant cultural contribution.
- Contributed to the development of Yakshagana Bayalata (a dance-drama) and the classical dance form that evolved into Kuchipudi.
Writings and Intellectual Legacy:
- Authored 15 works, with two surviving texts: Gita Bhasya and Bhavaprakasika.
- His teachings and writings significantly impacted the Madhva tradition and regional literature.
Discovery of the Idol:
- A three-foot idol of Narahari Tirtha was discovered at Simhachalam Temple in Visakhapatnam, Andhra Pradesh.
- The idol depicts Narahari Tirtha holding a script on palm leaves, flanked by devotees.
Contributions to Temple and Education:
- Transformed the Simhachalam Temple into a renowned center for Vaishnavism.
- Played a crucial role in safeguarding sacred idols like Moolarama and Moola Sita for Madhvacharya.
Cultural and Artistic Legacy:
- Promoted regional art forms, helping establish Kuchipudi as a classical dance style in Andhra Pradesh.
- Advocated for Yakshagana Bayalata, a form of dance-drama popular in coastal Karnataka.
Honors and Recognition:
- Bestowed titles such as "Loka Surak?a?a Ati Nipu?a?" and "Yo Avati Kalinga Bhu Sambhav?n" for his contributions to philosophy and governance.
Final Resting Place:
- Narahari Tirtha was consecrated near Chakratirtha at Hampi on the banks of the Tungabhadra River after his death.
- His legacy continues to influence the temple traditions, especially in Puri Jagannath, strengthening the Madhva influence in Odisha.
Year of Artificial Intelligence

- 05 Jan 2025
In News:
The All India Council for Technical Education (AICTE) has declared 2025 as the "Year of Artificial Intelligence" (AI), aiming to empower over 14,000 AICTE-approved colleges and benefit 40 million students. This initiative aligns with the Prime Minister’s vision to make India a global leader in AI and technology.
Key Objectives and Features of the AICTE AI Initiative:
- Positioning India as a Global AI Leader:
- Empowering students with AI skills to drive innovation and lead in the emerging AI-driven economy.
- Preparing India’s workforce for the technological advancements of the future.
- Core Elements of the AICTE AI Initiative:
- AI Affirmation Pledge: Institutions will adopt and display an AI Affirmation Pledge, focusing on innovation, ethics, and education in AI.
- Comprehensive AI Integration:
- Introducing interdisciplinary AI courses and research programs.
- Setting up AI labs in collaboration with industries to meet global standards.
- Promoting ethical AI practices with societal benefits in focus.
- AI Awareness Campaign:
- “AI for All: The Future Begins Here” campaign includes workshops, hackathons, and guest lectures.
- Formation of student-driven AI chapters to foster innovation and research.
- Faculty Development & Industry Partnerships:
- Workshops and certification programs for faculty to improve AI teaching.
- Collaboration with companies like Adobe, CISCO, and IBM for student exposure through internships and mentorships.
- Recognition of Excellence: Institutions excelling in AI integration will be recognized, serving as role models for others.
- Action Plan for Institutions:
- All institutions are required to submit AI Implementation Plans by December 31, 2024. These plans will be evaluated by the AICTE Approval Bureau and exemplary submissions will be highlighted as benchmarks.
- Shaping India as a Global AI Leader:
- AICTE aims to revolutionize India’s education system and enhance its position in the global AI race, focusing on building a self-reliant workforce.
Additional Context on AICTE and its Role:
- AICTE Overview:
- A statutory body and national-level council under the Ministry of Education.
- Established in November 1945 as a national-level apex advisory body for technical education in India.
Government Initiatives to Support AI and Consumer Protection:
- AI and Consumer Protection:
- AI-driven tools launched to enhance consumer protection, such as the National Consumer Helpline, e-MAAP Portal, and Jago Grahak Jago mobile application.
- New guidelines for regulating deceptive marketing in e-commerce to ensure consumer confidence in the digital market.
- Tools like the e-Daakhil Portal for online complaint filing.
Impact:
- This initiative will have a far-reaching impact, involving more than 14,000 institutions and 40 million students nationwide, preparing them for leadership roles in AI and technology, and helping India secure its future in the global AI-driven economy.
Translocation of Tigers from Madhya Pradesh
- 05 Jan 2025
In News:
Madhya Pradesh to translocate 15 Tigers to Rajasthan, Odisha and Chhattisgarh.
Key Highlights of the Translocation:
- Scale of Translocation: Largest relocation of big cats from a single state in India.
- Approval: NTCA has approved the translocation of 15 tigers from Madhya Pradesh to Rajasthan, Chhattisgarh, and Odisha.
- Source Reserves:
- Bandhavgarh, Panna, Kanha, and Pench Tiger Reserves in Madhya Pradesh.
- Distribution Plan:
- Rajasthan: 4 tigresses.
- Chhattisgarh: 2 male tigers and 6 tigresses.
- Odisha: 1 male tiger and 2 tigresses.
- Funding: States receiving tigers will bear all expenses related to translocation.
Objectives of the Translocation:
- Enhance Tiger Conservation: Reintroduce and bolster tiger populations in recipient states.
- Population Management: Relocate tigers to areas with suitable habitats to alleviate territorial disputes in overpopulated reserves.
- Genetic Diversity: Introduce new individuals to isolated tiger groups to prevent inbreeding and support long-term species survival.
About Kanha, Bandhavgarh, and Pench Tiger Reserves:
- Kanha Tiger Reserve:
- Location: Maikal range of the Satpura Mountains.
- Significance: Largest national park in Madhya Pradesh.
- Distinct Feature: First tiger reserve in India with an official mascot, ‘Bhoorsingh the Barasingha’.
- Flora and Fauna: Rich biodiversity with Royal Bengal Tigers, leopards, and the IUCN Vulnerable species, Barasingha.
- Bandhavgarh Tiger Reserve:
- Location: Between Vindhyan and Satpura ranges in Umaria district, Madhya Pradesh.
- Significance: Known for one of the highest densities of Royal Bengal Tigers in India.
- Historical Link: The ancient Bandhavgarh Fort, linked to the legend of Lord Rama and Lakshmana.
- Pench Tiger Reserve:
- Location: Spans Seoni and Chhindwara districts in Madhya Pradesh, extends into Maharashtra.
- Significance: Inspiration for Rudyard Kipling’s The Jungle Book.
- Flora and Fauna: Includes teak, saag, mahua forests; tigers, leopards, wild dogs, and gaur are key species.
Tiger Translocation Project Overview:
- First Project:
- Initiated in 2018, two tigers relocated from Kanha and Bandhavgarh to Satkosia Tiger Reserve in Odisha.
- Main Objectives:
- Reintroduce Tigers: In areas where they have been extirpated or extinct.
- Alleviate Territorial Disputes: Overpopulated reserves need additional tigers to reduce human-animal conflict.
Benefits of Translocation:
- Ecological Balance: Restores predator-prey dynamics in underpopulated reserves.
- Human-Animal Conflict Mitigation: Reduces conflict in overcrowded reserves.
- Rewilding Landscapes: Revives areas where tigers were locally extinct.
Concerns Associated with Translocation:
- Local Community Protests: Villagers fear tigers will pose a threat to their safety.
- Territorial Disputes: New tigers may face conflict with resident tigers.
- Poor Forest Management: Inadequate prey augmentation and habitat management may hinder success.
Madhya Pradesh’s Role in Tiger Conservation:
- Largest Tiger Population: Madhya Pradesh hosts the largest number of tigers in India, with 785 tigers as per NTCA’s 2022 report.
- Tiger Reserves: The state is home to nine tiger reserves, including the newly notified Madhav Tiger Reserve in Shivpuri.
- Translocation Strategy: Madhya Pradesh’s involvement helps reduce local tiger population pressure and contributes to broader conservation efforts across India.
Inter-State Tiger Translocation Goals:
- Reinforcement and Reintroduction: Introduce tigers into areas historically part of their range but from which they have been extirpated or extinct.
- Genetic Diversity: Introduce new tigers to isolated populations to maintain long-term population health.
Thanthai Periyar Memorial

- 05 Jan 2025
In News:
In a significant event for both Kerala and Tamil Nadu, Kerala Chief Minister Pinarayi Vijayan and Tamil Nadu Chief Minister M.K. Stalin are set to reunite at Vaikom, to inaugurate the extensively renovated memorial dedicated to Tamil reformist E.V. Ramasami Naicker, popularly known as Thanthai Periyar. This marks a historic occasion over a year and a half after they jointly inaugurated the centenary celebrations of the Vaikom Satyagraha.
Key Highlights:
Memorial History and Significance:
- Established: January 1994
- Location: 70-cent property near Valiyakavala Junction, Vaikom
- Ownership: Tamil Nadu Government
- Periyar Statue: Installed in 1985 on 84 cents of land provided by Kerala government; remains the centerpiece.
- Historical Neglect: The memorial suffered from years of neglect before the renovation.
Role of Periyar in Vaikom Satyagraha:
- Vaikom Satyagraha (1924–1925):
- First organized movement for the rights of the ‘untouchable’ communities in India.
- Led by prominent leaders like T.K. Madhavan, K.P. Kesava Menon, and K. Kelappan.
- Periyar, alongside his wife Nagamma, joined the movement, seeking access to public roads leading to the Sri Mahadeva Temple in Vaikom.
- Periyar’s Contribution:
- Was imprisoned twice for his participation in the movement.
- Honored with the title Vaikom Veeran for his leadership.
- Impact: The movement played a crucial role in securing social equality for all sections of society.
Periyar’s Legacy:
- Self-Respect Movement: Founded by Periyar to promote social equality and eliminate caste-based discrimination.
- Dravidar Kazhagam: A political and social organization founded by Periyar, advocating for the rights of the Dravidian people.
- Father of the Dravidian Movement: Periyar’s philosophy and activism laid the foundation for the Dravidian political ideology and social reforms in Tamil Nadu.
Rabbit Fever
- 05 Jan 2025
In News:
Tularemia, commonly known as "rabbit fever," is a rare but highly infectious bacterial disease caused by Francisella tularensis. Though uncommon, it can lead to severe health complications if left untreated. Over recent years, cases of tularemia have been on the rise in the United States, drawing attention to the broader environmental and epidemiological factors influencing the disease’s spread.
Rising Incidence of Tularemia
Between 2011 and 2022, the United States saw a 56% increase in the annual average incidence of tularemia infections compared to the previous decade, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Vulnerable populations include children aged 5 to 9, older men, and individuals of American Indian or Alaska Native descent. The increasing number of reported cases highlights the growing concern over this disease, despite its rarity.
Transmission Pathways
Tularemia is primarily transmitted through:
- Direct Contact with Infected Animals: Common carriers include rabbits, hares, and rodents, particularly those infected with Francisella tularensis. This presents a risk for individuals working closely with wildlife, such as hunters.
- Insect Bites: Ticks, especially in regions with high tick populations, and deer flies can spread the disease.
- Contaminated Food or Water: Consuming undercooked meat from infected animals or untreated water can lead to infection.
- Inhalation of Contaminated Dust or Droplets: This is a potential risk in agricultural or laboratory settings and can result in pulmonary tularemia.
Contributing Factors to the Rise in Cases
Several factors contribute to the increasing prevalence of tularemia:
- Climate Change: Rising temperatures are increasing tick activity and extending breeding seasons, allowing the bacteria to spread more easily.
- Habitat Encroachment: Deforestation and increased human interaction with wildlife are amplifying exposure to infected animals.
- Improved Diagnostic Tools: Advances in surveillance and testing methods have made it easier to detect tularemia, leading to more reported cases.
Early Symptoms and Diagnosis
Tularemia symptoms can vary depending on the route of infection. Symptoms typically appear 3 to 5 days post-exposure and may include:
- Sudden high fever (up to 104°F or 40°C)
- Chills, fatigue, and body aches
- Swollen lymph nodes, especially near the site of infection (e.g., under the arms or in the groin)
There are four primary forms of tularemia:
- Ulceroglandular: Characterized by skin ulcers and swollen lymph nodes.
- Glandular: Swollen lymph nodes without ulcers.
- Pneumonic: Lung infection, often resulting from inhalation.
- Typhoidal: A more systemic form, with symptoms like fever and abdominal pain.
Differentiating tularemia from other conditions such as flu, pneumonia, or lymphadenitis is key for diagnosis. A skin ulcer or swollen lymph nodes in individuals with recent exposure to wildlife or ticks is a critical diagnostic clue.
Treatment and Prognosis
Tularemia is treatable with antibiotics. First-line treatment includes streptomycin or gentamicin, while doxycycline or ciprofloxacin may be used for milder cases. Treatment typically lasts 10 to 21 days, and when initiated promptly, the disease has a high recovery rate and minimal complications. However, untreated cases can lead to chronic infections, lung abscesses, pneumonia, or severe sepsis, with mortality rates of 1-2% under treatment. Untreated severe cases can result in mortality rates between 30% and 60%.
Tularemia in India: A Potential Concern?
Tularemia is extremely rare in India, mainly due to the country's differing ecological conditions and limited interaction with the primary reservoirs of Francisella tularensis. However, awareness remains crucial, especially for individuals traveling to endemic regions or working in wildlife settings. Despite its rarity in India, the rising global incidence and changing environmental factors warrant continued vigilance.
Torrijos-Carter Treaties

- 04 Jan 2025
In News:
Recently, Donald Trump threatened to take back the Panama Canal, calling the transfer treaty “foolish”.
Why Trump Called the Panama Canal Transfer 'Foolish'?
- Transit Fees:
- Trump expressed frustration over high transit fees imposed by the Panama Canal Authority (ACP) on U.S. vessels.
- In 2023, due to droughts affecting Lakes Gatun and Alhajuela (which are crucial for canal operations), the ACP reduced crossing slots by 36%, leading to an increase in transit fees for ships.
- Chinese Presence:
- Trump is also concerned about the growing Chinese influence in the Panama Canal region.
- In 2017, Panama became the first Latin American country to sign a Belt and Road Initiative (BRI) agreement with China, increasing Chinese investments.
- Hutchison Ports PPC, a subsidiary of a Hong Kong-based company, operates ports near the canal, raising concerns over China's influence on logistical operations and potential surveillance capabilities.
The Torrijos-Carter Treaties and Canal Transfer:
- Panama Canal Treaty (1977):
- The treaty transferred control of the Panama Canal from the U.S. to Panama by December 31, 1999.
- The U.S. would no longer control the canal, and Panama would assume full responsibility for its operation and defense.
- Permanent Neutrality Treaty (1977):
- Declared the canal to be neutral and open to vessels of all nations.
- U.S. Right to Defense: The U.S. retained the right to defend the neutrality of the canal and had priority passage in case of military emergencies.
Panama’s Response to Trump’s Criticisms:
- Defense of Transit Rates:
- President José Raúl Mulino rejected Trump’s claims, defending the transit fees as being in line with international standards and based on a transparent procedure.
- Sovereignty:
- Mulino emphasized Panama’s sovereignty over the canal, asserting that Panama’s control over the canal was non-negotiable. He categorically denied the presence of Chinese soldiers in the canal, stating that there would never be any.
China’s Response:
- China's Position:
- China's Foreign Ministry responded by emphasizing that the Panama Canal is a neutral passageway, a vital infrastructure for Panama and the global trade system.
- China affirmed its respect for Panama's sovereignty and denied any military presence in the canal area.
Implications and Future:
- Diplomatic Tensions:
- The issue of transit fees and foreign influence, particularly China's presence in the region, is likely to remain a point of diplomatic negotiation.
- Panama is expected to assert its sovereignty and seek international support to prevent any external interference in the canal’s operations.
- U.S. Influence:
- The U.S. might attempt to renegotiate terms related to the Panama Canal's operations, especially concerning transit fees and military rights, although Panama remains firm on maintaining control.
Torrijos-Carter Treaties:
- Significance:
- Panama Canal Treaty and Permanent Neutrality Treaty marked a major shift in U.S.-Latin America relations, ending U.S. control and restoring Panamanian sovereignty.
- The treaties also ensured the neutrality of the canal while maintaining U.S. military access in emergencies.
- Impact:
- The treaties were a symbol of Panama’s regained sovereignty and played a key role in stabilizing relations between the U.S. and Panama, as well as resolving tensions over control of the canal.
Centralized Pension Payments System (CPPS)

- 04 Jan 2025
In News:
- The CPPS aims to enhance pension accessibility and simplify the disbursement process for over 7.85 million pensioners in India.
- Key Benefit: Pensioners can now receive their pension from any bank or branch across India, eliminating the need for physical verifications and providing seamless nationwide pension disbursement.
Key Highlights:
- Key Features:
- No need for physical verification: Pensioners do not have to visit the bank for verification at the time of pension commencement.
- Seamless pension disbursement: Upon release, the pension amount is credited immediately.
- Nationwide access: Pensioners can withdraw their pension from any bank or branch, without needing to transfer Pension Payment Orders (PPO) when relocating or changing banks.
- Significance:
- Eliminates the decentralised pension system, where each regional office maintained separate agreements with a few banks.
- Ensures pension portability, especially for pensioners who move or change banks.
Employees’ Provident Fund Organisation (EPFO):
- Overview:
- EPFO is a statutory body under the Employees' Provident Funds and Miscellaneous Act, 1952, and works under the Ministry of Labour and Employment.
- Structure:
- Administered by a tripartite board called the Central Board of Trustees, consisting of representatives from:
- Government (Central & State)
- Employers
- Employees
- The Central Board of Trustees is chaired by the Union Minister of Labour and Employment.
- Administered by a tripartite board called the Central Board of Trustees, consisting of representatives from:
- Key Schemes Operated by EPFO:
- Employees’ Provident Funds Scheme, 1952 (EPF): A savings scheme for workers.
- Employees’ Pension Scheme, 1995 (EPS): A pension scheme for employees after retirement.
- Employees’ Deposit Linked Insurance Scheme, 1976 (EDLI): Provides life insurance coverage to workers.
- Global Coverage: EPFO is also the nodal agency for implementing Bilateral Social Security Agreements with other countries, offering reciprocal social security benefits to international workers from countries with such agreements.
- Impact: The EPFO schemes cover Indian workers and international workers from countries with which EPFO has signed bilateral agreements.
Key Facts:
- CPPS improves the convenience and accessibility of pension services for millions of pensioners across India by simplifying the pension disbursement process and providing nationwide access without the need for physical verifications.
- EPFO, a statutory body under the Ministry of Labour and Employment, plays a crucial role in managing provident funds, pensions, and insurance schemes for both domestic and international workers, fostering social security across India.
Open Data Kit (ODK) Toolkit

- 04 Jan 2025
In News:
- The Comptroller and Auditor General (CAG) of India has deployed the Open Data Kit (ODK) platform to enhance transparency in government spending and improve accountability in the delivery of government schemes.
- The toolkit is being used for designing, collecting, and managing data relevant to audits.
Key Highlights:
Objective:
- Enhance transparency in public spending.
- Improve accountability in government schemes and projects.
- Collect real-time beneficiary feedback to aid audit planning and identify areas needing additional review.
Key Features:
- End-to-end encryption: Ensures secure data management.
- Integration with CAG’s Operating System (OIOS): Facilitates seamless analysis and management of data.
- Multi-language support: Allows for surveys in multiple languages, making it more accessible to diverse beneficiaries.
- User-friendly interface: Simplifies the design and management of data collection processes for auditors.
Usage and Applications:
- Beneficiary surveys are a key tool for gathering data, helping CAG identify problem areas in government schemes.
- The ODK toolkit was recently deployed in audits of AIIMS institutions in Mangalagiri (Guntur) and Bibinagar (Hyderabad) to assess patient satisfaction and gather evidence for performance reviews.
Working Process:
- Surveys are designed on the ODK platform and deployed to beneficiaries.
- Data is collected in real-time and analyzed using the OIOS system to generate actionable insights for audits.
- Beneficiary feedback is used to evaluate scheme delivery and improve efficiency.
Significance:
- Facilitates data-driven decision-making in audits, ensuring that audits are more transparent and evidence-based.
- Improves the citizen-centric evaluation of government schemes by gathering direct feedback from beneficiaries.
- Enhances the performance review of key institutions like AIIMS, contributing to better service delivery.
- The introduction of the ODK toolkit is part of the CAG’s efforts to use digital tools for better governance and accountability in the public sector. This also aligns with the growing trend of using technology for governance and auditing.
Project VISTAAR

- 04 Jan 2025
In News:
IIT Madras has partnered with the Ministry of Agriculture and Farmers’ Welfare on Project VISTAAR (Virtually Integrated System to Access Agricultural Resources). MoU signed between the Ministry and IIT Madras to integrate information about agricultural start-ups into the VISTAAR platform.
Key Highlights:
Project Objectives:
- Digitalisation of Agricultural Extension: To enhance the efficiency and effectiveness of the agricultural extension system through digital platforms.
- Access to Start-Up Innovations: Provide farmers easy access to over 12,000 start-ups in agriculture and allied sectors, connecting them to technological solutions and innovations.
- Support for Sustainable Agriculture: Focus on making farming more sustainable and climate-resilient by promoting adoption of innovative technologies.
Key Features of VISTAAR:
- Integration of start-up data via IIT Madras' startup information platform and its incubatee, YNOS Venture Engine.
- Advisory services covering:
- Crop production
- Marketing
- Value addition
- Supply chain management
- Information on government schemes for agriculture, allied sectors, and rural development.
- Real-time, contextual, and accurate information to enhance decision-making and improve farming practices.
Significance of the Project:
- The platform will expand the outreach of agricultural extension services, providing support to farmers across India.
- It will ensure farmers access high-quality advisory services that are critical for improving productivity and income.
- Integration of start-up-driven innovations will aid in the adoption of climate-resilient farming practices.
- Timely and accurate information will empower farmers to make informed decisions and improve the efficiency of agricultural processes.
Impact on Farmers:
- Digitalisation will provide farmers with easier access to expert advice and resources, enhancing productivity.
- Improved access to government schemes ensures farmers can avail themselves of financial and technical support for development.
- The project aligns with national objectives of enhancing agriculture’s contribution to India’s economy and ensuring food security.
Air India In-Flight Wi-Fi Connectivity
- 04 Jan 2025
In News:
- Tata Group’s Air India launched free Wi-Fi connectivity on select domestic and international flights.
- First Indian airline to offer Internet connectivity on domestic flights.
- The service is free for a limited introductory period on select domestic flights.
- Gradual expansion of Wi-Fi availability to more aircraft in the fleet.
Key Highlights:
Aircraft with Wi-Fi:
- Available on Airbus A350, Boeing 787-9, and select Airbus A321neo aircraft.
- Aircraft equipped with special hardware for Internet connectivity.
- Some aircraft, previously operated by Vistara, now part of Air India after the merger in November.
Technology Partner:
- Vistara’s in-flight Wi-Fi was facilitated by Tata Group’s Nelco, in collaboration with Panasonic Avionics.
- This service is now extended to select Air India domestic flights.
How to Access Wi-Fi:
- Passengers enable Wi-Fi on their devices and connect to the "Air India Wi-Fi" network.
- Redirected to an Air India portal where they enter details (PNR and last name) for access.
Connectivity Technologies:
- Air-to-Ground (ATG) Technology:
- Uses ground-based cellular towers to provide internet.
- Antenna on the aircraft’s belly picks up signals from nearby towers.
- Limited by tower availability, works best over land with dense coverage.
- Satellite-Based Connectivity:
- Uses satellites to provide internet by transmitting signals from ground stations to the aircraft.
- Provides wider coverage, particularly effective over oceans and sparsely populated areas.
In-Flight Wi-Fi Operation:
- Multiple in-cabin antennas collect signals from passengers’ devices.
- Signals are sent to an onboard server.
- For satellite-based systems, signals are transmitted via an antenna to satellites and then relayed to ground stations.
- For ATG systems, signals are sent directly to ground towers.
- In-flight Wi-Fi is slower compared to ground-based internet, though newer technologies are improving speed.
Cost Considerations:
- Airlines incur high initial costs for equipping aircraft with Wi-Fi technology (antennas and hardware).
- Air India is investing in a $400 million retrofit program for its fleet, which could include installing internet connectivity.
- Some airlines install Wi-Fi on new planes, while others retro-fit older models.
Revenue Model:
- Airlines often charge for Wi-Fi after offering a small volume of free internet.
- Some airlines provide free Wi-Fi for loyalty program members or premium passengers (business/first class).
- Air India is offering free Wi-Fi for now, but plans to introduce charges at a later date.
Future Outlook:
- In-flight internet is expected to become a significant source of ancillary revenue.
- Complimentary Wi-Fi for economy class passengers is unlikely in the near-to-medium term due to high costs involved in installation and operation.
Global Context:
- In-flight connectivity is becoming standard on major full-service carriers (FSCs) worldwide.
- Air India's move aligns with global trends, as it aims to be among the world’s leading airlines.
Ramesh Chand Panel
- 03 Jan 2025
In News:
The Government of India has formed an 18-member panel, headed by Ramesh Chand, a member of NITI Aayog, to revise the base year of the Wholesale Price Index (WPI) to 2022-23 from the current base year of 2011-12. The panel will also work on a roadmap for transitioning from WPI to the Producer Price Index (PPI).
Key Highlights:
Role and Mandates of the Panel:
- Revised Commodity Basket: The panel will recommend a new commodity basket for both WPI and PPI, reflecting structural changes in the economy.
- Review of Price Collection System: The panel will evaluate the current system for price collection and propose improvements.
- Computational Methodology: It will determine the computational methodology for both WPI and PPI to ensure accuracy in tracking price changes.
- The panel has been tasked with submitting its final report to the Office of the Economic Adviser at the Department for Promotion of Industry and Internal Trade (DPIT) within 18 months.
Understanding WPI vs. PPI:
- WPI (Wholesale Price Index) tracks the price of goods at the wholesale stage (i.e., goods sold in bulk to businesses), and excludes the service sector.
- Key Characteristics of WPI:
- Does not consider consumer-facing prices.
- Excludes services (about 55% of GDP).
- Can have double-counting bias due to multiple transactions before the final sale.
- Does not account for indirect taxes and may include export/import prices.
- Use: WPI helps in tracking bulk price movements between businesses, but doesn't fully represent consumer price inflation.
- Key Characteristics of WPI:
- PPI (Producer Price Index) tracks prices at various stages of production, considering both goods and services, and measures the average change in prices received by domestic producers.
- Key Characteristics of PPI:
- Excludes indirect taxes (making it more accurate for price movement tracking).
- Includes services, unlike WPI, giving a broader view of price trends across the economy.
- More aligned with international standards (System of National Accounts).
- Reflects prices before consumer consumption, providing a business-oriented perspective of price trends.
- Key Characteristics of PPI:
Why the Transition to PPI?
- The PPI is already used by major economies like the US, China, Germany, and Japan as it provides a more comprehensive measure of inflation from a producer’s perspective.
- It is expected to be a better indicator of inflationary trends in the overall economy, including both goods and services.
Challenges and Roadmap:
- The switch to PPI is complex, and the panel will need to ensure that the transition does not disrupt the current data collection and reporting systems. Both WPI and PPI will run concurrently until PPI stabilizes.
CGWB Report on Groundwater Contamination
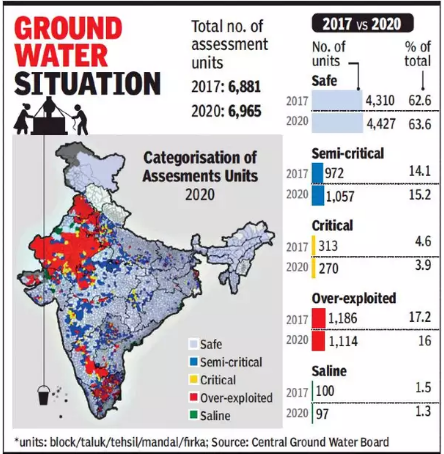
- 03 Jan 2025
In News:
The Central Ground Water Board (CGWB) report on groundwater quality reveals alarming levels of contamination in India's groundwater, with a focus on nitrate, fluoride, arsenic, and uranium. The report highlights the impact of agricultural practices, poor waste management, and urbanisation on water quality.
Key Highlights:
Nitrate Contamination:
- 440 districts in India report excessive nitrate levels in groundwater, with 20% of samples exceeding the permissible nitrate limit of 45 mg/L (WHO and BIS standards).
- High-risk regions: Rajasthan (49%), Karnataka (48%), and Tamil Nadu (37%) are the top states with high nitrate levels. Other affected states include Maharashtra, Telangana, Andhra Pradesh, and Madhya Pradesh.
- Causes: Nitrate contamination is mainly due to excessive use of nitrogen-based fertilizers, over-irrigation, and poor management of animal waste. Urbanisation and improper sewage systems exacerbate the problem.
Other Groundwater Contaminants:
- Fluoride contamination: A significant concern in Rajasthan, Haryana, Karnataka, Andhra Pradesh, and Telangana.
- Arsenic contamination: Elevated arsenic levels found in several states, especially in floodplains of the Ganga and Brahmaputra rivers (West Bengal, Jharkhand, Bihar, Uttar Pradesh, Assam, and Manipur).
- Uranium contamination: 42% of uranium-contaminated samples are from Rajasthan, and 30% from Punjab. Chronic exposure to uranium leads to kidney damage.
Groundwater Extraction and Availability:
- 60.4% of groundwater is being extracted across India.
- 73% of groundwater blocks are classified as in the ‘safe’ zone, an improvement from 67.4% in 2022.
Monsoon Impact:
- Nitrate contamination increases post-monsoon, with 32.66% of samples exceeding safe limits during the rainy season.
Health Implications:
- High nitrate levels, particularly dangerous for infants, can cause blue baby syndrome (methemoglobinemia).
- Long-term exposure to contaminants like fluoride and arsenic can lead to fluorosis and increase the risk of cancers and skin lesions.
Sources of Contamination:
- Agricultural practices: Excessive use of fertilizers, pesticides, and improper irrigation.
- Waste disposal: Leaking septic systems, sewage, and hazardous waste sites contribute to contamination.
- Urbanisation: Increased wastewater and sewage, along with poor waste management, worsen the issue.
Measures to Address Contamination:
- Jal Shakti Abhiyan (JSA) and Atal Bhujal Yojana (ABHY) aim to conserve and manage groundwater resources.
- National Aquifer Mapping and Management Program (NAQUIM) to assess and map aquifer systems.
- Pollution control programs: Under the Water (Prevention & Control) Act, 1974, and initiatives like sewage treatment plants and effluent treatment plants to manage wastewater.
- Public awareness: Campaigns like Swachh Bharat Mission and Catch the Rain educate communities on the importance of groundwater conservation.
Key Statistics:
- 56% of districts in India report groundwater nitrate levels exceeding the safe limit of 45 mg/L.
- Monsoon effects: Post-monsoon data shows a significant increase in contamination levels (32.66% vs. 30.77% pre-monsoon).
National e-Governance Awards (NAeG) Scheme 2025

- 03 Jan 2025
In News:
- The Department of Administrative Reforms & Public Grievances (DARPG) has issued the guidelines for the 28th National e-Governance Awards (NAeG) 2025.
- Nominations for the awards can be submitted online via the official portal: www.nceg.gov.in.
Key Highlights:
- Award Categories: Nominations for the awards can be submitted under the following six categories:
- Government Process Re-engineering: Digital transformation through the use of technology to improve government processes.
- Innovation by Use of AI and New Age Technologies: Fostering citizen-centric services via artificial intelligence and other modern technologies.
- Best e-Gov Practices in Cyber Security: Recognizing excellence in e-Governance practices focused on cybersecurity.
- Grassroot Level Initiatives: Initiatives at the Districts, ULBs (Urban Local Bodies), or Gram Panchayats that deepen service delivery.
- Replication and Scaling Up of Successful Projects: Projects awarded in the past (such as NAeG or Prime Minister’s Awards) that have been successfully replicated or scaled.
- Digital Transformation using Data Analytics: Projects that leverage data analytics on digital platforms for enhancing governance.
- Eligibility: The awards are open to Central Ministries/Departments, State Governments, District Collectors, Research Institutions, and other relevant entities.
- Award Details:
- The NAeG 2025 will feature 16 awards:
- 10 Gold Awards.
- 6 Silver Awards.
- The NAeG 2025 will feature 16 awards:
- Incentives:
- Gold Award winners will receive a Trophy, Certificate, and an incentive of Rs 10 lakh.
- Silver Award winners will receive a Trophy, Certificate, and an incentive of Rs 5 lakh.
- The incentive will be used for further implementation of the awarded projects or bridging resource gaps in public welfare.
- Objective: The goal of the National Awards for e-Governance is to recognize and promote excellence in the implementation of e-Governance initiatives and digital transformation efforts across India.
Tinnitus

- 03 Jan 2025
In News:
Researchers at IIT Bombay have created an affordable device to diagnose and manage tinnitus, a condition involving persistent ringing or buzzing in the ears. The device offers personalized treatment solutions and a comprehensive approach to managing tinnitus.
What is Tinnitus?
- Tinnitus is the perception of sound in the absence of external noise, meaning only the affected individual hears it. It is often caused by underlying conditions such as age-related hearing loss, ear injury, or circulatory system problems.
- It affects over 740 million adults globally, with 120 million experiencing severe symptoms (JAMA Neurology, 2022).
- Common symptoms include sleep disturbances, depression, anxiety, irritability, and significant impacts on mental health and social life.
- Treatment may include: Hearing aids, sound-masking devices, medications, and coping techniques to manage the noise.
Device Features:
- Precise Tinnitus Matching: Identifies the exact nature and frequency of sounds experienced by the patient.
- Customizable Treatment: Provides a tailored, multimodal approach to treatment, ensuring each patient gets a unique experience.
- Tracking Progress: Includes tools to monitor disease progression and patient improvement over time.
Affordability and Accessibility:
- The device is cost-effective, addressing the issue of high costs associated with current tinnitus management solutions.
- This breakthrough is especially beneficial for low-income regions, where access to expensive tinnitus treatment is limited.
Impact on Healthcare:
- The device empowers doctors with precise diagnostic tools, improving the accuracy of diagnosis and the efficacy of treatment.
- It aims to enhance patient quality of life by offering an affordable and accessible solution to tinnitus management.
Funding and Development:
- The project has received funding from Tata Centre for Technology and Design (TCTD), IIT Bombay, and Wadhwani Research Centre for Bioengineering (WRCB).
Significance:
- This development represents a technological advancement in tinnitus care, with the potential to greatly reduce the burden of the condition and improve the well-being of affected individuals worldwide.
Quad 20th Anniversary
- 03 Jan 2025
In News:
Quad Foreign Ministers reaffirmed their commitment to a free, open, and peaceful Indo-Pacific. Marked the 20th anniversary of Quad cooperation, originally formed to respond to the 2004 Indian Ocean earthquake and tsunami.
Key Highlights:
- What is the Quad?
- A strategic forum of the US, Japan, India, and Australia aimed at regional security and economic cooperation in the Indo-Pacific region.
- Founded on shared principles of democracy, human rights, rule of law, and countering China's influence.
- Origins:
- Quad traces its origins to the 2004 Tsunami relief efforts.
- Formed formally in 2007, but Australia withdrew in 2008 due to regional tensions. It rejoined in 2017 following strengthened US-Australia ties.
- Commitment to Regional Security:
- Focus on countering China’s assertive behavior in the Indo-Pacific.
- Ensuring maritime security, countering illegal fishing, promoting infrastructure, and advancing economic cooperation.
- Key Initiatives:
- IPMDA: Real-time monitoring of maritime activities.
- MAITRI: Capacity-building for maritime security.
- Quad Fellowship: Funds graduate-level STEM education in member countries.
- Open RAN: Promoting secure 5G infrastructure.
- Cancer Moonshot: Focus on cervical cancer prevention.
- Military and Naval Cooperation:
- Malabar Exercises: Joint naval drills between India, Japan, the US, and Australia.
- ASEAN and Regional Cooperation:
- Emphasis on ASEAN's central role in the Indo-Pacific region.
- Support for the Pacific Islands Forum and the Indian Ocean Rim Association (IORA).
- Future Developments:
- India to host the next Quad Summit in 2025.
- Continued focus on sustainable regional development, scientific collaboration, and disaster relief efforts.
- Significance of the Quad for India:
- Strategic Importance:
- Provides a platform to counter China's assertive policies, especially in the South China Sea and the "String of Pearls" strategy.
- Aligns with India’s Act East Policy, enhancing ties with East and Southeast Asia.
- Maritime Security: Ensures freedom of navigation and counters illegal activities like piracy and illegal fishing in India’s maritime domain.
- Economic Opportunities:
- Strengthens cooperation on infrastructure projects and trade initiatives, such as the Blue Dot Network.
- Post-COVID, Quad may aid India in attracting manufacturing units shifting from China.
- Scientific and People-to-People Collaboration: Supports STEM education and enhances soft power diplomacy through academic and cultural exchanges.
Rapid Chess Championship

- 02 Jan 2025
In News:
In a monumental achievement, Koneru Humpy from Vijayawada, India, claimed the 2024 FIDE Women’s World Rapid Chess Championship in New York. This victory marks her second World Rapid Chess title, five years after her first win in 2019 in Georgia, making her the first Indian and only the second player after China’s Ju Wenjun to win the title multiple times.
Key Highlights of Humpy’s Victory:
- Final Score: Humpy finished with an impressive 8.5 points from 11 rounds, securing the top spot by defeating Irene Sukandar of Indonesia in the final round.
- Strong Finish: Humpy surged ahead of the other joint leaders to clinch the title, with D. Harika, another Indian chess star, securing 5th place with 8 points.
World Rapid Chess Championship
- The World Rapid Chess Championship is a chess tournament that determines the world's top rapid chess player. The tournament is held annually by FIDE, the International Chess Federation.
- How it works
- The tournament uses a Swiss system, where players are paired with opponents of similar scores in each round.
- Players are not eliminated after losses.
- The player with the highest score at the end of the tournament wins.
- Time controls
- Players are given a set amount of time per move, plus an increment for each move.
- In the World Rapid Championship, players have 15 minutes per move, plus a 10-second increment for each move.
A Historic Year for Indian Chess:
- 2024 has been a remarkable year for Indian chess, with D. Gukesh becoming the youngest-ever World Chess Champion after his victory over Ding Liren (China) at the World Chess Championship in Singapore.
- India also made history by winning both the open and women’s sections at the 2024 Chess Olympiad in Budapest.
H-1B Visa
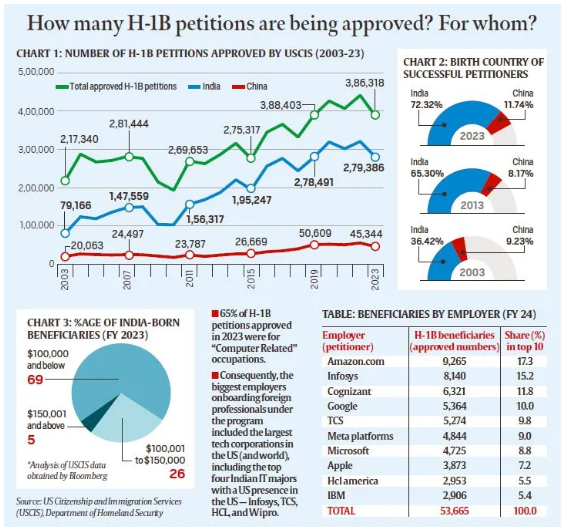
- 02 Jan 2025
In News:
In the weeks leading up to his return as US President, Donald Trump’s supporters are embroiled in a public dispute over skilled immigration and H-1B visas.
What is the H-1B Visa Program?
- Purpose and Overview:
- The H-1B visa is a non-immigrant visa allowing U.S. companies to employ foreign workers in specialized occupations like STEM (Science, Technology, Engineering, Mathematics) and IT, which require at least a bachelor’s degree.
- Introduced in 1990 to help U.S. employers fill positions when there’s a shortage of qualified domestic workers.
- It allows workers to stay in the U.S. for a maximum of six years, with the option to apply for permanent residence (Green Card) or leave for 12 months before reapplying.
- Annual Cap and Exemptions:
- 65,000 new visas are issued annually, with an additional 20,000 for those with a master’s degree or higher from a U.S. university.
- Certain petitions, such as for continuing employment or positions in higher education or nonprofit research, are exempt from the cap.
- Dominance of Indian Beneficiaries:
- Indians are the largest beneficiaries, accounting for over 70% of H-1B visa approvals annually since 2015, with China coming second at around 12-13%.
The Current Controversy
- Trigger for Debate:
- The controversy was sparked by Sriram Krishnan, a Chennai-born tech entrepreneur appointed as Donald Trump’s top AI adviser. His post on X (formerly Twitter) in November 2024, advocating for unlocking skilled immigration, led to backlash within Trump’s anti-immigration base.
- The Political Divide:
- Trump’s supporters, particularly from the MAGA (Make America Great Again) faction, voiced opposition to the H-1B visa program, arguing it undermines American workers and wages.
- This prompted pushback from pro-H-1B advocates like Elon Musk and Vivek Ramaswamy, who argue that the program is crucial for addressing the U.S.'s STEM talent shortages.
- Economic and Political Context:
- Immigration is a polarizing issue in the U.S., with a focus on low-skilled labor migration and its alleged effects on wages and job opportunities for American workers.
- Trump’s stance against low-skilled immigration echoes similar critiques about H-1B workers being employed at lower salaries in tech companies, which some claim depresses wages and reduces job opportunities for U.S. workers.
Criticisms of the H-1B Program
- Abuse of the System:
- Critics argue that companies exploit the H-1B program by hiring foreign workers, especially from India, at lower wages than American employees, particularly in tech industries.
- Elon Musk suggests that the program is “broken” and needs reform, proposing raising the minimum salary for H-1B workers to make it more expensive to hire overseas talent.
- Salary Disparities:
- Data from USCIS (U.S. Citizenship and Immigration Services) shows that 70% of H-1B petitions for Indian professionals in 2023 were for salaries below $100,000, while the median salary for U.S. IT professionals was $104,420.
- Impact on American Jobs:
- Critics argue that companies prefer to hire foreign workers at lower wages to save costs, despite the availability of qualified U.S. talent, thus taking away opportunities for American workers.
Support for the H-1B Program
- Filling the STEM Gap:
- Proponents, including Musk and Ramaswamy, argue that the H-1B visa is essential for filling the STEM skills gap in the U.S., given the global dominance of India and China in STEM fields.
- India and China lead the world in STEM graduates, with 2.55 million and 3.57 million, respectively, compared to the U.S. with 820,000.
- Proponents, including Musk and Ramaswamy, argue that the H-1B visa is essential for filling the STEM skills gap in the U.S., given the global dominance of India and China in STEM fields.
- Economic Benefits:
- The H-1B program helps U.S. companies access top global talent, boosting innovation and economic growth, especially in high-tech industries.
- Tech companies argue that without access to skilled foreign workers, they would struggle to fill critical positions in the technology sector.
Tamil Nadu's First Glass Bridge in Kanyakumari
- 02 Jan 2025
In News:
- The Chief Minister of Tamil Nadu inaugurated India’s first glass bridge over the sea in Kanyakumari, connecting the Thiruvalluvar Statue and the Vivekananda Rock Memorial.
- The bridge provides a safe and scenic walking route between these two iconic landmarks, eliminating the need for ferry trips.
Key Highlights:
- Dimensions and Design
- The bridge is 77 meters long and 10 meters wide, offering uninterrupted views of the sea from a unique vantage point.
- Designed to withstand marine conditions like corrosion and strong winds, ensuring durability and safety for visitors.
- Tourism Investment
- The bridge was built at a cost of ?37 crore, marking a significant investment in tourism infrastructure for Kanyakumari.
- This project aligns with the state’s vision to boost tourism and modernize amenities in the region.
- Significance as a Tourist Attraction
- The bridge is set to become a landmark tourist attraction, enhancing the visitor experience by providing a direct, scenic route between the two monuments.
- It is expected to play a pivotal role in boosting tourist footfall and the local economy.
About Thiruvalluvar Statue
- Location and Design
- The Thiruvalluvar Statue stands on a rock near the Vivekananda Rock Memorial in Kanyakumari.
- It is a symbol of wisdom, officially named the Statue of Wisdom by the Tamil Nadu government.
- Physical Specifications
- The statue stands at a total height of 133 feet (41 meters), with the statue itself measuring 95 feet (29 meters) and the pedestal adding 38 feet (12 meters).
- Weight: The statue weighs approximately 7000 tonnes and is designed in a hollow structure.
About Vivekananda Rock Memorial
- Location and Significance
- Situated on a rock in the Laccadive Sea, around 500 meters from the mainland in Kanyakumari.
- The memorial commemorates Swami Vivekananda, who represented India’s spiritual legacy at the 1893 Parliament of World’s Religions in Chicago.
- Historical and Religious Importance
- The rock is believed to be the site where Swami Vivekananda attained enlightenment.
- It is also associated with goddess Kanyakumari, who is said to have prayed to Lord Shiva on this rock, with an imprint of her feet preserved there.
- Architectural Features
- The memorial incorporates diverse architectural styles, including the Sripada Mandapam and the Vivekananda Mandapam.
- A life-sized bronze statue of Swami Vivekananda is located at the memorial.
- The rock is surrounded by the Bay of Bengal, Indian Ocean, and Arabian Sea, where these three water bodies converge.
Business Ready (B-READY) Report 2024

- 02 Jan 2025
In News:
- The B-READY report, launched by the World Bank in 2024, replaces the Ease of Doing Business (EoDB) index.
- Focus: It evaluates the global business environment to foster inclusive private sector growth, assessing 10 core topics covering a firm's lifecycle, such as business entry, taxation, labor, and international trade.
India’s Potential Challenges
- Business Entry: India faces multiple steps and incomplete digital integration, making it slower compared to benchmarks like Singapore, which achieves one-day registration at minimal cost.
- Labor Regulations: While India has introduced four labor codes, the implementation remains slow and inconsistent, affecting labor flexibility and compliance.
- International Trade: India struggles with customs delays, inconsistent enforcement, and high logistics costs, unlike countries like Germany and Singapore, which promote trade efficiently.
- Business Location: Regulatory delays and inconsistent approvals hinder the establishment of business facilities, affecting investment decisions.
- Public Services Gap: While regulations may be strong, there is often a gap in the provision of public services that support their effective implementation, leading to inefficiencies.
Key Strengths for India
- India is expected to score well in the areas of Quality of Regulations, Effectiveness of Public Services, and Operational Efficiency.
- The country shows promise in promoting digital adoption and aligning with global environmental sustainability practices, though gender-sensitive regulations need more emphasis.
Significance
- The B-READY report serves as an essential benchmark for assessing India's business environment, offering insights into regulatory reforms and operational efficiency.
- Key policy implications for India include the need to:
- Streamline business operations by digitizing registration and regulatory approval processes.
- Improve logistics and trade efficiency by reducing customs delays.
- Address labor market inefficiencies through better implementation of labor codes.
- Invest in public services and promote digital transformation for better compliance and operational ease.
- Focus on sustainability and inclusivity, ensuring gender-sensitive policies and fostering green business practices.
Global Findings from the B-READY Report
- Economies with strong regulatory frameworks and digital tools (e.g., Rwanda, Georgia) show that even countries with varying income levels can achieve high scores.
- High-income countries like Estonia and Singapore still have room for improvement, especially in areas like taxation and dispute resolution.
Comparison of B-READY with Ease of Doing Business (EoDB)
- Scope: B-READY is broader, covering a firm’s lifecycle and social benefits, while EoDB focused mainly on regulatory burdens.
- Indicators: B-READY uses 1,200 indicators from expert consultations and firm-level surveys, offering more comprehensive insights compared to the EoDB's limited metrics.
- Focus on Public Services: Unlike EoDB, which provided limited attention to public services, B-READY explicitly evaluates public service efficiency and operational effectiveness.
Policy Recommendations
- Streamline Business Operations: Inspired by countries like Singapore, India should simplify business registration and reduce delays in customs and regulatory approvals.
- Strengthen Public Services: Focus on improving tax portals, utility access, and dispute resolution systems through digital tools.
- Promote Sustainability: Encourage environmentally sustainable business practices and adopt gender-sensitive regulations to ensure inclusive growth.
- Peer Learning and Global Collaboration: Encourage India to learn from best practices in countries like Singapore and Estonia for effective reforms.
- Tailored Reforms: India must design policies addressing unique local challenges while adhering to global standards.
Stellaria bengalensis

- 02 Jan 2025
In News:
After a plant species of the genus Stellaria (family Caryophyllaceae) was reported from Kerala earlier this year, researchers have identified another member of the same genus at Kalimpong district in West Bengal.
Key Highlights:
Discovery and Identification:
- Published: The discovery was published in Phytotaxa.
- Location: Found in Kalimpong district, West Bengal, at altitudes of 2,245-2,450 metres in the Sangser forest.
- Named: The species is named Stellaria bengalensis after the state of West Bengal.
Taxonomy and Characteristics:
- Family: Caryophyllaceae.
- Type: Annual herb.
- Size: Grows to a height of 8 to 10.5 cm.
- Flowers: White in color, with shorter petals, often included within the sepal, and absence of bracts.
- Seeds: Sharp and pointed.
- Flowering and Fruiting: Occurs from May to September.
Distribution:
- Region: Primarily found in the Himalayan region.
- Similar Species: Stellaria mcclintockiae, identified earlier in Kerala (Nelliyampathy Hills).
- Both species grow in muddy soil slopes and are annuals.
Conservation Status:
- Under IUCN (International Union for Conservation of Nature) criteria, the species is assessed as "data deficient", pending further studies.
- Potential Habitat: There is a possibility of finding more populations in the western Himalayas.
Significance:
- Stellaria bengalensis is the second Stellaria species reported in India in 2025.
- India is home to about 22 Stellaria species, predominantly found in the Himalayan region.
- The discovery adds to biodiversity knowledge in India and underscores the importance of studying plant species in the region.
Smart Cities Mission (SCM)

- 31 Dec 2024
In News:
The introduction of smart classrooms as part of the Smart Cities Mission (SCM) has had a significant impact on education, leading to a 22% increase in enrolment across 19 cities, according to a report from the Indian Institute of Management, Bangalore (IIM-B). The study covers the period from 2015-16 to 2023-24 and highlights several key benefits of this initiative, which aims to improve the overall learning environment in government schools.
Key Findings:
- Increased Enrolment: The introduction of smart classrooms has been linked to a 22% increase in student enrolment across 19 cities, suggesting that the initiative has made education more appealing and accessible.
- Smart Classroom Development: By 2023-24, 71 cities had developed 9,433 smart classrooms in 2,398 government schools. The states with the most smart classrooms are:
- Karnataka (80 classrooms)
- Rajasthan (53 classrooms)
- Tamil Nadu (23 classrooms)
- Delhi (12 classrooms)
- West Bengal has a very limited number, with just two classrooms.
- Improved Learning Experience: Teachers have expressed positive feedback, agreeing that the smart classrooms have improved learning experiences and attendance among students. Additionally, the smart classroom setup has contributed to increased comfort for teachers and higher preference for these modern facilities.
- Teacher Training: Special training provided to teachers has enhanced their comfort with using the smart classroom tools, with senior secondary teachers showing the highest comfort levels.
- Digital Libraries: The study also found that 41 cities have developed Digital Libraries with 7,809 seating capacity, offering essential resources for students. Cities like Raipur (Chhattisgarh) and Tumakuru (Karnataka) have seen positive outcomes from these libraries, particularly in supporting students preparing for competitive exams.
Smart Cities Mission (SCM)
- Launched in June 2015, the Smart Cities Mission aims to promote cities that offer core infrastructure, a decent quality of life, a sustainable environment, and the application of smart solutions. As of November 2024, 91% of the projects under the mission have been completed.
SAAR Platform and Research
- In 2022, the Smart Cities Mission introduced the SAAR (Smart Cities and Academia towards Action and Research) platform to bridge the gap between academia and the government. Under this platform, 50 impact assessment studies have been initiated by 29 premier institutions, including six Indian Institutes of Management (IIMs), eight Indian Institutes of Technology (IITs), and 12 specialized research institutes.
Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease (MASLD)
- 31 Dec 2024
In News:
Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) has recently been renamed MASLD (Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease), reflecting a shift in understanding of the disease's root causes and its broader implications.
Why the Name Change?
- The primary reason for renaming NAFLD to MASLD is to highlight the metabolic dysfunction as the primary cause of the disease.
- Previously, the term NAFLD focused on the absence of alcohol consumption, which inadvertently shifted attention away from the true contributors, like obesity, type 2 diabetes, and abnormal cholesterol levels.
- The term MASLD eliminates the stigma associated with "non-alcoholic," which may have misled people into thinking alcohol consumption was the only factor, even though metabolic issues are the central cause.
- The term MASLD shifts the focus towards metabolic dysfunction, making it easier for healthcare professionals to understand, diagnose, and treat the condition more effectively.
The Connection to Metabolic Dysfunction
- MASLD is strongly associated with metabolic issues such as abdominal obesity, insulin resistance, and high blood sugar. These metabolic problems are key contributors to liver fat accumulation.
- People with abdominal obesity are 2-3 times more likely to develop fatty liver disease. MASLD affects about 25% of the global population, and the rates increase significantly (up to 50-70%) in individuals with type 2 diabetes or obesity.
- By focusing on metabolic dysfunction, MASLD encourages addressing the root causes rather than just the symptoms, offering a more effective approach to treatment and prevention.
How is MASLD Diagnosed?
Advancements in non-invasive diagnostic methods have improved the ability to diagnose MASLD more easily and accurately, including:
- FibroScan: A non-invasive, painless test to measure liver fat and stiffness, replacing the need for liver biopsy.
- MRI and Ultrasound Techniques: Reliable methods for assessing liver fat and scarring.
- Blood Tests: Common tests like ALT, AST, and GGT assess liver function. Researchers are also exploring new markers like CK-18 fragments and the ELF score (Enhanced Liver Fibrosis) to improve diagnostic accuracy.
Implications for Patient Care
The renaming of NAFLD to MASLD has important implications for patient care:
- Targeted Treatments: By focusing on the metabolic roots, treatments such as weight loss, blood sugar management, and cholesterol control can be prioritized. These interventions help reduce the risk of long-term complications such as heart disease, liver failure, and cirrhosis.
- Earlier Diagnosis: MASLD encourages earlier recognition of the condition, which can lead to better management and improved long-term outcomes.
Prevention
Preventing MASLD involves avoiding foods that exacerbate liver fat buildup. Dr. Punit Singla, director at Marengo Asia Hospitals, emphasizes limiting or avoiding:
- Fast food, junk food, and processed foods
- Foods high in sugar, including red and processed meats
A healthier lifestyle with a balanced diet rich in whole grains, fruits, vegetables, and lean proteins can significantly help prevent or manage MASLD.
61st Raising Day

- 31 Dec 2024
In News:
On December 20, 2024, Union Home Minister Shri Amit Shah attended the 61st Raising Day function of the Sashastra Seema Bal (SSB) in Siliguri, West Bengal. During the event, he e-inaugurated the Integrated Check Point (ICP) Agartala and a newly constructed residential complex for the Border Guard Force (BGF) at Petrapole. The event was attended by several dignitaries, including the Director of Intelligence Bureau (IB), Secretary of Border Management (MHA), and the Director-General of SSB.
Key Highlights from the Speech:
- Tributes to Martyrs: Shri Shah paid tributes to SSB martyrs, highlighting their sacrifices in protecting the country's borders and eliminating Left Wing Extremism in the eastern region. He acknowledged the 4 Padma Shri, 1 Kirti Chakra, and other national awards received by SSB for their exceptional service.
- Role in Connecting Borders: The Home Minister praised SSB’s role in connecting the culture, language, and heritage of border villages with mainstream India. He emphasized that the SSB has fulfilled its motto of "Service, Security, and Brotherhood" while maintaining a strong relationship with Nepal and Bhutan.
- Security and Vigilance: SSB is responsible for securing a 2,450 km border with Nepal and Bhutan. Shri Shah noted that SSB's vigilance has helped in stopping narcotics, arms smuggling, and human trafficking. Additionally, the force has worked to ensure that Bihar and Jharkhand are now Naxal-free.
- Zero-Tolerance Policy: The SSB has a zero-tolerance policy on encroachments, narcotics, and smuggling. Over the last three years, the SSB successfully removed more than 1,100 encroachments from government land and seized significant amounts of narcotics, weapons, and counterfeit currency.
- Impact in Jammu & Kashmir: SSB has played a critical role in combating terrorism in Jammu and Kashmir, killing more than 19 terrorists and arresting 14 through various operations.
- Humanitarian Efforts: Besides security, SSB has actively participated in disaster relief operations during floods and landslides, often at great personal risk.
- Government Schemes for CAPF Personnel: Under the leadership of Prime Minister Narendra Modi, various welfare schemes like Ayushman Cards, CAPF e-Housing, and scholarships have been launched to support CAPF personnel and their families.
- Self-Employment Initiatives: SSB has promoted self-employment for border youth, training them in areas like beekeeping, mobile repairing, and driving. They have also contributed significantly to the Nasha Mukt Bharat Abhiyan, creating awareness about drug addiction among 36,000 youth.
- Environmental Contribution: The force has planted over 6 crore trees as part of its environmental efforts.
Pegasus Spyware

- 31 Dec 2024
In News:
For the first time, a court in the US has held Israel’s NSO Group liable for its intrusive spyware Pegasus, which could set up a measure of accountability for the company that it has, for long, allegedly downplayed.
Overview:
- Pegasus is a spyware developed by the Israeli company NSO Group.
- It has been used for surveillance, allegedly targeting journalists, activists, politicians, and government officials across the world, including India.
Recent Legal Developments:
- US Court Ruling (2024):
- A US court held NSO Group liable for using Pegasus to surveil 1,400 WhatsApp users, including 300 from India.
- NSO Group violated the Computer Fraud and Abuse Act (CFAA) and the California Computer Data Access and Fraud Act (CDAFA).
- The ruling may revive debates on the accountability of spyware use and its implications on privacy.
Use of Pegasus in India:
- Targeted Individuals (2021):
- 300 Indian numbers allegedly targeted, including journalists, politicians, Union Ministers, and civil society members.
- High-profile targets included opposition leaders, constitutional authorities, and activists.
- Government Denial:
- The Indian government denied involvement, stating allegations lacked substance.
- In Parliament, IT Minister Ashwini Vaishnaw rejected claims, asserting India’s surveillance laws prevent unauthorized surveillance.
- NSO Group Response:
- NSO Group denied the allegations, calling them “false and misleading” and citing doubts about the sources.
Investigations and Legal Actions:
- Supreme Court Inquiry:
- The Supreme Court appointed a committee of technical experts in 2021 to investigate claims.
- August 2022 Report: Found no conclusive evidence of spyware use on examined devices but noted lack of cooperation from the government.
- State-Level Investigations:
- West Bengal: Set up a Commission of Inquiry into Pegasus surveillance, later halted by the Supreme Court.
- Andhra Pradesh: The issue became political, with allegations that the previous government used Pegasus to monitor opposition figures.
Pegasus Spyware Features:
- Capability: Can hack iOS and Android devices to collect data, record conversations, capture photos, and access app data.
- Exploitation Method: Uses zero-day vulnerabilities to exploit iOS and Android devices covertly.
- Invisibility: Operates without user knowledge, often only detected through signs like browser closings after phishing links are clicked.
Controversial Use of Pegasus:
- Global Use: Though intended for fighting terrorism and crime, Pegasus has been misused for spying on journalists, politicians, human rights activists, and opposition leaders.
- India Specifics:
- Pegasus Project: Targeted Indian citizens, including activists, journalists, and politicians.
- Amnesty International: Confirmed use of Pegasus to target Indian phones.
India's Legal Framework for Surveillance:
- Telecommunications Act (2023): Empowers the government to control telecom services during emergencies, but requires authorization for lawful interceptions.
- IT Act (2000): Allows the government to monitor, intercept, or decrypt information through computer resources under certain conditions.
- Digital Personal Data Protection (DPDP) Act (2023): Aims to protect personal data, including provisions on surveillance, data breaches, and rights of individuals over their data.
Privacy and Surveillance Concerns:
- Impact on Fundamental Rights:
- Surveillance infringes on the right to privacy under Article 21 of the Constitution.
- Freedom of speech and expression (Article 19) may be curtailed, with surveillance being used to suppress dissent.
- Lack of Transparency:
- Surveillance often occurs without judicial or parliamentary oversight, leading to potential executive overreach.
- Inability to Seek Legal Remedies:
- Citizens targeted by surveillance cannot challenge it due to lack of awareness, undermining constitutional rights.
- Executive Overreach and Suppression of Free Expression:
- Pegasus revelations have raised concerns about surveillance targeting constitutional functionaries, suppressing free speech, and stifling open discourse.
India-Australia Economic Cooperation and Trade Agreement (Ind-Aus ECTA)

- 31 Dec 2024
In News:
The India-Australia Economic Cooperation and Trade Agreement (Ind-Aus ECTA) completes two years of remarkable success, driving mutual growth and showcasing the complementarity of both economies.
Key Achievements:
- Bilateral Merchandise Trade Surge:
- Trade increased from USD 12.2 billion (2020-21) to USD 26 billion (2022-23).
- Trade moderated slightly in 2023-24 to USD 24 billion, but exports from India to Australia grew by 14%.
- From April-November 2024, bilateral trade reached USD 16.3 billion.
- Preferential Import Utilization:
- Export utilization: 79%
- Import utilization: 84%
- Sectoral Growth:
- Textiles, chemicals, and agriculture sectors have seen significant growth.
- New export products: Gold studded with diamonds, turbojets.
- India’s imports: Metalliferous ores, cotton, wood products that fuel Indian industries.
- Geopolitical Strengthening:
- Enhanced relations in forums like Quad, Indo-Pacific Economic Framework (IPEF), Supply Chain Resilience Initiative (SCRI).
Key Features of the Agreement:
- Tariff Reductions:
- Australian goods: 85% tariff-free access to India (rising to 90% by 2026).
- Indian goods: 96% tariff-free access to Australia (rising to 100% by 2026).
- Access to Key Markets:
- India: Access to Australia's fast-growing market.
- Australia: Access to India's labor-intensive sectors like gems, jewelry, textiles, leather, furniture, food, agriculture.
- Services and IT:
- 135 sub-sectors covered in services.
- India gains market access in 103 sub-sectors with Most Favoured Nation (MFN) status in 31.
- Fast-tracked approval of medicines and elimination of double taxation for India's IT sector.
- Job Creation & Skill Exchange:
- Expected creation of 1 million jobs in India.
- Opportunities for Indian yoga teachers, chefs, and 100,000 students with post-study work visas.
Future Prospects:
- Comprehensive Economic Cooperation Agreement (CECA): Builds on ECTA to advance bilateral trade, with 10 formal rounds and ongoing inter-sessional discussions.
- Trade Target: Aim to reach AUD 100 billion in trade by 2030.
- Global Economic Impact: Strengthening the partnership will contribute to a more resilient and dynamic global economy, with deeper economic integration between India and Australia.
World Audio Visual & Entertainment Summit (WAVES) 2025

- 30 Dec 2024
In News:
India to Host World Audio Visual & Entertainment Summit (WAVES) 2025.
Key Highlights:
- Purpose: The summit aims to bolster India's media and entertainment (M&E) industry, expand its global influence, and foster innovation and collaboration within the sector.
- Significance: First-ever global summit to cover the entire media and entertainment industry spectrum.
- Objective:
- Foster Dialogue and Trade: WAVES aims to be a premier platform for industry leaders, stakeholders, and innovators to engage in meaningful discussions, explore opportunities, and tackle challenges in the M&E sector.
- Promote India's M&E Industry: Attract trade and investment to India, highlighting its strengths in animation, gaming, entertainment technology, and cinema (both regional and mainstream).
- Focus Areas:
- Industry Advancements: Discussions will revolve around India’s progress in animation, visual effects, gaming, and cinema.
- Global Positioning: Establish India as a global powerhouse in the M&E sector, setting new standards for creativity, innovation, and global influence.
WAVES India - Vision and Mission:
- Vision: Position India as a Global Powerhouse: Enhance India’s standing in the dynamic M&E sector, making it a hub of creativity and innovation worldwide.
- Mission:
- Provide exclusive investment opportunities for global M&E leaders through WAVES.
- Drive India’s Creative Economy through Intellectual Property (IP) Creation for both domestic and international markets.
- Develop M&E Infrastructure: Strengthen industry infrastructure and create a skilled workforce to meet global demands.
- Adapt to New Trends: Embrace emerging technologies and transformations in the M&E landscape.
Expected Outcomes:
- Global Collaboration: Engage global M&E leaders in discussions that provoke ideas and facilitate collaborations.
- Attract Investment: Promote India as a business-friendly investment destination in the M&E sector.
- Skills and Capacity Building: Build capacity in the M&E industry and develop skilled human resources to support international needs.
PM CARES Fund Contributions and Utilization (2022-23)
- 30 Dec 2024
In News:
The Prime Minister’s Citizen Assistance and Relief in Emergency Situations Fund (PM CARES Fund) received Rs 912 crore in contributions during the financial year 2022-23 as donations continued to pour in even after the Covid pandemic.
Key Highlights:
Contributions Received:
- Total contributions in 2022-23: Rs 912 crore.
- Voluntary contributions: Rs 909.64 crore.
- Foreign contributions: Rs 2.57 crore.
Interest Income:
- Total interest income for 2022-23: Rs 170.38 crore.
- From regular accounts: Rs 154 crore.
- From foreign contributions account: Rs 16.07 crore.
Refunds and Additional Inflows:
- Rs 225 crore in refunds, including:
- Rs 202 crore refund from procurement of 50,000 ventilators for government hospitals.
Disbursements:
- Total disbursed in 2022-23: Rs 439 crore:
- Rs 346 crore for PM CARES for Children.
- Rs 91.87 crore for procurement of 99,986 oxygen concentrators.
- Rs 1.51 crore for refunds.
- Rs 24,000 for legal charges, and Rs 278 for bank and SMS charges.
Cumulative Contributions (2019-23):
- Rs 13,605 crore received from 2019-20 to 2022-23.
- Voluntary contributions: Rs 13,067 crore.
- Foreign contributions: Rs 538 crore.
- Interest income over these years: Rs 565 crore.
About PM CARES Fund:
Formation and Purpose:
- Established: March 27, 2020, as a Public Charitable Trust under the Registration Act, 1908.
- Purpose: To address emergencies like COVID-19, natural disasters, and man-made calamities. It also supports healthcare infrastructure and essential facilities.
Governance and Structure:
- Chairperson: The Prime Minister (ex-officio).
- Trustees: Defence, Home, and Finance Ministers (ex-officio).
- Additional Trustees: Appointed by the PM, serving on a non-profit basis (e.g., Justice K T Thomas (retd.) and Kariya Munda).
Tax Exemptions:
- Donations are eligible for 100% tax exemption under Section 80G of the Income Tax Act, 1961.
- Donations qualify as Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) expenditure under the Companies Act, 2013.
- The fund is exempt under the Foreign Contribution Regulation Act (FCRA), allowing it to receive foreign donations.
ASI Discovery at Srisailam Temple

- 30 Dec 2024
In News:
- The Archaeological Survey of India (ASI) uncovered ancient copper plates and gold coins at the Srisailam Temple in Andhra Pradesh, specifically in the Ghantamandapam area.
- The discovery includes 20 sets of copper plates, totaling 72 leaves, and various gold coins.
- The ASI's Epigraphy Branch in Mysore has completed the documentation of these findings, and the materials are being studied in detail.
Collaboration with Srisailam Devasthanam:
- In collaboration with the Srisailam Devasthanam, ASI plans to publish a book that will detail the findings and their historical significance.
- The book will be printed soon by Pragati Publications in Hyderabad.
Srisailam Temple Overview:
- The Srisailam Temple, also known as the Mallikarjuna Swamy Temple, is a prominent Hindu pilgrimage site in Andhra Pradesh.
- It is located in the Nallamala Hills, overlooking the Krishna River.
- The temple is dedicated to Lord Shiva in the form of Mallikarjuna Swamy and Goddess Parvati as Bhramaramba Devi.
- It is one of the 12 Jyotirlingas of Lord Shiva and one of the Shakti Peethas, making it significant in both Shaivism and Shaktism.
Architectural Significance:
- The temple is built in the Dravidian style, featuring lofty towers and expansive courtyards, and is considered a prime example of Vijayanagara architecture.
- Historical references to the temple date back to the Satavahana period (2nd century AD), and the temple was further endowed by the Kakatiyas and Vijayanagara rulers.
Cultural and Religious Importance:
- The Srisailam Temple is unique for housing both a Jyotirlinga (Lord Shiva) and a Shakti Peetha (Goddess Bhramaramba), a rare combination not found at other temples.
- The great religious figure Adi Shankaracharya is believed to have visited the temple and composed the Sivananda Lahiri there.
Historical Context:
- The copper plates and inscriptions discovered are likely to provide valuable insights into the historical and cultural significance of the temple, as well as the region's ancient religious practices.
Reassessment of Conjugal Visits in Delhi Prisons

- 30 Dec 2024
In News:
- The Delhi government is reassessing the proposal to permit conjugal visits for prisoners, following the suspension of a similar initiative in Punjab.
- Delhi Chief Minister has sought further input from the Law Department and explored if similar schemes are implemented in other states.
Conjugal Visits - Definition & Context:
- Conjugal visits involve allowing prisoners to spend private time with their legal partners or spouses, including intimate relations, within prison premises.
- No national policy exists in India for conjugal rights of prisoners, leading to varied implementations across states.
Punjab’s Pilot Project - ‘Parivar Mulakat’:
- Ludhiana Central Jail introduced the 'Parivar Mulakat' programme in September 2022, allowing face-to-face meetings with family in designated rooms.
- The initiative was suspended shortly after its launch due to security concerns, particularly difficulty in conducting thorough body checks on visitors.
Challenges in Delhi:
- Overcrowded prisons in Delhi make it challenging to manage the logistical demands of conjugal visits, especially with up to 1,200 daily visitations.
- The Home Department has received proposals but no progress has been made over the past year.
Legal Precedents on Conjugal Rights:
- Punjab and Haryana High Court (2014) ruled that prisoners have a right to conjugal visits to facilitate procreation.
- Madras High Court (2018) allowed a life convict on parole for conjugal relations, and in 2023, a judge called for similar considerations for Tamil Nadu.
Human Rights Argument:
- Advocates argue that denying conjugal visits to prisoners violates basic human rights of both prisoners and their spouses, particularly those aged 21-50, who are often in sexually active years.
- Amit Sahni, a social activist, filed a PIL highlighting that most prisoners in Delhi are denied conjugal rights despite their eligibility.
Government’s Position:
- Delhi DG (Prisons) had argued that temporary leave such as parole and furlough serve the purpose of family ties, questioning the need for conjugal visits within prison.
Need for Legal Framework:
- Legal experts suggest the creation of a law and policy framework to regulate conjugal visits, ensuring clear guidelines for their implementation.
- S.D. Singh, a Supreme Court advocate, emphasized that conjugal visits should be legally recognized as a right, requiring formal legislation for consistent implementation.
Future Considerations:
- The Delhi government’s reassessment may lead to a policy that considers both human rights and security concerns in its decision on conjugal visits.
Re-emergence of the Dodo in Kashmir’s Papier Mâché Craft
- 30 Dec 2024
In News:
Artisans in Srinagar, Kashmir, have revived the extinct dodo bird in papier mâché forms. These figurines are exported worldwide, particularly to Mauritius and Europe, ahead of the Christmas season. Over 50,000 dodo figurines have already been sent to international markets in 2024.
Key Highlights:
The Dodo:
- Scientific Name: Raphus cucullatus.
- Extinct Since: 1681, approximately 80 years after humans began interacting with them.
- Endemic to Mauritius: A flightless bird from the Indian Ocean island of Mauritius, a national symbol of the country.
- Extinction Causes: Overhunting and the introduction of invasive species like rats, pigs, and cats that preyed on their eggs.
- Physical Traits: Grey or brown plumage, about 3 feet tall, flightless and fearless.
Papier Mâché Craft in Kashmir:
- History: Practiced for over 600 years in Kashmir, introduced during the reign of King Zain-ul-Abidin (15th century).
- Techniques: Involves creating decorative objects using paper pulp, with traditional Persian motifs.
- Recent Addition of Dodo: The dodo was introduced to the papier mâché craft around two decades ago, likely by Mauritian tourists.
International Market and Demand:
- Mauritius: A significant market for the papier mâché dodo, as the bird is a national emblem of Mauritius.
- Europe: Exported to European countries during the Christmas season, contributing to the popularity of Kashmir’s handicrafts.
- Kashmir's Karkhanas: Local craft workshops in Srinagar are producing thousands of dodo figurines each season, with over 3,000 dodos produced this year.
Cultural and Economic Impact:
- Artisans' Contribution: Local artisans are helping keep the memory of the extinct dodo alive, while boosting Kashmir’s handicraft industry.
- Global Recognition: The dodo is now a sought-after item in global markets, linked to the traditional art of Kashmir.
- Kashmir Handicrafts: Several crafts from Kashmir, including papier mâché, have received Geographical Indication (GI) tags for their distinct cultural and regional significance.
Sambar Deer

- 29 Dec 2024
In News:
Three poachers were arrested for killing a sambar deer in the Daying Ering Memorial Wildlife Sanctuary (DEMWS), East Siang district, Arunachal Pradesh.
Action Taken:
- Poachers Arrested: The poachers were booked under the Wildlife Protection Act 1972 and Arms Act 1959. The seized articles were handed over to the police, and a FIR was registered.
- Sanctuary Protection Efforts: The Divisional Forest Officer (DFO) emphasized the need for intensified surveillance to prevent further hunting incidents. Public cooperation was urged to report such incidents for prompt action.
About Sambar Deer:
- Scientific Name: Rusa unicolor.
- Native Regions: Found across the Indian subcontinent and Southeast Asia.
- Other Names: Known as Jarao in Nepal and Four-eyed deer in China.
- IUCN Red List: Listed as Vulnerable.
Key Features:
- Size: Stands between 1.2–1.4 meters at the shoulder.
- Weight: Can reach up to 550 kg, making it the largest oriental deer.
- Coat: Dark brown with a ruff around the neck, and unspotted.
- Antlers: Male sambar bears long, rugged antlers with three points (tines).
- Behavior: Elusive, most active at dusk and night.
Habitat:
- Water Dependency: Always found near water sources.
- Habitat Range: Dry deciduous forests, rainforests, and mixed forests.
- Social Structure: Often found alone or in small groups.
About Daying Ering Memorial Wildlife Sanctuary (DEMWS):
- Location: Situated in East Siang district, Arunachal Pradesh.
- Established: Originally established as Lali Wildlife Sanctuary in 1976, renamed Daying Ering Memorial in 1986.
- Climate: Tropical, receiving both north-east and south-west monsoons.
- Waterways: Home to the Siang River, one of Arunachal's major rivers.
Flora:
- Vegetation: Composed mainly of riverine plains with a variety of thatch and grasses.
- Trees: Includes scattered patches of trees such as Termenelia myriocarpa, Dillenia indica, Albizia spp., and Bombax ceiba.
Fauna:
- Mammals: Includes Hog Deer, Wild Pig, Tiger, and Elephant.
- Birds: Over 150 species of birds, including endangered species like the White-Winged Wood Duck and Bengal Florican.
IIT Bombay Develops Painless Needle-Free Shock Syringes
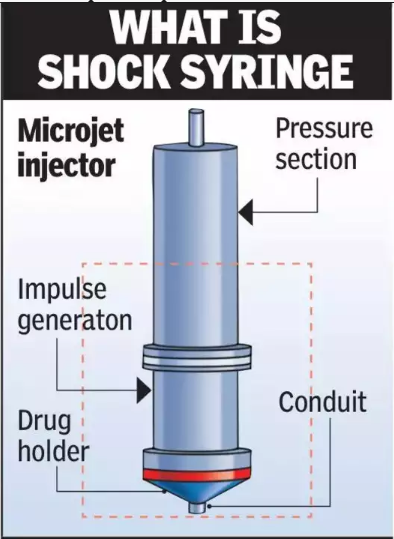
- 29 Dec 2024
In News:
Researchers at IIT Bombay, led by Viren Menezes from the Department of Aerospace Engineering, have developed a shockwave-based, needle-free syringe to deliver drugs painlessly and safely. The research was published in the Journal of Biomedical Materials and Devices.
Key Features of Shock Syringe:
- Unlike traditional syringes, the shock syringe uses high-energy shockwaves (traveling faster than the speed of sound) to deliver drugs, without the need for needles.
- The device is designed to reduce pain, tissue damage, and infection risk.
- The shock syringe aims to eliminate the discomfort and fear associated with needles.
How the Shock Syringe Works:
- The shock syringe is slightly longer than a ballpoint pen and contains a micro shock tube with three sections: driver, driven, and drug holder.
- Pressurized nitrogen gas is applied to the driver section, which creates a microjet of liquid drug. The microjet travels at speeds nearly twice as fast as a commercial airplane.
- The drug is then delivered through the nozzle of the syringe, penetrating the skin rapidly and gently.
Design Considerations:
- The syringe's nozzle has an opening of 125 μm (approximately the width of a human hair), ensuring a balance between precision and speed.
- Continuous monitoring of pressure ensures safe and effective drug delivery with minimal skin damage.
Testing and Results:
- Lab tests were conducted on rats, injecting three types of drugs:
- Anaesthetics (Ketamine-Xylazine): Shock syringe produced similar results to needles in terms of effect onset and duration.
- Viscous drugs (e.g., Terbinafine): The shock syringe outperformed needles, delivering the drug more deeply into the skin layers.
- Insulin for diabetic rats: The shock syringe lowered blood sugar levels more effectively and sustained the effect for a longer period.
- The skin analysis revealed less damage and inflammation with the shock syringe compared to traditional needles.
Advantages:
- Painless drug delivery: Patients experience little to no discomfort.
- Reduced tissue damage: The shock syringe causes less skin trauma and inflammation.
- Faster healing: Wounds from the injection heal quicker compared to traditional needles.
- Better drug absorption: Especially for viscous drugs, the shock syringe delivers more efficient and deeper drug penetration.
Potential Applications:
- The shock syringe could revolutionize immunization drives, making vaccinations faster and more efficient.
- It could significantly reduce the risk of bloodborne diseases caused by needle-stick injuries.
- The device is designed to perform over 1,000 injections, ensuring cost-effectiveness and reliability with minimal nozzle replacements.
Future Prospects:
- While promising, the future of shock syringes in clinical use depends on:
- Further innovation for human use.
- Obtaining regulatory approval.
- Ensuring the device’s affordability and accessibility.
PM- Ayushman Bharat Health Infrastructure Mission (PM-ABHIM) Scheme

- 29 Dec 2024
In News:
- The Delhi High Court has ordered the signing of a Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) between the Union Ministry of Health and Family Welfare and the Delhi Government.
- This MoU will facilitate the implementation of the PM-Ayushman Bharat Health Infrastructure Mission (PM-ABHIM) in Delhi.
About PM-Ayushman Bharat Health Infrastructure Mission (PM-ABHIM):
- Scheme Type: Centrally Sponsored Scheme (CSS) with some Central Sector Components (CS).
- Total Outlay: Rs. 64,180 Crores for the period 2021-22 to 2025-26.
- Objective:
- To strengthen healthcare infrastructure across India, focusing on:
- Building capacities in health systems at primary, secondary, and tertiary levels.
- Preparing health systems to effectively respond to current and future pandemics/disasters.
- Key Focus Areas:
- Filling critical gaps in health infrastructure, surveillance, and health research in both urban and rural areas.
- Improving healthcare delivery across the entire continuum of care.
- Central Sector Components (CS) under the Scheme:
- 12 Central Institutions: To act as training and mentoring sites with 150-bedded Critical Care Hospital Blocks (CCBs).
- Strengthening NCDC: Boosting the National Centre for Disease Control (NCDC) and establishing 5 new regional NCDCs.
- Health Surveillance: Creation of 20 metropolitan health surveillance units and expansion of Integrated Health Information Portal across all States/UTs.
- Public Health Units: Operationalization of 17 new Public Health Units and strengthening 33 existing units at Points of Entry (Airports, Seaports, Land Crossings).
- Emergency Health Infrastructure: Establishment of 15 Health Emergency Operation Centres and 2 mobile hospitals.
- Research and Virology Institutes: Setting up a national institution for One Health, 4 new National Institutes for Virology, and 9 Biosafety Level III laboratories.
- Support for States/UTs under CSS Component:
- Health and Wellness Centres (HWCs):
- 17,788 rural HWCs: To be built in areas with populations of 5000 (plain) or 3000 (difficult terrain like hills, tribals, desert).
- 11,024 urban HWCs: Focus on slum and vulnerable areas with a population of 15,000-20,000.
- Block Public Health Units (BPHUs): Establishment of 3,382 BPHUs at the block level to strengthen healthcare accessibility.
- Integrated Public Health Labs (IPHLs): Setting up 730 IPHLs across districts for better health monitoring.
- Critical Care Hospital Blocks (CCBs): Establishment of 602 CCBs in districts with populations exceeding 5 lakh and referral linkages in other districts.
- Overall Goal: PM-ABHIM aims to significantly enhance healthcare infrastructure in India, making healthcare more accessible and effective, especially in rural and underdeveloped areas.
UN Approves New AU Force to Combat Al-Shabaab in Somalia
- 29 Dec 2024
In News:
- On January 19, 2024, the UN Security Council approved a new African Union (AU) force in Somalia to counter the Al-Shabaab terrorist group.
- The resolution was supported by 14 of 15 members, with the US abstaining due to concerns about funding.
- The new force will replace the African Union Transition Mission in Somalia (ATMIS) after its mandate ends on December 31, 2024.
New Mission - AUSSOM:
- The new mission is named African Union Support and Stabilization Mission in Somalia (AUSSOM).
- AUSSOM will continue supporting Somali forces in stabilizing the nation and combating terrorism.
- The mission's objective is to enhance security and stability in Somalia, addressing the challenges posed by Al-Shabaab and ISIL.
Mandate and Operations:
- AUSSOM allows for the deployment of up to 12,626 personnel, including 1,040 police officers, until June 2025.
- The force will focus on counterterrorism, maintaining security, and assisting the Somali government in stabilizing the country.
Financing:
- A hybrid funding approach will be used:
- 75% of the mission’s costs will be covered by the UN, and 25% will come from African Union and partner countries.
- The US raised concerns about the UN's disproportionate funding of the mission, which led to its abstention from voting.
Contributing Countries:
- Egypt has announced its participation in the new force.
- Burundi and Ethiopia will not be contributing troops to AUSSOM.
- Ethiopia has its own ongoing disputes with Somalia, particularly regarding its maritime deal with the breakaway Somaliland region.
Background on Somalia's Challenges:
- Somalia has faced decades of civil war, an insurgency by Al-Shabaab, and recurring climate disasters.
- The country is one of the poorest in the world, and its internal conflicts are exacerbated by clannism, which has fragmented its political and social structure.
Historical Context of Peace Missions in Somalia:
- Previous UN peacekeeping missions in Somalia (1992-1995) faced significant failures, notably the Battle of Mogadishu and the failure to prevent the 1993 massacre.
- The rise of Al-Shabaab in the mid-2000s has further escalated the conflict, and the mission of AUSSOM aims to address these continuing threats.
The Role of Clannism:
- Clannism has hindered the establishment of a unified government in Somalia, with clan rivalries leading to a lack of national cohesion.
- Clannism refers to the prevalence of clan-centric politics, where allegiance to clan and sub-clan interests often takes precedence over national cohesion. In Somalia, the major clans are Darod, Hawiye, Dir, and Rahanweyn.
Importance of AUSSOM:
- AUSSOM represents a strategic shift in the international approach to stabilizing Somalia, relying more on African-led initiatives for peace and security in the region.
Global Peacekeeping Operations:
- The UN peacekeeping mission has been active globally, with over 1 million personnel deployed across 70+ operations.
- Success stories like Sierra Leone (1999-2005) and Liberia (2003-2018) demonstrate the potential impact of well-executed peace missions, but past failures like in Somalia (1992-1995) and Rwanda (1994) underline the challenges faced.
India’s Contribution:
- India has contributed significantly to UN peacekeeping missions, deploying over 253,000 personnel in 49 operations since 1948.
- India’s contributions to missions in Somalia, Rwanda, Sierra Leone, and Sudan reflect its active role in global peacekeeping efforts.
ASI Decodes Sanskrit Inscription Found in Pakistan-Occupied Kashmir (PoK)

- 29 Dec 2024
In News:
An ancient Sanskrit inscription found in Gilgit (PoK) was decoded by the Archaeological Survey of India (ASI).
About the Inscription:
- Location:
- Gilgit (PoK): Written in Brahmi script, dating back to 4th century CE.
- Peshawar (Pakistan): Written in Sharada script, dating to 10th century CE.
- Details of Gilgit Inscription:
- Mentions Pushpasingha, who installed a Mahesvaralinga for the merit of his guru.
- Written in Brahmi script, which was prevalent during the 4th century CE.
- Religious Context: Indicates significant religious connection, particularly with Shaivism.
- Details of Peshawar Inscription:
- Fragmentary: Engraved on a slab.
- Written in Sharada characters (10th century CE).
- Mentions Buddhist Dharini (chants), particularly referring to Da (Dha) rini in line six.
- The inscription is partially damaged, and further details are unclear.
- Earlier Discoveries:
- This is not the first Sanskrit inscription decoded from Pakistan. In the past, Sanskrit inscriptions have been found in various parts of Pakistan.
- Swat Valley: Known for numerous Buddhist rock inscriptions in Sanskrit using Nagari script, which were part of the Gupta Empire (circa 240–550 CE).
- Religious and Cultural Implications:
- The Gilgit inscription provides evidence of Shaivism as a prominent religious practice in the region during the 4th century CE.
- The Peshawar inscription suggests Buddhist influences, particularly related to Buddhist chants and rituals.
- Swat Valley's Role: The inscriptions found here highlight its importance as a center of Buddhist learning and cultural exchange.
China approves construction of World’s Largest Hydropower Dam on the Brahmaputra River

- 28 Dec 2024
In News:
China approved the construction of the world's largest dam, stated to be the planet's biggest infra project, on the Brahmaputra river in Tibet close to the Indian border, raising concerns in India and Bangladesh.
Key highlights:
Overview of the Project:
- Location: Lower reaches of the Yarlung Zangbo River (Tibetan name for Brahmaputra), where the river makes a U-turn in the Himalayan region before flowing into Arunachal Pradesh, India.
- Purpose:
- To support China’s carbon neutrality goals.
- To boost industrial growth and create jobs in Tibet.
- Expected to generate 300 billion kWh of electricity annually, over three times the capacity of the Three Gorges Dam in central China.
Significance:
- Scale: The dam is poised to be the world’s largest hydropower project, surpassing the Three Gorges Dam, and becoming the biggest infrastructure project globally, with an estimated cost of USD 137 billion.
- Engineering Challenges: The site is located in a seismic zone on the Tibetan plateau, prone to earthquakes, making construction and operational stability a major engineering challenge.
Concerns:
- Environmental Impact:
- Potential disruption to the local ecosystem and biodiversity.
- Risk of altering the river’s flow and course, which could impact agriculture and water resources downstream, particularly in India and Bangladesh.
- Geopolitical Risks:
- Water control: India and Bangladesh are concerned about China’s ability to control the water flow, with fears of China manipulating the flow to release excess water during conflicts, causing potential flooding in border areas.
- The project could also disrupt the hydrological cycle, affecting the region’s water availability, especially in Assam and Bangladesh.
Background:
- The Brahmaputra River is a trans-boundary river, flowing through China, India, and Bangladesh. Known by different names in these countries, it plays a vital role in the livelihoods of millions of people.
- China has already initiated hydropower generation on the upper reaches of the Yarlung Zangbo, with plans for additional projects upstream.
India-China Cooperation:
- China and India have an Expert Level Mechanism (ELM) in place since 2006 to manage trans-boundary river issues, under which China shares hydrological data with India, especially during the flood season.
- India is also constructing its own hydropower projects on the Brahmaputra in Arunachal Pradesh.
Potential Outcomes:
- Energy Generation: The dam could significantly contribute to China’s energy needs, providing a substantial amount of renewable energy.
- Regional Tensions: The dam’s construction may escalate tensions between China, India, and Bangladesh due to the control over water resources and environmental impact concerns.
Parker Solar Probe’s Closest-Ever Approach to the Sun

- 28 Dec 2024
In News:
NASA scientists announced that the Parker Solar Probe survived the closest-ever approach to the Sun. The craft was operating normally after it passed just 6.1 million km from the solar surface.
About the Parker Solar Probe:
- Launched: August 12, 2018, as part of NASA’s Living With a Star program.
- Named After: Eugene Newman Parker, a solar astrophysicist, marking the first NASA mission named after a living researcher.
- Mission Objectives:
- To study the Sun’s corona and the solar wind, investigating why the corona is hotter than the Sun’s surface.
- To explore the origins of solar winds and high-energy particles that impact space weather.
- To understand the structure and dynamics of plasma and magnetic fields around the Sun.
- To examine the mechanisms behind the acceleration and transportation of energetic particles.
Technological Feats:
- Heat Shield: Equipped with a 4.5-inch carbon-composite shield that withstands temperatures up to 1,377°C (2,500°F) while keeping the instruments cool at about 29.4°C (85°F).
- Speed: Travels at a speed of 692,000 km/h (430,000 mph), making it the fastest human-made object.
- Venus Flybys: Uses gravitational assists from Venus to gradually reduce its orbit and get closer to the Sun.
Historic Milestone:
- Closest Approach: On December 24, 2024, Parker Solar Probe reached a historic distance of 6.1 million km from the Sun's surface, the closest any human-made object has ever been.
- Comparison: If the Earth and Sun were 1 meter apart, Parker Solar Probe would be just 4 cm from the Sun.
- Temperature: At its closest, it endured temperatures up to 1,377°C.
Significance of the Mission:
- Scientific Contributions:
- Solar Wind: Helps scientists understand the origins of solar winds, which affect space weather and Earth’s technological systems.
- Corona Heating: Investigates why the Sun's corona is much hotter than its surface (a long-standing astrophysical mystery).
- Space Weather: Provides critical data for predicting space weather events that can impact satellites, communication systems, and power grids on Earth.
- Practical Implications:
- Improves understanding of space weather, potentially aiding in the protection of Earth’s infrastructure from solar storms.
- Technological and Engineering Marvel:
- Demonstrates advanced spacecraft technology that can withstand extreme conditions close to the Sun.
Recent Developments:
- Data Collection: As the probe passed through the Sun’s outer atmosphere (the corona), it collected valuable data expected to answer fundamental questions about solar behavior.
- Communication: Despite the extreme proximity to the Sun, the probe sent back a signal on December 26, confirming its status.
Key Dates:
- Launch: August 12, 2018.
- Closest Approach: December 24, 2024.
- Data Expected: Detailed telemetry data on January 1, 2025.
Exercise SURYA KIRAN

- 28 Dec 2024
In News:
Indian Army Contingent Departs for 18th Edition of Exercise SURYA KIRAN (India-Nepal Joint Military Exercise).
Key Highlights:
- Event Overview:
- Name: 18th Edition of Battalion-Level Joint Military Exercise SURYA KIRAN.
- Dates: 31st December 2024 to 13th January 2025.
- Location: Saljhandi, Nepal.
- Participants: Indian Army (334 personnel, led by a Battalion from the 11th Gorkha Rifles) and Nepal Army (Srijung Battalion).
- Objective of Exercise:
- Enhance interoperability in jungle warfare, counter-terrorism operations in mountainous terrain, and Humanitarian Assistance and Disaster Relief (HADR) under the UN Charter.
- Focus on operational preparedness, aviation training, medical aspects, and environmental conservation.
- Key Features:
- Training Focus: Improving combat skills and coordination to operate together in challenging situations.
- Exchange of Ideas: Soldiers from both nations will share best practices, enhance mutual understanding of operational procedures.
- Strengthening Bilateral Relations: Reinforces strong bonds of friendship, cultural linkages, and defense cooperation between India and Nepal.
- Significance:
- Historical Context: Exercise held alternately in India and Nepal since 2011.
- Enhances Combat Readiness: Prepares both armies to address shared security challenges and improve operational capabilities.
- Diplomatic Engagement: Fosters a productive professional environment between India and Nepal.
- Recent Developments:
- The exercise follows visits by General Upendra Dwivedi (Indian Army Chief) to Nepal and General Ashok Raj Sigdel (Nepali Army Chief) to India, strengthening military ties.
- Previous Editions:
- 17th Edition: Conducted in Pithoragarh, Uttarakhand (24th Nov - 7th Dec 2023).
Neolithic Age Grooves Discovery Near Boothapandi

- 28 Dec 2024
In News:
- Archaeological Survey of India (ASI) discovered rock grooves created during the Neolithic age near Boothapandi village, Kanniyakumari district.
- The discovery was made by K. Hari Gopalakrishnan (Archaeological Officer, Tirunelveli and Kanniyakumari districts) and M. Faisal (Sembavalam Research Centre).
Key Highlights:
- Groove Characteristics:
- The grooves are approximately 4,000 years old, formed by Neolithic people for tool sharpening.
- Tools used for activities like hunting, ploughing, and digging were sharpened here.
- The grooves resulted from wear and tear of tools that had broken or worn out during use.
- Groove Dimensions:
- Largest groove: 15 cm in length, 4 cm in width.
- Smallest groove: 8 cm in length, 3 cm in width.
- Similar Discoveries:
- Similar grooves have been found in other parts of Tamil Nadu, including Krishnagiri, Tiruvannamalai, and Villupuram.
- Significance:
- The grooves provide evidence of Neolithic human habitation in the region.
- Ongoing excavations are expected to uncover more about Neolithic culture in the area.The Hindu
Lighthouse Tourism in India

- 27 Dec 2024
In News:
Lighthouse tourism in India is rapidly emerging as an exciting and profitable segment of the country's travel and tourism industry. India's coastline, stretching over 7,500 kilometers, is home to 204 lighthouses, many of which are being transformed into vibrant tourist destinations, celebrating both India's rich maritime history and its natural beauty.
Key Highlights:
- Historical and Scenic Appeal: Lighthouses in India are often located in breathtaking coastal or island locations, offering panoramic sea views and access to surrounding natural beauty. Some of these structures are centuries old and are situated near significant cultural landmarks or UNESCO World Heritage Sites, adding cultural depth to the visitor experience.
- Economic Growth: As part of the broader Maritime India Vision (MIV) 2030 and Amrit Kaal Vision 2047, the Government of India is keen to transform these historic lighthouses into hubs of economic activity. By developing infrastructure, creating new tourism-related jobs, and fostering local entrepreneurship, lighthouse tourism aims to benefit coastal communities and boost India's tourism economy. As of 2023-24, 75 lighthouses across 10 states have been equipped with modern amenities, attracting 16 lakh visitors—a 400% increase from previous years.
- Government Initiatives:
- Lighthouse Festivals: The annual Indian Lighthouse Festival, inaugurated in 2023, serves as a key event to promote lighthouse tourism and cultural heritage.
- The 1st Indian Lighthouse Festival, “Bharatiya Prakash Stambh Utsav”, was inaugurated on 23rd September, 2023 by the Union Minister of Ports, Shipping & Waterways, Shri Sarbananda Sonowal and Goa Chief Minister, Shri Pramod Sawant at the historic Fort Aguada in Goa.
- The 2nd Indian Lighthouse Festival was held in Odisha. Union Minister of Ports, Shipping & Waterways, Shri Sarbananda Sonowal, was also joined by Odisha Chief Minister, Mohan Charan Majhi. Shri Sonowal dedicated two new lighthouses at Chaumuck (Balasore) and Dhamra (Bhadrak) and emphasized empowering coastal communities to preserve and promote lighthouses as part of India’s rich maritime heritage.
- Sagarmala Programme: This government initiative integrates infrastructure development with sustainable practices, ensuring that the growth of lighthouse tourism benefits local communities while preserving the environment.
- Tourism Infrastructure: The government has invested ?60 crore in enhancing these sites, providing facilities like museums, parks, amphitheaters, and more to enrich the visitor experience.
- Lighthouse Festivals: The annual Indian Lighthouse Festival, inaugurated in 2023, serves as a key event to promote lighthouse tourism and cultural heritage.
- Sustainable Development: The Indian government places a strong emphasis on eco-friendly tourism. This includes integrating lighthouses into broader coastal circuits and launching digital awareness campaigns to attract domestic and international tourists.
- Community Empowerment and Employment: Lighthouse tourism has already created direct and indirect employment, from hospitality to transportation, local handicrafts, and artisan work, with more than 500 jobs being generated. Local communities are being trained to offer skills in hospitality and tourism services.
Future Plans:
- Skill Development: Programs are being introduced to equip local people with the necessary skills to cater to the tourism industry.
- Sustainable Practices: Eco-friendly practices will continue to be emphasized to protect coastal ecosystems.
- Integration with Coastal Circuits: Lighthouses will become key points of interest in broader coastal tourism itineraries, further enhancing their appeal to tourists.
Household Consumption Expenditure Survey: 2023-24
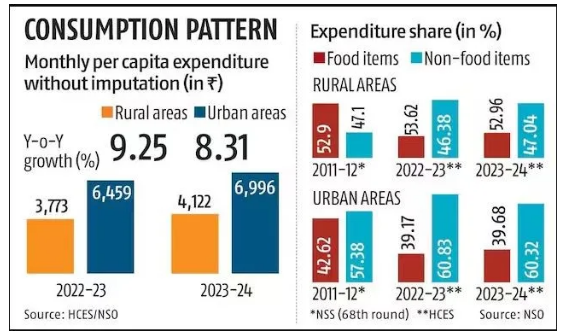
- 27 Dec 2024
In News:
The latest Household Consumption Expenditure Survey (HCES) for 2023-24 reveals notable trends in consumption patterns in rural and urban India, reflecting economic shifts post-pandemic.
Key Highlights:
- Food Spending Increase: The share of food expenditure in household budgets has increased both in rural and urban areas, likely due to rising food prices.
- Rural households allocated 47.04% of their expenditure to food in 2023-24, up from 46.38% in 2022-23.
- Urban households spent 39.68% of their budgets on food, slightly up from 39.17% last year.
- Narrowing Urban-Rural Gap: The gap in Monthly Per Capita Consumption Expenditure (MPCE) between rural and urban households has steadily reduced over the past decade.
- In 2023-24, rural consumption spending was 69.7% of urban consumption, an improvement from 71.2% in 2022-23 and 83.9% in 2011-12.
- Increased Rural Spending: Rural India has seen significant increases in spending. The average monthly spending per person in rural areas rose by 9.3% to Rs 4,122 in 2023-24, surpassing the 8.3% rise to Rs 6,996 in urban areas.
- This suggests a growing momentum in rural consumption, which has outpaced urban consumption growth in the last year.
- Spending Trends Across Income Groups: While the top 5% of both rural and urban populations saw a decrease in their consumption spending, every other income group, including the bottom 5%, registered an increase in spending.
- The bottom 20% in both rural and urban areas saw the highest growth in expenditure, signaling rising economic activity among lower-income groups.
- Non-Food Expenditure Dominates: Non-food items make up a larger share of household spending, particularly in urban areas, where they account for 60.32% of total expenditure compared to 52.96% in rural areas.
- In rural India, major non-food expenses include medical, conveyance, and clothing, while urban households allocate more to entertainment, education, and miscellaneous goods.
- Regional Consumption Patterns: Consumption expenditure varied significantly across states, with western and northern states like Maharashtra, Punjab, and Tamil Nadu spending more than the national average.
- In contrast, eastern and central states, including West Bengal, Bihar, and Odisha, spent less. Sikkim reported the highest per capita expenditure in both rural (Rs 9,377) and urban (Rs 13,927) areas, while Chhattisgarh recorded the lowest.
- Declining Consumption Inequality: The Gini coefficient, which measures consumption inequality, has declined in both rural and urban areas.
- This reflects reduced disparity in spending, indicating a trend toward more equitable economic growth across regions.
- Food Expenditure Trends: Food categories like beverages, processed foods, and cereals continued to see rising shares in total expenditure. The rise in spending on food items was particularly notable in rural areas for eggs, fish, and meat.
Operation Green Scheme

- 27 Dec 2024
In News:
The government’s flagship Operation Greens scheme, designed to stabilise crop prices and benefit farmers, has spent just 34 per cent of its allocated budget for 2024-25, according to a parliamentary report, even as onion farmers in Maharashtra reel from massive losses and potato shortages grip eastern states.
Key Highlights:
Overview:
- Launched: November 2018 under the Pradhan Mantri Kisan SAMPADA Yojana.
- Objective: Stabilize prices and improve farmers' income by enhancing the production and marketing of perishable crops, initially focusing on Tomato, Onion, and Potato (TOP).
- Expanded Scope (2021): Includes 22 perishable crops like mango, banana, ginger, apple, and shrimp.
- Implemented by: Ministry of Food Processing Industries (MoFPI).
- Funding: Managed by the National Agricultural Cooperative Marketing Federation of India (NAFED).
Key Aims:
- Reduce price volatility in agricultural markets.
- Minimize post-harvest losses.
- Strengthen farm-to-market linkages.
- Enhance farmers’ earnings by stabilizing market prices.
- Promote value addition and food processing.
Scheme Components:
- Short-term Interventions:
- Subsidies on transportation (50%) and storage (50%) to protect farmers from distress sales.
- Price stabilization during periods of surplus or shortage.
- Long-term Interventions:
- Development of farm-gate infrastructure like cold storage and processing facilities.
- Strengthening production clusters and Farmer Producer Organizations (FPOs).
- Building efficient agri-logistics systems.
- Promoting food processing and value addition capacities.
Key Features:
- 50% subsidy on transportation and storage costs for eligible crops.
- Projects eligible for 50% subsidy (up to ?50 crore per project), and for FPOs, a 70% subsidy.
- Demand-driven funding based on applications, with no fixed crop or state-wise allocation.
Key Findings from Parliamentary Standing Committee (PSC) Report (2024):
- Underutilisation of Budget: Only 34% (?59.44 crore) of the allocated ?173.40 crore for 2024-25 spent by October 2024, leaving 65.73% unspent.
- Slow Implementation: Out of 10 targeted projects, only 3 were completed by October 2024.
- Limited Impact on Price Stabilization:
- Onion prices fell by nearly 50% in Maharashtra, despite the scheme's intent to stabilize prices.
- Potato shortages in states like Odisha and Jharkhand due to weather-induced production dips in West Bengal.
- Inconsistent Policies: Export bans and fluctuating export duties caused frustration among onion farmers, undermining the scheme’s effectiveness in ensuring fair prices.
Impact on Farmers:
- Price Stabilization: Despite the scheme’s aims, price fluctuations continue to affect farmers, especially in Maharashtra with the onion price crash.
- Post-Harvest Losses: The scheme aims to reduce wastage by building infrastructure like cold storage, but challenges remain in implementation.
- Market Linkages: Attempts to connect farmers and FPOs with retail markets have not yet yielded significant results.
Operational Challenges:
- The scheme faces challenges in fulfilling its dual mandate of ensuring fair prices for farmers while keeping consumer prices affordable.
- The slow utilization of funds and incomplete infrastructure projects raise concerns about the effectiveness of the program.
- Inconsistent policy decisions, like the export ban and imposition of export duties, have contributed to farmer discontent.
Dr. Pushpak Bhattacharyya Committee

- 27 Dec 2024
In News:
- The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) has set up an eight-member committee to create a framework for the responsible and ethical use of Artificial Intelligence (AI) in the financial sector.
- The committee is chaired by Dr. Pushpak Bhattacharyya, Professor in the Department of Computer Science and Engineering at IIT Bombay.
Key Highlights:
Committee's Objective:
- The primary goal is to develop a Framework for Responsible and Ethical Enablement of AI (FREE-AI) in the financial sector.
- It will guide the ethical adoption of AI in financial services to enhance operational efficiency, decision-making, and risk management.
Scope of the Committee's Work:
- Assess the current global and domestic adoption of AI in financial services.
- Identify potential risks and challenges associated with the integration of AI in the sector.
- Recommend a framework for evaluating, mitigating, and monitoring AI-related risks.
- Propose compliance requirements for various financial entities (e.g., banks, NBFCs, fintech firms).
- Suggest a governance framework for ethical AI usage.
Key Benefits of AI in Financial Services:
- Operational Efficiency: AI can automate repetitive tasks, process large datasets, and enhance accuracy (e.g., loan application processing).
- Enhanced Decision-Making: Predictive analytics in AI help forecast market trends, aiding in better financial decision-making (e.g., algorithmic trading).
- Customer Relationship Management: AI-powered chatbots and virtual assistants enhance customer interaction, offering 24/7 support.
- Improved Risk Management: AI enables proactive fraud detection, improving security and preventing financial losses.
Concerns Associated with AI in Finance:
- Embedded Bias: AI models can replicate biases present in training data, leading to discriminatory outcomes and financial exclusion.
- Data Privacy and Security: The use of AI poses risks to personal data security, with potential violations of privacy regulations.
- Operational Challenges: AI systems may exhibit inconsistent responses, leading to challenges in trust and effectiveness.
- Cybersecurity Risks: Increased use of AI can heighten vulnerability to cyber-attacks and exploitation.
RBI's Role & Governance:
- The RBI aims to ensure that AI adoption in the financial sector is ethical, transparent, and aligned with global best practices.
- The committee's recommendations will influence policies to prevent misuse and safeguard consumer interests.
Rupee and Real Effective Exchange Rate (REER)

- 27 Dec 2024
In News:
The real effective exchange rate (REER) index of the rupee touched a record 108.14 in November, strengthening by 4.5 per cent during this calendar year, according to the latest Reserve Bank of India (RBI) data.
Key Highlights:
- Record REER Index:
- The Real Effective Exchange Rate (REER) of the rupee reached an all-time high of 108.14 in November 2024.
- This marks a 4.5% appreciation in REER during the calendar year 2024, according to RBI data.
- What is REER?
- REER is a weighted average of a country’s currency value against the currencies of its major trading partners, adjusted for inflation differentials.
- It considers 40 currencies accounting for about 88% of India's trade.
- REER Calculation:
- Nominal Exchange Rates: The exchange rate between the rupee and each partner's currency.
- Inflation Differentials: Adjusts for inflation differences between India and its trading partners.
- Trade Weights: Based on the trade share with each partner.
- Recent Trends in REER:
- In 2023, REER dropped from 105.32 in January to 99.03 in April.
- It has since been on an appreciating trend, reaching 107.20 in October and 108.14 in November 2024.
- Dollar Strengthening Impact:
- Despite the rupee weakening against the US dollar (from 83.67 to 85.19 between September and December 2024), it has appreciated against the euro, British pound, and Japanese yen.
- The dollar's strengthening was fueled by global economic factors, including inflation expectations in the US and high bond yields, which led to capital outflows from other countries, including India.
- Impact on Exports and Imports:
- Overvaluation: A REER above 100 signals overvaluation, which can harm export competitiveness (exports become costlier) while making imports cheaper.
- Undervaluation: A REER below 100 indicates a currency is undervalued, boosting exports but increasing the cost of imports.
- India's Inflation and REER:
- India's higher inflation relative to trading partners is a key factor behind the rupee’s rising REER, despite its depreciation against major currencies.
- This suggests the rupee is overvalued, which could explain why the RBI may allow the rupee to depreciate further against the dollar.
- Global Context:
- The strengthening of the US dollar, influenced by factors such as tariff policies under the Trump administration and tighter US monetary policies, plays a significant role in the depreciation of the rupee against the dollar.
- This dynamic affects India's trade balance, with potential consequences for export growth.
- Implications for India’s Economy:
- Overvalued currency (as indicated by REER above 100) can lead to a trade deficit, as imports become cheaper and exports less competitive.
- A weaker rupee, particularly against the dollar, could boost Indian exports but raise the cost of imports.
Strengthening Fisheries Extension Services

- 26 Dec 2024
In News:
India possesses diverse fisheries resources that provide livelihood opportunities to approximately three crore fishers and fish farmers. The country has witnessed an 83% increase in the national fish production since 2013-14, that stands at a record 175 lakh tons in 2022-23.
Importance of Fisheries Extension Services:
- Livelihood Support: Fisheries provide livelihoods to over 3 crore fishers and fish farmers in India. The sector's growth is crucial for enhancing sustainable practices and ensuring long-term productivity.
- Growth in Fish Production: India’s fish production has seen an 83% increase since 2013-14, reaching 175 lakh tons in 2022-23, with 75% of production coming from inland fisheries. India is the second-largest fish and aquaculture producer globally.
- Role of Extension Services: Extension services bridge the gap between scientific advancements and fishers, offering guidance on:
- Species lifecycle management
- Water quality management
- Disease control
- Sustainable rearing technologies and business models.
Government Initiatives to Strengthen Fisheries Extension:
- Matsya Seva Kendras (MSKs):
- Launched under PMMSY (Pradhan Mantri Matsya Sampada Yojana) in 2020, MSKs are one-stop centers providing comprehensive extension services.
- Support to Fish Farmers: MSKs offer:
- Disease testing, water, and soil analysis.
- Training on sustainable aquaculture practices.
- Technology infusion in seed/feed management.
- Focus on Inclusivity: Government assistance (up to 60%) is available for women and marginalized communities to set up MSKs.
- Examples:
- Thrissur, Kerala: Equipped with labs for water and microbial analysis.
- Maharashtra (Nasik and Sangli): Capacity-building efforts on seed/feed inputs.
- Collaborations: MSKs mobilize start-ups, cooperatives, and Fish Farmer Producer Organizations (FFPOs) to share best practices, including regenerative and conservation management in the face of climate change.
- Sagar Mitras:
- Role: Deployed in coastal states and union territories, Sagar Mitras act as a vital interface between the government and marine fishers.
- Functions:
- Collection and dissemination of daily marine catch data, price fluctuations, and market insights.
- Dissemination of important information: weather forecasts, fishing zones, local regulations, and hygienic fish handling.
- Provide support on disaster preparedness and natural calamities.
Enhancing Extension Services through Digital Platforms:
- AquaBazaar: A virtual learning platform initiated by the National Fisheries Development Board to provide expert guidance on:
- Seed production and breeding of commercially important fish species.
- Practical demonstrations to improve fishers' knowledge.
- Digital Outreach: Expanding such platforms will improve access to resources for fishers, especially in rural and remote areas.
Institutional Convergence and Capacity Building:
- Krishi Vigyan Kendras (KVKs): Fisheries extension services should be integrated with the over 700 Krishi Vigyan Kendras and state-level agricultural extension services for effective outreach.
- Formalizing the Sector: The World Bank-assisted project aims to create work-based digital identities for fishers and fish farmers, enhancing their access to extension services, training, and awareness programs.
Challenges in Fisheries Extension Services:
- Fragmented Initiatives: Multiple government schemes and programs lack institutional convergence, leading to inefficiencies in reaching the grassroots level.
- Digital Divide: Many rural and coastal areas face challenges in terms of digital literacy and internet connectivity, limiting the effectiveness of online platforms.
- Impact of Climate Change: Unpredictable weather patterns and resource depletion due to overfishing demand adaptive strategies and the promotion of climate-resilient practices.
Conclusion and Way Forward:
- Institutional Convergence: Combining existing extension machinery like Krishi Vigyan Kendras with fisheries extension services to leverage established networks and knowledge.
- Expand Digital Outreach: Platforms like AquaBazaar should be expanded to ensure wider access to expert knowledge, training, and best practices.
- Private Sector Collaboration: Encouraging public-private partnerships can enhance technology dissemination, capacity building, and resource mobilization in the fisheries sector.
- Focus on Sustainability: Developing climate-resilient and sustainable fisheries practices will be essential to address challenges posed by environmental changes and overfishing.
Private Aviation and Emissions

- 26 Dec 2024
In News:
Private aviation is releasing more than its ‘fair share’ of emissions.
Key Highlights:
- Aviation Sector's Global Emissions:
- The aviation sector contributed 2% of global CO2 emissions in 2022, around 800 Mt CO2 (International Energy Agency).
- If considered as a nation, aviation would rank among the top 10 emitters worldwide.
- Emissions from aviation have grown faster than other sectors like rail, road, or shipping in recent decades.
- Private Aviation and Its Impact:
- Private jets emit 5 to 14 times more CO2 per passenger than commercial flights and 50 times more than trains.
- Emissions from private aviation increased by 46% between 2019 and 2023.
- Each private flight contributes 3.6 tonnes of CO2 on average, intensifying global warming.
- Private aviation is responsible for significant nitrogen oxide (NOx) emissions and the creation of vapor trails, which further amplify environmental damage.
Trends in Private Aviation Growth:
- Global Trends:
- The number of private jets increased from 25,993 in December 2023 to 26,454 in February 2024.
- In the U.S., 69% of private aviation activity is concentrated.
- 8,500 more jets are expected to be delivered in the next 10 years globally.
- Private Aviation in India:
- 112 private planes were registered in India as of March 2024, placing it among the top 20 countries for private aircraft ownership.
- India's private aviation sector is expanding, driven by the growing billionaire and millionaire population.
- Private aircraft ownership in India stands at 1 per 1 lakh population, which is low compared to countries like Malta (46.51 per lakh) and the U.S. (5.45 per lakh).
Emission Reduction Efforts and Solutions:
- Sustainable Aviation Fuels (SAFs):
- SAFs are bio-based or waste-derived fuels that can reduce carbon emissions by up to 80% compared to conventional jet fuels.
- Airlines like SpiceJet (2018) and AirAsia (2023) have tested SAFs, but large-scale adoption is hindered by high costs and limited production.
- India aims to leverage its ethanol production chain, with potential to meet 15-20% of aviation fuel demand by 2050 if only surplus sugar is used.
- Hydrogen and Electric Aviation:
- Hydrogen offers a higher energy density than kerosene and emits only water vapor, making it a clean fuel alternative. However, hydrogen faces challenges with storage, infrastructure, and aircraft redesign.
- Battery-electric propulsion offers zero emissions but is currently limited by battery weight, energy density, and charging infrastructure.
India’s Policy and Initiatives:
- Government Initiatives:
- UDAN Scheme (Ude Desh ka Aam Nagrik) aims to enhance rural connectivity.
- NABH (Nextgen Airports for Bharat Nirman) seeks to increase airport capacity by five times.
- Sustainability Efforts:
- Indian airlines have tested SAFs, such as a 25% jatropha oil blend by SpiceJet in 2018.
- Ethanol for aviation fuel: India plans to use surplus sugar for ethanol, potentially fulfilling 15-20% of aviation fuel needs by 2050.
- Challenges to Decarbonisation:
- SAFs are costly and limited in availability.
- Hydrogen requires extensive infrastructure and aircraft redesign.
- Battery-electric solutions are currently unsuitable for long-haul flights due to energy limitations.
Ocean Anoxic Event 1a (OAE 1a)
- 26 Dec 2024
In News:
A recent study published in Science Advances has offered fresh insights into the timing and duration of the Ocean Anoxic Event 1a (OAE 1a).
What is OAE 1a?
- Definition: A period during the Cretaceous Period (~119.5 million years ago) when Earth's oceans became oxygen-depleted (anoxic), causing significant disruption in marine ecosystems.
- Cause: Triggered by massive volcanic eruptions that released large amounts of CO?, leading to global warming and depletion of oxygen in oceans. This caused the formation of anoxic marine basins.
- Impact: The depletion of oxygen led to the extinction of marine species, especially plankton, and the formation of black shales (organic carbon-rich layers).
Anoxic Marine Basins:
- Characteristics: These are bodies of water with extremely low or absent oxygen, allowing certain microbes and fungi to thrive, while most aerobic organisms perish.
- Significance: Anoxic basins contribute to carbon sequestration by slowing down the decay of organic material, helping in the reduction of atmospheric CO? levels. Examples include the Black Sea, Cariaco Basin, and Orca Basin.
Recent Study Findings (Published in Science Advances):
- Timing: OAE 1a began approximately 119.5 million years ago and lasted for about 1.1 million years, with a long recovery period for ocean ecosystems.
- Methodology: The study used isotopic analysis of volcanic tuffs from Japan's Hokkaido Island to pinpoint the timing of the event.
- Volcanic Eruptions: The study confirmed that volcanic eruptions, particularly from the Ontong Java Nui complex, released CO?, triggering oceanic oxygen depletion.
- Relevance to Modern Climate Change: The study draws parallels between past volcanic CO? emissions and current human-induced warming, warning that rapid modern warming could cause similar disruptions in marine ecosystems and potentially lead to a Holocene extinction.
Holocene Extinction:
- Definition: The ongoing Sixth Mass Extinction, primarily driven by human activities like overexploitation, habitat loss, pollution, climate change, and invasive species.
- Impact: Current extinction rates are 1,000-10,000 times higher than natural rates, with severe consequences for biodiversity and ecosystem services.
Key Mass Extinction Events:
- Permian Extinction (~250 million years ago): Linked to volcanic activity, global warming, and ocean anoxia, leading to the extinction of over 95% of species.
- Cretaceous Extinction (66 million years ago): Caused by an asteroid impact, exacerbated by volcanic eruptions, leading to the extinction of non-avian dinosaurs.
- Holocene Extinction: Caused by human activities, with long-term implications for biodiversity and ecosystem services.
Efforts to Mitigate Extinction:
- Climate Action: Limiting global warming to 1.5°C as per the Paris Agreement.
- Biodiversity Conservation: The 30X30 Initiative, aiming to conserve 30% of lands and oceans globally by 2030.
- Sustainable Practices: Encouraging sustainable resource management to reduce habitat destruction, pollution, and overexploitation.
Viksit Panchayat Karmayogi Initiative

- 26 Dec 2024
In News:
On Good Governance Day, commemorating the 100th birth anniversary of former Prime Minister Atal Bihari Vajpayee, Dr. Jitendra Singh, the Union Minister of State for various departments, launched the ‘Viksit Panchayat Karmayogi’ initiative. This initiative is part of the broader ‘Prashasan Gaon Ki Aur’ campaign, which aims to empower Panchayati Raj Institutions (PRIs) at the grassroots level by enhancing the capacity and competence of elected representatives and officials.
Objective of the ‘Viksit Panchayat Karmayogi’ Initiative
The initiative seeks to strengthen PRIs by providing innovative tools and frameworks for capacity building and participatory governance. It will focus on equipping local leaders and officials with the necessary knowledge and tools to make effective decisions and implement sustainable development initiatives. Piloted in Odisha, Assam, Gujarat, and Andhra Pradesh, it uses e-learning platforms, AI-powered chatbots, and mobile apps to address knowledge gaps and improve service delivery at the local level. This program aligns with the government's mission to decentralize governance and promote citizen-centric and equitable development across rural India.
Other Key Initiatives Launched on Good Governance Day
- iGOT Karmayogi Platform Dashboard: A new dashboard on the iGOT Karmayogi platform, which empowers ministries, departments, and state administrators to monitor progress in capacity-building efforts. The enhanced dashboard includes customizable views, robust data filtering tools, and insights to optimize decision-making, marking the introduction of the 1600th e-learning course. This development is part of the Mission Karmayogi initiative to strengthen the civil service through continuous learning.
- CPGRAMS Annual Report 2024: The CPGRAMS Annual Report provided a review of the Centralized Public Grievance Redress and Monitoring System (CPGRAMS). This platform has been instrumental in resolving over 25 lakh grievances annually, leveraging advanced technologies and multilingual support. The report also highlighted the implementation of the Grievance Redressal Assessment and Index (GRAI), which has improved transparency, accountability, and the efficiency of public service delivery.
- Single Simplified Pension Application Form: A new digital pension system was launched, combining nine separate pension forms into a single, streamlined application. This digital transformation integrates e-HRMS with Bhavishya, reducing processing time and ensuring timely pension disbursement with real-time tracking and Aadhaar-based e-signatures. This system enhances the user experience for pensioners, making the process more efficient and transparent.
- Compendium of Pension Related Instructions 2024: Dr. Singh introduced a comprehensive Compendium of updated rules, procedures, and guidelines related to pensions. This document serves as a reference for pensioners and administrative personnel, ensuring clarity in the pension process and aligning with the government's vision of simplifying and streamlining pension systems.
Good Governance Day 2024 (Sushasan Diwas)
- Observed on: December 25 annually, marking the birth anniversary of Atal Bihari Vajpayee (1924–2018).
- Introduced in 2014: By the Bharatiya Janata Party (BJP) government under Prime Minister Narendra Modi.
- Purpose: To honor Vajpayee's contribution and promote good governance practices in India.
- Objective of Good Governance Day:
- Promote Government Accountability: Ensuring government actions and services are transparent and citizens benefit equally.
- Instill Good Governance Values: Encourages civil servants to practice effective and responsible governance.
- Bridge the Gap: Between citizens and the government through active participation.
- Theme for 2024: "India’s Path to a Viksit Bharat: Empowering Citizens through Good Governance and Digitalisation."
Cephalopods

- 26 Dec 2024
In News:
Octopuses and their relatives are a new animal welfare frontier
- Cephalopods are highly intelligent, marine invertebrates that include species such as octopuses, squids, and cuttlefish.
- They are members of the class Cephalopoda in the phylum Mollusca, which is known for its diversity and complex morphology.
- Cephalopods are often considered one of the most behaviorally and morphologically complex classes within this phylum.
Key Features and Anatomy
Cephalopods exhibit several distinctive features:
- Body Structure: They have a head-foot structure, where the head is merged with the foot, and arms/tentacles surround the head. The arms and tentacles are derivatives of the foot, with some species possessing additional appendages for grasping or movement.
- Tentacles and Beak: Cephalopods possess tentacles, often with suction cups or hooks for capturing prey. They also have beak-like jaws, which are used to break down food.
- Eyes and Vision: Their unique W-shaped pupils enhance their vision. Most cephalopods are believed to be colorblind, but they exhibit remarkable visual camouflage through chromatophores (pigment cells) and reflectors beneath their skin, which can produce a wide range of colors and patterns.
- Movement: Cephalopods use jet propulsion to move. By expelling water from their mantle cavity, they can quickly travel through the water. Some species, like octopuses, also "walk" using their arms, while squids and cuttlefish employ fins for propulsion.
- Circulatory System: They have three hearts. Two hearts pump deoxygenated blood, while the third pumps oxygenated blood. Their blood is blue due to the presence of copper-based hemocyanin, which is effective in cold, low-oxygen environments.
- Neural Systems: Cephalopods are known for their advanced nervous systems. A significant portion of the neurons, especially in octopuses, are not located in the central brain but are distributed across the arms in “mini-brains” or ganglia, which helps coordinate movement and sensory functions independently.
Cognitive Abilities
Cephalopods have garnered significant attention due to their impressive cognitive abilities. Their intelligence is demonstrated in several areas:
- Problem-Solving: They are capable of using tools and strategies to solve complex tasks, such as escaping enclosures or catching prey.
- Learning and Memory: Cephalopods exhibit sophisticated learning behaviors, including associative learning and memory. Some species are known to delay gratification, choosing more preferred food items over immediate but less desirable ones. They also show evidence of "reversal learning," where they can adjust their behavior in response to changing environmental cues.
- Camouflage and Communication: Cephalopods can manipulate their skin's color and texture for camouflage, aiding in hunting and predator avoidance. For example, the Australian giant cuttlefish uses its chromatophores to communicate with potential mates or warn off competitors.
Species Diversity
Cephalopods are classified into three primary superorders:
- Octopodiforms: Includes octopuses (e.g., Octopus vulgaris), which are known for their intelligence and ability to solve problems.
- Decapodiforms: Includes squids and cuttlefish (e.g., Sepia officinalis, Architeuthis dux), which possess unique locomotion and hunting strategies.
- Nautiloids: Includes the chambered nautilus, the only cephalopod with an external shell, which is considered more primitive compared to other cephalopods.
Ethical and Conservation Concerns
Due to their intelligence and advanced nervous systems, cephalopods are becoming a focus of ethical debates regarding their treatment. Recently, California and Washington have enacted bans on octopus farming, and Hawaii is considering similar measures. These decisions are driven by the growing understanding of cephalopods' cognitive abilities and their capacity for suffering. As a result, there are increasing calls for humane treatment regulations similar to those for vertebrates.
Environmental and Ecological Role
Cephalopods play crucial roles in marine ecosystems. As carnivorous predators, they help maintain the balance of marine food chains by hunting smaller prey. Some species, such as the cuttlefish, also play important roles in communicating and signaling within their species through visual displays.
Kilauea Volcano
- 24 Dec 2024
In News:
Kilauea volcano erupts on Hawaii's Big Island.
Location:
- Kilauea is located on the southeastern shore of Hawaii’s Big Island, within Hawaii Volcanoes National Park.
Type of Volcano:
- Active Shield Volcano – Kilauea is a shield volcano, meaning it has broad, gentle slopes due to the eruption of fluid lava, which flows easily across large areas. Its eruptions tend to be less explosive than those of other types of volcanoes, creating a relatively safe environment for research and tourism compared to more volatile volcanoes.
Key Features:
- Summit Caldera: Kilauea has a large caldera at its summit, Halema'uma'u, which is a major volcanic feature. The caldera formed from the partial collapse of the volcano after the eruption of large amounts of magma. The caldera spans around 3 miles in length and 2 miles in width, covering an area of over 4 square miles.
- Rift Zones: Kilauea has two active rift zones stretching to the east and southwest, which are areas where lava can erupt and spread across the island. These rift zones are responsible for much of the volcanic activity.
- Lava Flows: Over the last 1,000 years, Kilauea has covered 90% of its surface with lava flows, making it one of the most active volcanoes in the world. It is known for producing highly fluid lava, which allows the lava to travel long distances from the eruption site.
- Historical Activity: Kilauea has had near-continuous eruptions in modern history, particularly between 1983 and 2018, with 34 eruptions since 1952. The volcano has remained active with frequent eruptions, and its lava lake was visible at the summit until 1924.
- Mythological Significance: The volcano is considered the home of Pele, the Hawaiian goddess of fire, lightning, and volcanoes. The Halema'uma'u crater is especially sacred, as it is believed to be the goddess's dwelling place.
Why is Kilauea Significant?
- Active and Young: Kilauea is one of the youngest volcanic products of the Hawaiian hotspot, a series of volcanic islands formed by the movement of the Pacific plate over a stationary plume of hot material beneath the Earth’s crust.
- Continuous Eruptions: It has been erupting regularly, with the exception of a quiet period between 1924 and 1952. Its eruptions are a significant natural phenomenon that scientists and visitors closely monitor.
- Proximity to Mauna Loa: Kilauea is located near Mauna Loa, another active shield volcano. Together, these two volcanoes form a large volcanic region, and their slopes merge seamlessly, making this area home to two of the world's most active volcanoes.
Shield Volcanoes and Kilauea
- Shield Volcanoes: A shield volcano is characterized by its broad, gentle slopes. These slopes are formed by repeated eruptions of fluid basalt lava, which spreads easily over large areas. Unlike composite volcanoes, which have steep, conical shapes, shield volcanoes like Kilauea have a much wider, dome-like appearance.
- Low Explosivity: Eruptions from shield volcanoes are generally low in explosivity, and lava flows are typically slow-moving. However, explosive events can occur if water interacts with lava, but this is relatively rare in Kilauea's eruptions.
Kilauea's Current Activity
In December 2024, Kilauea began erupting again, continuing its pattern as one of the most active volcanoes in the world. This eruption has once again drawn attention to the ongoing volcanic activity on the Big Island of Hawaii, as the volcano regularly contributes to the reshaping of the island and its landscape.
Other Volcanoes in India:
While Kilauea is known for its active status, India also has volcanic features, although most are dormant or extinct:
- Barren Island (Andaman Islands) – India’s only active volcano.
- Narcondam (Andaman Islands) – A dormant volcano.
- Baratang (Andaman Islands) – Known for mud volcanoes.
- Deccan Traps (Maharashtra) – A vast volcanic plateau formed by ancient eruptions.
- Dhinodhar Hills (Gujarat) – Extinct volcano.
- Dhosi Hill (Haryana) – An ancient volcanic site with historical significance.
GenCast AI
- 24 Dec 2024
In News:
Google’s GenCast AI is an advanced weather forecasting model developed by DeepMind that uses machine learning techniques to provide more accurate and longer-term weather predictions compared to traditional forecasting methods.
How GenCast Works:
- Training on Reanalysis Data:
- GenCast is trained on 40 years of reanalysis data (from 1979 to 2019). This data combines historical weather observations with modern weather forecasts, providing a comprehensive picture of past weather and climate conditions.
- Ensemble Forecasting with AI:
- Unlike traditional Numerical Weather Prediction (NWP) models, which run simulations based on physical laws and initial conditions, GenCast uses an ensemble forecasting approach where multiple predictions are generated by an AI model, not an NWP model.
- It produces a range of possible weather scenarios, each with different starting conditions, to reflect the uncertainty in weather forecasts.
- Neural Network and Diffusion Model:
- GenCast uses a neural network architecture with 41,162 nodes and 240,000 edges that process weather data. Each node accepts data, manipulates it, and passes it to another node, helping to refine and improve predictions.
- It uses a diffusion model, a type of AI model commonly used in generative AI. The model takes noisy input data, processes it through 30 refinement steps, and gradually produces a clearer forecast (de-noising the data).
- The result is a probabilistic forecast, such as "there's a 25% chance of rain in Chennai on December 25," rather than a deterministic forecast, which would provide exact quantities like "5 mm of rain."
- Faster Processing:
- The entire forecast process is incredibly efficient. GenCast can generate 50 ensemble forecasts at once with a spatial resolution of 0.25° x 0.25° (latitude-longitude) and temporal resolution of 12 hours.
- Using Google's TPU v5 units, it can produce these forecasts in just 8 minutes—far faster than traditional supercomputers, which can take several hours to run NWP simulations.
Key Features of GenCast:
- Better Performance on Extreme Weather: GenCast has shown superior accuracy in predicting extreme weather events, such as tropical cyclones, compared to traditional NWP models like those from the European Centre for Medium-Range Weather Forecasts (ECMWF).
- Probabilistic Forecasting: GenCast produces probabilistic forecasts, offering predictions like the likelihood of rain rather than precise measures, which helps with better preparation, especially for extreme weather events.
- Long-Term Forecasting: GenCast can generate forecasts for up to 15 days, which is longer than most traditional models, and is particularly useful for anticipating events like wind power generation and tropical cyclone tracking.
- Efficiency: GenCast's speed and resource efficiency set it apart from traditional NWP models, reducing forecast times dramatically.
Comparison with Traditional Weather Models:
- Numerical Weather Prediction (NWP): Traditional NWP models rely on solving complex physical equations to simulate the atmosphere and provide deterministic forecasts. These models require significant computational power and are typically limited to weather predictions for about a week.
- GenCast's Probabilistic Forecasts: In contrast, GenCast offers probabilistic predictions, making it better suited for providing early warnings about extreme weather, with better lead times for disaster preparation.
Future Developments:
While GenCast is impressive, Google acknowledges the importance of traditional NWP models for both supplying initial conditions and providing the foundational data needed to train AI models like GenCast. Ongoing collaboration with weather agencies is crucial to enhancing AI-based methods for weather prediction.
Overall, GenCast represents a significant leap forward in the use of AI for weather forecasting, with potential for greater accuracy, efficiency, and longer-term predictions compared to current methods.
National Human Rights Commission (NHRC)

- 24 Dec 2024
In News
Justice V. Ramasubramanian, a retired Supreme Court judge, has been appointed as the new chairperson of the National Human Rights Commission (NHRC). This decision was made by President Droupadi Murmu, and it comes following the completion of Justice Arun Kumar Mishra's tenure as NHRC chairperson in June 2023. After Justice Mishra's retirement, Vijaya Bharathi Sayani served as the acting chairperson. Alongside Justice Ramasubramanian, Priyank Kanoongo and Dr. Justice Bidyut Ranjan Sarangi (Retd.) have also been appointed as members of the commission.
Justice Ramasubramanian had been appointed a judge of the Supreme Court in September 2019 and retired in June 2023. His appointment to the NHRC is seen as a significant development for human rights advocacy and protection in India.
National Human Rights Commission (NHRC)
Establishment and Legal Framework
- Formation Date: The NHRC was established on October 12, 1993, under the Protection of Human Rights Act (PHRA), 1993.
- Paris Principles: It was created in alignment with the Paris Principles (1991), which were endorsed by the UN General Assembly in 1993, aimed at setting standards for national human rights institutions.
- Statutory Body: NHRC is a statutory body, meaning it is established by law, with a primary function to safeguard human rights in India.
Objectives
The NHRC's primary objective is to promote and protect human rights as defined in Section 2(1)(d) of the PHRA, which include fundamental rights such as:
- Right to Life
- Right to Liberty
- Right to Equality
- Right to Dignity
These rights are guaranteed by the Indian Constitution and are essential to the protection of individuals' freedoms and welfare.
Composition of NHRC
- Chairperson: A former Chief Justice of India or a former Supreme Court judge serves as the chairperson.
- Members:
- One former or sitting Supreme Court judge.
- One former or sitting Chief Justice of a High Court.
- Three members, with at least one woman, who have experience in human rights matters.
- Ex-Officio Members: The chairpersons of various National Commissions (e.g., SC/ST, Women, Minorities) and the Chief Commissioner for Persons with Disabilities are also part of the NHRC.
Functions and Powers
The NHRC has several crucial functions and powers to ensure the protection and promotion of human rights:
- Inquiry into Human Rights Violations: The commission can inquire into violations of human rights by public servants or negligence in protecting rights.
- Recommendations: It can make recommendations on how to protect, promote, and effectively implement human rights within India.
- Review of Laws: NHRC assesses various laws, treaties, and international instruments related to human rights.
- Research and Awareness: It promotes research, publications, and awareness about human rights issues, including educating the public about their rights and safeguards.
- Inspection of Institutions: NHRC has the authority to visit and inspect institutions such as jails, detention centers, and other places of confinement to ensure the humane treatment of individuals.
The ‘No-Detention’ Policy and Its Evolution

- 24 Dec 2024
In News:
The ‘no-detention’ policy was a significant part of India’s education reforms under the Right to Education (RTE) Act of 2009. This policy aimed to prevent the detention or expulsion of students until the completion of elementary education (Classes 1-8), with a focus on reducing dropout rates and ensuring every child receives at least basic education. However, the policy has been contentious, with arguments both for and against its implementation.
What was the ‘No-Detention’ Policy and Why Was It Introduced?
The RTE Act (2009) made education free and compulsory for children aged 6 to 14, under Article 21A of the Constitution. Section 16 of the Act specifically prohibited the detention or expulsion of students in elementary education (Classes 1-8). The rationale was to prevent the demotivation and fear of failure that might cause children to drop out of school, especially those from marginalized backgrounds. By promoting automatic progression through grades, the policy aimed to ensure that no child was left behind due to academic struggles.
Key to this system was Continuous and Comprehensive Evaluation (CCE), which assessed students on a holistic basis, beyond just formal exams, encouraging learning through regular feedback and assessments.
Amendments to the RTE Act (2017 and 2019)
In 2017, a Bill was introduced to amend the RTE Act, following concerns about the effectiveness of the ‘no-detention’ policy. The amended policy allowed for regular exams in Classes 5 and 8. If students failed, they would be given a re-examination within two months. If they still did not meet promotion criteria, detention could be enforced. This amendment empowered the Centre and states to decide whether to detain students in these grades.
The amendment came after criticism of the original policy for promoting students without sufficient learning progress. States like Madhya Pradesh and Punjab argued that no-detention was leading to poor academic performance, and called for a return to the traditional system of promoting students based on examination results.
Arguments for and Against the No-Detention Policy
Arguments for No-Detention:
- Reduced Dropout Rates: The policy helped ensure students, especially from disadvantaged backgrounds, continued in school without the fear of failure, leading to a drop in dropout rates.
- Holistic Development: It encouraged a child-centric learning approach where students were assessed on their overall development rather than just exam performance.
- Social Inclusivity: By promoting students regardless of performance, it was hoped that education would be more inclusive, preventing marginalization of students from lower socio-economic backgrounds.
Arguments Against No-Detention:
- Decline in Learning Outcomes: The policy led to a lack of motivation for students to perform academically. Without the accountability of exams, many students became less serious about their studies.
- Low Teacher Accountability: With automatic promotion, teachers had less incentive to ensure quality learning, leading to an overall dip in teaching standards.
- Impact on Educational Standards: Data indicated a decline in learning levels in government schools, as students were passed through the system without mastering the required skills.
In 2015, the Central Advisory Board of Education (CABE) conducted a study suggesting that more flexibility was needed in the policy, allowing schools to retain students who were significantly behind. However, there were differing views within the committee. Some members argued that detention had no proven benefits, and that the real issue was the poor quality of the education system itself.
In 2016, the TSR Subramanian Committee on the New Education Policy suggested continuing the no-detention policy until Class 5, citing evidence of reduced dropout rates and increased enrollment. However, other states pushed for scrapping it due to concerns over declining educational standards.
The Shift Toward Scrapping the No-Detention Policy
By 2019, the RTE Act was amended to give states the discretion to hold back students in Classes 5 and 8, if they failed to meet the promotion criteria. This change came after state feedback that the no-detention policy was having adverse effects on learning outcomes and teacher accountability.
In 2024, the Ministry of Education took further steps to formalize this shift by introducing new rules under the RTE Act Amendment. Students failing to meet the promotion criteria in Classes 5 and 8 will be given additional instruction and an opportunity for a re-examination. If they still fail, they can be detained, with specialized guidance provided to help them catch up.
Which States Continue or Scrapped the No-Detention Policy?
The decision to maintain or scrap the policy varies across states and union territories:
- States Retaining No-Detention Policy: Andhra Pradesh, Arunachal Pradesh, Goa, Karnataka, Kerala, Maharashtra, Odisha, Telangana, Uttar Pradesh, among others, continue to implement the no-detention policy, citing its role in minimizing dropouts and promoting inclusivity.
- States That Have Scrapped the Policy: Delhi, Punjab, Madhya Pradesh, Rajasthan, West Bengal, and Gujarat have already discarded the policy, opting for examinations and re-examinations in Classes 5 and 8 to ensure better academic accountability.
Why the Controversy?
The debate over the no-detention policy hinges on balancing academic accountability with social inclusivity. Supporters argue that it ensures children from marginalized communities receive their full elementary education, while opponents point to the decline in learning standards, especially in government schools, as a major issue.
In summary, while the no-detention policy was introduced with the noble aim of reducing school dropouts and ensuring every child completed at least elementary education, its effectiveness has been questioned due to concerns over declining learning outcomes. The recent changes represent a shift towards better accountability and quality in education, while still ensuring that children receive additional support before being detained.
Space Docking Experiment (SpaDeX) Mission
- 24 Dec 2024
In News:
The Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) is set to launch its Space Docking Experiment (SpaDeX) mission, a key milestone in India’s space capabilities. The mission will deploy two 220-kg satellites, SDX01 (Chaser) and SDX02 (Target), into a 740 km orbit using the PSLV-C60 rocket. SpaDeX aims to demonstrate the technology for satellite docking, a critical component for future space missions such as lunar exploration and the development of India's own space station, Bharatiya Antariksh Station (BAS).
Key Objectives of SpaDeX Mission:
- Primary Objective: To demonstrate the rendezvous, docking, and undocking of two small spacecraft (SDX01 and SDX02) autonomously.
- Secondary Objectives: Include testing electric power transfer between the docked spacecraft, composite spacecraft control, and post-docking payload operations.
The mission will see the two spacecraft gradually approach each other, performing a series of maneuvers, starting at a 20 km distance and closing to millimeter-scale distances before docking. Once docked, they will execute secondary tasks, such as scientific payload operations, using advanced technologies including high-resolution cameras, multi-spectral payloads, and radiation monitors.
Technological Innovations:
- Docking Mechanism: An indigenous, motor-driven, low-impact, androgynous docking system with capture, extension/retraction, and rigidization mechanisms. Both spacecraft are equipped with identical docking systems to simplify operations.
- Advanced Sensors: The spacecraft will use a Laser Range Finder (LRF), Proximity & Docking Sensors (PDS), and Rendezvous Sensors for precise distance measurement and to guide the docking process.
- Inter-Satellite Communication: The spacecraft will employ autonomous inter-satellite links (ISL) for real-time communication and data sharing.
- RODP Processor: This system, based on GNSS, ensures accurate position and velocity determination for the spacecraft during the docking procedure.
Significance of the SpaDeX Mission:
- Technological Milestone: SpaDeX positions India as the fourth country, after the US, Russia, and China, to develop space docking technology.
- Space Exploration: The successful demonstration will facilitate future space exploration, including Chandrayaan-4 and interplanetary missions.
- Modular Space Infrastructure: Space docking is essential for building multi-modular space stations, which allows the construction of large structures in space and enhances flexibility for future missions.
- Satellite Servicing: Docking enables satellite servicing, including repairs, refueling, and upgrades, which increases the operational lifespan of satellites.
SpaDeX Mission for India’s Space Station:
The SpaDeX mission is a crucial step towards India’s plans for the Bharatiya Antariksh Station (BAS). This will be India’s first modular space station, designed to conduct advanced scientific research, including in life sciences and medicine. BAS is expected to begin operations by 2035, and the development of docking technology is pivotal for its assembly and operation.
Mission Launch Details:
The PSLV-C60 rocket is set to launch the SpaDeX mission from Sriharikota. The mission is a demonstration of India's growing space capabilities and its indigenous technologies, including the Bharatiya Docking System (BDS).
Challenges and Technological Requirements:
The docking process requires extremely precise maneuvering, as the two spacecraft will be traveling at speeds of 28,800 km/h and must reduce their relative velocity to just 0.036 km/h before docking. This level of precision is crucial for future missions involving spacecraft servicing, crew transfers, and the construction of space infrastructure like BAS.
In addition to the docking demonstration, SpaDeX will carry 24 academic and startup payloads aboard the PSLV’s fourth stage, POEM (PSLV Orbital Experimental Module-4), offering a valuable platform for microgravity research.
Future Prospects:
The success of SpaDeX will pave the way for more complex missions, such as India’s lunar and Mars exploration programs, the development of the Bharatiya Antariksh Station, and international collaborations in satellite servicing and space infrastructure.
72nd North Eastern Council (NEC) Plenary Session

- 23 Dec 2024
Overview:
The 72nd Plenary of the North Eastern Council (NEC), concluded in Agartala, Tripura, marking the second time the city hosted this significant event since 2008. The plenary featured a series of high-level discussions focused on accelerating development and addressing the socio-economic challenges of the North Eastern Region (NER), which includes Arunachal Pradesh, Assam, Manipur, Meghalaya, Mizoram, Nagaland, Sikkim, and Tripura.
Key Highlights:
- Pre-Plenary Technical Sessions: Central ministries presented their developmental agendas for the NER, charting a path forward for the region's growth and addressing key challenges.
- Main Plenary:
- Presiding Officers: The session was chaired by the Union Home Minister and NEC Chairman, Shri Amit Shah, along with DoNER Minister, Shri Jyotiraditya M. Scindia, and Minister of State, Dr. Sukanta Majumdar.
- Participants: Governors, Chief Ministers, Chief Secretaries, Planning Secretaries, and high-ranking officials from all eight northeastern states will engage in strategic discussions to foster regional development.
- Agartala as Host:
- Agartala's selection as the venue signifies the evolving role of the city in regional development, as plenary sessions are usually held in Shillong and Guwahati.
- Significance of the NEC:
- The North Eastern Council (NEC), established in 1971, plays a pivotal role in the socio-economic development of the region. It was initially an advisory body but has evolved into a regional planning agency with a larger mandate.
- The NEC has contributed significantly to the development of critical infrastructure in the region, such as over 11,500 kilometers of roads, power generation through NEEPCO, and educational institutions like RIMS.
- Prime Minister's Vision for the NER:
- The Prime Minister’s vision for the region revolves around recognizing it as 'Ashta Lakshmi'—symbolizing immense potential and cultural richness. The NEC is central to realizing this vision through initiatives like the PM-DevINE scheme.
Key Achievements of the NEC:
- Over 11,500 kilometers of road construction, improving regional connectivity.
- Increased power generation capacity via projects managed by NEEPCO.
- Established institutions like the Regional Institute of Medical Sciences (RIMS) and others that cater to regional educational and technical needs.
Recent Focus and Shift in Governance:
- In the 72nd Plenary, the Union Home Minister highlighted a shift in the focus of police forces in northeastern states, urging them to focus not just on insurgency control but on ensuring the constitutional rights of citizens, reflecting a new governance phase in the region.
RBI's Report on State Finances (2024-25)

- 23 Dec 2024
In News:
The Reserve Bank of India's (RBI) report titled "State Finances – A Study of Budgets of 2024-25" provides a comprehensive analysis of the fiscal position of Indian states.
Key Highlights
- States' Performance Post-Pandemic
- Improved Tax Revenue: The average tax buoyancy has increased significantly from 0.86 (2013-2020) to 1.4 (2021-2025), reflecting enhanced tax collection efficiency.
- Capital Expenditure: There is a consistent rise in capital expenditure, which increased from 2.4% of GDP in 2021-22 to 2.8% in 2023-24 and is budgeted at 3.1% in 2024-25. This indicates a growing focus on investment in infrastructure like highways and bridges.
- Fiscal Discipline and Debt Levels
- Gross Fiscal Deficit (GFD): The gross fiscal deficit is projected at 3.2% of GDP in 2024-25, a slight increase from 2.9% in 2023-24.
- Debt-to-GDP Ratio: While states' debt-to-GDP ratio decreased from 31.0% in March 2021 to 28.5% in March 2024, it remains higher than the pre-pandemic level of 25.3% in 2019.
- Increased Borrowing and Debt Pressure
- Market Borrowings: States' reliance on market borrowings has increased, accounting for 79% of the GFD in FY25. Gross market borrowings surged by 32.8%, totaling Rs 10.07 trillion in FY23-24.
- Electricity Distribution Companies (DISCOMs): Continued losses in DISCOMs, accumulating Rs 6.5 lakh crore by 2022-23 (2.4% of India's GDP), continue to strain state finances.
- Rising Subsidy Burden
- Many states are offering subsidies and loan waivers, such as farm loan waivers and free services (electricity, transport, etc.), which risk diverting funds away from critical infrastructure projects. This includes significant subsidies for income transfers to farmers, women, and youth.
- Fiscal Transparency Concerns
- Revenue Generation Issues: Revenue growth from non-tax sources and central grants is slowing. The pace of State Goods and Services Tax (SGST) growth has also slowed down, which impacts overall state revenues.
- Lack of Fiscal Transparency: Inadequate reporting of off-budget liabilities obfuscates the true fiscal position, leading to a lack of clarity and accountability in state finances.
Recommendations by the RBI
- Debt Consolidation: States are encouraged to create clear and transparent debt reduction paths, with consistent reporting of off-budget liabilities to improve fiscal accountability.
- Expenditure Efficiency: Focus on outcome-based budgeting, ensuring funds are directed towards productive and sustainable investments, particularly in climate-sensitive areas.
- Subsidy Rationalization: States should contain and optimize subsidies to ensure they don't overshadow essential growth-promoting expenditure.
- Efficient Borrowings: Reduce over-reliance on market borrowings to control fiscal deficits and minimize financial risks.
- Revenue Generation: Improve collection mechanisms for SGST, strengthen non-tax revenue sources, and increase grants to reduce dependence on borrowings.
Balancing Subsidies and Fiscal Discipline
- Importance of Subsidies: Welfare programs like subsidies for healthcare, food security (e.g., Public Distribution System), and LPG connections (e.g., Pradhan Mantri Ujjwala Yojana) play a crucial role in human development and economic equality by supporting vulnerable populations.
- Importance of Fiscal Discipline: Excessive welfare spending without corresponding revenue generation can lead to high deficits and public debt, threatening long-term fiscal stability. Maintaining fiscal discipline ensures sustainable public finances, promotes investor confidence, and supports economic growth.
Green fixed deposits

- 23 Dec 2024
In News:
Green fixed deposits (FDs) are a type of investment scheme offered by banks and financial companies, aimed at environmentally-conscious investors. They function similarly to traditional fixed deposits, where funds are locked in with a bank for a fixed tenure. The primary distinction between green and regular deposits lies in the allocation of funds. While regular deposits are pooled into a common fund, the funds from green deposits are exclusively allocated to projects that promote environmental sustainability.
Key Features of Green Fixed Deposits:
- Investment Purpose: The funds raised through green FDs are directed towards environmentally beneficial projects, such as renewable energy initiatives (solar and wind power), clean technology, organic farming, and energy-efficient infrastructure.
- Eligibility: Green deposits are available to various entities, including individuals, Hindu Undivided Families (HUFs), societies, clubs, non-profit organizations, and sole proprietorships.
- Interest Rates: The interest rates on green deposits may or may not differ from regular deposits, depending on the policies set by the lending institution. Some banks and financial institutions, like IndusInd Bank, Federal Bank, DBS Bank India, and HDFC Ltd., offer green deposits, with Bank of Baroda recently launching the BOB Earth Green Term Deposit with an interest rate of up to 7.15% per annum.
- Safety: Like regular fixed deposits, green deposits are insured by the Deposit Insurance and Credit Guarantee Corporation (DICGC) under the provisions of the DICGC Act, 1961, ensuring the safety of the investment.
- Overdraft Facility: Banks may offer overdraft facilities against green deposits, providing more flexibility to investors.
- Premature Withdrawal: If the investor chooses to withdraw the deposit before the agreed tenure (after six months), the green FD will be converted into a regular fixed deposit.
- Denomination: Green deposits are denominated in Indian Rupees only.
Centenary of Belgaum session

- 23 Dec 2024
In News:
The Belagavi Session of 1924, marking its centenary in December 2024, holds significant historical and cultural value in India's freedom struggle. This session, the 39th All-India Congress session, was presided over by Mahatma Gandhi, the only instance he served as the Congress president. It took place in Belagavi, Karnataka, from December 26-27, 1924, amidst a growing momentum for India’s fight against British colonial rule.
Key Aspects of the Belagavi Session:
- Gandhi's Leadership: This was the only Congress session Gandhiji chaired, marking a pivotal moment in the freedom movement. His leadership emphasized non-violence, self-reliance, and unity among diverse groups, setting the stage for future movements like the Salt March and Quit India Movement.
- Focus on Social Change: Gandhi used the session to push for social reforms, including the abolition of untouchability, promotion of khadi (hand-spun cloth), and supporting village industries. These initiatives aimed to make Congress a movement for both political freedom and social upliftment.
- Promoting Hindu-Muslim Unity: Gandhi strongly advocated for Hindu-Muslim unity, recognizing its critical importance in the larger struggle for independence. His stance emphasized communal harmony during a time of social and political divisions.
- Cultural Impact: The session also featured musical performances, including contributions from Hindustani maestros like Vishnu Digambar Paluskar and Gangubai Hangal. The Kannada song “Udayavagali Namma Chaluva Kannada Nadu” became an anthem for the region's unification movement.
- Legacy: The session had a lasting impact, with initiatives such as promoting khadi, reducing Congress membership fees, and creating new avenues for peasant participation in the freedom movement. The Pampa Sarovara well, dug during the event, continues to provide water to parts of Belagavi.
Centenary Celebrations:
The centenary of the Belagavi Session is being celebrated with a range of events, including:
- A Congress Working Committee (CWC) meeting on December 26, 2024.
- A public rally with the theme “Jai Bapu, Jai Bhim, Jai Samvidhan.”
- Cultural events and exhibitions are also planned, including competitions, tableaux, and charkha marathons.
National Farmers' Day

- 23 Dec 2024
In News:
National Farmers' Day, also known as Kisan Diwas, is celebrated annually on December 23rd to honor the vital contributions of Indian farmers and commemorate the birth anniversary of Chaudhary Charan Singh, India's fifth Prime Minister. A passionate advocate for rural development and farmers' welfare, Charan Singh's policies laid the foundation for several reforms aimed at uplifting the agrarian economy. His contributions continue to inspire government initiatives that prioritize the welfare of farmers, fostering sustainable agricultural growth and ensuring food security for the nation.
The Legacy of Chaudhary Charan Singh
Chaudhary Charan Singh was born on December 23, 1902, in Noorpur, Uttar Pradesh. His deep understanding of rural issues and commitment to improving farmers’ lives earned him the title of "Kisan Leader". Throughout his political career, he championed reforms such as the Debt Redemption Bill (1939), which alleviated the financial burdens of farmers, and the Land Holding Act (1960), which promoted fair distribution of agricultural land. He also advocated for Minimum Support Price (MSP), and his policies laid the groundwork for NABARD and other farmer-centric institutions.
Significance of Kisan Diwas
Kisan Diwas highlights the importance of agriculture in India’s economy and employment, with farmers constituting nearly 50% of the workforce. The day emphasizes the need for policies that address farmers' challenges such as climate change, financial constraints, and technological adoption. It also serves as a reminder of the necessity to empower farmers through innovative solutions, financial security, and sustainable farming practices.
Key Government Initiatives for Farmer Welfare
The Indian government has launched several schemes to address the challenges faced by farmers and support their socio-economic upliftment:
- Pradhan Mantri Kisan Samman Nidhi (PM-KISAN): Provides direct income support to small and marginal farmers.
- Pradhan Mantri Fasal Bima Yojana (PMFBY): Offers crop insurance to mitigate financial risks due to crop loss.
- Pradhan Mantri Kisan Maandhan Yojana (PM-KMY): A pension scheme for farmers to ensure long-term social security.
- Soil Health Card Scheme: Promotes efficient fertilizer use and soil health by providing farmers with personalized soil health reports.
- Farmer Producer Organizations (FPOs): These entities help farmers collectively access markets, reduce costs, and improve bargaining power.
- Modified Interest Subvention Scheme (MISS): Provides affordable credit to farmers, especially for agriculture-related activities.
- Kisan Credit Card (KCC): Helps farmers access timely credit for agricultural purposes at concessional rates.
Significant Budget Allocations and New Schemes
The government has drastically increased its budget allocation to the agriculture sector. From Rs. 21,933.50 crore in 2013-14, the budget has risen to Rs. 1,22,528.77 crore for 2024-25, underlining the government's commitment to farmer welfare and sustainable agricultural development.
Notable Initiatives:
- Namo Drone Didi Scheme: This initiative, aimed at empowering Women Self-Help Groups (SHGs), supports the use of drones for agricultural purposes, including fertilizer and pesticide application, with 80% financial assistance.
- Clean Plant Programme (CPP): Enhances the quality and productivity of horticulture crops by ensuring disease-free planting material.
- Digital Agriculture Mission: Aims to modernize farming with digital infrastructure, including crop estimation surveys and e-agriculture platforms.
- National Mission on Natural Farming (NMNF): Encourages chemical-free, sustainable farming practices.
Farmers' Role in Nation-Building
India’s agricultural sector not only sustains the livelihoods of millions but also contributes significantly to the country's GDP. In FY 2023-24, agriculture contributed 17.7% to the Gross Value Added (GVA). With over 54% of the country's land dedicated to agriculture, farmers are critical to food security and rural development.
In 2023-24, India achieved a record foodgrain production of 332.2 million tonnes, illustrating the resilience of Indian farmers in ensuring food availability despite challenges like climate change.
IPBES Nexus Report

- 22 Dec 2024
In News:
The IPBES Nexus Report, formally titled The Assessment Report on the Interlinkages Among Biodiversity, Water, Food, and Health, was released to address the interconnected global challenges of climate change, biodiversity loss, food insecurity, water scarcity, and health risks. The report stresses that these challenges are deeply intertwined and cannot be solved separately; doing so would lead to ineffective or even counterproductive results.
Key Highlights of the Nexus Report
- Interconnections Between Global Challenges: The report emphasizes the strong interlinkages between the five major global challenges:
- Biodiversity Loss
- Water Scarcity
- Food Insecurity
- Health Risks
- Climate Change
It argues that efforts to address these challenges independently are ineffective and often exacerbate the problems. For example, scaling up food production to combat hunger can put more pressure on land, water, and biodiversity.
- Economic Cost of Biodiversity Loss:
- Global GDP Dependency: Over half of the global GDP (approximately $58 trillion annually) depends on nature. Biodiversity degradation significantly undermines productivity and economic output.
- Unaccounted Costs: The neglect of biodiversity in economic activities contributes to a loss of $10-25 trillion annually.
- Delayed Action: Delaying action on biodiversity conservation could double the costs within the next decade, potentially incurring $500 billion per year in additional costs.
- Synergistic Approach: The report identifies over 70 response options that promote synergistic outcomes across the five challenges. These include:
- Restoring Carbon-Rich Ecosystems: Such as forests, soils, and mangroves to address climate change and biodiversity loss.
- Managing Biodiversity to Prevent Disease Transmission: Effective biodiversity management reduces risks of diseases passing from animals to humans (zoonotic diseases).
- Sustainable Diets: Promoting diets that are both healthy and environmentally sustainable.
- Nature-Based Solutions: Implementing solutions that rely on natural processes to mitigate challenges like water scarcity and climate change.
- Inequality and Vulnerability: The report highlights how inequality exacerbates the challenges. Vulnerable populations, especially those living in areas where biodiversity has sharply declined, face increased health risks, malnutrition, and economic instability. 41% of people live in regions where biodiversity loss has been particularly severe, and 9% face high health burdens due to these declines.
- Principles for Transformative Change: The report outlines principles for achieving transformative change:
- Equity and Justice: Ensuring fair distribution of resources and opportunities for all.
- Pluralism and Inclusion: Embracing diverse perspectives and voices in policy-making.
- Respectful Human-Nature Relationships: Recognizing and nurturing reciprocal relationships between humans and nature.
- Adaptive Learning and Action: Continuously evolving policies and strategies based on feedback and new evidence.
- Urgency for Immediate Action: The report stresses that immediate action is critical. If the world continues to neglect biodiversity, it will face not only environmental collapse but also a missed opportunity for economic growth. Immediate implementation of nature-positive strategies could unlock $10 trillion in business opportunities and create 400 million jobs by 2030.
The IPBES Transformative Change Assessment Report
- This report builds upon the 2019 IPBES Global Assessment Report and advocates for transformative change to halt biodiversity loss and achieve global development goals. It defines transformative change as a system-wide shift in:
- Views: Changing how we think about nature and its value.
- Structures: Reforming systems of governance and organization.
- Practices: Changing behaviors and practices that harm nature.
Key Challenges to Transformative Change:
- Disconnection from Nature: Human societies' disconnection from nature, often rooted in historical domination, is a major cause of biodiversity loss.
- Economic Inequality: The concentration of power and wealth exacerbates environmental degradation.
- Unsustainable Consumption: Unsustainable patterns of consumption and production are significant drivers of environmental harm.
Synergistic Strategies for Transformation:
- Conserve and Regenerate: Restore ecosystems that have both ecological and cultural value.
- Mainstream Biodiversity: Integrate biodiversity considerations into sectors like agriculture, forestry, and infrastructure development.
- Transform Economic Systems: Adopt policies such as true cost accounting and sustainability-based tax principles to internalize the environmental costs of economic activities.
- Inclusive Governance: Promote governance systems that involve all stakeholders, especially local communities, in decision-making.
SAMARTH UDYOG BHARAT 4.0 INITIATIVE

- 22 Dec 2024
In News:
The SAMARTH Udyog Bharat 4.0 initiative, launched by the Ministry of Heavy Industries (MHI), aims to enhance the competitiveness of the Indian capital goods sector by promoting the adoption of Industry 4.0 technologies. This initiative is part of the Scheme for Enhancement of Competitiveness in the Indian Capital Goods Sector.
Key Features of SAMARTH Udyog Bharat 4.0 Initiative
- Establishment of Smart Manufacturing Hubs: Under this initiative, four Smart Advanced Manufacturing and Rapid Transformation Hub (SAMARTH) Centres have been set up across India:
- Centre for Industry 4.0 (C4i4) Lab, Pune
- IITD-AIA Foundation for Smart Manufacturing, IIT Delhi
- I-4.0 India @ IISc, Bengaluru
- Smart Manufacturing Demo & Development Cell, CMTI, Bengaluru
- Cluster Industry 4.0 Experience Centres: In addition to the above centres, 10 cluster Industry 4.0 experience centres have been approved. These will be established under a Hub and Spoke model, managed by the C4i4 Lab in Pune, and spread across India.
- Key Achievements:
- Model Factories: Development of an Industry 4.0 enabled Model Factory at C4i4, Pune, and a smart production-based factory at CMTI Bengaluru.
- Industry 4.0 Solutions: More than 50 use-cases for Industry 4.0 solutions were compiled to support implementation.
- Maturity Assessment Tool: Creation of the Industry 4.0 Maturity Model (I4MM), specifically designed to assess the readiness of Indian manufacturing companies for Industry 4.0.
- Online Assessment Tool: Launch of a free online assessment tool by C4i4 Lab, Pune, to help MSMEs evaluate their maturity in adopting Industry 4.0 technologies.
- Training and Awareness:
- Workshops and Seminars: Regular awareness seminars, workshops, and knowledge-sharing events are organized to educate industries about Industry 4.0.
- Workforce Training: The SAMARTH Centres have trained over 5000 professionals on smart manufacturing and Industry 4.0 technologies.
- Consultancy Services: The centres offer consultancy in areas such as IoT hardware, software development, and data analytics, along with incubation support for start-ups and MSMEs.
- Impact on MSMEs:
- Digital Maturity Assessments: Over 100 digital maturity assessments have been completed for the auto industry, and more than 500 improvement initiatives have been identified.
- Training and Capacity Building: Over 500 digital champions have been trained on Industry 4.0 technologies.
- Focus on MSMEs: While no direct financial assistance is provided to industries, including MSMEs, under this initiative, the SAMARTH Centres play a key role in helping them adopt Industry 4.0 technologies and build their capabilities.
Key Takeaways:
- The SAMARTH Udyog Bharat 4.0 initiative seeks to increase the global competitiveness of India's capital goods and manufacturing sectors.
- It leverages Industry 4.0 technologies such as IoT, automation, data analytics, and AI to modernize manufacturing processes.
- The initiative involves setting up 4 major Smart Manufacturing Hubs and 10 regional experience centres across the country to facilitate awareness, training, and adoption of Industry 4.0 among manufacturers, especially MSMEs.
- While it does not provide financial aid, it helps industries improve their digital maturity, trains workforce, and guides them through consultancy and workshops.
Next Generation DNA Sequencing Facility (NGS)

- 22 Dec 2024
Recently, the Union Minister Shri Bhupender Yadav inaugurated two groundbreaking facilities at the Wildlife Institute of India (WII), Dehradun: the Advanced Facility for Pashmina Certification and the Next Generation DNA Sequencing (NGS) Facility. These facilities are designed to enhance India’s capabilities in wildlife conservation and support the growth of traditional crafts like Pashmina weaving.
Key Highlights
Next Generation DNA Sequencing Facility (NGS)
The NGS facility is a cutting-edge research tool that enables the high-throughput analysis of entire genomes. This technology is pivotal in studying wildlife genetics and biodiversity by decoding millions of DNA sequences at once.
Applications in Wildlife Conservation:
- Genetic Diversity and Health: NGS helps assess the genetic diversity of species and their population health.
- Evolutionary Relationships: It aids in understanding the evolutionary history and unique adaptations of species.
- Disease Surveillance: The technology supports studying pathogen-host interactions and monitoring diseases affecting wildlife.
- Combating Illegal Wildlife Trade: NGS can help detect illegal wildlife trade and the movement of endangered species.
- Impact of Climate Change: It is crucial for studying how climate change affects genetic diversity and species survival.
This facility positions WII as a leading hub for molecular research, enabling more precise conservation efforts and studies on endangered species like tigers, elephants, and riverine dolphins.
Advanced Facility for Pashmina Certification
Launched under a Public-Private Partnership (PPP) model between WII and the Export Promotion Council for Handicrafts (EPCH), the Pashmina Certification Centre (PCC) has been significantly upgraded. The facility now includes a Scanning Electron Microscope (SEM) with Energy Dispersive Spectroscopy (EDS) for advanced wool testing and certification.
Key Features of the Upgraded Facility:
- Fiber Analysis: The SEM-EDS technology ensures accurate identification and certification of Pashmina fibers, free from any prohibited materials.
- Unique ID and E-certificates: Each certified product is tagged with a unique ID and e-certificate, enhancing traceability and authenticity.
- Global Trade Facilitation: The certification process eliminates delays at exit points, ensuring smoother international trade for certified Pashmina products.
The PCC has already certified over 15,000 Pashmina shawls and plays a crucial role in supporting the livelihoods of artisans and weavers in Jammu & Kashmir. By ensuring the authenticity of Pashmina, the facility also helps combat the illegal trade of Shahtoosh wool, which is harmful to the Tibetan antelope (Chiru).
Significance for Artisans and Conservation:
- Support for Artisans: The upgraded facility helps increase the credibility of Pashmina products in global markets, benefiting local artisans and weavers.
- Conservation Impact: By certifying genuine Pashmina products, the initiative indirectly contributes to the conservation of the Tibetan antelope by reducing illegal poaching and trade.
- Sustainability: The PCC is a self-sustaining model that not only supports conservation but also generates revenue and creates job opportunities.
Overview of the Genome India Project
The Genome India Project is a gene mapping initiative launched by the Department of Biotechnology, aiming to create a comprehensive database of genetic variations across the Indian population. The project focuses on understanding genetic diversity and its implications for health, agriculture, and biodiversity conservation in India.
Goals:
- Comprehensive Gene Mapping: The project seeks to map the genetic variations found within India’s diverse population, enabling better healthcare and disease management.
- Conservation and Biodiversity: Insights from the project will also aid in wildlife conservation by understanding the genetic health of endangered species and their ability to adapt to environmental changes.
This initiative is aligned with India’s broader goals of using advanced technologies to address modern conservation challenges and foster a sustainable future.
India State of Forest Report 2023

- 22 Dec 2024
In News:
The India State of Forest Report 2023 (ISFR 2023) was released by the Union Minister for Environment, Forest, and Climate Change at the Forest Research Institute in Dehradun. This biennial report, published by the Forest Survey of India (FSI), assesses the forest and tree resources of the country based on satellite data and field-based inventories. The ISFR 2023 is the 18th edition of this report, with the first published in 1987.
Key Findings
- Total Forest and Tree Cover:
- Area: 827,357 sq km (25.17% of India's geographical area)
- Breakdown:
- Forest cover: 715,343 sq km (21.76%)
- Tree cover: 112,014 sq km (3.41%)
- Increase from 2021: An increase of 1,445 sq km, including:
- Forest cover: +156 sq km
- Tree cover: +1,289 sq km
- State-wise Forest and Tree Cover:
- Top 3 States by Total Forest and Tree Cover Area:
- Madhya Pradesh (85,724 sq km)
- Arunachal Pradesh (67,083 sq km)
- Maharashtra (65,383 sq km)
- Top 3 States by Forest Cover:
- Madhya Pradesh (77,073 sq km)
- Arunachal Pradesh (65,882 sq km)
- Chhattisgarh (55,812 sq km)
- States with Maximum Increase in Forest and Tree Cover:
- Chhattisgarh, Uttar Pradesh, Odisha, and Rajasthan
- Mizoram, Gujarat, and Odisha showed the most significant increase in forest cover.
- Top 3 States by Total Forest and Tree Cover Area:
- Forest Cover Percentage (as a proportion of total geographical area):
- Lakshadweep: 91.33% (Highest)
- Mizoram: 85.34%
- Andaman & Nicobar Islands: 81.62%
- 19 States/UTs have over 33% forest cover, with 8 states having more than 75%.
- Mangrove Cover:
- Total Mangrove Cover: 4,992 sq km (a decrease of 7.43 sq km from 2021).
- Notable Changes: Gujarat saw the largest loss of mangroves, whereas Andhra Pradesh and Maharashtra reported increases.
- Carbon Stock and Climate Targets:
- Total Carbon Stock: 7,285.5 million tonnes (an increase of 81.5 million tonnes from the previous assessment).
- Nationally Determined Contributions (NDC):
- India’s carbon stock has reached 30.43 billion tonnes of CO2 equivalent.
- Achieved an additional 2.29 billion tonnes of carbon sink compared to the 2005 baseline, towards the 2030 target of 2.5-3.0 billion tonnes.
- Bamboo and Timber Production:
- Bamboo Bearing Area: Estimated at 154,670 sq km, an increase of 5,227 sq km since 2021.
- Timber Potential: Estimated annual potential production of 91.51 million cubic meters from trees outside forests.
Achievements:
- There has been a notable increase in the forest and tree cover, particularly in states like Chhattisgarh, Uttar Pradesh, Odisha, and Rajasthan.
- The carbon stock in forests has increased, helping India make significant progress in its climate change mitigation goals.
- The bamboo bearing area has also expanded, promoting biodiversity and economic benefits through bamboo cultivation.
Concerns:
- Mangrove Loss: Gujarat experienced a notable decrease in mangrove area, highlighting the need for focused conservation efforts in coastal regions.
Forest Survey of India (FSI) Overview
- Established: 1981, under the Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change (MoEFCC).
- Mission: To assess, monitor, and research forest resources across India, providing data for sustainable management, national planning, and conservation.
- Headquarters: Dehradun, Uttarakhand.
India’s National Quantum Mission

- 22 Dec 2024
In News:
India is preparing to launch its first quantum satellite within 2-3 years as part of its National Quantum Mission (NQM), a significant initiative aimed at positioning India as a global leader in quantum technologies. This satellite will play a pivotal role in enhancing the security of communications, particularly in the face of the potential threat posed by quantum computers to existing cryptographic systems.
What is a Quantum Satellite?
A quantum satellite is a type of communication satellite that uses quantum physics principles to secure data transmission. Unlike conventional satellites that rely on classical encryption, quantum satellites leverage quantum mechanics to achieve unbreakable encryption through Quantum Key Distribution (QKD).
Key Features:
- Quantum Key Distribution (QKD): Ensures secure key sharing, revealing any attempts of eavesdropping.
- Security Advantage: Provides "unconditional security" by detecting any interference during the transmission process.
- Data Transmission: Unlike conventional satellites that encode data in classical bits, quantum satellites encode information in quantum states or qubits.
What is Quantum Cryptography?
Quantum cryptography is a technique that uses the laws of quantum mechanics to secure communications. The most widely used method is Quantum Key Distribution (QKD), which ensures that the keys used to encrypt and decrypt messages remain secret and unbreakable.
Key Mechanisms:
- Quantum Measurement: Any attempt to measure the quantum state (such as a photon carrying information) changes its state, alerting the sender and receiver to potential eavesdropping.
- Quantum Entanglement: When two quantum particles (photons) are entangled, a change in one will instantaneously affect the other, ensuring that the key remains secure.
Why is Quantum Satellite Important?
The advent of quantum computing threatens the cryptographic methods that secure current digital communications. Quantum computers, with their vast computational power, could potentially crack encryption codes that are currently deemed secure. Quantum satellites aim to counteract this threat by using quantum cryptography to make communications tamper-proof.
Security in the Quantum Era:
- Classical Encryption: Relies on mathematical problems that are difficult to solve without the decryption key.
- Quantum Encryption: Uses quantum properties, such as superposition and entanglement, to offer superior security.
National Quantum Mission (NQM)
The National Quantum Mission (NQM) was approved by the Union Cabinet in April 2023 with a budget of ?6,000 crore for implementation over eight years (2023-2031). The mission aims to accelerate the development and application of quantum technologies, with a focus on quantum communication, quantum computing, quantum sensing, and quantum metrology.
Key Objectives:
- Development of Quantum Computers: Building intermediate-scale quantum computers with 50-1000 qubits.
- Quantum Communication: Establishing secure, satellite-based quantum communication systems within India and internationally.
- Research and Innovation: Fostering quantum technologies and creating a self-reliant ecosystem.
India’s Advancements in Quantum Technology
India is making significant progress in quantum research and communication. The Raman Research Institute in Bengaluru has identified Hanle, Ladakh as an ideal location for quantum communication experiments due to its optimal atmospheric conditions.
The Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) has already demonstrated successful free-space quantum communication over short distances (300 meters). The upcoming quantum satellite will build upon this progress to create secure quantum communication networks within India and internationally.
Global Context: Micius Satellite and China’s Lead
China is a global leader in quantum communications, having launched the world’s first quantum satellite, Micius, in 2016. Micius demonstrated the feasibility of secure quantum communication by generating pairs of entangled photons. India’s quantum satellite will build on this technology to create robust, long-range quantum communication networks.
Limitations of Quantum Key Distribution (QKD)
Despite its promise, QKD faces several limitations:
- Technological Maturity: The technology is still in the experimental phase, and large-scale commercial implementation is not yet feasible.
- Authentication Issues: QKD lacks reliable methods to authenticate the transmission source, leaving it vulnerable to impersonation attacks.
- Infrastructure Costs: Establishing and maintaining QKD networks requires specialized hardware, leading to higher costs.
- Denial-of-Service Risks: Eavesdroppers can trigger the abort mechanism, leading to transmission interruptions.
- Signal Loss: Atmospheric and distance-related attenuation can degrade the quality of quantum signals.
National Quantum Mission and Sectoral Impact
The NQM aligns with India's national priorities, including Digital India, Make in India, and Start-up India. The mission’s outcomes are expected to impact various sectors, such as:
- Healthcare: Quantum computing for drug design and medical research.
- Space Exploration: Enhancing communication security for space missions.
- Banking and Financial Services: Strengthening data security and transaction integrity.
- Energy: Improving energy systems and smart grids through advanced sensing technologies.
IRIS²: The European Union's Ambitious Satellite Network

- 21 Dec 2024
In News:
The European Union (EU) has announced the launch of IRIS² (Infrastructure for Resilience, Interconnectivity, and Security by Satellite), a highly ambitious space program that aims to enhance satellite connectivity, security, and resilience for both governmental and civilian applications. The initiative is set to rival major global satellite systems, such as Elon Musk's Starlink, and aims to provide secure, high-speed broadband connectivity, particularly in underserved regions.
Key Features of IRIS²:
- Satellite Constellation: The system will consist of 290 satellites, including 264 in Low Earth Orbit (LEO) and 18 in Medium Earth Orbit (MEO).
- First Launch: The first satellite for the program is scheduled for launch in 2029.
- Secure Connectivity: IRIS² is designed to provide secure, high-speed broadband services, particularly for European regions that lack reliable connectivity.
- Collaboration: The project is a collaboration between the EU, the European Space Agency (ESA), and private sector partners, including SES, Eutelsat, and Airbus.
- Funding: The program is funded through a €10.6 billion (~$11 billion) investment, with a 12-year concession for its implementation.
Applications of IRIS²:
- Governmental Use:
- Border Surveillance: Enhanced monitoring for national security.
- Crisis Management: Reliable communication during natural disasters and emergencies.
- Infrastructure Security: Safeguarding key national infrastructure.
- Defense: Boosting military communication resilience.
- Civilian Use:
- Broadband Access: Providing internet access in rural and underserved areas.
- Smart Energy: Supporting management of energy grids and related technologies.
- Transportation: Ensuring reliable communication and navigation in aviation, maritime, and automotive sectors.
- Remote Healthcare: Improving healthcare access in remote locations.
Significance of IRIS²:
- Strategic Asset: The program will strengthen EU sovereignty in space technology and improve its technological independence, reducing reliance on non-European satellite systems.
- Cyber and Communication Resilience: IRIS² is designed to enhance resilience against cyber threats and communication disruptions, ensuring uninterrupted service for both public and private sectors.
- Commercial Benefits: The satellite network will provide high-speed connectivity for businesses across Europe, offering a boost to commercial activities in remote and underserved areas.
- Complementary to Existing EU Programs: IRIS² complements other EU space initiatives, such as Copernicus (Earth observation) and Galileo (satellite navigation), enhancing the EU's capabilities in the space sector.
Overview of the IRIS² Satellite Network:
- Deployment in LEO and MEO:
- 264 satellites in LEO will provide low-latency communication for a wide range of applications.
- 18 satellites in MEO will offer broader coverage and support for global connectivity.
- Funding and Partners: The program is funded by the EU, ESA, and private firms, including SES, Eutelsat, and Airbus, ensuring both public and private sector involvement in the project.
- Applications:
- The network will provide secure satellite services for critical government functions, including surveillance, defense, and crisis management.
- It will also support civilian uses, such as broadband, smart grids, and transportation, and will facilitate cloud-based services.
Strategic and Geopolitical Importance:
- Boost to European Competitiveness: By developing its own satellite system, the EU will enhance its competitive position in the global space sector.
- Security and Autonomy: IRIS² will help Europe maintain control over its communication infrastructure, strengthening its autonomy and reducing dependence on external players for critical services.
- Resilience in Crisis Situations: In times of disruption (e.g., natural disasters, cyberattacks), IRIS² will ensure that Europe can maintain secure, reliable connectivity.
72% Decline in Bird Species at Bordoibam-Bilmukh Bird Sanctuary, Assam

- 21 Dec 2024
In News:
A recent study has revealed a dramatic decline in the number of bird species at Assam's Bordoibam-Bilmukh Bird Sanctuary (BBBS). The sanctuary, once home to a rich diversity of avian species, has experienced a 72% decline in bird species over the past 27 years. The study, published in the Journal of Threatened Taxa, highlights the severe biodiversity crisis facing the sanctuary.
Key Findings:
- Bird Species Count Decline:
- In 1997, the sanctuary recorded 167 bird species.
- Recent surveys (2022-2024) have only recorded 47 species, marking a 71.85% decline in species count.
- Surveys:
- 2011 Survey: Recorded 133 species (86 resident, 23 migratory, 24 local migrants).
- 2017-2018 Survey: Found 120 species, along with a variety of other biodiversity, including macrophytes, fish, and aquatic ferns.
- Impact on Migratory Birds:
- Migratory species like Brown Shrike, Citrine Wagtail, and White Wagtail (winter migrants), and the Lesser Kestrel (summer migrant) were recorded recently.
- Main Causes of Decline:
- Anthropogenic Activities: Overfishing, poaching, excessive harvesting of aquatic plants, and egg collection.
- Land Use Changes: Habitat degradation due to agriculture, machinery noise, and land being used as pasture areas.
- Disruption of Food Chain: Habitat loss and changes in foraging and breeding grounds for both migratory and resident birds.
- Species of Concern:
- Poached Birds: Lesser whistling duck, Fulvous whistling duck, White-breasted waterhen, Indian pond heron, Eastern spotted dove, and Yellow-footed green pigeon.
- Threatened Species: The sanctuary is home to globally threatened species like the Spot-billed Pelican and Lesser Adjutant.
About Bordoibam-Bilmukh Bird Sanctuary:
- Location: Situated between Dhemaji and Lakhimpur districts in Assam, the sanctuary spans 11.25 sq. km at an altitude of 90-95 meters above sea level.
- History: Declared a wildlife sanctuary in 1996, it was originally part of the Subansiri River which has now shifted 7 km from the wetland.
- Climate & Vegetation:
- Moist tropical climate with an average annual rainfall of around 2,000 mm.
- The vegetation includes flooded valley grasslands and wetland plants, providing crucial habitat for migratory birds.
- Significance for Avian Species:
- Hosts a variety of migratory waterfowl, especially during the winter.
- Home to globally threatened bird species like the Spot-billed Pelican and Lesser Adjutant, along with resident birds such as the Indian Pond Heron and Fulvous Whistling Duck.
Conservation Efforts:
- The decline in bird species at the sanctuary has raised alarm about the degradation of wetland habitats.
- The study emphasizes that habitat loss can disrupt the food chain, water table, and nutrient cycle, which in turn harms both the ecosystem and human communities.
- The authors of the study advocate for intense conservation efforts to restore and protect the sanctuary’s biodiversity.
Assam's Biodiversity:
- Assam is one of India's most biodiverse states, with around 950 bird species, including 17 endemic species.
- The state also hosts 55 Important Bird and Biodiversity Areas (IBA), which are vital hotspots for avian species.
New Undersea Cables to Boost India’s Digital Connectivity
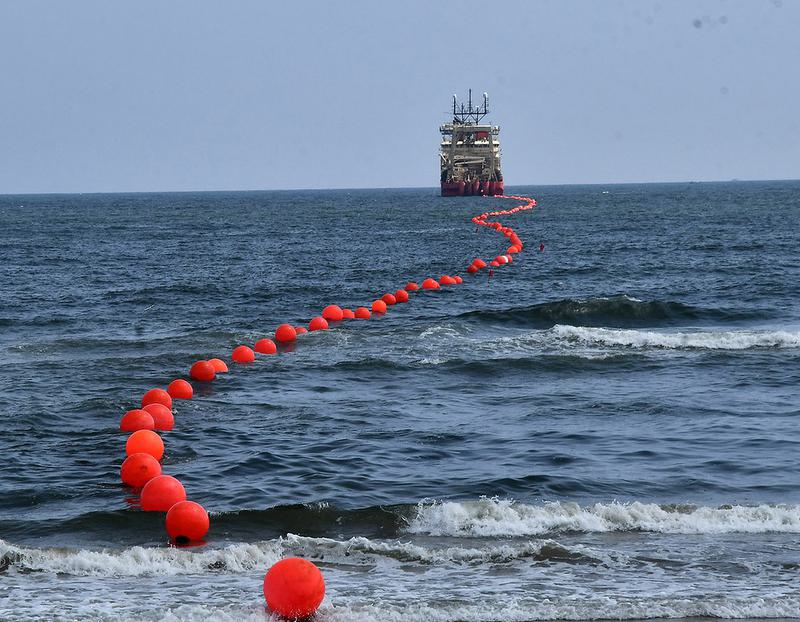

- 21 Dec 2024
In News:
India is expanding its digital infrastructure with the launch of two major undersea cable systems aimed at enhancing its Internet connectivity with Asia and Europe. The India Asia Xpress (IAX) and India Europe Xpress (IEX) are set to provide additional data links between India and these regions, supporting the growing demand for data usage. This also marks India’s increasing involvement in submarine cable resilience and security discussions.
Key Points:
- New Cable Systems:
- India Asia Xpress (IAX): Connects Chennai and Mumbai with Singapore, Thailand, and Malaysia.
- India Europe Xpress (IEX): Connects Chennai and Mumbai with France, Greece, Saudi Arabia, Egypt, and Djibouti.
- Total Length: Both cables, together spanning over 15,000 kilometers, will expand India’s undersea cable network.
- Ownership and Investment:
- Both cable systems are owned by Reliance Jio, with a strategic investment from China Mobile.
- Geopolitical Impact:
- These expansions are a response to growing Internet traffic, as well as India's rising geopolitical ambitions. They help bolster India’s defense strategy, improving cable resilience against disruptions from cyberattacks or physical damages.
- India’s active role in maritime cable network security is being closely watched, especially in key regions like the Bay of Bengal and the South China Sea.
- Past Cable Disruptions:
- In March, three cables connecting India to West Asia and Europe were disrupted, impacting Internet traffic. However, India’s alternate routing systems and data centers ensured services remained operational, highlighting the country’s resilience.
- International Role:
- India’s role in submarine cable resilience is growing. Telecom Secretary Neeraj Mittal is part of the International Advisory Body for Submarine Cable Resilience, established by the International Telecommunication Union (ITU).
Impact on India’s Connectivity:
- Bangladesh's Role:
- Plans to sell bandwidth from Bangladesh to Northeast India were recently put on hold. However, this does not significantly impact India as Northeast India already benefits from substantial fiber-optic connectivity through Power Grid Corporation of India’s transmission lines.
About Underwater Cables:
- What Are Undersea Cables?
- Undersea cables are fiber-optic cables laid under the ocean to transmit data across vast distances at high speeds.
- New Cable Systems:
- IAX: Connects India to Asia (Singapore, Thailand, Malaysia).
- IEX: Connects India to Europe (France, Greece, Saudi Arabia, Egypt, Djibouti).
- How They Work:
- Fiber-optic technology uses laser beams through thin glass fibers to transmit data.
- The cables are protected by multiple layers of insulation, plastic, and steel wires and are buried near shores or laid directly on the ocean floor in deep sea regions.
- Cable Features:
- Data Capacity: New cables can carry up to 224 Tbps (Terabits per second).
- Durability: Designed to avoid damage from fault zones, fishing areas, or anchors.
- Speed: Faster and more cost-efficient than satellite communications for large-scale data transfer.
Why Undersea Cables Over Satellites?
- Higher Capacity: Submarine cables handle far more data than satellites.
- Cost-Effective: More affordable for high-volume data transfers.
- Reliability: Cables provide more stable connections, especially for large-scale data, compared to satellites.
Strengthening Multimodal and Integrated Logistics Ecosystem (SMILE) program

- 21 Dec 2024
On December 20, 2024, the Government of India and the Asian Development Bank (ADB) signed a $350 million policy-based loan aimed at expanding India's manufacturing sector and improving the resilience of its supply chains. This loan is part of the Strengthening Multimodal and Integrated Logistics Ecosystem (SMILE) program.
Key Points:
- Loan Agreement Signatories:
- Department of Economic Affairs (DEA), Ministry of Finance, Government of India
- Department for Promotion of Industry and Internal Trade (DPIIT), Ministry of Commerce and Industry
- Asian Development Bank (ADB)
- SMILE Program:
- Goal: Strengthen the logistics ecosystem to enhance India's manufacturing sector and improve supply chain resilience.
- Structure: The program includes two subprograms focusing on strategic reforms in logistics and infrastructure development.
- Key Features of the SMILE Program:
- Strengthening Multimodal Infrastructure: Enhances logistics infrastructure at the national, state, and city levels.
- Standardization: Improves warehousing and other logistics assets to attract private sector investment.
- External Trade Logistics: Enhances efficiencies in external trade logistics.
- Smart Systems: Adopts systems for efficient, low-emission logistics to promote sustainability.
- Expected Outcomes:
- Cost Reduction & Efficiency: Strategic reforms will reduce logistics costs and improve efficiency.
- Job Creation: Infrastructure development and reforms are expected to generate substantial employment opportunities.
- Gender Inclusion: The program promotes gender inclusion through economic growth initiatives.
- Impact on India’s Economy:
- The transformation of India’s logistics sector will enhance the competitiveness of the manufacturing sector and drive sustainable economic growth.
About the Asian Development Bank (ADB):
- Headquarters: Mandaluyong, Metro Manila, Philippines.
- Established: December 19, 1966.
- Members: 69 countries, including both regional (e.g., India, China) and non-regional (e.g., USA, Japan) members.
- Function: ADB promotes social and economic development in Asia and the Pacific, providing loans, grants, and technical assistance for development projects.
- Key Shareholders:
- Japan: 15.57%
- USA: 15.57%
- India: 6.32%
- China: 6.43%
- Australia: 5.77%
2023 National Tansen Samman

- 21 Dec 2024
In News:
- The prestigious National Tansen Samman for 2023 was conferred upon Pt. Swapan Choudhary, a renowned tabla maestro from Kolkata, at the National Tansen Festival held in Gwalior, Madhya Pradesh.
Key Highlights:
- Tansen Festival: This festival, renowned for its celebration of classical music, is organized annually in Gwalior, which is considered the music capital of Madhya Pradesh.
- Prize Details: As part of the honor, Pt. Swapan Choudhary was presented with an honorarium of five lakh rupees, a citation plaque, and a shawl-shriphal.
- About the Award:
- The National Tansen Samman was established in 1980 by the Madhya Pradesh government to recognize exceptional contributions to Indian classical music.
- It is named after Tansen, one of India's most celebrated classical musicians.
- The award is the highest national honor in the field of Indian classical music.
- Additional Award:
- Raja Mansingh Tomar Samman for 2023 was awarded to Sanand Nyas, an institution from Indore. This institution has been active for 35 years in the promotion of classical music, drama, and cultural festivals.
- Pt. Swapan Choudhary’s Remark: In response to receiving the honor, Pt. Choudhary expressed his gratitude and pride in joining the ranks of distinguished artists awarded the National Tansen Samman.
About Tansen: The Iconic Musician
- Legacy: Tansen, also known as Miyan Tansen, was a prominent Indian classical musician, composer, and vocalist. He is credited with popularizing several ragas and revolutionizing the Indian classical music tradition.
- Role at Akbar’s Court: Tansen was one of the Navaratnas (nine jewels) in the court of Mughal Emperor Akbar. He held the title of Mian, meaning "learned man," bestowed upon him by Akbar.
- Contributions:
- Tansen is famous for his compositions, including the introduction of notable ragas such as Miyan ki Malhar, Miyan ki Todi, and Darbari.
- He also improved the plucked rabab, which is of Central Asian origin, enhancing its role in Indian classical music.
- Historical Influence: Tansen's life and work are surrounded by extensive legend, and his contributions remain deeply influential in the development of Indian classical music today.
Specialised Investment Fund (SIF)
- 20 Dec 2024
In News:
SEBI has introduced a new asset class called Specialised Investment Fund (SIF), designed to bridge the gap between Mutual Funds (MFs) and Portfolio Management Services (PMS). This new asset class is targeted at informed investors who are willing to take on higher risks.
SIFs offer a blend of the flexibility seen in PMS and the regulatory framework governing MFs, making them suitable for investors seeking more customized and riskier investment strategies.
Key Features of SIF:
- Minimum Investment: The minimum investment threshold for SIFs is Rs. 10 lakh. However, accredited investors (who meet specific eligibility criteria) can invest with lower amounts.
- Expense Structure: SIFs will follow the same expense structure as mutual funds. For equity schemes up to Rs 500 crore in size, the maximum allowable fee is 2.25% of assets under management (AUM), with the cap decreasing as the fund size grows. This ensures transparency and keeps management fees in line with existing mutual fund norms.
- Investment Strategies: SIFs can offer a mix of open-ended, close-ended, and interval investment strategies. Specific details on permissible strategies will be released by SEBI in the future.
- Investment Restrictions:
- For debt instruments, a single issuer's exposure is capped at 20% of the total AUM. However, this can be raised to 25% with approval from the Asset Management Company (AMC)’s trustees and board of directors. Government securities are exempt from this limit.
- For equities, the exposure is capped at 10% of the total AUM, in line with the norms for mutual funds.
- Ownership in Companies: The maximum permissible ownership in any company is raised to 15%, including the MF exposure.
- REITs and InvITs: SIFs can invest a maximum of 20% of their AUM in Real Estate Investment Trusts (REITs) and Infrastructure Investment Trusts (InvITs). However, the exposure to a single issuer in these areas is limited to 10%.
- Branding and Marketing: SEBI mandates AMCs to distinguish SIFs clearly from MFs through distinct branding, advertising, and website presence. This helps in creating a clear differentiation between the two products for investors.
- Risk Management and Compliance: AMCs managing SIFs are required to have robust risk management systems, internal control systems, and expertise to handle the investments effectively. Trustees are responsible for ensuring that the AMC complies with all risk management, investor protection, and disclosure norms.
Regulatory Context:
- The regulations on SIFs are similar to those governing mutual funds, including taxation and other compliance requirements.
- SEBI also introduced the Mutual Fund Lite regulations to encourage the growth of passively managed funds, such as exchange-traded funds (ETFs) and index funds. These regulations are designed to reduce compliance burdens and lower the barriers to entry for new players in the mutual fund industry.
Significance of SIFs:
- Targeted Audience: SIFs cater to investors who are knowledgeable and willing to take on riskier investments, thereby filling a gap between traditional MFs (which are more conservative) and PMS (which offer highly customized solutions).
- Higher Flexibility: While SIFs maintain some regulations of MFs, they offer more flexibility in investment choices, allowing AMCs to explore more dynamic strategies.
- Investor Protection: By maintaining the same expense structure as mutual funds and ensuring compliance with regulatory frameworks, SEBI aims to protect investor interests while allowing for higher returns that come with riskier investments.
Parliamentary Standing Committee on Rural Development & Panchayati Raj (PSC) and MGNREGA
- 20 Dec 2024
In News:
Recently, the Parliamentary Standing Committee (PSC) on Rural Development and Panchayati Raj highlighted several issues within the Mahatma Gandhi National Rural Employment Guarantee Scheme (MGNREGS). The committee recommended reforms to address these challenges, especially concerning wage rates, workdays, payment systems, and infrastructure.
Key Challenges in MGNREGS Implementation:
- Wages Not Aligned with Inflation:
- MGNREGA wage rates have failed to keep pace with inflation, diminishing the purchasing power of rural workers. This discourages workers from completing the full 100 workdays.
- The wage guarantee of 100 days per household often falls short, especially during times of natural calamities or post-pandemic recovery.
- Revision of Permissible Works:
- The list of allowable work under MGNREGA is outdated and doesn't cover all rural needs, such as flood protection or land erosion management. Delayed revisions limit its effectiveness in addressing region-specific challenges.
- Delayed Payment of Wages:
- Issues like Aadhaar-based payment system (ABPS) glitches, inactive Aadhaar details, or frozen bank accounts often lead to delayed wage payments.
- The delay in wages undermines the scheme's goal of providing livelihood support.
- Unemployment Allowance:
- Those who apply for work but are not provided employment within 15 days are entitled to a daily unemployment allowance. However, this allowance is rarely paid, and when it is, the amounts are insufficient.
- Weak Social Audits:
- Social audits are a vital mechanism to ensure transparency and accountability. However, in the 2020-21 fiscal year, only 29,611 Gram Panchayats out of a total were audited, pointing to the weak social audit system.
- Lack of Ombudsman:
- Despite the provision for 715 ombudsmen, only 263 have been appointed. This reduces the oversight and accountability of the scheme.
Recommendations for MGNREGS Reform by the PSC:
- Revision of Wage Rates:
- Link MGNREGA wages to an inflation index, ensuring wages reflect the rising cost of living in rural areas.
- The base year (2009-2010) should be updated to align with current inflation trends.
- Increase Days of Work:
- The PSC recommended increasing the guaranteed workdays from 100 to 150 days. This will provide better livelihood security, especially in times of economic distress.
- Improvement in Payment Mechanisms:
- The committee recommended maintaining alternative payment systems alongside ABPS to prevent wage delays.
- A streamlined process should be put in place to ensure timely wage disbursement, reducing bureaucratic hurdles.
- National Mobile Monitoring System (NMMS):
- The committee stressed the importance of training programs to help beneficiaries effectively use the NMMS.
- It also suggested retaining alternative attendance methods to avoid exclusion due to technological barriers. NMMS helps enhance transparency and accountability by tracking attendance and work progress.
- Sufficient Fund Allocation:
- The committee emphasized the need for adequate financial allocations for MGNREGS to make it more effective in providing livelihood security to rural households.
Additional Context and Statistics:
- In 2024-25, the average wage increase under MGNREGA was just Rs 28/day.
- The MGNREGA wage increase for 2023-24 ranged from 2%-10%.
- The Consumer Price Index for Agricultural Labour (CPI-AL) is used to determine wage rates, although Dr. Nagesh Singh Committee (2017) recommended using the CPI Rural instead.
About the Parliamentary Standing Committee on Rural Development & Panchayati Raj (PSC):
- Established: August 5, 2004.
- Jurisdiction: The committee oversees the Ministry of Rural Development and the Ministry of Panchayati Raj.
- Composition: 31 members – 21 from Lok Sabha and 10 from Rajya Sabha.
- Functions:
- Reviews Demands for Grants and reports.
- Examines Bills referred by the Speaker or Chairman.
- Reviews the annual reports of relevant ministries.
- Considers national policy documents.
About MGNREGA:
- Launched: 2005 by the Ministry of Rural Development.
- Objective: Provides 100 days of unskilled manual work at minimum wages for rural households annually.
- Key Features:
- Legal Guarantee: Work must be provided within 15 days of request.
- Unemployment Allowance: If work isn't provided within 15 days, beneficiaries are entitled to a daily allowance.
- Women-Focused: At least one-third of beneficiaries are women.
- Social Audits: Mandated by the Gram Sabha for all projects under the scheme.
Masali Village in Gujarat

- 20 Dec 2024
In News:
In Gujarat, Masali village in Banaskantha district has become country’s first solar border village.
Key Highlights:
Location:
Masali village is located in Banaskantha district, Gujarat, approximately 40 kilometers from the Pakistan border. The village, with a population of around 800 people, has recently achieved a significant milestone by becoming India’s first fully solar-powered border village.
Solarization Initiative:
Under the PM Suryaghar Yojana, the village has installed solar rooftops on 119 houses. These solar installations collectively generate over 225 kilowatts of electricity, which is more than sufficient to meet the village’s energy needs. This initiative marks a step forward in solarizing border areas of India, promoting sustainability and reducing dependency on conventional energy sources.
Significance of the Initiative:
- India's First Solar-Powered Border Village: Masali village is the first of its kind in India, making it a model for other border regions to adopt renewable energy solutions.
- Promotes Renewable Energy: The transition to solar power encourages sustainability, reduces dependence on traditional fossil fuels, and supports India's renewable energy goals.
- Part of the Border Development Project: Masali is part of a broader government plan that aims to solarize 11 villages in Vav taluka and 6 villages in Suigam taluka, strengthening energy access in these strategically vital areas.
- Energy Security: By harnessing solar energy, the village enhances its energy reliability and self-sufficiency, especially in remote areas with limited access to the national grid.
PM Suryaghar Yojana: Launched in 2024, the PM Suryaghar Yojana aims to provide free electricity to eligible Indian households by subsidizing the installation of rooftop solar panels. Key features of the scheme include:
- A subsidy covering up to 40% of the installation cost of solar panels.
- Eligible families receive 300 free electricity units per month, saving up to Rs. 18,000 annually.
- The scheme is expected to save the government approximately Rs. 75,000 crore annually on electricity costs.
- It encourages the use of renewable energy, lowers carbon emissions, and reduces the electricity expenses for the government.
Eligibility for the Scheme:
- Indian citizens who own a house with a suitable roof for installing solar panels.
- Households must have a valid electricity connection and should not have received any prior subsidy for solar panels.
Broader Implications:
The successful solarization of Masali village is not just an energy achievement but also a significant step toward promoting renewable energy usage, enhancing energy security, and fostering sustainable development in India’s border regions. It is expected that other regions in Gujarat and across the country will follow this example, improving both local living conditions and national energy resilience.
Reimposition of Protected Area Permit (PAP) in Manipur, Mizoram, and Nagaland

- 20 Dec 2024
In News:
The Ministry of Home Affairs (MHA) of the Government of India has recently reinstated the Protected Area Regime (PAR) for the states of Manipur, Mizoram, and Nagaland, which are strategically located along the international border with Myanmar. This move comes amid growing security concerns, particularly the influx of migrants from Myanmar, which has been cited as a significant factor in the ongoing conflicts in the region.
What is Protected Area Permit (PAP)?
A Protected Area Permit (PAP) is a special permission required for foreign nationals to visit certain areas of India deemed sensitive due to their proximity to international borders or other security-related concerns. The regulations governing the PAP are laid down under the Foreigners (Protected Areas) Order, 1958, which restricts the entry of foreigners to designated regions within India.
Purpose of PAP:
The PAP regime serves multiple critical objectives:
- National Security: It ensures the monitoring and regulation of foreign nationals in sensitive border areas.
- Preservation of Local Communities: The regime safeguards indigenous populations and their unique cultural heritage.
- Environmental Conservation: The permit helps minimize ecological disturbances in fragile regions, ensuring sustainable tourism and development.
Key Features of PAP Regime:
- Eligibility: All foreign nationals, excluding Bhutanese citizens, must obtain a PAP to enter these designated areas. The permit can be granted for specific regions, routes, and time periods.
- Validity: The PAP is typically valid for 10 days with the possibility of extension.
- Restricted Areas: Certain foreign nationals, particularly those from Afghanistan, China, and Pakistan, require prior approval from the MHA to enter these regions.
- Tourism and Other Permits: While foreign nationals can visit these regions for tourism purposes under the PAP, non-touristic visits require special permission from the MHA.
- Registration: Foreigners must register with the Foreigners Registration Officer (FRO) within 24 hours of arrival in the protected area.
Historical Context and Reimposition:
The PAP regime was lifted for Manipur, Mizoram, and Nagaland in 2011, as part of efforts to boost tourism in the region. However, due to rising security concerns related to illegal immigration and ethnic tensions, the MHA reimposed the PAP in 2025. The government’s move aligns with its broader national security strategy to better control foreign movements in sensitive border regions, particularly those with Myanmar, where the Free Movement Regime (FMR) had previously allowed easier cross-border travel.
Background on Security Concerns:
The influx of individuals from Myanmar, particularly members of the Chin community, which shares ethnic ties with the Kuki-Zomi communities in India, has been a source of tension. The Manipur government has repeatedly emphasized that uncontrolled migration has contributed to the unrest in the state. Additionally, the decision to end the FMR between India and Myanmar has further intensified the debate over border security and migration.
Impact on Tourism and Local Communities:
While the reimposition of the PAP is seen as a measure to strengthen security, it has raised concerns in states like Mizoram and Nagaland, which have been actively promoting tourism. For example, Nagaland’s Hornbill Festival recently attracted over 200,000 visitors, including foreign nationals. The reintroduced restrictions may dampen tourism in these states, which were previously exempt from the PAP to encourage foreign visits.
Key Legal Provisions Under the PAP Regime:
- Foreigners (Protected Areas) Order, 1958: This order mandates the requirement of a PAP for foreigners visiting areas close to international borders.
- Foreigners (Restricted Areas) Order, 1963: This order covers areas that require a Restricted Area Permit (RAP) for foreign nationals, such as the Andaman and Nicobar Islands.
States Affected by the PAP Regime:
The PAP regime affects regions close to India’s international borders, including the entire states of Arunachal Pradesh, Sikkim, Manipur, Mizoram, Nagaland, and parts of Himachal Pradesh, Jammu & Kashmir, Rajasthan, and Uttarakhand.
Dark Comets

- 20 Dec 2024
In News:
Dark comets are a newly identified class of celestial objects that challenge our traditional understanding of comets and asteroids. Unlike regular comets, these objects exhibit characteristics that blur the lines between comets and asteroids, leading astronomers to closely study their nature, origin, and significance.
Discovery and Background
The first hint of dark comets appeared in 2016, when asteroid 2003 RM exhibited strange orbital deviations that suggested it might be a comet in disguise. NASA further fueled this interest in 2017 when it discovered ‘Oumuamua, an interstellar object that entered our Solar System. Though initially classified as an asteroid, its erratic motion and lack of a visible tail led scientists to consider it a dark comet. Since then, several more objects with similar characteristics have been discovered, and astronomers now identify these objects as a new class—dark comets.
Characteristics of Dark Comets
- Appearance: Dark comets do not exhibit the brilliant, glowing tails typically associated with comets. Instead, they resemble asteroids, appearing as faint points of light in space. Unlike bright comets, they do not have a visible coma (a cloud of gas and dust) or a tail, making them much harder to detect.
- Size: Dark comets are typically small, ranging from a few meters to a few hundred meters in diameter. Due to their small size, there is less surface area for material to escape, preventing the formation of the iconic tails seen in traditional comets.
- Orbital Path: These objects follow elongated, elliptical orbits. While some of them travel close to the Sun, they can also venture to the outer reaches of the Solar System, far beyond Pluto, and even into the Oort Cloud—the distant region where long-period comets are believed to originate.
- Spin and Gas Dispersion: Dark comets often rotate rapidly, dispersing gas and dust in all directions. This rapid spin contributes to their invisibility, as the gas and dust are scattered evenly, making it more difficult for astronomers to detect their presence.
- Composition: The composition of dark comets may also play a role in their lack of visibility. Over time, the materials that form the bright tails of comets may be depleted, especially for older objects. As a result, dark comets may not release enough gas to produce a visible coma or tail.
Types of Dark Comets
There are two main categories of dark comets:
- Inner Dark Comets: These are smaller objects that reside closer to the Sun and typically travel in nearly circular orbits. They are often just a few meters in size, with less surface area for gas and dust to escape.
- Outer Dark Comets: These larger objects, measuring over 100 meters in diameter, travel in highly eccentric orbits, similar to Jupiter-family comets. These dark comets follow elliptical paths that bring them close to the Sun and then send them back toward the outer reaches of the Solar System.
Importance of Studying Dark Comets
Dark comets may hold critical clues about the early Solar System and the formation of Earth. Studying these objects can provide insights into the origins of water on Earth, as well as the ingredients necessary for life. Their unique composition and orbits also offer potential for understanding the processes that led to the formation of planets.
Recent Discoveries and Advancements
Astronomers recently discovered 10 new dark comets with the help of the Dark Energy Camera (DECam) on a large telescope in Chile. The DECam, designed to study distant galaxies and stars, has enabled researchers to detect these faint objects by analyzing images of the night sky. Further progress is expected with the upcoming Vera C. Rubin Observatory, which will feature the largest digital camera ever built. This new instrument will allow astronomers to capture more detailed images of the night sky and detect fainter objects, potentially doubling or even tripling the number of known dark comets in the next decade.
Key Facts:
- Dark comets lack the characteristic glowing tails of typical comets, instead resembling asteroids.
- They exhibit erratic motions and follow elliptical orbits, often extending beyond Pluto and into the Oort Cloud.
- They are typically small (a few meters to hundreds of meters wide) and spin rapidly.
- The first dark comet was identified in 2016, with more discoveries made in the years since.
- The Dark Energy Camera (DECam) in Chile has been instrumental in detecting these elusive objects, with a new Vera C. Rubin Observatory expected to further enhance detection in the future.
- Studies suggest that between 0.5% and 60% of Near-Earth Objects (NEOs) could be dark comets, many originating from the asteroid belt between Mars and Jupiter.
India's First-Ever Ganges River Dolphin Tagging in Assam

- 19 Dec 2024
In News:
India conducts the first-ever satellite tagging of the Ganges River Dolphin (Platanista gangetica) in Assam, a key step in wildlife conservation.
Key Highlights:
Objective of Tagging: The tagging aims to understand:
- Migratory patterns
- Range and distribution
- Habitat utilization, especially in fragmented river systems.
Key Participants:
- Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change (MoEFCC)
- Wildlife Institute of India (WII)
- Assam Forest Department
- Aaranyak (NGO)
- Funded by the National CAMPA Authority.
Significance of the Tagging:
- Technology Used: Lightweight satellite tags compatible with Argos systems were employed, minimizing interference with the dolphin’s movement despite its limited surfacing time (5-30 seconds).
- Insight into Dolphin Ecology: Helps fill knowledge gaps regarding habitat needs and seasonal migration, especially in disturbed river ecosystems.
Ganges River Dolphin – India's National Aquatic Animal:
- Endemic to India with around 90% of the population in India.
- Known for being nearly blind and using echolocation for navigation and hunting.
- Plays a crucial role as an apex predator and indicator species for river ecosystem health.
Project Dolphin:
- Launched by PM Narendra Modi in 2020, modeled after Project Tiger.
- Focuses on conservation of riverine and marine dolphins.
- A 10-year initiative funded by MoEFCC to safeguard dolphin populations and address ecosystem challenges.
Conservation Status:
- IUCN: Endangered.
- Protection: Included in Schedule I of the Wildlife Protection Act (1972) and CITES Appendix I.
- Major Threats: Habitat degradation, pollution, bycatch, and water abstraction, compounded by damming and sand mining.
Broader Impact:
- The tagging initiative contributes to evidence-based conservation strategies for Ganges River Dolphins.
- Will aid in the development of a comprehensive conservation action plan for the species.
- Expands the understanding of critical habitats within river ecosystems, benefiting both biodiversity and the communities dependent on these resources.
National Wildlife Health Policy (NWHP)

- 19 Dec 2024
In News:
The Central Zoo Authority, under the aegis of the Ministry of Environment Forest and Climate Change (MoEF&CC) has taken up the development of the ‘National Wildlife Health Policy in consultative workshop held in Indira Prayavaran Bhawan, New Delhi.
Key Highlights:
- Organized by: Central Zoo Authority (CZA), under the Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change (MoEF&CC).
- Event: Consultative workshop held at Indira Prayavaran Bhawan, New Delhi, on the development of the National Wildlife Health Policy (NWHP).
- Purpose: To address health threats to wildlife and integrate wildlife health management with public and animal health.
Goals of the National Wildlife Health Policy (NWHP):
- One Health Approach: Integrates human, animal, and environmental health, recognizing their interdependence.
- Focus Areas:
- Prevent and control zoonotic diseases.
- Improve disease surveillance and early detection, especially in protected areas.
- Promote biosecurity measures and epidemic preparedness.
- Enhance research and development in wildlife health management.
- Advocate for community awareness on wildlife health and conservation.
Key Features of the Policy:
- Wildlife Health Management Unit (WHMU): Proposed unit to oversee the policy's implementation.
- Collaboration: Involves coordination with various stakeholders including government ministries, NGOs, academic institutions, and veterinary universities.
- Disease Surveillance: Establish protocols for monitoring and controlling wildlife diseases, especially in protected areas.
- Capacity Building: Training programs for professionals involved in wildlife conservation and health management.
- Biosecurity Protocols: Strengthen measures to reduce disease transmission risks.
Supporting Institutions:
- GISE Hub, IIT Bombay and Office of the Principal Scientific Adviser to the Government of India are providing support in policy development.
Challenges Addressed:
- Wildlife in India faces various health challenges including:
- Infectious diseases (e.g., Canine Distemper Virus).
- Habitat loss and climate change impacts.
- Illegal wildlife trade and other anthropogenic pressures.
- India has over 91,000 wildlife species and more than 1,000 protected areas, making comprehensive health management crucial.
Expected Outcomes:
- Comprehensive Framework: A science-based framework for wildlife health, integrating ecological, human, and animal health.
- Disease Outbreak Response: Structured mechanisms for disease management, surveillance, and legal frameworks.
- Public Health Integration: Safeguard wildlife health, which directly impacts balanced ecosystems and biodiversity.
Policy’s Strategic Alignment:
- National Wildlife Action Plan (2017-31): The policy complements the action plan’s 103 conservation actions and 250 projects, including disease surveillance protocols in tiger reserves and other protected areas.
- Research & Development: Encourages the development of strategies to manage wildlife health and prevent disease outbreaks.
Eastern Maritime Corridor (EMC)
- 19 Dec 2024
In News:
In mid-2024, India surpassed China as the largest importer of Russian oil. This milestone has been accompanied by the operationalization of a new maritime route, the Eastern Maritime Corridor (EMC), which connects Chennai in India to Vladivostok in Russia. The new sea route is significantly reducing both shipping times and costs, facilitating smoother commodity trade between the two countries, particularly crude oil shipments.
The Eastern Maritime Corridor (EMC)
The EMC, covering a distance of about 5,600 nautical miles, has reduced the shipping time between India and Russia’s Far East by up to 16 days. The Chennai-Vladivostok route now takes just 24 days, compared to over 40 days using the traditional St. Petersburg-Mumbai route. This reduction in transit time makes it a highly efficient route for transporting goods such as crude oil, coal, LNG, fertilizers, and other commodities. Additionally, this new corridor supports India’s maritime sector and aligns with the country’s broader vision for maritime growth and regional strategic engagement.
Key Features of the EMC:
- Efficiency and Cost Savings: The route cuts shipping time and distance, reducing costs associated with longer transit periods. For example, a ship traveling between Vladivostok and Chennai now takes only about 12 days at cruising speed, compared to the traditional route's 40+ days.
- Strategic Importance: Vladivostok is Russia’s largest Pacific port, and the corridor strengthens India's strategic presence in the region. This maritime route bypasses traditional chokepoints like the Suez Canal, offering faster, more direct access to key markets.
- Diversification of Trade: Besides crude oil, the EMC facilitates the transportation of coal, LNG, fertilizers, and metals, diversifying India's trade portfolio with Russia. It also helps maintain supply chains for essential goods.
- Boosting India’s Maritime Sector: The corridor supports India’s Maritime Vision 2030, which aims to enhance the efficiency and reach of India's maritime trade, a sector responsible for over 70% of the country’s trade value.
Economic and Strategic Impact:
- The new Eastern Maritime Corridor is particularly significant for India’s energy needs. As the world’s third-largest consumer of crude oil, India imports over 85% of its crude oil demand. The growing imports of Russian crude, especially the Urals grade, are crucial for securing India’s energy future. Additionally, Russia’s competitive pricing on crude, coupled with the savings on shipping costs through the EMC, makes Russian oil even more attractive.
- Beyond the economic benefits, the EMC also supports India’s broader strategic goals, including strengthening ties with Russia, a key partner in defense, nuclear cooperation, and regional geopolitics. The closer maritime links also help counterbalance China's growing dominance in the Pacific region, aligning with India's Act Far East Policy and enhancing trade and diplomatic engagement with East Asia and Russia.
Other Key Maritime Corridors Relevant to India:
- International North-South Transport Corridor (INSTC): A 7,200 km multimodal route linking the Indian Ocean with Russia, offering alternative trade routes to Europe and Central Asia.
- India-Middle East-Europe Economic Corridor (IMEC): A recent project announced at the G20 Summit, which connects India, the Middle East, and Europe via rail, road, and maritime links, fostering greater regional integration.
- Northern Sea Route (NSR): A 5,600 km Arctic route offering shorter transit times between the Barents and Kara Seas and the Bering Strait, gaining importance due to growing imports of Russian energy resources.
In conclusion, the Eastern Maritime Corridor is reshaping India-Russia trade dynamics, boosting economic ties and strategic cooperation between the two nations. By facilitating faster and cheaper transportation, the EMC is not only beneficial for trade in crude oil but also for a range of other commodities, positioning India as a key player in the evolving global trade network.
One Nation, One Election
- 19 Dec 2024
In News:
The government has recently taken steps to implement "One Nation, One Election" by presenting two Constitution Amendment Bills in the Lok Sabha: the One Nation One Election – The Constitution 129th Amendment Bill 2024 and the Union Territories Laws Amendment Bill 2024.
Introduction to the Concept:
- Objective: Proposes synchronizing elections for Lok Sabha (national) and State Legislative Assemblies to be held on the same day.
- Purpose: Aims to reduce costs, minimize logistical challenges, and address governance disruptions caused by frequent elections.
- 2024 Report: The High-Level Committee Report on Simultaneous Elections, released in December 2024, outlines a roadmap for implementing this reform.
Historical Background:
- Previous Practice: From 1951 to 1967, Lok Sabha and State Assembly elections were conducted together.
- Disruptions: The practice was interrupted due to premature dissolutions and emergencies, leading to staggered elections across India.
High-Level Committee on Simultaneous Elections:
- Committee Formation: Headed by former President Ram Nath Kovind, formed on 2nd September 2023.
- Public Response: Over 21,500 responses, with 80% in favor.
- Political Party Responses: 32 political parties supported the idea, while 15 raised concerns about regional party marginalization.
- Expert Consultations: Majority of experts supported the reform, emphasizing resource optimization and reduced disruptions.
Committee Recommendations:
- Constitutional Amendments: Proposals to amend Articles 82A and 324A to enable simultaneous elections.
- Two-Phase Implementation:
- Phase 1: Synchronize elections for Lok Sabha and State Legislative Assemblies.
- Phase 2: Include Municipalities and Panchayats within 100 days.
- Single Electoral Roll: Creation of a unified electoral roll and EPIC for all levels of elections, reducing duplication and errors.
Rationale for Simultaneous Elections:
- Governance Consistency: Reduces focus on election preparation, allowing more attention to developmental work.
- Prevents Policy Paralysis: Mitigates disruptions caused by the Model Code of Conduct (MCC) during frequent elections.
- Resource Optimization: Reduces the need for personnel and resources for election duties, allowing better allocation to governance tasks.
- Preserves Regional Party Relevance: Local issues remain prioritized, ensuring regional parties' concerns are heard.
- Equitable Political Opportunities: Encourages diversification and inclusivity within political parties.
- Financial Benefits: Reduces the financial burden of conducting multiple elections, enhancing economic efficiency.
Conclusion:
- The concept of "One Nation, One Election" is a significant reform aimed at streamlining India's electoral processes. With broad public and political support, it promises improved governance, cost savings, and better resource management in the future.
Wroughton’s Free-Tailed Bat

- 19 Dec 2024
In News:
Wroughton’s free-tailed bat, a highly rare species of molossus bat, has been spotted at the Delhi Development Authority (DDA)’s Yamuna Biodiversity Park, marking a unique sighting.
Key Highlights:
- Species Overview: Wroughton’s free-tailed bat (Otomops wroughtoni) is a rare species of molossus bat, notable for its powerful flight and ecological importance in controlling insect populations and assisting in pollination.
- Conservation Status:
- IUCN: Listed as "Data Deficient".
- Protection: Listed under Schedule I of the Wildlife (Protection) Act, 1972.
- Geographical Distribution:
- Primarily found in the Western Ghats, with a single known breeding colony.
- Small colonies in Jaintia Hills, Meghalaya, and a solitary individual sighted in Cambodia.
- Physical Characteristics:
- Large in size, with huge ears extending beyond the muzzle.
- Bicoloured velvet fur.
- Noted for powerful flying capabilities, enabling long-distance foraging.
- Ecological Role:
- Regulates insect populations.
- Known for assisting in pollination.
- Habitat:
- Roosts in caves, or dark, damp, and slightly warm places, typically in moderate-sized colonies.
- Significance of the Delhi Sighting:
- The sighting at Yamuna Biodiversity Park is significant for Delhi, marking a rare occurrence in the region.
- Delhi's bat species: The city is home to about 14 bat species, with four species, including the Indian false vampire and Egyptian free-tailed bat, considered locally extinct.
- Conservation Efforts:
- Two decades of ecological restoration have created specialized niches in the area, aiding species rewilding and ecological balance.
- The Aravalli Biodiversity Park in Gurugram now serves as the only known roosting site for the Blyth’s horseshoe bat in Delhi NCR.
- Additional Notes:
- Wroughton’s free-tailed bat was considered critically endangered until 2000 due to its limited known population. However, the discovery of populations in other regions has led to a reclassification to "Data Deficient".
- Despite being discovered over a century ago, much about the bat's feeding ecology remains unknown.
Global Multidimensional Poverty Index (MPI) Report 2024

- 18 Dec 2024
In News:
The Global Multidimensional Poverty Index (MPI) Report 2024 was released by the United Nations Development Programme (UNDP) and the Oxford Poverty and Human Development Initiative (OPHI). The report focuses on the theme “Poverty Amid Conflict”, examining the interplay between violent conflict and multidimensional poverty.
Key Findings:
- Global Poverty Levels:
- 1.1 billion people (~18% of the global population) live in acute multidimensional poverty across 112 countries.
- India has the largest number of people living in multidimensional poverty, with 234 million people.
- Multidimensional Poverty Indicators:
- The MPI assesses poverty across three key dimensions:
- Health: Child mortality, malnutrition.
- Education: Years of schooling, school attendance.
- Living Standards: Access to clean water, sanitation, electricity, cooking fuel, housing quality, and ownership of basic assets.
- A person is considered MPI poor if they are deprived in one-third or more of the weighted indicators.
- The MPI assesses poverty across three key dimensions:
- Impact of Conflict:
- Countries experiencing violent conflict exhibit higher deprivations across all 10 MPI indicators when compared to non-conflict nations.
- 40% (455 million people) of those living in poverty are in conflict-affected regions. These regions include active war zones, fragile states, and areas with low peace.
- Child Poverty:
- 584 million children (27.9% of all children globally) are living in extreme poverty, highlighting the disproportionate impact on the younger population.
- In contrast, 13.5% of adults are living in extreme poverty.
- Regional Distribution:
- The regions with the highest poverty rates are Sub-Saharan Africa and South Asia, which together account for 83.2% of the global poor.
- Rural Poverty: A majority of the poor (83.7%, or 962 million people) live in rural areas, with 70.7% of the poor concentrated in rural parts of Sub-Saharan Africa and South Asia.
- Countries with the Highest Poverty:
- India: 234 million people.
- Pakistan: 93 million people.
- Ethiopia: 86 million people.
- Nigeria: 74 million people.
- Democratic Republic of the Congo: 66 million people. These five countries account for 48.1% of the global poor.
- Poverty Amid Conflict:
- The report underscores that 2023 witnessed the highest number of conflicts since World War II, leading to the displacement of 117 million people due to violent conflicts and other factors like natural disasters.
- Conflict zones continue to experience higher poverty, as nearly 40% of the world's poorest people live in these areas.
India's Poverty Situation:
- India's Poor Performance:
- India has 234 million people living in multidimensional poverty, making it the country with the largest share of the global poor.
- Regional Disparities: Poverty rates in rural areas remain high due to poor infrastructure, limited economic opportunities, and underdeveloped services outside of agriculture.
- Poor Nutrition: Malnutrition, especially among children, is a significant concern.
- Education: The quality of education remains subpar, especially in government-run schools, affecting learning outcomes.
- Water and Sanitation: Inadequate access to clean drinking water and sanitation is prevalent, especially in rural areas.
- Economic Setbacks: The COVID-19 pandemic worsened the economic situation, leading to job losses and reduced incomes.
Government Initiatives for Poverty Alleviation:
- National Food Security Act (NFSA): Provides subsidized food grains to 67% of India's population, targeting rural areas (75%) and urban areas (50%).
- Pradhan Mantri Ujjwala Yojana (PMUY): Aims to provide LPG connections to women from Below Poverty Line (BPL) families.
- Ayushman Bharat: Health insurance coverage up to ?5 lakh per family, designed to protect against catastrophic healthcare costs.
- POSHAN Abhiyaan: Focuses on reducing malnutrition, particularly among children, adolescent girls, pregnant women, and lactating mothers.
- Right to Education Act (RTE): Guarantees free and compulsory education for children between 6 and 14 years.
- Swachh Bharat Mission: Works to ensure universal sanitation coverage, including the construction of toilets and promoting cleanliness.
Schengen Zone Membership

- 18 Dec 2024
In News:
Recently, the European Union (EU) cleared Bulgaria and Romania for full membership in the Schengen Zone, effective January 1, 2025. This marks the end of a 13-year wait for these Eastern European nations, which joined the EU in 2007.
Key Highlights:
- Schengen Integration: Until now, Bulgaria and Romania were partially integrated into the Schengen Zone, with air and sea travel without border checks since March 2024. However, land border controls were still in place due to Austria's objections, mainly due to concerns over migration and border security.
- Austria's Shift: Austria had blocked full entry for years but finally lifted its veto on December 9, 2024, after a border protection package was agreed upon. This package includes joint border guard deployment at the Bulgarian-Turkish border and temporary land border controls for six months.
Schengen Zone Details:
- What is the Schengen Zone?
- Created by the Schengen Agreement (1985) and the Schengen Convention (1990), it is the world’s largest area without internal border controls, allowing free movement across most EU countries and some non-EU countries. It currently includes 29 countries (25 EU states and 4 non-EU countries: Iceland, Liechtenstein, Norway, and Switzerland).
- Key Features:
- Free Movement: Over 425 million people can travel freely within the zone without border checks.
- Uniform Visa Policy: Short-term stays of up to 90 days are allowed for tourists and business travelers from outside the Schengen Area.
- Cross-Border Cooperation: The Schengen Information System (SIS) facilitates security and border management by sharing critical data between countries.
- Temporary Border Controls: Countries can temporarily reintroduce border controls for security reasons, after notifying other member states and the European Commission.
Bulgaria and Romania
- Bulgaria:
- Capital: Sofia
- Location: Southeastern Europe, bordered by the Black Sea, Romania, Turkey, Greece, North Macedonia, and Serbia.
- Political System: Parliamentary Republic
- Romania:
- Capital: Bucharest
- Location: Bounded by Ukraine, Moldova, Black Sea, Bulgaria, Serbia, and Hungary.
- Political System: Semi-Presidential Republic
Implications of Full Schengen Membership:
- Security and Unity: Romania and Bulgaria's full integration into the Schengen Zone is seen as a boost to both EU security and unity. It solidifies the EU's commitment to free movement while enhancing border security across Europe.
- Impact on Migration: With Bulgaria and Romania’s full membership, the EU’s border management system will be more integrated, helping to address ongoing migration challenges.
World Bank Report on Poverty in India

- 18 Dec 2024
In News:
The World Bank has set a clear mission: ending extreme poverty and boosting shared prosperity on a livable planet. This new edition of the biennial series, previously titled Poverty and Shared Prosperity, assesses the three components of the mission and emphasizes that reducing poverty and increasing shared prosperity must be achieved without high costs to the environment.
Extreme Poverty in India:
- Current Poverty Status (2024):
- 129 million Indians are living in extreme poverty, defined as earning less than $2.15 (?181) per day.
- This marks a significant improvement from 431 million in 1990, demonstrating progress in poverty alleviation.
- Poverty Trends:
- In 2021, there was a reduction of 38 million people in extreme poverty, bringing the total to 167.49 million.
- However, higher poverty standards (set at $6.85 (?576) per day) now show more Indians below the poverty line than in 1990, mainly due to population growth.
- Survey Methodology:
- The 2022-23 Household Consumption and Expenditure Survey (HCES) in India used the Modified Mixed Reference Period (MMRP) method to improve data accuracy.
- The report suggests the need for careful analysis of the survey data, which may impact future poverty estimates.
Global Poverty Trends:
- Slowdown in Poverty Reduction:
- Global poverty reduction has slowed considerably, with 700 million people (8.5% of the global population) living in extreme poverty in 2024.
- The slowdown is attributed to factors like low economic growth, the COVID-19 pandemic, and increased fragility.
- Challenges in Achieving Targets:
- The global extreme poverty rate is expected to be 7.3% in 2030, which is double the World Bank's target of 3%.
- At current rates, extreme poverty eradication by 2030 is unlikely. It could take decades to eradicate extreme poverty, and over a century to lift people above the $6.85/day threshold.
- Impact of Polycrisis:
- Polycrisis refers to the confluence of multiple crises—slow growth, climate risks, and increased uncertainty—making global poverty reduction more challenging.
- Global prosperity has also been impacted, with slower income growth, particularly after the pandemic.
India's Role in Global Poverty Reduction:
- Contribution to Global Poverty:
- India’s contribution to global extreme poverty is expected to decline significantly over the next decade. However, even if India eradicates its extreme poverty by 2030, the global extreme poverty rate would only fall from 7.31% to 6.72%, still above the UN SDG target of 3%.
Proposed Pathways for Addressing Poverty:
- Faster and Inclusive Growth:
- Focus on increasing labor productivity, income, and employment to boost economic growth inclusively.
- Climate Resilience:
- Strengthen risk management and mitigation efforts to protect vulnerable populations from climate shocks, ensuring that growth does not worsen environmental degradation.
Global Priorities:
- Low-Income Countries: Prioritize poverty reduction through investments in human, physical, and financial capital to foster growth.
- Middle-Income Countries: Focus on inclusive income growth that reduces vulnerability, and seek synergies such as cutting air pollution alongside poverty reduction.
- High-Income Countries: Accelerate climate mitigation efforts while managing the transition costs involved.
Cyclone Chido
- 18 Dec 2024
In News:
Cyclone Chido makes landfall in Mozambique after leaving trail of destruction in French-administered Mayotte.
About Cyclone Chido:
- Location and Impact:
- Cyclone Chido struck Mayotte, a French overseas territory in the Indian Ocean, in December 2024.
- It is the strongest storm to hit Mayotte in at least 90 years.
- Cyclone Characteristics:
- Wind speeds exceeded 200 km/h (124 mph), with gusts surpassing 225 km/h (140 mph).
- The cyclone caused significant devastation to the region, prompting expressions of condolences from global leaders.
- Cyclone Classification:
- According to the Indian Meteorological Department (IMD), cyclones are classified based on wind speed:
- Depression: 31–49 km/h
- Deep Depression: 50–61 km/h
- Cyclonic Storm: 62–88 km/h
- Severe Cyclonic Storm: 89–117 km/h
- Very Severe Cyclonic Storm: 118–166 km/h
- Extremely Severe Cyclonic Storm: 167–221 km/h
- Super Cyclonic Storm: Above 222 km/h
- Cyclone Chido was classified as a Super Cyclonic Storm, based on its wind speeds exceeding 222 km/h.
- According to the Indian Meteorological Department (IMD), cyclones are classified based on wind speed:
About Mayotte:
- Geography:
- Mayotte is an archipelago in the Mozambique Channel, between Madagascar and the coast of Mozambique.
- It consists of two main islands: Grande Terre (the larger main island) and Petite Terre (the smaller island of Pamandzi).
- Political and Economic Context:
- Mayotte is an overseas department of France, and it is the poorest territory in both France and the European Union.
- France colonized Mayotte in 1843 and annexed the entire Comoros archipelago in 1904.
- A 1974 referendum showed that 95% of Comoros voters favored independence, but 63% of Mayotte's population voted to remain part of France. Subsequently, Grande Comore, Anjouan, and Moheli declared independence in 1975.
- Mayotte remains administratively under French governance.
- Biodiversity:
- Mayotte is renowned for its rich biodiversity, particularly for having one of the world’s largest enclosed lagoons.
Cyclones
- What is a Cyclone?
- A cyclone is a large-scale, rotating system of air that forms around a low-pressure area, bringing violent storms and extreme weather conditions.
- In the Northern Hemisphere, cyclones rotate anticlockwise, while in the Southern Hemisphere, they rotate clockwise due to the Coriolis effect.
- Tropical Cyclone Characteristics:
- Calm Centre (Eye): The cyclone’s center, or "eye," experiences relatively calm weather with low air pressure.
- High Wind Speed: Cyclones generally have average wind speeds around 120 km/h.
- Closed Isobars: Isobars (lines of equal atmospheric pressure) are tightly packed, leading to high wind velocities.
- Formation Over Oceans: Cyclones typically form over warm ocean waters.
- East-to-West Movement: Influenced by trade winds, cyclones usually move from east to west.
- Seasonal Nature: Cyclones occur during specific seasons based on regional climatic conditions.
Kisan Kavach

- 18 Dec 2024
In News:
Scientists develop ‘kisan kavach’ to shield farmers from pesticide sprays.
Key Highlights:
- Purpose: The Kisan Kavach is designed to shield farm labourers from harmful pesticide exposure. Pesticides, often neurotoxins, can be detrimental to health, causing symptoms like dizziness, headaches, vomiting, and even death with high exposure.
- Development:
- Developed by Biotechnology Research and Innovation Council (BRIC-inStem), Bangalore, in collaboration with Sepio Health Pvt. Ltd.
- Launched by Union Minister of State for Science and Technology.
- Fabric Technology:
- The suit uses oxime fabric, which chemically breaks down common pesticides on contact, preventing them from penetrating the skin.
- Mechanism: The fabric works through nucleophilic mediated hydrolysis, deactivating pesticides upon contact and preventing pesticide-induced toxicity and lethality.
- Components of the Kit:
- Consists of a trouser, pullover, and face-cover.
- Washable and reusable: The suit retains its protective properties even after 150 washes, in a wide temperature range, and under UV light exposure.
- Affordability:
- Priced at ?4,000 per kit, with efforts underway to reduce costs through increased production.
- Field Testing and Efficacy:
- Animal studies: Rodent tests showed that animals exposed to pesticides and covered with ordinary cotton cloth died within four days, while those with the activated fabric remained safe.
- Human trials are still pending.
- Health Implications:
- Pesticides are linked to chronic health issues, including cancer, as per studies by the National Institute of Nutrition (Indian Council of Medical Research).
- Global Context:
- In 2020, India used 61,000 tonnes of pesticides, despite producing much more (2,58,130 tonnes in 2022-2023).
- Pesticide-related health issues are a major concern, with 60% of India’s adult workforce engaged in agriculture.
- Impact:
- The suit aims to protect farm labourers from pesticide exposure and promote sustainable agriculture.
- It could help reduce health complications and improve working conditions for farmers, who often lack proper protective gear.
- Future Plans:
- Awareness campaigns will be conducted to inform farmers about this protective technology.
- Efforts are underway to make the kit more affordable as demand increases.
Credit Guarantee Scheme for e-NWR based Pledge Financing (CGS-NPF)

- 17 Dec 2024
In News:
The Credit Guarantee Scheme for e-NWR based Pledge Financing (CGS-NPF), launched by Union Minister Pralhad Joshi aims to support farmers by facilitating post-harvest finance using electronic negotiable warehouse receipts (e-NWRs). This initiative is part of the government’s efforts to minimize distress selling and ensure financial security for farmers, particularly small and marginalized ones.
Key Features of the Scheme:
- Total Corpus: ?1,000 crore for post-harvest finance.
- Loan Coverage:
- Agricultural purposes: Loans up to ?75 lakh.
- Non-agricultural purposes: Loans up to ?200 lakh.
- Eligible Borrowers: Small and marginal farmers, women, SC/ST/PwD farmers, MSMEs, traders, Farmer Producer Organizations (FPOs), and farmer cooperatives.
- Eligible Institutions: All scheduled and cooperative banks.
- Guarantee Coverage:
- Small and marginal farmers/Women/SC/ST/PwD: 85% for loans up to ?3 lakh, and 80% for loans between ?3 lakh to ?75 lakh.
- Other borrowers: 75% coverage for loans up to ?200 lakh.
- Risks Covered: Both credit risk and warehouseman risk.
- Guarantee Fees: 0.4% per annum for farmers, and 1% per annum for non-farmers.
Objectives:
- Minimize distress selling: By providing easy access to loans post-harvest, the scheme helps farmers avoid selling produce at low prices due to cash crunches.
- Instill confidence in banks: The scheme provides a guarantee cover to lenders, encouraging them to offer loans against e-NWRs.
- Encourage warehouse registration: The scheme emphasizes the need for more warehouses, particularly those closer to farmland, to improve accessibility for farmers.
About e-NWRs:
- e-NWRs are digital versions of traditional warehouse receipts that enable farmers to pledge stored commodities as collateral for loans.
- These receipts are governed by the Warehousing (Development and Regulation) Act of 2007, and since 2017, e-NWRs have been mandated for use in transactions related to agricultural produce stored in WDRA-accredited warehouses.
Expected Impact:
- This scheme is expected to boost post-harvest lending, with a target of increasing lending to ?5.5 lakh crore in the next decade.
- It will improve farmers’ income, reduce dependence on informal credit sources, and foster better financial inclusion.
- Additionally, it will create a more reliable supply chain for agricultural produce, enhancing food security.
Future Targets:
- Increase the number of registered warehouses under the WDRA to 40,000 in the next 1–2 years.
- Use platforms like e-Kisan Upaj Nidhi to streamline the lending process and avoid repeated visits to banks.
How La Niña Affects India's Climate?
- 28 Dec 2024
In News:
La Niña, a phase of the El Niño Southern Oscillation (ENSO), occurs when the Pacific Ocean region between Indonesia and South America is cooler than usual. This phenomenon influences global weather patterns, including those in India. Here’s how La Niña specifically affects India’s climate:
Monsoon Rainfall:
- La Niña typically results in normal to above-normal rainfall during the monsoon season in India. This is due to the cooling of sea surface temperatures in the central Pacific, which affects atmospheric circulation and strengthens the monsoon winds.
- In contrast, El Niño usually brings below-average rainfall and droughts to India, leading to agricultural stress.
- Recent La Niña years (2020-2022) saw above-normal monsoon rains, which benefited agricultural productivity, while the El Niño year of 2023 resulted in below-normal rains, impacting water availability and agriculture.
Winter Temperatures:
- During La Niña, winter temperatures in India are generally colder in the north, with cooler nights but relatively warmer days compared to El Niño winters. The planetary boundary layer height (PBLH) tends to be lower, trapping pollutants close to the surface. However, higher wind speeds during La Niña help to disperse air pollution, improving air quality.
- South India may experience colder-than-usual winters during La Niña, but current meteorological data suggests the ongoing winter in India is not strongly influenced by La Niña, as its expected onset has been delayed.
Impact on Summer Heat:
- La Niña generally provides relief from extreme summer heat, as it reduces the frequency and intensity of heatwaves. In contrast, El Niño summers are typically hotter and bring record-breaking heat waves.
- For example, April 2023 saw intense heatwaves across India, attributed to the El Niño phase, but if a La Niña forms and persists into the summer of 2025, it could help moderate the extreme heat.
The "Triple Dip" La Niña Phenomenon:
- A Triple Dip La Niña refers to a rare occurrence where three consecutive La Niña events happen, as was the case from 2020 to 2022. This is significant because these prolonged events can lead to stronger climatic impacts. In contrast, the current El Niño (2023) follows this period, potentially contributing to an irregular transition between La Niña and El Niño phases, which may intensify extreme weather patterns.
Global Climate Changes and La Niña:
- Climate change is believed to be increasing the frequency and intensity of both La Niña and El Niño events. Rising sea and land temperatures are disrupting the balance of the Pacific Ocean and could exacerbate extreme La Niña events, which might lead to harsher winters in India and other regions.
Forecast for 2024-2025:
- As of December 2024, the India Meteorological Department (IMD) and global meteorological bodies predict a weak La Niña event to emerge by late 2024 or early 2025. This could lead to colder winters and above-normal rainfall in the 2025 monsoon season, offering some relief from the heatwaves and dry conditions of the previous years.
Conclusion:
If a La Niña forms by the end of 2024, it is likely to bring cooler winters, a relief from extreme summer heat, and above-normal monsoon rainfall in 2025. Given the delayed onset and weakening of the current La Niña, the overall impact on India’s climate in the immediate future might be milder compared to previous La Niña years, but it still holds potential for more favorable conditions for agriculture and air quality.
Vijay Diwas 2024

- 17 Dec 2024
In News:
On December 16, 2024, India commemorated Vijay Diwas, marking the 53rd anniversary of its victory in the 1971 Bangladesh Liberation War. This day honors the bravery and sacrifices of Indian soldiers and the Mukti Bahini, whose collective efforts led to the creation of Bangladesh as an independent nation. On this occasion, leaders across India, paid heartfelt tributes to the fallen heroes who contributed to the victory, and to the enduring India-Bangladesh friendship.
The 1971 Bangladesh Liberation War culminated in the surrender of over 90,000 Pakistani soldiers, and India’s victory is celebrated as a defining moment in South Asian history.
The War’s Historical Context:
The 1971 Bangladesh Liberation War was a pivotal conflict between East Pakistan (now Bangladesh) and West Pakistan (now Pakistan), leading to Bangladesh’s independence. It was a direct result of decades of social, political, and economic discrimination faced by East Pakistan, despite its larger population and contribution to Pakistan’s economy. Major events leading to the war included:
- Cultural and linguistic marginalization, with East Pakistan's Bengali language and identity being suppressed by the West.
- The 1970 elections that saw the Awami League, led by Sheikh Mujibur Rahman, win a decisive victory in East Pakistan, but their demand for greater autonomy was rejected by West Pakistan.
- The violent crackdown by the Pakistani military in Operation Searchlight in March 1971, leading to widespread atrocities and a mass exodus of refugees into India.
India’s Role in the War:
India’s involvement in the conflict was initially cautious, but the refugee crisis—with over 10 million people fleeing to India—forced India to take action. India provided humanitarian aid and supported the Mukti Bahini, a guerrilla force of Bangladeshi fighters. On December 3, 1971, Pakistan’s preemptive airstrike on Indian military bases led to India's retaliation and full-scale military involvement, including air and naval operations.
India’s military, with assistance from the Mukti Bahini, launched a decisive campaign, ultimately leading to Pakistan’s surrender on December 16, 1971, and the creation of Bangladesh.
Vijay Diwas Observances:
- The 53rd Vijay Diwas celebrations at Fort William, Kolkata, saw a Bangladeshi delegation—including Mukti Joddhas (freedom fighters)—reflect on their memories of the war, highlighting India's crucial role in the liberation of Bangladesh.
- The event also featured a wreath-laying ceremony, military tattoo, and a salute to the shared sacrifice and friendship between India and Bangladesh.
The 1971 Surrender Painting and New Symbolism:
In an interesting development, the iconic 1971 surrender painting, depicting the surrender of Pakistani forces in Dhaka, was moved from the Army Chief’s lounge to the Manekshaw Centre. The painting was replaced by Karam Kshetra–Field of Deeds, a new artwork symbolizing India’s strategic and cultural heritage. This new piece incorporates elements like Lord Krishna’s chariot, Chanakya, and modern military assets, reflecting India’s military prowess and heritage.
Atmanirbhar Clean Plant Programme

- 17 Dec 2024
In News:
Recently, the Government of India and the Asian Development Bank (ADB) signed a $98 million loan agreement to enhance horticulture crop productivity by improving plant health management. This initiative is part of India’s Atmanirbhar Clean Plant Programme (CPP), aiming to provide farmers with access to certified disease-free planting materials to improve yields, quality, and resilience, particularly against climate change impacts.
Key Highlights of the Loan Agreement
- Objective: Improve access to certified, disease-free planting materials for horticulture crops.
- Implementation: The project will be implemented by the Ministry of Agriculture and Farmers Welfare through the National Horticulture Board (NHB) and the Indian Council of Agricultural Research (ICAR).
- Focus: The initiative will enhance farmers’ productivity, resilience to climate change, and pest/disease management through the Atmanirbhar Clean Plant Programme (CPP).
About the Atmanirbhar Clean Plant Programme (CPP)
The Atmanirbhar Clean Plant Programme aims to tackle critical challenges in horticulture by ensuring farmers have access to high-quality, virus-free planting materials. The program is designed to:
- Enhance crop yields and quality.
- Promote climate-resilient varieties to help farmers adapt to rising temperatures and extreme weather events.
- Safeguard the environment by controlling plant diseases and pests proactively.
Key Components of the CPP
- Clean Plant Centers (CPCs): Establishment of nine world-class CPCs across India, equipped with advanced diagnostic labs and tissue culture facilities to maintain disease-free foundation planting materials.
- Certification Framework: A robust certification system will be introduced to ensure accountability in planting material production, including accreditation for private nurseries.
- Climate Resilience: Focus on developing and disseminating climate-resilient plant varieties, addressing the growing concerns over extreme weather events and changing pest behavior due to climate change.
Significance of the Loan Agreement
- Climate Adaptation: The project will help farmers mitigate the effects of climate change, including unpredictable weather patterns and altered pest/disease behaviors.
- Economic Impact: The initiative aligns with India's vision of self-reliance in horticulture (Atmanirbhar Bharat), boosting agricultural productivity and sustainability.
- Long-term Benefits: Improved farm productivity, sustainability, and economic well-being for farmers, especially in the face of climate change.
Global Horticulture Significance
- India’s Position: India is the second-largest producer of fruits and vegetables globally, contributing 33% to the agricultural GDP.
- Land Coverage: Horticulture occupies 18% of India’s agricultural land, yet its production surpasses that of food grains.
Implementation and Impact
- Implementation Period: The project will be executed from 2024 to 2030, with 50% financial assistance from ADB.
- Institutional Strengthening: The initiative will bolster India’s ability to manage plant health, integrating advanced diagnostic techniques and capacity-building for horticulture professionals.
Exercise Agni Warrior

- 17 Dec 2024
In News:
The 13th edition of Exercise Agni Warrior (XAW-2024), a joint military drill between the Indian Army and the Singapore Armed Forces (SAF), concluded successfully at the Field Firing Ranges, Devlali, Maharashtra. The exercise focused on enhancing mutual understanding and interoperability between the two nations’ artillery units.
Key Facts:
- Participating Nations: India and Singapore
- Location: Field Firing Ranges, Devlali, Maharashtra
- Participants:
- 182 personnel from the Singapore Artillery
- 114 personnel from the Indian Army's Regiment of Artillery
- Objective: To maximize mutual understanding of drills and procedures for joint operations under the UN Charter, particularly in firepower planning and execution, utilizing advanced artillery technologies.
- Historical Context: The exercise began in 2004 under a bilateral agreement between India and Singapore and has evolved over the years, now marking 20 years of cooperation.
Purpose and Highlights:
The exercise aimed to reinforce the long-standing defense relationship between India and Singapore, focusing on:
- Joint Firepower Planning and Execution: Both forces demonstrated the use of New Generation Artillery Equipment, enhancing their firepower coordination.
- Enhancing Interoperability: The exercise emphasized seamless coordination between the two armies to operate as a multinational force under the UN Charter, addressing global security challenges.
- Knowledge Sharing: Personnel from both armies exchanged expertise on advanced artillery tactics, fostering a deeper understanding of each other's military capabilities.
- Technological Integration: Both sides integrated cutting-edge technologies, allowing the exchange of best practices in the use of artillery systems.
Key Objectives of XAW-2024:
- Enhanced Interoperability: To ensure smooth coordination in joint operations, fostering the ability to respond to regional security threats.
- Firepower and Coordination Techniques: Sharing expertise on artillery planning, coordination, and execution.
- Advanced Equipment Use: Testing and demonstrating modern artillery systems in joint operations, ensuring both forces are prepared for contemporary warfare.
Structure and Execution:
The exercise was structured to include pre-exercise training, field operations, and a post-exercise evaluation:
- Pre-Exercise: Both armies engaged in interactive sessions to familiarize themselves with each other's artillery tactics and advanced systems.
- Field Operations: Simulated combat scenarios tested joint firepower execution, emphasizing real-time problem-solving and decision-making under pressure.
- Post-Exercise Review: A thorough analysis identified areas for improving joint operations and coordination.
Strategic Significance:
- Strengthening Bilateral Ties: Agni Warrior reinforces the defense partnership, facilitating joint operations that support regional security.
- Regional Stability: The exercise underscores the commitment of both nations to peace and security in the Indo-Pacific region.
- Capacity Building: Both Indian and Singaporean forces gained exposure to sophisticated firepower planning and gained operational readiness for future deployments.
Little Bunting

- 16 Dec 2024
In News:
Little Bunting recently spotted in Mount Abu, Rajasthan, a sighting previously unseen in the region.
About the Little Bunting:
- Scientific Name: Emberiza pusilla
- Family: Bunting family (Emberizidae)
- IUCN Red List Status: Least Concern
Distribution:
- Breeding Range: Far northeast Europe and northern Eurosiberia to the Russian Far East (taiga region).
- Migratory Pattern: Migrates to the subtropics during winter, with sightings in northern India, southern China, and northern Southeast Asia.
Physical Features:
- Size: Small bird, measuring 12–14 cm (4.7–5.5 inches).
- Coloration:
- White underparts with dark streaking on the breast and sides.
- Chestnut face with a white malar stripe, black crown stripes, and a white eye-ring.
- Fine dark border behind chestnut cheeks.
- Similarity: Resembles a small female reed bunting but with distinct black crown stripes.
Call and Song:
- Call: Distinctive "zik".
- Song: A rolling "siroo-sir-sir-siroo".
Habitat and Behavior:
- Typically found in agricultural areas, feeding on grains.
- Migration: Avoids extreme cold conditions, possibly due to climate change influencing its movement into Rajasthan.
Recent Sightings in India: Spotted in Gurugram, Chandigarh, northern Punjab, and now Rajasthan.
Conservation Significance: The sighting underscores the need to preserve forest areas and wetlands for migratory species like the Little Bunting.
Search and Rescue Aid Tool (SARAT)

- 16 Dec 2024
In News:
The Indian National Centre for Ocean Information Services (INCOIS), under the Ministry of Earth Sciences, has developed SARAT Version 2 to aid Indian Search and Rescue (SAR) agencies like the Indian Coast Guard.
Key Highlights:
Purpose: SARAT is designed to assist in locating missing objects or individuals at sea by simulating the probable search area, considering factors like wind, currents, and waves.
Improvements in Version 2:
- The search area now starts from the last known position of the object, improving the accuracy of the search.
- Enhanced visualizations for better judgment of probable search areas, including colour coding of regions and markers to identify the last known position.
- Optimized search: Reduces the vast search area to a few high-probability regions, allowing for better utilization of limited search resources.
Technical Aspects:
- The tool uses model currents from the Regional Ocean Modelling System run on high-performance computers at INCOIS.
- It accounts for uncertainties in the initial location and the last known time of the missing object using model ensembling.
- Users can select from 60 types of missing objects based on shape and buoyancy.
Interactive Map & Multi-language Support:
- Results are shown on an interactive map, providing the probable search area.
- The tool also sends results as text messages to emails and mobile phones in languages of coastal states, enabling local fishermen to use it effectively during distress situations.
Launched in 2016, Updated in 2024: SARAT was launched in 2016 and the updated version (SARAT Version 2) has been designed with feedback from the Indian Coast Guard and other stakeholders involved in marine search operations.
Access: The updated SARAT Version 2 can be accessed at: https://sarat.incois.gov.in/sarat/home.jsp.
African Swine Fever

- 16 Dec 2024
In News:
African Swine Fever has been reported at two pig farms in Koottickal and Vazhoor grama panchayats in Kottayam district.
Action Taken:
- Culling of Pigs: All pigs in the affected farms and within a 1 km radius will be culled and disposed of according to Central Government guidelines.
- Infected Zone: A 1 km radius around the affected farms has been declared an infected zone.
- Surveillance Zone: A 10 km radius around the infected area has been designated a surveillance zone.
About African Swine Fever (ASF)
- African swine fever (ASF) is a highly contagious and hemorrhagic viral disease of domestic and wild pigs. It is a notifiable disease and its outbreak should be immediately reported to the higher authorities.
- ASF causes destructive effect on piggery due to high morbidity and mortality (up to 90-100 %). In India it was first confirmed in Arunachal Pradesh and Assam in February-March 2020.
- Currently, there is no effective vaccine available against ASF, so prevention by adopting strict biosecurity measures is the only way to prevent ASF.
CLINICAL SIGNS
- High fever (106-1080 F), lethargy and loss of appetite
- Increased respiration rate
- Blue-purple discoloration of skin of ears, abdomen and rear legs
- Discharge from the eyes and nose; bloody froth from the nose/mouth
- Constipation or bloody diarrhea
- Abortion
- Death of pigs in 6-15 days
Diagnosis: Confirmatory diagnosis in gov. laboratories
Zakir Hussain

- 16 Dec 2024
In News:
Ustad Zakir Hussain, the legendary tabla virtuoso, passed away at the age of 73 due to Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis (IPF).
Key Highlights:
- Career Highlights:
- Born on March 9, 1951, to Ustad Alla Rakha, a renowned tabla maestro.
- Began tabla training at age 7, with early guidance from his father.
- Co-founded Shakti in 1973 with John McLaughlin, blending Indian classical music with Western influences, pioneering world music.
- Worked with global artists, including George Harrison, John McLaughlin, and Mickey Hart.
- Awarded four Grammy Awards, including three at the 66th Grammy Awards (2024), and honored with the Padma Vibhushan in 2023.
- A visiting professor at Stanford and Princeton universities.
- Musical Style:
- Transformed the tabla from a background instrument into a dynamic, expressive solo performance.
- Known for his complex rhythms and spontaneous performances, making tabla accessible and glamorous.
- Emphasized the concept of "hazri" (attendance) in the court of music, seeing his music as an offering to a higher power.
- Cultural Influence:
- His music was a bridge between traditional Indian classical and contemporary global sounds, impacting audiences worldwide.
- Played a pivotal role in the cultural exchange of Indian classical music, gaining fans and respect across the globe.
- Participated in projects such as the Taj Mahal tea commercials and "Desh Raag", symbolizing unity and diversity in India.
What is Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis (IPF)?
- IPF is a chronic lung disease causing scarring of the lung tissue, leading to difficulty in breathing.
- Cause: The exact cause is unknown, hence termed "idiopathic" (unexplained).
- Risk Factors: Most common in older adults (over 50), men, and those with a history of smoking or viral infections.
About the Tabla:
- Structure: Composed of two drums—Tabla (right) and Bayan (left)—used primarily in Hindustani classical music.
- Material: Tabla has a wooden body, while Bayan can be made of clay or metal, both covered with animal skin and syahi paste.
- Role: Primarily accompanies vocal and instrumental performances, and is essential in various classical dance forms in northern India.
- Historical Note: Believed to have been invented by Amir Khusrau.
Prominent Tabla Players:
- Ustad Alla Rakha (father of Zakir Hussain).
- Zakir Hussain (himself).
- Shafat Ahmed and Samta Prasad.
India Maritime Heritage Conclave 2024

- 16 Dec 2024
In News:
The 1st India Maritime Heritage Conclave (IMHC 2024), a landmark event organized by the Ministry of Ports, Shipping and Waterways (MoPSW) was recently held.
Key Highlights:
Event Overview:
- Organized by the Ministry of Ports, Shipping, and Waterways (MoPSW), held on December 11-12, 2024.
- Theme: "Towards Understanding India's Position in Global Maritime History."
- Celebrated India’s maritime legacy and future vision as a maritime powerhouse.
India’s Maritime Heritage:
- Deeply rooted in ancient traditions; references in Rig Veda, mythology, literature, and archaeology.
- Modern India boasts a 7,500 km coastline, 13 major ports, 200 non-major ports, handling 95% of trade by volume and 70% by value.
- Ports handle 1,200 million tonnes of cargo annually, vital for economic growth.
Key Features of IMHC 2024:
- International Participation: Dignitaries from 11 countries, including Greece, Italy, UK.
- Exhibition: Showcased ancient shipbuilding techniques, navigation systems, historical trade routes.
- Cultural Program: Celebrated coastal traditions with performances and festivities.
- Key Focus: Sustainable maritime innovation, skill development, youth engagement, and cultural preservation.
National Maritime Heritage Complex (NMHC):
- Location: Lothal, Gujarat – an ancient Harappan site (2600 BCE).
- Significance: Home to the world’s oldest dry-dock (2400 BCE).
- Future Vision: NMHC to showcase maritime history with 14 galleries, open aquatic gallery, lighthouses, and a research institute.
Modern Maritime Significance:
- India’s Global Maritime Ranking: 16th largest globally, 3rd largest in ship recycling.
- Trade Backbone: 95% of India's trade by volume, 70% by value handled by maritime sector.
- Port Performance: India ranks 22nd in the World Bank’s Logistics Performance Index (2023).
Future Maritime Vision:
- Sustainable Blue Economy: Emphasis on eco-friendly practices, green shipping, and maritime tourism.
- Skill Development: Training programs to empower local communities and boost maritime workforce.
- Infrastructure Development: Upgrading ports and shipping infrastructure under the Sagar Mala Program.
- Policy Framework: Integrated policies for maritime heritage preservation and economic development.
Notable Initiatives:
- Maritime India Vision 2030: Focus on increasing maritime capacity and sustainability.
- SAGAR: Security and Growth for All in the Region initiative.
- Ship Repair & Recycling Mission: Promote India as a global leader in ship recycling.
- Green Hydrogen Hubs: Development of eco-friendly maritime infrastructure.
Santa Ana Winds

- 15 Dec 2024
In News:
The ongoing Franklin Fire in Malibu, California, has burned over 4,000 acres and affected around 22,000 people. Although the exact cause of the fire is still under investigation, experts point to two key factors contributing to the intensity of the blaze: Santa Ana winds and climate change.
Santa Ana Winds
- Santa Ana winds are powerful, dry winds that typically occur in Southern California from October to January.
- They are caused when high-pressure systems over the Great Basin (the area between the Rocky Mountains and Sierra Nevada) push air toward low-pressure areas over California’s coast.
- As the air moves downhill through mountain passes, it compresses and heats up, which significantly lowers the humidity—sometimes to levels below 10%—creating dry conditions. This extremely low moisture content dehydrates vegetation, making it highly susceptible to combustion.
- These winds have been a natural feature of California's weather, contributing to wildfires for years. However, when combined with other factors like climate change, their impact has become more severe.
The Role of Climate Change
While Santa Ana winds have long played a role in California's wildfires, climate change has exacerbated the situation in recent years. The state's wildfire season has lengthened due to rising global temperatures, which have led to:
- Warmer springs and summers.
- Earlier snowmelt in spring, which leaves vegetation drier for longer periods.
- Longer and more intense dry seasons, which cause increased moisture stress on vegetation.
As a result, forests and brushlands are now more vulnerable to fires. Climate change has also contributed to more extreme weather events, including heatwaves, which further dry out vegetation and create favorable conditions for wildfires.
Intensification of Wildfire Seasons
Recent studies have shown that California's wildfire season has grown longer over the past two decades. For example, a 2021 study in Nature Scientific Reports found that the state's annual burn season has shifted, with the peak fire season now occurring earlier in the year, from August to July. Additionally, research published in PNAS (Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences) in 2023 indicated that the largest wildfires in California history have occurred in the past 20 years, with five of the top 10 largest fires taking place in 2020 alone.
Looking Ahead
The situation is expected to worsen as climate change continues. If global temperatures rise by more than 3°C by the end of the century, as predicted by the United Nations, California’s wildfire risk will likely intensify. The combination of Santa Ana winds and increasingly dry conditions will continue to make areas like Malibu, and much of California, more prone to destructive wildfires.
In conclusion, while Santa Ana winds remain a natural contributor to California's wildfires, the influence of climate change has significantly lengthened the wildfire season, making wildfires more frequent, intense, and harder to control. The continued rise in global temperatures only accelerates these trends, posing a growing challenge for fire management and public safety in California.
'Jalvahak' Scheme for Inland Waterways Promotion

- 15 Dec 2024
In News:
Govt Unveils ‘Jalvahak’ To Boost Inland Waterways, Cargo Movement Incentivised on NW1, NW2 & NW16
Key Highlights:
- Launch of 'Jalvahak' Scheme:
- Launched by: Union Minister for Ports, Shipping & Waterways, Shri Sarbananda Sonowal, on December 15, 2024.
- Objective: The scheme aims to promote the use of inland waterways for long-haul cargo transportation, reduce logistics costs, and alleviate congestion in road and rail networks.
- Targeted Waterways:
- The scheme focuses on three major National Waterways (NWs):
- NW 1: River Ganga
- NW 2: River Brahmaputra
- NW 16: River Barak
- The scheme focuses on three major National Waterways (NWs):
- Incentives:
- The scheme offers up to 35% reimbursement on operating expenses for cargo transported over 300 km via these waterways, particularly using the Indo-Bangladesh Protocol Route (IBPR).
- Encouraging Private Operators: The scheme also incentivizes the hiring of vessels owned by private operators to promote competition and efficiency.
- Scheduled Cargo Service:
- Service Launch: Fixed, scheduled cargo vessel services have been introduced, running between key locations:
- Kolkata - Patna - Varanasi - Patna - Kolkata (for NW 1)
- Kolkata - Pandu (Guwahati) (for NW 2 via IBPR)
- Transit Times: Predefined and fixed for efficiency:
- Kolkata to Patna: 7 days
- Patna to Varanasi: 5 days
- Kolkata to Varanasi: 14 days
- Kolkata to Pandu: 18 days
- Pandu to Kolkata: 15 days
- Service Launch: Fixed, scheduled cargo vessel services have been introduced, running between key locations:
- Economic and Environmental Impact:
- Cargo Shift Target: The initiative aims to shift 800 million tonne-kilometres of cargo by 2027.
- Growth Projections:
- 200 million tonnes of cargo by 2030.
- 500 million tonnes by 2047, supporting the Blue Economy and Atma Nirbhar Bharat initiatives.
- The move to waterways aims to reduce the pressure on India's roads and rail systems, contributing to a more sustainable and cost-effective logistics system.
- Strategic Goals:
- Modal Shift: The scheme seeks to achieve a shift of 800 million tonne-kilometres by 2027 with an investment of ?95.4 crores.
- Sustainability: Inland waterways are considered an environmentally friendly, efficient, and low-cost transportation mode, with a focus on sustainability.
- Logistics Optimization: This initiative is expected to help optimize supply chains for major shipping companies, freight forwarders, and trade bodies involved in bulk and containerized cargo.
- Implementation Agencies:
- Inland Waterways Authority of India (IWAI): The main body responsible for the development and regulation of inland waterways.
- Inland & Coastal Shipping Limited (ICSL): A subsidiary of the Shipping Corporation of India, responsible for the operation of vessels.
- Broader Impact:
- Economic Growth: The scheme is expected to foster economic growth by improving logistics efficiency.
- Decongestion: The initiative aims to decongest the road and rail transport systems, facilitating smoother movement of cargo.
- Regional Connectivity: Enhances connectivity, particularly in eastern India, benefiting areas along the Ganga, Brahmaputra, and Barak rivers.
- About the National Waterways:
- India has 14,500 km of navigable inland waterways, which include rivers, canals, and backwaters. These waterways are significantly under-utilized compared to other countries.
- The National Waterways Act, 2016 declared 111 waterways (including both existing and newly identified ones) for navigation.
- The Jalvahak scheme is part of India's broader strategy to unlock the potential of its inland waterways, offering an efficient, economical, and environmentally sustainable alternative for cargo transport.
Rajmarg Saathi - Upgraded Route Patrolling Vehicles (RPV) by NHAI
- 15 Dec 2024
In News:
With an aim to enhance road safety and strengthen highway patrolling, NHAI plans to implement the upgraded and forward-looking Incident Management Services. The guidelines on the subject include updated specifications for new Route Patrolling Vehicles (RPVs) named ‘Rajmarg Saathi’ and outlines design, functions, technology, components and manpower specifications for the RPVs.
Key Highlights:
Launch of Rajmarg Saathi:
- Initiative by: National Highways Authority of India (NHAI).
- Objective: Enhance highway safety, emergency response, and road maintenance efficiency across India.
- Launched in: December 2024.
What is Rajmarg Saathi?
- Definition: An upgraded version of Route Patrolling Vehicles (RPVs), designed for effective highway patrolling and incident management.
- Main Aim: Improve highway safety and ensure smooth traffic flow through advanced technology and quick emergency responses.
Key Features:
- Advanced Design:
- Closed Cabinets: For organized storage and easy access to emergency tools and inventory, replacing earlier models with open storage space.
- AI-Powered Technology:
- Dashboard Cameras: Equipped with AI-enabled cameras to capture and analyze road conditions like cracks, potholes, and other distresses.
- Road Monitoring: The system also monitors vehicles, pedestrians, road signs, and other infrastructure elements.
- Integration with NHAI One: Data collected by AI systems is integrated into NHAI’s centralized application for efficient road maintenance.
- Emergency Preparedness: The RPVs are fully equipped with modern communication and safety tools, designed to minimize traffic disruptions during emergencies.
Data Collection and Maintenance:
- Weekly Analytics: The system will collect and analyze road condition data weekly to streamline maintenance activities and monitor highway safety.
Vehicle Usage and Replacement:
- Replacement Guidelines: RPVs will be replaced after 3 years of operation or 3,00,000 km to ensure they remain functional and service-ready.
Visibility and Branding:
- External Branding: RPVs are designed to be highly visible with enhanced branding for easy recognition as highway patrol vehicles.
- Uniform for Personnel: The patrolling personnel will wear updated uniforms, including bright blue colors and reflective jackets with authority logos for better identification.
Role in Incident Management:
- RPVs will play a crucial role in managing traffic incidents, ensuring smooth traffic flow, and enhancing road safety by addressing emergencies quickly.
Commitment to Road Safety:
- NHAI remains committed to improving road safety standards and ensuring a smooth, hassle-free travel experience for all users across the national highway network.
About NHAI:
- Establishment: NHAI was established under the National Highways Authority of India Act, 1988, and became operational in 1995.
- Responsibilities: It is responsible for developing, maintaining, and managing national highways in India.
- Objectives:
- Promote transparency in awarding contracts.
- Maintain high standards of project implementation.
- Ensure comfort and convenience for users of the national highway system.
India's Road Network:
- Size: India has the 2nd-largest road network in the world, spanning approximately 63.32 lakh km, which includes national highways, expressways, state highways, and rural roads.
India-Australia CCEA

- 15 Dec 2024
In News:
The 3-day stocktake meeting took place in New Delhi, marking a significant step in strengthening the India-Australia trade and strategic partnership.
Key Highlights:
- Key Discussion Areas:
- Trade in goods and services.
- Mobility, agri-tech cooperation, and market access.
- Focus on ensuring the CECA delivers balanced benefits for both nations.
- Food security concerns and market access modalities aligned with India’s goals.
- Background on Negotiations:
- The discussions in New Delhi were a continuation of the 10th round of negotiations held in Sydney (August 2024).
- Both sides aimed to outline a path forward for the early conclusion of the CECA.
- Importance of CECA:
- CECA is a Free Trade Agreement (FTA) aimed at eliminating tariffs and liberalizing services sectors to enhance business opportunities and cooperation.
- It addresses five key areas: Goods, Services, Digital trade, Government procurement & **Rules of Origin/Product Specific Rules
- New areas under discussion include: Competition policy, MSMEs, Gender, Innovation, Agri-tech, Critical minerals & Sports
- Historical Context:
- CECA negotiations began in May 2011, were suspended in 2016, and resumed in September 2021.
- The India-Australia Economic Cooperation and Trade Agreement (ECTA) was signed in 2022, serving as a foundational agreement and a precursor to CECA.
- Trade Statistics (2023-24):
- India's imports from Australia: $16.2 billion.
- India's exports to Australia: $8 billion.
- Trade has grown significantly, with India being Australia’s 5th-largest trading partner.
- Regional Cooperation Initiatives:
- India and Australia are partners in several regional initiatives:
- Indo-Pacific Economic Framework for Prosperity (IPEF)
- Trilateral Supply Chain Resilience Initiative (SCRI) with Japan.
- India and Australia are partners in several regional initiatives:
- India's CECA with Other Countries:
- India has similar CECA agreements with several nations, including: Singapore, Malaysia, Thailand & New Zealand
- Future Prospects:
- The stocktake discussions have paved the way for further cooperation in areas such as agricultural innovation, market access, and supply chain resilience.
- Both nations are optimistic about the early conclusion of the CECA and the broader economic partnership.
This recent stocktake visit represents a significant step in the ongoing efforts to solidify trade ties and deepen economic cooperation between India and Australia under the framework of the Comprehensive Economic Cooperation Agreement.
100-Day Intensified Nationwide TB Campaign

- 15 Dec 2024
In News:
- Union Health Minister Shri JP Nadda launched a 100-day intensified TB campaign in Panchkula, Haryana, aimed at reducing TB incidence and mortality. The campaign will focus on 347 high-risk districts across India.
Key Highlights:
- Campaign Goals:
- Find and treat missing TB cases, especially in high-risk groups.
- Significantly reduce TB-related deaths.
- Focus Areas:
- The campaign is part of India’s larger goal to eliminate TB before the 2030 SDG deadline.
- Strategies include early detection and rapid treatment of TB patients.
- Historical Context:
- TB was once seen as a "slow death" and patients were isolated.
- In 2018, the Prime Minister set the vision to end TB before 2030.
- Recent Government Initiatives:
- Ayushman Arogya Mandirs network of 1.7 lakh centers helps in early TB detection.
- Increased diagnostic infrastructure: Laboratories increased from 120 in 2014 to 8,293 today.
- Introduction of new drug regimens: Shorter and more effective treatments have increased the treatment success rate to 87%.
- Ni-kshay Support: Rs 3,338 crore transferred to 1.17 crore TB patients via direct benefit transfer.
- Key Achievements:
- TB decline rate in India has increased from 8.3% (2015) to 17.7% today, surpassing the global average.
- TB-related deaths have dropped by 21.4% over the past decade.
- Private Sector Involvement:
- Mandatory notification of TB patients by private practitioners has led to an 8-fold increase in TB case notifications.
- 4Ts Approach for TB Elimination: Test, Track, Treat, and Technology (use of advanced tools for diagnosis and treatment).
- New Initiatives:
- Ni-kshay Vahaan: Mobile vans to detect and treat TB patients in remote areas.
- Launch of national guidelines for a new drug-resistant TB regimen (BPaLM), which is a 4-drug combination therapy for multi-drug-resistant TB.
- Ni-kshay Poshan Yojana:
- Increase in nutritional support: Monthly support raised from Rs 500 to Rs 1000 per TB patient.
- The initiative also includes energy boosters for enhanced patient care.
- Mobile Diagnostics:
- Deployment of AI-enabled portable X-ray units and molecular tests to bring diagnostics closer to people, especially in remote areas.
- Monitoring and Data: Intensified data tracking via the Ni-kshay portal to provide timely updates to TB patients.
- Background of the Campaign:
- Part of the National TB Elimination Programme (NTEP).
- The 347 districts were selected based on indicators like death rates, presumptive TB examination rates, and incidence rates.
- Campaign Materials:
- Unveiling of Information, Education, and Communication (IEC) resources in regional languages.
- Honoring TB Champions and Ni-kshay Mitras during the event.
- Government’s Strategic Framework:
- India’s National Strategic Plan (NSP) for TB elimination (2017-2025).
- TB Harega Desh Jeetega Campaign and Pradhan Mantri TB Mukt Bharat Abhiyan.
- Tuberculosis (TB) Overview:
- TB is caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis and primarily affects the lungs, spreading through the air.
- Mortality rate has decreased from 28 per lakh (2015) to 23 per lakh (2022).
Desert Knight Air Combat Exercise

- 14 Dec 2024
In News:
India, France and UAE recently kicked off a major air combat exercise called “Desert Knight” over the Arabian Sea, strengthening trilateral defence cooperation and enhancing military interoperability amid the ongoing geopolitical churn.
Key Highlights:
- What It Is: A trilateral air combat exercise aimed at improving military interoperability and enhancing combat readiness among the participating nations.
- Nations Involved: India, France, and the UAE.
- Location: Conducted over the Arabian Sea, approximately 350-400 km southwest of Karachi.
- Aim of the Exercise:
- To strengthen trilateral defence cooperation among the three nations.
- To enhance combat skills and military interoperability of the air forces involved.
- Details of the Exercise:
- Duration: The exercise lasts for three days.
- The exercise involves large force engagement and intensive combat maneuvers in a realistic operational environment.
- Aircraft Involved:
- India: Deployed Sukhoi-30MKIs, Jaguars, IL-78 mid-air refuellers, and AEW&C (Airborne Early Warning and Control) aircraft from bases like Jamnagar.
- France: Deployed Rafale jets and other aircraft from Al Dhafra airbase.
- UAE: Deployed F-16 jets and other aircraft from Al Dhafra airbase.
Strategic Significance:
- The exercise is part of India’s efforts to build military interoperability with nations in the Persian Gulf region and strengthen defence ties with France and the UAE.
- Enhances combat readiness and strengthens cooperation against both traditional and non-traditional threats.
- Reflects the geopolitical shift and growing military cooperation in the Indo-Pacific region, especially in the context of China’s expansionist activities.
- Trilateral Framework: India, France, and the UAE launched a trilateral framework in 2022, focusing on areas like defence, technology, energy, and environment.
- Previous Exercises: In addition to Desert Knight, the countries also conducted their first trilateral maritime exercise in June 2023 to enhance cooperation in maritime security.
Broader Defence Relations:
- India-France: Long-standing strategic partnership with regular joint exercises like Shakti (army), Varuna (navy), and Garuda (air force).
- India-UAE: The defence relationship has grown significantly in recent years, with regular professional exchanges, combat exercises, and staff talks. India participates in the Desert Flag exercise at Al Dhafra airbase annually.
NASA Captures Active Volcano Erupting on Jupiter's Moon Io

- 14 Dec 2024
In News:
NASA has revealed new details about Io, Jupiter’s third-largest moon and the most volcanic world in our solar system.
Overview:
- NASA’s Juno mission has revealed new insights about Io, Jupiter's third-largest moon, known as the most volcanic world in the solar system.
- Io has over 400 active volcanoes, which send plumes and lava flows into space, creating its unique, fiery surface.
Recent Discoveries and Observations:
- Fiery Heart of Io:
- NASA's Juno mission has helped solve a 44-year-old mystery regarding Io’s volcanic activity, revealing that its volcanoes are likely powered by separate magma chambers rather than a single large magma ocean.
- This discovery was made during Juno’s close flybys in late 2023 and early 2024, using Doppler measurements and precise gravity data to understand the moon’s interior.
- Volcanic Activity:
- Io's volcanoes constantly erupt, spewing lava and plumes that shape its surface. The volcanic activity was first observed by NASA's Voyager 1 spacecraft in 1979.
- Tidal Flexing: Io experiences constant squeezing due to its elliptical orbit around Jupiter, which generates immense internal heat and causes frequent eruptions.
- Scientific Insights:
- The research suggests that tidal forces from Jupiter do not create a global magma ocean inside Io, as previously thought, but instead lead to localized magma chambers that fuel its volcanoes.
- Tidal flexing is the primary cause of the immense internal energy on Io, which melts portions of the moon's interior and drives volcanic activity.
- Broader Implications:
- Understanding Other Moons and Exoplanets: Juno's findings have broader implications for understanding the interiors of other moons like Enceladus and Europa, and even exoplanets and super-Earths.
- Future Missions:
- Juno will continue its mission, with the next close approach to Jupiter scheduled for December 27, 2024, bringing it 2,175 miles above Jupiter's cloud tops. Since entering Jupiter’s orbit in 2016, Juno has traveled over 645 million miles.
Switzerland Suspends MFN Clause in Tax Treaty with India

- 14 Dec 2024
In News:
Switzerland scraps MFN status to India, dividend income to face higher tax
Key Highlights:
- Reason for Suspension:
- The suspension follows a 2023 Supreme Court ruling in India, which clarified that the MFN clause in tax treaties is not automatically triggered when a country joins the OECD if the tax treaty with that country was signed before its OECD membership.
- The Court ruled that the Double Taxation Avoidance Agreement (DTAA) cannot be enforced unless it is notified under the Income-Tax Act, 1961.
- Details of the Suspension:
- Starting January 1, 2025, Switzerland will suspend the Most Favoured Nation (MFN) clause in its DTAA with India.
- The MFN clause was part of the India-Switzerland DTAA signed in 1994.
Impact of the Suspension:
- Higher Tax Liabilities for Indian Companies: Withholding tax on dividends from Switzerland will increase from 5% to 10% for Indian companies.
- Effects on Swiss Investments in India: Swiss companies will continue to face a 10% withholding tax on dividends from India, as per the India-Switzerland DTAA.
- Potential Re-evaluation of MFN Clauses by Other Countries: Other countries may reconsider how the MFN clause is applied in their tax treaties with India, following this development.
- No Change for Other Benefits: Other DTAA benefits and investments related to the European Free Trade Association (EFTA) will remain unaffected.
Most Favoured Nation (MFN) Clause Overview:
- Definition: The MFN principle ensures that favorable trading terms given by one WTO member country to another are extended to all other WTO members, promoting non-discrimination.
- Purpose: To ensure equal treatment among trading nations by preventing discrimination, and to promote fair trade and equitable market access.
- Key Features:
- Equal treatment in tariffs, quotas, and trade barriers.
- Members must extend the best terms to all other WTO members.
- Origin: The MFN principle was established after World War II as a cornerstone of the multilateral trading system under the WTO.
- Exceptions:
- Bilateral or regional trade agreements.
- Special access granted to developing countries.
- Non-WTO members (e.g., Iran, North Korea) are not bound by MFN rules.
- Removal of MFN:
- There is no formal procedure under the WTO to suspend MFN status.
- Countries are not obligated to notify the WTO when suspending or removing MFN treatment.
Recent Development:
- From January 1, 2025, Indian companies will face higher withholding tax (10%) on income sourced from Switzerland, as a result of the MFN clause suspension.
Empowering ASHA Workers

- 14 Dec 2024
In News:
ASHAs (Accredited Social Health Activists) are critical to India's healthcare system, particularly in rural and underserved areas. Since the program's launch in 2005, ASHAs have been integral in improving maternal health, increasing immunization rates, and promoting family planning and sanitation awareness. The network of ASHAs has grown to nearly 1 million members, making it one of the largest community health worker programs in the world.
Role of ASHAs: ASHAs work as community health activists, beyond basic healthcare delivery, by:
- Promoting health awareness.
- Mobilizing local participation in health programs.
- Increasing the utilization of existing health services.
They play a central role in improving maternal and child health, and their efforts have led to increased institutional deliveries and improved immunization rates in rural India.
Challenges Faced by ASHAs: Despite their essential role, ASHAs face several challenges:
- Inadequate compensation and delayed payments, which undermine motivation.
- Heavy workloads with insufficient support and resources.
- Social and economic marginalization, often leading to a lack of recognition and respect.
- Punitive systems that emphasize compliance and record-keeping, hindering autonomy.
This environment limits ASHAs' capacity to act as independent change agents, reducing their effectiveness in driving long-term health improvements.
Psychological Empowerment of ASHAs: To address these challenges, it's essential to empower ASHAs not just financially, but psychologically. Research in motivation theory, particularly Self-Determination Theory (SDT), provides a framework to achieve this. SDT emphasizes the importance of three key psychological needs:
- Autonomy: The need for ownership over one's work.
- Competence: The need to feel capable and effective in performing tasks.
- Relatedness: The need for social connection and recognition.
By fostering these three needs, ASHAs can become more intrinsically motivated and empowered to take ownership of their roles.
Strategies for Empowerment:
- Autonomy: Giving ASHAs more control over their work and decision-making can improve their engagement and efficacy. This can be achieved by reducing rigid monitoring and compliance systems.
- Competence: Providing continuous, quality training and resources will help ASHAs build the skills and confidence needed to perform their roles effectively. Digital tools and modern training programs can be used to enhance their capabilities.
- Relatedness: ASHAs should receive direct feedback from the communities they serve, fostering a sense of connection and accomplishment. Encouraging networks among ASHAs will also help combat isolation and provide peer support.
Government Efforts and Initiatives: The Indian government has recognized the need to support ASHAs through several initiatives:
- Increased remuneration and performance-based incentives.
- Insurance coverage under schemes like Ayushman Bharat.
- Training programs for skill development under the National Health Mission (NHM).
- Village Health Mapping and digital engagement platforms to enhance outreach and feedback mechanisms.
Moving Forward:
To further empower ASHAs, several key steps should be taken:
- Formalizing employment status: Transitioning ASHAs from volunteers to formal workers with benefits can ensure more stability and recognition.
- Improving compensation: Ensuring timely and adequate payments along with performance bonuses will incentivize ASHAs and increase job satisfaction.
- Enhancing infrastructure: Ensuring ASHAs have access to the necessary tools, medical supplies, and transportation to perform their tasks effectively.
- Digital integration: Expanding digital tools for data collection and communication can streamline their work and improve coordination with healthcare systems.
Under the Sal Tree Theatre Festival

- 14 Dec 2024
In News:
“Under the Sal Tree” Theatre Festival, held annually in Rampur, Assam, promotes eco-friendly and sustainable practices in theatre while showcasing rich cultural diversity.
Overview:
- Location: Rampur village, Goalpara district, Assam
- Organizer: Badungduppa Kalakendra, a social and cultural organization
- Founded: 1998 by Sukracharjya Rabha
- Festival Focus: Eco-friendly theatre practices, cultural diversity, and sustainability
Key Features
- Unique Setting: Open-air festival under Sal trees, with no artificial lighting or electric sound systems.
- Sustainability:
- No use of plastic.
- Carbon-neutral, with eco-friendly materials such as bamboo, straw, and cane.
- Performances in natural daylight, avoiding electric lights.
- International Participation: Theatre groups from countries like Poland, South Korea, Brazil, Sri Lanka, Bangladesh, North Korea, Bolivia, and Holland have performed.
- Cultural Celebration: Highlights indigenous art forms, languages, and traditions, e.g., Rabha and Bodo plays.
Festival Activities
- Performances:
- Includes plays like “Dadan Raja” (Rabha language play), “Kindhan Charithiram” (Tamil), and “Kisan Raj” (Hindi).
- Focus on themes such as societal change and resilience of farmers.
- Workshops & Community Projects: For performing artists, promoting artistic innovation and social impact.
- Anniversary Celebrations:
- 25th anniversary celebrated with special events and book releases, e.g., “Resonance: Echoing the Spirit of Badungduppa” and “Sukracharjya Rabha on the Back Stage”.
Impact & Legacy
- Theatre Movement: Celebrates art amidst nature, breaking geographical barriers despite the remote location.
- Founder’s Vision: Sukracharjya Rabha believed in the synergy between art and nature, aiming to bring social change through theatre.
- Local Involvement:
- 20 resident artists contribute to the festival’s success.
- Festival has become a major cultural attraction in Assam, drawing thousands of theatre enthusiasts.
One Nation, One Election Bill
- 13 Dec 2024
In News:
The One Nation, One Election Bill has made significant progress in India, passing the Lok Sabha with 269 votes in favor and 198 votes against. The bill proposes the synchronization of elections for the Lok Sabha, State Legislative Assemblies, and local bodies (Panchayats and Municipalities), aiming to streamline the electoral process, reduce costs, and enhance governance.
Key Updates:
- The bill has been approved by the Union Cabinet and will be reviewed by a Joint Parliamentary Committee (JPC), whose report will be presented for further approval and discussion in Parliament.
- The process will unfold in two phases:
- Phase 1: Simultaneous elections for the Lok Sabha and State Legislative Assemblies.
- Phase 2: Synchronizing local body elections (Panchayats and Municipalities) within 100 days of the general elections.
Historical Context:
- 1951-1967: India previously conducted simultaneous elections for the Lok Sabha and State Assemblies until disruptions, such as premature dissolutions of assemblies, led to staggered elections after 1967.
- The One Nation One Election concept has been revived to address inefficiencies in the current system, especially the high cost of conducting frequent elections.
Advantages of the One Nation, One Election Bill:
- Cost Reduction: Synchronizing elections can significantly lower the financial burden by eliminating the need for multiple election cycles, reducing the deployment of resources like security personnel and election staff.
- Long-Term Governance Focus: Politicians can prioritize governance and policy implementation rather than election campaigning, fostering long-term stability.
- Increased Voter Turnout: Voter fatigue, caused by frequent elections, may reduce, leading to higher turnout as elections occur less often.
- Fairer Political Competition: Smaller regional parties could have a better chance to compete with larger national parties by reducing election-related costs.
- Efficient Use of Resources: Security forces and administrative resources can be deployed more effectively, avoiding the redundancy caused by multiple election cycles.
Disadvantages of the One Nation, One Election Bill:
- Synchronization Challenges: Aligning elections across a vast and diverse country like India, especially in states with unstable political situations, may prove difficult.
- Federalism Concerns: The implementation may require constitutional changes that could impact India's federal structure, potentially limiting the autonomy of states in election matters.
- Impact on Regional Issues: National issues could overshadow regional concerns, diluting the focus on state-specific matters.
- Challenges for Regional Parties: Larger national parties may dominate the electoral landscape, reducing the influence of regional parties and undermining the federal nature of the political system.
- Accountability Risks: Fixed terms without frequent elections might reduce public scrutiny of elected officials, affecting their accountability.
Constitutional Amendments Required:
The implementation of One Nation, One Election requires amendments to several key constitutional provisions:
- Article 83: Regarding the duration of the Lok Sabha, amendments are needed to synchronize the timing of dissolution.
- Article 85: Deals with the sessions and dissolution of Parliament, which needs to be aligned with the new system.
- Article 172: Pertains to the duration of State Legislatures, requiring amendments for synchronization.
- Article 174: Similar to Article 85, it governs the sessions and dissolution of State Legislatures, needing standardization.
Implementation Challenges:
- Logistical Complexity: Conducting simultaneous elections would require immense logistical coordination, including vast numbers of electronic voting machines and trained personnel.
- Political Accountability: Fixed terms may reduce the accountability that frequent elections bring, potentially leading to governance stagnation.
- Impact on Federalism: Amendments to the Constitution regarding state legislatures might face resistance from states concerned about their autonomy.
International Mountain Day 2024
- 13 Dec 2024
In News:
On 11th December 2024, the Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change, in collaboration with the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) and G.B. Pant National Institute of Himalayan Environment (NIHE), hosted an event titled ‘Youth for the Himalaya: Innovate, Inspire, Impact’ to mark International Mountain Day.
Event Overview:
- The event was themed “Mountain Solutions for a Sustainable Future – Innovation, Adaptation, and Youth.”
- It emphasized the critical role of young people in addressing the environmental challenges faced by the Indian Himalayan Region (IHR).
- The aim was to showcase youth-driven innovations contributing to the region's sustainability, catalyzing active youth participation in environmental actions. This initiative aligns with the Mission LiFE (Lifestyle for Environment), launched by Prime Minister Narendra Modi, which encourages sustainable practices and collective environmental responsibility.
Key Highlights:
- Young changemakers, innovators, and stakeholders from across the country participated, including students, youth representatives, and members of the private sector, civil society, and government.
- The event highlighted discussions on sustainable solutions for the Himalayan region, integrating traditional knowledge with modern technological advancements in areas like eco-tourism, biodiversity conservation, and climate resilience.
- Short films and videos produced by NIHE and IUCN, such as "Promoting Conservation of Threatened Plant Species in the Western Himalayas" and "Himalayan Futures: Voices from the Ground," were also showcased.
International Mountain Day
- International Mountain Day, observed every year on December 11th since 2003, was established by the United Nations to raise awareness about the sustainable development of mountain regions.
- Mountains cover about one-fifth of the Earth's surface and provide essential freshwater to half of humanity, supporting agriculture, clean energy, and health.
Indian Himalayan Region (IHR)
- The IHR spans 13 Indian states and union territories, stretching approximately 2,500 kilometers from west to east. It is a biodiversity hotspot with significant ecological and cultural value. However, it faces challenges such as unsustainable development, climate change impacts, cultural erosion, and rising tourism.
Key Concerns for IHR:
- Unsustainable Development: Infrastructure projects and deforestation disrupt ecosystems.
- Climate Change: Glacial melting and rising temperatures affect water resources and increase flood risks.
- Cultural Erosion: Modernization threatens traditional practices of indigenous communities.
- Tourism Pressure: Waste generation due to growing tourism puts immense pressure on the region's fragile ecology.
Measures for Protection:
- Sustainable Tourism: Promoting eco-tourism and enforcing capacity limits to minimize environmental impact.
- Water Management: Capturing glacial meltwater for agriculture and ecosystem support.
- Disaster Preparedness: Developing disaster management strategies and early warning systems for events like landslides and floods.
- Bio-Cultural Conservation: Protecting both natural biodiversity and indigenous cultural practices through designated zones.
- Integrated Development: Establishing a "Himalayan Authority" for coordinated development in line with Sustainable Development Goals.
India’s Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) Journey Hits $1 Trillion Milestone
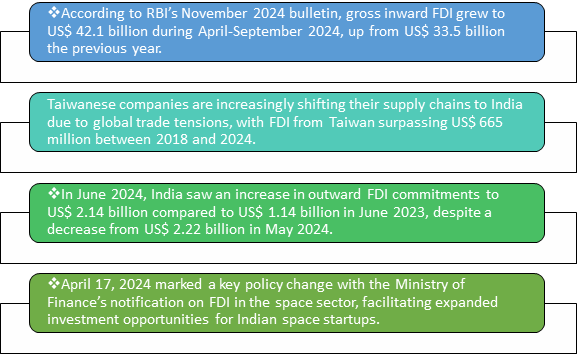
- 13 Dec 2024
In News:
India has reached a historic milestone, surpassing $1 trillion in foreign direct investment (FDI) inflows since April 2000. This achievement highlights India’s growing status as a major global investment hub and is further validated by a 26% increase in FDI inflows, which reached $42.1 billion during the first half of FY 2024-25.
Key Highlights of India’s FDI Growth:
- $1 Trillion Milestone: India has attracted a total of $1 trillion in FDI from April 2000 to September 2024. This figure includes equity, reinvested earnings, and other capital inflows.
- 26% Growth in FDI: FDI inflows surged by 26% in the first half of FY 2024-25, totaling $42.1 billion.
- Top Investors: Major investors include Mauritius (25%), Singapore (24%), and the United States (10%). These countries benefit from favorable tax treaties with India, boosting investment.
- Dominant Sectors: FDI has flowed into sectors like services, manufacturing, technology, and telecommunications, with significant investments also in pharmaceuticals, automobile, and construction development.
Factors Behind India’s FDI Success:
- Policy Reforms: India’s liberalized FDI policies, such as allowing 100% FDI in most sectors under the automatic route, have attracted foreign capital. Key reforms like abolishing angel tax and reducing corporate tax rates in the Income Tax Act of 2024 have also enhanced investor confidence.
- Business Environment: India’s rise in global competitiveness is evident in its improvement in rankings. It moved from 43rd to 40th in the World Competitiveness Index 2024 and climbed to 40th in the Global Innovation Index 2023, up from 81st in 2015.
- Investor Confidence: The government’s efforts, including initiatives like "Make in India", Goods and Services Tax (GST), and sector-specific incentives, have fostered a conducive environment for investment.
- Global Investment Standing: India has been the third-largest recipient of greenfield projects globally and saw a 64% increase in international project finance deals.
Contribution of Mauritius and Singapore:
- Mauritius and Singapore lead as the primary sources of FDI into India. Their favorable tax treaties with India make them attractive gateways for foreign investments. Mauritius accounted for 25%, and Singapore for 24% of the total FDI inflows.
Key Sectors Attracting FDI:
- Services Sector: Significant growth in services, especially financial services, has attracted substantial foreign investments.
- Manufacturing and Technology: These sectors have benefited from policies like the Production-Linked Incentive (PLI) schemes, which encourage foreign investments in high-tech manufacturing.
- Telecommunications and Pharmaceuticals: India’s growing digital ecosystem and strong pharmaceutical industry continue to attract international investments.
Importance of FDI for India:
- Infrastructure Development: FDI plays a crucial role in financing infrastructure projects, helping meet the country’s significant infrastructure needs.
- Balance of Payments: FDI helps bridge India’s current account deficit, ensuring stable foreign exchange reserves.
- Technology Transfer and Employment: Foreign investments bring advanced technology and create jobs, boosting productivity across sectors.
- Currency Stability: FDI supports the Indian Rupee in global markets by injecting foreign capital.
Challenges:
Despite the positive trends, India faces challenges such as geopolitical tensions, regulatory issues, global economic uncertainty, and infrastructure bottlenecks that can affect investor sentiment and capital inflows.
Way Ahead:
- Focus on Infrastructure: Continued investment in infrastructure development, including public-private partnerships (PPPs), will be crucial for sustained economic growth.
- Workforce Skilling: Collaborative efforts to upskill the workforce will ensure that India can meet the evolving demands of industries.
- Research and Development: Strengthening R&D and innovation will enhance India’s productivity and global competitiveness.
2024 World Chess Championship

- 13 Dec 2024
In News:
D. Gukesh became the youngest world chess champion after defeating Ding Liren of China in the final game of their match.
Key Facts about the 2024 World Chess Championship:
- Held At: Singapore, from November 25 to December 12, 2024.
- Players: Reigning champion Ding Liren (China) vs. Challenger D. Gukesh (India).
- Significance: This was the first-ever World Championship match contested by two Asian players. Gukesh became the third Asian to win the World Championship after Viswanathan Anand (India) and Ding Liren (China).
- Historical Context: The World Chess Championship was first established in 1886 with Wilhelm Steinitz as the first official World Champion.
- Governing Body: Organized by FIDE (Fédération Internationale des Échecs), which has been responsible for the event since 1948.
- Selection Process: Gukesh earned his spot through his victory in the 2024 Candidates Tournament in Toronto, while Ding Liren was the reigning champion after Magnus Carlsen declined to defend his title.
D. Gukesh: Key Details
- Birth: May 29, 2006, in Chennai, India.
- Grandmaster Title: Achieved at age 12 years, 7 months, and 17 days, making him the third-youngest Grandmaster in history.
- Chess Rating: He is the youngest player to reach a 2750 FIDE rating.
- Significant Wins:
- Gold medals in both team and individual events at the 2024 Chess Olympiad.
- Bronze medal in team events at the 2024 Asian Games.
- Remarkable Fact: Gukesh is four years younger than Garry Kasparov was when he won the World Championship in 1985.
FIDE World Chess Championship Overview:
- Founded: 1924 in Paris; headquartered in Lausanne, Switzerland.
- Governing Body: The International Chess Federation (FIDE) is recognized by the International Olympic Committee and governs global chess competitions. FIDE has 201 member countries.
Indian Chess Achievements:
- Viswanathan Anand: First Indian to win the World Chess Championship (5-time World Champion).
- D. Gukesh: Second Indian to win the World Chess Championship.
Disease X
- 13 Dec 2024
In News:
The recent outbreak reported in the first week of December 2024 in the Democratic Republic of Congo, which has claimed over 400 lives and remains unclassified, has raised concerns that it could be an instance of Disease X.
What is Disease X?
- Definition: Disease X is a hypothetical, unidentified pathogen that has the potential to cause a global health crisis, either as an epidemic or pandemic.
- Origins: Could arise from zoonotic spillover (animal-to-human transmission), antimicrobial resistance, bioterrorism, or lab accidents.
- Severity: Predicted to be 20 times more lethal than SARS-CoV-2, with rapid transmission and significant mortality.
- Features: Represents unknown threats, including viruses, bacteria, fungi, or prions.
- Emergence Factors: Driven by deforestation, urbanization, climate change, and human-wildlife interactions.
Historical Context
- Conceptualization: The term was coined by the World Health Organization (WHO) in 2018, post the 2014–2016 Ebola outbreak, which revealed gaps in global health responses.
- Zoonotic Origins: Around 70% of emerging diseases since 1940 have zoonotic origins, linked to human encroachment on wildlife habitats.
WHO’s Priority Pathogen List
- Purpose: To focus global resources and attention on diseases with high epidemic or pandemic potential but lacking sufficient vaccines or treatments.
- Pathogens Listed: Includes Ebola, Marburg, Lassa fever, Nipah virus, Rift Valley fever, Zika virus, and Disease X.
- Criteria: These diseases have high mortality rates, potential for rapid spread, and inadequate preventive or therapeutic options.
Why Disease X is a Concern
- Unpredictability: Its emergence, transmission, and impact remain uncertain, making preparedness challenging.
- Globalization: Increased global travel and trade facilitate rapid spread of diseases across borders.
- Environmental Drivers: Climate change, urbanization, and deforestation disrupt ecosystems, bringing humans into closer contact with wildlife and pathogens.
Patterns in Emerging Diseases
- Zoonotic Spillover: The majority of emerging diseases originate from animals, with over 1.7 million undiscovered viruses in wildlife that could infect humans.
- Increased Outbreaks: Since the mid-20th century, the frequency of new diseases has risen, reflecting environmental, demographic, and global factors.
Challenges in Predicting Disease X
- Uncertainty: The vast pool of potential pathogens (viruses, bacteria, fungi, etc.) makes it difficult to predict the exact nature, origin, or timing of Disease X.
- Environmental and Climatic Changes: Climate change reshapes disease transmission dynamics, expanding the range of diseases like malaria and dengue.
- Technological and Knowledge Gaps: Many pathogens that could cause pandemics are still unidentified. Genomic sequencing and AI are advancing but cannot fully predict Disease X.
Global Preparedness Initiatives
- WHO's Role: WHO’s priority pathogen list and Pandemic Treaty aim to ensure coordinated, global responses to future outbreaks.
- Pandemic Fund: Supports strengthening health systems, especially in low-income countries.
- mRNA Vaccine Hubs: Enhance vaccine production capacity, particularly in developing countries.
- Coalition for Epidemic Preparedness Innovations (CEPI): Works on "prototype pathogen" platforms to create vaccines within 100 days of identifying a new disease.
Indian Initiatives for Disease Surveillance and Preparedness
- Integrated Disease Surveillance Programme (IDSP): Tracks outbreaks, monitors trends, and strengthens the country’s epidemic preparedness.
- National Institute of Virology (NIV): Focuses on researching viral pathogens and zoonotic diseases.
- Biotech Initiatives: Indigenous vaccine development and diagnostic tools are crucial for combating future outbreaks.
- Emergency Response Fund: Allocates resources to support immediate pandemic response efforts.
Key Challenges in Tackling Disease X
- Prediction Complexity: The interactions between humans, animals, and the environment are too complex to predict the exact nature of Disease X.
- Health Disparities: Low- and middle-income countries often lack the infrastructure to effectively combat pandemics, making them more vulnerable.
- Climate Change: Alters transmission dynamics, expanding the range of diseases carried by vectors like mosquitoes.
Way Forward
- Strengthening Surveillance: Implementing real-time genomic sequencing and AI-driven tools for early outbreak detection.
- Global Cooperation: Promoting equitable sharing of vaccines, diagnostics, and treatments to ensure timely and efficient responses.
- Public Health Infrastructure: Invest in strengthening healthcare systems, especially in high-risk regions like the Congo Basin.
- Research and Development: Focus on universal vaccines, diagnostic tools, and prototype pathogen platforms that can be quickly adapted to new diseases.
Indian Scientists Develop Novel Gene Therapy for Haemophilia
- 12 Dec 2024
In News:
Indian scientists have developed a successful gene therapy treatment for severe haemophilia A, a rare inherited blood disorder causing spontaneous, potentially fatal bleeding episodes.
Key Highlights:
Trial Success:
- The trial, conducted at Christian Medical College (CMC), Vellore, involved five patients from Tamil Nadu.
- Results: None of the five patients reported bleeding episodes for over a year after receiving the treatment. The follow-up period averaged 14 months.
- This marks a significant improvement, as haemophilia patients typically experience frequent bleeding episodes requiring regular treatment.
Gene Therapy as a One-Time Solution:
- Traditional treatments involve frequent injections of clotting factors to prevent bleeding.
- The new gene therapy offers a one-time solution, teaching the body to produce enough clotting factor to prevent hemorrhages.
Haemophilia A - Overview:
- Caused by the absence of Factor VIII, a critical blood-clotting protein.
- Hemophilia A primarily affects males (since it's an X-linked disorder), though some females with two defective X chromosomes can also develop the condition.
- Symptoms include prolonged bleeding from minor injuries or internal bleeding in joints and muscles.
Current Treatment Challenges:
- Haemophilia treatments can be expensive and require lifelong care, costing up to ?2.54 crore over a 10-year period.
- The therapy requires repeated infusions of clotting factors or synthetic alternatives, which can be burdensome.
Gene Therapy Details:
- The gene therapy used in this trial involves fusing stem cells with the gene for Factor VIII using a lentivirus vector (safer than other vectors like adenovirus).
- This therapy eliminates the need for repeated Factor VIII infusions, providing a more cost-effective and sustainable solution.
Global Context:
- India has one of the world’s largest haemophilia populations, with an estimated 40,000 to 100,000 patients.
- The success of this gene therapy in India could lead to localized production, reducing treatment costs and increasing accessibility to gene therapy in resource-constrained settings.
Comparison with Roctavian:
- Roctavian, the only FDA-approved gene therapy for haemophilia A, also uses gene delivery to produce Factor VIII, but requires immunosuppressive therapy and is not approved for children.
- In contrast, the Vellore trial's lentivirus-based approach is considered safer, especially for children, with the potential for broader application.
Railways (Amendment) Bill, 2024

- 12 Dec 2024
In News:
The Railways (Amendment) Bill, 2024 was passed in the Lok Sabha on December 20, 2024, aiming to enhance the functioning and autonomy of Indian Railways.
Key Provisions:
- Repeal of the Indian Railway Board Act, 1905: The Bill repeals the 1905 Act and incorporates its provisions into the Railways Act, 1989, simplifying the legal framework by reducing the need to refer to two separate laws.
- Statutory Backing for Railway Board: The Bill provides statutory backing to the Railway Board, which previously lacked such a legal mandate. It grants the Union government the authority to determine the number of members, their qualifications, terms, and conditions of service.
- Decentralization of Power: The Bill aims to decentralize decision-making, granting greater autonomy to regional railway zones. This shift will allow more independence in budgeting, infrastructure projects, and recruitment, addressing long-standing calls for improved regional empowerment.
- Independent Regulator: The Bill proposes the creation of an independent regulator for overseeing tariffs, safety, and private sector participation. This idea has been supported by previous expert committees to encourage greater competition and transparency in the sector.
- Fast-Tracking Infrastructure and Services: The Bill will streamline approvals for new train services and infrastructure projects, helping meet demands from underserved regions, particularly in states like Bihar.
Objectives:
- Modernization of the Legal Framework: By incorporating the provisions of the 1905 Act into the 1989 Act, the Bill aims to simplify and modernize the legal architecture governing the railways.
- Empowerment of Railway Zones: Autonomy for railway zones is seen as a key step towards improving efficiency and accountability in operations.
- Private Sector Participation: The establishment of an independent regulator is expected to promote private participation in the railway sector, aligning with international standards.
Historical Context:
- The Indian Railways Act, 1890 established the foundations for Indian Railways as a government entity, which was further refined with the Indian Railway Board Act, 1905.
- This Bill aligns with recommendations from previous committees, including the Sreedharan Committee (2014) and the Committee on Restructuring Railways (2015), which have called for greater decentralization and autonomy for railway zones, as well as an independent regulatory body.
Challenges and Proposed Reforms:
- Financial Sustainability: The railways face challenges such as high operating costs, particularly from salaries and pensions, and losses in the passenger segment. Suggestions to improve finances include rationalizing passenger fares, enhancing freight revenue, and attracting private investment in infrastructure.
- Efficient Freight Operations: The Bill also addresses concerns about network congestion, especially for freight operations, and aims to increase the competitiveness of freight transport by improving infrastructure and reducing cross-subsidies from passenger fares.
Recommendations of various Committees on reforming the Railways
Regulatory Structure for Railway Sector
- Set up independent regulator to fix tariffs, promote competition, and protect consumer interests
Organisational structure of Indian Railways
- Corporatisation of Indian Railways
- Reorganise Railway Board to reflect a corporate business structure
- Envision the Railway Board as a policymaker alone
- Provide zones with full financial autonomy
Operations
- Separate core and non-core business (hospitals, schools, catering and security) of the Railways
- Permit private participation in some railway operations
Finances
- Clearly define social obligations and commercial business roles
- Restructure accounting procedure to reflect zone and route-wise profit and loss statements6,7,9
- Develop PPP models to attract private participation in: (i) developing and maintaining stations/ terminals, (ii) leasing of wagons, (iii) freight train operations, (iv) manufacturing of rolling stock, and (v) running non-core business operations
- Monetise railway assets
- Rationalise passenger tariffs
Regulatory Structure for Railway Sector
- Set up independent regulator to fix tariffs, promote competition, and protect consumer interests
Organisational structure of Indian Railways
- Corporatisation of Indian Railways
- Reorganise Railway Board to reflect a corporate business structure
- Envision the Railway Board as a policymaker alone
- Provide zones with full financial autonomy
Operations
- Separate core and non-core business (hospitals, schools, catering and security) of the Railways
- Permit private participation in some railway operations
Finances
- Clearly define social obligations and commercial business roles
- Restructure accounting procedure to reflect zone and route-wise profit and loss statements6,7,9
- Develop PPP models to attract private participation in: (i) developing and maintaining stations/ terminals, (ii) leasing of wagons, (iii) freight train operations, (iv) manufacturing of rolling stock, and (v) running non-core business operations
- Monetise railway assets
- Rationalise passenger tariffs
World Malaria Report 2024

- 12 Dec 2024
In News:
The World Malaria Report 2024 released by the World Health Organization (WHO) highlights significant progress in malaria control, particularly in India, but underscores the continued burden of malaria in Southeast Asia, where India accounts for half of all malaria cases.
About Malaria:
- Cause: Malaria is caused by Plasmodium parasites, primarily P. falciparum and P. vivax, transmitted through bites from infected female Anopheles mosquitoes.
- Transmission: Non-contagious; transmitted via mosquito bites.
- Symptoms: Fever, chills, and headaches appear 10–15 days after the mosquito bite. In some individuals, the symptoms may be mild.
- Prevention: Includes vector control strategies like insecticide-treated bed nets and indoor spraying. Malaria is treatable with early diagnosis and prompt medication.
India’s Malaria Status:
- Progress:
- India has made significant strides in reducing malaria, with cases decreasing from 22.8 million in 2000 to 4 million in 2023, a reduction of 82.4%.
- Similarly, malaria-related deaths dropped by 82.9%, from 35,000 in 2000 to 6,000 in 2023.
- Exit from High-Burden-High-Impact (HBHI) Group:
- India exited this group in 2024, signaling its success in reducing malaria burden.
- Cases dropped by 69% (from 6.4 million in 2017 to 2 million in 2023), and deaths fell by 68% (from 11,100 to 3,500 in the same period).
Key Strategies Behind India's Success:
- Artemisinin-Based Combination Therapy (ACT): Used to treat malaria effectively.
- Long-Lasting Insecticidal Nets (LLIN): Widely deployed to control mosquito populations.
- Targeted Interventions: Focused on forested and tribal areas where malaria transmission is higher, particularly in states like Jharkhand, Odisha, and the North-East.
- Effective Monitoring: Ensures proper implementation of strategies and interventions.
WHO's Global Malaria Report 2024 Highlights:
- Global Burden: In 2023, there were 263 million malaria cases globally and 597,000 deaths. The African region remains the hardest hit, accounting for 95% of malaria deaths.
- Progress Since 2000: Malaria incidence and deaths have significantly decreased. The global number of malaria cases and deaths dropped substantially, with over 2.2 billion cases and 12.7 million deaths averted.
- Malaria-Free Countries: As of November 2024, 44 countries and one territory, including Egypt, have been certified malaria-free.
- Emerging Threats: Drug resistance (especially to Artemisinin) and insecticide resistance are growing concerns, affecting control efforts.
India and Southeast Asia:
- India contributes nearly half of the malaria cases in Southeast Asia, while Indonesia accounts for about one-third. Despite progress, India and Indonesia together accounted for 88% of malaria deaths in the region.
- South-East Asia Progress: The region reduced malaria cases by 82.4% from 22.8 million in 2000 to 4 million in 2023. Timor-Leste and Bhutan reported zero indigenous malaria cases in 2023.
Global Recommendations:
- WHO stresses the need for continued investment, innovative strategies, and targeted actions, especially in high-burden areas like Africa, to sustain progress and tackle remaining challenges, such as drug resistance, insecticide resistance, and new vector species like Anopheles stephensi, which thrives in urban areas.
Smuggling in India Report 2023-24
- 12 Dec 2024
In News:
The annual ‘Smuggling in India - Report 2023-24’ report, which highlights DRI’s performance and experience over the last financial year as well as trends in the field of anti-smuggling and commercial fraud, will be released during the celebration.
Major Narcotics Hubs and Routes:
- Afghanistan, Iran, and Pakistan (The Death Crescent):
- Primary source of heroin trafficked into India.
- Routes via Africa, the Gulf, and India-Pakistan border.
- Myanmar, Laos, and Thailand (The Death Triangle):
- Significant source of synthetic drugs and heroin.
- Drugs often enter India through porous northeastern borders (e.g., Assam, Mizoram).
- Vulnerable regions: Moreh, Churachandpur, Zokhawthar.
- Maritime Routes:
- India’s vast coastline provides opportunities for drug trafficking, often through concealed shipping containers and fishing vessels.
- Air Routes:
- Increased trafficking due to international air traffic.
- Smuggled drugs often concealed in luggage, courier packages, or ingested by mules.
Major Narcotics Trends and Seizures (FY24):
- Cocaine:
- Significant increase in trafficking, particularly from South America and Africa.
- 47 seizures, up from 21 in the previous year.
- Seized quantity: 107 kg.
- Methamphetamine:
- Spiked in northeastern states like Assam and Mizoram.
- Seized quantity in FY24: 136 kg; increased in the first half of FY25 with 123 kg.
- Hydroponic Marijuana:
- Increasing smuggling from the US, Thailand, and other countries.
- Black Cocaine:
- New form of cocaine coated with substances like charcoal or iron oxide to evade detection.
- Contraband Cigarettes:
- Smuggling through sea routes, especially from Southeast Asia and the Middle East.
- Seizures increased by 19% in FY25, reaching 3.95 crore sticks.
- Illicit Gold:
- Significant destination for gold smuggling from West Asia (UAE, Saudi Arabia).
- Seized quantity fell slightly (1,319 kg in FY24), with land and air routes being primary methods.
- Wildlife Smuggling:
- Seizures included 53.5 kg of elephant tusks, leopard skins, live pangolins, and more.
Challenges and Issues:
- Porous Borders:
- Smuggling across eastern borders with Bangladesh, Myanmar, and Nepal remains a significant challenge.
- Difficult terrain in these regions aids traffickers.
- Air and Sea Routes:
- Growing use of air and maritime routes due to faster movement of goods.
- Technology and Detection:
- Emergence of “black cocaine” challenges traditional detection methods.
Anti-Smuggling and Drug Control Efforts:
- International Cooperation:
- United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime (UNODC) and the International Narcotics Control Board (INCB) lead global efforts.
- Paris Pact Initiative targets Afghan opiate trafficking.
- Indian Initiatives:
- Narcotic Drugs and Psychotropic Substances Act (1985) provides legal framework.
- Narcotics Control Bureau (NCB) and Anti-Narcotics Task Force (ANTF) work together for enforcement.
- National Action Plan for Drug Demand Reduction and Nasha Mukt Bharat Abhiyaan focus on awareness and rehabilitation.
ABOUT DRI
- The Directorate of Revenue Intelligence (DRI) is the premier intelligence and enforcement agency on anti-smuggling matters under the aegis of Central Board of Indirect Taxes & Customs (CBIC), Government of India.
- It came into existence on 4th December 1957.
- With its Headquarters at New Delhi, 12 Zonal Units, 35 Regional Units and 15 Sub-Regional Units, DRI has been carrying out its mandate of preventing and detecting cases of smuggling of narcotic drugs & psychotropic substances, gold, diamonds, precious metals, wildlife products, cigarettes, arms, ammunitions & explosives, counterfeit currency notes, foreign currency, SCOMET Special Chemicals, Organisms, Materials, Equipment and Technologies) items, hazardous & environmentally sensitive materials, antiques etc. and taking punitive action against the organised crime groups engaged therein.
- DRI is also engaged in unearthing commercial frauds and instances of customs duty evasion.
Hyperloop Technology
- 12 Dec 2024
In News:
India’s first hyperloop test track (410 meters) completed by Indian Railways, IIT-Madras’Avishkar Hyperloop team and TuTr (incubated startup) at IIT-M discovery campus, Thaiyur in Chennai, Tamil Nadu.
India’s First Hyperloop Test Track:
- Location: IIT Madras’ Discovery Campus, Chennai.
- Collaboration: Indian Railways, IIT-Madras' Avishkar Hyperloop team, and TuTr Hyperloop (startup).
- Track Length: 410 meters.
- Test Speed: Initial successful test at 100 km/h; plans for 600 km/h in the next phase.
- Passenger Capacity: 40–100 passengers per pod, depending on design.
What is Hyperloop Technology?
- Concept: A high-speed transport system using pods in low-pressure vacuum tubes, designed to achieve speeds similar to aircraft (up to 1,100 km/h).
- Working:
- Magnetic Levitation (Maglev): Pods float on magnets, eliminating friction.
- Vacuum Tubes: Reduces air resistance for high-speed travel.
- Propulsion: Linear induction motors propel pods.
- Energy: Solar-powered, designed for zero emissions.
India’s Hyperloop Projects:
- Current Status:
- Successful testing of a 410-meter test track at IIT Madras.
- Ongoing feasibility studies for routes like Chennai Airport–Parandur, Mumbai–Pune, and Amritsar–Chandigarh.
- Phase 1 & 2: First phase involves a 11.5-kilometer track; future expansion to 100 km.
- Mumbai–Pune Corridor: Planned as India’s first full-scale Hyperloop system, aiming to reduce travel time from 3–4 hours to 25 minutes.
Benefits of Hyperloop:
- Speed: Capable of reaching speeds up to 1,100 km/h (operational speed around 360 km/h).
- Efficiency: Reduces travel time, energy-efficient with reduced air resistance and friction.
- Sustainability: Powered by renewable energy (e.g., solar power), offering zero emissions.
- Point-to-Point Travel: No intermediate stops, making it more time-efficient.
Challenges:
- Infrastructure Costs: Expensive to build the vacuum tubes, stations, and supporting systems.
- Land Acquisition: Difficulty in acquiring land, especially in densely populated areas.
- Regulatory Issues: Lack of a specific regulatory framework for such advanced transport systems.
- Technological Barriers: Complex engineering challenges, including development of maglev systems and vacuum seals.
Global Context:
- Origin: Concept proposed by Elon Musk in 2013.
- Worldwide Adoption: Hyperloop is being explored globally, with projects in the U.S., UAE, and Europe.
GG Tau A System

- 11 Dec 2024
In News:
GG Tau A System: Located about 489 light-years from Earth, this system is a triple-star setup that is between 1 to 5 million years old. This makes it an ideal system for studying the early stages of planetary formation.
Findings from the Discovery:
- Protoplanetary Disk: The system features a protoplanetary disk made of gas and dust, where new planets are forming. Researchers from NISER (National Institute of Science Education and Research), Odisha detected emissions from key molecules in the disk.
- Chemical Molecules: The molecules are frozen on tiny dust particles in the coldest regions of the disk (temperatures between 12 K and 16 K). These frozen molecules could serve as the building blocks for new planets.
Significance of the Discovery:
- Triple-Star Configuration: GG Tau A’s triple-star system is rare, and it has complex gravitational interactions among the three stars. This complicates how the gas and dust disk behaves and provides unique insights into planetary formation in multi-star systems.
- Study of Planet Formation: Traditionally, planets form around single stars or in binary systems. However, multi-star systems like GG Tau A present challenges for planet formation. Studying this system helps scientists understand how planets can form in more complex environments.
- Cold Conditions for Planet Formation: The study found that icy conditions in the disk are essential for the accumulation of materials that form planets. These low temperatures (below the freezing point of carbon monoxide) allow dust and gas particles to clump together, creating the foundation for exoplanets.
Broader Implications:
- Exoplanet Diversity: This research enhances our understanding of how planets form in different types of star systems, contributing to the study of exoplanets and their potential diversity across the universe.
- Astrophysics and Planetary Science: This discovery plays a crucial role in improving our knowledge of the early stages of planet formation, especially in complicated star systems like triple-star setups, which are rare but can provide valuable insights into how planetary systems evolve under unique conditions.
Research Tools:
- The team used advanced radio telescopes located in the Atacama Desert (Chile) to observe the emissions from the disk, highlighting the role of cutting-edge technology in space exploration and astronomical research.
Champions of the Earth Award

- 11 Dec 2024
In News:
- Madhav Gadgil, an Indian ecologist, received the UN Environment Programme (UNEP)'s Champions of the Earth Award in 2024.
- The Champions of the Earth Award is UNEP’s highest environmental honor, recognizing individuals, organizations, and governments for significant contributions to environmental protection and sustainable development.
Contributions of Madhav Gadgil:
- Work in Western Ghats:
- Gadgil is recognized for his seminal work in the Western Ghats, an ecologically sensitive region in India, which is a global biodiversity hotspot.
- He chaired the Western Ghats Ecology Expert Panel (WGEEP), formed by the Indian government to assess the impacts of population pressure, climate change, and development on the region.
- Recommendations by WGEEP:
- Ecologically Sensitive Area (ESA): Recommended declaring the entire Western Ghats range as an ESA.
- The WGEEP suggested dividing the Western Ghats into three Ecologically Sensitive Zones (ESZ) based on environmental sensitivity.
- Development Restrictions: Proposed a ban on activities like mining, quarrying, thermal power plants, and large-scale hydropower projects in the most sensitive zones (ESZ-1).
- Governance Recommendations: Suggested a bottom-to-top governance approach, beginning with Gram Sabhas, and the creation of a Western Ghats Ecology Authority (WGEA) for effective management.
- Impact of Gadgil’s Work:
- His research and recommendations have played a crucial role in shaping environmental policy and public opinion in India.
- The UNESCO World Heritage status for the Western Ghats in 2012 was a significant step in global recognition of the region’s ecological importance.
About the Champions of the Earth Award:
- History & Significance:
- Established in 2005, the award recognizes trailblazers working towards addressing the triple planetary crisis: climate change, biodiversity loss, and pollution.
- Since its inception, it has honored 122 laureates who have shown outstanding leadership in environmental conservation.
- 2024 Awardees:
- Madhav Gadgil (India) – for his work on the Western Ghats.
- Sonia Guajajara (Brazil) – for advocacy for Indigenous rights and environmental protection.
- Amy Bowers Cordalis (USA) – for her work in Indigenous rights and ecosystem restoration.
- Gabriel Paun (Romania) – for defending Europe’s old growth forests from illegal logging.
- Lu Qi (China) – for contributions to afforestation and combating desertification.
- SEKEM (Egypt) – for advancing sustainable agriculture.
Key Facts about UNEP:
- UN Environment Programme (UNEP):
- Established in 1972, UNEP is a leading global authority on environmental issues.
- UNEP aims to address climate change, nature and biodiversity loss, and pollution through scientific research, policy support, and public advocacy.
- UNEP is headquartered in Nairobi, Kenya and works closely with 193 Member States to tackle the planet’s most pressing environmental challenges.
Ayush Visa

- 11 Dec 2024
In News:
- Recently, the government introduced a separate category of Ayush Visa for foreigners seeking treatment under the Ayush systems of medicine (Ayurveda, Yoga, Unani, Siddha, and Homeopathy).
- The Ayush Visa is available in four sub-categories:
- Ayush Visa: For foreigners visiting India for therapeutic care and wellness treatment in accredited hospitals/wellness centers.
- Ayush Attendant Visa: For attendants accompanying patients seeking Ayush treatment.
- e-Ayush Visa: An electronic version of the Ayush Visa for convenience.
- e-Ayush Attendant Visa: For attendants accompanying patients on an e-Ayush Visa.
- Visa Statistics (as of December 4, 2024):
- 123 regular Ayush visas have been issued.
- 221 e-Ayush visas issued.
- 17 e-Ayush attendant visas issued.
- Advantage Healthcare India Portal:
- The Ministry of Health and Family Welfare launched the Advantage Healthcare India portal, an official platform for Medical Value Travel (MVT).
- The portal facilitates information for international patients seeking medical treatment and wellness services in India.
- The website for accessing the portal is www.healinindia.gov.in.
- Government's Objectives: The government aims to sensitize stakeholders involved in MVT, including Ayush facility providers, to ensure smooth services for international patients.
Human Rights Day 2024

- 11 Dec 2024
In News:
Human Rights Day 2024 celebrated every year on 10th December is dedicated to promote protection of fundamental rights and freedom of all individuals.
Key Highlights:
- Purpose: Promote and protect human rights and freedoms worldwide.
- Theme (2024): “Our Rights, Our Future, Right Now” – highlights the importance of immediate action to protect and uphold human rights globally.
Historical Significance:
- Commemorates: The adoption of the Universal Declaration of Human Rights (UDHR) by the UN General Assembly in 1948.
- UN Resolution: Established by UN Resolution 423 (V) in 1950.
- First Observance: December 10, 1950.
- Father of Human Rights Day: Eleanor Roosevelt, for her pivotal role in drafting the UDHR.
Key Highlights:
- The UDHR:
- Adopted in 1948, it defines fundamental human rights for all individuals.
- Comprises 30 articles, addressing rights such as freedom, equality, and access to education, healthcare, and fair employment.
- Role of the UN: UN Human Rights Council (UNHRC): A body under the UN responsible for monitoring and promoting human rights worldwide, comprising 47 member states.
- Human Rights Day Focus in 2024:
- Emphasizes human rights education, particularly among the youth.
- Addresses emerging challenges like cybercrimes, AI impacts, and climate change.
- Reaffirms the importance of safeguarding human dignity globally.
Human Rights Declared by UDHR:
- Right to freedom and equality
- Right to life, liberty, and security
- Freedom from slavery and torture
- Right to recognition before the law
- Equal protection under the law
- Right to a fair trial
- Right to privacy and protection from attacks
- Right to work and fair employment
- Right to rest and leisure
- Right to education
- Right to an adequate standard of living
- Right to participate in government and cultural activities
AgeXtend
- 11 Dec 2024
In News:
- AgeXtend is developed by researchers at Indraprastha Institute of Information Technology – Delhi (IIIT-Delhi) to rapidly identify age-defying compounds, known as geroprotectors, to promote healthy aging.
Key Features of AgeXtend:
- What is AgeXtend?
- An AI-based platform designed to discover compounds with geroprotective (anti-aging) properties.
- Objective: To accelerate the identification of molecules promoting longevity by reducing the time and effort compared to conventional research methods.
- Development: Developed by researchers from the Indraprastha Institute of Information Technology (IIIT), Delhi.
- Working Mechanism:
- Scans over 1.1 billion compounds to predict, analyze, and validate molecules with anti-aging potential.
- Utilizes machine learning to determine efficacy, safety, and mechanisms of action.
- Experimental validation conducted using yeast, worms (C. elegans), and human cell models.
- Significance:
- The largest study on longevity, including compounds from commercial drugs, FDA-approved drugs, Ayurvedic, and Chinese medicine.
- Provides a scientific rationale for identifying geroprotective compounds, aiding targeted research.
- Open-source code and data promote collaboration and allow commercial exploration.
Platform Capabilities:
- AI Analysis:
- Uses bioactivity data from existing geroprotectors to predict new compounds with similar properties.
- Evaluates geroprotective potential, toxicity, and identifies target proteins and mechanisms of action for accuracy and safety.
- Unique Feature: Explains why a compound is considered geroprotective, revealing underlying mechanisms.
- Example Validation: Successfully identified benefits of metformin and taurine without prior knowledge, confirming the platform’s predictive power.
- Study Scale: The study involved scanning over 1.1 billion molecules, making it the largest study on longevity to date.
Open-Source and Commercial Use:
- Availability:
- The code and data are available as open-source for researchers and students. Commercial access is available for a fee.
- A Python package for AgeXtend is available via pip on pypi.org.
- Further Collaboration: The researchers have reached out to pharma companies to further investigate promising compounds.
- Exploring Natural Compounds: AgeXtend also explores natural compounds from the human microbiome, investigating their role in controlling cell aging.
Sora Turbo

- 10 Dec 2024
In News:
OpenAI officially launched Sora Turbo, its advanced text-to-video artificial intelligence (AI) tool, marking a significant development in the field of visual AI generation. This follows Google’s recent expansion of its video-generative AI tool, Veo, for Vertex AI customers. However, hours after Sora Turbo’s release, OpenAI temporarily disabled sign-ups due to overwhelming demand.
Key Features of Sora Turbo:
- Text-to-Video Generation: Users can input text prompts, and Sora Turbo will generate videos based on the provided descriptions. This makes it one of the first widely accessible AI-powered video generation models.
- Video Quality & Formats: Sora Turbo can generate videos in 1080p resolution, lasting up to 20 seconds. It supports both vertical and horizontal formats.
- Remix Options: Users can remix the AI-generated videos with their own assets, allowing for customization and extension of the content.
- Speed & Interface: The tool has been optimized for faster video generation compared to its previous version, with a new user interface designed to make the process more intuitive.
- Subscription Plans:
- ChatGPT Plus ($20/month): Users get up to 50 videos at 480p resolution per month or fewer videos at 720p resolution.
- ChatGPT Pro ($200/month): Offers 10 times more usage, with higher resolution and longer durations.
User Access and Availability:
- Access Requirements: To use Sora Turbo, individuals need to subscribe to either the ChatGPT Plus or ChatGPT Pro plans. The tool is included in these subscriptions without additional charges.
- Geographic Limitations: As of now, Sora Turbo is unavailable in the European Union, United Kingdom, and Switzerland.
Metadata & Safety Features:
- Transparency: All videos generated by Sora Turbo will include C2PA metadata for content provenance and authenticity, along with a visual watermark.
- Abuse Prevention: OpenAI has implemented safeguards to block the generation of harmful content, including child sexual abuse materials and sexual deepfakes.
Future Developments:
OpenAI has plans to offer tailored pricing for different users starting in early 2025. Additionally, Sam Altman, CEO of OpenAI, described Sora as a groundbreaking product, comparing it to the early days of GPT technology, and emphasized its potential for co-creation and innovative visual content generation.
INS Tushil Commissioned into the Indian Navy in Russia

- 10 Dec 2024
In News:
Recently, the Indian Navy officially commissioned INS Tushil, a multi-role stealth guided missile frigate, at Kaliningrad, Russia. This marks a significant milestone in India-Russia defense cooperation and strengthens India’s maritime capabilities.
About INS Tushil:
- Class & Design: INS Tushil is the seventh ship in the Krivak III class (Project 1135.6) of frigates. It is part of an upgraded series, following the Talwar-class and Teg-class frigates, and was built at the Yantar Shipyard in Kaliningrad, Russia.
- Development & Contract: The construction was initiated under a 2016 contract between the Indian Government, JSC Rosoboronexport (a Russian defense company), and the Indian Navy. The ship incorporates 26% indigenous technology, highlighting growing cooperation between Indian and Russian industries.
- Key Features:
- Stealth Design: With advanced radar-absorbing features, it is less detectable by enemy radar.
- Weaponry: Equipped with BrahMos supersonic cruise missiles, Shtil Surface-to-Air Missiles, anti-submarine torpedoes, electronic warfare systems, and more.
- Versatility: Designed for blue-water operations, the ship can engage in air, surface, underwater, and electromagnetic warfare.
- Helicopter Deck: Supports operations of upgraded Kamov 28 and Kamov 31 helicopters.
- Speed: Capable of exceeding 30 knots.
Significance:
- Enhanced Naval Capabilities: The commissioning of INS Tushil boosts India’s defense strength in the Indian Ocean Region (IOR), a vital area for global maritime trade and security.
- Maritime Security: INS Tushil is designed to support India’s vision of maintaining stability in the IOR and to act as a deterrent against piracy and other maritime threats.
- Defense Cooperation: This commissioning exemplifies the growing defense ties between India and Russia, underscored by joint development, technology transfer, and shared expertise. The ship reflects a major step in India's self-reliance in defense, in line with the “Aatmanirbhar Bharat” initiative.
- Strategic Role in Global Defense: The ship is a key asset in the Indian Navy's efforts to secure maritime trade routes, enhance regional security, and provide humanitarian assistance in times of need.
Key Events & Facts:
- Construction Timeline: The keel of INS Tushil was laid in 2013, and it launched in 2021. After completing extensive sea and weapon trials in 2024, it was formally commissioned into the Navy.
- Collaborative Effort: The ship is a product of collaborative efforts between Indian and Russian industries, marking a significant achievement in joint defense manufacturing.
Governor of the Reserve Bank of India (RBI)

- 10 Dec 2024
In News:
Recently, the Government of India announced the appointment of Sanjay Malhotra as the 26th Governor of the Reserve Bank of India (RBI). He replaces Shaktikanta Das, whose six-year tenure ends on December 10, 2024.
Background of Sanjay Malhotra:
- Education & Early Career: Sanjay Malhotra is a 1990-batch IAS officer from the Rajasthan cadre. He holds a degree in Computer Science Engineering from the Indian Institute of Technology (IIT) Kanpur and a Master’s in Public Policy from Princeton University.
- Professional Experience: Malhotra has over 33 years of experience in various sectors including power, finance, taxation, information technology, and mines. He is currently serving as the Revenue Secretary in the Ministry of Finance, a position he has held since October 2022. Prior to this, he was Secretary of the Department of Financial Services.
- Monetary Policy and Challenges: As RBI Governor, Malhotra will inherit the responsibility of steering India's monetary policy, especially as inflation has been a persistent issue and economic growth has slowed. His first monetary policy review is expected in February 2025.
About the Appointment Process:
RBI Governors are appointed by the Government of India, and the appointment process involves the Financial Sector Regulatory Appointment Search Committee, which includes the Cabinet Secretary, the current RBI Governor, the Financial Services Secretary, and two independent members. The committee prepares a list of eligible candidates, interviews them, and the final decision is made by the Cabinet Committee on Appointments, chaired by the Prime Minister.
RBI Governors Eligibility Criteria
- The RBI Act, 1934 does not mention any specific qualification for the governor. People with different educational backgrounds were selected to head the institution. However, the governor traditionally is either a civil services personnel or an economist.
- Candidates should have prior experience in areas such as:
- Working with the International Monetary Fund (IMF) or World Bank.
- Serving as Chairman or General Manager of a bank.
- Holding significant positions in reputable financial or banking organizations.
- Working in the Ministry of Finance of the Government of India.
- The candidate must be an Indian citizen aged 35 years or older.
- The candidate cannot be a member of Parliament, State Legislature, or hold any other office for profit
Key Responsibilities of the RBI Governor:
- Monetary Policy: The RBI Governor chairs the Monetary Policy Committee (MPC), which is responsible for setting benchmark interest rates and managing inflation.
- Regulation of Financial Institutions: The Governor oversees the regulation of banks, non-banking financial companies (NBFCs), and other financial institutions.
- Currency Management: The Governor ensures the proper issuance of currency and the withdrawal of unfit notes.
- Crisis Management and Policy Execution: The Governor is pivotal in managing financial crises and ensuring the execution of policies related to foreign exchange and financial inclusion.
National Panchayat Awards 2024

- 10 Dec 2024
In News:
The National Panchayat Awards 2024 celebrated the remarkable contributions of 45 Panchayats from across India for their role in driving sustainable and inclusive development in rural areas. The awards were presented on 11th December 2024 at Vigyan Bhawan, New Delhi, with President Smt. Droupadi Murmu and Union Minister of Panchayati Raj Shri Rajiv Ranjan Singh (Lalan Singh) presiding over the event.
Key Highlights:
- Categories of Awards: The awards focus on rural governance, social inclusion, environmental sustainability, and the achievement of the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) through Localization of SDGs (LSDGs).
- Deen Dayal Upadhyay Panchayat Satat Vikas Puraskar (DDUPSVP): Recognizes top-performing Gram Panchayats across 9 thematic areas like health, water, sanitation, and governance.
- Nanaji Deshmukh Sarvottam Panchayat Satat Vikas Puraskar: Awarded to the best Panchayats based on overall excellence across all LSDG themes.
- Gram Urja Swaraj Vishesh Panchayat Puraskar: Honors Panchayats for contributions to renewable energy.
- Carbon Neutral Vishesh Panchayat Puraskar: Awarded to Panchayats achieving net-zero carbon emissions.
- Panchayat Kshamta Nirmaan Sarvottam Sansthan Puraskar: Recognizes institutions supporting Panchayats in implementing LSDGs.
- Notable Achievements:
- Women’s Leadership: 42% of the award-winning Panchayats were led by women.
- States with Top Performers: States like Tripura, Odisha, and Maharashtra were prominently recognized for their achievements, especially in sustainability efforts like carbon neutrality and renewable energy adoption.
- Prize Distribution: A total of ?46 crore was awarded to the 45 winners, with funds directly transferred to their accounts.
Objectives:
The National Panchayat Awards aim to:
- Promote rural development through effective Panchayat governance.
- Encourage competition among Panchayats for improving public services and infrastructure.
- Recognize excellence in implementing sustainable development practices.
Key Themes of the Awards:
The awards are aligned with 9 LSDG themes that contribute to achieving 17 SDGs:
- Poverty-Free and Enhanced Livelihoods
- Healthy Panchayat
- Child-Friendly Panchayat
- Water-Sufficient Panchayat
- Clean and Green Panchayat
- Self-Sufficient Infrastructure
- Socially Just and Secured Panchayat
- Panchayat with Good Governance
- Women-Friendly Panchayat
The National Panchayat Awards 2024 underscore the significant role of Panchayats in shaping rural India by focusing on inclusive and sustainable development. The awards also promote the importance of localized governance in achieving SDGs, encouraging other Panchayats to adopt best practices and contribute to India's overall development goals.
Reforms in Merchant Shipping

- 10 Dec 2024
In News:
The Government is preparing to introduce several significant bills aimed at driving much-needed reforms in the shipping industry. Key among them are the Merchant Shipping Bill, 2024 and the Coastal Shipping Bill, 2024, both of which promise to bring transformative changes to boost the sector.
Context and Need for Reforms:
- Outdated Framework: The Merchant Shipping Act, 1958, and the Coasting Vessels Act, 1838, fail to address the current needs of the shipping sector, particularly offshore vessels.
- Regulatory Gaps: Inadequate regulation of offshore vessels, maritime training institutions, and welfare provisions for seafarers on foreign-flagged ships.
- Global Alignment: Need to align with international maritime conventions and modernize administration for competitiveness and better governance.
- Investment and Growth: Outdated laws hinder foreign investment and ease of doing business, necessitating a regulatory overhaul.
Key Features of the Merchant Shipping Bill, 2024:
- Ease of Vessel Registration:
- Reduces ownership threshold for Indian entities from 100% to 51%, enabling NRIs, OCIs, and foreign entities to invest.
- Facilitates registration of vessels chartered by Indian entities under the "bareboat charter-cum-demise" system, promoting capital-deficient entrepreneurs.
- Temporary registration provisions for vessels destined for demolition, boosting India's ship recycling industry.
- Expansion of Vessel Scope:
- Broadens the definition of "vessel" to include all types of mechanized and non-mechanized crafts, such as submersibles, hydrofoils, and Mobile Offshore Units (MOUs).
- Ensures comprehensive regulatory oversight, particularly in the offshore sector, enhancing transparency and safety.
- Coastal Security:
- Strengthens coastal security by empowering authorities to issue instructions to all types of vessels, addressing vulnerabilities highlighted by incidents like the 26/11 Mumbai attacks.
- Marine Pollution Measures:
- Incorporates global standards like the MARPOL convention to address marine pollution.
- Introduces measures such as reducing sulphur content in marine fuel and banning single-use plastics on Indian ships.
- Launch of the ‘Swachh Sagar’ portal to ensure proper disposal of ship-generated waste.
- Seafarer Welfare:
- Expands welfare provisions to include Indian seafarers working on foreign-flagged ships, offering protections under the Maritime Labour Convention (MLC).
- Ensures better working conditions and safety standards for a growing workforce of Indian seafarers abroad.
- Maritime Training Regulations:
- Establishes a legal framework to regulate maritime training institutions, addressing the rise of unauthorized institutes post-liberalization.
- Ensures standardized, high-quality education and eliminates fraudulent practices.
Coastal Shipping Bill, 2024:
- Focus on Commercial Utilization of Coastal Waters:
- Distinguishes between the technical regulation of ships and the commercial utilization of Indian coastal waters.
- Aims to streamline licensing, operations, and coastal planning, enhancing the integration of inland and coastal shipping.
- Alignment with ‘Sagarmala’ Program: Supports the promotion of coastal shipping through better infrastructure and connectivity, in line with the government's ‘Sagarmala’ initiative, which boosts port connectivity and coastal trade.
International Conventions India Has Ratified:
- MARPOL: Focuses on preventing ship-based pollution.
- Maritime Labour Convention (MLC): Protects seafarers' rights and ensures fair working conditions.
- Bunker Convention: Addresses liability for oil pollution damage.
- Wreck Removal Convention: Mandates safe removal of shipwrecks.
- Civil Liability Convention: Establishes liability for oil pollution incidents.
Significance of the Reforms:
- Modernized Framework: Aligns India’s maritime laws with global standards for enhanced competitiveness.
- Economic Growth: Encourages foreign investment and entry into the shipping sector by removing regulatory barriers.
- Environmental Sustainability: Focus on combating marine pollution and ensuring sustainable shipping practices.
- Enhanced Safety and Security: Strengthens coastal security and ensures stringent safety regulations for vessels.
- Seafarers’ Welfare: Extends benefits and protections to Indian seafarers working globally, ensuring better working conditions.
- Maritime Education: Provides a robust regulatory framework to ensure high-quality, standardized maritime training.
Turner Prize

- 09 Dec 2024
In News:
Jasleen Kaur, a 38-year-old Indian-origin Scottish artist, has won the prestigious Turner Prize 2024 for her exhibition "Alter Altar". This win highlights Kaur’s unique ability to weave together personal, political, and spiritual elements into a cohesive artistic expression. The exhibition explores themes such as plurality, migration, and cultural identity, drawing from Kaur’s own family history and experiences.
Exhibition Overview:
"Alter Altar," which was first showcased in Glasgow, features an array of everyday objects and cultural symbols, including:
- A vintage red Ford Escort covered in a large crocheted doily, symbolizing her father’s migrant aspirations.
- Worship bells, Irn-Bru orange resin, an Axminster carpet, and family photographs.
- Soundtracks, including music from Nusrat Fateh Ali Khan and Bob Marley, which reflect Kaur’s multicultural upbringing.
The exhibition blends these elements to examine migration, identity, and belonging. The jury, chaired by Alex Farquharson, Director of Tate Britain, praised Kaur’s ability to combine different voices through unexpected and playful material combinations, creating a visual and aural experience that evokes both solidarity and joy.
Personal and Political Reflection:
Kaur’s work reflects on the Sikh concept of Miri Piri, which represents the balance between the political and the spiritual. This duality is central to her exploration of cultural practices and the effects of violence, colonialism, and empire on these traditions. In her acceptance speech, Kaur also addressed political issues, calling for a ceasefire in Gaza and an end to institutional complicity in Israel's actions.
About the Turner Prize:
The Turner Prize, established in 1984, is one of the most prestigious awards in contemporary British art. It aims to recognize recent developments in British art. Kaur’s win is particularly significant as it marks the 40th anniversary of the award. Previous winners include renowned Indian-origin artists such as Anish Kapoor (1991).
Black holes in Webb data allay threat to cosmology’s standard model

- 09 Dec 2024
In News:
The James Webb Space Telescope (JWST), launched almost three years ago, has provided unprecedented insights into the early universe. Astronomers were surprised to find large, fully-developed galaxies when the universe was only 400-650 million years old, a timeframe previously thought to be too early for such structures.
The Challenge to the Standard Model:
- Cosmological Expectations: According to the standard model of cosmology, the first stars formed around 100-200 million years after the Big Bang, and galaxies began to form within the first billion years.
- Unexpected Findings: JWST observations seemed to show that galaxies were already large and well-formed much earlier than expected, raising questions about the timeline of galaxy formation.
New Study's Contribution:
- The Study: A study published in the Astrophysical Journal in August 2024, examined JWST data from the Cosmic Evolution Early Release Science (CEERS) Survey. They focused on galaxies from 650 to 1,500 million years after the Big Bang.
- Key Findings: One explanation for the unexpected size and number of early galaxies is that these galaxies formed stars much more efficiently than those in the modern universe. This could account for the larger-than-expected galaxies.
The Role of Black Holes:
- Impact of Black Holes: The study also explored the presence of black holes at the centers of early galaxies. These black holes, which emit significant light, were previously unaccounted for in the star mass estimations of galaxies. When the researchers removed the light from black holes (referred to as "little red dots"), they found that the galaxies were not as massive as initially thought.
- Correction to Previous Estimates: This adjustment in calculations helped align the data with the standard model of cosmology, sparing it from a major revision.
Implications for the Standard Model:
- Star Formation Efficiency: The study suggests that extreme conditions in the early universe, including abundant gas and less disruptive stellar events, could explain the higher efficiency of star formation.
- Cosmology's Stability: Despite earlier challenges to the standard model, the new findings support its predictions, showing that more efficient star formation and the role of black holes could explain the rapid growth of galaxies in the early universe.
Future Research Directions:
- Expanding Data Sets: The team plans to incorporate more data from JWST to study even earlier galaxies, which could help refine our understanding of galaxy formation in the early universe.
- Further Observations: As the team continues to explore galaxies from even earlier periods (around 400 million years after the Big Bang), they aim to strengthen their findings and provide further evidence to either support or challenge the current cosmological models.
Moths' Reproductive Choices Based on Plant Acoustic Emissions

- 09 Dec 2024
In News:
A new study, "Female Moths Incorporate Plant Acoustic Emissions into Their Oviposition Decision-Making Process," published last month, explores how female moths use sounds emitted by plants to choose where to lay their eggs.
Key Highlights:
Significance of Plant Emitted Sounds:
- Background: Last year, it was discovered that plants emit ultrasonic clicks or pops when stressed (e.g., dehydration). These sounds, although inaudible to humans, can be detected by animals, including insects.
- Moths’ Sensitivity: Moths, particularly the Egyptian cotton leafworm, are shown to be sensitive to these plant sounds, which they use as cues for laying eggs on plants.
Methodology:
- Experimental Setup: Researchers placed a hydrated tomato plant in an experimental arena with another hydrated plant that emitted distress sounds. They observed the behavior of female Egyptian cotton leafworms to understand how these sounds influenced their oviposition choices.
- Initial Finding: Moths typically choose healthy, thriving plants to lay eggs, as they provide better food sources for the larvae.
Study Findings:
- Moths’ Response to Sounds: The moths preferred to lay eggs on the “silent” plant rather than the one emitting distress sounds. This indicates that moths can not only detect the presence of a plant but also interpret acoustic signals to inform their egg-laying decisions.
- Implications: This behavior suggests that moths use a complex set of sensory inputs, including plant-emitted sounds, to select the most suitable plant for offspring development.
Broader Ecological Context:
- Moths as Insects: Moths belong to the order Lepidoptera and are found in diverse environments globally, except polar regions. With around 160,000 species, they are highly adapted and often nocturnal, though some species are diurnal.
- Impact on Agriculture: Certain moth species, especially during their caterpillar stage, are major agricultural pests (e.g., corn borers, bollworms), making understanding their behavior crucial for pest management strategies.
- Climate Change Considerations: Moths, like other species, are impacted by climate change, which can alter the timing and growth of plants they depend on, potentially influencing their reproductive strategies.
Conclusion:
- Innovative Findings: The study reveals a previously unknown aspect of moth behavior, showing that they incorporate plant acoustic emissions into their oviposition decisions.
- Future Implications: This discovery opens avenues for further studies on how environmental signals, like sound, affect the behavior of insects, and how these behaviors could be impacted by changing environmental conditions.
RBI's Stance on De-dollarisation and Risk Diversification

- 09 Dec 2024
In News:
- Governor Shaktikanta Das clarified that India is not pursuing "de-dollarisation," but rather aiming to diversify risk in trade. Measures like local currency trade agreements and Vostro accounts are intended to reduce reliance on the US dollar without eliminating it entirely.
- Objective: The goal is to de-risk India's trade, not to fully replace the dollar, especially amidst rising geopolitical tensions.
Key Highlights:
Vostro Accounts and Local Currency Trade:
- Vostro Accounts: These accounts, held by foreign banks in Indian rupees, facilitate transactions in local currencies, helping mitigate the risks of dollar dependency.
- International Currency Trade: By promoting trade in local currencies, the RBI seeks to reduce exposure to fluctuations in the dollar's value. However, these efforts have faced challenges due to India’s limited international presence in goods and services trade.
Gold Purchases by Central Banks:
- Surge in Gold Purchases: Global central banks, including the RBI, have significantly increased gold holdings. India added 27 tonnes in October 2024 alone, the largest increase among central banks.
- Motivations for Gold: The surge in gold buying reflects growing concerns about geopolitical risks, including the Ukraine war, and the potential for secondary sanctions. Gold is seen as a safe haven asset that diversifies reserves away from the US dollar.
Decline in Dollar Dominance:
- Global Shift: The share of the US dollar in global reserves has been gradually declining, partly due to the rise of the Chinese yuan. Central banks are increasingly turning to gold and alternative currencies as part of a diversification strategy.
- Impact on Emerging Markets: Countries like India are particularly motivated to reduce reliance on the dollar due to geopolitical tensions and economic vulnerabilities linked to the dollar’s dominance.
India’s Domestic Currency Trade Initiatives:
- Trade with Russia and UAE: India is actively exploring trade in domestic currencies with countries like Russia and the UAE to reduce dependence on the dollar. However, these efforts have faced slow uptake due to India’s trade deficit with most countries except the US.
- Challenges in Adoption: Despite efforts to internationalize the rupee, high transaction costs and lack of sufficient demand for rupee-based trade are significant barriers.
BRICS and Shared Currency Discussions:
- Geopolitical Complexity: BRICS nations, due to their geographical and economic diversity, have discussed the possibility of a shared currency, but no consensus has been reached.
- Reluctance Toward Yuan: India has resisted using the Chinese yuan for transactions, particularly for Russian oil imports, despite the yuan’s growing acceptance. This reflects India’s desire to maintain economic sovereignty and avoid over-reliance on a single currency.
Regional Implications of Dollar Volatility:
- Neighbourhood Impact: Countries like Sri Lanka, Bangladesh, Nepal, and Pakistan have experienced significant financial distress due to declining dollar reserves and surging oil prices, exacerbated by the Ukraine war.
- India’s Resilience: India’s strong dollar reserves have helped it maintain economic stability, but the country remains cautious of dollar volatility, particularly as oil prices rise.
Conclusion:
- Strategic Balance: India’s approach reflects a strategic balance of mitigating risks while ensuring global trade stability. The RBI’s emphasis on gold accumulation and pushing for rupee-based trade demonstrates a desire to reduce exposure to the dollar, but challenges like trade deficits and high transaction costs still hinder the full realization of these goals.
- Economic Sovereignty: Through these measures, India seeks to safeguard its economic sovereignty and financial stability in an increasingly unpredictable global economy.
Oilfields Amendment Bill, 2024

- 09 Dec 2024
In News:
To encourage domestic production of petroleum and other mineral oils, along with private investment in these sectors to reduce import dependence, the Rajya Sabha passed the Oilfields (Regulation and Development) Amendment Bill, 2024.
Key Details:
- Objective:
- Encourage domestic petroleum production.
- Reduce import dependence by promoting private investment in the oil sector.
- Key Amendments:
- Delinking petroleum from mining:
- The Bill separates petroleum and mineral oil production from mining activities.
- The Oilfields (Regulation and Development) Act, 1948, is amended to focus on mineral oils, distinct from the Mines and Minerals (Development and Regulation) Act, 1957.
- Expanded Definition of Mineral Oils:
- Includes hydrocarbons in various forms (natural gas, crude oil, petroleum, coal bed methane, and shale gas/oil).
- Excludes coal, lignite, and helium from the definition (falling under the Mines and Minerals Act).
- Petroleum Lease:
- Replaces the term "mining lease" with "petroleum lease."
- Covers activities such as exploration, development, production, and transportation of mineral oils.
- Private Investment:
- Provisions to attract private investment by clarifying rules for petroleum leases.
- Current mining leases remain valid without altering terms to the lessee's disadvantage.
- Decriminalization and Penalties:
- Replaces criminal punishment with financial penalties.
- Fines can go up to Rs. 25 Lakh, with additional penalties for ongoing violations.
- Rule-making Power of Central Government:
- Expands the Centre's authority over petroleum lease regulations, conservation, royalties, mergers, facility sharing, environmental protection, and dispute resolution.
- Delinking petroleum from mining:
- Significance of the Bill:
- Energy Access and Security: Ensures energy security by boosting domestic production.
- Attracting Investment: Creates a conducive environment for private sector investment.
- Environmental Safeguards: Provisions to control carbon emissions and promote renewable energy in oilfields.
- Opposition Criticism:
- State Rights on Mining: Concerns raised by opposition parties, particularly the DMK, about the reduction of state control over resource taxation (taxing mineral rights).
- Impact on Federal Balance: States traditionally manage mining rights under the Constitution’s State List (Entry 50). The Bill may shift control to the Union List (Entry 53), creating constitutional concerns.
- Environmental Concerns:
- Opposition figures like P.P. Suneer (CPI) argue for prioritizing public companies like ONGC, fearing privatization may worsen environmental governance.
- Adjudication of Disputes:
- Appeals against penalty decisions will be handled by the Appellate Tribunal, as per the Petroleum and Natural Gas Regulatory Board Act, 2006.
- Broader Significance:
- Energy Independence: Reduces reliance on fuel imports, fostering energy security and economic stability.
- Regulation: Strengthens the enforcement mechanism for petroleum operations while encouraging private participation.
Petroleum and Natural Gas Regulatory Board (PNGRB):
- Formation: Established under the Petroleum and Natural Gas Regulatory Board Act, 2006.
- Functions: Regulates refining, transportation, distribution, storage, marketing, and sale of petroleum products and natural gas.
- Role in the Bill: Ensures competitive markets for gas and handles appeals regarding regulatory decisions.
Markhor Spotted in North Kashmir's Baramulla

- 08 Dec 2024
In News:
Recently, a Markhor, a rare wild goat with spiral-shaped horns, was spotted in Noorkha village of Boniyar in Baramulla district, North Kashmir.The animal was seen near a waterfall in Noorkha, prompting locals to alert the authorities.
Key Highlights:
- The Markhor (Capra falconeri) is a large, wild goat species native to mountainous regions in Central and South Asia, including countries such as Pakistan, Afghanistan, India, and others.
- The species is considered endangered and is listed under Schedule I of the Wildlife Protection Act, 1972.
- The Markhor population in India is concentrated in areas like Shopian, Banihal Pass, Shamsbari, and Kazinag in Jammu and Kashmir.An estimated 300 Markhors live in Kashmir's dense pine and birch forests.
- Threats and Conservation Status:
- The Markhor faces threats due to human activities and natural factors, leading to a decline in its population.
- It is classified as 'Near Threatened' on the IUCN Red List and protected under the Indian Wildlife Protection Act and the Jammu and Kashmir Wildlife Protection Act.
- Significance of the Sighting:The sighting of the Markhor has excited both villagers and wildlife enthusiasts, as these animals are not typically found outside their natural habitats, particularly near human settlements.
Kawasaki Disease
- 08 Dec 2024
In News:
Comedian Munawar Faruqui recently opened up about a tough time in his life when his young son was diagnosed with Kawasaki disease.
What is Kawasaki Disease?
- Kawasaki disease is a rare condition that primarily affects children under the age of five.
- It causes inflammation in the blood vessels, including those that supply blood to the heart.
- With early treatment, most children recover without long-term health issues.
Possible Causes:
- The exact cause of Kawasaki disease is not well understood.
- Experts believe it may be triggered by a combination of genetic and environmental factors, including certain infections.
Symptoms: Kawasaki disease symptoms typically appear in two phases and may last for several weeks. Common symptoms include:
- High fever lasting more than five days.
- Red eyes without discharge.
- A rash on the body, particularly in the chest and groin area.
- Swollen hands and feet, sometimes accompanied by redness.
- Red, cracked lips and a swollen, red tongue.
- Swollen lymph nodes, particularly on one side of the neck.
Detection & Treatment:
- There’s no test that can directly detect Kawasaki disease. But healthcare providers can do tests that support a diagnosis of Kawasaki disease or rule out other possible illnesses.
- Treatment for Kawasaki disease includes:Immune globulin (IVIG), or human blood proteins you receive by IV. About 10% of children may not respond to the first dose of IVIG and will need a second dose or other medications.
Community and Individual Forest Rights in Anamalai Tiger Reserve (ATR)

- 08 Dec 2024
In News:
- The Coimbatore District Collector, granted community and individual forest rights under the Forest Rights Act, 2006, to tribal settlements in the Anamalai Tiger Reserve (ATR) on December 6, 2024.These rights were handed over to three tribal settlements and 14 families at a function in Coimbatore.
Key Highlights:
- Community Forest Rights:
- Three tribal settlements in ATR—Nagaroothu I, Nagaroothu II, and Chinnarpathi—were granted community rights.
- These rights allow the settlements to collect forest produce excluding timber, such as mango, amla, honey, tamarind, and grass for making brooms.
- Individual Forest Rights:
- Individual rights were granted to 14 families from the Old Sarkarpathy tribal settlement.
- The families had requested these rights for traditional cultivation practices passed down by their ancestors.
- The individual rights were approved after the recommendation of a sub-divisional committee and scrutiny by a district-level committee.
- About the Forest Rights Act (FRA), 2006:
- Purpose: The FRA was enacted to address historical injustices faced by forest-dwelling communities and ensure their livelihood and food security.
- Key Provisions:
- Individual Rights: Self-cultivation, habitation, and in-situ rehabilitation.
- Community Rights: Access to grazing, fishing, water bodies in forests, and protection of traditional knowledge and customary rights.
- Eligibility: Rights can be claimed by any community or individual who has lived in the forest for at least three generations (75 years) before December 13, 2005.
- Critical Wildlife Habitats: The Act mandates that critical wildlife habitats in national parks and sanctuaries remain inviolate for wildlife conservation.
- Authorities Involved in Vesting Forest Rights:
- Gram Sabha: Initiates the process for determining the nature and extent of rights.
- Sub-Divisional Level Committee: Examines resolutions passed by the Gram Sabha.
- District Level Committee: Grants final approval for forest rights.
- Challenges with Forest Rights Implementation:
- The Xaxa Committee pointed out several challenges in the implementation of the FRA, such as:
- Arbitrary rejection of claims.
- Lack of deadlines for claims processing.
- Unaddressed rights of communities displaced by development projects.
- The Xaxa Committee pointed out several challenges in the implementation of the FRA, such as:
- About Anamalai Tiger Reserve:
- Located in the Anamalai Hills of Pollachi and Coimbatore District, Tamil Nadu, at an altitude of 1,400 meters.
- Established as a tiger reserve in 2007, it is surrounded by multiple protected areas like the Parambikulam Tiger Reserve, Chinnar Wildlife Sanctuary, and Eravikulam National Park.
- Biodiversity in Anamalai Tiger Reserve:
- Habitats: The reserve contains wet evergreen forests, semi-evergreen forests, moist deciduous forests, dry deciduous forests, and unique habitats like montane grasslands and marshy grasslands.
- Flora: The reserve is home to around 2,500 species of angiosperms, including species like balsam, orchids, and wild relatives of cultivated crops such as mango, jackfruit, cardamom, and pepper.
- Fauna: It supports various wildlife species, including tigers, Asiatic elephants, sambars, spotted deer, leopards, jackals, and jungle cats.
Sacred Groves

- 08 Dec 2024
In News:
Preserving India’s sacred groves can help country achieve its conservation & climate goals.
Sacred Groves in India:
- Sacred groves are forest patches that are culturally and spiritually important for various communities.
- They are known by different names across India: sarnas in Jharkhand, devgudis in Chhattisgarh, and orans in Rajasthan.
- Groves vary in size from small clusters of trees to expansive forests covering several acres.
Threats to Sacred Groves:
- Sacred groves are increasingly under threat due to deforestation, mining, and development activities.
- Many sacred groves are being displaced or degraded, putting biodiversity and cultural practices at risk.
Ecological and Cultural Importance:
- Sacred groves are rich in biodiversity and serve as important carbon sinks, contributing to climate change mitigation.
- They have been maintained by indigenous communities for centuries, creating a deep connection between people and nature.
- Sacred groves also play a crucial role in preserving indigenous spiritual practices and cultural heritage.
Contribution to Climate and Conservation Goals:
- India’s climate commitment of achieving net-zero emissions by 2070 requires the protection of forests, including sacred groves.
- Sacred groves, when properly managed, can help in carbon sequestration and climate change mitigation.
- Preserving these groves can support forest conservation and foster coexistence with wildlife, ensuring a balance between development and environmental preservation.
Role of Indigenous Communities:
- Indigenous communities have long used sacred groves to regulate the use of forest resources and ensure environmental sustainability.
- Before modern ecological concepts, sacred groves were seen as natural conservation practices guided by spiritual beliefs.
- This traditional wisdom can be leveraged to enhance conservation efforts in India.
Examples of Successful Sacred Grove Conservation:
- Waghoba Grove in Maharashtra:
- Located in Chinchwadi village, the Taata chi Vanrai grove is dedicated to Waghoba, the tiger deity, and covers eight acres.
- Local communities, including the Thakars, have successfully resisted illegal timber extraction and helped conserve the grove, witnessing the return of wildlife like leopards.
- Worship of Waghoba has played a significant role in preserving forest patches and fostering human-animal coexistence.
- Tadoba-Andhari Tiger Reserve:
- Sacred groves around the Tadoba Reserve, dedicated to Waghoba, are important in reducing human-wildlife conflicts by promoting spiritual ties with the forest.
Government and Community Efforts:
- The Jharkhand government introduced the concept of gherabandi (boundary walls) in 2019 to conserve sacred groves.
- In Chhattisgarh, the renovation of sacred groves has been undertaken to protect and restore these areas.
- Despite these efforts, challenges remain in involving local communities and integrating sacred groves into broader conservation policies.
The Role of OECMs in Sacred Grove Conservation:
- Sacred groves are considered part of Other Effective Area-Based Conservation Measures (OECMs), which are areas conserved for biodiversity outside protected regions.
- OECMs recognize the cultural, spiritual, and socio-economic value of these areas and promote sustainable conservation practices that benefit both biodiversity and local communities.
- Sacred groves play an essential role in achieving long-term biodiversity conservation and ecosystem services.
World’s Oldest Wild Bird Lays Egg at 74 in Hawaii

- 08 Dec 2024
In News:
Wisdom, the world’s oldest known wild bird, a Laysan albatross, has laid her estimated 60th egg at the age of 74. This remarkable event occurred at the Midway Atoll National Wildlife Refuge in the Pacific Ocean, part of the Hawaiian Archipelago.
Background on Wisdom and Laysan Albatrosses
Wisdom, first banded as an adult in 1956, has been a part of the albatross population in the Pacific for decades. Laysan albatrosses are known for their strong migratory habits and lifelong pair bonding.
The Life Cycle of the Laysan Albatross
The egg incubation process for Laysan albatrosses is shared between both parents and lasts around seven months. Once the chick hatches, it takes five to six months to develop before it is ready to take its first flight over the ocean. These seabirds, which predominantly feed on squid and fish eggs, spend the majority of their lives soaring across the open seas.
Wisdom’s longevity and success in raising up to 30 chicks over her lifetime have been notable achievements. While Laysan albatrosses typically live up to 68 years, Wisdom’s age surpasses this average by several years.
About the Laysan Albatross
The Laysan albatross (Phoebastriaimmutabilis) is a large seabird found across the North Pacific. The Northwestern Hawaiian Islands host nearly the entire population of Laysan albatrosses, with most breeding pairs found on islands like Laysan and Midway Atoll. These birds are known for their long-distance soaring capabilities, with some covering hundreds of miles a day without flapping their wings.
Laysan albatrosses have blackish-brown upper wings and backs, with flashes of white in their primary feathers. They are monogamous, forming lifelong bonds with a single mate. Despite their impressive flying ability and vast range, their population is currently listed as "Near Threatened" by the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN).
Development Initiatives for North East Region (NER)

- 07 Dec 2024
In News:
Prime Minister’s Development Initiative for North East Region (PM-DevINE) was announced as a new Central Sector scheme, with 100% Central funding in the Union Budget 2022-23 with initial outlay of Rs.1500 crore.
PM-DevINE Scheme:
- Launched in 2022 as a Central Sector scheme, with 100% Central funding.
- Initial outlay: Rs. 1500 crore in the Union Budget 2022-23.
- Total outlay: Rs. 6600 crore for the period from FY 2022-23 to FY 2025-2026, approved by the Union Cabinet on 12 October 2022.
- Objectives:
- Fund infrastructure projects in the spirit of PM Gati Shakti.
- Support social development projects tailored to the felt needs of the NER.
- Enable livelihood opportunities for youth and women.
- Address development gaps in various sectors.
- 35 projects worth Rs. 4857.11 crore have been sanctioned under the scheme up to 30 November 2024, including 7 projects from the Union Budget 2022-23.
Industrialization Initiatives:
- North East Industrial Development Scheme (NEIDS):
- Launched on 1 April 2017, ended on 31 March 2022.
- Aimed at promoting industrialization in the NER.
- UNNATI Scheme:
- Launched on 9 March 2024 for enhancing regional infrastructure and promoting industrial growth.
- Provides specific incentives to industries, including:
- Capital Investment Incentive.
- Capital Interest Subvention.
- Manufacturing & Services Linked Incentive.
Budgetary Allocation for NER Development:
- Non-exempt Union Ministries/Departments are mandated to allocate at least 10% of their annual Gross Budgetary Allocation towards NER development.
- Between 2019-20 and 2023-24, these Ministries/Departments have incurred Rs. 3,53,412 crore towards the development of NER.
Role of State Governments and Central Support:The Government of India supplements state efforts with various schemes to promote industrialization and infrastructure development in the NER.
The PM-DevINE scheme, along with initiatives like UNNATI and the allocation of substantial funds by the central government, aims to accelerate the holistic development of NER. These efforts focus on infrastructure, social development, and industrialization, with specific emphasis on youth and women empowerment, ensuring long-term growth and prosperity for the region.
China Plus OneStrategy

- 07 Dec 2024
In News:
India had ‘limited success’ in capturing ‘China Plus One’ opportunity.
Limited Success in ‘China Plus One’ Strategy:
- India has had limited success in attracting multinational companies looking to diversify their supply chains under the ‘China Plus One’ strategy, aimed at reducing dependence on China.
- Vietnam, Thailand, Cambodia, and Malaysia have been more successful in benefiting from this shift due to factors like lower labor costs, simplified tax laws, and proactive Free Trade Agreements (FTAs).
Geopolitical Context - US-China Trade Conflict:
- The fresh US-China trade conflict involves tit-for-tat restrictions, with the US imposing export controls on Chinese high-tech goods and China retaliating by banning key materials.
- India's Position: As a "connecting economy" not directly aligned with the US or China, India stands to benefit from trade diversions arising from this conflict.
Opportunities for India Amid Trade Diversion:
- NITI Aayog CEO BVR Subrahmanyam highlighted opportunities arising from trade diversion, particularly due to US trade policies under President-elect Donald Trump, which could potentially create an economic boom for India.
- India has opportunities to capture a larger share of the global trade, especially in sectors where it currently holds a small market share (less than 1% of world trade in many areas).
Trade Policy Challenges:
- Steel Import Duty Proposal: NITI Aayog Vice Chairperson cautioned against imposing high duties on steel imports, arguing that it could reduce India’s competitiveness and lead to negative consequences for domestic industries reliant on steel.
- The global steel market has been affected by oversupply from China, with India’s iron and steel exports experiencing a sharp decline in Q1 FY25 due to weak domestic demand.
Impact of US Tariffs:
- A general 10% tariff on all imports by the US would not have a major negative impact on India.
- However, a 60% tariff on China could open significant opportunities for India, especially in sectors where it competes directly with China. There might be short-term shocks but long-term benefits.
Ongoing Trade Fragmentation:
- The report noted that trade fragmentation is driven by strict export controls on Chinese goods, implemented by the US to curb China’s growth, particularly in high-tech sectors.
Sectoral Competitiveness:
- While China remains India's key competitor across most export sectors, countries like Brazil, Indonesia, and South Africa generally lag behind India.
- Malaysia and Thailand outperform India in select sectors such as electrical machinery.
Challenges in the EU Market - Carbon Border Adjustment Mechanism (CBAM):
- Iron and steel industry facehigh exposure under the CBAM for EU exports, with tariffs potentially rising by 20-35% due to carbon emissions-related regulations.
- Indian firms could experience higher compliance costs due to the requirement for detailed emissions reporting, impacting competitiveness in the European market.
‘Anna Chakra’ and SCAN Portal

- 07 Dec 2024
In News:
The Union Minister of Consumer Affairs, Food and Public Distribution and New & Renewable Energy, launched ‘Anna Chakra’, the Public Distribution System (PDS) Supply chain optimisation tool and SCAN (Subsidy Claim Application for NFSA) portal a significant step towards modernizing the Public Distribution System and subsidy claim mechanisms of the States.
Anna Chakra: PDS Supply Chain Optimization Tool
- Purpose: A tool developed to enhance the efficiency of PDS logistics across India, optimizing food grain transportation.
- Collaboration: Developed by the Department of Food and Public Distribution, in collaboration with the World Food Programme (WFP) and IIT-Delhi’s Foundation for Innovation and Technology Transfer (FITT).
- Functionality: Uses advanced algorithms to identify optimal transportation routes for food grains.
- Key Features:
- Efficiency and Cost Savings: Achieves annual savings of Rs 250 crores by reducing fuel consumption, time, and logistics costs.
- Environmental Impact: Reduces transportation-related emissions by cutting transportation distance by 15-50%, contributing to a smaller carbon footprint.
- Wide Coverage: Impacts 30 states, 4.37 lakh Fair Price Shops (FPS), and 6,700 warehouses in the PDS supply chain.
- Technology Integration: Linked with the Freight Operations Information System (FOIS) of Railways and PM Gati Shakti platform, enabling geo-location mapping of FPS and warehouses.
SCAN Portal: Subsidy Claim Application for NFSA
- Objective: To streamline the subsidy claim process under the National Food Security Act (NFSA) 2013, ensuring better utilization of funds.
- Functionality: Provides a unified platform for states to submit food subsidy claims, reducing administrative complexity and delays.
- Key Features:
- Single Window Submission: Simplifies subsidy claim submission for states, enhancing coordination.
- Automated Workflow: End-to-end automation ensures efficiency, transparency, and faster settlements.
- Rule-Based Processing: Claims are scrutinized and approved through a rule-based system, speeding up the approval process.
Public Distribution System (PDS) Overview
- Purpose: Ensures food security by providing subsidized food grains to vulnerable populations under the NFSA, benefitting nearly 80 crore people.
- Management: A joint effort between the Central and State/UT Governments. The Food Corporation of India (FCI) handles procurement and transportation, while state governments manage local distribution.
- Commodities: Primarily wheat, rice, sugar, and kerosene, with some states also distributing pulses and edible oils.
Initiatives to Reform PDS in India
- One Nation One Ration Card (ONORC):
- Goal: To allow portability of ration cards, benefiting migrant workers and seasonal laborers.
- Features: Biometric authentication, digital payments, and enhanced inclusivity.
- SMART-PDS Scheme (2023-2026):
- Objective: To upgrade technology in PDS, including computerized FPS, point-of-sale (POS) machines, and GPS tracking for transparency and fraud reduction.
- Aadhaar and Direct Benefit Transfer (DBT):
- Purpose: Ensures proper beneficiary identification and cash transfers, allowing beneficiaries to purchase grains from the open market.
- Technology and Transparency Enhancements:
- GPS and SMS Monitoring: Ensures the proper delivery of food grains to FPS and provides citizens with updates via SMS.
PMeVIDYA DTH 24x7 Channel No. 31

- 07 Dec 2024
In News:
Union Minister for Education, launched the PMeVIDYA DTH 24x7 Channel No. 31 dedicated to Indian Sign Language (ISL) on December 6, 2024, in New Delhi.
Channel Purpose and Vision:
- Objective: To bridge the communication gap between the hearing-impaired and hearing populations by promoting ISL.
- Significance: Channel 31 aims to unlock talent and ensure equal opportunities for all, making society more inclusive and progressive.
- ISL's Role: Pradhan emphasized the importance of alternative communication methods like ISL, which ensures that individuals with hearing impairments have equal access to education, employment, and societal participation.
Government's Focus on Inclusivity:
- Legal Framework: Pradhan highlighted the expansion of recognized disabilities from 7 to 21, making the legal framework more comprehensive.
- National Education Policy (NEP) 2020: The policy focuses on inclusive education, with particular attention to Children with Special Needs (CwSN). The NEP promotes the standardization of ISL and its inclusion in educational curricula.
- Employment and Cultural Expression: ISL is not only essential for communication but also contributes to cultural expressions like dance and drama. Pradhan emphasized that learning ISL would open employment opportunities and allow individuals to express themselves fully.
Importance of Channel 31:
- The launch of Channel 31 aligns with India’s commitment to ensuring equal rights and access to education, as enshrined in the Constitution.
- Pradhan urged for widespread adoption of ISL, ensuring that more people learn the language to better support the hearing-impaired community.
PM e-Vidya Initiative:
- Launch Date: PM e-Vidya was launched as part of the Atmanirbhar Bharat Abhiyaan on May 17, 2020, to bridge the digital divide and ensure inclusive education.
- Key Components:
- DIKSHA: A national platform providing e-content for all grades.
- DTH TV Channels: Initially started with 12 channels, now expanded to 200, offering supplementary education in multiple languages.
- SWAYAM: A platform for online courses and MOOCs for both school and higher education.
- Community Radio & Podcasts: These platforms are used for wider educational outreach, especially in rural and remote areas.
- e-Content for Teachers: Interactive videos and resources aimed at enhancing teacher education.
Channel Content:
- Channel 31 will provide 24x7 educational content for children with hearing impairments, teachers, and other stakeholders.
- The content will include school curricula, career guidance, skill training, mental health support, and promotion of ISL as a subject.
- The content will be available on YouTube, increasing its reach and accessibility.
RBI Cuts CRR, Keeps Repo Rate Unchanged

- 07 Dec 2024
In News:
The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) has recently made significant monetary policy decisions that could have a broad impact on the economy.
Key Highlights:
Cut in Cash Reserve Ratio (CRR)
- CRR Reduction: The RBI has reduced the CRR by 50 basis points (bps), from 4.5% to 4%.
- Impact on Banks: This move will free up ?1.16 lakh crore in liquidity, which banks can use to lend, boosting the credit flow in the economy.
- Objective: The CRR cut is aimed at easing the liquidity stress in the financial system, which has been tightening due to RBI's foreign exchange interventions.
- Bank Benefits: Banks will benefit as they don’t earn interest on the CRR, and the extra liquidity may help them reduce deposit rates. Additionally, it may encourage banks to pass on benefits to borrowers, particularly in terms of lending rates.
Repo Rate Kept Unchanged at 6.5%
- Decision: The MPC decided to keep the key policy rate, the Repo rate, unchanged at 6.5%, continuing its stance for the 11th consecutive meeting.
- Reasons for Keeping Repo Rate Steady:
- Persistent inflation, particularly food prices, is a key concern. Despite strong growth in sectors like rural consumption, inflation remains high and continues to affect disposable income.
- RBI Governor emphasized that durable price stability is essential for strong, sustained economic growth.
Impact on Borrowers
- Borrowing Costs: With the Repo rate unchanged, external benchmark lending rates (EBLR) linked to the Repo rate will not rise, providing relief to borrowers by keeping Equated Monthly Installments (EMIs) stable.
- Deposit Rates: However, the CRR cut may lead to a marginal reduction in deposit rates due to increased liquidity in the system.
Economic Growth Forecast Adjusted
- Reduced GDP Growth Estimate: The RBI has downgraded the GDP growth forecast for FY25 to 6.6%, down from the earlier estimate of 7.2%. This revision comes after the economy showed signs of slowdown in the second quarter of FY25.
- Growth Outlook: Despite the downgrade, the RBI remains cautiously optimistic about recovery driven by festive demand and rural consumption. Governor Das indicated that the slowdown had likely bottomed out and the economy is set to recover in the coming quarters.
Inflation Forecast Raised
- Inflation Outlook: The inflation estimate for FY25 has been revised upward to 4.8%, compared to the earlier forecast of 4.5%. This is largely due to rising food prices, which surged to a 14-month high of 6.21% in October.
- Inflationary Pressures: The MPC noted that inflation has remained above the RBI’s target of 4%, primarily driven by food inflation. As inflation impacts consumption, the RBI aims to balance growth support with inflation management.
Monetary Policy Stance
- Neutral Stance Retained: The RBI has maintained a ‘neutral’ stance, meaning it is neither tightening nor easing monetary policy drastically, focusing instead on bringing inflation closer to its target of 4%.
- Inflation Control: While the RBI is aware of the economic slowdown, it continues to prioritize inflation control to ensure price stability and support sustainable growth.
Global and Domestic Economic Context
- Global Factors: The RBI has also been cautious about global developments, including capital outflows and the impact of U.S. monetary policy on the Indian economy. A rate cut could have further weakened the rupee by narrowing the interest rate differential with the U.S.
- Domestic Concerns: Domestically, the economy faces challenges such as weak manufacturing growth and high inflation. The GDP growth in Q2 FY25 dropped to 5.4%, a seven-quarter low, highlighting concerns over demand and inflationary pressures.
BharatiyaVayuyanVidheyak Bill, 2024

- 06 Dec 2024
In News:
In a significant move, the Indian Parliament passed the BharatiyaVayuyanVidheyak Bill, 2024 on December 5, 2024, bringing much-needed reforms to the aviation sector. The Bill, which replaces the Aircraft Act of 1934, aims to streamline aviation regulations and improve the ease of doing business in the industry.
Key Highlights of the BharatiyaVayuyanVidheyak Bill, 2024:
- Single-Window Clearance for Aviation Personnel: One of the major changes is the transfer of responsibility for the Radio Telephone Operator Restricted (RTR) certification from the Department of Telecom (DoT) to the Directorate General of Civil Aviation (DGCA). This move consolidates the certification process under a single authority, making it easier for aviation personnel like pilots, engineers, and flight dispatchers to obtain their licenses.
- Regulation of Aircraft Design: The Bill not only retains provisions for regulating aircraft manufacturing, maintenance, and repair, but also introduces new provisions to regulate aircraft design and the places where aircraft are designed.
- Enhanced Penalties for Violations: The Bill specifies severe penalties for violations, such as dangerous flying, carrying prohibited items (like arms or explosives), or littering near airports. Offenders may face imprisonment up to three years, fines up to ?1 crore, or both.
- Introduction of Second Appeal Mechanism: For the first time, the Bill introduces a second appeal process against decisions of regulatory bodies like the DGCA and BCAS, ensuring further scrutiny of decisions related to penalties.
- Improved Licensing Process: The shift of the RTR certification process from the DoT to DGCA aims to curb allegations of corruption associated with the previous system, where candidates often had to pay bribes to clear exams.
Organizational Setup and Authorities:
The Bill outlines the establishment of three key authorities under the Ministry of Civil Aviation:
- DGCA: Responsible for civil aviation safety, licensing, and ensuring compliance with international standards.
- BCAS: Ensures aviation security and develops relevant security measures.
- AAIB: Investigates aviation accidents and incidents.
The central government retains supervision over these bodies, with the power to modify or review their orders.
Criticisms and Concerns:
- Lack of Autonomy for DGCA: The DGCA, unlike independent regulators in other sectors (such as telecom or insurance), operates under direct government supervision. The lack of clear qualifications, selection process, and tenure for the DGCA Director General has raised concerns about the regulator's independence.
- Unilateral Appointment of Arbitrators: The Bill empowers the government to unilaterally appoint an arbitrator in certain cases, which has been criticized for potentially violating the right to equality under Article 14 of the Constitution. The Supreme Court has previously ruled that such unilateral appointments may be unconstitutional.
- Discretionary Criminal Penalties: The central government is granted the discretion to impose criminal penalties for rule violations, which some argue could undermine the principle of separation of powers, as it is the legislature's role to define criminal offenses and penalties.
- Exclusionary Hindi Title: Some critics argue that the Hindi title of the Bill may alienate non-Hindi-speaking populations, which make up a significant portion of India’s demographic.
Hornbill Festival

- 06 Dec 2024
In News:
The Hornbill Festival, a vibrant celebration of Nagaland's culture and tourism, is an annual event that takes place from December 1 to 10.
About the Hornbill Festival:
- Origin: First held in the year 2000.
- Purpose: The festival aims to foster inter-tribal communication, preserve the cultural heritage of Nagaland, and showcase the harmonious blending of traditional and modern elements.
- Significance: Referred to as the “festival of festivals,” it has become an essential part of the state’s cultural calendar.
- Organizers: It is organized by the Tourism and Art & Culture Departments of the Government of Nagaland.
- Location: The festival takes place annually at the Naga Heritage Village in Kisama, located about 12 kilometers from Kohima.
- Cultural Showcase: Over the years, it has evolved into a significant celebration that highlights the vibrant and diverse cultural traditions of the various tribes in Nagaland.
- Name Origin: The festival is named after the Hornbill bird, which holds cultural importance among the Naga tribes.
- Theme of the 2024 Hornbill Festival:The 2024 edition is themed “Cultural Connect,” celebrating the rich heritage and cultural diversity of Nagaland. The festival continues to merge modernity and tradition through a variety of activities, including Naga wrestling, traditional archery, food stalls, fashion shows, beauty contests, and musical performances. Additionally, the Archives Branch is presenting a special exhibition titled “Naga-Land & People in Archival Mirror” in partnership with the National Archives of India, offering a deeper look at the region's history and cultural practices.
- Recent Milestone:This year marks the 25th anniversary of the Hornbill Festival.
Festival Highlights:
- Annual Event: Held each year since its inception in 2000, it serves as a major cultural event for Nagaland.
- Symbolism: Named after the Hornbill bird, which represents boldness and grandeur in Naga folklore.
- Location: The festival is hosted at Kisama Heritage Village, a cultural center that preserves Naga traditions with 17 indigenous houses (Morungs) that represent each of the tribes.
- Cultural Diversity: Nagaland, known as the “Land of Festivals,” is home to 17 major tribes, each with its distinct festivals and cultural practices. The Hornbill Festival promotes inter-tribal interaction and celebrates the state’s rich heritage.
- National Significance: Reflecting India’s unity in diversity, the festival serves as a platform for different cultural practices to coexist, strengthening the nation’s collective identity.
India and Slovenia Announce Five-Year Collaboration Plan
- 06 Dec 2024
In News:
India and Slovenia have announced a five-year scientific collaboration plan (2024-2029) to deepen ties in research and technology. The Programme of Cooperation (PoC) was finalized during a meeting between Dr. Jitendra Singh (Indian Minister for Science and Technology) and Dr. Igor Papi? (Slovenian Minister for Higher Education, Science, and Innovation) on December 5, 2024.
Key Highlights:
- Joint Research Focus: The collaboration will focus on hydrogen technologies, sustainable innovation, AI, renewable energy, and smart cities.
- Over 20 Successful Projects: More than 20 joint initiatives in sectors like health, AI, and energy have already been implemented.
- Future Areas of Collaboration: New research projects will be launched, further strengthening academic exchanges and scientific networks between the countries.
- Hydrogen Technologies: Both ministers emphasized hydrogen's role in global energy sustainability, marking it as a critical area for future research.
- Historical Partnership: This builds on a partnership dating back to a 1995 agreement, with initiatives like the Joint Working Group on Scientific and Technological Cooperation.
What is the Programme of Cooperation (PoC)?
- The Programme of Cooperation (PoC) is a formal agreement between two countries designed to enhance collaboration in specific sectors, such as science, technology, and innovation.
- In the case of India and Slovenia, the PoC for the period 2024–2029 aims to promote joint research efforts, academic exchanges, and partnerships in emerging fields like hydrogen technologies, sustainable innovation, and other transformative areas.
- The PoC serves as a structured framework for long-term cooperation, enabling both nations to develop networks among scientists and researchers while addressing global challenges through collaborative innovation.
PM Surya Ghar: Muft Bijli Yojana

- 06 Dec 2024
In News:
The PM Surya Ghar: Muft Bijli Yojana, the world’s largest domestic rooftop solar initiative, is transforming India’s energy landscape with a bold vision to supply solar power to one crore households by March 2027.
Key Details:
Targeted Installations:
- 10 lakh installations by March 2025.
- 1 crore installations by March 2027.
Subsidy and Financing:
- Offers up to 40% subsidy for rooftop solar installations based on household electricity consumption.
- Collateral-free loans available for up to 3 kW solar systems at a 7% interest rate.
Key Benefits:
The PM Surya Ghar: Muft Bijli Yojana offers several significant benefits to participating households:
- Free Electricity for Households: The scheme provides households with free electricity through the installation of subsidized rooftop solar panels, significantly reducing their energy costs.
- Reduced Electricity Costs for the Government: By promoting the widespread use of solar power, the scheme is expected to save the government an estimated ?75,000 crore annually in electricity costs.
- Increased Use of Renewable Energy: The scheme encourages the adoption of renewable energy sources, contributing to a more sustainable and environmentally friendly energy mix in India.
- Reduced Carbon Emissions: The transition to solar energy under this scheme will help lower carbon emissions, supporting India's commitment to reducing its carbon footprint.
Eligibility Criteria:
1. The applicant must be an Indian citizen.
2. Must own a house with a roof that is suitable for installing solar panels.
3. The household must have a valid electricity connection.
4. The household must not have availed of any other subsidy for solar panels.
Impact
The PM Surya Ghar: Muft Bijli Yojana is expected to have far-reaching outcomes, both for individual households and the nation as a whole:
- Household Savings and Income Generation: Households will benefit from significant savings on their electricity bills. Additionally, they will have the opportunity to earn extra income by selling surplus power generated by their rooftop solar systems to DISCOMs. For instance, a 3-kW system can generate over 300 units per month on average, providing a reliable source of energy and potential revenue.
- Expansion of Solar Capacity: The scheme is projected to add 30 GW of solar capacity through rooftop installations in the residential sector, significantly contributing to India's renewable energy goals.
- Environmental Benefits: Over the 25-year lifetime of these rooftop systems, it is estimated that the scheme will generate 1000 BUs of electricity while reducing CO2 emissions by 720 million tonnes, making a substantial positive impact on the environment.
- Job Creation: The scheme is also expected to create approximately 17 lakh direct jobs across various sectors, including manufacturing, logistics, supply chain, sales, installation, operations and maintenance (O&M), and other services, thereby boosting employment and economic growth in the country.
Model Solar Village
- Under the "Model Solar Village" component of the scheme, the focus is on establishing one Model Solar Village per district throughout India.
- This initiative aims to promote solar energy adoption and empower village communities to achieve energy self-reliance.
- An allocation of ?800 crore has been designated for this component, with ?1 crore provided to each selected Model Solar Village.
- To qualify as a candidate village, it must be a revenue village with a population of over 5,000 (or 2,000 in special category states). Villages are selected through a competitive process, evaluated on their overall distributed renewable energy (RE) capacity six months after being identified by the District Level Committee (DLC).
- The village in each district with the highest RE capacity will receive a central financial assistance grant of ?1 crore.
- The State/UT Renewable Energy Development Agency, under the supervision of the DLC, will oversee the implementation, ensuring these model villages successfully transition to solar energy and set a benchmark for others across the country.
RangeenMachli App
- 06 Dec 2024
In News:
The app was developed by the ICAR-Central Institute of Freshwater Aquaculture (ICAR-CIFA) with support from the Pradhan Mantri MatsyaSampada Yojana (PMMSY) under the Ministry of Fisheries, Animal Husbandry & Dairying, Government of India.
Key Highlights:
- Target Audience: The app caters to hobbyists, farmers, and professionals in the ornamental fish industry.
- Multilingual Support: The app offers content in eight Indian languages, making it accessible to a broad and diverse audience.
- Main Objectives:
- Provide information on popular ornamental fish species and their care.
- Promote local aquarium businesses through dynamic directories.
- Enhance knowledge of ornamental aquaculture techniques for fish farmers and shop owners.
- Serve as an educational tool for newcomers and professionals in the ornamental fish industry.
- Salient Features:
- Multilingual Content: Ensures broader reach and user accessibility.
- Comprehensive Fish Information: Offers detailed guidance on fish care, breeding, and maintenance.
- Find Aquarium Shops Tool: A directory updated by shop owners, helping users find reliable local aquarium shops and promoting local businesses.
- Educational Modules:
- Basics of Aquarium Care: Covers key aspects like aquarium types, filtration, lighting, feeding, and maintenance.
- Ornamental Aquaculture: Focuses on breeding and rearing ornamental fish, particularly for farmers.
- Economic and Social Impact:
- Promoting Local Businesses: The app encourages economic growth by increasing visibility for local aquarium shops and creating opportunities for business owners.
- Authenticity and Reliability: Users can access verified information, reducing the reliance on unverified sources and promoting healthier aquariums.
- Sustainability and Growth: The app’s features are designed to foster sustainability and growth in the ornamental fish trade by providing reliable information and empowering users.
Pradhan Mantri MatsyaSampada Yojana (PMMSY):
- Objective: Aimed at transforming the fisheries sector, improving fish production, productivity, quality, technology, infrastructure, and management, while strengthening the value chain and promoting the welfare of fishers.
- Launch: The scheme was launched in 2020 with an investment of Rs. 20,050 crores for a 5-year period (2020-21 to 2024-25).
- Focus Areas:
- Inland fisheries and aquaculture.
- Fisheries management and regulatory framework.
- Infrastructure and post-harvest management.
- Doubling fishers' and fish farmers' incomes.
- Components:
- Central Sector Scheme (CS): Fully funded by the central government.
- Centrally Sponsored Scheme (CSS): Partially funded by the central government and implemented by states.
- Sub-Schemes:
- Pradhan Mantri MatsyaKisanSamridhiSah-Yojana (PM-MKSSY): Launched under PMMSY to formalize the fisheries sector and support micro and small enterprises with over Rs. 6,000 crore investment (FY 2023-24 to 2026-27).
- Beneficiaries: Includes fishers, farmers, fish vendors, fisheries cooperatives, SC/STs, women, differently-abled persons, state and central entities, and private firms.
Fisheries Sector Contribution:
- Supports around 30 million people.
- India is the 3rd largest fish producer globally, with a fish production of 175.45 lakh tons in FY 2022-23.
- Contributes 1.09% to the Gross Value Added (GVA) of India and 6.72% to agricultural GVA.
Related Schemes:
- Fisheries and Aquaculture Infrastructure Development Fund (FIDF): Launched with a fund of Rs. 7,522.48 crore.
- Kisan Credit Card (KCC): Extended to fishers and farmers from FY 2018-19.
- Sustainable fisheries development.
- Doubling income and job creation in the sector.
- Boosting exports and agricultural GVA.
- Social and economic security for fishers.
Trade Watch Quarterly
- 05 Dec 2024
In News:
NITI Aayog released its first quarterly report, Trade Watch Quarterly (TWQ), on December 4, 2024, focusing on India's trade developments during Q1 FY2024 (April-June).
Overview:
- Purpose: The publication aims to provide a comprehensive analysis of India’s trade performance, highlighting key trends, challenges, and opportunities.
- Target: To leverage insights for evidence-based policy interventions and foster informed decision-making, contributing to sustainable growth in India’s trade.
Trade Performance Highlights (Q1 FY24):
- Total Trade: $576 billion (5.45% YoY growth).
- Merchandise Exports: Growth was restrained due to declines in iron & steel, and pearls.
- Imports: Driven by high-value goods, including aircraft, spacecraft, mineral fuels, and vegetable oils.
- Services Exports: Displayed a surplus, particularly in IT services.
- Growth in Services Exports: A positive trend, rising by 10.09% YoY, particularly in IT services and business solutions.
Key Challenges for India’s Trade:
- Limited Success in China-Plus-One Strategy:Countries like Vietnam, Thailand, Malaysia have gained more from this strategy, benefitting from cheaper labor, simplified tax laws, and lower tariffs.
- CBAM (Carbon Border Adjustment Mechanism):Starting in 2026, CBAM will impose carbon taxes on imports like cement, steel, and fertilizers. India’s iron and steel industry could face significant risks due to this.
- Declining Share in Labor-Intensive Sectors:India’s global market share in labor-intensive sectors (e.g., textiles, leather) has declined despite a strong workforce.
- Geopolitical Instability (West Asia):
- Oil price hikes could increase India’s Current Account Deficit (CAD) and fuel inflation.
- Declining agricultural exports to markets like Iran further add to the challenges.
Strategic Recommendations for Overcoming Challenges:
- Infrastructure Modernization:
- Expansion of digital platforms like Trade Connect e-Platform to streamline processes and support exporters.
- Strengthening logistics via the National Logistics Policy.
- Export Incentives:Continuation of schemes like RoDTEP (Remission of Duties and Taxes on Exported Products) to maintain export competitiveness.
- Technological Integration:Leveraging digital trade to tap into high-growth sectors and foster innovation in trade.
- Strengthening FTAs (Free Trade Agreements):Focus on negotiating strategic FTAs with global partners (e.g., the UK and the EU) to reduce trade barriers and enhance global market access.
Geopolitical and Environmental Risks:
- U.S.-China Trade Tensions:Offers opportunities for India to diversify its supply chains, but also poses challenges in terms of overdependence on certain countries.
- Impact of CBAM:Risk to carbon-intensive Indian exports like steel and aluminium, which will face tariffs starting in 2026.
Sectoral Performance:
- Growing Sectors:
- IT Services: India’s market share of IT services reached 10.2%, continuing to be a strong contributor.
- Pharmaceuticals, Electrical Machinery, and Mineral Fuels: Significant contributors to export growth.
- Declining Sectors:Labor-Intensive Goods: Declines in global market share for textiles, pearls, and leather.
Pathway to $2 Trillion Exports by 2030:
- India's Export Aspirations:To achieve the target of $2 trillion in exports by 2030, India must address structural inefficiencies, diversify exports, and reduce trade barriers.
- Vision 2047:Aligning with India’s broader vision to become a developed nation, the report stresses the importance of strengthening trade, technology, and infrastructure to realize these ambitions.
- Trade's Role in Economic Growth:
- Trade is vital to India’s economic trajectory, contributing significantly to GDP growth.
- Through evidence-based policymaking, infrastructure modernization, and strategic global partnerships, India can achieve sustained growth in trade, leading to the realization of a Viksit Bharat (Developed India) by 2047.
Heat Shock Protein 70
- 05 Dec 2024
In News:
JNU scientists make big discovery that could change malaria, Covid-19 treatment.
Overview of the Discovery:
- Institution: Jawaharlal Nehru University (JNU), Special Centre for Molecular Medicine.
- Key Discovery: Identification of human protein Hsp70 as a critical factor in the spread of malaria and COVID-19.
- Research Collaboration: Involvement of Indian and Russian researchers.
- Outcome: Development of a small molecule inhibitor of Hsp70 that could act as a broad-spectrum treatment for multiple infections.
About Heat Shock Protein 70 (Hsp70):
- Definition: Hsp70 is a type of molecular chaperone protein.
- Function:
- Helps other proteins fold into their proper shapes.
- Prevents protein misfolding.
- Regulates protein synthesis and protects proteins from stress.
- Elevates during cellular stress to shield cells from damage.
- Role in Cellular Processes:
- Prevents protein aggregation and assists in protein transport across membranes.
- Plays a critical role in protein homeostasis and cell survival during stress conditions.
Hsp70's Role in Disease Spread:
- SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19) Interaction:
- Hsp70 interacts with the spike protein of SARS-CoV-2 and human ACE2 receptors.
- Facilitates viral entry into human cells by stabilizing this interaction during fever (when Hsp70 levels rise).
- Malaria:Pathogens like malaria parasites rely on the host's machinery for survival, including Hsp70.
Research Findings and Implications:
- Published in: International Journal for Biological Macromolecules.
- Inhibition of Hsp70:
- Targeting Hsp70 can disrupt viral replication.
- In lab tests, Hsp70 inhibitor (PES-Cl) blocked SARS-CoV-2 replication at low doses.
- Potential for Broad-Spectrum Treatment:
- Hsp70 could be a target for treating multiple infections, not limited to COVID-19 or malaria.
- Prevention of Drug Resistance:
- Host-targeting antivirals are less prone to resistance as the virus cannot mutate the host protein (Hsp70).
- This approach could be especially beneficial for combating rapidly evolving viruses like SARS-CoV-2 and its variants (e.g., Omicron).
Host-Targeting Approach vs. Traditional Drugs:
- Host-Targeting: Targets the host cell machinery (e.g., Hsp70) rather than the virus itself.
- Reduces the likelihood of viral mutation-induced resistance.
- Traditional Drugs: Target the virus directly, which can lead to resistance, especially with rapidly mutating viruses.
Global Health and Pandemic Preparedness:
- Universal Tool for Infectious Diseases: The discovery could serve as a universal tool for managing infections during health emergencies.
- Collaboration and Importance: Highlights the significance of international collaboration in addressing global health challenges (e.g., Dr. Pramod Garg of AIIMS, Ph.D. scholar Prerna Joshi).
- Future Implications:Preparation for future pandemics, as the world must remain vigilant even post-COVID-19.
Donald Trump's Threat on BRICS and US Dollar

- 05 Dec 2024
In News:
- US President-elect Donald Trump threatens BRICS countries (Brazil, Russia, India, China, South Africa) with 100% import tariffs if they create a new currency or support an alternative to the US dollar as the global reserve currency.
- Trump emphasizes that attempts to undermine the US dollar’s dominance will face economic retaliation, asserting the US economy won’t tolerate such moves.
Background
- Weaponization of the Dollar: The US has increasingly used its financial influence to impose sanctions (e.g., Russia, Iran) and cut off countries from systems like SWIFT (Society for Worldwide Interbank Financial Telecommunication).
- Concerns: Countries are concerned about their vulnerability to US monetary policies, which can have global impacts (e.g., rising US interest rates causing economic instability in other countries).
Efforts to Reduce Dependence on the US Dollar
- BRICS Countries’ Initiatives:
- Russian President Putin criticizes the weaponization of the dollar.
- Brazil's President Lula advocates for a new BRICS currency to increase payment options and reduce vulnerabilities.
- India's Steps:
- The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) allows invoicing and payments in Indian rupees for international trade (since 2022), particularly with Russia.
- Prime Minister Modi supports increasing financial integration and cross-border trade in local currencies within BRICS.
- External Affairs Minister Jaishankar emphasizes the importance of mutual trade settlements in national currencies.
- China-Russia Trade: Over 90% of trade between Russia and China is settled in rubles and yuan due to their more balanced trade relations.
Internationalization of the Indian Rupee
- RBI's Role:
- In July 2022, RBI allowed export/import settlements in rupees, starting with Russia in December 2022.
- More than 19 countries, including the UK and UAE, have agreed to settle trade in rupees.
- Challenges:
- The Indian rupee currently accounts for only 1.6% of global forex turnover.
- India’s trade imbalance with Russia limits the effective use of rupee reserves.
- Indian banks are cautious due to the risk of US sanctions.
Global Trends in Currency Diversification
- Multipolarity in Finance: Emerging economies like China, India, and Brazil are advocating for a more decentralized financial system, moving away from US dominance.
- Declining Dollar Share: The US dollar’s share of global reserves is gradually decreasing, with non-traditional currencies like the Chinese yuan gaining ground.
Risks of Moving Away from the US Dollar
- Chinese Dominance: Concerns about increasing Chinese economic influence, especially within BRICS, as China pushes for more use of the yuan in trade.
- Liquidity and Volatility Issues: Alternatives to the dollar may face challenges like lower liquidity and increased exchange rate volatility.
- Implementation Challenges: Countries, especially those with trade imbalances, find it difficult to adopt local currencies for international trade.
Potential Impact of 100% US Tariff on BRICS Imports
- Global Trade Dynamics: A blanket tariff would likely encourage deeper intra-BRICS trade and accelerate the move towards de-dollarization.
- Impact on the US: Higher import costs for American consumers and potential trade diversification to third countries could hurt the US economy without revitalizing domestic manufacturing.
- Retaliation: BRICS countries might retaliate with tariffs on US goods, escalating trade tensions.
India’s Strategic Approach
- Diplomatic Engagement: India should clarify to the US that diversifying trade mechanisms is not anti-American but seeks financial stability and multipolarity.
- Leadership Role in BRICS: India should support financial reforms within BRICS that align with its interests while maintaining strong ties with the US.
- Promotion of Digital Currency: India should accelerate its Central Bank Digital Currency (CBDC) and strengthen international platforms like UPI to enhance its global financial presence.
International Debt Report 2024
- 05 Dec 2024
In News:
Recently released, World Bank’s "International Debt Report 2024" highlights a worsening debt crisis for developing nations, with 2023 marking the highest debt servicing levels in two decades, driven by rising interest rates and economic challenges.
Key Highlights:
Rising Debt Levels:
- Total external debt of low- and middle-income countries (LMICs) reached $8.8 trillion by the end of 2023, an 8% increase since 2020.
- For IDA-eligible countries (those receiving concessional loans from the World Bank), external debt rose by 18%, reaching $1.1 trillion.
Debt Servicing Costs:
- Developing nations paid a record $1.4 trillion in debt servicing costs (principal and interest) in 2023.
- Interest payments surged by 33%, totaling $406 billion, putting immense pressure on national budgets, especially in critical sectors like health, education, and environmental sustainability.
Interest Rate Increases:
- Interest rates on loans from official creditors doubled to 4% in 2023.
- Rates from private creditors rose to 6%, the highest in 15 years, exacerbating the financial burden on developing countries.
Impact on IDA-Eligible Countries:
- IDA countries faced severe financial strain, paying $96.2 billion in debt servicing, including $34.6 billion in record-high interest costs (four times higher than a decade ago).
- On average, 6% of their export earnings were allocated to debt payments, with some countries dedicating up to 38%.
Role of Creditors:
- Private creditors reduced lending, leading to more debt-servicing payments than new loans.
- In contrast, multilateral lenders like the World Bank provided additional support, with the World Bank contributing $28.1 billion.
- Multilateral institutions have emerged as crucial support systems, becoming "lenders of last resort" for poor economies.
Debt Data Transparency:
- Efforts to improve debt transparency led to nearly 70% of IDA-eligible economies publishing accessible public-debt data in 2023, a 20-point increase since 2020.
- Accurate debt data can reduce corruption and promote sustainable investment.
Global Financial Reforms:
- There is a growing call for global financial reforms to address the systemic challenges of developing nations facing rising debt burdens.
- Proposed measures include increased concessional financing, improved restructuring mechanisms, and the establishment of a Global Debt Authority for better debt management.
Impact on Climate and Development Goals:
- Debt servicing has become a larger financial burden than climate initiatives in many countries, with developing nations spending more on debt servicing than climate goals (2.4% of GDP vs. 2.1% for climate investments).
- To meet climate commitments under the Paris Agreement, climate investments would need to rise to 6.9% of GDP by 2030.
Debt Relief Initiatives:
- Programs like the Heavily Indebted Poor Countries (HIPC) Initiative and the Multilateral Debt Relief Initiative (MDRI) provide debt relief to the world’s poorest nations, helping them meet Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs).
- For instance, Somalia saved $4.5 billion in debt service after completing the HIPC program in December 2023.
Global Sovereign Debt Roundtable (GSDR):
- The GSDR brings together debtor nations and creditors (both official and private) to improve debt sustainability and address restructuring challenges.
- Co-chaired by the IMF, World Bank, and G20, the forum aims to find coordinated solutions for sovereign debt issues.
Overview of Global Plastic Treaty Negotiations

- 05 Dec 2024
In News:
The recent negotiations for a global treaty aimed at curbing plastic pollution, held in Busan, South Korea, concluded without reaching a legally binding agreement. This marked the fifth round of discussions since the United Nations Environment Assembly (UNEA) initiated the process in March 2022, with the goal of finalizing a treaty by the end of 2024. The failure to adopt a treaty was primarily due to disagreements over production cap goals and the elimination of specific plastic chemicals and products.
Key Points of Dispute
- Production Cap Goals: A coalition of over 100 countries, including many from Africa, Latin America, and the European Union, pushed for clear production cap goals in the treaty. They argued that such measures are essential for effective regulation of plastic pollution.
- Opposition from Oil-Producing Nations: Conversely, a group of “like-minded countries” such as Saudi Arabia, Kuwait, Russia, and Iran opposed these provisions. They contended that regulating production cuts exceeded the original mandate set by UNEA and could lead to trade restrictions disguised as environmental measures. India and China aligned with this coalition, emphasizing their concerns regarding economic impacts.
Draft Treaty Highlights
Despite the failure to finalize an agreement, discussions produced a draft text that included both consensus points and contentious issues:
- Consensus Points:
- Proposals for banning open dumping and burning of plastics.
- Definitions for various plastic types were suggested but lacked clarity on contentious terms like microplastics.
- Contentious Issues:
-
- The draft did not adequately address definitions for microplastics or recycling standards.
- References to single-use plastics were included but faced pushback from certain nations.
India’s Position
India articulated its stance focusing on several key areas:
- Development Rights: Emphasized the need for recognizing varying responsibilities among countries in managing plastic pollution while considering their developmental rights.
- Technical and Financial Support: Advocated for provisions ensuring technical assistance and financial support for developing nations to manage plastic waste effectively.
- Opposition to Production Caps: India opposed any articles that would impose caps on polymer production, arguing that such measures were not directly linked to reducing plastic pollution.
Future Steps
The negotiations will continue with plans to reconvene in 2025. In the meantime, global plastic production is projected to rise significantly, potentially tripling by 2050 if no urgent action is taken. The ongoing dialogue will need to address both environmental concerns and developmental needs to create a balanced approach toward managing plastic pollution globally.
Global Context and Initiatives
The need for a global treaty is underscored by alarming statistics:
- Over 462 million tons of plastic are produced annually, with a significant portion contributing to pollution.
- Microplastics have infiltrated ecosystems worldwide, affecting biodiversity and human health.
Countries like Rwanda and Austria have implemented successful measures to reduce plastic waste, serving as models for global efforts. Initiatives such as the UNDP Plastic Waste Management Program in India aim to enhance waste management practices while addressing environmental impacts.
SheSTEM 2024

- 04 Dec 2024
In News:
Atal Innovation Mission (AIM), under the NITI Aayog and the Office of Science & Innovation, at the Embassy of Sweden, in partnership with Nordic collaborators - Innovation Norway, Innovation Centre Denmark, and Business Finland, announced the successful conclusion of SheSTEM 2024.
Key Highlights:
- Objective: To inspire youth, especially women, to explore careers in STEM (Science, Technology, Engineering, Mathematics) and promote innovative solutions for sustainability.
- Theme: Focus on Battery Technology and Energy Storage Systems (BEST), part of the India-Nordic BEST project, aimed at fostering sustainability through advanced energy solutions.
Key Features of the Challenge:
- Target Audience: Students from grades 6–12 across India.
- Participation: Over 1,000 submissions showcasing innovative energy storage solutions.
- Format: Students presented prototypes or concepts via a 2-minute video format.
- Focus Areas: Sustainability, energy storage, and innovative solutions to global challenges.
Significance of SheSTEM 2024:
- Youth Empowerment: Provides a platform for young innovators to showcase their ideas and contribute to global sustainability.
- Global Impact: Encourages collaboration between India and Nordic countries in academia, business, and government to explore energy storage and sustainable technologies.
- Women in STEM: Highlights the importance of gender inclusivity in STEM fields, particularly in sustainability and technology.
Key Facts about AIM (Atal Innovation Mission):
- Established: 2016 by NITI Aayog to foster innovation and entrepreneurship across India.
- Core Functions:
- Promote Entrepreneurship: Financial support, mentorship, and nurturing innovative startups.
- Promote Innovation: Creating platforms for idea generation and collaboration.
- Key Programs: Atal Tinkering Labs, Atal Incubation Centres, Atal New India Challenges, and Mentor India.
- Monitoring: Systematic monitoring of initiatives using real-time MIS systems and dashboards.
ICJ Hearing on Landmark Climate Change Case

- 04 Dec 2024
In News:
- The International Court of Justice (ICJ) has begun hearings on a landmark climate change case, seeking an advisory opinion on the obligations of countries under international law regarding climate change.
- The case stems from a UN General Assembly (UNGA) resolution initiated by Vanuatu in March 2023, co-sponsored by 132 countries.
Background:
- Vanuatu, a small island nation, faces existential threats from rising sea levels.
- The resolution was passed to clarify climate obligations in light of international laws, including the UNFCCC, Paris Agreement, and other legal instruments like the UN Convention on the Law of the Seas, and the Universal Declaration on Human Rights.
Global Impact of the Case:
- The outcome of the case could influence global climate governance, particularly in the context of climate negotiations.
- It may broaden the legal basis for climate obligations and underscore the legal consequences for non-compliance.
India’s Position:
- India has voiced concerns about the judicial process being the best approach to tackle climate issues, advocating for diplomatic efforts.
- India is scheduled to make its submission on December 5, highlighting its preference for a collaborative, non-top-down approach in climate discussions.
Implications for Developed and Developing Countries:
- The case highlights the historical responsibility of developed countries for climate change due to their higher emissions.
- The ICJ's advisory opinion could reinforce the argument that developed countries' obligations extend beyond the UNFCCC and Paris Agreement, incorporating broader international legal frameworks.
Climate Litigation and Precedent:
- The ICJ ruling could set a precedent for climate litigation, potentially influencing over 2,600 ongoing climate lawsuits globally.
- Notable rulings include the European Court of Human Rights, which held Switzerland accountable for failing to meet emissions targets, and India's Supreme Court recognizing the right to be free from adverse climate impacts in 2023.
Record Participation and Importance of the Case:
- The ICJ has received over 90 written submissions, with 97 countries and 12 international organizations participating in the hearings.
- The case is significant for the growing number of climate-related lawsuits and the evolving nature of international climate law.
Future Prospects:
- The ICJ’s advisory opinion, though non-binding, could significantly impact future climate negotiations, particularly in terms of responsibility sharing and climate finance.
- The outcome could also influence calls for compensation for climate damages, especially from vulnerable states like small island nations.
Places of Worship (Special Provisions) Act, 1991

- 04 Dec 2024
In News:
The Places of Worship (Special Provisions) Act, 1991, is once again in focus, albeit in a context in which its objectives are being ignored. Civil suits questioning the religious character of mosques at Varanasi and Mathura are progressing apace. These developments show that legislation freezing the status of places of worship is inadequate to stop Hindu claimants from making determined legal efforts to achieve their goal of replacing them with temples.
Places of Worship (Special Provisions) Act, 1991:
- Objective: To preserve the religious character of places of worship as they existed on August 15, 1947, and prevent changes in religious identity.
- Key Provisions:
- Section 3: Prohibits conversion of a place of worship from one religion to another.
- Section 4(1): Ensures the religious character remains unchanged from August 15, 1947.
- Section 4(2): Terminates ongoing or future legal proceedings seeking to alter the religious character of a place of worship.
- Exemptions:
- Ayodhya dispute: Exempted, allowing ongoing litigation.
- Ancient monuments & archaeological sites: Not covered by the Act.
- Already settled disputes or those agreed upon before the Act came into force.
- Penalties: Violators can face up to 3 years of imprisonment or fines.
- Criticism: The Act has been challenged for limiting judicial review, imposing a retrospective cutoff date, and restricting religious rights.
Recent Legal Disputes:
- Gyanvapi Mosque (Varanasi):
- Claim: Hindu worshippers assert the right to worship deities (e.g., Ma Sringar Gauri, Lord Vishweshwar) within the mosque premises.
- Legal Basis: Claim that the mosque was built over an ancient Hindu temple.
- Court's Ruling: The court allows the case to proceed, stating that the aim is to assert worship rights, not change the mosque’s status.
- Archaeological Survey: ASI report confirms the existence of a temple before the mosque’s construction.
- Key Legal Outcome: The Places of Worship Act does not bar these suits as they aim to ascertain the religious character of the site, not alter it.
- Shahi Idgah Mosque (Mathura):
- Claim: Hindu groups assert the mosque was built over Lord Krishna’s birthplace.
- Historical Context: The dispute was settled by a compromise in 1968, which was implemented in 1974, where part of the land was given to the mosque.
- Current Legal Dispute: New suits challenge the 1968 agreement as ‘fraudulent’ and seek the entire land to be transferred to the deity.
- Court's Ruling: The Act is not applicable as the 1968 agreement predates the 1991 Act, and the dispute pertains to the compromise, not the religious character.
- Shahi Jama Masjid (Sambhal, Uttar Pradesh):
- Claim: Allegation that the mosque was built over a Hindu temple (Hari Har Mandir).
- Survey Request: Petitioners seek a survey to verify the site’s historical and religious character.
- Legal Context: The mosque is a protected monument under the Ancient Monuments Preservation Act, 1904.
Key Legal Interpretations:
- Court’s Role: Courts have ruled that the Places of Worship Act does not prohibit suits related to the religious character of a site if they are aimed at determining, not altering, that character.
- Interpretation of ‘Religious Character’: The Allahabad High Court stated that a structure can’t have dual religious character (both Hindu and Muslim), and the religious character of a place must be determined through evidence.
Political and Social Implications:
- Ongoing Controversy: The Gyanvapi and Mathura mosque disputes continue to fuel political and religious debates, as Hindu organizations seek to assert their claims, while mosque committees and Muslim groups resist changes.
- Public and Legal Attention: The legal and political landscape surrounding the Places of Worship Act remains contentious, with several legal suits challenging its applicability.
1984 Bhopal disaster

- 04 Dec 2024
In News:
Forty years after the Bhopal disaster on December 2-3, 1984, several hundred tonnes of toxic waste still remain around the ill-fated Union Carbide plant.
Overview of the incident:
The 1984 Bhopal disaster, one of the world’s worst industrial accidents, was caused by the release of methyl isocyanate (MIC) gas, which was a key component in the production of pesticides at the Union Carbide India Limited (UCIL) plant. However, the toxic legacy of the disaster extends far beyond MIC, with a range of other harmful substances lingering in the environment. These include:
- Methyl Isocyanate (MIC):Primary toxic agent: MIC is a highly toxic, volatile compound. Exposure can cause severe respiratory distress, eye irritation, pulmonary edema, and even death.
- Heavy Metals:The site of the plant is contaminated with various heavy metals, including:
- Mercury: Known to accumulate in the body and affect the nervous system, kidneys, and liver. Even small doses over time can lead to chronic health problems.
- Chromium: Exposure to high levels of chromium, particularly hexavalent chromium, is associated with lung cancer and damage to the respiratory system.
- Lead: A potent neurotoxin, lead can cause developmental delays, memory problems, and damage to the kidneys.
- Nickel: Can cause respiratory and lung cancers when inhaled in significant quantities.
- Copper: High levels of copper exposure can damage the liver and kidneys.
- Organic Compounds:Several organic chemicals were found at the site, including:
- Hexachlorobutadiene: A suspected carcinogen that can cause liver damage, kidney damage, and neurological issues upon exposure.
- Chloroform (Trichloromethane): Known for its effects on the central nervous system, exposure can lead to dizziness, loss of consciousness, and even death at high concentrations. It is also a possible carcinogen.
- Carbon Tetrachloride: A potent liver toxin, exposure can result in liver damage, cancer, and nervous system toxicity.
- Trichlorobenzene: These compounds are volatile and can spread through air and water, accumulating in fatty tissues and causing damage to organs like the liver and kidneys.
- Persistent Organic Pollutants (POPs):Some of the contaminants, particularly the organic compounds, are classified as persistent organic pollutants, which do not degrade easily in the environment. These can lead to:
- Cancer: Several of these compounds are carcinogenic.
- Neurological damage: Prolonged exposure can affect both the central and peripheral nervous systems.
- Reproductive and developmental disorders: Exposure has been linked to adverse effects on fertility and developmental health in humans.
- Environmental and Long-term Health Effects:
- Even decades later, contamination continues to affect the health of people living around the site, with high rates of cancers, birth defects, respiratory diseases, and other health issues. Water sources in the region remain unsafe due to heavy contamination with toxic chemicals. Persistent organic pollutants have been identified in local communities, indicating that the contamination continues to spread.
Retired Sportsperson Empowerment Training (RESET) Programme

- 04 Dec 2024
In News:
At an event celebrating the National Sports Day, The Minister for Youth Affairs & Sports and Labour& Employment launched “Retired Sportsperson Empowerment Training” (RESET) Programme.
Key Highlights:
- Objective:
- Empower retired athletes through career development.
- Provide tailored education, internships, and skill enhancement.
- Address the human resource gap in the sports sector.
- Eligibility Criteria:
- Retired athletes aged 20-50 years.
- Winners of international medals or participants in international events.
- National/state-level medalists or participants in recognized competitions (e.g., National Sports Federations, Indian Olympic Association).
- Courses Offered (16 Courses):
-
- Strength & Conditioning Trainer
- Sports Nutritionist
- Sports Event Management
- Corporate Wellness Trainer
- Sports Masseur
- Sports Entrepreneurship
- Store Manager
- Fitness Centre Manager
- Physical Education Trainer
- Fitness Trainer
- Yoga Trainer
- Venue Supervisor
- Self-Defence Trainer
- Community Sports Trainer
- Camping & Trekking Guide
- Facility Caretaker
- Program Structure:
- Two levels based on educational qualifications:
- Class 12 and above
- Class 11 and below
- Hybrid learning mode:
- Self-paced learning via a dedicated portal.
- On-ground training and internships.
- Two levels based on educational qualifications:
- Internship and Placement:
- Internships offered in sports organizations, competitions, training camps, and leagues.
- Post-course placement assistance and entrepreneurial guidance.
- Implementing Agency:Lakshmibai National Institute of Physical Education (LNIPE) for the pilot phase.
- Importance:
- Provides sustainable career pathways for retired athletes.
- Utilizes the experience and skills of retired athletes to benefit future generations of athletes.
- Contributes to the growth of sports and nation-building.
- National Sports Day (29th August):
- Celebrated in honor of Major Dhyan Chand's birth anniversary.
- Promotes sports and physical fitness in India.
- Awards like Major Dhyan Chand Khel Ratna presented to honor excellence in sports.
26 Rafale-Marine Jets

- 03 Dec 2024
In News:
- Deal for 26 Rafale-M jets nearing completion, with final formalities expected to be completed by January 2025.
- These jets are designed for naval operations and will be deployed on INS Vikrant and INS Vikramaditya.
- Rafale-M Features: Multi-role, advanced avionics, AESA radar, and armaments like Meteor, MICA, SCALP, EXOCET.
- Three Scorpene Submarines: Additional three Scorpene-class submarines to be procured from France.
- These are part of a repeat order to Mazagon Dock Shipbuilders Limited (MDL), with five of the earlier six already inducted into service.
Nuclear Capabilities:
- INS Arighaat: Successfully fired a Submarine-Launched Ballistic Missile (SLBM), marking a significant milestone for India's nuclear deterrence.
- Indigenous Nuclear Attack Submarine (SSN): India’s first indigenous SSN expected by 2036-37.
Strategic Maritime Engagement:
- Indian Ocean Region (IOR): Active monitoring of maritime activities, especially of China's PLA Navy and Chinese research vessels.
- Pakistan Navy Expansion: Acknowledged Pakistan’s efforts to become a 50-ship Navy, including the acquisition of 8 Chinese submarines. Indian Navy is adapting its plans to address this.
Nuclear Submarine Program (SSBN):
- INS Arihant: Conducted multiple deterrence patrols.
- INS Arighaat: Ongoing trials including the recent K4 SLBM test, with a range of 3,500 km.
Naval Vision 2047:
- Navy Chief released Vision 2047 document, outlining the future direction and growth of the Indian Navy.
Bilateral and Multilateral Engagements:
- Participation in various bilateral and multilateral exercises, including RIMPAC 2024 (Hawaii) and Russian Federation Navy’s Raising Day (St. Petersburg).
Notre-Dame Cathedral

- 03 Dec 2024
In News:
The Notre-Dame Cathedral in Paris, a landmark symbol of French Gothic architecture, is set to reopen on after undergoing extensive renovations following a devastating fire in April 2019.
Historical and Architectural Significance:
- Location: Situated on Île de la Cité in the Seine River, Paris.
- Construction: Began in 1163 under Bishop Maurice de Sully and completed in 1260, showcasing a blend of early Gothic to Rayonnant Gothic styles.
- Key Features: The cathedral is renowned for its rib vaults, flying buttresses, stained-glass windows, and sculpted gargoyles.
- Cultural Importance: It has been a stage for significant historical events, including Napoleon Bonaparte's coronation in 1804. It also houses the Holy Crown of Thorns and relics from the crucifixion of Jesus.
- Literary Legacy: Featured in Victor Hugo's "The Hunchback of Notre-Dame" (1831), which drew attention to its architectural and historical significance.
Modern History and Renovation:
- The cathedral endured historical events such as the French Revolution, World War II, and attacks during the Protestant Reformation.
- In April 2019, a fire severely damaged the roof and spire, sparking an international outpouring of support for its restoration.
- Renovation efforts began soon after, involving more than 1,000 craftspeople, with President Emmanuel Macron calling it “the project of the century.”
Construction and Modifications Over Centuries:
- The Notre-Dame was a model for early Gothic architecture and has undergone multiple renovations, including the addition of flying buttresses and other structural changes during the 13th and 14th centuries.
- Modifications continued through the Renaissance and Classical periods, reflecting changing artistic styles and the political moods of the time.
Significance in French History:
- Witness to History: The cathedral has been central to 800 years of French history, serving as a backdrop for both brilliant and tumultuous events.
- Religious and Political Symbolism: It was the heart of Paris' religious and political life, acting as a symbol of the intertwined relationship between the church and the monarchy.
Madhya Pradesh’s 8th Tiger Reserve: Ratapani

- 03 Dec 2024
In News:
Recently, the Ratapani Wildlife Sanctuary in Madhya Pradesh was officially declared a Tiger Reserve, making it the 8th such reserve in the state. This declaration follows approval from the Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change through the National Tiger Conservation Authority (NTCA).
Key Details:
- Core Area: 763.8 sq. km
- Buffer Area: 507.6 sq. km
- Total Area: 1,271.4 sq. km
- Ratapani Tiger Reserve is located in the Raisen and Sehore districts, within the Vindhya hills, and is home to approximately 90 tigers.
- It also forms a crucial part of Madhya Pradesh’s tiger habitat and serves as a migration corridor from the Satpura ranges.
Economic and Ecotourism Benefits:
- The designation will boost ecotourism, generating employment and improving livelihoods for local communities.
- Eco-development programs will support residents, providing new opportunities and addressing the balance between conservation and human interests.
Wildlife Conservation and Management:
- The reserve will focus on habitat management, wildlife protection, and community engagement.
- The core area has been recognized as a critical tiger habitat under the Wildlife Protection Act, 1972.
- Efforts will include strengthening anti-poaching measures, improving surveillance, and enhancing prey base restoration.
Significance for Madhya Pradesh:
- This move places Madhya Pradesh as the "Tiger State of India", with significant conservation focus on the Ratapani and Madhav National Park (also in the process of becoming a tiger reserve).
- Madhya Pradesh now hosts 8 tiger reserves, contributing significantly to the country's overall tiger conservation efforts.
MahaKumbh Mela 2025

- 03 Dec 2024
In News:
- On December 1, 2024, the Uttar Pradesh government declared the MahaKumbh Mela area as a temporary district for four months.
- The new district will be known as the MahaKumbh Mela District, to streamline management for the 2025 MahaKumbh.
- Over 5,000 hectares of land will be part of this district, including 66 revenue villages from four tehsils: Sadar, Sorav, Phulpur, and Karchana.
Key Administrative Changes:
- Mela Adhikari (Kumbh Mela Officer) will act as the District Magistrate (DM) and will hold powers of Executive Magistrate, District Magistrate, and Additional District Magistrate.
- The Mela Adhikari will have authority under the Indian Civil Defense Code, 2023, and the Uttar Pradesh Revenue Code, 2006.
- The Mela Adhikari can appoint an Additional Collector for the district.
MahaKumbh Mela Overview:
- The Kumbh Mela is recognized by UNESCO as an Intangible Cultural Heritage of Humanity.
- It is the largest peaceful congregation of pilgrims, with participants bathing in sacred rivers at locations including Prayagraj, Haridwar, Ujjain, and Nashik.
- The PrayagrajKumbh takes place at the Sangam, the confluence of the Ganges, Yamuna, and the mythical Saraswati rivers.
- The event spans over a month and includes religious, cultural, and social activities, along with massive infrastructural setup including tented townships, civic facilities, and security measures.
International Day of Persons with Disabilities 2024

- 03 Dec 2024
In News:
- The International Day of Persons with Disabilities (IDPD), observed annually on December 3, celebrates the resilience, contributions, and leadership of persons with disabilities (PwDs) worldwide.
- Theme: “Amplifying the leadership of persons with disabilities for an inclusive and sustainable future”
History
- Proclamation: Established by the United Nations General Assembly in 1992 to promote the rights and well-being of persons with disabilities (PwDs).
- Convention on the Rights of Persons with Disabilities (CRPD): Adopted in 2006, further advanced the rights and well-being of PwDs and supports the 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development.
Initiatives
Department of Empowerment of Persons with Disabilities
- In order to give focused attention to policy issues and meaningful thrust to the activities aimed at the welfare and empowerment of Persons with Disabilities (PwDs), a separate Department of Disability Affairs was carved out of the Ministry of Social Justice and Empowerment on May 12, 2012.
- The Department was renamed the Department of Empowerment of Persons with Disabilities on December 8, 2014.
- The Department acts as a nodal agency for matters pertaining to disability and persons with disabilities, including effecting closer coordination among different stakeholders: related Central Ministries, State/UT Governments, NGOs, etc., in matters pertaining to disability.
Accessible India Campaign
- The Accessible India Campaign (Sugamya Bharat Abhiyan), launched on December 3, 2015 aims to achieve universal accessibility for Persons with Disabilities (PwDs) across India.
- The key focus areas include improving Built Environment Accessibility in public spaces, enhancing Transportation Accessibility for independent mobility, creating an accessible Information and Communication ecosystem, and expanding Sign Language Access through interpreter training and better media support.
Deendayal Divyangjan Rehabilitation Scheme (DDRS)
- DDRS is a central sector scheme to provide grant-in-aid to non-governmental organizations (NGOs) for projects relating to the rehabilitation of persons with disabilities aimed at enabling persons with disabilities to reach and maintain their optimal, physical, sensory, intellectual, psychiatric, or socio-functional levels.
District Disability Rehabilitation Centre (DDRC)
- The District Disability Rehabilitation Centre (DDRC) aims to address the needs of persons with disabilities through a multifaceted approach.
- Its objectives include early identification and intervention, raising awareness, and assessing the need for assistive devices along with their provision and fitment, arrangement of loans for self-employment and more. Additionally, it acts as an outreach center for services provided by National Institutes and works to promote a barrier-free environment for individuals with disabilities.
Assistance to Persons with Disabilities for Purchase/Fitting of Aids/ Appliances (ADIP) Scheme.
- The main objective of the Scheme is to provide grants-in-aid to the various implementing agencies (National Institutes/Composite Regional Centers/Artificial Limbs Manufacturing Corporation of India.
Schemes For Implementation Of Rights of Persons With Disabilities Act 2016 (SIPDA)
- The Scheme for Implementation of the Rights of Persons with Disabilities Act, 2016 (SIPDA) is a comprehensive "Central Sector Scheme" that encompasses 10 sub-schemes following its revision during the Expenditure Finance Committee (EFC) meeting on 11th August 2021.
- This revised scheme, approved by the Hon'ble Finance Minister, is designed to operate from 2021–22 to 2025–26.
Divya Kala Mela
- The Divya Kala Mela is a national-level fair dedicated to Divyangjan and represents a significant milestone in India’s journey toward inclusivity and empowerment of the Divyangjan, or differently-abled individuals.
PM-DAKSH
- PM-DAKSH (Pradhan Mantri DakshtaAurKushaltaSampannHitgrahi) Yojana is a one-stop destination for Persons with Disabilities (PwDs), skill training organizations, and employers across India to be a part of the National Action Plan for Skill Development of Persons with Disabilities implemented by the Department of Empowerment of Persons with Disabilities (DEPwD). Under this portal, there are two modules:
- Divyangjan Kaushal Vikas: Skill training is conducted for PwDs through the portal across the country.
- Divyangjan Rozgar Setu: The platform aims to act as a bridge between PwDs and employers having jobs for PwDs. The platform provides geo-tagged based information on employment/earning opportunities within private companies as well as PwDs across India.
Network Readiness Index 2024

- 02 Dec 2024
In News:
- India has climbed 11 positions to secure 49th rank in the Network Readiness Index (NRI) 2024, compared to 60th in NRI 2023.
- This improvement reflects India’s significant progress in the digital and telecommunication sectors.
NRI 2024 Overview:
- The NRI 2024 report assesses the network readiness of 133 economies based on four pillars: Technology, People, Governance, and Impact, using 54 variables.
- Published by the Portulans Institute, Washington DC.
India's Leading Indicators:
- Top rankings:
- 1st Rank: ‘AI scientific publications’, ‘AI talent concentration’, and ‘ICT services exports’.
- 2nd Rank: ‘FTTH/Building Internet subscriptions’, ‘Mobile broadband internet traffic’, and ‘International Internet bandwidth’.
- 3rd Rank: ‘Domestic market scale’.
- 4th Rank: ‘Annual investment in telecommunication services’.
Digital Progress:
- India has demonstrated remarkable digital transformation, especially in technological innovation and digital infrastructure.
Economic Grouping:
- India ranks 2nd in the lower-middle-income countries group, following Vietnam.
Telecommunication Achievements:
- Tele-density has increased from 75.2% to 84.69% in the past decade, with 119 crore wireless connections.
- Internet subscribers have surged from 25.1 crore to 94.4 crore, aided by Digital India initiatives and rural broadband expansion.
- 5G Launch: In 2022, India launched 5G services, significantly boosting global mobile broadband speed rankings from 118th to 15th.
Future Vision:
- India’s Bharat 6G Vision aims to position the country as a leader in future telecom technologies, backed by strong infrastructure and investments in emerging technologies.
Telecom Reforms:
- Spectrum management, ease of doing business, and consumer protection reforms have strengthened India’s telecom sector, contributing to its improved network readiness ranking.
World AIDS Day 2024
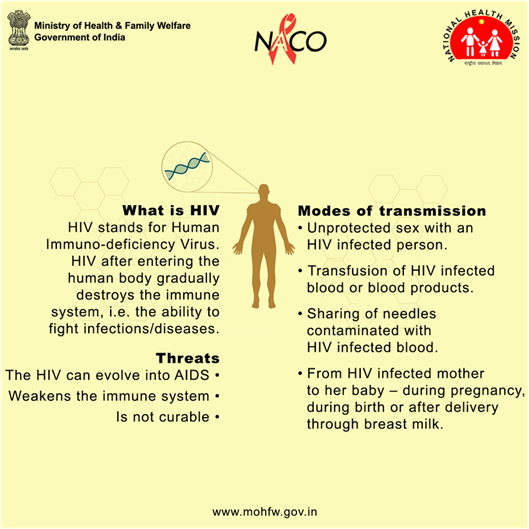
- 02 Dec 2024
In News:
World AIDS Day is observed annually on December 1 since 1988 to raise awareness about HIV/AIDS and demonstrate solidarity with affected individuals. It commemorates lives lost to AIDS and highlights progress and ongoing challenges in prevention, treatment, and care.
Key Highlights:
- 2024 Theme: "Take the Rights Path: My Health, My Right!"
- Focuses on healthcare access, human rights, and addressing systemic inequalities in HIV prevention and treatment services.
- Aims to empower individuals to manage their health and reduce stigma.
- Advocates for inclusivity and global cooperation to eradicate AIDS.
Global and National Perspective on HIV/AIDS
- Global Progress:
- According to UNAIDS Global AIDS Update 2023, significant strides have been made globally in reducing new HIV infections and improving treatment access.
- India has been acknowledged for its robust legal framework and financial investments in HIV control.
- India's HIV Statistics:
- Over 2.5 million people live with HIV in India.
- Annual new infections: 66,400, a 44% reduction since 2010.
- HIV prevalence among adults is 0.2%.
- Free lifelong treatment is provided to over 16 lakh people at 725 ART centers (as of 2023).
India’s Comprehensive HIV/AIDS Response
- Early Initiatives:
- India’s response to HIV/AIDS began in 1985 with sero-surveillance and blood safety measures.
- The National AIDS and STD Control Programme (NACP) was launched in 1992, evolving into one of the world’s largest HIV/AIDS control programs.
- Evolution of NACP:
- Phase I (1992-1999): Focused on awareness and blood safety.
- Phase II (1999-2007): Introduced direct interventions in prevention, detection, and treatment.
- Phase III (2007-2012): Expanded decentralized management at the district level.
- Phase IV (2012-2017): Increased funding and sustainability of interventions.
- Phase IV Extended (2017-2021): Passage of the HIV and AIDS (Prevention and Control) Act, 2017; introduction of the ‘Test and Treat’ policy; and response to the COVID-19 pandemic with IT innovations.
- NACP Phase V (2021-2026):
- Central Sector Scheme with an outlay of Rs. 15,471.94 crore.
- Goals: Reduce new HIV infections and AIDS-related deaths by 80% by 2025-26 from 2010 levels.
- Eliminate vertical transmission of HIV and syphilis, reduce stigma, and ensure universal access to STI/RTI services for vulnerable populations.
- Key strategies include community-centered approaches, technology integration, gender-sensitive responses, and public-private sector partnerships.
Key Objectives of NACP Phase V
- Prevention & Control:
- Ensure 95% of high-risk individuals access prevention services.
- Achieve the 95-95-95 targets: 95% of HIV-positive individuals know their status, are on treatment, and achieve viral suppression.
- Eliminate vertical transmission of HIV and syphilis.
- Reduce stigma and discrimination to less than 10%.
- STI/RTI Prevention:
- Universal access to high-quality services for at-risk populations.
Asia-Oceania Meteorological Satellite Users' Conference (AOMSUC-14)

- 02 Dec 2024
In News:
The 14th Asia-Oceania Meteorological Satellite Users' Conference (AOMSUC-14)was held in New Delhi, India, hosted by the India Meteorological Department (IMD) under the Ministry of Earth Sciences. This annual event brings together meteorologists, earth scientists, and satellite data users to discuss advancements in satellite technology for weather and climate monitoring.
Key Facts:
- Objective:
- Promote Satellite Observations: Highlight the importance of satellite data for meteorology and climatology.
- Advance Remote Sensing Science: Foster advancements in satellite technology and its application in weather forecasting and climate monitoring.
- Encourage Collaboration: Facilitate dialogue between satellite operators and users to enhance the use of satellite data across the Asia-Oceania region.
- Discuss Future Plans: Update on the current status and future plans of international space programs.
- Engage Young Scientists: Encourage the involvement of young researchers in satellite science and meteorology.
- Participants:
- Around 150 participants from various countries, including key international space organizations like WMO, NASA, ESA, JAXA, and other meteorological and space entities.
- The conference will feature oral presentations, poster sessions, panel discussions, and a training workshop focused on satellite data application.
- Significance of the Conference:
- Regional Cooperation: AOMSUC promotes stronger cooperation between countries in the Asia-Oceania region, addressing shared challenges in meteorology and satellite data usage.
- Improved Forecasting: Enhances satellite data utilization for more accurate weather forecasting, disaster prediction, and climate monitoring.
- Disaster Risk Management: Strengthens early warning systems for extreme weather events, improving disaster preparedness and response.
- Capacity Building: Offers training and workshops for local meteorologists, boosting the capacity of countries to use satellite data effectively for weather forecasting and climate services.
- Data Sharing: Encourages collaboration in satellite data sharing, facilitating better access to meteorological data across national borders.
- History of AOMSUC:The first AOMSUC was held in Beijing, China in 2010. Since then, the conference has been held annually in various Asia-Oceania locations and has become a leading event for the meteorological community.
KisanPehchaan Patra
- 02 Dec 2024
In News:
The Indian government is actively promoting the creation of digital identities for farmers through the KisanPehchaan Patra (Farmer ID). The initiative is an essential part of the Digital Agriculture Mission under the AgriStack initiative.
Key Details:
Objective:
- The main goal is to provide digital IDs linked to Aadhaar for farmers, capturing comprehensive agricultural data including land records, crop information, and ownership details.
- These digital identities are designed to enhance farmers' access to government schemes and digital agriculture services.
Farmer ID Creation Timeline:
- The government plans to create digital IDs for 11 crore farmers in phases:
- 6 crore farmers in FY 2024-25.
- 3 crore farmers in FY 2025-26.
- 2 crore farmers in FY 2026-27.
AgriStack Initiative:
- The AgriStack initiative aims to build a Digital Public Infrastructure (DPI) for the agriculture sector, which includes:
- Farmers' Registry.
- Geo-referenced village maps.
- Crop Sown Registry.
Implementation Strategy:
- Camp-mode approach: States have been instructed to organize field-level camps to ensure faster and inclusive registration of farmers.
- Financial Incentives:
- States will receive ?15,000 per camp for organizing these camps.
- Additionally, ?10 per Farmer ID issued.
- Funding is provided through the Pradhan Mantri KisanSamman Nidhi (PM-Kisan) scheme.
Benefits of Digital Farmer ID:
- Targeted Delivery of Benefits: Ensures subsidies and benefits reach legitimate farmers and eliminates duplication.
- Precision Agriculture: Supports data-driven policies for better crop planning, insurance, and market linkages.
- Financial Inclusion: Facilitates easy access to credit, loans, and crop insurance, empowering farmers financially.
- Better Monitoring: Helps in tracking the actual implementation of schemes and ensures that only eligible farmers benefit.
Progress in States:
- Advanced States: Gujarat, Madhya Pradesh, Maharashtra, and Uttar Pradesh have made significant progress in issuing digital Farmer IDs.
- Testing Phase: States like Assam, Chhattisgarh, and Odisha are still in the field-testing phase.
- Special Assistance Scheme: The Finance Ministry allocated ?5,000 crore in August 2024 to assist states in creating the Farmers' Registry, with funds available until March 2025.
Linkage with Land Records and Crop Data:
- The Farmer ID integrates with state land records and crop data, creating a dynamic and accurate database known as the Farmer’s Registry.
- This data helps in the development of better agricultural policies and decision-making.
Digital Agriculture Mission:
- The government approved a substantial outlay of ?2,817 crore for the Digital Agriculture Mission, which is intended to modernize agricultural practices and build robust digital infrastructure.
- The mission also includes the launch of the Digital Crop Estimation Survey (DGCES), which will help in crop estimation and better resource allocation.
National Policy on Female Labour Force Participation (FLFP)

- 02 Dec 2024
In News:
- India is working on a national policy to enhance female labour force participation (FLFP), focusing on creating a supportive care economy structure.
- The policy is being developed by an inter-ministerial team involving the Ministries of Skill Development, Labour, Rural Development, and Women and Child Development.
- Goal: To reduce barriers for women, especially related to caregiving responsibilities, and increase their participation in the workforce.
Key Focus Areas:
- Care Economy: Involves both paid and unpaid caregiving services, such as childcare, eldercare, domestic work, and health services.
- The policy aims to formalize care work, addressing its undervaluation and encouraging women's workforce participation.
- Proposes a core skilling package for caregivers, particularly for childcare in rural and informal sectors.
- Childcare Facilities: Targeting women working under schemes like MGNREGS (Mahatma Gandhi National Rural Employment Guarantee Scheme).
Current Challenges:
- Post-marriage employment drop: Women face a significant decline in workforce participation after marriage, often due to caregiving roles.
- In India, 53% of women are outside the labour force, mostly due to unpaid domestic work, unlike only 1.1% of men.
- The gender divide in caregiving is stark: Women spend over 5 hours daily on unpaid domestic work (81% of females), compared to 12.4% of males.
Key Initiatives:
- Palna Scheme: Provides daycare through Anganwadi-cum-Crèche facilities for working parents, benefiting children aged 6 months to 6 years. 1,000 crèches are operational.
- Women’s Employment Data:
- In rural India, 36.6% of women participate in the workforce, compared to 23.8% in urban areas.
- Post-marriage, female employment drops by 12 percentage points, even without children.
- Improving Female Labour Force Participation (FLFP): Key to India's growth, as matching women’s workforce participation with men could boost GDP by 27% (IMF).
Barriers to Women’s Workforce Inclusion:
- Unpaid Care Work: Women's disproportionate share of household duties limits paid employment opportunities.
- Cultural Norms: Gender expectations restrict women’s access to employment, especially in rural areas.
- Educational Barriers: Limited access to education for girls restricts skill development, lowering job prospects.
- Health & Safety Issues: Health challenges and safety concerns at workplaces hinder women's workforce participation.
- Lack of Supportive Policies: Absence of parental leave and flexible work arrangements for women, especially in the informal sector.
Government Initiatives for Women’s Employment:
- BetiBachaoBetiPadhao: Promotes girl child education and empowerment.
- National Education Policy (NEP): Ensures gender equity in education.
- Maternity Benefit (Amendment) Act, 2017: Extends paid maternity leave to 26 weeks and mandates crèche facilities in large establishments.
- Labour Codes (2019-2020): Codifies labor laws to provide a framework for improving women’s workplace safety and employment opportunities.
Global Examples & Inspiration:
- Japan’s Womenomics: Aimed at increasing female participation, Japan's womenomics reforms have grown women’s labour force participation from 64.9% to 75.2% (2013-2023).
- Flexible Work Models: Countries like Netherlands encourage part-time and remote work, offering flexibility to manage work-life balance.
- Sweden’s Investment in ECCE: Investing 1% of GDP in Early Childhood Care and Education (ECCE) has significantly reduced women’s workforce exclusion.
Way Forward:
- National Women’s Urban Employment Guarantee Act (WUEGA): Promotes gender-balanced work environments and childcare facilities at work sites.
- Flexible Work Options: Encouraging remote work, parental leave, and childcare support will empower more women to balance caregiving and employment.
- Investment in the Care Economy: To reduce the care burden on women, substantial investment in ECCE and related sectors is essential to increase women’s participation and economic independence.
Shahi Jama Masjid in Sambhal

- 01 Dec 2024
In News:
The controversy surrounding the Shahi Jama Masjid in Sambhal, Uttar Pradesh, has intensified following claims that the mosque, built during the Mughal Emperor Babur's reign (1526–1530), was constructed over a Hindu temple, the Hari Har Mandir. This claim has led to legal battles and violent clashes, making it part of a broader series of disputes involving mosques built during the Mughal era, such as the Gyanvapi mosque in Varanasi and the Eidgah Masjid in Mathura.
Background and Legal Context:
The dispute began when a petition was filed in Sambhal's district court on November 19, 2024, claiming the Jama Masjid was built on the site of an ancient temple. The petitioners, led by Hari Shanker Jain, demanded a survey to ascertain the religious character of the site. This petition follows a pattern seen in similar cases in Varanasi, Mathura, and Dhar, where Hindu groups have raised similar claims about mosque sites. The court ordered a photographic and videographic survey of the mosque, which, initially carried out peacefully, later sparked violence on November 24 when the survey was accompanied by chanting crowds. This led to protests, stone pelting, and allegations of police firing, resulting in several deaths.
The Jama Masjid is a protected monument under the Ancient Monuments Preservation Act, 1904, and is listed as a Monument of National Importance by the Archaeological Survey of India (ASI). This gives the case legal and cultural sensitivity, as it involves both national heritage and religious sentiments.
Historical and Architectural Context:
The Shahi Jama Masjid in Sambhal was constructed by Mir Hindu Beg, a general under Babur, in the early 16th century. It is one of three mosques commissioned by Babur, alongside those in Panipat and Ayodhya. The mosque is noted for its architectural style, which includes a large square mihrab hall, a dome, and arches, constructed using stone masonry and plaster. Some historians argue that the mosque might be a Tughlaq-era structure modified during Babur's reign. Locally, Hindu tradition holds that the mosque incorporates elements of a Vishnu temple, believed to be the site of Kalki, the tenth avatar of Vishnu.
The Places of Worship Act, 1991:
The dispute has reignited debates about the Places of Worship (Special Provisions) Act, 1991, which mandates that the religious character of any place of worship as it existed on August 15, 1947, should be maintained, with the exception of the ongoing Babri Masjid dispute. The Act aims to prevent any further contests regarding religious sites, and Section 3 of the Act explicitly prohibits converting a place of worship into a site of a different religious denomination.
The petition filed in Sambhal seeks to alter the religious character of the mosque, directly contravening the Places of Worship Act. The petitioners have cited remarks by Supreme Court Justice D.Y. Chandrachud in 2022, suggesting that a survey to ascertain the religious character of a place might not violate the Act. This has led to petitions challenging the Act in the Supreme Court, including cases from Varanasi, Mathura, Dhar, and now Sambhal.
The Legal and Social Implications:
The ongoing dispute over the Shahi Jama Masjid highlights the tension between historical narratives, legal frameworks, and communal harmony. The Supreme Court has intervened in the matter, temporarily halting further proceedings in the trial court, urging that the mosque's management committee approach the Allahabad High Court. The Court emphasized the importance of maintaining peace and harmony and cautioned against any actions that could escalate tensions.
The case underscores the challenges of balancing India's rich historical heritage with its diverse religious communities. As the legal process unfolds, the outcome of the Sambhal dispute could set significant precedents for how similar cases are handled in the future.
Conclusion:
The Sambhal mosque dispute, much like the Gyanvapi and Ayodhya cases, brings to the forefront the complex intersections of history, religion, and law. It also raises critical questions about the application of the Places of Worship Act and its implications for preserving India's pluralistic society. The outcome of this case, alongside the pending petitions in other states, will be crucial in shaping the future of religious site disputes in India.
India-Cambodia Joint Military Exercise CINBAX

- 01 Dec 2024
In News:
The first edition of CINBAX (Counter-Terrorism Counter-Bio-Terrorism and Intelligence Operations Exercise) was launched on December 1, 2024, at the Foreign Training Node, Pune.
Key Details:
- Participants: 20 personnel from each side – the Indian Army and the Cambodian Army – focusing on enhancing cooperation for UN peacekeeping operations.
- Objective:
- Enhancing Trust and Interoperability: CINBAX aims to foster mutual trust, build camaraderie, and improve operational efficiency between the two armies in conducting peacekeeping operations under UN guidelines.
- Focus Areas: Joint Counter-Terrorism (CT) operations, Intelligence, Surveillance, and Reconnaissance (ISR), cyber warfare, logistics, casualty management, and disaster relief operations.
- Phases of the Exercise:
- Phase I: Orientation for Counter-Terrorism operations in the context of UN peacekeeping missions.
- Phase II: Conduct of tabletop exercises to simulate and plan response scenarios.
- Phase III: Finalization of plans and review of lessons learned, focusing on operational strategies and tactical decision-making.
- Key Topics Covered:
- Discussions on setting up a Joint Training Task Force for intelligence, surveillance, and reconnaissance.
- Exploring cyber warfare, hybrid warfare, and unconventional tactics.
- Strategies for managing logistics, casualties, and coordination during Humanitarian Assistance and Disaster Relief (HADR) operations.
- Promotion of Indigenous Defence Equipment:
- The exercise will showcase Indian-made weapons and defence equipment, supporting India’s commitment to Atmanirbhar Bharat (self-reliance in defence production).
- Objective: To highlight India's advanced military technology and indigenous defence capabilities.
- Significance for India-Cambodia Relations:
- The exercise strengthens military ties between India and Cambodia, contributing to improved cooperation in regional peacekeeping efforts.
- CINBAX marks a significant milestone in India-Cambodiadefence collaboration and sets the stage for future joint operations.
India-Cambodia Bilateral Relations
- Historical Context:
- India and Cambodia share strong religious, cultural, and linguistic ties, with Hindu rituals influencing Cambodian culture and Sanskrit and Khmer sharing common words.
- Diplomatic relations were established in 1952, even before Cambodia's independence from France.
- Key Developments:
- 1954: Prime Minister Jawaharlal Nehru visited Cambodia, initiating strong diplomatic ties, particularly during the Non-Aligned Movement.
- Post-1970s: India played a pivotal role in Cambodia's recovery from the Khmer Rouge regime. India was the first democratic country to recognize the Heng Samrin regime in 1981 and contributed to Cambodia's political reconciliation.
- 1980s: India facilitated dialogue for the Paris Peace Accord and contributed to the success of UNTAC elections in 1993.
- Strategic and Economic Cooperation:
- Defence: Enhanced cooperation in defence capacity building, military training, and infrastructure development.
- Trade: India exports pharmaceuticals, bovine meat, automobiles, and leather products to Cambodia. In return, Cambodia exports organic chemicals, apparel, and footwear to India.
- Mekong-Ganga Cooperation (MGC): Established in 2000, MGC includes Cambodia and aims to enhance cooperation in sectors like trade, education, tourism, and cultural exchanges.
- Recent Collaboration:
- India has extended financial assistance for infrastructure projects in Cambodia, especially in restoring and conserving cultural heritage sites like Angkor Wat.
- MoUs signed in bilateral cooperation, cultural exchanges, and development projects highlight the growing India-Cambodia strategic partnership.
Key Highlights on India’s Horticulture and Plant Health Management Initiatives

- 01 Dec 2024
In News:
Government of India and ADB sign $98 million loan to promote plant health management in India’s horticulture.
Key Highlights:
$98 Million Loan Agreement with ADB:
- India and the Asian Development Bank (ADB) signed a $98 million loan to enhance horticulture productivity and resilience.
- Objective: Improve farmers' access to certified, disease-free planting materials, which will increase crop yield, quality, and climate resilience.
- Focus Areas: The project aligns with India’s Atmanirbhar Clean Plant Programme (CPP), aiming to strengthen plant health management in horticulture.
Atmanirbhar Clean Plant Programme (CPP):
- Implemented under MIDH: The Clean Plant Programme is part of the Mission for Integrated Development of Horticulture (MIDH).
- Goal: To provide virus-free, high-quality planting materials to farmers, boosting horticultural crop yields and promoting climate-resilient varieties.
- Implementation Period: 2024-2030, with 50% financial support from ADB.
- Key Components:
- Establishment of 9 Clean Plant Centers (CPCs) with state-of-the-art diagnostic, therapeutic, and tissue culture laboratories.
- Certification Framework: Developing a regulatory framework under the Seeds Act 1966 to certify clean plants.
- Support to Nurseries: Infrastructure development for large-scale nurseries.
- Significance: The programme strengthens India's self-reliance in horticulture and enhances adaptability to climate change impacts.
Mission for Integrated Development of Horticulture (MIDH):
- Nodal Ministry: Ministry of Agriculture and Farmers Welfare.
- Focus: Holistic development of the horticulture sector, including fruits, vegetables, mushrooms, spices, and more.
- Funding Pattern:
- General States: 60% by Government of India (GoI), 40% by State Governments.
- North-Eastern and Himalayan States: 90% by GoI.
Horticulture Sector at a Glance:
- Contribution to Agricultural GDP: Accounts for 33% of the gross value.
- Land Coverage: Occupies 18% of agricultural land in India.
- Global Standing: India is the second-largest producer of fruits and vegetables globally.
- Surpassing Food Grains: Horticulture production exceeds food grain production, occupying much less land (25.66 million hectares vs. 127.6 million hectares for food grains).
Key Benefits of the CPP:
- Climate Resilience: Promotes climate-resilient plant varieties and helps farmers adapt to climate change.
- Innovation: Encourages the use of advanced testing techniques and builds institutional capacity.
- Long-term Impact: Expected to improve sustainability, productivity, and the economic well-being of farmers.
Additional Horticulture Initiatives:
- CHAMAN (Horticulture Assessment using Geo-informatics): A programme to estimate area and production of horticultural crops using scientific methods.
- Kisan Rail Services: Facilitates transportation of perishable horticultural products like fruits and vegetables.
- Capital Investment Subsidy Scheme: By the National Horticulture Board to support the sector’s growth.
Grievance Redressal Assessment and Index (GRAI) 2023
- 01 Dec 2024
In News:
- It was launched by Dr. Jitendra Singh, the Union Minister of State for Science & Technology, Earth Sciences, PMO, Personnel, Public Grievances, Pensions, Atomic Energy, and Space, along with Shri V. Srinivas, the Secretary of the Department of Administrative Reforms and Public Grievances (DARPG).
- This initiative, conceptualized by DARPG, aims to evaluate and rank central Ministries and Departments based on their grievance redressal mechanisms.
Key Aspects of GRAI 2023:
- Objective: GRAI 2023 was designed to provide a comparative assessment of Ministries and Departments based on their grievance redressal systems. It was created based on recommendations from the Parliamentary Standing Committee of the Ministry of Personnel, Public Grievances, and Pensions.
- Assessment Method: The index evaluates 89 Central Ministries and Departments across four dimensions:efficiency, feedback, domain&organisational Commitment
- It is calculated using data from the Centralised Public Grievance Redressal and Management System (CPGRAMS) from January to December 2023. Ministries are grouped into three categories based on the number of grievances received in 2023:
- Group A: Ministries/Departments with more than 10,000 grievances (28 Ministries/Departments)
- Group B: Ministries/Departments with 2,000 to 9,999 grievances (33 Ministries/Departments)
- Group C: Ministries/Departments with fewer than 2,000 grievances (28 Ministries/Departments)
- Top Performers:
- Group A: The Department of Agriculture and Farmers Welfare topped the rankings.
- Group B: The Office of the Comptroller & Auditor General of India led.
- Group C: The Department of Investment & Public Asset Management ranked first.
- It is calculated using data from the Centralised Public Grievance Redressal and Management System (CPGRAMS) from January to December 2023. Ministries are grouped into three categories based on the number of grievances received in 2023:
- Analysis: GRAI 2023 includes an in-depth analysis of the root causes of effective grievance redressal for each Ministry/Department, presented in a color-coded, easily understandable format.
- Advancements: The report outlines a roadmap for improving grievance redressal, emphasizing:
- Utilization of advanced technologies such as AI and Machine Learning (ML) for predictive analytics and data analysis.
- The introduction of features like IGMS 2.0 and TreeDashboard within CPGRAMS.
- Improved training for Grievance Redressal Officers (GROs) and more rigorous audits to increase accountability.
- Expansion of CPGRAMS integration to local governments, enhancing the grievance redressal system across all levels of governance.
Commonwealth Secretariat recognized CPGRAMS as a best practice in grievance redressal at its meeting in April 2024.
SASCI Scheme for Tourism Development
- 01 Dec 2024
In News:
Centre clears scheme for development of 40 tourist destinations across 23 States at a cost of ?3,295 crore.
Key Details:
- Focus Areas: The scheme encourages the development of lesser-known destinations such as Bateshwar (Uttar Pradesh), Ponda (Goa), Gandikota (Andhra Pradesh), and Porbandar (Gujarat) to reduce overcrowding at popular sites.
- Implementation Timeline: Projects must be completed within two years, with funding released in stages until March 2026.
- Key Features:
- Long-term interest-free loans for 50 years.
- States responsible for project execution and maintenance, often through public-private partnerships (PPP).
- The Ministry of Tourism will monitor progress, and 66% of the funds have already been released.
- Emphasis on sustainability and boosting local economies by creating jobs through tourism.
- States must provide land at no cost and ensure proper infrastructure like safety, connectivity, and utilities.
Selection Criteria for Projects:
- Consultation Process: Detailed regional consultations led to the selection of 40 projects from 87 proposals received by the Ministry of Tourism. West Bengal was the only state not submitting proposals.
- Evaluation Criteria: Projects were evaluated based on:
- Connectivity, tourism potential, and ecosystem.
- Financial viability and sustainability.
- Impact on local economy and job creation.
- Funding Pattern:
- A maximum of ?100 crore for each project, with higher funding considered for exceptional projects.
- Total funding capped at ?250 crore per state, allocated on a first-come, first-served basis.
Importance of the Scheme:
- Economic Growth & Employment: Projects are designed to stimulate local economies, create employment, and promote sustainable tourism.
- Global Branding: The scheme aims to brand and market tourist destinations on a global scale.
- Tourism Infrastructure Growth: It aims to improve the entire tourism value chain, including transportation, accommodation, activities, and services.
Tourism Sector Overview:
- Current Status:
- India ranks 39th among 119 countries in the Travel and Tourism Development Index (TTDI) 2024.
- Foreign Tourist Arrivals (FTAs) increased by 47.9% in 2023, with 9.52 million tourists.
- Tourism contributed 5% to India’s GDP in 2022-23 and created 76.17 million direct and indirect jobs.
- India earned ?2.3 lakh crore in foreign exchange in 2023 through tourism.
- Projected revenue from tourism to exceed $59 billion by 2028.
- Initiatives for Promotion:
- Swadesh Darshan Scheme: To develop theme-based circuits.
- Dekho Apna Desh Initiative (2020): Promotes domestic tourism.
- PRASHAD & HRIDAY Schemes: Focus on pilgrimage and heritage city development.
MGNREGA Job Card Deletions Issue:
- Context: A significant surge in deletions of job cards under MGNREGA (Mahatma Gandhi National Rural Employment Guarantee Act) raised concerns over transparency and workers’ rights.
- Reasons for Deletion:
- Permanent migration, duplicate cards, forged documents, and refusal to work.
- Aadhaar-based payment system (ABPS) implementation led to deletions for non-linked cards.
- Implications:
- Violation of workers’ legal right to employment, especially when deletions were made without due process.
- The "Not willing to work" designation undermines livelihood opportunities, especially in high unemployment rural areas.
- Recommendations for Reform:
- Strengthening verification processes and ensuring deletions follow due procedure.
- Empowering Gram Sabhas to review and approve deletions.
- Regular audits and better grievance redressal mechanisms.
Other Government Initiatives in Tourism:
- National Mission on Pilgrimage Rejuvenation and Spiritual, Heritage Augmentation Drive (PRASHAD): For holistic and sustainable development of pilgrimage tourism.
- Incredible India & E-Visa Initiatives: To attract more foreign tourists.
- Regional Connectivity Scheme (UDAN): Enhances air connectivity to remote tourist destinations.
- National Heritage City Development and Augmentation Yojana (HRIDAY): Preserves and rejuvenates heritage sites.
13th National Seed Congress (NSC)

- 30 Nov 2024
In News:
- The 13th National Seed Congress (NSC), organized by the Ministry of Agriculture & Farmers' Welfare, concluded with significant discussions and outcomes focused on advancing India's seed sector.
- The theme for this year's congress, held in Varanasi, was "Innovating for a Sustainable Seed Ecosystem."
Key Highlights:
- Focus Areas:
- Seed Technologies and Biofortification: Emphasis on high-nutrition seeds like iron and zinc-enriched rice and Vitamin A-rich crops to combat malnutrition.
- Climate-Resilient Agriculture: Promoting practices like Direct Seeded Rice (DSR) and the development of stress-tolerant seed varieties to withstand climate change.
- Challenges in India’s Seed Ecosystem:
- Seed Replacement Rate (SRR): SRR in India is around 15-20%, with 100% for hybrid seeds, pointing to the need for higher adoption of certified seeds.
- Monoculture and Seed Market Monopoly: Issues like over-reliance on Bt cotton and domination by multinational companies (e.g., Bayer) in seed markets.
- Government Initiatives:
- National Seed Corporation (NSC): Produces foundation and certified seeds for over 600 varieties.
- Seed Village Programme (Beej Gram Yojana): Focus on improving the quality of farm-saved seeds.
- National Seed Reserve: Ensures seed availability during climatic disruptions.
- Policy Discussions:
- Proposed Seeds Bill: A new bill to regulate seed quality and promote sustainable practices.
- Public-Private Partnerships: Strengthening collaborations to improve seed production, accessibility, and quality.
- Outcomes:
- Biofortified Seeds: Increased development and distribution of nutrient-rich seeds.
- Climate-Resilient Seed Systems: Enhanced focus on developing crops that can withstand climate challenges.
- Public-Private Partnerships: Strengthening collaborations in seed technology and policy reform.
U.N. Peacebuilding Commission

- 30 Nov 2024
In News:
India has been re-elected to the United Nations Peacebuilding Commission (PBC) for the term 2025–2026, continuing its strong commitment to global peace and stability.
UN Peacebuilding Commission (PBC)
It is an advisory body established by the UN General Assembly and UN Security Council in 2005. It is tasked with supporting peace efforts in conflict-affected countries by advising and recommending strategies for post-conflict recovery and long-term peacebuilding.
Composition of PBC:
- The PBC is composed of 31 member states, elected from the General Assembly, Security Council, and Economic and Social Council.
- It includes key financial and troop-contributing countries, which play a central role in shaping global peacebuilding initiatives.
Key Mandates of the PBC
- Coordination of Resources and Strategies:The Commission brings together all relevant actors to propose integrated strategies for post-conflict recovery and peacebuilding.
- Reconstruction and Development:It focuses on rebuilding conflict-affected countries through institution-building and supporting sustainable development efforts.
- Improving Coordination:The PBC ensures better coordination within and outside the UN, develops best practices, and secures predictable financing for early recovery initiatives.
- Sustaining Peace:The Commission promotes sustained international attention to peacebuilding efforts and offers political support to countries emerging from conflict, with their consent.
- Integrated Approach:The PBC advocates for an integrated approach that links security, development, and human rights as interrelated and mutually reinforcing.
- Bridging Role:It serves as a platform to connect UN bodies, Member States, national authorities, civil society, and other stakeholders, sharing good practices in peacebuilding.
India’s Contributions to UN Peacebuilding and Peacekeeping
India has been at the forefront of UN peacebuilding initiatives due to its long-standing commitment to international peace and stability.
- Largest Contributor of Personnel:India is one of the largest contributors of uniformed personnel to UN Peacekeeping. Currently, around 6,000 Indian military and police personnel are deployed across multiple missions in Abyei, Central African Republic, Cyprus, Democratic Republic of Congo, Lebanon, Middle East, Somalia, South Sudan, and Western Sahara.
- Sacrifices in Service:India holds the tragic distinction of having lost over 180 peacekeepers, the highest number from any troop-contributing nation. These sacrifices reflect India's enduring commitment to global peace.
- Financial Support:India contributes to the Peacebuilding Fund, the primary financial instrument for conflict prevention and peacebuilding, which supports countries transitioning from conflict to peace.
- Championing South-South Cooperation:India has actively promoted South-South cooperation, a model for post-conflict recovery that emphasizes shared learning and capacity-building among developing nations.
- Women in UN Peacekeeping:India has led efforts for gender parity in UN peacekeeping. In 2007, India became the first country to deploy an all-women contingent to a UN peacekeeping mission. It has since deployed Female Engagement Teams (FETs) and Female Formed Police Units (FFPUs) in Lebanon and the Democratic Republic of Congo.
- Training and Capacity Building:India has invested in capacity development for both the UN and host nations. The Centre for UN Peacekeeping (CUNPK) in New Delhi, established by the Indian Army, trains over 12,000 troops annually in peacekeeping operations. India also deploys Mobile Training Teams to share best practices with other countries.
India’s Pledges at the UN Peacekeeping Ministerial (2023)
At the UN Peacekeeping Ministerial held in Accra, Ghana (December 2023), India made significant pledges:
- To contribute an Infantry Battalion Group, along with various sub-groups and pre-deployment training courses, for the next two years.
- India’s ongoing commitment to strengthening peacekeeping efforts and supporting the UN’s peacebuilding agenda was reaffirmed.
Global Engagement Scheme
- 30 Nov 2024
In News:
- The Ministry of Culture plays a pivotal role in promoting India’s rich cultural heritage across the globe through its Global Engagement Scheme.
- The scheme is designed to enhance India's cultural image internationally while fostering people-to-people connections and strengthening bilateral cultural ties with other nations.
- The scheme has three key components: Festival of India, Grant-in-aid to Indo-Foreign Friendship Cultural Societies, and Contribution Grants.
Key Components of the Global Engagement Scheme:
- Festival of India (FoI):
- Purpose: The Festival of India is organized abroad to celebrate and promote India's diverse culture. It provides a platform for artists from various cultural fields, including Folk Art (folk music, dance, theatre, puppetry), Classical and Traditional Dance, Classical and Semi-Classical Music, Experimental/Contemporary Dance, and Theatre.
- Impact: Since 2013-14, 62 Festivals of India have been held in different countries, with over 2,348 artists, including folk artists, participating. These festivals serve as a means to promote Indian folk art, culture, and music internationally.
- Artist Participation: Folk artists are remunerated with a performance fee of ?35,000 for the leader/main artist and ?7,000 for accompanying artists per performance.
- Grant-in-aid to Indo-Foreign Friendship Cultural Societies:
- Objective: This scheme supports cultural societies abroad that aim to strengthen cultural exchanges and promote Indian art forms. Grants are provided to these societies to organize various cultural programs and activities, fostering closer cultural ties between India and the host countries.
- Support to Folk Artists: This scheme also aids in bringing folk art to the global stage, showcasing India's traditional performances.
- Contribution Grant:
- Objective: The contribution grant is used for India’s membership in international organizations like UNESCO, ICOM, and the World Heritage Fund. This component also facilitates Indian participation in international meetings and helps host global events, further showcasing India’s cultural wealth.
Support for Veteran Artists:
In addition to promoting folk culture globally, the Ministry of Culture supports veteran artists through the Financial Assistance for Veteran Artists scheme. This initiative is aimed at supporting elderly and economically disadvantaged artists (aged 60 and above) who have made significant contributions to their respective art forms, including folk art.
- Financial Support: Artists selected under this scheme receive up to ?6,000 per month, adjusted for any state pension they may already receive.
Regional Contributions:
- The Ministry has empaneled folk artists and groups across India for participation in these international cultural exchanges. For instance, two folk artists/groups and one Kathak artist from Uttarakhand are currently empaneled.
- Notably, a troupe from Uttarakhand participated in the Freedom 70 Cultural Event in Cuba and the Dominican Republic in August 2017, showcasing the diversity of Indian folk art.
- The Financial Assistance for Veteran Artists has also benefitted several artists from Uttarakhand, with four artists from the state receiving support over the past two years.
Mahabodhi Mahotsav at Sanchi

- 30 Nov 2024
In News:
A two-day Mahabodhi Mahotsav is currently being held at the Great Stupa in Sanchi, Madhya Pradesh, a UNESCO World Heritage Site.
Key Highlights:
- The festival will include religious ceremonies and cultural activities centered around the relics of Lord Buddha’s chief disciples, Sariputra and Maudgalyayana.
- Cultural Significance: The Mahotsav serves as a platform for celebrating and reaffirming the cultural and spiritual heritage of the region, with a focus on the teachings of Lord Buddha.
About Sanchi Stupa:
Sanchi Stupa is one of the oldest and most significant monuments of Buddhist architecture in India. It has stood as a symbol of Buddhist history, spirituality, and culture for over two millennia.
- Historical Importance:Commissioned by Emperor Ashoka in the 3rd century BCE, the stupa was later expanded by the Shunga and Satavahana rulers. It stands as a testament to the spread of Buddhism across India and beyond.
- Architectural Features:
- Hemispherical Dome (Anda): The large dome represents the universe, encapsulating the essence of Buddhist cosmology.
- Chatras: The umbrella-like structures on top of the dome symbolize divine protection and royalty.
- Harmika: A small balcony on the dome, which is considered the abode of the gods.
- Medhi: The base of the stupa, which stores sacred relics.
- Toranas: Four intricately carved gateways that depict scenes from the life of Buddha and various Jataka tales. These gateways point to the four cardinal directions, symbolizing the universality of Buddha’s teachings.
- Vedica: The railings surrounding the stupa serve as sacred enclosures.
- Paradakshinapatha: Pathways for circumambulation, allowing devotees to walk around the stupa as a sign of respect.
- Symbolism:The stupa’s architecture is an example of early Buddhist aniconism, where the Buddha is not directly depicted but is represented symbolically through footprints, wheels, or empty thrones.
- Inscriptions:The stupa contains important inscriptions, including the Ashokan Lion Capital and inscriptions in Brahmi and Kharosthi scripts, reflecting the historical significance of the site.
- UNESCO World Heritage Status:In 1989, Sanchi Stupa was declared a UNESCO World Heritage Site, recognizing its exceptional historical and cultural importance as a center for Buddhist art, architecture, and philosophy.
Significance of the Mahabodhi Mahotsav:
The Mahabodhi Mahotsav at Sanchi not only provides a spiritual experience but also highlights the historical and cultural legacy of Buddhism in India. The event brings attention to the preservation and promotion of Buddhist heritage, reflecting India’s rich diversity and commitment to maintaining its ancient traditions. Through this festival, Sanchi continues to be a center of pilgrimage and learning, attracting visitors from around the world who seek to understand and experience the teachings of Lord Buddha.
Flexible UG Degree Completion Norms

- 30 Nov 2024
In News:
- The University Grants Commission (UGC) has approved new guidelines for undergraduate (UG) degree completion, offering flexibility in the duration of academic programs.
Key Details:
- Two Options for Degree Completion:
- Accelerated Degree Programme:Students with exceptional academic performance or those completing additional credits can graduate earlier than the standard duration.
- Extended Degree Programme:Students facing personal, financial, or academic challenges can extend the time for degree completion without facing penalties.
- Objective:
- Enhance flexibility and a student-centric approach to higher education.
- Address challenges like balancing education with personal or professional commitments.
- Institutional Autonomy:Higher Education Institutions (HEIs) can implement these options based on available infrastructure and academic resources.
- Recognition of Flexibility:Degrees completed earlier or later will be treated on par with those completed within the standard duration.
- Alignment with Global Trends:This initiative aligns with global educational trends towards flexible learning paths.
- Support for Interdisciplinary Studies:The new regulations are expected to benefit students pursuing interdisciplinary studies or professional courses.
- NEP 2020 Alignment:The move is in line with the National Education Policy (NEP) 2020, which promotes learner-centric education and skill development.
- Impact:The decision is likely to provide more options for students, making higher education more accessible and tailored to individual needs.
Ngada Festival

- 29 Nov 2024
In News:
The Rengma Naga tribe concluded a two-day celebration of the Ngada festival-cum-Mini Hornbill Festival at the Tseminyu RSA ground in Nagaland.
Ngada Festival Overview:
- Celebration: It is an annual celebration observed by the Rengma Naga tribe, marking the end of the agricultural cycle.
- Duration: Typically, an eight-day festival, it is celebrated towards the end of November.
- Significance: It is a festival of thanksgiving, joy, and cultural unity, with a focus on gratitude for the harvest and remembrance of departed souls.
Cultural and Ritual Aspects:
- Rituals: The festival involves rituals for protection from misfortunes, such as fire and evil spirits, as well as prayers for peace and prosperity in the community.
- Agricultural Link: The festival is celebrated after the harvest season, symbolizing the end of the agricultural cycle and the beginning of the storage of crops.
- Official Announcement: The village priest announces the start of the festival, and preparations begin shortly after.
Importance of Ngada:
- Gratitude for the Harvest: The festival is a celebration of the hard work of the agricultural year and the bountiful harvest.
- Cultural Identity: The festival serves as a vital reminder of the Rengma Naga’s cultural heritage and traditions, helping to preserve them for future generations.
- Symbol of Unity: It fosters cultural unity and strengthens community bonds within the tribe.
Tribal Demographics:
- Population: The Rengma Naga tribe has a population of around 62,951 in Nagaland and 22,000 in Assam (according to the 2011 Census of India).
- Ethnic Identity: The Rengmas belong to the Tibeto-Burman ethnic group and identify themselves as Njong or Injang.
Historical and Cultural Background:
- Migration: It is believed that the Rengmas, along with other Naga tribes, migrated from Southeast Asia, crossing the Yunnan Mountain ranges, and eventually settled in the upper Burma region.
- Slavery: Historically, slavery was practiced among the Rengmas, with slaves known as menugetenyu and it sakesa. However, by the time the British arrived, slavery was in decline, and no Rengma tribespeople were known to be slaves.
Economy:
- Agricultural Lifestyle: The Rengma Naga are primarily agriculturalists, relying on Jhum cultivation (shifting cultivation) and wet rice cultivation.
- Crops Grown: They grow staple crops like paddy, along with seasonal crops and fruits.
Religion:
- Traditional Beliefs: Traditionally, the Rengma Naga worship supernatural beings.
- Christianity: Today, most of the Rengma tribe has converted to Christianity.
Global Wage Report 2024-25

- 29 Nov 2024
In News:
A new report from the International Labour Organization (ILO) reveals that wage inequality has decreased in about two-thirds of all countries since 2000. Despite this positive trend, significant wage differentials persist worldwide.
Global Wage Inequality Trends:
- Wage inequality has decreased in about two-thirds of all countries since 2000.
- Average Annual Decrease in Wage Inequality:
- Ranges from 0.5 to 1.7% globally, depending on the measure used.
- More significant reductions have been observed in low-income countries, where the decrease has ranged from 3.2 to 9.6% over the past two decades.
- Wealthier Countries: Wage inequality has decreased at a slower pace:
- Upper-middle-income countries: annual decrease of 0.3 to 1.3%.
- High-income countries: annual decrease of 0.3 to 0.7%.
Global Real Wage Growth:
- Global real wages grew by 1.8% in 2023, with projections reaching 2.7% growth in 2024 (highest increase in over 15 years).
- This marks a recovery from the negative global wage growth of -0.9% in 2022 due to high inflation rates.
Regional Wage Growth:
- Emerging Economies: Saw stronger wage growth than advanced economies.
- Emerging G20 economies: 1.8% growth in 2022 and 6.0% growth in 2023.
- Advanced Economies: Faced real wage declines.
- G20 advanced economies: Declined by -2.8% in 2022 and -0.5% in 2023.
- Fastest Wage Growth: Observed in regions like Asia-Pacific, Central and Western Asia, and Eastern Europe.
Wage Inequality Persistence:
- Income Distribution: The lowest-paid 10% of workers earn just 0.5% of the global wage bill, while the highest-paid 10% earn nearly 38%.
- Wage Inequality in Low-Income Countries: Particularly high, with nearly 22% of wage workers classified as low-paid.
- Women and Informal Economy Workers: More likely to be among the lowest-paid workers, underscoring the need for targeted actions to close wage and employment gaps.
Non-Wage Workers:
- Globally, one in every three workers is a non-wage worker.
- In low- and middle-income countries, many workers are self-employed in the informal economy, which skews overall income inequality measures.
- Income inequality in these regions is higher when including self-employed workers, especially those in informal employment.
Policy Recommendations:
- Targeted Policies: To reduce wage inequality, countries need stronger wage policies and structural support for equitable growth.
- Focus Areas:
- Promote productivity and decent work.
- Formalization of the informal economy to help reduce income inequality.
- Inclusive Growth: The ILO emphasizes that national strategies should aim for inclusive economic growth to achieve fair wages and reduce wage gaps.
Key ILO recommendations include:
- Setting wages through social dialogue: wages should be set and adjusted through collective bargaining or agreed minimum wage systems involving governments, workers and employers.
- Taking an informed approach: wage-setting should take into account both the needs of workers and their families and economic factors.
- Promoting equality, and equal opportunity of treatment and outcomes: wage policies should support gender equality, equity and non-discrimination.
- Using strong data: decisions should be based on reliable data and statistics.
- Addressing root causes of low pay: national policies should reflect each country’s specific context and address the causes of low pay such as informality, low productivity and the under-valuing of jobs in sectors such as the care economy.
Mission Shukrayaan
- 29 Nov 2024
In News:
ISRO received approval for its first Venus mission, Shukrayaan. The probe will undertake a detailed investigation of Venus, including its surface, atmosphere and geological structure.
Shukrayaan Mission (Venus Orbiter Mission):
- Launch Timeline: Scheduled for 2028.
- Objective: Investigate Venus to gather data on its surface, atmosphere, and geological structure.
- Scientific Focus: Study weather patterns, geological activities, and atmospheric composition (e.g., carbon dioxide and sulfuric acid clouds).
- Instrumentation: Equipped with synthetic aperture radar, infrared, and ultraviolet imaging devices to study Venus’s ionosphere.
- Significance: Offers global coverage of Venus, addressing gaps in previous missions' spatial coverage.
- Cost: Estimated at Rs 1,236 crore.
- Launch Vehicle: ISRO plans to use the LVM-3 (GSLV Mk III) rocket to launch the mission into an elliptical parking orbit (170 km x 36,000 km).
- Mission Data Processing: Data will be archived and disseminated through the Indian Space Science Data Center (ISSDC).
Chandrayaan 4 Mission:
- Collaborative Effort: Joint mission between India (ISRO) and Japan.
- Launch Objective: Land on the moon's south pole, with a focus on the region at 90°S (compared to previous missions at 69.3°S).
- Mission Details:
- Includes a rover weighing 350 kg (12 times heavier than previous rover).
- The rover will be equipped with advanced scientific tools for lunar exploration.
- Government Approval: Awaiting approval, with a target execution date of 2030.
Gaganyaan Mission (Human Spaceflight Program):
- Timeline: Unmanned flight in 2026, followed by a manned mission.
- Indian Space Station: Construction approved; to be completed by 2035, comprising five modules.
- Purpose: To serve as a transit facility for deep space exploration, including future lunar missions.
Mars Exploration Plans:
- Future Missions: Plans to send satellites to Mars and attempt a landing on the Martian surface.
- Significance: Demonstrates India’s growing ambitions in interplanetary exploration.
INSAT-4 Series of Satellites:
- Goal: Launch of new meteorological and oceanographic sensors to improve weather forecasts and disaster management.
- Technological Advancements: Need for India to catch up with global advancements in space-based sensors.
International Collaboration in Space:
- Chandrayaan 4: A collaboration between ISRO and Japan to explore the moon’s south pole, showcasing India's growing international cooperation in space exploration.
Strategic Importance of Shukrayaan:
- Contribution to Science: The mission’s global dataset will provide unique insights into Venus, enhancing the understanding of planetary atmospheres and geological processes.
- Potential for Discoveries: Research on Venus’s ionosphere and possible volcanic activity.
'Bal VivahMukt Bharat' Campaign

- 29 Nov 2024
In News:
- The Union Minister for Women and Child Development launched the “Bal VivahMukt Bharat” campaign aimed at eradicating child marriage in India.
- Goal: Reduce child marriage rates to below 5% by 2029.
- Focus: Engage multiple stakeholders, raise awareness, and leverage technology for eradication.
Target Areas:
- Target States: West Bengal, Bihar, Jharkhand, Rajasthan, Tripura, Assam, Andhra Pradesh.
- High-Burden Districts: Nearly 300 districts with higher rates of child marriage.
Child Marriage Free Bharat Portal:
- A digital platform to raise awareness, report cases, and track progress on child marriage prevention.
- Real-time tracking by Child Marriage Prohibition Officers (CMPOs).
Monitoring and Accountability:
- Central nodal officers and CMPOs will oversee the campaign’s implementation at state and district levels.
- The portal facilitates citizens’ participation by allowing complaints and providing information on legal remedies.
Progress and Impact:
- Child marriage rates have reduced from 47.4% (2005-06) to 23.3% (2019-21).
- The goal is to reduce these rates further to below 5% by 2029.
Awareness and Community Engagement:
- Public campaigns and community mobilization to challenge societal norms and change attitudes towards child marriage.
- The campaign will continue through various channels, including the BetiBachaoBetiPadhao initiative.
Legal Framework:
- Strengthening the Prohibition of Child Marriage Act (PCMA), 2006, which sets the legal marriage age at 18 for women and 21 for men.
- Penalties for those involved in child marriage include imprisonment and fines.
Key Challenges for Child Marriage:
- Poverty: Families may view early marriage as a financial relief.
- Cultural Norms: Deep-rooted societal beliefs about preserving family honor.
- Gender Inequality: Patriarchal systems view girls as burdens.
- Lack of Education: Limited access to schooling forces early marriages.
- Fear of Sexual Assault: Misguided belief that early marriage protects girls.
- Weak Law Enforcement: Corruption and inadequate resources hinder the law’s implementation.
- Pandemic Impact: Economic hardships during COVID-19 led to an increase in child marriages.
Related Initiatives:
- Prohibition of Child Marriage Act (PCMA), 2006: Strengthens child marriage laws and establishes CMPOs.
- Success Stories: Individuals like BuchaRamanamma, Durga, and Roshni Perween have inspired others by stopping their own child marriages and advocating for change.
Campaign and National Vision:
- The campaign aligns with the Prime Minister’s vision for a Viksit Bharat (Developed India) by 2047.
- It aims to empower women and girls, providing them with opportunities for education, health, and safety.
- Collective effort from the government, social organizations, and citizens is crucial to eliminating child marriage.
Eklavya Digital Platform
- 29 Nov 2024
In News:
- The Indian Army launched the “Eklavya” online learning platformnmunder the leadership of General Upendra Dwivedi, Chief of the Army Staff (COAS).
- It is part of the Army’s “Decade of Transformation” initiative and aligns with the theme for 2024, “Year of Technology Absorption.”
Platform Development:
- Developed by the Army Training Command (ATC) and sponsored by the Army War College.
- Created at zero cost in collaboration with the Bhaskaracharya National Institute of Space Applications and Geoinformatics (BISAG-N), Gandhinagar.
- Hosted on the Army Data Network with scalable architecture to integrate various training establishments.
Key Features:
- Supports multiple courses from 17Category ‘A’ Training Establishments of the Army.
- Allows student officers to register for several courses simultaneously.
- Aims to decongest physical courses and integrate contemporary, application-focused content.
Categories of Courses:
- Pre-Course Preparatory Capsules: Online study material for physical courses, allowing focus on contemporary topics during offline training.
- Appointment-Specific Courses: Online courses for officers appointed to specialized roles (e.g., information warfare, financial planning, etc.), helping them gain domain-specific expertise before posting.
- Professional Development Suite: Includes courses on strategy, leadership, operational art, finance, emerging technologies, etc., focusing on holistic officer development.
Knowledge Highway:
- A searchable database featuring journals, research papers, and articles to support continuous professional education and development.
Impact:
- Promotes continuous professional military education.
- Enhances the efficiency and specialization of officers, particularly in emerging domains.
- Streamlines training processes and integrates modern technology in the Army’s educational system.
Supreme Court Ruling on EVMs

- 28 Nov 2024
In News:
The Supreme Court dismissed the PIL, remarking that EVMs are only questioned after electoral losses, not when elections are won. It emphasized that no evidence of tampering was found.
What Are EVMs and VVPATs?:
- EVMs: Electronic Voting Machines are used for conducting elections to the Parliament, state legislatures, and local bodies. They consist of two units: theControl Unit (operated by the polling officer) and the Ballot Unit (where voters cast their votes).
- VVPAT: The Voter Verifiable Paper Audit Trail enables voters to verify that their vote is recorded as cast. A slip is printed showing the candidate’s name, symbol, and serial number, visible for 7 seconds before being cut and stored in a sealed box.
Safeguards to Ensure EVM Integrity:
- Technical Safeguards:
- Microcontroller Security: EVMs use one-time programmable (OTP) microcontrollers, which cannot be altered after manufacturing.
- Standalone Operation: EVMs do not have wired or wireless connectivity, eliminating risks of remote tampering.
- Post-2013 Features: Advanced EVMs (M3) include tamper detection and mutual authentication protocols.
- Administrative Protocols:
- Randomized EVM Allocation: EVMs are randomly allocated to polling stations to avoid predetermined assignments.
- Mock Polls: Multiple mock polls are conducted to test the functionality of EVMs.
- Counting Procedures: EVMs are brought to counting tables under CCTV surveillance, and VVPAT slips are randomly cross-verified.
- Secure Storage: EVMs are stored under strict protocols, including double-lock systems, CCTV surveillance, and GPS-tracked transport.
Advantages of EVMs Over Ballot Papers:
- Elimination of Invalid Votes: EVMs ensure no invalid votes, a common problem with torn or mis-marked ballot papers.
- Prevention of Booth Capturing: EVMs restrict vote casting to 4 votes per minute, preventing fraudulent vote insertion.
- Accurate and Fast Counting: EVMs enable quick, error-free vote counting, reducing delays and human errors.
- Transparency: Voters can verify their votes through the VVPAT, and the vote count is displayed transparently without revealing candidate-wise results prematurely.
Evolution of EVMs in India:
- 1977: Concept of EVMs conceived.
- 1990: The Dinesh Goswami Committee recommended the use of EVMs.
- 2004: EVMs used nationwide in Lok Sabha elections.
- 2013: VVPAT was introduced to improve transparency.
- 2019: First nationwide use of EVMs backed by VVPAT.
India's Gig Economy
- 28 Nov 2024
In News:
The gig economy market is expected to grow at a compounded annual growth rate (CAGR) of 17 per cent to reach a gross volume of $455 billion by 2024, according to a white paper by the Forum for Progressive Gig Workers.
Key Sectors Supported by Gig Workers:
- E-commerce: Gig workers play a crucial role in driving growth in the e-commerce sector.
- Transportation and Delivery Services: These sectors are heavily dependent on gig workers for their operations and services.
Impact on Employment:
- Job Creation: The gig economy has the potential to create a significant number of jobs, especially in tier 2 and 3 cities, which are emerging as new growth hubs.
- Alternate Revenue Streams: Gig work provides diverse income opportunities for workers, especially for women, offering them a flexible mode of earning.
Contribution to GDP:
- The gig economy’s contribution is expected to add 1.25% to India’s GDP over time, highlighting its growing economic importance.
Technological Integration and Future Prospects:
- AI and Digital Innovation: Future growth is expected to be driven by the integration of artificial intelligence (AI), predictive analytics, and digital innovation, fostering sustainable and inclusive job opportunities.
Social and Economic Benefits:
- Women's Workforce Participation: The gig economy provides women with more earning opportunities and helps integrate them into the workforce.
- Welfare Initiatives: Platforms supporting gig workers are increasingly focusing on welfare initiatives, improving the overall working conditions in the sector.
Challenges and Opportunities:
- Challenges: The evolving dynamics between large companies and gig workers pose challenges in terms of worker rights and fair compensation.
- Opportunities: The growth of the gig economy presents opportunities for companies to innovate and create inclusive work environments, especially for underserved communities.
Future Developments:
- Formal Report: The Forum for Progressive Gig Workers plans to collaborate with global organizations to release a formal report with deeper insights and actionable recommendations for the future of gig work
Global Matchmaking Platform (GMP)
- 28 Nov 2024
In News:
- GMP was launched at COP29, on Energy Day, by the United Nations Industrial Development Organization (UNIDO) and the Climate Club.
- Aimed at accelerating industrial decarbonisation in heavy-emitting industries of emerging and developing economies (EMDEs).
- The platform addresses the annual funding gap of US$125 billion required to achieve net-zero emissions goals.
Key Highlights:
Support Mechanism:
- GMP operates as a support mechanism for the Climate Club, with the secretariat hosted by UNIDO.
- Activities are supported by the interim secretariat of the OECD and the International Energy Agency (IEA).
Key Objectives:
- Match country-specific decarbonisation needs with global technical and financial resources.
- Facilitate the decarbonisation of energy and emissions-intensive industrial sectors, such as steel, cement, chemicals, and aluminium.
- Offer assistance in policy development, technology transfer, and investment facilitation to promote low-carbon industrial practices.
Global Participation:
- Countries like Germany, Chile, Uruguay, Turkey, Bangladesh, and Indonesia are actively involved.
- Non-state actors include UNIDO, World Bank, Climate Investment Funds (CIF), and GIZ, supporting the platform’s initiatives.
Funding Gap:
- Industrial decarbonisation requires an increase in investments from US$15 billion (current) to US$70 billion by 2030, and US$125 billion by 2050, especially for sectors like steel and cement.
Climate Club Work Programme (2025-26):
- The GMP is part of the Climate Club's new work programme for 2025-26, focusing on:
- Advancing ambitious climate change mitigation policies.
- Transforming industries through decarbonisation.
- Boosting international climate cooperation.
Industrial Decarbonisation:
- Decarbonisation refers to reducing carbon dioxide (CO2) and greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions from industrial activities.
- Key sectors for decarbonisation include petroleum refining, chemical manufacturing, iron and steel, cement production, and the food and beverage sector.
Support for EMDEs:
- The platform focuses on helping emerging and developing economies overcome challenges such as lack of resources, technology, and capacity to adopt cleaner industrial methods.
- Climate finance is crucial to pilot and scale low-carbon technologies in these regions.
Future Role of GMP:
- The GMP will play a critical role in incorporating industrial decarbonisation into countries’ Nationally Determined Contributions (NDCs) for COP30.
- The platform aims to accelerate progress by connecting developing countries with finance, technology, and expertise to transition to low-emission industries.
E-Daakhil Portal
- 28 Nov 2024
In News:
- The E-Daakhil portal was launched by the Department of Consumer Affairs to promote consumer rights and ensure timely justice.
- The portal was launched nationwide with its final rollout in Ladakh on 22nd November 2024, making it operational across all states and union territories of India.
Background and Purpose:
- Introduced in September 2020, the portal was developed in response to the Consumer Protection Act 2019, which aims to address emerging consumer concerns.
- Aimed at providing a hassle-free, inexpensive, and speedy mechanism for filing consumer complaints, especially post the COVID-19 pandemic.
- E-Daakhil is an online platform that simplifies the grievance redressal process, allowing consumers to file complaints remotely, without the need for physical presence.
Portal Features:
- User-friendly interface: Simple and intuitive, allowing consumers to file and track complaints online.
- Registration process: Users can register through OTP on their mobile or an activation link via email.
- Paperless and transparent: The entire process, from filing complaints to tracking the case status, is digital and transparent.
- Consumers can file complaints, pay fees, and monitor the progress of their cases from the comfort of their homes.
Success and Impact:
- By the end of 2023, E-Daakhil was available in 35 states and union territories; with Ladakh being the latest addition in November 2024.
- Over 2.81 lakh users have registered, and 1.98 lakh cases have been filed, of which 38,453 cases have been disposed of.
Future Developments:
- E-Jagriti: A new initiative that will further streamline the case filing, tracking, and management process, reducing delays and paperwork.
- E-Jagriti aims to improve communication between parties, ensuring faster dispute resolution.
BioE3 Policy

- 28 Nov 2024
In News:
The BioE3 Policy outlines guidelines and principles for enabling mechanisms for ‘Fostering High Performance Biomanufacturing’ in the country across diverse sectors.
Key Highlights:
Primary Objective:
- Set a framework for the adoption of advanced technologies and innovative research to promote biomanufacturing in India.
- Focus on enhancing efficiency, sustainability, and quality in biomanufacturing.
Alignment with National Goals:
- Supports India’s vision of Green Growth (Union Budget 2023-24) and Lifestyle for Environment (LiFE), promoting sustainability.
- Aligns with India’s goal of achieving a Net-Zero carbon economy.
- Supports the Biomanufacturing and Biofoundry initiative announced in the Interim Budget 2024-25.
Key Objectives:
- Revolutionize biomanufacturing for better product quality and environmental sustainability.
- Accelerate the development and commercialization of bio-based, high-value products.
- Foster high-performance biomanufacturing across diverse sectors.
Achievements of Indian Bioeconomy (2014-2023):
- Contribution to GDP: Bioeconomy contributes 4.25% to India’s GDP of $3.55 trillion (as of Dec 2023).
- Growth of Bioeconomy: From $10 billion in 2014 to $151 billion in 2023, surpassing 2025 target.
- Increase in Biotech Startups: From 50 startups in 2014 to 8,531 startups in 2023.
Implementation Strategy:
- Establish BioEnablers including Bio-AI Intelligence Hubs, Biofoundries, and Biomanufacturing Hubs across India.
- Bio-AI Intelligence Hubs will support research and innovation using data-driven approaches and AI to develop technologies for bio-based products.
- Biofoundries and Biomanufacturing Hubs will provide infrastructure to scale up bio-based technology for commercial applications.
Focus on Human Resource Development:
- Bio-Enablers will offer training and internships to build a skilled workforce with interdisciplinary and technical skills required for biomanufacturing.
Sectoral Focus Areas:
- Based on consultations, six thematic sectors of national importance have been identified for implementation:
- Bio-based chemicals and enzymes
- Functional foods and smart proteins
- Precision biotherapeutics
- Climate-resilient agriculture
- Carbon capture and utilization
- Futuristic marine and space research
- Sectoral Expert Committees are addressing challenges and gaps identified for each of these sectors.
Government Support:
- The DBT-BIRAC (Department of Biotechnology and Biotechnology Industry Research Assistance Council) has called for proposals to establish Biofoundries and Biomanufacturing Hubs in academia and industry.
- These hubs will support innovation and commercialization of biomanufacturing technologies.
National Mission on Natural Farming (NMNF)
- 27 Nov 2024
In News:
The Union Cabinet approved the launching of the National Mission on Natural Farming (NMNF) as a standalone Centrally Sponsored Scheme under the Ministry of Agriculture & Farmers' Welfare.
Key Highlights
Objective & Focus:
- Launch of NMNF by the Union Cabinet to promote chemical-free farming in India.
- Aim to improve soil health, reduce input costs, and produce nutritious food.
- Support the shift to natural farming (NF), emphasizing local knowledge and agro-ecological principles.
Financial Allocation:
- Total Outlay: ?2481 crore (Government of India share ?1584 crore, State share ?897 crore) until FY 2025-26.
Key Features of NMNF:
- Coverage: Targeting 15,000 clusters in Gram Panchayats, covering 7.5 lakh hectares and impacting 1 crore farmers.
- Bio-Input Resource Centres (BRCs): 10,000 BRCs to supply ready-to-use natural farming inputs.
- Krishi Vigyan Kendras (KVKs) and Agricultural Universities (AUs): Establishment of 2,000 model demonstration farms for hands-on training in natural farming techniques.
- Farmer Training: 18.75 lakh farmers to be trained in NF practices such as preparation of organic inputs like Jeevamrit and Beejamrit.
- Krishi Sakhis/CRPs: Deployment of 30,000 workers for farmer mobilization and awareness.
Implementation Strategy:
- Farmer Certification System: Providing easy, simple certification for marketing natural farming produce with dedicated branding.
- Monitoring: Real-time, geo-tagged monitoring of implementation through an online portal.
- Convergence with other government schemes and organizations for market linkages and support.
Natural Farming Practices:
- Zero Budget Natural Farming (ZBNF): Promote sustainable farming by using local livestock and diverse crop systems.
- Benefits: Reduce dependence on external inputs like chemical fertilizers and pesticides, rejuvenate soil quality, and increase resilience to climate risks (e.g., drought, floods).
- Encourage biodiversity, and improve soil carbon content and water-use efficiency.
Targeted Areas and Farmer Support:
- Focus on areas where NF practices are already being followed or where farmer producer organizations (FPOs) or self-help groups (SHGs) are active.
- Training through model demonstration farms will focus on practical, location-specific NF techniques tailored to regional agro-ecologies.
Impact on Agriculture and Environment:
- Environmental Impact: Encourages sustainable farming by reducing chemical exposure, improving soil health, and promoting climate resilience.
- Farmer Well-being: By reducing input costs and promoting nutritious food, it aims to improve farmer incomes and family health.
- Contributing to the long-term health of the environment, ensuring a healthy Mother Earth for future generations.
Challenges and Concerns:
- Soil Nutrient Compromise: Concerns that some crops, like rice, might require chemical fertilizers (e.g., NPK) for optimal growth, which may not be sufficiently replaced by organic manure alone.
- The shift to natural farming requires significant awareness and training to ensure sustainable and productive yields.
Institutional Framework:
- Ministry of Agriculture and Farmers’ Welfare is the implementing body.
- Collaboration with KVKs, AUs, and farmer organizations ensures grassroots level support and knowledge dissemination.
Extension of Ban on ULFA

- 27 Nov 2024
In News:
- The Ministry of Home Affairs (MHA) extended the ban on United Liberation Front of Asom (ULFA) for five years under the Unlawful Activities Prevention Act (UAPA), 1967.
- The notification specifically includes all factions, wings, and front organizations associated with ULFA.
Reason for Extension:
- ULFA continues to pursue secessionist objectives (separation of Assam from India).
- The group is involved in criminal activities such as extortion, intimidation, and violent actions.
- ULFA has maintained links with other insurgent groups and continues to engage in illegal activities like the possession of arms and ammunition.
Peace Process:
- Pro-talks faction of ULFA, led by Arabinda Rajkhowa, signed a peace agreement with the central and Assam governments in December 2023.
- This faction has agreed to renounce violence, disband the organization, and join the democratic process.
- However, the hardline faction of ULFA, led by Paresh Baruah, remains active and continues its militant activities.
ULFA’s Formation and Objectives:
- ULFA was founded in 1979 with the goal of achieving the "restoration of Assam's sovereignty" through armed struggle.
- It has been a key player in the Assamese separatist movement for several decades.
Legal Framework:
- The UAPA (1967) empowers the government to declare an organization as unlawful or label individuals as terrorists if they engage in activities threatening India’s sovereignty, integrity, or promote terrorism and secession.
- The latest extension of the ban was made under Section 3(1) of UAPA.
Significance for Internal Security:
- This development is important for understanding insurgency and separatism in the Northeast and the government’s approach to national security and counterinsurgency.
- The ULFA issue highlights challenges in addressing regional insurgencies and the role of the UAPA in maintaining national integrity.
Socialist and Secular in Preamble

- 27 Nov 2024
In News:
Supreme Court upholds ‘secular, socialist’ in Preamble of the Constitution.
Key Highlights of the Supreme Court Judgment
- Judgment Overview:
- Supreme Court's Ruling: The Court upheld the inclusion of the terms ‘socialist’ and ‘secular’ in the Preamble of the Indian Constitution through the 42nd Amendment Act of 1976.
- Challenge: Petitioners, including BJP leader Subramanian Swamy, challenged the retrospective application of these terms, arguing they were not part of the original Preamble adopted in 1949.
- Court's Explanation:
- Socialist: The term represents a welfare state aimed at reducing inequality and ensuring social, political, and economic justice, but does not prescribe a specific economic policy (left or right).
- Secular: Denotes a state that treats all religions equally, ensuring religious freedom and neutrality in religious matters. It is linked to Articles 14, 15, and 16, which ensure equality and non-discrimination.
- Retrospective Application:The Court affirmed that Parliament’s amendment power under Article 368 extends to the Preamble, and the retrospective application of the terms was valid.
- Constitution as a ‘Living Document’:The Court emphasized that the Constitution is adaptable to societal changes and evolving needs. The inclusion of 'secular' and 'socialist' reflects India’s evolving democratic and social framework.
- Interpretation of Secularism and Socialism:
- Secularism in India refers to the state's neutral stance towards all religions, promoting religious harmony.
- Socialism signifies India’s commitment to ensuring equality of opportunity and promoting welfare policies, such as social justice and economic welfare.
Constitutional and Legal Framework
- Article 368: Grants Parliament the authority to amend the Constitution, including the Preamble. The Court affirmed that this power is unquestionable.
- Kesavananda Bharati Case (1973): Established the ‘basic structure doctrine,’ which means certain fundamental features of the Constitution cannot be altered. The inclusion of ‘secular’ and ‘socialist’ is in line with this basic structure.
- S.R. Bommai Case (1994): Reinforced the secular nature of the Indian state.
Preamble to the Constitution
- Definition: The Preamble is an introductory statement that outlines the fundamental values and goals of the Indian Constitution.
- Key Objectives: Justice (social, economic, political), Liberty (thought, expression, belief), Equality (status and opportunity), and Fraternity (national unity and dignity).
- Terms in the Preamble:
- Sovereign: India's independence in all matters.
- Socialist: Commitment to social justice and welfare.
- Secular: Equal respect for all religions.
- Democratic: Governance by the people, through elected representatives.
- Republic: Head of state elected, not hereditary.
42nd Amendment Act, 1976:
- Context: Introduced during the Emergency under Indira Gandhi's government.
- Key Changes: Added 'socialist' and 'secular' to the Preamble, revised 'Unity of the Nation' to 'Unity and Integrity of the Nation.'
- Significance: Strengthened constitutional values like inclusivity, equality, and justice.
Socialist and Secular Initiatives by Government
- Socialist Programs:
- MGNREGA: Rural employment guarantee.
- PDS: Food security system.
- Right to Education (RTE): Free, compulsory education.
- Housing Schemes: Awas Yojana for the economically weaker sections.
- Secular Programs:
- Minority Welfare: Scholarships and skill development.
- Religious Protection Laws: Protection of places of worship.
- Communal Violence Laws: Special courts for violence-related cases.
- Constitutional Safeguards: Equal rights for all religions under Articles 25-28.
Significance of the Supreme Court Judgment
- Reaffirmation of Constitutional Values: The inclusion of ‘socialist’ and ‘secular’ reinforces India’s commitment to equality, justice, and democratic principles.
- Legitimacy of Amendments: Affirms Parliament's constitutional power to amend the Preamble.
- Evolving Interpretation: Recognizes that the Constitution must evolve in response to societal and political changes.
Cyclone Fengal
- 27 Nov 2024
In News:
- A deep depression in the Southwest Bay of Bengal, 800 km south of Chennai and 500 km from Nagapattinam, is expected to become Cyclone Fengal within the next 24 hours.
- It is anticipated to move north-northwest towards Tamil Nadu and Puducherry.
Key Highlights:
Cyclone Fengal Naming:
- If the depression intensifies into a cyclone, it will be named Fengal, as suggested by Saudi Arabia.
- Fengal will follow Cyclone Dana, which made landfall in Odisha in October 2024.
Cyclone Naming Process:
- Panel Members: Cyclones in the North Indian Ocean are named by a panel of 13 countries under the World Meteorological Organization (WMO) and United Nations Economic and Social Commission for Asia and the Pacific (UNESCAP).
- Member countries include Bangladesh, India, Iran, Maldives, Myanmar, Oman, Pakistan, Qatar, Saudi Arabia, Sri Lanka, Thailand, the UAE, and Yemen.
- Process: Each member submits a list of 13 names, creating a rotational naming system. Names are assigned sequentially as cyclones form. Once used, a name is retired and not reused.
Cyclone Fengal’s Potential Impact:
- Fengal is expected to bring strong winds, heavy rainfall, and possible coastal flooding.
- The system’s trajectory is being closely monitored, and preparedness measures are being implemented.
Terminology of Tropical Cyclones:
Terminology Region Impact Areas
Typhoons China Sea, Pacific Ocean Japan, China, Philippines
Hurricanes Caribbean Sea, Atlantic Ocean United States, Mexico,
Caribbean nations
Tornadoes Guinea Lands (West Africa), Southern USA Southern USA, West Africa
Willy-willies Northwestern Australia Australia (especially
Northwestern region)
Riyadh Design Law Treaty (DLT)

- 27 Nov 2024
In News:
- India reaffirms its commitment to inclusive growth and strengthening its intellectual property (IP) ecosystem.The signing of the treaty comes after nearly two decades of negotiations.
Key Highlights:
Purpose of the DLT:
- Aims to harmonize industrial design protection frameworks across multiple jurisdictions.
- Improves efficiency and accessibility of design registration processes.
Key Features of the DLT:
- Grace Period: A 12-month grace period after the first disclosure of the design, ensuring its validity for registration.
- Flexibility for Applicants: Provides relief measures such as relaxed deadlines, reinstatement of lost rights, and flexibility in adding priority claims.
- Simplified Processes: Includes simplified procedures for design renewals, assignment, and license recording.
- E-Filing Systems: Promotes the adoption of electronic filing systems and exchange of priority documents.
Benefits of DLT:
- Empowering SMEs and Startups: Helps small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) and startups protect designs globally, enhancing competitiveness and market growth.
- Reduced Administrative Burden: Standardizes procedures, making the design protection process less complex, more predictable, and affordable.
- Support for Developing Countries: Offers technical assistance for implementation in developing and least-developed countries.
Significance for India:
- India’s rich heritage of design and craftsmanship underscores the importance of design protection for sustainable economic growth.
- Design registrations in India have surged, with a 120% increase in domestic filings over the last two years.
Supporting Programs:
- The treaty’s provisions align with India’s initiatives like Startup India and the Startups Intellectual Property Protection (SIPP) Scheme to boost the protection and commercialization of designs for Indian innovators.
Broader Impact:
- DLT aims to integrate design protection with traditional knowledge and cultural expressions, further enhancing protection for India’s diverse creative sectors.
About WIPO:
- The World Intellectual Property Organization (WIPO), headquartered in Geneva, Switzerland, is a specialized UN agency established in 1967, promoting IP rights globally.
- India is a member of WIPO, which has 193 member countries.
Overview of Intellectual Property (IP):
- IP includes creations like inventions, industrial designs, literary and artistic works, symbols, and more, which are used in commerce.
- IP rights protect creators, allowing them to benefit from their work when commercially exploited.
India's First Constitution Museum

- 26 Nov 2024
In News:
Lok Sabha Speaker Om Birla and Union law minister Arjun Ram Meghwal inaugurated the country's first Constitution Museum at OP Jindal Global University in Sonipat.
Museum Features
- Centrepiece: A photolithographic copy of the Indian Constitution (one of 1,000 reproductions).
- 360-Degree Experience: A visual presentation that takes visitors through pre-Independence India.
- Multimedia Presentation: Chronologically details significant events leading to the drafting of the Constitution.
- Constituent Assembly Members:
- Nearly 300 sculptured busts of members who contributed to the making of the Constitution.
- Hologram of Dr. BR Ambedkar: Located in the mezzanine section, showcasing his philosophies through interactive displays.
- Art Installations:
- ‘We, The People of India’ by Rajesh P Subramanian: Represents unity in diversity.
- ‘Echoes of Liberty’ by Rahul Gautam: Combines constitutional manuscripts with contemporary design.
- ‘Triad of Unity’ by Harsha Durugadda: Symbolizes unity, justice, and sovereignty.
- ‘Insaaf Ki Devi’ by Nishant S Kumbhatil: Depicts Lady Justice, representing judicial impartiality.
- ‘Equality Before Law’ by Pradeep B Jogdand: Illustrates equality and justice principles.
- ‘Map’ by Deval Verma: Encourages visitors to reflect on value and beauty.
- ‘Freedom’ by KR Nariman: Pays tribute to the people who uphold constitutional values.
- ‘Founding Mothers’ by Rahul Gautam: Honors the 15 women members of the Constituent Assembly.
One Nation One Subscription (ONOS)

- 26 Nov 2024
In News:
Cabinet approves One Nation One Subscription (ONOS) Scheme.
Key Highlights:
- Objective: It is a new initiative to provide unified access to international scholarly research articles and journals for all government-managed higher education institutions and research institutions in India.
- Scheme Overview:ONOS aims to make nearly 13,000 scholarly journals accessible to over 1.8 crore students, faculty, researchers, and scientists in more than 6,300 institutions across India. These journals will cover all academic disciplines, promoting both core and interdisciplinary research, including in tier 2 and tier 3 cities.
- Digital Platform:The scheme will be implemented through a fully digital process, coordinated by the Information and Library Network (INFLIBNET), an autonomous center under the University Grants Commission (UGC). The platform will provide easy access to the journals and facilitate a streamlined subscription process.
- Investment and Coverage:A total of ?6,000 crore has been allocated for ONOS for three years (2025-2027). The scheme will cover major international publishers such as Elsevier, Springer, Wiley, and Oxford University Press. It will enable institutions to access 13,000 journals from 30 global publishers.
Benefits of the Scheme:
- Access to Top-Quality Research:ONOS will provide wide access to top-tier scholarly journals, benefiting institutions, researchers, and students across various fields. It will significantly improve the research environment in the country, especially for institutions that previously lacked the resources to access high-impact journals.
- Fostering Research and Development:The initiative aligns with India's vision of becoming an Atmanirbhar and Viksit Bharat by 2047, supporting the government's goals under the National Education Policy (NEP) 2020 and the Anusandhan National Research Foundation (ANRF). It will help foster a culture of research and innovation in Indian institutions.
- Inclusivity:The scheme will particularly benefit institutions in smaller towns and rural areas, helping bridge the knowledge gap between urban and rural academic institutions.
- Simplified Access:The scheme eliminates the need for separate subscriptions to individual journals by different institutions, streamlining access to high-quality content through a single platform.
Implementation Details:
- Platform and Process:The ONOS platform will allow institutions to access journals through a unified portal, providing easy and coordinated access. The Department of Higher Education (DHE)will be responsible for conducting awareness campaigns about the initiative, ensuring widespread utilization among students and faculty.
- Review Mechanism:The ANRF will monitor and periodically review the usage of ONOS and track the contributions of Indian authors in the journals, ensuring that the initiative continues to support India’s research landscape.
- Operational Date:The ONOS platform is set to become operational on January 1, 2025, providing comprehensive access to research materials for government-managed higher education and research institutions.
The One Nation One Subscription scheme is a major step towards enhancing India's position in the global research ecosystem. It will provide unparalleled access to scholarly resources, supporting research excellence and innovation across the country.
Proba-3 mission

- 26 Nov 2024
In News:
The Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) will launch the European Space Agency’s Proba-3 mission on its PSLV rocket to study the solar corona, the outermost and hottest part of the Sun’s atmosphere, from Sriharikota on December 4.
Key Highlights:
- Mission Objective:The mission will study the Sun’s outermost and hottest atmosphere, the solar corona. The mission will also demonstrate the first-ever precision formation flying with two satellites working in tandem.
- Satellite Formation:Proba-3 consists of two satellites that will fly together, maintaining a fixed formation to study the Sun's corona.
What is Proba-3?
- Proba-3 is a solar mission developed by ESA, with an estimated cost of 200 million euros. The mission involves launching two satellites that will separate after launch, but fly in precise formation. The satellites will create a solar coronagraph, which blocks the Sun’s bright light to observe the solar corona, the Sun’s outermost atmosphere.
- Orbit: Proba-3 will orbit in a highly elliptical path (600 x 60,530 km) with an orbital period of 19.7 hours.
- Mission Duration: The expected mission life is two years.
What will Proba-3 Study?
The Sun's corona is extremely hot (up to 2 million degrees Fahrenheit), making it difficult to observe with conventional instruments. However, studying the corona is essential because it generates space weather phenomena such as solar storms and solar winds, which can impact satellite communications, navigation systems, and power grids on Earth.
Proba-3 will use three main instruments for its mission:
- ASPIICS (Association of Spacecraft for Polarimetric and Imaging Investigation of the Corona of the Sun):This coronagraph will observe the Sun’s outer and inner corona, similar to how the corona is visible during a solar eclipse. It features a 1.4-meter occulting disk to block the Sun’s light and facilitate close-up observations.
- DARA (Digital Absolute Radiometer):This instrument will measure the Sun’s total energy output (total solar irradiance).
- 3DEES (3D Energetic Electron Spectrometer):It will study electron fluxes as they pass through Earth's radiation belts, providing valuable data on space weather.
Why is Proba-3 Unique?
- Proba-3 is designed to mimic a natural solar eclipse, allowing continuous study of the Sun’s corona. Typically, solar scientists observe the corona for only about 10 minutes during an eclipse, occurring around 1.5 times a year. Proba-3 will provide up to six hours of data per day, equivalent to 50 eclipse events annually.
- The two satellites will maintain a precise formation, with one acting as an occulting spacecraft to cast a shadow, while the other (the coronagraph) stays in the shadow and observes the Sun’s corona. They will be positioned 150 meters apart, maintaining their formation autonomously.
- This artificial eclipse will enable scientists to study the corona and its less-understood features more effectively.
National Gopal Ratna Award 2024
- 26 Nov 2024
In News:
The Department of Animal Husbandry and Dairying (DAHD) declared the winners of the National Gopal Ratna Awards(NGRA); one of the highest National Awards in the field of livestock and dairy sector for the year 2024.
About the National Gopal Ratna Awards (NGRA):
- Purpose:Recognize and encourage individuals, AI technicians, dairy cooperatives, and farmer organizations in the livestock and dairy sector.
- Categories:
- Best Dairy Farmer (Indigenous Cattle/Buffalo Breeds)
- Best Artificial Insemination Technician (AIT)
- Best Dairy Cooperative/Milk Producer Company (MPC)/Dairy Farmer Producer Organization
- Addition (2024):Special awards for North Eastern Region (NER) to promote dairy development in the area, with winners in all three categories.
- and Prizes:
- Rs. 5 lakhs for 1st rank, Rs. 3 lakhs for 2nd rank, Rs. 2 lakhs for 3rd rank, and Rs. 2 lakhs for Special NER Award in the categories of Best Dairy Farmer and Best Dairy Cooperative/FPO/MPCs.
- For Best AIT, winners will receive a Certificate of Merit and a memento.
- Process:Winners selected from 2,574 applications via an online portal (https://awards.gov.in).
- The livestock sector is crucial for India's economy, contributing significantly to agriculture and providing livelihood, especially for small and marginal farmers, women, and landless laborers.
- Indigenous breeds have immense genetic potential, but their population and performance have been declining. To address this, the Rashtriya Gokul Mission was launched under the National Programme for Bovine Breeding and Dairy Development in 2014 to conserve and develop indigenous bovine breeds.
National Milk Day
- It is celebrated annually on November 26 in India to honor the significant contributions of milk and the dairy industry to the country's development.
- The day commemorates the birth anniversary of Dr VergheseKurien, the "Father of the White Revolution" in India, who played a pivotal role in transforming India into the largest producer of milk globally.
- National Milk Day was first celebrated on November 26, 2014, after the Indian Dairy Association (IDA), along with various dairy institutions across the country.
Nayi Chetna 3.0 – PahalBadlaav Ki

- 26 Nov 2024
In News:
Union Minister Shri Shivraj Singh Chouhan launches the third edition of ‘Nayi Chetna – PahalBadlaav Ki’ a month-long national campaign against gender-based violence in New Delhi.
Key Highlights:
- Organized by: Deendayal Antyodaya Yojana – National Rural Livelihoods Mission (DAY-NRLM) under the Ministry of Rural Development.
- Led by: DAY-NRLM’s extensive Self-Help Group (SHG) network.
- Aim of the Campaign: Raise awareness and encourage grassroots-level action to combat gender-based violence.
- Campaign Slogan: “EkSaath, EkAwaaz, HinsaKeKhilaaf” (United Voice Against Violence).
- Approach:
- Adopts a "whole-of-government" approach with collaboration from 9 key ministries:
-
- Ministry of Women and Child Development
- Ministry of Health and Family Welfare
- Department of School Education and Literacy
- Ministry of Home Affairs
- Ministry of Panchayati Raj
- Ministry of Social Justice and Empowerment
- Ministry of Youth Affairs and Sports
- Ministry of Information and Broadcasting
- Department of Justice
- Key Objectives:
- Raise awareness about all forms of gender-based violence.
- Mobilize communities to demand accountability and action.
- Facilitate access to timely intervention and support systems.
- Empower local institutions to take action against violence.
- Goals for Nayi Chetna 3.0:
- Generate widespread awareness about gender-based violence.
- Foster collective action at the grassroots level.
- Drive convergence among government ministries and community stakeholders.
- Create a sustainable and informed movement for gender equality and women’s empowerment.
Narasapur Crochet Lace Craft

- 25 Nov 2024
In News:
The Narasapur crochet lace craft, which has been a significant part of the cultural and economic fabric of the Godavari region in Andhra Pradesh, has recently been granted the prestigious Geographical Indication (GI) tag. The GI tag, registered by the Department of Promotion of Industry and Internal Trade (DPIIT) on March 1, 2024, acknowledges that this unique craft is geographically linked to the West Godavari and Dr. B.R. Ambedkar Konaseema districts in the Godavari region.
Key Details:
- Historical Background:
- The origins of the Narasapur crochet lace craft date back to 1844, when Macrae and his wife from Scotland introduced the lace-making technique to local women while they were associated with a Christian missionary in Dummugudem (now in Telangana).
- Over time, the craft became a crucial part of the region’s heritage and survived significant historical events like the Indian famine of 1899 and the Great Depression of 1929.
- Craftsmanship:
- The crochet lace is produced using thin threads and delicate crochet needles of varying sizes, resulting in intricate designs.
- The products made include doilies, pillow covers, cushion covers, bedspreads, table runners, and tablecloths, among others. These items are often exported to international markets like the US, UK, and France.
- Economic and Social Impact:
- The craft is predominantly carried out by women artisans, with over 15,000 women involved in its production. The GI tag is expected to revitalize the industry, especially after its stagnation due to the COVID-19 pandemic and competition from machine-made lace from China.
- The craft is also an important part of the Alankriti Lace Manufacturing Mahila Mutual Aided Co-operative Societies’ Federation Limited, which supports local women artisans and has revived operations at the Alankriti Lace Park in Narasapur.
- GI Tag Benefits:
- The Geographical Indication tag serves to protect the authenticity of the lace products, boost demand, and ensure better market recognition.
- It provides legal protection to the traditional craft, preventing unauthorized use of the term "Narasapur lace" by others and promoting the region's cultural heritage and economic growth.
- Future Outlook:
- With the GI tag, there is hope for increased demand for Narasapur lace products both in domestic and global markets, thus offering a fresh avenue for artisans to revive and sustain the craft.
- Alankriti Federation and other stakeholders are optimistic that the GI tag will significantly revitalize the local economy and empower women in the region.
Palparescontrarius

- 25 Nov 2024
In News:
Palparescontrarius is a species of antlion that was recently spotted for the first time in Tamil Nadu, on the Madras Christian College (MCC) campus. It is notable for being a large-sized adult antlion that resembles a dragonfly but has distinct characteristics that separate it from dragonflies, such as its clubbed antennae and fluttering flight.
Key Features of Palparescontrarius:
- Appearance:
- The adult Palparescontrarius is large and resembles a dragonfly in its general body structure.
- It has lacy wings, long clubbed antennae, and a slender, grayish body.
- Its wings are typically clear, although some species of antlions have spots on their wings.
- Flight and Behavior:
- Unlike dragonflies, Palparescontrarius has a distinct fluttering flight.
- It is a weak flier and can often be spotted at night near illuminated spots.
- Habitat and Lifestyle:
- Like other antlions, Palparescontrarius is found in dry, sandy regions and is mostly active at night.
- The larvae of this species are particularly known for their predatory behavior, as they trap ants and other small insects in cone-shaped pits they dig into the sand.
- Ecological Importance:
- Antlions, including Palparescontrarius, are harmless to humans and beneficial to the environment because they feed on ants and other insects, thus helping to control pest populations.
Breakthrough in Bacterial Computing
- 25 Nov 2024
In News:
Scientists at the Saha Institute of Nuclear Physics in Kolkatahave successfully engineered bacteria capable of solving mathematical problems, marking a major step forward in the field of synthetic biology and biocomputing. These engineered bacteria can function like artificial neural networks, performing tasks that were traditionally reserved for humans or conventional computers.
Key Highlights:
- Bacterial Computers:
- The research team introduced genetic circuits into bacteria, turning them into computational units capable of tasks like determining whether a number is prime or identifying vowels in an alphabet.
- These bacterial "computers" mimic artificial neural networks (ANNs), where each type of engineered bacterium (called a "bactoneuron") behaves like a node in a network, processing inputs to generate outputs.
- How it Works:
- The bacteria's genetic circuits are activated by chemical inducers, which represent binary 0s and 1s (the fundamental language of computing). The presence or absence of certain chemicals determines whether a bacterium expresses a specific fluorescent protein, representing the binary states.
- For example, when asked if a number between 0-9 is prime, the bacteria can express green fluorescent proteins (1) for "yes" or red fluorescent proteins (0) for "no", providing binary outputs that solve the problem.
- Complex Tasks:
- The team advanced to more complex tasks, such as asking the bacterial computers whether adding a number (like 2 + 3) results in a prime number or if a number's square can be expressed as the sum of factorials.
- In an even more complex test, the bacteria solved an optimization problem—calculating the maximum number of pieces a pie could be cut into with a given number of straight cuts. The bacteria’s fluorescent output represented binary numbers that were converted to decimal for the correct solution.
- Technical Details:
- The researchers used Escherichia coli (E. coli) bacteria, engineered with transcriptional genetic circuits, which recognize specific DNA sequences and trigger the expression of proteins based on the presence of chemical inducers.
- The system is similar to how ANNs work in traditional computing, where nodes (bactoneurons) take inputs, apply weights, and produce outputs based on activation functions.
- Implications and Future Prospects:
- Synthetic Biology & Biomanufacturing: This breakthrough could revolutionize industries such as pharmaceuticals and biomanufacturing by enabling biocomputers that perform specific tasks in a biological environment, potentially reducing reliance on silicon-based computers.
- Medical Applications: The ability of engineered bacteria to process data could lead to biocomputers capable of diagnosing diseases (such as cancer) at an early stage and even administering localized treatments.
- Understanding Intelligence: Bagh and his team hope to explore the biochemical nature of intelligence, pondering how intelligence could emerge from simple, single-celled organisms.
- Groundbreaking Research:
- The research, published in Nature Chemical Biology, has drawn significant attention in the synthetic biology community. Centre for Synthetic Biology highlighting the potential of bacteria programmed to solve complex problems.
This innovative work paves the way for future developments in biocomputing, where living organisms, instead of silicon chips, could be used to perform sophisticated calculations, offering new ways to think about computing, intelligence, and even the future of technology in medicine.
6th ASEAN-India Trade in Goods Agreement (AITIGA) Joint Committee Meeting
- 25 Nov 2024
In News:
The 6th ASEAN-India Trade in Goods Agreement (AITIGA) Joint Committee and related meetings for discussions on the review of the AITIGA were held recently in Vanijya Bhawan, New Delhi.
Key Highlights:
Key Negotiation Areas
- 8 Sub-Committees under the AITIGA Joint Committee discussed:
- Market access, rules of origin, SPS measures, standards and technical regulations.
- Customs procedures, economic and technical cooperation, trade remedies, and legal and institutional provisions.
- 5 Sub-Committees met physically during this round of negotiations.
Progress in Discussions
- Textual Discussions: Sub-Committees made progress in discussions on various provisions.
- Tariff Negotiations: Initial steps towards initiating tariff negotiations were covered.
High-Level Meetings Leading to AITIGA Review
- 21st ASEAN-India Economic Ministers Meeting: Held in September 2024 in Vientiane, Laos.
- 21st ASEAN-India Summit: Held in October 2024 in Vientiane, Laos.
Both meetings urged the Joint Committee to expedite negotiations and aim for the conclusion of the review in 2025.
Bilateral Meetings
- ASEAN delegates held separate bilateral meetings with Thailand and Indonesia to discuss bilateral trade issues.
- Indian and ASEAN Chief Negotiators met to align on the ongoing issues and future steps.
India's Review Demands
- Request for Review: India sought a review of AITIGA (implemented in 2010), citing disproportionate trade benefits favoring ASEAN countries.
- India’s Objectives:
- Enhanced Market Access: India pushed for ASEAN countries, especially Vietnam, to commit to greater market-opening for Indian goods.
- Stricter Rules of Origin (ROO): India requested more stringent ROO provisions to prevent Chinese goods from entering India via ASEAN countries at preferential rates.
Trade Relationship and Economic Impact
- Bilateral Trade:
- Total trade with ASEAN reached USD 121 billion in FY 2023-24.
- Trade during April-October 2024 was USD 73 billion, marking a 5.2% growth.
- Trade Deficit: India’s trade deficit with ASEAN widened from USD 4.98 billion in FY 2010-11 to USD 38.4 billion in 2023-24.
- ASEAN accounts for 11% of India’s global trade.
Future Outlook
- The next meeting of the AITIGA Joint Committee is scheduled for February 2025 in Jakarta, Indonesia.
- The review process aims to further enhance sustainable trade between India and ASEAN countries.
Access to Medicine Index Report 2024

- 25 Nov 2024
In News:
- Recently, Access to Medicine Index Report 2024 was released by the Access to Medicine Foundation. The report evaluates 20 leading pharmaceutical companies on their efforts to expand access to medicines in low- and middle-income countries (LMICs).The biennial report has been published since 2008.
- Key Highlights:
- Key Areas of Evaluation
- Governance of Access: Companies’ leadership in addressing access issues.
- Research & Development (R&D): Focus on innovations for diseases prevalent in LMICs.
- Product Delivery: Efforts to ensure medicines and vaccines are accessible.
- Findings from the 2024 Report
- Gaps in Access for Low-Income Countries:
- Many pharmaceutical companies are adopting ‘inclusive business models,’ but outcomes are mixed, with transparent reporting still lacking.
- 61% of products lack specific access strategies for low-income countries.
- Exclusion from Clinical Trials:Only 43% of clinical trials take place in LMICs, despite these countries representing 80% of the global population.
- Limited Technology Transfers & Local Availability:
- Technology transfers and voluntary licensing are concentrated in countries like Brazil, China, and India.
- Sub-Saharan Africa (excluding South Africa) remains largely overlooked.
- Decline in R&D for Priority Diseases:
- Pharmaceutical companies are moving away from diseases like malaria, tuberculosis, and neglected tropical diseases, which disproportionately affect LMICs.
- Gaps in Access for Low-Income Countries:
- Key Issues in Accessing Medicines in LMICs
- Economic Barriers:
- High costs of essential medicines, including patented drugs, limit access for patients in LMICs with low purchasing power.
- Out-of-pocket expenditures lead to catastrophic financial consequences for families.
- Infrastructure Challenges:
- Poor transportation and cold chain infrastructure hamper the efficient distribution of medicines, especially in rural areas.
- Disruptions in supply chains (e.g., during pandemics) exacerbate medicine shortages.
- Regulatory Issues:Weak enforcement of regulatory frameworks results in the proliferation of substandard and counterfeit medicines, compromising treatment efficacy.
- Workforce Limitations:
- A shortage of trained healthcare professionals restricts appropriate prescription and management of medicines.
- Cultural beliefs and low health literacy further complicate adherence to treatments.
- Economic Barriers:
- Challenges Specific to LMICs
- Dual Burden of Diseases:
- LMICs face both infectious diseases and non-communicable diseases (NCDs), putting strain on fragile healthcare systems.
- 17 million people die from NCDs before age 70 annually, with 86% of these deaths occurring in LMICs.
- Need for Local Manufacturing:
- Strengthening local pharmaceutical manufacturing and distribution networks is crucial to ensure a reliable supply of essential medicines and reduce dependence on imports.
- Dual Burden of Diseases:
- Recommendations for Improving Access
- Companies should scale up efforts to bridge the health equity gap and use innovative approaches and local partnerships to improve access.
- Focus on increasing transparency in access reporting and addressing the lack of strategies for low-income countries.
- Pharmaceutical companies should refocus on diseases prevalent in LMICs, such as malaria and tuberculosis, and ensure that their R&D addresses the needs of these regions.
- Key Areas of Evaluation
Chagas Disease
- 24 Nov 2024
In News:
A recent study by Texas A&M University has uncovered a concerning new risk for dogs in Texas related to Chagas disease—the parasite Trypanosoma cruzi (T. cruzi), which causes the disease, can survive in dead kissing bugs (Triatominae). This discovery was published in the Journal of Medical Entomology in October 2024 and has raised alarms about how dead insects, which might be found in insecticide-treated dog kennels, could still pose a transmission risk for dogs.
Key Findings:
- Chagas Disease is primarily spread by kissing bugs, which carry T. cruzi in their gut. Dogs can contract the parasite by ingesting the bug's feces, especially when they lick their bite wounds.
- The study shows that even dead kissing bugs, which are often discarded in kennels, can still carry viable T. cruzi. This is particularly worrying in areas where insecticides are used to control the insects but dead bugs remain accessible to dogs.
- Researchers collected live and dead triatomines from six Texas kennels between June and October 2022, using both genetic testing and culture methods to assess whether the bugs were carrying live T. cruzi.
- 28% of the collected bugs tested positive for T. cruzi.
- A dead kissing bug (Paratriatomalecticularia) was found to still harbor live T. cruzi cultures, demonstrating that the parasite can survive even after the insect has died.
Transmission and Risks:
- Kissing bugs typically feed on the blood of animals like dogs, rodents, and raccoons, defecating near the bite site. If the dog licks the contaminated area, they can ingest the parasite-laden feces and become infected.
- The new discovery suggests that dead kissing bugs may pose a secondary transmission route for T. cruzi. Dogs that ingest these dead bugs, either in insecticide-treated areas or natural environments, could still contract the parasite.
- Researchers noted that dead bugs with intact gut contents showed a higher rate of infection than desiccated ones, which suggests that the condition of the bug after death impacts how long the parasite survives.
Implications for Management:
- The findings challenge current insecticide-based control methods. While insecticides kill the bugs, dead insects could still serve as a source of infection, necessitating new approaches for managing Chagas disease transmission in dog kennels.
- The study underscores the importance of regularly removing dead insects in kennels and reconsidering control strategies beyond just using insecticides.
About Chagas Disease:
- Chagas disease is caused by the Trypanosoma cruzi parasite, commonly found in the feces of kissing bugs. It can cause long-term heart and digestive issues if left untreated.
- The disease is common in parts of South America, Central America, and Mexico, but it has been increasingly reported in the southern United States.
- Treatment focuses on killing the parasite in the acute phase, but once it progresses to the chronic phase, treatment is aimed at managing symptoms.
Next Steps and Ongoing Research:
- The Texas A&M team plans to explore how long T. cruzi survives in dead triatomines and whether insecticides affect the parasite’s ability to persist. They are also looking into developing integrated pest management strategies for environments with high kissing bug activity.
- The study also forms part of a broader "One Health" approach, recognizing that both human and animal health are interconnected, and research on Chagas disease in animals can help inform public health strategies.
Imperial Eagle(Aquila heliaca)

- 24 Nov 2024
In News:
- A rare Imperial Eagle (Aquila heliaca) was spotted in the PulluzhiKole wetlands. This marks a significant event as the species was last reported in Kannur in 2003.
Key Highlights:
- Habitat and Migration:
- The Imperial Eagle primarily breeds in southeastern Europe, west, and central Asia.
- During the winter months, it migrates to regions including northeastern Africa, West Asia, and parts of Southeast Asia.
- Conservation Status:The IUCN Red List lists the Imperial Eagle as a vulnerable species, indicating its potential risk of extinction, underscoring the need for its conservation efforts.
- Importance of Conservation:
- The Kole fields are a Ramsar-protected area, emphasizing their critical role in preserving migratory bird habitats.
- Ongoing conservation and observation efforts in these wetlands are essential for protecting the diverse bird species that use the area.
Features of the Imperial Eagle:
- Scientific Name: Aquila heliaca
- Physical Characteristics:
- Size: Length ranges from 68 to 90 cm, with a wingspan between 1.76 to 2.2 meters.
- Color: It has a pale golden crown and nape, with a grey base extending to the tail. Its wings feature prominent white "braces" on the scapulars.
- Sexual Dimorphism: Males are typically smaller than females.
- Habitat: Prefers old forests, mountainous regions, and riverside forests.
- Feeding: It has strong legs and curved talons for capturing and killing prey, and exceptional eyesight to spot prey from high altitudes.
- Conservation Efforts: Continued monitoring and protection of the Kole wetlands and other vital habitats are crucial for the survival of this vulnerable species and other at-risk birds.
Chinar Boat Race 2024

- 24 Nov 2024
In News:
- The Chinar Boat Race 2024 was successfully organized in Dal Lake, Srinagar, Jammu and Kashmir.
Key Highlights:
- Organizers:The event was hosted by the Indian Army in collaboration with White Globe NGO and the Lake Conservation and Management Authority (LCMA).
- Purpose:The race aimed to celebrate Kashmir’s culture and traditions while promoting conservation of Dal Lake.The event emphasized the ecological importance of Dal Lake and the need for its protection.
- Cultural Impact:The race attracted a large crowd of both locals and tourists, highlighting the vibrant culture of Kashmir.The event fostered a sense of community and unity, with people cheering for the participants.
- Military Engagement:The Army organizes sports and cultural events in the region to strengthen Army-public relationships, engage local youth, and promote an honourable profession in the military.
Dal Lake Overview:
- Location: Situated in Srinagar, Jammu and Kashmir, surrounded by the PirPanjal mountains.
- Area: 18 sq. km (lake); part of a 21.1 sq. km wetland.
- Islands: Includes 3 islands, two marked by Chinar trees: Roph Lank (Silver Island) and Sone Lank (Gold Island).
- Significance: Known as the “Jewel in the crown of Kashmir” or “Srinagar’s Jewel”.
- Floating Market: Famous for its floating market where vendors use wooden boats (Shikaras) to sell goods.
- Temperature: Can drop to −11°C in winter, sometimes freezing the lake.
Minke Whale

- 24 Nov 2024
In News:
Scientists have directly measured the hearing range of minke whales for the first time, finding that they can detect high-frequency sounds up to 90 kHz.
Key Highlights:
- Implication for Ocean Noise: The study suggests that baleen whales, including minke whales, may be more affected by anthropogenic ocean noise (e.g., naval sonar) than previously recognized, as their hearing range had been underestimated.
- Research Method: A novel catch-and-release technique was used to temporarily hold adolescent minke whales in Norway for auditory evoked potential (AEP) tests to measure their hearing sensitivity.
- Findings: Contrary to the belief that baleen whales are low-frequency specialists, minke whales can detect frequencies between 45 kHz to 90 kHz.
- Impact of Findings: The results could affect future regulations on ocean noise and its impact on marine mammals, as better hearing data is now available for baleen whales.
Minke Whale Overview:
- Family: Minke whales are members of the baleen or "great" whale family and are the smallest of the rorquals.
- Species: There are two recognized species:
- Common minke whale (Balaenoptera acutorostrata), found in various ocean basins.
- Antarctic minke whale (B. bonaerensis), found in the Southern Hemisphere.
- Subspecies:
- Dwarf minke whale: An unnamed subspecies of the common minke whale, mostly in the Southern Hemisphere.
- North Atlantic (B. a. acutorostrata) and North Pacific (B. a. scammoni) subspecies of common minke whales.
- Distribution: Minke whales are widely spread across tropical, temperate, and polar regions (65°S to 80°N), with common minke whales in all ocean basins and dwarf minke whales mostly in the Southern Hemisphere.
- Feeding Areas: They feed in cooler waters at higher latitudes and can be found both inshore and offshore.
- Conservation Status (IUCN):
- Common minke whale: Least Concern.
- Antarctic minke whale: Data Deficient.
Project Veer Gatha

- 24 Nov 2024
In News:
Over 1.76 crore school students from all 36 States and UTs participated in Project Veer Gatha 4.0.
Key Highlights:
- Activities: Students submitted poems, paintings, essays, videos, and other creative works in honor of the bravery and sacrifice of Armed Forces personnel.
- Objective: Instituted in 2021, the project aims to spread the inspiring stories of Gallantry Awardees to foster patriotism among students.
- Platform for Creativity: Students engage in creative projects based on the heroic deeds and sacrifices of Gallantry Award winners.
- Previous Editions:
- Edition 1 (2021): 8 lakh students.
- Edition 2 (2022): 19.5 lakh students.
- Edition 3 (2023): 1.36 crore students.
- School-Level Activities: Schools conducted various activities from 16.09.2024 to 31.10.2024, uploading 4 best entries per school to the MyGov portal.
- Awareness Programs: The Ministry of Defence organized virtual and face-to-face awareness sessions across schools.
- Winner Recognition:
- Past Editions: 25 winners in Editions I and II, and 100 winners in Edition 3.
- Project 4.0: 100 National winners, each receiving Rs. 10,000.
- District & State/UT Winners: 4 District-level and 8 State/UT-level winners will be felicitated by respective authorities.
- Collaborative Initiative: The project is a joint effort of the Ministry of Defence and Ministry of Education.
11th ASEAN Defence Ministers’ Meeting-Plus (ADMM-Plus)

- 23 Nov 2024
In News:
The 11th ADMM-Plus held in Vientiane, Laos saw Union Defence Minister Rajnath Singh engage in discussions with his counterparts from the United States, Japan, and the Philippines.
Focus: The talks centered on strengthening defence partnerships, regional security, and enhancing cooperation among Indo-Pacific nations.
ASEAN Defence Ministers’ Meeting-Plus (ADMM-Plus):
- Platform for Dialogue: The ADMM-Plus is a key platform for ASEAN and its eight Dialogue Partners—Australia, China, India, Japan, New Zealand, Republic of Korea, Russia, and the United States.
- Establishment: The inaugural ADMM-Plus was held in HàN?i, Vietnam on 12 October 2010.
- Annual Meetings: Since 2017, the ADMM-Plus has met annually to enhance dialogue and cooperation amidst an increasingly complex regional security environment.
Objectives:
- Capacity Building: To aid ASEAN members in addressing shared security challenges.
- Promote Trust and Transparency: Enhance mutual trust and confidence between ASEAN and partner nations.
- Regional Peace and Stability: Focus on cooperation in defence and security to counter transnational security challenges.
- ASEAN Security Community: Contribute to realizing the ASEAN Security Community, as per the Bali Concord II, aiming for peace, stability, democracy, and prosperity in the region.
- Vientiane Action Programme: Facilitate ASEAN's efforts towards a peaceful, secure, and prosperous ASEAN with outward-looking relations with Dialogue Partners.
Cicada

- 23 Nov 2024
In News:
North American cicadas have life cycles that last for prime numbers of years, putting pressure on the idea that humans created mathematics.
What are Cicadas?
- Classification: Cicadas are insects that belong to the order Hemiptera and the superfamily Cicadoidea.
- Physical Features: Hemipteran insects (also known as true bugs) have piercing-sucking mouthparts and two pairs of wings.
- Life Span: Cicadas spend the majority of their life underground, feeding on plant sap. Once they emerge from the soil, they have a short adult life span of about 2 to 4 weeks.
Habitat:
- Preferred Environment: Cicadas are typically found in natural forests with large trees and are considered canopy dwellers.
- Global Distribution: Cicadas are found on every continent except Antarctica. The highest genetic diversity of cicadas is found in India and Bangladesh, followed by China.
Cicada Emergence and Life Cycle:
- Life Cycle: Cicadas have a complex life cycle, involving long periods of underground development followed by brief adult emergence.
- Periodical Cicadas: There are species of cicadas that emerge in 13-year and 17-year cycles.
- Broods: Initially, 30 broods were categorized based on geography and emergence times, but currently, only about 15 broods remain active due to some broods becoming extinct.
- Unique Phenomenon: In April 2024, a rare event is expected where a trillion cicadas from two different broods will emerge simultaneously in the Midwest and Southeast regions of the United States.
Cicada's underground Development:
- Feeding on Sap: During their underground phase, cicadas feed on the sap of plants.
- Purpose of Long Development: Researchers believe the long development period helps cicadas evade above-ground predators by keeping them hidden in the soil.
Vulnerability after Emergence:
- Emergence Behavior: Once cicadas emerge, they construct a "cicada hut" to shed their nymphal skins, then climb onto nearby trees or vegetation.
- Predator Vulnerability: Adult cicadas are vulnerable to predators such as turtles and other forest creatures because they are clumsy and defenseless, making them easy prey for predators.
Significance of the 2024 Emergence:
- The coinciding emergence of cicadas from different broods (13-year and 17-year cycles) is a rare event that highlights the complexity and mathematical precision behind the cicada life cycle.
The science of plant communication

- 23 Nov 2024
In News:
More than any organism, plants understand the significance of communication the best.
Communication Through Chemical Warning (Volatile Organic Compounds - VOCs):
- Plants release volatile organic compounds (VOCs) when threatened, such as during herbivore grazing.
- VOCs act as distress signals, alerting neighboring plants to potential dangers.
- Neighboring plants respond by producing defensive compounds or toxins to deter herbivores.
- VOCs can travel through air and soil, enabling distant plants to prepare for threats, thereby enhancing survival across larger areas.
Wood Wide Web (Symbiotic Relationship with Mycorrhizal Fungi):
- Plants form a network with mycorrhizal fungi, connecting their roots in a symbiotic bond.
- This "Wood Wide Web" allows plants to communicate by sending chemical signals through their roots when under stress (e.g., pest attacks or drought).
- Fungi extend the root system and help share nutrients between plants, especially in times of distress.
- The network facilitates collective resilience and survival by ensuring nutrient sharing among plants.
Cooperative Behavior: Sharing Resources for Survival:
- Plants in close proximity, especially in dense forests, often share resources like water, nutrients, and light.
- When a plant detects a neighboring plant in distress, it prioritizes resource allocation to support its growth.
- This cooperative behavior promotes ecosystem stability and the overall health of forests.
- The mutual support system shows how cooperation enhances the survival of individual plants and the broader ecosystem.
Significance of Plant Communication in Ecosystem Health:
- Plants communicate through chemical signals, underground fungal networks, and cooperative behaviors.
- These interactions foster resilience, ensuring the survival of both individual plants and entire ecosystems.
- The silent communication among plants contributes to a dynamic, cooperative environment that thrives on mutual support.
GQ-RCP Platform
- 23 Nov 2024
In News:
Researchers have developed a technology for targeted better detection of HIV-genome derived G-Quadruplex (GQ).
Key Features of the GQ-RCP Platform
- Technology: GQ Topology-Targeted Reliable Conformational Polymorphism (GQ-RCP) platform developed by Jawaharlal Nehru Centre for Advanced Scientific Research (JNCASR).
- Detection Mechanism: Uses a fluorometric test to detect HIV-derived GQ DNA through reverse transcription and amplification.
- Advantage: Increases diagnostic reliability by reducing false positives associated with non-specific DNA probes.
- Process: pH-mediated transition of double-stranded DNA into GQ conformation for targeted detection.
- Flexibility: Initially designed for SARS-CoV-2, now adapted for HIV diagnosis.
About HIV
- Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV) attacks the immune system, specifically CD4 cells, weakening the body's ability to fight infections.
- Transmission: Spread through bodily fluids such as blood, semen, vaginal fluids, and breast milk.
- AIDS: Without treatment, HIV progresses to Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome (AIDS), where the immune system becomes severely damaged.
- Management: No cure; managed with antiretroviral therapy (ART), which controls viral replication.
Current HIV Situation in India
- Prevalence: As of 2021, ~2.4 million people living with HIV in India, with a 0.22% adult prevalence rate.
- Demographic Distribution: High prevalence among female sex workers (2.61%) and injecting drug users (5.91%). Women represent 39% of HIV-positive population.
- High-Prevalence States: Northeastern states have the highest prevalence (e.g., Mizoram - 2.70%) and southern states (e.g., Andhra Pradesh - 0.67%).
Government Initiatives on HIV
- National AIDS Control Program (NACP): Launched in 1992, aims for prevention, treatment, and care.
- Phase I (1992-1999): Focus on awareness, blood safety, and surveillance.
- Phase II (1999-2006): Expanded interventions for high-risk populations.
- Phase III (2007-2012): Increased targeted interventions and civil society involvement.
- Phase IV (2012-2021): Focused on integration of HIV services into public health systems.
- Phase V (2021-2026): Aim to reduce new infections and AIDS-related deaths by 80% by 2026.
- Legislative Framework: The HIV/AIDS Prevention and Control Act (2017) ensures the rights of people living with HIV and access to treatment without discrimination.
- International Support: India receives support from UNAIDS, WHO, the World Bank, and foundations like Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation.
Global Soil Conference 2024
- 23 Nov 2024
In News:
- Global Soil Conference (GSC) 2024 held in New Delhi.
- Focused on soil health's importance for food security, climate change mitigation, and ecosystem services.
What is the Global Soil Conference 2024?
- Organizers: Indian Society of Soil Science (ISSS) in collaboration with the International Union of Soil Sciences (IUSS).
- Objective: Address sustainable soil/resource management challenges and foster global dialogue.
- Theme: "Caring Soils Beyond Food Security: Climate Change Mitigation & Ecosystem Services."
Key Highlights of GSC 2024:
- Soil Health Issues:
- Soil degradation threatens productivity and global food security.
- 30% of India's soil is compromised by erosion, salinity, pollution, and organic carbon loss.
- Soil erosion is linked to SDG 15 (Sustainable Development Goal 15), aiming to protect terrestrial ecosystems.
- SDG 15:
- Goals: Promote sustainable land use, combat desertification, halt land degradation, protect biodiversity.
Concerns Regarding Soil Health in India:
- Soil Degradation:One-third of India's land faces degradation due to poor farming practices.
- Soil Erosion & Fertility Loss:
- India loses 15.35 tonnes of soil/hectare annually.
- Results in crop losses, economic damage, and environmental issues like floods and droughts.
- Soil Salinity:Reduces water infiltration, nutrient uptake, and aeration, making land infertile.
- Low Organic Content:
- Organic carbon in Indian soil is 0.54%, which hampers fertility.
- Over 70% of soils are affected by acidity or alkalinity, disrupting nutrient cycles.
- Desertification:Reduces soil fertility, increases erosion, and worsens food insecurity.
- Diversion of Fertile Land:Fertile agricultural land is diverted for non-agricultural purposes.
India's Initiatives for Soil Conservation:
- Soil Health Card (SHC) Scheme:Provides farmers with soil nutrient information.
- Pradhan Mantri Krishi Sinchai Yojana:Focuses on efficient water use.
- Zero Budget Natural Farming & Natural Farming Mission:Promotes sustainable farming practices to protect soil health.
Guided Pinaka Weapon System

- 22 Nov 2024
In News:
Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO) has successfully completed the Flight Tests of Guided Pinaka Weapon System.
Key Details of the Flight Tests:
- Conducted as part of Provisional Staff Qualitative Requirements (PSQR) Validation Trials.
- Tests Phases: Flight tests were carried out in three phases at different field firing ranges.
- Parameters Assessed:
- Ranging (the distance the weapon can accurately target).
- Accuracy (precision of hits).
- Consistency (performance over multiple trials).
- Rate of Fire (ability to fire multiple rockets simultaneously in salvo mode).
Guided Pinaka Weapon System:
- Design and Development:
- Developed by Armament Research and Development Establishment (ARDE) in association with other DRDO labs and production agencies, including:
- Research Centre Imarat,
- Defence Research and Development Laboratory,
- High Energy Materials Research Laboratory,
- Proof & Experimental Establishment.
- Production Agencies: Munitions India Limited, Economic Explosives Limited, Tata Advanced Systems Limited, and Larsen & Toubro.
- Developed by Armament Research and Development Establishment (ARDE) in association with other DRDO labs and production agencies, including:
- Key Features:
- Pinaka: A multi-barrel rocket launcher system named after Lord Shiva’s bow.
- Mobility: Highly mobile, providing quick deployment in battlefield scenarios.
- Firepower: Capable of delivering concentrated firepower on enemy targets.
- Upgraded Version (Pinaka Mark II):
- Extended range: 70 to 80 km.
- Future range targets: 120 km and 300 km.
- Salvo Mode: Tested for the ability to launch 12 rockets simultaneously.
- Significance:
- Strategic Importance: The successful trials enhance the artillery firepower of the Indian Armed Forces.
- Completion of Pre-requisite Trials: The system has successfully completed all flight trials before its induction into the Indian Army.
Prasar Bharati’s OTT Platform – WAVES

- 22 Nov 2024
In News:
Recently, Prasar Bharati launched its OTT platform WAVES, to cater to India’s increasing demand for digital streaming services.
Key Features of WAVES OTT Platform:
- Content Offered: A mix of classic content and contemporary programming, catering to various audiences.
- Target Audience: Aimed at Indians and those abroad wishing to stay connected to their Indian roots.
- Languages: Available in 12+ languages, including Hindi, English, Bengali, Marathi, Kannada, Malayalam, Telugu, Tamil, Gujarati, Punjabi, Assamese.
- Genres: Spanning 10+ genres, including infotainment, games, current affairs, and news.
- Free Access: Most content is available free to download and view, with exceptions for premium content.
- Additional Features:
- Video on demand.
- Free-to-play gaming.
- Radio streaming.
- Live TV streaming with 65 live channels.
- Online shopping via the Open Network for Digital Commerce (ONDC) supported e-commerce platform.
Content Highlights:
- Fauji 2.0: A modern adaptation of the iconic 1980s Shahrukh Khan show, focusing on lives of people who serve and protect India.
- Kakbhushandi Ramayana: An original show on DD National now available on WAVES, based on research of over 350 versions of the Ramayana worldwide. The show aims to provide a new portrayal of the epic, appealing to younger audiences.
Vision for WAVES OTT:
- WAVES aims to revive nostalgia while embracing modern digital trends.
- It serves as an inclusive platform that highlights Indian culture with an international outlook.
Rare Leucistic Peacock

- 22 Nov 2024
In News:
Tamil Nadu Forest Department staff and members of a non-governmental organisation rescued a rare peacock with white feathers, caused by a genetic condition called leucism, in Coimbatore.
Key Highlights:
Incident Details:
- Species: Indian peacock (Pavocristatus), known for its beautiful plumage.
- Condition: The peacock was rescued due to a leg injury and its rare white plumage.
- Cause of White Plumage: The bird's white feathers are caused by leucism, a genetic condition that reduces pigmentation in feathers while leaving eye color unaffected.
Expert Insights:
- Leucism: It causes partial loss of pigmentation in animals. A leucistic animal retains normal eye color but has pale or white coloration.
- Distinction from Albinism: Unlike albinism, which results in a complete lack of melanin and often causes red or pink eyes, leucistic animals retain normal eye pigmentation.
- Identification of Leucism in Peacock: The bird’s dark eyes and pink bill and feet confirmed it as fully leucistic.
Peacock Species:
- Indian Peacock (Pavocristatus): The National Bird of India, native to India and Sri Lanka. It belongs to the Phasianidae family, which also includes pheasants, quails, and jungle fowl.
- Green Peacock (Pavomuticus): Found from Myanmar to Java.
Conservation Status:
- IUCN Status: Listed as Least Concern.
- Wildlife Protection Act, 1972: The Indian peacock is listed under Schedule I, offering it the highest level of legal protection in India.
India’s First AI Data Bank

- 22 Nov 2024
In News:
The Ministry of Science and Technologyrecently launched India’s first Artificial Intelligence (AI) data bank that is aimed at propelling innovation and boosting the country’s national securityat the 7th Edition of the ASSOCHAM AI Leadership Meet 2024.
-
- The event theme: “AI for India: Advancing India’s AI Development – Innovation, Ethics, and Governance”.
Key Highlights:
- Objective:
- Propel innovation and enhance national security.
- Provide access to diverse, high-quality datasets for creating scalable and inclusive AI solutions.
- Key Features of the AI Data Bank:
- Target Audience: Researchers, startups, and developers.
- Data Types: Satellite, drone, and IoT data.
- Purpose:
- To enhance national security through real-time analytics.
- Enable predictive analytics for disaster management and cybersecurity.
Strategic Importance of AI in India:
- National Security: AI to strengthen national security by providing real-time analytics from satellite, drone, and IoT data.
- AI for Development:
- AI’s role in reshaping sectors like governance, business, healthcare, education, and space exploration.
- AI as a tool for economic growth, addressing climate change, improving public service delivery, and ensuring national security.
- Ethics and Governance:
- Ensuring responsible AI use with optimal handling.
- Addressing algorithmic bias and data privacy through robust governance frameworks.
- Commitment to transparent and fair AI systems that empower people rather than replace them.
- AI in Disaster Management and Cybersecurity:
- Aligning with India’s goals to use AI for predictive analytics in disaster management.
- Enhancing cybersecurity through AI technologies.
Government’s Vision on AI:
- Empowering Citizens: AI must bridge divides and ensure equitable access to its benefits.
- AI as Backbone for Future Development: India’s focus on making AI an integral part of its future economic and technological growth.
Climate Change Performance (CCPI 2025)
- 22 Nov 2024
In News:
Recently, the Climate Change Performance Index (CCPI 2025) report was released at the annual UN climate conference in Baku.
Key Highlights:
- It is published by think tanks German watch, New Climate Institute, and Climate Action Network International.It was first published in 2005.
- It tracks the progress of the world’s largest emitters in terms of emissions, renewables, and climate policy.
India's Ranking in Climate Change Performance (CCPI 2025)
- India's Rank: 10th (Dropped two places from the previous year).
- Key Factors for India's High Rank:
- Low per capita emissions: 2.9 tons of CO2 equivalent (global average: 6.6 tons).
- Rapid deployment of renewables: India is a leader in solar energy projects, including large-scale solar and rooftop solar schemes.
- Renewable energy targets: Aims for 500 GW of renewable energy capacity by 2030.
- Energy efficiency standards: Introduced, but coverage remains inadequate.
- Electric vehicle (EV) deployment: Significant progress, especially in two-wheelers.
- Challenges for India:
- Heavy reliance on coal: India remains one of the top 10 countries with the largest developed coal reserves.
- Growth-oriented approach: Economic growth and energy demand continue to drive climate action, with limited change in climate policy expected.
- Future Pledges:
- Net-zero emissions by 2070.
- Global leadership in green energy.
CCPI 2025 Rankings Overview
Rank
Country
Key Points
1-3
Empty
No country performed well enough to achieve a "very high" rating.
4
Denmark
Leading climate actions but ranks 4th technically.
5
Netherlands
Strong climate performance, follows Denmark.
6
U.K.
Notable improvement due to coal phase-out and halting new fossil fuel licenses.
10
India
High performer, despite challenges like reliance on coal.
55
China
Largest emitter, heavily reliant on coal, ranks 55th despite promising plans.
57
U.S.
Second-largest emitter, ranks 57th with insufficient climate targets.
59
Argentina
Major climate policy setbacks, including potential exit from Paris Agreement.
64-67
Iran, Saudi Arabia, UAE, Russia
Lowest-ranked, major oil and gas producers with weak climate policies.
General Findings of the Report
- CCPI Methodology: Assesses 63 countries (plus the EU) responsible for 90% of global emissions based on their emissions, renewable energy efforts, and climate policies.
- Global Trends:
- No country has been able to secure a "very high" rating across all categories.
- Denmark and Netherlands are among the top performers.
- The U.K. shows significant progress with its coal phase-out and fossil fuel policies.
Indira Gandhi Prize for Peace, Disarmament, and Development

- 21 Nov 2024
In News:
- Daniel Barenboim (Classical Pianist and Conductor) and Ali Abu Awwad (Palestinian Peace Activist) were jointly awarded the Indira Gandhi Prize for Peace, Disarmament, and Development for 2023.
- Daniel Barenboim was recognized for fostering peace through musical and cultural dialogue initiatives.
- Ali Abu Awwad was honored for his advocacy of peace through dialogue via his organization Roots, which he founded after serving time in Israeli prison.
Significance of the Indira Gandhi Peace Prize:
- The award is given to individuals or organizations who have made outstanding contributions to international peace, disarmament, and development.
- It includes a monetary award of ?25 lakh and a citation.
About the Indira Gandhi Peace Prize:
- Established: 1986 by the Indira Gandhi Memorial Trust in memory of former Prime Minister Indira Gandhi.
- Objective: To honor sustained efforts towards international peace, the development of humanity, and the promotion of disarmament.
- Past recipients: Includes prominent figures and organizations such as Mikhail Gorbachev, UNICEF, Jimmy Carter, Angela Merkel, ISRO, and Sir David Attenborough.
2022 Awardees:
- The Indira Gandhi Peace Prize for 2022 was awarded to the Indian Medical Association and the Trained Nurses Association of India, in recognition of their contribution as COVID-19 warriors.
Key Takeaways:
- The Indira Gandhi Peace Prize is regarded as one of the most prestigious awards for promoting peace, disarmament, and development worldwide.
- Daniel Barenboim's musical initiatives and Ali Abu Awwad's work through dialogue exemplify efforts to bridge divides and promote peaceful resolutions to conflict.
Green World Awards 2024

- 21 Nov 2024
In News:
Coal India Limited (CIL) under the aegis of the Ministry of Coal, has been conferred with the esteemed Green World Environment Award in the Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) category along with the distinguished tile of Green World Ambassador.
Key Highlights:
- Reason for the Award:
- The award was granted to CIL for its Thalassemia Bal SewaYojna, a CSR initiative aimed at providing permanent curative treatment for Thalassemia through Bone Marrow Transplants (BMT).
- The scheme provides financial assistance of up to ?10 lakh for BMT and has helped over 600 Thalassemia patients across India.
- Background of the Award:
- The Green Organization, an independent, non-political, non-profit environmental group, conferred the award.
- The organization has been recognizing and promoting environmental best practices and CSR initiatives globally since its establishment in 1994.
- CIL’s Role in CSR:
- CIL has been a pioneer in CSR, with its Thalassemia Bal SewaYojna being the first of its kind among public sector undertakings in India.
- The initiative partners with 17 prominent hospitals across India to provide stem cell transplants for Thalassemia patients.
- CIL’s Contribution to India's Energy Sector:
- CIL is responsible for producing over 80% of India's coal and contributes to 70% of the total coal-based power generation in the country.
- CIL accounts for 55% of India’s total power generation and meets 40% of the primary commercial energy requirements.
- Environmental Initiatives by CIL:
- CIL has adopted various measures to improve environmental sustainability, including:
- Expanding green cover over mined areas.
- Creating eco-parks and tourism spots.
- Providing mine water for domestic and agricultural use to surrounding villages.
- About Coal India Limited (CIL):
- Established: November 1975.
- Headquarters: Kolkata.
- Status: A Maharatna company and the largest coal-producing company in the world.
- Subsidiaries: CIL has seven producing subsidiaries and is a major corporate employer in India.
- About the Green Organization:
- Founded: 1994.
- Nature: Independent, non-political, non-profit organization.
- Objective: To recognize, reward, and promote environmental and CSR best practices worldwide.
- Initiatives: The Green World Awards are part of global efforts to encourage sustainability and corporate social responsibility.
- Significance of the Award:
- The Green World Environment Award highlights CIL’s commitment to social responsibility and environmental sustainability while maintaining its core role as an energy provider.
- The recognition underscores CIL’s leadership in integrating CSR initiatives with corporate operations to contribute to national development.
Bhu-Neer Portal
- 21 Nov 2024
In News:
- Minister of Jal Shakti, digitally launched the “Bhu-Neer” portal during the India Water Week 2024.
- Developed by the Central Ground Water Authority (CGWA), under the Ministry of Jal Shakti, in collaboration with the National Informatics Centre (NIC).
Key Highlights:
- Purpose of the Portal:
- Centralized platform for managing and regulating groundwater resources across India.
- Aims to ensure transparency, efficiency, and sustainability in groundwater usage, facilitating easier access to groundwater withdrawal permits.
Key Features:
- User-Friendly Interface: Simplified interface to streamline the application process for groundwater withdrawal.
- PAN-Based Single ID System: Allows seamless user registration, providing a unique identification for all stakeholders.
- NOC with QR Code: Enables verifiable and trackable compliance documents, ensuring authenticity.
- Improved Version: An enhanced version compared to the previous NOCAP system, with improved efficiency and features.
- Streamlined Process Flow: Simplifies the process for obtaining groundwater withdrawal permits.
Goals and Benefits:
- Promotes the sustainable use of groundwater and ensures compliance with legal frameworks at state and national levels.
- Supports Ease of Doing Business: Aligns with the Prime Minister’s vision by making the groundwater regulation process seamless and faceless, reducing bureaucratic delays.
Public Accessibility:
- The portal is now live and accessible to both project proponents and the general public.
- It offers services such as groundwater withdrawal related queries, tracking applications, and payment of statutory charges.
Impact on Groundwater Management:
- The platform is expected to bring improved groundwater regulation by providing centralized access to policies, compliance details, and sustainable practices related to groundwater use.
- It will contribute significantly to monitoring and sustainable management of India’s groundwater resources, crucial in light of increasing water scarcity.
Vision of the Portal:
- In line with the government’s broader goals of digitalization, transparency, and environmental sustainability, the “Bhu-Neer” portal marks a significant step in efficient water resource management.
India’s First Indigenous Antibiotic

- 21 Nov 2024
In News:
- Nafithromycin is India's first indigenously developed antibiotic aimed at combating drug-resistant pneumonia, developed with support from the Biotechnology Industry Research Assistance Council (BIRAC).
- The drug is being marketed under the trade name "Miqnaf" by Wockhardt.
Significance in Combating Drug Resistance:
- Nafithromycin addresses Community-Acquired Bacterial Pneumonia (CABP), a serious disease caused by drug-resistant bacteria.
- Pneumonia is responsible for over 2 million deaths globally annually, with India facing 23% of the global burden.
- The drug is 10 times more effective than current treatments like azithromycin, requiring only three doses for effective treatment, offering a safer and faster solution.
Biotechnology Sector and Public-Private Collaboration:
- BIRAC, under the Department of Biotechnology, supported the research and development of Nafithromycin.
- This achievement underscores the public-private collaboration between the government and pharmaceutical industry, demonstrating India’s capacity to develop indigenous solutions for global health challenges.
Global Health Implications:
- Antimicrobial Resistance (AMR) is a growing global health crisis that prolongs illnesses and raises healthcare costs.
- The new antibiotic offers a vital solution to multi-drug-resistant pathogens, contributing significantly to global health.
- India’s leadership in addressing AMR positions the country as a major player in biotechnology innovation.
Importance for Vulnerable Populations:
- Vulnerable populations, including children, the elderly, and those with weakened immune systems (e.g., diabetes, cancer patients), are particularly affected by drug-resistant pneumonia.
- Nafithromycin offers a much-needed therapeutic option for these groups.
Impact of AMR Awareness:
- The launch coincides with World AMR Awareness Week, emphasizing the urgency of tackling antimicrobial resistance.
- Public awareness, fostered by the COVID-19 pandemic, has increased the focus on biotechnology and its potential to address global health challenges.
Future Prospects:
- Nafithromycin is awaiting final approval from the Central Drugs Standard Control Organization (CDSCO) for manufacturing and public use.
- The launch is expected to lead to future breakthroughs in antibiotic development and contribute significantly to improving public health.
UNICEF’s State of the World’s Children 2024 (SOWC-2024) Report
- 21 Nov 2024
In News:
The world is facing an unprecedented crisis with nearly half of all children – about 1 billion – living in countries that face a high risk of climate and environmental hazards, the UNICEF’s State of the World’s Children 2024 (SOWC-2024) report, said.
Key Highlights:
Environmental Hazards and Children’s Health:
- Children face an increasingly unpredictable and hazardous environment due to climate change, environmental crises, and frontier technologies.
- Nearly 1 billion children live in countries facing high risks from climate and environmental hazards.
- Children’s developing bodies are especially vulnerable to pollution, extreme weather, and environmental hazards.
- Air pollution, rising temperatures, and extreme weather events harm children's respiratory health, increase the spread of diseases like malaria and dengue, and impact food security and access.
Impact of Climate Change:
- Climate destabilization, biodiversity loss, and pollution are intensifying globally.
- Climate-related disasters (e.g., floods) affect water supplies, causing waterborne diseases, a leading cause of death in children under five.
- Extreme weather events, such as floods, can cause trauma, anxiety, and displacement for children.
- By the 2050s, more children will be exposed to extreme climate hazards compared to the 2000s.
- School closures, affecting 400 million children since 2022 due to extreme weather, disrupt education and hinder economic growth.
Projections for Child Survival and Life Expectancy:
- Newborn survival rates: Projected to rise by nearly 4 percentage points to over 98% globally by the 2050s.
- Probability of surviving to age 5: Expected to increase to 99.5%.
- Life expectancy: Expected to rise to 81 years for girls and 76 years for boys by the 2050s.
Child Population Trends by 2050:
- Global child population expected to stabilize at 2.3 billion by the 2050s.
- South Asia, Eastern/Southern Africa, and West/Central Africa will have the largest child populations, facing significant challenges in meeting children’s basic needs.
- These regions also face climate risks, inadequate digital infrastructure, and socio-economic challenges.
Technological Advancements:
- Artificial Intelligence (AI), neurotechnology, renewable energy, and vaccine breakthroughs could significantly improve childhood well-being.
- Digitalization: While it can empower children, it also exposes them to online risks, including sexual exploitation and abuse.
Socio-Economic Conditions and Inequality:
- 23% of children projected to live in low-income countries by 2050, a significant increase from 11% in the 2000s.
- GDP per capita in East Asia, Pacific, and South Asia expected to more than double from the 2020s to the 2050s.
- Growing inequalities between high- and low-income countries, particularly in terms of digital access and infrastructure.
Urbanization and Child Welfare:
- By the 2050s, nearly 60% of children globally will live in urban areas, up from 44% in the 2000s.
- Ensuring healthier and more secure urban environments is critical for improving future childhoods.
- Over 95% of people in high-income countries are connected to the internet, compared to just 26% in low-income countries, exacerbating inequalities.
Key Takeaways:
- Children are facing a more hazardous environment than ever before, influenced by climate change, technological developments, and demographic shifts.
- Proactive measures are needed to mitigate environmental risks, promote digital inclusion, and ensure equitable access to resources and opportunities for children globally.
India’s Polio Eradication Journey

- 20 Nov 2024
In News:
India's achievement of becoming polio-free in 2014 stands as one of the most remarkable successes in global public health. This milestone, which was celebrated worldwide, represents decades of consistent efforts, collaboration, and innovative strategies, culminating in the elimination of wild poliovirus in the country.
Key Milestones in Polio Eradication
- Pulse Polio Programme Launch (1995):
- The Pulse Polio Immunization Programme was a game-changer, initiating large-scale vaccination campaigns across India, with the first nationwide campaign held on 2nd October 1994 (Gandhi Jayanti) in Delhi.
- The campaign used the Oral Polio Vaccine (OPV) and reached over 1 million children.
- The slogan "Do BoondZindagi Ki" (Two drops of life) became synonymous with India’s polio eradication efforts.
- Routine Immunization and System Strengthening:
- The Universal Immunization Programme (UIP), which launched in 1985, made polio one of the first diseases targeted for elimination. UIP is now one of the world’s largest immunization programs, aiming to provide vaccines against 12 preventable diseases, including polio.
- Cold chain management was improved through systems like the National Cold Chain Training Centre (NCCTE) and Electronic Vaccine Intelligence Network (eVIN), ensuring proper storage and distribution of vaccines.
- Inactivated Polio Vaccine (IPV) Introduction (2015):
- As part of the Global Polio Endgame Strategy, India introduced the Inactivated Polio Vaccine (IPV) in 2015 to provide enhanced protection, particularly against type 2 poliovirus.
- This move followed the global transition from trivalent OPV to bivalent OPV (which excludes the type 2 strain) and helped ensure continued protection against all forms of polio.
- Surveillance Systems:
- India implemented Acute Flaccid Paralysis (AFP) Surveillance to track unexplained paralysis in children, a symptom of polio.
- Environmental Surveillance, involving monitoring sewage water for poliovirus strains, played a critical role in identifying potential outbreaks and residual poliovirus transmission.
- Political Will & Community Engagement:
- Strong political commitment from both central and state governments ensured sustained resources and focus on the program.
- Community participation was also vital, with health workers and volunteers working to ensure vaccination coverage in the most remote areas.
The Final Leap: Certification and Maintenance
- 2011 marked the last case of wild poliovirus in Howrah, West Bengal, and India ramped up its surveillance and response efforts to ensure no further cases.
- India achieved polio-free certification from the World Health Organization (WHO) on 27th March 2014, after meeting strict criteria, including three years without wild poliovirus transmission and robust surveillance systems.
Post-Certification Efforts: Keeping Polio at Bay
Even after achieving polio-free status, India remains vigilant to maintain this achievement:
- Annual National Immunization Days (NID) and Sub-National Immunization Days (SNID) are held regularly to boost immunity levels and ensure no child is missed.
- Continuous surveillance and vaccination at international borders help prevent the risk of re-importation of the virus.
- Mission Indradhanush (MI), launched in 2014, aims to increase immunization coverage to 90%, focusing on hard-to-reach areas and improving vaccine coverage.
Ongoing Commitment to Immunization
India’s immunization programs continue to evolve:
- New vaccines like Rotavirus, Pneumococcal Conjugate Vaccine (PCV), and Measles-Rubella (MR) are being added to protect against other vaccine-preventable diseases.
- Mission Indradhanush’s intensified phase has played a crucial role in improving vaccination rates, particularly in underserved areas.
High-Altitude Sickness

- 20 Nov 2024
In News:
In September, a trekker from Idukki, Kerala, died in Uttarakhand while attempting to scale Garur Peak due to respiratory failure. Every year, numerous tourists like this succumb to the effects of high-altitude sickness in the pristine but challenging inner Himalayas. These regions present hidden dangers due to their extreme altitudes, where thinner air and reduced oxygen can lead to potentially fatal conditions.
What is High-Altitude Sickness?
- Acute Mountain Sickness (AMS) occurs when the body struggles to acclimatize to high altitudes, typically above 8,000 feet (2,400 meters), where oxygen levels are lower.
- As altitude increases, oxygen levels decrease, leading to hypoxia (lack of oxygen). Early symptoms include:Headache, Nausea, Fatigue&Shortness of breath
- If untreated, AMS can develop into:
- High-altitude pulmonary edema (HAPE): Fluid accumulation in the lungs, leading to severe breathing problems.
- High-altitude cerebral edema (HACE): Fluid in the brain causing confusion, hallucinations, or coma.
- Both conditions are life-threatening and require immediate descent to lower altitudes.
Infrastructural Issues
- Many Himalayan regions lack adequate healthcare facilities beyond major towns like Shimla.
- Leh is an exception, with specialized facilities for high-altitude ailments, but most areas lack preventive health measures.
- Implementing health screenings at entry points to high-altitude zones (like Kinnaur or Lahaul-Spiti) could significantly improve prevention and response to AMS.
Mandatory Registration System for Tourists
- Tourist Registration: A system where tourists must register before entering remote mountain areas would allow authorities to monitor movements and provide timely medical assistance.
- Benefits:
- Quick emergency responses by having data on tourists' locations.
- Research support: Tracking demographic patterns and risk factors to better understand how altitude impacts different populations.
Early Intervention for High-Altitude Sickness
- Gradual Ascent: To allow the body to acclimatize, gradual ascent is crucial. Every 3-4 days, take a rest day and avoid increasing sleeping altitude by more than 500 meters/day.
- Medications: Doctors recommend:
- Acetazolamide to promote better oxygenation.
- Dexamethasone for reducing inflammation in severe cases.
- For those with a history of HAPE, Nifedipine may be used preventively.
- However, no medication guarantees immunity from AMS. Travelers with pre-existing conditions should consult a doctor before traveling.
Treatment Strategies
- Descent: The best treatment for AMS is to descend to lower altitudes (300-1,000 meters), where symptoms improve rapidly.
- Additional Measures: If available, supplemental oxygen or a portable hyperbaric chamber can help in emergencies.
- Medications like acetazolamide and dexamethasone can provide short-term relief but are not substitutes for descent.
Policy Recommendations
- Medical Infrastructure: Establish state-of-the-art medical facilities in high-altitude regions of the Himalayas.
- Research: Set up research centers to study high-altitude illnesses.
- Air-ambulance Services: Equip states with air-ambulance services for rapid medical evacuation in emergencies.
- Health and Safety Information: Provide accessible information on government websites and at check-in points to educate tourists on preventing and managing AMS.
Preventive Measures Before Scaling the Himalayas
- Acclimatization: Gradual ascent is essential for preventing AMS.
- Health Checks: Get a medical check-up to assess risk factors before travel.
- Medications: Consult a doctor for potential preventive medications.
- Hydration and Rest: Stay hydrated and take ample rest during the ascent.
- Monitor Symptoms: Be aware of early symptoms like headaches or nausea and stop ascending if they occur.
By addressing these measures, the risks associated with high-altitude sickness can be mitigated, improving safety for tourists and trekkers in the Himalayas.
Army Tactical Missile System (ATACMS)

- 20 Nov 2024
In News:
- Russia reported that Ukraine fired six US-made Army Tactical Missile System (ATACMS) missiles at Bryansk, Russia, marking a significant escalation in the ongoing conflict.
- This came after US President Joe Biden authorized Ukraine to use long-range missiles to strike deeper inside Russian territory, easing previous restrictions on such weapons
About the Army Tactical Missile System (ATACMS)
- Overview:
- ATACMS is a surface-to-surface artillery weapon system designed to strike targets at much greater ranges than conventional artillery, rockets, or missiles.
- Manufacturer: Produced by Lockheed Martin, a leading US defense contractor.
- First Use: It was first used during the 1991 Persian Gulf War.
- Key Features:
- Guidance: ATACMS missiles are inertially guided ballistic missiles, capable of operating in all weather conditions.
- Range: Approximately 190 miles (305 km).
- Propulsion: It uses a single-stage, solid propellant for propulsion.
- Launch Platforms: Fired from platforms like the High Mobility Artillery Rocket System (HIMARS) and the M270 Multiple Launch Rocket System (MLRS).
- Payload: ATACMS missiles can carry cluster munitions, releasing hundreds of smaller bomblets over a targeted area, increasing their destructive power.
- Global Operators:Besides the US, ATACMS is also operated by countries such as Bahrain, Greece, South Korea, Taiwan, and the United Arab Emirates.
SanyuktVimochan 2024

- 20 Nov 2024
In News:
Recently, the Indian Army successfully conducted the Multilateral Annual Joint Humanitarian Assistance and Disaster Relief (HADR) Exercise, 'SanyuktVimochan 2024' at Ahmedabad and Porbandar, Gujarat.
Key Highlights:
- Conducted by: Konark Corps of Southern Command, Indian Army.
- Day 1: Tabletop Exercise (TTX)
- Theme: 'Cyclone in Coastal Region of Gujarat'.
- Focused on simulating a cyclone scenario affecting the Okha-Porbandar coastline.
- Discussed disaster relief strategies and interagency cooperation to improve response readiness.
- Attended by senior officials from NDMA, Armed Forces, State Disaster Management, and industry representatives, including delegates from nine foreign countries.
- Day 2: Multi-Agency Capability Demonstration
- Held at Chowpatty Beach, Porbandar.
- Simulated Disaster Scenario: Coordinated response to a cyclone, showcasing joint operations by:
- Indian Army, Navy, Air Force, Coast Guard, NDRF, SDRF, and other Central and State agencies.
- Key actions demonstrated:
- Requisition and Surveillance: Civil administration’s request for Armed Forces' assistance, followed by area surveillance.
- Rescue Operations: Insertion of personnel to rescue casualties.
- Casualty Evacuation: Use of resources to evacuate and assist victims.
- Resuscitation and Rehabilitation: Restoration efforts for affected citizens.
- Industrial Display &Atmanirbhar Bharat Initiative:
- Showcased indigenous HADR equipment from Indian defense industries.
- Highlighted technological advancements and self-reliance in disaster management.
- SanyuktVimochan 2024 enhanced India's disaster response capabilities, ensuring a coordinated and effective approach to humanitarian assistance.
- The exercise also bolstered India’s leadership in global disaster relief, contributing to international best practices and collaborative efforts in humanitarian assistance and disaster response.
Sickle Cell Eradication
- 20 Nov 2024
In News:
- On the occasion of Janjatiya Gaurav Diwason 15th November 2024, Hon’ble Governor of Madhya Pradesh, and Chief Minister unveiled a commemorative postage stamp dedicated to "Sickle Cell Eradication - 2047" at PG College, Dhar.
- Significance:Focuses on India’s commitment to eradicate Sickle Cell Anemia by 2047, especially in tribal communities.
Sickle Cell Anemia Overview
- What is Sickle Cell Anemia?
- Genetic blood disorder leading to abnormal hemoglobin.
- Red blood cells become sickle-shaped, blocking blood flow and causing pain, organ damage, and reduced life expectancy.
- Symptoms:
- Chronic anemia causing fatigue, weakness, and pallor.
- Painful episodes (sickle cell crisis) resulting in intense pain in bones, chest, and limbs.
- Delayed growth and puberty in children.
- Treatment Processes:
- Blood Transfusions: Relieve anemia and reduce pain crises.
- Hydroxyurea: Reduces the frequency of painful episodes.
- Gene Therapy: Includes bone marrow or stem cell transplants and methods like CRISPR for treatment.
Challenges of Sickle Cell Disease (SCD) in India
- Tribal Population Impact:
- India has the world’s largest tribal population (~67.8 million, 8.6% of total population as per 2011 Census).
- Sickle Cell Disease (SCD) is identified as one of the top 10 health issues for tribal communities.
- Challenges:
- Limited diagnostic and treatment facilities in remote tribal regions.
- Lack of awareness about genetic counseling and preventive care.
- High treatment costs (e.g., CRISPR therapy costs USD 2-3 million).
- Bone marrow donor availability is a challenge.
Government Initiatives for SCD Management
- National Sickle Cell Anaemia Elimination Mission (2023):
- Objective: Eliminate SCD as a public health issue by 2047.
- Key Features:
- Community Screening: Mass screening to identify at-risk individuals.
- Genetic Counseling: Educating families on genetic nature of SCD.
- Advanced Diagnostics: Use of tools like HPLC for accurate diagnosis.
- Prenatal Testing: Partnership with organizations like Sankalp India.
- Newborn Screening: AIIMS Bhopal provides early detection.
- Technology: A mobile app and National Sickle Cell Portal for tracking data.
- Progress:Over 3.37 crore people screened, with 3.22 crore confirmed negative.
- Target Groups:Focus on children, adolescents, youth, and adults for screening, counseling, and care.
- National Health Mission (NHM) (2013):
- Emphasizes disease prevention and management, particularly for hereditary conditions like sickle cell.
- Facilitates medications like hydroxyurea for treatment.
- National Guidelines for Stem Cell Research (2017):Regulates stem cell therapies and allows Bone Marrow Transplantation (BMT) for SCD.
- National Guidelines for Gene Therapy (2019):Guidelines for gene therapies for inherited disorders, including CRISPR treatment for SCD.
- State Haemoglobinopathy Mission of Madhya Pradesh:Addresses screening and management challenges of SCD in the state.
Global Awareness and Observances
- World Sickle Cell Awareness Day:
- Observed on 19th June annually, with the 2024 theme: "Hope Through Progress: Advancing Sickle Cell Care Globally".
- Aimed at raising awareness about SCD struggles, improving patient care, and finding a cure.
Bharat NCX 2024

- 19 Nov 2024
In News:
The Bharat National Cyber Security Exercise (Bharat NCX 2024), inaugurated on November 18, 2024, is a key initiative aimed at strengthening India’s cybersecurity resilience. This 12-day exercise is designed to equip cybersecurity professionals and national leadership with the skills to manage complex cyber threats, enhance incident response capabilities, and improve strategic decision-making. The event is organized by the National Security Council Secretariat (NSCS) in collaboration with Rashtriya Raksha University (RRU).
Key Details of Bharat NCX 2024:
- Cyber Defense and Incident Response Training
- The exercise focuses on defensive cybersecurity skills, preparing participants to defend against cyberattacks.
- Live-fire simulations will provide hands-on experience with real-time cyberattacks on IT and Operational Technology (OT) systems.
- Strategic Decision-Making Simulations
- A core component is the Strategic Decision-Making Exercise, where senior management from across sectors will simulate decision-making in a national-level cyber crisis.
- This exercise enhances their ability to respond swiftly and strategically in high-pressure scenarios.
- CISO’s Conclave
- The CISO's Conclave brings together Chief Information Security Officers (CISOs) from government, public, and private sectors.
- The conclave will feature panel discussions on the latest cybersecurity trends and government initiatives, allowing professionals to exchange knowledge and collaborate.
- Bharat Cybersecurity Startup Exhibition
- An exhibition will highlight innovative cybersecurity solutions developed by Indian startups. This showcases the growing role of the private sector in strengthening India’s cybersecurity infrastructure.
- Leadership Engagement and Capacity Building
- Leadership engagement is a key feature, ensuring that high-level decision-makers are prepared to lead national cybersecurity efforts.
- The exercise will foster a unified approach to dealing with emerging cyber threats.
Significance for India’s Cybersecurity Strategy
- National Cybersecurity Resilience: Bharat NCX 2024 is a vital step in fortifying India’s cybersecurity defenses, preparing professionals and leadership to address the evolving cyber threat landscape.
- Collaboration and Innovation: The inclusion of industry stakeholders, startups, and leaders from various sectors underscores the importance of collaboration in developing innovative solutions to cybersecurity challenges.
- Capacity Building: The exercise aims to improve decision-making at all levels, helping India build a robust cybersecurity framework to secure its critical infrastructure and respond effectively to potential cyber crises.
Grand Commander of the Order of the Niger

- 19 Nov 2024
In News:
PM Modi receives Nigeria’s second-highest national award.
Key Events and Achievements
- Award Conferred:
- Award Name: Grand Commander of the Order of the Niger (GCON).
- Significance: Nigeria’s second-highest national award, conferred on Prime Minister Narendra Modi.
- Historical Context: Modi becomes the second foreign dignitary to receive this award, after Queen Elizabeth in 1969.
Strategic and Developmental Ties Between India and Nigeria
- First Visit in 17 Years: Modi’s visit is the first by an Indian PM to Nigeria in 17 years, underscoring the significance of strengthening bilateral ties.
- Economic Cooperation:
- Over 200 Indian companies have invested around $27 billion in Nigeria across key sectors, making India a major economic partner.
- India has provided $100 million in development assistance through concessional loans and is actively involved in capacity-building training programs in Nigeria.
- MoUs Signed:
- Three Memoranda of Understanding (MoUs) were signed in the fields of:
- Cultural Exchange.
- Customs Cooperation.
- Survey Cooperation.
- Three Memoranda of Understanding (MoUs) were signed in the fields of:
- Relief Aid: Modi announced the dispatch of 20 tonnes of relief supplies to help Nigeria recover from the devastating floods that affected the country last month.
Diplomatic Discussions and Initiatives
- Strategic Partnership: Modi described the India-Nigeria partnership as one with immense potential in sectors like defence, energy, technology, trade, health, and education.
- Indian Expatriate Community: Modi acknowledged the 60,000-strong Indian diaspora in Nigeria, recognizing their role as a pillar of bilateral ties.
- Support for Africa:
- Modi highlighted India’s support for the African Union’s membership in the G20, an outcome of the India-hosted G20 summit in 2023.
- Nigeria’s Role: He noted Nigeria’s positive influence on Africa and its importance as a key partner in India’s Africa engagement.
Broader Implications for International Relations
- India-Nigeria Security Cooperation:
- The National Security Advisors (NSA) of India and Nigeria held in-depth discussions on counter-terrorism, extremism, and cybersecurity challenges.
- India and Nigeria are committed to jointly addressing global threats such as arms smuggling and international crime.
- India's Role as a Development Partner:
- India’s growing role as a development partner for African nations is becoming increasingly important, exemplified by Nigeria’s close ties with India.
- Global Diplomacy and Soft Power:
- Modi’s award and visit reflect India’s growing influence in Africa and its emphasis on fostering ties with resource-rich and strategically located nations like Nigeria.
- The Grand Commander of the Order of the Niger is also a reflection of the soft power India is wielding globally.
Key Facts about Nigeria:
- Location: Nigeria is located in West Africa, bordering Niger, Chad, Cameroon, and Benin, with access to the Atlantic Ocean.
- Significance:
- Known as the “Giant of Africa” due to its large population and economic power.
- It has the largest economy in Africa, largely driven by its oil reserves.
Graded Response Action Plan (GRAP-IV)

- 19 Nov 2024
In News:
As Delhi’s AQI worsened, the Commission for Air Quality Management issued the order to activate Stage-IV of the Graded Response Action Plan.
Restrictions Under GRAP-IV in Delhi-NCR
- Truck Movement:
- Banned except for essential goods and trucks using clean fuels (LNG, CNG, BS-VI diesel, or electric).
- Non-essential light commercial vehicles registered outside Delhi are also banned unless they are CNG or BS-VI diesel or electric vehicles (EVs).
- Delhi-registered BS-IV or older diesel vehicles (medium and heavy goods vehicles) are banned, except for those in essential services.
- Construction Activities:Suspension of all construction work, including public projects like highways, roads, flyovers, power lines, pipelines, etc.
- Schools and Work:
- Online classes for students of Classes 6 to 9 and Class 11.
- Work from home (WFH) recommendations for 50% office capacity in NCR.
- Central government employees may also be asked to work from home.
- Offline classes for Classes 10 and 12 continue, but schools for other classes must shift to online mode.
- Other Measures:
- State governments may impose additional measures such as:
- Closure of colleges.
- Odd-even vehicle scheme.
- Restrictions on non-essential commercial activities.
- State governments may impose additional measures such as:
About GRAP (Graded Response Action Plan)
- Purpose: A plan to reduce air pollution in the Delhi-NCR region based on AQI levels.
- Approved By: Supreme Court in 2016 (M.C. Mehta v. Union of India).
- Notified by MoEFCC: 2017.
- Implementation Authority: CAQM (Commission for Air Quality Management).
Stages of GRAP
GRAP is an incremental system, with measures activated as air quality deteriorates:
- Stage 1: Poor AQI (201-300) – Basic pollution control measures.
- Stage 2: Very Poor AQI (301-400) – Enhanced measures.
- Stage 3: Severe AQI (401-450) – Stricter actions like shutting down industries.
- Stage 4: Severe Plus AQI (Above 450) – Most stringent restrictions, as activated on November 18, 2024.
Air Quality Index (AQI)
- Introduced: 2014, by Central Pollution Control Board (CPCB).
- Categories:
- Good: 0-50
- Satisfactory: 51-100
- Moderately Polluted: 101-200
- Poor: 201-300
- Very Poor: 301-400
- Severe: 401-450
- Severe Plus: 451 and above (current status in Delhi).
- Pollutants Considered: PM10, PM2.5, NO?, SO?, CO, O?, NH?, and Pb.
- Measurement: 24-hour average values for PMs, and 8-hour averages for CO and O?.
Commission for Air Quality Management (CAQM)
- Established: Under the Commission for Air Quality Management in National Capital Region (NCR) Act, 2021.
- Mandate: To coordinate, research, and manage air quality issues in the NCR and adjoining areas.
- Composition: Includes government officials, technical experts, and NGO representatives.
- Jurisdiction: Covers Delhi and parts of Haryana, Uttar Pradesh, and Rajasthan.
Nepal-Bangladesh Power Transfer via India

- 19 Nov 2024
In News:
Nepal starts exporting energy to Bangladesh with Indian grid support.
Significance of the Power Transfer:
- Energy Cooperation:
- A major step in regional energy cooperation among Nepal, India, and Bangladesh.
- Strengthens sub-regional connectivity in the power sector.
- Nepal’s Hydropower Potential:
- Nepal, a Himalayan nation, possesses untapped hydropower resources, and this agreement opens the door for future cross-border electricity cooperation.
- Nepal’s energy exports are a green energy initiative, supporting sustainable industrial growth in Bangladesh and regional prosperity.
- Electricity Crisis in Bangladesh:
- Bangladesh is facing an ongoing electricity shortage, worsened by the suspension of power supply from Adani’s Godda plant and the maintenance of the Payra thermal unit.
- The addition of 40 MW of Nepalese hydroelectric power aims to alleviate the energy shortfall in Bangladesh.
Tripartite Power Sales Agreement:
- Agreement Details:
- The agreement for power transfer was signed in October 2023 between:
- NTPC Vidyut Vyapar Nigam (NVVN) (India)
- Nepal Electricity Authority (NEA) (Nepal)
- Bangladesh Power Development Board (BPDB) (Bangladesh).
- Power Export: Nepal has started exporting 40 MW of electricity, which marks a significant milestone in trilateral power cooperation.
- The agreement for power transfer was signed in October 2023 between:
Key Entities Involved:
- NTPC Vidyut Vyapar Nigam (NVVN):
- A wholly owned subsidiary of NTPC Ltd. (National Thermal Power Corporation), created to facilitate power trading.
- NVVN is diversifying into renewables, e-mobility, and green fuel solutions.
- NTPC Ltd.:
- A Maharatna PSU under India’s Ministry of Power, established to develop power resources in India.
- Involved in large-scale power generation and clean energy initiatives
Guru Ghasidas-TamorPingla Tiger Reserve

- 19 Nov 2024
In News:
The Guru Ghasidas-TamorPingla Tiger Reserve in Chhattisgarh has been officially notified as India's 56th tiger reserve, marking a significant milestone in the country's conservation efforts. Here's an overview of this new reserve:
Key Details:
- Location: The tiger reserve is located across the Manendragarh-Chirmiri-Bharatpur, Korea, Surajpur, and Balrampur districts of Chhattisgarh.
- Area: The reserve spans 2,829.38 square kilometers and includes both core and buffer zones.
- Core/critical habitat: 2,049.2 sq. km (includes the Guru Ghasidas National Park and TamorPingla Wildlife Sanctuary).
- Buffer zone: 780.15 sq. km.
- Rank: It is the third largest tiger reserve in India, after the Nagarjunasagar-Srisailam Tiger Reserve (Andhra Pradesh) and Manas Tiger Reserve (Assam).
Connectivity:
The reserve forms part of a landscape complex that extends over nearly 4,500 sq. km and is interconnected with other major tiger reserves:
- Sanjay Dubri Tiger Reserve (Madhya Pradesh) to the north.
- Bandhavgarh Tiger Reserve (Madhya Pradesh) to the west.
- Palamau Tiger Reserve (Jharkhand) to the east.
This connectivity supports greater wildlife movement, reducing the risk of inbreeding and strengthening the overall conservation efforts for the tiger population.
Biodiversity:
The Guru Ghasidas-TamorPingla Tiger Reserve is ecologically rich, harboring a wide array of species:
- 753 species have been documented, including:
- 230 bird species.
- 55 mammal species, including several threatened species such as tigers, leopards, sloth bears, and wolves.
- A variety of invertebrates, especially insects.
- The reserve's terrain includes dense forests, streams, rivers, and varied elevations, making it an ideal habitat for tigers and other wildlife.
Ecological Importance:
- Situated in the Chota Nagpur and Baghelkhand plateaus, the reserve has varied landscapes that contribute to its ecological diversity. The region's tropical climate and dense forests make it a critical habitat for tigers and other wildlife.
- The reserve's core area forms an important critical tiger habitat, providing a sanctuary for tigers to thrive with minimal human disturbance.
Conservation Impact:
With the addition of this tiger reserve, Chhattisgarh now boasts four tiger reserves, complementing the existing Udanti-Sitanadi, Achanakmar, and Indravati reserves. This bolsters the state's and the country's ongoing efforts to protect and conserve tigers, which are a keystone species in maintaining ecological balance.
Procedural Steps for Notification:
- Identification: The state government identifies a significant ecological area with potential for tiger conservation.
- NTCA Approval: After a thorough assessment, the National Tiger Conservation Authority (NTCA) evaluates and approves the proposal.
- State Notification: The state government officially notifies the area as a tiger reserve under the Wildlife Protection Act of 1972.
- Implementation: The state, with NTCA support, begins implementing conservation and management strategies.
Mystery mollusk
- 18 Nov 2024
In News:
- In a groundbreaking discovery, researchers have identified a new species of sea slug deep within the ocean’s midnight zone—a place that lies between 3,300 to 13,100 feet (1,000 to 4,000 meters) below the ocean's surface.
- The species, named Bathydeviuscaudactylus, is a glowing, swimming sea slug that exhibits several unique adaptations to survive in the extreme conditions of the deep ocean.
Key Features of BathydeviusCaudactylus
- Glowing Bioluminescence: One of the most striking features of this newly discovered mollusk is its ability to glow with bioluminescence. Bathydevius emits a soft, starry glow, an adaptation seen in only a few deep-sea species. The glowing feature plays a role in distracting predators and even includes the ability to detach glowing projections from its tail as a decoy.
- Unique Body Structure: Unlike most sea slugs that typically live on the seafloor, Bathydevius has evolved to thrive in the open water. It has a gelatinous, paddle-like tail and a large, bowl-shaped hood that covers its internal organs, making it appear somewhat like a “megaphone with a feathered tail.” This structure helps it capture prey, such as mysid shrimp, which it traps using its hood.
- Adaptations for Deep Sea Life: Bathydevius' transparent body, along with its ability to drift with ocean currents and flex its body to move vertically in the water column, allow it to navigate the depths of the midnight zone. Its hermaphroditic nature means it carries both male and female reproductive organs, allowing it to reproduce by attaching to the seafloor and laying eggs when needed.
Discovery and Exploration
- The unusual species was first encountered by researchers from the Monterey Bay Aquarium Research Institute (MBARI) during a deep-sea dive in February 2000 using a remotely operated vehicle (ROV) called Tiburon. Since then, more than 150 sightings have been made of the creature in the waters off the Pacific Coast of North America, ranging from Oregon to Southern California.
- Interestingly, similar creatures have been observed by the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) in the Mariana Trench, suggesting that Bathydevius may have a wider range than initially thought. A specimen was eventually collected for further study, revealing its identity as a nudibranch, a type of soft-bodied marine mollusk.
Survival Tactics and Behavior
- Prey Capture: Unlike typical sea slugs that scrape food from the seafloor, Bathydevius uses its large hood to trap crustaceans like mysid shrimp. This allows it to thrive in the open ocean where food can be harder to obtain.
- Defensive Mechanisms: When threatened, Bathydevius can glow with bioluminescence to distract predators. This glow, which creates a starry appearance across its back, has been seen in other deep-sea species but is rare in nudibranchs. Additionally, it can detach part of its tail (a glowing projection) to confuse attackers, similar to how lizards shed their tails as a defense mechanism.
- Reproduction and Movement: As a hermaphrodite, Bathydevius has the ability to self-fertilize or mate with other individuals. During reproduction, it descends to the seafloor and uses its foot to temporarily attach, releasing eggs before returning to its swimming lifestyle. It also relies on its flexible, transparent body to blend in with the surroundings and evade predators.
India Successfully Tests Long-Range Hypersonic Missile

- 18 Nov 2024
In News:
- India has made a major advancement in its defense capabilities with the successful flight test of its first long-range hypersonic missile, marking a historic moment in the country's defense technology.
- The test was conducted, by the Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO), took place off the coast of Odisha from the Dr. A.P.J. Abdul Kalam Island.
- The missile has a range of over 1,500 km and is capable of carrying various payloads for all branches of the armed forces.
Key Highlights of the Test:
- Successful Trial: The missile successfully completed its flight test with high accuracy, confirmed by the data gathered from down-range ship stations. It performed a series of terminal maneuvers, validating its precision targeting capabilities.
- Speed and Range: The missile achieved hypersonic speeds (Mach 6), or six times the speed of sound, and is designed for a range of more than 1,500 km, far exceeding the capabilities of many conventional missiles.
- Indigenous Development: This missile is a product of DRDO's indigenous efforts, developed with contributions from the Dr. APJ Abdul Kalam Missile Complex in Hyderabad, as well as other DRDO laboratories and industry partners.
What are Hypersonic Missiles?
- Definition: Hypersonic missiles are defined as weapons that travel at speeds greater than Mach 5 (five times the speed of sound), or about 3,836 miles per hour (6,174 km/h). At such speeds, they are incredibly difficult to track and intercept, posing a challenge for traditional missile defense systems.
- Types:
- Hypersonic Glide Vehicles (HGVs): These are launched from rockets and glide towards their target.
- Hypersonic Cruise Missiles (HCMs): These missiles use air-breathing engines like scramjets for sustained flight at hypersonic speeds.
- Advantages: Hypersonic missiles offer several advantages, including:
- Responsive strike capability: They can target time-sensitive threats quickly and with high precision.
- Manoeuvrability: Unlike ballistic missiles, which follow a predictable parabolic trajectory, hypersonic missiles can change course mid-flight, making them harder to defend against.
- Challenges:
- Heat and air resistance: Traveling at such high speeds generates tremendous heat due to friction, presenting engineering challenges.
- Tracking and interception: Their low-altitude flight and high speeds make them harder to detect and intercept with existing missile defense systems.
- High costs: Developing and deploying hypersonic weapons comes at a higher cost than traditional missile systems.
Global Context of Hypersonic Weaponry
- Russia and China: Both Russia and China are leaders in hypersonic missile technology. Russia has already deployed the Kinzhal hypersonic missile in Ukraine, demonstrating its effectiveness in combat situations.
- United States: The U.S. is also making significant advancements, with contracts like the Long Range Hypersonic Weapon (LRHW), awarded to Lockheed Martin for continued development.
- Other Nations: Countries such as France, Germany, Australia, Japan, and Israel are also actively working on developing hypersonic missile systems.
WIPO 2024 Report

- 18 Nov 2024
In News:
India continues to make significant strides in intellectual property filings, ranking among the top 10 countries for patents, trademarks, and industrial designs.
India’s Performance in Global Intellectual Property (IP) Filings:
- Overall Growth: India continues to make significant strides in intellectual property filings, ranking among the top 10 countries for patents, trademarks, and industrial designs.
- Patent Applications: India recorded a +15.7% growth in patent applications in 2023, marking its fifth consecutive year of double-digit growth, placing it among the top contributors to global patent filings.
- Trademark Filings: India ranks 4th globally in trademark filings, reflecting the country’s growing focus on brand protection.
- Industrial Designs: India saw a 36.4% surge in industrial design applications, emphasizing creativity and design innovation.
India’s Global Patent Ranking:
- Global Rank: India ranks 6th globally for patent applications with 64,480 filings in 2023.
- Resident Filings: For the first time, over half (55.2%) of India’s patent applications were filed by residents, highlighting growing domestic innovation.
- Patent Grants: A 149.4% increase in granted patents in 2023 underscores the efficiency of India’s patent office and the rising quality of applications.
Key Metrics and Trends in Patents:
- Patent-to-GDP Ratio: India’s patent-to-GDP ratio grew from 144 in 2013 to 381 in 2023, signaling a knowledge-driven economy.
- Sectoral Diversity: India’s patent filings span diverse sectors, including agriculture, pharmaceuticals, IT, and renewable energy, showcasing the broad scope of innovation.
Surge in Industrial Design Applications:
- Growth Rate: A 36.4% increase in industrial design filings in 2023, reflecting a shift towards value-added industries focused on product design and functionality.
- Leading Sectors: Key sectors driving design filings include textiles, accessories, tools, machines, and health & cosmetics.
- Manufacturing Transformation: This growth signals India’s transition from basic manufacturing to a more design-driven, innovation-focused ecosystem.
Trademark Filings:
- Global Rank: India ranks 4th globally in trademark filings with a 6.1% increase over the previous year.
- Resident Filings: Nearly 90% of trademark filings in India were made by domestic entities, highlighting a strong focus on brand protection.
- Active Trademarks: India now has over 3.2 million active trademarks, the second-largest in the world, reflecting a competitive and dynamic domestic marketplace.
Sectoral Trends in Trademarks:
- Leading Sectors: Health (21.9%), agriculture (15.3%), and clothing (12.8%) were the top sectors for trademark filings, underscoring India’s leadership in pharmaceuticals, food production, and fashion.
- Global Expansion: The rise in trademark filings also mirrors the increasing global demand for Indian products and services.
India’s Contribution to Global IP Growth:
- Global Trend: In 2023, a record 3.55 million patent applications were filed worldwide, with India contributing significantly to this surge, particularly in emerging markets.
- Local Innovation Focus: India’s rising resident filings in patents and trademarks point to a shift towards local innovation, with more Indian businesses and startups protecting their intellectual property.
Government Initiatives Fueling IP Growth:
- National IPR Policy: Launched in 2016, this policy fosters innovation, improves IP awareness, and supports domestic IP development.
- Key Measures: Modernization of IP offices, improvements in procedural requirements, and IP education initiatives.
- Atmanirbhar Bharat: Government campaigns like Atmanirbhar Bharat have supported local innovation and made Indian businesses more IP-conscious.
- Startup India & Atal Innovation Mission: These initiatives have further strengthened India’s innovation ecosystem by promoting entrepreneurship, research, and technological advancement.
- Startup India: Over 1,49,000 recognized startups as of September 2024.
- Atal Innovation Mission: More than 10,000 Atal Tinkering Labs in schools and 3,500+ startups incubated across India.
Assam’s Semiconductor Plant
- 18 Nov 2024
In News:
A Semiconductor Plant has been set up in Morigaon, Assam, projected for completion by mid-2025.
Overview of the Morigaon Semiconductor Plant:
- Location: Morigaon, Assam.
- Investor: Tata Semiconductor Assembly and Test Pvt Ltd (TSAT).
- Investment: ?27,000 crore.
- Production Capacity: Expected to produce 48 million semiconductor chips daily.
- Technology: Utilizes advanced packaging technologies such as flip chip and Integrated System in Package (ISIP).
- Sectors Served: Automotive, electric vehicles, telecommunications, consumer electronics.
- Completion: Projected to be completed by mid-2025.
- Job Creation: Expected to generate 15,000 direct jobs and 11,000-13,000 indirect jobs.
- Market Reach: Will serve both domestic and international markets, enhancing India's position in the global semiconductor supply chain.
India's Semiconductor Industry and Market Growth:
- Market Size (2023): Estimated at $38 billion.
- Projected Growth: Expected to grow to $109 billion by 2030.
- Government Initiatives: Several initiatives have been launched to promote domestic semiconductor manufacturing, including the India Semiconductor Mission (ISM) and the Semicon India Program.
India Semiconductor Mission (ISM):
- Objective: To build a self-reliant semiconductor ecosystem in India.
- Launched: 2021 with a financial outlay of ?76,000 crore.
- Scope: Covers semiconductor fabs, packaging, display manufacturing, Outsourced Semiconductor Assembly and Testing (OSAT), sensors, and other critical components.
- Support Schemes: Includes Modified Schemes for setting up Semiconductor and Display Fabs, as well as support for Compound Semiconductors, Silicon Photonics, and Sensors.
Key Projects in Semiconductor Industry:
- Morigaon Facility: Part of the broader government-backed initiative to enhance semiconductor production in India.
- Other Facilities: New semiconductor units by Tata Electronics (Dholera, Gujarat), CG Power (Sanand, Gujarat), and KaynesSemicon Pvt Ltd (Sanand, Gujarat).
- Modernization: The Semi-Conductor Laboratory in Mohali is being modernized, alongside initiatives like the Scheme for Promotion of Manufacturing of Electronic Components and Semiconductors (SPECS) and the Production Linked Incentive (PLI) Scheme.
Strategic Importance of Semiconductors:
- Role in Modern Electronics: Semiconductors are critical for a wide range of devices like computers, smartphones, solar cells, LEDs, and integrated circuits.
- Global Dependence: The global semiconductor market has significant reliance on suppliers like Taiwan (44%), China (28%), and South Korea (12%).
- Global Shortage: The 2021 chip shortage highlighted the vulnerability of global supply chains, prompting efforts by countries to boost domestic semiconductor production.
Government Support for Semiconductor Manufacturing:
- Financial Incentives: The government offers fiscal support for setting up semiconductor manufacturing plants:
- 50% of project cost support under the Semiconductor Fab Scheme and the Display Fab Scheme.
- Support for Compound Semiconductors and Chips to Startup (C2S) initiatives.
- Training 85,000 engineers through the C2S Programme in collaboration with academic institutions, R&D organizations, and MSMEs.
e-Tarang System
- 18 Nov 2024
In News:
Recently, the Ministry of Defence launched the AI-enabled e-Tarang System.
Key Highlights:
- Development Collaboration: Created in partnership with Bhaskaracharya National Institute for Space Applications and Geo-informatics (BISAG-N).
- Purpose:
- Improve planning for interference-free operation of defence equipment during both wartime and peacetime.
- Enable automated, efficient planning and management of Defence Spectrum.
- Support the development of newer technologies in higher frequency bands.
- Facilitate rapid decision-making and integration of critical modern defence technologies.
BISAG-N Overview:
- Status: Autonomous Scientific Society under the Ministry of Electronics & Information Technology (MeitY), Government of India.
- Key Roles:
- Technology development and management.
- Research and development in geo-spatial technologies.
- National and international cooperation in geo-spatial fields.
- Capacity building and entrepreneurship development in geo-spatial technology.
- Core Domains:
- Satellite Communication
- Geo-informatics
- Geo-spatial Technology
Joint Electromagnetic Board (JEMB) – Annual Meeting Highlights:
- Chairperson: Air Marshal Jeetendra Mishra, Deputy Chief of Integrated Defence Staff (Operations).
- Attendees: Senior officers from the Indian Army, Navy, Air Force, DRDO, DDP, and industry.
- Agenda: Focused on joint operations and integration in several areas:
- Electronic Warfare (EW)
- Signature Management
- Emerging Technologies
- Electromagnetic Interference/Compatibility (EMI/EMC)
- Spectrum Management
- Human Resource Management
- Key Outcome:
- Introduction of the AI-enabled e-Tarang System to enhance Defence Spectrum management.
- Release of the Technical News Letter (TNL) 2024, outlining future technologies for modern warfare.
- Development of a roadmap to enhance Spectrum Warfare capabilities and integration of EW assets across the three Services.
- Successful joint EW exercise conducted in September 2024, promoting the principle of “Victory through Jointness”.
Objective of the Meeting:
- Goal: Achieve synergy in joint electronic warfare operations across the Services.
- Focus: Establish technology development and training priorities for the future.
Exercise PoorviPrahar

- 17 Nov 2024
In News:
- From November 10 to 18, 2024, the Indian Army is conducting a high-intensity tri-services exercise named PoorviPrahar in the forward areas of Arunachal Pradesh.
- The exercise aims to enhance the combat effectiveness and coordination between the Indian Army, Navy, and Air Force, focusing on integrated joint operations in the challenging mountainous terrain of the region.
About Exercise PoorviPrahar
Objective: The primary goal of Exercise PoorviPrahar is to hone the combat readiness and synergy across the three branches of the Indian Armed Forces. It is designed to improve their ability to conduct integrated joint operations, especially in the difficult terrain of Arunachal Pradesh, which is crucial due to the region's strategic location along India's eastern frontier.
Key Features of the Exercise:
- Multidomain Integration:The exercise involves land, air, and sea operations, demonstrating India's capability to conduct multi-domain operations. This showcases the Indian Armed Forces' preparedness to tackle threats across all three domains simultaneously.
- Advanced Military Platforms:
- Aircraft: Advanced fighter jets, reconnaissance aircraft.
- Helicopters: Including Chinook heavy-lift helicopters and Advanced Light Helicopters (ALH Rudra).
- Artillery: The exercise makes use of the M777 Ultra-Light Howitzers, which provide mobility and precision firepower in rugged terrains.
- Swarm Drones and Loitering Munitions: These cutting-edge technologies enable precision strikes and enhanced situational awareness, contributing to more flexible and adaptive operations.
- Technological Integration:
- The exercise integrates next-generation technologies like Swarm Drones, Loitering Munitions, and First-Person View (FPV) Drones. These tools enhance operational flexibility, improve situational awareness, and enable precision in strike capabilities, marking a significant advancement in India's military technology.
- Operational Coordination:A core component of the exercise is the development of a Common Operating Picture (COP). This system integrates real-time data from land, air, and sea operations, improving coordination and decision-making. The system relies on AI-driven analytics and satellite communications, enabling rapid information sharing and quicker response times.
- Tactical Focus on Mountain Warfare:Arunachal Pradesh, with its mountainous and rugged terrain, is the perfect setting for honing skills required for mountain warfare. The region’s proximity to India’s border with China makes it a critical area for India’s defense strategy.
Key Takeaways:
- Integrated Joint Operations: The exercise focuses on improving the coordination between the Army, Navy, and Air Force to execute seamless operations across land, air, and sea.
- Advanced Technology Integration: The exercise features the use of Swarm Drones, Loitering Munitions, and AI-driven systems to enhance precision, situational awareness, and overall operational flexibility.
- Mountain Warfare Expertise: Conducted in the mountainous terrain of Arunachal Pradesh, the exercise is crucial for preparing the Indian Armed Forces to operate effectively in such challenging landscapes.
- Strategic Posture: The exercise reaffirms India’s ability to defend its Eastern frontier and maintain a robust defense posture in the face of potential threats in the region.
Unified Complex Radio Antenna
- 17 Nov 2024
In News:
- India and Japan recently signed a Memorandum of Implementation (MoI) to co-develop the UNICORN (Unified Complex Radio Antenna) mast for deployment on Indian Navy ships. This pact marks a significant milestone as it is India's first military technology transfer agreement with Japan.
- The deal follows a 2015 agreement on the transfer of defense equipment and technology, further strengthening defense ties between the two countries.
- The UNICORN mast is a cutting-edge communication and radar system designed to enhance the stealth characteristics of naval vessels. This agreement is seen as an important step towards deepening India-Japan defense cooperation.
What is UNICORN?
The UNICORN mast is an advanced, integrated antenna system that combines several communication and radar components into a single conical structure or radome (a radar-absorbing dome). It is designed to reduce the radar cross-section (RCS) of ships, improving their stealth capabilities.
Key features of the UNICORN mast include:
- Integration of multiple antennas: It consolidates various antennas used for tactical data links, communications, and navigation systems (e.g., TACAN - Tactical Air Navigation System).
- Stealth enhancement: By reducing the number of exposed components and consolidating them into a single radome, the mast significantly lowers the ship’s radar signature, making it harder to detect.
- Improved performance: The mast design minimizes mutual interference between antennas, enhances maintainability, and increases lightning resistance.
- Space efficiency: It saves valuable below-deck space and reduces ship-building time by integrating multiple systems into one mast.
The UNICORN system is currently deployed on Mogami-class frigates of the Japan Maritime Self-Defence Force.
India-Japan Defense Cooperation
- 2015 Defense Technology Transfer Agreement: This pact established a framework for defense cooperation between India and Japan, paving the way for joint projects like the UNICORN mast.
- Bilateral Military Exercises:
- Veer Guardian 2023: A bilateral exercise conducted between the Japan Air Self Defence Force (JASDF) and the Indian Air Force (IAF), which deepened defense interoperability between the two nations.
- Tarang Shakti 2024: The first multilateral air exercise hosted by the Indian Air Force, with Japanese fighter aircraft participating.
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands Development: Japan has also provided financial aid for infrastructure development in India’s strategically located Andaman and Nicobar Islands, contributing to enhancing India’s maritime security in the region.
Red-Headed Vulture
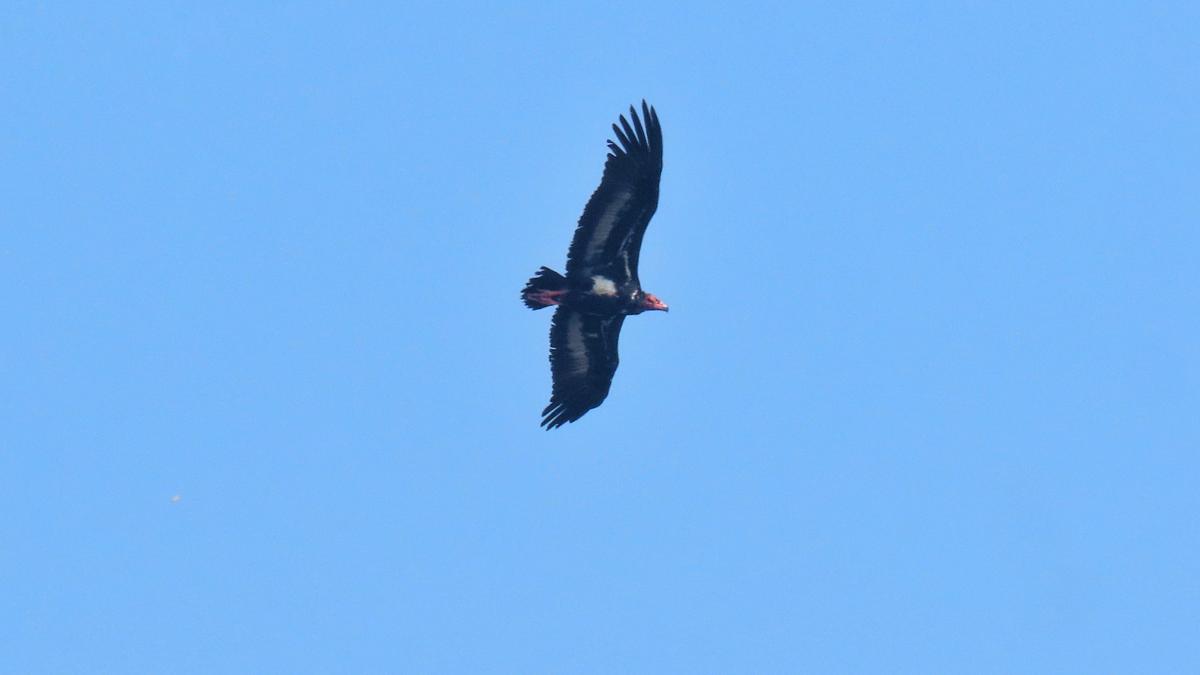

- 17 Nov 2024
In News:
- The Red-Headed Vulture, a critically endangered species, has been sighted for the first time in Kasaragod, Kerala, marking an important addition to the region’s avian biodiversity. This rare sighting occurred at Manhampothikunnu near Mavungal. Prior to this, the species was predominantly seen in the Wayanad region of Kerala.
- This discovery brings the total number of bird species recorded in Kasaragod to 407, showcasing the district's growing avian diversity.
About the Red-Headed Vulture:
- The Red-Headed Vulture (also known as the Asian King Vulture or Pondicherry Vulture) is one of the rarest and most critically endangered species of vultures in India. It is known for its distinctive scarlet red head and black body with a white patch on the abdomen.
- Physical Features: The bird is medium-sized, weighing around 5 kg, with a wingspan of up to 2.5 meters and a length of 80 cm. It is typically solitary, often found alone or with a mate.
- Distribution: Historically found in Central India, Nepal, Myanmar, Thailand, Vietnam, and parts of Kerala, Karnataka, and Tamil Nadu, the Red-Headed Vulture’s numbers have drastically declined in recent decades.
Conservation Status:
- IUCN Red List: The Red-Headed Vulture is classified as Critically Endangered.
- Wildlife Protection Act, 1972: It is listed under Schedule 1, offering it the highest level of legal protection.
- CITES: The species is also listed in Appendix II, indicating that it requires international conservation efforts to prevent it from becoming endangered.
Threats to Vultures:
- Diclofenac Poisoning: The significant decline in vulture populations in India, including the Red-Headed Vulture, is primarily due to the widespread use of diclofenac (a veterinary drug) to treat livestock. When vultures consume the carcasses of treated animals, they ingest the toxic drug, leading to kidney failure and death.
- Other threats include pesticide contamination, lead poisoning, habitat loss, and collisions with man-made structures like power lines and wind turbines.
Conservation Efforts in India:
- India has undertaken various efforts to protect vultures, including banning diclofenac in 2006 and expanding the ban to other harmful drugs like ketoprofen and aceclofenac in 2023.
- Vulture Conservation Breeding Centres (VCBCs): These centers are focused on captive breeding and reintroduction programs for vultures, helping to increase their populations. The Jatayu Conservation and Breeding Centre in Uttar Pradesh is one of the latest initiatives, set up to protect and rehabilitate vultures.
- Vulture Safe Zones have been created across India, providing safe habitats for vulture species to recover.
- Vulture Restaurant Initiative: In some regions, safe feeding centers (such as in Jharkhand) have been established, where vultures are provided uncontaminated carcasses, reducing their exposure to toxic substances.
- Legal Protection: Several species of vultures, including the Red-Headed Vulture, are protected under Schedule I of the Wildlife Protection Act, 1972, ensuring stringent legal measures against poaching and habitat destruction.
Global Conservation Efforts:
- India’s vulture conservation initiatives are part of a broader international effort under the SAVE (Saving Asia’s Vultures from Extinction) programme, which involves multiple regional and global organizations working to protect vulture species in South Asia.
Bali Jatra Cuttack Utsav 2024

- 17 Nov 2024
In News:
- Bali Jatra 2024 is being held from November 15 to November 22 in Cuttack, Odisha.
- The festival celebrates Odisha’s ancient maritime history and its cultural and trade links with Southeast Asia.
- The event has gained international attention due to the participation of diplomats and cultural troupes from ASEAN, BIMSTEC, and Pacific Island countries.
Historical and Cultural Significance:
- Bali Jatra ("Voyage to Bali") commemorates the 2,000-year-old maritime trade routes between ancient Kalinga (modern-day Odisha) and Southeast Asia, including regions like Bali, Java, Sumatra, Borneo, Burma (Myanmar), and Sri Lanka.
- The festival honors the skills of Kalinga sailors who contributed to the prosperity of the region through trade, including commodities like pepper, cinnamon, cardamom, silk, camphor, gold, and jewelry.
- It highlights Odisha’s maritime legacy and the cultural exchanges between India and Southeast Asia, particularly the cultural influence of Odia merchants on Bali.
Commercial and Economic Aspects:
- Bali Jatra is Asia’s largest open-air trade fair, featuring over 2,500 stalls selling a variety of products including artisanal crafts, household items, and food.
- The event is a major commercial activity with business transactions estimated to exceed ?100 crore over the course of the festival.
- The festival provides an opportunity for both local and national traders to exhibit products at competitive prices.
Cultural Performances and International Participation:
- The festival includes daily cultural performances showcasing Odissi dance, Chhau dance, Bihu, Mahari, Gotipua, Sambalpuri, and Santali folk dances.
- This year, cultural troupes from countries like Indonesia, Thailand, and Sri Lanka have participated, enhancing the international profile of the festival.
- Diplomats, including Ambassadors, High Commissioners, and Heads of Mission from 14 countries attended the inaugural ceremony.
Historical Background of Bali Jatra:
- The festival is linked to Kartika Purnima, the full moon night of the month of Kartika, marking the annual migration of traders from Odisha to Southeast Asia.
- Traders used boats called Boitas to travel to distant lands, which is now symbolically represented in the festival.
- The event’s cultural significance extends to the recognition of Odisha’s historic maritime routes, with ports like Tamralipti, Manikpatna, Chelitalo, Palur, and Pithunda playing key roles in global trade from as early as the 4th century BC.
Kalinga's Maritime Influence:
- The Kalinga Empire (present-day Odisha) had significant influence over the Bay of Bengal, referred to as the Kalinga Sea.
- Kalinga’s dominance in maritime trade is reflected in Kalidasa's Raghuvamsa, where the King of Kalinga is called "Lord of the Sea."
- Kalinga's Boitas (ships) were instrumental in connecting India with the Southeast Asian archipelago, including Bali.
Cultural Linkages with Bali:
- Odisha's trade with Bali influenced the culture, religion, and architecture of the region.
- Balinese Hinduism today still reflects Indian influences, with worship of Hindu deities like Shiva, Vishnu, Brahma, and Ganesha.
- The MasakapankeTukad festival in Bali, similar to Bali Jatra in Odisha, is a tribute to the maritime ancestors of Bali and commemorates the long-standing cultural ties.
Recognition and Milestones:
- Bali Jatra 2022 achieved a Guinness World Record for creating the largest collection of origami sculptures.
- The festival has evolved from a traditional trade fair to an international cultural event that highlights Odisha’s historical role in global trade and cultural exchanges.
TarunerSwapno Scheme

- 17 Nov 2024
In News:
Chief Minister Mamata Banerjee has ordered an inquiry after some intended beneficiaries of the ‘Taruner Swapna’ scheme, an initiative of the TMC government, alleged that they did not receive Rs 10,000 meant for the purchase of tablets (mobile device with a touchscreen display, rechargeable battery, and mobile operating system).
Overview:
- Aimed at bridging the digital divide by providing ?10,000 to Class 11 and 12 students in West Bengal for purchasing smartphones/tablets.
- In FY 2024-25, ?900 crore allocated for the scheme, targeting 16 lakh students.
- The main objective of the scheme is to provide scholarship to the students. So that the student can use their scholarship to buy a smartphone and tablet and can get education through online medium.
- This scheme will prove to be effective in making the future of the students bright and will also prove to be effective in strengthening them technically.
- Eligibility criteria for the scheme:
- Applicant must be a permanent resident of West Bengal State.
- The applicant should be a student.
- Students of 11th and 12th will be eligible for this scheme.
- The annual income of the family of the applicant student should not exceed Rs 2 lakh.
- Students with backlog are not eligible as this grant is for one-time only.
- This scheme will make the students technically strong and they will be able to improve their future with technology.
- Students of government/government-aided/sponsored schools and madrassas can avail assistance.
- TarunerSwapno Yojana will bridge the digital divide among students and facilitate modern education.
Europe’s Digital Euro

- 16 Nov 2024
In News:
The digital euro, a central bank digital currency (CBDC) being developed by the European Central Bank (ECB), aims to revolutionize Europe’s digital payment landscape. However, while the ECB has marketed it as a convenient, free, anonymous, and reliable alternative to existing cashless options like credit cards and mobile payment apps, the true purpose of the digital euro goes beyond these simplified claims.
Key Aspects of the Digital Euro
- Direct Issuance by the ECB: Unlike traditional digital payments that rely on intermediaries like banks or payment service providers, the digital euro is issued directly by the European Central Bank. This allows for peer-to-peer transactions without the need for third-party banks or payment gateways. It can be used for offline transactions, which is a major technical innovation that sets it apart from other digital currencies.
- A Digital Version of Cash: The digital euro is essentially a digital version of legal tender (cash), providing an alternative to cash in a world increasingly dominated by digital payments. Its key feature is direct payment between users, bypassing the traditional banking system. It aims to offer the same advantages as cash, such as anonymity, but with the convenience of digital transactions.
- Cost Reduction and Micro-Payments: The digital euro promises to lower transaction costs, especially for micro-payments that are currently prohibitively expensive using conventional bank transfers or digital services like PayPal. This cost efficiency is intended to enable new business models by lowering the friction in digital transactions, thus encouraging innovation in commerce.
The ECB’s Claims vs. the Real Motivation
While the ECB portrays the digital euro as a means to make payments easier, faster, and more secure, there is an underlying political and economic agenda that goes beyond improving consumer convenience.
- Sovereignty and Competition: One of the main drivers behind the digital euro is Europe’s desire to assert its digital sovereignty. The ECB positions the digital euro as a tool to strengthen the euro’s competitiveness against non-European payment providers, particularly those from the United States like PayPal, Apple Pay, and Google Pay. The EU is concerned that foreign companies may dominate the digital payment landscape, thereby reducing Europe's ability to control its own financial systems.
- This is a defensive measure to protect European financial interests. By creating a state-backed alternative to privately controlled digital payment systems, the EU aims to ensure that Europe does not become reliant on foreign corporations for essential services.
- Not About Citizens’ Convenience Alone: While the ECB frames the digital euro as a user-friendly solution for consumers, the real concern is about the control over digital currency. The digital euro offers a more centralized alternative compared to the decentralized nature of cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin. The ECB aims to harness the power of the state in regulating and controlling digital transactions, thus consolidating private property and ensuring the smooth functioning of Europe’s monetary policies.
- A Tool for Strengthening the Euro: The digital euro is also seen as part of Europe’s broader ambition to establish the euro as a dominant global currency. As the first fully-regulated digital currency issued by a central bank, it could position the euro to compete against other digital currencies, including the digital yuan or the U.S. dollar. The EU sees the digital euro as a way to expand its geopolitical influence by promoting its own currency as a global standard for digital payments.
Commemoration of Birsa Munda’s 150th Birth Anniversary

- 16 Nov 2024
In News:
On November 15, 2024, Prime Minister Narendra Modi launched a commemorative stamp and coin to mark the 150th birth anniversary of Birsa Munda, a prominent tribal freedom fighter and leader from Jharkhand.
Key Points about Birsa Munda:
- Iconic Tribal Leader: Birsa Munda, born in 1875, is often referred to as ‘Bhagwan’ (God) and ‘DhartiAaba’ (Father of the Earth) by the tribal communities. He is celebrated for his leadership in the fight against the exploitation of tribal people by both the British and non-tribal settlers.
- Ulgulan Movement: Birsa Munda led the Ulgulan (Great Tumult) against the alienation of land, forced labour, and the illegal appropriation of tribal land in the Chotanagpur Plateau. His efforts were critical in mobilizing tribal communities and challenging the colonial order.
- Religious and Social Reformer: He founded the Birsait faith, focusing on spiritual practices that emphasized prayer, worship of God, and abstaining from alcohol, fostering unity and resilience among tribal communities.
- Death and Legacy: Birsa Munda died in 1900 in British custody at the young age of 25. Despite his early death, his legacy lives on as a symbol of tribal pride and resistance.
- Janjatiya Gaurav Diwas: Since 2021, the Government of India observes November 15 as Janjatiya Gaurav Diwas (Tribal Pride Day) in honor of Birsa Munda's birth anniversary, recognizing the contributions of tribal communities and their role in India's history.
- Highlights of the 2024 Commemoration:
- Commemorative Stamp and Coin: To mark the 150th birth anniversary, the Prime Minister unveiled a commemorative stamp and coin in Bihar's Jamui district. This serves as a tribute to Munda's sacrifices for the country.
- Year-Long Celebrations: The 2024 event marks the beginning of year-long celebrations to commemorate Birsa Munda’s legacy, with a focus on tribal welfare and recognition of their historical contributions.
- Welfare Projects and Initiatives:
- Prime Minister Modi inaugurated and laid the foundation for tribal welfare projects worth over ?6,640 crore.
- The PM launched two tribal freedom fighter museums and tribal research institutes.
- 1.16 lakh homes were sanctioned under the Dharti Aba Janjati Gram Utkarsh Yojana.
- 25,000 homes for Particularly Vulnerable Tribal Groups (PVTGs) were approved under the Pradhan Mantri Janjati Adivasi Nyaya Maha Abhiyan (PM-JANMAN) scheme.
- The launch of 50 mobile medical units aims to improve healthcare access in tribal regions.
- 10 Eklavya Model Residential Schools (EMRS) were inaugurated to promote education for tribal students.
- DhartiAabaJanjatiya Gram Utkarsh Abhiyan:
- The DhartiAabaJanjatiya Gram Utkarsh Abhiyan aims to address gaps in social infrastructure, health, education, and livelihood in tribal-majority villages.
- The initiative is being implemented across 63,000 villages with the involvement of 17 ministries and departments.
- PM-JANMAN Scheme for PVTGs:
- Launched in November 2023, the PM-JANMAN initiative aims to uplift Particularly Vulnerable Tribal Groups (PVTGs) through various interventions like safe housing, clean drinking water, healthcare, education, and sustainable livelihoods. The scheme also supports Van Dhan Vikas Kendras for the trade of forest produce and solar-powered systems for households in tribal areas.
Partnerships for Accelerated Innovation and Research (PAIR)

- 16 Nov 2024
In News:
The Anusandhan National Research Foundation (ANRF) has launched the Partnerships for Accelerated Innovation and Research (PAIR) program to significantly boost research and innovation across Indian universities, especially those with limited research infrastructure. The program is designed to bring about a transformative change in India's academic research ecosystem, aligning with the broader goals of the National Education Policy (NEP) 2020.
Key Details:
- Launch Date: November 2024
- Ministry/Department: Department of Science and Technology (DST)
- Objective:
- To elevate research capabilities in universities that have limited resources by pairing them with well-established, top-tier institutions.
- To foster collaborations that can help these emerging universities enhance their research quality, drive innovation, and make significant, globally competitive research contributions.
- Operational Model: Hub-and-Spoke Framework
- Hub Institutions: These are well-established, top-tier institutions that will serve as mentors to less-researched universities. The hubs will be selected from:
- The top 25 institutions in the National Institutional Ranking Framework (NIRF).
- Institutions of National Importance ranked in the top 50 NIRF.
- Spoke Institutions: These are emerging universities or institutions with limited research infrastructure. These will include:
- Central and State Public Universities ranked within the top 200 NIRF Overall.
- Top 100 NIRF University/State Public Universities.
- Select NITs and IIITs.
- Hub Institutions: These are well-established, top-tier institutions that will serve as mentors to less-researched universities. The hubs will be selected from:
- Funding:
- The program has a budget allocation of up to ?100 crore per PAIR network.
- Distribution of Funds:
- 30% for the Hub institution.
- 70% for the Spoke institutions.
- Private Institutions serving as hubs will need to contribute 25% of their allocated budget.
- Mentorship & Research Focus:
- Hubs will provide mentorship to spoke institutions, guiding them in various aspects of research such as access to resources, advanced infrastructure, and best practices.
- The collaboration is expected to enhance research capabilities, foster innovation, and encourage the development of collaborative networks across institutions.
- Regional Diversity & Inclusion:
- The program ensures regional diversity, with at least one spoke institution located outside the hub's state.
- It also allows the inclusion of one promising university from Category III institutions that may not meet the eligibility criteria but show potential for growth in research.
- Phase-wise Rollout:
- The first phase will focus on institutions ranked within the top 25 NIRF and Institutions of National Importance.
- Future phases will expand the scope, allowing more universities and institutions to participate.
- Goals Aligned with NEP 2020:
- Fostering Research Excellence: By partnering top institutions with emerging ones, PAIR seeks to improve the quality of research in India’s higher education sector.
- Promoting Regional Diversity: Ensuring a geographically diverse set of institutions participate in the research ecosystem.
- Strengthening Innovation: Helping universities in less-researched areas to compete on an international level, particularly in cutting-edge and impactful research.
- Program Implementation:
- Prospective Program Directors from eligible Hub institutions are invited to apply online for the program at ANRF PAIR Application Portal.
About ANRF:
- ANRF was established under the ANRF Act 2023 as an apex body to provide strategic direction for scientific research in India.
- With the formation of ANRF, the Science and Engineering Research Board (SERB), previously established under an act of Parliament in 2008, has been subsumed into ANRF.
Global Maritime Conference
- 16 Nov 2024
In News:
In a bid to enhance India’s clout in the global merchant shipping sector, the government recently hosted a two-day global maritime conference – Sagarmanthan: The Great Oceans Dialogue.
Key Highlights:
- Purpose of the Conference:
- To enhance India's maritime influence and position India as a key player in the global maritime sector, especially in merchant shipping and maritime trade.
- To showcase India's ambitions in expanding its role in global maritime trade, governance, and collaboration.
- India's Maritime Ambitions:
- Despite being the most populous nation and one of the largest global economies, India’s maritime clout has been relatively lower than expected.
- The dialogue aims to shift global attention towards India's growing role and contributions to maritime trade and shipping.
- India's Maritime Growth:
- India contributed to 16% of global maritime growth in 2023 and is on track to become the third-largest global economy within three years.
- As India’s economic and geopolitical influence expands, maritime governance will become increasingly significant, necessitating deeper international collaborations in commerce, connectivity, and trade.
- Focus Areas of the Dialogue:
- Global Maritime Trade: India's expanding role in international shipping, trade routes, and maritime security.
- International Collaborations: Promoting deeper engagement in maritime governance and policy-making ecosystems.
- Human Well-being: Highlighting the role of maritime trade in supporting human welfare, particularly in the context of sustainable development and climate change.
- Significance for India:
- The conference serves as a platform to discuss India’s aspirations, policies, and presence in global maritime affairs.
- It is an opportunity to strengthen maritime relations and address issues of global relevance such as trade routes, shipping governance, and environmental sustainability
1st Bodoland Mohotsav

- 16 Nov 2024
In News:
- Recently, Prime Minister Narendra Modi inaugurated the 1st Bodoland Mohotsava two-day event focused on language, literature, and culture.
- Objective: Aims to promote peace, unity, and a vibrant Bodo society through cultural integration. The festival celebrates the rich Bodo culture and heritage.
Historical Context and Peace Initiatives:
- End of Violence: The event marks the end of 50 years of violence, following the Bodo Peace Accord (2020), which ended conflict in Bodoland and led to a path of peace and development.
- Peace Agreements: The Bodo Peace Accord served as a catalyst for other peace settlements, such as the KarbiAnglong Accord, Bru-Reang Accord, and NLFT-Tripura Accord.
Development in Bodoland Post-Peace Accord:
- Impact of the Peace Accord:
- Over 10,000 youth in Assam have renounced violence and joined the mainstream of development.
- Increased mutual trust between the people and the government.
- Economic Assistance:
- Rs 1,500 crore special package by the central government.
- Rs 700 crore spent on infrastructure development in education, health, and culture in Bodoland.
- Rs 5 lakh assistance for families affected by the Bodo conflict.
Government Support for Socio-Economic Development:
- Skill Development & SEED Mission:Focus on skilling, entrepreneurship, employment, and development through the SEED Mission for youth empowerment.
- Rehabilitation of Former Cadres:
- Over 4,000 former cadres of the National Democratic Front of Bodoland (NDFB) have been rehabilitated.
- Many youths have been recruited into Assam Police.
- Tourism & Employment:Growing tourism in Bodoland, with parks like Manas National Park and Raimona National Park, creating employment opportunities for youth.
Cultural Promotion:
- Bodo Culture and GI Tags:Promoting Bodo crafts like Aronnaye, Dokhona, Gamsa, etc., that have received Geographical Indication (GI) tags to preserve cultural identity.
- Bodoland Handloom Mission & Sericulture:Government efforts to promote sericulture and the Bodoland Handloom Mission to sustain Bodo weaving traditions.
- Literary Celebrations:
- Continuous Bodoland Literary Festival in Kokrajhar, enhancing the importance of Bodo literature and language.
- Celebration of Bodo Sahitya Sabha’s 73rd foundation day.
Key Government Initiatives for Development:
- Infrastructure Development:
- Rs 800 crore annually being spent by the Assam government for the development of Bodoland.
- Focus on healthcare, education, and employment.
- Medical Education:Expansion of medical colleges in Assam from 6 to 12, with plans for 12 more new colleges.
Operation Dronagiri

- 15 Nov 2024
In News:
- Recently, the Operation Dronagiri, launched under the National Geospatial Policy 2022 by the Department of Science and Technology (DST).
- Objective: It is a pilot project under India’s National Geospatial Policy 2022 aimed at showcasing the potential of geospatial technologies in sectors such as Agriculture, Livelihoods, and Logistics & Transport to improve quality of life and ease of doing business.
- Implementation:
- The first phase will cover five states: Uttar Pradesh, Haryana, Assam, Andhra Pradesh, and Maharashtra.
- Sectors Targeted: The focus will be on demonstrating the integration of geospatial data to solve real-world challenges in agriculture, transportation, and livelihoods.
National Geospatial Policy 2022
- Context: The National Geospatial Policy 2022 is aimed at liberalizing geospatial data and enabling widespread access and use of geospatial technologies across various sectors of governance, business, and development.
- Goals:
- Development of Geospatial Infrastructure: Promoting the creation of a robust infrastructure to make spatial data more accessible and usable.
- Geospatial Skill Development: Focus on creating a workforce proficient in geospatial technologies.
- Implementation of Standards: Establishing clear standards for geospatial data to ensure consistency and interoperability.
Role of Integrated Geospatial Data Sharing Interface (GDI)
- Launch: Alongside Operation Dronagiri, the Integrated Geospatial Data Sharing Interface (GDI) was also unveiled.
- Purpose: GDI is designed to facilitate seamless data sharing, access, and analysis of geospatial data.
- Key Features:
- Data Exchange: Enables smooth sharing of geospatial data for urban planning, disaster management, and environmental monitoring.
- Privacy and Security: Built with advanced data exchange protocols and privacy-preserving features to ensure secure data sharing.
- Collaboration: It will promote collaboration among stakeholders, including government agencies, industry, and startups, to unlock actionable insights for decision-making.
- Key Features:
Potential Applications of Geospatial Data
- Urban Planning: Assisting cities in designing efficient infrastructure.
- Disaster Management: Providing real-time data for better disaster response.
- Environmental Monitoring: Supporting initiatives for environmental protection and sustainability.
- Agriculture: Precision farming, crop monitoring, and improving supply chains.
- Logistics & Transport: Streamlining transportation networks, reducing traffic, and improving delivery systems.
Grand Challenge for Startups
- Objective: A Grand Challenge was announced as part of the initiative to support startups in developing Proofs of Concept (POCs) targeting specific problems in the focus sectors.
- Role of Startups: The challenge encourages innovation by early-stage and growth-stage startups in geospatial technology, offering mentorship, resources, and access to datasets.
- Geospatial Innovation Accelerators:
- The Geospatial Innovation Accelerators (GIAs) at prestigious institutions like IIT Kanpur, IIT Bombay, IIM Calcutta, and IIT Ropar will support this effort.
- Mentorship and Resources: These accelerators will provide the necessary support for startups to turn their innovations into scalable solutions.
Key Stakeholders and Operational Arms
- Geospatial Innovation Cell (DST): Responsible for overseeing the project’s implementation and execution.
- Navavishkar I-Hub Foundation (IITTNiF): Will manage the operational activities of Operation Dronagiri.
- Partnering Institutions: GIAs at IIT Kanpur, IIT Bombay, IIM Calcutta, and IIT Ropar will be the operational arms.
- Private Sector Involvement: Significant involvement of private sector companies, including startups, is crucial to ensuring the success and scalability of the project.
Impact and Significance
- Socioeconomic Benefits: The integration of geospatial data into agriculture, transport, and logistics will improve efficiency, reduce costs, and boost economic activity in critical sectors.
- Geospatial Innovation: The initiative marks a significant step towards making India a global leader in geospatial technology and positioning the country as a hub for innovative solutions using geospatial data.
- Government Engagement: The project will involve various government departments and corporates in a public-private partnership (PPP) model, similar to the successful implementation of the UPI payment system.
Mobility Arrangement for Talented Early-professionals Scheme (MATES)
- 15 Nov 2024
In News:
Australia has come up with a new scheme that allows talented young people from India to work in the country for some time.
What is the MATES Scheme?
- Full Name: Mobility Arrangement for Talented Early-professionals Scheme (MATES).
- Objective: To provide Indian university graduates and early-career professionals with an opportunity to live and work in Australia for up to two years.
- Establishment: The scheme is part of the Migration and Mobility Partnership Arrangement (MMPA) between Australia and India, signed on May 23, 2023.
- Launch Date: MATES will open for applicants in December 2024.
Eligibility Criteria
- Age: Applicants must be 30 years or younger at the time of application.
- Educational Qualifications: Must have graduated within the last two years from an eligible institution with a Bachelor’s degree or higher in one of the following fields:
- Renewable Energy
- Mining
- Engineering
- Information Communications Technology (ICT)
- Artificial Intelligence (AI)
- Financial Technology (FinTech)
- Agricultural Technology (AgriTech)
- English Proficiency: A minimum score of 6 overall in IELTS (or equivalent), with at least 5 in each module.
- Institutional Criteria: Graduates must be from the top 100 Indian universities as per the NIRF Ranking 2024 (e.g., Panjab University, Chandigarh University, Thapar Institute of Engineering, Lovely Professional University).
- Previous Participation: Applicants must not have previously participated in the MATES scheme.
Key Features of the MATES Scheme
- No Employer Sponsorship Required: Applicants are not required to have sponsorship from an Australian employer.
- Visa Duration: The visa allows a stay of up to 2 years in Australia, with multiple entries permitted.
- Dependents: Visa holders can bring dependents (spouse and children). Dependents will have work rights in Australia but will not count towards the annual cap.
- Visa Application Process:
- The visa will be granted through a ballot system (random selection).
- Application Fee: AUD 25.
- Shortlisted candidates will proceed to further formalities.
Program Features
- Targeted Sectors: MATES focuses on key sectors such as renewable energy, mining, engineering, ICT, AI, FinTech, and AgriTech, aligning with Australia’s demand for skilled professionals in these areas.
- Pilot Program: Initially, the scheme will offer 3,000 places per year for primary applicants.
- Work Flexibility: While the visa does not require applicants to work in their nominated field, it is designed to help young professionals expand their skills and network in Australia’s key industries.
Additional Benefits
- Career Development: Participants will gain international work experience, expanding their professional network and skills.
- Cultural Exchange: The scheme also promotes cultural exchange between India and Australia, fostering stronger bilateral relations.
- Pathway for Future Opportunities: Participants may apply for further temporary or permanent residence in Australia, provided they meet the eligibility requirements.
Impact and Significance
- Bilateral Cooperation: The MMPA, under which MATES is established, enhances migration and mobility between India and Australia while addressing concerns related to illegal migration.
- Youth Empowerment: The scheme offers young professionals a platform to develop their careers internationally, particularly in sectors of global relevance like AI, FinTech, and renewable energy.
- Skill Development: MATES aims to bridge skill gaps in Australia by attracting Indian professionals to key sectors where expertise is in high demand.
- Global Talent Mobility: This scheme supports the global mobility of young talent and strengthens the India-Australia economic and educational partnership.
Know Your Medicine (KYM) App

- 15 Nov 2024
In News:
Union Minister for Youth Affairs & Sports, Dr. Mansukh Mandaviya, has launched a nationwide appeal to strengthen the fight against doping in sports, urging athletes, coaches, and the entire sporting community to embrace the National Anti-Doping Agency (NADA) India's ‘Know Your Medicine (KYM)’ app.
Introduction to KYM App
- Launch: The app was launched by Dr. Mansukh Mandaviya, Union Minister for Youth Affairs and Sports, to combat doping in sports.
- Developer: National Anti-Doping Agency (NADA) India.
- Purpose: To prevent inadvertent doping by allowing athletes to check whether a medicine contains substances prohibited by the World Anti-Doping Agency (WADA).
Key Features of the KYM App
- Medicine Verification: The app enables athletes to verify if any medicine or its ingredients contain banned substances listed by WADA.
- Image and Audio Search: Unique search features help users easily search for specific sport-related information.
- Customizable Search: Users can select their sport category and receive relevant, sport-specific information.
- User-Friendly: Designed for athletes, coaches, and sports professionals to quickly verify medicines and ensure clean competition.
Importance of KYM App
- Supporting Clean Sports: The app promotes a fair and ethical sporting culture by reducing the risk of inadvertent doping.
- Integrity of Sports: Helps athletes avoid penalties or bans due to accidental doping, maintaining the integrity of the competition.
- Accessible Information: Provides easy access to information regarding medicines that may contain banned substances, which is crucial for athletes' health and careers.
NADA India's Mission
- Anti-Doping Awareness: The KYM app is part of NADA India’s broader initiative to educate athletes and raise awareness about the dangers of doping.
- Goal: To promote dope-free sports and ensure that athletes and coaches are equipped with the tools needed for compliance with anti-doping regulations.
NADA India: Background and Functions
- Established: NADA India was set up in November 2005 under the Societies Registration Act, 1860.
- Mission: To serve as the independent Anti-Doping Organization for India, aiming to create a doping-free sporting environment.
- Key Functions:
- Implementing Anti-Doping Code: Ensuring compliance with the World Anti-Doping Code among all sports organizations in India.
- Dope Testing Program: Coordinating a national dope testing program with stakeholders across various sports.
- Promoting Research and Education: Encouraging research on anti-doping and educating athletes on the importance of staying clean.
- Adopting Best Practices: Ensuring the implementation of high-quality standards for anti-doping programs.
Impact and Significance
- Preventing Doping: The KYM app helps prevent inadvertent doping incidents by providing athletes with the necessary tools to check their medicines.
- Supporting Athletes: It provides athletes with a reliable way to avoid banned substances in over-the-counter medications, thus safeguarding their careers.
- National and International Compliance: Supports India’s commitment to complying with international anti-doping norms, contributing to a global effort to maintain fairness in sports.
Operation Kawach

- 15 Nov 2024
In News:
The Delhi Police recently initiated Operation Kawach, arresting and detaining around 1,000 people in an attempt to crack down on various gangs and their operations in the wake of the recent incidents of shootings reported in the city.
Overview of Operation Kawach
- Objective: A crackdown on gang-related violence, drug trafficking, and other illegal activities like possession of firearms, banned drugs, and liquor.
- Agencies Involved:Delhi Police (Local Police, Special Cell, and Crime Branch)
- Duration: Initiated on November 12, 2024 (5 PM) and continued until November 13, 2024 (5 PM).
Key Details of the Operation
- Arrests and Detentions:
- Around 1,000 people detained.
- 486 people apprehended in Outer North Delhi (20% juveniles).
- Arrests made in Dwarka, Southwest, and North Delhi.
- Key Gangs Targeted:
- Associated with notorious gangs led by Lawrence Bishnoi, Neeraj Bawana, Kaushal Chaudhary, TilluTajpuria, Kala Jatheri, Manjeet Mahal, and Nandu gangs.
- Charges: Involvement in activities like:
- Possession of illegal firearms.
- Trafficking of liquor and banned drugs (NDPS Act).
- Theft and other criminal activities.
Significance of Operation Kawach
- Public Safety: Aimed at dismantling organized crime networks to enhance safety and reduce violence in Delhi.
- Impact on Gangs: Directly targets high-profile criminals, including those involved in gang wars and drug trafficking.
- Strategic Law Enforcement: Strengthens law enforcement capabilities, working in coordination across multiple police units.
Domestic Systemically Important Banks (D-SIBs)

- 15 Nov 2024
In News:
The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) retained the State Bank of India, HDFC Bank and ICICI Bank as Domestic Systemically Important Banks (D-SIBs).
Overview of D-SIBs
- Definition: D-SIBs are banks that are 'Too Big to Fail' (TBTF) and their failure could significantly disrupt essential banking services, affecting the economy.
- RBI Classification: The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) has designated SBI, HDFC Bank, and ICICI Bank as D-SIBs.
- Bucketing System: These banks are classified into different buckets based on their systemic importance.
Importance of D-SIBs
- Systemic Importance: Banks are considered systemically important due to their:
- Size
- Cross-jurisdictional activities
- Complexity
- Interconnectedness with the economy
- Impact of Failure: Failure of a D-SIB could cause significant disruption in the banking system and economy, impacting services like payments, loans, etc.
Why D-SIBs are Created
- Risk of Disruption: The failure of a large bank can disrupt essential services and lead to a broader economic crisis.
- TBTF Perception: These banks are often perceived as Too Big to Fail, leading to an expectation of government support during crises. This creates moral hazard, encouraging riskier behavior.
Assessment and Selection of D-SIBs
- Two-Step Process:
- Step 1: Selection of banks based on their size, complexity, and interconnectedness. Only banks with systemic importance are assessed (e.g., banks with assets > 2% of GDP).
- Step 2: Calculation of systemic importance score based on a range of indicators. Banks above a certain threshold are classified as D-SIBs.
- Indicators: Size (measured by Basel III Leverage Ratio Exposure Measure), interconnectedness, substitutability, and complexity are key factors.
Bucket Allocation and Capital Requirements
- D-SIBs are assigned to five buckets based on their systemic importance score:
- Bucket 1: Lowest capital surcharge (e.g., ICICI Bank).
- Bucket 5: Highest capital surcharge.
- Additional Capital Requirements:
- SBI: Additional 0.80% CET1 (Common Equity Tier 1) on Risk-Weighted Assets (RWAs).
- HDFC Bank: Additional 0.40% CET1.
- ICICI Bank: Additional 0.20% CET1.
- The higher the bucket, the higher the capital surcharge.
Global Systemically Important Banks (G-SIBs)
- Global List: Identified by the Financial Stability Board (FSB) based on data from the previous year.
- 2023 G-SIB List includes banks like JP Morgan Chase, Bank of America, HSBC, etc.
- Capital Requirement for G-SIBs in India: Foreign G-SIBs with branch presence in India must meet additional CET1 requirements, proportional to their operations in India.
Key Terms
- Risk-Weighted Assets (RWAs): These are used to calculate the minimum capital a bank must hold. It accounts for the risk level of a bank’s assets.
- Common Equity Tier 1 (CET1): The highest quality of capital a bank can hold, primarily made up of common stock, to absorb losses in times of distress.
World Diabetes Day 2024
- 14 Nov 2024
In News:
- World Diabetes Day is observed on November 14th each year to raise awareness about diabetes, its prevention, and management.
- It was created by the International Diabetes Federation (IDF) and the World Health Organization (WHO).
- Significance: Commemorates the birthday of Sir Frederick Banting, who co-discovered insulin in 1922 alongside Charles Best.
- Theme (2024): "Access to Diabetes Care: Empowering Better Health for All".
History:
- Established in 1991 by the International Diabetes Federation (IDF) and World Health Organization (WHO).
- Recognized as a global observance by the UN in 2006.
- Activities: Awareness campaigns, health check-ups, educational seminars, and lighting of Blue Circle Monuments worldwide as a symbol of unity in the fight against diabetes.
Global Diabetes Data (2022):
- Total Diabetic Adults: 828 million globally.
- India's Share: 212 million (approximately 25% of global cases).
- Other Countries:
-
- China: 148 million.
- USA: 42 million.
- Pakistan: 36 million.
- Indonesia: 25 million.
- Brazil: 22 million.
Risk Factors for Diabetes:
- Global Factors: Obesity and poor diets are key contributors.
- India-Specific Factors: Dietary habits, lack of exercise, and socio-economic disparities contribute significantly to the high prevalence.
Untreated Cases:
- Global untreated cases (2022): 445 million (59% of diabetics globally).
- India untreated cases (2022): 133 million (64 million men, 69 million women).
- Complications: Untreated diabetes leads to severe health complications, including heart disease, kidney failure, and premature death.
Types of Diabetes:
- Diabetes Mellitus: The most common type of diabetes, characterized by issues with insulin production or its efficient use.
- Type 1 Diabetes (T1D):
- Autoimmune condition where the pancreas produces little or no insulin.
- Primarily affects children and young adults.
- Type 2 Diabetes (T2D):
- Insulin resistance combined with reduced insulin production.
- Often linked to lifestyle factors like obesity and physical inactivity.
- Gestational Diabetes:
- Occurs in pregnant women, leading to high blood sugar.
- Typically resolves after childbirth.
- Diabetes Insipidus:
- Imbalance of water regulation due to inadequate secretion or response to antidiuretic hormone (ADH).
- Leads to excessive urination and dehydration.
- Type 1 Diabetes (T1D):
Symptoms of Diabetes:
- Frequent urination.
- Excessive thirst and hunger.
- Unexplained weight loss.
- Blurred vision.
- Fatigue.
- Slow-healing wounds.
Role of Insulin in Managing Diabetes:
- Function of Insulin: A hormone produced by the pancreas that helps regulate blood glucose levels by facilitating glucose uptake into cells.
- In Type 1 Diabetes: Insulin injections or pumps are essential for survival.
- In Type 2 Diabetes: Insulin or oral medications may be prescribed alongside lifestyle modifications like diet and exercise.
Government Initiatives in India:
- National Programme for Prevention and Control of Cancer, Diabetes, Cardiovascular Diseases, and Stroke (NPCDCS): Focuses on awareness, early diagnosis, and management of diabetes.
- National Health Policy (2017): Aims to reduce premature deaths from non-communicable diseases by 25% by 2025.
- Ayushman Bharat – Health and Wellness Centres: Provides free screenings and consultations for diabetes and other non-communicable diseases.
- Eat Right Movement: Promotes healthier dietary habits to combat obesity and reduce diabetes risks.
- School Health Programs: Aims to educate children on healthy lifestyles to prevent the early onset of Type 2 diabetes.
Decline in African Elephant Population

- 14 Nov 2024
In News:
- The population of African elephants has been declining rapidly, with data showing alarming drops across the African continent.
- Survey Period: The study covers population data from 475 sites in 37 countries over 52 years (1964-2016).
- Population Decrease:
- Savannah Elephants: A 70% decline on average across surveyed sites.
- Forest Elephants: A 90% decline on average across surveyed sites.
- Overall Impact: The study indicates a 77% average decline in elephant populations across both species.
Main Drivers of Decline
- Poaching: Illegal hunting for ivory and other body parts remains a major threat.
- Habitat Loss: Urbanization, agricultural expansion, and climate change are encroaching on the elephant’s natural habitats.
- Human-Elephant Conflict: Increased human settlements near elephant habitats lead to conflicts, further endangering elephant populations.
Species Overview
- Two Subspecies:
- Savannah Elephant (Loxodonta africana): Larger and more common, found in open savannas.
- Forest Elephant (Loxodonta cyclotis): Smaller and more elusive, found in dense rainforests.
- Conservation Status:
- Savannah Elephant: Endangered (IUCN).
- Forest Elephant: Critically Endangered (IUCN).
- CITES Listing: Both species are listed under CITES Appendix I, which bans international trade in endangered species.
Regional Impact
- Northern and Eastern Africa: These regions have seen drastic declines, particularly in the Sahel (Mali, Chad, Nigeria), where elephants have been extirpated (locally extinct) due to poaching and insufficient protection.
- Southern Africa: Positive Growth in some areas, particularly in Botswana, Zimbabwe, and Namibia, where elephant populations are growing due to strong conservation efforts.
Conservation Success
- Southern Africa: 42% of the surveyed sites showed increasing elephant populations, a testament to successful conservation strategies.
- Government and NGO Efforts: Successful population growth is often attributed to active management, including anti-poaching laws, protected areas, and conservation funding.
Elephant Behavior and Reproduction
- Social Structure: Elephants live in family units led by mature females, with strong social bonds.
- Low Sleep Time: Elephants sleep only 2 hours per day on average.
- Reproduction: They have a long gestation period of up to 2 years, and calves are cared for by mothers and allomothers (non-mother females).
Conservation Challenges
- Sustainability: Continued poaching and habitat destruction threaten to undo gains made in conservation.
- Fragmentation of Populations: With many elephants in isolated pockets, genetic diversity is declining, which could lead to long-term problems for species survival.
Jawaharlal Nehru Memorial Fund (JNMF)

- 14 Nov 2024
In News:
Jawaharlal Nehru Memorial Fund to launch ‘Nehru Archive’ next year.
Nehru Archive Initiative
- Launch Date: The Nehru Archive will go online on November 14, 2025, coinciding with Jawaharlal Nehru's birth anniversary.
- Purpose: The archive will showcase less-known published and unpublished works of India’s first Prime Minister, Jawaharlal Nehru, including his speeches, letters to Chief Ministers, and other writings.
Archive Content
- Key Features:
- 100 volumes of The Selected Works of Jawaharlal Nehru.
- Letters to Chief Ministers (1947-1964), documenting Nehru's communication with state leadership.
- Nehru’s iconic books like:
-
-
- The Discovery of India
- Glimpses of World History
- Letters from a Father to His Daughter
- An Autobiography
- The Unity of India
- A Bunch of Old Letters
-
-
- Speeches from 1917 to 1964.
- Writings on Nehru by his contemporaries.
- Global archival material from international sources.
- Objective: The goal is to provide dynamic, continuously updated, open-ended access to Nehru’s work, making it the most important research source on Nehru.
Significance
- Educational and Intellectual Contribution: The archive will serve as a comprehensive, accessible source of information for students, scholars, and the general public to understand Nehru’s contributions to the making of modern India.
- Preservation of Legacy: It will preserve and promote Nehru’s intellectual legacy and his vision for India's development post-independence.
- Historical Importance: The archive will help contextualize Nehru’s leadership during critical periods of Indian history, including India’s independence, partition, and post-independence challenges.
Governance and Establishment of JNMF
- Founded: The Jawaharlal Nehru Memorial Fund (JNMF) was established in 1964 through a Deed of Declaration of Trust following a National Committee chaired by Dr. S. Radhakrishnan, then President of India.
- Purpose: To preserve and promote Nehru's legacy, especially his role in shaping modern India.
- Governance: The JNMF is governed by 14 trustees and is currently headed by Sonia Gandhi, the Chairperson of the Congress Parliamentary Party.
Sea Ranching Initiative off Vizhinjam Coast

- 14 Nov 2024
In News:
- The State Fisheries Department in Kerala launched a sea ranching project by releasing 20,000 pompano (Trachinotus blochii) fingerlings off the Vizhinjam coast as part of the artificial reef project.
- Coordinates: The fingerlings were released near artificial reef modules placed 1.5 nautical miles off the coast.
- Follow-up to Artificial Reef Project: The release of fingerlings is a follow-up to the artificial reef project aimed at replenishing marine fishery resources and promoting sustainable fishing practices.
Project Details
- Fingerling Release: The first batch of 20,000 pompano was released as part of the broader initiative to release 10 lakh fingerlings (pompano and cobia) at 10 locations along the Thiruvananthapuram coast.
- Location and Quantity: At each location, 1 lakh fingerlings will be released, where artificial reefs have already been deployed under the Pradhan Mantri Matsya Sampada Yojana (PMMSY).
- Reef Design: Artificial reefs consist of 150 reef modules (triangular, flower, and pipe-shaped) created at 42 locations off 33 fishing villages in the Thiruvananthapuram district.
Objective and Benefits
- Marine Resource Replenishment: The primary aim is to replenish marine fishery resources in the region by enhancing biodiversity through the introduction of fingerlings.
- Sustainable Fishing: The project aims to promote sustainable fishing practices by supporting fish populations and ensuring long-term fishery health.
- Attraction of Fish Species: The artificial reefs have already attracted a variety of fish species, including tuna, trevally, and mackerel, enhancing the fishing ecosystem.
Implementation and Funding
- Scheme: The project is being implemented under the Pradhan Mantri Matsya Sampada Yojana (PMMSY), which focuses on sustainable fisheries development.
- Central Approval: The National Fisheries Development Board (NFDB) approved the ?3 crore funding for the initial phase in Thiruvananthapuram.
- Proposed Expansions:
- Phase II: A proposal for extending the artificial reef project to 96 villages in the districts of Kollam, Alappuzha, Ernakulam, and Thrissur with an estimated cost of ?29.76 crore.
- Phase III: A similar proposal for 96 villages in the northern districts of Malappuram, Kozhikode, Kannur, and Kasaragod with an estimated cost of ?25.82 crore.
Mission and Fingerlings Details
- Fingerlings:
- Pompano (Trachinotus blochii) and Cobia (Rachycentron canadum) fingerlings were reared at the Ayiramthengu fish farm.
- Each fingerling weighs between 8 to 10 grams.
- The release aims to stock marine areas with species that will contribute to biodiversity and fisheries sustainability.
Pradhan Mantri Matsya Sampada Yojana (PMMSY)
- Launched: PMMSY is a Centrally funded scheme under the Ministry of Fisheries, Animal Husbandry, and Dairying.
- Goal: The scheme focuses on sustainable fisheries development to enhance fisheries production, boost aquaculture, and promote responsible fishing practices.
- Funding: The scheme involves both Central and State Government funding for projects related to fisheries management, infrastructure development, and resource conservation.
Mission Fingerling
- Launched: 2017 by the Union Ministry of Agriculture and Farmers’ Welfare.
- Objective: To achieve the Blue Revolution by holistically developing and managing fisheries in India.
- Production Target: The mission aimed to increase fisheries production from 10.79 MMT (2014-15) to 15 MMT by 2020-21.
OECD Report on Indian Agricultural Policies

- 14 Nov 2024
In News:
- In 2023, the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD) revealed that Indian farmers faced the highest implicit taxation globally, amounting to USD 120 billion.
- Implicit Taxation: This taxation arises from government policies like export bans, duties, and price controls, aimed at lowering food prices for consumers but reducing the income of farmers.
- Export Restrictions: Key commodities affected include rice, sugar, onions, and de-oiled rice bran.
Impact on Indian Farmers
- Market Price Support (MPS):
- Negative MPS: In 2023, Indian agricultural policies resulted in a negative MPS of USD 110 billion.
- Farmers received lower prices than international market rates due to export bans and trade restrictions, impacting their income.
- Budgetary Support: Despite government subsidies and the Minimum Support Price (MSP) worth USD 10 billion, negative MPS outweighed positive support, leading to an overall loss for farmers.
- Farmer’s Share in Global Negative Support:
- India’s share of global negative price support in 2023 was 62.5%, a significant increase from 61% in 2000-02.
Global Agricultural Policy Trends
- Global Support: Total support for agriculture across 54 countries averaged USD 842 billion annually (2021-2023). However, there was a decline in support in 2022-23 from the pandemic-era peak.
- Challenges:
- Geopolitical Tensions (e.g., Russia-Ukraine war) and climate change are exacerbating global agricultural production and trade.
- Export Restrictions in various countries are distorting international agricultural markets.
- Farmer Protests across countries reflect the economic and social struggles of the farming community.
- Sustainability Issues: Global agricultural productivity growth is slowing, posing challenges to feeding a growing population sustainably.
India's Agricultural Policies
- Export Bans and Restrictions: These policies are intended to control domestic prices but undermine farmers’ income by lowering market prices for key agricultural products.
- Minimum Support Price (MSP): MSP is meant to protect farmers, but is often set below international market rates, leading to a negative price effect.
- Regulatory Constraints: Policies like the Essential Commodities Act (1955) and APMC Act (2003), though aimed at ensuring food security, often lead to price suppression for farmers.
- Price Depressing Policies: India's agricultural policies result in lower farm-gate prices due to price controls, government-set procurement prices, and lack of market access.
Negative Market Price Support (MPS)
- Historical Trends:
- From 2014-2016, India’s Producer Support Estimate (PSE) was -6.2%, driven mainly by negative MPS (-13.1%).
- The PSE measures the annual value of transfers to farmers, both from consumers and the government.
- Inefficiencies:
- Infrastructure Gaps: Poor infrastructure and high transaction costs lower the prices farmers receive.
- Inefficient Resource Allocation: Short-term subsidies for inputs (fertilizers, irrigation) don’t address long-term agricultural challenges like climate change and market access.
Government Support Programs
- Subsidies and Schemes:
- National Mission on Sustainable Agriculture (NMSA)
- Paramparagat Krishi Vikas Yojana (PKVY) for organic farming.
- Rashtriya Krishi Vikas Yojana (RKVY) to promote agricultural development.
- Digital Agriculture Mission and Unified Farmer Service Platform (UFSP) for modernizing agricultural practices.
- Sustainability Efforts:
- The government has introduced initiatives like AgriStack and Mission Organic Value Chain Development in the North East to enhance sustainable agricultural practices and reduce the negative impacts on farmers.
Global Context and Recommendations
- Environmental Public Goods Payments (EPGP): Only 0.3% of total producer support is dedicated to environmental sustainability, despite the growing need for climate-resilient agriculture.
- Sustainable Agricultural Practices: The OECD advocates for governments to tie producer support to sustainable farming practices, including the use of metrics like Total Factor Productivity (TFP) and Agri-Environmental Indicators (AEIs).
- TFP measures agricultural efficiency, while AEIs assess the environmental impacts of farming.
OECD Overview
- OECD Function: Founded in 1961, the OECD is an international organization of 38 countries that promotes prosperity, equality, and well-being through economic reports, data, and policy analysis.
- India’s Role: India has been an OECD Key Partner since 2007, engaging with the OECD on various policy issues, though it is not a member.
Global Nature Conservation Index (NCI) 2024
- 13 Nov 2024
In News:
India with an abysmal score of 45.5 (out of 100) has been ranked 176th in the Global Nature Conservation Index, 2024.
Key Highlights:
- India's Ranking:
- Ranked 176th out of 180 countries in the 2024 Global Nature Conservation Index (NCI).
- India is listed among the five worst performers, along with Kiribati (180), Turkey (179), Iraq (178), and Micronesia (177).
- Score: 45.5 out of 100, indicating significant conservation challenges.
- Key Factors Contributing to Low Rank:
- Inefficient land management practices.
- Rising threats to biodiversity, exacerbated by unsustainable development and climate change.
- Four Key Markers Assessed by the NCI:
- Land Management: Ineffective management leading to significant land conversion.
- Threats to Biodiversity: Habitat loss, fragmentation, and deforestation.
- Capacity and Governance: Need for stronger political will and better enforcement of conservation laws.
- Future Trends: Growing pressure from population density, climate change, and illegal wildlife trade.
- Sustainable Land Use Concerns:
- 53% of land has been converted for urban, industrial, and agricultural purposes.
- High use of pesticides and concerns over soil pollution.
- Sustainable nitrogen index of 0.77 indicates significant risks to soil health.
- Marine Conservation Issues:
- Only 0.2% of India’s national waterways are under protected areas, with no protected areas within its Exclusive Economic Zone (EEZ).
- Significant improvements needed in marine conservation despite 7.5% of terrestrial areas being protected.
- Deforestation and Habitat Loss:
- 23,300 sq. km of tree cover lost between 2001-2019 due to deforestation.
- Habitat fragmentation from agriculture, urbanization, and infrastructure development.
- Impact of climate change on sensitive ecosystems like alpine regions and coral reefs.
- Biodiversity Decline:
- Despite 40% of marine species and 65% of terrestrial species being within Protected Areas (PAs), many species continue to face population decline.
- 67.5% of marine species and 46.9% of terrestrial species are still experiencing population declines.
- Illegal Wildlife Trade:
- India is the fourth-largest illegal wildlife trading nation globally, with an estimated annual trade value of £15 billion.
- The NCI emphasizes the need for stronger enforcement and international cooperation to combat wildlife trafficking.
- Ecological Wealth Under Threat:
- India’s high population density (with a population that has doubled since the late 1970s) continues to put pressure on its ecological wealth.
- The country faces significant biodiversity challenges due to overpopulation and unsustainable development.
- Recommendations and Optimism:
- The NCI stresses the need for strong political will and commitment to sustainable development.
- India can improve its rank by strengthening conservation laws, improving governance, and securing funding for environmental initiatives.
- The NCI remains optimistic about India’s potential to address its conservation challenges and achieve more sustainable outcomes in the future.
- About the Nature Conservation Index (NCI):
- Developed by: Goldman Sonnenfeldt School of Sustainability and Climate Change (Ben-Gurion University) and BioDB.com (a biodiversity database).
- Purpose: Evaluates the conservation efforts of countries, using a data-driven approach to balance conservation and development.
- Key Focus Areas: Land management, biodiversity threats, governance, and future sustainability trends.
RBI's New Framework for Reclassification of FPI to FDI
- 13 Nov 2024
In News:
The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) directed foreign portfolio investors (FPIs) to obtain necessary approvals from the government and concurrence from the investee companies when their equity holdings go beyond the prescribed limits and they reclassify the holdings as foreign direct investment (FDI).
- Approval Requirement:
- FPIs (Foreign Portfolio Investors) must obtain necessary government approvals when reclassifying their foreign portfolio investments (FPIs) into Foreign Direct Investment (FDI).
- Approvals are mandatory, including those related to investments from countries sharing a land border with India.
- Investment Limits:
- According to FEMA (NDI) Rules, 2019, an FPI’s investment in an Indian company should not exceed 10% of the total paid-up equity capital (on a fully diluted basis).
- If the FPI exceeds this limit, it has 5 trading days from the settlement of trades to either divest or reclassify the excess holdings as FDI.
- Restrictions on Reclassification:
- Reclassification to FDI is not allowed in sectors where FDI is prohibited.
- FPIs must ensure compliance with FDI norms, such as entry routes, sectoral caps, investment limits, pricing guidelines, and other related conditions.
- Concurrence from Investee Companies:
- The FPI must obtain the concurrence of the investee company for reclassifying the investment into FDI.
- This ensures that the company adheres to conditions related to prohibited sectors, sectoral caps, and government approvals.
- Reclassification Procedure:
- The FPI must clearly state its intent to reclassify the investment to FDI and provide the necessary approvals and concurrence to its custodian.
- The custodian is responsible for freezing the FPI's purchase transactions in the investee company’s equity instruments until the reclassification is complete.
- Regulatory Adherence:
- The reclassification must follow the relevant provisions for FDI, including compliance with the Foreign Exchange Management Act (FEMA) and FDI guidelines.
India’s Vision of ‘Adaptive Defence’

- 13 Nov 2024
In News:
- Defence Minister Shri Rajnath Singh introduced the concept of ‘Adaptive Defence’ at the inaugural Delhi Defence Dialogue (DDD).
- Adaptive Defence aims to prepare India's military for the rapidly changing landscape of modern warfare, with evolving threats and technologies shaping global security.
Key Aspects of Adaptive Defence:
- Strategic Approach:
- Adaptive Defence is an evolving strategy where military and defence systems continuously adjust to emerging threats, focusing on proactive preparedness rather than reactive responses.
- It is based on anticipating future threats, fostering flexibility, resilience, and agility in both strategic and tactical responses.
- Core Elements:
- Situational Awareness: The ability to understand and respond to dynamic, often unpredictable environments.
- Flexibility & Agility: At both the strategic and tactical levels to ensure swift and effective responses.
- Resilience: The capacity to recover and adapt quickly to unforeseen circumstances.
- Integration with Emerging Technologies: Emphasis on adopting cutting-edge technologies like AI, drones, and cybersecurity to stay ahead of adversaries.
The Changing Nature of Warfare:
- Grey Zone & Hybrid Warfare:
- Modern conflicts now often occur in the grey zone and involve hybrid warfare, blending traditional and non-traditional threats like cyber-attacks, terrorism, and psychological warfare.
- These new threats demand continuous adaptation in strategies, doctrines, and military operations.
- Technological Transformation:
- Drones and swarm technologies are reshaping warfare. India aspires to become a global hub for drones, leveraging these technologies for both economic and military growth.
- The increasing significance of Artificial Intelligence (AI), cyber capabilities, and quantum technologies in defence highlights the need for international collaboration in research and innovation.
- Psychological Warfare:
- The rise of information overload and psychological warfare challenges traditional defence paradigms. Manipulation of information to influence public opinion and disrupt decision-making processes is now a key threat.
Government Initiatives for Adaptive Defence:
- Institutional Strengthening:
- Establishment of the Chief of Defence Staff (CDS) and initiatives to enhance jointness among the three armed services (Army, Navy, Air Force) to create a unified strategic force.
- Reform of training curricula and emphasis on integrated operations to ensure readiness for new-age warfare.
- Focus on Self-Reliance:
- Strengthening the indigenous defence sector through initiatives like Make in India and the Aatmanirbhar Bharat campaign.
- Increasing foreign direct investment (FDI) in defence and promoting defence exports, with India currently exporting to over 100 nations.
- Drone Hub Vision:
- India aims to become the world’s drone hub, supporting R&D and fostering innovation to develop reliable certification mechanisms and enhance Indian intellectual property in the drone sector.
- Programs like iDEX (Innovations for Defence Excellence) and ADITI are rewarding innovation and driving India's defence sector towards greater self-sufficiency.
- Technology and Innovation:
- Focus on cybersecurity, AI, and quantum technologies to develop solutions that address both national and global security challenges.
- India is also working on Theaterisation, integrating the three services into a unified force structure for enhanced coordination and joint operations.
- Defence Acquisition and Export:
- Introduction of the Defence Acquisition Procedure 2020, establishment of Defence Industrial Corridors in Uttar Pradesh and Tamil Nadu, and a Positive Indigenisation List to boost self-reliance.
- India is actively increasing defence exports, aiming for Rs 50,000 crore worth of exports by 2029, with key export destinations including the USA, France, and Armenia.
Strategic Vision for the Future:
- Collaborative Approach:
- Given the interconnectedness of global security, the defence minister emphasized the importance of a collaborative approach in dealing with transnational threats.
- Cross-border issues, cyberspace threats, and the potential of quantum and nanotechnologies demand the sharing of knowledge and strategies across borders.
- Joint Military Vision:
- Jointness in defence strategy should go beyond national borders and should involve international cooperation in response to global security challenges.
- The need for interconnected solutions in the face of transnational threats underscores the importance of multilateral cooperation.
Sudden Resurgence of H5N1 in Cambodia

- 13 Nov 2024
In News:
- Cambodia saw a resurgence of H5N1 avian influenza cases after over 10 years of no human infections.
- From February 2023 to August 2024, 16 human cases were reported, with 3 deaths caused by the A/H5 clade 2.3.2.1c virus.
- Notably, 14 of these cases were caused by a novel reassortant virus, involving a mixture of clade 2.3.2.1c and clade 2.3.4.4b gene segments.
Key Points:
- Reassortment of the Virus:
- The reassortment between clades 2.3.2.1c (Southeast Asia) and 2.3.4.4b (global spread) has created a new strain.
- This reassortant virus is responsible for the second wave of infections in humans, starting in October 2023.
- Zoonotic Transmission:
- Investigations confirmed that direct contact with sick poultry or bird droppings was the primary source of human infections.
- There have been no reported cases of human-to-human transmission.
- The novel reassortant virus appears to have replaced the 2.3.2.1c strain in Cambodian poultry.
- Geographic Spread and Spillovers:
- Clade 2.3.2.1c was first reported in Cambodian poultry in March 2014. It continued to circulate in both poultry and wild birds.
- Clade 2.3.4.4b viruses began circulating in Cambodian live bird markets by 2021, co-existing with clade 2.3.2.1c.
- There were two key spillovers to humans:
- The first spillover in February 2023, associated with clade 2.3.2.1c, involved two related individuals, with one death.
- The second spillover, beginning in October 2023, involved the novel reassortant virus.
- Genetic Analysis and Mutation Concerns:
- Genetic sequencing showed significant changes in the hemagglutinin (HA) gene of viruses from human cases, indicating a shift from older local strains to newer sublineages.
- The PB2 627K mutation in the novel reassortant is concerning, as it is linked to increased mammalian adaptation and the potential for airborne transmission, particularly in mammals like ferrets.
- This mutation raises concerns about the virus’s ability to adapt to humans or other mammals.
- Environmental and Epidemiological Factors:
- The reassortment is believed to have been facilitated by:
- High-density poultry farming.
- Wild bird migration.
- Cross-border poultry trade in Southeast Asia.
- These factors heighten the risk of zoonotic transmission, emphasizing the need for continued vigilance in the region.
- The reassortment is believed to have been facilitated by:
- Surveillance and Response:
- One Health investigations linked human cases to infected poultry, highlighting the importance of rapid response through whole genome sequencing.
- The ongoing surveillance is critical, as the novel reassortant strain has already replaced clade 2.3.2.1c in Cambodian poultry.
- Public Health Recommendations:
- There is an urgent need to strengthen sustained surveillance of avian influenza in both poultry and wild birds, particularly in Southeast Asia.
- Public health strategies should focus on:
- Reducing human exposure to infected poultry.
- Promoting safe poultry handling practices.
- Encouraging early healthcare-seeking behavior in individuals with potential symptoms.
Accessibility for Disabled Persons

- 13 Nov 2024
In News:
Recently, the Supreme Court of India delivered a significant ruling affirming that the right of persons with disabilities (PwDs) to access environments, services, and opportunities is a fundamental human right. The judgment was made in the case of RajiveRaturi vs. Union of India &Ors. and is based on a report submitted by the Centre for Disability Studies (CDS) at NALSAR University of Law.
Key Points of the Judgment:
- Social Model of Disability:
- The Court upheld the social model of disability, which focuses on societal changes to ensure the full inclusion and participation of PwDs.
- The model emphasizes removing social barriers and creating an inclusive environment that accommodates all disabilities.
- Challenges Faced by PwDs: The ruling highlighted various challenges faced by PwDs, as identified in the CDS NALSAR report:
- Accessibility Barriers: Significant gaps exist in accessibility measures across public spaces such as courts, prisons, schools, and public transport.
- Intersectionality & Compounded Discrimination: PwDs often face multiple layers of discrimination, such as caste, gender, and socio-economic status, which compound their marginalization.
- Inconsistent Legal Framework: The RPwD Act (2016) mandates mandatory compliance for accessibility standards, but Rule 15 under RPwD Rules (2017) only offers self-regulatory guidelines, which the Court found insufficient.
- Court's Analysis of Rule 15:
- The Court declared Rule 15(1) of the RPwD Rules, 2017, as ultra vires, meaning it is inconsistent with the mandatory compliance intended by the RPwD Act.
- The Court stressed the need for stronger legal and regulatory enforcement to ensure access for PwDs.
- Principles of Accessibility: The Court outlined several essential principles for achieving accessibility:
- Universal Design: Environments and services should be universally accessible to all, including PwDs.
- Comprehensive Inclusion: All types of disabilities, both visible and invisible, should be addressed.
- Assistive Technology Integration: Using technology to support PwDs in daily activities.
- Stakeholder Consultation: PwDs and disability advocacy groups must be consulted in planning and designing accessible spaces.
- Two-Pronged Approach:
- The Court recommended a two-pronged approach:
- Ensure accessibility in existing infrastructure: Modify and update current institutions and services to become accessible.
- Design future infrastructure with accessibility in mind: Plan and build new spaces and services that are inclusive from the start.
- The Court recommended a two-pronged approach:
Legal and Policy Framework:
- Rights of Persons with Disabilities (RPwD) Act, 2016:
- The RPwD Act mandates various accessibility standards and provisions to protect and promote the rights of PwDs, in alignment with India’s obligations under the United Nations Convention on the Rights of Persons with Disabilities (UNCRPD), which India ratified in 2007.
- The Act defines a person with a benchmark disability as someone with at least 40% of a specified disability.
- International Obligations:
- The ruling reaffirmed the importance of Article 9 of the UNCRPD, which emphasizes the right of PwDs to access the physical environment, transport, and information and communication technologies.
- Government Initiatives: The judgment highlights several initiatives aimed at improving accessibility:
- Accessible India Campaign (Sugamya Bharat Abhiyan): A nationwide effort to make public spaces and services accessible to PwDs.
- Assistance for Aids and Appliances: Government schemes to provide PwDs with necessary aids and appliances.
- Unique Disability Identification Portal: A platform for PwDs to register and obtain a disability certificate.
Notable Judicial Precedents:
The Court referred to several previous rulings that recognized the right to accessibility:
- State of Himachal Pradesh v. Umed Ram Sharma (1986): The Court included the right to accessibility under the Right to Life (Article 21) of the Constitution.
- Disabled Rights Group v. Union of India (2017): The Court directed that educational institutions ensure reserved seats for PwDs.
Nano-Coating Technology for Fertilizer Efficiency

- 12 Nov 2024
In News:
A mechanically stable, biodegradable, hydrophobic nanocoating material can enhance the nutrient use efficiency of chemical fertilizers by tuning them for slow release, thereby limiting their interaction with the rhizosphere soil, water and microbes.
Development of Slow-Release Fertilizers:
- A biodegradable, hydrophobic nanocoating has been developed to enhance the nutrient use efficiency of chemical fertilizers.
- The nanocoating allows for slow release of nutrients, thus limiting excessive interaction with soil, water, and microbes, and optimizing fertilizer usage.
Coating Composition:
- The coating is made from nanoclay-reinforced binary carbohydrates, primarily chitosan (a biopolymer from chitin) and lignin (a plant-based polymer).
- These materials are low-cost, naturally derived, and eco-friendly, ensuring sustainability and reducing the environmental impact of fertilizer use.
Technological Innovation:
- The coating process involves using a drum rotor method to uniformly coat fertilizers, improving their efficiency.
- The tuning of hydrophobicity in the nanocoating alters the release kinetics of fertilizers, ensuring that nutrients are released in accordance with the crop’s nutrient uptake needs.
Sustainability and Biodegradability:
- The nanocoating is biodegradable, which ensures that it does not harm the environment post-application, unlike conventional chemical fertilizers that may lead to soil degradation and water pollution.
- Life cycle assessment confirms the product's long-term sustainability compared to traditional fertilizers.
Enhanced Crop Productivity:
- The slow-release coating enables a reduced fertilizer dose, while maintaining or even increasing crop yields, particularly for staple crops like rice and wheat.
- This technology facilitates higher agricultural output with fewer inputs, contributing to food security.
Industrial Viability:
- The mechanical stability of the coated fertilizers ensures they can withstand transportation and handling, making them suitable for large-scale industrial application.
- The rotary drum system used for coating ensures uniform application and superior mechanical performance, ensuring that the fertilizers are not damaged during the supply chain process.
Economic Benefits:
- The use of slow-release fertilizers can reduce overall fertilizer costs for farmers while enhancing yields, leading to improved socio-economic conditions for farmers.
- The technology holds potential for economic growth by boosting agricultural productivity and reducing the financial burden on farmers for chemical fertilizer inputs.
Global Relevance:
- The research is significant in the context of global sustainable development goals, aiming to reduce the over-reliance on conventional chemical fertilizers that contribute to soil degradation, water contamination, and greenhouse gas emissions.
Research Collaboration:
- This breakthrough was achieved by scientists from the Institute of Nano Science and Technology (INST), Mohali, in collaboration with the Department of Science and Technology (DST).
- The findings were published in the peer-reviewed journal Environmental Science: Nano, highlighting its scientific validation.
3rd Indian Space Conclave
- 12 Nov 2024
In News:
- The 3rd Indian Space Conclave, held in New Delhi, was a significant event for India's growing role in global space exploration and strategic partnerships.
- Organized by the Indian Space Association (ISPA), the conclave brought together key stakeholders from the government, industry, academia, and space agencies to discuss India’s space ambitions and the transformative role of space technologies.
Key Highlights:
Satcom as a Transformative Force for Digital India
- Emphasis on Satellite Communication (Satcom) is more than a mere tool—it's a transformative force driving Digital India by connecting every household, village, and remote area of the country.
- Satcom has a wide array of applications that extend across essential sectors such as telecommunications, disaster management, healthcare, education, and agriculture, particularly in underserved regions.
Indo-EU Space Collaboration
- The event also showcased India’s growing space partnerships, particularly with the European Union (EU). The EU Ambassador recognized India as a dynamic space power and highlighted shared goals in Earth observation, space security, and human spaceflight.
- Proposed joint initiatives include training programs, collaborative research, and satellite missions, such as the Proba-3 satellite launch by ISRO, focusing on observing the Sun.
- India’s trustworthiness as a partner in space was underscored by its role in the successful launch of the Proba-1 and Proba-2 missions for the EU, with Proba-3 marking India’s third contribution to EU space exploration.
Space Startups and Innovation
- The rise of space-focused startups in India, spurred by the 2020 space sector reforms, was another key highlight. India now has over 300 space startups, contributing to both economic growth and innovation in the space industry.
- These reforms have helped curb brain drain, with many talented Indian professionals returning from global agencies like NASA to join the expanding Indian space ecosystem.
India’s Long-Term Space Goals
- The Indian space program has ambitious long-term goals, including:
- Gaganyaan, India’s human spaceflight mission.
- A crewed lunar landing by 2040.
- The establishment of an Indian space station by 2035.
- Plans for space tourism by 2040.
- These initiatives demonstrate India’s commitment to becoming a global leader in space exploration and technological innovation.
Space Sector Reforms (2020)
- The Space Sector Reforms 2020 were designed to increase the participation of private players in India’s space activities. The creation of agencies like the Indian National Space Promotion and Authorization Center (IN-SPACe) and the strengthening of New Space India Limited (NSIL) have been pivotal in boosting India’s global space market share.
- IN-SPACe serves as an autonomous body fostering industry, academia, and startups, while NSIL handles commercial activities and promotes high-tech space-related ventures.
India's First Mars and Moon Analog Mission
- ISRO's First Mars and Moon Analog Mission was inaugurated in Leh, Ladakh. This mission simulates the conditions of space habitats, specifically focusing on Mars and Moon environments.
- Ladakh's unique climate—high altitude, low oxygen levels, and extreme temperature fluctuations—makes it an ideal location for testing life support systems, space habitat technologies, and sustainable resource utilization.
Key Aspects of the Analog Mission:
- Life support systems like hydroponics (space farming) and standalone solar power systems to support sustainable food production and renewable energy in space habitats.
- Circadian lighting to simulate daylight cycles, maintaining astronaut health and well-being.
- The mission’s goal is to understand the psychological and operational challenges of living in isolation and extreme conditions, preparing India for future interplanetary exploration.
State of Food and Agriculture 2024Report
- 12 Nov 2024
In News:
- India's annual hidden costs from agrifood systems total $1.3 trillion, the third-largest globally, after China ($1.8 trillion) and the US ($1.4 trillion).
- These costs are mainly driven by unhealthy dietary patterns leading to non-communicable diseases (NCDs), such as heart disease, diabetes, and stroke.
Major Contributors to Hidden Costs:
- Unhealthy Diets: Over 73% of India’s hidden costs stem from unhealthy dietary habits, including:
- Excessive consumption of processed foods and additives ($128 billion).
- Low intake of plant-based foods, fruits, and beneficial fatty acids ($846 billion).
- These dietary risks contribute to a significant health burden, increasing the prevalence of NCDs and reducing labor productivity.
Global Context:
- Global hidden costs of agrifood systems amount to $12 trillion annually.
- 70% of these costs (~$8.1 trillion) arise from unhealthy dietary patterns, which include high intakes of sugar, salt, and processed foods, contributing to diseases and economic losses.
Health Impacts:
- The report identifies 13 dietary risk factors that contribute to NCDs, including insufficient intake of whole grains, fruits, vegetables, and excessive sodium, with varying effects across different agrifood systems.
Environmental and Social Costs:
- Environmental Costs: High costs from unsustainable agricultural practices, including greenhouse gas emissions and nitrogen runoff. In some agrifood systems, environmental costs can reach up to 20% of GDP.
- Social Costs: High poverty rates among agrifood workers and undernourishment in systems like protracted crises and traditional agrifood systems contribute significantly to the hidden costs.
India’s Agrifood System Profile:
- India’s agrifood system faces significant challenges related to low wages, poor productivity, and poverty among agrifood workers, driven by distributional failures.
- Climate Change and Environmental Degradation: Issues like droughts, floods, and soil degradation threaten food security and agricultural sustainability in India.
Recommendations for Transformative Change:
- True Cost Accounting: Implementing this method can help better capture hidden costs and enable more informed decision-making for a sustainable agrifood system.
- Healthier Diets: Policies to make nutritious food more affordable and accessible to reduce health-related hidden costs.
- Sustainability Incentives: Encouraging practices that reduce greenhouse gas emissions, harmful land-use changes, and biodiversity loss, using labelling, certification, and industry standards.
- Consumer Empowerment: Providing accessible information about the environmental, social, and health impacts of food choices, ensuring even vulnerable households benefit from healthier options.
India’s Path Forward:
- India has several ongoing initiatives for sustainable agriculture, including:
- National Mission for Sustainable Agriculture (NMSA).
- Eat Right Initiative.
- Digital Agriculture Mission (DAM).
- However, challenges like climate change, soil degradation, and low productivity among smallholder farmers hinder progress toward sustainable food systems.
Key Focus Areas for India’s Agrifood Systems:
- Support for Smallholder Farmers: Enhancing access to technology, markets, and financial services for marginalized farmers.
- Sustainable Practices: Adoption of water-efficient practices, soil health restoration, and environmentally friendly farming methods.
- Collaboration with International Agencies: Cooperation with FAO, WFP, and others to strengthen agricultural reforms and support smallholder farmers.
Diclipterapolymorpha

- 12 Nov 2024
In News:
A new species of Dicliptera, named Diclipterapolymorpha, has been discovered in the Northern Western Ghats of India.
Habitat and Location:
- Diclipterapolymorpha was found in the grasslands of Talegaon-Dabhade, a region known for its grasslands and fodder markets.
- The species thrives in the harsh climatic conditions of the Northern Western Ghats, an area vulnerable to summer droughts and frequent human-induced fires.
Unique Characteristics:
- The species is fire-resilient (pyrophytic), exhibiting a rare dual-blooming pattern:
- First Blooming: Occurs post-monsoon, typically from November to March/April.
- Second Blooming: Triggered by grassland fires in May and June, during which the plant produces dwarf flowering shoots.
- The inflorescence structure is unique in India, with its cymules developing into spicate inflorescences, a feature more commonly found in African species.
Taxonomy:
- The species is named Diclipterapolymorpha to reflect its diverse morphological traits.
- It is taxonomically distinct within the Dicliptera genus, with no known Indian species exhibiting similar characteristics.
Conservation Implications:
- The discovery highlights the need to carefully manage grassland ecosystems, as the species is adapted to fire but still vulnerable to habitat degradation.
- Human-induced fires are essential for the species' blooming cycle but must be managed to avoid overuse and degradation of habitat.
- The species' limited habitat range underscores the need for conservation efforts to protect the delicate ecosystems of the Western Ghats.
Publication:
- A research paper detailing the discovery of Diclipterapolymorpha has been published in the prestigious Kew Bulletin.
AntarikshaAbhyas 2024

- 12 Nov 2024
In News:
- ‘AntarikshaAbhyas – 2024’ is a three-day space exercise held from November 11-13, 2024, hosted by the Defence Space Agency (DSA), Headquarters Integrated Defence Staff.
- The exercise is the first of its kind and focuses on war-gaming the growing threats to space-based assets and services.
Objective of the Exercise:
- Enhance understanding of space-based assets and their operational dependencies.
- Identify vulnerabilities in military operations in case of denial or disruption of space services.
- Integrate India's space capabilities in military operations to secure national strategic objectives.
Participants:
- Defence Space Agency (DSA) and its allied units.
- Personnel from the Army, Navy, and Air Force.
- Specialist agencies under Headquarters Integrated Defence Staff, including:
- Defence Cyber Agency (DCA)
- Defence Intelligence Agency (DIA)
- Strategic Forces Command (SFC)
- Representatives from ISRO (Indian Space Research Organisation) and DRDO (Defence Research & Development Organisation).
Focus Areas:
- Space-based asset and service operational dependency.
- Securing national interests in space through technological innovation and development.
- Assessing space service vulnerabilities and impacts on military operations.
EV as a Service Programme

- 11 Nov 2024
In News:
- The 'EV as a Service'programme was launched by Shri Manohar Lal, Union Minister of Power and Housing & Urban Affairs, at the Major Dhyan Chand National Stadium.
- The initiative is spearheaded by Convergence Energy Services Limited (CESL), a subsidiary of Energy Efficiency Services Limited (EESL), to promote electric vehicles (EVs) in government offices.
Objective:
- The 'EV as a Service'programme aims to boost e-mobility within the government sector by deploying 5,000 electric cars in central and state government ministries, public sector enterprises (CPSEs), and various institutions over the next two years.
- The programme is designed to support India’s net-zero emissions goal by 2070 and advance the country's environmental sustainability vision.
Flexible Procurement Model:
- The programme utilizes a flexible procurement model, allowing government offices to choose from a range of E-Cars based on operational needs, making it adaptable for different government departments.
- It will help in reducing the reliance on fossil fuels, cutting carbon emissions, and contributing to energy security.
CESL’s Contribution:
- CESL has already deployed 2000 electric cars across India and is working on deploying around 17,000 electric buses.
- The 'EV as a Service'programme is a key step in helping India transition to clean mobility and reducing emissions from government fleets.
Alignment with National Initiatives:
- The launch complements the PM E-DRIVE Scheme, which aims to accelerate India’s transition to electric mobility.
- Vishal Kapoor, MD & CEO of CESL, emphasized that the initiative is helping to create a collaborative ecosystem involving manufacturers, fleet operators, policymakers, and users to scale up electric mobility in India.
Comics Commandos in Assam

- 11 Nov 2024
In News:
- "Comics Commandos" is an innovative initiative launched in Goalpara district, Assam, aimed at combating child labour and child marriage through the creative medium of comics.
- The initiative trains 30 local youths to create comic strips that use humour and minimal text for effective communication and public engagement.
Purpose and Objectives:
- Primary Goal: To raise awareness about child labour and child marriage, two major social issues prevalent in the region, by using visual storytelling.
- The initiative aims to resonate with the local community, focusing on everyday struggles like economic hardship, child abuse, and the social norms that perpetuate these issues.
- Rising Dropout Rates: Assam has witnessed an increase in school dropout rates, from 3.3% in 2020-21 to 6.02% in 2021-22, exacerbated by economic pressures like poverty, which force children to work or marry early.
Execution and Approach:
- Training: Thirty local youths are trained to design caricatures and doodles for the comics, ensuring the messages are both simple and engaging for a broader audience.
- Visual Storytelling: The use of visuals over text helps overcome literacy barriers and makes the message more impactful and accessible.
- Community Involvement: The program collaborates with teachers and school committees to facilitate wider participation and support in creating social awareness.
Government Support:
- Chief Minister HimantaBiswaSarma initiated a state-wide campaign in 2023 against child marriage, with the ambitious goal of eradicating it by 2026. This initiative aligns with the state's broader efforts to address social issues.
Impact of the Initiative:
- Comics Commandos is being seen as an effective tool for community empowerment and awareness generation in a region that faces persistent social challenges.
- By involving local youths in the campaign, the initiative ensures community participation and ensures that the message is communicated in a culturally relevant manner.
- The program also empowers young people to use their creativity for social change, thus helping build leadership and social responsibility among the youth.
Arpactophiluspulawskii
- 11 Nov 2024
In News:
- Arpactophiluspulawskii, a new species of aphid wasp, was discovered in Nagaland (Khuzama district), marking the first record of the genus Arpactophilus outside Australasia.
- This significant discovery highlights the biodiversity of Northeastern India, a region known for its rich and unexplored fauna.
Importance of Discovery:
- The Zoological Survey of India (ZSI) researchers cataloged the species, marking a major range expansion for the genus Arpactophilus, previously only found in Australasia, including regions like New Caledonia.
- The discovery expands the genus’s known distribution by thousands of kilometers, suggesting ecological connections between Nagaland and the Australasian region.
Species Characteristics:
- Arpactophiluspulawskii is distinguished by its square-shaped head, an inverted V-shaped uplifted clypeus, and rust-colored body markings.
- It features a uniquely textured thorax, setting it apart from other species in the genus.
- The wasp was collected from an altitude of over 1,800 meters, indicating Nagaland’s ecological diversity at high altitudes.
Ecological Significance:
- The Arpactophilus genus is known for its unique nesting behavior: females use silk from their abdomen to create protective cells in old termite galleries or mud nests.
- The discovery suggests that Nagaland’s ecological conditions (e.g., high altitude, diverse habitat) support the presence of such specialized fauna, making the region an important site for entomological research.
Taxonomic Contribution:
- The species is named Arpactophiluspulawskii in honor of Dr. Wojciech J. Pulawski, a distinguished expert in wasp taxonomy.
Scientific and Research Implications:
- The discovery is expected to stimulate further entomological research in Northeastern India, especially in areas like Nagaland, which are often overlooked in global biodiversity studies.
- Researchers believe that this discovery could lead to the identification of other unknown species in the region, expanding our understanding of species distribution and the ecological connectivity between regions.
Parliamentary Panel's Review on Mechanism to Curb Fake News

- 11 Nov 2024
In News:
- The Parliamentary Panel on Communications and Information Technology is reviewing mechanisms to curb fake news, following the Bombay High Court striking down a provision of the amended Information Technology (IT) Rules, 2021.
- The controversial provision allowed the government to identify and flag "fake news" on social media through its Fact Check Unit (FCU).
- The panel, led by BJP MP Nishikant Dubey, has summoned representatives from News Broadcasters and Digital Association and the Editors Guild of India to discuss the issue on November 21, 2024.
Issue with the Amended IT Rules:
- The IT Rules, 2021 were amended in April 2022 to include “government business” under the definition of fake news, expanding the scope of content flagged by the FCU.
- This amendment was challenged by media bodies and individuals like comedian Kunal Kamra, leading to the Bombay High Court striking it down in 2024.
- The court deemed the provisions unconstitutional, citing concerns about transparency and the potential misuse of power.
Types of Fake News:
- Misinformation: False information spread unintentionally.
- Disinformation: Deliberately false information meant to deceive and cause harm.
Status of Fake News in India:
- India as a major spreader of misinformation: The World Economic Forum's Global Risks 2024 report identifies disinformation as a significant short-term risk, with India as one of the largest consumers and producers of false information.
- Social Media Influence: Platforms like Facebook, WhatsApp, Twitter, and YouTube are widely used in India for news dissemination, making them a breeding ground for fake news.
- Spread of Political and Religious Misinformation: Fake news often serves political or religious agendas, leading to societal polarization and conflict.
Government Efforts to Combat Fake News:
- IT (Intermediary Guidelines and Digital Media Ethics Code) Amendment Rules, 2023: This amendment expanded the scope of "fake news" to include “government business” and gave the FCU the authority to flag misleading content.
- Press Information Bureau (PIB) Fact Check Unit: The PIB continues to run a fact-checking initiative, but it lacks the authority to remove flagged content from social media platforms.
- Digital Literacy Campaigns: Programs like Pradhan Mantri Gramin Digital Saksharta Abhiyan (PMGDISHA) aim to improve digital literacy, especially in rural areas, to help citizens identify and avoid fake news.
National Education Day 2024

- 11 Nov 2024
In News:
National Education Day is celebrated annually on November 11 to honor the birth anniversary of Maulana Abul Kalam Azad, India's first Education Minister and a prominent freedom fighter, scholar, and educator.
Key Highlights:
- Establishment:
- The observance was instituted by the Ministry of Human Resource Development (now Ministry of Education) in 2008 to recognize Azad’s pivotal contributions to India’s education system and his vision for a progressive, educated society.
- Azad's Contributions to Education:
- Azad played a significant role in shaping India's post-independence educational landscape, establishing critical institutions such as:
- University Grants Commission (UGC)
- All India Council for Technical Education (AICTE)
- Indian Institutes of Technology (IIT), including IIT Kharagpur
- Indian Council for Cultural Relations (ICCR)
- Promoted scientific research, cultural institutions, and technical education.
- Azad played a significant role in shaping India's post-independence educational landscape, establishing critical institutions such as:
- Significance of National Education Day:
- Reflects India’s commitment to promoting quality and inclusive education.
- Emphasizes the importance of education in empowering individuals and fostering national progress.
- Highlights educational reforms, literacy, and equal access to education as tools for societal transformation and empowerment.
- Theme for 2024:
- Although not officially published yet, the theme is expected to focus on inclusive, high-quality education, underlining the need for educational systems that equip students with skills to thrive in a rapidly evolving world.
- Focus Areas:
- Promoting literacy, equal access to education, and educational reforms.
- Developing critical thinking, creativity, and emotional intelligence in students.
Indian Military Heritage Festival 2024

- 10 Nov 2024
In News:
- Chief of Defence Staff General Anil Chauhan inaugurated the 2nd edition of the Indian Military Heritage Festival (IMHF) on November 8, 2024, in New Delhi.
- The two-day festival engages global and Indian experts, corporations, academicians, and non-profits focusing on India’s national security, foreign policy, military history, and military heritage.
Launch of Project Shaurya Gatha:
- Project ‘Shaurya Gatha’ was launched to conserve and promote India’s military heritage.
- The initiative, spearheaded by the Department of Military Affairs and USI of India, focuses on education and tourism to highlight India’s military history and valor.
- Publications Released:
- General Chauhan released important military publications:
- "Because of this: A History of the Indo-Pak Air War December 1971" by Air Marshal Vikram Singh (Retd).
- "Valour and Honour", a joint publication by the Indian Army and USI of India.
- "War-wounded, Disabled Soldiers, and Cadets", a joint publication by USI and the War Wounded Federation.
- General Chauhan released important military publications:
- Festival's Significance:
- The festival addresses the gap in public awareness regarding India’s military heritage and security concerns.
- It aims to enhance understanding of India’s military traditions, security issues, and the country’s efforts toward self-reliance in military capabilities under the Aatmanirbhar Bharat initiative.
Zhurong Rover

- 10 Nov 2024
In News:
Chinese rover helps find evidence of ancient Martian shoreline.
Mission Overview:
- Rover: Zhurong, part of China’s Tianwen-1 Mars exploration program.
- Mission Launch: Zhurong landed in 2021 in the Utopia Planitia region of Mars' northern hemisphere.
- Key Discovery: Evidence of an ancient ocean on Mars, suggesting a habitable past for the planet.
Key Findings:
- Geological Features Indicating a Coastline:
- Data from Zhurong and orbiting spacecraft (Tianwen-1 Orbiter, NASA's Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter) revealed geological features such as troughs, sediment channels, and mud volcano formations, suggesting the existence of a Martian coastline.
- Features indicate both shallow and deeper marine environments, supporting the idea of a past ocean.
- Age of the Ocean:
- The ocean likely existed around 3.68 billion years ago, with its surface potentially frozen in a geologically short period.
- The ocean is thought to have disappeared by 3.42 billion years ago.
Evolutionary Scenario of Mars:
- At the time of the ocean, Mars might have already begun transitioning away from a habitable planet, losing much of its atmosphere and becoming cold and dry.
- The ocean may have formed after Mars' climate began to change, suggesting that it was once more hospitable, possibly capable of supporting microbial life.
Implications for Life on Mars:
- The presence of water, a key ingredient for life, raises the possibility that Mars could have supported microbial life in its early history.
- When Mars had a thick, warm atmosphere, conditions might have been favorable for life, as microbial life would have been more likely to exist.
Significance of Zhurong's Contribution:
- Zhurong exceeded its original mission duration of three months, operating until May 2022, helping provide key data to understand Mars' ancient water history.
- The discovery adds to ongoing efforts to study the disappearance of water on Mars and its implications for the planet's habitability.
Future Exploration:
- Other studies, including seismic data from NASA’s InSight lander, suggest that liquid water might still exist deep beneath the Martian surface, hinting at the possibility of finding water in the planet's subsurface in the future.
World’s First CO? to Methanol Plant

- 10 Nov 2024
In News:
- NTPC has achieved the first-ever synthesis of CO? (captured from flue gas) and hydrogen (produced via a PEM electrolyzer) into methanol at its Vindhyachal plant.
- This marks a significant step in carbon management technology, aimed at advancing sustainable fuel production.
About CO?-to-Methanol Conversion:
- Carbon Dioxide Capture:
- CO? is captured from industrial sources, such as power plants, or directly from the atmosphere.
- Hydrogen Production:
- Renewable energy sources like solar or wind power are used to produce hydrogen through water electrolysis.
- Methanol Synthesis:
- The captured CO? is combined with hydrogen in the presence of a catalyst to produce methanol, typically under high pressure and temperature conditions.
Benefits of CO?-to-Methanol Conversion:
- Carbon Capture and Utilization (CCU):
- This technology reduces the impact of CO? on the atmosphere by converting it into useful products.
- Renewable Fuel Source:
- Methanol produced through this process can be used as a fuel for transportation, power generation, or as a feedstock for chemicals.
- Energy Storage:
- Methanol offers a more practical storage and transportation option than hydrogen, making it a potential energy storage solution and aiding the transition to hydrogen-based energy systems.
- Versatile Feedstock:
- Methanol is widely used in producing chemicals, solvents, and plastics, supporting various industrial applications.
What is Methanol?
- Brief: Methanol, also known as methyl alcohol or wood alcohol, is the simplest form of alcohol. It is a clear, colorless, and flammable liquid with a distinctive odor.
- Key Properties:
- Colorless, miscible with water, toxic if ingested, flammable.
QS World University Rankings
- 10 Nov 2024
In News:
The QS World University Rankings: Asia 2025 spotlights the top institutions in Eastern, Southern, South-Eastern, and Central Asia, emphasizing academic excellence, research, innovation, and internationalization.
India's Performance:
India has shown a remarkable upward trajectory, featuring:
- Two institutions in the Top 50:
- IIT Delhi ranked 44th (up from 46th), with a 99% employer reputation score.
- IIT Bombay ranked 48th, excelling with a 99.5% employer reputation score and 96.6% academic reputation score.
- Top 100 Institutions:
- IIT Madras (56th), IIT Kharagpur (60th), Indian Institute of Science (62nd), IIT Kanpur (67th), and University of Delhi (81st).
- Top 150 Institutions:
- IIT Guwahati, IIT Roorkee, Jawaharlal Nehru University, Chandigarh University (120th), UPES (148th), and VIT (150th).
Key Indicators for India:
- International Research Network and Citations per Paper contribute to India's growing global academic reputation.
- Papers per Faculty and Staff with PhD are India’s strongest indicators, reflecting robust research output and high teaching standards.
- Anna University achieved a perfect score of 100 in the Papers Per Faculty indicator, emphasizing high research output.
- North Eastern Hill University and University of Agricultural Sciences, Bangalore received a perfect score of 100 in the Faculty-Student Indicator.
Growth of Indian Institutions:
- India now has 46 institutions in the 2025 rankings, up from just 11 in 2015, marking a 318% increase over the past decade.
- India dominates Southern Asia with seven institutions in the top 10, showcasing the country's strengthening educational landscape.
India's Growing Global Influence:
- India's achievements underscore its commitment to academic excellence, competitiveness, and resilience in global higher education.
- Institutions like IIT Delhi and IIT Bombay highlight India’s ability to balance research productivity with high-quality teaching, enhancing its reputation as a global education hub.
One Sun One World One Grid (OSOWOG) Initiative

- 10 Nov 2024
In News:
- India is in talks with Oman, UAE, Saudi Arabia, Maldives, and Singapore to establish cross-border electricity transmission lines.
- This is part of the ambitious OSOWOG initiative to create a global renewable energy grid.
Key Points:
- Proposed by the Prime Minister of India at the 2018 International Solar Alliance (ISA) Assembly.
- Aims to create a transnational electricity grid that delivers power worldwide.
- Led by India and the UK, in collaboration with ISA and the World Bank Group.
Vision of OSOWOG:
- Connect regional grids through a common infrastructure for the transfer of renewable energy, focusing on solar power.
- Harness solar and other renewable energy from regions where the sun is shining and efficiently transmit it to areas of need.
- Aim to provide power to 140 countries using clean and efficient solar energy.
Phases of OSOWOG:
- Phase 1:
- Connect the Indian grid with grids in the Middle East, South Asia, and South-East Asia.
- Share solar and other renewable energy resources.
- Phase 2:
- Expand the interconnected grid to include renewable resources from Africa.
- Phase 3:
- Achieve a global interconnection aiming for 2,600 GW by 2050.
- Integrate as many countries as possible into a single renewable energy grid.
Global Collaboration:
- Involves national governments, international organizations, legislators, power operators, and experts.
- Focus on accelerating infrastructure development for a clean energy-powered world.
PyPIM platform
- 09 Nov 2024
In News:
Israeli researchers from the Israel Institute of Technology have developed the PyPIM platform, which allows computers to process data directly in memory, eliminating the need for a central processing unit (CPU). This breakthrough aims to address key challenges in modern computing, particularly in terms of energy consumption and processing efficiency.
Key Features of the PyPIM Platform:
- Integration with Python and PIM Technology:
- The PyPIM platform merges Python programming with digital processing-in-memory (PIM) technology, facilitating in-memory computing where computations occur directly within memory instead of transferring data to and from the CPU.
- Functionality and Innovations:
- Direct In-Memory Computations: PyPIM uses specialized instructions that enable computations to take place directly in memory, reducing the need for data movement between the CPU and memory.
- Developer-Friendly: It allows developers to use familiar languages like Python to write software for in-memory computing systems.
- Solving the "Memory Wall" Issue:
- The platform addresses the memory wall problem, where the speed of the CPU and memory exceeds the data transfer rates, creating bottlenecks that lead to inefficiencies.
- By performing calculations directly in memory, PyPIM reduces time and energy spent on data transfer, optimizing performance.
- Performance Improvements:
- Energy and Time Efficiency: By minimizing energy-intensive data transfers, PyPIM leads to significant energy and time savings.
- Simulation Tools: The platform includes tools that allow developers to simulate potential performance improvements from in-memory processing.
- Real-World Benefits:
- Faster Processing: Tasks performed using PyPIM have demonstrated faster processing speeds, with minimal code changes, particularly in mathematical and algorithmic tasks.
- The platform delivers a significant performance boost in areas like data analysis and algorithmic operations.
The PyPIM platform marks a pivotal advancement in computing architecture, providing a more energy-efficient and faster alternative to traditional CPU-dependent systems by reducing reliance on external memory processing and cutting down on data transfer delays.
AUSTRAHIND 2024

- 09 Nov 2024
In News:
- The 3rd edition of Exercise AUSTRAHIND started on 8th November 2024 at the Foreign Training Node in Pune, Maharashtra. The exercise will run until 21st November 2024.
Participating Forces:
- Indian Contingent: 140 personnel, primarily from the DOGRA Regiment and Indian Air Force (14 personnel).
- Australian Contingent: 120 personnel from the 13th Light Horse Regiment of the 10th Brigade of the 2nd Division.
Purpose of the Exercise:
- Enhance Military Cooperation between India and Australia.
- Promote Interoperability in conducting joint sub-conventional operations in semi-urban and semi-desert terrain.
- Focus on operations under Chapter VII of the UN mandate.
Key Objectives:
- Joint Tactical Drills and Planning to improve coordination between the forces.
- Training in counter-terrorism operations, special heli-borne operations, and drone countermeasures.
Phases of the Exercise:
Combat Conditioning and Tactical Training Phase:
- Includes drills such as terrorist response, territory capture, and Raid and Search & Destroy Missions.
- Establishment of Joint Operations Centre and securing critical infrastructure like helipads.
- Training on drone operations and counter-drone measures.
Validation Phase: Practical application and testing of skills learned in the previous phase.
Significance:
Best Practices Sharing: Both sides will exchange tactics, techniques, and procedures for conducting effective tactical operations.
Camaraderie Building: The exercise will foster a strong bond between soldiers from both countries.
Background: AUSTRAHIND is an annual exercise held alternately in India and Australia. The last edition took place in Australia in December 2023.
Digital Population Clock

- 09 Nov 2024
In News:
- Bengaluru's first digital population clock was inaugurated at the Institute for Social and Economic Change (ISEC) on November 8, 2024.
- The initiative is collaboration between ISEC and the Union Ministry of Health and Family Welfare (MoHFW).
Purpose:
- The clock provides real-time population estimates for Karnataka and India.
- It aims to enhance awareness about population dynamics and provide accurate demographic data for research and policy analysis.
Key Features:
- Real-time Updates:
- Karnataka’s population is updated every 1 minute and 10 seconds.
- India’s population updates every 2 seconds.
- Precision:
- The clock operates with satellite connections for real-time, accurate data updates.
- It functions autonomously with integrated components, ensuring continuous and precise tracking.
- Location: The clock is prominently displayed at the entrance of ISEC.
- National Expansion: Similar digital population clocks are being installed in 18 Population Research Centres across India by MoHFW.
Significance:
- Awareness: The clock serves as a visual tool to highlight the rapid pace of population growth and its implications for sustainable development.
- Research and Analysis: The clock is part of a broader effort to improve demographic studies and inform policy-making.
- Census Data Research Workstation:
- ISEC has introduced a new research workstation, supported by MoHFW, for in-depth demographic analysis.
- The facility is equipped with advanced software for studying population trends and supporting academic research.
RNA Editing

- 09 Nov 2024
In News:
Wave Life Sciences became the first biotechnology company to treat a genetic condition by editing RNA at the clinical level.
- What is RNA Editing?
- Definition: RNA editing is the modification of messenger RNA (mRNA) after it’s synthesized from DNA but before it is translated into proteins.
- Process: mRNA consists of exons (coding regions) and introns (non-coding regions). Exons code for proteins, while introns are removed before protein synthesis.
- Types of RNA Modifications:
- Addition: Insertion of a nucleotide.
- Deletion: Removal of a nucleotide.
- Substitution: Replacement of one nucleotide with another.
- Mechanism of RNA Editing:
- Involves Adenosine Deaminase Acting on RNA (ADAR) enzymes.
- ADAR enzymes modify adenosine to inosine, which is recognized as guanosine, allowing mRNA to be corrected.
- Guide RNA (gRNA) directs ADAR enzymes to the specific mRNA region for editing.
- Clinical Use of RNA Editing:
- Wave Life Sciences used RNA editing to treat α-1 antitrypsin deficiency (AATD), a genetic disorder.
- Other potential applications include treating diseases such as Huntington’s disease, Duchenne muscular dystrophy, Parkinson’s disease, obesity, and neurological disorders.
- Challenges in RNA Editing:
- Temporary Effects: RNA editing provides temporary changes, requiring repeated treatments for sustained effects.
- Delivery Issues: Current delivery methods, like lipid nanoparticles and adeno-associated virus vectors, have limitations in carrying large molecules.
- Specificity: ADARs may cause unintended changes in non-target regions of mRNA, leading to potential side effects.
- Comparison: RNA Editing vs. DNA Editing:
- Safety: RNA editing causes temporary changes and presents fewer risks than DNA editing, which makes permanent alterations to the genome.
- Immune Response: RNA editing uses enzymes naturally found in the body (ADAR), which reduces the risk of immune reactions, unlike DNA editing tools like CRISPR-Cas9 that can trigger immune responses.
- Significance of RNA:
- Structure: RNA is a nucleic acid, similar to DNA but typically single-stranded. It consists of a backbone of ribose sugars and phosphate groups, with bases adenine (A), uracil (U), cytosine (C), and guanine (G).
- Types of RNA:
- Messenger RNA (mRNA): Carries genetic information from DNA to ribosomes for protein synthesis.
- Ribosomal RNA (rRNA): Forms the core of the ribosome and catalyzes protein synthesis.
- Transfer RNA (tRNA): Transfers amino acids to ribosomes during protein synthesis.
- Regulatory RNAs: Regulate gene expression.
- α-1 Antitrypsin Deficiency (AATD):
- A genetic disorder where the protein α-1 antitrypsin accumulates in the liver, damaging both the liver and lungs.
- Treatments include weekly intravenous therapy or, in severe cases, liver transplants.
- RNA editing offers a potential new treatment approach.
- Global Impact:
- RNA editing is still in its early stages but shows promise for treating a wide range of genetic and chronic conditions.
- Ongoing research and clinical trials suggest RNA editing could become a key part of future gene-editing therapies.
Global Education Monitoring Report 2024

- 09 Nov 2024
In News:
- Released at the Global Education Meeting, hosted in Fortaleza by Brazil, the G20 President.
- Highlights progress and challenges in global education, with a focus on leadership, financing, and access.
Key Observations:
Leaders as Agents of Change:
- Education leadership is defined as social influence towards achieving common educational goals.
- Education leaders must:
- Define clear purposes and influence change.
- Balance learning outcomes with equity, quality, and inclusion.
Funding Deficits:
- 4 out of 10 countries spend less than 4% of their GDP on education.
Out-of-School Children:
- 251 million children and youth globally remain out of school, with only a 1% reduction since 2015.
Regional Disparities in Education Access:
- Central and Southern Asia show significant progress, but countries like Afghanistan, Bangladesh, India, and Pakistan still have large out-of-school populations.
Recommendations:
- Leadership Development: Empower school principals with the autonomy to manage schools effectively.
- Capacity Building for System Leaders: Strengthen the ability of education officials to act as system leaders.
- Climate Change Education: Introduce climate change topics in early education across subjects, not limited to science.
India’s Educational Initiatives:
- National Education Policy (NEP) 2020: Focuses on developing school leadership through training and workshops for principals.
- NISHTHA Program: Aims to improve leadership and management competencies of school heads and teachers.
Current Educational Landscape:
- Since 2015, 110 million children have entered school, and 40 million more complete secondary education.
- However, 33% of children in low-income countries remain out of school, compared to only 3% in high-income countries.
- Sub-Saharan Africa houses more than half of the global out-of-school youth.
Challenges in Education Financing:
- UNESCO–World Bank report highlights that 40% of countries allocate less than 15% of their public expenditure to education.
- Countries investing less than 4% of GDP in education face significant resource shortages.
- Low-income countries spend an average of $55 per learner, while high-income countries spend $8,543 per learner.
Need for Innovative Financing Mechanisms:
- Debt-for-Education Swaps: Proposes converting unsustainable debt into funding for education, leveraging past successful initiatives.
- Multilateral Platforms: Suggested to facilitate global negotiations for converting debt into educational investments, involving entities like UNESCO and the G20.
International Cooperation and Solidarity:
- Decline in Education Assistance: Official development assistance for education has decreased from 9.3% in 2019 to 7.6% in 2022.
- Strengthening Partnerships: The need for enhanced global cooperation to fill the educational financing gap and ensure equitable access to quality education.
Adaptation Gap Report 2024
- 08 Nov 2024
In News:
The Adaptation Gap Report 2024, published by the United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP), underscores the urgent need for enhanced climate adaptation efforts, particularly through increased financial support for developing countries. The report, titled Come Hell and High Water, provides an annual assessment of global adaptation progress in planning, implementation, and financing.
Key Findings
- Adaptation Gap:
- The adaptation finance gap is estimated at $187–359 billion per year.
- Current adaptation finance falls short, with only $28 billion provided in 2022, meeting just 5% of projected needs.
- Adaptation Progress:
- International public adaptation finance to developing countries rose to $27.5 billion in 2022, up from $19 billion in 2019, reflecting progress toward the Glasgow Climate Pact's goal of doubling finance by 2025.
- Significance of Adaptation:
- Ambitious adaptation measures could reduce global climate risk by 50%.
- For instance, $16 billion annually in agriculture could prevent climate-induced hunger for 78 million people.
- Impact of Global Warming:
- According to UNEP's Emissions Gap Report 2024, global temperatures may increase by 2.6°C–3.1°C above pre-industrial levels by 2100.
- Developing countries face severe vulnerabilities, evidenced by recent floods in Nepal, Nigeria, and Chad.
- National Adaptation Plans (NAPs):
- While 171 countries have at least one adaptation policy, progress in implementation remains slow.
- 10 countries have shown no interest in developing adaptation policies.
Challenges in Adaptation Financing
- Financial Burden: Adaptation projects such as seawalls and resilient infrastructure are costly for developing nations.
- Funding Shortfalls:
- Developed nations have failed to meet financial commitments like the $100 billion goal set for 2020.
- The adaptation finance gap remains significant in non-private sector-funded areas, such as ecosystem preservation.
- High-Interest Loans: Much current funding relies on high-interest loans, increasing the debt burden for recipient countries.
Recommendations
- Adopt New Financing Goals: Establish an ambitious New Collective Quantified Goal for climate finance at COP29.
- Strategic Adaptation Financing:
- Shift from project-based to anticipatory and transformational financing.
- Invest in harder-to-finance areas like ecosystem preservation and cultural heritage.
- Alternative Financing Models: Encourage risk finance, resilience bonds, debt-for-adaptation swaps, and payments for ecosystem services.
Global and Indian Initiatives
Global Initiatives:
- Paris Agreement: Sets a global adaptation goal to enhance resilience.
- UAE Framework for Global Climate Resilience: Introduced at COP28, focusing on agriculture, water, and health adaptation targets.
- Adaptation Fund: Provides project funding for developing nations under the Kyoto Protocol.
Indian Initiatives:
- National Action Plan on Climate Change (NAPCC): Includes eight missions, such as the National Adaptation Fund for Climate Change (NAFCC).
- Sectoral Schemes:
- MISHTI: Mangrove initiative for shoreline protection.
- Amrit Dharohar: Enhances wetland ecosystems.
- India's adaptation spending accounted for 5.6% of GDP in 2021–2022.
PM Vishwakarma Yojana

- 08 Nov 2024
In News:
The PM Vishwakarma Yojana is a landmark initiative by the Indian government aimed at revitalizing traditional craftsmanship and empowering artisans and craftspeople, often referred to as Vishwakarmas. Launched on September 17, 2023, during Vishwakarma Jayanti, the scheme highlights the government's commitment to preserving India's rich cultural heritage and supporting the unorganized sector.
Key Highlights
- Objective:
- To strengthen the Guru-Shishya tradition and improve the quality, reach, and marketability of products and services by artisans.
- To integrate Vishwakarmas into domestic and global value chains, making them self-reliant.
- To alleviate poverty by supporting rural and urban artisans across India.
- Financial Outlay:,Fully funded by the Union Government with a ?13,000 crore budget spanning five years (2023–2028).
- Eligibility:
- Open to rural and urban artisans and craftspeople involved in 18 traditional crafts, such as blacksmithing, goldsmithing, pottery, boat making, and carpentry.
- Covers 5 lakh families in the first year and aims to reach 30 lakh families over five years.
- Key Benefits:
- Financial Support:
- Collateral-free credit of ?1 lakh (first tranche) and ?2 lakh (second tranche) at a concessional 5% interest rate.
- Government provides 8% interest subvention upfront to banks.
- Toolkit Incentive: ?15,000 via e-vouchers for acquiring modern tools.
- Training and Skill Development: Basic and advanced skill training to create industry-ready manpower.
- Digital and Marketing Incentives: Encourages digital transactions and provides marketing support.
- Recognition: Beneficiaries receive a PM Vishwakarma Certificate and ID Card.
- Market Linkage: Facilitates better market access for artisan products.
- Financial Support:
- Achievements (as of Nov 4, 2024):
- 25.8 million applications received.
- 2.37 million artisans registered after verification.
- Over 1 million artisans benefited from toolkit incentives.
Significance
- Promotes inclusive development by supporting an underserved segment of the workforce.
- Recognizes and supports traditional skills passed down through generations, preserving India’s cultural diversity.
- Enhances productivity and competitiveness by integrating artisans into MSME sectors.
- Encourages sustainability through the promotion of handmade, eco-friendly crafts.
Key Institutions Involved
- Ministry of Micro, Small, and Medium Enterprises (MSME): Oversees implementation.
- Common Services Centres (CSC): Facilitates registration through biometric-based PM Vishwakarma Portal.
Challenges Addressed
- Lack of access to modern tools and financial support.
- Insufficient market linkages and exposure for traditional crafts.
- Limited opportunities for skill enhancement and product development.
Protected Planet Report 2024

- 08 Nov 2024
In News:
The Protected Planet Report 2024, released by UNEP-WCMC and IUCN, evaluates global progress toward achieving Target 3 of the Kunming-Montreal Global Biodiversity Framework (KM-GBF). This target aims to conserve 30% of Earth's terrestrial, inland water, coastal, and marine areas by 2030.
Key Highlights of the Report
- Current Global Coverage
- Land and Inland Waters: 17.6% protected.
- Oceans and Coastal Areas: 8.4% protected.
- Progress since 2020: Minimal increase (<0.5% for both realms), equivalent to an area twice the size of Colombia.
- Remaining Challenges to Achieve Target 3 by 2030
- Land: An additional 12.4% of land area must be protected (equivalent to Brazil + Australia).
- Ocean: 21.6% more marine areas must be safeguarded (larger than the Indian Ocean).
- Key Gaps:
- Only 8.5% of protected areas on land are well-connected.
- Only one-fifth of the areas critical for biodiversity are fully protected.
- Biodiversity representation remains uneven, with some ecological regions having no protection at all.
- Governance and Effectiveness Issues
- Less than 5% of protected land and 1.3% of marine areas have management effectiveness assessments.
- Only 0.2% of protected land and 0.01% of marine areas have undergone equitable governance assessments.
- Indigenous governance covers less than 4% of protected areas despite Indigenous and traditional territories covering 13.6% of the terrestrial areas.
- Ocean Conservation Progress: Most progress is in national waters; however, areas beyond national jurisdiction (the high seas) remain underrepresented (<11% coverage).
- Data Deficiency: Insufficient data to measure biodiversity outcomes, equity, and governance in protected areas.
Importance of Target 3
- Biodiversity Benefits: Protected areas play a critical role in halting and reversing biodiversity loss.
- Ecosystem Services: These areas contribute to clean air, water, climate regulation, and food security.
- Cultural and Economic Significance: They uphold the rights of Indigenous Peoples and local communities, ensuring equitable governance and sustainable resource use.
Key Recommendations
- Accelerate Conservation Efforts:
- Expand protected and conserved areas with a focus on biodiversity hotspots.
- Ensure areas are ecologically connected and effectively managed.
- Strengthen Indigenous and Local Contributions:
- Recognize and support the stewardship of Indigenous Peoples and local communities.
- Ensure their voices and knowledge systems are integrated into conservation planning.
- Improve Governance and Equity:
- Address gaps in equitable governance and include rights-based approaches.
- Global Cooperation:
- Increase international financing to developing nations for biodiversity conservation.
- Foster cross-border partnerships and support data-sharing initiatives.
- Enhance Data Availability:
- Collect and disseminate data on the effectiveness of protected areas and their biodiversity outcomes.
India’s Role and Strategy
- Commitment to KM-GBF: India updated its National Biodiversity Strategy and Action Plan (NBSAP) to align with the KM-GBF goals, aiming to protect 30% of natural areas by 2030.
- Focus on Restoration: Prioritizes the restoration of forests, rivers, and other ecosystems to maintain essential resources like clean air and water.
- Indigenous Participation: India emphasizes integrating Indigenous territories into its conservation framework.
Adoption Awareness Month 2024

- 08 Nov 2024
In News:
Adoption Awareness Month is an annual event where CARA and all its stakeholders come together to raise awareness about the legal process of adoption.
Context
- Celebrated by: Ministry of Women and Child Development (MWCD) and the Central Adoption Resource Authority (CARA).
- When: November 2024.
- Theme: “Rehabilitation of Older Children through Foster Care and Foster Adoption.”
- Purpose: To raise awareness about legal adoption, foster care, and the rehabilitation of older children in India.
Objectives
- Promote Legal Adoptions:
- Create awareness about the legal framework and processes for adoption.
- Encourage prospective adoptive parents (PAPs) to adopt older children or children with special needs.
- Foster Care Focus:
- Highlight the importance of foster care as a rehabilitative measure for older children.
- Public Engagement:
- Engage various stakeholders, including adoptive families, PAPs, older adoptees, and the general public, to share experiences and insights.
Key Activities
- Nationwide Campaigns:
- Offline events in states like Ladakh, Assam, Mizoram, Maharashtra, Karnataka, and West Bengal.
- Mega event in Lucknow, Uttar Pradesh, on November 21, 2024.
- Online Initiatives (via MyGov India):
- Storytelling, poster making, slogan writing, pledges, and online surveys.
- Informative content on adoption and foster care shared via social media.
- Interactive Engagements:
- Cultural programs, competitions, Q&A sessions with PAPs, and discussions with stakeholders.
- Sharing of experiences by older adoptees and adoptive parents.
Significance of Adoption Awareness Month
- Focus on Older Children:
- Addresses challenges faced by older children in finding permanent families.
- Promotes inclusive adoption practices for children with special needs or in foster care.
- Stakeholder Involvement:
- Builds trust and awareness by sharing real-life adoption experiences.
- Encourages societal participation in the rehabilitation of vulnerable children.
- Policy Awareness:
- Educates the public about the legal adoption process under CARA.
- Highlights the benefits and responsibilities of foster care and adoption.
Central Adoption Resource Authority (CARA)
- Role: Apex body for regulating adoption in India under the MWCD.
- Key Function: Ensures legal, ethical, and transparent adoption processes for orphaned, abandoned, and surrendered children.
Challenges in Adoption and Foster Care
- Limited awareness about adopting older children or children with special needs.
- Cultural and societal barriers.
- Complexities in the legal adoption process.
Way Forward
- Streamlining Processes: Simplify legal procedures to make adoption and foster care accessible.
- Increased Awareness: Continued campaigns to reduce stigma and misinformation about adoption.
- Policy Support: Strengthen programs for foster care and ensure periodic evaluation of their impact.
One Rank One Pension (OROP) Scheme

- 08 Nov 2024
In News:
As OROP completes the 10 years in 2024, it is essential to reflect on the immense benefits the scheme has brought to the armed forces community.
Overview:
- Implemented on: November 7, 2015.
- Announced in: Union Budget 2014, allocation of ?1,000 crore.
- Aim: To ensure uniform pension for military personnel retiring at the same rank with equal service duration, irrespective of retirement date.
- Significance: A landmark reform addressing a four-decade-long demand of ex-servicemen.
- Origin: Longstanding demand since the 1970s; first highlighted by the 3rd Central Pay Commission.
- Key Committees: K.P. Singh Dev Committee (1984) and Sharad Pawar Committee (1991) recommended reforms but faced financial and administrative hurdles.
Key Features:
The policy’s primary elements include:
- Re-fixation of Pensions: The pension of all past pensioners is re-fixed based on the pensions of personnel who retired in 2013, starting from July 1, 2014. This created a new benchmark for pensions, with all retirees getting equal benefits for their service.
- Periodic Revision: The pension is to be re-fixed every five years, ensuring that it continues to reflect changes in the pay and pension structure.
- Arrears Payments: Arrears of pension were to be paid in equal half-yearly installments, although the arrears for family pensioners and gallantry awardees were paid in a single installment.
- Safeguarding Above-Average Pension: For personnel drawing pensions higher than the average, their pensions are protected, ensuring that they do not lose out on the benefits of OROP.
- Inclusive of All Ex-Servicemen: The order covered all personnel who retired up to June 30, 2014, and provided a robust framework for revising pensions for all ranks, including family pensioners.
Impact:
- Veterans and Families:
- Benefited over 25 lakh ex-servicemen and families.
- Enhanced financial security, standard of living, and dignity.
- Emotional and Social Value:
- Strengthened trust between veterans and the government.
- Recognized sacrifices of armed forces personnel.
Okinawicius tekdi
- 07 Nov 2024
In News:
Researchers have recently discovered a new species of jumping spider in the Baner Hill area, underscoring the region's rich biodiversity and the growing need to preserve the natural landscapes around Pune.
About Okinawicius tekdi:
- The newly identified species, named Okinawicius tekdi, is a jumping spider that contributes to the growing diversity of India's spider population, now numbering 326 species of jumping spiders.
- The name "tekdi" comes from the Marathi word for "hill," reflecting the spider's habitat.
- The last time a spider species was identified in Pune was over three decades ago.
About Jumping Spiders:
- Jumping spiders belong to the family Salticidae and are known for their distinctive eight legs and remarkable jumping ability.
- These spiders possess a segmented body, a tough exoskeleton, and jointed legs.
- In addition to their agility, they are famous for spinning webs that they use to capture their prey.
World Cities Report 2024
- 07 Nov 2024
In News:
The World Cities Report 2024, released by UN-Habitat, highlights the urgent need for cities to address climate change, both as victims and major contributors.
Key Findings of the Report
- Temperature Increases by 2040: Nearly 2 billion people living in urban areas are projected to face at least a 0.5°C rise in temperature by 2040, exposing them to heatwaves and other climate-related risks.
- Urban Vulnerability and Climate Risk:
- Cities are disproportionately affected by climate change while being major contributors to greenhouse gas emissions, which exacerbates their vulnerability to events like floods, cyclones, and heatwaves.
- The urban population is facing a dual challenge: increased heat and extreme weather events such as flooding, cyclones, and erratic rainfall.
- Sea-Level Rise and Coastal Risks: Over 2,000 cities in low coastal areas, many located under 5 meters above sea level, are at heightened risk from sea-level rise and storm surges, potentially affecting more than 1.4 billion people by 2040.
- Riverine Flooding: Flood exposure in cities is growing 3.5 times faster than in rural areas, with 517 million people in urban areas projected to be exposed to riverine flooding by 2030.
- Investment Gap: Cities require between USD 4.5 trillion and USD 5.4 trillion annually to build and maintain climate-resilient systems, but current investments stand at only USD 831 billion, highlighting a massive funding shortfall.
- Decline in Urban Green Spaces: The average share of urban green spaces has dropped from 19.5% in 1990 to 13.9% in 2020, reducing cities' ability to absorb carbon, manage heat, and provide essential ecosystem services.
- Vulnerable Communities: Informal settlements and slums, often situated in environmentally sensitive areas, are disproportionately affected by climate impacts. These communities lack adequate infrastructure and are often unable to invest in necessary upgrades due to eviction fears or lack of legal recognition.
- Green Gentrification: While climate interventions like park creation can provide environmental benefits, they can also lead to green gentrification—displacing low-income households or increasing property values and rents, thus pricing vulnerable communities out.
Contributing Factors to Urban Global Warming
- Energy Consumption: Urban areas account for 71-76% of global CO? emissions from energy use, driven by dense populations, industrial activities, transportation, and high-energy demand for buildings.
- Industrial Activities: Urban industries and power plants release a variety of greenhouse gases (GHGs), including CO?, methane (CH?), and nitrous oxide (N?O).
- Land Use Changes: Urban expansion leads to deforestation and reduced carbon absorption, contributing to global warming. Urban land areas are expected to more than triple by 2050, accelerating environmental degradation.
- Waste Generation: Decomposing waste in landfills releases methane, a potent GHG, exacerbating the greenhouse effect.
- Urban Heat Island Effect: Urban Heat Islands (UHIs) occur when cities absorb and retain more heat due to their dense infrastructure (asphalt, concrete, and buildings), increasing local temperatures and energy consumption.
Impacts of Global Warming on Cities
- Heatwaves: Cities, especially in warmer regions like India, are experiencing more severe heatwaves and rising temperatures.
- Urban Heat Island Effect: UHIs increase the intensity of heatwaves, particularly in high-density cities, where buildings and roads trap heat, exacerbating energy demands and public health risks.
- Coastal Flooding: Rising sea levels threaten coastal cities with flooding and storm surges, displacing communities and disrupting economies.
- Wildfire Seasons: Warming temperatures and prolonged droughts increase the risk of wildfires in urban areas, particularly in forest-adjacent cities.
India's Climate Initiatives for Urban Areas
- Smart Cities Mission: Focuses on developing sustainable urban infrastructure, promoting smart technologies, and enhancing resilience to climate impacts.
- AMRUT Mission: Aims to provide basic infrastructure and sustainable urban development in cities, including water supply, sewage, and green spaces.
- Swachh Bharat Mission-Urban: Focuses on improving waste management and reducing pollution in urban areas.
- FAME India Scheme (Faster Adoption and Manufacturing of Hybrid and Electric Vehicles): Promotes electric vehicles to reduce urban air pollution and carbon emissions.
- Green Energy Corridor (GEC): Facilitates the integration of renewable energy sources into the national grid, encouraging clean energy use in urban centers.
21st India-US Military Cooperation Group (MCG) Meeting

- 07 Nov 2024
In News:
- The 21st India-US Military Cooperation Group (MCG) meeting was held from November 5 to 6, 2024, at the Manekshaw Centre, New Delhi.
- The meeting focused on strengthening defence ties between India and the US, covering a wide range of topics aimed at improving military cooperation.
Key Areas of Discussion
- Capacity Building: The meeting discussed initiatives for enhancing defence capacity through training exchanges, joint exercises, and sharing best practices.
- Defence Industrial Cooperation: Both countries explored opportunities for collaborative defence industrial ventures and technology sharing.
- Joint Exercises: The advancement of joint military exercises was highlighted to boost readiness against both conventional and hybrid threats.
- Strategic Objectives: The meeting aimed to enhance interoperability between the two countries' armed forces, enabling more effective joint operations.
Commitment to Strengthen Indo-US Defence Ties
- Strategic Partnership: Both nations reaffirmed their commitment to strengthening the Indo-US defence partnership, recognizing the shared challenges in the Indo-Pacific region.
- Focus on Regional Security: The discussions underscored the importance of ensuring regional security and global stability in the face of emerging threats.
The Role of the MCG
- Purpose: The MCG forum serves as a key platform for enhancing strategic and operational defence collaboration between India and the US.
- Long-term Goals: The MCG aims to build mutual defence capabilities, counter emerging threats, and ensure the security of both nations and the wider region.
Maha Kumbh Mela 2025

- 07 Nov 2024
In News:
- The Maha Kumbh Mela 2025 will be held in Prayagraj from January 13 to February 26.
- The event is a sacred pilgrimage that draws millions of pilgrims to bathe in the holy waters of the Triveni Sangam (the confluence of the Ganges, Yamuna, and Sarasvati rivers) for spiritual purification and liberation.
Significance and Spiritual Importance
- Sacred Rituals:
- The central ritual is the act of bathing in the holy waters of the confluence, believed to cleanse one’s sins and bring spiritual liberation (Moksha).
- Pilgrims also engage in worship, spiritual discourses, and seek blessings from revered sadhus and saints.
- Auspicious Dates:
- The event includes Shahi Snan (Royal Bath), where prominent saints and their followers bathe on specific dates, marking the beginning of the Mela.
- Paush Purnima marks the start of the auspicious bathing period.
- Cultural Ceremonies:
- The Mela features a grand procession (Peshwai) with Akharas (spiritual orders) on elephants, horses, and chariots.
- Cultural performances, traditional music, dance, and art are also part of the festivities, showcasing India’s vibrant cultural diversity.
Mythological and Historical Roots
- Mythology:
- The Kumbh Mela is deeply embedded in Hindu mythology, symbolizing humanity’s quest for spiritual unity and enlightenment.
- The timing of the event is based on astrological positions of celestial bodies, particularly the Sun, Moon, and Jupiter.
- Historical Significance:
- The origins of the Kumbh Mela trace back over 2,000 years, with references found in the Maurya and Gupta periods.
- Royal Patronage: Emperors like Akbar supported the Mela, symbolizing unity among different religions and cultures.
- British Colonial Era: British officials documented the Mela, fascinated by its scale and ritualistic practices.
- Modern Recognition:
- In 2017, the UNESCO recognized the Kumbh Mela as an Intangible Cultural Heritage of Humanity, underscoring its global significance.
Cultural Celebration and Unity
- Cultural Diversity:
- The Maha Kumbh Mela is a celebration of India's rich cultural heritage, where pilgrims experience traditional crafts, art, music, and dance, alongside spiritual practices.
- International Participation:
- Pilgrims from across the globe attend the Mela, drawn by its message of unity, tolerance, and the universal quest for spiritual growth and peace.
- Message of Unity:
- The Mela serves as a reminder of humanity’s shared desire for self-realization and spiritual fulfillment, transcending national, cultural, and religious boundaries.
PM-Vidyalaxmi Scheme
- 07 Nov 2024
In News:
- The Union Cabinet, chaired by Prime Minister Narendra Modi, approved the PM Vidyalaxmi scheme to provide financial assistance to meritorious students for higher education.
- Objective: The scheme aims to ensure that financial constraints do not hinder students from pursuing quality higher education.
Key Features of the scheme:
- Eligibility:
- Students admitted to top 860 Quality Higher Education Institutions (QHEIs) are eligible.
- Includes both government and private institutions, as per the NIRF (National Institutional Ranking Framework) rankings.
- Loan Provision:
- Collateral-free and guarantor-free education loans for tuition fees and other course-related expenses.
- Loans up to ?7.5 lakhs will have a 75% credit guarantee from the government to encourage banks to offer loans.
- Interest Subvention:
- For students with an annual family income of up to ?8 lakhs (and not eligible for other scholarships or schemes), a 3% interest subvention will be provided on loans up to ?10 lakhs.
- This subvention applies during the moratorium period (when repayment is deferred).
- Preference for interest subvention is given to students in technical/professional courses and those from government institutions.
- Target Beneficiaries:
- Around 22 lakh students are expected to benefit from the scheme annually.
- The government has allocated ?3,600 crore for the period 2024-2025 to 2030-2031, with 7 lakh fresh students anticipated to receive the benefit each year.
- Digital Process:
- A unified “PM-Vidyalaxmi” portal will allow students to apply for loans and interest subvention in a simplified, transparent, and digital manner.
- Payment Method:
- Interest subvention will be paid via E-vouchers or Central Bank Digital Currency (CBDC) wallets.
Loan Product Features
- Collateral-free & Guarantor-free: Loans will be accessible without the need for collateral or a guarantor.
- Loan Coverage:
- The scheme will cover full tuition fees and other related expenses.
- Eligibility Criteria:
- Students enrolled in NIRF top 100 HEIs, state institutions ranked 101-200, and central government institutions are eligible.
- The list of eligible institutions will be updated annually based on the latest NIRF rankings.
Government's Commitment
- The scheme is a part of the National Education Policy 2020’s vision to enhance access to quality education through financial support.
- Additional Support:
- It complements the existing Central Sector Interest Subsidy (CSIS) and Credit Guarantee Fund Scheme for Education Loans (CGFSEL) under PM-USP.
- The CSIS scheme provides full interest subvention for students with an annual family income of up to ?4.5 lakhs, pursuing technical/professional courses.
India-Algeria Strengthen Defence Ties

- 06 Nov 2024
In News:
- The Chief of Defence Staff (CDS) of India recently visited Algeria, culminating in the signing of a significant Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) on defence cooperation.
- Objective: The MoU aims to strengthen the strategic and military ties between India and Algeria.
Recent Developments in India-Algeria Relations
- Important Visit: The CDS’s visit coincided with Algeria’s 70th anniversary of its revolution, celebrated on November 1st, with military parades and ceremonies highlighting Algeria’s historical and political legacy.
- Defence Cooperation:
- India re-established its defence wing in Algeria, and Algeria reciprocated by considering the establishment of its defence wing in India.
- India emphasized its role as a “Vishwa Bandhu” (global partner) and offered to share defence expertise and experiences with Algeria.
- Strategic Discussion: The MoU aims to enhance mutual understanding, laying the foundation for long-term defence collaboration across multiple sectors, including manufacturing under India’s 'Make in India' and 'Make for the World' initiatives.
- Global Peace Support: CDS reiterated India’s commitment to peaceful conflict resolution and expressed support for Algeria’s defence interests.
Significant Areas of India-Algeria Relationship
- Diplomatic Relations:
- India and Algeria established diplomatic ties in July 1962, the same year Algeria gained independence from French colonial rule.
- India supported Algeria's liberation movement and both countries have maintained close ties as part of the Non-Aligned Movement.
- Bilateral Trade:
- Trade peaked at USD 2.9 billion in 2018 but dropped to USD 1.5 billion by 2021 due to COVID-19 and Algeria’s import restrictions.
- Trade rebounded in 2022, increasing by 24% to USD 2.1 billion.
- Exports from India (2023-24): Rice, pharmaceuticals, granite.
- Imports from Algeria: Petroleum oils, LNG, calcium phosphates.
- Bilateral Agreements:
- 2015 MoU: Between All India Radio (AIR) and Algerian National Radio for cooperation in broadcasting.
- 2018 Space Cooperation Agreement: Focuses on satellite technology for applications like crop forecasting and disaster management.
- Visa Waiver Agreement (2021): Diplomatic and official passport holders are exempt from visa requirements.
- Cultural Engagement:
- International Day of Yoga (2024): Celebrated in Algeria at the Jardin d’Essai du Hamma, attracting over 300 participants.
- Space Cooperation:
- The 2018 India-Algeria Space Cooperation Agreement focuses on joint space science, technology, and applications.
- India has launched four Algerian satellites (2016), and the 2022 Joint Committee Meeting expanded satellite capacity building efforts.
- Algeria’s space agency has engaged with ISRO on satellite applications like crop forecasting and disaster management.
- Indian Community in Algeria:
- Approximately 3,800 Indians live in Algeria, working in various sectors, including technical and semi-skilled roles.
- The community includes 13 Overseas Citizens of India (OCI), 10 Persons of Indian Origin (PIOs), and 15 Indian students.
Spraying Diamond Dust to cool the Earth

- 06 Nov 2024
In News:
- A new study in Geophysical Research Letters suggests that diamond dust could be more effective than any other material in reflecting solar radiation.
- Objective: The goal is to reduce global temperatures by 1.6°C by spraying approximately 5 million tonnes of diamonds annually into the atmosphere.
Background of Geoengineering Solutions:
- Geoengineering refers to large-scale interventions aimed at altering Earth's natural climate system to counteract global warming.
- One proposed solution involves spraying diamond dust in the Earth's upper atmosphere to cool the planet.
- This approach is part of Solar Radiation Management (SRM), which seeks to reflect sunlight away from Earth, thereby reducing global temperatures.
- Previous Materials Considered: Sulphur, calcium, aluminium, silicon, and other compounds have been studied to perform a similar function.
Context of Geoengineering and Climate Crisis:
- Inadequate Progress: Current efforts to mitigate global warming, such as reducing greenhouse gas emissions, have been insufficient. Global temperatures have continued to rise, and targets like the Paris Agreement's 1.5°C are increasingly out of reach.
- Rising Global Temperatures:
- 2023: Global temperatures were approximately 1.45°C higher than pre-industrial levels.
- Projected Challenge: To meet the Paris goal, global emissions must be reduced by at least 43% by 2030. However, current actions will likely result in only a 2% reduction by 2030.
Geoengineering Technologies:
- Geoengineering Methods:
- Solar Radiation Management (SRM): Reflects sunlight to cool Earth.
- Carbon Dioxide Removal (CDR): Involves capturing and storing CO?.
- SRM Techniques:
- SRM draws inspiration from natural events like volcanic eruptions, where large amounts of sulphur dioxide form particles that reflect sunlight.
- Mount Pinatubo (1991): One of the largest eruptions, which temporarily reduced global temperatures by 0.5°C due to the sulphur dioxide released.
Diamond Dust vs Other Materials:
- Study Comparison: Diamonds were found to be the most effective material compared to other compounds (sulphur, calcium, etc.) for reflecting solar radiation.
- Quantity Needed: To achieve a cooling of 1.6°C, 5 million tonnes of diamonds would need to be dispersed into the upper atmosphere each year.
Broader Geoengineering Context:
- Carbon Capture and Storage (CCS):
- CCS is already in practice, where CO? emissions from industries are captured and stored underground to reduce atmospheric carbon.
- However, CCS faces high costs and scalability issues, and safe storage sites for CO? are limited.
- Direct Air Capture (DAC): A more advanced method where CO? is directly removed from ambient air, but it faces even greater challenges in terms of infrastructure and cost.
VINBAX 2024 Exercise

- 06 Nov 2024
In News:
The 5th Edition of Vietnam Indian Bilateral Army Exercise “VINBAX 2024” had commenced at Ambala.
Key Participants
- Indian Army: A contingent of 47 personnel from the Corps of Engineers, along with personnel from other arms and services.
- Vietnam People's Army: A similar-sized contingent representing Vietnam's military forces.
- Bi-Service Participation: For the first time, personnel from both Army and Air Force of India and Vietnam are participating.
Objectives of VINBAX 2024
- Joint Military Capability Enhancement:
- Focus on enhancing joint military capabilities of both countries, specifically in the deployment of Engineer Companies and Medical Teams.
- Peacekeeping Operations (UN Context):
- The exercise prepares both sides for United Nations Peacekeeping Operations (PKO), under Chapter VII of the UN Charter, which deals with peace enforcement actions.
- Humanitarian Assistance & Disaster Relief (HADR):
- The exercise includes a 48-hour validation exercise with demonstrations of Humanitarian Assistance and Disaster Relief (HADR) operations.
- The HADR component will include equipment displays to assess the technical standards of both contingents while executing disaster relief and humanitarian missions in peacekeeping contexts.
Key Activities & Events
- Field Training Exercise: The exercise includes a field training component, with a larger scope than previous editions, focusing on:
- Engineer Tasks.
- Medical Support.
- Disaster Relief Operations.
- Validation Exercise: A critical 48-hour validation exercise to test the preparedness of the two forces in providing HADR, including:
- Demonstrations of disaster relief operations.
- Equipment displays to showcase capabilities in managing and executing peacekeeping and humanitarian operations.
- Cultural Exchange: The exercise will also provide an opportunity for cultural exchange, where the troops will learn about the social and cultural heritage of each other.
Background of VINBAX
- Inception: VINBAX was first conducted in 2018 as part of the growing defense cooperation between India and Vietnam. The inaugural edition took place in Jabalpur, Madhya Pradesh.
- Alternating Locations: The exercise alternates between India and Vietnam every year.
- Previous Editions:
- 2023 Edition: Held in Vietnam.
- Current Edition: This is the 5th edition, conducted in India (Ambala and Chandimandir).
Indian Defense Engagements in Southeast Asia
- India-Indonesia Joint Special Forces Exercise (Garud Shakti 2024): Held from November 1-12, 2024, in Cijantung, Jakarta, strengthening ties with Indonesian special forces.
- Singapore-India Maritime Bilateral Exercise (SIMBEX 2024): Held from October 23-29, 2024, in Visakhapatnam, focusing on maritime security cooperation in the Indo-Pacific.
Proba-3 Mission

- 06 Nov 2024
In News:
Europe's Proba-3 mission to arrive in India for launch aboard PSLV-XL by ISRO
Key Highlights:
- Objective: The Proba-3 mission, led by the European Space Agency (ESA), aims to observe the Sun’s corona by creating an artificial solar eclipse. This will allow continuous observation of the Sun’s faint outer atmosphere, which is typically only visible during a natural solar eclipse.
- Key Features:
- Artificial Solar Eclipse: The two spacecraft will fly in formation to maintain a shadow between them, enabling the uninterrupted observation of the solar corona.
- Formation Flying: The satellites must maintain a precise formation with an accuracy of one millimetre, equivalent to the thickness of a fingernail.
Mission Details
- Launch Date: Scheduled for December 4, 2024.
- Launch Location: Satish Dhawan Space Centre near Chennai, India.
- Launch Vehicle: The PSLV-XL rocket developed by ISRO will be used for the launch.
- Spacecraft Mass: The combined mass of the two spacecraft is 550 kg.
- Orbit: The spacecraft will be placed in a highly elliptical orbit with a maximum altitude of 60,000 km to facilitate the precise formation flying.
- This high altitude minimizes Earth’s gravitational pull and reduces the amount of propellant required to maintain their positions during the mission.
Mission Significance
- Solar Observation: The primary objective is to observe the Sun’s corona, which has been challenging to study due to its faintness. The artificial eclipse will allow continuous data collection on solar activity.
- Formation Flying: This technology will allow the two satellites to maintain autonomous flight with millimetre-level precision, which is a significant advancement in satellite formation control.
- Six-Hour Observation Windows: Each formation flying session will last for up to six hours, during which the satellites will observe the Sun's corona.
Technological and Scientific Contributions
- ASPIICS Instrument: The ASPIICS (AStronomical PIcture Camera for the Intense Corona of the Sun) will be the mission's primary instrument, developed by the Royal Observatory of Belgium. It will provide crucial data on solar activity and space weather.
- International Collaboration: The mission is a collaborative effort involving 14 ESA member states and various organizations across Europe.
- Mission Control: The mission will be managed from the ESA’s European Space Operations Centre (ESOC) in Belgium, with significant pre-launch training and preparations already underway.
ISRO's Role and Historical Context
- Launch by ISRO: The Proba-3 mission will be ISRO’s first launch for ESA since 2001, marking an important milestone in India-Europe space cooperation.
- PSLV-XL Rocket: ISRO’s PSLV-XL rocket is known for its reliability and capability in deploying satellites into precise orbits. It is well-suited to carry the 550 kg Proba-3 duo into a highly elliptical orbit for the mission.
Minuteman III ICBM

- 06 Nov 2024
In News:
The U.S. Army is scheduled to test launch a Minuteman III ICBM (Intercontinental Ballistic Missile) after the closure of voting on Election Day.
Missile Features
- Speed: Hypersonic, capable of reaching speeds up to 15,000 mph (Mach 23).
- Range: 13,000 km.
- Payload: Currently carries one nuclear warhead (as per arms control agreements with Russia), but originally designed for multiple independently targetable re-entry vehicles (MIRVs).
- Launch Time: Extremely fast, enabling near-instant global retaliation capabilities.
- Testing Reliability: Nearly 100% success rate in tests, with backup airborne launch controllers to ensure continuity of the retaliatory strike capability.
- Length: 18.2 meters.
- Diameter: 1.85 meters.
- Launch Weight: 34,467 kg.
- Type: Three-stage, solid-fuel missile.
Strategic Significance
- Land-Based Nuclear Deterrent: The Minuteman III is a key component of the U.S. nuclear triad, which includes land-based missiles, submarine-launched missiles (SLBMs), and strategic bombers.
- Cost-Effectiveness: The Sentinel weapon system (modernized Minuteman III) is viewed as the most cost-effective option for maintaining the land-based leg of U.S. nuclear deterrence until the planned Ground-Based Strategic Deterrent (GBSD) system replaces it in 2029.
- Global Reach: The missile can strike any target worldwide within minutes, demonstrating U.S. nuclear reach and power projection.
India's Green Leap

- 05 Nov 2024
In News:
India's journey toward a sustainable energy future has gained significant momentum with a series of policy reforms designed to reduce reliance on fossil fuels and accelerate the shift to clean energy. The recent Asia-Pacific Climate Report from the Asian Development Bank (ADB) highlights India's remarkable progress in reforming its fossil fuel subsidy system and its efforts to foster renewable energy, positioning the country as a leader in the region's green transformation.
Key Highlights from the Report:
India's Fossil Fuel Subsidy Reform
- India has successfully reduced fossil fuel subsidies by 85%, from a peak of $25 billion in 2013 to just $3.5 billion by 2023.
- The reform strategy is built on a "remove, target, and shift" approach, which involved phasing out subsidies on petrol and diesel from 2010 to 2014, followed by incremental tax hikes on these fuels through 2017.
- These fiscal changes created space for funding renewable energy projects, such as solar parks, electric vehicle initiatives, and infrastructure improvements.
Role of Taxation in Supporting Clean Energy
- Between 2010 and 2017, India introduced a cess on coal production and imports, which contributed significantly to funding clean energy projects. Approximately 30% of the cess was directed to the National Clean Energy and Environment Fund.
- This funding supported major renewable energy initiatives, including the National Solar Mission and Green Energy Corridor project, helping reduce the cost of utility-scale solar energy and expand off-grid renewable energy solutions.
- The introduction of the Goods and Services Tax (GST) in 2017 altered the financial landscape, redirecting the cess funds to GST compensation rather than directly to clean energy.
Government Schemes and Initiatives
- India is advancing its clean energy agenda through several key government schemes:
- National Green Hydrogen Mission: Aimed at establishing India as a leader in green hydrogen production.
- PM-KUSUM Scheme: Focused on promoting solar energy among farmers, allowing them to produce renewable power.
- PM Surya Ghar: Muft Bijli Yojana: A program designed to provide solar energy access to rural communities, reducing dependency on fossil fuels.
A Strategic Shift: From Subsidies to Clean Energy
- India’s subsidy reforms are an important part of its strategy to transition from a reliance on fossil fuels to a focus on renewable energy investments.
- These changes reflect India’s long-term goal of achieving net-zero emissions by 2070, as outlined in its climate action plans.
Global Significance of India’s Efforts
- The reduction in fossil fuel subsidies and the surge in clean energy investment serve as a model for other nations seeking to balance economic development with climate action.
- India’s approach demonstrates that policy reforms and innovative financing mechanisms can be used to accelerate the transition to a cleaner, greener economy while creating job opportunities and fostering economic growth.
IUCN’s First Global Tree Assessment

- 05 Nov 2024
In News:
More than one in three tree species threatened with extinction, finds IUCN’s first Global Tree Assessment
Key Highlights:
Global Tree Extinction Risk:
- 38% of the world’s tree species are now facing the risk of extinction — over one in three tree species is at risk.
- This means 16,425 out of 47,282 tree speciesanalyzed by the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) are under threat.
- Threatened tree species outnumber all threatened birds, mammals, reptiles, and amphibians combined, highlighting the urgent need for conservation action.
Key Drivers of Threat:
- Deforestation: The primary threat to trees is deforestation, driven by agriculture, livestock rearing, and urban development, especially in tropical regions.
- Climate Change: Rising sea levels and increasingly frequent storms exacerbate the threats, particularly in tropical regions and islands.
- Invasive Species & Pests: Non-native species, pests, and diseases are adding pressure to vulnerable tree populations.
Geographic Vulnerabilities:
- Islands are particularly vulnerable, with a high proportion of threatened species due to habitat destruction and urbanization.
- South America, which boasts the highest tree diversity, faces significant threats, with 3,356 out of 13,668 species at risk, mainly due to deforestation for agriculture.
Ecological and Economic Importance of Trees:
- Trees play a fundamental role in carbon, water, and nutrient cycles, and are critical for soil formation and climate regulation.
- The loss of trees poses a growing threat to thousands of other species of plants, fungi, and animals.
- Trees are essential for local communities, providing resources such as timber, medicines, food, and fuel. Over 5,000 species of trees are used for timber and construction, while more than 2,000 species are vital for food, fuel, and medicine.
Conservation Status:
- Tree species are threatened across 192 countries.
- The assessment is the first global analysis of the conservation status of trees, enabling better-informed conservation decisions.
Positive Actions and Strategies:
- Successful community-driven conservation efforts have had positive outcomes in places like the Juan Fernández Islands, Cuba, Madagascar, and Fiji.
- Some countries, including Ghana, Colombia, Chile, and Kenya, already have national strategies for tree conservation.
- Ex-situ conservation, such as seed banks and botanical gardens, is also crucial to safeguard species that may not survive in the wild.
Urgent Call for Action:
The IUCN Global Tree Assessment underlines the urgent need for enhanced conservation efforts, including:
- Habitat protection and restoration.
- Ex-situ conservation through seed banks and botanical gardens.
- Diversified and species-focused reforestation strategies.
- Supporting community-led conservation initiatives to safeguard vulnerable tree species.
Asia-Pacific Climate Report 2024

- 05 Nov 2024
In News:
Climate change to put APAC GDP on thin ice with 41% melt by 2100.
Key Highlights:
- Economic Losses Due to Climate Change:
- APAC Region: High-end greenhouse gas emissions could reduce GDP by 17% by 2070 and 41% by 2100.
- India: Projected to experience a 24.7% GDP loss by 2070, with neighboring countries like Bangladesh (30.5%), Vietnam (30.2%), and Indonesia (26.8%) facing even steeper declines.
- Major Drivers of Economic Losses:
- Sea-Level Rise: Up to 300 million people at risk of coastal flooding by 2070. Annual damages could reach $3 trillion by 2070.
- Labour Productivity: The APAC region could lose 4.9% of GDP from reduced labour productivity, with India facing a sharper 11.6% loss.
- Cooling Demand: Rising temperatures could reduce regional GDP by 3.3%, but India's cooling demands could cut its GDP by 5.1%.
- Flooding and Storms: Increased rainfall and storm intensity will exacerbate flooding and landslides, particularly in mountainous regions like the India-China border, where landslides could rise by 30-70% under severe warming.
- Impact on Key Sectors:
- River Flooding: By 2070, annual riverine flooding could cause $1.3 trillion in damages across the APAC, affecting over 110 million people. India could face over $1,100 billion in flood-related damages annually.
- Forest Productivity: Climate change could reduce forest productivity by 10-30% by 2070 across APAC. India could see losses over 25%, making it one of the hardest-hit countries, alongside Vietnam and Southeast Asia.
- Climate Risks and Vulnerabilities:
- Coastal Flooding: Coastal flooding could lead to widespread economic damage, with India expected to suffer significant losses, particularly in coastal areas.
- Ecosystem Threats: Intensified storms, rainfall, and landslides will affect ecosystems, forests, and agriculture across the region.
- Climate Change and Adaptation Needs:
- Investment Requirements: Developing Asia requires $102–431 billion annually for climate adaptation, far exceeding the $34 billion tracked from 2021 to 2022.
- Private Investment: The report highlights the need for greater private climate investment and regulatory reforms to attract capital for adaptation initiatives.
- Renewable Energy: APAC is well-positioned to embrace renewable energy for a net-zero transition, and the use of carbon markets could help achieve climate goals cost-effectively.
- Regional Net-Zero Goals and Progress:
- Net-Zero Targets: 36 out of 44 Asian economies have set net-zero emissions targets, but only 4 have legally committed to these goals. India and China target 2070 and 2060, respectively, while many OECD countries aim for 2050 targets.
- Policy Gaps: Developing Asia needs clearer policies and increased financing to meet climate ambitions. Institutions like ADB are crucial in supporting these efforts.
- Action Plan for the Future:
- Urgent Climate Action: The report stresses the importance of coordinated action to address escalating climate risks.
- Enhanced Adaptation Finance: There is a need to scale up adaptation-focused finance to tackle the growing climate challenges facing the region.
India's Vulnerability and Climate Challenges:
- Labour Impact: India is expected to experience a 11.6% GDP loss due to declining labour productivity, the highest among APAC countries.
- Cooling Demands: A 5.1% reduction in GDP due to increased cooling demand.
- Flood Damage: India’s flood-related losses could surpass $1.1 trillion annually by 2070, with damages to residential and commercial properties.
Bob Khathing

- 05 Nov 2024
In News:
- Defence Minister Rajnath Singh inaugurated the Major Ralengnao 'Bob' Khathing Museum of Valour in Tawang, Arunachal Pradesh, on October 31, 2023, coinciding with National Unity Day (Sardar Vallabhbhai Patel's birth anniversary).
- Significance: The museum honours Bob Khathing's contributions to India's security and the integration of Tawang into India.
Role in the Integration of Tawang:
- Tawang Expedition (1951): In January 1951, Major Bob Khathing, an officer of the Indian Frontier Administrative Service, led the expedition to peacefully integrate Tawang into India.
- Strategic Importance: At the time, there were concerns over Chinese intentions to enter Tibet and realign boundaries. Khathing's mission was crucial to prevent Chinese advances into the area.
- Expedition Details: Khathing set off with Assam Rifles troops from Charduar, Assam, and after overcoming extreme terrain and weather, he reached Tawang. On February 14, 1951, he hoisted the Indian flag, marking Tawang's official integration into India.
- Administrative Setup: Khathing established an administrative framework, including appointing Gaon Buras (village elders) to manage local governance.
Military Service and Recognition:
- World War II Service: Bob Khathing joined the Indian Army in 1939 and earned recognition for his role in the Second World War. He was awarded the Member of the British Empire (MBE) and the Military Cross (MC) for his bravery and leadership.
- Guerrilla Warfare: Khathing was part of the Victor Force, a British-led guerrilla unit tasked with countering the Japanese in Burma and India during WWII. Later, he became the adviser to SANCOL, a force set up to track Japanese forces in the region.
- Military Cross Citation: Khathing was praised for his tireless efforts in organizing local Naga support, gathering intelligence, and participating in successful ambushes, which played a critical role in defeating the Japanese.
Post-War Career and Civil Service:
- Ministerial Role in Manipur: After WWII, Khathing was demobilized and joined the interim government of Manipur, where he served as a minister in charge of the hill areas.
- Integration of Manipur: Following Manipur's merger with India in 1949, Khathing joined the Assam Rifles and served for two years before moving into civil administration.
- Key Positions: He served as Deputy Commissioner of Mokokchung (Nagaland), Development Commissioner in Sikkim, and Chief Secretary of Nagaland.
- Ambassadorship: In 1975, Khathing became India's ambassador to Burma, possibly the first person of tribal origin to hold such a position in independent India.
The Importance of His Contributions:
- Integration of Border Areas: Khathing’s role in integrating Tawang and securing India's northeastern frontier was pivotal in preventing further territorial disputes, especially with China.
- Institutional Development: He helped establish military and security institutions, including the Sashastra Seema Bal, Nagaland Armed Police, and the Naga Regiment, which played important roles in maintaining peace and security in the region.
- Heroic Leadership: Khathing's leadership, both as a soldier and civil servant, continues to be celebrated, symbolized by the Major Bob Khathing Museum of Valour.
NAMO DRONE DIDI

- 05 Nov 2024
In News:
Department of Agriculture & Farmers’ Welfare has released the Operational Guidelines of Central Sector Scheme “NAMO DRONE DIDI”
Key Highlights:
Objective:
- Empower women through Self-Help Groups (SHGs) by providing drones for agricultural rental services.
- Aim to support 14,500 SHGs from 2024 to 2026.
Scheme Overview:
- Type: Central Sector Scheme, under the Deendayal Antyodaya Yojana – National Rural Livelihood Mission (DAY-NRLM).
- Ministry: Ministry of Agriculture & Farmers Welfare.
- Target: Women SHGs for providing drone services in agriculture (e.g., nutrient and pesticide spraying).
Key Features:
- Financial Assistance:
- 80% subsidy (up to ?8 lakh) for SHGs to purchase drones.
- Loans for the remaining 20% via the National Agriculture Infra Financing Facility (AIF) with 3% interest subvention.
- Drone Package:
- Includes drones, spray assemblies, batteries, cameras, chargers, and measurement tools.
- Additional batteries and propellers allow up to 20 acres of coverage per day.
- Training Program:
- One SHG member will be selected for 15 days of mandatory training.
- Focus on drone operation and agricultural tasks (nutrient and pesticide spraying).
- Implementation & Oversight:
- Central Governance: Empowered Committee comprising secretaries from key ministries (Agriculture, Rural Development, Fertilizers, Civil Aviation, and Women and Child Development).
- State Level: Lead Fertilizer Companies (LFCs) will implement the scheme in coordination with state departments and SHG federations.
- Monitoring: IT-based Management Information System (MIS) through the Drone Portal for real-time tracking and fund disbursement.
- Financial Flexibility:
- SHGs can access loans through other Ministry of Rural Development schemes if needed.
Implementation Details:
- Governance: Central level oversight by the Empowered Committee and state-level execution by Lead Fertilizer Companies (LFCs).
- Ownership: Drones procured by LFCs will be owned by SHGs or their Cluster Level Federations (CLFs).
- Monitoring: The scheme will be tracked and managed through the Drone Portal, ensuring transparency and accountability.
LignoSat
- 04 Nov 2024
In News:
The world's first wooden satellite, LignoSat, is set to launch from the Kennedy Space Center aboard a SpaceX rocket. This pioneering satellite is a collaborative effort between Kyoto University and Sumitomo Forestry Co., marking a significant step towards exploring more sustainable materials in space exploration.
Key Highlights:
- Purpose:The primary goal of LignoSat is to test the viability of using wood in space technology, with a focus on the eco-friendliness and cost-effectiveness of using renewable materials in satellite construction. The satellite will be tested aboard the International Space Station (ISS) to assess its durability, strength, and ability to withstand extreme space conditions.
- Material:The satellite is crafted from magnolia wood, chosen for its durability and adaptability. Magnolia was selected for its strength, making it a suitable candidate to endure the harsh conditions of space travel and the intense environmental factors faced in space exploration.
- Mission Details:Once launched, LignoSat will be sent to the ISS, where it will be released from the Japanese Experiment Module (Kibo). Researchers will collect data on the satellite’s performance, examining its ability to handle the challenges of space, including temperature fluctuations and physical strain.
- Environmental Benefits:One of the key advantages of wooden satellites is their environmental impact. Traditional metal satellites, when re-entering the Earth's atmosphere, can generate metal particles that contribute to air pollution. In contrast, wooden satellites like LignoSat are designed to be eco-friendly during reentry. Wood is a natural material that burns up more cleanly during reentry, reducing the potential for harmful atmospheric pollution.
Tumaini Festival

- 04 Nov 2024
In News:
- The Tumaini Festival is held annually in the Dzaleka Refugee Camp in Malawi, one of the world’s few music festivals hosted within a refugee camp. It brings together refugees and locals for cultural exchange, showcasing music, art, and crafts.
- Dates: The festival runs from Thursday to Saturday each year, typically in November.
- Founded: In 2014 by Congolese poet Menes La Plume.
Festival Highlights:
- The festival features performances from a diverse range of artists, including refugees and local Malawians, as well as artists from South Africa, Zimbabwe, and beyond.
- In 2024, performances included Jetu, a 72-year-old singer, and Vankson Boy V, a Congolese refugee, alongside other acts like Maveriq Mavo from South Africa.
- The festival aims to:
- Celebrate cultural exchange and community solidarity between refugees and locals.
- Humanize the refugee experience by allowing refugees and locals to share common experiences and celebrate cultural diversity.
- Challenge stereotypes by showing refugees as people with the same aspirations, talents, and desires as locals.
Significance of Dzaleka Refugee Camp:
- Location: Situated near Lilongwe, Malawi, Dzaleka was originally a prison before becoming a refugee camp in 1994.
- Capacity: Initially designed for 10,000 refugees, the camp now hosts over 60,000 individuals from countries like Democratic Republic of Congo (DRC), Rwanda, Burundi, Ethiopia, and Somalia.
- Role: Dzaleka has evolved into a hub for humanitarian aid, cultural exchange, and empowerment of its residents.
First Science Result from India's Aditya-L1 Mission

- 04 Nov 2024
In News:
- The Aditya-L1 mission, launched by the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) on September 2, 2023, is India's first dedicated scientific mission to study the Sun.
- Primary Payload: The Visible Emission Line Coronagraph (VELC), developed by the Indian Institute of Astrophysics (IIAp), Bengaluru, is the spacecraft's main instrument.
Key Highlights:
- First Science Outcome:The first scientific result from the mission, involving VELC, has been released. It successfully estimated the onset time of a coronal mass ejection (CME) that occurred on July 16, 2023.
- CMEs are massive solar eruptions that can disrupt electronics in satellites and communications on Earth.
- Key Findings:
- VELC's Role: The VELC payload was crucial in observing the CME close to the solar surface, providing a detailed understanding of its onset.
- CMEs are typically observed in visible light after they have traveled far from the Sun. However, VELC’s unique spectroscopic observations allowed scientists to study the CME much closer to the Sun's surface.
- Publication:The results will be published in the Astrophysical Journal Letters.
- Future Significance:
- As the Sun approaches the maximum phase of its current solar cycle (No. 25), CMEs are expected to become more frequent. Continuous monitoring with VELC will provide valuable data for understanding these events.
- Monitoring the thermodynamic properties of CMEs near the Sun is essential to understand their source regions and behavior.
- Mission Details:
- The spacecraft is in a halo orbit around the Lagrange Point 1 (L1), about 1.5 million kilometers from Earth.
- Mission Lifetime: 5 years.
First Asian Buddhist Summit in New Delhi
- 04 Nov 2024
In News:
- The Government of India, in partnership with the International Buddhist Confederation (IBC), is hosting the First Asian Buddhist Summit in New Delhi.
- Theme: "Role of Buddha Dhamma in Strengthening Asia."
- Significance: The summit aligns with India’s Act East Policy, focusing on collective, inclusive, and spiritual development across Asia.
- Inauguration: The two-day event will be inaugurated by President Droupadi Murmu on November 5, 2024.
- Participants: Buddhist Sangha leaders, scholars, and practitioners from various Asian Buddhist traditions will gather to promote dialogue, understanding, and address contemporary challenges within the Buddhist community.
Key Themes of the Summit
- Buddhist Art, Architecture, and Heritage
- Focus on preserving and celebrating Buddhist landmarks in India (e.g., Sanchi Stupa, Ajanta Caves).
- Emphasizes the role of Buddhist art in fostering cross-cultural understanding.
- Buddha C?rik? and Dissemination of Buddha Dhamma
- Discusses Buddha’s journeys and how his teachings spread across India and beyond.
- Role of Buddhist Relics in Society
- Relics serve as symbols of Buddha's teachings, promoting devotion, mindfulness, and economic benefits through tourism and pilgrimages.
- Buddha Dhamma in Scientific Research and Well-Being
- Exploration of Buddhist teachings on mindfulness and compassion, and their integration into contemporary scientific practices to enhance well-being.
- Buddhist Literature and Philosophy in the 21st Century
- Delving into timeless Buddhist wisdom that continues to address the human condition, the nature of reality, and paths to enlightenment.
- Exhibition: "India as the Dhamma Setu (Bridge) Connecting Asia," showcasing India's role in the spread of Buddhism and its significance in fostering unity.
India’s Role in Promoting Buddhist Heritage
- Cultural Identity: Buddhism is integral to India's cultural fabric, influencing its national identity and foreign policy.
- Buddhist Tourism Circuit: The Indian government has developed a Buddhist Circuit covering key sites such as Bodh Gaya, Sarnath, and Kapilvastu.
- International Conferences and Symposia: India has hosted several events, including the First Global Buddhist Summit (2023), International Abhidhamma Diwas (2024), and Symposiums on Vipassana Meditation.
- Pali Language Recognition: On October 4, 2024, Pali was granted classical status, recognizing its significance in conveying Buddha’s teachings.
Buddhism’s Influence in Asia
- Historical Context: Buddhism, founded by Siddhartha Gautama in the 6th century BCE, spread across Asia with the support of figures like Emperor Ashoka (268-232 BCE), who promoted peace and harmony through Buddhist teachings.
- Spread of Buddhism: From its origins in India, Buddhism spread to Central Asia, East Asia, and Southeast Asia, adapting to local cultures and creating diverse schools: Theravada, Mahayana, and Vajrayana.
Ningol Chakkouba Festival

- 04 Nov 2024
In News:
Ningol Chakkouba is one of the biggest festivals of Manipur, primarily celebrated by the Meitei community, but over the years, it has seen participation from various communities.
Key Highlights:
- Date: The festival is celebrated annually on the second day of the lunar month of Hiyangei in the Meitei calendar.
- Main Celebration: The central tradition involves married sisters visiting their maternal homes for a grand feast, joyous reunion, and the exchange of gifts.
- Customary Invitation: A week before the festival, the son of the family formally invites his married sisters to join the celebration.
- Expansion of Celebration: While traditionally celebrated in Manipur, Ningol Chakkouba is now observed in other states and even outside India, where Manipuris are settled.
- Meaning of Ningol Chakkouba:
- Ningol means ‘married woman’.
- Chakouba means ‘invitation for feast’.
- Thus, the festival is a celebration where married women are invited to their parents' home for a special meal.
- Inclusion of Other Communities: Although originally a Meitei tradition, Ningol Chakkouba is now celebrated by various communities due to its emphasis on family reunion, happiness, and promoting peace and harmony in society.
- Cancellation in 2023: The festival was not held in the previous year due to ethnic violence in the state.
Kodo Millet

- 03 Nov 2024
In News:
Kodo millet is a staple food for many tribal and economically weaker sections in India. It is one of the 'hardiest crops, drought tolerant with high yield potential and excellent storage properties,' according to researchers
Background on Kodo Millet:
- Kodo millet (Paspalum scrobiculatum), also known as Kodra or Varagu, is a hardy, drought-tolerant crop widely grown in India, especially in Madhya Pradesh.
- It is a staple food for many tribal and economically weaker sections of India and is used to make various dishes like idli, dosa, and rotis.
- Kodo millet is valued for its high yield, nutritional benefits (rich in vitamins, minerals, antioxidants), and storage properties.
Incident in Bandhavgarh Tiger Reserve:
- 10 elephants from a herd of 13 died over three days in Madhya Pradesh’s Bandhavgarh Tiger Reserve.
- The cause of death was suspected to be mycotoxins associated with kodo millet, particularly Cyclopiazonic Acid (CPA), which is toxic to animals.
Historical Cases of Kodo Poisoning:
- The first human cases of kodo poisoning were reported in 1922 in the Indian Medical Gazette.
- Animals, including elephants, have also been affected by kodo millet consumption, with documented deaths as early as 1983.
- Cyclopiazonic Acid (CPA), a mycotoxin, was identified as the cause of kodo poisoning in the 1980s.
Why Does Kodo Millet Become Poisonous?
- Kodo millet is grown in dry and semi-arid regions and is vulnerable to fungal infections, particularly Ergot fungus, which produces CPA.
- When the crop encounters rainfall during maturing and harvesting, fungal infection can lead to "poisoned kodo," known locally as 'Matawna Kodoo' or 'Matona Kodo'.
- The mycotoxins in the infected millet are stable and resistant to standard food processing techniques.
Impact of Mycotoxins on Animals:
- Symptoms of poisoning: Vomiting, giddiness, unconsciousness, rapid pulse, cold extremities, limb tremors.
- Nervous and cardiovascular systems are primarily affected, causing liver dysfunction, heart damage, and gastrointestinal issues.
- In severe cases, consumption of infected kodo millet can cause death due to cardiovascular collapse and organ failure.
- Similar symptoms of depression and loss of mobility were observed in animal studies, including in mice.
Solution to Kodo Toxicity:
- Biocontrol agents (organisms that fight harmful pathogens) can help reduce fungal growth and mycotoxin production in kodo millet.
- Good agricultural practices: Sorting, proper storage in airtight containers, and avoiding moisture exposure during threshing can minimize contamination.
- Post-harvest management: Removing infected grains is crucial to preventing the spread of the disease.
Detection of Mycotoxins in Kodo Millet:
- Challenges: Mycotoxins are often undetectable by sight, and traditional methods like chromatography are time-consuming.
- Rapid detection tools: Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays (ELISA), lateral flow assays (LFAs), and biosensors offer faster, on-site methods for detecting mycotoxins in kodo millet.
Centre for Science and Environment

- 03 Nov 2024
In News:
Centre for Science and Environment release a report on Extended Producer Responsibility (EPR) for Plastic Packaging
Key Findings:
- EPR Guidelines (2022) were a step towards enforcing the "polluter pays" principle, but the system faces significant issues in its implementation and registration processes.
- Centre for Science and Environment (CSE) report, released on October 29, 2024, highlights gaps in the EPR system for plastic packaging and suggests corrective actions.
EPR Guidelines Overview:
- Issued by: Union Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change (MoEFCC).
- Objective: Hold producers, importers, brand owners (PIBOs), and plastic waste processors (PWPs) responsible for managing plastic packaging waste.
- Key Requirements:
- PIBOs must register on a centralized portal and set targets for collection, recycling, and reuse of plastic packaging.
- Registration involves compliance with targets on end-of-life recycling and recycled content usage.
Problems Identified in the Current EPR System:
- Low Registration and Enrollment:
- 41,577 registrations on the EPR portal, but a significant discrepancy in the type of stakeholders registered.
- 83% of registered entities are importers, 11% are producers, and only 6% are brand owners.
- Producers contribute 65% of the plastic packaging in the market but have low registration.
- Absence of Key Polluters:
- Manufacturers of virgin plastics are notably absent from the portal, despite being required to register.
- Fraudulent Practices:
- 700,000 fake certificates were generated by plastic recyclers, far exceeding the actual certificate generation capacity.
- The Central Pollution Control Board (CPCB) found that such fraudulent activities are undermining the integrity of the system.
- For example, end-of-life co-processing units (e.g., cement plants) claimed to have processed 335.4 million tonnes per annum of plastic waste, while their actual capacity is just 11.4 million tonnes per annum.
- Underreporting and Mismanagement:
- Despite 23.9 million tonnes of plastic packaging being introduced into the market, the CPCB’s estimation of plastic waste generation (4.1 MT annually) is underestimated.
- Lack of Stakeholder Representation:
- Urban local bodies and informal waste collectors—key contributors to plastic waste management—are not included in the EPR framework, which limits their incentives and support.
Recommendations for Improvement:
- Incorporate the Informal Sector:
- Recognize informal waste collectors and waste management agencies in the EPR framework to improve traceability and ensure better waste management.
- Eliminate Fraudulent Practices:
- Strict actions need to be taken against fraudulent recyclers and fake certificate issuers to restore credibility to the EPR system.
- Establish Fair Pricing for EPR Certificates:
- Undertake baseline cost studies to determine the true costs of plastic waste management, ensuring fair pricing for recycling certificates and preventing undervaluation.
- Standardize Packaging:
- Focus on product standardization to ensure that packaging materials are uniform and easily recyclable.
- Strengthen Monitoring:
- Improve oversight on the registration process and ensure that all polluters (producers, importers, brand owners) comply with the system’s guidelines.
EPR and Plastic Waste Management: Context and Importance
- Extended Producer Responsibility (EPR) is a policy approach where the responsibility of managing the entire lifecycle of plastic products (from production to disposal) lies with the producer.
- It is an essential part of India’s Plastic Waste Management Rules (2016), which mandate the recycling and proper disposal of plastic packaging waste.
Key Elements of EPR:
- Producer Accountability: Producers are responsible for the take-back, recycling, and final disposal of plastic packaging.
- Waste Minimization: Encourages reducing waste at the source by promoting sustainable packaging designs.
- Lifecycle Approach: Considers the entire lifecycle of the product, focusing on sustainability from production to disposal.
- Polluter Pays Principle: Ensures that the cost of waste management is borne by those responsible for generating the waste.
National Biodiversity Strategy and Action Plan (NBSAP) 2024-2030

- 03 Nov 2024
In News:
The updated NBSAP was released by India at the 16th Conference of Parties (COP16) to the Convention on Biological Diversity (CBD).
Overview of the NBSAP (2024-30):
- Title:Updated National Biodiversity Strategies and Action Plan: A Roadmap for Conservation of India’s Biodiversity.
- Objective: To provide a comprehensive roadmap for biodiversity conservation, aligning with global frameworks like the Kunming-Montreal Global Biodiversity Framework (KMGBF).
Key Features of the Updated NBSAP:
- Alignment with Global Frameworks:
- The Kunming-Montreal Global Biodiversity Framework (KMGBF) adopted in 2022 aims to halt and reverse biodiversity loss by 2030.
- India’s updated NBSAP aligns with KMGBF’s goals, focusing on biodiversity conservation, sustainable resource use, and ensuring fair benefit-sharing.
- 23 National Biodiversity Targets:
- The targets are focused on three key themes:
- Reducing threats to biodiversity
- Ensuring sustainable use of biodiversity
- Enhancing tools for biodiversity implementation
- The targets are focused on three key themes:
- Key Domains of Focus:
- Area-based conservation: Protecting ecosystems and habitats.
- Ecosystem resilience: Enhancing the ability of ecosystems to withstand environmental stressors.
- Recovery and conservation of threatened species.
- Conservation of agrobiodiversity: Ensuring the sustainability of agricultural biodiversity.
- Sustainable management of biodiversity.
- Enabling tools and solutions: Including financial and technical support for implementation.
- Financial Plan and Expenditure:
- Biodiversity Expenditure Review (BER) estimated an average annual expenditure of Rs 32,20,713 crore (FY 2017-2022) for biodiversity conservation.
- Future funding requirements (FY 2024-2030) estimated at Rs 81,664.88 crore annually at the central government level.
- Biodiversity Finance Plan suggests financing solutions, including public finance, corporate social responsibility (CSR), Ecological Fiscal Transfer (EFT), and Access and Benefit Sharing (ABS) mechanisms.
- Capacity Building:
- The NBSAP stresses the need for capacity building across various levels—national, state, and local.
- Focus on skills acquisition for biodiversity management and enhancing knowledge to implement conservation strategies.
Implementation Framework:
- Multi-Level Governance:
- At the national level, the Ministry of Environment, Forest, and Climate Change (MoEFCC) will oversee implementation with involvement from 22 other ministries.
- State-level: Involves State Biodiversity Boards and Union Territory Biodiversity Councils.
- Local level: Community-driven efforts through Biodiversity Management Committees.
- BIOFIN and Resource Mobilization:
- India is recognized as a leading country in the implementation of the Biodiversity Finance Initiative (BIOFIN).
- Encouragement for private entrepreneurs, businesses, and international donors to invest in biodiversity through innovative financial instruments like:
- Green Bonds
- Green Funds
- Payment for Ecosystem Services (PES)
- Incentives for Financial Solutions:
- India aims to explore funding from corporate social responsibility (CSR), ecological fiscal transfers, and access and benefit sharing mechanisms to meet the financial needs for biodiversity conservation.
Challenges and Strategies:
- Challenges India Faces:
- Habitat fragmentation
- Pollution
- Illegal wildlife trade
- Adverse effects of climate change
- Strategic Responses:
- The updated NBSAP provides strategies to address these challenges, ensuring comprehensive conservation and sustainable use of biodiversity.
First in the World Challenge
- 03 Nov 2024
In News:
ICMR announces ‘First in the World Challenge’ to encourage scientists to find innovative ideas to tackle health issues.
Key Highlights:
- Objective:
- Encourage bold, out-of-the-box ideas for solving difficult health problems.
- Aim to foster novel and groundbreaking biomedical innovations (vaccines, drugs, diagnostics, interventions, etc.).
- Target projects that are “first of their kind” and have never been tried or tested globally.
- Key Features of the Initiative:
- Focus on Groundbreaking Innovations:
- Emphasis on high-risk, high-reward ideas with potential for significant global health impact.
- Excludes proposals aiming for incremental knowledge or process innovation.
- Scope of Research:
- Breakthroughs in biomedical and health technologies such as:
- Vaccines
- Drugs/Therapeutics
- Diagnostics
- Interventions
- Breakthroughs in biomedical and health technologies such as:
- Focus on Groundbreaking Innovations:
- Funding & Support:
- Provides funding for projects at various stages, from proof-of-concept to prototype development and final product.
- Support for projects that have the potential to lead to “first-of-its-kind” biomedical innovations.
- Application Process:
- Open to individual researchers or teams (from single or multiple institutions).
- Teams must designate a Principal Investigator responsible for the project’s technical, administrative, and financial aspects.
- Selection Criteria:
- A selection committee will be formed with:
- Experts, innovators, policymakers, and distinguished scientists with an outstanding research record.
- Proposals evaluated based on originality, impact potential, and innovation.
- A selection committee will be formed with:
About the Indian Council of Medical Research (ICMR)
- History:Founded in 1911 as the Indian Research Fund Association (IRFA), renamed ICMR in 1949.
- Role & Mandate:
- Ministry of Health and Family Welfare, Government of India.
- Formulates, coordinates, and promotes biomedical research in India.
- Focus on improving public health and addressing national health challenges.
- Vision:“Translating Research into Action for Improving the Health of the Population.”
Wildlife Crime Control Bureau (WCCB)
- 03 Nov 2024
In News:
The Wildlife Crime Control Bureau (WCCB) of the Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate change has constituted a team to enquire into the death of ten elephants in Bandhavgarh Tiger Reserve of Madhya Pradesh. The team is conducting an independent enquiry in the matter.
- Incident Overview:
- Ten elephants found dead in Bandhavgarh Tiger Reserve, Madhya Pradesh, between October 29-31, 2024.
- Preliminary cause of death suspected to be poisoning; final cause pending postmortem and toxicological analysis.
- Government Actions:
- Union Government:
- The Wildlife Crime Control Bureau (WCCB) has set up a team to conduct an independent investigation into the deaths.
- Madhya Pradesh Government:
- Constituted a five-member State-level inquiry committee, headed by the Additional Principal Chief Conservator of Forests (APCCF, Wildlife).
- Committee includes members from civil society, scientists, and veterinarians.
- The State Tiger Strike Force (STSF) is conducting field investigations, combing surrounding areas for further clues.
- Other Involved Authorities:
- The Principal Chief Conservator of Forests (PCCF) and Chief Wildlife Warden of Madhya Pradesh are directly supervising the inquiry in Bandhavgarh.
- Senior officials from the National Tiger Conservation Authority (NTCA) have visited the site for discussions and investigation.
- Union Government:
About Wildlife Crime Control Bureau (WCCB):
- Mandate:
- Combats organized wildlife crime through intelligence gathering and coordination with enforcement agencies.
- Develops wildlife crime data and assists in prosecutions.
- Provides capacity building for wildlife crime enforcement agencies.
- Operations & Initiatives:
- Conducts operations like SAVE KURMA, THUNDERBIRD, WILDNET, and more to counter wildlife crimes.
- Nodal Ministry: Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change.
- Headquarters: New Delhi.
PARAKH RashtriyaSarvekshan 2024

- 02 Nov 2024
In News:
The National Achievement Survey (NAS), a nationwide survey meant to assess students’ learning progress, will be held on December 4 this year under a new name – PARAKH RashtriyaSarvekshan 2024. This year’s assessment involves a few changes from the last round in 2021.
Overview of PARAKH RashtriyaSarvekshan 2024:
- New Name: The National Achievement Survey (NAS) is now rebranded as the PARAKH RashtriyaSarvekshan 2024.
- Date: The survey will be held on December 4, 2024.
- Purpose: To assess students’ learning achievements across India.
- Organizing Bodies: Spearheaded by NCERT and CBSE.
What Does the Survey Assess?
- Assessment Focus: Evaluates students’ learning outcomes in various subjects.
- Survey Methodology: Uses multiple-choice questions to assess a sample of students.
- Target Groups: Students from government, government-aided, and private schools across every district in India.
History of NAS and PARAKH:
- NAS History: Conducted every three years since 2001 to capture learning progress.
- Involvement of Classes:
- 2001-2014: Included Classes 3, 5, and 8.
- 2014-15: Class 10 was introduced.
- 2017 and 2021: Covered Classes 3, 5, 8, and 10.
- Report Cards: Provides national, state, and district-level performance data.
Changes in 2024 Survey (PARAKH RashtriyaSarvekshan):
- Targeted Classes:
- Class 3 (End of foundational stage)
- Class 6 (End of preparatory stage)
- Class 9 (End of middle stage)
- Exclusion of Class 10: Unlike previous years, Class 10 students are not part of this year's assessment.
- Subjects Assessed:
- Class 3 & 6: Language, Mathematics, and The World Around Us (Concepts of Science, Social Science, and Environmental Education).
- Class 9: Language, Mathematics, Science, and Social Science.
Alignment with National Education Policy (NEP) 2020:
- NEP Structure: Aligns with the NEP 2020 framework, categorizing educational stages:
- Class 1-2: Foundational stage
- Class 3-5: Preparatory stage
- Class 6-8: Middle stage
- Class 9-12: Secondary stage
- The shift to Class 6 and 9 for this year’s survey matches the NEP's stage-wise educational framework.
Key Differences in 2024 Assessment:
- Survey Scale: In 2024, 75,565 schools and 22.9 lakh students from 782 districts will participate.
- 2021 Assessment Data:
- The 2021 survey revealed a drop in learning outcomes post-COVID-19.
- Class 3 students showed a performance below the national average in all states.
- Class 5: Only Punjab and Rajasthan had scores above the national average.
PARAKH's Role:
- PARAKH (Performance Assessment, Review, and Analysis of Knowledge for Holistic Development) was established in 2023 as the National Assessment Centre to oversee such achievement surveys.
- Mandate: One of PARAKH’s primary roles is to organize national surveys like the PARAKH RashtriyaSarvekshan.
Significance of the Survey:
- Data Utilization: The survey helps in shaping educational policies based on real-time data on student learning levels.
- Competency-Based Assessment: This year’s survey is focused on competency-based assessments, aligning with the goals of NEP 2020.
- Policy and Planning: The data helps in designing interventions to address regional or subject-wise disparities in education quality.
Hwasong-19

- 02 Nov 2024
In News:
- North Korea recently announced the successful test-firing of its latest intercontinental ballistic missile (ICBM), the ‘Hwasong-19’.
- Claims by North Korea: The missile was described as ‘the world’s strongest strategic missile’ and a ‘perfected weapon system’ by North Korean state media.
Key Features of the Hwasong-19:
- Solid-Fuel Propulsion: The Hwasong-19 reportedly uses solid-fuel propulsion, which enables quicker launches and greater secrecy. This contrasts with liquid-fuel missiles, which take longer to prepare and are more visible.
- Enhanced Performance: The missile is said to have improved altitude and flight duration compared to previous North Korean ICBMs, marking significant progress in missile technology.
- Size: The Hwasong-19 is estimated to be 28 meters long (92 feet), which is notably larger than many other ICBMs, including those from the U.S. and Russia, which are typically under 20 meters (66 feet).
Strategic Implications:
- Reach and Targeting: The Hwasong-19 is believed to have a range of over 13,000 kilometers, which is sufficient to target the U.S. mainland, signaling a significant advancement in North Korea’s missile capabilities.
- Nuclear Capability: While specific details on the missile’s payload remain undisclosed, the Hwasong-19 could potentially be equipped with a nuclear warhead, enhancing North Korea's strategic deterrence.
Impact on Regional and Global Security:
- US-North Korea Tensions: The launch occurred against the backdrop of ongoing U.S.-North Korea tensions, particularly over North Korea’s nuclear and missile programs. The missile could potentially alter the regional security dynamics, especially in East Asia.
What is an ICBM?
- ICBM Definition: An intercontinental ballistic missile (ICBM) is a long-range missile capable of carrying nuclear warheads (or other payloads) across continents.
- Range and Speed: ICBMs typically have a minimum range of 5,500 km (3,400 miles), with some capable of reaching up to 16,000 km or more, making them far faster and more capable than other ballistic missiles.
- Launch Mechanism: ICBMs are launched from land or submarine platforms, traveling through space before re-entering the Earth’s atmosphere and targeting distant objectives.
- Comparison with India's Agni-V: India’s Agni-V ICBM, which has a range of over 5,000 km, is often compared to North Korea’s missile systems.
Asset Recovery Interagency Network–Asia Pacific (ARIN-AP)

- 02 Nov 2024
In News:
- India, represented by the Directorate of Enforcement (ED), has joined the Steering Committee of the Asset Recovery Interagency Network-Asia Pacific (ARIN-AP).
- Leadership Role: India will assume the presidency of ARIN-AP and host the Annual General Meeting (AGM) in 2026, providing a platform for global cooperation in asset recovery and tackling economic crimes.
ARIN-AP Overview:
- Establishment: ARIN-AP is a multi-agency network formed to address the proceeds of crime across the Asia-Pacific region.
- Network Goals: Its mission is to facilitate cross-border collaboration in the areas of asset tracing, freezing, and confiscation.
- Membership: ARIN-AP includes 28 member jurisdictions and 9 observers, and operates as a key component of the Global CARIN Network (Camden Asset Recovery Inter-Agency Network).
- Functioning: ARIN-AP operates through a network of contact points that enable intelligence exchange among member agencies, promoting effective communication and coordination for asset recovery.
Significance of ARIN-AP's Work:
- Combating Economic Crimes: ARIN-AP enhances the efforts of law enforcement agencies in tracing and recovering assets linked to criminal activities, including both movable and immovable assets.
- Informal Exchange of Intelligence: The network allows for the informal exchange of intelligence between agencies, which often accelerates the identification and recovery of proceeds of crime. This can later lead to formal actions through bilateral or multilateral agreements.
- Global Impact: With over 100 jurisdictions in the broader CARIN Network, ARIN-AP plays a key role in global efforts to combat fugitive economic offenders and illicit financial flows.
India’s Contribution and Alignment with G-20 Priorities:
- India’s Leadership: India’s presidency in ARIN-AP will enhance its leadership in asset recovery, facilitating closer cooperation with regional and international law enforcement agencies.
- G-20 Alignment: This role aligns with India’s priorities under the G-20 framework, particularly focusing on the Nine-Point Agenda aimed at tackling fugitive economic offenders and improving asset recovery mechanisms.
Discovery of the First "Black Hole Triple" System

- 02 Nov 2024
In News:
Scientists have discovered a "black hole triple" system, which is a rare configuration in space involving one black hole and two stars.
Overview of the Discovery:
- Location: The system is located 8,000 light years away from Earth, in the constellation Cygnus.
- Key Features:
- A black hole at the center, currently consuming a star that is spiraling very close to it.
- A second, more distant star that orbits the black hole every 70,000 years, and another star that orbits it every 6.5 days.
What is a Black Hole Triple System?
- Black Hole and Two Stars: Unlike typical binary systems (comprising a black hole and one other object), this system contains a black hole surrounded by two stars, one nearby and one far away.
- V404 Cygni: The central black hole in the system is the V404 Cygni, one of the oldest known black holes, roughly 9 times the mass of the Sun.
Significance of the Discovery:
- Questions on Black Hole Formation: The discovery raises new questions about how black holes are formed. Traditionally, black holes are thought to form after the explosion of a massive star (supernova), but this system does not follow that model.
- New Formation Theory: Researchers suggest the black hole may have formed via a "direct collapse" process, where a star collapses into a black hole without undergoing a supernova explosion. This is referred to as a "failed supernova".
- In a failed supernova, the star's collapse happens too quickly for the explosive outer layers to be ejected, leading to the formation of a black hole without the typical violent explosion.
Implications for Other Binary Systems:
- The black hole’s gradual consumption of one of its stars may imply that some binary black hole systems could have originally been triple systems, with one star eventually being consumed by the black hole.
Research and Collaboration:
- Study: The discovery was made by researchers at California Institute of Technology (Caltech) and Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT).
- Published in: The findings were published in Nature in October 2024.
Additional Context:
- Distance: The system is about 8,000 light years away, which is vast but still observable with advanced telescopes.
- Mystery of the "Failed Supernova": The concept of a failed supernova offers new insights into the life cycle of massive stars and their transformation into black holes.
ISRO's Analogue Space Mission in Ladakh

- 02 Nov 2024
In News:
In a significant leap for the country’s space exploration aspirations, India has embarked on its first analogue space mission in Leh, a landmark step that will attempt to simulate life in an interplanetary habitat to tackle the challenges of a base station beyond Earth.
Mission Overview:
- Objective: To simulate living conditions in an interplanetary habitat, addressing challenges astronauts may face during deep-space missions (e.g., Moon, Mars).
- Goal: Study long-term isolation, habitat design, resource management, and psychological effects on astronauts.
- Partners: ISRO’s Human Spaceflight Centre, AAKA Space Studio, University of Ladakh, IIT Bombay, Ladakh Autonomous Hill Development Council.
Rationale for Ladakh:
- Geological Similarities: Ladakh’s terrain mirrors Martian and lunar surfaces, making it ideal for testing space technologies.
- Climate: Cold, dry, high-altitude conditions simulate the extreme environments of space.
- Focus Areas: Testing habitat construction, microbial studies, and survival strategies for long-duration space travel.
What are Analogue Space Missions?
- Definition: Simulated space missions on Earth designed to replicate the conditions of space exploration.
- Purpose:
- Test technologies (e.g., life support, habitat design, in-situ resource utilization).
- Study human behavior, psychological impacts of isolation, and operational readiness for extended space travel.
- Relevance: Crucial for preparing astronauts for missions to the Moon, Mars, or asteroids.
Significance of Analogue Missions:
- Technological Testing: Analogue missions help in evaluating systems for habitat design, life support, and health monitoring.
- Human Factors: They provide insights into crew health, teamwork under pressure, and performance during isolation.
- Psychological Studies: Address the impact of confinement, isolation, and communication delays on astronauts.
- Training: Participants (analogue astronauts) are trained for real-world space missions by conducting scientific experiments and managing emergencies.
Global Examples of Analogue Missions:
- NASA’s NEEMO: An underwater mission simulating microgravity conditions to train astronauts for space tasks.
- SIRIUS Program (UAE): Focuses on the psychological impacts of long-duration space isolation, featuring international collaborations.
- Arctic Mars Analogue Svalbard Expedition (AMASE): Uses the extreme Arctic environment of Svalbard to test Mars exploration technologies and procedures.
Relation to India’s Space Aspirations:
- Gaganyaan Mission: ISRO’s human spaceflight mission aiming to send Indian astronauts into space.
- Interplanetary Exploration: The analogue mission supports India’s broader goal of advancing human space exploration and technology development for Mars and beyond.
Melanistic Tigers
- 01 Nov 2024
In News:
- Odisha government relocated a tigress from Maharashtra’s Tadoba-Andhari Tiger Reserve to Similipal Tiger Reserve, Odisha, to address inbreeding issues among the tiger population.
- The tigress is part of a genetic diversification plan to remedy the increasing number of pseudo-melanistic tigers in the region.
Pseudo-melanistic Tigers:
- Pseudo-melanistic tigers, often referred to as "black tigers," exhibit a darker coat with broader, more prominent stripes.
- The mutation leads to the appearance of a mostly black fur, with occasional white-orange stripes.
Genetic Basis:
- This coloration is due to a mutation in the Taqpep gene, which causes the widening and darkening of stripes on the tiger's coat.
- The mutation is linked to genetic drift and inbreeding within the isolated Similipal population.
Historical Context:
- These tigers were once considered mythical until the 1700s, with sightings only being documented in the 1990s and 2017-18.
- The first confirmed genetic evidence of the black tiger appeared when a cub was born in captivity at Oklahoma City Zoo in the 1970s.
Distribution and Prevalence:
- Pseudo-melanistic tigers are predominantly found in Similipal Tiger Reserve, with 27 out of 30 tigers in Odisha exhibiting the trait.
- Other instances of such tigers exist in captivity, such as in Nandankanan Zoological Park (Bhubaneswar) and Arignar Anna Zoological Park (Chennai), both tracing ancestry to Similipal.
Genetic Studies:
- A 2021 study by the National Centre for Biological Sciences (NCBS) linked the Taqpep gene mutation to the unique appearance of these tigers.
- The mutation causes a missense change in the gene, replacing Cytosine with Thymine (C1360T), altering the tiger’s coat pattern.
High Frequency of Mutation in Similipal:
- Genetic analyses indicate a high frequency of the Taqpep gene mutation in Similipal tigers, with a 60% chance that a tiger born there will carry the mutated gene.
- Inbreeding and genetic isolation have contributed to this phenomenon, as Similipal’s tiger population is geographically cut off from other populations.
PM rolls out Ayushman Bharat for Citizens aged 70 and above

- 01 Nov 2024
In News:
Prime Minister Narendra Modi has expanded the Ayushman Bharat Pradhan Mantri Jan Arogya Yojana (PM-JAY) to provide health coverage to citizens aged 70 years and above, regardless of their income or economic status. This move is aimed at addressing the healthcare challenges faced by India's elderly population, which has been growing rapidly.
Key Highlights of the Ayushman Bharat Expansion:
- Health Coverage for Elderly:
- Ayushman Vaya Vandana Card: This new health card offers Rs 5 lakh annually for individuals aged 70 and above. The coverage is shared within the family, so if there are multiple elderly beneficiaries in one household, the total cover will be split.
- Scope: This initiative is designed to provide a safety net for elderly people, many of whom had previously been unable to access treatment due to high costs.
- Significance of the Scheme:
- India’s elderly population is rapidly growing, with the number of people over 60 expected to reach 319 million by 2050, up from 103 million in 2011.
- The expansion of PM-JAY to include those aged 70+ is a critical step in making universal health coverage more inclusive as India’s population ages.
- Eligibility and Registration:
- Individuals aged 70 years and above must register on the PM-JAY portal or through the Ayushman app. Those who already have an Ayushman Bharat card must complete an eKYC process to receive the new card and coverage.
- Exclusions: The scheme is not available in Delhi and West Bengal, as these states have not adopted the Ayushman Bharat scheme.
- Financial Details:
- The initial outlay for this expansion will be Rs 3,437 crore, covering the remainder of the current financial year and the next year.
- Cover for Overlapping Health Schemes: Elderly individuals who are already covered under other government schemes (e.g., CGHS, Ex-Servicemen Contributory Health Scheme) will have the option to either continue with their current coverage or choose Ayushman Bharat. Those with ESIC or private insurance can access both Ayushman Bharat and their existing cover.
- Coverage Scope:
- The expansion is expected to benefit approximately 6 crore individuals across 4.5 crore families.
- Existing Coverage: Around 1.78 crore elderly people are already covered under the scheme. Additional coverage will be provided to those not currently included in the scheme.
- Interoperability with Other Schemes:
- Those under the Central Government Health Scheme (CGHS), Ex-Servicemen Contributory Health Scheme (ECHS), or other similar schemes will need to choose between their current insurance and the Ayushman Bharat scheme.
- However, individuals enrolled in Employees' State Insurance Corporation (ESIC) can have both their existing cover and the Ayushman Bharat coverage.
- Rollout and Reach:
- The scheme will be implemented across 33 states and Union Territories, except Delhi, Odisha, and West Bengal.
- Over 29,600 hospitals, including more than 12,600 private facilities, are empanelled to provide treatment under PM-JAY.
Other Key Announcements:
- U-WIN Portal: A pan-India digital platform for routine vaccinations, aimed at enhancing the efficiency of vaccination programs.
- Critical Care Facilities: The Prime Minister also launched critical care infrastructure, including new facilities in AIIMS Bhubaneswar, Kalyani, and super-specialty units in Himachal Pradesh and Madhya Pradesh.
LiDAR (Light Detection and Ranging)
- 01 Nov 2024
In News:
LiDAR (Light Detection and Ranging) is a cutting-edge remote sensing technology that uses laser pulses to measure distances and create detailed 3D maps of Earth's surface. This technology has recently played a crucial role in discovering a lost Mayan city hidden under the dense Mexican jungle.
What is LiDAR?
- Definition: LiDAR is a remote sensing technology that uses pulsed laser light to measure distances and generate precise 3D models of Earth’s surface.
- Components: The system includes a laser, a scanner, and a GPS receiver. It is usually mounted on an aircraft to map large areas of terrain.
- Data Accuracy: LiDAR can create high-resolution 3D models with vertical accuracy up to 10 cm, making it highly precise for mapping ground elevation.
How LiDAR Works
- Laser Emission: LiDAR sends out rapid laser pulses toward the ground.
- Reflection: These pulses hit the Earth’s surface, reflecting off features like vegetation, buildings, and terrain.
- Measurement: The time it takes for the laser light to travel to the ground and back is measured, allowing the system to calculate the distance between the sensor and the surface.
- Point Cloud Data: The reflected light data is collected as a "point cloud", representing all the surfaces it hits, including trees, buildings, and other features.
- Refinement: This point cloud can be processed into a Digital Elevation Model (DEM), stripping away vegetation and structures to reveal the “bare earth,” which highlights features like roads, buildings, and hidden settlements.
Why LiDAR is Useful for Archaeologists
- Large-Scale Surveying: Traditional archaeological methods often involve labor-intensive fieldwork, such as walking over every square meter and manually cutting through thick vegetation. LiDAR, however, allows researchers to quickly survey vast areas of land, even through dense jungle, from the comfort of a lab.
- Visibility Under Vegetation: LiDAR’s ability to penetrate dense foliage and reveal features beneath the surface is a game changer. Even thick tree canopies that obscure the ground are no match for the laser pulses, which can pass through gaps to illuminate hidden structures.
The Discovery of the Lost Mayan City
- The City of Valeriana: Using publicly available LiDAR data from a forest monitoring project in 2013, archaeologist Luke Auld-Thomas discovered a lost Mayan city in Mexico’s Campeche region. The city, named Valeriana, had been hidden for centuries by the thick jungle.
- City Features: The city has all the hallmarks of a Classic Maya political capital, including:
- Multiple enclosed plazas
- Broad causeways
- Temple pyramids
- A ball court
- A reservoir formed by damming a seasonal watercourse
- Historical Significance: Valeriana is believed to date back before 150 CE and may have been a key political and cultural center in the Maya civilization.
Applications of LiDAR Beyond Archaeology
- Geography and Mapping: LiDAR is widely used to generate precise, three-dimensional data about the Earth’s surface, helping geographers and planners.
- Environmental Monitoring: It is also used in forest monitoring, flood risk assessment, and environmental conservation.
- Urban Planning and Engineering: Engineers use LiDAR for creating highly accurate topographical maps and planning infrastructure projects.
Anti-Counterfeiting Ink developed using Luminescent Nanomaterials

- 01 Nov 2024
In News:
- A novel anti-counterfeiting ink has been developed using luminescent nanomaterials, which significantly enhances security in currency, certificates, medicines, and branded goods.
- The ink utilizes the luminescent properties of rare earth ions and bismuth, enabling excitation-dependent luminescence under different light sources, providing a robust solution to combat counterfeiting.
Key Features:
- Multi-Wavelength Luminescence:
- The ink exhibits distinct colors when exposed to various wavelengths of light:
- Vibrant blue under 365 nm UV light
- Pink under 395 nm UV light
- Orange-red under 980 nm near-infrared (NIR) light
- These varying color emissions make it difficult for counterfeiters to replicate, as traditional covert tags are visible only under UV light and can be easily duplicated.
- The ink exhibits distinct colors when exposed to various wavelengths of light:
- Enhanced Durability:
- The ink remains effective under a wide range of conditions, including varying light, temperature, and humidity, ensuring long-term usability without degradation.
- Simple Application Method:
- The luminescent nanomaterials are synthesized through a co-precipitation method at 120°C.
- The resulting nanomaterials are then mixed into commercially available PVC ink using sonication, allowing for easy dispersion of nanoparticles.
- The ink is applied using screen printing to create patterns and texts that exhibit distinct color changes under different lighting conditions.
- Security Features:
- The ink combines rare earth ions with bismuth emissions, boosting its encryption and decryption capabilities. This creates a high level of security for applications on high-value items.
Applications:
- Currency and Certificates: Enhances the authenticity of financial instruments and official documents.
- Branded Goods: Protects products from counterfeiting and fraud.
- Medicines: Helps verify the authenticity of pharmaceutical products, preventing the distribution of fake medicines.
Benefits:
- Verification: Both consumers and manufacturers can easily verify the authenticity of products, providing an accessible solution to counterfeiting.
- Practical Solution: The ink offers a practical, reliable, and non-invasive method for detecting counterfeit products, addressing a global challenge in various industries.
MhadeiWildlife Sanctuary
- 01 Nov 2024
In News:
An adult tigress and three cubs have been spotted in the Mhadei wildlife sanctuary in Goa marking the first time evidence of the species has been recorded in the forests bordering the states of Maharashtra and Karnataka since 2020.
Key Highlights:
Location and Geography:
- It is located near Chorla Ghat, between North Goa and Belgavi, and borders Maharashtra and Karnataka.
- The sanctuary is traversed by the Mhadei River, which meets the sea at Panaji, Goa.
Ecological Significance:
- It is part of the Western Ghats, a UNESCO World Heritage site, and shares this ecosystem with Mollem National Park and other protected areas in Goa.
- The sanctuary is integral to wildlife corridors connecting the Sahyadri Tiger Reserve (Maharashtra) and Kali Tiger Reserve (Karnataka), critical for tiger conservation.
Flora and Fauna:
- It is home to diverse wildlife, including the critically endangered Long-billed vultures that nest at Vazra Falls.
- The region supports a variety of flora and fauna due to its biodiversity-rich Western Ghats ecosystem.
Conservation Status and Recommendations:
- Goa is the only state in India to have its entire portion of the Western Ghats under state protection, with Mhadei WLS being a key area.
- The National Tiger Conservation Authority (NTCA) has recommended that Mhadei WLS be designated as a tiger reserve to enhance protection efforts.
- The sanctuary is a potential candidate for inclusion under Project Tiger.
- In 2020, a Royal Bengal tigress and her cubs were tragically poisoned due to human-animal conflict.
Mahadayi Water Dispute:
- The Mahadayi (Madei, Mandovi) River is a source of dispute between Karnataka and Goa regarding water sharing.
- Karnataka seeks to divert water from the river to the Malaprabha River basin for drinking water supply in several districts, through the Kalasa-Banduri Nala project.
- The matter is currently being heard in the Supreme Court.
Report of The Lancet Countdown on Health and Climate Change, 2024

- 30 Oct 2024
In News:
The 2024 edition of The Lancet Countdown on Health and Climate Change presents critical insights into the intersection of health and climate change.
Key Findings from the 2024 Report
- Air Pollution and Mortality in India:
- In 2021, air pollution was responsible for 1.6 million deaths in India.
- Fossil fuels (coal and liquid gas) were identified as major contributors, accounting for 38% of these deaths.
- India was ranked as the second-highest emitter of PM2.5 globally in 2022, contributing 15.8% of consumption-based and 16.9% of production-based PM2.5 emissions.
- Impact of Heat Stress:
- In 2023, India experienced 2400 hours (or 100 days) of moderate to high heat stress, particularly during light outdoor activities like walking.
- Heatwaves have become more frequent, with adults over 65 years experiencing 8.4 heatwave days per year, a 58% increase from 1990-1999.
- This increased heat exposure has led to a loss of 181 billion labor hours globally, translating into an economic loss of approximately $141 billion.
- Global and National Trends in Air Pollution:
- PM2.5 is particularly hazardous because it is fine enough to enter the lungs and bloodstream, leading to severe health risks like respiratory and cardiovascular diseases.
- Nitrogen Dioxide (NO?), Sulphur Dioxide (SO?), Carbon Monoxide (CO), and Ozone (O?) were identified as other pollutants contributing to poor air quality in India.
- Health Impact of Extreme Weather:
- The 2023 heatwave was one of the hottest years on record, exacerbating health risks worldwide, especially for the elderly.
- Droughts and heatwaves also contributed to a rise in food insecurity, affecting millions globally.
- Disease Transmission and Climate Change:
- Dengue transmission potential rose by 85% from 1951-1960 to 2014-2023.
- Coastal areas suitable for the spread of Vibrio pathogens, which cause cholera, expanded by 23%, affecting over 210 million people.
- Health Effects of Fossil Fuel Pollution:
- Continued reliance on fossil fuels worsens air quality, leading to health problems such as respiratory diseases, cardiovascular issues, and adverse pregnancy outcomes.
Government Efforts to Tackle Air Pollution in India
- National Clean Air Programme (NCAP):
- NCAP is a national strategy to reduce air pollution across India, with specific action plans for 131 non-attainment cities. The initiative is supported through various central government schemes such as:
- Swachh Bharat Mission (Urban)
- Atal Mission for Rejuvenation and Urban Transformation (AMRUT)
- Smart City Mission
- Faster Adoption and Manufacturing of Hybrid and Electric Vehicles (FAME-II)
- NCAP is a national strategy to reduce air pollution across India, with specific action plans for 131 non-attainment cities. The initiative is supported through various central government schemes such as:
- Bharat Stage VI (BS-VI) Emission Norms:
- BS-VI standards aim to significantly reduce vehicular pollution, lowering permissible limits for NOx and particulate matter (PM) emissions from vehicles.
- System of Air Quality and Weather Forecasting and Research (SAFAR):
- SAFAR measures air quality and provides forecasts for metropolitan cities based on real-time data, helping authorities take preventive actions.
- Promotion of Renewable Energy:
- India achieved a record 11% of electricity from renewable energy in 2022. However, 71% of India’s electricity still comes from coal, underscoring the need for a faster transition to cleaner energy sources.
CRS Mobile App
- 30 Oct 2024
In News:
- Recently, the Union Home Minister Amit Shah launched the Civil Registration System (CRS) mobile app.
- The app aims to integrate technology with governance by making the registration of births and deaths more accessible, seamless, and hassle-free.
Key Features of the App:
- Anytime, Anywhere Registration: Citizens can register births and deaths from anywhere and at any time, in their State’s official language.
- The app is designed to significantly reduce the time required for registration, making it more efficient and convenient for users.
Legal and Policy Background:
- The Registration of Births and Deaths (Amendment) Act, 2023 mandates that all births and deaths in India, occurring from October 1, 2023, must be digitally registered through the Centre’s portal: dc.crsorgi.gov.in.
- This move is part of the broader effort to digitize civil records and create a centralized database.
Benefits of Digital Registration:
- Digital Birth Certificates: The new system will issue digital birth certificates which will serve as a single document to prove the date of birth for various services, such as:
- Admission to educational institutions
- Applying for government jobs
- Marriage registration
- Centralized Database: The integration of birth and death data into a centralized database will help update critical records such as:
- National Population Register (NPR)
- Ration cards
- Property registration
- Electoral rolls
National Population Register (NPR) Integration:
- The data collected through the CRS app will assist in updating the National Population Register (NPR), which was first collected in 2010 and updated in 2015 through door-to-door enumeration.
- The NPR serves as the first step toward the creation of the National Register of Citizens (NRC) under the Citizenship Act, aimed at identifying Indian citizens.
Replicas of Konark Wheels at Rashtrapati Bhavan

- 30 Oct 2024
In News:
- Four replicas of the Konark wheels, made of sandstone, have been installed at the Rashtrapati Bhavan Cultural Centre and Amrit Udyan.
- This initiative is aimed at showcasing India’s rich cultural heritage and promoting traditional historical elements among visitors to Rashtrapati Bhavan.
Significance of the Konark Sun Temple:
- Historical Background: The Konark Sun Temple was built in the 13th century under King Narasimhadeva I of the Eastern Ganga Dynasty in Konark, Odisha.
- Architectural Design: The temple is a colossal stone chariot with twelve pairs of intricately carved wheels, symbolizing the chariot of the Sun God.
- Materials Used: Constructed using Khondalite stones, the temple features detailed carvings that depict mythology and cultural life.
- Astronomical Significance: The temple's orientation is designed to capture the first light of the sun, reflecting ancient Indian knowledge of astronomy.
- UNESCO World Heritage Status: The Konark Sun Temple was declared a UNESCO World Heritage Site in 1984, recognizing its architectural and historical importance.
Symbolism of the Konark Wheel:
- Time and Progression: The Konark wheel represents time (Kalachakra), progression, and democracy. Its 24 spokes symbolize ancient Indian wisdom and the passage of time.
- Sundial Function: The wheel was historically used as a sundial in the temple, marking the passage of time and symbolizing India’s commitment to progress and resilience.
- National Emblem: The Konark wheel's design is also reflected in the Ashoka Chakra, the wheel on the national flag of India, symbolizing the nation’s resolve towards progress.
Cultural Heritage at Rashtrapati Bhavan:
- The installation of these replicas is part of a broader effort to introduce and promote traditional cultural and historical elements at Rashtrapati Bhavan.
- The Rashtrapati Bhavan Cultural Centre and Amrit Udyan serve as platforms to exhibit India’s diverse artistic legacy to visitors, allowing them to experience the grandeur of ancient Indian architecture and its cultural significance.
Belt and Road Initiative (BRI)
- 30 Oct 2024
In News:
- Brazilhas opted not to join China’s Belt and Road Initiative (BRI), becoming the second BRICS country after India to reject the multi-billion-dollar infrastructure project.
- Brazil prefers to explore alternative ways to collaborate with Chinese investors without signing a formal treaty, aiming to avoid the perceived risks of the BRI.
BRICS and India’s Role:
- Brazil’s decision follows India’s long-standing opposition to the BRI, particularly due to the China-Pakistan Economic Corridor (CPEC) passing through Pakistan-occupied Kashmir, which India views as a violation of its sovereignty.
- India has consistently argued that BRI projects should adhere to international norms, good governance, and transparency, emphasizing that such initiatives should be financially sustainable and not lead to debt traps.
Brazil’s Broader Economic Strategy:
- Brazil aims to balance its relationship with China, which is a major economic partner, but without being bound by the BRI. This decision reflects broader concerns within Brazil about the long-term financial sustainability of BRI projects, especially after witnessing debt crises in other countries like Sri Lanka.
Global Context and the BRI's Impact:
- The BRI, launched by China in 2013, spans several infrastructure sectors and has expanded globally, but it has faced criticism for its potential to trap smaller nations in unsustainable debt.
- India and Brazil’s resistance to the BRI highlights growing skepticism among emerging economies about the long-term implications of joining China's flagship project.
Ayurveda Day 2024

- 30 Oct 2024
In News:
Celebrated on 29th October 2024, marking the 9th Ayurveda Day, with the theme “Ayurveda Innovations for Global Health”.
- Global Participation: Over 150 countries participating, reflecting Ayurveda's growing global influence.
- Venue: Major events held at the All India Institute of Ayurveda (AIIA), New Delhi.
Key Highlights:
Significance of Ayurveda and its Global Outreach
- Ancient System: Ayurveda is one of the oldest healthcare systems, focusing on holistic well-being, rooted in Vedic traditions, and dating back over 5,000 years.
- Global Recognition: Recognized in 24 countries and Ayurveda products exported to over 100 countries.
- International Cooperation: Collaborative efforts through forums like BRICS, SCO, BIMSTEC, and WHO to integrate Ayurveda into global health policies.
Role of Dhanvantri in Ayurveda Day
- Dhanvantari Jayanti: Ayurveda Day coincides with Dhanteras, marking the birth anniversary of Lord Dhanvantri, considered the divine physician.
- Cultural & Religious Significance: Worshiped for promoting health and longevity, Dhanvantri symbolizes the healing powers of Ayurveda.
Innovations and Relevance of Ayurveda
- Research and Innovation: The theme emphasizes scientific advancements in Ayurveda to address global health challenges such as non-communicable diseases (NCDs), mental health, antimicrobial resistance (AMR), and geriatric care.
- Startup Ecosystem: Focus on fostering innovation through Ayurveda startups, particularly in the North Eastern states and across India.
Ayurveda’s Role in Addressing Global Health Issues
- Non-Communicable Diseases (NCDs): Ayurveda offers preventive and holistic treatment for diseases like diabetes, hypertension, and cardiovascular conditions.
- Mental Health: Ayurveda promotes balance in the mind, body, and spirit, with methods addressing stress, anxiety, and depression.
- Antimicrobial Resistance (AMR): Emphasizing traditional medicinal plants and natural remedies to combat resistance to antibiotics.
- Geriatric Health: Ayurveda's role in managing aging and enhancing quality of life through rejuvenation therapies.
Focus Areas for Ayurveda Innovation
- Women’s Health: Developing Ayurvedic solutions tailored for women's health issues, including reproductive health and hormonal balance.
- Workplace Wellness: Integrating Ayurveda in workplace settings to improve mental and physical health.
- School Wellness Programs: Promoting Ayurvedic practices in schools to boost immunity and overall health of children.
- Food Innovation: Modernizing Ayurvedic dietary concepts, focusing on nutritional balance and preventive health.
Government Initiatives and Digital Transformation
- Ayush Digital Platforms: Initiatives like Ayush Grid, Ayurgyan Scheme, Ayush Research Portal, and Namaste Portal are enhancing accessibility to Ayurvedic knowledge.
- WHO Integration: Ayurveda's inclusion in the WHO ICD-11 Traditional Medicine Module facilitates global standardization and recognition.
- I Support Ayurveda Campaign: A public awareness campaign aiming to garner over 250 million votes in support of Ayurveda.
Ayurvedic Education and Research
- Research Centers: Government-supported centers like the Research Centre for Innovation in Ayurveda Biology and WHO Global Traditional Medicine Centre advancing Ayurveda's global integration.
- Academic Contributions: Institutes like National Institute of Ayurveda, Institute of Teaching and Research in Ayurveda, and North Eastern Institute of Ayurveda and Homeopathy are leading innovation and education in Ayurveda.
Ayurveda and Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs)
- SDG 3 (Good Health and Well-being): Ayurveda contributes significantly to public health, with a focus on preventive care and holistic health.
- Universal Health Coverage (UHC): Ayurveda supports affordable, accessible healthcare solutions, complementing the global health agenda.
'Act4Dyslexia' Campaign

- 29 Oct 2024
In News:
- On October 27, 2024, prominent landmarks such as Rashtrapati Bhawan, Parliament House, India Gate, and the North and South Blocks in Delhi were illuminated in red to raise awareness for Dyslexia and other learning disabilities.
- Similar illuminations took place in major cities like Patna, Ranchi, Jaipur, Kohima, Shimla, and Mumbai, highlighting the importance of dyslexia awareness.
Key Highlights:
- Collaboration for Awareness:
- The campaign is organized in collaboration with UNESCO Mahatma Gandhi Institute of Education for Peace and Sustainable Development (MGIEP) and the ChangeInkk Foundation.
- Its goal is to remove stigma and foster understanding of dyslexia and other learning disabilities, which affect 20% of India’s population—around 35 million students.
- Flagging off the ‘Walk4Dyslexia’:
- The ‘Walk4Dyslexia’ event, aimed at promoting collective action for dyslexia awareness, was flagged off by Shri Rajesh Aggarwal, Secretary of the Department of Empowerment of Persons with Disabilities (DEPwD), along with Mr. Shombi Sharp, UN Resident Coordinator in India.
- The walk was organized by ChangeInkk Foundation, UNESCO MGIEP, Orkids Foundation, and Soch Foundation.
- Growth of the Campaign:
- The Act4Dyslexia campaign saw a significant expansion in 2024, with over 1,600 walks held across the country, from state capitals to villages, engaging over 4 lakh participants.
- The campaign mobilized 2 billion steps in support of dyslexia awareness, with 150+ organizations joining forces.
- Focus on Equal Rights and Opportunities:
- Dyslexia and other specific learning disabilities (SLDs) were officially recognized under the Rights of Persons with Disabilities Act, 2016. This law mandates equal educational and employment opportunities for individuals with disabilities.
- The National Education Policy (NEP) 2020 further emphasizes inclusive education, calling for early identification, teacher capacity building, and necessary support and accommodations.
- Understanding Dyslexia:
- Dyslexia is often misunderstood as a sign of being a "slow learner", but people with dyslexia often excel in areas like logical reasoning, problem-solving, and innovation.
- Notably, 40% of self-made millionaires have dyslexia, and historical figures like Albert Einstein were also dyslexic.
- Global Impact:
- The campaign aligns with the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), aiming to unlock the untapped potential of individuals with learning disabilities, thereby contributing to societal development at a global level.
New Disability Certificate Rules (RPwD Rules, 2024)

- 29 Oct 2024
In News:
- The Rights of Persons with Disabilities (RPwD) Rules, 2024, were amended by the Union Government in the wake of the Puja Khedkar controversy, where an IAS probationer was dismissed for alleged forgery in her disability and caste certificates.
- National Platform for the Rights of the Disabled (NPRD) has called for a rollback of the new rules, citing that they make the process of obtaining disability certificates more stringent and cumbersome.
Key Changes Under the New RPwD Rules, 2024
- Authority for Issuing Disability Certificates:
- Only a designated medical authority or a notified competent medical authority at the district level can issue disability certificates.
- NPRD had proposed that experts from non-profits also be authorized to carry out checks, but this suggestion was not accepted.
- Colour-Coded UDID Cards:
- The new rules introduce colour-coded UDID cards to represent levels of disability:
- White (general disability)
- Yellow (moderate disability)
- Blue (severe disability with 80% or higher).
- The new rules introduce colour-coded UDID cards to represent levels of disability:
- Mandatory Online Applications:
- Applicants are now required to apply for disability certificates online, which could be problematic for individuals who lack access to the internet, smartphones, or are digitally illiterate.
- The NPRD has urged the government to retain the option for in-person applications.
- Extended Time for Certificate Issuance:
- The new rules extend the time for issuing disability certificates from one month to three months.
- Reapplication Requirement:
- If there is no action taken on an application for two years, the applicant will have to reapply, which the NPRD considers unacceptable, as it punishes disabled individuals for system failures.
NPRD's Concerns
- Regressive and Burdensome:NPRD believes the amendments are regressive, adding more hurdles for genuine persons with disabilities to access certificates, which are crucial for identification and entitlement to services.
- Lack of Accountability:The NPRD argues that the rules do not address the systemic issues highlighted by the Puja Khedkar case, such as the lack of accountability at various levels in the certification process.
- Online Application Issues:Many people from the disabled community may struggle with technical jargon used in online applications and may not have the resources to complete the process digitally.
- Delay in Issuance:Extending the time for issuing certificates to three months could create delays for those in urgent need of certification for services or entitlements.
Mission for Integrated Development of Horticulture (MIDH)

- 29 Oct 2024
In News:
- The Union Government has decided to introduce four new components under the Mission for Integrated Development of Horticulture (MIDH), aimed at promoting modern farming techniques:Hydroponics, Aquaponics, Vertical Farming&Precision Agriculture
Key Features of MIDH:
- MIDH is a Central Sponsored Scheme (CSS) aimed at the integrated development of various horticulture crops, including:
- Fruits, vegetables, root and tuber crops, mushrooms, spices, flowers, aromatic plants, coconut, cashew, cocoa, and bamboo.
- The scheme focuses on pre-production, production, post-harvest management, processing, and marketing activities.
Revision of Operational Guidelines and Cost Norms:
- The Ministry of Agriculture and Farmers' Welfare is revising the MIDH operational guidelines and cost norms, which were last updated in April 2014.
- The revised guidelines are expected to be released within one month.
- Cost norms are likely to increase by 20% compared to the existing rates, addressing concerns from various states about outdated guidelines.
Reason for Revision:
- Several states, including Odisha, have raised concerns over the old rates under MIDH. For example, Odisha’s Agriculture Minister highlighted that the state was still using 10-year-old rates.
- The Union Cabinet had already approved the rationalization of all CSS operating under the Ministry into two umbrella schemes:
- Pradhan Mantri Rashtriya Krishi Vikas Yojana (PM-RKVY)
- Krishonnati Yojana (KY)
Growth in India's Horticulture Sector:
- India’s horticulture production has significantly increased in recent years:
- Total production reached 334.60 million metric tonnes in 2020-21, up from 240.53 million metric tonnes in 2010-11.
- India is now the second largest producer of fruits and vegetables globally, surpassing food grain production.
- MIDH Annual Budget:The annual allocation for MIDH in the current financial year (2024-25) is ?2,000 crore.
Greenhouse Gas Levels Hit Record High in 2023: World Meteorological Organization (WMO)

- 29 Oct 2024
In News:
According to the WMO, the last time the earth had a similar CO2 concentration was 3-5 million years ago, when temperatures were 2-3°C higher and sea levels were 10-20 metres higher than they are now
Key Highlights:
- Record High Greenhouse Gas (GHG) Levels:
- In 2023, annual mean carbon dioxide (CO2) levels rose by 2.3 parts per million (ppm), reaching a new record of 420 ppm.
- This marks the 12th consecutive year with an increase of over 2 ppm in CO2 levels.
- Historical Context:
- CO2 levels not seen in 3-5 million years, when temperatures were 2-3°C higher, and sea levels were 10-20 meters higher than they are today.
- Key GHGs at Record Highs:
- The globally averaged surface concentrations of CO2, methane, and nitrous oxide all reached new highs in 2023.
- Contributors to the Increase in CO2:
- Natural Variability: Natural factors such as large vegetation fires and reduced carbon absorption by forests contributed to higher CO2 levels.
- Human Activity: High fossil fuel emissions from human and industrial activities also played a major role.
- El Niño Phenomenon: The El Niño event led to higher temperatures and drier conditions, exacerbating the rise in GHG levels through increased wildfires and reduced carbon absorption by land sinks.
- Climate Feedback Loop Concerns:
- The WMO warned of a vicious cycle:
- Climate change could cause ecosystems to become larger sources of GHGs.
- Wildfires could release more carbon, and warmer oceans may absorb less CO2, leading to more CO2 remaining in the atmosphere, accelerating global warming.
- The WMO warned of a vicious cycle:
- Radiative Forcing:
- Radiative forcing (the warming effect on climate) from long-lived GHGs has increased by 51.5% from 1990 to 2023, with CO2 contributing 81% of this increase.
- Methane Concerns:
- Methane saw its largest three-year increase between 2020 and 2022.
- This increase was linked to warmer temperatures and wetter land conditions during the 2020-2022 La Niña conditions, which caused an uptick in methane emissions from natural wetlands.
- Long-Term Impact of CO2:
- Given CO2's long atmospheric lifetime, even with rapid emissions reductions, the warming effect will persist for several decades.
C-295 Aircraft
- 29 Oct 2024
In News:
- Recently, PM Narendra Modi inaugurated the Final Assembly Line (FAL) plant in Vadodara, Gujarat, for the manufacturing of the C-295 aircraft.
- The plant is a joint venture between Tata Advanced Systems Ltd (TASL) and Airbus.
- This is the first private sector final assembly line for military aircraft in India.
Key Details:
- Manufacturing Timeline
- Contract: In September 2021, India signed a ?21,935 crore deal with Airbus Defence and Space to procure 56 C-295 aircraft to replace the IAF’s ageing Avro-748 fleet.
- Production Plan:
- The first 16 aircraft will be delivered from Airbus’s plant in Seville, Spain, between September 2023 and August 2025.
- The remaining 40 aircraft will be produced in India by TASL, with the first “Made-in-India” C-295 rolling out in September 2026.
- The entire fleet (56 aircraft) is expected to be delivered by August 2031.
- Key Features and Specifications
- Type: Tactical transport aircraft with a capacity of 5 to 10 tonnes.
- Maximum Speed: 480 km/h.
- Cabin Dimensions: 12.7 meters (41 feet 8 inches), the longest unobstructed cabin in its class.
- Passenger Capacity: Can accommodate up to 71 seats.
- Cargo Handling: Rear ramp door for quick loading/unloading and para-dropping.
- Short Take-off and Landing (STOL): Capable of operating from airstrips as short as 2,200 feet.
- Significance for the Indian Air Force (IAF)
- The C-295 will enhance the medium-lift tactical capability of the IAF.
- It will replace the ageing Soviet-origin AN-32 aircraft, which are nearing the end of their operational life.
- The C-295 will bridge the capability gap in troop and cargo transport over short and medium distances.
- Indigenous Content
- Indigenous Electronic Warfare Suite: All 56 aircraft will be equipped with an indigenous electronic warfare suite, developed by Bharat Electronics Ltd (BEL) and Bharat Dynamics Limited (BDL).
- Made-in-India Components: 96% of the work that Airbus does in Spain will be done at the Vadodara plant, making it one of the highest-ever indigenous contributions for an aircraft in India.
- Global Operations of the C-295
- The C-295 is operational in various challenging terrains worldwide, including:
- Brazilian jungles, Colombian mountains (South America)
- Deserts of Algeria and Jordan (Middle East)
- Cold climates of Poland and Finland (Europe)
- Military operations in Chad, Iraq, and Afghanistan.
- The C-295 is operational in various challenging terrains worldwide, including:
- Roles and Capabilities
- Tactical Transport: Can transport troops and supplies from main airfields to forward operating airfields.
- Short Take-off and Landing (STOL): Capable of operating from short, unprepared airstrips.
- Low-level Operations: Can conduct low-speed, low-level missions at 110 knots.
- Other Missions: Suitable for casualty evacuation, special missions, disaster relief, and maritime patrol.
ISRO’s First Electric Propulsion-Led Spacecraft (TDS-1)

- 28 Oct 2024
In News:
India's first home-grown electric propulsion satellite to be launched in Dec.
Key Highlights:
- Objective of TDS-1:
- Purpose: To demonstrate electric propulsion technology for satellite steering, using solar-powered ionized gas.
- Goal: Reduce reliance on chemical fuel, making satellites lighter and more efficient.
- Key Benefits of Electric Propulsion:
- Weight Reduction: The technology can significantly cut down satellite mass. For example, a satellite weighing 4 tonnes could be reduced to around 2 tonnes.
- Fuel Efficiency: By using electric propulsion, the need for chemical fuel is minimized, allowing for a more efficient journey to geostationary orbit.
- Technology Details:
- Fuel Used: Gases like Argon are ionized using solar power to create propulsion.
- Process: The ionized gas is expelled at high speeds to generate thrust, pushing the satellite towards its desired orbit.
- Historical Context:
- The technology was first used in GSAT-9 (South Asia Satellite) in 2017 but with imported Russian components.
- TDS-1 marks the first fully indigenous development of electric propulsion technology by ISRO, highlighting India’s increasing space autonomy.
- Significance for India’s Space Program:
- Self-Reliance: TDS-1 reflects ISRO’s growing capacity to develop advanced space technologies domestically.
- Future Prospects: This breakthrough is expected to lead to more efficient satellite designs, enhancing India’s competitiveness in the global space industry.
Emissions Gap Report 2024

- 28 Oct 2024
In News:
The United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP) recently published the Emissions Gap Report 2024, in anticipation of the COP29 meeting of the UNFCCC to be held in Baku, Azerbaijan.
Key Highlights:
- Current Trajectory of Global Warming:
- If countries continue with current environmental policies, global temperatures are expected to rise by 3.1°C above pre-industrial levels.
- This is significantly higher than the Paris Agreement target of limiting global warming to well below 2°C, with an effort to cap it at 1.5°C.
- Paris Agreement at Risk:
- Even if all Nationally Determined Contributions (NDCs) are fully implemented (including both unconditional and conditional emissions reduction targets), the world would still experience 2.6°C of warming by 2030.
- This presents a major challenge to achieving the Paris Agreement’s climate goals.
- Urgent Need for Action:
- To limit global warming to 1.5°C, greenhouse gas emissions must peak before 2025 and decline by 43% by 2030.
- The report highlights the emission gap between current pledges and what is required to meet the 1.5°C goal.
- Record High Emissions:
- Global greenhouse gas emissions hit a record 57.1 gigatons of CO? equivalent in 2023.
- This represents an increase of 1.3% compared to 2022, continuing the upward trend from the previous decade.
- India’s Emissions:
- India’s greenhouse gas emissions grew by 6.1% between 2022 and 2023.
- Per capita emissions in India were 2.9 tCO?e in 2022, significantly lower than China (11 tCO?e) and the U.S. (18 tCO?e).
- G20 Countries’ Contribution:
- G20 countries, excluding the African Union, contributed 77% of global emissions in 2023.
- The six largest emitters (including China, U.S., and India) were responsible for 63% of global emissions.
- This shows a significant imbalance in emissions, with developed countries having much higher per capita emissions compared to developing nations like India and Africa.
- Necessary Emissions Cuts:
- To keep the 1.5°C target within reach, global emissions need to be cut by at least 7.5% annually until 2035.
- Cost of bridging the emissions gap: Achieving net-zero by 2050 will require USD 900 billion to USD 2.1 trillion annually, approximately 1% of global GDP.
- Emission Reduction Pathways:
- Renewable Energy: Scaling up solar and wind energy technologies could contribute up to 27% of the required emissions reductions by 2030.
- Forest Conservation: Protecting and restoring forests could provide 20% of the required emissions reductions by 2030.
- Other crucial measures include improving energy efficiency, transitioning to electric vehicles, and focusing on fuel switching in key sectors like transport, industry, and buildings.
- Disparities in Emissions:
- Despite changes over the past two decades, large disparities remain between emissions across regions.
- Developed countries have three times higher per capita emissions compared to the global average, while India, the African Union, and least developed countries continue to have much lower emissions.
- Call to Action:
- UNEP Executive Director Inger Andersen urged countries to act now, stating: “No more hot air, please.” The urgency is to ramp up climate pledges and ensure stronger actions in the upcoming COP29 talks in Baku, Azerbaijan (November 2024), where nations must work to get on a 1.5°C pathway.
United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP)
- Established: 1972, following the United Nations Conference on the Human Environment in Stockholm.
- Headquarters: Nairobi, Kenya.
- Governing Body: The United Nations Environment Assembly (UNEA), which is the world’s highest-level decision-making body on environmental matters, with 193 Member States.
- Programs & Initiatives: UNEP leads global efforts on climate action, ecosystem restoration, clean seas, and supports the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs).
- Reports: UNEP publishes crucial assessments like the Emissions Gap Report, Global Environment Outlook, and Adaptation Gap Report, influencing global environmental policies.
Hong Kong Discovers Dinosaur Fossils

- 28 Oct 2024
In News:
Hong Kong discovers dinosaur fossils for the first time
Key Details:
-
- Significance: This marks the first-ever discovery of dinosaur fossils in Hong Kong.
- Time Period:The fossils date back to the Cretaceous Period, approximately 145 million to 66 million years ago.
- Fossil Details:The fossils belong to a large dinosaur, but further studies are required to determine the exact species.Initial analysis suggests the dinosaur may have been buried by sand and gravel after death, later being washed to the surface by a flood before being buried again.
- Site and Protection:Port Island, part of a geopark, is closed to the public to facilitate ongoing fossil investigations and excavation work.
- Geological and Archaeological Importance:The discovery underscores the significance of Hong Kong's geoparks and its role in preserving and showcasing natural history.This finding contributes to global understanding of prehistoric life, especially in the Cretaceous period.
2024 Global Nature Conservation Index (NCI)
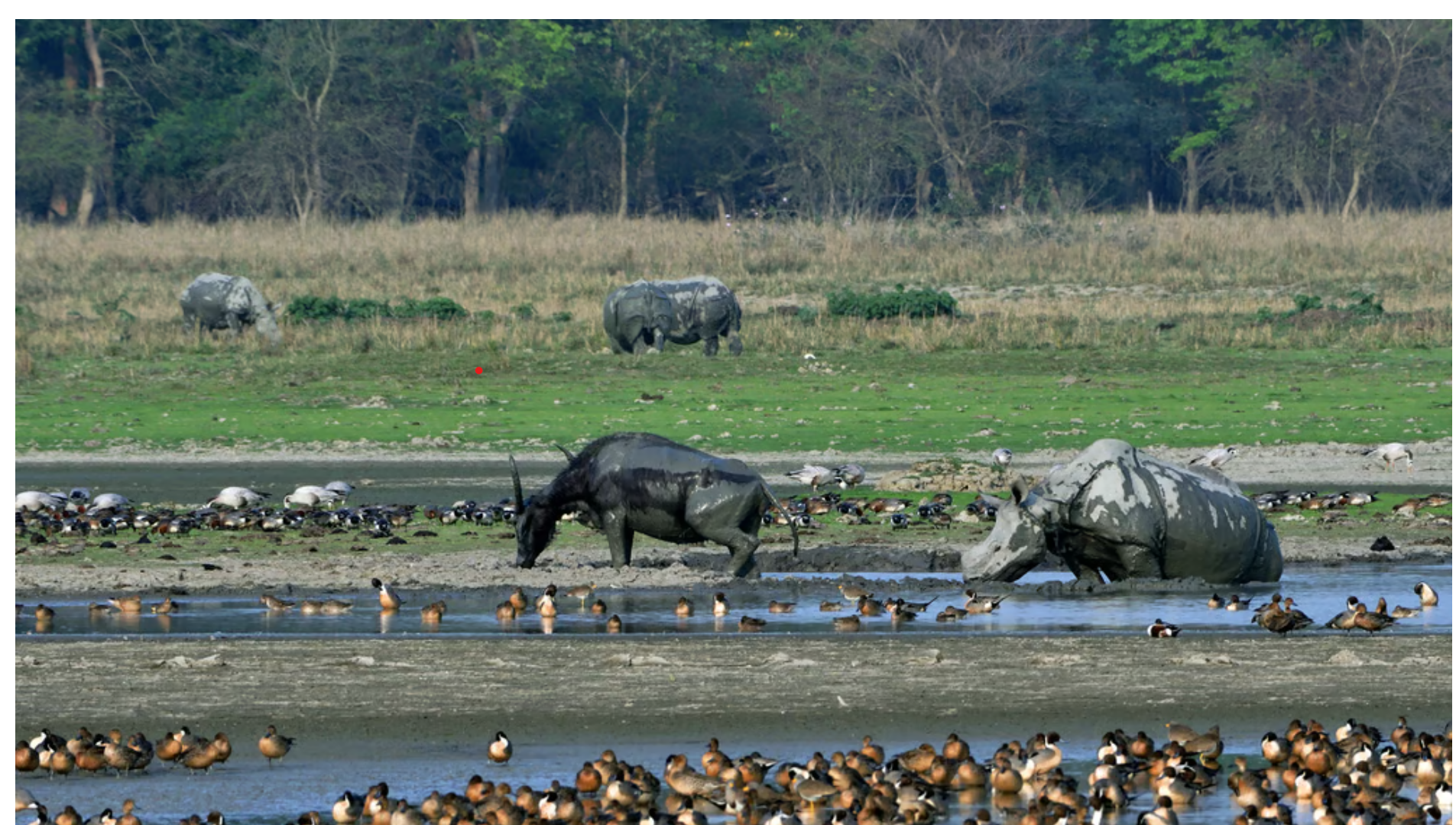

- 28 Oct 2024
In News:
India with an abysmal score of 45.5 (out of 100) has been ranked 176th in the Global Nature Conservation Index, 2024.
India's Ranking and Score:
- Rank: India ranks 176th out of 180 countries.
- Score: 45.5 out of 100.
- Context: India is listed among the five "worst performers," alongside Kiribati (180), Turkey (179), Iraq (178), and Micronesia (177).
Key Factors Affecting India’s Ranking:
- Inefficient Land Management: The main contributing factor to India's low ranking.
- Threats to Biodiversity: Rising threats due to habitat loss, deforestation, climate change, and pollution.
- Deforestation: Between 2001 and 2019, India lost 23,300 sq. km of tree cover, exacerbating biodiversity loss.
Focus Areas of the Nature Conservation Index (NCI):
- Land Management: Inefficient land use practices, with 53% of land converted for urban, industrial, and agricultural purposes.
- Biodiversity Threats: Habitat loss, fragmentation, and declining populations of marine and terrestrial species.
- Governance and Capacity: Challenges in enforcement of laws and governance structures that support conservation.
- Future Trends: India faces both opportunities and challenges, given its high population density and rapid development.
Key Findings:
- Land Conversion and Urbanization: High rates of land conversion (53%) for development purposes, contributing to habitat loss.
- Soil Pollution: Issues with pesticide use and soil pollution (low nitrogen index of 0.77), affecting soil health.
- Marine Conservation: Only 0.2% of national waterways and none within the Exclusive Economic Zone (EEZ) are protected.
- Deforestation Impact: Loss of 23,300 sq. km of forest between 2001-2019.
- Biodiversity Decline: Despite 40% of marine species and 65% of terrestrial species in protected areas, biodiversity continues to decline—67.5% of marine species and 46.9% of terrestrial species face population decreases.
Marine and Terrestrial Conservation:
- Marine Areas: Need for greater investment in marine conservation, as India's marine protected areas (MPAs) are limited.
- Protected Areas: While 7.5% of India’s terrestrial area is protected, significant threats like climate change and habitat fragmentation persist.
Biodiversity and Climate Change:
- Climate Change Risks: Impacts on vulnerable ecosystems, including coral reefs and alpine regions, further threaten biodiversity.
- Population Growth: India’s rapidly growing population (one of the highest in the world) places constant pressure on natural resources and ecosystems.
Illegal Wildlife Trade:
- Global Ranking: India is the fourth-largest illegal wildlife trader globally, with an annual trade worth approximately £15 billion.
- Call for Action: Stronger enforcement of wildlife protection laws and international cooperation are crucial to combat illegal wildlife trade.
SDGs and India’s Conservation Challenges:
- SDG 14 (Life Below Water) and SDG 15 (Life on Land): India faces significant challenges in meeting these Sustainable Development Goals, particularly in protecting marine life and terrestrial ecosystems.
Recommendations for Improvement:
- Stronger Political Will: Political commitment is essential for passing laws that promote sustainable development and biodiversity conservation.
- Enforcement and Funding: Increased funding for environmental initiatives and better enforcement of conservation policies are necessary to address the conservation challenges.
- Sustainable Development: Integrating sustainable land use practices and improving governance structures for conservation are key areas for focus.
New Space Missions and Developments

- 28 Oct 2024
In News:
The Space Commission also approved a joint moon mission with Japan called the Lunar Polar Exploration Mission. For LUPEX, ISRO is developing a different moon lander than the one it used for Chandrayaan-3
New Space Missions and Developments
- Chandrayaan-4 (Moon Mission):
- Type: Sample-return mission.
- Launch: Expected by 2027.
- Cost: ?2,104 crore.
- Objective: Sample collection of moon soil and rock to return to Earth.
- Mission Details: Two LVM-3 launch vehicles will launch components that will dock in Earth orbit before heading to the moon. The samples will be sent back using a bespoke canister.
- Lunar Polar Exploration Mission (LUPEX):
- Collaboration: Joint mission with Japan.
- Objective: Exploration of lunar poles with a new lander design, intended for potential crewed missions in future.
- Venus Orbiter Mission:
- Launch Window: March 2028.
- Cost: ?1,236 crore.
- Objective: Study Venus' surface and atmosphere to understand planetary evolution in the Solar System.
- Next Generation Launch Vehicle (NGLV):
- Development Budget: ?8,240 crore for first three development flights.
- Objective: A new launcher developed with private sector collaboration for future space missions.
Cabinet Approvals for Space Initiatives
- Human Spaceflight Programme (Gaganyaan):
- Four new missions under Gaganyaan, including an uncrewed Gaganyaan flight.
- Focus on developing technologies for India’s first space station, Bharatiya Antariksh Station (BAS), planned by 2028.
- Space-Based Surveillance (SBS) Missions:
- Phase 3: Approval for building 21 ISRO satellites, with 31 additional satellites by private companies.
- Total Cost: ?26,968 crore.
- Development of a Third Launch Pad:
- To support the NGLV and additional space missions at Sriharikota.
Upcoming Satellite Missions
- NISAR (NASA-ISRO Synthetic Aperture Radar):
- Launch: Early 2025 on a GSAT launch vehicle.
- Purpose: Earth observation using advanced radar technology.
- Issue: Protective coating added due to high temperatures during testing.
- Proba-3 (European Space Agency):
- Launch: November 29, 2024, aboard PSLV-XL.
- Objective: Study the Sun’s corona using two satellites in formation, mimicking an eclipse to capture unique solar data.
Private Sector Involvement
- Manastu Space & Dhruva Space:
- Collaboration: Testing green propulsion technology for the LEAP-3 mission.
- Technology: Hydrogen-peroxide-based green propulsion system.
- Launch: LEAP-3 mission in 2025.
- Bellatrix Aerospace:
- Project: Prototype satellite for ultra-low earth orbit at 200 km altitude.
- Ananth Technologies:
- Achievement: First private company to assemble, integrate, and test Space Docking Experiment (SpaDEx) satellites for ISRO.
Space Science and Research Updates
- Chandrayaan-3:
- Findings: The crater where Chandrayaan-3 landed is older than the South Pole-Aitken Basin (4.2-4.3 billion years old).
- Data Source: Optical High-Resolution Camera (Chandrayaan-2) and Pragyaan rover (Chandrayaan-3).
- Astrosat (India’s First Space Observatory):
- Mission Life: Expected to last two more years (originally planned for 5 years).
- Significance: Contributed to over 400 published papers based on multi-wavelength space observatory data.
ISRO-DBT Agreement for Biotechnology Experiments in Space

- 27 Oct 2024
In News:
- The Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) and the Department of Biotechnology (DBT) have signed an agreement to conduct biotechnology experiments on the upcoming Bharatiya Antariksh Station (BAS).
- Timeline for BAS:
- The BAS is expected to be operational from 2028-2035, with the initial module launches slated for 2028 and full expansion by 2035.
- It will be located at an altitude of 400 km above Earth and will support 15–20-day missions in space.
Focus Areas of Research
- Health Impact:
- Weightlessness & Muscle Health: Studying the effects of zero-gravity on muscle loss during space missions.
- Radiation Effects: Investigating how space radiation impacts astronaut health over long durations.
- Bio-Manufacturing:
- Algae Studies: Exploring algae for potential use in nutrient-rich, long-lasting food sources and biofuel production.
- Food Preservation: Identifying algae varieties that can help preserve food for longer periods in space.
- Integration with Gaganyaan Mission:
- Experiments may also be conducted during uncrewed test flights for the Gaganyaan mission (India’s first crewed mission to space, scheduled for 2025-2026).
BioE3 (Biotechnology for Economy, Environment and Employment) Policy
- Objective: The BioE3 policy aims to boost bio-manufacturing in India, which is projected to contribute $300 billion to the Indian economy by 2030.
- Key Focus Areas:
- High-Value Bio-Based Products: Promotes the development of bio-based chemicals, biopolymers, enzymes, and smart proteins.
- Climate-Resilient Agriculture & Carbon Capture: Aims to strengthen agricultural practices to withstand climate change and promote carbon capture technologies.
- Healthcare & Nutrition: Focuses on advancements in biotherapeutics, functional foods, and regenerative medicine.
- Marine & Space Biotechnology: Encourages research in space and marine biotechnology for new applications.
- Innovation & Entrepreneurship: Supports R&D-driven entrepreneurship through the establishment of bio-manufacturing hubs, bio-AI centers, and biofoundries.
- Employment Growth: Aims to create skilled jobs in the growing bioeconomy, promoting green growth and sustainable industries.
Bharatiya Antariksh Station (BAS) Overview
- Structure: The station will consist of:
- Command Module
- Habitat Module
- Propulsion Systems
- Docking Ports
- Objective: To support long-term research in space life sciences and bio-manufacturing, with a focus on human health, food sustainability, and biotechnology innovations.
21st Livestock Census

- 27 Oct 2024
In News:
The Livestock Census is a crucial tool for understanding the current status of India’s livestock sector and its contribution to the economy and society.
What is the Livestock Census?
- The Livestock Census is a nationwide survey conducted every five years to assess the number, species, breed, age, sex, and ownership status of domesticated animals and poultry, including stray animals.
- Purpose: It helps in collecting comprehensive data about the livestock population and their role in the economy and society.
- First Census: The first livestock census was conducted in 1919, and this is the 21st edition.
- Next Census: The 21st Livestock Census will be conducted between October 2024 and February 2025 by approximately 87,000 enumerators across 30 crore households in India.
Animals Covered in the Census
- The census will account for 16 species of animals, including:
- Cattle, Buffalo, Mithun, Yak, Sheep, Goat, Pig, Camel, Horse, Ponies, Mule, Donkey
- Dog, Rabbit, Elephant
- Poultry: Fowl, Chicken, Duck, Turkey, Geese, Quail, Ostrich, and Emu
- The census will also collect data on 219 indigenous breeds of these species recognized by the ICAR-National Bureau of Animal Genetic Resources (NBAGR).
Objectives of the Livestock Census
- Economic Contribution: The livestock sector contributes approximately:
- 30% of the Gross Value Added (GVA) of the agricultural sector
- 4.7% of India's overall GVA
- It plays a crucial role in rural employment, particularly in poultry and animal husbandry.
- Policy Formulation and Planning:
- The data from the census is critical for formulating and implementing policies related to livestock, ensuring sustainable growth in the sector.
- It helps in monitoring and estimating GVA from livestock.
- Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs):
- Provides vital data for tracking the progress towards Goal 2 of SDGs (Zero Hunger) and Target 2.5, which focuses on maintaining genetic diversity in livestock, particularly addressing local breeds at risk of extinction (Indicator 2.5.2).
- Sectoral Monitoring:
- The census helps in monitoring the performance and health of India’s livestock sector, which is vital for ensuring food security, rural livelihoods, and economic growth.
Key Features of the 21st Livestock Census
- Digitization:
- Like the 2019 Census, this year’s census will be fully digitized, with data collected via a mobile application.
- Digital Monitoring: A dashboard will monitor progress at various levels, and the latitude and longitude of the data collection locations will be recorded.
- A software-based livestock census report will be generated to streamline analysis.
- New Data Points:
- For the first time, data on pastoral animals and pastoralists will be collected, focusing on their socio-economic status and livestock holdings.
- Granular Data: The census will gather information on:
- Proportions of households that rely on livestock for major income.
- Gender-based data on stray cattle.
- Extended Scope:
- In addition to animal population statistics, the census will also focus on the socio-economic contributions of the livestock sector, gender inclusion, and employment.
Significance of the Livestock Census
- A Comprehensive Livestock Profile:
- Provides a holistic view of livestock population and the interlinkages between animal husbandry, agriculture, and rural economies.
- Assists in the management and preservation of indigenous animal breeds.
- Informed Decision-Making:
- Helps policymakers, researchers, and development organizations in formulating strategies for sectoral growth, genetic diversity preservation, and livelihood enhancement for rural communities.
- Monitoring Livestock Health:
- The census helps in tracking the health and sustainability of India’s livestock population, which is essential for ensuring food security and preventing animal diseases.
Findings of the 2019 Livestock Census
- Total Livestock Population: 535.78 million
- Cattle: 192.9 million
- Goats: 148.88 million
- Buffaloes: 109.85 million
- Sheep: 74.26 million
- Pigs: 9.06 million
- Other species contributed a small fraction to the total livestock population (0.23%).
Launch of 'Abhay'

- 27 Oct 2024
In News:
Recently, ‘Abhay’, the seventh ship in the Anti-Submarine Warfare Shallow Water Craft (ASW SWC) series was launched.
Key Details:
Project Background
- Contract Details: The Ministry of Defence (MoD) signed a contract with Garden Reach Shipbuilders & Engineers (GRSE), Kolkata, in April 2019 for the construction of eight ASW SWC ships.
- Class of Ships: The Arnala-class ships are intended to replace the older Abhay-class ASW Corvettes currently in service with the Indian Navy.
- Purpose: These ships are designed for anti-submarine warfare (ASW) operations in coastal waters and to conduct Low-Intensity Maritime Operations (LIMO) and mine-laying activities.
Design and Features of 'Abhay'
- Dimensions:
- Length: 77 meters
- Width: 10 meters
- Speed and Endurance:
- Maximum speed: 25 knots
- Endurance: 1800 nautical miles (NM).
- Propulsion: Waterjet-propelled, offering agility and swift response in tactical situations.
- Indigenous Content: Over 80% indigenous content, supporting India’s Aatmanirbhar Bharat (self-reliant India) initiative in defence manufacturing.
Capabilities of the ASW SWC
- Anti-Submarine Warfare:
- Designed to conduct subsurface surveillance and anti-submarine operations in coastal waters.
- Equipped with advanced sonar systems, including Hull-Mounted Sonar and Low-Frequency Variable Depth Sonar for enhanced underwater surveillance.
- Armament and Equipment:
- Torpedoes and ASW rockets for anti-submarine operations.
- Mines for mine-laying operations.
- Close-in Weapon System (CIWS): 30 mm for close-range defence against aerial and surface threats.
- 12.7 mm Stabilized Remote-Control Guns for additional defensive capability.
Strategic Importance
- Coastal Defence: The ASW SWC ships enhance the Navy’s capability to defend India’s extensive coastline and exclusive economic zone (EEZ) against submarine threats.
- Operational Role:
- In addition to anti-submarine warfare, these ships can conduct Low-Intensity Maritime Operations (LIMO), which include operations against non-traditional threats.
- Mine-laying capability to disrupt enemy naval operations.
- Advanced Detection: These ships are equipped to track both surface and underwater targets, enabling them to coordinate operations with aircraft, strengthening maritime security.
Center for Generative AI, Srijan

- 27 Oct 2024
In News:
IndiaAI and Meta have announced the establishment of the Center for Generative AI, Srijan (????) at IIT Jodhpur, along with the launch of the “YuvAi Initiative for Skilling and Capacity Building” in collaboration with the All India Council for Technical Education (AICTE), for the advancement of open source artificial intelligence (AI) in India.
Key Initiatives Launched
- Center for Generative AI, Srijan (????) at IIT Jodhpur:
- Focus on Generative AI (GenAI) research and innovation.
- Meta’s support for ethical and responsible development of AI technologies.
- Aim to empower researchers, students, and practitioners with the tools for responsible AI deployment.
- Focus Areas: Open science, AI policy advisory, and indigenous AI application development.
- YuvAi Initiative for Skilling and Capacity Building:
- Target: Empower 100,000 students and young developers (ages 18-30) with AI skills.
- Core Focus: Leveraging open-source Large Language Models (LLMs) for real-world solutions.
- Skills Development: Generative AI, open-source tools, and sector-specific AI applications (healthcare, education, agriculture, smart cities, mobility, and financial inclusion).
- Partnership: Collaboration with AICTE (All India Council for Technical Education).
Strategic Goals and Outcomes
- Research and Innovation:
- Strengthen India’s AI ecosystem through groundbreaking research and collaborations.
- Focus on open-source AI and indigenous AI solutions for national challenges.
- Empower India to lead in AI through ethical and responsible AI deployment.
- AI Talent Development:
- Bridge the AI talent gap by training young developers in open-source AI technologies.
- Develop AI solutions for critical sectors like healthcare, education, agriculture, smart cities, and financial inclusion.
- Program Components:
- GenAI Resource Hub with courses, case studies, and open datasets.
- Unleash LLM Hackathons for students to propose AI solutions for real-world challenges.
- Support for AI startups through an Innovation Accelerator.
Sectoral Focus and Impact
- Healthcare: AI for diagnostics, personalized medicine, and healthcare delivery.
- Education: AI tools for enhancing learning outcomes and personalized education.
- Agriculture: AI solutions for precision farming, pest control, and crop management.
- Smart Cities: AI in urban planning, traffic management, and public services.
- Mobility: AI applications in transportation, logistics, and urban mobility.
- Financial Inclusion: AI in fintech, digital payments, and financial services for underserved populations.
Additional Programs and Opportunities
- AICTE Collaboration: Mobilizing technical institutions across India to build AI capabilities.
- Master Training Activation Workshops: To introduce foundational AI concepts to students.
- Mentorship and Grants: Top AI solutions from hackathons will receive mentoring, seed grants, and market support.
- Student Startups: AI Innovation Accelerator will incubate 10 student-led AI startups experimenting with open-source models.
Pandemic Fund Project

- 27 Oct 2024
In News:
Recently, the Union Minister Shri Rajiv Ranjan Singh, Ministry of Fisheries, Animal Husbandry and Dairying launched the Pandemic Fund Project on "Animal Health Security Strengthening in India for Pandemic Preparedness and Response"in New Delhi.
Key Highlights:
Launch of Pandemic Fund Project
- Objective: Strengthening animal health security in India to enhance pandemic preparedness and response.
- Funding: $25 million initiative funded by the G20 Pandemic Fund.
- Location: New Delhi, Ministry of Fisheries, Animal Husbandry, and Dairying.
Context and Importance
- Livestock Sector: Crucial for socio-economic upliftment, contributing to employment and rural development.
- Growth in Livestock Sector: Significant progress in the last 9 years through schemes like the National Animal Disease Control Program (NADCP).
- Key Diseases Targeted:
- Foot and Mouth Disease (FMD): Aimed at eradication, with over 90.87 crore vaccines administered.
- Brucellosis: Over 4.23 crore vaccines administered.
Objectives of the Pandemic Fund Project
- Enhanced Disease Surveillance: Includes genomic and environmental monitoring for early warning systems.
- Laboratory Infrastructure Development: Upgradation for better diagnosis and disease management.
- Cross-Border Collaboration: Strengthening partnerships for global monitoring of zoonotic diseases.
- Integrated Monitoring System: Creation of a robust system for managing zoonotic diseases, with a focus on early detection and containment.
Documents Released for Strengthening Animal Health
- Standard Veterinary Treatment Guidelines (SVTG):
- Best practices for veterinary care to improve livestock health and productivity.
- Supports national action plans, especially for combating antimicrobial resistance.
- Crisis Management Plan (CMP) for Animal Diseases:
- Framework for effective response and containment during animal disease outbreaks.
- Ensures timely mitigation of animal disease crises.
One Health Approach
- Integration of Human, Animal, and Environmental Health: Key to preventing and managing future health crises.
- Zoonotic Risks: The project emphasizes reducing zoonotic disease transmission from animals to humans, crucial given the origins of many recent public health emergencies.
Implementation and Collaboration
- The project will be executed in collaboration with global institutions:
- Asian Development Bank (ADB)
- Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO)
- World Bank
Chanakya Defence Dialogue 2024

- 26 Oct 2024
In News:
- Recently, the Chanakya Defence Dialogue (CDD) 2024, second edition, was held at the Manekshaw Centre, New Delhi.
- Theme: "Drivers in Nation Building: Fueling Growth Through Comprehensive Security."
- Focus: Discussions on integrating national security into India's development trajectory and global strategy for a Viksit Bharat by 2047.
Key Objectives:
- The dialogue aimed to explore India’s strategic directions and development priorities by fostering discussions between policymakers, strategic thinkers, defence experts, and academia.
- Highlighted the link between national security and economic growth, stressing how security frameworks are vital for national progress.
Key Sessions and Discussions:
- Session 1: Social Cohesion and Inclusive Growth: Pillars of a Secure Nation:
- Focused on internal security, social unity, and inclusive development.
- Panelists discussed the role of community engagement, countering terrorism, and law enforcement reforms.
- Emphasized the need for integrating social progress and addressing challenges like separatism and terrorist narratives.
- Panelists called for evidence-based policies for equitable growth and stronger security frameworks to protect the country from internal threats.
- Session 2: Blurring Frontiers: The Convergence of Technology & Security:
- Addressed the intersection of technology and national security.
- Topics included AI, quantum computing, IoT, and blockchain for improving cyber resilience and data protection.
- Panelists emphasized the need to balance technological innovation with strong security measures, particularly in cybersecurity and critical infrastructure protection.
- Session 3: Ground-breakers: Shaping Land Warfare, Reflections for the Indian Army:
- Explored the integration of emerging technologies like AI, unmanned systems, and cyber warfare tools in enhancing military readiness.
- Focused on indigenous defense technologies under the Atmanirbhar Bharat initiative, promoting self-reliance and reducing dependency on foreign technologies.
- Emphasized multi-domain operations and the challenges of adapting to evolving security threats, especially from advanced cyber and space warfare.
Strategic Insights:
- Economic Growth & Security: The dialogue highlighted that national security and economic growth are interlinked, with a strong military infrastructure crucial for sustaining development.
- Role of Technology: Technological advancements like AI, space technology, and cybersecurity are pivotal for enhancing India's defense capabilities and strategic posture in a rapidly evolving global security landscape.
- Inclusive Security: Emphasized social cohesion and inclusive growth as key components of national security, acknowledging that a unified society contributes significantly to national resilience.
- Global Diplomacy: India’s global leadership in multilateral forums, its stance on peacekeeping, and its role in promoting sustainable development were discussed as part of the country’s soft power strategy.
National Mission for Manuscripts (NMM)

- 26 Oct 2024
In News:
- The Union Ministry of Culture plans to revive and relaunch the National Mission for Manuscripts (NMM) to enhance the preservation and accessibility of India’s ancient texts.
- The mission’s objective is to document, conserve, digitize, and disseminate India’s rich manuscript heritage, ensuring their protection and public access.
Formation of a New Autonomous Body:
- The National Mission for Manuscripts (NMM) is likely to be restructured into an autonomous body called the National Manuscripts Authority, which will be under the Ministry of Tourism and Culture.
- The new body will address the challenges and gaps in manuscript preservation and management, offering more focused and flexible governance.
Background and Achievements:
- Established in 2003, the NMM has been part of the Indira Gandhi National Centre for Arts (IGNCA).
- Key achievements:
- 52 lakh manuscripts have had metadata prepared.
- Over 3 lakh manuscripts have been digitized, though only one-third have been uploaded for public access.
- Preventive and curative conservation of over 9 crore folios of manuscripts has been undertaken over the last 21 years.
- The NMM has set up 100 Manuscripts Resource Centres and Manuscripts Conservation Centres across India.
Current Challenges and Gaps:
- Data Uploading and Access:
- Of the 130,000 digitized manuscripts, only 70,000 are accessible online due to the absence of a comprehensive access policy.
- A significant portion (around 80%) of manuscripts areprivately owned, restricting public access and usage.
- Digitization Mismatch:
- There have been concerns about discrepancies between the digitized data and the original manuscripts, which requires correction to ensure authenticity and accuracy.
- Lack of Comprehensive Access Policy:
- Limited public access to manuscripts due to policy restrictions hinders further research and public engagement with this rich heritage.
Scope and Future of NMM:
- India's Manuscript Heritage: India is believed to have around 10 million manuscripts, spread across various regions, languages, scripts, and topics.
- Digitization and Accessibility: Moving forward, the key challenge will be ensuring that a larger proportion of the manuscripts are digitized, uploaded, and made publicly available, particularly from private collections.
- The establishment of the National Manuscripts Authority is expected to streamline efforts and enhance coordination between government bodies, private institutions, and scholars.
Precision Medicine, Biobanks, and Regulatory Challenges in India
- 26 Oct 2024
In News:
Precision medicine is bringing in a new era of personalised healthcare. The field began to take concrete shape when scientists were wrapping up the Human Genome Project.
Introduction to Precision Medicine:
- Precision Medicine is a novel approach to healthcare that tailors treatments and preventive strategies based on an individual’s genetics, environment, and lifestyle, instead of using a one-size-fits-all approach.
- It leverages technologies like genomics, gene editing (CRISPR), and mRNA therapeutics to address various diseases such as cancer, chronic diseases, and genetic disorders.
- Recent breakthroughs include gene therapy for restoring vision and stem cell transplants for reversing diabetes, demonstrating the transformative potential of precision medicine.
Role of Biobanks in Precision Medicine:
- Biobanks are repositories storing biological samples (blood, DNA, tissues) along with associated health data. These samples are crucial for research and development of personalized treatments.
- Large and diverse biobanks are essential for ensuring that precision medicine benefits a wide demographic, as data from homogenous groups could limit the applicability of findings.
- Recent studies using biobank data have led to breakthroughs, such as identifying rare genetic disorders and developing organoid models for high-throughput drug screening.
Precision Medicine and Biobanks in India:
- Market Growth: India’s precision medicine market is growing at a CAGR of 16%, expected to surpass USD 5 billion by 2030, contributing 36% to the national bioeconomy.
- Policy Framework: The government’s BioE3 policy aims to promote biomanufacturing, with a focus on precision therapeutics and related technologies like gene editing and cancer immunotherapy.
- Biobank Initiatives:
- Genome India Programme: Completed sequencing of 10,000 genomes from 99 ethnic groups, aimed at identifying treatments for rare genetic diseases.
- Phenome India Project: Focused on collecting 10,000 samples for improving prediction models for cardio-metabolic diseases.
- Paediatric Rare Genetic Disorders (PRaGeD) Mission: Aiming to identify genes that could help develop targeted therapies for genetic diseases in children.
Regulatory and Ethical Challenges in Biobanking:
- India’s biobanking regulations are inconsistent, hindering the full potential of precision medicine. Unlike countries like the U.K., U.S., and Japan, which have comprehensive laws addressing issues like informed consent, data protection, and privacy, India lacks a cohesive regulatory framework.
- Informed Consent Issues: In India, participants provide samples without full knowledge of how their data will be used, who will have access to it, and for how long it will be stored. This lack of transparency undermines public trust in biobank research.
- Ethical Concerns: Without a clear regulatory framework, there is a risk of misuse of biological samples, such as non-consensual data sharing and sample mishandling.
- International Implications: The absence of robust laws allows foreign pharmaceutical companies to access Indian biobank data and samples without ensuring that the Indian population benefits from the resulting research or profits.
Global Comparison of Biobank Regulations:
- International Standards: Countries like the U.K., U.S., and Japan have established comprehensive biobank regulations, addressing:
- Informed consent for sample collection and data usage.
- Privacy protection and secure storage of genetic information.
- Withdrawal rights for participants at any stage of research.
- India’s biobank regulations lack clear provisions for data protection and participant rights, limiting the effectiveness of research and undermining public confidence in biobanks.
Microfinance Institutions (MFIs)

- 26 Oct 2024
In News:
Recently, the Financial Services Secretary stated that Microfinance institutions (MFIs) have played a crucial role in fostering financial inclusion but they should refrain from any reckless lending.
Microfinance Institutions (MFIs) and Financial Inclusion:
- MFIs provide small loans and financial services to low-income and marginalized groups, particularly those without access to formal banking services.
- Goal: To promote financial inclusion and empower marginalized communities, especially women, by enabling them to become self-sufficient and improve their socio-economic status.
- In India, over 168 MFIs serve around 3 crore clients across 29 states and 563 districts.
- The sector has grown significantly and is crucial for empowering Self-Help Groups (SHGs) and Joint Liability Groups (JLGs) to access credit and other financial services.
Concerns over Reckless Lending:
- The Financial Services Secretary, emphasized that MFIs should avoid reckless lending practices that could harm both borrowers and the sector.
- Poor underwriting and irresponsible lending could lead to unsustainable debt, especially for Self-Help Groups (SHGs) and Joint Liability Groups (JLGs) with limited financial literacy.
- Key Advice: Lending practices must be responsible, careful, and should aim to empower borrowers, not exploit their limited understanding.
Government Programs Supporting MFIs:
- SHG-Bank Linkage Programme: Over 77 lakh SHGs with a total loan outstanding of ?2.6 lakh crore, benefiting around 10 crore households.
- Lakhpati Didi Yojana: Aimed at empowering women, this scheme helps transform SHG members into women entrepreneurs.
Challenges Facing Microfinance Institutions:
- Regulatory Scrutiny: Many MFIs face scrutiny for high interest rates and non-compliance with borrower assessments. The RBI has urged MFIs to reassess lending practices.
- Over-Indebtedness: Many borrowers take loans from multiple MFIs, leading to unsustainable debt. As of March 2024, over 12% of borrowers had multiple loans, risking defaults.
- Low Financial Literacy: A significant challenge is low financial literacy among borrowers, which increases the risk of defaults and harms the reputation of MFIs.
RBI Guidelines on Microfinance (2022):
- Collateral-Free Loans: For households with income up to ?3 lakh, loans should be collateral-free.
- Repayment Cap: Monthly loan repayments should not exceed 50% of the borrower’s monthly income.
- Flexibility in Repayment: MFIs must offer flexible repayment options and ensure proper income assessment.
- Interest Rate Cap: The RBI has implemented guidelines to limit excessive interest rates charged by MFIs.
Government Schemes for Microfinance:
- Pradhan Mantri Mudra Yojana (PMMY): Provides financial assistance to non-corporate, non-farm small/micro enterprises.
- National Rural Livelihoods Mission (NRLM): Promotes rural livelihoods through the formation and capacity building of Self-Help Groups (SHGs).
- Deen Dayal Upadhyaya Antyodaya Yojana: Focuses on the empowerment of rural poor through skill development and income generation.
- Credit Guarantee Fund for Micro and Small Enterprises (CGTMSE): Provides guarantee cover to micro and small enterprises.
Way Forward for Microfinance Sector:
- Responsible Lending: MFIs must prioritize affordable lending practices, ensuring borrower’s repayment capacity is carefully assessed to avoid over-indebtedness.
- Enhancing Financial Literacy: MFIs should focus on financial education for borrowers, enabling them to make informed choices.
- Adherence to Regulatory Guidelines: MFIs should comply strictly with RBI regulations, including interest rate caps and borrower income assessments, to enhance sector transparency and trust.
- Malegam Committee Recommendations: Implementing suggestions like capping interest rates, tracking multiple loans, and improving transparency to prevent over-indebtedness.
- Diversifying Funding Sources: To reduce vulnerability to economic downturns, MFIs should work on diversifying their funding sources, reducing dependence on external capital.
Environmental Ship Index (ESI)
- 26 Oct 2024
In News:
- Mormugao Port Authority (MPA) has been globally recognized as an incentive provider on the Environmental Ship Index (ESI) platform, acknowledged by the International Association of Ports and Harbours (IAPH).
- Mormugao is India's first port to implement Green Ship Incentives through the ESI, contributing to global efforts to reduce maritime air emissions.
‘Harit Shrey’ Scheme:
- Launched in October 2023, the ‘Harit Shrey’ scheme provides discounts on port fees based on the Environmental Ship Index (ESI) scores of commercial vessels.
- Ships with higher ESI scores (indicating better environmental performance) are rewarded with incentives to encourage eco-friendly practices in shipping.
ESI and Global Efforts for Emission Reduction:
- The Environmental Ship Index (ESI) is a global system to evaluate and reward ships based on their environmental performance, particularly their emissions of nitrogen oxides (NOx) and sulphur oxides (SOx).
- The 2023 IMO greenhouse gas strategy aims to reduce the carbon intensity of international shipping by at least 40% by 2030.
Incentives and Benefits:
- The Harit Shrey scheme has already benefitted several vessels, promoting greenhouse gas emission reductions and contributing to sustainable maritime operations.
- The scheme aligns with global sustainability goals, particularly in reducing the carbon footprint of shipping operations.
Sustainability Recognition:
- The Mormugao Port Authority has submitted the Harit Shrey scheme for consideration in the IAPH Sustainability Awards under the World Port Sustainability Programme (WPSP), reflecting its commitment to environmental sustainability.
The Environmental Ship Index (ESI):
- ESI is a system that evaluates and rewards ships for better environmental performance than the standards set by the International Maritime Organization (IMO).
- Ships are assessed based on their emissions of NOx and SOx, with greenhouse gas reporting also included in the evaluation.
Main Features of ESI:
- Port-Centric: Developed as a port-to-port system, where ports can offer incentives based on the ESI score.
- Voluntary Participation: Shipowners participate voluntarily to demonstrate their vessels' environmental performance.
- Automated Calculation: The ESI score is automatically calculated and updated.
- Incentives: Ships with higher ESI scores may receive benefits such as reduced port fees and priority berthing.
Great Indian Bustard (GIB)
- 25 Oct 2024
A critically endangered Great Indian Bustard (GIB) chick was successfully born through artificial insemination (AI) at a breeding center in Jaisalmer, Rajasthan, marking a crucial step in efforts to save the species.
Endangered Status:
- The Great Indian Bustard is classified as critically endangered with fewer than 150 individuals left in the wild in India.
- About 90% of these birds are found in the desert areas of Rajasthan, with smaller populations in Gujarat, Maharashtra, Andhra Pradesh, and Karnataka.
Main Threats to the Species:
- Habitat Loss: The primary threat is the loss of habitat, which is often perceived as wasteland and is diverted for infrastructure projects like roads and development.
- Slow Reproductive Rate: The bustard’s low reproductive rate exacerbates its risk of extinction.
Conservation Efforts: Bustard Recovery Program
- In 2016, the Union Ministry of Environment, Forests and Climate Change launched the Bustard Recovery Program to focus on captive breeding and creating a sustainable environment for the reintroduction of GIBs into the wild.
- A dedicated GIB breeding center was set up at the Desert National Park in Jaisalmer, Rajasthan, as part of this initiative.
- Protection Status of GIB:
- IUCN: Critically Endangered
- CITES: Appendix 1
- Convention on Migratory Species (CMS): Appendix I
- Wildlife (Protection) Act, 1972: Schedule I
- It is also the state bird of Rajasthan, emphasizing its importance in the region’s biodiversity.
Introduction to Innovative Cancer Detection Technique
- 25 Oct 2024
In News:
- Scientists have developed an ultrasound-based technique for detecting cancer, aiming to replace traditional biopsies, which are invasive and painful.
- Promising Alternative: The method uses high-energy ultrasound to release biomarkers (RNA, DNA, and proteins) from cancerous tissue into the bloodstream, allowing for early cancer detection with minimal discomfort.
- Presented at Acoustical Society Conference: The technique was discussed at the joint meeting of the Acoustical Society of America and Canadian Acoustical Association in May 2024.
Traditional Cancer Detection vs. New Ultrasound Approach
- Current Gold Standard - Biopsy: Traditionally, cancer is diagnosed using biopsies, where a tissue sample is extracted using a needle from suspected cancerous areas. Although effective, biopsies are invasive, painful, and carry some risks.
- Ultrasound as a Non-Invasive Alternative: The new method involves using high-frequency ultrasound waves to break off cancerous tissue into droplets, which are then released into the bloodstream. The biomarkers in the droplets can be analyzed for cancerous mutations.
- Enhanced Sensitivity: This ultrasound-based technique increases the levels of genetic and vesicle biomarkers in blood samples by over 100 times, enabling the detection of cancers and specific mutations that are otherwise undetectable in blood.
Key Findings of the Research
- Single Cancer Cell Detection: The technique allows for the detection of a single cancer cell in blood samples. It works by passing ultrasound waves through isolated blood samples, which break apart circulating cancer cells, releasing biomarkers into the blood.
- Cost-Effective: Traditional methods for detecting circulating cancer cells are costly (e.g., the ‘CellSearch’ test costs $10,000). In contrast, this ultrasound method can detect cancer with a much lower cost, around $100 (?8,400).
- Potential for Early Diagnosis: The research shows promise for detecting cancer at an early stage, even before symptoms appear, using blood samples.
Challenges and Next Steps
- Need for Large-Scale Clinical Trials: While the technique shows potential, large cohort studies involving diverse patient groups across different geographies and ethnicities are needed to validate the approach.
- Long-Term Study for Effectiveness: Further research is required to ensure the accuracy and reliability of the technique across various cancer types and to determine the ideal biomarker thresholds for early detection.
- Regulatory Approval and Commercialization: If the clinical trials yield positive results, the method could be commercially available in approximately five years, following regulatory approval.
Understanding Cancer and Its Types
- Cancer Definition: Cancer refers to the uncontrolled growth of abnormal cells that can form tumors and spread to other parts of the body.
- Types of Cancer:
- Carcinoma: Cancer originating in epithelial cells (e.g., breast, lung, prostate cancer).
- Sarcoma: Affects connective tissues like bones and muscles.
- Leukemia: Affects blood-forming tissues, leading to abnormal white blood cell production.
- Lymphoma: Begins in immune cells, including Hodgkin and non-Hodgkin lymphoma.
- Melanoma: Cancer of pigment-producing skin cells.
- Key Differences Between Normal and Cancer Cells:
- Cancer cells grow uncontrollably and evade immune detection.
- Cancerous cells accumulate chromosomal abnormalities, unlike normal cells, which follow regulated growth patterns.
National Workshop on SATHI Portal

- 25 Oct 2024
In News:
Recently, the Department of Agriculture & Farmers' Welfare (DA&FW) organised a National Workshop on the SATHI (Seed Authentication, Traceability, and Holistic Inventory) Portal in New Delhi.
Key Highlights:
Purpose & Focus
- SATHI Portal: Focuses on Seed Authentication, Traceability, and Holistic Inventory to enhance seed certification, improve seed traceability, and streamline the seed supply chain.
- Primary Objective: Ensure availability of high-quality seeds to farmers through a transparent and efficient seed management system.
Key Features of the SATHI Portal
- Seed Certification: Aims to streamline seed certification processes across states for faster and more accurate seed certifications.
- Seed Traceability: Enhances transparency and traceability of seeds to ensure quality and authenticity.
- Inventory Management: The portal facilitates seed inventory management, helping farmers and stakeholders access reliable and transparent seed information.
- Technological Integration: Developed by the National Informatics Centre (NIC), the portal incorporates technology-driven solutions to minimize transactional time for registrations, approvals, and certifications.
Phase-II Rollout
- Focus on seed inventory management, with the objective of offering farmers reliable access to certified seed varieties.
- It aims to integrate state-specific seed processes into the national framework for greater standardization and efficiency.
Workshops & Technical Sessions
- NIC and ICAR Presentations: Covered the core components of the SATHI Portal, including:
- Seed Law Enforcement
- DNA Fingerprinting for ensuring seed authenticity.
- Seed Laboratory Processes to uphold quality control.
- Review of Phase-I: Discussions on achievements of Phase-I, focusing on improvements in seed certification processes across states.
- State Experiences: 10 state representatives shared insights on their experiences with the portal, discussing both benefits and challenges in the implementation phase.
Role of NIC & Technology
- The National Informatics Centre (NIC) is the technology partner behind the SATHI Portal, which is designed to enhance the efficiency of seed certification and inventory management.
- The portal contributes to larger digital initiatives like the Digital Agriculture Mission and Unified Farmer Service Platform (UFSP), which aim to support agricultural development through technology.
Chenchu Tribe

- 25 Oct 2024
In News:
The Chenchus of Penukumadugu have lived in the dense Nallamala forests for centuries, their existence intertwined with the wilderness around them. However, their inability to keep up with the relentless pace of modernisation has led to dwindling work opportunities under the MGNREGA.
Chenchu Tribe Overview
- Location: Primarily in the dense Nallamala forests, Andhra Pradesh (AP).
- Tradition: Historically hunter-gatherers, now relying on subsistence farming.
- Vulnerable Status: Classified as one of the 12 Particularly Vulnerable Tribal Groups (PVTGs) in Andhra Pradesh due to low literacy, stagnant population growth, and limited access to development.
- Livelihood: Dependent on forest resources (Non-Timber Forest Produce - NTFP) and agricultural labor.
Impact of MGNREGS (Mahatma Gandhi National Rural Employment Guarantee Scheme)
- MGNREGS Chenchu Special Project: Launched in 2009 to address specific needs of the Chenchus, such as physical strength, food insecurities, and cultural practices.
- Before Discontinuation: Provided 180 days of work per person annually, which helped Chenchus access regular income, improving food security and living conditions.
- Post-Discontinuation (2022):
- The project was integrated into a nationwide MGNREGS framework, reducing workdays to the standard 100 days per household.
- Consequences: Many Chenchus stopped engaging with MGNREGS due to bureaucratic hurdles (Aadhaar and bank linkage), reduced job days, and irregular wage payments.
- Only 1,500 out of 4,000 enrolled households currently participate in MGNREGS work.
Key Issues Post-MGNREGS Reform
- Aadhaar & Bank Account Challenges:
- Lack of literacy and digital skills makes the Aadhaar-based system intimidating.
- Many Chenchus are excluded from PDS and health benefits due to missing or unlinked Aadhaar cards.
- Absence of mobile phones and access to banks makes wage disbursement difficult.
- Irregular Payments & Trust Issues:
- The shift to bank payments has created trust issues, as many Chenchus are illiterate and cannot verify wage deposits.
- Distance from banks (up to 30 km) adds to the difficulty in accessing payments.
Forest Rights and Wildlife Conservation
- Forest Dependency: The Chenchus continue to depend on the forest for food and livelihood, but increasing restrictions due to wildlife conservation (e.g., Nagarjuna-Srisailam Tiger Reserve) have further curtailed their access to forest produce.
- Forest Rights Act (FRA): Many Chenchus have land pattas under the FRA but lack resources or support to utilize their land effectively due to the discontinuation of MGNREGS.
Government and Policy Response
- PVTG Initiatives: Various government initiatives like PM PVTG Mission, Viksit Bharat Sankalp Yatra, and Janjatiya Gaurav Divas aim to uplift PVTGs, but their impact remains limited without proper implementation of specialized support programs like the MGNREGS Chenchu Special Project.
United Nations Day 2024

- 25 Oct 2024
In News:
United Nations Day is celebrated each year on October 24 to mark the anniversary of the UN Charter's entry into force, aiming to raise awareness about the goals and achievements of the international body.
Key Highlights:
- Purpose: Celebrates the anniversary of the UN Charter coming into effect on October 24, 1945, after World War II.
- Goal: Raise awareness about the UN’s objectives and accomplishments.
UN Charter Overview
- Signing & Implementation:
- Signed on June 26, 1945, in San Francisco.
- Came into effect on October 24, 1945.
- India ratified the UN Charter on October 30, 1945.
- Predecessor: The League of Nations, created in 1919 after WWI, aimed at promoting international cooperation and peace.
- Content:
- Foundational document of the UN, binding all member states.
- Establishes principles of international relations, including equality of nations and the prohibition of force between countries.
- Amended three times: 1963, 1965, and 1973.
UN's Core Objectives
- Peace and Security: Maintaining global peace and preventing conflicts.
- Humanitarian Aid: Providing assistance to those in need.
- Human Rights: Protecting and promoting human rights globally.
- International Law: Upholding the rule of law on the global stage.
Main Organs of the UN
- General Assembly (UNGA):
- Comprises all 193 Member States, each with one vote.
- Main policy-making body, addressing international issues covered by the UN Charter.
- Security Council (UNSC):
- Consists of 15 members (5 permanent, 10 elected for two-year terms).
- Permanent members: China, France, Russia, UK, USA.
- India has been elected to the UNSC eight times.
- Economic and Social Council (ECOSOC):
- Composed of 54 members elected by the General Assembly.
- Coordinates policy and addresses economic, social, and environmental issues.
- Trusteeship Council:
- Established to oversee trust territories transitioning to independence.
- International Court of Justice (ICJ):
- The only international court resolving disputes between UN member states.
- Handles contentious cases and provides advisory opinions.
- Secretariat:
- Led by the Secretary-General, appointed by the General Assembly based on Security Council recommendations.
- Acts as the chief administrative body of the UN.
Note: Most UN organs, including the UNGA, UNSC, ECOSOC, Trusteeship Council, and Secretariat, are based in New York, while the ICJ is located in The Hague, Netherlands.
Nobel Peace Prize 2024

- 24 Oct 2024
In News:
The Nobel Peace Prize has been awarded to Nihon Hidankyo, an organisation of survivors of the Hiroshima-Nagasaki bombings. In doing so, the Nobel Committee has highlighted the power of their testimonies and the need for disarmament.
Key Points about Nihon Hidankyo and the Hibakusha Movement
- Nihon Hidankyo:
- Established on August 10, 1956, as the nation-wide organization for survivors of the Hiroshima and Nagasaki bombings.
- Focuses on the welfare of Hibakusha (A-bomb survivors), promoting nuclear disarmament, and advocating for compensation for victims.
- Works to share the stories and experiences of Hibakusha, both within Japan and globally.
- Hibakusha (Bomb-affected People):
- Survivors of the atomic bombings of Hiroshima and Nagasaki in 1945.
- Played a pivotal role in the global nuclear disarmament movement.
- Their testimonies have helped create the "nuclear taboo," ensuring nuclear weapons have not been used since 1945.
Role of Hibakusha in Nuclear Disarmament
- Global Impact:
- The bombings ignited a global movement for nuclear disarmament.
- Hibakusha's advocacy has highlighted the human cost of nuclear weapons, shaping international policy and promoting the nuclear taboo.
- Nihon Hidankyo’s Advocacy:
- The organization has been instrumental in documenting the effects of nuclear weapons and advocating for their abolition.
- Testimonies from Hibakusha have been key in raising awareness about the catastrophic humanitarian consequences of nuclear warfare.
Nobel Committee's Recognition and Current Nuclear Challenges
- Recognition of Hibakusha's Work:
- The Nobel Committee awarded the Peace Prize to Nihon Hidankyo for its role in promoting nuclear disarmament and for contributing to the nuclear taboo.
- The nuclear taboo is under increasing pressure as new countries seek nuclear weapons and existing powers modernize their arsenals.
- Current Nuclear Landscape:
- The US and Russia continue to maintain large nuclear stockpiles, with the US planning to spend over $1 trillion on upgrading its nuclear capabilities by the 2040s.
- New Threats: Geopolitical tensions, including regional conflicts, raise concerns about the resurgence of nuclear arms races.
Previous Nobel Peace Prizes for Disarmament
- Past Laureates:
- 1974: Former Japanese Prime Minister Eisaku Sato awarded for Japan's commitment to non-nuclear weapons policy.
- 2017: International Campaign to Abolish Nuclear Weapons (ICAN) awarded for its efforts to draw attention to the humanitarian consequences of nuclear weapons and push for a nuclear ban treaty.
- Link with Alfred Nobel’s Vision:
- Alfred Nobel, the founder of the Peace Prize, made his fortune with the invention of dynamite and sought to use his wealth to promote peace, especially through disarmament.
IMF's World Economic Outlook (WEO)
- 24 Oct 2024
In News:
- The International Monetary Fund (IMF) has maintained India’s GDP growth forecast at 7% for FY2024, marking a moderation from 8.2% in 2023.
- FY2025 Projection: Growth is expected to slow further to 6.5% in FY2025.
- India’s growth is expected to be stronger than most other large economies, yet the downward revision reflects challenges in the global economy and moderation in domestic economic momentum.
Global Economic Growth Projections:
- Global Growth (2024-2025): Global growth is projected at 3.2% in 2024 and 2025, which is stable but modest. This growth rate is largely unchanged from previous IMF forecasts.
- Long-Term Outlook: The IMF's long-term projection for global growth is 3.1%, which is considered subpar compared to pre-pandemic growth rates, signaling a potential era of low growth.
Key Risks and Uncertainties:
- The IMF highlights several downside risks to global growth, including:
-
- Monetary tightening: Central banks' high-interest rate policies to combat inflation could have long-term negative effects on economic growth and financial stability.
- Geopolitical Tensions: Ongoing conflicts, such as the Russia-Ukraine war, could disrupt global supply chains and trade, exacerbating inflation and slowing growth.
- China’s Economic Slowdown: China, the world’s second-largest economy, is facing a slower growth trajectory, especially in its real estate sector, which is dragging down its overall growth.
- Structural Challenges: The aging population and weak productivity are long-term growth inhibitors in many advanced economies, adding uncertainty to future growth prospects.
-
- Inflation and Monetary Policy:
- The IMF's inflation forecast shows global inflation cooling:
- 2023: Global inflation is expected to reach 6.7%.
- 2024: It is forecast to fall to 5.8%, with advanced economies expected to return to inflation targets sooner than emerging markets.
- 2025: A further decline to 4.3%.
- The primary driver of disinflation is not interest rate hikes but the unwinding of pandemic-related shocks, supply chain improvements, and the gradual return of labor supply.
- Monetary Policy: Central banks are likely to ease policies once inflation nears target levels, but risks of further commodity price spikes or geopolitical tensions could delay this.
- The IMF's inflation forecast shows global inflation cooling:
US and Europe Growth:
- Emerging Markets and Developing Economies:
- Growth Outlook: The IMF forecasts growth in emerging markets and developing economies at 4.2% for 2024 and 2025, with a slight moderation to 3.9% by 2026.
- Emerging Asia: Growth in emerging Asia (led by India and China) is expected to slow, from 5.7% in 2023 to 5% in 2025.
- India’s Relative Strength: India’s growth continues to outperform many emerging economies, though the slowdown from 8.2% in 2023 to 7% in 2024 reflects global economic headwinds.
- Income Inequality Risks:
- The IMF warns that low growth over an extended period (4+ years) could exacerbate income inequality within countries, as sluggish growth affects job creation and wage growth.
- Countries with slow economic recovery are likely to see a widening gap between rich and poor, undermining social cohesion and stability.
PM Young Achievers’ Scholarship Award Scheme for Vibrant India (PM YASASVI)

- 24 Oct 2024
In News:
With a vision of "Sabka Sath, Sabka Vikas", the Ministry of Social Justice and Empowerment has implemented the PM Young Achievers Scholarship Award Scheme for Vibrant India (PM-YASASVI).
- Objective of PM-YASASVI:
- The scheme aims to provide financial support and educational opportunities to students from Other Backward Classes (OBC), Economically Backward Classes (EBC), and Denotified Tribes (DNT).
- The goal is to help these students overcome financial barriers and pursue quality education, fostering a more inclusive and equitable society.
- Consolidation of Earlier Schemes:
- PM-YASASVI integrates multiple previous scholarship schemes:
- Dr. Ambedkar Post-Matric Scholarship for EBCs.
- Dr. Ambedkar Pre-Matric and Post-Matric Scholarship for DNTs.
- This consolidation aims to streamline the process and increase the impact on vulnerable groups.
- Key Components of the Scheme:
- Pre-Matric Scholarship: For students in Class 9-10 with annual family income below ?2.5 lakh. Provides ?4,000 annually.
- Post-Matric Scholarship: For students pursuing higher education, with academic allowances ranging from ?5,000 to ?20,000 based on course type.
- Top Class School Education: For meritorious students, offering ?1.25 lakh annually for students from OBC, EBC, and DNT categories in Classes 9-12.
- Top Class College Education: Covers tuition, living expenses, and educational materials for students in top institutions.
- Construction of Hostels for OBC Boys and Girls: Provides hostel facilities to socially and educationally backward students near government institutions.
- Scope and Financial Allocation (2023-24):
- Pre-Matric Scholarship: ?32.44 crore allocated to states and UTs for the year 2023-24, benefiting 19.86 lakh students.
- Post-Matric Scholarship: ?387.27 crore allocated for the year, benefiting 27.97 lakh students.
- Top Class School Education: ?6.55 crore for 2,602 students.
- Top Class College Education: ?111.18 crore for 4,762 students.
- Hostel Construction: ?14.30 crore allocated for the construction of hostels, accommodating 1,146 students.
- Key Benefits:
- Financial Assistance: Reduces the financial burden on students from marginalized communities, enabling them to continue their education without financial stress.
- Inclusive Education: Supports students from disadvantaged backgrounds, ensuring that they can access quality education from school through to higher education.
- Promotion of Merit: Focuses on meritorious students, ensuring that academic excellence is supported at all levels, from school to top-class institutions.
- Selection Process:
- The YASASVI Entrance Test (YET) is conducted by the National Testing Agency (NTA) for candidate selection under the scheme.
- Eligible students must appear for this test, and the results determine scholarship awards.
- Eligibility Criteria:
- The scheme is open to OBC, EBC, and DNT students with a family income not exceeding ?2.5 lakh annually.
- Additional specific eligibility criteria may apply for different scholarships under the scheme.
- Application Process:
- Interested students can apply for scholarships via the National Scholarship Portal (scholarships.gov.in), which is the official platform for application submission.
E. coli Outbreak Linked to McDonald's Burgers

- 24 Oct 2024
In News:
- An E. coli outbreak has been linked to McDonald's burgers in the United States. The infection has affected at least 10 states.
E. coli in India:
- Prevalence: E. coli infections are common in India, especially during the summer and rainy seasons, when there is an increase in gastrointestinal infections.
- Transmission: E. coli spreads mainly through contaminated food and water.
- National statistics: Over 500 outbreaks of diarrhoeal diseases were reported in India in 2023. E. coli is one of the most common pathogens causing gastrointestinal infections in India.
- ICMR data: According to the latest report from the Indian Council of Medical Research (ICMR), E. coli was found in 23.19% of patient samples from tertiary care hospitals across India.
- FSSAI's Role: The Food Safety and Standards Authority of India (FSSAI) is establishing a network of 34 microbiology labs to test food for pathogens like E. coli, salmonella, and listeria.
Symptoms of E. coli Infection:
- Common symptoms include:
- High fever (over 102°F)
- Persistent diarrhoea, sometimes bloody
- Vomiting
- Dehydration due to fluid loss
- Severe cases may lead to acute kidney injury.
Treatment of E. coli Infections:
- E. coli is treated with antibiotics, but medical consultation is necessary before taking any medication.
- Antimicrobial resistance is a growing concern, as E. coli's susceptibility to antibiotics, including carbapenem, has declined from 81.4% in 2017 to 62.7% in 2023.
When to Seek Medical Attention:
- Consult a doctor if:
- Diarrhoea lasts more than a couple of days.
- Frequent visits to the toilet (every half hour to an hour).
- Bloody diarrhoea.
- Vomiting frequently or inability to retain fluids.
Food Safety Measures:
- The FSSAI is working to improve food safety by implementing better testing protocols for microbial contamination in food products across India.
Cyberfraud Losses and Economic Impact

- 24 Oct 2024
In News:
- ?1.2 lakh crore is the projected financial loss due to cyber frauds in India over the next year (2024), according to the Indian Cyber Crime Coordination Centre (I4C) under the Union Home Ministry.
- This could amount to 0.7% of India’s GDP.
- Mule Accounts:
- Mule accounts are a significant contributor to cyber frauds. These accounts are used to facilitate money laundering and illegal transactions.
- On average, around 4,000 mule accounts are identified daily by I4C.
- Mule accounts typically facilitate the transfer of funds out of India, often through cryptocurrency transactions.
- Sources of Cyber Scams:
- A majority of frauds are linked to Chinese entities or China-based operations, with about half of the cybercrime complaints originating from China.
- Other major hubs for cyber frauds include Cambodia, Myanmar, and Laos, which house call-centre-like scam compounds.
- Azerbaijan has also been identified as a new hotspot for such scams.
- International Dimension:
- Fraudulent withdrawals have been reported from ATMs in Dubai, Hong Kong, Bangkok, and Russia using mule accounts.
- The international nature of these scams often involves routing stolen funds through various countries, using methods like cryptocurrency exchanges.
- Cybercrime and Terror Financing:
- Cyber scams have potential ramifications beyond financial losses; they can be used for terror financing and money laundering.
- Cryptocurrency is a common medium for laundering money, with an example cited of ?5.5 crore laundered through 350 transactions in a short span.
- ATM Hotspots and Fraudulent Withdrawals:
- 18 ATM hotspots have been identified across India where fraudulent withdrawals occur.
- Fraudsters exploit these locations to withdraw money, often using mule bank accounts and cross-border ATM networks.
- Government Response:
- The Ministry of Home Affairs (MHA) is working to combat these frauds by convening meetings with the Union Finance Ministry and the Reserve Bank of India (RBI).
- The objective is to curb the operation of mule accounts and strengthen the banking system to prevent such frauds.
- Banks are being urged to flag unusually high-value transactions or accounts with low balances that are engaging in suspicious activity.
- Fraudulent Calls and Scam Compounds:
- Indian fraudsters, in collaboration with international scam rings, use Indian mobile phone numbers to deceive citizens.
- Countries like Cambodia, Myanmar, Laos, and Azerbaijan have been identified as hubs for investment scams involving fraudulent calls.
- Helpline and Cyber Fraud Reporting System:
- The Citizen Financial Cyber Fraud Reporting and Management System (part of I4C) and the 1930 helpline provide mechanisms to report financial frauds.
- ?11,269 crore in financial frauds was reported during the first half of 2024 via these channels.
- The system also involves cooperation with over 200 financial intermediaries, including banks and wallets.
Tenkana

- 23 Oct 2024
In News:
- A team of arachnologists has discovered a new genus of jumping spiders, Tenkana, found across southern India and northern Sri Lanka.
- The discovery includes two previously known species, Tenkanamanu and Tenkanaarkavathi, and introduces a new species, Tenkanajayamangali, from Karnataka.
Name and Origin:
- The name Tenkana comes from the Kannada word for "south," reflecting the geographical region where all known species of this genus are found—southern India and northern Sri Lanka.
- The genus belongs to the Plexippina subtribe of jumping spiders, which is distinct from related genera like Hyllus and Telamonia.
Key Findings:
- Tenkanajayamangali was first discovered in Devarayanadurga reserve forest, Tumakuru district, Karnataka, at the origin of the Jayamangali river.
- The new species was identified through genetic analysis and physical examination, showing it did not match any known species.
Physical Characteristics:
- The male and female Tenkanajayamangali exhibit distinct physical differences.
- The male has pale hairs covering most of its carapace, while the female is grey with a pattern.
- The ocular area of T. jayamangali is uniformly covered with white hairs, in contrast to T. arkavathi and T. manu, which have distinctive markings.
Habitat and Distribution:
- Tenkana spiders are typically ground-dwelling and prefer dry, open habitats like short grasses, leaf litter, and rocky outcrops.
- These spiders have been observed in Tamil Nadu, Puducherry, Karnataka, Telangana, Andhra Pradesh, and some areas in Sri Lanka.
- The male and female spiders of T. jayamangali were discovered in different regions, 2 km apart, at the hilltop and foothills of the same forest.
Ecological and Behavioral Insights:
- The Tenkana genus is considered endemic to India, with species observed in diverse regions such as Bengaluru, Yercaud (Tamil Nadu), and Bannerghatta (Karnataka).
- These spiders are found in complex microhabitats, like shaded short grasses with dry leaf litter or rocky outcrops in relatively dry habitats.
- The movement of Tenkana spiders resembles that of Stenaelurillus, another ground-dwelling spider species.
Amazon Future Engineer Program (Phase 3)

- 23 Oct 2024
In News:
- The National Education Society for Tribal Students (NESTS) launched the third phase of the Amazon Future Engineer Program in 50 Eklavya Model Residential Schools (EMRS).
- Schools involved are spread across Andhra Pradesh, Gujarat, Karnataka, Madhya Pradesh, Odisha, Telangana, and Tripura.
Program Focus Areas:
- Emerging Technologies: The third phase introduces tribal students to key areas like:
- Blockchain technology
- Artificial Intelligence (AI)
- Coding and block programming
- The program is designed to equip students with skills in computer science fundamentals.
Teacher Training:
- A four-day in-person training workshop for teachers was conducted to empower them with the skills necessary to teach emerging technologies effectively.
- Teachers also participated in the EMRS Coders Expo, showcasing top student coding projects from the previous academic year.
Target Audience:
- Students: The program targets students from grades 6 to 9. Class 10 students will participate in project-based virtual sessions aligned with the CBSE AI Skills Curriculum.
- The goal is to enhance students' understanding of computer science and technology and prepare them for STEM (Science, Technology, Engineering, Mathematics) careers.
Program Expansion:
- Future Plans: The program will be rolled out in the next phase to cover a total of 410 EMRSs across India.
- Impact: Over 7,000 students in grades 6 to 8 have already benefited from the program’s introduction to computer science and block programming.
Key Goals of the Program:
- Empower Tribal Students: Provide tribal students with modern technological skills to prepare them for future STEM careers.
- Capacity Building: Equip both teachers and students with the knowledge and skills to engage with emerging technologies.
- Fostering Technological Literacy: The initiative aims to foster technological literacy and modernize education in tribal areas.
Recognition:
- During the event, Top 3 Student Coding Projects were felicitated for their creativity and innovation.
- The Top 3 IT Teachers were also recognized for their dedication in guiding students through the program.
Partnership with Amazon:
- The program is a collaboration between NESTS and Amazon, showcasing a joint effort to improve educational access and technological skill development among tribal students.
India's Mission Mausam and the Cloud Chamber

- 23 Oct 2024
In News:
Mission Mausamaims to not just improve weather forecasting in the country but also ‘manage’ certain weather events, and on demand, enhance or suppress rainfall, hail, fog and, later, lightning strikes.
- Focus Areas:
- Enhancing or suppressing rainfall, hail, fog, and later, lightning strikes on demand.
- Strengthening cloud physics research to better understand and modify weather conditions.
- Establishment of Cloud Chamber:
- Location: The cloud chamber is being built at the Indian Institute of Tropical Meteorology (IITM) in Pune.
- Purpose: To study cloud physics in detail and develop methods for weather modification.
- Key Feature: It will be a convective cloud chamber, capable of simulating conditions specific to Indian monsoon clouds.
What is a Cloud Chamber?
- A scientific apparatus that mimics the conditions required for cloud formation.
- Function: Water vapour, aerosols, and other particles are injected into the chamber, and under controlled temperature and humidity conditions, clouds can be formed.
- Global Context: While many countries have cloud chambers, India is building one with convection properties, which are essential for studying monsoon clouds. Only a few such chambers exist globally.
Why India Needs a Convective Cloud Chamber?
- Cloud Physics: The chamber will allow scientists to study various phenomena such as:
- Cloud behaviour under normal and extreme conditions.
- Formation of rain droplets and ice particles.
- Influence of moisture from cyclones or low-pressure systems.
- Interactions between different cloud layers.
- Objective: To gain insights into cloud formation specific to the Indian monsoon and develop strategies for weather modification.
Applications for Weather Modification:
- The cloud chamber will help scientists simulate and understand how to influence weather events like rain and fog, particularly in monsoon systems.
- It will allow testing of new ideas and theories under controlled conditions, adjusting temperature, humidity, and convection parameters to suit Indian weather conditions.
India’s Experience with Cloud Seeding:
- Cloud Seeding: A technique tested in India to enhance rainfall by introducing particles (seeds) into clouds.
- CAIPEEX Program: India conducted the Cloud Aerosol Interaction and Precipitation Enhancement Experiment (CAIPEEX) over a decade to study cloud seeding's effectiveness.
- Findings: Cloud seeding increased rainfall by up to 46% in some regions, showing its potential under specific conditions.
- Limitations: Cloud seeding is not a one-size-fits-all solution and is effective only under certain conditions.
Significance for India’s Weather Forecasting:
- Improved Weather Modification: The cloud chamber and insights from it could lead to better management of weather events, especially in regions affected by monsoon rains, cyclones, and droughts.
- Tailored Strategies: India will be able to implement targeted weather interventions, especially in agricultural regions, to reduce the negative impacts of extreme weather.
???????Global and Regional Relevance:
- Cloud Chamber: The Pune facility will be one of the few globally with the specific focus on convective properties needed to study Indian monsoon systems.
- Role in Climate Science: India’s investment in cloud physics research positions it at the forefront of developing technologies to manage climate variability and extreme weather events.
India-Pakistan Kartarpur Corridor Agreement Renewal
- 23 Oct 2024
In News:
- India and Pakistan have extended the Sri Kartarpur Sahib Corridor Agreement for another five years (until 2029).
- Purpose: The extension ensures uninterrupted operation of the corridor, allowing Indian pilgrims to visit Gurdwara Darbar Sahib Kartarpur in Pakistan.
- Significance: The extension reflects continued cooperation between India and Pakistan, with potential implications for improving bilateral relations.
Background of Kartarpur Corridor:
- Inception: The agreement was first signed on October 24, 2019, to allow visa-free access for Indian pilgrims to Gurdwara Darbar Sahib Kartarpur near Narowal in Pakistan.
- Pilgrimage Details:
- Eligibility: Indian nationals and Overseas Citizens of India (OCI) cardholders can visit the gurdwara on a daily basis.
- Return on Same Day: Pilgrims must return on the same day.
- No Religious Restrictions: Pilgrims of any faith can use the corridor.
- Capacity: Up to 5,000 pilgrims per day can visit the gurdwara.
- Historical Importance: The corridor facilitates the Sikh community's access to a key religious site, located just 4.7 km from the India-Pakistan border.
- Service Charge Dispute:
- Pakistan's Service Fee: Pakistan continues to charge a $20 service fee (approx. ?1,680) per pilgrim, which India has consistently urged Pakistan to waive.
- Pakistan’s Justification: Pakistan maintains the fee to cover the $17 million spent on refurbishing the gurdwara and developing infrastructure for the corridor.
- Geopolitical Context and Timing:
- Recent Developments: The agreement renewal follows External Affairs Minister S. Jaishankar’s visit to Pakistan to attend the Shanghai Cooperation Organization (SCO) Council of Heads of Government meeting.
- Improved Bilateral Relations: Jaishankar’s visit marked the first visit by an Indian foreign minister to Pakistan in nearly nine years, signaling potential thaw in relations, despite the lack of formal bilateral dialogue.
- Strategic and Religious Importance:
- Religious Diplomacy: The Kartarpur Corridor is viewed as a confidence-building measure and a symbol of religious diplomacy, particularly for the Sikh community.
- Historical Legacy: The corridor links Gurdwara Darbar Sahib Kartarpur in Pakistan to Gurdwara Dera Baba Nanak in India, facilitating access to a site of immense religious significance for Sikhs.
- Implications for India-Pakistan Relations:
- No Formal Bilateral Talks: Despite the successful renewal of the agreement, formal talks between India and Pakistan remain suspended, particularly after India’s revocation of Article 370 in Jammu and Kashmir in 2019, which led to a diplomatic freeze.
- Pakistan's Diplomatic Stance: Pakistan had recalled its high commissioner from India in August 2019, and tensions have remained high since then.
- Potential for Future Engagement:
- Diplomatic Channels Opened: The renewal of the Kartarpur agreement and Jaishankar’s visit suggest that diplomatic channels are still open, and there may be scope for further engagement if both sides take steps to address outstanding issues.
IMF retains India’s growth projection at 7% for FY25
- 23 Oct 2024
In News:
The International Monetary Fund (IMF) has revised India's GDP growth forecast for the fiscal year 2024-25 to 7%, up by 20 basis points from its previous estimate of 6.8%.
- India’s Growth Projections:
- Current Fiscal Year (FY2024-25): India’s GDP growth is projected at 7%, unchanged from June 2024 estimates.
- Next Fiscal Year (FY2025-26): Growth expected at 6.5%.
- Growth Decline from FY2023 (8.2%): The slowdown is attributed to the exhaustion of pent-up demand post-pandemic and the economy returning to its potential.
- Global Economic Growth:
- World Output: Projected global growth at 3.2% in both 2024 and 2025.
- Advanced Economies: U.S. GDP growth revised upward to 2.8% in 2024 and 2.2% in 2025.
- Emerging Markets & Developing Economies: Growth revised upwards, largely due to stronger economic activity in Asia, with China and India being key contributors.
- Global Inflation and Monetary Policy:
- Inflation Decline: Global inflation has decreased from its peak of 9.4% in Q3 2022 to 3.5% projected by end-2025.
- Inflation Outlook: Despite reductions in inflation, price pressures persist in some regions.
- Monetary Policy Tightening: IMF acknowledges challenges due to tight monetary conditions in several economies and their potential impacts on labor markets.
- Global Risks and Challenges:
- Geopolitical Tensions: Ongoing Russia-Ukraine war and escalating conflicts in West Asia (e.g., Lebanon) have increased geopolitical risks, potentially affecting commodity markets.
- Protectionism: Growing protectionist policies worldwide are a risk to global trade and economic stability.
- Sovereign Debt Stress: Debt burdens in several countries could become a source of instability.
- Weak Chinese Economy: Slower-than-expected recovery in China remains a significant concern for global economic growth.
- Monetary Policy Risks: Prolonged tight monetary policies in some countries could impact labor markets and economic recovery.
- IMF’s Policy Recommendations for Medium-Term Growth:
- Monetary Policy Neutrality: Countries should adopt a neutral monetary policy stance to balance growth and inflation control.
- Fiscal Policy Adjustment: Build fiscal buffers after years of loose fiscal policy to ensure stability.
- Structural Reforms: Implement structural reforms to boost productivity and cope with challenges like aging populations, the climate transition, and the need for youth employment.
- India’s Economic Outlook - Key Drivers:
- Rural Consumption Growth: The upward revision of India's FY2024-25 GDP forecast to 7% is driven by improved consumption, especially in rural areas.
- Upward Revisions for 2023: The increased growth forecast also reflects positive carryover effects from India's 8.2% growth in 2023.
- Emerging Asia's Growth: The growth outlook for emerging Asia is supported by India and China, though long-term growth prospects for China are weaker (projected to slow to 3.3% by 2029).
- Global Economic Outlook:
- World Growth Projections: Global growth is expected to remain at 3.2% in 2024 and 3.3% in 2025.
- Diverging Growth Rates: Growth across economies is converging as output gaps close, particularly in advanced economies (e.g., U.S. labor market cooling, euro area recovery).
Z-Morh Tunnel Project in Kashmir

- 22 Oct 2024
In News:
Seven people were killed in Jammu and Kashmir when suspected militants targeted the workers of infrastructure company APCO Infratech, which is constructing the Z-Morh tunnel on the Srinagar-Sonamarg highway. This is the first militant attack on a key infrastructure project in Jammu and Kashmir. In the past, militants have not targeted such infrastructure projects in the region.
What is the Z-Morh Tunnel?
- Length: 6.4 kilometers
- Connection: Links Sonamarg (a popular tourist destination) with Kangan town in central Kashmir’s Ganderbal district.
- Construction Site: Located near Gagangir village, ahead of Sonamarg.
- Naming: The tunnel gets its name from the Z-shaped road near the construction site.
Importance of the Z-Morh Tunnel
- All-Weather Connectivity: The tunnel is crucial for year-round access to Sonamarg, particularly in the winter when the road is often blocked by snow avalanches.
- Location: Situated at 8,500 feet above sea level, the tunnel provides a safe, all-weather route for tourists and locals, especially during winter months when access to Sonamarg is typically limited.
Strategic Importance
- Part of Zojila Tunnel Project:
- The Z-Morh tunnel is integral to the larger Zojila tunnel project, which aims to provide all-weather connectivity from Srinagar to Ladakh.
- The Zojila Tunnel, under construction at an altitude of around 12,000 feet, will connect Sonamarg (Kashmir) to Drass (Ladakh) and is expected to be completed by December 2026.
- Military and Strategic Significance:
- The Z-Morh tunnel is crucial for rapid military mobilization between Srinagar, Kargil, Leh, and Drass regions.
- It ensures quick access for military personnel to the Ladakh border, particularly in areas of heightened security like Siachen Glacier and the Turtuk sub-sector (on the Pakistan border).
- The tunnel will reduce dependence on air transport for troop and supply movements to forward areas, leading to cost savings and extended aircraft lifespan.
The case for a nature restoration law in India

- 22 Oct 2024
In News:
The Nature Restoration Law (NRL), which was enacted by the European Union (EU), is an inspiring model from which India can draw points to tackle its growing environmental crises.
Background of the NRL in the EU
- The Nature Restoration Law (NRL) was enacted by the European Union (EU) to restore ecosystems and combat biodiversity loss.
- Adopted on June 17, 2024, by the EU’s Environmental Council.
- Key objectives:
- Restore 20% of EU’s land and sea areas by 2030.
- Achieve full restoration of all ecosystems by 2050.
- Part of the EU’s Biodiversity Strategy for 2030 and European Green Deal.
- Target Areas:
- Forests, agricultural lands, rivers, urban spaces.
- Restoration measures include:
- 25,000 km of free-flowing rivers.
- Planting 3 billion trees by 2030.
- Global Impact: NRL is a critical tool in reversing Europe’s biodiversity loss, where 80% of habitats are in poor condition.
Environmental Crisis in India
- Land Degradation:
- 29.7% of India’s total geographical area is affected by land degradation (as per ISRO’s Desertification and Land Degradation Atlas, 2018-19).
- 97.85 million hectares of land degraded, with a significant increase since 2003-05.
- Major desertification hotspots in Gujarat, Karnataka, Maharashtra, and Rajasthan.
- Desertification: A growing concern, affecting 83.69 million hectares in 2018-19.
- Ongoing Efforts:
- Green India Mission, Pradhan Mantri Krishi Sinchayee Yojana, and National Afforestation Programme have had positive effects.
- Integrated Watershed Management Programme is the second-largest watershed programme globally.
Need for a Comprehensive Nature Restoration Law in India
- The scale of India’s environmental challenges requires a comprehensive nature restoration law similar to the EU’s NRL.
- The law should have legally binding targets to restore degraded landscapes and ensure ecosystem sustainability.
Key Features of an Indian Nature Restoration Law
- Restoration Targets:
- 20% of degraded land to be restored by 2030.
- Full restoration of ecosystems (forests, wetlands, rivers, agricultural lands, urban spaces) by 2050.
- Wetland Restoration:
- Target restoring 30% of degraded wetlands by 2030.
- Priority wetlands like Sundarbans and Chilika Lake play critical roles in biodiversity and carbon sequestration.
- Biodiversity in Agriculture:
- Promote agroforestry and sustainable agriculture practices.
- Use biodiversity indicators (e.g., butterfly or bird index) to monitor progress.
- River Restoration:
- Focus on free-flowing rivers such as the Ganga and Yamuna.
- Address pollution, obstructions, and ecosystem damage in major rivers.
- Urban Green Spaces:
- Ensure no net loss of urban green spaces.
- Promote urban forests in cities like Bengaluru and Delhi, where urban heat islands and air quality degradation are prominent.
Economic and Social Benefits of Ecosystem Restoration
- Global Economic Impact:
- Nature restoration could generate $10 trillion annually by 2030 (World Economic Forum estimate).
- Benefits for India:
- Agricultural Productivity: Restoring degraded land will enhance farm productivity.
- Water Security: Improved land restoration will contribute to better water availability.
- Job Creation: Millions of rural jobs could be created through ecosystem restoration efforts.
- Contributing to SDGs:
- The law would help India meet SDG 15 (sustainable management of forests, combating desertification).
- Climate Change Mitigation:
- Restoring ecosystems can help India enhance its carbon sinks, which is crucial for meeting Paris Agreement targets.
- Degraded lands lose their capacity to absorb carbon dioxide, contributing to global warming.
Caenorhabditis elegans (C. elegans)
- 22 Oct 2024
In News:
The tiny nematode Caenorhabditis elegans (C. elegans) has played an outsized role in scientific discovery, contributing to four Nobel Prizes over the years.
Key Discoveries from C. elegans Research
- C. elegans and Cellular Processes:
- The worm has helped scientists understand programmed cell death (apoptosis), a vital process in development and disease. This work contributed to the 2002 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine, addressing how cells are instructed to kill themselves and how this process goes awry in conditions like AIDS, strokes, and degenerative diseases.
- Gene Silencing and RNA Interference:
- In 2006, a Nobel Prize was awarded for the discovery of gene silencing via RNA interference (RNAi), a process first explored using C. elegans. This discovery led to the development of a new class of RNA-based drugs.
- Cellular Imaging Techniques:
- In 2008, C. elegans contributed to breakthroughs in cellular imaging, as its use helped invent cellular “lanterns” that allowed scientists to visualize the inner workings of cells, earning a Chemistry Nobel.
- Gary Ruvkun’s 2024 Nobel:
- Gary Ruvkun’s Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine in 2024 was the fourth in a series of Nobel recognitions stemming from C. elegans research, reinforcing its role in fundamental biological discoveries.
Key Facts About Caenorhabditis elegans (C. elegans):
- Size: 1 millimeter long.
- Life Cycle: Completes in 3-5 days.
- Cell Count: 959 cells.
- Genome: First multicellular organism to have its full genome sequenced in 1998.
- Sexual Reproduction: Hermaphroditic (self-fertilizing) and male.
- Scientific Role: Used to study genetics, developmental biology, neuroscience, and cell biology.
- Nobel Prize Contributions: Four Nobel Prizes, including those in Physiology, Medicine, and Chemistry, for advancements in cell death, gene silencing, and imaging.
IAEA’s 2024 Climate Change and Nuclear Power Report

- 22 Oct 2024
In News:
- The 2024 edition of the IAEA’s Climate Change and Nuclear Power report has been released, highlighting the need for a significant increase in investment to achieve goals for expanding nuclear power.
- The new report was launched last week on the margins of the Clean Energy Ministerial (CEM) in Brazil.
Key Highlights:
- Nuclear Power's Role in Climate Change Mitigation:
- Nuclear energy is gaining global interest as nations seek to enhance energy security and decarbonize economies.
- To meet net-zero emissions by 2050, nuclear power is projected to play a pivotal role, with a projected capacity increase of 2.5 times the current level by mid-century in the IAEA's high case scenario.
- Investment Needs for Nuclear Expansion:
- Annual investment required to meet the IAEA's high case scenario (2050 nuclear capacity) is USD 125 billion, a significant increase from USD 50 billion annually from 2017-2023.
- If the aspirational goal to triple nuclear capacity (as pledged by over 20 countries at COP28) is to be met, USD 150 billion annually would be necessary.
- Challenges in Financing: Upfront capital for nuclear power plants is expensive, posing challenges, especially in market-driven economies and developing countries.
- Private Sector and Multilateral Support:
- The private sector will need to play a larger role in financing nuclear projects.
- The IAEA is engaging with multilateral development banks to improve financing options for developing countries to invest in nuclear energy.
- Private finance initiatives: In September 2024, 14 major financial institutions signaled readiness to help fund nuclear newbuild projects.
- Nuclear Financing at Clean Energy Ministerial (CEM):
- The IAEA report was launched during the 15th CEM in Brazil, a high-level forum for advancing clean energy technologies.
- Key stakeholders from Brazil, the IAEA, the International Energy Agency (IEA), and the U.S. discussed strategies for securing nuclear power financing, especially in the context of COP29 (2024) where clean energy financing will be a key focus.
- Nuclear Energy in the EU’s Sustainable Financing:
- The EU taxonomy for sustainable activities now includes nuclear power, facilitating the issuance of green bonds for nuclear projects in Finland and France (2023).
- EDF received €4 billion in green bonds and around €7 billion in green loans (2022-2024).
- Investment in Nuclear Power:
- To meet global climate goals, nuclear power capacity must increase by 1.8 times by 2035.
- Effective financing mechanisms are crucial to scale up nuclear power and develop the workforce and supply chains needed for the energy transition.
- Policy Reform and International Partnerships:
- The report advocates for policy reforms and international partnerships to bridge the financing gap and accelerate nuclear power deployment, particularly in emerging markets and developing economies.
- Focus on technologies such as small modular reactors (SMRs), which could play a role in the energy transition.
- Key Areas to Support Nuclear Growth:
- Robust regulatory frameworks and new delivery models are essential to unlock investments.
- Development of skilled labor and effective stakeholder engagement is crucial for the expansion of nuclear energy.
- Energy System Modelling and Planning:
- The IAEA’s energy system modelling tools assist countries like Brazil in planning nuclear power projects, including cost analyses for electricity generation and financing strategies.
Role of the International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA):
- Mandate: The IAEA is the leading international body for promoting the safe, secure, and peaceful use of nuclear energy and technologies.
- Functions:
- Nuclear safeguards: Ensuring nuclear activities remain peaceful and preventing the diversion of nuclear materials for weapons purposes.
- Assisting member states with technical support, knowledge sharing, and strengthening nuclear safety and security.
- The IAEA also supports capacity-building and emergency response in case of nuclear or radiological incidents.
- Structure:
- The IAEA General Conference is made up of all 178 member states, meeting annually to approve budgets and policies.
- The Board of Governors (35 members) meets several times a year to oversee the agency's activities and appointments.
- Headquarters: Vienna, Austria
- The IAEA is part of the United Nations family, reporting to both the UN General Assembly and the Security Council.
Egypt becomes 2nd country in 2024 to be declared ‘malaria-free’
- 22 Oct 2024
In News:
Egypt was officially declared ‘malaria-free’ by the World Health Organization (WHO).
Key Highlights:
- Egypt became the second country (after Cabo Verde) to be certified malaria-free in 2024.
- It is the fifth African country to achieve this milestone, joining Morocco, UAE, and Cabo Verde in the malaria-free list.
- WHO Certification Criteria:
- A country is certified malaria-free if it can prove the Anopheles mosquito-borne malaria transmission chain has been broken for at least three years.
- The country must also have the capacity to prevent the re-establishment of transmission.
- About Malaria:
- Malaria is an acute febrile illness caused by Plasmodium parasites, transmitted through the bites of infected female Anopheles mosquitoes.
- It is a life-threatening disease primarily found in tropical countries.
- Symptoms include fever, headache, and chills, which can be mild and difficult to diagnose.
- Prevention mainly involves vector control interventions, and treatment involves early diagnosis and use of antimalarial drugs.
Russia's Izdeliye 305 (LMUR) Missile

- 21 Oct 2024
In News:
Russian state corporation Rostec has claimed that its Light Multipurpose Guided Rocket, also known as Izdeliye 305 or “Product 305,” has demonstrated remarkable resistance to jamming and interference on the battlefield in Ukraine.
Missile Overview
- Name: Izdeliye 305 (Product 305), also known as LMUR (Light Multipurpose Guided Rocket)
- Primary Use: Deployed by Russia’s Mi-28NM and Ka-52M attack helicopters.
- Function: Designed to target and destroy armored vehicles, fortifications, pillboxes, and watercraft with high precision.
Key Features
- Sniper-Like Accuracy: The missile is touted for its exceptional precision in targeting, making it one of Russia’s most successful guided weapons.
- Resistance to Jamming: The missile’s control channel has shown remarkable resistance to enemy electronic warfare (EW) systems, making it effective even in contested environments.
- No instances of the missile's control channel being suppressed during the ongoing Ukraine conflict.
- Versatile Guidance Systems: The missile operates in several modes:
- Fire-and-Forget: The missile locks onto the target before launch and operates autonomously post-launch.
- Remote Control Mode: The operator guides the missile to the target after it locks onto coordinates and transmits live imagery to the operator’s screen.
- Inertial + Homing Mode: The missile initially flies inertially toward target coordinates, then activates its homing system for final target guidance.
- High Explosive Warhead: Equipped with a 25-kg high-explosive fragmentation warhead, the LMUR is effective against a variety of targets.
Technical Specifications
- Weight: 105 kg (231 lbs)
- Range: Up to 9 miles, double the range of traditional Russian anti-tank missiles, providing the tactical advantage of engaging from beyond line-of-sight.
- Warhead: 25 kg high-explosive fragmentation for effective target destruction.
- Guidance: A combination of inertial navigation, satellite positioning, thermal imaging, and a two-way communication channel for real-time control.
Deployment and Use
- Helicopter Integration: Primarily used on Mi-28NM and Ka-52M attack helicopters, and also on the Mi-8MNP-2 for special operations.
- Combat Experience:
- The missile was actively used in Ukraine where it played a key role in countering Ukraine’s NATO-backed counteroffensive operations.
- It was previously tested in Syria against various targets, showcasing its capabilities before full operational deployment in 2022.
Significance in Ukraine Conflict
- Impact on Ukrainian Forces: The missile’s long range and resistance to EW have made it a critical component of Russia’s aerial operations, hampering Ukraine’s battlefield progress, particularly against heavily fortified positions and NATO-backed counteroffensive efforts.
Strategic Advantage: The missile’s ability to engage targets from a distance while evading jamming attempts gives it a significant edge in modern warfare.
National Water Awards 2023

- 21 Oct 2024
In News:
The Hon’ble President of India Smt. Droupadi Murmu will confer the 5th National Water Awards 2023 on October 22nd 2024 at Vigyan Bhawan, New Delhi.
Organizing Body:
- Ministry: Ministry of Jal Shakti
- Department: Department of Water Resources, River Development, and Ganga Rejuvenation (DoWR, RD & GR)
- Purpose: To recognize and honor individuals, organizations, and bodies that have made significant contributions to water conservation and management.
Award Categories
- Best State
- Best District
- Best Village Panchayat
- Best Urban Local Body
- Best School or College
- Best Industry
- Best Water User Association
- Best Institution (other than school or college)
- Best Civil Society Organization
Winners
- Best State:
- 1st Prize: Odisha
- 2nd Prize: Uttar Pradesh
- 3rd Prize (joint): Gujarat & Puducherry
- Other Awards: Winners in the remaining categories have been recognized, with citations, trophies, and cash prizes provided in certain categories.
Objectives of the National Water Awards
- Promote Water Conservation: Raise awareness about the importance of water and encourage effective water usage practices.
- Recognize Efforts: Celebrate the work of individuals, institutions, and organizations contributing to the government’s vision of a ‘Jal Samridh Bharat’ (Water-rich India).
- National Campaign: Under the guidance of Hon’ble Prime Minister, the Ministry of Jal Shakti has been working to spread awareness on water management and conservation through extensive national campaigns.
History and Background
- The National Water Awards (NWAs) were launched in 2018 by the DoWR, RD & GR to foster awareness and action on water-related issues.
- Awards were given for 2019, 2020, and 2022, but there were no awards in 2021 due to the COVID-19 pandemic.
- The awards aim to inspire best practices in water usage, conservation, and management across India, involving government bodies, industries, communities, and civil society.
Significance
- The National Water Awards serve as a platform to recognize the innovative initiatives taken by various stakeholders in addressing water challenges.
The awards contribute to furthering the government’s mission of achieving sustainable water management practices across the nation.
Funga Taxonomic Kingdom

- 21 Oct 2024
In News:
- Chile and the United Kingdom have prepared a proposal to recognize fungi as an independent kingdom, termed "Funga", alongside flora (plants) and fauna (animals).
- This will be presented at the 16th Conference of Parties (COP16) of the UN Convention on Biological Diversity (CBD), to be held in Cali, Colombia in October 2024.
- Why Funga?
- Fungi (e.g., mushrooms, moulds, yeast, lichen) play crucial ecological roles, but have historically been overlooked in conservation strategies.
- Fungi contribute significantly to decomposition, forest regeneration, carbon sequestration, and the global nutrient cycle.
- The recognition aims to strengthen fungal conservation by integrating fungi into global legislation and policies.
- Ecological Importance of Fungi:
- Decomposition: Fungi break down organic matter, facilitating nutrient recycling in ecosystems.
- Symbiotic Relationships: Many fungi form crucial symbiotic relationships with plants (e.g., mycorrhizal associations) and animals.
- Climate Mitigation: Boreal forest fungi absorb large amounts of carbon through symbiosis with plants, playing a role in mitigating climate change.
- Pollution Remediation: Fungi can help clean polluted soils by breaking down toxins.
- Food Production: Fungi are essential for producing common foods like bread, cheese, wine, beer, and chocolate.
- Health: Fungi produce antibiotics (e.g., penicillin) and aid in mammalian digestion.
- Scientific Recognition:
- In August 2021, the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) recognized fungi as one of the three kingdoms of life, alongside plants and animals.
- The 3F initiative (Flora, Fauna, and Funga), led by Giuliana Furci, aims to promote the international recognition and protection of fungi.
- Diversity and Research Gaps:
- Only 8% of the estimated 2.2 to 3.8 million fungal species have been formally described.
- Approximately 2,000 new fungal species are discovered annually, indicating the vast underexplored diversity of fungi.
- Threats to Fungi:
- Fungi face significant threats from deforestation, climate change, pollution, overharvesting, and fungicide use.
- These threats disrupt the symbiotic relationships fungi share with plants and animals, leading to ecosystem instability.
- Nitrogen enrichment in soils and habitat loss further exacerbate these risks.
Key Facts About Fungi
- Biological Characteristics:
- Fungi are eukaryotic organisms with rigid cell walls made of chitin (distinct from the cellulose found in plant cell walls).
- They are heterotrophic, meaning they absorb nutrients from their environment through external digestion (secreting enzymes to break down organic material before absorption).
- Reproductive Strategies:
- Fungi reproduce both asexually (via spores) and sexually, ensuring their proliferation across ecosystems.
- Growth Form:
- Fungi grow primarily as mycelium, a network of hyphae (filamentous structures) that helps in nutrient absorption and environmental interaction.
- Symbiotic Relationships:
- Fungi form mycorrhizal relationships with plants, enhancing nutrient exchange, and lichen associations with algae, providing mutual benefits in extreme environments.
WHO Approves First Mpox Diagnostic Test for Emergency Use

- 21 Oct 2024
In News:
- The World Health Organization (WHO) has listed the Alinity m MPXV Assay under its Emergency Use Listing (EUL) procedure.
- The test, developed by Abbott Molecular Inc., will help expand diagnostic capacity in countries experiencing Mpox outbreaks, particularly in Africa.
- Importance of Early Diagnosis:
- Early diagnosis enables timely treatment and virus control.
- It is critical for improving Mpox surveillance, especially in areas with high transmission.
Current Mpox Situation
- Global Context:
- Over 30,000 suspected cases reported in Africa in 2024.
- India has reported 30 cases since the WHO declared Mpox a global health emergency in August 2024.
- Testing Capacity:
- Limited testing capacity and delays in confirming cases have been a significant barrier to controlling the spread, especially in Africa.
- In India, 35 laboratories are currently equipped to test suspected Mpox cases.
Mpox Diagnostic Test Details
- Alinity m MPXV Assay:
- A real-time PCR test that detects monkeypox virus (MPXV) DNA from skin lesion swabs.
- Used by trained clinical laboratory personnel proficient in PCR techniques.
- Helps confirm suspected Mpox cases from pustular or vesicular rash samples.
- WHO's Role:
- The Emergency Use Listing (EUL) procedure accelerates the availability of life-saving products during public health emergencies.
- WHO aims to increase access to quality-assured diagnostics in regions most affected by Mpox.
About Mpox
- What is Mpox?
- Zoonotic disease caused by the monkeypox virus, part of the Orthopoxvirus genus (family Poxviridae).
- Closely related to smallpox, but generally less severe in humans.
- Transmission:
- Spread via physical contact with infected lesions, body fluids, or contaminated materials.
- Can also spread through animal bites, or activities like hunting, skinning, or eating infected animals.
- Two Clades:
- Clade I: Predominantly in Central and East Africa.
- Clade II: More common in West Africa; linked to the 2022 outbreak.
- Symptoms:
- Rashes, blisters, fever, sore throat, headache, muscle aches, back pain, swollen lymph nodes.
- Lesions typically scab over as they heal.
- Most people experience mild symptoms, but children, pregnant women, and immunocompromised individuals are at greater risk.
Treatment and Prevention
- No Specific Cure:
- Supportive care (e.g., pain relief, hydration) is recommended.
- In some cases, antivirals like tecovirimat (developed for smallpox) may be used under exceptional circumstances.
- Vaccination:
- Three smallpox vaccines are recommended for at-risk individuals: MVA-BN, LC16, and OrthopoxVac.
- Mass vaccination is not recommended by WHO.
New 'Lady Justice' Statue in the Supreme Court

- 21 Oct 2024
In News:
Recently, the Chief Justice of India unveiled the ‘new lady justice’ statue in the Supreme Court premises that replaced the ‘original lady justice’. The new statue is clothed in a saree, has shed the blindfold and holds scales on one hand and the Indian Constitution on the other.
Symbolism of the New Statue
- Design:
- Clad in a saree, symbolizing Indian tradition.
- No blindfold, with open eyes, conveying that justice "sees" all equally.
- Holds the Indian Constitution in one hand and scales of justice in the other.
- Significance:
- Aimed at decolonization of the judiciary, replacing colonial symbols with representations that reflect India's identity and values.
- The open eyes represent that justice is not blind, addressing social diversity, discrimination, and constitutional provisions for upliftment of underprivileged sections.
- The Constitution in place of a sword symbolizes its supremacy in India’s legal system.
Historical Context of Lady Justice
- Origin:
- Rooted in Roman mythology; Justitia, the goddess of justice, symbolized by scales, sword, and a blindfold.
- Blindfold added in the Renaissance as a satire on corrupt legal systems but later reinterpreted as a symbol of impartiality, representing justice without bias, irrespective of wealth, power, or social status.
- Scales: Balance in weighing both sides before judgment.
- Sword: Authority and power of law, to protect and punish.
Rationale for Change in India
- Colonial Legacy:
- The 'lady justice' symbol became prominent during British rule, reflecting colonial influence in India's legal system.
- Decolonial Intent:
- The shift from Western attire (robe) to a saree connects the statue to Indian traditions.
- Open eyes emphasize that Indian justice is not blind and addresses social inequalities directly.
- The Constitution's prominence underscores its role as the supreme guiding document in the Indian legal system.
Current Judicial System Challenges
- Pending Cases:
- Over 5 crore cases are pending across courts in India.
- Supreme Court recently dismissed a petition for a three-year timeline to resolve the backlog, citing the overwhelming volume of cases.
- Urgent Reforms Needed:
- Finalize the Memorandum of Procedure:
- Still pending after 8 years; addresses transparency and accountability in judicial appointments.
- Representation in Judiciary:
-
- Backward classes, SCs, STs, and minorities are underrepresented in higher judiciary (less than 25%), and women are underrepresented (less than 15%).
- Appointments should reflect India's social diversity.
-
- Vacancies in Courts:
-
- High Courts operate at 60-70% strength, contributing to a massive case backlog of over 60 lakh cases.
- Lower courts have 4.4 crore pending cases; vacancies must be filled by states promptly.
- Priority for Constitutional Cases:
-
- Cases concerning the constitutional validity of laws and individual liberty should be prioritized by the judiciary.
Conclusion
- The new Lady Justice statue is not just a symbolic change but reflects a broader effort to realign India’s judiciary with its social and constitutional values.
- To ensure fair and prompt justice, there is an urgent need to address systemic delays, fill vacancies, and improve diversity in judicial appointments.
- Only then will the judiciary truly embody the principles of impartiality and justice, as represented by the new statue.
2nd Indian Lighthouse Festival

- 20 Oct 2024
In News:
The 2nd Indian Lighthouse Festival was held with the aim of promoting lighthouse tourism and celebrating India’s maritime legacy.
Strategic Importance of the Lighthouse Projects
- The Ministry of Ports, Shipping & Waterways (MoPSW) has invested significantly in developing lighthouses as tourist hubs. The festival marks a concerted effort to integrate tourism with the preservation of these iconic structures.
- Lighthouse tourism has witnessed a remarkable increase of over 400% in visitor numbers since 2014, as part of India's broader vision to promote the blue economy.
-
- From just 4 lakh visitors in 2014, the footfall surged to 16 lakh in 2023-24, with over 9 lakh tourists already in the first half of FY 2024-25.
-
Key Projects and Announcements at the Festival
- New Lighthouses: The announcement of the two new lighthouses at Chaumuck and Dhamra along Odisha’s coastline is significant for enhancing coastal infrastructure and promoting maritime tourism in the state.
- Kalwan Reef Lighthouse: Located in Jamnagar, Gujarat, this lighthouse is part of a broader effort to enhance maritime navigation and heritage conservation along India’s western coastline.
- Development of Coastal Communities: Highlighted the importance of empowering coastal communities, particularly those living around lighthouses, to preserve and promote these structures as national cultural icons. These communities are expected to play a crucial role in lighthouse preservation, as well as in tourism and local economic development.
- Paradip Port Initiatives: Additionally, major infrastructure projects at Paradip Port, such as a stacker-cum-reclaimer and a flyover bridge, were inaugurated to further bolster the port’s capabilities and enhance its role in maritime logistics. The Sagarmala Programme also continues to transform Paradip Port into a mega port with a projected handling capacity of 500 MTPA by 2047.
Economic and Employment Impact
The development of 75 iconic lighthouses across 9 coastal states and one Union Territory is not only aimed at tourism development but also focuses on job creation. As of 2024:
- More than 150 direct jobs and 500 indirect jobs have been created in sectors such as hospitality, transportation, and local crafts, driven by the increasing footfall at these tourist destinations.
- The creation of modern amenities at these lighthouses, such as museums, amphitheaters, and children’s parks, has helped in transforming lighthouses into multifaceted tourism hubs that attract both domestic and international tourists.
Collaborative Efforts for Preservation and Promotion
- Public-Private Partnerships (PPP): Encouraging collaboration between the government, local communities, and private stakeholders to develop and maintain lighthouses as sustainable tourist destinations.
- National Framework: A central association will be created to manage coastal societies surrounding lighthouses, enabling local communities to actively participate in their preservation, protection, and promotion.
- Cultural Integration: The event also underscored the need for integrating cultural heritage with tourism development, using the lighthouses as platforms to showcase local art, cuisine, and history.
COP16 to the Convention on Biological Diversity (CBD)

- 20 Oct 2024
In News:
The 16th Conference of the Parties (COP16) to the Convention on Biological Diversity (CBD) will take place in Cali, Colombia, from October 21, 2024. This marks the first gathering since the adoption of the Kunming-Montreal Global Biodiversity Framework (KMGBF) in 2022.
About Convention on Biological Diversity (CBD)
- Adopted in 1992, the CBD is the most comprehensive international treaty focused on biodiversity conservation, the sustainable use of natural resources, and the fair sharing of benefits derived from genetic resources. It has been ratified by 196 countries, making it a key global instrument for biodiversity governance.
Key Objectives of the CBD
- Conservation of Biodiversity: Protecting genetic, species, and ecosystem diversity.
- Sustainable Use of Resources: Ensuring resources are used in a way that does not deplete or degrade biodiversity.
- Fair Sharing of Benefits: Ensuring that benefits from genetic resources are shared equitably with countries of origin.
Notable Frameworks within CBD
- Nagoya Protocol (2010): Establishes a framework for the fair and equitable sharing of benefits from the utilization of genetic resources.
- Cartagena Protocol (2000): Regulates the transboundary movement of living modified organisms (LMOs) resulting from modern biotechnology.
The Kunming-Montreal Global Biodiversity Framework (KMGBF)
- Adoption: The KMGBF was adopted at COP15 in 2022, following the Kunming Declaration.
- Targets: The framework includes 23 targets for 2030 and 4 global goals for 2050, aimed at reversing biodiversity loss and promoting sustainability.
- Notably, the 30x30 Target aims for 30% of the world’s land and oceans to be conserved by 2030. This is a key agenda item at COP16.
- The framework also emphasizes equitable access to genetic resources and the sharing of benefits from their use (Target 13).
Challenges and Issues at COP16
- Benefit-Sharing from Digital Sequence Information (DSI):
- A key issue is the fair sharing of benefits from digital sequence information (DSI) on genetic resources. The adoption of a global mechanism for this issue is still pending, as negotiations between developed and developing countries remain unresolved.
- Developed nations advocate for unrestricted access to genetic materials in exchange for voluntary contributions to a global fund.
- Developing nations seek a more equitable system, aligned with the CBD's principles of fair benefit-sharing.
- A key issue is the fair sharing of benefits from digital sequence information (DSI) on genetic resources. The adoption of a global mechanism for this issue is still pending, as negotiations between developed and developing countries remain unresolved.
- 30x30 Target Progress:
- The 30x30 target, which aims to conserve 30% of land and oceans by 2030, is far from being met:
- 17.5% of land and 8.4% of oceans are currently under protection.
- Concerns persist about the effectiveness of these protected areas, as studies suggest they may not be sufficient for long-term biodiversity conservation.
- The 30x30 target, which aims to conserve 30% of land and oceans by 2030, is far from being met:
- Financial Commitments (Target 19):
- Developed countries have pledged $20 billion annually for biodiversity financing by 2025. However, progress is slow:
- By September 2024, only $8.2 billion (41% of the target) had been committed.
- COP16 will assess whether this target can be met, with further announcements expected.
- Developed countries have pledged $20 billion annually for biodiversity financing by 2025. However, progress is slow:
- Implementation Gaps:
- Countries are required to set national targets aligned with the KMGBF. As of COP16, only 100 parties have submitted their targets, and 30 countries have updated their National Biodiversity Strategies and Action Plans (NBSAPs).
- A significant implementation gap remains in translating these targets into concrete actions.
Focus Areas for COP16
- Strengthening the 30x30 Target:
- COP16 will push for enhanced efforts to meet the 30x30 conservation goal. There is a need for better management and monitoring of protected areas to ensure they contribute to biodiversity preservation.
- Finalizing Benefit-Sharing Mechanism:
- Countries will focus on finalizing the multilateral benefit-sharing mechanism for genetic resources and DSI. The goal is to ensure that countries benefiting from genetic resources share those benefits with the countries of origin, addressing the issue of biopiracy and ensuring equitable access.
- Financial Commitment and Tracking:
- The financial shortfall for biodiversity conservation will be a critical discussion point. Effective monitoring of the biodiversity finance tracker will be needed to ensure that developed countries meet their $20 billion/year commitment.
- Addressing Implementation Gaps:
- There is a need to enhance monitoring and reporting mechanisms, improve national strategies, and align financial support with on-ground conservation efforts.
eShram-One Stop Solution

- 20 Oct 2024
In News:
- The ‘eShram-One Stop Solution’ will be launched on 21 October 2024 by the Union Minister of Labour & Employment and Youth Affairs & Sports.
- Objective: To provide easy access to various social security and welfare schemes for unorganized workers in India.
Key Features
- Mediator Platform: The eShram-One Stop Solution will act as an intermediary to facilitate the integration of multiple government schemes for unorganized workers, ensuring efficient access to services and support.
- Information Integration: It will integrate data on beneficiaries across various social security and welfare programs meant for unorganized workers, providing a single point of access.
- Target Group: Aimed at unorganized workers, including daily wage earners, migrants, and others who do not have regular formal employment.
Benefits
- Awareness & Accessibility: The platform will make unorganized workers aware of various government schemes tailored to their needs, helping them access benefits more easily.
- Effective Scheme Implementation: The eShram-One Stop Solution will aid in the identification and implementation of welfare schemes for faster saturation and coverage.
Integration with Existing Schemes
- 12 Integrated Schemes: Currently, 12 social security schemes from different ministries/departments have already been mapped with eShram.
eShram’s Progress So Far
- Launch: eShram was launched on 26 August 2021.
- Achievements: Over 30 crore unorganized workers have been enrolled, highlighting the widespread impact and popularity of the initiative among the target population.
Kala-azar Disease
- 20 Oct 2024
In News:
India to seek WHO certification for eliminating disease.
Overview of Kala-Azar (Visceral Leishmaniasis)
- Cause: Kala-azar is caused by the protozoan parasite Leishmania donovani, transmitted by the bite of infected female sandflies (Phlebotomus argentipes in India).
- Symptoms: Includes irregular fevers, weight loss, swelling of the spleen and liver, severe anaemia. If untreated, it is fatal in over 95% of cases.
- Affected Areas: Historically, Bihar, Jharkhand, West Bengal, and parts of Uttar Pradesh report the highest number of cases, with Bihar alone accounting for over 70% of India's cases.
India's Achievement in Kala-Azar Control
- Current Status:
- India has managed to maintain Kala-azar case numbers below 1 per 10,000 population for two consecutive years.
- This meets the WHO's criteria for elimination certification.
- 2023 and 2024 Statistics:
- 2023: 595 cases and 4 deaths.
- 2024 (so far): 339 cases and 1 death.
WHO Certification for Elimination
- WHO's Target: The World Health Organization aims to eliminate Kala-azar as a public health problem by 2030.
- Elimination Criteria: A country can be certified when:
- Local transmission is interrupted for a specified period.
- There is a system in place to prevent re-emergence of the disease.
- Global Context: Bangladesh is the first country to have eliminated Kala-azar, receiving WHO certification in October 2024, after reporting fewer than 1 case per 10,000 people for three consecutive years.
India's Kala-Azar Elimination Strategies
- National Health Policy (2002): Initially set the target to eliminate Kala-azar by 2010, revised multiple times, and is now aiming for 2030.
- Key Strategies:
- Active Case Detection: Identification and treatment of all cases.
- Vector Control: Targeting sandfly breeding grounds through insecticides and environmental management.
- Community Awareness: Educating the public on disease prevention and early diagnosis.
- Improved Surveillance: Ensuring rapid diagnosis and treatment access, including the use of the rK39 diagnostic kit.
- Integrated Vector Management: Combining insecticide spraying with environmental changes to reduce sandfly populations.
Challenges and Areas of Focus
- Root Causes: Persistent issues like poverty, inadequate sanitation, and malnutrition contribute to the spread of Kala-azar, particularly in rural, impoverished areas.
- Long-term Solutions:
- Strengthen vector control and improve sanitation.
- Address socio-economic factors like poverty and displacement.
- Invest in research for vaccines and new treatments.
Public Health Impact and the Way Forward
- Elimination Milestone: If India continues to reduce cases, it will join Bangladesh in eliminating Kala-azar as a public health threat.
- Sustaining Gains:
- Surveillance and quick response to new cases remain critical.
- Expand access to rapid diagnostic tools and effective anti-parasitic treatments.
- Focus on inter-sectoral convergence, integrating efforts from various government sectors, including health, sanitation, and housing.
Naseem-Al-Bahr 2024
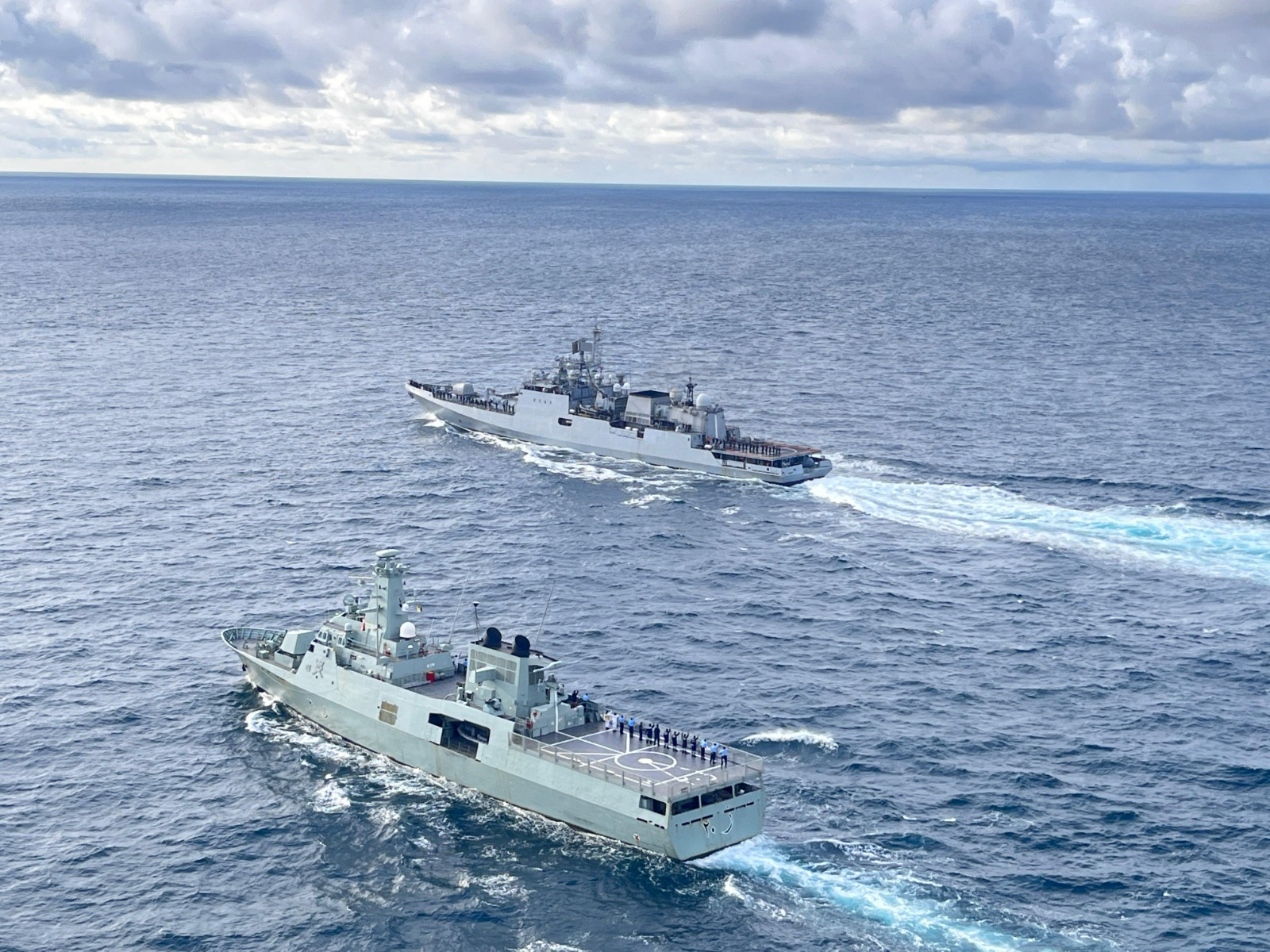

- 20 Oct 2024
In News:
Indo-Oman bilateral naval exercise Naseem-Al-Bahr was held in Goa from October 2024.
Naseem-Al-Bahr Exercise Overview
- Indian and Omani Participants:
- Indian Navy: INS Trikand (warship) and Dornier Maritime Patrol Aircraft.
- Royal Navy of Oman: Vessel Al Seeb.
- Initiation: Launched in 1993, marking a long-standing strategic partnership between India and Oman.
- Structure: The exercise is conducted in two phases:
- Harbour Phase:
- Professional Interactions: Subject Matter Expert Exchanges (SMEE), planning conferences.
- Social & Sports Engagements: Informal activities to foster mutual understanding.
- Sea Phase:
- Naval Operations:
- Gun firings at surface inflatable targets.
- Close-range anti-aircraft firings.
- Replenishment at Sea Approaches (RASAPS).
- Helicopter Operations: INS Trikand’s helicopter performed cross-deck landings and Vertical Replenishment (VERTREP) with RNOV Al Seeb.
- Aircraft Support: Dornier aircraft provided Over-the-Horizon Targeting (OTHT) data to enhance operational coordination.
- Naval Operations:
- Harbour Phase:
Key Highlights of the 2024 Exercise
- Interoperability: The exercise focused on improving operational coordination and enhancing mutual understanding of naval practices.
- Cohesion: The Indian Navy Sea Riders embarked on RNOV Al Seeb to further strengthen the bilateral relationship.
Strategic Significance
- Strengthening Ties: Naseem-Al-Bahr reaffirms the strong strategic relationship between India and Oman.
- Regional Collaboration: This exercise exemplifies India's growing collaboration with like-minded nations in the Indian Ocean Region (IOR).
- Broader Defence Relations:
- Oman is the first GCC country to conduct such bilateral naval exercises with India.
- Both countries also engage in other defence exercises:
- Army: Al Najah.
- Air Force: Eastern Bridge.
Trade Relations Between India and Oman (2022):
- Oil: India is the second-largest market for Oman's crude oil exports, following China.
- Non-oil Exports: India is Oman's fourth-largest market for non-oil exports, after UAE, US, and Saudi Arabia.
- Imports: India is the second-largest source of Oman's imports, following the UAE.
- Ongoing Trade Agreement: Both nations are currently negotiating a trade agreement to further boost bilateral economic cooperation.
Musaned Digital Platform

- 19 Oct 2024
In News:
Saudi Arabia Launches Musaned Digital Platform to Ensure Wage Protection for Foreign Workers.
Key Highlights:
- Purpose of Musaned:
- Musaned is a digital platform launched by Saudi Arabia to ensure wage protection and improve working conditions for foreign workers, particularly those in domestic (household) employment.
- The platform aims to safeguard workers' rights, create a stable working environment, and reduce illegal immigration.
- Coverage:
- The platform benefits foreign workers from 10 African countries (including Sudan, Ethiopia, Kenya) and 9 Asian countries (including India, Bangladesh, Pakistan, Vietnam, the Philippines, and Sri Lanka).
- Key Features:
- Employment Contract Access: Workers can check and track their employment contracts and receive updates via the Musaned labour app.
- Financial Transaction Tracking: The platform monitors financial transactions between employers and foreign workers, ensuring employers meet their contractual obligations.
- Integration with Benefits: Musaned can be linked to contract insurance and health benefits, providing additional protection for workers.
- Objectives:
- Wage Protection: Ensures timely and fair wages for foreign workers.
- Human Rights Protection: Promotes human rights by holding employers accountable for fulfilling their obligations.
- Vision 2030 Alignment: Supports Saudi Arabia’s Vision 2030 by improving the work environment and contributing to legal labor migration.
- Impact:
- The platform is expected to help secure workers’ rights, especially for domestic workers, and provide a more transparent, accountable framework for employment relations in the country.
Musaned is a significant step by Saudi Arabia to enhance the security and welfare of foreign workers, aligning with the Kingdom's broader goals of economic reform and social development under Vision 2030. The platform will provide greater transparency, protect workers’ rights, and contribute to a more regulated and sustainable labor market.
National Green Hydrogen Mission

- 19 Oct 2024
In News:
- The Union Government has sanctioned three pilot projects under the National Green Hydrogen Mission to explore the use of green hydrogen in steel production.
- The initiative aims to demonstrate safe and efficient hydrogen-based steelmaking processes, validate their technical feasibility, and evaluate economic viability for low-carbon steel production.
- Objectives of the Scheme:
- Identify and test advanced technologies for utilizing green hydrogen in the steel sector.
- Demonstrate safe and secure operation of hydrogen-based steel production.
- Validate technical and economic feasibility, contributing to decarbonization of iron and steel manufacturing.
- Pilot Project Components:
-
- 100% Hydrogen-based Direct Reduced Iron (DRI) using vertical shaft furnaces.
- Hydrogen use in Blast Furnace to reduce coal/coke consumption.
- Hydrogen injection in vertical shaft-based DRI units.
-
- Sanctioned Pilot Projects:
- Matrix Gas and Renewables Ltd
- Capacity: 50 tons per day (TPD).
- Consortium Partners: Gensol Engineering Ltd, IIT Bhubaneswar, Metsol AB (Sweden).
- Simplex Castings Ltd
- Capacity: 40 TPD.
- Consortium Partners: BSBK Pvt. Ltd., Ten Eight Investment, IIT Bhilai.
- Steel Authority of India Ltd (SAIL)
- Capacity: 3,200 TPD (Ranchi).
- Financial Support:
- Total Government Funding: ?347 crore for the three projects.
- These pilot projects are expected to be commissioned within the next three years and may serve as a blueprint for scaling up such technologies in India.
- About the National Green Hydrogen Mission:
- Launched: January 4, 2023.
- Total Budget: ?19,744 crore (up to FY 2029-30).
- Primary Goal: Establish India as a global hub for green hydrogen production and export while fostering decarbonization in sectors like steel, mobility, and energy.
- Key Features of the Mission:
- SIGHT (Strategic Interventions for Green Hydrogen Transition):
- Supports domestic manufacturing of electrolysers and promotes the production and use of green hydrogen.
- Expected Outcomes by 2030:
- Green Hydrogen Production: At least 5 million metric tons (MMT) annually.
- Renewable Energy: Addition of 125 GW in renewable energy capacity.
- Investment: Over ?8 lakh crore in green hydrogen technologies.
- Employment: Creation of 6 lakh jobs.
- Reduction in Fossil Fuel Imports: Savings of over ?1 lakh crore.
- GHG Emissions Reduction: Avoidance of nearly 50 MMT of annual greenhouse gas emissions.
- SIGHT (Strategic Interventions for Green Hydrogen Transition):
- Phase-wise Implementation:
- Phase I (2022-26): Focus on demand creation and initial deployment in existing hydrogen-using sectors (like steel and mobility).
- Phase II (2026-30): Expansion to new sectors with a push toward commercialization of green hydrogen.
The National Green Hydrogen Mission aims to significantly decarbonize India’s steel sector and other industries by leveraging hydrogen technology. With ?347 crore allocated for pilot projects in steelmaking, the initiative sets the stage for scalable, low-carbon steel production, contributing to India's clean energy transition and supporting its goal to become a global leader in green hydrogen.
Next Generation Missile Vessels (NGMV)

- 19 Oct 2024
In News:
GE’s LM2500 Marine Engines to Power Indian Navy’s Next Generation Missile Vessels (NGMV)
Key Highlights:
- Engine Selection:
- General Electric’s LM2500 marine gas turbines have been chosen to power the Indian Navy's Next Generation Missile Vessels (NGMV), currently being built by Cochin Shipyard Limited (CSL).
- Project Details:
- Number of Vessels: Six NGMVs are under construction.
- Contract Value: ?9,805 crore, awarded by the Defence Ministry.
- Delivery Schedule: The first deliveries are expected to commence in March 2027.
- Key Components and Suppliers:
- GE Aerospace will deliver six LM2500 engine kits to Hindustan Aeronautics Limited (HAL) for assembly and testing at their Industrial and Marine Gas Turbine Division in Bengaluru.
- GE will also supply the composite base, enclosure, and a full set of auxiliary systems for the gas turbines.
- LM2500 Marine Gas Turbine:
- The LM2500 turbine is known for its reliability and high power output, making it ideal for the NGMV mission.
- Top Speed: 35 knots (64 km/h).
- It is central to the propulsion system, meeting the stealth and power demands of the new missile vessels.
- Capabilities of NGMVs:
- Role: Designed for offensive missions, the NGMVs will be equipped for anti-surface warfare, maritime strike operations, and sea denial.
- Speed & Stealth: Capable of speeds up to 35 knots while maintaining stealth, these vessels will be difficult for enemy ships to detect.
- Weapons: They will carry a variety of anti-surface weapons, including the BrahMos supersonic cruise missile, loitering munitions, unmanned vehicles, and other guided weapons.
- Operational Roles:
- Offensive: The NGMVs will engage in attacking enemy warships, merchant ships, and land-based targets.
- Defensive: They will also be used for local naval defense operations, including the seaward defense of offshore development areas and defending choke points.
- Strategic Importance:
- The NGMVs will significantly enhance India’s maritime strike capability and provide a formidable presence in strategic sea routes, especially in regions like choke points and offshore development areas.
- Cochin Shipyard’s Role:
- After successfully constructing INS Vikrant, India’s first indigenous aircraft carrier, CSL is now focusing on the NGMV project, along with building anti-submarine warfare shallow water crafts for the Indian Navy, currently in various stages of construction.
- Partnerships:
- In 2023, GE Aerospace and HAL signed a Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) to expand their collaboration on marine gas turbines, including assembly, inspection, and testing (AIT) of the LM500 turbines.
- To date, GE Aerospace has delivered 24 marine gas turbine kits to HAL, supporting India’s Make-In-India initiative.
- Global Impact:
- The LM2500 gas turbine is used by 714 vessels globally, reinforcing its reputation for reliability and availability in critical maritime defense systems.
First Chief Minister of J&K UT Takes Charge
- 19 Oct 2024
In News:
Omar Abdullah sworn in as J&K CM; Surinder Kumar Choudhary is Deputy CM
Key Highlights:
- Omar Abdullah’s Political Context:
- This marks Omar Abdullah's second term as Chief Minister, after his tenure in 2009.
- He becomes the first Chief Minister of Jammu and Kashmir after the region’s special status was revoked and it was reorganized as a Union Territory in 2019.
- Challenges as CM of a Union Territory:
- Omar Abdullah acknowledged the unique challenges of serving as Chief Minister in a Union Territory and expressed hope that J&K’s Union Territory status would be temporary.
- Public Service and Security Measures:
- In his first official instructions, Abdullah asked the Director General of Police (DGP) to avoid creating “green corridors” or traffic halts during his movements. He also requested the minimization of sirens and aggressive security gestures, emphasizing minimal public inconvenience.
- Legal Context:
- Oath of Office: As per Article 164(3) of the Indian Constitution, the Chief Minister and other ministers are sworn in by the Governor or Lieutenant Governor in Union Territories.
- Abdullah is the first CM of the Union Territory of Jammu and Kashmir post the abrogation of Article 370 and the transition of J&K from a state to a Union Territory in 2019.
- Revocation of President's Rule:
- President’s Rule (under Article 356) was revoked following the election results, signaling the restoration of a functioning elected government after direct central governance in the region.
Karmayogi Saptah – National Learning Week

- 19 Oct 2024
In News:
Prime Minister Narendra Modi launched the ‘Karmayogi Saptah’ - National Learning Week on 19th October at Dr. Ambedkar International Centre, New Delhi.
Key Highlights:
- Context:
- The National Learning Week is a key event in the ongoing Mission Karmayogi initiative, aimed at building a civil service rooted in Indian ethos with a global outlook.
- Objective:
- To promote capacity building for civil servants through competency-linked learning.
- To align civil servants with national goals and foster a "One Government" approach.
- About National Learning Week (NLW):
- Largest learning event for civil servants, focused on individual and organizational growth.
- Encourages lifelong learning and continuous professional development.
- Provides fresh impetus to the Mission Karmayogi initiative, launched in September 2020, aimed at a future-ready, citizen-centric civil service.
- Learning Targets for Karmayogis:
- Each civil servant (Karmayogi) must complete at least 4 hours of competency-linked learning during the week.
- Learning opportunities include:
- Role-based modules on iGOT (Integrated Government Online Training platform).
- Webinars, public lectures, and policy masterclasses by prominent experts.
- Focus on improving skills for citizen-centric service delivery.
- Workshops & Seminars:
- Ministries, departments, and organizations organized domain-specific workshops and seminars.
- The goal is to enhance skills and knowledge, fostering better public service delivery.
- Outcomes:
- Strengthened alignment of civil servants with national priorities and goals.
- Enhanced individual competencies to better address citizen needs.
- A stronger commitment to continuous learning within the civil service.
Indian Development and Economic Assistance Scheme (IDEAS)

- 18 Oct 2024
In News:
- India has extended a ?487.60 crore Line of Credit (LoC) to Mauritius for financing a water pipeline replacement project.
- This initiative is part of the Indian Development and Economic Assistance Scheme (IDEAS), which supports developmental projects in partner countries through concessional loans.
About the IDEAS Scheme
- Origin: Launched in 2003-04 as the India Development Initiative, later renamed as IDEAS Scheme.
- Objective: To promote India’s political, economic, and strategic interests by providing developmental assistance to developing countries.
- Administering Body: The scheme is managed by the Ministry of External Affairs (MEA) with support from the Exim Bank.
Key Features of the IDEAS Scheme
- Lines of Credit (LoCs):
- Provides LoCs to developing countries for funding projects in various sectors, including:
- Infrastructure
- Water supply
- Education
- Other key developmental areas.
- Provides LoCs to developing countries for funding projects in various sectors, including:
- Project Recommendations:
- Projects funded under the scheme are recommended by MEA and are aimed at bolstering socio-economic development in the partner countries.
- Concessional Financing:
- The scheme offers concessional terms for the financing of these projects, reducing the financial burden on the recipient countries.
- Diplomatic and Strategic Benefits:
- The IDEAS scheme strengthens India’s diplomatic ties and fosters goodwill with countries in the Global South.
- Focus on Development:
- It aims to support key developmental goals in partner countries while advancing India's role as a leader in global development cooperation.
Significance
- The Mauritius water pipeline project is a part of the larger efforts under IDEAS to support infrastructure and socio-economic development in partner nations, helping to improve the quality of life and fostering closer bilateral relations.
Scam se Bacho Campaign

- 18 Oct 2024
In News:
Government and Meta join forces for "Scam se Bacho" Campaign to tackle rising online scams.
Key Details
- The "Scam Se Bacho" initiative aims to create a safer, more secure digital India by empowering users to protect themselves against growing cyber threats, contributing to the resilience of India’s digital progress.
- Objective: To combat rising online scams and cyber frauds by promoting digital safety and vigilance across India.
- Partners:
- Meta (formerly Facebook)
- Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology (MeitY)
- Ministry of Home Affairs (MHA)
- Ministry of Information and Broadcasting (MIB)
- Indian Cyber Crime Coordination Centre (I4C)
Purpose and Vision
- Goal: Empower Indian citizens with the knowledge and tools to protect themselves from online scams and cyber threats.
- Strategic Focus:
- Foster a culture of digital safety and vigilance.
- Align with the Digital India initiative, which has seen extraordinary growth in digital services, including 900 million internet users and leadership in UPI transactions.
- The campaign aims to build a national movement to safeguard citizens, emphasizing the importance of cyber literacy and digital security.
Key Points
- Growing Cybersecurity Threats:
- India has seen a surge in cyber frauds, with 1.1 million cases reported in 2023.
- The government is committed to addressing these threats through stronger cybersecurity measures and enhancing digital literacy.
- Meta’s Role:
- Meta’s global expertise in online safety will be leveraged to equip citizens with the knowledge to prevent cyber scams.
- Meta’s collaboration with the government aims to extend the reach of the campaign nationwide.
Features of the "Scam Se Bacho" Campaign
- Nationwide Reach:
- The initiative targets India’s 900 million internet users, making it a comprehensive national effort.
- Government Support:
- Backed by key ministries to ensure alignment with national digital and cybersecurity goals under Digital India.
- Whole-of-government approach to raise awareness on cyber safety.
- Educational Focus:
- The campaign emphasizes educating citizens on how to recognize and prevent online scams and threats.
Justice Sanjiv Khanna Appointed as Next Chief Justice of India

- 18 Oct 2024
In News:
Justice Sanjiv Khanna Appointed as Next Chief Justice of India, Will Assume Office on November 11
- Appointment:
- Justice Sanjiv Khanna has been appointed as the 51st Chief Justice of India by President Droupadi Murmu.
- He is set to take office on November 11, 2024, succeeding Chief Justice D.Y. Chandrachud, who is retiring on November 10, 2024.
- Tenure:
- Justice Khanna's tenure will be relatively short, lasting only six months, as he is scheduled to retire on March 13, 2025.
Career and Background
- Education and Early Career:
- Justice Khanna is a graduate of Delhi University’s Campus Law Centre.
- He enrolled as an advocate in 1983 and primarily practiced before the Delhi High Court.
- Prior to his elevation to the Delhi High Court in 2005, he served as the Senior Standing Counsel for the Income Tax Department and the standing counsel for civil matters for the Delhi government.
- Judicial Career:
- Supreme Court Appointment: Justice Khanna was appointed to the Supreme Court in January 2019, despite not having served as Chief Justice of a High Court. He was elevated over other senior judges from the Delhi High Court, such as Justices Rajendra Menon and Pradeep Nandrajog, whose names were initially recommended but not forwarded to the government.
- Key Contributions:
- Justice Khanna has been part of several significant rulings, including:
- February 2024: Part of the five-judge bench that struck down the Electoral Bond Scheme as unconstitutional.
- 2023: Contributed to upholding the abrogation of Article 370 of the Constitution.
- 2023: Authored a ruling granting the Supreme Court the power to directly grant divorce under Article 142 on the grounds of "irretrievable breakdown of marriage."
- Justice Khanna has been part of several significant rulings, including:
- Administrative Role:
- Justice Khanna currently serves as the Executive Chairman of the National Legal Services Authority (NALSA).
Process of Appointment of Chief Justice of India (CJI)
- Seniority Principle: The CJI is typically the senior-most judge of the Supreme Court.
- Memorandum of Procedure (MoP): The Law Ministry requests a recommendation from the outgoing CJI for his successor.
- Presidential Appointment: After receiving the recommendation, the President of India formally appoints the new CJI.
- Tenure and Retirement: The CJI serves until the age of 65. Upon retirement, the senior-most judge becomes the next CJI.
- Merit and Integrity Considerations: In addition to seniority, merit and integrity play crucial roles in the selection process for the CJI.
Hand-in-Hand Investment Forum

- 18 Oct 2024
In News:
Recently, the Director-General of the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) inaugurated the third Hand-in-Hand Investment Forum.
Purpose and Goals
- Objective: To accelerate the transformation of agrifood systems to address global challenges:
- Eradicate poverty (SDG 1)
- End hunger and malnutrition (SDG 2)
- Reduce inequalities (SDG 10)
- Target: Focuses on improving the lives of poor and vulnerable populations by:
- Raising incomes
- Enhancing nutritional status and overall well-being
- Strengthening resilience to climate change
Key Features of the HIH Initiative
- Launched: 2019 as a flagship program by the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO).
- Primary Focus Areas:
- Geospatial and analytics-driven approach: Utilizes advanced geospatial modeling, biophysical, socio-economic data, and analytics to identify key territories for intervention.
- Market-based transformation: Aims to create sustainable, market-based solutions for agricultural development and food systems transformation.
- Value Chain Development: Focus on developing value chains for priority commodities to boost incomes and food security.
- Agro-Industry Building: Strengthening agro-industries and introducing efficient water management and precision agriculture systems.
- Digitalization: Introducing digital services for better agricultural planning and productivity.
Key Areas of Intervention
- Agricultural Transformation: Identifying territories with the highest potential for transformation.
- Sustainable Management: Focus on sustainable practices in forestry, fisheries, and land management.
- Climate Resilience: Building systems to mitigate the effects of climate change and reduce vulnerability.
- Food Loss Reduction: Addressing food losses and waste across agricultural value chains.
Global Participation
- Member Countries: 72 countries have joined the initiative, collaborating on shared goals for agrifood systems transformation.
The Hand-in-Hand Investment Forum
- Purpose: A platform to mobilize investments for the successful implementation of agrifood transformation programs under the HIH initiative.
- Event: The third Hand-in-Hand Investment Forum was recently opened by the FAO Director-General to discuss challenges and solutions for global agrifood system transformation.
About the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO)
- Established: October 1945, it is the oldest permanent specialized agency of the United Nations.
- Mandate:
- Improve nutrition.
- Increase agricultural productivity.
- Raise the standard of living in rural areas.
- Contribute to global economic growth.
- Headquarters: Rome, Italy.
- Members: 194 Member States and the European Union.
Key Role of FAO:
- FAO leads international efforts to combat hunger and malnutrition worldwide.
- Supports member countries in implementing agricultural and food security programs.
Strategic Importance
- The Hand-in-Hand Initiative is integral to FAO’s mandate, focusing on countries with the most pressing needs due to poverty, hunger, or crises (natural or man-made).
- It enhances cooperation among nations to tackle global food security challenges, with a particular emphasis on countries with limited national capacities.
Strengthening Teaching-Learning and Results for States (STARS)

- 18 Oct 2024
In News:
The Department of School Education & Literacy (DoSE&L), Ministry of Education, hosted a two-day Strengthening Teaching-Learning and Results for States (STARS) knowledge sharing workshop in Bhopal, Madhya Pradesh.
- Event Overview:
- Two-day workshop hosted by the Department of School Education & Literacy (DoSE&L), Ministry of Education.
- Focus areas: School-to-Work Transition and Strengthening the Assessment System.
- Key Objectives:
- To enhance school-to-work transitions.
- To discuss strengthening educational assessment systems.
- Align education with future workforce needs as per the National Education Policy 2020.
Day 1: School-to-Work Transition
Panel Discussions:
- Policy Frameworks:
- Role of National Education Policy 2020, National Curriculum Framework (NCF), and National Credit Framework (NCrF) in school-to-work transitions.
- Focus on integrating skill education into school curricula, fostering multidisciplinary learning, and continuous evaluation to meet industry standards.
- Emphasis on internships, apprenticeships, and flexible learning pathways.
- Curriculum Integration:
- Need for integrated efforts across departments and aligning curriculum with industry demands.
- Focus on strengthening 21st-century skills in CBSE schools.
- Career Counselling and Psychometric Analysis:
- Focus on using psychometric assessments for career counselling and preparing students for future work environments.
- Work-Based Learning:
- Discussed partnerships with industry for work-based learning.
- Effective collaborations between schools and industry for internships, placements, and best practices.
Day 2: Strengthening Assessment System
- Psychometric Analysis & Career Counselling:
- Smt. Idzes Angmo Kundan (Principal Secretary, Maharashtra) presented the 3 P approach to career choices: Personal Interest, Parental Approach, and Possible Opportunities.
- Enhancing Student Outcomes:
- Discussed improving student outcomes by strengthening assessment systems.
- Shared innovations in educational assessments.
- Highlighted innovative assessment practices for future education.
- VSK Implementation (Chhattisgarh):
- Discussed VSK modes, data analysis, and strategies for integrating assessment outcomes with learning objectives.
- Strengthening Assessment Cells:
- Advocated for the establishment of assessment cells.
- Discussed best practices and challenges in strengthening assessment cells across states.
World Energy Outlook 2024

- 17 Oct 2024
In News:
The International Energy Agency's (IEA) World Energy Outlook 2024 offers an in-depth analysis of global energy trends, emphasizing the shift towards clean energy, growing energy demand, and the effects of geopolitical conflicts.
Key Highlights:
- Economic Growth:
- India was the fastest-growing major economy in 2023 with a 7.8% growth rate.
- On track to become the world’s third-largest economy by 2028.
- Surpassed China in 2023 to become the most populous country globally, despite a fertility rate below replacement level.
- Energy Demand Surge:
- India is projected to experience the highest increase in energy demand over the next decade.
- By 2035, India’s total energy demand is expected to rise by 35%, driven by rapid industrialization, urbanization, and increased living standards.
- Urbanization and Infrastructure Growth:
- Over 12,000 cars are expected to be added to Indian roads daily by 2035.
- Built-up space is set to increase by over 1 billion square meters annually, surpassing the total built space of South Africa.
- Industrial Expansion:
- Iron and steel production is expected to grow by 70% by 2035.
- Cement output is set to increase by 55%.
- Air conditioner stock to grow more than 4.5 times, with electricity demand from cooling expected to exceed Mexico’s total consumption in 2035.
- Energy Supply & Coal:
- India’s electricity generation capacity is projected to nearly triple to 1,400 GW by 2035.
- Coal remains a dominant energy source despite growth in renewables:
- Coal-fired power capacity will increase by 60 GW by 2030.
- Coal will continue to account for over 30% of electricity generation even as solar PV expands.
- By 2035, coal use in industries like steel and cement will grow by 50%.
- Renewable Energy & Clean Tech:
- India is on track to become a global leader in renewable energy, with a nearly 3x increase in electricity generation capacity.
- The country is expected to have the world’s third-largest installed battery storage capacity by 2030.
- By 2030, low-emission energy sources (solar, wind, nuclear) are expected to generate over 50% of India’s electricity.
- Electric Vehicles & Oil Demand:
- The rapid adoption of electric vehicles (EVs) is expected to peak India’s oil demand by the 2030s, reducing reliance on oil for transportation.
- Oil demand for transport will decline as EVs proliferate, though demand for oil in other sectors (e.g., petrochemicals) will continue.
- Net Zero Target:
- India aims to achieve net-zero emissions by 2070.
- By 2035, clean energy generation could be 20% higher than current policy projections, thanks to electric mobility, hydrogen use, and improved energy efficiency.
- CO2 emissions are projected to be 25% lower than under the Stated Policies Scenario (STEPS).
- Policy Support:
- India’s clean energy goals are backed by government initiatives, such as:
- PM-KUSUM scheme for solar energy in agriculture.
- National Solar Mission.
- Production Linked Incentive (PLI) Scheme to boost domestic solar PV manufacturing.
- India’s clean energy goals are backed by government initiatives, such as:
- Global Energy Trends:
- Geopolitical Risks: Global energy security remains affected by geopolitical tensions (e.g., Russia-Ukraine conflict, Middle East tensions).
- Energy Transition: Global shift toward clean energy, with solar and wind power investments accelerating.
- Oil & Gas Surplus: Oil and LNG supply expected to increase, putting downward pressure on prices by the late 2020s.
- Electric Mobility: EVs projected to account for 50% of new car sales by 2030.
- Energy Efficiency: Despite efforts, global targets for doubling energy efficiency by 2030 are unlikely to be met with current policies.
IEA Overview:
- The International Energy Agency (IEA) provides analysis and policy advice on energy security, economic development, and environmental sustainability.
- Established in 1974, it now includes 31 member countries and 13 association countries, including India.
- Major publications: World Energy Outlook, India Energy Outlook, World Energy Investment Report.
India’s Semiconductor Market Projected to Surpass $100 Billion by 2030
- 17 Oct 2024
In News:
India's semiconductor market is poised to exceed $100 billion by 2030, according to a report from the India Electronics and Semiconductor Association and Counterpoint Research. Currently valued at $45 billion in 2023, the market is projected to grow at an annual rate of 13%, driven by demand in mobile handsets and IT sectors, which together account for over 75% of revenues.
Key Highlights:
- Growth Drivers: The growth is supported by strong demand for electronics and government initiatives like the production-linked incentive scheme. Semiconductors are essential for various industries, including electronics, defense, healthcare, and automotive.
- Importance of Semiconductors: These materials, which include silicon and germanium, are crucial for electronic devices. They can conduct electricity under certain conditions, making them fundamental in transistors, integrated circuits, and devices like LEDs and solar cells.
- Global Context: The global semiconductor supply chain has shown vulnerabilities, particularly during the chip shortage of 2021. Major producers include Taiwan (44% market share), China (28%), South Korea (12%), the U.S. (6%), and Japan (2%). Countries are now focusing on building domestic chip industries to reduce dependency on a few key suppliers.
Factors Favoring India's Growth in Semiconductors:
- Skilled Workforce: India has a vast pool of STEM graduates, providing a skilled workforce for semiconductor manufacturing and design.
- Cost Advantage: Lower labor costs and efficient supply chains position India favorably for semiconductor manufacturing.
- Supply Chain Diversification: India is becoming a hub for back-end assembly and testing operations, with potential for front-end manufacturing.
- Government Support: Initiatives like Semicon India and the India Semiconductor Mission aim to create a robust semiconductor ecosystem, offering substantial fiscal incentives for companies.
Government Initiatives:
- Semiconductor Fab Scheme: Provides 50% project cost support for semiconductor manufacturing.
- Display Fab Scheme: Offers similar support for display manufacturing.
- Chips to Startup (C2S) Programme: Trains 85,000 engineers across academic and R&D institutions.
- Recent approvals for the establishment of semiconductor plants in Gujarat and Assam further bolster this initiative.
Nobel Prize for Economics 2024

- 17 Oct 2024
In News:
The winners of this year’s Economics Nobel, or the Sveriges Riksbank Prize awarded for economic sciences, Daron Acemoglu, Simon Johnson and James Robinson (AJR), pioneers in new institutional economics, emphasised the role of institutions in the direction of development.
The Great Divergence
- Definition: Refers to the economic and political development gap between the West and East, particularly during the 17th and 18th centuries.
- Key Factors:
- Industrialization in Western Europe enabled the projection of political power globally.
- Colonial institutions established during this period have long-lasting effects on post-colonial nations.
Role of Institutions in Development
- Nobel Prize Winners: Daron Acemoglu, Simon Johnson, and James Robinson (AJR) awarded for their work in new institutional economics.
- Institutions Defined: Set of rules constraining human behavior, ensuring law and order, and preventing coercion.
- Types of Institutions:
- Extractive Institutions: Concentrate wealth among elites, historically prevalent in colonized regions (e.g., Sub-Saharan Africa, Latin America).
- Inclusive Institutions: Promote broader participation in economic growth, more common in countries like the U.S., Canada, and Australia.
Research Contributions
- Natural Experiments: AJR used historical data to show how differing colonial practices influenced economic outcomes.
- Key Findings:
- Areas with landlord-based colonial systems had lower agricultural investment and productivity.
- Regions under direct colonial rule lagged in infrastructure like schools and health centers.
Implications of AJR's Work
- Economic Institutions: Reflect collective choices shaped by political power, which can be either de jure (formal) or de facto (informal).
- Challenges in Reform: Conflicting interests often hinder agreement on the nature of beneficial institutions.
Critical Perspectives
- Skepticism of AJR's Framework: Some scholars argue that AJR's emphasis on Western liberal institutions overlooks the complexities of historical contexts, including corruption and systemic inequalities in early U.S. history.
- Modern Economic Dynamics: AJR caution against assuming that inclusive institutions will automatically lead to prosperity, as evidenced by concerns regarding China's future growth under extractive political systems.
Insights from Nobel Prize Research
- Key Focus Areas:
- Institutional structures in colonized countries significantly shape economic prosperity.
- Example of Nogales, Arizona, and Nogales, Mexico illustrates the impact of institutions on economic opportunities.
About the Nobel Prize Recipients
- Daron Acemoglu:
- MIT professor and co-author of influential works on power and prosperity.
- Advocates for democracy's role in economic growth while acknowledging its challenges.
- Simon Johnson:
- Former IMF chief economist, current MIT professor.
- Emphasizes the complexity of addressing entrenched poverty due to institutional frameworks.
- James A. Robinson:
- University of Chicago professor, co-author of works on economic disparity.
- Highlights historical transitions toward inclusive societies and their importance in economic development.
Nobel Prize in Economic Sciences
- Established: 1968 by the Swedish central bank.
- Purpose: Complement existing Nobel Prizes, recognizing contributions to economic sciences.
- Notable Previous Laureates: Include Claudia Goldin (2023) for gender pay gap research and Abhijit Banerjee et al. (2019) for poverty alleviation studies.
SAMARTH Scheme

- 17 Oct 2024
In News:
Samarth is a demand-driven and placement-oriented umbrella skilling program of the Ministry of Textiles. Samarth Scheme has been extended for two years (FY 2024-25 and 2025-26) with a budget of Rs. 495 Crore to train 3 lakh persons in textile-related skills.
Key Details:
- Scheme Name: Samarth (Scheme for Capacity Building in Textile Sector)
- Nodal Ministry: Ministry of Textiles
- Extension Period: FY 2024-25 and 2025-26
- Budget: ?495 Crores
- Target: Train 3 lakh individuals in textile-related skills
Objectives
- Skilling Programs: Provide demand-driven, placement-oriented training.
- Industry Support: Encourage job creation in organized textile and related sectors.
- Skill Enhancement: Focus on upskilling and reskilling in traditional sectors (handloom, handicraft, silk, jute).
Implementation
- Implementing Partners:
- Textile Industry/Industry Associations
- Central/State government agencies
- Sectoral Organizations (e.g., DC/Handloom, Central Silk Board)
- Current Achievements:
- Total Trained: 3.27 lakh candidates
- Employment Rate: 2.6 lakh (79.5%) have secured jobs
- Women Empowerment: 2.89 lakh (88.3%) women trained
Scheme Features
- Coverage: Entire textile value chain, excluding spinning and weaving.
- Training Focus:
- Entry-level skilling
- Upskilling/reskilling existing workers in apparel and garmenting
- Beneficiaries: Handicraft artisans and job seekers in the textile sector.
Background
- Cabinet Approval: The scheme is a continuation of the Integrated Skill Development Scheme from the 12th Five Year Plan.
- Implementation Agency: Office of the Development Commissioner (Handicrafts).
Advancements of Research & Global Opportunities for Holistic Ayurveda - AROHA-2024

- 17 Oct 2024
In News:
All India Institute of Ayurveda, New Delhi is organising its first-ever international conference - Advancements of Research & Global Opportunities for Holistic Ayurveda - AROHA-2024.
Key Details:
- Theme: "Advancements in Research & Global Opportunities for Holistic Ayurveda"
- Conference Goals
- Position Ayurveda as a key pillar of global health and wellness.
- Facilitate dynamic exchanges among scholars, industry leaders, and practitioners.
- Explore the integration of traditional Ayurvedic wisdom with modern scientific advancements.
- Agenda Highlights
- Topics Covered:
- Ayurveda and ethnomedicine
- Quality control and standardization
- Diagnosis and drug delivery
- Evidence-based understanding and globalization
- Topics Covered:
- Institute Background
- All India Institute of Ayurveda (AIIA): Apex institute for Ayurveda with NAAC A++, NABH, and ISO accreditations.
- Facilities: 200-bed referral hospital, 44 specialty departments.
- Global Collaborations: Partnerships with institutions in 17 countries, including London School of Hygiene and Tropical Medicine and Western Sydney University.
- Innovations: Focus on research, drug development, and scientific validation of Ayurvedic practices.
- Participant Benefits
- Networking Opportunities: Engage with experts in Ayurveda and holistic healthcare.
- Learning Experiences: Attend plenary sessions, round table discussions, and exhibitions on medicinal plants and startups in Ayurveda.
- Recognition: Awards for contributions to Ayurveda.
- Research and Innovation Focus: Discussions on technology integration, including AI and bioinformatics.
DigiLocker Partners with UMANG
- 16 Oct 2024
In News:
The National e-Governance Division (NeGD) has announced the integration of the UMANG app with DigiLocker- India’s Digital Wallet. This collaboration aims to provide citizens with seamless access to a wide range of government services bringing greater convenience and allowing users to manage multiple services through a single platform.
UMANG app
- The UMANG app is accessible to all Android users with an expansion to iOS in the pipeline.
- The UMANG mobile app is an all-in-one single, unified, secure, multi-channel, multi-lingual, multi-service mobile app.
- It provides access to high-impact services of various organizations of the Union and States.
Simplified Citizen-Government interaction
This integration makes it easier for citizens to interact with the Government in an efficient, digital-first manner. DigiLocker has always been a pioneer in simplifying access to personal and official documents, and after integration with UMANG, it has expanded the range of services you can access on the go.
About DigiLocker
DigiLocker is a flagship initiative under the Digital India program aimed at providing secure cloud-based storage of essential documents. By integrating with e-governance services such as UMANG, DigiLocker further is committed to further enhance accessibility and ease of living.
World Food Day 2024

- 16 Oct 2024
In News:
World Food Day, observed annually on October 16, has its roots in the establishment of the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) by the United Nations in 1945.
Significance: World Food Day emphasizes the critical need to address global hunger and promote resilient food systems capable of overcoming challenges like climate change and economic disparities.
Introduction
- Food is vital for life, health, and well-being.
- Despite sufficient global food production, millions lack access to nutritious food.
- World Food Day serves as a reminder of ongoing challenges in achieving food security.
History and Theme
- Origins: Established by the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) in 1945, officially recognized in 1979.
- First Celebration: Took place in 1981 with the theme "Food Comes First."
- 2024 Theme: "Right to Food for a Better Life and a Better Future," highlighting that food security is essential for dignity and health. It emphasizes the need for sustainable practices and equitable distribution.
India’s Commitment to Food Security
- India has made significant strides in combating hunger through various programs aimed at malnutrition and poverty alleviation.
- Key initiatives include:
- National Food Security Act (NFSA): Provides subsidized food grains to 75% of the rural and 50% of the urban population, benefiting about 81 crore individuals.
- Pradhan Mantri Garib Kalyan Anna Yojana (PMGKAY): Offers free food grains to approximately 81.35 crore beneficiaries, extending support during the COVID-19 pandemic for an additional five years.
- PM POSHAN Scheme: Aims to improve children's nutritional status in government schools with a budget of ?12,467.39 crores for 2024-25.
- Antyodaya Anna Yojana (AAY): Focuses on the most vulnerable populations, supporting over 8.92 crore individuals and empowering women.
- Rice Fortification: Distribution of fortified rice through the Public Distribution System has improved nutritional intake for millions.
- Price Stability Initiatives: The government manages price volatility of essential commodities using the Price Stabilization Fund (PSF) and ensures affordability through strategic product launches.
Global Recognition of Indian Cuisine
- The Indian Thali has been recognized for its nutritional and sustainable qualities by the WWF Living Planet Report.
- Its plant-based composition contributes to lower resource use and reduced greenhouse gas emissions.
- If globally adopted, India’s dietary patterns could significantly lessen the environmental burden.
Significance
- India’s comprehensive initiatives reflect its dedication to food security and improving citizens' quality of life.
- By enhancing agricultural productivity and supporting vulnerable populations, India makes strides towards eradicating hunger.
- On World Food Day, these efforts underline India's commitment to achieving Sustainable Development Goal 2: Zero Hunger, while serving as a model for global food security initiatives.
PM GatiShakti National Master Plan

- 16 Oct 2024
In News:
- The Prime Minister commended the completion of three years of the PM GatiShakti National Master Plan, calling it a transformative initiative for India’s infrastructure development.
- Key Benefits: The plan enhances multimodal connectivity and improves efficiency across various sectors, contributing to logistics, job creation, and innovation.
Overview of PM GatiShakti National Master Plan
- Launch Date: October 2021
- Objective: A transformative initiative worth ?100 lakh crore aimed at revolutionizing India’s infrastructure over five years.
- Development Tool: Created as a Digital Master Planning tool by the Bhaskaracharya National Institute for Space Applications and Geoinformatics (BISAG-N).
- GIS Platform: Utilizes a dynamic Geographic Information System to integrate action plans from various ministries into a comprehensive database.
- Goals: Accelerate project completion, reduce timelines, and enhance India’s global competitiveness by addressing inter-ministerial challenges.
Key Features
- Digital Integration: A digital platform coordinating the efforts of 16 ministries for seamless infrastructure planning.
- Multi-Sector Collaboration: Incorporates initiatives from major programs like Bharatmala and Sagarmala.
- Economic Zones Development: Focuses on key areas such as textile clusters and pharmaceutical hubs to boost productivity.
- Technology Utilization: Employs advanced spatial planning tools and ISRO satellite imagery for data-driven project management.
Core Sectors Driving the Plan
- The National Master Plan is centered around seven primary sectors that enhance economic growth and connectivity, supported by sectors like energy transmission and social infrastructure.
Six Pillars of PM GatiShakti
- Comprehensiveness: Integrates various initiatives through a centralized portal, ensuring efficient planning.
- Prioritisation: Allows ministries to prioritize projects based on national importance and resource allocation.
- Optimisation: Identifies infrastructure gaps and selects the most efficient transportation routes.
- Synchronisation: Ensures coordinated efforts across ministries to avoid delays.
- Analytical Capabilities: Offers extensive data layers for improved spatial planning and decision-making.
- Dynamic Monitoring: Uses satellite imagery for real-time project tracking and adjustments.
Achievements of PM GatiShakti
- District-Level Expansion: Extended to 27 aspirational districts, with plans for 750 in the near future.
- Technological Integration: Enhanced real-time infrastructure planning using geospatial tools.
- Global Outreach: The GatiShakti tool showcased to 30 countries and highlighted at international conferences.
- Social Sector Benefits: Identified areas for new healthcare facilities and improved planning in various districts.
- Rural and Urban Development: Implemented projects for irrigation and city logistics in multiple states.
- Employment Initiatives: Utilized for setting up training institutes near industrial clusters.
Announcement of AI Centres of Excellence

- 16 Oct 2024
In News:
Union Minister for Education, Shri Dharmendra Pradhan, announced the establishment of three AI Centres of Excellence (CoE) focused on Healthcare, Agriculture, and Sustainable Cities in New Delhi.
Key Details:
- Establishment of Three AI-CoEs:
- Focus Areas:
- Healthcare: Led by AIIMS and IIT Delhi.
- Agriculture: Led by IIT Ropar, Punjab.
- Sustainable Cities: Led by IIT Kanpur.
- Collaboration: CoEs will work with industry partners and start-ups.
- Focus Areas:
- Financial Commitment:
- Total Approved Budget: ?990 crore for FY 2023-24 to FY 2027-28.
- Purpose: Support the establishment and operation of the CoEs.
- Vision and Impact:
- Pradhan emphasized the CoEs' role as solution providers for global public good.
- Expected to create a new generation of job and wealth creators.
- Aims to strengthen India's credentials in the global AI landscape.
- Leadership and Implementation:
- Apex Committee: Co-chaired by Shri Sridhar Vembu (Zoho CEO).
- Committee includes industry leaders and academic heads.
- Shri K. Sanjay Murthy highlighted the importance of interdisciplinary research and collaboration.
- Future Prospects:
- Dr. Vembu noted the CoEs will enhance the health of villages and cities, nurture talent, and generate opportunities.
- The initiative aligns with India's vision of "Viksit Bharat" (Developed India).
- Presentation and Film:
- Insights into the development of AI-CoEs presented by Smt. Saumya Gupta.
- A short film titled "Make AI in India and Make AI work for India" was showcased.
The establishment of these Centres of Excellence in AI signifies a major step toward fostering an effective AI ecosystem in India, aimed at developing scalable solutions and enhancing human resources in critical sectors.
International Abhidhamma Divas

- 16 Oct 2024
In News:
Recently, International Abhidhamma Divas was celebrated at Vigyan Bhavan, New Delhi, with PM Narendra Modi.
Key Details:
- India's Spiritual Legacy: Birthplace of Buddhism; site of Gautam Buddha's enlightenment.
- Sacred Sites: Veneration of locations like Bodh Gaya, symbolizing Buddha's journey and teachings.
- Core Teachings: Abhidhamma as a key philosophical component emphasizing mental discipline and self-awareness.
International Abhidhamma Divas
- Global Observation: Celebrates the significance of Abhidhamma in ethical conduct and mindfulness.
- Cultural Connection: Highlights India's role in preserving Buddhism and bridging ancient wisdom with contemporary practices.
Historical Background and Significance
- Commemoration: Marks Buddha’s descent from T?vati?sa to Sankassiya (Sankisa Basantapur).
- Teaching Period: Buddha taught the Abhidhamma to deities for three months; linked to the end of the Rainy Retreat and the Pav?ra?? festival.
Teachings of Abhidhamma
- Systematic Analysis: Provides a detailed exploration of mind and matter, differing from Sutta Pi?aka.
- Specialized Vocabulary: Key terms include "citta" (consciousness), "cetasika" (mental factors), "r?pa" (materiality), and "nibb?na" (liberation).
- Textual Framework: Six core books of Abhidhamma Piñaka cover moral states, aggregates, and causal relationships.
- Key Treatise: The Paññh?na offers in-depth causal analysis, essential for practitioners’ understanding.
Modern Observance and Celebrations
- Significance of Pali: Recognition of Pali as a classical language; promoting India's Buddhist heritage.
- Participants: Gathering of ambassadors, monks, scholars from 14 countries; emphasizes Abhidhamma's relevance today.
- Program Highlights: Dhamma discourse, academic sessions on Abhidhamma’s significance, exhibitions on Pali's evolution and Buddha's teachings.
Classical Status of Pali Language
- Pali's Role: Sacred language for delivering Buddha's teachings; recognized as a Classical Language by India.
- Buddhist Canon: Major texts include the Tipitaka (Vinaya, Sutta, Abhidhamma Pitaka) and commentarial traditions.
- Literary Heritage: Jataka Kathas reflect shared moral values; status enhances Pali studies in education and research.
Significance
- Significance of Celebration: Abhidhamma Divas underscores efforts to preserve and promote Buddhism’s legacy.
- Revitalization of Buddhism: Fosters global engagement and appreciation for Buddha’s teachings, reaffirming India's role in Buddhist studies.
e-Migrate Portal

- 15 Oct 2024
In News:
Recently, the Union Ministers for External Affairs and Labour and Employment launched the upgraded e-Migrate portal and mobile app, aimed at enhancing the migration experience for Indian workers seeking employment abroad. This initiative reflects the Indian government's commitment to ensuring the safety and welfare of its migrant workforce, aligning with global migration goals under the 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development.
About e-Migrate Portal
The e-Migrate portal is an online platform designed to facilitate and manage the migration of Indian workers. It promotes safe and legal mobility channels by providing a transparent framework for migrant workers, including:
- Information Access: Comprehensive resources to help migrants understand the migration process.
- Documentation Support: Tools to assist with necessary paperwork.
- Helpline Support: A 24/7 multilingual helpline that addresses issues faced by workers, particularly in the Gulf region.
- Awareness Campaigns: Initiatives to educate workers about their rights and responsibilities abroad.
The upgraded version of the portal, launched in October 2024, features enhanced functionality to better serve Indian migrants.
Key Features of e-Migrate v2.0
- Multilingual Helpline: Offers real-time support in multiple languages, ensuring that urgent issues are resolved efficiently.
- Integration with Digilocker: Facilitates secure, paperless submission of essential documents, such as passports and employment contracts.
- Social Security Net: Enhances social security measures for migrants, including insurance policies and partnerships with the State Bank of India for fee-free digital payment services.
- Mobile App: Introduced for the first time, this app provides easy access to services, including a job search marketplace for overseas employment opportunities.
- Rural Accessibility: Collaboration with Common Service Centres (CSCs) aims to expand immigration services to rural areas in local languages, making the platform more accessible to diverse populations.
Significance
The e-Migrate portal aligns with the United Nations' Sustainable Development Goal 10, which promotes orderly and responsible migration. By fostering safe migration practices, this initiative seeks to empower Indian workers and protect their rights while contributing to the country's international workforce.
Mission for Advancement in High-Impact Areas - Electric Vehicle (MAHA-EV) Mission

- 15 Oct 2024
In News:
The Anusandhan National Research Foundation (ANRF) has officially launched its first two initiatives: the Prime Minister Early Career Research Grant (PMECRG) and the Mission for Advancement in High-Impact Areas - Electric Vehicle (MAHA-EV) Mission. These initiatives aim to enhance India’s research landscape and support innovation in critical sectors.
Prime Minister Early Career Research Grant (PMECRG)
- Objective: The PMECRG is designed to empower early career researchers by providing flexible funding and support for high-quality innovative research. It aims to foster creativity and drive technological progress, positioning India as a global leader in science and technology (S&T).
- Significance: This grant recognizes the essential role of young researchers in advancing India's scientific agenda. By investing in their development, ANRF aims to cultivate a vibrant research ecosystem that encourages groundbreaking discoveries.
Mission for Advancement in High-Impact Areas - Electric Vehicle (MAHA-EV) Mission
- Focus: The MAHA-EV Mission targets the development of key technologies for electric vehicles, specifically in areas such as tropical EV batteries, power electronics, machines and drives (PEMD), and charging infrastructure.
- Goals:
- Reduce Import Dependency: By fostering domestic innovation in EV components.
- Global Leadership: Positioning India as a leader in the electric vehicle sector, aligning with the government's Atmanirbhar Bharat (self-reliant India) vision.
- Collaboration: The mission is designed to encourage multi-institutional and multi-disciplinary collaboration to address critical scientific challenges, thereby enhancing the competitiveness of India's EV sector.
Significance of Both Initiatives
- Bridging Gaps: Both initiatives aim to bridge the gap between academic research and industrial applications, a key goal of ANRF. This alignment is crucial for translating research into practical applications that benefit society.
- Strategic Interventions: These programs reflect the discussions held during the ANRF's Governing Board meeting, which emphasized global positioning in key sectors, capacity building, and fostering an innovation ecosystem.
- Long-term Vision: The initiatives contribute to India's goal of achieving a Viksit Bharat (Developed India) by 2047, accelerating the country's progress toward a sustainable and technologically advanced future.
The launch of the PMECRG and MAHA-EV Mission marks a significant step in enhancing India's research ecosystem. By supporting early career researchers and advancing electric vehicle technologies, ANRF is poised to drive innovation, foster collaboration, and strengthen India’s position on the global scientific stage. These initiatives reflect a commitment to sustainable development and technological leadership, paving the way for transformative advancements in various sectors.
Haber-Bosch process
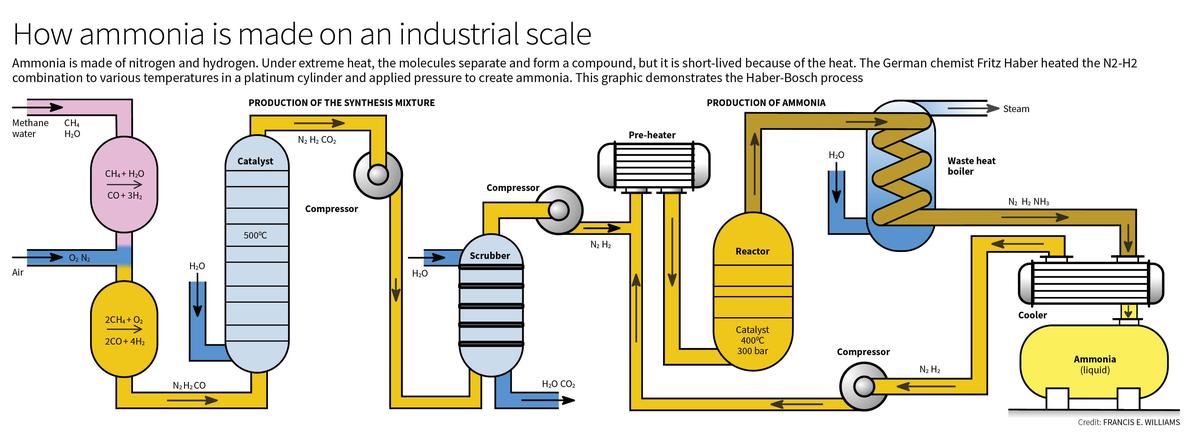
- 15 Oct 2024
In News:
The Haber-Bosch process has fundamentally transformed agricultural practices and global food production, enabling the conversion of atmospheric nitrogen into ammonia, which is essential for fertilizers.
The Nitrogen Molecule
- Composition: Nitrogen primarily exists as molecular nitrogen (N?) in the atmosphere, where two nitrogen atoms are bonded with a strong triple bond. This bond is very stable and requires significant energy (946 kJ/mol) to break, rendering N? largely inert and unavailable for direct use by plants.
Nitrogen in Nature
- Natural Fixation: In nature, the energy required to break the N? bond is typically provided by phenomena like lightning, which converts nitrogen to reactive forms such as nitrogen oxides (NO and NO?). These can subsequently form nitric acid when they react with water, depositing reactive nitrogen through rainfall.
- Microbial Processes: Certain bacteria, including Azotobacter and Rhizobia, can fix atmospheric nitrogen into reactive forms, supporting plant growth. Azolla, a fern with a symbiotic cyanobacterium, also helps in nitrogen fixation.
The Nitrogen Cycle
- Plant Uptake: Plants absorb reactive nitrogen in the form of ammonium (NH??) and nitrate (NO??) from the soil, essential for synthesizing proteins and other vital compounds. Humans and animals rely on plants for their nitrogen intake.
- Cycle Completeness: While nitrogen is returned to the soil through excretion and decomposition, some is lost back to the atmosphere as N?. This loss contributes to the depletion of soil nitrogen, especially in crops that do not fix their own nitrogen.
Ammonia Production
- Haber-Bosch Process: This process synthesizes ammonia from nitrogen and hydrogen under high pressure and temperature, using a catalyst to enhance efficiency. Initially developed by Fritz Haber and scaled by Carl Bosch, this method became the backbone of modern fertilizer production.
Benefits and Downsides of Fertilizers
- Food Security: The Haber-Bosch process has significantly increased food production, contributing to a remarkable rise in global food supply and preventing widespread hunger. It is estimated that one-third of the world’s population relies on fertilizers produced via this process for their food.
- Environmental Impact: The widespread use of nitrogen fertilizers can lead to environmental issues:
- Excess Nutrients: Over-application can result in nutrient runoff into water bodies, causing eutrophication, which depletes oxygen and harms aquatic life.
- Acid Rain: Reactive nitrogen can contribute to acid rain, affecting soil health and biodiversity.
- Soil Degradation: Continuous fertilizer use without adequate replenishment of nutrients can degrade soil quality over time.
While the Haber-Bosch process is crucial for modern agriculture and food security, it also presents significant environmental challenges. The balance between using fertilizers effectively and sustainably is essential to ensure that technological advancements do not come at the cost of ecological health. As such, addressing food security requires not just technological innovation, but also thoughtful political and social engagement to manage resources responsibly.
India's Renewable Energy Capacity Hits 200 GW Milestone
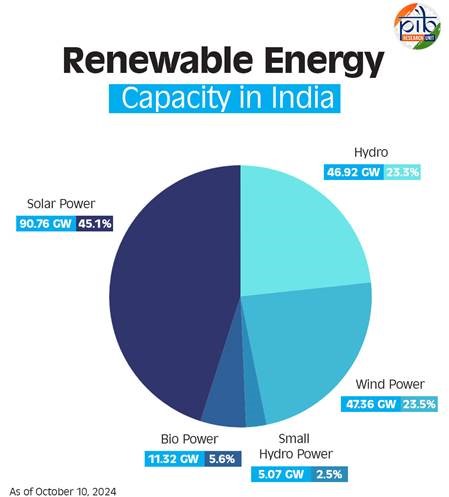
- 15 Oct 2024
In News:
India has recently celebrated a landmark achievement in its renewable energy sector, with its total renewable energy capacity surpassing 200 GW as of October 10, 2024. This milestone, reported by the Central Electricity Authority, showcases the country’s growing commitment to clean energy and its strategic shift towards a more sustainable future.
Overview of India’s Renewable Energy Landscape
As of October 2024, India's total electricity generation capacity stands at 452.69 GW, with renewable sources contributing a substantial 201.45 GW, representing 46.3% of the overall capacity. This shift highlights India’s increasing reliance on cleaner, non-fossil fuel energy.
Key contributors to this capacity include:
- Solar Power: Leading with 90.76 GW, capitalizing on India's abundant sunlight.
- Wind Power: Following closely at 47.36 GW, leveraging the country’s vast wind corridors.
- Hydropower: Large hydro projects add 46.92 GW, while small hydro contributes an additional 5.07 GW.
- Biopower: Incorporating biomass and biogas energy, contributing 11.32 GW.
Together, these resources are pivotal in reducing dependence on fossil fuels and enhancing energy security.
Leading States in Renewable Energy Capacity
Certain states are at the forefront of this renewable energy expansion:
- Rajasthan: 29.98 GW, benefiting from ample land and sunlight.
- Gujarat: 29.52 GW, driven by robust solar and wind initiatives.
- Tamil Nadu: 23.70 GW, utilizing favorable wind conditions.
- Karnataka: 22.37 GW, supported by a mix of solar and wind projects.
Key Schemes and Programs
The Indian government has introduced numerous initiatives to accelerate renewable energy capacity, aiming for 500 GW from non-fossil sources by 2030. Notable programs include:
- National Green Hydrogen Mission
- PM-KUSUM Scheme
- PM Surya Ghar Scheme
- Production-Linked Incentive (PLI) for solar PV modules
These efforts reflect the government's commitment to fostering a sustainable energy future while addressing the challenges posed by climate change and energy security. Here are some other ongoing key initiatives:
- Notification of a trajectory for renewable energy power bids of 50 GW per annum by Renewable Energy Implementation Agencies (REIAs) from FY 2023-24 to FY 2027-28.
- Foreign Direct Investment permitted up to 100 percent under the automatic route to attract investments.
- Waiver of Inter-State Transmission System charges for solar and wind power projects commissioned by June 30, 2025; green hydrogen projects until December 2030; and offshore wind projects until December 2032.
- Announced Renewable Purchase Obligation trajectory until 2029-30, including separate RPO for Decentralized Renewable Energy.
- A Project Development Cell has been established to attract and facilitate investments in the renewable sector.
- Standard Bidding Guidelines issued for tariff-based competitive bidding for procurement of power from grid-connected solar, wind, and wind-solar projects.
- Ultra Mega Renewable Energy Parks are being set up to provide land and transmission for large-scale renewable energy projects.
- Cabinet approval for a Viability Gap Funding scheme for offshore wind energy projects, facilitating the installation and commissioning of 1 GW of offshore wind energy capacity along the coasts of Gujarat and Tamil Nadu.
- Issued Electricity (Rights of Consumers) Rules, 2020, for net-metering up to 500 kilowatts or the electrical sanctioned load, whichever is lower.
- The “National Repowering and Life Extension Policy for Wind Power Projects, 2023” has been released.
- “Strategy for Establishment of Offshore Wind Energy Projects” outlines a bidding trajectory of 37 GW by 2030.
- Offshore Wind Energy Lease Rules, 2023, notified to regulate the grant of leases for offshore wind energy development.
- Procedure for Uniform Renewable Energy Tariff (URET) has been established.
- Standard & Labelling (S&L) programs for Solar Photovoltaic modules and grid-connected solar inverters have been launched.
- A transmission plan has been prepared to augment transmission infrastructure until 2030.
- The Electricity (Late Payment Surcharge and Related Matters) Rules have been notified.
- Green Energy Open Access Rules 2022 have been issued to promote renewable energy.
- Launched the Green Term Ahead Market (GTAM) to facilitate the sale of renewable energy power through exchanges.
- Orders issued to ensure that power is dispatched against Letters of Credit or advance payment for timely payments to renewable energy generators.
ITU World Telecommunication Standardization Assembly 2024

- 15 Oct 2024
In News:
- Prime Minister Narendra Modi inaugurated ITU WTSA 2024 and India Mobile Congress 2024, at Bharat Mandapam, New Delhi.
- First Time in India: WTSA hosted for the first time in India and the Asia-Pacific region.
- Participants: Over 3,000 industry leaders, policy-makers, and tech experts from more than 190 countries expected.
ITU WTSA 2024
- Significance: Governing conference for the standardization work of the International Telecommunication Union (ITU), held every four years.
- Focus Areas: Discussion on standards for next-generation technologies including:
- 6G
- Artificial Intelligence (AI)
- Internet of Things (IoT)
- Big Data
- Cybersecurity
- Opportunities for India: Enhances India’s role in shaping the global telecom agenda; insights into Intellectual Property Rights and Standard Essential Patents for startups and research institutions.
India Mobile Congress 2024
- Theme: "The Future is Now"
- Technological Focus: Highlight advancements in:
- Quantum Technology
- Circular Economy
- 6G and 5G use cases
- Cloud and Edge Computing
- IoT and Semiconductors
- Cybersecurity
- Green Technology
- Satellite Communication and Electronics Manufacturing
Importance for India
- Showcase of Innovation: A platform for India’s innovation ecosystem, demonstrating advancements in digital technology.
- Global Collaboration: Facilitates collaboration between government, industry, and academia to address global telecommunication challenges.
THAAD Missile Defence System

- 14 Oct 2024
In News:
The US pledged its THAAD missile defence system as well as several troops to Israel after Iran warned the country to not get involved.
In a new boost to Israeli forces, the United States will send a Terminal High Altitude Area Defence battery (THAAD) and troops to Israel amid its ongoing offensive against the Hezbollah.
THAAD battery:
- The Terminal High Altitude Area Defence system (THAAD) is an American anti-ballistic missile defence system. It can shoot down short, medium and intermediate range missiles in it's sphere.
- The THAAD has a “hit to kill” approach which blasts missiles as they before they enter their target zone during their descent.
- The THAAD was developed by the US after their experience of Iraq's Scud missile attacks during the Persian Gulf War in 1991. Out of a total of 88 Scud missiles, Iraq fired 42 into Israel and 46 into Saudi Arabia, killing many American soldiers in barracks as well.
- The first proposal for the THAAD was submitted to the US Defence Ministry in 1987 and a series of tests resulting in failures, finally led to a successful version in 1999.
- In 2008, the US deployed an early missile warning radar, a part of the THAAD system to Israel. Similar deployments were also made in 2012 and 2019, aiding Israel's ability to emerge as a military power in the Middle East.
Ladakh's Aurorae

- 14 Oct 2024
In News:
In October 2024, Ladakh witnessed spectacular auroras, typically seen in higher latitudes, indicating increased solar activity. This phenomenon was reported following intense solar storms, with red and green lights observed in the night sky. The auroras were captured by all-sky cameras operated by the Indian Institute of Astrophysics (IIA) in Hanle and Merak.
What Are Auroras?
Auroras are vibrant displays of light caused by interactions between charged particles from the Sun and Earth's magnetosphere. When solar winds—streams of charged particles—collide with atoms in the upper atmosphere, they create visible light, similar to how neon lights function.
Causes of Recent Auroras
The recent auroras in Ladakh were linked to several strong solar storms, particularly coronal mass ejections (CMEs), which are significant bursts of solar wind and magnetic fields rising above the solar corona. The storms, emanating from active solar regions, traveled towards Earth at remarkable speeds, disrupting the normal space weather and allowing auroras to be visible at lower latitudes, including Mexico and Germany.
Implications of Solar Activity
Astrophysicists at the Center of Excellence in Space Sciences India (CESSI) noted that these auroras validate ongoing efforts in space weather monitoring. The increased solar activity is part of the solar cycle, which peaks approximately every 11 years. Current predictions indicate that Solar Cycle 25 may reach its peak in 2024.
Monitoring Space Weather
Organizations like the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) closely monitor space weather to provide timely warnings about solar events that could disrupt satellite communications and other services. The CESSI team successfully predicted the occurrence of solar storms, enhancing confidence in their ability to forecast space weather and its potential impacts.
Potential Hazards
While auroras are visually striking, intense solar storms can have detrimental effects, including:
- Satellite Disruption: Increased drag and radiation can damage satellites in low Earth orbit, affecting navigation, communications, and military operations.
- Communication Blackouts: Severe storms can interfere with radio and satellite communications, impacting daily life and services.
Wayanad’s New X-Band Radar

- 14 Oct 2024
In News:
- Following devastating floods and landslides in July 2024 that resulted in over 200 fatalities in Wayanad, Kerala, the Union Ministry of Earth Sciences approved the installation of an X-band radar to enhance monitoring and early warning systems.
- Impact of Events: The floods were exacerbated by heavy rains, leading to significant debris flows and landslides, highlighting the need for advanced meteorological tools.
What is Radar?
- Definition: Radar stands for "Radio Detection and Ranging." It uses radio waves to determine the distance, velocity, and characteristics of objects.
- Functioning: A transmitter emits radio signals that reflect off objects, returning to a receiver for analysis. This technology is crucial in meteorology for monitoring weather patterns.
X-Band Radar Specifics
- Operating Frequency: X-band radar operates at 8-12 GHz, corresponding to wavelengths of 2-4 cm. This allows it to detect smaller particles, such as raindrops and soil.
- Advantages: The shorter wavelengths provide higher resolution images but have a limited range due to faster signal attenuation.
- Applications: In Wayanad, the radar will monitor particle movements like soil, enabling timely landslide warnings through high temporal sampling.
India’s Radar Network
- Historical Context: India has utilized radar for meteorological purposes since the early 1950s. The first indigenous X-band radar was established in 1970.
- Current Infrastructure: India operates both X-band and S-band radars (2-4 GHz) for various meteorological functions. The X-band network includes storm detection and wind-finding capabilities.
- Future Plans: The Indian government plans to add 56 more Doppler radars under the ?2,000-crore "Mission Mausam," enhancing weather forecasting capabilities across the country.
NISAR Satellite
- Collaboration: NISAR (NASA-ISRO Synthetic Aperture Radar) is a joint satellite project between NASA and ISRO, set to launch in 2025.
- Capabilities: It will feature L-band and S-band radars to monitor Earth’s landmass changes, further supporting environmental monitoring and disaster management.
Global Hunger Index 2024
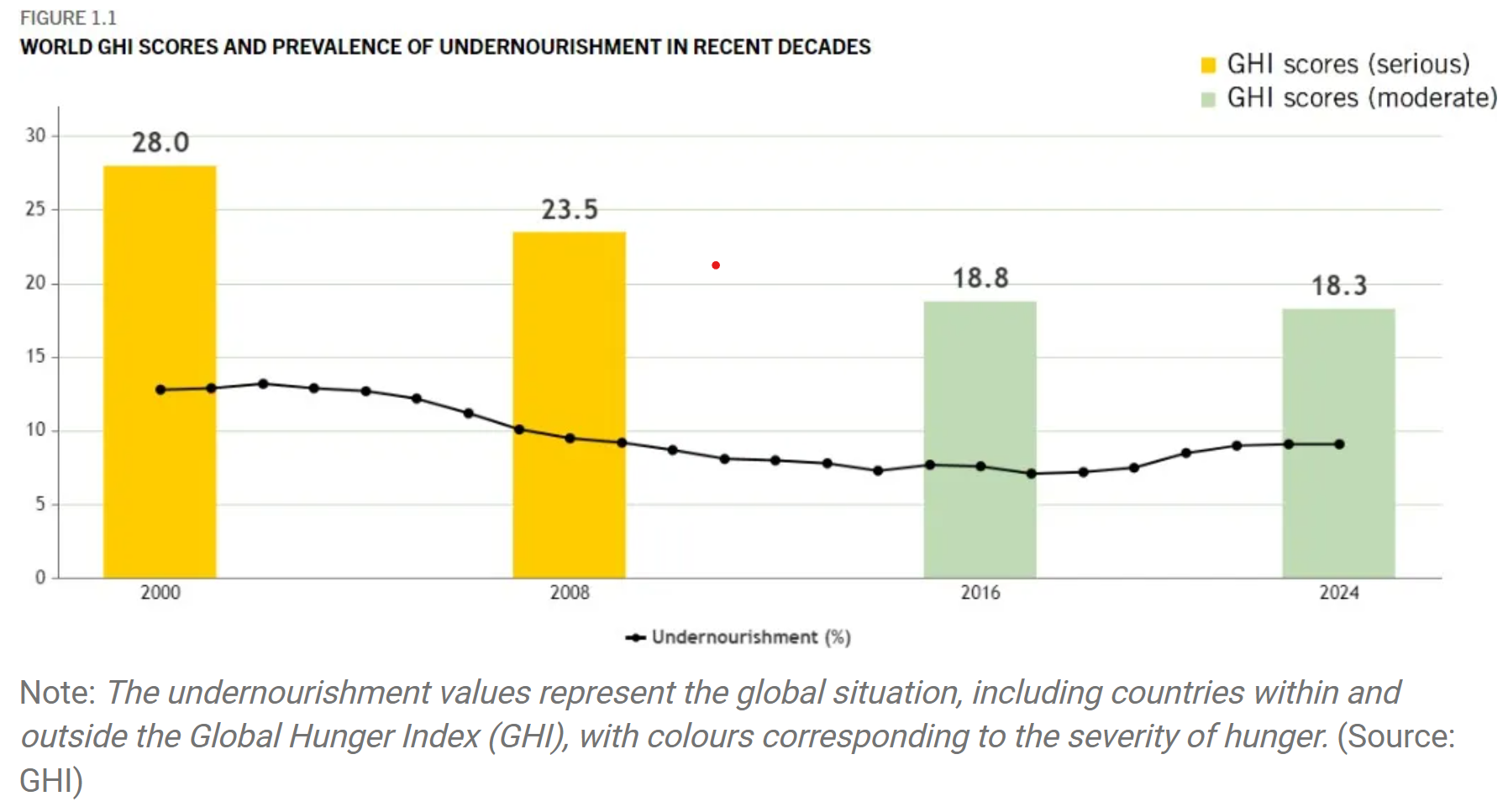
- 14 Oct 2024
In News:
The 2024 Global Hunger Index (GHI) emphasizes food as a fundamental human right, alongside air and water.
Key Highlights:
- Current Crisis: Despite adequate food production globally, around 350 million people face extreme hunger, with 49 million on the brink of famine.
- Statistics: Over 820 million people are chronically undernourished, and malnutrition claims the lives of five million children under five each year.
Top 10 Countries Most Affected by Hunger (2024)
- Somalia: GHI Score 44.1 (GHI 2000: 63.3)
- Yemen: GHI Score 41.2 (GHI 2000: 41.6)
- Chad: GHI Score 36.4 (GHI 2000: 50.5)
- Madagascar: GHI Score 36.3 (GHI 2000: 42.3)
- Democratic Republic of the Congo: GHI Score 34.9 (GHI 2000: 47.2)
- Haiti: GHI Score 34.3 (GHI 2000: 39.8)
- Niger: GHI Score 34.1 (GHI 2000: 53.1)
- Liberia: GHI Score 31.9 (GHI 2000: 48.0)
- Central African Republic: GHI Score 31.5 (GHI 2000: 48.0)
- Korea (DPR): GHI Score 31.4 (GHI 2000: 43.7)
India's Position
- Ranking: India ranks 105th in the GHI 2024, categorized as having a "serious" hunger situation.
- GHI Score: India’s score stands at 27.3, showing some improvement from a score of 38.4 in 2000 (previously classified as "alarming").
Key Concerns in India
- Undernourishment: 13.7% of the population is undernourished.
- Child Stunting: 35.5% of children under five are stunted.
- Child Wasting: 18.7% of children under five experience wasting.
- Child Mortality: 2.9% of children do not survive to age five.
Global Hunger Index (GHI):
A tool measuring hunger across countries based on four indicators:
-
- Undernourishment
- Child Wasting
- Child Stunting
- Child Mortality
- Data Sources: The GHI is based on data from credible organizations like the FAO, WHO, and UNICEF, as well as government surveys.
Hunger Indicators Explained
- Undernourishment: Reflects the overall food access situation.
- Child Wasting: Indicates acute malnutrition; a critical health issue.
- Child Stunting: Reflects chronic malnutrition; significant public health concern.
- Child Mortality: Represents the most severe consequence of hunger.
The 2024 GHI report reveals that while progress has been made in addressing hunger globally, significant challenges remain, particularly in countries like India and the most affected nations. Addressing these issues is crucial for achieving the goal of zero hunger by 2030.
Jipmer Launches ‘Tele-MANAS’ Mental Health Helpline

- 14 Oct 2024
In News:
- Jipmer (Jawaharlal Nehru Institute of Postgraduate Medical Education and Research) has launched the "Tele-MANAS" (Tele Mental Health Assistance and Networking Across States) helpline, a toll-free service (14416) aimed at providing mental health support.
- This initiative is part of the National Tele Mental Health Programme (NTMHP), launched by the Union Ministry of Health and Family Welfare.
Purpose and Need:
- With an estimated 1 in 10 people in India suffering from mental illness, and about 1% experiencing severe conditions, the service addresses significant gaps in mental health access, particularly in rural and remote areas.
- The helpline aims to provide immediate support for issues such as anxiety, depression, and emotional distress.
Training and Operations:
- Jipmer will train qualified counsellors who will subsequently train additional counsellors to expand the reach of the service.
- Counselors will be available 24/7, including holidays, to ensure continuous support.
Support Structure:
- Trained counselors will serve as the first point of contact for individuals seeking help, providing responses, suggestions, and necessary referrals to advanced mental health facilities.
- Jipmer will supervise the program, ensuring regular retraining and maintaining service quality.
Integration with National Programs:
- The initiative is coordinated by the National Institute of Mental Health and Neuro Sciences (NIMHANS), which acts as the National Apex Centre for the NTMHP.
- It includes a comprehensive information library on mental health and guidance for managing early signs of stress and emotional challenges.
Impact on Mental Health Services:
- The program aims to enhance the overall quality of mental health services across states and union territories in India, making them more accessible to a larger population.
- Emphasizes the importance of mental health as a public health priority.
South Karanpura Coalfield
- 11 Oct 2024
In News:
Recent research has highlighted significant shale gas generation potential in the eastern region of the South Karanpura coalfield, located in the Ramgarh district of Jharkhand, India. Evidence from microscopic palynomorphs and organic remains, combined with geochemical assessments, indicates that the eastern Sirka coalfield demonstrates a higher potential for hydrocarbon generation compared to the Giddi coalfield to the north.
Overview of the South Karanpura Coalfield
- Location and Size: The South Karanpura coalfield is situated along the Chingara fault and covers approximately 195 square kilometers, housing an estimated 5,757.85 million tonnes of coal reserves.
- Composition: This region is rich in coal, carbonaceous shale, and sandstone layers, making it well-established for its substantial coal deposits.
- Emerging Focus: With increasing energy demands and interest in hydrocarbon exploration, there is a growing emphasis on the potential for coal bed methane and shale gas generation in this area, aligning with national energy strategies for greener energy sources.
Research Methodology
Scientists from the Birbal Sahni Institute of Palaeosciences (BSIP) conducted a comprehensive study to evaluate hydrocarbon generation potential. The research involved:
- Sample Collection: Sediments were collected from coal, carbonaceous shale, and sandstone layers at the Sirka and Giddi C collieries in Hazaribagh district.
- Analysis Techniques: The study utilized palynological analysis of microscopic remains, alongside Rock-Eval pyrolysis to assess the potential of the rock samples. Key parameters analyzed included:
- Palynofacies
- Free hydrocarbons (S1)
- Heavy hydrocarbons (S2)
- Pyrolyzable carbon (PC)
- Residual hydrocarbon (RC)
The collected samples, which date back to the Permian (Barakar) period, indicate favorable conditions for high hydrocarbon resource potential in the eastern South Karanpura coalfield.
Shale Gas Overview
Shale gas is an unconventional natural resource found at depths of 2,500 to 5,000 meters, deeper than conventional crude oil. Its extraction involves deep vertical drilling followed by horizontal drilling, with hydraulic fracturing (fracking) being the most common method used to access gas trapped in low-permeability rocks.
New Cancer Therapy Target
- 11 Oct 2024
In News:
Scientists have identified a promising new target for cancer treatment by activating a DNA repair enzyme called TDP1. This approach suggests a combination therapy that could serve as a potential precision medicine for patients resistant to current treatments.
- Current Treatment Limitations:
- Existing anticancer drugs (e.g., Camptothecin, Topotecan, Irinotecan) target Topoisomerase 1 (Top1), essential for DNA replication and transcription.
- Cancer cells frequently develop resistance to these single-agent therapies, necessitating alternative treatment strategies.
- Research Insights:
- Conducted by scientists at the Indian Association for the Cultivation of Science (IACS), Kolkata, under the Department of Science and Technology (DST).
- The study focused on how cancer cells repair DNA during cell division and respond to chemotherapy targeting Top1.
- Key Findings:
- The research, published in The EMBO Journal 2024, highlights two critical proteins:
- Cyclin-dependent kinase 1 (CDK1)
- Tyrosyl-DNA phosphodiesterase 1 (TDP1)
- CDK1 regulates the DNA repair process, while TDP1 helps cancer cells survive by repairing drug-induced Top1 damage.
- The research, published in The EMBO Journal 2024, highlights two critical proteins:
- Mechanism of Action:
- TDP1 repairs Top1 that is trapped during the S phase of DNA replication.
- The role of TDP1 during the mitotic phase was previously unknown; CDK1 phosphorylates TDP1, enhancing its repair capabilities.
- Phosphorylation is crucial for efficient DNA repair, allowing cancer cells to withstand Top1-targeted chemotherapy.
- Potential for Combination Therapy:
- Targeting both CDK1 and TDP1 could help overcome drug resistance and improve treatment efficacy.
- Suggested use of CDK1 inhibitors (e.g., avotaciclib, alvocidib) alongside Top1 inhibitors may disrupt DNA repair and halt the cell cycle, increasing cancer cell mortality.
- Research Implications:
- Phosphorylation of TDP1 by CDK1 is essential for managing DNA damage in cancer cells.
- Inhibiting CDK1 may induce chromosome instability, effectively targeting cancer cells.
- The combination of CDK1 and Top1 inhibitors aims to enhance cancer treatment effectiveness.
- Future Directions:
- Identifying CDK1 and TDP1 as potential targets paves the way for developing new cancer therapies that inhibit DNA repair mechanisms.
- Further studies using animal models are ongoing to validate this innovative approach for precision medicine in treating resistant cancers.
NABARD Survey on Rural Financial Inclusion
- 11 Oct 2024
In News:
NABARD has published the findings from its second All India Rural Financial Inclusion Survey (NAFIS) for 2021-22, which offers primary data based on a survey of 1 lakh rural households, covering various economic and financial indicators in the post-COVID period.
Survey Overview:
- Inaugural survey conducted for 2016-17, results released in August 2018.
- Aims to analyze changes in rural economic conditions since 2016-17.
- Included all 28 states and Union Territories of Jammu & Kashmir and Ladakh.
Insights from NAFIS 2021-22
- Increase in Average Monthly Income:
- Average monthly income rose by 57.6% from Rs. 8,059 (2016-17) to Rs. 12,698 (2021-22).
- Nominal CAGR of 9.5%, with annual nominal GDP growth at 9%.
- Agricultural households earned Rs. 13,661; non-agricultural households earned Rs. 11,438.
- Salaried employment contributed 37% to total income; cultivation contributed one-third for agricultural households.
- Rise in Average Monthly Expenditure:
- Average monthly expenditure increased from Rs. 6,646 (2016-17) to Rs. 11,262 (2021-22).
- Agricultural households reported higher consumption (Rs. 11,710) compared to non-agricultural households (Rs. 10,675).
- Expenditure exceeded Rs. 17,000 in states like Goa and Jammu & Kashmir.
- Increase in Financial Savings:
- Annual average financial savings grew to Rs. 13,209 in 2021-22 from Rs. 9,104 in 2016-17.
- 66% of households saved in 2021-22, up from 50.6% in 2016-17.
- 71% of agricultural households reported savings, compared to 58% of non-agricultural households.
- States like Uttarakhand (93%) and Uttar Pradesh (84%) had high saving rates, while Goa (29%) and Kerala (35%) had lower rates.
- Kisan Credit Card (KCC) Coverage:
- 44% of agricultural households possessed a valid KCC.
- Among larger landholders and those with recent agricultural loans, 77% reported having a KCC.
- Insurance Coverage:
- Households with at least one insured member increased from 25.5% (2016-17) to 80.3% (2021-22).
- Vehicle insurance was most common (55%), followed by life insurance (24%).
- Pension Coverage:
- Households with at least one member receiving any form of pension rose from 18.9% to 23.5%.
- 54% of households with members over 60 years old reported receiving a pension.
- Financial Literacy:
- Good financial literacy increased by 17 percentage points, from 33.9% to 51.3%.
- Sound financial behavior improved from 56.4% to 72.8%.
Conclusion
- The NAFIS 2021-22 highlights significant advancements in rural financial inclusion since 2016-17.
- Improvements in income, savings, insurance coverage, and financial literacy are notable.
- Government welfare schemes (e.g., PM Kisan, MGNREGS) have positively impacted rural lives.
- Continued support and investment in rural development are essential for economic empowerment and financial security in India's rural population.
Colombo Security Conclave

- 11 Oct 2024
In News:
The Colombo Security Conclave (CSC) reached a milestone on August 30, 2024 with India, Sri Lanka, the Maldives and Mauritius signing a Charter and a memorandum of understanding, for the establishment of the CSC secretariat.
Key Facts:
Background of CSC:
- Originally called the NSA Trilateral on Maritime Security, the CSC was established in 2011 among India, Sri Lanka, and the Maldives. The initiative aimed to bolster maritime security in the Indian Ocean Region.
Membership:
- The founding members include India, Sri Lanka, and the Maldives. Mauritius joined in 2022, and Bangladesh became a member in 2024. Seychelles participates as an observer state.
Goals of CSC:
The CSC aims to foster cooperation in five main areas:
- Maritime safety and security
- Counterterrorism and prevention of radicalization
- Combating trafficking and transnational organized crime
- Cybersecurity and safeguarding critical infrastructure
- Humanitarian assistance and disaster relief
Defence Exercises:
- In November 2021, India, Sri Lanka, and the Maldives held Exercise Dosti XV in the Maldives, marking their first joint military exercise in the Arabian Sea under the CSC framework.
Nobel Prize in Literature 2024

- 11 Oct 2024
In News:
The Nobel Prize in Literature 2024 was awarded to South Korean author Han Kang “for her intense poetic prose that confronts historical traumas and exposes the fragility of human life.”
Key Details:
About South Korean author Han Kang
- Literary Style: Known for her physical empathy and metaphorical style; addresses extreme life stories.
- Career Beginnings:
- Started in 1993 with poetry in Literature and Society.
- Prose debut in 1995 with Love of Yeosu.
- Major Work:
- The Vegetarian (2007; English translation 2015).
- Explores violent consequences of protagonist Yeong-hye's refusal to conform to societal norms regarding food.
- Background:
- Born in 1970 in Gwangju, South Korea; later moved to Seoul.
- Comes from a literary family; father is a noted novelist.
- Engaged in art and music, influencing her writing.
- Significance: First South Korean writer to receive the Nobel Prize in Literature.
Previous Nobel Laureate
- 2023 Awardee: Jon Olav Fosse, Norwegian author.
- Contribution: Recognized for "innovative plays and prose which give voice to the unsayable."
Overview of the Nobel Prize
- Definition: Prestigious awards in six fields for those who have conferred the greatest benefit to humankind.
- Fields: Physics, Chemistry, Physiology or Medicine, Literature, Peace, and Economic Sciences.
- Peace Prize: Awarded for advancing international fellowship and promoting peace.
- Establishment: Founded by Alfred Nobel in his will dated 27 November 1895.
- Nobel's Background:
- Born on 21 October 1833 in Stockholm, Sweden.
- Noted for inventing dynamite; had interests in peace, poetry, and drama.
- Died in 1896; allocated his fortune for the prizes.
- First Award: Presented on 10 December 1901.
Prize Money
- Current award amount: $1.1 million per prize.
Note:
Rabindranath Tagore:
- Awarded the Nobel Prize in Literature in 1913 for his profound literary contributions.
- Notable works include Manasi, Gitanjali, and Chitra.
Unexpected Transformation of the Sahara Desert
- 10 Oct 2024
In News:
The Sahara Desert, one of the driest regions globally, is undergoing a surprising transformation due to an extratropical cyclone that impacted northwestern Africa on September 7-8, leading to patches of green across Morocco, Algeria, Tunisia, and Libya.
Key Details:
- Satellite Observations: NASA's satellite images reveal extensive greenery sprouting in areas typically known for drought conditions, as reported by NASA’s Earth Observatory.
- Flourishing Vegetation: Climate researcher Sylwia Trzaska noted that shrubs and trees are thriving in low-lying regions like riverbeds. Peter de Menocal, president of the Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution, highlighted that plant life can quickly respond to significant rainfall, transforming dunes into vibrant landscapes.
- Historical Context: Research indicates that the Sahara was once a lush environment with lakes and vegetation between 11,000 and 5,000 years ago. Recent heavy rains have replenished normally dry lakes.
- Rainfall Dynamics: The unusual rainfall event is attributed to the northward shift of the Intertropical Convergence Zone (ITCZ), which has moved further north than usual, resulting in equatorial-like downpours in the Sahara. Some areas experienced over half a foot of rain, surpassing typical annual precipitation levels.
- Impact of Rain Patterns: While the rains primarily affected less populated regions, severe flooding has resulted in over 1,000 fatalities and impacted around four million people across 14 African nations, according to reports from the World Food Programme and Associated Press.
- Climate Change Factors: Experts suggest that the repositioning of the ITCZ may be connected to record-high ocean temperatures and climate change, potentially altering rainfall patterns across Africa.
- Future Projections: As global ocean temperatures stabilize, de Menocal predicts that the rain belt may revert to a more southerly position, potentially crossing the equator.
- Sahara Desert Facts:
o The Sahara is the world's largest hot desert, spanning approximately 4,800 km in length and 1,800 km in width.
o It covers about 31% of the African continent, extending across 11 North African nations, including Algeria, Egypt, Mali, Morocco, Western Sahara, Tunisia, Chad, Libya, Mauritania, Niger, and Sudan
Universal Postal Union

- 10 Oct 2024
In News:
The Universal Postal Union (UPU) is set to assess the integration of the Unified Payment Interface (UPI) with cross-border remittances via the global postal network, according to a recent official announcement.
About the Universal Postal Union
The UPU is a specialized agency of the United Nations and serves as the main platform for international cooperation in the postal sector. Established by the Treaty of Bern in 1874, it stands as the second oldest international organization in the world.
Functions
The UPU coordinates postal policies among its member nations and oversees the global postal system. It establishes the rules for international mail exchanges and makes recommendations aimed at enhancing the volume and quality of mail, parcel, and financial services. Additionally, it plays an advisory, mediating, and liaison role while providing technical assistance when necessary.
Membership
Any member state of the United Nations is eligible to join the UPU. Non-member countries can also become UPU members, subject to approval by at least two-thirds of the existing member nations. Currently, the UPU comprises 192 member countries.
Structure
The UPU consists of four main bodies:
1. The Congress: The highest authority of the UPU, convening every four years.
2. The Council of Administration: Responsible for ensuring the continuity of UPU operations between Congresses and supervising activities related to regulatory, administrative, legislative, and legal matters.
3. The Postal Operations Council: Acts as the technical and operational hub of the UPU, composed of 48 member countries elected during Congress.
4. The International Bureau: Functions as the secretariat, providing logistical and technical support to the other UPU bodies.
The headquarters of the Universal Postal Union is located in Bern, Switzerland.
Caracal

- 10 Oct 2024
In News:
The Gujarat government has recently announced plans to establish a Caracal Breeding and Conservation Center in the Chadva Rakhal area of Kutch, with a budget of ?10 crore.
About the Caracal
- The caracal, known locally as "siya gosh" (meaning "black ear" in Persian), is a reclusive and primarily nocturnal feline celebrated for its agility and remarkable skill in catching birds mid-flight.
- In terms of nesting, caracals typically utilize abandoned porcupine burrows or rock crevices for denning and are often found with their young hidden among dense vegetation. They tend to live in small groups, and their elusive behavior makes them hard to spot in the wild.
Habitat and Distribution
Caracals inhabit various environments, including woodlands, savannahs, and scrub forests. In India, suitable habitats are found in regions such as Kutch, the Malwa Plateau, the Aravalli hills, and Bundelkhand. This species is also present in numerous countries across Africa, the Middle East, Central Asia, and South Asia.
Threats to Survival
The caracal faces significant threats from extensive hunting, illegal wildlife trade, and the destruction of its natural habitats.
Conservation Status
According to the IUCN, the caracal is classified as "Least Concern." In India, it is protected under Schedule I of the Wildlife (Protection) Act, 1972.
RBI's Recent Monetary Policy Review
- 10 Oct 2024
In News:
The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) maintained its benchmark interest rate at 6.5% for the 10th consecutive monetary policy review since April 2023. The policy stance was shifted to “neutral,” indicating potential for a future rate cut.
Monetary Policy Committee (MPC) Overview
- The decision to keep interest rates unchanged was supported by a majority of five out of six members of the MPC, which convened for three days starting October 7.
- The change in policy stance from “withdrawal of accommodation” to “neutral” was unanimously agreed upon.
Focus Areas
- The MPC emphasized the need for a durable alignment of inflation with targets while supporting economic growth.
- Macroeconomic parameters for inflation and growth were described as well balanced.
Inflation Insights
- A moderation in headline inflation is expected to reverse in September, likely remaining elevated due to adverse base effects.
- Retail inflation was below the central bank’s median target of 4% in July and August.
Growth Projections
- The RBI maintained its 7.2% GDP growth projection and a 4.5% average inflation estimate for 2024-25, with risks evenly balanced.
- Second-quarter inflation projection was revised down to 4.1% from 4.4%, while a rise to 4.8% is expected for the October to December quarter.
Domestic Growth and Investment
- Domestic growth remains robust, with private consumption and investment growing together.
- This growth has provided the RBI with the capacity to prioritize inflation control to achieve the 4% target.
Risks to Inflation
The Governor highlighted that unexpected weather events and escalating geopolitical conflicts pose significant upside risks to inflation.
National Maritime Heritage Complex (NMHC)

- 10 Oct 2024
In News:
The Union Cabinet has approved the development of NMHC in Lothal, Gujarat, under the Sagarmala programme.
- Purpose and Vision Aimed at showcasing India’s 4,500-year-old maritime heritage using an edutainment approach with modern technology.
Employment Generation
- Expected to create approximately 22,000 jobs: 15,000 direct and 7,000 indirect.
Project Phases
- Phase 1A
- Features a museum with 6 galleries, including:
- A large Indian Navy & Coast Guard gallery with external naval artifacts.
- Replica of Lothal township surrounded by an open aquatic gallery.
- A jetty walkway.
- Phase 1B
- Expansion includes:
- 8 additional galleries.
- The world's tallest Light House Museum.
- Bagicha complex with facilities for 1,500 cars, a food hall, and a medical center.
- Phase 2
- Development of Coastal States Pavilions by respective states and union territories.
- Hospitality zone featuring maritime-themed eco-resorts and museuotels.
- Recreation of ancient Lothal City and establishment of a Maritime Institute with hostel.
- Creation of four theme-based parks:
- Maritime & Naval Theme Park
- Climate Change Theme Park
- Monuments Park
- Adventure & Amusement Park
Governance and Management
- Governing Council
- Chaired by the Minister of Ports, Shipping & Waterways, overseeing project implementation and operation.
- Separate Society
- A dedicated society will manage future phases, governed under the Societies Registration Act, 1860.
Benefits and Funding
- Beneficiaries
- Local communities, tourists, researchers, government bodies, educational institutions, cultural organizations, conservation groups, and businesses.
- Funding
- Construction of the Light House Museum in Phase 1B will be financed by the Directorate General of Lighthouses and Lightships (DGLL).
Sagarmala Programme
- Objective
- A flagship initiative aiming to transform India’s maritime sector by enhancing logistics performance and fostering port-led development and coastal community upliftment.
- Background
- Approved in March 2015, the programme focuses on utilizing India’s extensive coastline and waterways for economic growth.
Pradhan Mantri Awas Yojana-Gramin (PMAY-G)

- 09 Oct 2024
Recent Initiatives:
- The Indian government has launched a nationwide survey of kutcha houses.
- Introduction of the Awas Sakhi mobile app to streamline housing assistance.
Purpose of the Kutcha House Survey
- Identify Housing Needs: The survey aims to collect data on families living in kutcha (temporary) houses, enabling targeted support for those in need.
- Support for Awas Sakhi App: The survey will enhance the functionality of the Awas Sakhi app, facilitating the application process and providing beneficiaries with vital housing information.
Overview of PMAY-G
- Launch: Initiated in 2016, PMAY-G aims to provide secure housing for the poorest communities.
- Beneficiary Selection Process: A comprehensive three-stage validation, including the Socio-Economic Caste Census 2011, Gram Sabha approvals, and geo-tagging, ensures that aid reaches those most deserving.
Benefits for PMAY-G Beneficiaries
- Financial Assistance:
- ?1.20 lakh for families in plain areas.
- ?1.30 lakh for families in hilly regions, including northeastern states and union territories.
- Support for Sanitation:
- An additional ?12,000 for toilet construction, aligned with the Swachh Bharat Mission – Gramin or MGNREGS.
- Employment Opportunities:
- Provision of 90/95 days of unskilled wage employment through MGNREGA for house construction.
- Access to Basic Amenities:
- Connections for water, LPG, and electricity facilitated through relevant schemes.
- Cost Sharing Structure:
- Expenses are shared in a 60:40 ratio for plain areas and a 90:10 ratio for northeastern states and selected Himalayan states. The Centre covers 100% of costs for other Union Territories.
Progress Under PMAY-G
- Targets: The government aims to construct 2.95 crore houses.
- Current Status: As of August 2024, 2.94 crore houses have been sanctioned, with 2.64 crore completed, enhancing living conditions for millions in rural areas.
Recent Developments
- In August 2024, the Union Cabinet approved funding for two crore additional houses at existing assistance rates.
- Eligibility Criteria Changes:
- Individuals owning bikes or scooters are now eligible.
- The income limit for eligibility has been raised from ?10,000 to ?15,000 per month.
Future Goals
- This initiative, spanning FY 2024-2029, aims to address ongoing housing demands, benefiting approximately 10 crore individuals by providing safe, hygienic, and socially inclusive housing.
2024 Nobel Prize in Chemistry

- 09 Oct 2024
In News:
U.S. Scientists David Baker and John Jumper and Britain’s Demis Hassabis won the 2024 Nobel Prize in Chemistry, for their work on understanding the protein structures.
Prize Distribution
- David Baker: Awarded half of the Prize for pioneering work in computational protein design.
- Demis Hassabis and John Jumper: Jointly awarded the other half for their revolutionary contributions to protein structure prediction using artificial intelligence.
Significance of Achievements
- The advancements in protein science represent a major milestone for healthcare and biotechnology.
- These innovations have unlocked new possibilities for designing proteins, potentially leading to breakthroughs in medicine, agriculture, and more.
David Baker's Innovations
- Baker has achieved the significant feat of creating entirely new types of proteins, enhancing our understanding of protein functionality.
- In 2003, he designed a novel protein using amino acids and custom software methods, which opened avenues for rapid protein creation.
- Applications include pharmaceuticals, vaccines, nanomaterials, and tiny sensors.
AI Contributions by Hassabis and Jumper
- Demis Hassabis and John Jumper employed advanced artificial intelligence to address the challenge of predicting complex protein structures.
- In 2020, they introduced the AI model AlphaFold2, which can predict the structure of nearly all identified proteins (approximately 200 million).
Notable Facts about the Nobel Prize in Chemistry
- The Nobel Prize in Chemistry has been awarded 116 times to 197 laureates from 1901 to 2024.
- Frederick Sanger and Barry Sharpless are the only recipients to have won the Prize twice.
- The inaugural Prize was awarded in 1901 to Jacobus H. van ‘t Hoff for his work on chemical dynamics and osmotic pressure.
- Marie Curie became the first woman to win the Prize in 1911 for her discovery of radium and polonium.
- Venkatraman Ramakrishnan, a citizen of Indian origin, received the Prize in 2009 for his research on ribosomes.
2024 Nobel Prize in Physics

- 09 Oct 2024
In News:
John Hopfield and Geoffrey Hinton won the 2024 Nobel Prize for physics “for foundational discoveries and inventions that enable machine learning with artificial neural networks”. Their work lies at the roots of a large tree of work, the newest branches of which we see today as artificially intelligent (AI) apps like ChatGPT.
Significance of ANNs
- Definition: ANNs are collections of interconnected nodes that mimic the networks of neurons in animal brains, enabling machines to process data, recognize patterns, and learn.
- Applications: Integral to AI applications such as facial recognition, language translation, and numerous fields including physics, chemistry, and medicine.
Historical Context
- Hopfield Network:
- Developed by John Hopfield in 1983.
- Based on Donald Hebb's neuropsychological theory of learning, emphasizing how connections between neurons strengthen through repeated interactions.
- Capable of storing and reconstructing images by adjusting node connections to achieve a low-energy state, effectively denoising input.
- Boltzmann Machine:
- Geoffrey Hinton's work on deep-learning machines, building on Ludwig Boltzmann's statistical mechanics.
- Introduced the concept of generative AI through networks that differentiate between probable outcomes.
- Developed Restricted Boltzmann Machines (RBMs) in the 2000s, enhancing learning efficiency through layered networks.
Evolution and Current State of ANNs
- Technological Progress: ANNs have evolved significantly, transitioning from individual computers to distributed networks like the cloud.
- Current Variants: Innovations include transformers, backpropagation, and long short-term memory techniques, making ANNs more capable and widely accessible.
Concerns and Risks
- Ethical Considerations: Rapid advancements in AI raise concerns about safety, misinformation, and job displacement.
- Expert Opinions: Both Hopfield and Hinton have expressed worries about the implications of AI systems surpassing human intelligence and the potential for misuse.
Trachoma

- 09 Oct 2024
In News:
The World Health Organization (WHO) has now recognised that India has successfully eliminated trachoma, a bacterial infection that affects the eyes, as a public health problem.
WHO Declaration:
- India has eliminated Trachoma as a public health problem (2024).
- Third country in the South-East Asia Region to achieve this milestone.
Trachoma Overview:
- Bacterial infection caused by Chlamydia Trachomatis.
- Contagious; spreads through contact with infected secretions.
- Can lead to irreversible blindness if untreated.
- Considered a neglected tropical disease.
Global Impact:
- WHO estimates 150 million affected worldwide; 6 million at risk of blindness.
- Most prevalent in underprivileged communities with poor living conditions.
Historical Context in India:
- Leading cause of blindness in the 1950s-60s.
- National Trachoma Control Program launched in 1963.
- Control efforts integrated into the National Program for Control of Blindness (NPCB).
Statistics:
- Blindness due to Trachoma was 5% in 1971; now reduced to less than 1%.
- Implementation of the WHO SAFE strategy (Surgery, Antibiotics, Facial hygiene, Environmental cleanliness).
Milestones:
- India declared free from infective Trachoma in 2017.
- Continued surveillance for cases from 2019 to 2024.
National Trachomatous Trichiasis (TT) Survey:
- Conducted in 200 endemic districts (2021-2024) under NPCBVI.
- Mandated by WHO to confirm elimination status.
MACE Observatory

- 09 Oct 2024
In News:
The MACE Observatory was recently inaugurated by the Secretary of the Department of Atomic Energy (DAE) and Chairman of the Atomic Energy Commission in Hanle, Ladakh.
About MACE Observatory
- Name: Major Atmospheric Cherenkov Experiment (MACE) Observatory.
- Significance:
- Largest imaging Cherenkov telescope in Asia.
- Highest imaging Cherenkov observatory in the world.
- Location: Situated at approximately 4,300 meters altitude in Hanle, Ladakh.
- Indigenous Development:
- Built by the Bhabha Atomic Research Centre (BARC).
- Supported by the Electronics Corporation of India (ECIL), Hyderabad, and other Indian industry partners.
Scientific Contributions
- Research Focus:
- Enhances understanding in astrophysics, fundamental physics, and particle acceleration mechanisms.
- Observes high-energy gamma rays to investigate cosmic phenomena like supernovae, black holes, and gamma-ray bursts.
- Global Impact:
- Aims to foster international collaborations in space research.
- Strengthens India’s position in the global scientific community.
Socio-Economic Role
- Local Impact: Contributes to the socio-economic development of Ladakh, promoting scientific awareness and opportunities.
Understanding Cherenkov Radiation
- Definition: A blue glow emitted when charged particles (e.g., electrons and protons) travel faster than light in a specific medium.
- Historical Note: Named after Pavel Cherenkov, who, along with Ilya Frank and Igor Tamm, received the Nobel Prize in Physics in 1958 for his work in demonstrating and explaining this phenomenon.
UK-Mauritius Treaty on Chagos Archipelago
- 08 Oct 2024
In News:
The United Kingdom said it would cede sovereignty of the strategically important Chagos Islands to Mauritius, calling it a “historic political agreement”. The UK has long controlled Chagos and the Diego Garcia military base located there, jointly operating it with the United States.
Background of the Chagos Archipelago
Historical Context
- The Chagos archipelago consists of 58 islands located about 500 km south of the Maldives.
- Initially uninhabited, the islands were populated in the late 18th century through the importation of slave labor.
- The islands were ceded to Britain from France in 1814, and in 1965, the UK established the British Indian Ocean Territory (BIOT), which includes Chagos.
Controversy Over Sovereignty
- Mauritius, a former British colony, claims that the detachment of Chagos from its territory during its independence in 1968 was illegal.
- The UK compensated Mauritius with a grant but retained control, establishing a military base on Diego Garcia.
Strategic Importance of Diego Garcia
Military Significance
- Diego Garcia has been a crucial U.S. military base since its operational status began in 1986.
- It played a key role in U.S. military operations during conflicts in the Gulf, Iraq, and Afghanistan.
- The base enables rapid response to crises and supports regional security, especially in light of U.S. interests in monitoring key trade routes like the Malacca Strait.
Geopolitical Implications
- The presence of the U.S. military in the Indian Ocean is vital for countering security threats, particularly regarding China's growing influence.
Recent Developments: The UK-Mauritius Agreement
Key Features of the Treaty
- On October 3, 2023, the UK agreed to cede sovereignty of the Chagos Islands to Mauritius, marking a significant political shift.
- The treaty allows Mauritius to resettle Chagossians (excluding Diego Garcia) and establishes a trust fund for their benefit.
- Despite this, the UK retains control over Diego Garcia for an initial period of 99 years.
Implications of the Agreement
- The resolution of the sovereignty issue may strengthen Western commitments to a stable and free Indo-Pacific region.
- If unresolved, tensions could push Mauritius toward seeking alliances with alternative powers like China.
India’s Position and Interests
Support for Mauritius
- India has historically supported Mauritius in its claims over Chagos, reflecting its stance against colonial legacies.
- In 2019, India voted in favor of Mauritius at the UN General Assembly regarding the Chagos dispute.
Strategic Partnerships
- With increasing Chinese assertiveness in the Indian Ocean, India has been strengthening its ties with Mauritius.
- Recent initiatives include the inauguration of an India-built airstrip and jetty in Agaléga, enhancing connectivity and support for Mauritius.
Conclusion
The UK-Mauritius treaty over the Chagos Archipelago marks a significant turning point in colonial legacies and geopolitical alliances in the Indian Ocean. For India, supporting Mauritius aligns with its broader strategic interests and enhances its influence in a region marked by competing global powers. As the dynamics evolve, India's role in fostering regional stability and partnerships will be crucial.
44th Session of Codex Committee on Nutrition and Foods for Special Dietary Uses

- 08 Oct 2024
In News:
India Participates in 44th Session of Codex Committee on Nutrition and Foods for Special Dietary Uses
Key Contributions:
- Nutrient Reference Values:
- Advocated for reference values for ages 6 to 36 months.
- Suggested combining NRV-R values by averaging those for 6-12 months and 12-36 months.
- This proposal was accepted by the committee.
- Probiotic Guidelines:
- Emphasized the need to update FAO/WHO probiotic guidelines, which are two decades old.
- Highlighted the lack of international harmonization in probiotic regulations affecting global trade.
- Committee agreed to revisit guidelines and requested FAO and WHO to conduct a literature review on probiotics.
- Discussion on Sweetness Assessment:
- Disagreed with the EU’s sensory testing proposal for carbohydrate sources in Follow-up Formula, citing lack of scientific validation.
- Supported by USA, Canada, and others; this led to the committee discontinuing the topic for now.
- Noted that ISO 5495 or other methods could be used in the absence of harmonized methods.
- Delegation:
- Included representatives from the Food Safety and Standards Authority of India, Ministry of Health and Family Welfare, and Ministry of Women and Child Development.
- Advocated for various food safety, consumer health, and trade-related issues.
- Outcome:
- India’s suggestions were officially incorporated into the final report, significantly influencing global food safety and nutrition standards.
- Additional Announcements:
- FAO/WHO plans for a Joint Statement on Healthy Diet Principles.
- Updates on reviewing benefits and risks of Alternative Animal Source Foods (A-ASFs).
- FAO introduced a new “Food and Diet” domain on its FAOSTAT database.
Marburg Virus
- 08 Oct 2024
In News:
- Definition:
- Marburg virus is one of the deadliest pathogens known to infect humans, causing severe hemorrhagic fever.
- Current Situation in Rwanda:
- Rwanda reported its first Marburg case late last month.
- At least 46 individuals have been infected, with 12 reported deaths.
- Approximately 80% of infections are among medical workers.
- The outbreak poses a significant threat to Rwanda’s fragile healthcare system, which has only 1,500 doctors for over 13 million people.
Characteristics of Marburg Virus
- Deadliness:
- Marburg virus disease (MVD) has case fatality rates ranging from 24% to 88%, depending on the strain and case management.
- The first outbreak occurred in Marburg, Germany, in 1967, with subsequent outbreaks primarily in Africa.
- Family:
- Marburg belongs to the filovirus family, which includes Ebola.
- Both viruses are clinically similar and can cause high-fatality outbreaks.
Transmission
- Initial Infection:
- Human infections initially occurred through prolonged exposure to mines or caves inhabited by Rousettus bats (notably the Egyptian fruit bat).
- Human-to-Human Transmission:
- MVD spreads directly through contact with blood and bodily fluids of infected individuals.
- Indirect transmission can occur via contaminated surfaces and materials (bedding, clothing).
- Risk for Medical Workers:
- Medical workers treating MVD cases are frequently infected, especially when infection control measures are inadequate.
Symptoms of Marburg Virus Disease (MVD)
- Incubation Period: Symptoms can appear 2 to 21 days after infection.
- Initial Symptoms: High fever, Severe headache, Muscle ache, Watery diarrhea, Abdominal pain and cramping, Vomiting
- Hemorrhagic Symptoms:
- Many patients develop bleeding from various sites, including the digestive system (fresh blood in feces and vomit), nose, gums, and vagina.
- Fatalities often occur due to severe blood loss and shock, typically 8 to 9 days after symptom onset.
Prevention and Treatment
- Current Status:
- No approved vaccines or specific treatments exist for MVD.
- Supportive Care:
- Rehydration (oral or intravenous fluids) and symptom management improve survival rates.
- Experimental Treatments:
- Rwanda is seeking experimental vaccines and treatments to address the outbreak.
- The US-based Sabin Vaccine Institute provided 700 doses of an experimental Marburg vaccine for healthcare professionals on the frontlines.
Genome Editing and Hereditary Cancers
- 08 Oct 2024
In News:
The International Agency for Research on Cancer’s estimates of the burden of 36 cancers in 185 countries suggest one in five individuals has a lifetime risk of developing cancer.
- Impact of CRISPR on Cancer Research:
- CRISPR screens have revolutionized the study of BRCA genes through high-throughput functional genetic analysis.
- Researchers use CRISPR-Cas9 to create specific mutations in BRCA genes, studying their effects on DNA repair and cancer development.
- Cancer Statistics:
- One in five individuals has a lifetime risk of developing cancer (International Agency for Research on Cancer).
- In 2022, there were approximately 20 million new cancer cases and 9.74 million cancer-related deaths; projections suggest these could rise to 32 million new cases and 16 million deaths by 2045, with Asia potentially accounting for half of the cases.
- Genetic Mutations and Inheritance:
- All cancers stem from genetic mutations; about 10% of cancer cases may involve inherited mutations.
- Specific inherited mutation prevalence:
- 20% in ovarian cancer patients.
- 10% in breast, colorectal, lung, and prostate cancers.
- 6% in cervical cancer.
- BRCA Genes Overview:
- The BRCA1 and BRCA2 genes, discovered in 1994 and 1995, are crucial for understanding hereditary cancer syndromes.
- Mutations in BRCA genes significantly increase the risk of breast, ovarian, and prostate cancers.
- BRCA mutations are estimated to occur in 1 in 400 individuals, with higher prevalence (1 in 40) among Ashkenazi Jews due to genetic bottlenecks and founder effects.
- Importance of Genetic Testing:
- Testing for BRCA mutations helps identify individuals at higher risk, enabling personalized prevention strategies such as increased surveillance or preventive surgery.
- The American Society of Clinical Oncology recommends testing for 15 genes related to breast and ovarian cancer risk.
- Targeted Therapies:
- PARP inhibitors represent a new class of chemotherapy drugs effective for cancers with BRCA mutations.
- Clinical trials show promising results, especially when combined with platinum-based chemotherapy.
- Advancements in Understanding Cancer Genes:
- CRISPR technology has improved our understanding of cancer-related genes, enabling researchers to study the effects of specific mutations.
- Studies have identified how different mutations influence responses to therapies like PARP inhibitors.
- Recent Research Findings:
- Research from the Wellcome Sanger Institute identified over 3,000 genetic changes in the RAD51C gene that could significantly increase breast and ovarian cancer risk.
- Variants disrupting RAD51C function can increase ovarian cancer risk six-fold and aggressive breast cancer risk four-fold.
- Risk Spectrum:
- Genetic risk is a spectrum based on how mutations affect protein function.
- Large-scale variant analysis is vital for personalized medicine and cancer prevention.
- Role of Population Studies:
- Population prevalence studies help identify hereditary cancer risks and inform genetic screening for at-risk individuals.
- Early cancer detection allows for better healthcare decisions and potential preventive therapies.
- Goals for Cancer Management:
- The ultimate aim is to reduce cancer morbidity and mortality, leading to healthier lives for individuals and families.
Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine 2024: MicroRNA Research

- 08 Oct 2024
Overview
The 2024 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine was awarded to Victor Ambros and Gary Ruvkun for their groundbreaking discovery of microRNA and its crucial role in post-transcriptional gene regulation. This award highlights their individual contributions to understanding how microRNAs influence gene expression, significantly advancing the field of molecular biology.
What are MicroRNAs?
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are small, non-coding RNA molecules typically 19-24 nucleotides long. They regulate protein production by interacting with messenger RNA (mRNA), ultimately influencing how much protein is synthesized from genetic information.
The Process of Gene Regulation
Gene expression involves two primary steps:
- Transcription: DNA is copied into mRNA in the nucleus.
- Translation: mRNA is translated into proteins by ribosomes with the help of transfer RNA (tRNA).
MicroRNAs play a critical role in regulating this process, particularly after transcription, by silencing mRNA and thereby controlling protein production.
Pioneering Research
Background
In the late 1980s, Ambros and Ruvkun utilized the model organism Caenorhabditis elegans, a small roundworm, to explore developmental processes. They focused on mutant strains, lin-4 and lin-14, which displayed abnormal development.
Key Discoveries
- Victor Ambros: Ambros cloned the lin-4 gene and discovered that it produced a short RNA molecule that did not code for proteins. This finding suggested that lin-4 could inhibit lin-14’s activity.
- Gary Ruvkun: Ruvkun investigated the regulation of the lin-14 gene and determined that lin-4 did not prevent the production of lin-14 mRNA. Instead, it inhibited protein production later in the gene expression process. He identified crucial segments in lin-14 mRNA essential for its inhibition by lin-4.
Collaborative Findings
Their subsequent experiments demonstrated that lin-4 microRNA binds to lin-14 mRNA, effectively blocking the production of lin-14 protein. Their findings were published in 1993 and laid the foundation for the understanding of microRNA.
Impact and Recognition
Initially, the significance of their discoveries was not widely recognized, as it was thought that microRNA regulation was specific to C. elegans. However, Ruvkun’s later identification of the let-7 gene, a microRNA found in various animal species, broadened the understanding of microRNAs' universal role in gene regulation.
Current Understanding
Today, it is known that humans possess over a thousand genes that code for different microRNAs. These molecules are crucial in regulating gene expression across multicellular organisms.
Applications and Future Directions
MicroRNAs can fine-tune gene expression, influencing various cellular functions despite similar genetic backgrounds. Abnormal microRNA regulation has been linked to diseases such as cancer and genetic disorders. While the Nobel Committee acknowledged that practical applications of miRNA research are still developing, understanding these molecules is vital for future research and therapeutic advancements.
Doddalathur Megalithic Burial Site

- 07 Oct 2024
In News:
A team of history and archaeology scholars and students from the University of Mysore have embarked on an excavation of megalithic burial sites in Chamarajanagar district.
- Location: Doddalathur village, Hanur taluk, Chamarajanagar district, situated in a valley by the Male Mahadeshwara Hill ranges.
- Team: A group of history and archaeology scholars and students from the University of Mysore, in collaboration with the Mythic Society, Bengaluru.
- Excavation Focus: Exploration of megalithic burial sites corresponding to the Iron Age (approximately 1200 BC to 300 CE).
- Site Features:
- Burials consist of circles made of large boulders, referred to as "megalithic."
- A small hillock is located to the west of the village.
- Historical Significance:
- The site was discovered by C. Krishnamurti of the Archaeological Survey of India in 1961.
- Originally contained over 1,000 burials, many of which have been lost due to agricultural expansion and development.
- Despite disturbances, many burials remain intact and are considered suitable for excavation.
- Goals of the Project:
- To enhance understanding of megalithic-Iron Age culture in southern Karnataka's hilly regions.
- To provide practical field training for archaeology students.
Maritime Exercise Malabar 2024

- 07 Oct 2024
In News:
Maritime Exercise Malabar 2024, Commencing at Visakhapatnam on 08 Oct Hosted by India, USA, Australia and Japan in Participation.
Background
- Origins: Initiated in 1992 as a bilateral naval drill between the United States and Indian Navy.
- Evolution: Has grown into a key multilateral exercise aimed at enhancing interoperability and addressing maritime challenges in the Indian Ocean and Indo-Pacific region.
Participating Naval Assets
- India: Various platforms, including:
- Guided missile destroyers
- Multi-purpose frigates
- Submarines
- Fixed-wing maritime reconnaissance aircraft
- Fighter aircraft and helicopters
- Australia:
- HMAS Stuart (Anzac Class Frigate)
- MH-60R helicopter
- P-8 Maritime Patrol Aircraft
- United States:
- USS Dewey (Arleigh Burke-Class Destroyer)
- Integral helicopter
- P-8 Maritime Patrol Aircraft
- Japan:
- JS Ariake (Murasame-class Destroyer)
Focus Areas of the Exercise
- Operational Enhancements:
- Discussions on special operations
- Surface, air, and anti-submarine warfare
- Subject Matter Expert Exchange (SMEE)
- Maritime Operations:
- Anti-submarine warfare
- Surface warfare
- Air defense exercises
- Emphasis: Improving situational awareness in the maritime domain.
Special Events
- Distinguished Visitors’ Day: Scheduled for October 9, 2024.
- Hosted by Vice Admiral Rajesh Pendharkar, Flag Officer Commanding-in-Chief, Eastern Naval Command.
- Joint Press Conference: Co-chaired by heads of delegations from all participating nations during the Harbour Phase.
Significance
- Comprehensive Exercise: Malabar 2024 is expected to be the most detailed edition to date, featuring complex operational scenarios and enhanced cooperation among the naval forces of the participating countries.GS Paper
DefConnect 4.0

- 07 Oct 2024
In News:
- DefConnect 4.0 was inaugurated by Union Defence Minister Rajnath Singh on October 7, 2024, at Manekshaw Centre, Delhi Cantonment.
- Organizer: Hosted by Innovations for Defence Excellence - Defence Innovation Organisation (iDEX-DIO) under the Department of Defence Production, Ministry of Defence.
Purpose and Focus
- Advancing Indigenous Innovation: Aims to enhance India’s defense ecosystem by promoting self-reliant defense technologies.
- Participants: Involves Armed Forces, Defence Public Sector Undertakings (DPSUs), start-ups, MSMEs, academia, incubators, investors, and policymakers.
Technology Showcase
- Exhibitions: iDEX innovators showcased cutting-edge technologies, products, and capabilities.
- Collaboration and Dialogue: Encourages partnerships and discussions to drive defense innovation and long-term collaborations.
Special Sessions
- Budget Insights: Focused on key takeaways from recent budget announcements impacting the defense innovation ecosystem.
- Semiconductor Domain: Highlighted initiatives and opportunities within the semiconductor sector.
Path Forward: Vision for 2047
- Viksit Bharat Goal: Aligns with India’s vision of becoming a global leader in defense innovation by 2047.
- Government Initiatives: Supports local talent and indigenous solutions through programs like iDEX.
iDEX Impact
- Defence India Start-up Challenges: 11 editions launched, garnering over 9,000 applications.
- Collaborations: Engages with over 450 start-ups/MSMEs on significant defense projects.
- Contribution to Self-Reliance: Supports the goal of achieving self-reliance in the defense and aerospace sectors.
India’s Tripartite Agreement

- 07 Oct 2024
In News:
Nepal, India, and Bangladesh have signed a tripartite agreement to facilitate cross-border electricity trade, enabling Nepal to export surplus electricity to Bangladesh via India.
Key Details of the Agreement
- Export Period: The agreement allows for electricity exports from June 15 to November 15 each year.
- Initial Export Volume: In the first phase, Nepal will export 40 MW of hydroelectricity to Bangladesh through Indian territory.
- Electricity Rate: The fixed rate per unit of electricity is set at 6.4 cents.
- Projected Revenue: Nepal is expected to earn approximately $9.2 million annually from this trade.
This agreement aims to enhance regional cooperation in energy trade and support sustainable development in the participating countries.
Increasing Frequency of Typhoons in Southeast Asia
- 07 Oct 2024
In News:
Overview of Typhoons
- Definition: A typhoon is a type of cyclone with wind speeds of 119 km/h or more, forming over warm ocean waters near the equator.
- Mechanism: As warm, moist air rises from the ocean, it creates a low-pressure system, leading to the characteristic circular wind patterns: anticlockwise in the Northern Hemisphere and clockwise in the Southern Hemisphere.
Recent Typhoon Events
- Typhoon Yagi: The most powerful tropical cyclone in Asia in 2024, with peak winds of 260 km/h. It caused significant destruction across Myanmar, Vietnam, Laos, and Thailand, displacing around 631,000 people and resulting in over 500 fatalities.
- Typhoon Bebinca: Reached wind speeds of 151 km/h, classified as a Category 1 storm, impacting eastern China with heavy rainfall and forcing evacuations for over 414,000 residents.
- Typhoon Shanshan: Affected Japan, bringing severe weather conditions.
Why are Typhoons more frequent?
- Rising Sea Surface Temperatures:
- Global warming has raised ocean temperatures, providing more energy for typhoon formation and intensification.
- Atmospheric Circulation Changes:
- Alterations in patterns, such as the weakening of the Walker Circulation, affect the frequency and paths of typhoons.
- El Niño and La Niña Effects:
- The El Niño-Southern Oscillation significantly influences typhoon activity. El Niño years often lead to increased typhoon occurrences in Southeast Asia, while La Niña can enhance cyclone activity in the Western Pacific.
- Increased Atmospheric Moisture:
- Higher global temperatures result in more evaporation, adding moisture to the atmosphere, which fuels stronger storms and increases rainfall intensity.
- Geographical Vulnerability:
- Southeast Asia’s location near warm ocean currents makes it a hotspot for typhoon activity, particularly along its extensive coastlines.
- Marine Heat Waves:
- Climate change has led to more frequent marine heat waves, causing extreme ocean warming, which contributes to intensified storms.
- Weaker Land-Sea Temperature Gradients:
- Changes in temperature differences between land and sea can prolong storm duration and severity.
- Urbanization and Environmental Degradation:
- Rapid urban development and the destruction of coastal ecosystems, like mangroves, diminish natural barriers against storm impacts.
Humanitarian Impact and Response
- The increasing intensity and frequency of typhoons have precipitated severe humanitarian crises in affected regions. The need for international cooperation in disaster response has become critical, involving collaboration among governments, civil societies, and humanitarian organizations to provide aid and support for those affected.
- Understanding the multifaceted reasons behind the rising frequency of typhoons is crucial for developing effective strategies to mitigate their impacts and enhance community resilience in Southeast Asia.
Mpox Diagnostic Test

- 06 Oct 2024
In News:
In an important move to improve global access to Mpox testing, the World Health Organization (WHO) has listed the first Mpox in vitro diagnostic under its Emergency Use Listing procedure.
- Context of Mpox Outbreak:
- Since January 2022, mpox has spread to 121 countries.
- By September 2024, there were 103,048 confirmed cases and 229 deaths.
- Diagnostic Test Approval:
- WHO approved Abbott Laboratories’ PCR diagnostic test, Alinity MPXV assay, for emergency use.
- This test detects mpox virus DNA from skin swabs, intended for trained lab personnel.
- Emergency Use Listing (EUL) Procedure:
- Allows WHO to expedite approval of unlicensed vaccines, treatments, and diagnostic tests during public health emergencies.
- In August, WHO called for manufacturers to submit diagnostic tools to aid low-income countries.
- Current Testing Landscape:
- Limited testing capacity has hindered response, especially in Africa, where over 30,000 suspected cases were reported in 2024.
- 35 laboratories in India are now equipped to test suspected mpox cases.
- Importance of Early Diagnosis:
- Early detection facilitates timely treatment and control of the virus, essential in outbreak areas.
- Characteristics of the Alinity MPXV Assay:
- Utilizes real-time PCR to detect mpox virus (clade I/II) DNA from lesion materials.
- Designed for skilled laboratory personnel familiar with PCR techniques.
- Ongoing Efforts:
- WHO is reviewing three additional mpox diagnostic tests and negotiating with more companies to enhance availability.
- Efforts include addressing the spread of a new variant, clade Ib, which is affecting more women and children.
- Public Health Implications:
- Expanding access to diagnostics is vital for managing the mpox outbreak and protecting populations, particularly in underserved regions.
- WHO emphasizes the importance of quality-assured medical products in containing the virus spread.
Discovery of New Hammerhead Shark Species

- 06 Oct 2024
In News:
A team of marine biologists led by a Florida International University researcher has described a new species of the shark genus Sphyrna from the Caribbean and the Southwest Atlantic.
- New Species: Named Sphyrna alleni (common name: shovelbill shark).
- Habitat: Found in coastal waters, estuaries, coral reefs, and seagrass beds from Belize to Brazil, with confirmed presence in:
- Caribbean: Belize, Panama, Colombia, Trinidad and Tobago.
- Southwestern Atlantic: Brazil.
- Characteristics:
- Small species, less than 1.5 m in length.
- Distinctive flat, shovel-shaped head lacking indentations on the anterior edge.
- Different from Sphyrna tiburo:
- More rounded anterior margin.
- Absence of lobules on the posterior margin.
- Higher precaudal vertebral count (80-83 vs. ~73 in Sphyrna tiburo).
- Evolutionary Insight: Possible sister lineage to Sphyrna vespertina, suggesting Sphyrna tiburo diverged later.
- Conservation Status:
- Hammerhead sharks are highly threatened, primarily due to overfishing.
- Most species, except Sphyrna gilberti, are listed as Vulnerable, Endangered, or Critically Endangered by the IUCN.
- Current IUCN assessment of Sphyrna tiburo as Globally Endangered may need reevaluation considering the new findings.
- Management Recommendations:
- Increased management efforts needed for Sphyrna alleni, particularly restrictions on gillnets and trawls, which significantly impact this species.
- Publication: Findings reported in the journal Zootaxa.
Shanghai Cooperation Organisation (SCO)

- 06 Oct 2024
In News:
- External Affairs Minister S. Jaishankar will attend the Shanghai Cooperation Organisation (SCO) Heads of Government meeting in Islamabad on October 15-16, 2023.
- This marks the first visit by an Indian External Affairs Minister to Pakistan since Sushma Swaraj in 2015.
Context of the Visit:
- The visit is primarily for the SCO meeting, reflecting India's focus on regional cooperation mechanisms.
- No bilateral meetings have been scheduled as of now, although Jaishankar's presence is based on "reciprocity" following Pakistan's participation in an earlier SCO meeting in India.
SCO Overview:
- Established on June 15, 2001, in Shanghai; evolved from the "Shanghai Five" formed in 1996.
- Original members included China, Russia, Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Tajikistan, and later Uzbekistan.
- Current members: India, Pakistan, Iran, and others, with Afghanistan and Mongolia holding Observer Status.
Significance of the SCO:
- Focuses on security cooperation, primarily among Asian nations.
- Seen as an alternative to Western international frameworks, especially with heavyweights like Russia and China positioning against US influence.
- India's inclusion alongside Pakistan in 2017 reflects the geopolitical jostling between Russia and China.
Geopolitical Dynamics:
- While SCO promotes cooperation, underlying tensions remain, particularly between India and Pakistan, and India and China.
- The organization has limited tangible outcomes due to member states' rivalries and differing interests.
India's Objectives in SCO:
- Provides a platform for enhancing relations with Central Asian countries, addressing common security concerns.
- Involves participation in the Regional Anti-Terrorist Structure (RATS) to combat terrorism and drug trafficking.
India-Pakistan Relations:
- Jaishankar's visit is seen in light of ongoing tensions; India shares difficult relations with both China and Pakistan.
- India canceled a summit under its presidency last year, opting for a virtual format instead.
Implications for Regional Politics:
- The visit comes shortly after the Jammu and Kashmir Assembly elections, with potential implications for India-Pakistan ties.
- Despite attending the SCO meeting, there is little expectation of progress in the India-Pakistan peace process.
- Recent statements from the Indian government criticize Pakistan for hosting wanted individuals, reflecting ongoing diplomatic tensions.
Strategic Importance:
- Participation in SCO allows India to engage with key regional players, including Russia, China, and Central Asian leaders.
- The meeting serves as preparation for India's participation in upcoming BRICS discussions, emphasizing the interconnectedness of these groupings.
Global Strategic Preparedness, Readiness and Response Plan (SPRP)

- 06 Oct 2024
In News:
The World Health Organization (WHO) launched the Global Strategic Preparedness, Readiness and Response Plan (SPRP) to tackle dengue and other Aedes-borne arboviruses.
Key Highlights:
- Purpose:
- Tackle dengue and other Aedes-borne arboviruses (e.g., Zika, chikungunya).
- Reduce disease burden, suffering, and deaths globally.
- Background:
- Rapid geographical spread of dengue due to:
- Unplanned urbanization.
- Poor water, sanitation, and hygiene practices.
- Climate change.
- Increased international travel.
- An estimated 4 billion people at risk, projected to increase to 5 billion by 2050.
- Significant increase in dengue cases; 12.3 million reported by August 2023, nearly double the total from 2022.
- Rapid geographical spread of dengue due to:
- Global Impact:
- Dengue endemic in over 130 countries, particularly affecting:
- South-East Asia.
- Western Pacific.
- Americas.
- Africa facing compounded health crises due to conflicts and disasters.
- Dengue endemic in over 130 countries, particularly affecting:
- Emergency Grade: WHO has graded the global dengue situation as grade 3, the highest emergency level.
- Key Components of SPRP:
- Emergency Coordination: Leadership and coordination activities for outbreak response.
- Collaborative Surveillance: Tools for early detection and control, including strengthened surveillance and epidemiological analysis.
- Community Protection: Engaging communities in local prevention and response measures.
- Safe and Scalable Care: Ensuring resilient health services for adequate patient care.
- Access to Countermeasures: Promoting research for better treatments and vaccines.
- Implementation Timeline: Over one year until September 2025, requiring US$ 55 million for health preparedness and response efforts.
- Alignment with Other Initiatives:
- Supports the Global Vector Control Response 2017-2030.
- Linked to the Global Arbovirus Initiative (2022) targeting mosquito-borne diseases.
- Call to Action:
- Encourages collaboration among government agencies, healthcare providers, and communities.
- Emphasizes the need for innovation and improved vector control strategies.
This plan aims to mobilize a coordinated response to the escalating threat of dengue and related diseases, emphasizing the role of all stakeholders in public health.
Very Short Range Air Defence System (VSHORAD)

- 06 Oct 2024
In News:
DRDO completed development trials of the 4th Generation miniaturised Very Short Range Air Defence System (VSHORAD).
Key Details:
- Trial Location: Conducted at Pokhran Field Firing Ranges, Rajasthan.
- Importance: VSHORAD addresses the Indian Army's need to replace legacy Igla systems, with past efforts making little progress.
- Recent Procurement: Army acquired small volumes of Igla-S through emergency procurement.
- Production Collaboration: Two production agencies involved in Development cum Production Partner (DcPP) mode for VSHORAD missiles.
- Trial Dates: Successful tests held on October 3 and 4, 2024.
Key Performance Metrics:
- Maximum Range and Altitude: Interception against high-speed aerial targets.
- Hit-to-Kill Capability: Demonstrated success in engaging targets in various scenarios (approaching, receding, crossing).
System Overview:
- Type: Fourth generation man-portable air defence system (MANPADS).
- Developer: Research Centre Imarat (RCI) in collaboration with other DRDO labs and industry partners.
Capabilities:
- Designed to neutralise low altitude aerial threats at short ranges.
- Features include Dual-band IIR Seeker, miniaturised Reaction Control System, and integrated avionics.
- More portable and lightweight than existing missile systems in the Army's arsenal.
Pradhan Mantri-Kisan Samman Nidhi (PM-KISAN) Scheme

- 05 Oct 2024
In News:
The Prime Minister of India is set to announce the 18th installment of the PM-KISAN scheme in Washim, Maharashtra. This will benefit over 9.4 crore farmers nationwide, with the government allocating more than ?20,000 crore for this initiative.
About PM-KISAN
The Pradhan Mantri Kisan Samman Nidhi (PM-KISAN) is a Central Sector Direct Benefit Transfer (DBT) initiative aimed at providing income support to farmers.
Key Features:
- Financial Assistance: The scheme offers ?6,000 annually to small and marginal farmer families, distributed in three equal installments.
- Eligibility: Initially targeted at families with up to 2 hectares of cultivable land, the scope was later broadened to include all farmer families, regardless of land size.
- Family Definition: The definition of a family under this scheme includes the husband, wife, and minor children.
- Identification of Beneficiaries: State governments and Union Territory administrations are responsible for identifying eligible farmer families based on the scheme's guidelines.
- Direct Transfers: The funds are directly credited to the beneficiaries' bank accounts.
Exclusion Criteria
Certain categories of individuals are not eligible for benefits under the PM-KISAN scheme, including:
- Institutional Land-holders: Those who hold land under institutional ownership.
- High-Profile Government Officials: This includes former and current holders of constitutional posts, ministers, members of legislative assemblies, mayors, and district panchayat chairpersons.
- Government Employees: Serving or retired officers and employees of central or state government ministries and departments are excluded.
- Pensioners: Retired pensioners receiving a monthly pension of ?10,000 or more, as well as those in the previously mentioned categories, are also ineligible.
- Income Tax Filers: Individuals who have paid income tax in the last assessment year.
- Registered Professionals: Professionals such as doctors, engineers, lawyers, chartered accountants, and architects who are engaged in practice and registered with professional bodies.
India's BRAP 2024 Alignment with World Bank's B-READY Index

- 05 Oct 2024
In News:
- The Indian government plans to align indicators of the BRAP 2024 index with the World Bank’s B-READY index to enhance business readiness rankings.
- State Involvement: States have been instructed to address gaps identified in the B-READY evaluations to improve their global rankings.
- Indicators Included: The upcoming 2024 BRAP rankings, prepared by the Department for Promotion of Industry and Internal Trade, will incorporate specific indicators from the B-READY index.
- Enterprise Survey Launch: An enterprise survey for the B-READY index in India is set to start in October, with support from the Ministry of Statistics and Programme Implementation.
- Participation Timeline: Although B-READY rankings will commence in 2024, India’s participation will begin in 2026. The initial rankings will cover 54 countries, expanding to 120 in 2025 and 180 in 2026.
- Successor to Previous Rankings: The B-READY index replaces the Ease of Doing Business rankings, which were discontinued in 2021 due to irregularities. It considers a broader range of factors in its assessments.
- Benchmark for Global Institutions: The B-READY framework will serve as a benchmark for global financial institutions and multinational companies to evaluate a country’s regulatory and policy environment.
- Historical Improvement: India improved its Ease of Doing Business ranking from 142 in 2014 to 63 in 2020.
- Technical Understanding: A team of government officials is tasked with understanding the technical aspects of the B-READY index to formulate strategies for improving India’s score.
- Lifecycle Parameters: The new index tracks ten parameters throughout a firm's lifecycle, including business entry, utility services, and labor, focusing on real-world applications rather than just legal changes.
- Recent BRAP Rankings: The BRAP 2022 rankings were recently announced, with Andhra Pradesh and Kerala achieving the top positions.
Co-district Initiative

- 05 Oct 2024
In News:
Assam has launched an innovative administrative initiative by inaugurating 21 'co-districts' as part of its Phase 1 rollout, which began on Friday and will extend into Saturday, ultimately introducing a total of 39 co-districts. This new structure replaces the previous system of 24 civil sub-divisions, aiming to bring governance closer to the citizens.
About the Co-District Initiative
- Structure: Co-districts serve as smaller administrative units within the larger district framework, each headed by an Assistant District Commissioner.
- Objective: This unique initiative, the first of its kind in India, seeks to enhance accessibility to governance and address administrative challenges faced by district administrations.
- Scope: The government plans to establish co-district offices in all 126 assembly constituencies in Assam.
Functions and Powers
The co-districts will handle a variety of important functions, including:
- Land Revenue Matters: Managing land-related issues and revenue collection.
- Development and Welfare Work: Overseeing development projects and welfare programs.
- Excise and Disaster Management: Addressing excise-related matters and coordinating disaster response efforts.
- Administrative Control: Co-districts will have authority over all departmental activities within their jurisdiction.
- Magisterial Powers: Commissioners will be empowered to issue permissions for events and manage other administrative tasks.
- Routine Administrative Tasks: Responsibilities include issuing ration cards, caste certificates, and land sale permissions.
India-U.S. MoU on Critical Minerals Supply Chains

- 05 Oct 2024
In News:
- The sixth Commercial Dialogue took place in Washington on October 4, 2024, led by Indian Union Minister of Commerce Piyush Goyal and U.S. Commerce Secretary Gina Raimondo.
- MoU Signing: A day prior, the leaders signed a memorandum of understanding (MoU) aimed at expanding and diversifying critical minerals supply chains to enhance resilience.
- Focus Areas:
- Identification of equipment, services, policies, and best practices for the development of U.S. and Indian critical minerals, covering:
- Exploration
- Extraction
- Processing and refining
- Recycling and recovery
- Identification of equipment, services, policies, and best practices for the development of U.S. and Indian critical minerals, covering:
- Context: This agreement follows China's export restrictions on gallium and germanium, critical for the semiconductor industry, and its ban on technology related to rare earth magnets and critical materials extraction.
- Strategic Goals:
- Promote open supply chains, technology development, and investment flows for green energy.
- Explore collaboration with other mineral-rich countries, particularly in Africa and South America.
- Progress on Semiconductor Supply Chains:
- Continued efforts to establish resilient semiconductor supply chains since the previous MoU.
- Completion of a "readiness assessment" by the U.S. Semiconductor Industry Association and India Electronics Semiconductor Association.
- Commitment to foster investments, joint ventures, and technology partnerships.
- Innovation Handshake: Success of roundtables in San Francisco and New Delhi aimed at enhancing innovation ecosystems and startup collaboration.
- Strategic Clean Energy Partnership: Discussions from the EIN Roundtable in March 2024 informed the U.S.-India Strategic Clean Energy Partnership meeting.
- IPEF Supply Chain Agreement: Significant progress noted in the IPEF ministerial meeting, focusing on semiconductors, chemicals, and critical minerals, particularly batteries and healthcare products.
- Future Collaborations:
- Focus on expanding U.S. Department of Commerce presence in India with approximately 70 Foreign Commercial Service staff.
- Plans for a U.S. trade mission to India in March 2025 aimed at supporting U.S. SMEs owned by underserved communities.
- Domestic Solar Manufacturing Protection: India reinstated the Approved List of Models and Manufacturers (ALMM) order to protect local solar PV module production against cheaper imports from China.
- Economic Context:
- The Economic Survey 2023-24 highlights China's expanding manufacturing trade surplus and its restrictive actions affecting India's access to solar equipment.
- India’s Production Linked Incentive (PLI) schemes have invested over $4.5 billion to bolster clean energy manufacturing but require additional policies to safeguard these investments.
Status of Elephant in India 2022-23

- 05 Oct 2024
In News:
- Shelved Census Report: The Environment Ministry has delayed the release of the elephant census report, “Status of Elephant in India 2022-23,” due to a lag in the Northeast census, with publication on hold until at least June 2025.
- Population Decline: Preliminary data from the report indicates significant drops in elephant populations across several regions:
- Southern West Bengal: 84% decline
- Jharkhand: 64% decline
- Odisha: 54% decline
- Kerala: 51% decline
- Developmental Threats: The report cites “mushrooming developmental projects,” including unregulated mining and infrastructure development, as major threats to elephant populations.
- Methodological Concerns: The Environment Ministry noted that refined counting methods could explain some discrepancies, suggesting new data may not be directly comparable to previous censuses conducted every five years since the 1990s.
- Old Counting Methods:
- Pre-2002: Elephants were counted using the “total direct count” method, which involved simple head counts but lacked scientific rigor for larger populations.
- 2002: Introduction of the “indirect dung count” method, where dung samples were used to estimate density based on decay rates.
- Sample Block Counts: Modified methods involved surveying limited areas (5 sq km) to improve detection accuracy.
- Elephants vs. Tigers: In 2021, a harmonized approach for estimating elephant and tiger populations was proposed, utilizing a similar block and co-variate methodology for both species.
- Genetic Mark-Recapture: The 2022-23 elephant census employed a genetic mark-recapture model using dung samples to identify individual elephants.
- Impact of Delay: Experts argue that withholding the available data hinders conservation efforts and governance. Delays could exacerbate the plight of elephant populations, particularly in regions facing specific threats, such as mining in Odisha.
Key Findings of the Unreleased Report:
- Overall Decline: The overall elephant population has decreased by 20% since 2017, with some areas reporting reductions of up to 41%.
- Regional Impact:
- Southern West Bengal, Jharkhand, and Odisha have seen losses of nearly 1,700 elephants.
- The Western Ghats region indicates an 18% decline.
- Northeast Region: The census for this area relies on extrapolated data from 2017, with approximately one-third of India's elephants located there.
- Contributing Factors: Habitat fragmentation, poaching, and human-elephant conflicts due to developmental activities are major threats.
- Conservation Recommendations: Strategies to strengthen elephant corridors, restore habitats, and enhance community involvement in conservation are vital.
- Challenges in the Northeast: Urban development, mining, and agriculture significantly threaten elephant movement and survival, underscoring the need for targeted conservation strategies.
- Conservation Status of Elephants in India:
- Leading States: Karnataka, Assam, and Kerala have the highest elephant populations.
- Conservation Status: Elephants are classified as Endangered on the IUCN Red List and are protected under multiple international conventions.
- Threats to Elephants:
- Habitat Loss: Rapid human population growth is diminishing elephant habitats.
- Fragmentation: Habitat disruption from construction and development projects is prevalent.
- Unlawful Killing: Human-elephant conflict often leads to retaliatory killings.
- Poaching: Targeting of male elephants for tusks continues to threaten genetic diversity.
- Conservation Measures:
- Financial support under various government schemes for habitat conservation and human-elephant conflict resolution.
- Establishment of 33 Elephant Reserves across 14 states.
- Collaborative efforts with railways and power departments to mitigate risks.
- Regular elephant census every five years by the Wildlife Institute of India (WII) for monitoring populations.
USCIRF Report on India: Key Highlights

- 04 Oct 2024
In News:
The United States Commission on International Religious Freedom (USCIRF), a Washington DC-based bipartisan U.S. federal government agency, has released a country update on India, flagging “collapsing religious freedom conditions”.
- Agency Overview:
- The United States Commission on International Religious Freedom (USCIRF) is an independent, bipartisan U.S. federal commission established under the 1998 International Religious Freedom Act (IRFA).
- Its primary functions include reviewing global religious freedom violations, providing policy recommendations to U.S. leaders, and publishing annual reports.
- Current Concerns:
- USCIRF's latest report indicates a “collapse” in religious freedom conditions in India, particularly worsening throughout 2024, especially around national elections.
- Legal and Policy Changes:
- Strengthening of discriminatory legislation, including:
- State-level anti-conversion and anti-terrorism laws.
- Implementation rules for the 2019 Citizenship (Amendment) Act (CAA).
- Passage of a State-level Uniform Civil Code (UCC) Bill in Uttarakhand.
- Strengthening of discriminatory legislation, including:
- Violations and Incidents:
- Expropriation of Places of Worship:
- Authorities have facilitated the construction of Hindu temples on former mosque sites.
- Increased attacks on religious minorities, particularly following the consecration of the Ayodhya temple in January 2024.
- Targeting of Religious Minorities:
- Arrests of Christians accused of forced conversions under anti-conversion laws.
- Anti-cow slaughter laws exploited by vigilante groups to target Muslims, Christians, and Dalits, often with little to no legal repercussions for perpetrators.
- Expropriation of Places of Worship:
- Recommendations:
- USCIRF urges the U.S. State Department to designate India as a “Country of Particular Concern” due to severe violations of religious freedom.
About USCIRF
- Composition: Comprised of nine commissioners appointed by the U.S. President or Congressional leaders, supported by non-partisan staff.
- Objective: To monitor and recommend actions on religious freedom violations aligned with international human rights standards.
Indian push needed to end AIDS as a global health threat by 2030: UNAIDS

- 04 Oct 2024
In News:
The UNAIDS Director recently highlighted the crucial role India plays in the global fight against HIV/AIDS, asserting that without its significant contributions, achieving the Sustainable Development Goal of ending AIDS as a public health threat by 2030 is unlikely.
Understanding HIV/AIDS
- HIV (Human Immunodeficiency Virus) is a virus that attacks the immune system, specifically targeting CD4 cells, which diminishes the body's ability to combat infections and diseases.
- When HIV progresses to its most severe form, it is diagnosed as AIDS (Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome), characterized by a severely compromised immune system, leading to life-threatening infections and cancers.
- The virus is transmitted through contact with infected bodily fluids, including blood, semen, and breast milk. While there is currently no cure, antiretroviral therapy (ART) can effectively manage HIV and prevent its progression to AIDS.
India’s Progress in Combating HIV/AIDS
- From 2010 to 2023, India has made significant strides in reducing annual new HIV infections by 44%, surpassing the global average.
- Additionally, AIDS-related deaths in India have decreased by nearly 80% during the same period, also exceeding global trends. However, challenges persist, with approximately 68,000 new infections reported in 2023, translating to around 185 daily.
- The Global AIDS Strategy emphasizes the need for 80% of prevention services to be delivered by community-led organizations, which are essential for reaching key populations but require sufficient resources and support.
About UNAIDS
UNAIDS, established in 1996, coordinates global efforts to combat HIV/AIDS and supports those affected. Headquartered in Geneva, Switzerland, it unites the efforts of 11 UN organizations and works in collaboration with various global and national partners to end the AIDS epidemic by 2030.
Key aspects of UNAIDS include:
- Global Mandate: To coordinate responses, support countries in prevention and treatment, and advocate for human rights and equality in access to services.
- Targets: The "90-90-90" targets aimed for 2020 sought to ensure that 90% of people living with HIV were diagnosed, 90% of those diagnosed were on treatment, and 90% of those on treatment achieved viral suppression.
- Current Strategy: The 2021-2026 Global AIDS Strategy focuses on eliminating inequalities that drive HIV and aims to ensure that 30 million people are on treatment by 2025.
- Funding and Advocacy: Funded by governments, private foundations, and corporations, UNAIDS organizes key campaigns, including World AIDS Day, to raise awareness and promote advocacy.
PM Internship Scheme

- 04 Oct 2024
In News:
The Prime Minister’s Internship Scheme, announced by Union Finance Minister Nirmala Sitharaman during her Budget speech on July 23, was launched on October 3. The PM Internship Scheme aims to provide internship opportunities to one crore youth in the top 500 companies over the next five years.
Companies will upload their internship positions, and candidates can submit applications starting October 12.
What is the Prime Minister’s Internship Scheme?
The PM Internship Scheme will enhance youth employability in India by offering them hands-on exposure to real-world business environments. The scheme represents a transformative opportunity to bridge the skills gap and drive sustainable growth in India.
A monthly stipend of ?4,500 will be provided to the interns from the central government via DBT (Direct Benefit transfer), with an additional ?500 offset provided by the company’s CSR fund.
Who is eligible for the PM internship scheme?
- Candidates aged between 21 and 24 years who are not engaged in full-time employment are eligible for the one-year internship programme.
- Internships are available to those who have passed class 10 or higher.
- Individuals from families with government jobs are excluded
- The scheme is not open to post-graduates
- A candidate who graduated from premier institutes such as IIT, IIM, or IISER, and those who have CA, or CMA qualification would not be eligible to apply for this internship.
- Anyone from a household that includes a person who earned an income of ?8 lakh or more in 2023-24, will not be eligible.
How to apply for the PM internship scheme?
- Interns can register in the portal and apply for internships. The portal, pminternship.mca.gov.in, is likely to be opened up for youngsters to enroll for consideration by companies on October 12. This window will be open till October 25 for the first batch of internships. Candidates must share and self-certify some data about their educational qualifications and residential pin codes.
- Candidates’ data will be matched with companies’ needs and locations using Artificial Intelligence tools, and a shortlist of candidates will then be generated for companies to consider.
- The portal is designed to streamline the application process and make candidate selection more transparent. Applicants can check the status of their applications in the portal once they have applied to the available posts.
What is the benefit of the scheme?
The scheme is to provide on-job training to youth and an exposure to real-life work environment. The scheme will also benefit the industry by creating a pipeline of skilled, work-ready youth who can be employed post-internship both in large as well as micro, small and medium enterprise.
National Mission on Edible Oils – Oilseeds (NMEO-Oilseeds)

- 04 Oct 2024
In News:
Cabinet Approves National Mission on Edible Oils – Oilseeds (NMEO-Oilseeds) (2024-25 to 2030-31).
Objective:
- Achieve self-reliance in edible oil production in seven years.
Financial Outlay:
- ?10,103 crore for the mission period.
Key Goals:
- Increase primary oilseed production from 39 million tonnes (2022-23) to 69.7 million tonnes by 2030-31.
- Boost domestic edible oil production to 25.45 million tonnes, meeting 72% of projected requirements.
Focus Areas:
- Enhance production of key oilseed crops: Rapeseed-Mustard, Groundnut, Soybean, Sunflower, Sesamum.
- Improve extraction efficiency from secondary sources (e.g., Cottonseed, Rice Bran).
Strategies:
- Promote high-yielding, high oil content seed varieties.
- Extend cultivation to rice fallow areas and encourage intercropping.
- Use advanced technologies like genome editing for seed development.
SATHI Portal:
- Launch of an online 5-year rolling seed plan for timely seed availability.
- Coordination with cooperatives, Farmer Producer Organizations (FPOs), and seed corporations.
Infrastructure Development:
- Establish 65 new seed hubs and 50 seed storage units.
- Develop over 600 Value Chain Clusters across 347 districts, covering over 1 million hectares annually.
Support for Farmers:
- Access to high-quality seeds, training on Good Agricultural Practices (GAP), and pest management advisory.
Environmental Benefits:
- Promote low water usage, improve soil health, and utilize crop fallow areas.
Background Context:
- India relies on imports for 57% of its edible oil demand.
- Previous initiatives include the National Mission on Edible Oils – Oil Palm (NMEO-OP) and significant increases in Minimum Support Price (MSP) for oilseeds.
- Imposition of 20% import duty on edible oils to protect local producers.
The NMEO-Oilseeds mission aims to enhance domestic oilseed production, reduce import dependency, and improve farmers' incomes while contributing to environmental sustainability.
Status of Classical Language: An Explainer

- 04 Oct 2024
In News:
The Union Cabinet has approved to confer the status of Classical Language to Marathi, Pali, Prakrit, Assamese and Bengali languages.
Why is a language declared as Classical?
Designating a language as classical acknowledges its historical significance and its role in preserving Bharat’s rich cultural heritage. These languages have been crucial in transmitting ancient knowledge, philosophies, and values for millennia. Government recognition emphasizes their deep antiquity and literary traditions, enhancing their status and promoting efforts for their preservation and research, ensuring their relevance in the modern world.
What are the criteria for declaring a language as classical?
In 2004, the Government of India, for the first time, created a new category of languages known as Classical Languages. It set the following as criteria for the status of Classical Language:
- High antiquity of its early texts/ recorded history over a thousand years.
- A body of ancient literature/ texts, which is considered a valuable heritage by generation of speakers.
- The literary tradition must be original and not borrowed from another speech community.
This criterion was revised in 2005 and 2024 based on the recommendations of Linguistic Experts Committees (LEC) under Sahitya Akademi to examine the proposed languages for the status of Classical Language. Later the criteria were revised in 2024 as follows:
- High antiquity of its early texts/recorded history over a period of 1500- 2000 years.
- A body of ancient literature/texts, which is considered a heritage by generations of speakers.
- Knowledge texts, especially prose texts in addition to poetry, epigraphical and inscriptional evidence.
- The Classical Languages and literature could be distinct from its current form or could be discontinuous with later forms of its offshoots.
The 2024 Linguistic Expert Committee also recommended the following languages to be fulfilling revised criteria to be considered as a Classical Language: Marathi, Pali, Prakrit, Assamese, Bengali
How many languages have been declared classical so far?
Languages Date of Recognition Notification by Source/Notification Date
Tamil October 12, 2004 Ministry of Home Affairs October 12, 2004
Ministry of Sanskrit November 25, 2005 Ministry of Home Affairs November 25, 2005
Telugu October 31, 2008 Ministry of Culture October 31, 2008
Kannada October 31, 2008 Ministry of Culture October 31, 2008
Malayalam August 8, 2013 Ministry of Culture August 8, 2013
Odia March 1, 2014 Ministry of Culture March 1, 2014
Steps Taken by the Ministry of Education for Advancing Classical Languages:
- Establishment of Central Universities (2020): Three universities created to promote Sanskrit through an Act of Parliament.
- Central Institute of Classical Tamil:
- Facilitates translation of ancient Tamil texts.
- Promotes research and offers courses for students and scholars.
- Centres for Excellence:
- Established for Classical Kannada, Telugu, Malayalam, and Odia under the Central Institute of Indian Languages in Mysuru.
- Awards: Introduction of national and international awards to recognize achievements in Classical Languages.
- Additional Benefits:
- National Awards for Classical Languages.
- Establishment of university chairs.
- Dedicated centers for promoting Classical Languages.
Annual Survey of Industries (ASI) Results for 2022-23
- 03 Oct 2024
In News:
- The Ministry of Statistics and Programme Implementation (MoSPI) has released the results of the Annual Survey of Industries (ASI) for the financial year 2022-23 (April 2022 to March 2023).
- The fieldwork for this survey was conducted from November 2023 to June 2024.
- The ASI provides critical insights into the dynamics of the manufacturing sector, covering aspects such as output, value added, employment, and capital formation.
Key Highlights
- Gross Value Added (GVA): Increased by 7.3% in current prices for 2022-23 compared to the previous year.
- Industrial Output: Grew by over 21% in 2022-23 compared to 2021-22.
- Employment: Estimated employment in the sector rose by 7.4% over the previous year, surpassing pre-pandemic levels.
The growth in key economic parameters such as invested capital, input, output, GVA, and wages indicates a robust recovery in the industrial sector. Notably, industries like Basic Metal Manufacturing, Coke & Refined Petroleum Products, Food Products, Chemicals, and Motor Vehicles were significant contributors, accounting for about 58% of total output and showing a 24.5% increase in output and 2.6% in GVA.
State Contributions
- Top GVA Contributors:
- Maharashtra
- Gujarat
- Tamil Nadu
- Karnataka
- Uttar Pradesh
Together, these states contributed over 54% of the total manufacturing GVA.
- Highest Employment States:
- Tamil Nadu
- Maharashtra
- Gujarat
- Uttar Pradesh
- Karnataka
Collectively, these states accounted for about 55% of total manufacturing employment in 2022-23.
Survey Details
The ASI encompasses various industrial units, including:
- Factories registered under the Factories Act, 1948.
- Bidi and cigar manufacturing establishments.
- Electricity undertakings not registered with the Central Electricity Authority.
- Units with 100 or more employees registered in the Business Register of Establishments.
The survey employs a comprehensive sampling strategy, dividing units into Central and State Samples to ensure accurate representation. Key components of the data collection include:
- Central Sample: Includes all units in less industrially developed states and specific industrial categories.
- State Sample: Comprises selected units based on employee count and other criteria.
Industrial Classification
Since 1959, the ASI has adopted various classifications to categorize industries. The current classification, NIC 2008, is based on the UN's international standards and has been in use since 2008-09.
Data Collection and Reliability
Data collection is conducted via a dedicated web portal, following the Collection of Statistics Act. Various quality checks ensure reliability, with the Relative Standard Errors (RSE) for important estimates remaining within acceptable limits.
Modified PKC-ERCP project
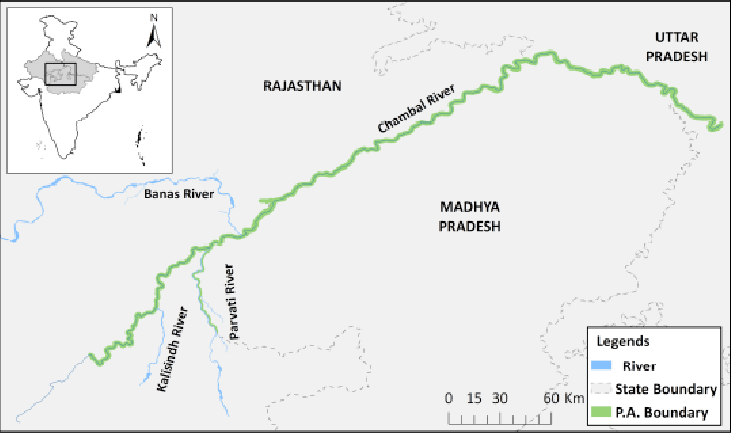
- 03 Oct 2024
In News:
Madhya Pradesh and Rajasthan governments signed an agreement for the implementation of the Rs 72,000 crore Parbati-Kalisindh-Chambal river linking project.
Modified PKC-ERCP Project Overview
- Signatories: Rajasthan, Madhya Pradesh, and the Union Ministry of Jal Shakti signed a MoU for implementation.
- Project Type: Inter-state river linking initiative.
- Integration: Combines the long-standing Parbati-Kalisindh-Chambal (PKC) project with the Eastern Rajasthan Canal Project (ERCP) under India's National Perspective Plan for interlinking rivers.
Objectives and Benefits
- Water Supply: Aims to provide drinking and industrial water to 13 districts in eastern Rajasthan and the Malwa and Chambal regions of Madhya Pradesh.
- Irrigation: Expected to irrigate approximately 5.6 lakh hectares across both states.
- Groundwater Management: Focus on improving groundwater levels and enhancing socio-economic conditions in rural Rajasthan.
Project Components
- Detailed Project Report (DPR): Currently under preparation, will outline water sharing, cost distribution, and implementation strategies.
- Historical Context:
- PKC Project: Proposed in 1980 as part of a national plan, initially focused on diverting water from Kalisindh and Newaj rivers to Chambal.
- ERCP: Proposed by Rajasthan in 2019 to optimize water resources by redistributing surplus monsoon water from various sub-basins to deficit areas.
Geographic Focus
- Beneficiary Districts in Rajasthan: Includes Alwar, Bharatpur, Dholpur, Karauli, and others.
- River Systems Involved:
- Chambal River: Originates in Madhya Pradesh, flows through Rajasthan, and joins the Yamuna.
- Kalisindh and Parbati Rivers: Serve as sources for water diversion.
Implementation Challenges
- Dependable Yield Issues: The original project proposal was based on a 50% dependable yield, contrary to the 75% norm, which was unacceptable to Madhya Pradesh. This led to discussions and revisions.
- Task Force Recommendations: Integrated discussions led to the proposal of the Modified PKC-ERCP, addressing both states' concerns.
Significance of the Project
- National Perspective Plan (NPP): Part of a larger initiative to manage water resources effectively across India, aiming to address water scarcity and improve irrigation.
- Support for Industrial Development: Enhances water availability for the Delhi-Mumbai Industrial Corridor, fostering economic growth.
PM E-DRIVE Scheme

- 03 Oct 2024
In News:
The Union Cabinet approved the PM Electric Drive Revolution in Innovative Vehicle Enhancement (PM E-DRIVE) Scheme to promote electric mobility in the country.
Objective:
- Accelerate electric vehicle (EV) adoption
- Establish essential charging infrastructure
- Promote cleaner and sustainable transportation
Key Highlights
- Significant Occasion: Launched on the eve of Mahatma Gandhi's 155th Birth Anniversary, aligning with the vision of ‘Swachh Bharat’ and ‘Swachh Vahan’.
- Financial Commitment: Union Cabinet approved a financial outlay of ?10,900 crore for the scheme over two years (approved on September 11, 2024).
Key Features of the PM E-DRIVE Scheme
- Subsidies/Demand Incentives:
- Total of ?3,679 crore allocated for:
- 24.79 lakh electric two-wheelers (e-2Ws)
- 3.16 lakh electric three-wheelers (e-3Ws)
- 14,028 electric buses (e-buses)
- Total of ?3,679 crore allocated for:
- E-Voucher Introduction:
- Aadhaar-authenticated e-vouchers for EV customers
- Simplifies access to incentives, with real-time generation for dealers.
- E-Ambulances:
- ?500 crore allocated for deployment
- Standards to be developed with relevant ministries.
- E-Buses:
- ?4,391 crore for 14,028 e-buses in nine major cities
- Focus on replacing scrapped state transport unit buses.
- E-Trucks:
- ?500 crore for incentivizing electric trucks
- Scrapping certificates required for incentives.
- Public Charging Stations:
- ?2,000 crore to install:
- 22,100 fast chargers for electric four-wheelers (e-4Ws)
- 1,800 for e-buses
- 48,400 for e-2Ws/3Ws
- ?2,000 crore to install:
- Test Agency Modernization:
- ?780 crore for upgrading Ministry of Heavy Industries test agencies to accommodate new EV technologies.
India’s Oil Imports from Saudi Arabia and Russia

- 03 Oct 2024
Context
- India’s crude oil imports are influenced by refinery maintenance cycles, which affect demand.
- August saw a dip in oil demand due to pre-maintenance preparations, but September recorded a recovery.
September Oil Import Trends
- Saudi Arabia:
- Imports rose 39.8% month-on-month to 0.73 million barrels per day (bpd), the highest since March.
- Saudi market share increased to 15.5% in September from 11.7% in August.
- Riyadh is reducing prices to regain lost market share, as earlier imports had plummeted to a multi-year low (0.42 million bpd in June).
- Russia:
- Remains India’s largest oil supplier with imports increasing by 6.4% from August to 1.88 million bpd.
- Russian crude constituted 40.2% of India’s total crude imports of 4.68 million bpd in September.
- Iraq:
- Supplied 0.87 million bpd, accounting for 18.7% of total imports.
- UAE:
- Oil imports increased by 18.6% month-on-month to 0.49 million bpd, the highest since June 2022.
Market Dynamics
- Price Sensitivity: Indian refiners are highly price-sensitive, which could lead to increased competition among suppliers.
- Potential for Increased Russian Imports: With Indian refiners expected to secure larger long-term contracts for Russian oil, further increases in imports from Russia are anticipated.
Strategic Implications
- Saudi Arabia is concerned about losing market share to Russia, especially as India’s refiners are currently favoring discounted Russian crude.
- Increased competition may benefit Indian refiners through better pricing from various suppliers.
Economic Context
- India, as the world's third-largest oil consumer with over 85% import dependency, is significantly affected by global oil price fluctuations.
- Although discounts on Russian crude have decreased, the overall savings from purchasing large volumes remain significant for Indian refiners.
The evolving landscape of India’s oil imports highlights the competitive dynamics among major suppliers, particularly Saudi Arabia and Russia, and underscores India’s strategic importance as a key market in the global oil sector.
Little Prespa Lake's Decline
- 03 Oct 2024
In News:
Little Prespa Lake on Albanian-Greek border slowly dying.
Overview of Little Prespa Lake's Decline
- Location and Geography:
- Little Prespa Lake is situated on the Albanian-Greek border, primarily in Greece with a southern tip extending into Albania.
- It covers approximately 450 hectares in Albania, now largely transformed into swamps or dry land.
- Ecological Changes:
- Once a crystal-clear lake, it has degraded into a marshy area, with about 430 hectares in Albania suffering from significant drying.
- Local wildlife has shifted; cows now roam where fish once thrived.
- Historical Context:
- The lake's decline began in the 1970s when Albanian authorities diverted the Devoll River to irrigate surrounding agricultural lands, severely limiting water inflow.
- Climate Change Impact:
- Rising temperatures, mild winters, and decreased precipitation have intensified the lake’s ecological crisis.
- Local experts warn that continued dry winters and hot summers could lead to irreversible damage.
Cruise Bharat Mission

- 01 Oct 2024
In News:
The central government launched the five-year Cruise Bharat Mission, aiming to boost cruise tourism in India to 1 million passengers and create 400,000 jobs by 2029.
Mission Goals
- Passenger Traffic: Increase from 0.5 million to 1 million sea cruise passengers by 2029.
- River Cruise Passengers: Grow from 0.5 million to 1.5 million.
- Job Creation: Generate 400,000 jobs in the cruise sector.
- Infrastructure Expansion:
- International cruise terminals: From 2 to 10.
- River cruise terminals: From 50 to 100.
- Marinas: From 1 to 5.
Implementation Phases
- Phase 1 (2024-2025):
- Conduct studies and master planning.
- Form alliances with neighboring countries.
- Modernize existing cruise terminals and destinations.
- Phase 2 (2025-2027):
- Develop new cruise terminals and marinas.
- Activate high-potential cruise locations.
- Phase 3 (2027-2029):
- Integrate cruise circuits across the Indian Subcontinent.
- Continue developing infrastructure and enhancing cruise experiences.
Strategic Focus Areas
- Sustainable Infrastructure:
- Develop world-class terminals, marinas, and water aerodromes.
- Emphasize digitalization (e.g., facial recognition) and decarbonization (shore power).
- Create a National Cruise Infrastructure Masterplan 2047.
- Operational Efficiency:
- Streamline operations using digital solutions (e.g., e-clearance and e-visa facilities).
- Cruise Promotion & Circuit Integration:
- Focus on international marketing and investment.
- Host events like the "Cruise India Summit."
- Form alliances with neighboring countries (UAE, Maldives, Singapore).
- Regulatory and Financial Policies:
- Establish tailored fiscal and financial policies.
- Launch a National Cruise Tourism Policy.
- Capacity Building & Employment:
- Create a Centre of Excellence for cruise-related economic research.
- Develop National Occupational Standards to enhance youth employment opportunities.
Expected Outcomes
- Tourism Growth: Position India as a global cruise destination.
- Cultural Promotion: Highlight the cultural, historical, and natural heritage of Bharat through cruise circuits.
- Community Benefits: Ensure inclusive growth for local communities and stakeholders in the cruise sector.
The Cruise Bharat Mission is set to redefine India's cruise tourism landscape, focusing on infrastructure development, operational efficiency, and promoting cultural heritage, while ensuring economic growth and job creation for the future.
BharatGen Initiative
- 01 Oct 2024
In News:
BharatGen is a pioneering generative AI initiative launched in New Delhi, aimed at revolutionizing public service delivery and enhancing citizen engagement, with Dr. Jitendra Singh, Union Minister of State, in virtual attendance.
- Significance
- Represents India's commitment to advancing homegrown technologies.
- Positions India as a global leader in generative AI, similar to achievements with UPI and other innovations.
- Marks the world's first government-funded Multimodal Large Language Model project focusing on Indian languages.
- Leadership and Implementation
- Spearheaded by IIT Bombay under the National Mission on Interdisciplinary Cyber-Physical Systems (NM-ICPS).
- Collaboration with the TIH Foundation for IoT and various academic partners, including IITs and IIMs.
- Key figures involved include Prof. Shireesh Kedare (Director, IIT Bombay) and Prof. Ganesh Ramakrishnan (consortium leader).
- Core Objectives
- Deliver generative AI models as a public good, prioritizing socio-cultural and linguistic diversity.
- Address broader needs such as social equity, cultural preservation, and inclusivity.
- Make AI accessible for industrial, commercial, and national priorities.
- Key Features
- Multilingual and Multimodal Models: Capable of handling text and speech in multiple languages.
- Bhartiya Data Sets: Focus on India-centric data collection and training.
- Open-Source Platform: Promotes collaboration and innovation in AI research.
- Ecosystem Development: Fosters a robust AI research community.
- Project Timeline and Impact
- Expected completion in two years, with benefits for government, private, educational, and research institutions.
- Ensures coverage of India’s diverse linguistic landscape through multilingual datasets.
- Emphasis on data sovereignty to strengthen control over digital resources.
- Alignment with National Goals
- Supports the Atmanirbhar Bharat vision by reducing reliance on foreign technologies.
- Aims to strengthen the domestic AI ecosystem for startups, industries, and government agencies.
- Focuses on democratizing access to AI for innovators and researchers.
- Research and Community Engagement
- Data-efficient learning for languages with limited digital presence.
- Development of effective models with minimal data through research collaborations.
- Initiatives to foster an AI research community, including training programs and hackathons.
- Future Roadmap
- Key milestones outlined up to July 2026, focusing on:
- Extensive AI model development and experimentation.
- Establishment of AI benchmarks tailored to India’s needs.
- Scaling AI adoption across industries and public initiatives.
- Key milestones outlined up to July 2026, focusing on:
Joint Military Exercise KAZIND-2024

- 01 Oct 2024
In News:
The 8th edition of the India-Kazakhstan Joint Military Exercise, KAZIND-2024, has commenced in Auli, Uttarakhand, running from September 30 to October 13, 2024.
Key Details:
- Joint Exercise KAZIND-2024 has been held annually since 2016.
- Last edition of the Joint Exercise was held at Otar, Kazakhstan from 30th October to 11th November 2023.
Participants:
- India:
- 120 personnel from KUMAON Regiment of the Indian Army
- Additional support from other arms and Indian Air Force
- Kazakhstan:
- Personnel primarily from Land Forces and Airborne Assault Troopers
Aim:
- Enhance joint military capability for counter-terrorism operations
- Focus on sub-conventional scenarios under Chapter VII of the UN Charter
Focus Areas:
- Operations in semi-urban and mountainous terrains
- High physical fitness levels
- Rehearsal and refinement of tactical drills
- Sharing best practices
Tactical Drills:
- Joint response to terrorist actions
- Establishment of a Joint Command Post
- Creation of an Intelligence and Surveillance Centre
- Securing helipad/landing sites
- Combat free fall and Special Heliborne Operations
- Cordon and Search operations
- Employment of drones and counter-drone systems
Outcomes Expected:
- Sharing of tactics, techniques, and procedures for joint operations
- Development of interoperability between the two armies
- Strengthening of bonhomie and camaraderie
- Enhancement of defense cooperation and bilateral relations between India and Kazakhstan.
La Nina and North India’s pollution
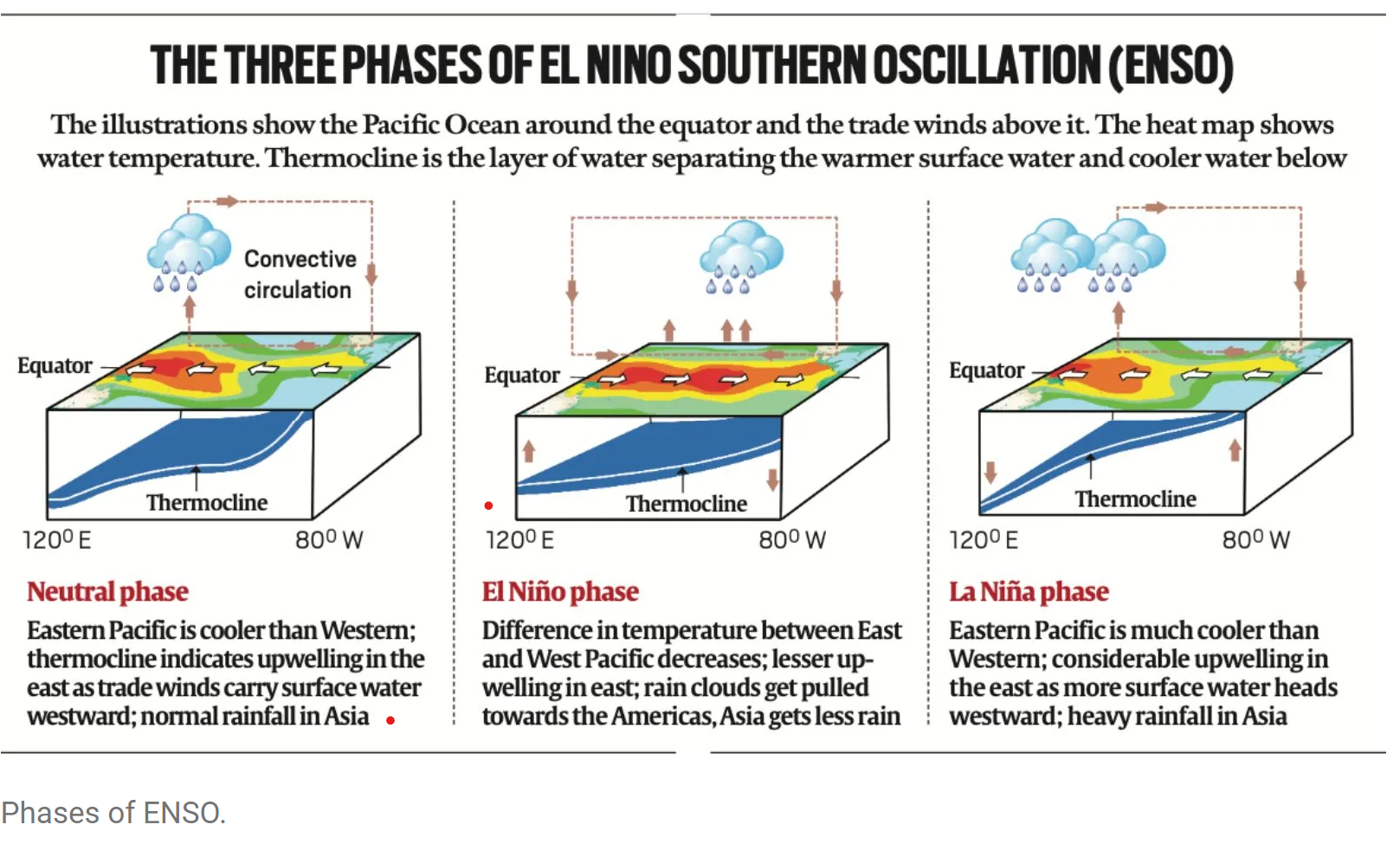
- 01 Oct 2024
In News:
Recent research by scientists at the National Institute of Advanced Science (NIAS) has underlined the links between climate change, La Niña and air quality.
Key Points on Air Quality Outlook for Delhi and North India
- Delayed La Niña & Monsoon Retreat:
- Erosion of optimism for improved air quality this winter in Delhi.
- Significant pollution challenges anticipated in early winter months.
- Possible relief in December and January, contingent on La Niña strengthening.
- Impact of Stubble Burning:
- If stubble burning occurs at half the intensity of previous years, November air quality may deteriorate.
- Research Insights:
- Study by National Institute of Advanced Science (NIAS) links climate change, La Niña, and air quality.
- Notable air quality improvement in winter 2022-23 was linked to La Niña conditions.
- Late onset of La Niña contributes to air quality uncertainty.
- Changing Pollution Dynamics:
- Shift from local emission-centric views to broader climatological factors is necessary.
- Air quality in Delhi worsens during winter due to high humidity, calm winds, and poor pollutant dispersion.
- La Niña Delays:
- Delayed La Niña onset means weak winds and stagnant conditions, worsening pollution.
- Expected development between September and November 2024.
- Effects of Stubble Burning:
- North-north-westerly winds could carry pollution from stubble burning in Punjab and Haryana into Delhi.
- Potential Outcomes of Late La Niña Onset:
- If La Niña develops in December or January, may improve air quality slightly.
- However, a longer, severe winter could exacerbate pollution issues due to lower inversion layers.
- NIAS-SAFAR Model Predictions:
- Early La Niña could have worsened air quality in the peninsular region.
- Early onset might have improved northern air quality.
- Link to Climate Change:
- Evidence suggests extreme air pollution correlates with climate change.
- Emphasizes the need for rigorous mitigation efforts and broader airshed management.
- Call for Rethinking Air Quality Strategies:
- Focus on integrating larger climatic factors into air quality policies.
- Prioritize health-centric measures through collaborative efforts with scientific bodies.
What is La Niña?
- La Niña (or ‘The Little Girl’ in Spanish) is a phase of what climatologists refer to as the El Niño Southern Oscillation (ENSO), a phenomenon that is a key driver of global natural climate variability.
- ENSO is characterised by changes in sea temperatures along the tropical Pacific Ocean due to atmospheric fluctuations overhead. These changes alter and interfere with the global atmospheric circulation, and influence weather worldwide.
- Occurring in irregular cycles of anywhere between two to seven years, ENSO has three phases — warm (El Niño or ‘The Little Boy’ in Spanish), cool (La Niña), and neutral.
- During the neutral phase, the eastern Pacific (off the northwestern coast of South America) is cooler than the western Pacific (around Philippines and Indonesia). This is because prevailing trade winds — caused by Earth’s rotation, between 30 degrees north and south of the equator — move east to west, sweeping warmer surface water along with them. The relatively cool waters from below rise to the surface to replace the displaced water.
- These wind systems weaken in the El Niño phase, leading to lesser displacement of warmer waters off the American coasts. Consequently, the eastern Pacific becomes warmer than usual. The opposite happens in the La Niña phase i.e. trade winds become stronger than usual and push larger quantities of water to the western Pacific.
Armed Forces (Special Powers) Act (AFSPA)

- 01 Oct 2024
In News:
- The Manipur government has extended the Armed Forces (Special Powers) Act (AFSPA) in the hill districts of the State for another six months.
- Effective October 1, the provisions of the Act will be extended to the whole State, except 19 police station limits in seven valley districts, thus maintaining the status quo, since three such notifications were passed since March 2023.
- It added that the “disturbed area” status could not be reviewed and a detailed ground assessment could not be done as “the sister security agencies are preoccupied with maintenance of law and order” and “it will be premature to arrive at any conclusion or decision on such sensitive matter without detailed assessment.”
Overview of the Armed Forces (Special Powers) Act (AFSPA)
- Enactment: The AFSPA was passed by Parliament and approved by the President on September 11, 1958.
- Context: It was introduced in response to rising violence in the North-eastern States, which state governments struggled to control.
Key Provisions of AFSPA
- Powers Granted:
- The Act empowers armed forces and Central Armed Police Forces in "disturbed areas" to:
- Kill anyone acting against the law.
- Arrest and search premises without a warrant.
- Receive protection from prosecution and legal action without Central government sanction.
- The Act empowers armed forces and Central Armed Police Forces in "disturbed areas" to:
- Issuance of Notifications:
- Both State and Union governments can issue notifications regarding AFSPA.
- The Ministry of Home Affairs issues "disturbed area" notifications for Arunachal Pradesh and Nagaland.
Definition of Disturbed Areas
- Criteria:
- A disturbed area is declared under Section 3 of AFSPA, indicating the need for armed forces' assistance in maintaining civil order.
- Factors leading to the declaration can include:
- Conflicts among different religious, racial, linguistic, or regional groups.
- Authority to Declare:
- The Central Government, the Governor of the State, or the administrator of a Union Territory can declare an area as disturbed.
- Duration:
- Once designated as disturbed, the area remains classified as such for three months, as per The Disturbed Areas (Special Courts) Act, 1976.
- State Government Input:
- State governments can recommend whether AFSPA should continue in their region.
Colombo Security Conclave (CSC)

- 03 Sep 2024
In News:
The Colombo Security Conclave (CSC) recently marked a significant milestone with the signing of the Charter and the Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) for the establishment of its Secretariat in Colombo. This initiative aims to strengthen regional security collaboration among member states.
Key Features of the Colombo Security Conclave
- Member States: The CSC comprises five member countries:
- India
- Bangladesh
- Sri Lanka
- Maldives
- Mauritius
Additionally, Seychelles participates as an observer nation.
- Core Objectives: The primary goal of the CSC is to enhance regional security by addressing transnational threats and challenges that are common concerns for member states. This includes a collaborative approach to ensure stability and safety in the region.
Origin and Evolution
- The CSC originated as the Trilateral for Maritime Security Cooperation, established through trilateral meetings among National Security Advisors (NSAs) and Deputy NSAs from India, Maldives, and Sri Lanka starting in 2011.
- The initiative faced a setback after 2014 due to heightened tensions between India and the Maldives.
- It was revived and rebranded as the CSC in 2020, expanding its membership to include Mauritius and, more recently, Bangladesh.
Structure and Cooperation
- The conclave facilitates interactions among NSAs and Deputy NSAs of member countries, fostering dialogue and cooperation on security matters.
- Cooperation under the CSC is organized around five key pillars:
- Maritime Safety and Security
- Countering Terrorism and Radicalization
- Combating Trafficking and Transnational Organized Crime
- Cybersecurity and Protection of Critical Infrastructure
- Humanitarian Assistance and Disaster Relief
Permanent Secretariat
- The establishment of a permanent Secretariat in Colombo is expected to enhance coordination and streamline operations among member states, bolstering the efficacy of the CSC in addressing regional security issues.
Thanjavur Veena

- 03 Sep 2024
In News:
The Thanjavur Veena has the distinction of being the first musical instrument in India to receive the Geographical Indication (GI) tag, highlighting its cultural and artistic significance. Here’s an overview of its features, types, and craftsmanship:
About Thanjavur Veena
- Construction:
- The Thanjavur Veena is known for its unique construction, which comes in two main types:
- Ekantha Veena: Carved from a single block of wood.
- Sada Veena: Composed of three sections—resonator (kudam), neck (dandi), and head—with joints.
- The Thanjavur Veena is known for its unique construction, which comes in two main types:
- Design Features:
- The instrument features 24 fixed frets (mettu), enabling musicians to play a wide range of ragas.
- Traditionally made from the bark of the Jackfruit tree, the bark undergoes extensive testing to ensure quality and durability.
- Craftsmanship:
- The process of crafting a Thanjavur Veena can take 15-20 days, involving cutting, intricate carving, shaping, and assembly of the wood to form the integral parts of the instrument.
Types of Veena
The Thanjavur Veena is one of several types of veenas used in Indian classical music:
- Rudra Veena and Vichitra Veena: Predominantly used in Hindustani classical music.
- Saraswati Veena and Chitra Veena: Associated with Carnatic classical music, with the Saraswati Veena being unique to Thanjavur.
Cultural Significance
- The Saraswati Veena is particularly notable as it is often associated with Goddess Saraswati, the deity of learning and arts, who is frequently depicted holding a veena. This connection emphasizes the instrument's importance in Indian culture and music.
7 New Schemes to Boost Farmer Income
- 03 Sep 2024
In News:
The Union Cabinet chaired by Prime Minister, Shri Narendra Modi, approved seven schemes to improve farmers’ lives and increase their incomes at a total outlay of Rs 14,235.30 Crore.
1. Digital Agriculture Mission: based on the structure of Digital Public Infrastructure, Digital Agriculture Mission will use technology for improving farmers’ lives. The Mission has a total outlay of Rs 2,817 crores. It comprises two foundational pillars
1. Agri Stack
- Farmers registry
- Village land maps registry
- Crop Sown Registry
2. Krishi Decision Support System
- Geospatial data
- Drought/flood monitoring
- Weather/satellite data
- Groundwater/water availability data
- Modelling for crop yield and insurance
The Mission has provision for
- Soil profile
- Digital crop estimation
- Digital yield modelling
- Connect for crop loan
- Modern technologies like AI and Big Data
- Connect with buyers
- Bring new knowledge on mobile phones
2. Crop science for food and nutritional security: with a total outlay of Rs 3,979 crore. The initiative will prepare farmers for climate resilience and provide for food security by 2047. It has following pillars:
- Research and education
- Plant genetic resource management
- Genetic improvement for food and fodder crop
- Pulse and oilseed crop improvement
- Improvement of commercial crops
- Research on insects, microbes, pollinators etc.
3. Strengthening Agricultural Education, Management and Social Sciences: with a total outlay of Rs 2,291 Crore the measure will prepare agriculture students and researchers for current challenges and comprises the following
- Under Indian Council of Agri Research
- Modernising agri research and education
- In line with New Education Policy 2020
- Use latest technology … Digital DPI, AI, big data, remote, etc
- Include natural farming and climate resilience
4. Sustainable livestock health and production: with a total outlay of Rs 1,702 crore, the decision aims to Increase farmers income from livestock and dairy. It comprises the following
- Animal health management and veterinary education
- Dairy production and technology development
- Animal genetic resource management, production and improvement
- Animal nutrition and small ruminant production and development
5. Sustainable development of Horticulture: with a total outlay of Rs 1129.30 crore the measure is aimed at increasing farmers’ income from horticulture plants. It comprises the following
- Tropical, sub-tropical and temperate horticulture crops
- Root, tuber, bulbous and arid crops
- Vegetable, floriculture, and mushroom crops
- Plantation, spices, medicinal, and aromatic plants
6. Strengthening of Krishi Vigyan Kendra with an outlay of Rs 1,202 crore
7. Natural Resource Management with an outlay of Rs 1,115 crore
Current State of Mental Healthcare in India

- 03 Sep 2024
Overview
India’s mental healthcare landscape is evolving, with increasing awareness and decreasing stigma around mental health issues. However, access to mental healthcare remains a significant challenge due to a shortage of professionals. Here are the key points:
Current State of Mental Healthcare in India
- Rising Demand: Shifts in societal attitudes have led to more individuals seeking mental health support. Awareness and willingness to access treatment have notably increased.
- Professional Shortage: Despite the rising demand, there are only 0.75 psychiatrists per one lakh population, far below the World Health Organization’s recommendation of three per lakh. As of the latest data, India has about 9,000 psychiatrists, while an estimated 36,000 are needed to meet the standard.
- Slow Workforce Growth: Approximately 1,000 psychiatrists enter the workforce annually, but with attrition and unemployment, it could take around 27 years to reach the WHO target without intervention.
- Comparative Analysis: India has one of the lowest psychiatrist-to-population ratios among BRICS nations, trailing only Ethiopia. However, it performs better than many South Asian countries.
Limitations of Current Data
- Outdated Survey: The data largely relies on the National Mental Health Survey (NMHS) conducted between 2015 and 2016, which is based on a limited sample size of around 40,000 people across 12 states.
- Narrow Focus: The NMHS primarily addressed specific mental illnesses and overlooked milder conditions, emotional issues, and vulnerable populations like prisoners and the homeless.
- Need for Updated Research: A second NMHS is scheduled for release next year, which may provide more comprehensive data and insights.
Improvements in Awareness and Attitudes
- Positive Attitudinal Shift: A study by the LiveLoveLaugh Foundation found significant improvements in how Indians perceive mental health. For instance, the percentage of people believing that individuals with mental illnesses can handle responsibilities rose from 32% in 2018 to 65% in 2021.
- Willingness to Seek Help: Over 90% of respondents in 2021 indicated they would seek treatment for themselves or support others in doing so, a substantial increase from 54% in 2018.
- Increased Awareness: Awareness of mental health issues has grown, with 96% of respondents in 2021 recognizing mental health compared to 87% in 2018.
Conclusion
While India is making strides in reducing stigma and increasing awareness around mental health, the critical shortage of mental health professionals poses a significant barrier to accessing timely care. Addressing this issue requires targeted policy interventions and incentives to boost the supply of mental health professionals and improve the overall infrastructure for mental healthcare in the country.
Digital Agriculture Mission

- 03 Sep 2024
Introduction
India's digital revolution has significantly transformed governance and service delivery in recent years by creating digital identities, secured payments and transactions. This progress has paved the way for a thriving digital ecosystem across various sectors, including finance, healthcare, education, and retail, positioning India as a leader in citizen-centric digital solutions.
For a similar transformation of the Agriculture Sector, the Union Cabinet Committee, chaired by Prime Minister Narendra Modi approved the 'Digital Agriculture Mission' with a substantial financial outlay of Rs. 2,817 Crore, including a central government share of Rs. 1,940 Crore, on September 2, 2024.
The Digital Agriculture Mission is designed as an umbrella scheme to support various digital agriculture initiatives. These include creating Digital Public Infrastructure (DPI), implementing the Digital General Crop Estimation Survey (DGCES), and supporting IT initiatives by the Central Government, State Governments, and Academic and Research Institutions.
The scheme is built on two foundational pillars:
- Agri Stack
- Krishi Decision Support System.
Additionally, the mission includes ‘Soil Profile Mapping’ and aims to enable farmer-centric digital services to provide timely and reliable information for the agriculture sector.
AgriStack: Kisan ki Pehchaan
AgriStack is designed as a farmer-centric Digital Public Infrastructure (DPI) to streamline services and scheme delivery to farmers. It comprises three key components:
1. Farmers' Registry
2. Geo-referenced village maps
3. Crop Sown Registry
- A crucial feature of AgriStack is the introduction of a 'Farmer ID', similar to Aadhaar card, serving as a trusted digital identity for farmers.
- These IDs, created and maintained by the State Governments/ Union Territories, will be linked to various farmer-related data, including land records, livestock ownership, crops sown, and benefits availed.
- The implementation of AgriStack is progressing through partnerships between the Central and State Governments, with 19 states having signed MoUs with the Ministry of Agriculture. Pilot projects have been conducted in six states to test the creation of Farmer IDs and the Digital Crop Survey.
- The six states include Uttar Pradesh (Farrukhabad), Gujarat (Gandhinagar), Maharashtra (Beed), Haryana (Yamuna Nagar), Punjab (Fatehgarh Sahib), and Tamil Nadu (Virudhnagar).
Key targets include:
- Creating digital identities for 11 crore farmers over three years (6 crore in FY 2024-25, 3 crore in FY 2025-26, and 2 crore in FY 2026-27)
- Launching the Digital Crop Survey nationwide within two years, covering 400 districts in FY 2024-25 and all districts in FY 2025-26
2. Krishi Decision Support System
- The Krishi Decision Support System (DSS) will integrate remote sensing data on crops, soil, weather, and water resources into a comprehensive geospatial system.
3. Soil Profile Mapping
Under the mission, detailed soil profile maps on a 1:10,000 scale for approximately 142 million hectares of agricultural land have been envisaged, with 29 million hectares of soil profile inventory already being mapped.
- Further under the Digital Agriculture Mission, the Digital General Crop Estimation Survey (DGCES) will be used for crop-cutting experiments to provide precise yield estimates, enhancing agricultural production accuracy.
- The mission is expected to create direct and indirect employment in agriculture, providing opportunities for around 2,50,000 trained local youth and Krishi Sakhis.
- By leveraging modern technologies like data analytics, AI, and remote sensing, the mission will improve service delivery for farmers, including streamlined access to government schemes, crop loans, and real-time advisories.
Key Components of the Mission
The Digital Agriculture Mission focuses on grassroots implementation, targeting farmers as the primary beneficiaries. Some of the key benefits of the mission include:
- Digital authentication for accessing services and benefits, reducing paperwork and the need for physical visits.
- Enhanced efficiency and transparency in government schemes, crop insurance, and loan systems through accurate data on crop area and yield.
- Crop map generation and monitoring for better disaster response and insurance claims.
- Development of digital infrastructure to optimize value chains and provide tailored advisory services for crop planning, health, pest management, and irrigation.
Digital Public Infrastructure for Agriculture
- Union Finance Minister Nirmala Sitharaman announced in the Union Budget 2024-25 that the Government, in partnership with states, will implement Digital Public Infrastructure (DPI) for agriculture over the next three years.
- This initiative will cover farmers and their lands, with a digital crop survey for Kharif planned for 400 districts this year. The goal is to update registries with details of 6 crore farmers and their lands.
- The Union Budget 2023-24 had previously introduced the DPI for agriculture, which aims to provide comprehensive data on farmers, including demographic details, land holdings, and crops sown. The DPI will integrate with state and central digital infrastructures to offer a range of farmer-centric services, including information on livestock, fisheries, soil health, and available benefits.
Conclusion
- The Union Cabinet also approved six major schemes alongside the Digital Agriculture Mission, with a total outlay of Rs 14,235.30 crore.
- These initiatives include Rs 3,979 crore for Crop Science aimed at ensuring food security and climate resilience by 2047, and Rs 2,291 crore for strengthening Agricultural Education, Management, and Social Sciences to support students and researchers. Rs 1,702 crore is allocated for Sustainable Livestock Health and Production to boost incomes from livestock and dairy, while Rs 1,129.30 crore is designated for Sustainable Development of Horticulture to increase income from horticulture. Additionally, Rs 1,202 crore will be invested in strengthening Krishi Vigyan Kendra, and Rs 1,115 crore towards Natural Resource Management.
- These comprehensive approaches leverage digital technologies to enhance productivity, efficiency, and sustainability in India's agricultural sector, potentially transforming the lives of millions of farmers across the country. By extending the digital revolution to agriculture, India aims to further solidify its position as a global leader in innovative, technology-driven solutions for critical sectors of the economy.
Supreme Court of India

- 02 Sep 2024
In News:
On August 31, 2024, Prime Minister Narendra Modi inaugurated the National Conference of District Judiciary at Bharat Mandapam, New Delhi. This event marked the 75th anniversary of the Supreme Court of India, highlighted by the unveiling of a commemorative stamp and coin.
Supreme Court of India: History and Key Insights
The Origins of the Judiciary
- The concept of law, or Dharma, in ancient India was significantly influenced by the Vedas, which outlined rules of conduct and rituals in the Dharma Sutras. These texts addressed the duties of individuals and the rights of kings, forming the foundation of Hindu Law. The earliest systematic examination of jurisprudence can be found in Kautilya's Artha Sastra (circa 300 B.C.), particularly its third chapter, which discusses legal transactions and disputes.
Establishment of the Supreme Court
- The Regulating Act of 1773, enacted by the British Parliament, initiated the establishment of the Supreme Court of Judicature at Calcutta, with its Letters of Patent issued on March 26, 1774. This court had the authority to hear all complaints and lawsuits involving His Majesty’s subjects in Bengal, Bihar, and Orissa. Additional Supreme Courts were later established in Madras (1800) and Bombay (1823).
- The Indian High Courts Act of 1861 replaced these Supreme Courts with High Courts in various provinces, which became the highest judicial authorities until the Federal Court of India was created under the Government of India Act 1935. After India gained independence in 1947, the Supreme Court of India was formally established on January 26, 1950, with its inaugural session held on January 28, 1950.
- The Supreme Court's rulings are binding across India, and it possesses the power of judicial review to ensure that legislative and executive actions align with constitutional provisions and fundamental rights.
Structure and Functioning
- Initially, the Supreme Court operated for only a few hours each day and convened for 28 days a year. Today, it functions extensively, meeting approximately 190 days annually. The court was temporarily housed in the Parliament House before moving to its current location on Tilak Marg, New Delhi, in 1958.
- The court's architecture symbolizes justice, featuring a prominent dome and spacious corridors. It began with a Chief Justice and seven judges, with Parliament later increasing this number as the workload grew. Currently, the Supreme Court includes a Chief Justice and 30 judges.
Appointment and Qualifications of Judges
- Judges are appointed by the President of India, based on recommendations from a committee of senior judges (Collegium System). A candidate must be a citizen of India and have served as a High Court judge for at least five years or as an advocate for ten years. The age of retirement for judges is 65 years.
Judicial Independence and Removal
- Judicial independence is constitutionally protected. A Supreme Court judge can only be removed by the President on grounds of proven misbehavior or incapacity, following a resolution supported by a two-thirds majority in both Houses of Parliament.
Judicial Salaries and Provisions
- Judges’ salaries and pensions are defined by the Supreme Court Judges (Salaries and Conditions of Service) Act, 1958, and are charged to the Consolidated Fund of India.
Acting Chief Justice
- In the absence of the Chief Justice, the President appoints another judge as the Acting Chief Justice, as stipulated in Article 126.
Post-Retirement Opportunities
- While retired judges cannot practice law in India, they often serve in governmental roles, such as leading commissions. There have been calls for a "cool-off" period before such appointments.
Ad Hoc Judges
- Ad hoc judges may be appointed when necessary, and must meet the qualifications for Supreme Court judges. Retired judges can also be called back to serve temporarily.
Courts of Record
- Both the Supreme Court and High Courts are classified as courts of record, with the authority to punish for contempt as per Article 129.
Seat of the Supreme Court
- The Supreme Court is based in Delhi but can convene anywhere in India, with such decisions made by the Chief Justice in consultation with the President.
Samudra Pratap

- 02 Sep 2024
In News
Recently, the Indian Coast Guard (ICG) proudly launched the first indigenously built Pollution Control Vessel, ‘Samudra Pratap’, in Goa.
Key Highlights of the Launch
- Vessel Details:
- Built by Goa Shipyard Limited (GSL), the vessel is specifically designed to combat oil spills along India’s coastlines.
- Dimensions: Length: 114.5m, Breadth: 16.5m, Displacement: 4170 T.
- The keel laying ceremony took place on November 21, 2022.
- Contract and Construction: GSL signed a contract worth Rs 583 crores for the construction of two Pollution Control Vessels for the ICG. This marks the first instance of such vessels being designed and built entirely in India.
- Significance of the Vessel: ‘Samudra Pratap’ stands as a testament to India's shipbuilding capabilities, showcasing GSL's expertise in producing advanced Pollution Control Vessels and reinforcing India's commitment to indigenization in defense manufacturing.
Retired Sportsperson Empowerment Training (RESET) Programme

- 02 Sep 2024
In News:
Union Minister of Youth Affairs & Sports and Labour & Employment, Dr. Mansukh Mandaviya launched “Retired Sportsperson Empowerment Training” (RESET) Programme on the occasion of National Sports Day in New Delhi.
Key Highlights:
This programme aims to empower retired athletes by equipping them with essential career skills and knowledge, enhancing their employability and enabling them to contribute meaningfully to the sports ecosystem.
Eligibility Criteria
- Age: Retired athletes aged 20 to 50 years.
- Achievements:
- Must be winners of international medals or participants in international events.
- Alternatively, must have been national or state medallists or participants in competitions recognized by:
- National Sports Federations
- Indian Olympic Association
- Ministry of Youth Affairs and Sports.
Programme Structure
- Levels: Two tiers based on educational qualifications:
- Class 12th and above
- Class 11th and below
- Learning Mode: A hybrid approach, combining:
- Self-paced online learning through a dedicated portal.
- On-ground training for practical skill development.
Lead Institute
- Lakshmibai National Institute of Physical Education (LNIPE) will oversee the implementation and administration of the programme.
Support and Opportunities
- Placement Assistance: Comprehensive guidance for job placements in relevant sectors.
- Entrepreneurial Guidance: Support for athletes looking to start their own ventures in sports or related fields.
- Internships: Opportunities for hands-on experience in:
- Sports organizations
- Competitions
- Training camps
- Leagues
Implementation and Benefits
- Self-Paced Learning: Flexibility for participants to manage their learning schedules effectively.
- On-Ground Training: Hands-on practical sessions aimed at enhancing skills relevant to various career paths.
- Evaluation and Certification: Participants will be assessed and awarded a certificate upon successful completion, adding value to their career prospects.
The RESET Programme not only recognizes the achievements of retired athletes but also empowers them to leverage their experiences in new and impactful ways, fostering a robust sports ecosystem in India.
Queers can open Joint Bank Accounts

- 02 Sep 2024
In News:
Recently, the Union Government issued an advisory that LGBTQIA+ individuals and queer couples can open joint bank accounts. They can nominate each other as beneficiaries.
Key Details:
- Supreme Court Background:
- In October 2023, the Supreme Court of India urged the government to consider equal entitlements for partners in queer relationships.
- This was part of a judgment that did not recognize same-sex marriage but suggested enabling joint bank accounts and beneficiary nominations.
- Clarification from the Department of Financial Services:
- Issued on August 28, 2023, confirming no restrictions on opening joint accounts for the queer community.
- The Reserve Bank of India also clarified this to Scheduled Commercial Banks on August 21.
- Private Banks' Initiatives:
- Some banks, like Axis Bank, have been allowing joint accounts and beneficiary nominations for LGBTQIA+ couples since September 2021.
- Axis Bank expressed support for the Finance Ministry's advisory, noting alignment with its inclusive banking initiative.
- Government Committee Formation:
- In April 2023, a six-member committee was established to define entitlements for queer couples.
- Chaired by the Cabinet Secretary, it includes Secretaries from various ministries.
- The committee can co-opt experts if needed.
Project NAMAN

- 02 Sep 2024
In News:
- The Indian Army launched the first phase of Project NAMAN, aimed at supporting Defence Pensioners, Veterans, and their families.
- Key Features of Project NAMAN:
- Implements the SPARSH (System for Pension Administration Raksha) digital pension system.
- Streamlines pension processes and provides accessible facilitation points for Veterans and Next of Kin (NOK).
- Importance:
- Ensures care and support for veterans and their families.
- Services extended to residents of military stations and surrounding localities.
- Establishment of Common Service Centres (CSCs):
- Tripartite MoU signed between:
- Indian Army’s Directorate of Indian Army Veterans
- CSC e-Governance India Limited
- HDFC Bank Limited
- CSCs provide:
- SPARSH-enabled pension services
- Government to Citizen (G2C) services
- Business to Consumer (B2C) services
- Tripartite MoU signed between:
- Phase One Deployment:
- 14 CSCs established in key locations: New Delhi, Jalandhar, Leh, Dehradun, Lucknow, Jodhpur, Bengdubi, Gorakhpur, Jhansi, Secunderabad, Saugor, Guntur, Ahmedabad, Bangalore.
- Future expansion plans for approximately 200 centres nationwide in the next 2-3 years.
- Infrastructure Support:
- HDFC Bank provided necessary IT infrastructure.
- Local military stations contributed physical facilities.
- Community Engagement:
- Concept developed based on feedback from the Defence community.
- Promotes camaraderie among serving and retired Armed Forces personnel.
- Management of CSCs:
- Each CSC managed by a Village Level Entrepreneur (VLE) selected from veterans or NOKs by Local Military Authorities (LMAs).
- VLEs receive training from CSC e-Governance India Limited.
- HDFC Bank offers monthly grants of ?20,000 for the first 12 months to support VLEs.
- Conclusion:
- Project NAMAN reflects the Indian Army's commitment to veteran welfare.
- Offers SPARSH-centric services and entrepreneurial opportunities for Veterans and NOKs, empowering them to contribute to their communities.
Foot-and-Mouth Disease (FMD)

- 01 Sep 2024
In News:
- Establishment of Disease-Free Zones:
- The Union government plans to create FMD-free zones in eight states: Karnataka, Tamil Nadu, Andhra Pradesh, Telangana, Uttarakhand, Punjab, Haryana, Maharashtra, and Gujarat.
- Aim: Expand export opportunities for Indian animal products and enhance global market presence.
- Vaccination Efforts:
- Advanced vaccination initiatives are underway in the identified states, as stated by Alka Upadhyaya, Secretary of the Department of Animal Husbandry and Dairying.
- Collaborative Workshop:
- A workshop on ‘Animal Infectious Disease Prioritisation’ was held in collaboration with the Food and Agriculture Organisation.
- Focus: Prioritized 20 major animal infectious diseases based on severity, transmissibility, and national importance.
- Action Plan:
- Formulated focusing on five critical areas:
- Coordination
- Communication
- Monitoring and surveillance
- Prevention and control
- Therapeutics and socio-economic planning
- Formulated focusing on five critical areas:
- Regional Disease Prioritization:
- Strengthening regional-level prioritization of animal diseases for tailored control strategies.
- Overview of FMD:
- Highly contagious viral disease affecting cloven-hoofed animals like cattle, swine, sheep, and goats, but not horses or cats.
- Significant economic impact due to its effect on livestock production and trade.
Key Characteristics of FMD:
- Transmission:
- Virus present in excretions and secretions; aerosolized virus can infect other animals via respiratory or oral routes.
- Symptoms:
- Fever, blister-like sores on the tongue, lips, and hooves.
- High mortality in young animals, with production losses noted even post-recovery.
- Vaccination:
- Available vaccines must be matched to specific virus types/subtypes.
Repairability Index for Mobile and Electronic Sectors

- 01 Sep 2024
In News:
- The Department of Consumer Affairs (DoCA), Government of India, has established a committee of experts to create a framework for the Repairability Index.
- Objective:
- Enhance consumer transparency regarding product repairability.
- Promote sustainable practices in the tech industry.
- National Workshop:
- Held on August 29, 2024, focusing on the Right to Repair in the Mobile and Electronics Sector.
- Aimed to gather industry stakeholders to agree on evaluating components for the Repairability Index.
- Key Goals:
- Address the rapid demand and short lifespan of mobile and electronic devices.
- Provide essential repair information and ensure access to spare parts, even for discontinued products.
- Repairability Index:
- A consumer-focused tool that helps in making informed product decisions based on repairability.
- Aims to standardize repairability assessments, enabling easier product comparisons.
- Consumer Empowerment:
- The index fosters mindful consumption and sustainability.
- Ensures affordable repair options and improves overall consumer satisfaction by addressing information gaps.
- Key components of the Repair Ecosystem:
- Comprehensive Repair Information: Access to repair manuals/DIYs, diagnostics, and a list of necessary tools and parts.
- Accessible Spare Parts: Easily identifiable and timely delivery of spare parts.
- Affordable Tools: Inexpensive, widely available, and safe tools for consumers.
- Modular Design: Key components designed for independent access and modularity.
- Economic Feasibility: Ensuring that the cost of repair parts and labor is affordable for consumers.
Taking into account the above necessities the committee is expected to recommend enabling framework for Policies/Rules/Guidelines which support repairability and integration of repairability index with the extant regulatory provisions in mobile and electronics sector to enhance consumer experiences in reusing the mobile and electronics products they own.
The committee will submit a comprehensive report including a framework for repairability index in Indian context by 15th November, 2024.
India's Biotech Revolution

- 01 Sep 2024
In News:
The Indian Cabinet has recently approved the BioE3 (Biotechnology for Economy, Environment, and Employment) proposal, a significant move to advance the country’s biotechnology sector.
Scheduled to take effect on April 1, 2025, the BioE3 policy aims to capitalize on India's biotechnology potential by focusing on six key areas: bio-based chemicals, functional foods, precision biotherapeutics, climate-resilient agriculture, carbon capture, and marine/space research.
Current Status of India’s Biotechnology Sector
India ranks among the top 12 biotechnology destinations globally and is the third-largest in the Asia-Pacific region. As of 2024, India's Bioeconomy is valued at an estimated USD 130 billion. The sector is integral to India’s goal of becoming a USD 5 trillion economy by 2024, with biotechnology contributing about 3% to the global market share.
Biotechnology Categories in India:
- Biopharmaceuticals: India is a major supplier of low-cost drugs and vaccines, leading in biosimilars with the highest number of approvals.
- Bio-Agriculture: India dedicates approximately 55% of its land to agriculture, holding the fifth-largest area of organic agricultural land worldwide. The sector's contribution to the Bioeconomy is expected to grow from USD 10.5 billion to USD 20 billion by 2025.
- Bio-Industrial: Biotechnology is enhancing industrial processes, manufacturing, and waste disposal.
- Bio IT & BioServices: India excels in contract manufacturing, research, and clinical trials, hosting the highest number of US FDA-approved plants outside the US.
Government Initiatives:
- 100% foreign direct investment (FDI) is permitted in greenfield pharma and medical devices.
- The National Biotechnology Development Strategy 2021-25 aims to make India a global leader in biotechnology, targeting a USD 150 billion Bioeconomy by 2025.
- The Department of Biotechnology has established 51 Biotech-KISAN hubs to connect farmers with scientific advancements.
- The Union Budget 2023-24 includes INR 10,000 crore for 500 ‘waste to wealth’ plants under the GOBARdhan scheme.
- The GenomeIndia Project focuses on sequencing and analyzing the Indian population’s genomes to aid public health.
Challenges and Recommendations
Challenges:
- Regulatory Hurdles: The complex approval process for GMOs and overlapping regulatory bodies slow down progress.
- Funding Issues: Limited funding and high risks deter investment. The biotechnology sector receives only 0.05% of India's GDP from the Central Government.
- Infrastructure Gaps: Inadequate research facilities and cold chain infrastructure hamper progress.
- IP Concerns: Intellectual property protection remains weak, affecting innovation.
- Global Competition: Indian firms face stiff competition from established global players.
- Talent Shortages: A brain drain and skills mismatch impede growth.
- Ethical Dilemmas: Ethical issues related to GMOs and gene editing pose challenges.
Recommendations:
- Regulatory Streamlining: Establish a unified Biotechnology Regulatory Authority and adopt a risk-based assessment approach.
- Innovative Funding: Create a Biotechnology Investment Fund with public-private partnerships.
- Talent Development: Launch skill development programs and integrate biotech training into various disciplines.
- Infrastructure Investment: Develop shared high-end research facilities and upgrade cold chain infrastructure.
- IP Strengthening: Enhance the IPR regime and establish a Biotech Patent Pool.
- Leverage Make in India: Expand the Production Linked Incentive (PLI) scheme to cover more biotech products and establish specialized manufacturing corridors.
Unified Pension Scheme

- 01 Sep 2024
In News:
The new Unified Pension Scheme (UPS), set to launch on April 1, 2025, aims to provide improved old age income security. Around 23 lakh Central government employees will benefit from this new scheme, and those currently under the National Pension System (NPS) will have the option to switch to UPS. States can also adopt the UPS for their employees, but they will need to secure funding from their own resources.
Key Components of UPS
The UPS introduces several enhancements to pension benefits:
- Pension Benefits: Employees will receive half of their average basic pay over the final 12 months of service as a monthly pension after completing a minimum of 25 years of service. For those with less than 25 years, the pension will be proportionately reduced, with a minimum pension of ?10,000 for those with at least 10 years of service.
- Family Pension: A family pension equivalent to 60% of the employee's pension will be provided to dependents upon the employee's death.
- Inflation Adjustment: Pension incomes will be adjusted in line with the consumer price trends for industrial workers, similar to the dearness relief provided to current government employees.
- Superannuation Payout: In addition to gratuity, a lumpsum superannuation payout will be given, amounting to 1/10th of the employee’s monthly emoluments for every six months of service.
Differences from the Current System
The new UPS combines features from the Old Pension Scheme (OPS) and NPS:
- Old Pension Scheme (OPS): Employees who joined before January 1, 2004, are covered under OPS, which guarantees a pension of 50% of the last drawn salary, adjusted for dearness allowance. It also offers a family pension of 60% of the last drawn pension, with provisions for commutation and additional increases for pensioners over 80 years of age.
- National Pension System (NPS): Introduced in 2004, NPS replaced OPS for new employees, shifting from a defined benefits system to a defined contribution scheme. Employees and the employer contribute a percentage of the salary to market-linked securities, with no guaranteed pension amount, only a corpus that must be used to buy an annuity upon retirement.
The UPS aims to blend the certainty of OPS with the funded approach of NPS. While employees' contributions will be capped at 10% of their salary, the government will contribute 18.5%, with potential adjustments over time. The government will cover any shortfall between investment returns and pension promises.
Reasons for the Change
The transition to UPS addresses concerns raised by government employees and political pressure regarding the NPS. Employees have criticized NPS for its lack of guaranteed pension benefits compared to OPS. The issue has become politically significant, with opposition parties promising to revert to OPS in various states.
In March 2023, Finance Minister Nirmala Sitharaman announced a review of NPS led by former Finance Secretary T.V. Somanathan. Though the review’s findings are yet to be made public, the introduction of UPS reflects a compromise balancing employee expectations with fiscal prudence.
Reactions and Future Impact
Central government employees generally welcome the UPS, recognizing it as a step toward addressing the shortcomings of NPS. However, there are concerns about the contributory nature of UPS and the absence of a commutation option like in OPS. Economists are analyzing the scheme's financial implications, with an expected additional cost of ?7,050 crore this year for the government. Future pension payouts may increase but are anticipated to be manageable with higher revenue growth.
The UPS marks a significant shift in pension policy, aiming to provide greater financial security for government employees while managing fiscal responsibilities.
New Target for Cancer Treatment Discovered by IACS Scientists

- 01 Sep 2024
In News:
In a significant breakthrough, scientists at the Indian Association for the Cultivation of Science (IACS) in Kolkata have identified a new target for cancer therapy. Their study, recently published in The EMBO Journal, focuses on how cancer cells manage DNA repair during cell division, potentially paving the way for more effective treatments.
Key Findings
The researchers explored how cancer cells respond to topoisomerase 1 (Top1)-targeted chemotherapy. Top1 inhibitors, such as camptothecin, topotecan, and irinotecan, disrupt DNA replication and transcription, causing damage that usually leads to cell death. However, cancer cells can sometimes develop resistance by employing internal DNA repair mechanisms, primarily involving a protein called TDP1.
Mechanism of Action
Top1 is crucial for relaxing DNA supercoils during cell division, a process necessary for accurate chromosome segregation. Drugs targeting Top1 can kill cancer cells by preventing this relaxation. Nonetheless, cancer cells counteract this damage with TDP1, which repairs the DNA and promotes cell survival.
The IACS team discovered that TDP1's function is influenced by its phosphorylation status, which changes during the cell cycle and drug treatment. This modification helps TDP1 detach from chromosomes during cell division, a mechanism that helps cells survive despite the presence of chemotherapy drugs.
Novel Therapeutic Approach
The researchers propose a novel approach that combines inhibitors of two key molecules: CDK1 protein and TDP1 enzyme. CDK1 plays a critical role in regulating the cell cycle, while TDP1 is involved in repairing DNA damage. By inhibiting both, the researchers aim to disrupt the cancer cell's ability to repair DNA damage caused by Top1 inhibitors.
This combinatorial targeting strategy could enhance the effectiveness of cancer treatments. While Top1 inhibitors induce DNA damage, CDK1 inhibitors could prevent the repair of this damage or halt the cell cycle, making it difficult for cancer cells to survive. This dual-target approach may also help overcome resistance mechanisms that cancer cells develop against single-agent therapies.
Clinical Implications
CDK1 inhibitors, including avotaciclib, alvocidib, roniciclib, riviciclib, and dinaciclib, are currently in various stages of clinical trials. These drugs can be used alone or in combination with other DNA-damaging agents. Combining CDK1 inhibitors with Top1 inhibitors holds promise for significantly improving cancer treatment outcomes by targeting different aspects of the cell cycle and DNA replication.
Although the study was conducted using human breast cancer cells, the findings suggest potential benefits for patients with other types of cancer, such as ovarian, colorectal, and small cell lung cancers (SCLC). SCLC, in particular, is associated with tobacco smoking and could potentially benefit from this new combinatorial approach.
Conclusion
The IACS study opens new possibilities for cancer treatment by targeting DNA repair mechanisms in cancer cells. By combining CDK1 and Top1 inhibitors, the researchers aim to enhance the effectiveness of chemotherapy and overcome resistance. Further research, including clinical trials, will be essential to validate these findings and develop personalized cancer therapies that could improve patient outcomes across various cancer types.
Recent Announcement on Dark Matter Research
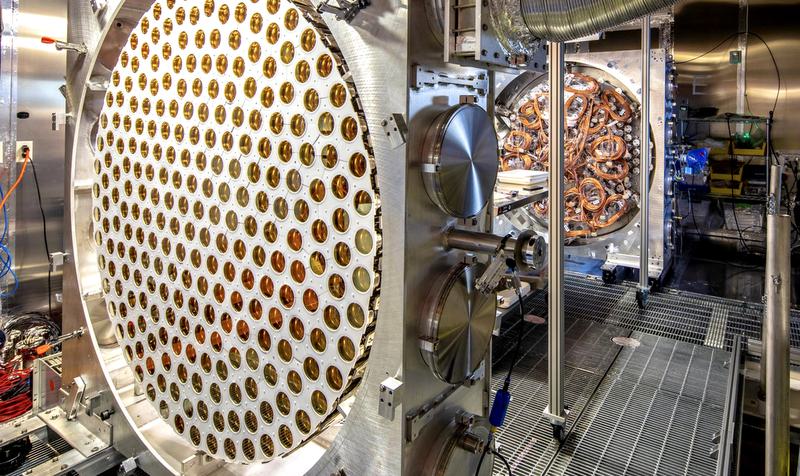

- 30 Sep 2024
In News:
Recently two representatives from the LUX-ZEPLIN (LZ) experiment, working 1.5 km underground at the Sanford Underground Research Facility in South Dakota, announced that they had placed the tightest restrictions yet on the identities of dark matter particles, resulting in a null finding that clarified which identities these particles could not have, leading to a sense of resignation rather than disappointment among the physics community, as similar experiments like XENON-nT in Italy and PandaX-4T in China have yielded empty results for decades despite significant efforts.
Background on Dark Matter
- Definition: Dark matter makes up most of the universe's mass, contributing to its structure.
- Composition: Likely consists of previously unknown particles that:
- Do not interact with photons.
- Remain stable over billions of years.
- Key Question: Can dark matter interact with atomic nuclei and electrons?
Experimental Strategies
- Proposed Method:
- Introduced by physicists Mark Goodman and Ed Witten in 1985.
- Concept: Use a “sail” (a chunk of metal) deep underground to detect dark matter interactions.
- Objective: Measure unknown mass and interaction rate (cross-section) of dark matter particles.
Scattering Cross-Section
- Concept:
- Similar to light interaction with different media (vacuum, glass, rock).
- Cross-sections indicate how readily a particle can scatter.
- Previous Limits: Proposed limits as small as 10−38cm210^{-38} text{cm}^210−38cm2.
- Current Achievements: Recent experiments have ruled out cross-sections as small as 10−44cm210^{-44} text{cm}^210−44cm2.
Challenges Ahead
- Neutrino Interference:
- As detectors increase in size, they also detect more noise from neutrinos, complicating dark matter detection.
- Both PandaX-4T and XENONnT report issues with neutrino signals.
- Resignation in Community:
- Scientists had hoped for clearer results before facing the challenge of distinguishing dark matter from neutrinos.
Alternative Research Avenues
- Focus on Lighter Particles:
- Exploring dark particles lighter than atomic nuclei for easier detection.
- Technological Development:
- Advancing technologies to measure minimal energy transfers using special materials.
Conclusion
- Ongoing Effort: The search for dark matter continues to unite scientific disciplines and require innovative approaches.
- Human Ingenuity: The pursuit reflects a broader effort to understand the universe, drawing on collective expertise and creativity.
NAMASTE programme

- 30 Sep 2024
In News:
A recent government survey has shed light on the demographics of workers engaged in the hazardous cleaning of urban sewers and septic tanks across India. This initiative, part of the Ministry of Social Justice and Empowerment's NAMASTE programme, highlights significant disparities within this labor sector.
Key Findings
- Community Representation: An overwhelming 91.9% of the 38,000 workers profiled belong to marginalized communities:
- Scheduled Castes (SC): 68.9%
- Other Backward Classes (OBC): 14.7%
- Scheduled Tribes (ST): 8.3%
- General Category: 8%
- Mortality Rates: Between 2019 and 2023, at least 377 individuals died while performing hazardous cleaning tasks, underscoring the dangers associated with this work.
The NAMASTE Programme
- Objective: The NAMASTE programme aims to mechanize sewer work to prevent fatalities linked to manual cleaning. It seeks to transition workers into safer, more sustainable roles as "sanipreneurs" by providing safety training, equipment, and capital subsidies.
- Background: This programme replaces the earlier Self-Employment Scheme for Rehabilitation of Manual Scavengers (SRMS), focusing on the more technical aspects of hazardous cleaning rather than manual scavenging.
- Namaste is a Central Sector Scheme of the Ministry of Social Justice and Empowerment (MoSJE) as a joint initiative of the MoSJE and the Ministry of Housing and Urban Affairs (MoHUA).
- The Scheme has been approved with an outlay of Rs. 360 crore for four years from 2022-23 to 2025-26.
- NAMASTE aims to achieve the following outcomes:
- Zero fatalities in sanitation work in India
- All sanitation work is performed by skilled workers
- No sanitation workers come in direct contact with human faecal matter
- Sanitation workers are collectivized into SHGs and are empowered to run sanitation enterprises
- All Sewer and Septic tank sanitation workers (SSWs) have access to alternative livelihoods
- Strengthened supervisory and monitoring systems at national, state and ULB levels to ensure enforcement and monitoring of safe sanitation work
- Increased awareness amongst sanitation services seekers (individuals and institutions) to seek services from registered and skilled sanitation workers
Progress and Coverage
- Implementation: Since the scheme's inception, 3,326 urban local bodies (ULBs) have begun profiling workers, with many reporting minimal or no workers engaged in hazardous cleaning.
- Data Collection: The government is gathering data from over 3,000 ULBs across 29 states and union territories to better understand the scope and risks associated with this labor.
AVGC: The Future of Media & Entertainment Industry

- 30 Sep 2024
Introduction
- The AVGC (Animation, Visual Effects, Gaming, Comics) sector is set to be the future of the media and entertainment industry.
- According to the FICCI-EY 2024 report, India now boasts the second-largest anime fan base globally and is projected to contribute 60% to the worldwide growth in anime interest in the coming years.
- In a significant step toward making India a global hub for AVGC, the Union Cabinet recently approved the establishment of a National Centre of Excellence (NCoE) for Animation, Visual Effects, Gaming, Comics, and Extended Reality (AVGC-XR) in Mumbai.
NCoE Background
- NCoE will be set up as a Section 8 Company under the Companies Act, 2013 in India with Federation of Indian Chambers of Commerce & Industry and Confederation of Indian Industry representing the industry bodies as partners with the Government of India.
- The establishment of the NCoE follows the Union Minister of Finance and Corporate Affairs 2022-23 budget announcement, which proposed the creation of an AVGC task force in the country.
- NCoE AVGC aims at creating a world class talent pool in India to cater to the Indian as well as global entertainment industry.
- Provisionally named the Indian Institute for Immersive Creators (IIIC), this center aims to revolutionize the AVGC sector and foster innovation in immersive technologies.
- It will be modeled after renowned institutions like the Indian Institutes of Technology (IITs) and Indian Institutes of Management (IIMs).
Objective of NCoE (IIIC)
Boasting a growth rate of 25% and an estimated value of ?46 billion by 2023 (FICCI-EY Report 2023), the animation industry in India is thriving and offers a promising future for passionate young talent.
Below are some of the key objectives of the NCoE (IIIC):
- Focusing of creating Indian IP
- Leveraging our cultural heritage in new age
- Create a multiplier effect in the industry
- An industry led initiative, in partnership with state and academia
- Integrated focus on education, skilling industry, development, innovation
- Hub and spoke model of development to be followed
- IIIC as the hub and several center’s as its spokes dedicated innovation and research fund to promote start-up ecosystem
Conclusion
The Union Cabinet's approval of the National Centre of Excellence (NCoE) for AVGC marks a pivotal step in strengthening India’s media and entertainment industry. This initiative is set to boost the economy while creating new job opportunities in the rapidly growing AVGC sector. As a global hub for filmmaking, India's advancements in technology and infrastructure will enable the production of high-quality content, positioning the country as a leader in technological innovation and creativity.
MARBURG VIRUS OUTBREAK IN RWANDA
- 30 Sep 2024
In News:
Rwanda is currently facing an outbreak of Marburg virus disease (MVD), leading to six fatalities, primarily among healthcare workers.
What is Marburg Virus Disease?
Marburg virus disease is a severe and often fatal illness first identified in 1967 in Germany. It is caused by the Marburg virus, which is primarily transmitted to humans through contact with infected animals, particularly fruit bats.
Current Situation in Rwanda
The ongoing outbreak has claimed six lives, most of whom were healthcare professionals. The Minister of Health has emphasized the need for heightened preventive measures and community vigilance.
Symptoms and Transmission
Common symptoms of MVD include high fever, severe headache, watery diarrhea, abdominal pain, and vomiting. The virus spreads through direct contact with the blood, secretions, and bodily fluids of infected individuals.
Available Treatments and Supportive Care
There is currently no specific treatment for Marburg virus disease. Supportive care, including symptom management and hydration, is critical, and early medical attention is essential for those exhibiting symptoms.
Preventive Measures and Recommendations
To prevent the spread of MVD, individuals should:
- Practice good hygiene.
- Avoid contact with infected persons.
- Ensure thorough cooking of animal products.
- Use protective equipment when caring for sick patients.
Global Context and Pandemic Risk
While Marburg virus disease poses a significant mortality risk and can spread between humans, its pandemic potential is lower than that of more contagious viruses. Rapid containment efforts are essential to prevent wider outbreaks.
INDIA DESERVES PERMANENT UNSC SEAT: BHUTAN

- 30 Sep 2024
In News:
With its significant economic growth and leadership of the Global South, India deserves a permanent seat at the UN Security Council, says Bhutan’s Prime Minister Tshering Tobgay.
Key Highlights:
- Economic Growth: Highlights India’s significant economic growth and its leadership in the Global South as justifications for this status.
- International Backing: India’s bid gains momentum with support from several UN Member States, including France, the UK, and the U.S.
- Need for Reform: Bhutan emphasized that the UNSC is outdated and must evolve to reflect contemporary geopolitical and economic realities.
- Advocacy for Representation: Bhutan has long called for a more representative and effective Security Council, backing India’s inclusion at the high table.
About UN Security Council (UNSC)
- Composition: Total of 15 member states.
- 5 permanent members (P5): China, France, Russia, the United Kingdom, and the United States (with veto rights).
- 10 non-permanent members elected for two-year terms.
- Election of Non-Permanent Members:
- Elected on a regional basis:
- 5 seats for African and Asian states.
- 2 seats for Latin American and Caribbean states.
- 1 seat for Eastern European states.
- 2 seats for Western European and other states.
- Elected on a regional basis:
- Presidency:
- Rotates monthly among members, following the English alphabetical order of country names.
- Primary Functions:
- Maintain international peace and security.
- Investigate and resolve disputes.
- Impose sanctions and authorize the use of force.
- Establish peacekeeping missions.
- Make recommendations to member states.
- Meeting Schedule:
- Regular meetings at UN headquarters in New York.
- Can convene at any time in response to emergencies.
- Decision-Making:
- Requires affirmative votes from at least 9 of the 15 members.
- Any of the P5 can veto resolutions, raising concerns about the Council's effectiveness.
- Subsidiary Bodies:
- Includes committees, working groups, and sanctions committees focused on specific issues like counter-terrorism, nuclear non-proliferation, and peacekeeping operations.
- Reforming the UN Security Council (UNSC)
- Charter Amendments:
- Reforming the UNSC requires amendments to the UN Charter.
- Voting Requirements:
- An amendment must be adopted by a two-thirds majority of the General Assembly.
- It must also be ratified by two-thirds of UN member states, including all permanent members of the UNSC.
- Charter Amendments:
Paryatan Mitra and Paryatan Didi

- 29 Sep 2024
In News:
- The Ministry of Tourism, Government of India, launched the national responsible tourism initiative ‘Paryatan Mitra & Paryatan Didi’ on September 27, 2024, coinciding with World Tourism Day.
- Vision: Aligned with the Prime Minister's vision to use tourism as a tool for social inclusion, employment, and economic development.
Pilot Locations
- Destinations: The initiative is piloted in six tourist destinations:
- Orchha (Madhya Pradesh)
- Gandikota (Andhra Pradesh)
- Bodh Gaya (Bihar)
- Aizawl (Mizoram)
- Jodhpur (Rajasthan)
- Sri Vijaya Puram (Andaman & Nicobar Islands)
Objectives and Training
- Enhancing Tourist Experience: The program aims to connect tourists with ‘tourist-friendly’ individuals who serve as local ambassadors and storytellers.
- Training Focus: Individuals interacting with tourists—such as cab drivers, hotel staff, street vendors, and students—receive training on:
- Importance of tourism and hospitality
- Cleanliness and safety
- Sustainability practices
- Local stories and attractions
Empowering Women and Youth
- Target Groups: Emphasis on training women and youth to develop tourism products such as:
- Heritage walks
- Food and craft tours
- Nature treks and homestays
- Employment Opportunities: Aims to enable locals to secure jobs as homestay owners, cultural guides, and adventure guides.
Digital Literacy
- Training in Digital Tools: Participants are also educated in digital literacy to enhance visibility of their offerings to tourists.
Impact and Recognition
- Training Success: Since the program's pilot in August 2024, approximately 3,000 individuals have been trained.
- Local Enthusiasm: Increased local interest in participating in tourism training programs and contributing to the tourism ecosystem.
- Future Recognition: The Ministry plans to award dedicated badges to Paryatan Mitra and Didi participants, ensuring tourists can identify those committed to providing exceptional experiences.
ETURNAGARAM WILDLIFE SANCTUARY

- 29 Sep 2024
In News:
A rare collision of two cyclones has led to significant environmental impact, including the flattening of thousands of trees within the sanctuary.
Key Details:
- Location: Situated in the Mulugu district of Telangana, near the borders of Maharashtra and Chhattisgarh. Approximately 100 km from Warangal and 250 km from Hyderabad.
- Establishment: Declared a wildlife sanctuary in 1952 by the Nizam government of Hyderabad.
- Area: Covers around 806 square kilometers.
Geographic Features
Rivers:
- Dayyam Vagu: A significant water source that divides the sanctuary into two parts.
- Godavari River: Flows through the sanctuary, contributing to its rich biodiversity.
Flora
- Vegetation: Dense tropical dry deciduous forest.
- Key Species: Includes teak, bamboo, madhuca, and terminalia trees, creating a lush habitat.
Fauna
- Wildlife: Home to diverse species such as:
- Mammals: Tiger, leopard, panther, wolf, wild dogs, jackals, sloth bear, chousingha, blackbuck, nilgai, sambar, spotted deer, and four-horned antelope.
- Reptiles: Notable for its population of mugger crocodiles and snakes, including cobras, pythons, and kraits.
Cultural Significance
- Temple: The famous Sammakka-Saralamma Temple is located within the sanctuary.
INDIA TO SUPPORT TRINIDAD AND TOBAGO IN DEVELOPING UPI-LIKE PAYMENT SYSTEM

- 29 Sep 2024
In News:
- NPCI International Payments Limited (NIPL) has partnered with Trinidad and Tobago's Ministry of Digital Transformation to create a payment platform for person-to-person and person-to-merchant transactions.
- Modeling on UPI: The new digital payments system will be based on India’s Unified Payments Interface (UPI), which is widely recognized as a leading digital payment solution.
- Role of NPCI: NIPL, a quasi-government body under the Reserve Bank of India, manages India’s retail payment systems, including UPI.
Previous Initiatives
- Global Expansion: Earlier in 2024, NIPL also committed to establishing digital payment systems in Peru and Namibia, leveraging the UPI model.
- Ongoing Talks: NIPL is exploring opportunities with additional countries in Africa and South America to assist in building their payment infrastructures.
Significance:
- UPI has emerged as a transformative force in India's financial landscape, registering nearly 15 billion transactions in August 2024, with an estimated value of USD 245 billion.
- This strategic partnership aims to empower Trinidad and Tobago to establish a reliable and efficient real-time payments platform for both person-to-person (P2P) and person-to-merchant (P2M) transactions, expanding digital payments in the country and fostering financial inclusion.
India’s Commitment to Social Determinants of Health at UNGA
- 29 Sep 2024
In News:
- Union Minister of State for Health and Family Welfare, represented India at the G20 Joint Finance-Health Task Force meeting during the 79th UN General Assembly.
- Focus: The session emphasized the importance of investing in health and addressing social determinants of health (SDH) through initiatives like debt-for-health swaps.
Key Highlights:
- Role of SDH: Underscored how social determinants such as housing, sanitation, water access, and income security are crucial for health investment priorities.
- Flagship Programs: India’s notable initiatives include:
- Ayushman Bharat: The world’s largest health insurance scheme.
- Swachh Bharat Mission: Aiming for a cleaner India.
- Jal Jeevan Mission: Ensuring water access for all.
- Pradhan Mantri Awas Yojana: Promoting housing for all.
- Impact of PM-JAY: Highlighted improvements in access to healthcare and outcomes, especially for non-communicable diseases.
Data and Policymaking
- Importance of Data: Stressed the need for enhanced data availability and standardization on SDH indicators to support effective policymaking.
- Unified Approach: Called for G20 nations to collaborate on data collection and analysis for better health systems globally.
Exploring Debt-for-Health Swaps
- Potential Mechanism: Discussed debt-for-health swaps as a means to relieve financial pressure while promoting health equity.
- Next Steps: Emphasized the need for stakeholder engagement and pilot programs to ensure effective implementation.
Conclusion
- Global Leadership: India reaffirmed its commitment to health equity through evidence-based policies and partnerships.
- Shared Vision: Advocated for a unified effort towards achieving “Health for All,” highlighting the significance of investments in social determinants of health.
About Social determinants of health (SDOH)
- SDOH are non-medical factors that affect a person's health, well-being, and quality of life. They include the conditions in which people are born, grow, work, live, and age.
- SDOH also include the broader systems that shape everyday life, such as economic policies, social norms, and political systems.
- Some examples of SDOH include:
- Safe housing, transportation, and neighborhoods
- Racism, discrimination, and violence
- Education, job opportunities, and income
- Access to nutritious foods and physical activity opportunities
- Polluted air and water
- Language and literacy skills
GST COMPENSATION CESS

- 29 Sep 2024
In News:
- GST compensation cess likely to continue beyond January 2026, with potential rebranding and new end-use defined.
- Revenue Collection: Estimated Rs 20,000 crore expected from the cess by February 2026, with recent receipts of Rs 12,068 crore in August 2024.
- Cess Nature: The compensation cess, originally intended for revenue shortfall, cannot merge with the 28% GST slab due to regulatory limitations.
Financial Context
- RBI Study Insights: Weighted average GST rate decreased from 14.4% at launch to 11.6%, now even below 11%, raising concerns among states.
- State Concerns: Many states, including Punjab and Kerala, seek a 2-5 year extension for the compensation period to stabilize finances.
Regulatory Framework
- Cess Legislation: GST Compensation Cess is governed by the Goods and Services Tax (Compensation to States) Act, 2017, initially set for five years.
- Taxpayer Obligations: All suppliers of designated goods/services must collect the cess, except exporters and those under the composition scheme.
Distribution Mechanism
- Calculation of Compensation: Based on projected revenue growth (14%) against actual revenue, with payments distributed bi-monthly.
- Surplus Distribution: Any surplus in the compensation fund post-transition period will be shared between the Centre and states.
Future Considerations
- Ministerial Panel: A panel established by the GST Council will recommend the cess's future and revenue sharing post-compensation.
- Tax Expert Opinions: Some experts argue against pursuing the revenue-neutral rate, suggesting broader tax base expansion instead.
- Revenue Gap Solutions: Options for addressing compensation fund deficits include revising cess formulas, increasing rates, or market borrowing.
IBSA (INDIA, BRAZIL, SOUTH AFRICA) GROUPING

- 28 Sep 2024
In News:
In a significant move for global security, the Foreign Ministers of the IBSA (India, Brazil, South Africa) grouping issued a strong declaration against terrorism during the 79th UN General Assembly in New York. This declaration condemned terrorism in all its forms and reaffirmed the collective responsibility of the international community to eliminate terrorist safe havens worldwide.
Key Points from the IBSA Declaration:
- Universal Threat: The ministers stressed that terrorism is a threat that transcends borders, cultures, and governments.
- Rule of Law: They emphasized that counter-terrorism efforts must adhere to international law, particularly the UN Charter and human rights laws, ensuring civil liberties are respected.
- International Framework: A call was made for establishing a comprehensive international counter-terrorism framework, with the United Nations at its core, to coordinate global efforts against terrorism.
- Cross-Border Security: The declaration highlighted the need for stringent actions against the movement of terrorists and the financing of terrorist networks, condemning groups like Al-Qaeda, ISIS/Daesh, Lashkar-e-Tayyiba (LeT), and Jaish-e-Mohammad (JeM).
- Comprehensive Convention: A renewed commitment to accelerate the adoption of the Comprehensive Convention on International Terrorism at the UN was emphasized, aiming to create a unified legal framework for combating terrorism.
POLITICAL DECLARATION ON ANTIMICROBIAL RESISTANCE (AMR)

- 28 Sep 2024
In News:
World leaders have officially adopted the Political Declaration on Antimicrobial Resistance (AMR) at the UN High-Level Meeting, highlighting the urgent need for coordinated global action to combat AMR, which claims 1.27 million lives annually. This declaration recognizes drug-resistant tuberculosis (DR-TB) as a critical component of the global AMR response, marking a significant moment in the fight against antimicrobial resistance.
Key Highlights of the Declaration
- DR-TB Priority: The declaration emphasizes the severe burden that DR-TB imposes on health systems, especially in low- and middle-income countries (LMICs), and the potential reversal of progress made against tuberculosis and the Sustainable Development Goals.
- Global Death Reduction Target: A target to reduce global deaths associated with AMR by 10% by 2030 and a funding goal of USD 100 million to help at least 60% of countries establish funded AMR plans by 2025.
- Support for Vulnerable Groups: Recognition of the socioeconomic challenges faced by those affected by AMR, affirming the need for integrated, person-centered healthcare, including support to reduce stigma.
- Independent Panel for Action: Agreement to establish an independent panel to provide evidence for actions against AMR by 2025.
Commitment to Action
The Stop TB Partnership applauds this commitment and urges UN Member States to provide necessary funding for implementing the declaration's commitments. The partnership aims to work closely with governments and civil society to translate these commitments into concrete actions.
Challenges of Antimicrobial Resistance
AMR poses a significant threat, particularly in LMICs, where it exacerbates existing healthcare challenges:
- Increased Infections: Medical facilities often become hotspots for treatment-resistant infections, making routine procedures riskier. In LMICs, about 11% of surgical patients experience infections.
- Lack of Resources: Access to clean water, proper diagnostics, and antimicrobial medicines is often limited, increasing vulnerability to drug-resistant infections.
- Impact of Conflicts: AMR complicates treatment in conflict zones, where drug-resistant infections spread rapidly among displaced populations, further emphasizing the need for peaceful resolutions.
Economic Implications of AMR
The economic case for addressing AMR is compelling:
- Without a stronger response, AMR could lead to an additional $412 billion in healthcare expenditures annually over the next decade, along with $443 billion in losses due to workforce participation and productivity declines.
- Implementing critical AMR interventions is considered a “best buy,” with a potential return of $7 to $13 for every dollar invested.
AYUSHMAN BHARAT DIGITAL MISSION (ABDM)

- 28 Sep 2024
In News:
Over 67 crore Ayushman Bharat Health Accounts (ABHA) have been created in the past three years under the Ayushman Bharat Digital Mission (ABDM). The digital healthcare mission marked its three-year anniversary.
Key Highlights:
- Launch Date: September 27, 2021.
- Vision: Establish a robust digital health infrastructure to enhance healthcare accessibility, efficiency, and transparency.
- Duration: A transformative three-year journey aimed at revolutionizing India’s digital healthcare ecosystem.
Objectives and Background
- Alignment with National Health Policy: The mission stems from the National Health Policy (2017), emphasizing accessibility and the integration of digital technologies.
- Building Blocks:
- National Health Stack (2018) introduced unique health identifiers and verified registries.
- National Digital Health Blueprint (2019) provided guidance for implementing ABDM.
Key Features of ABDM
- Unique Health Identifier (ABHA ID): Assigns a unique ID to every individual for managing health records.
- Healthcare Professionals Registry (HPR): Comprehensive database of healthcare professionals across all systems of medicine.
- Health Facility Registries (HFR): Repository of public and private health facilities, including hospitals, clinics, and pharmacies.
- Health Information Exchange and Consent Manager (HIE-CM): Allows secure access and sharing of health records based on informed consent.
- Unified Health Interface (UHI): Facilitates the discovery and delivery of health services.
- National Health Claims Exchange (HCX): Standardizes the insurance payment process for quicker claims.
- Data Privacy and Security: Ensures confidentiality and security of health-related information in compliance with the Digital Personal Data Protection Act, 2023.
- Interoperability: Enables seamless data exchange among stakeholders, supported by key gateways (HIE-CM, NHCX, UHI).
- Transparency: Offers individuals access to both public and private health services, ensuring transparent pricing and accountability.
Key Initiatives
- Scan and Share: QR-code based OPD registration reduces wait times and improves data accuracy.
- Digital Health Incentive Scheme (DHIS): Financial incentives to encourage participation in the ABDM ecosystem, launched on January 1, 2023.
- Microsites for Private Sector Adoption: Operationalized 106 microsites to facilitate ABDM adoption among private providers.
- End-to-End ABDM Adoption Pilot: Aimed at digitizing healthcare facilities across India, with 131 selected for participation.
Achievements
- Health Accounts Creation: Over 67 crore Ayushman Bharat Health Accounts (ABHA) established, linking 42 crore health records.
- Ecosystem Participation: Involvement of 236 private entities and leading public institutions, enhancing interoperability.
- Healthcare Facility Registration: 3.3 lakh health facilities and 4.7 lakh healthcare professionals registered.
Moving Towards Transformation
- Collaborations: Partnerships with IIT Kanpur and Maharashtra University of Health Sciences to drive digital health education and public goods development.
- Training Initiatives: Introduction of a WhatsApp Chatbot for stakeholder training on digital health practices.
- Digital Health Standards: Launched by the National Accreditation Board of Hospitals to promote digital health technology adoption.
- Integration of eSwasthya Dham Portal: Extends ABDM benefits to Char Dham Yatris.
Vision for the Future
ABDM aims to create a seamless digital health ecosystem, ensuring every Indian citizen has access to their health records through a unique ABHA ID. The initiative includes:
- Clinical Decision Support System (CDSS): Aids healthcare professionals in improving clinical decision-making and patient outcomes.
INDIA-UZBEKISTAN BILATERAL INVESTMENT TREATY (BIT)

- 28 Sep 2024
In News:
India and Uzbekistan signed the Bilateral Investment Treaty (BIT) aimed at boosting the confidence of investors of both the countries.
Key Highlights:
- Investor Protections:
- Assured Protection: The BIT guarantees protection for investors from both countries, aligning with international standards.
- Minimum Standards: It establishes a minimum standard of treatment and non-discrimination for investors.
- Dispute Resolution: An independent arbitration forum will be available for dispute settlement.
- Investment Safeguards:
- Protection from Expropriation: The treaty safeguards investments from unjust expropriation.
- Transparency and Compensation: Provisions are included for transparency and compensation for losses incurred.
- Regulatory Balance: While protecting investors, the treaty maintains a balance with the state's right to regulate, ensuring adequate policy space for both countries.
Economic Context
- Shared Commitment: The BIT reflects the commitment of both nations to foster economic ties and create a resilient investment environment.
- Expected Outcomes: It is anticipated that the treaty will facilitate increased bilateral investments, benefiting businesses and economies in India and Uzbekistan.
- Current Investment Landscape: As of August 2024, Overseas Direct Investment (ODI) from India to Uzbekistan stands at $20 million, with Indian investments notable in sectors such as pharmaceuticals, amusement parks, automobile components, and hospitality.
India and Bilateral Investment Treaties
BITs are reciprocal agreements between two countries designed to promote and protect foreign private investments within each other's territories.
- Key Guarantees Established:
- National Treatment: Foreign investors are treated on par with domestic companies.
- Fair and Equitable Treatment: Investors receive treatment aligned with international law.
- Protection from Expropriation: Limits the ability of a country to seize foreign investments without appropriate compensation.
- Status of BITs in India
- Historical Context:
- Until 2015, India had signed BITs with 83 countries, with 74 currently in force. These agreements were based on the Indian Model BIT established in 1993.
- Revisions and Current Approach: In 2015, India revised its Model BIT text. Since then, India has:
- Signed new BITs/Investment Agreements with four countries.
- Entered negotiations with 37 countries/blocks for new agreements.
- Terminated older BITs with 77 countries, with only six remaining in force.
- Historical Context:
- Key Features of the Revised Model BIT
- Investor Protection:
- Provides robust protection for foreign investors in India and Indian investors abroad.
- Balances investor rights with government obligations.
- Investor Confidence:
- Enhances investor confidence by ensuring non-discriminatory treatment and a level playing field.
- Establishes an independent arbitration forum for dispute resolution.
- Investment Definition:
- Adopts an "enterprise"-based definition of investment to encompass various forms of investment.
- Dispute Settlement Provisions:
- Refined Investor-State Dispute Settlement (ISDS) provisions require investors to exhaust local remedies before seeking international arbitration.
- Limits arbitration tribunals to awarding monetary compensation only.
- Regulatory Authority Preservation:
- Excludes government procurement, taxation, subsidies, compulsory licenses, and national security from BIT coverage, ensuring the government retains regulatory authority.
- Investor Protection:
- Strategic Impact
- Preferred FDI Destination: The revised BIT aims to position India as a preferred destination for foreign direct investment (FDI).
- Protection of Outbound FDI: It also focuses on safeguarding outbound investments made by Indian entities.
GLOBAL INNOVATION INDEX (GII) 2024

- 28 Sep 2024
In News:
- India has moved up to 39th place among 133 economies in the GII 2024, showcasing significant progress from its 81st position in 2015.
Key Details:
- Regional Leadership: India ranks first among the 10 economies in Central and Southern Asia, highlighting its emerging leadership in innovation within the region.
- Lower-Middle-Income Economies: India is also the top-ranked lower-middle-income economy in the GII.
- WIPO Science & Technology Ranking: India holds the 4th position in the World Intellectual Property Organization (WIPO) Science & Technology Cluster Ranking, indicating robust innovation capabilities.
- Top Science & Technology Clusters: Major Indian cities—Mumbai, Delhi, Bengaluru, and Chennai—are recognized among the world’s Top 100 S&T clusters, emphasizing urban centers' roles in fostering innovation.
- Intangible Asset Intensity: India ranks 7th globally in intangible asset intensity, reflecting a strong focus on knowledge-based assets and intellectual property.
Context and Significance of GII
- Purpose of GII: The GII evaluates innovation ecosystems of 133 economies, providing insights into trends that drive economic and social change through innovation.
- Global Leaders: The top five most innovative economies according to the GII 2024 are Switzerland, Sweden, the US, Singapore, and the UK.
- Fastest Climbers: India is among the fastest climbers in the GII over the past decade, alongside China, Turkey, Vietnam, and the Philippines.
Overview of WIPO
- Foundation and Mission: The World Intellectual Property Organization (WIPO), established in 1974 and part of the UN since then, aims to support global innovators and creators, ensuring the safe journey of their ideas to market.
- Membership: WIPO comprises 193 member states, including a diverse range of developing and developed countries, facilitating a broad exchange of intellectual property knowledge.
- Headquarters: Geneva, Switzerland.
WORLD TOURISM DAY 2024

- 27 Sep 2024
In News:
The Ministry of Tourism celebrated World Tourism Day on September 27, 2024, under the theme “Tourism and Peace.” The focus was on how tourism fosters global peace by encouraging cross-cultural interactions and understanding.
Key Details:
- World Tourism Day, established in 1980 by the United Nations World Tourism Organisation (UNWTO), celebrates the global impact of tourism and raises awareness about its economic, social, and cultural significance.
- This day celebrates the diverse experiences that tourism offers and commits to making travel more inclusive, sustainable, and beneficial for all; here’s all you need to know about the day.
- The date, September 27, was chosen to commemorate the adoption of UNWTO statutes in 1975
- The theme for World Tourism Day 2024 is “Tourism and Peace,” which will highlight the association between tourism and world peace, with the United Nations emphasising the significance of comprehending diverse cultures and encouraging sustainable tourism.
World Tourism Day: Significance and Celebrations
- World Tourism Day is a global event that celebrates the role of tourism in bridging cultural gaps, enhancing mutual understanding, and driving economic development.
- It focuses on responsible tourism practices, celebrating diverse cultural heritage, and addressing environmental sustainability and fair distribution of benefits.
- Events include seminars, workshops, and conferences on the theme of the year, cultural festivals, exhibitions, and public performances.
- Educational campaigns and community outreach activities raise awareness about responsible travel, supporting local economies, and protecting natural environments.
Note:
- The World Economic Forum, in its recently released Travel and Tourism Development Index (TTDI), shares the top countries gaining popularity in the travel and tourism industry.
- Notably, in Southeast Asia, India ranks 39th as the TTDI’s top lower-middle-income economy. India’s strong Natural (6th), Cultural (9th) and Non-Leisure (9th) resources drive its travel industry, with the country’s being only one of three to score in the top 10 for all the resources pillars.
- The TTDI measures the set of factors and policies that enable the sustainable and resilient development of the T&T sector, which in turn contributes to the development of a country. Among the 119 countries, here are the top 10 countries for travel and tourism in 2024 attracting travellers from all over the globe.
GlobE Network

- 27 Sep 2024
In News:
- India was elected to the 15-member GlobE Steering Committee on September 26, 2024, in a plenary session in Beijing. The election involved a multistage voting process.
- Role and Significance:
- India will play a vital role in shaping the global agenda on corruption and asset recovery.
- The Central Bureau of Investigation (CBI) highlighted India's expertise in combating corruption as a significant asset for the GlobE Network.
- About the GlobE Network:
- The Global Operational Network of Anti-Corruption Law Enforcement Authorities (GlobE Network) is a G-20 initiative, supported by India since 2020.
- Officially launched on June 3, 2021, during a UN General Assembly session against corruption.
- Currently comprises 121 member countries and 219 member authorities.
- Governance Structure:
- The Ministry of Home Affairs (MHA) serves as the central authority for India within the GlobE Network.
- Indian member authorities include the CBI and the Enforcement Directorate (ED).
- The Steering Committee consists of one chair, one vice-chair, and 13 members providing leadership and direction.
- Functionality and Objectives:
- The GlobE Network facilitates the sharing of best practices, criminal intelligence, and strategy development among international agencies to combat corruption.
- It is supported by the United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime (UNODC), which provides secretariat services.
- G-20 Presidency Initiatives:
- During India’s G-20 Presidency in 2023, two high-level principles for combating corruption were adopted, emphasizing the use of the GlobE Network to enhance global cooperation.
PLANETARY BOUNDARIES AND OCEAN ACIDIFICATION
- 27 Sep 2024
In News:
A new report from the Potsdam Institute for Climate Impact Research (PIK) indicates that the world's oceans are nearing critical acidity levels.
- Key Findings:
- Nine Crucial Factors: The report identifies nine essential elements for sustaining life on Earth.
- Exceeded Limits: Six of these factors have already surpassed safe limits due to human activities.
- Ocean Acidification: This is poised to become the seventh boundary breached.
- Crossed Boundaries:
- Factors Affected:
- Climate change
- Loss of natural species and habitats
- Depletion of freshwater resources
- Increase in pollutants, including plastics and agricultural chemicals
- Factors Affected:
- Causes of Ocean Acidification:
- Primarily driven by rising carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions from burning fossil fuels (oil, coal, gas).
- Implications of Acidification:
- Damage to corals, shellfish, and phytoplankton, disrupting marine ecosystems.
- Threats to food supplies for billions of people.
- Reduced capacity of oceans to absorb CO2, exacerbating global warming.
- Ozone Layer Status:
- Currently not close to being breached; showing recovery since the banning of harmful chemicals in 1987.
- Air Quality Concerns:
- A ninth boundary related to particulate matter is near danger limits.
- Improvements in air quality are noted, but industrializing nations still face pollution risks.
- Tipping Points:
- Crossing these boundaries could lead to irreversible and catastrophic consequences for humanity and future generations.
- All boundaries are interconnected; breaching one can destabilize the entire system.
- Opportunities for Solutions:
- Addressing critical issues, such as limiting temperature rise to 1.5 degrees Celsius above pre-industrial levels, can have widespread benefits across multiple environmental challenges.
Planetary boundaries
- The planetary boundaries were introduced in 2009 to define the global environmental limits within which humans can safely live.
- Johan Rockström, former director of the Stockholm Resilience Centre, led a group of 28 renowned scientists to identify the nine processes that regulate the stability and resilience of the Earth system.
- Climate Change: Greenhouse gas concentrations, primarily CO2, are the primary metric here. Exceeding the recommended levels risks amplifying global warming.
- Ocean Acidification: Oceans absorb CO2, leading to decreased pH levels. This boundary measures the carbonate ion concentration, vital for marine life like corals.
- Stratospheric Ozone Depletion: The ozone layer protects life from harmful ultraviolet radiation. This boundary emphasizes the ozone concentration in the stratosphere.
- Nitrogen and Phosphorus Cycles: Excess nitrogen and phosphorus, often from fertilizers, can disrupt ecosystems. Here, the focus is on their flow into the environment.
- Freshwater Use: Freshwater is vital for life. This boundary pinpoints the annual consumption of freshwater resources.
- Land-System Change: As we modify landscapes, particularly through deforestation, we alter habitats and carbon storage capabilities. This threshold concerns the amount of forested land remaining.
- Biodiversity Loss: Biodiversity underpins ecosystem resilience. This metric observes the extinction rate of species.
- Atmospheric Aerosol Loading: Aerosols influence climate and human health. This boundary examines their density in the atmosphere.
- Chemical Pollution: Synthetic chemicals can harm ecosystems and human health. This boundary reviews their concentration and spread.
INDIA WATER WEEK (IWW) 2024

- 27 Sep 2024
In News:
- The 8th edition of India Water Week (IWW) 2024 was held from September 17-20, 2024, at the Bharat Mandapam in New Delhi.
- Organized by the Ministry of Jal Shakti, this prestigious international event has established itself as a key platform for collaboration in water resource management.
- With participation from global water experts, government leaders, and private-sector representatives, the event aimed to address the critical challenges of water management, foster innovation, and promote sustainable water practices.
Theme and Focus
The theme for India Water Week 2024 was "Partnerships and Cooperation for Inclusive Water Development and Management." This theme underscored the importance of cross-sectoral and international collaboration to address the 21st-century's growing water challenges and the need for integrated efforts in water conservation, management, and equitable access to water resources.
India Water Week: An International Forum
- Since its inception in 2012, India Water Week has grown into a pivotal event in global water diplomacy, offering a platform for dialogue, innovation, and knowledge sharing.
- Each edition focuses on a specific water-related issue, providing policymakers, experts, and industry leaders the opportunity to present solutions and explore cooperative strategies.
International WASH Conference
- A key highlight of IWW 2024 was the International WASH Conference, organized by the Department of Drinking Water and Sanitation (DDWS), Ministry of Jal Shakti.
- This conference focused on global collaboration in Water, Sanitation, and Hygiene (WASH), aiming to address pressing sanitation challenges and promote hygiene standards.
- The conference was held between 17th-19th September 2024, in New Delhi. This three-day gathering, centered on the theme ‘Sustaining Rural Water Supply’, offered a platform for knowledge exchange, showcasing innovations, and sharing best practices aimed at addressing global WASH challenges, with a special focus on achieving Sustainable Development Goal 6 (SDG 6).
Key Takeaways from India Water Week 2024
The India Water Week 2024 concluded with several important takeaways:
- Collaboration and Cooperation: Water security can only be achieved through partnerships across sectors and borders.
- Innovation in Water Management: Startups and technological innovations are key to addressing the future challenges of water resource management.
- Community Participation: Local communities play a crucial role in water conservation efforts, and their involvement is vital to achieving sustainable development.
- Policy Recommendations: The event produced several policy recommendations for sustainable water governance, addressing challenges in climate resilience, infrastructure development, and groundwater management.
Conclusion
India Water Week 2024 was a landmark event that brought together a diverse group of stakeholders to address the complexities of water management in the 21st century. The event paved the way for a more sustainable and inclusive approach to water development through partnership, cooperation, and innovation, ensuring equitable access to water resources for all.
PARAM Rudra Supercomputers

- 27 Sep 2024
In News:
Recently, the Prime Minister of India launched three Param Rudra Supercomputing Systems and a High-Performance Computing (HPC) system for weather and climate research via a virtual event.
PARAM Rudra Supercomputers
- Development: Indigenously developed under the National Supercomputing Mission.
- Deployment Locations:
- Delhi: Inter University Accelerator Centre (IUAC) focuses on material science and atomic physics.
- Pune: Giant Metre Radio Telescope (GMRT) will explore Fast Radio Bursts (FRBs) and other astronomical phenomena.
- Kolkata: S N Bose Centre drives advanced research in physics, cosmology, and earth sciences.
High-Performance Computing (HPC) System
- Purpose: Tailored for weather and climate research.
- Location:
- Indian Institute of Tropical Meteorology (IITM), Pune.
- National Center for Medium Range Weather Forecast (NCMRWF), Noida.
- System Names: 'Arka' and 'Arunika', reflecting their solar connection.
Significance of the HPC System
- Enhanced Predictive Capabilities:
- High-resolution models improve accuracy and lead time for: Tropical cyclones, Heavy precipitation, Thunderstorms, Hailstorms, Heat waves, Droughts and Other critical weather phenomena
National Supercomputing Mission (NSM)
- Launch and Goals
- Launched in 2015 to position India among world-class computing power nations.
- Aims to connect national academic and R&D institutions with a network of over 70 high-performance computing (HPC) facilities.
- Implementation
- Managed by the Department of Science and Technology (DST) and the Department of Electronics and Information Technology (DeitY), Government of India.
- Estimated cost: Rs 4,500 crore over 7 years.
- Supports initiatives like 'Digital India' and 'Make in India'.
- Current Status
- India ranks 74th globally in supercomputing, with only 9 supercomputers out of more than 500 worldwide.
- The mission addresses the growing computing demands of the scientific community and aligns with international technology trends.
- Infrastructure and Networking
- Envisions a supercomputing grid with over 70 HPC facilities networked via the National Knowledge Network (NKN).
- NKN connects academic institutions and R&D labs through a high-speed network.
ASIA POWER INDEX

- 26 Sep 2024
In News:
In a major shift, India surpassed Japan to become the third-largest power in the Asia Power Index, reflecting its increasing geopolitical stature. This achievement is driven by India's dynamic growth, youthful population, and expanding economy, solidifying its position as a leading force in the region.
Key Factors Behind India’s Rise:
- Economic Growth: India has shown remarkable post-pandemic economic recovery, contributing to a 4.2-point rise in its Economic Capability. India’s massive population and strong GDP growth reinforce its standing as the world’s third-largest economy in PPP terms.
- Future Potential: India’s Future Resources score increased by 8.2 points, signalling a potential demographic dividend. Unlike its regional competitors, particularly China and Japan, India benefits from a youthful population that will continue to drive economic growth and labour force expansion in the coming decades.
- Diplomatic Influence: Prime Minister Narendra Modi’s leadership has garnered greater international recognition. India’s non-aligned strategic posture has allowed New Delhi to navigate complex international waters effectively. India ranked 6th in terms of diplomatic dialogues in 2023, reflecting its active engagement in multilateral forums.
- Further, India’s large population and economic capabilities offer it substantial promise. India’s score in Cultural Influence has also remained relatively strong, underpinned by its global diaspora and cultural exports.
- In addition, India’s role in multilateral diplomacy and security cooperation has been a point of emphasis. India's participation in dialogues, as well as its leadership in the Quad, has allowed it to play a significant role in regional security dynamics, albeit outside of formal military alliances.
Asia Power Index
- The Asia Power Index, launched by the Lowy Institute in 2018, is an annual measure of power dynamics in the Asia-Pacific region.
- It evaluates 27 countries across the Asia-Pacific, examining their ability to shape and respond to the external environment.
- The 2024 edition offers one of the most comprehensive assessments of power distribution in the region to date. Timor-Leste has been included for the first time, reflecting its growing importance in Southeast Asia.
- The Index focuses on both the material capabilities of states and the influence they exert on the international stage.
Criteria and Parameters of Power Measurement
Power in the Asia Power Index is divided into resource-based and influence-based determinants:
- Resource-Based Determinants:
- Economic Capability: The core economic strength of a country, measured through indicators like GDP at purchasing power parity (PPP), technological sophistication, and global economic connectivity.
- Military Capability: Evaluates conventional military strength based on defense spending, armed forces, weapon systems, and signature capabilities like long-range power projection.
- Resilience: The internal capacity to deter threats to state stability, including institutional robustness, geopolitical security, and resource security.
- Future Resources: Forecasts the future distribution of resources, including economic, military, and demographic factors projected for 2035.
- Influence-Based Determinants:
- Economic Relationships: The capacity to exercise leverage through trade, investment, and economic diplomacy.
- Defense Networks: The strength of alliances and partnerships, measured through military cooperation and arms transfers.
- Diplomatic Influence: The extent of a country's diplomatic reach, participation in multilateral forums, and foreign policy ambition.
- Cultural Influence: The ability to shape international public opinion through cultural exports, media, and people-to-people ties.
A country's overall power score is derived from a weighted average of these eight measures, encompassing 131 individual indicators. The results offer a nuanced understanding of how countries convert their resources into influence within the Asia-Pacific.
10 YEARS OF MAKE IN INDIA

- 26 Sep 2024
In News:
The “Make in India” initiative has completed 10 years. It was launched by Prime Minister Narendra Modi on September 25, 2014.
KEY TAKEAWAYS:
- The ‘Make in India’ campaign aims to facilitate investment, foster innovation, enhance skill development, protect intellectual property & build best in class manufacturing infrastructure.
- “Make in India” was designed to transform India into a global hub for design and manufacturing.
- Seen as an important ‘Vocal for Local’ initiative, its objective is twofold. Firstly, to boost India’s manufacturing capabilities and secondly to showcase its industrial potential on a global stage.
- The “Make in India 2.0” phase encompassing 27 sectors – both manufacturing and service.
4 pillars of “Make in India” initiative:
- New Processes: To enhance the business environment, promote entrepreneurship and startups – ‘ease of doing business’ became a crucial factor.
- New Infrastructure: Development of industrial corridors, smart cities, integrating state-of-the-art technology and high-speed communication to create world-class infrastructure, improving intellectual property rights (IPR) infrastructure etc.
- New Sectors: Opening of Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) in sectors like Defence Production, Insurance, Medical Devices, Construction, and Railway infrastructure.
- New Mindset: In order to support industrial growth and innovation – the government embraced a role as a facilitator rather than a regulator. The Government partners with industry in the economic development of the country.
Key Initiatives to enable Make in India initiative
Production linked Incentive (PLI) Schemes: The primary goals of the PLI Schemes are to attract substantial investments, incorporate advanced technology, and ensure operational efficiency. These schemes cover 14 key sectors aimed at fostering investment in cutting-edge technology and promoting global competitiveness.
PM GatiShakti: It is a strategic initiative aimed at achieving Aatmanirbhar Bharat and a US $5 trillion economy by 2025 through the creation of multimodal and last-mile connectivity infrastructure. PM GatiShakti is a transformative approach for economic growth and sustainable development. The approach is driven by 7 engines, namely:
- Railways
- Roads
- Ports
- Waterways
- Airports
- Mass Transport
- Logistics Infrastructure
Semiconductor Ecosystem Development: It encompasses four key schemes:
- Modified Scheme for Setting Up Semiconductor Fabs in India
- Modified Scheme for Setting Up Display Fabs in India
- Modified Scheme for Setting Up Compound Semiconductors, Silicon Photonics, Sensors Fabs, and Discrete Semiconductors, along with Semiconductor Assembly, Testing, Marking, and Packaging (ATMP) / OSAT Facilities in India
- Design Linked Incentive (DLI) Scheme
It aims to foster the development of a sustainable semiconductor and display ecosystem in the country.
The Semicon India Programme aims to provide a significant impetus to semiconductor and display manufacturing by facilitating capital support and promoting technological collaborations.
National Logistics Policy: Introduced to complement the PM GatiShakti National Master Plan. It focusses on enhancing the soft infrastructure of India’s logistics sector.
The Comprehensive Logistics Action Plan (CLAP) was rolled out. The key areas which it addresses are logistics systems, standardization, human resource development, state engagement, and logistics parks.
The National Industrial Corridor Development Programme: Aims to create “Smart Cities” and advanced industrial hubs.
Startup India: Several programs aimed at supporting entrepreneurs, building a robust startup ecosystem, and transforming India into a country of job creators instead of job seekers were rolled out.
Implementation of the Goods and Services Tax (GST): As India’s tax reforms, it is seen as crucial in the context of the Make in India initiative.
Unified Payments Interface: For India’s digital economy growth, it is seen as one of the key initiatives to enable ease of doing business.
Ease of Doing Business: The efforts aim to simplify regulations, reduce bureaucratic hurdles, and create a more business-friendly environment, significantly boosting investor confidence and supporting the objectives of the Make in India initiative.
China test-fires an intercontinental ballistic missile into the Pacific Ocean

- 26 Sep 2024
In News:
China stated that it test-launched an intercontinental ballistic missile, firing it into the Pacific Ocean in its first such exercise in decades.
- Launch Details:
- The missile carried a dummy warhead and fell into a designated area in the high seas.
- The specific flight path and landing location were not disclosed.
- Testing Objectives:
- The launch tested weapon performance and troop training levels, achieving its expected objectives.
- Historical Context:
- This is the first ICBM test over the Pacific Ocean in over 40 years.
- China's first ICBM, the DF-5, was test-fired in 1980.
- ICBM Specifications:
- The latest ICBM, likely the DF-41, has an estimated range of 12,000 to 15,000 kilometers (7,400 to 9,300 miles), capable of reaching the US mainland.
- Strategic Messaging:
- Analysts interpret the test as a warning to the US, suggesting direct intervention in Taiwan could expose the American homeland.
- The test signals China's ability to engage multiple fronts simultaneously.
- Regional Tensions:
- Recent weeks have seen heightened tensions with Japan, the Philippines, and Taiwan due to military incursions and exercises.
- International Norms:
- There is a global expectation to notify nations of long-range missile launches to avoid miscalculations. China has limited agreements regarding this, primarily with Russia.
- Military Buildup:
- Under Xi Jinping, China has enhanced its nuclear capabilities and revamped the PLA’s Rocket Force.
- Recent satellite imagery indicates the construction of hundreds of ICBM silos in China’s deserts.
- Future Projections:
- As of 2023, China has over 500 operational nuclear warheads, projected to exceed 1,000 by 2030 according to the Pentagon.
- Implications of the Test:
- The ICBM test may be aimed at demonstrating military readiness despite recent corruption scandals within the Rocket Force.
About ICBMs:
- An intercontinental ballistic missile (ICBM) is a long-range ballistic missile system primarily designed for nuclear weapons delivery. They are powerful and destructive weapons, capable of travelling vast distances at incredibly high speeds.
- Key features of ICBMs:
- Range: Range greater than 5,500 kilometres with maximum ranges varying from 7,000 to 16,000 kilometres.
- Speed: ICBMs can travel at speeds exceeding 20,000 kilometres per hour.
- Payload: Typically designed to carry nuclear warheads, though they could potentially be used to deliver other types of weapons, such as chemical or biological weapons.
- Deployment: ICBMs can be launched from silos underground, mobile launchers on land, or submarines at sea.
- Countries having operational ICBMs: Russia, United States, China, France, India, United Kingdom, Israel and North Korea.
INDIA'S BIOE3 POLICY AND SMART PROTEINS

- 26 Sep 2024
In News:
The Indian government recently approved the Biotechnology for Economy, Environment, and Employment (Bioe3) Policy, which prioritizes the production of "smart proteins". This initiative aligns with broader national goals of achieving a sustainable, circular bioeconomy and a Net Zero carbon economy.
What Are Smart Proteins?
Smart proteins are alternative proteins derived from unconventional sources such as:
- Algae
- Fungi
- Insects
- Fermentation processes
- Lab-grown cells
This category also includes plant-based proteins, designed to replicate the taste and nutritional value of animal products without the need for livestock farming.
Environmental Benefits
The production of smart proteins offers significant environmental advantages:
- Water Use: 72-99% less water compared to conventional meat.
- Land Use: 47-99% less land required.
- Water Pollution: 51-91% reduction in pollution.
- Greenhouse Gas Emissions: 30-90% fewer emissions.
Health and Safety
With rising incomes, India's protein consumption has increased, from 9.7% of calories in 1991 to 11% in 2021. Smart proteins:
- Enhance food safety by reducing the risk of zoonotic diseases.
- Foster ethical consumption and align with traditional Indian dietary preferences.
Objectives of the BioE3 Policy
The Bioe3 Policy aims to:
- Foster high-performance biomanufacturing.
- Promote sustainable growth and innovation in biotechnology.
- Support the transition towards a Net Zero carbon economy.
By emphasizing the development of smart proteins, the Bioe3 Policy represents a strategic move towards a more sustainable and resilient food system in India.
ACHIEVING GLOBAL NUCLEAR DISARMAMENT

- 26 Sep 2024
Overview
Global nuclear disarmament remains a top priority for the United Nations, initially emphasized in the General Assembly’s first resolution in 1946. Despite historical efforts, approximately 12,100 nuclear weapons still exist today, with ongoing modernization plans in many countries.
Key Historical Milestones
- 1945: Atomic bombings of Hiroshima and Nagasaki, killing an estimated 213,000 people.
- 1946: First UN resolution identifies nuclear disarmament as a key goal.
- 1959: General Assembly endorses the goal of general and complete disarmament.
- 1963: Opening of the Partial Test Ban Treaty.
- 1978: First Special Session of the General Assembly dedicated to disarmament.
- 1996: Comprehensive Nuclear-Test-Ban Treaty opens for signature.
- 2017: Adoption of the Treaty on the Prohibition of Nuclear Weapons.
Recent Developments
- 2019: U.S. withdrawal from the Intermediate-Range Nuclear Forces Treaty.
- 2023: Russia suspends participation in the New START Treaty, raising concerns over arms control.
The International Day for the Total Elimination of Nuclear Weapons
- Established: December 2013, following a high-level meeting on nuclear disarmament.
- Observed: Annually on September 26.
- Purpose: Raise awareness about the dangers of nuclear weapons and promote their total elimination.
Goals of the International Day
- Enhance public education on the humanitarian risks associated with nuclear weapons.
- Mobilize international efforts towards a nuclear-weapon-free world.
Continuing Challenges
- The doctrine of nuclear deterrence remains central to the security policies of nuclear-armed states and their allies.
- No nuclear weapons have been destroyed under a treaty framework, and current disarmament negotiations are stagnant.
- Growing frustration among UN Member States over the slow progress in nuclear disarmament.
NAGAR VAN YOJANA (NVY)

- 25 Sep 2024
In News:
Recently, the Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change, Government of India achieved a 100-Day Target of 100 Nagar Vans under Nagar Van Yojana (NVY) with the objective to Enhance Urban Greenery.
Key Details:
- Launch: Initiated in 2020 to enhance urban greenery, improve quality of life, and foster social cohesion.
- Financial Support: Offers ?4 lakh per hectare for creation and maintenance of urban forests.
- Area Specification: Nagar Van areas range from 10 to 50 hectares.
- Coverage: Applicable to all cities with Municipal Corporations, Municipalities, and Urban Local Bodies (ULBs).
Achievements
- 100-Day Target: The Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change achieved a target of 100 Nagar Vans, surpassing it with the approval of 111 Nagar Vans in just 100 days.
- Geographic Spread: These 111 Nagar Vans are distributed across six states and one Union Territory.
Features of Nagar Vans
- Biodiversity Focus: Emphasis on planting fruit-bearing, medicinal, and native species to attract wildlife and maintain ecological balance.
- Community Involvement: Engages citizens, students, and stakeholders through tree planting, educational programs, and sustainable management.
- Design Elements: Each Nagar Van includes two-thirds tree cover and features components like Biodiversity Parks, Smriti Vans, Butterfly Conservatories, Herbal Gardens, and Matri Vans.
Future Goals
- Expansion Plans: Target to develop 1,000 Nagar Vans by 2027, supported by the National Compensatory Afforestation Management and Planning Authority (National CAMPA).
- Environmental Impact: Aims to protect forest land from degradation and address urban environmental issues such as air pollution and habitat loss.
Ek Ped Maa Ke Naam Campaign
- Launch Date: Introduced on June 5, 2024, during World Environment Day.
- Purpose: Encourages tree planting as a tribute to mothers, fostering a culture of environmental stewardship.
- Tree Planting Goals: Aims to plant 80 crore trees by September 2024 and 140 crore by March 2025.
- Tracking Efforts: Participants can document their planting through the MeriLiFE portal, where over 75 crore saplings have been recorded.
Recent Initiatives
- Tree Plantation Drive: A recent drive on September 17, 2024, aimed at creating Matri Vans in newly approved Nagar Vans, highlighting community and governmental collaboration for sustainable urban development.
INDIA’s FIRST MISSION TO VENUS

- 25 Sep 2024
In News:
India is set to launch its first mission to Venus in March 2028, following the recent approval from the Union Cabinet. This mission, led by the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO), marks India’s second interplanetary endeavor after the successful Mars Orbiter Mission in 2013.
Importance of Studying Venus
- Earth's Twin: Venus is often referred to as Earth’s twin due to its similar mass, density, and size. Understanding Venus can provide insights into Earth’s own evolution.
- Extreme Conditions: The planet has a surface temperature around 462°C and an atmospheric pressure similar to that found deep under Earth’s oceans. Its atmosphere consists primarily of 96.5% carbon dioxide and features clouds of sulfuric acid.
- Historical Water Presence: Venus may have had water in the past, leading scientists to explore how it transitioned to its current hostile environment, likely due to a runaway greenhouse effect.
Mission Overview
- Launch Timeline: The mission will utilize a strategic launch window when Earth and Venus are closest, occurring every 19 months. It was initially planned for 2023 but is now set for 2028.
- Payload: The mission will carry around 100 kg of scientific instruments, including 17 Indian and 7 international experiments.
- Journey to Venus: After exiting Earth's orbit, the spacecraft will take about 140 days to reach Venus.
Aero-Braking Technique
- First-time Use: This mission will employ aero-braking, a technique to adjust the spacecraft’s orbit by skimming through Venus's atmosphere, creating drag that reduces altitude.
- Target Orbit: The satellite will initially be in a highly elliptical orbit of 500 km x 60,000 km and will be gradually lowered to an orbit of either 300 x 300 km or 200 x 600 km over about six months.
Scientific Payloads
- Synthetic Aperture Radar: For imaging the surface of Venus.
- Thermal Camera: To study temperature variations.
- Interplanetary Dust Analysis: Investigating dust particle flow.
- High-Energy Particle Studies: Examining particles entering the atmosphere and their ionization effects.
- Atmospheric Composition Study: Assessing the structure, variability, and thermal state of Venus’s atmosphere.
Which countries are trying to study Venus?
- There have been several missions to Venus in the past by the United States, the erstwhile USSR, Japan, and a collaborative mission of the European Space Agency (ESA) with Japan.
- The US has planned at least two more missions to Venus in the future — DaVinci in 2029 and Veritas in 2031 — and the ESA has planned the EnVision mission for 2030.
INDIA ATTENDS IPEF MINISTERIAL MEETING

- 25 Sep 2024
In News:
Recently, the Union Commerce and Industry Minister Piyush Goyal joined a virtual meeting of the Indo-Pacific Economic Framework for Prosperity (IPEF) alongside representatives from 13 other partner countries. This meeting marked the third gathering focused on the framework's key pillars: Supply Chain Resilience, Clean Economy, and Fair Economy.
Key Agreements and Future Steps
- Entry into Force of Agreements:
- The IPEF partners celebrated the upcoming implementation of the Clean Economy Agreement and the Fair Economy Agreement on October 11 and October 12, 2024, respectively. These agreements aim to enhance economic cooperation and deliver tangible benefits to member nations.
- Supply Chain Resilience:
- The ministers discussed the progress in operationalizing the Supply Chain Agreement, emphasizing collaborative efforts to create more competitive and resilient supply chains. Key actions include:
- The formation of action plan teams for critical sectors like semiconductors, critical minerals, and chemicals, addressing vulnerabilities revealed during the COVID-19 pandemic.
- India's election as Vice Chair of the Supply Chain Council, which aims to streamline communication and cooperation among member countries.
- The ministers discussed the progress in operationalizing the Supply Chain Agreement, emphasizing collaborative efforts to create more competitive and resilient supply chains. Key actions include:
- Clean Economy Initiatives:
- The Clean Economy Agreement focuses on energy security, climate resilience, and reducing fossil fuel dependence. Ministers acknowledged the advancement of eight Cooperative Work Programs (CWPs) addressing topics such as hydrogen and carbon markets.
- The first IPEF Investor Forum, held in Singapore, facilitated discussions on investment opportunities in climate-friendly technologies.
- Fair Economy Measures:
- The Fair Economy Agreement aims to bolster anti-corruption measures and improve tax administration efficiency. Upcoming workshops will address foreign bribery laws and public procurement oversight.
- India highlighted its own anti-corruption measures and commitment to transparency under Prime Minister Modi's leadership.
About IPEF
Launched on May 23, 2022, in Tokyo, IPEF includes 14 countries: Australia, Brunei, Fiji, India, Indonesia, Japan, South Korea, Malaysia, New Zealand, Philippines, Singapore, Thailand, Vietnam, and the USA. The framework seeks to enhance economic engagement, stability, and prosperity across the Indo-Pacific region through its four key pillars: Trade, Supply Chain Resilience, Clean Economy, and Fair Economy.
SPICED SCHEME

- 25 Sep 2024
In the News
The Union Ministry of Commerce and Industry has authorized the SPICED scheme (Sustainability in Spice Sector through Progressive, Innovative, and Collaborative Interventions for Export Development), which will run until 2025-26.
Overview
This initiative aims to expand the cultivation area and enhance the productivity of both small and large cardamom. It will also focus on improving the quality of spices for export through advancements in post-harvest processes and promoting value-added spice exports.
Key Objectives:
- Increase cardamom production and boost export potential.
- Improve post-harvest quality to meet export standards and ensure compliance with safety and quality regulations.
India holds the position of the largest producer, consumer, and exporter of spices globally.
Cardamom
Cardamom is sourced from the seeds of the Elettaria cardamomum plant (commonly known as green or true cardamom) and is a member of the ginger family. It is known for its unique, robust flavor that combines both spicy and sweet notes. There are two primary varieties: Small Cardamom and Large Cardamom.
Small Cardamom:
- Origin: Native to the evergreen forests of South India's Western Ghats.
- Major Producers: Primarily grown in Kerala, Karnataka, and Tamil Nadu.
- Growing Conditions: Thrives in loamy soil with thick shade, requires temperatures between 10°C and 35°C, and needs 1500 to 4000 mm of annual rainfall.
Large Cardamom:
- Distribution: Mainly cultivated in the Sub-Himalayan regions of Northeast India, Nepal, and Bhutan.
- Major Producers: Key production areas include Sikkim, Arunachal Pradesh, and the Darjeeling district of West Bengal.
- Growing Conditions: Prefers high altitudes (600 to 2000 meters), with average rainfall of 3000-3500 mm, and temperatures ranging from 6°C to 30°C. Well-drained, loamy soils rich in organic matter are ideal.
About the Spices Board of India
Established in 1987 under the Ministry of Commerce and Industry, the Spices Board of India serves as the apex organization for the promotion and export of a diverse array of spices, including black pepper, both small and large cardamom, ginger, turmeric, cinnamon, cumin, and fenugreek. The Board was formed by merging the Cardamom Board (1968) and the Spices Export Promotion Council (1960). Its headquarters is located in Kochi, Kerala.
Ideas4LiFE Initiative

- 25 Sep 2024
In News:
The Ideas4LiFE portal was launched by Union Minister for Environment, Forest and Climate Change, at IIT Delhi.
- Purpose: Designed to invite innovative ideas related to products and services that promote environmentally friendly lifestyles.
- Development Partner: Created in collaboration with UNICEF YuWaah.
Key Features of the Ideas4LiFE Portal
- Themes: Aligned with Mission LiFE, focusing on:
- Water Conservation
- Energy Efficiency
- Waste Reduction
- E-Waste Management
- Minimizing Single-Use Plastics
- Embracing Sustainable Food Practices
- Fostering Healthy Lifestyles
- Recognition: Winning ideas will be awarded attractive prizes for both individuals and institutions.
Engagement and Outreach
- Submissions: As of now, the portal has received approximately 3,300 registrations and over 1,000 ideas.
- Social Media Impact: The initiative has garnered 46.5 million impressions and a reach of 13.5 million through social media under the hashtag #Ideas4LiFE.
Collaboration with Educational Institutions
- Partnerships: Collaborations with the University Grants Commission (UGC), All-India Council for Technical Education (AICTE), and various educational institutions to promote the Ideathon among students and researchers.
- Objective: Encourage the academic community to contribute innovative, citizen-focused ideas that support sustainable living.
Future Plans
- Evaluation Process: Submitted ideas will be evaluated by a jury, leading to the announcement of shortlisted and winning ideas.
- Implementation: Winning ideas will be included in a national repository, allowing stakeholders, including government bodies and private entities, to nurture and scale these innovations.
Mission LiFE Context
- Definition: Mission LiFE (Lifestyle For Environment) is a campaign initiated at UN Climate Change Conference COP26 in 2021.
- Goals:
- Mobilize at least one billion people for environmental protection.
- Make 80% of villages and urban local bodies environment-friendly by 2028.
- Promote small, everyday actions to combat climate change.
- Philosophy: Emphasizes the P3 model—Pro Planet People—uniting individuals in the commitment to environmental stewardship.
SWACHH BHARAT MISSION 2.0

- 24 Sep 2024
Mission Overview:
- Launched on October 1, 2021, as the second phase of the Swachh Bharat Mission.
- Aims for "Garbage-Free Status" in all urban areas by 2026.
- Focuses on 100% source segregation, door-to-door waste collection, and scientific waste management.
Legacy Waste Issues:
- Legacy waste consists of improperly collected and stored solid waste, often found in landfills and abandoned sites.
- Approximately 15,000 acres of prime land are buried under nearly 16 crore tonnes of legacy waste in India.
- The mission seeks to convert legacy dumpsites into green zones and establish scientific landfills to manage untreated waste.
Current Progress:
- Of 2,424 identified dumpsites (each with over 1,000 tonnes of waste), only 470 have been fully remediated (16% reclaimed).
- 1,224 sites are under ongoing remediation, while 730 remain untouched.
- Out of 28,460 acres of affected land, 4,552 acres have been reclaimed, with 23,908 acres still to be addressed.
State Performance:
- Tamil Nadu: 837 acres reclaimed (42% of its total dumpsite area).
- Gujarat: Leads in percentage, reclaiming 75% of its landfill area (698 out of 938 acres).
Financial Aspects:
- Central assistance of ?3,226 crore has been approved for remediation efforts.
- States and Union Territories must provide a matching share to access these funds.
Challenges:
- Legacy waste management involves complexities such as radiological characterization, leachate management, and fire control.
- Current municipal solid waste generation in India is around 150,000 tonnes per day.
Historical Context:
- The original Swachh Bharat Mission (SBM-U 1.0) launched on October 2, 2014, focused on making urban areas Open Defecation Free (ODF).
GREENLAND LANDSLIDE AND GLOBAL SEISMIC WAVES

- 24 Sep 2024
In News:
Massive Greenland landslide sent seismic waves around earth for 9 days. One year ago, roughly 25 million cubic metres of ice and rock splashed into the Dickson Fjord in Greenland and displaced the water enough to give rise to a 200-metre high mega-tsunami; in this way, a melting glacier led to a planet-wide tremor, and researchers warn that it may not be the last
Seismic Observations
- Detection: Unusual seismic signals recorded by stations worldwide, characterized by a single frequency, unlike typical earthquake vibrations.
- Classification: Initially termed a "USO" (unidentified seismic object) due to its atypical properties.
- Duration: Waves persisted for nine days, unlike typical aftershock patterns.
Investigation Efforts
- Collaboration: Involved over 68 researchers from 40 universities across 15 countries.
- Data Sources: Combined seismic data, satellite imagery, water level monitors, and a classified bathymetric map from the Danish Navy.
- Conclusion: The seismic waves resulted from a massive landslide caused by the collapse of Hvide Støvhorn peak, which triggered a series of events leading to the tsunami.
Mega-Tsunami and Seiche
- Tsunami Details:
- Created by the avalanche crashing into the fjord, displacing water significantly.
- Resulted in waves that reflected off fjord walls, reaching heights of nearly 110 meters due to the fjord's unique shape.
- Seiche Phenomenon:
- Oscillations in the fjord persisted for over nine days, reflecting the energy from the landslide.
- Maximum amplitude of the seiche recorded at 7.4 meters, with a frequency of 11.45 MHz.
Climate Context
- Global Warming Impact: Thinning glaciers contributed to instability in the region, making such landslides more likely.
- Future Predictions: Researchers warn of increased frequency and scale of similar events as climate change continues to affect Arctic and subarctic regions.
Key Takeaways
- The Greenland landslide serves as a reminder of the unpredictable consequences of climate change, including massive geological events.
- The incident highlights the interconnectedness of natural systems and the potential for localized events to have global repercussions.
ROBOTIC MULES AND HIGH-ALTITUDE INNOVATIONS IN THE ARMY

- 24 Sep 2024
In News:
The Army has inducted 100 robotic mules, known as Multi-Utility Legged Equipment (MULE), under the fourth tranche of emergency procurements (EP).
- Purpose: These robotic mules are designed for surveillance and transporting light loads across challenging terrains, especially in high-altitude areas.
- Specifications:
- Endurance: Capable of operating for up to three years.
- Temperature Range: Functions effectively in extreme temperatures from -40°C to +55°C.
- Payload Capacity: Can carry up to 15 kg.
- Mobility: Can climb stairs, steep hills, and traverse obstacles; waterproof and able to cross rivers.
- Sensing Abilities: Equipped with electro-optics and infrared capabilities for object recognition.
- Control Mechanisms: Operable via an easy-to-use remote control, Wi-Fi, or Long-Term Evolution (LTE) connections.
- Mission Programming: Can be programmed for specific missions using waypoints or pre-recorded tasks.
- Combat Integration: Capable of integration with small arms for military applications.
- Logistics Drones: Logistics drones are currently undergoing trials to enhance support and movement in forward areas, particularly in high-altitude conditions.
- High-Altitude Habitat Evaluation: A new tent designed for extreme cold environments (operating at temperatures down to -40°C) is under evaluation. This tent, called Peak Pods, is intended for use in sub-zero conditions.
- Evaluation Locations: The tent has been tested in three high-altitude sites:
- Leh (11,500 feet)
- Daulat Beg Oldie (16,700 feet)
- Durbuk (12,500 feet)
- Significance: These advancements reflect the Army's focus on technological innovations to enhance operational capabilities in high-altitude areas, especially following the 2020 stand-off with China in Eastern Ladakh.
- Funding and Timelines: The EP process allows contracts up to ?300 crore, with a requirement for delivery within one year.
GINGEE FORT PROPOSED FOR UNESCO WORLD HERITAGE SITE

- 24 Sep 2024
In News:
Recently nominated for UNESCO’s World Heritage Site status, Gingee Fort is part of the Maratha Military Landscapes of India, which encompasses 12 historical sites, primarily located in Maharashtra, with Gingee being the sole representative from Tamil Nadu. The nomination highlights the fort’s historical importance, unique military architecture, and its integral role in Maratha military history.
Significance of Gingee Fort
Gingee Fort, often referred to as the "Troy of the East," stands as a crucial historical monument in Tamil Nadu. Perched atop three prominent hillocks—Rajagiri, Krishnagiri, and Chandragiri—it has served as a significant stronghold for numerous empires throughout Indian history, including the Vijayanagar Nayaks, Marathas, Mughals, French, and British. This fortification exemplifies India’s rich and diverse historical legacy.
Unique Features
The fort complex spans 11 acres and boasts an array of significant structures, including:
- Kalyana Mahal: An eight-storey royal residence.
- Durbar Hall: A ceremonial hall for gatherings.
- Stepped Well and Cannon: Examples of advanced engineering and military use.
- Clock Tower and Armory: Reflecting its historical military significance.
- Elephant Tank and Stables: Indicating its use for royal elephants.
- Temples and Mosques: Including the Venkataramana Temple with intricate carvings and the Sadathtulla Mosque.
Additionally, the fort features advanced water supply systems from various historical periods, ensuring adequate resources for its inhabitants.
Historical Timeline
The origins of Gingee Fort trace back to 1200 CE when built by Ananta Kon of the Konar Dynasty. The fort underwent significant renovations under the Vijayanagar Empire. Key historical events include:
- 1677: Captured by Chhatrapati Shivaji, it remained under Maratha control until 1698.
- 1698: Came under Mughal possession, later ruled by the Nawabs of Arcot and briefly by the French.
- 1750-1770: Occupied by the French before falling to the British.
This timeline reflects the fort's strategic and cultural significance across different dynasties.
Nomination Process for UNESCO
The process for securing UNESCO World Heritage Site status involves rigorous evaluation. Experts from UNESCO and the International Council on Monuments and Sites (ICOMOS) assess the site's historical significance, conservation state, and management strategies. A visit to Gingee Fort is scheduled as part of this evaluation, with a recommendation expected for the 2025 World Heritage designation.
Preparation of the Nomination Dossier
The Development and Research Organisation for Nature, Arts and Heritage (DRONAH) prepared the nomination dossier, aligning with UNESCO’s operational guidelines. This comprehensive document details the fort's historical context, conservation status, and management strategies, aimed at demonstrating its outstanding value for humanity.
SUPREME COURT RULING ON CHILD SEXUAL EXPLOITATIVE MATERIAL: KEY HIGHLIGHTS

- 24 Sep 2024
Overview of the Ruling
- Date: Recent ruling by the Supreme Court of India.
- Context: Determined that viewing, downloading, storing, or distributing material involving child sexual exploitation constitutes a criminal offense under the POCSO Act and the Information Technology Act.
- Appeal Background: Decision overturned a Madras High Court ruling that deemed private viewing of such material non-criminal.
Terminology and Legislative Recommendations
- Terminology Change: Supreme Court advocates replacing “child pornography” with “Child Sexual Exploitative and Abuse Material” (CSEAM) to avoid trivialization of the crime.
- Amendment Call: Court urged Parliament to amend the POCSO Act and advised promulgating an ordinance for immediate effect.
Key Highlights of the Ruling
- Redefinition of Terminology: Emphasizes that "pornography" may imply consensual acts, misrepresenting the nature of child exploitation.
- Expansion of Section 15 of the POCSO Act:
- Possession Without Reporting: Individuals must delete or report any stored CSEAM; failure results in penalties.
- Intent to Transmit: Possessing CSEAM with intent to share, barring reporting, is punishable.
- Commercial Possession: Storing CSEAM for commercial purposes faces the strictest penalties.
- Concept of Inchoate Offenses: Classifies offenses related to CSEAM as preparatory actions towards further crimes.
- Redefinition of Possession:
- Includes "constructive possession," where individuals can be liable without direct physical possession.
- Watching CSEAM online without downloading can still be deemed possession.
- Educational Reforms:
- Court urged for comprehensive sex education to counter stigma and misconceptions.
- Curriculum should cover consent, healthy relationships, and respect for diversity.
- Awareness of the POCSO Act: Central and state governments are mandated to promote awareness, supported by the National Commission for Protection of Child Rights (NCPCR).
- Formation of Expert Committee: To develop programs for health and sex education while increasing POCSO awareness among children.
- Victim Support and Awareness: Emphasized the need for psychological support, counseling, and educational assistance for victims.
Status of Crimes Against Children
- Increasing Incidents: India leads in online child sexual abuse imagery, with 25,000 uploads reported from April to August 2024.
- Geographical Distribution: Major uploads identified in Delhi, Maharashtra, Gujarat, Uttar Pradesh, and West Bengal.
- Rising Cases: From 331 cases in 2017 to 781 in 2018, with 1,171 cases of inappropriate content dissemination reported in 2022.
Overview of the POCSO Act
- Purpose: Addresses sexual exploitation and abuse of children, defining a child as anyone under 18.
- Features:
- Gender-Neutral: Recognizes that both genders can be victims.
- Victim Confidentiality: Mandates protection of victims’ identities.
- Mandatory Reporting: Requires reporting of suspected abuse.
Gaps in Implementation
- Support Persons: Lack of designated support persons for victims; 96% of cases showed inadequate support during legal processes.
- POCSO Courts: Only 408 designated courts across 28 states as of 2022, leading to access issues.
- Special Prosecutors: Shortage of trained public prosecutors for POCSO cases.
Conclusion
- Call for Collaboration: Emphasizes the need for a coordinated approach involving educators, healthcare providers, and law enforcement to combat child sexual exploitation.
- Societal Responsibility: A shift in societal attitudes is essential for preventing victimization and ensuring recovery for victims.
KEY FINDINGS ON ATROCITIES AGAINST SCS AND STS (2022)
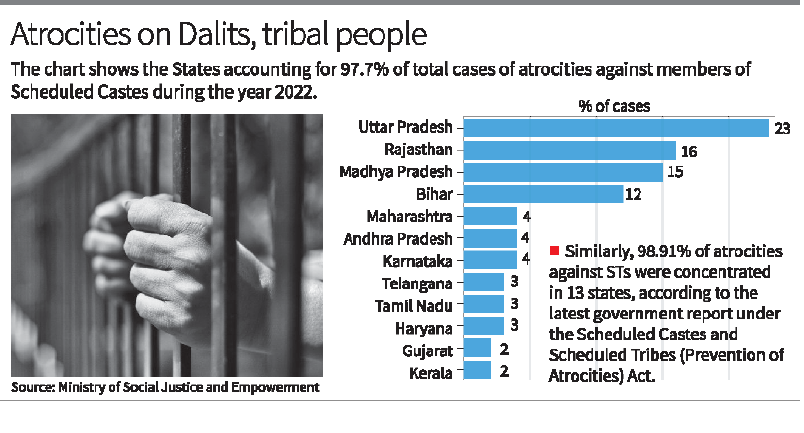
- 23 Sep 2024
In News:
According to the latest report under the Scheduled Castes and Scheduled Tribes (Prevention of Atrocities) Act by the Social Justice and Empowerment Ministry, the majority of atrocities against Scheduled Tribes (STs) were also concentrated in 13 states, which reported 98.91% of all cases in 2022.
- Case Statistics:
- Total cases of atrocities against Scheduled Castes (SCs): 51,656
- Total cases against Scheduled Tribes (STs): 9,735
- 97.7% of SC cases and 98.91% of ST cases reported from 13 states.
- States with Highest Incidents:
- SCs:
- Uttar Pradesh: 12,287 cases (23.78%)
- Rajasthan: 8,651 cases (16.75%)
- Madhya Pradesh: 7,732 cases (14.97%)
- Other significant states: Bihar (6,799), Odisha (3,576), Maharashtra (2,706)
- STs:
- Madhya Pradesh: 2,979 cases (30.61%)
- Rajasthan: 2,498 cases (25.66%)
- Odisha: 773 cases (7.94%)
- Other significant states: Maharashtra (691), Andhra Pradesh (499)
- SCs:
- Charge Sheets and Investigations:
- SC-related cases: 60.38% resulted in charge sheets; 14.78% ended with final reports (false claims/lack of evidence).
- ST-related cases: 63.32% led to charge sheets; 14.71% concluded similarly.
- Pending investigations by end of 2022: 17,166 SC cases, 2,702 ST cases.
- Conviction Rates:
- Decline from 39.2% in 2020 to 32.4% in 2022.
- Infrastructure Deficiencies:
- Only 194 out of 498 districts in 14 states have established special courts for these cases.
- Lack of identified atrocity-prone areas in states like Uttar Pradesh despite high case numbers.
- Protection Cells:
- SC/ST protection cells established in multiple states and union territories.
Reasons for Atrocities Against SCs and STs
- Caste Prejudice: Deep-rooted hierarchies and social exclusion lead to violence.
- Land Disputes: Conflicts over land access among historically deprived SC/ST communities.
- Economic Marginalization: Limited access to education and resources heightens vulnerability.
- Power Imbalance: Dominant castes wield political and social influence, perpetuating discrimination.
- Inadequate Law Enforcement: Weak implementation of protective laws and bureaucratic bias hinder justice.
- Political Exploitation: Caste tensions are sometimes used for electoral gains.
Scheduled Castes and Scheduled Tribes (Prevention of Atrocities) Act, 1989
- Objective: Protect SCs and STs from caste-based violence and discrimination.
- Key Provisions:
- Defines various offences against SC/ST members, prescribing stricter punishments.
- Excludes anticipatory bail provisions for accused under the Act.
- Mandates establishment of special courts for speedy trials.
- Investigations must be conducted by senior police officers and completed within stipulated time frames.
- Recent Amendments:
- 2015: Enhanced protections for SC/ST women.
- 2019: Restored original provisions for arrest procedures following a Supreme Court ruling.
Recommendations for Improvement
- Strengthen Legal Framework: Establish more special courts and train personnel in sensitive handling of SC/ST cases.
- Improve Reporting Mechanisms: Enhance systems for victims to report atrocities without fear.
- Awareness Campaigns: Educate communities on SC/ST rights and legal protections.
- Targeted Interventions: Identify and address issues in atrocity-prone districts.
- Monitoring and Evaluation: Implement frameworks for accountability and continuous improvement in addressing these issues.
- Collaborate with NGOs: Work with civil society to support victims and advocate for their rights.
100 YEARS OF ICAR-NISA

- 23 Sep 2024
Overview:
The ICAR-National Institute of Secondary Agriculture (NISA), originally established in 1924 as the Indian Institute of Natural Resins and Gums in Ranchi, Jharkhand, marks its centenary this year. Renamed in 2022, it operates under the Ministry of Agriculture and Farmers’ Welfare, focusing on enhancing the value of agricultural products.
Understanding Secondary Agriculture:
Secondary agriculture encompasses the transformation of primary agricultural products into higher-value commodities and includes activities such as:
- Beekeeping
- Poultry farming
- Agricultural tourism
This sector plays a crucial role in converting agricultural produce, residues, and by-products into valuable goods for various uses, including pharmaceuticals, food, and industrial applications. Examples of secondary agriculture practices include:
- Extracting vitamins from grains
- Producing oil from rice bran
- Making jaggery from sugarcane
- Cottage industries for jams and pickles
Growth Potential: The sector is poised for growth due to:
- Increasing consumer demand for value-added products like ready-to-eat meals.
- The need for innovative uses of renewable agro-bio resources.
- The significant availability of agricultural byproducts.
Significance of Secondary Agriculture:
- Environmental Sustainability: Proper utilization of crop residues can reduce waste and pollution.
- Enhanced Farmer Income: Activities like beekeeping and lac culture provide additional revenue streams for farmers.
- Value Addition: Processing agricultural products increases their shelf life and overall productivity.
- Promotion of Cottage Industries: Supports rural economies and fosters technology adoption.
Challenges Ahead: Despite its potential, secondary agriculture faces several hurdles:
- The industry for high-value products from agricultural byproducts, such as Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients, is still emerging.
- Small landholdings complicate the collection of crop residues.
- Limited research on suitable technologies hampers development.
- There is a lack of awareness among farmers regarding the processing of agricultural waste.
Conclusion
As ICAR-NISA celebrates its 100th anniversary, it remains crucial in shaping the future of secondary agriculture in India, addressing both challenges and opportunities to enhance sustainability and farmer livelihoods.
INDO-PACIFIC ECONOMIC FRAMEWORK (IPEF)

- 23 Sep 2024
In News:
India signed agreements within the US-led 14-member IPEF focused on a clean and fair economy.
- Objectives:
- Facilitate development, access, and deployment of clean energy and climate-friendly technologies.
- Strengthen anti-corruption measures and promote tax transparency among member countries.
- Clean Economy Agreement:
- Aims to accelerate energy security and mitigate greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions.
- Focuses on innovative methods to reduce reliance on fossil fuels and promote technical cooperation.
- Fair Economy Agreement:
- Seeks to create a transparent and predictable business environment to enhance trade and investment.
- Emphasizes information sharing, asset recovery facilitation, and strengthening cross-border investigations.
- Funding Mechanisms:
- IPEF offers platforms for technical assistance and concessional funding.
- IPEF Catalytic Capital Fund: Initial grant of $33 million aimed to catalyze $3.3 billion in private investments.
- PGI Investment Accelerator: Received $300 million from the US International Development Finance Corporation.
- Concerns Raised:
- Experts highlighted concerns over the secrecy of IPEF negotiations with limited public input.
- Expressed hope that India has not agreed to a non-derogation clause that could limit domestic regulatory flexibility for national projects.
- Potential Risks:
- Most standards discussed in IPEF are aligned with those in the US and OECD countries.
- India risks compliance pressures in future trade deals if it adopts these standards without adequate preparation.
- Strategic Importance of IPEF:
- Involves 14 member countries, focusing on economic cooperation through four key pillars: trade, supply chain resilience, clean economy, and fair economy.
- Represents 40% of the global economy and 28% of world trade, highlighting India's commitment to regional partnerships alongside the US, Japan, Australia, and other Indo-Pacific nations.
COP 29 AT BAKU

- 23 Sep 2024
In News:
Azerbaijan is making a significant move in the global climate finance landscape by proposing the Climate Finance Action Fund (CFAF) at the upcoming COP29 conference. This fund aims to gather voluntary contributions from fossil-fuel-producing nations and companies, with Azerbaijan itself making the initial investment. The fund’s goal is to support climate action in developing countries, which often struggle to finance their environmental initiatives.
Key Aspects of the CFAF:
- Voluntary Contributions: The fund seeks donations from fossil fuel entities, allowing them to contribute based on a fixed amount or production volumes.
- Bipartite Allocation: Proposed funds will be split equally—half for climate projects in developing nations and half for supporting those countries in executing their national climate action plans.
- Operational Threshold: The CFAF will only commence operations once it secures a minimum of $1 billion and commitments from at least ten countries to participate.
Context of COP29:
COP29, hosted in Baku from November 11 to 22, centers on finalizing a climate finance agreement, particularly the obligations of developed nations post-2025. This follows the ongoing struggle to meet the $100 billion annual financing target established in the Paris Agreement.
Additional Proposals:
Azerbaijan has also introduced several other initiatives as part of its agenda, including:
- Expanding Global Energy Storage: Aiming to increase capacity sixfold by 2030.
- Green Hydrogen Market: Fostering a global marketplace for green hydrogen.
- Minimizing Emissions from Digital Growth: Ensuring that the environmental impact of increasing digitalization and data centers is mitigated.
Challenges Ahead:
Despite the ambitious plans, there are significant hurdles to overcome, including establishing a robust framework for the CFAF, garnering international support, and ensuring compliance from contributors. As the conference approaches, ongoing negotiations will be crucial to achieving substantial agreements on climate finance that can lead to meaningful progress in combating climate change.
QUAD CANCER MOONSHOT

- 23 Sep 2024
In News:
The Quad Cancer Moonshot Initiative is a significant collaborative effort among the Quad countries—India, the United States, Australia, and Japan—aimed at combating cancer through innovative strategies. The initiative focuses on key areas such as preventing and detecting cancer, improving treatment, and alleviating the disease's impact on patients and families.
Key Highlights of the Quad Cancer Moonshot Initiative:
- Focus Areas:
- Cervical Cancer Screening: Enhancing access to screening programs.
- HPV Vaccination: Increasing vaccination rates against HPV, which is the leading cause of cervical cancer.
- Patient Treatment: Improving treatment protocols and accessibility for cancer patients.
- India’s Contributions:
- Financial Commitment: India has pledged $10 million to support the WHO’s Global Initiative on Digital Health, aimed at enhancing digital health technologies for cancer care in the Indo-Pacific region.
- Material Support: India will provide cervical cancer screening kits, detection tools, and HPV vaccines valued at $7.5 million to bolster healthcare initiatives in the region.
- AI-based Protocols: Development of AI-driven treatment protocols to improve care delivery for cancer patients.
- Capacity Building: India aims to enhance radiotherapy services and overall cancer prevention strategies in the Indo-Pacific.
This initiative represents a strong commitment to fostering international collaboration in healthcare, particularly in the prevention and treatment of cervical cancer. By empowering communities with accessible tools and resources, the Quad countries aim to significantly reduce the burden of cancer in the region.
AMUR FALCONS

- 22 Sep 2024
In News:
An order issued by the District Magistrate directed the owners of air guns to deposit their hunting weapons at the offices of respective village authorities.
Amur Falcons: An Overview
Scientific Classification:
- Common Name: Amur Falcon
- Scientific Name: Falco amurensis
- Family: Falconidae
Physical Characteristics:
- Size: Small raptors, approximately 28-30 cm in length.
- Distinctive Features: Dark plumage with white wing linings; reddish-orange eyes and feet.
Migration Patterns:
- Breeding Grounds: Southeastern Russia and northern China.
- Migratory Route: They leave their breeding areas in autumn, traveling south to round the Himalayas, stopping in Nagaland, and then heading towards the Western Ghats before crossing the Indian Ocean to reach South Africa.
- Distance: These falcons undertake an incredible journey of around 22,000 kilometers annually, making them one of the most remarkable long-distance migrants among raptors.
Diet:
- Primarily insectivorous, they also consume small vertebrates when available.
Conservation Status:
- IUCN Status: Least Concern
- Legal Protection:
- Wildlife Protection Act, 1972: Schedule IV
- Convention on Migratory Species (CMS): Appendix II
Recent Conservation Efforts:
- Ban in Manipur: The Tamenglong district administration has imposed a ban on hunting, catching, killing, and selling Amur falcons in preparation for their migratory arrival.
- Tagging Program: In 2016, radio transmitters were used to monitor their migration routes.
- Awareness Initiatives: An annual ‘Amur Falcon Festival’ in Tamenglong district promotes awareness and celebrates these migratory birds.
Threats:
- Amur falcons face various threats including habitat loss, hunting, and illegal trapping.
Cultural Significance:
- Locally known as ‘Kahuaipuina’ in Manipur and ‘Molulem’ in Nagaland, these birds hold ecological and cultural significance, particularly in regions that serve as critical stopover points during migration.
Summary
The Amur falcon is a small but remarkable migratory raptor known for its long-distance travels from its breeding grounds in Asia to Africa. Conservation efforts in India, particularly in the Tamenglong district of Manipur, aim to protect these birds from hunting and habitat loss, ensuring their continued survival and highlighting their importance in the ecosystem.
WORLD RHINO DAY
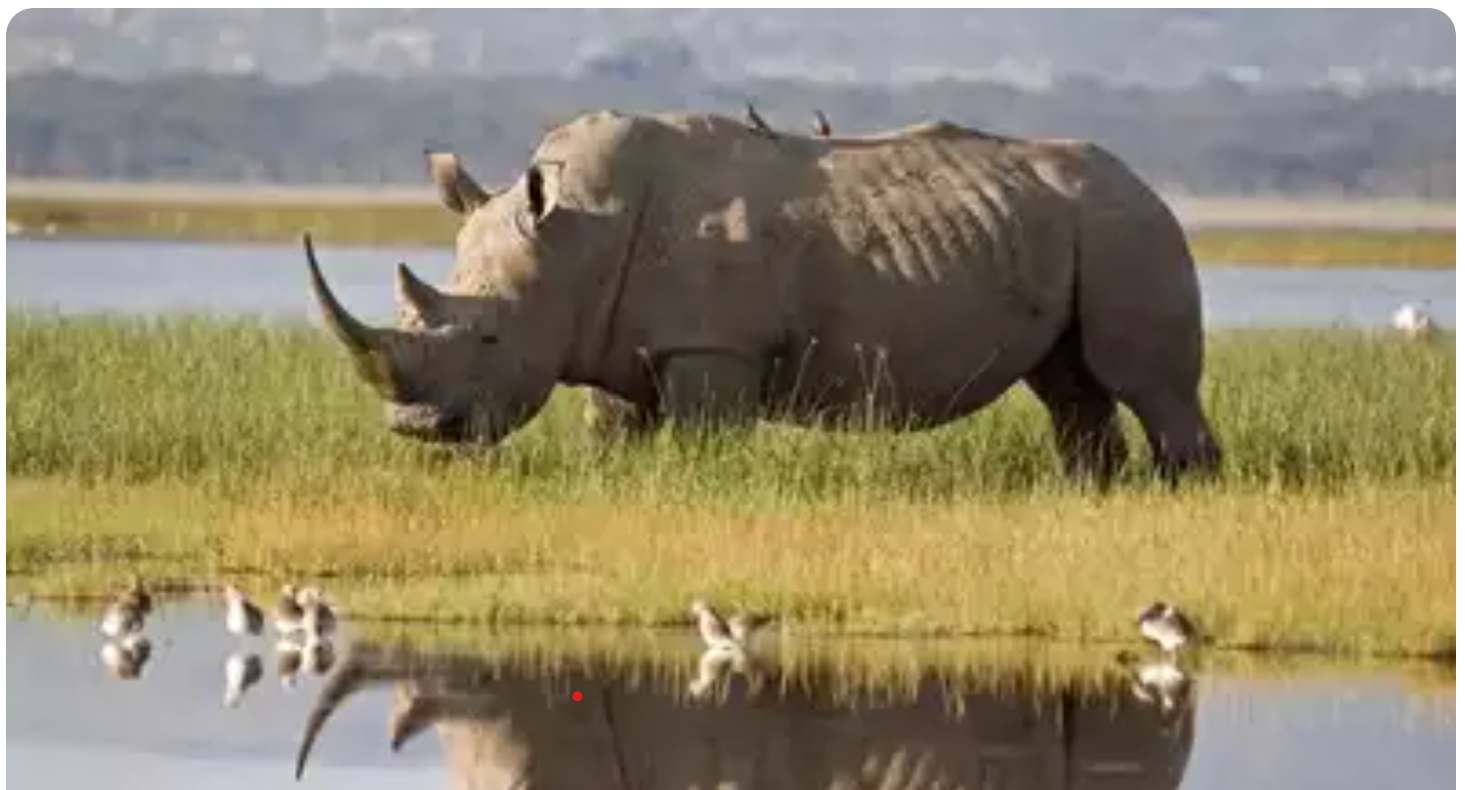

- 22 Sep 2024
In News:
Celebrated annually on September 22, World Rhino Day raises awareness about the critical conservation status of rhinoceroses and the myriad threats they face, such as poaching and habitat loss. This day, first initiated by the World Wildlife Fund South Africa in 2010, aims to highlight the need for the conservation of all five species of rhinos: the Javan, Sumatran, Black, Greater One-Horned, and White rhinos.
The Current Status of Rhino Species
- Among the five rhino species, three are classified as
- Critically Endangered: the Black, Javan, and Sumatran rhinos.
- The White Rhino is considered Near Threatened, with the Northern White Rhino itself critically endangered.
- The Greater One-Horned Rhino, primarily found in India, is listed as Vulnerable.
Notably, Kaziranga National Park in Assam is home to the largest population of Greater One-Horned Rhinos, boasting approximately 3,700 individuals.
Conservation Efforts
In India, initiatives like Project Rhino play a crucial role in safeguarding rhino populations. This project focuses on preventing poaching, enhancing habitat management, and increasing public awareness. It collaborates with various conservation groups and government agencies to strengthen law enforcement against poaching and to relocate rhinos to safer areas.
Another significant program is the Indian Rhino Vision 2020 (IRV 2020), aimed at boosting the population of Greater One-Horned Rhinos in Assam, particularly in regions where they had previously become extinct.
Surprising Facts About Rhinos
- Despite their thick skin, rhinos can get sunburned.
- Rhinos are related to zebras, horses, and tapirs.
- All five species are considered endangered.
- A group of rhinos is called a "crash."
- Rhinos' horns are made of keratin, the same protein found in human hair and nails.
- The term "rhinoceros" comes from two Greek words meaning "nose" and "horn."
- Rhinos and elephants are not natural enemies.
- One of the most famous depictions of a rhino is Albrecht Dürer's woodcut from 1515.
- The gestation period for rhinos can last up to 16 months.
- Rhinos have historically been used in traditional Asian medicine.
QUAD GROUPING

- 22 Sep 2024
In News:
Prime Minister Narendra Modi arrived in the United States, where he will participate in the fourth Quad Leaders Summit in Wilmington, Delaware.
What is the Quad Grouping?
The Quad, or Quadrilateral Security Dialogue, is an informal strategic alliance comprising India, the United States, Japan, and Australia. Originally formed in response to the Indian Ocean tsunami in 2004, the Quad aims to foster collaboration in various areas, but its primary focus has become countering the influence of China in the Indo-Pacific region.
Historical Background
- 2004: The Quad began as a response to the Indian Ocean tsunami, facilitating disaster relief.
- 2007: Japanese PM Shinzo Abe formalized the alliance.
- 2017: Amid rising Chinese assertiveness, the Quad was revitalized, expanding its objectives beyond maritime security.
Structure and Characteristics
- The Quad is not a formal organization; it lacks a secretariat or permanent decision-making body like the EU or UN.
- It focuses on strengthening bilateral and multilateral ties among member nations.
- Unlike NATO, the Quad does not include collective defense provisions but conducts joint military exercises to demonstrate unity.
Key Developments
- In 2020, the Malabar naval exercises expanded to include Australia, marking the first joint military exercises of the Quad since its resurgence.
- The first in-person summit took place in Washington, D.C. in 2021.
Objectives of the Quad
The Quad has outlined several primary objectives:
- Maritime Security: Ensuring safe and open sea routes in the Indo-Pacific.
- Climate Change: Addressing environmental challenges collaboratively.
- Investment Ecosystem: Creating opportunities for economic investment in the region.
- Technological Innovation: Promoting advancements and cooperation in technology.
- Public Health: Collaborating on initiatives like vaccine diplomacy during the COVID-19 pandemic.
Expansion and Future Directions
The Quad members have discussed expanding the partnership to include countries like South Korea, New Zealand, and Vietnam. In a joint statement, they reaffirmed their commitment to a free, open, resilient, and inclusive Indo-Pacific governed by international law.
Challenges and Opposition
China views the Quad as an effort to encircle and contain its influence. Beijing has criticized the grouping, labeling it as a strategy that incites discord among Asian nations.
45TH CHESS OLYMPIAD

- 22 Sep 2024
In News:
Recently, both the Indian men's and women's chess teams achieved remarkable success by winning gold medals at the Chess Olympiad in Budapest.
- In the final round of the 45th Chess Olympiad, the Indian men's team triumphed over Slovenia with a score of 3.5-0.5.
- At the same time, the Indian women's team showcased their skills by defeating Azerbaijan with the same score of 3.5-0.5.
- With this victory, India joins an elite group, as only China and the former Soviet Union had previously managed to win both men's and women's gold medals in the same Chess Olympiad edition.
- The Indian men's team had previously claimed bronze medals in 2014 and 2022.
- Meanwhile, the Indian women's team secured a bronze medal in the 2022 tournament held in Chennai.
About the Chess Olympiad:
- This prestigious event occurs every two years and features national teams from around the globe. It is organized by FIDE, which also selects the host nation.
- The inaugural Olympiad, which was unofficial, took place in 1924.
100 Years of the Discovery of the Indus Civilization
- 22 Sep 2024
Introduction
The centenary of the announcement of the Indus Valley Civilization (IVC) by Sir John Marshall on September 20, 1924, marks a significant milestone in archaeological history. This civilization, known for its advanced urban planning, encompasses over 2,000 sites across India, Pakistan, and Afghanistan.
Historical Context
Discovery of the Indus Civilization
- John Marshall's Role: As the Director-General of the Archaeological Survey of India (ASI), Marshall played a pivotal role in the excavations of Harappa and Mohenjodaro.
- Initial Findings: The civilization was revealed through meticulous work over two decades, beginning with Marshall's initial interest in the antiquities of India.
The Process of Discovery
The Concept of 'The Slow Hunch'
- Definition: Inspired by Steven Johnson's idea of 'the slow hunch,' this concept highlights how insights develop over time, similar to Joseph Priestley's early experiments with oxygen.
- Application to Marshall: Marshall's initial curiosity about the antiquity of India was nurtured through years of observations and explorations, culminating in the excavation of Harappa in 1921.
Key Individuals Involved
- Daya Ram Sahni: Conducted the first excavations at Harappa, uncovering evidence of an ancient culture.
- Rakhaldas Banerji: Excavated Mohenjodaro in 1922, leading to significant discoveries that indicated a widespread civilization.
Institutional Challenges
Limitations within ASI
- Lack of Collaboration: The ASI lacked a platform for archaeologists to share insights, impeding a collaborative approach to discoveries.
- Marshall's Focus: His dedication to ongoing projects, particularly at Taxila, resulted in delays in recognizing the significance of findings at Harappa and Mohenjodaro.
Announcing the Discovery
Marshall's Publication
- Impactful Presentation: In September 1924, Marshall's article vividly described the architectural and cultural features of the Indus Civilization, captivating readers.
- Scholarly Reception: The discovery sparked immediate scholarly interest, leading to further inquiries into the civilization's connections with ancient Mesopotamia.
Characteristics of the Harappan Civilization
Overview
- Timeframe: Flourished around 2500 BCE, classified as a Bronze-age civilization.
- Major Sites: Notable locations include Harappa, Mohenjodaro, and Lothal.
Key Features
- Urban Planning: Cities featured grid layouts, advanced drainage systems, and distinct public and private spaces.
- Agriculture and Economy: The economy thrived on agriculture, trade, and crafts, with evidence of cotton production and extensive trade networks.
Religious Practices
- Deities and Symbols: Terracotta figurines and seals indicate worship of fertility deities and animal figures, suggesting a rich spiritual life.
Reasons for Decline
Theories of Collapse
- Environmental Changes: Shifts in rainfall and tectonic activity may have disrupted agriculture and led to resource scarcity.
- Invasion Theories: While some suggest Indo-European invasions, evidence of cultural continuity challenges this narrative.
Recent Initiatives
Preservation and Promotion
- National Maritime Heritage Complex: Development at Lothal aims to highlight maritime history and attract tourism.
- UNESCO Recognition: Dholavira was added to the World Heritage list in 2021, showcasing the importance of IVC sites.
JORDAN
- 21 Sep 2024
In News:
Jordan has made history by becoming the first country in the world to be officially verified by the World Health Organization (WHO) as having eliminated leprosy. This achievement marks a significant advancement in global public health efforts.
Key Highlights:
- WHO Recognition: WHO Director-General Dr. Tedros Adhanom Ghebreyesus praised Jordan for this milestone, emphasizing the importance of stopping transmission and alleviating the suffering and stigma associated with leprosy.
- Historic Achievement: This success is not just about disease elimination but also about combating stigma and socio-economic harm.
- No Local Cases: Jordan has not reported any locally transmitted cases of leprosy for over two decades, demonstrating its effective public health strategies and strong political commitment.
- Independent Verification: WHO commissioned an independent team to conduct a thorough assessment, leading to the official recognition of leprosy elimination.
- Ongoing Vigilance: While celebrating this success, both the WHO and the Jordanian Ministry of Health emphasize the need for robust surveillance systems to detect and manage any future cases, including those from abroad.
Additional Context:
Leprosy, or Hansen's disease, is a chronic infectious condition caused by Mycobacterium leprae, primarily affecting the skin and nerves. Although it remains a neglected tropical disease, with over 200,000 new cases reported annually across more than 120 countries, Jordan's success showcases the potential for eradication through dedicated efforts.
This milestone serves as a beacon of hope, illustrating that with strong commitment, collaboration, and strategic planning, even longstanding public health challenges can be addressed effectively.
EXERCISE AIKYA

- 21 Sep 2024
In News:
The National Disaster Management Authority (NDMA), in partnership with the Indian Army's Southern Command and the Tamil Nadu State Disaster Management Authority (TNSDMA), recently conducted "EXERCISE AIKYA" in Chennai. This two-day Integrated Symposium and Table Top Exercise (TTEx) aimed to bolster disaster preparedness and response among key stakeholders across Peninsular India.
Key Highlights:
- Objective: "Aikya," meaning "Oneness" in Tamil, sought to unify India’s disaster management community by enhancing collaboration and preparedness.
- Participants: The exercise involved representatives from:
- Six southern states/UTs: Tamil Nadu, Kerala, Karnataka, Andhra Pradesh, Telangana, and Puducherry.
- Central ministries related to disaster management.
- State Disaster Management Authorities (SDMAs).
- Armed forces, including the Indian Army, Navy, and Air Force.
- Response agencies such as the NDRF, Indian Coast Guard, CRPF, CISF, and Railways.
- Early warning agencies including the IMD, NRSC, INCOIS, CWC, and FSI.
- Research institutions like NIDM, NIOT, IIT Madras, and DAE, with Prof. CVR Murty of IIT Madras serving as the Exercise Mentor.
- Focus Areas: The exercise simulated various emergency situations, covering:
- Tsunamis, landslides, floods, cyclones, industrial incidents, and forest fires.
- Recent disaster events in Tamil Nadu, Wayanad, and Andhra Pradesh.
- Discussions: Participants engaged in discussions about:
- Leveraging technology and AI for disaster management.
- Economic impacts of disasters.
- Vulnerabilities specific to the Peninsular region.
- Strategies for improving response times.
Future Plans
"EXERCISE AIKYA" marks a crucial step towards strengthening India’s disaster management framework. The NDMA and the Southern Command plan to conduct similar exercises with other military commands and institutions, including the Army War College and Naval War College, to further enhance national disaster preparedness and response capabilities.
EUROPA CLIPPER MISSION

- 21 Sep 2024
In news:
NASA is preparing to launch the Europa Clipper mission, which aims to investigate Jupiter's icy moon, Europa.
Key Details:
- Objective: This mission will place a spacecraft in orbit around Jupiter to conduct a thorough study of Europa, focusing on its potential habitability.
- Significance: Europa Clipper will be NASA's first mission specifically designed to explore an ocean world beyond Earth. Europa is believed to have a subsurface ocean beneath its icy surface, which raises the possibility of supporting life.
- Spacecraft Specifications:
- The spacecraft measures 100 feet (30.5 meters) from end to end and 58 feet (17.6 meters) across, making it the largest NASA spacecraft ever built for a planetary mission.
- Mission Plan:
- Europa Clipper will orbit Jupiter and conduct 49 close flybys of Europa to gather critical data regarding its environment and potential habitability.
- Instrumentation:
- Equipped with nine scientific instruments and a gravity experiment that leverages its telecommunications system, the spacecraft will maximize data collection by operating all instruments simultaneously during each flyby. This approach will allow scientists to compile comprehensive data layers, creating an in-depth understanding of Europa.
- Power Source:
- The spacecraft is outfitted with large solar arrays to harness sunlight for its energy needs while operating in the challenging environment of the Jupiter system.
Solar Array
A solar array is a collection of solar panels interconnected to generate electrical power. When combined with other components like an inverter and battery, it forms a complete solar energy system.
GLOBAL CYBERSECURITY INDEX 2024

- 21 Sep 2024
In News:
- India has achieved Tier 1 status in the Global Cybersecurity Index (GCI) 2024, published by the International Telecommunication Union (ITU), with an impressive score of 98.49 out of 100.
Role-Modeling Country: This accomplishment places India among ‘role-modeling’ countries, reflecting a strong commitment to cybersecurity practices globally.
Assessment Criteria: The GCI 2024 evaluates national efforts based on five pillars:
-
- Legal Measures
- Technical Measures
- Organizational Measures
- Capacity Development
- Cooperation
- Evaluation Methodology: The index utilized a comprehensive questionnaire comprising 83 questions, which cover 20 indicators, 64 sub-indicators, and 28 micro-indicators, ensuring a thorough assessment of each country's cybersecurity landscape.
- Tier Classification: The GCI 2024 report categorized 46 countries in Tier 1, the highest tier, indicating a strong commitment across all five cybersecurity pillars. Most countries fall into lower tiers, either “establishing” (Tier 3) or “evolving” (Tier 4) their cybersecurity frameworks.
Key Achievements
- Global Standing: India ranks at the top level of global cybersecurity rankings, showcasing its dedication to enhancing cyber resilience and securing its digital infrastructure.
- Government Initiatives:
- Robust Frameworks: Establishment of comprehensive frameworks for cybersecurity and cybercrime laws.
- Sectoral Support: Implementation of Sectoral Computer Incident Response Teams (CSIRTs) that provide technical support and incident reporting across various industries.
- Educational Integration: Cybersecurity has been integrated into primary and secondary education curricula to foster informed digital citizens.
- Public Awareness: Targeted campaigns have promoted secure online practices across multiple sectors, including private industry and academia.
- Skill Development and Innovation: The government has provided incentives and grants to enhance skill development and promote research within the cybersecurity sector.
- International Collaborations: India has engaged in numerous bilateral and multilateral partnerships to strengthen its capacity-building and information-sharing efforts.
About the International Telecommunication Union (ITU)
- Overview: Established in 1865, the ITU is the United Nations specialized agency for information and communication technologies, becoming a UN agency in 1947.
- Membership: ITU has 193 member countries and over 1,000 associated organizations, including companies and universities.
- Functions: ITU coordinates global radio spectrum allocation, sets technical standards for telecommunication, and works to improve ICT access in underserved communities.
- India's Involvement: India has been an active ITU member since 1869 and a regular participant in the ITU Council since 1952.
INDIA JOINS THE INTERNATIONAL BIG CAT ALLIANCE (IBCA)
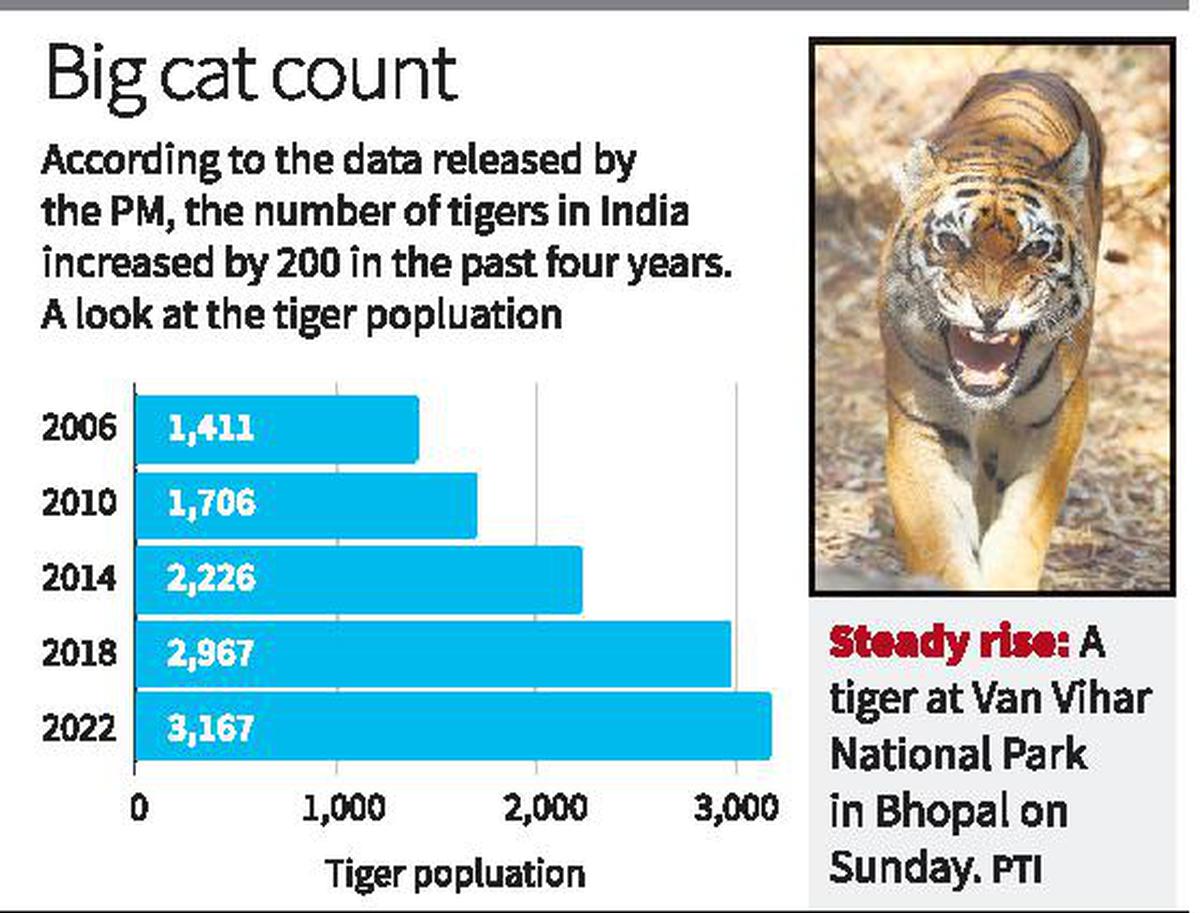
- 21 Sep 2024
In News:
India formally joined the International Big Cat Alliance (IBCA), launched by Prime Minister Narendra Modi on April 9, 2023, during the 50th anniversary of Project Tiger.
- Objective: The IBCA aims to conserve the world's seven big cat species: tiger, lion, leopard, snow leopard, cheetah, jaguar, and puma, focusing on their protection and natural habitats.
- Founding Members: India joins Nicaragua, Eswatini, and Somalia as founding members of the IBCA, which will collaborate with 24 countries and nine organizations.
- Headquarters: The IBCA will be headquartered in India, facilitating efforts to protect big cats and their ecosystems.
Purpose and Goals of IBCA
- Conservation Focus: The alliance addresses common challenges in the protection of the seven big cats, promoting sustainable resource use and tackling climate change.
- Collaboration and Support: The IBCA will provide a platform for member nations to share knowledge, expertise, and support recovery efforts in potential habitats.
- Mobilization of Resources: The alliance aims to mobilize financial and technical resources for effective conservation strategies based on global experiences.
Background and Evolution
- Inception: PM Modi proposed an international initiative against poaching and illegal wildlife trade in 2019, advocating for collaboration among tiger range countries.
- Extension of Project Tiger: The IBCA serves as an extension of India's long-standing commitment to wildlife protection, initially exemplified by the launch of Project Tiger in 1973.
Big Cat Species Overview
- Tiger (Endangered)
- Population: Approx. 3,167 in India, accounting for over 75% of the global population.
- Threats: Habitat loss, poaching, and climate change impacting their territory.
- Lion (Vulnerable)
- Population: Estimated 700 in India.
- Threats: Habitat reduction and targeted poaching.
- Leopard (Near Threatened)
- Population: Around 13,000 in India, with approximately 250,000 globally.
- Threats: Habitat loss and human-wildlife conflict.
- Snow Leopard (Vulnerable)
- Population: 400-700 in India, with global estimates of 4,000-6,500.
- Threats: Poaching, habitat loss, and human disturbances.
- Cheetah (Vulnerable)
- Population: Declined to less than 7,000 globally; declared extinct in India in 1952.
- Threats: Habitat loss, climate change, and illegal trafficking.
- Jaguar (Near Threatened)
- Population: Approximately 173,000 globally, primarily in South America.
- Threats: Deforestation, illegal hunting, and habitat fragmentation.
- Puma (Near Threatened)
- Population: Estimated 50,000, experiencing a decline.
- Threats: Habitat loss and human-wildlife conflict.
Future Initiatives
- Translocation Efforts: Following successful cheetah translocations from Namibia and South Africa, India plans to explore similar initiatives for other big cats.
- Global Cooperation: The IBCA will strengthen conservation efforts by working with a broader network of range countries to combat poaching and promote habitat preservation.
EARTH TO EXPERIENCE A TEMPORARY 'MINI-MOON' IN SEPTEMBER

- 20 Sep 2024
In News:
In late September, Earth will temporarily capture a small asteroid known as 2024 PT5. This phenomenon, where an asteroid becomes a "mini-moon," will last for about two months before the asteroid escapes back into space. While Earth has gained mini-moons before, such occurrences are quite rare; most asteroids either miss the planet entirely or burn up upon entering the atmosphere.
What Is a 'Mini-Moon'?
Mini-moons are small asteroids that get temporarily captured by Earth's gravity, orbiting the planet for a limited time. These asteroids are typically small and difficult to detect—only four mini-moons have been identified in Earth's history, and none remain in orbit today. Some objects previously thought to be mini-moons were later determined to be space debris, including rocket stages and satellites.
Details About 2024 PT5
Discovered on August 7 through the NASA-funded Asteroid Terrestrial-impact Last Alert System (ATLAS), 2024 PT5 measures approximately 33 feet in length, making it invisible to the naked eye and standard amateur telescopes. However, it is detectable by professional astronomical equipment.
According to Carlos de la Fuente Marcos, a professor at the Complutense University of Madrid, 2024 PT5 originates from the Arjuna asteroid belt, which consists of space rocks that share similar orbits with Earth. There is also speculation that it could be a fragment resulting from an impact on the moon, as noted by Paul Chodas from NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL).
However, some experts argue that 2024 PT5 may not fully qualify as a mini-moon. For an asteroid to be classified as such, it must complete at least one full orbit around Earth. Instead, 2024 PT5 will follow a horseshoe-shaped path, leading Lance Benner, a principal investigator at JPL, to express skepticism about its classification as a mini-moon.
Significance of the Event
Studying 2024 PT5 will provide valuable insights into asteroids that pass near Earth and their potential for future collisions. Additionally, many asteroids are believed to contain precious minerals and water, which could be harvested for future space missions and resource utilization. Observing this mini-moon will enhance our understanding of these celestial bodies and their behavior in Earth's vicinity.
TRISHNA MISSION

- 20 Sep 2024
In News:
During a recent event, the President of the French Space Agency, Centre National d’Etudes Spatiales (CNES), addressed various topics, celebrating 60 years of collaboration between France and India in space exploration, alongside discussions on the Gaganyaan and TRISHNA missions.
Overview of the TRISHNA Mission
The Thermal Infrared Imaging Satellite for High-resolution Natural Resource Assessment (TRISHNA) is a joint initiative by the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) and CNES.
Mission Objectives
TRISHNA aims to provide high-resolution, timely observations of Earth's surface temperature, monitor vegetation health, and analyze water cycle dynamics. It will facilitate:
- Assessment of urban heat islands
- Detection of thermal anomalies related to volcanic activity and geothermal resources
- Monitoring of snowmelt runoff and glacier behavior
- Collection of data on aerosol optical depth, atmospheric water vapor, and cloud cover
Satellite Payloads
TRISHNA is equipped with two main payloads:
- Thermal Infra-Red (TIR) Payload: Supplied by CNES, this payload includes a four-channel long-wave infrared imaging sensor that enables high-resolution mapping of surface temperature and emissivity.
- Visible-Near Infra-Red-ShortWave Infra-Red (VNIR-SWIR) Payload: Developed by ISRO, this payload consists of seven spectral bands aimed at detailed mapping of surface reflectance, which is crucial for calculating biophysical and radiation budget variables.
The data retrieved from both payloads will aid in solving surface energy balance equations to estimate heat fluxes.
Operational Details
- TRISHNA will operate in a sun-synchronous orbit at an altitude of 761 km, with a scheduled overpass time of 12:30 PM at the equator.
- This orbit will achieve a spatial resolution of 57 meters for land and coastal regions, and 1 km for oceanic and polar areas.
- The mission is expected to have an operational lifespan of five years.
PROJECT 200

- 20 Sep 2024
In News:
At the Bengaluru Space Expo 2024, Bengaluru-based start-up Bellatrix Aerospace launched Project 200, a pioneering satellite designed to operate in the Ultra-Low Earth Orbit (ULEO) range of 180 km to 250 km.
Revolutionary Capabilities
Bellatrix Aerospace claims that operating in this orbit dramatically enhances satellite capabilities and redefines their connection to Earth. The satellite's launch is part of a technology demonstration mission, showcasing an innovative propulsion system tailored for this low altitude.
Breakthrough Propulsion Technology
Traditionally, satellites are positioned above 450 km to minimize atmospheric interference. However, deploying at 200 km can significantly enhance capabilities, which has been hindered by propulsion technology limitations until now.
Enhanced Performance Metrics
The new propulsion system allows satellites to maintain their orbits for years, avoiding rapid deorbiting due to atmospheric drag. Key benefits of Project 200 include:
- Reduced Communication Latency: Halves the delay in satellite communication.
- Improved Image Resolution: Enhances clarity threefold.
- Cost Efficiency: Significantly lowers overall satellite costs.
Bellatrix's innovative approach not only addresses current limitations but also positions its satellite as a transformative solution for applications in high-resolution Earth observation, telecommunications, and scientific research.
PRADHAN MANTRI JANJATIYA UNNAT GRAM ABHIYAN

- 20 Sep 2024
In News:
The Union Cabinet, chaired by Prime Minister Narendra Modi, approved the Pradhan Mantri Janjatiya Unnat Gram Abhiyan. This mission aims to enhance the socio-economic conditions of tribal communities by saturating more than 63,000 tribal-majority villages and aspirational districts with a total budget of ?79,156 crore.
Budget Breakdown
- Total Outlay: ?79,156 crore
- Central Share: ?56,333 crore
- State Share: ?22,823 crore
Target Beneficiaries
The initiative is expected to benefit over 5 crore tribal people across 549 districts and 2,740 blocks in 30 States/UTs.
Context
- India's Scheduled Tribe (ST) population stands at 10.45 crore, according to the 2011 Census, with more than 705 tribal communities often residing in remote areas. This mission builds upon the successes of the Pradhan Mantri Janjati Adivasi Nyaya Maha Abhiyan (PM-JANMAN), launched on November 15, 2023.
Mission Objectives
- The mission aims to address critical gaps in social infrastructure, health, education, and livelihood through a comprehensive approach involving 25 interventions across 17 ministries.
Key Goals and Interventions
Goal 1: Developing Enabling Infrastructure
- Housing: Provision of pucca houses under the PMAY (Gramin) for eligible households, along with access to tapped water and electricity.
- Village Infrastructure: Improvement of all-weather road connectivity, mobile connectivity, and educational and health infrastructure.
Goal 2: Promotion of Economic Empowerment
- Skill Development: Enhanced training and self-employment opportunities for ST youth through initiatives like the Skill India Mission and support for tribal marketing.
Goal 3: Universal Access to Good Education
- Education Initiatives: Increase the gross enrollment ratio in schools and higher education, along with setting up tribal hostels for students.
Goal 4: Healthy Lives and Dignified Ageing
- Health Access: Provision of quality health facilities, aiming to meet national standards in maternal and child health indicators through mobile medical units.
Innovative Schemes
- Tribal Home Stay Initiative: Promotion of 1,000 homestays in tribal areas to boost tourism and provide alternate livelihoods. Each household can receive up to ?5 lakh for construction and ?3 lakh for renovations.
- Sustainable Livelihood for FRA Holders: Focus on 22 lakh FRA patta holders, enhancing their rights and providing livelihood support through various government schemes.
- Improving Educational Infrastructure: Upgrading tribal residential schools and hostels to improve local educational resources and retention rates.
- Sickle Cell Disease Management: Establishing Centers of Competence for affordable diagnostic services and prenatal care in regions where the disease is prevalent.
- Tribal Multipurpose Marketing Centres (TMMCs): Setting up 100 TMMCs to improve marketing of tribal products and facilitate better prices for producers.
WHITE REVOLUTION 2.0

- 20 Sep 2024
- Overview:
- India is the world's largest milk producer, with production reaching 230.58 million tonnes in 2022-23.
- White Revolution 2.0 focuses on cooperative societies, similar to the foundation laid by Operation Flood in the 1970s.
- Objectives of White Revolution 2.0:
- Increase daily milk procurement from 660 lakh kg (2023-24) to 1,007 lakh kg by 2028-29.
- Enhance the market access for dairy farmers, especially in uncovered areas.
- Generate employment and empower women through increased dairy cooperative involvement.
- Current Landscape:
- The Ministry of Cooperation has prioritized expanding the cooperative network since its formation in 2021.
- Dairy cooperatives operate in 70% of India’s districts with approximately 1.7 lakh dairy cooperative societies (DCSs).
- These DCSs serve around 2 lakh villages (30% of total villages) and account for 10% of milk production and 16% of marketable surplus.
- Regional Coverage:
- States like Gujarat, Kerala, and Sikkim have over 70% village coverage by dairy cooperatives.
- In contrast, states such as Uttar Pradesh, Uttarakhand, and Madhya Pradesh have only 10-20% coverage.
- Less than 10% coverage is observed in West Bengal, Assam, and several smaller northeastern states.
- Expansion Plans:
- NDDB plans to establish 56,000 new multipurpose dairy cooperative societies over the next five years and strengthen 46,000 existing DCSs.
- A pilot project initiated in February 2023 aims to set up dairy cooperatives in uncovered gram panchayats in Haryana, Madhya Pradesh, and Karnataka.
- Funding Sources:
- The National Programme for Dairy Development (NPDD) 2.0 will primarily fund White Revolution 2.0.
- Financial assistance will support village-level milk procurement, chilling facilities, and training initiatives.
- Current Production Insights:
- India’s milk production has grown significantly from 17 million tonnes in 1951-52 to 230.58 million tonnes.
- Average yield per animal is 8.55 kg/day for exotic/crossbred and 3.44 kg/day for indigenous animals.
- Per Capita Milk Availability:
- National average: 459 grams/day, higher than the global average of 323 grams/day.
- Significant regional variation: from 329 grams in Maharashtra to 1,283 grams in Punjab.
- Top Milk Producing States:
- Uttar Pradesh (15.72%), Rajasthan (14.44%), Madhya Pradesh (8.73%), Gujarat (7.49%), Andhra Pradesh (6.70%) contribute to 53.08% of total production.
- Indigenous buffaloes contribute 31.94%, while crossbred cattle contribute 29.81%.
- Market Dynamics:
- About 63% of total milk production is marketed; two-thirds of this is in the unorganised sector.
- Cooperatives hold a significant share in the organised sector, providing livelihoods to over 8.5 crore individuals, primarily women.
- Economic Impact:
- The dairy sector represents 40% (?11.16 lakh crore) of the agricultural value output in 2022-23, surpassing cereals.
One Nation, One Election

- 19 Sep 2024
In News:
The Union cabinet has recently approved the "One Nation, One Election" proposal, facilitating the conduct of simultaneous elections in India. This initiative follows a report submitted in March by a high-level committee chaired by former President Ram Nath Kovind, which unanimously recommended synchronizing Lok Sabha and State Assembly elections, along with local body polls, within 100 days.
What are Simultaneous Polls?
Simultaneous polls aim to align the timing of Lok Sabha and State Assembly elections across all states, thereby reducing the frequency of elections. Historically, simultaneous elections were held during the first four general election cycles (1952, 1957, 1962, and 1967), but this practice ended in 1959 after the dismissal of the Kerala government. Since then, due to premature dissolutions of various Assemblies, elections have been staggered. Currently, only four states—Andhra Pradesh, Odisha, Arunachal Pradesh, and Sikkim—hold simultaneous elections with the Lok Sabha.
Arguments For and Against
Proponents argue that simultaneous elections can significantly reduce election-related costs, which amounted to approximately ?3,870 crore during the 2014 general elections. They also highlight that the Model Code of Conduct triggers twice in a five-year cycle, leading to extended periods of governance downtime.
Opponents caution that this approach may favor larger political parties with national reach, potentially sidelining smaller regional parties. A 2015 study found that the likelihood of a party winning both Lok Sabha and Assembly elections when held simultaneously is 77%, dropping to 61% if elections are spaced six months apart.
Implementation Process
The committee proposed a two-step implementation:
- Simultaneous Elections: Conduct elections for both the Lok Sabha and State Legislative Assemblies together.
- Synchronizing Local Elections: Hold elections for municipalities and panchayats within 100 days following the general elections.
Following the announcement of the "appointed date," the terms of all State Assemblies constituted after that date would end with the Lok Sabha's term. This could lead to most State governments not completing their five-year terms, even if they maintain a majority.
Required Constitutional Changes
Several amendments to the Constitution have been proposed:
- Introduction of Article 82A: This would require all Legislative Assemblies elected after the appointed date to conclude with the Lok Sabha’s term.
- Amendment of Article 327: Expanding Parliament's powers to include the conduct of simultaneous elections.
- Revisions to Articles 83 and 172: Defining the five-year term as the "full term" and any remaining period after premature dissolution as the "unexpired term."
- Introduction of Article 324A: Empowering Parliament to ensure that municipality and panchayat elections occur alongside general elections.
- Amendments for Union Territories: Ensuring that Assembly elections in Union Territories align with simultaneous elections.
- Single Electoral Roll: Proposing a common electoral roll for all elections, to be managed by the Election Commission of India (ECI).
State Ratification
Under Article 368, amending the Constitution may require ratification by state legislatures. The panel believes that syncing Assembly elections with Lok Sabha elections will not need state ratification, but amendments for a common electoral roll and synchronization of local elections will require cooperation from the states. The ruling BJP, currently in power in several states, will need to navigate upcoming Assembly elections in Haryana, Maharashtra, and Jharkhand to secure this support.
Conclusion
The "One Nation, One Election" initiative aims to streamline India's electoral process, potentially enhancing governance and reducing costs. However, its success depends on achieving political consensus and implementing necessary constitutional amendments, which will require collaboration among various political parties and state governments.
Cabinet approves Chandrayaan-4 mission, first module of Bharatiya Antariksh Station, Venus mission, next-gen launcher

- 19 Sep 2024
In News:
The PM Modi-led Union Cabinet has approved several ambitious space initiatives, marking a significant leap for India's lunar and space exploration programs.
Chandrayaan-4 Mission
- Objective: The fourth lunar mission aims to collect lunar samples, return them safely to Earth, and analyze them.
- Timeline: Expected completion within 36 months post-approval, with a budget of ?2,104 crore.
- Significance: This mission will build foundational technological capabilities for a manned Moon landing planned by 2040.
- Remarks: ISRO Chairman S. Somanath emphasized that the mission's highlight is its low-cost execution and the step-by-step approach to developing the necessary technology.
Bharatiya Antariksh Station (BAS) and Gaganyaan
- BAS Development: Approval for the first module of the Bharatiya Antariksh Station, targeted for launch by 2028, with full completion by 2035.
- Gaganyaan Program: The program’s budget has been revised to ?20,193 crore, with an additional funding of ?11,170 crore to enhance its scope and include precursor missions for BAS.
- Mission Plan: Eight missions are envisaged by 2028, including four under the ongoing Gaganyaan program, development of BAS-1, and four additional missions for technology demonstration and validation.
Venus Orbiter Mission (VOM)
- Launch Timeline: Scheduled for March 2028, VOM will explore Venus's atmosphere, geology, and generate extensive scientific data.
- Budget: The Cabinet approved ?1,236 crore for VOM, with ?824 crore allocated for the spacecraft.
- Research Focus: The mission will provide insights into Venus's transformation and how different planetary environments evolve.
Next-Generation Launch Vehicle (NGLV)
- Development Approval: A reusable NGLV has been greenlit with a budget of ?8,240 crore.
- Capabilities: The new rocket will have three times the payload lifting capability compared to existing vehicles (10 tonnes to 30 tonnes to Low Earth Orbit) and will be cost-effective and commercially viable.
- Features: The NGLV will include reusability options and modular green propulsion systems, enhancing India's capacity for satellite launches.
Net Direct Tax inflows increase by 16.1%

- 19 Sep 2024
In News:
- Advance tax payments from corporates and personal taxpayers have risen by 22.6%, surpassing ?4.36 lakh crore. This increase is driven by a 39.2% rise in Personal Income Tax (PIT) receipts and an 18.2% uptick in corporate taxes.
Key Details:
- Overall net direct tax receipts have reached approximately ?9.96 lakh crore, reflecting a 16.1% increase, though this marks a slowdown from the 22.5% growth recorded as of August 11.
- As of September 17, corporate tax collections grew by 10.5%, while inflows from PIT increased by 18.9%.
- Securities Transaction Tax collections nearly doubled to ?26,154 crore, and refunds surged by 56.5% to ?2.05 lakh crore, according to data from the Income Tax Department.
- Personal taxes continue to outpace corporate taxes, contributing 51.7% of net direct tax receipts for the year.
- Gross tax collections, before accounting for refunds, have risen by 21.5%, totaling ?12.01 lakh crore.
Pradhan Mantri Annadata Aay Sanrakshan Abhiyan (PM-AASHA)
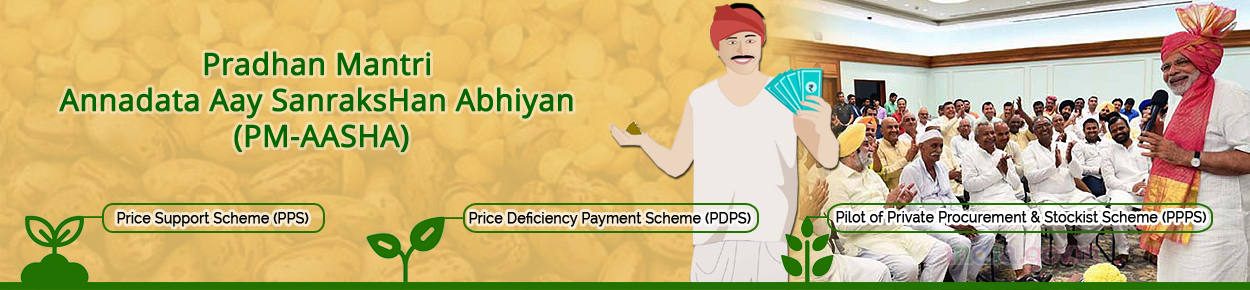
- 19 Sep 2024
In News:
- The Union Cabinet, chaired by Prime Minister Narendra Modi, approved the continuation of the PM-AASHA scheme to provide remunerative prices to farmers and control price volatility of essential commodities for consumers.
- Total Financial Outlay: ?35,000 crore during the 15th Finance Commission Cycle, up to 2025-26.
Scheme Integration
- The government has merged the Price Support Scheme (PSS) and Price Stabilization Fund (PSF) into PM-AASHA to enhance efficiency.
- Components of PM-AASHA:
- Price Support Scheme (PSS)
- Price Stabilization Fund (PSF)
- Price Deficit Payment Scheme (PDPS)
- Market Intervention Scheme (MIS)
Procurement Details
- MSP Procurement: Starting from the 2024-25 season, procurement of notified pulses, oilseeds, and copra at Minimum Support Price (MSP) will be on 25% of national production.
- Exceptions for 2024-25: 100% procurement of Tur, Urad, and Masur will be implemented.
- Government Guarantee: The existing government guarantee for procurement has been enhanced to ?45,000 crore.
Consumer Protection Measures
- The extension of the PSF scheme will help protect consumers from extreme price volatility by maintaining strategic buffer stocks of pulses and onions.
- Procurement of pulses at market prices will be handled by the Department of Consumer Affairs (DoCA) when prices exceed MSP.
Enhanced State Participation
- PDPS Coverage: The coverage for the Price Deficit Payment Scheme for notified oilseeds has been increased from 25% to 40% of state production.
- Implementation Period: Extended from 3 months to 4 months, with compensation limited to 15% of MSP.
Market Intervention Scheme (MIS) Adjustments
- The MIS has been extended to provide remunerative prices for perishable horticultural crops.
- Coverage for MIS has increased from 20% to 25% of production, with an option for direct differential payments to farmers.
- For TOP (Tomato, Onion, Potato) crops, the government will cover transportation and storage costs to ensure price stability.
Fast-track special courts (FTSCs)

- 19 Sep 2024
In News:
Fast-track special courts (FTSCs) are much more efficient than other courts in handling rape cases and those related to the Protection of Children from Sexual Offences (POCSO) Act, a report released by the India Child Protection.
Key Details:
West Bengal's Performance
- West Bengal recorded less than a 2% disposal rate for rape and POCSO cases, the lowest in India.
- Only five out of 123 earmarked FTSCs are currently functioning in the state.
Overview of the India Child Protection (ICP)
- Established in 2005, the ICP is dedicated to combatting child sexual abuse and related crimes, including:
- Child trafficking
- Exploitation of children in the digital space
- Child marriage
Efficiency of FTSCs
- The ICP report titled "Fast Tracking Justice" highlighted that FTSCs disposed of 83% of cases in 2022, compared to 10% by conventional courts.
- As of August 2023, 755 out of 1,023 earmarked FTSCs were operational.
- Among these, 410 FTSCs are exclusively for POCSO cases.
Historical Context
- The FTSC scheme was launched by the Centre in October 2019, following a Supreme Court directive for ensuring the swift disposal of cases, related to rape and those coming under the Protection of Children from Sexual Offences (POCSO) Act.
- It is a centrally sponsored scheme.
- Implemented by the Department of Justice, Ministry of Law and Justice.
Case Disposal Statistics
- FTSCs have disposed of 52% of the 4,16,638 rape and POCSO cases since the scheme's inception.
- Disposal rates improved from 83% in 2022 to 94% in 2023.
State-wise Disposal Rates
- Top Performing States:
- Maharashtra: 79.5%
- Punjab: 71.3%
- Kerala (Southern India): 69.5%
- Karnataka: 62.2%
- Tamil Nadu: 58.4%
- Lowest Performing States:
- West Bengal: 1.6%
- Jammu and Kashmir: 25%
- Meghalaya: 26.6%
- Delhi: 28.3%
Note: No data was available for Arunachal Pradesh, Ladakh, and Sikkim.
Need for Additional FTSCs
- The ICP report states that India needs at least 1,000 more FTSCs to manage the backlog effectively.
- The backlog of pending cases rose from 2,81,049 in 2020 to 4,17,673 by the end of 2022.
Advocacy for Reform
- Bhuwan Ribhu, a child rights activist, emphasized the urgent need for FTSCs to ensure justice for victims:
- Investment in the safety and security of women and children is crucial.
- All pending cases should be resolved within the next three years.
- Rehabilitation and compensation for victims should be prioritized.
- Time-bound policies for case disposal across all courts are necessary.
Funding and Resource Utilization
- The ICP report recommends optimizing the Nirbhaya Fund, created after the 2012 Delhi gang rape, to support additional FTSCs.
- There is currently ?1,700 crore unutilized, while the requirement for operationalizing new FTSCs is ?1,302 crore.
Strategic Clean Energy Partnership (SCEP)

- 18 Sep 2024
In News
The recent Strategic Clean Energy Partnership (SCEP) Ministerial between the United States and India aimed to enhance collaboration in clean energy innovation, energy security, and the transition to clean energy.
About the Partnership
The meeting reviewed significant achievements and future initiatives across five core pillars:
- Power and Energy Efficiency
- Responsible Oil and Gas
- Renewable Energy
- Emerging Fuels & Technologies
- Sustainable Growth
The SCEP facilitates bilateral cooperation on clean energy, focusing on power, efficiency, renewable resources, emerging technologies, and sustainable practices.
Key Highlights of SCEP
Renewable Energy Technology Action Platform (RETAP)
Launched in August 2023, RETAP aims to create actionable roadmaps for:
- Hydrogen
- Long-duration energy storage
- Offshore wind
- Geothermal technologies
Energy Storage Task Force
This public-private initiative seeks to address:
- Policy
- Safety
- Regulatory challenges
It explores alternatives to lithium-ion technologies, with projects like Battery Energy Storage Systems (BESS) in Assam and Haryana focusing on grid integration and renewable energy storage.
Modernization of Power Distribution
The meeting underscored India’s advancements in:
- Smart metering
- Power market reforms
- The Indian Railways’ goal of achieving net-zero emissions by 2030
India has successfully procured 1.5 GW of round-the-clock renewable energy.
Sustainable Aviation Fuel (SAF) & Transport Electrification
A comprehensive workshop was launched to enhance R&D, certification, and partnerships for SAF. India’s PM eBus Sewa scheme aims to deploy 10,000 electric buses, promoting electrification in medium and heavy-duty transport.
Carbon Capture, Utilization, and Storage (CCUS) & Methane Abatement
Cooperation on CCUS technologies and regulatory frameworks has increased, alongside efforts to reduce methane emissions in the oil and gas sector through collaboration with India’s Directorate General of Hydrocarbons.
Public-Private Collaborations
The importance of public-private dialogues in shaping policies and reducing the costs of clean energy technologies was emphasized.
Initiatives Supporting Clean Energy
- International Solar Alliance (ISA): A global coalition led by India, promoting solar energy collaboration among solar-rich countries.
- Renewable Energy Technology Action Platform (RETAP): A US-India initiative focusing on hydrogen, energy storage, offshore wind, and geothermal technologies.
- Green Hydrogen Mission (India): Promotes green hydrogen as a clean energy alternative, especially in heavy industries and transportation.
- EU’s Green Deal: A European strategy aimed at achieving climate neutrality by 2050 through clean energy investments and policies.
- PM KUSUM Scheme (India): Supports solar power generation for irrigation, reducing fossil fuel reliance in agriculture.
Union Budget 2024-25: Corridor Projects for Bihar's Temples

- 18 Sep 2024
Why in News?
The Union Budget 2024-25 announced plans to develop corridor projects for the Vishnupad Temple at Gaya and the Mahabodhi Temple at Bodh Gaya in Bihar. These initiatives aim to enhance both temples as significant pilgrimage and tourist destinations, modeled after the successful Kashi Vishwanath Corridor. The temples are located approximately 10 kilometers apart and hold considerable cultural significance.
Key Facts About the Temples
Vishnupad Temple at Gaya
- Location: Situated on the banks of the Phalgu/Falgu River in Gaya district, Bihar.
- Deity: Dedicated to Lord Vishnu.
- Legend: Local mythology recounts that a demon named Gayasur sought the power to help others attain moksha (liberation). After misusing this power, he was subdued by Lord Vishnu, who left a footprint at the temple, symbolizing this event.
- Architectural Features: The temple stands about 100 feet tall and is supported by 44 pillars made from large gray granite blocks (Munger Black stone), joined with iron clamps. The octagonal shrine is oriented towards the east.
- Construction: Built in 1787 under Queen Ahilyabai Holkar's orders.
- Cultural Practices: The temple is especially significant during Pitra Paksha, a time for honoring ancestors, attracting many devotees. The Brahma Kalpit Brahmins, or Gayawal Brahmins, have served as traditional priests since ancient times.
Mahabodhi Temple at Bodh Gaya
- Historical Significance: Believed to be the location where Gautam Buddha attained enlightenment under the Mahabodhi Tree.
- Construction: Originally built by Emperor Ashoka in the 3rd century BC, with the current structure dating back to the 5th–6th centuries.
- Architectural Features: The temple complex includes the 50-meter-high Vajrasana (the Diamond Throne), the sacred Bodhi Tree, and six other sacred sites associated with Buddha's enlightenment. The site is surrounded by numerous ancient Votive stupas and is protected by circular boundaries.
- Sacred Sites:
- Bodhi Tree: A direct descendant of the original tree under which Buddha attained enlightenment.
- Animeshlochan Chaitya: Where Buddha spent the second week of meditation post-enlightenment.
- Ratnachakrama: Site of Buddha's third week after enlightenment.
- Ratnaghar Chaitya: Site of Buddha's fourth week after enlightenment.
- Ajapala Nigrodh Tree: Site of Buddha’s fifth week after enlightenment.
- Lotus Pond: Site of Buddha’s sixth week after enlightenment.
- Rajyatana Tree: Site of Buddha’s seventh week after enlightenment.
- Recognition: Designated a UNESCO World Heritage Site in 2002, the Mahabodhi Temple attracts numerous national and international pilgrims, emphasizing its spiritual importance.
Other Tourist Attractions in Bihar
Additional notable tourist sites in Bihar include:
- Vishwa Shanti Stupa in Rajgir
- Nalanda
- Ancient city of Patliputra
- Valmiki Nagar Tiger Reserve in West Champaran
What is the Pilgrim Corridor Project (PCP)?
The Pilgrim Corridor Project (PCP) aims to upgrade religious sites into world-class destinations for spiritual and tourism purposes.
India-China Disengagement Along the LAC
- 18 Sep 2024
Overview of Disengagement Progress
Recently, India’s External Affairs Minister announced that about 75% of the “disengagement problems” with China along the Line of Actual Control (LAC) in Ladakh have been “sorted out.” However, notable areas such as Demchok and the Depsang plains have seen no progress toward resolution over the past two years.
Recent Developments on India-China Disengagement
Verified Disengagement
India and China have mutually agreed to and verified disengagement from five friction points, including:
- Galwan Valley
- Pangong Tso
- Gogra-Hot Springs
Despite this, issues in Demchok and Depsang remain unresolved.
Diplomatic Efforts
Recent high-level diplomatic interactions have facilitated the disengagement along the LAC. Key meetings include:
- India’s National Security Advisor Ajit Doval meeting Chinese Foreign Minister Wang Yi at the BRICS NSAs meeting in St Petersburg, Russia.
- Anticipation for further disengagement is linked to the upcoming BRICS Summit in October in Kazan, Russia, where leaders from both nations are expected to meet.
Significance of Disengagement
The 31st meeting of the Working Mechanism for Consultation & Coordination on India-China Border Affairs (WMCC) was described as “frank, constructive, and forward-looking.” Participants urged both parties to “narrow down the differences” and “find early resolution of the outstanding issues.” The phrase "narrow down the differences" marks a hopeful shift in the dialogue surrounding the border standoff.
Strategic Importance of Depsang Plains and Demchok
Depsang Plains
The Depsang Plains hold strategic significance due to the following reasons:
- The People’s Liberation Army (PLA)’s control threatens India’s position over the Siachen Glacier, potentially encircling the Indian Army between China and Pakistan.
- A coordinated attack from both China and Pakistan would leave India’s military position on the Siachen Glacier vulnerable.
- The Indian Army identifies this region as particularly susceptible to mechanized warfare due to its flat terrain, which also offers direct access to Aksai Chin.
Demchok
Demchok is crucial for several reasons:
- It facilitates effective surveillance of Chinese movements and activities in the Aksai Chin region.
- It supports essential road and communication links that enable rapid military mobilization and logistical support.
Key Areas in the India-China Standoff
Pangong Lake Region
- This area frequently sees patrols from both India and China intersecting.
- The north bank of the lake is divided into eight "fingers," with India claiming territory up to Finger 8 and China disputing it down to Finger 4.
Demchok Region
- Recent reports indicated increased Chinese activity and heavy equipment movement.
Galwan River Basin
- Satellite imagery revealed Chinese tents near the Galwan River basin, suggesting incursions into traditionally held Indian territories.
Gogra Post
- A Chinese military buildup near the Gogra post has escalated tensions.
Daulat Beg Oldie (DBO)
- Chinese encroachments have been reported in the DBO sector, located on the Indian side.
- The DBO airstrip is critical for winter operations and reinforcements, accessible via the 255 km-long Darbuk-Shyok-DBO road.
India Status Report on Road Safety 2024
- 18 Sep 2024
In News:
The "India Status Report on Road Safety 2024," prepared by the TRIP Centre at IIT Delhi, highlights India's slow progress in reducing road accident fatalities and emphasizes the need for a tailored approach to road safety.
Key Findings:
- Road Safety Analysis:
- The report analyzes road safety data from FIRs across six states and evaluates compliance with Supreme Court directives on road safety.
- There are significant disparities in road traffic death rates among states, with motorcyclists and truck-related fatalities being notably high.
- Road traffic injuries remain a critical public health issue, with little progress in reducing fatalities. Many states are unlikely to meet the UN goal of halving traffic deaths by 2030.
- Health Impact:
- In 2021, road traffic injuries ranked as the 13th leading cause of death in India and the 12th leading cause of health loss (measured in Disability-Adjusted Life Years, or DALYs). Six states listed road traffic injuries among their top 10 health loss causes.
- Crash Surveillance Deficiencies:
- India lacks a national crash-level database, relying on police station records, which are often incomplete and inaccurate. This hampers effective public policy and intervention strategies.
- State Performance:
- There is a threefold variation in per capita death rates across states. Tamil Nadu, Telangana, and Chhattisgarh have the highest rates, while West Bengal and Bihar have the lowest.
- Pedestrians, cyclists, and motorized two-wheeler riders are the most common accident victims, with trucks accounting for a large share of accidents.
- Helmet usage is low, especially in rural areas, and basic traffic safety measures are inadequate across many states.
- Global Comparison:
- India's road safety governance is starkly lagging compared to developed nations. By 2021, Indians were 600% more likely to die in road accidents compared to their counterparts in countries like Sweden.
Recommendations for Improvement
- National Database: Establish a comprehensive, publicly accessible database for fatal crashes to enhance understanding of risks and evaluate the effectiveness of interventions.
- Scaled Interventions: Prioritize road safety measures at both Central and State levels, tailored to the specific challenges of each region.
- Public Awareness and Safety: Increase public awareness of road safety measures, particularly helmet usage, and improve trauma care facilities.
- Infrastructure Audit: Conduct thorough audits of National and State Highways to identify safety gaps and implement necessary improvements.
By implementing these recommendations, India can take meaningful steps toward improving road safety and reducing fatalities.
Windfall tax on crude oil cut to zero

- 18 Sep 2024
In News:
The windfall tax on domestically produced crude oil will be slashed to ‘zero’ effective September 18. This marks its second reduction to nil since its introduction in July 2022.
Key Details:
- The windfall tax is revised every 15 days based on average oil prices over the previous two weeks, charged as Special Additional Excise Duty (SAED) on profits from domestically produced crude oil.
- The last revision, effective August 31, set the windfall tax at ?1,850 per tonne.
- The SAED on the export of diesel, petrol, and jet fuel (ATF) has been set to ‘nil’ following a major decline in crude oil prices.
- This is the second instance since the tax was imposed that it has been reduced to nil; the first reduction occurred on April 4, 2023.
Crude Oil Prices
- Crude oil prices increased by $1 per barrel due to supply chain issues; traders anticipate demand growth if the US Federal Reserve lowers borrowing costs.
- More than 12% of crude production from the US Gulf of Mexico was offline last week due to Hurricane Francine, contributing to price increases in three of the past four sessions. US crude futures rose by $1.31 (1.9%) to $71.40, while Brent crude futures increased by $1 (1.4%) to $73.75 per barrel.
- The windfall tax on crude oil companies was introduced in July 2022 to control extreme profits from gasoline, diesel, and aviation fuel exports.
What is a Windfall Tax?
- A windfall tax is a surtax imposed by governments on businesses or economic sectors that have benefited from economic expansion.
- The purpose is to redistribute excess profits in one area to raise funds for the greater social good; however, this can be a contentious ideal.
- Some individual taxes—such as inheritance tax or taxes on lottery or game-show winnings—can also be construed as a windfall tax.
Nipah viral infection

- 17 Sep 2024
In News:
- The district administration has imposed restrictions on social gatherings and made masks mandatory in Malappuram district after a 24-year-old man from Naduvath, near Wandoor, died from the Nipah viral infection.
- Five wards in Tiruvali and Mampad grama panchayats have been declared containment zones. Schools, colleges, madrasas, anganwadis and cinema halls in these zones will remain closed until further notice.
What is Nipah?
- Nipah is a viral infection that mainly affects animals such as bats, pigs, dogs and horses.
- It is known to cause infection in humans when they come in contact with saliva, urine, or faecal matter of infected animals — by eating fruits that have been bitten into by the animals or scaling trees were the bats live.
- It can also be transmitted human to human through close contact, but this is not the most common route of transmission.
- The case fatality ratio of Nipah can be extremely high at 40 to 75%. To compare, even at the peak of the Covid-19 pandemic, the case fatality ratio (CFR) – proportion of people who die among those who test positive – remained at around 3%.
What are the symptoms of Nipah?
People with Nipah start showing symptoms around four to 14 days after getting infected. The infection causes fever, headache, cough, sore throat and difficulty breathing. In later stages, the infection can also lead to brain swelling or encephalitis, leading to confusion, drowsiness, and seizures. With encephalitis, people can go into coma within 24 to 48 hours.
How does the Nipah monoclonal antibody work?
The monoclonal antibody binds with the part of the viral envelope that attaches to the human cells to gain entry. Given early in the disease, it prevents the virus from entering more and more cells, thereby stopping its proliferation and severe disease.
The monoclonal antibody has to be administered in the early stages of the disease, before encephalitis sets in.
India first imported 20 doses of the monoclonal antibodies — enough for ten patients — from a laboratory in Australia’s University of Queensland during the 2018 outbreak. Another 20 doses were requested last year. The monoclonal antibody has so far been used in 14 individuals globally and none of them died.
What can be done to protect yourself?
Usually, Nipah outbreaks are localised, meaning people from the rest of the country are not at risk of the infection at present. People from areas where cases are detected should refrain from coming in close contact with the family members and other contacts of the two case. With the infection transmitted by fruit bats, the government also suggests precautions like washing the fruits and peeling them before consumption. Fruits with signs of bat bites should be discarded. And, palm sap or juice must be boiled before consumption.
All-India Reservoir Status
- 17 Sep 2024
In News:
The southwest monsoon has provided significant rainfall across India, with total precipitation at 836.7 mm as of September 12, marking an 8% surplus for this time of year. The Central Water Commission (CWC) reports that reservoir levels are notably higher compared to last year and the 10-year average.
All-India Reservoir Status
- Total Capacity: 180.852 billion cubic metres (BCM) across 155 reservoirs.
- Current Storage: 153.757 BCM, which is 85% of total capacity.
- Last Year Comparison: 119.451 BCM (66%) and 10-year average of 130.594 BCM.
Regional Reservoir Highlights:
- North: 11 reservoirs at 68% capacity (13.468 BCM). Storage is lower than last year (81%) and decadal average (82%). Himachal Pradesh and Punjab saw significant rainfall deficits.
- East: 25 reservoirs at 76% capacity (15.797 BCM), improved from last year's 58%. Despite deficits in Nagaland and Bihar, overall rainfall has supported reservoir levels.
- West: 50 reservoirs at 90% capacity (33.526 BCM), a marked increase from 75% last year. Heavy rainfall, particularly in Gujarat, has led to flooding but boosted water reserves.
- Central: 26 reservoirs at 89% capacity (42.808 BCM), better than last year's 76%. This region has enjoyed normal or above-average rainfall.
- South: 43 reservoirs at 88% capacity (48.158 BCM), significantly higher than 49% last year. Regions traditionally receiving less monsoon rain have also seen improvements.
Comparison to 2023
- Improved Storage: Notable increases in states like Jharkhand, Odisha, West Bengal, and several others.
- Stable: No change in Goa and Telangana.
- Declines: Himachal Pradesh, Punjab, and Uttarakhand show worse conditions compared to last year.
River Basin Status
Major river basins exhibit normal or above storage levels, including:
- Barak (98.72%)
- Krishna (94.53%)
- Cauvery (93.54%)
- Narmada (92.19%)
- Godavari (91.85%)
- Others range from 83% to 66%.
Overall, the 2024 monsoon has led to improved water storage conditions across much of India, benefiting numerous states while highlighting specific areas of concern.
Precision Farming
- 17 Sep 2024
In News:
The Centre is contemplating to earmark Rs 6,000 crore to promote precision farming, a modern approach that uses smart technology such as Internet of Things, Artificial Intelligence, drones and data analytics to boost production through maximal use of resources while minimising environmental impact.
Key Details:
- Union Ministry of Agriculture is planning a Smart Precision Horticulture Programme under the existing Mission for Integrated Development of Horticulture (MIDH) scheme.
- It will cover 15,000 acres of land in five years from 2024-25 to 2028-29 and is expected to benefit about 60,000 farmers.
- At present, the Agriculture Infrastructure Fund (AIF), launched during Covid-19, has provisions for financing infrastructure projects for smart and precision agriculture.
- Under AIF, individual farmers as well as farmers’ communities such as Farmer Producer Organization, Primary Agricultural Credit Societies and SHGs are eligible for loans with interest subvention of 3% for using technological solutions in farm practices. These practices include farm/ harvest automation; purchase of drones, putting up specialised sensors on field; use of blockchain and AI in agriculture; remote sensing and Internet of Things (IoT).
Positive impact
- Smart and precision agriculture maximises use of resources like water, fertilisers and pesticides to increase production quality and quantity, all while insulating farmers from vagaries of climate change and other uncertainties, besides ensuring sustainable farming.
Apart from offering financial support, the Centre is also considering collaborating with the Netherlands and Israel, where tech-based modern farming solutions are being used, through Centres of Excellences (CoEs). The number of CoEs is likely to be 100 in the next five years. Under Indo-Israel Agriculture Project, 32 CoEs have already been set up across 14 states.
The Centre has also set up 22 Precision Farming Development Centres (PFDCs) across the country to test new technologies and modify them according to local needs.
According to the Ministry, these 22 PFDCs are located across State/Central Agricultural Universities, ICAR Institutes and IITs in TN, Karnataka, Madhya Pradesh, Odisha, Rajasthan, Haryana, Telangana, West Bengal, Ladakh, UP, Punjab, Gujarat, Uttrakhand, Maharashtra, Chhattisgarh, Jharkhand, Bihar, Himachal Pradesh, Kerala, Manipur and Assam. Besides, funds are released to states/UTs for projects involving use of AI and machine learning, under schemes like the National e-Governance Plan in Agriculture.
What is Precision Agriculture?
- Precision Agriculture is a farm management concept that revolves around the process of observing, measuring, and responding to various inter-and intra-field variability inputs for modern agriculture.
- Popular definitions of Precision Agriculture (PA) or Site-Specific Crop Management (SSCM) describe the term as a technology-enabled approach to farming management that observes, measures, and analyzes the needs of individual fields and crops.
- The goal of precision agriculture is to increase efficiency and productivity, reduce input costs, and improve environmental sustainability.
- Key Advantages:
- A refined set of cultivation practices and choice of crops based on the suitability of land
- Elimination of volatility and risk
- Waste management
- Reduced production costs
- Minimum environmental impact
- Optimized use of fertilizers
- Water management with optimized irrigation practices
- Improved soil health
What is the current status of the introduction of African cheetahs?

- 17 Sep 2024
In News:
Project Cheetah has encountered significant setbacks, including prolonged captivity and cheetah fatalities; with long-term success hinging on finding sufficient habitat, scientific management, and community support, the project’s future depends on overcoming these enormous challenges.
Overview of Project Cheetah:
- Cheetah Action Plan (CAP): India’s initiative to reintroduce African cheetahs, aimed at species conservation and ecosystem restoration.
- Long-term Commitment: Requires a minimum of 25 years of financial, technical, and administrative support from various governmental bodies.
Challenges Faced:
- Extended Captivity:
- Cheetahs have been held in captivity longer than planned, with only 12 of the original 20 surviving.
- Delays in the release process raise concerns about the cheetahs' fitness for survival in the wild.
- Health Issues and Fatalities:
- Several cheetahs have died due to pre-existing health conditions or management failures before being released.
- Captivity duration exceeds guidelines set by Namibian policy, rendering the cheetahs unfit for release.
- Environmental Adaptation Problems:
- Some deaths attributed to environmental stressors, such as heat stroke and improper management of conditions leading to health complications.
Location for Introduction:
- Kuno National Park: Chosen for its suitable habitat and prey base. However, many cheetahs remain confined, with release dates now pushed to late 2024 or early 2025.
- Additional Sites: Plans for a captive breeding facility in Gujarat and potential releases in Nauradehi Wildlife Sanctuary.
Management and Oversight:
- An expert committee, led by the National Tiger Conservation Authority (NTCA), oversees the project. Responsibilities include negotiating with African countries for cheetah procurement and implementing field activities.
Goals and Measurable Outcomes:
- Short-term Objectives: Achieve a 50% survival rate in the first year, establish home ranges, and generate eco-tourism revenue.
- Long-term Success: Establish a stable cheetah population, improve habitat quality, and support local economies.
Future Considerations:
- The project lacks a definitive sunset clause but will require ongoing management for decades.
- The key question remains whether India has sufficient habitat (4,000 to 8,000 sq. km) to support a viable population of free-ranging cheetahs.
Conclusion: Project Cheetah faces significant challenges in achieving its ambitious conservation goals, raising questions about its long-term viability and management practices.
Why is T.N.’s education funding on hold?

- 17 Sep 2024
In News:
Tamil Nadu is yet to receive this year’s funds from the Union government under the flagship education scheme Samagra Shiksha. According to the State government, the Centre has linked these funds to the complete implementation of the National Education Policy (NEP) 2020, which includes provisions that the State has opposed, including the contentious three-language formula.
What is Samagra Shiksha and why has Tamil Nadu not gotten funds under it?
- Samagra Shiksha is an integrated Centrally-sponsored scheme for school education from nursery till Class 12, with components for teacher training and salaries, special education, digital education, school infrastructure, administrative reform, vocational and sports education, with grants for textbooks, uniforms, and libraries, among others.
- The scheme’s estimated outlay between 2021 and 2026 is ?2.94 lakh crore, with the Centre and States contributing funds in a 60:40 ratio. For 2024-25, Tamil Nadu’s allocation under the scheme amounts to ?3,586 crore of which the Central share is ?2,152 crore, with a first quarterly instalment of ?573 crore, which has not yet arrived halfway through the financial year.
- In a letter to Prime Minister Narendra Modi last month, Tamil Nadu Chief Minister M.K. Stalin accused the Centre of imposing a prerequisite for the fund’s disbursal, namely, the signing of a Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) for another Centrally-sponsored education scheme called PM Schools for Rising India (PM Shri).
- This scheme, being run from 2022-2027, aims to create 14,500 model schools across the country to showcase the implementation of NEP 2020, and has a much smaller project cost of ?27,360 crore. The Centre has sent at least 10 letters to Tamil Nadu from September 2022, asking the State to sign the MoU, which included an agreement to fully implement the NEP.
In March 2024, Tamil Nadu committed to signing the PM Shri MoU due to its link to delayed funding for the larger Samagra Shiksha scheme. However, after signing a modified MoU in July that excluded NEP implementation, the Centre found it unacceptable. In August, Chief Minister M.K. Stalin noted that states signing the MoU received funds, accusing the Centre of “denying funds to the best-performing States” for not complying with NEP. The Union Education Ministry labeled these claims as misleading, but Tamil Nadu has not received Samagra Shiksha funds due to the incomplete MoU.
What is Tamil Nadu’s problem with the NEP 2020?
Tamil Nadu Education Minister highlighted the state's objections to specific NEP elements, such as the three-language formula and curriculum changes. He stated that Tamil Nadu is already implementing many acceptable aspects of the NEP through its own initiatives and warned that linking Samagra Shiksha funds to full NEP compliance infringes on the state's constitutional autonomy in education.
Tamil Nadu’s draft State Education Policy (SEP), submitted in July, clearly indicates that the State wants to stick to the 5+3+2+2 curricular formula, rather than the NEP, which includes the pre-school years. The SEP also proposes five years as the age of entry to Class 1, as against six years in the NEP. The State wants undergraduate college admissions to be based on Class 11 and 12 marks, rather than a common entrance test as proposed by the NEP. The biggest hurdle, however, is the NEP’s three-language formula.
Why does Tamil Nadu oppose the three-language formula?
The NEP 2020 recommends using the mother tongue or local language as the medium of instruction until Class 5, with all students learning at least three languages, including two native to India. This three-language formula has been part of every NEP since 1968 but has faced long-standing opposition in Tamil Nadu, rooted in historical movements against mandatory Hindi.
Tamil Nadu follows a two-language policy, requiring students to study Tamil and English, while allowing the choice of an optional third language, such as Hindi. Education Minister Anbil Mahesh emphasized Tamil's importance in the state's identity alongside English proficiency.
While the NEP offers flexibility and states that no language will be imposed on any state, allowing students to choose Tamil as a third language, all major political parties in Tamil Nadu have rejected the three-language formula. In response to concerns about opposing mother-tongue education, Mahesh affirmed the state prioritizes inclusive learning with Tamil at its core.
Pink Bollworm Attack

- 16 Sep 2024
In News:
Haryana has seen an overall fall in acreage under cotton cultivation to 4.76 lakh hectares (lh) this kharif season from 6.65 lh in 2023. This has been accompanied by an increase in the area under rice from 15.20 lh to an all-time-high of 16.44 lh in the state.
Key Details:
- The reduction in the cotton area — also reported in neighbouring Rajasthan (from 7.91 lh to 5.13 lh) and Punjab (2.14 lh to 1 lh) — has been attributed mainly to PBW infestation.
- In May-June this year, at the time of sowing, the price of kapas (raw unginned cotton) averaged Rs 6,700-6,800 per quintal in Haryana mandis. This was against the average Rs 11,100-11,200 per quintal two years ago.
Pink Bollworm (PBW) Infestation:
- Impact: The pink bollworm has devastated cotton yields by attacking the bolls, which affects the weight and quality of the cotton. This pest has been particularly damaging since its appearance in 2017-18 and has caused significant losses in Haryana, Rajasthan, and Punjab.
- Spread: PBW spreads through the air and infected crop residues, which harbor larvae and spread to future crops. This infestation has led to a dramatic decrease in cotton acreage.
The spread of pink bollworm
- The pink bollworm first appeared in north India during the 2017-18 season in a few districts in Haryana and Punjab, primarily cultivating Bt cotton, and spread to Rajasthan by 2021.
- PBW primarily spreads through the air. Residue of infected crops, often left by farmers on the field to be used as fuel, can also harbour PBW larvae which can then infect future crops. Infected cotton seeds are another reason behind the pest’s spread.
Economic Impacts:
- Price Decline: The price of kapas (raw cotton) has dropped from Rs 11,100-11,200 per quintal to Rs 6,700-6,800, significantly impacting farmers’ profitability.
- Farmer Losses: Farmers like Shyam Sundar have reported substantial losses due to low yields and poor quality, leading them to switch to more profitable and reliable crops like paddy and guar.
Transition to Paddy
Water Requirements:
- Challenges: Paddy requires much more water compared to cotton. Farmers need to flood their fields, which is challenging in regions where groundwater is saline or limited.
- Current Practices: Despite the increased water requirements, some farmers have transitioned to paddy due to its potentially better economic returns, especially when paddy prices are relatively high.
Monsoon and Irrigation:
- Weather Dependence: The monsoon this year has been favorable, allowing some farmers to successfully grow paddy. However, reliance on monsoon and supplementary irrigation from tubewells is not sustainable in the long term.
Government and Expert Perspectives
Government Incentives:
- Subsidies: The Haryana government is offering incentives for farmers switching to alternative crops and using water-saving techniques like direct seeding of paddy.
- Support: While there is support available, the effectiveness and reach of these measures are mixed, and some farmers have faced issues with insurance claims and financial aid.
Expert Opinions:
- Temporary Solution: Experts caution that while switching to paddy may be a temporary solution, it is not sustainable long-term due to water scarcity and environmental concerns.
- Environmental Impact: Paddy cultivation contributes to higher carbon and methane emissions, which adds to the environmental challenges in the region.
Economic and Industry Implications
Cotton Industry Concerns:
- Reduced Production: Lower cotton production affects the entire supply chain, from textile manufacturers to cottonseed oil and meal producers.
- Potential Recovery: There is hope that reduced PBW infestation this year may lead to a recovery in cotton yields, but the extent of this recovery remains uncertain.
NIDHI Companies

- 16 Sep 2024
In News:
The Registrar of Companies has imposed penalties on over two dozen Nidhi companies for breaches of the Companies Act, such as delayed financial filings and share allotment issues. Fines range from ?20,000 to ?12.5 lakh, with Sri Sathuragiri Nidhi receiving the highest penalty.
What is Nidhi Company?
A Nidhi Company is a unique NBFC regulated under the Companies Act, 2013, and the Nidhi Rules, 2014. Nidhi company signifies that these companies promote thrift and savings habits among their members by accepting deposits and providing loans. They primarily cater to their local communities and operate within a defined geographical area.
Requirements for Obtaining Nidhi Company Status:
Within One Year of Registration:
- Minimum Membership: A Nidhi company must have at least 200 members within one year of starting operations.
- Financial Strength: The company's net owned funds (equity share capital + free reserves - accumulated losses - intangible assets) must be ?10 lakh or more.
- Deposit Security: Unencumbered term deposits (deposits not pledged as security) must be at least 10% of the total outstanding deposits.
- Healthy Debt Ratio: The ratio of net owned funds to deposits should not exceed 1:20. This ensures the company has sufficient capital to back its deposit liabilities.
Compliance Filing:
If a Nidhi company meets all the above conditions within the first year, it must file form NDH-1 along with the prescribed fees within 90 days from the end of that financial year. The form needs to be certified by a practicing Chartered Accountant (CA), Company Secretary (CS), or Cost and Works Accountant (CWA).
Extension Option:
Companies that are unable to meet the requirements within the first year can apply for an extension of one additional financial year. To do so, they need to submit form NDH-2 to the Regional Director within 30 days from the end of the first financial year.
Strict Enforcement:
If a Nidhi company fails to meet the requirements even after the second financial year, it will be prohibited from accepting new deposits until it complies with the regulations. Additionally, it may face penalties for non-compliance.
Benefits of Nidhi Company Registration
Nidhi companies offer several advantages for entrepreneurs:
- Tax benefits: They can enjoy tax exemptions on their profits under certain conditions.
- Reduced regulatory burden: Compared to other NBFCs, Nidhi companies face less stringent regulations.
- Local focus: They cater to the specific financial needs of their communities, fostering local economic development.
- Enhanced credibility: Registration brings legitimacy and builds trust among members.
Eligibility for Nidhi Company Registration
For registration of Nidhi company, the following requirements must be met:
- Minimum members: A minimum of seven members are required at the time of incorporation.
- Minimum capital: The minimum paid-up capital must be Rs. 5 lakh.
- Business restrictions: Nidhi companies cannot undertake activities like issuing debentures or underwriting insurance.
- Profit distribution: They can only distribute a maximum of 20% of their net profit as dividend.
BHASKAR Platform

- 16 Sep 2024
In News:
The Department for Promotion of Industry and Internal Trade (DPIIT), Ministry of Commerce and Industry, is set to launch a groundbreaking digital platform aimed at strengthening India’s startup ecosystem.
Key Details:
- The Bharat Startup Knowledge Access Registry (BHASKAR) initiative, under the Startup India program, is a platform designed to centralize, streamline, and enhance collaboration among key stakeholders within the entrepreneurial ecosystem, including startups, investors, mentors, service providers, and government bodies.
- This initiative aligns with the Government of India’s vision to transform India into a global leader in innovation and entrepreneurship, reinforcing the country’s commitment to the startup movement.
Empowering Innovation Through a Centralized Platform
- India, home to over 1,46,000 DPIIT-recognized startups, has rapidly become one of the world’s most dynamic startup hubs. BHASKAR seeks to leverage this potential by providing an all-encompassing, one-stop digital platform that addresses the challenges faced by entrepreneurs and investors alike.
- By serving as a centralized registry, BHASKAR will enable seamless access to a wide array of resources, tools, and knowledge that will help fuel the entrepreneurial journey from ideation to execution.
- BHASKAR is designed to foster a conducive environment for networking, collaboration, and growth within the startup ecosystem.
- By providing personalized BHASKAR IDs for each stakeholder, the platform will facilitate easier interaction, enhance searchability, and allow for efficient discovery of relevant opportunities and partnerships.
Key Features of BHASKAR
- The primary goal of BHASKAR is to build the world’s largest digital registry for stakeholders within the startup ecosystem. To achieve this, the platform will offer several key features:
- Networking and Collaboration: BHASKAR will bridge the gap between startups, investors, mentors, and other stakeholders, allowing for seamless interaction across sectors.
- Providing Centralized Access to Resources: By consolidating resources, the platform will provide startups with immediate access to critical tools and knowledge, enabling faster decision-making and more efficient scaling.
- Creating Personalized Identification: Every stakeholder will be assigned a unique BHASKAR ID, ensuring personalized interactions and tailored experiences across the platform.
- Enhancing Discoverability: Through powerful search features, users can easily locate relevant resources, collaborators, and opportunities, ensuring faster decision-making and action.
- Supporting India’s Global Brand: BHASKAR will serve as a vehicle for promoting India’s global reputation as a hub for innovation, making cross-border collaborations more accessible to startups and investors alike.
Driving Forward India’s Startup Ecosystem
- The launch of BHASKAR marks a significant step forward in the government’s ongoing efforts to promote innovation, entrepreneurship, and job creation. It will serve as a central hub where startups, investors, service providers, and government bodies can come together to collaborate, exchange ideas, and accelerate growth.
- By facilitating easy access to knowledge and resources, BHASKAR will help unlock the full potential of India’s startup ecosystem, driving the country’s emergence as a global leader in entrepreneurship. The platform will be pivotal in creating a more resilient, inclusive, and innovation-driven economy, laying the foundation for a prosperous future.
BHASKAR: Shaping the Future of India's Startups
As India’s startup ecosystem continues to grow, BHASKAR will play a critical role in enhancing the country’s global standing in entrepreneurship. By fostering a culture of collaboration, the platform will help startups overcome challenges and build innovative solutions that address the needs of tomorrow.
With the launch of BHASKAR, the Government of India is reinforcing its commitment to making India a leader in global innovation, entrepreneurship, and economic growth.
International Day of Democracy

- 16 Sep 2024
In News:
Karnataka marked the 'International Day of Democracy' by forming a 'historic' 2,500-km-long human chain as a symbol of equality, unity, fraternity, and participative governance. The massive human chain, which according to the Karnataka government will be the "world's longest", is being formed across the state from Bidar to Chamarajanagar, covering all 31 districts.
Key Highlights:
- Democracy Day is an annual celebration observed on September 15.
- The United Nations General Assembly established this day in 2007 to emphasise the global significance of democracy. It serves as a reminder that democracy is not merely a fixed condition, but an ongoing pursuit. It calls for active engagement from international organizations, nation-states, civil society and people to pursue the democratic idea.
International Day of Democracy History
- The International Day of Democracy was accredited by the United Nations General Assembly (UNGA) on November 8, 2007, by passing a resolution entitled “Support by United Nations system of efforts of governments to promote and consolidate new or restored democracies.”
- September 15 was chosen to coincide with the anniversary of the Inter-Parliamentary Union’s Universal Declaration on Democracy, which was adopted in Geneva on September 15, 1997.
- This declaration outlines the tenets of democracy proclaiming that democracy is “a system of government based on the freely expressed will of the people to determine their own political, economic, social and cultural systems and their full participation, through free and fair periodic elections, in the composition of their representative government.”
- After the Universal Declaration on Democracy, Qatar spearheaded the campaign to observe an International Day of Democracy at the United Nations.
- The first-ever International Day of Democracy was held in 2008.
International Day of Democracy Significance
- The International Day of Democracy evaluates global democracy, emphasising that it requires commitment and engagement from the international community, the national state governments, civil societies and individuals.
- The day also reminds the nations of the need to uphold the principles of democracy such as the freedom of speech enshrined in Article 19 of the United Nations Universal Declaration of Human Rights.
Trilobite fossils from upstate New York reveal extra set of legs
- 15 Sep 2024
In News:
A new study finds that a trilobite species with exceptionally well-preserved fossils from upstate New York has an additional set of legs underneath its head.
Key details:
- The research, led by the American Museum of Natural History and Nanjing University in China, suggests that having a fifth pair of head appendages might be more widespread among trilobites than once thought.
- Published in the journal Palaeontology, the study helps researchers better understand how trilobite heads are segmented.
Trilobites
- Trilobites are a group of extinct arthropods whose living relatives include lobsters and spiders.
- Like other arthropods, the bodies of trilobites are made up of many segments, with the head region comprised of several fused segments.
- As with other parts of the trilobite body (the thorax and tail), these segments were associated with appendages, which ranged in function from sensing to feeding to locomotion.
- Trilobites are a group of extinct marine arthropods that first appeared around 521 million years ago, shortly after the beginning of the Cambrian period, living through the majority of the Palaeozoic Era, for nearly 300 million years. They died out at the end of the Permian, 251 million years ago, killed by the end Permian mass extinction event that removed over 90% of all species on Earth. They were very diverse for much of the Palaeozoic, and today trilobite fossils are found all over the world.
- The name 'trilobite' comes from the distinctive three-fold longitudinal division of the dorsal exoskeleton into a central axis, flanked on either side by lateral (pleural) areas.
Two ways
The segments in the trilobite head can be counted in two different ways: by looking at the grooves (called furrows) on the upper side of the trilobite fossil’s hard exoskeleton, or by counting the pairs of preserved antennae and legs on the underside of the fossil. The soft appendages of trilobites are rarely preserved, though, and when looking at the segments in the trilobite head, researchers regularly find a mismatch between these two methods.
In the new study, researchers examined newly recovered specimens of the exceptionally preserved trilobite Triarthrus eatoni from upstate New York. These fossils, known for the gold shine of the pyrite replacement preserving them, show an additional, previously undescribed leg underneath the head.
Resolving mismatch
By making comparisons with another trilobite species, the exceptionally preserved Olenoides serratusfrom the Burgess Shale in British Columbia, the researchers propose a model for how appendages were attached to the head in relation to the grooves in the exoskeleton.
This model resolves the apparent mismatch and indicates that the trilobite head included six segments: an anterior segment associated with the developmental origin of the eyes and five additional segments, associated with one pair of antennae and four pairs of walking legs, respectively.
PM Gram Sadak Yojana-IV

- 15 Sep 2024
In News:
- The Union Cabinet, chaired by the Prime Minister Shri Narendra Modi approved the proposal of the Department of Rural Development for “Implementation of the Pradhan Mantri Gram Sadak Yojana - IV (PMGSY-IV) during FY 2024-25 to 2028-29”.
- The financial assistance is to be provided for the construction of 62,500 Kms road for providing new connectivity to eligible 25,000 unconnected habitations and construction/upgradation of bridges on the new connectivity roads. Total outlay of this scheme will be Rs. 70,125 crore.
Details of the Scheme:
The details of the approval given by the Cabinet are as follows:
- Pradhan Mantri Gram Sadak Yojana -IV is launched for financial year 2024-25 to 2028-29. Total outlay of this scheme is Rs. 70,125 crore (Central Share of Rs. 49,087.50 crore and Sate Share of Rs. 21,037.50 crore).
- Under this scheme 25,000 unconnected habitations of population size 500+ in plains, 250+ in NE & Hill Sates/UTs, special category areas (Tribal Schedule V, Aspirational Districts/Blocks, Desert areas) and 100+ in LWE affected districts, as per Census 2011 will be covered.
- Under this scheme 62,500 Km of all-weather roads will be provided to unconnected habitations. Construction of required bridges along the alignment of the all-weather road will also be provided.
Benefits:
- 25,000 unconnected habitations will be provided all weather road connectivity.
- The all-weather roads will play the role of catalysts for the required socio-economic development and transformation of the remote rural areas. While connecting habitations, the nearby government educational, health, market, growth centers will be connected, as far as feasible, with the all-weather road for the benefit of the local people.
- The PMGSY -IV will incorporate international benchmarks and best practices under road constructions such as Cold Mix Technology and Waste Plastic, Panelled Cement concrete, Cell filled concrete, Full Depth Reclamation, use of construction waste and other wastes such as Fly Ash, Steel Slag, etc.
- PMGSY -IV road alignment planning will be undertaken through the PM Gati Shakti portal. The planning tool on PM Gati Shakti portal will also assist in DPR preparation.
Pradhan Mantri Gram Sadak Yojana (PMGSY)
- PMGSY is a central government scheme launched in 2000 to provide all-weather road connectivity to unconnected rural habitations.
- The scheme was originally a 100% centrally-sponsored initiative, but starting from the financial year 2015-16, the funding has been shared between the Central and State governments in a 60:40 ratio.
National Florence Nightingale Awards 2024

- 15 Sep 2024
In News:
President Droupadi Murmu honored 15 exemplary nursing professionals with the National Florence Nightingale Awards 2024, recognizing their extraordinary healthcare service.
Key Details:
- The National Florence Nightingale Award was instituted by the Ministry of Health and Family Welfare, Government of India in the year 1973 as a mark of recognition for the meritorious services rendered by the nurses and nursing professionals to the society.
- A total of 15 awards are given in the category of registered auxiliary nurses and midwife, registered nurses and midwife and registered lady visitor, the statement said.
- The award is given to outstanding nursing personnel employed in central, states and Union territories and voluntary organisations.
- The nurse in her/his regular job in the hospital or community settings, educational or administrative setting is eligible for the national award.
- Each award consists of a Certificate of Merit, a cash award of ? 1,00,000 and a medal.
A Legacy of Florence Nightingale
- The National Florence Nightingale Awards, are named in honor of Florence Nightingale, the founder of modern nursing.
- Nightingale’s pioneering work during the Crimean War laid the foundation for professional nursing, and her relentless efforts in promoting hygiene and compassionate care revolutionized healthcare practices worldwide.
- In her honor, International Nurses Day is celebrated every year on May 12, her birthday.
Chamran-1 satellite

- 15 Sep 2024
In News:
Iran successfully launched its Chamran-1 research satellite into orbit, utilising the Qaem-100 rocket developed by the paramilitary Revolutionary Guard.
Key Highlights:
- Satellite Details: Chamran-1, a research satellite, was designed and manufactured by Iranian engineers at Iran Electronics Industries (SAIran) in collaboration with the Aerospace Research Institute and private firms. It weighs approximately 60 kilograms.
- Launch Vehicle: The satellite was launched into orbit using the Ghaem-100, Iran's first three-stage solid-fuel space launch vehicle (SLV), developed by the Aerospace Force of the Islamic Revolutionary Guard Corps (IRGC).
- Mission Objectives: The primary mission of Chamran-1 is to test hardware and software systems for validating orbital maneuver technology. Additionally, it aims to assess the performance of cold gas propulsion subsystems and evaluate navigation and attitude control subsystems.
- Orbit Details: The satellite was placed into a 550-kilometer (341 miles) orbit above Earth.
What are Intercontinental ballistic missiles?
- Intercontinental ballistic missiles (ICBMs) are a type of ballistic missile with a range greater than 5,500 kilometers and are primarily designed to deliver nuclear warheads.
- They can carry conventional, chemical, and biological weapons, although the latter types have rarely been deployed on ICBMs.
- The United States, Russia, China, France, India, the United Kingdom, Israel, and North Korea are known to possess operational ICBMs, with Pakistan being the only nuclear-armed state that does not have them.
Operation Sadbhav

- 15 Sep 2024
In News:
India has launched Operation Sadbhav to deliver crucial humanitarian aid to Myanmar, Laos, and Vietnam, all of which have been devastated by Typhoon Yagi. This powerful storm, the most severe in Asia this year, has led to extensive flooding and widespread destruction across the affected countries.
Relief Efforts:
In response to the crisis, India has mobilized a significant amount of aid. The Indian naval ship INS Satpura has transported 10 tonnes of relief supplies, including dry rations, clothing, and medicines, to Myanmar. Concurrently, the Indian Air Force has dispatched a military transport aircraft with 35 tonnes of aid to Vietnam and an additional 10 tonnes to Laos. The aid includes essential items such as generators, water purification systems, hygiene kits, mosquito nets, blankets, and sleeping bags, which are crucial for addressing immediate needs during this emergency.
India's Proactive Approach:
Operation Sadbhav highlights India's proactive approach to humanitarian assistance and disaster relief, emphasizing its role as a leading responder in the region. This initiative reflects India's commitment to providing support to its neighboring countries in times of crisis and aligns with its broader 'Act East Policy,' which aims to strengthen relations with ASEAN member states through practical assistance and cooperation.
Strategic Importance:
The operation also underscores India's strategic goals of enhancing regional stability and reinforcing its position as a reliable partner in disaster management. By providing timely aid, India demonstrates its dedication to supporting regional stability and contributing to international humanitarian efforts.
Global Recognition and Cooperation:
India's response to Typhoon Yagi has received international acknowledgment for its effectiveness and promptness. The coordination of these relief efforts highlights the importance of global solidarity in addressing humanitarian crises and building resilience in disaster-affected regions.
Conclusion:
Operation Sadbhav is a clear demonstration of India's commitment to timely and substantial humanitarian assistance. It not only showcases India's proactive diplomacy but also strengthens its ties with ASEAN nations through meaningful cooperation in times of adversity. The ongoing relief efforts are a testament to India's role as a responsible global stakeholder in disaster response and recovery.
What is Operation Kawach, the new ‘war on drugs’ waged by Delhi Police?

- 05 Sep 2024
Aimed at identifying and apprehending people involved in the trafficking and distribution of narcotics, 'Operation Kawach' is a joint initiative launched by the Crime Branch in coordination with all district units of the Delhi Police.
In a major crackdown on the menace of drugs in the national capital, the Crime Branch of the Delhi Police conducted widespread raids, swooping down on over 100 locations across Delhi. Earlier, raids conducted during the intervening night of May 12 and 13 had led to the arrest of 31 drug offenders in 30 cases under the Narcotic-Drugs and Psychotropic Substances Act 1985.
As many as 12 bootleggers were also arrested in six cases of the Excise Act. The operation also saw the seizure of 957.5 grams of heroin, 57.8 kilograms of marijuana and 782 bottles of illicit liquor.
What is Operation Kawach?
Aimed at identifying and apprehending people involved in the trafficking and distribution of narcotics, ‘Operation Kawach’ is a joint initiative launched by the Crime Branch in coordination with all district units of the Delhi Police. The initiative aims to combat the harmful influence of drug addiction on youth and children and underscores the authorities’ commitment to safeguarding the well-being of young individuals and curbing the distribution of illicit substances in educational settings.
Operation Kawach is primarily intended to save the youth from the menace of drugs. Although the focus is to take stringent action on the supply side, it is also appealed to society to create awareness and reduce the demand of drugs. The parents, teachers and the social reformers are specially requested to sensitise the youth about the grave consequences of drug addiction.
Operation Kawach: The story so far
According to the official, the joint operations, which utilised a variety of resources such as undercover officers, surveillance, canine support and intelligence gathering, targetted both street-level dealers and high-level traffickers and have both ‘top-to-bottom’ and ‘bottom-to-top’ approaches to effectively counter drug trafficking in the national capital.
In this year, Delhi Police has arrested 534 narco-offenders in 412 NDPS cases. Around 35 kg of heroin/smack, 15 kg of cocaine, 1,500 kg of ganja, 230 kg of opium, 10 kg of charas and 20 kg of poppy have been recovered during these operations.
Black Coat Syndrome

- 05 Sep 2024
In News:
In her recent speech at the National Conference of District Judiciary, President Droupadi Murmu introduced the concept of 'black coat syndrome' to address the persistent issue of case delays in Indian courts. This term is intended to reflect the anxiety and reluctance that people experience when dealing with the judicial system, similar to the 'white coat syndrome' seen in medical settings.
Current Challenges in India's Judicial System
- Case Pendency: As of October 2023, there are over five crore cases pending across various levels of the judiciary in India. The current number of judges—20,580—falls short of effectively managing this caseload.
- Infrastructure Deficiencies: Many courts lack essential infrastructure and modern technology. For example, as of September 2023, 19.7% of district courts did not have separate toilets for women.
- Judicial Vacancies: There are notable vacancies in the judiciary. High courts have 347 unfilled positions out of a total of 1,114 sanctioned posts. Similarly, 5,300 out of 25,081 district judge positions are vacant.
- Gender Representation: The Supreme Court has three female judges, making up 9.3% of its bench. High courts have 103 female judges, representing 13.42%, while the district judiciary has a more balanced representation with 36.33% female judges.
Ongoing Initiatives to Address Judicial Challenges
- Technological Advancements:
- e-SCR (Electronic Supreme Court Reports): Provides digital access to Supreme Court judgments.
- Virtual Court System: Facilitates court proceedings through videoconferencing.
- eCourts Portal: Serves as a comprehensive platform for interaction among litigants, advocates, government bodies, and the public.
- National Judicial Data Grid (NJDG): Makes case statistics available at various levels for public and research use.
- Legal Reforms and Alternative Dispute Resolution (ADR):
- National Mission for Justice Delivery and Legal Reforms (2011): Focuses on improving justice access by tackling delays and arrears.
- ADR Methods: Includes Lok Adalats, Gram Nyayalayas, and Online Dispute Resolution to expedite justice.
- Commercial Courts Act 2015: Enforces pre-institution mediation for commercial disputes.
- Fast Track Courts: Designed to speed up cases involving serious crimes, senior citizens, women, and children.
Strategies for Future Improvement
- Increasing Court Efficiency: The Chief Justice of India has stressed the need for courts to function beyond their current capacity of 71% to better align case disposal with new case inflows.
- Filling Judicial Positions: With 28% of district court positions vacant, a regularized recruitment schedule is suggested to address these gaps. Additionally, integrating judicial recruitment on a national scale is recommended to reduce regional biases.
- Enhancing Case Management: Establish District-Level Case Management Committees to better manage cases by reconstructing records and identifying priority cases. Encouraging pre-litigation dispute resolution can also help manage the case backlog.
- Adjusting Judicial Vacations: The 2003 Malimath Committee report proposed reducing vacation periods to help address the backlog of cases.
- Bridging Judiciary Gaps: Addressing the disparity between district courts and high courts is crucial to create a more cohesive and unified judicial system.
Poshan Tracker Initiative
- 05 Sep 2024
In News:
The Ministry of Women and Child Development recently earned the National Award for e-Governance 2024 (Gold) for its Poshan Tracker initiative, which has made significant strides in enhancing child health and nutrition.
About the Poshan Tracker Initiative
The Poshan Tracker initiative focuses on identifying and addressing growth-related issues in children aged 0-6 years. By using real-time monitoring and WHO growth charts, the program ensures that children receive optimal nutrition.
Key components of the initiative include:
- Role of Anganwadi Workers (AWWs): These workers are essential in assessing children's health and implementing necessary interventions when deviations from expected growth are observed.
- Technology Integration: The program employs advanced ICT tools and Growth Measuring Devices (GMD) at Anganwadi Centers (AWCs) to enable precise data collection and regular monitoring.
- Impact: Real-time growth monitoring through the Poshan Tracker has substantially improved child health outcomes in India, benefiting millions of children under the Mission Poshan 2.0 initiative.
Key Features of the Poshan Tracker App
- Comprehensive Overview: The app offers a complete view of Anganwadi Centre activities, including service deliveries and beneficiary management for pregnant women, lactating mothers, and children under six.
- Digitization and Automation: It replaces physical registers used by workers with digital records, thereby enhancing the quality and efficiency of their work.
- Smartphone Provision: Anganwadi workers have been provided with smartphones through the Government e-Market (GeM) to streamline service delivery.
- Technical Support: Each state has a designated nodal person to provide technical assistance and resolve issues related to the Poshan Tracker application.
- Service Accessibility: Migrant workers who registered in their original state can access services at the nearest Anganwadi in their current location.
RHUMI-1

- 05 Sep 2024
In News:
India recently celebrated the launch of its first reusable hybrid rocket, RHUMI-1, developed by the Tamil Nadu-based start-up Space Zone India in collaboration with the Martin Group. The launch took place on August 24, 2024, from Thiruvidandhai in Chennai. This innovative rocket was propelled into a suborbital trajectory using a mobile launcher, carrying three Cube Satellites and fifty Pico Satellites designed to gather data on global warming and climate change.
Key Features of RHUMI-1:
- Hybrid Propulsion System: RHUMI-1 utilizes a combination of solid and liquid propellants, which enhances efficiency and lowers operational costs.
- Adjustable Launch Angle: The rocket's engine allows for precise trajectory control with adjustable angles ranging from 0 to 120 degrees.
- Electrically Triggered Parachute System: Equipped with an advanced and eco-friendly descent mechanism, this system ensures safe recovery of rocket components, offering both cost-effectiveness and environmental benefits.
- Environmentally Friendly: RHUMI-1 is entirely free of pyrotechnics and TNT, underlining its commitment to sustainability.
Reusable Launch Vehicles (RLVs):
Reusable Launch Vehicles are spacecraft designed to be launched, recovered, and reused multiple times. They offer several advantages:
- Cost Savings: RLVs can be up to 65% cheaper than constructing a new rocket for every launch.
- Reduced Space Debris: By minimizing discarded rocket components, RLVs help reduce space debris.
- Increased Launch Frequency: Shorter turnaround times allow for more frequent use of the rocket.
Unlike traditional multi-stage rockets, where the first stage is discarded after fuel depletion, RLVs recover and reuse the first stage. After separation, the first stage returns to Earth using engines or parachutes for a controlled landing.
Background on Space Zone India and Recent Missions:
Space Zone India is an aero-technology company based in Chennai, focusing on providing cost-effective, long-term solutions in the space industry. They offer hands-on training in aerodynamic principles, satellite technology, drone technology, and rocket technology while raising awareness about careers in the space sector. In 2023, Space Zone India conducted the "Dr. A.P.J Abdul Kalam Students Satellite Launch Mission," involving over 2,500 students from various schools across India. This mission resulted in the creation of a student satellite launch vehicle capable of carrying a payload of 150 Pico Satellites for research experiments.
Disaster Management (Amendment) Bill, 2024

- 05 Sep 2024
In News:
On August 1, 2024, the central government introduced the Disaster Management (Amendment) Bill in the Lok Sabha. This Bill, aimed at amending the existing Disaster Management Act of 2005, has been proposed in response to the increasing frequency of climate-induced disasters. However, the Bill’s provisions have raised concerns about further centralisation of disaster management processes, which may complicate and delay disaster response efforts.
Centralisation Concerns
The Bill continues the trend of centralising disaster management, a feature already prevalent in the 2005 Act. It grants statutory status to existing bodies like the National Crisis Management Committee (NCMC) and the High-Level Committee (HLC), potentially complicating the disaster response process. This centralised approach has previously led to delays, such as the late disbursement of funds to Tamil Nadu and Karnataka, contrary to the Act's intended rapid response.
Proposed Changes
Strengthening NDMA and SDMAs: The Bill aims to bolster the role of the National Disaster Management Authority (NDMA) and State Disaster Management Authorities (SDMAs) by having them prepare disaster management plans directly. It also introduces Urban Disaster Management Authorities (UDMAs) for state capitals and major cities, although these bodies may face challenges due to insufficient financial devolution.
Database and Staffing: The Bill mandates the creation of comprehensive disaster databases at national and state levels and allows the NDMA to appoint its own staff, subject to central government approval.
Issues with the Current Definition of ‘Disaster’
Heatwaves Exclusion: On July 25, 2024, the Minister of State for Science, Technology, and Earth Sciences announced that heatwaves will not be classified as a notified disaster under the Act. This decision aligns with the 15th Finance Commission’s view and maintains a restricted list of disasters eligible for assistance, which includes cyclones, droughts, earthquakes, and floods, but excludes climate-induced phenomena like heatwaves.
Inadequate Definition: The existing definition of "disaster" in the Act and the Bill remains narrow, failing to encompass climate-induced events such as heatwaves, which are increasingly recognized globally as significant disasters. Data from the India Meteorological Department shows a record number of heatwave days and related fatalities, highlighting the need for a broader disaster definition.
Critical Issues
Central-State Dynamics: The Bill’s centralisation raises questions about the balance of power between central and state governments. There are concerns that states will remain heavily dependent on central funds, complicating disaster management and response.
Lessons Unlearned: Despite being an update to the 2005 Act, the Bill appears to overlook past shortcomings, including delays in financial preparedness and response. A focus on cooperative federalism and effective disaster management should prioritize practical solutions over a central versus state blame game.
Future Directions: Addressing the challenges of climate-induced disasters and ensuring effective financial and operational preparedness requires revisiting and refining the disaster management framework. Emphasizing cooperative federalism and proactive disaster management strategies will be crucial in improving disaster resilience and response in the face of escalating climate risks.
India-France Bilateral Naval Exercise VARUNA

- 07 Sep 2024
In News:
The 22nd edition of the India-France bilateral naval exercise, VARUNA, took place in the Mediterranean Sea from September 2 to 4, 2024. This exercise highlights the strong maritime partnership between the Indian Navy and the French Navy, showcasing their commitment to enhancing interoperability and operational effectiveness.
Key Highlights:
- Participating Vessels and Aircraft:
- Indian Navy:
- INS Tabar: A frontline stealth frigate commanded by Captain MR Harish.
- Ship-borne Helicopter: Provided air support during the exercises.
- LRMR Aircraft P-8I: An advanced long-range maritime reconnaissance aircraft.
- French Navy:
- FS Provence: A French naval ship participating in the exercise.
- Submarine Suffren: A French attack submarine.
- Aircraft F-20: Providing air support.
- Atlantique 2: A French maritime patrol aircraft.
- Fighters MB339: Multi-role fighter aircraft.
- Helicopters NH90 and Dauphin: Providing additional aerial capabilities.
- Indian Navy:
- Exercise Activities:
- Tactical Maneuvers: Advanced maneuvers showcasing the operational capabilities of both navies.
- Anti-Submarine Warfare: Exercises designed to enhance capabilities in detecting and countering submarines.
- FLYEX (Flight Exercises): Coordinated air operations involving various aircraft.
- Air Defence Exercise: Training in defending against aerial threats.
- Live Weapon Firings: Demonstrations of weapon systems in action.
- PHOTO-EX (Photographic Exercise): Exercises designed for documenting and assessing naval operations.
- Steam Past: A ceremonial maneuver showcasing the participating ships.
- Significance of the Exercise:
- Evolution of VARUNA: Since its inception in 2001, VARUNA has become a key component of the India-France naval relationship. The exercise has evolved to improve interoperability and share best practices between the two navies.
- Strategic Importance: Conducting the exercise in the Mediterranean Sea reflects the Indian Navy's capability and commitment to operate far beyond the Indian Ocean Region (IOR). It underscores the strategic depth and outreach of the Indian Navy.
- Enhanced Interoperability: VARUNA demonstrates the mutual commitment of India and France to enhancing naval collaboration and operational effectiveness through joint exercises and shared experiences.
- Future Outlook:
- Commitment to Partnerships: The Indian Navy continues to prioritize building strong partnerships with like-minded navies worldwide. The VARUNA exercise is a testament to this ongoing commitment and the broader strategic goals of both India and France in strengthening maritime security and cooperation.
This bilateral exercise not only enhances the operational capabilities of both navies but also reinforces the strategic partnership between India and France in the maritime domain.
India’s $15 Billion Push for Chipmaking
- 07 Sep 2024
In News:
India is significantly ramping up its efforts to establish a semiconductor manufacturing industry, with plans to invest $15 billion in the second phase of its chipmaking incentive policy. This move aims to bolster the country's position in the global semiconductor supply chain, where it currently has minimal presence.
Key Points:
- Government Funding and Projects:
- Increased Investment: The Indian government is boosting its funding for chipmaking incentives to $15 billion, up from the $10 billion committed in the first phase.
- Approved Projects: Four major semiconductor projects have been approved, totaling over Rs 1.48 lakh crore ($18 billion). This includes:
- Tata and PSMC Fabrication Plant: India’s first commercial semiconductor fabrication plant, with an investment of more than Rs 91,000 crore ($11 billion), developed in partnership with Taiwan’s Powerchip Semiconductor Manufacturing Corporation (PSMC).
- Assembly and Testing Plants (ATMP/OSAT): Three plants:
- Micron Technology is building the first plant, approved in June 2023.
- Tata is constructing an assembly plant in Assam.
- C G Power and Industrial Solutions, in partnership with Japan’s Renesas Electronics, is developing the third plant.
- Government Subsidies:
- Capex Subsidies: The central government will provide nearly Rs 59,000 crore ($7 billion) in capital expenditure subsidies for these projects.
- State Support: State governments are offering incentives such as discounted land and electricity rates.
- Strategic Importance:
- Economic and Strategic Impact: Semiconductor chips are critical to a wide range of industries, including defense, automotive, and consumer electronics. Developing domestic chipmaking capabilities is seen as essential for economic growth and strategic independence.
- Global Competition: India is entering a highly competitive field dominated by Taiwan and the US. The US has a $50 billion chip incentive scheme, while the EU has a similar program. India’s efforts are part of a broader strategy to reduce dependence on global chip supply chains and capitalize on geopolitical shifts.
- Challenges and Realities:
- Technology Barriers: The Tata-PSMC plant will not produce cutting-edge chips, as the technology for advanced nodes is currently beyond their reach. Manufacturing chips with smaller node sizes involves significant technological expertise and innovation, areas where leading companies like Taiwan Semiconductor Manufacturing Company (TSMC) excel.
- High Entry Barriers: The chipmaking industry has high entry barriers, and India’s new plants will face challenges in achieving technological and competitive parity with established global leaders.
India's push into semiconductor manufacturing represents a major step in its economic development and strategic planning, aiming to position itself as a significant player in the global tech landscape while addressing critical supply chain vulnerabilities.
India-Maldives Defence Talks

- 07 Sep 2024
In News:
- India and the Maldives held their first defence talks since India withdrew its military personnel early this year.
Significance of Talks:
- The dialogue is notable given recent tensions in bilateral relations. Relations soured after President Mohamed Muizzu's election on an "India Out" platform, leading to the withdrawal of Indian troops. The last defence cooperation dialogue was held in March 2023 under President Ibrahim Solih.
Discussion Topics:
-
- Expediting ongoing defence cooperation projects.
- Planning forthcoming bilateral military exercises.
- Enhancing high-level exchanges and capability development.
Context of Tensions:
-
- Mohamed Muizzu, who took office in November 2023, had called for the removal of Indian military personnel, a significant shift from the previous administration’s stance.
- India agreed to withdraw 80 military personnel between March and May 2024. Indian technical personnel now operate key equipment like helicopters and a Dornier aircraft in the Maldives.
Recent Developments:
-
- Maldives Foreign Minister Moosa Zameer visited India in May.
- President Muizzu attended PM Narendra Modi’s swearing-in ceremony in June.
- In August, Indian External Affairs Minister S. Jaishankar visited the Maldives to reaffirm bilateral ties.
Historical Defence Cooperation:
-
- India gifted a Dornier aircraft to the Maldives in 2020 and a patrol vessel in 2019.
- India provided a coastal radar system last year and laid the foundation for the 'Ekatha Harbour' project, enhancing Maldivian Coast Guard capabilities.
Ongoing Projects:
-
- Greater Male Connectivity Project (GMCP) - a $500 million initiative financed by India.
- Building a new Coast Guard base at Uthuru Thilafalhu (UTF) atoll.
- India’s grant for High Impact Community Development Projects (HICDPs).
Strategic Importance:
-
- For Maldives: India is a key security partner and crisis responder, with historical assistance during emergencies (Operation Neer, Vaccine Maitri). Maldives seeks to restore Indian tourist numbers, vital for its economy.
- For India: The Maldives is crucial to India's Neighbourhood First Policy and Vision SAGAR. Its strategic location between major Indian Ocean chokepoints makes it a vital partner for maritime security and countering China's influence.
Recent Changes:
-
- The Muizzu government decided not to renew a 2019 MoU for hydrographic surveying with India, ending joint hydrographic surveys conducted under the pact.
Travel and Trade:
-
- Both countries benefit from an open skies arrangement and visa-free access for tourism, medical, and business purposes
India-Middle East-Europe Economic Corridor (IMEC)
- 07 Sep 2024
In News:
IMEC is an important initiative that can add to India's maritime security and faster movement of goods between Europe and Asia, said Union Minister of Commerce & Industry at the Confederation of Indian Industry (CII) India-Mediterranean Business Conclave 2024 in New Delhi.
Key Details:
- Corridors:
- East Corridor: Connects India to the Gulf.
- Northern Corridor: Links the Gulf to Europe.
- Components:
- Railroad: Provides a reliable and cost-effective cross-border ship-to-rail transit network.
- Ship-to-Rail Networks: Integrates road, sea, and rail transport routes.
- Road Transport: Complements the overall transport infrastructure.
- Expected Benefits:
- Increased Efficiency: Enhances transit efficiency and reduces costs.
- Economic Unity: Promotes economic integration and job creation.
- Environmental Impact: Lowers greenhouse gas emissions.
- Transformative Integration: Connects Asia, Europe, and the Middle East.
- Additional Features:
- Infrastructure: Includes laying cables for electricity and digital connectivity, and pipes for clean hydrogen export.
- Implementation:
- MoU Commitments: Participants will collaboratively address technical design, financing, legal, and regulatory aspects.
- Action Plan: A meeting is planned within 60 days to develop an action plan with specific timetables.
Geoeconomic Perspective
- Economic Integration and Interdependence:
- Prosperity Through Integration: IMEC aims to foster trade and investment among India, the Middle East, and Europe, potentially leading to mutual prosperity and regional stability.
- Building Bridges: Aligns with the liberal international order by promoting economic interdependence to reduce tensions and create shared interests.
- Support from Major Powers: Backed by the US, Europe, and India, signaling a strong commitment to economic ties and regional stability.
- Economic Potential:
- Infrastructure and Trade Routes: Enhances infrastructure and trade routes, boosting economic activity, trade volumes, and investment opportunities.
- Regional Development: Promotes job creation and development in economically disadvantaged areas along the corridor.
Geopolitical Perspective
- Strategic Rivalry with China:
- Countering the BRI: IMEC is seen as a strategic counterbalance to China's Belt and Road Initiative (BRI), offering an alternative aligned with US, European, and Indian interests.
- Regional Influence: Aims to limit China’s influence in the Middle East and South Asia by establishing a competing corridor.
- Geopolitical Alliances:
- Aligning Interests: Involves strategic partnerships among the US, Europe, and India, reflecting concerns about China’s global strategy and shifting power dynamics.
- Rivalry and Competition: The IMEC could be viewed as a global positioning move, responding to China’s growing influence and securing strategic interests.
Reasons for Joining the IMEC
- Economic Enhancement:
- Boosts Indo-Gulf Relations: Enhances trade and economic ties with the Arab Gulf, addressing infrastructure gaps.
- Regional Connectivity: Links India with key partners like Israel and Jordan, boosting economic opportunities.
- Strategic Trade Routes:
- Alternative Routes: Complements existing routes like Chabahar Port and INSTC, connecting India to southern Eurasia.
- Bypassing Choke Points: Offers a shorter route to Eastern Mediterranean and Western Europe, avoiding strategic choke points.
- Energy and Trade Opportunities:
- Access to Resources: Provides potential access to Eastern Mediterranean gas fields.
- Trade Bloc Connectivity: Links India with the EU and GCC, opening up growth opportunities.
- Geopolitical Aspirations:
- Global Power Ambitions: Supports India’s goal to enhance global influence and integrate with eastern and western neighbors.
- Economic Growth: Leverages economic integration to support development and influence.
- Infrastructure Development:
- Economic Integration: Facilitates infrastructure creation for increased trade volumes and regional stability.
e-Sankhyiki portal

- 07 Sep 2024
In News:
The Ministry of Statistics and Programme Implementation (MoSPI) has launched e-Sankhyiki portal with the objective to establish a comprehensive data management and sharing system for ease of dissemination of official statistics in the country.
Key Highlights:
- Launched on National Statistics Day 2024, the e-Sankhyiki portal is designed to create a comprehensive system for managing and sharing data, facilitating the easy dissemination of official statistics across the country.
- The portal is also accessible at - https://esankhyiki.mospi.gov.in. It aims to provide timely and valuable data inputs for policymakers, researchers, and the general public.
- It provides time series data for key macroeconomic indicators, with features for filtering and visualising the data. Users can also download customised datasets and visualisations and access them through APIs, enhancing the data's reusability.
- It consists of two modules viz. Data Catalogue and Macro Indicators.
- Data Catalogue Module:
- This module catalogues the Ministry’s major data assets, simplifying users' access. It enables searching within datasets and tables, downloading relevant data, and enhancing its value and reusability.
- The Data Catalogue includes seven core data products:
- Consumer Price Index
- Index of Industrial Production
- National Accounts Statistics
- Periodic Labour Force Survey
- Annual Survey of Industries
- Household Consumption Expenditure Survey
- Multiple Indicator Survey.
- It currently hosts over 2,300 datasets, each accompanied by specific metadata and visualisations for user convenience.
- Macro Indicators module:
- This module provides time series data on key macro indicators, featuring tools for filtering and visualising data.
- It allows users to download custom datasets, generate visualisations, and share data through APIs, promoting greater reusability. The initial phase of this module covering data from the past decade includes four major MoSPI products:
- National Accounts Statistics
- Consumer Price Index
- Index of Industrial Production
- Annual Survey of Industries
- The portal currently features over 1.7 million records, providing access to extensive vital data.
- Data Catalogue Module:
Government Initiatives for Safe Data Dissemination
- In response to the rapid data expansion, the Government of India has instituted robust data safety measures. These include storing data in the cloud facilities provided by the National Informatics Centre (NIC), conducting comprehensive security audits of applications, and implementing Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) technology for domain protection.
- Additionally, the government has focused on vulnerability assessments and ensured compliance with guidelines issued by organisations such as NIC and the Indian Computer Emergency Response Team (CERT-In).
- In addition , CERT-In under the Ministry of Electronics and Information technology (MeitY) also undertakes various activities like issuance of advisories and guidelines for cyber/information security, conduct of sensitization programmes/trainings/workshops, operating Cyber Threat exchange platform & Cyber Swachhta Kendra, formulation of a Cyber Crisis Management Plan, setting up of National Cyber Coordination Centre (NCCC) and empanelment of security auditing organisations etc. for data safety.
Rashtriya Poshan Maah 2024

- 06 Sep 2024
In News:
Union Minister of State for Women and Child Development, launched the Rashtriya Poshan Maah 2024 in Dhar district of Madhya Pradesh on 1st September,2024.
Key Highlights:
- As part of the 7th Rashtriya POSHAN Maah, awareness programs are being organized at various levels.
- Under the ICDS (Integrated Child Development Services) Project, complementary feeding activities were conducted at Anganwadi Centres (AWC) Paduck Bagicha, South Andaman.
- Also, at AWC, Champin Nancowrie, Nicobar district (Andaman & Nicobar) under the ICDS Tribal initiative, local food items and nutrition sources were displayed.
- These efforts aim to further the Prime Minister's vision of a ‘Suposhit Bharat’ by conducting diverse large-scale activities, harnessing the potential of Gram Panchayats and Urban Local Bodies.
Rashtriya Poshan Maah:
- The programme is annually celebrated in the month of September, with a different theme each year, primarily focusing on addressing malnutrition by ensuring convergence of various nutrition-related schemes and programmes.
- The objective of the Poshan Maah is to ensure community mobilisation and bolster people’s participation for addressing malnutrition amongst young children, and women and to ensure health and nutrition for everyone.
Poshan Abhiyaan:
- POSHAN Abhiyan (Prime Minister's Overarching Scheme For Holistic Nourishment) focuses on advancing nutritional outcomes for children under six years, adolescent girls, pregnant women, and lactating mothers.
- To cultivate widespread awareness about nutrition at each stage of life, it is celebrated annually as Poshan Maah (1st—30th September) and Poshan Pakhwada (fortnight of March).
- POSHAN Abhiyan (National Nutrition Month) aims to strengthen efforts to end hunger and malnutrition.
- It focuses to improving the nutritional outcomes among children, adolescent girls, pregnant women, and lactating mothers by focusing on prenatal care, diet, and optimal breastfeeding.
- The Ministry of Women and Child Development plans month-long activities under Poshan Maah, focusing on issues such as the hygiene and sanitation, anaemia prevention, maternal and infant health, among others.
- There are outreach programmes, identification drives, camps, and fairs with a special focus on pregnant and lactating women, children below six years, and adolescent girls in order to realise the vision of ‘Swasth Bharat’.
SAMRIDH Scheme
- 06 Sep 2024
In News:
- Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology (MeitY) launches 2nd Cohort of Startup Accelerators of MeitY for Product Innovation, Development and Growth (SAMRIDH).
About SAMRIDH Scheme:
- SAMRIDH is a flagship programme of MeitY for startups acceleration under National Policy on Software Products – 2019.
- The SAMRIDH programme, launched in August 2021 aims to support 300 software product startups with outlay of ?99 crore over a period of 4 years.
- SAMRIDH is being implemented through potential and established accelerators across India which provide services like making products market fit, business plan, investor connect and international expansion to startups plus matching funding upto ?40 lakh by MeitY.
- The scheme is being implemented by MeitY Start-up Hub (MSH), Digital India Corporation (DIC).
- In the first round of cohort, 22 Accelerators spread across 12 states are supporting 175 startups, selected through a multilevel screening process.
- Major Objective:
- The SAMRIDH scheme aims to support existing and upcoming Accelerators to select and accelerate potential IT-based startups to scale.
- Among others, the program focuses on accelerating the startups by providing customer connect, investors connect and connect to international markets
- Eligibility of Accelerator:
- Should be a registered Section-8/Society, [Not-for-Profit Company (eligible to hold equity)] having operations in India.
- The Accelerator and the team are recommended to have more than 3 years of startup experience and should have supported more than 50 start-ups of which at least 10 startups should have received investment from external Investors
- The Accelerator should have an experience of running startup program cohorts with activities listed as desirable under SAMRIDH program.
AgriSURE Fund and Krishi Nivesh Portal

- 04 Sep 2024
In News:
- Recently, the Union agriculture minister Shivraj Singh Chouhan launched two initiatives — a fund aimed at boosting farm-sector startups, and a single-window portal to process investments — as part of a slew of measures being taken by Prime Minister Narendra Modi-led government in its third term to bolster the farm economy.
Key Details:
- AgriSure is a ?750-crore fund established to support agricultural startups.
- Krishi Nivesh Nidhi is a portal designed to expedite the clearance of project proposals.
- Both initiatives aim to enhance farm incomes.
Awards for Credit Disbursal:
- Scheduled banks were recognized for their credit disbursals under the government’s agriculture infrastructure fund.
- First prize: State Bank of India (SBI).
- Second prize: HDFC Bank.
- Third prize: Canara Bank.
Significance of Agriculture Sector:
- Agriculture contributes 16% to India’s GDP.
- Farmers play a crucial role as both producers and consumers in the economy.
PM Modi’s Strategy to Double Farmers’ Incomes:
- The strategy includes:
- Increasing output.
- Reducing input costs.
- Ensuring profitable prices.
- Promoting crop diversification.
- Supporting natural farming.
- Enhancing value addition to crops.
Details of AgriSure Fund:
- Blended capital fund with a total corpus of ?750 crore:
- ?250 crore each from the Department of Agriculture and NABARD.
- ?250 crore to be raised from financial institutions.
- Managed by NabVentures, a subsidiary of NABARD.
- Provides both equity and debt support to startups and agripreneurs.
- Focuses on high-risk, high-impact activities within the agriculture value chain.
Agriculture Infrastructure Fund:
- Mobilized projects worth ?78,000 crore with ?45,000 crore in financing so far.
- Expanded areas of coverage approved by the Union Cabinet on August 28.
- Aims to create durable farm assets, such as warehouses and processing plants.
- Can be used by agricultural produce marketing committees (APMCs) for market facility improvements.
Funding and Loan Details:
- Part of the ?20-lakh crore stimulus package introduced during the Covid-19 pandemic.
- Total funding of ?1 lakh crore over four years:
- ?10,000 crore for 2020-21.
- ?30,000 crore each for the subsequent three financial years.
- Provides medium-to-long term debt financing for rural projects.
- Interest subvention of 3% per annum on loans up to ?2 crore for seven years, with the government covering part of the interest.
eShram portal

- 04 Sep 2024
In News:
The Ministry of Labour & Employment (MoLE) stated in a latest update that in the short span of three years since its launch, eShram has registered more than 30 crore unorganised workers, showcasing its rapid and widespread adoption among the unorganised workers.
Key Highlights:
- The Government envisages to establishing the eShram portal as a "One-Stop-Solution" for Country’s unorganised workers.
- During Budget speech 2024-25 it has been announced that, A comprehensive integration of eShram portal with other portals will facilitate such One-Stop-Solution.
- This initiative aims to facilitate access of various social security schemes being implemented by different Ministries/ Departments to unorganised workers through the eShram portal.
- As part of the eShram - One Stop Solution project, Ministry of Labour and Employment (MoLE) has been working to integrate major schemes like Pradhan Mantri Jeevan Jyoti Bima Yojana (PMJJBY), Pradhan Mantri Suraksha Bima Yojana (PMSBY), Ayushman Bharat Pradhan Mantri Jan Arogya Yojana (AB-PMJAY), Pradhan Mantri Street Vendors Atmanirbhar Nidhi (PM-SVANidhi), Mahatma Gandhi National Rural Employment Guarantee Act (MGNREGA), Pradhan Mantri Awas Yojana Gramin (PMAY-G), Ration Card scheme etc. for the benefit of the unorganised workers.
What is e-Shram and its purpose?
- e-Shram is a comprehensive National Database of Unorganised Workers (NDUW) launched by the Government of India under the Ministry of Labour & Employment.
- Its primary purpose is to facilitate delivery of welfare benefits and social security measures to unorganised sector workers across the country.
- The platform aims to register and provide identity cards to unorganised workers, enabling them to access various government schemes, benefits, and services more efficiently.
Who are unorganised workers?
Any worker who is a home-based worker, self-employed worker or a wage worker working in the unorganised sector and not a member of ESIC or EPFO, is called an unorganised worker.
What is unorganised sector?
Unorganised sector comprises of establishment/ units which are engaged in the production/ sale of goods/ services and employs less than 10 workers. These units are not covered under ESIC & EPFO.
What is UAN?
UAN or Universal Account Number is a 12 digit number uniquely assigned to each unorganised worker after registration on e-Shram portal. UAN is a permanent number i.e., once assigned, it will remain unchanged for any worker.
India Semiconductor Mission (ISM)
- 04 Sep 2024
In News:
The Union Cabinet, chaired by Prime Minister Narendra Modi, approved the proposal of Kaynes Semicon Pvt Ltd to setup a semiconductor unit in Sanand, Gujarat, with an investment of Rs 3,300 crore.
Key Highlights:
- The proposed unit, under the India Semiconductor Mission (ISM), will produce nearly 60 lakh chips per day.
- The chips produced in this unit will cater to a wide variety of applications which include segments such as industrial, automotive, electric vehicles, consumer electronics, telecom and mobile phones, etc.
- The initiative aligns with India’s goal of developing indigenous semiconductor capabilities.
- As per the reports, India’s semiconductor market is projected to reach $64 billion by 2026, positioning the country as a major global semiconductor hub.
- The first indigenously-developed chip is set to arrive in the country by the end of this year.
- In March, PM Modi laid the foundation stone of three semiconductor projects worth Rs 1.25 lakh crore.
- Tata Electronics is setting up a semiconductor fab in Dholera, Gujarat and one semiconductor unit in Morigaon, Assam.
- CG Power is setting up one semiconductor unit in Sanand. These units will produce lakhs of direct and indirect jobs.
- These four units will bring an investment of almost Rs 1.5 Lakh crore. The cumulative capacity of these units is about 7 crore chips per day, according to the Ministry of Electronics & IT.
- The Programme for Development of Semiconductors and Display Manufacturing Ecosystem in India was notified in 2021 with a total outlay of Rs 76,000 crore.
About India Semiconductor Mission (ISM)
- It is a specialized and independent Business Division within the Digital India Corporation that aims to build a vibrant semiconductor and display ecosystem to enable India’s emergence as a global hub for electronics manufacturing and design.
- ISM has all the administrative and financial powers and is tasked with the responsibility of catalysing the India Semiconductor ecosystem in manufacturing, packaging, and design.
- ISM has an advisory board consisting of some of the leading global experts in the field of semiconductors.
- ISM has been working as a nodal agency for the schemes approved under the Semicon India Programme.
Semicon India Programme:
- Launched in 2021 with a total budget of Rs. 76,000 crore, the ISM is overseen by the Ministry of Electronics and IT (MeitY), Government of India. This initiative is part of a broad effort to develop a sustainable semiconductor and display ecosystem within the country.
- The programme is designed to offer financial support to companies involved in semiconductor and display manufacturing and design. It also aims to foster the creation of domestic Intellectual Property (IP), and to promote and incentivize the Transfer of Technologies (ToT).
- Under this programme, four key schemes have been introduced:
- Scheme for establishing Semiconductor Fabs in India.
- Scheme for establishing Display Fabs in India.
- Scheme for setting up Compound Semiconductors/Silicon Photonics/Sensors Fabs and Semiconductor Assembly, Testing, Marking, and Packaging (ATMP)/OSAT facilities in India.
- Design Linked Incentive (DLI) Scheme.
Centre gives clearance for ‘Mission Mausam’

- 13 Sep 2024
The Union Cabinet approved 'Mission Mausam,' a groundbreaking initiative with an investment of ?2,000 crore over the next two years. The mission, spearheaded by the Ministry of Earth Sciences (MoES), aims to significantly advance India's capabilities in atmospheric sciences and climate resilience.
Objectives and Key Focus Areas
Mission Mausam is designed to improve the accuracy and effectiveness of weather forecasting and climate management through several critical components:
- Advanced Technology Deployment: The mission will focus on deploying next-generation radars and satellite systems equipped with advanced sensors. These technologies are crucial for enhancing weather surveillance and prediction accuracy.
- Research and Development: A key objective of Mission Mausam is to bolster research and development in atmospheric sciences. This will include the development of enhanced Earth system models and advanced weather forecasting techniques.
- GIS-Based Decision Support System: An automated decision support system based on Geographic Information Systems (GIS) will be developed to facilitate real-time data sharing and improve decision-making processes.
Institutional Framework and Implementation
The Ministry of Earth Sciences will oversee the implementation of Mission Mausam. The following institutions will play central roles in the mission:
- India Meteorological Department (IMD)
- Indian Institute of Tropical Meteorology
- National Centre for Medium-Range Weather Forecasting
Additional support will come from other MoES bodies:
- Indian National Centre for Ocean Information Services
- National Centre for Polar and Ocean Research
- National Institute of Ocean Technology
Sectoral Benefits
Mission Mausam is expected to bring significant improvements across various sectors:
- Agriculture: Enhanced agromet forecasts will aid farmers in optimizing crop management and increasing resilience to climatic variability.
- Disaster Management: Improved monitoring and early warning systems will enhance disaster preparedness and response, potentially reducing loss of life and property damage.
- Defence: Accurate weather forecasting will support strategic planning and operational efficiency within the defence sector.
- Energy and Water Resources: Better weather predictions will lead to more efficient management of energy and water resources.
- Aviation: Safer aviation will be supported by more reliable weather information, reducing risks and improving travel safety.
- Tourism: Sustainable tourism will benefit from accurate weather forecasting, contributing to safer and more enjoyable travel experiences.
Mission Mausam represents a significant investment in India’s ability to manage and mitigate the impacts of climate change and extreme weather events, ultimately aiming to enhance the resilience of communities and support sustainable development.
Delhi Declaration on Civil Aviation

- 13 Sep 2024
In the News:
The Prime Minister has announced the adoption of the Delhi Declaration on Civil Aviation.
Overview:
The Delhi Declaration was unanimously accepted following the conclusion of the 2nd Asia Pacific Ministerial Conference held in New Delhi. This Declaration provides a thorough framework designed to boost regional cooperation, tackle emerging challenges, and promote sustainable growth within the civil aviation sector across the Asia-Pacific region. The conference also marks the 80th anniversary of the International Civil Aviation Organization (ICAO).
Key Announcements:
- Prime Minister Narendra Modi highlighted significant achievements in Indian aviation, noting that women make up 15% of Indian pilots, a figure that surpasses the global average.
- A proposal for establishing an International Buddhist Circuit was introduced to enhance regional tourism and connectivity.
- India plans to build between 350 and 400 new airports by 2047, aiming to increase its global aviation presence.
- A Pacific Small Island Developing States Liaison Office will be created to help smaller nations manage aviation-related issues.
- The ‘Ek Ped Ma Ke Naam’ campaign was launched, with a goal to plant 80,000 trees in honor of ICAO’s 80 years, emphasizing green aviation and sustainability in future initiatives.
Significance of the Delhi Declaration:
- It marks a significant advancement in enhancing regional cooperation in civil aviation within the rapidly growing Asia-Pacific region.
- The framework tackles crucial issues such as sustainability, green aviation, and safety, which are vital for the current aviation industry.
- Initiatives like the International Buddhist Circuit are in line with broader regional objectives to improve connectivity, tourism, and economic development throughout Asia.
- India aims to assert itself as a major global aviation player with its ambitious plan to construct 350-400 airports by 2047, thereby becoming a key contributor to aviation infrastructure development.
Civil Aviation Sector in India:
- India ranks as the third-largest domestic aviation market globally and is projected to become the third-largest overall by 2025.
- The sector is expanding through significant government programs such as the UDAN Scheme, Pradhan Mantri Gati Shakti Plan, and NCAP 2016.
- With 136 operational airports and plans for an additional 100, the government is focused on modernizing infrastructure, improving regional connectivity, and promoting public-private partnerships for airport development.
International Civil Aviation Organization (ICAO):
- Established in 1947 by the Chicago Convention (1944).
- Headquarters: Montreal, Canada.
- Functions:
- Ensures the safety and efficiency of international air transport.
- Sets standards for aviation safety, security, and environmental performance.
- Encourages regional and international agreements to liberalize aviation markets.
- Promotes cooperation and dialogue among its 193 member states.
- Develops legal frameworks for aviation laws and standards.
SAARTHI APP

- 13 Sep 2024
In News:
Recently, the Open Network for Digital Commerce (ONDC) introduced the Saarthi app in partnership with Bhashini.
About the Saarthi App:
- The Saarthi app is a reference tool designed to help businesses create their own customized buyer-side applications.
- It facilitates network participants in developing buyer apps with multilingual capabilities. Initially, the app supports Hindi, English, Marathi, Bangla, and Tamil, with plans to expand to all 22 languages offered by Bhashini.
- The app features real-time translation, transliteration, and voice recognition, allowing businesses to broaden their market reach and attract customers from new regions.
What is Bhashini?
- Bhashini is India's AI-driven language translation platform. Its goal is to facilitate easy access to the internet and digital services in Indian languages, including through voice-based interactions, and to aid in the creation of content in these languages.
- The platform is designed to provide Artificial Intelligence and Natural Language Processing (NLP) resources to Indian MSMEs, startups, and individual innovators. This support will help developers offer all Indians access to the internet and digital services in their native languages.
- Additionally, Bhashini features a ‘Bhasadaan’ section for crowdsourcing contributions and is available through Android and iOS apps.
Exercise AL NAJAH

- 13 Sep 2024
In News:
- Indian Army contingent departed for the 5th edition of the India-Oman Joint Military Exercise AL NAJAH on September 12, 2024.
Key Details:
- Location: Rabkoot Training Area, Salalah, Oman.
- Frequency: Exercise AL NAJAH has been held biennially since 2015, alternating between India and Oman. Last edition was conducted at Mahajan, Rajasthan.
- Indian Army Contingent:
- Size: 60 personnel
- Composition: Battalion of the Mechanised Infantry Regiment, along with personnel from other arms and services.
- Royal Army of Oman Contingent:
- Size: 60 personnel
- Composition: Troops of the Frontier Force.
- Objective:
- Enhance joint military capability for counter-terrorism operations under Chapter VII of the United Nations Charter.
- Focus on operations in a desert environment.
- Tactical Drills:
- Joint Planning
- Cordon and Search Operation
- Fighting in Built-Up Areas
- Establishment of Mobile Vehicle Check Posts
- Counter Drone Operations
- Room Intervention
- Training Exercises:
- Combined field training exercises simulating real-world counter-terrorism missions.
- Outcomes Expected:
- Exchange of best practices in tactics, techniques, and procedures for joint operations.
- Foster interoperability, goodwill, and camaraderie between the two armies.
- Strengthen defense cooperation and enhance bilateral relations between India and Oman.
Battle of Saragarhi

- 13 Sep 2024
Why September 12 is Observed as Saragarhi Day:
- Historical Significance: The Battle of Saragarhi is considered one of the finest last stands in military history. On September 12, 1897, 21 soldiers of the 36th Sikh Regiment (now 4 Sikh) defended the fort against 8,000 Orakzai and Afridi tribal militants.
- 127th Anniversary: September 12 marks the 127th anniversary of this battle, which is now regarded as a legendary stand in global military history.
- The Battle: The 21 soldiers held the fort for seven hours despite being heavily outnumbered. They killed 200 militants and injured 600 before they were overwhelmed.
- Capt Amarinder Singh’s Account: In his book, he notes that the soldiers were aware of their certain death but chose to fight valiantly without surrendering, demonstrating unparalleled bravery.
What was Saragarhi and its Importance:
- Location and Role: Saragarhi was a communication tower between Fort Lockhart and Fort Gulistan in the North West Frontier Province (now Pakistan). It was crucial for linking these two forts, which housed a large number of British troops.
- Manning of Saragarhi: On that day, it was manned by only 21 soldiers from the 36th Sikh Regiment and a non-combatant, Daad, who performed odd jobs for the troops.
Details of the Battle:
- Initial Encounter: Around 9 am, the sentry spotted a large tribal army approaching, estimated between 8,000 and 15,000 strong.
- Communication: Sepoy Gurmukh Singh sent a Morse code message to Lt Col Houghton, requesting reinforcements. The response was to hold the position, as the supply route had been cut off.
- Challenges: The soldiers faced being outnumbered, limited ammunition (about 400 rounds per man), and communication issues. Sepoy Gurmukh Singh managed all heliograph communication tasks alone.
Key Figures:
- Havildar Ishar Singh: Leader of the defending troops, known for his bravery and independent nature. He was a respected and loved figure in his regiment.
- Sepoy Gurmukh Singh: The signalman who maintained communication during the battle, despite overwhelming challenges.
- Daad: The non-combatant who fought alongside the soldiers and killed five militants before being killed himself.
Recognition and Legacy:
- British Recognition: Queen Victoria awarded the 21 deceased soldiers the Indian Order of Merit (equivalent to the Victoria Cross), along with two ‘marabas’ (50 acres) and Rs 500 each.
- Current Observance: In 2017, the Punjab government declared September 12 as Saragarhi Day.
- Memorials: The Khyber Scouts regiment of the Pakistani army still mounts a guard at the Saragarhi memorial. The British built an obelisk with bricks from Saragarhi and commissioned gurdwaras at Amritsar and Ferozepur in honor of the martyrs. Shiromani Gurudwara Parbandhak Committee has named a hall after Saragarhi.
- Cultural Impact: The Battle of Saragarhi has inspired various media portrayals, including Akshay Kumar’s film Kesari.
INDUS-X Summit 2024

- 14 Sep 2024
The third edition of the INDUS-X Summit, held on September 9-10, 2024, in California, marked a significant advancement in the collaborative defence innovation ecosystem between India and the USA. Co-organized by the U.S.-India Strategic Partnership Forum (USISPF) and Stanford University, the summit emphasized the deepening of defence cooperation through innovation, joint research, and investment.
Key Outcomes
A major highlight of the summit was the signing of a Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) between India’s Innovations for Defence Excellence (iDEX) and the US Department of Defense’s Defence Innovation Unit (DIU). This agreement aims to enhance collaboration in defence innovation. The summit also saw the release of the INDUS-X Impact Report and the launch of a dedicated webpage for the initiative on both iDEX and DIU platforms.
Technological Showcase and Expert Dialogue
The summit provided a platform for startups and MSMEs to present cutting-edge technologies. Additionally, two advisory forums—the Senior Advisory Group and the Senior Leaders Forum—facilitated in-depth discussions on future technology trends, defence supply chain resilience, and funding opportunities for defence innovation. The discussions included contributions from experts across the defence industry, investment sectors, academia, and think tanks from both countries.
Leadership and Commitment
The Indian delegation was led by Amit Satija, Joint Secretary (Defence Industries Promotion), who underscored the commitment of both India and the USA to advancing defence technology through strategic collaboration. Since its launch in June 2023 during the Indian Prime Minister’s visit to the US, INDUS-X has achieved significant milestones, reinforcing its role in strengthening the US-India defence innovation partnership.
NEUROMORPHIC COMPUTING
- 14 Sep 2024
Indian Researchers Advance Neuromorphic Computing with Innovative Molecular Film
Researchers at the Indian Institute of Science (IISc) have made a groundbreaking development in neuromorphic computing, creating an analog computing system that leverages molecular films. This new system can store and process data across 16,500 different states, a significant leap from conventional binary computing methods.
Understanding Neuromorphic Computing
Neuromorphic computing is an advanced computing paradigm designed to emulate the structure and function of the human brain. By using artificial neurons and synapses, this approach marks a departure from traditional binary computing, enabling systems to learn and adapt from their environments.
How Neuromorphic Computing Works
Neuromorphic computing relies on Artificial Neural Networks (ANNs), which consist of millions of artificial neurons similar to those found in the human brain. These neurons communicate through electrical spikes or signals, following the principles of Spiking Neural Networks (SNNs). This setup allows the system to replicate the brain’s neuro-biological networks, performing tasks such as visual recognition and data interpretation with high efficiency.
Key Features of Neuromorphic Systems
- Brain-Inspired Architecture: Neuromorphic systems mimic the brain's structure, particularly the neocortex, which is involved in higher cognitive functions like sensory perception and motor commands.
- Spiking Neural Networks: These networks use spiking neurons that interact through electrical signals, mirroring the behavior of biological neurons. This design facilitates parallel processing and real-time learning.
- Integrated Memory and Processing: Unlike traditional von Neumann architecture, which separates memory and processing functions, neuromorphic systems combine these functions, leading to improved computational efficiency.
Advantages of Neuromorphic Computing
- Enhanced Efficiency: Neuromorphic computing enables faster problem-solving, pattern recognition, and decision-making compared to conventional systems.
- Revolutionizing AI Hardware: It holds the potential to transform AI hardware, allowing for complex tasks, such as training Large Language Models (LLMs), to be performed on personal devices. This advancement addresses current limitations related to hardware resources and energy efficiency.
- Energy Efficiency: Current AI tools are confined to data centers due to their high energy demands. Neuromorphic computing could overcome these constraints by providing energy-efficient hardware solutions.
Integration with Molecular Films
Molecular films, ultrathin layers engineered with specific electrical and optical properties, are central to this new advancement. These films act as neuromorphic accelerators, enhancing data storage and processing capabilities. They simulate brain-like parallel processing, improving performance in tasks such as matrix multiplication.
The recent development involves a molecular film that supports 16,500 possible states, a significant advancement over traditional binary systems. This film uses molecular and ionic movements to represent memory states, mapped through precise electrical pulses, creating what can be described as a "molecular diary" of states.
Comparison with Traditional Computing
- Parallel Processing: Neuromorphic computers can handle multiple streams of information simultaneously, unlike traditional computers that process data sequentially.
- Energy Efficiency: These systems consume less power by computing only when relevant events occur, making them suitable for real-time data processing applications.
- Analog vs. Binary: Traditional binary computing operates with bits that are either 0 or 1, akin to a light switch being on or off. In contrast, analog computing involves continuous values, similar to a dimmer switch with varying brightness levels.
This breakthrough by IISc researchers signifies a major step forward in neuromorphic computing, potentially transforming the way we approach data processing and artificial intelligence.
4 Years of Pradhan Mantri Matsya Sampada Yojana (PMMSY)

- 14 Sep 2024
Context:
Celebrating Four Years of Pradhan Mantri Matsya Sampada Yojana (PMMSY)
The Pradhan Mantri Matsya Sampada Yojana (PMMSY) has marked its fourth anniversary since its launch in 2020. This flagship scheme, managed by the Department of Fisheries under the Ministry of Fisheries, Animal Husbandry, and Dairying, aims to transform India’s fisheries sector into a vibrant and sustainable industry.
About PMMSY
The PMMSY is designed to invigorate the fisheries sector through a comprehensive approach that consolidates various existing schemes and initiatives. It operates as an umbrella scheme with two main components:
- Central Sector Scheme (CS)
- Centrally Sponsored Scheme (CSS)
The CSS component is divided into:
Non-Beneficiary Oriented Subcomponents:
- Enhancement of Production and Productivity
- Infrastructure and Post-Harvest Management
- Fisheries Management and Regulatory Framework
Fisheries Sector Overview
India stands as the third-largest fish producer globally and the second-largest in aquaculture production. It is also the fourth-largest exporter of fish and fisheries products, experiencing a notable 26.73% growth in exports from FY 2021-22 to FY 2022-23. Andhra Pradesh leads the country in fish production, followed by West Bengal and Gujarat. The sector supports the livelihoods of over 30 million people.
The Department of Fisheries is spearheading the PMMSY to foster a "Blue Revolution" through sustainable and responsible development of the fisheries sector.
Challenges Facing the Fisheries Sector
1. Overfishing: Excessive fishing pressure threatens fish stocks and disrupts ecosystem balance.
2. Illegal, Unreported, and Unregulated (IUU) Fishing: Practices such as fishing without proper authorization and using banned gear undermine conservation efforts.
3. Lack of Infrastructure and Technology: Outdated technology and inadequate storage and transportation facilities result in post-harvest losses and reduced productivity.
4. Poor Fisheries Management: Inefficient regulation enforcement and lack of comprehensive data exacerbate overfishing and IUU fishing.
5. Pollution and Habitat Destruction: Industrial pollution and habitat destruction from activities like coastal reclamation impact marine and freshwater ecosystems.
6. Climate Change: Altered oceanic and freshwater environments affect fish distribution and reproductive cycles, disrupting fisheries ecosystems.
7. Socio-Economic Issues: Poverty and limited livelihood options increase the vulnerability of fishing communities.
Government Initiatives for Sector Growth
1. National Fisheries Development Board (NFDB): Established in 2006, the NFDB plans and promotes fisheries development, enhancing production and infrastructure.
2. Blue Revolution: Launched in 2015, this initiative focuses on sustainable development, modern technology adoption, and strengthening fisheries governance.
3. Sagarmala Programme: Also launched in 2015, it aims to boost port-led development and includes projects to develop fishing harbors and cold chain infrastructure.
4. National Fisheries Policy: Introduced in 2020, this policy provides a framework for sustainable fisheries development, focusing on responsible management and socio-economic improvements.
5. Fish Farmers Development Agencies (FFDAs): Established at the district level to provide technical guidance and support to fish farmers.
6. Fisheries and Aquaculture Infrastructure Development Fund (FIDF): Created in 2018-19 with a fund of Rs 7,522.48 crore to address infrastructure needs, resulting in 121 approved projects.
7. Coastal Aquaculture Authority (CAA): Regulates coastal aquaculture to ensure sustainability and environmental conservation.
Way Forward
The fisheries sector in India holds immense potential due to its extensive coastline and water resources. Key measures to further enhance the sector include:
- Strengthening Monitoring and Enforcement: Combat IUU fishing with better monitoring and regulatory mechanisms.
- Supporting Sustainable Practices: Provide financial incentives for adopting modern technologies and sustainable practices.
- Protecting Aquatic Habitats: Ensure the conservation and restoration of vital habitats like mangroves and coral reefs.
- Improving Supply Chain Infrastructure: Develop better market linkages to ensure fair pricing and access to markets.
With these strategies, the PMMSY aims to drive the sustainable growth of India’s fisheries sector and bolster its contribution to the economy and livelihoods.
What is Helium & why is it used in rockets?

- 14 Sep 2024
The Crucial Role of Helium in Space Missions and the Challenges It Presents
Two NASA astronauts aboard Boeing’s Starliner will extend their stay on the International Space Station (ISS) due to issues with the spacecraft’s propulsion system, which includes problematic helium leaks. Meanwhile, SpaceX’s Polaris Dawn mission, which successfully launched on Tuesday, experienced delays due to similar helium-related issues with ground equipment.
The Importance of Helium in Spacecraft
Helium plays a critical role in space missions for several reasons. As an inert gas, it does not react with other substances or combust, which is crucial for maintaining the safety and stability of rocket systems. With an atomic number of 2, helium is the second lightest element after hydrogen. Its lightweight nature is essential for reducing the overall mass of rockets, which in turn minimizes fuel consumption and the need for more powerful (and costly) engines.
A key property of helium is its extremely low boiling point of –268.9 degrees Celsius. This allows it to remain in a gaseous state even in the super-cold environments where many rocket fuels are stored.
How Helium Is Utilized in Spacecraft
In spacecraft, helium is primarily used for:
- Pressurizing Fuel Tanks: Helium ensures that fuel flows smoothly to the rocket’s engines. As fuel and oxidizer are consumed during launch, helium fills the empty space in the tanks, maintaining consistent pressure.
- Cooling Systems: Helium is also used in cooling systems to manage the temperature of various components, preventing overheating and ensuring the proper functioning of the spacecraft.
Due to its non-reactive nature, helium can safely interact with the residual contents of the tanks without causing adverse reactions.
The Challenge of Helium Leaks
Despite its advantages, helium is prone to leakage. Its small atomic size and low molecular weight allow helium atoms to escape through even minor gaps or seals in storage tanks and fuel systems. This characteristic poses a significant challenge for space missions.
On Earth, helium leaks are easier to detect due to the gas’s rarity in the atmosphere. This makes helium a valuable tool for identifying potential faults in rocket or spacecraft fuel systems. The frequency of these leaks across various space missions, including those by ISRO and ESA, underscores a broader industry need for improved valve designs and more precise tightening mechanisms.
OpenAI’s powerful new AI model o1

- 14 Sep 2024
OpenAI Unveils New AI Model: Key Features and Implications
OpenAI has introduced its latest AI model, a significant advancement that aims to elevate the capabilities of artificial intelligence. This new model, part of the enigmatic ‘Project Strawberry,’ is designed to think more like a human when solving complex problems, offering a glimpse into the future of AI reasoning.
Introduction of OpenAI o1
The new OpenAI o1 model marks the beginning of a series of "reasoning" models intended to address intricate tasks in fields such as science, coding, and mathematics. This model, released as part of a preview in both ChatGPT and the API, represents a major leap forward in AI technology. OpenAI has announced that this is just the start, with regular updates and enhancements expected. Additionally, evaluations for the next model update, currently under development, are included in this release.
How It Works
The o1 model is designed to approach queries with a level of careful consideration similar to human problem-solving processes. It learns to tackle problems from various angles, verify its outputs, and improve through feedback. According to OpenAI, this model performs at a level comparable to PhD students in disciplines such as physics, chemistry, and biology. It is particularly adept in mathematics and coding, solving 83% of problems in a challenging math contest— a notable improvement from previous versions that only managed 13%. In coding, it has outperformed 89% of participants.
Sub-Models and Their Features
Alongside the main o1 model, OpenAI has also launched the o1-Mini. This version is a more cost-effective alternative, being 80% cheaper than the o1-preview. The o1-Mini is designed to offer fast and efficient reasoning, particularly beneficial for developers focused on coding tasks.
Implications for Jobs and Research
The advanced problem-solving capabilities of the o1 model are expected to impact various job sectors, particularly those involving routine coding, data analysis, and mathematical modeling. While this could reduce the need for human intervention in some tasks, it may also create new roles in AI safety and maintenance. For researchers, the model offers a powerful tool for accelerating breakthroughs in fields like physics, chemistry, biology, and healthcare. Its ability to generate formulas and analyze large datasets positions it as a valuable asset for advancing scientific research.
Access and Usage
The OpenAI o1 model is now accessible to ChatGPT Plus and Team users. The o1-preview and o1-mini can be selected using the model picker, with weekly message limits set at 30 for o1-preview and 50 for o1-mini. This rollout marks a new era in AI capabilities, showcasing OpenAI’s commitment to pushing the boundaries of artificial intelligence.
Key Points to Note
1. Not Artificial General Intelligence (AGI): Despite its advanced capabilities, o1-preview is not a step towards AGI, which aims for AI systems to perform cognitive tasks as well as or better than humans. The o1 models, while more adept at reasoning, still fall short of human-level intelligence.
2. Impact on Competition: While o1 gives OpenAI a temporary edge, it is expected to prompt competitors like Google, Meta, and others to accelerate their development of similar advanced models. These companies have the expertise to quickly develop models that could rival or surpass o1's capabilities.
3. Unknowns About Model Operations: Details on how o1 operates remain limited. It combines various AI techniques, including "chain of thought" reasoning and reinforcement learning, but specifics about its training data and internal mechanisms are not fully disclosed.
4. Cost Considerations: Using o1-preview comes at a higher cost compared to previous models. OpenAI charges $15 per million input tokens and $60 per million output tokens for corporate customers, compared to $5 and $15, respectively, for GPT-4o. The model’s complex reasoning requires more tokens, potentially making it more expensive to use.
5. Chain of Thought Transparency: OpenAI has chosen not to reveal the chain of thought process used by o1, citing safety and competitive reasons. This decision may cause issues for enterprise customers who lack visibility into their usage and billing accuracy.
6. New Scaling Laws: OpenAI's o1 models reveal new "scaling laws" suggesting that longer inference times can improve accuracy. This could increase the computing power and costs required to run these models effectively.
7. Potential Risks: o1 models could enable powerful AI agents, but they also present risks. Instances of “reward hacking” and unintended actions suggest that companies must carefully manage these agents to avoid ethical, legal, or financial issues.
8. Safety Assessments: OpenAI reports that o1 is generally safer than previous models, though it still poses a "medium risk" of assisting in biological attacks. This rating has raised concerns among AI safety and national security experts.
9. Concerns About Persuasion and Deceptive Alignment: AI safety experts are wary of o1’s persuasive capabilities and the potential for “deceptive alignment,” where a model might deceive users to achieve hidden goals. These concerns highlight the ongoing challenges in ensuring AI safety and transparency.
Overall, while the o1 models represent a significant leap forward in AI reasoning and problem-solving, they also introduce new complexities and risks that will need to be managed as they become more integrated into various applications.
Commission for Scientific and Technical Terminology (CSTT)

- 12 Sep 2024
In News:
The Commission for Scientific and Technical Terminology (CSTT) has recently unveiled a groundbreaking web portal, ‘shabd.education.gov.in,’ which is set to be a significant resource for technical terminology across all 22 official Indian languages. This initiative, supported by the Union Education Ministry, aims to consolidate and digitize scientific and technical terminologies, making them accessible to users in multiple languages.
Key Features of the Portal:
- Central Repository: The website serves as a central repository for glossaries developed by CSTT and other institutions. It currently hosts 322 glossaries with approximately 2.2 million words, with a goal to expand to 450 glossaries.
- Search Functionality: Users can search for technical terms using various criteria, including language, subject, type of dictionary, or specific language pairs. This comprehensive search capability allows for targeted and efficient access to information.
- Feedback Mechanism: The portal enables users to provide feedback on the terminologies, helping to refine and update the database based on real-world use and expert input.
- Expanding Technical Education: The launch of this platform supports the broader goal of enhancing technical education in Indian languages, which is crucial for fields like medicine and engineering.
Historical Context and Support:
- CSTT's Role: Established in 1961, CSTT is tasked with developing and defining scientific and technical terms in Hindi and other Indian languages. The commission also publishes textbooks, monographs, and journals, and organizes various academic events to promote standardized terminology.
- Process of Compilation: Terminologies are compiled through specialized committees for each subject area, with separate language committees ensuring the standardization of terms. The CSTT has been assisted by the National Translation Mission in this effort.
Impact and Usage:
- Since its launch in March 2024, the portal has seen significant engagement, with over 122,000 hits from both domestic and international users. This reflects the growing interest and need for accessible technical terminology in multiple languages.
- The portal is poised to play a crucial role in standardizing and disseminating technical knowledge across diverse linguistic communities in India, facilitating better understanding and education in various scientific and technical fields.
Ayushman Bharat Pradhan Mantri Jan Arogya Yojana (AB PM-JAY)

- 12 Sep 2024
In News:
- The Union Cabinet has approved a major expansion of the Ayushman Bharat Pradhan Mantri Jan Arogya Yojana (AB PM-JAY) to cover all senior citizens aged 70 years and above.
- This change allows anyone in this age group to be eligible for health insurance, regardless of their income level.
- This expansion aims to address the healthcare needs of the elderly, who often face higher medical expenses as they age.
- By lifting income restrictions, the government is ensuring that more senior citizens can benefit from much-needed health coverage, which will help ease the financial burden of healthcare.
How does the scheme work?
- The AB PM-JAY now covers an additional 6 crore individuals from 4.5 crore families, focusing on seniors aged 70 and above. Each senior citizen will be given a health card, allowing them easy access to healthcare services under the scheme.
- The scheme provides Rs 5 lakh coverage annually per family. If there are multiple senior citizens in the same family, this coverage is shared among them. The scheme is particularly beneficial for nuclear families, where the financial burden on elderly members can be more difficult to manage.
Key details of the scheme for senior citizens above 70
- Eligibility - All senior citizens aged 70 and above are eligible for Rs 5 lakh health coverage, regardless of income or social status.
- Top-up coverage - For families already enrolled in Ayushman Bharat, senior members will receive an extra Rs 5 lakh top-up, which is solely for their use.
- Private insurance - Senior citizens with private health insurance can still take advantage of the scheme without any conflict with their existing coverage.
- Public health schemes - Seniors who are part of other public health schemes like the Central Government Health Scheme (CGHS), Ex-Servicemen Contributory Health Scheme (ECHS), or Ayushman Central Armed Police Force (CAPF) will need to choose between their current insurance and the new Ayushman Bharat health coverage.
- New health cards - All eligible senior citizens will receive a separate health card, which will help them access the scheme’s benefits more efficiently.
Who pays for the coverage?
- The cost of this expanded coverage will be Rs 3,437 crore initially. State governments will bear 40% of the expenses, while the Centre will cover the remaining 60%. For states in hilly and northeastern regions, the Centre will fund 90% of the costs.
- As more senior citizens enrol, the costs may increase. Experts point out that covering elderly individuals often costs more than providing insurance for younger, economically weaker sections of society. However, the government is prepared to scale up the coverage based on demand.
Ayushman Bharat Pradhan Mantri Jan Arogya Yojana (AB PM-JAY)
- AB PM-JAY launched in 2018, is a flagship program designed to offer affordable and accessible healthcare to millions of vulnerable families across India.
- The primary aim is to provide health insurance coverage up to ?5 lakhs per family annually for secondary and tertiary care hospitalization.
- The scheme currently supports 55 crore individuals from 12.34 crore families throughout the country.
PM E-Drive replaces FAME India Phase II

- 12 Sep 2024
In News:
The Union Cabinet recently approved a new scheme called PM Electric Drive Revolution in Innovative Vehicle Enhancement (PM E-DRIVE) for the promotion of electric vehicles (EV) in India, replacing an earlier flagship scheme.
Key Highlights:
- The Ministry of Heavy Industries (MHI) will implement the new scheme with a total outlay of Rs 10,900 crore over a period of two years.
- The PM E-DRIVE will replace Faster Adoption and Manufacturing of Electric Vehicles in India Phase II (FAME India Phase II).
- The new scheme offers subsidies/demand incentives worth Rs 3,679 crore to incentivise adoption of electric two-wheelers, electric three-wheelers, e-ambulances, e-trucks and other emerging EVs.
- The scheme will support 24.79 lakh electric two-wheelers, 3.16 lakh e-three wheelers, and 14,028 e-buses.
- For e-ambulances, a total of Rs 500 crore has been allocated. In addition, Rs 4,391 crore has been provided for the procurement of 14,028 e-buses by state transport units and public transport agencies.
- To implement this, demand aggregation will be done by Convenience Energy Services Limited (CESL) in nine cities with a population of more than 40 lakh — Delhi, Mumbai, Kolkata, Chennai, Ahmedabad, Surat, Bengaluru, Pune, and Hyderabad. Intercity and interstate e-buses will also be supported in consultation with states.
- For availing benefits under the scheme, the ministry will introduce e-vouchers for EV buyers. At the time of purchase, the scheme portal will generate an Aadhaar authenticated e-voucher, which needs to be signed by the buyer and submitted to the dealer.
- Subsequently, the e-voucher will also be signed by the dealer and uploaded on the PM E-DRIVE portal. The signed e-voucher will be sent to the buyer and dealer via SMS, and will be essential for the OEM (original equipment manufacturer) to claim reimbursement of demand incentives under the scheme.
- The primary objective of the PM E-DRIVE scheme is to expedite the adoption of EVs by providing upfront incentives for their purchase, as well as by facilitating the establishment of essential charging infrastructure for EVs.
FAME India Phase II
Launched on April 1, 2019, with a budget of ?10,000 crores for three years. It is an extension of FAME India I, which began on April 1, 2015, with a ?895 crore budget.
Objectives:
- Promote the adoption of electric and hybrid vehicles.
- Provide upfront incentives for purchasing electric vehicles.
- Develop necessary charging infrastructure.
- Address environmental pollution and fuel security.
Focus Areas:
- Public transportation and shared transport.
- Incentives for electric buses through State/City Transport Corporations.
- For 3W and 4W vehicles, incentives are for public transport and commercial vehicles.
- For e-2Ws, focus is on private vehicles.
Targets:
- 10 lakh e-2Ws
- 5 lakh e-3Ws
- 55,000 e-4Ws
- 7,000 electric buses
Incentives:
- Applied to vehicles with advanced batteries, such as Lithium-ion and other new technologies.
Charging Infrastructure:
- 2,700 charging stations in metros, million-plus cities, smart cities, and hilly areas.
- Charging stations on major highways at 25 km intervals, on both sides of the road.
40% Amazon rainforest unprotected: why is this significant for climate change?

- 12 Sep 2024
In News
- Scientists agree that preserving the Amazon rainforest is critical to combating global warming, but new data published recently, indicate huge swathes of the jungles that are vital to the world’s climate remain unprotected.
- Nearly 40% of the areas of the Amazon rainforest most critical to curbing climate change have not been granted special government protection, as either nature or indigenous reserves, according to an analysis by nonprofit Amazon Conservation.
- The areas lie in the far southwest of the Amazon in Peru and the far northeast in Brazil, French Guiana, and Suriname, the data show.
- Those parts of the Amazon have the biggest, densest trees and the most continuous canopy cover. That means these areas hold the most carbon, which would be released into the atmosphere as climate-warming greenhouse gas if the jungle is destroyed by fire or logging.
What satellite data show
- Amazon Conservation analysed new data from the satellite imaging company Planet that used lasers to get a three-dimensional picture of the forest and combined it with machine-learning models.
- Only aboveground vegetation was considered, and not underground carbon in roots and soils.
- Amazon Conservation’s Monitoring of the Andean Amazon Project (MAAP)’s analysis shows that 61% of the peak carbon areas in the Amazon are protected as indigenous reserves or other protected lands, but the rest generally has no official designation.
- In Brazil, Suriname and French Guiana, only 51% of peak carbon areas are labeled for preservation. Peru protects a higher proportion of its critical areas, but some of the areas that have been left unprotected have been earmarked for logging.
Why the Amazon matters
- MAAP published an analysis last month showing that the Amazon contained 71.5 billion tonnes of carbon, roughly double the global carbon dioxide emissions for 2022. That analysis showed that the Amazon just barely absorbed more carbon than it released in the decade leading up to 2022, a positive signal for the world’s climate.
- But that remains an area of intense debate, with other studies showing the Amazon has flipped to become an emissions source.
- As the effects of anthropogenic climate change become more stark with each passing day, the Amazon becomes one of the most valuable assets for the planet’s health. Scientists say that if the Amazon becomes an emission source instead of a carbon sink — which absorbs carbon from the atmosphere — the impact on the planet may be cataclysmic.
Controversy over Mumbai's salt pans: why do these lands matter?

- 12 Sep 2024
In News:
Earlier this month, the Centre approved the transfer of 256 acres of salt pan land in Mumbai to the Dharavi Redevelopment Project Pvt Ltd (DRPPL), a joint venture between Adani Realty Group and the Maharashtra government, for building rental housing for slum dwellers.
What are salt pan lands?
- They comprise parcels of low-lying lands where seawater flows in at certain times, and leaves behind salt and other minerals. Along with Mumbai’s mangroves (also at risk due to development), this ecosystem is instrumental in protecting the city from flooding.
- According to the Coastal Regulation Zone (CRZ) notification of 2011, the ecologically sensitive salt pans fall under CRZ-1B category, where no economic activity is allowed with the exception of salt extraction and natural gas exploration.
- In all, 5,378 acres of land in Mumbai have been designated as salt pan lands, approximately nine times the size of the Dharavi slum. About 31% of this land is located in residential and commercial belts, and roughly 480 acres are encroached upon, a 2014 study by the state government found. The same study found that about 1,672 acres of Mumbai’s more than 5,000 acres of salt pan lands are “developable”.
- Nationally, some 60,000 acres have been demarcated as salt pan lands, spread across Maharashtra, Andhra Pradesh, Tamil Nadu, Odisha, Gujarat, and Karnataka. Andhra Pradesh (20,716 acres) boasts the largest expanse of such land, followed by Tamil Nadu (17,095 acres) and Maharashtra (12,662 acres).
Why are Mumbai’s salt pan lands at risk?
Development Pressure
- Land Scarcity: Mumbai faces severe land scarcity, with its burgeoning population and high demand for space. Salt pans, being some of the last undeveloped areas, are increasingly targeted for various projects.
- Development Plans: Multiple state governments have eyed salt pan lands for different uses.
Environmental Significance
- Flood Prevention: Salt pans are situated in low-lying areas that naturally collect rainwater and tidal flows, helping to mitigate flooding in Mumbai’s eastern suburbs. They act as natural buffers, absorbing excess water during heavy rains and high tides.
- Historical Context: During the July 2005 deluge, salt pans helped reduce the impact of flooding compared to other areas of Mumbai, highlighting their role in flood management.
- Ecosystems: Salt pans are home to various species of birds and insects and contribute to local biodiversity. The destruction of these lands could lead to loss of habitat and disruption of local ecosystems.
Risks of Development
- Flooding Concerns: Environmentalists argue that constructing on these low-lying areas will lead to increased flooding in areas like Vikhroli, Kanjurmarg, and Bhandup. This is because the land’s natural ability to absorb and manage water will be compromised.
- Quality of Life Issues: Relocating slum-dwellers to these areas raises concerns about their living conditions. Salt pans are prone to flooding, which could undermine the quality of life for new residents. The cost of making these lands habitable, including extensive land filling and waterproofing measures, could negate the benefits of affordable housing.
- Conflict with Climate Goals: There is a contradiction between Mumbai’s Climate Action Plan, which recognizes climate threats, and the push to develop areas critical for flood management.
SEMICON 2024

- 11 Sep 2024
In News:
Recently, Prime Minister Narendra Modi addressed the SEMICON 2024 conference on the outskirts of the national capital, advocating for increased investment in semiconductor manufacturing and resilient supply chains.
- Significance of Supply Chains: Emphasized the critical need for resilient supply chains, citing the COVID-19 pandemic as a stark reminder of their importance. The pandemic highlighted vulnerabilities in global supply chains, particularly affecting sectors dependent on chip imports from China.
- Investment in Semiconductors: Modi pitched India as a prime destination for semiconductor investments. He stressed that India aims to have an Indian-made chip in every global device and is committed to becoming a semiconductor powerhouse.
- India's Semiconductor Strategy:
- Reformist Government: Modi highlighted India’s reformist policies and stable business environment as key attractions for semiconductor investments.
- Growing Manufacturing Base: Expanding manufacturing infrastructure in India as a critical factor.
- Aspirational Market: The evolving technology market in India is seen as a strong incentive for semiconductor production.
- Government Commitment: Modi announced that over ?1.5 lakh crore has already been committed to semiconductor manufacturing, with several projects currently in the pipeline.
- Semicon India 2024 Focus:
- Event Goals: SEMICON India 2024 is a three-day conference designed to showcase India’s semiconductor strategies and policies, aiming to position the country as a global hub for semiconductor manufacturing.
- Workforce Development: The government is developing a semiconductor workforce of 85,000 engineers, technicians, and R&D experts.
- Market Growth: India’s semiconductor market, valued at $23.2 billion, is projected to reach $80.3 billion by 2028, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 17.10%.
- Importance of Semiconductors: Semiconductor chips as crucial for fulfilling the aspirations of millions and noted their role in India’s Digital Public Infrastructure (DPI), which remained effective during the pandemic when other countries’ banking systems struggled.
- Event Participation: SEMICON India 2024 will feature over 250 exhibitors and 150 speakers, including top executives from global semiconductor companies, industry leaders, businesses, and experts from around the world.
PresVu
- 11 Sep 2024
According to the company, the eye drop PresVu is the first of its kind in India, and that Entod has “applied for a patent for this invention in terms of its formulation and the process”.
Mumbai-based Entod Pharmaceuticals has announced that the Drug Controller General of India (DCGI) — the country’s apex drug regulator — has approved its new eye drop, which has been “specifically developed to reduce dependency on reading glasses for individuals affected by presbyopia.”
According to the company, the eye drop PresVu is the first of its kind in India, and that Entod has “applied for a patent for this invention in terms of its formulation and the process”.
What is presbyopia?
Presbyopia is an age-related condition in which the eyes gradually lose the ability to focus on nearby objects. People usually start to develop presbyopia at around the age of 40. According to doctors, spectacles are one of the most effective ways to manage the condition.
How does PresVu work?
- The active ingredient — chemical compounds in medicines that have an effect on the body — in PresVu is pilocarpine. The compound contracts the iris muscles, which control the size of the pupil and help humans see things clearly, thereby enabling one’s eyes to focus better on nearby objects, according to Entod Pharmaceuticals.
- The company also said that PresVu uses “advanced dynamic buffer technology” — essentially, a base solution — to adapt to the pH level (a scale used to measure how acidic or basic a substance is) of tears. This ensures that the eye drop has “consistent efficacy and safety for extended use, keeping in mind that such drops will be used for years at a stretch”.
- PresVu is a prescription-only medicine and, according to doctors, its impact is unlikely to last beyond four to six hours. It should not be used by people who have inflammation of the iris. Regular use of PresVu may lead to itching and redness, eyebrow pain, and muscle spasms in the eyes.
Is this a novel therapy?
- Although Entod’s claims make it seem that PresVu is a new therapy, pilocarpine, the main compound used in the eye drop, has been available in India for decades now.
- The United States Food and Drug Administration approved a pilocarpine eye drop for presbyopia in 2021.
- In India, the government decides on the ceiling price of pilocarpine in 4% and 2% concentrations. PresVu has pilocarpine in 1.25% concentration.
Strengthening India-UAE Relations

- 11 Sep 2024
The bilateral relationship between India and the UAE has flourished in recent years, marked by deepening strategic ties and multifaceted collaboration. The recent visit of Abu Dhabi's Crown Prince to India highlights the growing importance of this partnership. The UAE is now India's second-largest export destination, third-largest trading partner, and fourth-largest investor. The Comprehensive Economic Partnership Agreement (CEPA), effective from May 2022, has been transformative, boosting total trade by nearly 15% and increasing non-oil trade by 20% in the 2023-24 period.
Significance of the UAE for India
- Economic Gateway: The UAE is a crucial entry point for India into the Middle East and North Africa (MENA) region. As India's third-largest trading partner, bilateral trade reached USD 84.5 billion in FY 2022-23. The CEPA, removing tariffs on 80% of Indian exports to the UAE, has led to a 5.8% increase in non-oil trade early in 2023 and is expected to elevate trade to USD 100 billion by 2030. The UAE’s strategic location and infrastructure make it an ideal hub for re-exporting Indian goods to Africa and Europe.
- Energy Security: The UAE is India's fourth-largest crude oil supplier, with oil imports surging by 81% in January 2024. The partnership extends to renewable energy projects, aligning with India's goal of 500 GW renewable energy capacity by 2030, underscoring the UAE's role in India's energy transition.
- Investment Catalyst: FDI from the UAE to India has increased more than threefold, reaching USD 3.35 billion from USD 1.03 billion in 2021-22. The UAE-India High-Level Joint Task Force on Investments has played a key role, with significant investments like the Abu Dhabi Investment Authority’s Rs 4,966.80 crore in Reliance Retail Ventures Limited.
- Strategic Partner: The UAE has become a vital strategic ally for India in counterterrorism and maritime security. The bilateral naval exercise "Zayed Talwar" in 2021 and India's access to the UAE’s Al Dhafra air base highlight the expanding defense cooperation between the two nations.
- Remittances and Soft Power: The 3.5 million-strong Indian diaspora in the UAE is a major source of remittances and cultural influence. In 2022, India received nearly USD 111 billion in global remittances, with the UAE as a significant contributor. The diaspora also strengthens cultural ties, as evidenced by the BAPS Hindu Temple in Abu Dhabi, symbolizing the UAE’s commitment to religious tolerance.
- Tech and Innovation Hub: The UAE-India partnership is increasingly focused on technology and innovation. The I2U2 group (India, Israel, UAE, USA) aims to enhance cooperation in clean energy and food security. The UAE’s USD 2 billion investment in food parks in India and the UAE-India Artificial Intelligence Bridge, launched in 2018, facilitate joint research and position both countries at the forefront of technological advancement.
Areas of Friction
- Labor Rights: Persistent labor rights issues for Indian workers in the UAE, including passport confiscation and wage theft, remain a concern.
- Geopolitical Tensions: India’s growing ties with Israel and the UAE’s normalization with Israel complicate the geopolitical landscape, potentially entangling India in regional rivalries, especially with Iran. The UAE’s increasing ties with China also add strategic complexity.
- Energy Transition: Both nations’ commitments to net-zero targets—India by 2070 and the UAE by 2050—pose challenges to their traditional hydrocarbon-based relationship.
- Trade Imbalance: Despite growing trade, India’s trade deficit with the UAE stood at USD 16.78 billion in FY 2022-23. While the CEPA aims to address this, diversifying trade beyond hydrocarbons remains a challenge.
- Maritime Security: Coordinating responses to maritime security threats while respecting strategic autonomy is challenging. The UAE’s expanding naval presence and India’s growing maritime footprint require careful coordination.
Enhancing Relations
- Digital Diplomacy: India could use its IT capabilities to develop digital platforms for collaboration, including a real-time trade portal and a joint innovation hub, and expand cross-border digital payments.
- Green Energy Corridor: Proposing an "India-UAE Green Energy Corridor" could align with both nations’ climate goals through joint investments and research in renewable energy.
- Skill Bridge Program: A "Skill Bridge Program" could upskill Indian workers for the UAE job market, focusing on emerging sectors like AI and sustainable technologies.
- StartUp Synergy Scheme: Developing a "StartUp Synergy Scheme" could foster collaboration between Indian and UAE startups through joint incubation programs and market access facilitation.
- Maritime Cooperation Blueprint: Creating a comprehensive "India-UAE Maritime Cooperation Blueprint" could enhance collaboration in maritime security, blue economy initiatives, and port development, including joint patrols and deep-sea ports.
Polaris Dawn Mission: First Private Spacewalk Attempt

- 11 Sep 2024
Recently, a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket launched from Florida, carrying American billionaire Jared Isaacman and three other astronauts into orbit for the Polaris Dawn mission. This five-day mission marks a milestone as it aims to achieve the world’s first private spacewalk. Polaris Dawn is the inaugural flight of the Polaris Program, a collaborative effort between Isaacman and SpaceX, led by Elon Musk. The program's goal is to develop innovative technologies for future Mars missions.
What is a Spacewalk?
A spacewalk, or “extravehicular activity” (EVA), involves an astronaut conducting activities outside a spacecraft while in space. The concept of a spacewalk dates back to March 18, 1965, when Soviet cosmonaut Alexei Leonov performed the first EVA during the Space Race. Leonov's spacewalk lasted just 10 minutes.
Modern spacewalks typically occur outside the International Space Station (ISS) and can last between five and eight hours. Astronauts conduct spacewalks for various purposes, such as performing scientific experiments, testing new equipment, or repairing satellites and spacecraft.
During a spacewalk, astronauts wear specially designed spacesuits and use safety tethers to prevent floating away into space. These tethers have one end attached to the astronaut and the other secured to the spacecraft. An alternative safety device is the SAFER (Simplified Aid for EVA Rescue), a backpack with small jet thrusters controlled by a joystick, which helps astronauts maneuver in space.
Objectives of the Polaris Dawn Mission
The Polaris Dawn mission, utilizing SpaceX’s Dragon capsule, aims to reach an altitude of approximately 1,400 km from Earth. This altitude exceeds the previous record set by NASA’s Gemini XI mission in 1966, which reached 1,372 km. At this height, the mission will be deep within the Van Allen radiation belts, which start around 1,000 km altitude and are known for their high levels of radiation. The crew will study the effects of spaceflight and radiation on human health.
Following this high-altitude phase, the Dragon capsule will descend to a lower orbit to facilitate the spacewalk scheduled for the third day of the mission, Thursday. During the spacewalk, the capsule will be depressurized, and the hatch will open, exposing the interior to the vacuum of space. Only two crew members, Isaacman and Gillis, will exit the capsule, while Poteet and Menon will remain inside to manage safety tethers and monitor the mission’s status.
The primary objective of the spacewalk is to test SpaceX’s newly developed EVA spacesuits. These suits, designed specifically for this mission, feature built-in cameras and heads-up displays to provide real-time information about the suit's condition. They also incorporate advanced thermal management systems.
After the spacewalk, Isaacman and Gillis will return to the capsule, which will then be repressurized before resuming its mission activities.
Additional Mission Activities
Throughout the mission, the crew will conduct 40 scientific experiments. These include attempting to capture X-ray images using natural space radiation instead of traditional X-ray equipment. The mission will also test SpaceX’s Starlink satellite network for laser-based communication, allowing satellite-to-satellite communication without relying on ground-based infrastructure.
The grave threat from AMR
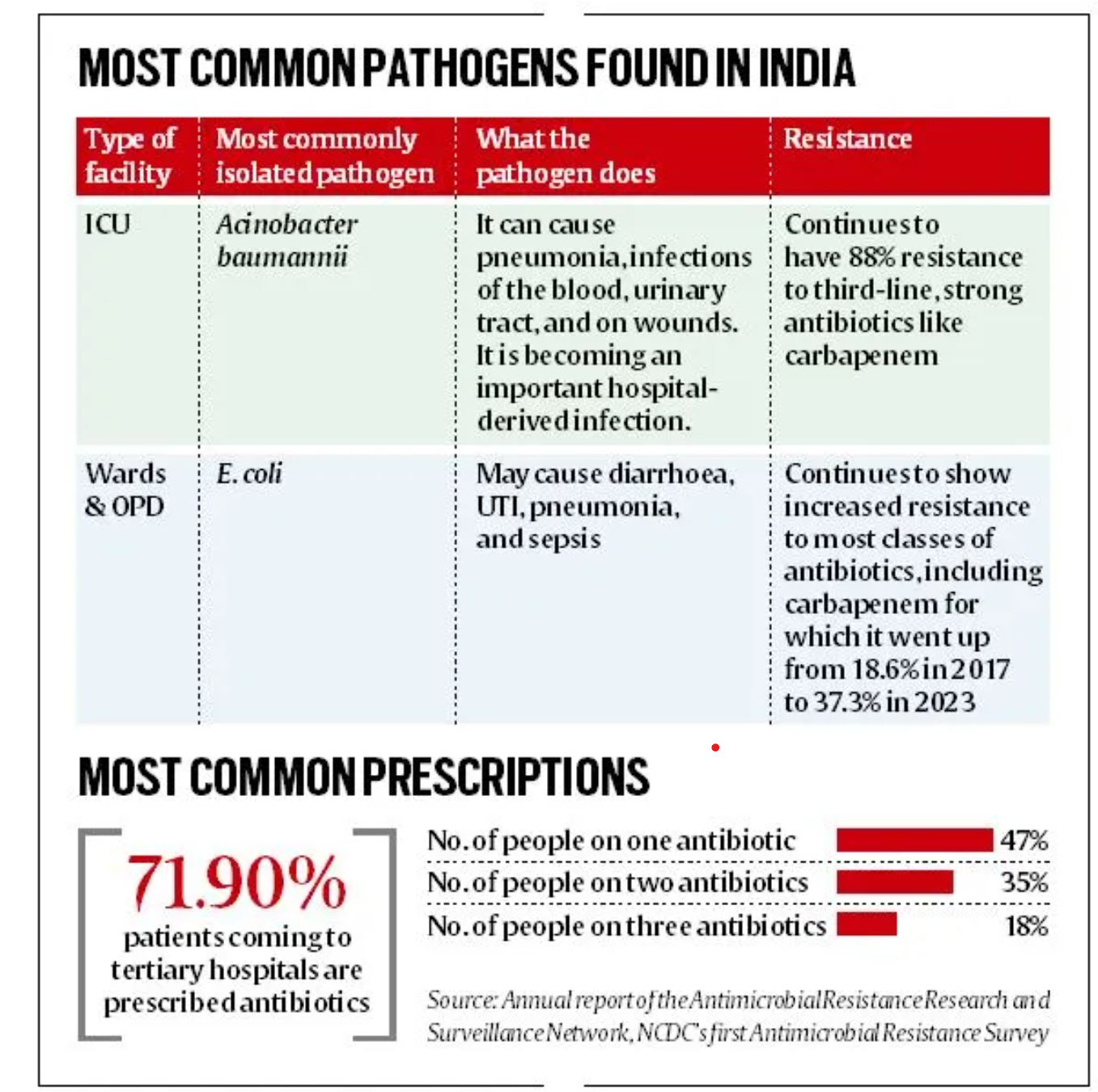
- 11 Sep 2024
Antimicrobial resistance (AMR) poses a significant threat globally, with escalating concerns in India. AMR arises when microbes evolve into drug-resistant ‘superbugs’ due to the misuse or overuse of antibiotics. This phenomenon is exacerbated by the September 26 UN General Assembly High-Level Meeting on antimicrobial resistance, which highlighted the World Health Organization’s (WHO) recent guidance on antibiotic pollution from manufacturing.
AMR and the emergence of "superbugs" have far-reaching implications for healthcare systems, particularly affecting patients with multiple health conditions. According to a survey by the Indian Council of Medical Research (ICMR), AMR is on the rise across India, underscoring the urgency of addressing this issue.
What is Antimicrobial Resistance (AMR)?
AMR occurs when pathogens gain the ability to survive and cause infections despite the presence of antimicrobial drugs. This resistance is a result of microbes evolving in response to inappropriate or excessive use of antibiotics. The proliferation of resistant strains can lead to the creation of 'superbugs' that are resistant to commonly prescribed antibiotics. These resistant pathogens can spread through hospitals, drinking water, and sewage systems, complicating the treatment of infections.
Why is AMR Increasing?
- Individual Practices: Many people in India take antibiotics without medical consultation, especially for viral infections like the flu, where antibiotics are ineffective. This misuse contributes to the development of resistance.
- Medical Practices: There is a need for improved education among doctors regarding the use of antibiotics. Broad-spectrum antibiotics, which target a wide range of infections, are more likely to induce resistance. A survey by the National Centre for Disease Control (NCDC) found that 71.9% of patients in hospitals were prescribed antibiotics, often not to treat existing infections but to prevent potential ones. This overprescription has diminished the efficacy of several antibiotics, such as Norfloxacin, and increased resistance to crucial antibiotics like carbapenems.
- Diagnostic Practices: Often, doctors prescribe antibiotics based on symptoms rather than diagnostic tests, leading to empirical treatments with broad-spectrum antibiotics. It is essential for doctors to use diagnostic tests to prescribe targeted antibiotics, minimizing unnecessary resistance development.
- Pharmaceutical Industry: The WHO’s recent guidelines on antibiotic pollution highlight the need for better management of wastewater and solid waste from antibiotic manufacturing facilities. Despite known high levels of antibiotic pollution, regulatory oversight remains limited.
Common Resistant Pathogens in India
In India, the most prevalent resistant pathogens include:
- E. coli: Responsible for gut infections, with susceptibility to carbapenems decreasing from 81.4% in 2017 to 62.7% in 2023.
- Klebsiella pneumoniae: Causes pneumonia and urinary tract infections, showing reduced susceptibility to carbapenems from 58.5% to 35.6% and 48% to 37.6% between 2017 and 2023.
- Acinetobacter baumannii: Primarily associated with hospital-acquired infections, with resistance to carbapenems at 88% in 2023.
Key Actions Required
- Prevention: Enhance infection prevention through better hygiene, sanitation, and vaccination.
- Education: Train doctors on the judicious use of antibiotics, reserving potent antibiotics for severe cases, and ensuring appropriate diagnostic testing.
- Regulation: Implement regulations to control antibiotic pollution from manufacturing processes and investigate resistance pathways.
Good Digital Public Infrastructure
- 08 Sep 2024
Good digital public infrastructure (DPI) integrates technology with societal needs, ensuring that it is secure, scalable, and inclusive.
India’s achievement of over 80% financial inclusion in just six years has drawn international praise, particularly as a model for the Global South. This accomplishment underscores India’s success in achieving both digital and financial inclusion for over a billion people. Consequently, the G20 summit in New Delhi in 2023 highlighted the critical role of digital public infrastructure.
In response, India’s G20 task force has released a comprehensive report outlining a global strategy for DPI development. This positions India to support other nations in achieving digital sovereignty, financial inclusion, and self-reliance.
The evolving digital landscape is marked by a variety of stakeholders—including private enterprises, government bodies, non-profits, and think tanks—each working to advance their DPI solutions. This raises two key questions: How can we identify genuine and reliable DPIs from the plethora available? And what differentiates a “good DPI” from a “bad DPI”?
Identifying effective DPI involves assessing how well technology meets societal needs while ensuring security, scalability, and inclusivity. Authenticity and adherence to core principles are essential for evaluating DPIs.
The Citizen Stack Model
Citizen Stack, built upon the proven success of India Stack, emerges as a trusted ecosystem in digital infrastructure. India Stack, a robust digital platform, has demonstrated its effectiveness and security on a vast scale, serving over a billion citizens. This strong foundation enhances Citizen Stack’s credibility and reliability. Unlike DPI manufacturers, Citizen Stack functions as a regulatory body or auditor, certifying and authenticating DPIs to ensure they meet high standards of quality and security.
Citizen Stack’s approach is comprehensive, focusing on security, scalability, and inclusivity. The DPI platforms approved by Citizen Stack are designed to meet the diverse needs of large populations while maintaining stringent security measures to protect user data and privacy. As an auditor, Citizen Stack ensures that certified DPIs are dependable, secure, and beneficial to the public.
In an era of abundant digital solutions and promises, distinguishing genuinely reliable platforms is essential. Citizen Stack offers assurance as a gold standard for DPI solutions.
Guiding Principles of a “Good DPI”
Citizen Stack has established five core principles—referred to as sutras—that define a good DPI:
- Maintain Citizen Relationships: Ensure that digital infrastructure supports a fair relationship between citizens, the market, and the state, free from undue influence.
- Protect Empowerment and Privacy: Implement consent-based data sharing systems that prioritize individual empowerment and privacy.
- Prevent Monopolistic Lock-In: Ensure interoperability to avoid citizens being restricted by monopolistic entities.
- Combine Techno-Legal Regulation: Integrate technology with legal frameworks to govern ethical tech use, ensuring innovation while safeguarding security and societal rights.
- Foster Public-Private Innovation: Encourage collaboration between public and private sectors, while avoiding corporate dominance. The focus should be on public good rather than corporate monopolies, and technology should prevent exploitation by state or corporate actors.
Barakah Nuclear Energy Plant
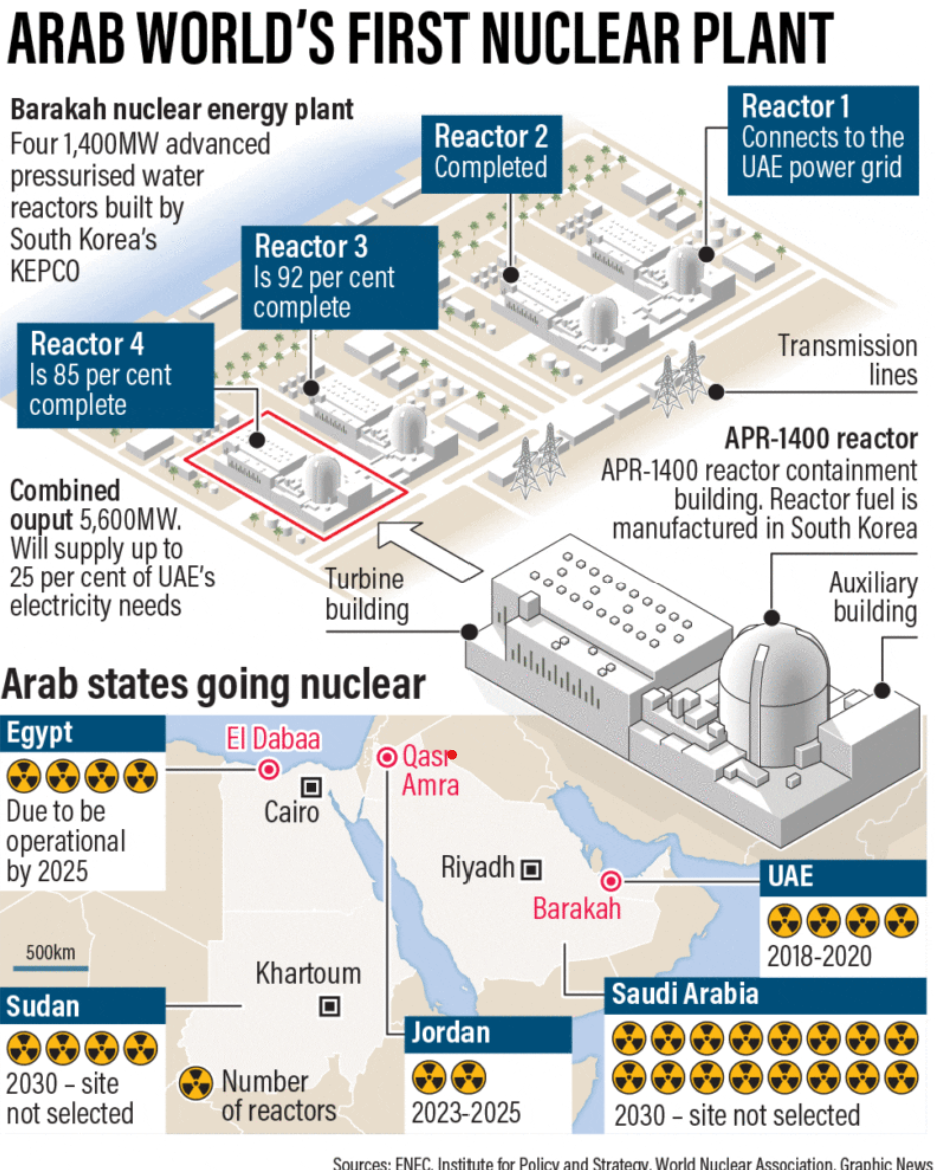
- 08 Sep 2024
Location: Situated in Al Dhafra, Emirate of Abu Dhabi.
Specifications:
- Reactor Count: Four nuclear reactors.
- Annual Output: 40 terawatt-hours (TWh) of electricity.
Objective and Significance:
- Energy Diversification: The plant is a key component of the UAE’s energy diversification efforts, providing clean and efficient power.
- Environmental Impact: It is projected to reduce carbon emissions by up to 22 million tons annually, equivalent to removing 4.8 million cars from the roads.
International Nuclear Energy Agreements
Purpose: Nuclear energy agreements are bilateral or multilateral treaties focused on the peaceful use of nuclear energy. They facilitate international cooperation in areas such as technology transfer, fuel supply, safety standards, and non-proliferation.
India’s Nuclear Energy Agreements:
- General Overview: India has established civil nuclear cooperation agreements with various countries including France, the United States, Russia, Namibia, Canada, Argentina, Kazakhstan, South Korea, Australia, Sri Lanka, and the United Kingdom.
Key Agreements:
- India-Russia: A longstanding partnership since the Cold War, with Russia significantly contributing to the construction of the Kudankulam Nuclear Power Plant in Tamil Nadu.
- India-US Civil Nuclear Agreement (2008): Known as the 123 Agreement, it marked India’s entry into the global nuclear market despite its non-signatory status to the Nuclear Non-Proliferation Treaty (NPT). This agreement enabled India to engage in nuclear trade with the US and other Nuclear Suppliers Group (NSG) members.
- India-France Civil Nuclear Agreement (2008): This agreement allows France to supply nuclear technology and fuel to India, including involvement in the proposed Jaitapur Nuclear Power Project in Maharashtra.
- India-Canada Nuclear Cooperation Agreement (2010): This historic deal marked a return to cooperation after a hiatus following Canada's sanctions in 1974, allowing uranium supply for India’s civilian reactors.
- India-Japan Nuclear Agreement (2016): This agreement facilitates the export of nuclear technology from Japan to India, reflecting Japan’s confidence in India's non-proliferation commitments.
- India-Kazakhstan: Agreements with Kazakhstan for uranium supply, given Kazakhstan’s status as a major uranium producer.
- India-Australia Civil Nuclear Cooperation Agreement: Permits Australia to export uranium for India’s civilian nuclear program. Notably, Australia typically exports uranium only to NPT signatories.
- India-United Kingdom Nuclear Agreement (2015): This agreement promotes collaboration on nuclear technology and research between India and the UK.
- India-UAE Civil Nuclear Energy Cooperation: Recently, India and the United Arab Emirates (UAE) formalized their collaboration in civil nuclear energy through an MoU.
National Initiative for Developing and Harnessing innovations (NIDHI) program
- 08 Sep 2024
- NIDHI is an umbrella programme conceived and developed by the Technology Translation and Innovation (TTI) Division/ National Science and Technology Entrepreneurship Development Board, of Department of Science & Technology, Government of India, for nurturing ideas and innovations (knowledge-based and technology-driven) into successful startups.
- The NIDHI programme works in line with the current national priorities and goals and its focus would be to build an innovation driven entrepreneurial ecosystem with an objective of national development through wealth and job creation.
- NIDHI aims to nurture Startups through scouting, supporting and scaling of innovations by providing them with a series of programme components tailored towards the critical initial phases of the Startup journey.
- The key stakeholders of NIDHI include Science & Technology based entrepreneurs, Startup Incubators, academic and R&D institutions, Startup mentors, financial institutions, angel investors, venture capitalists, relevant government & industry bodies and associations.
- NIDHI has been developed to suit the national aspirations and on the basis of DST’s three-decade long experience in propelling Startup Incubation centres and Science & Technology based entrepreneurs.
- The key components of NIDHI are :-
- NIDHI PRAYAS: Promotion and Acceleration of Young and Aspiring technology entrepreneurs – Support from Idea to Prototype
- NIDHI – EIR: Entrepreneur In Residence – Support system to reduce risk for entrepreneurs.
- NIDHI – TBI : Technology Business Incubator (NIDHI-TBI) – Converting Innovations to start-ups.
- NIDHI – iTBI : Inclusive- Technology Business Incubator – A new variant of the NIDHI-TBI launched in 2022-’23.
- NIDHI – Accelerator : Startup Acceleration Programme – Fast tracking a start-up through focused intervention.
- NIDHI – SSS : Seed Support System – Providing early stage investment
- NIDHI – COE : Centres of Excellence – Globally competitive facilities to help startups go global.
- While NSTEDB is the funding agency, the NIDHI programmes are implemented through Technology Business Incubators (TBIs) available around the country.
- Note: All the NIDHI-Startup funds and offerings are disbursed to eligible startups only through eligible NSTEDB associated incubators across India
Agni-4 ballistic missile successfully test-fired in Odisha

- 09 Sep 2024
In News:
India successfully test-fired the Agni-4 ballistic missile from the Integrated Test Range in Chandipur, Odisha. The test, conducted by the Strategic Forces Command (SFC) under India's Nuclear Command Authority (NCA), demonstrated the missile's operational and technical capabilities.
Key Details:
- Missile Specifications:
- Range: The Agni-4 missile has a maximum range of 4,000 kilometers.
- Payload: It can carry a payload of up to 1,000 kilograms.
- Length: The missile is approximately 20 meters long.
- Launch Platform: It is designed for deployment on a road-mobile launcher, enhancing its flexibility and mobility.
- Historical Context:
- Previous Test (2012): In its earlier test in 2012, Agni-4 successfully covered over 3,000 kilometers within 20 minutes. This was noted as the longest-range mission achieved by the Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO) at that time.
- Name Change: The Agni-4 was previously known as Agni-2 Prime.
- Development and Capabilities:
- Development: The Agni missiles, including the Agni-4, are developed by the DRDO, showcasing India's advancements in missile technology and strategic capabilities.
- Comparison with Agni-5: The Agni-4 is part of a series of Agni missiles that have progressively enhanced India's missile range and strike capabilities. The Agni-5 represents an even more advanced development in this series.
The successful test of Agni-4 underscores India's commitment to strengthening its strategic defense capabilities and maintaining its deterrence posture.
Swachh Bharat Mission averted 60,000-70,000 infant deaths annually: Study
- 09 Sep 2024
- Launched on October 2, 2014, the Swachh Bharat Mission (SBM) has been pivotal in advancing sanitation infrastructure in India.
- By 2020, the mission had facilitated the construction of over 11 crore household toilets under its Grameen component and over 63 lakh individual and 6.36 lakh community public toilets under its Urban component. This extensive sanitation drive aimed at eradicating open defecation and improving public health.
Impact on Infant Mortality
A recent study published in Nature has highlighted the significant health benefits resulting from SBM. According to the report, titled ‘Toilet Construction under the Swachh Bharat Mission and Infant Mortality in India,’ the initiative may have averted approximately 60,000 to 70,000 infant deaths annually between 2014 and 2020. The study, analyzed data from 35 states and 640 districts from 2011 to 2020, focusing on the infant mortality rate (IMR) and under-five mortality rate (U5MR).
Key Findings
- Decrease in Infant Mortality:
- The study established an inverse relationship between toilet access and infant mortality. It noted that districts with increased toilet coverage saw a marked decline in infant deaths.
- In 2003, the average toilet coverage in districts was below 40%, rising to over 60% by 2020. Correspondingly, infant mortality rates fell from an average of 48.9 per 1,000 live births in 2003 to 23.5 per 1,000 live births in 2020.
- Significant Decline:
- The research observed a substantial decline in infant mortality rates from 40 per 1,000 live births in 2012 to below 30 per 1,000 live births by 2019.
- The mortality rate for children under five also dropped from about 44 per 1,000 live births in 2012 to below 30 by 2019.
- Regional Variations:
- Despite the overall improvement, certain regions like parts of Uttar Pradesh, Madhya Pradesh, Odisha, and Andhra Pradesh continued to report higher infant mortality rates, ranging between 45-60 per 1,000 live births in 2020.
Conclusion
The SBM has demonstrably improved sanitation in India, with a notable reduction in infant mortality rates attributed to the increased availability of household toilets. While the mission has achieved significant progress, ongoing efforts and investments in broader public health infrastructure are essential to address persistent regional disparities and sustain health gains.
Jal Sanchay Jan Bhagidari Initiative

- 09 Sep 2024
In News:
Prime Minister Shri Narendra Modi recently launched the ‘Jal Sanchay Jan Bhagidari’ initiative via video conferencing from Surat, Gujarat.
Key Points:
- Campaign and Objectives:
- Objective: The initiative seeks to bolster water conservation through extensive public and governmental collaboration.
- Scope: About 24,800 rainwater harvesting structures will be constructed across Gujarat.
- Approach: Emphasizes a Whole-of-Society and Whole-of-Government approach to water management.
- Significance:
- Cultural Significance: PM Modi highlighted that water conservation is deeply embedded in Indian culture, with water revered as a divine entity and rivers considered Goddesses.
- Policy and Virtue: He stated that water conservation transcends policy and is both an effort and a virtue, reflecting social commitment and cultural consciousness.
- Future Challenges: The Prime Minister acknowledged the exacerbating impact of water scarcity due to climate change, urging a shift to the ‘Reduce, Reuse, Recharge, and Recycle’ mantra for sustainable water management.
- Impact of Drought and Water Scarcity:
- Recent Challenges: The drought affecting the Amazon region and other parts of India has highlighted the urgent need for effective water conservation strategies.
- Water Table Decline: Significant declines in river levels, such as the Rio Negro reaching its lowest minimum (12.7 meters) on record, and the death of endangered species due to low water levels underscore the crisis.
- Government Initiatives:
- Jal Jeevan Mission: Aims to provide piped water to every home, with significant progress noted from 3 crore households to over 15 crore.
- Jal Shakti Abhiyan: Focuses on renovation and construction of water sources with widespread public participation.
- Amrit Sarovar: Over 60,000 Amrit Sarovars have been constructed under this campaign, which began during the Azadi Ka Amrit Mahotsav.
- Innovative Solutions and Technological Integration:
- Drip Irrigation: Promotion of water-efficient farming techniques like drip irrigation to ensure sustainable agriculture.
- Support for Farmers: Encouragement for cultivating less water-intensive crops such as pulses and millets.
- Role of Industries:
- CSR Contributions: Industries have played a significant role in water conservation through initiatives like Net Zero Liquid Discharge Standards and the completion of 10,000 borewell recharge structures in Gujarat.
- Future Plans: The ‘Jal Sanchay-Jan Bhagidari Abhiyan’ aims to create an additional 24,000 recharge structures.
- Conclusion and Vision:
- Global Leadership: PM Modi expressed his belief that India can become a global leader in water conservation.
- Public Movement: Stressed the importance of continuing public participation in water conservation to make India a model for global sustainability.
Background: The ‘Jal Sanchay Jan Bhagidari’ initiative builds on the success of the earlier Jal Sanchay program by involving citizens, local bodies, and industries in water conservation efforts. The initiative aligns with the vision of water security and aims to mobilize collective action for long-term sustainability.
Key Data:
- Construction of 24,800 rainwater harvesting structures.
- Significant increase in tap water connections from 3 crore to over 15 crore households.
- Creation of more than 60,000 Amrit Sarovars across the country.
- Completion of 10,000 borewell recharge structures in Gujarat.
Climate change drives Amazon rainforest's record drought, study finds
- 09 Sep 2024
In News:
The drought that hit all nine Amazon rainforest countries - including Brazil, Colombia, Venezuela and Peru - is expected to worsen in 2024
Role of Climate Change:
- Likelihood Increase: Climate change made the drought 30 times more likely.
- Temperature and Rainfall: It drove extreme high temperatures and contributed to lower rainfall.
Future Projections:
- Expected Worsening: The drought is predicted to worsen in 2024, with the rainy season expected to recede in May.
Impact on Ecosystems:
- River Levels: Rivers have reached their lowest levels on record, with the Rio Negro river falling to its lowest minimum (12.7 meters) since records began in 1902.
- Dolphin Deaths: At least 178 endangered pink and gray Amazon river dolphins died due to low water levels and high temperatures.
- Fish Deaths: Thousands of fish died from low oxygen levels in Amazon tributaries.
Impact on Human Life:
- Disruptions: Waterways dried up rapidly, forcing people to undertake long journeys across dried river sections to access essential goods like food and medicine.
Contributing Factors:
- El Niño Influence: Periodic warming in the Eastern Pacific Ocean (El Niño) contributed to decreased rainfall but not to higher temperatures.
Potential Consequences:
- Forest Fires and Biome Health: The drought could exacerbate forest fires, combined with climate change and deforestation, potentially pushing the Amazon toward a point of no return where it ceases to be a lush rainforest.
- Previous Droughts: While the region has experienced at least three intense droughts in the past 20 years, this one’s impact on the entire Amazon basin is unprecedented.
Uncommon Cyclones in the Arabian Sea
- 09 Sep 2024
Cyclones are intense weather systems with low atmospheric pressure and rotating winds, forming over warm tropical waters. These storms cause severe weather, including heavy rainfall, strong winds, and storm surges. Cyclones are categorized based on wind speeds, from tropical depressions to severe cyclonic storms. Warm ocean surfaces and high humidity fuel these storms, with atmospheric conditions like wind shear and moisture influencing their strength and formation.
The North Indian Ocean plays a key role in global weather systems, particularly the summer monsoon. Warm waters from the Arabian Sea and Bay of Bengal are crucial for moisture generation during monsoon seasons. However, despite the warm ocean surfaces that typically promote cyclones, this region has fewer cyclones compared to other tropical oceans. A mix of factors—both promoting and suppressing cyclone formation—makes the North Indian Ocean a unique and less cyclone-prone area.
The Indian Ocean stands out due to its monsoonal circulation, marked by seasonal wind reversals north of the equator. It also has "oceanic tunnels" connecting it to the Pacific and Southern Oceans, which influence its weather. The Pacific tunnel introduces warm water into the upper layers, while the Southern Ocean brings cooler waters into deeper levels. These oceanographic features contribute to distinct weather patterns, including influencing the formation and behavior of cyclones.
As the pre-monsoon season begins and the Sun moves into the northern hemisphere, the Arabian Sea rapidly warms. The Bay of Bengal, typically warmer, heats further, driving atmospheric convection and rainfall. These warming patterns make the Bay of Bengal more prone to cyclones, while the Arabian Sea, with its cooler waters and stronger wind shear, experiences less cyclone activity. These conditions contribute to significant differences in cyclone formation between the two seas.
Impact of Climate Change on Cyclones in the Indian Ocean
Climate change is amplifying the Indian Ocean’s warming, bringing in more heat from the Pacific Ocean while the Southern Ocean pushes warmer waters into deeper layers. These changes, combined with shifts in winds and atmospheric humidity, are causing the Indian Ocean to warm at a rapid pace. This warming is affecting cyclone formation, increasing the frequency and intensity of storms. The Indian Ocean acts as a "clearinghouse" for ocean warming, impacting global weather patterns and intensifying cyclone activity.
Monsoon and Cyclone Seasons in the North Indian Ocean
- The monsoon heavily influences cyclone activity in the region. During the monsoon, strong winds cool the Arabian Sea, reducing the likelihood of cyclone formation. In contrast, the Bay of Bengal sees more low-pressure systems, although many do not become cyclones due to wind shear that weakens their energy.
- The North Indian Ocean experiences two distinct cyclone seasons—pre-monsoon and post-monsoon—unlike other regions that typically have just one. Cooler temperatures and stronger wind shear keep cyclone numbers low in the Arabian Sea, compared to the Bay of Bengal.
- Cyclone Asna, formed in August 2023, was a rare cyclone for this time of year. It developed from a land-based depression that moved over the Arabian Sea, marking the first August cyclone in the region since 1981. This rare occurrence highlights how rapidly warming oceans, influenced by climate change and El Niño, can drive unexpected cyclone formations.
India, UAE ink pact for civil nuclear cooperation

- 10 Sep 2024
In News:
- Recently, India and the United Arab Emirates (UAE) signed a significant Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) for civil nuclear cooperation.
- The agreement, established between the Nuclear Power Corporation of India Limited (NPCIL) and the Emirates Nuclear Energy Company (ENEC)-led Barakah Nuclear Power Plant Operations and Maintenance, was formalized during the visit of Sheikh Khalid bin Mohamed bin Zayed Al Nahyan, the Crown Prince of Abu Dhabi, to New Delhi.
Background:
- This MoU marks the first formal agreement of its kind between NPCIL and ENEC. The collaboration aligns with the broader commitment made during Prime Minister Narendra Modi’s visit to the UAE in August 2015, which focused on peaceful nuclear energy applications, including safety, health, agriculture, and science and technology.
Trilateral Cooperation:
- The agreement follows a series of discussions on nuclear cooperation between India and the UAE. On September 19, 2022, Foreign Ministers from France, India, and the UAE met in New York during the UN General Assembly and initiated a trilateral cooperation framework. This was further solidified by a phone call on February 4, 2023. The trilateral format aims to promote joint projects in energy, emphasizing solar and nuclear energy.
Additional Agreements:
During the Crown Prince’s visit, several other agreements were also signed:
- LNG Supply MoU: An agreement was reached between Abu Dhabi National Oil Company (ADNOC) and Indian Oil Corporation Limited for long-term LNG supply.
- Production Concession Agreement: Urja Bharat and ADNOC signed an agreement for Abu Dhabi Onshore Block 1.
- Food Parks Development: The Government of Gujarat and Abu Dhabi Developmental Holding Company PJSC (ADQ) signed an MoU for developing food parks in India. This initiative aligns with the I2U2 grouping (including Israel and the United States), which envisions food parks in Gujarat and Madhya Pradesh.
Conclusion:
The visit of the Crown Prince and the signing of these agreements reflect the strengthening ties between India and the UAE. This dynamic development coincides with the first India-Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC) Foreign Ministers’ meeting held in Riyadh on September 8-9. External Affairs Minister S. Jaishankar highlighted India's growing energy demands and its significant role in future global energy markets during his remarks at the meeting.
Govt dissolves Standing Committee on Statistics

- 10 Sep 2024
In News:
The recent dissolution of the 14-member Standing Committee on Statistics (SCoS) by the Union Ministry of Statistics and Programme Implementation has sparked considerable controversy and debate. The committee, which was chaired by Pronab Sen, a renowned economist and former chief statistician of India, was reportedly disbanded after its members raised concerns about the delay in conducting the decennial census.
Key Points:
- Dissolution of the Committee:
- The SCoS, formed in July 2023, was responsible for advising the Union government on survey methodology and statistical frameworks. According to the experts the decision to dissolve the SCoS was due to an overlap in functions with the newly formed Steering Committee for National Sample Surveys.
- Concerns and Criticism:
- Dr. Pronab Sen and other committee members expressed concerns over the delay in conducting the census, which was due in 2021 but has yet to be carried out. The last census, conducted in 2011, is now outdated, impacting the accuracy of various statistical surveys.
- Members of the SCoS reportedly questioned the delay in census operations during their meetings, leading to speculation that their concerns may have contributed to the committee's dissolution.
- Formation of the New Steering Committee:
- The new Steering Committee for National Sample Surveys, chaired by Rajeeva Laxman Karandikar, was established following a recommendation by the National Statistical Commission (NSC). The roles of this new committee are said to overlap with those of the SCoS, which the Ministry cited as a reason for disbanding the latter.
Standing Committee on Statistics (SCoS)
- The Standing Committee on Statistics (SCoS) was established by renaming and expanding the scope of the Standing Committee on Economic Statistics (SCES), which was originally formed in December 2019.
- The SCES, with 28 members, was tasked with reviewing economic indicators related to the industrial sector, services sector, and labor force statistics, including datasets like the Periodic Labour Force Survey, the Annual Survey of Industries, and the Economic Census.
Current Structure and Members: The newly formed SCoS comprises 14 members, including:
- Four Non-Official Members
- Nine Official Members
- One Member Secretary
The committee's total membership can be extended up to 16 based on requirements.
Functions:
1. Review and Address Issues:
o The SCoS reviews the existing frameworks and addresses issues related to all surveys as presented by the Ministry of Statistics and Programme Implementation (MoSPI). This includes evaluating survey results and methodologies.
2. Advisory Role:
o It advises on various aspects of survey methodology, including sampling frames, sampling designs, and survey instruments. The committee is also responsible for finalizing the tabulation plans and results of surveys.
3. Data Collection and Production:
o The SCoS oversees the design and implementation of all data collection and production efforts. It ensures that data collected by MoSPI adheres to high standards of statistical quality and accuracy.
Typhoon Yagi
- 10 Sep 2024
In News:
A devastating series of events unfolded in Vietnam, as a bridge collapsed and a bus was swept away by severe flooding, raising the death toll to at least 65. The fatalities are attributed to Typhoon Yagi and the subsequent heavy rains, which have wreaked havoc across the Southeast Asian country.
In Depth:
- The typhoon made landfall in Vietnam’s northern coastal provinces of Quang Ninh and Haiphong with wind speeds of up to 149 kilometers per hour (92 miles per hour) on Saturday afternoon.
- It raged for roughly 15 hours before gradually weakening into a tropical depression early Sunday morning.
- Vietnam’s meteorological department predicted heavy rain in northern and central provinces and warned of floods in low-lying areas, flash floods in streams and landslides on steep slopes.
What is a cyclone?
- The term 'Cyclone' is derived from the Greek word 'Cyclos' which means 'Coiling of the Snake'.
- Cyclones are created by atmospheric disturbances around a low-pressure area and are usually accompanied by violent storms and severe weather conditions. Basically, a tropical cyclone is a deep low-pressure area.
Sakthan Thampuran

- 10 Sep 2024
In News:
Minister of State for Tourism and Thrissur MP Suresh Gopi pledged to replace a statue of Sakthan Thampuran that was knocked over by a state transport bus in June with a new bronze statue if the Kerala government did not do so within 14 days.
Who was Sakthan Thampuran?
- Raja Rama Varma Kunjipillai or Rama Varma IX, better known today as Sakthan Thampuran, ruled over the Cochin kingdom from 1790 to 1805.
- He was born in 1751 to Ambika Thampuran and Chendose Aniyan Namboodiri of the Cochin royal family, but was raised by an aunt who called him Sakthan, meaning ‘powerful’.
- The word thampuran is believed to be an appropriation of the Sanskrit samrat, meaning emperor.
- The Cochin kingdom, which was part of the Late Chera Empire, covered the regions between Ponnani in Malappuram and Thottappally in Alappuzha in today’s Kerala.
Strategist and ruler
- Sakthan Thampuran became heir apparent in 1769 as an 18-year-old. He advised his king to maintain friendly relations with both the Dutch and the English, who were vying for a larger share of trade in the region.
- Sakthan is said to have orchestrated Mysore’s attempt to invade the Travancore kingdom, which had established relations with the English East India Company. This would result in the Powney treaty which freed the Cochin kingdom from its allegiance to Mysore, and helped formalise its relations with the British.
- Sakthan Thampuran put an end to the institution of the Yogiatirippads — the erstwhile spiritual heads of the Vadakkumnathan and Perumanam temples, who had conspired against the previous Cochin king in his wars against the Calicut Zamorin — and entrusted temple management to the government.
- He built a fearsome reputation for himself, and is said to have largely freed his kingdom of crime.
Thrissur and Pooram
- Sakthan Thampuran transferred the seat of the Cochin kingdom from Thrippunithura to modern-day Thrissur.
- The Thekkinkadu Maidanam and the surrounding Swaraj Round became the basis for the city’s elaborate road system and infrastructure.
- The king encouraged merchants of all religions and British officials to relocate to the city. He also overhauled and firmed up the kingdom’s finances, personally overseeing revenue management.
- Sakthan Thampuran started the Thrissur Pooram in 1797 as an alternative to the Arattupuzha Pooram, then the largest temple festival in the state.
- The Thrissur Pooram was conceived as an opportunity for the major temples in Thrissur to come to pay their respects to Lord Shiva, the presiding deity at the Vadakkumnathan Temple.
In a first, critically endangered elongated tortoise spotted in Aravallis

- 10 Sep 2024
In News:
- A critically endangered species, the elongated tortoise (Indotestudo elongata), was spotted in Haryana’s Damdama area during a research survey in the Aravallis.
Key Features:
- The tortoise is medium-sized with a yellowish brown or olive shell and distinct black blotches at the centre of each scute.
- The tortoise has on its nostril a pink ring, which appears in the breeding season.
- Mature individuals of both sexes develop a distinct pinkish colouration surrounding the nostrils and eyes during the season.
- Habitat:
- The tortoise, found in the Sal deciduous and hilly evergreen forests, is distributed across Southeast Asia from northern India, Nepal, Bhutan, and Bangladesh in the west, eastward through Myanmar, Thailand, and all of Indochina, north to Guangxi Province of China and south to Peninsular Malaysia.
- A disjunct tortoise population exists in the Chota Nagpur plateau in eastern India. It also inhabits lowlands and foothills of up to 1,000 m above sea level.
- There have not been enough surveys to ascertain its presence in Aravallis, but the tortoise is found in the foothills of the Himalayas.
- It inhabits wetter areas and discovering it here is an aberration than a norm, adding it cannot be ruled out that the tortoise was brought by trade.
Conservation Status:
- International Union for Conservation of Nature’s (IUCN) Status: Critically Endangered, under criteria A2cd.
Threats:
- Currently, I. elongata is heavily exploited for food and traditional medicine throughout its range.
- Local people often opportunistically capture tortoises while farming or extracting other forest resources. However, deliberate hunting also occurs and dogs continue to be widely used for finding tortoises.
India-Singapore Relations

- 04 Sep 2024
- High-Level Inter-Governmental Contacts:
- Frequent and high-level exchanges, including the Prime Minister's upcoming visit.
- Recent second India-Singapore Ministerial Roundtable with senior Indian ministers.
- Key Areas of Cooperation:
- Digitalisation, skills development, sustainability, healthcare, advanced manufacturing, and connectivity.
- Broader contacts include parliamentary and judicial exchanges.
- Economic Ties:
- Singapore is India’s largest trading partner among ASEAN countries and the sixth largest globally.
- Singapore is also the largest source of foreign direct investment (FDI) for India.
- People-to-People Exchanges:
- Large concentration of IIT and IIM alumni in Singapore.
- Historical ties, including the Indian National Army's presence and the contributions of early Indian diaspora in Singapore.
- Regional Policy and Strategic Importance:
- Singapore has supported India’s “Look East” and “Act East” policies.
- Facilitated India’s dialogue partnership with ASEAN.
- Regional implications due to Myanmar’s instability, with India and Singapore both having stakes.
- Defence and Maritime Cooperation:
- Important defence component and maritime collaboration.
- Focus on the Indo-Pacific region amidst growing Chinese influence and new regional architectures like the QUAD.
- Trade and Economic Outlook:
- The visit provides an opportunity to review and expand trade and economic partnerships.
- Potential for increased Chinese FDI into India, with Singaporean entities likely to play a role.
- Complementarities and Challenges:
- Singapore's role as a global trading and investment hub complements India’s economic landscape.
- Highlights India's regulatory and structural inefficiencies, pointing to areas needing improvement for enhanced bilateral cooperation.
World Bank hikes India's economic projection to 7% for FY 2024-25
- 04 Sep 2024
- The World Bank has forecast a growth of 7% for the Indian economy for the current fiscal year, upping its earlier estimate of 6.6%.
- In its report, India Development Update: India’s Trade Opportunities in a Changing Global Context, the World Bank said India’s growth continued to be strong despite a challenging global environment.
- The World Bank growth projection is in line with those of the International Monetary Fund (IMF) and Asian Development Bank (ADB).
- Both the institutions have raised their forecast to 7% for the financial year ending March 2025.
- The India Development Update [IDU] observes that India remained the fastest-growing major economy and grew at a rapid clip of 8.2% in FY 23/24.
- Growth was boosted by public infrastructure investment and an upswing in household investments in real estate.
- On the supply side, it was supported by a buoyant manufacturing sector, which grew by 9.9%, and resilient services activity, which compensated for underperformance in agriculture.
- Reflecting these trends, urban unemployment has improved gradually since the pandemic, especially for female workers. While female urban unemployment fell to 8.5 % in early FY24/25, the urban youth unemployment remained elevated at 17%.
- India’s robust growth prospects, along with declining inflation rate will help to reduce extreme poverty
- India can boost its growth further by harnessing its global trade potential. In addition to IT, business services and pharma where it excels, India can diversify its export basket with increased exports in textiles, apparel, and footwear sectors, as well as electronics and green technology products.
- A recovery in agriculture will partially offset a marginal moderation in industry and all services will remain robust. The rural private consumption will recover, thanks to the expected recovery in agriculture.
- The report also highlights the critical role of trade for boosting growth. The global trade landscape has witnessed increased protectionism in recent years. The post pandemic reconfiguration of global value chains, triggered by the pandemic, has created opportunities for India.
- The IDU recommends a three-pronged approach towards achieving the $1 trillion merchandise export target by reducing trade costs further, lowering trade barriers, and deepening trade integration.
23rd Law Commission of India

- 06 Sep 2024
Constitution and Tenure:
- Notification and Term:
- The 23rd Law Commission of India was notified by the Union government on September 2, with effect from September 1.
- The commission will have a three-year term, concluding on August 31, 2027.
- The tenure of the previous Law Commission, chaired by former Karnataka High Court Chief Justice Ritu Raj Awasthi, ended on August 31.
Role and Importance of the Law Commission:
- Purpose:
- The Law Commission is a non-statutory body formed by the Union Ministry of Law and Justice through a gazette notification.
- Its role includes reviewing the functioning of laws, recommending the repeal of obsolete legislation, and providing recommendations on issues referred by the government.
- Composition:
- Typically chaired by a retired Supreme Court or High Court judge.
- Includes legal scholars and can also have serving judges.
- Impact:
- Over the years, 22 Law Commissions have submitted 289 reports.
- Their recommendations have influenced significant legislation, such as the Code of Criminal Procedure, 1973 (CrPC), and the Right of Children to Free and Compulsory Education Act, 2009 (RTE Act).
Constitution of the 23rd Law Commission:
- Structure:
- The commission will consist of:
- A full-time chairperson.
- Four full-time members, including a member-secretary.
- Up to five part-time members.
- Ex officio members including the secretaries of the Legal Affairs and Legislative departments.
- The commission will consist of:
- Appointment and Remuneration:
- Chairperson and full-time members can be serving Supreme Court or High Court judges or other experts chosen by the government.
- The chairperson will receive a monthly salary of ?2.50 lakh, while members will receive ?2.25 lakh.
- The member-secretary must be an officer of the Indian Legal Service of the rank of Secretary.
- Serving judges appointed to the commission will serve until retirement or the end of the commission’s term, without additional remuneration.
Terms of Reference:
- Primary Tasks:
- Identify and recommend the repeal of obsolete or irrelevant laws.
- Create a Standard Operating Procedure (SOP) for periodic review and simplification of existing laws.
- Identify laws that are misaligned with current economic needs and suggest amendments.
- Directive Principles and Reforms:
- Examine laws in light of Directive Principles of State Policy and suggest improvements and new legislation to achieve constitutional objectives.
- Address laws affecting the poor, conduct post-enactment audits of socio-economic legislation, and review judicial administration for responsiveness.
Previous Commission's Contributions:
- Reports and Recommendations:
- The 22nd Law Commission produced 11 reports, including:
- A report in April 2023 recommending retention of Section 124A of the Indian Penal Code (sedition law), with suggested amendments for clarity.
- A report recommending a new law to protect trade secrets.
- A report on simultaneous elections, though it was not submitted to the government before the commission’s chairperson assumed office as a Lokpal member.
- The 22nd Law Commission produced 11 reports, including:
Upcoming Focus:
- The 23rd Law Commission is expected to continue examining key issues, including the implementation of a uniform civil code, which was also considered by the 22nd Commission but whose recommendations remain unpublished.
Can Kerala access funds from the Loss and Damage Fund?

- 06 Sep 2024
In light of the recent landslides in Kerala’s Wayanad district, the question arises whether subnational entities like Kerala can access the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC)’s Loss and Damage Fund (LDF). While the need for compensation is clear, the process of accessing climate funds is complex.
What is the Loss and Damage Fund (LDF)?
- Established at COP27 in Egypt, the LDF aims to support regions experiencing economic and non-economic losses from climate change.
- Includes extreme weather events and slow-onset processes like rising sea levels.
- Managed by a Governing Board, with the World Bank as the interim trustee.
- The Board is developing mechanisms for resource access, such as direct access, small grants, and rapid disbursement options.
- Concerns exist about the speed and accessibility of climate funds, which may affect their effectiveness in immediate disaster recovery.
What has been India’s Role?
- India faced over $56 billion in weather-related damages from 2019 to 2023. Despite this, its National Climate Action Policy prioritizes mitigation over adaptation, leading to limited engagement in Loss and Damage dialogues at COP meetings.
- High vulnerability in certain regions could benefit from active participation in these dialogues.
- India needs a clear legal and policy framework for climate finance, focusing on locally led adaptation, which is vital for vulnerable communities.
- The Union Budget 2024’s introduction of a climate finance taxonomy raises hopes for increased international climate finance.
- Without clear guidelines for accessing loss and damage funds, frontline communities remain at risk.
- India should advocate for decentralized fund disbursement methods from the LDF, contrasting with the centralized systems used for other climate funds.
What have been State Interventions?
- State governments, such as Kerala, often bear the financial burden of disaster recovery.
- Example: The Rebuild Kerala Development Programme post-August 2018 floods, funded by World Bank and KfW Development Bank loans.
- Focused on infrastructure reconstruction, including roads and bridges.
- Lack of a standardized method for comprehensive disaster damage assessments, especially for slow-onset events, may mean significant loss and damage needs go unassessed.
- This could hinder India’s ability to access the LDF.
- The Wayanad situation highlights broader challenges in accessing and managing climate finance for loss and damage.
- A clearer domestic policy framework focusing on locally led adaptation and defined guidelines for accessing loss and damage funds is needed for better climate change protection.
Vishvasya-Blockchain Technology Stack
- 08 Sep 2024
The Government of India has recently introduced several significant initiatives to advance blockchain technology and its applications.
1. Vishvasya-Blockchain Technology Stack
- Purpose: The Vishvasya-Blockchain Technology Stack is designed to offer Blockchain-as-a-Service (BaaS) with a geographically distributed infrastructure. This stack supports various permissioned blockchain-based applications, enhancing the security and efficiency of digital services.
2. NBFLite
- Description: NBFLite is a lightweight blockchain platform intended as a sandbox for startups and academic institutions. It allows for rapid prototyping, research, and capacity building, fostering innovation in blockchain applications.
3. Praamaanik
- Purpose: Praamaanik is a blockchain-enabled solution for verifying the origin of mobile apps. This ensures that users can trust the source of their applications, contributing to enhanced digital security.
4. National Blockchain Portal
- Function: The National Blockchain Portal serves as a central hub for accessing blockchain technologies and services developed under the National Blockchain Framework (NBF).
5. National Blockchain Framework (NBF)
- Overview: The NBF is designed to promote secure, transparent, and trusted digital service delivery. It includes:
- Distributed Infrastructure: Hosted across NIC Data Centers in Bhubaneswar, Pune, and Hyderabad.
- Core Framework Functionality: Provides the backbone for various blockchain applications.
- Smart Contracts & API Gateway: Facilitates interactions with blockchain-based systems.
- Security, Privacy & Interoperability: Ensures robust security and privacy while supporting integration with other systems.
- Applications Development: Supports the creation and deployment of blockchain applications.
- Goals: The NBF aims to address challenges such as the need for skilled manpower, vendor lock-in, and issues related to security, interoperability, and performance.
6. Strategic Objectives
- Digital Trust and Service Delivery: The framework is part of the government's effort to create trusted digital platforms and improve service delivery to citizens.
- Global Leadership: The initiative seeks to position India as a global leader in blockchain technology, driving economic growth, social development, and digital empowerment.
- Governance Transformation: Blockchain technology is envisioned to enhance transparency, efficiency, and accountability in public services.
7. Collaborative Efforts
- Development: The technologies have been developed through the collaborative efforts of organizations including C-DAC, NIC, IDRBT Hyderabad, IIT Hyderabad, IIIT Hyderabad, and SETS Chennai, with support from MeitY.
- Research and Patents: The NBF project has already resulted in several patents and research publications, reflecting its innovative and research-driven approach.
8. Future Directions
- Scaling Applications: There is an emphasis on scaling blockchain applications across various states and departments.
- Exploring New Innovations: Efforts will continue to onboard new applications and innovative components on the NBF stack.
Health Ministry approves new treatment regimen for multidrug-resistant TB
- 08 Sep 2024
The recent approval of the BPaLM regimen by India's Union Health Ministry marks a significant advancement in the fight against multidrug-resistant tuberculosis (MDR-TB). This new treatment combines four drugs—Bedaquiline, Pretomanid, Linezolid, and Moxifloxacin—and offers several benefits over traditional treatments.
Key Points:
- Enhanced Effectiveness: The BPaLM regimen has demonstrated a higher efficacy in treating MDR-TB compared to previous methods.
- Shorter Treatment Duration: Unlike traditional treatments, which can take up to 20 months and often come with severe side effects, the BPaLM regimen shortens the treatment period to just six months.
- Improved Safety: The new regimen is noted for its safety profile, potentially reducing the risk of adverse effects compared to older treatments.
- Cost Savings: By shortening the treatment duration and improving outcomes, the BPaLM regimen is expected to lower overall treatment costs.
- Integration into National TB Elimination Programme: This regimen will be incorporated into India’s National TB Elimination Programme, aligning with the country’s ambitious goal to eliminate TB by 2025, which is five years ahead of the global target.
- Infrastructure and Testing Facilities: India boasts a comprehensive TB laboratory network, including 7,767 rapid molecular testing facilities and 87 culture and drug susceptibility testing laboratories, which will support the implementation of the new regimen.
This development represents a significant step forward in TB care and aligns with broader global efforts to combat drug-resistant TB more effectively.
Agnibaan - SOrTeD: World’s First 3D-printed Rocket Engine

- 31 May 2024
Why is it in the News?
Indian space startup Agnikul Cosmos on Thursday successfully launched its first sub-orbital test vehicle powered by the world’s first single-piece 3D-printed rocket engine, after calling off its launch at least four times previously.
What is Agnibaan - SOrTeD?
- Agnibaan SOrTeD is a sub-orbital technological demonstrator of the Agnibaan launch vehicle, manufactured by Indian space startup Agnikul Cosmos.
- A sub-orbital launch reaches outer space but does not complete an orbit around Earth, intersecting the Earth's atmosphere or surface without becoming an artificial satellite or reaching escape velocity.
- This marks Agnikul’s fifth launch attempt since March 22. With this launch, AgniKul became the second private company to achieve a rocket launch in India, following Skyroot's successful flight in 2022.
Features:
- It is a customizable, two-stage launch vehicle capable of carrying up to 300 kg into an orbit approximately 700 km above Earth.
- Semi-Cryogenic Engine: Utilizes a combination of liquid and gaseous propellants, operating at temperatures higher than cryogenic engines but lower than traditional liquid rocket engines.
- Uses refined kerosene, which is lighter and can be stored at normal temperatures, allowing more propellant to be carried. When combined with liquid oxygen, kerosene provides higher thrust.
- The test flight aims to demonstrate in-house, homegrown technologies, gather crucial flight data, and ensure the optimal functioning of systems for AgniKul's orbital launch vehicle, Agnibaan.
- The rocket is designed for accessing both low and high-inclination orbits and is completely mobile, enabling launches from more than 10 ports.
Agnibaan Acheivments:
- World’s First 3D-Printed Engine: Agnibaan is the first rocket to use a 3D-printed engine.
- First Semi-Cryogenic Engine-Powered Rocket Launch: Pioneering the use of semi-cryogenic engines in rocket launches.
- India’s First Private Launchpad Rocket Launch: The first Indian rocket launch conducted from a private launchpad.
- Unique Engine Configuration: Powered by the only engine in India that uses both gas and liquid fuel (liquid oxygen/kerosene).
Significance:
- Typically, rocket engine parts are manufactured separately and assembled later.
- The 3D-printed manufacturing process is expected to lower launch costs and reduce vehicle assembly time, offering affordable launch services for small satellites.
About 3D Printing:
- 3D printing, also known as additive manufacturing, creates three-dimensional objects from digital models by adding material layer by layer.
- This process, which uses materials like plastic, composites, or bio-materials, allows for efficient and customized production, contrasting with traditional subtractive manufacturing methods.
Notable Examples of 3D Printing:
- Industry Applications: 3D printing is widely used in industries such as healthcare, automotive, and aerospace.
- Aerospace: In May, Relativity Space launched a test rocket made entirely from 3D-printed parts, standing 100 feet tall and 7.5 feet wide.
- However, the rocket experienced a failure shortly after takeoff.
- Healthcare: During the peak of the COVID-19 pandemic in 2020, 3D printers were utilized to produce essential medical equipment, including swabs, face shields, masks, and parts for ventilators.
Urban Heat Island Effect
- 31 May 2024
Why is it in the News?
Large parts of the country are witnessing a searing and longer-than-usual heatwave, with record-breaking day temperatures.
What is an Urban Heat Island?
- An urban heat island occurs when a city experiences much warmer temperatures than nearby rural areas.
- The difference in temperature between urban and less-developed rural areas has to do with how well the surfaces in each environment absorb and hold heat.
What is the Urban Heat Island Effect?
- Structures made of concrete — buildings, pavements, roads, and other infrastructure — absorb and re-emit the sun’s heat more than natural features like trees and water bodies.
- Cities, where these structures are concentrated, and greenery is limited, thus become “islands” of higher temperature compared to surrounding, greener, areas.
- This is called the urban heat island effect. And since heat is trapped in built-up structures, greater urbanisation has a direct correlation with the rise in night temperatures.
How do humidity and warm nights impact the human body?
- The rise in temperatures, humidity, and warmer nights together make the summer more deadly for human beings.
- Humans regulate their body temperatures by sweating, the evaporation of sweat from the skin cools our bodies.
- However high humidity prevents this from happening, which can take a toll on the body.
- Reacting to heat, “the heart starts pumping more blood to our skin.
- This activates the sweat glands which help regulate body temperature.
- But as a result of sweating, other organs get less blood flow.
- In humid conditions, the body continues to sweat with little avail.
- This not only leads to dehydration and salt imbalances but also takes a toll on organs due to reduced blood flow.
- And it leads to the body overheating as its temperature-regulation mechanism is not working.
- If the temperatures are too high, the cellular processes in the brain also get affected.
- This can initially lead to fainting, and in more serious cases, effects such as heat stroke and organ malfunction.
At the very basic level, more humidity and warmer nights do not allow our bodies to rest and recuperate”.
Recombinant Proteins
- 31 May 2024
Why is it in the News?
Researchers at the Department of Biochemistry, Indian Institute of Science, have developed a novel method for the production of recombinant proteins.
What are Recombinant Proteins?
- A recombinant protein is a protein that has been produced by the means of recombinant DNA – DNA that has been modified in order to encode the blueprint of a protein of interest.
- Recombinant proteins are produced in host cells, in which recombinant DNA has previously been inserted so that the cells’ ribosomes are instructed to express the recombinant protein instead of what the cells’ original DNA would have encoded.
What are recombinant proteins in biotechnology?
- In biotechnology, recombinant proteins are proteins that have been produced by host cells, according to artificially modified DNA (recombinant DNA) instead of the cells’ own DNA.
- The recombinant DNA is inserted into host cells by means of a suitable vector, after which protein expression commences according to this blueprint.
- Once harvested, recombinant proteins are used for various purposes within life sciences and medicine, e.g. in research, but also the treatment of several diseases.
What are the techniques in recombinant protein production?
- genetic engineering, DNA cloning and vector design
- transfection of host cells (bacterial, yeast, mammalian)
- protein expression and purification
Recombinant protein examples:
-
- human insulin
- human growth factors
- factor VIII – treatment for haemophilia
- therapeutic monoclonal antibodies
- various research reagents
What are recombinant proteins used for?
- Recombinant proteins are widely used in many fields of life sciences, e.g. for research purposes, but also in the treatment of various diseases.
- This is because they are frequently chosen in the production of biopharmaceuticals, for instance when designing monoclonal antibody therapies.
- In the treatment of diabetes, recombinant proteins are also an essential keystone, being used in the production of human insulin.
Benefits of recombinant proteins:
- High Purity: Recombinant proteins can be produced with a high degree of purity, reducing the risk of contamination or impurities in experimental applications.
- Customization: Researchers can design and produce recombinant proteins with specific modifications, tags, or mutations to suit their experimental needs.
- Scalability: The possibility to scale up recombinant protein production makes it suitable for industrial and therapeutic applications.
- Consistency: The production of recombinant proteins can be tightly controlled, ensuring consistent quality and reproducibility in experiments or drug manufacturing.
Cost-Effectiveness: Compared to traditional methods of obtaining proteins from natural sources, recombinant protein production can be more cost-effective, especially for rare or complex proteins.
Global Food Policy Report 2024

- 31 May 2024
Why is it in the News?
A new global report has raised concerns about dietary habits in India, highlighting a significant increase in the consumption of unhealthy foods compared to nutritious options.
Key Highlights of the Global Food Policy Report 2024:
- Diet Quality in India: At least 38% of the Indian population consumed unhealthy foods, while only 28% ate all five recommended food groups: one starchy staple, one vegetable, one fruit, one pulse/nut/seed, and one animal-source food.
- Trends in Food Consumption: The intake of calorie-dense, nutrient-poor foods is not only high but increasing, whereas the consumption of vegetables and other micronutrient-rich foods remains low.
- Processed Foods in South Asia: In India and other South Asian countries, the consumption of processed foods is on the rise. After cereals and milk, snacks and prepared foods make up a significant portion of Indian food budgets.
- Malnutrition Rates in India: The proportion of the population suffering from malnutrition in India increased from 15.4% in 2011 to 16.6% in 2021.
- Overweight Prevalence: The prevalence of overweight adults in India rose from 12.9% in 2006 to 16.4% in 2016.
- Packaged Foods: The share of household food budgets spent on packaged, highly processed, calorie-dense foods nearly doubled from 6.5% to 12% during this period.
- Cost of Nutrient-Rich Foods: In the South Asian region, micronutrient-rich foods are expensive, while cereals, fats, oils, sugar, and sugary and salty snacks are relatively inexpensive.
About the International Food Policy Research Institute (IFPRI):
- The International Food Policy Research Institute (IFPRI) provides research-based policy solutions to sustainably reduce poverty and end hunger and malnutrition in developing countries.
- Established in 1975, it is a research centre of CGIAR, the world’s largest agricultural innovation network.
Vision and Mission:
- IFPRI’s vision is a world free of hunger and malnutrition.
- Its mission is to provide research-based policy solutions that sustainably reduce poverty and end hunger and malnutrition.
IFPRI’s research focuses on five strategic research areas:
-
- Fostering Climate-Resilient and Sustainable Food Supply
- Promoting Healthy Diets and Nutrition for All
- Building Inclusive and Efficient Markets, Trade Systems, and Food Industry
- Transforming Agricultural and Rural Economies
- Strengthening Institutions and Governance
Headquarters: Washington, D.C
Cryonics

- 31 May 2024
Why is it in the News?
An Australian cryonics company, Southern Cryonics, sparked a widespread debate after successfully freezing their first client, known as ‘Patient One’.
What is Cryonics?
- Cryonics is the practice of preserving human bodies in extremely cold or cryogenic temperatures (−196°C) with the hope of reviving them sometime in the future.
- Cryonics procedures can begin only after the "patients" are clinically and legally dead.
- When a dead body is cryonically preserved, it is packed with ice and injected with anticoagulants, a treatment to stop blood from clotting.
- The body is then transported to one of three cryonic centres in the world.
- There, in a process known as vitrification, the body is drained of its blood, which is then replaced with chemicals and anti-freeze.
- The body is placed in a sleeping bag and housed in a tank of liquid nitrogen at -196 degrees Celsius.
- The premise of cryonics is based on a possibility rather than a probability of success.
- There is no scientific evidence to suggest that it is possible to revive a person back to a living state.
- Cryobiologists hope that with future technology, including nanotechnology, they will be able to repair cells and tissues that are damaged during the freezing process.
Is cryonics ethical?
- There are some arguments in favour of cryonics, the simplest of which is one of free will and choice.
- As long as people are informed of the very small chance of success of future re-animation, and they are not being coerced, then their choice is an expression of their autonomy about how they wish to direct the disposal of their bodies and resources after death.
- In this light, choosing cryonics can be seen as no different to choosing cremation or burial, albeit a much more expensive option.
- However, this case raises several other ethical and problematic concerns.
- There is the issue of potentially exploiting vulnerable people.
- Some might argue vulnerable people are trading hype for hope.
- The cryonic process might work, but imperfectly. During the process of re-animation, there may be some brain damage.
- That would mean rather than waking up, one might be unconscious or trapped in some disordered, uncontrollable painful stream of consciousness.
It might be heaven but it might also be hell. The key issue is that people must be made aware of the risks as well as the benefits, and are not exploited.
AMRUT scheme

- 30 May 2024
Why is it in the News?
Around 36% of India’s population is living in cities and by 2047 it will be more than 50%. The World Bank estimates that around $840 billion is required to fund the bare minimum urban infrastructure over the next 15 years.
About Atal Mission for Rejuvenation and Urban Transformation (AMRUT):
- AMRUT was launched to enhance the quality of life by providing basic civic amenities, especially benefiting the poor and disadvantaged.
- The mission focuses on infrastructure development to deliver better services to citizens.
- AMRUT covers 500 cities, including all cities and towns with a population of over one lakh that have notified Municipalities.
About AMRUT 2.0:
- AMRUT 2.0 will promote circular economy of water through development of City Water Balance Plan (CWBP) for each city focusing on recycle/reuse of treated sewage, rejuvenation of water bodies and water conservation.
- It will help cities to identify scope for projects focusing on universal coverage of functional water tap connections, water source conservation, rejuvenation of water bodies and wells, recycle/reuse of treated used water, and rainwater harvesting.
- Based on the projects identified in CWBP, Mission envisages to make cities ‘water secure’ through circular economy of water.
The target in the second phase of AMRUT is to:
-
- Improve sewage and septic management
- Make cities water-safe
- Ensure no sewage drains into rivers
- AMRUT 2.0 focuses on enhancing sewerage and septic management to make all Indian cities water secure.
Aim:
- Achieve 100% coverage of water supply to all households in around 4,700 urban local bodies by providing about 2.68 crore tap connections.
- Achieve 100% coverage of sewerage and septage in 500 AMRUT cities by providing around 2.64 crore sewer or septage connections.
Principles and Mechanism:
- Adopt principles of the circular economy to promote conservation and rejuvenation of surface and groundwater bodies.
- Promote data-led governance in water management and leverage the latest global technologies and skills through a Technology Sub-Mission.
- Conduct 'Pey Jal Survekshan' to encourage competition among cities for better water management.
Coverage:
- Extend coverage from 500 cities in the first phase to 4,700 cities and towns.
- Benefit more than 10.5 crore people in urban areas.
Analysis of the AMRUT Scheme:
Performance of the Scheme:
- As of May 2024, the AMRUT dashboard reports that ?83,357 crore has been disbursed. This funding has facilitated:
- 58,66,237 tap connections
- 37,49,467 sewerage connections
- Development of 2,411 parks
- Replacement of 62,78,571 LED lights
Criticism of the Sheme:
Despite these achievements, significant issues persist:
- Approximately 2,00,000 people die annually due to inadequate water, sanitation, and hygiene.
- In 2016, India's disease burden from unsafe water and sanitation was 40 times higher per person than China's, with minimal improvement since then.
- Large volumes of untreated wastewater increase disease vulnerability.
- Around 21 major cities are expected to run out of groundwater. A NITI Aayog report predicts that 40% of India's population will lack access to drinking water by 2030.
- Nearly 31% of urban households lack piped water, and 67.3% are not connected to a piped sewerage system.
- The average urban water supply is 69.25 litres per person per day, far below the required 135 litres.
- Air quality in AMRUT cities and other urban areas continues to worsen.
- While the National Clean Air Programme was launched in 2019 to address air quality, AMRUT 2.0 focuses primarily on water and sewerage issues.
Challenges:
The AMRUT scheme has faced several fundamental challenges:
- Project-Oriented Approach: The scheme adopted a project-oriented rather than a holistic approach.
- Lack of City Participation: It lacked significant involvement from elected city governments, being driven instead by bureaucrats, parastatals, and private companies.
- Governance Issues: Governance was dominated by non-elected officials, violating the 74th constitutional amendment.
- The apex committee was led by the MOHUA secretary, and state committees were headed by chief secretaries, excluding people's representatives.
- Private Nexus: The scheme favored a private nexus of consultants and professionals, sidelining local elected officials.
- Water Management: Effective water management in cities requires consideration of climate, rainfall patterns, and existing infrastructure, which the scheme did not adequately address.
- Inefficient Sewage Treatment: Sewage treatment plants were inefficiently designed, with faecal matter traveling longer distances than the average worker's commute.
- Urban Planning: Driven by private players and real estate developers, urban planning often led to the disappearance of water bodies, disrupted stormwater flows, and a lack of proper stormwater drainage systems.
Way Forward:
To improve the AMRUT scheme:
- Nature-Based Solutions: Implement nature-based solutions.
- Comprehensive Methodology: Adopt a comprehensive methodology that integrates all aspects of urban development.
- People-Centric Approach: Focus on a people-centric approach, involving local communities in decision-making.
Empower Local Bodies: Empower local bodies to take a leading role in governance and implementation.
New Light-based Tool to Detect Viral Infections

- 30 May 2024
Why is it in the News?
A viral infection can stress cells and change their shapes and sizes. Researchers have built a tool to detect these changes.
About the new Tool:
- A team of researchers has developed an innovative method to detect viral infections in cells using only light and principles of high-school physics.
- The key insight is that viral infections can stress cells, causing changes in their shapes, sizes, and other features.
- As the infection progresses and the body becomes diseased, these changes become more pronounced.
- The researchers have found a way to translate these cellular changes into recognizable patterns that can indicate whether a cell is uninfected, virus-infected, or dead.
- For example, virus-infected cells tend to be elongated and have clearer boundaries compared to uninfected cells.
- By analyzing the patterns of light interacting with cells, this method can non-invasively differentiate between uninfected, virus-infected, and dead cells.
- This approach has the potential to revolutionize viral disease diagnosis and monitoring, providing a simple, cost-effective, and powerful tool for detecting viral infections at the cellular level.
Significance:
- This light-based approach to detecting viral infections offers several significant advantages over the current standard methods:
- Accuracy: The new light-based technique can detect viral infections with equal or even greater accuracy compared to existing standard methods that rely on chemical reagents.
- Cost-effectiveness: The equipment required for this new method costs only around one-tenth of the $3,000 (approximately Rs 2.5 lakh) needed for the standard chemical-based approach, making it a far more affordable option, especially for resource-constrained settings.
- Rapid results: The light-based method can identify virus-infected cells in just about two hours, significantly faster than the 40 hours required by the current standard method.
- This time efficiency can be crucial in situations where rapid detection is essential, such as during a virulent disease outbreak.
- Early detection: By enabling the early detection of viral infections at the cellular level, this new technique could prove invaluable in containing the spread of highly contagious viral diseases, such as a severe influenza outbreak.
What are Viruses?
- Viruses are microscopic organisms capable of infecting various hosts such as humans, plants, animals, bacteria, and fungi.
- Structurally, they consist of genetic material (DNA or RNA) enclosed in a protective shell called a capsid, with some viruses also possessing an envelope.
- Unable to reproduce independently, viruses rely on host cells to replicate by utilizing the cell's machinery.
- Common types include influenza viruses, human herpesviruses, coronaviruses, human papillomaviruses, enteroviruses, flaviviruses, orthopoxviruses, and hepatitis viruses.
- Viruses are responsible for causing illnesses such as flu, the common cold, and COVID-19.
Dag Hammarskjold Medal

- 30 May 2024
Why is it in the News?
An Indian peacekeeper who lost his life serving under the UN flag is among over 60 military, police and civilian peacekeepers to be honoured posthumously with a prestigious medal for their service and supreme sacrifice in the line of duty.
What is Dag Hammarskjold Medal?
- The Dag Hammarskjold medal is a prestigious honour commemorating the ultimate sacrifice made by United Nations peacekeepers.
- Established in 1997, it pays tribute to those who have lost their lives while serving in UN peacekeeping missions under the organization's operational control and authority.
- This posthumous award is presented annually on Peacekeeper's Day at a solemn ceremony held at the United Nations headquarters in New York.
- Each member state that has had military or police personnel perish during peacekeeping duties receives the medal in recognition of their fallen compatriots.
- The medal bears the name of Dag Hammarskjold, the second Secretary-General of the United Nations, whose own life was tragically cut short in 1961 while working to resolve the Congo crisis.
- In naming this honour after him, the UN commemorates both his exceptional leadership and the courageous individuals who have followed in his footsteps by making the ultimate sacrifice for the cause of global peace and security.
India’s Role in Peacekeeping:
- India is currently the second largest contributor of uniformed personnel to UN Peacekeeping after Nepal.
- India is followed by Uganda with 5,764 personnel, and Bangladesh with 5,393.
- These personnel are deployed across 12 UN peacekeeping missions across the world.
- Traditionally, India has always been among the biggest contributors of UN peacekeepers.
- Since 1950, approximately 2, 86,000 Indian soldiers have served in the UN across the globe.
- UN peacekeeping missions are mandated under Article 99 by which the Secretary-General is granted the authority to independently address potential global conflicts or threats.
- Also seen as a very robust diplomatic tool, it is also a way in which the Secretary-General flags the issue to the UN Security Council.
- The functions of UN peacekeeping operations range from maintaining peace and security to escorting humanitarian relief, upholding human rights, supporting the fight against gender-based violence to assist in the restoration of the rule of law and facing the complex crises of today from climate change to pandemic.
Microcephaly
- 30 May 2024
Why is it in the News?
A study recently revealed that a gene called SASS6 and its variants have been implicated in a developmental process that causes microcephaly.
What is Microcephaly?
- Microcephaly is a condition where a baby's brain and head do not develop properly during pregnancy or after birth.
- While rare, it can have profound impacts on a child's cognitive and physical abilities.
- Several factors can disrupt normal brain growth, including infections the mother contracts while pregnant, exposure to toxic substances, genetic disorders, lack of proper nutrition, and injuries before or around the time of birth.
- Infants with microcephaly are born with abnormally small heads compared to others of the same age and sex.
- This small head size indicates an undersized brain.
- As they grow older, many children with microcephaly experience significant developmental delays and disabilities.
- Common symptoms include intellectual disability, impaired motor skills and speech, vision and hearing problems, seizures, and unusual facial features.
- Some cases may show no obvious symptoms at birth, only for challenges to emerge over time.
- Treatment: Unfortunately, there is no cure for microcephaly itself.
- However, early intervention programs, therapies, and educational supports can help manage symptoms and maximize the child's developmental potential within their abilities.
- While microcephaly's causes are varied, maintaining good health before and during pregnancy gives a baby the best chance for proper brain growth.
Preventing prenatal infections, avoiding toxins, getting prenatal screening for disorders, and ensuring adequate nutrition all reduce microcephaly risk.
eMigrate Project

- 30 May 2024
Why is it in the News?
External Affairs Ministry, Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology and Common Services Centers eGovernance Services India Limited have signed a Memorandum of Understanding today to provide the eMigrate services through CSC in the country.
What is the eMigrate Project?
- eMigrate project is undertaken to assist mainly the blue-collar workers going to Emigration Check Required (ECR) countries.
- The project was conceptualized to address issues faced by migrant workers by making the emigration process online seamless and also to bring foreign employers registered recruitment agents and insurance companies on one common platform aimed at promoting safe and legal migration.
- Over the years, the number of Indians going abroad for employment has been increasing as well as the contribution of remittances sent by them has been significant.
- Under this MoU, the eMigrate Portal of MEA would be integrated with CSC’s portal, to provide the following eMigrate services to the citizens through CSCs:
- Facilitate registration of applicants on the eMigrate portal through CSCs.
- Facilitation of uploading and processing of the required documents for the applicants on the eMigrate portal through CSCs.
- Facilitate and support booking for medical and other services required by migrant workers or applicants registered on the eMigrate portal through CSC.
- Creating awareness about eMigrate services amongst citizens across India.
About Common Service Centre (CSC):
- Common Services Centers (CSCs) are an integral part of the Digital India mission.
- The CSCs are frontend service delivery points for the delivery of digital services to the citizens, especially in rural and remote areas across the country.
- This helps in contributing towards the fulfilment of the vision of Digital India and the government’s mandate for a digitally and financially inclusive society.
- Currently, more than 5.50 lakh CSCs are delivering more than 700 digital services to citizens in assisted mode with enhanced ease and convenience.
- Apart from delivering essential government and public utility services, CSCs also deliver a range of social welfare schemes, financial services, educational courses, skill development courses, healthcare, agriculture services, digital literacy, etc.
Landslides in India

- 29 May 2024
Why is it in the News?
At least 36 people were killed in heavy rains and landslides in four northeastern states on Tuesday under the impact of Cyclone Remal while normal life came to a grinding halt in all the eight states of the region with road and rail links affected.
What are Landslides?
- Landslides in India are one of the major hydro-geological hazards affecting large parts of the landmass of the country.
- It refers to the gravitational movements of a mass of rock, debris, or earth down a slope.
- Landslides are a type of "mass wasting," which denotes any down-slope movement of soil and rock under the direct influence of gravity.
- As per a report from the Geological Survey of India (GSI), 13% of the total land area in India is prone to landslides.
- This covers almost all the hilly regions in the country.
- About 0.18 million square km, or 42% of this vulnerable area is in the Northeastern region, where the terrain is mostly hilly.
What Causes a Landslide in India?
- Deforestation: Removal of trees reduces the binding properties of soil and rocks. This enables the water to seep into the sub-surface, making the topsoil vulnerable.
- For example, the Himalayan region has become more vulnerable to landslides due to the indiscriminate cutting of trees.
- Shifting Cultivation: Shifting cultivation is common in hilly regions and Northeast areas. Every year, residents burn the forests for cultivation purposes.
- However, this deteriorates the quality of topsoil, causing erosion during heavy rainfall. This makes such regions more vulnerable to landslides.
- Heavy Rainfall and Earthquakes: Heavy rainfall and earthquakes often cause landslides.
- For example, heavy rain caused landslides in Talai village of Maharashtra in 2021.
- Mining: Human activities like mining or quarrying remove the vegetation cover and soil gravel. This lowers the groundwater retention capacity. Also, it increases the risk of flooding.
- Therefore, landslides occur due to loose debris or excess floods during an earthquake and heavy rainfall, respectively.
- Urbanisation: Intensive urbanisation and urbanization activities such as establishing commercial housing projects and road construction reduce the vegetation cover which leads to an increasing frequency of landslides.
What Are the Different Types of Landslides?
Landslides in India are divided into four categories:
- Topples: This occurs due to fractures in rocks. It causes tilting for gravitational pull without collapsing.
- Falls: This involves the collapse of rocks or debris from a cliff or slope. It results in the collection of debris at the base of a hill.
- Spread: It occurs in gentle slopes where soft debris or other materials are widely available.
- Slides: It occurs when debris, rocks or soil slide through a slope.
What Are the Impacts of Landslides in India?
- Mud, debris and rocks slide from the slope during landslides.
- This restricts human movement and creates a traffic barrier on highways and railway lines.
- Loss of human lives is one of the severe effects.
- Landslide is the primary factor behind the Joshimath sinking crisis which led to mass evacuation in January 2023.
- It damages houses, roads and buildings.
- This further creates a financial burden for rebuilding infrastructure to rehabilitate the masses.
- The debris sliding down from slopes blocks the river channel fully or partially.
- This makes it difficult for locals to get the water supply.
- Landslides also increase the risk of floods. This is because the debris increases the river sediment.
- As a result, irregular course rivers become frequent, resulting in floods.
What Are the Measures Required to Prevent Landslides?
- An increase in forest cover is a must in community lands to reduce the hazard of landslides.
- People must store the excess water in catchment areas.
- It will reduce the effect of flash floods and also recharge groundwater levels.
- People must restrict the grazing of their animals.
- Reduce the urbanisation activities such as building dams or other commercial projects.
Implementation of public awareness regarding preventive measures during landslides and other hazard management is necessary.
Kaza TFCA (Kavango Zambezi Transfrontier Conservation Area) Summit

- 29 May 2024
Why is it in the News?
Members states of the world’s largest transnational conservation initiative meet to review progress and strategise the way forward.
About the Kaza TFCA (Kavango Zambezi Transfrontier Conservation Area) Summit:
- The Kaza TFCA (Kavango Zambezi Transfrontier Conservation Area) Summit is a high-level meeting of the heads of state and government representatives from the countries that make up the Kaza TFCA.
- The Kaza TFCA is a conservation area that spans parts of Angola, Botswana, Namibia, Zambia and Zimbabwe.
Some key points about the Kaza TFCA Summit:
- It brings together the political leadership from the five Kaza member countries to discuss issues related to the conservation and sustainable development of the Kaza transfrontier area.
- Topics discussed include wildlife conservation, tourism development, community involvement, and joint management of shared natural resources across international boundaries.
- The Summit aims to strengthen political support, coordination and collaboration among the Kaza partner countries for effective transboundary natural resource management.
- It provides a platform for the member states to review progress made, agree on priorities, and give strategic direction for the Kaza program going forward.
- The Summits are held periodically, with the last one being hosted by Botswana in 2018 in Kasane.
About the Kavango Zambezi Transfrontier Conservation Area:
- The Kavango Zambezi Transfrontier Conservation Area is a 520,000-square-kilometre wetland and spans five southern African countries: Angola, Botswana, Namibia, Zambia and Zimbabwe.
- It is home to a high concentration of wildlife species, including the largest elephant population.
- The KAZA TFCA was formally established on the 18th of August 2011 when the Heads of State of the five governments signed its Treaty in Luanda, Angola, during the SADC Summit for Heads of States.
The KAZA TFCA was established to:
- Conserve the shared natural resources and cultural heritage of this vast area of southern Africa
- Promote and facilitate the development of a complementary and linked network of protected areas that protect wildlife and provide and restore dispersal corridors and migratory routes
- Develop the KAZA TFCA into a world-class tourism destination offering a variety of breathtaking adventures and luxurious relaxation
- Promote the free and easy movement of tourists across borders
- Implement programmes that ensure the sustainable use of natural resources in ways that improve the livelihoods of communities and reduce poverty in the region
- Harmonise conservation legislation and natural resource management of the TFCA
Magellan Mission

- 29 May 2024
Why is it in the News?
After analysing the archived data from the space agency’s Magellan mission, scientists suggest that Venus, the almost Earth-sized planet was volcanically active between 1990 and 1992.
What is the Magellan Mission?
- NASA's Magellan mission to Venus was one of the most successful deep space missions launched from Kennedy Space Center in Florida in the year 1989.
- It was the first spacecraft to image the entire surface of Venus and made several discoveries about the planet.
- Magellan burned up about 10 hours after being commanded to plunge into the Venusian atmosphere.
- Magellan's primary mission was to use a synthetic aperture radar (SAR) to create detailed maps of the surface of Venus.
- The SAR allowed Magellan to penetrate a thick cloud layer which made it challenging to study Venus from Earth.
- By mapping the planet's surface, scientists aimed to investigate the planet's geology and landforms, including its vast plains, steep mountains, and impact craters.
- Magellan was also sent to measure the planet's gravity and magnetic fields.
- This information was considered important to NASA scientists as it would provide more information about the planet's interior structure and composition.
- Because Venus is a planet close to Earth that compares in size and composition, mapping and studying Venus was considered an important mission as it added to understanding the evolution and geology of rocky planets like Earth.
What is the Magellan Spacecraft?
- The Magellan spacecraft was a space probe launched into space on May 4, 1989, by NASA on the Space Shuttle Atlantis.
- NASA named Magellan after the Portuguese explorer Ferdinand Magellan, who was the first documented person to circumnavigate the Earth.
- The Magellan probe aimed to map the planet Venus and collect data about its atmosphere and physical characteristics.
- Venus is the second planet from the sun in the Milky Way solar system and is, along with Mercury, one of two planets that orbit between Earth and the sun.
- Known for being the first spacecraft to map the surface of Venus, Magellan remained in Venus' orbit for four years before being burned up in its atmosphere in October 1994.
What does the study reveal?
- The study identified a 2.2 square kilometre volcanic vent associated with Maat Mons, the second-highest volcano on Venus, located in the Atla Regio near the planet's equator.
- The vent showed signs of drained lava, and the radar images indicated that it had doubled in size over eight months, with the lava lake seeming to have reached the rim. These changes suggested that the vent had been actively erupting and spewing lava.
This discovery provides new insights into the geology and activity of Venus and highlights the importance of studying the planet's surface features to better understand its history and evolution.
Vivekananda Rock Memorial

- 29 May 2024
Why is it in the News?
Prime Minister Narendra Modi will be visiting the Vivekananda Rock Memorial in Kanyakumari, to meditate between May 30 to June 1, to mark the culmination of the 2024 Lok Sabha polls.
About the Vivekananda Rock Memorial:
- The Vivekananda Rock Memorial is a monument and a popular tourist destination located approximately 500 metres off the mainland of Vavathurai, Kanyakumari in the state of Tamil Nadu.
- Situated on a big rock, it is surrounded by three water bodies – the Arabian Sea, the Bay of Bengal, and the Indian Ocean.
- Vivekananda is said to have arrived here after wandering across the country.
- It is believed that the monk and the philosopher meditated on the rock and attained a vision for a developed India.
- The memorial, designed by renowned architect Eknath Ranade and completed in 1970, is located at the southernmost point of India in Kanyakumari.
- This is where the eastern and western coastlines of India converge.
- The memorial features two primary structures:
- The Vivekananda Mandapam, which houses an impressive bronze statue of the revered Swami Vivekananda, and
- The Shripada Mandapam contains footprints believed to belong to Goddess Kanyakumari.
- This site holds profound cultural and spiritual significance, with legendary tales of Goddess Kanyakumari praying to Lord Shiva on this rock.
- This memorial is right next to a huge monolithic statue of Tamil poet and philosopher Thiruvalluvar which was created by the Indian sculptor V Ganapati Sthapati.
About Swami Vivekananda:
- Swami Vivekananda (1863–1902), born Narendranath Datta, was a renowned Hindu monk and spiritual leader.
- A foremost disciple of Sri Ramakrishna Paramhamsa, he was recognized as a meditation expert by his guru.
- Vivekananda sought to integrate Indian spirituality with Western material progress, viewing them as complementary.
- He emphasized self-purification through helping others and advocated for selfless service and societal betterment.
- His teachings covered the four yogas, the harmony of religions, the divinity of the soul, and serving humanity as God.
- He gained international recognition by representing Hinduism at the 1893 World's Parliament of Religions in Chicago.
Upon returning to India, he founded the Ramakrishna Order at Belur in 1897.
Golden Rice

- 29 May 2024
Why is it in the News?
A court in the Philippines recently revoked biosafety permits for commercial propagation of genetically modified golden rice and Bt eggplant.
What is Golden Rice?
- In the late 1990s, German plant scientists Ingo Potrykus and Peter Beyer developed Golden Rice to combat vitamin A deficiency, a leading cause of infant blindness and increased mortality from infectious diseases like measles.
- Golden Rice is a type of rice that produces beta-carotene, giving it a golden colour, unlike white rice, which lacks these nutrients.
- Vitamin A deficiencies are prevalent in countries where rice is a staple food.
- The widespread use of Golden Rice is expected to improve health by reducing rates of preventable blindness and mortality, especially among children and pregnant women.
Golden Rice and Vitamin A Deficiency:
- Potrykus and Beyer added two genes to white rice in 2004, creating Golden Rice, which they donated to impoverished nations as a solution to vitamin A deficiency (VAD).
- Governments approve Golden Rice cultivation only after ensuring it is safe for the environment, humans, and animals.
- Golden Rice can replace the daily intake of white rice without adverse effects, providing a natural source of vitamin A and beta-carotene to combat VAD.
Efficacy of Golden Rice:
- Adequate vitamin A levels in mothers support vision, immune health, and fetal development through the placenta and breastfeeding.
- Vitamin A deficiency is the leading cause of childhood blindness and weakens the body’s ability to fight common diseases, leading to high mortality rates among young children and their mothers.
- Natural sources of vitamin A include animal products like milk, butter, cheese, eggs, and liver, while plants do not contain vitamin A directly, they contain beta-carotene, which the body can convert into vitamin A.
- White rice is rich in carbohydrates but lacks beta-carotene, an antioxidant and precursor to vitamin A.
- Golden Rice, containing beta-carotene, can help prevent millions of deaths and alleviate suffering from VAD and micronutrient malnutrition in impoverished regions.
Additionally, expanding the cultivation of genetically modified, bio-fortified crops like Golden Rice could further address vitamin deficiencies in developing countries.
Denotified, Nomadic and Semi-Nomadic Tribes
- 28 May 2024
Why is it in the News?
Denotified and Nomadic Tribes, a group of marginalised communities across Andhra Pradesh, have been silently suffering neglect and caste-based discrimination for centuries.
Who are Denotified, Nomadic, and Semi-Nomadic Tribes?
- Denotified, Nomadic and Semi-Nomadic Tribes are among the most vulnerable and deprived communities in India.
- Denotified Tribes (DNTs): These communities were labelled as 'born criminals' under British colonial laws, starting with the Criminal Tribes Act of 1871.
- The Independent Indian Government repealed these Acts in 1952, thereby 'de-notifying' these tribes.
- Nomadic and Semi-Nomadic Tribes: These groups are characterized by their mobility, moving from place to place rather than settling permanently.
- Historically, they have not had access to private land or home ownership.
Social and Historical Context:
- Categorization: Many DNTs are classified within Scheduled Castes (SC), Scheduled Tribes (ST), and Other Backward Classes (OBC), but some remain uncategorized in these groups.
Historical Commissions:
- Criminal Tribes Inquiry Committee (1947): Investigated the status of these tribes in the United Provinces (now Uttar Pradesh).
- Ananthasayanam Ayyangar Committee (1949): Led to the repeal of the Criminal Tribes Act.
- Kaka Kalelkar Commission (1953): The first OBC Commission.
- B.P. Mandal Commission (1980): Made recommendations concerning these communities.
- National Commission to Review the Working of the Constitution (NCRWC, 2002): Highlighted the wrongful stigmatization and exploitation of DNTs, chaired by Justice M.N. Venkatachaliah.
Population and Distribution:
- South Asia: Hosts the largest nomadic population in the world.
- India: Approximately 10% of the population is comprised of Denotified and Nomadic Tribes.
- There are about 150 Denotified Tribes and around 500 different Nomadic Tribes in India.
Challenges Faced by Nomadic Tribes:
- Lack of Basic Infrastructure: Nomadic tribes often lack access to essential facilities such as drinking water, shelter, sanitation, healthcare, and education.
- Stigma and Treatment: Historically labelled as criminals, these communities still face discrimination and harsh treatment from local authorities and police.
- Lack of Social Security: Due to their frequent movement, nomadic tribes do not have permanent settlements, which makes it difficult for them to obtain social security documents like Ration Cards and Aadhaar Cards.
- This exclusion prevents them from accessing government welfare schemes.
- Unclear Caste Categorization: The classification of these tribes varies across states, with some being categorized as Scheduled Castes (SC) and others as Other Backward Classes (OBC).
- Many individuals lack caste certificates, hindering their ability to benefit from government programs.
Developmental Efforts for Nomadic Tribes:
- Dr Ambedkar Pre-Matric and Post-Matric Scholarship for DNTs: Launched in 2014-15, this centrally sponsored scheme supports DNT students not covered under SC, ST, or OBC categories.
- The pre-matric scholarship promotes education among DNT children, especially girls.
- Nanaji Deshmukh Scheme of Construction of Hostels for DNT Boys and Girls: Also launched in 2014-15, this scheme is implemented through state governments, UT administrations, and central universities.
- It provides hostel facilities for DNT students not covered under SC, ST, or OBC categories, enabling them to pursue higher education.
- Scheme for Economic Empowerment of DNTs: Aim to offer free competitive exam coaching, health insurance, housing assistance, and livelihood initiatives.
- Allocates Rs. 200 crores to be spent over five years starting from 2021-22.
The Development and Welfare Board for De-notified, Nomadic, and Semi-Nomadic Communities (DWBDNC) is responsible for its implementation.
Onset of Monsoon
- 28 May 2024
Why is it in the News?
The southwest monsoon is progressing normally, and conditions are suitable for its onset on the Kerala coast in the next five days, the India Meteorological Department (IMD) said on Monday (May 27).
What does the ‘onset of monsoon’ Mean?
- The onset of the monsoon over Kerala marks the beginning of the four-month, June-September southwest monsoon season over India, which brings more than 70% of the country’s annual rainfall.
- The onset of the monsoon is a significant day in India’s economic calendar.
- According to the IMD, the onset of the monsoon marks a crucial transition in the large-scale atmospheric and ocean circulations in the Indo-Pacific region, and the Department announces it only after certain defined and measurable parameters, adopted in 2016, are met.
Onset & Advance of Monsoon:
- Broadly, the IMD checks for the consistency of rainfall over a defined geography, its intensity, and wind speed.
- Rainfall: The IMD declares the onset of the monsoon if at least 60% of 14 designated meteorological stations in Kerala and Lakshadweep record at least 2.5 mm of rain for two consecutive days at any time after May 10. In such a situation, the onset over Kerala is declared on the second day, provided specific wind and temperature criteria are also fulfilled.
- The 14 enlisted stations are Minicoy, Amini, Thiruvananthapuram, Punalur, Kollam, Alappuzha, Kottayam, Kochi, Thrissur, Kozhikode, Thalassery, Kannur, Kasaragod, and Mangaluru.
- Wind field: The depth of westerlies, prevailing winds that blow from the west at midlatitudes — should be up to 600 hectopascals (1 hPa is equal to 1 millibar of pressure) in the area bound by the equator to 10ºN latitude and from longitude 55ºE to 80ºE.
- The zonal wind speed over the area bound by 5-10ºN latitude and 70-80ºE longitude should be of the order of 15-20 knots (28-37 kph) at 925 hPa.
- Heat: According to IMD, the INSAT-derived Outgoing Longwave Radiation (OLR) value (a measure of the energy emitted to space by the Earth’s surface, oceans, and atmosphere) should be below 200 watts per sq m (wm2) in the box confined by 5-10ºN latitude and 70-75ºE latitude.
- Northern Limit of Monsoon (NLM): Southwest monsoon normally sets in over Kerala around 1st June.
- It advances northwards, usually in surges, and covers the entire country around the 15th of July.
- The NLM is the northernmost limit of monsoon up to which it has advanced on any given day.
In general, the Andaman and Nicobar Islands start receiving monsoon rainfall between May 15 and May 20 every year, and it usually starts raining along the Kerala coast in the last week of May.
Mundra Port

- 28 May 2024
Why is it in the News?
Adani Ports and Special Economic Zone Ltd (APSEZ) on Sunday said its flagship Mundra Port has created yet another record by welcoming the largest container ship to call at an Indian port.
About Mundra Port:
- Mundra Port is the largest private and container port in India.
- It is situated on the northern shores of the Gulf of Kutch, near Mundra in the Kutch district of Gujarat.
- It is a deep-draft, all-weather port and a designated special economic zone (SEZ).
- Mundra Port handles 33% of India's container traffic and is a critical hub for the nation's trade.
Ownership and Operations:
- Adani Ports and Special Economic Zone Limited (APSEZ), India's largest commercial port operator, oversees nearly one-fourth of the country's cargo movement.
Handling Capacity:
- Capacity: The port has a capacity of 260 million metric tons (MMT) and handled over 155 MMT in the fiscal year 2022-23, which represents nearly 11% of India’s maritime cargo.
- Facilities: Equipped with 26 berths and two single-point moorings, Mundra Port can accommodate a diverse range of vessels and cargo types, including containers, dry bulk, break bulk, liquid cargo, and automobiles.
- Coal Terminal: It hosts the country's largest coal import terminal, ensuring rapid cargo processing with minimal turnaround time.
- Connectivity: The port's rail network connects seamlessly with the national rail system, facilitating cargo transportation to any location in India.
What is MSC Anna?
- MSC Anna is the largest container ship ever to dock at an Indian port.
- Size: The vessel measures 399.98 meters in length, approximately the length of four football fields, making it one of the largest container ships globally.
- Capacity: MSC Anna can carry up to 19,200 TEUs (20-foot equivalent units).
With an arrival draft of 16.3 meters, it can only be accommodated at Adani Ports' Mundra Port, as no other port in India has the capability to berth such a deep-draft vessel.
ZIG Currency

- 28 May 2024
Why is it in the News?
To address its long-standing economic instability, the Reserve Bank of Zimbabwe (RBZ) has launched a new gold-backed currency called the ZiG, short for Zimbabwe Gold, replacing the Zimbabwean dollar on April 5, 2024.
What is a ZiG Currency?
- Zimbabwe Gold, or ZIG, is the world's newest currency that was introduced by Zimbabwe to replace the Zimbabwe dollar in April.
- It is backed by the country's gold reserves and was launched in an effort to reduce currency instability and hyperinflation.
- It is the sixth currency Zimbabwe has used since the 2009 collapse of the Zimbabwe dollar amid hyperinflation of 5 billion per cent.
Features of ZiG currency:
- Gold-Backed: The ZiG is unique as it is backed by gold reserves, ensuring its value is supported by the physical gold held by the government.
- Denominations: ZiG notes and coins are issued in denominations of 1ZiG, 2ZiG, 5ZiG, 10ZiG, 20ZiG, 50ZiG, 100ZiG, and 200ZiG. This gold backing aims to provide stability and prevent currency devaluation.
Reasons for Launching a New Currency:
- High Inflation: Zimbabwe has struggled with extreme inflation, with rates exceeding 500% in recent years.
- Currency Instability: The Zimbabwean dollar, introduced in 1980, lost its value due to hyperinflation. The country's reliance on various foreign currencies, mainly the US dollar, has limited economic control.
- Historical Collapse: The collapse of the Zimbabwean dollar in 2009, with hyperinflation peaking at 5 billion per cent, is one of the worst currency crashes in history.
Economic Control: Converting the previous national currency, the Zimbabwe dollar, into ZiGs is intended to simplify monetary matters and provide certainty and predictability in the financial system.
Eucalyptus Tree

- 28 May 2024
Why is it in the News?
The Kerala government issued an order allowing the Kerala Forest Development Corporation (KFDC) to plant eucalyptus trees for its financial sustenance in 2024-2025.
What is the Eucalyptus Tree?
- Eucalyptus is an evergreen tree, one of the most widely cultivated trees native to Australia.
- In Australia, they are commonly referred to as gum trees or stringybark trees.
- The eucalyptus, which is an invasive species of flora, was planted in large numbers by the British in the areas surrounding Nilgiris.
- Many eucalyptus species are cultivated globally as shade trees and in forestry plantations.
Features:
- Bark: Eucalyptus trees have gum-infused bark.
- Leaves: They feature long stems and circular leaves, which are difficult to digest if eaten whole.
- Flowers: Small flowers grow on eucalyptus trees, available in various colours including white, yellow, and shades of red.
- Capsules: Eucalyptus produces small woody capsules that contain seeds.
Uses of Eucalyptus:
- Medicinal Properties: Eucalyptus is widely valued for its medicinal benefits. Some species' leaves contain oil with a strong aroma, primarily composed of cineole (eucalyptol), along with flavonoids and tannins, which have anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties.
- Respiratory Relief: Eucalyptus oil is well-known for relieving congestion and easing breathing during colds.
- Pain Relief: The oil is also used as a topical treatment for sore muscles, aching joints, and rheumatism, improving blood circulation when applied.
- Wood: Eucalyptus wood is tough and durable, making it ideal for building furniture and fences.
Eucalyptus Plantations in India:
- Species: The most widely planted eucalypts in India are Eucalyptus tereticornis and Eucalyptus hybrid.
- Regions: It is extensively grown in Tamil Nadu, Andhra Pradesh, Gujarat, Haryana, Mysore, Kerala, and the Nilgiri Hills.
- Growing Conditions: Eucalyptus thrives in deep, fertile, well-drained loamy soil with adequate moisture.
Dangers of Eucalyptus Tree:
- Water: Eucalyptus trees have a terrible reputation as extensive water users and significant contributors to soil depletion.
- While they do need copious quantities of water, their colossal taproot can find moisture even in the most barren areas.
- This voracious appetite helps maintain their incredibly rapid growth.
- Toxicity: Eucalyptus plant foliage is toxic to animals and humans if ingested.
- Exploding: Eucalyptus oil gives off flammable fumes, and these fumes can be ignited by lightning, flying sparks, and cinders, causing the tree to explode.
Fireballs: During brush or forest fires, the eucalyptus species releases great quantities of flammable gas that mix with air to produce fireballs full of sparks and embers exploding out in front of the fire.
WHO Pandemic Treaty

- 27 May 2024
Why is it in the News?
Health officials from the 194 member states of the World Health Organization hope next week to complete more than two years of negotiations on new rules for responding to pandemics when they gather in Geneva.
What is the Pandemic Treaty?
- The "Pandemic Treaty" or "Pandemic Accord" refers to an ongoing process at the World Health Organization (WHO) to negotiate an international agreement or convention on pandemic prevention, preparedness, and response.
- The idea was proposed in late 2020 amid the COVID-19 pandemic to strengthen global coordination and solidarity in addressing future pandemic threats.
- The WHO already has binding rules known as the International Health Regulations (2005) which set out countries’ obligations where public health events have the potential to cross national borders.
- These include advising the WHO immediately of a health emergency and measures on trade and travel.
- Adopted after the 2002/3 SARS outbreak, these regulations are still seen as functional for regional epidemics such as Ebola but inadequate for a global pandemic.
Key points about the proposed Pandemic Treaty/Agreement:
- Objective: To establish a global framework and rules to ensure better cooperation, data sharing, and coordinated response during future pandemics.
- Legal Status: It would be a legally binding international instrument, like a treaty or convention, requiring ratification by WHO member states.
- Core Elements: Likely to include provisions on equitable access to countermeasures, strengthening health systems, information sharing, One Health approach (human-animal-environment interface), and funding mechanisms.
- Negotiation Process: In December 2021, the World Health Assembly established an intergovernmental negotiating body to draft and negotiate the instrument through a member-state-led process.
- The goal is to learn from COVID-19 experiences and create a binding global framework that facilitates a more coherent, better-coordinated international response to potential future pandemic threats.
How will the Global Health Rules change?
- The updates to the International Health Regulations (IHR) include:
- A new alert system to provide different risk assessments for future outbreaks, addressing criticisms that the current system delayed the COVID-19 response.
- Introducing an intermediary alert stage called “early action alert,” in addition to the existing Public Health Emergency of International Concern (PHEIC).
- Considering a “pandemic emergency” designation for the most severe health threats, filling a gap in the current system which does not use the term "pandemic."
- Strengthening state obligations to inform the WHO of public health events, changing the language from “may” to “should.”
How Do Countries View the Pact?
- Negotiations have been marked by significant differences between wealthy and poor countries.
- The talks missed a key May 10 deadline, nearly collapsing and prompting WHO Director-General Tedros to call an emergency meeting to boost morale. Contentious issues include:
- The sharing of drugs and vaccines.
- Financing, with debates over setting up a dedicated fund versus using existing resources like the World Bank’s $1 billion pandemic fund.
- Political pressure, particularly from right-wing groups and politicians concerned about sovereignty, which the WHO denies.
What Happens Next?
- The new IHR rules and the pandemic accord are intended to complement each other, but opinions vary on whether one can exist without the other.
- Sources indicate that IHR negotiations are more advanced and likely to pass, with changes taking effect automatically after 12 months unless countries opt-out.
- In contrast, the pandemic treaty requires ratification, potentially taking years.
Virupaksha Temple Hampi

- 27 May 2024
Why is it in the News?
The historical Saalu Mantap (pillar line), located on the premises of the Virupaksha Temple in Hampi, a UNESCO World Heritage Site, collapsed after heavy rain lashed the region on Tuesday night.
What is the Historical Significance of Virupaksha Temple?
- The Virupaksha temple gained prominence and underwent extensive expansion in the 14th century during the Vijayanagara Empire (1336 to 1646).
- Founded by Harihara I of the Sangama dynasty, the Vijayanagara Empire expanded from a strategic position on the banks of the Tungabhadra River to become one of the most powerful kingdoms of its time.
- The temple was built by Lakkan Dandesha, a nayaka (chieftain) under the ruler Deva Raya II, also known as Prauda Deva Raya of the Vijayanagara Empire.
- The temple flourished under the patronage of the Vijayanagara rulers, who were great builders and patrons of art.
- It became a vital centre for the religious and cultural activities of its time.
- It is a prime example of Dravidian temple architecture, characterised by its grand gopurams (towering gateways), the shikhara towering over the sanctum sanctorum, its intricate carvings and pillared halls.
- Richly adorned with carvings and sculptures, the gopuram depicts various deities, mythological scenes and animals.
- The sanctum sanctorum houses the Shiva lingam, the main object of worship.
- Historians say all temples had pavilions where traders sold articles, such as those used in worship.
- Sometimes devotees visiting the temple also camped under the pavilions.
- With several other temples and structures located there, Hampi was the empire’s capital city and stands today as evidence of what is known as the last ‘great Hindu empire’ of South India.
- UNESCO also recognised its uniqueness and categorised the Group of Monuments at Hampi as a World Heritage Site.
Zero Debris Charter

- 27 May 2024
Why is it in the News?
Twelve nations have signed the Zero Debris Charter at the ESA/EU Space Council, solidifying their commitment to the long-term sustainability of human activities in Earth orbit.
What is the Zero Debris Charter?
- The Zero Debris Charter is an initiative of the European Space Agency (ESA) and a non-legally binding, technically driven and community-building instrument.
- It is a world-leading effort to become debris-neutral in space by 2030.
- It outlines high-level guiding principles and sets ambitious, collectively defined targets to realize the goal of Zero Debris.
- The charter has been endorsed by countries including Austria, Belgium, Cyprus, Estonia, Germany, Lithuania, Poland, Portugal, Romania, Slovakia, Sweden, and the United Kingdom.
What are Space Debris?
- Space debris encompasses all non-functional, man-made objects in Earth's orbit or re-entering the Earth's atmosphere.
- This category includes decommissioned satellites, spent rocket bodies, fragments resulting from spacecraft breakups or collisions, and debris from anti-satellite weapon tests.
- Presently, there are over one million pieces of space debris larger than one centimetre orbiting Earth.
What are the Concerns with Space Debris?
- Threat to Space Infrastructure: Collisions with operational satellites can disrupt navigation and communication systems on Earth.
- Kessler Syndrome: The uncontrolled accumulation of debris can trigger an escalating cascade of collisions, exacerbating the problem.
- Risk on Earth: Large space debris re-entering the atmosphere uncontrollably poses risks to the population on the ground.
- Increased Cost: Expensive collision avoidance manoeuvres must be performed to protect valuable space assets.
Initiatives for Space Debris Mitigation:
Global:
- Inter-Agency Space Debris Coordination Committee (IADC): A global entity that coordinates activities related to space debris among various space agencies worldwide.
- Space Debris Mitigation Guidelines: Established by the Committee on the Peaceful Uses of Outer Space (COPUOS), these guidelines provide recommendations for reducing the generation of space debris and promoting the long-term sustainability of outer space activities.
India:
- Debris-Free Space Missions (DFSM): An initiative by ISRO aimed at achieving debris-free space missions by 2030, implemented through the ISRO System for Safe & Sustainable Space Operations Management (IS4OM).
- Project NETRA (NEtwork for Space Object Tracking and Analysis): A project focused on enhancing space situational awareness to monitor and manage space debris.
Astronomical Transients
- 27 May 2024
Why is it in the News?
Recently the Indian-American astronomer Shrinivas Kulkarni was awarded the Shaw Prize for Astronomy in 2024 for his work on the physics of astronomical transients.
What are Astronomical Transients?
- Astronomical transients refer to celestial events or phenomena that occur suddenly, brighten or flare up for a brief period of time, and then fade away.
- These events are temporary and transient in nature, lasting from a few seconds to a few years.
Some examples of astronomical transients include:
- Supernovae: These are explosions that mark the end of a massive star's life cycle. They can briefly outshine an entire galaxy before fading away over several weeks or months.
- Gamma-ray bursts (GRBs): These are extremely energetic bursts of gamma-ray radiation that can last from a few milliseconds to several minutes.
- They are believed to be associated with the collapse of massive stars or the merging of compact objects like neutron stars or black holes.
- Novae: These are smaller explosive events on the surface of a white dwarf star in a binary system, caused by the accretion of material from a companion star.
- Tidal disruption events (TDEs): These occur when a star passes too close to a supermassive black hole and is torn apart by the black hole's gravitational forces, leading to a flare of electromagnetic radiation.
- Fast radio bursts (FRBs): These are intense bursts of radio waves that last only a few milliseconds and originate from distant galaxies. Their exact sources are still being investigated.
- Gravitational wave transients: These are transient events detected as gravitational waves, such as the merging of binary black holes or neutron stars, which produce a brief burst of gravitational radiation.
- Comets and asteroids: The close approach or impact of comets and asteroids can produce transient phenomena like outbursts, flares, or even temporary atmospheres around them.
- Astronomical transients are important for understanding various astrophysical processes, the evolution of celestial objects, and for studying the properties of the universe on different timescales.
Small Island Developing States

- 27 May 2024
Why is it in the News?
The Fourth International Conference on Small Island Developing States (SIDS-4) will be convened from May 27-30, 2024.
About Small Island Developing States (SIDS):
- Small Island Developing States (SIDS) are a distinct group of 39 States and 18 Associate Members of United Nations regional commissions that face unique social, economic and environmental vulnerabilities.
- The three geographical regions in which SIDS are located are:
- The Caribbean
- The Pacific
- The Atlantic, Indian Ocean and South China Sea (AIS)
- SIDS were recognized as a special case both for their environment and development at the 1992 United Nations Conference on Environment and Development held in Rio de Janeiro, Brazil.
- The aggregate population of all the SIDS is 65 million, slightly less than 1% of the world’s population, yet this group faces unique social, economic, and environmental challenges.
- SIDS face a host of challenges including for many, their remote geography.
- As a result, many SIDS face high import and export costs for goods as well as irregular international traffic volumes.
- For SIDS, the Exclusive Economic Zone (EEZ)—the ocean under their control—is, on average, 28 times the country’s land mass.
- Thus, for many SIDS the majority of the natural resources they have access to comes from the ocean.
- Factors like small population size, remoteness from international markets, high transportation costs, vulnerability to exogenous economic shocks and fragile land and marine ecosystems make SIDS particularly vulnerable to biodiversity loss and climate change because they lack economic alternatives.
- Climate change has a very tangible impact on SIDS.
- Slow onset events such as sea level rise pose an existential threat to small island communities, requiring drastic measures such as relocation of populations, and the related challenges this poses.
- These challenges are compounded by limited institutional capacity, scarce financial resources and a high degree of vulnerability to systemic shocks.
- Industries like tourism and fisheries can constitute over half of the GDP of small island economies.
- However, the importance of these natural resources extends beyond the economy; biodiversity holds aesthetic and spiritual value for many island communities.
- For centuries, these communities have drawn benefits from biodiversity in the form of food supply, clean water, reduced beach erosion, soil and sand formation, and protection from storm surges.
- At the regional level, SIDS are also supported by inter-governmental organisations, primarily the?Caribbean Community (CARICOM),?the?Pacific Islands Forum (PIF)?and the Indian Ocean Commission (IOC).
Kazi Nazrul Islam

- 25 May 2024
Why is it in the News?
One hundred and twenty-five years ago on May 25, 2024, a ‘rebel poet’ was born in undivided Bengal who would go on to create about 4,000 songs and several stories to remind his warring and impoverished country folks of the power of humanity to tide over hunger, poverty and disintegration of society.
Who was Kazi Nazrul Islam?
- Kazi Nazrul Islam (1899-1976) was a Bengali poet, writer, and musician whose oeuvre, Nazrulgeeti (Songs of Nazrul), constitutes a musical genre that is perhaps second in popularity to only Rabindrasangeet, the compositions of Rabindranath Tagore.
- He enjoys iconic status in West Bengal, Bangladesh, and the Bengali diaspora around the world, and is revered as the National poet of Bangladesh.
- Nazrul is known as the Bidrohi Kobi (Rebel Poet) because most of the more than 4,000 songs that he wrote and composed are songs of protest and revolution, which inspired the freedom fighters of Bengal in their struggle against colonialism and imperialism.
- In 1923, the British arrested Nazrul because of the strongly anti-British content of a magazine that he founded and edited.
- His first poem was published when he was still in Karachi, in the Bangiya Mussalman Sahitya Patrika.
- Some of the poems he had composed and contributed in Moslem Bharat included Shatil Arab, Moharram, Korbani, Fatiha, Doazdaham, Badal Prater Sharab, and Kheya Parer Tarani, amongst others.
- The political conditions in which Nazrul Islam eventually began his career as a writer were ones conditioned by extreme tensions and conflict including the Jallianwala Bagh massacre and launch of the Non-Cooperation Movement following the special session of the Indian National Congress, and especially in the context of the “divide and rule” policy which was adopted by the British.
- Several issues that the populace of the subcontinent had to deal with included economic backwardness, racial prejudices, and social inequality.
- In such circumstances, he joined a Bengali newspaper called Naba-Yug (New Era).
- His writings were later compiled and published as a book Yugabani (Message of the Age) which was immediately banned by the British government.
- Apart from writing and working for several other newspapers of the times, including Sevak, he had also started his own political weekly in 1922, named, Dhumketu (The Comet).
- The paper explicitly voiced their opinions against the British government and played an important role in steering the rebellious attitude and voices of the populace.
- As a result, Nazrul was charged with charges of sedition and he was sentenced to 1 year of rigorous imprisonment in 1923.
- On this occasion, Rabindranath Tagore had also dedicated a newly composed dance-drama Basanti to Nazrul, which was performed in Calcutta.
- Nazrul Islam was a prolific poet and composed several poems on various themes including themes of social messages, and resistance against the colonial government.
- He had effectively used his poems as a literary conduit to voice his opinions against British colonial rule.
- The highest point of his career as a poet was when he composed the poem Bidrohi (The Rebel).
- The poem was highly appreciated and established him as a well-respected poet.
- The poem was characterized by a revolutionary spirit and rife with heroic sentiments.
- It portrayed a revolutionary who had called upon the marginalized sections of the society to rise up and face the British despots.
- The compositions of Kazi Nazrul Islam in the form of songs, poems, and other forms of literature formed a very strong and powerful weapon against British colonial rule.
- The revolutionary themes which were explicit in his writings played an important role during the freedom movement.
- He consistently raised his voice against communalism, imperialism, fundamentalism and exploitation.
- His literary legacy is remembered and acknowledged to this date.
- He had earned the respect of not only his contemporaries but also of the later generations.
- His contributions thus are not limited to the efflorescence of Bengali literature but also extended to the cause of freedom during the Indian Independence Movement.
Gliese 12b

- 25 May 2024
Why is it in the News?
Recently, scientists have discovered a new planet that they say could "potentially support human life."
What is Gliese 12b?
- Gliese 12 b is a rocky planet just 40 light-years away from Earth.
- It orbits around a star called Gliese 12, a cool red dwarf in the constellation Pisces.
- This star is only 27 per cent of the size of our sun, with about 60 per cent of its surface temperature.
- But it's this lower temperature that makes Gliese 12 b theoretically habitable for humans.
- Gliese 12 b is one of the few known rocky planets where humans could theoretically survive according to scientists.
- The planet was discovered by an international team, in collaboration with NASA and the European Space Agency, using data from NASA's Transiting Exoplanet Survey Satellite (TESS) and ESA's Characterizing Exoplanet Satellite (CHEOPS).
- Gliese 12 b falls into this "Goldilocks zone," with an average temperature of 107 degrees Fahrenheit and a size somewhere between Venus and Earth.
- The researchers hope that by learning more about Gliese 12 b's atmosphere we may be able to answer questions about the evolution of our own solar system and other habitable planets.
About the Transiting Exoplanet Survey Satellite (TESS):
- TESS is a NASA mission dedicated to discovering exoplanets around nearby bright stars.
- It was launched on April 18, 2018, aboard a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket from Cape Canaveral.
- TESS operates in a unique high Earth orbit with a period of 12 to 15 days.
- This orbit is designed to keep the telescope's view largely unobstructed by Earth and the Moon.
- The prime mission concluded on July 4, 2020, but TESS continues to operate on an extended mission.
- TESS has identified a wide range of exoplanets, from small rocky worlds to giant planets, highlighting the diversity of planetary systems in our galaxy.
- TESS uses the transit method to find exoplanets. It monitors stars for periodic dips in brightness, which occur when a planet crosses in front of the star along our line of sight.
- The size of the dip indicates the planet's diameter and the duration of the transit provides information about the planet's orbit.
- The transit method allows scientists to determine the diameter and orbital size of exoplanets.
- Orbits within certain ranges fall into the "habitable zone," where conditions may allow liquid water to exist on the surface of Earth-like worlds.
World Intellectual Property Organization (WIPO) Meeting 2024

- 25 May 2024
Why is it in the News?
The Treaty on Intellectual Property, Genetic Resources and Associated Traditional Knowledge was adopted at the Diplomatic Conference held under the aegis of the World Intellectual Property Organization (WIPO) at its headquarters in Geneva recently.
What is the WIPO Meeting 2024?
- The World Intellectual Property Organization (WIPO) Meeting 2024 focuses on final-stage negotiations for a proposed treaty on intellectual property, genetic resources, and associated traditional knowledge.
- The aim is to protect the rights of communities that conserve genetic resources and hold traditional knowledge of their use.
- The main goal of the treaty is to enhance the efficacy, transparency, and quality of the patent system regarding genetic resources and traditional knowledge.
- It aims to prevent patents for non-novel or non-inventive inventions and ensure proper disclosure of genetic resources and traditional knowledge in patent applications.
Key challenges in the negotiations:
- Key challenges include reaching a consensus on mandatory disclosure requirements, addressing biopiracy, deciding on the inclusion of DSI in the treaty, and defining traditional knowledge.
- Countries like the United States, Japan, and South Korea generally oppose mandatory disclosure requirements, adding complexity to the negotiations.
What are genetic resources and traditional knowledge associated?
- Genetic resources are genetic material of actual or potential value found in plants, animals, and microorganisms.
- These resources are essential in fields like agriculture, pharmaceuticals, and biotechnology.
- Traditional knowledge associated with genetic resources refers to the knowledge, practices, and innovations of indigenous and local communities, developed and passed down through generations.
- This knowledge is often related to the use and conservation of genetic resources.
What is Biopiracy?
- Biopiracy refers to the unauthorized use and patenting of genetic resources and traditional knowledge without proper compensation or acknowledgement to the communities that developed and conserved them.
- The treaty seeks to address biopiracy by requiring the disclosure of genetic resources and traditional knowledge in patent applications and aligning with international agreements like the Nagoya Protocol.
What is Digital sequence information (DSI)?
- Digital sequence information (DSI) refers to the digital representation of genetic material.
- The treaty currently excludes DSI from its scope, which is a point of contention as it affects the management and protection of genetic resources.
- Including DSI in the treaty is under debate to ensure comprehensive protection.
Outcomes and Significance of this Meeting:
- Expected outcomes include finalizing the treaty's text, agreeing on substantive intellectual property provisions, and administrative issues.
- Once finalized, the treaty will be open for signature and aims to provide a robust framework for protecting genetic resources and traditional knowledge.
- The treaty also aims to protect the rights of indigenous and local communities by ensuring they receive fair compensation and recognition for their genetic resources and traditional knowledge.
- It also promotes the sustainable use and conservation of these resources, benefiting both global and local communities.
- The treaty has broader implications for international intellectual property law, biodiversity conservation, and the rights of indigenous and local communities.
- It aims to balance the interests of patent holders with the need to protect and sustainably use genetic resources and traditional knowledge.
India’s Role:
- India plays a significant role in the negotiations by advocating for strong disclosure requirements and a clear definition of traditional knowledge.
- India's participation helps ensure that the treaty provides sufficient policy space for countries to maintain their current stronger disclosure requirements under national laws.
Taiwan Strait/Formosa Strait
- 25 May 2024
Why is it in the News?
China ended two days of war games around Taiwan, in which it simulated attacks with bombers and practised boarding ships, and Taiwan's defence ministry detailed on Saturday the surge of Chinese warplanes and warships involved.
About the Taiwan Strait:
- Geography: The Taiwan Strait, also known as the Formosa Strait, is a 180 km-wide body of water separating mainland China from the island of Taiwan.
- It lies between the coast of Fujian Province in China and Taiwan.
- Location: The strait is part of the South China Sea and connects to the East China Sea in the north.
- The seafloor is primarily a continental shelf extending from the Asian continent, with Taiwan situated on the outer edge.
- The strait is relatively shallow, with an average depth of about 490 feet and a minimum depth of 82 feet.
- Islands: Major islands on the Taiwan side include Penghu (or Pescadores), Kinmen, and Matsu.
- On the Chinese side, Xiamen and Pingtan are significant islands.
- While Xiamen and Pingtan are administered by the People's Republic of China, Penghu, Kinmen, and Matsu are governed by the Republic of China (Taiwan).
- Shipping Corridor: The Taiwan Strait is a vital global shipping route, with nearly 50 per cent of global container shipping passing through the Taiwan Strait.
- Key ports in the region include Amoy in mainland China and Kao-hsiung in Taiwan.
- Historical Significance: The strait has been a site of military confrontations between the People's Republic of China and Taiwan since 1949, following the Chinese Civil War.
- The Kuomintang forces, led by Chiang Kai-shek, retreated across the strait and established their government in Taiwan.
- Median Line: The median line is an informal dividing line in the Taiwan Strait, established during the Cold War to reduce the risk of military clashes between China and Taiwan.
- Although not formalized by any treaty, it served as a tacit boundary until 2019, when Chinese military aircraft began crossing it.
- Beijing has since increasingly challenged the existence of the median line by frequently sending warplanes over it.
World Health Assembly 2024

- 25 May 2024
Why is it in the News?
The World Health Assembly will convene from May 27 to June 1 to discuss amendments to the International Health Regulations, aimed at improving the ability of countries to respond to public health emergencies and prepare a potential new pandemic agreement.
What is the World Health Assembly?
- The World Health Assembly is the decision-making body of the World Health Organization (WHO), the United Nations (UN) agency dedicated to promoting the global population's health and access to the highest levels of healthcare provision.
- Its main functions are to determine WHO's policies, elect the Organization's Director-General, supervise financial policies, and review and approve the proposed WHO budget.
- Delegates from WHO member states come together at an annual assembly held at the UN headquarters in Geneva, Switzerland, to focus on a specific healthcare agenda created by the organization's Executive Board.
- The Executive Board comprises 34 technically qualified members, each elected for a three-year term.
- They meet every year in January to agree on the agenda and any resolutions that will be put before the World Health Assembly for consideration.
- Now in its 76th session, the theme for this year’s event is “Health For All: 75 Years of Improving Public Health”.
What does the Assembly do?
- Delegates at the annual World Health Assembly discuss the Executive Board's policy agenda for the coming year and decide which health goals and strategies will guide the WHO's public health work.
- Other functions include voting to appoint the organization's Director-General to serve a five-year term.
- Dr Tedros Adhanom Ghebreyesus holds the post currently, having been re-elected in 2022 to serve a second term as head of the world's leading public health agency.
Why is it important?
- Since its inauguration, the Assembly has presided over WHO policies that have helped eradicate deadly diseases like smallpox and the poliovirus and helped foster international collaborations to develop and distribute vaccines for diseases like malaria and COVID-19.
About International Health Regulations (IHR):
- First adopted by the World Health Assembly (WHA) in 1969, the IHR was last revised in 2005. These regulations aim to maximize collective efforts in managing public health events while minimizing disruptions to travel and trade.
- The IHR has 196 State Parties, including all 194 WHO Member States, plus Liechtenstein and the Holy See.
- The IHR provide a comprehensive legal framework that outlines countries' rights and obligations in managing public health events and emergencies with the potential to cross borders.
- The regulations introduce crucial safeguards to protect the rights of travellers and others, covering the treatment of personal data, informed consent, and non-discrimination in the application of health measures.
- Legally Binding Instrument: As an instrument of international law, the IHR is legally binding on 196 countries.
Sweet Sorghum

- 24 May 2024
Why is it in the News?
Governments should be using their agriculture extension services to raise awareness among farmers, and consumers about the benefits & practical applications of sweet sorghum in people’s diet.
About Sweet Sorghum:
- Sweet sorghum is the most important millet crop occupying the largest area among the cereals next to rice.
- It is mainly grown for its grain and fodder.
- Alternative uses of sorghum include commercial utilization of grain in the food industry and utilization of stalk for the production of value-added products like ethanol, syrup jaggery and enriched bagasse as fodder and as a base material for cogeneration.
- Sweet sorghum has emerged as a supplementary crop to sugarcane in dry land pockets for the production of ethanol.
- The success rate is high because of the use of existing machinery available in the sugar factories and attached distilleries.
- The advantages of the crop are it can be grown with limited water and minimal inputs and it can be harvested in four months.
Climate and Soil:
- Sweet sorghum can be sown in June with the southwest monsoon, in September-October with the northeast monsoon (500-600 mm rainfall), or in summer with assured irrigation.
- The crop prefers moderate rainfall; excessive moisture or heavy rain after flowering can reduce sugar content.
- With irrigation, early sowing before June can prevent issues with heavy rains during flowering and grain maturation.
- Summer sowing may result in lower biomass and sugar yield. Sweet sorghum thrives in well-drained soils of medium depth (18" and above), with water requirements varying by soil type (red, black, laterite, and loamy).
Multiple Uses of Sweet Sorghum:
- Sweet sorghum is a versatile crop used for grain, animal feed, and sugary juice.
- Its grains are made into steamed bread, porridge, and beer, providing high nutritional value with proteins, carbohydrates, fibre, and essential minerals like potassium, calcium, sodium, and iron.
- Resilient in arid climates, sweet sorghum produces significant biomass, which, along with grains, serves as high-quality animal feed.
- The sugary juice from its stalks is used for bioethanol production, yielding more ethanol per hectare than maize, second only to sugarcane.
- Notably, sweet sorghum is drought-resistant, capable of dormancy during dry periods and resuming growth later.
- Its tolerance to low water, nitrogen inputs, salinity, and drought stress makes it ideal for arid regions, making it popular in the US, Brazil, and China.
Shallow Aquifer Management (SAM)

- 24 May 2024
Why is it in the News?
Securing water for the future as the mantra, the Greater Hyderabad Municipal Corporation (GHMC) in the latest intervention has taken up the Shallow Aquifer Management (SAM) model on a pilot basis in the city.
What is an Aquifer?
- An aquifer is a body of porous rock or sediment that is saturated with groundwater.
- Groundwater enters an aquifer through precipitation that seeps down through the soil.
- It can then move through the aquifer and emerge at the surface via springs and wells.
- Aquifers are classified into two types:
- Deep Aquifers
- Shallow Aquifers
What is Shallow Aquifer Management (SAM)?
- In 2022, the Atal Mission for Rejuvenation and Urban Transformation (AMRUT) launched a Shallow Aquifer Management (SAM) pilot program in ten cities across nine states:
- Bengaluru (Karnataka), Chennai (Tamil Nadu), Dhanbad (Jharkhand), Gwalior (Madhya Pradesh), Hyderabad (Telangana), Jaipur (Rajasthan), Kolkata (West Bengal), Pune and Thane (Maharashtra), and Rajkot (Gujarat).
- The SAM pilot is overseen by the National Institute of Urban Affairs (NIUA) and supported by the Advanced Center for Water Resources Development and Management (ACWADAM) in Pune and the Biome Environmental Trust in Bengaluru.
- Under SAM, the Greater Hyderabad Municipal Corporation (GHMC) has identified five municipal parks for implementation this year.
How does it work?
- The project involves drilling shallow water injection borewells to depths of 100-120 feet to extract water from shallow aquifers.
- This process helps recharge the underlying layers during rainfall events by collecting water from the surrounding watershed and directing it through recharge pits.
- Consequently, underground water layers are replenished, leading to a rise in the water table.
Tropical Cyclone Remal

- 24 May 2024
Why is it in the News?
The first cyclone in the Bay of Bengal this pre-monsoon season, Cyclone Remal, is expected to make landfall between Sagar Island in West Bengal and Bangladesh's Khepupara on Sunday midnight.
About Cyclone Remal:
- The IMD has forecasted that a depression in the Bay of Bengal is likely to concentrate into a severe cyclonic storm and make landfall between Sagar Island in West Bengal and Khepupara in Bangladesh around May 26 midnight.
Name of the cyclone:
- If the cyclone is formed, it will be named 'Remal', which means 'sand' in Arabic.
- The cyclone has been named ‘Remal’, according to a system of naming cyclones in the Indian Ocean region.
- A standard naming convention is followed for tropical cyclones forming in the North Indian Ocean, including the Arabian Sea and the Bay of Bengal.
- As the IMD is a part of the Regional Specialised Meteorological Centres (RSMCs), it gives names to the tropical cyclones after consulting 12 other countries in the region.
- The name 'Remal' has been suggested by Oman which means 'sand' in Arabic.
What is a Tropical Cyclone?
- A tropical cyclone is a rapidly rotating storm system characterized by a low-pressure centre, strong winds, and a spiral arrangement of thunderstorms that produce heavy rain.
- These cyclones develop over warm tropical or subtropical waters and can cause significant damage due to high winds, heavy rainfall, and storm surges.
How a Tropical Cyclone is Formed?
- Tropical cyclones form over warm ocean waters near the equator.
- The process begins when warm, moist air rises from the ocean surface, creating an area of low pressure.
- This causes surrounding air with higher pressure to move toward the low-pressure area, warming up and rising as well.
- As this air rises and cools, the moisture condenses to form clouds.
- The system of clouds and wind starts to spin and grow, fueled by the ocean's heat.
- When the wind speeds increase sufficiently, an eye forms in the centre of the cyclone.
Characteristics of a Tropical Cyclone:
- Calm Center: The eye of the cyclone is calm and clear, with very low air pressure.
- High Wind Speeds: The average wind speed of a tropical cyclone is around 120 km/h.
- Closed Isobars: These are lines on a weather map that connect areas of equal atmospheric pressure, leading to greater wind velocity.
- Oceanic Origin: Tropical cyclones develop over oceans and seas.
- Movement: They typically move from east to west under the influence of trade winds.
- Seasonal: Tropical cyclones are seasonal phenomena.
How are Cyclones Classified?
- The Indian Meteorological Department (IMD) classifies cyclones based on wind speeds:
- Depression: Wind speeds between 31–49 km/h
- Deep Depression: Wind speeds between 50-61 km/h
- Cyclonic Storm: Wind speeds between 62–88 km/h
- Severe Cyclonic Storm: Wind speeds between 89-117 km/h
- Very Severe Cyclonic Storm: Wind speeds between 118-166 km/h
- Extremely Severe Cyclonic Storm: Wind speeds between 166-221 km/h
- Super Cyclonic Storm: Wind speeds above 222 km/h
Global Species Action Plan (GSAP) SKILLS Platform

- 24 May 2024
Why is it in the News?
In response to the escalating biodiversity crisis, the Global Species Action Plan (GSAP) is designed to support the implementation of the Kunming-Montreal Global Biodiversity Framework (GBF).
About GSAP SKILLS Platform:
- The Global Species Action Plan (GSAP) SKILLS platform, standing for (Species Conservation Knowledge, Information, Learning, Leverage, and Sharing), brings the GSAP’s content online and enables real-time updates of technical tools and resources.
- This platform aims to facilitate global collaboration and partnership by connecting decision-makers, species conservation practitioners, and experts at all levels.
- It ensures accessibility and relevance by providing real-time updates on technical tools and resources.
- Each target within the Global Biodiversity Framework is accompanied by a summary and rationale for species conservation interventions, actions, and sub-actions, along with the actors involved and the technical tools and resources required, facilitating the scaling-up of implementation efforts.
- Managed proactively by the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN), the platform meets the needs of governments and stakeholders to take decisive action for species conservation.
- The development of the GSAP SKILLS platform has been principally supported by the Ministry of Environment, Republic of Korea, with additional resources from the Tech4Nature Initiative, launched by IUCN and Huawei in 2020.
What is the Global Species Action Plan?
- It has been developed to support the implementation of the Kunming-Montreal Global Biodiversity Framework (GBF) and to address the increasing biodiversity loss worldwide.
- It outlines strategic interventions and actions to conserve and sustainably manage species while ensuring equitable benefits.
About Kunming-Montreal Global Biodiversity Framework:
- The Kunming-Montreal Global Biodiversity Framework (GBF) is an outcome of the 2022 United Nations Biodiversity Conference.
- Its tentative title had been the "Post-2020 Global Biodiversity Framework".
- The GBF was adopted by the 15th Conference of Parties (COP15) to the Convention on Biological Diversity (CBD) on 19 December 2022.
- It has been promoted as a "Paris Agreement for Nature".
- It is one of a handful of agreements under the auspices of the CBD, and it is the most significant to date.
- It has been hailed as a "huge, historic moment" and a "major win for our planet and for all of humanity."
- UN Secretary-General António Guterres speaking at the 2022 biodiversity conference in Montreal which led to this treaty
- The Framework is named after two cities, Kunming, which was scheduled to be the host city for COP15 in October 2020 but postponed and subsequently relinquished the hosting duties due to China's COVID policy, and Montreal, which is the seat of the Convention on Biological Diversity Secretariat and stepped in to host COP15 after Kunming's cancellation.
The League of Arab States (LAS)/Arab League
- 24 May 2024
Why is it in the News?
The Arab League called recently for a UN peacekeeping force in the "occupied Palestinian territories" at an international summit dominated by the war between Israel and Hamas.
What is the Arab League?
- The League of Arab States was formed in Cairo on 22 March 1945 with six members: Egypt, Iraq, Transjordan (later renamed Jordan), Lebanon, Saudi Arabia and Syria, with Yemen joining on 5 May 1945.
- It currently has 22 member states; Algeria, Bahrain, Comoros, Djibouti, Egypt, Iraq, Jordon, Kuwait, Lebanon, Libya, Mauritania, Morocco, Oman, Palestinian Authority, Qatar, Saudi Arabia, Somalia, Sudan, Syria, Tunisia, United Arab Emirates and Yemen.
- Four countries have been admitted as observers: Brazil, Eritrea, India and Venezuela.
- Each member state has one vote in the League Council, while decisions are binding only on those states that have voted for them.
- The official language of the Arab League and its 22 member states is Arabic.
- The league seeks to promote the political, social, and military interests of its members.
- The head of the league is known as the secretary-general.
- The secretary-general is appointed to a five-year term by a two-thirds majority of league members.
- Headquarters: Cairo, Egypt.
Goals:
- The overall aim of the league is to promote Arab interests.
- Its main goals are to strengthen and coordinate the political, cultural, economic, and social programs of its members and to try to settle disputes among them or between them and third parties.
- In 1950 the members also agreed to provide military support to help defend each other.
The Arab League Council:
- The League Council is the highest body of the Arab League and is composed of representatives of member states, typically foreign ministers, their representatives, or permanent delegates.
- Each member state has one vote.
- The Council meets twice a year, in March and September. Two or more members may request a special session if they desire.
- The general secretariat manages the daily operations of the league and is headed by the secretary-general.
- The general secretariat is the administrative body of the league, the executive body of the council, and the specialized ministerial councils.
El Niño and La Nina
- 23 May 2024
Why is it in the News?
Last month, the India Meteorological Department (IMD) forecasted above-normal rain in the upcoming monsoon season in India, with “favourable” La Nina conditions expected to set in by August-September.
What are El Niño and La Nina?
- El Niño (meaning “little boy” in Spanish) and La Nina (meaning “little girl” in Spanish) are climate phenomena that are a result of ocean-atmosphere interactions, which impact the temperature of waters in the central and eastern tropical Pacific Ocean which affects global weather.
- The Earth’s east-west rotation causes all winds blowing between 30 degrees to the north and south of the equator to slant in their trajectory.
- As a result, winds in the region flow towards a southwesterly direction in the northern hemisphere and a northwesterly direction in the southern hemisphere which is known as the Coriolis Effect.
- Due to this, winds in this belt (called trade winds) blow westwards on either side of the equator.
- Under normal ocean conditions, these trade winds travel westwards along the equator from South America towards Asia.
- Wind movement over the ocean results in a phenomenon called upwelling, where cold water beneath the ocean surface rises and displaces the warm surface waters.
- At times, the weak trade winds get pushed back towards South America and there is no upwelling.
- Thus, warmer-than-usual sea surface temperatures are recorded along the equatorial Pacific Ocean, and this is known as the emergence of El Niño conditions.
- Conversely, during La Nina, strong trade winds push warm water towards Asia.
- Greater upwelling gives rise to cold and nutrient-rich water towards South America.
- Thus, climatologically, El Niño and La Nina are opposite phases of what is collectively called the El Niño Southern Oscillation (ENSO) cycle.
- It also includes a third neutral phase.
- El Niño events are far more frequent than La Nina ones.
- Once every two to seven years, neutral ENSO conditions get interrupted by either El Niño or La Nina.
- Recently, La Nina conditions prevailed between 2020 and 2023.
How could the incoming La Nina impact global weather?
- La Niña, driven by the cooling of ocean waters due to the ENSO (El Niño-Southern Oscillation) cycle, can significantly influence global weather patterns.
- The air circulation loop in the region, affected by these temperature changes, impacts precipitation levels in neighbouring areas and can alter the Indian monsoon.
- Currently, the El Niño event that began in June last year has significantly weakened.
- Neutral ENSO conditions are expected to be established by June.
- Following this, La Niña conditions are anticipated to emerge, with its effects likely becoming apparent from August.
La Nina’s Impact on India:
- With above normal rain forecast, the seasonal rainfall is expected to be 106 per cent of the Long Period Average (LPA), which is 880mm (1971-2020 average).
- Except in east and northeast India, all remaining regions are expected to receive normal or above-seasonal rainfall.
- Heavy rains could result in some regions witnessing riverine and urban flooding, mudslides, landslides and cloudbursts.
- East and northeast India region, during La Nina years, receive below average seasonal rainfall.
- Therefore, there may be a shortfall in water reserves there this year.
- During La Nina years, incidents of thunderstorms generally increase.
- “The east and northern India regions could experience thunderstorms accompanied by lightning.
- With increased farming activities undertaken during the July and August rainy months, which coincides with the season’s enhanced lightning and thunderstorms, there is a high risk of fatalities in these regions.
- In addition to ENSO, there are other parameters that can impact the monsoon.
- However, in a La Nina year, a deficit monsoon over India can be easily ruled out.
La Nina’s Impact on the World:
- Similar to India, Indonesia, the Philippines, Malaysia and their neighbouring countries receive good rainfall during a La Nina year.
- This year, Indonesia has already witnessed floods.
- On the other hand, droughts are common in southern regions of North America, where winters become warmer than usual.
- Canada and the northwestern coast of the United States see heavy rainfall and flooding.
- Southern Africa receives higher than usual rainfall, whereas eastern regions of the continent suffer below-average rainfall.
- ENSO has a huge impact on hurricane activity over the Atlantic Ocean.
- During a La Nina year, the hurricane activity here increases.
- For instance, the Atlantic Ocean churned out a record 30 hurricanes during the La Nina year 2021.
Is Climate Change Affecting ENSO?
- Over India, El Niño is known to suppress the southwest monsoon rainfall and drive higher temperatures and intense heat waves, like the present summer season.
- In the past, monsoon seasons during years following an El Niño were 1982-1983 and 1987-1988, with both 1983 and 1988 recording bountiful rainfall.
- At present too, a similar situation could play out.
- The 2020-2023 period witnessed the longest La Nina event of the century.
- Thereafter, ENSO neutral conditions developed, which soon gave way to El Niño by June 2023 which has been weakening since December last year.
- Scientists say that climate change is set to impact the ENSO cycle.
- Many studies suggest that global warming tends to change the mean oceanic conditions over the Pacific Ocean and trigger more El Niño events.
- The World Meteorological Organization (WMO) has also said that climate change is likely to affect the intensity and frequency of extreme weather and climate events linked to El Niño and La Nina.
Bay of Bengal Initiative for Multi-Sectoral Technical and Economic Cooperation (BIMSTEC)

- 23 May 2024
Why is it in the News?
The Bay of Bengal Initiative for Multi-Sectoral Technical and Economic Cooperation (BIMSTEC) will now be open to new members and observers after a historic first charter of the grouping came into force on 20 May.
What is BIMSTEC?
- The Bay of Bengal Initiative for Multi-Sectoral Technical and Economic Cooperation (BIMSTEC) is a multilateral regional organization that brings together seven member states located in the littoral and adjacent areas of the Bay of Bengal, forming a contiguous regional unity.
- Aims: The primary aim of BIMSTEC is to accelerate shared growth and cooperation among littoral and adjacent countries in the Bay of Bengal region.
- Formation: The organization was initially founded as BIST-EC in June 1997, following the adoption of the Bangkok Declaration.
- The founding members included Bangladesh, India, Sri Lanka, and Thailand.
- With Myanmar's entry in late 1997, the organization evolved into BIMST-EC (Bangladesh, India, Myanmar, Sri Lanka, and Thailand Economic Cooperation).
- In 2004, the inclusion of Nepal and Bhutan led to the formation of BIMSTEC, as we know it today.
- The current member states comprise five South Asian nations: Bangladesh, Bhutan, India, Nepal, and Sri Lanka, and two Southeast Asian nations: Myanmar and Thailand.
- BIMSTEC's Permanent Secretariat is situated in Dhaka, Bangladesh, serving as a hub for regional cooperation and coordination among member states.
Areas of cooperation:
- BIMSTEC functions as a sector-driven cooperative organization, initially focusing on six key sectors: Trade, Technology, Energy, Transport, Tourism, and Fisheries.
- Over time, the scope of cooperation has expanded, and as of now, BIMSTEC has identified 14 priority areas of cooperation.
- The inclusion of Climate Change in 2008 marked the 14th priority area.
- Within these priority areas, each member country takes responsibility for leading specific sectors.
- This allows for focused efforts and utilization of regional expertise.
- India, for example, is the leading country in several crucial areas, including Transport & Communication, Tourism, Environment & Disaster Management, and Counter-Terrorism & Transnational Crime.
- This leadership role involves coordinating initiatives, sharing best practices, and driving collaborative efforts within these sectors to enhance regional development and cooperation.
Planetary Alignment

- 23 May 2024
Why is it in the News?
Next month, on June 3, there will be a planetary alignment that may actually allow you to witness six planets align in the sky.
What is a Planetary Alignment?
- Planetary alignment is a term used to describe the positioning of planets in the solar system such that they appear to be in a straight line or close to one when viewed from a specific vantage point, for us that's Earth.
- It is an astronomical event that happens when, by coincidence, the orbits of several of the planets of the Solar System bring them to roughly the same side of the Sun at the same time.
- This phenomenon is more an illusion of perspective rather than the planets being in a perfect line in space.
- It’s important to emphasise that the planets aren’t forming a straight line in space – that’s a much rarer astronomical event called a syzygy.
- However, because all the planets, including the Earth, orbit around the Sun in roughly the same orientation (moving in which we call the “Plane of the Ecliptic”), when they’re on the same side of the Sun as each other, they appear to form a line in the sky when we view them from Earth.”
- Planetary alignments are rather common within themselves, especially when two, three, or even four planets align in the sky.
- Five or more planets aligning, however, is less common.
- April 8, 2024, was the last time the planets were all in alignment.
Which planets will align?
- Mercury, Mars, Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune will form a near-straight line, offering an extraordinary opportunity to witness this cosmic phenomenon.
Which planets will be visible?
- While six planets align, not all of them will be visible to the naked eye, due to their vast distance from Earth.
- Meanwhile, the Moon will also play a spoilsport as it distorts the visibility.
- Mercury and Jupiter will be tricky to see in the sky due to their proximity to the Sun in their orbit.
- However, Mars and Saturn will be visible to the naked eye, though very dim.
- Meanwhile, keen observers will need telescopes or high-powered binoculars to spot the distant planets Uranus and Neptune.
Economic Capital Framework (ECF)

- 23 May 2024
Why is it in the News?
The Central Board of the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) has approved a record surplus transfer of Rs 2.11 lakh crore to the Central government for the fiscal year 2023-24, determined based on the Economic Capital Framework (ECF).
What is the Economic Capital Framework (ECF)?
- The Economic Capital Framework (ECF) is an objective, rule-based, transparent methodology for determining the appropriate level of risk provisions (fund allocation to capital reserve) that is to be made under Section 47 of the Reserve Bank of India Act.
- The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) developed an Economic Capital Framework (ECF) for determining the allocation of funds to its capital reserves so that any risk contingency can be met as well as to transfer the profit of the RBI to the government.
- There are two clear objectives for the ECF.
- First, the RBI as a macroeconomic institution has the responsibility to fight any disorder especially a crisis in the financial system. Here, to meet such a crisis, the RBI should have adequate funds attached under the capital reserve.
- Second, is transferring the remaining part of the net income to the government.
- The process of adding funds to the capital reserve is a yearly one where the RBI allots money out of its net income to the capital reserve.
- How much funds shall be added to the capital reserve each year depends upon the risky situation in the financial system and the economy.
- The process of allocation of funds is technically called as provisioning (risk provisioning etc.,) to the reserves.
- After allotting money to the capital reserve, the remaining net income of the RBI is transferred to the government as profit.
- Since the government is the shareholder of the RBI, the latter’s income (means profit) should be transferred to the Government (Section 47 of the RBI Act).
- Previously, there were several attempts to frame an ECF for the RBI. However, under the changed circumstances, the RBI central board constituted a new committee (under Bimal Jalan) to design an ECF in 2018.
What is a Bimal Jalan Committee?
- The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) in November 2018 had constituted a six-member committee, chaired by former governor Dr Bimal Jalan, to review the current economic capital framework (ECF), after the Ministry of Finance asked the central bank to follow global practices.
What did the Bimal Jalan Committee Recommend?
- According to the Committee, a better distinction between the two components of RBI's economic capital, realised equity and revaluation balances, was needed.
- The realised equity can be used as a buffer in meeting losses, whereas the revaluation balances will be used only during market risks as they are unrealised valuation gains and cannot be distributed.
- The Committee has recommended the adoption of Expected Shortfall (ES) under stressed conditions for measuring the RBI’s market risk and asked to adopt a target of ES 99.5 per cent confidence level.
- It also asked to maintain a Contingent Risk Buffer (CRB) within 6.5 per cent and 5.5 per cent of RBI's balance sheet.
- The Jalan Committee recommended a surplus distribution policy that follows the realised equity maintained by the RBI.
- The panel also suggested that the RBI’s ECF should be reviewed every five years.
- In August 2019, the Central Board of the RBI, chaired by Governor Shaktikanta Das, finalised the RBI’s accounts for 2018-19 using the revised framework to determine risk provisioning and surplus transfer. According to the reports, the RBI had over Rs 9 trillion of surplus capital with it.
Personality Rights

- 23 May 2024
Why is it in the News?
Hollywood actress Scarlett Johansson has said she was “shocked” and “angered” to hear the voice of GPT-4o, OpenAI’s latest AI model, as it sounded “eerily similar” to her own voice.
What are Personality Rights?
- Personality rights or publicity rights are a subset of “celebrity rights” – a much broader term used to refer to certain rights enjoyed by celebrities.
- Besides personality rights, celebrities also have “privacy rights”, which include the right to be left alone.
- The name, voice, signature, images, or any other feature easily identified by the public are markers of a celebrity’s personality and are referred to as “personality rights.”
- These could include poses, mannerisms, or any other distinct aspect of their public persona.
- Several celebrities register aspects of their personalities as trademarks to use them commercially.
- For instance, footballer Gareth Bale trademarked the heart shape he makes with his hands as part of goal celebrations.
- The rationale behind such rights is that only the creator or owner of the unique features can gain commercial benefit from them.
- Therefore, unauthorised use could lead to revenue losses.
- In India, actors such as Rajnikanth, Anil Kapoor and Jackie Shroff have approached the courts over “personality rights” in India.
- Recently, the Delhi HC protected the personality and publicity rights of actor Jackie Shroff while restraining various e-commerce stores, AI chatbots, and social media from misusing Shroff’s name, image, voice, and likeness without his consent.
How are Personality Rights Protected in India?
- Although personality rights or their protection are not explicitly defined in Indian statutes, they usually fall under the right(s) to privacy and property.
- Concepts in intellectual property rights cases, such as passing off and deception, are usually applied in such cases while ascertaining if protection is warranted.
- Protection can be given through damages and injunctions.
International Criminal Court (ICC)

- 21 May 2024
Why is it in the News?
International Criminal Court (ICC) Chief Prosecutor recently announced that he has applied for arrest warrants against Israeli Prime Minister Benjamin Netanyahu and Defence Minister Yoav Gallant for crimes against humanity in the ongoing Gaza war.
What is the International Criminal Court (ICC)?
- The International Criminal Court (ICC) in The Hague (Netherlands) is a permanent global court established in 2002.
- The ICC was created as a result of the Rome Statute, a treaty established at a United Nations conference in Italy and signed in 1998 by 120 countries — giving the ICC its power.
- The ICC is independent of the United Nations (UN) but is endorsed by the UN General Assembly.
- It also maintains a cooperation agreement with the UN.
- It has the power to prosecute individuals and leaders for genocide, crimes against humanity and war crimes.
- Unlike the International Court of Justice (ICJ), which is an organ of the UN, the ICC does not prosecute states.
The Court does not have universal jurisdiction:
- Its jurisdiction only applies to crimes committed by nationals of States Parties or Non-States Parties that have recognized its jurisdiction through declaration and crimes committed in such States.
- The Court may also exercise its jurisdiction for crimes that have been referred to it by the United Nations Security Council, in accordance with a resolution adopted under Chapter VII of the Charter of the United Nations.
The Court’s jurisdiction is governed by the principle of complementarity:
- It does not relieve States of their primary responsibility and only intervenes when the States have been unable or did not wish, to try crimes under their jurisdiction.
- The Court is not a United Nations body. However, it is part of the international system to fight against impunity and prevent and handle crises.
How is the ICC governed?
- The Rome Statute created three bodies:
- The International Criminal Court
- The Assembly of States Parties
- The Trust Fund for Victims
- The Assembly of States Parties (ASP) is made up of representatives of States Parties.
- It provides general guidelines while respecting the independence of the Court and makes decisions relating to how it operates (in particular by electing judges and the Prosecutor and by approving the ICC’s budget).
- The Trust Fund for Victims was created by the ASP to grant individual reparations to victims by executing reparations orders handed down by the Court.
- It also contributes to their rehabilitation through psychological and physical recovery and material support.
- The Fund has financed projects in Uganda, the Central African Republic and the Democratic Republic of the Congo.
The International Criminal Court is made up of four bodies:
- The Presidency (made up of three judges) is responsible for external relations with States, organizes the Divisions’ judicial work and supervises the administrative work of the Registry;
- The Judicial Divisions – the Pre-Trial Division, the Trial Division and the Appeals Division – carry out judicial proceedings;
- The Office of the Prosecutor carries out preliminary analyses, investigations and prosecutions;
- The Registry carries out non-judicial activities related to safety, interpretation, information and outreach or support to lawyers for the defence and victims.
The recruitment process for judges at the ICC:
- Every three years, the ASP elects six new judges, a third of the 18 ICC judges, for a term of nine years.
- The candidates for the position of judge at the ICC are presented by the States Parties.
- The election of judges is governed by a unique procedure that aims to ensure, insofar as possible, that there is a balanced bench with regard to legal expertise, geographical representation and gender.
How does the International Criminal Court differ from the International Court of Justice?
International Criminal Court:
1. Part of the United Nations (UN)?
Ans. No, The International Criminal Court is independent but co-operates closely with the UN.
2. What is its aim?
Ans. To try individuals who are suspected of the crime of genocide, war crimes, crimes against humanity or the crime of aggression.
3. Where is it located?
Ans. The Hague
International Court of Justice:
1. Part of the United Nations (UN)?
Ans. No, The International Court of Justice is the principal judicial organ of the United Nations.
2. What is its aim?
Ans. To settle legal disputes between states,and to advise the UN on legal questions.
3. Where is it located?
Ans. The Hague
AI Agents

- 22 May 2024
Why is it in the News?
Known as ‘AI agents’, GPT-4o and Project Astra have been touted as far superior to conventional voice assistants such as Alexa, Siri, and Google Assistant.
What are AI Agents?
- AI agents are sophisticated AI systems that can engage in real-time, multi-modal (text, image, or voice) interactions with humans.
- Unlike conventional language models, which solely work on text-based inputs and outputs, AI agents can process and respond to a wide variety of inputs including voice, images, and even input from their surroundings.
- AI agents are designed to perceive their environment and take actions in order to achieve specific goals.
- They perceive their environment through sensors, process the information using algorithms or models, and then take actions using actuators or other means.
- AI agents can range from simple systems that follow predefined rules to complex, autonomous entities that learn and adapt based on their experiences.
- They're utilized in various fields, including robotics, gaming, virtual assistants, autonomous vehicles, and more.
- These agents can be reactive (responding directly to stimuli), deliberative (planning and making decisions), or even have learning capabilities (adapting their behaviour based on data and experiences).
How are they Different From Large Language Models?
- While large language models (LLMs) like GPT-3 and GPT-4 have the ability only to generate human-like text, AI agents make interactions more natural and immersive with the help of voice, vision, and environmental sensors.
- Unlike LLMs, AI agents are designed for instantaneous, real-time conversations with responses much similar to humans.
- LLMs lack contextual awareness, while AI agents can understand and learn from the context of interactions, allowing them to provide more relevant and personalised responses.
- Also, language models do not have any autonomy since they only generate text output.
- AI agents, however, can perform complex tasks autonomously such as coding, data analysis, etc.
- When integrated with robotic systems, AI agents can even perform physical actions.
What are the Potential Uses of AI Agents?
- AI agents can serve as intelligent and highly capable assistants.
- They are capable of handling an array of tasks, from offering personalised recommendations to scheduling appointments.
- AI agents can be ideal for customer service as they can offer seamless natural interactions, and resolve queries instantly without actually the need for human interventions.
- In the field of education and training, AI agents can act as personal tutors, customise themselves based on a student’s learning styles, and may even offer a tailored set of instructions.
- In healthcare, they could assist medical professionals by providing real-time analysis, diagnostic support, and even monitoring patients.
Risks and Challenges Associated With AI Agents:
- While AI agents showcase immense potential for the future, they are not without risks.
- Privacy and security are a key area of concern as AI agents gain access to more personal data and environmental information.
- Just like any AI model, AI agents can carry forward biases from their training data or algorithms, leading to harmful outcomes.
As these systems become more common, appropriate regulations and governance frameworks should be laid out to ensure their responsible deployment.
Doppler Radar Speed Guns

- 22 May 2024
Why is it in the News?
The Consumer Affairs Ministry has invited public comments by June 11 on draft rules for microwave Doppler radar equipment used to measure vehicle speeds on roads, according to a circular issued by the ministry.
What are Doppler Radar Speed Guns?
- Doppler radar speed guns are tools that use the Doppler effect to measure the speed of moving objects, such as vehicles.
- They consist of a radio transmitter and receiver that send out a narrow beam of radio waves.
- When these waves bounce off a moving object, their frequency changes due to the Doppler effect.
- This phenomenon occurs when the frequency of a wave changes as its source moves relative to an observer.
The Doppler Effect
- The Doppler effect refers to the change in frequency or wavelength of a wave in relation to an observer moving relative to the wave source.
- In the case of a radar speed gun, the waves in question are radio waves.
How do Doppler Radar Speed Guns work?
- As the object moves toward or away from the radar gun, the frequency of the reflected waves is altered.
- If the object is approaching the radar, the frequency increases
- If it's moving away, the frequency decreases
- The radar speed gun analyzes these changes to calculate the object's speed using the following equation:
- v = Δf/f × c/2
- where v is the object's speed, Δf is the frequency shift, f is the transmitted frequency, and c is the speed of light.
- Doppler radar speed guns are commonly used by law enforcement to monitor vehicle speeds, ensuring safety on the roads.
- They can also be found in various other applications, such as aviation, navigation, and meteorology.
Advantages
- Non-Contact Measurement: Measures speed without needing to be in contact with the vehicle.
- Quick and Accurate: Provides rapid speed measurements with high accuracy.
- Versatile: Can be used in various conditions and for different types of moving objects.
Census Begins for Blue Sheep and Himalayan ibex

- 22 May 2024
Why is it in the News?
Wildlife authorities in Himachal Pradesh’s high altitude, cold desert district of Lahaul & Spiti have started surveys as part of the census to estimate the population of blue sheep or bharal and the Himalayan ibex, the main prey of the iconic snow leopard.
About Himalayan Ibex:
- The Himalayan ibex, a subspecies of the Siberian ibex, is native to the Himalayan regions of India, Pakistan, Tibet, and Nepal.
- These sure-footed, sturdy wild goats belong to the genus Capra in the family Bovidae and are typically found in mountainous regions across Europe, Asia, and northeastern Africa.
- Scientific Name: Capra sibirica hemalayanus
- Habitat: Himalayan ibex inhabit the high-altitude regions of the Himalayas, including the Trans-Himalayan areas, at elevations between 3,000 and 5,800 meters.
- In India, they are primarily found in the states of Jammu and Kashmir, Himachal Pradesh, and Uttarakhand.
Features:
- Size: Adult Himalayan ibex weighs about 90 kg and stands around 40 inches tall.
- Sexual Dimorphism: Males are larger than females and have large, curved horns with front notches that grow each year.
- Coat: Their coat varies from light brown to reddish-brown with a white belly and distinctive black and white markings on their legs.
- The coat is thick and woolly in winter, shedding in early summer. A darker dorsal stripe is also present.
- Behaviour: They are typically found in small herds, sometimes numbering up to 50 individuals.
- They are agile and can run at speeds of up to 50 km/h.
Conservation Status:
- IUCN Red List: Near Threatened
About Blue Sheep/Bharal:
- The blue sheep, also known as the bharal, is a caprine species native to the high Himalayas.
- Its scientific name is Pseudois nayaur, and it is the sole member of the genus Pseudois.
Distribution:
- The bharal is found in several countries, including India, Bhutan, China (specifically in Gansu, Ningxia, Sichuan, Tibet, and Inner Mongolia), Myanmar, Nepal, and Pakistan.
Features:
- Size: Medium-sized caprids, measuring 115 to 165 cm (45 to 65 in) in length, with tails ranging from 10 to 20 cm (3.9 to 7.9 in).
- They stand 69 to 91 cm (27 to 36 in) at the shoulder.
- Sexual Dimorphism: Males are slightly larger than females.
- Coat: Their short, dense coat is slate grey, often with a bluish shine. The underparts and backs of the legs are white, while the chest and fronts of the legs are black.
- Horns: The horns grow upwards, curve out, and then back, resembling an upside-down arc.
- Behaviour: Bharal are diurnal, alternating between feeding and resting on grassy mountain slopes.
Conservation Status:
- IUCN Red List: Least Concern
- Wildlife Protection Act 1972: Schedule ICoat: Their short, dense coat is slate grey, often with a bluish shine. The underparts and backs of the legs are white, while the chest and fronts of the legs are black.
- Horns: The horns grow upwards, curve out, and then back, resembling an upside-down arc.
- Behaviour: Bharal are diurnal, alternating between feeding and resting on grassy mountain slopes.
Conservation Status:
- IUCN Red List: Least Concern
- Wildlife Protection Act 1972: Schedule I
Aircraft Turbulence

- 22 May 2024
Why is it in the News?
A passenger died and many were injured when a Singapore Airlines’ Boeing 777 headed from London to Singapore “severe turbulence” en route.
What is the Aircraft Turbulence
- Turbulence means disruption of airflow over the wings of an aeroplane, which causes it to enter irregular vertical motion.
- These pockets of disturbed air can have many causes, most obviously the unstable weather patterns that trigger storms.
- It is caused by the relative movement of disturbed air through which an aircraft is flying.
There are at least seven kinds of turbulence that an aircraft can run into:
- Wind Shear: It happens when there is a sudden change in wind direction, whether vertically or horizontally.
- Typically occurs close to thunderstorms, jet streams, etc.; tricky for pilots as tailwinds suddenly change to headwinds or vice versa.
- Frontal: Created in the frontal zone when warm air is lifted by a sloping frontal surface and friction between opposing air masses.
- Most palpable when warm air is moist; intensity increases with thunderstorms. Most commonly close to thunderstorms.
- Convective: When land surface temperature rises, the air above the ground heats up and rises, creating air pockets around it.
- Convection currents cause difficulties during approach as they tend to affect the rate of descent.
- Wake: It forms behind an aircraft when it flies through air-creating wingtip vortices.
- Mechanical: This type of turbulence occurs when tall solid objects such as mountains or highrise constructions disrupt the normal airflow, causing the air for planes to fly through to become dirty.
- Clear Air: It occurs when an aircraft crosses from one air mass to another, which has a different direction.
- Clear air turbulence could also happen when an aircraft moves out of a jet stream. Clear air turbulence is mainly caused by wind or jet streams.
- Mountain View: It is one of the most severe; these are oscillations that form on the downwind side of mountains when strong winds flow towards mountains in a perpendicular fashion.
- Aircraft tracking perpendicularly across, or downwind of a mountain, may experience a sudden loss of altitude followed by a sudden reduction in airspeed.
Are turbulence incidents dangerous?
- It depends on their nature and intensity.
- Aircraft undergo some form of turbulence on a regular basis and pilots are trained to deal with these.
- However, there have been several instances when turbulence has brought down modern jetliners.
Even in these cases, while intense turbulence has been the main cause of an accident, several other factors — such as lack of proper training, and poor dissemination of weather or wind-related information — have contributed to the accident.
Paris Principles on NHRIs

- 21 May 2024
Why is it in the News?
For the second year in a row, an organisation affiliated with the UN human rights office has deferred accreditation for India’s human rights body, the National Human Rights Commission (NHRC).
What are the Paris Principles?
- The Paris Principles, formally Principles Relating to the Status of National Human Rights Institutions, which were adopted by the UN General Assembly on December 20, 1993, set out minimum standards that NHRIs must meet in order to be considered credible and to operate effectively.
- The Paris Principles lay down six main criteria to determine which NHRIs are functioning effectively and would receive accreditation from GANHRI.
- They are
- broad mandate based on universal human rights norms and standards
- autonomy from the government
- independence guaranteed by the statute or Constitution
- pluralism, including membership that broadly reflects their society
- adequate resources and
- adequate powers of investigation
- These Principles also say that NHRIs should be equipped to receive complaints and cases brought by individuals, third parties, NGOs, trade unions, or other organisations representative of professionals such as lawyers and journalists.
Accreditation:
- Global Alliance of National Human Rights Institutions (GANHRI), which represents about 120 national human rights institutions, is responsible for reviewing and accrediting these institutions in compliance with the Paris Principles every five years.
- GANHRI acts through its Subcommittee on Accreditation (SCA), which categorises member NHRIs into two groups, ‘A’ and ‘B’. As of November 29, 2023, 120 NHRIs were accredited by GANHRI, 88 of which were given an ‘A’ rank, indicating full compliance with the Paris Principles; the remaining 32 were put under ‘B’, indicating partial compliance.
Why has India’s Accreditation Been Put on Hold?
- India’s accreditation status was put on hold after the Sub-Committee on Accreditation (SCA) meeting on May 1 in Geneva.
- The SCA, which meets twice a year, scrutinizes each country’s human rights institution.
- The May 1 meeting, chaired by New Zealand with participation from South Africa, Sri Lanka, and Spain, highlighted several concerns about the National Human Rights Commission (NHRC) of India.
- Issues raised include a lack of transparency in NHRC appointments, conflicts of interest with police overseeing investigations, and no minority or female representation on the panel.
- Additionally, nine human rights organizations, including Amnesty International and Human Rights Watch, expressed concerns about India’s human rights record, citing increasing restrictions on civic space and discrimination against minorities.
- UN human rights experts also highlighted “attacks on minorities, media, and civil society” in India.
What Happens if India Loses Accreditation?
- If India loses its 'A' status accreditation, its National Human Rights Institution (NHRI) will face significant limitations. With 'A' status, NHRIs can participate in the UN Human Rights Council, its subsidiary bodies, and some UNGA bodies and mechanisms, and hold full membership in the Global Alliance of National Human Rights Institutions (GANHRI) with voting and governance rights.
- With 'B' status, NHRIs can attend GANHRI meetings but cannot vote or hold governance positions. Without proper accreditation, India’s NHRC cannot represent the country at the UN Human Rights Council, vote, or hold governance roles.
- India’s review has been deferred, and a final decision is yet to be made.
What is India’s Record of Accreditation with GANHRI?
- India’s National Human Rights Commission (NHRC) was established in 1993 and first accredited by the Global Alliance of National Human Rights Institutions (GANHRI) in 1999.
- It achieved 'A' status in 2006 and retained it in 2011.
- However, in 2016, accreditation was deferred due to issues like the appointment of political representatives and lack of gender balance and pluralism in the NHRC staff.
- Despite these concerns, the NHRC regained 'A' status in 2017.
- In 2023, the Sub-Committee on Accreditation (SCA) withheld India’s accreditation again, citing six reasons, including the NHRC’s inability to operate without government interference and the presence of too many government officials and individuals affiliated with the ruling party in the commission.
Rangelands in India

- 21 May 2024
Why is it in the News?
A new report by the United Nations paints a concerning picture of the world’s rangelands, with up to 50 per cent estimated to be degraded.
What are Rangelands?
- A rangeland is an open area that is suitable for grazing livestock.
- Rangelands are home to grass and grass-like plants, shrubs, and scattered trees.
- They are, however, unfit for growing crops due to their aridity and poor soil quality.
- Rangelands cover 80 million square kilometres, or over 54 per cent of the terrestrial surface, constituting the largest land cover/use type in the world but accounting for one-sixth of global food production and representing nearly one-third of the planet’s carbon reservoir.
- According to the Rangelands Atlas, livestock production systems in rangelands cover 45 per cent of the global land surface, almost half of which is situated in drylands.
- In India, rangelands occupy about 121 million hectares and the area used for grazing is estimated at around 40 per cent of the total land surface of India, including grasslands (17 per cent), and forests (23 per cent).
Key Characteristics of Rangelands in India:
- Vegetation: Rangelands in India is primarily covered with grasses and shrubs, such as Dichanthium annulatum (gamhar), Cenchrus ciliaris (buffel grass), and Ziziphus nummularia (ber).
- The presence and type of vegetation vary based on rainfall and soil conditions, with trees being scattered or sometimes entirely absent.
- Climate: These areas experience semi-arid to arid climates with significant seasonal variations in rainfall.
- Droughts are a frequent challenge.
- Soil: Rangeland soils are typically thin and less fertile than those found in agricultural areas.
- Land Use: Rangelands are mainly used for grazing by domestic animals like cattle, sheep, and goats.
- Some of these lands also support wildlife herbivores.
The Significance and Management of Rangelands in India:
- Rangelands play a pivotal role in India's ecosystem, serving as primary grazing areas for livestock, maintaining biodiversity, and providing ecological services such as soil erosion prevention, water flow regulation, and carbon storage.
- These lands are also a crucial source of livelihood for millions through pastoralism, dairy production, and wool production.
- However, rangelands face multiple challenges, including overgrazing, climate change, and encroachment, which negatively impact their health and productivity.
- To address these issues, several management strategies have been employed:
- Rotational Grazing: This approach allows for controlled grazing periods, enabling vegetation to recover and promoting long-term sustainability.
- Reseeding: By reintroducing native grasses and shrubs, the quality of rangelands can be significantly enhanced.
- Community-Based Management: Engaging local communities in the decision-making process fosters sustainable practices and ensures the well-being of both the rangelands and the people relying on them.
- Understanding the significance of rangelands in India is essential for maintaining their vitality, supporting the livelihoods of those dependent on them, and ensuring the continued provision of vital ecological services.
Primary Amoebic Meningoencephalitis (PAM)
- 21 May 2024
Why is it in the News?
A five-year-old girl from Malappuram district in Kerala who had been undergoing treatment for amoebic meningoencephalitis at the Government Medical College Hospital Kozhikode has died.
What is the Primary Amoebic Meningoencephalitis?
- Primary amebic meningoencephalitis (PAM) is a rare brain infection that is caused by Naegleria fowleri.
- It is a free-living amoeba or a single-celled living organism.
- Naegleria fowleri lives in warm fresh water and soil around the world and infects people when it enters the body through the nose.
- Higher temperatures of up to 115°F (46°C) are conducive to its growth and it can survive for short periods in warm environments.
- The amoeba can be found in warm freshwater, such as lakes and rivers, swimming pools, splash pads, surf parks, or other recreational venues that are poorly maintained or minimally chlorinated.
How does Naegleria fowleri infect people?
- Naegleria fowleri enters the body through the nose, usually when people are swimming. It then travels up to the brain, where it destroys the brain tissue and causes swelling.
- Notably, people cannot get infected with Naegleria fowleri from drinking water contaminated with the amoeba.
- PAM is also non-communicable.
Symptoms of PAM:
- In the initial stage, the symptoms include headache, fever, nausea and vomiting.
- Later on, the patient may have a stiff neck and experience confusion, seizures, hallucinations and slip into a state of coma.
- According to the US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), “Most people with PAM die within 1 to 18 days after symptoms begin.
- It usually leads to coma and death after 5 days.”
What is the treatment for primary amoebic meningoencephalitis?
- As earlier reported, scientists haven’t been able to identify any effective treatments for the disease yet.
- At present, doctors treat it with a combination of drugs, including amphotericin B, azithromycin, fluconazole, rifampin, miltefosine, and dexamethasone.
Copernicus Emergency Management Service (CEMS) Programme

- 21 May 2024
Why is it in the News?
As part of a multi-agency effort to locate a helicopter carrying Iranian President Ebrahim Raisi that crashed in East Azerbaijan province recently, the European Union activated its emergency satellite mapping service at Iran’s request as adverse weather and darkness hampered search and rescue operations.
What is the Copernicus Emergency Management Service (CEMS)?
- The Copernicus Emergency Management Service (CEMS) is part of the Copernicus Programme, the European Union’s Earth Observation Programme.
- CEMS is managed directly by the European Commission via the Joint Research Centre.
- CEMS supports all actors involved in the management of natural or manmade disasters by providing geospatial data and images for informed decision-making.
- CEMS constantly monitors Europe and the globe for signals of an impending disaster or evidence of one happening in real-time.
- The service immediately notifies national authorities of their findings or can be activated on-demand and offers to provide them with maps, time series or other relevant information to better manage disaster risk.
- CEMS products are created using satellite, in-situ (non-space) and model data.
- CEMS comprises two components:
- On-demand Mapping
- Early Warning & Monitoring
- Copernicus EMS Early Warning and Monitoring offers critical geospatial information at European and global levels through continuous observations and forecasts for floods, droughts and forest fires.
- It includes the European Flood Awareness System (EFAS), the European Forest Fire Information System (EFFIS) and the European Drought Observatory (EDO).
- It also links to the global versions of the early warning systems and the Global Disaster Alert and Coordination System (GDACS) for tropical cyclones.
- These versions cover the overseas areas of Europe that are often affected by extreme events.
- The service is provided free of charge to all users either in rush mode, for emergency management activities that require immediate response and/or non-rush mode, to support emergency disaster management activities not related to immediate response, analysing pre-disaster risk assessment and population and asset vulnerability or post-disaster recovery and reconstruction.
- It can be activated only by designated authorised users.
R21/Matrix-M Vaccine
- 21 May 2024
Why is it in the News?
Vaccines manufacturer Serum Institute of India (SII) recently said it has started exports of the 'R21/Matrix-M' malaria vaccine to Africa as part of the global fight against the disease.
What is R21/Matrix-M Vaccine?
- The R21/Matrix-M vaccine is a newly approved preventive measure against malaria in children, marking the second malaria vaccine recommended by the World Health Organization (WHO) after the RTS, S/AS01 vaccine in 2021.
- Developed by the Jenner Institute at Oxford University and the Serum Institute of India, the vaccine received support from the European and Developing Countries Clinical Trials Partnership (EDCTP), the Wellcome Trust, and the European Investment Bank (EIB).
- This low-cost, high-efficacy vaccine is already licensed in several African countries.
How the R21/Matrix-M Vaccine Works?
- Vaccines work by presenting an antigen—a component of the virus or bacteria that the immune system can recognize and respond to—to immune cells.
- The R21/Matrix-M vaccine targets the plasmodium 'sporozoite', the initial form of the malaria parasite entering the human body.
- Infected mosquitoes inject only a few sporozoites (10-100) before the parasite multiplies, making them an ideal target for a vaccine.
- R21 is a subunit vaccine that delivers parts of a protein secreted by the sporozoite, combined with a component of the hepatitis B virus known to trigger a strong immune response.
- Additionally, the vaccine contains Matrix-M, an "adjuvant" that enhances the immune system’s response, making it more potent and long-lasting.
Key Facts about Malaria:
- Malaria is a life-threatening disease caused by parasites that are transmitted to people through the bites of infected female Anopheles mosquitoes.
- There are five parasite species that cause malaria in humans, with Plasmodium falciparum and Plasmodium vivax posing the greatest threat.
- Malaria is prevalent in tropical areas where it’s hot and humid.
- In 2020, there were an estimated 241 million malaria cases worldwide, resulting in approximately 627,000 deaths. Sub-Saharan Africa bears the heaviest burden, accounting for about 95% of malaria cases and 96% of deaths, primarily among children under five.
- Children under 5 years of age are the most vulnerable group affected by malaria.
- Symptoms include fever, chills, headache, nausea, and muscle pain, which can progress to severe illness and death if untreated.
- Cerebral malaria, the most severe form, can lead to coma and represents about 15% of deaths in children and nearly 20% of adult deaths.
- Malaria is preventable and curable; early treatment often results in full recovery.
- Treatment involves various antimalarial drugs, including chloroquine, hydroxychloroquine, primaquine, artemisinin-based therapy, and atovaquone-proguanil.
- The type of parasite determines the specific medication used.
- Continued efforts are essential to control and ultimately eradicate malaria, with vaccines like RTS, S/AS01 (Mosquirix) and R21/Matrix-M offering promising advances in prevention, especially for children in high-risk regions.
Contaminated Blood Scandal
- 20 May 2024
Why is it in the News?
An independent inquiry report on the UK’s contaminated blood scandal, to be published Monday (May 20), indicates Britain may pay over 10 billion pounds ($12.70 billion) in compensation to thousands infected with HIV or hepatitis.
What is the Contaminated Blood Scandal?
- During the 1970s and 1980s, thousands of people who had the blood-clotting disorder haemophilia were given blood donated or sold by people who were infected with the HIV virus and hepatitis.
- Tainted blood was also given to people who needed blood transfusions after childbirth or surgery.
- In the early 1970s, the NHS (Britain’s National Health Service) started using a new treatment for haemophilia called Factor VIII.
- This was a processed pharmaceutical product that was created by pooling plasma from many donors.
- Factor VIII was considered to be a “wonder drug” for patients with classical haemophilia and Von Willebrand Syndrome (which is a bleeding disorder in which the patient’s blood cannot clot fully), more efficient and convenient than earlier treatments.
- The nature of Factor VIII was such that even one infected donor could compromise the entire batch of the protein.
- The product used by the NHS was imported from the United States, where a large volume of donated plasma at the time came from prisoners and users of intravenous drugs who were paid for their blood.
- The inquiry report has estimated that more than 30,000 people were infected with HIV, hepatitis C or, as in the case of 1,250 haemophiliacs, both.
- Most hepatitis C infections were seen in transfusion recipients, and as many as 380 children were infected with HIV.
- Nearly two-thirds of those who were infected with HIV later died of AIDS-related illnesses, and an unknown number transferred HIV to their partners.
- The report said that 2,400-5,000 recipients of blood developed hepatitis C, with the exact figure not known yet, as symptoms can show up years later.
How did the government react after the scandal was widely known?
- It was only after 1985 that all Factor VIII products were heat-treated to kill the HIV virus.
- However, UK blood donations were not routinely screened for hepatitis C until 1991.
- Evidence provided to the inquiry suggests that the British government chose to turn a blind eye to the situation, mainly due to financial considerations.
- Official documents from the 1990s revealed that due to cost concerns, the NHS did not pursue adequate testing or awareness campaigns, despite warnings in the mid-1970s about the risks of viral infections from US blood donations.
- As early as 1953, the World Health Organisation (WHO), had warned of the hepatitis risks associated with the mass pooling of plasma products.
- It urged that dried plasma should be prepared from pools of between 10 to 20 donors to reduce the risk of contamination.
- In 1974, the UN agency warned Britain not to import blood from countries with a high prevalence of hepatitis, such as the US.
- Another warning of the risk of contracting HIV from blood products was issued in 1982.
- The following year, The Lancet and WHO said haemophiliacs should be told about the dangers of donated plasma.
Calcium Carbide

- 20 May 2024
Why is it in the News?
Food regulator FSSAI has asked traders and food business operators not to use the banned product 'calcium carbide' for ripening of fruits.
What is Calcium Carbide?
- Calcium carbide is a hazardous chemical that can have adverse effects on human health.
- It is a colourless, odourless substance that reacts with moisture to produce acetylene gas, which is a known carcinogen.
- This gas can cause respiratory problems, eye irritation, and even skin burns.
- In addition, calcium carbide also contains traces of arsenic and phosphorus, which are toxic substances that can lead to serious health complications.
- Calcium carbide is a commonly used chemical compound in the agriculture industry, especially for ripening fruits.
- It is a cheap and easily available substance that is widely used by fruit vendors and farmers in India to speed up the ripening process of fruits such as mangoes, bananas, and papayas.
- Due to these dangers, the use of calcium carbide for ripening fruits has been banned under the Regulation of the Food Safety and Standards (Prohibition and Restrictions on Sales) Regulations, 2011.
- This regulation explicitly states, "No person shall sell or offer or expose for sale or have in his premises for sale under any description, fruits which have been artificially ripened by use of acetylene gas, commonly known as carbide gas".
Ethylene gas as a safer alternative:
- Considering the issue of rampant use of banned calcium carbide, FSSAI has permitted the use of ethylene gas as a safer alternative for fruit ripening in India.
- Ethylene gas can be used at concentrations up to 100 ppm, depending upon the crop, variety and maturity.
- Ethylene, a naturally occurring hormone in fruits, regulates the ripening process by initiating and controlling a series of chemical and biochemical activities.
- The treatment of unripe fruits with ethylene gas triggers the natural ripening process until the fruit itself starts producing ethylene in substantial quantities.
- Further, the Central Insecticides Board and Registration Committee (CIB & RC) have approved Ethephon 39 per cent SL for the uniform ripening of mangoes and other fruits.
Nucleosynthesis
- 20 May 2024
Why is it in the News?
Stellar nucleosynthesis is the process by which stars forge elements inside their cores.
What is Nucleosynthesis?
- Nucleosynthesis is the process by which atomic nuclei undergo nuclear reactions and decay to form new nuclei.
- It is responsible for the production of new elements in the universe.
- Nucleosynthesis occurs in various environments, such as during the Big Bang, in the cores of stars through nuclear fusion, and in black hole accretion disks through nuclear burning.
- The process is temperature-dependent, and the rates of nuclear reactions are influenced by the temperature of the environment.
- The Big Bang Nucleosynthesis (BBN) model is a fundamental theory that explains the evolution of the early universe and predicts the abundance of light elements.
- Nucleosynthesis plays a crucial role in understanding the composition of the universe and can provide insights into physics beyond the standard model.
Types of nucleosynthesis:
- Nucleosynthesis occurs in several different environments and phases of the universe's evolution, including:
- Stellar Nucleosynthesis: This occurs within stars and is responsible for producing most of the chemical elements heavier than hydrogen and helium.
- As stars age and undergo various stages of nuclear fusion, they synthesize elements up to iron in their cores, and heavier elements during supernova explosions at the end of their life cycles.
- Big Bang Nucleosynthesis: This took place during the early moments of the universe's existence, shortly after the Big Bang.
- t primarily produced the lightest elements, hydrogen, and helium, along with trace amounts of lithium, beryllium, and boron.
- Cosmic Ray Spallation: High-energy cosmic rays interacting with interstellar matter can cause fragmentation of atomic nuclei, resulting in the production of lighter elements and isotopes.
Bacterial Pathogens Priority List (BPPL)

- 20 May 2024
Why is it in the News?
The World Health Organization (WHO) recently released its updated Bacterial Priority Pathogens List (BPPL) 2024.
What is the Bacterial Pathogens Priority List?
- The Bacterial Pathogens Priority List (BPPL) is a crucial tool in the global effort to combat antimicrobial resistance (AMR).
Background:
- In 2017, the World Health Organization (WHO) created the first BPPL to guide investment in the research and development (R&D) of new antibacterial treatments, listing 13 bacterial pathogens (phenotypes).
- The list was developed using the Multi-Criteria Decision Analysis (MCDA) method, a scientific approach that evaluates and ranks alternatives based on multiple criteria, ensuring systematic and transparent decision-making.
- The 2024 WHO BPPL expands to cover 24 pathogens across 15 families of antibiotic-resistant bacteria, categorizing them into critical, high, and medium priority groups to guide R&D and public health efforts.
Significance:
- The BPPL directs priorities for R&D and investment in AMR, highlighting the necessity for region-specific strategies to combat resistance effectively.
- It is aimed at developers of antibacterial medicines, academic and public research institutions, research funders, public-private partnerships involved in AMR R&D, and policymakers responsible for AMR policies and programs.
What is Antimicrobial Resistance (AMR)?
- Antimicrobial resistance (AMR) is the ability of microorganisms to persist or grow in the presence of drugs designed to inhibit or kill them.
- These drugs, called antimicrobials, are used to treat infectious diseases caused by microorganisms such as bacteria, fungi, viruses and protozoan parasites.
- When microorganisms become resistant to antimicrobials, standard treatments are often ineffective, and in some cases, no drugs provide effective therapy.
- Consequently, treatments fail and this increases illness and mortality in humans, animals and plants.
- For agriculture, this causes production losses, damages livelihoods and jeopardizes food security.
- Moreover, AMR can spread among different hosts and the environment, and antimicrobial-resistant microorganisms can contaminate the food chain.
- Antimicrobial resistance (AMR) is a major global threat of increasing concern to human and animal health.
- It also has implications for food safety, food security and the economic well-being of millions of farming households.
Project Astra

- 20 May 2024
Why is it in the News?
Recently, during the company's annual developer conference, Google unveiled an early version of Project Astra.
What is Project Astra?
- Project Astra is an experimental “multimodal” AI assistant developed by Google DeepMind.
- It's designed to be a versatile tool that can understand and respond to information from the real world through various means, like text, voice, images, and even videos.
- This makes it different from current AI assistants that mostly rely on internet searches and user input.
- Building on Google’s Gemini language model, Astra has multimodal capabilities to perceive visuals, sounds, and other real-world inputs.
- The aim is to create a universal AI helper that seamlessly assists us in daily life by comprehending the actual environment through sight and sound, not just text.
- Astra represents Google’s vision for next-gen AI assistants.
Key Features of Google's Project Astra:
- Visual Understanding: Astra can interpret and analyze visual input from its camera feed.
- It identifies objects, reads text, and describes scenes and environments in detail, allowing users to show Astra something and ask questions about it.
- Voice Interaction: Astra supports natural conversation without the need to repeatedly use wake words.
- It comprehends context and facilitates back-and-forth dialogue, even allowing users to interrupt its responses.
- Remembering Context: Astra retains memory of previous conversation parts, objects it has seen, and information provided by the user.
- This contextual awareness enhances the fluidity of interactions.
- Multimodal Integration: Astra integrates visual and auditory inputs to form a comprehensive understanding of the current situation, correlating what it sees and hears to fully grasp the context.
- Real-Time Assistance: Astra delivers real-time assistance by rapidly processing sensor data and queries, ensuring a responsive and interactive user experience.
What are Multimodal AI Models?
- Multimodal AI models are advanced artificial intelligence systems that process and integrate multiple types of data inputs, such as text, images, audio, and video, to develop a comprehensive understanding of context.
- By combining these different modalities, these models enhance their ability to interpret complex scenarios more accurately than unimodal systems.
- For instance, in autonomous vehicles, multimodal AI uses data from cameras, lidar, radar, and GPS for better navigation.
- In healthcare, these models integrate medical images with patient history for improved diagnostics.
- Applications also include virtual assistants, which understand and respond to spoken commands while recognizing objects in images, and educational tools that combine text, video, and interactive content for richer learning experiences.
- Multimodal AI models are often implemented using deep learning techniques, which allow the model to learn complex representations of the different data modalities and their interactions.
- As a result, these models can capture the rich, diverse information present in real-world scenarios, where data often comes in multiple forms.
Open Network for Digital Commerce (ONDC)

- 18 May 2024
Why is it in the News?
The ONDC Startup Mahotsav was held in New Delhi recently in collaboration between the Startup India initiative and the Open Network for Digital Commerce (ONDC).
About the Open Network for Digital Commerce (ONDC):
- The Open Network for Digital Commerce (ONDC) is a network based on open protocol and will enable local commerce across segments, such as mobility, grocery, food order and delivery, hotel booking and travel, among others, to be discovered and engaged by any network-enabled application.
- The platform aims to create new opportunities, curb digital monopolies support micro, small and medium enterprises and small traders and help them get on online platforms.
- It is an initiative of the Department for Promotion of Industry and Internal Trade (DPIIT) under the Ministry of Commerce and Industry.
Features of ONDC:
- ONDC, a UPI of e-commerce, seeks to democratise digital or electronic commerce, moving it from a platform-centric model to an open network.
- Through ONDC, merchants will be able to save their data to build credit history and reach consumers.
- The proposed government-backed platform aims to create a level playing field for e-commerce behemoths such as Amazon, Flipkart, and offline traders who have been crying foul at the unfair trade practices of these e-tailers.
- The platform will also be compliant with the Information Technology Act, 2000 and designed for compliance with the emerging Personal Data Protection Bill.
- In this system, ONDC plans to enable sellers and buyers to be digitally visible and transact through an open network, regardless of what platform or application they use.
- It will also empower merchants and consumers by breaking silos to form a single network to drive innovation and scale, transforming all businesses from retail goods, food to mobility.
- The new framework aims at promoting open networks developed on open-sourced methodology, using open specifications and open network protocols independent of any specific platform.
- It is expected to digitise the entire value chain, standardise operations, promote inclusion of suppliers, derive efficiencies in logistics and enhance value for consumers.
- According to the government's official statement, ONDC shall take all measures to ensure confidentiality and privacy of data in the network.
- ONDC shall not mandate the sharing of any transaction-level data by participants with ONDC.
- It will work with its participants to publish anonymised aggregate metrics on network performance without compromising on confidentiality and privacy.
- Presently, ONDC is in its pilot stage and the government has set up a nine-member advisory council, including Nandan Nilekani from Infosys and National Health Authority CEO R S Sharma, on measures needed to design and accelerate the adoption of ONDC.
Plunging Region of a Black Hole

- 18 May 2024
Why is it in the News?
For the first time, astronomers have observed the area right at the edge of a black hole where matter stops orbiting and plunges straight in at near-light speed.
What is the Plunging Region of a Black Hole?
- The plunging region of a black hole is an area where matter ceases to orbit the celestial object and instead falls directly into its incalculable depths.
- This phenomenon was initially predicted by Albert Einstein's groundbreaking theory of general relativity, which continues to shape our understanding of the cosmos.
- As matter approaches a black hole, it is torn apart and forms a rotating ring known as an accretion disc.
- According to general relativity, there exists an inner boundary within this disc, beyond which nothing can maintain its orbit around the black hole.
- Instead, the material is drawn towards the black hole at nearly the speed of light, marking the beginning of the plunging region.
- This region, situated just outside the event horizon, represents the point of no return for matter falling into a black hole.
- Despite the challenges posed by studying these enigmatic structures, researchers believe that investigating plunging regions could unveil new insights into the formation and evolution of black holes.
- Additionally, these studies may offer valuable information about the fundamental properties of space-time, potentially transforming our understanding of the universe and its most mysterious inhabitants.
What is a Black Hole?
- A black hole is a celestial phenomenon that arises from the remnants of a massive star that has exhausted its nuclear fuel and undergone gravitational collapse.
- It is characterized by an unfathomably dense core, known as a singularity, which is enveloped by a boundary called the event horizon.
- The event horizon serves as a point of no return; any matter or light that crosses this boundary is irrevocably drawn towards the singularity, making it impossible to escape the immense gravitational pull.
Black holes are classified into three categories based on their size and formation process:
- Stellar-mass black holes: These form when a massive star collapses at the end of its life cycle. They typically have masses ranging from approximately five to several dozen times that of our Sun.
- Supermassive black holes: Found at the centre of most galaxies, including our own Milky Way, these colossal structures boast masses that can reach billions of times the mass of the Sun.
- Intermediate-mass black holes: With masses between those of stellar mass and supermassive black holes, these entities are thought to form through the merger of smaller black holes or the collapse of dense clusters of stars.
- Due to their extreme nature, black holes have been the subject of extensive research and fascination in the scientific community.
- The study of these enigmatic structures continues to yield invaluable insights into the fundamental principles governing our universe.
World Telecommunication and Information Society Day

- 18 May 2024
Why is it in the News?
To commemorate the World Telecommunication and Information Society Day, C-DOT, the premier Telecom R&D Centre of the Department of Telecommunications (DoT) celebrates and announces special Initiatives “NIDHI” & “STAR Program” for the development of indigenous telecom solutions & technologies.
What is World Telecommunication and Information Society Day?
- World Telecommunication and Information Society Day (WTISD) is celebrated every year in May to honour the founding of the International Telecommunication Union (ITU) on May 17, 1969.
- The day can be traced back to commemoration of the two significant events in the history of global communication.
- World Telecommunication and Information Society Day (WTISD) commemorates two significant events in the history of global communication.
- Firstly, it marks the founding of the International Telecommunication Union (ITU) in 1865, when the first International Telegraph Convention was signed.
- Followed by, in November 2005, the World Summit on the Information Society (WSIS) called upon the United Nations General Assembly to also declare May 17th as World Information Society Day.
- And then in 2006, the ITU Plenipotentiary Conference in Antalya, Turkey, agreed to combine the two events as World Telecommunication and Information Society Day.
- This year’s World Telecommunications and Information Society Day 2024 focuses on the theme, “Digital Innovation for Sustainable Development,” underlying how digital innovation may help link everyone and create sustainable prosperity for all.
About the International Telecommunication Union (ITU):
- The International Telecommunication Union (ITU) is the United Nations specialized agency for information and communication technologies (ICTs).
- Established in 1865, it is the oldest among the UN’s 15 specialized agencies.
- ITU is responsible for allocating global radio spectrum and satellite orbits, developing technical standards to ensure network interconnectivity, and improving ICT access for underserved communities.
- Headquartered in Geneva, Switzerland, ITU is part of the UN Development Group and operates 12 regional offices worldwide.
- It functions as an intergovernmental public-private partnership with 193 member states and around 800 sector members. India, a member since 1952, was re-elected to the ITU Council for the 2019-2022 term.
Mitogenome
- 18 May 2024
Why is it in the News?
New research has found South African leopards originated from two unique clades in southern and central Africa approximately 0.8 million years ago.
What is a Mitogenome?
- DNA is found in the nucleus of cells and also in the mitochondrial genome, or mitogenome.
- Mitogenomes are DNA molecules that float around outside the nucleus of a cell.
- They store their own set of genetic information and are maternally inherited, which means they are only passed on from mother to offspring.
- Mitogenomes are a “genomic by-catch” when sequencing the whole genome.
- They are so abundant in cells that it is very easy to extract them.
- Studying mitogenomes is a reliable way to track the ancestry of a species.
- This is because genes mutate (change) at a regular rate over time.
- The changes in the mitogenome provide a picture of any species' evolution over hundreds of thousands of years.
What is DNA?
- DNA or Deoxyribonucleic Acid is the genetic material that codes the information for all the different processes that make an organism living like growth, replication, metabolism, etc.
- DNA is present in each cell (except for some viral species, RBCs, sieve cells, etc.) and is passed down from parents to their offspring. DNA is comprised of units called nucleotides.
- DNA is self-replicating, a long stretch of nucleotides.
- DNA is a form of nucleic acid and is one of the four major macromolecules that make up the living system.
- In eukaryotic cells, it is found in the nucleus of the cell whereas in prokaryotes it is found free-floating in the cell cytoplasm.
- Other than the nucleus DNA is also found in mitochondria, chloroplast, and in smaller forms called plasmid in certain bacterial species.
Materiovigilance Programme of India (MvPI)

- 18 May 2024
Why is it in the News?
The DCGI recently issued a directive to all medical device license holders and manufacturers, instructing them to report any adverse events associated with life-saving medical equipment on the government's Materiovigilance Programme of India (MvPI) platform.
What is the Materiovigilance Programme of India?
- The Materiovigilance Programme of India was launched on July 6, 2015, that monitors and evaluates the safety of medical devices across the country.
- It aims to systematically collect and scientifically analyze data on adverse events related to medical devices, offering guidance on their safe usage and supporting regulatory decision-making processes.
Objectives and Importance:
- The primary goal of the Materiovigilance Programme is to enhance patient safety in India by carefully recording, assessing, and determining the root causes of adverse events or risks associated with medical devices, including in-vitro diagnostics.
- By coordinating the reporting and analysis of such events, the programme seeks to inform regulatory bodies and healthcare professionals, promoting the appropriate use of medical devices and ultimately improving patient safety.
Governance and Regulation:
- Since 2018, the Indian Pharmacopoeia Commission (IPC) has served as the National Coordination Centre (NCC) for the programme.
- The Materiovigilance Programme is regulated by the Central Drugs Standards Control Organization (CDSCO), operating under the Ministry of Health and Family Welfare.
- The Drugs and Cosmetics Act, 1940, and Medical Device Rule, 2017, currently govern all medical devices in India.
- Given that the country is 80% dependent on imports for medical devices, the programme's role in ensuring the safety and efficacy of these essential healthcare tools is crucial.
About Drugs Controller General of India (DCGI):
- The Drugs Controller General of India (DCGI) leads the Central Drugs Standard Control Organization (CDSCO), ensuring the quality of drug supply nationwide.
- Nodal Ministry: Ministry of Health & Family Welfare
Functions:
- Approving new drugs and overseeing clinical trials.
- Establishing standards for drug manufacturing, sales, import, and distribution in India.
- Granting licenses for specific drug categories such as blood products, IV fluids, vaccines, and sera.
- Ensuring uniform implementation of the Drugs & Cosmetics Act, 1940, and its associated rules to safeguard patient safety, rights, and well-being.
Baobab Tree

- 17 May 2024
Why is it in the News?
A new study has uncovered the origins of baobabs, the tall and uniquely shaped deciduous trees that are famously spotted on the island of Madagascar.
What are Baobab Trees?
- Baobabs are known for their great heights, with some extending up to 50 metres, and exceptionally long lifespans going up to 2,000 years.
- In India too, a few baobab trees exist, including one near the Golconda Fort in Andhra Pradesh that is believed to be more than 400 years old.
- The trees have trunks with large circumferences and thin, spindly branches.
- In local cultures, the trees are also revered because of the multiple uses their parts have, with the fruits and seeds being edible, the seed oil used for cooking and the bark fibre for clothing.
- They are also called “upside down” trees because of their tops resembling an uprooted plant turned upside down.
Essential for the ecosystem:
- Baobab trees are fundamental to the entire dry African savanna ecosystem.
- They help keep soil conditions humid, aid nutrient recycling, and slow soil erosion with their massive root systems.
- As a succulent, the tree absorbs and stores water from the rainy season in its massive trunk, producing a nutrient-dense fruit in the dry season, which can grow up to a foot long.
- The fruit contains tartaric acid and Vitamin C, serving as a vital nutrient and food source for many species.
- They are also an essential source of water and shelter for hundreds of animals, including birds, lizards, monkeys, and even elephants – which can eat their bark for moisture when there is no water nearby.
In human culture:
- For humans, the baobab’s fruit pulp can be eaten, soaked in water to make a refreshing drink, preserved into a jam, or roasted and ground to make a coffee-like substance.
- The bark can be pounded to make everything from rope, mats, and baskets to paper and cloth.
- Leaves are also used, they can be boiled and eaten, or glue can be made from their flower’s pollen.
What Did the Study Find?
- The study highlighted the threats facing baobab trees and examined their genetic makeup.
- It reported that three Madagascar species of baobab trees are threatened with extinction, according to the IUCN Red List of Threatened Species.
- The study identified various threats, including residential and commercial development and livestock farming, which require land clearing.
- However, even species not currently endangered show declining populations, suggesting that more rigorous conservation strategies are needed to ensure their long-term survival.
- This necessitates a detailed understanding of the baobabs' genetics.
- Genomic sequencing revealed a consensus on the monophyly of the Malagasy lineage from Madagascar.
- According to DNA studies, baobab trees first arose in Madagascar 21 million years ago, with their seeds later carried by ocean currents to Australia and mainland Africa, where they evolved into distinct species.
- The study also warned that climate change poses severe threats to Adansonia suarezensis from Madagascar, predicting its possible extinction by 2080.
- Due to their unique ecological roles and low genetic diversity, these species are likely to have reduced resilience to environmental changes and habitat fragmentation.
Leopard Cat

- 17 May 2024
Why is it in the News?
The leopard cat (Prionailurus bengalensis), a small wild cat native to South, Southeast and East Asia, was recently spotted in Maharashtra’s Pench, in what is being billed as Central India’s first sighting of the species.
About Leopard Cat:
- The Leopard cat (Prionailurus bengalensis) is a small wild cat native to continental South, Southeast, and East Asia.
- With its distinctive leopard-like colouring, this small wildcat is known for its remarkable adaptability and extensive distribution across Asia.
Habitat and Distribution:
- Leopard cats can be found in a variety of environments, ranging from the Amur region in Russia to the Korean Peninsula, China, Indochina, the Indian Subcontinent, northern Pakistan, and as far south as the Philippines and the Sunda Islands of Indonesia.
- Although they can inhabit agriculturally used areas, leopard cats prefer forested habitats, including tropical evergreen rainforests, subtropical deciduous and coniferous forests, and plantations at various altitudes.
Physical Characteristics:
- Size and appearance vary considerably across their range, with a length of 45 to 75 cm (18 to 30 inches), excluding their 23-35 cm (9-13.8 inches) tail.
- Their colouration ranges from pale tawny to yellow, red, or grey, with white underparts and distinctive spots.
- Most leopard cats have four black stripes running from their forehead to the nape, breaking into short bands and elongated spots on their shoulders.
Behaviour and Diet:
- As solitary and nocturnal carnivores, leopard cats primarily feed on rodents, tree shrews, and hares, playing a crucial role in maintaining the balance of their ecosystems.
Conservation Status:
- Listed as "Least Concern" on the IUCN Red List, leopard cats face threats from habitat loss, poaching, and human-wildlife conflict. Continued monitoring and conservation efforts are essential to protect this species and its vital role in Asia's diverse ecosystems.
Facts about Pench Tiger Reserve:
- Location: Situated in the southern reaches of the Satpura hills, the Pench Tiger Reserve spans Seoni and Chhindwara districts in Madhya Pradesh and extends into Nagpur district in Maharashtra as a separate Sanctuary.
- It derives its name from the Pench River, which flows from north to south through the Reserve.
- The reserve encompasses the Indira Priyadarshini Pench National Park, the Pench Mowgli Sanctuary, and a buffer zone.
- The area served as the inspiration for Rudyard Kipling's renowned work, "The Jungle Book."
- Vegetation: The undulating topography supports a diverse range of vegetation, from moist, sheltered valleys to open, dry deciduous forests.
- Flora: Pench Tiger Reserve boasts a rich variety of flora, including teak, saag, mahua, and various grasses and shrubs.
- Fauna: Renowned for its wildlife diversity, the reserve is home to large herds of Chital, Sambar, Nilgai, Gaur (Indian Bison), and wild boar.
- Key predators include the tiger, leopard, wild dogs, and wolf. Additionally, the reserve supports over 325 species of resident and migratory birds, including the Malabar Pied Hornbill, Indian Pitta, Osprey, Grey Headed Fishing Eagle, and White Eyed Buzzard.
Deda Method of Preserving Seeds

- 17 May 2024
Why is it in the News?
In his 50s, Madakam Unga, a Muria tribal farmer who migrated from Chhattisgarh and settled in the dense forests of the Godavari Valley, is still practising ‘deda’, a traditional method of preserving seeds that his ancestors handed over to his family.
What is the Deda Method?
- The Deda Method is an ancestral seed preservation technique passed down through generations.
- This unique method involves the use of natural materials to create a protective, airtight environment for the seeds, ensuring their viability for future planting.
Preservation Process:
- Seeds are packed tightly and wrapped in leaves to form a sturdy bundle resembling a boulder.
- The seed-filled leaf packages are then woven together with Siali leaves (Bauhinia vahlii), locally known as 'addakulu,' forming the distinctive deda structure.
- A deda consists of three layers:
- The innermost layer contains wood ash spread over Siali leaves.
- The ash is then covered with lemon leaves, creating a protective casing.
- Lastly, seeds are preserved within this casing and sealed, with each deda supporting up to 5kg of seeds.
Advantages:
- The Deda Method effectively protects seeds from pests and worms, ensuring their quality and viability.
- Seeds preserved using this technique can be used for cultivation for up to five years.
- This method is particularly useful for preserving the seeds of various pulses, such as green gram, red gram, black gram, and beans.
- By utilizing the Deda Method, farmers can maintain a reliable, diverse collection of seeds, contributing to sustainable agricultural practices and supporting long-term food security.
Facts About Muria Tribe:
- Location: The Muria tribe is found in the states of Telangana, Andhra Pradesh, Chhattisgarh, and Odisha.
- Language: They speak Koya, a Dravidian language.
- Population and Status: In Andhra Pradesh, the Muria, also known as 'Gutti Koyas' by native tribes, are internally displaced people (IDPs) with a population of around 6,600.
- Cultural Practices: The Muria have a progressive outlook on marriage and life.
- A notable example is the Ghotul, a communal dormitory that provides an environment for Muria youth to explore and understand their sexuality.
Recognition: While most Gutti Koya belong to the Gond or Muria communities, which are recognized as Scheduled Tribes in Chhattisgarh, they lack such recognition in Telangana.
Synchrotron

- 17 May 2024
Why is it in the News?
China's latest scientific achievement, the High Energy Photon Source (HEPS), is poised to become Asia's first fourth-generation synchrotron light source which is scheduled to commence operations by the end of this year.
What is a Synchrotron?
- A synchrotron is a type of circular particle accelerator where particles travel in a loop.
- It functions by accelerating charged particles, typically electrons, through sequences of magnets until they approach the speed of light.
How Does It Work?
- Acceleration: Charged particles are accelerated through magnets.
- Production of Light: These high-speed electrons generate extremely bright light, known as synchrotron light.
- This light, predominantly in the X-ray region, is millions of times brighter than conventional sources and 10 billion times brighter than the sun.
- Beamlines and Workstations: The intense light is directed down beamlines to experimental workstations for research purposes.
Applications:
- Research: Scientists use synchrotron light to study tiny matter such as atoms and molecules.
- By examining how a sample scatters, diffracts, absorbs, or reemits the synchrotron light, they can uncover details about its structure and chemical composition.
Global Presence:
- There are approximately 70 synchrotrons worldwide in various stages of development.
- They have varying technical specifications and uses, ranging from practical applications to fundamental theoretical research.
In India:
- India has a synchrotron facility known as the "Indus Synchrotron."
- It is located at the Raja Ramanna Centre for Advanced Technology (RRCAT) in Indore, Madhya Pradesh.
- The Indus Synchrotron is a third-generation synchrotron radiation source that is used for various research applications in fields such as materials science, biology, and environmental science.
What is the High Energy Photon Source (HEPS)?
- HEPS (High Energy Photon Source) is recognized as the brightest synchrotron X-ray source in Asia.
- Location: The HEPS facility is situated in Huairou, China, approximately 50 kilometres from Beijing.
- Acceleration Capabilities: HEPS is designed to accelerate electrons up to energies of 6 gigaelectron volts within its 36-kilometer circumference storage ring, producing high-energy X-rays for research purposes.
- Nanoscale Investigations: The high-energy X-rays generated by HEPS can penetrate deep into samples, allowing researchers to study intricate details at the nanometer scale.
- Diverse Research Applications: HEPS will cater to various research fields, including energy, condensed matter physics, materials innovation, and biomedicine, by providing access to 14 specialized beamlines.
- Superiority to Existing Synchrotrons: Compared to China's current most advanced synchrotron, the Shanghai Synchrotron Radiation Facility (with a circumference of 432 meters), HEPS will offer a time resolution 10,000 times better.
PREFIRE (Polar Radiant Energy in the Far-InfraRed Experiment) Mission

- 17 May 2024
Why is it in the News?
NASA is set to launch the two small satellites of the PREFIRE mission from New Zealand on May 22 aimed at filling in critical gaps in data from Earth's polar regions.
What is the PREFIRE Mission?
- PREFIRE (Polar Radiant Energy in the Far-InfraRed Experiment) is a NASA mission that involves sending two tiny twin spacecraft, known as CubeSats, to the Earth's polar regions to gather data on the heat energy radiated out to space and its impact on our climate.
- PREFIRE consists of two, 6U CubeSats with a baseline mission length of 10 months.
- These shoebox-sized satellites will orbit at altitudes between 292 and 403 miles, crossing paths in the atmosphere.
Objectives:
- The mission will help close a gap in understanding how much of Earth’s heat is lost to space, especially from the Arctic and Antarctica.
- Analysis of PREFIRE’s measurements will inform climate and ice models, providing better projections of how a warming world will affect sea ice loss, ice sheet melt, and sea level rise.
- Improving climate models can ultimately help to provide more accurate projections on the impacts of storm severity and frequency, as well as coastal erosion and flooding.
- By studying the far-infrared radiation emitted from these regions, PREFIRE will help improve the accuracy of climate models, enhancing our understanding of phenomena such as Arctic warming, sea ice loss, and ice-sheet melting.
The mission will help in:
- Uncover the reasons behind the Arctic warming more than 2½ times faster than the global average since the 1970s.
- Provide scientists with a clearer understanding of how efficiently far-infrared heat is emitted by materials such as snow and sea ice, and how clouds affect the amount of far-infrared radiation that escapes to space.
- Enhance predictions about future changes in the heat exchange between Earth and space, and how these changes will impact phenomena like ice sheet melting, atmospheric temperatures, and global weather patterns.
How will the Satellites Work?
- The mission with cube satellites about the size of a shoebox will be launched aboard an Electron launch vehicle.
- It is equipped with technology proven on Mars and will measure a “little-studied portion” of the radiant energy emitted by Earth.
- Two satellites carrying a thermal infrared spectrometer will be in asynchronous near-polar orbits and will be passing over a given spot on Earth at different times. To maximize coverage, they will be overlapping every few hours near the poles.
- The instruments weighing less than 6 pounds (3 kilograms) each will make readings using a device called a thermocouple, similar to the sensors found in many household thermostats.
Why is it Important to Study the Polar Regions?
- According to NASA, Earth's climate balance hinges on the equilibrium between the heat energy the planet receives from the Sun and the amount it radiates back into space.
- The difference between incoming and outgoing energy determines Earth's temperature and climate.
- The polar regions are crucial in this balance.
- Changes in the polar regions can significantly impact global weather patterns.
- Extreme storms, flooding, coastal erosion – all of these phenomena are influenced by what’s happening in the Arctic and Antarctic.
- This underscores the importance of understanding polar dynamics to predict and mitigate global climate effects.
Digital Arrest

- 16 May 2024
Why is it in the News?
With the cases of extortion and ‘digital arrest’ frauds on the rise, the Indian Cyber Crime Coordination Centre (I4C) working under the Union Ministry of Home Affairs issued an advisory asking the citizens to be alert about such frauds.
What is ‘Digital Arrest’?
- ‘Digital arrest’ is a new and innovative tactic employed by cybercriminals to defraud gullible victims and extort money.
- The modus operandi in this cybercrime method is that fraudsters pose as law enforcement officials such as police, Enforcement Directorate, and CBI, among others, and manipulate them into believing that they have committed some serious crime.
- The cyber fraudsters deceive the victim into believing that he or she has been put under ‘digital arrest’ and will be prosecuted if they do not pay the scamsters a huge amount of money.
- The fraudster often uses the tactic of instilling fear and a sense of urgency in the victims, ensuring they part with their money before realizing it's a scam.
- The cyber criminals often force the naive victims to self-arrest or self-quarantine themselves, by tricking them into believing that they have been put under ‘digital arrest’ and cannot leave their house unless they pay up.
Modus Operandi of Digital Arrest Scams:
- Initial Engagement: Fraudsters initiate contact with unsuspecting individuals through various digital communication channels, such as phone calls, WhatsApp, or Skype.
- Fear and Urgency Manipulation: The scammers employ psychological tactics to instil fear and a sense of urgency in their victims.
- They present fabricated evidence and falsely claim that the victim is embroiled in criminal activities or is facing an imminent arrest warrant.
- Elaborate Scams: To enhance the legitimacy of their scheme, the scammers create elaborate setups, including simulated police stations, virtual interrogations, and video calls with individuals posing as senior police officers.
- Layered Interrogations: Victims are subjected to multiple rounds of “interrogations,” with the scammers assuming different roles, such as a “constable,” a “sub-inspector,” and finally a “DCP-level officer.”
- This layered approach aims to convince victims of the gravity of the situation and increase their susceptibility to the scam.
- Financial Exploitation: Under the imminent threat of arrest, victims are coerced into transferring substantial sums of money into designated accounts.
- The scammers deceitfully claim that these funds are necessary to clear the victim’s name or resolve the alleged criminal charges.
Actions Taken by the Centre:
- Intelligence agencies have determined that the incidents are part of a coordinated online economic crime network operated by transnational crime syndicates.
- The Indian Cyber Crime Coordination Centre (I4C), overseen by the Ministry of Home Affairs, has collaborated with Microsoft to block over 1,000 Skype IDs associated with such illicit activities.
- Additionally, efforts are underway to block SIM cards, mobile devices, and "mule" accounts utilized by cybercriminals.
- Money mules, also known as "smurfers," are individuals unwittingly used by fraudsters to launder stolen or illegal money through their bank accounts.
- Following reports of such incidents, these individuals often become the focus of police investigations due to their involvement, as highlighted in a security advisory by HDFC Bank.
- The Home Ministry is collaborating with other ministries, their agencies, the Reserve Bank of India (RBI), and various organizations to combat these criminal activities.
- I4C is actively providing technical support and inputs to the police forces of states and union territories to identify and investigate cases.
- I4C has leveraged its social media platform Cyberdost, along with its presence on platforms like Twitter, Facebook, and Instagram, to disseminate infographics and videos aimed at raising awareness about cybercrime.
- Citizens are urged to remain vigilant and help spread awareness about cybercrime.
- They are encouraged to report any such incidents promptly to the cybercrime helpline at 1930 or through the website http://www.cybercrime.gov.in.
- Additionally, filing a complaint and notifying the local police is advised.
India VIX

- 16 May 2024
Why is it in the News?
India VIX, which is an indicator of the market’s expectation of volatility over the near term, surged past the 21 mark recently.
What is India VIX?
- India VIX is a volatility index computed by the NSE based on the order book of NIFTY Options.
- For this, the best bid-ask quotes of near and next-month NIFTY options contracts, which are traded on the F&O segment of NSE are used.
- India VIX indicates the investor’s perception of the market’s volatility in the near term i.e. it depicts the expected market volatility over the next 30 calendar days.
- The higher the India VIX values, the higher the expected volatility and vice versa, as per NSE.
- ‘VIX’ is a trademark of the CBOE, and Standard & Poor’s has granted a license to NSE, with permission from the CBOE, to use such a mark in the name of the India VIX and for purposes relating to the India VIX.
What is the Volatility Index?
- The Volatility Index, VIX or the Fear Index, is a measure of the market’s expectation of volatility over the near term.
- Volatility is often described as the ‘rate and magnitude of changes in prices’ and in finance often referred to as risk.
- Usually, during periods of market volatility, the market moves steeply up or down and the volatility index tends to rise.
- As volatility subsides, the Volatility Index declines.
- The Volatility Index is a measure of the amount by which an underlying index is expected to fluctuate in the near term, (calculated as annualised volatility, denoted in percentage e.g. 20 per cent) based on the order book of the underlying index options.
- The Chicago Board of Options Exchange (CBOE) was the first to introduce the volatility index for the US markets in 1993 based on S&P 100 Index option prices.
- In 2003, the methodology was revised and the new volatility index was based on S&P 500 Index options.
- Since its inception, it has become an indicator of how market practitioners think about volatility.
- Investors use it to gauge market volatility and base their investment decisions accordingly.
Global Report on Internal Displacement 2024 (GRID-2024)

- 16 May 2024
Why is it in the News?
Floods, cyclones, earthquakes and other disasters triggered over half a million internal displacements in India in 2023, according to Geneva-based Internal Displacement Monitoring Centre (IDMC).
About Global Report on Internal Displacement 2024:
- The Global Report on Internal Displacement (GRID) 2024, published by the Internal Displacement Monitoring Centre (IDMC) based in Geneva, Switzerland.
- It is the authoritative source for data and analysis on the state of internal displacement for the previous year.
- Each year, IDMC presents the validated estimates of internal displacements by conflict and disasters, and the total cumulative numbers of IDPs worldwide.
- The GRID also provides an overview of the year’s most significant internal displacement situations, highlighting potential measures to address the issue across the humanitarian, development, disaster risk reduction and climate change agendas.
- The 2024 Global Report on Internal Displacement (GRID) report presents the data and analysis behind the 75.9 million people living in internal displacement as of the end of 2023.
- It is the ninth edition of the GRID and includes global and regional insights into the risk, scale and impacts of internal displacement.
Highlights of the GRID 2024:
- Rising Numbers of (IDPs): In 2023, the number of internally displaced persons (IDPs) reached 75.9 million, up from 71.1 million the previous year.
- Causes of Displacement: Disasters contributed to 7.7 million displacements, with earthquakes being responsible for one-fourth of these.
- Conflict and violence led to 68.3 million displacements.
- High-Displacement Countries: Sudan, Syria, the Democratic Republic of Congo (DRC), Colombia, and Yemen account for almost half of the world's IDP population.
- Significant Increases: Sudan had the highest number of IDPs recorded for a single country in 2023, reaching 1 million.
- The majority of new displacements occurred in Sudan, the Palestinian territories, and the DRC, accounting for nearly two-thirds of all cases.
- South Asia Displacement: Approximately 3 million people across South Asia experienced internal displacement due to conflict and violence, with 80% of them located in Afghanistan.
- Manipur violence resulted in 67,000 displacements, marking the highest number of conflict and violence-related displacements in India since 2018.
- Impact of Natural Disasters: There was a notable decrease in internal displacement due to natural disasters in India in 2023, dropping from 2.5 million in 2022 to 528,000.
About Internal Displacement Monitoring Centre (IDMC):
- Established in 1998, the IDMC is the leading source of information and analysis on internal displacement.
- It was created to address a significant gap in knowledge on global patterns and scales of internal displacement.
- IDMC defines internal displacement as the number of forced movements of people within their own country over a given year.
- The IDMC is a part of the Norwegian Refugee Council (NRC), an independent, non-governmental humanitarian organization.
- Primary Roles: The IDMC serves as a global monitor and advocate for evidence-based policy and action.
- It aims to influence governments, UN agencies, donors, international organizations, and NGOs.
- As the official repository of data and analysis on internal displacement, the IDMC's GRID provides critical insights into the global internal displacement crisis and aids in developing informed solutions.
Extra-pulmonary TB
- 16 May 2024
Why is it in the News?
Approximately 20% of tuberculosis (TB) patients suffer from Extra-pulmonary TB, yet the majority remain undiagnosed. Even among those diagnosed, access to appropriate care is limited to specialized health facilities, posing a challenge to effective treatment.
What is Extra-pulmonary TB?
- Extra-pulmonary tuberculosis (EPTB) is a form of tuberculosis (TB) that affects organs outside the lungs, such as the lymph nodes, pleura, bones, joints, and central nervous system.
- EPTB accounts for a significant portion of active TB cases, ranging from 20% to 40%, and occurs more frequently in immunosuppressed individuals and young children.
- In HIV-positive individuals, EPTB is present in more than 50% of cases.
- EPTB diagnosis remains challenging due to the difficulty in accessing affected sites and the low sensitivity of diagnostic tests.
- A combination of mycobacteriology and histopathologic examinations, along with molecular techniques such as polymerase chain reaction, can aid in the diagnosis.
- Biochemical markers, like adenosine deaminase or gamma interferon, can be useful adjuncts in diagnosing TB-affected serosal fluids.
Treatments:
- Treatment of EPTB typically involves standard anti-TB drug therapy, but the ideal regimen and duration have not yet been established.
- While the disease usually responds to treatment, complications and paradoxical responses may occur, necessitating the distinction from other causes of clinical deterioration.
- Surgery may be required to obtain diagnostic specimens or manage complications.
Challenges with EPTB:
- EPTB infections may leave disease markers lingering even after treatment, posing concerns about relapse.
- Standardized diagnosis and treatment protocols for various affected organs are lacking, complicating management.
- A lack of awareness among both patients and physicians, along with the absence of precise diagnostic and treatment criteria, adds to the challenge.
- Even after completing anti-TB therapy, some EPTB patients may experience lingering effects of the disease.
- The existing INDEX-TB guidelines, formulated over a decade ago, require updating to incorporate the latest insights and experiences.
Kadar Tribe

- 16 May 2024
Why is it in the News?
The recent death of a Kadar tribesman in Tamil Nadu’s Anamalai Tiger Reserve in an elephant attack has left the indigenous community and conservationists in shock as Kadars are known to co-exist with wild elephants for ages.
About Kadar Tribes:
- The Kadar tribes are a small indigenous tribal community residing in South India, primarily along the hilly border between Cochin in Kerala and Coimbatore in Tamil Nadu.
- Traditionally, they are forest dwellers who rely on forest resources for their livelihood, opting not to practice agriculture.
- Their shelters are typically thatched with leaves, and they frequently shift locations based on their employment needs.
- Rather than subsisting solely on gathered food, they prefer rice obtained through trade or wages.
- With a long history of specialization, the Kadars are known for collecting various forest products like honey, wax, sago, cardamom, ginger, and umbrella sticks, which they trade with merchants from the plains.
- They maintain a symbiotic relationship with nature, emphasizing the coexistence of Kadar and Kaadu (forest), and have established traditional protocols for the sustainable use of forest resources.
- Every resource collection practice, such as honey extraction, firewood gathering, resin tapping, or herb picking, is conducted with regeneration time in mind.
- The population of the Kadars was estimated to be around 2,000 individuals in the early 21st century, and they primarily speak Dravidian languages like Tamil and Kannada.
- Their religious beliefs include worshipping jungle spirits, a kindly creator couple, and local forms of Hindu deities.
- While recognized as a Particularly Vulnerable Tribal Group (PVTG) in Kerala, they do not hold the same status in Tamil Nadu.
About Anamalai Tiger Reserve:
- Anamalai Tiger Reserve is a protected area located in the Anamalai Hills of Pollachi and Coimbatore District of Tamil Nadu, India.
- Annamalai Tiger Reserve was originally called Anamalai Wild Life Sanctuary notified in the year 1974 and established in the year 1976.
- Later, it was renamed as Indira Gandhi Wildlife Sanctuary & National Park in honour of former Prime Minister Indira Gandhi's visit in 1961.
- According to the National Tiger Conservation Authority, the sanctuary was declared as Anamalai Tiger Reserve in 2007.
- The sanctuary presently includes a core area of 958.59 sq. km and a buffer area of 521.28 sq. km forming a total area of 1479.87 sq. km.
- It is located at an altitude of 1400 m in the Anamalai Hills of the Western Ghats.
Solar Storms
- 15 May 2024
Why is it in the News?
According to the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO), Indian satellites did not suffer any major outages due to the multiple powerful earth-bound solar storms recently.
What is a Solar Storm?
- Solar storms are a normal part of our Sun's solar cycle.
- It occurs when the Sun emits huge bursts of energy in the form of solar flares and coronal mass ejections.
- These phenomena send a stream of electrical charges and magnetic fields toward the Earth at a speed of about three million miles per hour.
- When a solar storm strikes the Earth, it often produces a dazzling “northern lights" display in parts of the atmosphere that can be seen in areas close to the Arctic Circle.
- Solar storms start with a huge explosion on the Sun.
- These explosions — called solar flares — can be about as powerful as billions of nuclear bombs!
- Solar flares usually go hand-in-hand with the release of huge streams of charged plasma that travel at millions of miles per hour.
- These streams are called coronal mass ejections, or CMEs.
- When CMEs hit the Earth, they can cause geomagnetic storms that disrupt satellites and electrical power grids.
- For example, in 2017 two massive solar flares fired out from the surface of the Sun disrupted devices such as GPS navigation systems on Earth.
How often do solar storms happen?
- Scientists who study solar storms have discovered that the frequency of solar flares appears to follow an 11-year solar cycle.
- At times of peak activity, there could be several solar storms each day.
- At other times, there might be less than one solar storm per week.
What is the Impact of Solar Storm?
- It majorly interferes with several services, including GPS navigation, weather forecasting, communication, and other satellite-dependent services.
- Besides that, it also has a significant impact on satellite networks and communication.
- They can create geomagnetically induced currents (GICs), which can overload electrical systems and cause damage to transformers, issues with voltage regulation, and widespread power outages.
- Furthermore, because solar storms increase the amount of solar and cosmic radiation that reaches the top regions of Earth's atmosphere, they also pose health concerns to people, especially aircraft crew and passengers, especially on flights at high latitudes.
- These storms have the potential to disrupt infrastructure in near-Earth orbit and on Earth's surface, affecting communications, the electric power grid, navigation, radio, and satellite operations.
Humboldt Glacier

- 15 May 2024
Why is it in the News?
Venezuela is thought to be the first nation in modern times to have completely lost all of its glaciers.
About Humboldt Glacier:
- Venezuela's Humboldt Glacier, also known as La Corona, held great significance as the country's last remaining glacier.
- Located in the Sierra Nevada de Mérida mountain range in the Andes, at an altitude of approximately 5,000 meters, the Humboldt Glacier was part of a group of six glaciers that once covered an area of 10 square kilometres.
- However, due to the accelerated melting caused by climate change, five of these glaciers had vanished by 2011, leaving Humboldt as the sole remnant.
- Humboldt Glacier's deterioration continued at an alarming pace in subsequent years.
- Recent studies conducted by the International Cryosphere Climate Initiative (ICCI), a scientific advocacy organization, revealed that the glacier had shrunk to an area of less than 2 hectares.
- As a result, it was downgraded from a glacier to an ice field, marking Venezuela as the first country in modern history to lose all of its glaciers.
- The demise of Humboldt Glacier serves as a stark warning of the global consequences of climate change.
- It exemplifies the rapid loss of ice in tropical regions, which not only impacts local ecosystems and water resources but also contributes to rising sea levels and exacerbates the effects of climate change worldwide.
About the International Cryosphere Climate Initiative (ICCI):
- International Cryosphere Climate Initiative (ICCI) was formed in 2009 following COP-15 in Copenhagen.
- It is a network of senior policy experts and researchers working with governments and organizations to create, shape and implement initiatives designed to preserve as much of the Earth’s cryosphere as possible.
- CCI's work focuses on three major areas of the cryosphere:
- The Arctic
- The Antarctic
- High mountain regions
- By connecting cutting-edge science to a variety of policy-making forums and supporting integrated projects worldwide to protect the cryosphere, ICCI advances climate action.
- ICCI programs target the unique climate dynamics at work in the cryosphere, while at the same time lending increased urgency to global climate efforts aimed at CO2 and other greenhouse gases by communicating the unexpected rapidity and global implications of cryosphere warming.
NISAR Satellite Can Monitor Earth’s Tectonic Movements

- 15 May 2024
Why is it in the News?
ISRO Chairman S. Somanath recently announced that the NISAR satellite has the capability to accurately monitor tectonic movements and complete full mappings of the Earth twice a month.
About the NISAR Satellite:
- NISAR is a joint Earth-observing mission between NASA and the Indian Space Research Organization (ISRO).
- It is a Synthetic Aperture Radar satellite with two bands.
- It will be launched into a polar Sun-synchronous dawn-dusk orbit.
- One is the S-band and the other is the L-band.
- The S-band payload has been made by the ISRO and the L-band payload by the U.S.
- The U.S. will contribute to the large deployable antenna.
- This being a dual-band polarizable radar, it can do a lot of things.
- First, because it has a large deployable antenna with an 18-metre diameter, it has a very high swath.
- It can fully cover the earth in approximately 14 to 15 days, according to radar.
- It can monitor various aspects in very high resolution.
- For example, it can monitor the tectonic movements to centimetre accuracy.
- It can do measurements of water bodies accurately.
- It can look at water stressing on the earth, wherever there is a deficiency of water.
- It can ground-penetrate to a certain depth.
- It is capable of monitoring the vegetation cover and snow cover.
- It, therefore, basically looks at the whole of the earth in terms of surface, water, greenery and all of that.
- It measures accurately and gives repetitive, full coverage of the earth two times a month.
- It means it is capable of a lot of observation and this data will be available to both India and the U.S.
- We can study the water-stressing, climate change-related issues, and agricultural changes through patterns, yield, desertification and continental movements precisely with respect to annual water cycle movements.
- It can measure tectonic plate movements accurately.
- So a lot of geological, agricultural and water-related observations can be obtained from this satellite.
Mission Objectives:
- The primary goal of NISAR is to provide precise measurements of tectonic plate movements, enabling comprehensive observations in geology, agriculture, and water-related domains.
- Additionally, it aims to analyze water stress, climate change impacts, agricultural shifts, desertification, and continental shifts with accuracy, particularly concerning annual water cycle variations.
- NISAR's data will facilitate global resource and hazard management, while also aiding scientists in comprehending climate change dynamics and its effects.
Launch Schedule:
- Initially planned for July, the launch is now expected in October-November due to issues on the U.S. side requiring corrections.
Memory of the World (MoW) Programme

- 15 May 2024
Why is it in the News?
Three Indian literary works, Ramcharitmanas, Panchatantra, and Sah?dayaloka-Locana, were added to UNESCO’s Memory of the World Asia-Pacific Regional Register during the tenth meeting of the Memory of the World Committee for Asia and the Pacific (MOWCAP).
About Memory of the World Programme:
- The Memory of the World (MoW) Programme is an international initiative by UNESCO launched in 1992 aimed at preserving and recognizing the world's significant documentary heritage.
- The program's objective is to identify and protect important documents in a manner similar to how UNESCO's World Heritage Convention and World Heritage List recognize significant natural and cultural sites.
The Memory of the World Programme aims to:
-
- Facilitating the preservation of documentary heritage, particularly in conflict-affected areas or regions impacted by natural disasters.
- Enabling universal access to documentary heritage worldwide.
- Enhancing public awareness about the significance of documentary heritage among the wider public.
Governance Body:
- The International Advisory Committee (IAC) serves as the main governing body for the MoW Programme, providing guidance to UNESCO on its planning and implementation.
- The IAC comprises 14 members appointed by UNESCO's Director-General, who are chosen for their expertise and authority in the field of documentary heritage.
Nominations for MoW:
- Nominations for inscription on the Asia Pacific Register are called every two years, alternating with the International Register.
- In even-numbered years, nominations are accepted for the Asia Pacific Register.
India has three items included in the Memory of the World Register:
- Ramcharitmanas: Written by Tulasidas in the 16th century in the Awadhi dialect, this text holds immense cultural and literary significance in the regions of Lucknow, Prayagraj, and Ayodhya.
- Panchatantra: This ancient Indian collection of fables, originally written in Sanskrit, consists of five sections that revolve around specific principles.
- It is widely believed to have been authored by Vishnu Sharma.
- Sah?day?loka-Locana: A Sanskrit commentary on the Dhvanyaloka, Sah?day?loka-Locana holds significant historical and literary value within India's rich cultural landscape.
- Through the Memory of the World Programme, UNESCO continues to protect and celebrate the diverse documentary heritage of humanity, ensuring its preservation and accessibility for future generations.
Indian Cyber Crime Coordination Centre (I4C)
- 15 May 2024
Why is it in the News?
The Indian Cyber Crime Coordination Centre (I4C), in collaboration with Microsoft, has blocked more than 1,000 Skype IDs involved in blackmail, extortion, and “digital arrests” by cybercriminals posing as police and law enforcement authorities.
About Indian Cyber Crime Coordination Centre (I4C):
- The Indian Cyber Crime Coordination Centre (I4C) is a comprehensive initiative to address cybercrime in India.
- It has been established under the Ministry of Home Affairs (MHA) Govt. of India.
- With a focus on improving coordination between various Law Enforcement Agencies (LEAs) and stakeholders, I4C serves as a nodal point in the fight against cybercrime.
- It is located in New Delhi.
Its primary functions include:
- Acting as the central hub for tackling cybercrime and coordinating efforts among LEAs.
- Identifying research needs and collaborating with academia and research institutes within India and abroad to develop new technologies and forensic tools.
- Preventing the misuse of cyberspace by extremist and terrorist groups.
- Suggesting amendments to cyber laws to keep pace with evolving technologies and fostering international cooperation.
- Coordinating activities related to the implementation of Mutual Legal Assistance Treaties (MLAT) with other countries concerning cybercrimes, in consultation with the concerned nodal authority in MHA.
Key Components of the Indian Cyber Crime Coordination Centre (I4C):
- The I4C is comprised of several specialized units designed to tackle various aspects of cybercrime:
- National Cybercrime Threat Analytics Unit (TAU): Regularly reports on cybercrime threats and provides crucial insights to support the nation's cybersecurity efforts.
- National Cybercrime Reporting Portal (NCRP): Offers a unified platform for citizens to report various cybercrime complaints around the clock from anywhere in India.
- National Cybercrime Training Centre (NCTC): Imparts essential training to government officials, primarily focusing on state law enforcement agencies.
- National Cybercrime Research and Innovation Centre: Conducts research and develops indigenous tools for preventing cybercrimes.
- Platform for Joint Cyber Crime Coordination Team: Facilitates coordination, sharing of cybercrime modus operandi, and data/information exchange among state/UT LEAs.
- Cybercrime Ecosystem Management Unit: Focuses on creating mass awareness regarding cyber hygiene and prevention of cybercrimes.
- National Cybercrime Forensic Laboratory (Investigation) Ecosystem: Assists LEAs in cyber forensics investigations.
- In addition to these components, the I4C also fosters collaboration between academia, industry, the public, and government entities in the prevention, detection, investigation, and prosecution of cybercrimes.
- Through the Cyber Crime Volunteers Program, the I4C unites passionate citizens who are committed to serving the nation and contributing to the fight against cybercrime.
Convention on Biological Diversity (CBD)

- 14 May 2024
Why is it in the News?
Technical experts from across the world are gathered at the United Nations headquarters in Kenya in preparation for the 16th Conference of Parties to the Convention on Biological Diversity (COP16).
About the Convention on Biological Diversity (CBD):
- The Convention on Biological Diversity (CBD), known informally as the Biodiversity Convention, is a multilateral treaty that has the main objective of developing national strategies for the conservation and sustainable use of biological diversity.
- It is a multilateral treaty established in 1992 at the United Nations Conference on Environment and Development (also known as the Earth Summit) held in Rio de Janeiro, Brazil.
- Signed by 150 government leaders, the Convention on Biological Diversity is dedicated to promoting sustainable development.
- Conceived as a practical tool for translating the principles of Agenda 21 into reality, the Convention recognizes that biological diversity is about more than plants, animals and microorganisms and their ecosystems – it is about people and our need for food security, medicines, fresh air and water, shelter, and a clean and healthy environment in which to live.
The CBD has so far produced two important international agreements:
- The Cartagena Protocol on biosafety entered into force in 2003, seeks to protect the environment from the potential risks of Genetically Modified (GM) organisms.
- The Cartagena Protocol on Biosafety to the Convention on Biological Diversity is an international treaty governing the movements of living modified organisms (LMOs) resulting from modern biotechnology from one country to another.
- It aims to ensure the safe handling, transport, and use of living-modified organisms (LMOs) that may have adverse effects on biological diversity, taking into account human health, especially focusing on transboundary movements.
- The protocol was adopted in January 2000 in Cartagena, Colombia, and entered into force on September 11, 2003.
- The Nagoya Protocol on Access to Genetic Resources entered into force in 2014, aims at sharing the benefits arising from the utilisation of genetic resources in a fair and equitable way.
- The Nagoya Protocol on Access to Genetic Resources and the Fair and Equitable Sharing of Benefits Arising from their Utilization is a supplementary agreement to the Convention on Biological Diversity.
- It provides a legal framework for the fair and equitable sharing of benefits arising from the utilization of genetic resources, with a particular focus on ensuring that benefits are shared with the countries and communities that provide those resources.
- The protocol aims to promote the conservation and sustainable use of biodiversity while also respecting the rights of indigenous and local communities over their traditional knowledge and genetic resources.
- It was adopted in Nagoya, Japan, in 2010 and entered into force in 2014.
- The Conference has also implemented many positive decisions that have contributed to the promotion of environmental integrity and the rights of Indigenous Peoples and Local Communities.
- In 2010, the conference in Nagoya adopted a Strategic Plan for Biodiversity, including the Aichi Biodiversity Targets for the 2011-2020 period.
- The convention provides a framework for member countries to develop national strategies and action plans for the conservation and sustainable use of biological diversity.
- As of now, 196 countries have ratified the convention, making it a widely accepted and crucial international agreement for addressing global environmental issues.
Silk Cotton Tree

- 14 May 2024
Why is it in the News?
Silk cotton trees are dwindling in south Rajasthan, triggering a chain of detrimental effects on both the forests and the local populace in the region.
About Silk Cotton Tree:
- The silk cotton tree, or the semal tree is a type of native cotton tree with large red flowers.
- The genus name Salmalia is derived from the Sanskrit name Shaalmali.
- Silk cotton trees comprise eight species in the genus Bombax, native to India, tropical southern Asia, northern Australia and tropical Africa.
- These trees bear beautiful red-coloured flowers from January to March and the fruit on maturity appears during March and April.
- These are full of cotton-like fibrous stuff.
- It is for the fibre that villagers gather the semul fruit and extract the cotton substance called "kopak".
- This substance was once used for stuffing pillows, sofas and mattresses.
- The fruit is cooked and eaten and also pickled.
- Semul is quite a fast-growing tree and can attain a girth of 2 to 3 m, and a height of about 30 m, in nearly 50 years or so.
- It thrives in moist deciduous and semi-evergreen forests, as well as in plains, with occasional sightings in coastal areas and up to 1400 m in hilly regions.
- The tree is not particularly frost-tolerant and may get damaged by prolonged exposure to cold temperatures.
- Among the Garasia tribe in Rajasthan, the tree holds cultural significance, with some believing their lineage traces back to semal trees.
Distribution:
- Its distribution spans across various regions in India, including Andaman & Nicobar Island, Assam, Bihar, Kerala, Madhya Pradesh, Maharashtra, Odisha, Punjab, Rajasthan, and Uttar Pradesh.
Importance of the Tree:
- The tree's importance lies in its resistance to fire and its renowned cooling properties, making it valuable for land reclamation efforts.
- It generates abundant biomass each season and aids in carbon sequestration by shedding leaves before flowering.
- The late flowering of the small tree is considered by some researchers as a potential indicator of a hot summer or delayed monsoon.
- The silk cotton tree is known for its medicinal properties.
- The tree’s bark, leaves, and seeds are utilised in traditional medicine to cure various ailments, including fever, diarrhoea and skin conditions.
- The tree is also used as a natural remedy for wounds and cuts.
- The tree also serves as a habitat for rock bees, as its spikes deter sloth bears, and its reddish roots are consumed by tribal communities during the monsoon.
- Furthermore, it offers opportunities for agroforestry and provides essential resources like food, fodder, and fuelwood, with its wood being used by various tribes for crafting musical instruments and utensils.
OpenAI’s GPT-4o

- 14 May 2024
Why is it in the News?
OpenAI introduced its latest large language model (LLM) called GPT-4o recently, billing it as its fastest and most powerful AI model so far.
What is GPT-4o?
- GPT-4o (“o” stands for “Omni”) is a revolutionary AI model by OpenAI, which has been developed to enhance human-computer interactions.
- It lets users input any combination of text, audio, and image and receive responses in the same formats.
- This makes GPT-4o a multimodal AI model – a significant leap from previous models.
- GPT-4o is like a digital personal assistant that can assist users with a variety of tasks.
- From real-time translations to reading a user’s face and having real-time spoken conversations, this new model is far ahead of its peers.
- GPT-4o is capable of interacting using text and vision, meaning it can view screenshots, photos, documents, or charts uploaded by users and have conversations about them.
- The new updated version of ChatGPT will also have updated memory capabilities and will learn from previous conversations with users.
What is the technology behind GPT-4o?
- LLMs are the backbone of AI chatbots. Large amounts of data are fed into these models to make them capable of learning things themselves.
- A large language model (LLM) is a computer program that learns and generates human-like language using a transformer architecture trained on vast text data.
- Large Language Models (LLMs) are foundational machine learning models that use deep learning algorithms to process and understand natural language.
- These models are trained on massive amounts of text data to learn patterns and entity relationships in the language.
- LLMs can perform many types of language tasks, such as translating languages, analyzing sentiments, chatbot conversations, and more.
- They can understand complex textual data, identify entities and relationships between them, and generate new text that is coherent and grammatically accurate.
What are GPT-4o’s limitations and safety concerns?
- GPT-4o is still in the early stages of exploring the potential of unified multimodal interaction, meaning certain features like audio outputs are initially accessible in a limited form only, with preset voices.
- Further development and updates are necessary to fully realise its potential in handling complex multimodal tasks seamlessly.
- Regarding safety, GPT-4o comes with built-in safety measures, including “filtered training data and refined model behaviour post-training”.
International Bullion Exchange (IIBX)

- 14 May 2024
Why is it in the News?
The State Bank of India (SBI) recently announced that it has secured the distinction of being the first bank to become a trading-cum-clearing (TCM) Member of the India International Bullion Exchange at the GIFT City in Gujarat.
What is the International Bullion Exchange (IIBX)?
- India International Bullion Exchange (IIBX) is India's first International Bullion Exchange.
- It is situated within the Gujarat International Finance Tech City (GIFT City) IFSC in Gandhinagar, Gujarat.
- Conceptualized to serve as a premier platform for importing bullion into India, IIBX aims to establish a world-class ecosystem for bullion trading, fostering investment in bullion financial products, and providing top-tier vaulting facilities.
What is Bullion?
- Bullion refers to high-purity physical gold and silver, typically stored in the form of bars, ingots, or coins.
- While sometimes recognized as legal tender, bullion primarily serves as a reserve for central banks and institutional investors.
Key Features:
- Transparent Price Discovery: IIBX prioritizes transparent price discovery mechanisms, ensuring fair and equitable transactions.
- Responsible Sourcing and Supply Chain Integrity: Emphasizing ethical practices, IIBX upholds responsible sourcing and supply chain integrity standards.
- Quality Assurance and Standardization: IIBX maintains rigorous quality assurance protocols and standardized practices to uphold the integrity of traded bullion.
Regulation and Oversight:
- Under the governance of the International Financial Services Centers Authority (IFSCA), IIBX operates under a unified regulatory framework dedicated to the development and oversight of financial products, services, and institutions within IFSCs.
Competitive Advantage:
- Offering a diverse array of products and cutting-edge technology, IIBX provides cost-effective solutions unparalleled by Indian exchanges and global counterparts in major financial hubs like Hong Kong, Singapore, Dubai, London, and New York.
What is the International Financial Services Centers Authority (IFSCA)?
- The International Financial Services Centers Authority (IFSCA) is a regulatory body established in India to oversee and regulate financial products, services, and institutions operating within International Financial Services Centers (IFSCs).
- IFSCA was formed to develop and promote the financial ecosystem within IFSCs, ensuring compliance with international standards and best practices.
- It regulates various entities such as banking, insurance, securities markets, and other financial intermediaries to foster growth and innovation in the financial sector within IFSCs.
- IFSCA's jurisdiction includes Gujarat International Finance Tech City (GIFT City) IFSC in Gandhinagar, Gujarat, which serves as a hub for international financial activities in India.
United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime (UNDOC)

- 14 May 2024
Why is it in the News?
The United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime released the 2024 World Wildlife Crime Report on May 13, 2024.
About the United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime (UNODC):
- The United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime (UNODC) is a global organization that operates under the umbrella of the United Nations and serves as a leading authority in the fight against illicit drugs, organized crime, corruption, and terrorism.
- UNODC works to promote justice, security, and integrity in various areas related to crime prevention and criminal justice.
Objectives:
- The primary objectives of UNODC are to assist member states in their efforts to combat drug trafficking, reduce drug abuse and its associated health and social consequences, dismantle transnational organized criminal networks, prevent and address corruption, counter terrorism, and promote the rule of law and effective criminal justice systems.
History of UNODC:
- It was established in 1997 through the merger of two precursor entities:
- The United Nations Drug Control Programme (UNDCP) - It was founded in 1991 as a response to the growing global drug problem.
- Its primary focus was to coordinate and support international efforts in combating illicit drug production, trafficking, and drug abuse.
- The Centre for International Crime Prevention (CICP) - The CICP, established in 1992, aimed to address a broader range of transnational crimes, including organized crime, corruption, and terrorism.
- The United Nations Drug Control Programme (UNDCP) - It was founded in 1991 as a response to the growing global drug problem.
- The merger of these two entities resulted in the creation of UNODC, which brought together expertise and resources in the fields of drug control and crime prevention under a unified structure.
- Since its inception, UNODC has expanded its mandate and activities to encompass a wide range of global challenges related to drugs, crime, corruption, and terrorism.
The mandate of UNODC:
- The mandate of UNODC is derived from several United Nations General Assembly resolutions and international conventions.
- The organization operates within the framework of the United Nations principles and aims to support member states in implementing these conventions and addressing the various aspects of crime and drug-related challenges.
Funding:
- It relies on voluntary contributions, mainly from governments, to carry out the majority of our work.
- Headquarters: Vienna, Austria
The Main Areas of UNODC's:
- Fighting Drugs: Implementing global drug control conventions, aiding in prevention and treatment, disrupting trafficking networks, and fostering international cooperation.
- Tackling Organized Crime: Helping states build legal frameworks, dismantle criminal networks, strengthen border control, and analyze emerging threats.
- Anti-Corruption Efforts: Supporting UNCAC implementation, establishing commissions, recovering stolen assets, and promoting integrity in public and private sectors.
- Strengthening Criminal Justice: Enhancing law enforcement, judiciary, and prison systems, improving access to justice, supporting rehabilitation, and promoting international legal standards.
- Combating Terrorism: Assisting in legal frameworks, enhancing law enforcement capacities, countering terrorist financing, and addressing online radicalization.
- Addressing Human Trafficking and Migrant Smuggling: Developing strategies, strengthening legislation, aiding victim protection, and fostering international cooperation.
What is the World Wildlife Crime Report?
- The World Wildlife Crime Report, now in its third edition (2024), continues the tradition established by earlier editions published in 2016 and 2020.
- It delves into trends related to the illegal trafficking of protected wildlife species, providing comprehensive analyses of the harms and impacts of wildlife crime.
- Furthermore, it investigates the driving factors behind wildlife trafficking trends and assesses the effectiveness of various interventions aimed at addressing this complex issue.
Xenotransplantation
- 13 May 2024
Why is it in the News?
The first recipient of a modified pig kidney transplant passed away recently, around two months after the surgery was carried out.
What is Xenotransplantation?
- Xenotransplantation is the transplantation of organs from different species, such as pigs to humans.
- It is a procedure that involves the transplantation, implantation or infusion into a human recipient of either (a) live cells, tissues, or organs from a nonhuman animal source, or (b) human body fluids, cells, tissues or organs that have had ex vivo contact with live nonhuman animal cells, tissues or organs.
- Essentially, it is the use of animal cells and organs to heal humans.
- Xenotransplantation involving the heart was first tried in humans in the 1980s.
- The need for such a procedure was felt because of the significant gap between the number of transplants needed by patients and the availability of donor organs.
How Does Xenotransplantation Happen?
- The process of implanting a pig kidney into a recipient is akin to a standard transplant procedure, including the use of post-surgery immunosuppressant drugs.
- However, several critical additional steps are involved.
- Firstly, the chosen animal organ undergoes genetic modifications to prevent rejection by the human body.
- Using CRISPR-Cas9 gene editing technology, specific pig genes responsible for producing antibodies reactive to the human immune system are removed. Simultaneously, certain human genes are introduced to enhance the kidney's compatibility with human recipients.
- Even after the surgery, vigilant monitoring is essential to assess the body's response to the transplanted organ.
Why are pigs often used for xenotransplantation?
- Pig heart valves have been used to replace damaged valves in humans for over 50 years now.
- The pig’s anatomical and physiological parameters are similar to those of humans, and the breeding of pigs on farms is widespread and cost-effective.
- Also, many varieties of pig breeds are farmed, which provides an opportunity for the size of the harvested organs to be matched with the specific needs of the human recipient.
What are the Complications of Xenotransplantation?
- Rejection: Despite genetic modifications, the recipient's immune system may still recognize the transplanted organ as foreign and mount an immune response, leading to rejection.
- Infection: Xenotransplantation introduces the risk of transmitting infectious diseases from the donor animal to the recipient, including viruses and bacteria that may not typically affect humans.
- Immunological Challenges: The interaction between the recipient's immune system and the transplanted organ may trigger inflammatory responses, leading to complications such as inflammation and tissue damage.
- Ethical Concerns: Xenotransplantation raises ethical dilemmas related to animal welfare, genetic engineering, and the potential exploitation of animals for human benefit.
- Long-term Health Risks: The long-term effects of xenotransplantation on recipient health, including the development of chronic conditions and the risk of cancer, are still not fully understood and require further research.
Vibrant Village Programme (VVP)

- 13 May 2024
Why is it in the News?
The government is likely to spend over ?2 crore on each kilometre of road to be constructed along the China border in Uttarakhand and Sikkim under the Vibrant Village Programme (VVP), according to the project’s details.
What is the Vibrant Villages Programme (VVP)?
- Vibrant Villages Programme (VVP) is a Centrally Sponsored Scheme approved on 15th February 2023 for the financial years 2022-23 to 2025-26.
Objective:
- For comprehensive development of the select villages in 46 blocks in 19 districts abutting the northern border in the States of Arunachal Pradesh, Himachal Pradesh, Sikkim, Uttarakhand and UT of Ladakh.
- It will aid in raising the standard of living for residents of designated border communities and encouraging them to remain there, reversing the outmigration from these villages and enhancing border security.
- Action plans for identified villages would be prepared by the district administration with assistance from the proper mechanisms at the block and panchayat levels, in order to guarantee complete saturation of federal and state programmes.
- Road connectivity, drinking water, power (including solar and wind energy), mobile and internet access, tourist attractions, multipurpose facilities, healthcare infrastructure, and wellness centres are the intervention areas with the highest priority for village development.
Scheme implementation:
- Scheme implementation involves identifying and fostering economic drivers in border villages along the northern border, following a "Hub and Spoke Model" to establish growth centres.
- This includes promoting social entrepreneurship, empowering youth and women through skill development and entrepreneurship, leveraging local tourism potential, preserving cultural heritage, and fostering sustainable eco-agribusinesses.
- Vibrant Village Action Plans will be developed by district administrations in collaboration with Gram Panchayats, ensuring full coverage of Central and state schemes.
Expected outcomes:
- Key outcomes that have been attempted are connectivity with all-weather roads, drinking water, 24x7 electricity – Solar and wind energy to be given focussed attention, and mobile and internet connectivity.
- Tourist centres, multi-purpose centres and health and wellness Centers.
Rat-Hole Mining

- 13 May 2024
Why is it in the News?
A one-member panel appointed by the High Court of Meghalaya to handle coal-related issues has flagged the lack of progress in restoring the environment damaged by rat-hole coal mining in the northeastern State.
What is Rat-hole Mining?
- Coal reserves are concentrated in Eastern India, spanning states such as Telangana, Madhya Pradesh, Maharashtra, Jharkhand, Chhattisgarh, and West Bengal, with significant deposits also found in the North-Eastern regions like Assam and Meghalaya.
- However, commercial mining isn't prevalent in the North-East due to unsuitable terrain and the nature of coal deposits.
- Open mining faces additional challenges, and the coal in this region often contains high sulfur content, reducing energy efficiency and classifying it as low-quality coal.
- A rat-hole mine involves digging of very small tunnels, usually only 3-4 feet deep, in which workers, more often children, enter and extract coal.
- Once the pits are dug, miners descend using ropes or bamboo ladders to reach the coal seams.
- The coal is then manually extracted using primitive tools such as pickaxes, shovels, and baskets.
- A major portion of these employees are children, who are preferred because of their thin body shape and ease of accessing depths.
- This practice has become very popular in Meghalaya.
- Here there are majorly hilly terrains, which make coal mining very difficult.
- Also, digging a big hole is very difficult because a big hole demands pillars and support.
- Since it’s a good opportunity to extract coal from there for big as well as local investors, because it involves less investment and good returns, people are drawn towards this dangerous business.
- The practice is to not make any professional tunnels, install pillars, and ensure safety measures, but to just dig a small tunnel and put children and labour to work.
- Rat-hole mining is primarily practised only in Meghalaya.
- Such cases are not witnessed in Jharkhand and Chhattisgarh because the coal seems to be thick in Jharkhand and Chhattisgarh while in Meghalaya coal seems to be very thin.
- So, economically it is not a good idea to do open mining, and therefore, they prefer rat-hole mining.
Types of rat-hole mining:
- The rat-hole mining is broadly of two types.
- In the side-cutting procedure, narrow tunnels are dug on the hill slopes and workers go inside until they find the coal seam.
- In the other type of rat-hole mining, called box-cutting, a rectangular opening is made, varying from 10 to 100 sqm, and through that a vertical pit is dug, 100 to 400 feet deep.
- Once the coal seam is found, rat-hole-sized tunnels are dug horizontally through which workers can extract the coal.
Environmental and Safety Concerns:
- Since rat-hole mining is illegal, it is practised behind closed doors, and therefore, no one is ready to invest in infrastructure development.
- Coal is stored near rivers because of a shortage of space which leads to pollution around water bodies.
- The water in the Kopili River (which flows through Meghalaya and Assam) has turned acidic.
- The entire roadsides in and around mining areas are for piling coal.
- This is a major source of air, water and soil pollution.
- Off-road movement of trucks and other vehicles in the area causes further damage to the ecology of the area.
- Due to rat-hole mining, during the rainy season, water gets flooded into the mining areas resulting in the death of many workers due to suffocation and hunger.
- If water has seeped into the cave, the worker can enter only after the water is pumped out.
- Also, the mines are typically unregulated, lacking safety measures such as proper ventilation, structural support, or safety gear for the workers.
When Was It Banned?
- The National Green Tribunal (NGT) banned rat-hole mining in 2014 and retained the ban in 2015.
- The ban was on grounds of the practice being unscientific and unsafe for workers.
- The NGT order bans not only rat-hole mining but all “unscientific and illegal mining.”
- But orders of the Tribunal have been violated without exception since The State Government has failed to check illegal mining effectively.
Caenorhabditis Elegans
- 13 May 2024
Why is it in the News?
Researchers found that after C. elegans worms ate a disease-causing bacteria, its children knew from birth to avoid making the same mistake.
What is Caenorhabditis Elegans?
- Caenorhabditis elegans is a small, free-living roundworm (nematode) that is widely used as a model organism in various fields of biological research, including genetics, developmental biology, neuroscience, and ageing.
- It was initially discovered in the soil of a nematode-infested plant in the city of Bristol, England, in the early 20th century.
C. elegans has several characteristics that make it an ideal model organism:
- Simple anatomy: The adult hermaphrodite worm consists of precisely 959 cells, allowing for a detailed understanding of its cellular anatomy.
- Rapid life cycle: The worm's life cycle, from fertilized egg to mature adult, takes only about 3 days at 20°C.
- Transparent body: The transparency of its body enables researchers to observe cellular structures and processes directly under a microscope.
- Ease of genetic manipulation: C. elegans is highly responsive to genetic manipulation techniques, facilitating the study of gene function and the effects of mutations.
- Research on C. elegans has led to groundbreaking discoveries, including insights into the molecular basis of cell death, the regulation of gene expression, and the neural basis of behaviour.
- These findings have provided valuable knowledge that can be applied to understanding the biology of more complex organisms, including humans.
What are Nematodes?
- Nematodes are long, thin round worms, so tiny that they can usually only be seen under the microscope.
- Nematodes are incredibly abundant organisms found in various environments worldwide.
- They can be parasites of animals and plants or exist as free-living organisms in soil, freshwater, marine habitats, and even unconventional places like vinegar and beer malts.
- These bilaterally symmetrical creatures are elongated with tapered ends and may possess a pseudocoel, a fluid-filled body cavity.
- Nematodes are ubiquitous, inhabiting diverse ecosystems ranging from deserts and swamps to oceans and even Antarctica.
- In animals, they commonly parasitize organs such as the alimentary, circulatory, and respiratory systems.
ASEAN-India Trade in Goods Agreement (AITIGA)

- 13 May 2024
Why is it in the News?
The 4th joint committee meeting for the review of AITIGA (ASEAN-India Trade in Goods Agreement) was held in Putrajaya, Malaysia recently.
About ASEAN-India Trade in Goods Agreement (AITIGA):
- The ASEAN-India Trade in Goods Agreement (AITIGA) is a trade deal between the ten member states of ASEAN and India.
- ASEAN and India signed the Agreement at the 7th ASEAN Economic Ministers-India Consultations in Bangkok, Thailand in 2009.
- The Agreement, which came into effect in 2010, is sometimes referred to as the ASEAN-India Free Trade Agreement.
- The Agreement has led to steadily increasing trade between ASEAN and India since its signing.
- In 2019-20, trade between India and ASEAN was worth US$86 billion.
- Though this represented a decline from US$97 billion in 2018-19 because of the COVID-19 pandemic, it was an increase from US$81.3 billion in the 2017-18 financial year.
- It covers trade in physical goods and products and it does not apply to trade in services.
- ASEAN and India signed a separate ASEAN-India Trade in Services Agreement in 2014.
About the Association of the Southeast Asian Nations (ASEAN):
- The Association of the Southeast Asian Nations (ASEAN) is a geopolitical and economic organization established to accelerate economic growth, social progress and cultural development among its ten (10) member states.
- It also aims to promote peace and stability in the region, active collaboration and mutual assistance on matters of common interest, Southeast Asian studies, and maintain close and beneficial cooperation with other regional and international organizations.
- It was established on 8 August 1967 in Bangkok, Thailand with the signing of the ASEAN Declaration by the founding members of ASEAN, namely Indonesia, Malaysia, the Philippines, Singapore and Thailand.
- Brunei Darussalam then joined in 1984, Viet Nam in 1995, Lao PDR and Myanmar in 1997, and Cambodia in 1999, making up the current 10 Member States of ASEAN.
- The ASEAN Secretariat was set up in February 1976 and is based in Jakarta, Indonesia.
PS4 Engine

- 11 May 2024
Why is it in the News?
Recently, the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) successfully tested a liquid rocket engine made with the help of additive manufacturing technology — commonly known as 3D printing.
About PS4 Engine:
- ISRO has successfully conducted a long-duration test of its PS4 engine, re-designed for production using cutting-edge additive manufacturing (AM) techniques, also known in common parlance as 3D printing, and crafted in the Indian industry.
- The PS4 engine is the uppermost stage of the Polar Satellite Launch Vehicle (PSLV), comprising two Earth-storable liquid engines.
- The engine uses the earth-storable bipropellant combinations of Nitrogen Tetroxide as oxidiser and Mono Methyl Hydrazine as fuel in pressure-fed mode.
- It was developed by ISRO's Liquid Propulsion Systems Centre (LPSC).
- LPSC redesigned the engine making it amenable to the Design for Additive Manufacturing (DfAM) concept thereby gaining considerable advantages.
- It was developed by ISRO's Liquid Propulsion Systems Centre (LPSC).
- The manufacturing of the engine was done by the Indian industry partner, Wipro 3D, and the engine was hot tested at ISRO Propulsion Complex, Mahendragiri, Tamil Nadu.
Why did ISRO use 3D printing to build the PS4 engine?
- The technology helped ISRO bring down the number of parts in the engine from 14 to a single piece.
- The space agency was able to eliminate 19 weld joints and saved 97% of the raw material.
- It also reduced the overall production time by 60%.
What is 3D Printing?
- 3D printing is a process that uses computer-created design to make three-dimensional objects layer by layer.
- It is an additive process, in which layers of a material like plastic, composites or bio-materials are built up to construct objects that range in shape, size, rigidity, and colour.
How is 3D printing done?
- To carry out 3D printing, one needs a personal computer connected to a 3D printer.
- All they need to do is design a 3D model of the required object on computer-aid design (CAD) software and press ‘print’.
- The 3D printer does the rest of the job.
- 3D printers construct the desired object by using a layering method, which is the complete opposite of the subtractive manufacturing processes.
- The (3D) printers act generally the same as a traditional inkjet printer in the direct 3D printing process, where a nozzle moves back and forth while dispensing a wax or plastic-like polymer layer-by-layer, waiting for that layer to dry, then adding the next level.
- It essentially adds hundreds or thousands of 2D prints on top of one another to make a three-dimensional object.
- Notably, these machines are capable of printing anything from ordinary objects like a ball or a spoon to complex moving parts like hinges and wheels.
- We can print a whole bike, handlebars, saddle, frame, wheels, brakes, pedals and chain–ready assembled, without using any tools.
- It’s just a question of leaving gaps in the right places.
Heatstroke

- 11 May 2024
Why is it in the News?
The Union Health Ministry has issued standardised guidelines for confirming heatstroke and heat-related deaths in the country.
What is a Heatstroke?
- Heatstroke, also known as sunstroke, is a medical emergency resulting from the body overheating due to exposure to high temperatures and humidity or prolonged physical exertion in hot conditions.
- Individuals experiencing heat exhaustion may exhibit symptoms such as fatigue, dizziness, headache, nausea, vomiting, low blood pressure, and increased heart rate.
Criteria for Heatstroke:
- Heatstroke is characterized by body temperatures of 40°C (104°F) or higher, accompanied by delirium, seizures, or coma, posing a potentially fatal condition.
Heatstroke Deaths in India:
- According to analysis of data from the National Crime Records Bureau, over 11,000 people in India died due to heatstroke between 2012 and 2021.
Government Initiatives:
- The Health Ministry released a National Action Plan on Heat-Related Illness in July 2021, outlining strategies to address health challenges posed by heat waves.
- The India Cooling Action Plan (ICAP) aims to mitigate heat impacts by ensuring sustainable cooling and thermal comfort for all by 2037-38.
First Aid Measures for Heatstroke:
-
- Move the affected person to a cool, shaded area.
- Offer water or a rehydrating drink if the person is conscious.
- Fan the person to promote cooling.
- Seek medical attention if symptoms worsen, persist, or if the person loses consciousness.
- Avoid giving alcohol, caffeine, or carbonated beverages.
- Apply a cool, wet cloth to the person's face or body.
- Loosen clothing to improve ventilation.
Key Points from the Guidelines:
- Rationale for the Guidelines: Between 2013 and 2022, there was an 85% increase in estimated annual heat-related mortality compared to 1991–2000, driven by global warming and changing demographics.
- Without significant adaptation progress, annual heat-related deaths could surge by 370% by mid-century if global temperatures continue to rise towards 2°C above pre-industrial levels.
- In light of these projections, enhancing our understanding and surveillance of heat-related health issues is imperative.
Preparation and Authorship:
- The guidelines were developed by the National Programme on Climate Change and Human Health (NPCCHH) in collaboration with the National Centre for Disease Control (NCDC).
Objective:
- The guidelines aim to assist hospitals in identifying criteria for categorizing deaths as heat-related or due to heat stroke, promoting evidence-based medical decision-making.
Autopsy Considerations:
- Decisions regarding autopsy should be based on factors such as the circumstances of death, the age of the deceased, and available resources.
- Where feasible, collecting blood, urine, etc., for toxicological examination is recommended, contingent on the condition of the body.
Challenges in Diagnosing Heat-Related Deaths
- Diagnosing heat-related deaths post-mortem presents several challenges, including:
- Frequently unavailable pre-terminal or terminal body temperatures.
- Non-specific autopsy findings vary based on the duration of survival after heat exposure.
- Reliance on-scene investigation for diagnosing hyperthermia, a condition resulting from the body's inability to regulate heat.
- Consideration of circumstances of death and exclusion of alternative causes.
- It's noted that autopsies are not mandatory for heat-related deaths.
Inter-Services Organisations (ISOs) (Command, Control, and Discipline) Act

- 11 May 2024
Why is it in the News?
The Inter-Services Organisations (Command, Control and Discipline) Act has been notified in a gazette and has been enforced with effect from May 10, the Defence Ministry said recently.
About Inter-Services Organisations (ISOs) (Command, Control, and Discipline) Act:
- During the Monsoon Session of 2023, both houses of Parliament passed a bill aimed at enhancing the operational efficiency and coordination of Inter-Services Organisations (ISOs).
- These organisations comprise personnel from the Army, Air Force, and Navy, such as joint training institutions like the National Defence Academy, National Defence College (NDC), Defence Services Staff College (DSSC), and the Andaman and Nicobar Command (ANC).
Key Provisions of the ACT:
- Inter-Services Organisation Establishment: Existing Inter-Services Organisations will be considered constituted under the Act.
- The central government may establish an Inter-Services Organisation comprising personnel from at least two of the following services: the Army, Navy, and Air Force.
- Control of Inter-Services Organisations: The Act empowers the Commander-in-Chief or Officer-in-Command of an Inter-Services Organisation to exercise command and control over its personnel.
- They are responsible for maintaining discipline and ensuring the proper discharge of duties by service personnel.
- Supervision of an Inter-Services Organisation will be under the purview of the central government.
- Commander-in-Chief Eligibility: Officers eligible for appointment as Commander-in-Chief or Officer-in-Command include:
- A General Officer of the regular Army (rank above Brigadier),
- A Flag Officer of the Navy (rank of Admiral of the Fleet, Admiral, Vice-Admiral, or Rear-Admiral), or
- An Air Officer of the Air Force (a rank above Group Captain).
- Commanding Officer Appointment: The Act establishes a Commanding Officer responsible for leading a unit, ship, or establishment within the Inter-Services Organisation.
- The Commanding Officer carries out duties assigned by the Commander-in-Chief or Officer-in-Command.
- They have the authority to initiate disciplinary or administrative actions for personnel within the Inter-Services Organisation.
Need for the Act:
- Theaterisation Drive: The enactment aligns with the ongoing push for theaterisation, a vital military reform aimed at optimizing resources for future combat scenarios.
- Existing Framework Challenges: Currently, armed forces personnel are governed by separate laws— the Air Force Act, 1950, the Army Act, 1950, and the Navy Act, 1957—resulting in disjointed disciplinary powers.
- Under the current setup, only officers from the same service possess disciplinary authority over personnel governed by the respective Act, leading to command, control, and discipline challenges.
- Financial Implications: The present framework entails time-consuming processes and financial expenditures for personnel transfers.
- The proposed legislation seeks to remedy these challenges by enhancing discipline enforcement, expediting case resolutions, and potentially saving public funds.
Auroras

- 11 May 2024
Why is it in the News?
The night sky was lit up by northern lights, or aurora borealis, at Hanle village in Ladakh early Saturday morning.
What are Auroras?
- Auroras are essentially natural lights that appear as bright, swirling curtains in the night sky and can be seen in a range of colours, including blue, red, yellow, green, and orange.
- These lights primarily appear near the poles of both the northern and southern hemispheres all year round but sometimes they expand to lower latitudes.
- In the north, the display is called the Aurora Borealis
- In the south, it is known as the Aurora Australis
Why do auroras occur?
- It is due to activity on the surface of the Sun.
- The star continuously releases a stream of charged particles, mainly electrons and protons, and magnetic fields called the solar wind.
- As the solar wind approaches the Earth, it is deflected by the planet’s magnetic field, which acts like a protective shield.
- However, some of the charged particles are trapped in the magnetic field and they travel down the magnetic field lines at the north and south poles into the upper atmosphere of the Earth.
- These particles then interact with different gases present there, resulting in tiny flashes that light up the night sky.
- When solar wind particles collide with oxygen, a green colour light is produced.
- Interaction with nitrogen produces shades of blue and purple.
- Auroras expand to midlatitudes when the solar wind is extremely strong.
- This happens when the activity on the Sun’s surface goes up, leading to solar flares and coronal mass ejections (CMEs), which are essentially extra bursts of energy in the solar wind.
- In such cases, the solar wind is so intense that it can result in a geomagnetic storm, also known as a magnetic storm, a temporary disturbance of the Earth’s magnetic field.
- It is during a magnetic storm that auroras can be seen in the mid-latitudes.
‘Hanooman’ GenAI Platform

- 11 May 2024
Why is it in the News?
Homegrown generative artificial intelligence (GenAI) platform Hanooman went live in 98 global languages, including 12 Indian languages recently.
What is the ‘Hanooman’ Platform?
- Hanooman is India's Gen AI platform, launched in 98 languages including 12 Indian languages such as Hindi, Marathi, Gujarati, Bengali, Kannada, Odia, Punjabi, Assamese, Tamil, Telugu, Malayalam, and Sindhi.
- Abu Dhabi-based AI investment firm 3AI Holding Limited and SML India have built this indigenous platform.
- Named after the revered Hindu deity Hanuman, known for his unparalleled strength, wisdom, and devotion, Hanooman embodies the core principles of intelligence, agility, and resilience.
- The development of Hanooman was driven by a vision to create an AI platform that combines human-like intelligence with advanced machine-learning capabilities to tackle complex problems and drive innovation across diverse domains.
Key Features and Capabilities:
- Natural Language Understanding (NLU): Hanooman boasts advanced NLU capabilities that enable it to understand and interpret human language with remarkable accuracy.
- Whether it's processing text, speech, or multimedia content, Hanooman can analyze and extract meaningful insights to facilitate intelligent decision-making.
- Contextual Awareness: Hanooman is equipped with contextual awareness technology that allows it to understand the context of a given situation and adapt its responses accordingly.
- This enables Hanooman to provide personalized recommendations, anticipate user needs, and deliver tailored experiences across various applications and interfaces.
- Deep Learning and Neural Networks: Leveraging state-of-the-art deep learning algorithms and neural networks, Hanooman is capable of learning from vast amounts of data and continuously improving its performance over time.
- This enables Hanooman to tackle complex problems, such as image recognition, natural language processing, and predictive analytics, with unparalleled accuracy and efficiency.
- Multi-Modal Learning: Hanooman supports multi-modal learning, allowing it to process and integrate information from multiple sources, including text, images, and audio.
- This enables Hanooman to understand and analyze complex data sets more comprehensively, leading to more informed decision-making and actionable insights.
Applications and Uses:
- Healthcare: Hanooman can be used to analyze medical imaging data, diagnose diseases, and develop personalized treatment plans based on individual patient profiles.
- Finance: It can analyze market trends, predict financial risks, and optimize investment strategies to maximize returns and minimize losses.
- Manufacturing: It can optimize production processes, detect anomalies in manufacturing equipment, and improve quality control measures to enhance operational efficiency and reduce downtime.
- Retail: It can analyze customer data, personalize marketing campaigns, and optimize inventory management to drive sales and increase customer satisfaction.
Oleander

- 10 May 2024
Why is it in the News?
Two Kerala government-controlled temple boards, which together manage 2,500-odd temples in the state, have banned the use of oleander flowers (locally known as arali) in temple offerings after a 24-year-old woman died after accidentally chewing some oleander leaves.
What is Oleander?
- Nerium oleander, commonly known as oleander or rosebay, is a plant cultivated worldwide in tropical, subtropical, and temperate regions.
- Known for its drought tolerance, the shrub is often used for ornamental and landscaping purposes.
- In Kerala, the plant is known by the names of arali and kanaveeram and is grown along highways and beaches as a natural, green fencing.
- There are different varieties of oleander, each with a flower of a different colour.
How is oleander used in traditional medicine?
- The Ayurvedic Pharmacopoeia of India (API), a government document that describes the quality, purity, and strength of drugs used in Ayurveda, mentions oleander.
- According to API, an oil prepared from the root bark can be used to treat skin diseases.
- The plant has been “frequently described in Brihattrayi, Nighantus and other classical Ayurvedic texts.
- Charka [Charak Samhita] has prescribed the leaves of white-flowered variety externally for chronic and obstinate skin diseases of serious nature including leprosy.
How toxic is oleander?
- Even though it is prescribed in some ayurvedic formulations, oleander’s toxicity has also long been recognised across the world.
- The plant has been “exploited therapeutically and as an instrument of suicide since antiquity.
- Moreover, ingestion or inhalation of smoke from burning oleander can also be intoxicating.
- This is due to the properties of cardiac glycosides (a type of chemical) including oleandrin, folinerin, and digitoxigenin, which are present in all parts of the plant.
- Cardiac glycosides are steroidal compounds capable of exerting pharmacological effects on cardiac muscle.
- The primary therapeutic value of these glycosides lies in their ability to exert profound tonic effects on the heart.
- However, the therapeutic window is small and overdose/toxicity is frequently encountered when using these drugs.
- Effects of oleander toxicity include nausea, diarrhoea, vomiting, rashes, confusion, dizziness, irregular heartbeat, slow heartbeat, and, in extreme cases, death.
- Symptoms last for 1 to 3 days and may require a hospital stay.
World Migration Report 2024

- 10 May 2024
Why is it in the News?
According to the recently released World Migration Report 2024, which is published by the International Organization for Migration (IOM), India has consistently been the top recipient of remittances globally.
Key Highlights of the World Migration Report 2024:
- Resilience Amidst COVID-19: Despite the challenges posed by the COVID-19 pandemic, international migration remains a vital driver of human development and economic progress.
- Notably, there has been a remarkable over 650 per cent surge in international remittances from 2000 to 2022, soaring from USD 128 billion to USD 831 billion.
- This growth defied predictions of a substantial decrease in remittances due to COVID-19.
- Remittances to Low and Middle-income Countries: Out of the total remittances, which amounted to USD 831 billion, a significant portion of USD 647 billion was sent by migrants to low and middle-income countries.
- These remittances play a crucial role in the GDPs of these nations, surpassing foreign direct investment globally.
- Persistent Challenges: While international migration continues to foster human development, the report underscores enduring challenges.
- The global population of international migrants has reached approximately 281 million, while the number of individuals displaced by conflict, violence, disasters, and other factors has surged to a record high of 117 million.
- Urgent action is imperative to address displacement crises effectively.
- Misinformation and Politicization: Despite the fact that most migration is regular, safe, and regionally focused, public discourse has been clouded by misinformation and politicization.
- It is essential to provide a clear and accurate depiction of migration dynamics to counteract this trend.
About the International Organization for Migration (IOM):
- Established in 1951, IOM, the UN Migration Agency, is the leading inter-governmental organization in the field of migration and works closely with governmental, intergovernmental and non-governmental partners.
- IOM works to help ensure the orderly and humane management of migration, promote international cooperation on migration issues, assist in the search for practical solutions to migration problems and provide humanitarian assistance to migrants in need, including refugees and internally displaced people.
- Membership: Currently, IOM counts 175 Member States and 8 states with Observer status.
- India joined as an IOM Member State on June 18, 2008.
- Headquarters: Situated in Geneva, Switzerland, IOM's headquarters serves as a hub for its global operations.
UN Counter-Terrorism Trust Fund

- 10 May 2024
Why is it in the News?
India recently contributed $5,00,000 to the UN Counter-Terrorism Trust Fund, reaffirming its unwavering commitment to the global fight against terrorism.
About the UN Counter-Terrorism Trust Fund:
- The United Nations Counter-Terrorism Trust Fund, founded in 2009 and transferred to the UN Office of Counter-Terrorism (UNOCT) in 2017, plays a crucial role in supporting global counter-terrorism initiatives.
- Contributions: Governments, inter-governmental and non-governmental organizations, private institutions, and individuals can all contribute to the fund.
- Contributions may be unearmarked or earmarked for specific global programmes or initiatives under UNOCT.
- India’s Contribution: India's contribution primarily supports UNOCT's global programmes, specifically focusing on Countering Financing of Terrorism (CFT) and the Countering Terrorist Travel Programme (CTTP).
- These initiatives aim to enhance the capacities of member states in eastern and southern Africa to combat terrorism financing and prevent the movement and travel of terrorists.
Key Facts about the UN Office of Counter-Terrorism (UNOCT):
- Established on June 15, 2017, through a UN General Assembly resolution, UNOCT is mandated to provide leadership and coordination on counter-terrorism efforts across the United Nations system.
- UNOCT's primary functions include enhancing collaboration among entities within the Global Counter-Terrorism Coordination Compact, ensuring a balanced implementation of the four pillars of the UN Global Counter-Terrorism Strategy, and strengthening capacity-building assistance for Member States.
- UNOCT also focuses on improving visibility, advocacy, and resource mobilization for UN counter-terrorism initiatives, while prioritizing the prevention of violent extremism within the broader counter-terrorism framework.
Maillard Reaction

- 10 May 2024
Why is it in the News?
The Maillard Reaction elucidates the intricate chemical processes responsible for the diverse array of flavours, aromas, and textures found in foods.
What is Maillard's Reaction?
- The Maillard reaction is a complex chain of chemical reactions that occurs when heat is exposed to amino acids and reducing sugars.
- The Maillard Reaction, named after the French scientist Louis-Camille Maillard, is a chemical phenomenon observed when amino acids, essential components of proteins, and sugars undergo heating.
- This reaction influences the taste, scent, and consistency of food items.
- It characterizes a non-enzymatic browning process in food, where colour alterations manifest without the involvement of enzymes.
How does the Maillard Reaction Induce Browning in Food?
- The Maillard reaction initiates a complex chemical process that yields various products. Chemist J.E. Hodge first delineated its steps in 1953 to simplify its understanding.
- An array of foods, from meats to bread to vegetables and coffee beans, contain both sugars and protein components.
- When subjected to heat, these sugars and proteins undergo a condensation reaction, forming an unstable compound known as Schiff base.
- This Schiff base undergoes rearrangement and dehydration, yielding diverse intermediate compounds.
- These intermediates further react to generate essential flavour components, enriching the food's aroma.
- Some intermediates undergo rearrangement, resulting in a more stable product. These products serve as vital precursors to melanoidins, pivotal in imparting the food's characteristic brown hue.
- Continued transformation, including condensation and polymerization, culminates in the formation of melanoidins—nitrogen-containing compounds responsible for the food's distinctive brown colouration.
What are the Factors Affecting the Reaction?
- The pace and magnitude of the Maillard reaction hinge on various elements, including temperature, acidity, moisture levels, and the composition of proteins and sugars in the food.
- Optimal Temperature: Temperatures typically fall within the range of 110 to 170 degrees Celsius, with levels surpassing this threshold potentially resulting in food burning and imparting bitter flavours.
- Elevated temperatures generally expedite the reaction, whereas acidic environments and moisture content can impede it.
- Hence, foods tend to brown more rapidly at higher temperatures, and dry items like bread crusts often acquire a rich brown hue during baking.
Non-market Economy Status

- 10 May 2024
Why is it in the News?
Vietnam has been pushing the President Joe Biden administration to quickly change its “non-market economy” classification to “market economy”, in a bid to avoid high taxes imposed by the US on the goods imported from the Southeastern country.
Why does Vietnam Want to Get the ‘Market Economy’ Status?
- Vietnam has argued that in recent years it has implemented enough economic reforms that get its name off the non-market economies list.
- The country does meet a number of criteria for the status to be changed.
- For instance, Vietnam allows foreign investment, wages are determined by free negotiations between workers and management, and most of the means of production are not owned by the state.
- The change in status will also help Vietnam get rid of the anti-dumping duties, making its products more competitive in the US market.
- Vietnam’s Center for WTO and International Trade has said that the method of calculating anti-dumping duties is flawed as it causes “the dumping margin to be pushed up very high” and does not actually reflect the situation of Vietnamese companies.
About Non-market Economy Status:
- Non-market economy status refers to a designation applied to countries by international trade authorities, particularly the World Trade Organization (WTO), based on their economic structure and policies.
- In a non-market economy, the allocation of resources, production decisions, and pricing mechanisms are predominantly influenced by the government rather than by market forces.
- This can include state ownership of key industries, government intervention in setting prices, and restrictions on foreign investment and trade.
- For trade purposes, countries classified as non-market economies may face different treatment in anti-dumping investigations and trade disputes.
- This designation can affect how trade regulations and tariffs are applied to goods originating from these countries.
- The US designates a country as a non-market economy based on several factors which are:
- If the country’s currency is convertible
- If wage rates are determined by free bargaining between labour and management
- If joint ventures or other foreign investments are allowed whether the means of production are owned by the state; and
- If the state controls the allocation of resources and price and output decisions.
- Other factors like human rights are also considered.
- The non-market economy label allows the US to impose “anti-dumping” duties on goods imported from designated countries.
Market Economies:
- Market economies operate based on the interactions between consumers and businesses, guided primarily by the law of supply and demand, rather than by central government policies.
- Theoretical Foundation: Developed by classical economists like Adam Smith, David Ricardo, and Jean-Baptiste Say, market economies emphasize the role of free markets in allocating resources efficiently.
- Modern Market Economies: Often referred to as mixed economies, modern market economies may still involve some government interventions, such as price-fixing, licensing, quotas, and industrial subsidies, but the majority of decisions are market-driven.
- Examples include countries like India, the USA, and the UK, where market forces play a significant role in shaping economic activities.
What is Anti-dumping Duty?
- An anti-dumping duty is a protectionist tariff that a domestic government imposes on foreign imports that it believes are priced below fair market value.
- In order to protect their respective economy, many countries impose duties on products they believe are being dumped in their national market; this is done with the rationale that these products have the potential to undercut local businesses and the local economy.
- While the intention of anti-dumping duties is to save domestic jobs, these tariffs can also lead to higher prices for domestic consumers.
- In the long term, anti-dumping duties can reduce the international competition of domestic companies producing similar goods.
- The World Trade Organization (WTO)–an international organization that deals with the rules of trade between nations–also operates a set of international trade rules, including the international regulation of anti-dumping measures.?
Antarctic Treaty Consultative Meeting (ATCM)

- 09 May 2024
Why is it in the News?
India is working with like-minded countries to promote regulated tourism in Antarctica as a steady increase in the number of tourists threatens to harm the fragile ecology in the White Continent.
About the Antarctic Treaty Consultative Meeting:
- The Antarctic Treaty Consultative Meeting (ATCM) is the annual meeting of the Parties to the 1959 Antarctic Treaty.
- The meeting serves as a platform for the exchange of information, discussion of common interests, and promotion of the principles and purposes of the Antarctic Treaty.
- The first ATCM was held in 1961, and initially occurred every other year, though the frequency has since increased.
- During the ATCM, representatives of the member countries address various issues related to Antarctica, such as environmental protection, scientific research, and tourism regulation.
- Key agenda items include strategic planning for sustainable management of Antarctica and its resources, policy, legal, and institutional operations, and biodiversity prospecting.
- The ATCM is organized by the Antarctic Treaty Secretariat, which is headquartered in Buenos Aires, Argentina, and was established in 2004.
- The Secretariat is responsible for facilitating communication and information exchange among the parties involved in the Antarctic Treaty System.
- In recent years, the ATCM has been hosted by various countries, with India hosting the 46th meeting in 2024.
- The Ministry of Earth Sciences (MoES), Government of India, through the National Centre for Polar and Ocean Research (NCPOR) and the Secretariat of the Antarctic Treaty will jointly organise the 46th Antarctic Treaty Consultative Meeting (ATCM 46) from 20 to 30 May 2024 at the Lulu Bolgatty International Convention Centre (LBICC) in Kochi, India.
What is the Antarctic Treaty?
- The Antarctic Treaty is an international agreement that aims to preserve and protect the Antarctic continent and its surrounding waters for scientific research and peaceful purposes.
- Signed on December 1, 1959, by 12 countries, the treaty came into effect on June 23, 1961.
- The treaty establishes Antarctica as a natural reserve devoted to scientific research, and it designates the area south of 60°S latitude as a region free of military and nuclear activities.
Key aspects of the treaty include:
-
- Freedom of scientific research and exploration, with cooperation among signatory nations
- Exchange of scientific information and personnel between treaty member nations
- Prohibition of military activities, such as the establishment of military bases or weapons testing
- Prohibition of nuclear explosions and disposal of radioactive waste
- Acknowledgement that no new territorial claims can be made on the continent
- Designation of Antarctica as a "Special Conservation Area" to protect its ecosystems and native species
- Currently, 54 countries have ratified the Antarctic Treaty, and 29 of these countries have Consultative Party status.
- Consultative Parties have the right to participate in decision-making processes related to the management and governance of the Antarctic region, while Non-Consultative Parties are encouraged to engage in scientific research and exchange information.
- On 12 September 1983, India became the fifteenth Consultative Member of the Antarctic Treaty.
- It participates in the decision-making process along with the other 28 Consultative Parties to the Antarctic Treaty.
- India’s first Antarctic research station, Dakshin Gangotri, was established in 1983.
- At present, India operates two year-round research stations: Maitri (1989) and Bharati (2012).
- The permanent research stations facilitate Indian Scientific Expeditions to Antarctica, which have been ongoing annually since 1981.
- In 2022, India enacted the Antarctic Act, reaffirming its commitment to the Antarctic Treaty.
Global Electricity Review 2024

- 09 May 2024
Why is it in the News?
In 2023, India overtook Japan to become the world’s third-highest producer of solar power, according to a report by international energy analytics agency Ember recently.
About Global Electricity Review 2024:
- The Global Electricity Review is published by Ember, a leading climate and energy think tank focused on accelerating the global transition to clean energy.
- The Global Electricity Review 2024 offers an in-depth analysis of the global electricity landscape in 2023.
- Drawing from a vast dataset encompassing 80 countries representing 92% of global electricity demand, and historical data from 215 countries, the report provides a robust and comprehensive examination of the current state of the electricity sector.
- The report's objective is to evaluate the progress made in transitioning the world's electricity systems towards cleaner, low-carbon sources, with a focus on limiting global temperature rise to 1.5 degrees Celsius.
Key Findings from the Report:
- Record Solar Energy Generation: Solar energy accounted for a record 5.5% of global electricity in 2023, solidifying its position as the fastest-growing electricity source for the nineteenth consecutive year.
- Renewables Surge: Renewable sources accounted for 30% of global electricity, marking a significant increase from 19% in 2000. Solar and wind power drove this expansion, with low-carbon sources contributing to nearly 40% of global electricity generation in 2023.
- Fossil Fuel Decline Forecast: The report predicts a decline in fossil fuel generation in 2024 and beyond, indicating a possible peak in global fossil fuel production in 2023.
- China's Dominance: China emerged as a significant contributor to renewable energy, accounting for 51% of the global solar generation increase and 60% of new global wind generation in 2023.
India-Specific Insights from the Report:
- India's Rise in Solar Generation: In 2023, India surpassed Japan to become the world's third-largest solar power generator, climbing from its ninth position in 2015.
- While India's installed solar capacity ranks fifth globally, its rapid growth demonstrates significant progress in harnessing solar energy.
- Share of Solar Energy in India's Electricity Mix: India generated 5.8% of its electricity from solar energy in 2023.
- This substantial contribution highlights the increasing role of solar power in meeting the country's energy demands.
- India's Contribution to Global Solar Growth: India experienced the world's fourth-largest surge in solar generation in 2023, adding 18 TWh to its capacity.
- Alongside China, the United States, and Brazil, India accounted for 75% of global solar growth in that year.
- Solar Generation Growth Since 2015: Global solar generation in 2023 was six times higher than in 2015, with India witnessing a remarkable seventeen-fold increase.
- India's Renewable Energy Target: India has committed to tripling its renewable capacity by 2030, aiming for 500 GW of installed renewable energy capacity.
- This ambitious target will require a significant acceleration in annual capacity additions.
AlphaFold 3

- 09 May 2024
Why is it in the News?
Google Deepmind has unveiled the third major version of its “AlphaFold” artificial intelligence model, designed to help scientists design drugs and target diseases more effectively.
About AlphaFold 3:
- AlphaFold 3 is a major advancement in artificial intelligence created by Google's DeepMind in collaboration with Isomorphic Labs.
- It's essentially a powerful tool that can predict the structures and interactions of various biological molecules such as:
- Predict structures of biomolecules: Unlike previous versions that focused on proteins, AlphaFold 3 can predict the 3D structure of a wide range of molecules, including DNA, RNA, and even small molecules like drugs (ligands).
- This is a significant leap in understanding how these molecules function.
- Model molecular interactions: AlphaFold 3 goes beyond just structure prediction.
- It can also model how these molecules interact with each other, providing valuable insights into cellular processes and disease mechanisms.
The potential applications of AlphaFold 3 are vast. It has the potential to revolutionize fields like:
- Drug discovery: By understanding how drugs interact with their targets, researchers can design more effective medications.
- Genomics research: AlphaFold 3 can help scientists understand the function of genes and how mutations can lead to disease.
- Materials science: By modelling the interactions between molecules, scientists can design new materials with specific properties.
- AlphaFold 3 is a significant breakthrough and is freely available for non-commercial use through AlphaFold Server.
- This makes this powerful tool accessible to researchers around the world, potentially accelerating scientific advancements.
Widal Blood Test

- 09 May 2024
Why is it in the News?
The Widal test's tendency to produce inaccurate results is clouding the understanding of India's typhoid burden, leading to increased costs, and exacerbating antimicrobial resistance risks.
What is the Widal Blood Test?
- A Widal test is a serological diagnostic test for typhoid fever.
- It helps evaluate the level of antibodies produced by the body in response to the Salmonella bacterial infection that causes typhoid fever in patients.
- Widal blood test is also known as a typhoid blood test report, as it is widely used for diagnosing typhoid fever.
- The symptoms of typhoid fever may be similar to those of other diseases, which can make the diagnosis of typhoid difficult without proper testing.
- Typhoid fever is a severe illness caused by a bacterium called Salmonella Typhi.
- This bacterium affects the gastrointestinal system and causes a range of symptoms such as high fever, diarrhoea or constipation, headache, abdominal pain, fatigue, weight loss, and red spots.
- The bacteria usually enter the body through contaminated food or water.
- Typhoid requires prompt treatment to prevent further complications such as severe intestinal perforation or bleeding.
- The Widal blood test is a quick and easy serological test that can help confirm or rule out whether a fever is due to a typhoid infection.
- Typically, typhoid symptoms appear within 6 to 30 days of exposure to the bacterial infection.
- The Widal test is designed to detect antibodies against O (somatic) and H (flagellar) antigens that cause the infection and typhoid fever.
- Infection through these antigens produces specific antibodies in response.
- The Widal blood test analyses the interaction between these two antigens and the antibodies produced in the patient's body through a blood sample.
- Detecting the presence of these antibodies in the Widal blood test indicates a bacterial infection.
- However, it has several limitations and has been phased out in many countries due to its potential for inaccuracy.
- The World Health Organization (WHO) advises against relying heavily on the Widal Test because various factors can influence its results.
- For example, a single positive result does not definitively confirm an active typhoid infection and a negative result does not necessarily rule it out.
- Additionally, obtaining an accurate diagnosis requires testing at least two serum samples taken 7-14 days apart, which can be time-consuming and often impractical.
- In areas with a continuous high burden of typhoid, baseline antibody levels may already be elevated, complicating the interpretation of results without knowing the appropriate cut-off values.
- Furthermore, cross-reactivity with antibodies produced against other infections or vaccinations can lead to false positives.
- Prior antibiotic therapy can also impact antibody levels, resulting in false negatives.
- Despite its accessibility and historical significance, the Widal Test's limitations emphasize the need for more accurate and reliable diagnostic methods for typhoid fever.
African Union (AU)

- 09 May 2024
Why is it in the News?
The African Union condemned Wednesday the Israeli military's moves into southern Gaza's Rafah, calling for the international community to stop "this deadly escalation" of the war.
About the African Union (AU):
- The African Union (AU) is a continental organization comprising 55 member states, representing the countries of the African continent.
- Established in 2002, it succeeded the Organization of African Unity (OAU), which was founded in 1963.
- The primary objective of the AU is to promote unity, cooperation, and development among African nations while advancing the continent's global interests.
- Guided by a vision of "An Integrated, Prosperous, and Peaceful Africa, driven by its own citizens and representing a dynamic force in the global arena," the AU plays a critical role in fostering collaboration and progress across the continent.
- To realize its objectives and attain the Pan-African Vision of an integrated, prosperous, and peaceful Africa, the AU developed Agenda 2063, a strategic framework for Africa's long-term socio-economic and integrative transformation.
- This ambitious agenda emphasizes the importance of collaboration and support for African-led initiatives to ensure the aspirations of the African people are achieved.
- The African Union is headquartered in Addis Ababa, Ethiopia, where it functions as a central hub for decision-making and policy development.
The African Union (AU) operates through a structured framework aimed at efficient decision-making and implementation. Its key components include:
- Assembly: Comprising the heads of state and government of member countries, the Assembly serves as the highest decision-making body within the AU.
- Executive Council: Comprised of foreign affairs ministers, the Executive Council focuses on policy matters and offers recommendations to the Assembly.
- AU Commission: Headquartered in Addis Ababa, the AU Commission serves as the administrative arm responsible for executing the decisions of both the Assembly and the Executive Council.
- Peace and Security Council: This council is entrusted with the vital task of preserving peace and security across the continent, addressing conflicts and promoting stability.
- Additionally, the AU structure fosters the active involvement of African citizens and civil society through institutions such as the Pan-African Parliament and the Economic, Social & Cultural Council (ECOSOCC), ensuring broader participation and representation in the union's endeavours.
West Nile Fever

- 08 May 2024
Why is it in the News?
The Kerala health department has issued an alert after cases of West Nile fever were reported in Malappuram, Kozhikode and Thrissur districts.
What is West Nile Fever?
- West Nile Fever is a viral infection transmitted primarily by mosquitoes, caused by the West Nile virus (WNV).
- The virus is commonly found in Africa, Europe, the Middle East, North America, and West Asia.
- Most people infected with the West Nile virus don’t experience any symptoms.
- About 20% of people who become infected with WNV will develop West Nile fever.
- However, for some, particularly the elderly or those with weakened immune systems, symptoms can range from mild flu-like symptoms such as fever, headache, body aches, fatigue etc.
- Transmission occurs when mosquitoes become infected after feeding on infected birds, and then bite humans.
Why is it named West Nile Fever?
- West Nile Virus was first isolated in a woman in the West Nile district of Uganda in 1937.
- According to the World Health Organisation (WHO), It was identified in birds in the Nile Delta region in 1953,
Symptoms:
- West Nile Fever can manifest with a range of symptoms, although the majority of individuals infected with the West Nile virus (WNV) remain asymptomatic.
- For those who do exhibit symptoms, they typically appear within 2 to 14 days after being bitten by an infected mosquito.
- Common symptoms include fever, headache, body aches, and fatigue, which are similar to those of the flu.
- Additionally, individuals may experience nausea, vomiting, diarrhoea, and swollen lymph glands.
- Skin rash and swollen joints are also reported in some cases.
- In more severe instances, West Nile Fever can lead to neurological complications.
- These may include meningitis (inflammation of the membranes surrounding the brain and spinal cord) or encephalitis (inflammation of the brain).
- Signs of neurological involvement may include severe headache, high fever, neck stiffness, disorientation, tremors, seizures, paralysis, and coma.
Treatment:
- While there is no specific treatment for West Nile Fever, supportive care such as pain management, fluids, and rest can help alleviate symptoms and aid recovery.
- Prompt medical attention is crucial, especially for those experiencing neurological symptoms, as these can be life-threatening.
Leber Congenital Amaurosis (LCA)

- 08 May 2024
Why is it in the News?
Scientists utilized a CRISPR-Cas9 tool to restore vision in individuals, including adults and children, afflicted with congenital blindness termed Leber congenital amaurosis (LCA).
What is Leber Congenital Amaurosis?
- Leber Congenital Amaurosis (LCA) is a rare genetic eye disorder where affected infants experience severe vision loss or blindness at birth.
- The condition results from the impaired function of light-gathering cells (rods and cones) in the retina.
Prevalence and Cause:
- LCA affects approximately one in 40,000 people.
- It is caused by a gene mutation that disrupts the proper function of the CEP290 protein, which is critical for vision.
Recent Development:
- Scientists have employed CRISPR-Cas9 gene editing technology to develop a novel therapy called EDIT-101.
- In a clinical trial called "BRILLIANCE," participants received a single dose of EDIT-101.
- The treatment involves cutting out the mutation in the CEP290 gene and replacing it with healthy DNA, restoring the normal function of the CEP290 protein and allowing the retina to detect light.
- This groundbreaking approach offers a promising treatment for individuals affected by LCA.
What is CRISPR-Cas9?
- CRISPR-Cas9 is a unique technology that enables geneticists and medical researchers to edit parts of the genome by removing, adding or altering sections of the DNA sequence.
- It is currently the simplest, most versatile and precise method of genetic manipulation.
How does CRISPR-Cas9 work?
- The CRISPR-Cas9 system operates through two primary molecules:
- Cas9, an enzyme often likened to "molecular scissors," which can precisely cut both strands of DNA at a designated location in the genome.
- Guide RNA (gRNA), a segment of RNA containing a specific pre-designed sequence (about 20 bases long) within a longer RNA scaffold.
- The scaffold binds to DNA, while the pre-designed sequence guides Cas9 to the intended genomic location, ensuring accurate DNA cleavage.
- The guide RNA is tailored to identify and bind to a particular sequence in the DNA, with RNA bases that complement those of the target DNA sequence.
- This specificity ensures that the guide RNA binds solely to the target sequence and avoids other genomic regions.
- Once bound, Cas9 cuts across both DNA strands at the targeted location.
- Subsequently, the cell's repair mechanisms recognize the DNA damage and attempt to rectify it.
- Scientists exploit this DNA repair process to introduce alterations to one or more genes within the genome of a selected cell.
Interactive Voice Response System (IVRS)

- 08 May 2024
Why is it in the News?
Political parties are currently reaching out to voters through Interactive Voice Response System (IVRS) calls on a daily basis.
What is an Interactive Voice Response System?
- Interactive voice response is a technology that allows telephone users to interact with a computer-operated telephone system through the use of voice and DTMF tones input with a keypad.
- IVR or Interactive Voice Response software accepts caller input, either voice or touch-tone, in response to pre-recorded prompts, and provides programmed responses.
- The responses can range from simple call routing to complex actions involving several external systems and data points depending on the software’s sophistication.
- The name, “interactive voice response” is derived from the caller responding to interactive options, offered by a pre-recorded voice.
Functionality:
- IVRS is powered by pre-recorded messaging or text-to-speech technology.
- It features a dual-tone multi-frequency (DTMF) interface.
Types:
- Touch-tone replacement: This system prompts callers to use a touch-tone keypad selection to access information.
- Directed dialogue: Provides specific verbal prompts to callers depending on their inquiry.
- Natural language: Employs speech recognition to better understand user requests.
- Industry Application: IVRS technology has been widely used across multiple industries, including banking, customer service, education, healthcare, and travel.
Benefits:
- Increased customer satisfaction by providing a streamlined experience.
- Improved contact centre operations and KPIs through call volume management.
- Reduced hold times during high call volume periods.
- Cost-effectiveness by reducing the need for customer service representatives.
Indian Ocean Dipole (IOD)
- 08 May 2024
Why is it in the News?
The Positive Indian Ocean Dipole (IOD), also known as the Indian Nino, could potentially resurface for the second consecutive year during the latter part of 2024.
What is the Indian Ocean Dipole (IOD)?
- The Indian Ocean Dipole (IOD) is defined by the difference in the sea surface temperature between the two equatorial areas of the Indian Ocean – a western pole near the Arabian Sea (in western Indian Ocean) and an eastern pole closer to the Bay of Bengal (in eastern Indian Ocean).
- The IOD affects the climate of Southeast Asia, Australia and other countries that surround the Indian Ocean Basin.
- The Indian Monsoon is invariably influenced by the IOD.
- IOD is simply the periodic oscillation of sea surface temperatures, from ‘positive’ to ‘neutral’ and then ‘negative’ phases.
- If the sea surface temperature of the western end rises above normal (0.4°C) and becomes warmer than the eastern end, it leads to a positive IOD.
- This condition is favourable for the Indian Monsoon as it causes a kind of barrier in the eastern Indian Ocean and all the southwesterly winds blow towards the Indian sub-continent.
- Accordingly, the waters in the eastern Indian Ocean cool down, which tends to cause droughts in adjacent land areas of Indonesia and Australia.
- Conversely, during a negative IOD period, the waters of the tropical eastern Indian Ocean are warmer than water in the tropical western Indian Ocean.
- This results in increased rainfall over parts of southern Australia.
Effects on India:
- A positive IOD can boost India's southwest monsoon performance depending on its development timing.
- Example: In 2019, a strong IOD event improved a 30% rainfall deficit during the late monsoon season.
- Benefits for agriculture through recharging water sources and reservoirs.
- The development of IOD likely benefits India's agricultural sector, particularly in areas with precarious water storage levels.
Difference between El Nino and IOD:
- The Indian Ocean Dipole (IOD) and the El Nino are independent climatic phenomena but often co-occur.
- Both IOD and El Nino result in changes in global wind patterns. To know about the change of wind patterns, click here.
- However, the cycle of IOD is shorter, while El Nino condition could last for even two years.
- IOD commences in the month of May and ends with the withdrawal of the Southwest Monsoon in the Indian sub-continent.
LockBit Ransomware

- 08 May 2024
Why is it in the News?
The U.S. Department of Justice has indicted Russian national Dimitry Yuryevich Khoroshev, 31, and announced a $10 million reward for any information leading to his apprehension.
What is LockBit Ransomware?
- LockBit is a type of ransomware involving financial payment in return for decryption.
- It mainly targets businesses and government agencies rather than consumers.
- Its potential targets are the institutions that would be hampered by the inconvenience and have sufficient means to pay a large payment.
- It is developed and operated by a cybercriminal group known as LockBit, which offers ransomware-as-a-service (RaaS) to other malicious actors.
- Formerly known as ABCD ransomware, has evolved into a distinct danger within the spectrum of extortion tools.
- It carries out its attacks mainly via email attachments.
- The cyber assaults through LockBit ransomware can be traced back to September 2019, when it got its first nickname, “abcd virus.”
- The nickname was derived from the filename used when encrypting a victim’s data.
- They are considered one of the most prolific and aggressive organizations in the industry, and their actions are raising anxiety among security professionals worldwide.
How LockBit Ransomware Operates?
- Exploitation: LockBit ransomware breaches systems through social engineering tactics like phishing or brute force attacks on intranet servers.
- Initial breach probes may take only a few days.
- Infiltration: Once inside a network, LockBit uses post-exploitation techniques to escalate privileges and move laterally to assess targets.
- It disables security programs and infrastructure for recovery, making independent recovery difficult.
- Deployment: LockBit spreads across the network, encrypting system files and leaving ransom notes in each folder.
- Payment of the ransom is often seen as the only viable option for victims to regain access to their systems.
How Does LockBit Ransomware Spread?
- LockBit typically spreads via phishing emails with malicious attachments or through drive-by downloading from infected websites.
- It utilizes common Windows tools like Windows PowerShell or Server Message Block, making it challenging for endpoint security systems to detect.
- Additionally, it disguises its encrypting executable file as a common PNG picture file, further evading system defenses.
Takes ransom in Bitcoins:
- LockBit hackers use so-called ransomware to infiltrate systems and hold them hostage.
- They demand payment to unlock the computers they’ve compromised and often threaten to leak stolen data to pressure victims to pay.
- The group typically demands ransom payments in Bitcoin.
Carbon Farming

- 07 May 2024
Why is it in the News?
Carbon farming offers a versatile solution applicable across diverse agro-climatic regions, simultaneously addressing issues such as soil degradation, water scarcity, and climate variability challenges.
What is Carbon Farming?
- Carbon farming refers to a set of agricultural practices designed to sequester carbon dioxide from the atmosphere and store it in the soil.
- The primary goal is to mitigate climate change by enhancing carbon capture and reducing greenhouse gas emissions.
- Through strategic land management, farmers can play a crucial role in offsetting carbon emissions and promoting environmental sustainability.
Principles of Carbon Farming:
- Carbon Sequestration: The core principle involves capturing carbon dioxide through photosynthesis and storing it in the soil.
- This is achieved by promoting the growth of plants and trees that absorb carbon from the atmosphere.
- Reduced Emissions: Carbon farming emphasizes practices that minimize greenhouse gas emissions.
- This includes optimizing fertilizer use, adopting no-till farming, and reducing reliance on synthetic inputs.
- Biodiversity Conservation: Integrating diverse crops and promoting agroforestry practices contribute to biodiversity conservation.
- This enhances ecosystem resilience and supports sustainable agricultural systems.
- Soil Health: Improving soil health is fundamental to carbon farming.
- Practices like cover cropping and rotational grazing not only sequester carbon but also enhance soil structure, water retention, and nutrient cycling.
Benefits of Carbon Farming:
- Climate Change Mitigation: The primary benefit is the significant contribution to mitigating climate change.
- Carbon farming helps offset carbon emissions, acting as a natural solution to reduce the concentration of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere.
- Improved Soil Fertility: The focus on soil health leads to increased fertility and productivity.
- Healthy soils contribute to better crop yields, reduced erosion, and enhanced resilience to climate-related challenges.
- Biodiversity Enhancement: Carbon farming practices support biodiversity by creating habitats for diverse plant and animal species.
- This contributes to ecological balance and resilience in the face of environmental changes.
- Economic Opportunities: Farmers engaged in carbon farming may access new revenue streams through carbon offset programs.
- These initiatives incentivize sustainable practices and provide financial benefits to farmers.
Challenges in Carbon Farming:
- Transition Period: Implementing carbon farming practices often requires a transition period, during which farmers may face initial costs and adjustments to new techniques. Financial support and education are crucial during this phase.
- Market Access: Connecting farmers to carbon offset markets can be challenging. Developing transparent and accessible markets for carbon credits is essential for the success of carbon farming initiatives.
- Education and Awareness: Many farmers may not be familiar with carbon farming practices.
- Education and awareness programs are necessary to disseminate information, build capacity, and encourage widespread adoption.
Conclusion
Carbon farming is a dynamic and evolving approach to agriculture that holds immense promise in the fight against climate change. By understanding its principles, benefits, and challenges, farmers and stakeholders can actively contribute to a more sustainable and resilient future. The key terms associated with carbon farming provide a foundation for navigating this innovative landscape and embracing practices that benefit both the environment and agriculture.
Wildlife Corridors

- 07 May 2024
Why is it in the News?
To revive the population of tigers in Sahyadri Tiger Reserve (STR) — the lone tiger reserve in the Maharashtra western region — the state’s forest department will soon translocate tigers from Tadoba-Andhari Tiger Reserve (TATR) in Chandrapur district.
What are Wildlife Corridors?
- Corridors are essentially habitats and pathways that connect wildlife populations, which are fragmented by human settlements and infrastructure works.
- They are crucial for the long-term survival of the tiger population as they help guard against localised extinctions and ensure the exchange of gene flow, which helps in population diversity.
- Tigers have large home ranges and often travel long distances in search of mates and food.
- In doing so, they make use of these wildlife corridors and cross several human-dominated landscapes.
- The role played by corridors in conservation is a well-established one and has been incorporated into policy decisions as well.
- Mitigation measures such as underpasses, and wildlife crossings are now routinely ordered to safeguard tigers and other wildlife in projects where linear infrastructure projects fragment habitats.
- Litigation, advocacy, and policymaking have all contributed to this.
- The construction of an overpass on the National Highway- 7 to protect the migratory route of tigers underneath between the Kanha and Pench Tiger Reserves is one instance of embedding mitigation measures to protect corridors.
- Tigers routinely use the space beneath the elevated stretch of the highway to cross the forests.
- In 2014-15, the National Tiger Conservation Authority and Wildlife Institute of India (WII) mapped 32 major tiger corridors in the country across four broad tiger landscapes – Shivalik Hills and Gangetic plains, Central India and Eastern Ghats, Western Ghats, and the North East Hills.
Is Translocation the Best Approach for Tiger Recovery?
- Tiger translocation projects have been undertaken in India since 2008.
- Sariska Tiger Reserve, in 2008, and Panna Tiger Reserve, in 2009, have witnessed successful tiger reintroduction and translocation projects.
- There have also been failures and shelving of reintroduction plans, like in the case of Satkosia Tiger Reserve in Odisha, which was the country’s first inter-state translocation project.
- However, before choosing translocation, other available options such as habitat improvement, prey augmentation, strengthening of tiger corridors, and vigilance improvement should be assessed.
- Even after translocations, one must ensure that corridors are strengthened and they are free of major disturbances.
- This will ensure the dispersal of tigers to other source population areas.
Sikhs for Justice (SFJ)

- 07 May 2024
Why is it in the News?
Delhi LG V K Saxena recently recommended a (NIA) probe against jailed Delhi CM Arvind Kejriwal for allegedly receiving political funding from Sikhs for Justice (SFJ), a New York-based pro-Khalistan organisation that is banned in India.
What is Sikhs for Justice (SfJ)?
- Sikhs for Justice (SFJ) formed in 2007, is a US-based group seeking a separate homeland for Sikhs, a “Khalistan” in Punjab.
- Its founder Gurpatwant Singh Pannun, a law graduate from Panjab University and currently an attorney at law in the US, is the face of SFJ and its legal adviser.
- Panun had launched the secessionist Sikh Referendum 2020 campaign, an initiative that eventually became defunct.
- He was among the nine individuals designated as “terrorists” by the Union Ministry of Home Affairs.
- ‘Referendum 2020’, claimed it wanted to “liberate Punjab from Indian occupation”.
- In Pannun’s words, “SFJ in its London Declaration (in August 2018) had announced to hold the first-ever non-binding referendum among the global Sikh community on the question of secession from India and re-establishing Punjab as an independent country.”
Banned in India:
- India refers to Gurpatwant Singh Pannun as a terrorist, and has banned SFJ under the Unlawful Activities (Prevention) Act, 1967.
- The Home Ministry’s 2019 notification issuing the ban says: “In the garb of the so-called referendum for Sikhs, SFJ is actually espousing secessionism and militant ideology in Punjab, while operating from safe havens on foreign soils and actively supported by inimical forces in other countries.”
- Currently, almost a dozen cases are registered against Pannun and SFJ in India.
FLiRT

- 07 May 2024
Why is it in the News?
There’s a new group of COVID-19 variants within the Omicron JN.1 lineage “which have demonstrated increased transmissibility and immune resistance” recently detected in the United States.
What is the New Covid-19 Variant FLiRT?
- FLiRT variants are sub-lineages of the Omicron COVID-19 variant.
- Detected in the United States, this variant group has been named Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) FLiRT variant KP.2 and is a spinoff of JN.1.11.1.
- According to the US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), FLiRT has led to increased hospitalisation rates, although it has not significantly raised mortality rates.
- Its primary impact is on the upper respiratory tract.
- The rapid emergence and diversification of the JN.1 variant and its descendant, KP.2, which shows significant alterations in spike (S) protein structure and increased resistance to existing vaccines, underscore the necessity for further research to understand the implications for public health and vaccine development.
Where does the name come from?
- The letters of FLiRT variation are derived from the technical names of the mutations:
- F and L are included in one, and R and T which is included in another.
What are the emerging symptoms?
- Symptoms associated with FLiRT are similar to those of other Omicron subvariants, including sore throat, cough, fatigue, nasal congestion, runny nose, headache, muscle aches, fever, and possible loss of taste and smell
Transmissibility:
- This variant is highly transmissible and can impact immunity and overall health.
- This variant spreads via respiratory droplets of the person to others or touching infected surfaces such as faucets, furniture, elevator buttons, and kitchen countertops, or coming in close contact with the person who is sick with this variant
Is there a concern for India?
- Currently, there are no reported cases of FLiRT variants in India, and our immunity is acquired.
- Thus far, no new vaccine is recommended.
Fusobacterium nucleatum
- 07 May 2024
Why is it in the News?
In a recent study, researchers have discovered a unique subtype of Fusobacterium nucleatum that is more prevalent in colorectal cancer (CRC) tumours.
What is Fusobacterium nucleatum?
- Fusobacterium nucleatum is a species of bacteria commonly found in the human mouth and gastrointestinal tract.
- It is a Gram-negative anaerobic bacterium, meaning it does not require oxygen to survive.
- While it is a normal component of the oral microbiota, Fusobacterium nucleatum can also act as an opportunistic pathogen, potentially causing infections in various parts of the body.
- In recent research, specific subtypes of Fusobacterium nucleatum have been associated with colorectal cancer tumours, highlighting its potential role in certain diseases.
- It plays a role in periodontal disease and is often associated with various human diseases and infections, including preterm births.
- F. nucleatum can aggregate with other bacteria species in the oral cavity and is considered a key component of periodontal plaque due to its abundance.
- Detection of F. nucleatum typically involves surgical tissue retrieval, faecal tests, or blood tests in patients showing symptoms, and early detection is crucial for preventing further disease progression.
Highlights of the Recent Research:
- Researchers examined genomes of F. nucleatum types from colorectal tumour samples and individuals without cancer. Among its subspecies, only one, known as Fusobacterium nucleatum animalis (or Fna), was consistently found in tumour samples.
- Further genetic analysis divided Fna into two distinct groups, with only one group, Fna C2, being prevalent in colorectal tumours.
- Fna C2 showed higher acid resistance, potentially allowing it to travel from the mouth to the intestines via the stomach.
- Additionally, Fna C2 demonstrated the ability to hide within tumour cells, evade the immune system, and utilize nutrients found in the gastrointestinal tract.
Boeing Starliner

- 06 May 2024
Why is it in the News?
Boeing’s Starliner spacecraft, carrying two NASA astronauts, will be launched by an Atlas V rocket from the Kennedy Space Center in Cape Canaveral, Florida, to the International Space Station (ISS).
What is Boeing’s Starliner?
- Starliner, a reusable spacecraft, has a pusher abort system.
- This allows the crew to safely escape throughout the launch and the ascent phases of the mission.
- In addition to being software-driven, the Starliner has wireless internet that will help with “crew communication, entertainment and docking with the International Space Station”
- The spacecraft can fly and course-correct on its own.
- It operates like advanced self-driving cars, with features similar to sophisticated cruise control and hands-free driving, allowing astronauts to simply enjoy the ride without intervention.
- It also allows astronauts to choose their level of control.
- Consisting of a crew capsule and a service module, the Starliner aims to revolutionize space travel with its advanced features and capabilities.
Crew Capsule:
- The crew capsule is the heart of the spacecraft, providing housing for astronauts during their journey.
- Designed to withstand the rigours of reentry, the capsule ensures a safe return to Earth for its occupants.
Service Module:
- The service module is equipped with essential systems for astronaut survival, such as air and temperature control, water supply, and sanitation facilities.
- Additionally, it contains the necessary engines and fuel required for manoeuvring the spacecraft in space.
- This module is not reusable and is designed for single use.
Starliner Specifications:
- With a width of over 4 meters, the Starliner can accommodate up to seven astronauts at once.
- The spacecraft boasts a unique weldless structure, making it both durable and reusable, with a potential for up to 10 missions and a six-month turnaround time between launches.
- Furthermore, the Starliner incorporates modern technologies like wireless internet and tablet interfaces for enhanced crew interaction.
Launch Vehicle:
- The Starliner is compatible with the Atlas V rocket, operated by United Launch Alliance (ULA), a joint venture between Boeing and Lockheed Martin.
- This collaboration ensures the seamless integration of the spacecraft and launch vehicle, optimizing mission success.
Why is the mission significant?
- In 2014, NASA selected Boeing and SpaceX to develop spacecraft for transporting astronauts to the International Space Station (ISS).
- While SpaceX has already conducted multiple successful missions with its Dragon crew capsule, the Starliner's success would mark the first time the United States has two domestically produced spacecraft capable of carrying astronauts to space.
- Once operational, Boeing and SpaceX will alternate missions to the ISS, with each crew's expedition lasting up to six months.
- This partnership will continue until the ISS is decommissioned in the next decade.
Air Independent Propulsion (AIP) Technology

- 06 May 2024
Why is it in the News?
The Indian Navy has initiated trials to modernize its conventional submarine fleet by issuing a Rs 60,000 crore tender for the acquisition of highly advanced submarines equipped with Air Independent Propulsion (AIP) technology.
What is an Air Independent Propulsion (AIP)?
- Air Independent Propulsion (AIP) is a propulsion system used in submarines that allows them to operate underwater for extended periods without the need to surface or snorkel for air.
- Unlike traditional diesel-electric submarines, which rely on diesel engines for surface propulsion and battery-powered electric motors for submerged propulsion, AIP-equipped submarines use a supplementary propulsion system that generates power independently of atmospheric oxygen.
- AIP systems typically employ technologies such as fuel cells, closed-cycle diesel engines, Stirling engines, or other innovative methods to generate electricity or mechanical power for propulsion while submerged.
- Closed Cycle Diesel Engines: These engines use stored liquid oxygen and an inert gas, such as argon, to run the diesel engine while submerged.
- Closed Cycle Steam Turbines: These systems generate steam using stored liquid oxygen and a fuel source, such as diesel or bioethanol, to power a turbine and produce electricity.
- Stirling Cycle Engines: This technology utilizes a closed-cycle heat engine to generate power using a temperature difference between a hot and cold source.
- Fuel Cells: These devices convert chemical energy from a fuel, such as hydrogen, and an oxidizing agent, like stored liquid oxygen, into electrical energy through an electrochemical reaction.
- These systems produce minimal noise and exhaust, allowing submarines to operate quietly and stealthily underwater, making them less vulnerable to detection by sonar and other detection systems.
- The implementation of AIP technology significantly enhances the stealth and endurance capabilities of submarines, enabling them to conduct longer-duration covert missions and remain submerged for extended periods, thereby enhancing their overall operational effectiveness.
- The Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO) is pioneering fuel cell-based AIP systems, unique for their hydrogen generation capabilities.
- Developed by the Naval Materials Research Laboratory (NMRL) of DRDO, these systems offer flexibility in operation modes to meet diverse user requirements.
China’s Chang’e-6 Mission

- 06 May 2024
Why is it in the News?
Recently, China launched its second mission to the far side of the Moon. If successful, it will be the world’s first mission to bring back samples from the part of the Moon that the Earth never gets to see.
What is Chang’e-6 Mission?
- China's Chang'e-6 spacecraft launched recently, on a mission to collect samples from the far side of the Moon.
- The mission aims to grab samples containing material ejected from the lunar mantle and thus provide insight into the history of the Moon, Earth, and Solar System.
- It is a 53-day-long mission. After reaching the Moon’s orbit, the mission’s orbiter will circle the natural satellite while its lander will descend into the 2,500-kilometre-wide South Pole-Aitken basin on the lunar surface.
- The impact that created the basin, among the largest in the history of the solar system, is thought to have dug up material from the lunar mantle.
- If that material can be retrieved, scientists can learn more about the history of the Moon’s insides.
- After collecting samples through scooping and drilling, the lander will launch an ascent vehicle, which will transfer the samples to the orbiter’s service module.
- This module will then return to the Earth.
- China is the only country to achieve a soft landing on the far side of the Moon.
- In 2019, its Chang’e-4 mission landed on the region and explored the Moon’s Von Karman crater with the help of a rover.
Why is the Far Side of the Moon Important?
- The Moon’s far side is often referred to as the dark side because it cannot be seen from the Earth, not because it does not catch the Sun’s rays.
- The Moon is tidally locked with the Earth and therefore, we see only one side of the Moon, also known as the near side.
- The far side has been under the spotlight in recent years as it is very different from the near side.
- It has a thicker crust, more craters and fewer maria, or plains where lava once flowed.
- Examining the samples from the far side can help scientists solve mysteries about the origin and evolution of the Moon — till now, scientists have only been able to analyse samples from the near side.
- The far-side samples can also give answers to the longstanding question: why is it different from the near side?
- Going to the far side, getting samples and doing different kinds of geophysical measurements is really important to figuring out this really long, long-standing mystery.
Anthropocene Epoch

- 06 May 2024
Why is it in the News?
For digital democracies, it is imperative to recognise the potential for self-inflicted social impoverishment by overlooking these long-term challenges of the Anthropocene.
What is an Epoch?
- Epochs form part of the Earth’s official timeline.
- All 4.6 billion years are split into Eons, Eras, Periods, Epochs and Ages - as designated by the International Commission on Stratigraphy.
- The Earth’s current epoch, the Holocene, started at the end of the last ice age, around 12,000 years ago.
- In comparison, the current Eon (in British English Aeon) is the Phanerozoic, which started some 540 million years ago.
What is the Anthropocene Epoch?
- The Anthropocene Epoch is an unofficial unit of geologic time, used to describe the most recent period in Earth’s history when human activity started to have a significant impact on the planet’s climate and ecosystems.
- The term, coined by biologist Eugene Stormer and chemist Paul Crutzen in 2000, combines the Greek words "anthropo" (man) and "cene" (new) to signify the dawn of a new human-centric era.
- Various phenomena characterize this proposed epoch, including global warming, sea-level rise, ocean acidification, mass-scale soil erosion, deadly heat waves, and the deterioration of the biosphere.
- These environmental changes highlight the unprecedented influence of human actions on the Earth's systems.
What is the Geological Time Scale?
- The geological time scale is based on the geological rock record, which includes erosion, mountain building and other geological events.
- Over hundreds to thousands of millions of years, continents, oceans and mountain ranges have moved vast distances both vertically and horizontally.
- For example, areas that were once deep oceans hundreds of millions of years ago are now mountainous desert regions.
- To understand the context of the Anthropocene Epoch, it is essential to explore the geological time scale.
- From longest to shortest, these divisions are called eons, eras, periods, epochs, and ages.
- The study of the correlation between strata and fossils is known as stratigraphy.
Current Epoch and Debate:
- Officially, the current epoch is the Holocene, which started 11,700 years ago after the last major ice age.
- However, there is ongoing debate within the scientific community regarding the distinction between the Holocene and the Anthropocene.
- The International Union of Geological Sciences (IUGS) has yet to formally adopt the term Anthropocene as an official epoch.
- The critical question the IUGS needs to address is whether human influence has significantly altered the Earth's systems to the extent that it is reflected in the rock strata.
- As the debate continues, the Anthropocene Epoch serves as a reminder of the profound impact of human activity on the planet and the urgent need to address environmental challenges for the sake of Earth's future.
GOLDENE

- 06 May 2024
Why is it in the News?
For the first time, researchers have created a free-standing sheet of gold (goldene) that is only one atom thick.
What Is Goldene?
- Goldene is an innovative, free-standing 2D metal with a thickness of just one atom.
- Created through a unique process, Goldene offers a wide range of potential applications in various industries, particularly in electronics and catalysis.
How is it created?
- Scientists first encapsulate an atomic monolayer of silicon between layers of titanium carbide.
- Gold is deposited on this structure, allowing the gold atoms to diffuse and replace the silicon atoms, creating a monolayer of trapped gold atoms.
- Using Murakami's reagent and a Japanese technique employed in forging katanas and high-quality knives, the titanium carbide layers are etched away, leaving a free-standing, one-atom-thick layer of gold.
Dimensions:
- Goldene sheets are approximately 100 nanometres thick, roughly 400 times thinner than the most delicate commercially available gold leaf.
Applications: Goldene's unique properties offer potential applications in various sectors:
- Electronics industry: Goldene's thinness and conductivity can enhance electrical components and circuitry.
- Carbon dioxide conversion: It can potentially aid in transforming carbon dioxide into useful products.
- Hydrogen-generating catalysis: Goldene could be utilized to efficiently produce hydrogen.
- Selective production of value-added chemicals: The material's properties enable the selective generation of chemicals for specific applications.
- Hydrogen production: It can contribute to the clean production of hydrogen.
- Water purification: Goldene could be implemented in water treatment technologies.
Significance:
- Goldene is an economically viable alternative to conventional, thicker gold structures, making it an appealing option for catalytic applications.
- Its unique characteristics position Goldene as a potentially revolutionary material for various industries.
Eta Aquariid Meteor Shower

- 04 May 2024
Why is it in the News?
The Eta Aquariid meteor shower, which has been active since April 15, will peak on May 4 and 5.
About Eta Aquariid Meteor Shower:
- The Eta Aquariids are a meteor shower associated with Halley's Comet.
- The shower is visible from about April 19 to about May 28 each year with peak activity on or around May 5.
- It is formed when Earth passes through the orbital plane of the famous Halley’s Comet, which takes about 76 years to orbit the Sun once.
- It seems to be originating from the Aquarius constellation, hence ‘Eta Aquariid’.
- The Eta Aquariid meteor shower is known for its rapid speed.
- This makes for long, glowing tails which can last up to several minutes.
- About 30 to 40 Eta Aquarid meteors can be seen per hour during the peak of the meteor shower if observed from the Southern Hemisphere.
- The number decreases to about 10 meteors per hour if being viewed in the Northern Hemisphere.
- This is due to the location of the “radiant” — the position in the sky where the meteor shower seems to come from.
- In the Northern Hemisphere, Eta Aquarid meteors most often appear as ‘Earthgrazers’ long meteors that appear to skim the surface of the Earth.
- In the South, however, they can be seen higher up in the sky and hence are more visible.
What are Comets?
- Comets are frozen leftovers from the formation of our solar system, some 4.6 billion years ago.
- They are composed of dust, rock and ice and orbit around the Sun in highly elliptical orbits which can, in some cases, take hundreds of thousands of years to complete.
- Billions of them are theorised to be orbiting the Sun beyond Neptune, in the Kuiper Belt and even more distant Oort cloud.
- Comets come in different sizes, although most are roughly 10 km wide.
- However, as they come closer to the Sun, comets “heat up and spew gases and dust into a glowing head that can be larger than a planet.
- This material also forms a tail that stretches millions of miles.
How are Meteor Showers Related to Comets?
- Meteors are simply grains of dust or rock that burn up as they enter the Earth’s atmosphere.
- This burning also creates a brief tail.
- Since most meteors are tiny they completely burn up in Earth’s atmosphere. However, once in a while, a large enough meteor passes through and hits the ground (at which time it is called a meteorite), often causing significant damage.
- A meteor shower can be observed when Earth passes through the clouds of dust left behind in a comet’s orbital plane.
- The sky lights up with small and large meteor tails as the debris left behind by the comet interacts with Earth’s atmosphere.
World Press Freedom Index 2024
- 04 May 2024
Why is it in the News?
India’s score on the World Press Freedom Index fell over the last year, from 36.62 to 31.28, according to World Press Freedom Index.
About World Press Freedom Index 2024:
- The World Press Freedom Index, an annual report published by Reporters Without Borders (RSF), evaluates the ability of journalists to work and report freely and independently across 180 countries.
- The index ranks nations based on a press freedom questionnaire covering five categories:
- Political context
- Legal framework
- Economic context
- Ssociocultural context, and
- Security
- It is important to note that the index focuses solely on press freedom and does not assess the quality of journalism or human rights violations in general.
Key Findings in the 2024 Index:
- Global decline: The report reveals an overall deterioration in press freedom worldwide, with an average drop of 7.6 points.
- Political repression: There has been a sharp increase in political repression against journalists and independent media outlets.
- Top-ranking countries:
- Norway ranks first, followed by Denmark and Sweden.
- European countries, particularly those within the European Union, continue to demonstrate strong press freedom.
- Regions with the worst performance: The Maghreb and Middle East regions face the most significant restrictions on press freedom imposed by government forces.
- Lowest-ranking countries:
- Eritrea ranks last, followed by Syria and Afghanistan.
India's Ranking:
- Although India's rank slightly improved from 161 in 2023 to 159 in 2024, this change is primarily due to other countries dropping in their rankings.
- India experienced a decline in all indicators except security.
- Notably, India ranks behind Turkey, Pakistan, and Sri Lanka, which hold positions 158, 152, and 150, respectively.
Artificial General Intelligence (AGI)

- 04 May 2024
Why is it in the News?
“GPT-4 is the dumbest model any of you will ever have to use again,” said the OpenAI’s CEO Sam Altman at a time when his company is going big on superintelligence or Artificial General Intelligence (AGI).
What Is Artificial General Intelligence (AGI)?
- Artificial general intelligence (AGI) is a team used to define the concept of development of AI to a level that can almost be capable of human intelligence and able to solve complex problems.
- Artificial intelligence (AI) is a broad field that encompasses various domains and applications, such as computer vision, natural language processing, machine learning, robotics, and more.
- AGI is a fictional Super Intelligence system that can match human intelligence.
- In Normal terms, AGI is also called strong AI, full AI, or general intelligent action.
- AGI systems are expected to have human-like or superhuman cognitive abilities, such as reasoning, planning, learning, communication, creativity, and problem-solving.
- AGI systems would be able to perform any task that humans can do, and even tasks that humans cannot do.
What is the Difference Between AI & AGI?
- AI systems are trained to perform specific tasks that require some level of intelligence, such as recognizing faces, translating languages, playing games, or diagnosing diseases.
- However, these systems are not able to generalize their skills and knowledge to other domains or tasks that they were not trained for.
- This is where artificial general intelligence (AGI) comes in.
- Artificial intelligence is an Umbrella containing the science of developing systems and processes that can replicate human intelligence.
- It's an umbrella containing multiple subdomains specifically built to develop such intelligence systems.
- Artificial General Intelligence is more like the system's ability to learn by itself, and behave like human intelligence. It's an evolved system with the help of heavily trained AI over time.
How can AGI Help Humanity?
- In theory, AGI has innumerable positive implications.
- For instance, in healthcare, it can redefine diagnostics, treatment planning, and personalised medicine by integrating and analysing vast datasets, far beyond the capabilities of humans.
- In finance and business, AGI could automate various processes and enhance overall decision-making, offering real-time analytics and market predictions with accuracy.
- When it comes to education, AGI could transform adaptive learning systems that work towards the unique needs of students.
- This could potentially democratise access to personalised education worldwide.
Blue Corner Notice

- 04 May 2024
Why is it in the News?
The Central Bureau of Investigation (CBI) is likely to issue a Blue Corner notice against absconding Janata Dal (Secular) MP Prajwal Revanna.
What is Interpol’s Colour-coded Notices?
- A Blue or a Blue Corner notice is a part of Interpol’s elaborate system of colour-coded notices, which enable countries to “share alerts and requests for information [on wanted persons/crimes] worldwide”.
- This sharing of critical crime-related information is crucial for tackling internationally spread-out criminal activities.
- There are seven types of notices — Red Notice, Yellow Notice, Blue Notice, Black Notice, Green Notice, Orange Notice, and Purple Notice. Each has a different implication.
- Red Notice: To seek the location and arrest of persons wanted for prosecution or to serve a sentence.
- Yellow Notice: To help locate missing persons, often minors, or to help identify persons who are unable to identify themselves.
- Blue Notice: To collect additional information about a person’s identity, location or activities in relation to a criminal investigation.
- Black Notice: To seek information on unidentified bodies.
- Green Notice: To provide a warning about a person’s criminal activities, where the person is considered to be a possible threat to public safety.
- Orange Notice: To warn of an event, a person, an object or a process representing a serious and imminent threat to public safety.
- Purple Notice: To seek or provide information on modus operandi, objects, devices and concealment methods used by criminals.
- These notices are issued by Interpol’s General Secretariat at the request of a member country’s Interpol National Central Bureau and are made available for all member countries.
What is Interpol?
- Interpol, or the International Criminal Police Organization, is an intergovernmental organization that facilitates global police cooperation and crime control.
- Founded in 1923, Interpol enables member countries to share data and collaborate on investigating cross-border crimes, such as terrorism, drug trafficking, cybercrime, and human trafficking.
- Interpol is composed of a network of 194 member countries, each having a National Central Bureau (NCB) that serves as the point of contact for international investigations. Key functions of Interpol include:
- Providing a secure communication system for member countries to exchange information on criminal activities.
- Facilitating operational support and assistance for member countries in managing crime-related crises and emergencies.
- Coordinating training and capacity-building initiatives to enhance the capabilities of law enforcement agencies.
- Issuing colour-coded notices (e.g., Red Notice for wanted persons) to alert member countries about international criminals and activities.
- Providing access to databases containing vital data on known criminals, fingerprints, DNA profiles, and stolen and lost travel documents.
- Interpol functions within the framework of international law and operates in accordance with the principle of neutrality, ensuring that it does not interfere in the political, military, religious, or racial affairs of member countries.
- Its main objective is to provide a platform for international police cooperation and create a safer world for all.
Oxytocin

- 04 May 2024
Why is it in the News?
Recently, the Delhi High Court called for action against the 'rampant use of Oxytocin' in dairy colonies.
What is Oxytocin?
- Oxytocin also known as the ‘love hormone’ is secreted by the pituitary glands of mammals during sex, childbirth, lactation, or social bonding.
- It is normally produced in the hypothalamus and released by the posterior pituitary.
- It can be chemically manufactured and sold by pharma companies for use during childbirth.
- It is administered either as an injection or a nasal solution.
Side effects of oxytocin:
- A few side effects of oxytocin in humans would include:
- Allergic reactions on the skin like rashes Itching, hives Swelling, lips, tongue, or throat
- Changes in the heart rhythm causing fast or irregular heartbeat, dizziness, feeling faint or lightheaded
- Pain in the chest
- Breathlessness and trouble breathing
- Nausea Vomiting
- Severe headache
- Blurred vision
- Pounding in the neck or ears
- Jaundice Seizure
- According to doctors, prolonged use of oxytocin injections also causes fertility disorders like poor oestrus signs, reduced lactation period, lower conception rate, and high embryonic mortalities.
- Oxytocin injection given to cattle to boost the delivery of milk production is one of the reasons for the early onset of puberty among girls, the development of breasts in males, and the lack of testosterone production due to hormonal imbalance.
Affects fertility in both men and women:
- Milk adulterated with oxytocin is to be avoided by pregnant women as it can cause abortion and babies may be born with deformities.
- It also increases the risk of haemorrhage in mothers after birth and can also inhibit breastfeeding.
- However, boiling milk can help eliminate traces of oxytocin.
What are Hormones?
- Hormones are special chemicals produced by glands in the endocrine system that act as messengers in the body, regulating various physiological processes like growth, metabolism, reproduction, and mood.
- They travel through the bloodstream to target organs and tissues, where they exert their effects by binding to specific receptors and influencing cellular activity.
Shaksgam Valley
- 03 May 2024
Why is it in the News?
India recently said it has lodged a strong protest with China for carrying out construction activities in the Shaksgam Valley in an "illegal" attempt to alter the situation on the ground.
Context:
- Recently, the Ministry of External Affairs (MEA) said that the Shaksgam Valley is a part of the territory of India amid reports of China building infrastructure in the valley.
- The Shaksgam Valley strategically located region that is now part of Pakistan-occupied Kashmir.
- MEA spokesperson Randhir Jaiswal recently said that India "never accepted the so-called China-Pakistan Boundary Agreement of 1963 through which Pakistan unlawfully attempted to cede the area to China".
- Lodging a strong protest with China for carrying out construction activities, India called it an "illegal" attempt to alter the situation on the ground.
Where is the Shaksgam Valley Located?
- The Shaksgam Valley, or the Trans Karakoram Tract, is part of the Hunza-Gilgit Region of PoK.
- It is bordered by the Xinjiang Province of the People's Republic of China to the north.
- The northern areas of PoK are to its west and south.
- And the Siachen Glacier region to the east.
How did Pakistan cede Shaksgam valley to China?
- In 1963, Pakistan ceded the Shaksgam Valley to China when it signed a border agreement with Beijing to settle their border disputes.
- But, Article 6 of the 1963 agreement clearly stated that “the two Parties have agreed that after the settlement of the Kashmir dispute between Pakistan and India, the sovereign authority concerned will reopen negotiations with the Government of the People's Republic of China, on the boundary as described in Article 2 of the present Agreement, to sign a formal Boundary Treaty to replace the present agreement.”
- The agreement laid the basis for the construction of the Karakoram Highway, which was jointly built by Chinese and Pakistani engineers during the 1970s.
What is the History of Shaksgam Valley?
- When the British asked the Mir of Hunza, a vassal of the Maharaja of Kashmir, to give up his rights to the Taghdumbash Pamirs and the Raskam valley in 1936, the Shaksgam valley to the south-west had remained in his possession.
- This remained the traditional frontier of British India until independence and was inherited by India following Jammu & Kashmir's accession in 1947.
- And, this was the border that Pakistan compromised in its 1963 agreement with China.
- Pakistan established diplomatic relations with the People's Republic of China in 1951.
- Back then, Pakistan was viewed as a member of the non-Soviet block due to its membership in two anti-communist military pacts -- SEATO and CENTO -- led by the United States.
- China was on the opposite side.
- After Chinese troops invaded Tibet in 1950, Pakistan even offered transit facilities to US aircraft so they could supply equipment to Tibetan rebels.
- Chinese troops began to cross the border in eastern Hunza after the Partition of India.
- This started in 1953 and in 1959 they took some livestock out of the area.
- This prompted a furious response from Pakistan, which was determined to protect its borders.
- The then President of Pakistan, Ayub Khan, however, saw an opportunity to appease the Chinese in the late 1950s as India-China relations were rapidly deteriorating.
- Subsequently, Beijing developed closer ties with Islamabad after the India-China War of 1962.
- China went on to support Pakistan diplomatically during the 1965 India-Pakistan war.
- Amid these developments, Pakistan chose to downgrade historical claims made by the Mir of Hunza and signed over the Shaksgam Valley to China in 1963.
What was the Consequence?
- In granting China's claim to a border along the Karakoram Range, Pakistan compromised India's traditional frontier along the KunLun Range to the northwest of the Karakoram Pass.
- It also allowed China to extend a claim eastward along the Karakoram in Ladakh.
- This enabled China to claim all of Aksai-Chin.
Electrolysers

- 03 May 2024
Why is it in the News?
Developing a domestic manufacturing infrastructure for electrolyzers is expected to reduce the cost of green hydrogen and strengthen India's competitive advantage.
What are Electrolysers?
- Electrolysers are devices that produce hydrogen through a chemical process called electrolysis, which splits water molecules into hydrogen and oxygen molecules using electricity.
How do They work?
- These devices consist of a stack of conductive electrodes separated by a membrane, to which a high voltage and current are applied.
- This induces an electric current in the water, causing it to decompose into its constituents: hydrogen and oxygen.
- The generated oxygen is either released into the atmosphere or stored for future use as a medical or industrial gas.
- The hydrogen produced can be stored as a compressed gas liquefied for industrial use or utilised in hydrogen fuel cells, which power various transportation vehicles like trains, ships, and aircraft.
Types of Electrolysers:
- Alkaline Electrolysers: This technology, predominantly used by the fertiliser and chlorine industries, employs thick membranes and nickel-based electrodes.
- It currently represents a significant portion of global electrolyser capacity.
- Proton Exchange Membrane (PEM) Electrolysers: Operating at high pressure, PEM electrolysers utilise thin perfluorosulfonic acid (PFSA) membranes.
- Though they require gold and titanium-plated electrodes and catalysts like platinum, iridium, and ruthenium, they produce high-purity hydrogen and are easy to cool, making them a popular choice.
- Solid Oxide Electrolysis Cell (SOEC) Electrolysers: These devices utilise heat to produce hydrogen from steam and are ideal for locations with available heat sources such as nuclear or industrial facilities.
- Operating at high temperatures ranging from 500 to 850 degrees Celsius.
- Anion Exchange Membrane (AEM) Electrolysers: Operating at significantly lower temperatures of 50 to 60 degrees Celsius, AEM electrolysers combine the less harsh conditions of alkaline electrolysers with the simplicity and high efficiency of PEM electrolysers.
Electrolyzers and Green Hydrogen Production:
- Green hydrogen is renewable hydrogen produced using water electrolysis technology and electricity generated from renewable energy sources, such as solar or wind.
- It is gaining unprecedented momentum globally, and it is believed that it is a key component in accelerating the shift to clean energy.
- The commercialization of electrolyzers can make green hydrogen more readily available and enable energy systems across the globe to undergo fundamental transformations to lower emissions and reduce their negative impact on the environment.
Diplomatic Passport

- 03 May 2024
Why is it in the News?
After allegations of sexual abuse by Janata Dal (Secular) MP Prajwal Revanna came to light, the politician fled to Germany on a diplomatic passport.
What is a Diplomatic Passport?
- Diplomatic passports are issued to people holding diplomatic status or deputed by the Government of India for official duty abroad.
- Unlike normal passports, which are valid for 10 years and have a dark blue cover, diplomatic passports are valid for five years or less and have maroon covers.
- Diplomatic passports, also known as 'Type D' passports.
- A diplomatic passport has 28 pages.
- Holders of such passports are entitled to certain privileges and immunities as per international law, including immunity from arrest, detention, and certain legal proceedings in the host country.
Issuing Authority:
- The Ministry of External Affairs’s (MEA) Consular, Passport & Visa Division issues diplomatic passports (‘Type D’ passports) to people falling in broadly five categories:
- Those with diplomatic status;
- Government-appointed individuals travelling abroad for official business;
- Officers working under the branches A and B of the Indian Foreign Service (IFS), normally at the rank of Joint Secretary and above; and
- Relatives and immediate family of officers employed in IFS and MEA.
- Select individuals who are authorised to undertake official travel on behalf of the government”.
- The MEA issues visa notes to government officials going abroad for an official assignment or visit.
What are the Benefits of Having a Diplomatic Passport?
- Official identification: The diplomatic passport serves as an official identification document for individuals representing the Indian government on diplomatic missions.
- It helps in establishing their identity and official status.
- Diplomatic immunity: Diplomatic passport holders are typically entitled to certain privileges and immunities as per international law.
- This includes immunity from arrest, detention, and certain legal proceedings in the host country, safeguarding their ability to perform official duties without hindrance.
- Visa facilitation: Diplomatic passports often enjoy certain privileges when it comes to visa facilitation.
- Many countries offer expedited visa processing or waive visa requirements altogether for diplomatic passport holders, simplifying travel arrangements for official purposes.
- Access to diplomatic channels: The diplomatic passport grants access to diplomatic channels and services provided by Indian embassies, consulates, and other diplomatic missions worldwide.
- This includes assistance with consular services, protection, and support while abroad.
- Priority services: Diplomatic passport holders may receive priority services at airports and during immigration procedures.
- This can include dedicated immigration counters or expedited security and customs clearance, saving time during travel.
- Official representation: The diplomatic passport signifies the official representation of the Indian government and confers a sense of authority and credibility while dealing with international counterparts, foreign officials, and diplomatic communities.
Can Diplomatic Passports be Revoked?
- According to The Passports Act, 1967, the passport authority may cancel a passport or travel document, with the previous approval of the Central government.
- The passport authority can impound or revoke a passport if the authority believes that:
- The passport holder or travel document is in wrongful possession
- If the passport was obtained by the suppression of material information or based on wrong information provided by the individual
- If it is brought to the notice of the passport authority that the individual has been issued a court order prohibiting his departure from India or has been summoned by the court.
- A diplomatic passport can be revoked upon orders from a court during proceedings with respect to an offence allegedly carried out by the passport holder before a criminal court.
Monkeypox (Mpox)
- 03 May 2024
Why is it in the News?
The Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC) is struggling to contain its biggest Mpox outbreak.
What Is Monkeypox (Mpox)?
- Mpox (formerly known as monkeypox) is a rare viral infection caused by the mpox virus, a member of the orthopoxvirus genus.
- It was first discovered in 1958 in monkeys but can also infect humans and other animals.
- Mpox typically presents with a range of symptoms and can be transmitted through close contact with infected individuals or animals.
Symptoms:
- Mpox symptoms often begin with fever, muscle aches, and sore throat, followed by a rash that starts on the face and spreads across the body.
- The rash evolves over two to four weeks, forming macules, papules, vesicles, and pustules before crusting over.
- Lesions can also appear on the palms of the hands and soles of the feet.
Causes:
- The mpox virus is primarily transmitted through direct contact with the skin lesions, body fluids, or respiratory droplets of infected individuals or animals.
- It can also be contracted through contaminated materials, such as bedding or clothing.
Prevention:
- Preventing mpox involves avoiding contact with infected individuals or animals, practising good hygiene, and disinfecting contaminated surfaces.
- Vaccines are also available for individuals at high risk of contracting the virus.
Treatment:
- There is currently no specific treatment for mpox, but symptoms can be managed with supportive care, such as fever reducers and pain medications. In some cases, antiviral medications may be used.
Five Eyes Intelligence-sharing Network

- 03 May 2024
Why is it in the News?
Recently, the Australian Broadcasting Corporation (ABC) reported that “Indian spies” had been “kicked out of Australia” after being caught trying to steal secrets about sensitive defence projects and airport security, as well as classified information on Australia’s trade relationships”.
What is the Five Eyes?
- The Five Eyes is an intelligence alliance comprising Australia, Canada, New Zealand, the United Kingdom and the United States, formed in 1946.
- The alliance is based on a series of bilateral agreements on surveillance and intelligence-sharing.
- These arrangements are commonly known as the United Kingdom-United States Communication Intelligence Act (UKUSA) agreement.
- The UKUSA agreement is a secret pact that, since 1946, has allowed the two countries to share intelligence with each other.
- The UKUSA agreement was so secret that its existence wasn't even acknowledged until 2005.
- Each of the Five Eyes states pursues interception, collection, and decryption activities and shares all intelligence information obtained with the others by default.
- These countries share information with each other through the ultra-sensitive STONEGHOST network, which has been claimed to contain "some of the Western world's most closely guarded secrets".
- The Five Eyes states share integrated programmes, staff, and bases.
Origins of the Five Eyes
- During World War II, informal secret meetings between British and American code-breakers laid the groundwork for establishing the FE alliance.
- After the Cold War, the information-sharing arrangement became formalised under the ECHELON surveillance system in the 1960s.
How does the Five Eyes Alliance operate?
- The alliance facilitates the sharing of signals intelligence among the five countries.
- The countries agree to exchange by default all signals intelligence they gather.
- The bedrock of the Five Eyes Alliance is based on the joint abilities of the United Kingdom's Government Communications Headquarters (GCHQ) and the USA's National Security Agency (NSA) to intercept intelligence.
- These agencies collect and decrypt signal intelligence, called SigInt, which involves internet, telephone, radio and satellite data from across the world.
- The UKUSA Agreement, which was made public in 2010, states:
- "It will be contrary to this agreement to reveal its existence to any third party whatsoever" and "each party will seek the agreement of the other to any action with third parties and will take no action until its advisability is agreed upon."
Supersonic Missile-Assisted Release of Torpedo (SMART) System

- 02 May 2024
Why is it in the News?
The Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO) recently tested a next-generation torpedo release system aimed at boosting the Navy’s anti-submarine warfare capabilities.
What is a SMART System?
- The SMART system, designed to bolster the Indian Navy's anti-submarine warfare capabilities, represents a fusion of cutting-edge technology and indigenous innovation.
- With its supersonic capabilities and torpedo release mechanism, the SMART system offers a formidable deterrent against potential submarine threats, enhancing the Indian Navy's operational readiness and maritime defence posture.
- The SMART system comprises a mechanism by which the torpedo is launched from a supersonic missile system with modifications that would take the torpedo to a far longer range than its own.
- For example, a torpedo with a range of a few kilometres can be sent a distance to the tune of 1000 km by the missile system from where the torpedo is launched.
- The system also gives flexibility in terms of the missile system’s launch platform.
- A number of DRDO laboratories including Defence Research and Development Laboratory (DRDL) and Research Centre Imarat (RCI), both in Hyderabad; Aerial Delivery Research and Development Establishment (ADRDE) in Agra; and Naval Science and Technology Laboratory (NSTL) Visakhapatnam have developed the technologies required for SMART.
Key Features of SMART Anti-submarine Missile System:
- It is a canister-based, long-range anti-submarine missile system.
- It has been developed by the DRDO for the Indian Navy.
- The objective behind the project is to develop a quick reaction system that can launch a torpedo from a standoff distance.
- The missile has a range of 643 km carrying a lightweight torpedo of range 20 km with a 50 kg high explosive warhead.
- SMART uses a two-way data link connected to airborne or ship-based submarine detection and identification systems.
- It can be launched from a surface ship or a truck-based coastal battery.
- The missile is powered by a dual-stage solid-propellant rocket and utilizes electro-mechanical actuators for course correction.
- The missile utilizes sea skimming to reduce detection range.
- The first successful test of SMART was done on 5 October 2020 from Abdul Kalam Island.
Significance:
- This missile-based mechanism to launch lightweight torpedoes can target submarines hundreds of kilometres away — far beyond the conventional range of lightweight torpedoes.
- It will be particularly employed in the absence of other assets for immediate action when an enemy submarine is detected.
Red Colobus

- 02 May 2024
Why is it in the News?
The Red colobus, a rare group of imperilled monkeys spread across Africa, is the primary indicator of biodiversity decline in the continent’s tropical forests.
What is Red Colobus?
- Red colobus monkeys (Piliocolobus spp.), a rare and imperilled group of primates endemic to Africa, serve as crucial indicators of the continent's biodiversity.
- They are part of the broader colobine family, which predominantly consists of leaf-eating species, distinguishing them from the omnivorous cercopithecines.
- Alongside Africa's red colobus monkeys, the colobine group also encompasses langurs found in South and Southeast Asia.
- These distinctive primates are distributed across diverse habitats, ranging from the forests of Senegal to the Zanzibar Archipelago.
- Despite their ecological significance, red colobus monkeys face a dire threat of extinction, with more than half of the known 18 distinct forms listed as Endangered or Critically Endangered on the IUCN Red List.
- Their survival is imperilled by various factors, primarily driven by human activities.
- Hunting for both trade and local consumption poses a significant threat, as does the relentless encroachment on their habitats.
- Habitat loss, degradation, and fragmentation result from activities such as logging, mining, charcoal production, and the conversion of forests into agricultural lands.
- These threats collectively endanger the existence of red colobus monkeys, highlighting the urgent need for conservation efforts to safeguard their future.
Conservation of Red Colobus Monkeys:
- The International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) Species Survival Commission Primate Specialist Group and the African Primatological Society have come together to initiate the Red Colobus Conservation Action Plan.
- This collaborative effort focuses on making red colobus monkeys a priority target in conservation, ultimately contributing to the preservation of Africa's tropical forests and addressing unsustainable hunting practices.
- To effectively implement the action plan, a Red Colobus Working Group (RCWG) has been established.
- This group will provide guidance and ensure that the plan's objectives are met. Additionally, a Red Colobus Conservation Network (RCCN) has been created to promote communication, capacity-building, and monitoring of the conservation efforts for red colobus monkeys.
- Through this joint venture, the IUCN and the African Primatological Society aim to secure the future of red colobus monkeys while safeguarding the ecosystems they inhabit.
Ajrakh from Kutch

- 02 May 2024
Why is it in the News?
The recent addition of Ajrakh from Kutch to the list of GI-tagged fabrics is a proud moment for India's rich textile heritage.
What is Ajrakh?
- The Ajrakh fabric is a traditional hand-block printing technique that originated in Kutch, Gujarat.
- It uses natural dyes and intricate patterns to create beautiful textiles, which are then used to make sarees, dupattas, stoles, and other garments.
- The unique feature of Ajrakh is its use of geometric patterns and rich earthy colours like indigo, madder, and mustard.
- This fabric has been an integral part of the Kutchi culture for centuries and has now gained recognition on a global level with its GI tag.
What is a GI tag?
- The GI tag is a certification that identifies a product as originating from a specific geographical location and possessing unique qualities due to that region's traditional knowledge and expertise.
- It not only adds value to the product but also protects it from imitation or misuse.
- Ajrakh's GI tag was granted by the Geographical Indications Registry after a long process of documentation and verification of its origin and production techniques.
Some other Indian textiles have received similar recognition.
- Banarasi Silk: The luxurious Banarasi silk sarees from Varanasi have been coveted by women all over the world for their exquisite designs and fine quality.
- This fabric has been granted a GI tag for its uniqueness in design, weaving technique, and use of pure silk and zari.
- The intricate designs of Banarasi silk sarees, inspired by Mughal and Persian art, make them stand out in the sea of Indian textiles.
- Chanderi Fabric: Chanderi, a small town in Madhya Pradesh, is known for its delicate and lightweight fabric.
- Chanderi sarees and suits are made from a combination of cotton and silk, giving them a sheer and lustrous appearance.
- This fabric has been granted a GI tag for its traditional handloom weaving technique, which dates back to the 13th century.
- The motifs used in Chanderi fabrics are inspired by nature and are intricately woven using golden zari.
- Kanjeevaram Silk: The Kanjeevaram sarees from Tamil Nadu are famous for their vibrant colours, fine silk, and intricate zari work.
- This fabric has been granted a GI tag for its traditional weaving technique that uses three shuttles to weave the body, border, and pallu of the saree separately and then join them together.
- The rich gold zari work on Kanjeevaram sarees makes them a must-have in every Indian woman's wardrobe.
- Kota Doria: One of the many varieties of sari clothing produced in Muhammadabad Gohna, Mau in Uttar Pradesh and the surrounding area, as well as in Kota, Rajasthan, is kota doria.
- Pure cotton and silk are used to make sarees, which are adorned with square-like designs called khats.
- Since these sarees were woven in Mysore, they were originally known as Masuria.
- The GI tag was given to Kota Doria in July 2005. Kota Doria cotton sarees are regarded as the lightest in India because of their transparency and low weight.
- Odisha Ikat: One type of ikat, which is a resist dyeing method, comes from Odisha and is called Orissa Ikat.
- It is sometimes referred to as "Bandha of Orissa" and has been an Orissan product since 2007.
- To produce the design on the loom before weaving, the warp and weft threads are tie-dyed.
Antares
- 02 May 2024
Why is it in the News?
The Bengaluru-based Indian Institute of Astrophysics (IIA) has filmed the passing of the moon in front of Antares, a bright red star.
What is Antares?
- Antares, also known as Alpha Scorpii, is one of the brightest stars in our night sky.
- Located in the constellation Scorpius, Antares has captivated stargazers and astronomers for centuries with its fiery red hue and impressive size.
- The name Antares is derived from the Greek word meaning “rival to Mars” due to its reddish appearance, similar to the planet Mars.
- Ancient cultures associated Antares with various mythological figures, including the Greek god Ares and the Egyptian god Osiris.
- It is also one of the largest known stars, with a diameter estimated to be around 700 times that of our Sun.
- Antares is located approximately 550 light-years away from Earth, making it a relatively close neighbour in astronomical terms.
- It is classified as a red supergiant star, belonging to the spectral type M1.5 Iab-Ib.
- Its surface temperature is about 3,500 Kelvin.
- Antares is a variable star, which means its brightness fluctuates over time.
- Scientists estimate that Antares is approximately 12 million years old.
- As a red supergiant, it is in the later stages of its stellar evolution and is expected to explode as a supernova in the future.
- Antares has a mass estimated to be about 15 times that of our Sun.
- It is primarily composed of hydrogen and helium, with traces of heavier elements.
- Antares has a companion star in a binary system known as Antares B.
- The two stars orbit each other, with a separation of several astronomical units.
- The visual apparent magnitude of Antares is around 1.06, making it one of the 20 brightest stars in the night sky.
- Antares emits a significant amount of infrared radiation, making it a prominent object in infrared observations.
- Antares experiences intense stellar winds, which cause it to lose mass at a rate of approximately one Earth mass every hundred thousand years.
- Antares played a crucial role in ancient navigation, particularly in the Southern Hemisphere, serving as a marker for determining the position of celestial objects.
Booker Prize

- 02 May 2024
Why is it in the News?
The Booker Prize, one of the most prestigious awards in the literary world, has recently come under fire for the historical links to slavery of its original sponsor, Booker Group.
What is the Booker Prize?
- The Booker Prize was founded in 1969, initially just for writers from the Commonwealth, but later opened to writers globally.
- Each year, the prize is awarded to a single work of fiction in the English language.
- In 2004, a separate International Booker Prize was instituted for translated works.
- The prize was co-founded by publishers Tom Maschler and Graham C Greene, and from 1969 to 2001, it was sponsored by, and named after Booker Group Ltd, a British wholesale foods company, established in 1835 as a shipping and trading company, and now owned by Tesco.
- In 2002, British investment management firm Man Group became the prize’s sponsor, and thus it came to be known as The Man Booker Prize.
- After Man Group ended its sponsorship in 2019, American charity Crankstart took over, and reverted the award’s name to its original ‘Booker Prize’.
- Irish author Paul Lynch wins the 2023 Booker Prize for his novel 'Prophet Song'.
About the International Booker Prize:
- The International Booker Prize (formerly known as the Man Booker International Prize) was launched in 2005.
- It was originally awarded every two years to a living author who has published fiction either originally in English or whose work is generally available in translation in the English language.
- It was an award for the body of work of the author, rather than awarded for an individual novel.
- Beginning in 2016, the award changed. It is now given annually to a single book in English translation, with a £50,000 prize for the winning title, shared equally between author and translator.
- Georgi Gospodinov and Angela Rodel have won the International Booker Prize 2023 for the novel ‘Time Shelter’.
- ‘Tomb of Sand’ Geetanjali Shree, translated by Daisy Rockwell Winner 2022 winner.
Nutrient-based Subsidy

- 01 May 2024
Why is it in the News?
Capping consumption of urea and DAP to correct worsening plant nutrient imbalance is likely to be on the priority list of the government post the Lok Sabha polls.
What is Meant by the Term "Balanced Fertilization"?
- Fertilisers are basically food for crops, containing nutrients necessary for plant growth and grain yields.
- Balanced fertilisation means supplying these primary (N, phosphorus-P, and potassium-K), secondary (sulphur-S, calcium, magnesium), and micro (iron, zinc, copper, manganese, boron, molybdenum) nutrients in the right proportion, based on soil type and the crop’s own requirement at different growth stages.
What is a Nutrient-based Subsidy?
- Nutrient-based subsidy (NBS) is a system started in 2010 to help farmers use the right amount of nutrients in fertilizers.
- Instead of giving a subsidy for each type of fertilizer, the government decided to give subsidies based on nutrients like Nitrogen (N), Phosphorus (P), Potassium (K), and Sulfur (S) in the fertilizers.
- The idea was to encourage farmers to use fertilizers with a balanced mix of nutrients, instead of just focusing on certain types like urea, DAP, and MOP.
- These balanced fertilizers contain a mix of N, P, K, S, and other nutrients in the right amounts.
- At first, this plan seemed to work. Between 2010 and 2012, farmers started using more balanced fertilizers and less of the ones with just one or two nutrients.
- But there was a problem: urea, which is heavily used by farmers, was not included in this plan.
- Since the government controlled the price of urea and only went up a little bit after the NBS was introduced, farmers kept using it more and more.
- This means that even though the NBS helped with other fertilizers, it didn't do much to reduce the use of urea.
Challenges:
- The challenges arise from recent changes in fertilizer pricing and consumption patterns.
- Earlier, companies set prices for non-urea fertilizers, with the government providing subsidies based on their nutrient content.
- However, in the past few years, even non-urea fertilizers have come under price control, especially since January 2024, possibly due to upcoming elections.
- This shift has led to imbalances in nutrient usage.
- For example, the current price of DAP is lower than certain NPKS complex fertilizers, even though it contains less nitrogen and phosphorus.
- As a result, farmers tend to overuse DAP, similar to urea. On the other hand, the price of MOP does not incentivize its use, leading to its reduced incorporation into fertilizers, despite its importance for crop immunity and nitrogen uptake.
- To address these issues, it's crucial to establish a proper price hierarchy among non-urea fertilizers.
- DAP should be priced highest, followed by complexes, with MOP priced the lowest. Additionally, DAP usage should be limited to rice and wheat, while other crops can fulfil their phosphorus needs through complexes and SSP.
- Improving the acceptability of SSP, despite its lower price, can be achieved by marketing it in granular form, which is less prone to adulteration and ensures a slower release of phosphorus without drift during application.
Goldman Environmental Prize

- 01 May 2024
Why is it in the News?
Chhattisgarh-based environment and forest activist Alok Shukla has been honoured with the prestigious Goldman Environmental Prize for his efforts and exemplary community campaign in safeguarding the biodiversity-rich forests in the mineral-rich state.
About Goldman Environmental Prize:
- The Goldman Environmental Prize recognizes grassroots environmental heroes from roughly the world’s six inhabited continental regions:
- Africa
- Asia
- Europe
- Islands & Island Nations
- North America
- South & Central America
- It is also called the Green Nobel.
- The Prize recognizes individuals for sustained and significant efforts to protect and enhance the natural environment, often at great personal risk.
- The Goldman Prize views “grassroots” leaders as those involved in local efforts, where positive change is created through community or citizen participation.
- Through recognizing these individual leaders, the Prize seeks to inspire other ordinary people to take extraordinary actions to protect the natural world.
History:
- Reflecting a lifetime commitment to philanthropy and environmental issues, the Goldman Environmental Prize was founded in 1989 by Richard and Rhoda Goldman.
- The duo envisioned the Prize as a way to demonstrate the international nature of environmental problems and draw public attention to the global need for action.
- By rewarding ordinary individuals for their outstanding environmental achievements, the Goldmans hoped to inspire others to emulate the examples set by the Prize recipients.
- The first Goldman Environmental Prize ceremony took place on April 16, 1990, and it was timed to coincide with Earth Day.
- The recipients of the Goldman Environmental Prize are announced annually in a live ceremony timed to coincide with Earth Day.
- The Prize is awarded in the city of San Francisco, California.
- Prize winners each receive a bronze sculpture in the shape of an Ouroboros.
- Common to many cultures around the world, the Ouroboros, which depicts a serpent biting its tail, is a symbol of nature’s power of renewal.
Patachitra Painting

- 01 May 2024
Why is it in the News?
The first-generation women patachitra artists of the village sell their work online & are recognized the world over, encouraging future generations to stay in the profession.
About Patachitra Painting:
- Pattachitra style of painting is one of the oldest and most popular folk art forms of Odisha.
- Pattachitra- literally meaning ‘Picture on cloth canvas’ is a traditional treasure that has mesmerized the common man.
- The Patachitras, the intricate and artistic folk art, of Orissa are icon paintings that include wall paintings, manuscript paintings, palm-leaf etchings, and paintings on cloth, both cotton and silk.
- Pattachitra paintings are made of tussar silk.
- The origin of the paintings is traced to the 8th century A.D., from the fragmented pieces of evidence of cave paintings in Khandagari, Udaigiri, and Sitabhinji.
- Having a reference in the earliest known treatise on a painting called ‘Chitralakshana’, this art form finds its strong roots in the traditions of Lord Jagannath, the presiding deity of Odisha.
- These paintings have a ritualistic significance even to this day.
- The picturesque village of Raghurajpur, on the banks of river Bhargavi is well known for this artistry, along with its neighbours Puri, Dandasahi, and Khasposak.
- The Pattachitra artists are called ‘Chitrakaars’ (Painters), mainly belonging to the Maharana and Mahapatra castes.
- The creation of the Pattachitra paintings is a disciplined art form, and the chitrakars maintain rigidity in their use of colours and patterns, restricting the colours to a single tone.
Making of Paintings:
- Preparing the paints is perhaps the most important part of the creation of Pattachitra, engaging the craftsmanship of the chitrakars in using naturally available raw materials to bring about indigenous paints.
- The gum of the Katha tree is the chief ingredient and is used as a base for making different pigments, on which diverse raw materials are mixed for diverse colours.
- Powdered conch shells, for instance, are used for making a white pigment, while lamp soot is used for a black pigment.
- The root of the keya plant is usually used for making the common brush, while mouse hair is used on the requirement of finer brushes, to be attached to wooden handles.
Street Vendors (Protection of Livelihood and Regulation of Street Vending) Act, 2014

- 01 May 2024
Why is it in the News?
Enacted on May 1, 2014, after decades of advocacy, the Street Vendors Act has achieved progress yet faces implementation challenges in safeguarding vendors' livelihoods.
About Street Vendors (Protection of Livelihood and Regulation of Street Vending) Act, 2014:
- The Street Vendors (Protection of Livelihood and Regulation of Street Vending) Act, 2014 was enacted to legitimize the rights of street vendors (SVs) and regulate their activities.
- It is implemented by respective States/UTs by framing Rules, schemes, Bye-laws and Plan for Street Vending as per provisions of the Act.
- It seeks to safeguard and manage street vending in urban areas, with State-level regulations and initiatives overseen by Urban Local Bodies (ULBs) through the formulation of by-laws, urban planning, and regulatory measures.
- The Act clearly defines the roles and obligations of both vendors and various levels of government.
- One of the primary objectives of the Act is to ensure the inclusion of all "existing" vendors within designated vending zones by issuing vending certificates (VCs).
- It establishes Town Vending Committees (TVCs) as a mechanism for participatory governance, with street vendor representatives comprising 40% of the committee members, including a sub-representation of 33% for women SVs.
- These committees are tasked with overseeing the allocation of vending spaces and ensuring the representation of all existing vendors within vending zones.
- Moreover, the Act provides mechanisms for addressing grievances and disputes, proposing the establishment of Grievance Redressal Committees chaired by a civil judge or judicial magistrate.
- Additionally, it mandates that States/ULBs conduct surveys to identify street vendors at least once every five years, ensuring an updated understanding of the street vending landscape and facilitating effective regulatory measures.
Look Out Circulars (LOCs)

- 01 May 2024
Why is it in the News?
The Bombay High Court has held that public sector banks (PSBs) cannot recommend or request the issuance of Look Out Circulars (LOCs) against loan defaulters and has set aside the provisions of the central government’s Office Memoranda (OM) that empowered PSBs to do so.
What are Look Out Circulars (LOCs)?
- Look Out Circulars (LOCs) is a governmental directive to immigration authorities, instructing them to regulate and restrict the physical movement of individuals.
- Law enforcement agencies utilize them to prevent individuals wanted by the police or under suspicion from leaving or entering the country through designated ports of entry, including land, air, and sea ports.
- Typically issued by police, intelligence agencies, or other authorized government bodies under the Ministry of Home Affairs (MHA), LOCs are not explicitly backed by legislation but are governed by executive directives, such as the Office Memorandum issued by the MHA in 2021.
- This memorandum outlines consolidated guidelines for opening LOCs against both Indian citizens and foreigners.
- The guidelines dictate that LOCs can only be opened in criminal or penal cases, with the reason for the circular clearly indicated.
- However, in exceptional circumstances, LOCs may be issued for reasons detrimental to the sovereignty, security, or integrity of India, bilateral relations with other states, or the strategic and economic interests of India.
- Basic details, including name, parentage, passport number, and date of birth, must be available before issuing an LOC, and the process requires constant monitoring to minimize inconvenience to genuine travellers.
- Additionally, agencies responsible for requesting LOCs must review their requests quarterly and annually, with the results reported to the MHA.
- While the legal consequences of issuing an LOC lie with the originating agency, the power to issue such directives is derived from The Passports Act, 1967, which governs the grant of passports, travel documents, and endorsements to travellers during emigration or immigration processes.
'Egg Shell Skull' Rule

- 30 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
Underlining that the state and central consumer courts incorrectly applied the ‘eggshell skull’ legal principle, the Supreme Court recently restored the compensation of Rs 5 lakhs awarded by the district consumer forum in a medical negligence case.
What is the ‘Eggshell Skull’ Rule?
- The eggshell skull rule is a common law principle applied in civil litigation.
- Essentially, when the offender would be liable for all injuries that might be intensified due to the peculiar conditions of the injured person that the offender might not have known.
- Simply put, the defendant would be held responsible for injuries caused to a person when he hit him on the head, even if the victim had a particularly delicate skull or an ‘eggshell’ for a skull.
- A person who has an eggshell skull would be more severely impacted by an act, which an otherwise “normal person” would be able to withstand.
- The rule is applied for claiming an enhanced compensation, for damage that is more than what could have been ordinarily anticipated to be caused by the defendant.
Origin of the ‘Eggshell Skull’ Rule:
- The 'eggshell skull' rule, also known as the 'thin skull rule,' is a legal doctrine that holds a defendant liable for all consequences resulting from their negligent or intentional actions, even if the victim's pre-existing vulnerability worsens the outcome.
- The rule's origins can be traced back to an 1891 US case, Vosburg v. Putney, in which a boy kicked another's shin without knowing about his prior injury, leading to complications.
- The Wisconsin Supreme Court held that the defendant was responsible for the subsequent harm, even though he did not intend to cause such severe damage.
- A similar case in England a decade later involved a pregnant woman who experienced severe shock and gave birth to a disabled child after a horse van was negligently driven into a public house where she worked.
- The King's Bench upheld the principle that defendants are liable for the harm caused to victims, regardless of pre-existing vulnerabilities.
- The eggshell skull rule has been applied in various legal cases across different jurisdictions, emphasizing that defendants are accountable for the consequences of their actions, even when victims' unique vulnerabilities contribute to more significant harm.
What was the Jyoti Devi Medical Negligence Case?
- In 2005, Jyoti Devi underwent an appendix removal surgery in Himachal Pradesh, India.
- However, her abdominal pain persisted, leading to a four-year ordeal and multiple hospital visits.
- Eventually, doctors discovered that a 2.5 cm needle had been left in her abdomen during the initial surgery, requiring another operation to remove it.
- Jyoti sought compensation for medical negligence and was initially awarded Rs 5 lakhs by the district consumer forum.
- The hospital appealed, leading to the state consumer forum reducing the compensation to Rs. 1 lakh, and the National Consumer Disputes Redressal Commission (NCDRC) increasing it to Rs. 2 lakhs.
What did the SC Rule?
- The Supreme Court (SC) restored the original Rs 5 lakh compensation, criticizing the lower compensation amounts as "paltry" and "unjust."
- The SC ruled that the 'eggshell skull' rule did not apply in Jyoti's case since there was no evidence of a pre-existing vulnerability or medical condition that contributed to her suffering.
- The court cited two factors for increasing the compensation: Jyoti's prolonged pain over five years and the decade-long legal battle she endured.
Global Leaders Group on Antimicrobial Resistance

- 30 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
The European Society for Clinical Microbiology and Infectious Diseases (ESCMID) and the Global Leaders Group (GLG) on AMR jointly organized a high-level event, ‘Forging partnerships between science and policy’, on April 26, 2024, in Barcelona, Spain.
About Global Leaders Group on Antimicrobial Resistance:
- Established in November 2020, the Global Leaders Group on Antimicrobial Resistance is a collaborative effort of world leaders and experts from various sectors working together to accelerate political action against antimicrobial resistance (AMR).
- The Group serves as an independent global advisory and advocacy entity, striving to maintain public support, political momentum, and visibility of AMR on the global health and development agenda.
- Background: The Group emerged from a recommendation by the Interagency Coordination Group on Antimicrobial Resistance, aiming to strengthen global leadership and political action against AMR.
- The first meeting of the Group was held in January 2021.
Secretariat Support:
- The Quadripartite Joint Secretariat (QJS) on Antimicrobial Resistance, a joint effort by the Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO), the United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP), the World Health Organization (WHO), and the World Organisation for Animal Health (WOAH), provides secretariat support for the Group.
- Through its collaborative and multisectoral approach, the Global Leaders Group on Antimicrobial Resistance is committed to addressing the growing threat of AMR and promoting responsible and sustainable access to antimicrobials.
What is antimicrobial resistance (AMR)?
- Antimicrobial resistance (AMR) refers to the ability of microorganisms, such as bacteria, viruses, fungi, and parasites, to develop resistance to the effects of antimicrobial drugs, such as antibiotics, antivirals, antifungals, and antiparasitics.
- As a result, the medications become less effective or even ineffective at treating infections caused by these resistant microorganisms.
- AMR occurs when microorganisms undergo genetic changes that enable them to survive exposure to antimicrobial drugs.
- These changes can be shared between different microorganisms, leading to the spread of resistance genes.
- Over time, the increased use and misuse of antimicrobial drugs have accelerated the development of AMR.
Common factors contributing to AMR include:
-
- Overprescription of antimicrobials
- Non-adherence to prescribed treatment regimens
- Misuse of antimicrobials in agriculture and livestock farming
- Poor sanitation and hygiene practices
- Lack of access to clean water
- The rise of AMR poses a significant threat to public health, as it makes the treatment of common infections more difficult and increases the risk of complications.
- Additionally, AMR has implications for global health security, as resistant infections can spread rapidly across regions and become a major public health challenge.
Taam Ja' Blue Hole

- 30 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
Recently, scientists have uncovered a massive sinkhole off the coast of the Yucatan Peninsula in Mexico.
What is Taam Ja' Blue Hole?
- Taam Ja' Blue Hole is the world's deepest known underwater sinkhole, recently discovered in Chetumal Bay off Mexico's Yucatan Peninsula.
- The blue hole extends approximately 420 meters (1,380 feet) below sea level, making it significantly deeper than the previous record holder, the Dragon Hole in the South China Sea.
- The nearly circular sinkhole covers an area of around 13,660 square meters and features steep sides covered in biofilms, sediments, limestone, and gypsum ledges.
- Named "Taam Ja'," meaning "deep water" in the Mayan language, the blue hole was initially discovered by a local diver in 2003 but only recently gained scientific attention.
- Further research is ongoing to explore the unique marine life and geological features within this remarkable underwater cavern.
What is a Blue Hole?
- A blue hole is a large, underwater sinkhole or cavern with a submerged opening that appears dark blue from above due to the depth and clarity of the water.
- The name "blue hole" originates from the striking contrast between the dark blue, deep water within the hole and the lighter blue shallower water surrounding it.
- These unique geological formations are typically formed through a combination of erosion and dissolution of limestone bedrock, resulting in circular or ovular depressions in the seafloor.
- Over time, blue holes can develop distinct ecosystems hosting a variety of marine life, including unique and rare species that have adapted to the specific conditions within these habitats.
- Blue holes can be found in various parts of the world, both in oceanic and inland settings.
- Some famous examples include the Great Blue Hole in Belize, the Dean's Blue Hole in the Bahamas, and the Taam Ja' Blue Hole in Mexico.
Thrombosis with Thrombocytopenia Syndrome (TTS)
- 30 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
Global pharmaceutical giant AstraZeneca has said that its AZD1222 vaccine against Covid-19, which was made under license in India as Covishield, could cause low platelet counts and formation of blood clots in “very rare” cases.
What is Thrombosis with Thrombocytopenia Syndrome (TTS)?
- Thrombosis with Thrombocytopenia Syndrome (TTS) is characterised by thrombosis formation (blood clots) combined with thrombocytopenia (low platelet count) with symptoms typically presenting in the 4-42 days after vaccination.
- Platelets are small cells that help blood to clot, so having too few of them can be dangerous.
- It often involves unusual blood clot locations, such as in the brain (cerebral venous sinus thrombosis) or abdomen.
- The condition was observed in people who received adenoviral vector COVID-19 vaccines, such as Vaxzevria, Covishield (AstraZeneca), and the Johnson & Johnson/Janssen COVID-19 vaccine.
- TTS seems to occur because the body's immune system reacts to the vaccine by making antibodies that attack a protein involved in blood clotting.
- According to the Centers for Disease Control (CDC), TTS is classified into 2 tiers based on the location of thrombosis and severity of symptoms.
Tier 1:
- Rare blood clots, like in the brain or gut, sometimes alongside more typical ones in the legs or lungs.
- Low platelet count (below 150,000 per microliter).
- Positive anti-PF4 ELISA tests can help confirm diagnosis but aren't always needed.
- Tier 1 cases are usually more severe and riskier.
- This is more common in younger people.
Tier 2:
- Common blood clots, like in the legs or lungs.
- Low platelet count (below 150,000 per microliter).
- A positive anti-PF4 ELISA test is necessary for diagnosis.
Symptoms of TTS:
- Symptoms of TTS can include severe headaches, stomach pain, swelling in the legs, trouble breathing, and problems with thinking or seizures.
Great Rift Valley

- 30 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
A dam burst near a village in the Rift Valley region of southern Kenya in the early hours of April 29, 2024. Some 45 people have been killed according to the police chief of Nakuru County, where the incident took place.
About the Great Rift Valley:
- The Great Rift Valley, part of the larger East African Rift System (EARS), is a significant geological feature extending across East Africa, from Jordan in southwestern Asia to central Mozambique's coast along the Indian Ocean.
- Running through numerous countries including Eritrea, Djibouti, Ethiopia, Kenya, Tanzania, Uganda, Rwanda, Burundi, the Democratic Republic of Congo, Malawi, Zambia, and Mozambique, the valley is one of Earth's most expansive rifts.
Formation:
- Resulting from tectonic plate movements about 40 million years ago, the Great Rift Valley's formation is linked to the East African Rift's emergence.
- Geologically active, the region experiences frequent earthquakes, volcanoes, hot springs, and geysers.
Notable Features:
- A series of approximately 30 lakes dot the Great Rift Valley, including Lake Tanganyika (the world's second-deepest lake) and Lake Victoria (the second-largest freshwater lake by surface area).
- Many of Africa's highest mountains, such as Mount Kilimanjaro, Mount Kenya, and Mount Margherita, form part of ranges fronting the valley.
What is a Rift Valley?
- A rift valley is a lowland region that forms where the Earth's tectonic plates move apart or rift.
- Rift valleys are a result of the tectonic processes that shape the Earth's surface, specifically in regions where tectonic plates are diverging or pulling away from each other.
- Rift valleys are characterized by a long, narrow depression, often with steep sides, running along the length of the rift.
- The depression is caused by the sinking of the ground between the two diverging plates as they pull away from each other.
- The thinning of the Earth's crust leads to subsidence and the formation of a valley.
- Rift valleys can be found on land as well as on the ocean floor.
Some notable examples of rift valleys include:
- The Great Rift Valley in East Africa is part of the larger East African Rift System.
- The Red Sea Rift separates the African and Arabian tectonic plates.
- The Rhine Valley in Europe was formed by the divergence of the European and African plates.
- Rift valleys are geologically active areas often associated with volcanic activity, earthquakes, and the formation of hot springs, geysers, and other hydrothermal features.
Global Alliance of National Human Rights Institutions (GANHRI)

- 29 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
The National Human Rights Commission (NHRC) is preparing to defend the government’s human rights processes at a meeting in Geneva this week, where a decision on whether India’s human rights body will retain its “A status” is expected to be made.
About Global Alliance of National Human Rights Institutions (GANHRI):
- The Global Alliance of National Human Rights Institutions (GANHRI) is a representative body of National Human Rights Institutions (NHRIs) from across the world.
- It assists in the establishment and strengthening of independent and effective NHRIs, which meet the international standards set out in the Paris Principles.
- GANHRI encourages joint activities and cooperation among NHRIs, organises international conferences, liaises with the United Nations and other international organisations, assists NHRIs under threat, and assists governments in establishing NHRIs.
- The Asia Pacific Forum of National Human Rights Institutions (APF) and other member institutions continue to make a significant contribution to the operations and human rights initiatives of GANHRI.
- The organisation is incorporated as a non-profit organisation under Swiss law.
- Its Statute, adopted in March 2009, sets out its objectives and how it operates.
Membership:
- NHRIs that comply fully with the Paris Principles – and which have been granted 'A status' by GANHRI – are eligible to become voting members of GANHRI and to hold governance positions.
- NHRIs that only partially comply with the Paris Principles – and which have been granted 'B status' by GANHRI – can participate in meetings of GANHRI but are not eligible to vote or to hold governance positions.
Bureau:
- The operations of GANHRI are managed by its Bureau, which is comprised of representatives from each of the four regional groupings:
- Africa, the Americas, Europe, and the Asia Pacific.
- Each regional grouping is represented by elected representatives from four 'A status' NHRIs.
- The APF is currently represented on the GANHRI Bureau by Australia, India, Korea, and Qatar.
- A key role of the Bureau is to assess applications for membership in the ICC.
- It also reviews and determines the accreditation status of NHRIs, following a recommendation from the Sub-Committee on Accreditation.
- In addition, the Bureau collaborates with the Office of the High Commissioner for Human Rights (OHCHR), in particular the National Institutions and Regional Mechanisms Unit, to facilitate the participation of NHRIs in the United Nations Human Rights Council.
- Bureau meetings are usually held twice a year; the first is in conjunction with the first quarter session of the UN Human Rights Council and the second is in conjunction with one of the NHRI regional network's meetings.
- A meeting is also held in conjunction with the bi-annual International Conference.
International Conference:
- The International Conference involves NHRIs, as well as representatives of United Nations agencies, international organisations, and civil society.
- The purpose of the International Conference is to strengthen cooperation between NHRIs, to discuss human rights issues of shared concern, and to ensure follow-up at the national level.
- The International Conference is held every two years, alternating between Europe, the Americas, Africa, and the Asia Pacific.
Officials:
- The positions of GANHRI Chairperson and Secretary are served on a rotational basis by representatives nominated by the four regional coordinating committees: Europe, Africa, the Americas, and the Asia Pacific.
- The current GANHRI Chairperson is Maryam Abdullah Al Attiyah, Chairperson of the National Human Rights Committee of Qatar (NHRC), representing the Asia Pacific region.
- The current GANHRI Secretary is Amina Bouayach, Chairperson of the National Human Rights Council of Morocco (CNDH), representing the African region.
Secretariat:
- The National Institutions and Regional Mechanisms Unit of OHCHR acts as the GANHRI secretariat.
- GANHRI has a permanent representative in Geneva to support and facilitate the participation of NHRIs in the UN Human Rights Council and its human rights mechanisms.
Critical Minerals Summit

- 29 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
Ministry of Mines today organized a summit to foster collaboration, share knowledge, and drive innovation in the field of critical mineral beneficiation and processing in New Delhi.
About Critical Minerals Summit:
- The Critical Minerals Summit was organized by the Ministry of Mines, Government of India, in collaboration with the Shakti Sustainable Energy Foundation (Shakti), the Council on Energy, Environment and Water (CEEW), and the Indian Institute of Sustainable Development (IISD).
- It aims to promote collaboration and innovation in critical mineral beneficiation and processing.
- This event brings together a wide range of stakeholders, including industry leaders, startups, government officials, scientists, academics, and policy experts from both India and abroad.
Key Objectives:
- Tackling Demand: The summit seeks to address the growing demand for Critical Raw Materials (CRMs) needed for renewable energy systems and electric vehicles as part of India's strategic development goals.
- Focus on Key Minerals: The Ministry of Mines has identified eight crucial minerals for focus, including Glauconite (Potash), Lithium – Rare Earth Elements (Laterite), Chromium, Platinum Group, Graphite, Tungsten, Rare Earths (RE), and vanadium-associated with Graphite.
- Diverse Participation: The summit offers a platform for a diverse group of stakeholders to collaborate, share knowledge, and drive innovation in the field of critical minerals.
What are Critical Minerals?
- Critical minerals are metallic or non-metallic elements essential for modern technologies, economies, and national security, with potentially vulnerable supply chains.
- Their 'criticality' changes over time due to shifting supply and societal needs.
- Applications: Critical minerals are vital for manufacturing advanced technologies like mobile phones, computers, semiconductors, and renewable energy systems such as electric vehicles, wind turbines, solar panels, and batteries.
- They are also used in common products like stainless steel and electronics.
- Examples of Critical Minerals are antimony, beryllium, cobalt, copper, gallium, germanium, lithium, vanadium, and more.
- Top Producers: Countries like Chile, Indonesia, Congo, China, Australia, and South Africa lead in critical mineral production.
- Critical Minerals in India: The Indian government has identified 30 critical minerals, including antimony, beryllium, cobalt, copper, gallium, graphite, hafnium, indium, lithium, molybdenum, nickel, niobium, phosphorous, potash, rare earth elements, rhenium, silicon, strontium, tantalum, tellurium, tin, titanium, tungsten, vanadium, zirconium, selenium, and cadmium.
- To meet the rising demand for critical minerals and ensure a stable supply, the Indian government is actively working on auctioning critical mineral blocks and fostering industry partnerships.
- These efforts are crucial for the country's economic development and energy transition goals.
Green Taxonomy

- 29 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
The RBI and the Finance Ministry could draw inspiration from the ASEAN region's evolving green taxonomy, continually updated with sectoral insights, to enhance sustainability efforts.
What is Green Taxonomy?
- Green taxonomy is a pivotal framework designed to delineate environmentally sustainable investments, providing clarity on which economic activities and assets qualify as "green" or environmentally sound.
- It plays a crucial role in advancing global sustainability objectives, particularly in the context of combating climate change and transitioning towards a low-carbon economy.
What is Green Taxonomy?
- At its core, green taxonomy serves as a comprehensive tool for classifying economic activities and assets based on their environmental sustainability.
- It is crafted by governments, regulators, and stakeholders with a commitment to achieving net-zero carbon emissions and fostering sustainable development.
Significance of Green Taxonomy:
- The significance of green taxonomy lies in its multifaceted role:
- Preventing Greenwashing: By establishing clear criteria and standards, green taxonomy helps prevent greenwashing, a deceptive practice wherein investments are portrayed as environmentally friendly when they may not be.
- Informing Investment Decisions: Investors are empowered to make informed decisions by utilizing the taxonomy as a guide. It offers transparency and guidance, enabling investors to align their investment strategies with environmental objectives.
- Directing Investments Towards Sustainability: The taxonomy serves as a tool for channeling investments towards sustainable economic activities and assets. By identifying and classifying green investments, it encourages the allocation of capital to projects that contribute positively to environmental goals.
Common Features of Green Taxonomies:
- Green taxonomies typically include objectives related to climate mitigation and adaptation, with some also incorporating additional environmental goals such as biodiversity conservation.
- To qualify as green, an activity must substantially contribute to at least one of these environmental objectives.
- Furthermore, green taxonomies often integrate "do no significant harm" criteria, ensuring that activities considered green do not compromise other environmental objectives.
- Additionally, they emphasize compliance with social safeguards, including human rights considerations.
Nuanced Approaches in Green Taxonomies:
- Some taxonomies adopt a nuanced approach, such as the "traffic light" system utilized by the Indonesian and proposed Singaporean taxonomies.
- Under this approach, economic activities are categorized into different tiers (green, amber, or red) based on their environmental sustainability.
- This system offers a more nuanced understanding of the environmental impact of various activities, allowing for tailored assessments and decision-making.
What Is Greenwashing?
- Greenwashing is the process of conveying a false impression or misleading information about how a company’s products are environmentally sound.
- Greenwashing involves making an unsubstantiated claim to deceive consumers into believing that a company’s products are environmentally friendly or have a greater positive environmental impact than they actually do.
- In addition, greenwashing may occur when a company attempts to emphasize sustainable aspects of a product to overshadow the company’s involvement in environmentally damaging practices.
- Performed through the use of environmental imagery, misleading labels, and hiding tradeoffs, greenwashing is a play on the term “whitewashing,” which means using false information to intentionally hide wrongdoing, error, or an unpleasant situation in an attempt to make it seem less bad than it is.
National Centre for Good Governance (NCGG)

- 29 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
A central government delegation is on a three-day visit to Bangladesh beginning Sunday to further boost bilateral ties on governance matters, according to an official statement.
About the National Centre for Good Governance:
- The National Centre for Good Governance (NCGG) was set up in 2014 by the Government of India as an apex–level autonomous institution under the Ministry of Personnel, Public Grievances and Pensions.
- The Centre traces its origin to the National Institute of Administrative Research (NIAR), which was set up in 1995 by the Lal Bahadur Shastri National Academy of Administration (LBSNAA), the Government of India's topmost training institute for civil services.
- NIAR was subsequently rechristened and subsumed into NCGG.
- NCGG deals with a gamut of governance issues from local, state to national levels, across all sectors.
- The Centre is mandated to work in the areas of governance, policy reforms, capacity building, and training of civil servants and technocrats of India and other developing countries.
- It also works as a think tank.
- Since its inception, the Centre has been extensively working in areas such as primary and elementary education, decentralized planning at district and block levels, capacity building of Panchayat Raj Institutions (PRIs), participatory models of learning and action, rural development, cooperatives, and public sector management, etc.
- In addition, it focuses on issues related to good governance, social accountability, water, sanitation, and hygiene (WASH), among other sectors.
- The Centre encapsulates the essence of good governance and weighs on the importance of the rule of law, bringing in transparency, working to promote public participation in governance, service delivery, and reforms, as well as in developing accountable institutions, access to information, etc.
Raja Ravi Varma

- 29 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
The first true copy of the painting Indulekha by legendary artist Raja Ravi Varma will be unveiled at the Kilimanoor Palace, where the eminent artist was born in 1848, on the occasion of his 176th birth anniversary celebrations.
Who was Raja Ravi Varma?
- Raja Ravi Varma was an Indian painter and artist.
- He is considered among the greatest painters in the history of Indian art.
- His works are one of the best examples of the fusion of European academic art with a purely Indian sensibility and iconography.
- Additionally, he was notable for making affordable lithographs of his paintings available to the public, which greatly enhanced his reach and influence as a painter and public figure.
- His lithographs increased the involvement of common people with fine arts and defined artistic tastes among common people.
- He was part of the royal family of erstwhile Parappanad, Malappuram district.
- He is also celebrated for inventing the first oleograph press in Ghatkopar, Mumbai.
- His paintings depicting Hindu gods and goddesses had a significant influence on their portrayal in art and cinema for many years.
- His artworks found popularity not only among Europeans but also among laymen, who appreciated his work for its simplicity.
- In a time when lower castes were barred from temples, they found solace in Varma's work.
- In addition to Indian mythology, he was admired for highlighting the beauty of South Indian women.
- Viceroy Lord Curzon honored him with the 'Kaisar-i-Hind' Gold Medal for his service.
- His paintings can be broadly classified into three categories: portraits, portrait-based compositions, and theatrical compositions based on myths and legends.
- Some of his popular paintings include 'A Family of Beggars,' 'A Lady Playing Swarbat,' 'Draupadi Dreading to Meet Kichaka,' 'Girl in Sage Kanwa's Hermitage (Rishi-Kanya),' 'Jatayu,' and 'Indulekha' among others.
About Indulekha Painting:
- The painting by Raja Ravi Varma draws inspiration from the novel as he creates an oil painting of Indulekha, who is depicted holding a letter addressed to her lover, Madhavan, the hero of the novel, with the salutation 'Dear Madhavan...' dated 1892.
- The painting, characterized by an over-the-top sense of symmetry and precise attention to micro-details, dates back to the 19th century.
- Another belief suggests that the famous painting 'Reclining Lady' by Ravi Varma was modeled on Indulekha.
- Recently, the painting was restored by Madhan S. of the Heritage Conservation and Research Academy.
Expanding Glacial Lakes in the Indian Himalayas: ISRO

- 27 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
Experts express concern over the ISRO analysis findings, indicating that the expansion of glacial lakes due to warming could result in cascading impacts in lower regions.
Highlights of the ISRO Report:
- The ISRO report said 601 glacial lakes, or 89 percent, have expanded more than twice, and 10 lakes have grown between 15 times and double their size. Sixty-five lakes have expanded 1.5 times.
- Of the 2,431 glacial lakes larger than 10 hectares, 676 have significantly expanded, and at least 130 of these lakes are in India 65 (Indus River basin), 7 (Ganga River basin), and 58 (Brahmaputra River basin).
- Elevation-based analysis shows 314 lakes are located in the 4,000 to 5,000 meters range, and 296 lakes are above 5,000 meters elevation.
What are Glacial Lakes?
- Glacial lakes emerge in hollows or basins shaped by glaciers' erosive force and are prevalent in areas where glaciers once existed or persist.
- They vary widely in size and shape, from tiny pools to expansive bodies of water.
- ISRO classifies them into four main types: moraine-dammed, ice-dammed, erosion-based, and 'others'.
- While vital as freshwater sources for rivers, glacial lakes also pose risks, particularly Glacial Lake Outburst Floods (GLOFs).
- GLOFs occur when these lakes discharge large volumes of meltwater, often due to natural dam failures, causing sudden and severe downstream flooding.
Formation Processes:
- Glacial Erosion: Glaciers, moving slowly, sculpt the landscape by eroding bedrock through abrasion and plucking, creating valleys and basins.
- Moraine Deposition: As glaciers move, they transport sediment, depositing it at their edges as moraines, which can act as natural dams, forming lake basins.
- Ice Melting: Rising temperatures or glacier retreat causes ice to melt, filling depressions created by erosion with water, and forming glacial lakes.
- Terminal Moraine Formation: Glaciers may leave behind ridges of sediment at their terminus, creating natural dams that trap water, forming terminal moraine lakes.
Utilization of Remote Sensing for Glacial Lake Monitoring:
- Monitoring glacial lakes in the Himalayan region presents challenges due to rugged terrain, making satellite remote-sensing technology indispensable.
- By analyzing satellite data, changes in glacial lakes can be tracked over time, offering insights into their evolving dynamics.
- This data is vital for understanding their environmental impact and devising strategies to manage risks such as glacial lake outburst floods (GLOFs) and adapt to climate change in glacier-influenced regions.
Mitigating Risks Associated with Glacial Lakes:
- Research suggests that reducing glacial lake levels by 10 to 30 meters can significantly alleviate downstream impacts, albeit not eliminate GLOF risks.
- One effective method involves siphoning off lake water using extended High-Density Polyethylene (HDPE) pipes.
- In 2016, the Sikkim State Disaster Management Authority successfully employed this technique to lower water levels in South Lhonak Lake, showcasing its practicality and efficacy in risk reduction efforts.
Haritha Karma Sena (HKS)

- 27 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
Adhering to green protocol, the Haritha Karma Sena workers have to ensure that the polling booths and surroundings are free of plastic and other waste materials in Kerala.
What is Haritha Karma Sena (HKS)?
- Haritha Karma Sena (HKS) is a professional team comprising Green Technicians and Green Supervisors, predominantly composed of Kudumbashree Women.
- Their duties include collecting, transporting, processing, recycling/disposing, and managing waste materials in collaboration with respective Local Self-Governments.
- Launched in 2013 by the Government of Kerala, it is part of the Haritha Keralam Mission.
What is the Haritha Keralam Mission?
- It is a comprehensive initiative aimed at transforming Kerala into a clean and green state.
- The mission strives to eliminate garbage, promote sustainable waste management practices, generate employment in the waste management sector, and raise environmental awareness.
What is the Success Story of the HKS?
- The 35,500 members of the HKS have tirelessly worked to change societal attitudes towards household waste management.
- Waste collection and segregation have become respected and remunerative occupations.
- The transition from centralized waste treatment to decentralized management reflects a community-driven approach to sustainability.
- Kudumbashree's empowerment of women and the government's emphasis on awareness and training are crucial for sustaining these efforts.
What More Needs to be Done?
- Future plans include improving segregation methods, promoting diversification, and expanding waste storage infrastructure.
- These initiatives reflect a holistic approach to waste management and economic development.
Symbol Loading Units (SLUs)

- 27 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
Recently, the Supreme Court rejected the plea for full verification of VVPAT slips against EVM counts and directed the ECI to seal the Symbol Loading Unit (SLU) for 45 days post-election results announcement.
What is a Symbol Loading Unit (SLU) and How Does it Work?
- Symbol Loading Units (SLUs) were introduced around the same time as VVPATs, a little over a decade ago.
- VVPATs help voters verify their votes, they see a slip with a printed image of the party symbol they voted for.
- But for the VVPAT to print a symbol correctly, information pertaining to the list of candidates and their symbols must be loaded onto the VVPAT machine in the correct order.
- This is where the Symbol Loading Unit, or SLU, comes in.
- The introduction of VVPATs necessitated the use of SLUs.
- The SLU is used to load the symbols of the candidates onto the VVPAT.
- It is a matchbox-sized device that is first connected to a laptop or personal computer, from where a symbol-loading application is used to load a bitmap file containing the candidates’ names, serial numbers, and symbols.
- The SLU is then connected to the VVPAT to transfer that file onto the paper audit machine.
- This is done under the supervision of a district election officer.
At Which Point in the Election Process Are SLUs Used?
- The SLUs come into the picture only a few days before polling in a particular seat, when the EVMs are being commissioned and the list/ order of contesting candidates is decided and set on the ballot unit and the VVPAT.
- Candidate-setting can happen at any time from five to two days before voting at a seat.
- Once the SLU is used to load symbols onto the VVPAT, the EVM is ready for use.
- After this, the SLU is of no relevance to the actual voting process.
What Happens to an SLU After Symbols Are Loaded?
- Typically, a small number of SLUs are enough to load symbols onto all VVPATs for a seat.
- According to EC officials, it takes an SLU two to three minutes to load each VVPAT.
- Once the symbol-loading is complete, the SLUs are handed over to the concerned district election officer for safekeeping.
- They remain in the officer’s custody until the day after voting. Afterward, the SLUs are released to the engineers of the two EVM manufacturers, Bharat Electronics Ltd (BEL) or Electronics Corporation of India Ltd (ECIL), so they can be used to load symbols onto VVPATs for other seats in subsequent phases.
- Thus, in a multi-phase election like the ongoing one for the 18th Lok Sabha, an SLU is typically reused after one phase of polling to load symbols onto VVPATs meant for other seats in subsequent phases.
Bambi Bucket

- 27 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
Recently, an Indian Air Force MI 17 V5 helicopter, equipped with a Bambi Bucket, was deployed to combat the forest fires in Nainital district, Uttarakhand.
What is a Bambi Bucket?
- Bambi Bucket is a specialised aerial firefighting tool that has been in use since the 1980s.
- It is essentially a lightweight collapsible container that releases water from underneath a helicopter to targeted areas.
- The water is released by using a pilot-controlled valve.
- One of its key features is that it can be quickly and easily filled.
- The bucket can be filled from various sources, including a lake, river, pond, and swimming pool, which allows firefighters to swiftly refill it and return to the target area.
- Bambi Bucket is available in a variety of sizes and models, with capacities ranging from 270 liters to more than 9,840 liters.
How was the Bambi Bucket Invented?
- The Bambi Bucket was invented by Don Arney, a Canadian business, in 1982.
- Arney came up with the idea after he realised that the aerial firefighting water buckets in use at the time were not efficient and had a high failure rate.
- These water buckets were generally made of “solid fiberglass, plastic, or canvas with metal frames” and were “too rigid to fit inside the aircraft” and had to be “trucked to fire sites or flown in on the hook of a helicopter thereby slowing the aircraft down.
- Another issue was that the water dropped from these containers used to get dispersed into a spray thereby reducing impact.
- Bambi Bucket does not have these limitations.
- One, it can be stored within the helicopter until development.
- Two, it discharges a solid column of water, “resulting in a more accurate and effective water dump, less evaporation on the descent, and greater impact force.
- It was an instant success and began to be widely used for firefighting.
- Today, Bambi Bucket is used in more than 115 countries around the world by more than 1,000 helicopter operators.
Carnation Revolution

- 27 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
Recently, Portugal commemorated its 50th anniversary of Portugal's Carnation Revolution – the peaceful uprising that toppled a dictatorship and ended a decade of colonial war.
About the Carnation Revolution:
- The Carnation Revolution, also known as the 25th of April, was a pivotal event in Portugal's history that marked the transition from an authoritarian regime to a democratic government.
- On April 25, 1974, a group of military officers orchestrated a nearly bloodless military coup, overthrowing the Estado Novo dictatorship that had ruled Portugal for over four decades.
- The revolution aimed to accelerate decolonization, end ongoing wars through negotiations, and improve socio-economic conditions within Portugal.
- This event not only transformed Portugal's political landscape but also had significant implications for the nation's African colonies.
- Several factors contributed to the success of the Carnation Revolution, including widespread discontent with the authoritarian regime, a costly and unpopular colonial war, and the growing desire for democracy and improved living conditions.
- The coup leaders, known as the Armed Forces Movement (MFA), garnered support from various factions, including the Communist Party, socialists, and moderate democrats.
- The Carnation Revolution was named after a Lisbon flower seller who offered red carnations to soldiers, which were then placed in the barrels of their rifles.
- This iconic gesture symbolized the peaceful nature of the coup and solidified the carnation as a symbol of Portugal's democratic movement.
- The 50th anniversary of the Carnation Revolution celebrated on April 25, 2024, signifies the enduring impact of this historic event on Portugal's political trajectory and its relationship with its former colonies.
Bathymetry

- 26 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
Scientists from the Indian National Centre for Ocean Information Services (INCOIS) recently conducted a study of the bathymetry, or ocean floor, in the Indian Ocean.
What is Bathymetry?
- Bathymetry is a technique dedicated to mapping the depths of water bodies, that is, it is the measurement and representation of the topography of the bottom of rivers, seas, and oceans.
- In addition to measuring depth, this study also includes identifying underwater relief and creating three-dimensional maps of the sea floor.
- The word “bathymetry” comes from the Greek "bathýs", meaning deep, and "metron", meaning measure.
- Bathymetry allows for obtaining information about the physical characteristics of the sea floor, such as seamounts, mountain ranges, valleys, abyssal plains, and underwater canyons.
How is Bathymetry Performed?
- To carry out bathymetry, specific equipment is used, such as multibeam sonar (MultiBeam Echosounder), IMU (Inertial Measurement Unit), and high-precision positioning systems (via satellite with RTK correction).
- Multibeam sonar emits sound pulses toward the sea floor and measures the time it takes for the sound to return to the sensor after being reflected by submerged surfaces.
- Based on this sound return time and knowledge of the exact position of the vessel and its attitude (roll, pitch, yaw), it is possible to calculate the depth at a given point.
- The bathymetry service generates charts, blueprints, and digital models (2D and 3D) of the sea floor.
- LiDAR sensors, on the other hand, are used to detect data through beams of light above the waterline, mapping slopes, rockfills, and channel walls.
- The fusion of bathymetry data with Lidar data allows the three-dimensional construction of the environment in very high resolution.
- Allowing the client to plan or verify works and/or assets in the region of interest.
About Indian National Centre for Ocean Information Services (INCOIS):
- Established in 1999, the Indian National Centre for Ocean Information Services (INCOIS) under the Ministry of Earth Science, Govt of India.
- It is mandated to provide ocean information and advisory services to a broad spectrum of users through sustained ocean observations and constant improvements through systematic and focused research.
- The activities include data services, consultancy, and capacity development.
- HQ: Hyderabad
- INCOIS is a permanent member of the Indian delegation to the IOC of UNESCO and a founding member of the Indian Ocean Global Ocean Observing System (IOGOOS) and the Partnership for Observing the Oceans (POGO).
Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD)
- 26 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
The rising incidence of Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD) across the globe has become a concern for doctors, while early diagnosis is lacking, diagnosis in itself is challenging considering that other conditions could mimic IBD.
What is IBD?
- Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) is a recurring and long-term (chronic) condition that affects the digestive tract.
- IBD causes inflammation of the stomach, small intestine, and colon.
- IBD is a progressive disease that can become worse over time and cause other damage if not properly diagnosed and treated.
- There are two types of IBD: Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis.
- Crohn’s disease: leads to inflammation anywhere in the gastrointestinal tract, however, it commonly affects the end of the small intestine (the ileum) and the beginning of the large intestine (the right colon).
- Crohn’s disease can also affect the entire thickness or alternating areas of the bowel wall.
- Ulcerative colitis: causes inflammation in the large intestine or colon.
- This form of IBD inflames the innermost lining of the colon and creates tiny open sores (ulcers).
- Crohn’s disease: leads to inflammation anywhere in the gastrointestinal tract, however, it commonly affects the end of the small intestine (the ileum) and the beginning of the large intestine (the right colon).
What causes IBD?
- The exact cause of IBD is unknown, but IBD is the result of a weakened immune system. Possible causes are:
- The immune system responds incorrectly to environmental triggers, such as a virus or bacteria, which causes inflammation of the gastrointestinal tract.
- There also appears to be a genetic component.
- Someone with a family history of IBD is more likely to develop this inappropriate immune response.
Symptoms of IBD:
- Although Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis are different conditions, IBD conditions have similar symptoms, such as:
- Abdominal pain
- Diarrhea
- Rectal bleeding
- Vomiting
- Weight loss
How Is Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD) Treated?
- While there is no curative treatment for IBD, it is managed through medication, dietary changes, and occasionally surgery.
- The treatment aims to alleviate symptoms, mitigate complications, prevent future flare-ups, and potentially promote the healing of inflamed intestines.
Indian Historical Records Commission (IHRC)

- 26 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
Recently, the Indian Historical Records Commission (IHRC) has adopted a new logo and motto.
About Indian Historical Records Committee (IHRC):
- The Indian Historical Records Committee (IHRC) is a national forum established in 1919, comprising creators, custodians, and users of records.
- Its primary purpose is to advise the Government of India on matters related to record management and their utilization for historical research.
Secretariat:
- The National Archives of India, New Delhi, serves as the Secretariat for the IHRC, formerly known as the Indian Historical Records Committee since 1911.
Leadership and Membership:
- Led by the Union Minister of Culture, the IHRC consists of 134 members, including government agencies, government-appointed nominees, representatives from State/UT Archives, universities, and learning institutions.
- Over the years, the IHRC has convened 62 sessions.
Committee Structure: The IHRC operates with two adjunct bodies:
- Editorial Committee: Responsible for reviewing and approving papers based on archival sources for presentation at committee sessions.
- Standing Committee: Tasked with reviewing the implementation of committee recommendations and providing input on meeting agendas.
- The Secretary of the Ministry of Culture chairs the Standing Committee of IHRC.
- The Indian Historical Records Commission (IHRC) has adopted a new logo and motto recently.
- The logo signifies the theme and uniqueness of IHRC entirely.
- The pages in the shape of lotus petals represent IHRC as the resilient nodal institution for maintaining historical records.
- The Sarnath pillar in the middle represents India's glorious past.
- Brown as the colour theme reinforces the organization's mission of preserving, studying, and honouring India's historical records.
- The motto translates as "Where history is preserved for the future."
- The IHRC plays a vital role in identifying, collecting, cataloging, and maintaining historical documents, manuscripts other sources of historical information.
- By doing so the Commission ensures that valuable historical knowledge is conserved for future generations.
- The motto, therefore, reflects the Commission's commitment to ensuring the safeguarding of historical documents and making these accessible for the benefit of present and future generations.
Nephrotic Syndrome
- 26 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
On the heels of recent news reports on how keratin-based hair-straightening products containing glycolic acid derivatives led to severe kidney injury in women, researchers from Kerala have reported a series of cases wherein, the use of fairness creams has been linked to nephrotic syndrome.
What is Nephrotic Syndrome?
- Nephrotic syndrome causes scarring or damage to the filtering part of the kidneys (glomeruli).
- This causes too much protein to be lost from the blood into the urine.
People with nephrotic syndrome often have:
-
- Low levels of protein in the blood (hypoalbuminemia)
- Very high levels of protein in the urine (proteinuria)
- Swelling (edema), especially around the eyes, feet, and hands
- High cholesterol
What causes nephrotic syndrome?
- Nephrotic syndrome results from damage to the kidneys' glomeruli.
- These are the tiny blood vessels that filter waste and excess water from the blood and send them to the bladder as urine.
- The glomeruli keep protein in the body. When they are damaged, protein leaks into the urine.
- Healthy kidneys allow less than 1 gram of protein to spill into the urine in a day.
- In nephrotic syndrome, the glomeruli let 3 grams or more of protein leak into the urine during 24 hours.
- Nephrotic syndrome may happen with other health problems, such as kidney disease caused by diabetes and immune disorders.
- It can also develop after damage from viral infections.
- The cause of nephrotic syndrome is not always known.
What are the symptoms of nephrotic syndrome?
- The symptoms of nephrotic syndrome include:
- Swelling or edema, typically in the ankles, feet, or legs
- Fatigue
- Loss of appetite
- Weight gain
- Foamy urine
Treatment:
- The treatment of nephrotic syndrome varies depending on its cause.
- However, it typically includes medications to treat the underlying cause, as well as changes in diet.
- Dietary changes that might help in treating nephrotic syndrome include Source:
- limiting sodium
- eating less protein
- reducing the intake of saturated fat and cholesterol
Complications of nephrotic syndrome:
- Serious complications of nephrotic syndrome include kidney failure or end-stage renal disease (ESRD).
- Dialysis may be needed if kidney failure develops which can happen in extreme cases.
Army Tactical Missile Systems (ATACMS)

- 26 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
The United States has confirmed providing long-range Army Tactical Missile Systems (ATACMS) to Ukraine to aid its war effort against Russia.
What is the ATACMS System?
- The Army Tactical Missile Systems (ATACMS) is one of the most potent missile systems built by US-based arms manufacturer Lockheed Martin.
- This is a surface-to-surface artillery weapon system.
- Its biggest strengths are the long-range of attack, the ability to fire cluster munitions, and the weapon system’s mobility.
- Range: There is a mid-range version of the ATACMS, called Block 1, and a long-range version, Block 1A.
- ATACMS Block 1 has a range of 165 kilometres. Ukraine was provided these systems last year and used them to attack targets in October.
- ATACMS Block 1A, on the other hand, has a maximum range of 300 km. However, this depends on the kind of munition the missile carries.
- With such a range, the long-range ATACMS Block 1A is capable of striking targets well beyond the range of existing Army cannons, rockets, and other missiles.
- Mobility: ATACMS missiles are fired from the High Mobility Artillery Rocket System (HIMARS) and M270 Multiple Launch Rocket System (MLRS) platforms. Both of these launching systems are highly mobile automatic systems.
Why Ukraine can’t use ATACMS to Target Russian Territories?
- Despite territories deep inside Russia now being within the range of the ATACMS, Ukraine cannot use it to hit targets in these locations.
- Ukraine has committed to only use the weapons inside Ukraine, not in Russia.
- The US administration has made it clear that the weapons cannot be used to hit targets inside Russia.
- The Biden administration is concerned that if Ukraine strikes deep into Russian territory, it will anger Moscow and escalate the conflict.
Microsoft Phi-3-Mini

- 25 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
A few days after Meta unveiled its Llama 3 Large Language Model (LLM), Microsoft recently unveiled the latest version of its ‘lightweight’ AI model – the Phi-3-Mini.
What is Phi-3-Mini?
- Phi-3 refers to a series of language models developed by Microsoft, with Phi-3-mini being a notable addition.
- Phi-3-mini is a 3.8 billion parameter language model trained on 3.3 trillion tokens, designed to be as powerful as larger models while being small enough to be deployed on a phone.
- Despite its compact size, Phi-3-mini boasts impressive performance, rivaling that of larger models such as ChatGPT-3.5.
- Furthermore, Phi-3-mini can be quantized to 4 bits, occupying approximately 1.8GB of memory, making it suitable for deployment on mobile devices.
- The model’s training data, a scaled-up version of the one used for Phi-2, is composed of heavily filtered web data and synthetic data, contributing to its remarkable capabilities.
Advantages and Challenges of Phi-3-Mini:
- Phi-3-mini exhibits strengths in its compact size, impressive performance, and the ability to be deployed on mobile devices.
- Its training with high-quality data and chat-finetuning contribute to its success. This allows it to rival larger models in language understanding and reasoning.
- However, the model is fundamentally limited by its size for certain tasks.
- It cannot store extensive “factual knowledge,” leading to lower performance on tasks such as TriviaQA.
- Nevertheless, efforts to resolve this weakness are underway, including augmentation with a search engine and exploring multilingual capabilities for Small Language Models.
- Safety: Phi-3-mini was developed with a strong emphasis on safety and responsible AI principles, in alignment with Microsoft’s guidelines.
- The approach to ensuring safety involved various measures such as safety alignment in post-training, red-teaming, and automated testing.
- It also involved evaluations across multiple categories of responsible AI (RAI) harm.
How is Phi-3-Mini Different From LLMs?
- Phi-3-mini is the Small Language Model (SLM). Simply, SLMs are more streamlined versions of large language models.
- When compared to Large Language Model (LLM), smaller AI models are also cost-effective to develop and operate, and they perform better on smaller devices like laptops and smartphones.
- SLMs are great for “resource-constrained environments including on-device and offline inference scenarios.
- Such models are good for scenarios where fast response times are critical, say for chatbots or virtual assistants.
- Moreover, they are ideal for cost-constrained use cases, particularly with simpler tasks.
- While LLMs are trained on massive general data, SLMs stand out with their specialisation.
- Through fine-tuning, SLMs can be customised for specific tasks and achieve accuracy and efficiency in doing them.
- Most SLMs undergo targeted training, demanding considerably less computing power and energy compared to LLMs.
- SLMs also differ when it comes to inference speed and latency.
- Their compact size allows for quicker processing and their cost makes them appealing to smaller organisations and research groups.
Ross Ice Shelf

- 25 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
New research has found a "missing piece of the puzzle" of West Antarctic Ice Sheet melt, revealing that the collapse of the ice sheet in the Ross Sea region can be prevented—if we keep to a low-emissions pathway.
About Ross Ice Shelf:
- The Ross Ice Shelf is a floating mass of land-ice, with a front between 15 and 50 meters high. ?
- It is the largest ice shelf in Antarctica.
- Situated in the Ross Sea, it extends off the coast into the ocean, covering an impressive 487,000 square kilometers, roughly the size of France.
- Despite its vast surface area, only 10% of the ice shelf is visible above the water, mostly concealed beneath hundreds of meters of ice.
- The thickness of the Ross Ice Shelf varies significantly, ranging from about 100 meters to several hundred meters at its thickest points near the areas where the shelf connects to the Antarctic continent.
- The formation of the Ross Ice Shelf is the result of snow accumulation and compaction over time, which ultimately transforms into ice.
- It is continuously fed by glaciers draining from both the East and West Antarctic Ice Sheets, creating a balance as new ice is added while existing ice is removed through melting at the base and calving at the front.
- This massive ice shelf plays a critical role in stabilizing the Antarctic ice sheet.
About the Ross Sea:
- Location and Size: The Ross Sea is a vast, remote bay located just 320 km from the South Pole, positioned south and slightly east of New Zealand.
- It covers an area of approximately 370,000 square miles (960,000 square km), making it the largest polar marine ecosystem in the world.
- The sea's dynamics are significantly shaped by the coastal East-Wind Drift, which establishes a vast clockwise gyre, complemented by deepwater upwelling phenomena.
- Notably, it holds the distinction of being Antarctica's first protected area, serving as a habitat for a plethora of penguin species and numerous whale species.
- Depth: Despite its vast size, the Ross Sea is relatively shallow, with an average depth of approximately 530 meters.
- Historical Exploration: The sea is named after British explorer Sir James Clark Ross, who first visited the area in 1841 during his expedition to Antarctica.
- The Ross Sea's importance to both the scientific community and global conservation efforts cannot be overstated, as it provides valuable insights into the effects of climate change on polar ecosystems.
Global Tiger Conservation Coalition

- 25 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
At the Sustainable Finance for Tiger Landscapes Conference, Bhutan and the Tiger Conservation Coalition pledged to mobilize $1 billion for tiger conservation efforts.
About the Tiger Conservation Coalition:
- The Tiger Conservation Coalition is a group of non-governmental organizations (NGOs) that have worked for many years with partners to conserve tigers.
- It brings together leading tiger biologists and experts in wildlife crime, human-wildlife coexistence, policy, finance, development, and communications with unprecedented alignment on achieving tiger conservation at scale.
- Its member organizations include the Environmental Investigation Agency (EIA), Fauna & Flora, the International Union for Conservation of Nature and Natural Resources (IUCN), Panthera, TRAFFIC, United Nations Development Programme (UNDP), Wildlife Conservation Society (WCS) and World Wide Fund for Nature (WWF).
- It is an independent group of organizations that combines and shares the vast knowledge, on-the-ground experience, and data of its members and partners to support Tiger Range Countries in developing and implementing effective approaches to tiger conservation.
- The Coalition was founded on strong relationships among eminent tiger experts already working together on major tiger assessments, including the latest assessment by the IUCN Red List of Threatened Species released in 2022, and the forthcoming Green Status Assessment, and coalesced around a common vision for tiger recovery.
- By engaging national and local civil society organizations from the region, and continuing to support the Global Tiger Initiative Council and the Global Tiger Forum, the coalition aims to further strengthen partnerships and impactful outcomes for tigers.
- In January 2022, the Tiger Conservation Coalition released its vision for tiger recovery through 2034, the next Year of the Tiger.
- “Securing a Viable Future for the Tiger” presents a set of measurable goals and high-level strategic approaches to achieve the long-term presence of viable and ecologically functional populations of wild tigers.
- Its suggested actions, grounded in the latest science and results, would lead to increasing numbers of tigers secure in current and expanded protected habitats, with distribution and connectivity across their indigenous range.
- Tiger Conservation Coalition members co-developed Tiger Conservation Landscapes 3.0, an integrated habitat modeling system to measure and monitor changes in tiger habitat at range-wide, national, biome, and landscape scales in near real-time.
- This work serves as a model for objective, range-wide, habitat monitoring as countries work to achieve the goals laid out in the 30x30 agenda, the Sustainable Development Goals, and the Kunming-Montreal Global Biodiversity Framework.
Global Report on Food Crises (GRFC) 2024

- 25 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
Nearly 282 million people faced high levels of acute food insecurity in 59 countries in 2023, with extreme weather being the second most significant factor driving food crisis, revealed the 2024 Global Report on Food Crisis (GRFC) released April 24, 2024.
About Global Report on Food Crises (GRFC) 2024:
- The Global Report on Food Crises (GRFC) 2024, released annually by the Food Security Information Network (FSIN), provides a comprehensive analysis of global food crises and their causes.
- Launched by the Global Network Against Food Crises, a multistakeholder initiative involving United Nations agencies, the European Union, the United States Agency for International Development, and various non-governmental agencies, the report highlights the alarming state of food insecurity worldwide.
Key findings from the GRFC 2024 include:
- Analysis of 1.3 billion people in 59 countries in 2023, with nearly 282 million facing high levels of acute food insecurity.
- Identification of 2023 as the fifth consecutive year of rising numbers of people suffering acute food insecurity, defined as life or livelihood-threatening food deprivation.
- Conflicts, extreme weather events, and economic shocks have been identified as the primary drivers behind worsening food crises globally.
- Conflict hotspots like Palestine's Gaza Strip and Sudan experienced a significant escalation in food crises during 2023, with conflict and insecurity becoming the main drivers in 20 countries, directly affecting 135 million people.
- The Gaza Strip emerged as the area with the most severe food crisis over the past eight years of GRFC reporting, while Sudan is facing one of the worst food crises globally, with nearly one-third of its population in need of emergency food assistance.
- Weather extremes were the main driver in 18 countries, causing over 72 million people to face high levels of acute food insecurity.
- The 10 countries experiencing the largest food crises in 2023 included the Democratic Republic of Congo, Nigeria, Sudan, Afghanistan, Ethiopia, Yemen, Syria, Bangladesh, Pakistan, and Myanmar.
- On a positive note, the food crisis improved in 17 countries, including the Democratic Republic of Congo and Ukraine.
- The GRFC 2024 report emphasizes the urgent need for coordinated global efforts to address the root causes of food crises and enhance the resilience of vulnerable populations.
- By understanding and responding to these challenges, we can work towards a more food-secure future for all.
International Conference on Disaster Resilient Infrastructure (ICDRI)

- 25 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
Countries must build “resilient infrastructure” against natural disasters that are becoming more frequent and severe, said Prime Minister Narendra Modi recently.
About the Coalition for Disaster-Resilient Infrastructure (CDRI):
- The Coalition for Disaster-Resilient Infrastructure (CDRI) is a global partnership comprising national governments, UN agencies and programs, multilateral development banks, private sector entities, and academic institutions.
- Established during the United Nations Climate Action Summit in 2019 in New York, CDRI is dedicated to addressing the challenges associated with building resilience in infrastructure systems and development processes.
Objectives:
- CDRI aims to enhance the resilience of infrastructure systems to climate and disaster risks, thereby promoting sustainable development.
- It seeks to expedite the development and retrofitting of resilient infrastructure to meet the imperatives of the Sustainable Development Goals, including universal access to basic services and fostering prosperity and decent work.
- Serving as an inclusive multi-stakeholder platform, CDRI is led and managed by national governments. It facilitates the exchange of knowledge on various aspects of infrastructure resilience.
- CDRI brings together diverse stakeholders to create mechanisms assisting countries in upgrading their capacities, systems, standards, regulations, and practices related to infrastructure development, tailored to their risk contexts and economic needs.
Membership:
- Since its inception, 39 countries, 7 international organizations, and 2 private sector organizations joined as members.
- International organizations include:
- The Asian Development Bank (ADB)
- World Bank Group
- United Nations Development Programme (UNDP)
- United Nations Office for Disaster Risk Reduction (UNDRR)
- European Union
- European Investment Bank, and
- The Private Sector Alliance for Disaster-Resilient Societies (ARISE)
- The CDRI is the second major coalition launched by India outside of the UN, the first being the International Solar Alliance.
Secretariat:
- CDRI's secretariat is based in New Delhi, India.
Golden trevally Fish

- 24 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
The golden trevally, a popular marine fish on Tamil Nadu’s coastline, has been successfully bred in captivity by scientists at ICAR-CMFRI’s Visakhapatnam station.
What is Golden trevally Fish?
- The Golden Trevally (Gnathanodon speciosus), also known as the Golden Kingfish or Banded Trevally, is a popular and fascinating marine fish species found in the Indo-Pacific and Eastern Pacific regions.
- It typically inhabits deep lagoons and seaward reefs, often in association with larger fish species.
- This fish is highly sought-after for both consumption and ornamental purposes due to its faster growth rates, good meat quality, and attractive appearance.
- According to fish landing observations in India, golden trevally are primarily landed at reef area fishing grounds in Tamil Nadu, Puducherry, Kerala, Karnataka, and Gujarat.
About the Central Marine Fisheries Research Institute (CMFRI):
- CMFRI was established in 1947 under India's Ministry of Agriculture and Farmers Welfare.
- It joined the Indian Council of Agricultural Research (ICAR) in 1967.
The institute's primary objectives include:
- Monitoring exploited marine fisheries resources and assessing under-exploited resources within India's Exclusive Economic Zone.
- Understanding fluctuations in marine fisheries resources in response to environmental changes.
- Developing sustainable mariculture technologies for finfish, shellfish, and other organisms to supplement capture fishery production.
- The CMFRI's notable achievements include developing the "Stratified Multistage Random Sampling Method" for estimating fishery catch and effort along India's 8,000 km coastline.
- Headquartered in Kochi, Kerala, the institute continues to contribute significantly to the growth and development of India's marine fisheries sector.
State of the Climate in Asia 2023 Report

- 24 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
As Asia is warming faster than the global average, it is witnessing more extreme weather, climate, and water-related events than any other region across the world.
Highlights of the State of the Climate in Asia 2023 Report:
- The 2023 State of the Climate in Asia Report, spearheaded by the World Meteorological Organization, sheds light on significant climate trends and events across the continent:
- In 2023, Asia witnessed 79 extreme climate events, affecting over nine million individuals, making it the most disaster-affected region.
- Atmospheric concentrations of carbon dioxide, methane, and nitrous oxide soared to unprecedented levels in 2022.
- Oceans have absorbed approximately a quarter of the carbon dioxide emitted annually into the atmosphere since 1960, resulting in record-high ocean heat content in 2023.
- Tropical cyclone activity over the North Indian Ocean surpassed the average.
- 2023 marked Asia's second-highest mean temperature on record, with Japan and Kazakhstan experiencing record warmth.
- Glacial retreat accelerated in 2023, particularly in the East Himalayas and Central Asia's Tian Shan mountains, due to elevated temperatures and arid conditions.
About the World Meteorological Organisation:
- The World Meteorological Organization (WMO) is a specialized agency of the United Nations with a membership of 193 member states and territories.
- It is the UN system's authoritative voice on the state and behavior of the Earth's atmosphere, its interaction with the oceans, the climate it produces, and the resulting distribution of water resources.
- WMO originated from the International Meteorological Organization, the roots of which were planted at the 1873 Vienna International Meteorological Congress.
- Established by the ratification of the WMO Convention on 23 March 1950, WMO became the specialized agency of the United Nations for meteorology (weather and climate), operational hydrology, and related geophysical sciences a year later.
- The Secretariat, headquartered in Geneva, is headed by the Secretary-General.
- Its supreme body is the World Meteorological Congress.
Psychoanalysis
- 24 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
Sudhir Kakar, a pioneering Indian psychoanalyst, author, and cultural critic, passed away on Monday at the age of 85.
What is Psychoanalysis?
- Psychoanalysis is a set of psychological theories and therapeutic methods that focus on the unconscious mind, as well as the role of repressed emotions and desires in shaping behavior and mental health.
- Developed by Sigmund Freud in the late 19th and early 20th centuries, psychoanalysis is based on the idea that many of our thoughts, feelings, and actions are influenced by unconscious motives and conflicts, often rooted in childhood experiences.
- Psychoanalysis has three core components:
- A method of investigation of the mind and the way one thinks.
- A systematized set of theories about human behavior.
- A method of treatment for psychological and emotional issues.
- Key concepts in psychoanalysis include the id, ego, and superego (the structural model of the psyche), the Oedipus complex, defense mechanisms (such as repression, denial, and projection), and dream interpretation.
- During psychoanalysis therapy, a patient works closely with a therapist to explore and understand unconscious thoughts and feelings, often by discussing dreams, memories, and other experiences.
- The goal is to bring repressed emotions to the surface and address any underlying conflicts in order to alleviate mental distress and improve overall well-being.
- While psychoanalysis has had a significant influence on psychology and mental health treatment, it remains a controversial approach due to its lack of scientific rigor and emphasis on subjective interpretation.
- Nevertheless, many of its concepts have been adapted or integrated into other forms of therapy, and psychoanalysis remains an important part of the history and development of psychology.
Significance:
- It has profoundly impacted the fields of psychology and mental health treatment, as well as culture, literature, and the arts. Its significance can be understood through the following points:
- Foundational Role: Psychoanalysis provided a groundbreaking approach to understanding the human mind and behavior, shifting the focus from conscious experiences to unconscious mental processes.
- Influence on Psychology: Many concepts introduced by psychoanalysis, such as the unconscious mind, defense mechanisms, and the influence of early childhood experiences, have been adopted and adapted by various schools of psychology, including cognitive-behavioral, humanistic, and psychodynamic approaches.
- Therapeutic Approach: Psychoanalysis revolutionized the way mental health issues were treated, moving away from a purely medical model and emphasizing the importance of talking therapy in addressing psychological problems.
- Cultural Impact: The ideas of psychoanalysis have permeated culture, literature, and the arts, influencing our understanding of human motivations, relationships, and emotions. Concepts like Freudian slips, dream interpretation, and the Oedipus complex have become part of everyday language.
- Interdisciplinary Applications: The principles of psychoanalysis have been applied in fields beyond psychology, including sociology, anthropology, literature, and film studies.
- Despite criticisms and revisions, psychoanalysis remains a significant and influential theory that has shaped our understanding of the human mind and behavior.
- It continues to contribute to the development of psychological theories and therapeutic approaches, enriching our comprehension of mental health and human nature.
Crystal Maze-2 Missile

- 24 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
The Indian Air Force achieved a milestone by successfully test-firing an air-launched ballistic missile, ROCKS or Crystal Maze 2, capable of hitting targets over 250 kilometers away.
About Crystal Maze-2 Missile:
- Crystal Maze 2 missile also known as ROCKS is an advanced air-launched missile developed by Israel, designed for precision strikes on high-value targets.
- This missile is capable of engaging heavily fortified positions from long distances, ensuring minimal collateral damage.
- It is renowned for its accuracy and reliability in combat scenarios, making it a preferred choice for missions requiring surgical precision.
- The missile’s integration into various platforms enhances its operational flexibility and effectiveness in diverse combat environments.
Features:
- Crystal 2 operates effectively in GPS-denied areas and can breach regions secured by air defense systems.
- This system allows for the choice between penetration or blast fragmentation warheads, making it suitable for targeting both surface and heavily fortified underground facilities.
- With a striking distance of over 250 kilometers, it offers versatility with options for either penetration or blast fragmentation warhead, ensuring the destruction of above-ground or well-protected underground targets.
- India is currently developing the Crystal Maze 2 missile.
- The Indian Air Force (IAF) has successfully conducted tests on this missile and aims to procure it in large numbers under the Make in India initiative.
- This move highlights India’s dedication to achieving self-sufficiency in defense manufacturing.
Marburg virus disease (MVD)
- 24 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
The Kitum cave in Mount Elgon National Park, Kenya, is known as the world's deadliest cave which may have some really dangerous viruses inside, like Ebola and Marburg.
What is Marburg Virus Disease (MVD)?
- Marburg virus disease (MVD), formerly known as Marburg hemorrhagic fever, is a severe, often fatal illness in humans.
- It affects both people and non-human primates.
- Marburg and Ebola viruses are both members of the Filoviridae family (filovirus).
- Though caused by different viruses, the two diseases are clinically similar.
- Both diseases are rare and can cause outbreaks with high fatality rates.
- The average MVD case fatality rate is around 50%.
- Rousettus aegyptiacus, fruit bats of the Pteropodidae family, are considered to be natural hosts of the Marburg virus.
Transmission:
- Human infection with MVD typically occurs after prolonged exposure to Rousettus bats inhabiting mines or caves.
- The virus can then spread through human-to-human transmission via direct contact with infected bodily fluids, contaminated materials, or broken skin and mucous membranes.
Symptoms:
- After an incubation period of 2-21 days, symptoms arise abruptly, including fever, chills, headache, and muscle pain.
- A maculopapular rash may appear around day five, most visible on the chest, back, and stomach.
- Other symptoms, such as nausea, vomiting, chest pain, sore throat, abdominal pain, and diarrhea, can manifest, with severity increasing to potentially include jaundice, organ dysfunction, severe weight loss, delirium, and massive hemorrhaging.
- The average MVD case fatality rate is around 50%, varying between 24% and 88% in past outbreaks.
Treatment:
- There is currently no specific treatment for MVD, but early supportive care involving rehydration and symptom management improves survival rates.
Viral Hemorrhagic Fevers (VHFs):
- Viral Hemorrhagic Fever (VHFs) is a group of diseases caused by several distinct families of viruses that affect multiple organ systems in the body.
- These illnesses range from mild to severe and life-threatening, with many having no known cure or vaccine.
- VHFs negatively impact the cardiovascular system and reduce overall bodily function.
Project Nimbus

- 23 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
Google's employees staged protests against the company's collaboration with the Israeli government on "Project Nimbus", a $1.2 billion cloud computing initiative.
What is Project Nimbus?
- Google’s Project Nimbus is a $1.2 billion cloud computing initiative with the Israeli government.
- The project aims to provide public cloud services to address challenges within various sectors in Israel, including healthcare, transportation, and education in Israel.
- However, the project has sparked controversy leading to protests and layoffs within the company.
- Project Nimbus involves Google establishing a secure instance of Google Cloud on Israeli soil.
- This would allow the Israeli government to perform large-scale data analysis, AI training, database hosting, and other forms of powerful computing using Google’s technology.
- The project is a joint contract between Google and Amazon signed in 2021.
- As part of the agreement, Google Cloud will work with the public sector on the formulation of best practices for cloud migration, integration, and optimization of cloud services.
- According to the official announcement in the year 2021, Google Cloud will also provide training to the country’s technical government employees and senior leaders to enhance digital skills.
What is the Controversy Surrounding Project Nimbus?
- Despite the potential benefits, Project Nimbus has sparked controversy due to concerns about the potential misuse of AI and other technologies.
- Employees fear that the technology developed under Project Nimbus could be used in harmful ways.
- There have been reports suggesting that Israel is using AI to eliminate its targets.
- Israeli outlets +972 Magazine and Local Call claimed that two AI systems, "Lavender" and "Where's Daddy?" were used to identify 37,000 Hamas operatives.
- However, there's no official confirmation regarding any connection between Project Nimbus and these AI systems.
- The use of AI also causes concern as it is still a relatively new technology on the battlefield and is yet to be regulated by governments across the globe.
Google Response to the Accusations Regarding Project Nimbus?
- Google clarified that the project is intended for use by Israeli government ministries in areas such as finance, healthcare, transportation, and education, emphasizing that it is not aimed at handling highly sensitive or classified military operations related to weaponry or intelligence services.
Netzah Yehuda Battalion

- 23 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
The US government may soon sanction a battalion of the Israeli Defence Forces (IDF) over alleged human rights violations, marking the first such move in the history of the two countries’ relations.
What is the Netzah Yehuda Battalion?
- The Netzah Yehuda battalion was set up in 1999 to accommodate the religious beliefs of ultra-Orthodox Jews and other religious nationalist recruits in the army.
- It was established to facilitate military service for these communities, accommodating their religious observances by scheduling prayer and study times, and restricting their interactions with female soldiers.
- The battalion is historically stationed in the occupied West Bank region and faces intense scrutiny for allegedly committing human rights violations against Palestinians.
- Netzah Yehuda came on the radar of United States agencies after the death of an elderly Palestinian-American man, who was detained by the battalion.
What is the Unit Accused Of?
- The United States called for a criminal investigation after Netzah Yehuda soldiers were accused of being involved in the death of a 78-year-old Palestinian-American, Omar Assad, who died of a heart attack in 2022 after he was detained and was later found abandoned at a building site.
- A Palestinian autopsy found Assad died from a stress-induced heart attack brought on by being manhandled.
- The case attracted unusual attention because of his dual nationality, his age, and a demand by the U.S. State Department for an investigation into his death.
- There have been several other incidents in recent years, some captured on video, in which Netzah Yehuda soldiers were accused of, or charged with, abusing Palestinian detainees.
- The battalion primarily operated in the West Bank before it was moved out of the territory in late 2022 after U.S. criticism.
- The unit has recently been serving in Gaza.
Star Campaigners

- 23 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
In the current general elections, political parties are selecting 'star campaigners' to lead their campaigns.
What are Star Campaigners in Election?
- Star campaigners are popular individuals with significant fan followings and are chosen by political parties to contest or campaign during elections.
Legal Provisions:
- The Representation of the People Act, 1951 (RPA) governs the expenditure incurred by 'leaders of a political party,' commonly referred to as star campaigners.
- A recognized political party (National or State) can appoint a maximum of 40-star campaigners.
- A registered unrecognized political party can appoint up to 20.
- The names of star campaigners must be communicated to the Election Commission (EC) and Chief Electoral Officer (CEO) within seven days from the date of election notification.
- For multi-phase elections, political parties can submit separate lists of star campaigners for different phases.
Expenses and Apportionment:
- If a star campaigner seeks votes for contesting candidates or shares the dais with them, rally/meeting expenses are apportioned to the election expenditure of those candidates.
- Boarding/lodging expenses incurred by the star campaigner while campaigning for candidates are included in the expenditure accounts of those candidates.
- If candidates travel with the star campaigner, 50% of the star campaigner's travel expenditure is apportioned to those candidates.
Special Cases:
- When a Prime Minister or former Prime Minister serves as a star campaigner, the government bears the expenditure on security, including bullet-proof vehicles.
- However, if the Prime Minister is accompanied by another star campaigner, the candidate must bear 50% of the expenditure on security arrangements.
Tundra Ecosystem

- 23 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
A recent study has warned that the warming planet may alter the characteristics of tundra environments and could transform them from carbon sinks to carbon sources.
About Tundra Ecosystem:
- The Tundra ecosystem is one of the unique ecosystems of the planet.
- The adverse climatic conditions of tundra regions like dry winds, meager precipitation, and extreme cold make it a unique and desert-like ecosystem with treeless fields.
- These harsh climatic conditions of the tundra region make the survival of plant and animal species quite severe.
Key Characteristics of Tundra Regions:
- Low Temperatures: Tundra areas experience frigid temperatures, ranging from -34 to -6 degrees Celsius (-30 to 20 degrees Fahrenheit).
- Short Growing Seasons: The tundra's summer growth period lasts merely 50 to 60 days, with sunlight persisting up to 24 hours a day.
- Permafrost: Below the surface lies a layer of permanently frozen soil, varying from a few inches to several feet thick.
- Minimal Precipitation: Despite being likened to deserts in terms of moisture, tundra regions receive low precipitation levels, primarily in the form of snow.
- Limited Biodiversity: Harsh conditions in the tundra support fewer plant and animal species compared to other biomes.
- Carbon Sink: Tundras serve as significant carbon storage areas due to the slow decomposition rates in their cold environments.
Types of Tundra:
- Arctic Tundra: Found north of the taiga belt in the far Northern Hemisphere, encompassing regions between the North Pole and the boreal forest, including parts of Canada, Russia, Greenland, Iceland, Norway, Sweden, and Finland.
- Alpine Tundra: Prevails above the tree line in mountain ranges worldwide, such as the Rockies, the Andes, the Himalayas, and the Alps.
- Antarctic Tundra: Encompasses several sub-Antarctic islands and portions of the Antarctic continent.
Flora and Fauna:
- Flora: Common plant species in tundra regions include mosses, lichens, sedges, cotton grass, and birches.
- Fauna: Wildlife in tundra ecosystems includes Arctic foxes, snow geese, polar bears, and other cold-adapted species.
Survey of India (SoI)

- 23 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
The Tamil Nadu government filed its objections in the Supreme Court recently, about the Survey of India (SOI) report on the construction of the mega car parking project near the Mullaiperiyar dam, and sought rejection of the report.
What is the Survey of India (SoI)?
- The Survey of India (SoI) serves as the National Survey and Mapping Organization of India, operating under the Department of Science and Technology.
- Established in 1767, it holds the distinction of being the oldest scientific department within the Government of India.
- Tasked with the critical role of being the country's primary mapping agency, SoI bears the responsibility of thoroughly exploring and mapping India's terrain to furnish foundational maps for comprehensive and efficient development initiatives.
- Originally comprising only five directorates in 1950, primarily focused on catering to the mapping requirements of the Defense Forces in the Northwest and Northeast regions, the department has since expanded to encompass 18 directorates spread across the nation, ensuring comprehensive map coverage essential for national development.
- SoI's expertise is widely utilized by various ministries and government undertakings for diverse purposes, including delineating international borders, and state boundaries, and facilitating the planned development of previously underserved areas.
- Moreover, SoI actively contributes to numerous national scientific endeavors in fields such as geophysics, remote sensing, and digital data transmission.
- Functioning as a key advisor to the Government of India on all survey-related matters, including geodesy, photogrammetry, mapping, and map reproduction, SoI fulfills a multitude of duties and responsibilities, which include:
- Conducting all geodetic control, geodetic, and geophysical surveys.
- Undertaking topographical control, surveys, and mapping within India.
- Producing geographical maps and aeronautical charts.
- Conducting surveys for developmental projects.
- Mapping forests, cantonments, large-scale city surveys, guide maps, cadastral surveys, etc.
- Engaging in surveys and mapping for specialized purposes.
- Demarcating India's external boundaries, depicting them on published maps, and advising on inter-state boundary demarcation.
- Conducting research and development in cartography, printing, geodesy, photogrammetry, topographical surveys, and indigenization.
- Predicting tides at 44 ports, including 14 foreign ports, and publishing tide tables one year in advance to support navigational activities.
- Reviewing and certifying India's external boundaries and coastline on maps published by other entities, including private publishers.
- Headquartered: Dehradun (Uttarakhand)
Zero Shadow Day
- 22 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
A group of students was provided a first-hand experience of the Zero Shadow Day (ZSD) phenomenon at an event organized by the Pondicherry Science Forum (PSF).
What is Zero Shadow Day?
- Zero Shadow Day occurs twice every year in locations between the Tropics of Cancer and Capricorn, where the Sun is positioned directly overhead at noon.
- The shadow typically appears elongated on the ground while being observed under normal circumstances.
- However, when the shadow perfectly aligns under the object, during a short period of time, it remains absent on the ground.
- This happens when the sun reaches the zenith, its highest point of revolution.
- The dates of the occurrence may vary depending on the specific location and its latitude.
Why does Zero Shadow Day occur?
- Zero Shadow Day is caused due to Earth's axial tilt of approximately 23.5 degrees and its orbit around the Sun.
- The Sun is never overhead causing it to maintain a slightly lower altitude either north or south.
- The tilting position is also responsible for different seasons on Earth.
- As the Earth orbits the sun, the angle at which the sun's rays hit the Earth's surface changes, causing shadows to be cast in different directions.
- In regions falling between the Tropic of Cancer (about 23.5 degrees north of the equator) and the Tropic of Capricorn (about 23.5 degrees south of the equator), there are instances when the Sun is exactly overhead.
- Since the sun's rays come down almost vertically, there is no or little shadow on vertical objects.
National Organ and Tissue Transplant Organization (NOTTO)
- 22 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
Each organ transplant case will receive a distinctive National Organ and Tissue Transplant Organisation (NOTTO) ID assigned to both the donor and the recipient.
Highlights of the News:
- The Union Health Ministry has mandated the cessation of commercial organ transactions, particularly those involving foreign nationals, and emphasized the need for stringent oversight by local authorities.
- For deceased donor transplants, a NOTTO-ID is required for organ allocation, while in living donor transplants, the ID must be generated within 48 hours post-surgery through the NOTTO website by the hospital.
What is the National Organ and Tissue Transplant Organization (NOTTO)?
- NOTTO is a national organization established under the Directorate General of Health Services, Ministry of Health and Family Welfare, Government of India.
It serves as the central coordinating hub for:
- Organ and tissue procurement and distribution.
- Maintaining a registry of organ and tissue donation and transplantation activities across the country.
NOTTO comprises two divisions:
- National Human Organ and Tissue Removal and Storage Network:
- Acts as the primary center for nationwide coordination of organ and tissue procurement, distribution, and registry.
- Established in accordance with the Transplantation of Human Organs (Amendment) Act 2011.
- National Biomaterial Centre (National Tissue Bank):
- This center focuses on filling the gap between demand and supply while ensuring quality assurance in tissue availability.
- The Transplantation of Human Organs (Amendment) Act 2011 has expanded NOTTO's scope to include tissue donation and registration of tissue banks.
Activities performed by NOTTO include:
-
- Coordinating tissue procurement and distribution
- Donor tissue screening
- Tissue removal and storage
- Tissue preservation
- Laboratory screening of tissues
- Tissue tracking
- Sterilization
- Record maintenance
- Data protection and confidentiality
- Quality management in tissues
- Patient information on tissues
- Developing guidelines, protocols, and standard operating procedures
- Training and assistance in registering other tissue banks
BFI Biome Virtual Network Program

- 22 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
Centre for Cellular and Molecular Platforms (C-CAMP) has joined the Blockchain for Impact (BFI) Biome Virtual Network Program to accelerate transformative healthcare solutions through biomedical innovation.
About BFI Biome Virtual Network Program:
- The BFI-Biome Virtual Network Program is a pioneering initiative uniting incubators and research institutes under a single umbrella.
- This fosters collaborations among the stakeholders in the translational pipeline, the process of transforming research discoveries into real-world applications.
- Through this program, BFI will allocate over 200,000 USD over the course of three years, leveraging C-CAMP’s expertise to develop essential programs for healthcare-based startups.
- C-CAMP being an organization to foster deep science research and innovation for societal impact, the goals and mandates of both partners naturally align and complement each other.
- The partnership is expected to blur disciplinary boundaries in approaching biotech R&D, promote cross-integration of expertise and infrastructure, and provide multidisciplinary insights into need identification, problem-solving, and solution implementation.
What is C-CAMP?
- Centre for Cellular And Molecular Platforms (C-CAMP) is an initiative of the Dept of Biotechnology, Ministry of Science and Technology, Govt. of India, with a mandate to be an enabler of cutting edge Life Science Research and Innovation.
- C-CAMP is also a member of the Bangalore Life Sciences Cluster (BLiSC).
- It facilitates Bioscience Research and Entrepreneurship by providing Research, Development, Training, and Services in state-of-the-art Technology Platforms.
- As a part of C-CAMP's mandate of promoting entrepreneurship and innovation, C-CAMP has created and fostered an entrepreneur-friendly culture in and around the Academic/Research environment through its involvement in Seed Funding Schemes for Startups, Entrepreneur Mentorship program, and Bio-Incubation facility.
- It has established State-Of-The-Art Platform Technologies which are essential requirements for success and leadership in the field of Life Sciences.
- C-CAMP allows Investigators to use Techniques as tools and not be limited by Technological barriers while pursuing challenging scientific questions.
Global Financial Stability Report (GFSR)

- 22 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
The International Monetary Fund (IMF) released the latest global financial stability.
About Global Financial Stability Report (GFSR):
- The Global Financial Stability Report (GFSR) is a semiannual report by the International Monetary Fund (IMF).
- It is released twice per year, in April and October.
- The GFSR provides an assessment of the global financial system and markets and addresses emerging market financing in a global context.
- It focuses on current market conditions, highlighting systemic issues that could pose a risk to financial stability and sustained market access by emerging market borrowers.
Key Points from the Report:
- The report highlights significant risks facing the global financial system, including persistent high inflation, increased lending in unregulated credit markets, and a rise in cyber-attacks targeting financial institutions.
- It underscores geopolitical tensions, such as conflicts in West Asia and Ukraine, as potential factors disrupting aggregate supply and driving up prices, possibly constraining central banks from lowering interest rates.
- India emerged as the second-largest recipient of foreign capital in 2023, following the United States, though this trend could shift rapidly if Western central banks signal prolonged high-interest rates.
- Of concern is the expansion of the unregulated private credit market, where non-bank financial institutions extend credit to corporate borrowers, posing potential threats to the broader financial system.
- Many borrowers in this market lack financial stability, with numerous entities unable to cover interest costs with current earnings, highlighting underlying risks.
World Earth Day 2024

- 22 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
On World Earth Day 2024, a global network promoting local food and traditional cooking has called for practical measures to cut down on plastic use in the food chain and to safeguard the environment.
About World Earth Day:
- World Earth Day, also known as International Mother Earth Day, is a globally recognized event dedicated to raising awareness and promoting the sustainability of our planet.
- Earth Day is celebrated on April 22 in the United States and on either April 22 or the day the spring equinox occurs throughout the rest of the world.
- Theme: The theme for World Earth Day 2024 is “Planet vs Plastics”.
- The theme aims to bring attention to the serious issue of plastic pollution and how it harms nature.
Earth Day History:
- The origin of Earth Day can be traced back to 1970.
- The idea behind the event originated from Gaylord Nelson, a US senator, and Denis Hayes, a Harvard student.
- They were both deeply disturbed by the deteriorating environment in the United States and the massive January 1969 oil spill in Santa Barbara, California.
- Deeply disturbed by the environmental impacts, Gaylord Nelson wanted to infuse the energy of student protests into an emerging public consciousness about air and water pollution.
- He recruited Denis Hayes, a young activist, to manage the campus teach-ins and to scale the idea of environment conservation to a broader public.
- They choose April 22, a weekday between Spring Break and Final Exams, to increase student participation.
- Its immediate success was evident with a massive turnout of 20 million people across the US.
- By 1990, Earth Day became a global event transcending national borders.
Earth Day Significance:
- Earth Day symbolizes the need to protect our mother nature.
- The day encourages every individual to think about environmental conservation and act accordingly.
- It speaks about the need to reduce carbon footprints, conserve natural resources, and protect wildlife and natural habitats.
- The day also serves as a platform to advocate for policy changes that can have a positive impact on the environment.
Ethylene Oxide
- 20 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
The Singapore Food Agency (SFA) has issued a recall on Indian spice brand Everest’s fish curry masala after detecting an ‘excessive’ amount of ethylene oxide–a pesticide–in it.
What is Ethylene Oxide?
- Ethylene oxide is a colorless and flammable gas with a slightly sweet odor and It dissolves easily in water.
- It is widely used in various industries due to its versatile properties.
- Its primary applications include the production of other chemicals, such as ethylene glycol for antifreeze and polyester, as well as the sterilization of medical equipment.
- It also has minor applications in agriculture.
- In this sector, it's used as a fumigant to control insect pests in stored agricultural goods, such as food commodities, to protect them from infestation.
- This usage makes up less than 1% of its applications, and it is combined with other gases to minimize potential toxicity to humans and the environment.
- While ethylene oxide plays a significant role in many industrial processes, it also poses health risks to those exposed to it.
- Potential health effects range from mild symptoms like headaches, nausea, and respiratory issues, to more severe problems such as cancer and reproductive harm.
- To minimize exposure risks, industries and facilities that use ethylene oxide are subject to environmental regulations and required to implement safety measures.
- These measures include emission-reducing and monitoring devices, on-site testing, site-specific operating parameters, and regular reporting and record-keeping.
- Despite these precautions, workers in factories that produce or use ethylene oxide, as well as people living near these facilities, may still face potential health risks.
How Do Pesticides Harm Our Bodies if Present in Food?
- Pesticides, designed to ward off unwanted organisms in agriculture, can pose extensive risks to human health if they find their way into our food chain.
- Even a brief exposure to some of them can cause acute poisoning and symptoms, including diarrhea, dehydration, and skin irritation.
- Some insecticides like Resmethrin, Cypermethrin, and Fenvalerate have been connected to chronic health issues, which include reproductive complications, immune system disruption, pores, and skin infection, and interference with the endocrine system.
- Even low-level exposure over the years can cause critical health implications.
How Long-term Issues Can be Combated?
- Some steps can be taken to mitigate the risks associated with pesticides and ethylene oxide exposure.
- It’s critical to prevent the runoff of insecticides into storm drains, which can contaminate water sources.
- While using insecticides, it’s essential to consider the characteristics of the application site to minimize unintended exposure.
- Attention to the geological factors and groundwater depth can prevent pesticide seepage into water reservoirs.
- By implementing these measures and maintaining strict regulations, we can minimize the health risks posed by these chemical substances.
Salas y Gómez
- 20 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
An international team of scientists last week announced they discovered 160 species when exploring 10 seamounts and two islands on the 2,900-kilometre-long ocean ridge Salas y Gómez.
What is ‘Salas y Gomez’?
- Salas y Gómez is a remarkable underwater mountain chain in the Southeastern Pacific Ocean.
- This 2,900-kilometer-long range stretches in a west-east orientation, connecting the East Pacific Rise and the Nazca Ridge.
- The western end of the chain lies within Chile's Exclusive Economic Zone near the Easter Islands, while the eastern part extends into areas beyond national jurisdiction and touches upon the national waters of Chile and Peru.
- The region is characterized by unique ecosystems isolated by the Atacama Trench, the Humboldt Current System, and an extreme oxygen minimum zone.
- Salas y Gómez and Nazca ridges are known for their extraordinary biodiversity, hosting some of the highest levels of marine endemism on Earth.
- Given the ecological significance of this underwater mountain range, there is a growing interest in designating Salas y Gómez and its surrounding areas as high-seas marine protected areas upon the ratification of the UN High Seas Treaty.
- This initiative aims to safeguard the region's unique ecosystems and contribute to global marine conservation efforts.
About the United Nations High Seas Treaty:
- The United Nations High Seas Treaty is a legal framework, or a set of legal tools, designed to protect the oceans that are beyond any country’s territory.
- The high seas are defined as the waters that are 200 nautical miles from any national jurisdiction; they are international open waters that all countries can use for marine business such as shipping, fishing, and marine research.
- The treaty’s formal name is the Biodiversity Beyond National Jurisdiction Treaty, or BBNJ Treaty for short.
Key Facts About the High Seas Treaty:
- The treaty was to be negotiated under the United Nations Convention on Laws of the Sea (UNCLOS) of 1982.
- It took 19 years to reach an agreement on it.
- Before now, laws to protect ocean waters and biodiversity beyond countries’ territorial boundaries only protected 1.2% of the high seas.
World Craft Council International

- 20 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
The World Crafts Council International (WCCI), a Kuwait-based organization working on the recognition and preservation of traditional crafts across the globe, has picked Srinagar for mapping its craft clusters before its final nomination as the World Craft City (WCC) from India this year.
About World Crafts Council:
- World Crafts Council AISBL is an international non-profit organization dedicated to fostering the preservation, promotion, and advancement of global craftsmanship and traditional crafts.
- It was founded by Ms. Aileen Osborn Vanderbilt Webb, Ms. Margaret M. Patch, and Smt Kamaladevi Chattopadhyay at the 1st World Crafts Council General Assembly in New York on June 12, 1964.
- Since its inception, the World Crafts Council AISBL has been affiliated with UNESCO under Consultative Status for many years.
- Its mission is to empower artisans, celebrate cultural diversity, and contribute to sustainable development by supporting the rich tapestry of global craftsmanship and preserving languishing crafts from extinction.
- Headquarters: The current headquarters for the term (2021-2024) is located in Kuwait.
Objectives:
- The main objective of the World Crafts Council AISBL is to strengthen the status of crafts in cultural and economic life.
- The Council aims to promote fellowship among craftspersons by offering them encouragement, help, and advice.
- It fosters and assists cultural exchange through conferences, international visits, research studies, lectures, workshops, exhibitions, and other activities.
- The WCC also seeks to foster wider knowledge and recognition of the craftspeople's work with due regard to the diversified cultural and national backgrounds and traditions of its members.
- In carrying out these principles, the Council shall consult with governments, national and international institutions, societies, and individuals.?
India has only 3 cities designated as World Craft City:
- Mysuru (Kinnal paintings, Sandalwood carvings, Rosewood Inlay, etc.)
- Mamallapuram (Stone Carving continuing since the Pallava dynasty (275 CE to 897 CE)
- Jaipur (Kundan Jadai (Gem setting), Meenakari Jewellery, Lac-based craft, Gotta Patti Work, etc.)
About the World Craft City Programme:
- The World Craft City Programme, initiated in 2014 by the World Crafts Council AISBL (WCC-International), recognizes the significance of local authorities, artisans, and communities in global cultural, economic, and social advancement.
- By establishing a vibrant network of craft cities worldwide, it embraces the ideals of the creative economy and acknowledges the valuable contributions of local entities to comprehensive development.
- Notably, Jaipur (Rajasthan), Mamallapuram (Tamil Nadu), and Mysore have already been designated as craft cities under this initiative in India.
National Curriculum for Early Childhood Care and Education 2024

- 20 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
For the first time ever, the Central government has released a curriculum advisable to be taught to children aged three to six years old, thus giving an impetus to pre-school learning in 14 lakh anganwadis across the country.
About National Curriculum for Early Childhood Care and Education 2024:
- The National Curriculum for Early Childhood Care and Education 2024 introduces Aadharshila, a comprehensive 48-week curriculum tailored for children aged three to six years attending anganwadis.
- Developed through collaboration among the Ministry of Women and Child Development, the Ministry of Health and Family Welfare, the Department of School Education and Literacy, the Ministry of Education, the NCERT, the Institute of Home Economics at Delhi University, and civil society organizations, Aadharshila serves as a foundational learning framework.
??Key Features:
- The curriculum introduces a weekly play calendar, initiating with four weeks of academic activities facilitating the transition from home to Anganwadi centers through engaging play.
- Over the subsequent 36 weeks, children engage in diverse activities such as storytelling, rhymes, arts, and crafts, fostering exploration, free play, conversation, creation, and appreciation.
- Storytelling themes promote values like conflict resolution, responsibility, and cooperation.
- Children delve into topics including colors, shapes, numbers, senses, family, and friends, enhancing skills in listening, following instructions, counting, and recognizing sounds, alongside exploring themes like seasons and festivals.
- The final eight weeks focus on reinforcing previous learnings through worksheets and performance observation.
- Activities and timetables are age-specific, with detailed material requirements, variations, teacher notes, curricular goals, and competency assessments.
- The curriculum spans three years, targeting at least 48 weeks of learning, fostering skills crucial for Grade 1 transition such as listening, vocabulary, imagination, and social development.
- Special provisions ensure screening, inclusion, and referrals for children with disabilities in all activities.
- The national framework lays the foundation for states to develop culturally relevant curricula, addressing future schooling challenges effectively.
Vasuki Indicus

- 20 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
Fossils recovered from Kutch in Gujarat may have belonged to the spine of one of the largest snakes to have ever lived, according to new research from the Indian Institute of Technology Roorkee.
Highlights of the Vasuki Indicus Discovery:
- A nearly 50-foot-long snake species, one of the longest and largest in recorded history, once existed in the Indian subcontinent.
- The reptile, Vasuki indicus, lived in India nearly 47 million years ago, fossil remains found from Gujarat’s Panandhro Lignite Mine in Kutch suggest.
- This giant snake, named Vasuki indicus, is estimated to have reached 15 meters in length, exceeding even a T-Rex.
- Scientists found 27 vertebrae, some even in their original position within the spine. They believe Vasuki resembled a large python and lacked venom.
- The species was given the specific name of Vasuki indicus in acknowledgment of the country of its origin, India.
- Vasuki is revered as the king of the snakes in Hindu mythology and is worshiped on special days like Nag Panchami.
About Vasuki Indicus:
- Vasuki indicus belongs to the Madtsoiidae family, and thrived during a “warm geological interval".
- Researchers suggest that the warm tropical temperatures of Gondwanaland, averaging around 28°C, may have contributed to the substantial size and growth of this giant reptile.
- There is a recognized correlation suggesting that higher ambient temperatures can enable larger growth in animals.
- Madtsoiids were also found in Europe and Africa, besides Asia.
- Vasuki indicus represents a large lineage of Madtsoiidae that originated in the Indian subcontinent and then spread to southern Eurasia, before reaching North Africa around 50 million years ago, that’s nearly 15 million years after the dinosaurs went extinct.
- Madtsoiidae, an extinct lineage of terrestrial snakes, thrived on the Indian subcontinent over a span of approximately 100 million years, from the Late Cretaceous to the Late Pleistocene, dating from roughly 98 million to 11,000 years ago.
- During the Late Cretaceous period, the supercontinent Pangea had fragmented into two major landmasses:
- Laurasia, encompassing North America, Europe, and Northern Asia to the north; and
- Gondwanaland to the south, which included present-day Africa, Antarctica, South America, Australia, and the Indian subcontinent.
- The fossils of Vasuki indicus extracted from the early Lutetian grey shale layers of the Naredi Formation at the Kutch mine include an “excellently preserved, partial vertebral column”.
- The discovery sheds light on the biogeographic patterns of dispersion and diversification within the Madtsoiidae, particularly across the Gondwanan continents.
- The presence of this giant snake in the Eocene of India indicates a complex history of faunal exchanges between the Indian subcontinent and other landmasses prior to complete integration into the Eurasian plate.
Coral Bleaching
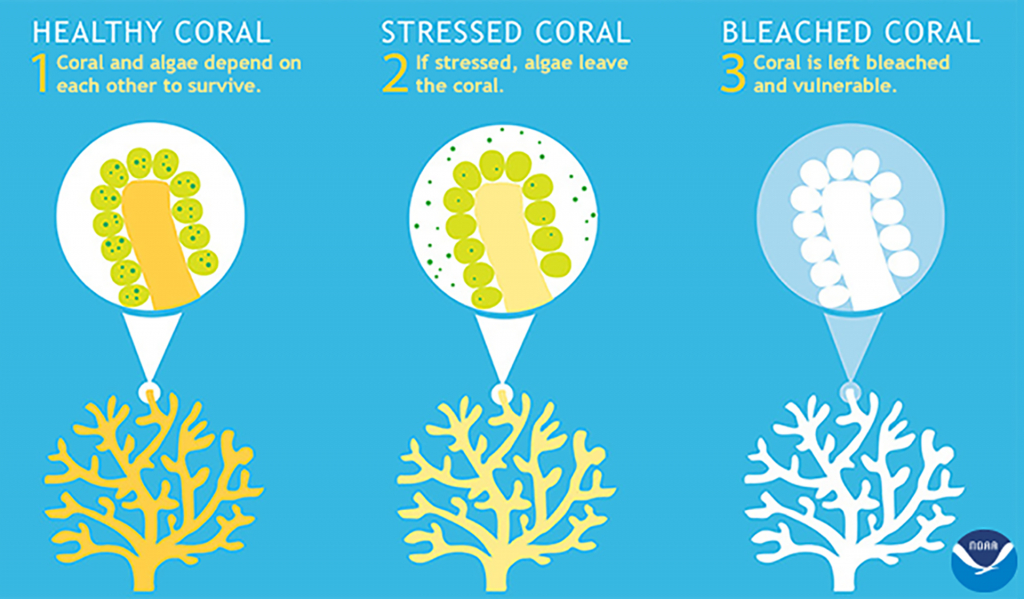
- 19 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
The fourth global mass coral bleaching event has been triggered by extraordinary ocean temperatures, the US National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) said recently.
What are Corals and Coral Reefs?
- Corals are essentially animals, which are sessile, meaning they permanently attach themselves to the ocean floor.
- They use their tiny tentacle-like hands to catch food from the water and sweep it into their mouth.
- Each individual coral animal is known as a polyp and it lives in groups of hundreds to thousands of genetically identical polyps that form a ‘colony’.
- Corals are largely classified as either hard coral or soft coral.
- It is the hard corals that are the architects of coral reefs — complex three-dimensional structures built up over thousands of years.
- Unlike soft corals, hard corals have stony skeletons made out of limestone that are produced by coral polyps.
- When polyps die, their skeletons are left behind and used as foundations for new polyps.
- Coral reefs, also referred to as “rainforests of the sea”, have existed on the Earth for nearly 450 million years.
- Australia’s Great Barrier Reef is the largest in the world, stretching across 2,028 kilometers.
What is the Significance of Corals?
- Coral reefs have a crucial role in marine ecosystems.
- Thousands of marine species can be found living on one reef.
- For instance, “the Great Barrier Reef contains over 400 coral species, 1,500 fish species, 4,000 mollusc species and six of the world’s seven sea turtle species”.
- Research has shown that there could be millions of undiscovered species of organisms living in and around reefs.
- These massive structures also provide economic goods and services worth about $375 billion each year.
- More than 500 million people across the world depend on coral reefs for food, income, and coastal protection from storms and floods.
- Coral reefs can absorb up to 97% of the energy from waves, storms, and floods, which prevents loss of life, property damage, and soil erosion.
- Therefore, the absence of coral reefs would not only result in severe ramifications for marine life but also for humans.
What is Coral Bleaching?
- Most corals contain algae called zooxanthellae ( plant-like organisms) in their tissues.
- Corals and zooxanthellae have a symbiotic relationship.
- While corals provide zooxanthellae a safe place to live, zooxanthellae provide oxygen and organic products of photosynthesis that help corals to grow and thrive.
- Zooxanthellae also give bright and unique colors to corals.
- Corals are very sensitive to light and temperature and even a small change in their living conditions can stress them.
- When stressed, they expel zooxanthellae and turn entirely white.
- This is called coral bleaching.
- Coral bleaching doesn’t immediately lead to the death of corals.
- They rather go under more stress and are subject to mortality.
- Coral bleaching reduces the reproductivity of corals and makes them more vulnerable to fatal diseases.
- If the bleaching is not too severe, corals have been known to recover.
- Global mass bleaching of coral reefs is when significant coral bleaching is confirmed in the Atlantic, Indian, and Pacific oceans.
- Such events are a relatively new phenomenon.
- The first one took place in 1998 in which 20% of the world’s reef areas suffered bleaching-level heat stress.
- The next two global bleaching events occurred in 2010 (35% of reefs affected) and between 2014 and 2017 (56% of reefs affected).
What can be the impact of the event?
- As the global mass bleaching event is still unfolding, its full impact will not be known for a while.
- With global temperatures soaring, such events are expected to become more frequent and longer.
- As a result, the world may lose the vast majority of its coral reefs at 1.5 degrees Celsius of warming, and virtually all at 2 degrees.
- Currently, the average global temperature of the Earth has increased by at least 1.1 degree Celsius since 1850.
- To curb global warming to no more than 1.5 degrees Celsius, countries need to bring GHG emissions to a net zero by 2050, according to the Paris Agreement.
The goal, however, is unlikely to be achieved as record levels of GHG emissions have continued to be emitted into the atmosphere.
Mount Ruang

- 19 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
A remote volcano in Indonesia’s outermost region erupted again on April 19 after the crater threw up columns of smoke and lava multiple times this week and forced thousands to evacuate.
About Mount Ruang:
- Mount Ruang is an active stratovolcano located in the Sangihe Islands arc, North Sulawesi, Indonesia.
- It is the southernmost volcano in the region, situated on an island that measures 4 by 5 kilometers wide.
- The summit features a partial lava dome and reaches an altitude of 725 meters.
- Mount Ruang has experienced multiple eruptions throughout its history, with the most recent ongoing eruption starting on April 18, 2024.
- The volcano's eruptions often generate ash columns, lava flows, and gas emissions, posing risks to nearby communities.
What is a Stratovolcano?
- A stratovolcano is a tall volcano shaped like a cone, formed by various layers of materials such as volcanic ash, hardened lava, pumice, and tephra.
- Stratovolcanoes are steep and have periodic explosive and effusive eruptions, although some have calderas, which are collapsed craters.
- The highly viscous lava that flows from this type of volcano cools and hardens and in turn, does not spread far.
- The magma that forms this lava is generally felsic.
- Stratovolcanoes are more common than shield volcanoes.
- One of the famous stratovolcanoes is Vesuvius which destroyed Herculaneum and Pompeii in 79 CE.
Formation Of Stratovolcanoes:
- Stratovolcanoes occur mostly in subduction zones, where the oceanic crust slides under continental crust.
- The descent of the oceanic plate causes the release of trapped water from hydrated minerals and porous rock, into the mantle rock in the area above the oceanic slab.
- This process occurs at different pressures depending on the minerals.
- The water lowers the mantle rock’s melting point, causing partial melting and its rise to the lithosphere forming a temporary pool.
- The magma then continues to rise through the crust collecting rock rich in silica.
- The magma finally pools in the magma chamber which is either within or under the volcano.
- The low pressure at this point causes the volatile compounds such as water, carbon dioxide, and sulfur dioxide dissolved in the magma to escape.
- When the magma and gas accumulate to a critical level, they overcome the rock blockage of the volcanic cone and erupt violently.
Global Alliance for Incinerator Alternatives (GAIA)

- 19 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
The Global Alliance for Incinerator Alternatives (GAIA) Asia Pacific, in collaboration with other environmental organizations, has called on the Association of Southeast Asian Nations (ASEAN) to take decisive action in response to plastic pollution.
About Global Alliance for Incinerator Alternatives (GAIA):
- The Global Alliance for Incinerator Alternatives (GAIA) is an alliance of over 1,000 grassroots groups, NGOs, and individuals working towards a transition from a linear, extractive economy to a circular system.
- GAIA's primary objective is to create a world that prioritizes people's right to a safe and healthy environment, free from toxic pollution and resource depletion.
- GAIA envisions a just, zero-waste world where communities' rights are respected, and ecological limits are acknowledged. To achieve this vision, the alliance focuses on:
- Eliminating Incineration: GAIA advocates for alternatives to incineration and promotes waste management practices that protect the environment and public health.
- Promoting Zero Waste: The alliance supports the adoption of zero-waste strategies, emphasizing waste reduction, reuse, and recycling to conserve resources and reduce pollution.
- Addressing Plastic Pollution: GAIA recognizes the global plastic pollution crisis and works on initiatives to reduce plastic waste and promote sustainable alternatives.
- Mitigating Climate Change: GAIA advocates for climate-friendly waste management practices, emphasizing the importance of reducing greenhouse gas emissions from waste disposal.
What is Incineration?
- Incineration is a waste treatment process that involves burning hazardous materials at high temperatures to destroy contaminants.
- This process takes place in an "incinerator," a furnace specifically designed to safely burn hazardous materials within a combustion chamber.
- Various types of hazardous materials can be treated through incineration, including soil, sludge, liquids, and gases.
- While incineration effectively destroys many harmful chemicals such as solvents, polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs), and pesticides, it does not destroy metals like lead and chromium.
- Modern incinerators are equipped with air pollution control mechanisms, such as fabric filters, scrubbers, and electrostatic precipitators.
- These technologies help remove fly ash and gaseous contaminants generated during the incineration process, mitigating its environmental impact.
- Despite its benefits in waste treatment, incineration remains a topic of debate due to concerns about residual pollutants and the potential for contributing to greenhouse gas emissions.
Wigner Crystals

- 19 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
In new peer-reviewed research, physicists from Princeton University have confirmed that electrons don’t even need atoms to party together.
What are Wigner Crystals?
- Wigner Crystals are composed entirely of electrons, unlike the common crystals which are formed by atoms or molecules.
- These negatively charged particles, which are known for their role in electricity and chemical bonding, can, under specific circumstances, arrange themselves into a lattice structure, creating a crystal made purely of electrons.
- The conditions required for the formation of Wigner Crystals are quite stringent.
- They occur at very low electron densities, where the repulsive Coulomb forces between the electrons dominate over their kinetic energy.
- This means that the electrons must be spread out enough so that their mutual repulsion causes them to settle into a fixed pattern, minimizing their potential energy.
- The discovery was made possible by cooling a two-dimensional electron system to near absolute zero and reducing the electron density to a critical level.
- Under these conditions, the electrons crystallized into a lattice, much like the atoms in a solid.
- The visualization of this electron lattice marks a monumental step in our understanding of the quantum phases of matter.
- The implications of this discovery are profound.
- Wigner Crystals could provide insights into the behavior of electrons in low-density environments, such as those found in semiconductors and other electronic materials.
- This could lead to the development of new technologies and materials with unique electronic properties.
- Moreover, the study of Wigner Crystals could shed light on other exotic states of matter and the fundamental principles of quantum mechanics.
- The confirmation of Wigner Crystals underscores the importance of theoretical physics and how ideas that once seemed purely speculative can lead to tangible discoveries.
- The realization of Wigner Crystals opens up a new chapter in the study of condensed matter physics.
- It stands as a bridge between the abstract world of quantum mechanics and the tangible reality of material science.
- As we continue to explore the quantum landscape, Wigner Crystals will undoubtedly play a pivotal role in unraveling the mysteries of the electron and the intricate dance of particles that constitute the fabric of our universe.
Added Sugars/Free Sugars

- 19 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
Nestlé’s products for babies in Asia, Africa, and Latin America were found to contain added sugars, while the same products sold in Europe did not have it, according to a recent report.
Highlights of the Report on Nestle:
- A report by the Swiss organization Public Eye titled 'How Nestlé gets children hooked on sugar in lower-income countries' scrutinized Nestlé for employing varying nutritional standards across its products depending on the country, with unclear sugar content labeling.
- The report highlighted Nestlé's Cerelac, the world's largest baby cereal brand, which contains significantly higher sugar levels in markets like India, Ethiopia, and Thailand compared to Germany and the UK.
- Despite sugar not being recommended for infants, Nestlé's baby food products with added sugars are allowed under some countries' national legislation, conflicting with WHO guidelines.
- WHO recommends reducing daily free sugar intake to less than 10% of total energy intake, preferably less than 5% (around 25 grams per person per day), for better health.
- Nestlé India claims to have reduced added sugars by up to 30% in their infant cereals portfolio over the last five years, depending on the variant.
What are Added Sugars?
- Sugar is a simple carbohydrate.
- Some food items have sugar that is naturally occurring.
- It is “found in milk (lactose) and fruit (fructose) or any product that contains milk (such as yogurt, milk, or cream) or fruit (fresh, dried) contains some natural sugars.
- Free sugar or added sugar is added separately to a food item during preparation or processing.
- It can “include natural sugars such as white sugar, brown sugar, and honey, as well as other caloric sweeteners that are chemically manufactured (such as high fructose corn syrup).
Why is Added Sugar Bad?
- Excessive consumption of added sugars poses several health risks.
- Limiting sugar intake is essential for maintaining a healthy diet and preventing various diseases.
The following are some reasons why added sugars can be harmful:
- Poor Nutritional Balance: Consuming too much-added sugar can lead to increased overall energy intake, often replacing nutritionally adequate calories from healthier food sources.
- This results in an unbalanced diet lacking essential nutrients, increasing the risk of malnutrition and other health problems.
- Increased Risk of Non-Communicable Diseases: Excessive sugar consumption is associated with a higher risk of developing non-communicable diseases such as diabetes, obesity, and cardiovascular ailments.
- These diseases can have severe long-term consequences on overall health and well-being.
- Unnecessary for Infants and Children: Adding sugar to foods offered to babies and young children is unnecessary and can be highly addictive, establishing unhealthy eating habits that continue into adulthood.
- Early exposure to sugar is also associated with tooth decay and can contribute to nutrition-based disorders later in life.
Cloud Seeding

- 18 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
The UAE recorded the heaviest rain ever after a severe thunderstorm hit the country on April 15, killing at least one person, causing damage to homes and businesses, and bringing air travel to a standstill in Dubai.
What Led to the Heavy Rains in Dubai?
- The primary reason for these heavy rains was a storm system, which was passing through the Arabian peninsula and moving across the Gulf of Oman.
- According to a different report, rains could have been exacerbated by cloud seeding, a process of spraying salt mixtures in clouds that would result in condensation of the cloud and eventually cause rainfall.
- Several reports quoted meteorologists at the National Center for Meteorology as saying they flew six or seven cloud-seeding flights before the rains.
Is climate change responsible for the event?
- Some experts have suggested that the soaring global temperatures could also be behind the event.
- Higher temperatures cause evaporation of water not only from land but also oceans and other water bodies, meaning a warmer atmosphere holds more moisture.
- Studies have found that for every 1 degree Celsius rise in average temperature, the atmosphere can hold about 7% more moisture.
- This makes storms more dangerous as it leads to an increase in precipitation intensity, duration, and/or frequency, which ultimately can cause severe flooding.
- While the average global temperature on the Earth has increased by at least 1.1 degrees Celsius since 1850, the UAE has witnessed an increase of almost 1.5 degrees Celsius in the past 60 years.
- The increase in temperatures is mainly caused by the rise of heat-trapping greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions since the Industrial Revolution.
- However, it is extremely difficult to attribute any particular extreme weather event to climate change.
- It is because there are multiple factors, like patterns of natural climate variability, such as El Niño and La Niña, that contribute to such events.
What is Cloud Seeding?
- Cloud seeding is a type of weather modification where substances like silver iodide or dry ice are dispersed into clouds to encourage precipitation, such as rain or snow.
- In countries like the UAE, where temperatures are high and annual rainfall is minimal, cloud seeding is employed to alleviate pressure on limited groundwater sources by enhancing precipitation.
What is UAE's cloud seeding programme?
- The UAE initiated its cloud seeding program in the late 1990s, making it one of the first Middle Eastern countries to use this technique.
- Collaborative research with institutions like the National Center for Atmospheric Research (NCAR) and NASA has bolstered their efforts.
How does cloud seeding work?
- Cloud seeding is a technique where “seeding agents" such as silver iodide or salt are introduced into clouds to stimulate condensation and trigger rainfall.
- Weather forecasters monitor atmospheric conditions and identify suitable clouds for seeding based on precipitation patterns.
- This technique can increase rainfall by up to 30-35 percent in clear conditions and 10-15 percent in more humid conditions.
What is the environmental impact of cloud seeding?
- Cloud seeding alters the precipitation patterns of a region/locality.
- This may negatively impact neighboring ecosystems, which were to receive rain for the seeded clouds originally.
- Introducing seeding agents might impact the natural hydrological cycle as it may change the natural soil moisture levels, groundwater recharge, and river flows.
- Some experts worry about the potential for silver toxicity if cloud seeding becomes widespread.
- Silver iodide is a common seeding agent.
- Silver toxicity could pose risks to aquatic life and soil health.
- Therefore, even with the promise cloud seeding holds, responsible stewardship and thorough evaluation of its environmental impacts are crucial.
Green Credit Programme (GCP)

- 18 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
The Environment Ministry recently has made significant changes to the Norms of the Green Credit Programme.
What is the Green Credit Programme (GCP)?
- An innovative initiative by the Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change (MoEF&CC).
- Announced under the 'Lifestyle for Environment' (LiFE) movement.
- It aims to establish a market-based mechanism to incentivize voluntary environmental actions by individuals, urban local bodies, communities, and the private sector.
Target Sectors and Stakeholders:
- Designed to encourage voluntary environmental actions across various sectors.
- Engages diverse stakeholders, including individuals, communities, private sector industries, and companies.
Initial Focus Areas:
- Water conservation: Encourages efficient use and management of water resources.
- Afforestation: Promotes tree planting and forest restoration to enhance carbon sequestration and biodiversity.
Programme Implementation:
- The GCP's governance structure is overseen by an inter-ministerial Steering Committee, with the Indian Council of Forestry Research and Education (ICFRE) serving as the program administrator.
- ICFRE manages the implementation, monitoring, and operation of the program.
- A user-friendly digital platform will simplify project registration, verification, and issuance of Green Credits.
- ICFRE, in collaboration with experts, is developing the Green Credit Registry and trading platform to facilitate the registration and trading of Green Credits.
- Entities and individuals must register their activities with the government to earn Green Credits.
- Verification of activities will be conducted by a designated agency, with self-verification available for small projects.
Programme Impact:
- The GCP strives to encourage environmentally beneficial actions by creating tradable green credits through a market-oriented approach.
- These green credits can be traded on a domestic market platform, providing further incentives for positive environmental actions.
- Additionally, if the generation of green credits results in measurable reductions or removals of carbon emissions, they may also qualify for carbon credits.
Programme Adjustments:
- In response to concerns regarding the potential misuse of the GCP for profit-driven tree planting, the government has emphasized the importance of prioritizing ecosystem restoration over mere tree planting.
- Indigenous species will be preferred, and naturally occurring seedlings will be preserved.
- The previous requirement of a minimum of 1,100 trees per hectare to qualify as a reforested area has been revised, with States now tasked to define specific criteria.
- State forest departments will be responsible for the actual implementation of afforestation efforts.
United Nations Entity for Gender Equality and the Empowerment of Women (UN Women)

- 18 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
According to a recent report by UN Women, six months into the war, Gaza is facing a humanitarian crisis disproportionately impacting women and girls.
What is UN Women?
- Founded in 2010 by the United Nations General Assembly as part of the UN reform agenda.
- Merges resources and mandates to create a more significant impact on gender equality and women's empowerment.
- Serves as a global advocate for women and girls, addressing their needs and accelerating progress.
Key Roles:
- Supports intergovernmental bodies like the Commission on the Status of Women in developing policies, global standards, and norms for gender equality.
- Assists member states in implementing these standards and offers technical and financial support upon request.
- Builds effective partnerships with civil society organizations.
- Leads and coordinates the UN system's work on gender equality while promoting accountability through regular monitoring of progress.
Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs):
- Works globally to realize the SDGs for women and girls.
- Promotes women's equal participation in all aspects of life.
Country-level Support:
- Collaborates with government and non-governmental partners in countries that request assistance.
- Helps implement policies, laws, services, and resources to advance gender equality.
Grant-making Funds:
- Fund for Gender Equality: Provides grants to support innovative, high-impact programs by government agencies and civil society groups.
- UN Trust Fund to End Violence against Women: Finances initiatives that address violence against women and girls.
Commission on the Status of Women (CSW):
- A global policy-making body focused on gender equality and women's advancement.
- Operates as a functional commission of the United Nations Economic and Social Council (ECOSOC).
Information and Advocacy:
- Regularly provides information on women's rights issues to the General Assembly, ECOSOC, and the Security Council.
- Maintains the UN Secretary-General's database on violence against women, tracking measures taken by UN Member States and organizations.
- UN Women plays a vital role in advancing gender equality and women's empowerment worldwide by providing crucial support, resources, and advocacy through its various initiatives and collaborations.
Submersible Platform for Acoustic Characterisation and Evaluation (Space)

- 18 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
A state-of-the-art Submersible Platform for Acoustic Characterisation and Evaluation (Space) was inaugurated by Secretary, Department of Defence (R&D) and DRDO Chairman Samir V Kamat at Underwater Acoustic Research Facility, Kulamavu in Idukki district of Kerala recently.
About Submersible Platform for Acoustic Characterisation and Evaluation (SPACE):
- Developed by the Naval Physical & Oceanographic Laboratory of the Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO), SPACE is a premier testing and evaluation hub for sonar systems used by the Indian Navy across various platforms, including ships, submarines, and helicopters.
Key Features:
- Two primary components:
- A floating platform on the water's surface and
- A submersible platform that can be lowered up to 100 meters using winch systems.
- Facilitates quick deployment and recovery of scientific packages like sensors and transducers.
- Suitable for surveying, sampling, and data collection of air, surface, mid-water, and reservoir floor parameters using advanced scientific instrumentation.
- Well-equipped scientific laboratories cater to data processing and sample analysis requirements.
Uses:
- Evaluating complete sonar systems, enhancing research capabilities in Anti-Submarine Warfare.
- SPACE enables researchers to explore innovative solutions for underwater acoustic challenges, improve naval capabilities, and ensure the security of Indian waters.
What is Sonar?
- SONAR, which stands for Sound Navigation And Ranging, is a technology that uses sound waves to detect, locate, and map objects underwater.
- It operates on the principle of echolocation, similar to how bats and dolphins use sound to navigate and find their prey.
- The Sonar system consists of a transmitter, a receiver, and a display.
- The transmitter sends out sound waves, which travel through water and reflect off objects in their path.
- These reflected waves, or echoes, are then received by the receiver.
- By measuring the time it takes for the echoes to return and the strength of the received signal, the system can determine the distance, direction, size, and shape of the underwater object.
Sonar has various applications, including:
- Maritime navigation: Commercial ships and submarines use sonar to navigate through unfamiliar waters, avoid obstacles, and create underwater maps.
- Military applications: Sonar plays a crucial role in military operations for detecting and tracking enemy submarines, underwater mines, and other threats.
- Fishing and underwater research: Sonar helps fishermen locate schools of fish and is also used by scientists and researchers to study marine life, underwater topography, and archaeological sites.
Iron Age Archaeological Sites Discovered in Telangana

- 18 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
A team of archaeologists claimed to have discovered a unique Iron Age megalithic site at Ooragutta near Bandala village in SS Tadvai mandal of Mulugu district, Telangana.
Recent Archaeological Discoveries in Telangana:
Ooragutta Iron Age Megalithic Site:
- Situated near Bandala village, SS Tadvai Mandal, Mulugu district, and boasts over 200 megalithic structures dating back to 1,000 BCE.
- Notable for its 'Dolmenoid Cists' featuring cap-stone-shaped side slabs, a rarity in India.
- Resembles European 'Passage Chambers', possibly influencing the design of squarish and rectangular monuments.
Rock Art Sites at Damaratogu:
- Two new sites were discovered in Gundala mandal of Bhadradri Kothagudem district.
- 'Devarlabanda Mula' site contains animal depictions, possibly dating back to the Mesolithic Age (8,000 - 3,000 BCE).
- No weapons or domestic animals are shown, suggesting the paintings may be from a pre-agricultural era.
About the Iron Age:
Timeframe:
- Began between 1200 BCE and 600 BCE, following the Stone Age and Bronze Age.
- Spanned across Africa, Europe, and Asia during prehistoric times in the Old World.
Discovery and Use of Iron:
- Iron replaced bronze as the preferred choice of metal in metalworking.
- First discovered in Turkey before spreading to other European countries.
- Used for making strong tools, enhancing agriculture through the development of the iron plow, and creating powerful weapons for armies.
Technological Advancements:
- Construction of large forts, bridges, and deep mines to extract valuable minerals.
- Improvements in pottery and weaving techniques.
Social and Political Impacts:
- Rulers gained significant power through the use of iron weapons and the ability to conquer other lands.
- The transition from prehistory to history as writing became widespread, marking the end of the Iron Age.
- Iron remains popular for various applications today, such as tools, building materials, and machinery.
- The Iron Age was a transformative period in human history, characterized by the discovery of iron, advancements in technology, and shifts in social and political structures. The use of iron revolutionized agriculture, warfare, and everyday life, leaving a lasting impact on human civilization.
B virus

- 17 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
A 37-year-old man wounded by a wild monkey in Hong Kong is in intensive care suffering from infection with B virus.
What is B virus?
- B virus, also known as herpes B virus or Macacine herpesvirus 1 (McHV-1), is a type of herpesvirus found in macaque monkeys, particularly rhesus macaques.
- While asymptomatic in these animals, it can cause severe neurological complications, including encephalitis, in humans if transmitted through bites, scratches, or contact with infected bodily fluids.
Is B virus infection fatal??
- B virus infections in humans are rare but potentially fatal, with symptoms ranging from fever and headache to neurological dysfunction and death.
- Of the 50 cases reported in the US, 21 have died.
- Prompt treatment with antiviral medication is essential if exposure to B virus occurs, and preventive measures are crucial for individuals working with or handling macaques.
How does it spread??
- The transmission of this virus among humans is rare.
- So far, only one case of human-to-human transmission has been recorded.
What are the symptoms of B virus infection??
- Disease onset typically occurs within 1 month of exposure, although the actual incubation period can be as short as 3–7 days.
- The common symptoms seen during the infection are:
- Fever, headache, myalgia, and localized neurologic symptoms (e.g., pain, numbness, itching) might occur near the wound site.
- Lymphadenitis, lymphangitis, nausea, vomiting, and abdominal pain also can occur.
Treatment:
- The treatment for B virus includes providing antiviral medications.
Green Bonds (SGrBs)

- 17 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
Recently, the RBI approved FIIs such as insurance companies, pension funds, and sovereign wealth funds to invest in India's Sovereign Green Bonds (SGrBs), which finance projects aiming to advance India's shift to a low-carbon economy.
What are Green Bonds?
- Green bonds are bonds issued by any sovereign entity, inter-governmental groups or alliances, and corporates with the aim that the proceeds of the bonds are utilised for projects classified as environmentally sustainable.
- The framework for the sovereign green bond was issued by the government on November 9, 2022.
Why are these bonds important?
- Over the last few years, Green Bonds have emerged as an important financial instrument to deal with the threats of climate change and related challenges.
- According to the International Finance Corporation (IFC), a World Bank Group’s institution, climate change threatens communities and economies, and it poses risks to agriculture, food, and water supplies.
- A lot of financing is needed to address these challenges.
- It’s critical to connect environmental projects with capital markets and investors and channel capital towards sustainable development – and Green Bonds are a way to make that connection.
When did Govt plan these bonds?
- In August 2022, the government said it stands committed to reducing the Emissions Intensity of GDP by 45 percent from the 2005 level by 2030 and achieving about 50 percent cumulative electric power installed capacity from non-fossil fuel-based energy resources by the same year.
- In line with the commitment to significantly reduce the carbon intensity of the economy, the Union Budget 2022-23 announced to issue of Sovereign Green Bonds.
- The country’s climate actions have so far been largely financed from domestic resources and it is now targeting the generation of additional global financial resources.
- The issuance of the Sovereign Green Bonds will help the Indian government in tapping the requisite finance from potential investors for deployment in public sector projects aimed at reducing the carbon intensity of the economy.
Where will the proceeds go?
- The government will use the proceeds raised from SGrBs to finance or refinance expenditure (in parts or whole) for various green projects, including renewable energy, clean transportation, energy efficiency, climate change adaptation, sustainable water and waste management, pollution and prevention control, and green buildings.
- In renewable energy, investments will be made in solar, wind, biomass, and hydropower energy projects.
Combined Maritime Forces (CMF)
- 17 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
The Indian Navy successfully intercepted and apprehended a dhow in the Western Arabian Sea recently and seized 940 kilograms of contraband narcotics.
About the Combined Maritime Forces (CMF):
- The Combined Maritime Forces (CMF) is a Bahrain-based multinational naval partnership dedicated to fostering security, stability, and prosperity throughout vital international waterways.
- Comprised of five task forces, CMF's primary objectives include countering terrorism, preventing piracy, enhancing regional cooperation, and maintaining a safe maritime environment.
- CMF's efforts focus on eliminating violent extremism and terrorist networks in its operational areas, collaborating with regional and global partners to bolster security and stability, assisting in capacity-building for regional maritime capabilities, and responding to environmental and humanitarian crises when needed.
- The five task forces within CMF are:
- CTF 150: Gulf of Oman Security and Counter-Terrorism
- CTF 151: Counter-piracy operations
- CTF 152: Arabian Gulf Security and Cooperation
- CTF 153: Red Sea and Gulf of Aden security and cooperation
- CTF 154: Maritime security training
- CMF comprises a diverse group of nations, each voluntarily contributing to the organization's efforts to maintain security and stability in international waters.
- Participating nations include:
- Australia, Bahrain, Belgium, Brazil, Canada, Colombia, Denmark, Ecuador, Egypt, France, Germany, Greece, India, Iraq, Italy, Japan, Jordan, Kenya, Republic of Korea, Kuwait, Malaysia, the Netherlands, New Zealand, Norway, Pakistan, the Philippines, Poland, Portugal, Qatar, Saudi Arabia, Seychelles, Singapore, Spain, Thailand, Türkiye, UAE, United Kingdom, United States, and Yemen.
- Members have the flexibility to contribute in various ways, from providing liaison officers at CMF's headquarters in Bahrain to supplying warships, support vessels, and maritime reconnaissance aircraft.
- CMF can also request support from warships not explicitly assigned to the organization.
- The headquarters of CMF is co-located with the US Naval Central Command and US Navy Fifth Fleet at Naval Support Activity (NSA) Bahrain.
- CMF is commanded by a US Navy Vice Admiral, with a UK Royal Navy Commodore serving as the Deputy Commander. Senior staff roles at CMF's headquarters are filled by personnel from member nations, ensuring a diverse and collaborative environment.
- Together, these task forces enable CMF to effectively address a wide range of challenges and promote a more secure maritime domain for all nations.
Gaia-BH3

- 17 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
European astronomers have made a groundbreaking discovery by identifying Gaia-BH3, a colossal black hole located just 2,000 light years away from Earth within the Milky Way, revolutionizing our comprehension of star formation.
What Is Gaia-BH3?
- Gaia-BH3, a stellar black hole in the Milky Way galaxy, has been identified as the most massive one discovered to date.
- The European Space Agency's Gaia mission detected Gaia-BH3 due to its distinctive 'wobbling' effect on a companion star orbiting it.
- Through the use of the Very Large Telescope at the European Southern Observatory in Chile's Atacama Desert and other ground-based observatories, researchers confirmed its enormous mass.
- With a mass 33 times greater than our sun, Gaia-BH3 is situated in the Aquila constellation at a distance of 1,926 light-years from Earth, earning it the title of the second-closest known black hole.
- Gaia BH1, located about 1,500 light-years away, remains the closest known black hole to Earth with a mass approximately 10 times that of our sun.
- While Gaia-BH3 holds the distinction of being the most massive stellar black hole in our galaxy, it pales in comparison to Sagittarius A*, the supermassive black hole at the Milky Way's center, which boasts a staggering mass of roughly 4 million times that of the sun.
Difference Between Stellar and Supermassive Black Holes:
- Stellar and supermassive black holes are two distinct types of cosmic phenomena, each with unique characteristics and origins.
- Stellar-mass black holes result from the gravitational collapse of a single star or the merger of two neutron stars, resulting in masses comparable to stars.
- Their mass typically ranges from three to fifty times that of our sun.
- In contrast, supermassive black holes boast a mass exceeding 50,000 times the solar mass, often reaching into the millions or billions.
- The formation of supermassive black holes remains a mystery to scientists, as they are too massive to have formed from a single star's collapse.
- Their consistent presence at the center of galaxies suggests a potential connection to galactic formation.
- While our understanding of these cosmic giants continues to evolve, one thing is clear: both stellar and supermassive black holes are awe-inspiring fixtures in our universe.
United Nations Conference on Trade and Development (UNCTAD)

- 17 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
Global trade dynamics are expected to remain sluggish in 2024, the United Nations Conference on Trade and Development (UNCTAD) has warned.
Key Highlights of the Report:
- UNCTAD’s latest projections indicate global growth of 2.6 percent in 2024, slightly slower than in 2023.
- This marks the third consecutive year in which the global economy will grow at a slower pace than before the pandemic when the average rate for 2015–2019 was 3.2 percent.
India’s growth is expected to be marginally lower than in 2023:
- Regarding India, the report stated that the economy grew at 6.7 percent in 2023 and is expected to be marginally lower at 6.5 percent in 2024.
- It noted that the expansion in 2023 was influenced by strong public investment and the services sector, which received a boost from robust local demand for consumer services along with assured external demand for business services exports.
- The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) is expected to keep interest rates constant in the near term, while strong public investment expenditures will offset restrained public consumption spending.
About the United Nations Conference on Trade and Development (UNCTAD):
- The United Nations Conference on Trade and Development (UNCTAD) is an intergovernmental organization established in 1964 to promote the interests of developing countries in global trade.
- With its headquarters in Geneva, Switzerland, UNCTAD has 195 member states and collaborates with numerous nongovernmental organizations worldwide.
- The organization focuses on formulating policies related to various aspects of development, including trade, aid, transport, finance, and technology.
- UNCTAD plays a crucial role in addressing the concerns of developing countries regarding international institutions, such as the World Trade Organization (WTO), the International Monetary Fund (IMF), and the World Bank.
- By providing a platform for these countries to discuss and tackle their unique challenges, UNCTAD contributes to global economic development and reduces inequalities.
- Some notable achievements of UNCTAD include the establishment of the Global System of Trade Preferences (now replaced by the World Trade Organization), which reduces tariffs and removes non-tariff trade barriers, the Common Fund for Commodities, providing financial assistance to countries dependent on commodity exports, and various agreements for debt relief.
- In recent years, UNCTAD has focused on addressing globalization challenges and helping the least developed countries integrate into the global economy.
Hydrocarbon Extraction: Processes, Methods, Environmental Impact

- 16 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
Over millennia, mighty geological processes in the earth’s crust heated and compressed together pieces of life forms that had been dead for a while.
What Is a Hydrocarbon?
- The term hydrocarbon refers to an organic chemical compound that is composed exclusively of hydrogen and carbon atoms.
- Hydrocarbons are naturally occurring and form the basis of crude oil, natural gas, coal, and other important energy sources.
- They are highly combustible and produce carbon dioxide, water, and heat when they are burned.
- As such, hydrocarbons are highly effective as a source of fuel.
Where are Hydrocarbons Located?
- Hydrocarbons, such as natural gas, coal, crude oil, and petroleum, are typically found in underground rock formations within reservoirs.
- These reservoirs form when less resistant rocks are overlayed by more resistant ones, creating a lid that traps hydrocarbons beneath.
- Petroleum geology tools, methods, and techniques are used to assess these rocks for their porosity and permeability, determining how much hydrocarbons they can hold and how easily they can flow through them.
- Kerogen, lumps of organic matter, is the primary source of hydrocarbons within these subterranean rocks.
- Kerogen can be deposited from lacustrine, marine, or terrestrial ecosystems.
- Over time, surrounding rocks can become warmer and more compactified, exerting forces on kerogen that cause it to break down into various hydrocarbons, such as waxy oils, light oils, gas, and coal.
- Petroleum geologists locate and characterize kerogen-containing source rocks, studying their geophysical and thermal properties.
- They conduct modeling activities, analyze observational data, and dig exploration wells to estimate hydrocarbon quantities.
- Once a profitable hydrocarbon source is identified, drilling can commence.
How are the Hydrocarbons Accessed?
- Drilling and reservoir engineers employ various methods to extract hydrocarbons efficiently without damaging the reservoir.
- The process begins with creating a production well, strategically positioned to maximize drainage.
- A drilling machine, consisting of a drill pipe, drill collars, and a drill bit, is used to create the well.
- As drilling progresses, steel casings are lowered into the tunnel, and cement slurry is pumped into the gap between the casings and the tunnel's outer edge.
- The solidifying cement prevents cave-ins and blocks surrounding fluids from entering the well.
- The tunnel is filled with drilling fluid, which cools the drill bit and carries rock fragments to the surface for removal.
- Controlling drilling fluid pressure is crucial to prevent hydrocarbon eruptions. Modern drilling setups use blowout preventers to manage such events.
- Meanwhile, mud-logging records rock properties at different depths, aiding the process.
- Drill pipes can be extended or replaced as needed during the drilling process, which is now conducted by advanced drilling rigs equipped with power sources.
- Offshore rigs feature additional facilities to ensure stability and facilitate extraction through the water column.
How are the Hydrocarbons Extracted?
- Upon drilling the production well, it must be prepared for hydrocarbon drainage, called completion.
- Engineers remove the drill string and perforate the casing, allowing hydrocarbons to flow into the well and rise to the surface.
- A narrower tube encourages one-directional flow and controls outflow using valves.
- When pressure differences are insufficient for natural fluid ascent, pump jacks or other artificial lift methods can aid extraction.
- Workovers may be required to maintain or improve production efficiency over time.
- Extraction phases include primary (relying on natural processes), secondary (inducing artificial pressure), and tertiary (enhanced recovery methods, like steam injection) phases, each contributing to the total hydrocarbon yield.
What Happens When a Well is Depleted?
- Wells may cease extraction before depletion if operations become unprofitable.
- Properly plugging abandoned wells prevents hydrocarbon and gas leakage into surrounding environments, yet deterioration and failure of plugs remain concerns.
- Decommissioning is the most thorough but often expensive solution.
- Improperly abandoned wells contribute significantly to methane emissions, alongside emissions from extraction and component use.
- A 2018 study estimated that 9,000 oilfields in 90 countries released 1.7 billion tonnes of carbon dioxide in 2015 alone.
- Overall, the pursuit of subterranean hydrocarbons, including natural gas, coal, crude oil, and petroleum, employs various extraction methods.
- However, it is essential to consider the environmental impact and sustainability of these operations.
Thiruvalluvar

- 16 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
Seeking to connect with the people of Tamil Nadu where his party is trying to gain a foothold, Prime Minister Narendra Modi recently announced that the BJP will work towards building Thiruvalluvar cultural centers all over the world.
Who was Thiruvalluvar?
- Thiruvalluvar, the author of the revered 'Thirukkural' or 'Sacred Couplets', remains a figure of historical debate.
- His exact period and religious affiliation are uncertain, with proposed dates ranging from the 3rd or 4th century CE to the 8th or 9th century.
- Various groups regard him as a Hindu sage, a Jain sage, or a Dravidian saint with no religious identifiers except his Dravidian heritage.
- Accounts of Thiruvalluvar's origins are diverse.
- In Edward Jewitt Robinson's 1873 book, 'Tamil Wisdom: Traditions Concerning Hindu Sages and Selections from their Writings', he described Thiruvalluvar as a "Pariah" with a mother from "the low class" and a possibly Brahmin father.
- According to this narrative, Thiruvalluvar was found in a grove near a Shiva temple in Mayilapur and was taken in by the wife of a high-ranking Velalan before being entrusted to a "Pariah family."
- Despite the ambiguity surrounding Thiruvalluvar's identity, his wisdom-laden verses in 'Thirukkural' continue to influence and inspire generations across religious and cultural divides.
Why does Thiruvalluvar matter?
- Thiruvalluvar, affectionately called Valluvar by Tamils, is revered as a cultural and moral icon across caste and religious lines.
- His 'Thirukkural', a compilation of 1,330 couplets, is an integral part of Tamil culture, comparable to the Bhagavad Gita or Ramayana in North Indian Hindu households.
- It serves as a foundational text for ethical living and tracing Tamil cultural roots.
- Beyond Tamil Nadu, Thiruvalluvar's wisdom is celebrated in the context of ancient India's rich philosophical heritage, emphasizing morality and ethics.
- His enduring influence is evident as successive Indian finance ministers reference his teachings in annual Budget speeches.
- However, competing claims to Thiruvalluvar's legacy have sparked controversy, such as the 2019 debate surrounding the BJP's depiction of him in saffron robes instead of traditional white garments.
- Despite these disputes, the profound impact of Thiruvalluvar's teachings continues to resonate across various cultures and languages, fostering unity and moral guidance.
Why Are Political Parties Asserting Thiruvalluvar's Legacy?
- Political parties, both national and regional, have long vied for ownership of Thiruvalluvar's legacy. For instance, the BJP, with a limited grassroots presence in Tamil Nadu, seeks to bolster its standing through the appropriation of Tamil saints and icons.
Trade and Economic Partnership Agreement (TEPA)
- 16 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
The new approach to intellectual property and investment through FTAs accepts an IP maximalist agenda of the United States Trade Representative; it threatens to upset the fine balance between public and private interests and push India away from essential innovations.
What is the Trade and Economic Partnership Agreement (TEPA)?
- The TEPA is a pact designed to foster trade and investment opportunities between India and the European Free Trade Association (EFTA).
- It endeavors to diminish or eliminate tariffs and non-tariff barriers across various product categories.
Objectives:
- Facilitate trade and investment by reducing tariffs and non-tariff barriers.
- Ensure equitable and transparent market access for service providers and investors.
- Enhance cooperation concerning the protection and enforcement of intellectual property rights.
- Streamline trade procedures, promote customs cooperation, and establish effective mechanisms for dispute resolution.
Coverage:
- The agreement encompasses 14 chapters, addressing key areas such as:
- Trade in goods
- Rules of origin
- Intellectual property rights (IPRs)
- Trade in services
- Investment promotion and cooperation
- Government procurement
- Technical barriers to trade
- Trade facilitation
- By addressing these comprehensive aspects, the TEPA seeks to bolster economic collaboration and foster mutually beneficial outcomes for both India and EFTA member states.
What is the European Free Trade Association (EFTA)?
- EFTA is an intergovernmental organization of four member countries that are not part of the European Union (EU): Iceland, Liechtenstein, Norway, and Switzerland.
- The association was set up in 1960 to promote closer economic cooperation and free trade in Europe.
How important is EFTA?
- Iceland, Liechtenstein, Norway, and Switzerland have a combined population of less than 14 million.
- But their association punches above its weight in terms of trade figures.
- In 2021, EFTA was the tenth-largest trader in the world in merchandise trade and the eighth-largest in trade in services.
What is EFTA’s history?
- EFTA was established in 1960 by seven countries: Austria, Denmark, Norway, Portugal, Sweden, Switzerland, and the United Kingdom.
- Iceland and Liechtenstein joined EFTA in 1970 and 1991, respectively.
- Denmark, the UK, Portugal, Austria, and Sweden then left EFTA to join the EU between 1973 and 1995.
UN Permanent Forum on Indigenous Issues

- 16 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
As the 23rd session of the UN Permanent Forum on Indigenous Issues begins in New York, United States on April 15, participants pointed out that though recognition of indigenous territories is increasing, it is not happening at the pace the planet needs.
About the UN Permanent Forum on Indigenous Issues:
- Established in 2000, the UNPFII serves as an advisory body to the United Nations Economic and Social Council (ECOSOC), focusing on indigenous issues related to economic and social development, culture, environment, education, health, and human rights.
- Alongside the Expert Mechanism on the Rights of Indigenous Peoples and the Special Rapporteur on the Rights of Indigenous Peoples, the UNPFII is one of three UN entities mandated to address Indigenous Peoples' issues.
The Permanent Forum's primary objectives include:
-
- Providing expert advice and recommendations to the Council, United Nations programs, funds, and agencies.
- Raising awareness and fostering integration and coordination of indigenous issues within the UN system.
- Preparing and disseminating information on indigenous issues.
Membership and Structure
- The UNPFII consists of sixteen independent experts who serve three-year terms and may be re-elected or re-appointed for one additional term.
- Eight members are nominated by governments, while the remaining eight are nominated directly by indigenous organizations from their respective regions.
- Following each session, the UNPFII submits a report containing recommendations and draft decisions to the ECOSOC, contributing to global efforts to address and improve the well-being of Indigenous Peoples worldwide.
Long Period Average (LPA) Rainfall

- 16 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
Ministry of Earth Sciences announced recently that the country as a whole is likely to receive above-normal rainfall during the southwest monsoon from June to September 2024.
What is the Long Period Average (LPA) of Rainfall?
- The India Meteorological Department (IMD) predicts a “normal”, “below normal”, or “above normal” monsoon in relation to a benchmark “long period average” (LPA).
- According to the IMD, the “LPA of rainfall is the rainfall recorded over a particular region for a given interval (like month or season) average over a long period like 30 years, 50 years, etc”.
- While this quantitative benchmark refers to the average rainfall recorded from June to September for the entire country, the amount of rain that falls every year varies from region to region and from month to month.
- Therefore, along with the countrywide figure, the IMD also maintains LPAs for every meteorological region of the country — this number ranges from around 61 cm for the drier Northwest India to more than 143 cm for the wetter East and Northeast India.
Why LPA is Needed?
- The IMD records rainfall data at more than 2,400 locations and 3,500 rain-gauge stations.
- Because annual rainfall can vary greatly not just from region to region and from month to month, but also from year to year within a particular region or month, an LPA is needed to smooth out trends so that a reasonably accurate prediction can be made.
- A 50-year LPA covers for large variations in either direction caused by freak years of unusually high or low rainfall (as a result of events such as El Nino or La Nina), as well as for the periodic drought years and the increasingly common extreme weather events caused by climate change.
What is the Range of Normal Rainfall?
- The IMD maintains five rainfall distribution categories on an all-India scale. These are:
- Normal or near normal, when the percentage departure of actual rainfall is +/-10% of LPA, that is, between 96-104% of LPA;
- Below normal, when the departure of actual rainfall is less than 10% of LPA, that is 90-96% of LPA;
- Above normal, when actual rainfall is 104-110% of LPA;
- Deficient, when the departure of actual rainfall is less than 90% of LPA; and
- Excess, when the departure of actual rainfall is more than 110% of LPA.
Space Tourism

- 15 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
Entrepreneur and pilot on the NS-25 mission of Blue Origin — a company founded by Jeff Bezos, who is also Gopi Thotakura is set to become the first Indian to venture into space as a tourist the founder of Amazon.
Context:
- In recent years, space tourism has grown by leaps and bounds.
- The space tourism market was valued at $848.28 million.
- It is expected to grow to $27,861.99 million by 2032.
- However, there are several challenges, such as high cost, and environmental concerns, that may limit the industry’s growth.
- The NS-25 mission, which Gopi Thotakura is a part of, is a sub-orbital mission. Thotakura and his other crew members will be taken to outer space via New Shepard, a fully reusable sub-orbital launch vehicle developed specifically for space tourism by Blue Origin.
What is Space Tourism?
- Space tourism is essentially a section of the aviation sector that seeks to provide tourists with the opportunity to become astronauts and experience space travel for recreational, leisure, or business purposes.
- There are two main types of space tourism, sub-orbital and orbital.
- The sub-orbital spacecraft takes passengers just beyond the Kármán line (it lies nearly 100 kilometers above our heads and is considered to be the boundary between Earth’s atmosphere and outer space).
- The passengers get to spend a few minutes in outer space and then come back to Earth.
- The orbital spacecraft, on the other hand, takes passengers much further than the Kármán line.
- Usually, passengers can spend from a couple of days to more than a week at an altitude of nearly 1.3 million feet.
- In September 2021, Space X’s Falcon 9 took four passengers to an altitude of 160 km where they spent three days orbiting the Earth.
What are the Challenges?
- Currently, space tourism is expensive as a passenger generally has to pay at least a million dollars to reach outer space.
- This amount is out of reach for almost everyone.
- Moreover, several studies have pointed out that space tourism may lead to environmental damage as rockets emit gaseous and solid chemicals directly into the upper atmosphere.
- A 2022 study done by researchers found that the soot emissions from rocket launches are far more effective at warming the atmosphere compared to other sources.
- Safety is also a concern when it comes to space tourism.
- Despite high safety standards, a total of 676 people have flown into space and 19 of them have died, as of November 2023, according to a report by Astronomy Magazine.
- This means that approximately 3% of astronauts died during their space flight which is quite a high fatality rate.
Special Olympics Bharat

- 15 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
Special Olympics Bharat (SOB), a National Sports Federation of India is forming district units across Tamil Nadu through elections on April 22.
About Special Olympics Bharat:
- Special Olympics Bharat is a National Sports Federation also registered under the Indian Trust Act 1882 in 2001 and is accredited by Special Olympics International to conduct Special Olympics Programs in India.
- It is recognized by the Ministry of Youth Affairs & Sports, Government of India as a National Sports Federation in the Priority Category, for the development of Sports for Persons with Intellectual Disabilities.
- It is a designated Nodal Agency for all disabilities on account of its national presence and experience, especially in rural areas which account for nearly 75 percent of the disabled population in India.
- Mission: The mission of Special Olympics is to provide year-round sports training and athletic competition in a variety of Olympic-type sports for children and adults with intellectual disabilities, giving them continuing opportunities to develop physical fitness, demonstrate courage, experience joy, and participate in a sharing of gifts, skills, and friendship with their families, other Special Olympics athletes and the community.
- Special Olympics Bharat works towards the social acceptance of people with intellectual disabilities, whereby they are respected and given equal chances to become productive citizens.
- They encourage athletes to move from the Special Olympics training and competition into school and community programs where they can compete in regular sports activities.
Special Olympics Bharat strives to:
- Focus on holistic development and training that goes beyond the classrooms into the playing fields, cultural and community centers, to motivate children with disabilities to join and remain in school
- Create role models who will inspire the children and also motivate parents to send their children to school and to participate in sports and other extra-curricular activities
- Train teachers to sensitize them to the needs of special children, and create a cadre of physical education teachers from among the disabled who can work with schools and community centers
- Ensure maximum involvement of the community for greater public understanding and acceptance of people with intellectual disabilities.
- Ensure all Special Olympics Bharat activities local, state, national, and international reflect the Olympic movement values, standards, ceremonies, and events.
What is Intellectual Disability?
- Intellectual disability is a lifelong condition that affects a person’s intellectual skills and their behaviour in different situations.
- It can include difficulties in communication, memory, understanding, problem-solving, self-care, social and emotional skills, and physical skills.
- People with intellectual disability have the same feelings, rights, and aspirations as everyone else.
- Intellectual disability does not define who a person is, how they should be treated, or how they want to live.
- An IQ test determines whether a person has an intellectual disability. IQ scores lower than 70 indicate an intellectual disability.
Precautionary Principle

- 15 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
The precautionary principle is becoming an established guideline for policymakers tackling environmental problems according to British environmentalist Norman Myers
What is the Precautionary Principle?
- The Precautionary Principle serves as a foundational concept in policymaking, advocating for the adoption of proactive measures to mitigate potential risks to public health or the environment:
- Proactive Risk Management: The principle legitimizes the implementation of preventative measures in situations where there are uncertainties regarding the extent of harm posed by certain activities or policies.
- Rather than waiting for conclusive scientific evidence, decision-makers are encouraged to take preemptive action to prevent serious or irreversible damage.
- Scientific Uncertainty: It acknowledges that in cases where scientific certainty is lacking, waiting for conclusive evidence before taking action may result in significant harm.
- Therefore, the principle emphasizes the importance of not using the absence of full scientific certainty as a justification for delaying necessary measures to prevent environmental degradation or protect public health.
- Risk-Averse Approach: By advocating for precautionary action, even in the absence of absolute certainty about potential harm, the principle prioritizes safety and prudence.
- It underscores the importance of erring on the side of caution to safeguard against potential risks, thus emphasizing a preventive rather than reactive approach.
- International Recognition: Originating in the 1970s, the Precautionary Principle has gained international recognition and has been enshrined in various international treaties and conventions related to environmental protection.
- It has been incorporated into the legal frameworks of organizations such as the European Union and has influenced decisions on issues ranging from climate change to biodiversity conservation.
- Application in Policy: The principle has influenced the development of laws and regulations worldwide, shaping policies related to endangered species, climate change, and genetically modified organisms (GMOs).
- Notably, it has played a significant role in determining the European Union's stance on GMOs and has been integral to the formulation of EU environmental law.
- The Precautionary Principle emphasizes the importance of taking proactive measures to address potential risks, particularly in situations where scientific evidence is uncertain but the potential consequences are significant.
- It embodies a proactive and risk-aware approach to policymaking, intending to prevent harm and promote sustainable development.
About Jim Corbett National Park:
- Jim Corbett National Park, named after the renowned naturalist and conservationist Jim Corbett, is situated in Uttarakhand's Nainital district.
- As the oldest national park in India, it was initially established as Hailey National Park in 1936 to protect the endangered Bengal tiger.
- The park is an integral part of the larger Corbett Tiger Reserve, with the Patli Dun Valley forming its core area.
- The Ramganga River flows through the park, contributing to its diverse ecosystem.
- Not only is it known for its rich biodiversity, but also for being the first area to come under the Project Tiger initiative in 1973.
Hubble Tension
- 15 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
One of the biggest mysteries in cosmology is the ‘Hubble tension’, the puzzle that the expansion of the Universe we see today doesn’t match what we think it should be from looking at the early cosmos.
What is Hubble Tension?
- The Hubble tension refers to a puzzling disagreement between two methods of measuring the universe's expansion rate, represented by the Hubble constant (H0).
- The Hubble constant describes how fast galaxies move away from each other due to cosmic expansion.
- Researchers employ two primary approaches to estimate H0: the cosmic distance ladder and analysis of the cosmic microwave background (CMB).
Cosmic Microwave Background (CMB):
- CMB constitutes a ubiquitous sea of photons, remnants of the Big Bang's aftermath.
- Scientists scrutinize CMB for temperature variations and employ intricate trigonometric techniques to analyze its large-scale properties.
- This analysis culminates in an estimation of cosmic expansion at approximately 68 (km/s)/Mpc.
Cosmic Distance Ladder:
- This method facilitates the measurement of distances to celestial objects spanning various proximity ranges.
- Notably, Cepheid variable stars, which exhibit predictable luminosity fluctuations over time, serve as crucial distance indicators.
- By gauging the brightness of Cepheid variables, researchers can infer their distances, leading to an estimation of H0 around 73 (km/s)/Mpc.
Discrepancy and Hubble Tension:
- The utilization of these two distinct measurement methods yields slightly divergent values for H0, resulting in the emergence of the Hubble tension.
Significance of the Hubble Tension:
- The presence of the Hubble tension suggests potential implications, including unexplored physical phenomena or systematic errors in measurement techniques.
- Resolving this tension is imperative to enhance our comprehension of the universe's expansion dynamics and the fundamental laws governing it.
Operation Meghdoot

- 15 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
India commemorates 40 years since the launch of Operation Meghdoot, a critical mission to secure the strategic heights of the Siachen glacier, acknowledged as the highest battlefield in the world.
About Operation Meghdoot:
- Operation Meghdoot was the codename for the Indian Army operation to take full control of the (Siachen Glacier in Ladakh).
- It was launched in 1984 and it was unique as it involved the first assault on the world's highest battlefield.
- This operation was launched on April 13, 1984, by the Indian Army and Indian Air Force (IAF), marking a pivotal moment in securing the Siachen Glacier, a strategically crucial region dominating Northern Ladakh.
- The operation involved airlifting Indian Army soldiers, with IAF helicopters operating in the area since 1978, including the first landing of an IAF helicopter on the glacier in October 1978.
- The need for Operation Meghdoot arose due to Pakistan's cartographic aggression in Ladakh, allowing foreign mountaineering expeditions in Siachen.
- Intelligence inputs about impending Pakistani military action prompted India to secure strategic heights on Siachen, deploying troops via airlifts and air-dropping supplies to high-altitude airfields.
What was IAF's Role and Evolution in Operation Meghdoot?
- The IAF played a crucial role in supporting Operation Meghdoot, initially focusing on transport and helicopter aircraft for troop and material transport.
- Gradually, the IAF expanded its role, deploying fighter aircraft like the Hunter, MiG-23s, and MiG-29s, operating from high-altitude airfields at Leh and Thoise.
- This expanded role included fighter sweeps and simulated strikes over the glacier, boosting morale and deterring adversaries.
- Operating on the highest battlefield globally, IAF helicopters are the lifeline for Indian troops, providing crucial support in emergencies, logistics supply, and evacuating the sick and wounded from the glacier.
- As the Indian Army celebrates 40 years on the Siachen Glacier, it reflects not only on the progress made in technological advancements and logistical improvements but also on the sacrifices and dedication of its personnel.
- 'Operation Meghdoot' stands as a testament to India's commitment to safeguarding its borders and ensuring the well-being of its troops in one of the world's most challenging terrains.
About Siachen Glacier:
- The Siachen Glacier, situated in the Eastern Karakoram range of the Himalayas, is located just northeast of Point NJ9842, where the Line of Control (LOC) between India and Pakistan ends.
- Administered by India since Operation Meghdoot in 1984, the glacier spans from northwest to southeast, originating at the Indira Col West and descending from an altitude of 6,115 meters to 3,570 meters.
- As the second-longest glacier in the world's non-polar areas, the Siachen Glacier is surpassed only by Tajikistan's Fedchenko Glacier.
- It lies south of the significant drainage divide separating the Eurasian Plate from the Indian subcontinent in the glaciated Karakoram region, sometimes referred to as the "Third Pole."
- The Nubra River finds its source in the Siachen Glacier, highlighting the glacier's ecological importance.
GRB 221009A - Gamma-ray Bursts (GRBs)

- 13 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
Northwestern University recently confirmed that the brightest gamma-ray burst ever recorded, GRB 221009A, was caused by the collapse and explosion of a massive star.
About GRB 221009A:
- GRB 221009A, also known as Swift J1913.1+1946, is the brightest gamma-ray burst ever detected, estimated to be ten times brighter than the previous record holder.
- The burst itself lasted around seven minutes, but its effects were observable for over ten hours.
- GRB 221009A originated from a galaxy estimated to be 2.4 billion light-years away, yet it was powerful enough to influence Earth's atmosphere.
- This exceptionally bright burst emitted across a vast range of the electromagnetic spectrum, providing a unique opportunity for scientists to study this rare phenomenon in detail.
- The cause of the burst is attributed to the collapse of a massive star, but scientists are still investigating why it was so much brighter than other gamma-ray bursts.
What are Gamma-ray Bursts?
- Gamma-ray bursts (GRBs) are the most powerful explosions in the universe.
- These brief flashes of high-energy light result from some of the universe's most explosive events, including the birth of black holes and collisions between neutron stars.
- Lasting a few milliseconds to several minutes, GRBs can be hundreds of times brighter than an average supernova, making them as luminous as a million trillion suns.
- Thus, when a GRB erupts, it briefly becomes the brightest source of electromagnetic radiation in the observable universe.
- Gamma Ray Bursts are difficult to study because they are so short-lived.
- They were first detected by the Vela satellites, which were designed to detect nuclear tests during the Cold War.
- It was only years after their detection that they were declassified.
- The location of gamma-ray bursts within their host galaxy and their surrounding environment informs us as to the formation and evolution of the progenitor system, providing insight into stellar evolution and star formation across the age of the universe.
What causes a gamma-ray burst?
- The cause of a gamma-ray burst depends on how long it lasts.
- GRBs that last less than two seconds are caused by the merger of two neutron stars or the merger of a neutron star and a black hole.
- Longer GRBs, which can last hours, are triggered when a massive star collapses and births a black hole.
- In both cases, GRBs result from jets of particles accelerated to around 99.9% of the speed of light.
How powerful are gamma-ray bursts?
- In just a few seconds, a gamma-ray burst can emit as much energy as the sun will put out over its entire 9 billion-year lifetime
Do gamma-ray bursts happen in the Milky Way?
- GRBs seem to be most closely associated with galaxies that are in the midst of intense star formation, a period that our galaxy seems to have matured out of 2 billion to 3 billion years ago.
- However, the Milky Way is filled with the supernova remnants that mark the deaths of massive stars, indicating that our galaxy was once home to GRBs.
Defence Attaché (DA)

- 13 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
As India expands its presence in defense diplomacy and plans to deploy Defense Attachés to Indian missions in Africa, Armenia, and the Philippines, experts and experienced diplomats advise against simply "rationalizing" their numbers.
What’s a Defense Attaché?
- According to the Geneva Centre for the Democratic Control of Armed Forces (DCAF), a defence attaché is a member of the armed forces serving at an embassy as a “representative of his/her country’s defence establishment abroad and in this capacity enjoys the diplomatic status and immunity.
- The defence attaché’s work usually concerns bilateral military and defence relations.
- Some countries send attachés for security issues, such as migration or matters relating to police and justice.
- The defence attachés are also responsible for facilitating communication and cooperation between their home nation’s armed forces and the host country’s military.
- They act as military and/or security advisors to their country’s ambassador and embassy staff.
- They can also promote their home nation’s military weapons industry.
- Defence attachés collect and examine military intelligence, facilitate military cooperation pacts, and give an evaluation of security issues to their home country’s government.
- They also act as a link between diplomats and the military.
India to Send Defence Attachés to New Countries:
- India has started dispatching defence attachés to many new countries, while reportedly downsizing the military personnel at its missions in some other nations.
- 15-16 new attaches from the Indian Navy, the Indian Air Force (IAF), and the Indian Army are being posted to Poland, the Philippines, Armenia, and the African countries of Tanzania, Mozambique, Djibouti, Ethiopia, and Ivory Coast.
- In the next phase, 10 entirely new defence wings will be created in different countries, with a particular focus on nations to which arms can be exported.
Why the Other Countries Matter?
- India dispatching a defense attaché to Poland, which is a part of the European Union (EU) and has emerged as an important security partner in Europe in recent years, is also significant.
- The EU posted a military attaché to its mission in India for the first time last year. India’s move to do the same in Poland is “reflective of the desire to expand two-way defence ties.
- Armenia has become a major exporter of India’s arms.
- India has already inked deals with the Asian country for Pinaka rockets, Akash missiles, ammunition, and multi-barrel rocket launchers, with some of them coming amid Armenia’s clash with Azerbaijan over Nagorno-Karabakh.
- Armenia has shown interest in expanding its defence ties with India.
- China’s military assertiveness in the South China Sea has prompted India to grow military ties with ASEAN countries.
- India’s decision to send defence attachés for the first time to the Philippines comes in the wake of the sale of Indian arms to Manila.
- India signed a $375 million deal with the Philippines in 2022 to supply three batteries of the BrahMos missile and will soon start the delivery of the missiles to the Southeast Asian country.
Science Based Targets Initiative (SBTi)

- 13 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
A contentious recent decision by the Science Based Targets Initiative (SBTi), permitting carbon offsetting for Scope 3 emissions of businesses with SBTi-based climate targets, has stirred controversy and skepticism.
About Science Based Targets Initiative (SBTi):
- The Science-based Targets Initiative (SBTi) is a global movement launched post the 2015 Paris Climate Agreement to mobilize companies in combating climate change.
- SBTi supports businesses in their decarbonization projects, ensuring compatibility with limiting global temperature rise to 1.5C° and achieving carbon neutrality by 2050.
- Backed by a scientific method, SBTi verifies company objectives are aligned with COP21 goals.
- SBTi was initiated by four international organizations:
- United Nations Global Compact (UNGC)
- World Wildlife Fund (WWF)
- Carbon Disclosure Project (CDP)
- World Resource Institute (WRI)
- The primary objective of SBTi is to guide businesses in setting greenhouse gas (GHG) emission reduction targets that align with the Paris Agreement, are scientifically valid, and contribute significantly to reducing global emissions.
To determine a 1.5C° trajectory compatibility, SBTi uses science-based targets that account for the following factors:
-
- A carbon budget focused on achieving the 1.5C° global warming limit.
- GHG emission scenarios from the IPCC or the IEA.
- Emission allocation method: emission intensity reduction, absolute emission reduction, or emission intensity convergence toward a sector-specific reference level
- Through this methodology, companies can establish clear and science-based GHG reduction targets, effectively contributing to global emission reduction efforts.
SBTi's Net Zero objective:
- In October 2021, SBTi introduced its "Net Zero" benchmark, challenging committed companies to achieve long-term reduction targets up to carbon neutrality.
The Net Zero goal builds upon the initial SBT approach and focuses on four essential components:
-
- Short-term targets: To align with the 1.5°C objective, companies must set targets for reducing their total emissions (Scopes 1, 2, and 3) within a maximum of 5 to 10 years.
- Long-term objectives: Alongside short-term targets, Net Zero requires companies to define long-term goals compatible with limiting global warming to 1.5°C and achieve them by 2050 (or 2040 for the energy sector).
- Carbon finance for short-term contributions: Companies are encouraged to invest in external carbon sequestration or avoidance projects by purchasing carbon credits, complementing their GHG reduction efforts. SBTi prioritizes sequestered emissions over avoided emissions, considering the latter's carbon credits less reliable.
- Neutralization: As the final stage in reaching carbon neutrality, companies must minimize residual emissions and then offset them through carbon sequestration actions.
- The SBTi movement has rapidly gained international recognition for its rigor, reliability, and the credibility of the people behind it.
- Several thousand companies of all sizes have rapidly adopted the scientific approach it promotes. To date, nearly 6,800 companies worldwide have signed up to the SBTi.
Gujarat Freedom of Religion Act

- 13 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
The Gujarat government recently clarified that Buddhism and Hinduism must be considered as two separate religions for religious conversions in the state.
Why did the Gujarat Government Issue the Circular?
- The Gujarat government issued the circular to address an issue regarding the application process for converting from Hinduism to Buddhism.
- The circular, issued by the Home Department highlights that the proper procedures outlined in the Gujarat Freedom of Religion Act (GFR Act) are not being followed.
- The circular points out that some offices are rejecting these conversion applications, arguing that under Article 25(2) of the Constitution, Sikhism, Jainism, and Buddhism are considered part of Hinduism.
- Therefore, applicants are told they don't need permission for religious conversion.
- This interpretation refers to Article 25, which guarantees religious freedom.
- Article 25(2)(b) allows laws for social welfare or reform for Hindus, which includes Sikhs, Jains, and Buddhists.
- Notably, the circular contrasts with a proposed 2006 amendment to the GFR Act, which suggested considering Jainism and Buddhism as part of Hinduism.
- However, the circular clarifies that, according to the GFR Act, Buddhism must be seen as a separate religion.
How does the GFR Act Govern Religious Conversions in Gujarat?
- The Gujarat Freedom of Religion Act (GFR Act) controls how people change their religion in Gujarat.
- According to the state government, this law aims to stop religious conversion by offering rewards, using force, lying, or tricking people.
- One part of the law, Section 3, makes it a crime to force or persuade someone to change their religion, whether by using force, offering rewards, trickery, or arranging marriages.
- Another part, Section 3A, added in 2021, lets anyone who feels harmed or their relatives report these crimes to the police.
- People who break Section 3 can be sent to jail for up to three years and fined up to Rs 50,000.
- If the person affected is a woman, a child, or from certain communities, the punishment is harsher – up to four years in jail and a fine of Rs 1 lakh.
- For a religious conversion to be legal, Section 5 says the person leading the ceremony must get permission from the District Magistrate beforehand.
- And the person who changes their religion must tell the District Magistrate afterward.
- Not doing this can result in a one-year jail term or a fine of up to Rs 1,000.
- In 2021, the GFR Act was changed to include more rules.
- It now makes it a crime to change religion through marriage (Section 4A) and says marriages are void if one person converts before or after getting married (Section 4B).
- It also punishes people involved in organizations that unlawfully convert others (Section 4C). The accused now have to prove that the conversion was legal (Section 6A).
Asian Development Bank (ADB)

- 13 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
The Asian Development Bank (ADB) recently raised its forecast for India’s GDP growth in the current fiscal year ending on March 31, 2025, to 7%, from 6.7% earlier, citing robust public and private investment as well as expectations of a gradual improvement in consumer demand as the rural economy recovers.
What is the Asian Development Bank?
- The Asian Development Bank (ADB) is a global development finance agency whose aim is to help developing member countries in reducing poverty and improving people’s quality of life.
- It came into existence in 1966 and it is headquartered in Manila, Philippines.
- It aids in pushing social and economic development by providing loans, technical assistance, grants, and equity investments.
- ADB is owned and financed by its 68 members, 49 of whom are from the Asia-Pacific region.
- ADB’s key partners are governments, the commercial sector, non-government organizations, development agencies, community-based groups, and foundations.
- ADB will follow three complementing strategic agendas: inclusive growth, ecologically sustainable growth, and regional integration, as outlined in Strategy 2020, a long-term strategic framework approved in 2008.
- The major objective of the Asian Development Bank is to ensure market prosperity and enhance collaboration among Asia-Pacific countries.
- The ADB oversees significant projects within the region and sometimes raises funding through international bond markets.
- To promote development, the Asian Development Bank provides grants, loans, technical support, and equity investments to its developing member nations, the private sector, and public-private partnerships.
- They also use co-financing activities to supply support while tapping official, commercial, and export finance sources.
- Members and associate members of the international organization Economic Commission for Asia and the Far East are eligible to affix the ADB.
- Other regional and non-regional developed countries that are members of the United Nations or any of its specialized agencies are eligible.
Who Controls the Asian Development Bank?
- The ADB is run by a board of governors, which represents the member countries of the ADB.
- As of 2022, ADB's five largest shareholders are Japan and the United States (each with 15.6% of total shares), the People's Republic of China (6.4%), India (6.3%), and Australia (5.8%).
Funding Sources:
- The ADB sustains its operations through various channels, including member contributions, earnings from lending activities, and the repayment of loans.
Volcanic Vortex Rings

- 12 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
Since last week, Mount Etna has been sending up almost perfect rings of smoke into the air which are a rare phenomenon that scientists refer to as volcanic vortex rings.
What are Volcanic Vortex Rings?
- Vortex rings are generated when gas, predominantly water vapor, is released rapidly through a vent in the crater.
- The vent that has opened up in the crater is almost perfectly circular so the rings.
- The phenomenon was first observed at Mt. Etna and Mt. Vesuvius in Italy in 1724 and has been documented in an engraved plate from 1755.
- In more recent times, volcanic vortex rings have been observed at volcanoes such as Redoubt in Alaska, Tungurahua in Ecuador, Pacaya in Guatemala, Eyjafjallajökull and Hekla in Iceland, Stromboli in Italy, Sakurajima in Japan, Yasur in Vanuatu, Whakaari in New Zealand, and Momotombo in Nicaragua.
- According to the report, the rings can remain in the air for up to 10 minutes but tend to disintegrate quickly if conditions are windy and turbulent.
About Mount Etna:
- Mount Etna, sometimes referred to simply as Etna, is an active volcano on the east coast of Sicily, the largest island in the Mediterranean Sea, lying just off the toe of the Italian “boot”.
- Etna’s peak is the highest in Italy south of the Alps, and it is Europe’s largest and one of the most active volcanoes.
- Etna’s summit has five craters, which are responsible for most of the volcano’s eruptions; there are also “flank” eruptions that occur out of 300-odd vents of varying sizes along the slopes of the mountain.
- Etna is in almost constant activity and has seen, since the year 1600, at least 60 flank eruptions and many more summit eruptions.
- In recent years, summit eruptions have occurred in 2006, 2007-08, on two occasions in 2012, 2018, and 2021; flank eruptions have taken place in 2001, 2002-03, 2004-05, and 2008-09.
- Etna has been a World Heritage Site since 2013, and according to UNESCO, the volcano’s eruptive history can be traced back 500,000 years.
- At least 2,700 years of this activity have been documented.
Apple Warns Users of "Mercenary Spyware"

- 12 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
Apple has cautioned its users in India and 91 other countries that their iPhone may have come under attack from “mercenary spyware”, including Pegasus, a malware developed by the Israeli company NSO Group.
What are Mercenary Spyware Attacks?
- Mercenary spyware attacks represent an elevated level of cyber threat, characterized by their intricate nature and highly targeted approach.
- These attacks, surpassing typical cybercriminal activity and consumer malware, are meticulously crafted to infiltrate specific individuals with significant resources.
- Due to their sophisticated design and substantial investment, mercenary spyware attacks pose a formidable challenge in terms of detection and prevention.
- Despite their potency, they have primarily targeted select users, leaving the majority relatively unaffected.
- This breed of cyber threat stands as one of the most advanced and elusive globally, prompting tech giant Apple to refrain from attributing them to specific perpetrators or regions.
- The primary objective of mercenary spyware is to clandestinely infiltrate smartphones and other devices, operating without the user's knowledge or consent.
- These surveillance tools are capable of monitoring movements, intercepting communications, and pilfering sensitive data.
- In troubling instances, reports indicate that governments, intelligence agencies, and law enforcement bodies have procured mercenary spyware for surveillance purposes, often targeting political dissidents and activists.
- Key players in the production of mercenary spyware include the NSO Group, FinFisher, and Hacking Team.
- The NSO Group's flagship spyware, Pegasus, facilitates remote infiltration of devices, granting access to calls, emails, messages, and various files.
- Similarly, FinFisher's FinSpy can intercept keystrokes, access data, and activate microphones and cameras without authorization.
- The Hacking Team's Galileo, also known as the Remote Control System (RCS), possesses similar capabilities, including keystroke capture, video call recording, and unauthorized access to device components like the camera and microphone.
About Pegasus Spyware:
- Pegasus Spyware, crafted by Israel's NSO Group, represents a potent cyber threat.
- This sophisticated malware is engineered to exploit zero-click vulnerabilities, granting it access to smartphones without any interaction from the user.
- Once infiltrated, Pegasus gains full control over the targeted device, enabling it to extract a wealth of data, including emails, texts, and phone calls.
- Additionally, it possesses the capability to remotely activate the smartphone's camera and microphone, further compromising the user's privacy.
What are Spyware and Malware?
Spyware:
- Spyware is a type of software that secretly collects information about a user's activities on their computer or device without their knowledge or consent.
- It may track keystrokes, capture browsing habits, record personal information, or monitor online activities.
- Spyware often operates stealthily in the background, making it difficult for users to detect.
Malware:
- Malware, short for malicious software, is a broad term that encompasses various types of harmful software designed to disrupt, damage, or gain unauthorized access to computer systems or networks.
- Malware includes viruses, worms, trojans, ransomware, and other malicious programs.
- Unlike spyware, which focuses on gathering information covertly, malware may aim to corrupt files, steal data, spread across networks, or carry out other harmful actions.
- Malware can enter a system through email attachments, infected websites, removable media, or software downloads from untrusted sources.
World Cybercrime Index

- 12 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
A new World Cybercrime Index developed by researchers shows that a majority of cybercriminals come from just a few countries.
About World Cybercrime Index:
- The World Cybercrime Index is a collaborative effort between the University of Oxford and UNSW Canberra that identifies global cybercrime hotspots by ranking countries based on their contribution to cybercrime.
- Data is collected from a survey of 92 cybercrime experts involved in intelligence gathering and investigations.
- The index ranks around 100 countries and identifies key hotspots for various cybercrime categories, such as ransomware, credit card theft, and scams.
Key Findings:
- Russia tops the list, followed by Ukraine, China, the USA, Nigeria, and Romania.
- India ranks 10th in the index, with a balanced distribution of cybercrime types but a notable specialization in scams.
- Certain countries were associated with specific types of cybercrime, like data and identity theft in the United States and technical products or services-related crimes in China.
- These insights highlight the need for international cooperation in addressing cybercrime and its various manifestations across different countries.
According to the Oxford University, the five major categories of cybercrime assessed by the study were:
-
- Technical products/services (e.g. malware coding, botnet access, access to compromised systems, tool production).
- Attacks and extortion (e.g. denial-of-service attacks, ransomware).
- Data/identity theft (e.g. hacking, phishing, account compromises, credit card comprises).
- Scams (e.g. advance fee fraud, business email compromise, online auction fraud).
- Cashing out/money laundering (e.g. credit card fraud, money mules, illicit virtual currency platforms).
Mange Disease

- 12 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
The forest department is monitoring an outbreak of mange among a pack of Asiatic wild dogs in the Mudumalai Tiger Reserve (MTR) in the Nilgiris, which they strongly suspect has spread to the animals through the local feral dog population.
What is Mange Disease?
- Mange is a distressing skin condition that affects dogs and is caused by microscopic parasites and different types of mites that infest the dog's skin and coat.
- The two most common forms of mange in dogs are Sarcoptic mange (caused by Sarcoptic scabies mites) and Demodectic mange (caused by Demodex Canis mites).
- Sarcoptic Mange- Scabies: Sarcoptic mange is highly contagious and can spread from dog to dog through direct contact. These microscopic mites burrow into the dog's skin, leading to intense itching and discomfort.
- Demodectic Mange: Demodectic mange, on the other hand, is not usually contagious and often results from an overgrowth of naturally occurring Demodex mites. A weakened immune system or genetic factors can contribute to the development of this form of mange.
- Common Symptoms of Mange in Dogs include:
- Intense Itching
- Skin Infections
- Crusty or Scaly Skin
- Ear Problems
- Mange in dogs is a treatable condition when detected early and managed appropriately.
About Mudumalai Tiger Reserve (MTR):
- The Mudumalai Tiger Reserve, nestled in Tamil Nadu's Nilgiris District at the tri-junction of Karnataka, Kerala, and Tamil Nadu, holds ancient significance, dating back 65 million years to the formation of the Western Ghats.
- It shares borders with the Wayanad Wildlife Sanctuary (Kerala) to the West and the Bandipur Tiger Reserve (Karnataka) to the.
- The Theppakadu Elephant Camp within the reserve is a popular tourist spot, boasting a rich variety of flora and fauna, including Elephants, Gaurs, Tigers, Panthers, and various deer species.
- This historic elephant camp, established over a century ago, sits on the banks of the Moyar River, serving vital roles in human-wildlife conflict resolution, monsoon patrolling, eco-tourism, elephant conservation, and education.
Sungrazing Comet
- 12 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
A tiny "sungrazer" comet was discovered, photographed, and destroyed during the recent total solar eclipse — all within 24 hours.
What is a Sungrazing Comet?
- Sungrazing comets are a special class of comets that come very close to the sun at their nearest approach, a point called perihelion.
- To be considered a sungrazer, a comet needs to get within about 850,000 miles from the sun at perihelion.
- Many come even closer, even to within a few thousand miles.
- Being so close to the sun is very hard on comets for many reasons.
- They are subjected to a lot of solar radiation which boils off their water or other volatiles.
- The physical push of the radiation and the solar wind also help form the tails. As they get closer to the sun, the comets experience extremely strong tidal forces or gravitational stress.
- In this hostile environment, many sungrazers do not survive their trip around the sun.
- Although they don't crash into the solar surface, the sun can destroy them anyway.
- Many sungrazing comets follow a similar orbit, called the Kreutz Path, and collectively belong to a population called the Kreutz Group.
- Close to 85% of the sungrazers seen by the SOHO satellite are on this orbital highway.
- Scientists think one extremely large sungrazing comet broke up hundreds, or even thousands, of years ago, and the current comets on the Kreutz Path are the leftover fragments of it.
- Comet Lovejoy, which reached perihelion on December 15, 2011, is the best-known recent Kreutz-group sungrazer.
- And so far, it is the only one that NASA's solar-observing fleet has seen survive its trip around the sun.
What is a Comet?
- A comet is a small celestial body made primarily of ice, dust, and rocky material that orbits the sun in an elongated path.
- When a comet approaches the sun, the heat causes the ice to vaporize, releasing dust and gas into a glowing coma, or halo, around the comet's nucleus.
- This glowing coma often forms a tail that stretches away from the sun due to the solar wind and radiation pressure.
- Comets are often referred to as "dirty snowballs" or "icy dirtballs" because of their composition.
- They are believed to be remnants from the early formation of the solar system and carry important information about its history.
- Comets can have highly elliptical orbits, sometimes taking thousands or even millions of years to complete a single orbit around the sun.
Invasive Alien Species

- 11 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
In a bid to manage the teeming population of chital (spotted deer) in Ross Island (officially known as the Netaji Subhash Chandra Bose Island), the Andaman and Nicobar Islands administration recently sought help from the Wildlife Institute of India.
What are Invasive Alien Species (IAS)?
- According to the Convention on Biological Diversity (CBD), Invasive alien species are plants, animals, pathogens, and other organisms that are non-native to an ecosystem, and which may cause economic or environmental harm or adversely affect human health.
- In particular, they impact adversely upon biodiversity, including the decline or elimination of native species - through competition, predation, or transmission of pathogens - and the disruption of local ecosystems and ecosystem functions.
- Invasive alien species, introduced and/or spread outside their natural habitats, have affected native biodiversity in almost every ecosystem type on Earth and are one of the greatest threats to biodiversity.
- Since the 17th century, invasive alien species have contributed to nearly 40% of all animal extinctions for which the cause is known (CBD, 2006).
- The problem continues to grow at great socio-economic, health, and ecological costs around the world.
- Invasive alien species exacerbate poverty and threaten development through their impact on agriculture, forestry, fisheries, and natural systems, which are an important basis of people’s livelihoods in developing countries.
- This damage is aggravated by climate change, pollution, habitat loss, and human-induced disturbance.
What are Some Examples of Invasive Wildlife in India?
- The list of invasive wildlife in India is dominated by certain species of fish such as the African catfish, Nile tilapia, red-bellied piranha, and alligator gar, and turtle species such as the red-eared slider.
- The red-eared slider, for instance, is a favorite among India’s exotic pet owners, and many have been abandoned in local water bodies.
- This turtle, native to North America, notoriously edges out local freshwater species, owing to its fast rates of reproduction, and the following competition for food.
- With regards to species of fish, many were introduced in India to feed the demand for those maintaining aquariums.
- For instance, the African catfish was brought over from Bangladesh specifically for aquaculture purposes. “
- The occurrence of C gariepinus (the species’ scientific name) has been reported from several inland systems of India including the mighty rivers like Ganga, Yamuna, Sutlej, Godavari, Periyar River, and the lakes like Vembanad Lake.
How do IAS Impact Native Flora and Fauna?
- The invasive species act as disruptors in the food chain and disturb the balance of the ecosystem.
- In habitats where there is no competition, invasive species can dominate the entire ecosystem
- For instance, “in Keoladeo Park, Bharatpur in Rajasthan, which is a UNESCO World Heritage site, the African catfish have been known to prey on waterfowls and migratory birds as well.
- Studies have shown that the proliferation of chital in the Andamans has affected the regeneration of native vegetation, as the deer are known to consume seeds and seedlings.
National Investment and Infrastructure Fund (NIIF)

- 11 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
iBUS, a digital infrastructure solutions company, said recently it has raised $200 million from the government-backed National Investment and Infrastructure Fund Limited (NIIF).
What is the National Investment and Infrastructure Fund (NIIF)?
- The National Investment and Infrastructure Fund (NIIF) stands as a pioneering fund manager dedicated to investing in India's infrastructure and related sectors.
- Established in 2015, NIIF marks India's inaugural sovereign wealth fund (SWF), embodying a collaborative investment platform for both international and domestic investors.
Key Aspects of NIIF:
- Investment Mandate: NIIF operates with a mandate to deploy equity capital into domestic infrastructure projects, spanning greenfield, brownfield, and stalled ventures.
- Its investment horizon extends across diverse asset classes, including infrastructure, private equity, and other sectors, all aimed at delivering attractive risk-adjusted returns.
- Ownership and Independence: With 49% ownership by the Indian government, NIIF boasts over $4.9 billion in assets under management, solidifying its status as the nation's largest infrastructure fund.
- Despite its close ties with the government, NIIF maintains autonomy in its investment decisions, ensuring a professional and impartial approach to its operations.
- Professional Management: The fund is predominantly owned by institutional investors and managed by a proficient team with expertise in both investments and infrastructure.
- This professional oversight ensures the strategic deployment of capital and efficient management of investments.
- Regulatory Compliance: NIIF operates within the regulatory framework as an Alternative Investment Fund (AIF) registered with the Securities Exchange Board of India (SEBI).
- It actively raises capital from a spectrum of domestic and international institutional investors, further bolstering its financial resources.
NIIF manages capital through four distinct funds:
- NIIF Master Fund: Focused on infrastructural projects such as roads, ports, airports, and power, it stands as India's largest infrastructure fund.
- NIIF Private Markets Fund: Invests in infrastructure and associated sectors through third-party managed funds.
- NIIF Strategic Opportunities Fund: Devoted to developing large-scale businesses and greenfield projects deemed strategically significant for the nation.
- India-Japan Fund: NIIF's bilateral initiative aimed at environmental preservation in India, with contributions from both the Indian government and the Japan Bank for International Cooperation.
- NIIF catalyzes fostering sustainable infrastructure development in India while facilitating fruitful collaborations between Indian and international stakeholders, exemplifying a robust model for investment-driven growth.
QS World University Rankings

- 11 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
Sixty-nine Indian universities made it to the rankings with 424 entries in the 2024 QS World University Rankings by Subject. This marks a 19.4 percent rise from the previous year’s 355 entries.
About QS World University Rankings:
- The QS World University Rankings, curated annually by Quacquarelli Symonds, are a comprehensive assessment of the world's top 1,000 universities.
- In the latest 2024 edition, universities were meticulously evaluated across 55 specific subjects and five broader subject areas, offering a nuanced perspective on academic excellence.
Key Highlights from the 2024 Rankings:
- Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) maintains its prestigious position as the top-ranked university globally for the 12th consecutive year, a testament to its enduring academic prowess.
- The Indian Institute of Technology Bombay (IITB) shines as the leading Indian institution, securing the 149th spot on the global stage.
- Noteworthy Progress: India demonstrates remarkable advancement with a total of 69 universities making their mark in the QS rankings, showcasing a notable 19.4% increase from the previous year.
- India stands as the second most represented country in Asia, highlighting its growing significance in the global academic landscape.
- Jawaharlal Nehru University (JNU) emerges as a standout, clinching the 20th position globally in development studies, reaffirming its commitment to excellence in specialized fields.
- India's Rise in Research: The nation exhibits a commendable 20% improvement in the Citations per Paper indicator, underscoring its burgeoning research capabilities.
- With a staggering 1.3 million academic papers produced, India emerges as the world's fourth-largest contributor to research, trailing only behind academic powerhouses like China, the United States, and the United Kingdom.
- Challenges Ahead: Despite significant strides, India grapples with the challenge of securing citations in premier global journals, with only 15% of its research receiving recognition in these esteemed publications between 2017 and 2021.
- Overall, India's journey in the QS World University Rankings reflects a narrative of progress, innovation, and resilience, while also highlighting areas for continued growth and enhancement in the global academic arena.
African Baobab Tree

- 11 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
In a groundbreaking conservation endeavor, the Global Society for the Preservation of Baobabs and Mangroves (GSPBM) has initiated a mission to rejuvenate the iconic Baobab trees.
About the African Baobab Tree:
- African baobab trees, scientifically known as Adansonia Digitata, are some of the oldest living organisms in the world.
- Baobab trees originated millions of years ago in West Africa and spread over time to other parts of the world, creating new species.
- There are 9 baobab species, of which 6 have originated in Madagascar, 2 in Australia, and 1 in Africa.
- These trees range in height from 5 to 20 meters and are typically found in deciduous forests composed primarily of broad-leaved trees that shed their leaves during one season.
- It is one of nine species of baobab, is native to mainland Africa, and also thrives in the African savanna ecosystem.
- The savanna features warm temperatures year-round and experiences its highest seasonal rainfall in the summer.
- It is characterized by grasses and dispersed trees, allowing ample sunlight to reach the ground.
- Age Record: Carbon-14 dating has revealed that an African baobab specimen in Namibia is approximately 1,275 years old, making it the oldest known angiosperm tree.
- Tree of Life: African baobabs, being succulents, absorb and store water in their expansive trunks during the rainy season.
- This unique adaptation enables them to produce nutrient-dense fruit during the dry season, even in arid environments.
- Utilization: Baobab trees, with lifespans exceeding a thousand years, offer a multitude of benefits including food, fodder for livestock, medicinal compounds, and raw materials for various purposes.
- Threats: Since 2005, nine of the thirteen oldest African baobab specimens and five of the six largest trees have either perished or experienced significant decline, possibly due to the impacts of climate change.
What are Angiosperms?
- Angiosperms, a taxonomic class of plants, are characterized by seeds enclosed within an ovule, such as those found in apples.
- This group is commonly known as hardwoods.
- Angiosperms typically comprise trees with broad leaves that undergo color changes and shed annually during autumn.
- Examples of deciduous angiosperms include oaks, maples, and dogwoods. However, certain angiosperms, such as rhododendrons, live oaks, and sweet bay magnolias, retain their leaves.
Gymnosperms:
- Gymnosperms, another taxonomic class, encompass plants with seeds not enclosed in an ovule, as seen in pine cones.
- The term "gymnosperm" translates to "naked seed," and this group is often referred to as softwoods.
- Gymnosperms commonly feature needle-like leaves that remain green throughout the year. Examples include pines, cedars, spruces, and firs.
- While many gymnosperms maintain their foliage year-round, some, like ginkgos, dawn redwoods, and bald cypresses, do shed their leaves.
Sulthan Bathery

- 11 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
BJP suggests renaming Sulthan Bathery to Ganapathivattam due to historical identity alteration by Tipu Sultan.
Where Does the Name Ganapathyvattam Come From?
- Sulthan Bathery, one of the three municipal towns in Wayanad has a stone temple that was once known as Ganapathyvattam.
- The temple, built in the prevalent architectural style of the Vijayanagar dynasty, was constructed by Jains who migrated to Wayanad from areas in present-day Tamil Nadu and Karnataka in the 13th century.
- The temple was partly destroyed during the invasions of Tipu Sultan, the ruler of Mysuru in the second half of the 18th century.
- Between 1750 and 1790, today’s northern Kerala was invaded several times by the rulers of Mysuru, Hyder Ali and his son Tipu.
- It remained abandoned for nearly 150 years.
- Later, it was taken over by the Archaeological Survey of India, which declared it as a monument of national importance.
- The town of Ganapathyvattam, on the route between Mysore and the ports of the Arabian Sea, also gained prominence as a trading center and a stopover.
The History of Sultan Bathery:
- The armies of Tipu destroyed temples and churches and forced many in the path of the invasion to flee to escape forced religious conversion.
- Tipu Sultan used the Maha Ganapathy temple in Sulthan Bathery as a battery or store for weapons for his army in the Malabar region (today’s North Kerala, including Wayanad).
- This led to the British recording Ganapathyvattam as “[Tipu] Sultan’s Battery”, and the name survived as Sulthan Bathery.
Higgs Boson

- 10 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
Peter Higgs, the eminent theoretical physicist who first proposed the idea of what we now know as the “Higgs Boson,” died at the age of 94 on April 8.
What is the Higgs Boson?
- Particles make up everything in the universe but they did not have any mass when the universe began.
- They all sped around at the speed of light, according to the European Council for Nuclear Research (CERN).
- CERN, the European Council for Nuclear Research, is where the Large Hadron Collider (LHC) is located, and it's where the discovery of the Higgs Boson was made in 2012 through experiments conducted at the LHC.
- Everything we see like planets, stars, and life, emerged after particles gained their mass from a fundamental field associated with the particle known as the Higgs boson.
- The particle has a mass of 125 billion electron volts making it 130 times bigger than a proton?, according to CERN.
- Interestingly, the subatomic particles known as bosons are named after Indian Physicist Satyendra Nath Bose.
How does the Higgs Boson Work?
- The Higgs boson is a fundamental component of a theory formulated by Higgs and colleagues in the 1960s to elucidate how particles acquire mass.
- According to this theory, a pervasive Higgs energy field permeates the universe.
- As particles traverse this field, they interact with and draw in Higgs bosons, which congregate around the particles in varying quantities.
- Likewise, envision the universe akin to a party: less prominent guests can swiftly traverse the room without notice, while more popular guests attract clusters of people (the Higgs bosons), thus decelerating their movement through the room.
- Similarly, particles navigating the Higgs field experience a comparable phenomenon.
- Certain particles attract larger assemblies of Higgs bosons, and the more Higgs bosons a particle draws in, the greater its mass becomes.
Why is the Higgs Boson Called the “God Particle?”
- The Higgs boson is popularly known as the "God Particle".
- The name originated from Nobel Prize-winning physicist Leon Lederman's book on the particle which he titled the "Goddamn Particle", owing to frustration over how difficult it was to detect.
- However, his publishers changed the name to "The God Particle", which often draws ire from religious communities.
Who was Peter Higgs?
- Born in UK's Newcastle upon Tyne in 1929, Mr Higgs studied at King's College in London and has taught at the University of Edinburgh since the 1950s.
- Described as a modest man who published only a few scientific papers, he disliked his sudden fame calling it "a bit of a nuisance", even cringing when the term "Higgs boson" was used.
- Even as a lifelong atheist, he disliked the name "God particle".
- In 2013, Higgs and Francois Englert won the Physics Nobel Prize for their work on the particle which was thought to be a key to explaining the universe.
CDP-SURAKSHA

- 10 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
The government has come up with a new platform to disburse subsidies to horticulture farmers under the Cluster Development Programme (CDP) — the Centre’s initiative to promote horticulture crops.
What is the CDP-SURAKSHA?
- The CDP-SURAKSHA is essentially a digital platform.
- SURAKSHA stands for “System for Unified Resource Allocation, Knowledge, and Secure Horticulture Assistance.”
- The platform will allow an instant disbursal of subsidies to farmers in their bank accounts by utilizing the e-RUPI voucher from the National Payments Corporation of India (NPCI).
- The CDP-SURAKSHA has features such as database integration with PM-KISAN, cloud-based server space from NIC, UIDAI validation, eRUPI integration, local government directory (LGD), content management system, geotagging, and geo-fencing.
How does the CDP-SURAKSHA work?
- The platform allows access to farmers, vendors, implementing agencies (IA), cluster development agencies (CDAs), and officials of the National Horticulture Board (NHB).
- A farmer can log in using their mobile number and place an order for planting materials such as seeds, seedlings, and plants based on their requirement.
- Once the demand has been raised by the farmer, the system will ask them to contribute their share of the cost of planting material.
- The subsidy amount paid by the government will appear on the screen automatically.
- After the farmer pays their contribution, an e-RUPI voucher will be generated.
- This voucher will then be received by a vendor, who will provide the required planting material to the farmer.
- Once the ordered planting material is delivered to the farmer, they have to verify the delivery through geo-tagged photos and videos of their field.
- It is only after the verification that the IA will release the money to the vendor for the e-RUPI voucher.
- The vendor will be required to upload an invoice for the payment on the portal.
- The IA will collect all the documents and share them with the CDA for subsidy release, then only the subsidy will be released to the IA.
- However, the farmer, who raised the demand for the plant material using the platform, can avail of the subsidy at the first stage only.
What is e-RUPI?
- The CDP-SURAKSHA platform uses e-RUPI vouchers from the NPCI.
- The voucher is a one-time payment mechanism that can be redeemed without a card, digital payments app, or internet banking access, at the merchants accepting e-RUPI.
- According to the NPCI, the e-RUPI can be shared with the beneficiaries for a specific purpose or activity by organizations or government via SMS or QR code.
What is the Cluster Development Program (CDP)?
- The CDP is a component of the central sector scheme of NHB.
- It is aimed at leveraging “the geographical specialization of horticulture clusters and promoting integrated and market-led development of pre-production, production, post-harvest, logistics, branding, and marketing activities.”
- So far, 55 horticulture clusters have been identified, out of which 12 have been selected for the pilot.
- These clusters are in different stages of development.
- Four more clusters:
- A floriculture cluster in West Bengal
- Coconut clusters in Kerala and Tamil Nadu, and
- White onion clusters in Gujarat
- Each cluster will have an implementing agency and a cluster development agency (CDA).
- According to the government, about 9 lakh hectares of area will be covered through all 55 clusters, covering 10 lakh farmers.
- It is estimated that the initiative will attract private investment of Rs 8,250 crore, in addition to the government’s assistance, which is fixed according to the size of the cluster, up to Rs 25 crore for mini cluster (size up to 5,000 ha), up to Rs 50 crore for medium clusters (5,000 to 15,000), and up to Rs 100 crore for mega clusters (more than 15,000 ha).
C-Dome Defense System

- 10 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
Israel for the first time used a seaborne missile defense system to shoot down a drone approaching from the Red Sea that had set off sirens in the port city of Eilat.
What is the C-Dome Defense System?
- The C-Dome is a naval version of Israel's Iron Dome air defense system, designed to protect against rocket and missile attacks.
- Drawing from Iron Dome's technology, C-Dome shares its 90% effectiveness rate and utilizes radars to detect and destroy short-range rockets with its missiles.
Operational Deployment and Integration:
- First unveiled in 2014 and declared operational in 2022, the C-Dome is mounted on Sa'ar 6-class corvettes and German-made warships.
- It employs the same interceptor as the Iron Dome but differs in its integration with the ship's radar for target detection, ensuring full-circular vessel protection.
Combatting Modern Threats:
- C-Dome's primary objective is to counter a wide range of modern maritime and coastal threats with high kill probability.
- Its successful deployment and performance underscore its pivotal role in safeguarding Israel's naval interests and assets against evolving security challenges.
About Iron Dome:
- Developed by Rafael Advanced Defense Systems and Israel Aerospace Industries, the Iron Dome is a cutting-edge air missile defense system that offers protection against short-range rockets by intercepting them above Israeli territory.
- With its multi-rocket handling capacity, Iron Dome became operational in 2011 and features:
- All-weather capabilities for day and night functionality
- Launching versatility with various interceptor missiles
- A range of approximately 40 miles
- Portable design for deployment on ships or land
- Adaptive defense through reloadable interceptors
Iron Dome consists of three key elements:
-
- Radar system for detecting incoming rockets
- Command-and-control mechanism to evaluate threat levels
- Interceptors are designed to neutralize incoming rockets before impact
- These components work in tandem to provide Israel with a robust and reliable defense against aerial threats.
India Imposed Import Restrictions on Solar PV Cells

- 10 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
Recent government orders on attempts to increase local sourcing of solar modules to support India’s renewables manufacturing ecosystem have been widely reported in the media as ‘import restrictions’.
What is the Approved List of Models and Manufacturers (ALMM) List?
- The Approved List of Models and Manufacturers of Solar Photovoltaic Modules (ALMM) comprises government-approved manufacturers eligible for use in government projects, government-assisted projects, and schemes.
- ALMM aims to boost the domestic solar industry and reduce dependence on imports, particularly from China.
ALMM's Suspension and Reinstatement:
- The ALMM was kept in abeyance for two years to address concerns raised by renewable energy producers with pre-existing government contracts.
- During this period, India's domestic solar industry struggled to compete with cheap Chinese imports.
- To support local manufacturers, the government launched initiatives like the Production Linked Incentive (PLI) scheme under the Atmanirbhar Bharat ('Self-Reliant India') Programme.
- With the PLI scheme enhancing the competitiveness of Indian manufacturers, the ALMM was reinstated in March 2024.
- The government believes that domestic companies can now meet India's solar equipment demand, making the ALMM an essential tool for promoting import substitution and self-reliance in the renewable energy sector.
Solar PV Imports:
- India heavily relies on solar cell and module imports, with China and Vietnam being the primary suppliers.
- Government data reveals that India imported approximately $11.17 billion worth of solar cells and modules over the past five years.
- As of 2023-24, China accounted for 53% of solar cell imports and 63% of solar PV modules.
China's Competitive Edge:
- Several factors contribute to China's dominance in solar PV exports:
- Cost-effective manufacturing due to lower power costs
- Government policies prioritizing the solar PV sector
- Economies of scale and continuous innovation driven by growing domestic demand
- These advantages have made China the most cost-competitive location for producing solar PV components, making it challenging for other countries to match their production capabilities.
What is the Scope of Solar Energy in India?
- India's solar sector holds immense potential, driven by the government's target of achieving 500 GW of installed non-fossil fuel capacity by 2030.
- Moreover, the country's rapid growth in electricity demand, fueled by economic activities and climate adaptation measures, positions solar power as a critical resource.
- Solar energy accounted for one-third of renewable energy generation from April 2023 to February 2024, showcasing its significance in India's energy mix.
- Despite an estimated solar power potential of 748.99 GW, the country has yet to fully exploit this resource.
- To harness this potential, the government is implementing various schemes and programs, paving the way for a sustainable and prosperous solar future.
Coordinated Lunar Time (LTC)

- 10 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
Recently, the US White House has officially instructed NASA to create a lunar time standard for international and private sector coordination on the Moon.
What is Coordinated Lunar Time (LTC)?
- Coordinated Lunar Time (LTC) is a lunar-based time system being developed by NASA in collaboration with other government agencies to establish a standardized time zone for the Moon.
- LTC aims to provide a precise timekeeping benchmark for lunar spacecraft and satellites, synchronizing communication between astronauts, bases, and Earth.
Importance of LTC:
- As lunar exploration and commerce expand, a unified time standard becomes essential for managing operations, ensuring transaction reliability, and coordinating logistics.
- Furthermore, LTC addresses the discrepancy in timekeeping between Earth and the Moon due to differences in gravity, as time ticks faster on the Moon, causing Earth-based clocks to lose an average of 58.7 microseconds per day.
- Establishing LTC will prevent potential problems in spacecraft docking, data transfer, communication, and navigation.
How Will a Lunar Time Standard Be Established?
- Like on Earth, atomic clocks can be deployed on the lunar surface to set a time standard.
- These clocks have to be placed on the Moon at different locations since the Moon’s rotation and even local lumps of mass, called mascons, beneath the crust of the Moon affect the flow of time ever so slightly.
- Mascons or mass concentrations are so dense that they alter the Moon’s local gravity field.
- These effects are minor but the output from these clocks can be synthesized to give the Moon its own independent time, which can be tied back to UTC for seamless operations from Earth as well.
How Does Earth’s Time Standard Work?
- Most of the clocks and time zones of the world are based on Coordinated Universal Time (UTC), set by the International Bureau of Weights and Measures in Paris, France.
- UTC is essentially an internationally agreed-upon standard for world time.
- It is tracked by a weighted average of more than 400 atomic clocks placed in different parts of the globe.
- Atomic clocks measure time in terms of the resonant frequencies — the natural frequency of an object where it tends to vibrate at a higher amplitude — of atoms such as cesium-133.
- In atomic time, a second is defined as the period in which a cesium atom vibrates 9,192,631,770 times.
- As the vibration rates at which atoms absorb energy are highly stable and ultra-accurate, atomic clocks make for an excellent device for gauging the passage of time.
- To obtain their local time, countries must subtract or add a certain number of hours from UTC depending on how many time zones they are away from 0 degree longitude meridian, also known as the Greenwich meridian.
- If a country lies on the west of the Greenwich meridian, it has to subtract from the UTC, and if a country is located on the east of the meridian, it has to add.
Black Swan Event

- 09 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
Army Chief Gen Manoj Pande on Monday called upon the force to be always prepared for 'black swan' events and "expect the unexpected" even as he identified technology as the new area for strategic competition among nations.
What is the Black Swan Event?
- A black swan is a rare, unpredictable event that comes as a surprise and has a significant impact on society or the world.
- These events are said to have three distinguishing characteristics:
- They are extremely rare and outside the realm of regular expectations
- They have a severe impact after they hit; and
- They seem probable in hindsight when plausible explanations appear.
When did the Term Originate?
- The black swan theory was put forward by author and investor Nassim Nicholas Taleb in 2001 and later popularised in his 2007 book – The Black Swan: The Impact of the Highly Improbable.
- In his book, Taleb does not try to lay out a method to predict such events but instead stresses building “robustness” in systems and strategies to deal with black swan occurrences and withstand their impact.
- The term itself is linked to the discovery of black swans.
- Europeans believed all swans to be white until 1697 when a Dutch explorer spotted the first black swan in Australia.
- The metaphor ‘black swan event’ is derived from this unprecedented spotting from the 17th century, and how it upended the West’s understanding of swans.
Implications of Black Swan Events:
- Black Swan events are characterized by their extreme rarity, severe impact, and widespread implications across various sectors.
- These unanticipated occurrences can trigger substantial disruptions, unveiling vulnerabilities in systems once thought resilient and prompting reassessments of risk management practices.
- Disruption: Black Swan events have the potential to disrupt economies, industries, and societies on a global scale.
- Their unforeseen nature can cause sudden shifts in financial markets, business operations, and everyday life, leaving lasting effects on the overall landscape.
- Uncertainty: The inability to predict Black Swan events using traditional methods injects considerable uncertainty into decision-making and planning for individuals, organizations, and governments.
- Navigating through such unpredictable circumstances can pose significant challenges for all affected parties.
- Vulnerability: These rare events can expose vulnerabilities in systems that were previously thought to be impervious or resilient.
- By doing so, Black Swan events emphasize the importance of preparedness and encourage the development of more robust risk management practices.
- Reassessment of Risk: In the aftermath of a Black Swan event, there is often a renewed focus on identifying and mitigating previously overlooked risks.
- This heightened awareness can lead to changes in investment strategies, regulatory policies, and overall risk management practices.
- Regulatory and Policy Responses: Governments and regulatory bodies may implement new regulations or policies in response to Black Swan events.
- These measures are designed to prevent or mitigate the impact of similar occurrences in the future, ultimately shaping the economic and social landscape.
- Behavioral and Attitude Changes: Black Swan events can significantly alter behaviors and attitudes as individuals and organizations adapt to the new reality.
- These shifts may include changes in consumer behavior, investment strategies, and approaches to risk management.
Examples of Black Swan Events:
- The Dot-com Bubble: In 2000, the valuation of many internet-based companies plummeted after a period of rapid growth.
- The 9/11 Terrorist Attacks: The events of September 11, 2001, had far-reaching consequences on global security, politics, and economies.
- The 2008 Financial Crisis: A series of shocks to Wall Street due to the unraveling of subprime lending practices caused significant economic turmoil.
- Brexit: The unexpected decision of the United Kingdom to leave the European Union in June 2016 caught many by surprise and caused the British pound to plummet against the US dollar.
- COVID-19 Pandemic: The ongoing global health crisis continues to significantly affect economies and markets worldwide.
- These instances illustrate the profound and widespread implications of Black Swan events, underscoring the importance of adaptability and resilience in an ever-changing global landscape.
Imposition of Anti-Dumping Duty on Sodium Cyanide

- 09 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
The Directorate General of Trade Remedies (DGTR) has now recommended the imposition of anti-dumping duty on sodium cyanide (NaCN) imported from China, the European Union, Japan, and Korea.
Key Facts About Sodium Cyanide:
- Sodium cyanide (NaCN) is a highly toxic, inorganic compound with a white, crystalline appearance.
- It is a solid at room temperature and has a high affinity for metals, making it useful in various industrial processes.
- Due to its toxic nature, proper handling and safety protocols must be followed when working with sodium cyanide.
Applications of Sodium Cyanide:
- Mining and Metallurgy: Sodium cyanide is widely used in the extraction of gold and silver from ores. It is employed in a technique called "cyanide heap leaching," where a dilute sodium cyanide solution is sprayed onto crushed ore.
- The cyanide forms a water-soluble complex with the precious metals, enabling their recovery from the ore.
- Electroplating: NaCN is utilized as an electrolyte in electroplating processes, particularly for the deposition of silver, gold, and other metals on various surfaces to improve their appearance, durability, or conductivity.
- Synthetic Fiber Production: Sodium cyanide is used in the manufacturing of synthetic fibers such as acrylic and nylon.
- It serves as a catalyst in the polymerization process, promoting the formation of long-chain polymers that make up the fibers.
- Pesticides: Due to its toxicity, sodium cyanide has been used as a fumigant to control pests and rodents.
- However, its use in this field has been largely phased out in many countries due to safety concerns and the development of safer alternatives.
- Dye and Pigment Production: NaCN can be used in the production of certain dyes and pigments, particularly those containing nitrogen.
- It acts as a precursor for the synthesis of these compounds.
What is Anti-Dumping Duty?
- An anti-dumping duty is a tariff imposed by a domestic government on foreign imports suspected of being sold at prices lower than those in the exporter's domestic market.
- This measure aims to prevent these products from undercutting local businesses and harming the local economy.
- The World Trade Organization (WTO) oversees a framework of international trade rules governing anti-dumping measures.
- Under this agreement, governments are permitted to address dumping practices if they pose a threat of significant harm to a domestic industry.
Calculation of Anti-Dumping Duty:
- The calculation of anti-dumping duty involves determining the difference between the normal value and the export value of the product.
- The normal value represents the market value of the product in the exporter's domestic market, while the export value denotes the price at which the product is sold when exported to India.
- The anti-dumping duty is levied to neutralize this price disparity and safeguard the domestic industry from the adverse effects of inexpensive imports.
Anti-Dumping Mechanism in India:
- India's anti-dumping mechanism is overseen by the Directorate General of Anti-Dumping and Allied Duties (DGAD) under the Ministry of Finance.
- The legal framework for anti-dumping in India is established by the Customs Tariff Act of 1975 and the Customs Tariff Rules of 1995.
- The DGAD conducts investigations to assess whether a surge in below-cost imports has negatively impacted the domestic industry.
Mangal Pandey

- 09 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
Sepoy Mangal Pandey likely didn't anticipate that his shot at the Sergeant Major of his regiment near Kolkata on March 29, 1857, would ignite a significant event in Modern Indian history—the Revolt of 1857, also known as the Sepoy Mutiny or the First War of Indian Independence.
Who was Mangal Pandey?
- Mangal Pandey was a prominent historical figure who played a pivotal role in India's struggle for independence from British colonial rule.
- Born in the kingdom of Awadh, which contributed significantly to the East India Company's army, Mangal Pandey joined the 34th Bengal Native Infantry at the age of 22.
Annexation of Awadh:
- In 1856, the British annexed Awadh in a treacherous act that provoked widespread anger and resentment among the local population.
- The deposition of the Nawab and the subsequent confiscation of villages from the taluqdars during the land revenue settlement of 1856 only exacerbated the situation.
Mangal Pandey's Mutiny and Execution:
- The introduction of the Enfield rifle, which used animal fat (beef and pork) in its cartridges, was met with fierce resistance from soldiers like Mangal Pandey.
- They perceived the use of these cartridges as a direct affront to their religious beliefs.
- On March 29, 1857, Mangal Pandey openly revolted, firing at his Senior Sergeant Major in protest.
- His act of defiance led to his capture, and he was subsequently hanged by order of a Court Martial at Lal Bagan in Barrackpore.
- Mangal Pandey's sacrifice and bravery in the face of British oppression have earned him a lasting place in India's history as a symbol of resistance against colonial tyranny.
The Expansion of the 1857 Revolt and Its Lasting Impact:
- The bravery exhibited by Mangal Pandey inspired a wave of resistance among other soldiers, notably those of the 7th Awadh Regiment.
- On May 11, 1857, a group of Sepoys from Meerut refused to use the new cartridges and killed their European officers, marching to the Red Fort in an act of defiance.
The Legacy of the 1857 Revolt:
- The revolt of 1857 had far-reaching consequences and reshaped the dynamics of British rule in India.
- In response to the growing unrest, the British Parliament passed the Government of India Act in 1858, effectively transferring all powers of the East India Company to the Crown.
- Queen Victoria was subsequently declared the Sovereign of British India.
- The Queen's Proclamation, announced by Lord Canning in 1858, introduced a new policy of perpetual support for the native Princes and pledged non-intervention in matters of religious beliefs in India.
- This policy was further reinforced in 1877 during the Delhi Durbar, where Queen Victoria assumed the title of Qaiser-e-Hind, reflecting her position as the Empress of India.
- The 1857 revolt, sparked by Mangal Pandey's actions, marked a turning point in India's struggle for independence and continues to be remembered as a pivotal moment in the nation's history.
ISRO’s ‘Zero Orbital Debris’ Milestone

- 09 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
The rise in satellite launches has led to a new crisis for spacefaring nations: space debris, which ISRO's recent mission successfully mitigated by leaving 'zero orbital debris'.
Context:
- Recently, ISRO announced that its PSLV-C58/XPoSat mission effectively minimized debris in Earth's orbit.
- This achievement was made possible by repurposing the final stage of the PSLV into a novel orbital station termed PSLV Orbital Experimental Module-3 (POEM-3), as outlined by ISRO.
What is POEM?
- POEM, developed by the Vikram Sarabhai Space Centre (VSSC) is a cost-effective space platform, that repurposes the spent fourth stage of a PSLV rocket into an orbital platform.
- It made its debut during the PSLV-C53 mission in 2022, serving as a stabilized platform for conducting in-orbit scientific experiments with various payloads.
- POEM-3, deployed during ISRO's PSLV C-58 mission in 2024, successfully positioned the XPoSat satellite into its targeted 650 km orbit.
- Subsequently, the fourth stage of the PSLV, functioning as POEM-3, was maneuvered to a circular orbit at 350 km altitude.
- Upon completing all payload objectives, POEM-3 re-entered Earth's atmosphere.
Significance of POEM-3's Achievement:
- The significance of POEM-3's achievement lies in its contribution to mitigating space debris, a pressing concern highlighted in ISRO's Space Situational Assessment Report 2022.
- With the world witnessing a surge in space object placement, reaching 2,533 in 179 launches in 2022, the proliferation of space debris poses substantial risks to space assets.
- Furthermore, it exacerbates the 'Kessler syndrome,' wherein cascading collisions from a single event generate additional debris, intensifying the threat to space operations.
International Law Pertaining to Space Debris:
- Regarding international regulation on space debris, presently, there exists no specific international law governing debris in Low Earth Orbit (LEO).
- However, the majority of spacefaring nations adhere to the Space Debris Mitigation Guidelines of 2002, which received endorsement from the UN in 2007.
How are Space Agencies Dealing with Debris?
- Various space agencies are actively addressing the issue of space debris.
- NASA initiated its Orbital Debris Program in 1979, while the European Space Agency (ESA) has committed to a 'Zero Debris charter,' aiming for the elimination of space debris by 2030.
- Japan has launched the Commercial Removal of Debris Demonstration (CRD2) project to confront space junk.
- Additionally, an Indian startup named Manastu Space is developing technologies such as in-space refueling, deorbiting of defunct satellites, and satellite life extension to contribute to debris mitigation efforts.
TSAT-1A Satellite

- 09 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
SpaceX successfully launched and deployed the TSAT-1A satellite developed by Tata Advanced Systems Limited (TASL) in partnership with Satellogic Inc.
About TSAT-1A Satellite:
- TSAT-1A is a groundbreaking optical sub-meter resolution Earth observation satellite developed by Tata Advanced Systems Limited (TASL) in collaboration with Latin American company Satellogic Inc.
- This collaboration began in late 2023, culminating in TSAT-1A's assembly at TASL's Assembly, Integration, and Testing (AIT) plant in Karnataka, India.
- Launched from the Kennedy Space Center in Florida, United States, via SpaceX's Falcon 9 rocket, TSAT-1A has since garnered attention for its advanced capabilities and strategic significance.
Key Features of TSAT-1A:
- Sub-meter resolution imagery: TSAT-1A's primary strength lies in its ability to capture high-resolution military-grade imagery of Earth's surface, providing precision of less than one meter per pixel.
- Multispectral and hyperspectral imaging: This technology enables TSAT-1A to gather data across a wide range of wavelengths in the electromagnetic spectrum, offering a detailed and nuanced understanding of land, water, and other natural resources.
- Enhanced performance: TSAT-1A offers improved collection capacity, a wider dynamic range, and low-latency data delivery, ensuring efficient and reliable intelligence gathering.
Strategic Applications and Implications:
- Designed for use by Indian defense forces, TSAT-1A is set to play a pivotal role in discreet information gathering, with the potential for data-sharing among friendly nations.
- By enhancing defense forces' preparedness, response capabilities, and strategic decision-making, TSAT-1A represents a significant milestone in India's space industry and a potential game-changer in the realm of defense and security.
About SpaceX's Falcon 9 rocket:
- The Falcon 9 is a partially reusable, two-stage rocket designed and manufactured by SpaceX.
- Known for its reliable and safe transportation capabilities, Falcon 9 is primarily used to launch payloads and crew into Earth orbit.
- Since its first launch in 2010, Falcon 9 has made significant strides in the aerospace industry, becoming the first commercial rocket to launch humans to orbit in 2020 and maintaining a strong safety record with only one flight failure to date.
Solar Eclipse

- 08 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
On Monday (April 8), a total solar eclipse will cross North America, passing over Mexico, the United States, and Canada. This type of solar eclipse is a rare event for any particular spot.
What is a Solar Eclipse?
- A solar eclipse takes place when the Moon moves in the middle of Earth and the Sun.
- The Moon blocks the light of the Sun, either fully or partially, which casts a huge shadow on some parts of the world.
There are four different types of solar eclipses, including:
- Total solar eclipse: When the Moon blocks the Sun entirely, the areas in the center of the Moon’s shadow at the time witness a total solar eclipse.
- The sky darkens and people who are in the path of a total solar eclipse can get a glimpse of the Sun’s corona — the outer atmosphere — which is usually not visible due to the bright face of the Sun.
- Annual solar eclipse: When the Moon passes in front of the Sun but is at or near the farthest point from Earth, an annular solar eclipse occurs.
- In this scenario, the Moon covers the Sun in such a way that only the periphery of the Sun remains visible — looking like a ring of fire.
- Partial solar eclipse: A partial solar eclipse takes place when the Moon blocks just a part of the Sun, giving it a crescent shape.
- During both partial and annular eclipses, the regions outside the area covered by the Moon’s umbra — the middle and the darkest part of the lunar shadow — will see a partial solar eclipse.
- Partial solar eclipse is the most common type of solar eclipse.
- Hybrid solar eclipse: A hybrid solar eclipse — the rarest type of solar eclipse — is witnessed when an eclipse shifts between annular and total as the shadow of the Moon moves across the globe.
- In this case, some parts of the world see a total solar eclipse, while others observe an annular solar eclipse.
How Often Does a Solar Eclipse Take Place?
- A solar eclipse is witnessed only during the new moon — when the Moon and Sun are aligned on the same side of Earth.
- A new moon occurs about 29.5 days because that is how long it takes the Moon to orbit Earth.
- This, however, does not mean that a solar eclipse happens every month. It takes place only between two to five times annually, because the Moon does not orbit Earth in the same plane as the Earth orbits the Sun.
- In fact, the Moon is tilted by about five degrees with respect to Earth.
- As a result, most of the time when the Moon is in between the Sun and Earth, its shadow is either too high or too low to fall on the Earth.
Why is a Total Solar Eclipse so Rare?
- While there can be between two and five solar eclipses every year, total eclipses only happen about once every 18 months or so.
- This is because a total eclipse is only visible if one is standing in the umbra — the other part of the shadow is called the penumbra, which is not as dark as the umbra.
- The umbral shadow is very small, covering only a small part of Earth.
- In fact, the entire path of the umbral shadow during a solar eclipse will only cover less than one percent of the globe.
- This is why only very few people will get to see a total eclipse at a time.
- Moreover, about 70 percent of the globe is underwater and half of the land is considered uninhabited.
- That’s why, it is quite rare when a total solar eclipse happens and a lot of people get to see it.
Umbra and Penumbra:
- During a solar eclipse, the Moon comes between the Earth and the Sun, casting a shadow on the Earth's surface.
- This shadow consists of two main parts: the umbra and the penumbra.
- The umbra is the central, darkest part of a shadow, such as during a total solar eclipse when the Moon completely covers the Sun.
- The penumbra is the outer part of the shadow where the obscuration is partial, resulting in a partial solar eclipse.
Consumer Confidence Survey (CCS)

- 08 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
Consumer confidence for the year ahead has improved further on the back of higher optimism, which resulted in the Future Expectations Index (FEI) rising by 2.1 points to 125.2, the highest level since mid-2019, according to a Reserve Bank of India survey conducted in March 2024.
What is the Consumer Confidence Survey (CCS)?
- The Consumer Confidence Survey (CCS) is a comprehensive assessment conducted by the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) to gauge consumer perceptions of the current economic landscape.
- Administered across various cities, the CCS measures consumer confidence based on key indicators such as economic conditions, employment prospects, price levels, income, and spending patterns.
- The survey collects valuable insights into consumer sentiments by posing a series of questions about both present and future economic scenarios.
- These responses offer a glimpse into consumers' perceptions of the prevailing financial environment, shedding light on economic trends, opportunities, and potential challenges.
- As a vital tool for policymakers, the Consumer Confidence Survey contributes to shaping effective strategies aimed at fostering sustainable economic growth and improving overall financial stability.
Highlights of the Survey:
- The survey revealed optimistic consumer sentiments across all parameters, reflecting a positive outlook on the current and future economic landscape.
- Key indicators, such as the Current Situation Index (CSI) and Future Expectations Index (FEI), showcased significant improvements, reaching their highest levels since mid-2019.
- Current Situation Index (CSI): Measuring overall consumer perception of the present economic situation, the CSI experienced a notable increase of 3.4 points compared to the previous survey, currently standing at 98.5.
- Future Expectations Index (FEI): Evaluating consumer sentiment for the next 12 months, the FEI witnessed a substantial surge, reaching its highest point since mid-2019 and indicating a positive outlook for the upcoming year.
- The CSI and FEI are calculated based on net responses concerning the economic situation, income, spending, employment, and price levels, comparing the current period with one year ago and the anticipated changes in the year ahead, respectively.
- Households’ Inflation Expectation Survey: There was a slight increase in the proportion of households anticipating an overall rise in prices and inflation within the next three months and one year, as observed across general prices and most product categories when compared to the previous survey round.
- Additionally, the survey results revealed noteworthy enhancements in households' perceptions regarding the general economic situation and employment prospects, signaling a sense of optimism for both the current period and the years ahead.
Oceanic Niño Index (ONI)
- 08 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
The US National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) has recently forecasted an 83% likelihood that the Oceanic Niño Index (ONI) will move into a neutral range between April and June 2024.
What is the Oceanic Niño Index?
- The Oceanic Niño Index (ONI) is the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration's (NOAA) primary indicator for monitoring El Niño and La Niña, which are opposite phases of the climate pattern called the El Niño-Southern Oscillation, or “ENSO” for short.
- NOAA is a US governmental agency responsible for monitoring and researching the Earth's oceans, atmosphere, and climate, and providing weather forecasts and environmental data.
- The ONI is the difference between a three-month running average of the sea surface temperature averaged over an area of the ocean from 120 West to 170 West longitude along the equator and the long-term average for the same three months.
- NOAA considers El Niño conditions to be present when the Oceanic Niño Index is +0.5 or higher, indicating the east-central tropical Pacific is significantly warmer than usual.
- La Niña conditions exist when the Oceanic Niño Index is -0.5 or lower, indicating the region is cooler than usual.
What is El Niño and La Niña?
- El Niño and La Niña are two natural climate phenomena that occur in the Pacific Ocean, characterized by fluctuations in ocean surface temperatures.
- They are part of the El Niño-Southern Oscillation (ENSO) cycle, which impacts global weather patterns.
- El Niño refers to the warming of ocean surface temperatures in the eastern tropical Pacific.
- This warming causes changes in atmospheric pressure and wind patterns, which can lead to drought conditions in parts of South America and heavy rainfall in other regions, such as the southern United States.
- La Niña is the opposite phase of the ENSO cycle, characterized by cooler-than-average ocean surface temperatures in the eastern tropical Pacific.
- This results in the strengthening of normal trade winds, causing increased rainfall in some regions, such as Indonesia and northern Australia, and drier conditions in other areas, including the southwestern United States.
- El Niño refers to the warming of ocean surface temperatures in the eastern tropical Pacific.
Effects of El Niño and La Niña on India:
- Both El Niño and La Niña have significant impacts on India's climate, particularly during the monsoon season.
- El Niño events often lead to weaker monsoon winds and reduced rainfall in India, causing droughts and impacting agricultural production.
- On the other hand, La Niña events typically result in stronger monsoon winds and higher rainfall, leading to better agricultural yields.
- However, excessive rainfall can also cause floods and landslides in some regions.
- Monitoring and predicting the occurrence of El Niño and La Niña events is crucial for India's weather forecasting and agricultural planning.
- Accurate predictions enable authorities to take necessary measures to mitigate potential adverse effects on agriculture and infrastructure.
SUVIDHA Portal

- 08 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
The Election Commission said that over 73 thousand applications had been received on the Suvidha Portal in just 20 days since the announcement of General Elections 2024.
About SUVIDHA Portal:
- The Suvidha portal is a technological solution developed by the Election Commission of India (ECI) to ensure a level playing field upholding the democratic principles of free, fair, and transparent elections.
- Suvidha's robust track record showcases its ability to streamline requests for permissions and facilities during election campaigns, catering to diverse needs such as rallies, canvassing, and temporary party offices.
- The Suvidha portal offers both online and offline submission options, ensuring inclusivity and equal opportunity for all stakeholders.
- Permission requests can be processed efficiently through a robust IT platform managed by nodal officers from various state departments.
- The portal's user-friendly design allows political parties and candidates to submit requests from anywhere, at any time.
- To enhance transparency and convenience, Suvidha also provides a companion app for real-time tracking of application statuses.
- Available on both iOS and Android platforms, the app ensures a seamless user experience.
- Moreover, the Suvidha portal promotes accountability by offering features such as real-time tracking, status updates, timestamped submissions, and SMS communication.
- Data collected on the Suvidha platform serves as a valuable resource for scrutinizing election expenditures, thereby promoting greater integrity in the electoral process.
- With Suvidha, the Election Commission of India demonstrates its commitment to facilitating a fair, efficient, and transparent electoral environment, granting equal access to all political parties and candidates seeking permissions and clearances during election campaigns.
Prevention of Money Laundering Act (PMLA)

- 08 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
In its manifesto for the Lok Sabha election, the primary opposition party pledged to cease the weaponization of the Prevention of Money Laundering Act (PMLA) if entrusted with power.
About the Prevention of Money Laundering Act:
- The Prevention of Money Laundering Act (PMLA) constitutes the cornerstone of India's legal framework aimed at combating money laundering, with its enactment and enforcement starting from July 1, 2005.
- Enacted by India's Parliament under Article 253, which authorizes legislation for implementing international conventions, the Act has three primary objectives:
- Prevention and control of money laundering
- Confiscation of proceeds derived from laundering, and
- Addressing related issues within India.
- The Act empowers the Director of the Financial Intelligence Unit-India (FIU-IND) and the Director (Enforcement) with exclusive and concurrent powers to enforce its provisions.
- Subsequent amendments were made in 2009 and 2012 through the Prevention of Money Laundering (Amendment) Acts.
What is Money Laundering?
- Money laundering is defined as the process through which an illegal fund, such as black money, is obtained from illegal activities and disguised as legal money, eventually portrayed as white money.
- The money laundered is passed on through various channels or phases of conversions and transfers to make it legal and eventually reach a legally acceptable institution, like a bank.
Brief History of the PMLA:
- In response to the emergence of global terrorism in the 1990s and the subsequent imperative to curb illicit financial flows, international efforts intensified, culminating in the establishment of the Financial Action Task Force (FATF) in 1989 to coordinate anti-money laundering endeavors worldwide.
Legislative Response:
- Against this backdrop, India, as a member of FATF, was prompted to enact domestic legislation to combat money laundering following the United Nations General Assembly's political declaration in 1998 urging member states to implement national anti-money laundering measures.
Enactment Process:
- The initial iteration of the Prevention of Money-Laundering Bill in 1998 was introduced by the NDA government, aiming to address various aspects such as the prevention of money laundering, confiscation of illicit proceeds, and establishment of coordinating agencies.
- However, concerns regarding potential misuse of the proposed law led to bipartisan opposition, prompting referral to the Department-related Standing Committee on Finance.
- Despite deliberations and amendments, the bill was eventually passed by Parliament in 2002, with enforcement commencing in 2005 following the formulation of accompanying rules under the subsequent UPA government.
Significant Amendments in the PMLA:
- Over the years, the Prevention of Money Laundering Act (PMLA) has undergone various revisions, but it was the amendments introduced in 2009 and 2012 that notably empowered the Enforcement Directorate (ED) to take coercive measures against politicians.
- In 2009, amendments expanded the PMLA's scope to include 'Criminal conspiracy' under Section 120B of the Indian Penal Code (IPC), enabling the ED to intervene in cases alleging conspiracy, even if the primary offense isn't listed in the PMLA.
- For instance, this broadening facilitated the ED's pursuit of cases like the land-grabbing accusations against a former Jharkhand CM, currently incarcerated in Ranchi.
- Furthermore, the 2009 amendments granted the ED international jurisdiction for tracking laundered money, enhancing its global reach.
- In 2012, the PMLA was amended to elevate the Prevention of Corruption Act, 1988 (PC Act) to Part A of the statute's schedule from Part B.
- This move imposed stricter bail conditions on corruption suspects, requiring courts to ascertain substantial evidence of guilt if bail opposition arises from the public prosecutor.
- Part A of the schedule encompassed various serious offenses, including acts like waging war against the nation, drug trafficking, and violations of the PC Act, among others.
Supreme Court's Verdicts on the Constitutionality of PMLA:
- In the case of Vijay Madanlal Choudhary & Ors vs Union of India (2022), a three-judge Bench of the Supreme Court upheld the constitutional validity of the Prevention of Money Laundering Act (PMLA), which faced challenges in over 200 individual petitions.
- One of the primary challenges was regarding the creation of an alternative criminal law system by the PMLA, as the Enforcement Directorate (ED) operates outside the ambit of the Code of Criminal Procedure (CrPC).
- Not being classified as 'police', the ED is not bound by CrPC provisions for searches, seizures, arrests, and property attachments.
- The judgment affirmed the ED's expansive powers, including the admissibility of statements made to it in court.
- In Nikesh Tarachand Shah v Union of India (2017), the PMLA, akin to the Unlawful Activities (Prevention) Act (UAPA), imposed stringent bail conditions, requiring accused individuals to prove the absence of a "prima facie" case against them and their commitment to refraining from future offenses.
- The Supreme Court initially struck down these provisions as unconstitutional.
- However, Parliament reintroduced them through an amendment to the PMLA via the Finance Act, of 2018, which the Supreme Court upheld in 2021.
- While certain aspects of the 2021 ruling, such as the ED's non-obligation to disclose the ECIR (similar to an FIR in criminal cases), are currently under review, the ruling stands as the prevailing law of the land.
Use of Green Hydrogen in the Transport Sector

- 06 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
The Ministry of New and Renewable Energy (MNRE) has announced a Rs-496-crore (until 2025-26) scheme to support pilot projects that either test the viability of green hydrogen as a vehicle fuel or develop secure supporting infrastructure such as refueling stations.
What is Green Hydrogen?
- Green hydrogen is a form of hydrogen gas produced through a process called electrolysis, where water (H2O) is split into hydrogen (H2) and oxygen (O2) using electricity.
- The electricity used in this process is generated from renewable sources such as solar, wind, or hydroelectric power, hence the term "green" hydrogen.
- Unlike conventional methods of hydrogen production, which often rely on fossil fuels and emit greenhouse gases, green hydrogen production is considered environmentally friendly because it doesn't generate carbon dioxide emissions.
- It can be used as a clean energy carrier in various sectors, including transportation, industry, and energy storage.
- The production of green hydrogen is still relatively expensive compared to other forms of hydrogen production, but ongoing advancements in renewable energy technologies and electrolysis processes are expected to reduce costs and increase the viability of green hydrogen as a sustainable energy source in the future.
India's Push for Green Hydrogen in the Transportation Sector:
- India is aggressively pushing for the adoption of green hydrogen in its transportation sector:
- Major Indian commercial vehicle manufacturers like Tata Motors, Volvo Eicher, and Ashok Leyland are intensifying their efforts to develop hydrogen-powered trucks and buses.
- Simultaneously, Indian energy companies are ramping up efforts to increase the production of green hydrogen while striving to decrease costs, making it competitive with other fuels.
- Given its vast and expanding market for both vehicles and energy, India stands poised to reap substantial benefits from widespread green hydrogen adoption as a vehicular fuel.
- India anticipates numerous advantages from this transition, including mitigating pollution, achieving climate objectives, and reducing reliance on expensive fossil fuel imports.
- Moreover, India views this shift as a significant business opportunity, aiming to establish itself as a global hub for the production and export of green hydrogen.
Scheme for Use of Green Hydrogen in the Transport Sector:
- The Scheme for Use of Green Hydrogen in the Transport Sector focuses on several key objectives:
- Validating the technical feasibility and performance of green hydrogen as a transportation fuel.
- Evaluating the economic viability of vehicles powered by green hydrogen.
- Demonstrating the safe operation of hydrogen-powered vehicles and refueling stations.
- Under the scheme, the Ministry of Road Transport & Highways will designate a scheme implementation agency responsible for inviting proposals for pilot projects.
- Once selected, the chosen company or consortium will serve as the project's executing agency and must complete the pilot project within a two-year timeframe.
- To support these initiatives, the Ministry of New and Renewable Energy (MNRE) will consider approving viability gap funding (VGF) based on the recommendations of a Project Appraisal Committee.
- The VGF amount will be determined by assessing the specific needs, merits, and feasibility of each project.
Advantages of Green Hydrogen in the Transportation Sector:
- Hydrogen Internal Combustion Engine (ICE) vehicles utilize hydrogen through combustion, akin to traditional diesel and petrol vehicles, but without emitting carbon.
- Hydrogen Fuel Cell Electric Vehicles (FCEVs) convert hydrogen electrochemically into electricity, leaving water as the sole byproduct, offering a clean and efficient alternative.
- While hydrogen ICE vehicles emit no carbon, studies indicate that converting hydrogen into electricity in a fuel cell is more energy efficient than burning it.
- Unlike Battery Electric Vehicles (BEVs) where the battery is heavy, hydrogen FCEVs are typically lighter due to hydrogen being a lighter element.
- This lightweight characteristic of hydrogen fuel cell technology makes it particularly promising for heavy-duty trucks, providing a viable alternative to EV battery technology.
- Green hydrogen presents a significant opportunity to reduce carbon emissions in the transportation sector without compromising revenue-generating payload capacity, addressing both environmental and economic concerns.
Challenges to the Large-Scale Adoption of Green Hydrogen in the Transportation Sector:
- Cost Prohibitions: The production cost of green hydrogen remains high, posing challenges to its viability as a fuel option.
- To compete with Battery Electric Vehicles (BEVs), the cost of green hydrogen needs to be reduced to between $3 and $6.5 per kilogram by 2030.
- Retail green hydrogen prices in California reached as high as $30 per kilogram in 2023, underscoring the current cost disparity.
- However, ongoing technological innovations and scale-up efforts are expected to drive cost reductions soon.
- Insufficient Infrastructure: Building hydrogen fueling stations for trucks can cost up to 72% more than those for battery electric trucks, according to the California Transportation Commission.
- Challenges with supply complications and market factors have led to the closure of hydrogen refueling stations, exemplified by Shell's recent decision in California.
- Storage and Transportation Challenges: Hydrogen storage requires high-pressure cylinders, which are costly and pose technical challenges.
- Existing natural gas pipeline infrastructure is unsuitable for transporting hydrogen.
- Specialized cylinders capable of safely storing green hydrogen are under discussion, necessitating infrastructure development.
- Handling and Safety Concerns: Hydrogen's flammability necessitates stringent safety protocols and infrastructure at refueling stations.
- Developing robust safety standards is imperative before widespread adoption can occur.
- Long-Term Viability: Advancements in battery technologies are continuously improving the weight and efficiency of EV batteries, potentially challenging the long-term viability of green hydrogen-powered vehicles, particularly in heavy-duty commercial applications.
World Anti-Doping Agency (WADA)

- 06 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
According to the recently released 2022 statistics by the World Anti-Doping Agency (WADA), out of 3865 samples handled by the National Anti-Doping Agency (NADA), 125 (3.2 percent) tested positive — the most in any country.
About World Anti-Doping Agency (WADA):
- WADA, or the World Anti-Doping Agency, is an international independent organization established in 1999.
- It operates with equal funding from both the global sports community and governments worldwide.
- WADA's primary objectives encompass scientific research, education, capacity-building in anti-doping measures, and oversight of the World Anti-Doping Code (Code), which standardizes anti-doping policies across all sports and nations.
- Headquartered in Montreal, Canada, WADA comprises various governing bodies, including a foundation board, executive committee, and several specialized committees.
- The foundation board, consisting of 42 members, holds the highest decision-making authority within WADA.
- It comprises equal representation from both the Olympic Movement and governments.
- Responsibilities for day-to-day operations and policy implementation are delegated by the foundation board to the executive committee, which comprises 12 members, also equally distributed between the Olympic Movement and governments.
- WADA's presidency is a voluntary role that alternates between representatives from the Olympic Movement and governments.
- Additionally, WADA's committees serve as advisory bodies, offering guidance and expertise to support the organization's programs and initiatives.
About National Anti-Doping Agency (NADA):
- The National Anti-Doping Agency (NADA) was established on November 24, 2005, under the Societies Registration Act of 1890.
- NADA operates to foster a culture of doping-free sports in India.
- NADA's key objectives include implementing anti-doping regulations in alignment with the World Anti-Doping Agency (WADA) code, regulating the doping control program, promoting education and research, and raising awareness about the detrimental effects of doping.
The primary functions of NADA are as follows:
- Enforcing the Anti-Doping Code to ensure compliance by all sports organizations in the country.
- Coordinating dope testing programs in collaboration with all relevant stakeholders.
- Facilitating anti-doping research and educational initiatives to instill the values of drug-free sports.
- Adopting best practices and quality standards to enhance the effectiveness and continual improvement of the anti-doping program.
Hydroponic Farming

- 06 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
In the wake of evolving consumer preferences, India is at the forefront of an agricultural transformation, pivoting towards sustainable farming with an emphasis on health.
What is Hydroponics?
- Hydroponics is a method of growing plants without soil, utilizing nutrient-rich water as the primary source of essential minerals and elements.
- The technique involves the circulation of nutrient-enriched water through a network of pipes or channels, directly supplying the roots of plants with the necessary nourishment for their growth and development.
Key Features and Benefits:
- Soilless Cultivation: Hydroponics eliminates the need for soil by providing an alternative substrate or a soil-like medium, such as rock wool, perlite, or vermiculite, to support the plants' roots.
- Nutrient Control: This technique enables precise control over the nutrient composition, concentration, and pH levels in the water, ensuring optimal nutrient availability for plants.
- Water Efficiency: Hydroponics recirculates and reuses water, significantly reducing water consumption compared to traditional soil-based farming.
- Space Optimization: Due to the compact nature of hydroponic systems, they can be used in urban areas, greenhouses, and indoor facilities, maximizing yield per unit area.
- Year-round Cultivation: With controlled environmental conditions, hydroponics allows for continuous cultivation, regardless of seasonal changes or weather fluctuations.
- Hydroponics provides a sustainable, efficient, and adaptable approach to agriculture, with potential benefits in resource conservation, food security, and sustainable urban food production.
Hydroponics in India:
- According to a report by Datamintelligence, India’s hydroponic market is poised for a remarkable growth trajectory, with a projected Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) of 13.53% by 2027, outpacing the global industry’s estimated growth of 6.8%.
- This surge underscores the vast potential of hydroponics in meeting the rising demand for sustainable food produce, particularly in metros and tier 1 cities where health-conscious consumers are willing to pay a premium for fresh, safe, and sustainably grown products.
- This transformative shift is not just a response to changing consumer preferences for fresh produce but also an adaptation to the geographical and environmental challenges that face traditional farming methods.
Suitable Regions for Hydroponic Farming:
- Hydroponic farming presents a viable solution in regions where traditional farming faces significant barriers:
- Areas with Limited Water Supply: Hydroponics drastically reduces water usage, making it ideal for drought-prone areas.
- Rocky Regions: In places where the terrain is unsuitable for soil-based agriculture, hydroponics offers a practical alternative.
- Low Soil Fertility Areas: Hydroponics bypasses the need for fertile soil, allowing cultivation in regions with poor soil quality.
- Demand-Driven Areas: Regions with a high demand for fresh products are perfect for hydroponic farms, catering to health-conscious consumers in urban and semi-urban locales
The Edge with Hydroponic Farming in India:
- Hydroponic farming’s ascendancy in India is attributed to several compelling benefits, underpinned by technological advancements that lower operational costs and facilitate scalability:
- Versatility in Location: It enables agriculture in environments traditionally deemed unsuitable, such as deserts or cold climates.
- Controlled Conditions: Farmers have precise control over nutrients, pH, and the growing environment, optimizing plant health and yield.
- Resource Efficiency: The recycling of water and nutrients significantly cuts down on input costs and environmental impact.
- Enhanced Growth Rates: Increased oxygen availability accelerates plant growth, leading to quicker harvest cycles.
- Pest and Disease Reduction: By eliminating soil, hydroponics reduces the risk of soil-borne diseases and pests.
- Higher Yields: The efficiency and controlled environment of hydroponic systems result in substantially higher crop yields.
- Labour and Maintenance Savings: The absence of weeding and traditional cultivation reduces labour requirements and costs.
- Improved Working Conditions: Elevating crops to a more accessible height improves ergonomics for farm workers, further reducing labour costs.
- No Need for Crop Rotation: Hydroponics eliminates the necessity for crop rotation, simplifying farm management.
- Reduced Transplant Shock: Plants grown hydroponically experience less stress when transplanted, enhancing survival rates.
Rakhigarhi

- 06 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
The NCERT has proposed updates to school textbooks, including adding findings from DNA analysis of skeletal remains at the Rakhigarhi archaeological site in Haryana and removing references to the Narmada Dam project's impact on tribals, leading to displacement and destitution.
About the Ancient Site of Rakhigarhi:
- The site of Rakhigarhi is one of the five known biggest townships of the Harappan civilization on the Indian subcontinent.
- The other four are:
- Harappa
- Mohenjodaro and Ganveriwala in Pakistan and
- Dholavira (Gujrat) in India
- Five interconnected mounds spread over a huge area from the Rakhigarhi's unique site.
- Two mounds, out of five, were thickly populated.
- This site was excavated by Shri Amarendra Nath of Archeological Survey of India.
- The archaeological excavations revealed a mature Harappan phase represented by a planned township having mud-brick as well as burnt-brick houses with proper drainage systems.
- The ceramic industry is represented by redware, which includes dish-on-stands, vases, jars, bowls, beakers, perforated jars, goblets, and hands.
- Animal sacrificial pits lined with mud brick and triangular and circular fire alters on the mud floor have also been excavated signifying the ritual system of Harappans.
- A cylindrical seal with five Harappan characters on one side and a symbol of an alligator on the other is an important find from this site.
- Other antiquities included blades; terracotta and shell bangles; beads of semiprecious stones, terracotta, shell, and copper objects; animal figurines, toy cart frame and wheel of terracotta; bone points; inscribed steatite seals and sealings.
- The excavations have yielded a few extended burials, which certainly belong to a very late stage, maybe the medieval times.
About Harappan Civilization:
- The Harappan civilization is believed to be one of the oldest world civilizations together with Egypt and Mesopotamia.
- It flourished around 2,500 BC, in the western part of South Asia, in contemporary Pakistan and Western India.
- The Harappan civilization developed along the mighty river, the Indus, and for that reason, it is also known as the Indus Valley Civilization.
- The Harappan civilization is identified as a Bronze-age civilization because many objects have been found that are made up of copper-based alloys.
- For example, the famous ‘dancing girl,’ a bronze figurine that provides an insight into the advances made in art and metallurgy, as well as the hairstyle and ornaments prevalent during the period.
- In the 1920s, the Archaeological Department of India carried out excavations in the Indus Valley wherein the ruins of the two old cities, viz. Mohenjodaro and Harappa were unearthed.
India Abstains from UNHRC Resolution on Gaza Ceasefire

- 06 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
India recently abstained on a resolution at the Human Rights Council that called on Israel for an immediate ceasefire in Gaza.
India's Voting Pattern on Israel-Palestine Issues at the UNHRC:
- India's stance on the Israel-Palestine conflict has been reflected in its voting behavior at the United Nations Human Rights Council (UNHRC).
- While India has voted in favor of resolutions criticizing Israel for human rights violations, occupation of the Syrian Golan, and affirming Palestinian self-determination, it has also abstained from certain resolutions.
- In a significant development, India abstained from a resolution calling for an immediate ceasefire in Gaza and an arms embargo on Israel.
- This decision followed instances of violence, including the killing of aid workers and airstrikes.
- India's abstention is believed to be in line with its previous votes on resolutions involving "accountability."
- India's approach indicates its belief that both parties should be held accountable for their actions.
- As a result, it refrains from supporting resolutions that single out one side for condemnation.
- By taking a balanced stance, India aims to promote peace and stability in the region while advocating for the rights of all parties involved.
About the United Nations Human Rights Council (UNHRC):
- The United Nations Human Rights Council (UNHRC) is an inter-governmental body established by the United Nations General Assembly (UNGA) in 2006.
- Headquartered in Geneva, Switzerland, the council serves as a key platform for addressing human rights issues globally.
- The High Commissioner for Human Rights serves as the principal human rights official within the UN system.
- The council convenes three times annually to address human rights violations worldwide.
Membership:
- Comprising 47 member states, the council is responsible for promoting and safeguarding human rights across the globe.
- Member states are elected individually via secret ballot by a majority vote of the General Assembly.
- The election of members occurs within geographical groups to ensure equitable representation.
Tenure:
- Council members serve for a term of three years and are not eligible for immediate re-election after two consecutive terms.
The UNHRC's primary functions include:
- Promoting universal respect for human rights and fundamental freedoms.
- Addressing violations of human rights, including gross and systematic violations.
- Developing international human rights law and making recommendations to the UN General Assembly.
- Conducting investigations into alleged human rights abuses through special rapporteurs and working groups.
- Reviewing the human rights records of all UN member states through the Universal Periodic Review process.
3D Cosmic Map May Open Window To Dark Energy
- 05 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
An international team of researchers has just released the most comprehensive “three-dimensional” map of the universe, which, scientists hope, could reveal some clues about dark energy, the mysterious force that is believed to be causing the universe to expand uncontrollably.
Context:
- An international team of researchers has unveiled an extensive 3D map of the universe, aiming to unlock secrets about dark energy, the enigmatic force thought to be driving the universe's rapid expansion.
- Led by Shadab Alam from the Tata Institute of Fundamental Research in Mumbai, the team collaborated on this groundbreaking project, utilizing the Dark Energy Spectroscopic Instrument (DESI), a specialized tool capable of simultaneously gathering light from 5,000 galaxies when attached to a telescope.
- The DESI collaboration has measured that the expansion rate of the universe was increasing by 68.5 km per second after every 3.26 million light-years of distance, a unit astronomers define as megaparsec.
About Dark Energy Spectroscopic Instrument (DESI):
- The Dark Energy Spectroscopic Instrument (DESI) is a remarkable tool designed to capture light from an impressive 5,000 galaxies simultaneously when attached to a telescope.
- This collaborative effort involves over 900 researchers from institutions worldwide, with the Tata Institute of Fundamental Research (TIFR) representing India's sole participating institution.
- DESI, stationed atop the Mayall 4-Meter Telescope in Arizona, United States, has enabled researchers to analyze light emissions from an astounding six million galaxies, some dating as far back as 11 billion years ago.
- This wealth of data has facilitated the creation of the most intricate map of the universe to date.
Dark Energy Vs Dark Matter:
- Dark energy and dark matter are two distinct yet mysterious components of the universe, with vastly different properties and effects on cosmic structures.
Nature and Composition:
- Dark Energy: Dark energy is a hypothetical form of energy that permeates all of space and is responsible for the accelerated expansion of the universe.
- It is often associated with a cosmological constant or Einstein's "cosmological antigravity."
- Dark energy is thought to exert a repulsive force that counteracts gravity on cosmic scales, driving galaxies away from each other at an accelerating rate.
- However, its precise nature remains one of the greatest mysteries in modern physics.
- It's important to note that dark energy does not matter; rather, it's an energy density inherent in space itself.
- Dark Matter: Dark matter is a form of matter that does not emit, absorb, or reflect electromagnetic radiation, making it invisible and detectable only through its gravitational effects.
- Unlike dark energy, dark matter exerts an attractive gravitational force, influencing the motion of galaxies and other cosmic structures.
- It interacts with ordinary matter and with itself only through gravity and possibly through weak nuclear force, but not through electromagnetic forces like photons.
- Various astrophysical observations strongly suggest the existence of dark matter, but its precise composition and particle nature are still unknown.
Effects on the Universe:
- Dark Energy: The primary effect of dark energy is to drive the accelerated expansion of the universe.
- This expansion results in the increasing separation between galaxies over time. Dark energy is thought to dominate the energy density of the universe, comprising approximately 68% of the total mass-energy content.
- Dark Matter: Dark matter plays a crucial role in the formation and structure of galaxies and larger cosmic structures.
- Its gravitational influence binds galaxies together and provides the framework for the large-scale cosmic web.
- While dark matter does not emit or interact with light, its presence can be inferred from gravitational lensing, galaxy rotation curves, and the large-scale distribution of matter in the universe.
- Dark matter is estimated to constitute about 27% of the total mass-energy content of the universe.
Detectability:
- Dark Energy: Dark energy is challenging to detect directly because it does not interact with electromagnetic radiation.
- Its existence is inferred from the observational data related to the accelerating expansion of the universe, such as measurements of distant supernovae and the cosmic microwave background radiation.
- Dark Matter: Dark matter is also challenging to detect directly due to its non-interaction with light.
- However, its gravitational effects on visible matter and radiation allow astronomers to indirectly infer its presence.
- Various experimental efforts, such as those involving particle accelerators and underground detectors, aim to detect dark matter particles directly, though success has not yet been achieved.
Agni-Prime Ballistic Missile

- 05 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
India has successfully flight-tested the new generation ballistic missile Agni-Prime from the APJ Abdul Kalam Island off the coast of Odisha.
About Agni-Prime Missile:
- Agni-P or Agni-Prime is a new generation nuclear-capable medium-range ballistic missile (MRBM) developed by the DRDO that incorporates technological advances from Agni-IV and Agni-V and is considered a successor for Agni-I and Agni-II missiles in the operational service of the SFC.
- Agni-Prime, with a strike range of 1,000 to 2,000 km, has significant upgrades, which include composite motor casing, maneuverable reentry vehicle (MaRV), improved propellants, and navigation and guidance systems.
- It is a two-stage, surface-to-surface, road-mobile, and solid-fueled missile that is transported by a truck and launched via a canister.
- It is a ballistic missile with a dual redundant navigation and guidance system.
Features:
- Although Agni-Prime looks similar to Agni-III, the weight is reduced by half.
- Agni-P will replace older generation missiles such as Prithvi-II (350 km), Agni-II (2,000 km), Agni-III (3,000 km), and Agni-4 (4,000 km) ballistic missiles.
- Agni-Prime incorporates upgrades such as propulsion systems, composite rocket motor casings, and advanced navigation and guidance systems.
- Along with Agni-V, Agni-P will provide India with stronger deterrence against countries such as China and Pakistan.
- While Agni-V brings all of China within its strike range, Agni-P seems to have been developed to counter Pakistan's forces.
- Agni-P is developed to achieve maximum maneuverability against missile defense systems and higher accuracy for precision strikes.
What is a Ballistic Missile and why is it named so?
- A Ballistic missile follows a ballistic flight path - which comprises three phases of flight.
- In the first phase or the boost phase, the solid-fuel rocket engine propels the missile upwards and it has to rapidly gain velocity and altitude, by knifing through the densest parts of the earth's atmosphere.
- The second and unpowered phase of flight happens in the upper reaches of the earth's atmosphere or in space, where the missile travels along its pre-determined path, but without the power of its engines.
- It is known as the coast phase or mid-course phase and during this time, it travels along a horizontal path.
- During the coasting, the missile is either in space or the upper atmosphere, where it faces minimal resistance or drag.
- In the third and final phase or the terminal phase, the missile descends and gets back into the earth's atmosphere and flies towards its target, while being guided by its on-board systems.
Sannati: Ancient Buddhist Site
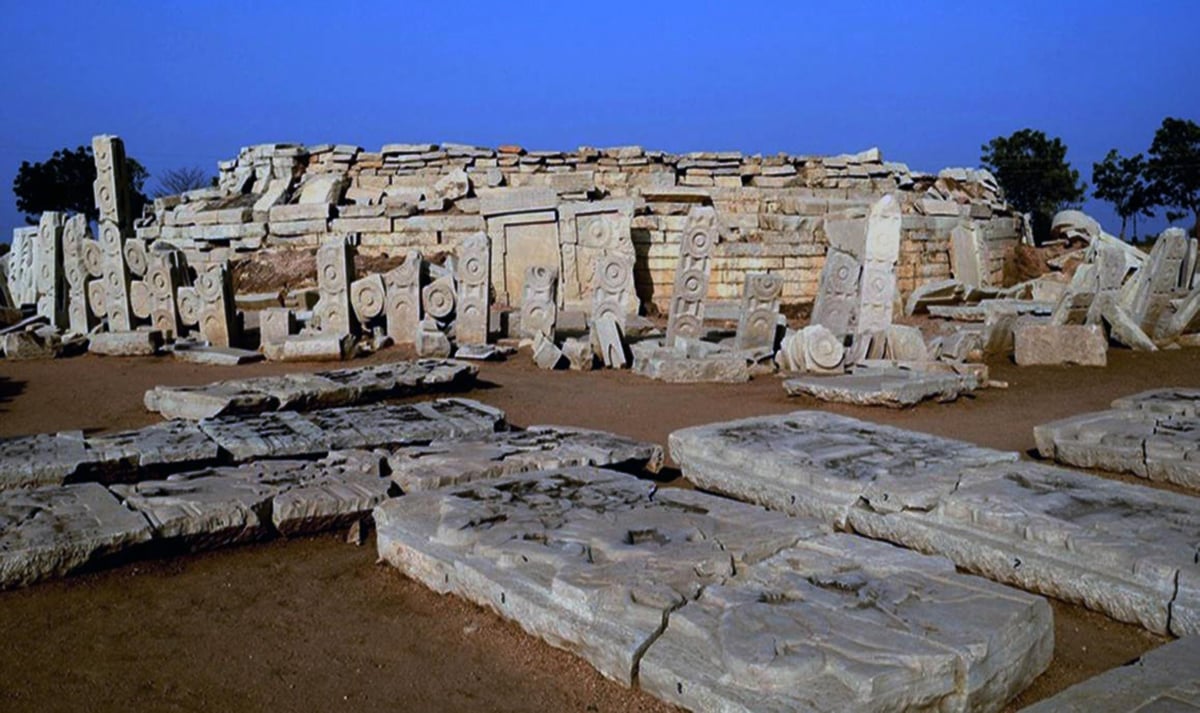

- 05 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
Left neglected for many years after it came to light through the ASI excavations in the 1990s, the ancient Buddhist site of Sannati on the bank of the Bhima River got a restoration project in 2022.
About Ancient Sannati Buddhist site:
- This ancient Sannati Buddhist site, situated alongside the Bhima River near Kanaganahalli in Karnataka's Kalaburagi district, offers a rich historical and cultural experience.
- Notably, it also boasts the Chandrala Parameshwari Temple, a popular attraction among tourists.
Key discoveries at this site include evidence of development across three distinct phases:
- Maurya, Early Satavahana, and Later Satavahana periods, span from the 3rd Century B.C. to the 3rd Century A.D.
- The Ranamandala area of Sannati presents a unique chronological timeline from prehistoric to early historic eras.
- Among the remarkable findings is an inscription in the Prakrit language, inscribed using Brahmi script.
- Noteworthy is the recovery of a significant stone sculpture portraying Mauryan Emperor Ashoka, surrounded by his queens and attendants, with the inscription "Raya Asoko" in Brahmi script, leaving no doubt about the identity of the depicted figure.
- The excavation also yielded around 60 dome slabs featuring sculptural depictions of Jataka stories, significant events in the life of Buddha, portraits of Shatavahana monarchs, and unique representations of Buddhist missionaries dispatched by Ashoka to various regions.
- Moreover, the ancient Nagavi Ghatikasthana, often dubbed as the Takshashila of the South, lies approximately 40 km from Sannati.
- Functioning as a prominent educational center akin to a modern-day university during the Rashtrakuta and Kalyana Chalukya dynasties from the 10th to 12th Centuries, it held great historical significance.
Microplastics
- 05 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
Recently, scientists have created plant-based plastic that doesn't create cancer-causing microplastics because 97% of it breaks down in the environment.
What is Microplastics?
- Microplastics are small plastic particles measuring less than 5 millimeters in diameter.
- These particles, which are distinguished from larger "macroplastics" like bottles and bags, stem from both commercial product development and the breakdown of larger plastics.
- Microplastics are commonly found in a variety of products, including cosmetics, synthetic clothing, plastic bags, and bottles.
- Unfortunately, many of these products can easily enter the environment as waste.
- Composed of carbon and hydrogen atoms linked in polymer chains, microplastics often contain additional chemicals such as phthalates, polybrominated diphenyl ethers (PBDEs), and tetrabromobisphenol A (TBBPA).
- There are two categories of microplastics: primary and secondary.
- Primary microplastics are intentionally designed for commercial use, including in cosmetics and microfibers shed from textiles like clothing and fishing nets.
- Secondary microplastics, on the other hand, result from larger plastic items breaking down due to environmental factors such as sunlight and ocean waves.
- Understanding the sources and types of microplastics is crucial for addressing their impact on the environment, wildlife, and human health, ultimately promoting more sustainable production and waste management practices.
Environmental Impacts of Microplastics:
- Microplastics pose significant environmental concerns due to their resistance to breaking down into harmless compounds, much like larger plastic items.
- Consequently, both primary and secondary microplastics accumulate and endure once introduced into the environment.
- In marine ecosystems, microplastics have the potential to amalgamate with harmful chemicals before being consumed by marine organisms.
- Despite efforts, conventional water treatment facilities struggle to completely eliminate microplastics from water sources.
- Additionally, microplastics contribute to air pollution as they are present in dust and airborne fibrous particles, further highlighting their pervasive impact on various environmental systems.
Project Akashteer

- 05 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
The Army has started the induction of control and reporting systems under ‘Project Akashdeer’ to bolster its air defense capabilities.
What is 'Project Akashteer'?
- 'Project Akashteer' is a cutting-edge initiative designed to automate air defense control and reporting processes by digitizing them.
- Developed by Bharat Electronics Limited (BEL) as part of the 'Atmanirbhar Bharat' initiative, this project is poised to significantly enhance the operational efficiency and integration of the Army's air defense mechanisms.
- By integrating radar and communication systems at all levels into a unified network, 'Akashteer' aims to deliver an unprecedented level of situational awareness and control.
- This will enable swift engagement of hostile targets, significantly reduce the risk of fratricide, and ensure the safety of friendly aircraft in contested airspace.
- A noteworthy aspect of 'Akashteer' is its emphasis on mobility and resilience.
- The system's control centers, designed to be vehicle-based and mobile, can maintain operational capabilities even in challenging communication environments.
- The system will facilitate the achievement of complete automation of air defense operations and significantly enhance the air defense posture of India.
- The induction of the systems has commenced in the Indian Army's Corps of Army Air Defense, marking a significant move towards enhancing India's defense capabilities and technology absorption.
How it will help India's air defense system?
- The 'Akashteer Command and Control Systems will significantly enhance India's air defense capabilities in several ways:
- Efficiency and Integration: By digitizing Air Defence Control and Reporting processes, 'Akashteer' will usher in unprecedented levels of efficiency and integration.
- This will enable the Indian Army to respond swiftly to hostile threats while minimizing the risk of friendly fire incidents.
- Situational Awareness: 'Akashteer' integrates radar and communication systems into a unified network, providing the Indian Army with unprecedented situational awareness.
- This will enable them to detect and engage hostile targets more effectively, ensuring the safety of friendly aircraft in contested airspace.
- Mobility and Resilience: The system's vehicle-based and mobile Control Centers are designed to maintain operational capabilities even in challenging communication environments.
- This ensures that the Indian Army can operate effectively in diverse terrain and under adverse conditions.
- Automation: Overall, the deployment of 'Akashteer' signifies a leap towards complete automation of air defense operations.
- This will enhance the Indian Army's ability to defend its airspace, ensuring a safer and more secure future for the country.
- The Indian Army has declared 2024 as the 'Year of Technology Absorption' and is undertaking various initiatives to induct niche technology and systems into its inventory.
- The induction of 'Akashteer' control centers is one of the major milestones achieved by the Army on its path to transformation to meet the current and futuristic requirements of complex air defense operations.
Ring of Fire
- 04 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
Nine people died and more than 1,000 were injured in Taiwan after the island was hit by its biggest earthquake in at least 25 years on Wednesday (April 4) morning.
What is the Ring of Fire?
- The Ring of Fire is essentially a string of hundreds of volcanoes and earthquake sites that run along the Pacific Ocean.
- It is a semicircle or horseshoe in shape and stretches nearly 40,250 kilometers.
- The Ring of Fire traces the meeting points of numerous tectonic plates, including the Eurasian, North American, Juan de Fuca, Cocos, Caribbean, Nazca, Antarctic, Indian, Australian, Philippine, and other smaller plates, which all encircle the large Pacific Plate, according to a report by National Geographic.
- It runs through 15 more countries including the USA, Indonesia, Mexico, Japan, Canada, Guatemala, Russia, Chile, Peru, and the Philippines.
Why is the Ring of Fire Vulnerable to Earthquakes?
- The Ring of Fire witnesses so many earthquakes due to constant sliding past, colliding into or moving above or below each other of the tectonic plates.
- As the edges of these plates are quite rough, they get stuck with one another while the rest of the plate keeps moving.
- An earthquake occurs when the plate has moved far enough and the edges unstick on one of the faults.
Why are There so Many Volcanoes in the Ring of Fire?
- The existence of volcanoes in the Ring of Fire is also due to the movement of tectonic plates.
- Many of the volcanoes have been formed through a process known as subduction.
- It takes place when two plates collide with each other and the heavier plate is shoved under each other, creating a deep trench.
- “When a ‘downgoing’ oceanic plate [like the Pacific Plate] is shoved into a hotter mantle plate, it heats, volatile elements mix, and this produces the magma.
- The magma then rises through the overlying plate and spurts out at the surface,” which leads to the formation of volcanoes, according to a report by DW.
- Most of the subduction zones on the planet are located in the Ring of Fire and that’s why it hosts a large number of volcanoes.
Why is Taiwan so Exposed to Earthquakes?
- Taiwan lies along the Pacific “Ring of Fire,” the line of seismic faults encircling the Pacific Ocean where most of the world’s earthquakes occur.
- The area is particularly vulnerable to temblors due to the tension accumulated from the interactions of two tectonic plates, the Philippine Sea Plate and the Eurasian Plate, which may lead to sudden releases in the form of earthquakes.
- The region’s mountainous landscape can magnify the ground shaking, leading to landslides.
myCGHS App

- 04 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
Recently, the government has launched the 'myCGHS' app for iOS to provide Central Government Health Scheme beneficiaries access to electronic health records, information, and resources.
About myCGHS app:
- The Union Health Ministry launched the myCGHS app for iOS (Apple Users) to provide easy access for the Central Government Health Scheme (CGHS) beneficiaries to their Electronic Health Records, information, and other resources.
- The myCGHS iOS app is developed by the technical teams of the National Informatics Centre (NIC) Himachal Pradesh and the NIC Health Team.
- It is a convenient mobile application offering features aimed at enhancing information and accessibility for CGHS beneficiaries.
- The app is said to offer a range of services including:
- Online appointment booking and cancellation
- Downloading CGHS card and index card
- Accessing lab reports from CGHS labs
- Checking medicine history
- Monitoring medical reimbursement claim status
- Accessing referral details
- Locating nearby wellness centers
- Staying updated with news and highlights, and
- Finding nearby impaneled hospitals, labs, and dental units.
- Additionally, users can access the contact details of wellness centers and offices conveniently.
- To ensure data security, the app also features security measures such as two-factor authentication and mPIN function to be able to access the app once they are logged in.
- Users on the Apple ecosystem can find the app on the App Store and download it free of charge.
- The myCGHS app has been available for Android users since February 2022.
Key Highlights of the Central Government Health Scheme (CGHS):
- CGHS provides healthcare services to registered employees and pensioners of the Central Government of India.
- Enrolled members receive reimbursement and cashless healthcare facilities through this scheme.
- It encompasses healthcare services from various systems of medicine including Allopathy, Homeopathy, Ayurveda, and Unani.
- CGHS beneficiaries have the flexibility to undergo treatment at any impaneled private hospital of their preference.
Ahobilam Temple

- 04 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
The Forest Department and Sri Lakshmi Narasimha Swamy Devasthanam (SLNSD) at Ahobilam have imposed certain restrictions on visitors arriving at the shrine, which is composed of nine different temples, situated within the Nallamala forest.
About Ahobilam Temple:
- The Ahobilam is a famous temple situated on the Nallamalai ranges in the state of Andhra Pradesh.
- The Nallamalai ranges south of river Krishna, down to Tirupati, and are called `Sesha Parvatha`.
- Sesha is the name of the king of serpents.
- The hood of the sesha is at Tirupati, the tail is at Srisailam, and the middle is situated at Ahobilam.
- Nallamalais at the tail are called Sringiri
- In the middle are called Vedagiri and
- Garudagiri referred to as the hood
- The shrine of the Ahobilam temple is situated on the top of the first range and is referred to as Upper Ahobilam and down below is called Lower Ahobilam.
- A huge temple surrounded by several buildings can be seen at the Upper Ahobilam.
- The main shrine or the "sacro sanctum" at Upper Ahobilam was carved out of a big egg-like rock with mandapams.
- There is a tank here, which supplies water to the residents of the Upper Ahobliam temple.
- There is a Lower Ahobilam in the below with a big temple and enclosures, It was built according to the South Indian style (Dravidian architecture).
Significance:
- Ahobilam is traditionally regarded as the place where Vishnu in the form of Narasimha killed the Rakshasa Hiranyakashipu to save his devotee Prahlada.
- The legend says that Narasimha emerged from a rock pillar to slay the Rakshasa.
- The moment is represented in several murtis in the various temples.
- Also, Garuda prayed for a vision of Narasimha in the form of Avathara, to fulfill his wish, and settled in nine forms across the hills in Ahobilam.
About Nallamala Forest:
- Nallamala Forest is among South India's largest expanses of untouched woodland, besides the Western Ghats.
Location:
- Situated across five districts in Andhra Pradesh and Telangana, it sprawls across the Nallamala Hills, a segment of the Eastern Ghats, south of the Krishna River.
- Part of the forest falls within the Nagarjunsagar-Srisailam Tiger Reserve, the nation's largest tiger reserve, boasting a significant tiger population.
Climate:
- Experiencing warm to hot conditions year-round, with scorching summers and mostly cool, dry winters.
- The majority of rainfall occurs during the southwest monsoon.
Vegetation:
- Tropical dry deciduous.
Flora:
- Nallamala Forest is rich in endemic species like Andrographis nallamalayana, Eriolaena lushingtonii, Crotalaria madurensis var, Dicliptera beddomei, and premna hamitonii.
Fauna:
- Home to over 700 animal species, including tigers, leopards, black bucks, wild hogs, peacocks, pangolins, Indian Pythons, King Cobras, and numerous rare bird species.
Glacial Lake Outburst Floods

- 04 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
Recently, the Uttarakhand government has constituted two teams of experts to evaluate the risk posed by five potentially hazardous glacial lakes in the region.
What is Glacial Lake Outburst Flood (GLOF)?
- A GLOF denotes the sudden release of meltwater from a moraine or ice-dammed glacial lake, typically due to dam failure.
- These events pose significant hazards, often resulting in catastrophic flooding downstream, leading to substantial loss of life and property.
- GLOF can be triggered by several factors, including earthquakes, heavy rains, and avalanches.
Key Features of GLOFs:
-
- Sudden water releases.
- Rapid occurrences lasting hours to days.
- Large downstream river discharges.
Threats Posed by GLOFs in the Himalayan Regions:
- Climate Change Impact: Climate change-induced glacier melt accelerates the formation or expansion of glacial lakes, heightening the risk of GLOFs.
- Vulnerability of Moraines and Dams: Glacial lakes situated behind unstable moraines or natural dams are prone to breaching, as evidenced by events like the Kedarnath floods in 2013.
- Immediate Flood Risks: Abrupt water releases trigger massive floods, causing extensive damage to homes, and infrastructure, and triggering landslides and sedimentation.
Mitigation Strategies for GLOFs:
- Risk Assessment and Zonation: Identify high-risk areas and implement necessary mitigation measures, including mapping and modeling, as outlined in the 'Guidelines for Preparation of Disaster Management Plans for Glacial Lake Outburst Floods (GLOF)'.
- Early Warning Systems: Establish monitoring networks with sensors to detect changes in glacial lakes and provide timely warnings to vulnerable communities.
- Utilization of Technology: Leverage remote sensing and GIS-based tools for monitoring glacial lakes and surrounding areas.
- Regulation of Construction: Implement construction codes to regulate development in high-risk zones, exemplified by the 'Guidelines for the Construction of Earthquake Resistant Buildings' developed by the NDMA.
- Capacity Building Initiatives: Enhance skills and resources through training programs conducted by institutions like the National Centre for Disaster Management, in collaboration with the private sector and NGOs.
- Infrastructure Development: Invest in infrastructure to redirect potential floodwaters away from communities and critical infrastructure.
The Marine Products Export Development Authority (MPEDA)

- 04 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
Officials recently emphasized that India's shrimp export value chain is certified by the Marine Products Export Development Authority (MPEDA), ensuring that abusive conditions are not tolerated at shrimp farms.
About the Marine Products Export Development Authority (MPEDA):
- The Marine Products Export Development Authority (MPEDA) was set up by an act of Parliament in 1972.
- The erstwhile Marine Products Export Promotion Council established by the Government of India in September 1961 was converged into MPEDA on 24th August 1972.
- MPEDA is given the mandate to promote the marine products industry with special reference to exports from the country.
- It is the nodal agency for the holistic development of the seafood industry in India to realize its full export potential as a nodal agency.
- Based on the recommendations of MPEDA, the Government of India notified new standards for fishing vessels, storage premises, processing plants, and conveyances.
- MPEDA’s focus is mainly on Market Promotion, Capture Fisheries, Culture Fisheries, Processing Infrastructure & Value addition, Quality Control, Research and Development.
- It is envisaged that this organization would take all actions to develop and augment the resources required for promoting the exports of “all varieties of fishery products known commercially as shrimp, prawn, lobster, crab, fish, shellfish, other aquatic animals or plants or part thereof and any other products which the authority may, by notification in the Gazette of India, declare to be marine products for (the) Act”.
- The Act empowers MPEDA to regulate exports of marine products and take all measures required for ensuring sustained, quality seafood exports from the country.
- MPEDA is given the authority to prescribe for itself any matters that the future might require for protecting and augmenting the seafood exports from the country.
- It is also empowered to inspect marine products, their raw materials, fixing standards, specifications, and training as well as take all necessary steps for marketing the seafood overseas.
Major Functions of MPEDA:
-
- Infrastructure registration for seafood export trade.
- Trade information collection and dissemination.
- Promotion of Indian marine products overseas.
- Assistance for infrastructure development and modernized processing.
- Aquaculture promotion for export production augmentation.
- Deep-sea fishing project promotion and equipment upgrade.
- Market promotion and publicity activities.
- Inspection of marine products and raw materials, setting standards.
- Training for fishermen, fish processing workers, and aquaculture farmers.
- Research and development through RGCA.
- Extension activities through NETFISH and NaCSA.
- Matters related to protecting and increasing seafood exports.
- Headquarters of MPEDA is located in Kochi, Kerala.
- Nodal Ministry: Ministry of Commerce and Industry.
- It has Trade Promotion offices in New Delhi, Tokyo, and New York.
South Korea’s ‘Artificial Sun’ KSTAR Reaches 100 Million Degrees Celsius
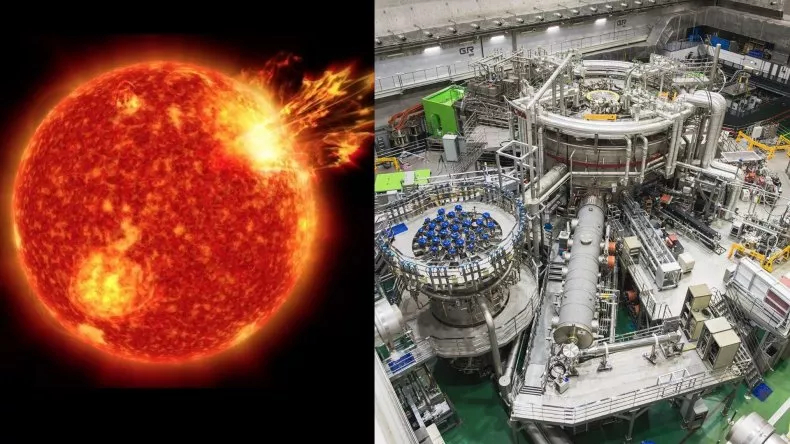
- 03 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
South Korean scientists have set a new world record for the length of time they sustained temperatures of 100 million degrees Celsius.
Key Highlights:
- The Korea Superconducting Tokamak Advanced Research (KSTAR) fusion reactor reached temperatures of 100 million Celsius for 48 seconds.
- Scientists hope to harness this unlimited energy.
- It is also significant that the KSTAR maintained the high confinement mode (H-mode) for over 100 seconds.
- H-mode is a stable plasma state.
- The earlier record of achieving this temperature was for 30 seconds which took place in 2021.
- The scientists at the Korea Institute of Fusion Energy (KFE) said they managed to extend the time by tweaking the process.
- They also used tungsten instead of carbon in the 'diverters', which extract heat and impurities produced by the fusion reaction.
- The International Thermonuclear Experimental Reactor in southern France has the world's biggest tokamak and what the scientists in South Korea achieve will help French scientists.
What is an Artificial Sun?
- An artificial sun typically refers to a device or facility designed to replicate some aspects of the nuclear fusion processes that occur naturally in stars like the Sun.
- These facilities aim to generate and sustain controlled nuclear fusion reactions, usually through the use of high temperatures, pressures, and magnetic fields.
- Scientists generally use a donut-shaped reactor called a tokamak in which hydrogen variants are heated to extraordinarily high temperatures to create a plasma.
- High temperatures and high-density plasmas are vital for the future of nuclear fusion reactors.
- This is called artificial Sun because it replicates the reaction of fusion taking place there and unleashes a massive amount of heat energy.
- The goal is to harness fusion energy as a potential future source of clean and abundant energy for various applications, including electricity generation.
What is Nuclear Fusion?
- Fusion is the reaction that makes the sun and other stars shine.
- It involves fusing hydrogen and other light elements to release massive power that experts in the field hope to harness for unlimited, zero-carbon electricity.
- In this reaction, two atoms of hydrogen or helium come together and fuse to unleash huge amounts of energy.
Wadge Bank
- 03 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
While India 'gave away' rights to Katchatheevu, in a subsequent pact, it secured sovereign rights in Wadge Bank near Kanyakumari.
What is Wadge Bank?
- Wadge Bank is a 10,000 square kilometer submarine plateau, of the sea south of Kanyakumari that is rich in biodiversity and considered India’s richest fishery resource.
- Wadge Bank, located near Cape Comorin, is home to more than 60 species of ornamental fish and other oceanic animals.
- It is a productive coastal area where three seas meet and tides create a rich fishing ground from May to October.
- Moreover, it is an invaluable treasure that indigenous people and communities depend on for food and resources, and is important to their culture.
How did India get control of the Wadge Bank?
- Wadge Bank came to India as part of the second of the two accords signed with Sri Lanka in the 1970s.
- Following the 1974 agreement under which Prime Minister Indira Gandhi ‘gave away’ Katchatheevu island to Sri Lanka, New Delhi, and Colombo signed another pact in 1976 under which the former bought Wadge Bank.
- On March 23, 1976, India and Sri Lanka signed the agreement on the maritime boundary in the Gulf of Mannar and the Bay of Bengal as part of which it was agreed that the Wadge Bank “lies within the exclusive economic zone of India, and India shall have sovereign rights over the area and its resources”.
- In the general description of Wadge Bank annexed with the treaty shared with the United Nations, it is described as “outside the territorial waters of India”.
- The Wadge Bank near Kanyakumari is rich in biodiversity and considered India’s richest fishery resource.
- As per the 1976 pact, Sri Lankan fishermen can’t engage in activities here.
- ??But at the request of Sri Lanka and as a gesture of goodwill, India agreed that Lankan fishing vessels licensed by the Government of India could fish in Wadge Bank for three years from its establishment as an exclusive economic zone of India with the stipulation that only six such vessels can fish and their catch cannot exceed 2,000 tonnes in a year.
- And, again at the request of the Sri Lankan government, India agreed to provide Colombo with 2,000 tonnes of fish of the quality, species, and at the price mutually agreed by the two sides for five years after the Lankans stopped fishing at the Wadge Bank.
BIMSTEC Charter

- 03 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
Recently, a significant majority in Nepal's Lower House backed the proposal to endorse the BIMSTEC Charter.
About the BIMSTEC Charter:
- The BIMSTEC Charter, officially signed and adopted during the Fifth BIMSTEC Summit in Colombo, Sri Lanka in 2022, serves as a cornerstone legal and institutional framework for the Bay of Bengal Initiative for Multi-Sectoral Technical and Economic Cooperation (BIMSTEC).
- This charter aims to establish a structured environment conducive to rapid economic development by delineating specific cooperation projects within the agreed areas of collaboration, along with potential expansions into additional areas as mutually agreed upon by Member States.
- Furthermore, the charter reaffirms the enduring commitment to the foundational principles and objectives of BIMSTEC, as articulated in the Bangkok Declaration of 1997.
The Importance of the BIMSTEC Charter:
- By officially adopting the BIMSTEC Charter, the organization transforms into a structured institution comprising member states situated along the Bay of Bengal, thereby formalizing their cooperation and dependence on this vital maritime region.
- The Charter grants BIMSTEC the authority to establish external relations with non-member states, developmental partners, as well as regional, UN, and international organizations, facilitating broader collaboration and engagement.
- Moreover, it underscores the imperative for a fair, just, equitable, and transparent global order while reiterating the commitment to multilateralism, with the United Nations at its core, and advocating for a rule-based international trading system.
About the Bay of Bengal Initiative for Multi-Sectoral Technical and Economic Cooperation (BIMSTEC):
- The Bay of Bengal Initiative for Multi-Sectoral Technical and Economic Cooperation (BIMSTEC) is a regional organization comprising seven Member States lying in the littoral and adjacent areas of the Bay of Bengal constituting a contiguous regional unity.
- This sub-regional organization came into being on 6 June 1997 through the Bangkok Declaration.
- It constitutes seven Member States:
- Five derive from South Asia, including Bangladesh, Bhutan, India, Nepal, and Sri Lanka, and
- Two from Southeast Asia, including Myanmar and Thailand.
- Initially, the economic bloc was formed with four Member States with the acronym ‘BIST-EC’ (Bangladesh, India, Sri Lanka, and Thailand Economic Cooperation).
- Following the inclusion of Myanmar on 22 December 1997 during a special Ministerial Meeting in Bangkok, the Group was renamed ‘BIMST-EC’ (Bangladesh, India, Myanmar, Sri Lanka and Thailand Economic Cooperation).
- With the admission of Nepal and Bhutan at the 6th Ministerial Meeting (February 2004, Thailand), the name of the grouping was changed to ‘Bay of Bengal Initiative for Multi-Sectoral Technical and Economic Cooperation’ (BIMSTEC).
Swell waves

- 03 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
As a result of the low-pressure area formed over the Atlantic Ocean moving into the Indian Ocean, high swell waves in the range of 11 m were formed.
What Are Swell Waves?
- Swell waves are characterized by the formation of long wavelength waves on the surface of the seas, propagating along the interface between water and air.
- They are commonly known as surface gravity waves due to their nature.
Origin:
- Unlike waves generated by immediate local winds, swell waves originate from distant weather systems.
- These waves are the result of prolonged wind action over a significant area of water, known as fetch.
- Even after the wind subsides or shifts, or the waves move away from the wind source, swell waves persist and continue to propagate.
Influencing Factors:
- The speed of the wind, the extent of ocean surface area affected by consistent wind direction (fetch), and the duration of time the winds persist over the same part of the ocean are all contributing factors to the formation and behavior of swell waves.
Characteristics of Swell Waves:
- Limited Frequency and Direction Range: Swell waves exhibit a narrower range of frequencies and directions compared to wind-generated waves occurring locally.
- Defined Shape and Direction: Swell waves assume a more distinct shape and direction, displaying less randomness than waves generated by local winds.
- Directional Orientation: Unlike wind waves, swell waves are characterized by the direction from which they originate rather than where they are headed.
- Wavelength Variation: Swell waves typically possess long wavelengths, although this can vary depending on the size of the water body.
- Generally, their wavelengths seldom exceed 150 meters.
- However, on occasion, particularly severe storms may produce swells with wavelengths surpassing 700 meters.
What are the Differences Between a Normal Wave and Swell Waves?
Normal Waves:
- Random Nature: Normal waves encompass any spontaneous disturbance occurring in the sea, exhibiting a wide array of forms, types, shapes, heights, periods, directions, and speeds.
- Varied Characteristics: Waves can manifest in diverse forms and attributes, subject to the prevailing conditions in the ocean.
Swell Waves:
- Deep-water Linear Waves: Swell waves are a distinct category of deep-water, linear waves originating or emerging from a chaotic wave system during external weather events due to wave dispersion.
- Defined Characteristics: Swells travel in a specific direction as uniform, high-speed, long waves that maintain consistency over time, with speeds determined by their wavelengths and periods.
- Extensive Travel: Swell waves traverse significantly greater distances compared to typical wave packets, exhibiting remarkable endurance.
- Independence from Local Weather: Swell waves remain unaffected by local weather systems, retaining their characteristics even in the presence of nearby weather phenomena.
OptiDrop Platform

- 03 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
The Centre for Cellular and Molecular Platforms (C-CAMP) in Bengaluru recently announced that it has developed a new platform that makes it easier and cheaper to study single cells.
About the OptiDrop Platform:
- The OptiDrop platform is an innovative microfluidic chip-based technology that simplifies and reduces the cost of single-cell analysis.
- Developed by the Centre for Cellular and Molecular Platforms (C-CAMP) in Bengaluru, India, OptiDrop enables precise and cost-effective analysis of single cells encapsulated in droplets.
- The platform boasts unique features, including live data visualization, a smaller data footprint, and a 'closed' system design that prevents external contamination.
- OptiDrop has potential applications in diagnostics, therapeutics, agriculture, and animal health, making it a versatile tool for various research areas.
Applications:
- This cutting-edge technology holds vast potential across diverse fields including diagnostics, therapeutics, agriculture, and animal health. Its versatility enables:
- Precise examination of individual cells during drug screening processes.
- Environment control for monitoring and addressing water contamination.
- Identification and sorting of CAR-T cells in immuno-oncotherapeutics.
- Selection of CRISPR-modified single cells.
- Identifying high-efficiency clones in single-cell genomics paves the way for advancements in personalized medicine and beyond.
- This platform is a testament to the potential of combining microfluidic technologies with advanced optical sensing techniques, paving the way for more efficient and cost-effective single-cell analysis.
What is the Centre for Cellular and Molecular Platforms (C-CAMP)?
- The Centre for Cellular and Molecular Platforms, or C-CAMP, was conceptualized by the Department of Biotechnology, Govt. of India in 2009 as an enabler or catalyst of cutting-edge research and innovation in the life sciences.
- C-CAMP has established itself as a major platform technology base, industry-oriented innovation hub, and incubator unit for life science research.
- With state-of-the-art technology platforms, a rich academic environment, and networks of business and industry-related resources, it encourages researchers and entrepreneurs to develop scientific tools and solutions for socially relevant problems.
- It is an institution with the core mandate of enabling cutting-edge life science research and innovation.
Havana Syndrome
- 02 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
The mysterious so-called Havana Syndrome symptoms experienced by U.S. diplomats in recent years have been linked to a Russian intelligence unit, according to a joint media investigation released on April 1.
What is Havana Syndrome?
- Havana Syndrome is a term used to describe a set of mental health symptoms experienced by US intelligence and embassy officials in various countries.
- The symptoms include hearing sounds without any external noise, nausea, vertigo, headaches, memory loss, and balance issues.
- The syndrome first came to light in 2016 when US officials stationed at the country's embassy in Havana, Cuba, began reporting these symptoms.
- The exact cause of the syndrome remains unknown, but it has been linked to high-frequency microwave transmissions.
- The syndrome was named after the city where it was first reported, Havana, and has since been reported by US government officials and military personnel serving at various stations across the world.
- The symptoms of Havana Syndrome are diverse and range from pain and ringing in the ears to cognitive dysfunction.
- Some individuals have also reported hearing loss, memory loss, and nausea.
- The exact cause of these symptoms remains unknown, with theories ranging from sonic weapons to mass psychogenic illness.
- Despite ongoing investigations, there is currently no known cure for Havana Syndrome.
- Research continues into the potential causes and treatments for this perplexing condition.
Affected Regions:
- As per reports from US media outlets, over the past few years, officials have documented more than 130 instances worldwide, including in Moscow, Russia, Poland, Georgia, Taiwan, Colombia, Kyrgyzstan, Uzbekistan, and Austria, among others, with similar accusations emerging in early 2018 from US diplomats stationed in China.
- Status in India: The first such incident was reported in 2021 when a US intelligence officer accompanying CIA director William Burns to New Delhi exhibited symptoms of Havana Syndrome.
Recent Investigation Findings and Russia's Response:
- A year-long investigation revealed evidence suggesting that unexplained anomalous health incidents, commonly known as Havana Syndrome, may be linked to the use of directed energy weapons wielded by members of Russia's GRU Unit 29155, responsible for foreign operations and implicated in various international incidents, including the 2018 attempted poisoning of defector Sergei Skripal in Britain.
- Moscow has dismissed the allegations as "groundless," asserting the absence of convincing evidence, deeming the accusations baseless and unfounded.
What are Microwave Weapons?
- Microwave weapons, a type of directed energy weapon, utilize high-frequency electromagnetic radiation to generate heat in the water within a target's skin, resulting in pain and discomfort.
- Several nations are believed to have developed such weapons for use against both humans and electronic systems.
- China unveiled its "microwave weapon," the Poly WB-1, at an air show in 2014, while the United States has also designed a prototype called the "Active Denial System."
- The existence of these weapons has raised concerns regarding their potential misuse, and further research is necessary to understand their long-term effects and implications on human health and security.
Bridge Fuel
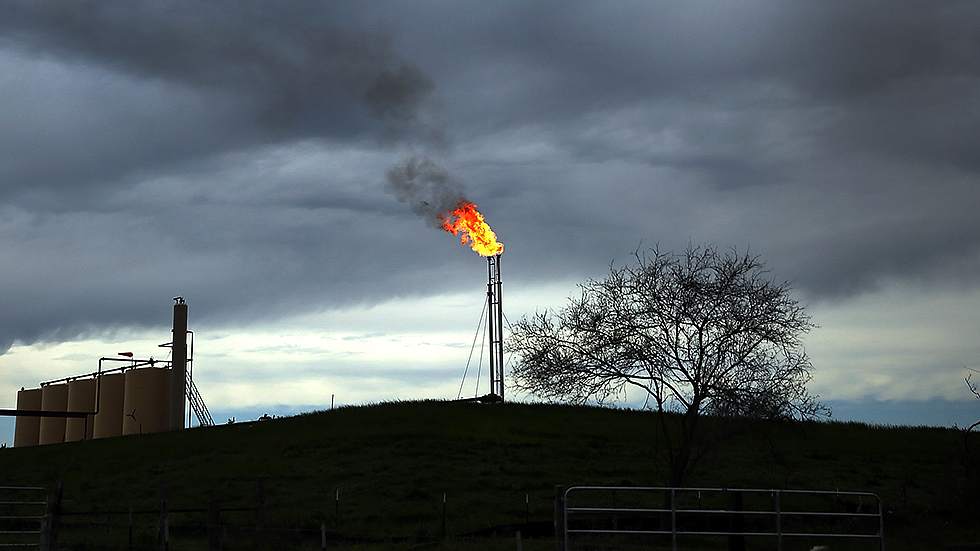

- 02 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
Natural gas has been called a ‘bridge fuel’ for countries looking to transition away from coal and oil dependency, and as they pursue a pathway towards renewables and electrification.
What is Bridge Fuel?
- Bridge fuel is a widely recognized term for fuels that aim to meet society's energy needs while minimizing environmental impacts during the transition to a clean, renewable energy economy.
- The primary objective of bridge fuels is to replace current fossil-fuel-dependent energy sources and pave the way for a greenhouse gas emission-free future.
- Natural gas is often considered a bridge fuel due to its lower greenhouse gas emissions during combustion compared to other fossil fuels.
- However, an ideal bridge fuel should also contribute to national energy independence and reduce pollution-related costs.
- Bridge fuels play a crucial role in balancing current energy demands with the long-term goal of achieving a sustainable, renewable energy landscape.
What is Natural Gas and How is it Formed?
- Natural gas, a non-renewable fossil fuel, is a mixture of hydrocarbon-rich gases.
- This colorless, odorless gas consists primarily of methane (70-90%), with smaller amounts of ethane and propane.
- Possible impurities include carbon dioxide, hydrogen sulfide, and nitrogen.
- Natural gas formation dates back millions to hundreds of millions of years ago when layers of organic matter (such as plants, animals, and diatoms) accumulated on land and ocean floors.
- Over time, these layers were buried under sediment and rock. Intense pressure and heat transformed this carbon and hydrogen-rich material into coal, oil, and natural gas.
- Today, natural gas reserves are found deep within the Earth's crust, often alongside other hydrocarbon deposits like coal and crude oil.
- The extraction, processing, and utilization of natural gas play a critical role in meeting global energy demands while transitioning towards cleaner, renewable energy sources.
Applications of Natural Gas:
- Natural gas undergoes processing and conversion into cleaner fuels for various applications.
- During processing, several valuable by-products like propane, ethane, butane, carbon dioxide, and nitrogen are extracted for further use.
Key uses of natural gas include:
- Generating electricity and heat, serving as a primary energy source for power plants.
- In compressed form (CNG), it fuels vehicles, providing a cleaner alternative to traditional gasoline or diesel.
- Powering boilers and air conditioning systems for residential, commercial, and industrial purposes.
- Manufacturing fertilizers, particularly ammonia, support the agricultural sector.
- As a cleaner fossil fuel, natural gas has a lower environmental impact than coal, emitting 50% less CO2.
- This makes it a critical component in the global shift towards more sustainable and eco-friendly energy solutions.
Leap Second

- 02 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
Glaciers are melting so fast that we may need to delay adding that 'negative leap second' to keep clocks aligned with Earth's rotation.
What Is a Leap Second?
- Leap seconds serve as a tool to synchronize global timekeeping with the Earth's gradually slowing rotation due to factors such as the melting and refreezing of ice caps.
- Introduced in the early 1970s, leap seconds are added periodically to Coordinated Universal Time (UTC) to align it with the Earth's actual rotation time.
- UTC is derived from the combined output of over 300 highly precise Atomic clocks worldwide, which offer accuracy within 1 second over millions of years.
- In contrast, Astronomical Time (UT1) corresponds to the Earth's rotation and determines day length.
- The primary reason for leap second additions is the irregularity of Earth's rotation, influenced by various factors like the moon's gravitational forces, causing ocean tides.
- This creates a gradual desynchronization between UTC and UT1. When the discrepancy between UTC and UT1 nears 0.9 seconds, a leap second is added to UTC, ensuring global timekeeping remains aligned with the Earth's rotation.
- Since its introduction, 27 leap seconds have been added to UTC, typically on June 30 or December 31.
- The leap second system continues to serve as an essential mechanism for maintaining synchronization between atomic timekeeping and the Earth's rotation.
What is Negative Leap Second?
- A negative leap second is a proposed time adjustment involving the subtraction of one second from our clocks to synchronize them with Earth's rotation.
- Unlike positive leap seconds, which are added to account for slower rotation, a negative leap second would address the Earth spinning faster than usual.
- So far, no negative leap second has been implemented since Earth's rotation has generally been slow in recent decades.
- However, as Earth's rotation has recently accelerated, timekeepers are considering using negative leap seconds for the first time.
- The International Earth Rotation and Reference Systems Service (IERS) closely monitors the Earth's rotation and determines when to add or subtract leap seconds.
- A decision to implement a negative leap second would serve as a corrective measure, ensuring our timekeeping systems remain aligned with the planet's rotation.
- While negative leap seconds have yet to be utilized, they offer a potential solution to the challenge posed by variations in Earth's rotational speed, ensuring the ongoing synchronization of our timekeeping methods with the planet's natural rhythms.
Presence of Ozone on Jupiter's Moon Callisto

- 02 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
An international team of scientists, including from India, has discovered strong evidence indicating the presence of ozone on Jupiter’s moon Callisto, shedding light on the complex chemical processes taking place on icy celestial bodies in the Solar System.
Study on the Formation of Ozone in Callisto's Icy Environment:
- A recent study examined the chemical evolution of sulfur dioxide (SO2)-rich astrochemical ice found on Callisto's surface when exposed to ultraviolet (UV) radiation.
- The investigation revealed a unique signature indicating the formation of ozone, which could have implications for the potential habitability of the Jovian moon.
- Callisto is Jupiter's second-largest moon and the third-largest moon in our solar system.
- It has a relatively stable surface, which could play a vital role in preserving subsurface oceans or potential habitats beneath its icy crust.
- The study analyzed UV absorption spectra data from ice samples containing SO2, a primary component of Callisto's surface ice, and observed the generation of ozone under UV irradiation.
- Ozone formation on Callisto could have implications for the moon's astrobiological potential, as ozone can protect the surface from harmful radiation.
- Further research is needed to better understand the implications of this discovery on Callisto's habitability and the potential for future exploration missions.
Callisto's Distinctive Environment:
- Following Saturn, Jupiter boasts the second-highest number of moons in the Solar System, with Callisto ranking among its largest moons and holding the position of the third-largest moon overall, after Ganymede and Titan.
- Comprised predominantly of water ice, rocky elements, sulfur dioxide, and traces of organic compounds, Callisto presents a compelling potential for harboring life beyond Earth within the Solar System.
- The moon's extensively cratered surface bears witness to a lengthy history of impacts from asteroids and comets.
Importance of the Research:
- The identification of ozone on Callisto hints at the existence of oxygen, a crucial component essential for the development of intricate molecules vital for life, including amino acids, thus prompting inquiries into the moon's potential for sustaining life.
- This finding also has implications for other icy moons within our Solar System, offering insights that could broaden our comprehension of habitable environments beyond Earth.
Significance of Ozone:
- Consisting of three oxygen atoms bonded together, the ozone molecule plays a pivotal role in shielding life on Earth.
- Situated in the lower region of the Earth's stratosphere, approximately 15-35 kilometers above the surface, the ozone layer acts as a protective barrier.
- Without this layer, ultraviolet radiation would intensify, posing significant threats to various species and disrupting ecosystems.
- Ultraviolet-B and ultraviolet-C, with wavelengths ranging from 290 to 320 nanometers and 100 to 280 nanometers respectively, can cause DNA damage, and mutations, and elevate the risk of skin cancer and cataracts in humans.
- Furthermore, ultraviolet light can impede plant growth and adversely affect diverse organisms.
Voter Verifiable Paper Audit Trail (VVPAT)
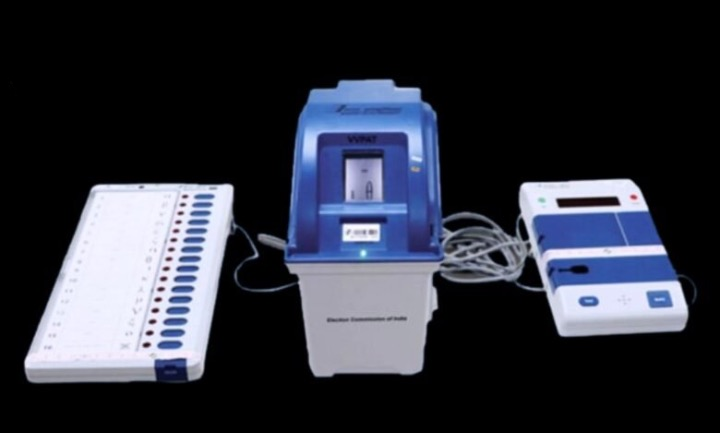

- 02 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
The Congress has hailed as an “important first step” the Supreme Court’s notice to the Election Commission and the Centre on a plea seeking a complete count of VVPAT slips and said the matter should be decided before the Lok Sabha polls commence.
What is the Voter Verifiable Paper Audit Trail (VVPAT)?
- The Voter Verifiable Paper Audit Trail, or VVPAT system, was first introduced in 2014 for the first time during the 2014 Lok Sabha Elections.
- The ECI conducted pilot tests of VVPAT systems in a few constituencies in 2011, and after successful trials, VVPAT was gradually deployed across all polling stations in subsequent elections.
- It is connected to Electronic Voting Machines (EVM) and enables voters to confirm that their votes were cast as intended.
- The concept of VVPAT was to enhance the credibility and transparency of EVMs.
What are VVPAT Slips?
- VVPAT slips are an integral part of the EVMs used in elections.
- It provides a physical paper trail for voters to verify that their vote has been correctly recorded by the EVM.
- It ensures transparency and accountability in the electoral process by allowing voters to verify their vote before casting it finally.
- The VVPAT produces a paper slip that permits the voter to confirm the accuracy of their vote on the EVM.
- This slip displays the name and symbol of the party chosen by the voter.
- Additionally, the machine features a transparent window through which the voter can observe the printed slip.
- Subsequently, the slip is securely deposited into a sealed compartment within the machine.
- However, in the event of a dispute, this sealed box can be opened for further examination.
Controversies Surrounding VVPAT:
- Despite its intended purpose of enhancing transparency, VVPAT has been subject to several controversies over the years.
- Some critics have raised concerns about the reliability of VVPAT systems, citing instances of malfunctioning printers, paper jams, and discrepancies between electronic and paper records.
- The Opposition parties within the INDIA bloc have been advocating for the full counting of VVPATs, to bolster public trust in the EVMs, which itself has been subjected to intense scrutiny recently.
- Their concern has mostly stemmed from allegations of delay in the printing and displaying of VVPAT slips for every vote, which they claim can significantly increase the time required for vote counting.
Supreme Court’s intervention in VVPATs:
- In April 2019, the SC asked the poll panel to increase the number of EVMs that undergo VVPAT physical verification from one to five per assembly segment in a parliamentary constituency.
- In the month of May the same year, the Supreme Court dismissed a writ petition seeking 100 percent counting of VVPAT in the 2019 Lok Sabha elections.
- Earlier in the same month, the Supreme Court had also dismissed the review petition filed by opposition parties to increase verification of VVPAT-EVM to 50 percent.
Katchatheevu Island
- 01 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
Prime Minister Narendra Modi once again attacked the Congress about its decision to “callously give away” the island of Katchatheevu.
About the Island of Katchatheevu:
- Katchatheevu is an uninhabited area located between India and Sri Lanka in the Palk Strait.
- It measures around 1.6 km in length and slightly over 300 m wide at its broadest point.
- Situated northeast of Rameswaram, it is approximately 33 km away from the Indian coast.
- Moreover, it is positioned about 62 km southwest of Jaffna, at the northern tip of Sri Lanka, and 24 km from the inhabited Delft Island, which is a part of Sri Lanka.
- Katchatheevu is not suited for permanent settlement as there is no source of drinking water on the island.
History of the island:
- Being the product of a 14-century volcanic eruption, Katchatheevu is relatively new in the geological timescale.
- In the early medieval period, it was controlled by the Jaffna kingdom of Sri Lanka.
- In the 17th century, control passed to the Ramnad zamindari based out of Ramanathapuram, about 55 km northwest of Rameswaram.
What is the dispute?
- The island became part of the Madras Presidency during the British Raj.
- But in 1921, both India and Sri Lanka, at the time British colonies, claimed Katchatheevu to determine fishing boundaries.
- A survey marked Katchatheevu in Sri Lanka, but a British delegation from India challenged this, citing ownership of the island by the Ramnad kingdom.
- This dispute was not settled until 1974.
What is the Agreement on Katchatheevu Island?
- In 1974, Indira Gandhi made attempts to settle the maritime border between India and Sri Lanka, once and for all.
- As a part of this settlement, known as the ‘Indo-Sri Lankan Maritime Agreement’, Indira Gandhi ‘ceded’ Katchatheevu to Sri Lanka.
- At the time, she thought the island had little strategic value and that ceasing India’s claim over the island would deepen its ties with its southern neighbor.
- Moreover, as per the agreement, Indian fishermen were still allowed to access Katchatheevu “hitherto”.
- Unfortunately, the issue of fishing rights was not ironed out by the agreement.
- Sri Lanka interpreted Indian fishermen’s right to access Katchatheevu to be limited to “rest, drying nets and for visit to the Catholic shrine without a visa”.
- Another agreement in 1976, during the period of Emergency in India, barred either country from fishing in the other’s Exclusive Economic Zone.
- Again, Katchatheevu lay right at the edge of the EEZs of either country, retaining a degree of uncertainty about fishing rights.
How did the Sri Lankan Civil War Impact Katchatheevu?
- Between 1983 and 2009, the border dispute remained on the back burner as a bloody civil war raged in Sri Lanka.
- With the Sri Lankan naval forces preoccupied with their task of cutting off supply lines of the LTTE based out of Jaffna, incursions by Indian fishermen well into Sri Lankan waters were commonplace.
- Bigger Indian trawlers were especially resented as they would not only tend to overfish but also damage Sri Lankan fishing nets and boats.
- In 2009, the war with the LTTE ended, and things dramatically changed. Colombo beefed up its maritime defenses and turned its focus to Indian fishermen.
- Facing a depletion of marine resources on the Indian side, they would frequently enter Sri Lankan waters as they had been doing for years, but finally began facing consequences.
- To date, the Sri Lankan navy routinely arrests Indian fishermen and there have been many allegations of custodial torture and death.
- The demand for Katchatheevu is revived each time such an incident happens.
Indian Government Stance on Katchatheevu Island:
- The Union government’s position on Katchatheevu has largely remained unchanged.
- It has argued that since the island had always been under dispute, “no territory belonging to India was ceded nor sovereignty relinquished.”
Kodaikanal Solar Observatory (KOSO)

- 01 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
Since ancient times, seafarers, mathematicians, astronomers, and physicists have all diligently studied and tracked the Sun and its phenomena, with the establishment of the Madras Observatory by the British East India Company in 1792 marking a pioneering effort in this region.
About Kodaikanal Solar Observatory:
- The Kodaikanal Solar Observatory is a solar observatory owned and operated by the Indian Institute of Astrophysics (IIA), Bengaluru.
- It is on the southern tip of the Palani Hills 4 kilometers from Kodaikanal (Tamil Nadu).
- The Government of India separated Astrophysics from the India Meteorological Department (IMD) in April 1971.
- From solar data recorded on basic photographic plates or films, the 125-year-old KoSO boasts a mammoth digital repository containing 1.48 lakh digitized solar images of 10 terabytes.
- These include 33,500 white-light images (showing sunspots) and thousands of other images of the Sun recorded every day since the start of the 20th century.
- KoSO is the only observatory offering high-resolution digitized images for such a long period (with coverage of more than 75 percent).
- Today, it houses a spectrum of advanced instruments like the H-alpha telescope to perform full disc imaging, a White light Active Region Monitor (WARM) with calcium and sodium filters to make full disc simultaneous observations of the photosphere and chromosphere layers of the Sun, a solar tunnel telescope and more.
Links to the Great Drought:
- Scanty rainfall over south India during the winter monsoon of 1875 triggered one of the worst droughts the country had experienced till then.
- Multiple failed crops over the famine-stricken peninsular India killed 12.2 to 29.3 million people across the Madras and Mysore Provinces during 1875-1877.
- India, along with China, Egypt, Morocco, Ethiopia, southern Africa, Brazil, Columbia, and Venezuela, suffered concurrent multi-year droughts during 1876-1878, later named the Great Drought, and an associated global famine that killed nearly 50 million.
- The drought was thought to be due to multiple reasons:
- Solar activity
- Cool Pacific Ocean conditions followed by a record-breaking El Nino (1877-1878)
- Strong Indian Ocean Dipole and
- Warm North Atlantic Ocean conditions.
Solar Physics Observatory in Palani Hills:
- Established in response to the British Raj's acknowledgment of solar activity's link to India's weather patterns, the Palani Hills Solar Physics Observatory, also known as the Indian Solar Observatory, was founded to conduct systematic studies on solar phenomena and their correlation with Indian meteorology.
- Located in Kodaikanal, selected for its favorable atmospheric conditions after careful consideration by Charles Michie Smith (a Professor of Physics at the Madras Christian College), the observatory was officially sanctioned by the Government of India in August 1893 and inaugurated by Lord Wenlock (the then Governor of Madras) in 1895.
- Commencing systematic observations in 1901, it merged with the Madras Observatory, enriching its instrumentation.
- Notable discoveries ensued, including the identification of the Evershed Effect.
- Over time, the observatory expanded its research domains to encompass cosmic rays, radio astronomy, and ionospheric physics, among others, solidifying its status as a pioneering institution in the field of astrophysics.
- Notably, it initiated solar radio observations in 1952, marking a significant milestone in Indian solar research.
- Despite the closure of contemporaneous observatories, the Palani Hills Solar Physics Observatory has endured, continuing to contribute to our understanding of the Sun and its effects on Earth's climate and space weather.
Why Study the Sun?
- Being the primary source of energy, life on Earth is supported by the Sun.
- Any change on the solar surface or its periphery could significantly affect the Earth’s atmosphere.
- Powerful solar storms and solar flares can be potentially harmful to Earth’s satellite-based operations, power grids, and navigational networks.
- The KoSO (Kodaikanal Solar Observatory), which has been imaging the Sun for over a century now, has a rich repository of data.
- This is extremely useful not only to reconstruct the Sun’s historic past but also to link its behavioral changes to better understand and predict its future and its impact on life on Earth and Space weather.
Fukushima Water Issue

- 01 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
Recently, Japan announced that its experts have engaged in discussions with their Chinese counterparts to address Beijing's concerns regarding the release of treated radioactive wastewater from the damaged Fukushima Daiichi nuclear power plant into the sea.
What is the Fukushima Water Issue?
- In 2021, the Japanese government unveiled plans to gradually discharge over one million tonnes of contaminated water from the Fukushima nuclear plant into the ocean over the next three decades.
- The contaminated water is a residual product of the devastating 2011 earthquake and tsunami that incapacitated the Fukushima Daiichi nuclear power plant, resulting in the release of radioactive materials.
- After more than ten years of storing this wastewater, Japan asserts that they are facing storage space limitations and contends that the treated water is now safe for release.
Concerns Surrounding the Fukushima Water Discharge:
- Tritium and Carbon-14: The water from Fukushima undergoes filtration via the Advanced Liquid Processing System (ALPS), effectively reducing most radioactive contaminants to acceptable safety levels, except tritium and carbon-14.
- While both emit low levels of radiation, consumption in large quantities could potentially pose risks.
- Insufficient Research: Scientists emphasize the need for further investigation into the potential impact of the water discharge on the ocean bed and marine ecosystems.
- The Pacific Islands Forum regional group has labeled the proposed plan as "another significant nuclear contamination disaster," citing ongoing challenges faced by its member nations due to past US nuclear testing.
Pacific Islands Forum (PIF):
- The Pacific Islands Forum (PIF) is an inter-governmental organization that aims to enhance cooperation among countries and territories of Oceania, including the formation of a trade bloc and regional peacekeeping operations.
- It was founded in 1971 as the South Pacific Forum (SPF), and changed its name in 1999 to "Pacific Islands Forum", to be more inclusive of the Forum's Oceania-spanning membership of both north and south Pacific island countries, including Australia.
- It is a United Nations General Assembly observer.
- The PIF secretariat is located in Suva, the capital of Fiji.
Nuclear Incidents:
- A nuclear and radiation incident denotes an occurrence that has resulted in significant repercussions for individuals, the environment, or the facility involved.
- These may entail fatal consequences for individuals, substantial releases of radioactivity into the environment, or reactor core meltdowns.
- Globally, there have been a total of 99 incidents at nuclear power plants.
- Fifty-seven of these incidents have transpired since the Chornobyl disaster, with the United States accounting for 57% of all nuclear-related incidents.
- Noteworthy nuclear power plant mishaps encompass:
- Fukushima Daiichi nuclear disaster (2011)
- Chernobyl disaster (1986)
- Three Mile Island accident (1979), and
- The SL-1 accident (1961).
Real Estate (Regulation and Development) Act, 2016

- 01 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
Eight years after Parliament passed the Real Estate (Regulation and Development) Act, 2016, the Union Ministry of Housing and Urban Affairs is in the process of reviewing the functioning of the Act, including by holding regular meetings with homebuyers and setting up a data collection unit within the Ministry.
What Is Real Estate (Regulation & Development) Act, 2016 (RERA)?
- The Real Estate (Regulation & Development) Act, 2016 is an act of the Parliament of India that strives to protect home buyers and helps escalate the investment made in the real estate industry.
- It was established under this Act to regulate the real estate sector.
- Additionally, it acts as the adjudicating body for faster dispute resolution related to the real estate industry.
The Primary Objectives of the Act:
- Ensuring Transparency: Promoting transparency in the real estate sector regarding the sale of flats, apartments, plots, buildings, or any real estate project.
- Establishing Dispute Resolution: Setting up an adjudicating mechanism to swiftly resolve disputes.
- Protecting Buyer Interests: Safeguarding the interests of buyers/allottees in the real estate domain.
- Building Trust: Fostering trust between buyers and promoters by leveraging regulatory authority.
- Furthermore, the Act mandates that Real Estate Regulatory Authorities establish and maintain a web portal containing pertinent details of all registered real estate projects for public access.
Reasons for RERA Implementation:
- The introduction of RERA was necessitated by challenges faced by the Indian real estate sector since 2012, including factors such as unemployment, recession, low rental yield, inventory pile-up, and ambiguous tax and arbitration frameworks.
Projects Covered by RERA:
- RERA covers commercial and residential projects, including plotted developments, that exceed 500 square meters or comprise more than 8 units.
- Additionally, projects lacking a Completion Certificate prior to the Act's commencement are subject to its provisions.
Benefits of RERA Implementation:
- Standardization: RERA ensures uniformity in the real estate sector concerning aspects like carpet areas and common areas, thereby preventing malpractices such as alterations in layout, area, agreements, and specifications.
- It also mandates disclosure of details regarding brokers, architects, and contractors.
- Timely Delivery: Developers are obligated to adhere to scheduled delivery timelines for office spaces or homes.
- Failure to comply may result in stringent penalties or imprisonment for the developer.
- Regulatory Compliance: RERA mandates obtaining clearance from government departments before the sale of any residential or commercial property.
- Financial Transparency: Developers are required to maintain separate bank accounts for each project, enhancing financial transparency and accountability.
- Warranty Protection: Buyers are empowered to report any structural defects in the building to the developer within one year of possession, with the developer obligated to rectify them free of charge.
Challenges Associated with RERA:
- Limited Scope: The regulations of RERA do not extend to ongoing projects or those stalled due to clearance issues, potentially leaving certain projects outside its jurisdiction.
- Approval Delays: Delays in approval and clearance from government agencies may impede the timely completion and delivery of real estate projects, affecting both developers and buyers.
- Exemption for Small Developers: Small-scale developers overseeing projects smaller than 500 square meters are exempt from RERA's provisions, and registration with the regulatory authority is not compulsory for them.
- Project Launch Delays: Projects cannot be launched without necessary clearances, which may result in delays in the commencement of new projects.
International Network for Terrestrial Research and Monitoring in the Arctic (INTERACT)

- 01 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
In a recent development, Arctic research stations under INTERACT reported a significant loss of over 1,000 billion tonnes of ice over the past four decades.
About the International Network for Terrestrial Research and Monitoring in the Arctic (INTERACT):
- The International Network for Terrestrial Research and Monitoring in the Arctic (INTERACT) is an infrastructure project under the auspices of SCANNET.
- INTERACT specifically seeks to build capacity for research and monitoring in the European Arctic and beyond and is offering access to numerous research stations through the Transnational Access program.
- It aims to build capacity for identifying, understanding, predicting, and responding to diverse environmental changes throughout the wide environmental and land-use envelopes of the Arctic.
- The project, which is funded by the EU, has the main objective of building capacity for identifying, understanding, predicting, and responding to diverse environmental changes throughout the wide environmental and land-use envelopes of the Arctic.
- INTERACT is a multidisciplinary initiative; collectively, its stations host thousands of scientists worldwide who collaborate on projects spanning glaciology, permafrost studies, climate research, ecology, biodiversity, and biogeochemical cycling.
About the Scandinavian Network for Coordinated Observation of the Atmosphere and Terrestrial Environment (SCANNET):
- SCANNET is a circum-Arctic network of currently 77 terrestrial field bases in northern Europe, Russia, the US, Canada, Greenland, Iceland, the Faroe Islands, and Scotland as well as stations in northern alpine areas.
- The primary aim of SCANNET is to facilitate coordinated observations and research activities focused on the atmosphere and terrestrial environment in the Arctic region.
- These observations cover a wide range of scientific disciplines, including meteorology, climatology, ecology, geology, and environmental science.
- By leveraging the diverse geographical locations of its field bases, SCANNET enables scientists to study various environmental phenomena, such as changes in weather patterns, shifts in ecosystems, permafrost dynamics, and the impact of climate change on Arctic landscapes.
- Moreover, SCANNET serves as a platform for collaboration and information sharing among researchers from different institutions and countries.
- It fosters partnerships and promotes the exchange of data, methodologies, and best practices, thereby enhancing our understanding of Arctic processes and their global implications.
X-Class Solar Flares

- 30 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
Recently the Earth was hit by an X-class solar flare that was strong enough to ionize part of the planet's atmosphere.
What are Solar Flares?
- Solar flares are large explosions from the surface of the sun that emit intense bursts of electromagnetic radiation.
- The intensity of the explosion determines what classification the flare belongs to.
- The most powerful are X-class flares, followed by M-, C-, and B-class; A-class flares are the smallest.
- These flares can be visible as bright flashes in a particular region of the sun and can last several minutes.
- Solar flares occur when magnetic energy builds up in the solar atmosphere and is released suddenly.
- These outbursts are intrinsically linked to the solar cycle — an approximately 11-year cycle of solar activity driven by the sun's magnetic field.
What Causes Solar Flares?
- The sun's surface is a magnetically mixed-up place.
- Magnetic fields are created from electrically charged gases generating electrical currents that act as a magnetic dynamo inside the sun.
- These magnetic fields twist, tangle, and reorganize themselves due to the turbulent nature of the gases that create them.
- This unsettled magnetic field behavior — also known as solar activity — can trigger solar flare eruptions from the surface that release vast amounts of electromagnetic radiation — a form of energy that includes radio waves, microwaves, X-rays, gamma rays, and visible light.
- Solar flares tend to originate from regions of the solar surface that contain sunspots — darker, cooler portions of the solar surface where magnetic fields are particularly strong.
- As such, the number of sunspots can indicate the likelihood of a solar flare eruption.
- Solar activity follows an approximately 11-year cycle with the peak of sunspot activity coinciding with the solar maximum and a sunspot hiatus coinciding with the solar minimum.
- During periods of low solar activity when no sunspots are present, it is unlikely that a solar flare will occur.
What are X-Class Solar Flares?
- Solar flares are categorized into five classes based on the intensity of emitted X-rays, with each class letter denoting a 10-fold increase in energy output, akin to the Richter scale for earthquake strength assessment.
- X-class flares are the most powerful solar flares.
- Then there are M-class flares that are 10 times smaller than X-class flares, then C-class, B-class, and finally A-class flares which are too weak to significantly affect Earth.
- Within each letter class, a finer scale from 1 to 9 gives the flare assessment greater precision with larger numbers representing more powerful flares within the class.
- However, X-class flares can break this nine-point rating mold with higher ratings, since there is no class more powerful than X-class.
- Fortunately, X-class flares occur on average about 10 times per year.
How do Solar Flares Affect the Earth?
- Disruption of Satellite Communications: Solar flares can interfere with satellite communications, GPS signals, and radio transmissions, causing disruptions or blackouts in telecommunications and navigation systems.
- Auroral Displays: Intense solar flares can trigger colorful auroras, or Northern and Southern Lights, as charged particles interact with Earth's magnetic field, creating stunning light displays in the polar regions.
- Power Grid Disturbances: Severe solar flares have the potential to induce geomagnetic storms that can overload power grids, leading to widespread power outages and damage to electrical infrastructure.
- Radiation Hazards: Solar flares emit harmful radiation, particularly in the form of ultraviolet and X-rays, which can pose risks to astronauts in space and airline passengers at high altitudes.
- Impact on Electronics: The influx of charged particles during solar flares can induce currents in electrical circuits, potentially damaging or disrupting sensitive electronic devices, such as computers, satellites, and spacecraft.
Vaikom Satyagraha

- 30 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
Vaikom, a temple town in the princely state of Travancore, saw the start of a non-violent agitation on March 30, 1924 — the first among temple entry movements that would soon sweep across the country.
What is Vaikom Satyagraha?
- Vaikom Satyagraha was a significant non-violent protest against the caste-based discrimination prevalent in the princely state of Travancore, characterized by a feudal, militaristic governance system entrenched with rigid social norms and customs.
- Discriminatory practices, such as the prohibition of lower castes like the Ezhavas and Pulayas from temple entry and even walking on roads near temples, were pervasive.
Contribution of Leaders:
- In 1923, the issue was brought to attention as a resolution by Madhavan during the Kakinada meeting of the All India Congress Committee.
- Subsequently, the Kerala Pradesh Congress Committee formed the Congress Untouchability Committee in January 1924 to address the matter.
- Pioneers of the Vaikom Satyagraha movement include Madhavan, K.P. Kesava Menon, then secretary of the Kerala Pradesh Congress Committee, and K. Kelappan, a prominent Congress leader and educationist known as Kerala Gandhi.
Factors Leading to Satyagraha:
- The expansion of Christian missionaries, backed by the East India Company, led to conversions among lower castes seeking liberation from an oppressive system.
- Maharaja Ayilyam Thirunal initiated several progressive reforms, notably the establishment of a modern education system providing free primary education for all, including lower castes.
- These reforms, alongside the influence of capitalism, contributed to the emergence of new social hierarchies, sometimes conflicting with traditional ones.
Commencement of Satyagraha:
- On March 30, 1924, the Satyagrahis embarked on a procession towards the restricted public roads, where a board warned oppressed communities against walking (near the Vaikom Mahadeva temple).
- Despite being halted 50 yards away, individuals such as Govinda Panikkar (Nair), Bahuleyan (Ezhava), and Kunjappu (Pulaya), adorned in khadi attire, courageously defied the prohibition orders.
- Subsequently, they were stopped by the police and, in protest, sat on the road, resulting in their arrest.
- Following this incident, three volunteers from different communities were designated each day to walk on the prohibited roads. Within a week, the movement's leaders were all apprehended by authorities.
Role of Women:
- Large-scale participation of women was witnessed for the first time during the Satyagraha, marking the passage of women into the socio-political consciousness of the country.
- Nagammai, the wife of Periyar, and Kannammal, his sister, played unprecedented roles in the struggle.
Arrival of Gandhi:
- In March 1925, Gandhi arrived at Vaikom and engaged in discussions with leaders from various caste groups.
- He also met with the Maharani Regent at her Varkala camp.
Withdrawal of Vaikom Satyagraha:
- The Vaikom Satyagraha was officially terminated on November 30, 1925, following consultations between Gandhi and W.H. Pitt, the police commissioner of Travancore.
- A compromise was reached, leading to the release of all prisoners and the granting of access to roads.
Temple Entry Proclamation:
- In 1936, the historic Temple Entry Proclamation was signed by the Maharaja of Travancore, abolishing the age-old ban on temple entry.
Significance:
- During a period of growing nationalist fervor and widespread agitation, the Vaikom Satyagraha emerged as a pivotal catalyst for social reform.
- Introducing Gandhian principles of nonviolent resistance to Travancore for the first time, marked a significant departure from traditional modes of protest.
- Enduring for over 600 consecutive days, despite social pressure, police interventions, and even a natural disaster in 1924, the steadfastness of the movement is commendable.
- The Vaikom Satyagraha fostered unprecedented unity across caste lines, showcasing a remarkable display of solidarity among diverse communities.
India-led ‘Group of Friends’

- 30 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
At a high-level meeting of the India-led 'Group of Friends (GOF), India launched a new database designed to record crimes against UN peacekeepers and monitor progress in holding perpetrators accountable.
About the 'Group of Friends':
- The Group of Friends (GOF) was launched by India in 2022 to promote accountability for crimes against the Blue Helmets during its presidency of the UN Security Council.
- India, Bangladesh, Egypt, France, Morocco, and Nepal are co-chairs of the GOF, which comprises 40 member states.
Key objectives of the group include:
- Engaging and sharing information with the UN Secretary-General to assist member states hosting or having hosted peacekeeping operations in bringing perpetrators of crimes against peacekeepers to justice.
- Serving as an informal platform at the UN to exchange information, share best practices, and mobilize resources to facilitate accountability for crimes against peacekeepers.
- Monitoring progress on bringing accountability for crimes against peacekeepers.
- The 'Group of Friends' will convene two meetings of its members per year and organize one event annually involving Permanent Missions and other stakeholders, ensuring greater safety and security for peacekeepers.
- This initiative represents the political will of member states, particularly troop and police contributing countries, to champion the implementation of UN Security Council resolution 2589, adopted in August 2021 under India's Presidency of the Council.
- Resolution 2589 called upon member states hosting or having hosted UN peacekeeping operations to take all appropriate measures to bring to justice perpetrators of violence against UN personnel, including their detention and abduction.
- The 'Group of Friends serves as a crucial platform for advancing this resolution, promoting accountability, and enhancing the protection of peacekeepers worldwide.
India's Significant Role in UN Peacekeeping:
- As a longstanding advocate for global peace and stability, India has demonstrated its commitment to United Nations (UN) peacekeeping operations.
- Over the past seven decades, India has contributed more than 260,000 peacekeepers, making it the largest cumulative contributor to UN peacekeeping missions.
- Despite the risks associated with such endeavors, India has remained steadfast in its support of peacekeeping efforts.
- Tragically, 177 Indian peacekeepers have made the ultimate sacrifice in the line of duty, reflecting India's dedication to fostering stability worldwide.
- Presently, India has more than 6,000 peacekeepers deployed in nine out of the twelve UN peacekeeping missions.
- As a strong proponent of accountability for crimes against peacekeepers, India plays a crucial role in advocating for the safety and security of these dedicated personnel.
C-Vigil App

- 30 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
Ever since the general election was announced two weeks ago, a total of 79,000 violations have been reported on the Election Commission of India’s (ECI) cVigil app across the country.
About C-Vigil App:
- cVigil is a user-friendly and easy-to-operate application, that connects vigilant citizens with the District Control Room, Returning Officer and Field Unit (Flying Squads), or Static Surveillance Teams.
- By using this app, citizens can immediately report incidents of political misconduct within minutes and without having to rush to the office of the returning officer.
- As soon as the complaint is sent on the cVigil app, the complainant receives a unique ID, through which the person will be able to track the complaint on their mobile.
- This creates a rapid and accurate reporting, action, and monitoring system.
The cVIGIL app enabled voters to
- Register Complaints: The app allows every citizen within the election boundaries to report the Model Code of Conduct / Expenditure Violations by taking photos/audio/video through their mobile phones by signing into the application.
- Anonymous User: The app also allows the citizen to complain anonymously, without revealing their details/ identity.
- Geotagging: The app automatically enables a geo-tagging feature when users switch on their camera in the cVIGIL to report a violation, which helps the field unit to know the precise location of the incident.
Benefits of the Application:
- cVIGIL is a convenient and user-friendly app allowing citizens to send pictorial evidence of the model code of conduct violations in their vicinity.
- Each reported incident is tracked and scrutinized from the beginning to the endpoint, thus bringing accountability into the system.
- The immediate location verification feature of the cVIGIL will act as a strong deterrence for miscreants and wrong-doers as they can be easily tracked.
- A combination of all these factors will encourage citizens to keep vigil over unhealthy electoral practices and bring them to the notice of the Election Commission.
- This in turn will help the commission reach its objective of conducting free and fair elections.
Hume’s Empathic Voice Interface (EVI)

- 30 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
AI startup Hume unveiled a new voice interface yesterday that the company claims is “the first conversational AI with emotional intelligence.
What is an Empathic Voice Interface (EVI)?
- Empathic Voice Interface (EVI) by Hume, a New York-based research lab and technology company, is the world’s first emotionally intelligent voice AI.
- It accepts live audio input and returns both generated audio and transcripts augmented with measures of vocal expression.
- By processing the tune, rhythm, and timbre of speech, EVI unlocks a variety of new capabilities, like knowing when to speak and generating more empathic language with the right tone of voice.
- These features enable smoother and more satisfying voice-based interactions between humans and AI, opening new possibilities for personal AI, customer service, accessibility, robotics, immersive gaming, VR experiences, and much more.
- Developers can now seamlessly integrate EVI into various applications using Hume’s API, offering a unique voice interface experience.
EVI boasts several distinctive empathic capabilities:
- Human-Like Tone: EVI responds with tones resembling human expressions, enhancing the conversational experience.
- Responsive Language: It adapts its language based on the user’s expressions, addressing their needs effectively.
- State-of-the-Art Detection: EVI uses the user’s tone to detect the end of a conversation turn accurately, ensuring seamless interactions.
- Interruption Handling: While it stops when interrupted, EVI can effortlessly resume from where it left off.
- Self-Improvement: EVI learns from user reactions to continuously improve and enhance user satisfaction over time.
- In addition to its empathic features, EVI offers fast, reliable transcription and text-to-speech capabilities, making it versatile and adaptable to various scenarios.
- It seamlessly integrates with any Language Model Library (LLM), adding to its flexibility and utility.
What is an AI with Emotional Intelligence and How Can it be Used?
- Artificial Intelligence with emotional intelligence, also known as affective computing or emotion AI, refers to the integration of emotional awareness and intelligence into AI systems, enabling them to recognize, understand, and respond to human emotions.
- This capability draws inspiration from the concept of emotional intelligence in humans, which involves perceiving and managing emotions in both oneself and others.
- The development of emotionally intelligent AI involves leveraging advanced techniques in machine learning, natural language processing, and computer vision to enable AI systems to recognize emotions in facial expressions, speech, and text.
- These systems can adapt their responses based on recognized emotions, creating more empathetic and nuanced interactions between humans and AI.
Potential applications of AI with emotional intelligence include:
- Healthcare: Emotion-sensitive AI could help detect depression, anxiety, or other mental health issues by analyzing speech patterns, facial expressions, or social media posts.
- Education: AI systems could adapt to individual students' emotions, providing customized support and facilitating better learning experiences.
- Customer Service: Emotion AI could enable businesses to respond more appropriately to customer emotions, improving customer satisfaction and fostering long-term loyalty.
- Entertainment: Affective computing could make games and other entertainment experiences more immersive and engaging by adapting to users' emotions in real-time.
Great Indian Bustard (GIB)

- 29 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
The Supreme Court last week said it will review its April 2021 order to bury underground all power lines in the habitat of the Great Indian Bustard (GIB), after the Centre found the order “practically impossible to implement” over long distances.
About Great Indian Bustard:
- Great Indian Bustard (GIB) is an agro-grassland bird endemic to the Indian Subcontinent.
- Known locally as Godawan in Rajasthan, it is a Critically Endangered species as per the IUCN Red List.
- It belongs to the family Otididae and exhibits sexual dimorphism.
- The GIB is an omnivorous bird.
- The species has a current viable population of around 150 individuals in India and mainly survives in the Thar Desert of Rajasthan which holds about 100 individuals.
- Of the remaining individuals, these birds are found in Gujarat, Maharashtra, Karnataka, and Andhra Pradesh respectively.
- With fewer than 150 individuals, they are caught in a deadly maze of power lines that crisscross its last refuge in the Kutch and Thar deserts of western India.
Why Do Power Lines Kill Bustards?
- Power lines pose a risk to all flying birds.
- In 2020, a study carried out by the Wildlife Institute of India (WII) in 4,200 sq km of GIB habitat in and around Desert National Park (DNP) in Rajasthan estimated that power lines killed around 84,000 birds of multiple species every year.
- GIBs are especially vulnerable because of their narrow frontal vision and large size.
- Unlike some birds that have a panoramic vision around the head, species like raptors and bustards have extensive blind areas above their heads.
- When they stretch their head forward to scan the ground below, they fly blind in the direction of travel.
Arguments of the Centre:
- The Centre said taking lines of 66 KV and higher voltage underground was not feasible for the evacuation of bulk power due to constraints such as transmission losses, maintenance challenges, multiple cable joints, increased time requirements, and safety concerns.
- The cost implications of undergrounding all power lines in the large area identified are very heavy — running into many thousands of crores and the cost of externalities that will burden the nation was “huge” and “disproportionate”.
- Harnessing renewable power from high-potential areas of Rajasthan and Gujarat was “essential for meeting rising power demand and India’s international commitments on climate change”.
Other threats faced by GIB:
- Free-ranging dogs pose a significant threat to the Great Indian Bustard (GIB) population, particularly in the Thar landscape, with feral packs responsible for a substantial portion of Chinkara depredation in the Desert National Park (DNP) as of 2017.
- Although sporadic hunting of GIBs persists, the prevalent use of pesticides in agricultural areas poses a more substantial risk to the bird's survival.
- Additionally, habitat loss, particularly the decline of grasslands essential for nesting, and diminishing support from local communities are growing concerns.
CoViNet
- 29 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
The World Health Organization (WHO) has launched a global network of laboratories to identify and monitor potentially novel coronaviruses that could emerge shortly.
What is CoViNet?
- The Coronavirus Network (CoViNet) is a global collaboration of laboratories with expertise in human, animal, and environmental coronavirus surveillance.
- This network aims to identify and monitor potential new coronaviruses that could emerge and impact public health worldwide.
- To enhance pandemic preparedness, CoViNet will expand its scope to include animal health and environmental surveillance, as well as timely risk assessments.
- This will allow the World Health Organization (WHO) to develop more informed policies and protective measures against future viral outbreaks.
- CoViNet will also play a pivotal role in building and supporting laboratory capacities in low- and middle-income countries to monitor MERS-CoV and other emerging coronaviruses of public health importance.
- By fostering knowledge exchange and capacity building, CoViNet aims to strengthen the global response to coronavirus threats.
- Furthermore, data generated through CoViNet's efforts will guide the work of the WHO's Technical Advisory Groups on Viral Evolution (TAG-VE) and Vaccine Composition (TAG-CO-VAC). These groups rely on cutting-edge research and surveillance data to inform public health policies and vaccination strategies.
- With 36 laboratories from 21 countries across all six WHO regions, CoViNet currently encompasses a wide range of expertise and resources.
- Three Indian institutions, namely, the Council of Scientific and Industrial Research-National Environmental Engineering Research Institute, the Indian Council of Medical Research-National Institute of Virology in Pune, and the Translational Health Science and Technology Institute, proudly represent the country in this global network dedicated to coronavirus surveillance and preparedness.
About the World Health Organization (WHO):
- The World Health Organization (WHO) stands as a paramount global health authority, dedicated to promoting health, preventing diseases, and improving healthcare systems worldwide.
- Established in 1948, WHO operates as a specialized agency of the United Nations, with its headquarters in Geneva, Switzerland.
- It collaborates with governments, international organizations, and civil society to address pressing health challenges and provide guidance and support to countries in need.
- WHO's mandate encompasses a wide array of health-related issues, including infectious diseases, non-communicable diseases, mental health, maternal and child health, and environmental health.
- Through research, policy development, and technical assistance, WHO plays a vital role in shaping health policies, setting standards, and coordinating responses to health emergencies such as pandemics and natural disasters.
- With a mission to ensure the highest attainable level of health for all people, WHO continues to lead efforts in global health governance, advocacy, and capacity-building, striving for a healthier, safer, and more equitable world.
Food Waste Index Report 2024

- 29 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
As per the Food Waste Index Report for 2024, households worldwide discarded more than one billion meals daily in 2022.
About UNEP Food Waste Index Report 2024:
- The United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP) Food Waste Index Report 2024, co-authored with the Waste and Resources Action Programme (WRAP), offers a comprehensive analysis of the state of global food waste.
- The report reveals alarming trends, including the wastage of over 1 billion meals per day in 2022, highlighting the urgency to address this critical issue.
Key findings from the report include:
- Per Capita Waste: The average annual food waste per person amounts to approximately 79 kilograms (or around 174 pounds).
- This equates to over a billion meals being wasted daily worldwide, underscoring the significant inefficiencies in current food consumption habits.
- Sources of Waste: Household waste constitutes the majority, around 60%, with food service establishments (such as restaurants) contributing approximately 28%, and retailers making up about 12%.
- This breakdown suggests that interventions targeting consumer behavior could have a substantial impact on reducing overall waste.
- Environmental Impact: Food loss and waste contribute to 8 to 10% of global greenhouse gas emissions.
- Comparatively, if food waste were considered a country, it would rank as the third-largest emitter of greenhouse gases globally, trailing only China and the United States.
- This stark comparison underscores the urgent need to address food waste not only for resource efficiency but also as a crucial aspect of climate action on a global scale.
- Global vs. Local Impact: The report highlights that food waste is a pervasive issue affecting both high-income and lower-income countries alike.
- This universality implies that solutions must be adaptable and scalable across various socioeconomic contexts.
- Collaborative Solutions: Governments, regional entities, industry stakeholders, and non-profit organizations are increasingly involved in public-private partnerships to combat food waste.
- Effective strategies, such as food redistribution through initiatives like food banks and charities, are recognized as vital for reducing waste while simultaneously supporting vulnerable communities.
Recommendations:
- The Food Waste Index Report by UNEP emphasizes the urgent need for comprehensive action, both globally and locally, to tackle the issue of food waste.
- By illuminating the extent and origins of waste, as well as its significant environmental and social repercussions, the report advocates for collaborative efforts across all sectors to establish sustainable food systems.
- The target of halving food waste by 2030 is not only in line with environmental goals but also represents a crucial step towards reducing global hunger and promoting a fairer distribution of food resources.
- As nations strive to achieve this objective, the report underscores the interconnectedness of food security, environmental sustainability, and economic viability.
- It presents addressing food waste not only as a moral and environmental imperative but also as a practical opportunity to bolster global food security and combat climate change.
Protection of Children from Sexual Offences (POCSO) Act

- 29 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
The Kerala High Court has held that a child charged with offenses under the Protection of Children from Sexual Offences (POCSO) Act, 2012, is to be prosecuted as per the provisions of the Juvenile Justice (Care and Protection of Children) (JJ) Act.
About the Protection of Children from Sexual Offences Act (POCSO Act):
- Enacted in 2012, the POCSO Act stands as India's pioneering legislation dedicated to addressing child sexual abuse comprehensively.
- Under the administration of the Ministry of Women and Child Development (MoWCD), its primary objective is safeguarding children under 18 from sexual assault, harassment, and exploitation, alongside establishing Special Courts to adjudicate such cases swiftly and efficiently, ensuring justice and protection for victims.
Salient Features of the Act:
- The POCSO Act adopts a gender-neutral approach, defining a child as "any person" under 18, ensuring inclusivity for all victims of child sexual abuse.
- It delineates various forms of sexual abuse, encompassing penetrative and non-penetrative assault, sexual harassment, and pornography.
- Certain circumstances, such as mental illness or abuse by a trusted individual like a family member, escalate the severity of sexual assault as per the Act.
- Individuals involved in trafficking children for sexual exploitation are subject to punishment under the Act's provisions on abetment.
- Attempting to commit an offense under the Act incurs penalties up to half the prescribed punishment for the completed offense.
- There's no time limit for reporting abuse, empowering victims to come forward at any point, regardless of when the abuse occurred.
- The Act mandates reporting of sexual abuse, penalizing failure to do so with imprisonment or fines.
- It includes child-friendly procedures for reporting, evidence recording, investigation, and trial, ensuring a supportive environment for victims.
- These procedures include recording the child's statement in a preferred location, preferably by a female officer, and avoiding aggressive questioning or character attacks.
- Medical examinations occur in the presence of a trusted individual, and the child is shielded from seeing the accused during testimony.
- Trials are held in camera, with the Special Court aiming to complete proceedings within a year of cognizance, prioritizing swift justice for victims.
Amendment to the Act:
- In 2019, the Act underwent its inaugural amendment to intensify penalties for particular offenses, aiming to dissuade perpetrators and safeguard the dignity of childhood.
- This amendment introduced the death penalty for aggravated penetrative sexual assault against children.
- Additionally, it empowered the imposition of fines and sentences of up to 20 years in prison to combat child pornography.
United Nations High Commissioner for Refugees (UNHCR)

- 29 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
According to the United Nations High Commissioner for Refugees (UNHCR), in 2023, more than 4,500 Rohingya refugees embarked on a perilous journey across the Bay of Bengal and the Andaman Sea.
About the United Nations High Commissioner for Refugees (UNHCR):
- UNHCR, the UN Refugee Agency, is a global organization dedicated to saving lives, protecting rights, and building a better future for people forced to flee their homes because of conflict and persecution.
- It leads international action to protect refugees, forcibly displaced communities, and stateless people.
- Formally known as the Office of the High Commissioner for Refugees, UNHCR was established by the General Assembly of the United Nations in 1950 in the aftermath of the Second World War to help the millions of people who had lost their homes.
- Today, UNHCR operates in 137 countries and provides life-saving assistance, including shelter, food, water, and medical care for people forced to flee conflict and persecution, many of whom have nobody left to turn to.
- UNHCR defends their right to reach safety and helps them find a place to call home so they can rebuild their lives.
- UNHCR also collaborates with countries to improve and monitor refugee and asylum laws and policies, ensuring that human rights are upheld.
- UNHCR considers refugees and those forced to flee as partners, putting those most affected at the center of planning and decision-making.
Who are the Rohingya Refugees?
- Rohingya are an ethnic group, largely comprising Muslims, who predominantly live in the Western Myanmar province of Rakhine.
- They speak a dialect of Bengali, as opposed to the commonly spoken Burmese language.
- Though they have been living in the South East Asian country for generations, Myanmar considers them as persons who migrated to their land during Colonial rule so, it has not granted Rohingyas full citizenship.
- According to the 1982 Burmese citizenship law, a Rohingya (or any ethnic minority) is eligible for citizenship only if he/she provides proof that his/her ancestors have lived in the country before 1823. Otherwise, they are classified as “resident foreigners” or as “associate citizens” (even if one of the parent is a Myanmar citizen).
- Since they are not citizens, they are not entitled to be part of civil service. Their movements are also restricted within the Rakhine state.
T+0 Settlement Cycle

- 28 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
The BSE and NSE introduced trading in the T+0 rolling settlement cycle in the equity segment on an optional basis today.
What is Trade Settlement?
- Trade settlement encompasses the bilateral process of transferring funds and securities on the designated settlement date.
- It signifies the completion of a trade transaction when the purchased securities of a listed company are successfully delivered to the buyer, and the seller receives the agreed-upon payment.
- The evolution of the trade settlement cycle in India has seen notable adjustments over time.
- Initially shortened by SEBI to T+3 from T+5 in 2002 and further to T+2 in 2003, the current cycle in the Indian stock market stands at T+1.
- This migration to the T+1 cycle took effect in January 2023, positioning India as the second country globally, after China, to implement the T+1 settlement cycle for top-listed securities.
What is the T+0 Trading Settlement Cycle?
- In December last year, the capital markets regulator SEBI proposed to introduce a facility for clearing and settlement of funds and securities on T+0 (same day) on an optional basis, in addition to the existing T+1 settlement cycle.
- The regulator has also proposed to introduce optional instant settlement at a later stage.
- Under the T+0 trade cycle, the settlement of trades will happen on the same day after the closure of the T+0 market.
- If investors sell a share, they will get the money credited to their account the same day, and the buyer will also get the shares in their demat account on the very day of the transaction.
What are the Benefits of T+0 Trade Settlement?
- A shortened settlement cycle will bring cost and time efficiency, transparency in charges to investors, and strengthen risk management at clearing corporations and the overall securities market ecosystem.
- The T+0 trade cycle is expected to provide flexibility in terms of faster pay-out of the funds against the securities to the sellers and faster pay-out of securities against the funds to the buyers.
- It will allow better control over funds and securities by the investors.
- For the securities market ecosystem, a shorter settlement cycle will further free up capital in the securities market, thereby enhancing the overall market efficiency.
- It will enhance the overall risk management of Clearing Corporations (CCs) as the trades are backed by upfront funds and securities.
Who can Participate in the T+0 Settlement Cycle?
- All investors are eligible to participate in the segment for the T+0 trade settlement cycle if they are able to meet the timelines, process, and risk requirements as prescribed by the Market Infrastructure Institutions (MIIs).
Solar and Heliospheric Observatory (SOHO)
- 28 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
Recently, NASA's Soho mission, which is tasked with observing the Sun, has captured its 5000th comet as it dives around the star in our Solar System.
About Solar and Heliospheric Observatory (SOHO):
- SOHO was built as a general solar observatory, with twelve suites of scientific instruments to track all of these properties of the Sun.
- During its operations, it has provided important insights, including:
- Details about the interior of the Sun,
- What sunspots look like beneath the surface,
- Measurements of the speed of the solar wind,
- The charged particles that escape from the corona,
- Mapping the magnetic field behavior over the Sun’s surface; and
- Revealing new phenomena such as “solar tornadoes”.
- Built in Europe, SOHO is operated jointly by ESA and NASA, with contributions from a large number of scientists, engineers, and other staff around the world.
- The spacecraft was launched in 1995 with a planned two-year mission.
- Its work was successful enough to justify keeping the observatory going, and it’s still operating more than 20 years later.
- The probe orbits the Sun at a place where the gravity of the Sun and Earth balance each other out, known as the first Lagrange point (L1).
- Center for Astrophysics (CfA) scientists and engineers provided SOHO’s Ultraviolet Coronagraph Spectrometer (UVCS), which operated until 2013 and measured the ultraviolet spectrum of the hot solar atmosphere.
- UVCS provided the insight that the corona is too hot to be produced by ordinary thermal transfer, where particles collide and pass energy to each other.
- Instead, the corona and solar wind must be accelerated by the magnetic field interactions in some way.
- Other SOHO instruments measure the speed and composition of the solar wind; the seismic waves that travel across the Sun’s surface; the fluctuations in the temperature, composition, and density of different parts of the corona; and the motion of matter upward from the Sun’s interior to its surface.
South East Africa Montane Archipelago (SEAMA)

- 28 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
A recent investigation in southern Africa has revealed a plethora of previously undiscovered biodiversity within a newly identified ecoregion known as the South East Africa Montane Archipelago (SEAMA).
About South East Africa Montane Archipelago (SEAMA):
- It represents a newly identified mountainous ecoregion spanning from northern Mozambique to Mount Mulanje in Malawi, which is the second-highest peak in southern Africa.
- This ecoregion comprises 30 granitic inselbergs rising over 1000 meters above sea level, hosting both the largest (Mt Mabu) and smallest (Mt Lico) mid-elevation rainforests in southern Africa, alongside uniquely diverse montane grasslands.
- SEAMA experiences notably higher annual rainfall and humidity, particularly during the dry season, compared to its surrounding areas.
- Since 2000, SEAMA has witnessed a loss of 18% of its primary humid forest cover, with rates reaching up to 43% in certain locations—marking one of the most rapid deforestation rates across Africa.
- The principal cause of montane forest depletion in SEAMA stems from slash-and-burn agricultural practices, predominantly employed for subsistence food cultivation by local communities, alongside charcoal production for household cooking and economic purposes.
What are Inselbergs?
- Inselbergs are solitary geological formations characterized by isolated, steep-sided hills or small mountains rising abruptly from flat or gently sloping terrain.
- Composed of erosion-resistant rock, such as granite or quartzite, inselbergs stand out prominently in landscapes, with steep or even vertical sides resulting from differential erosion processes.
- These formations, found predominantly in arid or semi-arid regions, take various shapes, including dome-shaped hills, conical peaks, or sheer-sided cliffs.
- Despite their isolated nature, inselbergs support unique ecosystems and biodiversity, creating microclimates and habitats for specialized plant and animal species.
- Rock crevices, caves, and pockets of soil on inselbergs harbor distinct flora and fauna adapted to harsh conditions, making these formations biodiversity hotspots.
- Additionally, inselbergs often hold cultural and spiritual significance for indigenous peoples and local communities, serving as sites for religious rituals, cave paintings, or archaeological artifacts.
- However, inselbergs face threats such as deforestation and habitat degradation due to human activities like slash-and-burn agriculture and charcoal production.
- Conservation efforts are crucial to protect these geological wonders and preserve their ecological and cultural significance for future generations.
Carlsberg Ridge & Afanasy-Nikitin Seamount
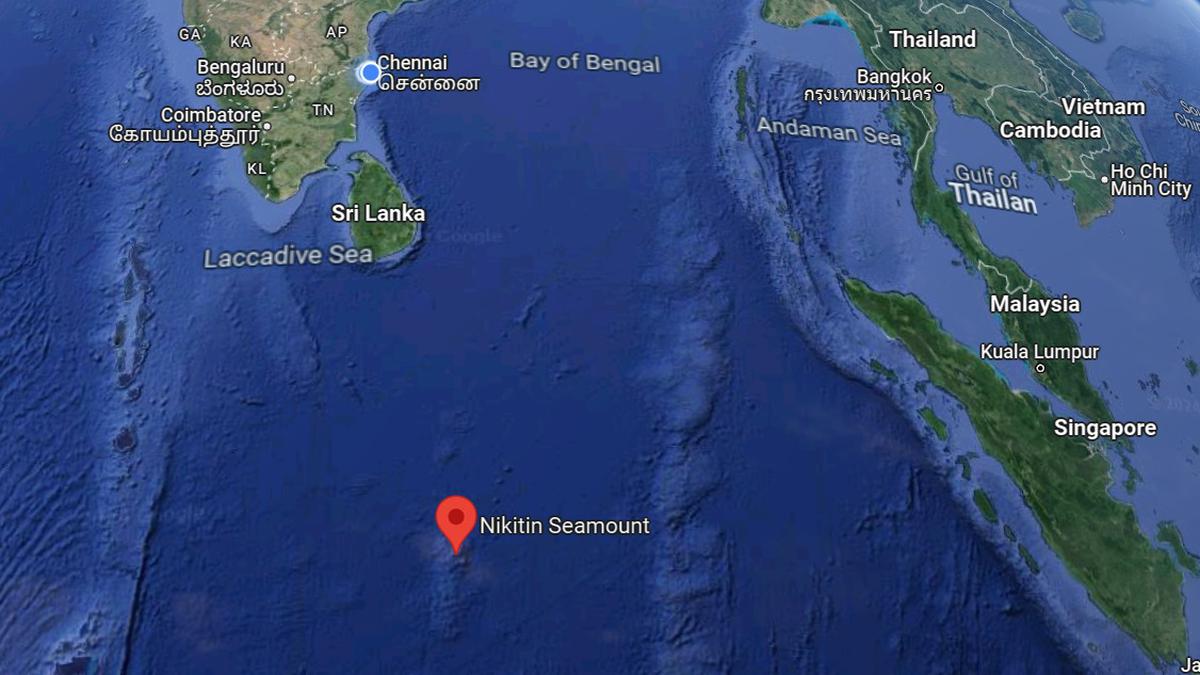
- 28 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
Indian delegates have been visiting the International Seabed Authority (ISA), Jamaica to strengthen efforts to explore two deep sea regions in the Indian Ocean for mining, according to reports this week.
What is the Carlsberg Ridge?
- The Carlsberg Ridge is the northern section of the Central Indian Ridge, a divergent tectonic plate boundary between the African Plate and the Indo-Australian Plate, traversing the western regions of the Indian Ocean.
- The ridge of which the Carlsberg Ridge is a part extends northward from a triple point junction near the island of Rodrigues (the Rodrigues Triple Point) to a junction with the Owen Fracture Zone.
- The ridge started its northwards propagation in the late Maastrichtian and reached the incipient Arabian Sea in the Eocene.
- Then it continued to accrete basalt but did not propagate for nearly 30 million years ago.
- Then, in the early Miocene, it started to propagate westwards towards the Afar hot spot, opening the Gulf of Aden.
- The Carlsberg Ridge is seismically active, with a major earthquake being recorded by the U.S. Geological Survey at 7.6 on the moment magnitude scale in July 2003.
- The ridge was discovered by the Danish research vessel Dana during the Carlsberg Foundation's Oceanographic Expedition around the world (1928–1930), better known as the 2nd Dana Expedition, and named after the Carlsberg Foundation, which funded the entire expedition and subsequent analysis and publication of results.
About the Afanasy Nikitin Seamount (ANS) Seabed:
- The ANS is a major structural feature in the Indian Ocean, rising up above the sea bed but below the surface, and forming a seamount.
- It is 400 km long and 150 km wide, and is located in the Central Indian Basin — southeast of Sri Lanka, right below the equator, to the west of Singapore.
- It was formed about 80 million years ago, while dinosaurs still roamed the Earth.
- The Seamount is named after Afanasy Nikitin, a 15th-century Russian merchant who was one of the first to document his travels to India.
- A black monolith is also erected in his honor at Revdanda, about 100 km away from Mumbai, where he is thought to have first set foot in the country.
- The ANS seamount is about 3,000 km from India’s coast and is rich in cobalt, copper, manganese, and nickel.
What are Seamounts?
- Seamounts are submarine mountains originating from volcanic eruptions beneath the ocean's surface, serving as critical habitats for diverse marine ecosystems.
- Similar to terrestrial volcanoes, seamounts can exhibit varying states of activity, including active, dormant, or extinct stages.
- They typically form near mid-ocean ridges, where tectonic plates separate, allowing magma to ascend and solidify on the seabed.
- Notably, seamounts also emerge near intraplate hotspots and oceanic island chains, such as island arcs, characterized by volcanic and seismic activity.
- These underwater formations hold significant scientific value, offering insights into mantle composition, plate tectonics, and oceanic circulation dynamics.
- Moreover, seamounts play a crucial role in nutrient cycling and marine life proliferation, fostering localized upwelling of nutrient-rich waters that support diverse biological communities.
Australia’s Carbon Credits System

- 28 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
A recent study revealed that a prominent reforestation initiative operating within the Australian Carbon Credit Unit (ACCU) Scheme has been deemed a significant underperformer, amounting to a 'catastrophe' in terms of its outcomes.
What is the Australian Carbon Credit Unit (ACCU) Scheme?
- The ACCU Scheme plays a pivotal role in the Australian carbon market, incentivizing various entities including individuals, businesses, and governmental bodies to engage in endeavors aimed at mitigating emissions or sequestering carbon.
- Participants encompass a broad spectrum ranging from individuals and sole traders to corporations, local and state government entities, and trusts.
- Achievement of the scheme's objectives is facilitated through diverse means such as the adoption of innovative technologies, equipment upgrades, the adoption of sustainable business practices to enhance productivity or energy efficiency, and the implementation of novel vegetation management techniques.
How Does It Work?
- The ACCU Scheme operates by rewarding participants who execute projects focused on either reducing or avoiding greenhouse gas emissions (emissions avoidance) or capturing and storing atmospheric carbon (sequestration).
- These projects contribute significantly to mitigating climate change and advancing environmental sustainability in Australia.
- For each tonne of carbon dioxide equivalent (t CO?-e) emissions that a participant's project successfully stores or avoids, they are eligible to earn one Australian Carbon Credit Unit (ACCU).
- These ACCUs serve as a tangible representation of the project's positive environmental impact and can be traded on the secondary market or sold to the Australian Government through carbon abatement contracts.
- In essence, the ACCU Scheme establishes a robust framework for quantifying and monetizing emission reduction and carbon sequestration efforts, providing a strong financial incentive for individuals and businesses to actively engage in climate-friendly initiatives.
- By fostering an active carbon market, the scheme helps ensure the continued growth and development of innovative projects that combat climate change and support Australia's transition to a low-carbon economy.
Criticisms and Controversies:
- The ACCU Scheme has encountered criticisms and controversies regarding its overall effectiveness and the integrity of the carbon credits it generates.
- One such concern is based on research indicating that native forests in Australia's desert regions are experiencing either stagnant growth or shrinking woodlands.
- This finding raises questions about the capacity of these areas to sequester carbon at the levels claimed in ACCU projects.
- Furthermore, critics argue that Australia has amassed substantial quantities of carbon credits through these projects, despite the questionable integrity of the underlying data.
- The scheme's reliability and effectiveness are, thus, scrutinized, as the quality and accuracy of the carbon credits generated are essential to maintaining trust and credibility in the carbon market.
- As the ACCU Scheme evolves, addressing these concerns and ensuring that it genuinely contributes to emission reduction and carbon sequestration efforts is crucial.
- Regular evaluations and transparency in data collection and analysis will help enhance public confidence and secure the scheme's role as a central pillar of Australia's climate change mitigation strategy.
Krishi Integrated Command and Control Centre (ICCC)

- 27 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
Earlier this month, Agriculture Minister Arjun Munda inaugurated a Krishi Integrated Command and Control Centre (ICCC) set up at Krishi Bhavan in New Delhi, a big-screen dashboard of all digital innovations in the sector.
What is the Krishi ICCC?
- The ICCC is a tech-based solution involving multiple IT applications and platforms, designed to help make informed decisions.
- The center is housed in the Ministry of Agriculture & Farmers’ Welfare and is responsible for legislation, policy formation, and implementation of initiatives in the agriculture sector.
- The ICCC uses state-of-the-art technologies such as artificial intelligence, remote sensing, and Geographic Information Systems (GIS) to collect and process large amounts of granular data.
- The ICCC uses platforms including the Krishi Decision Support System (DSS) to collect micro-level data, process it, and present the macro picture.
How does the Krishi ICCC Operate?
- Using AI and machine learning, the system will initially identify a farmer either through their mobile number or Aadhaar details.
- Next, it will cross-reference this information with the farmer's field data retrieved from land records, as well as historical crop sowing data from the crop registry, and weather information from IMD, among other sources.
- Subsequently, the system will generate personalized advisories tailored to the farmer's needs, presented in their local language.
- This functionality will be facilitated through the Bhashini platform, enabling translations into multiple Indian languages.
What Information Does the Krishi ICCC Offer?
- Displayed on eight expansive 55-inch LED screens within the ICCC, the system provides comprehensive data covering various aspects such as temperatures, rainfall, wind speed, crop yields, production statistics, drought conditions, cropping patterns (both geographically and over time), and production forecasts.
- This information is presented in a graphical, map-based, timeline, and drill-down formats for enhanced visualization and analysis.
- Additionally, users can access pertinent trends, including periodic and non-periodic variations, outliers, and Key Performance Indicators (KPIs), alongside receiving insights, alerts, and feedback concerning agriculture schemes, programs, projects, and initiatives.
- Moreover, the system facilitates direct interaction between farmer beneficiaries and officials or the Minister through video conferencing facilities, ensuring effective communication and support.
Practical Applications:
- Farmer’s Advisory: The ICCC allows visualization of GIS-based soil carbon mapping as well as soil health card data for a particular district together in one place.
- This, when visualized with weather-related data from IMD for the selected district, will allow a customized and authentic advisory to be sent to the farmer about the type of crops that can be grown, and water and fertilizer requirements.
- Drought Actions: An increase or decrease in yield from a specific region (as per GCES data) can be correlated with weather, rainfall, and other information visualized through the Drought Portal, enabling the administration to understand the reason for the increase/ decrease in yield and to take decisions proactively.
- Crop Diversification: An analysis of crop diversification maps, together with field variability for paddy, will enable decision-makers to identify regions with scope for diversified cropping so that farmers can be advised accordingly.
- Farm Data Depository: Krishi Decision Support System (K-DSS), a platform under development, will act as an agriculture data repository. Integrated spatial and non-spatial data will be superimposed as a layer on the GIS map, and various AI/ ML models will be run on the data.
- The K-DSS will help in evidence-based, efficient, and data-driven decision-making, and assist in preparing customized advisories for farmers.
- Validation of Yield: Yield, as captured through Krishi MApper, can be analyzed with the yield generated through GCES application for a plot.
Archaeological Survey of India will ‘Delist’ Some ‘Lost’ Monuments

- 27 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
The Archaeological Survey of India (ASI) has decided to delist 18 “centrally protected monuments” because it has assessed that they do not have national importance.
Context:
- ASI has decided to delist 18 protected monuments
- ASI says the monuments have ceased to be of 'national importance'
- The 18 'lost' monuments include eleven in Uttar Pradesh
Significance of Delisting Monuments:
- Several monuments are currently facing the prospect of delisting, including historical landmarks such as a medieval highway milestone in Mujessar village, Barakhamba Cemetery in Delhi, Gunner Burkill’s tomb in Jhansi district, a cemetery at Gaughat in Lucknow, and Telia Nala Buddhist ruins in Varanasi.
- The exact whereabouts or condition of these monuments remain uncertain.
Meaning of Delisting:
- Delisting a monument entails its removal from the roster of protected sites, thereby relinquishing its conservation, protection, and maintenance responsibilities by the Archaeological Survey of India (ASI).
- Under the Ancient Monuments and Archaeological Sites and Remains (AMASR) Act, delisted monuments no longer enjoy protection against construction-related activities in their vicinity, enabling regular urbanization and development activities to proceed uninhibited.
Status of Protected Monuments:
- The inventory of protected monuments is subject to change through additions and removals. Presently, the ASI oversees 3,693 monuments, a number set to decrease to 3,675 following the ongoing delisting initiative.
- This marks the first extensive delisting endeavor in several decades.
Procedures for Monument Delisting:
- The regulations governing the List of Protected Monuments are stipulated under the Ancient Monuments and Archaeological Sites and Remains Rules, 1959.
- This legislation safeguards structures and sites aged over a century, encompassing a diverse array of architectural and historical marvels.
- The government possesses the authority to eliminate certain monuments from the protected list via official notification in the Gazette.
- Through such notifications, the government can declare that certain ancient monuments, archaeological sites, or relics no longer hold national significance under the purview of the AMASR Act (Section 35 of the AMASR Act).
Lost Monuments:
- The Ancient Monuments and Archaeological Sites and Remains (AMASR) Act safeguards monuments and sites aged over a century.
- Nevertheless, numerous structures, particularly smaller or lesser-known ones, have gradually disappeared over time due to factors like urbanization, encroachments, dam and reservoir construction, or neglect.
- In some instances, the lack of public memory hampers efforts to locate these monuments.
Extent of Loss:
- According to a submission by the Ministry of Culture to the Parliamentary Standing Committee on Transport, Tourism, and Culture in December 2022, 50 out of India's 3,693 centrally protected monuments were unaccounted for.
- Among these, 14 succumbed to rapid urbanization, 12 were submerged by reservoirs or dams, and the remaining 24 remain untraceable.
- The Committee noted that budget constraints limited the provision of security guards to historical sites, with only 2,578 guards assigned to 248 sites out of the required 7,000.
- Additionally, a 2013 report by the Comptroller and Auditor General (CAG) of India highlighted the disappearance of at least 92 centrally protected monuments nationwide.
About the Archaeological Survey of India (ASI):
- Founded in 1861 by Alexander Cunningham, the Archaeological Survey of India (ASI) was later formalized as a statutory body under the Ancient Monuments and Archaeological Sites and Remains Act, 1958 (AMASR Act) following India's independence.
- ASI's primary mandate encompasses archaeological research and the safeguarding, conservation, and preservation of cultural monuments across the nation.
- Its operational scope includes conducting surveys of antiquarian remains, exploring and excavating archaeological sites, and overseeing the conservation and maintenance of protected monuments, among other responsibilities.
- The ASI operates under the purview of the Ministry of Culture.
Armed Forces (Special Powers) Act (AFSPA)

- 27 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
Union Home Minister Amit Shah has said the Jammu and Kashmir Assembly elections will be held before September and that the Centre will consider revoking the Armed Forces (Special Powers) Act there.
What is AFSPA?
- The AFSPA empowers the armed forces to uphold law and order in “disturbed areas.”
- They have the right to prevent a gathering of five or more people in a given location, use force, or even open fire after providing a sufficient warning if they believe someone is breaking the law.
- Armed forces are also permitted to enter and search any location if they suspect illegal activity.
- According to the AFSPA Act, the Army also has the authority to detain someone without a warrant, seize weapons and ammunition, and offer protection to someone acting in good faith.
Salient features of the AFSPA Act:
- The Central Government or the Governor of a State has the right to declare all or a part of any state to be a disturbed region if they believe it is necessary to stop the terrorist activity or any other activity that could jeopardize India’s sovereignty or be disrespectful to the national anthem, flag, or constitution.
- According to Section 3 of the AFSPA, the Central Government may send out armed forces to support the civilian authorities if the governor of a state publishes a formal announcement in the Gazette of India.
- According to the Disturbed Areas Act of 1976, a territory must maintain the status quo for a minimum of three months after being designated “disturbed.”
- Section (4) of the AFSPA grants army officers specific authority to shoot the only requirement is that the officer must sound the alarm before firing.
- Security forces have the authority to search without permission and arrest anyone without a warrant.
- After being taken into custody, a person must be delivered to the closest police station as soon as possible.
- The Central Government must first provide its consent before prosecuting an on-duty officer for alleged human rights violations.
What are the “Disturbed areas” under the AFSPA Act?
- The state governor, the administrator of the union territory, or the central government may declare a region as a “disturbed area” by publishing a notice in the official gazette, the entire territory or an order to implement it may be declared disturbed.
- It is up to the state governments to decide whether or not to implement the Act.
- However, the governor or the Center may disregard their judgment under Section (3) of the Act.
- The state governor was the only person with the authority to confer AFSPA when the act came into force in 1958.
- The 1978 amendment granted the central government this authority.
List of states that implement the AFSPA Act:
- Four states and one union territory currently have AFPSA activities, while 12 districts are still partially subject to the act, and 31 districts have fully implemented the law.
The AFSPA states include:
-
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Nagaland
- Assam
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Manipur
Black Carbon

- 27 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
As per a study, the residential sector is responsible for 47% of India's overall black carbon emissions.
What is Black Carbon?
- Black carbon is the dark, sooty material emitted alongside other pollutants when biomass and fossil fuels are not fully combusted.
- It contributes to global warming and poses severe risks.
- Studies have found a direct link between exposure to black carbon and a higher risk of heart disease, birth complications, and premature death.
- Most black carbon emissions in India arise from burning biomass, such as cow dung or straw, in traditional cookstoves.
- According to a 2016 study, the residential sector contributes 47% of India’s total black carbon emissions.
- Industries contribute a further 22%, diesel vehicles 17%, open burning 12%, and other sources 2%.
- Decarbonization efforts in the industry and transport sectors in the past decade have yielded reductions in black carbon emissions, but the residential sector remains a challenge.
- Black carbon is a potent contributor to global warming due to its efficient absorption of light and subsequent heating of its surroundings.
- This process leads to the conversion of incoming solar radiation into heat.
- Moreover, black carbon influences cloud formation and affects regional circulation and precipitation patterns.
- When deposited on ice and snow, it diminishes surface albedo, reducing their ability to reflect sunlight and causing surface warming.
Impacts:
- Black carbon significantly contributes to global warming and poses substantial risks to human health.
- Exposure to black carbon has been linked to increased incidences of heart disease, birth complications, and premature mortality.
- Its warming effect on climate is estimated to be 460-1,500 times more potent than that of CO2.
Magnetofossils
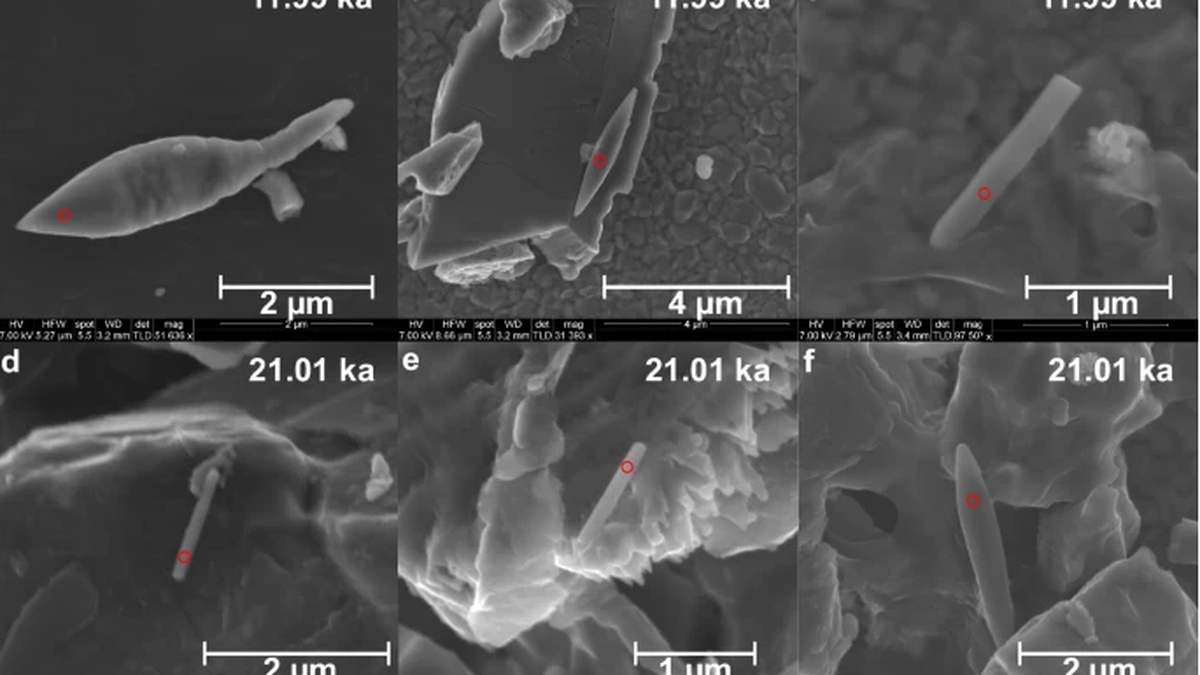
- 27 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
In the depths of the Bay of Bengal, scientists have discovered a 50,000-year-old sediment — a giant magnetofossil and one of the youngest to be found yet.
What are Magnetofossils?
- Magnetofossils represent the fossilized remnants of magnetic particles originated by magnetotactic bacteria, also referred to as magnetobacteria, encapsulated within the geological archives.
About Magnetotactic Bacteria:
- Magnetotactic bacteria, predominantly prokaryotic microorganisms, possess the unique ability to align themselves in alignment with Earth's magnetic field.
- These organisms were traditionally believed to utilize the Earth's magnetic field as a navigational aid to locate environments with optimal oxygen levels.
- Comprising distinctively structured particles abundant in iron, these bacteria harbor small sacs that function akin to a compass.
- Magnetotactic bacteria synthesize minute crystals composed of iron-rich minerals such as magnetite or greigite, facilitating their navigation amidst fluctuations in oxygen concentrations within their aquatic habitats.
Key Findings of the Study:
- Sediment Composition: The sediment core, measuring three meters in length and extracted from the southwestern Bay of Bengal, primarily comprised "pale green silty clays."
- Foraminifera Abundance: Researchers observed abundant benthic and planktic foraminifera, which are single-celled organisms characterized by shells found near the seabed and freely floating in water.
- Oxygen Concentration: At depths ranging from approximately 1,000 to 1,500 meters, the Bay of Bengal exhibited notably low oxygen levels.
- Analysis of the sediment sample confirmed fluctuations in monsoon activity, as evidenced by the presence of magnetic mineral particles from distinct geological periods.
- Role of Rivers: Rivers such as the Godavari, Mahanadi, Ganga-Brahmaputra, Cauvery, and Penner, which discharge into the Bay of Bengal, played a pivotal role in magnetofossil formation.
- Nutrient Supply: The nutrient-rich sediment transported by these rivers supplied reactive iron, which, combined with organic carbon in the suboxic conditions of the Bay of Bengal, created a conducive environment for magnetotactic bacteria growth.
- Impact of Oceanographic Processes: Factors such as freshwater discharge from rivers and oceanographic phenomena like eddy formation influenced the oxygen content in these waters, distinguishing them from other low-oxygen zones.
- Persistence of Suboxic Conditions: The presence of magnetofossils indicated the prolonged persistence of suboxic conditions in the Bay of Bengal, fostering an environment conducive to the proliferation of magnetotactic bacteria.
Ola’s ‘Krutrim AI’

- 26 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
Earlier this year, Ola, the Indian multinational ridesharing company, introduced Krutrim AI as "India's own AI," with plans for substantial enhancements to its initial iteration to expand its foundation upon launch.
What is Krutrim AI?
- Krutrim AI is a generative AI assistant that converses in 10+ languages, including Hindi, English, Tamil, Telugu, Malayalam, Bengali, Marathi, Kannada, Gujarati, etc., making it India’s own AI by an artificial intelligence startup.
- It was founded by Bhavish Aggarwal, the founder of Ola Cabs.
- Krutrim AI has been natively created to ensure a creative AI tool designed for over 1.4 billion Indians to provide 100% contextually relevant responses.
- It is a critical milestone in developing public-facing artificial intelligence in India.
These are 4 benefits of Krutrim AI:
-
- Supports multiple Indian languages.
- Native experience is built to cater to cultural diversity.
- They are trained on local language tokens and sources.
- Allows user interaction without charge on its free version.
What is the Tech Behind Krutrim AI?
- Krutrim AI uses Natural Language Processing (NLP) — a component of AI — to understand the nuances of human language, including colloquialisms and cultural contexts.
- Machine Learning (ML) algorithms enable it to learn from vast data sets and improve its responses over time.
- Moreover, Deep Learning, a sophisticated branch of ML, helps it recognize patterns and analyze complex data, which could be crucial for Krutrim AI’s performance.
- While the exact technologies used are not disclosed, these methodologies align with the AI’s demonstrated functions.
How Krutrim AI Works?
- Krutrim AI works through prompts given in the chat field, similar to other generative AI chatbots.
- Generative AI chatbots like Krutrim AI are large language models that understand prompts in the language used for daily communication and respond with language similar to humans.
- Krutrim AI allows users to reply, modify the details, or add additional elements to the response, similar to the experience a user would have with a human assistant.
Benefits of Using Krutrim AI:
- Krutrim AI offers 4 benefits.
- Multilingual as it responds in over 10 Indian languages, which is helpful for users not proficient in English.
- Cultural context provides a native experience, as Krutrim’s training data was specifically geared towards being culturally relevant and understanding the Indian context.
- The development of (AI) start-up Krutrim was done natively from the ground up.
- It is trained on over 2 trillion language tokens, with the largest representation of Indian languages in the artificial intelligence landscape.
- Krutrim’s base model offers a free AI chatbot experience, with a premium version (Krutrim Pro) in the works, that will have larger knowledge-based capabilities.
Post-Vaccination Immunity
- 26 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
A recent review revealed that only a handful of vaccines offer durable protection lasting beyond 20 years.
About Post-vaccination immunity:
Mechanism:
- The fundamental immunological process involves the production of memory B cells in lymph nodes, providing long-term protection against diseases.
- These memory B cells recognize antigens delivered by vaccines, prompting the production of potent antibodies upon encountering similar antigens from foreign objects like viruses, effectively eliminating infections.
- T cell support is essential for the activation of memory B cells, thus vaccines stimulating T cells are capable of inducing their production.
- Notably, certain vaccines, such as polysaccharide typhoid and pneumococcal vaccines, may not prompt the production of B cells.
- To extend the duration of immunity conferred by memory B cells, frequent boosters may be necessary, ranging from six months to several years.
- However, the presence of memory B cells alone does not guarantee protection, as the effectiveness of vaccines in triggering their production varies.
- Long-lasting plasma cells (LLPCs) migrate from lymph nodes to the bone marrow, where they may persist for decades, constituting a crucial aspect of vaccine-induced immunity.
- Every vaccine aims to generate LLPCs in the bone marrow for lifelong protection, with vaccines like those for measles and rubella known to stimulate LLPC production.
- Notably, some potent vaccines, such as mRNA COVID-19 shots, may not effectively activate LLPCs in the bone marrow.
- For vaccines to confer long-term protection, they must generate both memory B cells and LLPCs in the bone marrow, with variations in vaccine effectiveness in producing these cells explaining differences in their durability.
Smart Meter National Programme (SMNP)

- 26 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
Kerala's shift towards an alternative approach for the implementation of smart electricity meters, sidelining the Central government's Rs 3 lakh crore project, poses a challenge to the Union Government's initiative of replacing 250 million traditional meters with smart meters in all households by March 2025.
About the Smart Meter National Programme (SMNP):
- The Indian government has initiated the Smart Meter National Programme (SMNP) to revolutionize the country's energy sector through the implementation of smart meters.
- By replacing 25 crore conventional meters, the SMNP aims to enhance the operational efficiency and revenue management of distribution companies (DISCOMs).
- Under the leadership of Energy Efficiency Services Limited (EESL), a joint venture of four National Public Sector Enterprises, the scheme is set to make waves in the energy sector.
- EESL, comprised of NTPC Limited, PFC, REC, and POWERGRID, operates under the Ministry of Power and is committed to undertaking the necessary capital and operational expenditures with zero upfront investment from states and utilities.
- The Build-Own-Operate-Transfer (BOOT) model facilitates the recovery of smart meter costs via the monetization of energy savings resulting from improved billing accuracy, reduced meter reading costs, and increased efficiency.
- In accordance with guidelines set forth by the Central Electricity Authority (CEA), the strategic deployment of these smart meters adheres to industry standards.
Smart meters offer a multitude of advantages:
-
- Consumers can monitor their electricity usage and make informed decisions to reduce their bills.
- Utilities benefit from enhanced operational efficiency, enabling better power demand management.
- Web-based Monitoring: The interconnected smart meter network can mitigate utilities' commercial losses, enhance revenue generation, and propel power sector reforms.
- The Smart Meter National Programme (SMNP) paves the way for a more efficient and sustainable energy landscape in India, revolutionizing the way utilities operate and consumers engage with their electricity usage.
What are Smart Meters?
- A smart meter serves as an advanced tool for recording electricity consumption and voltage levels, offering a significant upgrade over traditional metering systems.
- While conventional meters simply measure power usage, smart meters take it a step further by transmitting real-time data to utility providers at intervals of 15 minutes or hourly.
- Smart meters truly live up to their name by utilizing internet connectivity to facilitate two-way communication.
- On one hand, they empower consumers with up-to-date information on energy usage patterns, enabling them to make informed decisions and manage consumption more efficiently.
- On the other hand, utility providers gain valuable insights for monitoring purposes and ensuring accurate billing.
- In essence, smart meters pave the way for improved energy management, increased transparency, and enhanced efficiency, catering to the evolving needs of both consumers and utility providers in today's digital era.
Cannabis

- 26 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
During the celebration of Holi across India, Bhang, derived from the Cannabis sativa plant or true hemp, is widely favored for consumption.
What is Cannabis?
- Cannabis is found mainly in the Indo-Gangetic plains – in Himachal Pradesh, Punjab, Haryana, Uttar Pradesh, Bihar, and West Bengal – along with the Deccan region.
- Cannabis is termed Ganzai in Telugu, Ganja in Tamil, and Bangi in Kannada.
- The cannabis plant can be 4 to 10 feet tall at maturity.
- Its plant also grows on wastelands and can easily be spotted on roadsides.
- Three products can be obtained from the plant – fiber, oil, and narcotics.
- Bhang is obtained from the seeds and leaves of the plant, which are reduced to powder.
- Then, the powder is filtered and prepared for drinking, mixed often with cold, flavored milk or thandai on Holi.
Additional Uses and Benefits of Cannabis:
- According to the Indian Council of Agricultural Research (ICAR), cannabis ash can be applied to animals' skin in cases of hematoma, a condition characterized by blood clotting outside of blood vessels.
- Hemp-seed oil is employed in varnish industries as a substitute for linseed oil and in soft soap manufacturing, as well as possessing numerous medicinal properties.
- In Himachal Pradesh, cannabis cultivation is concentrated in Chhota/Bada Bhangal of Kangra and the Karsog area of Mandi district.
- While cultivating cannabis for addictive narcotics is illegal, states permit regulated cultivation for industrial or horticultural purposes, focusing on fiber and seed extraction.
- Cannabis-based treatments, such as bhang application on paddy seeds, can enhance germination and control threadworms in paddy nurseries, particularly in the temperate regions of Jammu and Kashmir.
- Heated and crushed cannabis leaves are often transformed into a paste to alleviate pain from a honey bee or wasp stings.
District Election Management Plan

- 26 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
Effective execution of elections demands thorough planning, where a crucial aspect is the meticulous formulation and implementation of the District Election Management Plan (DEMP).
About the District Election Management Plan (DEMP):
- The District Election Management Plan (DEMP) is a comprehensive document designed to ensure the smooth conduct of elections, employing statistics and analysis.
- According to the Election Commission of India, the DEMP must be prepared at least six months before the tentative poll day.
- Collaboration among election officials, administrative authorities, law enforcement agencies, etc., is crucial for the execution of the DEMP.
Key components of the DEMP include:
- District Profile: A district profile providing foundational electoral strategy, featuring political maps outlining constituencies, key demographic and infrastructure statistics, and a brief on the district’s administrative setup and socio-economic features.
- Polling Stations: Detailed strategies for enhancing the availability and accessibility of polling stations, ensuring essential facilities such as ramps, electricity, lighting, drinking water, toilets, and internet connectivity.
- Special Attention to PwD and Senior Citizens: Addressing the requirements of voters with disabilities and senior citizens through dedicated help desks, round-the-clock control rooms, home voting options, and advanced postal ballot voting for essential service personnel.
- Systematic Voters’ Education and Electoral Participation (SVEEP) Plan: Integration of the Systematic Voters’ Education and Electoral Participation (SVEEP) plan, focused on increasing electoral participation.
-
- Planning, training, welfare, and deployment strategies for election personnel, along with training initiatives for district-level teams to enforce the Model Code of Conduct (MCC) and equip all election personnel with the necessary skills and knowledge.
Regarding Electronic Voting Machines (EVMs)?
- Management of Electronic Voting Machines (EVMs) is vital to uphold the integrity of the electoral process, encompassing strategies for secure storage, availability, transportation, and maintenance of both EVMs and Voter Verifiable Paper Audit Trails (VVPATs).
- The District Election Management Plan (DEMP) contributes to enhancing the voting process by ensuring its organization and accessibility to all voters.
- Furthermore, the principles employed in the DEMP, such as meticulous planning, collaboration, and transparency, offer valuable insights applicable beyond elections, providing lessons for broader governance.
- The emphasis on advanced planning, data-driven decision-making, and stakeholder collaboration highlighted by the DEMP is instrumental in addressing challenges effectively.
ISRO’s Reusable Launch Vehicle (RLV) LEX 02 Landing Experiment

- 23 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
The Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) successfully conducted the Pushpak Reusable Landing Vehicle (RLV) LEX 02 landing experiment at the Aeronautical Test Range in Chitradurga recently.
What is a Reusable Landing Vehicle (RLV) LEX 02?
- Continuing our exploration into reusable landing vehicles, RLV-LEX-02 marks the second mission in our series conducted at the Aeronautical Test Range.
- Following the success of RLV-LEX-01 last year, this latest endeavor showcases the remarkable autonomous landing capability of our reusable launch vehicle (RLV).
- Notably, RLV-LEX-02 demonstrates the vehicle's ability to navigate and safely land from off-nominal initial conditions immediately upon release from a helicopter.
Methodology of the Experiment:
- The RLV LEX-02 mission showcased the autonomous landing prowess of our reusable launch vehicle under demanding circumstances following its release from a helicopter.
- Dubbed 'Pushpak', this winged vehicle was airlifted by an Indian Air Force Chinook helicopter and released from a height of 4.5 km.
- Navigating autonomously, it adeptly approached the runway, making precise cross-range corrections before executing a flawless landing.
- Utilizing a combination of its brake parachute, landing gear brakes, and nose wheel steering system, it safely came to a stop.
- Notably, the winged body and all flight systems previously employed in RLV-LEX-01 were repurposed for RLV-LEX-02 after undergoing necessary certification and clearances.
- This remarkable mission was executed collaboratively by the Vikram Sarabhai Space Centre (VSSC), the Liquid Propulsion System Centre (LPSC), and the ISRO Inertial Systems Unit (IISU).
What is the Reusable Launch Vehicle?
- The reusable launch vehicle represents a pioneering space plane design characterized by a low lift-to-drag ratio, which mandates high glide angles during approach and consequently requires landing at velocities reaching 350 kmph.
- Integral to its innovation are a multitude of indigenous systems developed meticulously. These encompass sophisticated navigation systems, leveraging pseudolite technology for precise localization, as well as instrumentation and sensor arrays, among other advancements, all spearheaded by ISRO.
Order of the Druk Gyalpo

- 23 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
Prime Minister Narendra Modi recently received Bhutan’s highest civilian award, the ‘Order of the Druk Gyalpo’, during his two-day State visit to the neighboring nation.
What is the ‘Order of the Druk Gyalpo’ Award?
- The Order of the Druk Gyalpo, Bhutan's most prestigious civilian award, was recently conferred upon Indian Prime Minister Narendra Modi during his two-day State visit to the neighboring nation.
- As the first foreign Head of Government to receive this esteemed accolade, Prime Minister Modi joins a select group of individuals honored for their exceptional contributions to Bhutanese society, service, integrity, and leadership.
- According to the ranking and precedence established within Bhutan's honor system, the Order of the Druk Gyalpo represents the pinnacle of lifetime achievement, taking precedence over all other orders, decorations, and medals.
- Prime Minister Modi received the award in recognition of his outstanding contributions to strengthening India-Bhutan relations and his dedicated service to the Bhutanese nation and its people.
- Past recipients of the Order of the Druk Gyalpo include:
- Her Majesty The Royal Queen Grandmother Ashi Kesang Choden Wangchuck in 2008
- His Holiness Je Thrizur Tenzin Dendup in 2008, and
- His Holiness Je Khenpo Trulku Ngawang Jigme Choedra in 2018.
- With Prime Minister Modi's recent addition to this esteemed list, the Order of the Druk Gyalpo continues to symbolize Bhutan's appreciation for remarkable individuals who significantly impact the country and its people.
Netravati River

- 23 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
The principal bench of the National Green Tribunal (NGT) in New Delhi has initiated action on the Netravati Waterfront Promenade Development Project in Mangaluru.
About the Netravati River:
- The Netravati River, also known as Netravathi Nadi, originates from the Bangrabalige valley, Yelaneeru Ghat in Kudremukh, Chikkamagaluru district, Karnataka, India.
- It passes through the revered pilgrimage site Dharmasthala, earning recognition as one of India's sacred rivers.
- Converging with the Kumaradhara River at Uppinangadi, it eventually flows into the Arabian Sea, south of Mangalore city, serving as the primary water source for Bantwal and Mangalore.
- The Netravati railway bridge, a prominent structure, acts as the gateway to Mangalore.
- Historically known as the Bantwal River, it was documented as unfordable during the South-West Monsoon in the 1855 Gazetteer of Southern India.
- The river's navigability by small country craft and its influence on local geography and transport, including the naming of the Netravati Express train, underscores its significance in the region's history.
- Instances of flooding, notably in 1928 and 1974, have shaped the lives of residents, prompting relocations and resilience
About the National Green Tribunal:
- The National Green Tribunal (NGT) was established under the National Green Tribunal Act of 2010.
- While its principal seat is located in New Delhi, it also holds sessions in Bhopal, Pune, Kolkata, and Chennai.
- The NGT is entrusted with the responsibility of adjudicating applications or appeals, ensuring their final disposition within six months of filing.
Composition:
- The tribunal comprises a Chairperson, Judicial Members, and Expert Members, each serving a non-renewable term of five years.
- The appointment of the Chairperson is made by the Central Government in consultation with the Chief Justice of India (CJI).
- A Selection Committee, constituted by the Central Government, is responsible for appointing both Judicial and Expert Members.
- The tribunal can accommodate a minimum of 10 and a maximum of 20 full-time Judicial and Expert Members.
Powers & Jurisdiction:
- Established to efficiently handle cases concerning environmental protection and conservation of natural resources, including forests.
- It possesses appellate jurisdiction akin to a court.
- While not bound by the procedural formalities outlined in the Code of Civil Procedure, 1908, the NGT operates based on the principles of natural justice.
Hepatitis B
- 23 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
Public knowledge and awareness about Hepatitis B, a deadly disease that can cause end-stage liver cirrhosis and liver cancer, is dismal in India, according to a new study conducted by Sir Ganga Ram Hospital, New Delhi.
What is Hepatitis B?
- It is a severe liver infection that can lead to liver damage, cancer, and death.
- The virus spreads through contact with an infected person's blood or bodily fluids.
- One can get hepatitis B through sexual contact, sharing needles or other drug-injection equipment, or from mother to child during childbirth.
Symptoms of Hepatitis B:
- Hepatitis B is a severe viral infection of the liver that can cause inflammation and scarring.
- Symptoms include fatigue, fever, abdominal pain, dark urine, joint pain, and jaundice.
Causes of Hepatitis B:
- Hepatitis B is caused by the hepatitis B virus (HBV).
- HBV is found in the blood and body fluids of an infected person. It can spread through contact with fluids, such as:
- Blood, through needle sharing or accidental needle sticks
- Contact with body fluids, such as saliva, etc.
- Sexual contact with someone who has HBV
- From a mother to a child through childbirth
- Hepatitis B can also spread through contact with contaminated surfaces, such as:
- Sharing personal items like toothbrushes or razors with someone who has HBV
- Getting a tattoo or body piercing with contaminated equipment
Types of Hepatitis B:
- There are three main types of hepatitis B: acute, chronic, and carriers.
- Acute hepatitis B is a short-term illness that occurs within the first six months after exposure to the virus. It is the most common type of hepatitis B in children.
- Chronic hepatitis B is a long-term illness that can lead to serious health problems, including liver failure and liver cancer.
- Carriers of hepatitis B have the virus in their blood but do not show any symptoms.
Treatment for Hepatitis B
- Several medications can help treat hepatitis B.
- These include antiviral drugs, which can help reduce the amount of virus in the body, and immunomodulators, which can help boost the immune system to better fight the virus.
- If the liver is damaged, one may also need medication to help protect it from further damage.
- HBIG (Hepatitis B Immuno Globulin) is one of the best ways to treat hepatitis B.
- Adults who have been exposed to hepatitis should get HBIG and vaccination as soon as possible, preferably within 24 hours but not later than 14 days after the exposure.
Prevention of Hepatitis B:
- The best way to prevent hepatitis B is to get vaccinated.
- The vaccine is given as a series of shots.
- The first shot is usually given at birth; the rest at 1–2 months old, 6–18 months old, and 4–6 years old.
- If one was not vaccinated as a child, they can receive the vaccines as an adult.
Jaipur’s traditional celebrations with ‘Gulaal Gota’

- 23 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
In Jaipur, Rajasthan, a centuries-old tradition called "Gulaal Gota" will be observed during Holi, involving the throwing of colors through a unique medium, dating back around 400 years.
What is a Gulaal Gota?
- A Gulaal Gota is a small ball made of lac, filled with dry gulaal.
- Weighing around 20 grams when filled with gulaal, these balls are thrown at people on Holi, getting smashed to bits on impact.
- Local artisans say that making Gulaal Gotas involves first boiling the lac in water to make it flexible.
- Lac is a resinous substance that is secreted by certain insects. It is also used to make bangles.
- After shaping the lac, colour is added to it. At first red, yellow, and green are added as other colours can be obtained through their combinations.
- After the processing is done, artisans heat the lac.
- It is then blown into a spherical shape with the help of a blower called “phunkni”.
- Then, gulaal is filled in the balls before they are sealed with lac.
Where does the raw material for Gulaal Gota come from?
- Lac is brought from Chhattisgarh and Jharkhand.
- The female scale insect is one of the sources of lac.
- To produce 1 kg of lac resin, around 300,000 insects are killed.
- The lac insects also yield resin, lac dye, and lac wax.
How did Gulaal Gotas become a tradition in Jaipur?
- Gulaal Gotas are made by Muslim lac makers, called Manihaars, only in Jaipur.
- Manihaars’ ancestors were shepherds and horse traders who arrived from Afghanistan.
- They settled in Bagru, a town located close to Jaipur, and learned lac-making from Hindu lac makers or Lakhere.
- The city of Jaipur was established in 1727. Its founder Sawai Jai Singh II, an admirer of art, dedicated a lane at the Tripoliya Bazaar to the Manihaar community.
- This is where lac bangles, jewelry, and Gulaal Gota are mostly sold, to date.
What is the economics of this tradition?
- One box of six Gulaal Gota balls is sold for Rs 150, which is much costlier than water balloons.
- Usually, the whole family of artisans is engaged in this work, including women.
- For Manihaars, lac bangles are the main source of sustenance as making Gulaal Gota is a seasonal work.
- Artisans say that the bangles are eco-friendly as they are made without any chemicals.
Why the demand is falling?
- Jaipur has of late become a hub of many factories where cheap, chemical-based bangles are made with minimum lac.
- Original lac bangles are costlier than the manufactured ones. Hence, the demand for lac-only bangles has fallen.
- Many of the community’s younger members are also more interested in taking up blue-collar jobs instead of artisan work.
Government Support and Artisan Empowerment:
- The Indian government has issued artisan cards to Lac Bangle and Gulaal Gota craftsmen, enabling them to access benefits under various government schemes.
- Many artisans have ventured abroad to exhibit their craft, such as Awaz Mohammad, who was invited to showcase his work at the G20 summit in New Delhi last year.
- In efforts to preserve tradition, some Gulaal Gota artisans are advocating for a Geographical Indication (GI) tag, which can enhance product visibility and underscore its unique regional identity.
PIB Fact Check Unit (FCU)

- 22 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
Recently, the Supreme Court stayed the Centre’s notification of the Fact Check Unit (FCU) under the Press Information Bureau (PIB) until the Bombay High Court arrives at a final decision on the challenge to the amended Information Technology (IT) Rules.
Background:
- Under the Government of India (Allocation of Business) Rules, 1961, the Ministry of Information and Broadcasting (MIB) is entrusted with the responsibility of disseminating information about government policies, schemes, and programs through various mediums of communication.
- In fulfilling its role, the Ministry publicizes the policies, initiatives, schemes, and programs of the Government of India through press releases, press conferences, webinars, publication of books, etc.
- To carry out this crucial function, the Ministry has several attached and subordinate offices, including the Press Information Bureau (PIB).
- A significant aspect of the responsibility of facilitating public information about the functioning of the Government of India involves countering the dissemination of fake, false, and misleading information.
- The PIB has been carrying out this function for a long through a wide distribution of accurate and reliable information, issuing rebuttals, etc.
- In the age of social media where information spreads rapidly, the spread of fake and manipulated information, especially related to the functioning of a democratically elected Government, is dangerous to society as it has the potential to intensify social, economic, and political conflicts, weaken public trust in democratic institutions, and even endanger the life of the citizens.
What is the PIB Fact Check Unit (FCU)?
- The Press Information Bureau has been at the forefront of taking proactive measures to combat fake news related to the Government of India.
- In November 2019, PIB established a Fact Check Unit (FCU) to tackle the issue of fake news about the Government of India, its various ministries, Departments, Public Sector Undertakings, and other Central Government organizations.
- The unit verifies claims about government policies, regulations, announcements, and measures.
- Through an established rigorous fact-checking procedure, the PIB Fact Check Unit helps dispel myths, rumors, and false claims and provides accurate and reliable information to the public.
Organization
- The PIB Fact Check Unit is headed by a senior DG/ADG level officer of the Indian Information Service (IIS).
- The day-to-day operations of the Unit are handled by IIS officers at various levels. The Unit reports to the Principal Director General, PIB who functions as the Principal Spokesperson of the Government of India.
Fact-Check Mechanism
- Users send requests over WhatsApp, email, or a web portal. Each such request received is considered a ‘Query’.
- Queries are segregated by the Unit based on their relevance to matters about the Government of India.
- Only queries about the Government of India are considered and taken up as Actionable Queries, while others are deemed not relevant for action.
- The information in question is checked rigorously through multiple layers of cross-checking through Government Open-source information, use of technological tools, and verification from the concerned Government of India organization.
- Should the Unit come across a piece of information that the Unit ascertains must be busted publicly for the larger benefit of the people of India, after investigation and verification from official & authoritative sources, it publishes a 'Fact Check' on its social media platforms.
- Often a single fact check can be a result of multiple queries.
Fact-checked content can be segregated into the following three categories:
- Fake: any factually incorrect news, content, or, piece of information related to the Government of India, spread intentionally or unintentionally, that can deceive or manipulate the audience, with or without the intention to cause potential harm, can be flagged as Fake
- Misleading: any information presented, either partially true or with selective presentation of facts or figures or with distortion of facts or figures and to deceive or mislead the recipient of the information.
- True: any information that is found to be factually correct after investigation
Shanghai Cooperation Organisation (SCO) Startup Forum

- 22 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
India will host the fifth meeting of the Shanghai Cooperation Organisation startup forum in January next year according to the commerce and industry ministry.
About the Shanghai Cooperation Organisation Startup Forum:
- The SCO Startup Forum is a platform for the stakeholders from the startup ecosystems from all SCO Member States to interact and collaborate.
- The entrepreneurial activities aim to empower the local startup communities in the SCO Member States.
- The SCO Startup Forum aims to create multilateral cooperation and engagement for startups among the SCO Member States.
- This engagement will empower the local startup ecosystems in the SCO Member States.
The following are the objectives of the engagement:
- Sharing of best practices to promote entrepreneurship and innovation to build knowledge-exchange systems
- Bringing Corporations and Investors across to work closely with startups and provide local entrepreneurs with much-needed support and market access
- Increasing scaling opportunities for startups by providing solutions in the field of social innovation and providing Governments with a plethora of innovative solutions
- Creating open procurement channels to enable matchmaking for procuring innovative solutions from startups
- Facilitating cross-border incubation and acceleration programs that will enable the startups to explore international markets and get focused mentorship.
Upcoming Events:
- India is set to host the second meeting of the Special Working Group for Startups and Innovation (SWG) in November 2024 and the SCO Startup Forum 5.0 in January 2025.
Past Initiatives:
- SCO Startup Forum 1.0: Established in 2020, laying the groundwork for multilateral cooperation among SCO Member States' startups.
- SCO Startup Forum 2.0: Held virtually in 2021, introducing the SCO Startup Hub, a centralized platform for the SCO startup ecosystem.
- SCO Startup Forum 3.0: Organized physically in 2023 by the Department for Promotion of Industry and Internal Trade (DPIIT), marking a significant milestone for SCO Member States' startup collaboration.
- 1st Meeting of the SWG: Led by India, the first meeting of the SCO Special Working Group on Startups and Innovation in 2023 focused on the theme 'Growing from Roots', emphasizing foundational growth within the startup ecosystem.
Usha Mehta

- 22 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
A recent film has been launched, depicting the inspiring life story of Indian freedom fighter Usha Mehta.
About Usha Mehta:
- Born in 1920 in the village of Saras, near Surat in Gujarat, Usha Mehta, affectionately known as Ushaben, embodied the Gandhian principles of non-violence and civil disobedience from a young age.
Early Activism:
- At the tender age of eight in 1928, she participated in a protest march against the Simon Commission, demonstrating her early commitment to India's independence struggle.
- The Secret Congress Radio: In 1942, amidst the fervor of the Quit India Movement, Usha Mehta and her colleagues boldly established the Secret Congress Radio.
- This clandestine radio station played a pivotal role in connecting freedom movement leaders with the masses, ensuring the dissemination of crucial information, and maintaining the spirit of resistance against colonial rule.
Establishing an Underground Radio Station:
- With the outbreak of the War in 1939, the British government imposed stringent measures, including the suspension of all amateur radio licenses throughout the Empire.
- Operators were mandated to surrender their equipment to the authorities, under threat of severe repercussions for non-compliance.
Key Figures in the Operation:
- Usha Mehta, alongside Babubhai Khakar, Vithalbhai Jhaveri, and Chandrakant Jhaveri, played instrumental roles in orchestrating the Congress Radio initiative, defying the ban on amateur radio broadcasting.
The Congress Radio Trial:
- The trial of the five accused individuals—Usha Mehta, Babubhai Khakar, Vithalbhai Jhaveri, Chandrakant Jhaveri, and Nanak Gainchand Motwane, who facilitated crucial equipment—captivated public attention in Bombay.
- While Vithalbhai and Motwane were acquitted, Mehta, Babubhai, and Chandrakant faced severe sentences for their involvement.
Usha Mehta's Legacy:
- Following her release from Pune's Yerawada Jail in March 1946, Usha Mehta was lauded in nationalist circles as "Radio-ben," symbolizing her courageous defiance and commitment to the freedom struggle through underground broadcasting.
Independence, PhD, & Padma Vibhushan
- When India finally achieved independence in 1947, the British had divided the country into two parts – India and Pakistan, sending the region into chaos.
- The divide results in massive bloodshed with more than 10 million Hindus, Muslims, and Sikhs seeking to find their home.
- Mehta was torn. “In a way, I was very happy, but sad at the same time because of partition.
- It was an independent India but a divided India,” she was quoted as saying in the book Freedom Fighters Remembered.
- She was away from active politics in independent India due to her ill health but continued to remain a staunch Gandhian till the very end.
- She penned the script for a documentary on Gandhi produced by her colleague at the radio station, and earned a PhD in Gandhian thought at the University of Bombay.
- She taught political science and ran the politics department at the university.
- She also taught at Wilson College for 30 years.
- She was also the president of the Gandhi Peace Foundation.
- In 1998, she was awarded India’s highest civilian honor, the Padma Vibhushan.
- She lived a simple life and never married or had children.
- She died on 11 August 2000 at the age of 80.
International Telecommunication Union (ITU)

- 22 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
Dr. Neeraj Mittal's unanimously elected as co-chair of the International Telecommunication Union (ITU)'s digital innovation board recently.
About the International Telecommunication Union (ITU):
- Established in 1865 as the International Telegraph Union, the ITU has evolved into the United Nations specialized agency for information and communication technologies (ICT).
- Recognized as a vital intergovernmental organization, the ITU facilitates collaboration between governments and private sector entities to advance global telecommunication and ICT services.
Key Points:
- Status: Designated as a specialized agency of the United Nations in 1947.
- Membership: Boasting a diverse membership of 193 countries and over 1000 companies, universities, and international and regional organizations.
Functions:
- Allocation of global radio spectrum and satellite orbits.
- Coordination and establishment of technical standards about telecommunication/ICT.
- Initiatives to enhance ICT accessibility in underserved communities worldwide.
- India's Engagement: India has maintained an active presence within the ITU since 1869, consistently participating in its endeavors.
- Notably, India has been a regular member of the ITU Council since 1952.
- Headquarters: Located in Geneva, Switzerland, the ITU serves as the global epicenter for fostering collaboration and innovation in the realm of ICT.
What is the Digital Innovation Board?
- The Digital Innovation Board is a pivotal component of the Innovation and Entrepreneurship Alliance for Digital Development, aimed at addressing pressing needs within the realm of innovation as outlined in the Kigali Action Plan, which was adopted at the World Telecommunication Development Conference 2022.
- Comprised of Ministers and Vice Ministers of Telecom/ICT from 23 Member Countries of the International Telecommunication Union (ITU), spanning across Asia, Europe, Africa, and North, and South America, this board serves as a strategic advisory body.
- ITU initiated the Innovation and Entrepreneurship Alliance for Digital Development to tackle significant challenges and opportunities in innovation.
- This alliance operates through three key mechanisms:
- The Digital Transformation Lab
- The Network of Acceleration Centers, and
- The Digital Innovation Board.
- The Digital Innovation Board's primary objective is to offer strategic guidance, expertise, and advocacy in promoting local capacity building, fostering innovation, and encouraging entrepreneurship in digital development.
- Its overarching mission is to cultivate a more inclusive and equitable digital future for all stakeholders.
Enforcement Directorate (ED) Arrests Delhi Chief Minister

- 22 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
Delhi Chief Minister Arvind Kejriwal was recently arrested in the Delhi excise policy case, in which he had been issued multiple summons by the Enforcement Directorate (ED).
About the Enforcement Directorate (ED):
- Established in 1956 as the 'Enforcement Unit' under the Department of Economic Affairs, the Enforcement Directorate (ED) underwent a name change in 1957.
- Presently, ED operates under the Department of Revenue (Ministry of Finance) administrative control for operational purposes.
Roles and Responsibilities:
- ED is responsible for enforcing the Foreign Exchange Management Act, 1999 (FEMA) and certain provisions of the Prevention of Money Laundering Act (PMLA).
- In case of FEMA violations, ED has the authority to attach the assets of offenders.
- ED is also empowered to conduct searches, seizures, arrests, prosecutions, and surveys against PMLA offenses.
Appointment Process for ED Director:
- The Central Government appoints the ED Director based on the recommendations of a committee, which comprises:
Chairperson: Central Vigilance Commissioner
Members: Vigilance Commissioners, Home Secretary, Secretary DOPT, and Revenue Secretary.
What is the Delhi Excise Policy 2021-22?
- The Delhi Excise Policy 2021-22, also known as the new liquor policy, was introduced on November 17, 2021, to transform liquor sales in the city.
- This policy marked a significant departure from the traditional model by privatizing liquor shops and aiming to enhance customer experience while curbing black market activities.
- However, amidst controversy and allegations of procedural irregularities, Delhi ultimately reverted to its previous excise regime.
Key Features:
- The new policy divided Delhi into 32 zones, each open for bidding by firms, departing from individual licenses to zone-based bidding.
- 849 retail vend licenses were auctioned by the Excise department.
- Notably, the policy allowed for discounts to retail customers and reduced dry days to three from 21.
- It proposed innovative measures such as home delivery of liquor and lowering the drinking age from 25 to 21, although these were not implemented.
Controversy:
- Before implementation, the policy underwent scrutiny by the Chief Secretary, who alleged procedural lapses and irregularities.
- The report implicated the Deputy CM for making unilateral decisions, leading to financial losses and allegations of kickbacks.
- These kickbacks were purportedly used to influence elections in other states, leading to a CBI investigation and subsequent arrest of the Deputy CM and others.
- The Enforcement Directorate (ED) also initiated investigations into alleged money laundering, with claims of substantial proceeds of crime and kickbacks reaching prominent political figures.
- In essence, the Delhi Excise Policy 2021-22, while aiming for modernization and improved governance in liquor sales, was marred by controversy and allegations of corruption, prompting a thorough investigation into its implementation and aftermath.
International Day of Forests 2024

- 21 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
On March 21, 2024, people around the world celebrate World Forest Day. It's a day to remind everyone about how important forests are and all the good things they do for us.
About World Forest Day:
- World Forestry Day, also known as International Day of Forests, is celebrated on March 21 each year.
- The day aims to promote the sustainable management, conservation, and development of all types of forests for the benefit of current and future generations.
The theme for International Day of Forests 2024:
- This year's theme, "Forests and Innovation: New Solutions for a Better World" highlights the critical role of innovation and technology in protecting our forests.
- From advanced monitoring systems that track deforestation to sustainable forestry practices, innovation is key to overcoming the challenges threatening our forests.
History of International Day of Forests:
- The United Nations General Assembly announced March 21 to be the International Day of Forests in 2012.
- The day aims to respect and promote the value of a wide range of forests. Countries are encouraged to take part in regional, global, and local drives to set up a scope of forest and tree-related campaigns, like planting campaigns.
- The Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO) and the United Nations Forum on Forests are the coordinators of the International Day of Forests.
Importance of International Day of Forests:
- As per the UNGA, "The United Nations Forum on Forests and the Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO), in collaboration with Governments, the Collaborative Partnership on Forests and other relevant organizations in the field are responsible for organizing the events and campaigns related to the World Forestry Day."
- The importance of the International Day of Forests is to spread awareness and give instruction at all levels to guarantee feasible forest management and biodiversity preservation.
The Enduring Significance of Forests:
- Forests are often referred to as the "lungs of the planet" for a reason.
They play a vital role in:
- Combating Climate Change: Forests act as carbon sinks, absorbing and storing vast amounts of carbon dioxide, a major greenhouse gas.
- Protecting Biodiversity: Forests provide habitats for countless species of plants and animals, ensuring the health and balance of ecosystems.
- Providing Clean Air and Water: Forests filter air and water, regulating our climate and providing us with essential resources.
- Supporting Livelihoods: Millions of people around the world depend on forests for food, medicine, and income generation.
Celebrating and Taking Action:
- World Forestry Day is a springboard for action and we can get involved by:
- Support Organizations: Donate to or volunteer with organizations working towards forest conservation and sustainable forestry practices.
- Reduce Consumption: Make conscious choices to reduce consumption of paper and wood products, minimizing environmental footprint.
- Plant a Tree: Plant a tree in our community or support tree-planting initiatives.
- Spread Awareness: Educate ourselves and others about the importance of forests and the threats they face.
- By taking action, big or small, we can all contribute to a future where our forests continue to thrive, ensuring a healthier planet for generations to come.
World Inequality Lab Report

- 21 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
India’s top 1 percent income and wealth shares have reached historical highs and are among the very highest in the world, according to a paper released by World Inequality Lab.
What is the World Inequality Lab?
- The World Inequality Lab is a global research center that focuses on studying inequality and public policies that promote social, economic, and environmental justice.
The lab's main missions include:
- Expanding the World Inequality Database: The lab gathers and analyzes data on income, wealth, and capital asset distribution across various countries.
- Publishing research: The lab releases working papers, reports, and methodological handbooks to contribute to the understanding of global inequality dynamics.
- Collaborating with international researchers: The lab works with a network of researchers from around the world to compile and analyze data for the World Inequality Database.
- Promoting public debate: The lab aims to raise awareness about inequality by disseminating their findings and engaging in public discourse.
- The World Inequality Lab is known for producing the World Inequality Report, which offers up-to-date and comprehensive data on different aspects of inequality globally, including wealth, income, gender, and ecological inequality.
Key Insights from the Research Paper Released by the WIL:
- A team of four economists, including Nitin Kumar Bharti, Lucas Chancel, Thomas Piketty, and Anmol Somanchi, has compiled comprehensive time series data on income and wealth inequality in India.
- Titled "The Billionaire Raj," the paper asserts that India's current level of inequality surpasses that of the British Raj era.
- In the fiscal year 2022-23, India witnessed its highest recorded levels of income and wealth concentration among the top 1%: 22.6% and 40.1%, respectively.
- India's top 1% income share is noted to be among the highest globally, even surpassing countries like South Africa, Brazil, and the US.
- While India's top 1% holds a significant share of income, the wealth share of this segment is comparatively lower than in South Africa and Brazil.
- The paper accentuates the stark disparities among various income groups in India.
- For instance, the wealthiest 1% possess an average wealth of Rs 5.4 crore, 40 times the national average, whereas the bottom 50% and the middle 40% hold significantly lower amounts: Rs 1.7 lakh (0.1 times the national average) and Rs 9.6 lakh (0.7 times the national average), respectively.
- At the pinnacle of the wealth distribution, approximately 10,000 individuals out of 92 million Indian adults possess an average wealth of Rs 2,260 crore, a staggering 16,763 times the average Indian wealth.
Key Recommendations from the Research Paper:
- The research paper has meticulously compiled data from various sources to construct its estimates on income and wealth inequality.
- Given the absence of official income estimates and wealth statistics based on surveys in India, the paper underscores the necessity for reliable data sources in these domains.
- To tackle the issue of inequality in India, the paper proposes a range of policy interventions.
- These measures encompass a comprehensive overhaul of the tax structure to encompass both income and wealth considerations, alongside substantial public investments in critical areas such as healthcare, education, and nutrition.
- A notable suggestion outlined in the report is the implementation of a "super tax" of 2% on the net wealth of the 167 wealthiest families recorded in 2022-23. This levy is projected to generate revenues equivalent to 0.5% of the national income.
- Furthermore, the imposition of such a tax is envisaged not only to create fiscal leeway for essential investments but also to serve as an effective tool in combatting entrenched inequality within the society.
Project GR00T

- 21 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
AI chip leader Nvidia on Tuesday (March 19) announced Project GR00T or Generalist Robot 00 Technology, which promises to revolutionize the evolution of humanoid robots.
What is Project GR00T?
- Project GR00T stands for Generalist Robot 00 Technology.
- It is essentially a general-purpose foundation model for humanoid robots.
- This ambitious project aims to create a general-purpose foundation model for humanoid robots, enabling them to understand natural language, learn new skills from observing humans, and solve various tasks in real-time.
- Robots built on this platform are designed to understand natural language and emulate movements by observing human actions, such as instantly learning coordination, dexterity, and other skills.
- This can help the robots navigate and engage with the real world around them.
- The goal of Project GR00T is to advance the field of embodied artificial general intelligence (AGI) and drive breakthroughs in robotics.
- NVIDIA intends to leverage its expertise in AI and its technological resources to develop this foundational model, which would provide humanoid robots with human-like abilities, such as emotion, reaction, and movement.
The Potential Consequences of Project GR00T and Humanoid Robots in the Workforce:
- As humanoid robots, such as those envisioned by NVIDIA's Project GR00T, become more advanced and capable of handling various hazardous or repetitive tasks, concerns arise over potential job displacement.
- For instance, Nvidia's partnership with Hippocratic AI to develop AI-powered healthcare agents may lead to a reduction in the demand for nurses.
- However, proponents argue that these robots can serve as valuable aids for humans, enhancing their quality of life and complementing their skills rather than supplanting them entirely.
- Consequently, the impact of humanoid robots on the workforce may ultimately depend on their successful integration into existing labor structures, as well as the willingness and ability of society to adapt to this transformative technology.
Lianas and its Impact on Forest Ecosystem

- 21 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
Amidst escalating global temperatures, a pioneering study spearheaded by the University of the Sunshine Coast, Australia, sheds light on an unexpected threat posed by Lianas.
What are Lianas?
- Lianas are long-stemmed, woody vines that have their roots in the ground but use the trunks and branches of trees to climb their way up toward the canopy in order to reach sunlight.
- The term “liana” applies more to this type of lifestyle than to any specific family of plants, as lianas come from a variety of different taxonomic groups.
- They are found in tropical forests all over the world.
- These plants have developed a unique climbing strategy to reach the forest canopy and maximize their access to sunlight for photosynthesis.
- Their flexible stems, adventitious roots, and specialized structures such as tendrils and hooks allow them to twist, twine, and ascend the trunks and branches of trees.
How do Lianas Impact the Forest Ecosystem?
- Lianas can have both positive and negative influences on forest ecosystems, depending on their abundance and the specific environmental context.
Positive Impacts of Lianas on Forests:
- Biodiversity: Lianas enhance forest biodiversity by creating additional habitats, providing food resources, and supporting the life cycles of numerous organisms.
- Insects, birds, mammals, and even some epiphytic plants rely on lianas for food, shelter, and reproductive sites.
- Nutrient Cycling: Lianas play a crucial role in nutrient cycling within forests. By absorbing nutrients from the forest floor and transferring them to the canopy through their stems, lianas facilitate nutrient exchange between different vertical layers of the forest.
Negative Impacts of Lianas on Forests:
- Competition for Resources: High densities of lianas can lead to competition with trees for essential resources like light, water, and nutrients.
- This competition may impede tree growth, reduce seedling establishment, and hinder forest regeneration.
- Impact on Forest Structure and Stability: By increasing the likelihood of tree fall during storms or strong winds, lianas can negatively affect forest structure and composition.
- When lianas grow on tree crowns, they increase the weight and wind resistance of trees, making them more susceptible to uprooting.
- Economic Implications: Lianas can also impact the growth and reproduction of commercially valuable tree species, which has economic implications for forest management and timber production.
- Moreover, liana-infested trees often have reduced timber quality due to distortions in the tree trunk and branches.
- Low Carbon Sequestration: Their lower carbon sequestering capacity compared to trees further exacerbates the threat to carbon storage.
Pusa Basmati Rice

- 21 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
Even as basmati rice exports from the country are poised to scale a new high, scientists at the Indian Agricultural Research Institute (IARI) have red-flagged the “illegal” cultivation of its blockbuster varieties in Pakistan.
Unauthorized Cultivation and Export of Pusa Basmati Rice Varieties in Pakistan:
- Despite being officially registered and protected Indian varieties, several IARI-bred Basmati rice varieties, such as Pusa Basmati 1121, Pusa Basmati-6, and Pusa Basmati 1509, are being illegally cultivated and marketed in Pakistan.
- Recent YouTube videos even feature newer IARI varieties like Pusa Basmati-1847, PB-1885, and PB-1886, released in late 2021.
- Pakistan's unauthorized Basmati exports have been substantial, with 7.58 lt ($694.55 million) in 2021-22 and 5.95 lt ($650.42 million) in 2022-23 (July-June).
- This growth is partly due to the depreciation of the Pakistani rupee, allowing the country to offer lower export prices than India.
- The proliferation of these protected varieties in Pakistan can be attributed to the ease of seed multiplication.
- With just a small quantity of seeds, large-scale cultivation can be established within two years of the variety's release in India.
- This unauthorized cultivation not only undermines India's intellectual property rights but also impacts the competitiveness of India's Basmati rice exports in the global market.
What is the Basmati Crop Improvement Program?
- The Basmati Crop Improvement Program focuses on refining the unique qualities of Basmati rice, such as its distinct grain characteristics, cooking properties, and pleasing aroma.
- IARI has played a crucial role in the genetic enhancement, leading to the development of high-yielding, semi-dwarf, and photo-insensitive Basmati varieties like Pusa Basmati 1.
- These improvements have significantly reduced the crop duration from 160 to 120 days and increased productivity from 2.5 to 6-8 tons per hectare.
- As a result, these advanced Basmati varieties account for approximately 90% of India's projected $5.5 billion exports in 2023-24.
- This achievement contributes to substantial foreign exchange earnings and economic growth for the country.
Key Features of IARI-Developed Basmati Rice Varieties:
- IARI has cultivated various Basmati rice varieties with distinct characteristics, including:
- Pusa Basmati 1121: Known as the world's longest Basmati rice, it matures in 145 days with an average yield of 45 q/ha.
- Pusa Basmati 1509: Derived from Pusa 1121 x Pusa 1301, this variety addresses Pusa Basmati 1121's weaknesses, matures in 115 days, and yields 5 tons/ha.
- Improved Pusa Basmati 1 (Pusa 1460): This variety, the first product of molecular breeding in Indian rice, is an enhanced Pusa Basmati 1 with bacterial leaf blight resistance.
- Pusa Basmati 6 (Pusa 1401): Offering superior grain quality, this variety improves upon Pusa 1121's yielding ability, agronomy, and cooking quality.
- Pusa RH10: The world's first superfine grain aromatic rice hybrid, it was released in 2001 for commercial cultivation in specific irrigated ecosystems.
Registration and Cultivation Areas of Pusa Basmati Rice in India:
- All Pusa Basmati rice varieties are officially recognized under the Seeds Act 1966 and can be cultivated within the designated Geographical Indication (GI) area of Basmati rice in India, encompassing seven northern states.
- These varieties are further registered under the Protection of Plant Varieties and Farmers' Rights Act 2001, which permits only Indian farmers to sow, save, re-sow, exchange, or share the seeds of protected/registered varieties.
Six Heritage Sites on Tentative UNESCO List

- 20 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
In a significant boost to its rich cultural and historical legacy, 6 new sites from Madhya Pradesh have found a place in the tentative UNESCO list of World Heritage Sites (WHS).
Six New Sites From MP In the UNESCO Tentative List:
- The sites included in the tentative list are Gwalior Fort, the Historical Group of Dhamnar, Bhojeshwar Mahadev Temple, Rock Art Sites of Chambal Valley, Khooni Bhandara, Burhanpur, and God Memorial of Ramnagar, Mandla.
- The UNESCO tentative list includes those that provide a forecast of the properties that a State Party may decide to submit for inscription in the next five to ten years.
- Gwalior Fort: An imposing fortress atop a hill, featuring impenetrable walls, exquisite sculptures, and stunning architecture.
- Built-in the 6th century AD by Rajput warrior Suraj Sen and expanded by Tomar ruler Maan Singh in 1398.
- Dhamnar Caves: Rock-cut temple site in Mandsaur district, constructed in the 7th century AD.
- It comprises 51 caves, stupas, chaityas, and dwellings, with a colossal Gautam Buddha statue.
- Bhojeshwar Mahadev Temple: Located near Bhopal, this temple is dedicated to Lord Shiva, with a huge Linga carved from a single stone.
- Built between 1010 and 1053 AD by Raja Bhoj but was never completed.
- Chambal Valley Rock Art Sites: The world's largest concentration of rock art sites across MP, Rajasthan, and Uttar Pradesh, depicting ancient daily life, rituals, and hunting scenes.
- Khooni Bhandara: A unique water supply system built in Burhanpur in 1615 by ruler Abdurrahim Khankhana, still operational today.
- Gond Statue, Mandla: Moti Mahal, a five-storied palace built in Mandla in 1667 by Gond king Hriday Shah, showcasing the strong willpower of the king despite limited resources.
What is UNESCO’s Tentative List?
- A World Heritage Site is a site with outstanding universal value.
- It also denotes cultural and natural significance that transcends national boundaries and is of common importance for current and future generations of all humanity.
- According to UNESCO, a tentative list lists the properties each State Party intends to consider for nomination.
- The government of any nation must have a nomination document ready for the UNESCO World Heritage Committee to review once as soon as UNESCO includes it in a location on the Tentative List.
- After this, a UNESCO representative will evaluate the situation and inspect it.
What is the Tentative List Process?
- The States Parties are encouraged to submit their Tentative Lists of properties that they consider cultural and natural heritage of outstanding universal value and, therefore, suitable for inscription on the World Heritage List.
- The States Parties are encouraged to prepare their Tentative Lists with the participation of stakeholders such as site managers, local and regional governments, local communities, NGOs, and other interested parties and partners.
- The States Parties should submit the Tentative Lists to the World Heritage Centre at least one year before submitting any nomination.
- The list should not be exhaustive.
- The States Parties can re-examine and re-submit their list at least every ten years.
- The States Parties are also requested to submit their lists using a submission format (English or French) that should contain the name of the properties, geographical location, a brief description of the properties, and why the property is of outstanding universal value.
- Nomination will only be considered once the property is added to the State Party's Tentative List.
State of Global Climate Report 2023

- 20 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
In line with a host of observations by climate agencies in the preceding three months, the World Meteorological Organisation (WMO) has officially confirmed 2023 to be the hottest year on record.
About the State of Global Climate Report 2023:
- Published annually by the World Meteorological Organization (WMO), the State of Global Climate Report provides a detailed analysis of the Earth's climate system.
- Contributors to the report include various UN organizations, National Meteorological and Hydrological Services, Global Data and Analysis Centers, Regional Climate Centres, the World Climate Research Programme (WCRP), and more.
Highlights of the 2023 Report:
- Record-Breaking Global Temperatures: 2023 was the hottest year on record, with a global average near-surface temperature of 1.45°Celsius (±0.12°C) above the pre-industrial baseline.
- The past ten years were also the warmest decade recorded.
- Extensive Marine Heatwaves: Nearly one-third of the global ocean experienced a marine heatwave on an average day in 2023.
- Over 90% of the ocean had faced heatwave conditions at some point during the year, negatively impacting ecosystems and food systems.
- Unprecedented Glacier Ice Loss: Preliminary data reveals the largest loss of ice since 1950 for the global set of reference glaciers, driven by extreme melt in western North America and Europe.
- Surge in Renewable Energy Capacity: Renewable capacity additions in 2023 increased by almost 50% from 2022, totaling 510 gigawatts (GW) and marking the highest rate in the past two decades.
- These findings emphasize the pressing need to address climate change through effective international cooperation, policymaking, and sustainable practices.
About the World Meteorological Organisation (WMO):
- The World Meteorological Organization (WMO) is a specialized agency of the United Nations that fosters international cooperation in atmospheric science, climatology, hydrology, and geophysics.
- Founded in 1950, WMO originated from the International Meteorological Organization established in 1873 to facilitate the exchange of weather data and research.
- Today, WMO comprises 193 member countries and territories and promotes the free exchange of meteorological and hydrological data, information, and research.
- By collaborating with various partners, WMO contributes to environmental protection, climate change mitigation, and sustainable development efforts worldwide.
- Headquarters: Geneva, Switzerland.
Small-Scale LNG (SSLNG)

- 20 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
India's largest gas utility GAIL (India) Ltd commissioned the country's first SSLNG unit at its Vijaipur complex in Madhya Pradesh recently.
India Unveils Its First Small-Scale LNG Plant:
- In a significant step towards a cleaner energy mix, GAIL (India) Ltd. has commissioned India's first Small-Scale LNG (SSLNG) plant in Vijaipur, Madhya Pradesh.
- This plant will produce 36 tonnes of Liquefied Natural Gas (LNG) daily, utilizing cutting-edge technology like treatment skids and liquefaction skids to convert natural gas into LNG.
- As part of India's commitment to increasing the proportion of natural gas in its primary energy mix from 6% to 15% by 2030, the SSLNG plant will play a pivotal role in reducing pollution emissions while catering to the nation's growing energy demands.
- This milestone achievement paves the way for a greener future and positions India as a significant player in the global LNG landscape.
What is Small-Scale LNG?
- Small-scale LNG (SSLNG) is an emerging industry that offers a novel approach to natural gas distribution.
- While there is no standard international definition, SSLNG typically involves the liquefaction and transportation of natural gas in smaller quantities using specialized trucks and vessels.
- This allows for the supply of LNG to industrial and commercial consumers in regions without pipeline connectivity.
- SSLNG can be sourced from existing large-scale LNG import terminals or small liquefaction plants in gas-rich locations.
- End-users regasify the LNG using small vaporizers for traditional use cases like supplying Compressed Natural Gas (CNG) for vehicles and piped gas for households and industries.
- Alternatively, LNG can be supplied in its liquid form for direct use.
Benefits of Small-Scale LNG (SSLNG):
- Expanded Accessibility: SSLNG overcomes the constraints of traditional pipeline infrastructure, enabling natural gas delivery to regions previously lacking access.
- This opens new avenues for cleaner fuel alternatives and widespread energy availability.
- Operational Flexibility: SSLNG's modular design allows for rapid deployment in response to local demand fluctuations, making it an ideal solution for remote locations, industrial environments, and diverse transportation requirements.
- Sustainability Promotion: By fostering the adoption of cleaner fuels, SSLNG significantly reduces emissions in various transportation sectors, including trucks, buses, and marine vessels. This contributes to a greener future and combats climate change.
- Strengthened Energy Security: Decentralized SSLNG distribution systems diversify fuel sources and bolster energy security, ensuring reliable and stable energy supply amid global fluctuations and uncertainties.
Challenges of Small-Scale LNG (SSLNG) Implementation:
- Vehicle Availability Constraints: Limited options for LNG-powered vehicles impede the widespread adoption of LNG as a fuel source, underscoring the need for increased production and diversification of vehicle models.
- Insufficient Retail Infrastructure: The lack of a well-established LNG retail network hinders convenient consumer access to LNG fuel, emphasizing the importance of infrastructure expansion and enhancement.
- Higher Upfront Investment: The comparatively higher initial costs of LNG vehicles compared to traditional diesel options may deter potential buyers, necessitating innovative financial solutions and incentives.
- Financing Barriers: The absence of dedicated financing options for LNG vehicles poses obstacles for interested buyers, requiring tailored financial instruments to support SSLNG uptake.
- Restricted Pipeline Coverage: SSLNG faces logistical challenges in areas without existing natural gas pipeline networks, highlighting the need for infrastructure development to extend its reach to remote regions.
- Regulatory and Permitting Hurdles: SSLNG projects may encounter regulatory and permitting setbacks, including environmental and safety concerns, potentially prolonging project timelines and inflating costs.
- Addressing these challenges is essential for expediting SSLNG implementation and fostering its growth.
FSSAI Launches Comprehensive Lab Network for Pathogen Testing

- 20 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
With food poisoning and diarrhea becoming a common occurrence, the Food Safety and Standards Authority of India (FSSAI) is working towards creating a network of 34 microbiology labs across the country that will be equipped to test food products for 10 pathogens, including E coli, salmonella, and listeria.
About the Initiative:
- To address the growing concern of microbial contamination in food products, a network of 34 advanced microbiology laboratories has been established across the country.
- These state-of-the-art facilities are specifically designed to test and monitor a wide range of food products for the presence of harmful pathogens, including E. coli, salmonella, and listeria, among others.
- The nationwide initiative aims to strengthen the existing food safety framework by enhancing the early detection and prevention of foodborne illnesses.
- By analyzing food samples collected during routine surveillance, the labs will play a pivotal role in ensuring the safety and quality of consumable goods.
- With a focus on safeguarding public health and well-being, this collaborative effort will contribute significantly to the overall improvement of food security and foster greater confidence in the food industry.
- As the network continues to expand and evolve, it will undoubtedly become an essential asset in the ongoing battle against foodborne pathogens and contamination.
Need for the Initiative:
- India has witnessed a surge in food poisoning and diarrhea cases in recent years, emphasizing the critical need for improved food safety measures.
- According to data from the National Centre for Disease Control (NCDC), over 1,100 outbreaks of acute diarrhoeal disease and around 550 incidents of food poisoning occurred within the last four years.
- These troubling statistics underscore the urgency to address this pressing public health issue.
- State food safety laboratories, responsible for ensuring the safety of consumable products, currently lack the necessary resources and infrastructure to effectively identify and mitigate the presence of dangerous pathogens.
- The complexities of maintaining live reference samples, the high costs of reagents, and the requisite expertise of microbiologists pose significant challenges in maintaining optimal food safety standards.
- Consequently, the establishment of a comprehensive microbiology lab network becomes crucial in effectively addressing the growing threat of foodborne illnesses.
- By enhancing testing capabilities and promoting early detection, this initiative will ultimately contribute to a safer food supply, improved public health outcomes, and increased consumer confidence in the food industry.
About the Food Safety and Standards Authority of India (FSSAI):
- As an autonomous body under India's Ministry of Health and Family Welfare, the FSSAI was established in 2006 under the Food Safety and Standards Act.
- This act serves as a consolidating statute focusing on food safety and regulation in India.
- The FSSAI's mission is to set global standards for food, encourage adherence to these standards, promote good manufacturing and hygiene practices, and enable citizens' access to safe and nutritious food.
Key functions include:
-
- Protecting public health by regulating and supervising food safety.
- Setting standards and guidelines for food articles.
- Issuing licenses, registrations, and accreditations for food businesses.
- Controlling food imports to prevent harmful ingredients.
- Accrediting food testing laboratories nationwide.
- Overseeing food certification in India, including accreditation of certification systems and food safety management systems for food businesses.
- Through these efforts, the FSSAI plays a vital role in maintaining high food safety standards and safeguarding the well-being of India's citizens.
Reverse Flipping
- 20 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
Payments major Pine Labs and quick commerce firm Zepto are among the startups looking to relocate their headquarters from foreign shores to India, to capitalize on the country's burgeoning tech landscape.
What is Reverse Flipping?
- Reverse flipping is a growing trend where overseas startups relocate their domicile to India and list on Indian stock exchanges.
- The primary motivation behind this shift is the potential for a higher valuation and more certain exit opportunities in India's thriving economic landscape.
Several factors contribute to the rise of reverse flipping:
- Access to a large, expanding economy: India's significant market size and sustained economic growth offer foreign startups attractive prospects for business expansion and success.
- Abundant venture capital: India's substantial venture capital resources provide a strong financial foundation for startups, fueling innovation and growth.
- Favorable tax policies: The country's tax regulations encourage foreign startups to establish operations in India, helping them maximize profits and minimize costs.
- Enhanced intellectual property protection: India's robust IP protection framework fosters innovation and creativity, safeguarding the unique ideas and technologies of startups.
- Skilled, youthful workforce: The availability of a talented, young, and educated population provides startups with a valuable human resource pool to drive growth and success.
- Supportive government policies: The Indian government actively promotes entrepreneurship and innovation through various initiatives and policies, creating a conducive environment for startups.
- The Economic Survey 2022-23 acknowledged the importance of reverse flipping and suggested measures to expedite the process, including simplifying tax vacation procedures, ESOP taxation, capital movement, and reducing tax layers.
- These efforts aim to further enhance India's appeal as a destination for foreign startups and foster economic growth.
What is Flipping?
- Flipping refers to the process by which an Indian company becomes a 100% subsidiary of a foreign entity after moving its headquarters overseas, involving a transfer of intellectual property (IP) and other assets.
- This transforms an Indian startup into a fully-owned subsidiary of a foreign entity, with founders and investors maintaining their ownership through the new overseas structure by exchanging their shares.
The process of flipping poses several concerns for India:
- The brain drain of entrepreneurial talent: As Indian startups move their operations overseas, India experiences a loss of innovative and entrepreneurial talent, which could otherwise contribute to the country's economic growth and development.
- Value creation in foreign jurisdictions: Flipping redirects potential value creation to foreign countries, depriving India of the economic benefits that could result from successful startups and innovations.
- Loss of Intellectual Property: When companies relocate and transfer their intellectual property overseas, India loses valuable IP assets, undermining the country's competitive advantage and innovation potential.
- Reduced tax revenue: Flipping also contributes to decreased tax revenue for India as companies shift their operations and profits to other jurisdictions, which may have more favorable tax policies.
Developing Countries Trading Scheme (DCTS)

- 19 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
Exporters seeking to avail duty concessions on shipments to the UK will have to adhere to the new British rules under the Developing Countries Trading Scheme (DCTS).
What is the Developing Countries Trading Scheme (DCTS)?
- The Developing Countries Trading Scheme (DCTS) is a preferential trading scheme introduced by the United Kingdom to promote trade with developing countries and support their economic growth.
- The DCTS is designed to support sustainable growth in these countries through a more generous unilateral offer compared to the current Generalised Scheme of Preferences (GSP).
Key provisions of the DCTS include:
- Tariff Reduction: Lowering tariffs facilitates easier exportation of goods from developing countries to the UK market.
- Liberalized Rules of Origin: Simplifying rules of origin requirements streamlines trade between developing nations and the UK.
- Simplified Conditions: The scheme's conditions are simplified to facilitate easier access for developing nations.
- The DCTS extends to countries currently benefiting under the UK's GSP, encompassing 47 Least Developed Countries (LDCs) and 18 additional low-income (LIC) and lower-middle-income (LMIC) countries or territories identified by the World Bank.
- However, it excludes countries classified as upper-middle income by the World Bank for three consecutive years or those with a free trade agreement (FTA) with the UK.
- The UK government's policy response to the DCTS introduction is structured into four sections, addressing rules of origin, tariffs, goods graduation, and scheme conditions.
- Overall, the DCTS signifies the UK's commitment to bolstering trade opportunities and sustainable growth in developing countries by providing improved market access and favorable trade terms.
Significance For India:
- The Developing Countries Trading Scheme (DCTS) has significant implications for India, as it offers preferential access to the United Kingdom's market.
- India, being classified as a lower-middle-income country by the World Bank, is eligible to benefit from the DCTS.
- Trade opportunities: The scheme provides reduced or eliminated tariffs on various goods, making it easier for Indian exporters to access the UK market.
- This results in enhanced trade opportunities and increased competitiveness for Indian products.
- Economic growth: By improving access to a major global market, the DCTS can contribute to India's economic growth, creating jobs and boosting the country's export sector.
- Diversification: The scheme encourages Indian businesses to diversify their export portfolio, helping to reduce reliance on specific sectors or trading partners.
- Sustainable development: Through its focus on promoting sustainable development and economic growth in participating countries, the DCTS aligns with India's own goals to foster inclusive and sustainable economic progress.
Overall, the DCTS presents a positive outlook for trade between India and the UK. It offers Indian exporters improved access to the UK market, reduced trade barriers, and a conducive environment for sustainable growth. India can leverage the opportunities provided by the DCTS to strengthen its trade relationship with the UK and potentially increase its exports, benefiting its economy and the livelihoods of its people.
Haemodialysis
- 19 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
Findings from a nationwide private hemodialysis network show that there is a variation in the survival of patients receiving hemodialysis in India depending on various factors, and stress on the need to standardize dialysis care across centers.
What is Hemodialysis?
- Haemodialysis, also known as dialysis, is a medical procedure that helps individuals with kidney failure by removing waste products and excess fluid from their blood.
- This procedure essentially performs the functions of the kidneys, which are responsible for filtering waste and maintaining the body's electrolyte balance.
Key points about hemodialysis:
- Process: During hemodialysis, a patient's blood is circulated through a machine with a semipermeable membrane, called a dialyzer or an artificial kidney.
- The dialyzer filters out waste products, such as urea and creatinine, and excess fluid from the blood, which is then discarded, while essential components are returned to the patient's bloodstream.
- Access: To perform hemodialysis, a patient typically requires vascular access, which is a surgically created connection between an artery and a vein, usually in the arm.
- This connection allows for the efficient flow of blood from the patient to the dialysis machine and back.
- Duration: Haemodialysis treatment typically lasts for around 3-5 hours and is performed several times per week, depending on the patient's needs and kidney function.
- Indications: Haemodialysis is prescribed for patients with end-stage kidney failure, also known as end-stage renal disease (ESRD), who need immediate intervention while waiting for a kidney transplant or when a transplant is not a suitable option.
- Side effects: Some common side effects of hemodialysis include low blood pressure, muscle cramps, itching, and fatigue.
- Complications such as infection, access problems, and blood clotting may also occur, but these risks can be minimized with proper medical supervision and management.
- In summary, hemodialysis is a life-sustaining treatment for patients with kidney failure, offering a means to maintain their health and well-being despite the loss of kidney function.
SAKHI App To Assist Gaganyaan Crew

- 19 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
The Vikram Sarabhai Space Centre (VSSC), the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) facility at Thumba in Thiruvananthapuram, has developed a multi-purpose app that will help astronauts on the Gaganyaan space flight mission carry out a range of tasks such as looking up vital technical information or communicating with one another.
About SAKHI App:
- The Vikram Sarabhai Space Centre (VSSC), an ISRO facility in Thumba, Thiruvananthapuram, has created the versatile 'SAKHI' app for astronauts on the Gaganyaan space flight mission.
- SAKHI stands for 'Space-borne Assistant and Knowledge Hub for Crew Interaction'.
Purpose:
- During the mission, the app will assist Gaganyaan crew members in various tasks such as accessing vital technical information and communicating with each other.
Utility:
- Health Monitoring: It will monitor key health parameters like blood pressure, heart rate, and oxygen saturation, providing crucial insights into the crew's physical condition during the mission.
- Additionally, it will remind them of hydration, dietary schedules, and sleep patterns.
- Connectivity:
- Astronauts can use the app to maintain mission logs in various formats, including voice recordings, texts, and images.
- It will ensure seamless communication between the crew, the onboard computer, and ground-based stations.
- Current Status: An engineering model of the custom-built hand-held smart device featuring SAKHI has been tested, with the development of a flight model underway.
About the Gaganyaan Mission:
- The primary objective of the mission is to demonstrate the capability to launch and safely return three crew members to low Earth orbit.
- The Launch Vehicle Mark-3 (LVM3) is designated as the launch vehicle for the Gaganyaan mission.
- Crew Escape System (CES): A vital component of the mission, CES is powered by quick-acting, high-burn rate solid motors.
- It ensures the safe evacuation of the Crew Module and crew in case of emergencies during launch or ascent.
- Orbital Module: Comprising the Crew Module (CM) and Service Module (SM), the Orbital Module orbits the Earth, providing safety and support throughout the mission phases.
- Crew Module (CM): Designed to offer a habitable space with Earth-like conditions for the crew during their time in space.
- Service Module (SM): This module supports the CM during orbit, containing essential systems such as thermal, propulsion, power, avionics, and deployment mechanisms.
- This will mark ISRO's inaugural manned spaceflight mission, joining the ranks of the US, Russia, and China, which have previously conducted human spaceflights.
Nilgiris Forest Fire

- 19 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
The Indian Air Force (IAF) has deployed its assets to aid the local administration in dousing the raging forest fire that started recently in Tamil Nadu's Nilgiris district.
What is a Forest Fire?
- A forest fire, also known as a wildfire, is an uncontrolled fire that occurs in forested areas or other vegetated landscapes.
- These fires can spread rapidly, fueled by dry vegetation, high temperatures, low humidity, and strong winds.
- Once ignited, they can quickly grow in size, consuming vast areas of land, vegetation, and wildlife habitat.
- Wildfires pose significant risks to human safety, property, ecosystems, and air quality.
Causes of Forest Fire:
- Forest fires are caused by Natural causes as well as man-made causes.
- Natural causes: Many forest fires start from natural causes such as lightning which sets trees on fire.
- However, rain extinguishes such fires without causing much damage. High atmospheric temperatures and dryness (low humidity) offer favorable circumstances for a fire to start.
- Man-made causes: Fire is caused when a source of fire like naked flame, cigarette or bidi, electric spark, or any source of ignition comes into contact with inflammable material.
- Natural causes: Many forest fires start from natural causes such as lightning which sets trees on fire.
Types of forest fire:
- Surface Fire: This type of forest fire spreads primarily along the ground, consuming surface litter such as dry leaves, twigs, and grasses.
- The flames engulf the forest floor as they advance.
- Underground Fire: Underground fires, also known as muck fires, burn with low intensity beneath the surface, consuming organic matter and surface litter.
- These fires often spread slowly and can continue burning for months, destroying vegetative cover.
- Ground Fire: Ground fires occur in sub-surface organic fuels such as duff layers under forest stands or organic soils of swamps.
- They burn herbaceous growth and organic matter beneath the surface, often transitioning from smoldering underground fires.
- Crown Fire: Crown fires involve the burning of the crowns of trees and shrubs, sustained by a surface fire.
- They are particularly hazardous in coniferous forests, where resinous material can fuel intense flames.
Frequency of Forest Fire in India:
- Seasonality: Forest fires in India are prevalent from November to June, with peak activity typically occurring in April and May, encompassing both small-scale and large-scale incidents.
- Vulnerability: The 2019 India State of Forest Report (ISFR) highlighted that over 36% of the country's forest cover is susceptible to frequent fires, with 4% categorized as extremely prone and an additional 6% as highly fire-prone.
- Affected Regions: Dry deciduous forests experience severe fires, with Northeast India, Odisha, Maharashtra, Jharkhand, Chhattisgarh, and Uttarakhand being particularly vulnerable areas.
- Recent Incidents: Notable fire outbreaks occurred in 2021 across Uttarakhand, Himachal Pradesh, Nagaland-Manipur border, Odisha, Madhya Pradesh, and Gujarat, including wildlife sanctuaries.
- In 2023, Goa faced large bushfires under investigation for potential human causes.
- 2024 Trends: Recent reports indicate heightened fire activity in Mizoram, Manipur, Assam, Meghalaya, and Maharashtra, with increased incidents along the Konkan belt, coastal Gujarat, southern Rajasthan, Madhya Pradesh, coastal Odisha, Jharkhand, Andhra Pradesh, Karnataka, and Tamil Nadu.
- Southern India: While Andhra Pradesh and Telangana witness fire incidents, forests in southern India, primarily evergreen or semi-evergreen, are less prone to fires, although Tamil Nadu has experienced recent wildfires.
Reasons Behind This Year's Fires:
- Climate Factors: Dry conditions, high temperatures, clear skies, and light winds have fueled forest fires in southern India.
- Temperature Trends: February 2024 was exceptionally hot, making it the hottest month in southern India since 1901.
- Heat Accumulation: Above-average temperatures over the past months led to a buildup of heat, drying out biomass in forests ahead of the summer season.
- Excess Heat Factor: Western Andhra Pradesh and Karnataka are experiencing higher-than-normal EHF values, increasing the risk of heat waves.
- Mild Aridity: Lack of rain and high temperatures have classified most districts in southern India as mildly arid.
World Air Quality Report 2023

- 19 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
India had the third worst air quality out of 134 countries in 2023 after Bangladesh and Pakistan according to the World Air Quality Report 2023 by IQAir.
About World Air Quality Report 2023:
- The World Air Quality Report is an annual publication by IQAir, a Swiss air quality monitoring firm.
- The report provides an in-depth analysis of global air quality, shedding light on the impact of air pollution on human health and the environment.
Key highlights from the report include:
- India ranks third in poor air quality: With an average annual particulate matter 2.5 (PM2.5) concentration of 54.4 micrograms per cubic meter, India trails only Bangladesh and Pakistan in terms of poor air quality.
- South Asian dominance in pollution rankings: Bangladesh and Pakistan occupy the top two positions in the air pollution rankings, while ten out of the eleven most polluted cities in the world are in India.
- Delhi's alarming status: For the fourth consecutive year, Delhi has been identified as the world's most polluted capital city.
- Additionally, Bihar's Begusarai has been termed the world's most polluted metropolitan area.
- India's widespread exposure: An overwhelming 96% of the Indian population experiences PM2.5 levels more than seven times the WHO annual PM2.5 guideline, emphasizing the need for urgent interventions to mitigate the health impacts of air pollution.
What is Particulate Matter (PM)?
- Particulate Matter (PM) is a term used to describe a mixture of solid particles and liquid droplets found in the air.
- These particles can be made up of various components such as dust, dirt, soot, smoke, and organic chemicals.
- They are classified based on their size, with PM2.5 and PM10 being the most commonly referenced categories.
- PM2.5 refers to fine particulate matter with a diameter of 2.5 micrometers or less, which is about 30 times smaller than the width of a human hair.
- These particles are produced by various sources such as vehicle emissions, industrial processes, and wildfires.
- Due to their small size, they can penetrate deep into the lungs and even enter the bloodstream, posing significant health risks.
- PM10, on the other hand, refers to coarse particulate matter with a diameter of 10 micrometers or less.
- These particles are larger and primarily originate from activities such as construction, road dust, and agricultural practices.
- While not as harmful as PM2.5, they can still enter the respiratory system and cause health problems.
Equity Issues in IPCC Reports

- 18 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
In a study published recently, researchers analyzed more than 500 future emissions scenarios the UN Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) assessed in its latest reports.
About the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC):
- The IPCC was created in 1988 by the World Meteorological Organization (WMO) and the United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP).
- It is the leading international body for the assessment of climate change.
- It is a key source of scientific information and technical guidance to the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC) and the Paris Agreement.
- The IPCC provides governments with scientific information for use in developing climate policies.
- The IPCC currently has 195 members.
- The IPCC does not undertake new research. Instead, it synthesizes published and peer-reviewed literature to develop a comprehensive assessment of scientific understanding.
- These assessments are published in IPCC reports.
- They are subject to multiple drafting and review processes to promote an objective, comprehensive, and transparent assessment of current knowledge.
- The IPCC’s work is guided by principles and procedures that govern all main activities of the organization.
- IPCC member governments and observer organizations nominate experts and the IPCC's scientific governing body, the IPCC Bureau, selects authors and editors with expertise in a range of scientific, technical, and socio-economic fields.
What are IPCC Assessment Reports?
- Typically, IPCC reports comprise three Working Group reports:
- One on physical science
- One on climate adaptation, and
- One on mitigation action.
- One synthesis report consolidates findings from the three Working Group reports.
- Then there are thematic special reports.
- Each report assesses climate-related scientific literature to capture the state of scientific, technical, and socio-economic knowledge on climate change.
- The IPCC is currently in its Seventh Assessment cycle (AR7).
How Does it Assess Future Scenarios?
- The IPCC uses ‘modelled pathways’ to estimate what it will take to limit the warming of the earth’s surface.
- These pathways are drawn using Integrated Assessment Models (IAMs) that describe human and earth systems.
- IAMs are complex models that examine possible futures of the energy and climate systems and economies.
- Its macroeconomic models can point to future growth levels in terms of GDP;
- Its energy models can project future consumption
- Vegetation models can examine land-use changes; and
- Earth-system models use the laws of physics to understand how climate evolves.
- With such integration across disciplines, IAMs are meant to provide policy-relevant guidelines on climate action.
- However, these models also have shortcomings. They prioritize least-cost assessments — for example, the absolute cost of setting up a solar plant or undertaking afforestation in India is lower than in the U.S.
- However, experts have said they could exercise the option of enabling countries to equitably share the burden of action, where the richest undertake more drastic mitigation action more immediately.
About the Latest Study:
- Conducted by a team of specialists from Bengaluru and Chennai, the study scrutinized 556 scenarios outlined in the IPCC's AR6 report.
- Their findings indicate that by 2050, per-capita GDP in Sub-Saharan Africa, South Asia, West Asia, and other parts of Asia will remain below the global average.
- Collectively, these regions account for 60% of the global population.
- Additionally, the study highlighted disparities in the consumption of goods and services, as well as energy and fossil fuel consumption, between the Global North and the Global South.
Why Does Equity Matter?
- Equity is crucial in climate action as per the UNFCCC, which mandates developed nations to lead in combating climate change.
- However, current modeling approaches often overlook equity, burdening poorer nations disproportionately.
- Researchers highlight the need for modeling techniques that prioritize climate justice and equitable distribution of responsibilities.
- They argue that mitigation pathways should ensure developed regions accelerate towards net negative emissions and allocate carbon budgets to less developed regions.
- Addressing this gap requires a paradigm shift in scenario building, emphasizing both equity and environmental sustainability.
- This approach is vital for fostering global cooperation and achieving meaningful climate action.
Lisu and Singpho Communities

- 18 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
Children of the Lisu and Singpho communities in Arunachal Pradesh and Assam are named according to the order they are born in the family, incorporating numbers into their names.
News Summary:
- In the Lisu or Yobin community of Arunachal Pradesh, names reflect the birth order of children, a tradition emphasizing familial hierarchy and cultural heritage.
- This practice underscores the community's deep-rooted connection to family and tradition.
- Recently, Birdwatchers discovered a new species of wren babblers in remote northeastern Arunachal Pradesh, aptly named the Lisu wren babbler.
Lisu and Singpho communities:
- The Lisu and Singpho communities, belonging to the Tibeto-Burman ethnic family, share a unique tradition of employing numbered names to denote birth order within their families, serving as a testament to their ethnic cohesion and rich cultural legacy.
- This naming tradition is prevalent among the Lisus, spanning regions such as Arunachal Pradesh, China, Myanmar, and Thailand, as well as the Singphos, who are prominent in Arunachal Pradesh and Assam in India.
- The Singphos, an ethnic community believed to have originated from the Kachin peoples, migrated from regions including upper Myanmar, Southwestern China, and Northern Thailand to settle in the eastern areas of Arunachal Pradesh.
- Both communities adhere to specific naming sequences for boys and girls, supplemented by strategies to prevent confusion in cases of similar name counts within families, such as the use of prefixes or suffixes.
- Furthermore, names may incorporate clan or ancestral references, adding layers of cultural and familial significance to the naming tradition, which underscores the profound connection to tradition and the enduring importance of family and clan identities within these communities.
About Wren Babblers:
- Belonging to the babbler family Timaliidae, Wren Babblers encompass approximately 20 small Asian bird species.
- Characteristics: These birds typically measure between 10 to 15 centimeters (4 to 6 inches) in length, featuring short tails and straight bills.
- Natural Habitat: Primarily found in southern Asia, Wren Babblers inhabit various ecological niches.
- Grey-bellied Wren Babblers: A closely resembling species to this newly discovered one, predominantly inhabit regions of Myanmar, with smaller populations also found in China and Thailand.
Revenue-Based Financing

- 18 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
Revenue-based financing (RBF) is increasingly popular among startups and digital SMEs due to a lack of venture capital and limited access to traditional credit options.
What Is Revenue-Based Financing?
- Revenue-based financing is a method of raising capital for a business from investors who receive a percentage of the enterprise's ongoing gross revenues in exchange for the money they invested.
- In a revenue-based financing investment, investors receive a regular share of the business's income until a predetermined amount has been paid.
- Typically, this predetermined amount is a multiple of the principal investment and usually ranges between three to five times the original amount invested.
How Revenue-Based Financing Works?
- Capital investment: An investor or a group of investors provides capital to a company (but not as a traditional loan nor in exchange for equity in the company).
- Revenue percentage agreement: In return for the capital, the company agrees to give the investor a fixed percentage of its gross revenues each month.
- Repayment structure: The company repays the invested capital through payments based on monthly or annual revenue.
- The amount paid each month varies as it is directly tied to the company’s revenue for that month.
- Repayment cap or term: There is usually a cap on the total amount to be repaid, often set as a multiple of the original investment (e.g., 1.5x or 2x the initial amount).
- Alternatively, the repayment might continue until a specific term is reached, such as a number of years.
Comparing Revenue-based Financing to Debt and Equity-based Models:
- While revenue-based financing shares similarities with debt financing in terms of regular investor repayments, it differs notably as it doesn't involve interest payments.
- Instead, repayments are based on a predetermined multiple, yielding returns higher than the initial investment.
- Moreover, unlike traditional debt arrangements, revenue-based financing doesn't necessitate collateral.
- Additionally, unlike equity-based models, it doesn't entail transferring ownership stakes in the company to investors.
Chausath Khamba

- 18 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
Characterized by its marble pillars and intricate latticework, Chausath Khamba (64 pillars) stands adjacent to the Nizamuddin dargah, a 14th-century shrine erected in honor of the revered Sufi saint Hazrat Nizamuddin Auliya.
About the Chausath Khamba:
- Chausath Khamba was built in AD 1623 - 24 to serve as a tomb for Mirza Aziz Koka, the foster brother of Mughal Emperor Akbar.
- It is so called on account of the 64 (chausath) monolithic marble pillars (khamba) and stands close to his father, Atgah Khan’s tomb, at the edge of the Dargah of Hazrat Nizamuddin Auliya.
- The tomb enclosure is entered through a lofty arched gateway and has a large sunken forecourt.
- The mausoleum is unique on account of it being built entirely of marble, with 25 marble domes supporting the flat roof of the structure.
- The plan for Chausath Khamba could have been inspired by the wooden garden pavilions from Persia - such as the Chihil Sutun, and in turn, the Chausath Khamba seems to have inspired the architectural design for Emperor Shahjahan’s Diwan-i-Aam, Hall of Audience.
- Each facade of the square structure has five marble arches inset with marble jaallis or lattice screens and a doorway in the central arch providing access to the tomb.
- The column capitals are intricately carved with simple yet striking pendentives bridging the square floor plan to the circular dome above.
- The structure also finds mention in Sir Gordon Risley Hearn’s book The Seven Cities of Delhi.
- As per author and historian Sam Dalrymple, the edifice embodies the architectural style of Gujarat and Ahmedabad within Delhi, serving as the Urs Mahal for hosting festivities during the commemoration of Nizamuddin's passing.
- This illustrates the historical dissemination of regional architectural influences across India over centuries.
Predictive AI: Its Applications and Advantages

- 18 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
Predictive AI is revolutionizing data analysis, decision-making, and industry leadership, offering businesses unprecedented insights and strategic advantages.
What is Predictive Artificial Intelligence (AI)?
- Predictive artificial intelligence (AI) utilizes machine learning techniques to analyze historical data and forecast future events, distinguishing it from traditional AI focused solely on retrospective analysis.
- This cutting-edge technology employs advanced algorithms and machine learning models to sift through extensive datasets, identifying subtle patterns and trends.
- Unlike conventional approaches, Predictive AI doesn't just analyze data; it transforms it into actionable insights, enabling organizations to:
- Anticipate future outcomes,
- Predict market shifts, and
- Make strategic decisions with unprecedented foresight.
- By continuously learning from past data and adapting to changing trends, Predictive AI becomes an invaluable tool, guiding businesses through uncertain landscapes.
How Predictive AI Work?
- Leveraging Big Data: Predictive AI relies on access to extensive datasets, often referred to as "big data," as larger datasets typically lead to more accurate analyses.
- Utilizing Machine Learning (ML): As a subset of AI, ML involves training computer programs to analyze data autonomously, without human intervention.
- In the realm of predictive AI, ML algorithms are applied to vast datasets to extract valuable insights.
- Autonomous Processing: Predictive AI models are capable of autonomously processing massive datasets, eliminating the need for human oversight.
- Pattern Recognition: Through ML techniques, predictive AI learns to recognize patterns within datasets, associating specific data points or occurrences with potential future events.
- By examining numerous factors, predictive AI can identify intricate patterns indicative of recurring events, enabling organizations to anticipate future outcomes effectively.
Difference Between Predictive AI and Generative AI:
- Predictive AI and generative AI both employ machine learning techniques and leverage extensive datasets to generate their outputs.
- However, while predictive AI utilizes machine learning to forecast future outcomes, generative AI employs machine learning to produce original content.
- For instance, a predictive AI model may inform fishermen about impending storms, whereas a generative AI model may craft a fictional narrative depicting various scenarios involving weather and fishing expeditions.
- While both types of AI rely on statistical analysis to discern patterns, their objectives, machine learning methodologies, and applications differ significantly.
Various Applications of Predictive AI:
- Assessing the Impact of Natural Disasters: With the recent eruption of a volcano in Iceland, the potential repercussions on air travel echo concerns from a similar event in 2010, which disrupted flights across Europe.
- Predictive AI leverages data analysis to identify patterns and anticipate the impact of such extreme weather events on air travel. Platforms like Yandex offer interactive maps for real-time monitoring of ash clouds post-eruption.
- Enhancing Oil and Gas Exploration: In the realm of oil and gas exploration, companies possess extensive historical geological data that can inform predictive AI systems.
- By analyzing past drilling successes, these systems can predict optimal locations for new oil wells.
- For instance, Saudi Aramco utilizes its meta-brain generative AI to optimize drilling plans, analyze geological data, and forecast drilling outcomes accurately.
- By analyzing past drilling successes, these systems can predict optimal locations for new oil wells.
- Inventory and Supply chain management: Predictive AI aids in inventory and supply chain management by identifying peak consumer demand periods, facilitating proactive stock adjustments, and optimizing resource allocation to address fluctuations in road congestion and meet increased user demands.
- Marketing campaigns: Just as predictive AI can anticipate user or customer behavior, it can help prognosticate what kinds of content or products prospective customers may be interested in.
- Advancing Medical Research: Predictive AI plays a pivotal role in drug discovery, a cornerstone of contemporary medical research.
- Pharmaceutical companies are increasingly collaborating to leverage predictive AI models for analyzing vast datasets and identifying potential drug candidates. Initiatives like the 'MELLODDY Project', supported by the EU Innovative
- Medicines Initiative and multiple pharmaceutical firms, exemplify this collaborative effort in pooling data and leveraging predictive AI for drug discovery.
First Drug to Treat Common, Lethal Liver Disease Gets US Nod
- 16 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
Madrigal Pharmaceuticals Inc.’s drug Rezdiffra gained the first US approval to treat a potentially deadly liver disease that affects millions worldwide, succeeding in an area where some bigger rivals have failed.
What is Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis (NASH)?
- Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) is a condition in which fat builds up in the liver.
- NASH (or nonalcoholic steatohepatitis) is a type of NAFLD that can damage the liver.
- NASH occurs when the fat buildup in the liver leads to inflammation (hepatitis) and scarring.
- NASH can be life-threatening, as it can cause liver scarring (called cirrhosis) or liver cancer.
- It is estimated that 3% to 5% of the global population is affected by NASH, though the disease is considered to be underdiagnosed.
Who gets NASH?
- The condition may be hereditary.
- If a person has family members who have had NASH or NAFLD, they are at risk.
- Additionally, having certain health conditions may increase a person’s risk of developing NASH. These include:
- Being overweight or obese.
- Having high cholesterol or high triglyceride levels.
- Having type 2 diabetes, insulin resistance, or prediabetes.
What are the signs and symptoms of NASH?
- NASH is known as a “silent” disease because many people present with few or no symptoms.
- However, some people will experience tiredness, pain, and discomfort in the upper right part of the abdomen.
How is NASH diagnosed?
- Diagnosing NASH can be challenging because symptoms may not be noticeable until the disease progresses.
- Healthcare providers typically suspect NASH based on abnormal blood or liver test results or imaging showing liver fat.
- Confirmation requires a liver biopsy, an invasive procedure with risks and expenses, involving taking a small liver sample for microscopic examination.
How is NASH treated?
- To manage NASH, losing weight is often recommended as it can reduce liver fat, inflammation, and scarring.
- This involves losing around 3% to 5% of body weight by limiting fats and sugars in the diet.
- Heavy alcohol use should also be avoided to prevent further liver damage.
- If NASH progresses to cirrhosis, treatment may involve medications, medical procedures, or even a liver transplant.
- Currently, there are no approved medications specifically for treating NASH, but ongoing research aims to develop new treatments.
Google Deepmind’s new AI that can play video games with you

- 16 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
Google DeepMind recently revealed its latest AI gaming agent called SIMA or Scalable Instructable Multiworld Agent, which can follow natural language instructions to perform tasks across video game environments.
What is SIMA?
- Scalable Instructable Multiworld Agent (SIMA) is an AI Agent, which is different from AI models such as OpenAI’s ChatGPT or Google Gemini.
- AI models are trained on a vast data set and are limited when it comes to working on their own.
- On the other hand, an AI Agent can process data and take action themselves.
- SIMA can be called a generalist AI Agent that is capable of doing different kinds of tasks.
- It is like a virtual buddy who can understand and follow instructions in all sorts of virtual environments – from exploring mysterious dungeons to building lavish castles.
- It can accomplish tasks or solve challenges assigned to it.
- It is essentially a super-smart computer program that can be thought of as a digital explorer, having the ability to understand what you want and help create it in the virtual world.
How does SIMA work?
- SIMA can understand commands as it has been trained to process human language.
- So when we ask it to build a castle or find the treasure chest, it understands exactly what these commands mean.
- One distinct feature of this AI Agent is that it is capable of learning and adapting.
- SIMA does this through the interactions it has with the user.
- The more we interact with SIMA, the smarter it gets by learning from its experiences and improves over time.
- This makes it better at understanding and fulfilling user requests.
- Based on the current stage of AI development, it is a big feat for an AI system to be able to play even one game.
- However, SIMA goes beyond that and can follow instructions in a variety of game settings.
- This could potentially introduce more helpful AI agents for other environments.
Tesla’s India entry gets boost as government approves new EV policy
- 16 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
The government announced a new electric vehicle (EV) policy recently that is expected to provide a major boost to Tesla's plans to start operations in India.
What is the Revised EV Policy Offering Tax Incentives?
- The Government of India has sanctioned a new initiative aimed at positioning India as a premier manufacturing hub, fostering the production of cutting-edge electric vehicles (EVs) within the nation.
- Crafted to entice investments from renowned global EV manufacturers, this policy seeks to provide Indian consumers access to state-of-the-art EV technology while bolstering the Make in India campaign.
- By cultivating a competitive environment among EV players, the policy endeavors to fortify the EV ecosystem, stimulating innovation and efficiency.
- Furthermore, it is anticipated to stimulate substantial production rates, capitalize on economies of scale, and drive down production costs, consequently curbing crude oil imports, narrowing trade imbalances, and mitigating urban air pollution, thereby fostering a healthier environment for all.
Key Features of the Policy:
- Minimum Investment Requirement: Companies are mandated to invest a minimum of Rs 4,150 Crores.
- Investment Ceiling: There is no upper limit on the investment amount.
- Manufacturing Timeline: Companies must establish manufacturing facilities in India within 3 years and commence commercial production of e-vehicles.
- Within 5 years, they should achieve 50% domestic value addition.
- Domestic Value Addition (DVA): Localization levels of 25% by the 3rd year and 50% by the 5th year are mandatory during manufacturing.
- Customs Duty: A customs duty of 15%, applicable to Completely Knocked Down (CKD) units, will be enforced for 5 years.
- Import Limits: Import of at most 8,000 EVs annually is permitted under this scheme, with provisions for carrying forward unutilized import quotas.
- Bank Guarantee Requirement: Investment commitments necessitate bank guarantees to cover the forgone customs duty.
EV Adoption in India:
- In 2023, electric vehicle sales in India surged by 49.25% year-on-year, surpassing 15 lakh units, as the Federation of Automobile Dealers' Association (FADA) reported.
- This notable increase follows a total sale of approximately 10 lakh units recorded in 2022, indicating a rapid growth trajectory.
- Factors contributing to this surge include improved product availability, escalating fuel prices, state subsidies, and incentives provided under the FAME-II Initiative.
What is the FAME-II Scheme?
- The FAME India scheme, initiated in 2015, serves as an incentive program aimed at accelerating the adoption of electric and hybrid vehicles, with its acronym standing for "Faster Adoption and Manufacturing of Electric and Hybrid Vehicles in India."
- In 2019, the Central government sanctioned Phase II of the FAME Scheme with a budgetary allocation of 10,000 Crore over three years, extending until March 31, 2024.
- The primary objective of Phase II is to stimulate demand by facilitating the deployment of 7000 e-Buses, 5 lakh e-3 Wheelers, 55,000 e-4 Wheeler Passenger Cars (including Strong Hybrid), and 10 lakh e-2 Wheelers, thereby fostering the growth of the electric vehicle ecosystem.
- Under the FAME-II scheme, nearly 2 lakh vehicles have received support, signifying a significant stride towards electric vehicle adoption in the country.
Government Initiatives to Promote EV Usage:
- Battery Swapping Policy: The Battery Swapping Policy offers an alternative approach wherein discharged batteries are exchanged for charged ones, enabling efficient charging without vehicle downtime.
- NITI Aayog has recently unveiled a draft battery-swapping policy, prioritizing metropolitan cities with populations exceeding 40 lakh for the establishment of battery-swapping networks in the initial phase.
- Switching to EVs: Central and State governments extend upfront subsidies to mitigate the overall costs associated with electric vehicles, incentivizing consumers to transition towards cleaner mobility options.
- E-AMRIT Portal: The e-AMRIT portal serves as a comprehensive platform, furnishing resources and support to facilitate the seamless transition to electric vehicles, thereby bolstering the nation's electrification agenda.
Pandavula Gutta designated an exclusive Geo-heritage site in Telangana

- 16 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
Pandavula Gutta, a geological marvel older than the Himalayan hills, has been officially recognized as the sole Geo-heritage site in Telangana.
What is Pandavula Gutta?
- Pandavula Gutta holds historical significance, being older than the Himalayas and renowned for its ancient rock paintings portraying diverse animals such as bison, antelope, tiger, and leopard, along with intricate geometric designs and symbols like swastikas, circles, and squares.
- These paintings indicate continuous human habitation from the Mesolithic period (around 12,000 to 6,000 BCE) through medieval times.
About Geo-heritage Sites:
- Geo-heritage sites encompass geological features of inherent or cultural significance, providing insights into the Earth's evolution or history, valuable for earth science and educational purposes.
- In India, the Geological Survey of India (GSI) identifies and designates these special places as Geo-Heritage Sites (GHS) to ensure their preservation, akin to UNESCO's protection of world heritage sites worldwide.
About the Geological Survey of India (GSI):
- The Geological Survey of India (GSI), established in 1851 initially to locate coal deposits for the Railways, has evolved into a comprehensive repository of geo-science information vital for various sectors in India.
- Its objective is to provide impartial and current geological expertise and geoscientific data to inform policy-making decisions and address commercial and socio-economic needs.
- Designated as the primary agency for geological mapping and regional mineral resources assessment under the National Mineral Policy (NMP) 2008, GSI emphasizes systematic documentation of geological processes across India and its offshore areas.
- Utilizing advanced techniques and methodologies, including geological, geophysical, and geochemical surveys, the organization operates from its headquarters in Kolkata, along with six regional offices and state units across the country.
- Presently, GSI operates as an attached office to the Ministry of Mines.
'ETHANOL 100' hits the road at 183 Indian Oil stations in five states

- 16 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
In a strategic advance towards cleaner fuel alternatives, India commenced the sale of ETHANOL 100 across 183 Indian Oil outlets in Maharashtra, Karnataka, Uttar Pradesh, New Delhi, and Tamil Nadu.
What is ETHANOL 100 Fuel?
- ETHANOL 100 fuel represents a significant advancement in automotive technology, offering a high-octane rating ranging from 100 to 105.
- This elevated octane level is particularly advantageous for high-performance engines, delivering improved efficiency and power output while simultaneously reducing environmental impact.
- One of the key features of ETHANOL 100 is its remarkable versatility, making it suitable for a diverse range of vehicles, including flex-fuel vehicles (FFVs) designed to accommodate various fuel types such as gasoline, ethanol, or any blend thereof.
- This adaptability ensures that ETHANOL 100 can seamlessly integrate into existing automotive fleets without requiring extensive modifications or infrastructure upgrades.
- The composition of ETHANOL 100 consists of approximately 93 to 93.5 percent ethanol blended with 5 percent petrol and 1.5 percent co-solvent acting as a binder.
- This well-balanced formulation not only enhances fuel performance but also contributes to its practicality as a mainstream fuel option.
- In addition to its performance benefits, ETHANOL 100 stands out as a cleaner and greener alternative to traditional gasoline.
- By emitting lower levels of greenhouse gases and pollutants, such as carbon dioxide and particulate matter, ETHANOL 100 plays a crucial role in mitigating climate change and improving air quality in our communities.
- With the right infrastructure and support mechanisms in place, ETHANOL 100 has the potential to revolutionize the automotive industry by offering a sustainable and eco-friendly fuel solution that aligns with the global efforts to combat environmental degradation and promote sustainable development.
What are Flex-fuel Vehicles?
- Flex-fuel vehicles are engineered to operate on a diverse range of fuels, offering consumers the flexibility to choose between petrol, ethanol, or methanol at the point of refueling.
- Equipped with an internal combustion engine (ICE), these vehicles can seamlessly switch between different fuel types, providing versatility and convenience to drivers.
- While possessing similarities to conventional petrol-only cars, flex-fuel vehicles undergo minor modifications to accommodate the use of alternative fuels, ensuring compatibility and optimal performance across various fuel options.
Devin AI, an AI software engineer, can handle coding projects end-to-end

- 15 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
Recently, a US-based startup Cognition has unveiled an AI-powered tool, Devin, which it calls the “world’s first fully autonomous AI software engineer”.
What is Devin?
- Devin is a super-smart computer program created by a company called Cognition.
- It's like having a clever assistant for software engineering tasks.
- With just a simple instruction, Devin can write code, build websites, and make software all on its own.
- But Devin isn't trying to replace human engineers, instead, it's meant to work together with them to make their jobs easier.
- The special feature of Devin is its ability to think ahead and solve tricky problems.
- It can learn from its mistakes and keep getting better over time.
- Plus, it has all the tools that a human engineer needs, like a way to write code and browse the internet.
- Devin has been tested against other AI programs, and it did way better, solving almost 14 out of 100 problems compared to just under 2 for others.
- So, in simple terms, Devin is like a super-smart assistant that helps engineers do their work faster and better, without taking their jobs away.
How does Devin work?
- Devin works by using advanced artificial intelligence (AI) algorithms to understand and execute tasks related to software engineering.
- When given a prompt or instruction, Devin analyzes the request and uses its vast database of knowledge and problem-solving techniques to generate code, design websites, or develop software.
- One of Devin's key features is its ability to think ahead and plan complex tasks.
- It can make thousands of decisions based on the given task and learn from its mistakes to improve its performance over time.
- Devin also has access to essential tools like a code editor and web browser, enabling him to complete tasks from start to finish.
- It can learn new technologies, tackle a wide range of engineering challenges, and even train its own AI models.
- Additionally, Devin can collaborate with human engineers in real time, providing updates, accepting feedback, and contributing to design choices.
- Overall, Devin works by harnessing the power of AI to automate routine tasks, streamline workflows, and empower engineers to focus on more complex problems.
- By combining human expertise with machine intelligence, Devin represents a significant advancement in software engineering technology.
Conservationists to propose Kazhuveli watershed region in T.N. for nomination to World Monuments Fund Watch 2025

- 15 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
The Eri (tank) network in the Kazhuveli watershed region in the Villupuram district which comprises an incredible network of tanks created thousands of years ago is to be proposed for nomination to the World Monuments Fund Watch 2025 program.
About the World Monuments Fund (WMF)?
- The World Monuments Fund (WMF) is a non-profit organization headquartered in New York, committed to safeguarding and conserving endangered ancient and historic sites worldwide.
- Collaborating with local partners globally, the WMF offers financial and technical assistance to support preservation efforts.
- With a track record of raising over $300 million and securing an additional $400 million from other entities, the WMF has successfully preserved over 700 sites and championed the protection of more than 800 cherished landmarks since its establishment.
World Monuments Watch:
- The World Monuments Watch, initiated in 1996, is a program centered on nominations, fostering a link between local heritage conservation and international engagement.
- Through this initiative, the WMF has allocated over $110 million towards projects at over 300 Watch sites, enabling communities to utilize the platform's visibility to secure an additional $300 million from various funding sources.
World Monuments Fund in India:
In India, the World Monuments Fund (WMF) has focused on conserving significant cultural and ecological sites, including:
- The Kazhuveli Watershed Region: Renowned for its ancient 'Eri' network, an intricate system of tanks dating back thousands of years.
- Situated in the Villupuram district of Tamil Nadu, spanning from Gingee to Marakkanam and extending to the Auroville plateau.
- Proposed pilot projects in Munnur village aim to develop a heritage toolkit applicable across the watershed and beyond if the nomination is successful.
- Suranga Bawadi: An ancient water management system located on the Deccan Plateau in Karnataka.
- Included in the World Monument Watch list for 2020, highlighting its significance for preservation efforts.
Vision for Edible Oil Self-Reliance takes root in the North-East

- 15 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
Prime Minister Narendra Modi has reiterated the Government’s commitment to move towards self-sufficiency in edible oils production and harped on the importance of oil palm cultivation in the northeast region.
About the National Mission for Edible Oils - Oil Palm (NMEO-OP):
- The National Mission for Edible Oils - Oil Palm (NMEO-OP) is an initiative launched by the Government of India in August 2021 to significantly enhance oil palm cultivation and crude palm oil production.
- This centrally sponsored scheme prioritizes the North East region and the Andaman and Nicobar Islands, aiming to boost the area and productivity of oilseeds and Oil Palm.
- The targets of NMEO-OP include expanding the oil palm area to 10 lakh hectares by 2025-26, a substantial increase from 3.5 lakh hectares in 2019-20, along with elevating Crude Palm Oil production to 11.20 lakh tonnes by 2025-26 from 0.27 lakh tonnes in 2019-20.
- Furthermore, the mission seeks to enhance consumer awareness to maintain a consumption level of 19.00 kg/person/annum until 2025-26.
- Implementation of NMEO-Oil Palm involves various stakeholders such as the State Departments of Agriculture and Horticulture, Central University, ICAR-Institutions, CDDs, SAUs, KVKs, Central Agencies/Cooperatives, Oil palm processors/ Associations, DD Kisan, AIR, DD, TV channels.
- The salient features of NMEO-OP encompass assistance for planting material, inputs for intercropping up to a gestation period of 4 years, the establishment of seed gardens and nurseries, micro-irrigation, bore well/pump set/water harvesting structure, vermicompost units, solar pumps, harvesting tools, custom hiring center cum harvester groups, farmers and officers training, and replanting of old oil palm gardens, among others.
Oil Palm Production in India:
- Originating in West Africa, Oil Palm (Elaeis guineensis) is a relatively recent crop in India known for its high vegetable oil yield per hectare.
- It yields two main oils, palm oil, and palm kernel oil, utilized in both culinary and industrial applications.
- The primary oil palm-growing states in India include Andhra Pradesh, Telangana, and Kerala, which collectively contribute to 98% of the total production.
- Additionally, Karnataka, Tamil Nadu, Odisha, Gujarat, and Mizoram also have significant areas dedicated to oil palm cultivation.
India ranks 134th in global human development index

- 15 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
India has moved up a rank on the global Human Development Index (HDI), according to the United Nations Development Programme (UNDP) report ‘Breaking the gridlock: Reimagining cooperation in a polarised world’ released recently.
Highlights of the Recent Report:
- The latest report revealed that India's global ranking improved slightly from 135th in 2021 to 134th in 2022, with a total of 193 countries assessed in 2022 compared to 191 in the previous year.
- In 2022, India exhibited progress across all Human Development Index (HDI) parameters, including life expectancy, education, and Gross National Income (GNI) per capita.
- Notable advancements were observed in life expectancy, which increased from 67.2 to 67.7 years, while expected years of schooling reached 12.6, mean years of schooling rose to 6.57, and GNI per capita saw an uptick from $6,542 to $6,951.
- Despite these positive strides, India continues to lag behind its South Asian counterparts, such as Bangladesh (129th), Bhutan (125th), Sri Lanka (78th), and China (75th).
What is the Human Development Index (HDI)?
- The Human Development Index is published by the United Nations Development Programme (UNDP).
- It is the most well-known index of human development.
- It is based on the idea that human development means that people have long and healthy lives, are knowledgeable, and have a decent standard of living.
- More specifically, these three dimensions are measured with four indicators:
- A long and healthy life: measured by life expectancy at birth
- Knowledge: measured by expected years of schooling (for children of school entering age) and average years of schooling (for adults aged 25 and older)
- A decent standard of living: measured by Gross National Income (GNI) per capita
- Represented on a scale from 0 to 1, the HDI value reflects a country's level of human development, with higher values indicating greater development.
- Computed as the geometric mean of normalized indices for each dimension, it offers a nuanced understanding of a nation's progress.
- Furthermore, the HDI aligns with Amartya Sen's 'capabilities' approach, emphasizing the significance of achieving substantive ends in human well-being beyond mere economic indicators.
- Since its inception in 1990, the United Nations Development Programme (UNDP) has annually published the Human Development Report, which incorporates the latest HDI findings and insights.
Honoring, the Architect of Mumbai (Bombay)

- 15 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
The Maharashtra cabinet recently decided to ask the Ministry of Railways to rename Mumbai Central Station after Nana Jagannath Shankarseth.
Who was Nana Jagannath Shankarseth?
- Nana Jagannath Shankarseth was a social reformer, educationist, and philanthropist and often described as the “architect” of Mumbai (then Bombay).
- He made extremely valuable contributions in terms of both ideas and money to multiple sectors, to lay a strong foundation for the city.
- Shankarseth was greatly inspired by the legendary merchant and philanthropist Sir Jamsetjee Jeejeebhoy.
- As a social reformer and community leader, Shankarseth earned the goodwill of both Indians and the British.
- He became the first Indian to be nominated to the Legislative Council of Bombay.
Shankarseth’s Most Significant Contributions:
- Education: Shankarseth was deeply committed to the growth and spread of education in Bombay, and donated land owned by his family for educational institutions.
- Like many social reformers of his age, he believed that Indians could progress through education.
- He also worked for the education of girls and women.
- Shankarseth founded the Native School of Bombay, which was renamed first as the Bombay Native Institution, and then as the Board of Education.
- Finally, this institution evolved into the prestigious Elphinstone College.
- Museum, Temples: Shankarseth was among the wealthy donors who helped promote Dr Bhau Daji Lad Museum in Byculla, which was designed by a famous London-based architect.
- The Bhawani Shankar Temple near Nana Chowk was Shankarseth’s tribute to his late mother Bhawanibai Murkute.
- He also built a Ram temple.
- Railways: The first train in India ran between Boribunder and Thane on April 16, 1853.
- The 34-km project was undertaken by the Great Indian Peninsular Railway Company.
- The committee that gave the project impetus included Sir Jamsetjee Jeejeebhoy and Nana Shankarseth.
World Pi Day 2024: International Day Of Mathematics And Worldwide Celebrations

- 14 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
Every year, International Day of Mathematics (IDM) is celebrated on March 14 to spread awareness about its role in solving real-world problems.
About International Day of Mathematics:
- Every year, International Day of Mathematics (IDM) is celebrated on March 14 to spread awareness about its role in solving real-world problems.
- The United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO) declared the International Day of Mathematics at the 40th General Conference on November 19, 2019.
- This day also sheds light on Mathematics' importance in different areas like climate change, energy, artificial intelligence, and sustainable development.
- International Day of Mathematics coincides with International Pi Day.
- Pi is one of the most widely known mathematical constants and it is rounded to 3.14, which is why it is observed on March 14.
- IDM is an opportunity to educate students about the role and importance of mathematics in improving quality of life.
- It also empowers women and girls to contribute to achieving sustainable development goals for the 2030 agenda.
History:
- The 205th session of UNESCO’s Executive Council adopted the International Day of Mathematics.
- The 40th session of UNESCO's General Conference adopted March 14 as the International Day of Mathematics, which was the first official celebration with the theme 'Mathematics is Everywhere'.
- It is an opportunity to understand the importance of mathematics in daily life promoting mathematics use for the advancement of society.
Significance:
- International Day of Mathematics is celebrated to promote Mathematics in different fields highlighting the role of mathematics in solving the real-life world and addressing social concerns.
- IDM shows the application of mathematics in different fields of life including science, technology, engineering, and economics.
- IDM promotes mathematics at different levels encouraging educators, policymakers, parents and to stress the importance of mathematics and inspire students to pursue careers in STEM fields.
- STEM stands for Science, Technology, Engineering, and Mathematics. It is an opportunity to share research, discoveries, and insights with the general public and demystify the subject to make it more accessible.
- International Day of Mathematics is a global initiative to foster collaboration and exchange ideas across borders, cultures, and disciplines.
- The day aims to promote mathematics and help address global challenges through it.
The theme for International Day of Mathematics 2024:
The theme for International Day of Mathematics 2024 is 'Playing With Math.'
News-sharing service by Prasar Bharati launched, content to be ‘free of copyright’

- 14 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
Ahead of the Lok Sabha polls, public broadcaster Prasar Bharati launched a news-wire-like service to offer free content across mediums, which will be free of copyright or credit obligations.
What is PB-SHABD?
- PB-SHABD, an acronym for Prasar Bharti - Shared Audio Visuals for Broadcast and Dissemination, is a comprehensive platform designed to deliver daily news feeds encompassing video, audio, text, photos, and other formats to media subscribers.
- Leveraging the expansive network of Prasar Bharati reporters, correspondents, and stringers, the service offers up-to-the-minute news coverage spanning various regions of the country.
- Functioning as a centralized hub for news content, SHABD serves as a valuable resource for organizations, offering a wide array of news stories across fifty categories in all major Indian languages.
- Furthermore, the shared feeds facilitate tailored storytelling across diverse platforms, catering to the specific needs of newspapers, TV channels, and digital portals.
- In an inaugural gesture, the service is provided free of charge for the initial year, extending invaluable support to smaller media outlets and contributing to enhanced accessibility to news content.
About Prasar Bharti:
- Prasar Bharti functions as the nation's Public Service Broadcaster, operating under the Prasar Bharati Act established in 1997 as a statutory autonomous body.
- Its primary objective is to deliver public broadcasting services aimed at informing and entertaining the public.
- Comprising the former media units of the Ministry of Information and Broadcasting, namely the Doordarshan Television Network and All India Radio, Prasar Bharti plays a vital role in disseminating news and entertainment content.
- Headquartered in New Delhi, Prasar Bharti serves as a cornerstone of India's media landscape, dedicated to fulfilling its mandate of public service broadcasting.
Lab to monitor seawater quality and testbed to track monsoon systems inaugurated
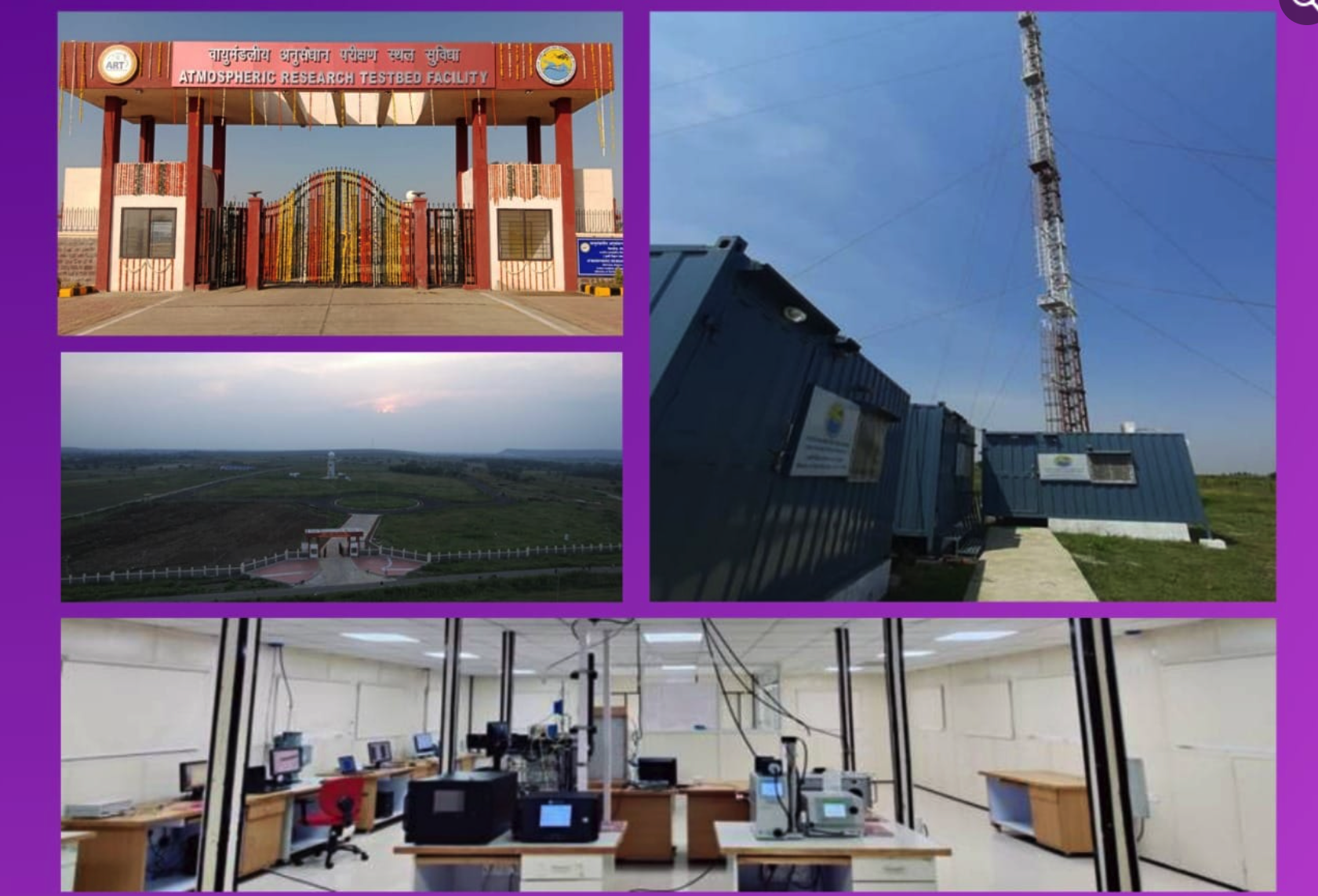

- 14 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
Recently India commissioned the atmospheric testbed facility near Bhopal, equipped with high-end instruments to record vital parameters for enhancing weather models and conducting advanced studies on the Indian monsoons, with construction commencing in early 2018.
What is the Atmospheric Research Testbed (ART)?
- The ART is an open-field, focused observational and analytical research programme at Silkheda.
- The facility aims to conduct ground-based observations of weather parameters like temperature, wind speeds, etc., and in-situ (on-site) observations of the transient synoptic systems – like low-pressure areas and depressions that form in the Bay of Bengal – during the southwest monsoon season from June to September.
- Studying these systems and their associated cloud parameters will be used to generate high volumes of data over a long period.
- It can then be compared with the existing weather models so that improvements can be made to obtain accurate rainfall predictions.
- The setup at ART will also be used for calibrating and validating various satellite-based observations, part of weather predictions and forecasting.
- Spread over 100 acres, the ART has been developed by the Ministry of Earth Sciences for Rs 125 crore.
- The Indian Institute of Tropical Meteorology (IITM), Pune, is in charge of the operations.
- Under the first phase, remote sensing-based and in-situ measurements using 25 meteorological instruments have commenced.
- In the second phase, ART will deploy instruments such as a radar wind profiler and balloon-bound radiosonde, and soil moisture and temperature measuring equipment.
What instruments are ART equipped with?
- To obtain continuous observations of convection, clouds, and precipitation, and monitor the major modes of variabilities, the ART is equipped with over two dozen high-end instruments, radars, and more.
- At 72 meters, ART will house India’s tallest meteorological tower.
- Some of the instruments deployed are an aethalometer for performing aerosol studies, a cloud condensation nuclei counter, a laser ceilometer to measure cloud sizes, a micro rain radar to calculate raindrop size and its distribution, and a Ka-band cloud radar and a C-band Doppler weather radar to help track the movement of rain-bearing systems over this zone.
Why is having an Atmospheric Research Testbed important?
- At present, 45% of India’s labor force is employed in the agriculture sector and much of Indian agriculture is rain-fed.
- Cultivation along the Monsoon Core Zone (MCZ), which spans the central India region from Gujarat to West Bengal, is primarily rainfall-fed.
- The southwest monsoon season accounts for 70 percent of the country’s annual average rainfall (880mm).
- Throughout India, the majority of Kharif cultivation is undertaken between July and August, which see an average monthly rainfall of 280.4mm and 254.9mm (1971–2020 average), respectively.
- During this four-month-long season, several rain-bearing synoptic systems, namely the low pressures or depressions, develop in the Bay of Bengal.
- Inherently, these systems move westwards/northwestwards over to the Indian mainland and pass through the MCZ, causing bountiful rainfall.
Why is it important to have data about monsoons over central India?
- Studies have correlated the all-India rainfall performance to the rainfall received over the central India region, highlighting its importance.
- The India Meteorological Department (IMD) issues rainfall forecasts for the country’s four homogeneous regions – north, west, east, and south peninsular India.
- In addition, it issues a special rainfall forecast for the MCZ, which is considered India’s food bowl.
- However, there is still limited understanding of the role of these synoptic systems, their associated cloud physics, cloud properties, and their overall role in enhancing the monsoon rainfall.
- Central India, therefore, acts as a natural laboratory for scientists and meteorologists to perform a hands-on study of the Indian monsoons.
- They can record data and make observations about the allied systems, clouds, and other associated physical and atmospheric parameters.
- Additionally, climate change is driving erratic rainfall patterns in tropical regions, like India.
- It has also strengthened the low-pressure systems, which are aided by high temperatures.
- This results in very heavy rainfall recorded along their trajectory during the monsoons.
- Now, with ART, scientists will be able to generate and obtain long-term observations on cloud microphysics, precipitation, convection, and land-surface properties, among a host of other parameters.
- This information will be assimilated and fed into the numerical weather models to enhance forecast output, especially the rainfall forecasts.
- More accurate forecasts will ultimately help the farming community plan their activities better.
Why Madhya Pradesh?
- The ART has been established at Silkheda, a location that falls directly in line with the path of major rain-bearing synoptic systems.
- This will facilitate direct monitoring and tracking.
- Besides, the locality is pristine and free of anthropogenic and other pollutants, making it the best site in central India for setting up sensitive, high-end meteorological instruments and observatories for recording data.
Methane emissions from fossil fuels remain high despite progress, US tops list of emitters: IEA

- 14 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
As per the International Energy Agency’s (IEA) Global Methane Tracker 2024, methane emissions from fuel consumption in 2023 approached record levels, nearing their highest point in history.
About the Global Methane Tracker:
- The Global Methane Tracker is an annual publication issued by the International Energy Agency (IEA), presenting the latest data on methane emissions primarily from the energy sector. It integrates recent scientific research, measurement campaigns, and satellite data.
Key Highlights from the Global Methane Tracker 2024:
- Methane emissions from fuel usage in 2023 approached record levels, reaching approximately 120 million tonnes (Mt), marking a slight increase from the previous year.
- Bioenergy, derived from plant and animal waste, contributed an additional 10 million tons of emissions.
- Out of the total methane emissions, around 80 million tons originated from ten countries, with the United States and Russia leading in emissions from oil and gas operations, and China leading in emissions from coal operations.
- Despite indications of declining emissions in certain regions, the overall methane emissions remain alarmingly high, posing a significant challenge to achieving global climate objectives.
- To align with the Paris Agreement goal of limiting warming to 1.5°C, there is a critical need to reduce methane emissions from fossil fuels by 75 percent by 2030.
- Achieving this target would require an estimated investment of approximately $170 billion, representing less than 5 percent of the revenue generated by the fossil fuel industry in 2023.
About the International Energy Agency (IEA):
- The International Energy Agency is an intergovernmental organization headquartered in Paris, established in 1974.
- Its primary mandate is to ensure stability in the international oil supply, a response to the oil crisis of 1973, which led to temporary disruptions in the global oil supply chain.
- Operational Framework: The IEA functions within the broader scope of the Organization for Economic Co-Operation and Development (OECD).
- Membership: As of 2022, the IEA comprises 31 member nations, with India joining as an associate member in 2017.
- Key Requirement: Member countries are obligated to maintain reserves equivalent to 90 days of the previous year's net oil imports.
- These reserves must be readily accessible by the government to address potential disruptions in the global oil supply chain, even if the reserves are not owned directly by the government.
NITI Aayog launches 'vocal for local' initiative to promote grassroots-level entrepreneurship

- 14 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
NITI Aayog on Wednesday launched the 'Vocal for Local' initiative under its Aspirational Blocks Programme to bolster local economies and foster grassroots-level entrepreneurship, an official statement said.
What is the ‘Vocal for Local’ Initiative?
- The 'Vocal for Local' initiative, led by NITI Aayog through its Aspirational Blocks Programme, aims to foster self-reliance and sustainable development.
- Under this initiative, products from 500 aspirational blocks have been curated and unified under the Aakanksha brand.
- Aakanksha is an overarching brand, with potential extensions into various sub-brands to tap into global markets.
- A dedicated section has been established on the Government e-Marketplace (GeM) portal under the Aakanksha brand to promote these products.
- Additionally, partners in the initiative offer support in areas such as e-commerce facilitation, establishing market linkages, financial and digital literacy, documentation and certification, and skill enhancement.
About Aspirational Blocks Programme:
- Inspired by the Aspirational District Programme launched in 2018, the Aspirational Blocks Programme extends its reach to 112 districts nationwide.
- This new initiative targets the enhancement of underperforming blocks across various development indicators.
- It aims to foster comprehensive growth in regions requiring additional support.
- Initially encompassing 500 districts across 31 States and Union Territories, the programme focuses on blocks in six key states: Uttar Pradesh (68 blocks), Bihar (61), Madhya Pradesh (42), Jharkhand (34), Odisha (29), and West Bengal (29).
What is the Government e-Marketplace (GeM)?
- Established in 2016 by the Ministry of Commerce and Industry, Government of India, the Government e-Marketplace (GeM) serves as an online platform for public procurement.
- GeM acts as a centralized portal, streamlining the procurement process for common-use Goods & Services required by various Government Departments, Organizations, and PSUs.
- Purchases made through GeM by Government users are mandated by the Ministry of Finance under the General Financial Rules, 2017.
- GeM is operated by GeM SPV (Special Purpose Vehicle), a 100% Government-owned, non-profit company operating under the Ministry of Commerce and Industry.
On Dandi March anniversary, PM Modi launches master plan for Sabarmati Gandhi Ashram redevelopment

- 13 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
Describing various initiatives of his government as “a way of its dedication towards Mahatma Gandhi”, Prime Minister Narendra Modi launched a master plan for the Sabarmati Gandhi Ashram redevelopment project in Ahmedabad recently, on the anniversary of the historic Dandi March.
About Sabarmati Gandhi Ashram redevelopment project:
- On the anniversary of the historic Dandi March, Prime Minister Narendra Modi launched a master plan for the Sabarmati Gandhi Ashram redevelopment project in Ahmedabad.
- This joint initiative by the central government and the Gujarat government, known as the Gandhi Ashram Memorial and Precinct Development Project, is set to cost around Rs 1,200 crore.
- During the inauguration, PM Modi emphasized the importance of conserving heritage sites, stating that "a country which cannot conserve its heritage also loses its future."
- He highlighted the collective responsibility of all Indians to preserve this globally renowned site, which holds immense historical and cultural significance.
- The government's commitment to restoring old buildings to their original form, with the aim of eliminating the need for new constructions, was outlined by PM Modi.
- This approach aligns with the principle of preserving the authenticity and integrity of heritage sites, ensuring that future generations can experience and appreciate their true essence.
- The Sabarmati Gandhi Ashram, established by Mahatma Gandhi in 1917, played a pivotal role in India's struggle for independence.
- By undertaking this redevelopment project, the government seeks to honor the legacy of the father of the nation and create a space that inspires future generations to learn from his life and teachings.
About Dandi March:
- The Dandi March, also known as the Salt March or Salt Satyagraha, was a significant non-violent protest action led by Mahatma Gandhi in March-April 1930.
- This landmark event marked the beginning of a larger civil disobedience campaign that Gandhi waged against British rule in India, which extended into early 1931.
- The Dandi March garnered widespread support for Gandhi among the Indian populace and drew considerable international attention.
- The motivations behind the Dandi March were rooted in the British monopoly over salt production and distribution in India.
- A series of laws prohibited Indians from producing or selling salt independently, forcing them to purchase heavily taxed salt that was often imported.
- This affected the majority of Indians, who were poor and could not afford the high cost of salt. Indian protests against the salt tax had begun in the 19th century and remained a major point of contention throughout British rule.
- By undertaking the Dandi March and defying the salt laws, Gandhi sought to mobilize the Indian populace against British oppression and galvanize support for the Indian independence movement.
- The march, which covered over 240 miles from Sabarmati Ashram to Dandi, symbolized the spirit of nonviolent resistance and civil disobedience that would come to characterize India's struggle for freedom.
Impact of Dandi March:
- The Dandi March had a profound impact on the Indian independence movement and left an indelible mark on the country's history.
- The mass civil disobedience that ensued after Gandhi's iconic march led to millions of Indians breaking the salt laws by making or buying illegal salt.
- Gandhi's unwavering commitment to satyagraha against the salt tax inspired countless others to join the movement, including prominent leaders like Jawaharlal Nehru.
- Thousands were arrested and imprisoned, including Gandhi himself, but the spirit of resistance only grew stronger.
- News of Gandhi's detention galvanized tens of thousands more to join the satyagraha, and the march on the Dharasana salt works went ahead as planned in May 1931.
- Despite facing violent opposition from the police, the peaceful marchers, led by the poet Sarojini Naidu, persisted in their nonviolent resistance.
- Gandhi's release from custody in January 1931 marked a turning point, as he began negotiations with Lord Irwin aimed at ending the satyagraha campaign.
- These efforts culminated in the Gandhi-Irwin Pact, signed on March 5, 1931, which formalized a truce between the Indian independence movement and the British government.
- The Dandi March, therefore, served as a catalyst for change, uniting Indians from all walks of life in a shared struggle for freedom and justice.
- The events of the Salt Satyagraha remain an enduring symbol of the power of nonviolent resistance and the indomitable spirit of the Indian people in their quest for self-determination.
Khelo India Rising Talent Identification will take sports to the doorstep of aspiring champions

- 13 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
Union Minister for Youth Affairs and Sports, Shri Anurag Singh Thakur inaugurated the unique Khelo India Rising Talent Identification (KIRTI) programme amidst much enthusiasm at the Sector 7 sports complex, in Chandigarh recently.
About the KIRTI Programme:
- The KIRTI Programme is an ambitious nationwide initiative aimed at school children between the ages of nine and 18.
- With a dual focus, the scheme strives to uncover hidden talent from every corner of the country while simultaneously utilizing sports as a powerful tool to combat addiction to drugs and digital distractions.
Primary Objectives of KIRTI's Programme:
- Identifying and nurturing talented young athletes from across India, ensuring that no potential goes unnoticed.
- Leveraging sports as a means to steer youth away from harmful addictions and encourage a healthier, more active lifestyle.
- To achieve these goals, KIRTI plans to conduct 20 lakh assessments throughout the year at designated Talent Assessment Centres across the nation.
- The programme launched with a strong start at 50 centers in India, assessing 50,000 applicants in the first phase across 10 sports such as athletics, boxing, wrestling, hockey, and football.
- KIRTI's athlete-centric approach is characterized by its transparent selection methodology, which is grounded in Information Technology.
- The programme employs data analytics based on Artificial Intelligence to predict sporting potential in aspiring athletes, ensuring that talent identification is both objective and data-driven.
- By channeling India's youth towards sports and providing them with the necessary support, KIRTI aims to foster a new generation of athletes and promote a healthier, more active society.
About Khelo India Scheme:
- The Khelo India Scheme is the flagship initiative of the Ministry of Youth Affairs & Sports, Government of India.
- This Central Sector Scheme is designed to instill a sports culture and achieve sporting excellence in the country by leveraging the transformative power of sports and its cross-cutting influence.
- The Khelo India Scheme encompasses multiple verticals, with "Sports Competitions and Talent Development" being a key focus area.
- Within this vertical, the "Talent Identification and Development" component plays a crucial role in identifying and nurturing athletes at both the grassroots and elite levels.
- The primary objective is to strengthen the sports ecosystem in India by cultivating talent and providing athletes with the necessary resources and support to excel in their respective disciplines.
- Through the Khelo India Scheme, the government aims to promote sports as a way of life, encouraging greater participation and creating a robust platform for athletes to showcase their skills.
- By investing in sports infrastructure, training, and competition opportunities, the scheme seeks to establish India as a global sporting powerhouse and inspire future generations to embrace the spirit of sportsmanship and athletic achievement.
Govt's new code bars unethical marketing of drugs by pharma firms

- 13 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
The government has notified a new legal code to curb the unethical marketing of drugs and banning medical representatives from using “inducement” to access healthcare professionals
About the Uniform Code of Pharmaceutical Marketing Practices (UCPMP) 2024:
- The UCPMP 2024 has been implemented to regulate unethical practices within the pharmaceutical industry, with a focus on promoting transparency and ethical conduct.
- The updated guidelines encompass various aspects, including drug endorsement, promotion, ethical behavior for medical representatives, and the maintenance of professional relationships with healthcare professionals.
Key provisions of the UCPMP 2024 include:
- Prohibiting the offering of gifts and travel facilities to healthcare professionals or their family members by pharmaceutical companies.
- Mandating that medical representatives should not use any form of inducement or subterfuge to gain interviews with healthcare professionals, nor should they provide payment for access under any guise.
- Holding pharmaceutical companies responsible for the actions of their medical representatives.
- Banning the supply of free drug samples to individuals who are not qualified to prescribe such products.
- Requiring each pharmaceutical company to maintain detailed records of free samples provided to healthcare practitioners, with the total value of distributed samples not exceeding two percent of the company's domestic sales per year.
- Compulsory constitution of an Ethics Committee for Pharmaceutical Marketing Practices (ECPMP) by all pharmaceutical associations, along with the establishment of a dedicated UCPMP portal on their websites for implementation and monitoring purposes.
- Detailed guidelines on how drugs should be promoted in textual and audio-visual marketing materials, ensuring that information is balanced, up-to-date, verifiable, and non-misleading.
- Restrictions on making unverified claims and comparisons about a drug's usefulness, as well as using terms like "safe" and "new" without proper qualification.
- Assigning responsibility for adherence to the UCPMP 2024 to the Chief Executive Officers of pharmaceutical companies.
- Outlining penalties for violating the code and establishing a clear process for handling complaints, ensuring accountability and effective oversight.
- The UCPMP 2024 serves as a comprehensive framework for promoting ethical practices within the pharmaceutical industry, aiming to protect the interests of patients, healthcare professionals, and other stakeholders while fostering an environment of transparency and integrity.
India world’s top arms importer between 2019-23: SIPRI

- 13 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
India was the world’s top arms importer for the period 2019-23 with imports having gone up by 4.7% compared to the period 2014-18, according to the SIPRI.
Highlights from the SIPRI Report 2023:
- The report highlights that India continues as the world’s largest arms importer, maintaining this position despite ongoing efforts to enhance its defense-industrial base, accounting for a significant 9.8% of global arms imports between 2019 and 2023.
- There has been a steady increase in India's arms imports, with a 4.7% rise observed between 2014-18 and 2019-23, attributed in part to emergency procurements prompted by the prolonged military standoff with China.
- The dynamics of arms suppliers are changing, with Russia historically serving as India's primary weapons supplier, still accounting for 36% of its arms imports, although there is a shift towards diversification, with India increasingly turning to Western countries and domestic manufacturers.
- Notably, between 2019-23, Russian deliveries constituted less than half of India's arms imports for the first time since 1960-64.
- Western suppliers like France and the United States are emerging as key players, collectively accounting for 46% of India's arms imports, with significant contracts in progress, such as India's procurement of 31 armed MQ-9B Sky Guardian drones from the US and 26 Rafale-M fighters from France.
- In the global arms trade landscape, India ranks as the top importer, followed by Saudi Arabia, Qatar, Ukraine, Pakistan, Japan, Egypt, Australia, South Korea, and China, while the United States leads among exporters with a 42% share, followed by France and Russia.
- India's role as a major arms customer is underscored by its position as the largest arms customer for France, Russia, and Israel, highlighting its significance in global arms procurement.
- Meanwhile, China remains a dominant supplier to Pakistan, accounting for 61% of its exports, and also exports 11% of its arms to Bangladesh, consolidating its influence in the region.
Challenges Encountered by India in Indigenous Production of Defense Equipment:
- Efforts to promote indigenous defense production, exemplified by initiatives like 'Make in India', have encountered persistent challenges, notably the failure to materialize any projects under the Strategic Partnership (SP) model, which was introduced to foster collaboration between the public and private sectors within the defense industry.
- The SP model, designed to facilitate joint endeavors between government-owned defense entities and private companies, has yet to yield tangible results, necessitating a thorough review of the policy framework.
- Key areas for improvement include a reevaluation of pricing methodologies, ensuring long-term orders to sustain production, and addressing bottlenecks that impede project implementation.
- Furthermore, India's defense sector has seen minimal Foreign Direct Investment (FDI), amounting to only Rs 5,077 crore since the sector was opened to private companies in 2001.
- Despite efforts to liberalize FDI regulations, such as allowing up to 74% through the automatic route and up to 100% through the government route in 2020, investment inflows remain disproportionately low.
About Stockholm International Peace Research Institute (SIPRI):
- The Stockholm International Peace Research Institute (SIPRI) is a renowned independent international institute committed to investigating various aspects of conflict, armaments, arms control, and disarmament.
- Founded in 1966 and headquartered in Stockholm, Sweden, SIPRI consistently ranks among the world's most respected think tanks.
SIPRI's mission is multi-faceted and encompasses the following key objectives:
- Conducting in-depth research and activities related to security, conflict, and peace, with the aim of developing a deeper understanding of the complex factors that influence global stability.
- Providing insightful policy analysis and recommendations to policymakers, international organizations, and civil society actors, helping them make informed decisions and develop strategies to address security challenges.
- Facilitating dialogue and building capacities among various stakeholders, including governments, academia, and non-governmental organizations, to foster cooperation and promote mutual understanding on peace and security issues.
- Promoting transparency and accountability in the field of international security by maintaining comprehensive databases on arms transfers, military expenditure, and other relevant data, which contribute to a more accurate assessment of global security trends.
- By adhering to these core principles and objectives, SIPRI plays a vital role in advancing the global discourse on peace and security, while supporting efforts to mitigate conflict and promote stability worldwide.
Decoding the Trillion-Dollar Impact of GPUs on the AI Industry
- 13 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
As the global demand for the latest AI technologies surges, one unexpected item has emerged as a highly sought-after commodity: the graphics processing unit (GPU).
What is a Graphics Processing Unit (GPU)?
- A Graphics Processing Unit (GPU) is a specialized computer chip designed to efficiently render graphics and images by performing rapid mathematical calculations.
- Widely used in both professional and personal computing, GPUs were initially developed to handle the rendering of 2D and 3D images, animations, and video content.
- Similar to a Central Processing Unit (CPU), a GPU is an integral component of computing devices.
- However, the primary distinction lies in the GPU's specialized design to handle and accelerate graphics workloads and display graphics content on devices like PCs or smartphones.
- While a typical modern CPU consists of between 8 and 16 "cores" that process complex tasks sequentially, GPUs contain thousands of smaller cores.
- These cores are engineered to work simultaneously ("in parallel") to achieve fast overall processing, making GPUs ideal for tasks involving numerous simple operations that can be executed concurrently.
- GPUs operate using a technique called parallel processing, where multiple processors manage separate parts of a single task.
- They also possess their own dedicated RAM to store and process large amounts of data for graphics-intensive applications.
- In graphics applications, the CPU sends instructions to the GPU for drawing graphics content on the screen.
- The GPU then executes these instructions in parallel at high speeds, displaying the content on the device—a process known as the graphics or rendering pipeline.
- They also possess their own dedicated RAM to store and process large amounts of data for graphics-intensive applications.
- Modern GPUs have expanded beyond their traditional role in graphics rendering and are now employed in various applications such as creative content production, video editing, high-performance computing (HPC), and artificial intelligence (AI).
- By offloading graphics-related tasks from the CPU, GPUs enable fast and smooth rendering of content on computer screens.
- As technology continues to advance, the applications of GPUs will likely expand even further, solidifying their position as an essential component in the computing landscape.
Mission Divyastra: India's Agni-V missile makes maiden flight with MIRV

- 12 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
India on Monday announced the successful testing of an Agni missile capable of carrying multiple warheads meant to hit multiple targets simultaneously.
What are Agni-5 Missiles?
- Agni is a long-range missile developed indigenously by the Defence Research and Development Organisation, DRDO.
- The family of Agni missiles has been in the arsenal of the Indian armed forces since the early 1990s.
- This latest variant of the missile is equipped with what is known as MIRV (Multiple Independently Targetable Re-entry Vehicle) technology, first developed at least five decades ago but in possession of only a handful of countries.
Salient Features of Agni-5:
- Powered by a three-stage solid-fuel engine, Agni-5 boasts a range exceeding 5,000km.
- The Agni series encompasses medium to Intercontinental variants, spanning Agni-1 to Agni-5, with ranges varying from 700 km to over 5,000 km.
- DRDO’s successful June 2021 test of Agni P, a canisterized missile, demonstrated a range capability ranging between 1,000 and 2,000 km.
- With its ability to be launched from both road and rail platforms, Agni-5 ensures ease of deployment and swift launch capabilities.
What is MIRV Technology?
- The MIRV have revolutionized the concept of ballistic missile payloads by enabling a single missile to carry multiple warheads, each capable of targeting enemies at different locations.
- The technology was first introduced in the US with the successful test of the Minuteman III in 1968, which brought the technology into actual use in the 1970.
- The Soviet Union developed their own MIRV-enabled ICBM and SLBM technology by the end of the 1970s.
- The strategic shift started by MIRV has enabled many nations to greater target damage and reduce the effectiveness of enemy missile systems, altering the landscape of global nuclear deterrence.
- The warheads on MIRVs can be launched at different speeds and in different directions.
- Some MIRVed missiles can hit targets as far as 1,500 km apart.
- The technology requires a delicate combination of large missiles, small warheads, precise guidance, and a complex mechanism for releasing warheads sequentially during flight.
How does MIRV Work?
- The MIRV-equipped missile follows a trajectory into space similar to other ballistic missiles.
- After the boost phase, the missile’s upper stage, known as ‘bus’, reaches suborbital spaceflight, and aligns itself based on designated targets.
- The ‘bus’ sequentially deploys multiple warheads along with decoys and countermeasures.
- Each warhead can be assigned a different target or trajectory.
- After the deployment, the warheads re-enter the Earth’s atmosphere and proceed to their respective targets.
What are the Challenges?
- The MIRV technology enhances first-strike proficiency and complicates the calculus of mutual assured destruction.
- With the ability to deploy multiple warheads from a single missile, nations can achieve a broader spread of targets, making the defense system less effective and more costly.
- Although MIRVs were not initially made to defeat ballistic missile defenses, they are much more difficult to defend against than traditional missiles.
- Possession of MIRV technology not only exhibits a country’s nuclear prowess but plays a crucial role in shaping international security and nuclear deterrence strategies.
STPI launches 24th Centre of Entrepreneurship FinGlobe in Gandhinagar to nurture startups in fintech & banking services

- 12 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
Software Technology Parks of India (STPI) recently launched its 24th Center of Entrepreneurship (CoE) - "FinGlobe," dedicated to fostering innovation and growth in the financial technology sector, at STPI-Gandhinagar, GIFT City.
About Software Technology Parks of India (STPI):
- Software Technology Parks of India (STPI) was set up in 1991 as an autonomous society under the Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology (MeitY).
- STPI’s main objective has been the promotion of software exports from the country. STPI acts as ‘single-window in providing services to the software exporters.
- The services rendered by STPI for the software exporting community have been statutory services, data communications services, incubation facilities, training and value-added services.
- STPI has played a key developmental role in the promotion of software exports with a special focus on SMEs and start-up units.
Services of STPI:
- Main services of STPI include Statutory services, Incubation and Data communication services to the IT/ITES/ESDM sector.
- Statutory services: STPI has been implementing the Software Technology Park (STP) scheme and the Electronics Hardware Technology Park (EHTP) scheme for the promotion of the IT/ITES industry.
- STP Scheme is a unique scheme, designed to promote the software industry and growth of start-ups and SMEs without any locational constraints.
- Incubation services: STPI is offering ultra-modern office facilities to small units and entrepreneurs.
- Plug-n-Play facilities for start-ups enable a short gestation period.
- This has encouraged many entrepreneurs to start their own operations and grow in a competitive environment.
Objectives of STPI:
- Promotion of software and software services development and exports, including IT Enabled Services (ITES)/Bio-IT.
- Provision of statutory and promotional services to exporters through the implementation of schemes like Software Technology Park/Electronics and Hardware Technology Park, among others.
- Offering data communication services, along with value-added services, to industries related to IT/ITES.
- Encouraging micro, small, and medium entrepreneurs by fostering an entrepreneurial environment in the IT/ITES sector.
. India ‘one of the worst autocratisers’: V-Dem report on democracy

- 12 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
India, which was downgraded to the status of an “electoral autocracy” in 2018, has declined even further on multiple metrics to emerge as “one of the worst autocratizers”, according to the ‘Democracy Report 2024’ released by the Gothenburg-based V-Dem Institute that tracks democratic freedoms worldwide.
About V-Dem (Varieties of Democracy):
- The V-Dem Institute, established in 2014 by Swedish political scientist Staffan Lindberg, is a research institution dedicated to studying the various forms of democratic governance around the world.
- Headquartered at the University of Gothenburg in Sweden, V-Dem produces several high-profile datasets that assess the qualities of different governments based on hundreds of indicator variables.
- These datasets are widely used by political scientists due to their comprehensive coverage of various aspects of government and are freely available to the public.
- V-Dem's annual publications provide valuable insights into the functioning of governments worldwide, promoting transparency and understanding of democratic institutions.
About The Democracy Report:
- The Democracy Report presents a comprehensive analysis of the state of democracy worldwide, with a particular focus on the trends of democratization and autocratization.
- The report classifies countries into four distinct regime types based on their performance on the Liberal Democracy Index (LDI): Liberal Democracy, Electoral Democracy, Electoral Autocracy, and Closed Autocracy.
- The LDI is a composite index that encompasses both liberal and electoral dimensions of democracy.
- It is based on 71 indicators, which are grouped into the Liberal Component Index (LCI) and the Electoral Democracy Index (EDI).
- The LCI assesses various aspects of individual and minority rights, as well as legislative constraints on the executive.
- The EDI evaluates the extent to which elections are free and fair, considering factors such as freedom of expression and association.
- In addition to the LCI and EDI, the LDI also incorporates three other component indices:
- The Egalitarian Component Index (measuring social group equality)
- The Participatory Component Index (assessing the vibrancy of citizen groups and civil society organizations), and
- The Deliberative Component Index (evaluating whether political decisions are based on public reasoning or emotional appeals, solidarity attachments, and coercion).
- The Democracy Report, along with the underlying dataset, scientific articles, and working papers, is publicly available for download on the V-Dem Institute's website.
- The website also offers interactive graphic tools to facilitate the exploration and visualization of the data.
Key Insights from the Democracy Report 2024:
- The Democracy Report 2024, a collaborative effort involving 4,200 scholars from 180 countries, draws from 31 million datasets spanning 202 countries from 1789 to 2023.
Global Trends:
- In 2023, 42 countries (home to 35% of the world’s population) experienced autocratization.
- Autocracies now encompass 71% of the world's population, up from 48% a decade ago.
- The overall level of democracy has regressed to 1985 levels for the average global citizen.
- Eastern Europe, South, and Central Asia witnessed the most significant decline in democracy.
- Freedom of expression, clean elections, and civil society engagement were the most affected aspects in autocratizing nations.
Focus on 2024 Elections:
- Of the 60 countries holding elections in 2024, 31 are experiencing democratic backsliding.
India's Situation:
- India, classified as an electoral autocracy since 2018, has further deteriorated, earning the title of "one of the worst autocratizers."
- The report notes that India's level of liberal democracy has plummeted to levels comparable to those during the 1975 emergency declared by Indira Gandhi.
- Under the V-Dem classification, a liberal democracy requires robust mechanisms for judicial independence, checks on executive power, and strong protection of civil liberties and equality under the law.
- India currently falls into the category of electoral autocracy, characterized by multiparty elections but lacking adequate freedom of expression and fair electoral processes.
India launches revamped scheme to help advance pharma industry's tech capabilities

- 12 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
India's Department of Pharmaceuticals recently unveiled the Revamped Pharmaceuticals Technology Upgradation Assistance Scheme (RPTUAS) to help advance the technological capabilities of India's pharmaceutical industry and align it with global standards.
What is the Pharmaceuticals Technology Upgradation Assistance Scheme?
- In an effort to support pharma companies aligned with global quality standards, the Department of Pharmaceuticals (DoP) has announced a revamped Pharmaceuticals Technology Upgradation Assistance (RPTUAS) Scheme.
- It has been incorporated as a sub-scheme under the Scheme - Strengthening of Pharmaceutical Industry (SPI), which was launched in July 2022.
Objective:
- To facilitate Micro, Small and Medium Pharma Enterprises (MSME) of proven track record to upgrade their technology to meet WHO-GMP or Schedule M standards.
Intended Beneficiaries:
- Micro, Small and Medium Enterprises of the pharma sector.
Key Features of the Revised Scheme:
- Broadened Eligibility Criteria: Reflecting a more inclusive approach, eligibility for the PTUAS has been expanded beyond Micro, Small and Medium Enterprises to include any pharmaceutical manufacturing unit with a turnover of less than 500 crores that requires technology and quality upgradation.
- Preference remains for MSMEs, supporting smaller players in achieving high-quality manufacturing standards.
- Flexible Financing Options: The scheme introduces more flexible financing options, emphasizing subsidies on reimbursement basis, over traditional credit-linked approaches.
- Comprehensive Support for Compliance with New Standards: In alignment with revised Schedule-M and WHO- Good Manufacturing Practice (GMP) standards, the scheme now supports a broader range of technological upgrades.
- Eligible activities include improvements such as HVAC systems, water and steam utilities, testing laboratories etc.
- State Government Scheme Integration: The revised scheme allows integration with state government schemes, enabling units to benefit from additional top-up assistance. This collaborative approach aims to maximize support for the pharmaceutical industry in their technology upgradation efforts.
- The new benefit limit is based on turnover of the company. Units with less than Rs 5 crore turnover will get an incentive of 20 percent of investment under eligible activities.
- The units with turnover ranging from Rs 50 crore to less than Rs 250 crore will get an incentive of 15 percent of investment, while for those with turnover ranging from Rs 250 crore to less than Rs 500 crore, it will be 10 percent of investment under eligible expenses.
New sensor can detect 'forever chemicals' in drinking water

- 12 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
A team of chemists from the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) has designed a breakthrough method for the detection of perfluoroalkyl and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS).
What are Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS)?
- Per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) are a class of man-made chemicals that have been in use since the 1940s.
- Due to their unique properties, such as high chemical stability and resistance to heat, grease, and water, PFAS have been widely used in various industrial and commercial applications.
- They are commonly found in products such as stain- and water-resistant fabrics, cleaning products, paints, and fire-fighting foams.
- PFAS are often referred to as "forever chemicals" because they do not break down naturally in the environment.
- This is due to the strong carbon-fluorine bond that characterizes these compounds, making them highly persistent and resistant to degradation.
- The widespread use of PFAS has resulted in increasing levels of environmental contamination, with PFAS being detected in air, water, and soil samples worldwide.
- Exposure to these chemicals has been linked to a range of health risks, including decreased fertility, developmental effects in children, interference with body hormones, increased cholesterol levels, and an increased risk of certain cancers.
Due to their persistent nature and potential health risks, there is growing concern about the widespread use of PFAS and the need for improved regulation and remediation strategies to manage their environmental and health impacts.
- Environmental Persistence: Due to their strong carbon-fluorine bonds, PFAS do not break down easily in the environment.
- They can accumulate in soil, water, and living organisms, posing a long-term risk to ecosystems and human health.
- Bioaccumulation: PFAS can accumulate in living organisms, including humans, through the food chain.
- Even small amounts of PFAS in the environment can build up to harmful levels in animals and humans over time.
- Regulatory Action: Due to the potential health and environmental risks associated with PFAS, many countries are taking regulatory action to restrict their use and manage their environmental impacts.
- This includes banning certain PFAS-containing products, setting drinking water standards, and requiring the clean-up of contaminated sites.
MNRE to discuss specialized cylinders for hydrogen storage with stakeholders

- 11 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
The Ministry of New and Renewable Energy (MNRE) plans to convene a meeting with relevant stakeholders to discuss the development of specialized cylinders for green hydrogen storage.
What is Green Hydrogen?
- Green Hydrogen is produced through the process of electrolysis of water, utilizing electricity generated from renewable energy sources.
- The carbon intensity of green hydrogen depends on the carbon neutrality of the electricity source, with higher renewable energy content resulting in greener hydrogen.
- With its potential to decarbonize various sectors, reduce carbon emissions, and achieve energy independence, green hydrogen holds significant promise.
- Its production from renewable sources like solar, wind, and hydropower makes it a sustainable and environmentally friendly alternative to traditional fossil fuels in transportation and industry, offering a consistent and reliable energy source.
- Storage: Hydrogen is stored in cylinders at high pressure, categorized into four types based on materials used. Type 1 and Type 2 are suited for storage, while Type 3 is ideal for storage and transportation, and Type 4 is recommended for on-board storage.
- Unlike compressed natural gas (CNG) stored at around 3,600 psi, hydrogen is stored at 5,000-10,000 psi.
- Vehicles can utilize hydrogen either by burning it in an internal combustion engine or by using a fuel cell to convert it into electricity to charge on-board batteries.
- Type 3 and Type 4 cylinders are reinforced with carbon fiber, making them lightweight and suitable for vehicles.
- Type 4 cylinders, lined with a polymer instead of aluminum like Type 3, are even lighter.
Application of Green Hydrogen:
- Green hydrogen finds diverse applications, including powering vehicles and generating electricity through fuel cells.
- It also serves in heating systems and the production of chemicals and fertilizers.
- Additionally, green hydrogen supports microgrids, facilitating electricity provision to remote areas and fostering energy independence.
Advantages and disadvantages of green hydrogen:
- 100 % sustainable: Green hydrogen does not emit polluting gasses either during combustion or during production.
- Storable: Hydrogen is easy to store, which allows it to be used subsequently for other purposes and at times other than immediately after its production.
- Versatile: Green hydrogen can be transformed into electricity or synthetic gas and used for commercial, industrial or mobility purposes.
However, green hydrogen also has negative aspects that should be borne in mind:
- High cost: Energy from renewable sources, which are key to generating green hydrogen through electrolysis, is more expensive to generate, which in turn makes hydrogen more expensive to obtain.
- High energy consumption: The production of hydrogen in general and green hydrogen in particular requires more energy than other fuels.
- Safety issues: Hydrogen is a highly volatile and flammable element and extensive safety measures are therefore required to prevent leakage and explosions.
NHAI to start rolling out satellite-based tolling on national highways soon

- 11 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
Road Transport and Highways Minister Nitin Gadkari said in Parliament in February that the government plans to implement a new highway toll collection system based on the global navigation satellite system before the model code of conduct for the 2024 election kicks in.
What is the Global Navigation Satellite System (GNSS)?
- GNSS refers to a constellation of satellites providing signals from space that transmit positioning and timing data to GNSS receivers.
- The receivers then use this data to determine location.
- Examples of GNSS include Europe’s Galileo, the USA’s GPS, Russia’s GLONASS and China’s BeiDou
How will the GNSS-Based Toll System work?
- The system will use an automatic number plate recognition (ANPR) system through cameras installed on highways and deduct tolls based on the distance traveled by a vehicle.
- The device monitors the movements while driving, accurately marking the entry and exit points on tolled segments. By analyzing travel distance, it computes the charges accordingly.
- This eliminates the uniformity of fixed tolls at booths, ensuring fairness for drivers traversing shorter distances.
Difference between FASTags and ANPR technology:
- FASTags streamline electronic toll payments at toll plazas equipped with scanners, enabling vehicles to pass through without stopping.
- Conversely, GNSS-based systems utilize ANPR technology to deduct tolls based on distance traveled, rendering traditional toll plazas unnecessary.
What are the Challenges?
- Detection of Non-Compliance: Without physical barriers, detecting non-compliant vehicles, such as those without an On-Board Unit (OBU) or engaging in fraudulent activities, poses a challenge.
- Infrastructure Requirements: Deploying gantry-mounted Automatic Number-Plate Recognition (ANPR) systems along highways is essential for capturing violations and enforcing toll payments.
- License Plate Quality: The effectiveness of ANPR systems relies on the quality of license plates; subpar plates hinder accurate recognition and enforcement efforts.
- Data Privacy and Security: GNSS-based toll systems entail collecting and processing sensitive location data, necessitating robust privacy and security measures.
Inflection AI rolls out new large language model to its Pi chatbot

- 11 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
Recently, Inflection AI launched its latest LLM, Inflection 2.5, an upgrade to its model that powers its friendly chatbot Pi personal assistant.
About Inflection 2.5:
- Inflection-2.5 is an “upgraded in-house model that is competitive with all the world’s leading LLMs like GPT-4 and Gemini.
- The newly upgraded LLM comes with its signature personality and uniquely empathetic fine-tuning.
- Its latest model achieved GPT-4’s performance with only 40 per cent of the OpenAI model’s computation power for training.
- Besides, it seems Inflection 2.5 has made some stellar strides in areas of IQ such as coding and mathematics.
- This means that the model has made substantial improvements on key benchmarks.
- With the new upgrade, Pi has now been endowed with world-class real-time web search capabilities to ensure that users get access to high-quality and up-to-date information in real-time.
What is the Pi chatbot?
- Pi is an advanced chatbot powered by Inflection AI's cutting-edge language model, Inflection 2.5 which allows one to have deep and meaningful conversations.
- To access the chatbot, one needs to log on to Inflection.AI, click on Meet Pi, and simply start talking to the chatbot right away.
- Pi is more humane and has been promoted as a chatbot that has a personality.
- In other words, Inflection AI dubbed it as a chatbot that is “supportive, smart, and there for you anytime”.
- Pi is more like a companion to humans and is free to use.
- The chatbot comes with a voice, in six distinct voices, to choose from adding life to conversations.
Pi chatbot boasts a number of impressive features that make it stand out from other conversational AI systems:
- Real-time web search capabilities: Pi can access and present up-to-date information on a wide range of topics, ensuring that users always have access to accurate and relevant information.
- Empathetic personality: Pi's unique empathetic fine-tuning allows it to understand and respond to the emotional nuances of human communication, making it a more engaging and personable conversational partner.
- Versatile conversation topics: Whether you're discussing current events, asking for local recommendations, studying for an exam, drafting a business plan, coding, or just talking about hobbies, Pi is equipped to handle a wide range of conversational topics.
- User-friendly interface: Designed with accessibility in mind, Pi's intuitive interface makes it easy for users of all technical abilities to engage with the chatbot and get the most out of their conversations.
Health ministers of 11 African countries commit to end malaria deaths

- 11 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
In a historic gathering in Cameroon’s capital Yaoundé, African health ministers, global malaria partners, funding agencies, scientists, civil society organizations and other principal malaria stakeholders pledged to end malaria deaths, especially given the tools and systems available.
What is the Yaounde Declaration?
- The Yaounde Declaration was endorsed by health ministers from 11 African nations with the highest malaria burden, aiming to expedite efforts to eliminate malaria-related deaths.
- Signed during the Yaoundé conference, co-hosted by the World Health Organization (WHO) and the Government of Cameroon, the declaration underscores a collective commitment to combat malaria.
- The signatory countries include Burkina Faso, Cameroon, the Democratic Republic of the Congo, Ghana, Mali, Mozambique, Niger, Nigeria, Sudan, Uganda, and Tanzania, together accounting for approximately 70% of the global malaria burden.
- Commitments entail stronger leadership and increased domestic funding for malaria control programs, leveraging data technology, adhering to updated technical guidance, and intensifying efforts at national and sub-national levels.
- Ministers pledged augmented health sector investments to fortify infrastructure, personnel, and program implementation, fostering multi-sectoral collaboration, and cultivating partnerships for funding, research, and innovation.
- Signatories affirmed their resolute dedication to hasten malaria mortality reduction and to ensure mutual accountability for the declaration's outlined commitments.
Current Status of Malaria:
- Between 2019 and 2022, global malaria cases increased from 233 million to 249 million, with Africa experiencing a substantial rise from 218 million to 233 million cases, highlighting the continent as the epicenter of the malaria crisis.
- The 11 African countries represented at the conference bear the highest burden of malaria infections and deaths.
Progress and Challenges:
- Despite some progress, malaria incidence has only declined by 7.6% and mortality by 11.3%, falling short of the African Union’s interim goals.
- Only seven out of 46 member states have achieved a 40% reduction in malaria incidence or mortality.
- Urgent action is imperative to bridge a financial gap of $1.5 billion to sustain basic malaria services, especially for vector control.
- Additional funding of $5.2 billion annually for progress towards elimination and $11 billion for climate adaptation in the health sector is crucial to avert significant surges in cases and deaths, particularly among vulnerable populations like children and pregnant women.
UGC notifies framework for private universities to set up off-campus centers

- 11 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
In line with the “future academic vision” instead of “commercial interests”, the UGC has notified modalities on March 6 for state private universities to set up off campus centers within their respective states.
News Summary:
- The University Grants Commission (UGC) recently permitted private universities to establish off-campus centers and outlined regulations for the same.
- Previously, private universities in the country were restricted from opening off-campus centers in other states.
- In a meeting held on March 5, the UGC decided to authorize state private universities to establish off-campus centers across the country, provided they meet specific criteria.
- Criteria include a minimum of five years of establishment and accreditation from the National Assessment and Accreditation Council (NAAC), without requiring an A or B grade.
- Universities seeking to establish off-campus centers must meet staff, infrastructure, and financial requirements mandated by the commission and obtain approvals from statutory and regulatory bodies.
- These universities must ensure the provision of infrastructure, faculty, and courses offered at the main campus to students at their off-campus centers.
- A one-time establishment fee of Rs 10 lakh is required to be paid to the UGC by the universities.
- The UGC reserves the right to conduct inspections and take punitive actions against universities in case of irregularities or complaints.
- Additionally, the UGC may order the closure of a university’s off-campus center for violations, with the university responsible for relocating affected students to the main campus.
About University Grants Commission (UGC):
- The University Grants Commission (UGC) of India operates as a statutory body established under the UGC Act, 1956.
- Its primary mandate encompasses coordinating, determining, and upholding standards within higher education institutions across India.
- UGC holds the authority to grant recognition to universities and colleges within the country and allocates funds to these recognized institutions.
- Nodal Ministry: Department of Higher Education, Ministry of Education.
Mandate of UGC:
- Facilitating and coordinating university education initiatives.
- Establishing and maintaining standards in teaching, examination, and research activities within universities.
- Formulating regulations to define minimum education standards.
- Monitoring advancements in collegiate and university education while disbursing grants to these institutions.
- Serving as a crucial intermediary between the Union and State governments and higher education institutions.
- Providing advisory services to the Central and State governments concerning measures aimed at enhancing university education standards.
Conclusion
Academic experts said that this decision may prove beneficial for students as they will get more options to choose from. However, it also means that the 16 government-run universities in the state will face more competition. More students may shift to these centers, leaving a large number of approved seats in the public universities vacant every year.
India’s indigenous fifth-gen fighter jet AMCA

- 09 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
The Cabinet Committee on Security (CCS) this week cleared a Rs 15,000 crore project to design and develop the Advanced Medium Combat Aircraft (AMCA), India’s fifth-generation fighter multirole fighter jet.
About Advanced Medium Combat Aircraft (AMCA)?
- The AMCA will be India’s indigenous fifth-generation fighter aircraft.
- The indigenous Light Combat Aircraft (LCA) Tejas is a 4.5-generation single-engine multirole aircraft.
- The Aeronautical Development Agency (ADA) under the Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO) will be the nodal agency for executing the programme and designing the aircraft.
- It will be manufactured by state-owned Hindustan Aeronautics Limited (HAL).
- The aircraft will put India in a select group of nations that have their own fifth-generation fighter aircraft.
- Discussions for developing the AMCA started in 2007.
- The initial plan was to jointly develop the aircraft with Russia under a Fifth Generation Fighter Aircraft (FGFA) programme.
- However, India withdrew from the FGFA project in 2018.
Features of AMCA:
- Stealth: The 25-tonne twin-engine aircraft, which will be bigger that other fighters in the Indian Air Force inventory, will have advanced stealth features to avoid detection by enemy radar.
- With stealth features, this aircraft (AMCA) would be able to compete with other stealth fighters in the world.
- Fuel & Weapons: The aircraft will have a large, concealed internal fuel tank of 6.5-tonne capacity, and an internal weapons bay for a range of weapons, including indigenous weapons, to be buried in its belly.
- Engine: The AMCA Mk1 variant will have the US-built GE414 engine of the 90 kilonewton (kN) class, while the more advanced AMCA Mk2 will fly on the more powerful 110kN engine, which will be developed indigenously by DRDO’s Gas Turbine Research Establishment (GTRE) in collaboration with a foreign defense major.
- India has been talking with Safran SA of France, one of the world’s largest manufacturers of aircraft engines and related equipment, in order to finalize the roadmap for the development of the combat aircraft engine
- Another important aspect would be to ensure a higher utilization time and smaller serviceability or maintenance periods for the aircraft.
- This will be aided by the inclusion of a comprehensive Integrated Vehicle Health Management (IVHM) system to keep track of multiple structural components, and to assess the condition of the aircraft in real time.
- Other features such as a diverterless supersonic inlet for controlling air flow into the engines, and a serpentine air intake duct to shield the engines from radar emissions, are likely to be part of the AMCA.
Other Fifth-generation Fighters:
- Only a few countries have built a fifth-generation stealth fighter aircraft.
- The list of the aircraft currently in service includes:
- The F-22 Raptor and F-35A Lightning II of the US
- The Chinese J-20 Mighty Dragon, and
- The Russian Sukhoi Su-57.
India to restart Penicillin G manufacture
- 09 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
India will start manufacturing the common antibiotic Penicillin G later this year, three decades after the country’s last plant shut down, Union health minister Mansukh Mandaviya announced last week.
What is Penicillin G?
- Penicillin G serves as a key active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) utilized in the production of various common antibiotics.
- Its molecular formula is C16H18N2O4S.
- Penicillin G (potassium or sodium) is an FDA-approved antibacterial medication primarily indicated for treating severe bacterial infections like pneumonia, meningitis, gonorrhea, syphilis, among others.
- This natural penicillin antibiotic is typically administered intravenously or intramuscularly due to limited oral absorption.
- Additionally, Penicillin G may be employed in certain instances as prophylaxis against susceptible organisms.
Why did Penicillin Manufacturing Stopped in India?
- The discontinuation of Penicillin G production in India, along with numerous other active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs), resulted from the influx of cheaper Chinese products driven by subsidies.
- Torrent Pharma in Ahmedabad was the final plant to halt Penicillin G production, with at least five companies, including Torrent, manufacturing the antibiotic in the country during the 1990s.
- In the early 1990s, India boasted nearly 2,000 API manufacturers, while approximately 10,000 units produced formulations. However, the allure of cheaper Chinese alternatives grew, particularly with the relaxation of customs rules during the country's economic liberalization.
- The Drug Prices Control Order, which imposed price caps on essential medicines, further incentivized companies to opt for cheaper imported products.
- While India previously sold Penicillin G for around Rs 800 per kg, China drastically reduced prices to nearly Rs 400 per kg, rendering domestic manufacturing economically unviable.
Why the Delay in Restarting Production?
- Lack of Urgency: Despite awareness within the industry and government about the decline in API production in India due to the availability of cheaper alternatives globally, there was limited emphasis on restarting domestic production.
- The supply chain disruptions caused by the pandemic highlighted the need for self-reliance, prompting the government to launch initiatives like the PLI scheme to bolster domestic manufacturing.
- High Initial Investment: API manufacturing, particularly for fermented compounds like Penicillin G, entails significant upfront costs.
- Establishing a production facility requires substantial capital investment, with companies often needing several years to break even.
- Dominance of China: China has emerged as a dominant supplier, significantly expanding its manufacturing capacity over the past three decades.
- Competing with Chinese prices would necessitate substantial investments in larger facilities.
What's the Impact of PLI Schemes?
- Reduction in API Imports: Since the implementation of the PLI scheme, there has been a notable decrease in API imports.
- For instance, the import dependency for paracetamol, which was previously two-thirds of the required volume, has now halved.
- Incentive Structure: The PLI scheme offers incentives structured as follows:
- 20% support for the first four years, gradually reducing to 15% in the fifth year and 5% in the sixth year for eligible sales of fermentation-based bulk drugs like antibiotics, enzymes, and hormones such as insulin.
- Chemically synthesized drugs receive a 10% incentive for six years on eligible sales.
The ‘Architecture Nobel’: Why Pritzker laureate Riken Yamamoto’s work stands out

- 09 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
Japanese architect Riken Yamamoto was this week declared winner of the 2024 Pritzker Architecture Prize, the highest international award in the field, which is sometimes referred to as the “Architecture Nobel”.
About Pritzker Architecture Prize:
- The Pritzker Architecture Prize is an international prize awarded each year to a living architect or a group of architects for significant achievements.
- It was established by the Pritzker family of Chicago in 1979 through their Hyatt Foundation, which until today is responsible for the prestigious award.
- The idea behind the Pritzker Prize is to honor contemporary architects “whose built work demonstrates a combination of those qualities of talent, vision, and commitment, which has produced consistent and significant contributions to humanity and the built environment through the art of architecture.”
- The award consists of a bronze medallion and a prize money of 100,000 USD.
- It is conferred during a ceremony held at an architecturally significant site throughout the world.
- The prize, which is also known as the Nobel Prize of architecture, is awarded “irrespective of nationality, race, creed, or ideology”.
- Nominations come from a range of architects, academics, and critics and the jury consists of five to nine experts.
History of the Prize:
- The idea for the Pritzker Prize came from Jay and Cindy Pritzker, who wanted to encourage and stimulate a greater public awareness of architecture, while also inspiring more creativity in the profession.
- The name Pritzker comes from the family who are based in Chicago and own the Hyatt Hotels.
Riken Yamamoto's Notable Works:
- Yamamoto, the ninth laureate from Japan, is known for his iconic architectural designs, such as the Hiroshima Nishi Fire Station (2000), featuring a transparent façade with glass walls and floors, offering passersby a glimpse inside.
- His design of the Koyasu Elementary School (2018) incorporates spacious, open terraces that facilitate arts education in dance, music, and painting while fostering student interaction.
Every village to have agricultural credit societies by 2027

- 09 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
Union Cooperation Minister Amit Shah Friday said that the Centre has decided to ensure formation of Primary Agricultural Credit Societies (PACS) in every village by 2027.
Context:
- Union Cooperation Minister Amit Shah recently announced the Centre's commitment to establishing Primary Agricultural Credit Societies (PACS) in every village by 2027, introducing 20 new activities to enhance their profitability.
- Emphasizing the significance of computerization in PACS, Shah highlighted its role in fostering development opportunities.
- He also inaugurated the National Cooperative Database and unveiled the 'National Cooperative Database 2023: A Report' to bridge existing gaps through comprehensive analysis.
- The database initiative progressed through three phases, including mapping approximately 2.64 lakh societies across agriculture, dairy, and fisheries sectors in the first phase.
- Subsequent phases involved data collection from various federations, banks, and mapping of the remaining 8 lakh primary cooperative societies in other sectors.
- The unveiling revealed over 8 lakh registered societies in the country, connecting more than 30 crore citizens.
What are Primary Agricultural Credit Societies (PACS)?
- PACS are grassroots cooperative credit societies, constituting the final tier in a three-tier cooperative credit system led by State Cooperative Banks (SCBs) at the state level.
- SCBs channel credit to District Central Cooperative Banks (DCCBs) operating at the district level, which collaborate with PACS, directly serving farmers.
- PACS operate as cooperative entities, with individual farmers as members and elected office-bearers from within the community. Villages may host multiple PACS.
- These societies extend short-term and medium-term agricultural loans to farmers for various farming activities.
Number of PACS in India:
- Established since 1904, India currently boasts over 1,00,000 PACS nationwide, engaging a significant member base exceeding 13 crore farmers.
- However, operational PACS stand at only 63,000, indicating the need for enhanced functionality and outreach.
Why are PACS Appealing?
- PACS offer crucial last-mile connectivity, ensuring farmers have access to capital at the onset of agricultural activities.
- They streamline credit extension processes, providing farmers with timely financial support with minimal paperwork, unlike traditional banks known for cumbersome procedures.
- PACS simplify paperwork and administrative tasks, offering farmers collective strength and assistance from PACS office-bearers.
- Unlike individual interactions required with commercial banks, PACS enable farmers to navigate loan processes collectively, reducing reliance on intermediaries.
Challenges Faced by PACS:
- Political influences often overshadow financial prudence within PACS, impacting loan recovery.
- Various committees have highlighted systemic issues within the cooperative system, including low member participation, lack of professionalism, inadequate governance, bureaucratic hurdles, and a workforce with aging and disengaged employees.
Union Cabinet approves India AI Mission with 10,372 cr outlay

- 08 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News
India has made its first move to address a key shortcoming it currently has in unlocking opportunities around generative artificial intelligence (AI) – that of computing hardware.
What is IndiaAI Mission?
- India's AI Mission entails the launch of an artificial intelligence (AI) initiative, announced by the Prime Minister at the Global Partnership on Artificial Intelligence (GPAI) Summit 2023 in New Delhi, with implementation overseen by the 'IndiaAI' Independent Business Division (IBD) under Digital India Corporation (DIC).
- Led by the Ministry of Electronics and IT (MeitY), the mission aims to establish a computing capacity exceeding 10,000 graphics processing units (GPUs) and develop foundational models trained on datasets encompassing major Indian languages, focusing on priority sectors such as healthcare, agriculture, and governance.
- Additionally, the mission will involve the establishment of AI Curation Units (ACUs) in 50-line ministries and the creation of an AI marketplace to provide AI services and pre-trained models to AI application developers.
- Implementation of the AI computer infrastructure will follow a public-private partnership model, with 50% viability gap funding, with Rs 4,564 crore allocated from the total outlay of Rs 10,372 crore for building computing infrastructure.
Key Features of the IndiaAI Mission:
- IndiaAI Compute Capacity: Establishing a scalable AI computing ecosystem to meet the growing demands of India's burgeoning AI start-ups and research community.
- IndiaAI Innovation Centre: Focusing on the development and deployment of indigenous Large Multimodal Models (LMMs) and domain-specific foundational models in critical sectors.
- IndiaAI Datasets Platform: Streamlining access to high-quality non-personal datasets to fuel AI innovation.
- IndiaAI Application Development Initiative: Promoting the adoption of AI applications in critical sectors, addressing problem statements sourced from Central Ministries, State Departments, and other entities.
- IndiaAI FutureSkills: Mitigating barriers to entry into AI programs by expanding AI courses at undergraduate, master's, and Ph.D. levels.
- IndiaAI Startup Financing: Supporting and accelerating deep-tech AI startups by providing streamlined access to funding for futuristic AI projects.
- Safe & Trusted AI: Ensuring the responsible implementation of AI projects through the development of indigenous tools and frameworks to foster trust and safety in AI applications.
The Significance of the IndiaAI Mission:
- The IndiaAI Mission aligns with the vision of fostering indigenous AI development and leveraging AI technology for the benefit of India.
- It aims to demonstrate to the international community the positive impact of AI technology on society, thereby enhancing India's global competitiveness.
- By establishing a comprehensive ecosystem for AI innovation through strategic partnerships across public and private sectors, the mission will catalyze AI-driven advancements.
- It will foster creativity and bolster internal capabilities, ensuring India's technological sovereignty.
- Furthermore, the mission is poised to create employment opportunities that demand advanced skills, leveraging India's demographic advantage.
After 10 years struggle, Mendha gets separate Panchayat status under Gramdan Act

- 08 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News
The Maharashtra government recently notified Mendha, a village deep inside the forests of the state’s Gadchiroli district, as a separate Gram Panchayat under The Maharashtra Gramdan Act, 1964.
What is Gramdan?
- Gramdan is an expansion of the Bhoodan Movement started in 1951 by Aacharya Vinoba Bhave.
- ‘Bhoodan’ meant redistribution of land from bigger landowners to the landless.
- Under Gramdan, the entire village will put its land under a common trust.
- This way, the land will not be sold outside the village or to one who has not joined Gramdan in the village.
- But the landowners can continue to cultivate it and reap the benefits.
- The Movement paved the way for the protection of natural resources by giving equal rights and responsibilities to everyone in the community and empowering communities to move towards self-governance.
- Under the Act, at least 75 percent of landowners in the village should surrender land ownership to the village community for it to be declared as ‘gramdan’.
- Such land should at least be 60 percent of the village land. Five per cent of the surrendered land is distributed to the landless in the village for cultivation.
- Recipients of such land cannot transfer the same without the permission of the community.
- The rest remains with the donors.
- They and their descendants can work on it and reap the benefits.
- But they cannot sell it outside the village or to a village resident who has not joined Gramdan.
- Today, seven states in India have 3,660 Gramdan villages, the highest being in Odisha (1,309).
- The states are Andhra Pradesh, Bihar, Maharashtra, Odisha, Rajasthan, Tamil Nadu and Uttar Pradesh.
- In September 2022, the Assam government repealed the Assam Gramdan Act, 1961 and Assam Bhoodan Act, 1965, bypassing The Assam Land and Revenue Regulation (Amendment) Bill, 2022.
- This, it said, was done to counter encroachment on donated lands in the state.
- Till that time, Assam had 312 Gramdan villages.
About Mendha’s Village Struggle:
- The village, comprising around 500 Gond Adivasis, has fought for its forests for years.
- It is popular as the first village in India to secure community forest rights (CFR), following the passing of the Scheduled Tribes and Other Traditional Forest Dwellers (Recognition of Forest Rights) Act, 2006.
- Some 80 per cent of the area in the village is covered with dense forest.
- People here believe that land is not a private property but a collective resource that provides food and livelihood and should be saved and passed on to the next generation.
- All villagers in Mendha have surrendered their land, which is unique. In all other villages, only about 75-80 per cent of landowners had agreed to do so.
- The village fulfilled these conditions of the Act in 2013 and notified the district collector about its decision to implement the Act.
Amit Shah launches National Cooperative Database, to help in policy making
- 08 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News
Cooperation Minister Amit Shah on Friday launched the National Cooperative Database and stressed that it would help in policy making.
About National Cooperative Database (NCD):
- The National Cooperative Database (NCD) is an initiative spearheaded by the Ministry of Cooperation, responding to the pressing need for a robust database to effectively capture essential information concerning India's extensive cooperative sector.
- Developed collaboratively with State Governments, National Federations, and stakeholders, the NCD is designed to promote a cooperative-centric economic model, offering a web-based digital dashboard for seamless data management.
- Acting as a centralized repository, the NCD aggregates data from cooperative societies, including National/State Federations, with information entered and authenticated by nodal officials at RCS/DRCS offices for cooperative societies and provided by various national/state federations for federations.
- The collected data encompasses diverse parameters, such as registered names, locations, membership numbers, sectoral details, operational areas, financial statements, audit statuses, and more, providing a comprehensive overview of the cooperative landscape.
- Serving as a vital communication tool, the NCD facilitates efficient interaction between the Central Ministry, States/UTs, and Cooperative Societies, fostering collaboration and synergy within the cooperative sector.
- Key features and benefits of the NCD include single-point access, comprehensive and updated data, user-friendly interface, vertical and horizontal linkages, query-based reports and graphs, Management Information System (MIS) reports, data analytics, and geographical mapping capabilities.
Kerala declares man-animal conflict a state-specific disaster

- 08 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
Amid repeated deaths from animal attacks and rising anger over them, Kerala recently declared man-animal conflict as a state-specific disaster, becoming the first state in the country to do so.
What is Man-animal Conflict?
- Man-animal conflict refers to the interaction between wild animals and humans, resulting in adverse outcomes for both people and wildlife, as well as their habitats.
- Escalating Conflict: In states across India, human-wildlife conflict has intensified, leading to a significant rise in human casualties.
- For instance, in Maharashtra, the conflict resulted in 86 in 2021 and 105 deaths in 2022, marking a sharp increase compared to previous decades.
Causes:
- Factors contributing to this conflict include the encroachment of grodeathswing human and animal populations into each other's territories, habitat fragmentation due to legal and illegal land use changes, alterations in cropping patterns attracting wildlife to agriculture, and habitat destruction from invasive alien species.
- Despite having over 700 protected areas, a substantial portion of elephant, lion, and tiger ranges lie outside these protected zones, exacerbating the conflict.
Ecologist Perspective:
- Ecologist Madhav Gadgil highlights that the Wildlife Protection Act of 1972 has inadvertently facilitated an environment where wild animals can invade human habitats with impunity.
- He cites the optimal foraging theory in ecology, which underscores animals' efforts to maximize nutrient intake while minimizing time, effort, and risks.
Solutions:
- Addressing the issue requires robust enforcement and pragmatic policies to mitigate conflict incidences.
- Engaging local communities, as suggested by the Future for All Report 2021 (by WWF and UNEP), fosters coexistence between humans and wildlife, acknowledging that complete elimination of conflicts is impractical.
- Additionally, awareness campaigns aimed at educating the public about man-animal conflict and skill development initiatives for communities living near forests can alleviate pressures on agricultural and forest lands.
Kerala's Decision to Declare Man-Animal Conflict as a State-Specific Disaster:
- Implications of the Decision: Currently, the management of man-animal conflict falls under the jurisdiction of the forest department, operating in accordance with the Wildlife Protection Act.
- By designating man-animal conflict as a state-specific disaster, the responsibility for addressing it shifts to the state disaster management authority, empowered by the Disaster Management Act, enabling swifter and more decisive action.
- Rationale for the Decision: Instances of loss of life due to man-animal conflict have prompted calls to tranquilize, capture, or eliminate the responsible animals.
- Presently, the chief wildlife warden, holding the sole authority in the state, makes decisions regarding wild animals causing disturbances in human settlements.
- Past decisions to tranquilize aggressive animals, like wild elephants, have faced legal challenges.
- Under the disaster management authority, actions can be taken that supersede other regulations, including those outlined in the Wildlife Protection Act.
- According to the Disaster Management Act, except for the Supreme Court or a High Court, no court has jurisdiction to entertain suits or proceedings regarding actions taken by relevant authorities in line with the Act.
- Additionally, the Act stipulates that its provisions hold precedence over any other law during the specific period of a declared disaster.
Kerala's Success in Managing Man-Animal Conflict:
- Kerala, with approximately 5,700 wild elephants in 2017, comprising 19% of the nationwide population of 30,000, witnessed a significantly lower incidence of human fatalities caused by elephants, accounting for only 81 (4%) of the 2,036 deaths recorded in India between 2018 and 2021.
- Factors Contributing to Kerala's Effective Management of Man-Animal Conflict:
- Maintenance of Unchanged Wilderness Boundaries: Kerala has largely preserved the boundaries between wilderness and civilization in recent years, contributing to the mitigation of man-animal conflicts.
- Evolution of Agricultural Practices: Changes in agricultural practices, such as the cultivation of crops like coffee, pepper, and tea, which hold less appeal for elephants, have helped reduce conflicts between humans and elephants.
- Unique Elephant Characteristics: Individual elephants are identified and named based on their distinct characteristics, such as Kabali, an elephant residing in the Athirapally jungle in Thrissur district, known for its tendency to attack or chase automobiles.
- These factors collectively contribute to Kerala's successful management of man-animal conflict, resulting in relatively fewer human fatalities caused by elephants compared to other regions in India.
Countries hope to bring BBNJ or High Seas treaty into force by 2025

- 08 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News
The Blue Leaders High-Level Event on Biodiversity Beyond National Jurisdiction was held in Belgium on March 7, 2024, to urge nations to ratify a new treaty to protect the high seas from pollution, climate change and overfishing.
What is the BBNJ Treaty?
- The BBNJ Treaty, also referred to as the Treaty of the High Seas, is an international agreement aimed at conserving and sustainably managing marine biological diversity in areas beyond national jurisdiction, operating within the framework of the UNCLOS.
- These areas encompass the high seas beyond exclusive economic zones or national waters.
- It represents nearly half of the Earth's surface and is characterized by minimal regulation and understanding of their biodiversity, with only 1% currently under protection.
- Launched at the One Ocean Summit in February 2022, the High Ambition Coalition on Biodiversity Beyond National Jurisdiction seeks to unite various delegations involved in BBNJ negotiations toward a comprehensive and ambitious outcome.
- The negotiations focus on key elements agreed upon in 2015, including the conservation and sustainable use of marine genetic resources, area-based management tools such as marine protected areas, environmental impact assessments, and initiatives for capacity-building and technology transfer in marine science and management.
- India is yet to sign the treaty. However, it called on efforts for entry into force and implementation of the treaty at the G20 New Delhi Leaders’ Declaration held in September 2023.
The Importance of a Legally Binding Instrument for BBNJ:
- Biodiversity in areas beyond national jurisdiction is crucial for ocean health, coastal communities' welfare, and global sustainability, constituting 95% of the ocean and offering essential ecological, economic, social, cultural, scientific, and food-security benefits.
- Despite their significance, these areas face escalating threats such as pollution, overexploitation, and the impacts of climate change, compounded by the anticipated rise in demand for marine resources in the future.
- Even the deep seafloors, considered one of the most inhospitable habitats, are experiencing the onset of extinction processes, with alarming statistics showing that 62% of assessed mollusc species are threatened, including critically endangered, endangered, and vulnerable species, while the International Seabed Authority permits deep sea mining contracts.
- It is imperative to establish a legally binding framework for managing and regulating biodiversity in areas beyond national jurisdiction, as over 60% of this resource in the global seas remains unmanaged and unprotected, necessitating comprehensive conservation measures.
ISRO’s second rocket launchport in Tamil Nadu’s Kulasekarapattinam

- 07 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
Prime Minister Narendra Modi laid the foundation stone of the second rocket launchport of the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) at Kulasekarapattinam on February 28.
Why does India need a new launchport?
- With the Union government’s recent policy announcing the opening of the space sector to private players, a sharp rise in the number of commercial launches is certain.
- To ensure that ISRO’s first launchport, the Satish Dhawan Space Centre (SDSC) SHAR in Sriharikota, is not overburdened with a high number of launches, the space agency has decided to build another facility.
- While SHAR will be only used for launching bigger and heavy-lift-off missions, the Kulasekarapattinam launchport will be used to launch smaller payloads.
- SHAR will also be available for India’s big ticket missions to the Moon, Venus, and much touted human-flight mission, the Gaganyaan.
- Private players could develop space-qualified sub-systems, build satellites, and even launch vehicles using the new launchport.
- It will also facilitate dedicated launch infrastructure for all the on-demand commercial launches.
Why is the new ISRO launchport located in Tamil Nadu?
- Geographically, scientifically, and strategically, the Kulasekarapattinam launchport provides a natural advantage to ISRO’s future launches pertaining to the Small Satellite Launch Vehicle (SSLV).
- Allowing a direct southward and smaller launch trajectory for the light weight SSLVs carrying less fuel, the Kulasekarapattinam facility will boost ISRO’s attempts to enhance payload capacities.
- Currently, the trajectory followed by all launches from SHAR are longer as they follow a path which requires the vehicle to skirt eastwards around Sri Lanka before taking the actual southward flight.
- This consumes additional fuel. However, the same would not be required for future launches from Kulasekarapattinam, which is geographically located several kilometers to the west of Colombo, thereby allowing a straight southward flight and simultaneously saving the already limited fuel available onboard SSLV.
- Notably, both the launch ports are located in Southern India, near the equator.
- For a launch site close to equator the magnitude of the velocity imparted due to Earth’s rotation is about 450 m/s, which can lead to substantial increase in the payload for a given launch vehicle.
- Geostationary satellites must necessarily be in the equatorial plane.
- So, for such satellites, the closer the launch site is to the equator the better it is.
What are SSLVs?
- SSLV is the new small satellite launch vehicle developed by ISRO to cater for the launch of small satellites.
- It has a three-stage launch vehicle, having a lift-off weight of about 120 tonnes and is 34 meters in length and 2 meters in diameter.
- SSLV is designed with a three-stage solid propulsion and a liquid propulsion stage, which is the terminal stage.
- The SSLV missions are useful to launch small-sized satellites weighing anywhere between 10 to 500kg into the Low Earth Orbit.
- Going by their size and weight, these are typically referred to as mini, micro or nano satellites.
- They are low on cost and intended satellite insertion into orbits takes a shorter flight time.
- SSLV are best suited for commercial and on-demand launches.
- Previously, satellite projects built by college students and private players involved in the space sector have benefitted from SSLV missions.
What are the features of SHAR?
- SHAR is situated along the east coast of Andhra Pradesh and is located 80 km off Chennai.
- It currently provides launch infrastructure to all ISRO missions.
- It is equipped with a solid propellant processing setup, static testing, and launch vehicle integration facilities, telemetry services — tracking and command network to oversee the launch — and a mission control center.
- SHAR has two launch complexes that are routinely used to launch the Polar Satellite Launch Vehicle (PSLV), the Geosynchronous Space Launch Vehicles (GSLV) and the Geosynchronous Satellite Launch Vehicle Mk-III, now renamed as LVM3.
Haiper, the text-to-video model created by Google DeepMind and Tiktok alumni

- 07 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
Recently, a company founded by former members of Google DeepMind, TikTok, and top labs from research academia — introduced an eponymous new text-to-video model Haiper.
What is Haiper?
- Haiper is an all-in-one visual foundation model that allows everyone, with or without technical training, to generate high-quality video content with ease.
- The founders claim that Haiper brings forward cutting-edge machine learning with the belief that creativity should be “fun, surprising, and shareable”.
- The company has built Haiper as a powerful, industry-agnostic creativity tool.
- It was released by Google DeepMind and Tiktok alumni.
What does Haiper do?
- Haiper offers tools such as text-to-video, animated static images, video repainting tools, etc.
- Users can go on to the website, log in with their email addresses, and start generating videos for free by typing in text prompts.
- At present, users can only generate HD video spanning 2 seconds, and a slightly lower-quality video could go up to four seconds.
Strengths and limitations:
- While the short length is a limitation, the company is working towards extending the video outputs.
- Presently, the tool is free to use, with an aim to build a community.
- While OpenAI’s Sora is still not available for the public, Haiper is offering users to try its tool for free on its website.
Controversy Erupts as Tamil Nadu Governor Refers to Ayya Vaikundar as 'Sanatan Dharma Savior'

- 07 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
Tamil Nadu Governor R N Ravi’s recent remarks about the 19th-century social reformer Ayya Vaikundar — that he was Lord Vishnu incarnated to prevent the destruction of Sanatan Dharma — have evoked sharp reactions in the state, from politicians as well as Vaikundar’s followers.
Who was Ayya Vaikundar?
- Ayya Vaikundar, born in 1809, is revered as a social reformer and the founder of the Ayyavazhi sect, primarily in southern Tamil Nadu.
- His teachings focused on equality, fraternity, and the eradication of caste-based discrimination, challenging the established religious and social hierarchies of the time.
- At a time when rigid casteism and caste-based atrocities were the norm, Vaikundar introduced measures to challenge these divisions.
- He organized Samapanthi-bhojana or community eateries for people from all backgrounds.
- He would send his disciples to the homes of lower castes to eat with them.
- When lower castes were not allowed to fetch water from wells used by upper caste Hindus, Vaikundar initiated the digging of common wells, called Muthirikinarus.
- At a time when priests threw vibhuti and sandal paste at devotees from a distance to avoid touching them and lower castes were not allowed to enter temples at all, Vaikundar introduced Thottu Namam, in which he inspired priests to apply the sacred paste on devotees’ forehead, irrespective of their caste.
- The paste would be applied in the form of a lamp, indicating the soul and God, representing the form of God inside every life.
- Vaikundar also encouraged all devotees to wear turbans and dhotis, promoting equality.
- He initiated the Thuvayal Panthy programme, teaching vegetarianism and discipline to followers, who spread these teachings across Tamil Nadu.
- He established Nizhal Thangals as community worship spaces, which did not have any idol or deity, and only Tamil was used for worship.
- These community worship centers also had community kitchens and even basic schools.
- He pioneered education for the lower castes and opposed discriminatory taxes.
- One of his significant interventions was the introduction of simplified, inclusive marriage customs without a Brahmin priest or Sanskrit mantras.
Trees in Corbett fell prey to greedy nexus, says Supreme Court
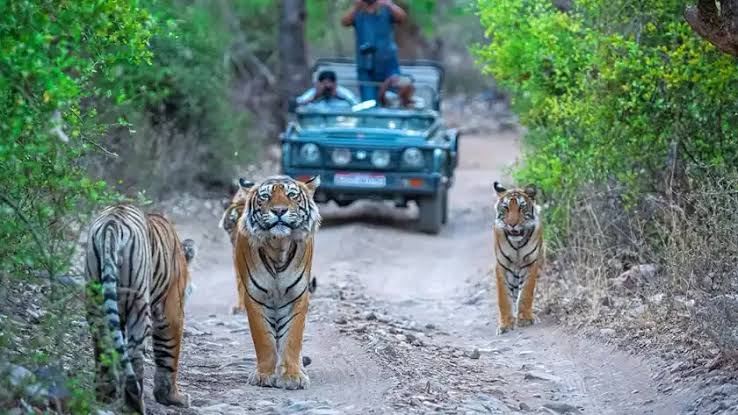

- 07 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
The Supreme Court on Wednesday condemned the illegal felling of over 6,000 trees to construct buildings, ostensibly for “eco-tourism” at the Jim Corbett National Park in Uttarakhand, as a “classic case” of nexus between politicians and officials working to ransack the environment for short-term commercial ends.
News Summary:
- In 2023, a series of applications brought attention to the creation of alleged illegal buildings and encroachment on water bodies, prompting court intervention.
- Petitioners highlighted violations of environmental norms and encroachment into core wildlife habitats.
- Evidence presented during proceedings revealed unauthorized constructions within the national park, including concrete and iron enclosures purportedly intended for a 'safari' experience.
- Moreover, it was disclosed that over 6,000 trees had been felled in the national park under the pretext of safari development.
Supreme Court’s Observations:
- The Court has raised concerns regarding the necessity of developing facilities within natural forest environments, particularly in areas designated for the protection of endangered species like tigers.
- Directing the Government to establish a committee, the Supreme Court seeks recommendations on whether tiger safaris should be permitted in buffer or fringe areas and what guidelines should govern their establishment if allowed.
- Additionally, the Court has strongly criticized the illegal constructions and extensive tree felling in Uttarakhand's Corbett National Park.
What are the Core and Buffer Areas in Tiger Reserves?
- As per the Wild Life (Protection) Amendment Act of 2006, a Tiger Reserve comprises core or critical habitat and a buffer zone surrounding it.
- Core areas hold the legal status of a National Park or a Sanctuary.
- Buffer zones consist of a mix of forest and non-forest land, managed as a multiple-use area.
- The buffer area acts as a protective barrier, absorbing the impact of poaching pressure on tiger and other wildlife populations.
About Jim Corbett National Park:
- Location: Situated in the Nainital district of Uttarakhand, Jim Corbett National Park is renowned for its rich biodiversity.
Key Facts:
- Established in 1935, it is India’s oldest national park.
- Initially named Hailey National Park after its founder Sir Malcolm Hailey, it was renamed Corbett National Park in 1956 to honor Jim Corbett's contributions to wildlife preservation in India.
- Corbett National Park boasts the highest population of tigers in India, highlighting its importance for tiger conservation efforts.
- Flora: Dominated by Sal, Semal, Kharpat, Sissoo, Khair, Dhak, Khingan, Bakli, Bel, Ber, Bamboo, Khingam, Jamun, Kanju, Rohini, and Pula trees.
- Sal, Khair, and Sissoo are prominently featured throughout the park.
- Fauna: Home to diverse wildlife including Tiger, Leopard, Elephant, Chital Deer, Sambar Deer, Hogg Deer, Barking Deer, Wild Boar, Langur, Wild pig, Rhesus Monkey, Jackal, Rabbit, Yellow Throated Martin, and Otters.
- Various reptiles such as Crocodile, Gharial, King Cobra, Common Krait, Cobra, Russell's Viper, Rock Python, and Monitor Lizard inhabit the park.
- The Kosi River feeds the eastern periphery of Corbett National Park.
- The Ramganga River (West) and its tributaries Sonanadi, Palain, and Mandal serve as significant hydrological resources for the park.
Vaishnaw bats for further simplification of economic laws at ‘NITI for States’ platform launch

- 07 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
The Union IT, Communications, and Railways Minister Ashwini Vaishnaw Thursday stressed on the need to further simplify economic laws in a modern and relevant way at the launch of NITI Aayog’s ‘NITI for States’ platform.
About “NITI For States” Platform:
- It serves as a cross-sectoral knowledge hub envisioned to be a Digital Public Infrastructure (DPI) for Policy and Good Governance.
Key features include:
- A comprehensive repository comprising Best Practices, Policy documents, datasets, data profiles, and NITI publications across various sectors.
- Knowledge products spanning 10 sectors and two cross-cutting themes (Gender and Climate Change), such as Agriculture, Education, Energy, Health, Manufacturing, MSME, Tourism, Urban, and Water resources & WASH.
- An intuitive and user-friendly interface accessible via multiple devices, including mobile phones.
- The platform aims to catalyze digital governance transformation by providing government officials with contextualized, actionable knowledge and insights, thereby enhancing decision-making quality.
- It supports district collectors and block-level functionaries by granting access to innovative best practices from various States and Union Territories.
What is the Viksit Bharat Strategy Room?
- It serves as an interactive platform enabling users to visualize data, trends, best practices, and policies in an immersive manner, facilitating a comprehensive assessment of any problem statement.
- The platform features voice-enabled AI for user interaction and facilitates connectivity with multiple stakeholders through video conferencing.
- Designed as a plug-and-play model, it enables replication by states, districts, and blocks for widespread adoption.
- Collaboration with various government organizations by NITI Aayog includes:
- iGOT Karmayogi's "SAMARTH" online training modules accessible through the platform.
- Integration of NITI Aayog’s National Data and Analytics Platform (NDAP) to provide access to government datasets.
- Support from the National E-Governance Division (NeGD) in developing the innovative Viksit Bharat Strategy Room.
- Multi-lingual support provided by Bhashini.
- Integration of PM Gatishakti BISAG-N team, with DPIIT support, to offer geospatial tools for Area Based Planning.
INS Jatayu, India’s new naval base in Lakshadweep

- 06 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
On Wednesday (March 6), Naval Detachment Minicoy will be commissioned as INS Jatayu, an upgraded naval base, marking an important milestone in the Indian Navy’s resolve to incrementally augment security infrastructure at the strategic Lakshadweep Islands.
About INS Jatayu Naval Base:
- The existing Naval Detachment Minicoy, which is under the operational command of the Naval Officer-in-Charge (Lakshadweep), will be commissioned as INS Jatayu.
- A naval detachment has administrative, logistics, and medical facilities.
- INS Jatayu will be upgraded to a naval base with additional infrastructure such as an airfield, housing, and personnel, after obtaining the requisite environmental and other clearances.
- The fragile ecology of the island may pose challenges for the construction but there are plans to construct a new airfield that will be capable of operating both military and civil aircraft.
Significance of INS Jatayu?
- The basing of an independent naval unit with requisite infrastructure and resources will enhance its overall operational capability in the islands.
- The establishment of the base is in line with the government’s focus on comprehensive development of the islands.
- The base will enhance its operational reach, facilitate its anti-piracy and anti-narcotics operations in the western Arabian Sea, and augment its capability as the first responder in the region.
- With the commissioning of INS Jatayu, the Indian Navy will add to its strength on the western seaboard.
- The proposed airfield will allow operations for a range of aircraft, including P8I maritime reconnaissance aircraft and fighter jets, and extend the Navy’s reach and operational surveillance capabilities at a time when India is seeking to counter the growing Chinese influence in the Indian Ocean Region.
- This has an immediate bearing at a time when India’s relations with the Maldives have come under strain since the election of the pro-China President Mohamed Muizzu.
About the Lakshadweep Islands:
- Lakshadweep, ‘a hundred thousand islands’ in Sanskrit and Malayalam, is an archipelago of 36 islands located between 220 km and 440 km from Kochi.
- The islands, only 11 of which are inhabited, have a total area of only 32 sq km.
- The Lakshadweep are part of a chain of coralline islands in the Indian Ocean that includes Maldives to the south, and the Chagos archipelago farther beyond, to the south of the equator.
- Given their location in the Indian Ocean, the Lakshadweep are of huge strategic importance to India.
- Minicoy straddles vital Sea Lines of Communications (SLOCs) — the world’s main maritime highways — including the Eight Degree Channel (between Minicoy and Maldives) and the Nine Degree Channel (between Minicoy and the main cluster of Lakshadweep islands).
- In consequence, the Lakshadweep Islands are also vulnerable to marine pollution.
Exclusive-World on brink of fourth mass coral reef bleaching event- NOAA

- 06 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
The world stands on the brink of witnessing its fourth mass coral bleaching event, a phenomenon that threatens to hit vast expanses of tropical reefs, including significant portions of Australia's iconic Great Barrier Reef.
Key Findings from the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA):
- Impending Fourth Mass Coral Bleaching Event: The world is on the brink of a fourth mass coral bleaching event, following those in 1998, 2010, and 2014.
- To classify as global, widespread bleaching must occur across three ocean basins: the Atlantic, Pacific, and Indian.
- Impact of Previous Events: The last global mass coral bleaching event occurred from 2014 to 2017, resulting in the loss of nearly a third of the Great Barrier Reef's corals.
- Preliminary data indicates that approximately 15% of the world's reefs experienced significant coral die-offs during this event.
- Current Situation: This year is witnessing even more severe bleaching events, with the Caribbean experiencing its worst coral bleaching on record following the Northern Hemisphere summer last year.
- Link to Climate Phenomena: Coral bleaching is often associated with the naturally occurring El Niño climate phenomenon, which leads to warmer ocean waters.
- Climate Change Impact: The world recently experienced its first 12-month period with an average temperature exceeding 1.5 degrees Celsius (2.7 degrees Fahrenheit) above pre-industrial levels.
- A temperature rise of 1.5°C is considered the tipping point for mass coral die-offs, with scientists estimating that 90% of the world's corals could be lost as a result.
About the Corals and Coral Reefs:
- Corals: Corals are animals known as polyps, which engage in a symbiotic relationship with tiny algae called zooxanthellae.
- These algae provide corals with food and oxygen, while corals offer them a safe habitat.
- Coral Reefs: Coral reefs are limestone structures formed by thousands of tiny coral animals and are predominantly found in tropical climates.
Coral Bleaching and Its Concerns:
- Coral bleaching occurs when corals are exposed to stressful conditions like high temperatures, pollution, or changes in water chemistry, leading them to expel the zooxanthellae.
- Without these algae, corals lose their color and turn white, hence the term 'bleaching,' and cannot survive for long in this state.
- Recovery Potential: Despite its severity, coral bleaching doesn't necessarily mean the end of the reef; timely removal of stressors can facilitate the return of zooxanthellae and coral recovery.
- Ecological Importance: Coral reefs serve as habitats and food sources for numerous fish and marine species.
- They also offer coastal protection from erosion and storms and play a critical role in regulating the Earth's climate by absorbing and storing carbon dioxide.
- Cultural and Aesthetic Value: Beyond their ecological functions, coral reefs represent stunning biodiversity and natural beauty, making their loss a tragic prospect for future generations.
- Impacts: When coral reefs suffer, so do the ecosystems and communities reliant on them, underscoring the far-reaching consequences of coral degradation.
Google-backed satellite to track global oil industry methane emissions
- 06 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
MethaneSAT — a satellite which will track and measure methane emissions at a global scale — was launched aboard a SpaceX Falcon9 rocket from California recently.
What is MethaneSAT?
- MethaneSAT will orbit the Earth 15 times a day, monitoring the oil and gas sector.
- It will create a large amount of data, which will tell “how much methane is coming from where, who’s responsible, and are those emissions going up or down over time”.
- The data collected by MethaneSAT will be made public for free in near real-time.
- This will allow stakeholders and regulators to take action to reduce methane emissions.
Institutions involved in the development:
- The entity behind MethaneSAT is the Environmental Defense Fund (EDF) — a US-based nonprofit environmental advocacy group.
- To develop the satellite, EDF partnered with Harvard University, the Smithsonian Astrophysical Observatory, and the New Zealand Space Agency.
Features of MethaneSAT:
- Historically, tracking the source of methane emissions and measuring them has been quite challenging.
- ?While some satellites can provide high-resolution data, they can only scan specific, pre-targeted sites.
- Others can examine larger areas and detect large emitting events, but cannot scan “smaller sources that account for the majority of emissions in many, if not most, regions,” the EDF statement added.
- Due to this discrepancy, according to an International Energy Agency (IEA) report, global methane emissions are about 70 per cent higher than levels reported by national governments.
- MethaneSAT is expected to fix the issue.
- Equipped with a high-resolution infrared sensor and a spectrometer, the satellite will fill critical data gaps.
- It can track differences in methane concentrations as small as three parts per billion in the atmosphere, which enables it to pick up smaller emissions sources than the previous satellites.
- MethaneSAT also has a wide-camera view — of about 200 km by 200 km — allowing it to identify larger emitters so-called “super emitters”.
Significance of MethaneSAT:
- Advancing the Goals of the Global Methane Pledge 2021: The Global Methane Pledge, signed by over 150 countries in 2021, aims to reduce collective methane emissions by at least 30% from 2020 levels by 2030.
- During the previous year's COP, over 50 companies pledged to significantly reduce methane emissions and routine flaring.
- MethaneSAT will play a crucial role in helping these entities achieve their targets.
- Enhancing Transparency: The satellite will usher in a new era of transparency by providing publicly available data accessible to anyone worldwide.
- This data will enable monitoring of methane commitments made by governments and corporations, promoting accountability and transparency in emission reduction efforts."
Why Do We Need to Track and Measure Methane Emission?
- Methane is an invisible but strong greenhouse gas, and the second largest contributor to global warming after carbon dioxide, responsible for 30 percent of global heating since the Industrial Revolution.
- According to the United Nations Environment Programme, over a period of 20 years, methane is 80 times more potent at warming than carbon dioxide.
- The gas also contributes to the formation of ground-level ozone — a colorless and highly irritating gas that forms just above the Earth’s surface.
- According to a 2022 report, exposure to ground-level ozone could be contributing to one million premature deaths every year.
- Therefore, it is crucial to cut methane emissions and the main culprit, fossil fuel operations, which account for about 40 percent of all human-caused methane emissions.
- The objective of MethaneSAT is to help achieve this goal.
Holistic Progress Card: How NCERT is planning to change student assessment

- 06 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
The New Education Policy (NEP), established in 2020, proposed redesigning the assessment system of school students in India recently.
About the Holistic Progress Card (HPC):
- It Is Developed by Performance Assessment, Review, and Analysis of Knowledge for Holistic Development (PARAKH), a standard-setting body under the NCERT.
- The Holistic Progress Card (HPC) marks a significant departure from traditional assessment methods for students in the foundational stage (Classes 1 and 2), preparatory stage (Classes 3 to 5), and middle stage (Classes 6 to 8), aligning with the recommendations of the National Education Policy (NEP) 2020.
Key Features:
- Incorporates feedback from parents, classmates, and self-evaluation by students.
- Aims to provide a comprehensive view of students' academic performance, cognitive abilities, socio-emotional skills, and creativity during class activities.
- Aligns with the National Curriculum Framework for School Education (NCFSE) to prioritize learner-centric evaluation.
- Emphasizes a shift from numerical grades to a 360-degree evaluation, focusing on students' active engagement in class activities and the demonstration of diverse skills and competencies.
- Enables teachers to identify students' strengths and weaknesses, fostering personalized support and intervention.
- Encourages students to reflect on their progress and set academic and personal goals, fostering self-awareness and accountability.
- Involves parents in the learning process, integrating their insights on homework, classroom engagement, and extracurricular activities.
- Includes peer evaluation, allowing students to assess their classmates' contributions to activities.
Benefits:
- Goes beyond numerical grades, providing descriptive and analytical evaluations that encompass academic achievements and critical skill development.
- Promotes a shift from summative to formative assessment, fostering competency-based evaluation and holistic growth.
Majuli Island's Mask Craft Celebrated With Geographical Indication Tag

- 06 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
Adding to their growing national and international recognition, the traditional Majuli masks in Assam were given a Geographical Indication (GI) tag by the Centre recently.
What are Majuli Masks?
- These handmade masks are traditionally used to depict characters in bhaonas, or theatrical performances with devotional messages under the neo-Vaishnavite tradition.
- Majuli, the largest river island in the world and the seat of Assam’s neo-Vaishnavite tradition, has been home to the art of mask-making since the 16th century.
- It was introduced by the 15th-16th century reformer saint Srimanta Sankardeva.
- The masks can depict gods, goddesses, demons, animals and birds — Ravana, Garuda, Narasimha, Hanuman, Varaha Surpanakha all feature among the masks.
- They can range in size from those covering just the face (mukh mukha), which take around five days to make, to those covering the whole head and body of the performer (cho mukha), which can take up to one-and-a-half months to make.
- According to the application made for the patent, the masks are made of bamboo, clay, dung, cloth, cotton, wood and other materials available in the riverine surroundings of their makers.
Why is This Art Practiced in Monasteries?
- Sattras are monastic institutions established by Srimanta Sankardev and his disciples as centers of religious, social and cultural reform.
- Today, they are also centers of traditional performing arts such as borgeet (songs), sattriya (dance) and bhaona (theater), which are an integral part of the Sankardev tradition.
- Majuli has 22 sattras, and the patent application states that the mask-making tradition is by and large concentrated in four of them:
- Samaguri Sattra
- Natun Samaguri Sattra
- Bihimpur Sattra and
- Alengi Narasimha Sattra
What is Majuli Manuscript Painting?
- It is a form of painting which also received the GI tag.
- It originated in the 16th century done on sanchi pat, or manuscripts made of the bark of the sanchi or agar tree, using homemade ink.
- The earliest example of an illustrated manuscript is said to be a rendering of the Adya Dasama of the Bhagwat Purana in Assamese by Srimanta Sankardev.
- This art was patronized by the Ahom kings.
- It continues to be practiced in every sattra in Majuli.
India ranks 113 out of 190 countries in the World Bank’s legal gender gap index

- 05 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
India's ranked improved to 113 out of 190 countries in the World Bank’s Women, Business and Law index, according to the 10th edition of the report released Monday.
About Women, Business and Law Index:
- The "Women, Business and the Law (WBL)" index is a project of the World Bank Group, specifically designed to measure the legal environment for women's economic opportunities across 190 economies.
- It's distinct from a general "Gender Equality Index" as it focuses specifically on legal frameworks and their impact on women's involvement in business and professional life.
What does it Measure?
- The WBL index assesses legal frameworks across eight indicators:
- Mobility (freedom of movement)
- Workplace (discrimination, maternity leave, etc.)
- Pay (equal pay for equal work)
- Marriage (property rights, domestic violence)
- Parenthood (parental leave, child custody)
- Entrepreneurship (starting and running a business)
- Assets (ownership and inheritance)
- Pension (access to and benefits)
- Scoring: Each indicator is scored on a scale of 0 to 100, with 100 representing the highest level of legal rights and protections for women.
- The overall score for a country is the average of these eight indicators.
- Latest version: The latest edition is "Women, Business and the Law 2024", released in October 2023.
- This version also introduces two new indicators:
- Safety (addressing violence against women)
- Childcare (availability, affordability, and quality)
Highlights of the Report:
- Women spend an average of 2.4 more hours a day on unpaid care work than men—much of it on the care of children.
- Only 62 economies—fewer than a third—have quality standards governing childcare services, which has an adverse impact on the employment opportunity of women as mothers with young children have their battles to pick.
- Women face hindrances in areas such as entrepreneurship as just one in every five economies mandate gender-sensitive criteria for public procurement processes, meaning women are deprived of significant economic opportunities.
About India:
- According to the 10th edition of the Women, Business and Law index, India ranks 113 out of 190 countries in the Index.
- The addition of Safety and childcare as indicators in the new index is believed to have improved India’s ranking slightly.
- The index shows that in India, women enjoy 60% of the legal rights compared to men, which is lower than the global average of 64.2%, but much higher than the 45.9% of the legal protections compared to men.
- Over the years, India’s score has remained constant at 74.4%, whereas a total of 14 countries around the world, including Denmark, Canada, and Finland, score a perfect 100 in the legal framework score.
- Some of the less developed countries like Ethiopia, Namibia, and even Burundi have better scores than India.
- India’s performance is much lower in providing supportive frameworks, such as programs, services, budgets, procedures, inspections, and sanctions for non-compliance with quality standards.
- Only 54.2% of the supportive frameworks needed were established in the country.
Venice Biennale, ‘the Olympics of the art world’, set to open on April 20

- 05 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
The 60th edition of the Venice Biennale, known as “the Olympics of the art world”, will open on April 20.
What is the Venice Biennale?
- The Venice Biennale is one of the biggest and most prestigious art fairs in the world.
- Biennale is an Italian word which means ‘every other year’. Over the years, however, it has come to mean a large international exhibition that takes place every two years.
- A biennale exhibition is different from a regular exhibition as it is organized on a large scale and involves multiple venues.
- Biennales feature contemporary art by artists from various countries that are usually linked by a common curatorial theme, providing a framework for exploring contemporary social, economic and political ideas in an international context.
India’s participation:
- India made its debut at the Biennale in 1954. Recording robust sales, the exhibition comprised over 50 paintings of masters such as M F Husain, S H Raza, Jamini Roy, Amrita Sher-Gil, and Francis Newton Souza.
- After 1954, the country officially participated in the event in 2011. The exhibition was organized by Lalit Kala Akademi and curated by Ranjit Hoskote.
- It featured works by artists like Zarina Hashmi, Gigi Scaria, Praneet Soi, and the Desire Machine Collective.
- At the 2019 Venice Biennale, the Ministry of Culture, Confederation of Indian Industry, National Gallery of Modern Art, and Kiran Nadar Museum of Art (KNMA) in collaboration organized the Indian pavilion.
Will India have a presence at the 2024 Venice Biennale?
- This year, the Biennale is helmed by its first Latin American curator — the artistic director of the São Paulo Museum of Art, Adriano Pedrosa.
- His theme for the event is “Foreigners Everywhere”, which will delve into the experiences of those living on the margins, as outsiders, immigrants or indigenous populations.
- Works by Indian artists will also feature in this central exhibition.
- This includes the late modernists Ram Kumar, B Prabha, SH Raza, Jamini Roy, Amrita Sher-Gil, FN Souza, and Goa-based Monika Correa.
- Representing the contemporary will be the public art collective Aravani Art Project, led by trans and cis women.
India halts Pakistan-bound ship suspected of carrying CNC machines from China

- 05 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
Recently, Prime Minister Narendra Modi witnessed the start of the process of core-loading the indigenous prototype fast breeder reactor (PFBR) at the Madras Atomic Power Station in Kalpakkam, Tamil Nadu.
What is the PFBR?
- The PFBR, or Prototype Fast Breeder Reactor, is a nuclear reactor designed to produce more nuclear fuel than it consumes.
- In nuclear fission, the nucleus of an atom absorbs a neutron, becomes unstable, and splits into two, releasing energy.
- If the unstable nucleus releases additional neutrons, the reactor’s facilities can utilize them to initiate more fission reactions.
How does the PFBR work?
- PHWRs use natural or low-enriched U-238 as the fissile material and produce Pu-239 as a byproduct.
- This Pu-239 is combined with more U-238 into a mixed oxide and loaded into the core of a new reactor together with a blanket.
- This is a material the fission products in the core react with to produce more Pu-239.
- A breeder reactor is a nuclear reactor that produces more fissile material than it consumes.
- In a ‘fast’ breeder reactor, the neutrons aren’t slowed, allowing them to trigger specific fission reactions.
- The PFBR is designed to produce more Pu-239 than it consumes.
- It uses liquid sodium, a highly reactive substance, as coolant in two circuits. Coolant in the first circuit enters the reactor and leaves with (heat) energy and radioactivity.
- Via heat-exchangers, it transfers only the heat to the coolant in a secondary circuit.
- The latter transfers the heat to generators to produce electricity.
DoT launches Digital Intelligence Portal, ‘Chakshu’ facility to curb cyber crimes, financial frauds

- 05 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
The Department of Telecommunications (DoT) recently launched its ‘Digital Intelligence Platform (DIP)’ to curb the misuse of telecom resources in cybercrimes and financial frauds, and the ‘Chakshu’ facility on the Sanchar Saathi portal to enable citizens to report suspected fraud communication.
About Digital Intelligence Platform (DIP):
- Digital Intelligence Platform (DIP) is developed by the Department of Telecommunications.
- It is a secure and integrated platform for real time intelligence sharing, information exchange and coordination among the stakeholders i.e. Telecom Service Providers (TSPs), law enforcement agencies (LEAs), banks and financial institutions (FIs), social media platforms, identity document issuing authorities etc.
- The portal also contains information regarding the cases detected as misuse of telecom resources. The shared information could be useful to the stakeholders in their respective domains.
- It also works as a backend repository for the citizen-initiated requests on the Sanchar Saathi portal for action by the stakeholders.
- The DIP is accessible to the stakeholders over secure connectivity and the relevant information is shared based on their respective roles.
- The said platform is not accessible to citizens.
What is the Chakshu Facility?
- Chakshu is the latest addition to the citizen centric facilities already available on the Sanchar Saathi portal of DoT.
- It facilitates citizens to report suspected fraud communication received over call, SMS or WhatsApp with the intention of defrauding like KYC expiry or update of bank account / payment wallet / SIM / gas connection / electricity connection, sextortion, impersonation as government official / relative for sending money, disconnection of all mobile numbers by Department of Telecommunications etc.
- In case, a citizen is already a victim of cyber-crime or financial fraud, it is advised to report at cyber-crime helpline number 1930 or website https://www.cybercrime.gov.in of Government of India.
Carbon Capture and How it Can Help Save the Planet

- 05 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
Germany has recently declared its approval for carbon capture and offshore storage for specific industrial sectors.
What is Carbon Capture and Storage?
- CCS refers to a host of different technologies that capture CO2 emissions from large point sources like refineries or power plants and trap them beneath the Earth.
- Notably, CCS is different from carbon dioxide removal (CDR), where CO2 is removed from the atmosphere.
- CCS involves three different techniques of capturing carbon, including: Post-combustion, Pre-combustion, and Oxyfuel combustion.
- In post-combustion, CO2 is removed after the fossil fuel has been burnt. By using a chemical solvent, CO2 is separated from the exhaust or ‘flue’ gasses and then captured.
- Pre-combustion involves removing CO2 before burning the fossil fuel. “First, the fossil fuel is partially burned in a ‘gasifier’ to form synthetic gas. CO2 can be captured from this relatively pure exhaust stream,” according to a report by the British Geological Survey. The method also generates hydrogen, which is separated and can be used as fuel.
- In oxyfuel combustion, the fossil fuel is burnt with almost pure oxygen, which produces CO2 and water vapor. The water is condensed through cooling and CO2 is separated and captured. Out of the three methods, oxyfuel combustion is the most efficient but the oxygen burning process needs a lot of energy.
- Post-combustion and oxyfuel combustion equipment can be retro-fitted in existing plants that were originally built without them. Pre-combustion equipment, however, needs “larger modifications to the operation of the facility and are therefore more suitable to new plants.
- After capture, CO2 is compressed into a liquid state and transported to suitable storage sites.
- Although CO2 can be transported through ship, rail, or road tanker, pipeline is the cheapest and most reliable method.
Can Carbon Capture Help Save the world?
- Operational CCS projects generally claim to be 90 percent efficient, meaning they can capture 90 per cent of carbon and store it.
- Studies, however, have shown that a number of these projects are not as efficient as they claim to be.
- For example, a 2022 study by the Institute for Energy Economics and Financial Analysis (IEEFA) found most of the 13 flagship CCS projects worldwide that it analyzed have either underperformed or failed entirely.
- Moreover, CCS technologies are quite expensive.
- When CCS is attached to coal and gas power stations it is likely to be at least six times more expensive than electricity generated from wind power backed by battery storage.
- It is far cheaper and more efficient to avoid CO2 emissions in the first place.
- There are also only a few operational CCS projects across the world even though the technology has been pushed for decades.
- According to the International Energy Agency (IEA), there were 40 operational CCS projects in 2023, which captured more than 45 metric tonnes (Mt) of CO2 annually.
- To ensure the planet doesn’t breach the 1.5 degree Celsius temperature increase limit, it would take an “inconceivable” amount of carbon capture “if oil and natural gas consumption were to evolve as projected under today’s policy settings.
- It added that the electricity required to capture that level of carbon as of 2050 would be more than the entire planet’s use of electricity in 2022.
- Therefore, there couldn’t be an overreliance on carbon capture as a solution to tackle climate change.
Grey-zone Warfare Latest Entry in Lexicon of Warfare

- 04 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
On the last day of the 2024 Raisina Dialogue (February 24), India’s Chief of Defence Staff General Anil Chauhan said that “grey zone warfare” is the latest in informal warfare.
What is the Grey Zone Warfare?
- Grey zone warfare refers to a strategic approach where a nation seeks to gain advantages over others without engaging in overt conflict.
- It involves a series of tactics, including cyberattacks, disinformation campaigns, and economic pressures, aimed at subtly undermining or destabilizing adversaries.
- China has notably employed this strategy against India and neighboring countries.
What are the China's Grey Zone Tactics Against India?
- South China Sea Activities: China asserts its dominance in the South China Sea using naval and civilian vessels, raising tensions with neighboring countries like India.
- Infrastructure Near Borders: China constructs infrastructure and settlements near India's borders, bolstering territorial claims and strategic positioning.
- Digital Investments: China invests in Indian digital platforms and media, influencing public narratives and perceptions.
India's Counter-Measures:
- Inter-Agency Collaboration: India promotes collaboration among defense, intelligence, and law enforcement agencies to devise comprehensive strategies to counter grey zone threats.
- Enhanced Vigilance: India increases surveillance and presence in border areas and strategic locations to detect and respond to covert Chinese activities.
- Regulating Foreign Investments: India scrutinizes foreign investments in critical sectors, particularly technology, to safeguard national security interests.
Long-Term Implications for India:
- Information Warfare: Grey zone conflicts often involve digital misinformation, influencing public opinion and perceptions.
- Economic Leverage: Dependency on foreign investments poses vulnerabilities if used as leverage by investing nations.
- Technology Dependency: Heavy reliance on foreign technology exposes India to risks, emphasizing the need to bolster indigenous technological capabilities.
Conclusion
Grey zone warfare encompasses a multifaceted strategic landscape, blending digital, economic, and geopolitical tactics. India recognizes these challenges and is actively devising strategies to navigate this complex terrain.
PM Modi hails those supporting wildlife conservation efforts on World Wildlife Day

- 04 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
On the occasion of World Wildlife Day on March 3, Prime Minister Narendra Modi lauded those at the forefront of sustainable practices and supporting wildlife conservation efforts.
About the World Wildlife Day:
- World Wildlife Day is observed to advocate for sustainable practices that contribute to biodiversity conservation and to enhance public consciousness about the importance of safeguarding and nurturing animals.
- It endeavors to underscore the interconnectedness of all life forms on Earth and to foster harmonious coexistence between humans and animals through activism, advocacy, and education.
Origins:
- Initially proposed by Thailand to the UN General Assembly in 2013, World Wildlife Day aimed to dedicate a day to spotlight the significance of wild animals and plants worldwide.
- On December 20, 2013, the General Assembly adopted a resolution, designating March 3 as World Wildlife Day from 2014 onwards.
- Coinciding with the day, the Convention on International Trade in Endangered Species of Wild Fauna and Flora (CITES) was signed in 1973, emphasizing the importance of safeguarding species from the threats of international trade.
The theme of WWD 2024:
- The theme, "Connecting People and Planet: Exploring Digital Innovation in Wildlife Conservation," underscores the potential of technological advancements to revolutionize conservation efforts.
- In today's digital era, technological breakthroughs offer novel solutions to persistent conservation challenges, making this theme particularly relevant.
Significance:
- World Wildlife Day serves as a vital global awareness platform for animal protection and conservation.
- It reinforces the intrinsic value of animals and advocates for treating them with compassion, integrity, and reverence.
About the Convention on International Trade in Endangered Species of Wild Fauna and Flora (CITES):
- CITES is an international treaty that aims to regulate and monitor the trade of endangered plants and animals, including their parts and derivatives, to ensure their survival in the wild.
- Under CITES, member countries are required to regulate and monitor the trade of endangered species through a system of permits and quotas.
- They must also report regularly on their implementation of the treaty and collaborate with other countries to ensure its effectiveness.
- Currently, CITES has 184 parties.
Supreme Court’s ban on Patanjali ads

- 04 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
Recently, the Supreme Court restrained Patanjali Ayurved from discrediting allopathy in its campaigns, and from advertising products that claim to cure chronic conditions.
What is the Magic Remedies Act?
- The Drugs and Magic Remedies (Objectionable Advertisements) Act of 1954 is a legislative framework to control the advertisement of drugs and prohibit claims of magical qualities in remedies.
- The Act encompasses various forms of advertisements, including written, oral, and visual mediums.
What does the Magic Remedies Act entail?
- Under the Act, “drug” refers to medicines intended for human or animal use, substances for diagnosis or treatment of diseases, and articles affecting the body’s functions.
- Other than articles meant for consumption, the definition of “magic remedy” under this Act also extends to talismans, mantras, and charms that allegedly possess miraculous healing powers or influence bodily functions.
Regulations on advertisements under the Magic Remedies Act:
- The Act imposes strict regulations on the publication of advertisements related to drugs.
- It prohibits advertisements that give false impressions, make false claims, or are otherwise misleading.
- The term “advertisement,” under the Act, extends to all notices, labels, wrappers, and oral announcements.
- Violations of these provisions can result in penalties upon conviction, including imprisonment or fines.
Punishment:
- Violating the Act can result in imprisonment, fines, or both.
- If this is the first conviction for the violator, they may face up to six months in prison, fines, or both.
- For a subsequent conviction, imprisonment may extend to one year, a fine, or both.
- The Act does not include any limits for the fines that may be imposed on individuals or organizations.
Who comes under the Magic Remedies Act?
- The Act applies to all individuals and entities involved in the publication of advertisements, including manufacturers, distributors, and advertisers.
- The Act can hold both individuals and companies accountable for contraventions.
Several OPEC+ nations extend oil cuts to boost prices

- 04 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
Moscow, Riyadh, and several other OPEC+ members announced extensions to oil production cuts first announced in 2023 as part of an agreement among oil producers to boost prices following economic uncertainty.
What is the OPEC+ Oil Alliance?
- OPEC+ is a coalition of oil-exporting nations that convenes regularly to determine the quantity of crude oil to offer on the global market.
- Origin: This alliance was established in late 2016 to formalize a framework for collaboration between OPEC and non-OPEC oil-producing nations on a consistent and sustainable basis.
- The primary objective of these nations is to collaborate on regulating crude oil production to stabilize the oil market.
- OPEC+ collectively controls approximately 40% of global oil supplies and holds over 80% of proven oil reserves.
- At its core, OPEC+ consists of OPEC member states, predominantly comprising nations from the Middle East and Africa.
- Membership: It includes OPEC member states along with Azerbaijan, Bahrain, Brunei, Kazakhstan, Russia, Mexico, Malaysia, South Sudan, Sudan, and Oman.
About the Organization of the Petroleum Exporting Countries (OPEC):
- OPEC, short for the Organization of the Petroleum Exporting Countries, is a permanent intergovernmental organization comprised of oil-exporting nations.
Mission:
- To coordinate and harmonize the petroleum policies of its member countries.
- To ensure the stability of oil prices in global oil markets, aiming to eliminate detrimental and unnecessary fluctuations.
- Formation: Founded in 1960 by the five original members - Iran, Iraq, Kuwait, Saudi Arabia, and Venezuela.
- Presently, it consists of 13 member countries, which include Algeria, Angola, Congo, Equatorial Guinea, Gabon, Libya, Nigeria, and the United Arab Emirates.
- Headquarters: Located in Vienna, Austria.
India halts Pakistan-bound ship suspected of carrying CNC machines from China

- 04 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
Recently, Indian security agencies have intercepted a Pakistan-bound ship from China at Mumbai's Nhava Sheva port.
What are CNC Machines and Wassenaar Arrangements?
- CNC machines are controlled by a computer and offer efficiency, consistency, and accuracy not possible manually.
- These machines have been included in the Wassenaar Arrangement since 1996.
- This international arms control regime aims to stop the proliferation of equipment with both civilian and military uses, with India being among the 42 member countries exchanging information on transfers of conventional weapons and dual-use goods and technologies.
About the Wassenaar Arrangement:
- The Wassenaar Arrangement is a voluntary export control framework established in July 1996.
- Comprising 42 member nations, it facilitates the exchange of information regarding transfers of conventional weaponry and dual-use goods and technologies.
- Dual-use items possess the capacity for both civilian and military applications.
- The arrangement's secretariat is headquartered in Vienna, Austria.
Membership:
- The arrangement boasts 42 member states, predominantly consisting of NATO and EU nations.
- Members are obligated to report arms transfers and dual-use goods and technology transfers or denials to destinations beyond the arrangement biannually.
- India became a member of the Arrangement in 2017.
Objectives:
- Central to its operation is the continual exchange of technology-related information, encompassing both conventional and nuclear-capable technologies, among member states.
- This information exchange involves the maintenance and refinement of comprehensive lists of materials, technologies, processes, and products deemed militarily significant.
- The primary goal is to regulate the movement of technology, materials, or components to entities or nations that could jeopardize global security and stability.
Wassenaar Arrangement Plenary:
- The WA Plenary is the decision-making and governing body of the Arrangement.
- It is composed of representatives of all Participating States who normally meet once a year, usually in December.
- Chairmanship of the Plenary is subject to annual rotation among Participating States.
- In 2018, the United Kingdom held the Plenary Chair, while Greece assumed the position in 2019.
- Decisions within the Plenary are made through consensus.
Bengaluru's Rameshwaram cafe blast puts the spotlight on IEDs

- 02 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
At least nine people were injured after an explosion at the bustling Rameshwaram Cafe in Bengaluru’s Whitefield area recently, possibly by an improvised explosive device (IED).
What is Improvised Explosive Devices (IEDs)?
- An Improvised Explosive Device (IED) refers to a makeshift explosive device constructed and deployed unorthodoxly or improvised.
- These devices are typically crafted using commonly available materials, including explosives, triggers, and containers, often to cause destruction, injury, or death.
- IEDs can vary widely in design and complexity, ranging from simple pipe bombs to more intricate devices incorporating timers, remote controls, or even cellular communication for activation.
- IEDs can be deployed using a vehicle, carried, placed, or thrown by a person, delivered in a package, or concealed on the roadside.
- Due to their adaptable nature, IEDs are commonly used by insurgents, terrorists, and other malicious actors to carry out attacks against both military and civilian targets.
- Their unpredictable nature and often concealed placement make them particularly challenging for security forces to detect and mitigate.
- Efforts to counter IED threats involve a combination of technological advancements, intelligence gathering, and counterinsurgency strategies aimed at identifying and neutralizing these devices before they can cause harm.
Types of IEDs:
- Vehicle-Borne IEDs: Among the most destructive forms of IEDs are those concealed within vehicles. These can be driven to specific locations and detonated, causing massive explosions capable of levelling buildings.
- Suicide Bombings: Suicide bombings involve individuals strapping IEDs to their bodies, becoming human carriers of destruction. This method inflicts maximum damage in densely populated areas.
- Package IEDs: Package IEDs are small devices hidden in innocuous-looking packages. They are often placed in public spaces, targeting unsuspecting victims.
Methods of IED Initiation:
- Remote Control: IEDs can be remotely triggered using various methods, such as cell phones or radio signals, allowing attackers to maintain a safe distance from the explosion.
- Pressure Activation: Pressure-sensitive IEDs detonate when a certain amount of pressure is applied, making them lethal traps for those who inadvertently trigger them.
- Timers: IEDs can also be equipped with timers, which delay the explosion to occur at a specific time, further complicating detection and prevention.
The Devastating Impact of IEDs:
- The aftermath of IED explosions is often catastrophic, leading to loss of life, severe injuries, and widespread damage to infrastructure.
- The psychological impact on survivors and affected communities can be long-lasting.
Detection Technologies and Challenges:
- Detection technologies such as (Metal Detectors, X-ray and Imaging Scanners, Explosive Trace Detection (ETD), and Sniffer Dogs) play a critical role in countering the threat of Improvised Explosive Devices (IEDs), but they also face numerous challenges due to the evolving nature of these devices.
India to Make Climate Risk Disclosures Mandatory for Banks

- 02 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
While acknowledging the importance of the environment and its long-term impact on organizations and the economy as a whole, the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) has now released a draft framework for banks to follow.
What are Climate-led Financial Risks?
- “Climate-related financial risks” means the potential risks that may arise from climate change or from efforts to mitigate climate change, their related impacts, and economic and financial consequences according to RBI.
- These risks manifest through two primary channels: physical risks and transition risks.
- Physical Risks: These entail the economic and financial consequences arising from the escalating frequency and severity of extreme weather events linked to climate change. Such events can exert pressure on the financial sector in various ways:
- Renewable Energy Sector (REs) Vulnerability: The occurrence of local or regional weather events may strain the anticipated cash flows to REs, impacting their financial stability. Furthermore, chronic flooding or landslides pose risks to the collateral that REs have pledged as security for loans.
- Infrastructure and Property Damage: Severe weather phenomena can inflict damage on the physical assets and data centres owned or leased by REs, impairing their capacity to deliver financial services effectively.
- Transition Risks: These risks stem from the transition toward a low-carbon economy, influenced by factors such as evolving climate-related policies, technological advancements, and changing consumer behaviours. Key considerations include:
- Policy and Regulatory Shifts: Changes in climate-related regulations and policies, along with advancements in technologies, can significantly influence the transition process. Moreover, alterations in customer sentiments and behaviour patterns play a pivotal role in shaping this transition.
- Economic Impact: The transition toward reducing carbon emissions carries substantial implications for the economy at large. It entails a shift toward sustainable practices and investments, which can impact various sectors and industries differently.
- Recognizing and addressing these climate-related financial risks is imperative for ensuring the resilience and stability of the financial sector in the face of evolving environmental challenges.
About the Framework:
- Commencing from the financial year 2025-26, all major financial institutions across India, including top-tier NBFCs and renowned NBFCs, will be mandated to furnish details about governance, strategy, and risk management strategies.
- Additionally, they will be required to initiate disclosure of metrics and targets from the fiscal year 2027-28.
Key highlights of the framework include:
- Enhanced Disclosure Requirements: Banks will be obligated to unveil climate-related risks that could potentially impact their financial stability.
- This measure aims to facilitate a comprehensive understanding of climate-related financial risks and opportunities, fostering early assessment and proactive management.
- Scope of Coverage: The framework encompasses various financial entities, including scheduled commercial banks (excluding local area banks, payments banks, and regional rural banks), Tier-IV primary urban cooperative banks (UCBs), and top and upper layer non-banking financial companies (NBFCs).
- Disclosure Obligations for Renewable Energy Sector (REs): REs are mandated to disclose crucial information related to climate-related risks and opportunities across short-, medium-, and long-term horizons. Key areas of disclosure include:
- Identification of Climate-Related Risks and Opportunities: REs are required to identify and disclose climate-related risks and opportunities relevant to their operations and financial outlook.
- Assessment of Impact: REs must delineate the impact of climate-related risks and opportunities on their business strategies and financial planning, enabling stakeholders to comprehend the implications on their overall strategy.
- Resilience Evaluation: REs are tasked with evaluating the resilience of their strategies in light of diverse climate scenarios, thereby ensuring robustness in navigating potential challenges and capitalizing on emerging opportunities.
Significance:
- A pressing requirement exists for an improved and standardized disclosure framework for regulated entities to mitigate financial risks.
- Without such a framework, there is a risk of assets being mispriced and capital being misallocated, which could have adverse repercussions on financial stability. Consequently, the imperative for a standardized disclosure framework on climate-related financial risks became evident.
How India’s first semiconductor fabrication plant can help plug into the global value chain

- 02 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
The Union Cabinet recently approved the country's first semiconductor fab to be made by the Tata Group in collaboration with Powerchip Taiwan.
What is Semiconductor Fabrication?
- The semiconductor fabrication process is a complex and highly specialized series of steps that transform raw materials into functional electronic components.
- This process involves a multitude of techniques and technologies, with each stage requiring precise control and attention to detail.
- A semiconductor fab -- short for fabrication -- is a manufacturing plant in which raw silicon wafers are turned into integrated circuits (ICs).
- A fab lab features a clean room where ICs are etched onto wafers.
- The completed chips are sent to a back-end assembly and test facility before they are packaged and sold.
- A semiconductor fab facility always includes a clean room -- so known because its environment is carefully controlled to eliminate dust and vibrations and to keep the temperature and humidity within a specific narrow range.
- Contamination can enter the fab environment through external sources, resulting in damage to products that can affect overall yield.
- To minimize the losses, all potential sources of contamination are thoroughly analysed and cleaned.
- For example, the tools used in the chip manufacturing process have low levels of particulates and fibres.
- The goal is to ensure that extraneous contamination is not introduced into the semiconductor fab to ensure the highest quality of the final products.
Technology Used in Semiconductor Fab Labs:
- Photolithography: Photolithography is a crucial optical process in the fabrication process, as it is used to create intricate circuit patterns on a single wafer's surface.
- This is achieved by coating the wafer with a photosensitive material, called a photoresist, and then exposing it to high-wavelength deep ultraviolet (DUV) or extreme ultraviolet (EUV) light through a mask containing the desired pattern.
- The exposed photoresist undergoes a chemical change, which allows it to be selectively removed.
- It leaves behind a patterned layer that serves as a protective layer for subsequent processing steps, such as etching and deposition.
Minimum age to cast postal ballots hiked to 85 years

- 02 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
For the upcoming Lok Sabha and State Assembly elections, senior citizens who are 85 years and older will be able to opt for postal ballots as the government recently amended the rule to increase the eligibility from the current limit of 80 years and above.
News Summary:
- The government, in collaboration with the Election Commission, has introduced amendments to the Conduct of Election Rules (1961), specifically targeting the eligibility criteria for voting by postal ballot.
- Notably, the minimum age for senior citizens eligible for postal voting has been increased from 80 years to 85 years.
- Previously, Rule 27A of the Conduct of Election Rules had extended the postal ballot facility to senior citizens above 80 years, persons with disabilities, poll officers, and individuals diagnosed with COVID-19.
- This provision was first implemented during the 2020 Bihar assembly polls, coinciding with the onset of the pandemic.
- Despite the initial extension of postal voting rights to senior citizens aged 80 and above, a subsequent review by the Election Commission revealed that only a small fraction, approximately 2-3%, of eligible voters in this age group opted for postal ballots.
- The majority preferred to physically visit polling stations to cast their votes.
- Considering the statistics indicating that the total number of senior citizens above 80 years stands at 1.75 crore, with 98 lakh falling within the age range of 80-85 years, the government deemed it necessary to amend the existing rule.
- This adjustment reflects a nuanced approach aimed at ensuring efficient electoral processes while addressing the preferences and needs of elderly voters.
What is Postal Voting?
- Postal voting is only available to a specific group of voters.
- By retyping her choices on the ballot paper and returning it to the inspection officer before counting, a voter can remotely cast her ballot using this feature.
Who Can Avail This?
- Armed forces members such as those in the Army, Navy, and Air Force, armed police officers serving outside their home states, government workers stationed outside of India, and their wives are only eligible to vote by mail.
Features:
- Voters may use this service from any location outside of the designated constituency.
- This system makes it easier to create voter electoral roll data for services.
- It has two layers of security, making it a secure system:
- 1. Downloading the encrypted electronically transmitted postal ballot (ETPB) file requires an OTP (one-time password).
- 2. To decrypt, print, and deliver ETPB, a PIN is necessary.
- By sending postal ballots electronically to eligible service voters, this system addresses the time constraint associated with mailing postal ballots.
- The specific quick response code ensures confidentiality and prevents the duplication of cast ETPB.
Concerned Raised by Political Parties:
- Parties argue that allowing voters 65 and older to cast postal ballots violates voting confidentiality since many of the population lacks education and may ask for help from others at various points, ultimately identifying their chosen candidate.
- Their exposure to "administrative influence or influence by the government or the ruling party" also results from this.
How the development of Agaléga figures in India’s vision for its maritime neighbourhood
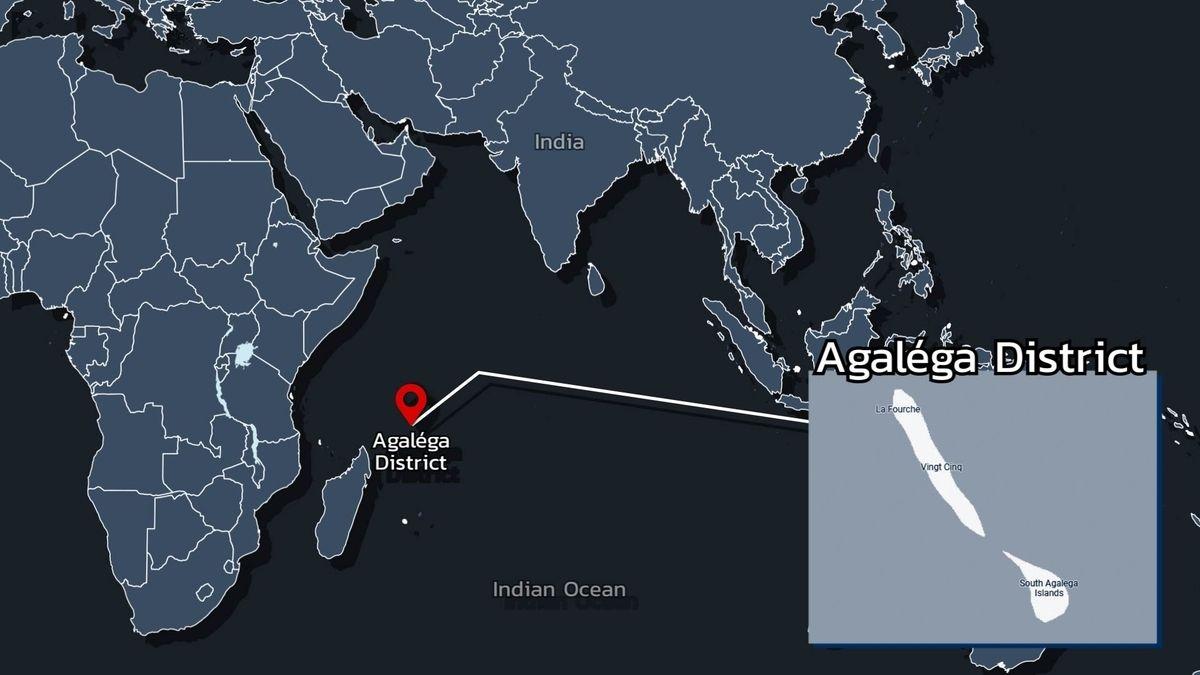
- 02 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
Recently, Prime Ministers Narendra Modi and Pravind Jugnauth jointly inaugurated an airstrip and the St James Jetty on North Agaléga Island in the Indian Ocean.
About Agalega Islands:
- Agaléga Island comprises two islets, a long and thin northern island and a shorter, round southern island.
- It is slightly over 3,000 kilometres from the nearest mainland Indian coast, deep in the Indian Ocean near Madagascar.
- Despite its pristine appeal, Agaléga remains largely undiscovered by tourists and there are no hotels, water bungalows, or bustling tourist shops.
- Instead, approximately 300 islanders sustain themselves through coconut cultivation and fishing, maintaining a way of life passed down through generations.
Importance of Agalega Islands:
- The development of the Agalega Islands holds significant socio-economic and national security implications for Mauritius, aligning closely with India's maritime vision.
- Despite being a dependency of Mauritius, the islands have long remained underdeveloped, posing challenges to the sustainability and well-being of their inhabitants.
- Necessities often required referral to Mauritius due to the lack of infrastructure.
- Moreover, the absence of an official government or security presence posed a serious vulnerability, necessitating urgent attention.
- Recognizing the potential to transform this vulnerability into a strategic asset, Mauritius prioritized the development of the islands and the establishment of facilities capable of accommodating ships and aircraft.
- In this regard, the construction of a jetty and an airstrip emerged as imperative steps to bolster the islands' infrastructure.
- Given the shared interests and cooperation between Mauritius and India, the government of Mauritius selected India as its preferred development partner for this ambitious initiative.
Why did Mauritians Choose India?
- Ties between India and Mauritius go back to 1948, 20 years before the country’s independence from Britain.
- Seventy percent of the inhabitants of Mauritius are of Indian origin, and the two countries share deep historical, social, and cultural bonds.
- The consistent feature in the history of bilateral relations has been friendship and trust at all levels — the political leadership, the diplomatic and military communities, as well as between the peoples of the two countries.
- The development of these strategically located islands required trust more than anything else. India was the obvious choice.
Significance for India:
- The goodwill and trust between the two countries will be further enhanced. India will welcome opportunities to further develop these islands in collaboration with Mauritius as the latter deems appropriate.
- The joint development of Agaléga underscores India’s commitment to the vision of Security And Growth for All in the Region (SAGAR), and its willingness to assist smaller maritime nations in building capacity and developing capability.
- It will indicate to other maritime neighbours that India is a benign and friendly country that respects the sovereignty of independent nations.
- India would like to emerge as the preferred development and security partner in the Indian Ocean Region.
PM Modi launches India’s first hydrogen-powered ferry built at Cochin Shipyard

- 01 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
Prime Minister Modi recently virtually launched India’s first indigenously developed hydrogen fuel cell ferry manufactured by Cochin Shipyard Limited (CSL), which will be deployed for service at Varanasi in Uttar Pradesh.
What is the "Harit Nauka" (Green Boat) Initiative?
- Initiated by the Ministry of Ports, Shipping, and Waterways, "Harit Nauka" aims to facilitate a sustainable transition of inland vessels.
- In January 2024, the shipping ministry introduced the "Harit Nauka" guidelines, outlining the path towards environmentally friendly practices for inland vessels.
- According to these guidelines, all states are mandated to progressively adopt green fuels for 50% of their inland waterway-based passenger fleets within the next decade, to achieve 100% adoption by 2045. This initiative aligns with the Maritime Amrit Kaal Vision 2047, aimed at reducing greenhouse gas emissions.
- The implementation of this initiative not only contributes to reducing emissions but also paves the way for replicating such environmentally friendly ferry models across the country to enhance urban mobility.
- Furthermore, it serves as a significant catalyst for advancing the objectives of the National Green Hydrogen Mission.
What are Hydrogen Fuel Cells?
- Hydrogen fuel cells harness the chemical energy of hydrogen to generate electricity, offering a clean energy solution with electricity, heat, and water as the sole products and by-products.
Functioning:
- Similar to batteries, fuel cells continuously produce electricity and heat as long as fuel is supplied. A typical fuel cell comprises two electrodes—an anode (negative electrode) and a cathode (positive electrode)—surrounding an electrolyte.
- Hydrogen fuel is supplied to the anode, while air is directed to the cathode. At the anode, a catalyst separates hydrogen molecules into protons and electrons, which then travel different paths.
- Electrons create an electric current through an external circuit, while protons migrate through the electrolyte to the cathode, combining with oxygen and electrons to form water and heat.
Challenges in India:
- High Cost: Fuel cell systems remain relatively expensive compared to conventional energy sources.
- Infrastructure Deficiency: India currently lacks the necessary infrastructure for the widespread adoption of fuel cell technology, including hydrogen production and distribution networks.
- Technical Hurdles: Despite ongoing advancements, fuel cell technology is still in its nascent stages, facing persistent technical challenges.
- Policy Constraints: The absence of a comprehensive policy framework from the Indian government has constrained the development and adoption of fuel cell technology, impeding research and investment.
India's Initiatives:
- In response to these challenges, India has formulated the National Green Hydrogen Policy, delineating a vision for the growth of the hydrogen and fuel cell industry.
- The policy aims to position India as a global hub for the production, utilization, and export of Green Hydrogen and its derivatives, signalling a strategic commitment to advancing sustainable energy solutions.
Characteristics of the Hydrogen-Powered Ferry:
- Length and Capacity: The hydrogen fuel cell vessel is a 24-meter-long catamaran, capable of accommodating up to 50 passengers in its air-conditioned passenger area.
- Battery-Free Operation: Distinguished by its innovative design, this ferry does not rely on conventional batteries for storing electrical energy.
- Instead, it utilizes hydrogen fuel, stored in cylinders onboard the vessel. With five hydrogen cylinders capable of carrying 40kg of hydrogen, the ferry can sustain operations for eight hours. Additionally, it features a 3-kW solar panel to complement its power source.
- Fuel Cell Technology: Equipped with a 50-kW PEM (proton-exchange membrane) fuel cell, coupled with Lithium-Ion Phosphate batteries, the ferry boasts adaptability in response to varying power demands.
- PEM fuel cells, renowned for their lower operating temperature, lightweight, and compactness, are commonly employed in automotive applications.
- Environmental Sustainability: With zero emissions and noise, coupled with enhanced energy efficiency, the hydrogen fuel cell-powered ferry stands as an environmentally friendly alternative.
- Its minimal moving parts contribute to reduced maintenance requirements compared to combustion vessels.
- Additional Advantages: While hydrogen fuel cell technology has been in development for maritime purposes, only a handful of countries worldwide have executed demonstration projects.
- Thus, this ferry positions India at the forefront, providing an early advantage in harnessing the potential of hydrogen as an emerging green fuel within the marine sector.
Doomsday Glacier has lost 50 billion tons of ice, melting began 80 years ago

- 01 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
Antarctica's Doomsday Glacier, the world's widest glacier, has lost over 50 billion tons of ice and the melting rate is on the rise as the continent gets warmer.
What is Doomsday Glacier?
- The Thwaites Glacier (also known as Doomsday Glacier), a massive and world’s widest glacier is located in West Antarctica.
- The Doomsday nickname reflects the potential for catastrophic flooding if the glacier were to collapse completely.
- Scientists are particularly concerned about Thwaites Glacier because of its size and location.
- If it were to collapse or significantly retreat, it could lead to a more rapid flow of ice from the interior of West Antarctica into the ocean, contributing to rising sea levels.
- The collapse could lead to a 65 cm rise in global sea level.
- The ice loss in the region has been observed to be accelerating since the 1970s, however, so far it remained unclear as to when this retreat began.
- The significant glacial retreat began in the 1940s and the findings coincide with previous work that studied retreat on Pine Island Glacier and found glacial retreat began in the ‘40s as well.
- This change is not random nor specific to one glacier but It is part of a larger context of a changing climate.
Why Did the Melting Begin?
- The meeting was kicked off by an extreme El Nino climate pattern that warmed the west Antarctic, and since then the glacier has not been able to recover from the damage.
- It is significant that El Niño only lasted a couple of years, but the two glaciers, Thwaites and Pine Island remain in significant retreat.
- Once the system is kicked out of balance, the retreat is ongoing.
- The Doomsday Glacier's melting remains one of the most crucial events triggered and accelerated by climate change and could lead to the submergence of several coastal regions of the world.
ZSI names a newly discovered head-shield sea slug after President Droupadi Murmu
- 01 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
The Zoological Survey of India named a new marine species of head-shield sea slug with ruby red spot which was discovered from West Bengal and Odisha coast after President of India Droupadi Murmu.
About Melanochlamys Droupadi:
- Melanochlamys Droupadi is a newly discovered marine species of head-shield sea slug distinguished by its striking ruby red spot.
- This species, belonging to the Melanochlamys genus, was first identified along the coasts of Digha in West Bengal and Udaipur in Odisha.
Key Features:
- This small invertebrate typically measures up to 7 mm in length.
- It primarily inhabits wet and soft sandy beaches.
- Adorned in brownish-black hues, it features a distinctive ruby-red spot towards its hind end.
- Melanochlamys Droupadi exhibits hermaphroditic characteristics, possessing both male and female reproductive organs. However, it requires another sea slug for successful reproduction.
- Internally, it possesses a shell and a posterior segment comprising 61 per cent of its body length.
- To safeguard against sand infiltration, it continuously secretes transparent mucus, forming a protective sheath around its body.
- When in motion, it burrows beneath smooth sand, creating a moving capsule where its body remains mostly concealed, akin to a turtle, leaving behind a discernible trail.
What are Sea Slugs?
- Sea slugs are a diverse group of molluscs inhabiting marine environments, characterized by their slug-like appearance.
- They occupy a wide range of habitats, spanning from shallow intertidal zones to the depths of the ocean, and from polar regions to tropical waters.
- As agile predators, sea slugs prey on mobile organisms such as other shelled and unshelled sea slugs, roundworms, marine worms, and small fish.
- Currently, researchers have identified 18 species of sea slugs worldwide.
- While sea slugs predominantly inhabit temperate regions within the Indo-Pacific Oceanic realm, three species exhibit truly tropical distributions: Melanochlamys papillata from the Gulf of Thailand, Melanochlamys bengalensis from the West Bengal and Odisha coast, and the newly discovered species.
World's First Vedic Clock to be Unveiled by PM Modi in Ujjain

- 01 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
Prime Minister Narendra Modi inaugurated the Vedic Clock in Ujjain as part of the 'Vikramotsav' celebration in Madhya Pradesh.
Features of the Vikramaditya Vedic Clock:
- This is the world's first 'Vedic Clock', designed to display time according to the ancient Indian traditional Panchang (time calculation system).
- The clock is installed on an 85-foot high tower constructed at Jantar Mantar in Ujjain, adjacent to the Government Jiwaji Observatory.
- It will display 30 Muhurats, tithi, and all other time calculations of Vedic Hindu panchang.
- Additionally, Samvat, Mas, moon position, Parva, Shubhshubh Muhurat, Ghati, Nakshatra, solar eclipse, and lunar eclipse, among other things
- It will be the world’s first clock in which Indian time calculation will be displayed.
- The Vedic clock installed in Ujjain as the city has been considered the centre of time calculation.
- The Tropic of Cancer passes through Ujjain.
Time calculation:
- The unique timepiece calculates time-based on Vedic Hindu Panchang, planetary positions, Muhurat, astrological calculations, solar eclipse, and lunar eclipse, among other things, and also indicates the Indian Standard Time (IST) and Greenwich Mean Time (GMT).
- The period from one sunrise to the next is used to calculate time.
- The clock will calculate time from one sunrise to another.
- The time period between the two sunrises will be divided into 30 parts, with each hour consisting of 48 minutes according to ISD.
- The reading will start from 0.00 with the sunrise functions for 30 hours (an hour of 48 minutes).
- Also, there will be a dedicated mobile application for the readings of the Vedic Clock, and citizens will be able to use it on their smartphones, computers, televisions, and other devices.
Why It is Located in Ujjain?
- The standard time of the world was determined from Ujjain 300 years ago.
- Throughout the world, the time prescribed and transmitted from Ujjayini (Ujjain) has been followed.
- The shortest fraction of time is included in Indian time calculations based on the Indian astronomical theory and the motions of planetary constellations.
- Ujjain was previously thought to be India’s central meridian, and the city determined the nation’s time zones and time differences, according to Hindu astronomical belief.
- The city of Lord Mahakal is situated exactly where the Tropic of Cancer and Zero Meridians meet.
- Additionally, it is situated in the oldest observatory in India, which Sawai Jai Singh II of Jaipur constructed in the early 1700s.
- Mirzapur in Uttar Pradesh, which is located at 82°30’ East longitude, is the location of the zero meridians on the Prime Meridian, or IST, four hours ahead of GMT, according to the 1884 convention on meridians.
India to set up International Big Cat Alliance

- 01 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
The Union Environment Ministry plans to set up and coordinate an International Big Cat Alliance (IBCA), along the lines of the International Solar Alliance, an India-headquartered initiative to promote solar installations globally.
About the International Big Cat Alliance (IBCA):
- The idea of the International Big Cat Alliance (IBCA) was first given by Prime Minister Modi during his speech on the occasion of Global Tiger Day in 2019.
- He called for developing an alliance of global leaders to curb poaching in Asia.
- The alliance was formally announced on April 9, 202, in Mysuru, as India commemorated the completion of 50 years of Project Tiger.
- The alliance will focus on the conservation of seven big cats, which include Tiger, Lion, Leopard, Snow Leopard, Puma, Jaguar, and Cheetah. Out of these, five are found in India.
- Membership to the IBCA is open to 97 'range' countries, encompassing the natural habitats of these big cats, as well as other interested nations and international organizations.
- The alliance aims to facilitate cooperation among countries to advance the conservation agenda for mutual benefit.
- Operating with a multifaceted approach, the IBCA endeavours to establish robust linkages across various domains, including knowledge sharing, capacity building, networking, advocacy, financial and resource support, research, technical assistance, education, and awareness.
- Governance of the alliance consists of a General Assembly comprising all member countries, a Council comprised of seven to fifteen member countries elected by the General Assembly for a five-year term, and a Secretariat.
- The IBCA Secretary General, appointed by the General Assembly upon the Council's recommendation, serves a specific term.
- To support its initiatives, the IBCA has secured initial funding of Rs. 150 crore from the Government of India for the period spanning from 2023-24 to 2027-28.
RBI tweaks norms related to the Regulatory Sandbox scheme

- 29 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
The Reserve Bank recently tweaked guidelines for the Regulatory Sandbox (RS) scheme under which participating entities will have to comply with digital personal data protection norms.
About the Regulatory Sandbox Scheme:
- The Regulatory Sandbox scheme denotes a controlled regulatory environment where new products or services can undergo live testing.
- Functioning as a "safe space" for businesses, regulators may offer certain relaxations for testing purposes within this environment.
- It serves as a structured platform for regulators to engage with the industry and develop regulations that foster innovation and enable the delivery of cost-effective financial products.
- The scheme holds potential as a tool for creating dynamic regulatory environments that adapt to emerging technologies through evidence-based learning.
Objectives:
- Offering innovative technology-led entities an opportunity for limited-scale testing of new products or services, potentially involving regulatory relaxations before broader implementation.
- At its core, the Regulatory Sandbox is a formal program allowing market participants to test new products, services, or business models in live settings, under appropriate oversight.
- Proposed financial services under the scheme should leverage new or emerging technology to address consumer needs or offer benefits.
- The overarching goal is to promote responsible innovation in financial services, enhance efficiency, and deliver consumer benefits.
- The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) introduced the 'Enabling Framework for Regulatory Sandbox' in August 2019 after extensive consultations.
- The updated framework mandates compliance with the Digital Personal Data Protection Act of 2023 for sandbox entities.
- Furthermore, the timeline for various stages of the Regulatory Sandbox process has been extended from seven to nine months.
- Fintech companies, including startups, banks, financial institutions, and other entities providing support to financial services businesses, are among the target applicants for entry into the Regulatory Sandbox.
PM Modi lays stone for India’s second spaceport at Kulasekarapattinam
- 29 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
Prime Minister Narendra Modi laid the foundation stone for the country’s second spaceport at Kulasekarapattinam in Tuticorin district recently.
About Kulasekarapattinam Spaceport:
- The Kulasekarapattinam Spaceport is a forthcoming space launch facility located in Kulasekarapattinam, a coastal village near the temple town of Tiruchendur in Thoothukudi district, southern Tamil Nadu.
- It will become the second operational spaceport in India after the Satish Dhawan Space Centre, established in Sriharikota, Andhra Pradesh, in 1971, and will feature two launch pads.
- The primary focus of the Kulasekarapattinam Spaceport will be to facilitate the commercial launch of Small Satellite Launch Vehicles (SSLVs).
- Spanning 2,350 acres, the spaceport will comprise 35 essential facilities, including a launch pad, rocket integration facilities, ground range and checkout facilities, and a mobile launch structure (MLS) equipped with checkout computers.
- With the capability to launch up to 24 satellites annually using a mobile launch structure, it offers a strategic advantage by enabling direct southward launches over the Indian Ocean, thus conserving fuel for small rocket launches.
- This stands in contrast to the Satish Dhawan Space Centre, where launching into a polar orbit necessitates additional fuel due to the curved trajectory required to avoid crossing landmasses, particularly Sri Lanka.
- The estimated cost of the Kulasekarapattinam Spaceport project is Rs. 986 crore.
About the Small Satellite Launch Vehicles (SSLVs):
- The SSLV, or Small Satellite Launch Vehicle, is a three-stage launch vehicle characterized by three solid propulsion stages and a liquid propulsion-based Velocity Trimming Module (VTM) serving as a terminal stage.
- Measuring 2 meters in diameter and 34 meters in length, the SSLV boasts a lift-off weight of 120 tonnes.
- Designed for versatility, the SSLV can effectively launch a 500kg satellite into a 500 km planar orbit.
- Notable features of the SSLV include its cost-effectiveness, rapid turnaround time, ability to accommodate multiple satellites, feasibility for launch-on-demand, and minimal infrastructure requirements.
New waste management technology could improve life in rural India

- 29 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
A new waste management technology that allows pyrolysis at a community level could help rural Indians cut indoor air pollution, improve soil health, and generate clean power, a recent study has claimed.
What is BioTRIG?
- BioTRIG represents a novel waste management technology centered around pyrolysis, poised to mitigate indoor air pollution, enhance soil quality, and foster clean energy generation across rural India.
- This community-oriented pyrolysis system is ingeniously crafted to utilize locally generated waste, offering a sustainable solution tailored to village environments.
- The innovative process yields three valuable by-products: bio-oil, syngas, and biochar fertilizer, presenting multifaceted benefits for rural communities, from cleaner energy sources to enhanced agricultural productivity.
- Moreover, the self-sustaining nature of BioTRIG enables the utilization of syngas and bio-oil to fuel subsequent pyrolysis cycles, with excess electricity catering to local energy needs, fostering self-reliance and sustainability.
- By harnessing the clean-burning properties of bio-oil and the soil-enriching qualities of biochar, BioTRIG empowers rural households to transition away from traditional cooking fuels while concurrently enhancing agricultural resilience and carbon sequestration efforts.
Significance:
- Computer simulations indicate that the BioTRIG system holds the potential to significantly mitigate greenhouse gas emissions from communities, potentially reducing them by nearly 350 kg of CO2-eq per capita per year.
- This projection underscores a noteworthy positive influence on both climate emissions and public health.
- The BioTRIG technology could mark a paradigm shift in waste management practices and energy generation methods within rural India, promising transformative benefits for communities.
What is Pyrolysis?
- Pyrolysis is a transformative chemical recycling method that disassembles residual organic matter into its fundamental molecular components.
- This innovative process entails confining the waste within an oxygen-deprived enclosure and subjecting it to temperatures exceeding 400 degrees Celsius.
Education Minister launches SWAYAM Plus platform

- 29 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
The Union Minister of Education and Skill Development and Entrepreneurship Dharmendra Pradhan recently launched the ‘SWAYAM Plus’ platform to offer courses developed collaboratively with the industry.
About the SWAYAM Plus Platform:
- SWAYAM is a Massive Open Online Course (MOOC) platform providing educational opportunities by bringing the best teaching and learning resources to everyone.
- Operated by the Indian Institute of Technology (IIT)-Madras, this platform aims to extend educational opportunities to both traditional students and working professionals, aligning with the provisions of the NEP 2020 for flexible entry and exit points in education.
- By enabling individuals to balance work and studies through online courses, SWAYAM Plus empowers them to enhance their skills and career prospects, thus contributing to India's knowledge economy.
Objectives and features:
- SWAYAM Plus primarily focuses on achieving the following:
- Building an ecosystem for all stakeholders in professional and career development, including learners, course providers, industry, academia, and strategic partners;
- Enabling a mechanism that provides credit recognition for high?quality certifications and courses offered by the best industry and academia partners;
- Reaching a large learner base by catering to learning across the country, with a focus on reaching learners from tier 2 and 3 towns and rural areas and Offering employment-focused courses, based on learner needs – across chosen disciplines with options to learn through resources in vernacular languages.
- Enhanced employability: SWAYAM Plus empowers individuals to balance work and studies through online courses, enhancing skills and career prospects.
- Industry partnerships: Courses are tailored to industry requirements in collaboration with industry leaders.
Key features:
- Multilingual content, AI guidance, credit recognition, and pathways to employment are prominent features.
Implementation and reach:
- SWAYAM Plus aims to offer high-quality courses with credit recognition, reaching learners nationwide, especially from tier 2 and 3 towns and rural areas.
Value-added services:
- Value-added services like mentorship, scholarships, and job placements will be provided, creating a digital ecosystem for upskilling and reskilling at all education levels.
- SWAYAM, launched in 2017, had enrolled 72 lakh learners by 2023.
- Now, in line with the NEP 2020, SWAYAM Plus will incorporate courses tailored to industry requirements, developed in collaboration with industry leaders like L&T, Microsoft, and CISCO.
European Parliament adopts nature restoration law

- 29 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
The European Parliament recently adopted the first European Union (EU) law to restore degraded ecosystems across the 27-nation political and economic bloc.
About the Nature Restoration Law:
- The Nature Restoration Law is hailed as a significant stride toward rejuvenating Europe’s natural habitats, with a staggering 81% currently classified as being in poor health.
- It sets a pioneering example for global emulation, emphasizing the criticality of safeguarding and revitalizing our natural environment for the welfare of forthcoming generations.
Objectives:
- This legislation aims to rejuvenate ecosystems, habitats, and species across the European Union's (EU) terrestrial and marine domains, fostering the enduring recuperation of diverse and robust nature.
- Additionally, it endeavors to contribute to the EU's climate mitigation and adaptation objectives while fulfilling international commitments.
- These directives aspire to encompass a minimum of 20% of the EU's land and marine territories by 2030, with the ultimate goal of restoring all ecosystems in need by 2050.
Specific Targets:
- Wetlands, forests, grasslands, rivers, lakes, heath & scrub, rocky habitats, and dunes: The objective is to enhance and restore biodiverse habitats on a large scale, fostering the recovery of species populations through habitat improvement and expansion.
- Pollinating Insects: The target is to reverse the decline of pollinator populations by 2030, aiming for a positive trajectory in pollinator numbers.
- Forest Ecosystems: The aim is to promote an upward trend in standing and fallen deadwood, varied aged forests, forest connectivity, common forest bird populations, and organic carbon reserves.
- Urban Ecosystems: The objective is to achieve zero net loss of green urban spaces by 2030 and expand the total area covered by green urban spaces by 2040 and 2050.
- Agricultural Ecosystems: The goal is to bolster grassland butterfly and farmland bird populations, increase organic carbon reserves in cropland mineral soils, and augment the proportion of agricultural land featuring diverse landscape characteristics.
About the European Union (EU):
- The European Union (EU) is a political and economic union of 27 European countries that collaborate on various issues, including trade, security, and environmental protection.
- Founded after World War II to promote peace and economic cooperation, the EU has evolved into a complex organization with its own institutions, laws, and currency (the euro).
- It operates on the principles of democracy, human rights, and the rule of law, with the European Commission, European Parliament, and European Council among its key decision-making bodies.
- The EU's single market allows for the free movement of goods, services, capital, and people across member states, fostering economic growth and prosperity.
- Additionally, the EU plays a prominent role in global affairs, advocating for multilateralism, sustainable development, and climate action.
Scientists are closer to creating a reference genome for Indians; 10,000 samples sequenced already

- 28 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
The Government’s ambitious Genome India initiative achieved a significant milestone Tuesday as researchers completed sequencing 10,000 healthy genomes from different regions of the country, representing 99 distinct populations.
News Summary:
- The Department of Biotechnology has announced the successful completion of India's '10,000 genome' project, aimed at establishing a comprehensive reference database of whole-genome sequences within the country.
- This milestone marks the creation of a detailed genetic map of India, offering significant potential for both clinicians and researchers in diverse fields.
- With India emerging as the largest genetic laboratory globally, this rich dataset is poised to catalyze advancements in the country's biology sector.
- Notably, India's bio-economy has witnessed remarkable growth, expanding from $10 billion in 2014 to over $130 billion in 2024, signaling a promising trajectory for future development.
- The entirety of the genomic dataset will be housed at the Indian Biological Data Centre (IBDC), serving as a valuable digital resource for research purposes.
- Established in 2022, the IBDC represents India's sole indigenous databank, eliminating the need for Indian researchers to rely on foreign servers for hosting biological datasets.
What is Genome Sequencing?
- Genome sequencing is the process of determining the exact order of the building blocks (nucleotides) that make up an organism's entire DNA, or genome.
- It's like reading the complete instruction manual for life, containing the information needed to create and maintain an organism.
Applications of Genome Sequencing:
- Healthcare: Doctors can diagnose diseases with greater accuracy, personalize treatments, and uncover the causes of rare conditions.
- Agriculture: Scientists can engineer crops with desired traits like disease resistance and improved yield, while breeders select animals with specific characteristics.
- Forensics: DNA profiling aids criminal investigations and paternity testing.
- Conservation: Studying the genetic diversity of endangered species helps with conservation efforts while analyzing invasive species' origins aids in controlling their spread.
What is the Human Genome Project (HGP)?
- Initiated in 1990, the Human Genome Project aimed to elucidate the entire sequence of the human genome.
- In 2023, the project culminated in the release of the latest version of the complete human genome, boasting a mere 0.3% error margin.
- Enabled by the Human Genome Project, whole-genome sequencing facilitates the examination of an individual's genome to uncover deviations from the average human genome.
- These deviations, or mutations, offer insights into an individual's susceptibility to diseases, their responsiveness to specific stimuli, and other pertinent genetic attributes.
About the Genome India Project:
- The Genome India Project stands as a pioneering initiative approved by the Department of Biotechnology, geared towards gene mapping.
- This project sets out with the ambitious objective of compiling an exhaustive repository documenting genetic diversity across the Indian populace.
- At its core, the endeavor seeks to conduct genome sequencing for more than 10,000 individuals spanning various geographic and ethnic backgrounds within India, ultimately laying the groundwork for a standardized reference genome specific to the Indian demographic.
Significance of the Genome India Project:
- Unveiling Unique Genetic Variants: The Genome India Project holds the key to unraveling genetic variants exclusive to India’s diverse population, enabling tailored drug formulations and therapeutic interventions.
- For instance, mutations like MYBPC3, linked to premature cardiac arrest and prevalent in 4.5% of Indians, underscore the necessity of region-specific genetic insights, contrasting with global rarity.
- Similarly, the discovery of the LAMB3 mutation, causing a severe skin disorder and impacting nearly 4% of the population around Madurai, emphasizes the localized genetic complexities absent in global databases.
- Comprehensive Database for India's Population: With a colossal population exceeding 1.3 billion, India boasts a mosaic of over 4,600 distinct population groups, many practicing endogamy.
- This vast demographic diversity underscores the need for a comprehensive genetic database tailored to India's populace, crucial for identifying and addressing disease-causing mutations prevalent within specific groups.
- Unlike extrapolating findings from global datasets, the Genome India Project provides precise genetic insights essential for Indian-centric healthcare strategies.
African leaders demand financial systems reform; launch ‘Africa Club’ at 37th African Union Summit
- 28 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
Recently, during the 37th African Union Summit, member countries initiated the formation of the Africa Club.
What is the Africa Club?
- The Africa Club is an alliance of African Multilateral Financial Institutions, established at the African Union summit, designed to enhance Africa's influence in the global financial system.
- The initiative aims to align its operations with the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) and the African Union's Agenda 2063, fostering innovative financial instruments, facilitating debt management discussions, and promoting collaborative efforts to address the specific needs of African nations.
- Its membership comprises key institutions such as the African Export-Import Bank, Trade and Development Bank, Africa Finance Corporation, African Reinsurance Corporation, African Trade and Investment Development Insurance, Shelter Afrique Development Bank, and ZEP – RE (PTA Reinsurance Co).
About the African Union:
- The African Union is a continental organization consisting of 55 member states across the African continent, established on May 26, 2001, in Addis Ababa, Ethiopia.
- The AU's objectives include promoting peace, security, and stability on the continent, accelerating political and socioeconomic integration, defending the sovereignty and territorial integrity of member states, and advancing sustainable development.
- It serves as a platform for African countries to coordinate their efforts in various fields, including governance, human rights, economic development, infrastructure, health, education, and culture.
- The AU's structures include the Assembly of Heads of State and Government, the Executive Council, the Pan-African Parliament, the African Court of Justice and Human Rights, and various specialized technical committees and organs.
- Through its initiatives and programs, the AU works towards realizing the vision of an integrated, prosperous, and peaceful Africa, driven by its citizens and representing a dynamic force in the global arena.
Google unveils Genie AI which can create video games from text and image prompts

- 28 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
Recently, Google DeepMind unveiled Genie, a novel model capable of creating interactive video games based solely on textual or image prompts.
What is Genie AI?
- Genie is a foundation world model that is trained on videos sourced from the Internet.
- The model can “generate an endless variety of playable (action-controllable) worlds from synthetic images, photographs, and even sketches.”
- It is the first generative interactive environment that has been trained in an unsupervised manner from unlabelled internet videos.
- When it comes to size, Genie stands at 11B parameters and consists of a spatiotemporal video tokenizer, an autoregressive dynamics model, and a simple and scalable latent action model.
- These technical specifications let Genie act in generated environments on a frame-by-frame basis even in the absence of training, labels, or any other domain-specific requirements.
What does Genie do?
- Genie is a new kind of generative AI that enables anyone – even children – to dream up and step into generated worlds similar to human-designed simulated environments.
- It can be prompted to generate a diverse set of interactive and controllable environments although it is trained on video-only data.
- It is a breakthrough as it makes playable environments from a single image prompt.
- According to Google DeepMind, Genie can be prompted with images it has never seen.
- This includes real-world photographs, and sketches, allowing people to interact with their imagined virtual worlds.
- When it comes to training, they focus more on videos of 2D platformer games and robotics.
- Genie is trained on a general method, allowing it to function on any type of domain, and it is scalable to even larger Internet datasets.
Why is it Important?
- The standout aspect of Genie is its ability to learn and reproduce controls for in-game characters exclusively from internet videos.
- This is noteworthy because internet videos do not have labels about the action that is performed in the video, or even which part of the image should be controlled.
- It allows you to create an entirely new interactive environment from a single image.
- This opens up many possibilities, especially new ways to create and step into virtual worlds.
- With Genie, anyone will be able to create their own entirely imagined virtual worlds.
Ex-SC Judge Justice AM Khanwilkar Appointed As Lokpal Chairperson

- 28 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
Nearly 19 months after he retired as a Supreme Court judge, Justice A M Khanwilkar was appointed the chairperson of the anti-corruption ombudsman Lokpal on Tuesday. The post fell vacant nearly two years ago.
Who is AM Khanwilkar?
- Justice Ajay Manikrao Khanwilkar was a Supreme Court judge between May 2016 and July 2022.
- He has also served as chief justice of the Madhya Pradesh High Court and the Himachal Pradesh High Court and as a judge of the Bombay High Court.
- Recently appointed as the Chairperson of the anti-corruption ombudsman Lokpal on Tuesday.
- The appointment came nearly two years after the post fell vacant.
- Khanwilkar was elected for the post following discussions by a high-level committee, which included:
- Prime Minister Narendra Modi
- Chief Justice of India DY Chandrachud
- Leader of the Opposition in Lok Sabha, Adhir Ranjan Chowdhury
- The Lokpal has been functioning without its permanent chief since the conclusion of Justice Pinaki Chandra Ghose's term on May 27, 2022.
About Lokpal:
- The Lokpal is a statutory body established under the Lokpal and Lokayuktas Act of 2013.
- Its primary mandate is to investigate allegations of corruption against certain public officials and handle related matters.
- The organizational structure of Lokpal includes a chairperson and a maximum of eight members.
- The chairperson must be a former Chief Justice of India, a former Judge of the Supreme Court, or an eminent individual meeting specified eligibility criteria.
- Half of the maximum eight members are judicial members, who must be former Judges of the Supreme Court or former Chief Justices of High Courts.
- Additionally, a minimum of fifty percent of the members are drawn from SC/ST/OBC/minority backgrounds and include women.
How are Members Appointed?
- The President of India appoints the Chairperson and Members based on recommendations from a selection committee.
- This committee comprises the Prime Minister as Chairperson, the Speaker of Lok Sabha, the Leader of Opposition in Lok Sabha, the Chief Justice of India or a nominated Judge, and one eminent jurist.
- Members serve a term of five years or until they reach 70 years of age, whichever comes first, starting from the date they assume office.
- The Chairperson receives salary, allowances, and other benefits equivalent to those of the Chief Justice of India.
- Similarly, Members receive salary, allowances, and other benefits equivalent to those of a Judge of the Supreme Court.
Jurisdiction:
- The Lokpal has the authority to investigate allegations of corruption against current or former Prime Ministers, Union Ministers, Members of Parliament, and officials from various levels of the Union Government categorized under Groups A, B, C, and D.
- Its jurisdiction extends to include chairpersons, members, officers, and directors of entities established by parliamentary acts or financed by the Union or State government, as well as any organization receiving foreign contributions exceeding Rs 10 lakh.
- However, there are exceptions regarding the Prime Minister's jurisdiction. The Lokpal cannot investigate allegations related to international relations, external/internal security, public order, atomic energy, and space. Moreover, complaints against the PM require approval from at least two-thirds of the Lokpal's members before initiation of an inquiry.
Powers of Lokpal:
- The Lokpal possesses the authority to oversee and issue directives to the Central Bureau of Investigation (CBI).
- Once the Lokpal has referred a case to the CBI, the investigating officer cannot be transferred without the Lokpal's approval.
- It holds the power to authorize the CBI to conduct search and seizure operations related to these cases.
- The Inquiry Wing of the Lokpal is endowed with powers akin to those of a civil court.
- In specific circumstances, the Lokpal can confiscate assets, proceeds, receipts, and benefits obtained through corrupt means.
- It is empowered to recommend the transfer or suspension of public servants implicated in corruption allegations.
- The Lokpal can issue directives to prevent the destruction of records during the preliminary inquiry phase.
- As per Section 48 of the Act, the Lokpal is mandated to submit an annual report on its activities to the President, which is subsequently laid before both Houses of Parliament.
First Pey Jal Survekshan Awards to be conferred by President on 5th March

- 28 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
President Droupadi Murmu will present the first Pey Jal Survekshan Awards on the 5th of next month in New Delhi.
About the Pey Jal Survekshan Awards:
- The Pey Jal Survekshan Awards feature a prestigious lineup of 130 accolades, spotlighting outstanding contributions in the realm of water management.
- The awards span various categories, including the Pey Jal Gold, Silver, and Bronze City Awards, with each tier symbolizing excellence in specific population segments (ranging from 1 to 10 Lakh, 10 to 40 Lakh, and more than 40 Lakh).
- In addition to these, commendations are also extended for commendable efforts in areas such as Best Water Body, Sustainability Champion, Reuse Champion, Water Quality, City Saturation, and the prestigious AMRUT 2.0 Rotating Trophy of the Year.
Comprehensive Evaluation Parameters:
- Embracing a multifaceted approach, the evaluation criteria encompass a wide array of parameters, including accessibility, coverage, water quality maintenance at treatment facilities and household levels, sustainability practices ensuring the health of water bodies, adoption of SCADA/flowmeters, and efficient reuse of treated wastewater.
- Cities are meticulously graded using a star rating system, ranging from 5 stars to No star, meticulously reflecting their performance across these pivotal benchmarks.
- Ensuring Water Purity and Transparency: The Pey Jal Survekshan reinforces the assurance of clean water through rigorous independent NABL lab testing at both the source and consumer ends.
- Leveraging advanced technological tools such as GIS-enabled web portals, geo-tagging, and infrastructure mapping, the survey captures precise and transparent data, facilitating informed decision-making.
- Enhancing Urban Governance and Citizen Engagement: Anticipated to serve as a catalyst for urban local body (ULB) decision-making processes, the outcomes of the Pey Jal Survekshan are poised to elevate service delivery standards while fostering active citizen participation.
- By nurturing a sense of ownership and disseminating knowledge on water conservation and optimal utilization, the awards endeavor to empower communities toward sustainable water management practices.
What is the AMRUT Mitra initiative?
- The AMRUT Mitra initiative is geared towards active engagement of women Self-Help Groups (SHGs) in urban water management, recognizing women as pivotal stakeholders and highlighting their vital role in household water governance.
- Tasked with executing AMRUT 2.0 projects, the Mitras will undertake various responsibilities, including billing, collection, leak detection, plumbing, water quality monitoring, and infrastructure upkeep.
- At its core, AMRUT Mitra seeks to cultivate a sense of ownership among women, fostering inclusivity and diversity in traditionally male-dominated domains while ensuring equitable access to safe drinking water and addressing gender disparities.
- Expected outcomes encompass the empowerment of women SHGs, socio-economic upliftment, alignment with AMRUT 2.0 objectives, heightened community awareness, and the establishment of a blueprint for future endeavors.
An initiative to improve nutrition in adolescent girls using Ayurveda under Mission Utkarsh

- 27 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
The project for anemia control under Mission Utkarsh will be a joint public health initiative by the Ministries of Ayush and Women and Child Development and will be launched in five aspirational districts first as a pilot project.
About Mission Utkarsh:
- Mission Utkarsh was launched in January 2022, a new initiative of “rapid improvement of selected Districts” to improve.
- Under this mission, 15 central ministries and departments are working to bring select key performance indicators in bottom districts to the state and national average.
- Over 94,000 adolescent girls between the age group of 14-18 years registered under Poshan Tracker at approximately 10,000 Anganwadi Centres will benefit in 12 12-month periods of the program.
- The coordinating agency for the project will be the Central Council for Research in Ayurvedic Sciences (CCRAS).
- Classical Ayurveda medicines (Drakshavaleha and Punarnavadi mandoor) for better nutrition to improve the health of the anemic adolescent girls will be provided for a period of 3 months.
- These five districts are Dhubri in Assam, Bastar in Chhattisgarh, Paschimi Singhbhum in Jharkhand, Gadchiroli in Maharashtra, and Dholpur in Rajasthan.
- Building research capacity through training, conferences, workshops, and seminars with the active participation of researchers of integrative healthcare would be enhanced.
What is Anaemia?
- According to WHO, anemia occurs when there is a lower-than-normal count of red blood cells or a reduced hemoglobin concentration within them, crucial for oxygen transport throughout the body.
Symptoms
- This condition leads to symptoms like fatigue, weakness, dizziness, and shortness of breath due to decreased oxygen-carrying capacity in the blood.
Causes:
- Iron deficiency is the most common nutritional cause, although deficiencies in folate, vitamins B12 and A can also contribute.
- Chronic diseases like kidney or liver disease, cancer, and genetic conditions such as sickle cell anemia further exacerbate anemia.
Significance:
- Anaemia has significant implications, particularly affecting vulnerable populations like pregnant women and children under five, impacting reproductive health and reducing work capacity, thus posing an economic burden.
Anaemia in India:
- India faces a substantial anemia burden, with recent surveys indicating alarming prevalence rates among women aged 15-49 and children aged six months to five years, highlighting the urgent need for public health interventions.
RBI Allows Lending And Borrowing Govt Securities

- 27 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
In a bid to deepen the bond market, the Reserve Bank of India on Wednesday issued guidelines for lending and borrowing in government securities.
What are Government Securities?
- Government securities, also known as G-Secs, refer to the debt instruments issued by the government to finance its fiscal requirements.
- These securities are backed by the government’s guarantee of repayment and are considered risk-free investments.
- They are an integral part of the fixed-income market and are traded on the government securities market.
- Government securities serve as a means for the government to raise funds from the public to meet its expenditure needs, bridge budget deficits, and fund developmental projects.
- Investors who purchase these securities lend money to the government in return for regular interest payments and the principal amount at maturity.
- These securities come in mainly two categories:
- Short-Term: Often known as “Treasury Bills,” these have initial maturities of less than a year.
- Long-Term: Typically referred to as Government Bonds or Dated Securities, these have an original maturity of one year or more.
- In India, the Central Government issues both treasury bills and bonds or dated securities while the State Governments issue only bonds or dated securities, which are called State Development Loans (SDLs).
Treasury Bills (Short-Term G-Secs)
- Treasury Bills, commonly known as T-Bills, are short-term government securities with a maturity period of less than one year.
- They are issued at a discount to their face value and are highly liquid instruments.
- T-Bills serve as a mechanism for the government to efficiently manage its short-term funding requirements.
Dated Securities (Long-Term G-Secs)
- Dated Securities are long-term government securities with a fixed maturity period, typically 5 to 40 years.
- They pay regular interest to investors, known as coupon payments, and return the principal amount at maturity.
- Dated Securities are vital for financing long-term projects and meeting government borrowing needs.
Centre approves interest-free loans to FCV tobacco growers in Andhra Pradesh

- 27 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
The Central Government has approved a 10 thousand rupees interest-free Loan to the Flue Cured Virginia (FCV) Tobacco growers in Andhra Pradesh.
What is Flue Cured Tobacco?
- There are three types of tobacco curing methods traditionally used: Air-Cured, Fire-Cured, and Flue-Cured.
- Each of the different curing methods results in a tobacco product that is distinguishable by both its nicotine content and its aroma.
Flue-Cured:
- Flue-curing tobacco is raised with a low level of nitrogen and harvested by priming method.
- Harvested leaves are strung on sticks which are then stacked into to flue curing barn.
- The barn is artificially heated.
- Green leaves should be loaded in the upper half of the barn and the lighter ones in the lower half.
- The three steps are Yellowing, Fixing the color, and Drying.
Grading:
- After curing, leaves are graded by sorting leaves into uniform lots according to body, color, and degree of blemish or damage.
- The most important elements of quality in FCV tobacco are color, texture, size, blemish, strength, even burning with white ash, and agreeable flavor.
Why is Tobacco Cured?
- To create smoking tobacco, the tobacco leaves need to be cured, or dried out.
- The wet, green tobacco leaves of a tobacco plant initially contain too much moisture to catch fire.
- They also have a higher chlorophyll content.
- By releasing a certain amount of chlorophyll from the leaves during the drying-out process, the natural tannins come out giving the smoked tobacco its flavor and scent.
- The curing process makes the leaf dry enough to smoke while increasing the sugar and natural tannins found in each leaf to create the sweetly aromatic and mild taste tobacco is known for.
Key Characteristics of Flue-cured Tobacco:
-
- Produces primarily cigarette tobacco
- Contains a high sugar content
- Contains medium to high levels of nicotine
- Rich in natural tannins which creates its distinct mild and slightly sweet flavor and aroma
- FCV tobacco is mainly produced in Andhra Pradesh and Karnataka in India.
India gets desi Garbhini GA2 for evaluation of foetal growth
- 27 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
Specifically tailored to address the unique characteristics of foetal growth within the Indian population, India has finally got its locally made ‘Garbhini-GA2’, a groundbreaking Artificial Intelligence model.
What is Garbhini-GA2?
- The Garbhini-GA2 model, developed as part of the DBT India initiative (GARBH-Ini) program by researchers at the Indian Institute of Technology (IIT) Madras and the Translational Health Science and Technology Institute (THSTI), Faridabad, addresses the challenge of accurately estimating foetal age (gestational age, GA) in the Indian population, particularly in the second and third trimesters.
- Unlike existing formulas designed for Western populations, Garbhini-GA2 accounts for variations in foetal growth specific to the Indian context, significantly reducing estimation errors by nearly threefold.
- This innovative model is crucial for ensuring precise prenatal care and determining accurate delivery dates, thereby enhancing maternal and foetal health outcomes.
- Garbhini-GA2 marks a milestone as the first late-trimester GA estimation model validated using Indian population data, offering a tailored approach to foetal age determination that is essential for effective maternal healthcare."
About Translational Health Science and Technology Institute (THSTI):
- THSTI, an autonomous institute under the Ministry of Science and Technology, was founded in 2009 in Faridabad, Haryana, with a core commitment to advancing research beyond mere discovery.
- By fostering collaboration among diverse teams in medicine, science, and technology, THSTI leverages translational expertise to drive clinical research and innovation.
- In addition to its core mission, THSTI plays a pivotal role in fostering social innovation and entrepreneurial endeavors, particularly in the domain of maternal and child healthcare.
. First-of-its-kind Micro Turbojet Engine made in India

- 27 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
A micro turbojet engine designed and developed indigenously by Hyderabad-based firm Raghu Vamsi Machine Tools with the support of the IIT Hyderabad has been unveiled.
Key Highlights of the Micro Turbojet Engine “INDRA RV25: 240N”:
- It is an indigenous micro turbojet engine made in India.
- Its primary focus is on serving unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) or drones.
- Beyond UAVs, the engine exhibits versatile applications in air taxis, jetpacks, auxiliary power units, range extenders, and potential use in power generation for the future.
- Indigenous design and development: Engineered entirely in India by the Raghu Vamsi Machine Tools (RVMT) team of skilled engineers & supported by IIT, Hyderabad.
- A great demonstration of the potential of Industry-Academia partnership
- Self-reliance and autonomy: By reducing reliance on imported technologies, components, and expertise, the Micro Turbojet Engine contributes to India’s goal of achieving self-sufficiency in critical sectors, bolstering national security and economic resilience
- Empowering local manufacturing: The launch of the indigenous Micro Turbojet Engine not only drives technological innovation but also stimulates the growth of the domestic aerospace and defense manufacturing ecosystem, creating jobs and fostering economic growth.
What Is a Turbojet Engine and How Does It Work?
- Turbojet engines are jet engines that, like other jet engines, generate propulsion by discharging or expelling heated air.
- They feature a combustion chamber in which they burn fuel and air.
- As they burn this mixture, turbojet engines will discharge heated air.
- It can find turbojet engines in commercial airplanes, civilian airplanes, and military aircraft.
How Turbojet Engines Work?
- The process begins by drawing air through an intake.
- Turbojet engines feature an air intake, which is typically located near the front of the engine.
- Air will flow into this intake, at which point it will be redirected to the engine’s interior.
- After entering the engine, the air will become compressed.
- Turbojet engines feature a set of rotating blades. Known as compressors, these rotating blades are designed to compress the air.
- The next step in the process is combustion which involves the burning of fuel and air.
- Turbojet engines will inject fuel into the same combustion chamber where the compressed air is located.
- A spark will then ignite the mixture of fuel and compressed air, thereby generating hot, high-pressure exhaust gas.
- The exhaust gas generated by the combustion is expelled out the rear of the turbojet engine.
- This rearward expulsion allows for forward propulsion.
- As the exhaust gas is discharged out the rear of the turbojet engine, the airplane will be propelled forward.
PM Modi Inaugurates 'Sudarshan Setu', India's Longest Cable-Stayed Bridge
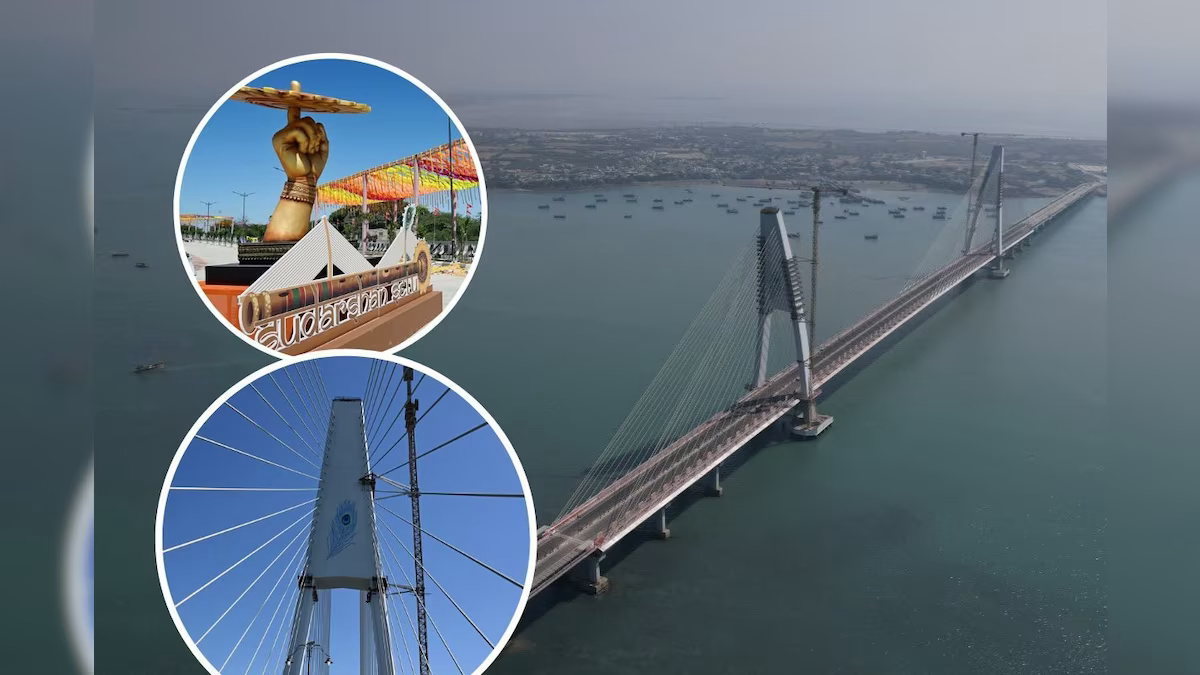

- 26 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
PM Modi recently inaugurated the Sudarshan Setu, a four-lane cable-stayed bridge connecting Okha to Beyt Dwarka island in Gujarat.
About the Sudarshan Setu:
- 'Sudarshan Setu' is the country's longest cable-stayed bridge 2.32 km on the Arabian Sea connecting Beyt Dwarka island to mainland Okha in Gujarat's Devbhumi Dwarka district.
- It boasts a unique design, featuring a footpath adorned with verses from the Bhagavad Gita and images of Lord Krishna on both sides.
- It also has solar panels installed on the upper portions of the footpath, generating one megawatt of electricity.
- The 2.32 km bridge, including 900 metres of a central double-span cable-stayed portion and a 2.45 km long approach road, has been constructed at a cost of Rs 979 crore.
About Beyt Dwarka:
- Bet/Beyt (pronounced ‘Bait’ Dwarka also known as Shankhodara, is an island located near the shores of Okha which is situated around 30 km from Dwarka, in the Gulf of Kutch.
- It said that Lord Krishna resided here while Dwarka was his constitutional seat.
History:
- Bet Dwarka derived its name from the word ‘bet’ which translates to ‘gift’ and is believed that Lord Krishna received it from his friend Sudama.
- In the ancient epic, Mahabharata, Bet Dwarka is known by the name of ‘Antardvipa’ to which people of the Yadava clan needed to travel by boat.
- Explorations and excavations carried out under the sea have revealed the presence of settlements whose age can be traced back to the era of the Harappan civilisation and that of the Mauryan rule.
- In the later years, the region was under the administration of the Gaekwad clan of the state of Baroda.
- During the revolt of 1857, Vaghers attacked the region and captured it, but had to concede defeat in two years and return the region back to the Gaekwads.
Ladakh: Centre agrees to examine demand for statehood, inclusion in Sixth Schedule of Constitution

- 26 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
Recently, the Centre has agreed to examine whether the provisions of the Sixth Schedule of the Constitution can be implemented in Ladakh.
What is the Sixth Schedule?
- The Sixth Schedule under Article 244 provides for the formation of autonomous administrative divisions — Autonomous District Councils (ADCs) — that have some legislative, judicial, and administrative autonomy within a state.
- ADCs have up to 30 members with a term of 5 years and can make laws, rules and regulations with regard to land, forest, water, agriculture, village councils, health, sanitation, village- and town-level policing, inheritance, marriage and divorce, social customs and mining, etc.
- The Bodoland Territorial Council in Assam is an exception with more than 40 members and the right to make laws on 39 issues.
- The Sixth Schedule applies to the Northeastern states of Assam, Meghalaya, Mizoram (three Councils each), and Tripura (one Council).
Why does Ladakh want to be part of the Sixth Schedule?
- There was much enthusiasm initially, mostly in Leh, after the August 5, 2019 decisions that created two new Union Territories.
- The Buddhist-dominated Leh district had long demanded UT status because it felt neglected by the erstwhile state government, which was dominated by politicians from Kashmir and Jammu.
- This development has sparked concerns among locals regarding potential challenges related to identity preservation, resource allocation, and administrative oversight.
- Also, the changed domicile policy in Jammu and Kashmir has raised fears in the region about its own land, employment, demography, and cultural identity.
- The UT has two Hill councils in Leh and Kargil, but neither is under the Sixth Schedule.
- Their powers are limited to the collection of some local taxes such as parking fees and allotment and use of land vested by the Centre.
- The Sixth Schedule empowers the Governor of the State to designate specific areas as administrative units within the Autonomous Districts and Autonomous Regions.
Can Ladakh be included in the Sixth Schedule?
- In September 2019, the National Commission for Scheduled Tribes recommended the inclusion of Ladakh under the Sixth Schedule, noting that the new UT was predominantly tribal (more than 97%), people from other parts of the country had been restricted from purchasing or acquiring land there, and its distinct cultural heritage needed preservation.
- Notably, no region outside the Northeast has been included in the Sixth Schedule.
- In fact, even in Manipur, which has predominantly tribal populations in some places, the autonomous councils are not included in the Sixth Schedule.
- Nagaland and Arunachal Pradesh, which are totally tribal, are also not in the Sixth Schedule.
- “Ladakh’s inclusion in the Sixth Schedule would be difficult.
- The Constitution is very clear, the Sixth Schedule is for the Northeast.
- For tribal areas in the rest of the country, there is the Fifth Schedule.
- However, it remains the prerogative of the government — it can, if it so decides, bring a Bill to amend the Constitution for this purpose.
IGNCA’s ‘language atlas’ to shine a light on India’s linguistic diversity

- 26 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
The Indira Gandhi National Centre for Arts, an autonomous body under the Union Culture Ministry, proposes to conduct a linguistic survey across the country to create a ‘Language Atlas’ of India.
About the Language Atlas of India:
- The Language Atlas of India traces its roots back to the seminal Linguistic Survey of India (LSI) conducted by Sir George Abraham Grierson, which was first published in 1928.
- Since its inception, the linguistic landscape of India has undergone significant transformations, necessitating a comprehensive reevaluation.
- The proposed linguistic survey aims to capture the myriad languages and dialects prevalent across the country, acknowledging the dynamic nature of linguistic diversity.
- It seeks to document not only the languages and dialects actively spoken but also those that have faced extinction or are teetering on the brink of disappearance.
- Engaging a wide array of stakeholders, including the Ministries of Culture, Education, Tribal Affairs, Home, Social Justice and Empowerment, and Development of the North East Region, the survey endeavours to be inclusive and representative of diverse language communities.
- Phased Approach: The Detailed Project Report (DPR) advocates for a structured approach, commencing with state-wise data collection followed by regional assessments.
- Furthermore, the proposal advocates for the preservation of linguistic heritage through the digital archiving of audio recordings encompassing the linguistic richness of the nation.
- Significance: Languages serve as conduits of communication and repositories of cultural heritage, encapsulating local wisdom, traditions, narratives, and medicinal knowledge.
- For instance, many indigenous communities possess indigenous knowledge of medicinal plants and herbs, which are transmitted through generations via their native languages, emphasizing the intrinsic link between language and cultural preservation.
About the Indira Gandhi National Centre for the Arts (IGNCA):
- Established in 1987 as an autonomous institution under the aegis of the Ministry of Culture, the Indira Gandhi National Centre for the Arts (IGNCA) serves as a pivotal hub for research, academic endeavours, and dissemination within the realm of the arts.
- Governance Structure: Operating with a Board of Trustees, the IGNCA convenes regularly to provide overarching guidance and direction for its multifaceted activities.
- Under the stewardship of a Chairman, the Executive Committee, composed of select Trustees, oversees the operational facets of the centre.
- Integral Role in Project Mausam: Embracing its role as a research unit, the IGNCA actively contributes to Project Mausam, a collaborative initiative spearheaded by the Ministry of Culture in partnership with the Archaeological Survey of India (ASI), New Delhi.
- Project Mausam endeavours to explore the intricate tapestry of cultural routes and maritime landscapes that historically linked diverse regions along the Indian Ocean littoral, fostering connections between coastal centres and their hinterlands.
- Engagement in the Vedic Heritage Portal: In alignment with its commitment to cultural heritage preservation, the IGNCA embarks on a project dedicated to designing and developing a Vedic Heritage Portal, under the auspices of the Ministry of Culture, Government of India.
- This portal serves as a digital platform aimed at elucidating the profound messages encapsulated within the Vedas, contributing to the dissemination of ancient wisdom and knowledge.
G-33 calls for progress on agricultural trade ahead of WTO Ministerial Conference

- 26 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
The G-33 group of countries recently expressed serious concern over the lack of progress in agriculture trade negotiations and urged the members of the World Trade Organisation (WTO) to work on a permanent solution to the issue of public stockholding of grains for food security purposes.
Key Highlights of the G33 Trade Ministers Meeting in Abu Dhabi:
- Special Safeguard Mechanism: The G33 group emphasized the importance of the Special Safeguard Mechanism (SSM) as a crucial instrument against significant import surges or sudden price declines.
- They called for WTO members to reach an agreement and adopt a decision on SSM by the 14th WTO Ministerial Conference (MC).
- Permanent Solution for Public Stockholding: The G33 nations sought a permanent solution during the 13th Ministerial Conference, which commenced in Abu Dhabi recently.
- The MC serves as the highest decision-making body of the WTO.
- Critical Importance of Public Stockholding: The G33 statement highlighted the critical significance of public stockholding for food security in developing countries.
- It enables governments to procure crops from farmers at the minimum support price (MSP) and store and distribute food grains to the poor.
- This program supports low-income or resource-poor producers and contributes to rural development.
- The 13th WTO Ministerial Conference provides a crucial platform for WTO members to engage in constructive discussions and work towards finding mutually beneficial solutions.
What is G 33?
- The G33 is a forum of developing countries including India, Brazil, South Africa etc. formed during the Cancun ministerial conference of the WTO (2003), to protect the interest of the developing countries in agricultural trade negotiations.
- It was created to help group countries which were all facing similar problems.
- The G33 has proposed special rules for developing countries at WTO negotiations, like allowing them to continue to restrict access to their agricultural markets.
- Dominated by India, the group has "defensive" concerns regarding agriculture in relation to World Trade Organization negotiations, and seeks to limit the degree of market opening required of developing countries.
- The group has advocated the creation of a "special products" exemption, which would allow developing countries to exempt certain products from tariff exemptions, and also a "special safeguard mechanism" which would permit tariff increases in response to import surges.
Analysis of Household Consumption Expenditure Survey 2022-23 Report

- 26 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
The per capita monthly household expenditure more than doubled in 2022-23 as compared to 2011-12, according to the latest study by the National Sample Survey Office (NSSO).
Context:
- As per the 2022-23 report, rising inequality between the top and bottom of the pyramid.
- Urban and rural households register higher expenditure, spending less on food items.
- New methodology and questionnaire used in Household Consumption Expenditure Survey (HCES) 2022-23.
About the National Sample Survey Office (NSSO):
- The National Sample Survey Office (NSSO) comes under the Ministry of Statistics and Program Implementation headed by a Director General.
- It is responsible for the conduct of large-scale sample surveys in diverse fields on an All-India basis.
- Primarily data are collected through nationwide household surveys on various socio-economic subjects, Annual Survey of Industries (ASI), etc.
- Besides these surveys, NSSO collects data on rural and urban prices and plays a significant role in the improvement of crop statistics through supervision of the area enumeration and crop estimation surveys of the State agencies.
- It also maintains a frame of urban area units for use in sample surveys in urban areas.
The NSSO has four Divisions:
- Survey Design and Research Division (SDRD): This Division, located at Kolkata, is responsible for the technical planning of surveys, formulation of concepts and definitions, sampling design, designing of inquiry schedules, drawing up of tabulation plans, and analysis and presentation of survey results.
- Field Operations Division (FOD): The Division, with its headquarters at Delhi/Faridabad, is responsible for the collection of primary data for the surveys undertaken by NSS.
- Data Processing Division (DPD): The Division, with its headquarters at Kolkata is responsible for sample selection, software development, processing, validation and tabulation of the data collected through surveys.
- Survey Coordination Division (SCD): This Division, located in New Delhi, coordinates all the activities of different Divisions of NSS.
- It also brings out the bi-annual journal of NSS, titled “Sarvekshana”, and organizes National Seminars on the results of various Socio-economic surveys undertaken by NSS.
Key Insights From the 2022-23 Survey:
- Evolution of Food Expenditure: Over the past two decades, there has been a notable shift in spending patterns on food in India.
- Between 1999-2000 and 2022-23, both urban and rural households witnessed a gradual decline in the share of expenditure allocated to food.
- This period marks the first instance where food expenditure has dropped to below 50% in rural India and below 40% in urban India.
- Changing Dietary Preferences: The composition of food consumption has also undergone significant changes.
- Cereals and pulses have seen a reduction in their share of overall food consumption expenditure, while spending on milk has surged, surpassing that on cereals and pulses combined.
- In a noteworthy shift, the average Indian now spends more on fruits and vegetables than on food grains.
- Furthermore, expenditure on animal proteins like eggs, fish, and meat has shown a growing trend, indicating a preference for animal-based proteins over plant-based ones.
- Rise in Processed Food Consumption: There has been an observed increase in the share of expenditure allocated to processed foods, beverages, and purchased cooked meals.
- This trend aligns with the Engel Curve hypothesis, suggesting that as incomes rise, households allocate a smaller proportion of their spending to food and tend to prefer superior items over inferior ones.
- Closing Rural-Urban Consumption Gap: Consumption growth in rural areas has outpaced that in urban areas, leading to a narrowing of the rural-urban consumption divide.
- If this trend continues, it could potentially lead to parity in urban and rural incomes and consumption patterns in the future.
- Challenges in Inflation Calculation: The findings of the latest Household Consumption Expenditure (HCE) Survey underscore the need to review the inflation basket.
- The current Consumer Price Index (CPI)-based inflation calculation, established in 2012, may not accurately reflect contemporary consumption patterns.
- For instance, the disparity between the weightage assigned to cereals in the CPI basket and actual expenditure on cereals by rural households highlights the need for recalibration.
- Insights on Poverty Reduction: According to NITI Aayog CEO B V R Subrahmanyam, the latest survey indicates a reduction in poverty to five per cent nationwide.
- Both rural and urban areas are witnessing increased prosperity, as evidenced by rising per capita monthly expenditure.
- Demand for Legal Guarantee to MSP: While there is a demand for a legal guarantee to Minimum Support Price (MSP) for 23 crops, including food grains and sugarcane, the survey data suggests that the growth in the farm sector is being primarily driven by livestock, fisheries, and horticulture crops.
- This poses a pertinent question regarding the promotion of production: should the focus be on crops outside the MSP purview, such as milk, fish, poultry products, fruits, and vegetables, given their growing consumption trends?
BharatGPT Unveils Hanooman, a New Suite of Indic Generative AI Models

- 24 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
Recently, the BharatGPT group, led by IIT Bombay along with seven other elite Indian engineering institutes announced that it would launch its first ChatGPT-like service next month.
What is Hanooman?
- Hanooman is a series of large language models (LLMs) that can respond in 11 Indian languages like Hindi, Tamil, and Marathi, with plans to expand to more than 20 languages.
- It is unveiled by Seetha Mahalaxmi Healthcare (SML) in partnership with the IIT Bombay-led BharatGPT ecosystem.
- The BharatGPT group, which is backed by Reliance Industries.
- Hanooman has been designed to work in four fields, including health care, governance, financial services, and education.
- According to BharatGPT, the series isn’t just a chatbot but It is a multimodal AI tool, which can generate text, speech, videos and more in multiple Indian languages.
- One of the first customised versions is VizzhyGPT, an AI model fine-tuned for healthcare using reams of medical data.
- The size of these AI models ranges from 1.5 billion to a whopping 40 billion parameters.
Are There Any Other Indian Language Models?
- Apart from BharatGPT, a host of different startups like Sarvam and Krutrim, backed by prominent VC investors such as Lightspeed Venture Partners and billionaire Vinod Khosla’s fund, are also building AI models customised for India
What are Large Language Models (LLMs)?
- Large language models use deep learning techniques to process large amounts of text.
- They work by processing vast amounts of text, understanding the structure and meaning, and learning from it.
- LLMs are ‘trained’ to identify meanings and relationships between words.
- The greater the amount of training data a model is fed, the smarter it gets at understanding and producing text.
- The training data is usually large datasets, such as Wikipedia, OpenWebText, and the Common Crawl Corpus.
- These contain large amounts of text data, which the models use to understand and generate natural language.
The NB8 visit to India focuses on cooperation and trust
- 24 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
External Affairs Minister S Jaishankar hosted the India-Nordic-Baltic meeting on the sidelines of the ongoing Raisina Dialogue 2024 recently.
What are the Nordic-Baltic Countries?
- The Nordic-Baltic countries, also known as the NB8, are a group of Northern European countries that share historical, cultural, and geopolitical ties.
- The group includes
- Nordic countries of Denmark, Finland, Iceland, Norway, and Sweden, and
- Baltic countries of Estonia, Latvia, and Lithuania.
- These countries collaborate on various regional issues, such as security, economy, environment, and culture, and often work together within international organisations and forums.
- The term "Nordic-Baltic" highlights the close relationship and cooperation between these neighbouring states in the Baltic Sea region.
India's Relations with NB8 Countries:
- India's collaboration with NB8 nations is broadening, exemplified by initiatives like the India-Denmark Green Strategic Partnership, the India-Norway Task Force on Blue Economy, and cooperation on sustainability and ICT with Finland, including the 'LeadIT' (Leadership for Industry Transition) initiative with Sweden.
- Cooperation extends across various sectors, including innovation, green transition, maritime affairs, healthcare, intellectual property rights, emerging technologies, space exploration, and artificial intelligence.
- Trade and investment between the NB8 region and India are on a steady rise, reflecting deepening economic ties.
- Moreover, the security dynamics of the Nordic-Baltic region and the Indo-Pacific are intertwined, underlining the interconnectedness of regional security challenges.
Significance of NB8:
- The NB8 nations embody advanced economies characterised by their outward orientation, emphasis on innovation, complementarity, and seamless integration into the European Common Market, the world's largest single market area.
- The Baltic states, in particular, stand out as pioneers in IT, digitization, cyber technology, and green innovations, showcasing their leadership in these critical domains.
- Moreover, all NB8 members share a steadfast commitment to democracy and human rights, serving as advocates for an international order grounded in principles of multilateralism and adherence to international law.
NB8 Proposals for India:
- In light of the Ukraine conflict and its ripple effects on global food and energy security, supply chains, macro-financial stability, inflation, and growth, the NB8 seeks to collaborate with India in the following ways:
- Recognizing Shared Challenges: In an increasingly interconnected world, challenges such as the Ukraine conflict, global health crises, climate-related events, and geopolitical tensions affect us all.
- Acknowledging these shared challenges underscores the necessity for collaborative efforts to address them effectively.
- Embracing a Positive Agenda: There is an urgent imperative to pivot towards a more positive agenda for global cooperation.
- Leveraging our mutual commitment to the multilateral system, the NB8 proposes to enhance dialogue and cooperation on issues that are paramount to India's priorities and those of other global partners.
PM Modi unveils of Sant Ravidas statue in Varanasi on 647th birth anniversary

- 24 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
Prime Minister Narendra Modi recently said that the present government is taking forward the teachings and ideals of Sant Ravidas while following the mantra of ‘Sabka Saath Sabka Vikas, Sabka Vishwas aur Sabka Prayas’.
Who is Guru Ravidas?
- Guru Ravidass (also Ravidas, Rohidas and Ruhidas in eastern India) was a North Indian Guru mystic of the bhakti movement who was active in the 15th century CE.
- Venerated in the region of Uttar Pradesh as well as the Indian state of Maharashtra, his devotional songs and verses made a lasting impact upon the bhakti movement.
- He is often given the honorific Guru.
- He was a socio-religious reformer, a thinker, a theosophist, a humanist, a poet, a traveller, a pacifist and a spiritual figure before whom even head-priests of Benaras lay prostrate to pay homage.
- His birthday comes every year at Puran Mashi in the month of Magh.
- His mother’s name was Mata Kalsi and his father’s name was Baba Santokh Dass.
- Guru Ravidass was born into a humble family which was considered untouchable as per the social order prevailing at that time in Hindu society.
- He spearheaded the fight against man-made discrimination based on caste, colour or creed and preached the lofty ideas of socialism, secularism, equality and fraternity.
- He taught the lessons of universal brotherhood, tolerance, and the message of loving your neighbour, which got more importance in today’s world.
- Guru Ravidass fulfilled Guru Nanak Dev’s request by donating old manuscripts, which contained a collection of Guru Ravidass’s verses and poems.
- The earliest collection of these poems is available in Sri Guru Granth Sahib.
- It was compiled by Guru Arjan Dev, the fifth Guru of the Sikhs.
- There are 41 verses of Guru Ravidass in the Sikh Holy Book, Guru Granth Sahib.
- Meera Bai, a revered figure in Hindu spiritualism, is said to have considered Guru Ravidas as her spiritual Guru.
- It is said that Guru Ravidass disappeared from the world, leaving behind only his footprints.
- Some believe that Guru Ravidass lived in Banaras during his last days, dying a natural death at the age of 126 years.
Govt amends electricity rules to speed up new connections, promote EVs and solar PV systems
- 24 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
Recently, the government amended the Electricity (Rights of Consumers) Rules 2020, allowing consumers to now obtain separate electricity connections for charging their electric vehicles, and reducing the time period for obtaining a new electricity connection.
Context:
- The Government of India has recently approved the amendments to the Electricity (Rights of Consumers) Rules, 2020.
- According to the Union Minister for Power and New & Renewable Energy, Shri R. K. Singh, these amendments aim to expedite the process of obtaining new electricity connections.
- Encompassing various facets including billing, grievance redressal, compensation, and timeframes for new connections, these rules are designed to streamline consumer experiences.
- Moreover, they extend support to prosumers engaged in renewable energy generation.
- The amendments, as highlighted by the Minister, are poised to enhance consumer empowerment, fostering a more consumer-centric electricity ecosystem.
Major Amendments to the Electricity (Rights of Consumers) Rules, 2020:
- Streamlining Rooftop Solar Installation: Amendments exempt the requirement for technical feasibility studies for rooftop solar systems up to 10 kW capacity.
- For systems exceeding 10 kW, the timeframe for feasibility studies has been condensed from twenty to fifteen days, with automatic approval if deadlines are missed.
- Commissioning timelines for distribution licensees have been shortened from thirty to fifteen days.
- Dedicated Connections for Electric Vehicle Charging: Consumers can now secure separate electricity connections for charging Electric Vehicles (EVs), aligning with national emission reduction targets and Net Zero aspirations by 2070.
- Accelerated Connection Processes: New electricity connection timelines have been slashed from seven to three days in metropolitan areas, from fifteen to seven days in other municipal areas, and from thirty to fifteen days in rural regions.
- Exceptions apply in rural hilly terrains, maintaining the existing thirty-day period.
- Enhanced Consumer Rights in Residential Complexes: Residents in cooperative housing societies and residential colonies gain the option of individual or single-point connections, decided through transparent ballots conducted by Distribution Companies.
- Tariff parity is ensured between single-point and individual connections.
- Prompt Meter Installation for Complaints: Distribution licensees are mandated to install additional metres within five days of receiving complaints to verify consumption for a minimum of three months, enhancing consumer confidence and billing accuracy.
First moon-landing by private company

- 24 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
Fifty-two years after the last successful Apollo mission, a US-made spacecraft landed on the Moon recently which also marks the arrival of private space companies on the lunar surface.
What is Odysseus Lunar Exploration?
- Odysseus is a spacecraft built by Intuitive Machines, embarked on its journey from Earth aboard a Falcon 9 rocket by SpaceX recently.
- Intuitive Machines, headquartered in Houston, USA, boasts a decade-long legacy in space exploration endeavours.
- Loaded with six NASA payloads, Odysseus set its course for the Moon.
- Its lander module, Nova-C, achieved the milestone of landing in the Moon's south pole region, following Chandrayaan-3's similar feat last year.
- This marks the third successful moon-landing event in under a year, alongside Chandrayaan-3 and Japan's SLIM (Smart Lander for Investigating Moon).
Mission Objectives:
- The primary aim of the lunar lander is to assess the environmental conditions at the Moon's south pole.
- This assessment holds significant importance as NASA gears up for a crewed mission in September 2026 with Artemis III.
- Before sending astronauts to this area, NASA seeks to gather crucial data, including insights into water presence and accessibility, to inform mission planning.
Funding:
- Under the Commercial Lunar Payload Services (CLPS) program, NASA allocated $118 million to Intuitive Machines for this mission.
- CLPS has engaged at least 14 private companies to ferry NASA payloads to the Moon, fostering a collaborative environment aimed at nurturing the private space industry's capabilities in lunar exploration technology and science.
The Significance of Odysseus:
- Advancing Long-Term Lunar Presence: Odysseus' successful landing heralds a transformative phase in lunar exploration, aiming to establish infrastructure and a technological ecosystem capable of sustaining extended human presence.
- Diverging from Past Lunar Missions: In contrast to the moon landings of the 1960s and 1970s spearheaded by the US and the Soviet Union, Odysseus' mission focuses on leveraging lunar resources for sustained exploration.
- While historic moon landings were remarkable feats, technological limitations of the time hindered the immediate utilisation of lunar resources such as mining.
- Supporting US Commitment to Moon Exploration via Artemis Program: Odysseus' touchdown aligns with the US commitment to rekindle lunar exploration through the ambitious Artemis program.
- This endeavour transcends mere lunar landing missions, aiming to establish essential infrastructure and a thriving lunar economy conducive to comprehensive exploration.
- Unlocking Lunar Potential as a Gateway to Deep Space: By laying the groundwork for lunar infrastructure and economic activity, missions like Odysseus pave the way for leveraging the Moon as a springboard for deeper space exploration, offering nations unprecedented opportunities for cosmic discovery.
Kiru Hydropower Corruption Case: CBI Searches J&K Ex-Governor Satya Pal Malik’s Premises

- 23 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
The CBI conducted searches at the premises of former Jammu and Kashmir governor Satya Pal Malik and 29 other locations recently in connection with alleged corruption in the Rs 2,200-crore Kiru Hydropower project.
What are the Corruption Allegations Surrounding the Kiru Hydel Project?
- During his tenure as the governor of Jammu and Kashmir from August 23, 2018, to October 30, 2019, Satya Pal Malik claimed that he was offered a Rs 300-crore bribe to approve two files, one of which pertained to the project.
- In 2022, the J&K government requested a CBI investigation into alleged misconduct, previously highlighted by Satya Pal Malik, in the awarding of two government contracts.
- Concerns have been raised regarding the award of civil works, particularly to Patel Engineering Ltd, a prominent infrastructure and construction company established in 1949.
- The CBI has initiated action against the former CVPPPL chairman, MD, and Directors, as well as Patel Engineering.
- According to the FIR, an inquiry by the J&K Anti-Corruption Bureau and the Power Department had been conducted.
- The FIR alleges non-compliance with e-tendering guidelines in the awarding of civil works for the project.
- Additionally, accusations of substandard work and failure to employ local youth have been levelled against the hydel project.
What is the Kiru Hydel Power Project?
- The 624MW Kiru hydroelectric project is being developed as a run-of-river scheme in the Kishtwar district of Jammu and Kashmir, a union territory in India.
- Location of the Kiru project: The Kiru hydropower project is being built along the Chenab River near the villages of Patharnakki and Kiru, approximately 42 km from Kishtwar.
- It will be located between the Kirthai II hydroelectric project to its upstream and the Kwar hydroelectric project to its downstream.
- The project is being developed by the Chenab Valley Power Projects (CVPPPL) joint venture (JV) between:
- National Hydroelectric Power (NHPC, 49%)
- Jammu & Kashmir State Power Development (JKSPDC, 49%) and
- The Power Trading Corporation (PTC, 2%)
- The Ministry of Environment Forests and Climate Change (MoEF&CC) awarded environmental clearance for the hydroelectric project in 2016 while the foundation stone was laid in February 2019.
- The project is being constructed at an estimated cost of Rs 4,287 crore and is expected to start commercial operations in July 2025.
- The Cabinet Committee on Economic Affairs (CCEA) approved the investment in the project in March 2019.
- Apart from helping address the energy demand across northern India and the state’s rural areas, it could aid small-scale and cottage industries.
Advantages of the Kiru Hydroelectric Power Project:
- This project aims to alleviate the energy shortage in Northern India while also enhancing the transportation, education, healthcare, and road infrastructure in the area.
- By bringing electricity to rural communities, the project will lessen the reliance of residents on alternative energy sources.
- The heightened power availability will foster the growth of small-scale and cottage industries, generating employment opportunities and revenue for the local populace.
What is a Run-of-river Project?
- Run-of-river hydropower is a facility that channels flowing water from a river through a canal or penstock to spin a turbine.
- Typically a run-of-river project will have little or no storage facility.
- Run-of-river provides a continuous supply of electricity (base load), with some flexibility of operation for daily fluctuations in demand through water flow that is regulated by the facility.
Race to the global eradication of Guinea worm disease nears the finish line
- 23 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
The world is on the brink of a public health triumph as it closes in on eradicating Guinea worm disease. There were more than 3.5 million cases of this disease in the 1980s, but according to the WHO, they dwindled to 14 cases in 2021, 13 in 2022, and just six in 2023.
What is Guinea Worm Disease?
- Dracunculiasis is also called guinea worm disease (GWD).
- It is an infection caused by a parasite called Dracunculus medinensis (guinea worm).
- This parasite is an organism that survives by deriving nutrients and feeding off another organism.
- GWD spreads through drinking contaminated water.
- It is presently eradicated in most parts of the world but is still seen in remote parts of Africa and some remote rural areas in the world where there is no access to clean drinking water.
- GWD is considered endemic in three African countries, Sudan, Ethiopia, and Mali.
- In recent years, a few cases of GWD in animals, especially dogs, have been reported in developed countries as well.
- GWD is a serious condition, that causes debilitating pain and complications, affecting the quality of life
Symptoms:
- People infected with Guinea worm don’t typically have any symptoms until about a year after they're first infected.
- It’s not until the worm is about to erupt from the skin that people start to feel sick.
- What that happens, the symptoms of Guinea worm disease can include Fever, Nausea and vomiting, Diarrhoea, Shortness of breath, Burning, itching, pain, and swelling where the worm is in the body (often the legs and feet) and Blister where the worm breaks through the skin.
Impact:
- Guinea worm disease isn’t often deadly, but it can cause serious complications, lifelong disabilities, and financial hardship for those involved.
- The pain involved is often so intense that it’s difficult for people to work, go to school, or care for themselves or others.
- This lasts an average of 8.5 weeks, though lifelong disability is common.
Dracunculiasis Treatment:
- There is no vaccine or drug developed to prevent or treat this disease.
- The only means available is the management of the disease which is removing the whole worm and caring for the wound caused by it and avoiding infection in the process or exposure to the guinea worm larvae at all costs, especially by avoiding contaminated drinking water and stagnant water sources.
- Without proper treatment, wounds caused by the worm can become infected by bacteria, leading to sepsis, septic arthritis, and contractures (when joints lock and deform).
- In some cases, these infections become life-threatening.
Earth’s early evolution: Fresh insights from rocks formed 3.5 billion years ago

- 23 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
Exploring ancient cratons such as the Singhbhum Craton in India, alongside similar formations in South Africa and Australia, provides unparalleled insights into the early stages of our planet's development, reaching back approximately 3.5 billion years.
What is Singhbhum Craton?
- The Singhbhum Craton encompasses a vast expanse of rugged terrain, primarily spanning regions in Jharkhand and Odisha, situated between the Chhota Nagpur plateau and the Eastern Ghats.
- Dating back approximately 3.5 billion years, this ancient segment of the Earth's crust offers valuable insights into early geological processes.
- Its oldest rock formations consist predominantly of volcanic and sedimentary rocks, referred to as greenstone successions.
- Greenstones are characterised by submarine volcanic rocks with minor sedimentary components.
- Geologically akin to greenstone belts in South Africa's Barberton and Nondweni regions and the Pilbara Craton in Western Australia, these areas experienced extensive submarine mafic volcanic activity, rich in magnesium oxide, between 3.5 and 3.3 billion years ago, with preserved features like pillowed lava and komatiites.
Significance:
- The Singhbhum Craton sheds light on early tectonic activities during the Archaean era, enhancing our understanding of the Earth's formative stages.
- Its distinctive geological characteristics, particularly the presence of greenstone belts, yield invaluable data on surface and atmospheric processes crucial for theorising about early habitable conditions and the emergence of life on Earth.
What are Cratons?
- A craton is a stable and ancient part of Earth's lithosphere that has experienced long-term tectonic and geomorphic stability.
- It is considered to be the nucleus of a continent and is characterised by its thick and cold lithosphere.
- Cratons can undergo destruction, which is defined as a geological process resulting in the loss of craton stability due to changes in its physical and chemical properties.
- The mechanisms responsible for craton destruction include oceanic plate subduction, rollback and retreat of subducting plates, stagnation and dehydration of subducting plates in the mantle transition zone, melting of the mantle caused by dehydration of stagnant slabs, non-steady flow in the upper mantle induced by melting, and changes like the lithospheric mantle.
- Craton destruction can lead to crustal thinning, surface uplift, and the concentration of mineral deposits.
Atal Vayo Abhyuday Yojana (AVYAY)

- 23 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
The Department of Social Justice and Empowerment, being the Nodal Department for the welfare of senior citizens, develops and implements programmes and policies for these groups in close collaboration with State Governments, Non-Governmental Organisations and civil society.
About the Atal Vayo Abhyuday Yojana (AVYAY):
- It is a Central Sector Scheme to improve the quality of life of the Senior Citizens.
- The project is implemented by the Department of Social Justice and Empowerment.
Aims and Objectives:
- The main objective of the Scheme is to improve the quality of life of Senior Citizens by providing basic amenities like shelter, food, medical care and entertainment opportunities and by encouraging productive and active ageing through providing support for capacity building of State/ UT Governments/Non-Governmental Organisations (NGOs)/Panchayati Raj Institutions (PRIs) / local bodies and the community at large.
The components of the AVYAY Scheme are as under:-
-
- Integrated Programme for Senior Citizens (IPSrC)
- State Action Plan for Senior Citizens (SAPSrC)
- Rashtriya Vayoshri Yojana (RVY)
- Elderline – National Helpline for Senior Citizens
- Senior-care Ageing Growth Engine (SAGE)
- Geriatric Caregivers Training
Components of the AVYAY Scheme:
- Integrated Programme for Senior Citizens (IPSrC): Grant aid is provided to Non-Governmental/ Voluntary Organizations for running and maintenance of Senior Citizens' Homes (old age homes), continuous care homes, etc.
- Facilities like shelter, nutrition, medicare and entertainment are provided free of cost to indigent senior citizens.
- State Action Plan for Senior Citizens (SAPSrC): Grant in aid is released to States/ UTs for the creation of a pool of trained Geriatric Caregivers for senior citizens, for carrying a special drive for Cataract Surgeries for Senior Citizens and State Specific Activities for the welfare of senior citizens, especially who are indigent in the States/UTs.
- Rashtriya Vayoshri Yojana (RVY): To provide for senior citizens, suffering from any age-related disability/infirmity such as low vision, hearing impairment, loss of teeth and loco-motor disabilities.
- The eligible senior citizens under this component are those who are in the BPL Category or have monthly income up to Rs.15000/.
- Generic and non-generic devices are distributed to the senior citizens through the camps.
- Elderline: National Helpline for Senior Citizens (14567): The Ministry has set up the National Helpline for Senior Citizens to provide free information, Guidance, Emotional Support and field intervention in cases of abuse and rescues.
- Senior-care Ageing Growth Engine (SAGE): To promote out-of-the-box and innovative solutions for commonly faced problems, innovative start-ups are identified and encouraged to develop products, processes and services for the welfare of the elderly under this initiative.
- The initiative is implemented through IFCI Venture Capital Funds Ltd. (Investment Manager).
- Geriatric Caregivers Training: To bridge the gap in supply and increasing demand in the field of geriatric caregivers and also to create a cadre of professional caregivers in the field of geriatrics.
- The component is implemented through the National Institute of Social Defence and at present 3,180 geriatric caregivers have been trained.
In a first, CERN scientists carry out laser cooling of Positronium

- 23 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
In a first, an international team of physicists from the Anti-hydrogen Experiment: Gravity, Interferometry, Spectroscopy (AEgIS) collaboration has achieved a breakthrough by demonstrating the laser cooling of Positronium.
About Anti-hydrogen Experiment: Gravity, Interferometry, Spectroscopy (AEgIS):
- AEgIS is an experiment at the Antiproton Decelerator facility at CERN (European Organization for Nuclear Research).
- It is a collaboration of physicists from a number of countries in Europe and from India.
- In 2018, AEgIS demonstrated the first pulsed production of antihydrogen atoms, by interacting pulse-produced positronium (an atom consisting of only an electron and a positron) with cold, trapped antiprotons.
- The primary scientific goal of the Antihydrogen Experiment: Gravity, Interferometry, Spectroscopy (AEgIS) is the direct measurement of the Earth's gravitational acceleration, g, on antihydrogen.
What is Positronium?
- Positronium is a bound state system of a positron and an electron, similar to the hydrogen atom, where an electron orbits around a proton.
- In the case of positronium, the positron and the electron orbit around their common centre of mass.
- The system is unstable, and the two particles eventually annihilate each other, releasing two or more gamma ray photons.
- Positronium has two possible states:
- The singlet state (para-positronium), in which the electron and the positron spins are antiparallel and the system has a shorter lifetime, and
- The triplet state (ortho-positronium), in which the electron and the positron spins are parallel, and the system has a longer lifetime.
- Positronium has been studied extensively in experimental and theoretical physics because it provides a simple system for testing quantum electrodynamics (QED) and for studying the properties of matter and antimatter.
- It also has potential applications in fields such as material science, plasma physics, and astrophysics.
What is Antimatter?
- Antimatter shares similarities with ordinary matter, except for its opposite electric charge.
- Often referred to as "mirror" matter, antimatter pairs with ordinary matter particles.
- For example, while an electron possesses a negative charge, its antimatter counterpart is a positron, which carries a positive charge and has the same mass as an electron.
- Positrons, antiprotons, and antineutrons are the antimatter counterparts of electrons, protons, and neutrons, respectively, collectively known as antiparticles.
- These antiparticles can combine to form anti-atoms and theoretically could lead to the formation of antimatter regions within our universe.
- However, the coexistence of matter and antimatter is short-lived due to their tendency to annihilate upon contact, resulting in the release of substantial energy in the form of gamma rays or elementary particles.
- Antimatter, like matter, emerged during the Big Bang.
- Scientists have produced antimatter particles through high-speed collisions in large particle accelerators like the Large Hadron Collider operated by CERN outside Geneva.
- Additionally, antiparticles are sporadically generated throughout the universe through natural processes.
Eminent Jurist Senior Advocate Fali Nariman passes away

- 22 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
Recently, eminent jurist and senior advocate of the Supreme Court Fali S Nariman died at the age of 95.
Who was Fali S Nariman?
- Fali S Nariman was born on January 10, 1929, in Rangoon, then part of British India.
- He began his legal career by enrolling as an advocate of the Bombay High Court in November 1950.
- His stature grew, and he was designated as a senior advocate in 1961.
- In 1972, he moved to New Delhi to practise in the Supreme Court of India.
- In May 1972, Nariman assumed the role of additional solicitor-general of India; however, he resigned a day after the Emergency was imposed on June 26, 1975.
- He also served as the president of the International Council for Commercial Arbitration and chaired the Executive Committee of the International Commission of Jurists, Geneva, from 1995 to 1997.
- His son, Justice Rohinton F Nariman, formerly served as a judge on the Supreme Court.
- Nariman received the Padma Bhushan in January 1991 and in 2007 he was awarded the Padma Vibhushan.
What Were Some of Nariman's Landmark Cases?
- The Golak Nath case: In the historic judgement, the Supreme Court held that the Parliament cannot make a law which is capable of infringing the fundamental rights of citizens.
- It came up after two brothers in Punjab challenged the Constitution (17) Amendment Act, 1964, which came into effect by amending Article 31A of the Constitution. (This article deals with the acquisition of estates).
- Nariman, not only supported the petitioners but also appeared to argue on the issue representing the intervenors in the case.
- They argued that Parliament’s power to amend the Constitution under Article 368 did not include articles contained in Part III of the Constitution dealing with fundamental rights.
- Following the hearing of the case submitted in 1967, an eleven-judge bench agreed with the petitioner’s submissions pointing out that Article 13(2) states that Parliament cannot make a law which infringes fundamental rights.
- The Kesavananda Bharati case: The Kesavananda Bharati case is known for setting a benchmark in the Indian judiciary and had Nariman’s prompt representation in the SC.
- He assisted noted Advocate Nanabhoy Palkhivala in the famous case that led to the path-breaking judgement laying down the basic structure doctrine of the Constitution, clipping Parliament’s power to amend the Constitution.
- The 1973 verdict simultaneously gave the judiciary the authority to review any constitutional amendment on grounds of violation of the basic structure of the Constitution.
- The Bhopal Gas Tragedy case: In 1984, the Bhopal gas tragedy where 42 tons of toxic chemicals leaked from a pesticide plant owned by Union Carbide India Limited, resulting in thousands of deaths and environmental damage in the following years.
- The Supreme Court began hearing the case for compensation to the victims in 1988.
- Senior Advocate Nariman appeared, representing Union Carbide, and offered to pay a sum of 426 million dollars as compensation to the victims of the tragedy.
- In 1989, Union Carbide settled with the central government and agreed to pay 470 million dollars as compensation.
- The Cauvery Water Dispute case: Nariman represented Karnataka for over 30 years in the water-sharing dispute with Tamil Nadu.
- In 2016, the Supreme Court ordered the Karnataka government to release 6,000 cusecs (cubic feet per second) of water from September 21 to September 27.
- The Karnataka legislative assembly, however, passed a resolution stating that they did not have water to spare and chose to defy the court’s orders.
- Due to this non-compliance, Nariman refused to argue the case on behalf of the Karnataka government any further.
- On February 16, 2018, the court in its final judgement took note of Nariman’s stance on the issue and necessarily mentioned that Nariman had courageously lived up to the highest tradition of the Bar.
- The court then proceeded to reduce Karnataka’s annual water releases to 177.25 thousand million cubic feet (TMC) from 192 TMC.
- Disproportionate assets case against former Tamil Nadu Chief Minister J Jayalalithaa: AIADMK leader and former- Tamil Nadu CM Jayalalitha had been accused of misappropriating funds during her tenure between 1991 and 1995.
- A Sessions Court in Bangalore in September 2014 found that she had acquired property disproportionate to her known income and imposed a Rs 100 crore fine on her.
- This sentence was upheld by the Karnataka High Court a month later leading to an appeal at the Supreme Court.
- Nariman appeared on behalf of Jayalalitha in October 2014 and convinced the court to grant bail against executing the fine and suspend the sentence passed by the Sessions judge in Bangalore.
- The 1981 Second Judges case: The Supreme Court held that the primacy of the Chief Justice of India’s recommendation in judicial appointment and transfer can be turned down on cogent grounds by the government.
- However, the judicial discussions finally led to the creation of the collegium system of appointment of judges to constitutional courts in 1993, when the top court came out with its judgement in the second judge’s case.
- Nariman had stated that the advice given through consultation with the CJI must be seen as binding to protect the independence of the judiciary, as judges would be in a better position to determine the suitability and competence of candidates.
- In 1993, the nine-judge bench agreed with Nariman’s arguments and established the Supreme Court Collegium.
- The COVID-19 case: Nariman represented the Parsi community in its dispute over the protocol and standard operating procedure for handling of dead bodies of Parsi Zoroastrian COVID-19 victims under which metallic nets were to be installed above ‘Tower of Silence’ so that birds did not feed on the corpses and carry the killer virus elsewhere
Cabinet approves Flood Management and Border Areas Programme (FMBAP) for the period 2021-26

- 22 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
Recently, the Union Cabinet approved the continuation of “Flood Management and Border Areas Programme (FMBAP)” with a total outlay of Rs. 4,100 crore for a period of 5 years from 2021-22 to 2025-26.
About the Flood Management and Border Areas Programme (FMBAP):
- The FMBAP Scheme is being implemented throughout the country for effective flood management, erosion control and anti-sea erosion and to help in maintaining peace along the border.
- The scheme benefits towns, villages, industrial establishments, communication links, agricultural fields, infrastructure etc. from floods and erosion in the country.
- The catchment area treatment works will help in the reduction of sediment load into rivers.
- The Scheme aims at the completion of the ongoing projects already approved under FMP.
The Scheme has two components:
- Under the Flood Management Programme (FMP) component of FMBAP with an outlay of Rs. 2940 crore, central assistance will be provided to State Governments for taking up critical works related to flood control, anti-erosion, drainage development and anti-sea erosion, etc.
- The pattern of funding to be followed is 90% (Centre): 10% (State) for Special Category States (8 North-Eastern States and Hilly States of Himachal Pradesh, Uttarakhand and UT of Jammu & Kashmir) and 60% (Centre):40% (State) for General/ Non-Special Category States.
- Under the River Management and Border Areas (RMBA) component of FMBAP with an outlay of Rs. 1160 crore, flood control and anti-erosion work on common border rivers with neighbouring countries including hydrological observations and flood forecasting, and investigation & pre-construction activities of joint water resources projects (with neighbouring countries) on common border rivers will be taken up with 100% central assistance.
- The Scheme has the provision of incentivizing the States which implement flood plain zoning, recognized as an effective non-structural measure for flood management.
Importance:
- While the primary duty of flood management lies with the State Governments, the Union Government actively promotes and advocates for the adoption of modern technology and innovative approaches.
- Additionally, projects executed under the RMBA component serve to safeguard critical installations of security agencies and border outposts situated along border rivers from the perils of floods and erosion.
- Furthermore, the scheme includes provisions for incentivizing states that implement flood plain zoning, a recognized and effective non-structural measure for flood management.
Will the ‘Paruveta Festival’ celebrated in Andhra’s Ahobilam get UNESCO recognition?

- 22 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
INTACH is striving to obtain UNESCO recognition for the yearly 'Paruveta' festival, emphasising its cultural significance.
About the Paruveta Festival:
- Paruveta Festival, also known as the 'mock hunting festival', is a celebrated tradition at the Sri Narasimha Swamy temple in Ahobilam, Andhra Pradesh.
- It stands out as a symbol of communal harmony, where devotees from various religious backgrounds, including Muslims, come together to offer prayers.
Origin and Significance:
- According to folklore, the festival commemorates Lord Vishnu's incarnation as Narasimha, who married Chenchulakshmi, a tribal girl, symbolising unity across different communities.
- The festival's rituals, typically observed during Vijayadashami or Sankranti, extend for a 'mandala' period of forty days in Ahobilam.
Activities and Customs:
- During the festival, the temple deity is carried to the 32 Chenchu tribal villages surrounding Ahobilam for forty days.
- The journey begins with a symbolic act where tribals shoot arrows at the deity's palanquin, signifying protection and reverence.
- Chenchus participated by undertaking 'Narasimha Deeksha', wearing yellow robes and Tulasi Mala, while observing celibacy.
- The temple staff reside in these villages throughout the festival, showcasing the tradition of a casteless society with no traces of untouchability.
Key Points about Chenchu Tribes:
- Geographic Distribution: Chenchu tribes primarily inhabit the hills of southern India, particularly in Andhra Pradesh.
- Additionally, Chenchu communities can be found in Tamil Nadu, Karnataka, and Orissa.
- Language and Communication: Their native language, known as Chenchu, belongs to the Dravidian language family.
- While many Chenchu individuals speak Telugu, their traditional language holds cultural significance.
- Livelihood and Occupation: Historically, Chenchu people pursued a nomadic lifestyle, relying on food gathering.
- However, due to factors such as agricultural expansion, many have transitioned to working as farmers or forest labourers.
- Housing and Settlements: Chenchu dwellings are typically hive-shaped structures constructed from wattle thatch, composed of interwoven poles, twigs, reeds, or branches.
- These houses reflect their traditional architectural style and are adapted to their environment.
- Social Structure: Chenchu society is organised into clans, which are extended family units, as well as local groups and individual families.
- They adhere to exogamous marriage practices, prohibiting unions within the same clan.
- Additionally, Chenchu kinship is patrilineal, tracing descent through male lineage.
Unauthorised online lending apps high on the FSDC scanner

- 22 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
Fresh measures to curb unauthorised online lending apps’ operations could be on the anvil, following deliberations on the issue at the Financial Stability and Development Council (FSDC) chaired by Finance Minister Nirmala Sitharaman recently.
About the Financial Stability and Development Council (FSDC):
- The Financial Stability and Development Council (FSDC) is a high-level body established by the Government of India in 2010 to address macroeconomic and financial stability issues.
- Although not a statutory body, it operates under the Financial Stability Division of the Department of Economic Affairs within the Ministry of Finance.
Background:
- In response to the global financial crisis of 2008, recommendations were made by the Raghuram Rajan Committee for the creation of a centralised regulatory body to oversee India's financial system.
- The establishment of FSDC reflects India's proactive approach to enhance preparedness for future financial challenges.
Composition:
- Chaired by the Union Finance Minister, the council comprises key stakeholders including the Governor of the Reserve Bank of India (RBI), finance and economic affairs officials, regulatory body chairpersons, and other relevant authorities.
- The Secretary of the Department of Economic Affairs serves as the council's secretary.
Responsibilities:
- FSDC is entrusted with the task of promoting financial stability, coordinating policy responses to systemic risks, and fostering the development of India's financial sector.
Concerns and Future Directions:
- Concerns have been raised about potential encroachment on the autonomy of sectoral regulators due to FSDC's leadership by the Union Finance Minister.
- To address this, it's crucial to safeguard the independence of regulatory bodies and establish clear guidelines to ensure effective coordination without undermining regulatory authority.
What is Digital Lending?
- Digital lending refers to the process of accessing credit online, facilitated through web platforms or mobile applications.
- This approach leverages technology across various stages of the lending process, including customer acquisition, credit assessment, approval, fund disbursement, recovery, and customer service.
Key Features:
- Utilises technology for end-to-end lending operations, enhancing efficiency and accessibility.
- Offers flexibility in credit options and facilitates swift transactions, appealing to modern borrowers.
- Prominent examples include Buy Now, Pay Later (BNPL) schemes, which provide short-term financing for purchases, allowing consumers to defer immediate payments.
Drivers of Growth:
- Increased adoption is driven by widespread smartphone usage and the convenience of online transactions.
- Flexibility in credit offerings and simplified application processes contribute to the popularity of digital lending platforms.
- BNPL services, in particular, cater to consumers seeking deferred payment options for purchases and services.
Centre increases Fair and Remunerative Prices of sugarcane

- 22 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
The Cabinet Committee on Economic Affairs recently approved ?340/quintal as the Fair and Remunerative Price (FRP) of sugarcane for the sugar season 2024-25 at a sugar recovery rate of 10.25%.
What is the Fair and Remunerative Price (FRP)?
- FRP was introduced by the government in 2009 by an amendment to the Sugarcane (Control) Order, 1966.
- It replaced the Statutory Minimum Price (SMP) on the Commission for Agricultural Costs and Prices (CACP) consultation.
- The FRP system assured timely payment to farmers, irrespective of the profit and loss to sugar mills.
- Further, the new system made it mandatory for sugar mills to pay the farmers within 14 days of delivery of sugarcane.
- Additionally, the FRP system introduced grading on the basis of sugar recovery rate from sugarcane wherein a premium was paid to the farmer on higher recovery and a reduction in rates on lower recovery.
- The FRP is based on the Rangarajan Committee report on reorganising the sugarcane industry.
Factors Considered for Announcing FRP:
-
- Cost of production of sugarcane
- Return to the growers from alternative crops and the general trend of prices of agricultural commodities
- Availability of sugar to consumers at a fair price
- The price at which sugar produced from sugarcane is sold by sugar producers
- Recovery of sugar from sugarcane
- The realisation made from the sale of by-products viz. molasses, bagasse and press mud or their imputed value
- Reasonable margins for the growers of sugarcane on account of risk and profits
Effect of the New FRP:
- Sugar production in India was hit hard in the October-December 2023 quarter as production fell by 11.21 million metric tonnes;
- It was 12 million in the same quarter the previous year.
- The increase in FRP is going to increase the cost for producers.
- The increased FRP will benefit over five crore sugarcane farmers in the country, however, the increase in production cost could affect end-consumers as well.
- Factors such as FRP hikes, akin to MSP, make it attractive to farmers but also increase prices in the local market as mills pass on that cost to consumers
WHO launches digital health platform agreed upon in India’s G20 presidency

- 21 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
Achieving one of the three priority areas agreed upon during India’s G20 presidency in 2023, the World Health Organization (WHO) recently launched the Global Initiative on Digital Health (GIDH) virtually, a platform for sharing knowledge and digital products among countries.
About Global Initiative on Digital Health (GIDH):
- The Global Initiative on Digital Health (GIDH) is a network managed by the World Health Organization (WHO), dedicated to enhancing and coordinating efforts for country-led digital health transformation through collaborative partnerships and knowledge sharing.
- It was launched by the WHO and the Government of India during the G20 Health Ministerial Meeting in Gandhinagar.
- Functioning as a platform for inter-country knowledge exchange and digital product dissemination, GIDH strives to achieve several key objectives through collective action:
- Assess and prioritise countries' requirements for sustainable digital health transformation.
- Enhance the alignment of digital health resources and address unfunded priorities at the country level.
- Facilitate the accelerated attainment of the strategic objectives outlined in the Global Strategy on Digital Health 2020-2025.
- Promote capacity building and synergize efforts to support local development, maintenance, and adaptation of digital health technologies to evolving needs.
- Comprising four primary components, GIDH operates as a network of networks:
- Country Needs Tracker: Tracks and prioritises country-specific digital health requirements.
- Country Resource Portal: Provides a comprehensive map of available digital health resources within each country.
- Transformation Toolbox: Shares quality-assured digital tools to support country-led digital health initiatives.
- Knowledge Exchange: Facilitates the exchange of insights and best practices among member countries.
- GIDH extends support to countries in three fundamental ways:
- By attentively addressing their needs
- By fostering resource alignment to prevent fragmentation, and
- By offering access to quality-assured digital products.
- Membership in GIDH is open to all institutions actively involved in the digital health domain.
What is Digital Health?
- Digital health denotes the utilisation of technology, encompassing mobile devices, software applications, and various digital tools, to enhance health outcomes and streamline healthcare delivery.
- Essentially, it represents an interdisciplinary field at the intersection of technology and healthcare, integrating a diverse array of concepts and innovations.
- This encompasses a broad spectrum of technologies and services, spanning telemedicine, electronic health records, wearable devices, health information exchange, and more.
- Examples of notable digital health initiatives include India’s CoWIN platform and UNICEF's RapidPro and FamilyConnect programs.
- RapidPro, UNICEF’s real-time information platform, serves as a foundational component in its digital health portfolio.
- FamilyConnect, another UNICEF initiative, delivers targeted, lifecycle-based messages via SMS to various recipients, including pregnant women, new mothers, and heads of households.
India Initiatives on Digital Health:
- National Digital Health Mission (NDHM): Designed to establish a comprehensive national digital health ecosystem featuring unique health IDs, electronic health records (EHRs), and a platform for health data exchange.
- Ayushman Bharat Digital Mission (ABDM): Aims to develop a digital infrastructure for the Ayushman Bharat Health Infrastructure Mission (ABHIM), incorporating health registries, electronic claim processing, and telemedicine services.
- E-Sanjeevani Telemedicine Platform: Enables virtual consultations between healthcare providers and patients nationwide, enhancing access to medical care.
- Jan Arogya Setu App and CoWIN Platform: Offers access to healthcare services, facilitates appointment scheduling, and disseminates COVID-19-related information.
- Digital Aarogya Mitra (DAM): Implements a community health worker program utilising technology for data collection and community-based health interventions.
Malta becomes the 119th member of the International Solar Alliance

- 21 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
Malta became the 119th country to join the International Solar Alliance recently.
About the International Solar Alliance (ISA):
- The International Solar Alliance (ISA) is an alliance of more than 120 signatory countries that aims to reduce the dependence on non-renewable sources of energy like fossil fuels.
- Currently, 118 countries are signatories to the ISA Framework Agreement.
- The ISA is an action-oriented, member-driven, collaborative platform for increased deployment of solar energy technologies as a means for bringing energy access, ensuring energy security, and driving energy transition in its member countries.
- The platform strives to develop and deploy cost-effective and transformational energy solutions powered by the sun to help member countries develop low-carbon growth trajectories, with a particular focus on delivering impact in countries categorised as Least Developed Countries (LDCs) and the Small Island Developing States (SIDS).
- The ISA was conceived as a joint effort by India and France to mobilise efforts against climate change through the deployment of solar energy solutions.
- It was conceptualised on the sidelines of the 21st Conference of Parties (COP21) to the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC) held in Paris in 2015.
Role of India:
- As a founding member, India holds a pivotal position within the alliance, serving both as a host nation and a major contributor to achieving its objectives.
- The ISA marks a historic milestone as the first international organisation to establish its secretariat in India.
- With a target of generating 100 GW of solar energy by 2022, India's commitment represents a significant portion of the ISA's overall goal.
Recent Developments:
- The ISA was granted Observer Status by the UN General Assembly, fostering closer collaboration between the alliance and the United Nations to advance global energy growth and development.
- The approval of the 'Solar Facility' by the ISA introduces a payment guarantee mechanism aimed at incentivizing investments in solar projects, further driving progress towards sustainable energy initiatives.
India contributes $1 million to fund combating poverty and hunger

- 21 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
Recently, India has contributed 1 million US Dollars to the Poverty and Hunger Alleviation Fund established by India, Brazil, and South Africa, IBSA.
What is the IBSA Fund?
- Established in 2004 and operational since 2006, the IBSA Fund embodies the collaborative efforts of India, Brazil, and South Africa.
- Contributing one million dollars annually each, the IBSA countries unite in a spirit of partnership to champion Southern-led, demand-driven projects in developing nations.
- With a focus on identifying replicable and scalable initiatives, the fund aims to address pressing development challenges in recipient countries.
- Supported projects align with partner countries' national priorities and international development agendas, including the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs).
- The fund's objectives encompass diverse areas such as promoting food security, combating HIV/AIDS, and expanding access to safe drinking water, among others, to advance sustainable development.
- To date, the IBSA Fund has allocated USD 50.6 million, funding 45 projects across 37 countries in the Global South.
- The United Nations Office for South-South Cooperation (UNOSSC) fulfils the roles of Fund Manager and Secretariat for the IBSA Fund.
What is IBSA?
- IBSA stands for the India, Brazil, and South Africa Dialogue Forum, a unique platform that unites three major democracies and significant economies from diverse continents, collectively addressing common challenges.
- Formally established as the IBSA Dialogue Forum during a historic meeting of the Foreign Ministers from India, Brazil, and South Africa in Brasilia on June 6, 2003, the forum's inception was marked by the issuance of the Brasilia Declaration.
- To date, five IBSA Leadership Summits have been convened, with the 5th Summit held in Pretoria on October 18, 2011.
- In 2021, India held the chairmanship of IBSA under the theme "Democracy for Demography and Development."
- On March 2, 2023, Brazil assumed the rotating presidency of the India, Brazil, South Africa Dialogue Forum (IBSA), further advancing the forum's collaborative agenda.
Global leaders converge in Delhi for Raisina Dialogue 2024

- 21 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
The ninth edition of the Raisina Dialogue will be held from today till Friday (February 23) in New Delhi.
What is the Raisina Dialogue?
- The Raisina Dialogue is India’s premier conference on geopolitics and geoeconomics committed to addressing the most challenging issues facing the global community.
- Every year, leaders in politics, business, media, and civil society converge in New Delhi to discuss the state of the world and explore opportunities for cooperation on a wide range of contemporary matters.
- The Dialogue is structured as a multi-stakeholder, cross-sectoral discussion, involving heads of state, cabinet ministers and local government officials, who are joined by thought leaders from the private sector, media and academia.
- The conference is hosted by the Observer Research Foundation in partnership with the Ministry of External Affairs, Government of India.
- This effort is supported by a number of institutions, organisations and individuals, who are committed to the mission of the conference.
- The theme of the 2024 edition is “Chaturanga: Conflict, Contest, Cooperate, Create”.
- During the three-day conference, the participants will engage with each other over six “thematic pillars”. These include:
- Tech Frontiers: Regulations & Realities
- Peace with the Planet: Invest & Innovate
- War & Peace: Armouries & Asymmetries
- Decolonising Multilateralism: Institutions & Inclusion
- The Post 2030 Agenda: People & Progress; and
- Defending Democracy: Society & Sovereignty.
After 30 years, Buddha relics travel to Thailand

- 21 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
Four of the 20 relics of Lord Buddha preserved at the National Museum are being taken to Thailand for a month-long exposition beginning recently, in a rare trip abroad for the delicate antiquities recovered more than a century ago.
About the Relics of Lord Buddha:
- The relics of Lord Buddha and his disciples Arahata Sariputra and Arahata Maudgalayana are known as the ‘Kapilvastu Relics.’
- The relics date back to around the 4th or 5th Century BC.
- They were found in Bihar’s Piprahwa — a site that is believed to be the ancient city of Kapilvastu.
- Piprahwa today is located in Uttar Pradesh’s Siddharthnagar district.
- The relics were discovered by a team of Archaeological Survey of India (ASI) officials in the 1970s.
- The ASI conducted excavations at Piprahwa from 1971-77 under the supervision of the archaeology director KM Srivastava.
History:
- Lord Buddha achieved Mahaparinirvana at the age of 80 in Kushinagar.
- The Mallas of Kushinagara cremated his body with ceremonies befitting a ‘Universal King’ (‘cakravartin’).
- His holy relics, from the funeral pyre, were collected, divided and given by Brahmin priest Dhona of Kushinagar to kings and priests.
- The eight shares were distributed among Ajatashatru of Magadha, the Licchavis of Vaishali, the Sakyas of Kapilavastu, Mallas of Kushinagar, Bullies of Allakappa, the Mallas of Pava, the Koliyas of Ramagrama and a Brahmana of Vethadipa.
- The sacred relics were commemorated in eight different stupas.
- Two more stupas came into existence, one over the urn in which the relics had been collected and one over the embers.
- Thus, stupas erected over the bodily relics of Buddha (Saririka-stupas) are the earliest surviving Buddhist shrines.
- It is stated that Ashoka (circa 272-232 BC), being an ardent follower of Buddhism, opened up seven of these eight stupas, and collected a major portion of the relics for enshrinement within innumerable stupas built by him to popularise Buddhism and spread dharma.
- In 1898, the discovery of an inscribed casket by William Claxton Peppé, a British colonial engineer and an estate manager at a Buddhist stupa site at Piprahwa, was an epoch-making incident.
- The inscription on the lid referred to the relics of Buddha and his community.
- The bone relics present in the stone coffer were presented to King Rama V of Thailand.
- The relics were further divided into three shares and gifted to Thailand, Myanmar and Sri Lanka.
- In Thailand, the holy relic has been enshrined in a chedi on the top of Suwanbanphot, Bangkok.
- Every year, during the Loi Krathong Festival, there is a seven-day and seven-night celebration, which has become a tradition to worship the Buddha’s relics.
La Nina impacted air quality in India in the winter of 2022
- 20 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
A new study suggests that monsoon rainfall over India, which is strongly influenced by El Niño and La Niña events—alternating warming and cooling of the eastern Pacific Ocean impacting global weather may also affect air quality in the country.
Key Findings of the New Study on the Impact of La Niña on Air Quality in India:
- According to the researchers at the National Institute of Advanced Studies (Bengaluru) and the Indian Institute of Tropical Meteorology (Pune), the strong influence of El Niño and La Niña events on monsoon rainfall over India, driven by the alternating warming and cooling of the eastern Pacific Ocean, with far-reaching effects on global weather patterns.
- Remarkably, this study marks the first time that air quality in Indian cities has been directly linked to a La Niña event, suggesting an indirect connection to climate change, which intensifies the severity of El Niño and La Niña occurrences.
- Traditionally, northern Indian cities, notably Delhi, face elevated concentrations of PM2.5 pollutants from October to January.
- However, the winter of 2022 witnessed a notable deviation from this trend, with northern cities experiencing cleaner air than usual, while western and southern cities like Mumbai, Bengaluru, and Chennai saw worsened air quality.
- Specifically, Delhi observed a 10% reduction in PM2.5 concentrations, contrasted with a 30% increase in Mumbai and a 20% rise in Bengaluru.
- The researchers, investigating this anomaly, identified the potent effects of the La Niña event, notably stronger than typical occurrences, leading to significant changes in wind circulation patterns over India.
- This impact became pronounced in the third year of La Niña, suggesting a cumulative effect that may amplify over time.
- While La Niña events are associated with improved air quality in northern India, the study emphasizes the need for further research to understand the potential impacts of El Niño events, which may produce contrasting effects on air quality across the country.
What are El Niño and La Niña?
- El Niño refers to a band of warmer water spreading from west to east in the equatorial Pacific Ocean.
- Similarly, a La Niña occurs when the band of water spreads east to west and is cooler.
- Both phenomena affect the weather worldwide and can have drastic effects on economies that depend on rainfall.
- Together, El Niño and La Niña make up a cyclical process called the El Niño Southern Oscillation.
- An El Niño year creates a global warming crisis in miniature because the warm water spreading across the tropical Pacific releases a large amount of heat into the atmosphere.
- El Niño: El Niño is characterized by warmer-than-average sea surface temperatures in the central and eastern Pacific Ocean.
- In India, El Niño events often correlate with below-average rainfall during the monsoon season.
- This can lead to drought conditions in some regions, affecting agriculture and water resources.
- El Niño can also influence temperature patterns, with some parts of India experiencing warmer temperatures during El Niño events.
- La Niña: La Niña is characterized by cooler-than-average sea surface temperatures in the central and eastern Pacific Ocean.
- In India, La Niña events often correlate with above-average rainfall during the monsoon season.
- This can lead to increased precipitation in some regions, potentially causing flooding, while other areas may experience drought conditions.
- La Niña can also influence temperature patterns, with some parts of India experiencing cooler temperatures during La Niña events.
Impact of La Niña on Air Quality in India:
- Altering Wind Patterns: During the winter of 2022, the typical north-westerly winds, carrying agricultural pollutants from Punjab and Haryana towards Delhi and the Gangetic plains, were disrupted.
- Instead, wind circulation shifted to a north-south direction, diverting pollutants away from Delhi.
- Consequently, pollutants bypassed Delhi, travelling over Rajasthan and Gujarat towards southern regions.
- Modifying Local Wind Circulation near Mumbai: In Mumbai, the local wind circulation, which alternates between land-to-sea and sea-to-land flows every few days, experienced prolonged unidirectional winds.
- This sustained wind pattern prevented the dispersal of pollutants from the city, leading to their accumulation within Mumbai's atmosphere throughout the winter of 2022.
- These changes in wind patterns, influenced by La Niña, significantly impacted air quality dynamics in India, highlighting the intricate relationship between climate phenomena and regional atmospheric conditions.
Gold Hunt by Villagers Reveals Ancient Harappan Settlement in Gujarat

- 20 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
The newly discovered Harappan settlement at Lodrani village in the Kutch region of Gujarat has sparked widespread interest in the fascinating remains of this ancient civilisation, making it an important site for archaeological exploration and research.
Features of Harappan site Morodharo:
- Morodharo is a fortified settlement of the Harappan era, with the fortification measuring 102 m to the west and 58 m north to the south.
- The thickness of the wall is 3.3 m on average.
- Morodhara has a 10x10 m platform on the southwest side and a well on the northeast side.
- Burial cairns have been found at Morodharo.
- A cairn is an intentionally constructed mound of stones, typically created for marking a location or serving as a burial mound.
- Harappan pottery with perforated jar sherds, reserved slipware and terracotta cakes have also been unearthed.
- All these items have a striking resemblance to those found in Dholavira.
About Harappan Civilization:
- The Harappan civilization, also known as the Indus Valley civilization was South Asia's first urban civilization, flourishing concurrently with Mesopotamia and Egypt.
- It encompassed the most extensive territory, covering approximately 800,000 square kilometres, compared to its contemporaries.
- Prominent cities during the Harappan period included Harappa and Mohenjo-Daro in present-day Pakistan, along with Dholavira, Lothal, and Surkotada in Gujarat, India, among others.
- Urban planning in Harappan cities followed a meticulous grid layout, with streets intersecting at right angles, dividing the cities into neat rectangular blocks.
- The streets and alleys were deliberately designed for efficient movement, accommodating carts and pedestrians, often featuring covered drains alongside.
- For defence and security, the cities were enclosed by sturdy walls made of mud bricks, shielding against intruders and natural calamities.
- Each city was structured into an elevated citadel and a lower town, with the former housing monumental structures like granaries and administrative buildings.
- Residential areas comprised multi-story brick houses clustered around courtyards, some equipped with private wells and well-ventilated bathrooms.
- A sophisticated drainage system ensured efficient waste disposal, with individual house drains connected to street-level drainage networks.
- Granaries and storage facilities were strategically positioned to manage surplus agricultural yields, reflecting advanced urban planning and resource management.
India, and ASEAN discuss the review of the trade agreement

- 20 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
India hosted the 3rd meeting of the AITIGA Joint Committee, which focused on reviewing the ASEAN-India Trade in Goods Agreement at Vanijya Bhawan in New Delhi from February 16th to 19th, 2024.
About the ASEAN-India Trade in Goods Agreement (AITIGA):
- The ASEAN-India Trade in Goods Agreement (AITIGA) is a trade deal between the ten member states of ASEAN and India.
- ASEAN and India signed the Agreement at the 7th ASEAN Economic Ministers-India Consultations in Bangkok, Thailand in 2009.
- The Agreement, which came into effect in 2010, is sometimes referred to as the ASEAN-India Free Trade Agreement.
- The Agreement originated out of the Framework Agreement on Comprehensive Economic Cooperation between India and ASEAN created in 2003.
- The Framework Agreement laid a sound basis for the establishment of an ASEAN-India Free Trade Area (FTA), which includes FTA in goods, services and investment.
- The Agreement has led to steadily increasing trade between ASEAN and India since its signing.
- In 2019-20, trade between India and ASEAN was worth US$86 billion.
About ASEAN:
- The Association of Southeast Asian Nations, or ASEAN is an intergovernmental organization of ten Southeast Asian countries:
- Brunei, Cambodia, Indonesia, Laos, Malaysia, Myanmar, the Philippines, Singapore, Thailand, and Vietnam.
- ASEAN's primary objectives are to promote political and economic cooperation and regional stability among its member states.
- The organization operates on the principles of mutual respect, non-interference in internal affairs, and consensus-building. ASEAN's motto, "One Vision, One Identity, One Community," underscores its commitment to fostering unity and solidarity among Southeast Asian nations.
- Economically, ASEAN has made significant strides towards integration through initiatives like the ASEAN Economic Community (AEC), aimed at creating a single market and production base.
- This has facilitated trade, investment, and economic development within the region.
- Additionally, ASEAN serves as a platform for dialogue and cooperation on a wide range of issues, including security, environmental sustainability, cultural exchange, and disaster management.
BSNL floats Rs 65,000 crore tender for phase-III BharatNet project

- 20 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
BSNL, the state-owned telecommunications company, has initiated a tender process amounting to approximately Rs 65,000 crore for the implementation of the phase-III BharatNet project.
What is the BharatNet Phase III Project?
- The BharatNet phase-III project adopts a three-level architecture:
- Internet leased line bandwidth
- Middle-mile connectivity, and
- Last-mile connectivity
- It aims to involve village-level entrepreneurs or Udyamis in providing last-mile connectivity to households on a revenue-sharing basis.
- BSNL aims to provide 15 million home fibre connections over five years using the BharatNet Udyami model.
About BharatNet Project:
- The BharatNet Project is one of the largest rural telecom projects in the world.
- It aimed at providing broadband connectivity to all Gram Panchayats across India in a phased manner.
- Its core objective is to ensure equitable access to broadband services for all telecom service providers, fostering the deployment of services like e-health, e-education, and e-governance in rural and remote areas.
- Initiated in 2011 and executed by Bharat Broadband Network Limited (BBNL), a Special Purpose Vehicle established in 2012, the project operates in three phases.
- Phase I launched in 2011, focused on creating the National Optical Fibre Network, leveraging existing infrastructure and laying additional fibre to bridge connectivity gaps up to the Gram Panchayat level.
- Phase II, approved in 2017, builds upon Phase I’s experiences, aligning with the Digital India vision.
- It adopts a flexible approach, integrating various media such as Optical Fibre Cable (OFC), Radio, and satellite to connect Gram Panchayats, utilizing models like State-led, Private Sector, and CPSU Models for implementation.
- Phase III, spanning from 2019 to 2023, aims to establish a robust, future-ready network with district-to-block fibre connectivity, featuring ring topology for redundancy.
- This comprehensive approach ensures the creation of a resilient and inclusive telecom infrastructure, facilitating socio-economic development in rural India.
Hundred years ago, Satyendra Nath Bose changed physics forever
- 20 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
In 2024, we commemorate the centenary of Bose's pivotal discovery of the precise equations governing the behaviour of collections of photons, fundamental particles of light.
About Satyendra Nath Bose:
- Satyendra Nath Bose (1894-1974) was an eminent Indian physicist renowned for his pioneering contributions to theoretical physics, notably in the realms of quantum mechanics and statistical mechanics.
- His groundbreaking research laid the groundwork for Bose-Einstein statistics and the theoretical elucidation of Bose-Einstein condensate, a novel state of matter.
- Bose's profound insights not only advanced the understanding of fundamental physics but also played a pivotal role in refining the Standard Model of Particle Physics.
- His visionary work eventually paved the way for significant discoveries in particle physics, including the identification of the Higgs Boson, colloquially referred to as the "God Particle."
Major Contributions of Satyendra Nath Bose:
- Foundation of Bose-Einstein Statistics and Bosons: In 1924, Bose formulated a revolutionary explanation for Planck's law of black-body radiation using quantum mechanics principles, introducing the concept of "Bose-Einstein statistics."
- This theory delineates the behaviour of particles known as "bosons," characterized by integer spin.
- Bose-Einstein statistics elucidate how bosons, such as photons and atoms, preferentially occupy the same quantum state, a behaviour distinct from fermions governed by the Pauli exclusion principle.
- This groundbreaking work laid the groundwork for understanding particle behaviour at low temperatures and foretold the existence of the Bose-Einstein condensate, a novel state of matter.
- Prediction of Bose-Einstein Condensate: Bose's collaboration with Einstein in statistical mechanics led to the theoretical prediction of the Bose-Einstein condensate (BEC), a revolutionary concept in quantum physics.
- According to Bose-Einstein statistics, at ultra-low temperatures approaching absolute zero, bosons can congregate in the lowest energy state, forming a condensed state.
- Often dubbed the "fifth state of matter," BEC occurs when bosons lose sufficient energy to coalesce into a single quantum state, creating a cohesive "super-particle" cloud.
- Experimental confirmation of Bose-Einstein condensation in 1995, decades after Bose's theoretical proposal, garnered Eric Cornell, Carl Wieman, and Wolfgang Ketterle the Nobel Prize in Physics in 2001.
- Together with Meghnad Saha, he published the first English translation of Einstein’s papers on general relativity.
- His dedication to research and scientific integrity earned him numerous accolades, including the Padma Vibhushan and the Fellowship of the Royal Society.
Warming up to climate change: How does climate change impact extreme weather events?

- 19 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
Extreme weather is becoming more frequent and more intense in many places around the world because of climate change.
How Does Climate Change Impact Extreme Weather Events?
- The Earth's average temperature has gone up by at least 1.1 degrees Celsius since 1850, mostly because of human activities like burning fossil fuels and deforestation.
- This temperature rise has led to more frequent and stronger extreme weather events worldwide, such as heatwaves, droughts, floods, hurricanes, and wildfires.
- It's hard to directly blame one single weather event on climate change because there are many factors involved.
- However, studies can tell us if climate change made a particular event worse or more likely to happen.
- For example, after a deadly heatwave in Western Europe in 2019, a study found that climate change made that heatwave five times more likely to occur.
- In India, heatwaves have become longer because of global warming, and they're expected to get even worse in the future.
- Climate models predict that by the 2040s, heatwaves might become 12 times more common.
- Higher temperatures also make droughts worse.
- In East Africa, for instance, a severe drought happened between 2020 and 2022, leading to famine and displacing millions of people.
- A report found that climate change made droughts like this at least 100 times more likely in that region.
- Warmer temperatures also contribute to wildfires by drying out land and making it easier for fires to start and spread.
- In Canada, for example, a study showed that climate change doubled the chances of extreme fire conditions.
- This was particularly concerning because Canada recently faced its worst wildfire season ever.
- As temperatures rise, the air can hold more moisture, leading to heavier rainfall and more flooding during storms.
- Warm air can also dry out the soil, making droughts worse. But when warm, moist air meets cooler air, it can lead to more intense storms and flooding.
- There's also evidence that climate change is making hurricanes stronger and more frequent.
- Warmer oceans provide more energy for hurricanes to form and intensify.
- The oceans have absorbed a lot of the extra heat from greenhouse gases, making them warmer.
- This, in turn, leads to stronger storms and more damage when they hit land.
- So, while climate change doesn't directly cause any single weather event, it's making extreme weather events more common and more severe, putting people and ecosystems at risk.
Bird flu outbreak in Andhra: Could H5N1 spark the next pandemic?

- 19 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
A bird flu outbreak in poultry in Andhra Pradesh’s Nellore district was reported recently. Laboratory tests by the National Institute of High-Security Animal Diseases in Bhopal confirmed that it was caused by the type A strain of the H5N1 variant of the avian influenza virus.
What is Bird Flu/Avian Influenza?
- Bird flu, also known as avian influenza, is a viral respiratory illness primarily affecting birds.
- It's caused by specific strains of the Influenza A virus.
- Bird flu spreads between both wild and domesticated birds.
- It has also been passed from birds to humans who are in close contact with poultry or other birds.
- There is no clear evidence that the virus can be transmitted from human to human.
- However, this may have happened in rare cases, where a person has become ill after caring for a sick family member.
- While most types don't infect humans, certain strains like H5N1, H7N9, and H5N6 have caused concern due to their ability to transmit to humans in rare cases.
- Transmission:
- Birds: Spreads easily between birds through bodily fluids (saliva, faeces, nasal discharge) and contaminated environments.
- Humans: Primarily occurs through direct contact with infected birds or surfaces, inhaling infected droplets, or consuming undercooked poultry meat from infected birds.
- Symptoms:
- The symptoms of bird flu in humans are similar to those of regular influenza and include:
- Can range from mild (fever, cough, sore throat, muscle aches) to severe (pneumonia, respiratory failure, multi-organ failure, death).
- Symptoms usually appear within 3-7 days of exposure.
- Treatment: Antiviral medications like Tamiflu have proven effective in managing human infections caused by avian influenza viruses, reducing both the severity of symptoms and the likelihood of fatalities.
Avian Influenza in India:
- Initial Incidence: The first instance of Highly Pathogenic Avian Influenza (HPAI) H5N1 in India occurred in 2006 in Navapur, Maharashtra, marking the onset of recurrent annual outbreaks.
- The emergence of H5N8 was documented in India in November 2016, primarily affecting wild birds in five states, with Kerala reporting the highest number of cases.
- This disease has been identified in 24 states and union territories, prompting the culling of over 9 million birds to curb its spread.
- Corresponding Strategy: India's strategy for managing Highly Pathogenic Avian Influenza (HPAI) revolves around a "detect and cull" approach, as delineated in the National Action Plan for Prevention, Control, and Containment of Avian Influenza (revised - 2021).
Banks to conduct periodic performance reviews of empanelled advocates to fast-track cases in DRTs

- 19 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
Banks will conduct periodical reviews of the performance of empanelled advocates at debt recovery tribunals (DRTs) and rationalise the cases assigned to them based on performance.
What is the Debt Recovery Tribunal?
- Debt Recovery Tribunal is a quasi-judicial body formed under the Recovery of Debts Due to Banks and Financial Institutions (RDDBFI) Act, 1993 to facilitate recovery of loans by banks and financial institutions to the customers.
- It was introduced as a response to the growing issue of Non-performing Assets (NPAs) and the need for a dedicated mechanism to resolve disputes related to debt recovery.
- These tribunals were instituted to offer a swifter and more effective alternative to traditional civil courts for the resolution of matters concerning debt recovery by banks and financial institutions.
- Its Appellate Tribunal is the Debt Recovery Appellate Tribunal (DRAT).
- Under Section 22 of the RDDBFI Act, 1993, both DRT and DRAT are mandated to adhere to the principles of natural justice, and proceedings before them are deemed to be judicial.
Jurisdiction of Debt Recovery Tribunal:
- They are empowered to adjudicate cases brought forth by banks, financial institutions, and related entities seeking the recovery of outstanding amounts.
- DRTs preside over matters surpassing a designated monetary threshold, and their rulings carry the weight of civil court decrees.
- The scope of DRT jurisdiction encompasses a broad spectrum of financial claims, encompassing loans, advances, and financial aid extended by banks and financial institutions.
Powers of DRT:
- Under Section 22(2) of the RDDBFI Act, 1993, the DRT possesses the following powers:
- Summoning individuals and compelling them to testify under oath.
- Demanding the disclosure and presentation of documents.
- Accepting evidence through affidavits.
- Issuing commissions to examine witnesses or documents.
- Revisiting its rulings.
- Rejecting applications due to default or adjudicating them in absentia.
- Revoking any order of dismissal stemming from default or any order passed in absentia.
- Addressing any other matters stipulated by regulations.
- The organisational framework of the Debt Recovery Tribunal:
- DRTs fall under the purview of the Ministry of Finance and operate akin to judicial courts.
- Each DRT is helmed by a Presiding Officer, who must hold qualifications equivalent to that of a District Judge.
- The Presiding Officer is appointed for a tenure of five years or until reaching the age of 62, whichever comes first.
- Appointment of the Presiding Officer is vested in the Central Government.
- At present, 39 DRTs and 5 DRATs are functioning across the country.
- Each DRT and DRAT are headed by a Presiding Officer and a Chairperson respectively.
Key aspect in poll bond case still alive: Money Bill route

- 19 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
Even as a five-judge bench of the Supreme Court struck down the electoral bonds scheme as unconstitutional recently, it saved one aspect of the challenge for another day and a larger bench – the issue of the government using the money Bill route to bring in the laws that introduced the electoral bonds.
News Summary:
- A recent ruling by a five-judge bench of the Supreme Court invalidated the electoral bonds scheme, citing it as unconstitutional.
- However, the court reserved one aspect of the challenge for further review by a larger bench – specifically, the government's use of the money Bill route to enact the laws introducing the electoral bonds.
The Supreme Court highlighted that:
- The examination of introducing these amendments through a money Bill under Article 110 of the Constitution was not addressed.
- The interpretation of Article 110 of the Constitution has been referred to a seven-judge Bench and remains pending judicial review.
What are Money Bills?
- According to Article 110, a money Bill encompasses provisions related to taxes, government borrowing, and expenditure from the Consolidated Fund of India, among other financial matters.
- Article 109 outlines the process for the passage of such Bills, granting predominant authority to the Lok Sabha in their enactment.
- The Speaker is responsible for certifying a Bill as a Money Bill, with the Speaker's decision being final.
- In the past seven years, the government has utilised the money Bill route to introduce various legislations, notably including the Aadhaar Act, 2016, and the Finance Act, 2017.
Other Instances of Government Utilising Money Bill Route:
- Several significant legislations have been enacted by the government through the money Bill route, including:
- The Finance Acts of 2016 and 2018, introduced amendments to the Foreign Contribution Regulation Act, of 2010.
- The Tribunals Reforms Act was passed as a money Bill in 2017.
- The rigorous amendments to the Prevention of Money Laundering Act (PMLA) in 2022, alongside the enactment of the Aadhaar Act in 2018.
- The Supreme Court has upheld the validity of the PMLA amendments and the legality of the Aadhaar Act.
- Notably, Chief Justice of India Chandrachud dissented in the five-judge bench decision that upheld the Aadhaar Act, criticising the government's use of the money Bill route as a subversion of the Constitution.
- However, these laws may still face scrutiny and potential invalidation if the court determines that they were enacted through improper procedure, namely, utilising the money Bill route.
Difference Between Money Bills and Financial Bills:
- While every Money Bill is categorised as a Financial Bill, not every Financial Bill qualifies as a Money Bill.
- For instance, a Finance Bill solely dedicated to tax proposals is deemed a Money Bill.
- Conversely, a Financial Bill may include provisions on taxation or expenditure alongside other subjects.
- The Compensatory Afforestation Fund Bill, 2015, which establishes funds under the Public Account of India and states, serves as an example of a Financial Bill.
The process for passing these two types of bills varies considerably.
-
- The Rajya Sabha lacks the authority to reject or amend a Money Bill.
- Following passage by the Lok Sabha, Money Bills are referred to the Rajya Sabha for recommendations.
- Within 14 days, the Rajya Sabha must return the Bill to the Lok Sabha with its suggestions, which are not binding.
- Should the Lok Sabha reject the recommendations, the Bill is considered passed by both Houses in its original form from the Lok Sabha.
- If the Rajya Sabha fails to provide recommendations within 14 days, the same outcome applies.
- However, both Houses of Parliament must approve a Financial Bill.
- While an ordinary Bill can originate in either House, a Money Bill can only be introduced in the Lok Sabha, per Article 117(1).
- Moreover, only on the President's recommendation can anyone introduce or propose Money Bills in the Lok Sabha.
- Amendments related to reducing or abolishing any tax are exempt from requiring the President's recommendation.
- The essential conditions for a Financial Bill to attain Money Bill status are that it must solely originate in the Lok Sabha, not the Rajya Sabha, and must be introduced upon the President's recommendation.
INCOIS, ISRO to study rip currents for safer beaches

- 19 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
Indian National Centre for Ocean Information Services (INCOIS) and Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) have embarked on a project to continuously monitor and issue operational forecast alerts of rip currents.
What is a Rip Current?
- Rip currents are channelled currents of water flowing away from shore at surf beaches.
- They typically extend from near the shoreline, through the surf zone and past the line of breaking waves. (The surf zone is the area between the high tide level on the beach to the seaward side of breaking waves.)
Formation of Rip Currents:
- Rip currents form when waves break near the shoreline, piling up water between the breaking waves and the beach.
- One of the ways this water returns to sea is to form a rip current, a narrow stream of water moving swiftly away from shore, often perpendicular to the shoreline.
Size of the Rip Currents:
- Rip currents can be as narrow as 10 or 20 feet in width though they may be up to ten times wider.
- The length of the rip current also varies.
- Rip currents begin to slow down as they move offshore, beyond the breaking waves, but sometimes extend for hundreds of feet beyond the surf zone.
Speed of the Rip Current:
- Rip current speeds can vary. Sometimes they are too slow to be considered dangerous.
- However, under certain wave, tide, and beach-shape conditions the speeds can quickly become dangerous.
Are All Rip Currents Dangerous?
- Rip currents are present on many beaches every day of the year, but they are usually too slow to be dangerous to beachgoers.
- However, under certain wave, tide, and beach-shape conditions they can increase to dangerous speeds.
- The strength and speed of a rip current will likely increase as wave height and wave period increase.
How Do Rip Currents Result in the Drowning of Swimmers?
- Drowning deaths occur when people pulled offshore are unable to keep themselves afloat and swim to shore.
- This may be due to any combination of fear, panic, exhaustion, or lack of swimming skills.
- Rip currents are the greatest surf zone hazard to all beachgoers. They can sweep even the strongest swimmer out to sea.
- Rip currents are particularly dangerous for weak and non-swimmers.
ISRO’s ‘Naughty Boy’ Rocket Launches INSAT-3DS (Indian Express)

- 17 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
The Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) recently launched its weather satellite INSAT-3DS board spacecraft Geosynchronous Launch Vehicle (GSLV) F14, nicknamed the ‘naughty boy’ for its spotty record.
What is the GSLV-F14?
- The Geosynchronous Satellite Launch Vehicle (GSLV), standing at a height of 51.7 metres, is a three-stage launch vehicle with a liftoff mass of 420 tonnes.
- First stage: Its first stage (GS1) features a solid propellant (S139) motor with 139 tons of propellant and four earth-storable propellant stages (L40) strapons, each carrying 40 tons of liquid propellant.
- Second Stage: The second stage (GS2) also utilises an earth-storable propellant system with a 40-ton propellant load.
- Third Stage: The third stage (GS3) is equipped with a cryogenic system containing 15 tons of propellant, consisting of liquid oxygen (LOX) and liquid hydrogen (LH2).
- GSLV-F14 serves as a versatile launch vehicle, capable of deploying various types of spacecraft for communication, navigation, earth resource surveys, and other specialised missions.
GSLV-F14/INSAT-3DS Mission Overview and Key Goals:
- INSAT-3DS Satellite marks a significant advancement in the Third Generation of Meteorological Satellite series from Geostationary Orbit, with substantial contributions from Indian industries.
- Fully funded by the Ministry of Earth Sciences (MoES), the mission aims to enhance meteorological services, complementing the existing capabilities of INSAT-3D and INSAT-3DR satellites.
Key Objectives:
- Earth Observation and Oceanic Monitoring: Utilise various spectral channels to monitor Earth's surface, conduct oceanic observations, and assess environmental conditions critical for meteorology.
- Atmospheric Parameter Profiling: Provide vertical profiles of essential meteorological parameters within the atmosphere, enhancing our understanding of atmospheric dynamics.
- Data Collection and Dissemination: Facilitate the collection and dissemination of data from Data Collection Platforms (DCPs), ensuring timely access to crucial meteorological information.
- Satellite Aided Search and Rescue (SAR) Services: Enable Satellite Aided Search and Rescue services, enhancing emergency response capabilities through advanced satellite technology.
Significance of the GSLV-F14/INSAT-3DS Mission:
- The launch of INSAT-3DS holds a lot of significance for India's space agency as it is equipped to provide extremely accurate weather forecast information by studying the surface of the ocean, also being helpful in disaster prevention.
- The GSLV has encountered challenges in the past, with four out of 15 launches facing setbacks, contrasting with the higher success rates of ISRO's PSLV and LVM-3.
- The success of this mission is critical, especially considering the upcoming launch of the Earth observation satellite, NISAR, later this year, a collaborative effort between NASA and ISRO.
- INSAT-3DS, with a mission lifespan of 10 years, will assume the roles of INSAT-3D (2013) and INSAT-3DR (2016), which have reached the end of their operational lives.
- This mission will enhance meteorological forecasting capabilities, enabling better prediction of extreme weather events like thunderstorms, providing visibility assessments for aviation, and facilitating research on forest fires, smoke, snow cover, and climate dynamics.
OpenAI launches Sora (Indian Express)

- 17 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
OpenAI has unveiled a new generative artificial intelligence (GenAI) model that can convert a text prompt into video, an area of GenAI that was thus far fraught with inconsistencies.
What is OpenAI's Sora?
- Sora is an AI model developed by OpenAI –– built on past research in DALL·E and GPT models –– and is capable of generating videos based on text instructions.
- It can also animate a static image, transforming it into a dynamic video presentation.
- Sora can create full videos in one go or add more to already created videos to make them longer.
- It can produce videos up to one minute in duration, ensuring high visual quality and accuracy.
- Sora can generate complex scenes with various characters, precise actions, and detailed backgrounds.
- Not only does the model understand the user's instructions, but it also interprets how these elements would appear in real-life situations.
- The model has a deep understanding of language, enabling it to accurately interpret prompts and generate compelling characters that express vibrant emotions.
- Sora can also create multiple shots within a single generated video that accurately portrays characters and visual style.
Limitations:
- Despite its impressive capabilities, OpenAI acknowledges certain limitations in the current iteration of Sora.
- The model may encounter challenges in accurately simulating complex physics within scenes, leading to potential discrepancies in cause-and-effect scenarios.
- For instance, while depicting a person taking a bite out of a cookie, Sora may struggle to consistently render a corresponding bite mark on the cookie in subsequent frames.
RBI Put Restraints on a Certain Card Network (Indian Express)

- 17 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) has ordered a certain card network to stop “unauthorised payments” made using business cards.
What is a Card Network?
- Card networks connect banks, merchants, and customers (card users) to one another so that transactions can be carried out smoothly and securely.
- Card networks are operating in the background every time a customer uses her card to make a payment.
- There are five authorised card networks in India:
- Visa
- Mastercard
- RuPay
- Diners Club, and
- American Express
Reasons Behind the RBI Order:
- Payments to Non-Card-Accepting Entities: The network facilitated card payments from corporations for commercial transactions, transferring the funds to non-card-accepting recipients via IMPS, RTGS, or NEFT without proper authorization, violating the Payment and Settlement Systems (PSS) Act, 2007.
- Non-Adherence to KYC Requirements: Additionally, the RBI expressed concerns regarding non-compliance with Know Your Customer (KYC) norms in these transactions.
What are the RBI’s Concerns?
- Under Section 4 of the PSS Act, such a payment system requires authorisation, which had not been obtained in this case.
- There were two other concerns as well.
- First, the intermediary in such an arrangement pooled a large amount of funds into an account that was not a designated account under the PSS Act.
- Second, transactions processed under this arrangement did not comply with the ‘originator and beneficiary information’ requirements, as stipulated under the ‘Master Direction on KYC’ issued by the RBI.
- Steps taken by the RBI: The RBI has instructed the card network to suspend all such arrangements until further notice.
- However, regular usage of business credit cards remains unaffected.
Stratospheric Observatory for Infrared Astronomy (SOFIA) (Indian Express)

- 17 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
Researchers have now, for the first time, detected the presence of water molecules on the surface of an asteroid using the data from NASA's now-retired SOFIA airborne observatory.
About Stratospheric Observatory for Infrared Astronomy (SOFIA):
- SOFIA is a powerful, general-purpose infrared observatory used to study the birth of new stars, planetary nebulae and supernova remnants, the atmospheres of Solar System objects, and many more.
- Earth’s atmosphere protects us from harmful radiation, but it also blocks a lot of light useful for astronomy.
- For that reason, NASA and the German Aerospace Center (DLR) built the Stratospheric Observatory for Infrared Astronomy (SOFIA) to fly aboard a modified commercial aircraft capable of flying above 99% of the light-blocking atmosphere.
- SOFIA is carried aboard an aeroplane capable of flying at an altitude of 13 kilometres, higher than 99% of the infrared-absorbing atmosphere.
- First flown in 2007, SOFIA provided the first measurements of Pluto’s atmosphere, mapped the dust and magnetic fields around black holes, and provided a wealth of information about star-forming nebulae.
- The telescope consists of a 2.5-meter (8.2-foot) mirror and a suite of scientific instruments including:
- Photometers to measure the brightness of sources
- Spectrometers to split the light into its component wavelengths, and
- A polarimeter to measure the polarisation of light caused by dust particles.
- Astronomer Gerard Kuiper is best known for his prediction of the Kuiper Belt of icy outer Solar System bodies, but in 1965, he used a high-flying NASA aeroplane to study Venus in infrared light, pioneering the use of aircraft for astronomy.
- SOFIA is Kuiper’s spiritual descendant, built on a larger scale and using a dedicated aeroplane.
- The SOFIA telescope is carried by a Boeing 747SP (“special purpose”) designed for long-duration flights.
- The aeroplane was modified in several ways, including a large opening on the side of the telescope.
- To operate under these conditions, SOFIA is lightweight and built to withstand mechanical vibrations and turbulence from air flowing across the opening in the side of the aeroplane.
- The aeroplane is capable of ten-hour flights, with flight paths chosen to keep ahead of the sunrise and maximise the amount of darkness.
- SOFIA achieved full operational capability in 2014 and prematurely ended in 2022 after operating for 12 years.
India initiates Anti-Dumping Probe into Solar Glass Imports from China and Vietnam (TOI)

- 17 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
India has launched an anti-dumping investigation into the import of solar glass from China and Vietnam following a complaint from domestic players.
What is Anti-Dumping Duty?
- Anti-dumping duty is a tariff levied on imports from foreign countries when their prices are lower than the fair market value of similar goods in the domestic market.
- It's implemented by governments to counteract the practice of "dumping," where foreign goods are sold at unfairly low prices in the domestic market, posing a threat to local businesses.
- The primary objective of anti-dumping duty is to safeguard domestic industries from unfair competition and restore fair trade practices.
- This measure is permitted by the World Trade Organization (WTO) to address instances where dumping causes genuine harm to domestic industries.
- To impose anti-dumping duties, governments must provide evidence of dumping, quantify its extent in terms of costs, and demonstrate the resulting injury or threat to domestic markets.
- While aimed at protecting local industries, anti-dumping duties can sometimes lead to increased prices for consumers within the country.
About Countervailing Duty (CVD):
- Countervailing duty (CVD) is a type of tariff imposed by a government to offset the adverse effects of import subsidies on domestic producers.
- It serves as an import tax applied by the importing country on subsidised products from abroad.
- CVD is imposed to address situations where foreign governments provide subsidies to their producers, lowering the cost of their goods and potentially disrupting fair competition.
- To prevent the influx of subsidised products into their markets, importing countries levy CVD, effectively neutralising the price advantage enjoyed by these imports.
- The imposition of CVD is permitted by the World Trade Organization (WTO) to help maintain fair trade practices among its member countries.
Difference Between Anti-dumping Duty and Countervailing Duty:
- Anti-dumping duty is enacted to safeguard domestic markets from the harmful effects of low-priced foreign goods, while CVD targets products benefiting from government subsidies, resulting in artificially low prices.
- The amount of Anti-dumping duty is determined by the margin of dumping, whereas CVD is calculated based on the subsidy value granted to foreign goods.
Melting Glaciers Threaten Gulf Stream Collapse by 2025 (India Today)
- 16 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
As the world grapples with the escalating impacts of climate change, a recent study has sounded the alarm on the potential collapse of the Gulf Stream by 2025.
What is the Gulf Stream?
- The Gulf Stream is a strong ocean current that brings warm water from the Gulf of Mexico into the Atlantic Ocean.
- It extends all the way up the eastern coast of the United States and Canada.
What Causes the Gulf Stream?
- The Gulf Stream is caused by a large system of circular currents and powerful winds, called an oceanic gyre.
- There are five oceanic gyres on Earth.
- The Gulf Stream is part of the North Atlantic Subtropical Gyre.
- The ocean is constantly in motion, moving water from place to place via currents.
- The Gulf Stream brings warm water from the Gulf of Mexico all the way up to the Norwegian Sea.
- As the warm water comes in, colder, denser water sinks and begins moving south—eventually flowing along the bottom of the ocean all the way to Antarctica.
How Does the Gulf Stream Impact Weather and Climate?
- This strong current of warm water influences the climate of the east coast of Florida, keeping temperatures there warmer in the winter and cooler in the summer than the other southeastern states.
- Since the Gulf Stream also extends toward Europe, it warms Western European countries as well.
- In fact, England is about the same distance from the equator as the cold regions of Canada, yet England enjoys a much warmer climate.
- If it weren’t for the warm water of the Gulf Stream, England would have a much colder climate.
How Long Have We Known About the Gulf Stream?
- We’ve known about the Gulf Stream for more than 500 years.
- In 1513, Spanish explorer Ponce de Leon noted that there was a strong current in this location.
- A few years later, Ponce de Leon’s ship pilot realized that the Gulf Stream could help speed up the sailing trip from Mexico to Spain.
- In the late 18th century, Benjamin Franklin became the first to chart out the path of the Gulf Stream on a map.
Coal Ministry Hosts Industry Interaction on Coal Gasification (ET)
- 16 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
The Ministry of Coal has announced it will host an Industry Interaction on February 16, 2024, in Hyderabad to discuss the development of coal and lignite gasification projects across India.
What is Coal Gasification?
- Coal gasification is a process where coal undergoes partial oxidation with air, oxygen, steam, or carbon dioxide to produce a fuel gas.
- This gas serves as an alternative to piped natural gas or methane for energy generation.
- Underground Coal Gasification (UCG) is a technique involving the conversion of coal into gas within the seam, extracted through wells.
- Production of Syngas: This process yields Syngas, a mixture primarily comprising methane (CH4), carbon monoxide (CO), hydrogen (H2), carbon dioxide (CO2), and water vapour (H2O).
- Syngas finds applications in producing fertilisers, fuels, solvents, and synthetic materials.
- Significance: In manufacturing, steel companies traditionally rely on costly imported coking coal. Syngas derived from coal gasification offers a cost-effective alternative.
- It is utilized in electricity generation, chemical feedstock production, and hydrogen-based applications like ammonia production and fueling a hydrogen economy.
Advantages of Coal Gasification:
- Coal gasification offers a solution to local pollution issues.
- It is deemed environmentally cleaner than direct coal combustion.
- Decreasing dependence on imported natural gas, methanol, ammonia, and other vital commodities, enhances energy security.
- This technology has the potential to mitigate environmental impacts by curbing carbon emissions and promoting sustainable approaches, aligning with India's global objectives for a more environmentally sustainable future.
Concerns Associated with Coal Gasification Plants?
- The main disadvantage of coal gasification is that it is an expensive process.
- The process can produce a number of harmful emissions, including carbon dioxide, sulphur dioxide, nitrogen oxides, and mercury.
- The process produces a lot of ash, which can pollute the environment.
- The process uses a lot of water, which can lead to water shortages in areas where it is used.
The Global Pulses Conference (The Hindu)
- 16 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
The Global Pulses Conference, an annual meeting of pulses producers, processors and traders, suggested that India augment the production of pulses to meet the nutritional requirements.
About the Global Pulses Confederation (GPC):
- The Global Pulses Confederation (GPC) serves as a global representative body for the pulse industry.
- Stakeholders: It encompasses various stakeholders within the pulse industry, such as growers, researchers, traders, government entities, processors, and consumers.
- Headquarters: The GPC is based in Dubai and operates under the licensing of the Dubai Multi Commodity Centre (DMCC).
- The Global Pulses Conference, held annually, took place in New Delhi this year.
Key Observations from the Conference:
- Self-Sufficiency Target: India aims to achieve self-sufficiency in pulses production by 2027, having already attained this status in chickpeas and various other pulse crops, with minor gaps remaining in pigeon peas and black gram.
- Decadal Growth: Pulse production has witnessed a significant 60% growth, increasing from 171 lakh tonnes in 2014 to 270 lakh tonnes in 2024.
- Minimum Support Price (MSP): The government has guaranteed farmers a minimum support price set at 50% above the actual cost of production, ensuring lucrative returns on investment.
- Current MSP rates reflect remarkable increases, such as 117% in masoor, 90% in moong, and substantial hikes in chana dal, toor, and urad compared to a decade ago.
- Government Initiatives: Efforts include the introduction of new seed varieties and the expansion of tur and black gram cultivation to bolster production.
- Importance of Pulse Crops: Pulse cultivation not only enriches soil health but also provides nutritional benefits, particularly for smallholding farmers.
- Improved cultivation practices promise widespread benefits for all stakeholders involved.
Status of Pulse Production in India:
- Production Trends: Over the past decade, pulse production in India has surged by 60%, escalating from 171 lakh tonnes in 2014 to 270 lakh tonnes in 2024.
- Global Standing: India boasts the distinction of being the world's largest producer, consumer, and importer of pulses. It contributes 25% to global production, consumes 27% of the world's total, and imports 14%.
- Agricultural Landscape: Pulses occupy approximately 20% of the foodgrain area in India and contribute 7-10% to the nation's total foodgrain production.
- Cultivation Seasons: While pulses are cultivated in both Kharif and Rabi seasons, Rabi pulses account for over 60% of the total production.
- Variety Distribution: Among pulse varieties, Gram leads the production, comprising roughly 40% of the total output, followed by Tur/Arhar at 15-20%, and Urad/Black Matpe and Moong each contributing approximately 8-10%.
- Self-Sufficiency: India has achieved self-sufficiency in chickpeas (chana) and various other pulse crops, with minor shortfalls, observed only in pigeon peas (tur) and black gram.
DoT Unveils 'Sangam: Digital Twin' Initiative (TOI)

- 16 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
The Department of Telecommunications has introduced the 'Sangam: Digital Twin' initiative, which aims to transform infrastructure planning and design through innovation and the integration of advanced technologies.
What is Sangam: Digital Twin initiative?
- Digital Twin technology creates virtual replicas of physical assets, enabling monitoring, simulation, and analysis for adaptive outcomes.
- 'Sangam: Digital Twin' consists of two stages:
- The first is exploratory for creative exploration, and
- The second is for the practical demonstration of specific use cases, creating a future blueprint for collaboration in future infrastructure projects.
- The initiative aligns with advancements in communication, computation and sensing over the past decade, fostering a collaborative approach to reshape infrastructure planning and design.
- 'Sangam: Digital Twin' integrates 5G, IoT, AI, AR/VR, AI native 6G, Digital Twin and next-gen computational technologies to break silos and promote a whole-of-nation approach.
- The new initiative aims to transform ideas into solutions, bridging the gap between conceptualisation and realisation, and fostering advancements in infrastructure.
- Sangam encourages a holistic approach to innovation, uniting stakeholders to harness unified data and collective intelligence.
- It is aimed at creating an ecosystem that maximises the value of technological advancements for development.
- Sangam aims to demonstrate the practical implementation of innovative infrastructure planning solutions, providing a model framework for collaboration and a future blueprint for scaling successful strategies in future projects.
- The platform also offers a blog for pre-registered participants to connect, share insights, and engage in discussions.
Significance of Digital Twins:
- Facilitates remote monitoring, making it applicable for use in hazardous operations.
- Enhances predictive capabilities, assisting in making informed policy decisions.
- Improves operational efficiency, thereby ensuring the maintenance of output quality.
- Assists in urban planning by generating various simulations and forecasts.
The Schengen Area in Europe (The Hindu)
- 16 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
Kosovo recently achieved visa-free entry to the Schengen zone in Europe, the world's largest area of unrestricted movement. Now, citizens of Kosovo can visit the Schengen zone as tourists for up to 90 days within 180 days.
Why Kosovo's Schengen Application Was Delayed for Years?
- Despite the European Commission's clearance of Pristina's readiness to address issues like illegal migration and corruption in 2018, Kosovo faced prolonged delays in obtaining Schengen visa-free status.
- The primary obstacle stemmed from opposition from various EU members who did not acknowledge Kosovo's unilateral declaration of independence from Serbia in 2008.
- Moreover, Kosovo lacks legal statehood recognition from the UN and is not acknowledged by key global players like Russia and China.
What is the Schengen Zone?
- The Schengen Zone is an area that encompasses much of Europe and enables visa-free and border-free travel within it.
- The Schengen zone is named after the Schengen Agreement, which was signed in 1985 in Schengen, Luxembourg.
- The Schengen Zone acts as a single jurisdiction that allows travellers to cross borders without stopping for any border checks and therefore enables those who live close to international borders to come and go with ease.
- It currently includes 27 countries in Europe, though not all are members of the European Union.
- The exceptions are Norway, Liechtenstein, Switzerland, and Iceland.
- Croatia, an EU member since 2013, joined Schengen in 2023, while Romania and Bulgaria, EU members since 2007, will gain partial Schengen entry from 31 March 2024.
Is Admission to Schengen Mandatory for EU Members?
- When the Schengen agreement took effect in 1995, only seven of the entire 15-member union at the time joined the passport-free area.
- Today, 23 of the 27 EU states are part of the passport-free zone, excluding Cyprus, Romania, Bulgaria and Ireland.
- The Schengen area comprises 27 countries, including four non-EU members: Iceland, Liechtenstein, Switzerland and Norway.
- It is important not to confuse the status of the four countries with the recent entry of Kosovo and the other five western Balkan entrants which are not counted among the Schengen 27 members.
What are the Advantages of the EU’s Border-free Policy?
- For nationals of any country, the benefit is the freedom to travel with a single Schengen visa to other European nations within the borderless area.
- For EU states, the Visa-free borderless travel, alongside the single currency adopted by 20 EU countries, is the most visible symbol of European integration.
What are the Challenges Faced by the Schengen Region?
- The Schengen region faced significant challenges, particularly during the Eurozone sovereign debt crisis of the past decade.
- The influx of migrants from conflict areas in Africa and West Asia, coupled with the rise of anti-immigrant sentiments fueled by far-right populist parties in Europe, added strain to the region.
- At one point, there were discussions within the EU about potentially excluding Mediterranean border countries from the Schengen Area, as some individual states considered reintroducing border controls unilaterally.
8th Century Kotravai Sculpture from Pallava Period Discovered (Indian Express)

- 15 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
Recently, archaeologists discovered an eighth-century Kotravai sculpture, an artefact that dates back to the Pallava period, near Ulundurpet, Tamil Nadu.
About the Kotravai Sculpture:
- Kotravai sculpture is made in a slab stone of five-feet height and four-feet width.
- The idol is depicted with eight hands, indicating its origin in the eighth century during the Pallava period.
- The sculpture depicts various elements such as chakkara, sword, bell, and abhaya mudra in the right hands.
- Conch, bow, shield, and Uru Mudhra are shown in the left side hands along with bangles in all hands.
- The presence of trishul (soolam) and lion (simmam) on the right side of head, and blackbuck (kavarimann) on the left side.
- Kotravai is portrayed standing on the head of a buffalo, with two guards on each side.
About the Pallava Dynasty:
- The Pallava Dynasty, a prominent power in South India, thrived from the 3rd to the 9th centuries.
- Their dominion encompassed the northern regions of Tamil Nadu, portions of Karnataka, Andhra Pradesh, and Telangana, with Kanchipuram serving as their capital.
- The Pallavas were known for their patronage of Buddhism, Jainism, and Brahminical faith, as well as their support for music, painting, and literature.
- Origins: Initially vassals of the Andhra Satavahanas, the Pallavas gained autonomy following the latter's decline in Amaravati.
- Gradually expanding southward, they established their capital in Kanchipuram during the 4th century CE.
- Under the reigns of Mahendravarman I (571 - 630 CE) and Narasimhavarman I (630 - 668 CE), the Pallava realm experienced significant growth in wealth and power.
- According to the accounts of Chinese traveller Hiuen Tsang, Bodhidharma, the founder of the Chan (Zen) school of Buddhism in China, was purportedly a prince of the Pallava empire.
- The Chinese traveller Hiuen Tsang visited Kanchipuram, the capital of Pallavas, during the reign of Narasimha Varman I and lauded their benevolent governance.
Architectural Contributions of the Pallavas:
- The Pallava Dynasty is renowned for its patronage of Dravidian architecture, particularly temple construction.
- They played a pivotal role in the evolution from rock-cut architecture to stone temples.
- Their most celebrated architectural achievements can be found in Mahabalipuram, which flourished as a significant hub of art, architecture, and literature during Pallava rule.
- Narasimhavarman II commissioned notable structures such as the Kailasanatha Temple in Kanchipuram and the Shore Temple.
- Among these temples, Kailasanatha and Vaikuntaperumal stand out for their architectural excellence.
- The Vaikuntaperumal shrine, erected in the 8th century AD, is renowned for its intricate sculptures depicting Pallava history.
- Religion: The Pallavas embraced Shaivism, a predominant local religion, thereby aligning themselves with Dravidian cultural traditions.
Military Engagements and Decline of the Pallava Dynasty:
- Throughout their reign, the Pallavas engaged in persistent conflicts with both the Chalukya Dynasty to the north and the Tamil kingdoms of Chola and Pandyas to the south.
- The Pallavas faced ongoing battles with the Chalukyas of Badami and ultimately succumbed to the supremacy of the Chola kings in the 8th century CE.
- The ascent of the Rashtrakutas marked the decline of the Pallava Dynasty.
- In 897 AD, Vijayalaya, the Chola King, decisively defeated Aparajitavarman, the last Pallava King, thereby sealing the fate of the Pallava Dynasty.
Alaskapox Claims One Life in US (TOI)

- 15 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
An elderly man has died from Alaskapox, the first known fatality from the recently discovered virus.
What is Alaskapox?
- Alaskapox is caused by orthopoxvirus, a family of brick-shaped viruses that can infect both animals and humans, leading to skin lesions or pox.
- The virus was first identified in a woman living near Fairbanks, Alaska, and has since been primarily detected in small mammals like red-backed voles and shrews.
- However, domestic pets such as dogs and cats may also be carriers of the virus.
What are the symptoms of Alaskapox?
- Symptoms of Alaskapox include the development of one or more bumps or pustules on the skin, accompanied by joint or muscle pain and swollen lymph nodes.
- While the majority of the seven known human cases in Alaska over the past nine years have experienced mild illnesses that were resolved without intervention, the virus poses a greater threat to individuals with weakened immune systems.
How is Alaskapox Transmitted?
- Transmission of Alaskapox is believed to occur through direct contact with infected animals.
- Unlike some of its orthopoxvirus relatives, there have been no documented instances of Alaskapox spreading from person to person.
- Though it's not clear how Alaskapox is transmitted, researchers say that it may be zoonotic meaning it can jump from animals to humans.
PM Modi addresses World Government Summit 2024 in Dubai (MEA)

- 15 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
Prime Minister Modi attended the World Government Summit 2024 as guest of honour in Dubai recently.
What is the World Governments Summit?
- The World Governance Summit serves as a worldwide platform committed to shaping the trajectory of government initiatives across the globe.
- This annual gathering takes place in Dubai, United Arab Emirates, convening leaders and experts from various sectors.
- Each year, the Summit sets the agenda for the forthcoming era of governance, emphasising the utilisation of innovation and technology to address pressing global challenges.
- Since its establishment in 2013, the Summit has been steadfast in its mission to influence the evolution of governmental practices and foster a brighter future for humanity.
World Governance Summit Organization:
- The World Governance Summit Organization operates as an impartial, nonprofit entity with a global reach, dedicated to influencing the future landscape of governance.
- Headquartered in Dubai, United Arab Emirates, the organisation serves as a nexus for collaboration and idea exchange among governmental and non-governmental stakeholders.
- 2024 Summit: Dubai, United Arab Emirates
- Theme - 'Shaping Future Governments'
Key Highlights of PM Modi's Speech:
- Streamlining Government Operations: The Prime Minister addressed the evolving landscape of governance, emphasising India's adoption of transformative reforms under the ethos of "Minimum Government, Maximum Governance.”
- Human-Centred Governance: Drawing from India's experience leveraging digital technology for welfare, inclusivity, and sustainability, he advocated for a human-centred approach to governance.
- He highlighted India's focus on people's participation, last-mile delivery, and women-led development to foster an inclusive society.
- Need for Global Collaboration: Given the interconnected nature of the world, the Prime Minister stressed the importance of governments collaborating and learning from each other to tackle future challenges effectively.
- Model of Governance: Highlighting the current imperative, the Prime Minister underscored the necessity for governance to be inclusive, technologically adept, transparent, and environmentally sustainable.
- He outlined priorities such as Ease of Living, Justice, Mobility, Innovation, and Business in public service delivery.
- India's Climate Change Commitment: Reaffirming India's unwavering commitment to climate change action, he urged people to join Mission LiFE (Lifestyle for Environment) to foster a sustainable world.
- Leadership Role of India: The Prime Minister elaborated on India's leadership role, particularly as the chair of G-20, highlighting efforts to address global challenges and elevate development concerns of the Global South.
- He advocated for reforming multilateral institutions to give greater voice to the Global South in decision-making processes.
- India as a Global Partner: Emphasising India's commitment to global progress, he reiterated India's role as a "Vishwa Bandhu" (friend of the world), pledging continued contributions to global advancement.
China Moves its Nationals into its Vacant ‘Defence Villages’ Along LAC (Indian Express)

- 15 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
Chinese nationals have started occupying several of their model “Xiaokang” border defence villages across India’s north-eastern borders which the country has been building along the Line of Actual Control (LAC) since 2019.
News Summary:
- Chinese activity has been observed in several villages situated on its side of the Line of Actual Control (LAC) opposite the Lohit Valley and the Tawang sector of Arunachal Pradesh.
- Over the past five years, China has been undertaking the construction of 628 "well-off villages" along India's borders with the Tibet Autonomous Region, encompassing regions like Ladakh and Arunachal Pradesh.
- The precise purpose of these villages remains ambiguous, although the structures are believed to serve as "dual-use infrastructure," serving both civilian and military functions.
What is the Line of Actual Control (LAC)?
- The LAC serves as the boundary separating areas under Indian administration from those under Chinese administration.
- However, it is not a formally agreed-upon boundary, lacking delineation on maps or physical demarcation on the ground.
- India views the LAC as approximately 3,488 km in length, while China's perspective estimates it to be around 2,000 km.
- The LAC is segmented into three sectors: the eastern sector covering Arunachal Pradesh and Sikkim, the middle sector spanning Uttarakhand and Himachal Pradesh, and the western sector in Ladakh.
- India's official boundary line, as depicted on maps released by the Survey of India, encompasses both Aksai Chin and Gilgit-Baltistan, diverging from the LAC.
- Consequently, the LAC does not coincide with India's claim line.
- For China, the LAC generally aligns with its claim line, except in the eastern sector, where it asserts control over the entire territory of Arunachal Pradesh, which it regards as South Tibet.
Dispute over the LAC and Controversy Surrounding Claim Lines in Ladakh:
- India disputes the validity of the Line of Actual Control (LAC), asserting that it is a construct devised by China.
- The Chinese demarcation appears as a series of disconnected points on a map, lacking a clear and consistent delineation.
- India contends that the line should exclude territorial gains made through aggression in 1962 and instead reflect the positions as of September 8, 1962, before the Chinese incursion.
- This ambiguity in the Chinese definition of the LAC leaves room for China to pursue incremental changes on the ground through military actions, as evidenced by the clash in the Galwan Valley between the Indian Army and the Chinese PLA in 2020.
- Aksai Chin, located in the Ladakh region of the princely state of Jammu and Kashmir, was not part of British India, despite being under British Empire control.
- As a result, while the eastern boundary was clearly defined in 1914 with the signing of the Shimla Agreement on the McMahon Line by British India, the western boundary in Ladakh remained unresolved.
- These historical maps, still officially recognized today, formed the basis of engagements with China, ultimately culminating in the 1962 War.
Infrastructure Development along the LAC:
- Consistently, China has enhanced its existing infrastructure along the Line of Actual Control (LAC), focusing on improving connectivity through mountain passes, constructing roads, bridges, and model villages.
- Additionally, China has been constructing infrastructure, including border villages, within Bhutanese territory.
- Over the past three to four years, India has intensified efforts to bolster its border infrastructure, encompassing initiatives to enhance forward connectivity, establish alternative routes to the LAC, and connect remote areas.
- India's Vibrant Villages program aims to modernise 663 border villages, providing them with essential amenities in the initial phase.
- Notably, 17 of these villages located along the borders with China in Ladakh, Himachal Pradesh, Uttarakhand, Sikkim, and Arunachal Pradesh have been earmarked for development as pilot projects under this program.
- Moreover, significant progress is underway on three major highways in Arunachal Pradesh:
- The Trans-Arunachal Highway
- The Frontier Highway, and
- The East-West Industrial Corridor Highway.
Stone Age Wall Discovered Beneath the Baltic Sea (India Today)
- 15 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
A megastructure found in the Baltic Sea may represent one of the oldest known hunting structures used in the Stone Age — and could change what’s known about how hunter-gatherers lived around 11,000 years ago.
About the Blinkerwall:
- The Blinkerwall is the oldest known megastructure crafted by humans in Europe.
- It is around a kilometre-long structure that lies hidden in the Bay of Mecklenburg, submerged under 21 metres of water.
- It consists of approximately 1,400 smaller stones intricately positioned to connect almost 300 larger boulders, some of which were deemed too massive for human groups to have manoeuvred.
- The total weight of the wall's stones exceeds 142 tonnes, making it improbable that natural processes, such as tsunamis or glacial movements, formed it.
- It likely dates back over 10,000 years, sinking beneath rising sea levels around 8,500 years ago.
- This positions it among the oldest known examples of hunting architecture globally and potentially designates it as the oldest man-made megastructure in Europe.
About the Baltic Sea:
- The Baltic Sea is a semi-enclosed inland sea situated in Northern Europe.
- As an arm of the North Atlantic Ocean, it stretches northward from the latitude of southern Denmark nearly to the Arctic Circle, acting as a divider between the Scandinavian Peninsula and the rest of continental Europe.
- With a coastline spanning approximately 8,000 km, the Baltic Sea is bordered by several countries, including Sweden, Poland, Lithuania, Latvia, Finland, Estonia, Germany, Denmark, and Russia.
- Covering an area of around 377,000 sq.km, the sea measures approximately 1,600 km in length and 193 km in width.
- It is linked to the White Sea via the White Sea Canal and to the North Sea's German Bight through the Kiel Canal, while it connects to the Atlantic Ocean through the Danish Straits.
- The Baltic Sea encompasses three significant gulfs: the Gulf of Bothnia to the north, the Gulf of Finland to the east, and the Gulf of Riga slightly to the south.
- Renowned as the world's largest brackish inland water body, the Baltic Sea exhibits lower water salinity levels compared to the World Oceans due to freshwater influx from the surrounding land and its shallow depth.
- More than 250 rivers and streams discharge into the Baltic Sea, with the Neva River being the largest among them.
- The sea boasts over 20 islands and archipelagos, with Gotland, located off the coast of Sweden, ranking as the largest island in the Baltic Sea.
Farmers’ Protest 2.0 and MSP Demand (The Hindu)

- 14 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
India's Farmers are back on the streets yet again, demanding guarantees on Minimum Support Prices, work on the Swaminathan Committee report, Electricity amendment bill, and debt waiver.
Why are Farmers Protesting?
- Farmers have demanded MSP assurance across all crops, implementing Swaminathan Commission recommendations, debt relief, pensions for farmers, and withdrawing cases against past protestors.
- Advocacy for India's exit from WTO and free-trade agreements are also demands that have been put forth by the farmers.
What is the Minimum Support Price (MSP)?
- Minimum Support Price (MSP) is the lowest rate at which government procurement agencies buy crops from farmers.
- It shields farmers from market fluctuations, offering stability and income security.
- MSP is crucial for ensuring fair prices for farmers and is determined by the Commission for Agricultural Costs and Prices (CACP), considering factors like production costs, market trends, and demand-supply dynamics.
- Established in 1965, CACP operates under the Ministry of Agriculture and Farmers Welfare.
- After the CACP submits its recommendations, the Cabinet Committee on Economic Affairs (CCEA), chaired by the Prime Minister of India, makes the final decision on MSP levels.
Which Crops are Covered Under MSP?
- Kharif crops such as Paddy, Jowar, Bajra, Ragi, Maize, Arhar, Moong, Urad, Cotton, Groundnut, Sunflower Seed, Soybean, and Sesamum.
- Rabi crops such as Wheat, Barley, Gram, Masur, Rapeseeds & Mustard, Safflower, and Toria.
- Additionally, MSP is announced for Copra, De-husked Coconut, and Jute, and Fair Remunerative Prices are declared for Sugarcane.
How is MSP Calculated?
- The Minimum Support Price (MSP) is calculated by considering both the explicit and implicit costs incurred by farmers.
- Explicit costs cover expenses like chemicals, fertilisers, seeds, and hired labour, while implicit costs include factors such as family labour and rent.
- These variables are represented by A2, FL, and C2.
- A2 refers to the expenses for inputs like chemicals, fertilisers, seeds, and hired labour for crop growth, production, and maintenance.
- A2 + FL includes both actual and implicit costs, such as family labour.
- C2 incorporates A2 + FL along with fixed capital assets and rent paid by farmers.
- Additionally, the Commission for Agricultural Costs and Prices (CACP) takes into account various other factors:
- Cost of cultivation per hectare and crop costs in different regions.
- Cost of production per quintal and regional differences.
- Market prices of relevant crops and their fluctuations.
- Other production and labour costs, along with associated changes.
- Prices of commodities bought or sold by farmers and any fluctuations.
- Information on product supply, including area, yield, production, imports, exports, and stocks with public agencies or industries.
- Demand information across regions, including total and per capita consumption, processing industry trends, and capacity.
What Changes Did the Swaminathan Formula Propose?
- The National Commission on Farmers, chaired by agricultural scientist M S Swaminathan, in 2004, submitted a report to the government in 2006, suggesting that the solution to the farm crisis was to provide remunerative prices to the farmer.
- The commission recommended that the MSP should be 1.5 times the farmers’ input costs.
- For the calculation of input costs, however, the Swaminathan Commission laid down a different formula.
- Along with the paid-out cost (A2) and the imputed value of family labour (FL), also included the interest on the value of owned capital assets, rent paid for leased-in land, or the rental value of owned land (C2).
- Key difference:
- The government sets MSP at 1.5 times the Cost of Production (CoP), where Cop is A2+FL.
- The Swaminathan Commission, however, suggests that CoP should be based on C2, proposing the 'C2+50 per cent' formula for setting MSP.
National Generic Document Registration System (PIB)
- 14 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
Recently, the Secretary, Department of Land Resources, rolled out the National Generic Document Registration System (NDGRS) throughout Assam along with the launch of Unique Land Parcel Identification Number (ULPIN) seeding of geo-referenced Cadastral Maps.
About National Generic Document Registration System:
- The Department of Land Resources has developed the National Generic Document Registration System (NGDRS) as part of the Digital India Land Records Modernisation Programme (DILRMP).
- As many as 28 States / UTs have adopted the NGDRS for Land Records.
- The NGDRS application is developed by the National Informatics Centre, Pune.
- It is a common, generic application developed for registration departments across the country under the One Nation One Software initiative.
Objectives of NGDRS:
- With technology being one of the major enablers, it is ensured that registrations and delivery of documents to the parties happen faster in comparison to the conventional methods. The broad level objectives are:
- One Nation One Software
- Generic platform for registration of properties and document across the country
- Citizen empowerment by enabling property valuation and online document submission
- A single platform of all the stakeholders in registration process
Features of NGDRS:
- It is a nationwide registration department application that is generic, standardised, and adaptable.
- Sub-registrars, citizens, and apex users from registration departments are the intended users of this program.
- NGDRS makes it easier for states to set up state-specific instances and customise the program to meet their needs.
- With its comprehensive user interface for document and property registration, the program makes it possible for citizens to continue with online land purchases.
- They are able to determine the circle rate for land, determine the type of land, and value properties based on current rates.
- The inability to transact in properties that are prohibited—such as government, tribal, mortgaged, etc.—helps them eventually determine where and what kind of land to purchase.
- After that, clients may schedule appointments in advance, apply online for document submission, and make quick payments.
- Purchasers of real estate only need to make one visit to the sub-registrar's office, and that should be during the final registration and signing process.
What is ULPIN?
- It is the distinct blockchain ID, and the land parcel's ULPIN from BhuNaksha allows for a unique identification.
- Every land parcel has a unique 14-digit alphanumeric identification number, often known as the AADHAR or fingerprint for land.
- The identification relies on georeferenced cadastral maps and is based on the land parcel's longitude and latitude.
- ULPIN has the following advantages: it guarantees transaction uniqueness, maintains current spatial records, connects property transactions, shares land record data across departments and financial institutions, and gets rid of fraudulent transactions.
Revised Guidelines for Community Radio Stations (ET)

- 14 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
With a view to ensuring the growth of the community radio sector, the Union government on Tuesday increased the advertising time for community radio stations as well as the tariff rate for advertisements.
What are Community Radio Stations (CRSs?
- Community radio stations (CRSs) are low-power radio stations with a coverage area of approximately a 10-15 km radius, depending on the area’s geography, which is meant to be set up and operated by local communities.
- They offer a platform where content is disseminated in localized dialects and regional languages.
- Local, context-specific issues are raised and discussed in these stations in local idioms.
- India's first community radio station (CRS) was inaugurated on the campus of Anna University in 2004.
- Currently, there are 481 CRSs in India.
About the Revised Policy Guidelines:
- Under the revised policy, the government has permitted any eligible organisation functional in multiple districts to set up a maximum of six community radio stations in different districts.
- The advertising time for community radio stations has been increased from seven minutes per hour to 12 minutes per hour, while the rate of advertisement has been hiked from Rs 52 to Rs 74 per 10 seconds, the guidelines stated.
- The policy also fixed the validity of the letter of intent issued to an organisation to one year, with a buffer of three months to the applicant for any unforeseen circumstances.
- The revised policy guidelines are expected to fuel the growth of the community radio sector.
- The guidelines stated that the licensee would set up an advisory and content committee comprising members of the local community, with 50 per cent representation for women.
Carbon Nanotubes (CNTs) (DST)
- 14 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
Recently, researchers at the Institute of Advanced Study in Science and Technology (IASST) have pioneered a novel method for directly synthesising CNTs on glass substrates at a temperature of 750 °C.
What are Carbon Nanotubes (CNTs)?
- A carbon nanotube is a small cylindrical carbon structure made out of graphene.
- The tube comprises hexagonal structures.
- Despite their very small size, carbon nanotubes are very strong.
- Carbon nanotubes are also known as “Buckytubes” because they resemble R. Buckminster Fuller’s geodesic domes.
- They are pivotal in advancing modern technology by showcasing extraordinary properties.
- Applications: They have found applications in diverse fields, including rechargeable batteries, flexible electronics, aerospace, transparent electrodes, touch screens, supercapacitors, and medicine.
- Recent Developments: The experiment employs the Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapour Deposition Technique (PECVD), in which a spiral-shaped fused hollow cathode source is specifically constructed to create plasma.
- This novel method avoids the requirement for high temperatures and does not require a transition metal catalyst.
Why is It Necessary?
- Metal catalysts (Fe, Co, and Ni) and high temperatures (~1000 0C) are needed for conventional CNT production procedures.
- Concerns about biocompatibility arise with these catalysts for possible biomedical uses.
- A fascinating area of nanotechnology, the removal of these catalysts from CNTs presents a huge financial hurdle, underscoring the urgent need for cleaner, more sustainable CNT synthesis techniques.
- Clean CNTs that can be used in biomedical settings, optoelectronics, and energy studies may now be produced.
Atlantic Meridional Overturning Circulation (AMOC) (Earth Org)
- 14 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
The circulation of the Atlantic Ocean, a key component in global climate regulation, is “on route” to a tipping point, according to a new study, which describes the findings as “bad news for the climate system and humanity.”
What is Atlantic Meridional Overturning Circulation (AMOC)?
- The ocean’s water is constantly circulated by currents.
- Tidal currents occur close to shore and are influenced by the sun and moon and the surface currents are influenced by the wind.
- However, other, much slower currents that occur from the surface to the seafloor are driven by changes in the saltiness and ocean temperature, a process called thermohaline circulation.
- These currents are carried in a large "global conveyor belt," which includes the AMOC.
- AMOC stands for Atlantic Meridional Overturning Circulation.
- The AMOC circulates water from north to south and back in a long cycle within the Atlantic Ocean.
- This circulation brings warmth to various parts of the globe and also carries nutrients necessary to sustain ocean life.
- The circulation process begins as warm water near the surface moves toward the poles (such as the Gulf Stream in the North Atlantic), where it cools and forms sea ice.
- As this ice forms, salt is left behind in the ocean water.
- Due to the large amount of salt in the water, it becomes denser, sinks down, and is carried southwards in the depths below.
- Eventually, the water gets pulled back up towards the surface and warms up in a process called upwelling, completing the cycle.
- The entire circulation cycle of the AMOC, and the global conveyor belt, is quite slow.
- It takes an estimated 1,000 years for a parcel (any given cubic meter) of water to complete its journey along the belt.
- Even though the whole process is slow on its own, there is some evidence that the AMOC is slowing down further.
Is the AMOC Slowing Down?
- As our climate continues to change, there is a possibility that the AMOC will slow down, or come to a complete stop.
- While research shows it is weakening over the past century, whether or not it will continue to slow or stop circulating completely remains uncertain.
- If the AMOC does continue to slow down, however, it could have far-reaching climate impacts.
- For example, if the planet continues to warm, freshwater from melting ice at the poles would shift the rain belt in South Africa, causing droughts for millions of people.
What Would Happen if AMOC Failed?
- AMOC acts as a sort of "switch" for the climate, particularly in Europe and the northern hemisphere.
- It would result in less precipitation in regions like Europe, North America, China, and certain regions of Russia in Asia, as well as widespread cooling throughout the northern hemisphere.
- The Amazon rainforest might become dry and drought-prone as a result of the extra heat brought on by a collapsing AMOC, and it might even become a savannah state.
- In certain areas, monsoon development and rainfall might be impeded by a slowing in AMOC.
- There might be less rainfall in the Sahel (the West African monsoon area), less summer monsoon circulation in South Asia and India, and more winter storms in Europe.
- The summer monsoon circulation over the Indian subcontinent and the sea level pressure gradient are both weakened by a weakening of the land-sea heat gradient.
India's retail inflation moderates to 5.10 per cent in January (The Hindu)

- 13 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
India's retail inflation has eased to 5.10% on an annual basis, according to data released by the Ministry of Statistics & Programme Implementation.
What is Retail Inflation or CPI-based Inflation?
- Retail inflation, also known as Consumer Price Index (CPI) inflation tracks the change in retail prices of goods and services which households purchase for their daily consumption.
- CPI is released by The National Statistical Office (NSO), Ministry of Statistics and Programme Implementation (MoSPI).
- To measure inflation, we estimate how much CPI has increased in terms of percentage change over the same period the previous year.
- If prices have fallen, it is known as deflation (negative inflation).
- The Central Bank (RBI) pays very close attention to this figure in its role of maintaining price stability in the economy.
- The CPI monitors retail prices at a certain level for a particular commodity; and price movement of goods and services at rural, urban and all-India levels.
- The change in the price index over a period of time is referred to as CPI-based inflation or retail inflation.
- Generally, CPI is used as a macroeconomic indicator of inflation, as a tool by the central bank and government for inflation targeting and for inspecting price stability, and as a deflator in the national accounts.
- CPI also helps understand the real value of salaries, wages, and pensions, the purchasing power of the nation’s currency, and regulating rates.
- CPI, one of the most important statistics to ascertain economic health, is generally based on the weighted average of the prices of commodities.
- It basically gives an idea of the cost of the standard of living.
- CPI specifically identifies periods of deflation or inflation for consumers in their day-to-day living expenses.
- If there is inflation (when goods and services cost more) the CPI will rise over a period of time.
- If the CPI drops, that means there is deflation or a steady reduction in the prices of goods and services.
How is CPI calculated (CPI formula)?
- To calculate CPI, multiply 100 by the fraction of the cost price of the current period and the base period.
- CPI formula: (Price of the basket in current period / Price of the basket in base period) x 100
Odisha’s Gupteswar Forest Is Now A Biodiversity Heritage Site (TOI)
- 13 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
Gupteswar forest in the Koraput district of Odisha has been officially declared the fourth biodiversity heritage site (BHS) in the state.
What is a Biodiversity Heritage Site (BHS)?
- A Biodiversity Heritage Site (BHS) is a unique ecosystem with rich biodiversity that is designated for special protection and conservation.
- These sites are typically declared by individual states or local bodies under the provisions of the Biological Diversity Act, of 2002, in India.
Who can Declare BHS?
- Under Section 37 of the Biological Diversity Act, 2002 the State Government in consultation with local bodies may notify areas of biodiversity importance as Biodiversity Heritage Sites (BHS).
- The ‘Biodiversity Heritage Sites’ (BHS) are unique ecosystems having rich biodiversity comprising of any one or more of the following components:
- The richness of wild as well as domesticated species or intra-specific categories.
- High endemism.
- Presence of rare and threatened species, keystone species, and species of evolutionary significance.
- Wild ancestors of domestic/cultivated species or their varieties.
- Past pre-eminence of biological components represented by fossil beds and having significant cultural, ethical or aesthetic values are important for the maintenance of cultural diversity, with or without a long history of human association with them.
- “The creation of BHS may not put any restriction on the prevailing practices and usages of the local communities, other than those voluntarily decided by them.
- The purpose of declaring BHS is to enhance the quality of life of the local communities through conservation of such sites.”
The main objectives of declaring an area as a BHS are:
- To conserve biological diversity, including genetic diversity, ecosystem diversity, and species diversity.
- To protect habitats of rare, endemic, and threatened species.
- To promote sustainable use of biodiversity.
- To maintain cultural diversity and traditional knowledge associated with biodiversity.
- To raise awareness about the importance of biodiversity conservation.
Biodiversity Heritage Sites (BHS) of India:
Revival of Weimar Triangle (The Hindu)
- 13 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
The governments of Poland, France and Germany vowed Monday to make Europe a security and defence power with a greater ability to back Ukraine, amid concerns that former U.S. President Donald Trump might return to the White House and allow Russia to expand its aggression on the continent.
What is the Weimar Triangle?
- The Weimar Triangle is a regional alliance of three European countries:
- France
- Germany
- Poland
- It was established in 1991 in the German city of Weimar, with the aim of promoting cooperation between the three countries on cross-border and European issues.
- The Weimar Triangle is not a formal organization, but rather a platform for dialogue and cooperation.
- The three countries hold regular summits, typically at the level of heads of state or government, and their foreign ministers also meet frequently.
- The Weimar Triangle also includes cooperation between parliaments, militaries, scientists, and cultural institutions.
Significance of the Weimar Triangle:
- The Weimar Triangle has played a significant role in European integration.
- It helped to support Poland's emergence from communism and its accession to the European Union in 2004.
- In recent years, the Weimar Triangle has taken on a renewed importance as Europe has faced a number of challenges, including the Ukraine crisis and the rise of populism.
- The three countries have worked together to promote stability and cooperation in Europe.
Some of the key areas of cooperation between the Weimar Triangle countries:
- Security: The three countries cooperate on a range of security issues, including defence, counterterrorism, and cybersecurity.
- Economy: The Weimar Triangle countries are major trading partners, and they work together to promote economic growth and integration.
- Energy: The three countries are working together to develop a more secure and sustainable energy supply.
- Climate change: The Weimar Triangle countries are committed to combating climate change and have pledged to meet the targets of the Paris Agreement.
- Culture: The three countries have a rich cultural heritage, and they work together to promote cultural exchange and understanding.
Greening India's Wastelands with Agroforestry (GROW) Report and Portal (DD News)

- 13 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
NITI Aayog recently unveiled the Greening and Restoration of Wasteland with Agroforestry (GROW) report and portal, aiming to bolster efforts in environmental conservation and sustainable land use across India.
About the Greening India's Wastelands with Agroforestry (GROW) Portal:
- The "Greening and Restoration of Wasteland with Agroforestry (GROW)-Suitability Mapping" portal offers universal access to state and district-level data.
- Hosted on the Bhuvan website, the GROW initiative aligns with national commitments to restore 26 million hectares of degraded land by 2030 and create an additional carbon sink of 2.5 to 3 billion tonnes of carbon dioxide equivalent.
- Led by NITI Aayog, the initiative involved collaboration from various institutions and utilized advanced technologies like remote sensing and GIS to assess agroforestry suitability across all Indian districts.
- Through thematic datasets, the project developed an Agroforestry Suitability Index (ASI) for national-level prioritization of greening and restoration projects.
- Based on analysis of five remote sensing-derived thematic layers - land use, wasteland, slope, water proximity, and soil organic content - the system provides information on areas suitable for agroforestry across India.
- It classifies areas as highly suitable, moderately suitable, and less suitable for agroforestry.
- Key features include generating district-level information on wasteland areas suitable for agroforestry, area prioritization regimes, live maps, area analysis-statistic reports, and an interactive mode/tool for flexibility in handling weights based on local conditions/needs.
Government Emphasis on Agroforestry in Budget Allocation:
- The Union Budget for the fiscal year 2022-23 has underscored the promotion of agroforestry and private forestry as a priority.
- Recognizing the critical goods and services provided by agroforestry, the budget aligns with the country's commitment to sustainable land use practices.
India's Agroforestry Leadership and Global Alignments:
- As the seventh-largest country globally, India faces challenges such as increased build-up areas, degraded land, and imbalanced resources.
- Approximately 16.96% of the Total Geographical Area (TGA) is a wasteland, necessitating transformation for productive use.
- India's pioneering National Agroforestry Policy, initiated in 2014, aims to enhance productivity, profitability, and sustainability through agroecological land use systems.
- Agroforestry aligns with global commitments, including the Paris Agreement, Bonn Challenge, UN Sustainable Development Goals, United Nations Convention on Combating Desertification (UNCCD), Doubling Farmers Income, Green India Mission, and more.
- India's proactive stance in promoting agroforestry contributes significantly to these international efforts, fostering a sustainable and resilient future.
Floor Test in the Bihar Legislative Assembly (Indian Express)
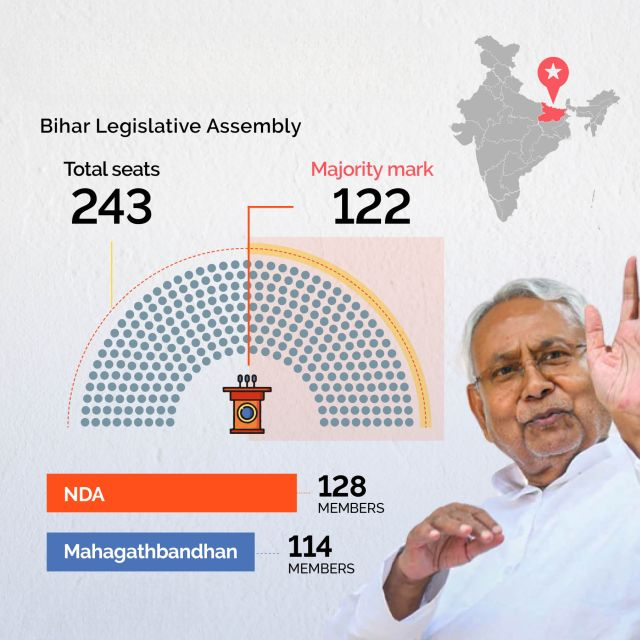
- 13 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
Bihar Chief Minister Nitish Kumar's coalition government with the Bhartiya Janata Party (BJP) on Monday won a crucial trust vote in the Bihar Assembly.
What is a Floor Test?
- A floor test (also called a ‘trust vote’) is held in legislative bodies, to find out whether the government that is suspected to have lost the majority still retains the confidence of the House.
- This is done through a vote among the members.
- When the House is in session, it is the Speaker who can call for a floor test but when the Assembly is not in session, the Governor’s residuary powers under Article 163 allow him to call for a floor test.”
- Further, “In 2020, the Supreme Court, in Shivraj Singh Chouhan & Ors versus Speaker, Madhya Pradesh Legislative Assembly & Ors, upheld the powers of the Speaker to call for a floor test if there is a prima facie view that the government has lost its majority.”
What Happens During a Floor Test?
- In case the majority held by the government is questioned, the leader of the party which claims to have the majority has to move a vote of confidence and prove a majority among those present and voting.
- The CM moves a motion seeking a vote of confidence, on which MLAs who are present in the House vote.
- If the majority of members vote in favour, the government survives;
- If the CM loses the vote, the government has to resign.
- This happens both in Parliament and the state Legislative Assemblies.
- Voting can be conducted by either a voice vote, in which MLAs respond to the motion verbally.
- Voting electronically involves the casting of votes by pressing a button, after which the numbers for each side are displayed on a board.
- In a physical division of votes, lawmakers cast votes in a ballot box, which are then counted.
- Also in situations when there are differences within a coalition government, the Governor can ask the Chief Minister to prove majority in the house.
- There is another test, the Composite Floor Test, which is conducted only when more than one person stakes a claim to form the government.
- When the majority is not clear, the governor might call for a special session to see who has the majority.
- The majority is counted based on those present and voting.
- This can also be done through a voice vote where the member can respond orally or through division voting.
- Some legislators may be absent or choose not to vote.
- In division vote, voting can be done through electronic gadgets, ballots or slips.
- The person who has the majority will form the government.
- In case of a tie, the speaker can also cast his vote under Article 100 of the constitution.
Regulating India's Online Gaming Industry (Indian Express)

- 12 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
The government will act as a regulator for the online gaming sector rather than an industry-led self-regulatory organization (SRO).
What are Online Games?
- Online games refer to games that are played over some form of computer network, most often the Internet.
- Online games can range from simple text-based games to games incorporating complex graphics and virtual worlds populated by many players simultaneously.
Types of Online Gaming:
- e-Sports: Originally played offline or on gaming consoles, e-Sports now thrive in the online realm, featuring structured competitions among professional players or teams.
- Fantasy Sports: These games involve assembling virtual teams composed of real-life athletes from different sports teams.
- Points are earned based on the actual performance of these athletes, as seen in platforms like Dream11.
- Online Casual Games: These diversions can be skill-based, where success relies on mental or physical prowess, or chance-based, where outcomes are determined by random events, like dice rolls.
How Big is India's Online Gaming Industry?
- The online gaming sector in India is primarily nurtured by a burgeoning startup ecosystem, boasting a robust 27% compound annual growth rate (CAGR).
- Projections suggest that the integration of AI and online gaming could contribute up to $300 billion to India's GDP by 2026-27.
- India leads the global charts in terms of the percentage of new paying users (NPUs) in gaming, soaring from 40% in 2020 to an anticipated 50% in 2021.
- Transactional gaming revenue witnessed a notable 26% surge in India, with the number of paying players escalating from 80 million in 2020 to 95 million in 2021, as per a FICCI report.
Challenges Confronting India's Online Gaming Sector:
- Regulatory Void: The absence of a regulatory framework poses challenges in implementing essential measures such as grievance redressal, player protection, data security, and curbing deceptive advertisements.
- Illegal Offshore Markets: Illicit offshore gambling and betting platforms pose threats to financial integrity and national security, with estimated annual tax losses to India amounting to $45 billion.
- Interstate Quandary: Varied state regulations on online gaming create inconsistencies, compounded by the Internet's borderless nature, making enforcement difficult.
- Societal Implications: The surge in online gaming raises concerns about addiction, mental health, financial fraud, and privacy breaches, warranting a comprehensive approach to address these issues.
The Problem of Self-Regulatory Bodies Under the IT Rules:
- The implementation of the IT (Intermediary Guidelines and Digital Media Ethics Code) Rules 2021 represented a significant stride in regulatory oversight.
- According to these rules, online real-money gaming platforms must obtain approval from a regulatory authority, while those not involving real money are exempt from such requirements.
- In April 2023, the government issued online gaming regulations and provided a three-month window for the industry to propose Self-Regulatory Organizations (SROs).
- However, the proposals submitted were predominantly influenced by gaming companies and their industry associations, raising concerns about their ability to function as impartial regulatory bodies.
NAL Successfully Tested High Altitude Pseudo-Satellite (HAPS) at Challakere, Karnataka (TOI)

- 12 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
Scientists from city-based National Aerospace Laboratories (NAL), a Council of Scientific and Industrial Research (CSIR) lab, achieved a breakthrough by successfully testing an unmanned aerial vehicle called High-Altitude Pseudo Satellite (HAPS) at Chitradurga's Challakere in Karnataka.
News Summary:
- National Aerospace Laboratories (NAL) has achieved a milestone with the successful testing of an unmanned aerial vehicle known as the High Altitude Pseudo-Satellite (HAPS) in Challakere, Karnataka.
- This innovative system, measuring 5 meters in length with an impressive 11-meter wingspan and weighing 23 kg, soared to an altitude of approximately 3 km and maintained its position for an impressive duration of eight hours.
- A comprehensive series of tests is slated, with the ultimate goal of developing a full-fledged aircraft boasting a remarkable 30-meter wingspan comparable to a Boeing 737 by the year 2027.
- This advanced craft is anticipated to ascend to an impressive altitude of 23 km and remain airborne for a remarkable period of at least 90 days.
- NAL's ambitious agenda includes the design and construction of various components essential for the HAPS, including propellers, battery management systems, carbon-composite airframes, flight-control systems, and high-powered electric motors capable of withstanding extreme temperature variations.
- Additionally, in a separate endeavour, a Bengaluru-based private company recently conducted the inaugural test flight of a solar-powered, long-endurance drone, achieving an impressive flight duration of 21 hours.
About High Altitude Pseudo-Satellite (HAPS):
- Since the 1990s, numerous global initiatives have been undertaken to explore the potential applications of High Altitude Pseudo Satellites, also known as High Altitude Platform Stations (HAPS).
- Positioned above 20 km altitude in the stratosphere, these unmanned aircraft are designed for exceptionally long-duration flights, spanning months or even years.
- HAPS encompass various aircraft types, including airplanes, airships, and balloons.
Benefits/Advantages of HAPS:
- These solar-powered vehicles bridge the gap between unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) operating in lower altitudes and traditional satellites in space.
- They offer a wide array of applications, including telecommunications, emergency/public safety communications, intelligent transportation systems, maritime surveillance, environmental monitoring, and land border control.
- Compared to ground-based communication networks, HAPS can cover larger areas with minimal interference and facilitate data transfer between satellites and ground-based telecom networks.
- Unlike traditional satellites, which are costly to construct and launch, HAPS are more cost-effective and easier to deploy.
- It has both military and civilian applications, including intelligence, surveillance, telecommunication, and disaster response.
- The technology offers lower latency and can connect to multiple ground stations.
Significance for India:
- In India, Hindustan Aeronautics Limited (HAL) announced in 2022 its collaboration with a startup company to develop a "futuristic" high-altitude pseudo satellite.
- Given India's extensive land borders stretching approximately 15,000 km and a coastline spanning 7,500 km, securing these borders is paramount, necessitating diverse solutions.
- Hovering at the Earth's atmospheric edge, HAPS offer valuable services for efficient border surveillance, tracking enemy movements deep into territories or seas, and conducting round-the-clock missions.
- Equipped with advanced optical and infrared cameras, state-of-the-art sensors, and other sophisticated technology, these aerial platforms are ideal for border patrolling, target tracking, maritime surveillance, navigation, and even missile detection.
- China's Aviation Industry Corporation of China (AVIC), a state-owned aerospace and defense conglomerate, has been actively developing various HAPS platforms for surveillance purposes.
- In 2018, it successfully tested the solar-powered Morning Star drone, renowned for its prolonged airborne endurance.
What Is Nazool Land Which Is At The Heart Of Haldwani Violence? (Indian Express)

- 12 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
Violence erupted in Uttarakhand’s Haldwani district recently after the administration conducted a demolition drive at the site of a mosque and madrasa, allegedly on Nazool land, killing five and injuring many more.
What is Nazool Land?
- Nazool land is owned by the government but most often not directly administered as state property.
- The state generally allots such land to any entity on lease for a fixed period, between 15 and 99 years.
- In case the lease term is expiring, one can approach the authority to renew the lease by submitting a written application to the Revenue Department of the local development authority.
- The government is free to either renew the lease or cancel it — taking back Nazool land.
- In almost all major cities of India, Nazool land has been allotted to different entities for a variety of different purposes.
How did Nazool Land Emerge?
- During British rule, kings and kingdoms which opposed the British frequently revolted against them, leading to several battles between them and the British Army.
- Upon defeating these kings in battle, the British would often take their land away from them.
- After India gained Independence, the British vacated these lands.
- But with kings and royals often lacking proper documentation to prove prior ownership, these lands were marked as Nazool land — to be owned by the respective state governments.
How Does the Government Use Nazool Land?
- The government generally uses Nazool land for public purposes like building schools, hospitals, Gram Panchayat buildings, etc.
- Several cities in India have also seen large tracts of land denoted as Nazool land used for housing societies, generally on lease.
- Very often, the state does not directly administer Nazool land but rather leases it to different entities.
- While several states have brought in government orders for framing rules for Nazool land, The Nazool Lands (Transfer) Rules, 1956 is the law mostly used for Nazool land adjudication.
New Education Policy Taking Forward Swami Dayanand’s Vision (Indian Express)

- 12 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
The National Education Policy 2020 is taking forward the vision of social reformer Swami Dayanand Saraswati, Prime Minister Narendra Modi said recently.
Who was Maharishi Dayanand Saraswati?
- Maharishi Dayanand Saraswati, born on February 12, 1824, in Tankara, Gujarat, was a pioneering social reformer.
- He established the Arya Samaj in 1875 with the aim of addressing prevailing social injustices.
Religious and Social Reforms:
- Rejection of Idolatry and Ritualism: Dayanand Saraswati staunchly opposed idol worship and ritualistic practices, advocating instead for the worship of a formless, attributeless God as outlined in the Vedas.
- Shuddhi Movement: He initiated the Shuddhi Movement to reclaim individuals who had converted to religions like Islam or Christianity, aiming to reintegrate them into Hinduism.
- Back to Vedas: Recognizing the importance of Vedic wisdom, he spearheaded a movement to revive the teachings of the Vedas, emphasizing their relevance in modern society.
- Women’s Rights: Dayanand Saraswati championed women’s rights, advocating for their education and equal participation in social and religious spheres alongside men.
- Opposition to Child Marriage and Sati: He vehemently opposed practices like child marriage and sati, viewing them as detrimental to society and antithetical to Vedic principles.
Educational Reforms:
- Dayanand Saraswati established several Gurukuls to impart Vedic knowledge to his followers and empower them to disseminate this wisdom further.
- Influenced by his philosophy and vision, his disciples founded the Dayanand Anglo Vedic (DAV) College Trust and Management Society following his demise in 1883.
- The first DAV High School was founded in Lahore on June 1, 1886, under the leadership of Mahatma Hans Raj.
Literary Contributions:
- Dayanand Saraswati's philosophical ideas are encapsulated in his notable works like "Satyartha Prakash" and "Veda Bhashya," shedding light on his vision for Hindu reform.
- His thoughts were further disseminated through the journal "Arya Patrika," which he edited, reflecting his philosophical convictions.
Arya Samaj:
- Founded by Dayanand Saraswati in Bombay in 1875, the Arya Samaj, meaning "society of the nobles," aimed to reform Hinduism by steering it away from superstition.
- With the motto "Krinvanto Vishwam Aryam" meaning "Make this world noble," the Samaj advocated for a return to the true essence of Hinduism, rejecting ritualistic practices like idol worship, pilgrimage, and animal sacrifice.
- In the 1880s, the Samaj actively supported widow remarriage, promoting social reforms aligned with its principles.
- The Arya Samaj's influence extends beyond India, with active branches worldwide.
PM-SVANidhi Boosted the Annual Income of Street Vendors (Indian Express)

- 12 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
A study that evaluated the impact of the PM SVANidhi, a small working capital loan scheme for street vendors, has found that the first tranche of `10,000 led to an additional annual income of `23,460 for each beneficiary.
News Summary:
- Commissioned by the Union Ministry of Housing and Urban Affairs, the study was conducted by the Centre for Analytical Finance at the Indian School of Business (ISB) from January to June 2023.
- Although the report's findings will inform the Ministry's assessment of the PM SVANidhi scheme, it is not expected to be publicly released.
Key Findings of the Report:
- 94% of beneficiaries who received the initial Rs 10,000 loan reported using it for business investments, rising to 98% for those who received a second loan.
- The first loan contributed to an average additional monthly income of Rs 1,955, totalling Rs 23,460 over the one-year loan period.
- Approximately 13.9% of disbursed loans were categorized as non-performing assets (NPAs), indicating no payments for three months or more.
- Beneficiaries demonstrated a lower debt-to-income (DTI) ratio compared to typical small businesses, indicating high creditworthiness.
- Despite the PM SVANidhi program, there was limited improvement in street vendors accessing formal credit from other sources, with only 9% having loans from financial institutions.
What is PM SVANidhi?
- The Prime Minister Street Vendor’s AtmaNirbhar Nidhi (PM SVANidhi) stands as a flagship initiative of the Ministry of Housing and Urban Affairs, Government of India, launched on June 1, 2020.
- Its core aim is to extend accessible credit to street vendors, enabling them to revive their businesses and achieve self-reliance.
- The scheme is specifically tailored to empower street vendors, including hawkers, rehri walas, thelewala, and those operating in urban and peri-urban areas.
- PM SVANidhi facilitates eligible street vendors to obtain working capital loans devoid of collateral requirements.
- These loans, with a maximum cap of Rs. 10,000 and a one-year tenure, are intended to support vendors in procuring essential items, securing raw materials, and meeting their operational expenses.
- Furthermore, the scheme offers a 7% interest subsidy to vendors who repay their loans promptly, promoting timely repayments and fostering financial discipline.
How Does PM SVANidhi Work?
- The PM SVANidhi scheme operates through a streamlined and accessible application process designed to maximize participation and outreach among street vendors.
- Vendors can apply for the scheme via a dedicated online portal or through Common Service Centers (CSCs) established nationwide.
- Once the application is submitted, it undergoes a brief verification process conducted by relevant authorities.
- Upon successful verification, the loan amount is directly transferred to the vendor's bank account.
- Vendors can then utilize the funds to revive their businesses, purchase inventory, and cover operational expenses.
Key Features and Benefits of PM SVANidhi:
- Affordable Credit: PM SVANidhi offers accessible working capital loans of up to Rs. 10,000 to street vendors, facilitating credit access without the need for collateral.
- Interest Subsidy: The scheme provides a 7% interest subsidy to vendors who repay their loans promptly, incentivizing timely repayments and easing financial burdens.
- Digital Empowerment: PM SVANidhi promotes digital transactions and payments among street vendors, fostering adaptation to evolving business practices and enhancing financial literacy.
- Enhanced Livelihood: By availing of PM SVANidhi benefits, street vendors can improve their livelihoods, expand their businesses, and generate sustainable income for themselves and their families.
- Access to Social Security Schemes: Street vendors enrolled in PM SVANidhi are eligible for various social security schemes, including Pradhan Mantri Suraksha Bima Yojana (PMSBY) and Pradhan Mantri Jeevan Jyoti Bima Yojana (PMJJBY), providing financial coverage and protection during unforeseen events.
Conclusion
The Prime Minister Street Vendor’s AtmaNirbhar Nidhi (PM SVANidhi) scheme stands as a beacon of hope for street vendors throughout India. By offering accessible credit, digital empowerment, and access to social security schemes, PM SVANidhi is propelling the advancement and prosperity of street vendors, empowering them to establish sustainable livelihoods. This groundbreaking initiative, with its manifold advantages and inspiring success stories, underscores the Government of India's dedication to fostering an inclusive and self-sufficient economy.
7th Indian Ocean Conference 2024 (The Hindu)

- 10 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
During the inauguration of the Indian Ocean Conference in Perth, Sri Lankan President Ranil Wickremesinghe highlighted the escalating concerns of smaller countries in the region regarding the militarization of the Indian Ocean and the increasing "great power rivalry."
What is the Indian Ocean Conference (IOC)?
- The Indian Ocean Conference (IOC) is an annual international event that centres on the geopolitical, economic, and strategic significance of the Indian Ocean region.
- It serves as a platform for policymakers, scholars, business leaders, and civil society representatives to discuss security, trade, and cooperation within the Indian Ocean area.
- Established in 2016, the conference's first edition took place in Singapore.
- Notably, the 6th IOC convened in Dhaka, Bangladesh, in 2023.
- Organized by the India Foundation in collaboration with various regional organizations, the IOC facilitates dialogue and collaboration on key issues impacting the Indian Ocean region.
Key Points from EAM Jaishankar’s Speech:
- Addressing Challenges in the Indian Ocean: Jaishankar highlighted the spectrum of challenges in the Indian Ocean, ranging from threats to maritime traffic like piracy and terrorism to concerns about international law, freedom of navigation, and sovereignty.
- He emphasized the interconnected nature of transnational and non-traditional threats, including those arising from illegal activities.
- Concerns about Grey Areas: Expressing concern about grey areas, Jaishankar noted that some issues, such as those related to climate change and natural disasters, are increasingly visible.
- He also discussed disruptive events and their impact, along with the consequences of distant crises like fuel and food shortages.
- Additionally, unsustainable debt, opaque lending practices, and unviable projects are affecting countries in the region.
- Structural Challenges of Globalization: Jaishankar discussed the structural challenges inherent in the current form of globalization, emphasizing over-concentrations in manufacturing and technology.
- He highlighted the importance of dispersing production across different geographies, especially in light of the COVID-19 pandemic, and emphasized the need for reliable and resilient supply chains.
- Additionally, he noted the significance of trust and transparency in the digital era and the emergence of artificial intelligence.
- Drivers of the Future: Jaishankar underscored the importance of focusing on drivers of the future, such as digital technology, electric mobility, green hydrogen, and sustainable shipping, for a sustainable future.
About the Indian Ocean Region (IOR):
- The Indian Ocean Region (IOR) comprises the Indian Ocean and its adjacent territories, including coastal states and islands.
- Extending from the African coast in the west to the Australian coast in the east, and from the Arabian Peninsula and the Persian Gulf in the north to the southern coast of Sri Lanka and Australia in the south, the IOR covers approximately 70.6 million square kilometres, making it the world's third-largest ocean.
Significance of the Indian Ocean Region (IOR):
- Geopolitical Importance: Positioned as a major transit route for global trade, the IOR facilitates the transportation of vital commodities, including oil and gas.
- It hosts critical chokepoints like the Strait of Malacca and the Bab-el-Mandeb Strait, connecting Asia, Europe, and Africa.
- Economic Importance: Boasting several rapidly developing economies like India, China, and various Southeast Asian nations, the IOR is rich in natural resources, attracting substantial foreign investment.
- With 64% of the global population and 60% of the global GDP, the region plays a significant role in the global economy.
- Security Importance: The IOR is a region of paramount security significance, confronting challenges such as terrorism, piracy, and maritime security threats.
- It has witnessed heightened military activity from major powers like the US, India, and China in recent times.
- Environmental Importance: Home to diverse marine ecosystems like coral reefs and mangrove forests, the IOR supports biodiversity and sustains local communities.
- However, it faces environmental risks due to climate change, including rising sea levels and more frequent extreme weather events.
Monetary Policy Committee (MPC) of RBI (The Hindu)

- 10 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
The RBI’s Monetary Policy Committee (MPC) has prudently opted to persist with its objective of ‘ensuring that inflation progressively aligns to the target’ by keeping benchmark interest rates unchanged, and sticking with its stance of ‘withdrawal of accommodation’.
About the Monetary Policy Committee (MPC):
- The Monetary Policy Committee (MPC) is a committee of the Reserve Bank of India (RBI), chaired by its Governor.
- The RBI shall organise at least four meetings of the Monetary Policy Committee in a year.
- Established under Section 45ZB of the RBI Act, 1934, the government forms this six-member committee.
Composition of MPC:
- Comprising six members, three are from the RBI, while the remaining members are appointed by the Government of India.
- Members include the RBI Governor (Chairperson), the RBI Deputy Governor responsible for monetary policy, one official nominated by the RBI Board, and three members proposed by the Government of India (chaired by the Cabinet Secretary).
- MPC members serve a single four-year term and are not eligible for reappointment.
Functions:
- The primary responsibility of the MPC is to determine the benchmark policy interest rate (repo rate) to manage inflation within the prescribed target level.
- The current mandate of the committee is to maintain annual consumer price index (CPI) inflation at 4% within a band of +/- 2% until March 31, 2026.
Earth System Model (HT)
- 10 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
The Indian Institute of Tropical Meteorology is developing a first-for-India Earth System Model to improve climate forecasts and predict climate impacts.
What is an Earth System Model (ESM)?
- An Earth System Model (ESM) is a complex computer program that simulates the interactions between the various components of our planet's climate system, including the atmosphere, oceans, land, ice, and biosphere.
- These models are crucial for understanding past, present, and future climate trends, and are used for purposes like:
- Improving weather forecasts: By accounting for intricate interactions between different parts of the Earth system, ESMs can potentially lead to more accurate weather predictions, particularly for longer-term forecasts.
- Predicting climate change impacts: By simulating different scenarios of greenhouse gas emissions and other influencing factors, ESMs can project how climate change might affect specific regions and aspects like temperature, precipitation, and sea level rise.
- Informing adaptation and mitigation strategies: With insights into potential climate impacts, policymakers and individuals can make informed decisions about adapting to and mitigating the effects of climate change.
India's Earth System Model:
- Recognizing the importance of such models, India is currently developing its first-ever indigenous Earth System Model, led by the Indian Institute of Tropical Meteorology (IITM) and the Centre for Climate Change Research (CCCR).
- An amount of ?192.28 crores has been sanctioned under the Monsoon Convection, Clouds and Climate Change (MC4) sub-scheme to develop the climate forecasting system
- This project, funded by the Ministry of Earth Sciences, aims to:
- Enhance forecast accuracy: The model will incorporate advanced features to improve the reliability of weather forecasts, particularly for monsoons that are crucial for India's agriculture.
- Facilitate long-term climate studies: By simulating various climate scenarios, the model will provide valuable insights into potential future climate changes affecting India.
- Predict climate impacts: This model will help assess the risks and potential impacts of climate change on various sectors like agriculture, water resources, and coastal ecosystems.
- The project is expected to be completed by 2025 and is believed to be a significant step towards improving India's understanding and preparedness for the challenges posed by climate change.
About the Monsoon Convection, Clouds, and Climate Change (MC4) Sub-Scheme:
- The MC4 initiative aims to enhance our understanding of monsoonal precipitation changes and their implications in a warming climate by enhancing observational databases and climate models.
- Its overarching objective is to refine our understanding of the interactions between monsoon dynamics, clouds, aerosols, precipitation, and the water cycle within a changing climate context.
The nodal ministry overseeing this effort is the Ministry of Earth Sciences (MoES).
What is an Earth System Model (ESM)?
- An Earth System Model (ESM) is a complex computer program that simulates the interactions between the various components of our planet's climate system, including the atmosphere, oceans, land, ice, and biosphere.
- These models are crucial for understanding past, present, and future climate trends, and are used for purposes like:
- Improving weather forecasts: By accounting for intricate interactions between different parts of the Earth system, ESMs can potentially lead to more accurate weather predictions, particularly for longer-term forecasts.
- Predicting climate change impacts: By simulating different scenarios of greenhouse gas emissions and other influencing factors, ESMs can project how climate change might affect specific regions and aspects like temperature, precipitation, and sea level rise.
- Informing adaptation and mitigation strategies: With insights into potential climate impacts, policymakers and individuals can make informed decisions about adapting to and mitigating the effects of climate change.
India's Earth System Model:
- Recognizing the importance of such models, India is currently developing its first-ever indigenous Earth System Model, led by the Indian Institute of Tropical Meteorology (IITM) and the Centre for Climate Change Research (CCCR).
- An amount of ?192.28 crores has been sanctioned under the Monsoon Convection, Clouds and Climate Change (MC4) sub-scheme to develop the climate forecasting system
- This project, funded by the Ministry of Earth Sciences, aims to:
- Enhance forecast accuracy: The model will incorporate advanced features to improve the reliability of weather forecasts, particularly for monsoons that are crucial for India's agriculture.
- Facilitate long-term climate studies: By simulating various climate scenarios, the model will provide valuable insights into potential future climate changes affecting India.
- Predict climate impacts: This model will help assess the risks and potential impacts of climate change on various sectors like agriculture, water resources, and coastal ecosystems.
- The project is expected to be completed by 2025 and is believed to be a significant step towards improving India's understanding and preparedness for the challenges posed by climate change.
About the Monsoon Convection, Clouds, and Climate Change (MC4) Sub-Scheme:
The MC4 initiative aims to enhance our understanding of monsoonal precipitation changes and their implications in a warming climate by enhancing observational databases and climate models.
- Its overarching objective is to refine our understanding of the interactions between monsoon dynamics, clouds, aerosols, precipitation, and the water cycle within a changing climate context.
- The nodal ministry overseeing this effort is the Ministry of Earth Sciences (MoES).
Preamble to the Constitution of India (Indian Express)

- 10 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
The Supreme Court recently wondered if the Preamble to the Constitution could have been amended while retaining the date when the Constitution was adopted.
Background:
- In historical context, the Preamble underwent a solitary amendment in December 1976 via the 42nd Constitutional Amendment during the Indira Gandhi Government.
- This amendment introduced two modifications: replacing "unity of the nation" with "unity and integrity of the nation," and inserting "socialist" and "secular" between "sovereign" and "democratic."
- Initially, the Preamble described India as a "sovereign, democratic republic."
- Notably, the Supreme Court affirmed in the Kesavananda Bharati case that the Preamble constitutes an integral component of the Constitution, subject to Parliament's amending authority, provided the fundamental structure remains intact.
About the Preamble of the Indian Constitution:
- The Preamble to the Constitution of India draws inspiration primarily from the 'Objective Resolution' penned by Jawaharlal Nehru in 1946.
- It serves as a concise introduction, outlining the foundational principles and aspirations of the nation. Key components include:
- Source of Constitutional Authority: It affirms that the Constitution derives its authority from the people of India.
- Nature of the Indian State: It declares India as a Sovereign, Socialist, Secular, Democratic, and Republican Polity.
- Objectives of the Constitution: It articulates Justice, Liberty, Equality, and Fraternity as the core objectives.
- Adoption Date: It designates November 26, 1949, as the date of adoption.
- Significance:
- Acts as a guiding framework for interpreting the Constitution and formulating laws.
- Defines the national aspirations and goals.
- Highlights the importance of fundamental rights and values for all citizens.
- Fosters a sense of national unity and identity.
Is the Preamble a Part of the Constitution of India?
- In the Berubari Union Case of 1960, the Supreme Court stated that the Preamble is not a formal part of the Constitution.
- However, it acknowledged that the Preamble provides insight into the intentions of the Constitution makers, thus aiding in interpreting any ambiguities within the Constitution.
- The Kesavananda Bharati Case of 1973 marked a reversal of this stance.
- The Supreme Court declared the Preamble as an intrinsic part of the Constitution, attributing it significant interpretive value.
- It emphasized that the Preamble plays a crucial role in understanding the spirit and objectives of the Constitution, guiding the interpretation of its provisions.
- In the LIC of India Case of 1995, the Supreme Court reiterated that the Preamble is indeed an integral component of the Constitution.
- However, it clarified that while the Preamble holds symbolic importance and helps in understanding the Constitution's essence, it cannot be directly enforced as a law in Indian courts.
Can the Preamble be Amended?
- An essential debate revolves around whether the Preamble can undergo amendments under Article 368.
- In the Kesavananda Bharati Case of 1973, the Supreme Court established that the Preamble constitutes a fundamental aspect of the Constitution and is therefore amenable to amendments.
- However, any such amendment must adhere to the principle that the 'Basic Structure' of the Constitution remains untouched.
Polygamy in India: Insights and debates surrounding Uniform Civil Code (Indian Express)

- 10 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
The Uttarakhand Legislative Assembly recently passed the Uniform Civil Code (UCC) Bill, 2024 after a two-day discussion. The Bill brings uniformity in personal laws, governing things such as marriage, divorce, and inheritance, across communities in the state (excluding tribals).
What is Polygamy?
- Polygamy involves the practice of having multiple spouses simultaneously, which can include either wives or husbands.
- It manifests in two primary forms:
- Polygyny, where a man is married to several women concurrently, and
- Polyandry, where a woman is married to multiple men concurrently.
Who can have "multiple wives"?
- Under Hindu law, which applies to Hindus, Sikhs, Jains, and Buddhists, the practice of polygamy is prohibited.
- Individuals governed by Hindu law can face criminal proceedings under Sections 494 and 495 of the Indian Penal Code.
- The Special Marriage Act, as well as Christian and Parsi laws, also outlaw bigamy.
- However, the Shariat Protection Act exempts Muslims in India from the ban on polygamy.
- Additionally, due to the protection granted to cultural practices of scheduled tribes, polygynous marriages can be found in tribal groups across northeastern states, Odisha, Telangana, and other regions.
- Courts have had to face cases where a man converted to Islam from other religions to marry a second wife.
- While the Supreme Court, in its 1994 Sarla Mudgal verdict, declared that conversion solely for a second marriage is invalid, the Law Commission reports from 1961 and 2009 have emphasized the need to clarify the legal position of the "second wife" in a converted Muslim marriage and address the rights of any children born from such a union.
What does the data say?
- Government data on polygamy can be obtained from two main sources — the decadal census and the National Family Health Survey (NFHS). Both have certain limitations.
- The census does not directly collect data on polygamy.
- Rather its incidence is inferred from the difference in the number of married men and the number of married women in the country.
- More married women than men point to the prevalence of situations where men have married more than once.
- Rather its incidence is inferred from the difference in the number of married men and the number of married women in the country.
What does the census data say?
- According to the census of 2011, there are 28.65 crore married men in India, compared to 29.3 crore married women.
- The difference between the two numbers — 65.71 lakh — can be explained either by the incidence of polygamy or men going abroad.
- The highest discrepancy in the population of married men and women can be found among Hindus (who make up the largest number of Indians), followed by Muslims, Sikhs, Christians, Sikhs, and Buddhists.
- However, when compared to their respective shares in the total population, Muslims and Christians report the greatest difference.
What does NFHS data say?
- The NFHS-5 showed the prevalence of polygamy (the percentage of women who reported their husbands had other wives) was highest among Christians (2.1%), followed by Muslims (1.9%), and Hindus (1.3%), looking at religion.
- Overall, Scheduled Tribes reported the highest incidence at 2.4%.
- A June 2022 study by the International Institute of Population Sciences (IIPS) showed that polygynous marriages (one man married to more than one woman at a time) have decreased from 1.9% in 2005-06 to 1.4% in 2019-21, among the whole population.
- Buddhists, who reported a 3.8% incidence of polygyny in 2005-06, saw the sharpest dip of 65.79% to 1.3% in 2019-21.
- The incidence of polygyny in the total population fell by 26.31%.
Constitutional Perspective and Supreme Court's Insights:
- India, as a secular state, upholds the principle of equality among religions, ensuring that no religion holds superiority or inferiority over another.
- The Indian Constitution guarantees fundamental rights to all citizens, and any legislation conflicting with these rights is considered unconstitutional.
- Article 13 of the Constitution invalidates any law inconsistent with Part III of the Constitution.
- Article 14 ensures equal treatment and protection under the law for every individual within India's territory.
- In a 2021 verdict, the Supreme Court highlighted India's recognition of a plural legal system, allowing different religious communities to abide by distinct 'personal laws.'
- However, these personal laws must adhere to constitutional validity and morality, ensuring they do not infringe upon Articles 14, 15, and 21 of the Constitution.
Bharat Ratna for former PMs Charan Singh and PV Narasimha Rao, scientist Swaminathan (Indian Express)

- 09 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
The Union government on February 9, 2024, announced former Prime Ministers Chaudhary Charan Singh, P.V. Narasimha Rao and agriculture scientist M.S. Swaminathan will be honoured with the country’s highest civilian honour, the Bharat Ratna posthumously.
News Summary:
- The government recently conferred the Bharat Ratna for former Prime Ministers Chaudhary Charan Singh and PV Narasimha Rao and agricultural scientist MS Swaminathan, who is known for his leading role in India's 'Green Revolution', posthumously.
- Earlier, the government had announced Bharat Ratna, for veteran BJP politician LK Advani and socialist icon and former Bihar Chief Minister Karpoori Thakur.
Who was PV Narasimha Rao?
- Pamulaparthi Venkata Narasimha Rao (28 June 1921 – 23 December 2004) was a lawyer and a towering Congress leader in undivided Andhra Pradesh, who became the 9th prime minister of India.
- He ruled the country between 1991 and 1996.
- In 1991, when India was facing a foreign reserves crisis, Narasimha Rao's government brought about three big-ticket economic reforms -- globalisation, liberalisation and privatisation.
- PV Narasimha Rao was the first person from South India to become the prime minister of India.
- He was born in a Telugu Niyogi Brahmin family in the Laknepalli village of Narsampet mandal, Warangal.
- The district is currently in Telangana.
- He was a freedom fighter who took part in Hyderabad's Vande Mataram movement in the late 1930s.
- After Independence, PV Narasimha Rao became a full-time politician.
- He was elected as an MLA for the first time in 1957.
- Till 1971, he assumed many ministerial positions in the state government. He became the chief minister of Andhra Pradesh in 1971.
- He was known as an Indira Gandhi loyalist and supported her in 1969 when the Congress vertically split into two parts.
- Rao also served as a member of parliament from Andhra Pradesh and handled home, defence and foreign affairs portfolios as a central minister.
- In 1991, he had almost retired, however, he came back to active politics after the assassination of Congress President and Prime Minister Rajiv Gandhi's assassination.
- He was also the first Congress PM outside the Nehru-Gandhi family.
- He broke several conventions as the prime minister.
- He appointed economist Manmohan Singh as his finance minister.
- Together, they brought about economic reforms.
Who was Chaudhary Charan Singh?
- Chaudhary Charan Singh was born in a middle-class farmer family in Meerut in 1902.
- He started his political career with the Congress.
- He was first elected to the Uttar Pradesh assembly in 1937 from Chhaprauli and later got re-elected in 1946, 1952, 1962 and 1967.
- Chaudhary Charan Singh was appointed as a parliamentary secretary in Govind Ballabh Pant's government in 1946.
- He worked in several departments before being appointed a cabinet minister for justice and information in 1951.
- In 1967, he quit the Congress and became the chief minister of Uttar Pradesh for the first time after being elected as the leader of the Sanyukta Vidhayak Dal coalition.
- He became the chief minister for the second time in 1970.
- In 1979 after the Jana Sangh (BJP's predecessor) pulled out of the 18-month-old Morarji Desai-led Janata Party government.
- Congress (I) decided to extend support to Chaudhary Charan Singh who took oath as prime minister on July 28, 1979.
- But before he could prove his majority in the Lok Sabha, Indira Gandhi withdrew support to his government and Singh resigned.
- He continued to remain as caretaker PM till January 14, 1980.
Who was MS Swaminathan?
- M.S. Swaminathan is an eminent Indian agricultural scientist and geneticist hailed as the "Father of the Green Revolution" in India.
- Born on August 7, 1925, Swaminathan's groundbreaking research and advocacy have significantly contributed to India's agricultural development and food security.
- He played a crucial role in introducing high-yielding varieties of wheat and rice, which revolutionized agricultural productivity in the country during the 1960s and 1970s.
- Swaminathan has received numerous awards and honours for his contributions to agriculture and sustainable development, and he continues to be a leading voice in global efforts to address food security and environmental sustainability.
Pradhan Mantri Matsya Kisan Samridhi Sah-Yojana (PM-MKSSY) (PIB)

- 09 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
Recently, the Union Cabinet approved the Pradhan Mantri Matsya Kisan Samridhi Sah-Yojana (PM-MKSSY), a sub-scheme under the Pradhan Mantri Matsya Sampada Yojana.
About Pradhan Mantri Matsya Kisan Samridhi Sah-Yojana:
- Implemented as a Central Sector Sub-scheme within the broader framework of the PMMSY, this initiative aims to bolster the fisheries sector.
- Funding: With an estimated outlay of Rs. 6,000 crore, the scheme comprises 50% public finance, including contributions from the World Bank and the AFD, and the remaining 50% anticipated investment from beneficiaries and the private sector.
- Duration: Operational for four years from FY 2023-24 to FY 2026-27, spanning all States and Union Territories.
Intended Beneficiaries:
- Fishers, Fish (Aquaculture) Farmers, Fish workers, Fish Vendors or such other persons directly engaged in the fisheries value chain.
- Micro and Small enterprises in the form of Proprietary Firms, Partnership Firms and Companies registered in India, Societies, Limited Liability Partnerships (LLPs), Cooperatives, Federations, Village Level Organizations like Self Help Groups (SHGs), Fish Farmers Producer Organizations (FFPOs) and Startups engaged in fisheries and aquaculture value chains.
- FFPOs also include Farmer's Producer Organizations (FPOs).
- Any other beneficiaries that may be included by the Department of Fisheries, Gol as targeted beneficiaries.
Aims and objectives of PM-MKSSY:
- Gradual Formalization of the unorganized fisheries sector through self-registration of fishers, fish farmers and supportive workers under a National Fisheries Sector Digital Platform including the creation of work-based digital identities of fish workers for improved service delivery.
- Facilitating access to institutional financing fisheries sector micro and small enterprises.
- Providing a one-time incentive to beneficiaries for purchasing aquaculture insurance.
- incentivising fisheries and aquaculture microenterprises through performance grants for improving fisheries sector value-chain efficiencies including the creation and maintenance of jobs.
- Incentivising micro and small enterprises through performance grants for the adoption and expansion of fish and fishery product safety and quality assurance systems including the creation and maintenance of jobs.
What is a White Paper in Economics? Types and Main Purpose (Indian Express)

- 09 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
Finance Minister Nirmala Sitharaman presented a “white paper” on the Indian economy in Parliament recently.
What is a White Paper?
- A White Paper is a report, guide, research-based paper or formal government document that presents expert analysis about a topic or solution to a problem, or policy proposals, often bound in white covers.
- They have been used historically to introduce new policies or legislation and gauge public reaction to government initiatives, schemes or policies.
Types of White Paper:
- There are three types of white paper Economic White Paper, Budget White Paper, and Policy White Paper.
- Economic White Paper: It contains an analysis of the current state of the economy and talks about the challenges, and opportunities it faces.
- The paper also contains the government’s plans and strategies to address the issues.
- Budget White Paper: A Budget White Paper contains government budgetary priorities, spending schemes, revenue sources, and fiscal projections among other issues.
- Policy White Paper: A Policy White Paper talks about a specific policy, scheme or program of the government to address a particular issue or problem in the economy.
- Economic White Paper: It contains an analysis of the current state of the economy and talks about the challenges, and opportunities it faces.
What is the use of White Paper?
- The purpose of a white paper on the economy is to inform the public, Parliament, and stakeholders about a government's policy, vision, goals, plans, and actions being taken to safeguard the economic interests of the country.
- The document can also be used as a tool for consultation and feedback, as it invites comments and suggestions from various parties on the proposed policies or programs.
- A white paper can also influence public opinion and shape the political debate on economic issues.
Key Insights from the White Paper on the Indian Economy and its Objectives:
- The comprehensive 58-page document is structured into three primary segments.
- Section 1 delves into the macroeconomic landscape during the UPA's 10-year tenure.
- Section 2 presents an overview of various corruption scandals that occurred under the UPA administration.
- Section 3 outlines the strategies employed by the NDA to revitalize the economy.
Objectives of the white paper presented by FM:
- To elucidate the governance, economic, and fiscal challenges inherited by the NDA government upon assuming office in 2014.
- To shed light on the policies and initiatives undertaken by the NDA government since 2014 to rejuvenate the economy.
- To stimulate a more informed discourse on the significance of national interest and fiscal responsibility in governance, transcending political expediency.
Most Important Claims in the White Paper:
- The UPA era was marred by policy missteps and corruption scandals, notably non-transparent auctions of public resources like coal and telecom spectrum.
- In the aftermath of the 2008 Global Financial Crisis, the UPA's pursuit of high economic growth undermined macroeconomic stability, leading to challenges such as high inflation and fiscal deficit.
- Capital expenditure as a percentage of total expenditure declined significantly during the UPA tenure, impeding infrastructure development and economic growth.
- The White Paper highlights improvements under the NDA, including lower inflation rates and enhanced efficacy of schemes like Jan Dhan and Swachh Bharat Mission.
- The NDA government's proactive measures have steered the economy away from crisis, positioning India as one of the top global contributors to growth.
- Overall, the White Paper underscores the NDA's efforts to address economic challenges and foster sustainable growth in India.
What Insights Can We Draw from the Above Assertions?
- Examining the economic performance spanning two decades, especially in consecutive terms, presents a formidable challenge due to the multitude of factors influencing both the economy and its measurement methodologies.
- For example, the significant fluctuations in domestic inflation during the latter years of the UPA administration can largely be attributed to the volatile cost of crude oil.
- During FY12 to FY14, crude oil prices fluctuated between $111 and $105 per barrel, significantly impacting inflation rates. Subsequently, oil prices declined to $84 in FY15 and further to $46 in FY16.
- While the NDA government has achieved noteworthy milestones such as the implementation of GST and IBC, the white paper fails to acknowledge shortcomings within the economy.
- Notably, it overlooks critical issues such as unemployment, and the absence of a formal measure of poverty since 2011 is not addressed.
Kyasanur Forest Disease (KFD) (The Hindu)

- 09 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
Karnataka is currently facing challenges posed by the spread of Kyasanur Forest Disease (KFD), also recognized as monkey fever.
What is KFD?
- The disease was first noticed in the Kysanur Forest area of Sorab Taluk in Shivamogga district in 1956 and was named after the region.
- It is also known as monkey fever, as monkeys also get infected.
- The death of a monkey serves as a warning of a KFD outbreak.
- The scientists concluded that the virus (Flaviviridae virus family) must have been present in the forests of the Malnad region.
- It became active due to ecological changes.
- The disease spreads through ticks.
- Primates that come in contact with infective ticks contract the disease.
- Human beings who visit the forest area either for livelihood, to graze cattle, or to collect firewood contract the disease.
- Normally, the transmission begins from late November to June.
- It peaks between December and March, according to studies.
- A blood test is done to identify if someone has KFD.
Symptoms:
- Symptoms start to appear three to eight days after the bite, of an infective tick.
- The common symptoms are:
- Fever
- Redness of the eyes
- Severe headache, and
- Body pain
- Three to four days after the onset of initial symptoms, the patient may have gastrointestinal symptoms.
- In severe cases, bleeding from the nose is noted.
Treatment:
- There is no specific treatment, doctors handle the symptoms and monitor the vitals daily.
- An attempt to use a vaccine was given up after studies showed it to be ineffective.
- The ICMR is said to be in consultation with Indian Immunologicals for the development of a vaccine.
About 400 Smart Cities Mission Projects are Likely to Miss June 30 Deadline (Indian Express)

- 09 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
Recently, the Union Housing and Urban Affairs Secretary Manoj Joshi told the Parliamentary Standing Committee on Housing and Urban Affairs that Some projects under the Smart Cities Mission would not be able to meet the June 30 deadline and the respective state governments would be responsible for completing them thereafter.
Key Highlights of the Report:
- Approximately 400 Smart City Mission (SCM) projects are facing challenges in meeting the extended deadline of June 2024, according to a recent report by the Parliamentary committee.
- These projects, being implemented by around ten cities under the Center's flagship SCM, are at risk of not being completed within the timeframe.
- The Ministry of Housing and Urban Affairs (MoHUA) has granted a second extension to the Smart Cities Mission, giving it until June 2024 to finalize pending work.
- However, if these projects are not completed by then, the respective state governments will be responsible for completing them at their own expense.
- The role of the ministry extends beyond merely transferring funds; it also involves overseeing project execution and ensuring successful completion.
- Despite the challenges, the ministry has emphasized that there will be no further extensions to the mission.
- Delays have been attributed to various factors, including difficulties in relocating local populations, legal hurdles such as land procurement issues, frequent turnover of smart cities' CEOs, and delays in projects requiring coordination with other government entities.
- In light of these challenges, the committee has proposed extending the Smart Cities Mission to Tier-2 cities located within 50-100 km of capital cities and tourist destinations.
- Additionally, the committee has highlighted the importance of protecting privacy rights, especially given the extensive deployment of surveillance technology like CCTV cameras and Integrated Command and Control Centers across all 100 cities involved in the mission.
What is the Smart Cities Mission (SCM)?
- The Smart Cities Mission (SCM) was initiated on 25th June 2015, to foster urban centers that offer essential infrastructure and a sustainable, clean environment.
- Through a competitive process spanning from 2016 to 2018, 100 cities were selected for development as Smart Cities, each receiving five years from their selection to complete designated projects.
- Administered as a Centrally Sponsored Scheme under the Union Ministry of Housing and Urban Affairs (MoHUA), the program entails financial support from the Central Government amounting to Rs. 48,000 crores over five years, equating to an average of Rs. 100 crore per city per year, matched by an equivalent contribution from the State or Urban Local Body (ULB).
- Guided by six core principles, the Smart Cities initiative aims to enhance the quality of life for residents through the implementation of innovative solutions, fostering economic growth, and addressing social, economic, physical, and institutional aspects of urban development. It prioritizes sustainable and inclusive progress, endeavouring to establish scalable models that can serve as beacons for other cities aspiring for advancement.
- Financing for the Smart Cities Mission entails shared responsibilities between the Central Government, state governments, and ULBs, requiring equal contributions for project implementation.
- As of December 1, 2023, significant progress has been made, with 6,419 projects worth Rs. 1,25,105 crore completed out of a total of 7,970 projects valued at Rs. 1,70,400 crore.
- An additional 1,551 projects worth Rs. 45,295 crore are currently in progress, though certain cities, particularly those in the North-Eastern and Himalayan regions, as well as small Union Territories, face challenges in keeping pace.
- Budget allocations for the Smart Cities proposal have seen adjustments, with a reduction in the outlay from Rs. 7,634 crores to Rs. 7,535 crores in the revised budget for 2023-24, and a further decrease to Rs. 2,236 crores for the 2024-25 fiscal year.
Prithvi Vigyan Scheme to Bolster Earth Science Research Approved by Cabinet (Indian Express)

- 08 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
The Union Cabinet has approved a Rs 4,797 crore research scheme to boost and maintain research momentum in the fields of ocean, atmospheric and polar sciences.
What is PRITHvi VIgyan (PRITHVI)?:
- The PRITHvi VIgyan (PRITHVI) will be an umbrella scheme spearheaded by the Ministry of Earth Sciences to help continue many of the ongoing research projects covering the period from 2021 to 2026.
- This scheme encompasses five existing sub-schemes:
- Atmosphere & Climate Research-Modelling Observing Systems & Services (ACROSS)
- Ocean Services, Modelling Application, Resources and Technology (O-SMART)
- Polar Science and Cryosphere Research (PACER)
- Seismology and Geosciences (SAGE)
- Research, Education, Training and Outreach (REACHOUT)
- The principal objectives of the comprehensive PRITHVI Scheme are as follows:
- Enhancing and maintaining long-term observations across the atmosphere, hydrosphere, geosphere, cryosphere, and biosphere to monitor critical indicators of the Earth System and its changes.
- Developing modelling systems to comprehend and forecast weather patterns, ocean dynamics, and climate-related hazards, while advancing the understanding of climate change science.
- Exploring the polar and high seas regions to uncover new phenomena and resources.
- Innovating technology for the exploration and sustainable utilization of oceanic resources benefits society at large.
- Translating insights from Earth systems science into services that contribute to societal well-being, environmental preservation, and economic prosperity.
- This scheme is poised to foster the development of integrated, multidisciplinary earth science research and innovative initiatives across various institutes under the MoES umbrella.
Significance of the PRITHVI Scheme:
- Under the PRITHVI Scheme, the Ministry of Earth Sciences (MoES) plays a pivotal role in delivering vital services concerning weather, climate, oceanography, coastal conditions, hydrology, seismology, and natural hazards.
- These services play a crucial role in issuing forecasts, warnings, and alerts for a wide array of natural disasters, including tropical cyclones, floods, tsunamis, and earthquakes.
- By facilitating disaster preparedness and risk mitigation, they contribute significantly to safeguarding lives and property.
- Earth System Sciences encompass a comprehensive study of the interconnected components of the Earth, including the atmosphere, hydrosphere, geosphere, cryosphere, and biosphere, along with their intricate interactions.
- The PRITHVI Scheme is designed to address these components comprehensively, enhancing our understanding of Earth System Sciences and delivering dependable services for the nation's benefit.
- Through integrated research and development endeavours across diverse MoES institutes, the scheme is poised to tackle major challenges in weather forecasting, climate science, oceanography, cryospheric studies, and seismology.
- These efforts aim to explore sustainable methods for harnessing both biological and non-biological resources, ensuring responsible utilization of our planet's resources.
Support to Students for Participating in Competitions Abroad (SSPCA) Initiative (India Today)

- 08 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
The All India Council for Technical Education (AICTE) recently introduced a scheme named 'Support to Students for Participating in Competitions Abroad' (SSPCA).
About the Support to Students for Participating in Competitions Abroad (SSPCA) Initiative:
- The SSPCA Initiative, spearheaded by the All India Council for Technical Education (AICTE), aims to enhance the global competitiveness of Indian students in technical education.
- Crafted to provide financial backing to students aspiring to excel in international scientific events, the initiative offers a comprehensive support system.
Financial Assistance and Mentorship:
- Under the SSPCA scheme, individual students or student teams can avail themselves of travel grants to engage in international competitions.
- This assistance encompasses financial aid, mentorship, logistical support, and networking opportunities, empowering students to effectively represent India on the global stage.
- Financial aid extended by the AICTE scheme amounts to up to Rs 2 lakh per student, covering various expenses such as international and domestic travel, registration fees, visa applications, accommodation, airport taxes, travel insurance, and equipment costs associated with the competition.
Eligibility:
- Eligibility for the SSPCA initiative extends to students enrolled in diploma, B.E./B. Tech, integrated M. Tech, and M./M. Tech programs in AICTE-approved institutions.
- Each team of students is entitled to financial support under the scheme once during the course of their study.
About the All India Council for Technical Education (AICTE):
- Established as the statutory body and national-level council for technical education in India, the AICTE has played a pivotal role in shaping the landscape of technical education in the country.
- Founded in 1945 as an advisory body, it gained statutory status through an Act of Parliament in 1987.
Functions:
- The AICTE is responsible for granting approval for the establishment of new technical institutions, the introduction of new courses, and variations in intake capacity.
- It sets and upholds norms and standards for technical institutions to ensure quality development.
- Additionally, the AICTE promotes technical education through various schemes aimed at fostering innovation, faculty development, research and development, and inclusivity for women, the handicapped, and marginalized sections of society.
- Technical institutions under the AICTE's purview encompass a wide array of programs, including post-graduate, undergraduate, and diploma courses across multiple disciplines.
- Headquartered in New Delhi, the AICTE continues to be at the forefront of advancing technical education and innovation in India.
World Sustainable Development Summit 2024 (TERI)

- 08 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
Vice-President Jagdeep Dhankhar inaugurated the World Sustainable Development Summit in New Delhi recently in the presence of Prime Minister of Guyana Mark Phillips.
About the World Sustainable Development (WSDS) Summit:
- The WSDS Summit, organized annually by The Energy and Resources Institute (TERI), stands as a flagship event in the realm of sustainable development.
- Instituted in 2001, the Summit series boasts a distinguished legacy spanning over two decades, dedicated to advancing 'sustainable development' as a universally embraced objective.
- Distinguished as the sole independently convened international summit on sustainable development and environment originating from the Global South, the WSDS endeavours to forge enduring solutions for the global community.
- It achieves this by convening the world's foremost leaders and intellectuals on a singular platform.
- The upcoming WSDS 2024 marks the 23rd edition of this significant summit, revolving around the theme 'Leadership for Sustainable Development and Climate Justice'.
Key Facts about The Energy and Resources Institute (TERI):
- TERI stands as a premier think tank committed to conducting research aimed at fostering sustainable development in India and across the Global South.
- Established in 1974 as an information centre focusing on energy issues, TERI expanded its scope to encompass multifaceted research, policy analysis, consultancy, and implementation initiatives.
- TERI's research endeavours, commencing in the late 1980s, are rooted in its steadfast belief that the efficient utilization of energy and sustainable management of natural resources are indispensable for developmental progress.
- Across various sectors, TERI concentrates its efforts on:
- Promoting the efficient utilization of resources
- Enhancing access to and adoption of sustainable practices and inputs
- Mitigating environmental and climate impacts
- TERI's headquarters are located in New Delhi, serving as a hub for its diverse activities and initiatives.
Lok Sabha passes Finance Bill (Indian Express)

- 08 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
The Lower House of Parliament recently passed the Finance Bill moved by Union Finance Minister Nirmala Sitharaman.
Context:
- The Lok Sabha passed the Finance Bill, 2024 by voice vote recently.
- Also, the House passed the Appropriation Bill, granting authorization for government expenditures for four months in the upcoming fiscal year.
- The Appropriation Bill is a significant legislative measure that empowers the government to utilize public funds allocated in the annual budget.
- It serves to uphold accountability and transparency by necessitating parliamentary approval for expenditures and prevents unauthorized withdrawals from the Consolidated Fund of India.
- Furthermore, the lower house sanctioned the Rs 1.8 lakh crore budget for the Union Territory of Jammu and Kashmir.
What is a Finance Bill?
- The Finance Bill, classified as a Money Bill under Article 110 of the Constitution, is an annual presentation in the Lok Sabha following the Union Budget announcement.
- It encapsulates the government's fiscal proposals concerning taxation, expenditure, and other financial affairs.
- Through this bill, the government submits its proposals for imposing new taxes, altering the existing tax framework, or extending the current tax structure beyond the approved period to Parliament.
- Accompanied by a Memorandum elucidating its provisions, the Finance Bill is exclusively introduced in the Lok Sabha, though amendments can be recommended by the Rajya Sabha.
- Approval from both houses of Parliament is requisite for the bill to become law, with a mandate for passage within 75 days of its introduction.
- While all Money Bills fall under the category of Financial Bills, not all Financial Bills qualify as Money Bills.
- For instance, a Finance Bill solely focusing on tax proposals is classified as a Money Bill.
- Conversely, a Bill addressing taxation or expenditure alongside other subjects is categorized as a Financial Bill.
- Thus, if a Bill entails government expenditure along with other matters, it is designated as a financial bill.
Highlights of the 2024 Finance Bill:
- Stability in Income Tax: With the impending general elections in April-May 2024, the bill prioritizes continuity by retaining the current tax framework for the fiscal year 2024-2025.
- Targeted Relief Measures: Incorporates slight tax concessions tailored to particular sectors or taxpayer groups.
- Promotion of Economic Expansion: Encompasses provisions aimed at fostering infrastructure enhancement, investment stimulation, and streamlining business operations.
- Fiscal Discipline: Pursues fiscal consolidation objectives through proposed strategies to manage expenditures or enhance revenue generation.
Extending the Retirement Age of Supreme Court and High Court Judges (Indian Express)

- 08 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
The government has told a parliamentary panel that extending the retirement age of Supreme Court and High Court judges based on their performance may not be practical.
Key Insights from the Report on Judicial Processes and Reform:
- On August 07, 2023, the Standing Committee on Personnel, Public Grievances, and Law and Justice, chaired by Mr. Sushil Kumar Modi, presented its findings.
- Among its significant findings and recommendations, the Committee emphasized the necessity of raising the retirement age for judges.
- They highlighted the importance of aligning this age with advancements in medical sciences and increased life expectancy.
- At present, Supreme Court (SC) and High Court (HC) judges retire at 65 and 62 years, respectively.
- The Committee proposes amending relevant Articles (124 and 217) of the Constitution to extend these retirement ages.
- The retirement age of the High Court Judges was increased from 60 to 62 years, after the 15th constitutional Amendment according to section 4 of the Constitutional Act 1963.
- Furthermore, the Committee suggests implementing a system of appraisal by the SC Collegium to assess judges' performance and health conditions, as well as the quality and quantity of judgments delivered, before extending their tenure.
Debate Regarding the Retirement Age for Supreme Court (SC) and High Court (HC) Judges:
- Retiring SC judges have frequently reflected on their time in office, often feeling that their tenure didn't allow them sufficient opportunity to make meaningful contributions to the judiciary.
- In 2022, former Chief Justice of India (CJI) N.V. Ramana engaged in a dialogue with Justice Stephen Breyer of the US Supreme Court, who chose to retire at age 83 after serving for 27 years.
- Expressing his views, CJI Ramana, who was scheduled to retire after 8.5 years on the SC bench, remarked that 65 seemed 'too early an age for retirement.'
- Despite this, CJI Ramana's tenure surpassed that of most other SC judges.
- Among the current 32 Judges of the SC, only CJI Chandrachud, and Justices J.B. Pardiwala, K.V. Viswanathan, and Dipankar Datta are expected to exceed the 8-year mark.
- These judges represent a minority who surpass the average tenure of sitting SC judges, which stands at 5.4 years.
Why is the Government Resistant to Elevating the Retirement Age for SC and HC Judges?
- The government asserts that raising the retirement age for Supreme Court (SC) and High Court (HC) judges might lead to potential issues of favouritism.
- They argue that such a move would grant excessive authority to the SC Collegium, potentially diminishing parliamentary oversight in evaluating judges for tenure extensions.
- Additionally, the government expresses concerns that this change could subject judges to external pressures, compromising their ability to maintain impartiality.
- Moreover, they highlight the strain it would place on the already limited human resources within the Judiciary and the Executive involved in the appointment process.
Additional Insights from the Report on Judicial Processes and Reform:
- Establishment of Regional SC Benches: The Committee highlighted the challenge faced by litigants from distant regions due to the centralized nature of the Supreme Court in Delhi.
- They proposed leveraging Article 130 to create regional benches in four or five locations.
- These regional benches would handle appellate matters, while constitutional issues would remain under Delhi's jurisdiction.
- Enhancing Social Diversity in Judicial Appointments: Recognizing a diversity deficit in the higher judiciary, the Committee pointed out the low representation of marginalized communities.
- They noted that since 2018, only a small percentage of High Court judges belonged to Scheduled Castes and Scheduled Tribes.
- To address this, the Committee recommended that the Supreme Court and High Court Collegiums prioritize the nomination of women and candidates from marginalized communities, including minorities.
- Implementation of Mandatory Asset Declaration: While constitutional functionaries and government servants are obligated to declare their assets annually, judges are exempt from this requirement.
- The Committee urged the central government to enact legislation mandating higher judiciary judges to disclose their assets and liabilities each year to the appropriate authority.
- Revision of Vacation Practices in SC and HCs: The Committee observed that simultaneous vacations for the entire court contribute to case backlog and inconvenience for litigants.
- They proposed a staggered vacation system, wherein judges take leave at different times throughout the year, to mitigate this issue.
- Publication of Annual Reports by HCs: Presently, only a few High Courts publish annual reports, unlike the Supreme Court, which regularly issues its report.
- The Committee recommended that the Department of Justice collaborate with the Supreme Court to ensure that all High Courts prepare and publish their annual reports, promoting transparency and accountability in judicial operations.
Rajya Sabha passes Bills to add PVTGs of Odisha, A.P. in ST lists (Indian Express)

- 07 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News
The Rajya Sabha recently passed two Bills, which seek to modify the list of Scheduled Castes and Scheduled Tribes in Odisha and Andhra Pradesh.
News Summary:
- The Rajya Sabha recently approved the Constitution (STs) Order Amendment Bill 2024 and the Constitution (SCs and STs) Order Amendment Bill 2024, introduced by the Ministry of Tribal Affairs.
- This development paves the path for the inclusion of numerous new communities in the Scheduled Tribes (STs) list of Odisha, along with the incorporation of synonyms and phonetic variations of existing tribes in the ST lists of both Andhra Pradesh and Odisha.
About the Legislation:
- The recently passed bills introduced notable changes to the Scheduled Tribes (STs) lists of Odisha and Andhra Pradesh, particularly focusing on the inclusion of seven Particularly Vulnerable Tribal Groups (PVTGs), a subset of STs, with four additions in Odisha and three in Andhra Pradesh.
- In Odisha, the PVTGs added include:
- Pauri Bhuyan and Paudi Bhuyan as synonyms of the Bhuyan tribe.
- Chuktia Bhunjia as a synonym of the Bhunjia tribe.
- Bondo as a sub-tribe of the Bondo Poraja tribe.
- Mankidia as a synonym for the Mankirdia tribe.
- In Andhra Pradesh, the PVTGs added are:
- Bondo Porja and Khond Porja as synonyms of the Porja tribe.
- Konda Savaras as a synonym for the Savaras tribe.
- These additions mark a significant step as these groups, belonging to PVTGs, have been included in the scheduled list after 75 years of independence.
Additional Changes:
- Apart from these additions, the bills also facilitated changes in Odisha's ST list, including the relocation of two entries, Tamadia and Tamudia, from the Scheduled Castes list to the Scheduled Tribes list.
- Furthermore, synonyms, phonetic variations, and sub-tribes of at least eight existing communities in Odisha's ST list were added through the bill.
- Expanding Odisha's ST list, the bills introduced two new entries:
- The Muka Dora community (and synonyms) in undivided Koraput District, which comprises Koraput, Nowrangapur, Rayagada, and Malkangiri districts.
- The Konda Reddy (and synonyms) community.
Who are Particularly Vulnerable Tribal Groups (PVTGs)?
- Particularly Vulnerable Tribal Groups (PVTGs), as defined by the Ministry of Tribal Affairs (MoTA), comprise 75 distinct tribal communities in India.
- These groups are characterized by:
- Pre-agriculture level of technology,
- Stagnant or declining population trends,
- Extremely low literacy rates, and
- Subsistence level of economy.
- PVTGs were identified as a separate category based on the recommendations of the 1961 Dhebar Commission. Initially, there were 52 PVTGs, and over time, the list has expanded to include 75 groups across 18 states and Union Territories.
- According to data from the MoTA and the 2011 Census, Odisha has the largest population of PVTGs, with 8.66 lakh individuals, followed by Madhya Pradesh with 6.09 lakh and Andhra Pradesh (including Telangana) with 5.39 lakh.
- Overall, the total PVTG population exceeds 40 lakh, with Odisha's Saura community being the largest PVTG, numbering 5.35 lakh individuals.
SAMARTH Centers (PIB)

- 07 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News
Recently, the Minister of State for Heavy Industries informed the Lok Sabha about SAMARTH Centres.
About SAMARTH Centres:
- The Smart Advanced Manufacturing and Rapid Transformation Hub (SAMARTH) centers are established under the Scheme for "Enhancement of Competitiveness in the Indian Capital Goods Sector."
- These centers play a crucial role in assisting Micro, Small, and Medium Enterprises (MSMEs) by providing workforce training and raising awareness about Industry 4.0 technologies through:
- Organizing seminars, workshops, and knowledge-sharing events on Industry 4.0.
- Conducting training sessions to create awareness about Industry 4.0.
- Offering consultancy services (including in areas such as IoT hardware, software development, and data analytics) and providing incubation support to start-ups, including MSMEs.
Key Highlights of the Enhancement of Competitiveness in the Indian Capital Goods Sector Scheme:
- Initiated by the Ministry of Heavy Industries, this scheme aims to address technological obsolescence and improve access to quality industrial infrastructure and common facilities.
- Phase I of the scheme was launched in November 2014, focusing on skill development, infrastructure enhancement, and technology development in the Capital Goods Sector.
- Phase II, commenced on January 25, 2022, aims to amplify the impact created by Phase I by fostering a strong and globally competitive capital goods sector, contributing at least 25% to the manufacturing sector.
Components of the Scheme:
- Identification of Technologies through Technology Innovation Portals.
- Establishment of four New Advanced Centres of Excellence and augmentation of Existing Centres of Excellence.
- Promotion of skilling in the Capital Goods Sector, including the creation of qualification packages for skill levels 6 and above.
- Establishment of four Common Engineering Facility Centres (CEFCs) and augmentation of existing CEFCs.
- Augmentation of Existing Testing and Certification Centres.
- Establishment of ten Industry Accelerators for Technology Development.
Pradhan Mantri Bhartiya Jan Aushadhi Kendras (PIB)

- 07 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News
PACS have been allowed by the Government to operate Pradhan Mantri Bhartiya Jan Aushadhi Kendras (PMBJK) under the Pradhan Mantri Bhartiya Jan Aushadhi Pariyojana of Department of Pharmaceuticals, Ministry of Chemicals and Fertilizers (GOI).
About Pradhan Mantri Bhartiya Jan Aushadhi Kendras:
- Pradhan Mantri Bhartiya Jan Aushadhi Kendras are established as part of the Pradhan Mantri Bhartiya Janaushadhi Pariyojana, initiated by the Department of Pharmaceuticals, Ministry of Chemicals and Fertilisers in November 2008.
Objective:
- The primary objective is to ensure the availability of quality medicines at affordable prices for all segments of society, particularly the economically disadvantaged, thereby reducing out-of-pocket healthcare expenses.
- These Kendras offer generic drugs that are equivalent in quality and efficacy to expensive branded drugs but are available at significantly lower prices.
- All essential therapeutic medicines are stocked in Jan Aushadhi Stores, along with allied medical products commonly found in chemist shops, enhancing the viability of operating a Jan Aushadhi store.
- The Pharmaceutical & Medical Devices Bureau of India (PMBI), established under the Department of Pharmaceuticals, Government of India, with the support of all Central Public Sector Undertakings (CPSUs), coordinates the procurement, supply, and marketing of generic drugs through the PMBKs.
Eligibility to Open a Jan Aushadhi Kendra:
- State Governments, reputable NGOs, trusts, private hospitals, charitable institutions, doctors, unemployed pharmacists, and individual entrepreneurs are eligible to apply for establishing a new Jan Aushadhi Kendra.
- Applicants are required to employ a Bachelor of Pharmacy (B Pharma) or Diploma in Pharmacy (D Pharma) degree holder as a pharmacist in their proposed store.
The Nagoya Protocol (Down To Earth)

- 07 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News
Cameroon, a central African country recently adopted the Nagoya Protocol on Access and Benefit Sharing.
About the Nagoya Protocol:
- The Nagoya Protocol on Access to Genetic Resources and the Fair and Equitable Sharing of Benefits Arising from their Utilisation (the Protocol) is a globally binding agreement designed to fulfill the access and benefit-sharing obligations outlined in the Convention on Biological Diversity (CBD).
- Adopted in Nagoya, Japan, in October 2010, the Protocol came into effect on October 12, 2014, following the deposit of the fiftieth instrument of ratification.
- It establishes a transparent legal framework to ensure the fair and equitable distribution of benefits derived from the use of genetic resources, a key objective of the CBD.
Benefits of the Protocol:
- It provides researchers with a structured framework to access genetic resources for biotechnological research and development while ensuring a fair share of benefits derived from their utilization.
- Indigenous and local communities stand to benefit from the recognition and protection of traditional knowledge associated with genetic resources.
Scope of the Protocol:
- The Protocol covers genetic resources within the scope of the CBD and addresses the benefits arising from their utilization.
- Additionally, it encompasses traditional knowledge linked to genetic resources covered by the CBD and the benefits derived from its utilization.
Key Facts about the Convention on Biological Diversity (CBD):
- With 196 contracting parties, the CBD is the most comprehensive binding international agreement for conserving nature and sustainably managing natural resources.
- Opened for signing at the UN Conference on Environment and Development in Rio de Janeiro in 1992, the CBD aims to conserve biological diversity, ensure its sustainable use, and promote the fair and equitable sharing of benefits.
- The CBD covers biodiversity across ecosystems, species, and genetic resources.
- The Conference of the Parties (COP) serves as the highest decision-making body of the Convention, with the Secretariat based in Montreal, Canada.
- To further CBD objectives, two internationally binding agreements were adopted: the Cartagena Protocol in 2000, regulating the transboundary movement of living modified organisms, and the Nagoya Protocol in 2010, facilitating access to genetic resources and the equitable sharing of benefits.
Vidyanjali Scholarship Programme (India Today)

- 07 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News
Recently, the Union Minister of Education and Skill Development & Entrepreneurship launched the EdCIL Vidyanjali Scholarship Programme.
About the Vidyanjali Scholarship Programme:
- The Vidyanjali Scholarship Programme ensures equitable access to high-quality educational systems by facilitating a seamless transition from secondary to higher education and providing financial support to meritorious students from Navodaya Vidyalayas who lack financial means.
- It embodies a holistic approach to empowerment, aiming to expand educational opportunities, especially for students from economically disadvantaged backgrounds.
- The programme aims to secure assistance and funding from non-governmental partners and private sources, including CSR grants, national and international donors, and impact investors.
- Initially, the programme will benefit students in grades XI and XII studying in Navodaya Vidyalayas across the country.
- A dedicated fintech platform has been developed under Vidyanjali to disburse sponsorships to students through Direct Benefit Transfer (DBT).
- This platform plays a crucial role in data management, application processing, progress tracking, grant disbursement monitoring, fund utilization monitoring, generating impact reports for Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), recognizing notable student achievements, and publicly acknowledging the support of funders, among other functions.
What is EdCIL?
- Educational Consultants India Limited (EdCIL) is the sole Public Sector Undertaking under the Ministry of Education, Government of India.
- Established on June 17, 1981, under the Companies Act, 1956, it holds the distinction of being categorized as a 'Mini Ratna Organisation' by the Government of India.
- EdCIL provides consultancy and technical services in various domains of education and human resource development, both domestically and globally.
- Its clientele includes numerous state and central government departments, public sector undertakings (PSUs), and autonomous bodies such as Indian Institutes of Technology (IITs), Indian Institutes of Management (IIMs), Indian Institutes of Information Technology (IIITs), Kendriya Vidyalayas, and Navodaya Vidyalayas.
India to sign 78 bn deal to extend Qatar LNG imports (Indian Express)

- 06 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
India and Qatar are likely to ink a deal recently to extend the supply of 7.5 million tonnes per annum (mtpa) of liquefied natural gas (LNG) for another 20 years beyond 2028.
Context:
- India wants to increase the share of natural gas in its primary energy mix to 15 per cent by 2030 from a little over 6 per cent at present.
- The country already depends on LNG imports to meet around half of its gas demand, and as demand grows, imports of the natural gas are also set to grow.
- World’s largest exporter of LNG, Qatar, accounts for over half of India’s imports.
- India imported a total of 19.85 million tonnes of LNG in 2022-23 (FY23), of which 10.74 million tonnes, or 54 per cent, came from Doha.
- India’s total imports from Qatar in FY23 were valued at $16.81 billion, of which LNG imports alone were worth $8.32 billion, or 49.5 per cent of the overall imports from Doha.
- Natural gas is seen as a significantly cleaner alternative to conventional petroleum fuels like diesel and petrol and is usually cheaper than crude oil.
- For India, which has an import dependency of over 85 per cent in the case of crude oil, natural gas is seen as more affordable as well as a transition fuel in the country’s energy transition pathway.
Trade Relationship Dynamics between India and Qatar:
- In the trade relationship between India and Qatar, there exists a significant trade imbalance favoring Qatar.
- Qatar stands as India's largest source of liquefied natural gas (LNG), which is gas cooled to liquid form for sea transportation.
Import Dependency on Gas:
- India's import reliance on natural gas stands at around 50%, with a governmental focus on increasing gas consumption likely leading to further import escalation in the future.
- Petronet LNG, India's primary LNG importer, holds a long-term contract with Qatar for importing 8.5 million tonnes per annum (mtpa) of LNG. Moreover, Qatar's gas holds a substantial share in India's LNG procurements from the spot market.
Demand for Natural Gas in India:
- India has set an ambitious target to elevate the share of natural gas in its primary energy mix to 15% by 2030, up from slightly over 6% at present.
- This aspiration is poised to drive a rapid surge in LNG imports in the upcoming years. Natural gas is perceived as a notably cleaner alternative to traditional petroleum fuels like diesel and petrol, and often comes at a lower cost than crude oil.
- Given India's over 85% import dependency on crude oil, gas emerges as both more economically viable and a smoother transition fuel in the energy transformation trajectory.
Trade Dynamics: India's Import from Qatar and Export to Qatar
- In FY 2022-23, India's total imports from Qatar amounted to $16.81 billion, with LNG imports constituting $8.32 billion of the total.
- While Indian LNG importers are endeavoring to diversify their sources, reducing heavy reliance on Qatar may take considerable time.
- On the export front, India's exports to Qatar were valued at only $1.97 billion in FY 2022-23, encompassing cereals, copper articles, iron and steel articles, vegetables, fruits, spices, and processed food products.
Global LNG Market Trends:
- The global LNG market currently leans towards sellers, especially following Russia's invasion of Ukraine, which disrupted Russian natural gas supplies to Europe.
- This disruption triggered a surge in LNG spot cargo prices globally.
- Unlike term contracts, spot LNG market prices are subject to higher volatility, with prices rising steeply in times of tight supply and falling sharply during a supply glut.
Future Outlook of the LNG Market:
- Industry experts predict a shift in the global LNG market dynamics over the next few years, transitioning into a buyer's market due to the surge in new LNG export projects.
- A buyer's market arises when there is an excess supply of goods or services compared to demand, granting buyers more negotiating leverage.
- Despite this anticipated shift, it may take several years for this scenario to materialize, with a substantial portion of new LNG export capacity expected to originate from Qatar itself.
International Centre for Integrated Mountain Development (DownToEarth)

- 06 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
Experts from The International Centre for Integrated Mountain Development (ICIMOD) called for ‘bold action’ and ‘urgent finance’ to prevent collapse of nature in High Mountain Asia on February 5, 2024, in the Nepalese capital of Kathmandu.
About the International Centre for Integrated Mountain Development (ICIMOD):
- The International Centre for Integrated Mountain Development (ICIMOD) is an intergovernmental knowledge and learning center dedicated to serving the communities of the Hindu Kush Himalaya (HKH) region.
- Established and inaugurated on December 5, 1983, its mission is to generate and share knowledge that informs regional policy and action, attracting investments to facilitate the transition to greener, more inclusive, and climate-resilient development.
Membership and Governance:
- ICIMOD's member countries include Afghanistan, Bangladesh, Bhutan, China, India, Myanmar, Nepal, and Pakistan.
- Its highest governing body is the Board of Governors, composed of representatives from each member country and independent members nominated by the ICIMOD Support Group based on their professional expertise and experience.
Functions and Objectives:
- The center serves the HKH region by generating and sharing information and knowledge to address critical mountain-related challenges.
- It bridges scientific research with policy formulation and practical on-the-ground implementation.
- Furthermore, ICIMOD provides a regional platform for experts, planners, policymakers, and practitioners to exchange ideas and perspectives, facilitating sustainable mountain development.
- Headquarters of ICIMOD is in Kathmandu, Nepal.
Key Facts about the Hindu Kush Himalaya (HKH) Region:
- The Hindu Kush Himalaya (HKH) region spans 3,500 km across eight countries, from Afghanistan in the west to Myanmar in the east.
- It serves as the source of ten major Asian river systems, including the Amu Darya, Indus, Ganga, Brahmaputra, and others.
- The HKH region plays a vital role in providing water, ecosystem services, and livelihoods to the people living within its boundaries.
Israel discovers 6-million-year-old giant underwater canyon of Messinian Event (TOI)

- 06 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
The Israel Geological Survey announced recently that Israeli geologists discovered a huge underwater canyon on the bottom of the Eastern Mediterranean that was formed about 6 million years ago.
What is Messinian Event?
- The Messinian Event, also referred to as the Messinian Salinity Crisis (MSC).
- It marks a significant geological occurrence during which the Mediterranean Sea experienced a cycle of partial or near-complete desiccation, making it one of the most severe ecological crises in Earth's history.
- This event unfolded approximately 6 million years ago (MYA) and persisted until around 5.3 MYA.
- The process began with the severance of the connection between the Atlantic Ocean and the Mediterranean Sea.
- This disconnection resulted from a combination of reduced sea levels globally and the collision of the European and African plates, causing the land to rise.
- Consequently, the Mediterranean experienced significant evaporation, as its evaporation rate exceeded its precipitation rate.
- Without a substantial influx of water from the Atlantic, the sea began to evaporate rapidly.
- During this period, a vast underground canyon formed, with rivers cutting deep into the basin floor, creating a canyon much larger than the Grand Canyon, reaching depths of up to 2,000 meters (6562 feet).
- As the Mediterranean water evaporated, salt deposits, primarily composed of Halite and Gypsum, accumulated on the basin floor, some reaching depths of 800 meters (2,500 feet).
- Despite the rapid evaporation, salt deposition did not keep pace, resulting in an increase in water salinity.
- The heightened salinity levels made the Mediterranean inhospitable to marine life, leading to a decline in biodiversity.
- Eventually, the sea dried up almost entirely, culminating in the Zanclean flood when the Atlantic Ocean reclaimed the basin.
What is Deep-sea Canyon?
- Deep-sea canyons, such as those formed during the Messinian Event, are steep valleys carved into the seafloor of the continental slope, extending onto the continental shelf.
- These canyons vary in size and shape and have been sculpted by various erosional processes, including river flows during periods of low sea levels, mudslides, debris flows, and turbidity currents.
Water (Prevention and Control of Pollution) Amendment Bill, 2024 (Indian Express)

- 06 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
The Centre on Monday introduced a Bill that would enable it to prescribe the norms for nominating chairpersons of State Pollution Control Boards, exempt certain industrial units from restrictions, and decriminalize “minor offenses” related to water pollution.
News Summary:
- The Water (Prevention and Control of Pollution) Amendment Bill, 2024 has been introduced in the Rajya Sabha.
- It is applicable to Himachal Pradesh and Rajasthan, with the potential to extend to other states through resolutions under the Water (Prevention and Control of Pollution) Act, 1974.
- The Bill empowers the Centre to exempt certain industrial plants from restrictions and issue guidelines related to industry establishment.
About Water (Prevention and Control of Pollution) Amendment Bill, 2024:
- Enacted in 1974, the Water (Prevention and Control of Pollution) Act aimed to prevent and control water pollution, establishing penal provisions for non-compliance.
Rationale for the Amendment:
- The Amendment Bill underscores the importance of democratic governance, emphasizing trust in people and institutions. It addresses the outdated regulations leading to a trust deficit.
Key Amendments Proposed:
- The Amendment Bill seeks to modernize the existing penal provisions, replacing imprisonment with fines for minor violations. This move aligns with the principles of Ease of Living and Ease of Doing Business.
Major Features of the Amendment Bill:
- The Bill proposes several key changes, including:
- Prescribing the process for nominating the chairman of the State Pollution Control Board by the Central Government.
- Granting the Central government authority to exempt certain industrial plants from restrictions on new outlets and discharges.
- Issuing guidelines on matters related to the establishment of industries by the Central government.
- Decriminalizing minor offenses and substituting them with monetary penalties.
- Specifying the adjudication process for penalties by officers of appropriate rank.
- Outlining penalties for non-compliance with regulations regarding new outlets, discharges, and sewage.
- Allocation of penalty amounts to the Environmental Protection Fund established under the Environment (Protection) Act, 1986.
Mera Gaon, Meri Dharohar (MGMD)(PIB)

- 06 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
The Government of India has decided to map and document all villages under Mera Gaon, Meri Dharohar (MGMD) Programme.
About the Mera Gaon Meri Dharohar Programme:
- The Mera Gaon Meri Dharohar (MGMD) programme is a nationwide initiative led by the Ministry of Culture, launched on July 27, 2023, under the National Mission on Cultural Mapping.
- Its primary aim is to compile detailed information about the life, history, and cultural essence of Indian villages and make this data accessible to both virtual and real-time visitors.
Key Components and Categories:
- Under the MGMD, information is collected across seven broad categories, including:
- Arts and Crafts Village
- Ecologically Oriented Village
- Scholastic Village Linked with Textual and Scriptural Traditions of India
- Epic Village linked with Ramayana, Mahabharata, and/or Puranic legends and oral epics
- Historical Village linked with Local and National History
- Architectural Heritage Village
- Any other distinctive characteristic, such as fishing village, horticulture village, shepherding village, etc.
Objectives:
- The primary objective of the project is to culturally map India's 6.5 lakh villages across 29 States and 7 Union Territories on a comprehensive virtual platform.
- Through MGMD, individuals will have the opportunity to immerse themselves in India's diverse and vibrant cultural heritage.
Core Ideals and Benefits:
- The fundamental aim of the project is to foster appreciation for India's rich cultural traditions, thereby promoting economic growth, social harmony, and artistic development in rural communities. The programme is envisioned as a catalyst for showcasing and preserving India's cultural diversity.
Financial Outlay and Scheme Components:
- A financial outlay of Rs. 353.46 Crore has been approved under the scheme of Financial Assistance for Promotion of Art and Culture, comprising eight scheme components:
- Financial Assistance to Cultural organizations with National Presence
- Cultural Function & Production Grant (CFPG)
- Financial Assistance for the Preservation & Development of Cultural Heritage of the Himalayas
- Financial Assistance for the Preservation & Development of Buddhist/Tibetan Organization
- Financial Assistance for Building Grants including Studio Theatres
- Financial Assistance For Allied Cultural Activities
- Scheme for Safeguarding the Intangible Cultural Heritage
- Through these components, the programme aims to provide comprehensive support for the preservation and promotion of India's rich cultural heritage.
National Agriculture Market or eNAM (Financial Express)

- 05 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News
With more states opening up or facilitating trade of agricultural commodities on the electronic -National Agriculture Market (eNAM), a spurt in trading among various markets within the state as well as at the inter-state level is being witnessed.
What is the National Agriculture Market (eNAM)?
- eNAM is an online trading platform dedicated to agricultural commodities in India.
- Launched on April 14, 2016, it is wholly funded by the Government of India.
- The Small Farmers Agribusiness Consortium (SFAC), operating under the Ministry of Agriculture and Farmers Welfare, takes the lead in implementing e-NAM
Objectives of eNAM:
- The primary goal is to enhance marketing opportunities for farmers by establishing a competitive and transparent price discovery system.
- It also facilitates online payment options for buyers, aiming to streamline the selling process for farmers.
Network and Structure:
- The NAM portal connects existing agricultural markets, including APMC/RMC market yards, sub-market yards, private markets, and unregulated markets.
- By creating a centralized online platform, e-NAM unifies agricultural markets nationwide for efficient commodity price discovery.
Key Features:
-
- Farmers can showcase products in nearby markets, allowing traders from any location to provide quotes.
- Single-window services encompass all APMC-related activities, including commodity details, buy-and-sell offers, and direct e-payment settlements to farmers' accounts.
- Facilitating Trade:
- eNAM allows traders, buyers, and commission agents to obtain licenses from state-level authorities without physical presence requirements.
- Quality standards and infrastructure for testing are harmonized in every market, including provision for Soil Testing Laboratories in selected mandis.
- Stakeholder Benefits:
- Designed for the collective benefit of farmers, mandis, traders, buyers, Farmer Producer Organizations (FPOs), and exporters.
- Stakeholder advantages include transparent online trading, real-time price discovery, reduced transaction costs, and availability of commodity prices on the e-NAM mobile app.
- Additional Benefits:
- Farmers receive details of commodity prices, quantity sold, and quality certification through SMS.
- The system promotes a more efficient supply chain and facilitates warehouse-based sales.
- Online payments are directly deposited into farmers' bank accounts, ensuring a seamless and secure financial transaction process.
INS Sandhayak - the Indian Navy’s First Survey Vessel Large (SVL) Ship (TOI)

- 05 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News
Defense minister Rajnath Singh commissioned survey vessel INS Sandhayak into the Indian Navy at the Naval Dockyard recently.
About INS Sandhayak:
- INS Sandhayak stands as the first unit in a series of four Survey Vessel (Large) ships under construction at Garden Reach Shipbuilders & Engineers (GRSE), Kolkata.
- Its primary mission is to conduct thorough coastal and deep-water Hydrographic Surveys, focusing on Port and Harbour approaches, navigational channels, and routes.
- The operational scope extends to maritime limits, encompassing the Exclusive Economic Zone (EEZ) and extended continental shelf.
Features:
-
- The vessel is equipped to gather oceanographic and geophysical data, serving the needs of both defense and civil applications.
- In a secondary role, it provides limited defense capabilities and can function as a hospital ship during wartime or emergencies.
- Cutting-Edge Technology:
-
- Equipped with advanced hydrographic tools, including a Data Acquisition and Processing System, Autonomous Underwater Vehicle, Remotely Operated Vehicle, DGPS Long-range positioning systems, and Digital side-scan sonar.
- Performance Specifications:
-
- Powered by two diesel engines, INS Sandhayak boasts a speed capability exceeding 18 knots.
- With a length of 110 meters and a displacement of 3400 tons, the vessel maintains an indigenous content exceeding 80 per cent by cost.
- Historical Continuity:
-
- This ship has been re-incarnated in its current form from the previous Sandhayak, decommissioned in 2021.
Hydrothermal System Beneath the Waters of Lake Rotorua in New Zealand's North Island (India Today)

- 05 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News
In a big revelation, scientists have unveiled a hidden hydrothermal system beneath the waters of Lake Rotorua, a site steeped in Maori legend and situated atop a dormant volcanic crater on New Zealand's North Island.
What are Hydrothermal Systems?
- Hydrothermal systems manifest in regions with intense heat, occurring both on continents near convergent plate boundaries and on the ocean floor in proximity to mid-ocean ridges.
- Three essential components—fluids, heat, and permeable rock structures—are crucial for their formation.
- Formation Dynamics:
- These systems are frequently situated near mid-ocean ridges, where tectonic plates diverge, leading to the creation of new seafloor.
- Operational Mechanism:
- Hydrothermal systems initiate as seawater infiltrates fractures in the oceanic crust, gaining heat from the Earth's interior as it descends.
- Interacting with the oceanic crust, the seawater, reaching temperatures of 350-400 degrees Celsius, undergoes chemical modifications, extracting elements from the rocks.
- Despite the extreme pressure at ocean depths preventing boiling, this process generates hydrothermal fluid—a mixture of gasses and dissolved elements, including metals.
- Return to the Seafloor:
- The superheated fluid is ejected back to the seafloor and rapidly cools upon contact with near-freezing ocean bottom waters.
- Chimney-Like Deposits:
- Chemicals dissolved in the fluid precipitate at the vent, creating chimney-like deposits.
- These formations support unique deep-sea chemosynthetic communities—organisms relying on chemicals, not photosynthesis, to sustain their metabolism.
Uniform Civil Code (Indian Express)

- 05 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News
The Uttarakhand Cabinet on Sunday approved the final draft of the Uniform Civil Code (UCC) without any changes, a day before the state Assembly convenes for a special session to take up the Bill.
What is Uniform Civil Code (UCC)?
- A Uniform Civil Code signifies a unified legal framework for the entire country, applicable across all religious communities concerning personal matters like marriage, divorce, inheritance, and adoption.
- The objective is to replace the current fragmented personal laws that govern interpersonal relationships within different religious communities.
Constitutional Framework:
- Article 44 of the Constitution mandates the State to strive for a Uniform Civil Code applicable to all citizens.
- Positioned in Part-IV as a Directive Principle, Article 44, while not justiciable, serves as a fundamental governance guideline.
- These principles, outlined in Article 37, provide overarching ideas for the State to consider in policy formulation and law enactment.
Current Landscape of Personal Laws:
- In the Concurrent list of the Constitution, matters such as marriage, divorce, and inheritance fall under both Parliament and state legislature jurisdictions.
- Hindu personal laws have been codified into four parts since 1956, while Muslim laws, not codified per se, draw from religious texts.
- Christians, Zoroastrians, and Jews are governed by their own personal laws. Goa stands as an exception, following the Portuguese Civil Code.
Need for Uniform Civil Code:
- A UCC aims to establish equal status for all citizens, addressing the inconsistency and lack of uniformity in personal laws across different religions.
- This inconsistency, conflicting with Article 14's Equality before the Law guarantee, often results in gender disparities.
Challenges and Criticisms:
- While advocating equality, the UCC concept raises concerns about potential clashes with the Right to Freedom of Religion (Article 25).
- Critics argue that separate personal laws uphold the right to practice one's religion, particularly crucial for minorities.
- Striking a balance, the Law Commission's 2018 report suggests preserving diversity in personal laws while ensuring alignment with fundamental rights.
The Way Forward:
- Encouraging a progressive mindset through education, awareness, and sensitization is vital for understanding the spirit of the UCC.
- Simultaneously, discriminatory personal laws should be amended or abolished.
- The Law Commission recommends codifying different personal laws to derive universal principles prioritizing equity, rather than imposing a blanket Uniform Civil Code
“Pineapple Express” Sweeps California, Atmospheric River Leaves State In Distress (India Today)
- 05 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
A strong and grievous atmospheric river storm is predicted to hit California during the later part of Saturday, leaving over another storm, which resulted in extreme flooding in the last week.
What is an Atmospheric River?
- Atmospheric rivers are long and relatively narrow bands of water vapor that form over an ocean and flow through the sky, transporting much of the moisture from the tropics to northern latitudes.
- They occur globally but are especially significant on the West Coast of the United States, where they create 30% to 50% of annual precipitation and are vital to water supplies but also can cause storms that produce flooding and mudslides.
- While they are an incredibly important source of rainfall, they can also bring flash flooding, mudslides, and landslides, sometimes killing people and destroying property.
- Formation: Formed by winds associated with cyclones, atmospheric rivers typically range from 250 miles to 375 miles (400 to 600 kilometers) in width and move under the influence of other weather.
- Many atmospheric river events are weak. But the powerful ones can transport extraordinary amounts of moisture.
- Studies have shown that they can carry seven to 15 times the average amount of water discharged daily by the Mississippi River.
- Forty-six atmospheric rivers made landfall in the U.S. West Coast during the water year 2023.
- Nine were categorized as strong, two were extreme and one was exceptional.
- California experienced extensive flooding and massive snowfall.
What Happens When an Atmospheric River Reaches Land?
- When the moisture-laden air moves over mountain ranges such as the Sierra Nevada along the California-Nevada line, the water vapor rises and cools, becoming heavy precipitation that falls as rain or snow.
- While traditional cold winter storms out of the north Pacific build the Sierra snowpack, atmospheric rivers tend to be warm.
- Snow may still fall at the highest elevations but rain usually falls on the snowpack at lower elevations.
- That can quickly prompt melting, runoff and flooding and decrease the snowpack needed for California’s water supply.
What is a Pineapple Express?
- It is a nickname for a strong atmospheric river in the tropical Pacific near Hawaii.
Where did the Term Atmospheric River Come From?
- The name came from research published in the 1990s by scientists Yong Zhu and Reginald E. Newell of the Massachusetts Institute of Technology.
Multidimensional Poverty in India (Indian Express)

- 03 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
Recently, In her Interim Budget speech, the Union Finance Minister informed that nearly 25 crore people have been raised from multi-dimensional poverty in the last 10 years.
What is Multidimensional Poverty?
- Multidimensional Poverty refers to the complex nature of poverty, where individuals or communities experience various simultaneous disadvantages.
- These may include inadequate health, malnutrition, limited access to clean water and electricity, substandard living conditions, and limited educational or employment opportunities.
- Merely focusing on income as a poverty indicator fails to fully grasp the depth and breadth of deprivation experienced by individuals.
- Multidimensional Poverty recognizes that poverty encompasses more than just economic factors; it encompasses a range of dimensions that impact well-being and quality of life.
- This approach to measuring poverty incorporates not only income or consumption levels but also considers deprivations in education and access to essential infrastructure.
- The international poverty line, set at $2.15 per day (in 2017 purchasing power parity terms) by the World Bank, serves as a benchmark for evaluating monetary value but is complemented by a broader assessment of various dimensions of deprivation.
What is the Global Multidimensional Poverty Index?
- The Global Multidimensional Poverty Index (MPI) serves as a vital tool for assessing acute multidimensional poverty in over 100 developing nations.
- Published collaboratively by the Oxford Poverty and Human Development Initiative (OPHI) and the UNDP's Human Development Report Office, it provides a comprehensive framework for tracking deprivation across three key dimensions and ten indicators.
- This index operates on a scale from 0 to 1, with higher values indicating greater levels of poverty.
- According to MPI methodology, individuals experiencing deprivation in a third or more of the weighted indicators are classified as "MPI poor."
India's Progress and Comparison:
- According to the 2023 Global MPI report, India successfully uplifted 415 million people out of poverty between 2005-06 and 2019-21, marking a significant achievement in poverty alleviation efforts.
- India is among 25 nations that have effectively halved their global MPI values within 15 years.
Comparison with India's National MPI:
- In addition to the global MPI, India has its own National Multidimensional Poverty Index.
- Published by NITI Aayog, India's MPI incorporates two additional indicators:
- Maternal health (under the health dimension) and
- Bank account ownership (under the standard of living dimension).
- This modification aligns the MPI with India's specific national priorities, offering a nuanced understanding of poverty dynamics within the country.
GHAR (GO Home and Re-Unite) Portal for Restoration and Repatriation of Child (PIB)

- 03 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
The Ministry of Women and Child Development developed the “Track Child Portal”, which enables tracking of the missing and found children in all States/UTs including Maharashtra, Chhattisgarh, North Eastern States and Jharkhand.
What is the GHAR Portal?
- National Commission for Protection of Child Rights (NCPCR) has developed and launched the portal GHAR - Go Home and Reunite, with the sole purpose of restoration and repatriation of children.
- The GHAR portal has been developed to digitally monitor and track the restoration and repatriation of children.
- Here's how the portal can help strayed children go home and reunite with their families:
- The portal digitally tracks and monitors children who are in the juvenile justice system and have to be repatriated to another country, state or district.
- It allows the digital transfer of cases of children to the Juvenile Justice Board/Child Welfare Committee of the state concerned.
- It will help in speedy repatriation of children.
- Where there is a requirement for a translator/interpreter/expert, a request will be sent to the state government concerned.
- Child welfare committees and district child protection officers can ensure proper restoration and rehabilitation of children by digitally monitoring the progress of the case of the child.
- A checklist format will be provided in the forms so that the children who are being hard to repatriate or children who are not getting their entitled compensation or other monetary benefits can be identified.
- A list of government-implemented schemes will be provided so that at the time of restoration the Child Welfare Committees can link the child with the schemes to strengthen the family and ensure that the child remains with his/her family.
- The Ministry of Women and Child Development is administering the Juvenile Justice (Care and Protection of Children) Act, 2015 (JJ Act, 2015) (as amended in 2021) and the Rules thereunder, to ensure the safety, security, dignity and well-being of children.
- The Act provides for the protection of children in need of care and protection and those in conflict with the law by catering to their basic needs through care, protection, development, treatment and social reintegration.
- Under the JJ Act, 2015, the Child Welfare Committees have been empowered to make decisions regarding the children in need of care and protection for the children’s best interest.
- They are also mandated to monitor the functioning of the Child Care Institutions (CCIs).
- Similarly, under section 106 of the JJ Act, 2015, every state government has to constitute a District Child Protection Unit (DCPU) for every district to take up matters relating to children to ensure the implementation of the JJ Act, 2015 and its rules thereunder.
- To ensure effective coordination in child safety, protection and development, District Magistrates have been made the heads of DCPUs.
- DMs have been empowered to review the functioning of DCPUs and CWCs at regular intervals to ensure prompt decisions as per provisions of the JJ Act and Rules are taken by these bodies, keeping in mind the best interests of the children.
: Law Commission of India (Indian Express)

- 03 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
The 22nd Law Commission of India led by Justice Ritu Raj Awasthi has recommended that the offense of criminal defamation should be retained in the new criminal laws.
About the Law Commission of India:
- The Law Commission of India is a non-statutory body, constituted by the Government of India from time to time.
- The commission's function is to research and advise the government on legal reform, and is composed of legal experts, and headed by a retired judge.
- The commission is established for a fixed tenure and works as an advisory body to the Ministry of Law and Justice.
- The first Law Commission was established during colonial rule in India by the East India Company under the Charter Act of 1833 and was presided over by Lord Macaulay.
- After that, three more commissions were established in British India.
- The first Law Commission of independent India was established in 1955 for a three-year term.
- Since then, twenty-one more commissions have been established.
- The 22nd Law Commission has been notified with effect from 21st February 2020 for a term of 3 years.
- Cabinet approves the extension of the term of the 22nd Law Commission of India up to 31st August 2024.
- Justice Rituraj Awasthi (Former Chief Justice of the Karnataka HC) was appointed as the chairperson of the current 22nd Law Commission.
- The last chairman of the 21st Law Commission was retired Supreme Court judge Justice B.S. Chauhan.
The Responsibilities of the Law Commission:
- Identification of laws which are no longer relevant and recommending the repeal of obsolete and unnecessary enactments;
- Suggesting enactment of new legislations as may be necessary to implement the Directive Principles and to attain the objectives set out in the Preamble of the Constitution;
- Considering and conveying to the Government its views on any subject relating to law and judicial administration that may be specifically referred to it by the Government through the Ministry of Law & Justice (Department of Legal Affairs);
- Considering the requests for providing research to any foreign countries as may be referred to it by the Government through the Ministry of Law & Justice (Department of Legal Affairs);
- Preparing and submitting to the Central Government, from time to time, reports on all issues, matters, studies and research undertaken by it and recommending such reports for effective measures to be taken by the Union or any State; and
- Performing such other functions as may be assigned to it by the Central Government from time to time.
Govt To Sell Bharat Rice At Rs 29/Kg in Retail Market (Indian Express)

- 03 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
The government will launch retail sales of Bharat Rice at ?29 per kg from next week to provide relief to consumers. It has also directed traders to disclose rice stock to control prices.
Context:
- The recent announcement by the Union government regarding the retail sale of rice at Rs 29 per kg through three cooperatives has garnered attention in the news.
- This initiative, known as 'Bharat Rice,' seeks to address the upward trend in rice prices.
- Over the past year, retail prices have surged by 14.5%, while wholesale prices have seen a 15.5% increase.
- This move aims to mitigate the impact of rising rice prices on consumers and ensure the affordability and accessibility of this staple food item.
Recent Developments:
- In response to escalating domestic rice prices and to ensure food security within the country, the Union government implemented measures in 2023.
- These included a ban on the export of white (non-basmati) rice and the imposition of a 20% export duty on par-boiled rice.
- The decision to restrict rice exports was driven by the need to stabilize domestic prices and guarantee an ample food supply for the nation.
- Experts predict that these restrictions are likely to remain in place until the upcoming general election scheduled for April-May 2024.
- Challenges in rice production during the 2023-24 kharif season, exacerbated by dry weather conditions attributed to El Nino, have further complicated the supply situation.
- Despite these trade limitations, local rice prices have remained firm, prompting government warnings to retailers.
Government Intervention:
- Union Food Secretary Sanjeev Chopra highlighted a 14.51% increase in retail rice prices over the past year.
- In response to rising rice prices, the government has mandated traders, wholesalers, retailers, and processors to report their rice and paddy stocks every Friday to manage food inflation and curb speculative activities.
- To counter inflationary pressures, the government has initiated the retail sale of 'Bharat Rice' to the general populace.
- Initially, 5 lakh tonnes of rice will be allocated for retail sale under this brand through agencies like NAFED, NCCF, and Kendriya Bhandar, priced at ?29 per kilogram in 5 kg and 10 kg bags.
- Furthermore, the Food Corporation of India (FCI) has ample stocks of good-quality rice available for sale to traders and wholesalers under the open market sales scheme at a reserve price of ?29 per kilogram.
Status of India’s Rice Exports:
- India holds the position of the world's largest rice exporter, accounting for 45% of the global rice market share.
- During April-May 2023, overall rice exports witnessed a notable increase of 21.1% compared to the previous fiscal year.
- Basmati rice exports in May 2023 alone surged by 10.86% compared to May 2022, reflecting a sustained upward trend.
- The export of non-Basmati rice has been steadily rising over the past three years, with Basmati rice exports in 2022-2023 surpassing the previous year's figures.
- Recent data provided by the government indicates a 15% increase in total rice exports (excluding broken rice) by August 17 compared to the corresponding period in the previous year.
- Regional Dynamics: Thailand anticipates a nearly 25% decrease in rice production for the 2023-2024 season, while Myanmar has halted raw rice exports.
- Similarly, rice availability is expected to be limited in Iraq and Iran.
- India annually exports more than 4 million tons of basmati - a premium long-grain variety famed for its aroma - to Iran, Iraq, Yemen, Saudi Arabia, the United Arab Emirates and the United States, among others.
Three New Major Railway Corridors Announced Under PM GatiShakti in the Interim Budget 2024-25 (PIB)

- 03 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
The Interim Budget for 2024-25 announcement for implementation of three Economic Railway Corridors identified under the PM GatiShakti for enabling multi-modal connectivity.
Context:
- The Interim Budget for 2024-25 has laid the groundwork for implementing three major Economic Railway Corridors under the PM GatiShakti initiative.
- This will enable multi-modal connectivity, including:
- Energy, mineral, and cement corridors
- Port connectivity corridors and
- High-traffic density corridors
Significance of the Three Corridors:
- Logistics Efficiency Boost: These Corridors serve as catalysts for enhancing logistics efficiency, thereby cutting down on the costs associated with rail transportation.
- By streamlining rail movements, they pave the way for smoother and more cost-effective logistics operations.
- Alleviating Rail Congestion: One of their primary roles is to alleviate congestion on heavily trafficked rail routes.
- By diverting some of the traffic to these designated Corridors, the strain on high-density rail networks is relieved, ensuring smoother and more reliable transportation across the board.
- Promoting Modal Shift: The Corridors play a pivotal role in encouraging a modal shift from road to rail and coastal shipping.
- By providing efficient rail connections and integrating coastal shipping options, they offer viable alternatives to traditional road transport, thereby reducing congestion on highways and minimizing environmental impact.
- Environmental Sustainability: A key benefit of these Corridors is the reduction of the carbon footprint associated with logistics operations.
- By promoting more environmentally friendly modes of transportation such as rail and coastal shipping, they contribute to mitigating the environmental impact of freight movement, fostering sustainability in logistics practices.
About PM GatiShakti National Master Plan:
- The government of India initiated the Pradhan Mantri Gati Shakti National Master Plan to transform the nation's infrastructure.
- PM Modi launched the PM Gati Shakti National Master Plan (NMP) on 13th October 2021, on the 75th Independence Day to provide multimodal connectivity infrastructure to various economic zones.
- The scheme is expected to smooth out the execution of projects across the nation and foster coordination between different ministries engaged with these projects.
Advantages of PM Gati Shakti:
- It lays out a centralised portal to unite the infrastructural initiatives of 16 central ministries and departments.
- Facilitates these ministries, gives a centralised transportation and logistics grid for smoother data flow and sped up project clearance.
- Large-scale infrastructure projects like UDAAN, expansion of the railway network, Bharatmala, Sagarmala, inland waterways, and Bharat Net will be executed by the Gati Shakti master plan.
- The Gati Shakti master plan aims to create employment potential for a large number of individuals.
- The plan's three primary targets are smooth multimodal connectivity, enhanced prioritisation and optimal usage of resources to create capacities on time, and resolution of issues like standardisation, disjointed planning and clearances.
- The Gati Shakti mission aims to create world-class infrastructure in the country and foster logistical synergy across various modes of movement.
- The general objective of the drive is to increase competitiveness and economic development in India.
Expansion of Nano DAP (Indian Express)

- 02 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
Finance Minister Nirmala Sitharaman, presenting the interim budget on (February 1), announced the expansion of the application of Nano DAP on various crops in all agro-climatic zones.
What is DAP?
- Di-ammonium Phosphate (DAP) is a fertilizer containing phosphorus and nitrogen, crucial nutrients for plant growth.
- Its chemical formula is (NH?)?HPO?. DAP is widely utilized in agriculture to offer plants a quick and easily accessible nutrient source.
- It ranks as the second most utilized fertilizer in India, following urea. Notably, DAP is rich in phosphorus (P), which plays a vital role in promoting root establishment and development.
- Application of DAP is typically done just before or at the time of sowing to ensure optimal plant growth and development.
What is Nano DAP?
- Nano DAP is an innovative liquid fertilizer formulation comprising nanoparticles of Diammonium Phosphate (DAP).
- Serving as a rich source of nitrogen and phosphorus, the two primary nutrients crucial for crop growth, Nano DAP offers unique advantages.
- Its small particle size, measuring less than 100 nm, coupled with a high surface area, facilitates easy absorption by plant leaves.
- This novel nano-formulation contributes to enhanced crop growth and yield, decreased environmental impact, and improved profitability for farmers.
Why Nano DAP?
- In addition to being more efficient than conventional DAP, Nano DAP has a few other benefits.
- First, it is more pocket-friendly than its conventional counterpart.
- A 500 ml bottle of Nano DAP, equivalent to a 50-kg bag of conventional DAP, is priced at only Rs 600 (compared to Rs 1,350 for the bag).
- Since the government provides significant subsidies on DAP, the adoption of a more inexpensive fertiliser will likely be a significant relief to the government’s subsidy burden.
- Second, for farmers, Nano DAP is also significantly more convenient.
- Simply put, 500 ml bottles are easier to transport, store, and use than 50kg bags.
- The fertiliser is sprayed on crops, with 250-500 ml of DAP, dissolved in water, required per spray, per acre.
- Most importantly, however, India currently imports significant quantities of fertiliser to meet domestic demand.
- The adoption of domestically-produced Nano DAP — produced in Kalol, Gujarat — is set to significantly reduce this import burden.
- This revolutionary step will not only take Indian agriculture forward in foodgrain production but it will also make India self-reliant in fertiliser production.
- The adoption of Nano DAP will help in achieving self-sufficiency in fertilisers and greatly benefit our farmers.
US Approved Sale of 31 Predator Drones to India (India Today)

- 02 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
In a significant development that underscores the deepening strategic partnership between India and the United States, the US State Department has approved a landmark Foreign Military Sale to the Indian government.
News Summary:
- The US Defense Security Cooperation Agency has formally notified the US Congress regarding a potential military sale of MQ-9B SkyGuardian drones and associated equipment to the Government of India.
What is a Drone?
- Drones are aerial vehicles powered by various means, capable of autonomous flight or remote piloting, and can carry payloads, lethal or nonlethal, depending on the mission.
Key Features of MQ-9B SkyGuardian Drones:
- Designed for extended over-the-horizon flights lasting over 30 hours, facilitated by satellite connectivity.
- Incorporates advanced capabilities to safely operate in civilian airspace, facilitating joint operations with civil authorities for real-time situational awareness.
- Equipped with sophisticated maritime intelligence, surveillance, and reconnaissance (ISR) systems, enabling real-time monitoring and patrolling both above and below the ocean's surface.
Significance of Drone Technology in Defense:
- Strategic Importance: Drones offer valuable intelligence, surveillance, and reconnaissance (ISR) capabilities, providing real-time visuals and data to support decision-making processes.
- They also reduce risks to personnel and offer cost-effective alternatives to conventional manned aircraft.
- Tactical Advantages: Drones enable precision strikes with minimal collateral damage, enhance coordination and logistics in challenging terrains, and facilitate operations in remote or hostile environments.
Challenges Associated with Drones:
- Complex Airspace Management: The integration of drones into India's airspace necessitates a robust management framework to ensure safe and efficient operations.
- Adverse Weather Conditions: Factors like strong winds can affect drone operations, highlighting the need for resilient systems capable of operating in varied environmental conditions.
- Privacy and Safety Concerns: There are concerns regarding the potential misuse of drones for breaching privacy and safety regulations, emphasizing the importance of stringent regulations and oversight mechanisms.
Animal Husbandry Infrastructure Development Fund (PIB)

- 02 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
The Union Cabinet chaired by Prime Minister Shri Narendra Modi approved the continuation of the Animal Husbandry Infrastructure Development Fund (AHIDF) to be implemented under the Infrastructure Development Fund (IDF) with an outlay of Rs.29,610.25 crore for another three years up to 2025-26.
About the Animal Husbandry Infrastructure Development Fund:
- This initiative operates as a Central Sector Scheme aimed at incentivizing investments from various entities, including individual entrepreneurs, private companies, MSMEs, Farmer’s Producers Organizations (FPOs), and Section 8 companies.
- These investments are directed towards establishing infrastructure for:
- Dairy processing and value addition
- Meat processing and value addition
- Animal feed plants
Objectives:
- Facilitating the expansion of milk and meat processing capacity and diversification of products, thereby granting unorganized rural milk and meat producers greater access to organized markets.
- Enhancing price realization for producers and ensuring the availability of quality milk and meat products for domestic consumers.
- Promoting exports and elevating the sector's contribution to export revenue.
- Providing quality concentrated animal feed to cattle, buffalo, sheep, goat, pig, and poultry, ensuring balanced rations at affordable prices.
- The Government of India offers a 3% interest subvention for a period of 8 years, including a two-year moratorium, for loans covering up to 90% of the investment.
- These loans are accessible from scheduled banks, the National Cooperative Development Corporation (NCDC), NABARD, and NDDB.
- Notably, government entities and cooperatives are excluded from availing benefits under this scheme.
What is Animal Husbandry?
- Animal husbandry encompasses the controlled cultivation, management, and production of domestic animals, with a focus on enhancing desirable qualities through breeding.
- It serves as a vital branch of agriculture dedicated to animals raised for various purposes such as meat, fibre, milk, and other products.
- This involves day-to-day care, selective breeding, and the overall management of livestock.
- In India, animal husbandry plays a crucial role in the livelihoods of many farmers, offering significant self-employment opportunities, particularly for landless labourers, small and marginal farmers, and women.
- The sector contributes to providing affordable and nutritious food to millions of Indians through the production of meat, eggs, milk, and other essential items.
- Additionally, it serves as a valuable source of raw materials such as hides, skins, bones, blood, and fat.
- Animals are often regarded as the best insurance against natural calamities like drought, famine, and other adversities, providing a degree of stability to farmers in unpredictable conditions.
Digital Detox for Responsible Gaming (TOI)

- 02 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
The Karnataka government recently said it would launch a 'Digital Detox' initiative in collaboration with the All India Game Developers Forum (AIGDF), with special emphasis on gaming and social media.
What is Digital Detox?
- A digital detox entails voluntarily refraining from using digital devices like smartphones, computers, and social media platforms for a defined period.
- This period can range from a few hours to as long as a week or even a month.
- Research indicates that approximately 25% of smartphone owners aged 18 to 44 cannot recall the last time they were separated from their phones.
Benefits:
- Overcoming Technology Addiction: Studies reveal that around 61% of individuals acknowledge their addiction to the internet and digital screens.
- A digital detox aids in combating this addiction.
- Enhanced Mental Health: Disconnecting from technology can alleviate stress and anxiety, thereby fostering improved mental health and overall well-being.
- Increased Productivity and Creativity: Taking a break from continuous digital engagement bolsters focus and concentration, leading to heightened productivity and creativity.
- Improved Sleep: Excessive screen time has been linked to poor sleep quality. A digital detox helps in promoting better sleep by reducing exposure to blue light and stimulating content.
- Enhanced Communication Skills: Reducing online time allows for more face-to-face interactions, nurturing better communication skills and social connections.
Challenges:
- Feelings of Disconnection: Detox participants may feel disconnected from friends and family members.
- Fear of Missing Out: Participants may experience FOMO (fear of missing out) or anxiety about missing important information.
- Boredom or Restlessness: Detoxes may lead to feelings of boredom or restlessness.
- Withdrawal Symptoms: Some individuals may experience withdrawal symptoms such as anxiety or boredom.
Way forward:
- Start Small: Initiate the detox with shorter periods and gradually extend the duration.
- Inform Others: Notify friends and family about the detox to avoid misinterpretations.
- Engage in Healthy Activities: Utilize detox time for activities like reading, spending time outdoors, or exercising.
- Minimize Notifications: Turn off device notifications and store them out of sight.
- Reward Progress: Offer yourself incentives for achieving detox goals.
Conclusion
Digital dependence can contribute to mental health issues, shorter attention spans, and strained interpersonal relationships. While technology offers convenience and connectivity, excessive screen time exacts a toll. A digital detox presents an opportunity to enhance mental and physical well-being, as well as nurture healthier relationships. With proper planning and commitment, a successful and fulfilling detox experience is achievable.
Improved Fiscal Resilience Amid Modest Tax Buoyancy (Indian Express)

- 02 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
The government’s aim to restrict the fiscal deficit to 5.8 per cent of the Gross Domestic Product (GDP) as against 5.9 per cent budgeted earlier for the financial year and the push to restrict the fiscal deficit target to below 4.5 per cent by 2025-26 rides on the back of a strong buoyancy in tax revenues.
What is Tax Buoyancy?
- Tax buoyancy elucidates the correlation between fluctuations in government tax revenue growth and changes in Gross Domestic Product (GDP).
- This concept underscores the intrinsic link between the government's tax earnings and economic expansion.
- Essentially, as the economy accelerates, government tax revenue experiences a corresponding increase.
- Tax buoyancy delineates the responsiveness of tax revenue growth to alterations in GDP, signifying its sensitivity to economic fluctuations.
- A buoyant tax exhibits a revenue surge without necessitating a rise in tax rates, contingent upon factors such as the tax base's magnitude, tax administration efficiency, and the simplicity and rationality of tax structures.
- Typically, direct taxes demonstrate higher buoyancy, being more responsive to GDP growth rates.
What is Tax Elasticity?
- Tax elasticity, akin to tax buoyancy, refers to variations in tax revenue consequent to changes in tax rates.
- For instance, assessing how tax revenue fluctuates when the government reduces corporate income tax from 30 percent to 25 percent illustrates tax elasticity.
- This concept underscores the dynamic relationship between tax rates and revenue generation, reflecting the degree of responsiveness of tax revenue to alterations in tax rates.
About the Laffer Curve:
- The Laffer Curve, pioneered by economist Arthur Laffer in 1974, illustrates the interplay between tax rates and government tax revenue collection.
- This economic theory posits that tax rates exceeding a certain threshold diminish tax revenue by disincentivizing workforce participation.
- It suggests the existence of an optimal tax rate that maximizes total tax revenue.
- By visually depicting the inverse relationship between tax rates and tax revenue, the Laffer Curve highlights the complexities of tax policy and the importance of balancing tax rates to achieve revenue optimization.
RBI Action Against Paytm Payments Bank (Indian Express)

- 01 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) recently barred Paytm Payments Bank from offering all its core services — including accounts and wallets — from March, effectively crippling the company’s business.
News Summary
- The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) has directed Paytm Payment Bank to halt accepting money in any customer account, including wallets and prepaid instruments like FASTags, from March 1.
- This action comes due to ongoing non-compliance and significant supervisory concerns highlighted by the RBI.
What Does the RBI Directive Include?
- Barred Services: Paytm Payment Bank is prohibited from offering most of its essential services.
- Account Closure: Paytm cannot accept deposits or top-ups after February 29, and nodal accounts of its parent company, One97 Communications, and Paytm Payments Services, must be terminated by February 29.
- Transaction Settlement: All pending transactions and nodal accounts initiated by February 29 must be settled by March 15.
- Customer Withdrawals: Customers are permitted to freely withdraw or use the money from their Paytm accounts, including savings and current accounts, prepaid instruments, FASTags, etc., within their available balance.
Reasons Behind the Action:
- Ongoing Scrutiny: Paytm Payment Bank has been under RBI scrutiny since 2018.
- Compliance Concerns: While specifics were not disclosed, it's believed the action stems from RBI's concerns about KYC compliance and IT-related issues.
- Data Security: RBI is cautious about safeguarding depositors' money and protecting data.
- Concerns arose when Paytm Payment Bank and its parent company lacked sufficient barriers to prevent unauthorized access to data by China-based entities with indirect stakes in the parent company.
What is a Payments Bank?
- Payment banks function similarly to traditional banks but on a smaller scale and without engaging in credit risk.
- Established based on recommendations from the Nachiket Mor Committee, their primary objective is to promote financial inclusion by providing banking and financial services to underserved areas, including migrant workers, low-income households, and small entrepreneurs.
Legal Framework and Features:
- Registered as public limited companies under the Companies Act 2013 and licensed under Section 22 of the Banking Regulation Act 1949, payments banks operate under various regulations such as the Banking Regulation Act 1949, RBI Act 1934, and Foreign Exchange Management Act 1999.
Key features include:
- Differentiation: Payments banks are distinct from universal banks and operate on a smaller scale.
- Capital Requirement: The minimum paid-up equity capital for payment banks is set at 100 crores, with promoters required to contribute at least 40% during the first five years of operation.
- Permissible Activities: Payments banks can accept deposits up to Rs. 2,00,000, invest in government securities to meet statutory liquidity requirements and provide various banking services such as remittance, mobile payments, ATM/debit cards, and net banking.
- Additionally, they can serve as banking correspondents for other banks.
- Limitations: Payments banks are restricted from issuing loans and credit cards, accepting time deposits or NRI deposits, and establishing subsidiaries for non-banking financial activities.
Blue Economy 2.0 (Indian Express)

- 01 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
The Interim Budget presented by Finance Minister Nirmala Sitharaman on (February 1) stressed environment-friendly development through the promotion of a ‘blue economy’.
What are the Proposals in the Interim Budget Regarding the Blue Economy?
- Finance Minister Nirmala Sitharaman announced plans to launch a scheme focusing on restoration, adaptation measures, coastal aquaculture, and mariculture, adopting an integrated and multi-sectoral approach.
- Restoration and adaptation measures aim to preserve ocean health during economic activities, while aquaculture involves farming aquatic plants and animals, and mariculture focuses on rearing marine creatures in saltwater.
- Additionally, five integrated aqua parks will be established, and the Pradhan Mantri Matsya Sampada Yojana (PMMSY) will be strengthened to increase aquaculture productivity, double exports to Rs 1 lakh crore, and create 55 lakh employment opportunities in the near future.
What is the Blue Economy?
- While the term blue economy can simply refer to economic activities related to the sea and the coasts, it is generally understood to have an element of sustainability in it.
- Thus, the European Commission defines it as “all economic activities related to oceans, seas and coasts.
- It covers a wide range of interlinked established and emerging sectors”; the World Bank says the blue economy is the “sustainable use of ocean resources for economic growth, improved livelihoods, and jobs while preserving the health of ocean ecosystems.”
- For a country like India, with a long coastline, diversity in terms of fish and other ocean produce, and multiple tourism opportunities, the blue economy is highly significant.
Does India Have a Blue Economy Policy?
- The blue economy 2.0. a draft policy framework on India’s Blue Economy was first released in July 2022.
- The policy document contained “key recommendations on National Accounting Framework for Blue Economy and Ocean Governance, Coastal Marine Spatial Planning and Tourism Priority, Marine Fisheries, Aquaculture and Fish Processing.
- Manufacturing, Emerging Industries, Trade, Technology, Services and Skill Development, Logistics, Infrastructure and Shipping, Coastal and Deep-Sea Mining and Offshore Energy and Security, Strategic Dimensions and International Engagement.”
- When the G20 summit was hosted in New Delhi under India’s presidency, the Comptroller & Auditor General of India (CAG) chaired the Engagement Group for Supreme Audit Institutions (SAls) of the member countries in June 2023. Two priorities for the SAI20 deliberations were blue economy and responsible Artificial Intelligence.
CBSE Proposes New Plan For Class 10 & 12 (Indian Express)

- 01 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
CBSE is reported to have proposed significant changes to the academic framework for secondary and higher secondary education, including a shift from studying two languages to three in Class 10, with the requirement that at least two must be native Indian languages.
Key Highlights of the Proposal:
Proposed Changes for Class 10:
- Transition from studying two languages to three, with a stipulation that at least two must be native Indian languages.
- Potential requirement for students to pass in 10 subjects, contrasting with the current mandate of five.
Proposed Changes for Class 12:
- Shift to studying two languages instead of one, with the condition that at least one must be a native Indian language.
- Introduction of a necessity to clear examinations in six subjects for high school graduation, up from the existing requirement of five.
The objective behind the Proposed Changes:
- These modifications are part of CBSE's broader initiative to implement a national credit framework in school education, addressing the absence of a formalized credit system in the standard curriculum.
Academic Year and National Learning Hours:
- According to the CBSE plan, an academic year will comprise 1200 notional learning hours, equivalent to earning 40 credits.
- Notional learning denotes the specified time required for an average student to achieve set outcomes.
- This encompasses both academic learning at school and non-academic or experiential learning outside of it.
Storage of Earned Credits:
- The scheme of studies has been adjusted to outline teaching hours and credits earned for each subject.
- These earned credits will be digitally stored in the Academic Bank of Credits, accessible through a linked Digilocker account.
What is the National Credit Framework (NCrF)?
- The draft NCrF was introduced by the Union Ministry of Education (MoE) in 2022, based on recommendations from an inter-ministerial committee.
- It serves as a guideline for schools, colleges, and universities to adopt the credit system, marking the inclusion of the entire school education system under its purview.
- Previously, only the National Institute of Open Schooling (NIOS) followed a credit system, but the NCrF extended its coverage to include skill and vocational education.
Proposed Benefits of NCrF for Various Stakeholders:
- Students:
- Facilitates multidisciplinary education with flexible curricula.
- Eliminates distinctions between different streams like arts, science, social sciences, and commerce.
- Rewards students with credits for academic, skill, and experiential learning.
- Expands core learning to encompass both foundational and cognitive aspects.
- Institutions:
- Fosters collaboration between institutions.
- Simplifies and standardizes credit mechanisms.
- Emphasizes research and innovation.
- Utilizes institutional infrastructure efficiently.
- Government:
- Expected to increase student enrollment rates.
- Complements India's demographic dividend, aiming to become the Skill Capital of the World.
- Industry:
- Enables students to acquire NSQF-approved foundational skills from the industry, enhancing employability.
- Allows for quick educational upgradation and up-skilling through micro-credentials.
Significance of NCrF:
- Aligns with the vision of the National Education Policy (NEP) 2020 by integrating academic and vocational domains for flexibility and mobility.
- Facilitates re-entry into the education system for students who have dropped out.
- Promotes Recognition of Prior Learning, acknowledging skills acquired informally through various means.
Enforcement Directorate (ED) Arrests Jharkhand CM in a Corruption Case (Indian Express)

- 01 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
Recently Jharkhand CM Hemant Soren was arrested by the officials of the Enforcement Directorate (ED) in the land scam case.
News Summary:
- Jharkhand CM Hemant Soren became the third state chief minister to be arrested after the Enforcement Directorate took him into custody in a money laundering case.
- Before Hemant Soren, his father Shibu Soren and Madhu Koda were arrested.
- He was arrested in a case related to an illegal change of ownership of land in Jharkhand.
What is the Enforcement Directorate (ED)?
- The Enforcement Directorate (ED) is a multi-disciplinary agency tasked with investigating money laundering offenses and violations of foreign exchange laws.
- It operates under the Department of Revenue within the Ministry of Finance and upholds strict compliance with the Constitution and laws of India.
Structure:
- Headquarters: Located in New Delhi, the ED is headed by the Director of Enforcement.
- Regional Offices: The agency has five regional offices situated in Mumbai, Chennai, Chandigarh, Kolkata, and Delhi, each overseen by Special Directors of Enforcement.
- Recruitment: Officers are recruited directly and transferred from other investigative agencies, comprising personnel from the Indian Revenue Services (IRS), Indian Police Services (IPS), and Indian Administrative Services (IAS), including roles such as Income Tax officers, Excise officers, Customs officers, and police officials.
- Tenure: Typically, officers serve a two-year term, extendable to five years with three annual extensions.
- Amendments to the Delhi Special Police Establishment (DSPE) Act, 1946, and the Central Vigilance Commission (CVC) Act, 2003, enable the government to extend the tenure of directors for one year after completing their initial two-year terms.
Functions:
- COFEPOSA: Empowered by the Conservation of Foreign Exchange and Prevention of Smuggling Activities Act, 1974 (COFEPOSA), the ED can initiate cases of preventive detention related to violations of the Foreign Exchange Management Act (FEMA).
- Foreign Exchange Management Act, 1999 (FEMA): This civil law aims to regulate external trade and payments, with the ED responsible for investigating suspected contraventions, adjudicating cases, and imposing penalties.
- Prevention of Money Laundering Act, 2002 (PMLA): Enacted to combat money laundering, the ED is tasked with tracing assets derived from crime proceeds, attaching property, and prosecuting offenders through Special Courts.
- Fugitive Economic Offenders Act, 2018 (FEOA): Introduced to address economic offenders seeking refuge abroad, the ED enforces this law by attaching properties of fugitives and confiscating assets, thereby deterring offenders from evading Indian law.
5 Wetlands Added to The Global List of Wetlands of International Importance under Ramsar Convention (TOI)

- 01 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
Ahead of World Wetlands Day, five more wetlands in India got the tag of international importance under the Ramsar Convention, making it the fourth largest country in terms of the number of sites on the list.
About the New Ramsar sites:
- The five newly added Indian sites in the list are Karaivetti Bird Sanctuary and Longwood Shola Reserve Forest in Tamil Nadu, and Magadi Kere Conservation Reserve, Ankasamudra Bird Conservation Reserve and Aghanashini Estuary in Karnataka.
- In India, Tamil Nadu continues to have the maximum number of Ramsar sites (16) followed by Uttar Pradesh (10).
- Karaivetti Bird Sanctuary (Tamil Nadu): Karaivetti Bird Sanctuary is one of the largest inland wetlands of Tamil Nadu and is a significant source of groundwater recharge for the area.
- Water from the wetland is utilized by the villagers for cultivating crops such as paddy, sugar cane, cotton, corn, and split red gram.
- Karaivetti has one of the largest congregations of waterbirds in the State of Tamil Nadu.
- The Longwood Shola Reserve Forest (Tamil Nadu): The Longwood Shola Reserve Forest derives its name from the Tamil word, "Solai", which means ‘tropical rainforest’.
- The ‘Sholas’ are found in the upper reaches of the Nilgiris, Anamalais, Palni hills, Kalakadu, Mundanthurai and Kanyakumari in Tamil Nadu.
- These forested wetlands serve as habitats for the globally endangered Black-chinned Nilgiri Laughing thrush (Strophocincla cachinnans), Nilgiri Blue Robin (Myiomela major), and vulnerable Nilgiri Wood-pigeon (Columba elphinstonii).
- As many as 14 out of 26 endemic bird species of the Western Ghats are found in these wetlands.
- Ankasamudra Bird Conservation Reserve (Karnataka): Ankasamudra Bird Conservation Reserve is a human made Village Irrigation Tank built centuries back and is spread over an area of 98.76ha.
- It is an ecologically important wetland, rich in biodiversity, comprising over 210 species of plants, mammal species, reptiles, birds etc.
- It supports more than 1% of the biogeographic population of Painted Stork and Black-headed Ibis.
- Aghanashini Estuary (Karnataka): Aghanashini Estuary is formed at the confluence of the Aghanashini River with the Arabian Sea.
- The brackish water of the Estuary provides diverse ecosystem services including flood and erosion risk mitigation, biodiversity conservation and livelihood support.
- The wetland also provides livelihoods to families by supporting fishing, agriculture, collection of edible bivalves and crabs, shrimp aquaculture, traditional fish farming in the estuarine rice fields (locally known as Gazni rice fields), bivalve shell collection and salt production.
- Magadi Kere Conservation Reserve (??Karnataka): Magadi Kere Conservation Reserve, is a human-made wetland with an area of nearly 50 hectares which was constructed to store rainwater for irrigation purposes.
- The wetland harbors two vulnerable species, namely the Common pochard and River tern and four near-threatened species, namely the Oriental Darter Black-headed Ibis Woolly-necked Stork and Painted Stork.
- It is also one of the largest wintering grounds for the Bar-headed goose (Anser indicus) in Southern India.
- The wetland is a designated Important Bird Area (IBA) and is also listed as a priority area for conservation in India.
What is the Ramsar Convention?
- The Ramsar Convention was signed on 2nd February 1971 to preserve the ecological character of their wetlands of international importance.
- It is named after Ramsar, the Iranian city where the treaty was signed in 1971, and places chosen for conservation under it are given the tag ‘Ramsar site’.
- The World Wetlands Day, celebrated on 2 February to raise global awareness about the importance of wetlands for human prosperity and a healthy planet.
India Ranks 93 on Corruption Perceptions Index 2023 (The Hindu)
- 31 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News?
India ranked 93 out of 180 countries on the corruption perceptions index for 2023 as its overall score remained largely unchanged, according to a Transparency International report.
Key Facts About Corruption Perceptions Index 2023:
- India ranked 93 out of 180 countries on the corruption perceptions index for 2023 tied with Maldives, Kazakhstan, and Lesotho also ranking at 93 out of 180 countries.
- In 2023, India's overall score was 39 while in 2022, it was 40.
- India's rank in 2022 was 85.
- Denmark (90) tops the index for the sixth consecutive year, with Finland and New Zealand.
- In South Asia, both Pakistan (133) and Sri Lanka (115) grapple with their respective debt burdens and ensuing political instability.
- Bangladesh (149) emerges from the least developed country (LDC) status, with economic growth supporting a continued reduction in poverty and improving living conditions.
- China (76), with its aggressive anti-corruption crackdown, has punished more than 3.7 million public officials for corruption over the last decade.
- Somalia (11), Venezuela (13), Syria (13), South Sudan (13) and Yemen (16) take the bottom spots in the index.
What is the Corruption Perceptions Index (CPI)?
- The Corruption Perceptions Index (CPI) scores and ranks countries/territories based on how corrupt a country’s public sector is perceived to be by experts and business executives.
- It is a composite index, a combination of 13 surveys and assessments of corruption, collected by a variety of reputable institutions including the World Bank, World Economic Forum, private risk and consulting companies, think tanks and others.
- The CPI ranks 180 countries and the results are given on a scale of 0 (highly corrupt) to 100 (very clean).
- The CPI is released annually by Transparency International, an independent nonprofit organization that aims to fight corruption, especially in the public sector.
- Transparency International is a global independent, nongovernmental nonprofit organization (NPO) that aims to stop corruption by promoting transparency in various sectors of society.
- The organization's international secretariat is located in Berlin and it has national chapters in more than 100 countries.
- The agency is funded through donations from governments, individuals, private donors, and other organizations.
- The organisation conducts research, and advocacy work, and undergoes various projects in its fight against corruption.
- In 1995, the organization created the first Corruption Perceptions Index, ranking 45 countries based on how much corruption they were perceived to have in the public sector.
Economic Impact of Corruption:
- Corruption continues to be a big hurdle to political, economic, and social development.
- Those who are economically challenged are the most affected by the effects of corruption and related fraud.
- That's because they often rely heavily on public services and can't afford to pay bribes.
- The International Finance Corporation also cites increases in the cost of business as a result of corruption.
Elon Musk's Neuralink implants Brain Chip in First Human (Indian Express)
- 31 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News?
Recently, Elon Musk announced his brain chip company, Neuralink, has completed its first implant on a human patient.
What is Neuralink?
- Neuralink is an upcoming medical device called a brain-computer interface that can help paralysed persons or amputees regain some sense of movement.
- It will decode signals from a part of the brain that plans movements.
- These signals will then be used to control external devices such as computers and mobile phones, allowing the participants to browse the web or play online games with just their thoughts even as their limbs are immobile.
- Under the PRIME Study (short for Precise Robotically Implanted Brain-Computer Interface) an N1 implant will be surgically placed by an R1 robot in the brain.
- The N1 implant has 1,024 electrodes distributed across 64 threads that are thinner than human hair.
- The R1 robot has been designed to insert these threads very accurately in a specific region of the brain.
Current Scenario in the Brain-Computer Interface?
- Recent breakthroughs in brain-computer interfaces have led to remarkable advancements, including systems capable of translating neural signals into speech at nearly the speed of natural speech and bi-directional interfaces that offer sensory feedback to the brain.
- In a notable development, researchers in Switzerland documented a case involving a man paralyzed from the waist down who regained the ability to walk.
- This feat was achieved through the use of a digital bridge that bypassed the damaged portion of his spinal cord.
- By employing a brain-spine interface, the signals from his brain were converted into stimulation for his spine, enabling him to walk again.
- While it may take several years before such devices are commercially available, the scientific progress in this field is remarkable.
- These advancements hold promise for individuals paralyzed due to accidents, offering potential mobility with the assistance of spinal implants.
What are the Challenges?
- One of the main challenges of the technology is establishing the connection between the brain and the chips, allowing it to reliably interpret the signals from the brain.”
- The use of conventional electronics for developing brain-computer interfaces results in a “mismatch with the soft tissue of the brain.”
- This can lead to tissue damage and immune response to the sensors.
- Flexible electronics with tissue-like properties can help build interfaces that do not face these problems.
- It can also help the systems adapt to changes in the brain volume during development, ageing and disease.
Eravikulam National Park to Close From February 1 for Nilgiri Tahr Breeding Season (The Hindu)

- 31 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News?
The Eravikulam National Park (ENP), the natural habitat of the Nilgiri tahr, will be closed for the calving season of the species from February 1 to March 31.
About Eravikulam National Park:
- Eravikulam National Park also known as Rajamala National Park, is located in Kerala's Idukki district.
- The park is administered under the Kerala Forest and Wildlife Department and became a National park in 1978.
- It is a 97 km2 national park located along the Western Ghats, Kerala.
- Anamudi, the highest peak in south India was located on the southern side of the park.
- This is also the land of "Neelakurinji", a flower that blooms once in twelve years.
- Wildlife in the Park: The park holds the maximum viable population of the endangered Nilgiri Tahr including other little-known fauna Nilgiri marten, ruddy mongoose, small clawed otter, dusky striped squirrel etc.
- Flora: Important flora includes Microtropis ramiflora, Actinodaphne bourdilloni, Pittosporum tetraspermium, Chrysopogon Zelanieus, Strobilanthus Kunthianus (Neela Kurinji) etc.
- Mostly the park is busted with rolling grasslands, but several patches of shola forests are also found in the upper part of the valley.
- The shola grasslands are exceptionally rich in balsams and orchids including the long thought extinct variety Brachycorythis wightii.
- The Atlas moth, the largest of its kind in the world, is seen in this park.
Key Facts about Nilgiri Tahr:
- Nilgiri Tahr is a rare mountain animal found only in the southern part of the Western Ghats.
- Scientific Name: Nilgiritragus hylocrius
- Local Name: Varayaadu
- They are famous for their ability to climb steep cliffs, which has earned them the nickname Mountain Monarch.
- It is the official state animal of Tamil Nadu.
- Distribution: Nilgiri Tahrs are mainly found in Kerala and Tamil Nadu, covering only about 5% of the Western Ghats.
- Eravikulam National Park in Kerala is home to the largest population of Nilgiri Tahrs.
- Habitat: They live in open grasslands at elevations between 1200 and 2600 meters in the South Western Ghats.
- Characteristics: Nilgiri Tahrs have a sturdy body with short, coarse fur and a rough mane.
- Both males and females have curved horns, with males having larger horns, up to 40 cm long.
- Adult males have a light grey area on their backs, known as a 'saddle,' hence the name 'saddlebacks.'
- They have a short grey-brown or dark coat.
- Conservation Status:
- IUCN Red List: Endangered
- Protected under the Wildlife (Protection) Act of India, 1972: Schedule I
Employer Rating Survey to Assess Women Participation in Workforce (Business Standard)

- 31 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News?
To bolster the representation of women in the workforce and advance gender equality, various ministries of the central government issued a series of advisories and surveys on Tuesday, aimed at industries and employers.
About the Survey:
- This survey aims to evaluate the prevalence of women-friendly practices across the nation's workplaces.
- The government is collecting information on several key aspects, including the establishment of internal complaints committees (ICC) for preventing sexual harassment, the provision of childcare facilities, ensuring pay equity, offering flexible or remote work options for women, and providing safe transportation during late hours.
- Additionally, various ministries of the Central government have issued advisories to enhance women's representation in the workforce.
Factors Affecting Low Women Workforce Participation:
- Cultural and Social Norms: Traditional gender roles and societal expectations often discourage women from pursuing full-time employment due to responsibilities for caregiving and homemaking, limiting their participation in the workforce.
- Educational Barriers: Limited access to quality education can hinder women from acquiring the necessary skills and qualifications for certain jobs, further reducing their workforce participation.
- Gender Pay Gap: Disparities in wages between men and women discourage women from entering or remaining in the workforce, contributing to lower participation rates.
- Structural Constraints: India's manufacturing and service sectors often have rigid structures that limit employment opportunities, particularly in the informal sector where many women work.
- Security Concerns: Instances of sexual harassment in the workplace create safety concerns for women, acting as a barrier to their participation in the labour force.
Government Initiatives Supporting Women's Empowerment:
- Code on Wages, 2019: Ensures equal pay for equal work without discrimination based on gender, fostering fairness in wage practices across establishments.
- Code on Occupational Safety, Health And Working Conditions (OSH), 2020: Proposes amendments to improve employment conditions for women workers, particularly in above-ground mines, ensuring their safety and well-being.
- Maternity Benefit Act, 2017: Enhances maternity benefits and fosters a healthier work environment for pregnant and nursing women, promoting their well-being and work-life balance.
- Rashtriya Mahila Kosh (RMK): A national organization offering microfinance services to empower economically disadvantaged women, supporting their livelihood projects and economic independence.
- National Rural Livelihoods Mission (NRLM): Focuses on creating sustainable self-employment opportunities for rural women through skill training, capacity building, and financial assistance, enabling them to engage in income-generating activities.
- MGNREGA (Mahatma Gandhi National Rural Employment Guarantee Act): Guarantees 100 days of wage employment annually to rural households, actively encouraging women's participation and ensuring equitable employment opportunities.
Way Forward
Continued government initiatives aimed at empowering women in the workforce through skill development and expanded employment opportunities have yielded positive results, as evidenced by the Periodic Labour Force Survey (PLFS) released by the Labour Bureau in 2023. This survey indicated a notable increase in women's participation, rising from 23.3% in 2017-18 to 37% in 2022-23.
Draft Indian Stamp Bill, 2023 (Indian Express)

- 31 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News?
The Centre has proposed repealing the Indian Stamp Act, of 1899 and bringing in a new law for the stamp duty regime in the country.
What is Stamp Duty?
- A stamp duty is essentially a government tax, which is levied to register documents, like an agreement or transaction paper between two or more parties, with the registrar.
- Usually, the amount specified is fixed based on the document’s nature or is charged at a certain percentage of the agreement value stated in the document.
- Stamp duties can be levied on bills of exchange, cheques, promissory notes, bills of lading, letters of credit, policies of insurance, transfer of shares, debentures, proxies and receipts.
- Accepted as valid evidence in a court of law, stamp duties are levied by the Centre but appropriated by the concerned states within their territories under Article 268 of the Constitution.
Notable Provisions of the Draft Indian Stamp Bill, 2023:
Several provisions of the Indian Stamp Act, of 1899 have now become “redundant” or “inoperative” Therefore, the ministry has proposed repealing the existing Act and substituting it with new legislation to “reflect the present realities and objectives.”
- The draft Bill has introduced provisions for digital e-stamping.
- “Electronic stamp” or “e-stamp” means an electronically generated impression denoting the payment of stamp duty by electronic means or otherwise, according to Section 2 (18) of the Bill.
- There are also provisions for digital signatures.
- Section 2 (17) of the Bill states that the words “executed” and “execution”, used for instruments, will mean “signed” and “signature” and include attribution of electronic records and electronic signatures, as defined under the Information Technology (IT) Act, 2000.
- The IT Act defines “electronic records” as “data, record or data generated, image or sound stored, received or sent in an electronic form or micro film or computer generated microfiche.”
- Meanwhile, digital or electronic signature refers to the authentication of any electronic record by a subscriber through an electronic method or procedure.
- The draft Bill also proposes to raise penalties.
- It seeks to increase the maximum penalty amount from Rs 5,000 to Rs 25,000 for contravening any provisions of the law and impose Rs 1,000 per day for repeated offences.
What is the Indian Stamp Act, of 1899?
- The Indian Stamp Act, of 1899 is a fiscal or money-related statute that lays down the law relating to tax levied in the form of stamps on instruments recording transactions.
- Under Section 2 of the Act, an instrument includes every document by which any right or liability is or purports to be, created, transferred, limited, extended, extinguished or recorded.
- According to this Act, a “stamp” has been defined as “any mark, seal or endorsement by any agency or person duly authorised by the State Government, and includes an adhesive or impressed stamp, for the purposes of duty chargeable under this Act”.
- Section 3 of the 1899 Act prescribes that certain instruments or documents shall be chargeable with the amount indicated in Schedule 1 of the Act.
- These include bills of exchange or promissory notes.
Framework for Voluntary Carbon Market in Agriculture Sector (Down To Earth)

- 30 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News?
The central government recently launched a framework to promote voluntary carbon markets in the agriculture sector.
What are Carbon Markets?
- Carbon markets are trading systems in which carbon credits are sold and bought.
- Companies or individuals can use carbon markets to compensate for their greenhouse gas emissions by purchasing carbon credits from entities that remove or reduce greenhouse gas emissions.
- One tradable carbon credit equals one tonne of carbon dioxide or the equivalent amount of a different greenhouse gas reduced, sequestered or avoided.
- When a credit is used to reduce, sequester, or avoid emissions, it becomes an offset and is no longer tradable.
Why are Carbon Markets Important?
- Scientists warn that 2°C of warming will be exceeded during the 21st century unless we achieve deep reductions in GHG emissions now.
- Effective action will require concerted and sufficient investment, knowing also that the costs of inaction will be far higher.
- The latest IPCC report finds all countries are falling way short, with financial flows three to six times lower than levels needed by 2030 – and even starker differences in some regions of the world.
- Many countries are turning to carbon markets as a key component in driving and financing the necessary transformation to tackle the climate crisis.
How Many Types of Carbon Markets Are There?
- There are broadly two types of carbon markets: compliance and voluntary.
- Compliance markets are created as a result of any national, regional and/or international policy or regulatory requirement.
- Voluntary carbon markets (VCM)– national and international – refer to the issuance, buying and selling of carbon credits, on a voluntary basis.
- The current supply of voluntary carbon credits comes mostly from private entities that develop carbon projects, or governments that develop programs certified by carbon standards that generate emission reductions and/or removals.
Importance of Establishing a VCM Framework in the Agricultural Sector:
- Emission Concerns: Agriculture in India contributes approximately 15% of the nation's greenhouse gas emissions, highlighting the urgent need for mitigation strategies.
- Vulnerability: With around 50% of cultivated land being rainfed and more than 80% of farmers categorized as small or marginal, the sector is highly susceptible to the impacts of climate change.
- National Mission on Sustainable Agriculture (2010): This initiative focuses on promoting adaptation measures such as agroforestry, micro irrigation, and soil health management, which not only reduce emissions but also offer opportunities for carbon sequestration.
- Additional Income Opportunities: Through the implementation of these practices, farmers can potentially generate additional income streams.
'Maratha Military Landscapes' to be India's nomination for UNESCO World Heritage List for 2024-25 (The Hindu)

- 30 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News?
'Maratha Military Landscapes' representing extraordinary fortification and military system envisioned by the Maratha rulers will be India's nomination for inclusion in the UNESCO World Heritage List for the 2024-25 cycle, the Culture Ministry said on January 29.
About Maratha Military Landscapes:
- Developed between the 17th and 19th centuries, the nomination comprises the 12 components of Salher Fort, Shivneri Fort, Lohgad, Khanderi Fort, Raigad, Rajgad, Pratapgad, Suvarnadurg, Panhala Fort, Vijaydurg, Sindhudurg in Maharashtra, and Gingee Fort in Tamil Nadu.
- These components are strategically distributed across diverse geographical and physiographic regions, highlighting the military prowess of the Maratha rule.
- The landscapes showcase the integration of landscape, terrain, and physiographic characteristics distinctive to the Sahyadri mountain ranges, the Konkan Coast, the Deccan Plateau, and the Eastern Ghats in the Indian Peninsula.
- Out of the more than 390 forts in Maharashtra, only 12 have been chosen under the 'Maratha Military Landscapes of India'.
- The inception of the Maratha Military ideology dates back to the 17th century during the reign of the Maratha King Chhatrapati Shivaji Maharaj, continuing through subsequent rules until the Peshwa rule of 1818 CE.
UNESCO Nomination Criteria:
- There are two categories of nomination- cultural and natural criteria.
- The Maratha Military Landscapes is nominated under cultural criteria.
- To fulfil this criterion, a site should bear unique testimony to cultural tradition, it should be an outstanding example of a type of building, architectural or technological ensemble, or landscape that illustrates significant stage(s) in human history and it should be directly or tangibly associated with events or living traditions, ideas or beliefs, artistic and literary works of outstanding universal significance.
World Heritage Sites In India:
- India presently boasts 42 World Heritage sites, with 34 cultural sites, 7 natural sites, and 1 mixed site.
- Maharashtra alone has six World Heritage Sites including:
- The Ajanta Caves
- Ellora Caves
- Elephanta Caves
- Chhatrapati Shivaji Maharaj Terminus
- Victorian Gothic and Art Deco Ensembles of Mumbai, and
- The Western Ghats (a natural site)
Tentative List Recognition:
- The Maratha Military Landscapes of India, included in the Tentative List of World Heritage sites in 2021, is the sixth cultural property nominated for inclusion in the World Heritage List from Maharashtra.
Govt Brings Non-urea Fertilisers Under Price Control (Indian Express)

- 30 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News?
The Modi government has brought di-ammonium phosphate (DAP), muriate of potash (MOP) and all other fertilisers that receive nutrient-based subsidy (NBS) support under “reasonable pricing” controls.
What is the Central Government's Decision on Non-Urea Fertilizers?
- The Department of Fertilisers (DoF) under the Ministry of Chemicals & Fertilisers has issued comprehensive guidelines for assessing the fairness of Maximum Retail Prices (MRPs) for all non-urea fertilisers covered by the Nutrient Based Subsidy (NBS) scheme.
- Effective from April 1, 2023, these guidelines set maximum allowable profit margins for different types of fertilizer companies: 8% for importers, 10% for manufacturers, and 12% for integrated manufacturers.
- Companies deemed to be earning excessive profits beyond these thresholds during a financial year (April-March) are required to reimburse the surplus to the DoF by October 10 of the following fiscal year.
- Failure to comply within the specified timeframe will result in the imposition of a 12% per annum interest rate on the refund amount, calculated from the day after the end of the financial year.
- Any unreasonable profits will be deducted from future fertilizer subsidy payments by the government.
How will Companies Unreasonable Profit be Determined?
- Fertilizer companies are required to conduct a self-assessment of unreasonable profits, using cost auditor's reports and audited cost data approved by their board of directors.
- This information must be submitted to the Department of Fertilisers (DoF) by October 10 of the subsequent fiscal year.
- The DoF will then review the reasonableness of Maximum Retail Prices (MRPs) submitted by companies by February 28 for each completed previous financial year.
- Subsequently, it will prepare a report on any unreasonable profits earned and to be recovered from the companies.
Significance of the New DoF Guidelines:
- Non-urea fertilizers are already informally price-controlled, a measure expected to continue until the conclusion of the Lok Sabha elections.
- The new guidelines establish indirect MRP controls on non-urea fertilizers by limiting the profits companies can earn from their sales.
- These limits will be based on the total cost of sales, encompassing production or import costs, administrative overheads, selling and distribution expenses, as well as net interest and financing charges.
- Essentially, the new guidelines extend the detailed cost monitoring and price control regime currently applied to urea to other fertilizers.
What is the Nutrient Based Subsidy (NBS) Scheme?
- NBS fertilisers are technically decontrolled unlike urea, whose maximum retail price (MRP) is fixed by the government.
- Under the NBS scheme, introduced in April 2010, their MRPs are supposed to be market-determined and set by the individual companies selling them.
- The government merely pays a fixed per-tonne subsidy on each of these fertilisers, linked to their nutrient content or specific percentage of nitrogen (N), phosphorous (P), potassium (K) and sulphur (S).
- Unlike the previous system, where subsidies were product-specific, the NBS Scheme encourages balanced fertilization by discouraging excessive use of high-nutrient fertilizers like urea, DAP, and MOP.
- It aims to promote innovation in fertilizer products and encourages the use of complex fertilizers and single super phosphate to address nutrient imbalances.
- However, the scheme faced challenges as urea consumption increased significantly, leading to nutrient imbalances and subsequent failure.
Delhi HC Upholds Validity of Anti-profiteering Provision of CGST Act (TOI)

- 30 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News?
Delhi High Court has upheld the constitutional validity of the anti-profiteering clause in the GST law, which mandates companies to pass on the benefit of lower taxes and input tax credits to consumers.
What is an ‘Anti-profiteering’ Activity?
- Any reduction in the rate of GST tax on any supply of goods or services or the benefit of input tax credit should have been passed on to the recipient by way of a commensurate reduction in prices.
- The wilful action of not changing the final price of the good or service by various means, despite the reduction in the rate of the tax for that particular good or service, amounts to “profiteering”.
How is the Anti-profiteering Mechanism Under the CGST Act?
- CGST mandate a 3-tier structure for investigation and adjudication of the complaints regarding profiteering.
- a) National Anti-profiteering
- b) Authority Directorate General of Safeguards
- c) State-level screening committees and standing committee
How Does the Screening Committee and Standing Committee Work?
- GST council may constitute a standing committee, having members from both state and central government.
- Every state shall constitute one state-level screening committee.
- It will have one member from the state government and one member from the central government as nominated by the respective appropriate authority.
- The complaints or issues of local nature will be first examined by the screening committee.
- State-level screening and standing committee will examine the complaint and determine the prime facie evidence to support the validity of the complaint.
- If any committee satisfies that the supplier has contravened section 171 of the CGST Act, the case shall be transferred to DG Safeguards for further investigation.
- The committees shall complete the investigation within a period of a month from the date of the receipt of the application.
What is the Role of DG Safeguards in the Anti-profiteering Mechanism?
- DG safeguards are the main investigation arm in the anti-profiteering mechanism.
- It can summon the interested parties make inquiries or call the relevant documents.
- It can seek help from technical experts in the due course of investigation.
- DG Safeguards shall complete the investigation within a period of three months from the date of receipt of the report from either screening or standing committee.
- The period can be extended for another three months.
Who Can File the Complaint Against Profiteering?
- Any consumer or organisation experiencing a non-reduction in the price of the goods or service despite the reduction in the rate of GST can file a complaint with proper evidence.
- Any supplier, trader, wholesaler or retailer, who could not get the benefit of input tax credit on account of a reduction in the rate of GST, can also file the complaint with proper evidence.
Western Countries Halt UNRWA Funding Amid Gaza War (Indian Express)

- 30 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News?
UN officials recently urged countries to reconsider their decision to suspend funding for UNRWA, promising strict action against any staff member implicated in Hamas’ October 7 attack on Israel.
Context:
- Recently UN officials urged countries to reconsider their decision to suspend the funding for the United Nations agency for Palestinian refugees (UNRWA).
- The agency highlighted that two million Palestinians in Gaza are dependent on UNRWA services.
- The US and eight other Western countries, which together provided more than half of UNRWA’s 2022 budget, cut the money after Israel accused some of the agency’s staff members of involvement in the October 7 attack.
What is the United Nations Refugee Agency for Palestinians (UNRWA)?
- UNRWA stands for UN Relief and Works Agency for Palestinian Refugees in the Near East.
- It was founded in 1949 to provide aid to about 700,000 Palestinians who were forced to leave their homes in what is now Israel during the 1948 Arab-Israeli war.
- The UN agency operates in Gaza and the Israeli-occupied West Bank, as well as Lebanon, Syria, and Jordan — countries where the refugees took shelter after their expulsion.
- It runs education, health, relief and social services, microfinance and emergency assistance programmes inside and outside refugee camps based in the aforementioned areas.
- Currently, around 5.9 million Palestine refugees — most of them are descendants of original refugees — access the agency’s services.
- Over 1 million are sheltering in UNRWA schools and other facilities in Gaza.
- Funding: UNRWA is funded almost entirely by voluntary contributions by donor states like the US.
- It also gets a limited subsidy from the UN, which is used only for administrative costs, the agency’s website said.
What has Israel accused UNRWA of?
- Israel has alleged that 12 staff members of UNRWA were involved in the October 7 attack.
- It has also claimed that Hamas siphons off funds given to UNRWA and fights from in and around the agency’s facilities.
- Israel has alleged that “Hamas tunnels (are) running next to or under UNRWA facilities and accuses the agency of teaching hatred of Israel in its schools.
How has UNRWA Responded?
- The UNRWA has denied all the allegations, saying it has no links to Hamas.
- In the statement, UN officials said out of 12 staff members who were accused of being involved in the attack, nine have been terminated.
- One is confirmed dead and the identity of the two others is being clarified.
What Happens Now?
- UNRWA is crucial for the survival of people living in Gaza, which has plunged into a humanitarian crisis after the outbreak of the conflict.
- The agency has been the main supplier of food, water and shelter to civilians of the enclave.
- UNRWA, however, would run out of money needed for its aid work within weeks if the funding isn’t restored.
Modified Parbati-Kalisindh- Chambal-ERCP (PKC-ERCP) Link Project (Indian Express)
- 29 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News?
An MoU was signed by Rajasthan and MP with the Union Ministry of Jal Shakti Sunday for implementation of the Modified Parbati-Kalisindh-Chambal-ERCP (Modified PKC-ERCP) Link Project.
What is the Modified PKC-ERCP?
- The Modified PKC-ERCP is an inter-state river linking project.
- A Memorandum of Agreement (MoA) will be finalised among Rajasthan, Madhya Pradesh, and the Centre, covering the sharing of water, exchange of water, sharing of costs and benefits, implementation mechanisms, arrangements for management and control of water in the Chambal basin, etc.
What is the PKC link project?
- The Parbati-Kalisindh-Chambal (PKC) link project is one of the 30 links included in the National Perspectives Plan formulated by the erstwhile Union Ministry of Irrigation (now Ministry of Water Resources) and the Central Water Commission in the year 1980.
- As per the National Water Development Agency (NWDA), the preliminary feasibility report of the Kalisindh-Chambal link canal project was prepared and circulated to the states concerned in September 1991.
- The report proposed the diversion of water from river Newaj (a tributary of Kalisindh) and Kalisindh to the river Chambal at either the Rana Pratap Sagar dam or the Gandhi Sagar dam.
- Rajasthan came up with the proposal of the ERCP in 2019, and to utilise water resources optimally, the Task Force for Interlinking of Rivers (TFILR) discussed its merger with the PKC link project.
- This integration was approved by the Special Committee for Interlinking of Rivers in December 2022.
What is the ERCP?
- The Eastern Rajasthan Canal Project (ERCP) is aimed at the intra-basin transfer of water within the Chambal basin, by utilising surplus monsoon water available in the Kalisindh, Parvati, Mej and Chakan subbasins and diverting it into water deficit sub-basins of Banas, Gambhiri, Banganga and Parbati.
- This will provide drinking and industrial water to 13 districts of eastern Rajasthan, namely Alwar, Bharatpur, Dholpur, Karauli, Sawai-Madhopur, Dausa, Jaipur, Ajmer, Tonk, Bundi, Kota, Baran, and Jhalawar.
What are the benefits of the modified project?
- According to the Jal Shakti Ministry, the link project proposes to provide drinking and industrial water in 13 districts of eastern Rajasthan, and Malwa and Chambal regions of Madhya Pradesh, apart from providing irrigation in 2.8 lakh ha. area (or more) each in both states (total of 5.6 lakh ha or more).
What is River Interlinking?
- River Interlinking involves the creation of artificial channels to connect rivers and water bodies, facilitating the transfer of water from regions of surplus to those facing deficits.
- Importance of River Interlinking:
- Disaster Management: River Interlinking plays a crucial role in mitigating floods and droughts, aiding in effective disaster management strategies.
- Economic Benefits: It offers economic advantages such as enhanced irrigation facilities, increased hydro-power generation capacity, and improved inland navigation, contributing to regional development.
- Ecological Restoration: River Interlinking initiatives contribute to the restoration of river ecosystems and provide support to biodiversity in water-deficient regions, fostering ecological balance.
- Concerns Associated with River Interlinking:
- Biodiversity Loss: One major concern revolves around the potential loss of biodiversity resulting from altering natural river courses and habitats.
- Community Displacement: Another significant issue is the displacement of communities residing in areas affected by river interlinking projects, highlighting social and humanitarian challenges.
About the National Perspective Plan:
- The National Perspective Plan was formulated in 1980 under the purview of the Ministry of Irrigation (currently known as the Ministry of Jal Shakti) and the Central Water Commission.
- Objective:
- The plan aims to address regional disparities by facilitating the inter-basin transfer of water resources, thereby minimizing imbalances across different regions of the country.
- Components:
- The plan consists of 30 link projects categorized into two main components:
- the Himalayan component, comprising 14 projects, and
- the Peninsular component, consisting of 16 projects.
- The plan consists of 30 link projects categorized into two main components:
World's First 'Black Tiger Safari', to be Established in Odisha (TOI)
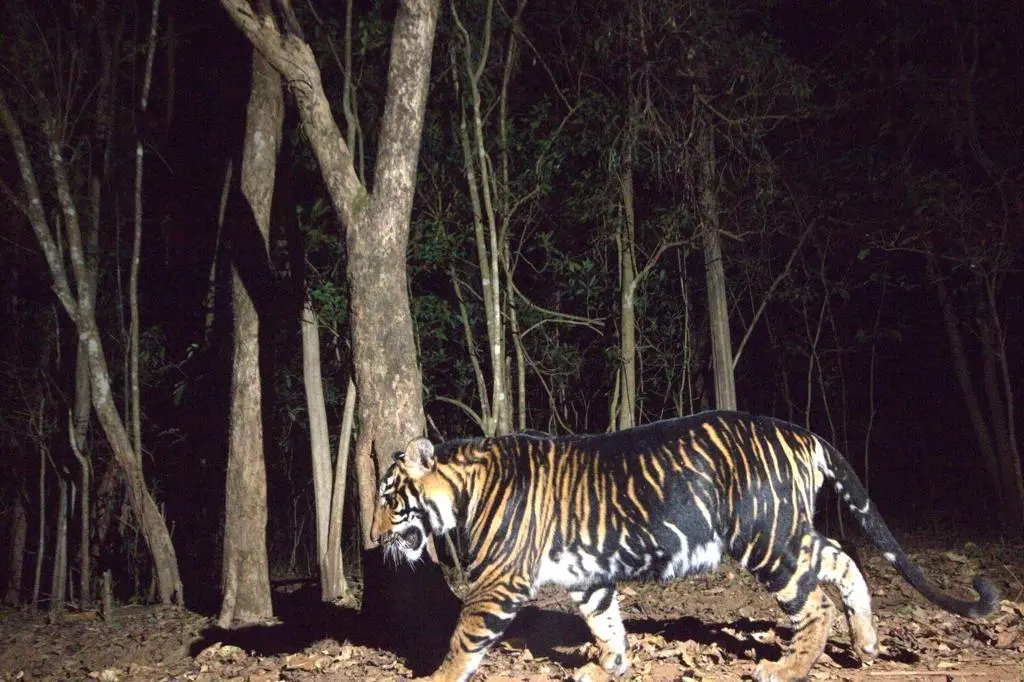

- 29 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News?
Odisha is gearing up to provide an unparalleled experience to visitors through its upcoming black tiger safari, offering a rare glimpse into the lives of these majestic creatures in their natural habitat.
What are Black Tigers or Melanistic Tigers?
- Black tigers, also known as melanistic tigers, are a unique phenomenon resulting from a genetic condition called melanism.
- Melanism causes an increased production of melanin, a pigment responsible for hair, eye, and skin colouration, resulting in black or nearly black skin, feathers, or hair in animals.
- In Simlipal Tiger Reserve, many royal Bengal tigers belong to a distinct lineage characterized by higher-than-normal levels of melanin.
- These tigers exhibit black and yellow interspersed stripes on their coats, though they are not entirely black.
- Therefore, they are more accurately described as pseudo-melanistic.
- As per the 2022 All-India Tiger Estimation, 16 tigers were recorded in Similipal Tiger Reserve, out of which 10 were melanistic.
- However, ongoing tiger surveys conducted by the state government suggest that the actual number of royal Bengal tigers in Similipal Tiger Reserve may be higher than reported by the National Tiger Conservation Authority.
- Factors Contributing to (Pseudo) Melanism:
- Research conducted by the National Centre for Biological Sciences (NCBS) in Bengaluru indicates that a single mutation in the gene Transmembrane Aminopeptidase Q (Taqpep) is responsible for the enlargement or spreading of black stripes into the yellow background of black tigers.
- Genetic analyses and computer simulations suggest that Similipal's black tigers may have originated from a very small founding population of tigers and are likely inbred.
- Additionally, the isolation of tigers in Similipal Tiger Reserve leads to breeding within the population, further contributing to the prevalence of melanism among these tigers.
About Similipal Tiger Reserve (STR):
- Similipal, which derives its name from the ‘Simul’ (Silk Cotton) tree, is a national park and a Tiger Reserve situated in the northern part of Orissa’s Mayurbhanj district.
- It spans an expansive area of 2,750 square kilometres (1,060 square miles), bordering Jharkhand and West Bengal.
- Similipal Tiger Reserve is a key component of the Mayurbhanj Elephant Reserve, which encompasses three protected areas:
- Similipal Tiger Reserve
- Hadagarh Wildlife Sanctuary, and
- Kuldiha Wildlife Sanctuary
- Biodiversity: Similipal is renowned for its rich biodiversity, boasting a diverse array of wildlife including the majestic Bengal tiger, the iconic Asian elephant, the formidable gaur, and the elusive chausingha.
- Recognized as a UNESCO World Network of Biosphere Reserves site since 2009, it stands as Asia's second-largest biosphere reserve, following the Gulf of Kachchh in Gujarat.
- Notably, Similipal Tiger Reserve holds the distinction of being the sole natural habitat in India for melanistic royal Bengal tigers, adding to its ecological significance.
The Procedure of Appointment of a Chief Minister (The Hindu)

- 29 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News?
Janata Dal (United) president Nitish Kumar took oath as Bihar Chief Minister for a record ninth time on Sunday, returning to the BJP-led National Democratic Alliance just 18 months after he left it, in his fifth switch in political loyalties since 2015.
About Chief Minister:
- According to Article 163 of the Indian Constitution, each state shall have a Council of Ministers led by the Chief Minister (CM) to assist and provide advice to the Governor in carrying out the state's functions.
- In the parliamentary system of governance, the Chief Minister holds the actual executive authority within states.
- While the Governor serves as the ceremonial head of the state, the Chief Minister serves as the head of the government.
- In the Indian political framework, the Chief Minister's role is analogous to that of the Prime Minister at the national level.
Appointment Process of Chief Minister:
- The Constitution of India does not lay down specific criteria for the appointment of a Chief Minister.
- Article 164 of the Indian Constitution stipulates that the Governor is responsible for appointing the Chief Minister, albeit with certain limitations.
- Traditionally, the leader of the largest party in the state legislature is typically chosen as the Chief Minister, following parliamentary conventions.
- Even individuals who are not members of the state legislature (both Houses) can be appointed as Chief Minister for a temporary period of six months, during which they must secure election or nomination (in the case of a bicameral legislature).
- In situations where no single party or pre-poll coalition secures a majority in the assembly (known as a hung assembly), the Governor exercises discretionary powers to appoint the Chief Minister, relying on individual judgment.
- The Constitution does not mandate the Chief Minister-elect to demonstrate majority support in the state assembly before assuming office.
- However, after the formation of the ministry, the Governor may request the Chief Minister to prove majority support within a reasonable timeframe.
Oath and Affirmation of Chief Minister:
- The third Schedule of the Indian Constitution outlines the "Forms of Oaths or Affirmations" to be taken by public officials.
- Typically, the Chief Minister's oath, solemnly administered by the Governor, constitutes a formal commitment to uphold the constitution and execute the responsibilities of the position with integrity and diligence.
Roles and Responsibilities of the Chief Minister:
- The Chief Minister serves as the principal advisor to the Governor on matters pertaining to the convening and adjournment of state legislative sessions.
- As the head of the State Legislative Assembly, the Chief Minister acts as the primary liaison between the Governor and the Council of Ministers.
- The Chief Minister possesses the authority to propose the dissolution of the legislative assembly to the Governor when deemed necessary.
- Additionally, the Chief Minister assumes the role of vice-chairman of the relevant zonal council on a rotational basis, serving a term of one year.
Alabama in USA Carried Out the First Ever Execution Using Nitrogen Gas (Indian Express)

- 29 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News?
Alabama inmate Kenneth Smith was executed on January 25 by nitrogen hypoxia, marking the United States’ first execution using the method, and the first time in over four decades that a new method of execution was introduced since lethal injection was first used in 1982.
News Summary:
- An Alabama death row inmate has been put to death by nitrogen gas, in the first known execution of its kind in the US.
- His case marks the first known execution by nitrogen hypoxia, which his lawyers had argued amounted to a form of “cruel and unusual punishment”.
- Death by nitrogen gas is an untested procedure, and its opponents say it can cause unnecessary suffering.
- Kenneth Smith, 58, was a contract killer who had been on the death row since 1996.
What is Nitrogen Hypoxia?
- Nitrogen hypoxia is a style of execution wherein an inmate is made to inhale nitrogen instead of oxygen, leading to gradual asphyxiation.
- To achieve this, a respirator mask is placed over the head of the inmate on death row.
- While the air we breathe is made up of 80 per cent nitrogen, it exists in combination with oxygen, rendering the colourless, odourless gas harmless.
- However, if a person is deprived of oxygen and made to breathe in just nitrogen, the gas proves lethal.
- When a high concentration of nitrogen is inhaled, it replaces the oxygen in the body and disables the respiratory system, causing death.
Why Nitrogen Hypoxia?
- Nitrogen hypoxia is the first new method of execution to be introduced since 1982 when lethal injections began being used.
- The drug needed to administer lethal injections to inmates on death row became harder to access over time, pushing authorities to scout for alternatives.
- Further, there were reports of a surge in complications associated with the procedure as well.
- As of now, only three states in the United States have approved the use of nitrogen gas to execute death row inmates, namely, Alabama, Oklahoma, and Mississippi.
Is Nitrogen Hypoxia Ethical?
- There is little research regarding death by nitrogen hypoxia.
- When the State is considering using a novel form of execution that has never been attempted anywhere, the public has an interest in ensuring the State has researched the method adequately and established procedures to minimise the pain and suffering of the condemned person.
- The risks associated with this method of execution include the risks surrounding the chances of a gas leak if the mask is not secured well on the inmate.
- The law requires that this execution not be cruel.
Key facts about Nitrogen:
- The air around us, the atmosphere, is made up of about 78% nitrogen and only 21% oxygen.
- The rest comprises water vapour, argon, neon, helium, hydrogen and xenon.
- Those are known as "permanent gases".
- There is also a range of "variable gases" in the atmosphere.
- They include methane, ozone and carbon dioxide — with concentrations that can vary from day to day and region to region.
- At a concentration of 78% in the atmosphere, nitrogen is safe to breathe.
- But it grows dangerous and potentially fatal once levels of nitrogen reach 80% or more.
- Nitrogen has no odour, is tasteless, and colourless.
- Nitrogen gas is inert, but certain soil bacteria can "fix" nitrogen into a usable form for plants and animals.
- French chemist Antoine Laurent Lavoisier named nitrogen azote, meaning without life.
- Nitrogen was sometimes referred to as 'burnt' or 'dephlogisticated' air.
- Nitrogen compounds are found in foods, fertilizers, poisons, and explosives.
- It is responsible for the orange-red, blue-green, blue-violet, and deep violet colours of the aurora.
- Nitrogen has a valence of 3 or 5.
- Discovery: Scottish physician Daniel Rutherford in 1772
- Nitrogen is the fifth most abundant element in the universe.
PM Modi Inaugurates the Diamond Jubilee Celebration of the SC (The Hindu)

- 29 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News?
Prime Minister Narendra Modi on Sunday said ?800 crore has been approved for the expansion of the Supreme Court building complex while underlining that “ease of justice is the right of every Indian citizen and the Supreme Court is its medium”.
About the Supreme Court of India (SC):
Historical Context:
- The Supreme Court of India, inaugurated on January 26, 1950, coinciding with India's Republic Day, stands as the apex judicial body of the nation.
- Article 124 of the Constitution states that “There shall be a Supreme Court of India.”
- Situated on Tilak Marg, New Delhi, it initially operated from the Parliament House before relocating to its current edifice.
- The present building of the Supreme Court was inaugurated on August 4, 1958, by the first President of India, Dr. Rajendra Prasad.
Judicial Composition:
- The original Constitution envisioned a Supreme Court comprising a Chief Justice and seven puisne Judges, with subsequent increments authorized by Parliament to meet the burgeoning caseload.
- Presently, the Supreme Court consists of 34 Judges, including the Chief Justice, who convene in smaller benches of two or three, while larger benches of five or more, known as Constitution Benches, address critical constitutional matters or resolve conflicting decisions.
Jurisdiction and Powers:
- Endowed with original, appellate, and advisory jurisdiction, the Supreme Court serves as the final interpreter of the Constitution and the ultimate court of appeal.
- Its exclusive original jurisdiction extends to disputes between the Government of India and States or between States (Article 131), while Article 32 empowers it to safeguard Fundamental Rights through writs.
- Additionally, the Supreme Court exercises appellate jurisdiction over High Courts and other judicial bodies, with the power to entertain appeals on substantial questions of law and issue special leave to appeal under Article 136.
- Special advisory jurisdiction is vested in the Supreme Court under Article 143, allowing it to deliberate on matters referred by the President of India.
Judicial Powers and Enforcement:
- Empowered to issue writs and directions for the enforcement of Fundamental Rights, the Supreme Court wields authority to punish for contempt of court, including self-contempt.
- It can reconsider its final judgments through curative petitions and holds the authority to transfer cases between High Courts and adjudicate on election petitions.
Binding Authority:
- As the apex judicial body, judgments rendered by the Supreme Court carry binding precedent on all subordinate courts and tribunals across India, ensuring uniformity and consistency in legal interpretation and application.
AISHE report shows higher enrollment of women in higher education for 8 consecutive years (Indian Express)

- 27 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News?
In the last eight years, more women have enrolled in higher education compared to men, according to the 2021-22 All India Survey on Higher Education (AISHE) released recently.
Major Highlights of the AISHE Report 2021-22:
- The All India Survey on Higher Education (AISHE) for 2021–2022 has recently been released, and it highlights a notable change in enrolment trends.
- Women have enrolled in higher education at a higher rate than men during the last eight years, which is a significant step toward gender parity in academic fields.
Women Lead the Surge:
- According to the AISHE report, women now constitute 55 percent of the total increase in higher education enrollment, accounting for a staggering 91 lakh individuals since the academic year 2014-15.
- The latest statistics indicate that out of the overall enrollment of 4.33 crore, 48 percent, or 2.07 crore, are women—a marginal uptick from the 2.01 crore recorded in the previous academic year.
- The trend, characterized by a continuous surge in female enrollment since 2014-15, is particularly noteworthy.
- The report highlights an 18.7 percent increase in the enrollment of women from 2017-18 to 2021-22, showcasing a consistent upward trajectory.
Narrowing the Gender Gap:
- The gender gap in higher education is steadily narrowing, with the science stream standing out as a domain where women are making significant strides.
- Notably, 52.1 percent of the 57.18 lakh students enrolled in science at the undergraduate, postgraduate, MPhil, and PhD levels are women.
- The undergraduate level alone witnesses 51 percent of women in the science stream.
- However, disparities persist in certain disciplines, such as engineering and technology, where female enrollment lags significantly behind.
- The AISHE survey reveals that of the total students in undergraduate engineering programs, only 11.3 lakh are females, while 27.6 lakh are males.
- In addition to undergraduate programs, the report sheds light on postgraduate and PhD levels, showcasing a remarkable 61.2 percent of women in postgraduate science programs and a significant 62 percent representation in PhD programs in the sciences.
- State-wise Enrolment: The top 6 states in terms of student enrollment are Uttar Pradesh, Maharashtra, Tamil Nadu, Madhya Pradesh, West Bengal, and Rajasthan, constituting 53.3% of total enrollment.
- Number of Foreign Students: There are 46,878 foreign students enrolled in higher education, with the highest share from Nepal (28%).
- Teaching Staff in Higher Education: The total number of faculty/teachers in 2021-22 is 15.98 lakh, with about 56.6% male and 43.4% female, showing an increase of 46,618 teachers over 2020-21.
- This emerging trend is not only indicative of changing societal dynamics but also underlines the need for continued efforts to foster inclusivity and equal opportunities within the realm of higher education.
- The report serves as a testament to the progress made while emphasizing the areas that still require attention and intervention.
About the All India Survey on Higher Education (AISHE) Report:
- The All India Survey on Higher Education serves as the primary source of comprehensive data regarding the state of higher education in India.
- Published by the Ministry of Education, this survey has been ongoing since 2011, covering all higher educational institutions across the country.
- It gathers detailed information on various aspects including student enrollment, faculty data, infrastructure, and finances.
- The report relies on voluntary data submission by higher education institutions listed on the aishe.gov.in portal, with the accuracy of the data overseen by the respective institution's Nodal Officers.
What are incestuous ‘sapinda’ marriages, and why has the Delhi High Court reaffirmed the ban on them? (Indian Express)

- 27 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News?
Delhi High Court this week rejected a challenge to the constitutionality of Section 5(v) of the Hindu Marriage Act, 1955 (HMA), which prohibits marriage between two Hindus if they are “sapindas” of each other — “unless the custom or usage governing each of them permits of a marriage between the two”.
What was the Case?
- In 2007, the marriage of a woman was declared void after her husband proved it was a sapinda marriage and she did not come from a community where such marriages were customary.
- This decision was challenged in the Delhi High Court, which dismissed the appeal in October 2023.
- The woman then petitioned the High Court again, challenging the legality of the sapinda marriage ban.
- She claimed that sapinda marriages take place even when there is no evidence of custom.
- As a result, Section 5(v), which prohibits sapinda marriages unless an established custom exists, violates the right to equality guaranteed by Article 14 of the Constitution.
- The petitioner also claimed the marriage had received the consent of both families, demonstrating its legitimacy.
What are Sapinda Marriages?
- A sapinda marriage is one between two people who are related to each other to some extent.
- According to Section 3(f)(ii), “Two persons are said to be sapindas of each other if one is a lineal ascendant of the other within the limits of sapinda relationship, or if they have a common lineal ascendant who is within the limits of sapinda relationship with reference to each of them.”
- According to the Hindu Marriage Act (HMA), on the mother's side, a Hindu person cannot marry anyone within three generations of them in the "line of ascent".
- On the father's side, this prohibition applies to anyone within five generations of the individual.
- This means that on their mother's side, a person cannot marry their sibling (first generation), parents (second generation), grandparents (third generation), or anyone else who shares this ancestry within the three generations.
- On their father's side, this prohibition would apply to their grandparents' grandparents as well as anyone within five generations of this ancestry.
Exceptions to the Prohibition Against Sapinda Marriages?
- The only exception can be found within the same provision.
- An exception arises when the customs of the individuals involved permit sapinda marriages.
- The term "custom" is defined in Section 3(a) of the HMA.
- According to this section, a custom must have been consistently and uniformly practised for an extended period and must have gained sufficient recognition among Hindus in a specific locality, community, or family to be deemed legally binding.
Are Marriages Similar to Sapinda Marriages Allowed in Other Countries?
- In several European countries, the laws on relationships that are considered incestuous are less stringent than in India.
- In France, the crime of incest was abolished under the Penal Code of 1810, so long as the marriage was between consenting adults.
- Portuguese law also does not criminalise incest.
- Under Italian law, incest is a crime only if it causes a “public scandal”.
- In the United States, incestuous marriages are banned in all 50 states, though incestuous relationships between consenting adults are allowed in New Jersey and Rhode Island.
CSIR’s Republic Day Tableau highlights the Purple Revolution through Lavender Cultivation in Jammu & Kashmir (PIB)

- 27 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News?
The Council of Scientific & Industrial Research's Republic Day Tableau highlighted the unleashing of a Purple Revolution ushered through Lavender cultivation in Jammu & Kashmir.
What is the Purple Revolution?
- The Purple Revolution or Lavender Revolution, launched by the Ministry of Science & Technology, aims to promote the indigenous aromatic crop-based agro-economy through the ‘aroma mission’ of the Council of Scientific and Industrial Research (CSIR).
- The mission aims to increase the income of the farmers and promote lavender cultivation on a commercial scale.
- Lavender oil, which sells for, at least, Rs. 10,000 per litre, is the main commodity.
- Other popular products include medicines, incense sticks, soaps, and air fresheners.
- The cultivation of lavender is very cost-effective as it yields revenue immediately.
- Jammu and Kashmir’s climatic conditions are conducive to lavender cultivation since the aromatic plant can withstand both chilly winters and pleasant summers.
- Additionally, it is a low-maintenance crop, which can be used from its second year of plantation and blossoms for fifteen years.
- In its entirety, lavender production gives better returns when compared to other traditional crops.
- Under the One District One Product-Districts as Export Hubs (ODOP-DEH) initiative, lavender cultivation in Jammu and Kashmir has experienced a significant boom.
- Lavender has been designated by the central government as a "Doda brand product" to promote the rare aromatic plant and boost the morale of farmers, entrepreneurs, and agribusinesses involved in its cultivation as part of this Aroma Mission.
- The Aroma Mission through the Purple Revolution aims to bring about a revolutionary change in the fragrance industry, consequently promoting the expansion of the aroma sector and generating rural employment, through targeted interventions during cultivation, product refinement, market development and curating an expansion strategy for the lavender crop.
About Aroma Mission:
- The Aroma Mission, launched in 2016, aims to enhance the cultivation of plants like lavender, Aloe Vera, Mehndi, Menthol, and Mint, known for their aromatic and medicinal properties.
- Developed by the Council of Scientific & Industrial Research (CSIR), this mission employs new technologies.
- It seeks to revolutionize the aroma sector by improving agricultural practices, processing methods, and product development.
- Additionally, it provides technical and infrastructure support to farmers and growers nationwide, ensuring fair prices through buy-back mechanisms.
- The mission targets to expand cultivation by 30,000 hectares and catalyze aromatic crop cultivation in 60,000 hectares overall.
- This expansion is expected to yield an extra 700 tonnes of essential oils used in perfumery, cosmetics, and pharmaceuticals, creating a business worth at least 200 crores.
Interim Budget 2024: Exporters seek higher allocation for MAI scheme (Business Standard)

- 27 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News?
Ahead of the interim Budget 2024, exporters have urged the government to allocate funds worth $3.88 billion for the Market Access Initiative (MAI) scheme to promote Indian exports and help them hit the ambitious $2 trillion target by 2030.
What is the Market Access Initiatives (MAI) Scheme?
- The Market Access Initiative (MAI) Scheme is an Export Promotion Scheme envisaged to act as a catalyst to promote India’s exports on a sustained basis.
- The scheme is formulated on a focus product-focus country approach to evolve specific markets and specific products through market studies/surveys.
- Assistance would be provided to Export Promotion Organizations/Trade Promotion Organizations/National Level Institutions/ Research Institutions/Universities/Laboratories, Exporters etc., for enhancement of exports through accessing new markets or through increasing the share in the existing markets.
- Under the Scheme, the level of assistance for each eligible activity has been fixed.
- The following activities will be eligible for financial assistance under the Scheme:
- Marketing Projects Abroad
- Capacity Building
- Support for Statutory Compliances
- Studies
- Project Development
- Developing Foreign Trade Facilitation Web Portal
- To support Cottage and handicraft units
How does the MAI Scheme work?
- The scheme’s primary goal is to facilitate export growth by enabling entities to enter new markets or enhance their presence in existing markets.
- To accomplish this, the scheme provides predetermined levels of assistance for each eligible activity.
- By directing attention to key products and specific markets, the MAI Scheme serves as a catalyst for driving India’s export expansion in a sustainable and strategic manner.
Who is eligible to receive assistance under the MAI Scheme?
- Various entities are eligible to receive financial assistance under the MAI Scheme, including:
- Export promotion organizations
- Trade promotion organizations
- National level institutions
- Research institutions
- Universities
- Laboratories
- Individual exporters
- Start-ups
Who administers the MAI Scheme?
- The MAI Scheme is administered by the Ministry of Commerce and Industry, Government of India, through the Directorate General of Foreign Trade (DGFT).
Rare Golden Tiger takes a stroll in Assam’s Kaziranga National Park, video stuns people (HT)

- 27 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News?
A rare golden tiger was recently spotted in Kaziranga National Park taking a stroll and is the only known golden big cat in India.
What is a Golden Tiger?
- A Golden Tiger, also called a Golden Tabby Tiger, is a Bengal tiger with a unique colour variation caused by a recessive gene.
- The tiger looks golden because it has a mutation or a genetic variant.
- Basically, tigers have three colours: black, orange and white.
- In the Golden Tiger, the black colour is missing and it is slightly faded.
- The golden colouring of these tigers comes from a recessive trait called 'wideband,' affecting how black pigments are produced during hair growth.
- Golden tigers are not a distinct subspecies but rather a product of genetic diversity among Bengal tigers.
- They are extremely rare in the wild and even more so in captivity.
About Kaziranga National Park:
- Kaziranga National Park lies partly in the Golaghat District and partly in the Nagaon District of Assam.
- It is the oldest park in Assam and covers an area of 430 sq km along the river Brahmaputra on the North and the Karbi Anglong hills on the South.
- The National Highway 37 passes through the park area and tea estates, hemmed by table-top tea bushes.
- Kaziranga National Park a world heritage site is famous for the Great Indian one-horned rhinoceros, the landscape of Kaziranga is of sheer forest, tall elephant grass, rugged reeds, marshes & shallow pools.
- It was declared a National Park in 1974.
- It is one of the last areas in eastern India undisturbed by a human presence.
- It is inhabited by the world's largest population of one-horned rhinoceroses, as well as many mammals, including tigers, elephants, panthers and bears, and thousands of birds.
- Vegetation: Due to the difference in altitude between the eastern and western areas of the park, mainly four main types of vegetation’ like alluvial inundated grasslands, alluvial savanna woodlands, tropical moist mixed deciduous forests, and tropical semi-evergreen forests.
- Flora: Kumbhi, Indian gooseberry, cotton tree, and elephant Apple are among the famous trees that can be seen in the park.
- Fauna: The forest region of Kaziranga Park is home to the world’s largest population of Indian Rhinoceros.
- Other animals that can be seen in the elephant grass, marshland and dense tropical moist broadleaf forests of Kaziranga are Hoolock Gibbon, Tiger, Leopard, Indian Elephant, Sloth Bear, Wild water buffalo, swamp deer, etc.
- Also in this park the good number of migratory bird species from Central Asia.
- With the increase in tiger population every year, the government authorities declared Kaziranga a Tiger Reserve in the year 2006.
As Army launches Op Sarvashakti, recalling Sarpvinash of 2003, that crushed terror base in Pir Panjal (Indian Express)

- 25 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News?
The Army has launched Operation Sarvashakti in the Rajouri-Poonch sector of Jammu and Kashmir, deploying forces on both sides of the Pir Panjal range to target terrorists who have carried out a series of attacks on troops in the area.
What is Operation Sarvashakti?
- In a bid to combat increasing terrorist activities in Jammu and Kashmir, the Army has initiated Operation Sarvashakti, under which terrorists operating on both sides of the Pir Panjal mountain ranges in the Union Territory will be neutralised.
- There were three major attacks on the security forces in 2023, and over the past few years, 20 soldiers have been killed in terrorist ambushes in this area.
- Operation Sarvashakti, as part of which at least three brigades of additional troops are being deployed in the sector from various reserve and strike corps formations in order to increase the density of troops and, therefore, the likelihood of contact with terrorists, recalls an earlier operation by the Army in the same forests more than two decades ago.
- Back in 2003, Indian forces launched Operation Sarpvinash to flush out terrorists who had infiltrated from across the border and set up camps in the thick forests south of the Pir Panjal range, especially in the Hilkaka area in Poonch.
What was Operation Sarpvinash?
- Operation Sarpvinash, launched in April 2003, marked a significant counter-insurgency effort in Jammu and Kashmir.
- In response to intelligence indicating over 300 foreign terrorists establishing secure camps in Surankote and Hilkaka post-infiltration across the Line of Control (LoC), the three-month-long operation involved 10,000 troops in a challenging 150 sq km area.
- Employing helicopters and ground forces, the operation neutralized approximately 100 terrorists, dismantled bunkers, and recovered weapons, explosives, and supplies.
- Operation Sarpvinash successfully restored peace to the region until 2017-18, impacting the region's security dynamics.
- However, since 2021, there has been a resurgence of high-intensity attacks on security forces in this area.
Why is this area important strategically?
- The areas south of Mendhar leading to the Pir Panjal range through Hilkaka constitute among the shortest routes of access for infiltrators from across the LoC into the Kashmir valley.
- The terrorists chose this region to set up camps because dominating this area can potentially provide a conduit to personnel in the event of a military operation by the Pakistanis, and easier infiltration of terrorists.
- The dense forests and steep mountain slopes offer both adequate cover and visual domination of the area.
- Terrorists were able to merge with the foliage whenever Indian troops carried out searches in the area and inflicted casualties in case of contact.
- All of these locational advantages for terrorists remain intact to some degree even now.
Centre approves incentive of Rs 8,500 crore for coal gasification projects (Indian Express)

- 25 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News?
In a bid to achieve the target of coal gasification of 100 million tonnes (MT) of coal by 2023 in India, the government recently approved Rs 8,500 crore incentives.
What is Coal Gasification?
- Coal gasification is a thermo-chemical procedure wherein the pressure and heat of the gasifier disintegrate coal into its chemical components.
- The resulting "syngas" are mostly carbon monoxide (CO) and hydrogen, with some other gaseous substances thrown in for good measure.
- Coal gasification is an in-situ method wherein oxygen is infused into the seam together with water and ignited at high temperatures, causing coal to partly oxidised into hydrogen, CO, carbon dioxide (CO2), methane (CH4), and hydrogen sulphide (H2S).
- Ex-situ reactors are designed to simulate the gasification process above the ground's surface.
- Sulphur in coal is transformed to H2S and trace volumes of carbonyl sulphide during the gasification process (COS).
- Acid gas removal technology can easily and cost-effectively discard these sulphur compounds.
- There is no scrubber sludge produced by coal gasification plants, which necessitates careful and expensive disposal.
- The majority of the wash water is reprocessed, and residual wastewater from gasification plants can be treated effectively.
- As a result, coal gasification is regarded as a cleaner coal technology when compared to coal combustion.
- Furthermore, coal could be used to generate a range of products using clean coal innovations such as hydrogen, methanol, and fertilisers via coal gasification.
- Carbon fibres and plastic composites made from coal power plant ash/residue.
How can it be used?
- Syngas, according to proponents of coal gasification, can be used to generate power, in energy-efficient fuel cell technology, or as chemical "building components" for industrial applications.
- The hydrogen can also be extracted and used to power a hydrogen economy.
- Coal gas can also be transformed into a transportation fuel to be used in automobiles as a replacement for gasoline, but it is less efficient than the current output and combustion of petroleum-based gasoline.
- Coal gasification is said to be more efficient than traditional coal burning since it can use the gases two times: the coal gases are first purified of contaminants before being fired inside a turbine to produce energy.
- The gas turbine exhaust heat can be then collected and used to produce steam for a steam turbine generator.
- This is known as a combined process, and according to DOE, a coal gasification processing facility using this dual method can possibly attain an efficiency of 50% or higher, compared to the customary coal power plant, which is typically just above 30%.
Significance of Coal Gasification:
- India announced environmental targets as its Nationally Determined Contribution (NDC) under the Paris Agreement in 2016.
- In order to meet these objectives, coal gasification aids in the decrease of emission levels and the advancement of non-fossil fuel-based energy resources.
- The syngas produced by coal gasification can be used to generate urea and a variety of products such as methanol, Dimethyl ether (DME), and olefins, allowing India to minimise imports and become self-sufficient.
- Syngas CO and H2 are essential reducing agents for steel production and are regarded as an environmentally friendly technique of steel production because they reduce the import of furnace oil.
- India has ambitious plans to produce active pharmaceutical ingredients (API) domestically rather than importing them from China.
- As a result, the potential of Syngas requirement for making APIs, as well as methanol as a solvent, is being investigated.
- The synthesis gas can be used in an Integrated Gasification Combined Cycle (IGCC) system to generate electricity in an efficient and environmentally friendly manner.
Initiatives taken by India:
- The Ministry of Coal, through Atmanirbhar Bharat Abhiyaan, has taken the initiative, National Coal Gasification Mission, that is to utilise coal through coal gasification, with the goal of achieving 100 MT coal gasification by 2030.
- It has also been recommended that all coal companies assign a nodal officer and formulate a plan for gasifying at least 10 per cent of their coal production.
- SHAKTI policy was implemented in coal gasification projects to minimise operating costs by allocating long-term coal linkages through auction.
What is National Voters’ Day?: Govt plans events around theme for 2024 (Indian Express)

- 25 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News?
India today is celebrating its 14th National Voters’ Day. It is celebrated annually on January 25 since 2011 to mark the foundation day of the Election Commission of India. The ECI was founded on January 25, 1950.
Why is National Voters’ Day celebrated?
- National Voters’ Day aims to promote people’s participation in elections by encouraging and felicitating young voters and increasing voter enrolment.
- It is also utilised to spread awareness among voters and to promote informed participation in the electoral process.
- The day is celebrated at the national, state, district, constituency and polling booth levels, which makes it one of the largest celebrations in the country.
- The date chosen for National Voters' Day commemorates the formation of the Election Commission of India (ECI) on January 25, 1950.
- The ECI is an autonomous constitutional body under Article 324 entrusted with the sacred responsibility of conducting free, fair, and credible elections across the country.
- Since its inception, the ECI has played a pivotal role in upholding the democratic principles of India, ensuring the voice of every citizen is heard.
- The first National Voters’ Day was celebrated in 2011 under the leadership of the then Chief Election Commissioner (CEC) S Y Quraishi.
- Emulating India’s example, six countries, including Sri Lanka, Pakistan, Nepal and Bhutan, have started celebrating National Voters Day.
- National Voters’ Day pledge: As a part of the celebrations, all government offices, autonomous bodies, and organisations take a pledge on the day.
- Schools and educational Institutions across the country are encouraged to conduct activities such as debates, discussions, and competitions on the theme of Voters’ Day.
What is the theme for National Voters’ Day 2024?
- The theme for this year is ‘Nothing Like Voting, I Vote For Sure’, which is a continuation of last year’s theme, and conveys an individual’s feeling and aspiration towards participation in the electoral process through the power of their vote.
- The logo for this year’s theme is designed in such a way that it showcases the festivity and inclusivity of the electoral process.
- The Ashoka Chakra in the background represents the largest democracy in the world, whereas the inked finger represents the participation of each and every voter of the country.
- The tick mark in the logo stands for informed decision-making by the voter.
A shallow lake in Canada could reveal how life on Earth began (Space.com)

- 25 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News?
Scientists have discovered a lake that could be a good match for Darwin's "warm little ponds" where life got started on the primordial Earth.
What is a Soda Lake?
- A soda lake is a lake with a pH value of more than the usual measure of 6 or 7, usually between 9 and 11.
- High carbonate concentration, especially sodium carbonate, is responsible for the alkalinity of the water.
- A soda lake may also contain a high concentration of sodium chloride and other salts making it saline or hypersaline Lake.
- Soda lakes are highly productive ecosystems compared to freshwater lakes with a global primary production rate of over 10 grams of carbon per square meter per day.
- Therefore Soda lakes are the most productive aquatic environment on Earth because of the availability of dissolved carbon dioxide.
- Soda lakes occur naturally in both arid and semi-arid areas.
Geology And Genesis Of Soda Lakes:
- A topography that limits the outflow of water from the lake is needed.
- An endorheic basin is formed when the water is confined without the outflow.
- The pH of the water in the depression rises through the evaporation of the lake which requires a suitable climate like the desert climate to balance between the inflow and evaporation.
- The rate at which carbonate salt dissolves in the lake water depends on the ecology of the surrounding area.
- The relative absence of magnesium and calcium is critical in the formation of the soda lake since magnesium or calcium is likely to dissolve quickly and displace the carbonate ion thus neutralizing the PH of the lake water.
Biodiversity Of Soda Lakes:
- Soda lakes are inhabited by a rich diversity of microbial life making them a productive ecosystem.
- They are permanent and seasonal habitats for algae which are visible in many of the lakes.
- Soda lakes are dominated by prokaryotes like bacteria and archaea, especially in lakes with higher levels of alkalinity.
- Multicellular organisms such as brine shrimp and fish are found in plenty if not most of the soda lakes.
- Soda lakes also harbour unique species which are adapted to the alkali conditions.
- These organisms which are adapted to the high alkalinity are called haloalkaliphiles.
Examples Of Soda Lakes:
- Africa and Asia have the highest number of soda lakes since the two continents have vast desert conditions which are perfect for the formation of soda lakes.
- Most of the soda lakes in Africa are located in Eastern Africa, especially in Kenya, Tanzania, and Ethiopia.
- Lake Natron in Tanzania is one of the most outstanding soda lakes in Africa because of the high PH of water which is always about 12.
- India and China have the highest number of soda lakes in Asia.
- Some of the soda lakes in India include Tso Kar Salt Lake, Pangong Salt Lake, and Lonar Lake.
NFRA to inspect Big 4, others in 2024 too (Financial Express)

- 25 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News?
The National Financial Reporting Authority (NFRA) is going to inspect the Big Four audit firms as well as other top auditors of large listed entities in 2024, an official familiar with the development told FE.
What is the National Financial Reporting Authority (NFRA)?
- The National Financial Reporting Authority (NFRA) is a statutory body and was constituted on 1st October 2018 by the Government of India under Sub Section (1) of section 132 of the Companies Act, 2013.
- It is responsible for setting accounting standards in the country.
- The Punjab National Bank fraud prompted the government to establish an NFRA as the legal regulator for the auditing profession.
- Its mandate is to improve the quality and consistency of financial statements in the country and ensure that businesses and financial institutions disclose accurate and fair information.
- The National Financial Reporting Authority (NFRA) is located in New Delhi.
- The chairperson since March 2022 is Ajay Bhushan Pandey.
- The NFRA can probe listed as well as unlisted public companies.
- Companies must have a paid-up capital of ?500 crores and an annual turnover of ?1,000 crores.
Functions and Duties:
- As per Sub Section (2) of Section 132 of the Companies Act, 2013, the duties of the NFRA are to:
- Recommend accounting and auditing policies and standards to be adopted by companies for approval by the Central Government;
- Monitor and enforce compliance with accounting standards and auditing standards;
- Oversee the quality of service of the professions associated with ensuring compliance with such standards and suggest measures for improvement in the quality of service;
- Perform such other functions and duties as may be necessary or incidental to the aforesaid functions and duties.
Composition of the NFRA:
- As mandated by the Companies Act, NFRA is comprised of a chairperson appointed by the Central Government and a maximum of 15 members.
- The individuals selected for these roles must possess expertise in accountancy, auditing, finance, or law.
- Furthermore, they are required to declare to the Central Government that there is no conflict of interest or lack of independence in their appointment.
Membership Qualifications:
- All members, including the chairperson, who are in full-time employment, are prohibited from association with any audit firm (including related consultancy firms) during their term of office and for a period of two years after the completion of their term.
Powers of the NFRA:
- The NFRA has the same powers as the Civil Court.
- The NFRA has the authority to investigate matters of misconduct involving CAs and Chartered Accountants.
- It can impose a penalty of not less than ?1 lakh but not exceeding 5 times the fees collected.
- Also, the NFRA may also investigate and take action against individuals who violate the rules of professional conduct.
- It has the power to initiate investigations on its own and upon referral from the Central Government.
India overtakes Hong Kong as the world’s fourth-largest stock market by market capitalisation (Live Mint)

- 24 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News?
Recently, India’s stock market has overtaken Hong Kong’s to rank as the fourth-biggest equity market globally for the first time.
News Summary:
- As of January 22, 2024, data compiled by Bloomberg indicates that the combined value of shares listed on Indian exchanges has reached USD 4.33 trillion, surpassing Hong Kong's USD 4.29 trillion.
- The top three global stock markets are currently the United States, China, and Japan.
What is Stock Market?
- A stock market is a platform where individual and institutional investors trade various securities, including stocks, bonds, Exchange Traded Funds (ETFs), and derivatives.
- Stock markets are categorized into two types:
- Primary Market: Involves the initial offering of new shares, bonds, etc.
- Secondary Market: Encompasses the trading of existing securities like equities and bonds.
- Examples include stock exchanges such as the Bombay Stock Exchange.
Importance of Stock Market:
- For Businesses: Facilitates access to capital, risk diversification, and supports business expansion.
- For Investors: Offers better returns compared to traditional savings instruments, provides tax benefits, and contributes to capital growth.
- For Society: Drives social impact through instruments like Social Impact Bonds, encourages sustainable investment via Green bonds and promotes responsible financial practices.
- For Economy: Mobilizes idle savings, fosters entrepreneurship through venture capital funds, and plays a vital role in economic development.
Challenges in Indian Stock Markets:
- High Volatility: Market fluctuations can be significant, posing challenges for investors.
- Limited Issuer and Investor Base: Constraints on both issuers and investors can adversely impact liquidity.
- Sub-optimal Corporate Debt Market: Dominance of government bonds hampers the growth of the corporate debt market.
- Other Issues: Various factors, such as regulatory complexities and market inefficiencies, can affect the optimal functioning of Indian stock markets.
How is the Stock Market Regulated in India?
- The stock market in India is regulated by various bodies, with the primary regulatory authority being the Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI).
- SEBI is a statutory regulatory body established in 1992 to protect the interests of investors and promote the development of the securities market in India.
- It operates under the Securities and Exchange Board of India Act, 1992.
- Also, while SEBI is the primary regulatory authority for the Indian stock market, the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) supports its efforts by ensuring overall financial stability, implementing monetary policies, and regulating aspects related to banking and foreign investments.
- Additionally, these bodies contribute to the nation's economic progress by facilitating capital formation.
What is end-to-end encryption? How does it secure information? (The Hindu)
- 24 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News?
There are several ways to encrypt information depending on the level of secrecy and protection required.
What is End-to-end Encryption (E2EE)?
- End-to-end encryption (E2EE) is a type of messaging that keeps messages private from everyone, including the messaging service.
- When E2EE is used, a message only appears in decrypted form for the person sending the message and the person receiving the message.
- The sender is one "end" of the conversation and the recipient is the other "end"; hence the name "end-to-end."
How Does Encryption Work?
- Encryption works by altering data so that only someone who possesses a specific piece of knowledge — known as the key — can interpret the data.
- Keys can take different forms in different contexts.
- With communications over the Internet, a key is a string of bits that plays a role in the complex mathematical equations used to scramble and unscramble data.
- With E2EE, the key that can encrypt and decrypt messages remains saved on a user's device.
What Kind of Encryption Does E2EE Use?
- End-to-end encryption uses a specialized form of encryption called public key encryption (also sometimes called asymmetric encryption).
- Public key encryption enables two parties to communicate without having to send the secret key over an insecure channel.
- Public key encryption relies on using two keys instead of one: a public key and a private key.
- While anyone, including the messaging service, can view the public key, only one person knows the private key.
- Data encrypted with the public key can only be decrypted with the private key (not the public key).
- This contrasts with symmetric encryption, where only one key is used to both encrypt and decrypt.
How Does End-to-end Encryption Support Privacy?
- E2EE ensures that no one can see messages except for the two people who are communicating with each other.
- When implemented properly, it does not require users to trust that a service will handle their data properly.
- Thus, E2EE gives people total control over who can read their messages, enabling them to keep their messages private.
What are the Limitations of End-to-end Encryption?
- E2EE keeps messages secure in transit (as they pass from one person to another).
- But it does not protect messages once they reach their destination.
- E2EE is not guaranteed to be future-proof. When implemented correctly, modern encryption methods are strong enough to resist encryption-breaking efforts from even the most powerful computers in the world.
- But the more powerful in the future like Quantum computers, if developed, would be able to crack modern encryption algorithms.
- Using E2EE keeps messages secure in the present, but it may not keep them secure permanently.
Karpoori Thakur’s vision of social justice inspires our governance model: PM Modi (The Hindu)

- 24 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News?
Former Bihar CM Karpoori Thakur will be awarded India's highest civilian award, Bharat Ratna, posthumously.
About Jan Nayak Karpoori Thakur:
Pre-Independence Influence:
- Inspired by Mahatma Gandhi and Satyanarayan Sinha, Karpuri Thakur actively participated in the Quit India Movement in 1942 during his schooling days.
- Aligned with the All India Students Federation (AISF), he left his graduation studies to join the movement for India's independence.
Post-Independence Contributions:
- Commencing his career as a village teacher, Thakur re-entered politics, winning the Bihar Legislative Assembly election in 1952 from the Tajpur constituency.
- Notable for his representation of the Socialist Party, he gained legendary status for championing workers' rights and advocating for reservations for backward classes.
- He launched a fast-unto-death agitation in 1970 for labourers' rights at Telco, leading worker strikes and facing arrest.
Key Contributions:
- Social Justice: Thakur dedicated his political journey to addressing systemic inequalities, striving for fair resource distribution and equal opportunities for all.
- OBC Politics: Recognized as the pioneer of OBC politics in Bihar, he implemented quotas for backward classes, laying the foundation for Mandal Commission recommendations.
- Affirmative Action: Strengthened affirmative action for backward classes, ensuring representation and opportunities deserving of their status.
- Selflessness: As Chief Minister, he refrained from benefiting personally from a scheme meant for political leaders' colonies.
- Alcohol Ban: Implemented a comprehensive ban on alcohol in Bihar in 1970.
- Education: Instrumental in establishing schools and colleges, particularly in underdeveloped regions, to make education accessible to historically marginalized communities.
The need to overhaul a semiconductor scheme (The Hindu)
- 24 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News?
The semiconductor Design-Linked Incentive (DLI) scheme, set to undergo a mid-term appraisal, has so far approved only seven start-ups, falling significantly short of its intended goal of supporting 100 over a span of five years since its announcement.
About Design-Linked Incentive (DLI) Scheme:
- Under the DLI scheme, government will provide financial incentives and design infrastructure to domestic companies, start-ups and MSMEs focussed on semiconductor design.
- The DLI scheme has been announced by the Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology (MeitY) to offset the disabilities in the domestic industry involved in semiconductor design in order to not only move up in value-chain but also strengthen the semiconductor chip design ecosystem in the country.
- C-DAC (Centre for Development of Advanced Computing), a scientific society operating under MeitY, will serve as the nodal agency for implementation of the DLI scheme.
Objectives:
-
- Nurturing and facilitating the growth of the domestic companies, startups and MSMEs.
- Achieving significant indigenization in semiconductor content and IPs involved in the electronic products deployed in the country, thereby facilitating import substitution and value addition in the electronics sector.
- Strengthening and facilitating access to semiconductor design infrastructure for startups and MSMEs.
Duration: The scheme shall initially be for three (3) years from 01-01-2022.
- The scheme has three components – Chip Design infrastructure support, Product Design Linked Incentive and Deployment Linked Incentive.
- Under the Chip Design infrastructure support, C-DAC will set the India Chip Centre to host the state-of-the-art design infrastructure (viz. EDA Tools, IP Cores and support for MPW (Multi Project Wafer fabrication) & post-silicon validation) and facilitate its access to supported companies.
- Under the Product Design Linked Incentive component, reimbursement of up to 50% of the eligible expenditure subject to a ceiling of ?15 Crore per application will be provided as fiscal support to the approved applicants who are engaged in semiconductor design.
- Under the Deployment Linked Incentive component, an incentive of 6% to 4% of net sales turnover over 5 years subject to a ceiling of ?30 Crore per application will be provided to approved applicants whose semiconductor design for Integrated Circuits (ICs), Chipsets, System on Chips (SoCs), Systems & IP Cores and semiconductor linked design are deployed in electronic products.
- The DLI Scheme will also take a graded and pre-emptive approach to Identify the Products of national priorities and implement strategies for their complete or near complete indigenisation & deployment thereby taking steps towards the import substitution & value addition in strategic & societal sectors.
Rahul Gandhi prevented from visiting Batadrava Than Significance of this Assam shrine (Indian Express)

- 24 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News?
Congress leader Rahul Gandhi recently prevented from visiting Assam’s Batadrava Than, where he was going as part of his Bharat Jodo Nyay Yatra.
What is the Batadrava Than?
- The Batadrava Than, or Bordowa Than, is a temple complex at the birthplace of revered Vaishnavite reformer-saint Srimanta Sankardeva (1449-1568).
- Located in Nagaon district, the Batadrava Than, or Bordowa Than, is one of the most sacred sites for Assamese Vaishnavites.
- Sankardeva founded the first-ever Kirtan Ghar at Bordowa in 1494 AD to practise and preach the neo-Vaishnavite faith during the fifteenth century in Assam and propagated the Ek Saran Naam Dharma.
- Various structures within the campus include Natghar (drama hall), Alohighar (guest room), Sabhaghar (assembly hall), Rabhaghar (music room), Hatipukhuri, Aakashi Ganga, Doul mandir (festive temple), and more.
- There is also a mini-museum displaying historical articles and artefacts.
- Bordowa Than has a history of disputes over ownership, leading to its division into two satras: Narowa and Salaguri. In 1958, it was reunified under the banner of 'Bordowa Than,' with both former Satras combined, and a single Namghar was established.
What was Srimanta Sankardeva’s Philosophy?
- He propagated the Ek Saran Naam Dharma.
- The Ek Saran Naam Dharma focussed on worship in the form of bhakti (devotion) to Lord Krishna, through singing and congregational listening of His name and deeds.
- Sankardeva espoused a society based on equality and fraternity, free from caste differences, orthodox Brahmanical rituals and sacrifices.
- His teaching focused on prayer and chanting (naam) instead of idol worship. His dharma was based on the four components of deva (god), naam (prayers), bhakats (devotees), and guru (teacher).
- The Neo-Vaishnavite reformist movement that Sankardeva started is behind the monastic institutions called Thans/Sattras that dot Assam.
- As the saint travelled across Assam, spreading his teachings, these Sattras/Thans were established as centres of religious, social and cultural reforms in the 16th century.
- Today, the Sattras promulgate Sankardeva’s unique “worship through art” approach with music (borgeet), dance (xattriya) and theatre (bhauna).
- Each Sattra has a naamghar (worship hall) as its nucleus and is headed by an influential “Sattradhikar”.
Literary Contributions:
- Srimanta Sankardev's significant literary works include 'Kirtan Ghosa' and 'Gunamala.'
- He is credited with composing sacred songs known as 'Borgeet.'
- His penned dramas, recognized as 'Ankia Naat,' featured Sattriya Dance as an integral component during that era.
- In these 'Ankia Naats,' Srimanta Sankardev employed a narrative style through drama, often portraying the lives of Lord Krishna and Lord Rama.
- His inaugural dramatic piece was 'Chihnajatra,' followed by others like 'Kaliya Daman' and 'Patni Prasad.'
- Remarkably, at the age of twelve, when he commenced formal education, he crafted a poem extolling Lord Vishnu titled 'Karatala Kamala Kamala Dala Nayana.'
- Notably, during this early phase, he composed the poem using only consonants, having not yet learned about vowels.
First meeting of Social Audit Advisory Body reviews social justice schemes (ET)

- 23 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News?
The first meeting of the Social Audit Advisory Body (SAAB) was held last week at the conference hall, Dr Ambedkar International Centre, New Delhi.
What is the Social Audit Advisory Body (SAAB)?
- Social Audit Advisory Body (SAAB) is a first-of-its-kind advisory body in India.
- It is set up under the National Institute of Social Defence (NISD), which functions under the Department of Social Justice & Empowerment (DoSJE), Ministry of Social Justice and Empowerment.
- It will guide the Ministry as it institutionalizes social audits for each of its programs.
- It will support the Social Justice Cell of the Social Audit Unit members in developing their abilities.
What is a Social Audit:?
- A social audit is a procedure that involves looking over and evaluating a plan or program.
- People actively participate in the process, which involves comparing government data with actual ground realities.
- Important tenets of SA include:
- Protection of citizens (Suraksha)
- Participation (Bhagidari), and
- Information access (Jaankari).
Implementation of Social Audit:
- The Mahatma Gandhi National Rural Employment Guarantee Act (MGNREGA), among other hallmark programs, now include the provision of Social Audit (SA) with the efforts of the Union Government.
- In order to guarantee SA through specialized Social Audit Units at the state level, DoSJE developed the National Resource Cell for Social Audit (NRCSA).
- The first state to put a social audit statute into effect was Meghalaya.
Significance: Promote transparency and accountability,
-
- strengthen institutions at the grassroots level etc.
Challenges: Lack of awareness among stakeholders, apathetic attitude of implementing agency etc.
Steps for SocialAudit:
- Orientation and Sensitization:: Conducted by the implementing agency.
- Presentation: Creating a social audit team.
- Verification: Verifying information with beneficiaries, inmates, stakeholders, and institution staff.
- Validation: Presenting the initial report for validation.
- Presentation and Action: Sharing findings at the district level with all stakeholders present.
Restoring Lake Victoria: CSE, Tanzanian authorities hold multi-nation stakeholder consultation (DownToEarth)
- 23 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News?
Lake Victoria, the largest freshwater lake in Africa and the world’s second-largest faces numerous environmental challenges that demand collective efforts for restoration and conservation.
About Lake Victoria:
Geography:
- Located in East Africa and bordered by Tanzania, Uganda, and Kenya.
- Africa's largest lake by area (approximately 59,947 km²) and the world's second-largest freshwater lake after Lake Superior.
- Lies in a shallow depression within the East African Rift Valley.
- The average depth of 40 meters, maximum depth of 80-81 meters.
Hydrology:
- The main source of water is rainfall, supplemented by rivers like the Kagera.
- The only outlet is the Victoria Nile, which flows into the White Nile and ultimately the Nile River.
- Plays a crucial role in the water supply and livelihoods of millions of people in East Africa.
Ecology:
- Supports a diverse ecosystem with over 200 fish species, including the Nile perch and Nile tilapia.
- Important habitat for birds, reptiles, and amphibians.
- Facing challenges like pollution, overfishing, and invasive species.
History and Culture:
- Named after Queen Victoria by British explorer John Hanning Speke in 1858.
- Has been a vital source of transportation, trade, and food for centuries.
- Plays a significant role in the cultural traditions and folklore of the surrounding communities.
With no iron or steel, Ayodhya temple is a study in sandstone (The Hindu)
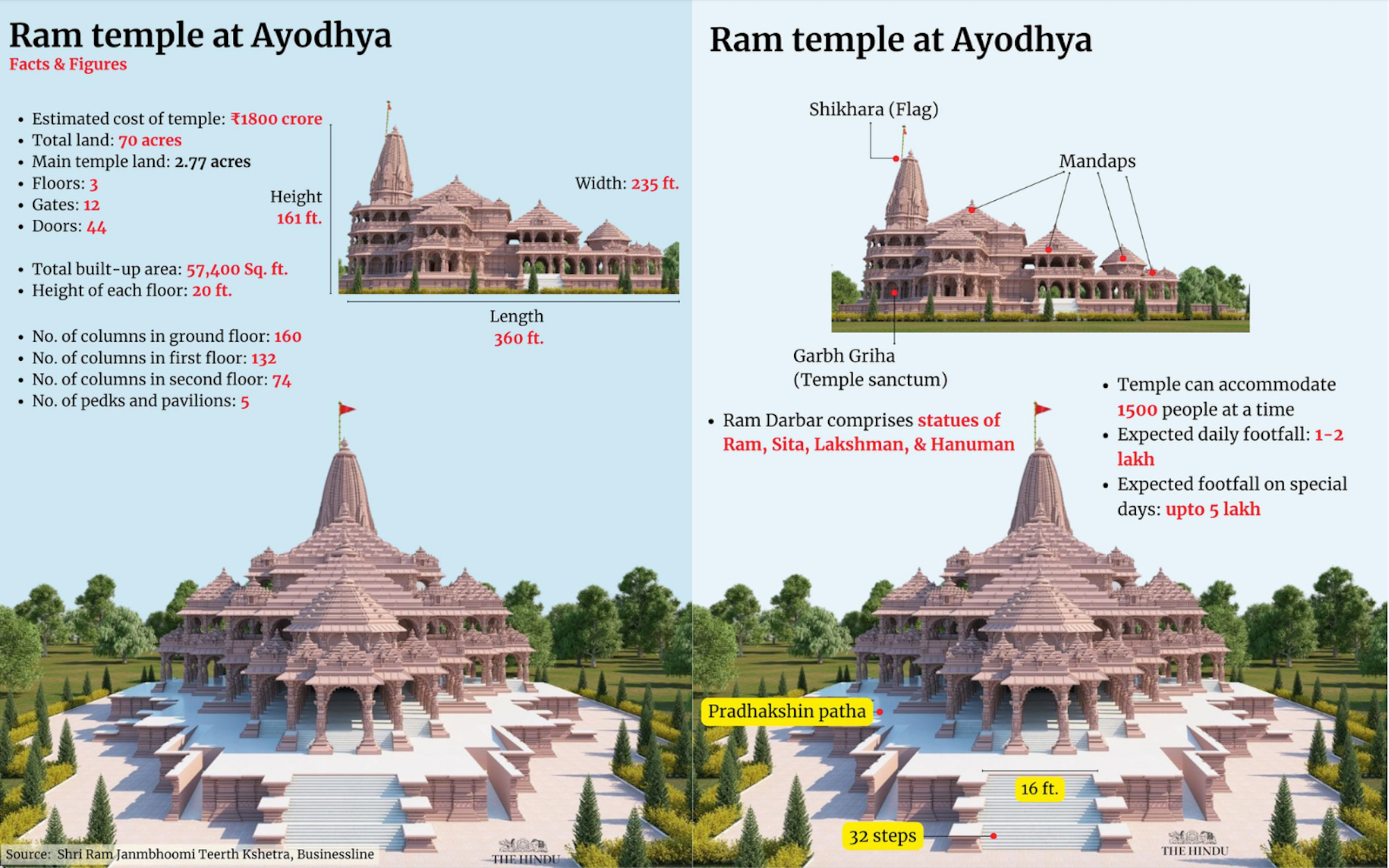
- 23 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News?
A new landmark of India — both structural and spiritual — rose on Ayodhya's horizon on January 22 in the form of a new-age architectural marvel of elegant sandstones, diligently carved by craftspeople with dedication and devotion to Lord Ram.
Major Features of the Ram Temple:
- No iron or steel has been used in the construction of the grand structure.
- Stones have been sourced from Rajasthan's Bansi Paharpur area.
- The entire temple superstructure will eventually be three storeys — ground plus two floors.
- Nagara style: The temple complex, built in the traditional Nagara style, will be 380 feet long from the east to the west, 250 feet wide and 161 feet high.
- Each floor of the temple will be 20 feet high and have a total of 392 pillars and 44 gates.
- Images of Lord Hanuman, other deities, peacocks and flower patterns have been carved onto the stones, lending the structure a divine look.
- Unique feature: Around the grand temple is a rectangular periphery called percota, a feature found in temples in south India, but not generally in north India.
- The percota will be 14 feet wide and the periphery span 732 metres.
- The temple will be nestled within the percota periphery.
- Ornate statues of elephants, lions, Lord Hanuman and Garuda were installed at the main entrance leading to the temple.
- These statues have also been made using sandstone brought from Bansi Paharpur.
- An ancient Shiva temple that exists on the Kuber Tila has also been revitalised.
- Green Complex: About 70 per cent of the complex will be a green area.
- "The green area includes portions which are very dense and, in some segments, even sunlight hardly filters through.
- The complex will have two sewage treatment plants — a water treatment plant and a dedicated electricity line from the powerhouse.
- The fire brigade post will be able to source water from an underground reservoir.
Additional Architectural Aspects:
- A time capsule, located approximately 2,000 feet below the ground beneath the temple, houses a copper plate inscribed with pertinent information about the Ram Mandir, Lord Rama, and Ayodhya.
- The objective of this time capsule is to preserve the temple's identity for posterity, preventing it from fading into obscurity in the years to come.
- Engineered as an earthquake-resistant structure, the temple boasts an estimated age of 2500 years.
PM Modi extends his greetings to the people of India on Parakram Diwas (Indian Express)

- 23 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News?
Prime Minister Narendra Modi extended greetings to the people of India on Parakram Diwas on 23rd January.
Why Parakram Diwas is Celebrated?
- The government officially announced on January 19, 2021, that January 23 be observed as Parakram Diwas in order to pay tribute to Netaji’s relentless pursuit of India’s freedom.
- The government of India has decided to celebrate his birthday on the 23rd day of January every year as “PARAKRAM DIWAS” to inspire people of the country, especially the youth, to act with fortitude in the face of adversity as Netaji did, and to infuse in them a spirit of patriotic fervour,” the Centre had said in a notification.
- Parakram Diwas, which translates to “Day of Valour”.
- In 2021, the first event took place at Victoria Memorial Hall, Kolkata.
- In 2022, a hologram statue of Netaji was unveiled at India Gate, and in 2023, the 21 largest unnamed islands of Andaman & Nicobar Islands were named after the 21 Param Vir Chakra awardees and a model of National Memorial dedicated to Netaji which was supposed to be built on Netaji Subhas Chandra Bose Dweep, was unveiled.
Key Facts About Subhas Chandra Bose:
- Born on January 23, 1897, in Cuttack, Orissa.
- In 1920, he successfully passed the civil service examination but resigned from his position in April 1921 after learning about the nationalist turmoil in India.
- A prominent Indian nationalist leader, he played a pivotal role in the Indian independence movement against British colonial rule.
- Joined the Indian National Congress and actively participated in the struggle for independence.
- Elected president of the Indian National Congress for two consecutive terms but resigned due to ideological conflicts with Mahatma Gandhi.
- In 1939, Bose founded the Forward Bloc, an organization aimed at unifying anti-British forces in India.
- Fled from India at the beginning of World War II, travelling to the Soviet Union, Germany, and Japan in pursuit of an alliance against British forces in India.
- With Japanese assistance, reorganized and led the Indian National Army, comprising Indian prisoners-of-war and plantation workers from Southeast Asia.
- Established the Azad Hind Government in exile with Japanese support, leading the Indian National Army in battles against the allies in Imphal and Burma.
PM Modi announces solar roof-top scheme for one crore households (HT)

- 23 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News?
Prime Minister Narendra Modi on Monday announced the 'Pradhan Mantri Suryodaya Yojana' under which one crore households will get rooftop solar across the nation.
What is 'Pradhan Mantri Suryodaya Yojana'?
- The scheme aims to equip one crore poor to middle-class households with rooftop solar panels in a bit to provide electricity from solar energy.
- The scheme would not only reduce the electricity bill of the poor and middle class but would also make India self-reliant in the energy sector.
- Rooftop solar panels are the photovoltaic panels installed on the roof of a building which is connected to the main power supply unit.
- Thus, it reduces the consumption of grid-connected electricity and saves electricity costs for the consumer.
- In a solar rooftop system, there is only an upfront capital investment and minimal cost for maintenance.
- Under this scheme, one crore households will get solar rooftops.
- Moreover, it will offer additional income for surplus electricity generation.
- The consumer can choose any vendor on the national portal and after installation, the subsidy is sent directly to the bank account of the consumer.
- The Pradhanmantri Suryodaya Yojana is a new scheme but very similar to the previously announced Rooftop Solar Programme in 2014.
- The previous scheme had aimed to produce 40,000 megawatts (MW) or 40 gigawatts (GW) of solar power by 2022.
India's Advancements in Solar Energy:
- At the end of last year, 2023, India’s solar power generation stood at 73.31 GW, up from 2022’s 63.3 GW.
- However, rooftop solar power generation only stands at around 11.08 GW as of December 2023.
- The total solar power generated in the nation, Rajasthan leads the pack with 18.7 GW while Gujarat follows with 10.5 GW.
- However, when talking about rooftop solar power, Gujarat is at peak position — with 2.8 GW — followed by Maharashtra at 1.7 GW.
- India has more than 300 million households and an average of 300 sunny days each year, which has tremendous potential for rooftop solar installations in residential spaces.
- However, experts note that despite several measures, India’s rooftop solar power generation is not where it should be, listing reasons for the situation.
- The primary reason for rooftop solar not becoming popular is that it is still an expensive option for many.
- There is also a lack of awareness.
Importance of Solar Power to India:
- Harnessing the power of the sun to generate electricity is important to India for multiple reasons.
- If India wants to achieve its aim of becoming net zero by 2070, it has to look towards the sun.
- In fact, at COP26, in November 2021, India committed to meet 50 per cent of its electricity requirements from renewable energy sources by 2030.
- For these aims to be met, India has to harness the full capacity of the sun.
- Moreover, India’s share of global energy demand is predicted to double to 11 per cent in 2040, making it imperative to enhance energy security and self-sufficiency in power generation without increasing environmental costs.
- This increase in power demand is likely to increase India’s reliance on coal, oil and natural gas as a source of energy.
- However, additional imports of oil and increased domestic production of coal will not only fall short of energy demand but will also entail economic and environmental costs.
- The expansion of solar power units and increased reliance on solar power allow India to enhance energy security in the face of rising demand.
- Furthermore, India is already facing depleting groundwater levels, owing to which the nation must shift its energy resources away from water.
Davos meeting 2024: 5 key takeaways (Indian Express)

- 22 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News?
This year’s edition of the World Economic Forum (WEF) annual meeting was held from January 15 to January 19.
Key Highlights from Davos Meeting 2024:
- Artificial Intelligence (AI): The focal point of discussion at this year's World Economic Forum (WEF) meeting was Artificial Intelligence (AI).
- Conversations delved into its transformative potential for human welfare, addressing concerns such as the necessity for regulation, apprehensions about job losses, risks associated with impersonation and misinformation, and the potential exacerbation of inequalities.
- Despite acknowledging these challenges, participants generally agreed that the positive aspects of AI outweigh the negatives, with no substantial threat to human intelligence.
- War and Uncertainty: The summit underscored the risks emanating from a delicate geopolitical landscape, ongoing conflicts in the Middle East and Europe, threats to global supply chains, and uncertainties surrounding food security.
- Notably, the head of the Palestine Investment Fund estimated a requirement of at least $15 billion solely for the reconstruction of houses in Gaza.
- However, Arab states asserted their reluctance to fund reconstruction without a guarantee of lasting peace.
- Climate: The imperative for businesses to adapt to climate change and nations to collaborate despite differences in combating it emerged as another key theme.
- Discussions emphasized the necessity for developed countries to assist in financing climate action in developing nations to prevent a widening inequality that could result in winners and losers.
- China's Economy: Against the backdrop of a slowing economy, China sought increased investment from the West, which has experienced some cooling.
- With a GDP growth of 5.2% in 2023, still below pre-pandemic levels, China grappled with efforts by the United States to isolate it, particularly evident in the semiconductor trade standoff.
- India-Specific Observations: McKinsey and Company's assessment of Davos 2024 highlighted India's rapid transformation as one of the fastest-growing large economies globally.
- The summit marked the launch of the Global Good Alliance for Gender Equity and Equality, endorsed by the WEF and the Government of India.
- Originating from the G20 Leaders' Declaration, the alliance aims to bring together global best practices, knowledge sharing, and investments in women's health, education, and enterprise.
- Supported by the Bill and Melinda Gates Foundation, the alliance will be hosted by the CII Centre for Women Leadership, with the World Economic Forum as a 'Network Partner' and Invest India as an 'Institutional Partner.'
About the World Economic Forum:
- The World Economic Forum is the International Organization for Public-Private Cooperation.
- The Forum engages the foremost political, business, cultural and other leaders of society to shape global, regional and industry agendas.
- It was established in 1971 by German engineer and economist Klaus Schwab.
- It is a not-for-profit foundation and is headquartered in Geneva, Switzerland.
- The Forum strives in all its efforts to demonstrate entrepreneurship in the global public interest while upholding the highest standards of governance.
Reports released by WEF:
-
- Global Gender Gap Index
- Global Risks Report
- Fostering Effective Energy Transition Report
- Global Cyber Security Outlook
- Global Competitiveness Report
- Travel and Tourism Development Index
About Davos Meet:
- The World Economic Forum (WEF) organizes a meeting annually at the end of January in Davos, a mountain resort in Graubünden, in the eastern Alps region of Switzerland.
- The Annual Meeting, also known as the Davos Agenda, has the objective of orienting global leaders on the imperatives of the year ahead.
- This year's theme for the Annual Meeting in Davos is 'From Lab to Life: Science in Action'.
MeitY signs MoU with Cuba for cooperation on digital public infrastructure (ET)

- 22 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News?
India and Cuba have signed an MoU for cooperation in the field of sharing successful digital solutions implemented at the population scale for digital transformation.
India and Cuba Bilateral Relations:
- India and Cuba share a robust and longstanding diplomatic camaraderie, marked by warmth and amity.
- In a gesture of early support, India was among the first nations to acknowledge and establish relations with the new Cuban government post the revolutionary events in January 1959.
- Trade Dynamics: The bilateral trade engagement, while moderate, exhibits a diverse array of commodities.
- India exports pharmaceutical products, organic chemicals, plastic goods, medical equipment, engineering items, textiles, metal products, mineral oil products, and tools to Cuba.
- Conversely, Cuba primarily imports pharmaceuticals and tobacco products from India.
- Energy Partnership: A pivotal facet of India-Cuba relations is their collaboration in the energy sector.
- As a member country and Vice-President of the Latin America & the Caribbean region at the International Solar Alliance (ISA), Cuba plays a significant role in fostering energy cooperation between the two nations.
- Advancements in Science & Technology, Biotechnology, and Health: The bilateral relations in the domains of science, technology, and health have been fortified through ministerial-level visits from both nations.Development Collaboration: Prioritizing development assistance has been a cornerstone of their bilateral ties.
- India has extended disaster relief assistance to Cuba in the aftermath of hurricanes that have afflicted the region over the years.
- Cultural Relations: Cuban appreciation for Indian culture and civilization is evident, with figures like Mahatma Gandhi, Jawaharlal Nehru, and Rabindranath Tagore holding a special place in Cuban hearts.
- Indian Diaspora: Although the Indian community in Cuba is relatively small, it includes descendants of Indians who migrated to Cuba in the early twentieth century from Jamaica and other parts of the West Indies to contribute to sugarcane plantations.
What is Digital Public Infrastructure (DPI)?
- DPI is a digital network that enables countries to safely and efficiently deliver economic opportunities and social services to all residents.
- DPI can be compared to roads, which form a physical network that connects people and provides access to a huge range of goods and services.??
- DPI allows people to open bank accounts and receive wages faster and more easily.
- It allows governments to support citizens more quickly and efficiently, especially during emergencies.
- And it enables entrepreneurs to reach customers far and wide.??
- A strong DPI has three foundational systems—identity, payments, and data exchange—that together can make life easier in important ways.?
- When the three core systems—identity, payments, and data exchange—exist simultaneously and can talk to one another, people, businesses, and governments can reap the full benefits of DPI.
- Over time, safe and inclusive DPI creates vibrant and competitive economies.?
Indigenous mobile hospital saves life at ‘Pran Pratishta’ event in Ayodhya (The Hindu)

- 22 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News?
An Indigenous mobile hospital at the 'Pran Pratishta' event in Ayodhya played a life-saving role as 65-year-old Dharmacharya Pramukh and VHP member Ramkrishna Srivastava, experiencing a heart attack and sudden medical emergency, collapsed unconscious.
What is Aarogya Maitri Aid Cube?
- It is India’s first portable hospital that can be airlifted to a disaster area and assembled in an hour.
- This “flatpack” field hospital consists of 72 small cubes equipped with tents and customised medical equipment.
- It is built under the Bharat Health Initiative for Sahyog Hita and Maitri (BHISHM) and the hospital is reportedly designed to treat up to 200 patients.
- The cubes, each of which weighs below 15kg and measures 38cm x 38cm x 38cm, are resilient enough to be dropped from a plane or helicopter.
- The ‘Aarogya Maitri Cube Cage’ has three frames containing 12 mini-cubes.
- A single cage can fit a total of 36 mini-cubes.
- At least five trained people are needed to assemble the cubes into a functional hospital in an hour.
- These cubes can be flown to a war zone or a remote area hit by natural disasters such as earthquakes and floods.
- The product was developed under Prime Minister Narendra Modi’s ambitious ‘Project BHISHM’ which aims to support developing countries affected by natural disasters or humanitarian crises.
How the portable hospital will help?
- The portable hospital is capable of facilitating life-saving surgery on remote and tough terrains.
- The 72 cubes contain different equipment such as portable ventilators, solar panel-based generators, ultrasound machines, digital imaging radiography machines, defibrillators, high-mounted OT lights, stretchers, modern surgical devices, and portable laboratories.
- A line of Ayurvedic products was added to the list of items in the cubes at the suggestions of PM Modi.
- “HLL Life Care is the government’s nodal agency for sourcing the Aarogya Maitri Cube, whereas the manufacturing has been undertaken by multiple sellers as it includes a variety of products.
- Billed as the “world’s first portable disaster hospital”, the kit is waterproof and corrosion-proof.
- A tablet computer is installed inside the cube pack to prevent mistakes while setting up the structure.
- If the immediate need at the site is for life-saving surgery, then the operating theatre can be assembled first. This takes just 10 minutes. The doctors can start surgery while the remaining cubes are assembled.”
- The portable hospital can “provide critical medical care to 100 survivors for up to 48 hours, making it a lifeline on remote and tough terrains where immediate medical attention is needed. The cubes [which are self-sustained healthcare units] can handle bullet, burn, head, spinal and chest injuries, fractures, and major bleeding.
- India is now equipped and ready to supply this to any country in need.
- t can also be utilised in regions across India that need medical support due to epidemics, high elevations, or challenging landscapes.
- This could play a significant role in the management of public health.
- As a goodwill gesture, India has already given two Aarogya Maitri Cubes to Myanmar and one is being prepared for Sri Lanka.
After tiny chopper Ingenuity, NASA planning to send giant fixed-wing plane Maggie to Red Planet (TOI)
- 22 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News?
In its pursuit of extensively exploring Mars to find signs of water, Nasa is considering a proposed idea to send a giant fixed-wing plane to the Red Planet.
What is Ingenuity Mars Helicopter?
- The Ingenuity Mars Helicopter is a small, autonomous aircraft that is part of NASA's Mars 2020 mission.
- It was deployed to the surface of Mars on April 3, 2021, and made its first powered, controlled flight on another planet on April 19, 2021.
- Ingenuity is a technology demonstration mission, and its main goal is to show that powered flight is possible on Mars.
- The helicopter has four carbon-fiber blades creating enough lift to overcome the thin Martian atmosphere.
- It is powered by solar cells and can fly for up to 90 seconds at a time.
- Since its first flight, Ingenuity has completed 72 flights, far exceeding its original planned five flights.
- It has flown a total of 17 km and reached an altitude of 24 m.
- The helicopter has also helped to scout ahead for the Perseverance rover, taking images and collecting data from areas that the rover cannot reach.
- Ingenuity's success has paved the way for future aerial exploration of Mars.
- Future helicopters could be used to scout for landing sites, study the Martian surface in more detail, and even carry small payloads of scientific instruments.
About Perseverance Rover:
- Perseverance is a robotic rover exploring Jezero Crater on Mars as part of NASA's Mars 2020 mission.
- Launched on July 30, 2020, it successfully landed on February 18, 2021, making it the most sophisticated and heaviest rover ever sent to Mars.
Mission Highlights:
- Seeking signs of ancient microbial life: Perseverance is equipped with several instruments to analyze Martian rocks and soil for potential signs of past life.
- Collecting rock samples: The rover drills and collects rock samples that will be cached on Mars for potential return to Earth by future missions.
- Testing technology for future missions: Perseverance is demonstrating new technologies that will be crucial for future human exploration of Mars, such as the MOXIE instrument that produces oxygen from the Martian atmosphere and the Ingenuity helicopter, the first powered aircraft to fly on another planet.
- Perseverance Achievements:
- Finding evidence of an ancient lake in Jezero Crater that may have been habitable for microbial life.
- Collecting the first rock samples from Mars that will be returned to Earth.
- Demonstrating the feasibility of using a helicopter on Mars (the Ingenuity helicopter hitched a ride with Perseverance).
Indian Immunologicals rolls out indigenously developed Hepatitis A vaccine (Financial Express)
- 22 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News?
Indian Immunologicals Ltd (IIL), a wholly-owned subsidiary of the National Dairy Development Board (NDDB) recently announced that it has launched India’s first indigenously developed Hepatitis A vaccine, Havisure.
About Havisure Vaccine:
- The vaccine is effective in preventing the disease and is recommended for children in routine immunization.
- It is a two-dose vaccine wherein the first dose is administered at above 12 months of age and the second dose is given at least after 6 months of the first dose.
- The vaccine is also recommended for individuals who are at risk of exposure or travel to the regions with high hepatitis A prevalence.
- In addition to this people with occupational risk of infection and suffering from chronic liver diseases also need Hepatitis A vaccination.
Key Facts About Hepatitis A:
- Hepatitis A is an inflammation of the liver caused by the hepatitis A virus (HAV).
- The virus is primarily spread when an uninfected (and unvaccinated) person ingests food or water that is contaminated with the faeces of an infected person.
- The disease is closely associated with unsafe water or food, inadequate sanitation, poor personal hygiene and unprotected sex.
- Unlike hepatitis B and C, hepatitis A does not cause chronic liver disease but it can cause debilitating symptoms and rarely fulminant hepatitis (acute liver failure), which is often fatal.
- Hepatitis A occurs sporadically and in epidemics worldwide, with a tendency for cyclic recurrences.
- Epidemics related to contaminated food or water can erupt explosively, such as the epidemic in Shanghai in 1988 that affected about 300,000 people.
- They can also be prolonged, affecting communities for months through person-to-person transmission.
- Hepatitis A viruses persist in the environment and can withstand food production processes routinely used to inactivate or control bacterial pathogens.
- Geographical distribution: Infection is common in low- and middle-income countries with poor sanitary conditions and hygienic practices, and most children (90%) have been infected with the hepatitis A virus before the age of 10 years, most often without symptoms.
- Transmission: The hepatitis A virus is transmitted primarily by the fecal-oral route; that is when an uninfected person ingests food or water that has been contaminated with the feces of an infected person.
- In families, this may happen through dirty hands when an infected person prepares food for family members.
- Waterborne outbreaks, though infrequent, are usually associated with sewage-contaminated or inadequately treated water.
- Symptoms: Symptoms of hepatitis A range from mild to severe and can include fever, malaise, loss of appetite, diarrhoea, nausea, abdominal discomfort, dark-coloured urine and jaundice (yellowing of the eyes and skin).
- Not everyone who is infected will have all the symptoms.
- Treatment: There is no specific treatment for hepatitis A.
- Recovery from symptoms following infection may be slow and can take several weeks or months.
- Prevention: Improved sanitation, food safety and immunization are the most effective ways to combat hepatitis A.
‘Global Good Alliance for Gender Equity and Equality’ launched at Davos with support from India (DD)

- 20 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News?
Recently, India announced a new alliance for global good, gender equity, and equality at the World Economic Forum Annual Meeting.
About Global Alliance for Global Good- Gender Equity and Equality:
- It primary aims to unite global best practices, promote knowledge-sharing, and invest in women's health, education, and enterprise.
- It follows the initiatives of the G20 framework, including the Business 20, Women 20, and G20 EMPOWER, building on the commitments of G20 leaders for the global community's benefit.
- Aligned with multiple Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), such as Good Health and Well-Being (SDG 3), Quality Education (SDG 4), Gender Equality and Empowerment (SDG 5), and Global Partnership for Development (SDG 17), this initiative underscores India's dedication to gender equality in global development.
- Supported by the Bill and Melinda Gates Foundation, anchored by the CII Centre for Women Leadership, and with partnerships from the World Economic Forum and Invest India, the alliance reflects India's commitment to addressing gender-related issues within G20 nations under the principles of 'Vasudhaiva Kutumbakam' and 'Sabka Saath, Sabka Prayaas.'
About the World Economic Forum:
- The World Economic Forum is the International Organization for Public-Private Cooperation.
- The Forum engages the foremost political, business, cultural and other leaders of society to shape global, regional and industry agendas.
- It was established in 1971 by German engineer and economist Klaus Schwab.
- It is a not-for-profit foundation and is headquartered in Geneva, Switzerland.
- The Forum strives in all its efforts to demonstrate entrepreneurship in the global public interest while upholding the highest standards of governance.
Reports released by WEF:
-
- Global Gender Gap Index
- Global Risks Report
- Fostering Effective Energy Transition Report
- Global Cyber Security Outlook
- Global Competitiveness Report
- Travel and Tourism Development Index
Police think tank Bureau of Police Research and Development warns users of scams, data-breach acts on WhatsApp (The Hindu)

- 20 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News?
The Bureau of Police Research and Development (BPRD) has warned users of different scams perpetrated through messaging platform WhatsApp.
About the Bureau of Police Research and Development (BPRD):
- The Bureau of Police Research & Development (BPR&D) was set up in 1970 under the Ministry of Home Affairs to identify the needs and problems of the police in the country.
- It was also mandated to keep abreast of the latest developments in the fields of science and technology, both in India and abroad, to promote the use of appropriate technology in police work.
- Over the years, the BPR&D has also been entrusted with the responsibility of monitoring the training needs and quality of training in the States and Central Police Organisations and assisting the same, as also assisting the States in modernization of the State Police Forces and Correctional Administration.
- In the process, the BPR&D has also been tasked to assist the Ministry of Home Affairs and the CPFs, etc., in the development of Standards, Quality Requirements (QRs), etc., concerning various types of equipment and items about infrastructure.
- More recently, the BPR&D has also been entrusted with the responsibility of anchoring and coordinating the work of the National Police Mission.
BPRD's Roles and Responsibilities:
- The Bureau of Police Research and Development (BPRD) plays a crucial role in elevating the functioning of police forces across the nation:
- Policy Formulation and Guidance: Assists in formulating policies and strategies for police development.
- Guides to enhance the efficiency of police forces.
- Interdepartmental Interface: Acts as a bridge between the police and other government departments for efficient resource and technology sharing.
- Financial Assistance: Offers financial support to state governments for surveys, studies, and the development of specialized infrastructure and training.
- Training and Awareness: Conducts seminars and workshops to educate police personnel on crime prevention and effective policing.
- Promotes awareness of policing importance and public order maintenance.
- Development of Systems: Works towards developing systems like Community Policing, modern investigations, and effective technology and data management.
BPRD's Vision and Mission:
- Vision: To facilitate the optimal deployment of police forces and related activities, enabling them to meet contemporary challenges.
- Mission: To enhance police capabilities and those of stakeholders by providing resources and research-based knowledge, bridging gaps between evidence-based practice, policy formulation, and public outreach.
- Focus Areas: BPRD prioritizes innovation, knowledge initiatives, and research in policing, public order, security, and related fields, creating models relevant to contemporary needs.
- Overall Objective: BPRD is committed to developing capacity, fostering police professionalism, and promoting safety and public order in India through research, innovation, and strategic initiatives.
How the new Education Ministry guidelines will affect the coaching institutes (HT)

- 20 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News?
Taking cognisance of coaching centres charging exorbitant fees from students, promoting unhealthy competition and stress among students, and a rise in student suicides and other malpractices, a set of new guidelines were released by the Education Ministry.
Guidelines for Registration and Regulation of Coaching Centers 2024:
- The guidelines define a 'coaching centre' as an establishment providing coaching for study programs, competitive exams, or academic support to more than 50 students at the school, college, and university levels, established, run, or administered by any person.
Key aspects of the guidelines include:
- Registration Process: Coaching centres must apply for registration within their local jurisdiction, adhering to specified forms, fees, and document requirements.
- Each branch of a coaching centre is considered a separate entity, requiring individual registration.
- Marketing Standards: Coaching centres are prohibited from making misleading promises or guarantees regarding ranks or marks.
- Transparency is mandated, with centres required to maintain an updated website containing detailed information.
- Student Enrollment: Students below the age of 16 are not permitted for enrolment, and entry is allowed only after the completion of secondary school examinations.
- Fee Structure: Tuition fees must be fair, with detailed receipts provided.
- A comprehensive prospectus must include information on courses, duration, facilities, fees, and refund procedures. Any fee increase during the course is prohibited.
- Exit Policy: Pro-rata refunds are mandated within 10 days for mid-course withdrawals.
- Infrastructure Requirements: Coaching centres must allocate a minimum of one square meter per student.
- Compliance with fire safety and building codes is essential, along with proper electrification, ventilation, lighting, security measures, and medical assistance.
- Study Hours: Classes should not coincide with school hours, and weekly off for students and tutors is mandatory.
- Class sizes must align with a healthy teacher-student ratio.
- Mental Wellbeing: Centers should establish mechanisms for immediate intervention and counselling for students in distress.
- Complaint Mechanism: Students, parents, or tutors/employees can file complaints, to be resolved within thirty days by the competent authority or an inquiry committee.
- Penalties: Penalties for violations include ?25,000 for the first offence, ?1 lakh for the second, and registration revocation for subsequent breaches.
PM declares Khelo India Youth Games 2023 open in Chennai (Indian Express)

- 20 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News?
Prime Minister Narendra Modi recently declared the Khelo India Youth Games 2023 open at the Nehru Indoor Stadium in Chennai.
What is Khelo India?
- The Khelo India programme has been introduced to revive the sports culture in India at the grassroots level by building a strong framework for all sports played in our country and establishing India as a great sporting nation.
- Talented players identified in priority sports disciplines at various levels by the High-Powered Committee will be provided annual financial assistance of INR 5 lakh per annum for 8 years.
About the Khelo India Youth Games 2023:
- The 6th edition of the Khelo India Youth Games is being hosted by Tamil Nadu, marking the first occurrence of the Games in South India.
- Spanning from January 19th to 31st, 2024, the event will unfold across four cities in Tamil Nadu – Chennai, Madurai, Trichy, and Coimbatore.
- With over 5600 athletes participating in more than 275 competitive events spanning 26 sports disciplines and one demo sport, this edition introduces Silambam, a traditional sport of Tamil Nadu, as a demo sport and includes Squash for the first time.
- Archery, athletics, badminton, and squash have been introduced first time in this edition.
- The mascot, 'Veera Mangai,' pays tribute to Rani Velu Nachiyar, an Indian queen who courageously resisted British colonial rule.
- The logo integrates the image of the poet Thiruvalluvar.
- Objectives: The overarching objective of the Khelo India Youth Games is to rejuvenate India's grassroots sports culture, aiming to build a robust framework for all sports and position the nation as a prominent sporting entity.
- Organized by the Ministry of Youth Affairs & Sports, the Games have been an annual tradition since their inception in 2018 in Delhi.
What is the Nagara style, in which Ayodhya’s Ram temple is being built (Indian Express)

- 20 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News?
The Ram temple in Ayodhya will be inaugurated on January 22. Chandrakant Sompura, 81, and his son Ashish, 51, have designed the complex in the Nagara style of temple architecture.
What is the Nagara style?
- Originating around the 5th century AD, the Nagara style influenced temple architecture in several regions of India, from Northern India to Karnataka to parts of Madhya Pradesh, Odisha and Gujarat, giving it its pan-India appeal.
- Given that the temple will attract Hindu devotees from across the country, this is the most "inclusive" architectural style of Hinduism in that respect.
- The word “Nagara” means “city,” and the style's close association with urban architectural principles made it suitable for a bustling town like Ayodhya while retaining Hindu temple elements that are familiar to devotees.
- With carved pillars and towering spires, it seeks to echo the magnificent craftsmanship of the Khajuraho temples of Madhya Pradesh and the Sun Temple in Odisha’s Konark.
- The Nagara style is not confined to a specific period — it flourished during the Gupta dynasty but continued to evolve through various regional kingdoms and empires that ruled over the northern parts of India.
- The temple's architecture is characterised by its tower-like structures, known as 'shikhara' or spires, which rise vertically, symbolising the sacred mountain, Mount Meru, considered to be the centre of the physical, metaphysical and spiritual dimensions in Hindu, Jain and Buddhist cosmology.
- This temple architecture is also closely associated with both the Shaivite and Vaishnavite sects of Hinduism and known for its sculptural elements that echo scenes from Hindu epics like Ramayana and Mahabharata.
The typical Nagara temple layout:
- The layout of Nagara-style temples follows a distinct pattern, reflecting the cosmic order and the journey of the soul towards liberation
The typical plan of the Nagara-style temple:
- Vastu Purusha Mandala: At the core of Nagara temple design is the concept of Vastu Purusha Mandala, a sacred diagram representing the cosmic man.
- The temple’s plan is aligned with this mandala, ensuring that the deity’s sanctum aligns with the cosmic forces.
- This alignment reflects the belief that the temple is a microcosm of the universe, establishing a cosmic resonance.
- Garbhagriha (Sanctum Sanctorum): The sanctum sanctorum, or garbhagriha, is the innermost and holiest chamber where the principal deity resides and is always located directly below the highest Sikhara.
- Often square, this chamber is a symbol of the womb of creation.
- The placement of the deity within this sacred space is meticulously calculated to maintain harmony with cosmic energies.
- Pradakshina Patha (Circumambulation): Around the garbhagriha, there is a circumambulatory path called the pradakshina patha.
- This path allows devotees to walk in a clockwise direction around the deity, as a symbolic act of paying respect, seeking blessings, and expressing devotion.
- The pradakshina patha may be enclosed within the temple or form an outer pathway surrounding the main temple complex.
- It is believed that circumambulation harmonizes the individual with the divine and creates a spiritual connection.
- Vimana (Tower): The Vimana, or tower, is the crowning glory of Nagara temples.
- The shikhara, as the main spire, represents Mount Meru, the mythical abode of the gods, meant to symbolize the ascent from the earthly realm to the celestial plane, creating a visual narrative of the soul’s journey towards spiritual awakening.
- Mandapa (Congregation Hall): The mandapa, or congregation hall, serves as a communal space for rituals, gatherings, and celebrations. Supported by intricately carved pillars, the mandapa’s design is often open, allowing devotees to participate in ceremonies.
- The pillars themselves are adorned with sculptures depicting deities, mythological narratives, and celestial beings, contributing to the immersive spiritual experience.
- Antarala (Vestibule): The antarala acts as a transitional space between the garbhagriha and the mandapa.
- It serves functional and symbolic purposes, symbolising the journey from the material to the divine.
- The antarala may house additional deities or intricate sculptures, further enhancing the spiritual ambience.
- Ardhamandapa (Entrance Porch): The ardhamandapa, or entrance porch, serves as the threshold between the external world and the sacred interior.
- Often featuring ornate pillars and intricate carvings, the ardhamandapa is a visual prelude to the architectural splendour within.
- Devotees traverse this space as they enter the sanctified realm of the temple.
- Peripheral Structures: Surrounding the central shrine are often smaller shrines and subsidiary structures, creating a complex architectural ensemble.
- These structures, known as subsidiary shrines or parivara devatas, pay homage to various deities associated with the main deity.
- The arrangement of these structures follows a harmonious pattern, contributing to the overall visual appeal of the temple complex.
Regional variations:
- As a pan-India style, the Nagara architecture has regional variations that reflect the cultural ethos of where it is built.
- Odisha: The Nagara style in the state is characterised by its exquisite stone carvings and towering spires.
- The temples of Bhubaneswar, Puri, and Konark in the state of Odisha exemplify this style.
- The temples showcase carvings of deities, mythical creatures, dancers, and musicians, evoking a sense of dynamic movement.
- Gujarat: Known for its elegance and simplicity, the Gujarati Nagara style is epitomised by the Sun Temple in Modhera and the famous Somnath Temple.
- The main 'shikhara' in the state's temples are relatively modest in height compared to northern iterations.
- The emphasis is on the overall harmony of the temple’s complex measurements and the sculptural beauty.
- Rajasthan: The style in this state has been noticeably influenced by distinctive elements of Rajput architecture — from fortified walls and ornate entryways.
- Look no further than the Dilwara Temples in Mount Abu and the Sun Temple of Ranakpur for examples of this style.
- Distinct features include marble carvings and delicate detailing.
- Karnataka: Nagara temples in the South have subdued shikharas compared to their northern temples.
- What is more, the emphasis is on pillar carvings and the subject matter is often famous scenes from mythology.
- The Virupaksha Temple in Hampi and the Lepakshi Veerabhadra Temple are notable Nagara-style temples in the south.
- Madhya Pradesh: Central Indian temples often feature a variety of spires, emphasising the stepped shape.
- The sculptures focus on a wide range of themes, including mythological narratives, daily life, and spiritual pursuits.
- The Khajuraho complex, including the Lakshmana Temple, exemplifies the Nagara style in Central India.
- Combining spiritual principles with aesthetics and craftsmanship, the Nagara style is an indelible part of India’s cultural and religious legacy.
- The Ram temple draws from this same architectural legacy of Hinduism to create a religious monument that seeks to inspire the same awe that the centuries-old Indian temples continue to do.
Comparison to Dravida style:
- The Dravida counterpart to the shikhara is the vimana. There exists, however, a fundamental difference.
- In the Dravida-style temples, vimanas are typically smaller than the great gatehouses or gopurams, which are the most immediately striking architectural elements in a temple complex.
- Moreover, while shikharas are mentioned in southern Indian architectural sources, they refer to only the dome-shaped crowning cap atop the vimana.
- The existence of gopurams also points to another unique feature of the Dravida style — the presence of a boundary wall.
- A few Nagara-style temple complexes are lined with distinctive boundary walls that are a part of the temple’s design.
- This is one of Ayodhya’s Ram temple’s ‘hybrid’ features — although no elaborate gopuram has been built (citing paucity of space), a 732m long wall runs around the temple compound.
Pakke Paga Hornbill Festival begins in Arunachal; effective conservation of iconic birds urged (DTE)

- 19 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News?
The 9th edition of the Pakke Paga Hornbill Festival (PPHF) commenced in the town of Seijosa in Arunachal Pradesh’s Pakke Kessang district on January 18, 2024, with a call to protect and conserve hornbills.
About Pakke Paga Hornbill Festival:
- The first Pakke Paga Hornbill Festival (PPHF) took place in 2015 with the primary goal of acknowledging the Nyishi tribal group's significant role in hornbill conservation within the Pakke Tiger Reserve (PTR).
- Additionally, the festival aimed to generate alternative sources of income for the region and raise awareness across India about the marvels of PTR and its surroundings.
- The current year's festival is themed "Domutoh Domutoh, Paga hum Domutoh," meaning 'Let Our Hornbills Remain' in the Nyishi language.
- The focus of this year's festival is to emphasize the crucial importance of preserving these iconic birds.
About the Great Indian Hornbill:
- The Great Indian Hornbill is a bird family found in tropical and subtropical Africa, Asia, and Melanesia.
- It is the state bird of Kerala and Arunachal Pradesh in India.
- The Great Indian Hornbill is now considered “Vulnerable” due to high hunting pressure, habitat loss, and deforestation.
Key Facts About Pakke Tiger Reserve:
- Pakke Tiger Reserve is located in the East Kameng district of Arunachal Pradesh.
- It is bordered by the Tenga Reserve Forest to the North, the Doimara Reserve Forest to the West, and Nameri National Park and Tiger Reserve (Assam) to the South.
- The region exhibits high species diversity and endemicity, acting as a transitional zone between the Indian and Malayan ecoregions.
- Located North of the Brahmaputra River, Pakke Tiger Reserve is positioned in the transition zone between the Assam plains and the hilly forests of Arunachal Pradesh.
- Vegetation primarily comprises tropical evergreen and semi-evergreen forests.
- Flora: Notable flora includes Polyalthia simiarum, Pterospermum acerifolium, Sterculia alata, Stereospermum chelonioides, Ailanthus grandis, and Duabanga grandiflor. Additionally, about eight species of bamboo are found in the area.
- Fauna: The fauna of the reserve includes iconic species like the Tiger and elephant, as well as predators such as the Leopard and the Clouded leopard, contributing to the rich biodiversity of the region.
ISRO develops second-generation Distress Alert Transmitter (The Hindu)

- 19 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News?
Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) has developed an improvised Distress Alert Transmitter (DAT) with advanced capabilities and features for the fishermen at sea to send emergency messages from fishing boats.
What is a Distress Alert Transmitter (DAT)?
- The first version of DAT has been in operation since 2010, allowing fishermen at sea to send emergency messages from their fishing boats.
- These messages are transmitted via a communication satellite to the Indian Mission Control Centre (INMCC), the central control station, where the alert signals are decoded to determine the identity and location of the distressed fishing boat.
- The extracted information is then relayed to Maritime Rescue Coordination Centres (MRCCs) under the Indian Coast Guard (ICG), enabling coordinated Search and Rescue operations to assist fishermen in distress.
About the Second Generation DAT (DAT-SG):
- Leveraging advancements in satellite communication and navigation technology, ISRO has enhanced DAT into the Second Generation DAT (DAT-SG). DAT-SG not only allows fishermen to send distress alerts but also provides them with acknowledgements, assuring them that rescue operations are underway.
- In addition to transmitting distress signals, DAT-SG can receive messages from control centres.
- This feature enables the sending of advance alert messages to fishermen about adverse weather conditions, cyclones, tsunamis, or other emergencies.
- Moreover, the system transmits information on Potential Fishing Zones (PFZs) to fishermen at regular intervals.
- DAT-SG can be connected to mobile phones using a Bluetooth interface, and messages can be read in the native language through a mobile app.
- The central control centre employs a web-based network management system called "SAGARMITRA," which maintains a database of registered DAT-SGs.
- This system assists MRCCs in accessing real-time information about distressed boats, allowing the Indian Coast Guard to initiate Search & Rescue operations promptly during distress situations.
Why Kashmir and Ladakh are without snow this winter, its implications (Indian Express)

- 19 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News?
The Indian Himalayas are experiencing an unusual lack of snowfall this winter, impacting ski resorts and prompting holiday cancellations.
Key Highlights of the Report:
- Unprecedented precipitation deficit: December witnessed an alarming 80% precipitation deficit in the western Himalayan region.
- The ongoing dry spell in January is attributed to the absence of active western disturbances this winter season, as reported by the India Meteorological Department (IMD).
- Impact on freshwater resources: Experts warn of potential impacts on freshwater availability in the Himalayan region.
- The extended dry spell poses a threat to horticulture and agricultural production, raising concerns among experts.
- Unseasonal blooming and alarming temperature anomalies: Despite being peak winter, Ladakh and Kashmir experienced unusually warm temperatures, leading to early crop blooming.
- A report by IMD scientists reveals maximum temperatures 5-8 degrees Celsius below normal over the northern plains since December 29.
- Challenges to water levels and ecosystems: Experts also highlight the significance of the Chillai Kalan snowfall period as the only freshwater source.
- The prolonged dry spell has resulted in reduced water levels in rivers and streams, posing challenges to the region's ecosystems.
Factors contributing to severe weather conditions:
- Scientists attribute the severe weather to three main factors:
- Lack of active western disturbances
- Prevailing El Nino conditions, and
- A strong jet stream.
- El Nino, characterised by abnormal warming in the central Pacific Ocean, contributes to altered weather patterns.
- Mechanics of fog formation: Scientists explain the three conditions required for fog formation: weak low-level winds, moisture, and overnight cooling.
- The lack of strong western disturbances disrupts these conditions, contributing to the prolonged fog.
- Persistent jet streams and cold wave conditions: Strong jet streams prevailing over north India for the last five days have led to the subsidence of cold air, enhancing cold wave/cold day conditions.
These conditions are expected to continue over the next five days, intensifying the challenges posed by the ongoing weather anomalies.
National Quantum Mission to call for proposals to set up four tech hubs (PTI)

- 19 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News?
The government will set up a coordination cell to implement the National Quantum Mission (NQM) with a focus on establishing four technology hubs in the format of consortia of academia, research and development labs and industry.
What is the National Quantum Mission (NQM)?
- The National Quantum Mission (NQM) will assist India take a giant leap into the future of technology.
- India has entered the ranks of the select few nations actively pursuing the advancement of quantum technology by establishing this programme.
- In 2023, the government sanctioned the National Quantum Mission (NQM), spanning from 2023-24 to 2030-31, with the following key features:
- The mission aims to initiate, foster, and amplify scientific and industrial research and development in Quantum Technology (QT), establishing a dynamic and innovative ecosystem.
- Its ultimate goal is to propel quantum technology-led economic growth, foster the QT ecosystem, and position India as a leading nation in the field of Quantum Technologies & Applications.
- It willl be implemented by the Department of Science & Technology (DST) under the Ministry of Science & Technology.
Key Objectives:
- Develop intermediate-scale quantum computers with 50-1000 physical qubits across platforms like superconducting and photonic technology within eight years.
- Implement satellite-based secure quantum communications over a 2000-kilometre range within India, ensuring long-distance secure quantum communications with other countries.
- Establish inter-city quantum key distribution over 2000 km and multi-node Quantum networks with quantum memories.
- Develop highly sensitive magnetometers in atomic systems and Atomic Clocks for precision timing, communications, and navigation.
- Support the design and synthesis of quantum materials like superconductors, novel semiconductor structures, and topological materials for quantum device fabrication.
- Develop single photon sources/detectors and entangled photon sources for applications in quantum communications, sensing, and metrology.
Implementation:
- The mission involves the establishment of four Thematic Hubs (T-Hubs) in leading academic and National R&D institutes, focusing on Quantum Computing, Quantum Communication, Quantum Sensing & Metrology, and Quantum Materials & Devices.
- These hubs will concentrate on generating new knowledge through basic and applied research and promote R&D in their respective domains.
Significance:
- NQM has the potential to elevate India's Technology Development ecosystem to global competitiveness.
- It is expected to significantly benefit various sectors such as communication, health, finance, and energy, with applications ranging from drug design to space, banking, and security.
- The mission aligns with national priorities, including Digital India, Make in India, Skill India, Stand-up India, and Start-up India, and contributes to Sustainable Development Goals (SDG).
- With the launch of this mission, India will be the seventh country to have a dedicated quantum mission after the US, Austria, Finland, France, Canada and China.
What is Quantum Technology?
- The term "quantum technology" is used to describe the research and development of techniques to build supercomputers with enhanced speed, security, and efficiency in data processing above conventional computers.
- Quantum mechanics, which governs the behaviour of subatomic particles, is used to design these novel systems.
- The peculiar characteristics of subatomic particles are the key to quantum technology's capabilities in processing massive quantities of information concurrently.
Telco body seeks USOF, tax reliefs in FY25 Union Budget (Live Mint)

- 19 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News?
Telecom services providers have urged the Ministry of Finance to suspend the Universal Service Obligation Fund (USOF) till the existing corpus is exhausted.
About Universal Service Obligation Fund (USOF):
- The USOF was established through a parliamentary amendment to the Indian Telegraph (Amendment) Act, 2003.
- Its primary goal is to ensure non-discriminatory access to affordable telecom services in rural and remote areas, thereby narrowing the digital gap between urban and rural regions.
- For financially unviable rural and remote areas, the USOF provides subsidy support in the form of Net Cost or Viability Gap Funding (VGF).
- This encourages telecom service providers to expand their services to these areas, enhancing telecommunications and broadband accessibility.
- Funding Mechanism: Telecom operators contribute to the USOF through a Universal Service Levy (USL), a percentage of their Adjusted Gross Revenue (AGR).
- Administration: The USOF is overseen by the Administrator, USO Fund, appointed by the Central Government.
- It operates as an attached office under the Department of Telecommunications (DoT), Ministry of Communications.
Telecom Technology Development Fund (TTDF):
- Launched by USOF on October 1st, 2022, the TTDF Scheme targets domestic companies and institutions engaged in designing, developing, and commercializing telecommunication products and solutions.
- The scheme aims to facilitate affordable broadband and mobile services in rural and remote areas.
- The initiative fosters connections between schools and diverse volunteers from the Indian Diaspora, including young professionals, retired teachers, retired government officials, NGOs, private sector companies, corporate institutions, and more.
- Under the scheme, USOF is committed to developing standards to meet nationwide requirements and establishing an ecosystem for research, design, prototyping, use cases, pilots, and proof-of-concept testing.
- The scheme provides grants to Indian entities, encouraging the integration of indigenous technologies tailored to domestic needs.
Cellular Operators Association of India (COAI)
- The Cellular Operators Association of India (COAI), was constituted in 1995 as a non-governmental society registered under the Societies Act, 1860.
- The Association is dedicated to the advancement of modern communications through the establishment of a world-class cellular infrastructure and to delivering the benefits of affordable mobile communication services to the people of India.
- Today it is regarded as an important interface between the main stakeholders of the Indian Telecom Ecosystem, i.e. Government, Operators, Consumers, Equipment Manufacturers, and Content Providers.
- COAI provides a forum for discussions and exchange of ideas between Service Providers, Policy Makers, Regulators, Technologists, etc., who share a common interest in the development of mobile telephony in the country.
India’s first graphene centre becomes reality (Indian Express)

- 18 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News?
The Union government recently launched India’s first graphene centre ‘India Innovation Centre for Graphene (IICG)’ at Maker Village Kochi.
About India Innovation Centre for Graphene (IICG):
- India Innovation Centre for Graphene (IICG) is India’s first Graphene Centre.
- It is a joint venture of the Digital University of Kerala, the Centre for Materials for Electronics Technology (C-MET) and Tata Steel Limited.
- Key Aspects: IICG is committed to advancing research and development, fostering product innovation, and enhancing capacity building in the field of Graphene and two-dimensional materials (2DM).
- With a vision to bridge the gap between research and commercialization, IICG actively supports the Graphene-Aurora program initiated by the Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology (MeitY).
- This program aims to provide a comprehensive facility for startups and industries to facilitate seamless progression from research and development to commercialization.
About Graphene:
- Graphene is a one-atom-thick layer of carbon atoms arranged in a hexagonal lattice, serves as the fundamental building block of Graphite, utilized in various applications, including pencil tips.
- Scientists first isolated Graphene in 2004.
Properties of Graphene:
- Recognized as the world's thinnest material, Graphene boasts a thickness of only one atom, making it one million times thinner than human hair.
- Despite its extreme thinness, Graphene exhibits exceptional strength, surpassing even steel and diamond.
- It functions as an outstanding conductor of both heat and electricity, surpassing copper in electrical conductivity.
- Remarkably transparent, Graphene absorbs only 2% of light.
- Impermeable to gases, including lightweight gases like hydrogen and helium.
Applications:
- Mechanical Strength: Used to enhance the strength of various materials.
- Thermal Applications: Ideal for creating heat-spreading solutions, such as heat sinks or heat dissipation films.
- This has applications in microelectronics (e.g., improving the efficiency and lifespan of LED lighting) and larger applications like thermal foils for mobile devices.
- Energy Storage: Due to its minimal thickness, Graphene possesses an exceptionally high surface-area-to-volume ratio, making it promising for use in batteries and supercapacitors.
- It holds the potential to enable energy storage devices, including batteries, supercapacitors, and fuel cells, with increased energy storage capacity and faster charging capabilities.
- Future Potential: Graphene shows promise in various potential applications, including anti-corrosion coatings and paints, precise sensors, efficient electronics, flexible displays, solar panels, accelerated DNA sequencing, drug delivery systems, and more.
Telangana signs agreement with WEF for setting up C4IR in Hyderabad (The Hindu)

- 18 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News?
Recently, Telangana has signed an agreement with the World Economic Forum (WEF) to establish the Centre for Fourth Industrial Revolution (C4IR) in the state capital, Hyderabad.
About the Centre for Fourth Industrial Revolution (C4IR):
- C4IR is a global initiative of the World Economic Forum (WEF) to collaborate with governments, businesses, academia, and civil society to address the challenges and opportunities posed by the Fourth Industrial Revolution (4IR).
- The focus of this collaboration is to use technology for advancements in the life sciences and healthcare sector, particularly aiming to meet healthcare targets for the state’s population.
- Telangana aims to become a hub for health technology and a global centre for healthcare services.
About Fourth Industrial Revolution (4IR):
- Klaus Schwab, the executive chairperson of the World Economic Forum (WEF), coined the term 4IR in 2016.
- This term refers to advancements in artificial intelligence, machine learning, 5G technology, the Internet of Things, robotics, biotechnology, quantum computing, and more.
- These technologies offer new possibilities for organizations, allowing them to dream big and expand into areas that were previously unimaginable.
The World Economic Forum
- The World Economic Forum is the International Organization for Public-Private Cooperation.
- The Forum engages the foremost political, business, cultural and other leaders of society to shape global, regional and industry agendas.
- It was established in 1971 by German engineer and economist Klaus Schwab.
- It is a not-for-profit foundation and is headquartered in Geneva, Switzerland.
- The Forum strives in all its efforts to demonstrate entrepreneurship in the global public interest while upholding the highest standards of governance.
Jagannath Temple corridor | An attempt to counter BJP’s Hindutva push ahead of elections (The Hindu)

- 18 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News?
Odisha Chief Minister Naveen Patnaik on Wednesday unveiled a sprawling heritage corridor around the Jagannath Temple in Puri, a project being seen as an attempt to counter the BJP’s Hindutva push ahead of the Lok Sabha and State Assembly elections later this year.
About the Puri Heritage Corridor Project:
- The Shree Jagannath Heritage Corridor, officially named Shree Mandir Parikrama, is a 75-metre-long heritage corridor around the Jagannath Temple in Puri, Odisha.
- Initiated in 2016, the Puri Heritage Corridor Project aims to enhance pilgrim amenities, bolster the temple's safety, and contribute to Puri's transformation into a world heritage city.
- The comprehensive project entails the redevelopment of significant areas within the town and in proximity to the temple, catering to the needs of both visitors and tourists.
- A phased implementation of 22 distinct projects is planned under the Augmentation of Basic Amenities and Development of Heritage and Architecture at Puri (ABADHA) scheme.
- The project also aims to provide ample facilities and amenities for pilgrims and visitors, ensuring a hassle-free and memorable experience, while strengthening the safety and security of the temple and its devotees.
About Jagannath Temple:
- Jagannath Temple believed to be built in the 12th century by King Anatavarman Chodaganga Deva of the Eastern Ganga Dynasty.
- People call it ‘Yamanika Tirtha’ because they believe that the presence of Lord Jagannath nullifies the power of ‘Yama,’ the god of death, in Puri.
- The temple, also known as the “White Pagoda” and part of the Char Dham pilgrimages, has four gates:
- The main Eastern ‘Singhdwara’ with two crouching lions,
- Southern ‘Ashwadwara,’
- Western 'Vyaghra Dwara,' and
- Northern ‘Hastidwara.’
- Each gate has unique carvings representing different forms.
- In front of the entrance stands the Aruna stambha or sun pillar, originally from the Sun Temple in Konark, adding to the historical and artistic significance of the Jagannath Temple.
An ancient system that could bring water to dry areas (DownToEarth)
- 18 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News?
Some of Africa’s dry areas face serious water shortages due to minimal rainfall. An ancient system of drawing water from aquifers, the “qanat system”, could help.
What is the Qanat system?
- The qanats have been used for centuries in arid and semi-arid parts of North Africa, the Middle East and Asia, where water supplies are limited.
- It’s known by a variety of names, “foggara” in North Africa, “falaj” in Oman and “qarez” in parts of Asia.
- It’s thought to have been developed in Persia in the first millennium BC.
- As the Islamic Empire spread across the Arabian Peninsula, the Levant, north Africa and parts of Europe from 661 to 750 CE, so did knowledge about qanats.
- Today, some of the region’s qanat systems, like those in Iran, are protected under heritage status.
- Some of these qanats, although declining in number, are still used.
- They are largely protected for historical and cultural reasons.
How does the qanat system work?
- There are bodies of water underground known as aquifers, some of which can be found at the tops of valleys or near mountains.
- A qanat system taps these aquifers and, using underground tunnels, moves the water, using gravity, over many kilometres.
- The tunnel then exits at a lower-lying area.
- When the water exits the tunnel, farmers can use it to irrigate their crops.
- People can also access the water along the stretch of the tunnel using wells.
- It’s a system that’s managed by everyone and its benefits are shared.
- Everybody has a vested interest and a role to play and community bonds can be strengthened.
Advantages of qanat systems:
- Efficient use of water: Qanats allow for the extraction and transport of groundwater from deep underground sources to the surface.
- This allows for a more efficient use of water resources, as the water is extracted and transported to the surface for irrigation and other purposes.
- Sustainable water supply: Qanats can provide a reliable and sustainable source of water for communities, even in arid regions where surface water is scarce.
- Cool and humid air supply: The cool and humid air that flows through the qanat can be used to provide a natural air conditioning system for buildings, as well as to irrigate crops and orchards.
- Low maintenance: Qanats require minimal maintenance once they are constructed, making them a cost-effective and long-lasting water supply solution.
- Disaster resilience: Qanats are resilient to natural disasters such as earthquakes and floods, as they are located underground and protected from damage.
Who are the Shankaracharyas — and who was Adi Shankara? (Indian Express)

- 18 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News?
Recently, the four Shankaracharyas have said they will not attend the inauguration of the Ram temple in Ayodhya on January 22.
Who are the Shankaracharyas?
- The Shankaracharyas are the "supreme authority" in Hinduism and for interpreting Hindu scriptures.
- The shankaracharyas head the four principal monasteries or mutts that were established by the eighth-century Hindu saint Adi Shankara.
- They are based in Uttarakhand, Odisha, Karnataka and Gujarat.
- Each mutt, called peetha or pitha in Sanskrit, was tasked to serve as the custodian of one Veda each and keep alive Vedic literature.
- Govardhan Math in Puri is the custodian of the Rig Veda.
- Dwarka Sharada Peetham in Gujarat is responsible for the Sam Veda.
- The Sringeri Sharada Peetham in Karnataka is responsible for the Yajur Veda and
- Jyotir Math in Uttarakhand's Joshimath for the Atharva Veda.
- All the peethas are situated in the four cardinal directions and are amongst the most-revered pilgrimages in India.
Who was Adi Shankara?
- The title "Shankaracharya", in fact, is derived from Adi Shankara, a Vedic scholar credited with reforming and reviving Hinduism during a time when Buddhists and Jains wielded influence.
- Adi Shankara was born in Kalady village on the bank of the River Periyar in today Kerala’s Ernakulam district in the month of Vaishakha in 788 CE.
- Also known as Jagadguru, Shankara had a short life (it is believed he died when he was just 32) but he had a big impact on Hindu religion.
- Revered as an avatar of Lord Shiva, it is believed that he mastered the Vedas when he was just 16.
- At a very young age, Shankara started criss-crossing the length and breadth of India to spread his commentaries on Brahama Sutras, Upanishads and the Bhagavad Gita amid a rise in Jainism and Buddhism.
What is the legacy of Shankara?
- Shankara’s legacy today transcends his contributions to metaphysics and theology.
- His travels across the subcontinent have often been interpreted as a near-nationalistic project where faith, philosophy and geography are yoked together to imagine a Hindu India which transcended the political boundaries of his time.
- And his four mathas, located in the North and South, East and West of India, are seen as the ultimate examples of this project.
- His mathas are thus also seen as keepers of Hindu faith and traditions.
What is Advaita Vedanta?
- Shankara is most associated with Advaita Vedanta, a school of Hindu philosophy and spiritual discipline.
- Advaita Vedanta articulates an ontological position of radical nondualism — it posits that all that we perceive is ultimately illusory (maya) and that the principle of Brahman (not the caste Brahmin) is the only true reality of all things, transcending empirical plurality.
- The fundamental thrust of Advaita Vedanta lies in the unity of atman or individual consciousness, and brahman or the ultimate reality.
Four Peethas aren't the four Dhams
- The four peethas established by Adi Shankara should not be confused with the four dhams.
- The four dhams, known as Char Dham, were also established by Adi Shankara.
- The four dhams are at;
- Badrinath
- Dwarka
- Puri and
- Rameswaram.
- The peethas are basically associated with the preservation and propagation of Hindu philosophy.
India signs an agreement to acquire five lithium mines in Argentina (Business Standard)

- 17 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News?
Recently the Indian govt. signed an agreement to acquire five lithium brine blocks for exploration and development in Argentina.
Context:
- The Mines Ministry, operating through KhanijBidesh India Limited (KABIL), has entered into an agreement with Argentina's state-owned CAMYEN for the development of five lithium blocks.
- CAMYEN, officially known as Catamarca Minera Y Energetica Sociedad Del Estado, is headquartered in the Catamarca province of the Latin American nation.
- Key Points: KABIL, a government-owned entity, will initiate the exploration and development activities for five lithium brine blocks—Cortadera-I, Cortadera-VII, Cortadera-VIII, Cateo-2022-01810132, and Cortadera-VI, collectively spanning an area of approximately 15,703 hectares.
- As part of its expansion, KABIL is planning to establish a branch office in Catamarca, Argentina.
- This marks a significant milestone as it represents the first lithium exploration and mining project undertaken by a government company in India.
- Argentina, situated within the global "Lithium Triangle" alongside Chile and Bolivia, collectively possesses more than half of the world's total lithium resources.
Khanij Bidesh India Ltd. (KABIL):
- It is a Joint Venture Company among National Aluminium Company (NALCO), Hindustan Copper Limited (HCL) and Mineral Exploration Corporation Limited (MECL).
- It has been formed in August 2019.
- KABIL is focusing on identifying and sourcing battery minerals like Lithium and Cobalt.
- KABIL is a joint venture company focused on identifying, acquiring, developing, processing and making commercial use of strategic minerals in overseas locations for supply in India.
Current Statistics About Lithium in India:
- India has recently discovered 5.9 million tonnes of lithium reserves in Jammu & Kashmir and ranks seventh globally.
- The primary lithium reserve in India has been discovered in the Salal-Haimana area of Reasi District in Jammu and Kashmir, with additional smaller reserves identified in Karnataka.
- Presently, India fulfils its entire lithium demand through imports.
- In the fiscal year 2023, there was a notable increase in lithium imports in India, reaching approximately $3 billion (around ?24,900 crore), indicating a 58% growth compared to the figures in FY22.
- More than 95% of India's lithium imports are sourced from China and Hong Kong.
Global Reserves of Lithium:
- Approximately half of the world's lithium resources are concentrated in Latin America, primarily in countries such as Bolivia, Argentina and Chile along with significant deposits in USA, Australia and China.
- Bolivia has the highest identified lithium resources in the world with 20 million tonnes, as per the US Geological Survey data.
- Argentina has the second-largest lithium reserve estimated to be close to 20 million tonnes.
- The United States follows Argentina with 12 million tonnes of lithium reserves.
- Chile ranks fourth globally with 11 million tonnes of lithium reserves.
- Australia occupies the fifth spot with 7.9 million tonnes of lithium reserves, according to the available data.
- China, the largest country in Asia, ranks sixth globally with 6.8 million tonnes of lithium reserve. China, without having the largest lithium reserves, continues to dominate lithium mining and processing in the world.
- Argentina holds a substantial portion, accounting for 20% of the world's total lithium resources, making it the second-largest contributor after Bolivia.
- Argentina is a key participant in the 'Lithium Triangle,' alongside Chile and Bolivia.
- Collectively, these three nations possess over two-thirds of the global lithium resources.
- The Lithium Triangle is a region in the Andes known for its rich lithium reserves.
- Notably, Argentina ranks second globally in terms of lithium resources, third in lithium reserves, and fourth in lithium production.
Importance of the Agreement:
- This agreement holds strategic value as it enables India to enhance its lithium supply, fostering the growth of both countries' lithium mining and downstream sectors.
- It contributes to the diversification of the supply chain for essential materials, aligning with the pursuit of Global Net Zero objectives.
- Given that a significant portion, approximately 54%, of India's lithium imports are currently sourced from China, which dominates 80% of the global supply, this deal helps reduce dependence on a single supplier.
- The initiative aligns with the Mineral Security Partnership (MSP), of which India is an active participant.
Union Minister Rao Inderjit Singh launches the MPLADS e-SAKSHI Mobile Application for the Revised Fund Flow Procedure under the MPLAD Scheme (PIB)

- 17 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News?
Recently, the Minister of State (Independent Charge) of the Ministry of Statistics and Programme Implementation (MoSPI) Rao Inderjit Singh launched the MPLADS e-SAKSHI Mobile Application at Khurshid Lal Bhawan, New Delhi.
What is the e-SAKSHI Mobile Application?
- The e-SAKSHI mobile application was devised for the revamped fund flow procedure within the Members of Parliament Local Area Development Scheme (MPLAD).
- It is poised to revolutionize the way Members of Parliament (MPs) engage with and oversee development projects in their constituencies.
Key Features of e-SAKSHI:
- Convenience and Accessibility: MPs can seamlessly propose, track, and supervise projects with the application, ensuring convenience and accessibility at their fingertips.
- Real-time Access: The application provides real-time access, enhancing decision-making by enabling swift responses to emerging needs or issues.
- Streamlined Communication: e-SAKSHI facilitates streamlined communication between MPs and relevant authorities, promoting an efficient exchange of information.
- Transparency: MPs receive instant updates on the status and progress of proposed projects, promoting transparency in the implementation process.
- Budget Management: The application includes features for budget management, empowering MPs to monitor expenditures effectively.
Key Points about the MPLAD Scheme:
- Introduced in 1993, MPLAD is a fully funded Government of India scheme where funds are released directly to district authorities as grants-in-aid.
- The funds are non-lapsable, allowing the carry-forward of entitlement not released in a specific year to subsequent years, subject to eligibility.
- MPs have an annual entitlement of ?5 crore per constituency, with their role limited to recommending works.
- District authorities are responsible for sanctioning, executing, and completing the recommended works within stipulated timelines.
- Lok Sabha members recommend works in their respective constituencies, while Rajya Sabha members can recommend works anywhere in their elected state.
- Nominated members can recommend works nationwide.
- MPLADS works can be implemented in areas affected by various natural calamities, ensuring a flexible and responsive approach to development needs.
In Assam, creeper conservation rides revived Karbi traditional game (The Hindu)

- 17 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News?
A dying traditional game, given a fresh lease of life at the ongoing Karbi Youth Festival (KYF) in central Assam’s Karbi Anglong district, has fuelled a drive for conserving a creeper with an African connection.
About African Dream Herb:
- The African dream herb, also known by various names such as Giant sea bean, snuff box, and Entada rheedii, is a perennial climbing vine valued by African traditional healers for its ability to induce vivid dreams, facilitating efficient communication with ancestors.
- Indigenous to Africa, Asia, Australia, and Madagascar, this vine thrives in tropical lowlands, along coastlines, river banks, woodlands, thickets, and riverine rainforests.
- Uses: A paste derived from its leaves, bark, and roots serve purposes ranging from wound cleaning to treating burns and addressing jaundice in children.
- The plant's tea, made from its entirety, aids in improving blood circulation to the brain and healing the aftermath of a stroke.
- The bark is employed to treat ailments such as diarrhoea, dysentery, and parasitic infections.
- This vine produces dark brown, spherical seeds, almost the size of a human patella or kneecap, used in the traditional game 'Hambi Kepathu,' associated with the origin of the Karbi community.
What is Hambi Kepathu?
- Also known as Simrit in some regions of Karbi Anglong, Hambi Kepathu is played on three rectangular courts with two teams of three members each.
- In this male-only game, players place a 'hambi' (glazed creeper seed) vertically on the midpoint of the boundary line for opponents to hit with their 'hambi.'
- The name Hambi Kepathu is derived from the first syllables of the names of a Karbi sister-brother duo, adding to the array of traditional Karbi games such as 'Pholong' (spinning top), 'Thengtom Langvek' (torch swimming), and 'Kengdongdang' (bamboo stilt race).
PM pays homage to Sri Guru Gobind Singh Ji on his Parkash Utsav (The Hindu)

- 17 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News?
January 17 marks the 357th birth anniversary of Guru Gobind Singh, the revered Sikh leader born in Patna, Bihar.
About Guru Gobind Singh:
- Guru Gobind Singh, the 10th and the last Guru of the Sikhs, was born as Gobind Rai on December 22, 1666, in Patna, Bihar, to Guru Teg Bahadur, the ninth Guru of Sikhism.
- Following the martyrdom of his father by the Mughal emperor Aurangzeb in 1675, Guru Gobind Singh assumed leadership at the age of nine.
- Renowned as a warrior, poet, and prophet, Guru Gobind Singh is cherished by Sikhs for his defence of faith and advocacy for equality and justice.
- In 1699, Guru Gobind Singh formed the institution of the Khalsa and introduced the Five Ks — Kesh (uncut hair), Kangha (wooden comb), Kara (iron or steel bracelet), Kirpan (sword), and Kacchera (short breeches).
- He fought 14 wars against his oppressors and tyrants, but with ethical and moral principles, never taking captives, nor damaging places of worship; he was never the first to be the aggressor.
- The notable conflicts include the Battle of Bhangani, the Battle of Nadaun, the Battle of Anandpur, the Battle of Chamkaur, the Battle of Muktsar, and the Battle of Khidrana
- While continuing to lead with steely determination, Guru Gobind Singh faced with fortitude, the execution of his two sons, Zorawar Singh and Fateh Singh.
- The duo was bricked alive at Sirhind by the then-governor.
- He lost two more sons in the battle of Chamkaur Sahib, yet he stayed true to his goal.
- When the Mughal army, numbering over a lakh, marched against his troop of 40 soldiers, he marched on bravely, penning his famous hymn, mitr pyare nu haal muridan da kehna (Oh beloved friend of the Lord, see the plight of your disciples).
- Guru Gobind is credited with finalising the manuscript of Guru Granth Sahib, declaring it to be the ultimate Guru of the Sikhs.
- His metaphysical, sublime and exquisite poetry has been immortalised in his composition, Dasam Granth, reflected in Jaap Sahib, Chandi Di Vaar, Tav Prasad savaiye and Benti Chaupai, among others.
- He wrote in Punjabi, Arabic, Braj Bhasa, Sanskrit and Persian and remains a much-revered guru.
- He was assassinated in 1708, at the age of 41.
Defence upgrade roadmap: Apex body led by Prime Minister, MoD sci-tech unit (Indian Express)
- 17 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News?
The expert committee, led by Vijay Raghavan, the former principal scientific advisor, proposed that the country's defence technology roadmap be overseen by an apex body called the Defence Technology Council, with the Prime Minister serving as its chair.
The context in which the Vijay Raghavan Committee was Established:
- Formed by the government last year, the committee was tasked with assessing the functioning of the Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO).
- The committee's report, submitted this month, follows the government's initiative to address significant delays in various DRDO projects.
- This scrutiny comes in response to concerns raised by the Parliamentary Standing Committee on Defence, which noted that 23 out of 55 mission mode projects faced substantial delays.
- In 2022, the Comptroller and Auditor General (CAG) highlighted that 67% of the 178 scrutinized projects failed to meet their initially proposed timelines.
- The CAG attributed these delays to factors such as persistent alterations in design specifications, delays in completing user trials, and delays in placing supply orders.
- The prevalent practice of seeking multiple extensions for projects, particularly those designated under the Mission Mode category, has been identified as undermining the intended purpose of these initiatives.
Major Recommendations of the Vijay Raghavan Committee:
- Establishment of the Defence Technology Council: Headed by the Prime Minister, with the Defence Minister and the National Security Advisor serving as Vice Presidents.
- This council is envisioned to play a pivotal role in charting the nation's defence technology roadmap, deciding on significant projects, and overseeing their execution.
- An executive committee, led by the Chief of Defence Staff, is proposed, featuring members such as the Principal Scientific Advisor, the three service chiefs, their vice chiefs, and representation from academia and industry.
- Creation of the Department of Defence Science, Technology, and Innovation: To be led by a technocrat, this department aims to foster defence research and development within the academic and startup ecosystem.
- Additionally, it is designated as the secretariat for the Defence Tech Council chaired by the Prime Minister.
- Drawing expertise from scientists in the Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO) and academia, it will compile a knowledge repository on production expertise, conduct background research for the Defence Tech Council, and contribute to informed decisions on technology production.
- Restructuring of DRDO's Focus: Recommends that DRDO concentrate on its original mission of research and development for defence purposes.
- The suggestion is for DRDO to abstain from involvement in productization, production cycles, and product management, tasks deemed more suitable for the private sector.
- Currently, DRDO is engaged in all aspects of its projects, spanning from research and development to production.
The last batch of Mizoram Bru refugees permanently settled in Tripura (The Hindu)

- 16 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News?
The Tripura government has allocated land for the rehabilitation of the last batch of Mizoram Bru refugees, who were granted permanent settlement in Tripura through a Home Ministry-initiated quadripartite agreement signed on January 16, 2020.
Who are Bru refugees?
- Brus, also referred to as Reangs, are a tribal community indigenous to northeast India and have historically resided in parts of Mizoram, Tripura, and Assam.
- In the state of Tripura, the Brus are a designated Particularly Vulnerable Tribal Group (PVTG).
- Most Brus residing in Tripura today have suffered more than two decades of internal displacement, fleeing ethnic persecution primarily from the neighbouring state of Mizoram.
Bru-Reang Refugee Crisis:
- It all started in 1995 when the Young Mizo Association and the Mizo Students' Association demanded that Brus be eliminated from Mizoram’s electoral rolls as they were not indigenous inhabitants.
- Being ethnically distinct from the majority of Mizos, the Brus are often referred to as “Vai” in the state, meaning outsiders or non-Mizos.
- Tensions escalated after the Brus retaliated against the Mizos’ attempts to disenfranchise them, and organized themselves into an armed group, the Bru National Liberation Front, and a political entity, the Bru National Union.
- They also demanded the creation of a separate Bru Autonomous District Council (ADC) in western Mizoram as per the provisions of the sixth schedule of the Indian Constitution.
- However, their attempts at seeking greater autonomy were foiled and resultant ethnic clashes forced many Reangs in Mamit, Kolasib and Lunglei districts of Mizoram to migrate to neighbouring Tripura in 1997.
- Today, roughly 35,000 Reangs continue to reside in north Tripura’s Kanchanpur camp as refugees, as per Home Ministry estimates.
Have there been any attempts to resettle the Brus?
- The state governments, along with the union government have made multiple attempts to send Brus back to their homeland in Mizoram.
- But until 2014, following eight rounds of resettlement, only an estimated 5,000 individuals, or 1622 Bru-Reang families returned to Mizoram in various batches.
- In July 2018, the governments of Tripura, Mizoram, and the central government concluded a quadripartite pact with Bru community representatives to resettle refugees in Mizoram.
- This was however opposed by not only native Mizo groups but also by the Reangs who feared threats to life and further ethnic repression in their home state.
- Efforts were still made to pursue the terms of this pact. The supply of free ration to relief camps was halted on instructions of the Home Ministry in a bid to hastily complete the repatriation of refugees, which resulted in at least six starvation deaths.
- Sensing a failure of the 2018 pact, the four groups once again came together in January 2020 to sign another quadripartite pact to resettle the Brus, this time in the state of Tripura.
- The central government earmarked a Rs 600 crore package to aid the rehabilitation efforts, and the Bru families were promised a residential plot, a fixed deposit of Rs 4 lakh, a Rs 1.5 lakh grant to construct their houses, as well as free ration and a monthly stipend of Rs 5,000 for a period of two years.
- Additionally, the renewed 2020 pact also promised to include the displaced Reangs in the electoral rolls in Tripura.
Darjeeling zoo’s success with snow leopards: Why wild cats are fussy breeders (Indian Express)

- 16 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News?
The Padmaja Naidu Himalayan Zoological Park (PNHZP) in Darjeeling has made headlines for successfully breeding 77 snow leopards since the 1980s, placing it next only to New York’s Bronx Zoo, which has produced 80 snow leopard cubs since it started breeding experiments with the species in the 1960s.
About Snow Leopard:
- The snow leopard, also known as the ounce, is a large Asian cat belonging to the family Felidae, classified as Panthera uncia.
- It preys on various animals, including marmots, wild sheep, ibex, and domestic livestock. As the apex predator in the mountain ecosystem, snow leopards serve as vital indicators of ecosystem health.
- Habitat: Native to the mountain ranges of Central and South Asia, snow leopards are found in India, specifically in the western Himalayas covering Jammu and Kashmir, Ladakh, Himachal Pradesh, Uttarakhand, Sikkim, and Arunachal Pradesh in the eastern Himalayas.
- Threats to Survival: With an estimated 4,000 to 6,500 snow leopards remaining in the wild, around 500 of them are in India.
- Human settlement expansion, particularly livestock grazing, has escalated conflicts.
- Climate change, causing a rise in average temperatures across their habitat, poses an additional threat.
- Poaching, driven by illegal trades in pelts and body parts used in traditional Chinese medicine, further endangers their lives.
- Protection Status:
- IUCN Red List: Vulnerable
- CITES: Appendix I
- Wildlife (Protection) Act, 1972: Schedule I
- Conservation Efforts: The Government of India initiated Project Snow Leopard in 2009 to safeguard and conserve the snow leopard population and their habitats through participatory policies.
- Under the UNDP's SECURE Himalaya project in 2020, India's first Snow Leopard Conservation Centre was launched in Uttarkashi, Uttarakhand, promoting conservation efforts in the region.
About Padmaja Naidu Himalayan Zoological Park (PNHZP):
- Formerly known as the Himalayan Zoological Park, the PNHZP was established in August 1958 in Darjeeling, West Bengal.
- Dedicated to the preservation of ecological balance in the Eastern Himalayas, the park pursues the following objectives:
- Ex-situ Conservation and Captive Breeding: The park focuses on the ex-situ conservation and captive breeding of endangered Himalayan animal species.
- Awareness and Education: Aiming to educate and motivate both local residents and visitors, the park conducts awareness campaigns highlighting the significance of Himalayan ecosystem conservation.
- Applied Research: The PNHZP initiates applied research in animal biology, behaviour, and healthcare, contributing to a better understanding of these aspects.
- Conservation Pioneering: Recognized as a conservation pioneer, the zoo initiated the first ex-situ conservation breeding program in 1986, commencing with the Snow Leopard conservation breeding project.
- The Red Panda project followed suit in 1990.
- High-Altitude Zoo: The PNHZP holds the distinction of being the largest high-altitude zoo in the country, making significant strides in the conservation of endangered Eastern Himalayan species in India.
How do flights land safely despite fog and low visibility? The wizardry tech that makes it possible! (Financial Express)

- 16 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News?
In the past few days, the Delhi airport has experienced chaos, resulting in over 100 flight delays, 10 flights being diverted, and some even cancelled due to low visibility caused by dense fog conditions affecting flying operations.
What is an Instrument Landing System?
- Fog, which is the suspension of water droplets near the ground, poses a considerable obstacle to aircraft operations during instances of reduced visibility.
- This atmospheric condition results in thick mist which hampers flight operations, necessitating the reliance on instruments like the “Instrument Landing System” (ILS) to navigate through the obscured surroundings.
- ILS is a standard International Civil Aviation Organisation (ICAO) precision landing aid that is used to provide accurate azimuth (angular measurement in a spherical coordinate system) and descent guidance signals for guidance to flight for landing on the runway under adverse weather conditions.
- To put things in perspective, ILS operates in tandem with ground-based equipment and avionic components on the aircraft, providing precise guidance to pilots during the critical phases of approach and landing.
- The ILS guiding system helps planes land in low visibility with the help of radio signals and also sometimes high-intensity lighting arrays.
- Among the various categories of ILS, Category 3 (CAT III) is the most significant due to its capability to support landing operations in low visibility conditions, thereby enhancing flight safety and operational efficiency.
- At present, airports like Delhi, Amritsar, Jaipur, Lucknow, and Kolkata among others use CAT IIIB technology in India.
- However, the absence of pilots or the ILS technology can lead to massive delays and cancellations.
- Moreover, a lot of financial and logistics are required to operate the technology which is still a distant dream at many airports around the country.
How does this system work?
- Consisting of two main components—the localizer and the glide slope—the CAT safe system functions by transmitting radio signals that help pilots align their aircraft with the correct runway and maintain the appropriate descent path.
- The localizer ensures lateral alignment, guiding the aircraft along the correct azimuth toward the runway centerline.
- Simultaneously, the glide slope provides vertical guidance, aiding pilots in maintaining the proper descent angle for a safe landing.
- Together, these components create a reliable and accurate navigational reference, allowing pilots to execute precision landings even when external visibility is severely compromised.
- Notably, ILS-equipped runways are equipped with ground-based transmitters positioned at the end of the runway, emitting signals that are received by the aircraft’s onboard ILS receiver.
- As the aircraft approaches the runway, the pilot uses the visual and audible cues provided by the ILS to make real-time adjustments, ensuring that the aircraft remains aligned with the desired glide path.
- In essence, the technology significantly enhances aviation safety and operational reliability by enabling pilots to conduct precise landings even in conditions that would otherwise pose a considerable risk.
NHAI cracks down on multiple FASTags for a single vehicle, launches ‘One Vehicle, One FASTag’ program (Financial Express)

- 16 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News?
The National Highways Authority of India (NHAI) announced on Monday (January 15) that FASTags with valid balances but incomplete KYC will be deactivated by banks after January 31, 2024.
What is the ‘One Vehicle, One FASTag’ Program?
- In a bid to enhance the efficiency of the electronic toll collection system and facilitate seamless movement at toll plazas, NHAI has initiated the ‘One Vehicle, One FASTag’ program, discouraging the use of a single FASTag for multiple vehicles or linking multiple FASTags to a particular vehicle.
- NHAI encourages FASTag users to complete the ‘Know Your Customer’ (KYC) process for their latest FASTag, aligning with RBI guidelines.
- To prevent inconvenience, users must ensure KYC completion for their latest FASTag and discard all previously issued FASTags through their respective banks.
- The initiative aims to deactivate or blacklist previous tags after January 31, 2024.
- Ensuring seamless and comfortable journeys: The ‘One Vehicle, One FASTag’ initiative, coupled with the high penetration rate of FASTag at around 98% and over 8 crore users, is poised to streamline toll operations, ensuring efficient and comfortable journeys on national highways.
About FASTags:
- FASTag serves as an electronic toll collection system in India, administered by the NHAI.
- Utilising Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) technology, it facilitates toll payments directly from the linked prepaid or savings account or directly from the toll owner.
- FASTag utilizes Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) technology, allowing seamless toll payments while the vehicle is in motion.
- Windscreen Affixation: FASTag is affixed on the vehicle's windscreen, providing a hassle-free experience for customers to drive through toll plazas without the need to stop for payments.
- Automatic Deduction: Toll fares are automatically deducted from the linked account of the customer, ensuring a swift and cashless transaction.
- Vehicle Specific: Once affixed to a vehicle, FASTag becomes vehicle-specific, preventing transferability to another vehicle.
- Purchase from NETC Member Banks: FASTag can be conveniently purchased from any of the National Electronic Toll Collection (NETC) Member Banks.
- Prepaid Account Recharge: In the case of linking FASTag to a prepaid account, customers need to recharge or top-up the tag based on their usage.
Govt cuts windfall tax on petroleum crude to Rs 1,700 per tonne (The Hindu)

- 16 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News?
The government has cut the windfall tax on domestically-produced crude oil to ?1,700 per tonne from ?2,300 per tonne with effect from January 16.
What is Windfall Tax?
- A Windfall Tax is imposed by governments on specific industries that experience exceptionally high profits due to economic conditions surpassing the norm.
- The term "windfall" denotes an unforeseen surge in profits, leading to the imposition of the windfall tax on the excess gains.
- Imposition Criteria: Governments impose the Windfall Tax when there is a sudden and substantial increase in an industry's revenue.
- Notably, this increase must be unrelated to the company's intentional actions, such as business strategies or expansions, but instead linked to external events beyond its control.
- A Windfall Tax is typically triggered by external occurrences, such as the unexpected surge in profits observed in the oil and gas industries amid the Russia-Ukraine conflict.
- Tax Rates: Governments tax these windfall gains at rates higher than the standard tax rates applicable to regular profits.
- Target Industries: Commonly, industries such as oil, gas, and mining become targets for windfall gains tax.
Objectives:
- Redistribution of Gains: To redistribute unexpected profits, especially when high prices benefit producers at the expense of consumers.
- Funding Social Welfare Schemes: Utilizing the windfall tax revenue to support social welfare initiatives.
- Supplementary Revenue Source: Acting as an additional revenue stream for the government.
- Addressing Trade Deficit: Providing a means for the government to mitigate the widening trade deficit in the country.
When Did India Introduce Windfall Tax?
- To address the shortage of energy products on the domestic market, the Indian government added a special additional excise duty on the export of gasoline and diesel, known as the Windfall Tax, on July 1st, 2022.
Why are Countries Levying Windfall Taxes Now?
- Since the past few years, gasoline prices, crude oil, gas, and coal have significantly increased.
- COVID-19 and the conflict between Ukraine and Russia made this increase even more pronounced.
- Because of this, energy companies profited handsomely at the expense of consumers, who now pay much higher prices for their energy use.
- The UN Secretary-General, therefore, encouraged nations to impose windfall taxes on those companies that have greatly benefited from the rise in the price of fossil fuels.
- As a result, many countries, including the UK, Germany, and others, besides India, are considering imposing Windfall Taxes.
Conclusion
In conclusion, a windfall tax is a tax that a government may impose or an additional tax that may be imposed on a business when it generates a sizable unanticipated profit, particularly if the company has benefited from favourable economic conditions.
Companies in specific economic sectors, such as the oil and gas industry, that profit from circumstances like commodity shortages that significantly drive up the cost of their goods at the expense of consumers may be subject to windfall taxes.
Goyal asks FCI officers to turn whistleblowers to curb corruption (The Hindu)

- 15 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News?
Recently, the Food Minister said the role of FCI is not only to deliver ration but also to instil confidence in farmers and beneficiaries by bringing in transparency, efficiency and accountability.
About the Food Corporation of India (FCI):
- FCI is a statutory body with multifaceted objectives aimed at ensuring national food security.
- It was established through the enactment of the Food Corporation Act, of 1964 by the Parliament.
- As part of the Ministry of Consumer Affairs, Food and Public Distribution, FCI plays a pivotal role in supporting farmers, managing food distribution, and maintaining strategic food grain stocks.
Key Objectives:
- Effective Price Support Operations: FCI focuses on safeguarding farmers' interests through efficient price support operations.
- Public Distribution System (PDS): The distribution of food grains nationwide for the PDS forms a crucial aspect of FCI's mandate.
- Operational and Buffer Stocks: FCI is entrusted with maintaining optimal levels of operational and buffer stocks to ensure national food security.
Role in Ensuring Food Security:
- Procurement at Minimum Support Price (MSP): FCI actively engages in procuring food grains, primarily wheat and paddy, under the Price Support Scheme to guarantee MSP for farmers and provide affordable food to vulnerable sections.
- Coarse Grains Procurement: Additionally, FCI oversees the procurement of coarse grains, such as Jowar and Bajra, in coordination with state government agencies.
- Storage Capacity: To meet storage obligations, FCI boasts an extensive network of storage depots and silos strategically positioned across the country.
- Movement and Distribution: FCI undertakes the movement of food grain stocks from surplus to deficit regions, ensuring planned delivery through PDS, creating buffer stocks, and supplying food grains for defence, paramilitary forces, and natural calamities.
In conclusion, FCI's multifaceted role encompasses procurement, storage, and distribution, contributing significantly to the nation's food security and the well-being of farmers.
Medical care on India’s trains is running late, with passengers at risk (The Hindu)

- 15 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News?
The Balasore train accident in June 2023 raised important concerns about rail safety, but it was largely about accident-related safety.
Provision of Medical Care in Railway:
- In 1995, a ‘Special first aid box’ was provided in long-distance superfast trains, Shatabdi and Rajdhani trains.
- In 1996, as part of a pilot project, Railways stationed a medical team in two long-distance trains.
- This team consisted of a medical officer, a male nurse, and an attendant.
- The Railways subsequently discontinued the service – but to make healthcare accessible, it decided to give doctors travelling on trains a 10% discount if they were willing to provide medical services en route.
- In 2017, the Supreme Court directed the Railways to set up a committee consisting of experts from the All India Institute of Medical Sciences (AIIMS) to recommend further measures.
- Based on the committee’s recommendations, the Railways decided to modify the contents of the first aid boxes and provide them at all railway stations and in all passenger-carrying trains.
- It also mandated first-aid training for railway staff at the time of joining and once every three years.
- In 2021, the Railways launched an integrated helpline number – 139 – for all queries concerning the railways, including medical assistance.
Way Forward
- Railways should ensure the updated 88-item first-aid list is in place on all trains and that passengers are aware of these services.
- Periodic inspections are necessary to maintain the quality of care as well.
- Finally, the Railways need to install a system to capture data on the healthcare needs of people travelling on trains and use that to inform policy.
In a big push for India's energy security, ONGC makes two significant gas discoveries in the Mahanadi basin block (Business World)

- 15 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News?
In a significant stride towards bolstering India's energy security, the state-owned Oil and Natural Gas Corporation (ONGC) has successfully unearthed two substantial natural gas reserves within the Mahanadi basin block in the Bay of Bengal.
About the Mahanadi River Basin:
- Ranked as the 8th largest river basin in the country, the Mahanadi River Basin boasts a substantial catchment area spanning 139,681.51 sq. km, representing approximately 4.28% of the total geographical area of India.
- Encompassing significant portions of Chhattisgarh and Odisha, along with smaller segments of Jharkhand, Maharashtra, and Madhya Pradesh, this basin stretches across diverse terrains and is surrounded by the Central India hills to the north, the Eastern Ghats to the south and east, and the Maikala range to the west.
- The basin's physiographic features are categorized into four regions:
- The northern plateau
- The Eastern Ghats
- The coastal plain (a fertile delta area), and
- The erosional plains of the central tableland.
- Notably, the basin receives about 90% of its rainfall during the monsoon season.
- Agriculture dominates the landscape, covering 54.27% of the total area, while water bodies occupy 4.45%. Predominant soil types include red and yellow soils.
Key Characteristics of the Mahanadi River:
- As one of the major east-flowing peninsular rivers in India, the Mahanadi River originates from the Sihawa range of hills in the Dhamtari district of Chhattisgarh.
- Water Potential: Second only to the Godavari River in terms of water potential among peninsular rivers, the Mahanadi River spans a total length of 851 km, with 357 km flowing through Chhattisgarh and 494 km through Odisha.
- Tributaries: The river is augmented by left bank tributaries including the Seonath, Hasdeo, Mand, and Ib, while the right bank receives contributions from the Ong, Tel, and Jonk.
- Hirakud Dam: An engineering marvel, the Hirakud Dam, recognized as the world's longest earthen dam at 26 km, is strategically located about 15 km from Sambalpur in Odisha, providing essential water management for the region.
- The Mahanadi River plays a crucial role in the hydrology of Chilika Lake, designated as a wetland of international importance under the Ramsar Convention.
- Approximately 61% of the lake's inland flow originates from the Mahanadi River system, mainly through its distributaries, Daya and Bhargabi.
Global surgery: why access to essential surgery is important (The Hindu)

- 15 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News?
Global surgery is the neglected stepchild in global health. The neglect is more shocking in South Asia which has the largest population globally lacking access to essential surgery.
What is global surgery?
- Global surgery focuses on equitable access to emergency and essential surgery.
- While it predominantly focuses on low- and middle-income countries (LMICs), it also prioritises access disparities and under-served populations in high-income countries (HICs).
- These “surgeries” include essential and emergency surgeries such as surgery, obstetrics, trauma, and anaesthesia (SOTA).
- Despite small differences, there is largely a consensus across multiple international groups on about thirty or so procedures that fall under the umbrella of emergency and essential surgery.
The Global Scenario:
- As per the Lancet Commission on Global Surgery (LCoGS), more than 70% of the global population, which amounts to five billion individuals, lacks timely access to safe and affordable surgical care.
- Notably, over 1.6 billion of these individuals reside in South Asia. Access gaps are particularly acute, with 99% and 96% of people in low- and lower-middle-income countries (LLMICs), respectively, facing challenges compared to 24% in high-income countries (HICs).
Concerns and Impact:
- In 2010, surgically treatable conditions contributed to around 17 million deaths, surpassing the combined mortality burden of HIV/AIDS, tuberculosis, and malaria.
- The global disease burden also translates into a significant economic impact, with a projected cumulative loss of $20.7 trillion to the GDP across 128 countries by 2030 if the scale-up of surgical care remains inadequate.
Measures implemented for Global Surgery:
- India's Pradhan Mantri Jan Arogya Yojana has played a pivotal role by providing millions of surgeries at either zero or negligible cost, specifically benefiting the bottom 40% of the Indian population.
- In South Asia, Pakistan has developed a National Surgical Care Vision, while Nepal has initiated a comprehensive National Plan Encompassing Surgical, Obstetric, and Anaesthesia Care (NSOAP).
Way Ahead
- Addressing global surgery challenges requires a multi-faceted approach, emphasizing research, innovation, policy focus, and sustained financing.
- Key stakeholders, including organizations like the World Health Organization (WHO) and various non-profit groups, hold significant potential in advancing and supporting global surgery initiatives.
- Collaborative efforts on these fronts are crucial for ensuring equitable and accessible surgical care on a global scale.
India celebrates 76th Army Day with pride and gratitude (TOI)

- 15 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News?
Prime Minister Narendra Modi and President Droupani Murmu conveyed their warm wishes to Indian Army personnel on the occasion of Army Day.
Why is Army Day celebrated?
- On January 15, KM Cariappa took charge of the Indian Army from General Sir Francis Roy Bucher in 1949, who was the last British-serving Army chief.
- KM Cariappa became the first-ever Indian General to command the Army in its long eventful journey.
- Later, General Cariappa also became the Field Marshal of India.
- KM Cariappa, who is popularly known as Kipper, received King's commission in 1919 and was part of the first group of Indian cadets at the Royal Military College in Sandhurst, UK.
- He was the first Indian who attended Staff College in Quetta and the first one to command a battalion.
- In 1942, Cariappa raised the 7th Rajput Machine Gun which was later known as 17 Rajput.
- He was conferred with Field Marshal Rank in 1986 and passed away in 1993 at the age of 94.
Indian Army Day 2024: Theme
- The theme of the Indian Army Day 2024 is “In Service of the Nation”.
- The theme of 2024 focuses on the main essence of the Army.
- This year’s theme also resembles the motto of the Indian Army, “Service Before Self.”
- This year marks the 76th Army Day.
- The parade will be held under the command of the Army's Central Command, which is headquartered in Lucknow.
Indian Army Day 2024: Significance
- Indian Army Day is also known as Bhartiya Sena Diwas.
- The day promises a grand celebration to honour the valour and service of the Army officers.
- It also proves to be a day dedicated to spreading awareness and enthusiasm among the youth of the nation to join the Bhartiya Sena and serve the country selflessly.
- Army Day is dedicated to appreciating and acknowledging the sacrifice and dedication of the Indian Army towards protecting the country from the illegal invasion of enemies and attacks.
Indian Army Day 2024: History
- The Indian Army was established on 1 April 1895 by the British.
- Initially, the Indian Army was known as the Royal Indian Army.
- India attained Independence on 15 August 1947.
- On 15 January 1949, the first Commander-in-Chief of India General K.M. Cariappa took over the rule of British Army Official General Sir Francis Roy Bucher. Since then, this historic moment has been celebrated as Bhartiya Sena Divas.
- India is following the tradition of celebrating this grand day with great zeal and patriotism.
- Since 15 January 1949, India has been self-reliant in the field of defence.
The first-ever IUCN assessment of the Himalayan Wolf is out. And it is grim (DownToEarth)

- 13 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News?
The Himalayan Wolf is a prominent lupine predator found across the Himalayas the taxonomic status which was a puzzle till late, has been assessed for the first time in the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN)’s Red List.
Key Findings:
- Population Decline: The IUCN assessment highlights a persistent reduction in the habitat area, extent, and quality of Himalayan wolves.
- The estimated total population ranges from 2,275 to 3,792 mature individuals, with 227 to 378 in India.
Primary Threats:
- Depredation Conflict: Arising from habitat modification, encroachment, and depletion of wild prey populations.
- Hybridization with Dogs: Particularly in Ladakh and Spiti, where feral dog populations are on the rise.
- Illegal Hunting: Driven by trade in fur and body parts, including paws, tongues, and heads.
About the Himalayan Wolf (Canis lupus chanco):
- It is also called Tibetan wolves, which live at more than 4,000 metres altitudes.
- Habitat: It is found in the Himalayas (Nepal and India) and the Tibetan Plateau.
- Exhibits genetic adaptations to cope with hypoxic conditions.
- Characteristics: Adorned with thick fur, displaying brown colouration on the back and tail, complemented by paler yellows on the face, limbs, and underside.
- Larger than Indian and European wolves.
- Shows a preference for wild prey over domestic options.
- Conservation Status:
- IUCN’s Red List: Categorized as Vulnerable.
- Wildlife Protection Act, 1972: Listed under Schedule I.
- CITES: Included in Appendix I.
Recommended Actions for the Conservation of Himalayan Wolves:
- Ensure the preservation and restoration of robust wild prey populations and their natural habitats.
- Foster collaborative transboundary initiatives to safeguard and conserve the species across its range of countries.
- Integrate the Himalayan Wolf into comprehensive conservation programs for enhanced protection and sustainable management.
How GM mustard was developed, why the question of its approval has now reached the Supreme Court (Indian Express)

- 13 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News?
The Supreme Court recently questioned the Centre on why reports of the court-appointed Technical Experts Committee (TEC) on the biosafety of genetically modified (GM) crops were not looked into by the Genetic Engineering Appraisal Committee (GEAC).
Context:
- The Supreme Court has raised concerns about the approval process for the transgenic mustard hybrid DMH-11, developed by Delhi University with herbicide-tolerant traits through genetic modification.
- The Genetic Engineering Appraisal Committee (GEAC) had recommended its environmental release in 2022, but the court questioned whether the reports from the court-appointed Technical Experts Committee (TEC) were adequately considered before approval.
- DMH-11 contains two alien genes isolated from a soil bacterium called Bacillus amyloliquefaciens.
- Indian scientists improvised the barnase/barster male sterility technique to produce the DMH-11.
-
- Barnase/barster male sterility technique is a 1990s breeding innovation technique pioneered in Belgium.
- Indian scientists arranged the genes in a way that will allow a large number of high-yielding varieties of mustard to be developed, which is normally not possible.
- Genetically Modified Organisms (GMOs) undergo genome alterations, and transgenic organisms result from the introduction of foreign DNA sequences.
- Approval process for transgenic crops:
-
- Safety assessments by committees are conducted before the open field tests.
- Transgenic plants must be better than non-GM variants and environmentally safe for commercial clearance.
- GEAC recommends environmental release.
- Final approval by MoEFCC.
- Benefits of GM crops:
-
- Resistance against plant diseases.
- Improved yields
- Increased food security.
About the Genetic Engineering Appraisal Committee (GEAC):
- Establishment: GEAC operates as a statutory body mandated by the Environment Protection Act of 1986.
- Responsibility: It holds the responsibility for evaluating proposals concerning the environmental release of Genetically Modified (GM) organisms and associated products.
- GEAC operates under the purview of the Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change.
SC directs UOI to frame a policy to phase out heavy-duty diesel vehicles & replace them with BS VI (The New Indian Express)
- 13 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News?
The Supreme Court has directed the Centre to frame a policy within six months to replace heavy-duty diesel vehicles and replace them with BS VI vehicles, observing that the right to clean air is not the entitlement of people living in Delhi alone.
What are BS-VI Norms?
- Bharat stage (BS) emission standards are laid down by the government to regulate the output of air pollutants from internal combustion engines and spark-ignition engine equipment, including motor vehicles.
- The central government has mandated that vehicle makers must manufacture, sell and register only BS-VI (BS6) vehicles from April 1, 2020.
- The first emission norms were introduced in India in 1991 for petrol and in 1992 for diesel vehicles.
- Following this, the catalytic converter became mandatory for petrol vehicles and unleaded petrol was introduced in the market.
What is the Difference Between BS4 and BS6?
- Both BS-IV and BS-VI are unit emission norms that set the maximum permissible levels for pollutants that an automotive or a two-wheeler exhaust can emit.
- Compared to the BS4, BS6 emission standards are stricter
- Whereas makers use this variation to update their vehicles with new options and safety standards, the biggest modification comes in the permissible emission norms.
What area unit BSI, BSII, BSIII, BSIV, and BSVI emission norms?
- The abbreviation BS refers to ‘Bharat Stage’.
- It is prefixed to the iteration of the actual emission norms.
- The primary rules with the soubriquet Asian nation 2000 were introduced in the year 2000, with the second and third iterations being introduced in 2001 and 2005 with the soubriquet BSII (BS2) and BSIII (BS3), respectively.
- The fourth iteration, BSIV, was introduced in 2017 and therefore the delay between the introduction of BS3 and BS4 resulted in fast-tracking the BSVI or BS6 emission norms rather than BSV (BS5) norms.
- On 29 April 1999, the Supreme Court of India ruled that all vehicles in the country had to meet Euro I or India 2000 norms by June 1, 1999, and Euro II would be mandatory in the National Capital Region (NCR) from April 2000.
- Carmakers were not prepared for this transition and in a subsequent judgment, the implementation of Euro II was deferred.
- On 29 April 1999, the Supreme Court of India ruled that all vehicles in the country had to meet Euro I or India 2000 norms by June 1, 1999, and Euro II would be mandatory in the National Capital Region (NCR) from April 2000.
- In 2002, the government accepted the report submitted by the Mashelkar committee, which proposed a road map for the rollout of Euro-based emission norms in India.
- It also recommended a phased implementation of future norms, with regulations being implemented in major cities first and extended to the rest of the country after a few years.
- Based on the recommendations of the committee, the National Auto Fuel policy was announced officially in 2003.
- The road map for the implementation of the BS norms was laid out in 2010.
- The policy also created guidelines for auto fuels, reduction of pollution from older vehicles and R&D for air quality data creation and health administration.
- The standards and the timeline for implementation are set by the Central Pollution Control Board under the Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change.
- Since October 2010, Bharat Stage (BS) III norms have been enforced across the country.
- BS-IV emission norms were put in place in 13 major cities from April 2010, and the entire country from April 2017.
- In 2016, the government announced that the country would skip the BS-V norms altogether and adopt BS-VI norms by 2020.
Science Ministry team visits Hawaii to take stock of international telescope project (The Hindu)

- 13 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News?
In a signal of renewed enthusiasm for a global scientific project, an official delegation from the Department of Science and Technology visited Mauna Kea, an inactive volcano on the island of Hawai’i in the United States, to discuss “challenges” to the Thirty Meter Telescope (TMT) project.
About Thirty Meter Telescope (TMT) Project:
- The name "Thirty Metre" denotes the telescope's substantial 30-meter mirror diameter, composed of 492 glass segments seamlessly integrated.
- It is an international collaboration involving institutions such as CalTech, the Universities of California, Canada, Japan, China, and India, facilitated by the Department of Science and Technology (DST) and the Department of Atomic Energy (DAE).
- Significance: Upon completion, it will surpass the world's largest existing visible-light telescope in width by threefold.
- A larger mirror enables greater light collection, enhancing the telescope's capability to observe distant, faint objects.
- It is projected to be over 200 times more sensitive than current telescopes and possess 12 times the resolving power of the Hubble Space Telescope.
- Application: The TMT's primary purpose includes the study of exoplanets, specifically exploring whether their atmospheres contain water vapour or methane, potential indicators of extraterrestrial life.
- Opposition against Construction: The proposed site, Mauna Kea in Hawaii, is contested due to its sacred significance to native Hawaiians, who perceive such projects as desecrating the mountain.
Contribution of India:
- India expects to be a major contributor to the project and will provide:
- Hardware (segment support assemblies, actuators, edge sensors, segment polishing, and segment coating)
- Instrumentation (first light instruments), and
- Software (observatory software and telescope control systems) worth $200 million.
- Of the 492 precisely polished mirrors that the telescope needs, India will contribute 83.
- The Indian Institute of Astrophysics (IIAP) is leading the consortium of Indian institutions that are involved with the TMT project.
India gears up for HPV vaccine drive against cervical cancer (Indian Express)
- 13 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News?
In a bid to reduce cases of cervical cancer, the government is likely to roll out an immunisation campaign against Human Papillomavirus (HPV) in the second quarter of the year.
What Is Cervical Cancer?
- Cervical cancer starts in the cells lining the cervix -- the lower part of the uterus (womb).
- Cancer starts when cells in the body begin to grow out of control.
- It typically develops slowly, primarily caused by persistent infection with certain high-risk types of human papillomavirus (HPV).
- Human papillomavirus (HPV) is a common sexually transmitted infection which can affect the skin, genital area and throat.
- Women living with HIV are 6 times more likely to develop cervical cancer compared to women without HIV.
- Cervical cancer can be cured if diagnosed at an early stage and treated promptly.
- According to WHO, countries around the world are working to accelerate the elimination of cervical cancer in the coming decades, with an agreed set of three targets to be met by 2030.
How does the vaccine prevent cancers?
- The quadrivalent vaccines, including the Serum Institute of India’s Cervavac, prevent the entry of four of the most common types of HPV 16, 18, 6 and 11 thereby preventing infections, genital warts, and eventually cancer.
- At least 14 HPV types have been identified to have the potential to cause cancer.
-
- Among these, HPV types 16 and 18 are considered to be the most oncogenic, causing about 70 per cent of all cervical cancer cases globally.
- Universal immunisation of girls also reduces the transmission of the infection to boys and protects them from other cancers.
Who should get the HPV vaccine?
- The vaccine has to be administered to adolescent girls before they are sexually active.
- This is because the vaccine can only prevent the entry of the virus.
- “HPV is a very common infection and 90% of sexually active women already have it.
- Other than that, the response to the vaccine is also better in adolescents.
- This is the reason a booster is needed for girls over the age of 15 years who get the shot.
- Although not covered by the planned government campaign, the vaccine can also be administered to adolescent boys and is recommended for men who have sex with men.
Why is an HPV vaccination campaign important?
- More than 95% of all cervical cancer cases are linked to persistent infection with certain high-risk strains of HPV.
- What this essentially means is vaccination can be effectively used to prevent the infection and thereby cervical cancer cases.
- This is especially necessary in a country like India which accounts for nearly a fifth of the cervical cancer cases globally.
-
- India reports around 1.25 lakh cases and about 75,000 deaths each year.
- “The vaccine is 97% effective in preventing cervical cancer. This is the reason more than 100 countries have now implemented HPV vaccination programmes and they have seen a decline in the incidence as well.
Ganga mission gets the power to allow treated sewage into water bodies (Indian Express)

- 12 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News?
The National Mission for Clean Ganga (NMCG), the Centre’s nodal agency responsible for the abatement of pollution in river Ganga and its tributaries, has assumed new powers under which it may now permit the discharge of treated sewage and effluent that conforms to the prescribed “norms” into the river, canal or water bodies.
About the National Mission for Clean Ganga (NMCG):
- The National Clean Ganga Mission (NMCG) is a flagship programme developed by the National Council for the Rejuvenation, Protection and Management of the Ganga River, also known as the National Ganga Council.
- It is registered as a society under the Societies Registration Act, 1860.
- It came into existence on August 12th 2011 and is supported by the State-Level Program Management Groups (SPMGs) in Uttar Pradesh, Uttarakhand, Bihar, Jharkhand and West Bengal.
- The Government of India established this body to encourage a coordinated effort by the listed states to tackle the contamination of the Ganga River by offering financial and technological assistance.
Key objectives of the National Mission for Clean Ganga (NMCG):
- The project entails rehabilitating and boosting existing STPs and immediate short-term action to reduce pollution at the exit points on the riverfront in order to control the inflow of sewage.
- To preserve the consistency of the water cycle without altering the fluctuations of the natural season.
- Restore and control surface and groundwater supply.
- Regenerate and preserve the natural flora of the city.
- To preserve and invigorate the aquatic biodiversity and the riparian biodiversity of the Ganga River basin.
- Enable the public to engage in the process of protecting, rejuvenating and maintaining the water.
Major functions of the National Mission for Clean Ganga (NMCG):
- Execution of the National Ganga River Basin Authority (NGRBA) work program
- Integration of the National Ganga River Basin Project supported by the World Bank
- Supervise and manage the execution of projects approved by the Government of India under NGRBA
- To perform some additional research or duties as may be delegated by MoWR, RD & GJ in the context of restoration of the Ganga River
- Layout regulations and procedures for the conduct of NMCG affairs and contribute or revise, vary or amend them as and when required
- Grant or accept financial aid, loan securities or properties of any kind, and undertake and approve the management of any endowment trust, fund or gift that is not incompatible with the objectives of the NMCG.
- Take all such action and take any other action that might seem appropriate or relevant to the accomplishment of the goals of the NGRBA.
Article 30 Not Intended To Ghettoise Minorities, Minority Institution Can Include Others In Administration: Supreme Court In AMU Case Hearing (Indian Express)

- 12 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News?
In a recent observation, the Supreme Court, headed by Chief Justice of India D Y Chandrachud, highlighted that the right granted to religious and linguistic minorities to establish and administer their educational institutions under Article 30(1) of the constitution was not intended to "ghettoise" them.
What is Article 30 of the Indian Constitution?
- Article 30 of the Indian Constitution states the right of minorities to establish and administer educational institutions.
- It says: “All minorities, whether based on religion or language, shall have the right to establish and administer educational institutions of their choice.”
When was Article 30 adopted?
- Article 30 was adopted on December 8, 1948.
Features of Article 30 of the Indian Constitution:
- Article 30 of the Indian constitution consists of provisions that safeguard various rights of the minority community in the country keeping in mind the principle of equality as well.
- Article 30(1) says that all minorities, whether based on religion or language, shall have the right to establish and administer educational institutions of their choice.
- Article 30(1A) deals with the fixation of the amount for the acquisition of property of any educational institution established by minority groups.
- Article 30(2) states that the government should not discriminate against any educational institution on the ground that it is under the management of a minority, whether based on religion or language while giving aid.
The debate around Article 30:
- On December 8, 1948, the Constituent Assembly debated the need for imparting primary education in one's mother tongue.
- One of the members of the Assembly moved an amendment to restrict the scope of this article to linguistic minorities.
- He argued that a secular state should not recognise minorities based on religion.
- Another member of the Assembly proposed to guarantee linguistic minorities the fundamental right to receive primary education in their language and script.
- He was concerned about the status of minority languages, even in regions which had a significant minority population.
- The Constituent Assembly rejected the proposals.
What is Article 29 of the Indian Constitution?
- Both Article 29 and Article 30 guarantee certain rights to minorities.
- Article 29 protects the interests of minorities by making a provision that any citizen/section of citizens having a distinct language, script or culture has the right to conserve the same.
- Article 29 mandates that no discrimination would be done on the grounds of religion, race, caste, language or any of them.
Concept of Minority in the Indian Constitution:
Religious minorities:
- While Article 30 and Article 29 of the Constitution do not specify 'minorities' in India, it is classified into religious minorities and linguistic minorities.
Religious Minorities in India:
- The basic ground for a community to be nominated as a religious minority is the numerical strength of the community.
- For example, in India, Hindus are the majority community.
- As India is a multi-religious country, it becomes important for the government to conserve and protect the religious minorities of the country.
- Section 2, clause (c) of the National Commission of Minorities Act, declares six communities as minority communities. They are:
- Muslims
- Christians
- Buddhists
- Sikhs
- Jains and
- Zoroastrians (Parsis)
Linguistic Minorities:
- A class or group of people whose mother language or mother tongue is different from that of the majority groups is known as the linguistic minority.
- The Constitution of India protects the interests of these linguistic minorities.
Swachh Survekshan Awards 2023 | Surat, Indore are the cleanest cities (The Hindu)

- 12 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News?
The President of India recently presented the ‘Swachh Survekshan Awards 2023’ at Bharat Mandapam in New Delhi.
What is Swachh Survekshan?
- Conducted annually, Swachh Survekshan is a comprehensive evaluation of cleanliness, hygiene, and sanitation standards in cities and towns throughout India.
- This initiative was launched as an integral component of the Swachh Bharat Abhiyan, specifically falling under the urban segment (SBA-Urban).
- Initiated by the Ministry of Housing and Urban Affairs (MoHUA), the survey is executed in collaboration with the Quality Council of India (QCI).
- The Swachh Bharat Abhiyan, launched on October 2, 2014, aims to achieve cleanliness and the eradication of open defecation in India by October 2, 2019.
- The campaign is bifurcated into rural (SBA-Gramin, overseen by the Department of Drinking Water and Sanitation under the Ministry of Jal Shakti) and urban (SBA-Urban, supervised by MoHUA).
- Recently, on October 1, 2021, SBM-U 2.0 was introduced, focusing on ensuring universal access to sanitation facilities. Within this framework, the vision of attaining a Garbage-Free India has been emphasized.
- Commencing with the first survey in 2016, covering 73 cities, Swachh Survekshan has expanded significantly to encompass 4242 locations in the 2020 survey.
- The evaluation methodology centres on two primary criteria: citizen feedback and field assessment.
- Objectives of Swachh Survekshan: The primary goal of Swachh Survekshan is to encourage large-scale citizen participation and create awareness amongst all sections of society about the importance of working together towards making towns and cities better places to reside in.
About Swachh Survekshan Awards 2023:
- Swachh Survekshan Awards 2023 were presented by President Droupadi Murmu at Bharat Mandapam, New Delhi, under the auspices of the Ministry of Housing and Urban Affairs (MoHUA).
- The theme for the year 2023 centred around "Waste to Wealth" emphasizing sustainable waste management practices.
- For 2024, the theme is “Reduce, Reuse and Recycle”.
- Indore (Madhya Pradesh) and Surat (Gujarat) jointly clinched the title of the cleanest cities in the country, with Navi Mumbai (Maharashtra) securing the third position.
- Remarkably, Indore maintained its top-ranking status for the seventh consecutive year.
- In the category of clean cities with a population of less than 1 lakh, Sasvad, Patan, and Lonavala secured the top three positions, while Madhyamgram, Kalyani, and Haora in West Bengal found themselves at the bottom.
- The cleanest cantonment was declared as Mhow Cantonment Board in Madhya Pradesh, and Chandigarh earned the SafaiMitra Surakshit Sheher recognition.
- In the Ganga Towns category, Varanasi and Prayagraj secured the first and second positions, respectively.
- Acknowledging overall cleanliness efforts, Maharashtra claimed the title of the best-performing state, followed by Madhya Pradesh and Chhattisgarh in the second and third positions.
- Odisha secured the fourth spot, with Telangana, Andhra Pradesh, Punjab, Gujarat, Uttar Pradesh, Tamil Nadu, Sikkim, Karnataka, Goa, Haryana, and Bihar following suit.
- Conversely, Rajasthan, Mizoram, and Arunachal Pradesh found themselves at the lower end of the ranking.
Govt’s ZED scheme for MSMEs hits 1 lakh certification milestone; check scheme’s details (Financial Express)

- 12 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News?
The Zero Effect, Zero Defect scheme (ZED) by the MSME Ministry, which aims to encourage environmentally sustainable manufacturing practices among MSMEs, has achieved the 1 lakh certification milestone
What is the Zero Effect, Zero Defect (ZED) Scheme?
- Launched in October 2016 and revamped in April 2022, the ZED scheme offers certification for environmentally conscious manufacturing under three certification levels (gold, silver and bronze) classified according to 20 performance-based parameters such as quality management, timely delivery, process control, waste management, etc.
- The scheme provides financial assistance of up to 75 per cent of the total cost of certification, with a maximum subsidy ceiling of Rs 50,000 along with up to Rs 2 lakh support for handholding/consultancy to achieve the next certification level.
- For technology upgradation, the scheme offers assistance of up to Rs 3 lakhs for moving towards zero effect solutions/pollution control measures/cleaner technology.
- MSMEs are charged Rs 10,000 for bronze certification, Rs 40,000 for silver certification, and Rs 90,000 for gold certification.
- In December 2023, the MSME Ministry made the ZED scheme free for women-led MSMEs.
- In addition, the government will now make a guaranteed payment of 100 per cent financial support for the certification cost under the scheme.
- The ZED certification is valid for three years and the MSME units are required to re-apply for the certificate as per the validity of the scheme.
- Currently, the scheme is applicable for manufacturing MSMEs only.
- The government hasn’t announced the scheme’s model for services MSMEs yet.
- The scheme is in line with the government’s plan to reduce the country’s CO2 emissions by 1 billion tons by 2030, reduce carbon intensity below 45 per cent by 2030 and finally make way for achieving a Net-Zero emission target by 2070.
- The ZED Certification envisages the promotion of Zero Defect Zero Effect (ZED) practices amongst MSMEs so as to:
- Encourage and enable MSMEs to manufacture quality products using the latest technology, and tools & to constantly upgrade their processes for the achievement of high quality and high productivity with the least effect on the environment.
- Develop an Ecosystem for ZED Manufacturing in MSMEs, to enhance competitiveness and enable exports.
- Promote the adoption of ZED practices and recognise the efforts of successful MSMEs.
- Encourage MSMEs to achieve higher ZED Certification levels through graded incentives.
- Increase public awareness of demanding Zero Defect and Zero Effect products through the MSME Sustainable (ZED) Certification.
- Identify areas to improve upon, thereby assisting the Government in policy decisions and investment prioritization.
Mamata asks PM to officially list Bengali as a ‘classical language’ (The Hindu)

- 12 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News?
West Bengal Chief Minister Mamata Banerjee in a letter to Prime Minister Narendra Modi on Thursday asked the central government to officially list Bengali as a “classical language”
About the Classical Languages in India:
- The Ministry of Culture plays a significant role in providing guidelines concerning Classical languages.
- At present, six languages in India hold the status of 'Classical.'
- These include:
- Tamil (2004)
- Sanskrit (2005)
- Kannada (2008)
- Telugu (2008)
- Malayalam (2013) and
- Odia (2014)
- All these Classical Languages find a place in the Eighth Schedule of the Constitution.
The criteria for designating a language as 'Classical' encompass several key factors:
- Historical Significance: A language must boast high antiquity, with early texts or recorded history spanning 1500-2000 years.
- Rich Literary Heritage: The language should possess a substantial body of ancient literature or texts considered a valuable heritage by successive generations of speakers.
- Originality: The literary tradition of the language should be original, not borrowed from another speech community.
- Distinctive Identity: A Classical language and its literature must maintain a distinct identity from modern iterations, potentially featuring a discontinuity between the classical language and its later forms or derivatives.
Upon achieving Classical status, the Human Resource and Development Ministry extends various benefits to promote the language, including:
- International Recognition: Two significant annual international awards are instituted for scholars of eminence in classical Indian languages.
- Centers of Excellence: Establishing a dedicated Centre of Excellence for Studies in Classical Languages.
- Academic Support: Encouraging the University Grants Commission to initiate Professional Chairs for Classical Languages, particularly in Central Universities, to foster academic research and development.
The Bengali Language:
- Bengali serves as the official language of West Bengal and holds the same status in Bangladesh.
- It stands as the second most spoken language in India and ranks as the seventh most spoken language globally.
- As an Indo-Aryan language indigenous to the Bengal region of South Asia, Bengali employs a script derived from Brahmi, an ancient Indian script.
- Notably, Bengali is written from left to right.
World Employment and Social Outlook: Trends 2024 Report (The Hindu)

- 11 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News?
The global unemployment rate is set to increase in 2024 while growing social inequalities remain a concern, according to the International Labour Organisation’s (ILO) World Employment and Social Outlook: Trends 2024 report released in Vienna recently.
Key Findings:
- Employment Trends: Joblessness and the jobs gap have both decreased below pre-pandemic levels, but global unemployment is expected to rise in 2024.
- The macroeconomic environment witnessed a significant deterioration in 2023.
- Global Economic Challenges: Ongoing geopolitical tensions and persistent inflation led to frequent and aggressive actions by central banks.
- Monetary authorities in both advanced and emerging economies implemented the fastest interest rate increases since the 1980s, with widespread global repercussions.
- Economic Slowdown in Key Economies: China, Türkiye, and Brazil experienced notable slowdowns, adversely affecting global industrial activity, investment, and trade.
- Despite the economic slowdown, global growth in 2023 surpassed expectations, and labour markets displayed unexpected resilience.
- Unemployment Dynamics: The global unemployment rate in 2023 improved modestly to 5.1% compared to 2022.
- Labour market participation rates largely recovered from pandemic lows, but concerns arise about structural imbalances persisting.
- Wage Trends: Real wages declined in most G20 countries as increases failed to keep pace with inflation.
- Workers living in extreme poverty (earning less than US$2.15 per day per person in PPP terms) increased by about one million globally in 2023.
- Positive real wage growth was observed in China, the Russian Federation, Mexico, India, and Türkiye.
Recommendations As per the Report:
- Inclusive Labor Policies: Policymakers in rapidly ageing countries should focus on supporting the participation of groups with weak labour market attachment, including youth, women, and older workers.
- Investment and Skills Strategies: Investment and skills policies should aim to enhance productivity, and potential growth, and promote a more productive utilization of technological progress.
- Sectoral Improvements: Motivating workers who leave due to low pay and challenging working conditions can be achieved by improving conditions in sectors and occupations with these challenges.
- International Workforce Matching: Facilitating the matching of internationally mobile workers to suitable jobs could alleviate some of the shortages in the labour market.
- Long-Term Engagement: Recognizing that structural challenges in labour market adjustment are unlikely to vanish in the short term, it is crucial for governments and social partners to engage in ongoing efforts to address these challenges.
International Labour Organization (ILO)
- The International Labour Organization (ILO) stands as the United Nations agency dedicated to the world of work.
- Mission: The core mission of the ILO is to promote social and economic justice by establishing and advancing international labour standards.
- Motto: At the heart of the ILO's mission is the pursuit of Decent Work for all, encapsulating the commitment to fostering conditions that are fair and dignified.
- Headquarters: Situated in Geneva, Switzerland, the ILO operates from its global headquarters.
- Parent Organization: Functioning under the Economic and Social Council of the United Nations, the ILO is a vital component of the UN system.
- Additionally, it is a member of the United Nations Development Group (UNDP), collaborating with other UN organizations to achieve Sustainable Development Goals.
- Historical Background: Established in 1919 under the Treaty of Versailles, following the conclusion of World War I, the ILO was conceived with the conviction that enduring and universal peace could only be realized through a foundation of social justice.
- In 1946, it transitioned into a specialized agency within the newly formed United Nations.
- Membership: The ILO boasts a diverse membership, with 187 member states, encompassing 186 out of the 193 UN member states along with the Cook Islands.
- Organizational Structure: Distinguishing itself as the only tripartite U.N. agency, the ILO brings together representatives from governments, employers, and workers of its 187-member states, fostering collaborative efforts in shaping global labour standards and policies.
The Process of Selecting Tableaux for the Republic Day Parade (Indian Express)

- 11 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News?
India’s Republic Day celebrations are incomplete without colourful tableaux cantering down the Kartavya Path (formally Rajpath). Showcasing India’s rich and diverse cultural heritage, they add colour to the grand event on January 26.
Who can send tableaux to the Republic Day parade?
- According to the Ministry of Defence (MoD), each year, a select number of “State Governments/UT Administrations/Central/Ministries/Departments” send their tableaux to the Republic Day parade.
- There is a rigorous application process which begins with interested parties submitting a concept note, along with design blueprints to the MoD.
How does the selection process work?
- The tableaux proposals received are evaluated by a committee of experts appointed by the MoD, comprising prominent persons in the fields of art, culture, painting, sculpture, music, architecture, choreography, etc. The selection process happens in a phased manner.
- STAGE 1 involves the assessment of the initial proposals and the design sketch/blueprint.
- The Committee sits alongside official representatives of the participants and suggests modifications, if necessary.
- A number of proposals may be rejected in this stage itself.
- STAGE 2 involves the assessment of three-dimensional models of the proposals.
- If the Committee is satisfied with the model, then the tableau is selected and further sent for fabrication.
- The Committee can also suggest changes to models before selection.
- Crucially, while the process is envisioned to be collaborative, the Committee has the final say on which tableaux are chosen, and can order any modifications they feel are required.
What is the basis of selection?
- Selection depends upon a combination of factors including but not limited to visual appeal, impact on the masses, idea/theme of the tableaux, degree of detailing involved in the tableaux, music accompanying the tableaux, local artists used etc.
- Each year, the MoD comes up with an overarching theme, under which, participants can showcase elements relevant to their respective state/UT/department in their tableaux.
- This year’s theme is “Viksit Bharat” (Developed India) and “Bharat: Loktantra ki Matrika” (India: the Mother of Democracy).
- The Defence Ministry also shares the basic guidelines about what all the tableaux can or should include.
- The participating entities must engage “young qualified designers from renowned institutions”, electronic display walls for a bright display of images or content, moving elements using robotics or mechatronics, 3D printing could be used for certain elements, use of augmented or virtual reality, and special effects to improve the optics and visual effects of the tableau.
- Extra weightage is given to tableaux which conform to these guidelines.
- Importantly, the tableaux of two different states/ UTs must not be too similar, and eco-friendly materials must be used for their construction.
'Report Fish Disease' to Monitor Fish Diseases (TOI)

- 11 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News?
A mobile app titled ‘Report Fish Disease’ has been introduced to help aquaculture farmers to report diseases on their farms.
What is the 'Report Fish Disease' App?
- The mobile application is designed to empower fish farmers by offering a convenient and effective platform for reporting diseases on their farms.
- Developed as part of the NSPAAD project, with the lead institute being ICAR-NBFGR and a collaborative partnership with the Central Institute of Fisheries Technology (CIFT), this app brings a host of features and benefits.
Key Features:
- User-Friendly Interface: The app provides fish farmers with an intuitive and user-friendly interface, ensuring easy accessibility.
- Efficient Disease Reporting: A simplified reporting format allows farmers to easily report disease outbreaks by providing essential information such as location, affected species, observed symptoms, and images.
Significance:
- Swift Response through Geo-tagging: Utilizing geo-tagging technology, the app facilitates a rapid response from authorities.
- Farmers receive real-time updates on the status of their reported cases, ensuring transparency and accountability in disease management.
- Information Hub: Beyond reporting, the app serves as an information hub, offering farmers valuable resources on disease prevention, treatment, and best aquaculture practices.
- Comprehensive Disease Management: The app is a comprehensive package aimed at diagnosing, preventing, controlling, and treating aquatic animal diseases.
- It provides solutions to encourage aquaculture farmers to maintain the health of their stocks.
Anticipated Impact:
- By transforming disease management in aquaculture, the app aims to enhance the sustainability and productivity of this critical sector.
- It achieves this through early disease detection, data-driven decision-making, capacity building, and efficient resource allocation.
The ultimate goals of the app include:
- Improved Livelihood: Enhancing the livelihood of fish farmers through proactive disease management.
- Food Security: Safeguarding the nation’s food security by ensuring the health and well-being of aquatic animal stocks.
- Industry Growth: Contributing to the sustainable growth of the aquaculture industry by fostering a proactive approach to disease prevention and management.
Henley Passport Index 2024 (Indian Express)

- 11 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News?
The Henley Passport Index, which ranks the world’s most travel-friendly passports, has released its list for 2024, with European nations of France, Germany, Italy and Spain, and Asia’s Japan and Singapore sharing the number one spot.
Highlights of Henley Passport Index 2024:
- The Henley Passport Index for 2024 ranks different passports according to the number of destinations their holders can visit without a prior visa or can avail of a visa on arrival, a visitor’s permit, or an electronic travel authority (ETA) on entering the destination.
- The rankings are based on the analysis of data provided by the International Air Transport Association (IATA).
- It then provides a ‘Visa-free score’ which, essentially, is the number of destinations that the holders of that particular passport can travel to without a prior visa or can avail of a visa on arrival or other similar permits.
- For instance, those holding the passports of the countries in the #1 spot had access to 194 visa-free destinations while those holding the Afghanistan passport ranked last at #104, had visa-free access to only 28 of them.
- As per the latest rankings, France, Germany, Italy, Japan, Singapore, and Spain hold the top spot as the world's most powerful passports, allowing visa-free entry to 194 global destinations.
- Finland, Sweden and South Korea shared the second rank, while Austria, Denmark, Ireland and Netherlands occupied the third spot.
- India, meanwhile, has improved its ranking and moved up to the 80th position from the previous year’s ranking of 84.
- Those holding an Indian passport have visa-free access to 62 destinations.
- World’s least powerful passports:
- Afghanistan (Score: 28) - visa-free access to only 28 destinations
- Syria (Score: 29) - visa-free access to only 29 destinations
- Iraq (Score: 31) - visa-free access to only 31 destinations
- Pakistan ( (Score: 34) - visa-free access to only 34 destinations
About Henley Passport Index:
- The Henley Passport Index is the original, authoritative ranking of all the world’s passports according to the number of destinations their holders can access without a prior visa.
- The index is based on exclusive data from the International Air Transport Association (IATA) – the largest, most accurate travel information database – and enhanced by Henley & Partners’ research team.
- It started in 2006 as the Henley & Partners Visa Restrictions Index (HVRI).
- The Henley Passport Index compares the visa-free access of 199 different passports to 227 travel destinations.
Carbon Border Adjustment Mechanism (CBAM) (Indian Express)

- 11 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News?
Recently India has flagged concerns relating to sensitive and confidential trade data of its exporters getting compromised while complying with the European Union’s Carbon Border Adjustment Mechanism (CBAM).
What Is Carbon Border Adjustment Mechanism (CBAM)?
- CBAM is a policy tool introduced by the European Union (EU) to reduce carbon emissions by imposing a carbon tax on imported products, ensuring that they are subject to the same carbon costs as products produced within the EU.
- It is part of the EU's "Fit for 55 in 2030 package" to reduce greenhouse gas emissions by at least 55% by 2030 compared to 1990 levels.
- The aim of CBAM is to prevent carbon-intensive imports from undermining the EU's climate objectives and to encourage the adoption of cleaner production practices around the world.
- To implement CBAM, importers will need to declare the quantity of goods imported and their greenhouse gas emissions on an annual basis.
- They will need to surrender a corresponding number of CBAM certificates to offset these emissions, and the price of these certificates will be based on the weekly average auction price of EU Emission Trading System (ETS) allowances in Euro/tonne of CO2 emitted.
- It encourages non-EU countries to adopt stricter environmental regulations, reduce global carbon emissions, and prevent carbon leakage by discouraging companies from moving to countries with weaker environmental regulations.
- Additionally, the revenue generated from CBAM will be used to support EU climate policies, which can serve as an example for other countries to promote green energy.
Impact of CBAM on India:
- The EU's carbon border adjustment mechanism will have a negative impact on India's exports of metals such as iron, steel, and aluminium products.
- The mechanism will subject these exports to extra scrutiny and impose carbon levies ranging from 19.8% to 52.7%, which could threaten India's major exports to the EU.
- From 1st January 2026, the EU will start collecting the carbon tax on each consignment of steel, aluminium, cement, fertilizer, hydrogen and electricity, which could further harm India's exports to the EU.
- The high carbon intensity of Indian products, due to coal being the dominant energy source, is a concern for the country as it may result in higher carbon tariffs from the EU.
- India's use of coal is much higher than the EU and the global average, with coal-fired power accounting for almost 75% of India's energy consumption.
- This makes direct and indirect emissions from industries like iron, steel and aluminium a significant worry for India.
- The lack of a domestic carbon pricing scheme in India poses a risk to its export competitiveness, particularly for sectors such as refined petroleum products, organic chemicals, pharma medicaments, and textiles, which are among the top 20 goods imported by the EU from India.
- Countries with a carbon pricing system may have a competitive advantage as they may pay less carbon tax or receive exemptions.
- This risk could expand to other sectors in the future.
What can be done?
- India can take a multi-pronged approach to mitigate the impact of the EU's Carbon Border Adjustment Mechanism (CBAM) on its exports.
- One of the ways is to implement a Decarbonization Principle, which refers to reducing or eliminating greenhouse gas emissions from human activities such as transportation, power generation, manufacturing, and agriculture.
- The government could complement its existing schemes such as the National Steel Policy and the Production Linked Incentive (PLI) scheme with a Decarbonization Principle.
- This would encourage industries to focus on carbon efficiency, making their products more competitive in a carbon-conscious world.
- Another way is to negotiate with the EU to recognize its energy taxes as equivalent to a carbon price.
- India could also negotiate with the EU to transfer clean technologies and financing mechanisms to aid in making India's production sector more carbon efficient.
- One way to finance this is to propose that a portion of the EU's CBAM revenue could be set aside to support India's climate commitments.
- Additionally, India could begin preparing for the new system by establishing a Carbon Trading System, as China and Russia do.
- India can encourage sustainable and eco-friendly production by providing incentives, which will enable the country to stay competitive in a more carbon-conscious future while achieving its 2070 Net Zero Targets. This will help India pursue its developmental goals and economic aspirations without any compromise.
DRDO anti-drone tech ready, handed over to BEL, private firms (The Hindu)

- 09 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News?
The counter-drone system developed by the Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO) is ready for production and has already been demonstrated to armed services and other internal security agencies with some orders already placed.
Key Highlights from the Report:
- The Defence Research and Development Organization (DRDO) has successfully engineered an indigenous counter-drone technology designed to counter various types of drone attacks, encompassing both soft and hard kill capabilities, particularly effective against micro drones.
- Significance: This cutting-edge system employs a laser-based kill mechanism for the detection and destruction of drones in the airspace.
- Notably, it can proficiently detect and disrupt micro drones within a range of 3 kilometres, employing laser signals to neutralize targets situated at distances between 1 to 2.5 kilometres.
- The technology has been seamlessly transferred to private industries, including Bharat Electronics Limited (BEL), Adani, Larsen & Toubro (L&T), and Icom.
- This strategic transfer enhances collaboration between the public and private sectors for the continued advancement and deployment of this crucial anti-drone technology.
What are Counter-Drone Systems?
- Counter-drone systems serve as defensive mechanisms designed to thwart potential drone attacks through the processes of detection, identification, and neutralization.
- These systems are broadly categorized as kinetic or non-kinetic.
- Kinetic Systems: Kinetic counter-drone systems employ projectiles, such as bullets or missiles, to destroy an intruding drone.
- They integrate advanced sensors like radar for drone detection, coupled with a motorized platform to precisely aim and fire the weapon.
- Non-Kinetic Systems: Non-kinetic counter-drone systems focus on disrupting flight capabilities or corrupting signals crucial for control and navigation.
- This is achieved by emitting noise signals at specific frequencies, rendering the drone incapable of receiving command signals.
- Additionally, non-kinetic systems may transmit false GPS signals, creating confusion in the drone's navigation system.
Centre asks Manipur government to study representation on removing Kuki-Chins from ST list (The Hindu)
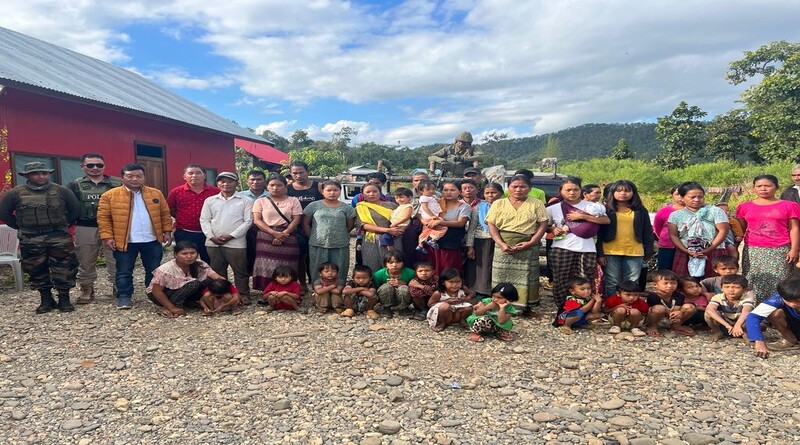

- 09 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News?
The Manipur government has been asked by the Centre to examine a representation seeking deletion of the “Nomadic Chin-Kuki” from the list of Scheduled Tribes in Manipur.
Context:
- The petition advocates that the primary criterion for categorizing Scheduled Tribes in the country should be based on Indigeneity, referencing a Supreme Court ruling dated January 2011.
- The petition specifically highlights the case of the "Zou" tribe, asserting that their origin in Myanmar's Chin state, a foreign territory, was not documented in pre-independence Indian Censuses.
- Consequently, the plea argues against the inclusion of the "Zou" tribe in the Scheduled Tribe list of Manipur.
About Kuki and Zomi Tribes:
- The Kuki-Zomi Tribes represent an ethnic group originating from the Bangladesh region, primarily residing in Manipur and Mizoram in India.
- Also recognized as Chin or Mizo people, they share a unified ancestry and culture.
- Their communication is conducted through various dialects within the Chin-Kuki-Mizo language family, belonging to the Tibeto-Burman branch of the Sino-Tibetan languages.
- The Kuki-Zomi Tribes are interconnected with the broader Zo people, alongside other tribes such as Chin and Mizo.
What is the Process of amendment in the ST List?
- The inclusion or exclusion of any tribe or tribal community from the Scheduled Tribes list is exclusively governed by legislation enacted by the Parliament of India.
- Amendments to the list are effectuated through notifications issued under clause (1) of Article 342, specifying Scheduled Tribes.
- According to a Supreme Court ruling, the authority to modify, amend, or alter the Scheduled Tribes list specified in the notification under Article 342(1) is not vested in State governments, courts, tribunals, or any other entity.
- Contrary to this, the central government asserts that the initiation of proposals for inclusion or exclusion from the ST list must originate from the respective State government.
- The Parliament then takes action based on this proposal.
- The Lokur Committee, in 1965, laid down the criteria employed by the government to designate communities as Scheduled Tribes, and these criteria persist in use today.
- They encompass primitive traits, distinctive culture, geographical isolation, shyness of contact with the larger community, and backwardness.
PM Modi wishes Indian diaspora on Pravasi Bharatiya Diwas (The Hindu)

- 09 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News?
Prime Minister Narendra Modi has extended his wishes to the Indian diaspora on the Pravasi Bharatiya Diwas and said their dedication towards preserving our rich heritage and strengthening global ties is commendable.
What is Pravasi Bharatiya Diwas?
- Pravasi Bharatiya Divas (PBD), also known as Non-Resident Indian (NRI) Day, is celebrated on January 9 to mark the contribution and achievements of the overseas Indian community to the development of India.
- The day also commemorates the return of Mahatma Gandhi, the greatest Pravasi, from South Africa to India in 1915, who led India's freedom struggle and changed the lives of Indians forever.
- Its format was later revised in 2015 to celebrate the event once every two years and to hold theme-based conferences during the intervening period with participation from overseas diaspora experts, policy-makers, and stakeholders.
- The Pravasi Bharatiya Divas is the flagship event of the Ministry of External Affairs.
- It is held in different cities, to showcase the diversity and progress of different regions of India.
Pravasi Bharatiya Divas: History
- Pravasi Bharatiya Diva was first celebrated in 2003.
- It was an annual event earlier, but in 2015, the government revised its format to celebrate PBD once every two years.
- To date, 17 conventions have been held.
- The last Pravasi Bharatiya Divas was celebrated in the Indore of Madhya Pradesh in 2023.
Pravasi Bharatiya Samman Awards:
- Another aspect of the Pravasi Bharatiya Divas is the Pravasi Bharatiya Samman Awards.
- The awards were initiated in 2003 by the Indian Government to recognize the achievements and contributions of NRIs and PIOs in various fields such as education, science and technology, arts and culture, social work, public service, trade and industry, and philanthropy.
Pravasi Bharatiya Divas: Significance
- These conventions provide a platform for the overseas Indian community to engage with the Indian government and people of the land of their ancestors for mutually beneficial activities.
- These conventions are also very useful in networking among the overseas Indian community residing in various parts of the world and enable them to share their experiences in various fields.
Switzerland’s decision to eliminate import duties limits FTA utility for India’ (Indian Express)

- 09 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News?
Switzerland’s policy to allow tariff-free entry for all industrial goods from all countries significantly limits India’s prospects of gains from India and the European Free Trade Association (EFTA) free trade agreement (FTA) that is currently being negotiated.
Context:
- Within the broader context, the Global Trade Research Initiative (GTRI) asserts that Switzerland's approach of granting tariff-free entry to all nations places constraints on the benefits India could potentially derive from the envisioned trade agreement with the European Free Trade Association (EFTA).
- This limitation arises as Switzerland has eliminated tariffs on various products, encompassing chemicals, consumer goods, vehicles, and clothing.
About the European Free Trade Association (EFTA):
- The European Free Trade Association (EFTA) is a regional trade organization and free trade area consisting of four European states: Iceland, Liechtenstein, Norway and Switzerland.
- The organization operates in parallel with the European Union (EU), and all four member states participate in the European Single Market and are part of the Schengen Area.
- They are not, however, party to the European Union Customs Union.
- It was established in 1960.
- Trade Dynamics with India:
- In 2022, the combined merchandise trade between EFTA and India exceeded USD 6.1 billion.
- The predominant EFTA imports included organic chemicals (27.5%), with machinery (17.5%) and pharmaceutical products (11.4%) constituting the primary exports to India.
India’s Trade and Economic Partnership Agreement (TEPA) with EFTA:
- Negotiations on the trade deal commenced in 2008 and resumed in 2016.
- The latest rounds covered diverse aspects such as trade in goods and services, rules of origin, Intellectual Property Rights (IPR), trade and sustainable development, sanitary and phytosanitary measures, technical barriers to trade, trade remedies, and customs and trade facilitation.
Impact of Switzerland’s Policy on India's Gains under EFTA:
- Effect on Negotiations: Switzerland's decision significantly alters the dynamics of the ongoing India-EFTA trade agreement negotiations, posing implications for India's potential gains.
- Increase in Market Competitiveness: Switzerland, as India's primary export destination in EFTA, has eliminated import duties, intensifying competition for Indian products despite the Free Trade Agreement (FTA) with EFTA.
- No Gains in Agricultural Exports: Exporting agricultural produce to Switzerland remains challenging due to tariff complexities, quality standards, and approval requirements. EFTA, including Switzerland, has shown reluctance to eliminate tariffs on basic agricultural produce.
- Trade Deficit with Switzerland: In FY2023, India faced a substantial trade deficit with Switzerland, with imports totalling $15.79 billion compared to exports of $1.34 billion. Switzerland's policy is anticipated to widen this trade deficit further.
- In essence, Switzerland's tariff-free policy introduces complexities in India's negotiations and hampers potential gains, particularly in the realm of agricultural exports, impacting the overall trade balance with EFTA.
: In a first, India set to chair, and host UNESCO's World Heritage Committee session in Delhi (HT)

- 09 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News?
In a historic development, India is poised to chair and host UNESCO's World Heritage Committee session in New Delhi from July 21 to 31 this year, the Permanent Representative of India to UNESCO.
About the World Heritage Committee:
- The World Heritage Committee operates as a subsidiary of the United Nations Educational, Scientific, and Cultural Organization (UNESCO).
- Its primary responsibilities encompass executing the World Heritage Convention, determining the utilization of the World Heritage Fund, and disbursing financial assistance in response to requests from States Parties.
- The committee holds authoritative decision-making power regarding the inscription of properties on the World Heritage List, scrutinizes reports on the conservation status of listed properties, and prompts States Parties to rectify mismanagement issues.
- Additionally, it plays a pivotal role in determining the inclusion or removal of properties on the List of World Heritage in Danger.
- Structure:
- Comprising representatives from 21 States Parties elected by their General Assembly, the Committee operates with members serving six-year terms.
- However, many state parties opt for a four-year term voluntarily, allowing other state parties an opportunity to participate on the committee.
- Bureau of the World Heritage Committee:
- The Bureau, consisting of seven state parties elected annually by the Committee, includes a Chairperson, five Vice-Chairpersons, and a Rapporteur.
- This body is responsible for coordinating the Committee's activities, determining meeting schedules, and organizing the agenda.
What is UNESCO?
- The United Nations Educational, Scientific, and Cultural Organization (UNESCO) stands as a specialized agency within the United Nations (UN), dedicated to fostering global peace and security through collaborative efforts in education, arts, sciences, and culture.
- Established in 1945 as the successor to the League of Nations' International Committee on Intellectual Cooperation, UNESCO boasts a membership of 193 states and 11 associate members, along with partnerships in the non-governmental, intergovernmental, and private sectors.
- The organization is headquartered at the World Heritage Centre in Paris.
- UNESCO's foundational mission is to promote peace, sustainable development, and human rights by fostering cooperation and dialogue among nations.
- It pursues this overarching goal through five primary program areas: Education, Natural Sciences, Social/Human Sciences, Culture, and Communication/Information.
- The governance of UNESCO lies in the hands of the General Conference, comprising member states and associate members, convening biannually to establish the agency's programs and budget.
- The General Conference also elects members of the Executive Board, responsible for managing UNESCO's initiatives.
- Every four years, the Director-General is appointed by the General Conference to serve as the chief administrator of UNESCO.
- India has been a founding member of UNESCO, having ratified UNESCO’s Constitution on 4th November 1946.
The logic behind momentum investing (The Hindu)

- 10 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News?
Traditionally, experts have advised investors to buy assets when they are selling at low prices, such as during times of a financial crisis, as assets could be found selling at prices well below their intrinsic value. Momentum investing is in stark contrast to this traditional logic.
What is Momentum investing?
- Momentum investing refers to a style of investing wherein investors purchase assets such as stocks or bonds that are consistently rising in price while selling assets whose prices are falling.
- Momentum investors buy assets with rising prices in the hope that the upward price momentum of these assets would continue, thus allowing them to sell these assets at higher prices in the future to make profits.
- Similarly, they sell assets that are falling in price expecting the fall in prices to continue for some time.
- Momentum investing is based on the philosophy that there can be discernible trends in asset prices and that these trends tend to persist over time.
- The persistence of such trends gives investors an opportunity to recognise and participate in them early enough to make significant profits from their investments.
What is the Counter-logic?
- Momentum investors often invest money in assets whose prices have scaled new all-time highs, even if these assets are trading at prices that are far above their intrinsic value.
- Many academic studies have shown that momentum investing can generate high returns that comfortably beat the benchmark indices.
- Momentum investors generally do not conduct a deep analysis of the fundamental or intrinsic value of the assets in which they invest their money.
- They invest purely based on whether the price of an asset is showing a strong trend, either upward or downward, that they can ride on.
- For this reason, many critics argue that momentum investing can cause an unsustainable rise or fall in prices as momentum investors are blind to the actual value of these assets.
- This, they argue, can eventually lead to heavy losses for investors who are late to sell when the prices of these momentum-driven assets suddenly catch up with the assets’ intrinsic value.
- Some investors may combine value investing, which is based on assessing the intrinsic value of an asset, with momentum investing.
- These investors believe that taking into account the existing trend in the price of an asset can help save time and boost investment returns.
- It should be noted that traditional value investors believe in purchasing assets that are undervalued and selling them when the price of the asset has risen to match the asset’s intrinsic value.
- It might, however, take many years before the price of an asset rises to fully match its intrinsic value.
- Investors who combine value investing with momentum investing may be able to purchase an undervalued asset at just about the time when its price starts to trend towards its intrinsic value.
- This prevents investor money from being locked in for years in assets whose prices go nowhere.
Land Ports Authority Releases Report on Gender-Inclusive Framework for Cross-Border Trade in India (NewsOnAIR)

- 10 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News?
Land Ports Authority of India (LPAI) today released a report on 'Engendering Land Ports in India' in New Delhi. The main objective of the report is to develop a framework for gender-inclusive cross-border trade and tourism through land Ports in the country.
About the Land Ports Authority of India (LPAI):
- LPAI was established In 2012 as a statutory body under the LPAI Act of 2010.
- It comes under the purview of the Department of Border Management, Ministry of Home Affairs.
- Mandate: LPAI is entrusted with the development of cutting-edge infrastructure for its land ports.
- This infrastructure includes the construction of a Cargo Terminal Building, Passenger Terminal Building, deployment of mechanized equipment for cargo handling, implementation of security and surveillance measures at land ports, and the provision of forex counters.
- Growth: From its inception with just two land ports in 2012, LPAI has played a significant role in expanding India's operational land ports to 11, facilitating connections across the country's land borders with Bangladesh, Nepal, and Pakistan.
Land Ports in India:
- Integrated Check Posts (ICPs) are the official designations for land ports in India.
- The country currently boasts 11 operational land ports, namely Attari, Agartala, Dawki, Petrapole, Raxaul, Rupaidiha, Jogbani, Moreh, Sutarkandi, Srimantapur, and the Passenger Terminal Building (PTB) at Dera Baba Nanak.
- In the year 2023, significant trade activities were conducted through seven primary land ports: Attari, Agartala, Petrapole, Raxaul, Jogbani, Sutarkandi, and Srimantapur.
- These land ports played a crucial role in facilitating trade valued at Rs 76,000 crore and accommodating the movement of approximately 24 lakh passengers in the year 2023.
Why there is a Need for Land Ports in India?
- Given its strategic central location, India shares an extensive international land border spanning over 15,000 kilometres with seven South Asian countries: Afghanistan, Bangladesh, Bhutan, China, Myanmar, Nepal, and Pakistan.
- Numerous specified entry and exit points facilitate cross-border movements involving individuals, goods, and vehicles.
- However, the persistent challenge of inadequate infrastructure at these designated border checkpoints has posed a significant hurdle to regional trade, adversely affecting the smooth transit of both commodities and passengers.
- Recognizing this obstacle, the Committee of Secretaries recommended the establishment of Integrated Check Posts (ICPs) in 2003.
- These ICPs were envisioned to offer state-of-the-art infrastructure facilities, addressing the deficiencies in the existing border infrastructure and promoting more efficient cross-border interactions.
Launch of the Traditional Medicine Morbidity codes of Ayurveda, Siddha and Unani Chapter in International Classification of Diseases (ICD) 11 as Module 2 (PIB)

- 10 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News?
The launch event for Module 2 of the World Health Organization's International Classification of Diseases (ICD) 11 TM Morbidity Codes is scheduled to take place in New Delhi on January 10, 2024.
What is the International Classification of Diseases?
- Developed by the World Health Organization (WHO), the International Classification of Diseases (ICD) serves as a global standard for classifying diseases.
- The existing global data on diseases is primarily rooted in modern biomedicine practices, guiding diagnoses within healthcare systems worldwide.
- ICD plays a significant role on a global scale, offering crucial insights into the prevalence, causes, and consequences of human diseases and mortality.
- It achieves this by incorporating reported and coded data, forming the basis for clinical terms in health records and disease statistics across primary, secondary, and tertiary care, as well as cause-of-death certificates.
- The data and statistics derived from ICD coding contribute to various essential functions, including supporting payment systems, aiding in service planning, facilitating quality and safety administration, and driving health services research.
- Moreover, the standardized data collection associated with ICD categories allows for large-scale research initiatives.
- It's important to note that the WHO ICD series currently does not include the classification of data and terminology related to diseases based on Ayush systems such as Ayurveda, Siddha, Unani, etc.
- The Central Bureau of Health Intelligence (CBHI), operating under the Ministry of Health and Family Welfare, serves as the WHO Collaboration Centre for ICD-related activities.
- The CBHI plays a crucial role in collecting and disseminating data on various diseases and mortality.
What is the TM2 module of ICD11?
- The Ministry of Ayush has introduced the Code for Ayurveda, Siddha, and Unani Medicine, utilizing the National Ayush Morbidity and Standardised Electronic Portal (NAMASTE).
- In partnership with the World Health Organization (WHO), the Ministry of Ayush has collaboratively developed a comprehensive categorization of data and terminology about diseases based on Ayush systems, namely Ayurveda, Siddha, and Unani, within the TM2 module of the ICD11 series.
- Furthermore, the Ministry of Ayush has formalized this collaboration by signing a Donor Agreement with the World Health Organization for the implementation of these initiatives.
Karnataka High Court bans mining around KRS Dam in Mandya: ‘can’t turn Nelson’s eye to possible danger’ (Indian Express)

- 10 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News?
The Karnataka High Court has suspended all mining licenses for stone quarrying within a 20-km radius of the Krishna Raja Sagar (KRS) Dam in the Mysore-Mandya region of the state under provisions of the Dam Safety Act, 2021.
About the Krishnaraja Sagar (KRS) Dam:
- Krishnaraja Sagar (KRS) Dam is a gravity dam strategically positioned beneath the confluence of the Kaveri River with its tributaries, Hemavati and Lakshmana Tirtha, in Karnataka's Mandya district.
- Usage: The dam serves crucial roles, providing water for irrigation in Mysore and Mandya while acting as a primary drinking water source for Mysore, Mandya, and Bengaluru.
- Additionally, it facilitates power generation at the Shivanasamudra hydroelectric power station.
- Water released from the KRS Dam travels into Tamil Nadu and is stored in the Mettur Dam in the Salem district.
- History: Constructed during the reign of Maharaja Krishnaraja Wadiyar IV, the dam, completed in 1931, bears his name.
- The eminent Indian engineer Sir M. Visvesvaraya designed this impressive structure, commencing construction in 1911.
- Features: Built with a combination of surki mortar and limestone, the dam spans 2,621 meters (8,600 ft) in length and stands 40 meters (130 ft) high.
- Exhibiting an arch type, it boasts 177 iron sluices, some equipped with automatic doors.
- The reservoir covers about 130 square kilometres, making it the largest in Asia at the time of construction.
- A captivating addition to the site is the Brindavan Gardens, an ornamental garden intricately linked with the dam.
Key Details About the Kaveri River:
- Kaveri River, also spelt Cauvery, is a revered river in southern India, often referred to as the Ganga of South India.
- Origin: The river originates from the Brahmagiri Hill in the Western Ghats of southwestern Karnataka.
- Course: Flowing southeastward for a span of 765 km, Kaveri traverses through the states of Karnataka and Tamil Nadu, descending the Eastern Ghats with impressive cascades.
- Basin Coverage: The Kaveri basin spans the states of Tamil Nadu, Karnataka, Kerala, and the Union Territory of Puducherry.
- Outflow: Ultimately, the river empties into the Bay of Bengal at Poompuhar in the Mayiladuthurai district of Tamil Nadu.
- Left Bank Tributaries: Notable left bank tributaries include Harangi, the Hemavati, the Shimsha, and the Arkavati.
- Right Bank Tributaries: Major right bank contributors encompass Lakshmantirtha, the Kabbani, the Suvarnavati, the Bhavani, the Noyil, and the Amaravati.
Autonomous systems becoming the preferred choice in Order of Battle for nations across the globe: Navy Chief (The Hindu)

- 10 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News?
Chief of Naval Staff Admiral R Hari Kumar officially initiated the maiden indigenously produced Drishti 10 'Starliner' Unmanned Aerial Vehicle (UAV) for the Indian Navy.
What is Drishti 10 Starliner UAV?
- Drishti 10 Starliner Unmanned Aerial Vehicle is an advanced intelligence, surveillance, and reconnaissance (ISR) platform, developed by Adani Defence and Aerospace, and represents a significant leap forward in India’s defence technology.
- The Drishti 10 Starliner boasts an impressive 36 hours of endurance and a substantial 450 kg payload capacity.
- It stands out as the only all-weather military platform certified with NATO’s STANAG 4671 (standardized agreement 4671) for airworthiness, allowing it to operate in both segregated and unsegregated airspace.
- The UAV is equipped with state-of-the-art sensors, an extended endurance of 36 hours, and advanced communication capabilities.
- Its incorporation of new-age technologies such as Automatic Take Off and Landing (ATOL) positions it as a formidable asset.
- Notably, this UAV is a home-assembled version of the Hermes-900 MALE UAV, featuring an impressive 70% indigenous content.
- A notable feature of the Drishti 10 'Starliner' is its low maintenance demands, contributing to cost-effectiveness and operational efficiency.
- This quality enhances operational readiness, minimizing downtime and optimizing deployment opportunities.
- The Drishti 10 is outfitted with cutting-edge communication systems, encompassing satellite communication and Line-of-Sight (LOS) data links, guaranteeing dependable and secure data transmission.
What is Unmanned Aerial Vehicle (UAV)?
- A drone, also referred to as an unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV), is an aircraft that operates without a human pilot, crew, or passengers on board.
- UAVs are integral components of unmanned aircraft systems, comprising a ground-based controller and a communication system linked with the UAV.
Drones are categorized based on their weight, adhering to existing regulations:
- Nano: Equal to or less than 250 grams
- Micro: Between 250 grams and 2 kilograms
- Small: From 2 kilograms to 25 kilograms
- Medium: Between 25 kilograms and 150 kilograms
- Large: Exceeding 150 kilograms
Ram Temple opening brings fresh hope to Moradabad brass traders as orders for idols shoot up (The Hindu)

- 08 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News
The industry, which till now produced utensils and home decorative items with intricate designs, is now flooded with orders for idols of Ram, Sita, Laxman and Hanuman
Brassware Industry Moradabad:
- Moradabad was founded in 1600 by Murad, the son of Mughal Emperor Shahjahan, and hence became known as Moradabad.
- It is well-known for its brass work and has made a name for itself in the global handicraft market.
- Moradabad, often referred to as the "Brass City" or Peetal Nagri, exports brassware to countries like the US, Britain, Canada, Germany, the Middle East, and Asia.
- Brass, an alloy of copper and zinc, holds historical significance due to its exceptional hardness and workability.
- In the 1980s, the industry witnessed diversification with the introduction of various metal wares such as brass, iron, and aluminum.
- This expansion brought new technologies like electroplating, lacquering, and powder coating to Moradabad's art industry.
- Notably, Moradabad Metal Craft (Word Mark) has received a geographical indication (GI) tag, emphasizing its unique identity and craftsmanship.
- In the 18th century, Moradabad’s brass industry was boosted when the British East India Company began ordering large quantities of brass products for export.
- The demand for Moradabad’s brassware continued to grow throughout the 19th and 20th centuries, making it one of the most critical industries in the city.
What Categories of Brass are made in Moradabad?
Moradabad’s manufacturers produce a wide range of brass products, including:
- Brass utensils: It includes a variety of brass utensils, such as pans, kettles, and jugs.
- Brass lamps: Moradabad is also known for its brass lamps, which are used for decoration and lighting homes and businesses.
- Brass statues: Brass spiritual suppliers also produce a wide range of brass God idols, Goddess statues, and Home decor statues.
- Other brass products: In addition to the items mentioned above, Moradabad’s manufacturers also produce various other brass products, such as vases, ashtrays, candlesticks, and door knockers.
How AI can help detect cancer and why India’s biggest cancer treatment hospital is utilising it (Indian Express)

- 08 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News
Given the escalating cases of cancer, the shortage of specialists poses a significant challenge in curbing fatalities. To address this gap, Mumbai’s Tata Memorial Hospital (TMH), the biggest cancer hospital in India, is turning to artificial intelligence (AI).
Context:
- With the rising cancer cases, a notable challenge is the shortage of specialists, impacting efforts to reduce fatalities.
- To tackle this issue, Tata Memorial Hospital (TMH) in Mumbai, India, the country's largest cancer hospital, is embracing artificial intelligence.
- The hospital is leveraging deep learning to establish a Bio-Imaging Bank for cancer, employing AI to develop a tailored algorithm specific to cancer diagnosis.
What is the Role of AI in Cancer Detection and Treatment?
- Early Detection through Identification of Tissue Changes and Potential Malignancies: AI analyzes radiological and pathological images, learning from extensive datasets to recognize unique features associated with various cancers.
- This technology facilitates early detection by identifying tissue changes and potential malignancies.
- Predictive Models for Tumor Survival and Treatment Guidance: Comprehensive imaging generates longitudinal patient data, aiding in understanding behavior, treatment response, disease recurrence, and overall survival.
- AI and machine learning protocols utilize this data to develop predictive models for tumor survival and guide treatment aggressiveness.
- Avoiding Unnecessary Chemotherapy: The creation of a tumor image bank allows for the development of algorithms for different tumors, assessing treatment responses directly from images and avoiding unnecessary chemotherapy for predicted non-responders.
- Maintaining Diagnostic Quality while Decreasing Radiation Exposure: Tata Memorial Hospital has added data from 60,000 patients to the biobank over the past year.
- Using this data, AI successfully reduces radiation by enhancing images with AI algorithms, ensuring a significant decrease in radiation exposure to children without compromising diagnostic quality.
- Potential to Reduce Cancer Fatalities in the Future:
- AI is poised to play a transformative role in cancer treatment, particularly in mitigating fatalities in rural India.
- Its potential lies in tailoring treatment approaches based on diverse patient profiles, optimizing therapy outcomes.
- AI swiftly detects cancer, eliminating the need for extensive tests and enabling even general practitioners to diagnose complex cancers.
- This technology is set to significantly enhance precision in cancer solutions.
What is Bio-Imaging Bank?
- The overarching objective is to establish a robust repository incorporating radiology and pathology images intricately linked with clinical information, outcome data, treatment specifics, and additional metadata.
- This strategic design aims at facilitating the training, validation, and rigorous testing of AI algorithms.
- Functioning: In conjunction with creating the database, the project involves training and testing multiple AI algorithms using the accumulated data.
- It is tailored to address medically relevant tasks, including screening for lymph node metastases, nucleus segmentation and classification, biomarker prediction, and therapy response prediction.
- Institutions Involved: The multi-institutional project receives funding from the Department of Biotechnology and collaborates with IIT-Bombay, RGCIRC-New Delhi, AIIMS-New Delhi, and PGIMER-Chandigarh.
Sarbananda Sonowal to chair the First Inland Waterways Development Council Meeting to be held tomorrow in Kolkata (PIB)

- 08 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News
The Inland Waterways Authority of India, under the Ministry of Ports, Shipping, and Waterways (MoPSW), is set to host the inaugural 'Inland Waterways Development Council' meeting on January 8, 2023, in Kolkata.
Key Initiatives to be Unveiled during the Meeting:
- Marking the first session of the Inland Waterways Development Council.
- The Inland Waterways Development Council (IWDC) meeting will address vital issues related to the advancement of inland waterways in India through a comprehensive agenda.
- Initiatives such as the “Harit Nauka – Guidelines for Green Transition of Inland Vessels” and the “River Cruise Tourism Roadmap 2047” will be launched as integral components of the agenda.
- The meeting will center on critical aspects like fairway development, private sector engagement, and enhancing cargo transport efficiency in Inland Water Transport (IWT).
- The agenda will also focus on promoting eco-friendly vessels for passenger transportation, exploring economic benefits in river cruise tourism, and advocating for sustainable practices in the development of inland waterways.
What is the Inland Waterways Development Council?
- The Government of India established the Inland Waterways Development Council in 2023 with the active aim of comprehensively developing inland waterways and the associated Inland Water Transport (IWT) ecosystem.
- The focus is on improving cargo efficiency, facilitating passenger movement, and promoting river cruise tourism, with the active engagement of States and Union Territories.
About Inland Waterways Authority of India (IWAI):
- The Inland Waterways Authority of India (IWAI) came into existence on 27th October 1986 for development and regulation of inland waterways for shipping and navigation.
- The Authority primarily undertakes projects for development and maintenance of IWT infrastructure on national waterways through grants received from the Ministry of Shipping.
- The head office of the Authority is at Noida.
- The Authority also has its regional offices at Patna, Kolkata, Guwahati and Kochi and sub-offices at Allahabad, Varanasi, Farakka, Sahibganj, Haldia, Swroopganj, Hemnagar, Dibrugarh, Dhubri, Silchar, Kollam, Bhubaneswar and Vijayawada.
From red ant chutney to black rice, the 7 Odisha products that have bagged GI tags (Indian Express)

- 08 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News
Seven products from Odisha, ranging from the Similipal Kai chutney made with red weaver ants to the embroidered Kapdaganda shawl, have bagged the coveted Geographical Indication (GI) tag in recognition of their exclusivity to the state.
What is Geographical Indication (GI) Tag?
- Geographical Indications of goods refer to the place of origin of a product.
- Such tags are accorded as they convey an assurance of quality and distinctiveness, attributable to the fact of its origin in a specific geographical locality, region or country.
- In India, the Department for Promotion of Industry and Internal Trade, Ministry of Commerce and Industry, awards GIs.
- A GI registration is given to an area, not a trader, but once a product gets the registration, traders dealing in the product can apply to sell it with the GI logo.
- Authorised traders are each assigned a unique GI number.
- If any unauthorised trader tries selling the product under that name, they can be prosecuted under The Geographical Indications of Goods (Registration and Protection) Act, 1999.
- A marker of authentic products, the GI tags also help protect the interests of the local growers and artisans by preventing duplicity of the products and sale from unauthorised traders.
- Consumers, through the tags, can know which goods are certified.
The Seven Products and Their Distinctiveness:
- Kapdaganda shawl: Woven and embroidered by the women of the Dongria Kondh tribe, a particularly vulnerable tribal group (PVTG) in the Niyamgiri hills in Odisha’s Rayagada and Kalahandi districts, the shawl reflects the rich tribal heritage of the Dongria Kondhs.
- It is embroidered on an off-white coarse cloth with red, yellow and green coloured threads, with each colour holding significance.
- Green symbolises the mountains and hills, and yellow stands for peace and happiness.
- Red stands as the symbol of blood.
- The motifs in the shawls are mostly lines and triangles, believed to be a reflection of the importance of mountains for the community.
- The shawl is worn by both men and women and the Dongrias gift it to their family members as a token of love and affection.
- It is embroidered on an off-white coarse cloth with red, yellow and green coloured threads, with each colour holding significance.
- Lanjia Saura Painting: The painting is also known as Idital. The artworks are famous for their beauty, aesthetics, ritualistic association and iconography.
- The art form belongs to the Lanjia Saura community, a PVTG largely residing in the Rayagada district.
- These paintings are in the form of exterior murals painted on the mud walls of homes.
- White paintings figure over a crimson-maroon background.
- It is believed that the Lanjia Sauras paint their walls with Idital artworks to show gratitude to their deities and forefathers, and also for the well-being of their community.
- Reflecting the love and affection of the primitive tribes for nature, they feature subjects like tribal humans, trees, animals, birds, the Sun and the Moon.
- Koraput Kala Jeera Rice: The black-coloured rice variety, also known as the ‘Prince of Rice’, is famous for its aroma, taste, texture and nutritional value.
- Tribal farmers of the Koraput region have preserved the rice variety for around 1,000 years.
- As the rice grains resemble cumin seeds, it is also called Kala Jeera. Consumption of the rice variety helps in increasing haemoglobin levels and improves metabolism in the body.
- The farmers and producers of Koraput Kala Jeera rice have followed the traditional knowledge and practices in cultivation.
- Similipal Kai chutney: The chutney made with red weaver ants is a traditional delicacy of the tribals in Odisha’s Mayurbhanj district.
- The ants are found in the forests of Mayurbhanj, including in the Similipal forests – Asia’s second-largest biosphere.
- Rich in medicinal and nutritional value, the chutney is believed to be a good source of nutrients like protein, calcium, zinc, vitamin B-12, iron, magnesium, potassium, etc.
- The tribals prepare the Kai chutney by grinding the ants manually on a Sil Batta or the grinding stone.
- Mayurbhanj’s tribals also earn their livelihood by selling the red ants and the chutney made from the ants.
- They believe that its consumption helps boost immunity and prevents diseases.
- Nayagarh Kanteimundi Brinjal: Nayagarh Kanteimundi Brinjal is known for its prickly thorns on the stems and the whole plant.
- The green and round fruits contain more seeds as compared to other genotypes.
- It is famous for its unique taste and relatively short quick cooking time. The plants are resistant to major insects and can be grown with minimal pesticide.
- It is being widely cultivated in Nayagarh district of the state.
- Odisha Khajuri Guda: Odisha’s “Khajuri Guda” or jaggery is a natural sweetener extracted from date palm trees and has its origin in the Gajapati district.
- Traditionally, the jaggery is prepared in a trapezoidal form called ‘Patali Gur’ and is organic by nature.
- It is dark brown and has a unique taste.
- Dhenkanal Magji: Dhenkanal Magji is a type of sweet made from cheese from buffalo milk, with distinct characteristics in terms of appearance, taste, flavour, shape, and size.
- It also has unique nutritional values that distinguish it from other cheese-based sweets.
- The sweet is prepared by draining moisture from the cheese and then frying it, finally forming balls from the mixture.
iDEX innovators to exhibit futuristic technologies at Vibrant Gujarat summit (ET)

- 08 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News
The Ministry of Defence on Sunday said that Innovations for Defence Excellence-Defence Innovation Organization (iDEX-DIO) will participate in the 10th edition of the Vibrant Gujarat Summit from January 10 to 12 in Gandhinagar.
About iDEX:
- iDEX (Innovations for Defence Excellence), the flagship scheme of the Ministry of Defence, Govt of India launched by Prime Minister Modi in 2018.
- The objective of the scheme is to cultivate an innovation ecosystem in the Defence and Aerospace sector by collaborating with startups, innovators, MSMEs, incubators, and academia.
- iDEX offers grants and support for R&D with significant potential for future adoption in Indian defense and aerospace.
- It is currently engaged with around 400+ Startups and MSMEs, till now procurement of 31 items worth over Rs 2000 Cr. has been cleared.
- Recognized as a game-changer in the defense ecosystem, iDEX has received the PM Award for Innovation in the defense sector.
What is the Vibrant Gujarat Summit?
- The Government of Gujarat organizes the Vibrant Gujarat Global Summit, also known as Vibrant Gujarat, a biennial global business event held in the state of Gujarat, India.
- It attracts business leaders, investors, corporations, thought leaders, and policymakers, serving as a platform to understand and explore business opportunities in Gujarat.
- Launched in 2003 and now held every two years, the summit aims to promote Gujarat as an attractive investment destination, fostering partnerships and collaborations across various sectors.
- Industry associations, both nationally and internationally, support the summit, making it one of Gujarat's crucial economic forums.
- The event creates a platform for business leaders, policymakers, and investors to explore opportunities for investment, collaboration, and partnership in sectors such as energy, manufacturing, infrastructure, information technology, agriculture, healthcare, and more.
- It facilitates discussions, negotiations, and agreements in these key sectors.
- The Tenth edition of Vibrant Gujarat Global Summit is being held from 10 to 12 January 2024 in Gandhinagar, Gujarat.
- Its theme is 'Gateway to the Future'.
- This Tenth Edition of the Summit will celebrate “20 Years of Vibrant Gujarat as the Summit of Success”.
- There are 34 Partner countries and 16 Partner organizations for this year’s Summit.
- Further, the Ministry of Development of North-Eastern Region will utilize the Vibrant Gujarat platform to showcase investment opportunities in the North-Eastern regions.
‘Deep tech’ policy to be sent to Cabinet for approval, says scientific adviser (The Hindu)

- 06 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News
The government will be sending a note, on a new ‘deep tech’ policy for India in the coming weeks to the Union Cabinet for approval, said Prof. Ajay Kumar Sood, Principal Scientific Advisor at a public event on January 5.
Key Details in the Draft NDTSP:
- The Draft National Deep Tech Startup Policy (NDTSP) stands out through its key highlights, enhancing the existing Startup India policies by fostering an environment conducive to the growth of deep tech startups.
- It addresses the unique challenges these startups face.
- The draft NDTSP introduces new policy instruments and recommends essential policy changes under several themes, including nurturing research, development, and innovation, strengthening the intellectual property regime, facilitating access to funding, enabling shared infrastructure and resource sharing, creating supportive regulations, standards, and certifications, attracting human resources, initiating capacity building, promoting procurement and adoption, ensuring policy and program interlinkages, and sustaining deep tech startups.
India's 'Deep Tech' Startup Ecosystem faces significant challenges as outlined in the draft 'deep tech' policy:
- As of May 2023, the DPIIT recognizes 10,298 startups, but only about 10% fall under the 'deep tech' category, indicating a need for more effort and support.
- A major hurdle is the inadequate funding for 'deep tech' startups. Unlike fintech or retail software startups that require comparatively smaller funds, 'deep tech' startups demand significantly larger financial investments.
- This financial gap poses a notable obstacle to their growth and development.
What is Deep Tech?
- Deep technology, often referred to as "deep tech," encompasses advanced technologies rooted in substantial scientific or engineering innovations.
- These innovations are considered "deep" due to their sophisticated and highly advanced nature, providing solutions to complex challenges or issues.
- Examples of breakthroughs in deep tech include genomics, robotics, nanotechnology, and clean energy initiatives emerging from research labs and academia.
- Deep-tech startups and companies are characterized by their pursuit of solutions to intricate problems through technologies and processes involving lengthy research and development cycles.
- Importantly, businesses and startups that rely on easily replicable ideas do not qualify as deep tech startups.
- Deep tech stands apart from high tech, which denotes a broader scope of technical innovations and advancements.
- Unlike high-tech companies, those in deep tech are primarily focused on profound scientific or engineering breakthroughs.
Isro’s futuristic fuel cell system could power space station (TOI)

- 06 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News
Recently, a futuristic fuel cell-based power system was successfully tested by Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) to provide a sustainable and reliable power source for space stations.
What is a Fuel Cell?
- Fuel cells, intricate devices powered by chemical reactions, have diverse applications spanning transportation, industrial sectors, commercial and residential buildings, and reversible grid energy storage systems.
- Operationally, fuel cells consist of two electrodes—an anode and a cathode—immersed in an electrolyte.
- The anode, supplied with hydrogen fuel, undergoes oxidation to produce hydrogen ions and electrons.
- Simultaneously, the cathode, exposed to an oxidizer like oxygen, results in the production of water as hydrogen ions absorb electrons.
- The voltage per unit cell is determined by the energy level disparity at the electrodes. While a single fuel cell generates a modest amount of direct-current electricity, practical use often involves assembling stacks of these cells.
- Advantages: Advantages of fuel cells include lower or zero emissions, particularly with hydrogen fuel cells emitting only water, addressing climate concerns by avoiding carbon dioxide emissions.
- They operate quietly with few moving parts, achieve higher efficiencies compared to combustion engines, and resemble batteries but offer prolonged electrical energy due to continuous external fuel and air/oxygen sources.
- This longevity distinguishes them from batteries that rely on finite fuel material and oxidant, making fuel cells a sustainable and efficient choice for various applications.
About ISRO:
- The Indian Space Research Organization (ISRO) is the pioneer space exploration agency of the Government of India, headquartered at Bengaluru.
- ISRO was formed in 1969 with a vision to develop and harness space technology in national development, while pursuing planetary exploration and space science research.
- ISRO replaced its predecessor, INCOSPAR (Indian National Committee for Space Research), established in 1962 by India’s first Prime Minister Pt. Jawaharlal Nehru and scientist Vikram Sarabhai, considered amongst the founding fathers of the Indian space program.
BRO Implements Indigenous Technology for Road Construction Near China Border in Arunachal Pradesh (TOI)

- 06 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News
In order to improve operational capacity of the defence forces in the high-altitude areas along the Indo-China border in Arunachal Pradesh, the BRO will build bituminous roads using an indigenous technology, “Rejupave” developed by India’s oldest and premier road research organisation, CSIR-Central Road Research Institute (CSIR-CRRI).
What is Rejupave Technology?
- CSIR-Central Road Research Institute (CSIR-CRRI), India's oldest road research organization, developed the Rejupave Technology.
- It is beneficial for constructing high-altitude bituminous roads in low and sub-zero temperatures.
- The technology actively reduces production and rolling temperatures of bituminous mixes by 30 to 400 degrees Celsius, ensuring minimal heat loss during transit in snowy conditions and long haulage times.
- The bio-oil-based asphalt modifier of this technology significantly lowers the heating requirements of bituminous mixes and preserves mix temperature during transit.
- In cold climatic regions, the 'Rejupave' asphalt modifier enhances long-term durability and resistance to thermal cracking under low-temperature conditions.
- Additionally, it plays a crucial role in reducing greenhouse gas emissions in the eco-sensitive mountainous environment of Arunachal Pradesh.
About CSIR-Central Road Research Institute (CRRI):
- Established in 1952, CSIR-Central Road Research Institute (CRRI) stands as a premier national laboratory under the Council of Scientific and Industrial Research (CSIR).
- CRRI's major research and development programs encompass a range of projects, including the design, construction, and maintenance of roads and runways, traffic and transportation planning for large and medium cities, management of roads in diverse terrains, improvement of marginal materials, utilization of industrial waste in road construction, and landslide control.
- The institute extends its expertise by providing technical and consultancy services to various organizations both within India and internationally.
- CRRI actively contributes to capacity building in highway engineering, empowering human resources to undertake and execute road and runway projects.
High-frequency waves detected in the Martian Upper Atmosphere could help understand plasma processes over Mars (PIB)
- 06 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News
Recently, scientists have detected the existence of high-frequency plasma waves in the Martian Upper Atmosphere with novel narrowband and broadband features that can help to understand plasma processes in the Martian plasma environment.
What are Plasma Waves?
- Plasma waves, commonly observed in Earth's magnetosphere, denote short-time scale fluctuations in electric and magnetic fields.
- These waves play a crucial role in energizing and transporting charged particles within Earth's magnetosphere.
- Specific plasma waves, like electromagnetic ion cyclotron waves, serve as a safeguard, cleansing Earth's radiation belt, known to pose threats to satellites.
- Researchers, intrigued by this phenomenon, seek to understand the presence of diverse plasma waves around planets without intrinsic magnetic fields, such as Mars.
Key Observations:
- Scientists utilized high-resolution electric field data from NASA's Mars Atmosphere and Volatile Evolution Mission (MAVEN) spacecraft to examine high-frequency plasma waves in the Martian environment.
- These waves manifest as either parallel-propagating electron oscillations (Langmuir waves) or perpendicular-propagating electron oscillations (upper-hybrid type waves) in Mars' magneto sheath region.
- Two distinct wave modes, below and above the electron plasma frequency, were observed in the Martian magnetosphere.
- Broadband and narrowband waves exhibited identifiable features in the frequency domain, with broadband waves displaying periodic patchy structures at intervals of 8–14 milliseconds.
Significance:
- The presence of these waves offers a valuable tool to investigate how electrons gain or dissipate energy within the Martian plasma environment.
Cabinet clears PRITHVI initiative for ease of research in earth sciences (Indian Express)

- 06 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News
The government Friday approved an initiative that will give it the flexibility to pursue research and use funds allocated to five different sub-schemes related to earth sciences over a five-year period.
About the PRITHVI Scheme:
- The PRITHVI Scheme is an initiative by the Ministry of Earth Sciences (MoES) designed to deepen our understanding of the Earth and its essential indicators.
- With a substantial allocation of Rs 4,797 crore spanning 2021-26, this comprehensive initiative aims to significantly advance research, modeling, and service delivery in critical domains like weather, climate, oceans, and polar regions.
- The scheme amalgamates five existing sub-schemes:
- Atmosphere and Climate Research-Modelling Observing Systems and Services (ACROSS)
- Ocean Services, Modelling Application, Resources and Technology (O-SMART)
- Polar Science and Cryosphere Research (PACER)
- Seismology and Geosciences (SAGE)
- Research, Education, Training, and Outreach (REACHOUT).
- Collectively, these programs strive to deepen our comprehension of Earth's vital signs and translate scientific knowledge into practical services for the benefit of society, the environment, and the economy.
Objectives:
- A primary aim of PRITHVI is to enhance and sustain long-term observations across the atmosphere, ocean, geosphere, cryosphere, and solid earth.
- This facilitates the recording and monitoring of vital signs and changes within the Earth System.
- The scheme places emphasis on developing predictive models for weather, ocean, and climate hazards while advancing our understanding of climate change science.
- Exploring polar regions and high seas is a significant aspect, targeting the discovery of new phenomena and resources.
- The scheme underscores the development of technology for exploring and sustainably harnessing oceanic resources for societal applications.
Implementation:
- Various components of the PRITHVI scheme are interdependent, executed in an integrated manner through the collective efforts of the institutes under the MoES.
10th century Kadamba inscription written in Kannada, Sanskrit found in Goa (The Hindu)

- 05 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News?
An inscription written in Kannada and Sanskrit and said to be of 10th century A.D. Kadamba period has been discovered in the Mahadeva temple at Cacoda in southern Goa.
About the Kadamba Inscription:
- Discovery and Study of the Inscription: The inscription illuminates the Kadamba period in Goa, commencing with the auspicious phrase 'Be it well' (Swasthi Shri).
- It was discovered between the temples of Mahadev and Sateri-Betal at Cacoda in Goa.
- Epigraphic Details: It chronicles the story of Gundayya, Talara Nevayya's son, who vowed to fulfill his father's desire by capturing a Gopura in the port of Goa.
- The inscription is engraved in Kannada and Nagari characters.
- Its literary style mirrors the Talangre inscription of Jayasimha I from the same period.
- The deciphering of the Kadamba stone inscription has brought to light its historical and socio-cultural importance.
- Historical Narrative: The Kadambas of Goa served as subordinates to the Chalukyas.
- Kadamba Shasthadeva, appointed as Mahamandaleshwara of Goa by Chalukyan emperor Tailapa II, played a key role in overthrowing the Rashtrakutas.
- In 960 A.D., Kadamba Shasthadeva conquered Chandavara and the port of Gopakapattana (present Goa).
- Gundayya, Talara Nevayya's son, actively participated in the battle, successfully securing the port but sacrificing his own life.
- To commemorate his son's heroic fight, Talara Nevayya erected a memorial stone with the inscription in the Mahadev temple at Cacoda.
- Socio-cultural Importance: Cacora village, situated near navigable waterways, establishes connections to the Upper Ghat region through the ancient route of Diggi ghat leading to Karnataka.
- Currently a census town under the Municipality of Curchorem Cacora in Goa, Cacoda hosts the Mahadev temple with its affiliated deities, showcasing the cultural richness and historical significance of the area.
Justice Gavai nominated as SC Legal Services Committee Chairman: What law says on free legal aid in India (Indian Express)

- 05 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News
Supreme Court judge Justice BR Gavai has been nominated as the Chairman of the Supreme Court Legal Services Committee (SCLSC), replacing Justice Sanjiv Khanna – the seniormost judge of the top court after the Chief Justice of India (CJI).
What is the Supreme Court Legal Services Committee?
- The Supreme Court Legal Services Committee was constituted under Section 3A of the Legal Services Authorities Act, 1987, to provide “free and competent legal services to the weaker sections of society”, in cases falling under the top court’s jurisdiction.
- Section 3A of the Act states that the Central Authority (the National Legal Services Authority or NALSA) shall constitute the committee.
- It consists of a sitting SC judge, who is the chairman, along with other members possessing the experience and qualifications prescribed by the Centre.
- Both the chairman and other members will be nominated by the CJI. Further, the CJI can appoint the Secretary to the Committee.
Who does the SCLSC comprise?
- As of date, the SCLSC consists of chairperson BR Gavai and nine members nominated by the CJI.
- The Committee, in turn, can appoint officers and other employees as prescribed by the Centre, in consultation with the CJI.
- Besides this, Rule 10 of the NALSA Rules, 1995, entails the numbers, experience, and qualifications of the SCLSC members.
- Under Section 27 of the 1987 Act, the Centre is empowered to make rules in consultation with the CJI, by notification, to carry out the provisions of the Act.
What is the need for legal services and how is it dispensed to the people?
- The need for providing legal services has been underlined in many provisions of the Indian Constitution.
- Article 39A states, “The State shall secure that the operation of the legal system promotes justice, on a basis of equal opportunity, and shall, in particular, provide free legal aid, by suitable legislation or schemes or in any other way, to ensure that opportunities for securing justice are not denied to any citizen by reason of economic or other disabilities.”
- Moreover, Articles 14 (right to equality) and 22(1) (rights to be informed of grounds for arrest) also make it obligatory for the State to ensure equality before the law and a legal system that promotes justice based on equal opportunity.
- Although the idea of a legal aid programme was earlier floated in the 1950s, it was in 1980 that a committee at the national level was established under the chairmanship of then SC judge Justice PN Bhagwati.
- The Committee for Implementing Legal Aid Schemes started monitoring legal aid activities throughout India.
What the Legal Services Authorities Act says?
- In 1987, the Legal Services Authorities Act was enacted to give a statutory base to legal aid programmes.
- It aims to provide free and competent legal services to eligible groups, including women, children, SC/ST and EWS categories, industrial workers, disabled persons, and others.
- Under the Act, NALSA was constituted in 1995 to monitor and evaluate the implementation of legal aid programmes and to lay down policies for making legal services available.
- A nationwide network has been envisaged under the Act for providing legal aid and assistance.
- It also disburses funds and grants to State Legal Services Authorities and NGOs for implementing legal aid schemes and programmes.
- Subsequently, in every state, State Legal Services Authorities (SLSA) were established to implement NALSA’s policies and directions, give free legal services to people, and conduct Lok Adalats.
- An SLSA is headed by the Chief Justice of the respective High Court and includes the senior HC judge as its Executive Chairman.
- While the HC Chief Justice is the patron-in-chief of the SLSA, the CJI is the patron-in-chief of NALSA.
- Similarly, District Legal Services Authorities (DLSAs) and Taluk Legal Services Committees were established in districts and most taluks.
- Situated in the District Courts Complex in every district, each DLSA is chaired by the District Judge of the respective district.
- The Taluka or Sub-Divisional Legal Services Committees are headed by a senior civil judge.
- Collectively, these bodies organise legal awareness camps, provide free legal services, and supply and obtain certified order copies and other legal documents, among other functions.
How graphene semiconductors can revolutionise electronics and computing (Front Line)
- 05 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News
Recently, Scientists have made a breakthrough in electronics, creating the world’s first functional semiconductor made from graphene—a material known for being tough, flexible, light and with a high resistance.
What is Graphene?
- Graphene is a single sheet of carbon atoms—a 2D material held together by the strongest chemical bonds known.
- These carbons are arranged in tessellated hexagons, much like honeycomb.
- It is an incredibly strong material. It’s so strong we can hold up a football with just one atomic layer of graphene.
- Graphene is also incredibly flexible, making it ideal for use in electrical devices and batteries, or even printed on glass, plastics or fabrics.
Keys Properties of Graphene:
- Strength: it is the strongest material ever measured, about 200 times stronger than steel.
- This is because the strong covalent bonds between carbon atoms in the hexagonal lattice make it very difficult to break apart.
- Conductivity: Graphene is also an excellent conductor of heat and electricity.
- In fact, it is the best conductor of heat at room temperature of any known material.
- This is because the electrons in graphene can move freely through the lattice without encountering any obstacles.
- Transparency: Graphene is almost completely transparent to light, absorbing only about 2.3% of visible light.
- This makes it a promising material for use in transparent electronics and solar cells.
- Flexibility: Graphene is also incredibly flexible, and can be bent and folded without breaking.
- This makes it a good candidate for use in flexible electronics, such as wearable devices.
- These properties make graphene a potential game-changer for a wide range of industries, including electronics, energy, transportation, and medicine.
Potential Applications of Graphene:
- Electronics: Graphene could be used to make transistors that are much faster and more efficient than the silicon transistors used in today's electronics.
- This could lead to the development of smaller, lighter, and more powerful devices.
- Energy: Graphene could be used to make solar cells that are more efficient at converting sunlight into electricity.
- It could also be used to make batteries that are lighter and have longer lifespans.
- Transportation: Graphene could be used to make lighter and stronger airplanes and cars.
- It could also be used to make more efficient batteries for electric vehicles.
- Medicine: Graphene could be used to make sensors that can detect diseases at an early stage.
- It could also be used to deliver drugs directly to diseased cells.
Drawback of Graphene:
- Graphene has major drawbacks, which has prevented its use in electronics.
- One major issue is known as the “band gap problem.”
- The band gap is a crucial electronic property that allows semiconductors to switch on and off.
- Graphene didn’t have a band gap—until now.
- Despite its promise, graphene is still a relatively new material and there are a number of challenges that need to be overcome before it can be widely used.
- One challenge is that it is difficult and expensive to produce large sheets of high-quality graphene.
- Another challenge is that graphene is very sensitive to its environment, and its properties can be easily affected by the presence of even small amounts of impurities.
- However, researchers are making rapid progress in overcoming these challenges, and it is likely that graphene will become a common material in the near future.
- With its unique properties, graphene has the potential to revolutionize many different industries and improve our lives in countless ways.
PM’s school becomes base for week-long residential programme for students (The Hindu)

- 05 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News
The Ministry of Education on Thursday launched ‘Prerana’, an experiential learning programme, which will operate from the vernacular school in Prime Minister Narendra Modi’s birthplace Vadnagar, Gujarat where Mr. Modi studied when he was a student.
Context:
- The Department of School Education & Literacy, operating under the Ministry of Education, Government of India, has unveiled 'Prerana: An experiential learning program.'
- This innovative initiative is specifically crafted to deliver a profound, distinctive, and motivational learning experience to its participants.
- The overarching goal of this program is to cultivate and nurture leadership qualities among the individuals involved, thereby contributing to their holistic development and empowering them with the skills necessary for effective leadership in various contexts.
What is ‘Prerna’ Program?
- Prerana is driven by a strong commitment to integrate principles of Indian education system and the philosophy of value-based education which is a corner stone of the National Education Policy (NEP) 2020.
- It is a week-long residential program for selected students of class IX to XII.
- It is an experiential and inspirational learning program for students with the best-in-class technology where heritage meets innovation.
- A batch of 20 selected students (10 boys and 10 girls) will attend the program, every week from various parts of the country.
- Prerana program will run from a Vernacular School, established in 1888, in one of the oldest living cities of India, Vadnagar, district Mehsana, Gujarat.
- The curriculum of Prerana School prepared by IIT Gandhi Nagar is rooted in nine value based themes:
- Swabhiman and Vinay
- Shaurya and Sahas
- Parishram and Samarpan
- Karuna and Sewa
- Vividhta and Ekta
- Satyanishtha and Shuchita
- Navachar and Jigyasa
- Shraddha aur Vishwas, and
- Swatantrata and Kartavya.
- The program based on above themes will inspire the youth and foster respect for Bharat's unity in diversity, embodying the spirit of "Vasudhaiva Kutumbakam" and will contribute by making the youth of today, a flame holder for Viksit Bharat.
- Towards this endeavour, the participants will be guided by mentors from prestigious institutions.
- Selection Procedure: Students can register through the portal, wherein applicants can fill the requisite details to be a part of the ambitious and aspirational Prerana program.
- The registered applicants will go through a selection process, as prescribed on the portal.
- Applicants can also join the selection procedure conducted at the School/block level, on designated ‘Prerana Utsav’ day, through various activities based on the ethos of Prerana to evaluate for well rounded personalities keen to shape the future of our nation.
- Upon selection, the 20 participants (10 boys and 10 girls) will be attending the Prerana program and embark on a journey of inspiration, innovation, and self-discovery.
- After the program, the participants will carry the ethos of Prerana into their respective communities, become change makers and spark positive change to inspire others.
Ministry of Environment, Forest, and Climate Change submits proposals for Wetland City Accreditation under the Ramsar Convention on Wetlands for cities of Indore, Bhopal and Udaipur (The New Indian Express)

- 05 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News
MoEF&CC has submitted three nominations from India for Wetland City Accreditation (WCA) of Indore (Madhya Pradesh), Bhopal (Madhya Pradesh) & Udaipur (Rajasthan) under the Ramsar Convention on Wetlands.
What is Wetland City Accreditation (WCA)?
- Recognizing the importance of wetlands in urban and peri-urban environments and to take appropriate measures to conserve and protect these wetlands, the Ramsar Convention during COP12 held in the year 2015 approved a voluntary Wetland City Accreditation system under Resolution XII.10.
- It recognizes cities which have taken exceptional steps to safeguard their urban wetlands.
- The Wetland City Accreditation scheme aims to further promote the conservation and wise use of urban and peri-urban wetlands, as well as sustainable socio-economic benefits for local populations.
- Additionally, the Accreditation seeks to encourage cities that are close to and dependent on wetlands.
- Primarily Wetlands of International Importance, but also wetlands with other conservation category status, to develop and strengthen a positive relationship with these valuable ecosystems.
- To be formally accredited, a candidate for the Wetland City Accreditation should satisfy the standards used to implement each of the six international criteria mentioned Operational Guidance for WCA of the Ramsar Convention on Wetlands.
- This voluntary scheme provides an opportunity for cities that value their natural or human-made wetlands to gain international recognition and positive branding opportunities for their efforts in demonstrating strong positive relationships with wetlands.
- The ongoing Amrit Dharohar initiative of the MoEF&CC announced as part of this year’s budget also aims to achieve similar goals by promoting unique conservation values of Ramsar Sites.
- In this context, WCA will not only generate public awareness about conservation of urban and peri-urban wetlands but will also help in implementation of Amrit Dharohar across the country.
The Three Nominated Cities Include:
- Indore: Founded by Holkars, Indore is the cleanest city in India and the recipient of India’s Smart City Award 2023 for its best sanitation, water and urban environment.
- Sirpur Lake, a Ramsar Site in the city, has been recognised as an important site for water bird congregation and is being developed as a Bird Sanctuary.
- A strong network of more than 200 wetland mitras is engaged in bird conservation and sensitising local community to protect Sarus Crane.
- Bhopal: One of the cleanest cities in India that has proposed conservation zones around the wetlands in its draft City Development Plan 2031.
- Bhoj Wetland, Ramsar Site is the city’s lifeline, equipped with the world-class wetlands interpretation centre, Jal Tarang.
- Additionally, the Bhopal Municipal Corporation has a dedicated Lake Conservation Cell.
- A network of more than 300 wetland mitras is engaged in wetland management and conservation of Sarus Crane.
- Udaipur: Located in Rajasthan, the city is surrounded by five major wetlands, namely, Pichola, Fateh Sagar, Rang Sagar, Swaroop Sagar, and Doodh Talai.
These wetlands are an integral part of the city’s culture and identity, help maintain the city’s microclimate, and provide a buffer from extreme events.
India to use SpaceX rocket to launch communications satellite (Indian Express)

- 04 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News?
The Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) is gearing up for the launch of its communication satellite GSAT-20, weighing 4,700kg, an initiative marking India's entry into a new era of satellite technology.
Context:
- The commercial arm of ISRO, NewSpace India Limited (NSIL) will launch GSAT-20 (renamed as GSAT-N2), on-board SpaceX’s Falcon-9 during the second quarter of 2024.
- ISRO's current flagship rocket, the LVM3, holds a maximum carrying capacity of four tons.
- Falling short by 700kg for the GSAT-20.
- This satellite will cater to cellular backhaul service needs particularly to remote and unconnected regions.
What is GSAT 20 Satellite?
- GSAT-20 is an Indian geostationary Ka-band high-throughput communications satellite.
- GSAT 20 is built on the I-3K unified modular bus with electric-only propulsion.
- It will be India's first satellite to rely entirely on electric propulsion, which can be five to six times more efficient than chemical-based propulsion.
- It features a Ka × Ka high-throughput communications payload with 70 Gbps throughput utilizing 32 spot beams with each 2 polarisations providing broadband services across the Indian region.
- The satellite was initially set for a 2020 launch on a GSLV Mk.3 (2) rocket but got moved up to 2019 on an Ariane-5ECA+.
- In 2021, the plan returned to a GSLV Mk.3 (2) launch.
- In early 2024, a contract with SpaceX was signed for a Falcon-9 v1.2 (Block 5) launch.
What is SpaceX’s Falcon-9 Rocket?
- Falcon 9 is a reusable, two-stage rocket designed and manufactured by SpaceX “for the reliable and safe transport of people and payloads into Earth orbit and beyond".
- It is the world’s first orbital-class reusable rocket.
- Reusability allows SpaceX to re-fly the most expensive parts of the rocket, which in turn drives down the cost of space access," it added.
- Till now, it has undertaken 285 launches, 243 landings, and 217 re-flights.
Centre, SEBI will regulate short selling, Solicitor-General tells Supreme Court (The Hindu)

- 04 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News?
The Supreme Court judgement records a statement made by Solicitor General Tushar Mehta that the Union government and the Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI) will take measures to regulate short selling.
What is Short Selling?
- Short selling is a financial strategy where an investor or trader borrows securities, such as stocks, from a broker and sells them in the market with the expectation of buying them back at a lower price in the future.
- Short selling is regulated by a circular notified by SEBI in December 2007.
- This technique is employed by individuals who anticipate a decline in share prices, aiming to profit from their predictions.
- The process involves selling shares that the trader does not own.
- To initiate a short position, the trader borrows shares from a broker, who lends them with an agreement for return at the settlement time.
- The borrowed stocks are then sold at the prevailing market rate, creating a short position.
- Subsequently, the trader waits for the prices to decrease before buying back the shares to close the position.
- The ultimate goal of short selling is to 'sell high and buy low.'
- Profits are made when share prices fall, and the trader benefits from the difference between the selling and repurchasing prices.
- Conversely, if the trader's analysis is incorrect and share prices rise, they incur a loss.
How Does Short Selling Work?
Short selling is an activity that allows market participants to profit from the fall in the price of a financial instrument. It involves borrowing an asset from a broker, selling it in the market, and then repurchasing it later at a hopefully lower price to return it to the lender.
- Borrowing the Asset: The trader borrows the asset (usually stocks) from a broker or another trader.
- This borrowed asset is typically done through a margin account, where the investor agrees to certain terms and pays a fee or interest for the borrowed amount.
- Selling the Asset: After obtaining the borrowed asset, the trader immediately sells it on the market.
- This is where they take advantage of their belief that the asset's price will decrease.
- Waiting for Price Drop: The trader waits for the price of the asset to fall. If the price drops as anticipated, the investor can buy back the asset at a lower price.
- Repurchasing the Asset: Once the price has dropped, the trader uses the proceeds from the initial sale to repurchase the same asset at a lower price.
- Returning the Borrowed Asset: Finally, the trader returns the borrowed asset to the lender, typically the broker, from whom they originally borrowed it.
- Profit or Loss: The profit or loss in short selling is the difference between the price at which the asset was sold and the price at which it was repurchased, minus any borrowing fees, interest, or transaction costs.
Short selling is considered a more advanced and riskier trading strategy, and it requires careful monitoring of market conditions. It is often used by experienced investors or hedge funds seeking to profit from anticipated price declines in specific securities or markets.
A first in 100 years, the Indian Science Congress was postponed amid a tussle between organisers, Govt (Indian Express)

- 04 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News?
The Indian Science Congress, the largest gathering of scientists and students of science in the country and a permanent annual fixture in the calendar of the participant group for more than a century has been postponed.
Postponement of the Indian Science Congress:
- Unprecedented Interruption: The postponement of the Indian Science Congress holds unprecedented significance.
- Since its inception in 1914, the Congress has been an annual event, except for the years immediately following the onset of the Covid-19 pandemic (2021 and 2022).
- Tradition and Prime Ministerial Engagement: A cornerstone of scientific tradition, the Indian Science Congress is inaugurated by the Prime Minister, making it a fixture on the PM's calendar.
- Typically, it stands as the Prime Minister's first public engagement of the new year.
Why has the Science Congress Been Postponed This Year?
- This year's postponement stems from a protracted dispute between the Indian Science Congress Association (ISCA), the organizing body, and the Department of Science and Technology (DST) within the Union Ministry of Science and Technology.
- The DST, a key funding entity, withdrew support in September 2023, citing financial irregularities.
- The ISCA refuted the allegations and contested the DST's directive prohibiting government funds for Science Congress-related expenses, leading to an impasse that has resulted in the postponement.
- A legal challenge to the DST's decision is currently pending.
What is the Indian Science Congress (ISC)?
- The Indian Science Congress (ISC) is a unique event in the country that serves as a platform for scientific communities to interact with students and the general public on science-related matters.
- Organized by the Indian Science Congress Association (ISCA), an independent body supported by the Department of Science and Technology (DST) in the central government, the Science Congress is an annual five-day event from January 3 to 7, considered a permanent fixture on the Prime Minister’s calendar.
- The inaugural session of the Indian Science Congress took place in 1914 at the premises of the Asiatic Society, Calcutta.
- In recent years, the Indian Science Congress (ISC) has faced criticism due to issues such as a lack of substantial discussions, the promotion of pseudoscience, and outlandish claims by certain speakers.
- This has led to concerns among prominent scientists, with some advocating for the discontinuation of the event or, at the very least, the withdrawal of government support.
- While the government provides an annual grant for organizing the Science Congress, it does not play a direct role in its organization.
Namibian cheetah Aasha gives birth to 3 cubs in Kuno; ‘indicator that animals are acclimatising’ (Indian Express)

- 04 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News?
Recently, a Namibian cheetah named Aasha has given birth to three cubs at Kuno National Park in Madhya Pradesh.
About Kuno National Park (KNP):
- Location: Situated in the Sheopur district of Madhya Pradesh, Kuno National Park is nestled near the Vindhyan Hills.
- The park is aptly named after the Kuno River, a significant tributary of the Chambal River that traverses its expanse.
- Originally designated as a wildlife sanctuary, Kuno National Park attained the status of a national park in 2018.
- This transformation aligns with its pivotal role in the 'Action Plan for Introduction of Cheetah in India.'
- Vegetation and Flora: Kuno predominantly features a grassland landscape, punctuated by occasional rocky outcrops.
- The flora encompasses a diverse mix, including dominant species such as Kardhai, Salai, and Khair trees.
- The park boasts a rich composition with 123 tree species, 71 shrub species, 32 exotic and climbing species, and 34 bamboo and grass species.
- Fauna: The protected region of Kuno National Park shelters an array of wildlife, including the jungle cat, Indian leopard, sloth bear, Indian wolf, striped hyena, golden jackal, Bengal fox, and dhole.
- The park also delights bird enthusiasts with a habitat supporting over 120 bird species.
What is Project Cheetah?
- The Wildlife Trust of India started talks in 2009 to bring the cheetah back to India.
- Over five years, 50 cheetahs will be imported from African nations and placed in various national parks as part of the "Action Plan for Reintroduction of Cheetahs in India."
- Prime Site Selection - Kuno Palpur National Park (KNP): Among the surveyed sites in central Indian states, Kuno Palpur National Park (KNP) in Madhya Pradesh emerged as the most suitable location.
- This acclaim is attributed to its conducive habitat and ample prey base.
- KNP is deemed capable of supporting 21 Cheetahs, uniquely standing as a wildlife site where villages have been entirely relocated from within the park.
- Moreover, Kuno offers the prospect of harmoniously accommodating four of India's prominent big cats - tiger, lion, leopard, and Cheetah.
- Additional Recommended Sites: The project identifies other potential sites, including Nauradehi Wildlife Sanctuary (Madhya Pradesh), Gandhi Sagar Wildlife Sanctuary - Bhainsrorgarh Wildlife Sanctuary complex (Madhya Pradesh), Shahgarh bulge in Jaisalmer (Rajasthan), and Mukundara Tiger Reserve (Rajasthan).
- Implementation Progress: As a significant stride in the project's realization, 20 Cheetahs, comprising 8 from Namibia and 12 from South Africa, were introduced to Kuno Palpur National Park last year.
- This marks a historic initiative to establish a free-ranging Cheetah population in India, reviving their presence after a 70-year absence.
PM inaugurates Kochi-Lakshadweep Islands Submarine Optical Fibre Connection (PIB)
- 04 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News?
PM Modi recently, in Kavaratti, Lakshadweep, inaugurated the Kochi-Lakshadweep Islands submarine optical fibre connection (KLI-SOFC) project including various developmental projects worth more than Rs 1,150 crore.
Background-Kochi-Lakshadweep Submarine OFC (KLI) Project:
- The need for digitally connecting the Lakshadweep Islands through a high-capacity submarine cable link with the mainland has been felt for some time.
- Earlier, the only means of communication with the Islands was through Satellite medium, which had limited bandwidth capacity and was not able to meet the growing bandwidth demand.
- In the Kochi-Lakshadweep Islands Submarine Cable (KLI) project submarine cable connectivity from Mainland (Kochi) to eleven Lakshadweep Islands namely, Kavaratti, Agatti, Amini, Kadmat, Chetlet, Kalpeni, Minicoy, Androth, Kiltan, Bangaram and Bitra has been extended.
- The project is funded by the Universal Services Obligation Fund (USOF), Department of Telecommunication.
- Bharat Sanchar Nigam Limited (BSNL) was the Project Executing Agency and the work was awarded to NEC Corporation India Pvt Ltd.
- Major activities related to the project include Marine Route Survey, Submarine Cable laying, Civil Construction of CLS stations, Installation, Testing and Commissioning of End Terminals (SLTE).
- Highlights of the KLI Project:
- Total link distance: 1,868 kilometres.
- Total cost of project: Rs 1072 crore
???????Benefits of the KLI Project:
- The project will play a significant role in achieving the objective of ‘Digital India’ and ‘National Broadband Mission’ and in rolling out various e-governance projects of the Government of India in Lakshadweep Islands.
- E-Governance, Tourism, Education, Health, Commerce and Industries will get a boost
- It will also help in further improvement in the standards of living of the people on the Island and will accelerate overall social and economic development in these areas.
- The population of Lakshadweep Islands will be provided high-speed wireline broadband connectivity.
- High-speed broadband will be provided through FTTH and 5G/4G Mobile networks.
- The bandwidth created under this project will be available to all Telecom Service Providers (TSPs) to strengthen their telecom services in the Lakshadweep Islands.
Govt ready with rules for CAA, set to be notified before Lok Sabha polls announcement (Indian Express)

- 03 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News?
The rules for the Citizenship (Amendment) Act of 2019 are ready with the central government and will be notified "much before" the announcement of the Lok Sabha elections.
What is the Citizenship (Amendment) Act (CAA) 2019?
- The Citizenship (Amendment) Act of 2019 proposes amendments to the definition of illegal immigrants, specifically benefiting Hindu, Sikh, Parsi, Buddhist, Jain, and Christian immigrants (excluding Muslims) from Pakistan, Afghanistan, and Bangladesh.
- These individuals, residing in India without documentation, are eligible for expedited Indian citizenship within 5 years (reduced from 11 years).
Key Provisions:
- Cancellation of OCI Registration: The Act empowers the cancellation of Overseas Citizen of India (OCI) registration if the holder violates Citizenship Act provisions or other applicable laws.
Eligibility Criteria:
- Forced Migration: The CAA 2019 applies to those compelled to seek refuge in India due to religious persecution.
- Cut-off Date: Applicants must have entered India on or before December 31, 2014.
- Exceptions: The Act excludes areas under the Constitution's sixth schedule (autonomous tribal regions in Assam, Meghalaya, Tripura, and Mizoram) and states with an inner-line permit regime (Arunachal Pradesh, Nagaland, and Mizoram).
- Implementation Status: Despite lacking notified rules, leading to non-implementation, the government has repeatedly sought extensions for rule formulation.
Rules for the the CAA:
- The authorities have finalized the rules, and the online portal is operational.
- Upon issuing the rules, the authorities can implement the law, granting Indian citizenship to eligible individuals.
- The entire application process will be conducted online, allowing applicants to apply, even using their mobile phones.
- Applicants must declare the year of their entry into India without travel documents, with no requirement for additional documents.
- Requests from applicants who applied after 2014 will be processed according to the new rules.
Factors Contributing to the Delay in CAA Implementation:
- The CAA has encountered robust opposition, particularly in states like Assam and Tripura, leading to significant delays in its implementation.
- Demographic Concerns in Assam: In Assam, concerns have arisen over the perceived demographic impact of the CAA, with fears that it might contradict the 1985 Assam Accord's provisions.
- Assam Accord Violation Perception: The CAA is viewed in Assam as a potential breach of the 1985 Assam Accord, which permits citizenship for migrants arriving between January 1, 1966, and March 25, 1971.
- Nationwide Protest: Protests initially concentrated in the northeast expanded nationwide, contributing to a complex socio-political environment surrounding the CAA.
- Legal Challenges: The Supreme Court is handling petitions, including one from the Indian Union Muslim League, challenging the constitutional validity of the CAA.
- Allegations of Selectivity: Critics argue that the law is discriminatory, excluding persecuted communities like Rohingya, Tibetan Buddhists, and Sri Lankan Tamils, raising concerns about its arbitrary nature.
Counterarguments Responding to CAA Petitions:
- Basis of Classification: The government asserts that the CAA's classification is not based on religion but on addressing "religious discrimination" faced by minorities in neighbouring countries with a state religion.
- Parliamentary Deliberation: Emphasizing over seven decades of deliberation, the government highlights that the Parliament has considered issues related to minorities and enacted the CAA as a targeted amendment.
- Specific Problem Resolution: The CAA is portrayed as a focused amendment designed to address a specific issue prevalent in identified countries, rather than serving as a comprehensive solution for global challenges.
- Limited Legislative Scope: It is clarified that the legislation has a delimited scope, addressing the specific concerns of minorities in certain nations.
- The Indian Parliament is not obligated to address potential persecutions worldwide.
Another eye in the sky, on the ground: India is now part of the world’s largest radio telescope project (Indian Express)

- 03 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News?
The Indian government’s recent approval to join the SKA project, accompanied by a financial commitment of Rs 1,250 crore, marks the initial step towards this ratification.
What is the Square Kilometre Array Observatory (SKAO)?
- SKAO is an intergovernmental organisation dedicated to radio astronomy and is headquartered in the UK.
- At the moment, organisations from ten countries are a part of the SKAO.
- These include Australia, Canada, China, India, Italy, New Zealand, South Africa, Sweden, the Netherlands and the UK.
What is significant about the SKA telescope?
- The telescope, proposed to be the largest radio telescope in the world, will be located in Africa and Australia whose operation, maintenance and construction will be overseen by SKAO.
- The completion is expected to take nearly a decade at a cost of over £1.8 billion.
- Some of the questions that scientists hope to address using this telescope include:
- Beginning of the universe
- How and when the first stars were born
- The life cycle of a galaxy
- Exploring the possibility of detecting technologically-active civilisations elsewhere in our galaxy and
- Understanding where gravitational waves come from.
- As per NASA, the telescope will accomplish its scientific goals by measuring neutral hydrogen over cosmic time, accurately timing the signals from pulsars in the Milky Way, and detecting millions of galaxies out to high redshifts.
- Significantly, the development of SKA will use the results of various surveys undertaken using another powerful telescope called the Australian Square Kilometre Array Pathfinder (ASKAP), which is developed and operated by the country’s science agency CSIRO.
- This telescope, which has been fully operational since February 2019 mapped over three million galaxies in a record 300 hours during its first all-sky survey.
- ASKAP surveys are designed to map the structure and evolution of the Universe, which it does by observing galaxies and the hydrogen gas that they contain.
What are radio telescopes?
- Unlike optical telescopes, radio telescopes can detect invisible gas and, therefore, they can reveal areas of space that may be obscured by cosmic dust.
- Significantly, since the first radio signals were detected by physicist Karl Jansky in the 1930s, astronomers have used radio telescopes to detect radio waves emitted by different objects in the universe and explore them.
- According to NASA, the field of radio astronomy evolved after World War II and became one of the most important tools for making astronomical observations.
- The Arecibo telescope in Puerto Rico, which was the second-largest single-dish radio telescope in the world, collapsed in December 2020.
- The telescope was built in 1963 and because of its powerful radar, scientists employed it to observe planets, asteroids and the ionosphere, making several discoveries over the decades, including finding prebiotic molecules in distant galaxies, the first exoplanets, and the first millisecond pulsar.
Prime Minister pays tributes to Savitribai Phule and Rani Velu Nachiyar on their Jayanti (PIB)

- 03 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News?
The Prime Minister, Shri Narendra Modi paid tributes to Savitribai Phule and Rani Velu Nachiyar on their Jayanti.
Who is Savitribai Phule?
- Recognized as India's first woman teacher, Savitribai Phule was a pioneer who defied prevailing societal conventions to advance women's education, equality, and justice.
- She was a Dalit lady from the Mali community and was born on January 3, 1831, in Satara District's Naigaon (Maharashtra).
- Despite prevailing norms that limited education to affluent men, the Phules established India's first girls' school in Bhidewada, Pune, in 1848.
- Savitribai's commitment to social reform led to the establishment of Mahila Seva Mandal in 1852, advocating for women's rights.
- In 1860, she initiated a strike against shaving the hair of widowed women.
- Savitribai actively promoted inter-caste marriages, and widow remarriage, and fought against social issues like child marriage, sati, and dowry.
- In collaboration with Jyotirao, she founded the Balhatya Pratibandhak Griha, offering support to pregnant widows.
- The couple further established the Satyashodhak Samaj in 1873, aimed at dismantling caste, religion, and class hierarchies.
- Her literary contributions include "Kavya Phule" (1854), her first collection of poems, and "Bavan Kashi Subodh Ratnakar" (1892).
- Savitribai Phule's enduring legacy lies in her unwavering commitment to education and social reform, making her a pioneering figure in Indian history.
About Rani Velu Nachiyar:
- Rani Velu Nachiyar, born on January 3, 1730, in Ramanathapuram, Tamil Nadu, India, holds the distinction of being the first queen to actively resist British rule, predating the Sepoy Mutiny.
- Revered as Veeramangai among Tamils, she was extensively trained in martial arts, including Valari, Silambam, horse riding, archery, and various languages such as French, English, and Urdu.
- Married to King Muthuvaduganathaperiya Udaiyathevar of Sivagangai, Rani Velu Nachiyar entered the battlefield when her husband fell victim to British soldiers.
- Collaborating with Hyder Ali and Gopala Nayaker, she waged a successful war against the British, displaying exceptional military prowess.
- In 1780, she delegated authority to the Marudu brothers for the administration of the country.
- Rani Velu Nachiyar's courageous stand against colonial rule and her strategic alliances in the face of adversity mark her as an iconic figure in India's history of resistance and resilience.
Protesting new hit-and-run law, truckers dial down after talks with Home Secretary (Indian Express)

- 03 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News?
The All India Motor Transport Association (AIMTC) decided to end the nationwide truck drivers protests against the new hit-and-run law, after a meeting with Union Home Secretary Ajay Bhalla.
What is the New Hit-and-run Law?
The recently enacted Bharatiya Nyay Sanhita introduces stringent penalties for hit-and-run incidents in India.
- The law specifies that an accused individual causing a fatal crash and fleeing the scene without reporting to authorities could face imprisonment for up to 10 years along with a fine of Rs 7 lakh.
- Bharatiya Nyay Sanhita has established two distinct categories under the umbrella of "causing death by negligence."
- The first category addresses causing death through any rash or negligent act that does not amount to culpable homicide.
- Offenders in this category may face imprisonment for up to five years and a fine.
- The second category deals with causing death through rash and negligent driving, not amounting to culpable homicide.
- If the individual escapes without promptly reporting the incident to a police officer or magistrate, they could be subjected to up to 10 years of imprisonment and a fine.
What was the Hit-and-run Law Before?
- The old, British-era Indian Penal Code (IPC) did not have a specific provision for hit-and-run cases.
- Actions in such cases were taken under Section 304 A of the IPC.
- According to that section, a person causing the death of another due to a rash or negligent act could invite a jail term of a maximum of 2 years or be fined.
- "Whoever causes the death of any person by doing any rash or negligent act not amounting to culpable homicide, shall be punished with imprisonment of either description for a term which may extend to 2 years, or with fine, or with both," the section stated.
- All cases of hit-and-run along with other forms of activities that came under the ambit of causing death by a "rash and negligent act" were lodged under Section 304 A of the IPC.
South Africa files genocide case against Israel at ICJ: Why the African nation supports Gaza so strongly (Indian Express)

- 03 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News?
Amid international criticism of Israel for its continued bombing of Gaza, South Africa recently moved the International Court of Justice (ICJ), for an urgent order declaring that Israel was in breach of its obligations under the 1948 Genocide Convention.
About the International Court of Justice (ICJ):
- The International Court of Justice (ICJ) is the principal judicial organ of the United Nations (UN).
- It was established in June 1945 by the Charter of the United Nations and began work in April 1946.
- The seat of the Court is at the Peace Palace in The Hague (Netherlands).
- Of the six principal organs of the United Nations, it is the only one not located in New York (United States of America).
- The Court’s role is to settle, in accordance with international law, legal disputes submitted to it by States and to give advisory opinions on legal questions referred to it by authorized United Nations organs and specialized agencies.
- Its official languages are English and French.
- Powers and Functions: The ICJ handles two types of cases—contentious cases, involving legal disputes between States, and advisory proceedings, responding to legal questions referred by UN organs and specialized agencies.
- Contentious cases involve only UN member States or other States that have accepted the Court's jurisdiction.
- While the Court's judgments in contentious cases are final and binding, advisory opinions are not binding.
- Deciding disputes in line with international law, the ICJ relies on conventions, international custom, general principles, judicial decisions, and expert writings.
- Composition: The Court is composed of 15 judges, who are elected for terms of office of nine years by the United Nations General Assembly and the Security Council.
- It is assisted by a Registry, its administrative organ.
- To be elected, a candidate must secure an absolute majority in both UNGA and UNSC.
- The Court sees one-third of its composition renewed every three years, and judges are eligible for re-election.
- Once elected, judges declare their commitment to the impartial and conscientious exercise of their powers.
- They act independently, detached from any governmental influence.
- This comprehensive structure ensures the ICJ's role as a pivotal entity in the international legal landscape, providing judgments on contentious matters and advisory opinions on significant legal questions.
About the Genocide Convention 1948:
- The term 'genocide,' often casually employed in reference to attacks on various communities globally, finds its precise definition in the UN's Convention on the Prevention and Punishment of the Crime of Genocide, presented to the General Assembly in 1948.
- According to this Convention, genocide entails any of the following acts carried out with the intent to wholly or partially destroy a national, ethnic, racial, or religious group:
- Killing members of the group.
- Causing serious bodily or mental harm to group members.
- Deliberately inflicting conditions of life to bring about the group's physical destruction.
- Imposing measures to prevent births within the group.
- Forcibly transferring children of one group to another.
- This Convention categorizes genocide as a crime, applicable irrespective of whether it occurs during wartime or peacetime. India ratified the convention in 1959, although no specific legislation addressing genocide has been enacted to date.
NREGS payments: Aadhaar-based system mandatory now, Govt says may consider exemptions on case basis (Indian Express)

- 02 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News?
With the Aadhaar-based payment system (ABPS) now mandatory for payment of wages to NREGS workers, the Government on Monday said it may consider exemptions on a “case-by-case basis” should any gram panchayat face “technical issues”.
What is the Aadhaar Enabled Payment System (AePS)?
- The Aadhaar Enabled Payment System (AEPS) is a payment service that allows a bank customer to use Aadhaar as his/her identity to access his/her Aadhaar-enabled bank account and perform basic banking transactions like balance enquiry, cash withdrawal, remittances through a Business Correspondent.
- It is a service developed by the National Payments Corporation of India.
Key features of AePS:
- Aadhaar-linked transactions: AePS enables Aadhaar card holders to make transactions through their Aadhaar-linked bank accounts, similar to debit/credit card transactions.
- Biometric authentication: Transactions are completed by submitting the Aadhaar number and biometric details (iris or fingerprint scan) at Points of Sale (PoS) or micro ATMs, using Aadhaar authentication.
- Bank account privacy: Users are not required to share their bank account details during the transaction, enhancing privacy and security.
- Fund transfers: AePS allows users to transfer funds between bank accounts, providing a convenient way to send and receive money.
- Secure transactions: AePS transactions are considered safe and secure as they require biometric authentication, ensuring the identity of the user.
- By leveraging the Aadhaar infrastructure, AePS simplifies and secures financial transactions, making it accessible to a wide range of individuals, particularly those who may not have access to traditional banking services.
ABPS Implementation for NREGS:
- Since 2017, the Mahatma Gandhi National Rural Employment Guarantee Scheme (NREGS) has adopted the Aadhaar-enabled Payment System (ABPS).
- This system involves linking workers' 12-digit Aadhaar numbers with their job cards and NREGS workers' bank accounts.
- With nearly universal coverage of Aadhaar numbers among the adult population, the Government of India opted to expand ABPS for beneficiaries within the scheme.
- Payments are exclusively directed through ABPS to the associated accounts, ensuring a secure and swift method of fund transfer.
- Out of the total 14.33 crore active beneficiaries, Aadhaar has been successfully linked for 13.97 crore individuals.
- Among these Aadhaar-linked beneficiaries, 13.34 crore Aadhaar authentications have been completed, making 81.89% of active workers eligible for ABPS.
- In July 2023, approximately 88.51% of wage payments were executed through the Aadhaar-enabled Payment System.
Mandatory Adoption of ABPS for NREGS Workers:
- Initially mandated by the Rural Development Ministry starting from February 1, 2023, the implementation of the Aadhaar-enabled Payment System (ABPS) witnessed several extensions, ultimately being permitted until December 31, 2023.
- As of January 1, 2024, ABPS has become obligatory for NREGS workers, with no further extensions granted to states beyond December 31.
- The integrated approach of ABPS and the National Automated Clearing House (NACH), an interbank system, will be employed for bulk payments, including subsidies and salaries.
- The use of ABPS for wage payments to unskilled workers ensures the seamless transfer of benefits to their bank accounts, even in instances of frequent changes in the beneficiary's bank account.
Exemption Decision in the Event of Technical Issues:
- If a gram panchayat encounters technical or Aadhaar-related challenges, the Government of India may evaluate exemptions from Aadhaar-enabled Payment System (ABPS) requirements on a case-by-case basis until the resolution of the issue.
- This announcement followed criticism from opposition parties, labeling ABPS as a harsh New Year measure that could potentially exclude millions of the most vulnerable and marginalized Indians from accessing basic income.
- The government was accused of "weaponizing technology, especially Aadhaar.
India, Pakistan exchange list of nuclear installations and facilities (ET)

- 02 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News?
India and Pakistan exchanged the list of nuclear installations and facilities, covered under the Agreement on the Prohibition of Attack against Nuclear Installations and Facilities between the two countries.
About the Prohibition of Attack against Nuclear Installations and Facilities:
- The Agreement on the Prohibition of Attack against Nuclear Installations and Facilities, also known as the India-Pakistan Non-Attack Agreement, was signed on 31 December 1988 and became effective on 27 January 1991.
- It was signed by the then Pakistani PM Benazir Bhutto and Indian PM Rajiv Gandhi.
- According to this agreement, both India and Pakistan are required to annually communicate the list of nuclear installations and facilities covered by the agreement on the first of January of each calendar year.
- The agreement stipulates that neither party shall engage, directly or indirectly, in any actions aimed at causing destruction or damage to any nuclear installation or facility in the other country.
- The term 'nuclear installation or facility' encompasses nuclear power and research reactors, fuel fabrication, uranium enrichment, isotopes separation, reprocessing facilities, as well as any other installations involving fresh or irradiated nuclear fuel and materials in any form, along with establishments storing significant quantities of radioactive materials.
Need for the Agreement:
- In 1986, heightened concerns arose when the Indian army conducted a large-scale exercise named 'Brasstacks,' prompting fears of a potential assault on nuclear facilities.
- Subsequently, negotiations ensued between the two nations aimed at fostering an understanding regarding the management of nuclear weapons, ultimately leading to the formulation of the treaty.
Importance of the Agreement:
- Both nations reiterate their dedication to enduring peace and the cultivation of amicable and harmonious bilateral relations.
- They recognize the significance of confidence-building measures in fostering such relations built on mutual trust and goodwill.
- The potential consequences of even a limited nuclear exchange between India and Pakistan are grave, with the potential to cause the loss of 20 million lives within a week.
Radiocarbon dating brought the first verifiable way to keep time to many fields of science, significantly transforming them (The Hindu)

- 02 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News?
From thermodynamics to GPS, from social systems theory to studies of consciousness, time plays an essential role in how we study, interpret, and understand the natural universe and the peoples and technologies that occupy it.
What is radiocarbon dating?
- Radiocarbon dating is a technique employed to determine the age of an object by utilizing radiocarbon, a specific isotope known as carbon-14.
- Formation of Carbon-14: Carbon-14 is generated in the Earth's atmosphere through a process initiated by cosmic rays—energetic streams of charged particles originating from outer space.
- These cosmic rays collide with atmospheric gas atoms, releasing neutrons in the process.
- When these neutrons interact with nitrogen-14 isotopes, carbon-14 is produced.
- Given the continuous influx of cosmic rays penetrating the Earth's atmosphere, a constant production of carbon-14 takes place.
- Subsequently, this newly formed carbon-14 readily combines with atmospheric oxygen, resulting in the creation of radioactive carbon dioxide.
- The carbon-14 compound enters various ecosystems through the carbon cycle, including plants (via photosynthesis), animals (through the consumption of plants), and other forms of biomass.
- It assumes the form of carbon dioxide and other carbon compounds, facilitating its diffusion into the Earth's diverse ecosystems.
- This ensures that the concentration of carbon-14 in the atmosphere remains comparable to its concentration in the planet's other biospheres.
How does radiocarbon dating work?
- The process of radiocarbon dating hinges on the principles of carbon exchange within living organisms, such as the human body.
- While alive, these organisms continuously interact with their environment by engaging in activities like breathing, consuming food, excreting, and shedding skin.
- During these dynamic processes, carbon-14 is both released from the body and replenished, maintaining a relatively constant concentration within the organism that is in equilibrium with its surroundings.
- However, upon death, the cessation of these activities results in a diminishing concentration of carbon-14 in the body due to radioactive decay.
- As time elapses, the quantity of carbon-14 steadily decreases, and its decay rate can be theoretically predicted.
- Radiocarbon dating assesses the age of an object by measuring the remaining amount of carbon-14, a value used by scientists or computers to estimate the time since the organism's demise.
- In contemporary radiocarbon dating methodologies, advanced techniques are employed, with one of the most sensitive approaches being accelerator mass spectrometry (AMS).
- This sophisticated method allows for the analysis of organic samples as minute as 50 mg, enhancing the precision and accuracy of radiocarbon dating.
What are the limitations of carbon-14 dating?
- Age Restriction: Carbon-14 dating is effective for dating organic materials up to approximately 60,000 years old.
- Sample Size Requirements: Conventional radiocarbon dating necessitates relatively large samples, typically ranging from 10 to 100 grams (0.35 to 3.5 ounces), depending on the material being analyzed.
- Advancements in Sample Size: While newer dating methods have emerged that can work with smaller sample sizes, allowing for analyses with quantities as low as 20 to 50 milligrams (0.0007 to 0.0018 ounces).
- Contamination Sensitivity: Radiocarbon samples are highly susceptible to contamination, making it crucial for accurate dating that they remain clean and well-preserved throughout the analysis process.
Two-Month-Old Infant Breaks Records as Youngest to Undergo Successful Bone Marrow Transplant in Mumbai (Times Now)

- 02 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News?
A two-month-old girl, diagnosed with the rare disease ‘bubble baby syndrome,' becomes the youngest to receive a bone marrow transplant from an unrelated donor at Bai Jerbai Wadia Hospital for Children in Parel.
What is Bubble Baby Syndrome?
- 'Bubble baby syndrome,' medically known as Severe combined immunodeficiency (SCID) is a group of rare, life-threatening diseases that cause a child to be born with very little or no immune system.
- As a result, the child’s body is unable to fight off infections and can become very sick from infections like chickenpox, pneumonia and meningitis and can die within the first year of life.
- This condition falls under the category of primary immune deficiencies.
- The term "Bubble Baby Syndrome" is derived from the necessity for affected individuals to live in a highly controlled environment, as exposure to ordinary surroundings can pose fatal risks to children with SCID.
- What happens in Severe combined immunodeficiency (SCID)?
- In the developing fetus, the immune system originates in the bone marrow, where versatile stem cells can differentiate into three crucial types of blood cells: red blood cells, white blood cells (WBCs), and platelets.
- Among these, white blood cells, particularly lymphocytes, play a vital role in safeguarding the body against infections.
- Lymphocytes consist of two main types: B-cells and T-cells.
- T-cells identify, attack, and eliminate invaders, while B-cells produce antibodies that "remember" infections for future defence.
- SCID is classified as a "combined" immunodeficiency as it impacts both of these infection-fighting white blood cell types.
- In SCID, the child's immune system exhibits either an insufficient quantity of lymphocytes or dysfunctional lymphocytes.
- Consequently, the compromised immune system struggles to combat various germs such as viruses, bacteria, and fungi, leading to recurrent and severe infections.
- Causes: SCID results from inherited mutations in multiple genes, with one or both birth parents passing down the condition to their child.
- Symptoms: Although infants with SCID may initially appear healthy, signs of the disorder may manifest shortly after birth. These symptoms include
- Failure to thrive
- Chronic diarrhoea
- Frequent, often severe respiratory infections
- Oral thrush (a type of yeast infection in the mouth)
- Other challenging-to-treat bacterial, viral, or fungal infections
- Treatment: SCID is considered a pediatric emergency, and without prompt intervention, affected babies are unlikely to survive beyond their first birthday.
- The primary treatment method involves a stem cell transplant, also known as a bone marrow transplant.
- In this procedure, the child receives stem cells from a donor with the hope that these new cells will reconstruct the compromised immune system, offering a chance for a healthier and more sustainable life.
Bone marrow transplant
- The most common treatment for SCID is an allogeneic bone marrow transplant, which will introduce normal infection-fighting cells into your child’s body.
- Allogeneic transplants use stem cells from a relative or an unrelated donor from the National Marrow Donor Program.
- An allogeneic bone marrow transplant involves taking cells from the bone marrow (the soft, spongy tissue found in bones) of a healthy donor and giving them to a child after the child’s diseased bone marrow has been eliminated.
- Doctors at Children’s Hospital will screen your child’s family for potential bone marrow matches.
- While a tissue-matched sibling offers the greatest chance of curing SCID, they are not often available.
- Instead, most patients receive bone marrow donations from their parents or unrelated matched donors.
Govt extends PLI scheme for the auto sector by a year with 'partial amendments' (Business Standard)

- 02 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News?
Recently, the Ministry of Heavy Industries announced the extension of the Production Linked Incentive (PLI) Scheme for Automobile and Auto Components by one year with "partial amendments".
PLI Scheme for Automobile Sector:
- The Union Cabinet approved the PLI-Auto Scheme in 2021, allocating a budgetary outlay of Rs. 25,938 crore for five years (FY2022-23 to FY2026-27).
- Aimed at enhancing the production of Advanced Automotive Technology (AAT) Products, the PLI-AUTO Scheme is designed to promote extensive localisation for AAT products and facilitate the development of both domestic and global supply chains.
- This scheme primarily targets Zero Emission Vehicles (ZEVs), specifically Battery Electric Vehicles and Hydrogen Fuel Cell Vehicles.
- In a recent amendment, the incentive period was extended to cover five consecutive financial years, commencing from the financial year 2023-24, with disbursement scheduled for the subsequent financial year, 2024-25.
- The amended scheme stipulates that approved applicants can avail benefits for five consecutive financial years, but the eligibility period will not extend beyond the financial year ending on March 31, 2028.
- Additionally, the amendments specify that if an approved company fails to meet the determined threshold for an increase in Determined Sales Value over the initial year's threshold, it will not receive any incentives for that particular year.
What is the Production-Linked Incentive (PLI) Programme?
- Around 5 years ago, the Indian government aimed to stimulate domestic manufacturing by encouraging more companies to produce goods.
- Recognizing manufacturing as a crucial driver of economic growth with a multiplier effect, wherein each job and investment in manufacturing positively influences other sectors, the government introduced the Production-Linked Incentive (PLI) scheme.
- Under the PLI scheme, both foreign and domestic companies engaged in manufacturing receive financial incentives from the government.
- The annual incentive payout is determined as a percentage of the revenue generated by these companies and is applicable for a period of up to five years.
10th phase of Sagar Parikrama covering AP and Puducherry coastal districts to start from Mon (PIB)

- 01 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News?
Union Minister for Fisheries, Animal Husbandry and Dairying Shri Parshottam Rupala along with Minister of State Dr L Murugan will participate in the Sagar Parikrama (Phase X) event being organized from 1st January 2024 to 6th January 2024 at various locations of Andhra Pradesh and Puducherry
About Sagar Parikrama Phase-10:
- Sagar Parikrama Phase-X is poised to be a pivotal event in the ongoing efforts to promote sustainable fisheries, empower stakeholders, and contribute to the economic growth of coastal communities.
- It will continue and cover the remaining coastal districts of Andhra Pradesh namely Nellore, Prakasam, Bapatla, Krishna, West Godavari, Konaseema, Kakinada, Visakhapatnam, Vizianagaram, Srikakulam and Yanam (Union Territory of Puducherry).
What is “Sagar Parikrama”?
- Sagar Parikrama is a testament to the transformative power of visionary leadership for the welfare of the fishing community and coastal development.
- It is an initiative taken by the Government, with an aim to resolve the issues of the fishers, and other stakeholders and facilitate their economic upliftment through various fisheries’ schemes and programs being implemented by the Government such as Pradhan Mantri Matsya Sampada Yojana (PMMSY) and Kisan Credit Card for Fisheries (KCC).
- It represents a transformative voyage along the coastal belt, symbolizing unity with fisherfolk, fish farmers, and all stakeholders in the spirit of the 75th Azadi Ka Amrit Mahotsav.
- The Sagar Parikrama Yatra features the interactions of ministers with fishermen, fish farmers and other relevant stakeholders.
- State fisheries officials, fishermen representatives, fish farmers, entrepreneurs, fishermen cooperative society leaders, professionals, scientists, and other stakeholders from across the nation will accompany the events.
- The journey of the first phase of “Sagar Parikrama” started from Mandvi, Gujarat on 5th March 2022.
- So far, the total 9 phases of Sagar Parikrama have been covered in the coastal States/UTs of Gujarat, Daman & Diu, Maharashtra, Goa, Karnataka, Andaman & Nicobar, Kerala, Tamil Nadu, Puducherry, and part of Nellore district of Andhra Pradesh during initiation of its tenth phase.
- Nodal Ministry: Ministry of Fisheries, Animal Husbandry & Dairying.
- Sagar Parikrama is making a notable impact on improving the quality of life and economic well-being of the fishing community.
- By providing a platform for direct interaction with Ministers and senior government officials, the initiative ensures that the concerns and issues of fishermen and fish farmers are addressed promptly.
How two choke points could turn into a perfect storm for global trade (Indian Express)
- 01 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News?
Shipping giant Maersk on Sunday suspended passage of its vessels through the Red Sea route for 48 hours after fresh attacks by Yemen-based Houthi rebels. This comes barely a week after the company announced plans to resume operation citing the deployment of a US-led military operation to guard the crucial sea route.
What do the ongoing Red Sea and Panama Canal crises mean for world trade?
- A disruption in maritime transport is a crucial concern for the world economy, as over 80 per cent of the global goods trade is carried by sea.
- The share of trade via sea is much higher for developing countries such as India.
- Currently, two important shipping routes are facing blockages.
- Bab-el-Mandeb Strait which leads to the Suez Canal in the Red Sea region connects Asia and parts of North East and East Africa to Europe.
- The 100-year-old Panama Canal connects the Atlantic and Pacific Oceans.
- Both these routes are among the busiest in the world and a blockage results in forcing global shipping lines to take longer alternate routes, pushing up freight rates.
- The disruption at the Red Sea route, for instance, is estimated to push the prices of Indian agricultural products by 10 to 20 per cent, as shipments would be routed around Africa via the Cape of Good Hope.
- This comes at a time when much of the West is witnessing higher interest rates to curb inflation.
- Higher prices could further fuel demand concerns for global and Indian exporters.
Why is trade via the Panama Canal slowing?
- Shipping via the Panama Canal has dropped by over 50 per cent due to drought conditions at the 51-mile stretch.
- Due to the shortage of water, ships moving from Asia to the US are being forced to use the Suez Canal, which takes six more days compared to the Panama Canal.
- Moreover, Panama is facing its driest rainy season in decades, raising fears of prolonged canal bottlenecks.
How have the attacks impacted freight rates?
- Ever since the attacks along the Bab-el-Mandeb Strait began, global shipping firms have begun imposing war risk surcharges over and above the normal freight rates.
- Indian exporters said that freight rates for Indian shipments headed to Europe and Africa could surge as much as 25-30 per cent if the ongoing security concern along the Red Sea trade route continues.
- This is troubling, as the European Union is one of India’s second-largest export destinations.
- Slowing demand from the region has impacted India’s labour-intensive sectors, such as textiles, gems and jewellery exports.
Panama Canal
- It is an artificial canal that spans the Isthmus of Panama and links the Atlantic and Pacific oceans.
- Together with the Suez Canal, it is one of the two most strategically important man-made waterways in the world.
- It has a length of around 80 kilometres.
- The United States constructed the canal between 1904 and 1914, and on August 15, 1914, it was formally inaugurated.
- Since 1999, when control of the Canal was moved from the United States to Panama, it has been owned and operated by the Republic of Panama.
- To make it easier for ships to cross the continental divide, the Panama Canal is made up of a network of locks that raise and decrease the water level.
Over 1 lakh people availed free treatment under Delhi Arogya Kosh scheme till October (Indian Express)

- 01 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News?
As many as 1.13 lakh people have availed of free health treatment being provided under the city Government’s ‘Delhi Arogya Kosh’ scheme, till October last year, according to government data.
What is the 'Delhi Arogya Kosh' Scheme?
- Constituted in 2011, the Delhi Arogya Kosh (DAK) has five components/schemes:
- Financial assistance to EWS patients
- Free High-End Radiological Diagnostic Test Scheme
- Cashless Specified Surgeries scheme
- RTA (Road Traffic Accident) Scheme (‘i.e. Farishtey Scheme’) and
- Cashless Dialysis Scheme.
- There are 4 schemes under the name of Delhi Arogya Kosh which include financial support from the government for medical implants, various types of surgeries, 136 types of medical tests and the Farishtey scheme for treatment of accident victims.
- Under this scheme, if any citizen of Delhi goes to Delhi government hospitals for treatment and has to face a waiting period for examination or treatment and the patient needs immediate care, then the patient can avail the above-mentioned services in a private hospital with a doctor’s reference.
- Cashless check-ups and treatment will be provided for them in all the empanelled hospitals and the cost of this will be borne by the government.
- Under this scheme, every citizen of Delhi who has Delhi's voter card can get treatment.
- Children below 19 years of age can avail this facility based on their parents' voter cards.
Schemes Under 'Delhi Arogya Kosh':
- Financial assistance up to 5 lakh for different types of medical implants: Under this scheme, the government provides financial assistance up to Rs 5 lakh to the patients.
- To avail of the benefit of this scheme, patients need to submit their application and relevant documents.
- After their screening, the government bears the cost of implants and the treatment of the patient up to Rs 5 lakh.
- It is a cashless scheme.
- 136 free medical test facilities at private labs for patients: In the case of a long waiting list at government hospitals, patients can get the tests done at private hospitals or labs.
- Under this scheme, patients can get about 136 types of medical tests done for free.
- Under this, while waiting in a government hospital, patients can get all medical tests from private hospitals and labs free of cost, including X-ray, MRI, PET scan, CT scan and ultrasound.
- Free Surgery Scheme for patients to get the surgery done in private hospitals: If a patient goes to Delhi government hospital for treatment and has to undergo surgery but the waiting time is more than 30 days, then patients can avail free surgery in private hospitals under the 'Free Surgery Scheme' under this scheme.
- The government bears all the expenses incurred in the surgery.
- Accident victims’ free treatment : The Farishtey Scheme is also covered under Delhi Arogya Kosh.
- Under this scheme, if a person meets with an accident, he or she is provided immediate treatment in a government hospital for free and if the patient gets admitted within 72 hours of an accident, he or she can also avail treatment at a private hospital for free.
-
- All the expenses of patients will be borne by the Delhi government.
SC’s translation projects raced ahead in 2023 as retd. HC judges and law clerks help AI (The Hindu)

- 01 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News?
The Supreme Court’s monumental project of translating all of its 36,000 judgments into Scheduled Languages achieved unprecedented speed in 2023, with the E-SCR portal starting with just 2,238 translated judgments in January and ending the year with over 31,000.
Background:
- In 2023, the Supreme Court of India embarked on a groundbreaking venture to translate its extensive archive of 36,000 judgments into Scheduled Languages.
- This innovative initiative, powered by collaboration between retired High Court judges, law clerks, and artificial intelligence, has made significant strides.
- However, concerns linger regarding the practical application of these translated judgments and the absence of a standardized legal vocabulary across diverse regional languages.
- The launch of the E-SCR portal in 2023 marked a modest beginning with 2,238 translated judgments in January, reaching a commendable milestone of over 31,000 rulings translated by the year's end.
- Recent statistics reveal that Hindi leads with the highest number of translated judgments at 22,396, followed by Punjabi (3,572), Kannada (1,899), Tamil (1,172), and Gujarati (1,112).
- While the translation speed witnessed a significant improvement in 2023, legal experts express concerns about the practical utility of translated judgments, particularly when High Courts, except in the Hindi-speaking States, cannot conduct proceedings in regional languages.
What is the Supreme Court Vidhik Anuvaad Software (SUVAS)?
- SUVAS was introduced in November 2019 by the then-Chief Justice of India (CJI) S.A. Bobde.
- It was created to encourage and ensure the use of regional languages in judicial proceedings.
- It is an artificial intelligence (AI)--trained machine translation tool.
- Constitutional Standing: While Article 348(1)(a) of the Indian Constitution mandates that proceedings in the Supreme Court and every High Court be conducted in English, Article 348(2) provides a provision.
- It allows a State Governor, with the President's consent, to authorize the use of Hindi or another state language in the High Court of that particular State.
- In this context, SUVAS is vested with authority under Article 348, serving as a pivotal tool to promote linguistic diversity within the constitutional framework.
Planning to invest in green deposits? RBI releases latest guidelines to explain key provisions (Live Mint)

- 01 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News?
In a recent guideline, the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) said banks and Non-Banking Financial Companies (NBFCs) don’t need to raise green deposits.
What are Green Deposits?
- A green deposit is essentially a fixed-term deposit designed for individuals seeking to invest in eco-friendly projects.
- Similar to a standard Fixed Deposit scheme, the green deposit offers interest to investors and has a predetermined term.
Key Features:
- Allocation to Green Finance: The funds deposited in a green deposit are specifically earmarked for allocation to green finance initiatives, promoting environmentally conscious investments.
- Environmentally Friendly Focus: Also referred to as an environmentally friendly fixed deposit, this financial instrument encourages sustainable development by directing funds toward projects related to renewable energy, clean technology, and other environmentally beneficial initiatives.
- Priority Sector Classification: Green activities or projects financed through this framework may be classified under the priority sector, provided they meet the requirements outlined in the Priority Sector Lending (PSL) guidelines of the Reserve Bank of India (RBI).
- Overdraft Facility: Banks are permitted to offer overdraft facilities to customers against their Green Deposits, providing added flexibility.
- Currency Denomination: As per the current framework, green deposits can only be denominated in Indian Rupees.
- Insurance Coverage: Deposits raised under this framework are covered by the Deposit Insurance and Credit Guarantee Corporation (DICGC) in accordance with the Deposit Insurance and Credit Guarantee Corporation Act, 1961, and the relevant regulations.
- Renewal or Withdrawal: Upon maturity, depositors have the option to either renew or withdraw their green deposits, providing flexibility and choice.
Advantages of Green Deposits:
- Contribution to Climate-Friendly Initiatives: Green deposits empower depositors to actively participate in climate-friendly initiatives, aligning with India's net-zero goals and promoting environmental sustainability.
- Support for Socially Responsible Activities: Although higher interest rates may not be the primary focus, depositors indirectly contribute to socially and environmentally responsible endeavours.
- Their funds play a pivotal role in supporting activities that benefit the community and the planet.
- Positive Environmental Impact: By investing in green deposits, depositors contribute to positive outcomes such as reduced emissions, improved air quality, and sustainable resource allocation.
- These actions foster positive externalities, creating a healthier environment for all.
- Contribution to Reduced Income Inequality: The support for eco-friendly initiatives and fair resource allocation facilitated by green deposits contributes to long-term reductions in income inequality, fostering a more equitable and sustainable society over time.
Challenges Associated with Green Deposits:
- Design Limitations: Flaws in the design of green deposit frameworks may restrict the scope of eligible green projects that banks can invest in, limiting the diversity of environmentally beneficial initiatives.
- Perceived Reality vs. Impact: There is a concern that some green investment products may serve more as a psychological boost for investors rather than delivering substantial environmental benefits.
- The actual impact on the environment may not align with the positive perception created.
- Uncertain Project Sustainability: The long-term sustainability of green projects funded by banks remains uncertain, raising questions about the enduring impact of investments in environmentally friendly initiatives.
- Lack of Awareness: Insufficient awareness among bank staff can result in delays in the process of acquiring green deposits, hindering the seamless integration of eco-friendly financial products into banking operations.
- Lower Interest Rate Perception: Investors often prioritize high returns, and the perception that green deposits may offer lower interest rates could deter them from choosing environmentally conscious financial products.
Index of Eight Core Industries (ICI) increases by 7.8% (provisional) in Nov 2023 as compared to the Index of Nov 2022 (PIB)

- 30 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
The combined Index of Eight Core Industries (ICI) increased by 7.8 per cent (provisional) in November 2023 as compared to the Index of November 2022.
About the Index of Industrial Production (IIP):
- The IIP is a comprehensive index that assesses the growth rate of industry groups, categorized into:
- Broad sectors: Mining, Manufacturing, and Electricity.
- Use-based sectors: Basic Goods, Capital Goods, and Intermediate Goods.
- In India, the initiation of computing the IIP predates international recommendations. The Central Statistical Organization, now known as the National Statistics Office (NSO), assumed the responsibility for compilation and publication in 1951.
- The Ministry responsible for this process is the Ministry of Statistics and Programme Implementation.
Key Information:
- Base Year: The base year was changed to 2011-12 from 2004-05 in the year 2017.
- Sources of Data: The NSO compiles the IIP using secondary data from 14 source agencies across various Ministries/Departments and their attached/subordinate offices.
- The Department of Industrial Policy and Promotion (DIPP) contributes a significant portion of the data for the calculation.
- Utilization of IIP Data: The Industrial Production Index (IIP) is a valuable resource employed by several entities, including government bodies like the Ministry of Finance and the Reserve Bank of India (RBI), as well as private firms and analysts.
- It serves as a critical tool for analytical purposes.
- Additionally, the data is instrumental in computing the quarterly Gross Value Added (GVA) of the manufacturing sector within the Gross Domestic Product (GDP).
About the Index of Eight Core Sectors:
- The Index of Eight Core Industries (ICI) assesses the combined and individual production performance of eight vital industries.
- Together, these sectors account for 40.27% of the items measured in the Index of Industrial Production (IIP).
- Listed in descending order of their weightage, the eight core industries are:
- Refinery Products, Electricity, Steel, Coal, Crude Oil, Natural Gas, Cement, and Fertilizers.
162 cases of Covid sub-variant JN.1 detected in India; highest from Kerala, Gujarat: INSACOG (Live Mint)
- 30 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
India reported a total of 109 JN.1 COVID variant cases in the country as of December 26, Health Ministry sources recently said.
What is Indian SARS-CoV-2 Genomics Consortium (INSACOG)?
- Established in December 2020, INSACOG is a collaborative initiative involving the Union Ministry of Health, the Department of Biotechnology (DBT) under the Ministry of Science and Technology, the Council for Scientific & Industrial Research (CSIR), and the Indian Council of Medical Research (ICMR).
- The consortium's primary mission is to expand whole-genome sequencing of SARS-CoV-2, the coronavirus responsible for Covid-19, across India.
- This initiative aims to comprehend the virus's spread and evolution.
- INSACOG initially engaged 10 national research laboratories of the central government and has grown into a network of 38 labs, including private labs, following a hub-and-spoke model.
- The consortium's Genome Sequencing Laboratories guide new laboratories, working in tandem to monitor genomic variations through sentinel sequencing facilitated by the National Centre for Disease Control (NCDC) under the Integrated Disease Surveillance Programme (IDSP) of the central government.
- Beyond sequencing efforts, INSACOG endeavors to establish a systematic correlation between genome sequencing and clinical outcomes.
- It is actively building a nationwide hospital network to investigate clinical correlations in mild versus severe cases of Covid-19.
- Additionally, the consortium is conducting a longitudinal study to comprehend long-term post-Covid complications and changes in immunity.
- Looking ahead, INSACOG is exploring sewage surveillance as an early detection tool and assessing the spread of variants in hotspot localities.
Minister Bhupendra Yadav launches NTPS, a unified system for forest goods’ transport across India (Indian Express)
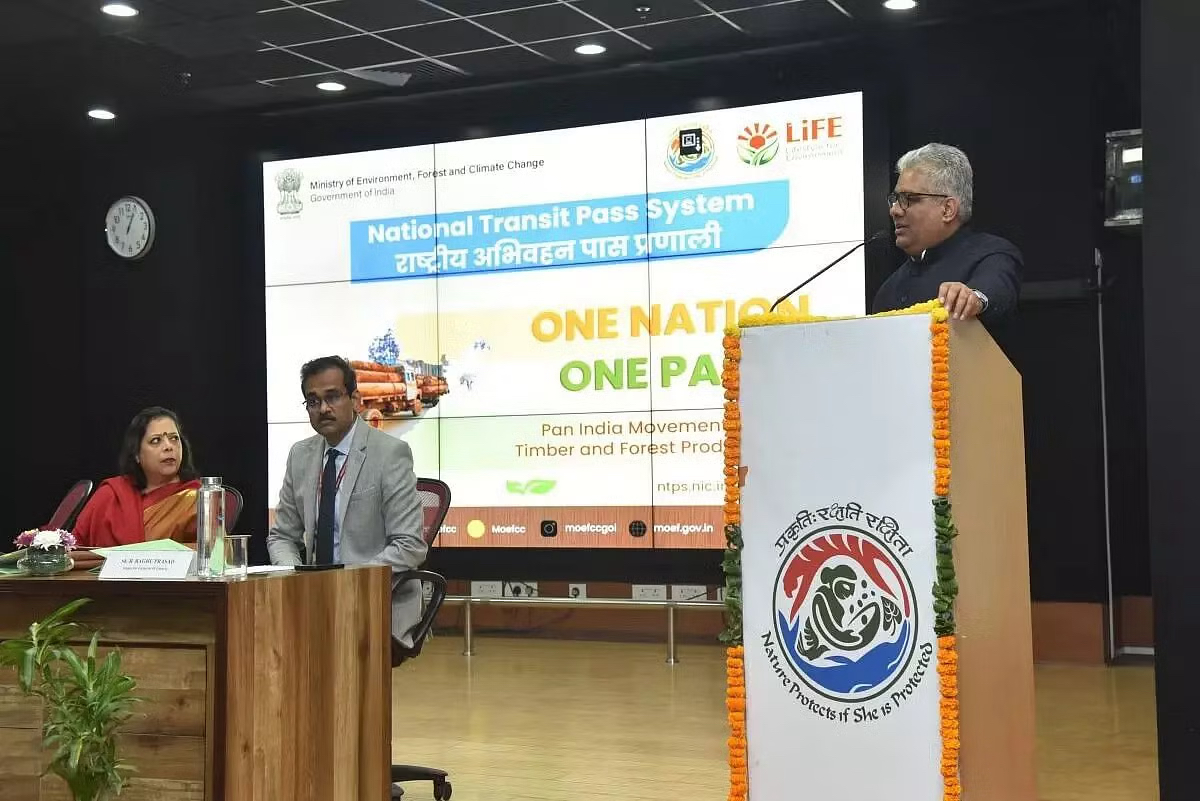

- 30 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
The central government on Friday launched the National Transit Pass System (NTPS) to facilitate seamless transit of forest goods across the country through a single permit.
About the National Transit Pass System (NTPS):
- The National Transit Pass System (NTPS) is established to facilitate the smooth transit of timber, bamboo, and other forest produce across the country.
- Currently, transit permits are issued based on state-specific rules, leading to a fragmented system.
- The NTPS aims to implement a "One Nation-One Pass" regime, ensuring seamless transit across the entire nation.
- This initiative streamlines the issuance of timber transit permits by providing a unified online platform for tree growers and farmers engaged in agroforestry, contributing to a more business-friendly environment.
Key Features of NTPS:
- Unified Online Platform: The NTPS offers a unified, online mode for obtaining timber transit permits, simplifying the process for tree growers and farmers involved in agroforestry nationwide.
- Record Management: It manages records for both inter-state and intra-state transportation of timber, bamboo, and other forest produce from various sources, including private lands, government-owned forests, and private depots.
- QR Coded Transit Permits: The system generates QR coded transit permits, enabling check gates across states to verify the permits' validity and ensure seamless transit.
- User-Friendly Applications: NTPS provides desktop and mobile applications for easy registration and permit applications, enhancing user convenience.
- Regulated Species and Exemptions: Transit permits are issued for regulated tree species, while users can self-generate No Objection Certificates for exempted species.
- State Participation: Presently, 25 States and Union Territories have adopted the unified permit system, simplifying interstate business operations for producers, farmers, and transporters.
- Nodal Ministry: The NTPS operates under the guidance of the Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change.
Horticulture boost: Litchi cultivation has expanded to 19 Indian states, according to officials (DownToEarth)

- 30 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
Litchi which is synonymous with India's hot summers, is now under cultivation in 19 Indian states, extending beyond its traditional confinement to Muzaffarpur in Bihar.
About Litchi Cultivation:
- Litchi, a delicious and succulent fruit of superior quality, belongs to the Sapindaceae family from a botanical perspective.
- Its translucent and flavorful aril, or edible flesh, is widely enjoyed as a table fruit in India.
- Agro-climatic Requirements: Litchi is a sub-tropical fruit that thrives optimally in moist sub-tropical climates.
- Ideally cultivated at low elevations, it can be grown up to an altitude of 800 meters.
- The crop flourishes in deep, well-drained loamy soil rich in organic matter, with an ideal pH range of 5.0 to 7.0.
- Temperature: The crop's temperature tolerance ranges from avoiding extremes, not exceeding 40.5 degrees Celsius in summer and staying above freezing point in winter.
- Rainfall: Prolonged rainfall, especially during flowering, can be detrimental as it interferes with pollination.
- Young trees necessitate protection from frost and hot winds until firmly established, although some temperature variation is necessary for proper fruiting.
- Frost during winter and intense summer heat are limiting factors for successful cultivation.
- Traditionally, commercial cultivation in India was confined to the northern foothills of the Himalayas from Tripura to Jammu & Kashmir, and the plains of Uttar Pradesh and Madhya Pradesh.
- However, due to increasing demand and the crop's viability, commercial cultivation has expanded to various states such as Bihar, Jharkhand, Madhya Pradesh, Chhattisgarh, etc.
- India ranks second in the world in production of Litchi production after China.
- Other significant producers include Thailand, Australia, South Africa, Madagascar, and the US.
- Statewise, Bihar tops in Litchi production followed by West Bengal (12 % of the total) and Jharkhand (10 %).
About National Research Centre on Litchi (NRCL):
- The National Research Centre on Litchi (NRCL) serves as the leading national institute dedicated to research and development in the field of litchi.
- It plays a pivotal role in providing national leadership, serving as a repository for comprehensive information on litchi production, processing, value addition, and extending consultancy services to end-users.
MEA’s Flagship ‘Know India Programme’ for youth diaspora completes 20 years (MEA GOI)

- 30 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
The flagship programme of the Ministry of External Affairs (MEA) for the youth diaspora, the ‘Know India Programme’, has completed 20 years.
About the Know India Programme (KIP):
- The Know India Programme is a flagship initiative of the Ministry of External Affairs designed to enhance awareness about India, its cultural heritage, and art, and to familiarize participants with various aspects of contemporary India and their ancestral homeland.
- This program is open to Persons of Indian Origin (21-35 years) (excluding non-resident Indians) from all over the world, with a preference for youth from Girmitiya countries, such as those from Mauritius, Fiji, Suriname, Guyana, Trinidad & Tobago, South Africa, and Jamaica.
- The program has been in existence since its inception in 2003.
Features of Know India Programme (KIP):
- It is a 21 days’ programme (excluding international travel) during which the participant will visit Delhi, Agra and a select state in India alongwith visits to places of historical, cultural, and religious significance.
- KIP participants will also have a 2-day orientation programme in New Delhi.
- Participants will meet opinion makers, leaders, and officials to get an overview of India’s economy, society and ongoing growth and development story.
- Participants are provided local hospitality e.g. boarding and Internal transportation in India, return air tickets from their country of residence to India provided participants bear 10% of the cost of total air fare.
- Gratis visa shall be granted to participants by the Indian Missions/Posts abroad.
- Some of the key elements of the Programme include:
- Visits to places of historical and cultural importance;
- Familiarisation with Yoga, Ayurveda, and classical forms of Music and Dance;
- Visit to institutions of democracy and governance like Parliament of India, Election Commission of India, Rashtrapati Bhawan;
- Interaction with leading educational institutions;
- Exposure to flagship economic and development schemes like Digital India, StartUp India, and Make in India; and
- visits to industrial sites, public and private firms to highlight India’s strength in Manufacturing & Service sector.
Eligibility Criteria:
- Minimum qualification required for participating in KIP is graduation from a recognized University /Institute or enrolled for graduation and the ability to speak in English.
- The applicant should not have visited India through any previous Programme of Government of India.
- Those who have not visited India before will be given preference.
- Applicant must provide documentary evidence to prove Indian origin or an undertaking about Indian origin which must be countersigned by the Indian Embassy/High Commission/Consul General.
States Returning to OPS Pose Significant Financial Burden: RBI (Indian Express)

- 12 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
Recently, the RBI released a report saying, the return to the Old Pension Scheme (OPS) by a few states would put a huge burden on their finances, restricting them from undertaking capital expenditure to drive the growth.
What is the Old Pension Scheme (OPS)?
- The Old Pension Scheme (OPS), popularly OPS, is for state and central government employees who have completed 10 or more years of service.
- The appeal of the Old Pension Scheme lies in its commitment to provide a guaranteed or 'defined' benefit to retirees, classifying it as a 'Defined Benefit Scheme.'
- It provides government employees with pensions based on their final salary, amounting to 50% of the last drawn salary.
- For instance, if a government employee's final monthly salary upon retirement was Rs 10,000, they would receive a guaranteed pension of Rs 5,000.
- Similar to government employees' salaries, pension payouts increased with government-declared dearness allowance (DA) hikes.
- The Central government discontinued OPS in 2003.
What were the issues with the OPS?
- The primary concern was the unfunded nature of the pension liability, lacking a dedicated corpus that could grow over time to meet payment needs.
- The annual Government of India budget allocated funds for pensions without a clear strategy for sustaining future payments.
- The 'pay-as-you-go' approach raised inter-generational equity concerns, burdening the present generation with the escalating load of pension responsibilities.
- Recently, the RBI expressed alarm over some states, including Himachal Pradesh, Jharkhand, Punjab, Chhattisgarh, and Rajasthan, reverting to the OPS, citing it as a significant fiscal challenge.
- The RBI warned that by deferring current expenses to the future, states risk accumulating unfunded pension liabilities in the years to come.
What is the New Pension Scheme (NPS)?
- Introduced by the Central government in 2004 as an alternative to OPS, NPS is accessible to employees across public, private, and unorganized sectors, excluding those in the armed forces.
- This pension initiative encourages individuals to invest in a pension account regularly during their employment.
- Upon retirement, subscribers can withdraw a specific percentage of the accumulated corpus.
- The remaining amount is disbursed as a monthly pension post-retirement.
- Regulated by the Pension Fund Regulatory and Development Authority (PFRDA).
How does NPS differ from OPS?
- Old Pension Scheme (OPS) ensures a fixed and guaranteed pension amount.
- In contrast, the National Pension Scheme (NPS) is an investment-cum-pension scheme, exposing returns to market volatility.
- NPS contributions are defined, but benefits are contingent on market performance.
Why Rural India Needs Women Drone Pilots? (Indian Express)

- 12 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
The NAMO Drone Didi Scheme provides new work opportunities to women and makes them the backbone of the rural economy.
What is the NAMO Drone Didi Scheme?
- The Prime Minister has recently approved the Central Sector Scheme (NAMO Drone Didi Scheme) for providing Drones to the Women Self Help Groups (SHGs), with an outlay of Rs. 1261 Crore.
- The scheme aims to provide drones to 15,000 selected Women SHGs during the period 2023-24 to 2025-2026 for providing rental services to farmers for agriculture purposes.
- The scheme seeks to empower women Self Help Groups (SHGs) and bring new technologies through drone services in the agriculture sector.
The highlights of this scheme are as follows:
- Departments involved: The scheme converges the resources and efforts of the Department of Agriculture & Farmers Welfare (DA&FW); Department of Rural Development (DoRD); Department of Fertilizers (DoF); Women SHGs and Lead Fertilizer Companies (LFCs).
- Identification of SHGs: The women SHGs would be identified from the total 89 lakh SHGs formed under the Deendayal Antyodaya Yojana.
- Financial Assistance:
- Central Financial Assistance covering 80% of drone costs up to a maximum of Rs. 8 Lakh will be provided.
- The remaining amount can be raised through the National Agriculture Infra Financing Facility (AIF) with a provision of interest subvention @ 3% on the AIF loan.
- Training:
- One of the members of SHGs will be trained in drone piloting skills and agriculture purposes of nutrient and pesticide application.
- Another member will be trained as a drone technician.
- This will allow them to not just operate the drone but also repair and maintain it.
- Nano Fertilizers: The scheme also promotes the use of Nano Fertilizers like Nano Urea and Nano DAP through drone services.
- Opportunities for Start-ups: The scheme not only empowers women but also opens avenues for dynamic start-ups in the field of drone aeronautics, tapping into significant untapped potential in this emerging sector.
Significance of the NAMO Drone Didi Scheme:
- Empowering Rural Women: Fosters technological empowerment of rural women, positioning them as the backbone of the rural economy.
- Places drone technology in the hands of women pilots from Self-Help Groups (SHGs).
- Modernizing Agricultural Practices: Addresses the imperative to modernize agricultural practices.
- Aims to elevate agricultural productivity through cutting-edge technology, contributing to a new agricultural revolution.
- Job Opportunities in Drone Aeronautics: Creates opportunities in the emerging field of drone aeronautics with substantial untapped potential.
- Opens avenues for rural women as pilots, mechanics, and spare-part dealers.
- Efficient Fertigation System Development: Facilitates the development of an efficient fertigation system.
- Introduces innovative liquid fertilizers like Nano Urea and Nano DAP with foliar application.
- Time-Efficient Spraying System: Automation of the spraying system through agri-drones ensures a time-saving and efficient application system.
- Equitable Agrarian Family Culture: Contributes to making the agrarian family culture more equitable and robust.
Article 356 of the Indian Constitution (The Hindu)

- 12 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
The Supreme Court recently held that the declaration of State emergency under Article 356 and the subsequent actions of the President should have a “reasonable nexus”.
What is Article 356 of the Indian Constitution?
Article 356 of the Constitution of India is based on Section 93 of the Government of India Act, 1935. According to Article 356, the President's Rule can be imposed on any state of India on the grounds of the failure of the constitutional machinery.
There are two types:
- If the President receives a report from the state's Governor or otherwise is convinced or satisfied that the state's situation is such that the state government cannot carry on the governance according to the provisions of the Constitution.
- Article 365: As per this Article, President's Rule can be imposed if any state fails to comply with all directions given by the Union on matters it is empowered to.
In simple words, President's Rule is when the state government is suspended and the central government directly administers the state through the office of the governor (centrally appointed. It is also called State Emergency or Constitutional Emergency.
President's Rule:
- Parliamentary approval is necessary for the imposition of the President's Rule on any state.
- The proclamation of President's Rule should be approved in both Houses of Parliament within two months of its issue.
- The approval is through a simple majority.
- The President's Rule is initially for a period of six months.
- Later, it can be extended for a period of three years with parliamentary approval, every six months.
- The 44th Amendment to the Constitution (1978) brought in some constraints on the imposition of the President's Rule beyond a period of one year. It says that the President's Rule cannot be extended beyond one year unless:
- There is a national emergency in India.
- The Election Commission of India certifies that it is necessary to continue the President's Rule in the state because of difficulties in conducting assembly elections in the state.
What happens after the President's Rule is imposed?
- The governor carries on with the administration of the state on behalf of the President. He or she takes the help of the state's Chief Secretary and other advisors/administrators whom he or she can appoint.
- The President has the power to declare that the state legislature's powers will be exercised by the Parliament.
- The state legislative assembly would be either suspended or dissolved by the President.
- When the Parliament is not in session, the President can promulgate ordinances with respect to the state's administration.
When is the President's Rule imposed?
- President's Rule is typically imposed when any of the following circumstances occur:
- The state legislature is unable to elect a leader as the Chief Minister within the time prescribed by the state's governor.
- Breakdown of a coalition in the state government, resulting in the Chief Minister having minority support in the legislature, and the CM is unable to prove a majority within the time prescribed by the governor.
- A vote of no confidence in the legislative assembly leads to a loss of majority.
- Postponement of elections due to unavoidable reasons such as a natural disaster, epidemic, or war.
Revocation of President's Rule:
- President's Rule can be revoked anytime after such a proclamation has been made by a subsequent proclamation by the President.
- A proclamation of revocation does not require approval by the Parliament.
- This occurs when the leader of a political party produces letters indicating majority support for him in the assembly and stakes his claim to form the state government.
How do web browsers work? (The Hindu)

- 12 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
Web browsers are our digital passports to the vast universe of the internet. Their simplicity is deceptive: beneath their user-friendly interfaces lies a world of intricate processes that transform clicks into the web pages we interact with every day.
What are web browsers?
- Fundamentally, the browser is an application that people use to send and receive messages via the internet.
- In other words, the browser is a program that runs on our device, with its purpose being to fetch information in different formats from the internet and show it on the device.
- It also does the reverse, receiving your input (say, a click), translating it to code, and transmitting it to some other machine across the internet.
- In the year 1990, the English computer scientist Tim Berners-Lee introduced the concept of the World Wide Web also named ‘WorldWideWeb’.
What Constitutes a Web Browser?
Web browsers today comprise numerous essential components, each representing a sophisticated technology. Additionally, they depend on various supporting technologies and adhere to established standards governing the functioning of the Internet.
- Request and Response: When we enter a website's URL, the browser sends a request to a server, asking for the specific web page.
- The server processes the request and sends back a response containing the information needed to construct the page.
- This response, akin to a digital blueprint, travels back to our browser.
- Deconstructing the Response: The server's response comprises various files encoded in HTML, CSS, and JavaScript.
- HTML outlines the webpage structure, CSS adds style and aesthetics, while JavaScript brings interactivity, making the page dynamic and engaging.
- Rendering: The browser deciphers HTML, applies CSS for styling, and executes JavaScript for interactivity, rapidly assembling the final webpage.
- Rendering engines are crucial technology enabling quick and cohesive visual presentation.
- Managing Data: Browsers use cookies for retaining site preferences and cache for storing frequently accessed files.
- Cookies act like post-it notes, preserving login status and preferences, while the cache accelerates page loading by retrieving stored files instead of downloading them again.
- Security: Browsers prioritize security by employing encryption protocols like HTTPS for data exchange.
- They create secure 'tunnels' to shield information during transmission. Warning systems alert users about potential threats, enhancing overall online safety.
As technology advances, web browsers are on a trajectory of continuous evolution. They are integrating state-of-the-art technologies such as WebAssembly, facilitating near-native performance within the browser. The future holds promises of support for virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR) experiences, offering immersive online interactions. Privacy features are also being fortified, empowering users with enhanced control over their digital presence.
Oil Producers Water Down Provision on Fossil Fuel Phase-out (Indian Express)

- 12 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
After four days of deadlock, a new draft agreement text emerged at the COP28 climate meeting that severely watered down earlier provisions on fossil fuel elimination but singled out coal for a rapid phase-down, which could be problematic for India.
Context:
- The 28th Conference of the Parties (COP 28) to the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change is underway in the United Arab Emirates from November 30 to December 12, 2023.
- During the climate meeting on December 10, negotiators took an initial step toward enhancing action on adapting to climate change.
- A draft text outlining potential "global goals" on adaptation was introduced for the first time, serving as a starting point for further negotiations.
- Negotiators are actively discussing various topics, including the contentious issue of fossil fuel phase-out, in informal sessions to find common ground.
- The draft document is titled 'Global Goal on Adaptation' (GGA) and aims to establish a shared global objective for adaptation, similar to the global goal of limiting temperature rise below the 1.5 degrees Celsius threshold for mitigation.
- This initiative addresses a longstanding demand from developing countries, emphasizing the need for increased focus and resource mobilisation for adaptation efforts.
- Notably, the draft removes the term 'phasing out' of fossil fuels but includes stronger language against coal, urging a "rapid phase-down of unabated coal," a point that may face objections from major consumers like India, Indonesia, and China, all developing countries heavily reliant on coal power.
Responses to the Draft Text 'Global Goal on Adaptation':
- The European Union (EU) and certain small island states promptly dismissed the draft agreement text.
- The EU climate commissioner criticized the overall insufficiency of the text, deeming it inadequate in addressing the climate change challenge.
- Primary dissatisfaction arose from the weakening of a provision related to the use of fossil fuels.
- The draft initially urged countries to "reduce both consumption and production of fossil fuels, in a just, orderly, and equitable manner."
- Notably, fossil fuels, responsible for nearly 80 percent of greenhouse gas emissions, have never been explicitly mentioned in prior COP decisions.
- While previous decisions emphasized the need to cut emissions, they avoided specifying actions for emission reduction.
- COP28 marked the first formal discussion of a fossil fuel phase-out but attempts to incorporate a robust provision faced resistance from oil-producing nations like Saudi Arabia and Russia.
- India, while not offering an immediate reaction to the draft agreement, has consistently asserted that singling out coal for accelerated reduction is discriminatory.
Youth for Unnati and Vikas with AI (YUVAi) (NewsOnAir)

- 11 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
YUVAi Student Finalists to showcase their AI-enabled social impact projects at the GPAI summit.
About Youth for Unnati and Vikas with AI (YUVAi) Initiative:
- YUVAi is aimed at fostering a deeper understanding of AI, to equip school students from classes 8th to 12th across the nation with AI skills, and to empower them to become human-centric designers and users of AI.
- In addition, the program offers an applied learning experience for students to understand and identify how AI technology can tackle critical problems and lead to the inclusive development of the nation.
- It is a collaborative initiative of the National e-Governance Division (NeGD), Ministry of Electronics & Information Technology (MeitY), Government of India and Intel India.
- The objectives of YUVAi are to :
- Foster a deeper understanding of AI-tech and social skills
- Enable youth to develop AI-enabled solutions as a sign of achievement
- Empower youth to become human-centric designers and users of AI
- The program will be conducted in three phases.
- In the initial phase, teachers will be selected to identify students from their respective schools and share their details with the organizing team.
- Next, online orientation sessions will be conducted for registered students around core AI concepts by experts to facilitate understanding of the ideation process.
- Finally, students will be encouraged to submit ideas (individually or in teams of 2) through a 120-second video explaining a proposed AI-enabled solution for any one of the eight core themes- agriculture, healthcare, education, environment and clean energy, transportation, rural development, smart cities and law and justice.
- Shortlisted students will attend online deep dive AI training in the second phase.
- A 3-day face-to-face boot camp will be organized to provide adequate mentorship and guidance by YUVAi coaches.
- After the mentorship camps, students will use this newly gained knowledge to develop AI-enabled innovations/projects on any of the eight core themes and submit final entries.
- Finally, the most innovative AI-based solutions will be announced and invited to a national showcase and felicitation ceremony.
- Rewards: Upon a successful idea submission, students will be awarded a Certificate of Appreciation.
Protein from Budgett’s frog can block enzymes of disease-causing pathogens (The Hindu)

- 11 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
Researchers from the Indian Institute of Science’s (IISc.) molecular biophysics unit in a study have identified that peptides (short protein) produced from Budgett’s frog can combat enzymes of disease-causing pathogens.
Key Research Findings:
- The research focused on peptides, or short proteins, derived from amphibian skin, a subject of prolonged study due to their capacity to counter adverse environmental conditions, including harmful pathogens.
- A peptide secreted by frogs demonstrated inhibitory effects on two crucial enzymes, namely subtilisin Carlsberg and proteinase K, which are produced by pathogens.
- These enzymes play a crucial role in fostering infections by breaking down specific protective proteins within the infected individual.
- The studied peptide exhibited its inhibitory action through a slow-tight binding pathway, proving to be as effective as SSI, a well-established subtilisin inhibitor.
- The researchers illustrated the formation of a Michaelis complex—an intact, noncovalent complex with the inhibitor—during the process.
About Budgett’s frog:
- Budgett’s frogs exhibit high intelligence and a notably assertive nature.
- When alarmed, they employ a defensive strategy by inflating themselves, standing on short legs, and, if necessary, lunging at potential threats with an open, imposing mouth accompanied by a distinctive shriek.
- During the dry season, these frogs take refuge in burrows they construct at the bottoms of water pools.
- Within these burrows, they shed multiple layers of skin to create a waterproof cocoon, ensuring their moisture retention.
- Equipped with exceptional night vision and a keen sensitivity to movement, Budgett’s frogs showcase effective hunting skills.
- Habitat/Range: Found in proximity to permanent or seasonal bodies of water, Budgett’s frogs inhabit regions across Paraguay, Argentina, and Bolivia.
- Conservation Status:
- IUCN Red List: Classified as Least Concern.
Royal Bengal Tiger spotted in Pangalokha Wildlife Sanctuary (PTI)

- 11 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
Recently a Royal Bengal Tiger was spotted in Pangalokha Wildlife Sanctuary in Sikkim at an altitude of 3,640 metres.
Context
- Royal Bengal Tiger has been sighted in the Pangalokha Wildlife Sanctuary in Sikkim roaming at an altitude of 3,640 meters.
- The Royal Bengal Tiger was captured by trap cameras of a team of the Bombay Natural History Society (BNHS) which is conducting a study in the sanctuary in collaboration with the Sikkim Forest Department.
- It was under a larger project called "Conservation and Use of Five Wetlands in three Himalayan States to Secure Habitats of Birds Migrating within the Central Asian Flyway (CAF)."
- This project was sanctioned under the National Mission on Himalayan Studies (NMHS), and aims to protect and conserve wetland sites in Ladakh, Himachal Pradesh, and Sikkim.
About Pangalokha Wildlife Sanctuary:
- The Pangalokha Wildlife Sanctuary is located at the tri-junction of Sikkim, Bengal and Bhutan and is spread over 128 square kilometres.
- The sanctuary is strategically located in the East Sikkim district, connecting the forests of Bhutan and the Neora Valley National Park in West Bengal.
- It is the largest wildlife sanctuary in Sikkim.
- Vegetation: The Sanctuary has typical alpine-temperate-subtropical vegetation with high-altitude lakes around Jelep La.
- Flora: Rhododendron, Silver Fir, Juniper forest and associated ground flora, moss-filled oak forests with dense bamboo thickets etc.
- Fauna: It is home to various species, including red pandas, snow leopards, Himalayan musk deer, Himalayan goral, and Himalayan black bears.
EU’s Landmark Deal on Artificial Intelligence Regulation (Indian Express)

- 11 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
Recently European Union policymakers agreed on a provisional deal on landmark rules governing the use of artificial intelligence (AI).
On December 8, EU member states and lawmakers reached a consensus on the formulation of "historic" rules governing artificial intelligence models like ChatGPT, concluding prolonged negotiations.
However, these rules are slated to come into effect no earlier than 2025, allowing room for technological advancements in the interim.
Key Highlights:
- The inception of the Artificial Intelligence Act dates back to 2021, aiming to instil transparency, trust, and accountability in AI practices.
- Its overarching goal is to establish a framework to address risks to safety, health, fundamental rights, and democratic values within the EU.
- Featuring a two-tier approach, the Act imposes transparency requirements on all general-purpose AI models, with more stringent measures for the more powerful ones.
- The Act proposes the creation of an EU-wide database cataloguing high-risk AI systems, with provisions for the inclusion of future technologies meeting high-risk criteria.
- The legislation seeks a delicate balance between fostering AI adoption and preventing or mitigating harms associated with specific applications of the technology.
Global Perspectives on Artificial Intelligence Governance:
- The dynamic evolution of Artificial Intelligence (AI) development has prompted diverse global perspectives on the regulation of these technologies.
- In May 2023, members of the European Parliament reached a preliminary agreement on a revised draft of the European Union's ambitious Artificial Intelligence Act.
- This Act envisions the creation of an EU-wide database for high-risk AI systems and outlines criteria for the inclusion of future technologies that meet these high-risk parameters.
- In contrast, the United States currently lacks comprehensive AI regulations and has adopted a relatively hands-off approach.
- On the opposite end of the spectrum, China has, in the past year, introduced some of the world's initial nationally binding regulations specifically targeting certain types of algorithms and AI.
- It has implemented a law to govern recommendation algorithms, with a particular focus on how these algorithms disseminate information.
India’s Position on Artificial Intelligence:
- Initially, the Union Minister for Electronics and Information Technology stated that the government was not contemplating any legislation to oversee the development of AI in India.
- However, in the lead-up to the G20 summit in September 2023, the Indian government hinted at the potential regulation of AI.
- Officials indicated that the forthcoming Digital Personal Data Protection Bill 2022 would extend to AI developers engaged in creating and facilitating AI technologies.
- Given the substantial data collection and utilization by AI developers to train their algorithms and enhance AI solutions, they may be classified as data fiduciaries and held accountable for the responsible use of personal data.
- Prime Minister Modi recently expressed India's aspiration to "take a giant leap in AI to empower its citizens and actively contribute to its evolution."
- India is gearing up to host the Global Partnership on Artificial Intelligence (GPAI) Summit 2023 in New Delhi from December 12-14.
- As a co-founder of GPAI, India, along with 28 member countries and the EU, is committed to guiding the responsible development and utilization of AI.
India's Ambitious Initiative to Expand Renewable Energy Capacity (Indian Express)

- 11 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
The Ministry of New and Renewable Energy (MNRE) has proposed an exemption for green hydrogen developers from adhering to its list of authorised manufacturers to enable them to import solar PV modules and wind turbine models from China.
What Does The Ministry of New and Renewable Energy (MNRE) Propose?
- The Ministry of New and Renewable Energy (MNRE) is exploring the option of granting an exemption to green hydrogen developers from its list of authorized manufacturers.
- This proposed exemption would enable these developers to import solar PV modules and wind turbine models from China, aiming to enhance the competitiveness of green hydrogen exports.
- It's noteworthy that Chinese manufacturers are presently absent from MNRE's Approved List of Models and Manufacturers (ALMM) and Revised List of Models and Manufacturers (RLLM).
The MNRE’s Proposal Background:
- After the 2020 Galwan Valley skirmishes, the Indian government issued directives to restrict the involvement of Chinese vendors in public procurement.
- Recently, the Indian procurement portal GeM announced the removal of hundreds of Chinese vendors over the past three years.
- At a time when energy companies are intensifying efforts to mass-produce green hydrogen, essential for which are renewable energy equipment and electrolysers, the government has sidelined Chinese manufacturers.
- This aligns with the MNRE's policy to enhance domestic manufacturing of renewable energy equipment.
- While central PSUs may face restrictions on importing electrolysis machinery from China, others continue to do so.
- In FY23, India witnessed a 40% increase, in importing machines and apparatus for electroplating, electrolysis, and electrophoresis, worth $45.61 million, compared to the preceding fiscal year.
What is the Significance of the MNRE’s Proposal?
- ??The proposal to import solar PV modules from China carries significance in bolstering the supply chain and enhancing the global competitiveness of Indian green hydrogen exports.
- Central PSUs such as Indian Oil Corporation Ltd and NTPC Ltd, both actively involved in green hydrogen projects, would benefit by sourcing equipment from Chinese manufacturers.
- This move is poised to strengthen India's position in the global green hydrogen market, aligning with the objectives outlined in the National Green Hydrogen Mission and facilitating the achievement of set targets.
Painkiller Meftal could cause DRESS syndrome (Financial Express)

- 07 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
Indian Pharmacopoeia Commission (IPC) has recently issued a drug safety alert for doctors and patients about the use of the commonly used painkiller mefenamic acid, popularly sold under the brand name Meftal.
Context:
- The Pharma standard body, Indian Pharmacopoeia Commission (IPC) in its preliminary analysis of Adverse Drug Reactions (ADRs) from the PvPI database revealed that Meftal can lead to Drug Reactions with Eosinophilia and Systemic Symptoms (DRESS) Syndrome.
- According to doctors, this syndrome causes a diverse array of clinical symptoms, anywhere from 2 to 8 weeks after initiating the offending drug.
What is DRESS syndrome?
- DRESS syndrome (Drug Rash with Eosinophilia and Systemic Symptoms) is an adverse reaction term that is currently used to describe a hypersensitivity reaction.
- Experts classify DRESS syndrome as a type 4 hypersensitivity reaction.
- It is a serious drug reaction affecting the skin and other organs, with a mortality rate of up to 10%.
- It manifests when the immune system excessively responds to specific medications, leading to a type 4 hypersensitivity reaction.
- This reaction can manifest with various symptoms across the body, including fever, abnormalities in blood, and inflammation of organs.
What are the symptoms of DRESS syndrome?
- Patients diagnosed with DRESS syndrome typically present with a rash, fever, and eosinophilia but can have a variety of symptoms including liver, lung, or kidney involvement.
- “DRESS syndrome should be suspected if a diffuse rash erupts and is accompanied by fever, facial edema, and enlarged lymph two to six weeks after starting a new high-risk medication.
How to treat DRESS Syndrome?
- The most important step to treat DRESS Syndrome is to stop the medication involved in the reaction, and sometimes, no further treatment is needed.
- Topical steroids can be given to treat the rash and in certain cases, further treatment is needed to protect the organs from damage, such as with steroids, which can be given either intravenously or orally.
- “Treatment with steroids can be needed for weeks or even months, and lab work is monitored carefully during this time.
- The average time to recovery is six to nine weeks.
Odisha Invokes ESMA to Ban Strikes by Health Department Staffs (The Hindu)

- 07 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
The Odisha Government invoked the Orissa Essential Services (Maintenance) Act (ESMA) prohibiting strikes by paramedical staff, including nurses, pharmacists, technicians, Class III and IV employees, to ensure that medical services are not disrupted.
About Essential Services Maintenance Act (ESMA):
The Indian Parliament enacted ESMA in 1968 to ensure the continuous provision of critical services crucial to people's daily lives. This legislation prohibits employees in essential services from striking, regardless of bandhs or curfews.
- Designated Essential Services: Public conservation, sanitation, water supply, hospitals, national defense, petroleum, coal, electricity, steel, fertilizer production, and banking-related services fall under the ambit of essential services.
- Communication, transportation, and government initiatives for food grain acquisition and distribution are also covered.
- State-Specific Application: State governments, individually or collaboratively, can enforce ESMA within their territories, each having its own version with slightly varied provisions.
- This allows states to address disruptions that impact specific regions.
- Central Government Activation: In the case of a nationwide disruption, especially in sectors like railways, the central government may invoke ESMA.
- Consequences for Striking Employees: Employees engaging in illegal strikes under ESMA can face disciplinary action, including dismissal. Legal consequences may involve arrests without a warrant, with imprisonment for up to one year, fines, or both for those participating or instigating the strike.
UN Secretary-General Invokes Article 99 on Humanitarian Crisis in Gaza (The Hindu)

- 07 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
Amid Israel’s ongoing military attacks on the Gaza Strip, particularly in its southern region, United Nations Secretary-General Antonio Guterres has invoked Article 99 of the UN Charter in a bid to establish a ceasefire.
Context:
- The United Nations Secretary-General Antonio Guterres has decided to invoke Article 99 of the UN Charter as the death toll in Israeli bombardments on Gaza crosses 16,000.
- He also urged the UN Security Council to act on the humanitarian crisis in Gaza.
- The development comes as Israel increased the intensity of its operations, especially in the areas of southern Gaza with Israel's defence leadership claiming that “half of Hamas’ battalion commanders" are killed.
What is Article 99 of the UN Charter?
- The Secretary-General may bring to the attention of the Security Council any matter which in his opinion may threaten the maintenance of international peace and security.”
- It is seen as a discretionary power.
- The responsibility it confers upon the Secretary-General will require the exercise of the highest qualities of political judgment, tact and integrity” according to a 1945 report of the Preparatory Commission of the United Nations.
- According to the UN, the President of the Security Council is under the obligation to call a meeting of the Council if the Secretary-General brings to the attention of the Council any matter under Article 99.
When has Article 99 Been Activated in the Past?
- 1960: Following the Congo Crisis, Secretary-General Dag Hammarskjöld invoked Article 99 to address the aftermath of Belgium's withdrawal and the ensuing internal conflict.
- 1971: Amid the Bangladesh Liberation War, Secretary-General U Thant activated Article 99 to draw attention to the humanitarian crisis, urging international intervention.
- 1979: In response to the Iranian Revolution and hostage crisis, Secretary-General Kurt Waldheim triggered Article 99 to underscore the seriousness of the situation and the necessity for a peaceful resolution.
- 1989: Confronted with the ongoing Lebanese Civil War and hostage abductions, Secretary-General Javier Pérez de Cuéllar invoked Article 99 to emphasize the requirement for international support and engagement.
‘Garba Of Gujarat’ Declared as Intangible Cultural Heritage by UNESCO (Indian Express)

- 07 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
Garba, the folk art of Gujarat, receives the intangible cultural heritage of humanity (ICH) tag from Unesco.
Context:
- 'Garba of Gujarat' has been inscribed in the Representative List of Intangible Cultural Heritage (ICH) of Humanity by UNESCO.
- The decision was taken at the 18th session of the UNESCO’s Intergovernmental Committee for Safeguarding of Intangible Cultural Heritage held in the Republic of Botswana.
- Garba of Gujarat is the 15th ICH element from India to join this list.
- This inscription underscores Garba’s pivotal role as a unifying force that fosters social and gender inclusivity.
About Garba Dance:
- Garba is a ritualistic and devotional dance deeply rooted in the traditions of Gujarat, India.
- This vibrant dance is a central part of the nine-day Navratri festival, dedicated to the worship of feminine energy or Shakti.
- The cultural richness of Garba vividly expresses the divine feminine through its performances and visuals.
- Taking place in various settings, from homes and temple courtyards to public spaces, streets, and open grounds, Garba transforms into a widespread, inclusive community celebration.
- Beyond its religious significance, Garba serves as a social equalizer, breaking down barriers related to socio-economic status, gender, and sect divisions.
- This inclusive dance form fosters community unity, bringing together diverse and marginalized groups and reinforcing social bonds.
- Notably, Garba holds the distinction of being the 15th cultural element from India to be recognized by UNESCO.
What is Intangible Cultural Heritage?
- Cultural heritage extends beyond physical structures and object collections.
- It encompasses traditions and living expressions transmitted from our forebears to descendants.
- This includes oral traditions, performing arts, social practices, rituals, festive events, and the knowledge associated with nature, the universe, as well as the skills involved in traditional craftsmanship.
Chandrayaan-3 Propulsion Module Retraces Steps to Earth Orbit (Indian Express)

- 07 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
Scientists have brought the Propulsion Module (PM) of the Chandrayaan-3 mission , which initially brought the Vikram lander to within 100 km of the Moon's surface before detaching and executing a historic controlled descent on August 23, back into Earth orbit.
What is a Propulsion Module in Chandrayaan-3?
- The Propulsion Module is a rectangular component of the Chandrayaan-3 spacecraft, equipped with solar panels for power.
- Its primary purpose was to transport the Lander module to the lunar polar circular orbit and facilitate its separation.
- Following separation, the SHAPE payload within the Propulsion Module was activated.
- Initially intended for a three-month operation during the mission, the ISRO announced on December 4th that the Chandrayaan-3's Propulsion Module had been manoeuvred out of lunar orbit.
- Placed high above Earth for an additional mission, the module is currently sustained by residual fuel.
- This bonus mission will showcase technologies crucial for future lunar sample retrieval, according to ISRO.
- As of now, the ISRO has not disclosed its plans for the spacecraft once it depletes its fuel.
Importance of Propulsion Module's Return to Earth's Orbit:
- ISRO highlighted the key achievements resulting from the return manoeuvres conducted on the Propulsion Module (PM) in connection to upcoming missions:
- Planning and executing the trajectory and manoeuvres for the return journey from the Moon to Earth.
- Developing a software module for planning such manoeuvres, along with its initial validation.
- Planning and executing a gravity-assisted flyby around a planet or celestial body.
- Preventing uncontrolled crashing of the PM onto the Moon's surface at the end of its life, aligning with the requirement of avoiding debris creation.
What is Chandrayaan-3 Mission?
Mystery of megamouth shark solved after one washes up in Philippines (Business Insider)

- 06 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
Recently a dead 18-foot megamouth shark that washed up on the beach in the Philippines was pregnant, confirming for the first time that these mysterious creatures give birth to live young.
About Megamouth Shark:
- Researchers have found Megamouth sharks to be particularly elusive.
- Since their discovery in 1976, there have been fewer than 300 sightings of these deep-sea sharks.
- Uncovering fewer than 150 specimens, scientists have identified them as the smallest of three species of filtering sharks.
- Their scientific name is Megachasma pelagios.
- Similar to their relatives, the basking sharks, Megamouth sharks feed on krill suspended in seawater, utilizing their oversized mouths to sieve their food.
- Although most sightings have occurred near the Philippines and Taiwan, these sharks have been observed around the world.
- These sharks are found in deep, warm oceanic water and inhabit the Atlantic, Indian, and Pacific oceans.
- Characterized by their substantial size, Megamouth Sharks can reach weights of up to 2700 pounds (1215 kg) and lengths ranging from 425 to 515 cm. Females are generally larger than males.
- Easily recognizable by their large, soft head and anteriorly positioned mouth, their colouration varies from grey to bluish-black above and pale grey below.
- They possess small, hooked teeth along both top and bottom jaws.
- As filter feeders, they swim with their mouths continuously wide open, filtering their preferred planktonic prey.
- The inside of their mouths is equipped with light-producing organs that may attract pelagic crustaceans and other potential prey.
- On the conservation front, the Megamouth Shark is listed as "Least Concern" on the IUCN Red List.
Closest-ever Sun photo captured by Solar Orbiter (India Today)

- 06 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
The European Space Agency's Solar Orbiter has captured the most detailed image of the Sun's full disc and outer atmosphere, the corona, to date.
What is the Solar Orbiter?
- Solar Orbiter is a Sun-observing satellite, equipped with 10 state-of-the-art science instruments, that aims to provide unprecedented insights into the workings of the Sun.
- It intends to conduct an in-depth study of both the Sun and the inner heliosphere, exploring the uncharted regions closest to our Solar System.
- A collaboration between the European Space Agency (ESA) and NASA, it represents the most intricate scientific laboratory ever dispatched to study the Sun.
- Distinguished by its capability to capture images of the Sun from a closer vantage point than any preceding spacecraft, it also marks the first exploration of the Sun's previously uncharted polar regions.
- Launched on February 10, 2020, the mission unveiled its initial images in June of the same year.
- Following gravitational assist manoeuvres at Earth and Venus, it commenced full science operations in December 2021.
- Solar Orbiter actively orbits the Sun in an elliptical trajectory, with its closest point, the perihelion, located approximately 25 million miles (40 million kilometres) from the Sun—closer than the orbit of Mercury.
- In terms of instrumentation, it actively carries six remote-sensing instruments for observing the Sun and the solar corona, along with four in-situ instruments for measuring the solar wind, energetic particles, and electromagnetic fields.
- The mission actively aims to continue its scientific operations until at least 2027.
Panchayat Development Index (PIB)

- 06 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
The Union Minister of State for Panchayati Raj recently informed Lok Sabha about the Panchayat Development Index.
About the Panchayat Development Index:
- The Panchayat Development Index serves as a comprehensive and versatile metric designed to actively evaluate the holistic advancement, efficacy, and ongoing progress of panchayats.
- This index actively considers a spectrum of socio-economic indicators and parameters, offering an actively nuanced understanding of the well-being and developmental status of local communities within the panchayat's jurisdiction.
- Objectives: The primary objective is to actively play a pivotal role in assessing performance and progress towards actively achieving Sustainable Development Goals at the grassroots level.
- An active component of this initiative is the Local Indicators Framework, which encompasses nine key themes for actively localising Sustainable Development Goals.
- These themes actively encompass creating poverty-free and thriving livelihoods, ensuring health and actively child-friendly environments, actively promoting water sufficiency, actively fostering clean and green spaces, actively developing self-sufficient infrastructure, actively establishing socially just and secure communities, actively promoting good governance, and actively creating women-friendly villages.
How Ranking Works?
- Ranks within the index are actively assigned based on scores, actively categorising panchayats into four grades.
- Those actively scoring below 40 percent are actively classified as Grade D,
- 40-60 percent as Grade C,
- 60-75 percent as Grade B
- 75-90 percent as Category A
- and those actively surpassing 90 percent are actively designated as A+.
- Significance of this Index: The significance of this index lies in its ability to actively offer valuable insights into areas requiring attention and improvement within rural areas under panchayat jurisdiction.
- It actively aids in identifying disparities, gauging the achievement of development goals, and actively crafting targeted policies and interventions to elevate the overall well-being and quality of life in rural communities.
Elephant Endotheliotropic Herpesvirus (EEHV) (DST Gov)

- 06 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
The study by ICAR-Indian Veterinary Research Institute (ICAR-IVRI), Izatnagar, Bareilly has found the exact status of EEHV and its subtypes circulating among the Asian elephant population in India.
What is Elephant Endotheliotropic Herpesvirus (EEHV)?
- Elephant endotheliotropic herpesvirus (EEHV) is responsible for one of the most devastating viral infectious diseases in elephants worldwide, especially young Asian elephants.
- EEHV is a double-stranded DNA virus that is classified in the family Herpesviridae.
- The mortality rate is very high (70-85%) and death occurs within a short period (2-4 days).
- In India, the incidence of EEHV-HD was first reported in 1997.
- 9 of 15 potential cases were confirmed from Southern India in wild free-ranging calves in Kerala, Karnataka, Tamil Nadu forest reserves, and Madras Zoo.
- Transmission of the disease: EEHV is mostly spread through mucosal secretions which include:
- Saliva, Breast milk, Nasal secretions, Trunk to trunk contacts etc
- The disease can only affect elephants and is not infectious to humans or other animals.
- Symptoms: Some elephants show symptoms such as reduced appetite, nasal discharge and swollen glands.
- Treatment: Treatment involves a combination of strategies such as antiviral therapy, aggressive fluid therapy to counter haemorrhaging, immuno-stimulant drugs like selenium and Vitamins C and E, as well as antipyretics and analgesics to manage fever.
- It's important to note that there is no definitive cure for herpesviruses in animals or humans since these viruses typically enter a latent state.
Scientists uncover seismic clues in Kopili Fault zone, advancing earthquake preparedness (PIB)
- 06 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
Recently, scientists at the Indian Institute of Geomagnetism (IIG) have detected seismogenic liquefaction characteristics within the dynamically active Kopili Fault (KF) zone.
About Kopili Fault Zone:
- The Kopili Fault extends from the western part of Manipur up to the tri-junction of Bhutan, Arunachal Pradesh and Assam.
- It covers a distance of about 400 km and is closer to the Himalayan Frontal Thrust.
- The Kopili fault bisects the Meghalaya Plateau and isolates the Mishmi block from the main part of the plateau.
- The Kopili fault is almost passing through the Kopili River.
- The river Kopili rises in the North Cachar Hills District in Borail Range at an altitude of 1525 meters.
- From a field study, it is observed that the Kopili Fault region is moving in the northeast direction at an average velocity of 28.397N mm/yr and 40.227E mm/yr.
- This region is characterized by heightened seismic activity, classified within the most critical Seismic Hazard Zone V.
- The geological dynamics are attributed to collisional tectonics, where the Indian Plate subducts beneath the Eurasian Plate.
- The fault itself is a transpressional fracture, producing dextral strike-slip earthquakes in the lower crust.
- The Kopili fault zone, a tectonic depression filled by the alluvium of the Kopili River and its tributaries, has experienced numerous seismic events, notable among them being the 1869 earthquake (magnitude 7.8) and the 1943 earthquake (magnitude 7.3).
Iyothee Thass Pandithar (The Hindu)

- 02 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
Tamil Nadu Chief Minister M.K. Stalin on Friday unveiled a statue of late anti-caste activist Iyothee Thass Pandithar installed at the Gandhi Mandapam campus at Guindy in Chennai.
About Iyothee Thass Pandithar:
- Iyothee Thass Pandithar was an important anti-caste activist and practiced Siddha medicine.
- He was born on 20 May 1845 in Madras presidency.
- In the 1870s, Thass brought together the Todas and other tribes of the Nilgiri Hills for the freedom movement.
- In 1876, he started the Advaidananda Sabha and, with Rev. John Rathina, launched a magazine called Dravida Pandian.
- In 1891, he founded the "Dravida Mahajana Sabha'' with Rettamalai Srinivasan.
- Also, he established the Sakya Buddhist Society in Madras, which had branches all over South India.
- This society, also known as the Indian Buddhist Association, was formed in 1898.
- To organize and oversee the society's activities, he began a weekly magazine, Tamizhan, in 1907.
INS Trinkat (Indian Express)
- 02 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
The Navy has appointed the first woman commanding officer in a naval ship in line with the Navy’s philosophy of “all roles-all ranks” to deploying women in the service, Navy Chief Admiral R Hari Kumar said on Friday.
About INS Trinkat:
- INS Trinkat is a patrol vessel crafted by Garden Reach Shipbuilders and Engineers in Kolkata, West Bengal, and serves the Indian Navy.
- The role of the INS Trinkat is for anti-poaching operations, counter-insurgency operations, and Search and Rescue Operations in Andaman and Nicobar Islands, Lakshadweep Islands, and India's Exclusive Economic Zone.
- It is capable of detecting and destroying fast-moving surface craft.
- It can also carry out policing anti-smuggling and fisheries protection operations.
- These patrol vessels are aptly named after Trinkat Island, one of the 24 islands constituting the Nicobar Islands chain situated in the northeast Indian Ocean, between the Bay of Bengal and the Andaman Sea.
About Group Captain Shaliza Dhami:
- Group Captain Shaliza Dhami, is an esteemed officer in the Indian Air Force (IAF).
- She holds the distinction of being the first woman officer in the IAF to secure a permanent commission and the pioneer woman to attain the role of a Flight Commander.
- Adding to her achievements, she became the first woman IAF officer selected for a front-line combat unit.
- Shaliza Dhami is an officer who is a qualified navigation instructor and has been involved in training observers inducted into the Navy.
- She is also learned to be the first woman officer who served as an observer in the Navy’s Tupolev Tu-142 maritime patrol aircraft.
- It's noteworthy that she is poised to make history once again by assuming command of a ship, marking a significant milestone in her career.
Sub-Neptune Planets (The Hindu)
- 02 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
Recently astronomers have discovered an uncommon star system located just 100 light-years away from us, with six planets huddled immensely close to their host star.
What about sub-Neptunes?
- Sub-Neptunes are generally any planet that has a smaller radius than Neptune, although some could still be more massive.
- There are no sub-Neptunes in our solar system even though they are now known to be more common around other stars than Neptune-sized worlds.
- They might be rocky planets with thick atmospheres of hydrogen and helium gas, planets made of rock and ice bearing warm and water-rich atmospheres.
- These sub-Neptune planets were Initially detected in 2020 by NASA's Transiting Exoplanet Survey Satellite (TESS) and are about two to three times as big as Earth.
What are the findings?
- The newly discovered sub-Neptunes range from 1.9 to 2.9 times Earth's diameter.
- All appear to possess a large atmosphere.
- They and their star are located around 100 light-years from Earth.
- A light year is the distance light travels in a year, 5.9 trillion miles (9.5 trillion km).
- The system has six planets, all about the same size and they've barely changed since its formation up to 12 billion years ago.
- Their star, called HD110067, is visible in Earth's night sky in the northern constellation Coma Berenices.
- These undisturbed conditions make it ideal for learning how these worlds formed and whether they host life.
Clearing Corporation of India Limited (CCIL) (The Hindu)

- 02 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) and the Bank of England (BoE) on Friday signed a Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) concerning cooperation and exchange of information in relation to the Clearing Corporation of India Ltd (CCIL).
About Clearing Corporation of India Limited (CCIL):
- The Clearing Corporation of India Ltd. (CCIL) was set up in April 2001 to provide guaranteed clearing and settlement functions for transactions in Money, G-Secs, Foreign Exchange, and Derivative markets.
- Objective: The prime objective has been to improve efficiency in the transaction settlement process, insulate the financial system from shocks emanating from operations-related issues, and undertake other related activities that would help to broaden and deepen the money, debt, and forex markets in the country.
- Promoters of CCIL: State Bank of India, IDBI Bank Ltd, ICICI Bank Ltd, Life Insurance Corporation of India (LIC), Bank of Baroda, and HDFC Bank Ltd.
- The company was incorporated with an authorised equity share capital of Rs. 50 crores.
- CCIL’s adherence to the stringent principles governing its operations as a Financial Market Infrastructure (FMI) has resulted in its recognition as a Qualified Central Counterparty (QCCP) by the Reserve Bank of India in 2014.
- CCIL is also the trade repository for all OTC transactions in the Forex, Interest Rate, and Credit derivative transactions.
- Through its fully owned subsidiary, Clearcorp Dealing Systems Limited (CDSL), CCIL has introduced various platforms for the electronic execution of deals in various market segments.
- Further, CDSL has developed, implemented, and manages the NDS-OM, the RBI-owned anonymous electronic trading system for dealing in G-Secs and also for reporting OTC deals, as well as the NDS-CALL platform, which facilitates electronic dealing in the Call, Notice & Term Money market.
Codex Alimentarius Commission (CAC) (PIB)

- 02 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
The Codex Alimentarious Commission (CAC) has recently praised India’s Standards on Millets and accepted its proposal for the development of global standards for millets during its 46th session held in Rome, Italy.
About Codex Alimentarius Commission (CAC):
- The Codex Alimentarious Commission (CAC) is an international food safety and quality standard-setting body created by WHO and FAO of the United Nations with 188 member countries.
- It is the body responsible for all matters regarding the implementation of the Joint FAO/WHO Food Standards Programme.
- Membership of the Commission is open to all Member Nations and Associate Members of FAO and WHO which are interested in international food standards.
- The Commission meets in regular session once a year alternating between Geneva and Rome.
- The programme of work of the Commission is funded through the regular budgets of WHO and FAO with all work subject to approval of the two governing bodies of the parent organizations.
- The Commission works in the six UN official languages.
- India has been a member of this commission since 1964.
- The 46th session of the Codex Alimentarius Commission (CAC) was held from 27 November to 2 December (2023) in Rome, Italy.
- In the current session, India has framed a comprehensive group standard for 15 types of millets specifying 8 quality parameters, which received resounding applause at the international meet.
- India put forward a proposal for the development of global standards for millet, particularly for Finger millet, Barnyard millet, Kodo millet, Proso millet, and Little millet as group standards as in the case of pulses.
Exercise Milan (The Hindu)

- 01 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
Indian Navy To Conduct One Of Its Largest Naval Exercises — MILAN — Next February; More Than Fifty Countries Expected To Participate
About Exercise Milan:
- Exercise Milan is a biennial multilateral naval exercise that began in 1995, and has since significantly expanded in scope and scale to become the largest exercise held by India.
- Initially involving only Indonesia, Singapore, Sri Lanka, and Thailand, it has evolved significantly in terms of participants and exercise complexity.
- Aligned with India's 'Look East Policy' initially, Milan expanded under the 'Act East Policy' and Security And Growth for All in the Region (SAGAR) initiative, welcoming Friendly Foreign Countries (FFCs).
- The mid-planning conference for Milan-24 occurred in October.
- The last edition of Milan, which is held off Visakhapatnam, saw participation from over 40 countries showcasing its substantial growth in scale and international engagement.
- The next edition of Exercise MILAN is scheduled to be held in February 2024 and is expected to see the participation of over 50 countries.
- It reflects the significant expansion of the Navy’s engagements as well as its capacity to assist countries in the Indian Ocean Region (IOR) as the first responder and Preferred Security Partner.
Sindhudurg Fort (Financial Express)

- 01 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
The Indian Navy is gearing up to showcase its operational prowess in a significant ‘Operational Demonstration’ scheduled for December 4, 2023, at Sindhudurg Fort in Maharashtra.
About Sindhudurg Fort:
- Sindhudurg Fort is a historically significant stronghold situated on an islet in the Arabian Sea, just off the coast of Maharashtra in western India.
- Positioned on Kurte Island near Malvan town in Sindhudurg District within the Konkan region of Maharashtra, this formidable fortress was commissioned and constructed under the reign of Chhatrapati Shivaji Maharaj of the Maratha Empire in 1664.
- The primary objective behind its construction was to counteract the escalating influence of foreign colonizers, including English, Dutch, French, and Portuguese merchants, and to curb the rise of the Siddis of Janjira.
- The Bakhar (a form of historical narrative written in Marathi prose) written by Chitragupta aptly mentions this fort as the most invaluable asset to Shivaji Maharaj.
Key Features:
- The fort spans 48 acres and boasts fortified walls that are 29 feet high and 12 feet thick, extending for a distance of two miles.
- Guarding these walls are 52 bastions equipped with embrasures for cannons.
- Access to the fort is through the Dilli Darwaja, the main gate, uniquely designed to blend seamlessly with the walls and visible only from close quarters.
- The fort is surrounded by several smaller forts, including Padmagad, Rajkot, and Sarjekot.
- An intriguing feature within the fort is a slab bearing the handprint and footprint of Chhatrapati Shivaji Maharaj.
- Additionally, a small temple dedicated to the Maratha King is situated within the fort's bounds
Asola Bhatti Wildlife Sanctuary (Indian Express)

- 01 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
The Delhi High Court has criticized the forest department's proposal to hold a walkathon and cyclathon in a wildlife sanctuary, calling it a "haphazard exercise."
About Asola Bhatti Wildlife Sanctuary:
- Asola Bhatti Wildlife Sanctuary covers 32.71 sq. km on the Southern Delhi Ridge of the Aravalli hill range, bordering Delhi and Haryana.
- It's in Southern Delhi and parts of Faridabad and Gurugram districts in Haryana.
- It's a part of the Sariska-Delhi Wildlife Corridor, linking Sariska Tiger Reserve in Rajasthan to Delhi Ridge.
- The sanctuary gets its name from the contiguous Asola village near Tughlaqabad in the Delhi NCR.
- Vegetation: The vegetation is classified as Northern Tropical Thorn Forests, known for thorny appendages and special leaves.
- The climate has extreme summer heat and significant winter cold due to its inland position.
- Flora: The main exotic plant is Prosopis juliflora, and the primary native plant is Diospyros montana.
- Fauna: The sanctuary is home to various animals like Golden Jackals, striped hyenas, Indian Crested Porcupines, Civets, Jungle Cats, Snakes, Monitor Lizards, and Mongoose.
- This sanctuary plays a crucial role in connecting wildlife across different areas.
World AIDS Day 2023 (Indian Express)

- 01 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
On the World AIDS Day 2023, observed each year on December 1, the World Health Organisation emphasised recognising and remembering the contribution of communities in controlling HIV-AIDS.
About World AIDS Day 2023:
- World AIDS Day which is observed every year on December 1 is a global movement to unite people in the fight against HIV and AIDS.
- Since 1988, when the World Health Organisation (WHO) recognised the day, communities have stood together on World AIDS Day to show strength and solidarity against HIV stigma and to remember lives lost.
- It is an opportunity to reflect on the progress made to date and raise awareness about the challenges that remain to achieve the goals of ending AIDS by 2030.
- The theme of World AIDS Day 2023 is– “Let Communities Lead"
What is HIV/AIDS?
- Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV) is a virus that attacks the immune system, compromising the body's ability to fight off infections and diseases.
- Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome (AIDS) is the advanced stage of HIV infection, characterized by severe immune system damage.
- Transmission: HIV spreads through unprotected sexual contact, sharing contaminated needles, and from an infected mother to her child during childbirth or breastfeeding.
- Treatment: Antiretroviral Therapy (ART) is the primary treatment for HIV/AIDS, managing the virus and supporting the immune system.
- Lifelong adherence is essential, ensuring viral suppression.
- Regular monitoring by healthcare providers is vital, and global challenges such as stigma and healthcare access persist in the fight against HIV/AIDS.
Gajraj Suraksha (Elephant Safety) System (New Indian Express)

- 01 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
"In a first", through cutting-edge indigenous technology, the Indian Railways has successfully developed a system, preliminarily called as ‘Gajraj Suraksha (Elephant safety) system’ to prevent elephant–train collisions in the forest areas.
About Gajraj Suraksha:
- Gajraj Suraksha uses an AI-based algorithm and a network of sensitive optical fiber cables to detect elephants approaching railway tracks, aiming to address elephant fatalities resulting from train accidents.
- How this will work?
- The system functions by sensing pressure waves generated by elephant movements along the tracks.
- As elephants move, the optical fibers detect vibrations from their footsteps, triggering signals within the fiber network.
- This enables the system to identify elephants up to 200 meters ahead of their arrival on the track.
- The Optical Fibre Cable (OFC)-based Intrusion Detection System sends alarms to station masters upon detecting movement along the tracks.
- The network is designed to accurately track elephant movement, allowing prompt communication to nearby station masters.
- This ensures timely information to locomotive drivers, facilitating the slowing down or stopping of trains to prevent potential collisions with elephants.
- The Indian Railway plans to introduce this system in West Bengal, Odisha, Jharkhand, Assam, Kerala, certain parts of Chhattisgarh, and Tamil Nadu.
Digital Crop Survey System (Indian Express)

- 19 Oct 2023
Why in the News?
Emphasizing the current manual nature of crop area and production estimation, the Central Government has urged states and Union Territories (UTs) to transition to a digital approach by implementing the Digital Crop Survey System starting in July next year.
About the Digital Crop Survey:
- As a part of the Digital Crop Survey initiative, the Ministry of Agriculture and Farmers Welfare (MoA&FW) has instructed states to capture data on essential parameters, encompassing:
- Village name, year, season, farmer ID, farm ID,
- Crop name (at the farm plot level),
- Crop variety,
- Crop sown area (at the farm plot level),
- Geotags of crop photos,
- Geotags of the farm boundary where the crop is cultivated,
- Sowing/planting date (at the farm plot level),
- Irrigation type (at the farm plot level), and
- Irrigation source (at the farm plot level).
- This directive follows the introduction of a pilot Digital Crop Survey across multiple states earlier this year.
- In a parallel initiative, the MoA&FW has also revised the release timelines for crop estimates.
- Previously conducted in five phases, the ministry has streamlined the process by eliminating the fourth phase traditionally released in August.
- The ministry now plans to unveil comprehensive final estimates encompassing all states and seasons (kharif, rabi, summer) in September-October, departing from the earlier practice of releasing final estimates in February of the subsequent year.
Guidelines for the Digital Crop Survey:
- According to sources, the Economics, Statistics and Evaluation Division (ESED) under the Ministry of Agriculture and Farmers’ Welfare (MoA&FW), has finalised the guidelines.
- According to the guidelines, all states/ UTs shall automate/digitise the process of area enumeration/girdawari of crops at field level, i.e., Digital Crop Survey, from 2024-25 Agricultural Year.
- In India, the agriculture year begins in July and ends in June, the following year.
- Under the guidelines, states and UTs shall use GPS-enabled mobile applications for collecting crop-sown data of each plot for each season and share the village-level aggregated data with DA&FW through API only.
Need for the Digital Crop Survey:
- The current methodology for gathering and consolidating crop statistics relies entirely on manual processes across most states, leading to delays and human errors in the data compilation.
- Only a handful of states, such as Karnataka, Telangana, and Andhra Pradesh, have embraced a digital approach to data collection through GPS-enabled mobile applications, particularly for the recording of crop area and Collection of Cost of Cultivation and Equipment Survey (CCEs) data directly from the fields.
- While Maharashtra and Madhya Pradesh have implemented digital systems, they are primarily focused on recording crop areas.
- India faces a challenge due to the lack of dependable agricultural production estimates, accentuating the necessity for a "real-time assessment estimate" of crops.
- Recognizing this gap, there is a compelling need to modernize the current production estimation system by incorporating technological interventions.
Organized Crime and Corruption Reporting Project (OCCRP) (The Hindu)

- 19 Oct 2023
Why in the News?
The Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI) has recently requested the Organized Crime and Corruption Reporting Project (OCCRP) to provide access to "essential documents" related to the accusations of stock manipulation and accounting fraud against the Adani Group.
About the Organized Crime and Corruption Reporting Project (OCCRP):
- The Organized Crime and Corruption Reporting Project (OCCRP) is a nonprofit investigative reporting platform that collaborates with over 50 independent media outlets worldwide, producing over 100 investigations annually.
- Established in 2006, its mission is to conduct transnational investigative reporting and advocate for technology-based approaches to expose organized crime and corruption on a global scale.
- The organization strives to cultivate and empower a global network of investigative journalists, publishing their stories to shed light on crime and corruption, enabling the public to hold those in power accountable.
Vision:
- OCCRP envisions a world where lives, livelihoods, and democracy are not jeopardized by crime and corruption.
- The organization is committed to exposing malfeasance so that the public can actively hold institutions accountable.
Core Initiatives:
- Global Investigative Network: OCCRP facilitates a global network of investigative journalists, providing them with essential resources and tools.
- This includes digital and physical security measures, enabling journalists covering sensitive topics to collaborate effectively with trusted editors.
- An investigative data platform, OCCRP Aleph empowers journalists to search and cross-reference over three billion records, unveiling criminal connections and patterns.
- This platform facilitates efficient cross-border collaboration among journalists.
- Training and Skill Development: OCCRP offers training programs to reporters and partners, equipping them with advanced journalism techniques, and enhancing their investigative capabilities.
- Partnerships for Change: OCCRP collaborates with advocacy groups, arming civil society with information to advocate for justice and transformative change.
- The organization also uncovers evidence that empowers law enforcement to take meaningful action.
Kati Bihu (PIB)

- 19 Oct 2023
Why in the News?
The Prime Minister, Narendra Modi recently extended best wishes on the auspicious occasion of KatiBihu to the people of Assam.
About Kati Bihu:
- Kati Bihu is an annual celebration observed in the state of Assam, signifying the relocation of rice saplings.
- The term "Kati" translates to cutting, representing the agricultural activity during this period.
- Also known as Kongali Bihu, with "Kongali" connoting a state of poverty, the festival holds cultural significance in Assam alongside two other Bihu festivals—Bhogali or Magh Bihu in January and Rongali or Bohag Bihu in April.
Significance:
- In this month, food resources are scarce, prompting people to celebrate by illuminating their homes with earthen lamps or candles.
- Lighting lamps near the Tulsi plant are a central aspect of the festival, signifying devotion and auspiciousness.
- People light a special lamp known as "Akash Banti" (Sky candle) in their paddy fields. Fueled by mustard oil, these lamps are elevated on bamboo poles.
- The belief prevails that the illuminated lamps guide the spirits of ancestors toward their heavenly abode.
Bhimashankar Temple (HT)

- 19 Oct 2023
Why in the News?
Tensions escalated at the Bhimashankar temple recently as a dispute unfolded between two groups of religious leaders, referred to as pujaris, regarding the leadership of the puja ceremony, leading to a brawl.
Bhimashankar Temple Overview:
- The Bhimashankar Temple is an ancient Hindu shrine dedicated to Lord Shiva, located amidst the Sahyadri hills in the Pune District of Maharashtra.
- Recognized as one of the 12 holy Jyotirlinga shrines in India, it holds immense spiritual significance.
- In recent times, it has gained additional importance as it was designated a "Wildlife Sanctuary," forming part of the Western Ghats and serving as the source of the Bhima River.
Historical Significance:
- Constructed around the 13th century, the temple is a testament to the craftsmanship of Vishwakarma sculptors.
- Subsequent enhancements, including the addition of spires (shikhara) by Maratha Empire statesman Nana Phadnavis in the 18th century, contribute to its historical evolution.
- Chhatrapati Shivaji Maharaj, the Maratha ruler, is believed to have played a role in fostering worship at the temple through his endowments.
Architectural Marvel:
- A blend of old and new structures in the Nagara style of architecture, the Bhimashankar Temple boasts spacious courtyards, intricate wall carvings, and imposing pillars.
- The sanctum, or Garbhgriha, houses the sacred Jyotirlinga, positioned at a lower level. The Swayambhoo, a self-emanated Shiv Linga, holds a central place in the Sanctum Sanctorum.
- Exquisite mythological carvings adorn the massive pillars and doorframes, depicting divine figures and sacred symbols.
- Additionally, the temple encompasses an ancient shrine dedicated to Lord Shani, considered auspicious by devotees, and features the revered Nandi statue at its entrance.
What are Jyotirlingas?
- Jyotirlingas are shrines where Lord Shiva is worshipped in the form of a Jyotirlingam, representing different manifestations of the deity.
- Among the 12 main Jyotirlingas in India, Bhimashankar Jyotirlinga is one.
- Each of these sacred shrines is named after its presiding deity and holds unique spiritual significance for devotees across the country:
- Somnath Jyotirlinga in Gir, Gujarat
- Mallikarjuna Jyotirlinga in Srisailam, Andhra Pradesh
- Mahakaleshwar Jyotirlinga in Ujjain, Madhya Pradesh
- Omkareshwar Jyotirlinga in Khandwa, Madhya Pradesh
- Baidyanath Jyotirlinga in Deoghar, Jharkhand
- Bhimashankar Jyotirlinga in Maharashtra
- Ramanathaswamy Jyotirlinga in Rameshwaram, Tamil Nadu
- Nageshwar Jyotirlinga in Dwarka, Gujarat
- Kashi Vishwanath Jyotirlinga in Varanasi, Uttar Pradesh
- Trimbakeshwar Jyotirlinga in Nasik, Maharashtra
- Kedarnath Jyotirlinga in Rudraprayag, Uttarakhand
- Ghrishneshwar Jyotirlinga in Aurangabad, Maharashtra
Siena Galaxy Atlas (SGA) (Space)

- 19 Oct 2023
Why in the News?
Astronomers have recently crafted a stunning atlas comprising 400,000 galaxies situated in the cosmic vicinity of the Milky Way, aptly named the Siena Galaxy Atlas.
About the Siena Galaxy Atlas:
- It is a digital atlas designed to help learn more about our universe by highlighting a number of well-known galaxies.
- It was produced using information gathered from three astronomical surveys conducted at Kitt Peak National Observatory (KPNO) and Cerro Tololo Inter-American Observatory (CTIO) between 2014 and 2017. These surveys collectively are referred to as the DESI Legacy Surveys.
Distinguishing Features:
- Setting itself apart from previous atlases, the Siena Galaxy Atlas relies on state-of-the-art digital images captured by advanced technology.
- Unlike its predecessors, which utilized outdated equipment and photographic plates, this atlas leverages highly sensitive instruments to produce the most precise and accurate data available.
- Notably, it marks the first cosmic atlas to showcase the light profiles of galaxies—a curve illustrating the variation in brightness from the galaxy's brightest point to its dimmest.
Significance:
- The introduction of the Siena Galaxy Atlas carries immense importance in astronomical exploration for several reasons:
- By relying on digital images captured with advanced instruments, the atlas ensures a level of precision and detail that surpasses previous methods, enhancing the overall quality of data.
- Light Profiles of Galaxies: A pioneering feature, the inclusion of light profiles in the atlas provides a unique perspective, allowing astronomers to glean valuable insights into the structure and characteristics of galaxies.
- Pattern Recognition: Cosmic atlases, such as the Siena Galaxy Atlas, play a pivotal role in aiding astronomers in identifying patterns.
- This capability is particularly valuable in categorizing phenomena like transient events, such as stars that exhibit sudden flares and then disappear.
- The atlas facilitates the identification of celestial objects worthy of more detailed follow-up studies, enabling astronomers to delve deeper into specific areas of interest.
- From unravelling the mysteries surrounding the birth and evolution of galaxies to investigating the distribution of dark matter and the propagation of gravitational waves through space, the Siena Galaxy Atlas serves as a versatile tool for astronomers in their cosmic pursuits.
AERA Warns Indian Airport Operators Against Charging Unapproved Tariffs (TOI)

- 13 Oct 2023
Why in the News?
The Airport Economic Regulatory Authority (AERA) issued a warning to major airports about levying aeronautical charges without approval.
About Airports Economic Regulatory Authority (AERA):
- Airports Economic Regulatory Authority (AERA), established under the Airports Economic Regulatory Authority of India Act, 2008, is a statutory body entrusted with the crucial task of regulating tariffs and associated charges for aeronautical services at major airports.
- This includes overseeing air traffic management, aircraft landing and parking, and ground handling services.
- The designation of an airport as "major" hinges on the 2008 Act, considering an annual passenger traffic threshold of at least 15 lakh.
- An amendment in 2019 elevated this criterion to 35 lakh annual passengers.
- For other airports, tariff determination falls under the purview of the Airports Authority of India (AAI).
- As an independent economic regulator, AERA operates with the objective of creating an equitable playing field, fostering healthy competition among major airports, promoting investment in airport facilities, and ensuring transparent regulation of aeronautical service tariffs.
- This initiative arose from the recognition of the need for an independent regulatory body capable of safeguarding the interests of both service providers and consumers.
- Headquartered in Delhi, AERA's history traces back to a time when most Indian airports were under the governance of the central government.
- The shift towards private sector participation in airport infrastructure development prompted the need for a distinct regulator.
- The Naresh Chandra Committee set up in 1997, recommended the establishment of an independent regulatory authority.
- Subsequently, the Airports Economic Regulatory Authority of India Act, 2008 (AERA Act), was enacted, leading to the creation of AERA.
About Airports Authority of India (AAI):
- Airports Authority of India (AAI), established through an Act of Parliament on April 1, 1995, resulted from the merger of the National Airports Authority and the International Airports Authority of India.
- Entrusted with a significant role, AAI is responsible for creating, upgrading, maintaining, and managing civil aviation infrastructure both on the ground and in the airspace of the country.
- Main Functions of AAI Include
- Construction, modification, and management of passenger terminals.
- Development and management of cargo terminals.
- Development and maintenance of apron infrastructure, encompassing runways, parallel taxiways, aprons, etc.
- Provision of Communication, Navigation, and Surveillance, involving DVOR / DME, ILS, ATC radars, visual aids, etc.
- Provision of air traffic services.
- Provision of passenger facilities and related amenities at its terminals.
Bihar’s Only Ramsar Site 'Kanwar Lake' Drying Up (DownToEarth)

- 13 Oct 2023
Why in the News?
Bihar’s only wetland of international importance under the Ramsar Convention lies neglected and is on the brink of drying up, even as the state is pitching other waterbodies for classification.
About Kanwar Lake:
- Kanwar Taal, known as Kabar Taal or Kabartal Wetland, is an oxbow lake in Begusarai district, Bihar, India.
- It is the largest freshwater oxbow lake in Asia, covering an area of 67.5 km².
- The lake was established as a bird sanctuary in 1987 and is now a designated Ramsar site since 2020.
- Covering the majority of the Indo-Gangetic plains in northern Bihar, this lake was declared a Ramsar site in 2020, making it the first wetland in Bihar to be included in the Ramsar convention.
- Kanwar Taal is a significant wetland in Bihar and is an essential stopover for migratory waterbirds along the Central Asian Flyway.
- The lake provides vital flood absorption during the monsoon season and supports agriculture during the dry season.
- It also houses five critically endangered species and over 50 fish species.
- Biodiversity: Kanwar Taal is rich in biodiversity.
- It is home to a wide range of plant and animal species.
- It supports 165 plant species and 394 animal species, including 221 species of birds.
- These bird species include both resident and migratory birds, with the lake serving as an important stopover point for migratory waterbirds travelling along the Central Asian Flyway.
- Flood Absorption: The wetland plays a crucial role in flood absorption during the monsoon season.
- It helps in reducing the impact of floods in the region by absorbing excess water, which is important for flood control and the protection of nearby areas.
- Agricultural Support: During the dry season, Kanwar Taal supports agriculture in the surrounding areas.
- The water from the lake is used for irrigation, benefiting local farmers and contributing to the region's agricultural productivity.
- Endangered Species: The wetland is home to five critically endangered species, highlighting its significance in conserving rare and threatened wildlife.
- Additionally, it hosts over 50 fish species, contributing to the aquatic biodiversity of the region.
What are Oxbow Lakes?
- Oxbow lakes are crescent-like water bodies formed due to erosion and deposition in meanders of rivers.
- Meanders are loops or curved structures formed in the course of a river due to friction or tectonic activity.
- The speed of water flow in the outer section of this meander is more than the inner part causing its neck to become narrower over time.
- Eventually, the size of this loop increases making it harder for the river to flow through it so it opts for a straight path.
- Finally, the ends of this meandered loop are separated by deposition of sediments or silt separating the river and a horseshoe-like structure called oxbow lake.
Data Analytics Dashboard” and “Poorvottar Sampark Setu” Portal Launched (PIB)

- 13 Oct 2023
Why in the News?
The Union Ministry of Development of the North-East Region virtually launched the “MDoNER Data Analytics Dashboard” and “Poorvottar Sampark Setu” portal at Vigyan Bhawan, New Delhi recently.
About Poorvottar Sampark Setu Portal:
- The Poorvottar Sampark Setu portal is a robust tool designed to streamline and improve the monitoring of Union Ministers' fortnightly visits to the North Eastern Region (NER)
Key features include:
- Insightful Dashboard: The portal offers a comprehensive dashboard presenting valuable insights and graphical information on state-wise/district-wise visits to NER by Union Ministers, serving as a centralized resource for stakeholders.
- Curated Minister List: It generates a curated list of Ministers eligible for nomination for visits to NER in the upcoming months, facilitating efficient planning.
- Online Tour Reporting: After their visit, Ministers can conveniently submit tour reports and recommendations online, streamlining the reporting process.
- Recommendation Analysis: MDoNER (Ministry of Development of North Eastern Region) can analyze and forward the received recommendations to respective line Ministries, Departments, and State Governments for prompt action.
- Summary Report Generation: The portal offers a one-click summary report generation feature, simplifying the overview of visits for effective decision-making.
What is the MDoNER Data Analytics Dashboard?
- The MDoNER Data Analytics Dashboard is a comprehensive platform integrating data from 112 schemes across 55 Departments and Ministries.
Its key benefits include:
- Data-Driven Decision Making: Empowers stakeholders with data-driven insights for informed decision-making.
- Operational Efficiency: Streamlines operations, ensuring a seamless and efficient workflow.
- Centralized Monitoring: Provides a centralized hub for monitoring diverse schemes and initiatives.
- Policy-Level Decision Tool: Functions as a valuable tool for crafting policies based on robust data analysis.
- Information Integration: Integrates information seamlessly, fostering coherence and accessibility.
- Focused Monitoring: Keeps a vigilant eye on NER Aspirational districts, North East border districts, and the most backward districts in NER for targeted interventions.
Modi’s Visit to Gunji Irks Nepal Opposition (Indian Express)

- 13 Oct 2023
Why is it in the News?
Prime Minister Narendra Modi’s visit to Gunji near Kalapani, Uttarakhand has triggered an uproar in Nepal.
About Gunji Village:
- Gunji Village, situated in the Dharchula tehsil of Pithoragarh district in northern Uttarakhand, holds a strategic location near the borders of Tibet and Nepal.
- Nestled at an altitude of 3500 meters, it marks the confluence of the Kuthi Yankti and Kalapani Rivers at the eastern end of the Kuthi Valley, offering stunning views of Mount Api in Nepal.
- Covering a geographical area of 188.9 hectares, Gunji is a seasonal abode for its inhabitants.
- During winters, the residents, totalling 335 people in 194 households as per the 2011 census, migrate to lower altitudes, primarily to Dharchula within the same district.
- The village is under the administration of a Sarpanch, the elected head.
- Renowned for its connection to the traditional Indian/Nepalese route to Kailas–Manasarovar, Gunji attracts visitors seeking its breathtaking vistas.
- To embark on a journey to Gunji, obtaining an Inner Line permit is a prerequisite.
What is an Inner line permit (ILP)?
- An Inner Line Permit (ILP) is an official travel document issued by the Government of India, facilitating the inward travel of Indian citizens into a protected area for a limited duration.
- It is mandatory for Indian citizens residing outside these specific states to secure a permit before entering the designated state.
- This document serves as a regulatory measure by the government to manage and monitor the movement of individuals into areas located in proximity to India's international borders.
- The concept originates from the Bengal Eastern Frontier Regulations of 1873, designed to safeguard the Crown's interests in trades such as tea, oil, and elephants by restricting the entry of "British subjects" into these designated "Protected Areas.
- In 1950, the term "British subjects" was replaced by "Citizen of India."
- ILPs come in various types, including those for tourists and others intended for individuals planning extended stays, often for employment purposes.
CSIR-CCMB Study to Understand the Genetics Behind Diseases (The Hindu)

- 13 Oct 2023
Why in the News?
The project — “Diverse Epigenetic Epidemiology Partnership (DEEP)” — aims to uncover the effects of genomic and environmental diversity on disease risk observed in people across the world, including those in Asia, Africa and North and South America.
About the Project, The Diverse Epigenetic Epidemiology Partnership (DEEP):
- The Diverse Epigenetic Epidemiology Partnership (DEEP) is a pioneering genomics and epigenomics initiative aimed at unravelling the genetic underpinnings of Non-Communicable Diseases (NCDs) in diverse populations, including South Asians.
- This five-year international project seeks to illuminate the impact of genomic and environmental diversity on disease risk across global populations, spanning Asia, Africa, and North and South America.
- Researchers will examine individuals from varied genetic and environmental backgrounds, analyzing DNA methylation patterns to discern their contributions to disease risk within each context.
- The study involves the development of software, infrastructure, and advanced statistical analyses to create new resources, integrated with existing international health and genetics databases for assessing trends in DNA methylation variation.
- This initiative holds significance as it aims to identify common and region-specific disease-causing mechanisms, addressing questions about the universal effectiveness of medicines and paving the way for targeted interventions to reduce global health disparities.
What is DNA methylation?
- DNA methylation is a molecular process involving the attachment of chemical groups to DNA, influencing the activation and deactivation of genes.
- This epigenetic modification plays a crucial role in enabling the body to respond to environmental signals, thereby contributing to overall systemic health and disease status.
- The intricate interplay between DNA methylation, genetics, and the environment is essential for unravelling the pathways that underlie health and disease, providing insights into their interconnected consequences.
DGCA Implements New Rules for Hang Gliders (Business Standard)

- 18 Oct 2023
Why in the News?
Aviation regulator DGCA has issued amended norms for operating powered hang gliders in the country.
About Hang Gliders:
- A hang glider is a distinctive type of aircraft that relies on air currents to remain airborne, setting it apart from conventional aircraft with engines and propellers.
- These aerodynamic marvels depend on wind dynamics for lift rather than propulsion.
- Operational Mechanics: Due to their unpowered nature, hang gliders necessitate launching from elevated points such as hills or mountains.
- Gravity, acting as the primary force, encompasses the weight of both the pilot and the wing.
- This weight generates thrust, propelling the aerofoil through the air.
- The aerofoil's distinctive shape prevents the hang glider from descending rapidly and facilitates lift.
- The aerofoil's design manipulates airflow, compelling the air above the wing to move faster, creating a low-pressure area.
- Simultaneously, the wing's downward and forward motion compresses the air beneath, fostering lift as the aerofoil is drawn into the low-pressure zone.
- Pilots maintain control during flight by manipulating the trapeze and adjusting direction and speed.
- Powered Hang Gliders: In a departure from traditional hang gliders, powered hang gliders integrate features of both hang gliders and powered aircraft.
- Equipped with a small engine, these variants enable pilots to take off and sustain flight without relying on natural elements like thermals or wind conditions, making them accessible to less-experienced aviators.
DGCA Regulations for Powered Hang Gliders:
The Directorate General of Civil Aviation (DGCA) mandates strict regulations governing powered hang gliders:
- Operation Authorization: Individuals must obtain prior authorization from a DGCA-approved examiner or instructor before operating a powered hang glider.
- Examiner Qualifications: Approved examiners must possess a minimum of 50 hours of experience on powered hang gliders, including at least 10 hours on a dual machine.
- Test Flight Criteria: Individuals conducting test flights must meet specific criteria, holding a valid Commercial Pilot Licence (CPL) with at least 25 hours of flying experience on a powered hang glider or authorization with 50 hours of flying experience.
- Transaction Certification: The sale or transfer of a powered hang glider requires a DGCA-issued certificate following a background check conducted by the Ministry of Home Affairs (MHA).
- Lease and Operation Restrictions: Owners or operators are prohibited from leasing, renting, or lending powered hang gliders.
- The use of certain equipment and devices is strictly regulated, with explicit permissions required.
- Safety Protocols: Security measures endorsed by the Bureau of Civil Aviation Security (BCAS) are obligatory at parking and operational locations, ensuring compliance with established guidelines for safe flight operations.
Is Halley’s Comet returning? (India Today)

- 18 Oct 2023
Why in the News?
The celestial calendar for 2023 is set to offer a spectacular show as the Orionid meteor shower is expected to rain down its greatest number of meteors on the mornings of October 21 and 22.
About the Orionid Meteor Shower:
- An annual celestial spectacle illuminating the night sky every October, the Orionid meteor shower is a captivating phenomenon with a fascinating origin.
- This cosmic event transpires as Earth traverses the remnants of debris left by Halley's Comet, officially designated as 1P/Halley.
- Halley's Comet, on a roughly 76-year orbit around the sun, sheds dust particles from its nucleus during each passage through the inner solar system.
- This process creates a distinctive trail of debris along its path.
- In late October each year, Earth intersects this celestial trail, giving rise to the mesmerizing display known as the Orionid meteor shower.
- Measuring about five by nine miles in size, Halley's Comet undergoes a remarkable transformation, losing between three to ten feet of material with each journey through the inner solar system.
- The resulting debris becomes the source of the Orionid meteors.
- This celestial event offers a visual treat for observers in both the Northern and Southern hemispheres, particularly during the post-midnight hours.
- It provides an opportunity to witness the graceful streaks of light as the meteors traverse the night sky.
What are Meteors?
- Meteors, often referred to as "shooting stars," are a captivating manifestation of meteoroids entering Earth's atmosphere at high speed and subsequently burning up.
- Meteor showers, occurring annually or at regular intervals, are linked to the Earth passing through the dusty debris trail left behind by a comet.
- In the case of the Orionid meteor shower, the meteors are named after the constellation Orion, close to where these luminous streaks appear in the sky.
- This annual celestial event not only captivates observers with its dazzling display but also serves as a reminder of the dynamic interactions between Earth and the celestial bodies that grace our cosmic neighbourhood.
Microalgae are Adapting to Warming Climate (DownToEarth)
- 18 Oct 2023
Why in the News?
A recent study finds microalgae are firing up a light-responsive protein to use sunlight for growth.
What is the Microalgae?
- Microalgae are microscopic algae prevalent in freshwater and marine environments, consisting of unicellular species that can exist independently or in chains and groups.
- Comprising unicellular algal varieties such as green algae, diatoms, and dinoflagellates, these organisms exhibit sizes ranging from a few micrometres to several hundred micrometres.
- Their colour, determined by predominant pigments, categorizes them into groups like green, red, or brown.
- Unlike higher plants, microalgae lack roots, stems, or leaves, and they predominantly engage in photosynthesis, fueled by photosynthetic pigments.
- Heterotrophic microalgae, lacking these pigments, rely on other organisms for sustenance.
Significance:
- Microalgae play a foundational role in the aquatic food chain, offering vital nutrients for zooplankton, small fish, and various aquatic organisms.
- They serve as a primary food source for filter-feeding organisms.
- Moreover, photosynthetic microalgae contribute significantly to global carbon and oxygen cycles, absorbing carbon dioxide and generating oxygen through photosynthesis.
- Approximately half of atmospheric oxygen is produced by these organisms.
- Microalgae can also establish symbiotic relationships, as seen in their association with corals (zooxanthellae), providing nutrients through photosynthesis.
- Certain microalgae, like Nostoc, Anabaena, and Oscillatoria, exhibit nitrogen-fixing capabilities.
- Additionally, microalgae are rich in nutrients and can be consumed by humans. Notable examples like Spirulina and Chlorella are often utilized as dietary supplements.
What are Macroalgae?
- Macroalgae, commonly known as seaweeds, are marine plants engaging in photosynthesis but reproducing without flowers.
- Visible to the naked eye, in contrast to microalgae, they typically grow attached to the seabed or reef substrate.
- These macroscopic algae play crucial roles in reef ecosystems, providing both food and habitat for a diverse array of species while contributing significantly to nutrient dynamics.
Diphtheria Outbreak in Guinea (WHO)
- 18 Oct 2023
Why in the News?
The World Health Organization (WHO) has announced that Guinea's Health Ministry has officially notified them of a diphtheria outbreak.
What is Diphtheria?
- Diphtheria, an extremely contagious and infectious disease, instigates severe inflammation in the nose, throat, and trachea (windpipe).
- This ailment is caused by strains of bacteria known as Corynebacterium diphtheriae, which produce a potent toxin responsible for the onset of illness.
Causes:
- The bacterial infection spreads through various means, including respiratory droplets emitted during coughing or sneezing.
- Transmission can also occur through contact with infected open sores or ulcers. The bacteria's toxin is the primary culprit behind the illness.
Symptoms:
- Manifesting 2-5 days post-infection, symptoms of diphtheria encompass a thick, grey membrane covering the throat and tonsils, a sore throat, hoarseness, swollen glands in the neck, difficulty breathing, nasal discharge, fever, chills, and fatigue.
- If the toxin enters the bloodstream, it can lead to damage to the heart, nerves, and kidneys.
Infection and Spread:
- Diphtheria bacteria thrive on person-to-person transmission, emphasizing respiratory droplets as a common mode of contagion.
- Skin infections are possible but seldom result in severe disease.
Treatment:
- Combatting diphtheria involves a dual-pronged approach:
- Antitoxin (Anti-diphtheritic Serum): This neutralizes bacterial toxins and is specifically employed for respiratory system infections. The antitoxin acts on toxins that haven't bound with cells and tissues.
- Antibiotics (Erythromycin or Penicillin): These medications eradicate the bacteria, preventing further spread. Antibiotics are effective against both the respiratory system and skin infections caused by diphtheria.
RISC-V Technology (The Hindu)
- 18 Oct 2023
Why in the News?
Chip designer Qualcomm said on Tuesday it is partnering with Alphabet's Google to make wearable devices like smartwatches using chips based on RISC-V technology.
What is RISC-V Technology?
- RISC-V technology, colloquially pronounced as "risk five," stands as a pioneering open-source initiative in computer architecture.
- Functioning as an open-source Instruction Set Architecture (ISA), it serves as the foundation for crafting customized processors tailored to various end applications.
- Positioned as the fifth generation of processors rooted in the Reduced Instruction Set Computer (RISC) philosophy, RISC-V originated as a project at UC Berkeley.
- Initially conceived for academic purposes, it has since matured into a robust standard now overseen by RISC-V International.
- RISC-V operates as an open-standard architecture, with its definition shaped collaboratively by member companies associated with RISC-V International—a global nonprofit organization steering the ISA.
- This collaborative approach fosters innovation and design freedom among member companies, paving the way for groundbreaking advancements in processor technology.
- At its core, RISC-V features a concise set of instructions upon which all software designs run.
- This streamlined architecture empowers designers to tailor and construct processors in alignment with the specific requirements of their intended applications.
Key Advantages:
- The merits of RISC-V extend beyond its technical specifications. Its open-standard nature facilitates industry-wide collaboration and innovation, enabling diverse stakeholders to contribute to the evolution of processor technology.
- Moreover, the entire RISC-V architecture is subject to scrutiny in the public domain, mitigating concerns related to back doors and concealed channels.
Applications:
- RISC-V finds application across a broad spectrum of industries, including wearables, industrial processes, Internet of Things (IoT), home appliances, smartphones, automotive systems, high-performance computing (HPC), and data centres.
- Its versatility makes it a compelling choice for diverse technological landscapes, showcasing its adaptability and efficacy across various domains.
Life through geometry in Warli (The Hindu)

- 29 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
Warli Whisperers, an exhibition by the Inherited Arts Forum, traces the artistic journey of the celebrated Mashe family from Maharashtra.
About the Warli Art:
- Origin: Warli art is a tribal form originating from the North Sahyadri region of Maharashtra, with roots dating back to the 10th century AD.
- However, it gained recognition for its unique style in the early 1970s.
- Practitioners: Traditionally, Warli art was practiced by Suvasinis, the women of the Warli tribe, who adorned the Lagn Chowk or wedding square with their artistic expressions.
- Characteristics: Warli artists draw inspiration from nature, depicting scenes of farming, food gathering, village life, and elements from the natural world.
- These paintings are mainly dominated by basic geometric shapes like circles, triangles and squares.
- These geometric shapes stand as a symbol of natural elements in our environment.
- For example, the circles represent the sun and moon, the triangles represent the mountains and the squares are considered as the central motifs of the painting.
- Techniques and Materials: The paintings showcase triangles, circles, and lines in stark white against a mud brown background, narrating stories of village life, customs, and traditions.
- Modified bamboo sticks serve as paintbrushes, and the colours are derived from nature, such as brown and orange from henna, indigo from dye, red from bricks, and white from thick rice paste.
- Warli art serves as a vibrant portrayal of the everyday and social occurrences within the Warli tribe of Maharashtra, serving as a means to adorn the walls of village houses.
- Concerns: It was not recognised as an art form even though it was in practice for centuries.
Warli Tribe
- The Warli tribe, categorized as indigenous Adivasis, inhabit both the mountainous and coastal regions near the Maharashtra-Gujarat border.
- Their communication is conducted through an unwritten Varli language, classified within the southern zone of Indo-Aryan languages.
SC Collegium recommends names for Chief Justices of five High Courts (The Hindu)

- 29 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
The Supreme Court Collegium headed by Chief Justice of India D.Y. Chandrachud has recommended the appointment of Chief Justices to five High Courts.
What is the Collegium System?
- It is a system under which appointments and transfers of judges are done in the Supreme Court and High Courts.
- It is not rooted in the Constitution, iInstead, it has evolved through judgments of the Supreme Court.
- The Supreme Court Collegium, headed by the Chief Justice of India, consists of the court's four other most senior judges.
- Similarly, the High Court Collegium is chaired by its Chief Justice, along with the four other most senior judges of that specific high court.
Appointment of Judges: Constitutional Framework
- Constitutional Provision: Under Article 217, the President holds the authority to appoint judges of a high court.
- The appointment of the Chief Justice involves consultation with the Chief Justice of India and the respective state's governor.
- Similarly, consultation with the Chief Justice of the concerned high court is essential for appointing other judges.
- In cases where a high court serves multiple states, the President consults with the governors of all relevant states.
- No Minimum Age Requirement: The Constitution does not specify a minimum age for the appointment of high court judges.
- Qualifications of Judges: To qualify for a high court judge, an individual must:
- Be a citizen of India.
- Have held a judicial office within India's territory for ten years; or
- Have been an advocate of a high court (or successive high courts) for ten years.
Supreme Court Judgements:
- Second Judges Case (1993): The Supreme Court decreed that the appointment of a high court judge must align with the Chief Justice of India's opinion.
- Third Judges Case (1998): The Supreme Court emphasized that for the appointment of high court judges, the Chief Justice of India should consult a collegium comprising the two most senior judges of the Supreme Court.
- The consultation process involves more than the Chief Justice of India's individual opinion.
Is Pegasus spyware targeting journalists in India? (The Hindu)

- 29 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
Amnesty International and Washington Post recently announced that it has found the presence of Pegasus spyware, sold only to governments, on two Indian journalists’ phones.
What is Pegasus Spyware, and How Does it Infiltrate Devices?
- Pegasus is a sophisticated form of malware, covertly designed to gather information without the user's knowledge.
- Developer: Developed by the Israeli security firm NSO Group.
- Objectives: Pegasus serves three primary purposes:
- Collecting historical data on a device discreetly.
- Continuously monitoring user activities and gathering personal information.
- Transmitting the collected data to third parties.
Infiltration Mechanisms:
- Pegasus utilizes "zero-click exploits," exploiting vulnerabilities in popular apps like iMessage and WhatsApp.
- Notably, zero-click exploits require no user interaction, differentiating them from typical cyberattacks.
- Network injection attacks are another method employed by Pegasus, where unsecured websites are used to infiltrate devices within milliseconds of the user's visit.
What is a Zero-click exploit?
- A zero-click exploit involves the installation of malicious software on a device without the device owner's consent.
- Notably, it does not require any action from the device owner to initiate or complete the installation.
Specific Exploit in the Recent Case with Indian Journalists:
- The particular exploit reportedly used in the incidents is known as BLASTPAST (previously identified as BLASTPASS), unfolding in two phases.
- Initial Phase: The attack aims to establish a connection with Apple HomeKit, a platform enabling users to control various smart devices on their network.
- The primary objective of this phase might be to assess how the device could be vulnerable to exploitation or to maintain visibility for potential future attacks.
- Second Phase: Malicious content is sent through the iMessage app to the target device.
- This stage is pivotal as it delivers the complete spyware payload, enabling extensive surveillance and data collection.
Mines Ministry unveils draft rules for offshore minerals auction (The Hindu Business Line)

- 29 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
India’s Mines Ministry has proposed a new set of rules for the auction of offshore mineral blocks. It is also in the process of identifying such mineral blocks, including those in exclusive economic zones beyond territorial waters.
Context:
- To implement the amended Offshore Areas Mineral (Development & Regulation) Act, 2002 (OAMDR Act), the ministry has unveiled two draft rules:
- Offshore Areas Mineral Auction Rules: These rules delineate provisions governing the auctioning of production leases.
- Offshore Areas Existence of Mineral Resources Rules: These rules set forth norms for the exploration of minerals and deposits in offshore areas.
Offshore Areas Mineral (Development & Regulation) Act, 2002 (OAMDR Act):
- The OAMDR Act governs the development and regulation of mineral resources in India's territorial waters, continental shelf, exclusive economic zones, and other maritime zones.
About Offshore Areas Minerals (Development and Regulation) Amendment Bill, 2023:
- The Bill proposes amendments to the Offshore Areas Mineral (Development and Regulation) Act, 2002, governing mining activities in India's maritime zones.
Key highlights include:
- Empowering the government to reserve offshore areas without operating rights.
- Granting the administering authority the discretion to issue composite licenses or production leases to the government or a government company.
- Eliminating the provision for renewing production leases and setting a fixed fifty-year period, aligning with the Mines and Minerals (Development and Regulation) Act, 1957.
- Mandating the grant of production leases to the private sector through competitive bidding.
- Allowing non-competitive bidding for operating rights in mineral-bearing areas reserved by the central government for government entities or corporations.
- Restricting the grant of exploration licenses or production leases for atomic minerals to government or government corporations.
- Introducing a four-year timeline for the commencement of production and dispatch after executing a composite license or production lease, with a two-year timeline (extendable by one year) for re-commencement after discontinuation.
- Authorizing the central government to establish rules for mineral conservation, systematic development, and environmental protection in offshore areas, preventing or controlling pollution from exploration or production operations.
India's Maritime Zone Mineral Resources:
- India's maritime zone hosts diverse mineral resources, including lime mud off the Gujarat and Maharashtra coasts within the Exclusive Economic Zone (EEZ).
- Additionally, the region boasts construction-grade sand along the Kerala coast and heavy mineral placers in the inner-shelf and mid-shelf regions off Odisha, Andhra Pradesh, Kerala, Tamil Nadu, and Maharashtra.
- Phosphorite is found in the Eastern and Western continental margins, while the Andaman Sea and Lakshadweep Sea house Polymetallic Ferromanganese (Fe-Mn) nodules and crusts.
Govt issues PMLA notice to Binance, 8 other offshore crypto firms, asks IT Min to block URLs (Indian Express)

- 29 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
India's Financial Intelligence Unit has issued show cause notices to nine offshore crypto-currency operators, including Binance, for not complying with the anti-money laundering PML Act.
About the Financial Intelligence Unit India:
- Financial Intelligence Unit – India (FIU-IND) was set by the Government of India in November 2004 as the central national agency responsible for receiving, processing, analyzing and disseminating information relating to suspect financial transactions.
- FIU-IND is also responsible for coordinating and strengthening efforts of national and international intelligence, investigation and enforcement agencies in pursuing the global efforts against money laundering and financing of terrorism.
- It is an independent body reporting directly to the Economic Intelligence Council (EIC) headed by the Finance Minister.
Key Functions of FIU-IND:
- Information Collection: Act as the central hub for receiving various reports, including Cash Transaction Reports (CTRs), Non-Profit Organisation Transaction Reports (NTRs), Cross Border Wire Transfer Reports (CBWTRs), Reports on the Purchase or Sale of Immovable Property (IPRs), and Suspicious Transaction Reports (STRs) from diverse reporting entities.
- Information Analysis: Analyze the received information to unveil transaction patterns indicative of potential money laundering and associated criminal activities.
- Information Sharing: Collaborate by sharing intelligence with national intelligence/law enforcement agencies, national regulatory authorities, and foreign Financial Intelligence Units, fostering a collective effort against financial crimes.
- Central Repository: Establish and maintain a national database by consolidating reports received from reporting entities.
- Coordination: Strengthen the collection and sharing of financial intelligence through efficient national, regional, and global networks to combat money laundering and related crimes.
- Research and Analysis: Conduct ongoing monitoring and identification of strategic areas related to money laundering trends, typologies, and developments.
What are Virtual Digital Assets?
- As per the Income Tax Act, a 'virtual digital asset' is described as any information, code, number, or token (excluding Indian currency or foreign currency) generated through cryptographic means and blockchain technologies.
- These assets can be electronically transferred, stored, or traded.
- The definition explicitly covers non-fungible tokens (NFTs) or tokens of a similar nature, regardless of nomenclature.
Forest Department Relies on Muthuvan Tribe's Indigenous Knowledge for Nilgiri Tahr Conservation (The Hindu)

- 17 Oct 2023
Why in the News?
Members of the Muthuvan tribe of the Anamalai hills, who are known for coexisting with the wildlife with their traditional knowledge, have joined hands with the Tamil Nadu Forest Department for a unique task.
About the Muthuvan Tribe:
- Inhabiting the border hill forests of Kerala and Tamil Nadu, the Muthuvan tribe is distributed across this region.
- The tribe communicates in distinct dialects, identifying themselves as Malayalam Muthuvan and Pandi Muthuvan.
- Cultural Beliefs: Embracing animism and spirit worship, the Muthuvan tribe venerates forest gods and attributes the spirits of their ancestors as the initial settlers in the hill forests.
- Renowned for their harmonious coexistence with wildlife, the Muthuvan people leverage traditional knowledge to navigate their relationship with the natural environment.
- Unique Governance System - 'Kani System': Operating under the 'Kani System,' each village is overseen by a 'Kani' responsible for village administration, reflecting their distinctive form of governance.
- Traditional Medicine Expertise: Proficient in traditional medicines, the Muthuvan tribe safeguards their effective remedies, preserving and passing down this knowledge across generations.
- Occupation: Agriculture serves as the primary occupation for Muthuvan tribes, yielding various products such as ragi, cardamom, and lemongrass.
About Project Tahr:
- Project Tahr aims to enhance comprehension of the Nilgiri Tahr population through surveys and radio telemetry studies.
- The initiative focuses on reintroducing Tahrs to their historical habitat, fostering their return to natural landscapes.
- Addressing immediate threats, the project employs strategic measures to mitigate challenges facing the Nilgiri Tahr.
- A key component involves intensifying public awareness efforts to garner support and understanding for the conservation of this species.
- Project Tahr is slated for a comprehensive 5-year implementation, spanning from 2022 to 2027.
INS Sumedha Visits Nigeria as part of its deployment to the Gulf of Guinea (PIB)

- 17 Oct 2023
Why in the News?
Indian Naval Ship INS Sumedha recently made a port visit at Lagos, Nigeria as part of its deployment to the Gulf of Guinea (GoG).
About INS Sumedha:
- INS Sumedha is the third vessel among the indigenously crafted Saryu-class Naval Offshore Patrol Vessels (NOPV).
- Constructed and designed domestically, Goa Shipyard Limited played a pivotal role in the indigenous creation of INS Sumedha.
- The vessel officially joined the Indian Navy's fleet on March 7, 2014.
- Operational Base: A key asset of the Indian Navy's Eastern Fleet, INS Sumedha operates from its base in Visakhapatnam.
- Primary Functions: The vessel is tasked with a diverse range of functions, including EEZ surveillance, anti-piracy patrols, fleet support operations, maritime security provision to offshore assets, and execution of escort operations for high-value assets.
- Features:
- With a displacement of 2,230 tonnes, INS Sumedha boasts dimensions of 105 meters in length and 12.9 meters in beam.
- Equipped with a cutting-edge weapon and sensor package, the vessel ensures enhanced operational capabilities.
- Designed to carry an Advanced Light Combat Helicopter onboard, adding to its versatility in maritime operations.
- Powered by two of the largest diesel engines deployed in the Indian Navy, INS Sumedha attains a top speed of 25 knots.
- Featuring a remarkable range of 6,000 nautical miles (11,000 km) at 16 knots (30 km/h), the offshore patrol vessel is well-suited for prolonged missions and operations.
About the Gulf of Guinea:
- Location: Situated as the northeasternmost part of the tropical Atlantic Ocean, the Gulf of Guinea is positioned off the western coast of the African continent.
- The Gulf lies at the confluence of the Prime Meridian and the Equator, specifically at 0°0’N and 0°0'E.
- Extent and Coastline: Encompassing an area of 2.3 million square kilometres, the Gulf features an extensive coastline stretching approximately 6,000 kilometres.
- Characterized by a narrow continental shelf, it boasts a distinctive coastal landscape.
- Oceanic Conditions: The Gulf of Guinea experiences warm tropical waters characterized by relatively low salinity, influenced by the inflow of rivers and high regional rainfall.
- Notable tributaries include the Volta and Niger rivers.
- Coastal Countries: 16 countries border the Gulf of Guinea, including Angola, Benin, Cameroon, Cote d'Ivoire, Democratic Republic of Congo, Republic of Congo, Guinea, Equatorial Guinea, Guinea-Bissau, Gabon, Nigeria, Ghana, São Tomé and Principe, Togo, and Sierra Leone.
- Topography: The coastal region is predominantly low-lying, featuring mangrove swamps, marshes, and lagoons.
- Geological Significance: The Gulf's coastline bears a striking resemblance to the continental margin of South America, affirming the theory of continental drift.
- Holding over 35% of the world’s petroleum reserves, the Gulf of Guinea is a significant global repository of petroleum.
- Security Challenges: Regrettably, the Gulf of Guinea has gained notoriety as one of the world’s most perilous gulfs due to widespread piracy, significantly impacting West African countries and attracting international concern.
BCCC Cautions Entertainment Channels on Depicting SCs, STs. (Business Standard)

- 17 Oct 2023
Why in the News?
The Broadcasting Content Complaint Council (BCCC) on Tuesday asked entertainment channels to exercise "extreme caution" while portraying the scheduled castes and scheduled tribes in television programmes to avoid hurting the sentiments of the members of the two communities.
About the Broadcasting Content Complaints Council (BCCC):
- The Indian Broadcasting and Digital Foundation (IBDF) established the BCCC in June 2011 as an independent self-regulatory body.
- Regulatory Role: The primary function of the BCCC is to enforce self-regulatory guidelines for non-news channels, covering general entertainment, kids, and special interest channels.
- Formulation of Guidelines: Guidelines address crucial areas, including national interest, racial and religious harmony, treatment of children, social values, explicit content (sex and nudity), violence, crime, gambling, drugs, smoking, tobacco, alcohol, defamation, harm, and offence.
- Complaint Lodging Process: Any viewer can file a complaint regarding television programs, non-news channels, and digital content of IBDF India members.
- Composition of BCCC:
- The council comprises 13 members, including a chairperson, four non-broadcast members, four representatives from national-level statutory commissions, and four members from the broadcast industry.
- Functioning Mechanism: Upon receiving a valid complaint, the concerned channel is required to present its viewpoint on the contested content within one working week.
- If the BCCC committee finds the channel's response unsatisfactory, it holds the authority to issue directives, mandating modifications or withdrawal of the content.
- Reporting to Authorities: In case of non-compliance with directives, the BCCC promptly submits a detailed report to the Ministry of Information and Broadcasting within 24 hours.
Key Details about the Indian Broadcasting & Digital Foundation (IBDF):
- Founded in 1999, the Indian Broadcasting Foundation initially served as the apex body for broadcasters.
- Recently rebranded as the Indian Broadcasting and Digital Foundation (IBDF) to encompass digital platforms, consolidating oversight over all digital over-the-top streaming firms.
- Representative Role: Recognized as the official spokesperson for the Indian broadcasting industry, IBDF plays a crucial role in articulating industry perspectives.
- IBDF's membership includes a diverse range of channels, covering both news and non-news categories such as General Entertainment Channels (GEC), sports, music, movies, and infotainment.
- Actively involved in providing research-based legislative inputs to the government, IBDF engages in advocacy efforts on various fronts, including fiscal, regulatory, and business issues.
- The organization plays a pivotal role in facilitating the formulation of favourable policies, addressing industry challenges, and advocating for essential changes in the overall system.
New Plant Species Curcuma kakchingense Discovered in Manipur (HT)

- 17 Oct 2023
Why in the News?
In a remarkable botanical discovery, a team of researchers from the Department of Life Sciences at Manipur University and Kwaklei and Khonggunmelei Orchids Pvt. Ltd. has unveiled a hitherto unknown plant species named "Curcuma kakchingense."
About Curcuma Kakchingense:
- Recently identified flowering plant species in Manipur, belong to the Zingiberaceae family.
- Member of the angiospermic family Zingiberaceae, which includes well-known plants like turmeric, gingers, and cardamom.
- Plant Characteristics: Robust plant reaching a height of eight feet, characterized by large terminal inflorescence.
- Natural Habitat: Thrives along the banks of the Sekmai River in the Kakching District of Manipur.
- Resemblance to Other Species: Bears a striking resemblance to local "Yaingung" (Curcuma longa) and Curcuma phrayawan from Thailand.
- Distinguished by lemon-yellow rhizomes with a notably bitter taste.
- IUCN Red List Classification: Classified as "Data Deficient" (DD) under the IUCN Red List category.
Importance of Curcuma Plants:
- Culinary and Traditional Uses: Various Curcuma species, including turmeric (Curcuma longa), play a vital role in cuisines, traditional medicines, spices, and dyes.
- Biological Activities: Curcumin and curcuminoids found in Curcuma species are nontoxic polyphenolic compounds with diverse biological activities.
- Pharmacological Properties: Essential oil of Curcuma species possesses pharmacological properties, including anti-inflammatory, anti-cancerous, anti-diabetic, and anti-microbial effects.
- Versatile Applications: Widely utilized in cosmetics, perfumes, and as ornamental plants, contributing to various industries and daily life.
New Artificial Intelligence System BTSbot Discovers Supernova (India Today)

- 17 Oct 2023
Why in the News?
An international team led by Northwestern University has successfully created an artificial intelligence (AI) tool Bright Transient Survey Bot (BTSbot) that can detect, identify, and classify supernovae.
What is the Bright Transient Survey Bot (BTSbot)?
- The Bright Transient Survey Bot operates as a machine-learning algorithm, undergoing training with a vast dataset comprising over 1.4 million images from nearly 16,000 sources.
- Utilizing data from the Zwicky Transient Facility (ZTF), it successfully identified the recently discovered supernova named SN2023tyk.
- Functionality: The algorithm seamlessly automates the process of seeking potential supernovae across the night sky.
- In the case of SN2023tyk, it autonomously requested the supernova's spectrum from the Palomar Observatory.
- Subsequently, the Spectral Energy Distribution Machine (SEDM), another robotic telescope, performed comprehensive observations to obtain the source's spectrum.
- Advantages: This innovative system not only streamlines the entire workflow of searching, detecting, confirming, classifying, and announcing new supernovae but also eradicates human error, significantly enhancing the speed of the process.
- The Bright Transient Survey Bot showcases the potential of automated technology in advancing astronomical discoveries.
What is artificial intelligence?
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) refers to the interdisciplinary field of computer science dedicated to developing algorithms and computational models that emulate human cognitive processes.
- Rooted in machine learning and advanced data analytics, AI aims to create systems capable of reasoning, problem-solving, and decision-making.
- AI involves the study and design of intelligent agents, encompassing areas like natural language processing, computer vision, and expert systems.
- It seeks to enhance machines' ability to learn from experience, adapt to new information, and perform tasks that traditionally necessitate human intelligence, fostering innovation across diverse domains, including healthcare, finance, and robotics.
Chennai's Pallikaranai Wetlands Welcoming Migratory Bird Flocks (The Hindu)

- 16 Oct 2023
Why in the News?
With over 150 garganeys, and several other species, including waders and raptors, flocking the Pallikaranai marshland, the curtain for the migratory season has been raised.
About Pallikaranai Marshland:
- Location: Pallikaranai marshland is a freshwater and partly saline wetland, located approximately 20 kilometres south of Chennai, Tamil Nadu.
- The eastern border of the marsh is flanked by the Buckingham Canal.
- Rich Ecosystem: The diverse ecosystem of Pallikaranai supports an impressive array of wildlife, including 115 bird species, 10 mammals, 21 reptiles, 10 amphibians, 46 fish, nine molluscs, five crustaceans, and seven butterfly species.
- Notable Species: Among the diverse wildlife are noteworthy species such as the Russell’s viper (Daboia siamensis), glossy ibis (Plegadis falcinellus), grey-headed lapwings (Vanellus cinereus), and Pheasant-tailed jacana (Hydrophasianus chirurgus).
- Biodiversity Significance: Beyond its biodiversity, the marshland serves a crucial role in flood prevention for Chennai, absorbing water during wet periods and releasing it during dry spells.
- Environmental Threats: Despite its ecological importance, the site faces threats from invasive non-native species, household sewage, urban wastewater, and periodic droughts.
- Ramsar Designation: Acknowledging its ecological significance, Pallikaranai marshland holds the status of being one of India's Ramsar sites, recognized for its importance in wetland conservation on an international scale.
INS Beas to Be Upgraded (PIB)

- 16 Oct 2023
Why in the News?
The Ministry of Defence signed a contract on October 16, 2023, in New Delhi for the life Upgrade and Re-Powering of "INS Beas" with Kochi-based M/S Cochin Shipyard Limited (CSL) at an overall cost of Rs. 313.42 Cr.
Context:
- The INS Beas is gaining attention as the first Brahmaputra Class Frigate to undergo a transition from steam to diesel propulsion.
- The completion of its Mid-Life Upgrade and Re-Powering in 2026 is expected to result in the INS Beas joining the active fleet of the Indian Navy, equipped with a modernized weapon suite and upgraded combat capabilities.
About INS Beas:
- INS Beas (F37) stands as a Brahmaputra-class frigate within the Indian Navy, constructed at the Garden Reach Shipbuilders and Engineers (GRSE) in Kolkata.
- Commissioned on July 11, 2005, it is the second ship in the Indian Navy to carry this name, with the first being a Leopard-class frigate commissioned in 1960 and decommissioned in 1992.
- Role: Functioning as a versatile warship, INS Beas is proficient in various missions, encompassing anti-aircraft, anti-submarine, and anti-ship warfare.
- Additionally, it plays a crucial role in patrolling, surveillance, and safeguarding India's maritime interests.
- Features: The ship's design and construction are wholly Indian, derived from the modification of the Godavari-class frigate.
- With a displacement of about 3,850 tonnes, INS Beas boasts a length of 126 meters (413 feet) and a beam width of 14.5 meters (48 feet).
- Propulsion: Powered by 2 steam turbines, INS Beas demonstrates remarkable agility, capable of reaching speeds exceeding 30 knots during naval operations.
- Technology: Equipped with modern sensor suites and matching weapon systems, the ship embodies cutting-edge technology to enhance its operational capabilities.
Amazon River Hits Lowest Levels in a Century Amid Drought in Brazil (Business Standard)

- 16 Oct 2023
Why in the News?
The Amazon River fell to its lowest level in over a century on Monday at the heart of the Brazilian rainforest as a record drought upended the lives of hundreds of thousands of people and damaged the jungle ecosystem.
About the Amazon River:
- The Amazon River holds the distinction of being the world's largest river in terms of both water volume and width.
- Length and Course: Spanning an impressive 6,400 kilometres, it is the second-longest river globally, surpassed only by the Nile.
- Originating high in the Andes Mountains, the river courses its way eastward through vast rainforests and lowlands before reaching its culmination at the northeastern coast of Brazil, where it empties into the Atlantic Ocean.
- Dynamic Width: During the dry season, the Amazon River exhibits a width ranging from 4 to 5 kilometres, expanding significantly to 50 kilometres in certain areas during the wet season.
- Unparalleled Drainage Area: The Amazon boasts the largest drainage area globally, with its watershed spanning across Brazil, Peru, Ecuador, Colombia, Venezuela, and Bolivia.
- Approximately two-thirds of the Amazon's mainstream and the majority of its basin lie within the borders of Brazil.
- Water Discharge and Global Impact: With a staggering water discharge of 300,000 cubic meters per second into the Atlantic Ocean, the Amazon contributes one-fifth of the total freshwater volume entering the world's oceans.
- This immense water flow plays a pivotal role in regulating global oxygen and carbon cycles.
- Extensive Tributaries: Featuring over 1,100 tributaries, including seventeen exceeding 1,500 kilometres in length, notable contributors include the Rio Negro, the Madeira River, and the Xingu River.
- Environmental Significance: The Amazon Rainforest, constituting approximately half of the Earth's remaining rainforest, stands as the largest repository of biological resources.
- Often referred to as the "lungs of the Earth," the Amazon plays a crucial role in maintaining the planet's oxygen and carbon balance.
US Says Egypt Border Crossing to Gaza to Reopen (Business Today)
- 16 Oct 2023
Why in the News?
Hundreds of tons of aid from multiple countries have been stationed in Egypt's Sinai Peninsula, awaiting an agreement for secure transportation to Gaza for several days.
About the Sinai Peninsula:
- Geographical Location: The Sinai Peninsula is a triangular landmass located in northeastern Egypt, serving as a critical land bridge that connects the continents of Asia and Africa.
- Size and Sovereignty: Encompassing an expansive area of 23,500 square miles (61,000 square km), the Sinai Peninsula is recognized as a sovereign territory within the boundaries of Egypt.
- Geographical Boundaries: It is bordered to the north by the Mediterranean Sea and to the east by Israel and the Gaza Strip.
- The Suez Canal lies to the west, acting as a separation from the African part of Egypt.
- To the southwest, the Gulf of Suez and the Red Sea border the peninsula, while the Gulf of Aqaba marks its southeastern boundary.
- Egypt shares maritime borders in the Sinai with Jordan and Saudi Arabia.
- Historical Significance: In the late 19th century, including the Sinai Peninsula, Egypt became part of the British Empire until gaining independence in 1922.
- During the Six-Day War of June 1967, the peninsula was occupied by Israeli forces and returned to Egypt in 1982 as part of the peace treaty signed in 1979.
- Diverse Geography: The Sinai Peninsula is characterized by a diverse landscape, featuring mountain ranges, deserts, plateaus, and coastal regions.
- Population Composition: With a relatively sparse population, the Sinai is home to about 600,000 people, predominantly consisting of Arab Egyptians and Bedouins.
Hailstorms Damage Apple Orchards in Kulgam, Shopian (HT)

- 16 Oct 2023
Why in the News?
A hailstorm in the evening caused massive damage to the crops and fruits in south Kashmir’s Kulgam and Shopian districts. Residents said the hailstorm damaged the apple fruit which was ready for harvesting.
What are Hailstorms?
- Hail, a solid form of rain composed of ice balls or lumps, leads to the formation of hailstorms when they descend to the ground.
- Typically lasting around 15 minutes, these storms can inflict injuries and damage to structures, vehicles, and more, particularly prevalent in midlatitude regions.
- Hailstorms occasionally coincide with other severe weather phenomena such as cyclones and tornadoes.
- The size of hailstones varies widely, ranging from small pellets under 1/4 inch to larger stones measuring several inches in diameter.
- Conditions: Conditions conducive to hailstorm occurrence involve the presence of highly developed Cumulonimbus clouds, massive anvil-shaped formations observed during thunderstorms that can reach heights of up to 65,000 feet.
- Strong updrafts, or ascending air currents within these clouds, and high concentrations of supercooled liquid water are essential elements.
- Formation of Hail: Hail formation begins with a water droplet lifted by an updraft inside a thundercloud.
- As it ascends, supercooled water droplets adhere to its surface, creating layers of ice.
- With continued ascent, the hail embryo grows by accumulating more supercooled particles until gravity pulls it down.
- Large hailstones often display alternating layers of clear and opaque ice due to irregular rates of freezing during their development.
Vice President Interacted With Inter-Parliamentary Union (IPU) President During P20 Summit (PTI)

- 14 Oct 2023
Why in the News?
Vice President Jagdeep Dhankhar recently hosted a lunch for heads of parliamentary delegations attending the G20 Parliamentary Speakers' Summit (P20) and also interacted with Inter-Parliamentary Union (IPU) President Duarte Pacheco.
About the Inter-Parliamentary Union (IPU):
- Established in 1889 in Paris, the Inter-Parliamentary Union (IPU) is the international organization of Parliaments, dedicated to promoting representative democracy and world peace.
- It serves as the first multilateral political organization globally, fostering cooperation and dialogue among all nations.
- Mission and Slogan: The IPU's mission revolves around parliamentary diplomacy, empowering parliaments, and parliamentarians to advance peace, democracy, and sustainable development worldwide.
- Its slogan, "For democracy. For everyone," encapsulates its commitment to democratic values.
- Membership and Promotion of Democracy: Currently comprising 179 member parliaments and 13 associate members, the IPU actively promotes democracy by strengthening parliaments, and fostering youth inclusion, gender balance, and diversity.
- A dedicated committee defends the human rights of parliamentarians globally.
- Headquarters and Funding: The IPU relocated its headquarters to Geneva in 1921.
- Financed primarily by its members using public funds, the organization sustains its operations and initiatives.
Organizational Structure:
- IPU Assembly: Principal statutory body expressing IPU views on political issues.
- Gathers parliamentarians to study international problems and make actionable recommendations.
- Governing Council: Plenary policymaking body composed of three representatives from each member parliament.
- Establishes the IPU's annual program, and budget, and considers substantive issues.
- Executive Committees: A 17-member body overseeing IPU administration and advising the Governing Council.
- Fifteen members elected by the Council for a four-year term.
- Standing Committees: Three committees set up by the Governing Council to assist the Assembly in its work.
- Meeting of Women Parliamentarians: A separate organ meeting during the first round of Statutory Meetings, reporting to the Governing Council.
- Attended by parliamentarians of both sexes, focusing on specific substantive items for debate within the Assembly's competence.
India, Sri Lanka Launch Ferry Service Across Palk Strait (The Hindu)

- 14 Oct 2023
Why in the News?
An international, high-speed passenger ferry service between Nagapattinam on the eastern coast of Tamil Nadu and Kankesanthurai in the northern province of Sri Lanka, has resumed as of Saturday, October 14, 2023, after a gap of nearly four decades.
About the Palk Strait:
- Palk Strait, situated between the Indian state of Tamil Nadu and the island nation of Sri Lanka, derives its name from Robert Palk, the governor of Madras Presidency (1755-1763) during the British Raj.
- Bounded by Pamban Island (India), Adam's (Rama's) Bridge, the Gulf of Mannar, and Mannar Island (Sri Lanka) to the south, the strait serves as a crucial link connecting the Bay of Bengal in the northeast with the Gulf of Mannar in the southwest.
- The southwestern segment of the strait is referred to as Palk Bay.
- Spanning 40 to 85 miles (64 to 137 km) in width, 85 miles in length, and with a depth of less than 330 feet (100 meters), it features the inflow of several rivers, including Tamil Nadu's Vaigai River.
- The port of Jaffna, serving as the commercial hub for northern Sri Lanka, is situated along this significant waterway.
Facts About Adam's Bridge:
- Adam's Bridge, also recognized as Rama's Bridge or Rama Setu, constitutes a series of limestone shoals situated between Pamban Island (Rameswaram Island) off the south-eastern coast of Tamil Nadu, India, and Mannar Island off the north-western coast of Sri Lanka.
- Geological evidence supports the idea that this bridge once formed a land connection between India and Sri Lanka.
- Extending over 50 km, it delineates the separation between the Gulf of Mannar to the southwest and the Palk Strait to the northeast.
- Featuring dry sandbanks and shallow waters ranging from 1 to 10 meters in depth, hindering navigation, scientists posit that Ram Setu is a natural formation resulting from tectonic movements and the entrapment of sand in corals.
- Significantly, this structure holds cultural significance in Hindu and Muslim mythology.
- Hindus believe it to be the bridge constructed by Lord Ram and his army for their journey to Lanka to confront Ravan.
- According to Islamic legend, Adam traversed this bridge to reach Adam’s Peak in Sri Lanka, where he purportedly stood on one foot in repentance for 1,000 years.
Manipur to Conduct Census of Amur Ffalcon (The New Indian Express)

- 14 Oct 2023
Why in the News?
The Manipur Forest Department will conduct the first-ever Amur falcon census. This initiative in India is one of the several programs the agency is running to safeguard migrating birds.
About Amur Falcon:
- The Amur Falcon, a diminutive member of the falcon family locally known as Akhuipuina, predominantly frequents Manipur and Nagaland.
- Originating from southeastern Siberia and northern China, these birds embark on extensive migrations in vast formations to winter in Southern and East Africa, covering a one-way journey of approximately 20,000 km through India twice a year.
- In terms of conservation, the Amur Falcon is safeguarded by the Wildlife Protection Act of 1972, listed under Schedule IV.
- Hunting or possession of its meat is subject to legal repercussions, including imprisonment for up to three years, a fine of up to 25,000, or bonds.
- Initiating a conservation effort in 2018, the forest department employed radio tagging to study the birds' migratory routes.
- As per the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN), the Amur Falcon is categorized as "Least Concern."
- Despite this, the species faces threats such as illegal trapping and killing during migration, along with habitat loss due to agricultural practices and land reclamation.
Egypt is Racing to Eliminate Hepatitis C (The Hindu)
- 14 Oct 2023
Why in the News?
Recently the WHO announced that Egypt had made “unprecedented progress” towards eliminating hepatitis C.
Context:
- As per the World Health Organization (WHO), Egypt has attained a significant milestone by becoming the inaugural country to reach the "gold tier" status in its pursuit of eliminating hepatitis C, meeting the criteria established by the global health organization.
- Egypt has successfully identified 87% of individuals with hepatitis C and has administered curative treatment to 93% of those diagnosed, surpassing the WHO's gold-tier benchmarks.
- These targets include diagnosing a minimum of 80% of individuals with hepatitis C and offering treatment to at least 70% of those identified, marking a commendable achievement for Egypt in the global effort against the disease.
What is Hepatitis C?
- Hepatitis C is a viral infection impacting the liver, causing both acute (short-term) and chronic (long-term) illnesses that can be life-threatening.
- Transmission occurs through contact with infected blood, such as sharing needles, unsafe medical procedures like unscreened blood transfusions, and vertical transmission from an infected mother to her baby.
- It can also be transmitted through certain sexual practices involving blood exposure.
- Contrary to misconceptions, Hepatitis C is not spread through breast milk, food, water, or casual contact like hugging, kissing, or sharing food/drinks with an infected person.
- Symptoms encompass fever, fatigue, loss of appetite, nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, dark urine, and jaundice (yellowing of the skin or eyes).
- Geographically, this viral infection is present in all WHO regions, with the Eastern Mediterranean Region and European Region bearing the highest disease burden.
- New infections often lack symptoms, making diagnosis challenging, and chronic infections may remain asymptomatic for decades until severe liver damage prompts noticeable symptoms.
- While no vaccine exists for Hepatitis C, antiviral medications offer effective treatment options.
What is Gold Tier Status?
- Gold tier status involves fulfilling distinct criteria, which encompass:
- Guaranteeing 100% blood and injection safety, with a commitment to maintaining a minimum of 150 needles/syringes annually for individuals who inject drugs (PWID).
- Achieving a diagnosis rate of over 80% for individuals living with chronic hepatitis C virus (HCV).
- Providing treatment to over 70% of individuals diagnosed with HCV.
- Instituting a sentinel surveillance program for hepatitis sequelae, with a focus on conditions such as liver cancer.
Centre Notifies Green Credit Programme and Ecomark Scheme (DownToEarth)

- 14 Oct 2023
Why in the News?
The Union Ministry of Environment, Forests and Climate Change on October 13, 2023, notified the ‘green credit’ programme, a first-of-a-kind market-based instrument designed to incentivise individuals, industries and local bodies for their voluntary environmental actions across diverse sectors.
About Green Credit Programme (GCP):
- Green Credit Program (GCP ) is an innovative market-based mechanism designed to incentivize voluntary environmental actions across diverse sectors, by various stakeholders like individuals, communities, private sector industries, and companies.
- The GCP's governance framework is supported by an inter-ministerial Steering Committee and The Indian Council of Forestry Research and Education (ICFRE) serves as the GCP Administrator, responsible for program implementation, management, monitoring, and operation.
- In its initial phase, the GCP focuses on two key activities: water conservation and afforestation.
- A user-friendly digital platform will streamline the processes for registration of projects, verification, and issuance of Green Credits.
- The Green Credit Registry and trading platform, being developed by ICFRE along with experts, would facilitate the registration and thereafter, the buying and selling of Green Credits.
- To obtain Green Credits, individuals and entities must register their activities through the central government's dedicated app/website www.moefcc-gcp.in.
- The Administrator will verify the activity through a designated agency, with self-verification for small projects.
- Once verification is complete, the Administrator will grant a Green Credit certificate which will be tradable on the Green Credit platform.
What is the Ecomark Scheme?
- The Ecomark Scheme provides accreditation and labelling for household and consumer products that meet specific environmental criteria while maintaining quality standards as per Indian norms.
- Products accredited under the Ecomark Scheme will adhere to specific environmental criteria, ensuring minimal environmental impact.
- It will build consumer awareness of environmental issues and encourage eco-conscious choices.
- It will also motivate manufacturers to shift towards environmentally friendly production. The scheme seeks to ensure accurate labelling and prevent misleading information about products.
- The Central Pollution Control Board administers the Ecomark Scheme in partnership with the Bureau of Indian Standards (BIS), which is the national body for standards and certification.
Both initiatives mark significant steps in promoting sustainable living, and environmental conservation, and, through individual and collective choice, embody eco-friendly practices in India. They align with global sustainability goals and reflect the government's commitment to conservation and protection of the environment.
A New Discovery: Unveiling an Underwater Mountain Range in the Southern Ocean (India Today)

- 28 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
Scientists have discovered an ancient underwater mountain range hidden within the world's strongest ocean current, the Antarctic Circumpolar Current.
Context:
- During a recent research expedition, scientists discovered a previously unknown mountain range deep beneath the Southern Ocean’s surface.
- Using state-of-the-art sonar technology, researchers were able to map out the underwater landscape with astonishing accuracy, revealing a vast range of peaks, ridges, and valleys.
- This newfound mountain range spans hundreds of miles and is estimated to be millions of years old.
- Geological Significance: This discovery holds immense importance for our understanding of the Earth’s geological history.
- The underwater mountain range provides key evidence of plate tectonics and the movement of Earth’s crust, as well as the formation of new landmasses.
- By studying the composition and structure of these underwater formations, scientists will be able to gain insights into the geological processes that have shaped our planet over millions of years.
- Moreover, the discovery raises intriguing questions about the relationship between underwater mountains and the surface landscapes they may be connected to.
- Researchers are eager to investigate whether similar mountain ranges exist on land and whether they share a common origin.
- Implications for Climate and Ecosystems: The newfound underwater mountain range also has significant implications for climate and marine ecosystems.
- These underwater peaks can act as barriers, influencing ocean currents and affecting nutrient distribution.
- Understanding the impact of these formations on ocean dynamics is crucial for predicting climate patterns and better managing marine resources.
- Additionally, these underwater mountains create a unique habitat for a diverse range of marine species.
- The ridges and valleys provide sheltered zones where marine life can thrive, with the potential for new species discoveries.
- Protecting these habitats will be critical in preserving the delicate balance of marine ecosystems.
About the Southern Ocean:
- The Southern Ocean, also referred to as the Antarctic Ocean is one of the Earth's five major ocean basins.
- Its formation traces back approximately 34 million years when Antarctica and South America underwent a gradual separation, resulting in the creation of the Drake Passage.
- This passage, situated between the tip of the Antarctic Peninsula and South America, delineates the Southern Ocean from the Pacific, Atlantic, and Indian Oceans, encompassing their tributary seas surrounding Antarctica below the 60° S latitude.
- Physiography: The ocean floor structure features a continental shelf, typically less than 160 miles (about 260 km) wide, expanding to a maximum width exceeding 1,600 miles (2,600 km) near the Weddell and Ross seas.
- Renowned for its robust winds, intense storms, marked seasonal variations, and frigid temperatures, the Southern Ocean is predominantly influenced by the Antarctic Circumpolar Current (ACC).
- This current, the longest, strongest, and deepest-reaching on Earth, follows a clockwise circulation around the continent, surpassing all others in the volume of water it transports globally.
- Biodiversity: The Southern Ocean sustains diverse flora and fauna, with a majority of marine life relying on the nutrient-rich phytoplankton found in the Antarctic Convergence.
- Notable species include whales, penguins, orcas, and seals, contributing to the region's rich biodiversity.
A new non-invasive formaldehyde sensor can detect adulterated fish at room temperature (DST GOI)
- 28 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
A new low-cost sensor made of metal oxide nanoparticles-reduced graphene oxide composite can detect formalin adulteration in fishes at room temperature in a non-invasive way. The sensor shows long-term stability with a low detection limit.
Context:
- A sensor designed for the detection of formalin in fish has been developed by the Nanomaterials and Nanoelectronics Laboratory at Guwahati University, Assam.
- The formalin sensor utilizes a composite of tin oxide-reduced graphene oxide, synthesized through a process involving the wet chemical approach for Graphene Oxide (GO) and the hydrothermal route followed by calcination for the tin oxide-reduced graphene oxide composite (rGO-SnO2).
- Testing of the sensor has been conducted both at the laboratory scale and on fish procured from the fish markets in the Guwahati region, specifically targeting potential adulteration.
- This groundbreaking research has received support from DST-PURSE (Promotion of University Research and Scientific Excellence) and has been documented in the journal ACS Appl. Nano Mater.
- Research Support: The research behind this innovative sensor is backed by DST-PURSE (Promotion of University Research and Scientific Excellence).
About Non-Invasive Formaldehyde Sensor:
- This non-invasive formaldehyde sensor incorporates a composite of tin oxide-reduced graphene oxide (rGO-SnO2) as its key materials.
- While reduced graphene oxide (rGO) has been widely utilized for detecting various toxic gases and volatile organic compounds (VOCs), tin oxide (SnO2) has demonstrated notable efficacy in formaldehyde detection, both in its pristine form and when combined with different compounds, including graphene.
- This combination is favoured for its heightened stability and sensitivity to low concentrations of formaldehyde.
- Synthesis Process: The fabrication process involves a wet chemical approach for the production of graphene oxide (GO), followed by the hydrothermal route and subsequent calcination to synthesize the tin oxide-reduced graphene oxide composite (rGO-SnO2).
- Comparison with Existing Sensors: Unlike commercial formalin sensors for fish, which are primarily electrochemical-based or colorimetric-based and often invasive, this novel sensor, made from metal oxide nanoparticles and reduced graphene oxide, offers a cost-effective and non-invasive method for detecting formalin adulteration in fishes at room temperature.
- Challenges with Existing Sensors: Traditional electrochemical sensors, though widely used, tend to be expensive, and colourimetric sensors, while more cost-effective, share the invasive nature of their electrochemical counterparts. Both face challenges related to low-level and selective detection.
- Significance of the New Sensor: The development of gas sensors based on 2D materials, such as graphene, opens up new possibilities for the effective detection of toxic vapours at room temperature.
- These sensors hold promise for accurately detecting formalin emanating from adulterated food products.
What is Formaldehyde?
- Formaldehyde (CH?O) is an odorless, colorless gas with high toxicity and flammability under standard room temperature conditions.
- Primary Applications:
- Production of fertilizers, paper, plywood, and certain resins.
- Utilized as a food preservative.
- Found in glues, resins, dyes, textiles, disinfectants, building materials, automotive components, embalming processes, and laboratory settings.
- Incorporated into household items like antiseptics, medications, and cosmetics.
- Potential Health Effects:
- Exposure to formaldehyde may result in irritation of the skin, throat, lungs, and eyes. Additionally, formaldehyde is recognized as a carcinogenic substance.
For Huntington’s disease clues, scientists are looking in fruit flies (The Hindu)
- 28 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
Scientists at the University of Szeged in Hungary have made significant progress in advancing our understanding of Huntington's disease through the study of fruit flies.
What is Huntington’s Disease?
- Huntington’s disease (HD) is a brain disorder that is passed down in families from generation to generation.
- It is caused by an error in the DNA instructions that build our body and keep it running.
- DNA is made up of thousands of genes, and people with HD have a small defect in a gene called huntingtin.
- Over time, this error causes damage to the brain and causes symptoms of Huntington’s disease.
- Huntington’s disease causes a person’s physical, mental and emotional abilities to deteriorate, usually during their prime at work, and there is currently no cure.
- Most people start developing symptoms in adulthood, between the ages of 30 and 50, but HD can also occur in children and young adults.
- Huntington’s disease is known as a family disease because each child of a parent with HD has a 50/50 chance of inheriting the defective gene.
Huntington’s Disease Symptoms:
- Symptoms of Huntington’s disease can vary greatly from person to person but typically include:
- Personality changes, mood swings and depression
- Forgetfulness and impaired judgment
- Unsteady gait and involuntary movements (chorea)
- Slurred speech, difficulty swallowing and significant weight loss.
- Symptoms typically worsen over the course of 10 to 25 years, affecting the ability to reason, walk, and speak.
- The person with HD or their friends and family may notice difficulty planning, remembering, and concentrating on the task.
- They can develop mood swings such as depression, anxiety, irritability, and anger.
- Most people with Huntington’s disease become “fidgety” and develop facial and limb movements known as chorea, which they cannot control.
- The symptoms of Huntington’s disease are sometimes described as ALS, Parkinson’s, and Alzheimer’s all at the same time.
Huntington’s Disease Treatment:
- No treatment can stop or reverse the progression of Huntington’s disease.
- Antipsychotic medications can relieve chorea and help control hallucinations, delusions, and violent outbursts.
- Huntington’s disease causes disability that gets worse over time.
How the PM JANMAN scheme can help Particularly Vulnerable Tribal Groups (Indian Express)

- 28 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
Recently, the Union Cabinet approved the Pradhan Mantri Janjati Adivasi Nyaya Maha Abhiyan (PM JANMAN), aimed at providing PVTG households and habitations with basic facilities such as safe housing, clean drinking water and sanitation, improved access to education, health and nutrition, road and telecom connectivity, and sustainable livelihood opportunities.
What is the PM-JANMAN Scheme?
- PM-JANMAN is a government initiative aimed at integrating tribal communities into the mainstream of development.
- The scheme, comprising both Central Sector and Centrally Sponsored Schemes, will be executed collaboratively by the Ministry of Tribal Affairs, State governments, and Particularly Vulnerable Tribal Groups (PVTG) communities.
Key Features:
- Implementation Scope: The scheme focuses on 11 critical interventions managed by 9 line Ministries, ensuring the effective execution of existing schemes within villages inhabited by PVTGs.
- Sectoral Coverage: PM-JANMAN spans various sectors, encompassing initiatives such as ensuring safe housing through the PM-AWAS Scheme, access to clean drinking water, improved healthcare, education, nutrition, road and telecommunications connectivity, and the promotion of sustainable livelihoods.
- Special Initiatives: The plan includes specific initiatives such as the establishment of Van Dhan Vikas Kendras to facilitate the trade of forest produce, deployment of off-grid solar power systems for 1 lakh households, and installation of solar street lights.
- Objectives: PM-JANMAN aims to enhance the quality of life and overall well-being of PVTGs by addressing the various forms of discrimination and exclusion they face.
- Additionally, it recognizes and values the unique and significant contributions of PVTGs to both national and global development.
How Does PM-JANMAN Differ?
- Distinctive Identification and Recognition: Criticism has arisen over outdated criteria for identifying Particularly Vulnerable Tribal Groups (PVTGs).
- The presence of repetitive names and discrepancies in recognition across states has led to confusion and exclusion.
- Addressing these concerns, PM-JANMAN introduces a Human Development Index for PVTGs, aiming to enhance proper identification and tailored development planning based on updated and comprehensive data.
- Participatory Bottom-Up Approach: In a departure from the 'one-size-fits-all' approach, PM-JANMAN adopts customised strategies that respect the unique needs and priorities of PVTGs.
- Emphasizing a participatory bottom-up approach, the scheme actively involves PVTGs in decision-making processes, particularly regarding land rights, social inclusion, and cultural preservation.
- Livelihood Promotion: PM-JANMAN focuses on sustainable livelihoods for PVTGs by providing skills training, essential resources such as land and credit, and implementing the Forest Rights Act (FRA) to secure land titles, particularly under Section 3(1)(e) for primitive tribal groups and pre-agricultural communities.
- The scheme encourages the preservation of cultural heritage through the promotion of traditional technologies and skill enhancement via industry partnerships.
- Health, Nutrition, and Education: To address the unique challenges faced by PVTGs, PM-JANMAN incorporates Mobile Medical Health Units for healthcare outreach in remote areas.
- The scheme also emphasizes cultural sensitivity in education by integrating PVTG culture and language into the curriculum, providing transportation, and training teachers about PVTG cultural contexts.
- Infrastructure Development: Recognizing that PVTG habitations may not meet standard criteria for existing schemes, PM-JANMAN relaxes guidelines for infrastructure schemes like Pradhan Mantri Grameen Sadak Yojana, Pradhan Mantri Awas Yojana, and Jal Jeevan Mission.
- This ensures improved access to housing, water, sanitation, electricity, and connectivity for PVTGs.
What are Particularly Vulnerable Tribal Groups (PVTGs)?
- PVTGs represent the most vulnerable segments within tribal communities, facing heightened challenges in various aspects of development.
- Due to their distinct vulnerabilities, more developed and assertive tribal groups often receive a significant portion of tribal development funds, necessitating a focused allocation of resources for the advancement of PVTGs.
- The designation of PVTGs dates back to 1975 when, based on the recommendations of the Dhebar Commission, the Government of India identified 52 tribal groups with unique vulnerabilities.
- Presently, there are 75 PVTGs among the 705 Scheduled Tribes in India.
- Geographically, PVTGs are distributed across 18 states and one Union Territory, as per the 2011 census, with Odisha having the highest number, exceeding 2.5 lakh individuals.
- Distinctive Characteristics of PVTGs:
- Stagnant or declining trends.
- Primarily pre-agricultural practices.
- Exceptionally low educational attainment.
- Predominantly subsistence level, indicating a reliance on basic, self-sustaining economic activities.
How Japan’s moon-landing attempt in January will affect Chandrayaan 4 (The Hindu)

- 28 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
Recently, the “Moon Sniper” lander developed by Japan’s space agency successfully entered lunar orbit.
About the Smart Lander for Investigating Moon (SLIM) Mission:
- The Smart Lander for Investigating Moon (SLIM) is a spacecraft crafted and launched by the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) on September 7, 2023, from the Tanegashima spaceport.
- Remarkably lightweight at 590 kg, SLIM embarked on its mission alongside XRISM, a cutting-edge X-ray space telescope, on an H-2A rocket.
- Upon launch, SLIM assumed an elliptical orbit around the moon within a span of approximately three minutes.
- Notably, the apogee (farthest point) of this orbit extends to 4,000 km, while the perigee (closest point) hovers at 600 km above the lunar surface.
Objectives of SLIM on the Lunar Surface:
- Before its lunar descent, SLIM is programmed to release two compact rovers known as Lunar Excursion Vehicle (LEV) 1 and 2.
- Working in tandem with SLIM, LEV-1, and LEV-2 are tasked with conducting a comprehensive study of the lunar surface near the designated landing area.
- Their mission encompasses the collection of temperature and radiation readings, as well as endeavours to investigate the moon's mantle.
- This collaborative effort by SLIM and its rovers aims to enhance our understanding of lunar conditions and contribute valuable insights to lunar exploration.
What is the XRISM Mission:
- The X-Ray Imaging and Spectroscopy Mission (XRISM) is a collaborative effort between the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) and the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA), with valuable contributions from the European Space Agency (ESA).
- Mission Objective: XRISM is designed to observe X-rays emanating from deep space, aiming to precisely identify their wavelengths with an unprecedented level of accuracy.
- The mission employs cutting-edge spectroscopy techniques to measure changes in the brightness of celestial objects across various wavelengths.
- Technological Advancements: Leveraging state-of-the-art spectroscopy, XRISM can detect X-rays within a broad energy spectrum ranging from 400 to 12,000 electron volts.
- To provide a perspective, the energy of visible light typically falls within the 2 to 3 electron volts range.
- This expanded energy range enables astrophysicists to gain novel insights into some of the universe's most dynamic regions, vast structures, and entities characterized by formidable gravitational forces.
India, Russia ink pacts on the construction of future power units of the Kudankulam nuclear plant (The Hindu)

- 27 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
In a major boost to their time-tested partnership, India and Russia recently signed some "very important" agreements related to the construction of the future power-generating units of the Kudankulam nuclear power plant.
About the Kudankulam Nuclear Power Project:
- The Kudankulam Nuclear Power Project is India's largest nuclear power plant situated in the Tirunelveli district of Tamil Nadu.
- It is being developed by the Nuclear Power Corporation of India (NPCIL) in collaboration with Russia's Rosatom State Atomic Energy Corporation.
- The construction began in March 2002.
- Since February 2016, the first power unit of the Kudankulam NPP has been steadily operating at its design capacity of 1,000 MW.
- The plant is expected to start operating at full capacity in 2027.
- Water-Water Energy Reactor: The Kudankulam Nuclear Power Project employs VVER (Water-Water Energy Reactor) technology, a pressurized water reactor design developed in the former Soviet Union, known for its safety and reliability.
- Power Generation Capacity: The current power generation capacity is 2×1,000 MWe VVER, expected to significantly increase with the construction of four additional reactors, estimated at ?89,470 crore.
- All units are subject to International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA) safety analysis, except the Kalpakkam nuclear plant, reserved for strategic use under the India-US Nuclear Agreement.
What is the 3-Stage Nuclear Programme of India?
- India's nuclear program is structured into three stages, strategically designed to harness the extensive Thorium deposits within the country, constituting approximately 25% of the world's total reserves.
- This focus on Thorium is crucial as India possesses limited Uranium reserves, accounting for about 2% of the global uranium reserves.
- 1st Stage: The initial stage employs Pressurized Heavy Water Reactors that operate on natural uranium, consisting of 99.3% U-238 and 0.7% U-235.
- The fissile U-235 triggers a chain reaction, while the non-fissile U-238 transforms into Pu-239 as a byproduct (spent fuel).
- This Pu-239 is subsequently utilized in the Fast Breeder Reactors in the 2nd stage.
- 2nd Stage: Fast Breeder Reactors primarily rely on Plutonium, utilizing a combination of Plutonium-239 from the 1st stage and the abundant U-238 found on Earth to generate additional Plutonium inside the reactor.
- As U-238 does not initiate a chain reaction, the reactors are termed Breeder reactors.
- To maximize the chances of neutron interaction with U-238, these reactors, known as Fast Breeder Reactors, omit a moderator to slow down neutrons.
- Once Plutonium-239 is fully consumed, Thorium is introduced to convert it into U-233, to be used in the 3rd stage.
- 3rd Stage: Thermal Breeder Reactors utilize U-233 produced in the 2nd stage, incorporating thorium-232.
- Notably, Thorium is non-radioactive and non-fissile. Since these reactors also generate U-233 from Thorium-232, they are classified as breeder reactors.
- India's significant reserves of thorium, particularly in the form of monazite sand, emphasize the critical role of the 3rd stage in India's nuclear energy portfolio.
PM Narendra Modi calls upon religious leaders and social organizations to launch a mass movement against drugs (NewsOnAir)

- 27 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
On the occasion of Veer Bal Diwas in New Delhi, PM Narendra Modi calls upon religious leaders and social organizations to launch a mass movement against drug menace.
Drug Menace in India:
- Alcohol, cannabis, opium, and heroin constitute the primary drugs abused in India.
- Approximately 13% of substance abusers in the country are under 20 years old.
- Adolescence is identified as a critical-risk period for the initiation of substance use.
- Children impacted by substance abuse fall under the category of children in need of care and protection as per the Juvenile Justice (Care and Protection of Children) Act 2015.
- In various regions, including Punjab, Assam, Mizoram, Chhattisgarh, Gujarat, Haryana, Bihar, Delhi, etc., drug abuse prevalence is notably high.
- Key causes of drug abuse include factors such as poverty, peer pressure, illiteracy, low self-esteem, and genetic predisposition.
Challenges in Combating the Drug Menace:
- India, strategically located between the Death Triangle (Thailand, Myanmar, and Laos) and Death Crescent (Pakistan, Afghanistan, and Iran), is a prominent hub for drug trafficking, particularly in major opium production regions globally.
- Porous borders exacerbate the problem, and technological advancements, such as the utilization of the dark net and cryptocurrency for drug trafficking, further complicate law enforcement efforts.
- Criminalizing drug abuse contributes to social stigma for addicts, deterring them from seeking essential medical assistance.
- There is a notable absence of comprehensive studies assessing the societal impact of drug abuse, hindering the formulation of informed strategies.
Efforts to Combat the Drug Menace:
- The Narcotics Drugs and Psychotropic Substances (NDPS) Act of 1985 outlines measures for identification, treatment, and rehabilitation.
- The Nasha Mukt Bharat Abhiyaan targets 272 highly vulnerable districts with a focus on community outreach.
- The Seizure Information Management System (SIMS) portal facilitates the management of cases involving substantial drug seizures.
- The National Action Plan for Drug Demand Reduction (NAPDDR) spanning 2018-2025 adopts a comprehensive, multi-pronged strategy.
- Furthermore, adherence to international conventions, including the Convention on Narcotic Drugs (1961) and the Convention on Psychotropic Substances (1971), reinforces India's commitment to addressing the global issue of drug abuse.
Atomic watchdog report says Iran is increasing production of highly enriched uranium (Indian Express)

- 27 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
Iran has increased the rate at which it is producing near weapons-grade uranium in recent weeks, reversing a previous slowdown that started in the middle of this year, the International Atomic Energy Agency said in a report.
What is Uranium Enrichment?
- Natural uranium is comprised of two isotopes, with approximately 99% being U-238 and only about 0.7% being U-235.
- U-235 is a fissile material capable of sustaining a chain reaction within a nuclear reactor.
- The enrichment process involves increasing the proportion of U-235 through isotope separation, effectively isolating U-238 from U-235.
- For the production of nuclear weapons, enrichment is necessary up to 90% or more, referred to as weapons-grade uranium.
- Low-enriched uranium, typically containing a 3-5% concentration of U-235, is suitable for generating fuel for commercial nuclear power plants.
- In contrast, highly enriched uranium, boasting a purity of 20% or more, finds application in research reactors.
Key Facts About Uranium:
- Discovered in 1789 by the German chemist Martin Klaproth, Uranium is a silvery-white metallic chemical element found in the periodic table, characterized by its atomic number 92.
- This element holds the distinction of having the highest atomic weight among all naturally occurring elements.
- Naturally present in low concentrations in soil, rock, and water, uranium is commercially extracted from minerals like uraninite.
- The mining of uranium ore can be undertaken through open pits or underground excavations, followed by crushing and processing at a mill to isolate the valuable uranium.
- An alternative method involves the direct dissolution of uranium from ore deposits in the ground, known as in-situ leaching, with the extracted uranium then pumped to the surface.
About the International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA):
- The International Atomic Energy Agency is an intergovernmental organization that seeks to promote the peaceful use of nuclear energy and to inhibit its use for any military purpose, including nuclear weapons.
- Established as an autonomous entity through its international treaty, the IAEA Statute, the organization, nonetheless, reports to both the United Nations General Assembly and the Security Council.
- Headquartered in Vienna, Austria, the IAEA collaborates with its Member States and various global partners to advance the safe and peaceful utilization of nuclear technologies.
- It employs nuclear safeguards, encompassing monitoring, inspection, information analysis, and other measures, to ensure the peaceful nature of nuclear activities and to detect and deter any potential diversion towards weapons-related purposes.
- The IAEA plays a crucial role in implementing comprehensive safeguards agreements mandated by the Nuclear Non-Proliferation Treaty (NPT), acting as a frontline defense against nuclear weapons proliferation.
- Additionally, the agency facilitates the exchange of scientific and technical information among its Member States.
- A key function of the IAEA is to bolster national, regional, and international capabilities to respond effectively to nuclear and radiological incidents, thereby minimizing their impact.
Zombie deer disease: Why are scientists concerned over its transmission to humans? (TOI)
- 27 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
Researchers in the US have warned that Chronic Wasting Disease (CWD) spreading among wildlife across North America, could also spread to humans.
What is Zombie Deer Disease??
- According to the US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), Zombie deer disease or chronic wasting disease is a prion disease that affects deer, elk, reindeer, sika deer and moose.
- Prion diseases affect both humans and animals and are distinguished by long incubation periods.
- In the case of chronic wasting disease or the zombie deer disease, "it may take over a year before an infected animal develops symptoms.
- History of the Disease?: The zombie deer disease was first discovered in Colorado (USA) in 1967.
- Until now, reports of humans getting affected have not come to the fore.
- However, the findings of several studies suggest that it can easily jump to human beings.
Why are health experts and scientists worried about a possible transmission??
- Experts are giving examples of the mad cow disease or the Bovine Spongiform Encephalopathy (BSE).
- “The BSE outbreak in Britain provided an example of how, overnight, things can get crazy when a spillover event happens from livestock to people.
Symptoms of the Disease:
- The common signs of the disease are drastic weight loss (wasting), stumbling, and other neurologic symptoms.
- Other symptoms seen in animals infected with this disease are listlessness, drooling, excessive thirst or urination, drooping ears, and lack of fear of people.
It is difficult to eradicate this disease??
- The chronic wasting disease is extremely difficult to eradicate from the environment once the infection has started.
- It can persist for years in dirt or on surfaces, and it is resistant to disinfectants, formaldehyde, radiation, and incineration at 600C (1,100F).
- Chronic Wasting Disease (CWD) is fatal to animals, and there are no treatments or vaccines.
Prevention?:
- To avoid the spread of the disease, humans should avoid shoot, handling, or eating meat from deer and elk that look sick or are acting strangely or are found dead.
- Individuals should wear latex or rubber gloves when dressing the animal or handling the meat.
Speed up measures for a new dam at Mullaperiyar, Kerala tells Central Water Commission (The Hindu)

- 27 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
Recently the State government of kerala has urged the Centre to speed up measures for building a new dam at Mullaperiyar in the Idukki district at a meeting with the Central Water Commission.
About the Central Water Commission (CWC):
- The Central Water Commission (CWC) is a leading technical organization in India dedicated to water resources management.
- Currently operating as an attached office of the Ministry of Jal Shakti, Department of Water Resources, River Development, and Ganga Rejuvenation, Government of India, it plays a pivotal role in overseeing various aspects of water resource management nationwide.
Key Functions:
- Initiation and Coordination: The Commission is responsible for initiating, coordinating, and advancing schemes in collaboration with concerned State Governments.
- These schemes focus on controlling, conserving, and utilizing water resources for Flood Control, Irrigation, Navigation, Drinking Water Supply, and Water Power Development.
- Investigation and Execution: The CWC undertakes the investigation, construction, and execution of water resource schemes as deemed necessary.
- Leadership and Structure: The Commission is led by a Chairman, holding the status of Ex-Officio Secretary to the Government of India.
- The organizational structure includes three wings:
- Designs and Research (D&R) Wing
- River Management (RM) Wing
- Water Planning and Projects (WP&P) Wing
- Each wing is overseen by a full-time member with the status of Ex-Officio Additional Secretary to the Government of India.
- Headquarters: The headquarters of the Central Water Commission is located in New Delhi.
Key Facts About Mullaperiyar Dam:
- The Mullaperiyar Dam is a masonry gravity dam, situated on the Periyar River in Thekkady, Idukki district of Kerala.
- Situated at an elevation of 881 meters above sea level, it graces the Cardamom Hills within the Western Ghats.
- The dam is strategically located at the convergence of the Mullayar and Periyar rivers.
- Its construction, led by the British Corps of Royal Engineers under Pennycuick, commenced in 1887 and concluded in 1895.
- Utilizing limestone and "Surkhi" (a blend of burnt brick powder, sugar, and calcium oxide), the dam serves the purpose of redirecting west-flowing River Periyar waters to the rain shadow regions of Theni, Madurai, Sivaganga, and Ramanathapuram districts in Tamil Nadu.
- The Periyar National Park is located around the dam's reservoir.
- Despite its location in Kerala, the dam is operated and maintained by Tamil Nadu under a 999-year lease agreement established during British rule.
New Toad Species Discovered in Dampa Tiger Reserve of Mizoram (HT)

- 12 Oct 2023
Why in the News?
A group of scientists from India and the United Kingdom have discovered a new species of toads, the third of a genus found only in a very narrow area in northeast India.
About the Recently Discovered Toad Species:
- This newfound toad species, belonging to the bufoides genus, marks the third identified within a limited area in northeast India.
- Distinguished by its interdigital webbing, unique colouration, skin tuberculation, and the existence of ovoid, tuberculated, and depressed parotid glands, this species adds to the diversity of its genus.
- The preceding species from the same genus, Bufoides meghalayanus and Bufoides kempi, were previously identified in the region of Meghalaya.
- In recognition of its discovery and to honour the significant contributions of the renowned herpetologist S. Bhupathy, this new species has been aptly named after him.
About the Dampa Tiger Reserve:
- Situated in the Lushai Hills on the western side of Mizoram, the Dampa Tiger Reserve holds significance for its unique features.
- Establishment: Designated as a tiger reserve in 1994 under the Project Tiger initiative.
- Geographical Boundaries: Bordered on the west by the Chittagong hill tracts (Sazek hill range) of Bangladesh.
- The terrain is characterized by hills, with elevations ranging from 49 to 1095 meters above mean sea level.
- Prominent peaks include Chhawrpialtlang (1095m), Dampatlang (869m), and Pathlawilunglentlang (780m).
- Vegetation Diversity: Encompassing tropical evergreen to semi-evergreen forests, the reserve boasts a diverse range of vegetation.
- River Systems: Drained by the Khawthlangtuipui River in the west and the Teirei River in the east, with tributaries like Keisalam, Seling, and Aivapui flowing through the reserve.
- Fauna: Diverse mammalian species inhabit the reserve, including Hoolock Gibbon, Rhesus Macaque, Assamese Macaque, Pig-Tailed Macaque, Stump-Tailed Macaque, and Phayre’s Leaf Monkey.
- Flora: The reserve boasts a rich flora, featuring species such as Dipterocarpus turbinatus, Dipterocarpus marcocarpus, Terminalia myriocarpa, and Michelia champaca, among others.
Project Nilgiri Tahr’ Launched in Tamil Nadu (The Hindu)

- 12 Oct 2023
Why in the News?
Consolidating efforts towards the conservation of Tamil Nadu’s State Animal, Chief Minister M.K. Stalin on Thursday, October 12, 2023, launched the ‘Project Nilgiri Tahr’ from the Secretariat in Chennai.
About Nilgiri Tahr:
- The Nilgiri Tahr, scientifically known as Nilgiritragus hylocrius, is an endangered mountain ungulate that is native to the southern part of the Western Ghats.
- Locally referred to as 'Varayaadu,' these creatures are renowned for their remarkable climbing abilities on steep cliffs, earning them the moniker "Mountain Monarch."
- Notably, the Nilgiri Tahr holds the distinction of being the state animal of Tamil Nadu.
Distribution:
- The current range of Nilgiri Tahrs is confined to approximately 5% of the Western Ghats in southern India, specifically in the states of Kerala and Tamil Nadu.
- The Eravikulam National Park in Kerala is home to the highest density and the largest surviving population of Nilgiri Tahrs.
Habitat:
- Nilgiri Tahrs inhabit open montane grassland habitats, thriving at elevations ranging from 1200 to 2600 meters in the South Western Ghats.
Distinctive Features:
- Characterized by a stocky body, short coarse fur, and a bristly mane, Nilgiri Tahrs exhibit sexual dimorphism, with mature males being larger and darker in colour.
- Both males and females possess curved horns, with males having larger ones measuring up to 40 cm, while females' horns reach approximately 30 cm.
- Adult males develop a light grey area or 'saddle' on their backs, leading to the term 'saddlebacks.' The species is recognized by its short grey-brown or dark coat.
Conservation Status:
- The Nilgiri Tahr is classified as Endangered on the IUCN Red List, signifying the critical need for conservation efforts.
- Additionally, it is accorded the highest protection under the Wildlife (Protection) Act of India, 1972, listed in Schedule I.
ICRISAT Joins One CGIAR Global Initiative (The Hindu BusinessLine)

- 12 Oct 2023
Why in the News?
The International Crops Research Institute for the Semi-Arid Tropics (ICRISAT), a Hyderabad-based international research institute with a focus on tropical dryland agrifood system innovation, has joined the One CGIAR integrated partnership.
What is One CGIAR Global Initiative?
- The One CGIAR global initiative is designed to establish a cohesive approach to transform food, land, and water systems in response to the challenges posed by the climate crisis.
- This collaborative effort involves the CGIAR System Organisation and 12 research centres operating under the umbrella of One CGIAR.
- CGIAR is a publicly-funded network of research centres focused on agrifood systems, operating in over 80 countries.
Key Facts about ICRISAT:
- ICRISAT, a non-profit, non-political international research organization, is dedicated to agricultural research for development in Asia and sub-Saharan Africa.
- Its mission is to support farmers by providing improved crop varieties and hybrids, particularly aiding smallholder farmers in arid regions to combat climate change.
- The organization specializes in research on five highly nutritious, drought-tolerant crops: chickpea, pigeonpea, pearl millet, sorghum, and groundnut.
- Recognized for its impactful work, ICRISAT was awarded the 2021 Africa Food Prize for the Tropical Legumes Project, contributing to improved food security across 13 countries in sub-Saharan Africa.
- ICRISAT is headquartered in Hyderabad, Telangana State, India, with two regional hubs in Nairobi, Kenya, and Bamako, Mali.
- Through its research and initiatives, ICRISAT plays a crucial role in addressing agricultural challenges and promoting sustainable development in diverse regions.
India Ranks 111 in Global Hunger Index (The Hindu)

- 12 Oct 2023
Why in the News?
India ranks 111 out of a total of 125 countries in the Global Hunger Index (GHI) 2023, with its progress against hunger nearly halted since 2015, reflecting a global trend.
Key Findings of Global Hunger Index (GHI) 2023:
- India holds a Global Hunger Index score of 28.7 on a 100-point scale, categorizing its severity of hunger as "serious."
- The global GHI score for 2023 is 18.3, considered moderate.
- Latin America and the Caribbean stand out as the only region in the world where GHI scores have deteriorated between 2015 and 2023.
- South Asia and Africa South of the Sahara emerge as the global regions with the highest hunger levels, each having GHI scores of 27.0.
About the Global Hunger Index:
- The Global Hunger Index (GHI) is a tool designed to comprehensively measure and track hunger at global, regional, and national levels, reflecting multiple dimensions of hunger over time.
- The GHI is intended to raise awareness and understanding of the struggle against hunger, provide a way to compare levels of hunger between countries and regions and call attention to those areas of the world where hunger levels are highest and where the need for additional efforts to eliminate hunger is greatest.
- It is prepared jointly by Irish aid agency Concern Worldwide and the German organisation Welt Hunger Hilfe.
- How the GHI Is Calculated?
- Each country’s GHI score is calculated based on a formula that combines four indicators that together capture the multidimensional nature of hunger:
- Undernourishment: the share of the population whose caloric intake is insufficient;
- Child stunting: the share of children under the age of 5 who have low height for their age, reflecting chronic undernutrition;
- Child wasting: the share of children under the age of five who have low weight for their height, reflecting acute undernutrition; and
- Child mortality: the share of children who die before their 5th birthday, reflecting in part the fatal mix of inadequate nutrition and unhealthy environments.
- The indicators included in the GHI formula reflect caloric deficiencies as well as poor nutrition.
- The undernourishment indicator captures the food access situation of the population as a whole, while the indicators specific to children reflect the nutrition status within a particularly vulnerable subset of the population for whom a lack of dietary energy, protein, and/or micronutrients (essential vitamins and minerals) leads to a high risk of illness, poor physical and cognitive development, and death.
- The inclusion of both child wasting and child stunting allows the GHI to document both acute and chronic undernutrition.
- By combining multiple indicators, the index minimizes the effects of random measurement errors.
- These four indicators are all part of the indicator set used to measure progress toward the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs)
Good Governance Day: Govt launches 3 new features on iGOT Mission Karmayogi platform (TOI)

- 26 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
On the occasion of Good Governance Day, Union Minister Dr Jitendra Singh launched the Extended Version of Mission Karmayogi by introducing three new features on the iGOT Karmayogi platform that include My iGOT, Blended Programs and Curated Programs..
About Mission Karmayogi:
- Mission Karmayogi, the National Programme for Civil Services Capacity Building (NPCSCB), is geared towards equipping Civil Servants with enhanced creativity, constructiveness, and innovation, utilising transparency and technology to prepare them for future challenges.
- This innovative program serves as a cornerstone for the country's civil servants, emphasizing a balanced approach between 'on-site learning' and traditional 'off-site learning.'
- Approved by the Government on September 2, 2020, Mission Karmayogi encompasses six key pillars:
- Policy Framework
- Institutional Framework
- Competency Framework
- Digital Learning Framework (iGOT-Karmayogi)
- The electronic Human Resource Management System (e-HRMS), and
- The Monitoring and Evaluation Framework.
- Encompassing all civil servants, including contractual employees, across various ministries, departments, organizations, and agencies of the Union Government, the program introduces three new features on the iGOT Karmayogi platform:
- My iGOT: Delivers targeted training courses on the home page of individual officers, directly addressing their unique capacity-building needs identified in the Capacity-Building Plan for their Ministries/Departments.
- Blended Programs: Facilitates equitable access to training methodologies across all levels by integrating traditional offline (in-person) classroom courses with online learning components.
- This approach enables officers and faculty to benefit from both the flexibility of online courses and the invaluable interactions of face-to-face classroom sessions.
- Curated Programs: Designed to cater to diverse learning needs of Ministries/Departments and Training Institutions, offering a custom approach to address the specific requirements of different segments within the civil services.
Six armed poachers, timber mafia held by forest officials at Similipal National Park (New Indian Express)
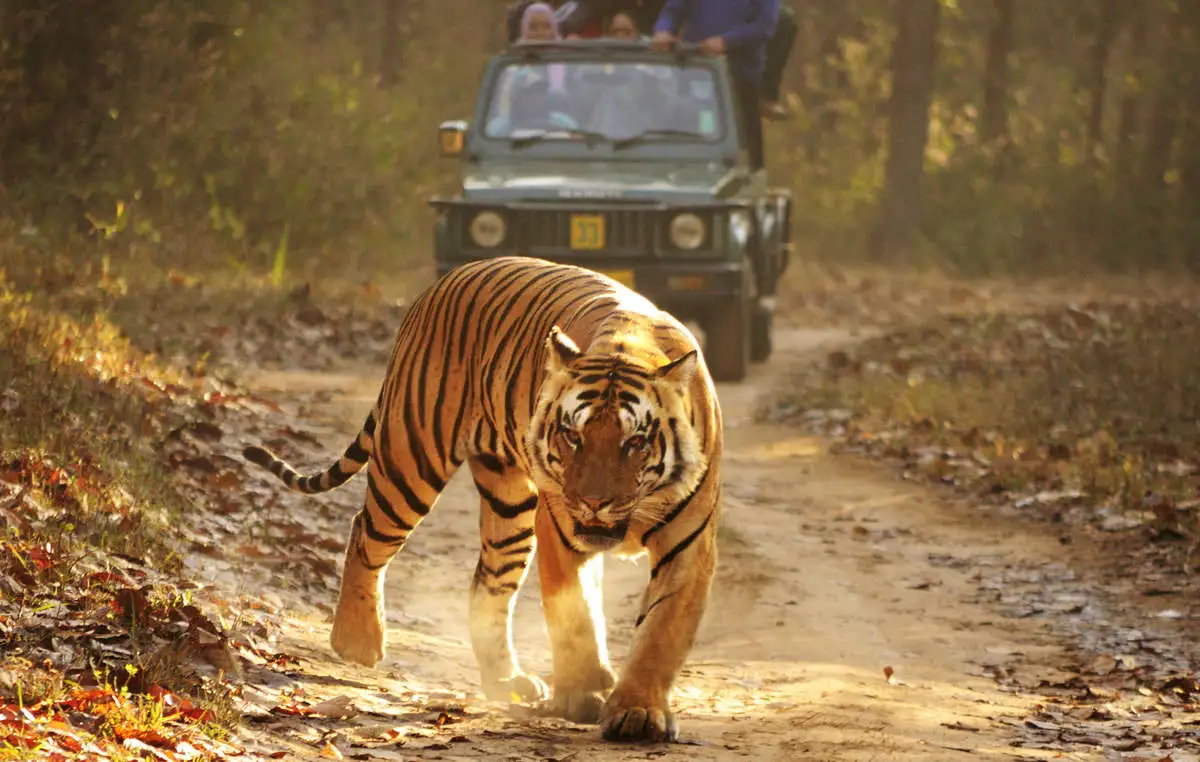

- 26 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
In a significant breakthrough, forest officials at Similipal National Park apprehended four armed poachers and two members of the timber mafia in separate locations on Saturday night.
About Similipal Tiger Reserve (STR):
- Similipal Tiger Reserve is located within the Mayurbhanj District, in the Northernmost part of Odisha.
- Declared a 'Tiger Reserve' in 1956, STR became a part of the national conservation initiative 'Project Tiger' in 1973.
- Recognized by UNESCO in 2009, STR, along with a transitional area covering 2250 sq. km, was included in the World Network of Biosphere Reserves.
- Terrain: Surrounded by high plateaus and hills, STR boasts the twin peaks of Khairiburu and Meghashini, reaching 1515m above mean sea level.
- The undulating and hilly terrain features open grasslands and wooded areas, with the inclined plateau rising abruptly from the low coastal plains.
- Hydrography: The region is crisscrossed with perennial water sources, contributing to rivers like Budhabalanga, Salandi, and various tributaries of the Baitarani River.
- Vegetation: STR encompasses a diverse mix of forest types and habitats, with Northern tropical moist deciduous dominating alongside semi-evergreen patches.
- Notably, it hosts the world's only landscape with melanistic tigers.
- Tribes: The vicinity of STR is inhabited by various tribes, including Kolha, Santhala, Bhumija, Bhatudi, Gondas, Khadia, Mankadia, and Sahara.
- Flora: Home to an impressive 1078 plant species, including 94 orchid species, STR is characterized by the dominance of Sal trees.
- Fauna: The reserve is home to a variety of wildlife, including leopard, gaur, elephant, langur, barking and spotted deer, sloth bear, mongoose, flying squirrel, porcupine, turtle, monitor lizard, python, sambar, pangolin, and more.
What is the Special Tiger Protection Force (STPF)?
- Realizing the importance of ‘tiger protection’ in biodiversity conservation, the Finance Minister announced policy initiatives in February 2008, for constituting the ‘Special Tiger Protection Force’ (STPF).
- Based on the one-time grant of Rs. 50 crore was provided to the National Tiger Conservation Authority (NTCA) for raising, arming and deploying a Special Tiger Protection Force, the proposal for the said force has been approved by the competent authority for 13 tiger reserves.
- The STPF has been made operational in the States of Karnataka (Bandipur), Maharashtra (Pench, Tadoba-Andhari, Nawegaon-Nagzira, Melghat), Rajasthan (Ranthambhore), Odisha (Similipal) and Assam (Kaziranga), out of 13 initially selected tiger reserves, with 60% central assistance under the ongoing Centrally Sponsored Scheme of Project Tiger (CSS-PT).
Goan Cashew (kernel) Got the Geographical Indication (GI) Tag (Indian Express)

- 12 Oct 2023
Why in the News?
Goa Chief Minister Pramod Sawant hailed the recognition as a great opportunity for the cashew industry in the state and “a milestone towards the Swayampurna Goa mission”.
About Goan cashew:
- Cashew is one of the most important plantation crops in India, with significant cultivation in the state of Goa.
- Its introduction to India traces back to the 16th century (1570) when the Portuguese brought it from its native region in northeast Brazil, Latin America.
- Originally recognized for afforestation and soil conservation, cashews quickly gained prominence in Goa, occupying the largest area among horticultural crops.
- The climatic conditions conducive to its growth are well-suited to the Indian coastal areas, thriving under hot and humid circumstances.
Climatic Conditions:
- Soil and Climate: Well-drained deep sandy loam soils, ranging from sandy to laterite, prove to be ideal for cashew cultivation.
- Goa, known for its sandy loam, is a particularly favourable region for this crop.
- Adaptability: Cashew exhibits excellent adaptability to the coastal regions of India, thriving under temperatures ranging from 20 to 38 degrees Celsius.
- The relative humidity in the range of 60 to 95% is also conducive to its growth.
- Rainfall: Annual precipitation between 2000 to 3500mm supports the cultivation of cashews, ensuring optimal growth and development.
- Geographical Expansion: While traditionally associated with Goa, the cultivation of cashews is expanding to non-traditional areas in the plains of Karnataka, Madhya Pradesh, Chhattisgarh, and some parts of the Northeast hill region.
- Cashew's journey from its introduction by the Portuguese to becoming a vital crop in Goan agriculture highlights its adaptability and significance in the diverse agro-climatic regions of India.
What is a Geographical Indication Tag?
- A Geographical Indication (GI) tag is a distinctive emblem affixed to products originating from a specific geographical area, signifying unique qualities or a reputation inherently tied to that origin.
- Primarily employed for agricultural products, foodstuffs, wine and spirit drinks, handicrafts, and industrial items, the Geographical Indications of Goods (Registration and Protection) Act, 1999 in India aims to facilitate the registration and enhanced safeguarding of geographical indications associated with various goods.
- Under this act, the granted GI tag holds validity for a period of 10 years, with the provision for renewal upon expiration.
Union Health Minister Launches MedTech Mitra Platform to Empower Medical Technology Innovators (NewsOnAir)

- 26 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
Union Health Minister Dr Mansukh Mandaviya has launched MedTech Mitra - a strategic initiative to empower MedTech innovators and advance healthcare solutions.
What is the MedTech Mitra Portal?
- The MedTech Mitra portal is an online platform designed to support medtech innovators by assisting in clinical evaluation, regulatory facilitation, and the adoption of new products in the medical technology sector.
- This collaborative initiative is overseen by the Indian Council of Medical Research (ICMR) and the Central Drugs Standard Control Organisation (CDSCO), operating under the direction/guidance of NITI Aayog’s Atal Innovation Mission.
Significance:
- In conjunction with recent policies and incentive schemes, such as the medical devices policy and the production-linked incentive scheme, the MedTech Mitra platform aims to catalyze growth in the medical devices sector and promote domestic manufacturing.
- These initiatives seek to foster the indigenous development of affordable and high-quality MedTech devices and diagnostics, thereby significantly reducing the sector's reliance on imports.
- The platform is envisioned to streamline the innovation process and facilitate research and development for emerging start-ups, ensuring a smoother journey from concept to product.
- By offering comprehensive guidance, including support for animal and clinical trials, the platform aims to bridge gaps for startups and promote ease of innovation.
- The MedTech Mitra portal is poised to foster collaborations between engineers, scientists, and clinicians, addressing a previously existing gap in partnerships within the sector.
About the Indian Council of Medical Research (ICMR):
- The Indian Council of Medical Research (ICMR) serves as the apex institution in India responsible for formulating, coordinating, and advancing biomedical research.
- With a primary mandate to conduct, coordinate, and implement medical research for societal benefit, ICMR is dedicated to translating medical innovations into tangible products and processes, subsequently integrating them into the public health system.
- Financial support for ICMR is provided by the Government of India through the Department of Health Research, Ministry of Health & Family Welfare.
AstroSat detects millisecond X-ray bursts from high magnetic field neutron stars (DD News)

- 26 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
India’s first multi-wavelength space-based observatory, AstroSat, has detected intense sub-second X-ray bursts emanating from a neutron star with an ultrahigh magnetic field, known as a magnetar.
What is X-ray Bursts?
- X-ray bursts manifest in low-mass X-ray binary systems featuring a neutron star and a low-mass main sequence star orbiting each other.
- The occurrence of these bursts is intricately linked to the gravitational dynamics of the neutron star and its companion.
- In this system, the proximity and intense gravitational forces of the neutron star cause the companion star to exceed its Roche-lobe, leading to the formation of an accretion disk around the neutron star.
- This disk becomes a repository for hydrogen drawn from the overflowing companion star.
- As hydrogen accumulates on the neutron star's surface, the extreme temperatures and pressures prevailing there catalyze its transformation into helium.
- This ongoing process results in the formation of a thin surface layer of helium.
- When this helium layer reaches a critical mass, a sudden explosive ignition occurs, elevating the entire neutron star's surface temperature to several tens of millions of degrees and releasing a burst of X-rays.
- Following the outburst, the binary system returns temporarily to a quiescent state, allowing the neutron star to reaccumulate the helium surface layer gradually.
- This cyclic process leads to the recurrence of X-ray bursts, typically unfolding at regular intervals separated by several hours or days.
About Indias’ AstroSat:
- AstroSat stands as India’s first dedicated multi-wavelength space observatory, pioneering a mission focused on the simultaneous study of celestial sources across X-ray, optical, and UV spectral bands.
- Launched with a lift-off mass of 1515 kg, AstroSat took flight aboard the Indian launch vehicle PSLV from the Satish Dhawan Space Centre in Sriharikota on September 28, 2015.
- It entered a 650 km orbit, inclined at an angle of 6 degrees to the equator.
- The Mission Operations Complex (MOX) at ISRO Telemetry, Tracking and Command Network (ISTRAC) in Bengaluru oversees the satellite throughout its mission life.
- With a minimum useful life of around 5 years, AstroSat is dedicated to achieving the following scientific objectives:
- Understanding high-energy processes in binary star systems housing neutron stars and black holes.
- Estimating magnetic fields associated with neutron stars.
- Investigating star birth regions and high-energy processes in star systems beyond our galaxy.
- Detecting new, briefly bright X-ray sources in the celestial sphere.
- Conducting a limited deep-field survey of the Universe in the Ultraviolet region.
India shedding mentality of slavery, says PM Modi (The Hindu)

- 26 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
Speaking at a "Veer Bal Diwas" event to commemorate the martyrdom of two sons of Guru Gobind Singh, PM Modi said their sacrifices are not only being remembered in India but also globally through programmes in other countries as well
About Veer Bal Diwas:
- Veer Bal Diwas is observed annually on December 26th to commemorate the valour and sacrifice of the four sons of Guru Gobind Singh, the tenth Sikh guru.
- The four sons, named Zorawar Singh, Fateh Singh, Jai Singh, and Kulwant Singh, played a significant role in resisting the Mughal emperor Aurangzeb and his army.
- Zorawar Singh and Fateh Singh were captured by the Mughals at the ages of six and nine, respectively, after defending the fort of Anandpur Sahib from a siege.
- Subsequently, they were taken to Sirhind, where, steadfast in their faith, they refused to convert to Islam and were sentenced to a tragic death by being bricked alive in 1705.
- Jai Singh and Kulwant Singh, also captured at Anandpur Sahib, managed to escape from Sirhind with the assistance of loyal followers.
- They later joined their father in his final battle at Sirhind, where Guru Gobind Singh was wounded by a musket shot.
- The unwavering courage and sacrifice of Guru Gobind Singh's sons became a symbol of inspiration for generations of Sikhs, reflecting their dedication to the cause of Sikhism.
About Guru Gobind Singh:
- Guru Gobind Singh, the last of the ten Sikh Gurus, was born on December 22, 1666, in Patna, Bihar.
- His birth anniversary is observed according to the Nanakshahi calendar.
- Assuming the role of Sikh Guru at the tender age of nine after the passing of his father, Guru Tegh Bahadur, he served until his assassination in 1708.
Contributions:
- Religious: Guru Gobind Singh made profound contributions to the Sikh religion, introducing practices such as wearing a turban to cover hair.
- He laid the foundation for the Khalsa (1699), embodying the Five 'K's: kesh (uncut hair), kanga (wooden comb), kara (iron or steel bracelet), kirpan (dagger), and kachera (short breeches).
- These articles of faith became integral to the identity of a Khalsa.
- Establishing various rules for Khalsa warriors, including abstaining from tobacco, alcohol, and halal meat, Guru Gobind Singh emphasized their duty to protect innocent people from persecution.
- Guru Gobind Singh designated Guru Granth Sahib as the spiritual guide for both the Khalsas and Sikhs.
- Martial: Engaging in the battle of Muktsar in 1705, Guru Gobind Singh fiercely opposed the Mughals.
- The Battle of Anandpur in 1704 resulted in the tragic loss of the Guru's mother and two minor sons, who were executed. His eldest son also fell in battle.
- Literary: Guru Gobind Singh's legacy includes compositions like Jaap Sahib, Benti Chaupai, and Amrit Savaiye.
- Notably, he wrote the Zafarnama, a letter addressed to the Mughal Emperor Aurangzeb, showcasing his literary prowess and resilience.
‘Dunki’ and immigration: How the first modern passports came to be (Indian Express)

- 23 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
The recently released Shah Rukh Khan’s movie ‘Dunki’ is said to be based on the ‘donkey route’ or ‘donkey flight’ that lakhs of Indians take to reach countries like the US, the UK or some other European countries.
What is a Donkey Journey?
- Dunki is the Punjabi idiom that means to "hop from place to place", according to the Migration Policy Institute (MPI).
- It is a colloquial term for "donkey flights" or the "donkey flights method", which is a dangerous illegal immigration technique involving crossing a country's borders through a backdoor route via multiple stops in other countries.
How does the donkey flight method or dunki work?
- The desire for a higher quality of life has given rise to an industry driven by "agents" who charge exorbitant fees to help smuggle people to the country of their choice.
- Some agents may even run legitimate businesses while offering this dangerous option.
- The agents can offer various services, from fake papers to help through otherwise legal migration processes to smuggling people through ship containers.
Which countries are most targeted using the Dunki method?
- While donkey flight can be used to enter any country, the US, Canada, and the UK are some of the most popular destinations undertaken by Indian immigrants.
- According to a report, between February 2019 and March 2023, as many as 149,000 Indians were detained for attempting to enter the US illegally.
- Of this, most of those detained were from Gujarat and Punjab.
Risks involved in the dunki method:
- Dunki comes with tremendous risks, including the risk of capture, imprisonment, and deportation.
- When facilitated by an agent, the system is highly exploitative.
- Many sell off their assets, including ancestral land, to pay these agents.
- Agents may also withhold people's passports or other important documents to extort more money and assets.
- Moreover, smuggled migrants are also more vulnerable to becoming victims of other crimes during the smuggling process.
- The terrains of the places through which immigrants may have to travel pose a range of risks, including harsh weather conditions, rugged terrains, and access to basic resources like food and water.
- It must be noted that migrant smuggling is not the same as human trafficking.
- However, these crimes may sometimes interlink, adding another layer of risk for those engaging in illegal immigration.
About Passports:
- Rooted in history, passports trace back to mentions in the Hebrew Bible and structured systems in nations like France and the UK.
- The evolution into modern passports was catalyzed by the British Nationality and Status of Aliens Act in 1914, introducing features such as photographs and distinctive characteristics.
- The League of Nations' 1920 conference sought to standardize passport regulations, contributing to the establishment of a common British system.
- During the 1920s, the United States linked immigration laws to passports, imposing limitations on inflows.
- Despite initial reservations, passports have persisted as an integral element of contemporary citizenship.
- Indian Passports: The initiation of issuing Indian passports dates back to the First World War (1914-1918) through the Defence of India Act, as mandated by the British government for travel.
Assam-Meghalaya panels for boundary dispute to submit reports by December 31 (The Hindu)
- 23 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
The regional committees on the boundary dispute between Assam and Meghalaya have been asked to submit their reports by December 31, a Meghalaya government official said on Friday, December 22.
What is the Assam-Meghalaya Border Dispute?
- The Assam and Meghalaya have a longstanding dispute in 12 stretches of their 884-km shared border.
- The areas include Upper Tarabari, Gazang Reserve Forest, Hahim, Langpih, Borduar, Boklapara, Nongwah, Matamur, Khanapara-Pilangkata, Deshdemoreah Block I and Block II, Khanduli, and Retacherra.
Historical Context:
- During British rule, undivided Assam encompassed present-day Nagaland, Arunachal Pradesh, Meghalaya, and Mizoram.
- Meghalaya was delineated in 1972, following the Assam Reorganisation (Meghalaya) Act of 1969, but differing interpretations of the border emerged.
- In 2011, Meghalaya identified 12 disputed areas, covering approximately 2,700 sq km.
Key Point of Contention:
- A focal point of discord is Langpih in West Garo Hills, bordering Kamrup district in Assam.
- Post-Independence, Langpih transitioned from Kamrup district to Garo Hills and Meghalaya.
- Assam contends it's part of the Mikir Hills, while Meghalaya questions the inclusion of Blocks I and II of the Mikir Hills (now Karbi Anglong) in Assam.
Efforts to Resolve Dispute:
- In 1985, an official committee, led by former Chief Justice of India Y V Chandrachud, was formed but didn't yield a resolution.
- Both states identified six out of 12 disputed areas for resolution, resulting in a Memorandum of Understanding in March 2022.
- The second round of discussions for the remaining areas commenced in November 2022.
Potential Solutions:
- Utilizing satellite mapping for precise border demarcation.
- Leveraging constitutional provisions like Article 263 for the Inter-state Council to advise on disputes and coordinate policies.
- Reviving Zonal Councils to address common concerns among states in each zone, including border disputes and economic planning.
- Embracing the spirit of cooperative federalism to strengthen India's unity in diversity.
IIT Guwahati researchers devise mathematical model to help prevent riverbank erosion (Indian Express)

- 23 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
A team of researchers at the Indian Institute of Technology (IIT) Guwahati has developed a new award-winning mathematical model to help prevent erosion of rivers like Brahmaputra.
What is BRAHMA-2D?
- BRAHMA-2D (Braided River Aid: Hydro-Morphological Analyzer) is a sophisticated mathematical model designed for assessing the flow dynamics of expansive braided rivers such as the Brahmaputra.
- Functioning as a quasi-3D river flow model, BRAHMA-2D offers insights into water velocity at various depths within the river and the circulation patterns around structures like spurs, crucial for preventing river bank erosion.
- Developed through collaboration between researchers at IIT Guwahati and the Brahmaputra Board under the Union Ministry of Jal Shakti, this innovative model plays a pivotal role in the design of sustainable hydraulic structures.
- Engineers can leverage BRAHMA-2D to create effective structures like spurs, river bends, and other protective measures to combat river bank erosion.
- The model's successful validation on the Brahmaputra River near Majuli Island in Assam, a region prone to river bank erosion, underscores its practical applicability.
- BRAHMA-2D integrates a two-dimensional water movement model with entropy theory, focusing on disorder or randomness.
- Notably, it identifies a unique dip phenomenon near spurs, where water flows underneath intensifies—a phenomenon absent at points away from these structures.
- Beyond erosion prevention, BRAHMA-2D extends its utility to environmental studies by assessing the habitat suitability of aquatic species, particularly endangered ones.
- This assessment is based on factors such as required depth and flow velocity, showcasing the model's versatility in addressing multifaceted challenges in river ecosystems.
About Brahmaputra River:
- Originating as Siang or Dihang from the Chemayungdung glacier in the Kailash range near Mansarovar Lake, the Brahmaputra enters India to the west of Sadiya town in Arunachal Pradesh.
- Tributaries: Dibang, Lohit, Siang, Burhi Dihing, Tista, and Dhansari contribute to its flow.
- This perennial river exhibits distinctive features influenced by its geography and prevailing climatic conditions.
- Experiencing biannual flooding, the first occurs from the melting Himalayan snow in summer, and the second is a consequence of monsoon flows.
- Climate change has amplified the frequency and intensity of these floods, posing a threat to populations and food security in the lower riparian states of India and Bangladesh.
- Known for its dynamism, the Brahmaputra undergoes frequent changes in course, driven by landslides and geological activities.
Three heritage projects in Punjab and Haryana bag UNESCO Asia-Pacific Awards 2023 (Business Standard)

- 23 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
The resilient urban revitalisation of Rambagh Gate and Ramparts in Punjab, and heritage conservation projects related to Haryana's Church of Epiphany and Delhi's Bikaner House won Unescoawards on Thursday.
About Rambagh Gate & Ramparts:
- A three-story architectural marvel, the Rambagh Gate underwent meticulous restoration employing traditional building techniques.
- Locally sourced materials, including Nanak Shahi bricks set in lime mortar, were integral to the restoration process.
About Pipal Haveli, Gurdaspur:
- Pipal Haveli in Gurdaspur stands as a testament to ecological and traditional building methods, incorporating locally sourced materials and embracing vernacular architectural language.
- Notably, it actively promotes women's empowerment through initiatives like the BaRi Collective, offering programs that enhance women's livelihoods through environmentally conscious craft practices.
What is the UNESCO Asia-Pacific Awards for Cultural Heritage Conservation?
- UNESCO aims to promote private sector engagement and foster collaborations between the public and private sectors to preserve the cultural heritage of the Asia-Pacific region for the benefit of present and future generations.
- Since the year 2000, the UNESCO Asia-Pacific Awards for Cultural Heritage Conservation have been acknowledging the accomplishments of private sector entities and public-private initiatives in effectively conserving or restoring structures, places, and properties of significant heritage value in the region.
- Noteworthy, among the recognized sites, five are located in China, six in India, and one in Nepal.
- Highlights of Award-Winning Sites in India:
- Rambagh Gate in Amritsar: Received the prestigious "Award of Excellence," the highest recognition across all categories.
- Pipal Haveli in Punjab: Honored for its sustainable development as a heritage rural homestay.
- Karnikara Mandapam at Kunnamangalam Bhagawati Temple in Kerala: Earned the esteemed "Award of Distinction."
- Epiphany in Haryana, David Sassoon Library and Reading Room in Mumbai, and Bikaner House in New Delhi: Recognized with the "Award of Merit" for their outstanding contributions to cultural heritage conservation.
CISF to take over security of Parliament complex after Lok Sabha breach | What's the plan (Indian Express)

- 23 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
The Union Home Ministry has approved the deployment of the Central Industrial Security Force (CISF) in the Parliament complex, according to a government order.
News Summary:
- Following the security breach on December 13, the Union Home Ministry has given the green light for CISF deployment in the Parliament complex.
- Collaborating with Parliament Security Services, CISF will oversee access control for both the new and old Parliament buildings.
What are the Current Security Arrangements in Parliament?
- The Delhi Police currently handles access control, including frisking and baggage scanning.
- In response to the recent incident, eight Delhi Police security personnel responsible for these duties were suspended.
- In the event of armed intervention, the Parliament Duty Group (PDG), an armed unit of the Central Reserve Police Force (CRPF), is deployed.
- The overall responsibility for security lies with the Parliament Security Service under the Lok Sabha Speaker.
About Central Industrial Security Force (CISF):
- Established under the Central Industrial Security Force Act, 1968, CISF is a key Central Armed Police Force (CAPF).
- Initially formed in 1969 with three battalions, it has evolved into a versatile organization boasting a current strength of 1,63,590 personnel.
- Operating under the administrative purview of the Ministry of Home Affairs, CISF's headquarters is situated in New Delhi.
Key Operations:
- Critical Infrastructure Protection: Safeguarding 353 establishments nationwide, including Atomic Power Plants, Space Installations, Defence Production Units, Mines, Oil Fields, and Refineries.
- Fire Protection: Maintaining a dedicated Fire Wing catering to 104 establishments for fire safety services.
- VIP Security: Mandated to provide security to VIP protectees categorized as Z+, Z, Y, and X across the country.
- Airport Security: Entrusted with the specialized task of airport security since 2000, following the hijacking of Indian Airlines Flight IC-814 to Kandahar.
- Private Sector Security: Authorized by an amendment to the CISF Act, the force offers security services, on a payment basis, to vital private and joint venture industrial entities contributing to the nation's security and economy.
- Examples include Infosys campuses, Patanjali Food and Herbal Park, and the Reliance refinery.
- Overseas Deployment: Contributing contingents to the United Nations Stabilization Mission in Haiti (MINUSTAH).
- CISF stands out as the only Central Armed Police Force with a daily public interface, playing a crucial role in securing airports, the Delhi Metro, and iconic monuments.
NSG Takes on Invasive Vilayati Kikar/Prosopis Juliflora (Indian Express)

- 11 Oct 2023
Why in the News?
The National Security Guard (NSG) is actively combating the encroachment of the invasive plant species known as vilayati kikar at its Manesar campus, situated near the Delhi-Ajmer highway.
What is Prosopis Juliflora?
- Prosopis juliflora, a shrub or small tree belonging to the Fabaceae family and classified as a type of mesquite, is indigenous to Mexico, South America, and the Caribbean.
- Introduced to Delhi by the British in the 1920s during the construction of the national capital, this species is locally known by various names in India, including Bellary jaali, seemai karuvelam, seemai jaali, gando baval, and vilayati kikar.
- Known for its high ecological adaptability, Prosopis juliflora can thrive in diverse soil types, ranging from sand dunes to clay, and from saline to alkaline soils.
- It exhibits a wide altitude range, growing below 200 to above 1500 meters above sea level, with a mean annual rainfall varying from 50 to 1500 mm.
- However, despite its adaptability, it is recognized as an invasive plant with a propensity for vigorous growth, enabling it to outcompete indigenous plant species.
Impacts on the Environment: This invasive species pose significant environmental challenges:
- Prosopis juliflora absorbs more than four litres of water to produce one kilogram of biomass.
- The plant generates less oxygen and more carbon dioxide, making it less conducive to supporting bird habitats.
- It has the potential to contaminate groundwater, posing risks to the overall quality of this vital resource.
- The species contributes to land erosion by displacing grasslands that serve as habitats for native plants and animals.
- The invasive nature of Prosopis juliflora raises concerns about its ecological impact and necessitates efforts to manage and control its spread in affected regions.
Govt Notifies Changes in PLI Scheme for White Goods (Business Standard)

- 11 Oct 2023
Why in the News?
The central government has introduced changes to the rules governing the production-linked incentive (PLI) scheme for white goods, specifically air conditioners and light-emitting diode lights, with the goal of ‘simplifying the scheme’s operations’ and promoting the ease of doing business, according to an official statement on Wednesday.
What are White Goods?
- Major home appliances, commonly known as white goods, encompass substantial household devices like stoves, refrigerators, freezers, washing machines, tumble dryers, dishwashers, and air conditioners.
- While these durable consumer durables were initially available only in white, contemporary options offer a variety of colours, yet they persistently retain the term "white goods."
- Renowned for their robustness and extended lifespan, white goods are engineered to endure the rigours of daily use.
- Additionally, the term "white goods" may extend to white fabrics, particularly linen or cotton, including items like curtains, towels, or sheets, which historically were crafted from white cloth.
- In the beverage industry, the term "white goods" refers to colourless spirits such as vodka or gin.
What is Brown Goods?
- Brown goods refer to relatively lightweight electronic consumer durables, including computers, digital media players, TVs, and radios.
- In contrast to large household appliances (white goods), brown goods are primarily geared towards entertainment, communication, and convenience.
- Typically featuring electronic components, these devices are designed to deliver audio, video, or data-related services as their primary functions.
What is Grey Goods?
- When a commodity is traded through distribution channels, which are unofficial but legal are known as the grey goods.
- They are goods that are traded in a specific area, where the manufacturer does not intend to sell the product, but with different specifications.
- Grey goods are sold without the knowledge of the original manufacturer.
- They are typically less costly than the ones that are available by the authorised distributor.
- Also, they might be made to pertain to some jurisdiction.
- Example: A factory-unlocked version of the iPhone. It is made to suit US standards but is sold in India for a lesser price than the iPhone made for Indian standards.
- When it comes to such Grey goods, the manufacturer does not provide any warranty for the product.
Migratory Birds Arrive in Odisha’s Chilika Before Winter (DownToEarth)

- 11 Oct 2023
Why in the News?
Migratory birds have started their annual journey to Chilika Lake—India’s largest waterbird habitat in Odisha — ahead of winter this year.
About Chilika Lake:
- Chilika Lake is the largest brackish water lake and a shallow lagoon with estuarine character spread across the districts of Puri, Khurda and Ganjam in the state of Odisha in eastern India.
- It is considered to be the largest lagoon in India and is counted amongst the largest lagoons in the world.
- It is the largest wintering ground for migratory waterfowl found anywhere on the Indian sub-continent.
- It is one of the hotspots of biodiversity in the country, and some rare, vulnerable and endangered species listed in the IUCN Red List of threatened Animals inhabit the Lake area for at least part of their life cycle.
- On account of its rich bio-diversity, Chilika Lake was designated as a "Ramsar Site", i.e. a wetland of International Importance.
- The Nalaban Island within the lake is notified as a Bird Sanctuary under the Wildlife (Protection) Act, 1972.
- The National Wetlands, Mangroves and Coral Reefs Committee of the Ministry of Environment & Forests, Government of India, have also identified the lake as a priority site for conservation and management.
- The Lake is a highly productive ecosystem, with rich fishery resources.
- The rich fishing grounds sustain the livelihood of more than 0.2 million fisherfolk who live in and around the lake.
- It has a great heritage value and maritime trade to the far east countries used to take place from here.
- It is the largest winter ground of migratory birds in the Indian sub-continent and home to more than 150 highly threatened Irrawaddy dolphins, which is the largest lagoonal population globally.
- It supports some of the largest congregation of migratory birds from large parts of Asia, particularly during the winters that arrive from as far as the Caspian Sea, Lake Baikal, Aral Sea, remote parts of Russia, Kirghiz steppes of Mongolia, Central and South East Asia, Ladakh and the Himalayas to feed and breed in its fertile waters.
NASA Recently Shared a Satellite Image of Deception Island (Tribune India)
- 11 Oct 2023
Why in the News?
National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) recently shared a satellite image of Deception Island, one of the only places in the world where a ship can sail directly into the centre of an active volcano.
About Deception Island:
- Deception Island is situated within the South Shetland Islands, forming part of an archipelago northwest of the Antarctic Peninsula.
- This volcanic island is notable for its dynamic features and distinct geography.
- Originating from a colossal volcanic eruption, Deception Island's formation resulted in the collapse of its central structure, allowing seawater to inundate the resulting caldera.
- The landscape is characterized by desolate volcanic slopes, steaming beaches, and glaciers adorned with ash layers, creating a unique horseshoe-shaped entrance to the sea via Neptune’s Bellows.
- The island encircles Port Foster, recognized as one of the safest harbours in the Antarctic, offering vessels a rare opportunity to navigate into the heart of an active volcano.
- Among the few places globally where this is possible, Deception Island has experienced over twenty eruptions since the 19th century.
- Notably, the island witnessed three volcanic eruptions from 1967 to 1970, leading to the destruction of Chilean and British stations.
- Presently, Argentina and Spain maintain summer scientific stations on the island.
- Deception Island is safeguarded under the Antarctic Treaty, designating it as a protected area with restricted human visits and minimized environmental impact.
Cabinet Approves Establishment of an Autonomous Body Mera Yuva Bharat (PIB)

- 11 Oct 2023
Why in the News?
The Union Cabinet, chaired by Prime Minister Shri Narendra Modi, has approved the establishment of an autonomous body Mera Yuva Bharat (MY Bharat).
About Mera Yuva Bharat (MY Bharat):
- Mera Yuva Bharat (MY Bharat), an autonomous body will benefit the youth in the age group of 15-29 years, in line with the definition of ‘Youth’ in the National Youth Policy.
- In the case of programme components specifically meant for adolescents, the beneficiaries will be in the age group of 10-19 years.
- It will help in Setting the focus of the Government on youth-led development and to make the Youth “active drivers” of development and not merely “passive recipients”.
- It will be launched on 31st October 2023 on National Unity Day.
Objective:
- The primary objective of Mera Yuva Bharat (MY Bharat) is to make it a whole of Government platform for youth development.
- With access to resources & connection to opportunities, youth would become community change agents and nation builders allowing them to act as the Yuva Setu between the Government and the citizens.
- It seeks to harness the immense youth energy for nation-building.
The establishment of Mera Yuva Bharat (MY Bharat) would lead to:
- Leadership Development in the Youth:
- Improve leadership skills through experiential learning by shifting from isolated physical interaction to programmatic skills.
- Investing more in youth to make them social innovators, and leaders in the communities.
- Setting the focus of the Government on youth-led development and making the Youth “active drivers” of development and not merely “passive recipients”.
- Better alignment between youth aspirations and community needs.
- Enhanced efficiency through Convergence of existing programmes.
- Act as a one-stop shop for young people and Ministries.
- Create a centralized youth database.
- Improved two-way communication to connect youth government initiatives and activities of other stakeholders that engage with youth.
- Ensuring accessibility by creating a digital ecosystem.
Why There is a Need for Such Initiative?
- India’s youth are to play a critical role in defining the future of the nation.
- There is a need to establish a new contemporary technology-led platform for the Government to engage with the present-day youth.
- Ensuring accessibility by creating a digital ecosystem
- Mera Yuva Bharat supported by a technology platform would help to increase the Youth outreach efforts of the Department of Youth Affairs.
Mukundra Hills Tiger Reserve in Rajasthan Now Opens for Safari Tours (TOI)

- 10 Oct 2023
Why in the News?
The forest department started the inaugural jungle safari at the Mukundra Hills Tiger Reserve on Monday, which marks the beginning of organised tiger reserve tours for tourists in four locations across the state.
About Mukundra Hills Tiger Reserve:
- Location: Mukundra Hills Tiger Reserve, also known as Darrah Wildlife Sanctuary, spans across four districts – Bundi, Kota, Jhalawar, and Chittorgarh in Rajasthan.
- The reserve is nestled in a valley formed by two parallel mountains, Mukundra and Gargola.
- Establishment: In 2013, the tiger reserve was formed, encompassing Mukandra National Park, Dara Sanctuary, Jawahar Sagar Sanctuary, and a section of Chambal Sanctuary.
- Initially, it served as a hunting preserve for the Maharaja of Kota.
- River: Positioned on the eastern bank of the Chambal River, the reserve is crisscrossed by its tributaries.
- Vegetation: The reserve features a Dry Deciduous Forest.
- Flora: The dominant species is Kala Dhok or Kaladhi (Anogeissus pendula), accompanied by Khair, Ber, Kakan, Raunj, and more.
- On elevated slopes, Anogeissus pendula gives way to Anogeissus latifolia, coexisting with Bel, Salar, Uum, and Shisham.
- Fauna: Noteworthy fauna include Leopard, Sloth bear, Nilgai, Chinkara, Spotted Deer, Small Indian Civet, Toddy Cat, Jackal, Hyena, Jungle Cat, and Common Langur, among others.
- The region is also home to various reptiles and amphibians, such as Pythons, Rat Snake, Buff-striped keelbacks, Green keelbacks, crocodiles, turtles, Gharial and Otters.
Periodic Labour Force Survey (PLFS) Says Unemployment Rate Declined (The Hindu)

- 10 Oct 2023
Why in the News?
The Periodic Labour Force Survey (PLFS) has reported that the unemployment rate in the country has shown a decrease between April and June 2023.
Key Observations of the Periodic Labour Force Survey (PLFS):
- Improved Work Metrics: Both the Labour Force Participation Rate (LFPR) and Worker-Population Ratio (WPR) showed positive trends in the recent period.
- Urban Employment Trends: In urban areas, LFPR increased from 47.5% (April-June 2022) to 48.8% (April-June 2023) for individuals aged 15 and above.
- The WPR in urban areas rose from 43.9% (April-June 2022) to 45.5% in the corresponding months this year.
- Gender-specific Changes:
- Male LFPR increased from 68.3% to 69.2%.
- Female LFPR showed notable growth from 18.9% to 21.1% during the observed period.
What is the Periodic Labour Force Survey (PLFS):
- Conducted by the National Sample Survey (NSO) under the Ministry of Statistics and Programme Implementation (MoSPI).
- Launched in April 2017 by the National Statistical Office (NSO) to provide more frequent labour force data.
Objectives:
- Estimate key employment and unemployment indicators every three months for urban areas.
- Annually estimate indicators for both 'Usual Status' and 'Current Weekly Status' in rural and urban areas.
- Key Indicators:
- Labour Force Participation Rate (LFPR): Percentage of individuals in the population who are part of the labour force (working, seeking, or available for work).
- Worker Population Ratio (WPR): Percentage of employed persons in the population.
- Unemployment Rate (UR): Percentage of unemployed persons among those in the labour force.
- Current Weekly Status (CWS): Activity status determined based on the activities in the last 7 days before the survey.
India to Hold Satellite Spectrum Auctioning (The Hindu BusinessLine)

- 10 Oct 2023
Why in the News?
The Elon Musk vs Mukesh Ambani battle on whether to auction or allocate satellite spectrum has attracted intervention from the Prime Minister’s Office (PMO).
What is Satellite Spectrum?
- The satellite spectrum is like a special section of radio waves reserved for satellites when they're up in space.
- It's part of the larger family of radio waves that we use for things like Wi-Fi, TV, and radio.
- This spectrum serves as a vital resource for countries, facilitating satellite broadcasting, communication, and weather services.
Key Points:
- Limited Resource: The satellite spectrum is finite, allocated for activities like satellite broadcasting and communication.
- It plays a crucial role in facilitating services provided by communication satellites and weather satellites.
- Frequency Bands: The spectrum is categorized into different frequency bands, chosen based on diverse applications.
- The frequency assigned during a satellite's construction remains unchanged post-launch.
- Impact on Data Transfer: The frequency of a signal dictates the speed of data transfer.
- Higher frequencies enable faster data transmission, but they also entail shorter wavelengths, leading to signal attenuation over distances and increased interference risks.
- Frequency Range: Satellites typically transmit in the frequency range of 1.5 to 51.5 gigahertz.
- High-speed broadband operations often use the higher end of this spectrum.
About International Telecommunication Union (ITU):
- Founded in 1865 as the International Telegraph Union, later becoming a specialized agency of the United Nations in 1947.
- Functions:
- Allocates global radio spectrum and satellite orbits.
- Coordinates and sets technical standards for telecommunication/ICT.
- Strives to enhance ICT access in underserved communities globally.
- Headquarters: Geneva, Switzerland.
- Membership: Comprises 193 countries and nearly 800 private sector entities and academic institutions.
- India's Association with ITU: India has actively participated in the ITU since 1869, maintaining a consistent presence on the ITU Council since 1952.
New Species of Bagworm Moth discovered From Idukki (The Hindu)

- 10 Oct 2023
Why in the News?
Researchers from the Zoology Department at St. Thomas College (Autonomous), Thrissur, have discovered a new species of bagworm moth, Wizard Bagworm, from near the Nariyampara Falls in the Idukki district.
What is a Bagworm Moth?
- Belonging to the family of moths in the order Lepidoptera, bagworm moths are recognized for their protective larval cases.
- These moths are distributed globally, with notable populations in North America and Africa.
- In their larval stage, these perennial moths inhabit various evergreen trees and junipers.
- They derive their name from the bag-like cases constructed by the larvae around themselves.
- The larvae can pose a threat to trees, particularly evergreens.
About Eumasia Venefica:
- This recently identified species earned its name due to the unique shape of its bag, resembling a wizard's hat.
- It is the fourth species within this genus to be documented in India.
- Distinctive Features:
- The species exhibits effective camouflage techniques to evade predators.
- Larval cases of Eumasia venefica are discovered attached to rocks adorned with lichens.
- These cases join together, forming a colony covered with lichens.
- The larval bags bear a resemblance to a 'witch's hat,' featuring a disc-like anterior and a tubular posterior part.
- Unlike polyphagous pests, the larvae of this species exclusively feed on algae and mosses present on rocks.
Pontus Tectonic Plate: Geologist Unexpectedly Finds Remnants of a Lost Mega-Plate (Science Daily)
- 10 Oct 2023
Why in the News?
Geologists have reconstructed a massive and previously unknown tectonic plate that was once one-quarter the size of the Pacific Ocean.
About Pontus Tectonic Plate:
- Recently discovered in the west Pacific Ocean, the Pontus Tectonic Plate is a long-lost geological plate that holds significance in Earth's history.
- Believed to have measured about 15 million square miles at its zenith, roughly equivalent to one-quarter of the Pacific Ocean, this massive tectonic plate dates back as far as 160 million years, with more recent traces extending to approximately 20 million years ago.
- Over millions of years, the Pontus Plate underwent a gradual subduction process, pulled downward beneath a neighbouring plate by the force of gravity.
How was this Discovery Made?
- The subducting process involves the plate sinking into Earth's mantle due to its higher density compared to the surrounding mantle.
- Traces of a subducted plate are discernible in the form of rock fragments concealed in mountain belts.
- During subduction, upper portions of the plate are occasionally scraped off.
- Researchers employed geological data and computer modelling to reconstruct the movements of current plates, revealing a substantial area potentially vacated by the subducted Pontus Plate.
- Utilizing magnetic techniques, scientists identified basalt remnants in Borneo as Pontus relics, suggesting that this fragmentary evidence was left behind during the plate's subduction some 85 million years ago.
What is Plate Tectonics?
- Tectonic plates are large, rigid pieces of Earth's lithosphere, the outer shell comprising the crust and uppermost part of the mantle.
- These plates, which vary in size and shape, constantly move and interact, shaping the Earth's dynamic surface.
- The Earth's lithosphere is divided into several major plates, such as the Pacific, North American, and Eurasian plates, among others.
- The interactions at plate boundaries result in various geological phenomena, including earthquakes, volcanic eruptions, and the formation of mountain ranges.
- Plate tectonics, the theory explaining these movements, underscores how heat-driven convective currents in the Earth's mantle cause plates to diverge, converge, or slide past each other.
- Tectonic plate movements influence the planet's topography, seismic activity, and the distribution of continents and oceans, playing a fundamental role in Earth's geological evolution.
Reliance General gets ?923cr GST notices from the Directorate General of GST Intelligence (DGGI) (TOI)

- 09 Oct 2023
Why in the News?
Reliance General Insurance Company (RGIC), a subsidiary of the Anil Ambani-led Reliance Capital, has received multiple show-cause notices worth Rs 922.58 crore from the Directorate General of GST Intelligence (DGGI).
About Directorate General of GST Intelligence (DGGI):
- Formerly known as the Directorate General of Central Excise Intelligence (DGCEI), the Directorate General of GST Intelligence (DGGI) stands as a premier intelligence organization operating under the Central Board of Indirect Taxes & Customs, within the Department of Revenue, Ministry of Finance.
- Its primary focus is on collecting, collating, and disseminating intelligence pertaining to Goods and Services Tax (GST) evasion and duties related to Central Excise and Service Tax on a pan-India basis.
- Evolution: Originally designated as the Directorate General of Anti-Evasion (DGAE), it was established in 1979 as an independent wing under the Directorate of Revenue Intelligence, New Delhi.
- Became a full-fledged Directorate in 1983, headed by a Director.
- In 1988, attained the status of Directorate General under a Director General.
- Currently comprises 04 offices of the Director General (East, West, North, and South), 26 Zonal Units, and 40 Regional Units.
Key Responsibilities:
- Intelligence Gathering: Collects information from various sources, including GST returns, financial statements, and other documents, to identify potential GST law violations.
- Investigation: Empowered to conduct investigations into suspected cases of GST evasion or non-compliance, involving summoning individuals, examining records, and executing searches and seizures.
- Enforcement: Enforces provisions of the GST law, taking legal action against offenders, imposing penalties, and recovering taxes or duties owed.
- Additional Functions: Collaborates with agencies like the Central Board of Indirect Taxes and Customs (CBIC) and State GST authorities for effective GST law implementation.
- Plays a crucial role in raising awareness about GST compliance and educating taxpayers on their legal obligations.
- Provides technical and legal assistance to field officers and other government entities involved in GST administration.
Mandarin-Trained Territorial Army Inducted At LAC (ET)

- 09 Oct 2023
Why in the News?
Recently the Territorial Army (TA) has inducted its first batch of Mandarin-trained officers to support the regular Army's efforts to enhance expertise in the Chinese language.
What is the Territorial Army (TA)?
- The Indian Territorial Army (TA) acts as the second line of defence, complementing the regular Indian Army.
- It is distinct in its role, being neither a profession, occupation, nor a source of employment.
- Reserved for individuals engaged in mainstay civilian professions, gainful employment or self-employment in a civil field is a prerequisite for joining the TA.
Key Roles:
- Relieving Regular Army: Primarily tasked with relieving the Regular Army from static duties.
- Assistance in Emergencies: Provides crucial assistance to civil authorities during natural calamities and tragedies.
- Essential Services: Aids civil administration in delivering essential services, particularly in areas facing stretched state machinery or security threats.
Service Commitment:
- Part-Time Service: TA volunteers typically serve in uniform for a few days annually, ensuring their readiness to bear arms for national defence during emergencies.
Historical Background:
- Established by the British in 1920 through the Indian Territorial Act, organized into 'The Auxiliary Force' for Europeans & Anglo-Indians and 'The Indian Territorial Force' for Indian Volunteers.
- The Territorial Army Act of 1948 formalized the TA, inaugurated by the first Indian Governor General, Shri C Rajagopalachari, on 9th October 1949.
- Motto: Savdhani Va Shoorta (Vigilance and Valour).
Eligibility Criteria:
- Nationality: Open to Indian citizens (Men & Women).
- Age: 18 to 42 years.
- Education: Graduate from any recognized university.
- Physical Standards: Must be physically and medically fit.
- Employment: Gainful employment in civilian professions.
- Exclusions: Serving members of the Regular Army/Navy/Air Force/Police/GREF/Para Military and similar forces are ineligible.
New Ensign for the Indian Air Force (HT)

- 09 Oct 2023
Why in the News?
Indian Air Force (IAF) Chief Air Chief Marshal (ACM) Vivek Ram Chaudhari on Sunday unveiled a new Ensign for the force, as it marked its 91st anniversary, by the inclusion of the Air Force Crest in the top right corner of the Ensign, towards the fly side.
About the Indian Air Force (IAF) Ensign:
- The new IAF Ensign exclusively incorporates the IAF Crest, featuring distinctive elements that symbolize the spirit and ethos of the Indian Air Force.
Key Elements:
- IAF Crest: The crest prominently showcases the national symbol, the Ashoka Lion, atop, with "Satyamev Jayate" in the Devanagari script beneath.
- Himalayan Eagle: Positioned below the Ashoka Lion, a Himalayan eagle with outstretched wings symbolizes the formidable fighting spirit of the IAF.
- Light Blue Ring: Encircling the Himalayan eagle, a light blue ring bears the words "Indian Air Force."
- IAF Motto: Derived from the Bhagavad Gita, the motto "Nabha Sparsham Deeptam" (touching the sky with glory) is inscribed in golden Devanagari below the eagle.
- The IAF crest serves as a powerful symbol of inspiration and encouragement.
Variations:
- IAF has adopted various crests for commands, squadrons, and other establishments, all adhering to a standard frame featuring the formation sign and a motto at the foot.
Historical Evolution:
- British Era: During the British era, the IAF was known as the Royal Indian Air Force, and its ensign featured the Union Jack and the RIAF roundel.
- Post-Independence: The current IAF Ensign, created post-independence, replaces the Union Jack with the Indian tricolour and the RAF roundels with the IAF tri-colour roundel in the lower right canton.
Govt Mulling Incentives for ASHA Workers (ET)

- 09 Oct 2023
Why in the News?
The government is planning to give incentives to ASHA health activists for mobilising eligible individuals for sickle cell disease screening and distribution of sickle cell cards for prevention and early detection of the disease.
About Accredited Social Health Activist (ASHA):
- ASHA serves as a trained female community health activist integral to the National Rural Health Mission initiated by the Government of India.
- Selected from the community and accountable to it, ASHA is trained to bridge the gap between the community and the public health system.
Key Functions:
- Acts as a care provider at the community level.
- Facilitates access to healthcare, medicine, and sanitation services.
- Health Awareness: Raises awareness of health issues among marginalized sections within the community.
- Advocate for Women's Health: Champions female health and hygiene standards.
- Advocates for a health-conscious approach to livelihood.
Implementation:
- The ASHA scheme is operational in all States/UTs, except Goa.
- States are mandated to employ at least one ASHA worker per every 1000 people.
- Inclusive Selection Process: The selection process involves various community groups, self-help groups, Anganwadi Institutions, and local committees.
Selection Criteria:
- Rural ASHA: Preferably a literate woman resident, married/widowed/divorced, aged 25 to 45 years, and preferably educated up to the 10th standard.
- Urban ASHA: Identified from vulnerable clusters, belonging to specific vulnerable groups, with good communication and leadership skills.
Compensation:
- Primarily an honorary volunteer compensated for specific situations.
- Ranges from Rs 2,000 to Rs 7,000, depending on the state.
- Incentives: Eligible for incentives under various national health programs.
Adani Ports' Flagship Mundra Port Completes 25 Years (ET)

- 09 Oct 2023
Why in the News?
Mundra Port in Gujarat has completed 25 years of its operations, highlighting its expansion and evolution as one of the largest ports globally.
About Mundra Port:
- Mundra Port stands as India's largest private and container port, situated on the north shores of the Gulf of Kutch near Mundra in the Kutch district of Gujarat.
- As a deep-draft, all-weather port, it holds the distinction of being a Special Economic Zone (SEZ).
- Managed by Adani Ports and Special Economic Zone Limited (APSEZ), the port is a pivotal player in India's cargo movement, accounting for nearly one-fourth of the nation's total.
- Mundra Port plays a crucial role in managing 33% of the country's container traffic.
- Key Features: Strategic Location: Positioned on the Gulf of Kutch, Gujarat.
- Handling Capacity: With an impressive capacity of 260 MMT, the port efficiently manages over 155 MMT (FY 2022-23), contributing to almost 11% of India's maritime cargo.
- Infrastructure: Boasting 26 berths and two single-point moorings, the port accommodates diverse vessels and handles various cargo types, including containers, dry bulk, break bulk, liquid cargo, and automobiles.
- Coal Import Terminal: Home to the nation's largest coal import terminal, Mundra facilitates swift cargo evacuation with minimal turnaround time.
- Rail Connectivity: The port's rail network is seamlessly integrated into the national rail network, ensuring efficient cargo handling for destinations across India.
SUGAM REC Mobile App for 54EC Bonds Investors (PIB)

- 07 Oct 2023
Why in the News?
Recently, REC Limited, the Maharatna Central Public Sector Enterprise launched a SUGAM REC mobile application.
What is the SUGAM REC App?
- The SUGAM REC App caters exclusively to current and prospective investors in REC's 54EC Capital Gain Tax Exemption Bonds.
- Users can conveniently download e-bond certificates, apply for new investments, access essential forms for KYC updates, and connect with REC's Investor Cell through call, email, or WhatsApp.
What are 54EC Bonds?
- Also known as Capital Gain Bonds, these fixed-income instruments offer capital gains tax exemption under section 54EC.
- Investors can save on income tax for long-term capital gains by investing in these bonds within six months of the gain.
- With a fixed lock-in period of 5 years, the bonds can be held in either Physical or Demat form.
- Issued by government-managed institutions, they fund specific capital projects and derive their name from the relevant section of the Income Tax Act, 1961.
Key Facts about REC Limited:
- A 'Maharatna' company under the Ministry of Power, Government of India.
- Registered with RBI as a non-banking finance company (NBFC), Public Financial Institution (PFI), and Infrastructure Financing Company (IFC).
- Established in 1969 to address severe drought and famine, focusing on energizing agricultural pump sets for irrigation and reducing reliance on monsoons.
- Provides long-term loans and financing products to State, Centre, and Private Companies for infrastructure asset creation.
- It is the nodal agency for initiatives like Pradhan Mantri Sahaj Bijli Har Ghar Yojana (SAUBHAGAYA), Deen Dayal Upadhaya Gram Jyoti Yojana (DDUGJY), and National Electricity Fund (NEF) Scheme.
NGT Investigates Removal of Invasive Mussels in Ennore-Pulicat Wetland (The Hindu)

- 07 Oct 2023
Why in the News?
The Southern Bench of the National Green Tribunal (NGT) has asked the Fisheries Department and the Tamil Nadu State Wetland Authority to file a detailed report on the removal of invasive mussel species from the Ennore-Pulicat wetland.
What is Mytella strigata?
- Mytella strigata is a moderately large mussel known for its symmetrical shell, commonly found in the middle intertidal and subtidal waters of estuaries and coastal areas.
- These mussels attach to surfaces using byssus threads.
- Appearance: Individual mussels display diverse external colours such as black, dark bluish, brown, grey, orange, and occasionally green.
- The species exhibits various shell patterns, including zigzags, spots, or concentric bands.
- Habitat and Distribution: Found in dense clusters on hard substrates and in epibenthic habitats, Mytella strigata is prevalent along the Atlantic and Pacific coasts of tropical South and Central America.
- It has also expanded its presence to regions like Taiwan, the Philippines, Singapore, the Gulf of Thailand, the west coast of India, and the southeastern United States.
- Threats: These mussels pose a threat as they spread across river bottoms, forming carpets that hinder prawns from grazing or burying themselves in the sediment.
About Pulicat Lake:
- Pulicat is an extensive brackish-to-saline lagoon with marshes and a brackish swamp on the north.
- This is the second-largest saltwater lagoon in India and a Ramsar site (internationally recognized wetland under the Ramsar Convention).
- Only 16% of the lagoon is in Tamil Nadu; the rest is in Andhra Pradesh.
- It is fed by the Araani River at the southern tip and the Kalangi River from the northwest.
- Buckingham Canal, a navigation channel, passes through the lagoon.
- On the eastern boundary of this lagoon is Shriharikota Island, which separates the lagoon from the Bay of Bengal.
- The lagoon is shallow with large areas of mudflats and sandflats.
Watermeal May Become an Essential Food for Astronauts (India Today)

- 07 Oct 2023
Why in the News?
Scientists from Mahidol University in Thailand have been exploring the potential of watermeal, the smallest flowering plant on Earth, as a source of nutrition and oxygen for astronauts.
What is Watermeal?
- The Watermeal scientifically known as Wolffia, is often mistaken for algae, but they're actually the smallest flowering plants in the world!
- Its simplicity and rapid growth rate make it an ideal candidate for studying the effects of altered gravity on plant development.
- this tiny plant is aquatic, predominantly floating on the surface of water bodies.
- Because watermeal doesn’t have any roots, stems or leaves, it is basically just a sphere floating on a body of water.
- It's a prolific producer of oxygen through photosynthesis and belongs to the duckweed family (Lemnaceae).
- Each individual watermeal plant is extremely small, roughly the size of a pinhead.
- It has a simple, globular, and rootless structure, often appearing like minute green grains on the water.
- Watermeal thrives in quiet, nutrient-rich freshwater environments like ponds, lakes, and marshes.
- The plant is found globally, with a significant presence in Asia and Thailand.
- Watermeal is known to be a rich source of protein, making it a nutritious foodstuff.
- In Thailand, it has been part of the local diet for generations, appearing in dishes ranging from soups to salads.
Atmospheric Perturbations around the Eclipse Path (APEP) mission (HT)

- 07 Oct 2023
Why in the News?
Dr Aroh Barjatya, an Indian-origin scientist is set to lead the multi-institution NASA rocket mission on October 14.
About Atmospheric Perturbations around the Eclipse Path (APEP) mission:
- The APEP mission entails the launch of three rockets, each equipped with scientific instruments, to explore changes in the upper atmosphere during a solar eclipse, particularly during the critical phase of sudden light reduction.
- Mission Objective: To investigate alterations in the ionosphere induced by the abrupt decrease in sunlight during an eclipse, leading to the generation of waves in this atmospheric layer.
- Measurements will encompass changes in electric and magnetic fields, as well as variations in density and temperature.
- Launch Details: The launch site is the White Sands Missile Range in New Mexico, with a specific focus on studying the ionosphere's response during an eclipse.
- Potential Impact on Communications: NASA notes projections indicating a temperature and density reduction in the ionosphere during the eclipse, potentially causing disruptive wave disturbances that could affect GPS and satellite communications.
- Process: Rockets will be strategically positioned just beyond the path of annularity, where the Moon directly aligns with the Sun.
- Each rocket will deploy four compact scientific instruments designed to capture data on electric and magnetic fields, density, and temperature changes.
- NASA's primary objective is to achieve unprecedented simultaneous measurements from multiple ionospheric locations during a solar eclipse.
- Rationale for Rocket Selection: Sounding rockets were chosen for their precision in pinpointing and measuring specific regions of space.
- Their ability to investigate lower altitudes, inaccessible to satellites, makes them ideal for this mission.
- Sounding rockets offer precise data recording as they ascend and descend during suborbital flights, covering altitudes ranging from 45 to 200 miles (70 to 325 kilometres) above Earth's surface along their flight path.
Gangetic River Dolphin (The Hindu)

- 07 Oct 2023
Why in the News?
A recent publication by scientists and researchers has revealed that 19 Gangetic river dolphins had been rescued from the irrigation canals of the Ganga-Ghagra basin in Uttar Pradesh between 2013 and 2020.
About Gangetic River Dolphin:
- The Gangetic River dolphin is a freshwater species, representing one of the rare river dolphins worldwide.
- Distribution: It thrives in the river systems of Ganges-Brahmaputra-Meghna and Karnaphuli-Sangu, spanning across Nepal, India, and Bangladesh.
- Common Names: Known by various names such as Blind dolphin, Ganges dolphin, Ganges susu, hihu, side-swimming dolphin, and South Asian River Dolphin.
- Designated as India's National Aquatic Animal.
- Physical Features: Characterized by a long, thin snout, rounded belly, stocky body, and large flippers.
- Primarily feeds on fish, often found in counter-current systems of the main river channel.
- Eyes lack a lens, earning it the moniker 'blind dolphin.'
- Possesses an advanced bio-sonar system for effective hunting, even in murky waters.
- Requires surfacing every 30-120 seconds for breathing; its audible breathing sounds have led to the affectionate term 'Susu.'
- Conservation Status: IUCN categorizes it as Endangered.
- Protected under Schedule-I of the Wildlife (Protection) Act.
- Listed in CITES Appendix I.
Ayushman Arogya Mandir (The Hindu)

- 30 Nov 2023
Why is it in the News?
Recently, the Union Government has decided to rename the current Ayushman Bharat Health and Wellness Centres (AB-HWCs) as 'Ayushman Arogya Mandir.'
About Ayushman Arogya Mandir:
- The government has decided to rename the Ayushman Bharat-Health and Wellness Centres as 'Ayushman Arogya Mandir'
- The rebranded AB-HWCs will also have a new tagline -- 'Arogyam Parmam Dhanam'.
- Under the Government of India's flagship Ayushman Bharat Yojana, more than 1.6 lakhs AB- HWCs have been successfully established across states and UTs over the last five years with 219 crore footfalls so far.
- Ayushman Arogya Mandir is an attempt to move from a selective approach to health care to deliver a comprehensive range of services spanning preventive, promotive, curative, rehabilitative, and palliative care.
- It has two components which are complementary to each other.
- Under its first component, 1,50,000 Ayushman Arogya Mandir will be created to deliver Comprehensive Primary Health Care, that is universal and free to users, with a focus on wellness and the delivery of an expanded range of services closer to the community.
- The second component is the Pradhan Mantri Jan Arogya Yojana (PM-JAY) which provides health insurance cover of Rs. 5 lakhs per year to over 10 crore poor and vulnerable families seeking secondary and tertiary care.
- Ayushman Arogya Mandirs are envisaged to deliver an expanded range of services that go beyond Maternal and child health care services.
- It includes care for non-communicable diseases, palliative and rehabilitative care, Oral, Eye, and ENT care, mental health, and first-level care for emergencies and trauma , including free essential drugs and diagnostic services
- More than 2.71 crore wellness sessions have been held at these centers.
Fast Track Special Court (FTSC) (The Hindu)

- 30 Nov 2023
Why is it in the News?
The Union Cabinet recently gave its approval for the three-year extension of fast-track courts that are specifically used to handle sexual offense cases.
About Fast Track Special Court (FTSC):
- The Fast Track Special Court (FTSC) initiative started in August 2019 as a centrally sponsored scheme to handle cases related to rape and the POCSO Act.
- Originally planned for one year, it got extended to March 2023, and now it's extended further until March 2026 with a financial allocation of Rs. 1952.23 crore from the Nirbhaya Fund.
- These specialized courts, totaling 761, including 414 exclusive POCSO Courts, operate across all States and Union Territories.
- The Department of Justice, Ministry of Law & Justice, oversees their implementation.
- The primary aim is to expedite justice, offering quick relief to victims and reinforcing the nation's commitment to ending sexual and gender-based violence.
- The expected outcomes of this scheme are significant.
- They include a substantial reduction in pending cases related to Rape & POCSO Act, providing swift access to justice for victims through improved facilities and expedited trials, and reducing the burden on the judicial system by managing the number of cases effectively.
Angkor Wat Temple (TOI)

- 30 Nov 2023
Why is it in the News?
Angkor Wat, in the heart of Cambodia, has beaten Pompeii in Italy to become the eighth Wonder of the World.
About Angkor Wat Temple:
- Angkor Wat is among the most significant archaeological sites of Southeast Asia, located in the northern province of Siem Reap in Cambodia.
- The temple was constructed by the Khmer King Suryavarman II in the early 12th century.
- It was originally built as a Hindu temple, dedicated to Lord Vishnu by the Khmer Emperor Suryavarman II, it was converted into a Buddhist temple by his successor Jayavarman VII, who also built the famous Buddhist temple of Bayon nearby.
- The transition from Hinduism to Buddhism is evident in the intricate carvings that adorn the temple walls, depicting scenes from Hindu and Buddhist mythology.
- An interesting fact about Angkor is that it is also known as Yasodharapura.
- The name Angkor is derived from nokor, a Khmer word meaning "kingdom," which is derived from Sanskrit nagara, which means "city."
- Angkor Wat is said to represent Mount Meru, the home of the gods, according to both Hindu and Buddhist faiths.
- It is also famous for its statue of eight-armed Vishnu, also revered by the locals as their protecting deity.
- It holds the Guinness World Record for being the largest religious structure in the world, spread across some 400 km sq.
- In 1992 the temple complex was named a UNESCO World Heritage site.
Syrian Golan/Golan Heights (The Hindu)
- 30 Nov 2023
Why is it in the News?
India has voted in favour of a draft resolution in the United Nations General Assembly (UNGA) that expressed deep concern over Israel not withdrawing from the Syrian Golan.
About the Syrian Golan/Golan Heights:
- Location: Situated in south-western Syria, the Golan Heights is a rocky plateau sharing borders with Israel, Lebanon, and Jordan.
- The elevated terrain overlooks the Jordan Rift Valley, housing the Sea of Galilee and the Jordan River, with Mount Hermon as a dominant feature.
- Demography: Over 40,000 people reside in the Israeli-occupied Golan, with a majority being Druze, an Arab minority practicing a distinct form of Islam.
- Although Israel offered Druze residents citizenship after annexation, most identified as Syrian and declined.
- Additionally, about 20,000 Israeli settlers live in the region.
- History of Conflict: Originally part of Syria, Israel captured the Golan Heights in 1967 during the Six-Day War and formally annexed it in 1981.
- Syria attempted to reclaim the area in the 1973 Middle East war but was unsuccessful.
- While an armistice was signed in 1974, international recognition of Israel's annexation is lacking, and Syria insists on the territory's return.
- Significance of Golan Heights: Israel argues that maintaining the Golan as a buffer zone is vital due to the Syrian civil war, protecting Israeli towns from neighboring instability.
- Concerns also include the fear of Iran, an ally of the Syrian president, establishing a permanent presence near the border for potential attacks on Israel.
- Both nations value the Golan's water resources and fertile soil.
The Booker Prize 2023 (Indian Express)

- 30 Nov 2023
Why is it in the News?
The 2023 Booker Prize has been awarded to Prophet Song, a dystopian vision of Ireland in the grips of totalitarianism.
Key Facts:
- Irish author Paul Lynch won the 2023 Booker Prize for his novel "Prophet Song," a dystopian work about an Ireland that descends into tyranny.
- Set in Dublin, it tells the story of a family grappling with a terrifying new world in which the democratic norms they are used to begin to disappear.
- He becomes the fifth Irish writer to win the high-profile literary prize, which has propelled to fame countless household names, including past winners Salman Rushdie, Margaret Atwood, and Hilary Mantel.
What is a Booker Prize?
- The Booker Prize is a literary prize awarded every year to the best novel written in the English language which is published in the UK or Ireland.
- It is a high-profile literary prize and thus, is much anticipated among book lovers.
- Background: It was established in 1969 by Booker McConnell Ltd, the prize transitioned to the Booker Prize Foundation in 2002, sponsored by the Man Group.
- Initially, the award was £21,000, increased to £50,000 in 2002.
- Selection Process: An advisory committee, comprising diverse literary figures, appoints a judging panel annually.
- BOOKER PRIZE winners: Indians
- VS Naipaul, In a Free State (1971)
- Salman Rushdie, Midnight’s Children (1981)
- Arundhati Roy, The God of Small Things (1997)
- Kiran Desai, The Inheritance of Loss (2006)
- Aravind Adiga, The White Tiger (2008)
Parthenon Sculptures (Indian Express)

- 29 Nov 2023
Why is it in the News?
A diplomatic row sparked between Greece and the UK recently after British Prime Minister Rishi Sunak canceled a meeting with his Greek counterpart Kyriakos Mitsotakis over the status of the Parthenon Sculptures housed at the British Museum.
What are the Parthenon Sculptures?
- The Parthenon Sculptures at the British Museum are more than 30 ancient stone sculptures from Greece that are more than 2,000 years old.
- Most of them originally adorned the walls and grounds of the Parthenon temple on the rocky Acropolis hill in Athens.
- Completed in 432 BC, the temple is dedicated to the goddess Athena and is seen as the crowning glory of Athens’ Golden Age.
- While one notable sculpture, which is 75 meters long, depicts a procession for the birthday of Athena, others show gods, heroes, or mythical creatures.
How did the sculptures reach Britain?
- They were removed from the Parthenon in the early 19th century by Thomas Bruce, the 7th Earl of Elgin and then-British ambassador to the Ottoman Empire.
- The marbles were taken to Britain and purchased by the British Museum in 1816.
Swine Flu (TOI)
- 29 Nov 2023
Why is it in the News?
UK public health officials recently said they had confirmed a first human case of a swine flu strain similar to one that has been circulating in pigs.
About Swine Flu:
- Swine flu, scientifically known as H1N1 influenza, is a contagious respiratory illness caused by the H1N1 virus that commonly affects pigs.
- However, this virus can also infect humans, leading to a range of symptoms from mild to severe, and in some cases, it can be fatal.
- The virus spreads among humans through respiratory droplets produced when an infected person coughs or sneezes, making it highly transmissible.
- Swine flu symptoms resemble those of seasonal influenza, including fever, cough, sore throat, body aches, and fatigue.
- In severe cases, individuals may experience respiratory distress and pneumonia.
- One of the distinctive features of the H1N1 virus is its ability to affect younger age groups more severely compared to typical seasonal flu viruses.
- The World Health Organization declared a global pandemic of H1N1 influenza in 2009, emphasizing the need for international cooperation in monitoring and controlling the spread of the virus.
- Oseltamivir is an antiviral medication used to treat and prevent influenza A and influenza B.
Comet P12/Pons-Brooks (The Hindu)

- 29 Nov 2023
Why is it in the News?
Astronomers at the Indian Institute of Astrophysics (IIA) have used the Himalayan Chandra Telescope (HCT) in Hanle, Ladakh, to photograph the Comet P12/Pons-Brooks.
About Comet P12/Pons-Brooks:
- Comet 12P/Pons-Brooks is a Halley-type periodic comet that was first discovered by Jean-Louis Pons on July 12, 1812.
- It is nicknamed the 'Devil Comet' or likened to the 'Millennium Falcon' for its distinctive appearance.
- It has an orbital period of about 71.3 years.
- During its closest approach to the Sun or perihelion, the comet comes within about 0.78 astronomical units (AU) of the Sun, while at its furthest point, or aphelion, it is located at a distance of about 17.2 AU.
- Comet 12P/Pons-Brooks is also known for being the probable parent body causing the κ-Draconids meteor shower.
- It will make its return in 2024 and it is expected to reach its maximum brightness (potentially visible to the naked eye) during the month of April.
- With its closest approach occurring just a few days before a total solar eclipse on April 8, 2024, it presents a unique opportunity for skywatchers to potentially view the comet during the eclipse.
- However, since the comet's brightness can be unpredictable, there is no guarantee it will be visible.
- Comet 12P/Pons-Brooks is currently in the constellation of Lyra Constellation.
Indian Ocean Tuna Commission (IOTC) (PIB)

- 29 Nov 2023
Why is it in the News?
The Department of Fisheries, Ministry of Fisheries, Animal Husbandry & Dairying, GoI is organizing the 19th Working Party on Data Collection and Statistics (WPDCS19) of the Indian Ocean Tuna Commission (IOTC) from 28th November to 2nd December 2023.
About the Indian Ocean Tuna Commission:
- The Indian Ocean Tuna Commission (IOTC) is an intergovernmental organisation responsible for the management of tuna and tuna-like species in the Indian Ocean.
- It works to achieve this by promoting cooperation among its Contracting Parties (Members) and Cooperating Non-Contracting Parties in order to ensure the conservation and appropriate utilisation of fish stocks and encouraging the sustainable development of fisheries.
- The Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations adopted the Agreement for the Establishment of the Indian Ocean Tuna Commission during its 105th Session in Rome on 25 November 1993.
- The Indian Ocean holds the position as the second-largest tuna fishery globally, making it a crucial focus for the IOTC.
- Currently, the IOTC boasts 31 contracting parties, including countries and two cooperating non-contracting parties, Liberia and Senegal.
- Membership is open to Indian Ocean coastal countries, countries or regional economic integration organizations that are UN members, countries that are members of UN special organizations, and countries involved in tuna fishing in the Indian Ocean.
- India is an active member of the IOTC, with its headquarters located in Victoria, Seychelles.
INS Imphal (Business Standard)

- 29 Nov 2023
Why is it in the News?
Defence Minister Rajnath Singh recently unveiled the crest of the Indian Navy's stealth-guided missile destroyer Imphal.
About INS Imphal:
- INS Imphal is the third ship in the Visakhapatnam-class stealth-guided missile destroyers.
- INS Imphal is the third of the four Project 15B stealth-guided missile destroyers.
- It's one of the biggest destroyers made in India, measuring 164 meters long and weighing over 7500 tonnes.
- Powered by Combined Gas and Gas (COGAG) propulsion, the ship is capable of achieving speeds in excess of 30 knots (56 km/hour).
- It's equipped to handle various tasks in maritime warfare.
- The ship boasts a high indigenous content of approximately 75 percent that includes BrahMos surface-to-surface missiles, medium-range surface-to-air missiles, anti-submarine indigenous rocket launchers, and 76mm super rapid gun mount.
- "Designed by the Indian Navy's Warship Design Bureau and built by Mazagon Dock Shipbuilders Limited, Imphal is a hallmark of indigenous shipbuilding and is amongst the most technologically advanced warships in the world.
- The crest design on the ship represents the Kangla Palace and 'Kangla-Sa.'
- The Kangla Palace is a historical and archaeological site in Manipur, serving as the traditional seat of the past kingdom.
- On the right side of the crest, 'Kangla-Sa' is depicted—a mythical being with a dragon's head and lion's body from Manipur's history, symbolizing the guardian of its people.
- ‘Kangla-Sa' is also the state emblem of Manipur.
- Interestingly, INS Imphal is the first capital warship named after a city in the northeast—Imphal, the capital of Manipur.
Himalayan Black Bear (The Hindu)

- 28 Nov 2023
Why is it in the News?
An animal keeper died after being attacked by a Himalayan black bear in the animal’s enclosure of Indira Gandhi Zoological Park (IGZP) here recently.
About Himalayan Black Bear:
- The Himalayan black bear (Scientific Name: Ursus thibetanus laniger) is a subspecies of the Asian black bear found in the Himalayas of India, Bhutan, Nepal, China, and Pakistan.
- In India, habitat covers the entire Himalayan range from Jammu & Kashmir to Arunachal Pradesh, extending to hilly areas in other northeastern states.
- Habitat: Thrives in heavily forested regions with broadleaved and coniferous forests.
- It utilizes orchards, agricultural fields, and human habitats to navigate between forest patches.
- Physical Features: Possesses soft and shiny fur, featuring a distinctive white V patch on the chest.
- Average length ranges from 1.4 to 1.7 meters, weighing between 90 to 200 kg (higher weight typically before hibernation).
- Life Span: In the wild, their life expectancy is approximately 25 to 30 years.
- Diet: Omnivorous nature, consuming acorns, nuts, fruit, honey, roots, and various insects like termites and beetle larvae.
- Behavior: Primarily diurnal by nature but often shifts to a nocturnal lifestyle to avoid human contact.
- Conservation Status: IUCN Red List classification: Vulnerable
- Due to encroachment of human population, forest fires and the timber industries; these have all reduced the bear's habitat.
- There is also a high mortality rate among the newborn.
ISRO's AstroSat (PTI)

- 28 Nov 2023
Why is it in the News?
India's AstroSat space telescope has achieved a significant milestone by detecting more than 600 Gamma-Ray Burst (GRB), each marking the death of a massive star or merging of neutron stars.
About ISRO’s AstroSat:
- AstroSat is the first dedicated Indian astronomy mission aimed at studying celestial sources in X-ray, optical, and UV spectral bands simultaneously.
- One of the unique features of the AstroSat mission is that it enables the simultaneous multi-wavelength observations of various astronomical objects with a single satellite.
- AstroSat, with a lift-off mass of 1515 kg, was launched by the Indian launch vehicle PSLV from Satish Dhawan Space Centre, Sriharikota, on September 28, 2015, into a 650 km orbit inclined at an angle of 6 degrees to the equator.
- The minimum useful life of the AstroSat mission is expected to be 5 years.
- It carried a total of five scientific payloads, enabling imaging and studying the temporal and spectral properties of galactic and extra-galactic cosmic sources in a wide range of wavelengths on a common platform.
- The scientific objectives of AstroSat’s mission are:
- To understand high energy processes in binary star systems containing neutron stars and black holes.
- Estimate magnetic fields of neutron stars.
- Study star birth regions and high energy processes in star systems lying beyond our galaxy.
- Detect new briefly bright X-ray sources in the sky.
- Perform a limited deep-field survey of the Universe in the Ultraviolet region.
- At present, all the payloads are operational and are observing the cosmic sources.
Rythu Bandhu Scheme (The Hindu)

- 28 Nov 2023
Why is it in the News?
The Election Commission recently canceled the Telangana government's approval to give money to farmers through the Rythu Bandhu Scheme.
About Rythu Bandhu Scheme:
- Rythu Bandhu Scheme, also known as the Farmer's Investment Support Scheme (FISS), was initiated by the Telangana government in 2018.
- Objectives:
- Provide timely cash grants for the initial investment needs of farmers.
- Prevent farmers from falling into the debt trap.
- Financial Assistance: Rs 5,000 per acre per farmer per season directly transferred to their accounts.
- Distribution: Biannual support for both kharif and rabi harvests.
- Usage: Farmers can use funds for purchasing seeds, fertilizers, pesticides, labor, and other field operations of their choice.
- Eligibility: Open to all resident land-owning farmers, including those in forest areas with a Record of Forest Rights (ROFR).
- Special Inclusion: Farmers in forest areas, mainly from Scheduled Tribe communities, with a ROFR document, are eligible for benefits.
- It’s India's first direct farmer investment support scheme, providing cash directly to beneficiaries.
Kalakkad Mundanthurai Tiger Reserve (TOI)

- 28 Nov 2023
Why is it in the News?
Recently a new plant species belonging to the 'Impatiens' genus (Balsaminaceae) has been identified in the Kalakkad Mundanthurai Tiger Reserve, Tirunelveli.
About Kalakkad Mundanthurai Tiger Reserve:
- The Kalakkad Mundanthurai Tiger Reserve, is situated in the Southern Western Ghats within the Tirunelveli and Kanyakumari districts of Tamil Nadu.
- This reserve combines three major sanctuaries:
- The Kalakkad Sanctuary
- The Mundanthurai Sanctuary, and
- A portion of the Kanyakumari Sanctuary.
- The Agasthyamalai Hills, nestled between Kerala and Tamil Nadu, forms the sanctuary's core and is part of one of the world's 18 biodiversity hotspots.
- This reserve is also recognized as the “River Sanctuary,” with 14 rivers originating from it.
- Flora: The flora in this region exhibits a gradual transition from dry thorn forest to dry deciduous, moist deciduous, and a patch of West Coast wet evergreen forests at higher elevations.
- Fauna: Diverse fauna includes species such as Lion-tailed Macaque, Nilgiri Tahr, Nilgiri Pipit, Grey Headed Bulbul, Blue Winged Parakeet, and more.
Details about the New Plant Species:
- The species, named 'Impatiens Karuppusamyi,' pays tribute to S. Karuppusamy for his significant contributions to the taxonomy of South Indian angiosperms.
- This particular plant is exclusively found in the Agasthyamalai region within the southern Western Ghats.
- Belonging to the scapigerous group (stemless group), the plant is observable only during the monsoon season, lasting for a few weeks.
- Impatiens, a genus comprising over 1,000 flowering plant species, is widely distributed across tropical Africa, Madagascar, India, Sri Lanka, and China.
Iran has threatened to close the Strait of Gibraltar linking the Mediterranean and the Atlantic for shipping (The Hindu)
- 25 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
Recently, Iran has threatened to close the Strait of Gibraltar and the Mediterranean Sea unless Israel stops bombing Gaza.
About the Strait of Gibraltar:
- The Strait of Gibraltar is a narrow water passage that serves as a crucial link connecting Europe and Africa, facilitating the connection between the Mediterranean Sea and the Atlantic Ocean.
- Historical Significance: Prior to the inauguration of the Suez Canal in 1869, the Strait of Gibraltar held exclusive prominence as the sole gateway to the Mediterranean Sea.
- Geographical Borders: Positioned between Spain and the British Overseas Territory of Gibraltar in the north, and Morocco and the Spanish exclave of Ceuta in the south, the strait spans approximately 58 km and reaches a width of about 13 km at its narrowest point.
- Depth and Geological Formation: With depths ranging from 300 to 900 meters, the strait constitutes a significant divide between the elevated plateau of Spain and the Atlas Mountains of Northern Africa.
- Geological studies indicate that the strait originated from the northward movement of the African Plate towards the European Plate.
- High Maritime Activity: Recognized as one of the world's busiest waterways, the Strait of Gibraltar witnesses the daily transit of around 300 ships, equivalent to approximately one ship every 5 minutes.
- The Moroccan port of Tanger-Med, situated near Tangier, is a prominent port along the strait.
- Pillars of Heracles: Marking the eastern extremity of the strait, the area between the Rock of Gibraltar in the north and Mount Hacho or Jebel Moussa in the south spans approximately 23 km.
- These two land features referred to as the Pillars of Heracles, hold historical and geographical significance.
About the Mediterranean Sea:
- The Mediterranean Sea, an intercontinental body of water, is flanked by Europe to the north, Asia to the east, and Africa to the south.
- In the western expanse, it connects to the Atlantic Ocean through the narrow Strait of Gibraltar.
- To the extreme northeast, it links to the Black Sea via the Dardanelles Strait, the Sea of Marmara, and the Bosporus Strait.
- In the southeast, the Mediterranean Sea is connected to the Red Sea through the Suez Canal.
- Historical Significance: Recognized as the cradle of Western civilization, the Mediterranean Sea has played a pivotal role in the development of ancient cultures.
- Notable civilizations, including the Phoenicians, Ancient Greece, and the Roman Empire, flourished along its shores.
- Countries and Territories Along the Coast: A total of 22 countries, along with one territory (Gibraltar, a British Overseas Territory), have coastlines along the Mediterranean Sea.
- European nations with Mediterranean coastlines include Spain, France, Italy, Malta, Monaco, Slovenia, Croatia, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Montenegro, Albania, and Greece.
- Countries from the West Asian (Middle Eastern) region bordering the Mediterranean Sea include Turkey, Syria, Lebanon, Israel, Palestine (Gaza Strip), and the divided island of Cyprus.
- Additionally, five North African nations, namely Morocco, Algeria, Tunisia, Libya, and Egypt, have coastlines along the Mediterranean.
Mycoplasma Pneumonia (Indian Express)
- 28 Nov 2023
Why is it in the News?
What is Mycoplasma Pneumonia?
- Mycoplasma pneumoniae is a type of bacteria that can cause illness by damaging the lining of the respiratory system (throat, lungs, windpipe).
- It acts more like a virus and spreads faster from person to person.
- It is a common cause of pneumonia in children, adolescents, and young adults.
- Vulnerable groups, who already have respiratory issues, are prone to developing this infection in a severe form.
- Most people with respiratory infections caused by Mycoplasma pneumoniae don’t develop pneumonia.
- For this reason, MP is known as an atypical pneumonia and is sometimes called walking pneumonia.
- Symptoms: Symptoms of Mycoplasma pneumoniae infection can include:
- Fever, Cough, Headache, Sore throat, Fatigue, Muscle aches, and Shortness of breath
- In most cases, Mycoplasma pneumoniae infection is mild and goes away on its own within a few weeks.
- However, some people may develop more serious complications, such as meningitis or encephalitis.
- It spreads through close contact with an infected person, such as through coughing or sneezing.
- It can also be spread through contact with contaminated surfaces.
- There is no vaccine to prevent Mycoplasma pneumoniae infection however there are multiple antibiotics that effectively cure this infection.
PM to release ‘Collected Works of Pandit Madan Mohan Malaviya’ on 25th December (PIB)

- 25 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
On the occasion of the 162nd birth anniversary of Mahamana Pandit Madan Mohan Malaviya, Prime Minister Shri Narendra Modi will release the first series of 11 volumes of ‘Collected Works of Pandit Madan Mohan Malaviya’, on 25th December, 2023.
About Pandit Madan Mohan Malaviya:
- Pandit Madan Mohan Malviya, born on December 25, 1861, in Allahabad, Uttar Pradesh, made significant contributions to India's education system and actively participated in the Indian Independence movement.
- Acknowledged as a venerable soul, Mahatma Gandhi bestowed upon him the title of 'Mahamana,' considering him an elder brother.
- In 2014, posthumously, Pandit Malviya was honoured with the Bharat Ratna, the highest civilian award in the country.
- In tribute to his legacy, the Indian Railways launched the Varanasi-New Delhi Mahamana Express in 2016.
Significant Contributions:
- Banaras Hindu University: In 1916, Pandit Madan Mohan Malviya played a pivotal role in the Indian independence struggle against British rule and established the Banaras Hindu University (BHU).
- Serving as the Vice-Chancellor at BHU from 1919 to 1938 showcased his dedication to education and leadership.
- Hindu Mahasabha: A founding member of the Hindu Mahasabha in 1906, Malaviya demonstrated his early leadership in this organization.
- As a social reformer and accomplished legislator, he contributed significantly during his 11-year tenure (1909–20) as a member of the Imperial Legislative Council.
- Scout and Guide Movement: Pandit Malviya was instrumental in establishing the Scout and Guide movement in India, showcasing his commitment to youth development and character building.
- 'Satyamev Jayate': Renowned for coining the famous slogan 'Satyamev Jayate,' Pandit Malviya proclaimed it during the 1918 Indian National Congress session when he served as the President.
- President of INC: Pandit Madan Mohan Malviya's leadership extended to the Indian National Congress, where he held the position of President for four sessions (1909, 1913, 1919, and 1932).
- His active role in the Civil Disobedience and Non-cooperation movements, led by Mahatma Gandhi, underscored his commitment to India's struggle for independence.
- Media Role: From 1924 to 1946, Pandit Malviya served as the Chairman of Hindustan Times and also founded several Hindi and English newspapers, including The Leader, Hindustan Dainik, and Maryada.
- Advocacy for Education and Social Causes: Malaviya championed free and compulsory primary education, opposed the system of indentured labour in the British Empire, and advocated for the nationalization of railways, reflecting his dedication to societal progress and reform.
“FLip” mutations of SARS-COV-2 may be evading immunity and leading to a surge in COVID cases, suggest researchers (DownToEarth)
- 25 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
The omicron subvariant JN.1. is likely to soon become the dominant lineage of the SARS-CoV-2 virus worldwide, according to researchers at the University of Tokyo. The subvariant has a mutation in its spike protein, L455S, also called a “FLip” mutation.
Context:
- The mutations denoted as L455S and L455F are termed "FLip" mutations due to their role in interchanging the positions of amino acids F and L within the spike protein.
- These mutations enhance the virus's transmissibility.
- The substitution associated with these mutations reduces the receptor binding capacity of angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2), a protein present in epithelial cells across various body parts, including the lungs, heart, and kidneys.
- ACE2 serves as a crucial entry point for the SARS-CoV-2 virus, binding through its spike-like protein on the virus's surface.
- The FLip mutations, specifically L455F and F456L, are characterized by the swapping of positions between two amino acids, F and L, within the spike protein.
What is Flip Mutation?
- A flip mutation, also known as bit flip mutation, is a genetic operator used in evolutionary algorithms, particularly genetic algorithms (GAs).
- It works by randomly flipping the values of individual genes (bits) within a chromosome, introducing small changes to the genetic makeup of an individual.
- Imagine a chromosome as a string of 0s and 1s, representing the genetic code for a specific trait or characteristic.
- A flip mutation randomly selects one or more of these bits and changes their values.
- For example, a 0 might be flipped to a 1, or vice versa.
- The following image depicts flip mutation:
How does it work:?
- Individual selection: An individual is selected from the population.
- Gene selection: One or more genes (bits) within the individual's chromosome are randomly chosen.
- Bit flipping: The value of each selected gene is flipped. This means that a 0 is changed to a 1, and vice versa.
World Climate Action Summit 2023 (NewsOnAir)

- 27 Nov 2023
Why is it in the News?
Prime Minister Modi will be on a two-day visit to Dubai, UAE from 30th November to attend the World Climate Action Summit.
About World Climate Action Summit:
- The World Climate Action Summit is the High-Level Segment of the 28th Conference of Parties (COP-28) to the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC).
- COP-28 is being held from 28 November to 12 December 2023 under the Presidency of the UAE.
- The Conference of Parties to the UNFCCC provides a unique opportunity to impart momentum for collective action towards combating the shared challenge of climate change.
- The World Climate Action Summit will bring together heads of state and governments, leaders from civil society, business, youth, indigenous peoples' organisations, frontline communities, science, and other sectors.
- The summit aims to facilitate discussions on actions and plans to scale climate action.
- The COP 28 will focus on four paradigm shifts:
- Fast-tracking the energy transition and slashing emissions before 2030;
- Transforming climate finance, by delivering on old promises and setting the framework for a new deal on finance;
- Putting nature, people, lives, and livelihoods at the heart of climate action; and
- Mobilizing for the most inclusive COP ever.
- The summit may witness intense negotiations on unfulfilled promises of financial aid, particularly the yet-to-materialize $100 billion pledged by rich countries by 2020.
- Additionally, some countries, notably the European Union, are expected to advocate for a global deal to phase out unabated fossil fuels during COP28.
- During COP-26 in Glasgow, the Prime Minister announced five specific targets, titled "Panchamrit”, as India’s unprecedented contribution to climate action.
- The Prime Minister also announced Mission Lifestyle for Environment (LiFE) on that occasion.
- Climate change has been an important priority area of India’s G20 Presidency, and significant new steps have been captured in the New Delhi Leaders’ Declaration and other outcomes during our Presidency.
- COP-28 will provide an opportunity to take forward these successes.
Odisha Government has declared Leprosy as a 'Reportable Disease' in the State (New Indian Express)
- 25 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
The Odisha government on Friday declared leprosy a reportable disease in the state and asked hospitals and persons dealing with diagnosis and treatment, institutions imparting medical education and providing diagnostic services to report all cases to the respective district health authorities.
What is Leprosy?
- Leprosy, often referred to as Hansen's disease, is a persistent infectious illness brought on by the bacteria Mycobacterium leprae.
- The skin, eyes, mucosal surfaces of the upper respiratory tract, and peripheral nerves are the main areas affected by this condition.
- If left untreated, the condition has the potential to produce gradual and irreversible impairments.
- Prevalent in tropical and subtropical regions, leprosy qualifies as a neglected tropical disease (NTD) found in over 120 countries.
- Its occurrence spans all age groups, encompassing early childhood to advanced age.
- Transmission of Disease: Transmission of leprosy transpires through droplets from the nose and mouth, necessitating prolonged, close contact with an untreated individual.
- Contrary to misconceptions, casual interactions such as handshakes, hugs, shared meals, or proximity do not facilitate transmission.
- Symptoms: Symptoms usually manifest 3 to 5 years post-exposure to the leprosy-causing bacteria.
- Red patches on the skin.
- Skin Lesion
- Numbness in arms, hands, and legs.
- Ulcers on the soles of feet.
- Muscle Weakness and excessive weight loss.
- Nerve damage can result in loss of sensation in limbs and potential mucous membrane complications like a stuffy nose or nosebleeds.
- Treatment: Leprosy is curable through Multi-Drug Therapy (MDT), with early intervention crucial in preventing disability.
- Importantly, the commencement of treatment not only aids in recovery but also halts the transmission of the disease.
About the National Leprosy Eradication Programme (NLEP):
- The National Leprosy Eradication Programme is a centrally sponsored Health Scheme under the National Health Mission of the Ministry of Health and Family Welfare, Govt. of India.
- The Programme is headed by the Deputy Director of Health Services (Leprosy ) under the administrative control of the Directorate General Health Services, Govt. of India.
- While the NLEP strategies and plans are formulated centrally, the programme is implemented by the States/UTs.
- The major concern of the Programme is to detect cases of leprosy at an early stage and provide complete treatment, free of cost, in order to prevent the occurrence of Grade II Disability (G2D) in affected persons.
- India has achieved the elimination of leprosy as a public health problem as per WHO criteria of less than 1 case per 10,000 population at the National level in 2005.
- However, there are few districts within States where leprosy is still endemic.
Real Estate Investment Trusts (REITs) (Indian Express)

- 27 Nov 2023
Why is it in the News?
SEBI on Saturday decided to bring entities facilitating fractional investment in real estate under a regulatory framework, whereby they will be required to operate as Small and Medium Real Estate Investment Trusts.
About Real Estate Investment Trusts (REITs):
- A Real Estate Investment Trusts (REITs) is a company that owns and typically operates income-generating real estate or related assets.
- It pools funds from investors, directing them into various commercial real estate ventures, including office buildings, shopping malls, apartments, hotels, resorts, self-storage facilities, warehouses, and mortgages or loans.
- In contrast to conventional real estate firms, REITs don't develop properties for resale; rather, they acquire and develop properties primarily for inclusion in their investment portfolio.
- REITs offer individual investors an opportunity to share in the income generated by commercial real estate without the need to directly purchase such properties.
- Typically specializing in specific real estate sectors, REITs may focus on diversified or specialty portfolios, encompassing various property types like office and retail spaces.
- Most REITs are publicly traded on stock exchanges, similar to stocks, providing high liquidity compared to physical real estate investments.
- This stock-like nature allows investors to buy or sell REIT shares on the exchange at any time.
Sports Ministry requests IOA to constitute an ad-hoc committee to manage WFI affairs (Indian Express)

- 25 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
After suspending the newly elected Wrestling Federation of India (WFI) body on Sunday, the Sports Ministry have requested the Indian Olympic Association to constitute an ad-hoc committee to manage and control the affairs of the federation.
News Summary:
- Three days after the Wrestling Federation of India (WFI) elected a new governing council to run the sport in India, the Union Ministry of Youth Affairs and Sports directed the body to suspend all activities.
- It issued a letter to the Indian Olympic Association (IOA) to create an ad-hoc committee to manage and control the affairs of the WFI.
About the Wrestling Federation of India (WFI):
- Established in 1958 and headquartered in New Delhi, the Wrestling Federation of India (WFI) serves as the governing body for wrestling.
- Mission: WFI plays a pivotal role in nurturing and promoting wrestling talent for prestigious events such as the Olympics, Asian Games, National Wrestling Championships, and World Wrestling Championships.
- Affiliation: As an integral part of the Indian Olympic Association (IOA), WFI operates in accordance with the rules and regulations set forth by both the International Olympic Committee (IOC) and United World Wrestling (UWW).
- The UWW, recognized as the international governing body for wrestling, holds responsibilities ranging from overseeing wrestling competitions at the World Championships to ensuring adherence to standards at the Olympic level.
- WFI's Contract System for Wrestlers: In a groundbreaking move in 2018, WFI introduced an innovative contract system designed to support wrestlers.
- This system categorizes wrestlers into four grades:
- Grade A, providing financial assistance of 30 lakh rupees.
- Grade B offers a financial support package of 20 lakh rupees.
- Grade C, extending support amounting to 10 lakh rupees.
- Grade D provides a support package of 5 lakh rupees.
- To ensure relevance and fairness, the contracts undergo a thorough review on an annual basis, reflecting WFI's commitment to the ongoing development and support of wrestling talent.
About Indian Olympic Association (IOA):
- The Indian Olympic Association acts as the governing body overseeing the Olympic Movement and the Commonwealth Games within India.
- It holds affiliation with prominent international bodies, including the International Olympic Committee (IOC), Commonwealth Games Federation (CGF), Olympic Council of Asia (OCA), and Association of National Olympic Committees (ANOC).
- In fulfilling its role, the IOA manages key aspects of sports governance and prioritizes the welfare of athletes across the nation.
- Responsibilities: As a recognized entity by the Ministry of Youth Affairs and Sports, the IOA undertakes the crucial responsibility of coordinating the representation of athletes and teams in major international multi-sport events such as the Olympic Games, Commonwealth Games, Asian Games, and others sanctioned by the IOC, CGF, OCA, and ANOC.
- Historical Perspective: Established in 1927 with Sir Dorabji Tata serving as the Founding President and Dr. A.G. Noehren as the Secretary-General, the IOA operates as a Non-Profit Organization under the Societies Registration Act of 1860.
- This history underscores its enduring commitment to the promotion of sports.
- Governance Structure: Currently governed by a 32-member Executive Council, the IOA is led by a President.
- Elections for the Executive Council occur once every four years, emphasizing democratic and periodic leadership changes within the organization.
Supplementary Grants (The Hindu BusinessLine)

- 27 Nov 2023
Why is it in the News?
The Supplementary Demands for Grants (SDG) are likely to see additional allocation for fertliser, food and fuel subsidy along with Rural Employment Guarantee Scheme.
About Supplementary Grants:
- According to Article 115 of the Indian Constitution, there's a provision for additional funds known as supplementary, additional, or excess grants.
- When the funds approved by the Parliament are not enough for the planned expenses, an estimate is submitted to the Parliament for extra grants.
- These additional grants are reviewed and approved by the Parliament before the conclusion of the financial year.
- If the actual spending surpasses the approved grants, the Ministry of Finance and the Ministry of Railways make a request for an Excess Grant after the financial year ends.
- The Comptroller and Auditor General of India highlight these excesses to the Parliament.
- The Public Accounts Committee then examines these cases and provides recommendations to the Parliament.
- The Demand for Excess Grants is presented to the Parliament after the financial year, once the actual expenditures have been incurred.
High-energy Particle "Amaterasu" (Indian Express)

- 27 Nov 2023
Why is it in the News?
Scientists have detected one of the most powerful cosmic rays ever slamming into Earth but they have no idea what caused it or where it came from.
What is Amaterasu?
- The particle, named Amaterasu after the sun goddess in Japanese mythology, is one of the highest-energy cosmic rays ever detected.
- The Amaterasu particle has an energy exceeding 240 exa-electron volts (EeV).
- It is millions of times more than particles produced in the Large Hadron Collider, the most powerful accelerator ever built, and equivalent to the energy of a golf ball traveling at 95mph.
- It comes only second to the Oh-My-God particle, another ultra-high-energy cosmic ray that came in at 320 EeV, detected in 1991.
- Amaterasu appears to have emerged from the Local Void, an empty area of space bordering the Milky Way galaxy.
What are Cosmic Rays?
- Cosmic rays are high-energy particles, primarily protons and atomic nuclei, that originate from outer space and bombard Earth from all directions.
- They possess extraordinary energies, often exceeding those achievable in human-made accelerators.
- Created through various astrophysical processes, such as supernova explosions and the remnants of massive stars, cosmic rays travel through the vast expanse of space.
- Upon entering Earth's atmosphere, they collide with air molecules, initiating cascades of secondary particles.
- These rays play a crucial role in astrophysics, providing insights into the universe's most energetic phenomena.
- They contribute to our understanding of cosmic structures, magnetic fields, and the dynamics of celestial bodies.
- Despite their significance, the origins of certain ultra-high-energy cosmic rays remain mysterious, prompting ongoing research to unveil the secrets of these enigmatic particles.
Ministry of Textiles launches “Paat-Mitro” application to facilitate jute farmers (PIB)

- 22 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
To provide important information about MSP and agronomy to jute farmers, the Ministry of Textiles launched “Paat-Mitro” - a mobile application, developed by The Jute Corporation of India Limited (JCI) during the ‘Jute Symposium’.
What is Paat Mitro?
- Paat Mitro is a mobile application crafted by the Jute Corporation of India Limited (JCI) with the primary aim of furnishing vital information on Minimum Support Prices (MSP) and agronomy to jute farmers.
Key Features:
- The application is accessible in six languages, ensuring inclusivity.
- All functionalities within the app are provided to users free of charge.
- Paat Mitro offers a comprehensive range of information, encompassing the latest agronomic practices, MSP details, Jute Gradation Parameters, farmer-centric schemes like ‘Jute-ICARE,’ weather forecasts, locations of JCI’s Purchase Centres, and Procurement Policies.
- Farmers can conveniently track the payment status for the raw jute they sell to JCI under the MSP Operation.
- The app integrates advanced technology features such as a Chatbot, facilitating farmers in resolving queries effectively.
Key Information about the Jute Corporation of India Limited (JCI):
- Established in 1971 under the aegis of the Government of India, the Jute Corporation of India Limited (JCI) serves as the official agency dedicated to ensuring minimum support prices (MSP) for jute cultivators.
- JCI functions as the executing body for several Government of India initiatives aimed at enhancing the jute crop and the welfare of jute growers.
- It operates under the administrative purview of the Ministry of Textiles.
- The geographical reach of JCI spans seven states renowned for jute cultivation in India, including West Bengal, Bihar, Assam, Meghalaya, Tripura, Orissa, and Andhra Pradesh.
- With an authorized and paid-up capital of Rs. 5 crore, JCI plays a pivotal role in implementing the government's policy decisions, obligatorily purchasing any quantity of jute offered by growers at support rates without quantitative limitations.
- Incurred losses during policy implementation by JCI are subject to reimbursement by the Government of India.
Rating agencies too subjective, loaded against India, need reform: CEA (Indian Express)

- 22 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
Credit rating agencies need to reform their sovereign rating process to correctly reflect the default risk of developing economies, saving billions in funding costs, the government’s chief economic adviser, V Anantha Nageswaran, said recently.
What is a Sovereign Credit Rating?
- A Sovereign Credit Rating serves as an assessment of a government's ability to meet its debt obligations, with a lower rating reflecting higher credit risk.
- Rating agencies typically consider multiple factors such as growth rate, inflation, government debt, short-term external debt as a percentage of GDP, and political stability.
- A positive credit rating not only boosts credibility but also indicates a history of timely loan repayments, aiding banks and investors in evaluating loan applications and determining appropriate interest rates.
- The global credit rating industry is dominated by three major agencies: Moody's, Standard & Poor's, and Fitch.
- Despite India's ascent from the 12th to the 5th largest economy globally in 2023, with the second-highest growth rate among comparable economies, its credit ratings from S&P and Fitch stand at BBB, while Moody's rates it at Baa3—indicating the lowest investment-grade level.
Concerns Regarding Credit Rating Methodology:
- A quantitative examination revealed that more than 50% of credit ratings rely on qualitative components.
- Institutional Quality, predominantly gauged through the World Bank’s Worldwide Governance Indicators (WGIs), emerges as the primary factor influencing the credit rating of a developing economy.
- This poses a challenge as these metrics are often non-transparent, perception-driven, and derived from a limited group of experts, making them inadequate in representing the sovereign's willingness to meet its financial obligations.
- The non-trivial impact of these indicators on ratings implies that developing economies must exhibit progress along subjective indicators to secure a credit rating upgrade.
CEA's Suggestions for Credit Rating Reform:
- The Chief Economic Advisor (CEA) proposed a shift towards primarily considering a country's historical debt repayment record as a key determinant of its 'willingness to pay,' in contrast to relying on potentially suboptimal qualitative information.
- Embracing such a model would significantly enhance the credibility of Credit Rating Agencies (CRAs).
- The use of qualitative information and judgment should only be a last resort when genuine, verifiable data options are unavailable.
- If governance indicators are to be employed, they should be grounded in clear, well-defined, and measurable principles, steering away from subjective assessments by CRAs.
- CRAs possess a comprehensive database of global best practices, influencing their judgments.
- Sharing this knowledge with the countries they assess would empower sovereigns to take targeted actions to enhance their creditworthiness.
Kambala (Indian Express)

- 27 Nov 2023
Why is it in the News?
On the weekend of November 25 and 26, 160 pairs of buffaloes and their jockeys will race on specially made slush tracks for Kambala races at City Palace Grounds in Bengaluru.
What is Kambala?
- Kambala is a folk sport rooted in coastal Karnataka, particularly in areas where Tulu speakers are predominant.
- In the past, families and groups used to organize races in the muddy paddy fields after the harvest season.
- For many families, especially those from the Bunt community in coastal regions, Kambala holds significant prestige.
- Throughout the year, they groom pairs of buffaloes with the aim of winning major Kambala events and other races.
Kambala consists of four main categories:
- Negilu (plough): Lighter ploughs are used to tie buffaloes for the race.
- This category is for entry-level buffalo pairs participating in their first Kambala race.
- Hagga (rope): Buffaloes are raced by jockeys with just a rope tied to both buffaloes.
- Adda Halage: Participants stand over a horizontal plank dragged by buffaloes.
- Unlike Hagga and Negilu, where jockeys run behind the animals, buffaloes drag the jockeys in Adda Halage.
- Kane Halage: A wooden plank is tied to buffaloes.
- The plank, on which jockeys stand, has two holes through which water gushes out as it is dragged along the slush tracks.
- The height of water splashes determines the winner of the event.
Coming soon, a ‘Cafeteria’ for oil spill-hit birds at Ennore Creek (The Hindu)

- 22 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
Experts from the Wildlife Trust of India (WTI) and the Besant Memorial Animal Dispensary (BMAD) are planning to establish feeding stations for birds at the creek, where contamination due to an oil spill from industries in Manali has brought down the bird population drastically.
About Ennore Creek:
- Ennore Creek, situated in Thiruvallur District, Tamil Nadu, is a backwater channel branching off from the Kosathalaiyar River.
- It merges with the Bay of Bengal at Mugathwara Kuppam, while its northern channel links to Pulicat Lake, the country's second-largest brackish water lake.
- For generations, this creek has been a lifeline for communities in the neighbouring villages, designated as CRZ IV (Water Body) in the coastal zone management plan by the Tamil Nadu State Coastal Zone Management Authority.
- Its significance is heightened for local fisherfolk, alongside the Buckingham Canal and the broader Pulicat water system.
- The Ennore Creek has historically fostered a robust aquatic ecosystem renowned for its biodiversity.
- This ecologically sensitive area once boasted extensive mangrove swamps, contributing not only to sustainable fish resources but also playing a crucial role in flood mitigation during periods of heavy rainfall, high tides, and cyclones.
About the Wildlife Trust of India:
- Wildlife Trust of India (WTI) is an Indian Non-profit Organisation (NGO) committed to nature conservation.
- Motto: In Service of Nature
- It was formed in November 1998, in response to the rapidly deteriorating condition of the country's wildlife.
- Its mission is to:
- Conserve wildlife and its habitat and
- Work for the welfare of individual wild animals, in partnership with communities and governments.
- WTI has earned recognition for accomplishing significant conservation milestones, including the recovery of populations for critically endangered species, successful species translocation, and the mitigation of human-animal conflicts.
How an AI tool can make weather forecasts more accurate and help tackle climate change (Indian Express)

- 22 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
At the recent COP28, NASA and IBM announced that an Artificial Intelligence (AI) tool called watsonx.ai would be available on the open-source AI platform Hugging Space.
What is watsonx.ai?
- Watsonx.ai is a collaborative Artificial Intelligence tool developed by IBM and NASA.
- Its primary function is to enable users to monitor Earth from space, assessing past environmental changes and offering predictions about future occurrences.
- User-Friendly Interface: The tool is designed for simplicity, requiring users to select a location and a date.
- Watsonx.ai then highlights changes in floodwater, reforestation efforts, and other pertinent factors.
Functionality:
- Watsonx.ai is built on a foundation model trained on a diverse set of uncategorized data, allowing it to extrapolate information from one context to another.
- NASA provides datasets in the form of satellite images, and IBM developed the foundation model to interpret these visual inputs.
- The model's training involves comprehending visual sequences over time by reconstructing images with blank areas. This process enhances its ability to understand the connections between photos.
- Adjustments were made to the model for specific tasks such as segmenting and categorizing photos.
Additional Components:
- Watsonx.data: A specialized data store optimized for governed data and AI workloads.
- It facilitates the scaling of AI workloads by leveraging the entire data landscape.
- Watsonx.governance: An end-to-end toolkit encompassing both data and AI governance. It aids clients in establishing responsible, transparent, and explainable AI workflows.
- The toolkit provides governance capabilities for model management throughout the AI lifecycle.
Why rain and flood woes have hit Tamil Nadu hard in December (Indian Express)

- 22 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
Tamil Nadu has battled heavy rainfall throughout December. At the beginning of the month, parts of Chennai and its neighbourhood experienced massive flooding because of Cyclone Michaung.
News Summary:
- Tamil Nadu has experienced significant rainfall, recording 450mm since October 1.
- Among the 38 districts, only 14 have reported deficient rainfall until December 20.
Seasonal Rainfall Norms:
- December rainfall is typical for Tamil Nadu, with the northeast monsoon being crucial for the region.
- Nearly 48% of the annual rainfall (443.3mm) in Tamil Nadu occurs from October to December, impacting rabi cultivation.
Recent Rainfall Patterns in Southern Tamil Nadu:
- Three districts in southern Tamil Nadu witnessed 'exceptionally' heavy rainfall from December 17 to 19.
- The India Meteorological Department (IMD) reported a 100% or more surplus during this period compared to the previous week (December 6-13, 2023).
Factors Contributing to Record Rainfall:
- Vigorous northeast monsoon over Tamil Nadu and Kerala, particularly in the southern regions.
- Development of a cyclonic circulation in the southwest Bay of Bengal on December 16, enhancing northeast monsoon winds.
- The persistence of this system over southern Tamil Nadu on December 18 and 19, led to heavy cloud convection and hefty rainfall.
IMD's Forecast:
- The cyclonic circulation has moved away from the Indian landmass, currently positioned over the southeast Arabian Sea.
- No significant rainfall is expected in Tamil Nadu, but the IMD predicts light to moderate intensity rainfall (up to 64mm in 24 hours) in certain areas of southern Tamil Nadu.
What is Northeast Monsoon?
- The northeast monsoon stands as a significant and permanent element within the Indian subcontinent's climate system.
- Its nomenclature originates from the prevailing direction of the monsoon winds—blowing from the northeast to the southwest.
- In their trajectory, these winds accumulate moisture from the Bay of Bengal, subsequently depositing it over southern states such as Tamil Nadu, Andhra Pradesh, Kerala, south Telangana, and Karnataka.
- This monsoon is alternatively known as the winter monsoon, retreating monsoon, or reverse monsoon.
- Period: The northeast monsoon maintains activity throughout the three-month span from October to December.
- Causes and Influences: One of the primary instigators of the northeast monsoon is the southward shift of the Inter Tropical Convergence Zone (ITCZ).
- The ITCZ, a dynamic belt near the Equator, marks the convergence of trade winds from the northern and southern hemispheres.
- The southward displacement of the ITCZ, coupled with the warming of the Indian Ocean, induces a reversal in the lower-atmosphere moisture-laden winds' direction—from southwest to northeast—thereby triggering the Northeast Monsoon (NEM).
Sangai Deer (Indian Express)

- 25 Nov 2023
Why is it in the News?
The Manipur Government has expressed its reservations to the Centre over a hydro-electric modernisation plan in the state’s famous Loktak Lake saying it could be detrimental to the endangered species of Sangai deer apart from disturbing the biodiversity of the lake.
About Sangai Deer:
- The sangai is an endemic and endangered subspecies of Eld's deer found only in Manipur, India.
- It is also the state animal of Manipur.
- Its common English name is Manipur brow-antlered deer or Eld's deer and the scientific name is Rucervus eldii eldii.
- It is believed to have originated from a common ancestor of the brow-antlered deer family, which is thought to have existed in the region during the Pleistocene epoch, around 12,000 years ago.
- Its original natural habitat is the floating marshy grasslands of the Keibul Lamjao National Park, located in the southern parts of the Loktak Lake, which is the largest freshwater lake in eastern India.
- Appearance: is a medium-sized deer that is unique in appearance and behavior.
- The Sangai deer is a slender and graceful deer, with long legs and a thin neck. They have a height of around 90-100 cm at the shoulder and can weigh between 70 to 120 kg.
- Food Habits: The Sangai deer is primarily found in the marshy wetlands of the Loktak Lake in Manipur, where they feed on the vegetation growing on the floating biomass called “Phumdis.”
- They are known to feed on a wide variety of plants, including grasses, sedges, and herbs.
- Vulnerable Species: The Sangai is an endangered species and is listed in Schedule I of the Indian Wildlife Protection Act of 1972.
- The population of Sangai deer has been severely threatened due to habitat loss, hunting, and poaching.
- In the 1950s, the population of the Sangai deer was estimated to be around 600-700 individuals.
- However, by the 1970s, the population had declined to less than 100 individuals due to extensive hunting and habitat loss.
- The Government of India and the State Government of Manipur took several conservation measures, including the establishment of the Keibul Lamjao National Park in 1977, to protect and conserve the Sangai deer.
- The Sangai deer is a social animal and is usually found in small herds of 2-20 individuals.
- Protecting and conserving their natural habitats is one of the most effective ways to ensure the survival of these species.
- This can be achieved through the creation and management of protected areas, such as national parks and wildlife reserves, and the restoration of degraded habitats.
Digital Twins (TOI)

- 25 Nov 2023
Why is it in the News?
Recently, the Survey of India (SoI) and Genesys International, a prominent Indian mapping company, revealed a strategic collaboration for the implementation of a three-dimensional (3D) digital twin-mapping initiative in India.
About Digital Twin:
- Digital twins are digital representations of physical objects, people or processes.
- They aid decision-making through high-fidelity simulations of the twinned physical system in real-time and are often equipped with autonomous control capabilities.
- These replicas serve as dynamic and detailed counterparts, providing a real-time, data-driven simulation of their physical counterparts.
- The concept of digital twins has gained prominence with the advent of technologies like the Internet of Things (IoT), data analytics, and machine learning.
- In essence, a digital twin continuously collects and processes data from its physical counterpart, offering a comprehensive view of its behavior, status, and interactions.
- This real-time synchronization enables organizations to monitor, analyze, and understand the performance of physical assets or processes more effectively.
Applications:
- Manufacturing Sector: One primary application of digital twins is in the manufacturing sector.
- Manufacturers use digital twins to create virtual models of products and production processes.
- This allows for simulation, analysis, and optimization before physical prototypes are built, leading to reduced development costs and improved product quality.
- Healthcare: In healthcare, digital twins are employed to create personalized models of patients.
- These models, based on individual health data, help in predicting health outcomes, optimizing treatment plans, and advancing medical research.
- Transportation: Transportation industries utilize digital twins for optimizing logistics and predictive maintenance.
- For example, digital twins of aircraft engines can simulate performance under various conditions, aiding in proactive maintenance and minimizing downtime.
- Urban Planning: Urban planning benefits from digital twins by creating virtual models of entire cities.
- This assists in designing and optimizing infrastructure, managing resources efficiently, and planning for future growth and development.
- Industries: In industrial settings, digital twins of production processes enable real-time monitoring, troubleshooting, and optimization, leading to increased efficiency and reduced downtime.
Farlowichnus rapidus (The Hindu)

- 25 Nov 2023
Why is it in the News?
Brazil's geological service recently announced a new species of dinosaur, a speedy animal that lived in the desert during the early Cretaceous period.
About Farlowichnus Rapidus:
- The new species of dinosaur was a small carnivorous animal about the size of a modern-day seriema bird, or about 60-90 cm (2-3 feet) tall.
- it was a very fast reptile that ran across the ancient dunes.
- These fossilized dinosaur "trackways," were first found in the 1980s by Italian priest and paleontologist Giuseppe Leonardi in the city of Araraquara, in Sao Paulo (Brazil).
- It lived during the early Cretaceous period.
About Cretaceous Period:
- The Cretaceous Period, spanning from approximately 145 to 66 million years ago, represents the third and final epoch of the Mesozoic Era.
- It is characterized by significant geological and biological events.
- The climate was generally warm, and the world's continents were positioned closer to their present locations.
- The Cretaceous witnessed the proliferation of diverse and iconic dinosaurs, including the formidable Tyrannosaurus rex and the enormous herbivorous sauropods.
- Additionally, flowering plants, or angiosperms, experienced a remarkable evolutionary expansion during this period, transforming terrestrial ecosystems.
- Towards the end of the Cretaceous, a catastrophic event, possibly a large asteroid impact, led to the mass extinction of dinosaurs and numerous other species, marking the boundary between the Cretaceous and the subsequent Paleogene Period.
- This extinction event profoundly shaped the course of Earth's biological evolution.
Deepfakes (TOI)

- 25 Nov 2023
Why is it in the News?
The government has warned top social media and internet companies that their platforms may be temporarily suspended and even be ordered blocked in case they are unable to tackle the menace of deepfakes.
What are Deepfakes?
- The term "deepfake" combines the concepts of deep learning with the fabrication of content.
- Deepfakes involve the creation of synthetic images and audio using machine-learning algorithms, intending to disseminate misleading content by replacing a real person's appearance, voice, or both with artificially generated likenesses or voices.
- These manipulated creations can either depict nonexistent individuals or simulate real people engaging in actions or utterances they never did.
- Originating in 2017, the word "deepfake" emerged when a Reddit user named "deepfakes" shared explicit videos featuring celebrities.
- The process of crafting deepfakes utilizes machine learning models employing neural networks to manipulate visual and auditory elements.
- To generate a convincing deepfake video, creators train the neural network on extensive real footage of the targeted person, facilitating a realistic understanding of their appearance from various angles and lighting conditions.
- This trained network is then combined with computer graphics to overlay the person onto a different actor.
- Regrettably, this technology is increasingly exploited for malicious purposes, including scams, celebrity impersonation, election interference, social engineering, disinformation attacks, identity theft, and financial fraud.
- The distinguishing factor of deepfakes lies in their challenging detection due to their sophisticated nature.
Sundarbans Tiger Reserve (STR) (Indian Express)

- 25 Nov 2023
Why is it in the News?
The annual tiger census in West Bengal’s Sundarbans is scheduled to commence on November 27.
About Sundarbans Tiger Reserve (STR):
- Sundarbans Tiger Reserve (STR) is situated in the coastal districts of West Bengal, i.e. South 24- -Parganas and part in North 24-Parganas.
- It lies at the southernmost extremity of the lower Gangetic delta bordering the Bay of Bengal.
- It is one of the first nine Tiger Reserves declared under the Project Tiger scheme in the year 1973.
- It is the only mangrove forest throughout the world (besides Bangladesh) to harbour a significant tiger population.
- Borders: The Sundarbans Tiger Reserve is bound on the east by the international boundary with Bangladesh formed by the rivers Harinbhanga, Raimangal, and Kalindi.
- On the south lies the Bay of Bengal.
- The western border is formed by the river Matla, which acts as a common boundary with the territorial Forest Division of South 24- Parganas.
- Towards the northwest, the area is bound by rivers Bidya and Gomdi.
- The Sundarban Tiger Reserve is a part of the Sundarban Biosphere Reserve.
- It harbours significant populations of the river terrapin (Batagur baska), which was once believed to be extinct.
- It is the nesting ground for marine turtles like Olive Ridley (Lepidochelys olivacea), Green sea turtle (Chelonia mydas), and Hawksbill turtle (Eretmochelys imbricata).
- Flora: These comprise true mangroves or major elements, minor elements of mangroves or/and mangrove associates, shrubs, non-halophytic non-mangrove associates, halophytic herbs, shrubs, weeds, epiphytes, and parasitic plants.
- Fauna: It is to a large number of endangered and globally threatened species like the tiger (Panthera tigris tigris), fishing cat (Prionailurus viverrina), and estuarine crocodile (Crocodilus porosus), Gangetic (Platanista gangetica) and Irrawaddy Dolphin (Oracella brevirostris), king cobra (Ophiophagus hannah), water monitor lizard (Varanus salvator), etc.
Black-spotted Croaker, or the Ghol Fish (Indian Express)

- 24 Nov 2023
Why is it in the News?
The black-spotted croaker, or the ghol fish — considered a fisherman’s lottery — was declared the state fish of Gujarat on Tuesday.
About Ghol Fish:
- The Ghol fish is a rare and valuable marine species known for its richness in essential nutrients such as iodine, omega-3, DHA, EPA, iron, taurine, magnesium, fluoride, and selenium.
- Habitat: Typically found in the Indo-Pacific region, stretching from the Persian Gulf to the Pacific Ocean, the Ghol fish thrives in the marine areas of Gujarat and Maharashtra in India, exhibiting a distinctive golden-brown color.
- Size and Price: With a length of around one-and-a-half meters, the Ghol fish's price increases with its size, reaching up to Rs 5 lakh per unit length.
- Referred to as 'Sea Gold,' the Ghol fish earns this moniker due to a pouch in its stomach with potent medicinal properties, making it highly valued in the overseas market.
- Health Benefits:
- Eye Health: Rich in vitamins, minerals, and proteins, the Ghol fish contributes to maintaining eyesight.
- Anti-Ageing: The collagen content in the fish helps prevent wrinkles, preserving skin elasticity.
- Cognitive Development: The omega-3 content supports the growth of brain cells, enhancing the IQ of infants if consumed regularly.
- Muscle Toning: The fish is known for its muscle-toning properties.
- Economic Value: In high demand for both its meat and air bladder (sold separately), the Ghol fish serves various purposes, from culinary use to making beer and wine, with its air bladder finding applications in pharmaceuticals.
Psyche Mission (Indian Express)

- 24 Nov 2023
Why is it in the News?
A NASA experiment on the Psyche spacecraft has beamed back a near-infrared laser that contains test data from almost 16 million kilometers away.
About the Psyche Mission:
- Psyche is a NASA mission to study a metal-rich asteroid ‘Psyche’, located in the main asteroid belt between Mars and Jupiter.
- The mission launched on October 13, 2023, from Kennedy Space Center and will arrive at Psyche in August 2029.
- The spacecraft will orbit the asteroid for about two years, studying its geology, composition, and magnetic field.
- Scientists believe that Psyche may be the exposed core of an early planet that never fully formed.
- If so, studying Psyche could provide important insights into the formation of our solar system.
- It is also the first in a series of NASA science missions to be the primary payload launched on a SpaceX Falcon Heavy rocket.
- The goals of the Psyche mission are to:
- Understand the composition and structure of a metallic asteroid.
- Determine how Psyche formed and evolved.
- Learn more about the formation of planetary cores.
- The Psyche spacecraft is a solar-powered spacecraft that uses Hall effect thrusters for propulsion.
- The spacecraft also carries a suite of scientific instruments, including:
- A magnetometer to measure Psyche's magnetic field.
- A spectrometer to measure the composition of Psyche's surface.
- A gamma-ray spectrometer to measure the abundance of elements on Psyche's surface.
Mythimna Separata (DownToEarth)

- 24 Nov 2023
Why is it in the News?
Persistent high temperatures over an extended period might be responsible for the severe infestation of the Mythimna separata pest in Assam, causing damage to paddy crops in at least 15 districts.
About Mythimna Separata:
- This is a common long-distance migratory insect and a significant pest for various grain crops.
- Distribution: Mythimna separata is widely distributed in tropical and subtropical regions of Asia, including China, Japan, Southeast Asia, India, and eastern Australia.
- It has also been introduced to New Zealand and some Pacific islands.
- In India, it was initially identified as a sporadic pest in Tamil Nadu in 1937 and later in Kerala and Odisha in 1957.
- Known by various names such as the ear-head-cutting caterpillar, rice ear-cutting caterpillar, or armyworm, this pest feeds on leaves and has the capability to cut off panicles from the base of a crop plant.
- Its feeding habits often leave the field resembling it has been grazed by cattle.
- During an outbreak, the pest multiplies rapidly and moves in swarms from one field to another, similar to an army, causing harm to crops.
- The pest population tends to increase under favorable conditions, particularly when there is a rise in temperatures coupled with dryness.
Investor Risk Reduction Access platform (Indian Express)

- 24 Nov 2023
Why is it in the News?
Recently, the chairperson of the Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI) launched the Investor Risk Reduction Access platform.
About the Investor Risk Reduction Access Platform:
- The Investor Risk Reduction Access Platform is created to make investing safer, especially when technical issues occur at the trading member's end, both at the primary site and the disaster recovery site.
- Its purpose is to let investors close their open positions and cancel pending orders using the IRRA platform when technical problems or unexpected outages make the trading member's site inaccessible.
- It's designed to minimize risks for investors involved in the market.
- The platform is not for making new positions or orders;
- its role is solely to cancel pending orders.
- This platform is accessible to trading members supporting internet-based trading (IBT) and Security Trading through Wireless Technology (STWT) for their investors.
- However, it is not available for algo trading and institutional clients.
- All major stock exchanges – BSE, NSE, NCDEX, MCX, and Metropolitan Stock Exchange of India (MSE) – have collaborated to develop this platform.
- Stock exchanges can keep an eye on factors such as connectivity, order flow, and social media updates.
- They can independently activate the IRRA service if necessary, without waiting for a request from the trading member.
Global Digital Public Infrastructure Repository (Financial Express)

- 24 Nov 2023
Why is it in the News?
Prime Minister announced the launch of two India-led initiatives: the Global Digital Public Infrastructure Repository and a Social Impact Fund aimed at promoting the development of Social Impact Fund to advance Digital Public Infrastructure (DPI) in the Global South during the Virtual G20 Leaders’ Summit on 22nd November 2023.
About the Global Digital Public Infrastructure Repository:
- It was developed by the Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology (MeitY).
- It is an extensive resource center that combines knowledge and insights from G20 members and visiting countries.
- Its primary objective is to fill the knowledge gap in the decision-making processes and methodologies necessary for designing, constructing, deploying, and governing Digital Public Infrastructures (DPIs).
- The GDPIR presents information in a standardized format from countries and organizations that have successfully implemented DPIs on a large scale.
- This includes elements such as maturity scales, source codes (where available), and governance frameworks.
- Currently, the GDPIR showcases 54 DPIs from 16 countries.
- The DPIs from India featured in the GDPIR include
- Aadhaar, Unified Payments Interface (UPI), eSanjeevani, Ayushman Bharat Digital Mission (ABDM), DigiLocker, Umang, Co-WIN, Government e-marketplace, API Setu, Diksha, E-Hospital and Poshan Tracker etc.
What about the Social Impact Fund?
- The fund will financially support countries developing DPIs, providing “upstream technical and non-technical assistance”.
- The platform allows other governments, international organisations, and philanthropies to contribute to the fund too.
- India has pledged an initial commitment of $25 million (USD) to the fund.
Nugu Wildlife Sanctuary (The Hindu)

- 23 Nov 2023
Why is it in the News?
The National Tiger Conservation Authority (NTCA) has recommended to the authorities that the Nugu Wildlife Sanctuary abutting the Bandipur Tiger Reserve be declared as a core critical tiger habitat.
About Nugu Wildlife Sanctuary:
- The Nugu Wildlife Sanctuary is situated in the Heggadadevanakote Taluk of Mysore district in Karnataka and comprises the Lakshmanapura State Forest.
- In 1974, Nugu was declared as a Wildlife Sanctuary and later during the year 2003-2004, the area of Nugu Wildlife Sanctuary was added to the Nilgiri Biosphere Reserve.
- On the western side of the sanctuary lies the backwater of Nugu Dam which forms the part of the Nugu Wildlife Sanctuary.
- On the southwestern side, the area touches the Alaganchi State Forest which comes under the Bandipur Tiger Reserve.
- During the summer, elephants migrate from the adjoining area and congregate on the foreshore area because here, the backwater recedes and the area becomes temporary vast grassland due to the availability of fodder and water.
Geology of Nugu Wildlife Sanctuary:
- The Nugu region has red loamy type of soil with boulders.
The climate of Nugu Wildlife Sanctuary:
- The climate in the Nugu Wildlife Sanctuary is of moderate type with the temperature ranging between14°C to 38°C.
- The area receives rainfall both from southwest and northeast monsoons.
- The average amount of rainfall received in this area is 1000mm.
- Flora: The flora of the Nugu Wildlife Sanctuary is similar to that of the Bandipur National Park.
- The forests comprise southern mixed deciduous trees and dry deciduous scrubs.
- Some of the tree species found in this region include Dipterocarpus indicus, Calophyllum tomentosum, and Hopea parviflora.
- Fauna: Nugu Wildlife Sanctuary has a vast list of fauna with a wildlife population that includes elephants, wild boar, jungle cats, tigers, leopard, bonnet macaque, small Indian civet, back nappe hare, along with reptiles like the marsh crocodile, monitor lizard, cobra, rat snake, etc.
- With the adoption of the Wildlife Protection Act of 1972, hunting and poaching is banned and illegal in this sanctuary.
- In recent times, the Nugu Wildlife Sanctuary has been declared to be an eco-sensitive zone, which means there will be no commercial or industrial activity including mining in this area.
Tantalum (NewsOnAir)

- 23 Nov 2023
Why is it in the News?
The Indian Armed Forces contingent comprising 81 personnel departed for Australia on Wednesday to take part in the second edition of Joint Military Exercise AUSTRAHIND-23.
About Exercise AUSTRAHIND-23:
- Exercise AUSTRAHIND-23 was established in 2022, with its first edition held in Mahajan, Rajasthan.
- It is planned as an annual training event, alternating between India and Australia.
- The primary goal of the exercise is to cultivate collaborative partnerships and share best practices between the two sides.
- This year, the exercise is scheduled to take place in Perth, Australia, spanning from November 22nd to December 6th, 2023.
- The Indian Army contingent, consisting of 60 personnel from a Gorkha Rifles battalion, will actively participate in this exercise.
- A key focus is on promoting interoperability during multi-domain operations in urban and semi-urban terrain, aligned with Chapter VII of the United Nations on peacekeeping operations.
- The joint exercise serves as a platform for exchanging ideas and collectively rehearsing tactics, techniques, and procedures for conducting tactical operations.
- Additionally, the exercise contributes to fostering understanding between the two militaries, further strengthening defense cooperation between the two friendly nations.
Other Exercises between India and the Aus:
- AUSINDEX - Naval exercise between India and Australia
- Exercise Pitch Black - It is a biennial warfare exercise hosted by the Royal Australian Air Force (RAAF).
Inter Command Ocean Sailing Race 2023 (NewsOnAir)

- 23 Nov 2023
Why is it in the News?
The second edition of the Inter-Command Ocean Sailing Race to Goa was flagged off from the Naval Base in Kochi on Wednesday.
About the Inter Command Ocean Sailing Race 2023:
- The Inter Command Ocean Sailing Race 2023 features four 40-footer sailboats for an exciting journey in the Arabian Sea which was:
- INSV Bulbul
- INSV Neelkanth
- INS Kadalpur, and
- INSV Hariyal
- Each boat has a team of eight people from three naval commands and a combined team from Andaman and Nicobar Command, including the Delhi area.
Details of the Race:
- Distance and Route: The race covers around 667km from Naval Base, Kochi, to Goa in about five days.
- Engine-Free Journey: Boats will use the wind to reach Goa without engines.
- Inclusive Crew: This edition includes both men and women officers and sailors, promoting equal opportunities.
- Competition: With 32 participants, each competing for the title, the boats will navigate through the Arabian Sea's currents and winds.
Organizational Framework:
- Event Host: The Southern Naval Command organizes the race with the Indian Naval Sailing Association in New Delhi.
- Coordination: The Indian Navy’s Offshore Sailing Club in Kochi and the Ocean Sailing Node in INS Mandovi, Goa, coordinate the event.
- Purpose: The race helps the Navy improve risk management and technical skills while fostering a spirit of adventure among the crew.
Rapid Innovation and Startup Expansion (RISE) (Financial Express)

- 23 Nov 2023
Why is it in the News?
The AIM and NITI Aayog have recently introduced a new accelerator known as Rapid Innovation and Startup Expansion (RISE) aimed at providing support to startups in the circular economy sector in both Australia and India.
About Rapid Innovation and Startup Expansion (RISE):
- RISE, a collaborative initiative between Australia’s national science agency (CSIRO), and Atal Innovation Mission (AIM), the Government of India’s flagship initiative for fostering innovation and entrepreneurship, is a dedicated accelerator.
- This program is designed to support startups and small to mid-sized enterprises (SMEs) in India and Australia focusing on circular economy technologies and solutions.
Key Highlights:
- Focus Themes: The RISE Accelerator targets startups in India and Australia engaged in circular economy technologies, specifically in:
- Climate Smart Agriculture
- Clean Energy
- Circular Economy and Waste Management, and
- Climate Smart Mobility.
- Nine-Month Program: Over the course of nine months, the RISE Accelerator aims to assist startups in navigating early steps in a new region, establishing connections with the right partners, customers, and talent, and building credibility to succeed in international markets.
- First Round Focus: In its initial round, the accelerator concentrates on supporting startups and SMEs involved in technologies and solutions related to waste and the circular economy.
- Financial Support: Participating startups have the opportunity to receive up to INR 40,00,000 in non-equity grants.
- Future Rounds: Subsequent rounds of the accelerator will shift focus to climate-smart agriculture, clean energy, and climate-smart mobility.
New Frog Species- Music Frog (The Hindu)

- 23 Nov 2023
Why is it in the News?
Recently, scientists have discovered a new species of 'music frog' in Arunachal Pradesh.
About the New Frog Species:
- Scientists discover a new 'music frog,' Nidirana noadihing, in Arunachal Pradesh.
- Both male and female frogs are vocal with a unique call pattern of two-three notes.
- The discovery was made during field surveys in the Changlang and Lohit districts in August-September.
- Male frogs with 'robust' bodies were found calling loudly in vegetation near water bodies.
- The new species is named after the Noa-Dihing River, near where it was discovered.
- The species confirms the presence of the Nidirana genus in India for the first time.
- Nidirana species are known in Japan, Taiwan, China, Vietnam, Laos, and Thailand.
- Appearance: The amphibians have "irregularly shaped and sized spots" on their eyelids and they have dark stripes around their moderately large eyes.
- Their pupils are gold-rimmed and their irises are dark brown and have a golden spackle.
- Habitat: Noa-Dihing Music Frogs inhabit swamps, ponds, and paddy fields, constructing nests for egg laying.
- The discovery emphasizes the importance of exploring specialized habitats like marshlands, often overlooked in scientific studies.
Naval Anti-Ship Missile Short Range (NASM-SR) (TOI)

- 22 Nov 2023
Why is it in the News?
The Indian Navy successfully test-fired an indigenous anti-ship missile over the Arabian Sea, marking a significant step in India's efforts towards self-reliance in defense technologies.
About Naval Anti-Ship Missile Short Range (NASM-SR):
- This revolutionary missile NASM-SR, entirely developed by Indian scientists and engineers, represents a huge stride in the indigenization of India's defense infrastructure.
- The project is a collaborative effort between various esteemed agencies, including the Defense Research and Development Organisation (DRDO).
- The successful trial brings a sense of pride and accomplishment to India's defense realm.
- Launch Capability: This advanced missile is designed for launch from attack helicopters, presenting a versatile addition to the naval arsenal.
- Replacement for Sea Eagle: NASM-SR is slated to replace the existing Sea Eagle missiles currently in use by the Navy, aligning with the imperative of modernization and technological advancement.
- Integration with MH-60R Helicopters: As Sea King helicopters are phased out, the NASM-SR is anticipated to integrate seamlessly with the new MH-60R multi-role helicopters, a pivotal component of the Navy's evolving fleet.
Key Features:
- The missile incorporates a state-of-the-art guidance system and integrated avionics.
- It introduces indigenous launcher technology tailored for helicopter deployment.
- Possessing a striking range of approximately 60 km.
- Travels at a speed of Mach 0.8, slightly below the speed of sound.
- Equipped with a 100kg warhead, rendering it capable of neutralizing patrol boats and causing substantial damage to larger warships.
- Employs an imaging infrared seeker to target heat emissions, enhancing precision in homing onto its designated targets.
- During the approach to its target, the NASM-SR operates at just 5 meters above sea level, a strategic feature known as sea skimming.
- This low-level approach minimizes the susceptibility to detection, tracking, and interception by enemy radars or surface-to-air missiles.
Exercise Vajra Prahar 2023 (The Hindu)

- 22 Nov 2023
Why is it in the News?
A joint exercise of the special forces of India and the United States commenced in Meghalaya’s Umroi Cantonment on Tuesday.
About Exercise Vajra Prahar 2023:
- Exercise Vajra Prahar is a collaborative effort between the Indian Army and the US Army Special Forces.
- It is the 14th such exercise aimed at sharing the best practices and experiences in areas such as joint mission planning and operational tactics
- Representing the US, personnel from the 1st Special Forces Group (SFG) of the US Special Forces are actively engaged.
- The Indian Army contingent, led by Special Forces personnel from the Eastern Command, contributes to this joint training effort.
- The first edition took place in India in 2010, and the 13th edition occurred at the Special Forces Training School (SFTS), Bakloh (HP).
- This continuity highlights the longstanding commitment to strengthening Indo-US defense ties.
- The 14th edition is currently underway at Umroi Cantonment, Meghalaya, spanning from 21st November to 11th December 2023.
- This location serves as the backdrop for intensive training and cooperation.
- Exercise Vajra Prahar serves as a crucial platform to enhance inter-operability between the Indian and US armies.
- This emphasis on seamless coordination aims to bolster defense cooperation and strategic alignment.
Other Exercises between India and the USA:
- YUDHABHAYAS- Army
- VAJRA PRAHAR- Army
- Exercise MALABAR (Multilateral)- Indian Navy
- RED FLAG 16-1- Air Force
- Exercise COPE India 23- Air Force
Risk weight (LiveMint)

- 22 Nov 2023
Why is it in the News?
Spooked by the strong growth in unsecured loans to consumers, the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) has increased the cost of funds for banks and non-bank financial companies (NBFCs), by increasing the risk weight of such loans.
What are Risk Weights?
- Every rupee lent by the bank is a cost or has an implication on its capital position.
- Depending on the nature of the loan and the inherent risk associated with it, risk weights are attributed.
- Banks have to ensure that their capital is enough to cover these risk-weighted assets.
- Total assets as disclosed in the financials and total risk-weighted assets are different things.
- Each asset class has varying risk weights.
- For instance, risk weights for home loans could range from 50 percent to 75 percent, for gold loans it is 75 percent.
- Corporate loans are charged 100 percent given the risk they carry.
How do they affect borrowers?
- Lower the risk weight, and lower the rate of interest. This is the thumb rule.
- Therefore, risk weights impact borrowers indirectly and are felt through the pricing of loans.
- For instance, home loans have the lowest interest rate among retail products because lower risk weights allow banks to pass on the advantage of capital consumption.
- Personal loans and credit cards have the highest interest rate because of their tenure and charge on capital.
Gambusia Fish (The Hindu)

- 22 Nov 2023
Why is it in the News?
Government and non-government groups in Andhra Pradesh, Odisha, and Punjab have recently put Gambusia fish into local water sources to deal with mosquito issues.
About Gambusia fish:
- Gambusia, also known as mosquitofish, is a genus of small, freshwater fish in the family Poeciliidae.
- There are over 40 species of Gambusia, most of which are found in North America, Central America, and the Caribbean.
- Gambusia fish are known for their voracious appetite for mosquito larvae, and they have been widely introduced around the world for mosquito control.
- They are small, with females typically reaching a maximum length of 7 cm and males a maximum length of 4 cm.
- They have a slender body with a pointed snout and a small mouth.
- They are typically green or silver in color, with some species having dark spots on their sides.
- Gambusia fish are livebearers, meaning that they give birth to live young.
- Females can produce up to 1,000 fries (baby fish) per year.
- They are opportunistic feeders and will eat a variety of foods, including mosquito larvae, small insects, and zooplankton.
- Gambusia fish have been introduced to many parts of the world for mosquito control.
- However, they have also been shown to have negative impacts on native fish populations.
- In some cases, Gambusia fish have been known to outcompete and displace native fish species.
- The International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) declares Gambusia one of the 100 worst invasive alien species in the world.
Tantalum (Indian Express)

- 22 Nov 2023
Why is it in the News?
A team of researchers from the Indian Institute of Technology (IIT), Ropar has found the presence of tantalum, a rare metal, in the Sutlej river sand in Punjab.
What is Tantalum?
- Tantalum is a rare metal with the atomic number 73.
- Tantalum was first discovered by Anders Gustaf Ekenberg, a Swedish chemist, in 1802.
- It has been named after a Greek mythological figure Tantalus.
Properties:
- It’s grey, heavy, very hard, and one of the most corrosion-resistant metals in use today.
- It possesses high corrosion resistance because when exposed to air, it forms an oxide layer that is extremely difficult to remove, even when it interacts with strong and hot acid environments.
- When pure, tantalum is ductile, meaning it can be stretched, pulled, or drawn into a thin wire or thread without breaking.
- Moreover, it “is almost completely immune to chemical attack at temperatures below 150°C, and is attacked only by hydrofluoric acid, acidic solutions containing the fluoride ion, and free sulphur trioxide.
- Notably, tantalum also has an extremely high melting point, exceeded only by tungsten and rhenium.
Applications:
- Tantalum is most prominently used in the electronic sector.
- The capacitors made from tantalum are capable of storing more electricity in smaller sizes without much leakage than any other type of capacitor.
- This makes them ideal for use in portable electronic devices such as smartphones, laptops, and digital cameras.
- As tantalum has a high melting point, it is frequently used as a substitute for platinum, which is more expensive.
- The rare metal is also used to make components for chemical plants, nuclear power plants, aeroplanes, and missiles.
- Tantalum does not react with bodily fluids and is used to make surgical equipment and implants, like artificial joints.
Government bans anti-cold drug combination for kids aged under four (Indian Express)

- 21 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
The Central Drugs Standard Control Organisation (CDSCO) has prohibited the use of anti-cold fixed drug combinations in children below four years of age.
What are Fixed Dose Combination (FDC) Drugs?
- Fixed-dose combination (FDC) drugs, also referred to as combination products, embody a formulation containing two or more active drugs within a single dosage form.
- The United States Food and Drug Administration (FDA) defines a combination product as a composition involving a drug and a device, a biological product and a device, or a combination of a drug, device, and biological product.
- While the conventional approach favours formulating drugs as single compounds, the acceptance of fixed-ratio combination products hinges on two key criteria:
- Dosage Requirements: Each ingredient in the combination must meet the dosage criteria tailored to a specific population group.
- Proven Advantages: The combination should demonstrate a clear advantage over administering individual compounds separately in terms of therapeutic effect, safety, or compliance.
- FDCs have witnessed significant popularity in the Indian pharmaceutical market, experiencing notable growth in recent years.
About the Central Drugs Standard Control Organization (CDSCO):
- The Central Drugs Standard Control Organization (CDSCO) serves as the National Regulatory Authority (NRA) in India, overseeing the medical devices industry per the Drugs & Cosmetics Rules.
- Positioned under the Ministry of Health & Family Welfare, it is led by the Drugs Controller General of India (DCGI) with its headquarters situated in New Delhi.
- Operationalizing under the provisions of the Drugs and Cosmetics Act, CDSCO is entrusted with several crucial responsibilities, including the approval of new drugs, the facilitation of clinical trials, the establishment of standards for drugs, ensuring control over the quality of imported drugs, and coordination of activities among State Drug Control Organizations.
- One of its significant roles lies in collaboration with state regulators for granting licenses related to specialized categories of critical drugs.
- These encompass vital medical components such as blood and blood products, I.V. fluids, vaccines, and sera.
- The CDSCO plays a pivotal role in upholding standards, ensuring quality, and fostering coordination across the regulatory landscape for the benefit of public health in India.
Why the UK banned Air France, Lufthansa, and Etihad ads over ‘greenwashing’ claims (Indian Express)

- 21 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
Earlier in December, the United Kingdom’s ad regulator banned advertisements from Air France, Lufthansa, and Etihad for allegedly misleading consumers regarding the environmental impact of air travel.
What is Greenwashing?
- Greenwashing is the deceptive practice of creating a false impression or providing misleading information about the environmental sustainability of a company's products.
- It involves making unverified claims to lead consumers to believe that a company's products are more environmentally friendly or have a more positive impact on the environment than is accurate.
- Furthermore, greenwashing can occur when a company highlights the sustainable aspects of a product to divert attention from its involvement in environmentally harmful practices.
- Companies may employ greenwashing tactics by using vague claims that lack substantiated data or scientific validation.
- For instance, a car vendor might assert that a vehicle is eco-friendly due to increased fuel efficiency, conveniently overlooking or downplaying the broader environmental impact of vehicle manufacturing processes.
What are the Concerns With Greenwashing?
The practice of greenwashing raises apprehensions on several fronts:
- Authenticity of Climate Goals: There is a risk of undermining the authenticity of climate goals when misleading or exaggerated information about environmental initiatives is presented.
- Unwarranted Recognition and Benefits: Entities involved in greenwashing may receive undeserved recognition or benefits, potentially rewarding irresponsible behaviour and discouraging genuine sustainability efforts.
- Market Distortion: Greenwashing can distort markets by creating an uneven playing field.
- Entities engaging in deceptive practices might gain an unfair advantage over those genuinely adhering to stringent environmental standards.
- Lack of Comprehensive Regulations: The absence of comprehensive regulations and standards for environmental claims allows greenwashing to persist without adequate scrutiny, contributing to a lack of transparency.
- Challenges to Carbon Credit Systems: The practice of greenwashing introduces challenges to the integrity of carbon credit systems.
- This is particularly evident in informal markets, where the expansion of credit sources and certification by unofficial entities raise concerns about transparency and reliability.
- It's crucial to note that in the context of carbon credits, one credit represents the removal of one metric ton of carbon dioxide or equivalent greenhouse gases from the atmosphere.
- The concept of carbon credits was introduced by the Kyoto Protocol, providing rewards to countries or firms surpassing emission reduction mandates.
Global Initiatives Addressing Greenwashing:
- During the 27th Conference of Parties (COP27), the United Nations Secretary-General declared a zero-tolerance stance against greenwashing.
- Private corporations were urged to rectify their practices to align with genuine environmental efforts.
- In a landmark move in October 2023, the European Union approved the world's first green bond standards.
- These standards, under the "European Green Bond" label, mandate transparency and direct 85% of funds towards sustainable activities within the EU.
- The legislation aims to support the EU's transition to climate neutrality.
Laws in India:
- In India, greenwashing is classified as an unfair trade practice under the Consumer Protection Act, 2019.
- This legislation prohibits deceptive claims and outlines penalties and remedies for consumers adversely affected by such misleading practices.
- In February 2023, the Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI) issued guidelines for issuers of green debt securities.
- These guidelines are designed to ensure transparency, prevent greenwashing, protect investors, and regulate the development of the securities market.
- The Advertising Standards Council of India (ASCI), a voluntary self-regulatory organization, plays a crucial role in monitoring advertising practices.
- It holds jurisdiction over allegations of greenwashing, ensuring that ads are not only legal but also honest and fair.
- The ASCI's regulatory efforts aim to safeguard consumer interests and promote fair competition within the Indian advertising landscape.
Bhoomi Rashi Portal is revolutionizing land acquisition for Highway projects – Here’s how (Financial Express)

- 21 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
Union Minister of Road Transport and Highways Nitin Gadkari revealed in a recent statement to the Rajya Sabha that the Bhoomi Rashi portal is instrumental in expediting the development of highway infrastructure in India.
About the Bhoomi Rashi Portal:
- The acquisition of land was done manually before the year 2018. The data files were moved physically, leading to some limitations. This included delays in issuing notices, errors in land details, etc.
- To overcome the issues, the Ministry of Road Transport and Highways came up with a system.
- It is known as “Bhoomi Rashi”.
- The portal came into force on 1st April 2018
- The system is digital and automates the whole land acquisition (LA) process.
- It made and still makes the LA process more transparent and error-free.
- The portal processes the notices at every stage on a real-time basis.
Key Objectives:
- Acceleration of Land Acquisition: The primary goal is to facilitate a quicker and more efficient land acquisition process for National Highways.
- Centralized Processing: Acting as a singular online platform, it consolidates the processing of land acquisition notifications, contributing to the swift development of highway infrastructure projects.
- Transparency and Accountability: Ensures transparency and accountability throughout the land acquisition process.
- Direct Benefit Transfer: Facilitates the electronic transfer of benefits directly to the accounts of the beneficiaries involved in the land acquisition.
Salient Features:
- Bilingual application with Hindi and English for easy usability
- Preparation of interface for adding basic details of the project, including land acquisition sanction details
- Preparation of interface for Land Acquisition locations. villages
- Preparation of Interface for Competent Authority for Land Acquisition (CALA) details. CALA is a revenue functionary of the State Government appointed for each NH Project.
- Interface for generating land acquisition notification
- Interface for land Details
- Interface for generation of notification: organisational email IDS for all those involved in the process flow to ensure smooth e-office management
- Interface for Objections and processing
- Interface for compensation determination and finalisation
- Interface for land owners and affected parties
- Interface for reports generation
The portal is seamlessly integrated with the Public Financial Management System (PFMS) of the Ministry of Finance, ensuring real-time deposit of compensation into the accounts of affected/interested individuals.
What is Land Acquisition?
- Land acquisition is the governmental process, whether at the state or union level, through which private land is procured for infrastructure development, urbanization, or industrialization.
- In exchange, the government provides appropriate compensation to the landowner based on market value and assumes responsibility for the rehabilitation and resettlement of those affected by the land acquisition.
SAT quashes Sebi's order against Kishore Biyani, and others (Live Mint)

- 21 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
The Securities Appellate Tribunal (SAT) on Wednesday quashed regulator Sebi's order banning Future Retail chairperson Kishore Biyani and some other promoters from the securities market for one year in an insider trading case.
About the Securities Appellate Tribunal (SAT):
- Established as a statutory and autonomous entity under the Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI) Act, 1992, the Securities Appellate Tribunal (SAT) serves as a crucial forum for adjudicating appeals against decisions made by SEBI or its adjudicating officers.
Key Functions:
- Appeals Jurisdiction: Primarily tasked with hearing appeals against orders issued by SEBI or its adjudicating officers under the SEBI Act.
- Extended Jurisdiction: Additionally, SAT entertains appeals concerning orders from the Insurance Regulatory and Development Authority of India (IRDAI) and the Pension Fund Regulatory and Development Authority (PFRDA) related to cases filed before them.
Composition:
- Presiding Officer: A retired or sitting Supreme Court judge, Chief Justice of a High Court, or a High Court judge with at least seven years of service.
- Judicial Member: High Court judge with a minimum of five years of service.
- Technical Member: Individual with expertise and a minimum of 15 years of experience in the financial sector, including securities market, pension funds, commodity derivatives, or insurance.
- This member can be a senior official in the Central or State Government or a person of proven ability and integrity.
Appointment and Tenure:
- Appointments made by the Central Government in consultation with the Chief Justice of India or its nominee.
- Presiding Officer and members serve a term of five years, eligible for reappointment for an additional term of up to five years.
- No member shall hold office after reaching the age of 70.
Powers and Authority:
- They are empowered with the same powers as a civil court under the code of civil procedure when adjudicating suits.
- Appeals to SAT can be made by any person aggrieved by SEBI or adjudicating officer orders, excluding those made with the consent of all parties.
Appeals Process:
- Appeals against SAT decisions can be filed in the Supreme Court, limited to questions of law.
- No appeal is permissible against orders made with the consent of all parties.
- The SAT, with its specific mandate and composition, plays a pivotal role in ensuring fairness and justice in the regulatory framework of the securities market in India.
What is Insider Trading?
- Insider trading is the act of buying or selling securities of a publicly traded company based on material information not yet disclosed to the public.
- Material information encompasses any data that could significantly influence an investor's decision to buy or sell the security.
- For instance, Consider a scenario where a government employee, possessing knowledge about an upcoming regulation that would favour a sugar-exporting company, takes advantage of this information by purchasing the company's shares before the regulation becomes public knowledge.
MSME Ministry launches 3 sub-schemes under RAMP programme; makes ZED scheme free for women (Financial Express)

- 21 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
MSME Minister Narayan Rane recently launched three sub-schemes under the ministry’s existing RAMP ((Raising and Accelerating MSME Productivity) programme.
About the RAMP Programme:
- The Raising & Accelerating MSME Performance (RAMP) program, supported by the World Bank and inaugurated in 2022, is dedicated to enhancing the performance of micro, small, and medium enterprises (MSMEs) across India.
Program Objectives:
- Market and Credit Access: Facilitate improved access to markets and credit for MSMEs.
- Institutional Strengthening: Enhance institutional and governance structures at both central and state levels.
- Center-State Collaborations: Foster improved linkages and partnerships between central and state entities.
- Delayed Payment Issues: Address challenges related to delayed payments within the MSME sector.
- Greening of MSMEs: Promote sustainable practices and the adoption of green technologies within MSMEs.
- The National MSME Council has been set up by the Ministry to work as an administrative and functional body of the RAMP Programme.
Sub Schemes under RAMP:
- MSME GIFT Scheme: Aims to support MSMEs in adopting green technology through interest subvention and credit guarantee assistance.
- MSE SPICE Scheme: Focuses on promoting circular economy projects, with credit subsidy mechanisms, aligning with the MSME sector's goal of achieving zero emissions by 2070.
- MSE ODR Scheme: A pioneering initiative leveraging modern IT tools and Artificial Intelligence to address delayed payment incidents for Micro and Small Enterprises.
- Implementing Agencies for Sub Schemes:
- MSME GIFT and MSME SPICE Schemes: Small Industries Development Bank of India (SIDBI)
- MSE ODR Scheme: National Informatics Centre Services Inc. (NICSI)
- These sub-schemes, under the RAMP umbrella, signify a comprehensive effort to fortify and propel the growth of MSMEs, incorporating technological advancements and sustainable practices.
Chimaeras (The Hindu)

- 21 Nov 2023
Why is it in the News?
In a recent landmark study, scientists reported successfully generating a live chimaera in non-human primates
About Chimaeras:
- A genetic chimaera is a single organism made up of cells from more than one distinct genotype (or genetic makeup).
- Examples of varying degrees of chimerism exist in the animal kingdom.
- For instance, the half-sider budgerigar, a common pet parakeet, displays different colors on each side of its body due to chimerism.
- In anglerfish, the male fuses with the female, eventually being absorbed, creating a single animal with a merged genetic makeup.
- Marine sponges are known to have up to four distinct genotypes in one organism.
- In humans, natural chimaeras occur when the genetic material in one cell changes, leading to a clonal population of cells different from the rest.
- Fusion of two fertilized zygotes early in embryonic development can result in a condition where two genetic makeups coexist in a single individual.
- Chimerism can also arise from twin or multiple pregnancies evolving into a single fetus or a twin fetus being absorbed into a singleton.
Hard Currency (Financial Express)

- 21 Nov 2023
Why is it in the News?
Recently, the Global Trade Research Initiative (GTRI) said in a statement that Conditions are not ripe to make INR a hard currency.
What is Hard Currency?
- Usually, developed countries issue hard currency, and this currency is easier to trade and receive funds from other countries or investors from other nations.
Key characteristics of hard currencies:
- Hard currency means a stable currency, and its value does not fluctuate much in the international markets.
- It makes hard money currency easily tradable.
- It is issued by a sound economy. Developed countries issue hard currency and it is accepted by all nations across the world.
- It is highly liquid and several countries prefer to accept hard currency instead of local currency as it has lesser fluctuations and can be easily converted to local currency.
- Hard currency is universally accepted and international investors have a sense of faith in hard currency for trading.
- Countries across the globe consider hard currency as a foreign currency reserve, further adding to its value.
- As hard currency is easily convertible and stable, it is widely used in international exchanges.
- The value of the hard currency does not change much in response to global events.
- When domestic currencies struggle, people start holding on to hard currencies to protect their wealth.
Examples of hard currencies:
- US dollar (USD)
- Euro (EUR)
- Japanese yen (JPY)
- British pound (GBP)
- Swiss franc (CHF) etc.
The E Prime Layer (HT)
- 21 Nov 2023
Why is it in the News?
Recently, an international team of scientists found a new mysterious layer called the E prime layer on the outer part of the Earth's core.
About the E Prime Layer:
- Before, it was thought that there's only a small exchange of materials between the Earth's core and mantle.
- However, experiments showed that when water reaches the boundary between the core and mantle, it reacts with silicon in the core and creates silica.
Development of this Layer:
- New research proposes that over billions of years, tectonic plates carrying surface water transported it deep into the Earth.
- When this water reaches about 1,800 miles below the surface at the core-mantle boundary, it triggers significant chemical changes, affecting the core's structure.
- Scientists observed that under high pressure, subducted water chemically reacts with core materials.
- This reaction forms a hydrogen-rich, silicon-depleted layer on the outer core, resembling a film.
- Silica crystals produced in this process rise and mix into the mantle, impacting the overall composition.
- Changes in the liquid metallic layer could potentially lead to reduced density and altered seismic characteristics, consistent with anomalies detected by seismologists.
Importance of this Discovery:
- This finding deepens researchers' understanding of the Earth's internal workings, revealing a more extensive and complex global water cycle than previously known.
- The altered core layer has significant implications for the interconnected geochemical processes that link surface water cycles with the deep metallic core.
What is ROV ‘Daksh’? (HT)

- 21 Nov 2023
Why is it in the News?
The Defence Research Development Organisation's robotics team utilized the Remotely Operated Vehicle (ROV) Daksh to aid in the ongoing rescue operations during the Uttarakhand tunnel collapse.
What is ROV Daksh?
- Daksh is a remotely operated vehicle (ROV), designed by the Defence Research & Development Organisation (DRDO) for the recovery of unexploded bombs.
- It can negotiate various hurdles in an urban setting and can also be utilised to survey and monitor nuclear and chemical contamination levels.
- 90% of its components are indigenous.
- It has ladder climbing abilities and can function for three continuous hours, with the capability to operate over distances exceeding 100 to 500 meters.
- It serves the bomb disposal units (BDU) of an army, police, and paramilitary forces, aiding in handling IEDs and other dangerous substances.
- Its manipulator arm can handle hazardous objects weighing up to 20kg from 2.5 meters and 9kg from 4 meters away.
- Daksh demonstrates the ability to climb stairs and maneuver steep slopes, with durable rubber wheels capable of withstanding blast impacts.
- It is equipped with multiple cameras, IED handling tools, nuclear biological chemical (NBC) reconnaissance systems, a master control station (MCS), and a shotgun.
- The equipment is specifically designed for use on a motorized pan-tilt platform, which can help reach the risky terrain.
Atmospheric Waves Experiment (Indian Express)
- 21 Nov 2023
Why is it in the News?
Atmospheric Waves Experiment is a first-of-its-kind NASA experimental attempt aimed at studying the interactions between terrestrial and space weather.
What is the Atmospheric Waves Experiment (AWE)?
- AWE is a first-of-its-kind NASA experimental attempt aimed at studying the interactions between terrestrial and Space weather.
- Planned under NASA’s Heliophysics Explorers Program, the $42 million mission will study the links between how waves in the lower layers of the atmosphere impact the upper atmosphere, and thus, Space weather.
- AWE will be launched and mounted on the exterior of the Earth-orbiting International Space Station (ISS).
- From the vantage point, it will look down at the Earth and record the colourful light bands, commonly known as airglow.
- It will try to understand the combination of forces that drive the Space weather in the upper atmosphere.
- “AWE could open a new window of study, wherein scientists are attempting to understand if Space weather is affected by terrestrial and bottom-up forces.
- It will measure the airglow at mesopause (about 85 to 87 km above the Earth’s surface), where the atmospheric temperatures dip to minus 100 degrees Celsius.
- At this altitude, it is possible to capture the faint airglow in the infrared bandwidth, which appears the brightest enabling easy detection.
- AWE will be able to resolve waves at finer horizontal scales than what satellites can usually see at those altitudes, which is part of what makes the mission unique.
- The health of the ionosphere, whose lower layers sit at the edge of Space, is important for maintaining seamless communication.
- It is still not fully understood if the ionosphere is affected by the transient events or intense perturbations resulting from hurricanes or tornadoes.
- It was expected to launch in the month of August 2022, but the fresh launch is planned for later this month.
Rhododendron (The Hindu)

- 20 Nov 2023
Why is it in the News?
Recently rhododendron blooms in parts of Uttarakhand in November, worries experts.
About Rhododendron:
- Rhododendron is a diverse genus of flowering plants, encompassing over a thousand species, which include trees, shrubs, and creepers.
- These woody flowering plants belong to the heath family (Ericaceae) and are recognized for their appealing flowers and handsome foliage.
- Habitat: Rhododendrons thrive in various habitats, ranging from alpine regions and coniferous and broadleaved woodlands to temperate rainforests and even tropical areas.
- Distribution: Native to temperate regions of Asia, North America, and Europe, as well as tropical regions in Southeast Asia and northern Australia, rhododendrons have a broad geographical distribution.
- They flourish in slightly acidic soil conditions.
- Diversity: This genus displays an extensive range of sizes and shapes, from low-growing prostrate ground covers to towering trees exceeding 100 feet in height.
- In India, there are 132 taxa, including 80 species, 25 subspecies, and 27 varieties of rhododendrons.
- Local Names and Significance: In the local language, rhododendrons are known as "Lali Guras."
- Notably, they hold cultural significance as the national flower of Nepal and the state tree of Uttarakhand in India.
Nitrogen-9 Nucleus (Indian Express)

- 20 Nov 2023
Why is it in the News?
Researchers have found "compelling evidence" supporting the existence of the uncommon nitrogen-9 isotope. This discovery challenges previous interpretations and provides a fresh perspective on subatomic structures.
About Nitrogen-9 Nucleus:
- Nitrogen-9 is a radioactive isotope of nitrogen.
- This means that it is unstable and will eventually decay into a different isotope of nitrogen or a different element.
- It is considered unusual because it has an uncommon combination of seven protons and two neutrons (7:2) in its atomic nucleus.
- This creates an unusually high ratio of protons to neutrons.
- Generally, elements have a balanced ratio for stability, but Nitrogen-9’s high proton content makes it less stable, challenging the conventional stability thresholds.
- This oddity raises questions about its existence in this state and how it maintains stability, introducing complexity to our understanding of atomic nuclei.
- The reason for nitrogen-9's short half-life is that the strong force, which is responsible for holding nuclei together, is not strong enough to overcome the Coulomb repulsion between the positively charged protons in the nitrogen-9 nucleus.
- The discovery of nitrogen-9 is a major breakthrough in our understanding of nuclear physics.
- It showed that nuclei with very high proton-to-neutron ratios can exist, even if they are only for a very short time.
- This discovery has led to new research into the limits of nuclear stability and the role of nucleons (protons and neutrons) in holding nuclei together.
What is an Isotope?
- An isotope is a variant of a chemical element that has the same number of protons but a different number of neutrons in its atomic nucleus.
- This variance in neutron count results in different atomic masses for isotopes of the same element.
- Isotopes of an element share similar chemical properties but may exhibit differences in physical properties, such as stability and radioactivity.
Onattukara Sesame (The Hindu)

- 20 Nov 2023
Why is it in the News?
Efforts are being made to expand the cultivation of geographical indication (GI)-tagged Onattukara sesame.
About Onattukara Sesame:
- Onattukara sesame is a special sesame seed variety native to the Onattukara region of Kerala.
- It is renowned for its distinctive flavor, rich aroma, and exceptional nutritional and health value.
- In 2023, it received a geographical indication (GI) tag, recognizing its unique characteristics and link to the Onattukara region.
- This recognition serves as a testament to the exceptional qualities of Onattukara sesame and is expected to propel its demand and further empower the farmers of the region.
- Onattukara sesame distinguishes itself from other sesame varieties through its unique flavor profile.
- This distinctive flavor profile makes Onattukara sesame an indispensable ingredient in traditional Kerala cuisine, where it graces a variety of dishes, from curries and chutneys to sweet snacks.
- Distinguishing Features:
- Flavor and Aroma: Onattukara sesame has a nutty, slightly sweet flavor and a rich, earthy aroma.
- Nutritional Value: It is a rich source of vitamins and minerals, including vitamin E, calcium, magnesium, and iron.
- It also contains healthy fats, such as omega-3 and omega-6 fatty acids.
- Medicinal Properties: Traditionally, Onattukara sesame oil has been used in Ayurveda for its medicinal properties, including its ability to promote skin health, reduce inflammation, and relieve joint pain.
Freemartins (The Hindu)

- 20 Nov 2023
Why is it in the News?
Farmers in agricultural settings often identify freemartins by observing their physical and/or behavioral traits since these animals are unable to reproduce.
About Freemartins:
- A freemartin is an infertile female cattle with masculinized behavior and non-functioning ovaries.
- This condition is caused by the exchange of cells between female and male twins in utero.
- The male twin produces a hormone called anti-Müllerian hormone (AMH), which suppresses the development of the female reproductive tract.
- As a result, the female twin is born with an underdeveloped reproductive system and is unable to reproduce.
- Freemartinism occurs in about 90% of female cattle twins that share a placenta with a male twin.
- This is because the placentas of cattle twins are often fused together, allowing cells to move between the two fetuses.
- The fusion of placentas usually occurs between 40 and 120 days of gestation.
- In addition to being infertile, freemartins may also exhibit some masculine characteristics, such as a deeper voice, coarser hair, and a more muscular build.
- This is because they have been exposed to AMH from their male twin.
- There is no treatment for freemartinism, as the animal is infertile and cannot produce offspring.
- However, freemartins can still be used for other purposes, such as meat production or draft work.
Sophisticated Analytical & Technical Help Institutes (SATHI) Initiative (The Hindu)

- 20 Nov 2023
Why is it in the News?
The cancellation of a call for proposals under the Department of Science and Technology's SATHI program by the Centre has raised concerns among higher education institutions.
About Sophisticated Analytical & Technical Help Institutes (SATHI) initiative:
- The Department of Science and Technology (DST) is starting a project to create a shared Science and Technology infrastructure facility called Sophisticated Analytical & Technical Help Institute (SATHI).
- This facility will be available for use by academic institutions, startups, manufacturing units, industries, and R&D labs.
- The goal is to offer efficiently managed services with high transparency, accessibility, and effectiveness all in one place, catering to the needs of industries, startups, and academia.
- In the first phase, SATHI facilities will be set up at IIT-Delhi, IIT-Kharagpur, and BHU-Varanasi.
- This initiative aims to benefit less-endowed organizations like MSMEs, startups, state universities, and colleges, fostering a strong culture of research collaboration across different institutions and disciplines.
Aims & Objectives of SATHI:
- Provide shared, professionally managed Science and Technology services and infrastructure.
- Ensure efficiency, accessibility, and transparency for the demands of faculty, researchers, scientists, and students from various institutes and organizations.
- Enable round-the-clock R&D activities with minimal downtime.
- Offer facilities for fabrication work, rapid prototyping, material testing, characterisation, device fabrication, smart manufacturing, and more.
- Attract and support R&D labs, industrial R&D, MSMEs, Incubators, Start-ups, etc.
- Organize short-term courses, workshops, seminars, and hands-on training programs on the use and application of various instruments and techniques.
- Provide technical help and scientific knowledge to both external and internal users/researchers.
- Train technicians for maintaining and operating sophisticated scientific instruments.
- Maintain a record of trained personnel for better societal outreach and utilization of trained manpower across different SATHI centers when needed.
State of the Cryosphere Report 2023 (DownToEarth)

- 18 Nov 2023
Why in the News?
As per the 2023 State of the Cryosphere report, the anticipated disappearance of almost all tropical glaciers, a significant majority of mid-latitude glaciers, and polar regions is expected, even if global efforts successfully limit the rise in temperatures to 2 degrees Celsius above preindustrial levels.
About the State of the Cryosphere Report 2023:
- The State of the Cryosphere Report annually assesses the condition of Earth's snow and ice regions, and has been reviewed and endorsed by over 60 leading cryosphere scientists.
- This report is published by The International Cryosphere Climate Initiative (ICCI.)
- The cryosphere is a term for the regions of our globe that are covered in ice and snow – either seasonally or year-round.
- The Report describes how a combination of melting polar ice sheets, vanishing glaciers, and thawing permafrost will have rapid, irreversible, and disastrous impacts worldwide.
Key findings in the report on the impact of 2°C of warming include:
- Ice sheets: nearly all of Greenland, much of West Antarctica, and even vulnerable portions of East Antarctica will be triggered to very long-term, inexorable sea-level rise.
- Glaciers: extensive, irreversible ice loss from the world’s glaciers in many major river basins, with some disappearing entirely.
- As glaciers melt, risks of catastrophic events such as landslides, sudden ice shears, and glacial lake outburst floods increase.
- Sea ice: extensive sea ice loss at both poles, with severe feedback to global weather and climate.
- By 2°C, the Arctic Ocean will be sea ice-free in summer every year, potentially for several months.
- Permafrost: extensive permafrost thaw and resulting greenhouse gas emissions will cause temperatures to continue to rise, even once human emissions reach zero.
- At 2°C, annual total permafrost emissions (both CO2 and methane) would total the size of the entire European Union’s emissions from 2019.
- Polar ocean acidification: year-round, permanent corrosive ocean acidification conditions in many regions of Earth’s polar and near-polar seas.
- Shell-building animals and commercial fisheries that rely on them in the food chain may not survive.
About International Cryosphere Climate Initiative (ICCI):
- It was formed in 2009 following COP-15 in Copenhagen
- ICCI is a network of senior policy experts and researchers working with governments and organizations to create, shape, and implement initiatives designed to preserve as much of the Earth’s cryosphere as possible.
- ICCI programs target the unique climate dynamics at work in the cryosphere, while at the same time lending increased urgency to global climate efforts aimed at CO2 and other greenhouse gases by communicating the unexpected rapidity and global implications of cryosphere warming.
Dwarf Planet Eris (The Hindu)

- 18 Nov 2023
Why in the News?
Recently, scientists have discovered the inside structure of the enigmatic dwarf planet Eris.
About Dwarf Planet Eris:
- This new dwarf planet is the largest object found in orbit around the sun since the discovery of Neptune and its moon Triton in 1846.
- It was discovered on Jan. 5, 2005, and It is larger than Pluto, discovered in 1930.
- Like Pluto, the new dwarf planet is a member of the Kuiper belt, a swarm of icy bodies beyond Neptune in orbit around the sun.
- Eris is named for the ancient Greek goddess of discord and strife.
- The surface of Eris is extremely cold, so it seems unlikely that life could exist there.
- With a radius of about 1,163 kilometers, Eris is about 1/5 the radius of Earth.
- Eris, like Pluto, is a little smaller than Earth's Moon.
- Eris takes 557 Earth years to make one trip around the Sun.
- As Eris orbits the Sun, it completes one rotation every 25.9 hours, making its day length similar to ours.
- Moons: Eris has a very small moon called Dysnomia.
- Dysnomia has a nearly circular orbit lasting about 16 days.
- Eris most likely has a rocky surface similar to Pluto.
- Atmosphere: The dwarf planet is often so far from the Sun that its atmosphere collapses and freezes, falling to the surface as snow.
- As it gets closest to the Sun in its faraway orbit, the atmosphere thaws.
Card-on-File Tokenisation (CoFT) (Business Standard)

- 18 Nov 2023
Why in the News?
Recently, Visa has highlighted that the primary advantage of tokenization is a decreased risk of data breaches.
What is Card-on-File Tokenisation?
- Tokenisation is a process where the cardholder’s original card number, one which is written on the card and is extensively used for transactions and card identification, is replaced with a surrogate term called ‘token.’
- This process allows enhanced card protection by converting the customers’ card numbers into tokens.
- The exchange of tokens happens between the token requestor and the network, which empowers customers to receive a secure and reliable online payment experience.
- All relationship evidence of such exchange between token and crucial card information is securely saved in a vault that is only accessible to the card networks.
- Resultantly, the customers’ card details will be highly protected from online fraud and hackers.
How Does Card-on-File Tokenisation Work?
- When a customer makes a transaction by using their card at a tokenisation-based-authentication server:
- A credit/debit card is used for transactions at a POS device or an e-commerce website
- The tokenisation system receives and interprets the credit card number
- The tokenisation system goes on to replace the original credit card number with a 16-digit random character token for security
- The tokenisation system then provides the converted 16-digit random token number to the e-commerce marketplace and replaces the user’s credit card number with the same in their system
- For instance, card number (example): 4018 2255 6984 7854 will be replaced with token number: 4325 5214 8574 6658.
- The tokenisation system is an important tool for separating crucial data in ecosystems and databases while also offering enhanced card protection to cardholders.
Measles (Indian Express)
- 18 Nov 2023
Why in the News?
An estimated 11 lakh children in India missed their crucial first dose of measles vaccine in 2022, according to a report by the World Health Organization and US Centres for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC).
What is Measles?
- Measles is a highly contagious disease caused by a virus.
- It is caused by the Morbillivirus of the Paramyxoviridae family.
- It spreads easily when an infected person breathes, coughs, or sneezes.
- It can cause severe disease, complications, and even death.
- Measles can affect anyone but is most common in children.
- Measles infects the respiratory tract and then spreads throughout the body.
- Symptoms: Symptoms include a high fever, cough, runny nose, and a rash all over the body.
- Measles typically starts with a strong fever about 10 to 14 days after getting infected.
- In the beginning, it starts with a runny nose, cough, red and watery eyes, and small white spots inside the cheeks.
- After a few days, a rash appears, usually on the face and upper neck.
- This rash spreads over about three days, reaching the hands and feet, and lasts for five to six days before fading away.
- Any non-immune person (not vaccinated or vaccinated but not developed immunity) can become infected.
- If a woman catches measles during pregnancy, this can be dangerous for the mother and can result in her baby being born prematurely with a low birth weight.
- Treatment: There is no specific treatment for measles.
Amazon Yellow Spotted River Turtle (The Hindu)

- 18 Nov 2023
Why in the News?
In the Peruvian Amazon, an extended heat wave and drought have shortened the incubation period for thousands of turtle hatchlings released into the river by biologists as part of a local environmental program.
About Amazon Yellow Spotted River Turtle:
- This species is one of the largest South American river turtles.
- It is characterized by its dark upper shell and yellow spots on the head, which fade with age.
- They are considered side-necked turtles because they cannot pull their heads into their shells.
Native Habitat:
- Yellow-spotted River turtles are native to the Amazon River basin and can be found in the Amazon and Orinoco river systems in Venezuela, eastern Colombia, eastern Ecuador, northeastern Peru, the Guianas, Brazil and northern Bolivia.
- These turtles spend time basking along the riverbanks and in the calm waters of big rivers and streams.
- They avoid fast-moving waters.
Food/Eating Habits:
- They are omnivorous, feeding on both vegetation and small animals.
Reproduction and Development:
- Females lay their eggs in the peak of the dry season and the nests are sometimes destroyed by rising flood waters.
Sleep Habits:
- The turtles are diurnal, meaning they are most active in mid-morning and afternoon.
Lifespan:
- The oldest known yellow-spotted Amazon River turtle living in human care reached 23 years of age.
- They can live up to 70 years.
Exercise MITRA SHAKTI (PIB)

- 17 Nov 2023
Why in the News?
A joint military exercise, “Exercise MITRA SHAKTI-2023” is being conducted from November 16th to 29th, 2023, in Aundh (Pune).
About Exercise MITRA SHAKTI:
- Exercise MITRA SHAKTI is the ninth edition of a joint military exercise between the Indian and Sri Lankan armies.
- The Indian contingent, consisting of 120 personnel mainly from the MARATHA LIGHT INFANTRY Regiment, is participating alongside personnel from the Indian Air Force and the Sri Lankan Air Force.
- This exercise is the first bilateral and bi-service endeavor between the two countries.
- The primary goal is to jointly practice sub-conventional operations under Chapter VII of the United Nations Charter, emphasizing coordinated responses in counter-terrorism operations.
- The exercise includes training in Army Martial Arts Routine (AMAR), combat reflex shooting, Yoga, and the use of Drones and Counter Unmanned Aerial Systems, along with helicopters.
- Joint drills will cover securing helipads and conducting casualty evacuation during counter-terrorist operations.
- The collective focus is on enhancing interoperability among troops, minimizing risks to life and property, and prioritizing the interests and agenda of the UN in peacekeeping operations.
- Additionally, the exercise aims to strengthen bilateral relations between the neighboring nations.
Sickle Cell Disease (TOI)
- 17 Nov 2023
Why in the News?
The UK's medicines regulator has granted approval for the world's first gene therapy treatment for sickle cell disease.
What is Sickle Cell Disease?
- Sickle cell disease (SCD) is a blood disorder that is passed through the genes and results in abnormal hemoglobin.
- (Hemoglobin is a part of the red blood cells that carry oxygen through the body.)
- People with SCD have red blood cells that sickle or change shape when exposed to low oxygen levels in the cell.
- These sickled cells also become stiff and sticky compared to normal red blood cells.
- They can block blood flow, leading to tissue damage and pain.
- Over time, these blockages can lead to organ dysfunction and result in other serious medical complications.
Sickle Cell Disease Types
- There are several different forms of sickle cell disease, and it is different for each person.
- Hemoglobin SS, also known as sickle cell anemia
- Hemoglobin SC disease
- Hemoglobin sickle beta-thalassemia
- The most common and usually the most severe form is sickle cell anemia.
- The SCD type affects the severity and frequency of complications.
- The type of SCD also impacts the timing of complications.
- Some people have symptoms at a very young age while others will not show symptoms until adulthood.
Sickle Cell Disease Symptoms
- Anemia: Sickled blood cells are less able to carry oxygen, leading to anemia.
- Symptoms can include fatigue, weakness, dizziness, headache, shortness of breath and chest pain.
- Bone Pain: Decreased blood flow to the bones leads to periodic spikes in bone pain known as bone crises.
- SCD can also cause avascular necrosis, which is a breakdown of the bone and joint.
- Eye Disease or Blindness: Sickled blood cells can damage the fragile blood vessels in the back of the eye, leading to retina damage called retinopathy. This can lead to blindness.
- Infections: The spleen fails in SCD patients at a young age, decreasing the body’s ability to fight infections.
- Kidney Issues: Blood in the urine (papillary necrosis), frequent urination, kidney disease.
Treatments:
- A bone marrow transplant (stem cell transplant) can cure sickle cell disease.
- However, there are treatments that can help relieve symptoms, lessen complications, and prolong life.
- Gene therapy is also being explored as another potential cure. The UK recently became the first country to approve gene therapy treatment for sickle cell disease
Indian Computer Emergency Response Team (CERT-In) (Business Standard)

- 17 Nov 2023
Why in the News?
Among 1.39 million cyber security cases last year, vulnerable services made up 875,892 of the total incidents tackled by Cert-In
What is CERT-In?
- CERT-In stands for the Indian Computer Emergency Response Team.
- It is a government agency that functions under the Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology (MeitY).
- It was established in January 2004 with the objective of securing Indian cyberspace.
- It is the national nodal agency for dealing with cyber security threats like hacking and phishing.
- It strengthens the security-related defence of the Indian Internet domain.
- The Information Technology Act of 2000 designated CERT-In to serve as the national agency to perform the following functions in the area of cyber security:
- Prevention of cyber attacks: CERT-In works to prevent cyber attacks by issuing advisories and guidelines to organizations and users.
- It also conducts vulnerability assessments and penetration testing to identify and remediate security weaknesses.
- Incident response: It provides technical assistance to organizations that have been affected by cyber-attacks.
- It helps them to contain and recover from the incident, and to minimize the damage.
- Cyber security awareness: It raises cyber security awareness among the Indian public through various initiatives, such as workshops, seminars, and online resources.
- Coordination with other agencies: CERT-In coordinates with other cyber security agencies in India and around the world to share information and best practices.
- The constituency of CERT-In is the Indian cyber community and Indian cyberspace.
- CERT-In provides services to organisations in the Government, Public, and Private sectors.
- In addition, CERT-In provides services to individuals and home users as well.
- Disclosure of information will be followed in accordance with Indian Constitutional laws.
Worldwide Governance Indicators (Indian Express)

- 17 Nov 2023
Why in the News?
The Indian Chief Economic Adviser recently expressed worry about credit rating agencies using the World Bank's Worldwide Governance Indicators to assess ratings, particularly for developing countries.
About Worldwide Governance Indicators:
- The Worldwide Governance Indicators is based on a long-standing research programme of The World Bank.
- It was first established in 1996 to measure the quality of governance in over 200 countries.
- These aggregate indicators are derived from over 30 individual data sources produced by a variety of survey institutes, think tanks, non-governmental organizations, international organizations, and private sector firms.
- The indicators capture six key dimensions of governance including:
- Voice and Accountability
- Political Stability and Absence of Violence
- Government Effectiveness
- Regulatory Quality
- Rule of Law
- Control of Corruption
- According to The World Bank, corruption is the single greatest obstacle to economic and social development.
About The World Bank:
- The World Bank is an international financial institution that provides financial and technical assistance to developing countries around the world.
- Its goals are to reduce poverty and support development.
- It helps by offering a growing range of free tools, research, and knowledge to help people address the world’s development challenges, for instance, comprehensive, downloadable indicators about development in countries around the globe.
Wasp-107b (TOI)

- 17 Nov 2023
Why in the News?
In its latest discovery, NASA's James Webb Space Telescope has discovered a planet "Wasp-107b" where specks of sand fall as rain.
What is “Wasp-107b”?
- WASP-107b is a warm exoplanet with Neptune’s mass and Jupiter’s radius.
- This makes it ‘fluffy’ compared to the giant gas planets in our Solar System.
- This unusual size-to-mass ratio has given astronomers a unique opportunity to probe its atmosphere roughly 50 times deeper than more dense planets like Jupiter.
- This gas giant, often referred to as a "super-Neptune," holds several remarkable characteristics that set it apart from other known exoplanets.
Key Characteristics of WASP-107b:
- Size and Mass: WASP-107b is roughly the size of Jupiter, but with only about 12% of Jupiter's mass.
- This makes it one of the least dense exoplanets ever discovered.
- Orbit and Proximity: WASP-107b orbits its host star, WASP-107, very closely, completing an orbit in just 5.7 days.
- It is located about 200 light-years from Earth in the constellation Virgo.
- Sand Rain: WASP-107b exhibits a unique water cycle similar to Earth's, but with a peculiar twist: instead of water droplets, the planet experiences sand rain.
- These sand grains, composed of silicates, rise from lower atmospheric levels and condense into clouds before falling back down.
- Atmosphere: WASP-107b possesses a puffy atmosphere, likely due to its low density.
- In 2018, scientists using the Hubble Space Telescope detected helium in its atmosphere, marking the first detection of this element in an exoplanet's atmosphere.
- Potential for Atmospheric Characterization: WASP-107b's large size and proximity to its star make it a promising target for future atmospheric characterization studies.
- Scientists hope to glean more insights into the composition and dynamics of its atmosphere.
Pradhan Mantri Kisan Samman Nidhi (PM-KISAN) Scheme (TOI)

- 16 Nov 2023
Why in the News?
Prime Minister Narendra Modi released the 15th installment of the Pradhan Mantri Kisan Samman Nidhi (PM-Kisan) scheme worth over Rs 18,000 crore to more than 8 crore farmers on November 15, 2023.
About Pradhan Mantri Kisan Samman Nidhi (PM-KISAN):
- The Pradhan Mantri Kisan Samman Nidhi (PM-KISAN) is a Central Sector scheme with 100% funding from the Government of India.
- Under the scheme, income support of Rs. 6,000 per year in three equal installments is provided to all land-holding farmer families, providing them with socio-economic security.
- The amount is directly transferred to the bank accounts of the beneficiaries without any involvement of intermediaries, making it one of the largest Direct Benefit Transfer (DBT) schemes in the world.
- So far, more than Rs. 2.42 lakh crore have been disbursed to over 11 crore farmers.
- As per the study by the International Food Policy Research Institute (IFPRI), PM-KISAN had numerous benefits for the farmers and agriculture sector.
- It addresses the liquidity constraints of farming households, enabling essential input procurement.
- The scheme boosts modern cultivar adoption through Krishi Vigyan Kendras.
- The cash transfer to farmers increases their total net income and enhances their risk-taking capacity, leading to productive investments.
- PM-KISAN has empowered the farmers by boosting agriculture investments, easing credit constraints, and spurring rural economic growth.
- Consequently, farmers have been able to invest in their farms, including purchasing seeds, fertilizers, and necessary equipment, leading to increased agricultural production and improved crop yields.
Voice of Global South Summit (NewsOnAir)

- 16 Nov 2023
Why in the News?
Prime Minister Narendra Modi will inaugurate the second Voice of Global South Summit on November 17. This will be the second Voice of Global South Summit in less than a year hosted by India.
About ‘Voice of Global South Summit’ 2023:
- India is hosting the ‘Voice of Global South Summit’ 2023 in virtual format.
- The theme of the inaugural Leaders’ Session is "Together, for Everyone’s Growth, with Everyone’s Trust” and that of the Concluding Leaders’ Session is "Global South: Together for One Future”.
- The Summit will focus on sharing with the countries of the Global South, the key outcomes achieved in various G20 meetings over the course of India’s Presidency.
- The Summit will serve as a platform to discuss ways to sustain the momentum generated toward the common aspiration of a more inclusive, representative, and progressive world order.
What is the Voice of Global South Summit?
- Voice of Global South Summit has been India's endeavor to provide a common platform to deliberate on the concerns, interests, and priorities that affect the developing countries and also to exchange ideas and solutions, and most importantly, to unite in voice and purpose in addressing the concerns and priorities.
- The initiative is inspired by Prime Minister Narendra Modi’s vision of Sabka Saath, Sabka Vikas, Sabka Vishwas, and Sabka Prayaas, and is underpinned by India’s philosophy of “Vasudhaiva Kutumbakam”.
- India will work to ensure that the valuable inputs generated from partner countries in the Voice of Global South Summit deliberations receive due cognizance globally.
What is Global South?
- he term ‘Global South’ began by loosely referring to those countries that were left out of the industrialization era.
- These countries had a conflict of ideology with the capitalist and communist countries, accentuated by the Cold War.
- It includes countries that are in Asia, Africa, and South America.
- ‘Global South’ is just the opposite of ‘Global North’, defined essentially by an economic division between the rich and poorer countries.
Viksit Bharat Sankalp Yatra (The Hindu)

- 16 Nov 2023
Why in the News?
Prime Minister Narendra Modi launched the programme "Viksit Bharat Sankalp Yatra" across the country on November 15 to promote the Centre’s welfare schemes.
On the occasion of the Janjatiya Gaurav Divas (15th Nov), marking the birth anniversary of tribal icon Birsa Munda, Prime Minister Narendra Modi flagged off the Viksit Bharat Sankalp Yatra from Khunti, Jharkhand.
About Viksit Bharat Sankalp Yatra:
- The central idea of Viksit Bharat Sankalp Yatra is to publicise schemes, to get data on those who have benefitted from these schemes, and to mark those who are eligible but haven't got the schemes yet.
- It aims to cover over 2.55 lakh Gram Panchayats and over 3,600 urban local bodies by January 25, 2024, touching every district of the country.
- Its focus will be on reaching out to people and creating awareness about the benefits of welfare schemes like sanitation facilities, essential financial services, electricity connections, access to LPG cylinders, housing for the poor, food security, proper nutrition, reliable healthcare, clean drinking water, etc.
- Five specially designed IEC (Information, Education, and Communication) Vans has been flagged off marking the launch of the massive outreach programme of the government.
- The IEC Vans have been branded and customised to enable dissemination of information through audio visuals, brochures, pamphlets, booklets, and flagship standees in Hindi and state languages showcasing the major schemes, highlights and their achievements at the national, state and district level.
- The schemes being publicised include Ayushman Bharat, PMJAY, PM Garib Kalyan Anna Yojana, Deendayal Antyodaya Yojana - National Rural Livelihoods Mission, PM Awas Yojana (Rural), PM Ujjwala Yojana, PM Vishwakarma, PM Kisan Saman, Kisan Credit Card (KCC), PM Poshan Abhiyan, Har Ghar Jal - Jal Jeevan Mission, Survey of villages and mapping with improvised technology in village areas (SVAMITVA), Jan Dhan Yojana, Jeevan Jyoti Bima Yojana, Suraksha Bima Yojana, Atal Pension Yojana, PM PRANAM, Nano Fertiliser.
- Since schemes are aimed at tribals, specific concerns of tribal areas such as the Sickle Cell Anaemia Elimination Mission, Enrolment in Eklavya Model Residential Schools, Scholarship Schemes, Forest Right Titles, Individual and Community Land, Van Dhan Vikas Kendra, Organising Self Help Groups are also being addressed.
- The officers in charge will make sure that they reach out to the tribals and give out information about schemes meant for them.
India International Science Festival (PIB)

- 16 Nov 2023
Why in the News?
The 9th edition of the India International Science Festival (IISF) 2023 will be held at Faridabad, Haryana from January 17th-20th, 2024.
About the India International Science Festival (IISF):
- The India International Science Festival (IISF) is an annual science festival organized by the Ministry of Science and Technology, the Ministry of Earth Science, and Vijnana Bharati in India.
- The festival aims to promote science and technology in India and to showcase the latest advancements in these fields.
- The IISF has been held every year since 2007.
- The festival typically lasts for four days and features a variety of events, including exhibitions, seminars, workshops, and competitions.
- The exhibitions feature displays of scientific and technological innovations from India and around the world.
- The seminars and workshops provide opportunities for scientists and technologists to share their knowledge with the public.
- The competitions encourage students to participate in science and technology.
- The IISF is a major event in the Indian scientific community and has been praised for its role in promoting science education and public awareness of science.
- The festival has also been successful in attracting international participation, with scientists and technologists from around the world attending the event.
- The 2022 IISF was held in Bhopal, Madhya Pradesh, from January 21 to 24.
India International Science Festival (IISF) 2023:
- It will be held at the Campus of Translational Health Science and Technology Institute (THSTI) and Regional Centre for Biotechnology (RCB) of the Department of Biotechnology in Faridabad.
- Theme: 'Science and Technology Public Outreach in Amrit Kaal'.
- IISF 2023 will have a total of 17 themes to showcase scientific achievements, offering diverse benefits to participants and the general public.
Indo-Pacific Economic Framework (IPEF) (Indian Express)

- 16 Nov 2023
Why in the News?
India, the US, and 12 other members of the Indo-Pacific Economic Framework (IPEF) on Wednesday entered into a supply chain resilience agreement that aims to cut dependence on China and help shift manufacturing of crucial goods to member nations.
About Indo-Pacific Economic Framework for Prosperity (IPEF):
- The Indo-Pacific Economic Framework (IPEF) is an economic initiative launched by U.S. President Joe Biden in Tokyo on May 23, 2022.
- The framework aims to strengthen economic cooperation among countries in the Indo-Pacific region, which is home to over 40% of the world's population and generates nearly 60% of global GDP.
- Except Cambodia, Laos, and Myanmar, other Southeast Asian nations are a part of the IPEF.
- It has currently 14 members including Australia, Brunei Darussalam, Fiji, India, Indonesia, Japan, the Republic of Korea, Malaysia, New Zealand, Philippines, Singapore, Thailand, the United States, and Vietnam.
- The IPEF has four pillars:
- Trade;
- supply chains;
- clean energy, decarbonisation and infrastructure;
- tax and anti-corruption.
- IPEF Significance: The IPEF is a significant development in the Indo-Pacific region.
- It is the first major economic initiative launched by the United States in the region since the Trans-Pacific Partnership (TPP) negotiations collapsed in 2017.
- The IPEF is also unique in that it is open to all countries in the Indo-Pacific region, regardless of their economic development level.
- India and IPEF: India has been actively involved in the Indo-Pacific Economic Framework (IPEF) since its launch in May 2022.
- The country has joined three of the four pillars of the framework: supply chains, clean energy, and fair economy.
- However, India has not yet joined the trade pillar, which is the most sensitive and contentious pillar of the framework.
- There are a number of reasons why India has been hesitant to join the trade pillar.
- One concern is that the pillar could lead to tariff cuts on agricultural products, which would harm Indian farmers.
- India is also concerned about the potential for the trade pillar to lead to increased data flows, which could raise privacy concerns.
Tadoba-Andhari Tiger Reserve (TOI)

- 15 Nov 2023
Why in the News?
A dominant tiger named Bajrang said to have sired at least 50 cubs during his lifetime, recently died in a territorial fight with another powerful tiger, Chhota Matka, in the Tadoba-Andhari Tiger Reserve (TATR).
About Tadoba Andhari Tiger Reserve:
- Tadoba Andhari Tiger Reserve is the oldest and largest National Park in the Chandrapur district of Maharashtra.
- It is one of India's 47 project tiger reserves existing in India.
- The total area of the tiger reserve is 1,727 Sq.km, which includes the Tadoba National Park, created in the year 1955.
- The Andhari Wildlife Sanctuary was formed in the year 1986 and was amalgamated with the park in 1995 to establish the present Tadoba Andheri Tiger Reserve.
- The word 'Tadoba' is derived from the name of God "Tadoba" or "Taru," which is praised by local tribal people of this region, and "Andhari" is derived from the name of the Andhari river that flows in this area.
- Tadoba is presently home to more than 115 tigers, which is one of the highest in India.
- The vegetation of Tadoba forest is of Southern tropical dry deciduous type and is spread on around 626 sq. km.
- Teak is the prominent tree species in the forest.
- The Tadoba Tiger Reserve is rich in flora and fauna
- Flora: Some of the famous and widely seen flora of this park include Teak, Ain, Bija, Bamboo, Black Plum, and many others.
- Fauna: Tigers, Indian leopards, Sloth bears, Gaur, Nilgai, Striped Hyena, Spotted Deer, Barking Deer, Marsh Crocodile, etc.
Igla-S Missiles (TOI)

- 15 Nov 2023
Why in the News?
Recently, Russia has announced that it will supply the Igla-S man-portable air defense missile system to the Indian armed forces through licensed production by an Indian private company.
About Igla-S Missile System:
- The Igla-S is a man-portable air-defense system (MANPADS) developed by Russia.
- It is a surface-to-air missile (SAM) system which is also known as SA-24 Grinch in the West.
- The Igla-S entered service in 2004 and is currently in service with over 30 countries, including Russia.
- It is a highly effective and versatile weapon system that can be used to engage a wide variety of targets, including fixed- and rotary-winged aircraft, helicopters, unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs), and cruise missiles.
- The Igla-S has a range of 5 km and an altitude of 3,500 meters including a speed of Mach 2.5.
- It is a "fire-and-forget" weapon, meaning that the operator does not need to track the target after launch.
- The missile's infrared homing seeker automatically guides it to the target.
- It is a very compact and lightweight weapon system, making it ideal for use by infantry troops.
- It can be easily transported and deployed in a matter of minutes.
- The Igla-S is used by a number of countries, including Algeria, Azerbaijan, Belarus, China, India, Iran, Iraq, Kazakhstan, Libya, Malaysia, Myanmar, Nicaragua, North Korea, Peru, Poland, Russia, Serbia, Syria, Venezuela, and Vietnam.
INS Sumedha (Financial Express)

- 15 Nov 2023
Why in the News?
In a strategic move as part of the Indian Navy’s mission-based deployment to West Africa and the Atlantic, INS Sumedha conducted a port call at Walvis Bay, Namibia recently.
About INS Sumedha:
- INS Sumedha is a Saryu-class, Naval Offshore Patrol Vessel (NOPV) of the Indian Navy.
- It is the third ship of the class to be commissioned and was built by Goa Shipyard Limited in India.
- The ship was commissioned in March 2014.
- INS Sumedha is designed to undertake a variety of missions, including fleet support operations, coastal and offshore patrolling, ocean surveillance, and monitoring of sea lines of communication and offshore assets.
- The ship is also capable of carrying out humanitarian assistance and disaster relief (HADR) operations.
- INS Sumedha has been deployed on a number of operational missions, including:
- Operation Kaveri, the evacuation of Indian citizens from Sudan in April 2023.
- The ship has also participated in a number of international exercises, including Exercise Bright Star 2023 in Egypt.
About Walvis Bay:
- Walvis Bay is a city on the coast of Namibia, in the Erongo Region.
- It is the second-largest city in Namibia, after Windhoek, and is the capital of the Erongo Region.
- It is a major port city, and is the main port for Namibia.
- The port is home to a number of shipping companies and is a major export center for Namibian goods, such as fish, minerals, and diamonds.
- Originally a German enclave during the colonial era, Walvis Bay became a vital part of Namibia after gaining independence in 1990.
- The official language of the city is English, but Afrikaans, German, and Portuguese are also spoken.
Asian Development Bank (The Hindu BusinessLine)

- 15 Nov 2023
Why in the News?
The central government recently signed a USD 400 million policy-based loan with the Manila-based Asian Development Bank (ADB) to support its urban reform agenda to create high-quality urban infrastructure, improve service delivery, and promote efficient governance systems.
About Asian Development Bank (ADB):
- The Asian Development Bank (ADB) is a regional development bank headquartered in Manila, Philippines.
- It was established in 1966 to promote economic development and cooperation in Asia and the Pacific.
- The ADB's primary goal is to reduce poverty in its member countries.
- The bank provides loans, grants, technical assistance, and policy advice to its member countries.
- It also mobilizes private sector investment through its private sector arm, the Asian Development Bank Private Sector Operations.
- It has 68 member countries, including 49 countries in Asia and the Pacific, and 19 non-regional developed countries.
- The ADB's annual lending volume is around $32 billion.
- As of 2022, ADB's five largest shareholders are Japan and the United States (each with 15.6% of total shares), the People's Republic of China (6.4%), India (6.3%), and Australia (5.8%).
- Source of Funding: It relies on member contributions, retained earnings from lending, and the repayment of loans for the funding of the organization.
The bank's strategy is focused on four key areas:
- Promoting sustainable growth: The ADB is committed to supporting its member countries in achieving their sustainable development goals by financing infrastructure, clean energy, and climate change mitigation and adaptation projects.
- Tackling poverty and inequality: The ADB is providing financing for education, health, social protection, and other programs that benefit the poor and vulnerable to reduce poverty and inequality in its member countries.
- Strengthening regional cooperation: The ADB is promoting regional cooperation and integration in Asia and the Pacific.
- The bank is supporting its member countries in developing regional infrastructure, trade, and investment projects.
- Responding to crises and disasters: The ADB is helping its member countries prepare for and respond to crises and disasters by providing finances for disaster risk reduction and resilience projects.
One Station One Product’ scheme (New Indian Express)

- 15 Nov 2023
Why in the News?
The Indian Railway has established more than a thousand outlets in railway stations across the nation under its ‘One Station One Product’ (OSOP) initiative which aimed at providing a platform for skilled artisans to sell their indigenous products.
About One Station One Product’ (OSOP):
- The OSOP scheme is a unique initiative by the Indian Railways and aims to provide livelihood opportunities through skill development to local artisans, potters, weavers, and craftsmen.
- It was announced in the Union Budget 2022-23.
- The scheme, designed by the National Institute of Design, Ahmedabad, provides distinctive outlets that give high visibility to indigenous products, benefiting local craftsmen.
- Railways allot the outlets at its stations through a tendering process.
- The scheme’s outreach measures include advertising, social media, public announcements, press notifications, and personal visits to artisans.
- The products at these outlets range from artifacts and handicrafts to textiles and traditional appliances, indigenous to the region, and are crafted by local artisans or tribals.
- They also include locally made or grown food products in processed or semi-processed forms.
- It provides uniquely designed sale outlets for locals to sell indigenous products, and is now operational at 1,037 stations nationwide.
PM PVTG Development Mission (NewsOnAir)

- 14 Nov 2023
Why in the News?
Prime Minister Narendra Modi is going to launch the PM PVTG (Particularly Vulnerable Tribal Groups) Development Mission in a huge step to empower tribal people.
About PM PVTG Development Mission:
- The PM PVTG Development Mission plans to saturate PVTG families and habitations with basic facilities such as road and telecom connectivity, electricity, safe housing, clean drinking water, and sanitation, improved access to education, health and nutrition, and sustainable livelihood opportunities.
- The Mission will be implemented through the convergence of 11 interventions of nine Ministries.
- In addition, saturation will be ensured for schemes such as the Pradhan Mantri Jan Arogya Yojna, Sickle Cell Disease Elimination, TB Elimination, 100 percent immunisation, PM Surakshit Matritva Yojana, PM Matru Vandana Yojana, PM Poshan, and PM Jan Dhan Yojana.
Who are Particularly Vulnerable Tribal Groups (PVTGs)?
- PVTGs, or Particularly Vulnerable Tribal Groups, represent the most vulnerable subsets within India's diverse tribal communities, requiring heightened support and development efforts.
- There are 75 PVTGs in 18 States and Union Territories living in 22 thousand 544 villages having a population of around 28 lakhs.
- These tribes stay in scattered, remote, and inaccessible habitations, often in forest areas.
- The Government of India employs specific criteria for their identification, encompassing pre-agricultural technological levels, low literacy rates, economic disadvantages, and either a declining or stagnant population.
- The origin of the PVTG category dates back to 1975 when the government identified 52 vulnerable tribal groups, later augmented by an additional 23 in 1993.
- Notable examples of PVTGs include:
- the Cholanaikayan in Kerala
- Kathodi in Gujarat
- Jarawas in the Andaman & Nicobar Islands and
- Koraga in Karnataka
- The distinctive classification of PVTGs underscores a commitment to addressing the unique challenges faced by these marginalized tribal communities, aiming to uplift them through targeted support and development initiatives.
Cloud Seeding (LiveMint)
- 14 Nov 2023
Why in the News?
The Delhi government is mulling the use of artificial rain through cloud seeding this month to combat the air pollution crisis in the national capital.
What is Cloud Seeding?
- Cloud seeding is a weather modification technique aimed at increasing precipitation by dispersing substances into the air that serve as cloud condensation or ice nuclei.
- The primary goal is to encourage the formation and growth of precipitation particles within clouds.
- Commonly used substances for cloud seeding include silver iodide, potassium iodide, and liquid propane.
There are two main types of cloud seeding:
- Static cloud seeding: This type of seeding is used to increase precipitation in areas that are experiencing drought
- It involves releasing silver iodide or dry ice into clouds that are already producing precipitation.
- The silver iodide or dry ice acts as ice nuclei, which causes water droplets in the clouds to freeze and form snowflakes.
- The snowflakes then grow larger and fall to the ground as rain or snow.
- Dynamic cloud seeding: This type of seeding is used to increase the amount of precipitation that falls from clouds that are not yet producing precipitation.
- It involves releasing silver iodide into clouds that are still in the development stage.
- The silver iodide acts as condensation nuclei, which causes water vapor in the clouds to condense and form water droplets.
- The water droplets then grow larger and fall to the ground as rain or snow.
- Cloud seeding is typically done using aircraft, but it can also be done using ground-based generators or rockets.
- The aircraft or other seeding platform will fly into the clouds and release the silver iodide or dry ice.
- The seeding material will then spread throughout the cloud and begin to alter the microphysical processes.
- The effectiveness of cloud seeding is debated.
- Some studies have shown that it can increase precipitation by up to 30%, while other studies have shown that it has little or no effect.
- The effectiveness of cloud seeding is likely to vary depending on the type of clouds being seeded, the atmospheric conditions, and the seeding method used.
- Cloud seeding is used in a variety of countries around the world, including the United States, China, Russia, and Australia.
GPS Anklets (Indian Express)

- 14 Nov 2023
Why in the News?
For the first time in India, a prisoner in J&K has been given bail on the condition that his movements are monitored constantly.
About GPS Anklets/Tracker:
- The GPS tracker is a compact wearable gadget secured around the ankle, offering real-time location details.
- It is designed to be tamper-proof, triggering an alarm if any attempt is made to interfere with it.
- Removal by the wearer or any unauthorized individual without causing damage is virtually impossible.
- This versatile tracker can be attached to either the ankle or the arm, presenting as GPS anklets or GPS bracelets.
- While commonplace for bail conditions in countries such as the United States, the United Kingdom, and Malaysia, this marks the inaugural use of GPS trackers for this purpose in India.
What is GPS?
- GPS, or the Global Positioning System, is a satellite-based navigation system with a global reach.
- It functions through a network of satellites orbiting Earth, transmitting signals to GPS receivers.
- This technology has revolutionized navigation, offering precise location and time information for diverse applications, from driving to hiking.
- Originally developed for military purposes, GPS is now widely used in civilian life, integrated into smartphones for location-based services and emergency response.
- Its applications extend to real-time tracking of vehicles and assets, contributing to enhanced security and efficient management.
- Ongoing advancements ensure that GPS remains a crucial tool in modern navigation.
Vadhavan Port (HT)

- 14 Nov 2023
Why in the News?
The Vadhavan Port Project Ltd. (VPPL) has started the procedures to build a port with an estimated cost of ?76,220 crore. Public hearings are expected to commence in the coming months.
About Vadhavan Port:
- The Vadhavan Port is a proposed deep-sea port to be located in Palghar District, Maharashtra.
- It is expected to be one of the largest ports in the world, with a capacity to handle over 20 million TEUs (twenty-foot equivalent units) of containers per year.
- The port is being developed by a joint venture between the Jawaharlal Nehru Port Authority (JNPA) and the Maharashtra Maritime Board (MMB).
- The Vadhavan Port is being designed as a "green port" with a focus on sustainability.
- The port will use renewable energy sources and implement energy efficiency measures.
- The port will also have a dedicated waste management system to minimize environmental impact.
- It is expected to be operational by 2040 and is a critical project for India's economic growth and development.
- The Vadhavan Port is expected to be a major boost to the Indian economy.
- It will create thousands of jobs and attract billions of dollars in investment.
- The port will also help to reduce congestion at the JNPA, which is currently India's busiest container port.
- The Vadhavan Port is a major infrastructure project that is expected to have a significant impact on India's economy and society.
Birsa Munda (New Indian Express)

- 14 Nov 2023
Why in the News?
On Birsa Munday's birthday on Nov. 15th, PM Modi is scheduled to visit Ulihatu village, where the great leader's descendants live in an asbestos house.
About Birsa Munda:
- Birsa Munda was a tribal leader and folk hero who belonged to the Munda tribe.
- He was born on November 15, 1875, in the village of Ulihatu in the present-day Khunti district of Jharkhand.
- Birsa Munda is known for leading a rebellion against British colonial rule and the exploitation of tribal communities in the late 19th century.
- He was a charismatic leader and a devout Hindu.
- He preached a message of social and religious reform and advocated for the revival of traditional Munda culture and values.
- He also led a campaign against the conversion activities of Christian missionaries.
- In 1895, Birsa Munda launched a rebellion against the British.
- He and his followers attacked police stations, government buildings, and the homes of zamindars (landlords).
- The British responded with a heavy crackdown, and Birsa Munda was arrested in 1897.
- He was released from prison in 1898 but was rearrested in 1900 after he resumed his rebellion.
- Birsa Munda died in prison on June 9, 1900, at the age of 25.
- Birsa Munda's rebellion was a watershed moment in the history of the Indian independence movement.
- It inspired other tribal leaders to rise up against the British, and it helped to raise awareness of the plight of tribal communities in India.
- Birsa Munda is revered as a hero by tribal communities across India, and he is considered to be one of the pioneers of the Indian independence movement.
- In addition to his political activism, Birsa Munda was also a religious reformer.
- He founded a new religious movement called Birsait, which combined elements of Hinduism and tribal animism.
- Birsaitism is still practiced by some tribal communities in Jharkhand today.
- Birsa Munda's legacy continues to inspire people today, and he is remembered as one of the greatest heroes of the Indian independence movement.
- To honor Birsa Munda's significant influence on the national movement, the state of Jharkhand was established on his birthday in 2000.
- Recognizing his contributions, the Central Government declared November 15 as 'Janjatiya Gaurav Divas' in 2021.
Saturn’s Rings (Earth.com)

- 13 Nov 2023
Why in the News?
According to a recent report, Saturn's rings will vanish in just 18 months.
What are Saturn’s Rings?
- Saturn’s ring system is made up of countless small particles, ranging from micrometers to meters in size, that orbit the planet.
- These particles are mostly made of ice, with a smaller amount of rocky debris and dust.
- The rings are named alphabetically in the order they were discovered, with the main rings being A, B, and C.
- The rings are also home to countless icy fragments and are shrouded in a layer of cosmic dust.
- Recent research suggests that these objects might be relatively new in the cosmic timeline, potentially forming a mere 400 million years ago, making them younger than one-tenth of Saturn’s age.
About the Planet Saturn:
- Saturn is the sixth planet from the Sun and the second-largest in the solar system, after Jupiter.
- Saturn is a gas giant composed primarily of hydrogen and helium.
- It has a radius about nine times that of Earth, although it has a low density and is only about 95 times more massive than Earth.
- It has the highest number of satellites or moon, i.e., 146 in the solar system.
- Pioneer 11 and Voyagers 1 and 2 conducted flybys of Saturn, but Cassini extensively orbited the planet, completing 294 orbits from 2004 to 2017.
Exercise ‘CORPAT’ And ‘Bongosagar’ (NewsOnAir)

- 13 Nov 2023
Why in the News?
Recently, Exercise CORPAT and BONGOSAGAR between the Indian Navy and Bangladesh Navy were conducted in the Northern Bay of Bengal from 07 - 09 Nov 2023.
About Exercise CORPAT and Bongosagar:
- The 4th edition of the Bilateral Exercise between the Indian Navy and Bangladesh Navy, BONGOSAGAR-23, and the 5th edition of Coordinated Patrol (CORPAT) by the two navies were held at Visakhapatnam.
- Ships and aircraft from both navies undertook joint patrolling along the International Maritime Boundary Line and maritime exercises to enhance interoperability.
- Indian Navy Ships Kuthar, Kiltan, and Maritime Patrol Aircraft (MPA) Dornier participated in the exercise.
- The ships undertook communication drills, surface gun-shoots, tactical maneuvers, and other exercises.
- INS Kuthar is an indigenously built guided-missile Corvette, whereas INS Kiltan is an indigenously built anti-submarine Corvette.
- Both ships are part of the Indian Navy's Eastern Fleet based at Visakhapatnam, which functions under the operational command of the FOCINC ENC.
- CORPAT-23 also included the maiden Humanitarian Assistance and Disaster Relief drills held between the two navies.
- The bilateral exercises and coordinated patrols have strengthened mutual understanding and cooperation between the two navies.
India-OPEC Energy Dialogue (PIB)

- 13 Nov 2023
Why in the News?
The 6th High-Level Meeting of the India-OPEC Energy Dialogue took place on 9 November 2023, at the OPEC Secretariat in Vienna, Austria
Highlights of the India-OPEC Energy Dialogue 2023:
- The 6th High-Level Meeting of the India-OPEC Energy Dialogue took place on November 9th, in Vienna, Austria.
- The Meeting was co-chaired by HE Haitham Al Ghais, Secretary General of OPEC, and Hardeep Singh Puri, Minister of Petroleum and Natural Gas and Minister of Housing and Urban Affairs of India.
- Discussions revolved around ensuring availability, affordability, and sustainability in energy markets, emphasizing India's crucial role in global economic growth and energy demand.
- The 6th High-Level Meeting concluded with both parties underscoring the importance of fostering enhanced cooperation between India and OPEC moving forward.
- It was agreed to hold the next High-Level Meeting of the India-OPEC Energy Dialogue during the course of 2024 in India.
About the Organization of the Petroleum Exporting Countries(OPEC):
- OPEC, or the Organization of the Petroleum Exporting Countries, is a permanent international organization comprising oil-exporting nations.
- Its core mission is to coordinate and unify the petroleum policies of its member countries.
- This coordination aims to stabilize oil prices in global markets, working towards eliminating harmful and unnecessary price fluctuations.
- It was established in 1960 by Iran, Iraq, Kuwait, Saudi Arabia, and Venezuela, OPEC has since expanded to include 13 members.
- Member countries are Algeria, Angola, Congo, Equatorial Guinea, Gabon, Iran, Iraq, Kuwait, Libya, Nigeria, Saudi Arabia, United Arab Emirates, and Venezuela.
- With the addition of another 11 allied major oil-producing countries including Russia, the grouping is known as OPEC+.
- The organization's headquarters is located in Vienna, Austria.
World Energy Outlook 2023 (IEA)

- 13 Nov 2023
Why in the News?
Recently, the International Energy Agency (IEA) released the World Energy Outlook (WEO) Report 2023.
About World Energy Outlook 2023:
- This flagship publication of the International Energy Agency (IEA) has appeared every year since 1998.
- It provides in-depth analysis and strategic insights into every aspect of the global energy system.
- This year, the report delves into how changes in economies and energy usage are meeting the increasing demand for energy amid geopolitical tensions and fragile energy markets.
- It evaluates the evolution of energy security fifty years after the establishment of the IEA and looks at what's necessary at the COP28 climate conference in Dubai to support the 1.5 °C goal.
- The publication analyzes today's energy trends, covering areas like investment, trade flows, electrification, and energy access.
About the International Energy Agency (IEA):
- The International Energy Agency (IEA) is an independent inter-governmental organization operating within the framework of the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD).
- Its mission involves collaborating with governments and industry to create a secure and sustainable energy future.
- Established in 1974 to safeguard oil supplies, it was a response to the 1973-1974 oil crisis, which exposed the vulnerability of industrialized nations to oil import dependencies due to an oil embargo.
- Comprising 31 member countries and eleven association countries, IEA candidates must be OECD members.
- India joined as an Associate member in 2017.
- The IEA publishes reports such as the World Energy Outlook, World Energy Balances, Energy Technology Perspectives, World Energy Statistics, and Net Zero by 2050.
AAINA Dashboard for Cities’ Portal (PIB)

- 13 Nov 2023
Why in the News?
‘AAINA Dashboard for Cities’ portal aims to create a robust database of key performance metrics of Urban Local Bodies
About AAINA Dashboard for Cities:
- AAINA – Dashboard for cities, an initiative of the Ministry of Housing and Urban Affairs (MoHUA) is being envisaged which would serve as a tool for comparing similarly placed Urban Local Bodies (ULBs) and promoting peer learning amongst ULBs.
- This dashboard will inspire the ULBs by pointing to possibilities and areas of improvement and providing them the opportunity to learn and engage with frontrunners.
- It will provide information on the status and progress of the cities on five broad thematic areas viz.
- Political and Administrative Structure
- Finance
- Planning
- Citizen Centric Governance and
- Delivery of Basic Services.
- Urban Local Bodies (ULBs) can voluntarily submit their key data through a simple form on the portal.
- ULBs will submit audited accounts and performance metrics, which they can update when needed.
- The dashboard aims to be a permanent platform for ULB data, regularly updated for stakeholders and eventually open for public view.
- The Ministry, through the Digital India Corporation, will help ULBs/States with the data submission process.
- Currently, information about all the ULBs in the country isn’t available on one platform.
- The idea is to provide a platform for ULBs to learn from each other and also have critical data, which can be used in the future for planning new schemes and taking policy decisions
Attenborough's Long-beaked Echidna (The Hindu)

- 11 Nov 2023
Why in the News?
An elusive echidna feared extinct after disappearing for six decades has been rediscovered in a remote part of Indonesia, on an expedition that also found a new kind of tree-dwelling shrimp.
About Attenborough's long-beaked echidna:
- Attenborough's long-beaked echidna (Zaglossus attenboroughi), also known as Sir David's long-beaked echidna or the Cyclops long-beaked echidna.
- It is an egg-laying mammal native to the Cyclops Mountains in the northern Indonesian region of Papua.
- It is one of three species of long-beaked echidna, and is the smallest and most threatened of the three.
- The echidna was named after naturalist Sir David Attenborough.
- The echidna is a nocturnal animal, and it is most active at night.
- It spends its days sleeping in burrows, and it emerges at night to forage for food.
- The echidna's diet consists of ants, termites, beetles, and other insects.
- Attenborough's long-beaked echidna is classified as Critically Endangered by the IUCN.
5th Annual India- US ‘2+2’ Dialogue (The Hindu)

- 11 Nov 2023
Why in the News?
India and the U.S. on November 10 held extensive deliberations to further expand their global strategic partnership through greater defence industrial ties, enhancing engagement in the Indo-Pacific and boosting cooperation in key areas such as critical minerals and high technology.
Context:
- The fifth annual ‘2+2’ dialogue between India and the United States is underway in New Delhi.
- The U.S. delegation at the 2+2 ministerial talks was led by U.S. Secretary of State Antony Blinken and U.S. Defence Secretary Lloyd Austin.
- External Affairs Minister S Jaishankar and Defence Minister Rajnath Singh headed the Indian side.
What is the 2+2 Dialogue?
- The 2+2 Ministerial Dialogue, an annual diplomatic summit being held since 2018, brings together India's foreign and defence ministers with their US counterparts.
- Its purpose is to address and collaborate on common concerns to enhance and strengthen India–United States relations.
- A 2+2 ministerial dialogue enables the partners to better understand and appreciate each other’s strategic concerns and sensitivities taking into account political factors on both sides, in order to build a stronger, more integrated strategic relationship in a rapidly changing global environment.
- India has 2+2 dialogues with four key strategic partners: the US, Australia, Japan, and Russia.
- Besides Russia, the other three countries are also India’s partners in the Quad.
- The US is India’s oldest and most important 2+2 talks partner.
Cell Broadcast Alert System (CBAS) (The Hindu)

- 11 Nov 2023
Why in the News?
The Cell Broadcast Alert System (CBAS) of the National Disaster Management Authority (NDMA) did not effectively disseminate mass alerts during natural disasters, despite recent testing.
About Cell Broadcast Alert System (CBAS):
- The Cell Broadcast Alert System (CBAS) is a public warning system that uses mobile networks to send emergency alerts to mobile phones within a specific geographic area.
- It is a one-way messaging system that allows authorized authorities to send short messages to all mobile phones within a designated area, regardless of whether the recipients are subscribed to the mobile network or not.
Benefits of CBAS:
- Rapid and widespread dissemination of information: CBAS can reach a large number of people within a short period of time, making it an effective tool for communicating critical information during emergencies.
- No user interaction required: CBAS messages are automatically displayed on mobile phones, so there is no need for users to take any action to receive them.
- Effective for reaching all mobile phone users: CBAS messages can be received by all mobile phone users, regardless of whether they are subscribed to a particular mobile network or not.
- Not affected by network congestion: CBAS messages are not affected by network congestion, so they can be delivered even when network traffic is heavy.
CBAS can be used to send a variety of emergency alerts, including:
- Weather warnings: CBAS can be used to warn people of impending severe weather, such as tornadoes, hurricanes, and flash floods.
- Amber Alerts: CBAS can be used to broadcast information about missing children.
- Public safety alerts: CBAS can be used to warn people of other public safety threats, such as fires, terrorist attacks, and chemical spills.
Phreatomagmatic Eruptions (TOI)

- 11 Nov 2023
Why in the News?
Recently a new island emerged near Japan's Ogasawara island chain after an undersea volcano erupted.
What is Phreatomagmatic Eruption?
- A phreatomagmatic eruption is a volcanic eruption caused by the interaction of magma and water.
- They differ exclusively from magmatic and phreatic eruptions.
- Unlike phreatic eruptions, the products of phreatomagmatic eruptions contain juvenile (magmatic) debris.
- Large explosive eruptions typically contain magmatic and phreatomagmatic components.
- Phreatomagmatic ash is formed by the same mechanism over a wide range of basic and acidic compositions.
- A blocky and uniform crust with low vesicle content is formed.
- Deposits from phreatomagmatic eruptions are thought to be better classified and finer-grained than those from magmatic eruptions.
- This is the result of higher fragmentation of phreatomagmatic eruptions.
About Ogasawara Islands:
- The Ogasawara Islands are a group of more than 30 small subtropical islands in the North-Western Pacific Ocean roughly 1,000 km south of the main Japanese Archipelago.
- It is also known as the Bonin Islands.
- It is one of the famous UNESCO World Heritage sites of Japan.
Vampire Viruses (TOI)
- 11 Nov 2023
Why in the News?
For the first time, several ‘vampire viruses have been detected in the soil samples in the USA recently.
About Vampire Viruses:
- "Vampire viruses", also known as virophages, are viruses that parasitize other viruses.
- They have been known to science for decades, but this is the first time they have been discovered in the United States.
- The viruses were found in soil samples from Maryland and Missouri.
- Virophages are thought to attach themselves to other viruses and inject their own genetic material into the host-virus.
- This genetic material then takes over the host virus's replication machinery, allowing the virophage to reproduce itself.
- The host-virus is eventually destroyed in the process.
- Virophages could be used to control harmful viruses that infect crops or livestock.
- They could also be used to design new antiviral drugs that target viruses in a more specific way than current drugs.
- However, the discovery of virophages also raises some concerns.
- Virophages could potentially kill beneficial viruses that play an important role in the environment.
- For example, some viruses help to break down organic matter in soil, while others help to control populations of harmful bacteria.
Energy Conservation Building Code (ECBC) (Indian Express)

- 10 Nov 2023
Why in the News?
Paris-based International Energy Agency highlighted India’s Energy Conservation Building Code (ECBC), 2017 as something that sets it apart from other developing economies where “energy efficiency in buildings stands out as a laggard”.
About Energy Conservation Building Code (ECBC):
- Energy Conservation Building Code (ECBC) Released by the Bureau of Energy Efficiency (BEE).
- It was first released in 2007 and again updated in 2017.
- The purpose of ECBE is to set minimum energy standards for commercial buildings, with the objective of enabling energy savings of between 25 and 50% in compliant buildings.
- Commercial buildings include hospitals, hotels, schools, shopping complexes and multiplexes which have a connected load of 100 kW or more, or contract demand of 120 kVA or more.
- Also the code is for both new buildings and retrofitting existing buildings.
- Assessment Parameters: The Energy Conservation Building Code (ECBC) primarily looks at parameters like building design including envelope (walls, roofs, windows), lighting systems, and renewable energy integration among others.
- Tagging of buildings: Compliant buildings are assigned one of three tags in ascending order of efficiency, namely ECBC, ECBC Plus, and Super ECBC.
- 23 out of 28 states have notified ECBC rules. But only 15 states have notified rules based on the latest ECBC,2017.
- Five states — Gujarat, Maharashtra, J&K, Ladakh, and Manipur — are yet to notify ECBC rules.
Aurora (Indian Express)

- 10 Nov 2023
Why in the News?
Recently, NASA shared this incredible image of an aurora taken from the International Space Station.
What is Aurora?
- An aurora is a natural light display that shimmers in the sky.
- They are only visible at night, and usually only appear in lower polar regions.
- Auroras come in colors like blue, red, yellow, green, and orange.
- They're mostly visible near the Arctic and Antarctic Circles, known as the aurora borealis and aurora australis, respectively.
- These natural light shows occur when the solar wind from the sun meets Earth's magnetic field, creating a beautiful halo of light around the poles.
- This collision between solar wind ions and Earth's atmosphere atoms leads to stunning auroras.
- Their color depends on altitude and the atoms involved.
- Red comes from oxygen ions higher up, while the familiar green-yellow hues arise from interactions at lower altitudes.
- Sometimes, reddish and bluish tints appear, created by ions colliding with nitrogen atoms.
- The most active auroras happen when the solar wind is strongest, affected by solar weather changes, which follow an 11-year cycle.
- Equinoxes and magnetic storms can cause auroras to be seen even in mid-latitudes, affecting communication signals and occasionally causing disruptions.
- Auroras are a natural spectacle, painted by the collision of solar wind and Earth's atmosphere, creating these dancing lights in the night sky.
Bioluminescent Fungi 'Mycena Chlorophos' (The New Indian Express)

- 10 Nov 2023
Why in the News?
A team of researchers and the forest department have found a rare bioluminescent mushroom in the Kanyakumari Wildlife Sanctuary (KKWLS).
About Mycena chlorophos:
- Mycena chlorophos is a species of bioluminescent fungus, meaning that it can produce its light.
- It is primarily found in subtropical Asia, including India, Japan, Taiwan, Polynesia, Indonesia, and Sri Lanka, as well as in Australia and Brazil.
- The bioluminescence is produced through a chemical reaction that involves luciferin, a light-emitting molecule, and the enzyme luciferase.
- Luciferase catalyzes the oxidation of luciferin, which produces light.
- The luciferin in Mycena chlorophos is a compound called trans-3-hydroxyhispidin.
- This compound is also found in other bioluminescent fungi, such as Neonothopanus nambi and N. gardneri.
- The bioluminescence of Mycena chlorophos is thought to serve several functions.
- It may help the fungus to attract insects, which can help to disperse its spores.
- It may also help the fungus to ward off predators.
What is Bioluminescence?
- It is the ability of living organisms to emit light.
- It occurs due to a biochemical reaction between luciferins, oxygen, and the enzyme luciferase.
- The benefit of bioluminescence in fungi is to attract insects to facilitate their spore dispersal.
Radiative Cooling Paint (The Hindu)
- 10 Nov 2023
Why in the News?
Researchers from Jawaharlal Nehru Centre for Advanced Scientific Research (JNCASR) have developed a radiative cooling paint, which is specifically engineered to cool structures like buildings, pavers, and tiles in hot weather conditions.
What is Radiative Cooling Paint?
- Material Composition: Radiative Cooling Paint is composed of a mix of magnesium oxide (MgO) and polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF), derived from easily accessible, cost-effective, and safe materials.
- The optimized MgO-PVDF with dielectric nanoparticles resulted in a large solar reflectance of 96.3% and a record high thermal emission of 98.5% due to Mg?O bond vibrations, and other stretching/bonding vibrations from the polymer.
- Cooling Mechanism: This paint stands out not only for its appearance but for its function.
- It reflects nearly all of the sun's heat and emits a significant amount of its heat, effectively maintaining cooler surfaces.
- Heat Management: Tailored for hot climates, it efficiently reduces the need for excessive electricity use to cool buildings during sweltering days.
- Temperature Reduction: Once applied, it notably lowers surface temperatures by approximately 10 degrees under intense sunlight, surpassing the performance of regular white paint.
- Application Ease: Additionally, it showcases water-resistant properties and excellent adhesion to various surfaces, simplifying the application process on structures like walls and roofs.
Green Firecrackers (The Hindu)

- 10 Nov 2023
Why in the News?
Both government agencies and conscious citizens in Bengaluru are actively ensuring that only less polluting green crackers are being sold and bought this Deepavali.
What are Green firecrackers?
- Green firecrackers are a type of fireworks designed to produce fewer pollutants and emissions compared to traditional firecrackers.
- They are crafted to be more environmentally friendly by using cleaner ingredients, and emitting less smoke and harmful chemicals upon combustion.
- There are mainly three types of green firecrackers: SWAS, SAFAL, and STAR.
- They are not only eco-friendly but 15-20 % cheaper than the conventional ones.
- In 2018, the Council of Scientific and Industrial Research-National Environmental Engineering Research Institute (CSIR-NEERI) introduced the idea of green crackers.
What are they made of?
- Green firecrackers are marked by reduced size of shell, elimination of ash usage, reduced usage of raw material in the compositions, and have a uniformly acceptable quality.
- They use additives as dust suppressants to reduce emissions with specific reference to particulate matter (PM).
- These crackers lack the barium compounds responsible for their unique green hue.
- Barium, a metallic oxide, is known to contribute to air pollution and noise pollution.
- When green crackers are ignited, they produce water vapor, thereby minimizing dust emissions.
- In terms of sound levels, green firecrackers generate noise ranging from 110 to 125 decibels, making them significantly quieter than traditional firecrackers, which typically produce around 160 decibels, resulting in nearly 30% less noise.
Cops lose Rs 12 crore in chit fund scheme, probe on (TOI)

- 20 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
Around 70 persons belonging to AP special police have lost nearly Rs 12 crore in a chit fund scheme in Mangalagiri, said the police. Mangalagiri police registered a case and launched an public sector investigation.
What are Chit Funds?
- Chit funds, also known as Kuri and Chitty, serve as versatile financial instruments encompassing both borrowing and saving components.
- In this financial arrangement, a group of individuals collectively contributes a fixed sum at regular intervals, with the understanding that one member will receive the total pooled amount during each interval.
- This process repeats until every member has received their share.
- Typically managed by a chit-fund company, this financial instrument operates by having a group of contributors make regular contributions toward the chit value for a duration equivalent to the total number of subscribers.
- The recipient of the pooled money is determined through an auction or lucky draw, employing a reverse auction system where the individual willing to accept the lowest amount is chosen.
- The sum forfeited by the winning bidder is distributed among other bidders, deducting a foreman's charges and commission.
- The share each bidder receives is termed a dividend. Interestingly, a winning bidder can continue to invest in subsequent intervals, even after claiming their sum.
Types of Chit Funds:
Chit funds can be categorized into three types:
- Chit Funds Run by State Governments:
- Managed and regulated by state governments.
- Public sector undertakings (PSUs) also fall under this category.
- These funds are considered safe, with limited chances of loss. Business processes are transparent and well-regulated.
- Private Registered Chit Funds:
- Registered under the Chit Funds Act of 1982.
- Typically initiated by well-established financial institutions or business entities.
- While participation in these funds may not be as secure as state-run or public-sector funds, the calculated risk is manageable due to their association with reputable private-sector entities.
- Unregistered Chit Funds:
- These chit-funds lack legal recognition, and participation involves a higher risk.
- Commonly found throughout India, they are often formed by a close-knit group of associates.
- Participation in unregistered chit funds is discouraged due to the potential for disputes, which rely heavily on the integrity and honesty of the members involved.
What is Saradha Chit Fund Scam?
- The Saradha scam, also known as the Saradha Group financial scandal, was a major financial scam that surfaced in 2013.
The Saradha scheme:
- The scheme, run by Saradha Group (an umbrella company with 200 private players), was launched in the early 2000s by businessman Sudipto Sen.
- Aimed at small investors, the scheme became popular in a very short time as it promised high returns.
- The money was collected through a wide network of agents, who were paid commissions of over 25 per cent.
- The Saradha Group raised about Rs 2,500 crore in a few years time.
- The company used varied marketing means to build its brand.
- Apart from popular marketing techniques like celebrity endorsements, the company used to sponsor cultural events such as Durga Puja and invest in popular football clubs to attract more investors.
- The scheme soon expanded to Odisha, Assam, and Tripura, and the number of investors reached close to 1.7 million.
US launches Red Sea force as ships reroute to avoid attacks (The Hindu)
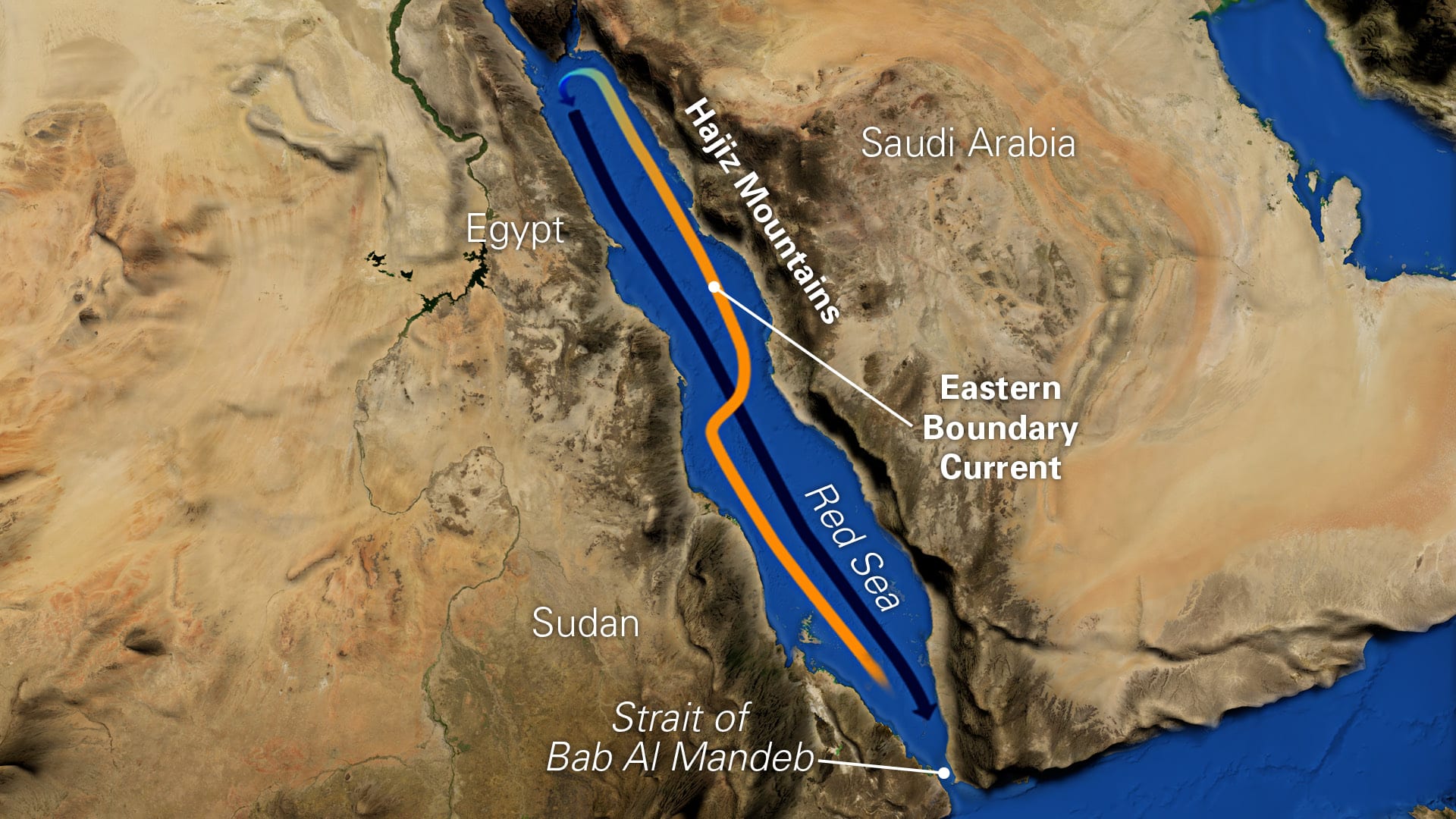
- 20 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
U.S. Defense Secretary Lloyd Austin on Tuesday announced the creation of a multinational operation to safeguard commerce in the Red Sea following a series of missile and drone attacks by Yemen's Iran-aligned Houthis.
Context:
- The U.S. Defense Secretary recently revealed the establishment of a multinational operation to protect commerce in the Red Sea.
- This decision comes in response to a string of missile and drone attacks by Yemen's Iran-aligned Houthis.
- The gravity of these attacks has prompted several shipping companies to instruct their vessels to remain stationary and avoid entering the Bab el-Mandeb Strait until the security concerns are addressed.
About the Red Sea:
- The Red Sea is a narrow waterway extending southeastward from Suez, Egypt, to the Bab el-Mandeb Strait.
- The Bab-el-Mandeb Strait links the Red Sea to the Gulf of Aden, providing a connection between the Mediterranean Sea and the Arabian Sea.
- Essentially, it is a narrow inland sea positioned between the Arabian Peninsula and Africa.
- The Red Sea acts as a boundary, separating the coastlines of Egypt, Sudan, and Eritrea from those of Saudi Arabia and Yemen.
- The Gulf of Aqaba, an extension to the northeast, stretches into southern Israel and southwestern Jordan.
- Significance: The Red Sea boasts some of the planet's hottest and saltiest seawater.
- It stands as one of the most heavily traversed water routes globally, facilitating maritime traffic between Europe and Asia.
- Relevance for India:
- Potential disruptions along this route could lead to a significant surge, up to 25-30%, in freight rates for Indian shipments bound for Europe and Africa.
- For India, the Red Sea trade route serves as the most direct path for ships traveling from Asia to Europe.
- India heavily depends on the Bab-el-Mandeb Strait for crucial aspects such as crude oil, LNG imports, and trade with regions in West Asia, Africa, and Europe.
- This passage is critical, accounting for 30% of global container traffic.
Who are the Houthi Rebels?
- The Houthis are a Shiite Muslim sect with roots that date back centuries in Yemen.
- Members of the religion are a minority in Yemen, which is predominantly Sunni Muslim, but they are a significant one, numbering in the hundreds of thousands and making up as much as a third of the overall population.
- Named after the Houthi tribe, they adhere to Zaydi Shia beliefs within Islam, emphasizing the lineage of Prophet Muhammad's family as the political leaders of the state.
- Also recognized as Ansar Allah, translating to "Supporters of God."
- Involvement in Yemen's Civil War: A major faction in Yemen's nearly decade-long civil war, starting in 2014 when Houthi insurgents seized control of Yemen's capital, Sanaa.
- By early 2015, Saudi Arabia, supported by other Gulf states and the U.S., conducted airstrikes against the Houthis, who have backing from Iran.
- Although a ceasefire was signed in 2022, it lapsed after six months, with the parties involved not returning to full-scale conflict.
- Houthi Attacks on Red Sea Ships:
- Iran-backed Houthi rebels from Yemen have targeted ships in the Red Sea in response to Israel's military actions in Gaza.
- The Houthis, supporting Hamas, declared on November 19 their intent to attack vessels they believe are traveling to and from Israel.
Full-blown late blight attack damages potato crops in Punjab (Indian Express)

- 20 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
Days after the experts from Punjab Agricultural University (PAU) had cautioned farmers against the late blight disease attack on potato crop, the worst fears of the potato farmers have come true.
About Late Blight Disease:
- Late Blight disease is attributed to the fungus Phytophthora infestans and stands as a significant threat to potato crops, potentially causing rapid failures if appropriate control measures are not implemented.
- Common in humid regions with specific temperature conditions, this disease manifests with initial symptoms of small, light to dark green, circular to irregular water-soaked spots.
- In cool, moist weather, these spots rapidly expand into large, dark brown or black lesions, often exhibiting a greasy appearance.
- A pale green to yellow border typically surrounds these lesions.
- The spread of Late Blight is facilitated by infected tubers and soil, acting as a primary source of infection.
- Infected tubers play a crucial role in the disease's persistence from one crop to another. Airborne infection occurs through sporangia.
- Effective control measures involve the prompt destruction of infected crop residue in the field to prevent the disease from spreading to nearby areas.
Diseases Caused by Bacteria on Potato Crops:
- Ring Rot
- Brown Rot
Diseases Caused by Fungi on Potato Crops:
- Late Blight
Diseases Caused by Virus on Potato Crops:
- Leaf Roll
- Mosaic
First Prehistoric Pictorial Cave Art Found in Madagascar Offers Clues Regarding Ancient Connections Between Borneo, Egypt (The Hindu)

- 20 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
Recently, distinctive prehistoric rock art depictions were unearthed within the Andriamamelo Cave in western Madagascar.
Key Discoveries:
- Within this cave's truly pictorial art, human-like and animal-like figures depicting scenes from nature have been revealed.
- The remarkable findings unveiled surprising cultural connections, with some scenes directly linking to Egyptian religious motifs from the Ptolemaic period (300-30 BCE).
- Additionally, symbols and inscriptions on the cave walls indicated connections to the Ethiopian and Afro-Arab regions.
- Furthermore, the prevalent symbology and motifs echoed a cave art style from Borneo dating back two millennia.
- Notably, depictions within the cave may include three extinct animals of Madagascar — a giant sloth lemur, an elephant bird, and a giant tortoise.
- The potential connection to Egypt is suggested by eight significant images, including representations of a falcon (Horus), the bird-headed god Thoth, the ostrich goddess Ma`at, and two human-animal figures resembling Anubis, the ancient Egyptian god typically portrayed with a canine head.
About Andriamamelo Cave:
- The Andriamamelo Cave is situated in western Madagascar, nestled within the karstified limestone of the Paysage Harmonieux Protege de Beanka.
- This cave is a component of a vast karst region that encompasses the UNESCO World Heritage site, Parc National de Bemaraha, to the south, and the less-explored Antsingimavo karst area to the north.
Goa Liberation Day: Why India waited for 14 years after independence to move troops to Goa (Indian Express)

- 20 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
Goa Liberation Day is commemorated annually on December 19. In 2023, we observe the 62nd anniversary of the liberation of Goa.
Key Highlights:
- This day commemorates the liberation of Goa in 1961 by the Indian armed forces, ending 450 years of Portuguese rule.
- Portuguese colonization in India began in 1510, but by the late 19th century, their colonies were limited to Goa, Daman, Diu, Dadra, Nagar Haveli, and Anjediva Island.
- After India's independence in 1947, attempts to persuade Portugal to cede their territories were unsuccessful.
- The Goa liberation movement gained momentum from small-scale revolts, peaking between 1940 and 1960.
- In 1961, diplomatic efforts failed and Operation Vijay was executed, leading to the annexation of Daman, Diu, and Goa to the Indian mainland on December 19.
About Operation Vijay:
- Operation Vijay, a 36-hour military initiative initiated on December 18, 1961, and concluded on December 19, 1961, aimed at liberating the Portuguese territories of Goa, Daman, and Diu.
- This marked a significant milestone as possibly the first tri-service operation by the Indian armed forces.
- The Indian Air Force executed bombings on the Portuguese airbase at Dabolim, complementing the army's advancement from the north and east into Goa.
- Simultaneously, the Indian Navy played a crucial role in preventing hostile actions by Portuguese warships, securing access to Mormugao harbor, and establishing control over the Anjadip Island off the coast of Karwar.
- By the evening of December 19, 1961, Portuguese Governor General Vassalo De Silva signed the surrender document as the Indian armed forces, led by the army with support from the air force and navy, had effectively outnumbered and outgunned the Portuguese forces.
Granting Statehood to Goa after Liberation:
- Following its liberation, Goa came under the administration of the Indian government, becoming a constituent of the Indian Union as the Union Territory of Goa, Daman, and Diu.
- However, in 1967, a plebiscite was conducted to decide on the potential merger of the state with Maharashtra.
- The majority of Goans voted against the merger, leading to the continuation of its status as a Union Territory.
- This arrangement persisted until 1987 when Goa was accorded statehood, emerging as the 25th state of India.
- Meanwhile, Daman and Diu retained their status as a Union Territory.
Electoral Trusts (ET) Scheme (Indian Express)

- 09 Nov 2023
Why in the News?
After a three-day hearing, the Supreme Court has reserved its judgment on the challenge to the Central government’s Electoral Bonds Scheme.
About Electoral Trusts (ET):
- As per Section 17CA of Income Tax Rules (1962), an Electoral Trust (ET) is a non-profit organization established for the orderly receipt of voluntary contributions from any person for distributing the same to political parties, registered under Section 29A of the Representation of People Act, 1951.
- This Scheme was notified in January 2013 by the then UPA government.
- Objective of Electoral Trust:
- Electoral Trusts are designed to bring more transparency in the funds provided by corporate entities to the political parties.
- The objective of an Electoral trust is not to receive any profit or pass on any direct or indirect benefit to its members or contributors.
- An Electoral trust will distribute funds only to eligible Political parties.
- These trusts are approved by the Central Board of Direct Taxes (CBDT) in accordance with the Electoral Trust Scheme of 2013.
- The ET may receive voluntary contributions from:
- an Individual (citizen of India)
- a Company registered in India
- a Firm or HUF or Associations of Persons or Body of Individuals resident in India
- The electoral trusts have to apply for renewal every three financial years.
INDUS-X Initiative (Financial Express)

- 09 Nov 2023
Why in the News?
On the eve of the India-US 2+2 Ministerial Dialogue, the inaugural INDUS-X Investors Meet was held in New Delhi.
What is the INDUS X Initiative?
- The INDUS-X initiative, also known as the India-U.S. Defense Acceleration Ecosystem, was launched in June 2023 during the State Visit of the Prime Minister of India to the United States.
- Its primary objective is to expand the strategic technology partnership and defense industrial cooperation between the governments, businesses, and academic institutions of India and the United States.
- INDUS-X is envisioned as a defense innovation bridge, encompassing Joint Challenges, a Joint Innovation Fund, academia engagement, industry-startup connections, private sector investment in defense projects, mentorship by experts, and niche technology projects, among other initiatives.
- This collaborative effort holds the promise of ushering in a new era of defense innovation and cooperation between India and the United States.
About INDUS X Investors Meet:
- The first-ever INDUS-X Investors Event brought all the stakeholders including Startups, Investors, Incubators, and Industry from both sides under one roof to discuss the collaborative agendas and opportunities thereon.
- The event also had focused panel discussions with a select audience of 50 thought leaders, including start-ups, investors, government officials, and business leaders from the defence industry.
- The panel discussed ‘Investment Opportunities in the Defence Sector’, elaborating upon establishing a sustainable commercial foundation for defence collaboration and co-production.
- The INDUS-X Educational Series (Gurukul) was also launched during the event.
- The Gurukul initiative is aimed at helping innovators and startups to navigate the defence eco-system of the US and India.
Palamu Tiger Reserve (TOI)

- 09 Nov 2023
Why in the News?
A recently captured image in the Palamu Tiger Reserve (PTR) reveals a new tiger, distinct from the one caught earlier this year.
About Palamau Tiger Reserve:
- The Palamau Tiger Reserve is located on the western side of Latehar district on the Chhotanagpur plateau in Jharkhand.
- It is one of the first 9 tiger reserves established in the country at the inception of ‘Project Tiger’, in the year 1973 in India and the only one in the state of Jharkhand.
- This reserve forms a part of the Betla National Park.
- The total area of the Tiger Reserve is 1129.93 sq. km
- It is the first reserve in the world in which a tiger census was carried out as a pugmark count, as early as 1932 under the supervision of J.W. Nicholson.
- The Palamau Tiger Reserve is very important for its biodiversity.
- The project area is constituted mainly of Sal forests, mixed deciduous forests, and bamboo groves.
- The reserve zone is the watershed area for 3 important rivers Koel, Burha, and Auranga.
Hermes 900 Star Liner (The Hindu)

- 09 Nov 2023
Why in the News?
Adani Aerospace and Defence in partnership with Elbit Systems manufactures the complete carbon composite aerostructures for Hermes 900 and Hermes 450 in Hyderabad.
About Hermes 900 Starliner:
- The Hermes 900 StarLiner is an Israeli-made, medium-size, multi-payload, medium-altitude long-endurance (MALE) unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) designed for tactical missions.
- It is also known as the Hermes 900 Heavy-Fuel Engine (HFE).
- It is developed by Elbit Systems.
- It is a successor to the Hermes 450 series of drones, one of the most widely used military drones in the world.
- The aircraft has a service ceiling of 30,000ft and offers a flight endurance of up to 36 hours.
- The Hermes 900 has a wingspan of 15 m (49 ft) and can carry a range of multi-sensor payloads weighing up to 450kg for multiple applications.
- Payload options include electro-optical/infrared sensors, synthetic-aperture radar/ground-moving target indication, communications and electronic intelligence, electronic warfare, and hyperspectral sensors.
- The drone has direct and indirect lighting strike capability and can perform missions under instrument flight rules (IFR) in all weather conditions.
'World's Largest Meditation Centre': PM Modi inaugurates Swarved Mahamandir in Varanasi (ET)

- 19 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
Prime Minister Narendra Modi inaugurated the world’s largest meditation centre, Swarved Mahamandir, in Varanasi on December 18.
About the Swarved Mahamandir:
- The Swarved Mahamandir stands as the world's largest meditation centre, accommodating 20,000 individuals in collective contemplation.
- Situated in Varanasi, Uttar Pradesh, this spiritual haven aspires to cast a luminous spiritual aura, enveloping the globe in a state of tranquil attentiveness.
- Named after the Swarved, a profound spiritual text penned by Sadguru Shri Sadafal Deoji Maharaj, the visionary behind Vihangam Yoga and an enduring yogi, the temple serves as a bastion for disseminating Swarveda teachings.
- Emphasizing Brahma Vidya, a profound body of knowledge, it guides spiritual seekers toward sustaining an unwavering equilibrium of peace and happiness.
- Architecturally, the Mahamandir is an imposing seven-floor superstructure, adorned with a captivating design featuring 125-petal lotus domes.
- Crafted from teakwood, the intricate carvings embellishing the ceiling and doors add to its allure.
- Pink sandstone envelops the temple walls, complemented by an enchanting garden featuring medicinal herbs.
- Imprinted on the Mahamandir's walls are verses from the Swarveda, serving as an enduring testament to the spiritual wisdom that resonates within its sacred confines.
What is Vihangam Yoga?
- Vihangam Yoga, an indigenous form of Yoga and meditation, was established by Sadguru Sadafal Deo Ji Maharaj in 1924.
- The nomenclature of this practice is derived from two foundational words: "Vihag," signifying bird, and "Yog," denoting union.
- The name encapsulates the profound concept of a bird ascending from the terrestrial realm, soaring high and unbounded in the sky.
- This symbolism mirrors the ultimate aim of Vihangam Yoga – the liberation of the soul from attachments to the material world, allowing it to recognize and embrace its innate, unshackled essence.
- Only through this liberation can an individual's consciousness seamlessly merge with the universal consciousness, often referred to as the Supreme Being, leading to a state of enduring tranquillity and bliss.
Telecommunications Bill, 2023: The changes it seeks in the telecom sector, why some have raised concerns (Indian Express)

- 19 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
The Telecommunications Bill, 2023, was introduced in the Lok Sabha on Monday. The bill allows the government to take over, manage or suspend telecommunication services or a network over national security.
Key Features of the Telecommunications Bill, 2023
- Repeal of Existing Laws: The bill annuls the Indian Telegraph Act, 1885, the Indian Wireless Telegraphy Act, 1933, and the Telegraph Wires (Unlawful Possession) Act, 1950, while introducing amendments to the Telecom Regulatory Authority of India (TRAI) Act, 1997.
- Authorization for Telecom Activities: Central government approval is mandatory for telecommunication services, network establishment, operation, maintenance, expansion, or possession of radio equipment.
- Existing licenses remain valid for their granted period or five years if unspecified.
- Spectrum Assignment: Spectrum allocation, except for specific purposes, will be through auction.
- Exceptions include national security, disaster management, and services by state-owned entities.
- Interception and Search Powers: Messages may be intercepted, monitored, or blocked for public safety, emergencies, or specified grounds like state security and prevention of offences.
- Government's Extraordinary Powers: The government can take temporary possession of telecom infrastructure during public emergencies, with the authority to suspend telecom services.
- Authorized officers may search for unauthorized equipment.
- Standards Specification Authority: The central government can prescribe standards for telecom equipment, infrastructure, networks, and services.
- Right of Way for Telecom Infrastructure: Facility providers can seek a right of way over public or private property for telecom infrastructure on a non-discriminatory basis.
- User Protection Measures: The government may implement measures to protect users, including consent for specific messages, creation of Do Not Disturb registers, and a mechanism for reporting malware.
- TRAI Appointments and Experience Requirements: Amendments allow individuals with at least 30 years of professional experience to serve as TRAI chairperson and those with at least 25 years of membership.
- Digital Bharat Nidhi: The Universal Service Obligation Fund (USOF) is renamed Digital Bharat Nidhi, allowing its use for research and development (R&D).
- Adjudication Process: An adjudicating officer, of the rank of joint secretary and above, will handle inquiries and orders against civil offences.
- Appeals can be made to the Designated Appeals Committee and further to TDSAT.
- Offences and Penalties: The Bill outlines criminal and civil offences, imposing penalties and imprisonment for unauthorized telecom services, network access, and equipment possession.
- Civil penalties apply for breaches of authorization terms.
What are the Reasons behind the introduction of the Telecommunications Bill, of 2023?
- The telecommunications sector plays a pivotal role in fostering economic and social progress, serving as the conduit for digital services.
- Given its significance, the security of our nation relies substantially on the robustness of telecommunication networks.
- Hence, there is an imperative to establish a legal and regulatory structure that prioritizes the security and resilience of telecommunication networks, fostering a digitally inclusive trajectory for growth.
- The dynamic evolution of telecommunication, its patterns of use, and underlying technologies in recent years underscores the necessity for legislation that aligns with the evolving needs of our society.
Stable Auroral Arc (SAR) (New Indian Express)

- 09 Nov 2023
Why in the News?
In a rare phenomenon, researchers from the Indian Institute of Astrophysics (IIA) have recorded the auroral activity that is normally witnessed over the North Pole- at Hanle and Merak in Ladakh through the all-sky cameras recently.
What is Stable Auroral Arc (SAR)?
- An aurora is a glorious curtain of light that is usually seen at high latitudes like in the Scandinavian countries, and they are not expected to occur at lower latitudes.
- They occur due to the interaction between the Earth’s magnetosphere and the incoming solar wind that carries charged particles and magnetic fields.
- They are typically several hundred kilometers wide and can extend for thousands of kilometers.
- A Stable Auroral Arc (SAR) is red in colour as opposed to the usual green-blue curtains of light seen from high latitudes.
- It is a rare phenomenon and it was not exactly an aurora-like one witnessed from close to the North Pole.
- SAR arcs are typically subvisual, meaning that they cannot be seen with the naked eye.
- However, they can be detected using specialized instruments, such as photometers and spectrographs.
- It was observed in Ladakh during a strong G3-class geomagnetic storm and this event was registered in many parts of the world.
Mines Ministry to Launch National Geoscience Data Repository Portal To Foster Innovation in Exploration (PIB)

- 19 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
Ministry of Mines is to launch the National Geoscience Data Repository (NGDR) Portal on 19th December 2023 in a ceremony in New Delhi.
What is the National Geoscience Data Repository Portal?
- This extensive online platform facilitates the retrieval, exchange, and examination of geospatial information nationwide.
- Spearheaded by the Geological Survey of India (GSI) and the Bhaskaracharya Institute of Space Applications and Geoinformatics (BISAG-N), the NGDR initiative marks a notable advancement in democratizing crucial geoscience data.
- It empowers stakeholders in various industries and academia by providing unparalleled access to invaluable resources.
About the Geological Survey of India (GSI):
- The Geological Survey of India (GSI) originated in 1851 with the primary objective of identifying coal deposits for the Railways.
- Since its inception, GSI has transformed into a repository of geo-scientific information, achieving international recognition for its contributions.
- The organization is dedicated to creating and updating national geoscientific data, conducting mineral resource assessments, and providing impartial geological expertise crucial for policy decisions, commercial ventures, and socio-economic needs.
- GSI focuses on comprehensive documentation of geological processes, employing state-of-the-art techniques in geological, geophysical, and geochemical surveys.
- As an attached office of the Ministry of Mines, GSI operates from its headquarters in Kolkata, with six regional offices in Lucknow, Jaipur, Nagpur, Hyderabad, Shillong, and Kolkata, along with state unit offices across India.
About BISAG (N):
- Bhaskaracharya National Institute for Space Applications and Geo-informatics (BISAG-N) operates as an Autonomous Scientific Society registered under the Societies Registration Act, 1860, falling under the MeitY, Government of India.
- Its multifaceted mission encompasses technology development and management, research and development, fostering national and international collaboration, capacity building, and facilitating technology transfer and entrepreneurship development in the realm of geospatial technology.
- BISAG-N has played a pivotal role in implementing GIS and geospatial technologies for major ministries and nearly all states, integrating diverse technological domains such as geo-spatial science, information science systems, and mathematics science systems.
- The institute operates as a state agency under the Department of Science and Technology, Government of Gujarat, situated in Gandhinagar, Gujarat.
mRNA, easy to customise, is the next frontier for personalised medicine (The Hindu)

- 19 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
The therapeutic use of messenger RNA (mRNA) has fueled great hope to combat a wide range of incurable diseases.
What is mRNA?
- mRNA, or messenger RNA, represents a type of nucleic acid responsible for conveying genetic instructions.
- Within cells, mRNA serves as a messenger, transporting codes from the DNA located in the nucleus to the sites of protein synthesis in the cytoplasm, where ribosomes are situated.
- The genetic information in DNA undergoes transcription, or copying, into mRNA before proteins can be synthesized.
- Each mRNA molecule encodes information for a specific protein, with every sequence of three nitrogen-containing bases dictating the inclusion of a particular amino acid in the protein.
Advantages of mRNA-Based Medicine:
- Scalability: The production of mRNA in the laboratory is highly scalable, as the method for generating mRNA remains consistent across different types.
- This contrasts with traditional drugs, where each compound has distinct chemistry, requiring varied manufacturing methods.
- Patient-Centric: mRNA, being naturally degradable by cells when no longer needed, allows for flexible dosage adjustments to cater to changing patient requirements.
- Broad Therapeutic Potential: mRNA-based medicine holds promise for addressing a wide range of diseases rooted in cellular errors, such as the production of incorrect proteins, mutant protein versions, or insufficient normal protein levels.
- By delivering corrected mRNA to affected cells, scientists aim to facilitate the production of the correct proteins.
Prospects of mRNA-Based Medicine:
- Diverse Treatment Applications: The future of mRNA-based medicine extends to addressing conditions like heart disease, neurodegenerative diseases, and bone loss, among others.
- Enhanced Wound Healing: mRNA drugs exhibit the potential to stimulate the formation of new blood vessels.
- This capability is particularly beneficial for diabetic patients with compromised blood circulation, reducing the risk of amputation.
- Treatment for Rare Conditions: mRNA-based medicine holds promise in treating rare disorders like propionic acidaemia, characterized by insufficient levels of liver proteins crucial for preventing the accumulation of toxic by-products in the body, especially in children.
Way Forward
- The capacity to tailor and manufacture mRNA easily enhances its prospects as a potent and personalized therapy, offering the potential for reduced side effects and widespread applicability.
- Despite these advancements, mRNA-based therapeutics are in the early stages of development, facing challenges such as the short lifespan of mRNA in cells and limited protein production duration.
- Addressing these hurdles is crucial to optimizing mRNA effectiveness and minimizing the quantity of mRNA needed.
MoEFCC has launched the Indian Forest & Wood Certification Scheme to promote sustainable forest management and agroforestry practices across the country (Indian Express)

- 19 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
Amid rising international concerns about deforestation and illicit trade in timber, the government has launched its own “national” forest certification scheme to validate entities that adhere to sustainable practices in the management of forests and their products.
About the Indian Forest & Wood Certification Scheme (IFWCS):
- The Indian Forest & Wood Certification Scheme (IFWCS) serves as the national forest certification initiative, focusing on fostering sustainable forest management and the sustainable utilization of Trees outside Forests (TOF) across India.
- Voluntary Participation: The scheme provides a voluntary third-party certification mechanism to encourage agroforestry practices within the country.
- Alternatives to Foreign Certifications: IFWCS presents an indigenous alternative to foreign certification agencies that have been prevalent in the Indian market for the past two decades.
- Applicability: The certification applies nationwide, covering both forest areas and TOF plantations on government, private, agroforestry, and other lands.
- It encompasses both timber and non-timber forest produce (NTFP).
- Necessity: With major export markets like Europe and the United States imposing stricter rules on forest product imports due to deforestation concerns related to climate change, IFWCS can provide market incentives for entities practising responsible forest management.
- Significance: The scheme aims to enhance trust, transparency, and international acceptability of Indian forest-based products.
- It is especially beneficial for state forest departments, individual farmers, or Farmer Producer Organizations engaged in agroforestry.
- Compliance and Legal Status: While the certification may gain recognition from various regulatory authorities, it does not serve as legal advice on compliance with specific laws, regulations, or requirements.
- Foundation: Forest Management certification relies on the Indian Forest Management Standard, a crucial component of the National Working Plan Code 2023, introduced this year.
- The Indian Forest and Wood Certification Council, acting as a multi-stakeholder advisory body, will supervise the scheme.
- The council comprises members from esteemed institutions like the Indian Council of Forestry Research and Education, Forest Survey of India, and the Indian Institute of Forest Management, along with representatives from relevant ministries.
- Implementation: The Indian Institute of Forest Management in Bhopal will serve as the scheme's operating agency.
- Certification bodies conducting independent audits will be accredited by the National Accreditation Board for Certification Bodies under the Quality Council of India.
Management of Forests in India:
- The administration of forests in India aligns with individual working plans specific to each forest area.
- Recently, these plans have undergone revisions incorporating the newly formulated Indian Forest Management Standards.
- Comprising 8 criteria, 69 indicators, and 254 verifiers, these standards are obligatory for implementation across all forest divisions nationwide.
- While forest divisions are not compelled to obtain certification, adhering to these standards renders them eligible.
- The decision to pursue certification is contingent upon specific requirements and considerations.
India's Akash missile engages four targets at once at 25km, a global first (ET)
- 18 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
India demonstrated the capability of the Akash missile system to engage four aerial targets simultaneously at a range of 25 kilometres, the Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO) said on Sunday.
Context:
- During the recent Exercise Astrashakti 2023, a solitary unit of the Akash weapon system demonstrated its capability by effectively engaging and eliminating four unmanned targets simultaneously.
- This showcase positions India as the pioneer, being the first country to showcase the proficiency of engaging multiple targets at considerable distances concurrently through command guidance from a single firing unit.
About the Akash Surface-to-Air Missile (SAM) Defence System:
- The Akash Surface-to-Air Missile (SAM) Defence System is a Short-Range Surface-to-Air Missile (SRSAM) designed to safeguard vulnerable areas and points from airborne threats.
- Developed indigenously by the Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO), it boasts several notable features:
- Versatility: Capable of simultaneously engaging multiple targets and effectively neutralizing manoeuvring threats, including unmanned aerial vehicles, fighter aircraft, cruise missiles, and helicopter-launched missiles.
- Electronic Counter-Counter Measures (ECCM): Equipped with built-in ECCM features, enhancing its resilience against electronic countermeasures.
- Flexible Deployment: The entire system is configured for launch from both static and mobile platforms such as battle tanks and wheeled trucks, ensuring adaptable deployment options.
- Transportability: Road and rail transportable, with swift mobilization and deployment capabilities, facilitating rapid response scenarios.
- Range: Capable of engaging aerial targets at a distance of approximately 25 km.
- Altitude of Operation: Ranging from 100 meters up to 20 km.
- Weight: 710 kg.
- Guidance System: Command Guidance.
- Automation: Fully automatic with a quick response time from target detection to neutralization.
- Open-System Architecture: Designed with an open-system architecture, ensuring adaptability to current and future air defence environments.
What is ‘noma’, the latest addition to WHO’s list of neglected tropical diseases (DownToEarth)

- 18 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
The World Health Organization (WHO) on December 15, 2023, added one of the world’s most under-recognised health challenges, noma, to its official list of neglected tropical diseases (NTD).
About the Noma disease:
- Noma is a severe gangrenous disease of the mouth and face with a mortality rate of approximately 90 per cent.
- It is also known as cancrum oris or gangrenous stomatitis and is often associated with extreme poverty, malnutrition and poor access to sanitation and oral hygiene.
- The name of the disease comes from the Greek word “nom?”, meaning “to devour”, as noma eats away facial tissue and bones if not treated early.
- Noma mainly affects children aged 2-6 years old and is found most commonly among those living in poor communities.
- The illness’s ‘hidden’ or neglected nature is most likely due to the fact that it affects the world’s most marginalised children.
- Noma is associated with a number of risk factors, including poor oral hygiene, malnutrition, weakened immune systems, infections, and extreme poverty.
- While the disease is not contagious, it prefers to attack when the body’s defences are weak.
- The NTD often starts as an ulcer on the mucous membrane lining, commonly after a bout of measles or other diseases, stated another 2003 study.
- “It quickly develops into a massive necrosis, moving from the inside outward, often involving major portions of the face.
- Treatment: “Early treatment with antibiotics, rehydration, correction of electrolytic imbalances, and administering nutritional supplements will halt the disease.
- The patients who survive face many consequences, like significant facial disfigurement, spasms of the jaw muscles, oral incontinence and speech problems.
- The disease is also called the ‘face of poverty’, as effective drugs like sulfonamides and penicillin and adequate surgical treatment for the effects remain inaccessible for many due to extreme poverty.
- “The recognition of noma as an NTD aims to amplify global awareness, catalyse research, stimulate funding, and boost efforts to control the disease through multisectoral and multi-pronged approaches.
Surat Diamond Bourse to create 150,000 jobs! Modi is confident ‘world’s largest office building’ will be a boon for artisans and businessmen (Financial Express)

- 18 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
In the inauguration ceremony of the Surat diamond bourse in Gujarat, Prime Minister Narendra Modi revealed plans for the creation of 150,000 new jobs, emphasising the bourse’s role as a “one-stop shop” for artisans and businessmen.
About Surat Diamond Bourse:
- Established in February 2015 by the former Chief Minister of Gujarat, Smt. Anandiben Patel, the Surat Diamond Bourse (SDB) is a prominent diamond trade centre situated in DREAM (Diamond Research and Mercantile) city, Surat, Gujarat.
- Recognized as the "diamond city" due to its diamond industry, which processes 85 to 90% of the world's rough diamonds, the SDB stands as the world's largest diamond trading hub, spanning an expansive floor space of 660,000 square meters and surpassing The Pentagon as the largest office building globally.
- Themed around the 'panch tatva,' symbolizing the five elements of nature – air, water, fire, earth, and sky, the SDB is designed with thematic landscaping.
- As a global centre for both rough and polished diamond and jewellery trading, it unifies various facets of the diamond industry, including cutting, polishing, and trading activities, within its vast expanse.
- The Bourse features a state-of-the-art 'Customs Clearance House' for Import-Export, a Jewelry mall for retail jewellery business, and facilities for International Banking and Safe Vaults.
Importance of the SDB Project:
- The Surat Diamond Bourse (SDB) is set to accommodate a diverse range of diamond-related enterprises, encompassing the sale of both rough and polished diamonds, diamond manufacturing machinery, diamond planning software, diamond certificate firms, lab-grown diamonds, and more.
- Anticipated to be a major contributor to employment, the SDB is poised to generate substantial job opportunities.
- With an expected direct employment impact on over 1.5 lakh individuals across various roles within the diamond industry, it aims to bolster economic activity and livelihoods.
- Acknowledging its commitment to environmental responsibility, the complex has earned pre-certification as a green building by the Indian Green Building Council (IGBC).
- This recognition is a testament to the SDB's implementation of eco-friendly and sustainable practices in its operations.
What is DREAM City?
- DREAM City, short for Diamond Research and Mercantile City, is an emerging business district located in Surat.
- Encompassing 810 hectares (2,000 acres) of land near Khajod, it follows the model of the Gujarat International Finance Tec (GIFT) City and Dholera Smart City near Ahmedabad.
- Envisioned as a comprehensive urban development, DREAM City is slated to feature office spaces, residential areas, and associated amenities.
- The project is under the purview of a special-purpose vehicle established by the Government of Gujarat.
- With an anticipated opening in 2030, DREAM City is poised to become Gujarat's third smart city, aligning with the state's commitment to fostering modern and sustainable urban environments.
Scientists find hydrogen cyanide, a key molecule for life formation, in Saturn’s icy moon Enceladus (Sci News)
- 18 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
Recently, planetary scientists have detected several compounds of strong importance to the habitability of Saturn’s icy moon Enceladus, including hydrogen cyanide, acetylene, propylene and ethane, using data from NASA’s Cassini mission.
What is Enceladus?
- Enceladus is the sixth-largest icy moon of Saturn. It has a white, streaky surface made of water ice.
- Beneath this frozen crust lies a warmer, salty ocean that covers the whole moon.
- This circular moon is just about 500 km wide, with a surface temperature of -200°C.
- But its interiors host several sources of energy and heat.
- Enceladus is tugged and pulled in all directions by Saturn’s gravity and the gravity of other more massive moons, thus creating heat in its interior.
- Its rocky core may also be undergoing radioactive decay and chemical reactions that generate heat.
- Moreover, it is also an active source of water volcanism, where giant plumes of water, ice, dust, and gases are ejected into space like volcanic explosions.
- The material from the plumes replenishes one of the rings of Saturn as well, as the icy particles that make up the rings slowly drift inwards and get pulled into Saturn.
- The presence of a global saltwater ocean with nutrients and a heat source suggests a suitable aquatic environment for life.
- However, no life has been found on Enceladus or anywhere else beyond Earth.
About Hydrogen cyanide:
- Hydrogen cyanide is a chemical compound with the formula HCN and structural formula H−C≡N.
- It presents itself as a colourless or pale-blue liquid or gas, characterized by a bitter, almond-like fragrance.
- Alternatively referred to as hydrocyanic acid or HCN, this substance has the potential to disrupt the body's oxygen utilization, posing risks to the brain, heart, blood vessels, and lungs.
- While Hydrogen cyanide boasts excellent solvent properties for numerous salts, its utilization as a solvent is limited due to its inherent toxicity.
- In various industrial settings, it finds application in tasks such as fumigation, electroplating, mining, chemical synthesis, and the manufacturing of synthetic fibres, plastics, dyes, and pesticides.
How Indian states fare on logistics: What the Centre’s latest survey says (Indian Express)

- 18 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
The Logistics Ease Across Different States (LEADS) perception survey, released by the Union Ministry of Commerce and Industry, flags some challenges in logistics and states performance on a regional basis.
Key highlights of the Report:
- Only five states namely Gujarat, Tamil Nadu, Karnataka, Maharashtra and Telangana continue to make up 70 per cent of exports. Over the years this has caused a widening gap in income and job generation between the landlocked states and coastal states.
- Performance of Landlocked States: Bihar, Himachal Pradesh, Jharkhand, and Chhattisgarh have received low perception scores on these counts while user satisfaction in Telangana, Uttar Pradesh, and Punjab improved.
- Notably, Jharkhand saw below-average scores across all indicators, encompassing infrastructure, services, and operating and regulatory categories.
- Performance of North-East Group: In Manipur, user satisfaction levels for the state are generally lower than the average of the North-East Group for all indicators across pillars.
- The data indicated relatively high stress in the ‘easy of entry’ category.
- While Assam performed better than average on most counts, the user performance assessment was also below the average of North-East Group in the case of Meghalaya.
- Odisha, West Bengal Lag Among Coastal States: Indian coastal states including Andhra Pradesh, Goa, Gujarat, Karnataka, Kerala, Maharashtra, Odisha, Tamil Nadu and West Bengal account for 75 per cent of total exports from the country and have fared well in logistics historically.
- Gujarat accounts for 33% followed by Maharashtra with 16% and Tamil Nadu with 9% share.
- However, the survey showed that Goa, Odisha and West Bengal continue to perform below the average among coastal states.
- In the case of Odisha, the survey said that there has been an improvement in the overall perception of the state’s logistics ecosystem since 2019 but despite this, the indicator averages for this year have remained below the Coastal Group average.
What is Logistics Ease Across Different States (LEADS)?
- Initiated in 2018 by the Department for Promotion of Industry and Internal Trade (DPIIT), Ministry of Commerce and Industry, LEADS draws inspiration from the World Bank's Logistics Performance Index (LPI).
- Unlike the LPI, which relies solely on perception-based surveys, LEADS incorporates both perception and objectivity, thereby enhancing the robustness and comprehensiveness of its evaluation.
- LEADS focuses on three pivotal pillars:
- Logistics Infrastructure
- Logistics Services, and
- Operating and Regulatory Environment.
- The recently released 5th edition, LEADS 2023, illuminates the evolving performance of states and union territories across these pillars.
- It provides valuable insights into the enhancement of logistics performance at the State/UT level, emphasizing an augmented stakeholder perception and the impact of various reforms.
- This report not only signals a positive transformation in the performance of states but also empowers State/UT Governments with region-specific insights, facilitating informed decision-making and comprehensive growth.
Importance of the LEADS Initiative:
- The LEADS report serves as a catalyst in fostering healthy competition among States/UTs, driving improvements in logistics performance.
- Notably, 23 States/UTs have aligned their State Logistics Policies with the National Logistics Policy, while 16 have accorded industry status to logistics, collectively contributing to the elevation of India's global positioning in the logistics ecosystem.
- This initiative significantly enhances the overall competitiveness of India's logistics sector, as evidenced by the country's ascent by six places to the 38th position in the 2023 Logistics Performance Index.
- Integral to this success are digital reforms like PM GatiShakti, Logistics Data Bank, Unified Logistics Interface Platform (ULIP), and GST, which have propelled India's improved global ranking.
- Developed collaboratively and through a consultative approach, the LEADS report introduces objectivity in assessing both infrastructure development and process-related reforms.
Saint Lucia’s Tax Inspectors without Borders (TIWB) programme launched in partnership with India (ET)

- 16 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
India will help Saint Lucia in strengthening its tax administration by transferring technical knowledge and skills to its tax administration, and sharing best practices under the ‘Tax Inspectors Without Borders (TIWB) programme’.
Key Highlights:
- India has been chosen as the Partner Administration and will provide Tax Experts for this programme.
- This programme is expected to be of 12-18 months’ duration in which India, in collaboration with the TIWB Secretariat and support of the UNDP Country Office, Barbados and the Eastern Caribbean, aims to aid Saint Lucia in strengthening its tax administration by transferring technical knowledge and skills to its tax administration, and through sharing of best practices.
- The focus of the programme will be on the effective use of automatic exchange of information under the Common Reporting Standard (CRS) framework.
What is Tax Inspectors without Borders programme?
- Tax Inspectors Without Borders (TIWB) is a joint initiative of the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD) and the United Nations Development Programme (UNDP).
- It is designed to support developing countries to build tax audit capacity.
- TIWB facilitates well-targeted, specialised tax audit assistance in developing countries around the world.
- Under TIWB, tax audit experts work alongside local officials of developing country tax administrations on tax audit and tax audit-related issues.
- TIWB aims to transfer technical know-how and skills to developing countries’ tax auditors, as well as share general audit practices.
- The host administrations of developing countries are the lead partners in TIWB programmes, clearly specifying their needs and scope of work.
- A dedicated central unit (TIWB Secretariat) jointly managed by OECD and UNDP operates as a clearing house to match the demand for auditing assistance with appropriate expertise.
- TIWB is a capacity-building programme.
State Bank of India (SBI) has raised its marginal cost of funds-based lending rate (MCLR) by up to 10 basis points for selected tenures (Financial Express)

- 16 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
State Bank of India (SBI) on Friday hiked its marginal cost of funds-based lending rate (MCLR) on various tenures by 5-10 basis points (bps), a move that could make consumer loans, such as auto or home loans, more expensive for borrowers.
What is the Marginal Cost of Funds Based Lending Rate (MCLR)?
- The MCLR, or Marginal Cost of Funds Based Lending Rate, represents the minimum lending rate below which a bank is not authorized to lend.
- This mechanism aims to facilitate the calculation of the minimum interest rate applicable to various types of loans offered by banks.
- Introduced by the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) on April 1, 2016, the MCLR methodology serves to improve the effectiveness of monetary policy transmission and enhance transparency in the interest rate-setting process, replacing the earlier base rate structure established in July 2010.
- Calculation of MCLR: MCLR is internally determined by the bank, considering the remaining period for the loan repayment. This rate is closely tied to actual deposit rates and is calculated based on four key components:
- The marginal cost of funds
- Negative carry-on account of the cash reserve ratio
- Operating costs
- Tenor premium
- Under the MCLR framework, banks have the flexibility to offer loans at fixed or floating interest rates across all categories.
- The actual lending rates for various loan categories and tenors are determined by adding the components of spread to the MCLR.
- Consequently, the bank is restricted from lending at a rate lower than the MCLR for a specific maturity concerning all loans linked to that benchmark.
- Banks review and publish MCLRs for different maturities on a monthly basis.
- Certain loan rates, such as those for fixed-rate loans with tenors exceeding three years and special loan schemes offered by the government, remain unaffected by MCLR fluctuations.
Difference Between MCLR and Base Rate:
MCLR stands as a more evolved iteration of the base rate, presenting several distinctions between the two:
- Origin and Regulation: The base rate is the RBI-set minimum interest rate, and financial institutions cannot lend below this rate.
- MCLR, on the other hand, is an internal benchmarking system used by financial institutions, allowing them to set lending rates based on a predetermined spread.
- Cost Calculation: The base rate relies on the average cost of funds.
- MCLR is rooted in the marginal or incremental cost of money, providing a more dynamic reflection of the current cost scenario.
- Impact of RBI's Repo Rate: The base rate remains unaffected by changes in the RBI's repo rate.
- MCLR, however, is directly influenced by revisions in the repo rate, adjusting accordingly.
- Consideration Factors: The base rate typically considers the minimum rate of return or profit margin.
- In contrast, when determining the MCLR, factors such as the tenor premium are taken into account, resulting in a more nuanced rate-setting process.
‘Sacrifice forever etched in our hearts’: PM Modi, leaders across parties pay tributes on Vijay Diwas (Indian Express)

- 16 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
Leaders across the political lines paid tributes to the soldiers who fought in the 1971 war, on the occasion of 52nd Vijay Diwas on Saturday.
About Vijay Diwas:
- Vijay Diwas, observed on December 16 annually, is a commemoration honouring the triumph of the Indian armed forces over Pakistan in the 1971 war and paying tribute to the soldiers who made the ultimate sacrifice for their country.
- This day is also recognized in Bangladesh as 'Bijoy Dibos' or Victory Day, symbolizing the nation's formal independence from Pakistan.
Historical Background:
- The roots of the 1971 war lay in the genocide perpetrated by the oppressive Pakistani military regime, led by General Yahya Khan, against the people of East Pakistan.
- The conflict emerged following the victory of the Sheikh Mujibur Rahman-led Awami League in the 1970 elections.
- Post-elections, the Pakistani military used force to manipulate the results, resulting in a mass exodus from East Pakistan.
- India intervened during this critical period, with then-Prime Minister Indira Gandhi offering refuge to those fleeing from the other side of the border.
- Tensions escalated on December 3, 1971, when Pakistan initiated air strikes on 11 Indian airbases.
- In response, Indira Gandhi instructed India's Army Chief, General Sam Manekshaw, to launch a full-scale war against Pakistan.
- India supported Bangladesh nationalist groups and executed 'Operation Trident,' led by the Indian Navy, to target Karachi Port.
- After a 13-day battle, India achieved a decisive victory on December 16, 1971, leading to the establishment of Bangladesh from the former East Pakistan.
- On this momentous day, General Amir Abdullah Khan Niazi of Pakistan signed the Instrument of Surrender, capitulating with 93,000 Pakistani soldiers before the Indian Army and the Mukti Bahini of Bangladesh, marking the most substantial military surrender post-World War II.
How the hottest summer ever affected the Arctic: 5 things you need to know (Indian Express)

- 16 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
Rising temperatures in the Arctic have led to unprecedented wildfires that forced communities to evacuate, a decline in sea ice extent, devastating floods, food insecurity, and a rise in sea level.
Highlights from the Arctic Report Card 2023:
- The period from October 2022 to September 2023 ranked as the sixth-warmest year in the Arctic since the initiation of record-keeping in 1900.
- Notably, this timeframe aligns with the Arctic monitoring year, spanning from October to September to cover the region's cold season.
- This marks the 14th consecutive year wherein Arctic temperatures surpassed the average recorded between 1991 and 2020.
- The elevated temperatures observed in the northern polar region had significant consequences, including unprecedented wildfires necessitating community evacuations, a reduction in sea ice coverage, severe floods, concerns about food security, and an elevation in sea levels.
The most severe consequences of the soaring temperatures in the Arctic:
- Thawing of Subsea permafrost: Subsea permafrost is essentially frozen soil beneath the seabed that contains organic matter.
- While it has been gradually thawing for thousands of years, warmer ocean temperatures are accelerating this process.
- When subsea permafrost thaws, the organic matter it contains decays and releases methane and carbon dioxide – greenhouse gases that contribute to global warming and worsen ocean acidification.
- Food insecurity: Due to the impact of climate change on freshwater bodies and marine ecosystems, Western Alaska recorded another year of extremely low numbers of Chinook and chum salmon. The size of adult salmon has also decreased.
- It led to fishery closures, worsened user conflicts, and had profound cultural and food security impacts in Indigenous communities that have been tied to salmon for millennia.
- Interestingly, while the population of Chinook and chum salmon declined, sockeye salmon increased in Western Alaska.
- According to scientists, the diverging impacts are affecting Indigenous communities that depend on the salmon for food, and challenging fishery managers as the different species respond in unique ways to the warming climate.
- Raging wildfires: Canada with 40% of its land mass is considered Arctic and Northern was among the worst affected regions when it comes to wildfires.
- Canada witnessed its worst wildfire season on record with fires burning more than 10 million acres in the Northwest Territories.
- This happened as high temperatures dried up vegetation and soil, coupled with below-average rainfall, creating perfect conditions for wildfires.
- Canada witnessed its worst wildfire season on record with fires burning more than 10 million acres in the Northwest Territories.
- Severe flooding: Rising temperatures have led to dramatic thinning of the Mendenhall Glacier, located in Alaska, over the past 20 years.
- As a result, over the years, the meltaway water has annually caused floods in the region.
- One such disaster took place in August 2023, when a glacial lake on a tributary of the Mendenhall Glacier burst through its ice dam.
- It caused unprecedented flooding and severe property damage” in Alaska’s Juneau.
- Greenland ice sheet melting: The highest point on Greenland’s ice sheet experienced melting for only the fifth time in the 34-year record.
- Not only this, the ice sheet continued to lose mass despite above-average winter snow accumulation.
- Between August 2022 and September 2023, it lost roughly 350 trillion pounds of mass.
- Notably, Greenland’s ice sheet melting is the second-largest contributor to sea-level rise.
India joins the elite club of countries to have mastered the controls for flying wing technology in tailless configuration (Indian Express)
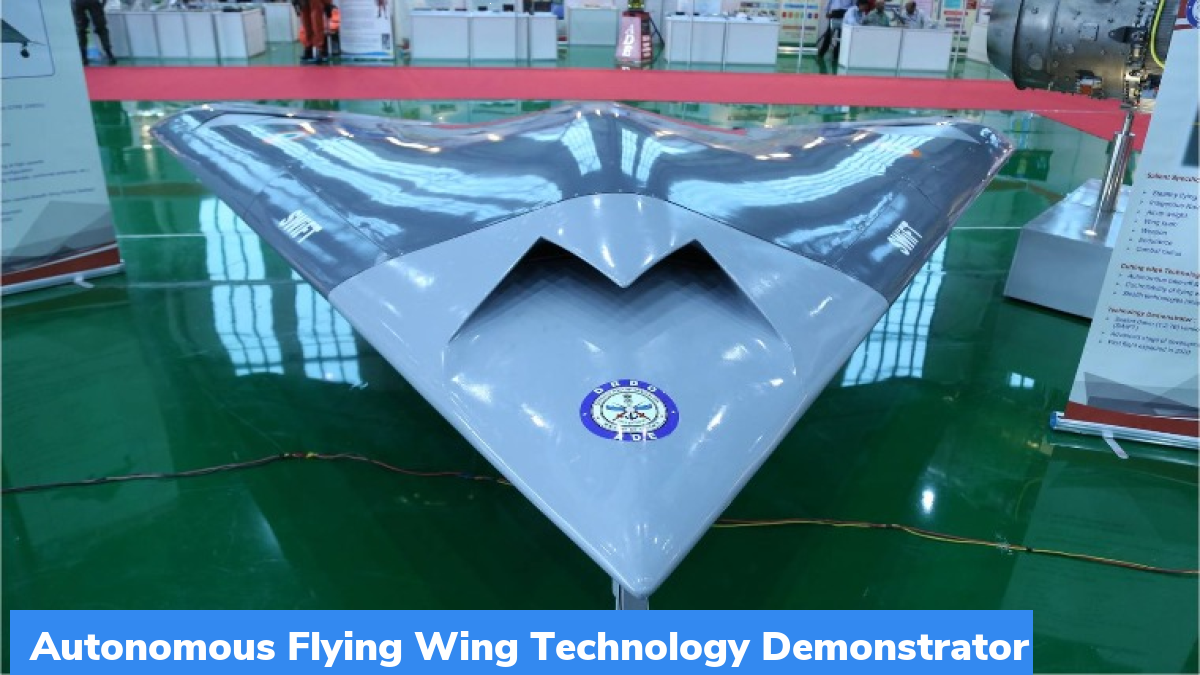

- 16 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
Recently Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO) successfully carried out a flight trial of the Autonomous Flying Wing Technology Demonstrator, an indigenous high-speed flying-wing Unmanned Aerial Vehicle (UAV) from the Aeronautical Test Range, Chitradurga in Karnataka.
About the Flying Wing Technology Demonstrator:
- The Flying Wing Technology Demonstrator is a domestically developed high-speed flying-wing Unmanned Aerial Vehicle (UAV) crafted by the Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO)’s Aeronautical Development Establishment.
- Its inaugural flight took place in July 2022, marking significant progress in the development of robust aerodynamic and control systems, real-time integration, hardware-in-loop simulation, and an advanced Ground Control Station.
- The project team successfully optimized avionic systems, integration processes, and flight operations, culminating in the seventh and final flight in the ultimate configuration.
- Constructed with a complex arrowhead wing platform, the UAV prototype utilizes a lightweight carbon prepreg composite material developed indigenously.
- A noteworthy feature is the autonomous landing capability, eliminating the need for ground radars, infrastructure, or a pilot.
- This unique capability demonstration allows take-off and landing from any runway with surveyed coordinates.
- This technology demonstrator has been developed for India's secretive stealth combat drone called Ghatak.
- The successful flight in a tailless configuration has propelled India into the prestigious group of nations that have perfected the controls for the Flying wing configuration
Indian Joins Elite Club:
- With this flight in the tailless configuration, India has joined the elite club of countries to have mastered the controls for the flying wing technology.
- These flight tests led to achievements in the development of robust aerodynamic and control systems; integrated real-time and hardware-in-loop simulation, and a state-of-the-art Ground Control Station, informed the DRDO.
Aatmanirbharta
- The DRDO team had optimised the avionic systems, integration and flight operations towards the successful seventh flight in the final configuration.
- The aircraft prototype, with a complex arrowhead wing platform, is designed and manufactured with lightweight carbon prepreg composite material developed indigenously.
- Also, the composite structure, impregnated with fibre interrogators for health monitoring, is a showcase of ‘Aatmanirbharta’ in aerospace technology.
'Pralay' Missile (The Hindu)

- 08 Nov 2023
Why in the News?
India on November 7 successfully test-fired its surface-to-surface short-range ballistic missile (SRBM) 'Pralay' from the Abdul Kalam Island off the Odisha coast.
About the Pralay missile:
- The Pralay missile is a short-range ballistic missile developed by India’s Defense Research and Development Organization (DRDO).
- It is similar in design and functionality to Russia’s Iskander-M quasi-ballistic missile.
- With a range that can vary from 150-500 km, the Pralay is equipped with a 500 kg payload that gives it a reach of 400 km.
- One of the key features of the Pralay missile is its ability to switch from a ballistic to a flat trajectory after launch.
- This quasi-ballistic trajectory, combined with high speeds and terminal maneuvering capabilities, makes it incredibly difficult for adversary air defense systems to intercept.
- The Pralay missile is a land mobile quick reaction system, launched from storage and transportation canisters and housed in either a 12×12 or an 8×8 launcher configuration.
- Furthermore, the missile’s jet vane system allows for evasive maneuvers in the terminal phase of flight, and it is even speculated that the Pralay has the capability to release decoys, adding an additional layer of defense.
- Its indigenously developed Fused Silica Radar-dome (RADOME) further enhances its radar transparency, making it even more challenging for enemy radars to detect.
- With the Pralay missile, India is reaffirming its commitment to developing and deploying advanced defense systems that can effectively counter adversary air defense systems.
- In an era where stealth technology is being challenged, the Pralay missile presents a formidable solution for striking targets deep behind enemy lines with minimal risk.
Treaty of Conventional Armed Forces in Europe (CFE) (Indian Express)

- 08 Nov 2023
Why in the News?
NATO on Tuesday announced the formal suspension of a key Cold War-era security treaty in response to Russia’s pullout from the deal.
About Treaty of Conventional Armed Forces in Europe (CFE):
- During the final years of the Cold War, negotiators signed the CFE, a treaty that placed restrictions on the deployment of military equipment to maintain a military balance between the North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO) and the then-Warsaw Pact countries.
- The treaty's purpose was to prevent the rapid build-up of forces that could be used in a swift assault.
- On November 19, 1990, twenty-two member states from both NATO and the Warsaw Pact came together in Paris to sign the agreement, a year after the fall of the Berlin Wall.
- The CFE finally entered into force on November 9, 1992, following the disintegration of the Warsaw Pact.
- The Treaty set specific limits on the number of battle tanks, armored combat vehicles, artillery pieces, combat aircraft, and attack helicopters that NATO and Warsaw Pact states could have on their respective territories.
- To meet these limits, CFE state parties destroyed over 50,000 weapons systems over subsequent years.
- These actions were monitored through a compliance mechanism that involved information sharing and reciprocal inspections.
- Furthermore, the treaty's scope was expanded to cover troop numbers in a 1992 follow-up agreement known as the CFE-1A.
- This arrangement arranged limits on military personnel levels.
- In 1999, during the Istanbul summit of the Organization for Security and Co-operation in Europe (OSCE), CFE Treaty partners reached an agreement on an updated and modified arrangement known as the Adapted CFE Treaty.
- One significant change was that limitations on conventional weapon systems were no longer linked to two military blocs but to the territorial borders of individual states.
- However, Russia suspended its participation in the treaty in 2007 and ceased active participation in 2015.
Krishi 24/7 7 (The Hindu Business Line)

- 08 Nov 2023
Why in the News?
Recently, the Union Agriculture Ministry partnered with the Wadhwani Institute for Artificial Intelligence (Wadhwani AI) to create a solution known as Krishi 24/7.
About Krishi 24/7:
- Krishi 24/7 is a groundbreaking AI-powered solution developed with support from Google.org, designed for automated monitoring and analysis of agricultural news.
- Key Features:
- This tool scans news articles in various languages and translates them into English for easy access.
- It extracts crucial information from news articles, including headlines, crop details, event types, dates, locations, severity, summaries, and source links.
- This ensures that the ministry receives timely updates on relevant events found on the internet.
- Significance:
- Krishi 24/7 addresses the vital need for an efficient system to identify and manage agricultural news articles.
- This aids in making timely decisions.
- It serves the Department of Agriculture and Farmers Welfare (DA&FW) by identifying pertinent news, delivering timely alerts, and facilitating swift action to protect the interests of farmers and promote sustainable agricultural growth through informed decision-making.
Vaigai Dam (The Hindu)

- 08 Nov 2023
Why in the News?
The third and final flood warning has been issued for five southern districts after the water level in Vaigai dam touched 69 feet (full reservoir level 71 ft) at 7 a.m. on Wednesday, November 8.
About Vaigai Dam:
- Built across the Vaigai River, the Vaigai Dam is located near Andipatti in Tamil Nadu's Theni district.
- The dam was inaugurated by then Chief Minister K. Kamaraj on January 21, 1959, and is often referred to as the lifeline of the people of this region.
- The farmers in the region are completely dependent on the water from the dam for irrigation purposes.
- With a height of 111 feet, the dam has the capacity to store up to 71 feet of water.
- Its main purpose is to provide irrigation water for the Madurai and Dindigul districts, as well as drinking water for Madurai and Andipatti residents.
- Close to the dam, the Government of Tamil Nadu has established an Agricultural Research Station dedicated to crop research.
- Additionally, there is a charming garden called Little Brindavan situated near the dam, offering a delightful place for visitors.
Project Dolphin (The Hindu)

- 08 Nov 2023
Why in the News?
In an effort to conserve dolphins and their habitat, the Tamil Nadu government has issued orders to implement Project Dolphin under the Union government’s Integrated Development of Wildlife Habitats scheme.
About Project Dolphin:
- Project Dolphin is a national conservation initiative approved in 2019 during the first meeting of the Prime Minister-led National Ganga Council (NGC) and launched in 2021 to safeguard both riverine and oceanic dolphin species.
- It's part of the larger Arth Ganga program, which is a government initiative.
- It is modeled after Project Tiger, the successful conservation program that has played a significant role in the resurgence of tigers in India.
- The Project Dolphin will strengthen the marine ecology and overall health of the marine Environment and will be implemented at a cost of Rs.8.13 crore.
- The major habitats of the dolphins are found in the Gulf of Mannar Biosphere Reserve (Tamil Nadu).
- The Ministry of Environment, Forests, and Climate Change is responsible for implementing Project Dolphin.
- The main goal is to ensure the long-term survival of these dolphins and, by extension, the overall health of the river's aquatic life.
- The National Mission for Clean Ganga (NMCG) started a dolphin conservation program in 2016 to work towards this important mission.
- Dolphins play an important role in keeping the marine environment in balance.
- Dolphins worldwide face various natural and human-induced threats which include hunting, entanglement in fishing nets, overfishing, climate change, ship strikes, tourism activities, toxic contamination, noise pollution, oil and gas development, and habitat degradation.
- The conservation of dolphins and their aquatic habitat through the use of modern technology by engaging with fishermen and other ocean-dependent populations is proposed under the project.
- The project will focus on key activities including strengthening of protection activities through better patrolling anti-poaching activities and strengthening of the surveillance and patrolling teams with modern equipment and technology;
- Rescue and rehabilitation activities through the strengthening of veterinary services, patrolling and training, etc;
- Dolphin habitat improvement through the restoration of coastal eco-system like mangroves, corals, sea grass, etc;
- Removal of ghost nets and reduction of pollution in coastal areas;
- enhancing awareness through the celebration of “National Dolphin Day”
Euclid Mission (NASA)

- 07 Nov 2023
Why in the News?
The Euclid mission, which will investigate the mysteries of dark matter and dark energy, released its first five science images recently.
About Euclid Mission:
- Euclid is a European mission, built and operated by European Space Agency (ESA), with contributions from NASA.
- Euclid is designed to give important new insights into the "dark side" of the universe -- namely dark matter and dark energy, both thought to be key components of our cosmos.
- It was launched from Cape Canaveral, Florida, (USA) on 1 July 2023 and the launch vehicle used was ‘SpaceX Falcon 9’.
- The mission derives its name from Euclid of Alexandria, an ancient Greek mathematician from around 300 BC, who laid the foundations of geometry.
- Euclid Mission Objective: The primary goal of the Euclid mission is to create a three-dimensional map of the universe, with time as the third dimension.
- This will be achieved by observing billions of galaxies, extending up to 10 billion light-years away, and covering over a third of the celestial sphere.
- Euclid will explore how the Universe has expanded and how structure has formed over cosmic history, revealing more about the role of gravity and the nature of dark energy and dark matter.
- The Euclid Consortium – consisting of more than 2,000 scientists from 300 institutes in 13 European countries, the U.S., Canada, and Japan – is responsible for providing the scientific instruments and scientific data analysis.
- NASA provided the detectors of the Near-Infrared Spectrometer and Photometer, NISP.
- Euclid is a medium-class mission in ESA’s Cosmic Vision Programme.
World Local Production Forum (WLPF) (PIB)

- 07 Nov 2023
Why in the News?
The Indian delegation led by Shri Bhagwant Khuba, Union Minister of State for Chemicals and Fertilizers participated in the Second World Local Production Forum (WLPF) held in Hague, Netherlands.
About the World Local Production Forum (WLPF):
- The World Local Production Forum (WLPF) is an initiative by the World Health Organization (WHO).
- The inaugural WLPF took place virtually in 2021.
- Main Objective: The core aim of this forum is to enhance access to essential medicines and other health technologies.
- Role and Function: The WLPF serves as a regular platform for Member States and the global community to collaboratively develop strategies, mobilize collective efforts, and establish partnerships.
- These actions are directed towards promoting sustainable local production, ensuring timely and equitable access to high-quality health products.
- Secretariat: The Local Production and Assistance (LPA) Unit at the WLPF is responsible for overseeing the forum's activities.
- Second WLPF Goals: The second WLPF has several key objectives:
- To create a global platform for discussions addressing the primary challenges related to local production and technology transfer.
- To explore opportunities and mechanisms for overcoming obstacles in this regard.
- To champion sustainable local production capabilities that lead to improved access to safe, effective, and high-quality health products and technologies.
Indo-Pacific Maritime Domain Awareness (IPMDA) initiative (The Hindu)
- 07 Nov 2023
Why in the News?
The Indian Navy Chief Admiral recently stated that the Indo-Pacific Maritime Domain Awareness (IPMDA) effort demonstrates the commitment to a free, open, inclusive, and rules-based Indo-Pacific region.
About the Indo-Pacific Maritime Domain Awareness (IPMDA) initiative:
- Announcement: It was announced at the 2022 Quad Leaders’ Summit in Tokyo.
- The primary objective is to track "dark shipping" and develop a more comprehensive, timely, and precise understanding of maritime activities in the Indo-Pacific region.
- Geographic Coverage: IPMDA integrates three critical regions in the Indo-Pacific:
- the Pacific Islands, Southeast Asia, and the Indian Ocean region.
- Purpose: IPMDA is a technology and training initiative aimed at enhancing maritime domain awareness in the Indo-Pacific.
- It seeks to increase transparency in critical waterways in the region.
- Technology Utilized: Innovative technology, including the collection of commercial satellite radio frequency data, is employed.
- The goal is to provide partners across Southeast Asia, the Indian Ocean region, and the Pacific with near real-time information on activities occurring in their maritime zones.
Graded Response Action Plan (GRAP) (Indian Express)

- 07 Nov 2023
Why in the News?
As the Air Quality Index (AQI) in the National Capital Region reaches 'severe' levels, the Commission for Air Quality Management (CAQM) activated Stage 4 measures from the Graded Response Action Plan (GRAP) recently.
What is the Graded Response Action Plan (GRAP)?
- GRAP is a set of emergency measures that kick in to prevent further deterioration of air quality once it reaches a certain threshold in the Delhi-NCR region.
- Approved in 2016 after the Supreme Court’s order in M. C. Mehta vs. Union of India (2016) and notified in 2017.
- The Supreme Court-appointed Environment Pollution (Prevention & Control) Authority (EPCA) to implement GRAP measures till 2020.
- However, the EPCA was dissolved and replaced by the Commission for Air Quality Management (CAQM) in 2020.
- From 2021, the Commission for Air Quality Management (CAQM), a statutory body responsible for implementing GRAP.
- CAQM relies on air quality and meteorological forecasts by the India Meteorological Department (IMD) and the Indian Institute of Tropical Meteorology (IITM).
- GRAP is incremental in nature and thus, when the air quality dips from ‘poor’ to ‘very poor,’ measures listed under both sections have to be followed.
- Stage 1 of GRAP is activated when the AQI is in the ‘poor’ category (201 to 300),
- Stage 2 is when it’s in the ‘Very poor’ category (301-400),
- Stage 3 is when the AQI is the ‘Severe’ category (401-450) and finally
- Stage 4 is when it rises to the ‘Severe +’ category (more than 450).
Global Landscape of Climate Finance 2023 (DownToEarth)

- 07 Nov 2023
Why in the News?
According to a new report, global climate finance is on the rise, yet it is not increasing at a scale and pace sufficient to address the climate crisis effectively.
About Global Landscape of Climate Finance 2023:
- The Global Landscape of Climate Finance is an annual report published by the Climate Policy Initiative (CPI).
- It provides the most comprehensive overview of global climate-related primary investment, covering both public and private finance.
- The report tracks climate finance flows across a range of sectors, including renewable energy, energy efficiency, transport, climate adaptation, and mitigation.
- This report concludes by calling for governments and investors to increase their support for climate finance, particularly for adaptation finance.
- It also recommends that more data be collected on climate finance flows to better understand where the gaps are and how to address them.
- It is an important tool for tracking global progress on climate finance and identifying areas where further investment is needed.
- It is an essential resource for policymakers, investors, and other stakeholders who are working to finance the transition to a low-carbon and climate-resilient economy.
- Key findings from the 2023 edition of the Global Landscape of Climate Finance report:
- Global climate finance reached an estimated USD 1.3 trillion on an annual average in 2021/2022, up from USD 653 billion in 2019/2020.
- The majority of climate finance is still directed towards mitigation activities, such as renewable energy and energy efficiency.
- There was a significant increase in climate finance for adaptation activities in 2021/2022.
- The growth in global climate finance was concentrated in a handful of geographies, with China, the US, Europe, Brazil, Japan, and India receiving 90% of increased funds.
- Private finance accounted for 60% of global climate finance in 2021/2022, up from 52% in 2019/2020.
Guindy National Park (The Hindu)

- 06 Nov 2023
Why in the News?
Guindy National Park, packed with blackbucks and birds, is one of the few national parks located in an Indian metropolis.
About the Guindy National Park:
- Guindy National Park is a protected area, located in the heart of Chennai’s metropolitan area of Tamil Nadu.
- It's the 8th smallest national park in India, covering an area of 2.70 square kilometers (1.04 square miles).
- This national park is unique because it is situated within the city of Chennai and is an extension of the grounds around Raj Bhavan, which was formerly known as the 'Guindy Lodge' and serves as the official residence of the governor of Tamil Nadu.
- Guindy National Park plays a crucial role in both ex-situ and in-situ conservation efforts.
- It provides a habitat for various wildlife species, including 400 blackbucks, 2,000 spotted deer, 24 jackals, numerous snakes, geckos, tortoises, and over 130 bird species.
- Flora: Guindy National Park features a diverse range of vegetation, including dry evergreen scrub and thorn forests, grasslands, and water bodies.
- Fauna: The park is home to 14 mammal species, over 60 species of butterflies and spiders each, and a wide variety of invertebrates such as grasshoppers, ants, termites, crabs, snails, slugs, scorpions, mites, earthworms, and millipedes.
Cnemaspis Rashidi (The Hindu)

- 06 Nov 2023
Why in the News?
A new species of gecko has been found recently in Tamil Nadu's Western Ghats, near Rajapalayam.
About Cnemaspis Rashidi:
- Cnemaspis Rashidi, also known as Rashid's dwarf gecko, is a recently discovered species of gecko in the Western Ghats of India.
- It is the smallest species in the genus Cnemaspis, measuring approximately two inches long from its snout to the vent.
- It is characterized by its beautiful color patterns of yellow, white, and black on its back.
- Cnemaspis rashidi is endemic to the Western Ghats.
- It was discovered in 2023 by a team of scientists from the Indian Institute of Science Education and Research (IISER) Pune and the Madras Crocodile Bank Trust.
- The scientists found the gecko at an altitude of 1,245 meters at the Kottamalai estate near Rajapalayam in Tamil Nadu.
- This is the 94th species of gecko that has been identified to date, out of 93 that have been reported.
- It is also a reminder of the rich biodiversity of the Western Ghats, which is one of the world's most important biodiversity hotspots.
National Mineral Development Corporation (NMDC) (PIB)

- 06 Nov 2023
Why in the News?
Recently, Shri Nagendra Nath Sinha, Secretary, Ministry of Steel, unveiled a groundbreaking ceremony for the Mining operations at Mount Celia Gold Project located in Western Australia.
About National Mineral Development Corporation (NMDC):
- National Mineral Development Corporation (NMDC), a Navratna Public Sector Enterprise under the Ministry of Steel, Government of India.
- It is the single largest producer of iron ore in India.
- It owns and operates highly mechanized iron ore mines in Chhattisgarh and Karnataka.
- The registered office is situated in Hyderabad, Telangana.
- NMDC is considered to be one of the low-cost producers of iron ore in the world.
- It also operates the only mechanized diamond mine in India at Panna, Madhya Pradesh.
- The company is involved in the exploration of a variety of minerals, including iron ore, copper, rock phosphate, limestone, dolomite, gypsum, bentonite, magnesite, diamond, tin, tungsten, graphite, and beach sands.
- Most of the high-quality iron ore produced by NMDC is sold to the Indian domestic steel industry through long-term contracts.
Zanzibar (Indian Express)
- 06 Nov 2023
Why in the News?
An IIT-Madras campus was inaugurated in Zanzibar on Monday, becoming the first campus of an IIT to be opened abroad.
Context:
- The first IIT campus outside of India was inaugurated on Monday with the opening of the IIT-Madras campus in Zanzibar.
- The pioneering venture is part of the central government’s initiative to project India’s education system onto the global stage.
- The campus is located in Bweleo district, a short distance from Zanzibar Town.
- The Zanzibar campus will benefit from an array of academic collaborations, including study abroad programs, internships with companies, and opportunities at the IIT-Madras campus in Chennai.
- It is open to students of all nationalities.
Key facts about Zanzibar (Tanzania):
- Zanzibar is a Tanzanian archipelago in the Indian Ocean, 25–50 kilometers located off the coast of east-central Africa and a semi-autonomous province of Tanzania.
- It comprises the main island of Unguja (informally referred to as Zanzibar), and Pemba Island, along with numerous smaller islands.
- Zanzibar City, on Unguja, is the archipelago's capital and largest city.
- The official languages of Zanzibar are Swahili and English.
- Zanzibar has a rich history, dating back to the 1st century AD.
- It was once a major center for the trade of spices, slaves, and ivory.
- The archipelago has been ruled by various empires and dynasties over the centuries, including the Portuguese, Omanis, and British.
- In 1964, Zanzibar gained independence from Britain and merged with Tanganyika to form the United Republic of Tanzania.
- Stone Town, the historic center of Zanzibar City, is a UNESCO World Heritage Site.
- The raised sands and sandstones with varied residual deposits are found on Zanzibar and Pemba islands which are similar to the alluvial deposits present on the African mainland.
- It is known for its vast wilderness areas.
- They include the plains of Serengeti National Park, populated by the “big five” game (elephant, lion, leopard, buffalo, rhino), and Kilimanjaro National Park, home to Africa’s highest mountain.
GST Amnesty Scheme (TOI)

- 06 Nov 2023
Why in the News?
The finance ministry has come out with an amnesty scheme for filing appeals against Goods and Services Tax (GST) demand orders.
What is the GST Amnesty scheme?
- The GST Amnesty scheme was introduced by the Centre to help businesses comply with the Goods and Services Tax laws in the country.
- Every entity that needs to file its GST returns must conduct the process in a sequential manner.
- If the taxpayer misses the last date, they may have to pay penalties for not filing the returns.
- In such a situation, the GST Amnesty scheme helps taxpayers file their returns without hefty penalties.
- The plan also aids businesses whose registration stands canceled for non-filing of returns.
- Under the GST Amnesty scheme, taxpayers can file for the revocation of their cancellation as well.
How can one benefit from the GST Amnesty scheme?
- Taxpayers cannot file the GST return for a particular period without submitting the previous ones.
- A heavy penalty will also be levied on them for missing their filings.
- The GST Amnesty scheme allows taxpayers to file their pending returns without incurring a hefty fine.
- It will help them in complying with the indirect taxation laws of the country.
- It also aids business entities to appeal against the cancellation of their registration if they have not submitted the GST returns for three consecutive quarters.
- The scheme will be open till January 31, 2024.
Pavana River (TOI)
- 04 Nov 2023
Why in the News?
Recently residents of Thergaon area in Pune, are worrieda a lot owing to the thick layer of toxic foam on Pavana river near Kejudevi temple.
About the Pavana River:
- Location: The Pavana River is in the western part of Maharashtra, specifically in the Pune District.
- It crosses Pune City and acts as a natural boundary between Pune City and the Pimpri-Chinchwad area.
- Origin: The river begins in the Western Ghats, approximately 6 kilometers south of Lonavala.
- It's a tributary of the Bhima River and meets the Mula River within Pune city.
- Initially flowing east, it turns south and passes through the suburbs of Dehu, Chinchwad, Pimpri, and Dapodi before joining the Mula River.
- There is a dam is built on this river at Pavana Nagar, called the "Pavana Nagar Dam".
- The Pavana Nagar Dam is an earthfill gravity dam.
- It's 1,329 meters (4,360 feet) long and 42.37 meters (139.0 feet) high.
- The dam has a total storage capacity of 30,500.00 cubic kilometers.
- Its main purpose is to supply sufficient water to the nearby areas and is a crucial water source for the region.
Kaleshwaram Lift Irrigation Project (KLIP) (HT)
- 04 Nov 2023
Why in the News?
A controversy over alleged engineering lapses in the ?1 lakh crore Kaleshwaram lift irrigation project on the Godavari river triggered an electoral slugfest in poll-bound Telangana.
About Kaleshwaram Lift Irrigation Project (KLIP):
- Location: The Kaleshwaram Lift Irrigation Project (KLIP) is situated at Kaleshwaram village in Telangana, along the Godavari River.
- Confluence Point: It is located at the confluence of the Pranhita and Godavari Rivers.
- At this confluence, the Wardha, Painganga, and Wainganga rivers also meet, forming the seventh-largest drainage basin in the subcontinent.
- Originally called Pranahita-Chevella project in erstwhile Andhra Pradesh, it was redesigned, extended and renamed as Kaleshwaram project in Telangana in 2014.
- KLIP is known as the world's largest multi-stage and multi-purpose lift irrigation project.
- A significant feature of KLIP includes a series of underground and surface water pumping stations, claimed to be the world's largest of their kind.
- This lift irrigation system stretches over 300 kilometers and moves large volumes of water from rivers or reservoirs to be distributed through channels and additional reservoirs before reaching the next stations.
- Objective: The project's goal is to provide water to 45 lakh acres of land in Telangana for irrigation and drinking water.
- KLIP started in 2016 and will utilise approximately 283 thousand million cubic feet (TMC) of water from the Godavari River to serve 13 districts in Telangana.
Adaptation Gap Report 2023 (DownToEarth)

- 04 Nov 2023
Why in the News?
The Adaptation Gap Report states that funding for adaptation measures in developing nations has been declining and is insufficient of what is required.
About the Adaptation Gap Report:
- The Adaptation Gap Report (AGR) is an annual United Nation Enviroment Programme (UNEP) flagship publication.
- The report's primary objective is to inform the negotiators of the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC) Member States, and the broader UNFCCC constituency, about the status and trends within climate adaptation at global and regional levels.
- AGR offers science-based recommendations to policymakers and decision-makers to enhance climate adaptation efforts in key climate-sensitive sectors.
- Since 2014, UNEP has been producing these assessments to support effective adaptation responses aligned with the UNFCCC's temperature and adaptation goals.
- The "adaptation gap" refers to the difference between actual adaptation efforts and the goals set by society, influenced by factors like climate change impacts, available resources, and competing priorities.
Key Findings of the Report:
- Adaptation costs are expected to rise significantly by 2050, especially in high-warming scenarios.
- The financial needs for adaptation are 10-18 times higher than the current international public adaptation fund flows.
- Urgent action is required to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and enhance adaptation efforts to protect vulnerable populations worldwide.
- In 2021, funding from developed countries to support adaptation projects in developing countries decreased by 15% compared to previous years.
- The report suggests seven strategies to bridge the adaptation gap, including increasing international financial support and mobilizing domestic resources.
- It also calls for a reform of the global financial system to facilitate easier access to climate-related funding from multilateral agencies such as the World Bank or the IMF.
Lucy Mission (NASA) (Indian Express)

- 04 Nov 2023
Why in the News?
Recently NASA's Lucy mission has discovered that the asteroid Dinkinesh is actually a binary system of two asteroids.
About Lucy Mission:
- The Lucy Mission is a NASA space probe designed to explore the Trojan asteroids.
- These are the asteroids that share an orbit with Jupiter around the Sun.
- It's on a twelve-year journey to visit eight different asteroids and the entire mission costs around $981 million.
- It was launched on October 16, 2021, from Cape Canaveral Space Force Station or Kennedy Space Centre in Florida.
- The Lucy Mission is named for the fossilized skeleton of a human ancestor, which was named for the Beatles song "Lucy in the Sky with Diamonds."
- The mission's scientists hope that Lucy will help them to better understand our own origins, just as the Lucy fossil helped us to better understand our evolutionary history.
- The Lucy spacecraft is equipped with a suite of instruments that will be used to study the asteroids it encounters. These instruments include:
- A high-resolution visible camera
- A near-infrared spectrometer
- A thermal emission spectrometer
- A dust detector
- A radio occultation instrument
- Lucy's mission will provide new insights into the diversity of the Trojan asteroids, their formation, and their role in the early solar system.
- The mission will also test new technologies for deep space exploration, such as a solar-powered propulsion system and a terminal tracking system.
- It made its first gravity assist from Earth on October 16, 2022, and on November 1, 2023, it flew by its first asteroid, Dinkinesh, a binary asteroid in the main belt.
- Lucy will make another gravity assist from Earth in 2024, and in 2025, it will fly by the inner main-belt asteroid 52246 Donaldjohanson.
World Food India 2023 (HT)

- 04 Nov 2023
Why in the News?
Prime Minister Narendra Modi stated that India's food diversity benefits investors worldwide as he inaugurated the second edition of "World Food India 2023" at Bharat Mandapam in Delhi recently.
What is World Food India 2023?
- World Food India 2023 provides a gateway of access to the Indian food market, promoting collaborations between domestic and foreign investors.
- It is organized by India's Ministry of Food Processing Industries in New Delhi from November 3rd to 5th.
- Objective: It aims to exhibit India's rich food culture and attract global investments in the food processing sector.
- The event brings together manufacturers, producers, investors, policymakers, and organizations from around the world involved in the food industry.
- Key Areas of Focus: The event is focused on leveraging millets as a superfood, positioning India as a global hub for food processing, unlocking growth potential in strategic segments, establishing an efficient ecosystem, and promoting sustainable development.
- India's Vision: This event aligns with India's vision to become a global leader in the food processing industry, highlighting the country's production, consumption, and export potential across various food sectors.
- India is taking steps to create an inclusive and sustainable ecosystem, attract foreign investment, and improve the ease of doing business in the food processing sector.
- Notably, the first edition of World Food India took place in 2017.
- India is a global leader in the production of various agricultural products, such as milk, bananas, mangoes, papayas, guavas, ginger, okra, and buffalo meat.
- It also ranks second in the production of rice, wheat, potatoes, garlic, and cashew nuts.
- Moreover, the United Nations has declared 2023 as the International Year of Millets (IYM 2023) with the goal of increasing millet production and consumption worldwide.
ENCORE (NewsOnAIR)

- 03 Nov 2023
Why in the News?
Recently, the Election Commission of India (ECI) has developed in-house software named ‘ENCORE’ designed for efficient candidate and election management.
About ‘ENCORE’:
- The Election Commission of India has designed in-house software for complete Candidate and election management through ‘ENCORE’ which stands for Enabling Communications on Real-time Environment.
- This provides a seamless facility for Returning Officers to process candidate nomination, affidavit, Voter turnout, counting, results and data management.
- The ENCORE counting application is an end-to-end application for returning officers to digitize the votes polled, tabulate the round-wise data and then take out various statutory reports of counting.
- An additional application, the ENCORE Scrutiny Application, allows Returning Officers to scrutinize online nominations submitted by candidates.
- This process involves verifying and marking the status of nominations as Accepted, Rejected, or Withdrawn, facilitating the creation of the final list of contesting candidates and symbol assignment.
- The ECI offers an online portal for candidate nomination and affidavit submission.
- Candidates can create accounts, complete nomination forms, submit security deposits, and plan their visits to the Returning Officer through this portal.
- The Candidate Affidavit portal is designed to display information about a candidate's financial assets and liabilities, offering transparency in candidates' financial disclosures.
- The ENCORE Nodal App serves as a platform for various government departments, including fire, education, police, environment, and CPWD, to issue 'no objection' certificates.
- These certificates are required before granting permission for political parties or candidates to hold rallies, road shows, and meetings, ensuring that all necessary clearances are obtained before public events.
Gundla Brahmeswaram Wildlife Sanctuary (New Indian Express)

- 03 Nov 2023
Why in the News?
In a first-of-its-kind, over 50 grass species were identified during a two-day workshop and survey on ‘Grasses Identification and Grassland Management’ at the Gundla Brahmeswaram Wildlife Sanctuary in the Nagarjunasagar-Srisailam Tiger Reserve (NSTR).
About Gundla Brahmeswaram Wildlife Sanctuary:
- Location: It is located in the Kurnool & Prakasam of Andhra Pradesh with an area of 1194 sq km.
- Located between two important hill passes known as "Mantralamma kanuma" and "Nandi kanuma".
- The Northern part of this Sanctuary forms a major part of the Southern boundary for Nagarjunasagar-Srisailam Tiger Reserve.
- River: The Gundlakamma River stretches across the sanctuary.
- It also has many, mesic sites and ancient rock formations.
- Indicator Species: Tiger, Panther, Wild dog, Bats, Fig trees.
- It was declared a wildlife sanctuary on September 18, 1990.
- Forest Type: Dry mixed deciduous forest, moist dry deciduous, semi-evergreen, dry deciduous scrub forest and dry savannahs.
- Flora: The forest is an adobe to medicinal plants of which 10 are critically endangered, 21 are Endangered and 27 species are vulnerable.
- The plants like Madhuca longifolia, Dellenia pentagyna, Aristolochia indica, Terminalia arjuna, Pithecolobium ducle, Adina cordifolia, Vanda spp; etc; thrive here.
- Fauna: Wildlife like Tiger, Leopard, Flying squirre. angur, jungle cat, panther, tiger, mouse deer, hyena, bonnet monkey etc; are found here.
Hydroclimate Extremes (PIB)
- 03 Nov 2023
Why in the News?
A recent study conducted at Banaras Hindu University explored the impact of global warming on hydroclimate extremes in the Indian River Basins (IRBs).
About Hydroclimate Extremes:
- Hydroclimatic extremes are severe events with significant impacts on both human societies and ecosystems.
- These events encompass phenomena such as floods, droughts, heat waves, and heavy rainstorms.
Key Findings:
- The research utilized highly detailed simulated precipitation data derived from the Coupled Model Intercomparison Project-6 (CMIP6) experiments.
- The study's results suggest an anticipated rise in the frequency of extreme rainfall in the Western Ghats and Northeast River basins.
- Additionally, heavy rainfall intensity is predicted to increase in the Upper Ganga and Indus basins.
- The research sheds light on an agricultural drought in the lower Ganga basin, attributed to a reduction in average rainfall.
Importance:
- This study underscores the importance of policymakers creating strategies to address both excess and shortage of water resources.
- It anticipates a 4% to 10% rise in intense rainfall in the western regions of Indian river basins, along with noteworthy shifts in precipitation patterns in specific areas.
- These alterations in hydroclimate extremes could greatly impact agriculture, public health, and socio-economic conditions.
- Furthermore, the research identifies critical areas prone to urban flooding in densely populated cities, emphasizing the need for policymakers to devise tailored climate adaptation and mitigation plans.
- These should encompass policies related to water management and emergency services to mitigate the risks posed by extreme events in these basins.
UN Office for the Coordination of Humanitarian Affairs (OCHA) (TOI)

- 03 Nov 2023
Why in the News?
??The UN Office for the Coordination of Humanitarian Affairs (OHCA), on Friday, launched an emergency aid appeal seeking $1.2 billion to help some 2.7 million people in Gaza and the West Bank.
About the UN Office for the Coordination of Humanitarian Affairs (OCHA):
- OCHA is part of the United Nations (UN) and focuses on humanitarian issues.
- It coordinates and leads UN responses to humanitarian crises worldwide.
- It was established by the General Assembly of the United Nations in 1991.
- OCHA's goal is to save lives, protect people, and help those affected by disasters and conflicts.
- It works with governments, non-governmental organizations (NGOs), and other partners to respond to emergencies.
- It provides funding to support relief efforts in crisis-affected regions.
- There are two types of pooled funds:
- The Central Emergency Response Fund (CERF) can provide financial support for emergencies anywhere on the globe.
- Country-Based Pooled Funds (CBPFs) are specific to individual countries.
- These funds operate from two central hubs located in Geneva and New York, serving as global operational centres.
- The office works to ensure that humanitarian aid reaches those in need.
- It has two headquarters locations, Geneva and New York, which act as centres of global operations.
- It helps plan and manage humanitarian responses, ensuring efficiency and effectiveness.
- OCHA promotes coordination among humanitarian organizations to avoid duplication and ensure better outcomes.
Bletchley Declaration 2023 (Indian Express)

- 03 Nov 2023
Why in the News?
The United Kingdom hosted a major Artificial Intelligence (AI) meeting, bringing together political leaders and technological professionals to explore the potential benefits and risks of this fast-evolving technology.
About the Bletchley Declaration:
- The Bletchley Declaration provides a comprehensive overview of the worldwide perspective on the potential benefits and risks associated with artificial intelligence (AI).
- It underlines the necessity of aligning AI systems with human intentions and encourages a deeper exploration of AI's full capabilities.
- Furthermore, the document acknowledges the potential for significant harm caused by AI, whether intentional or unintentional, including the possibility of catastrophic consequences.
- The Bletchley Declaration places great emphasis on safeguarding human rights, promoting transparency, ensuring explainability, upholding fairness, ensuring accountability, establishing regulation, prioritizing safety, incorporating human oversight, adhering to ethical standards, addressing bias issues, safeguarding privacy, and protecting data.
- This document is a reflection of the intricate negotiations between nations with differing interests and legal systems, encompassing countries such as the United States, the United Kingdom, the European Union, and China.
- The Bletchley Declaration highlights the crucial role of civil society in addressing AI safety concerns, despite some criticism from civil society groups that felt excluded from the summit.
- It also places a significant responsibility on companies engaged in the development of cutting-edge AI systems, emphasizing the need to ensure their safety through rigorous testing, evaluation, and the implementation of appropriate measures.
Global Stocktake should account for failures of developed nations: BASIC nations at COP28 (The Hindu)

- 04 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
The BASIC grouping, comprising Brazil, South Africa, India and China, has pushed during annual climate talks here that the Global Stocktake should also account for the failures of the developed nations.
About Global Stocktake:
- The global stocktake serves as a mechanism for nations and stakeholders to collectively assess their progress in achieving the objectives outlined in the Paris Climate Change Agreement, highlighting areas of success and areas needing improvement.
- In essence, it is akin to taking inventory on a global scale.
- Essentially, the global stocktake involves a comprehensive examination of everything related to the world's status regarding climate action and support.
- It entails identifying gaps and collaboratively strategizing to steer a more effective course towards accelerating climate action.
- This evaluation occurs every five years, with the inaugural stocktake scheduled to conclude at COP28.
- Background: In 2015, during COP21 in Paris, it became obligatory for all countries to establish emissions reduction targets and adapt to climate change impacts, known as Nationally Determined Contributions (NDCs).
- The agreement mandated that countries evaluate their progress, starting in 2023 and subsequently every five years.
- Initial Assessment: The UN released a technical report on the first Global Stocktake in September 2023.
- According to this report, while the global community demonstrated some progress, it fell short of the necessary scale.
- The report emphasizes the need to expedite implementation, adopting an all-of-society approach to enhance ambition across all aspects, aligning with the goals of the Paris Agreement and addressing the climate crisis.
- The report acknowledges existing progress but underscores the urgency for more concerted efforts.
- Recognizing well-known gaps, the technical findings also spotlight opportunities and creative solutions, addressing both current challenges and those emerging.
- Additionally, the report notes that the average global temperature has risen by nearly 1.2 degrees Celsius since pre-industrial times.
INCOIS wave rider buoy washes ashore in Gopalpur (New Indian Express)

- 04 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
A wave rider buoy, equipped belonging to the Indian National Centre for Ocean Information Services (INCOIS), with GPS and various weather-related instruments, was found ashore at the Gopalpur Military Station in Ganjam district on Saturday.
About Indian National Centre for Ocean Information Services (INCOIS):
- INCOIS is an autonomous organization under the Ministry of Earth Sciences (MoES).
- It is a unit of the Earth System Science Organization (ESSO), New Delhi.
- It is located in Hyderabad & was established in 1999.
- The ESSO operates as an executive arm of the Ministry of Earth Sciences (MoES) for its policies and programmes.
- It is mandated to provide the best possible ocean information and advisory services to society, industry, government agencies and the scientific community through sustained ocean observations and constant improvement through systematic and focused research.
What is the Earth System Science Organisation (ESSO)?
- Earth System Science Organisation (ESSO) is a virtual organisation set up by the Ministry of Earth Sciences GOI in 2007 and it is the executive arm of MoES.
- It has three major branches of earth sciences viz.,
- Ocean Science & Technology
- Atmospheric Science & Technology
- Geosciences and Technology.
- The overall vision of the ESSO is to excel in knowledge and technology enterprise for the earth system science realm towards the socio-economic benefit of the Indian sub-continent and in the Indian Ocean region.
- The ESSO contributes to the areas of Weather (General) and Weather advisories specific to agriculture, aviation, shipping, sports, etc. Monsoon, Disasters (cyclones, earthquakes, tsunamis, sea level rise), Living and non-living resources (fishery advisory, poly-metallic nodules, gas hydrates, freshwater etc), Coastal and Marine Ecosystems and Climate Change, Underwater Technology.
Scientists Create Tiny Robots Called 'Anthrobots' From Human Cells (India Times)
- 04 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
Scientists have created 'Anthrobots' , tiny living robots from human cells and the robots are able to move around in a lab dish and one day may be helpful in healing wounds or damaged tissue.
What is an Anthrobots?
- Anthrobots are self-assembling biological robots made from human tracheal cells, capable of movement and encouraging neuron growth.
- They can be created from adult human cells without genetic modifications, making them a potential patient-specific therapeutic tool.
- Anthrobots represent a significant advancement in regenerative medicine, potentially aiding in treating a variety of diseases and injuries.
- The multicellular robots, ranging in size from the width of a human hair to the point of a sharpened pencil, were made to self-assemble and shown to have a remarkable healing effect on other cells.
- The discovery is a starting point for the researchers’ vision to use patient-derived biobots as new therapeutic tools for regeneration, healing, and treatment of disease.
What are Tracheal cells?
- Tracheal cells come from the lining of the bronchi and trachea, forming the network of tubes that transport air to the lungs.
- These cells, a type of epithelial cell, are crucial for producing lubricating mucus to maintain the functionality of the airways.
- They are responsible for generating not only mucus but also various other compounds, all of which play a vital role in the process of respiration.
Is White Lung Syndrome caused by a new pathogen? Here is what you need to know (Indian Express)
- 04 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
An outbreak of a respiratory illness in northern China and Ohio in the US — the White Lung Syndrome as people are calling it — has sparked speculation online of a new pandemic threat after COVID-19.
About White Lung Syndrome:
- “White lung syndrome” is a term used to describe a severe form of pneumonia characterized by the appearance of white patches on chest X-rays.
- While the term suggests a specific disease, it is actually used to describe a variety of conditions that cause similar symptoms.
- Symptoms: The specific symptoms of white lung syndrome can vary depending on the underlying cause, but some of the most common symptoms include:
- Cough, feThere is no specific way to prevent white lung syndrome.
- ver, shortness of breath, chest pain, fatigue, loss of appetite and wheezing
- In severe cases, white lung syndrome can lead to respiratory failure, which is a life-threatening condition.
- Causes: There are many different causes of white lung syndrome, including:
- Viral infections: These are the most common cause of white lung syndrome, including viruses like influenza, respiratory syncytial virus (RSV), and COVID-19.
- Bacterial infections: These are less common than viral infections, but can still cause white lung syndrome.
- Fungal infections: These are rare, but can occur in people with weakened immune systems.
- Inhalation of harmful substances: This can include inhaling dust, fumes, or chemicals.
- Autoimmune diseases: These are diseases in which the body’s immune system attacks healthy tissues.
- Prevention: There is no specific way to prevent white lung syndrome.
- However, there are vaccines available for some of the viruses that can cause white lung syndrome, such as influenza and COVID-19.
- Treatment: The treatment for white lung syndrome depends on the underlying cause.
- In some cases, antibiotics or antiviral medications may be prescribed.
- In more severe cases, oxygen therapy or mechanical ventilation may be necessary.
11 bodies recovered after the volcanic eruption in Indonesia, and 12 climbers are still missing (Indian Express)

- 04 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
The bodies of 11 climbers were recovered on Monday a day after a furious eruption of the Mount Marapi volcano as Indonesian rescuers searched for 12 apparently still missing.
About Mount Marapi:
Don't confuse it with Mount Merapi, which is located on Java Island.
- ‘Mount Marapi’ located is a volcanic mountain located in West Sumatra of Indonesia.
- It also known as Marapi or Gunuang Marapi in Minangkabau.
- According to legend, the mountain is the site first settled by the Minangkabau people after their ship landed on the mountain when it was the size of an egg and surrounded by water.
- There are large numbers of upright burial stones in the region which are oriented in the direction of the mountain, indicating its cultural significance.
- A significant eruption occurred in 1979, and in April-May 2018, ashfalls to the southeast were recorded.
About Mount Merapi:
- Mount Merapi is a volcanic mountain on the island of Java in Indonesia and is the most active volcano in Indonesia (out of a total of 30 active volcanoes).
- Although Mount Merapi was discovered by humans in 1754, geologists have estimated that the volcanic mountain is over 400,000 years old.
- The last major eruption of Mount Merapi back in 2010. This eruption took the lives of 347 people, and a further 20,000 locals were forced to evacuate the area.
- The local name for Mount Merapi is Gunung Merapi which can be translated to Fire Mountain or Mountain of Fire.
- Mount Merapi is considered sacred by local people. They believe that a supernatural kingdom exists there.
- Mount Merapi has erupted countless times, which haven't been recorded in modern history.
- However, we do know that Merapi has erupted over 68 since 1548.
- Merapi has now been active for approximately 10,000 years.
PM Formalisation of Micro food processing Enterprises (PMFME) Scheme" launched under the Atmanirbhar Bharat Abhiyan with an outlay of Rs. 10,000 Crore supports 2 lakh micro food processing enterprises following One District One Product (ODOP) approac

- 08 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
As part of Atmanirbhar Bharat Abhiyan, the Ministry of Food Processing Industries (MoFPI) is implementing a centrally sponsored "PM Formalisation of Micro food processing Enterprises (PMFME) Scheme" for providing financial, technical and business support for setting up / upgradation of micro food processing enterprises in the country.
About PM Formalisation of Micro food Processing Enterprises (PMFME) Scheme:
- Launched on 29th June 2020, PMFMPE is a Centrally Sponsored Scheme by the Ministry of Food Processing Industries.
- It is designed to address the challenges faced by the micro-enterprises and to tap the potential of groups and cooperatives in supporting the upgradation and formalization of these enterprises.
- Aims:
- Enhance the competitiveness of existing individual micro-enterprises in the unorganized segment of the food processing industry and promote formalization of the sector; and
- Support Farmer Producer Organizations (FPOs), Self Help Groups (SHGs), and Producers Cooperatives along their entire value chain.
- Objectives: To build the capability of microenterprises to enable:
- Increased access to credit by existing micro food processing entrepreneurs, FPOs, Self Help Groups, and Co-operatives.
- Integration with an organized supply chain by strengthening branding & marketing.
- Support for the transition of existing 2,00,000 enterprises into a formal framework.
- Increased access to common services like common processing facilities, laboratories, storage, packaging, marketing, and incubation services.
- Strengthening of institutions, research, and training in the food processing sector; and
- Increased access for the enterprises, to professional and technical support.
- Outlay:
- The scheme envisages an outlay of ? 10,000 crores over a period of five years from 2020-21 to 2024-25.
- The expenditure under the scheme would be shared in a 60:40 ratio between Central and State Governments, in a 90:10 ratio with the North
- In Eastern and the Himalayan States, a 60:40 ratio with UTs with the legislature and 100% by the Center for other UTs.
- Coverage:
- Under the scheme, 2,00,000 micro food processing units will be directly assisted with credit-linked subsidies.
- Adequate supportive common infrastructure and institutional architecture will be supported to accelerate the growth of the sector.
The Supreme Court directed the governments to provide details on “the estimated inflow of illegal migrants into India.. after March 25, 1971”. (Indian Express)
- 08 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
The Supreme Court on Thursday asked the Centre and Assam government to provide details on the “estimated inflow of illegal migrants” to Assam and other Northeastern states after March 25, 1971, and the status of border fencing.
News Summary:
- During the hearing of petitions, a five-judge bench of the Supreme Court expressed concerns about the perceived 'unlimited influx' of illegal migrants from Bangladesh, impacting demographics and straining resources for Indian citizens.
- The court questioned the application of Section 6A, granting Indian citizenship benefits to illegal migrants, solely in Assam and not in West Bengal, which shares a larger border with Bangladesh.
- The Supreme Court directed the Home Secretary to submit an affidavit by May 11, 2023, detailing the estimated inflow of illegal migrants, steps taken to address illegal immigration, and specifics on border-fencing extent and timelines.
- The government was also instructed to provide information on illegal immigration along the West Bengal border post on March 25, 1971.
Why Section 6A of the Citizenship Act, 1955 is Under Challenge?
- Presently, a Supreme Court bench is reviewing petitions from indigenous Assamese groups challenging Section 6A of the Citizenship Act.
- These groups assert that the special provision serves as a 'beacon' for illegal entrants to settle in Assam, gain Indian citizenship, and subsequently deprive locals of political, and economic rights, jeopardizing Assamese cultural identity.
- The petitioners question the constitutional validity of Section 6A, claiming it is arbitrary, specifically singles out Assam, violates Article 14, and has led to an influx of illegal migrants from Bangladesh.
- They advocate for establishing 1951 as the cutoff date for inclusion in the National Register of Citizens instead of 1971.
- The primary petitioner, Assam Sanmilita Mahasangha (ASM), argues that Section 6A is discriminatory, arbitrary, illegal, and infringes upon the rights of indigenous Assamese people by establishing a different citizenship cutoff date for Assam compared to the rest of India (July 1948).
What are the Arguments of the Central Government?
- The central government refutes the accusation of unfairly burdening the state with the responsibility of handling illegal migrants, contending that different states of India can be classified differently based on historical and geographical factors.
- According to the government, the classification implied in Section 6-A is founded on intelligible differentia.
- Dismissing claims of arbitrariness, the Centre asserts that the guarantee against non-arbitrariness under Article 14 does not mandate universal application for every law, irrespective of dissimilarity or the nature of the individuals it pertains to.
Global River Cities Alliance with 267 river cities including India, USA and Denmark to be launched on December 10, 2023 (PIB)

- 08 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
The National Mission for Clean Ganga (NMCG) on behalf of River Cities Alliance (RCA), has signed a Memorandum of Common Purpose (MoCP) with the Mississippi River Cities and Towns Initiative (MRCTI), representing 124 cities/towns situated along the banks of the Mississippi River, USA.
What is River Cities Alliance (RCA)?
- The River Cities Alliance (RCA) is a joint initiative of the Department of Water Resources, River Development & Ganga Rejuvenation under the Ministry of Jal Shakti (MoJS) & the Ministry of Housing and Urban Affairs (MoHUA), with a vision to connect river cities and focus on sustainable river centric development.
- Beginning with 30 member cities in November 2021, the Alliance has expanded to 109 river cities across India and one international member city from Denmark.
- 30 cities include Dehradun, Rishikesh, Haridwar, Srinagar, Varanasi, Kanpur, Prayagraj, Farrukhabad, Mirzapur, Mathura, Bijnor, Ayodhya, Patna, Bhagalpur, Begusarai, Munger, Sahibganj, Rajmahal, Howrah, Jangipur, Hugli-Chinsurah, Berhampore, Maheshtala, Aurangabad, Chennai, Bhubaneshwar, Hyderabad, Pune, Udaipur and Vijayawada.
- The Alliance is open to all river cities of India. Any river city can join the Alliance at any time.
- Objective: To provide the member cities with a platform to discuss and exchange information on aspects that are vital for sustainable management of urban rivers, sharing best practices and supporting innovation.
- It focuses on three broad themes- Networking, Capacity Building and Technical Support.
- The Secretariat of the Alliance is set up at the National Institute for Urban Affairs (NIUA) Delhi.
About the National Mission for Clean Ganga (NMCG):
- The Ministry of Jal Shakti, Government of India, established the National Mission for Clean Ganga (NMCG) as a registered society to take proactive measures for preventing, controlling, and abating environmental pollution in the Ganga River.
- Its mission includes ensuring a continuous and adequate flow of water to rejuvenate the river.
- Initially serving as the implementation arm of the dissolved National Ganga River Basin Authority (NGRBA), NMCG aims to achieve effective pollution abatement and river rejuvenation through a river basin approach, promoting inter-sectoral coordination and environmentally sustainable development.
- Post the dissolution of NGRBA in 2016, NMCG continues its objectives through the National Council for Rejuvenation, Protection, and Management of River Ganga, also known as the National Ganga Council.
- The mission focuses on maintaining minimum ecological flows in the Ganga to ensure water quality and sustainable development.
- Structure: NMCG follows a two-tier management structure comprising the Governing Council and the Executive Committee, both led by the Director General.
- The Executive Committee holds the authority to approve projects up to Rs. 1000 crores.
- At the state level, State Programme Management Groups (SPMGs) serve as the implementing arms of State Ganga Committees.
- The Director General of NMCG holds the position of Additional Secretary in the Government of India.
Mining for critical minerals: what is the auction process, and why is it important? (Indian Express)

- 08 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
A total of twenty critical mineral blocks are currently open for commercial bidding by private entities. The auction process commenced on November 29, and interested parties have the opportunity to submit bids until January 22 of the following year.
What are Critical Minerals?
- A mineral attains critical status when there is a relatively higher risk of supply shortage and its impact on the economy compared to other raw materials.
- These minerals play a pivotal role in economic development and national security, and their scarcity, concentration in specific geographic locations, or limited extraction/processing options may pose potential vulnerabilities in the supply chain.
- Critical minerals, including lithium, graphite, cobalt, titanium, and rare earth elements, are indispensable for advancements in various sectors such as high-tech electronics, telecommunications, transport, and defense.
- They are integral to strategic value chains, including initiatives for clean technologies (e.g., zero-emission vehicles, wind turbines, solar panels), information and communication technologies (e.g., semiconductors), and advanced manufacturing inputs and materials (e.g., defense applications, permanent magnets, ceramics).
What are the Estimated Reserves of Key Critical Minerals in these Blocks?
- J&K Block: In the J&K block, there is an inferred reserve of 5.9 million tonnes of bauxite, containing over 3,400 tonnes of lithium metal content.
- Additionally, this block boasts more than 70,000 tonnes of titanium metal content.
- Odisha Block: In the Odisha block, the National Institute of Transforming India (NITI) estimates an inferred value of 2.05 million tonnes of nickel ore, equivalent to 3,908 tonnes of nickel metal content.
- Chhattisgarh Block: While the Chhattisgarh block contains lithium and rare earth elements (REEs), no drilling has been conducted to assess total reserves as of yet.
- Other Blocks: Nickel ore reserves have been identified in three blocks, situated in Bihar, Gujarat, and Odisha.
- However, drilling has not been carried out for the Bihar and Gujarat blocks.
How does India presently source these minerals?
- In the fiscal year 2022-23, India imported 2,145 tonnes of lithium carbonate and lithium oxide.
- Lithium carbonate, containing up to 19% lithium, and lithium oxide, typically converted to lithium hydroxide and containing 29% lithium, were part of the imports.
- Additionally, India imported 32,000 tonnes of unwrought nickel and 1.2 million tonnes of copper ore during the same period.
- Notably, India is entirely dependent on imports for its lithium and nickel demand, while for copper, this reliance stands at 93%.
Recent Initiatives by the Indian Government to Boost the Critical Minerals Sector:
- Identification of 30 Critical Minerals: In July 2023, the Indian government released a list of 30 critical minerals, including Antimony, Beryllium, Bismuth, Cobalt, Copper, Gallium, Germanium, Graphite, Hafnium, Indium, Lithium, Molybdenum, Niobium, Nickel, PGE, Phosphorous, Potash, REE, Rhenium, Silicon, Strontium, Tantalum, Tellurium, Tin, Titanium, Tungsten, Vanadium, Zirconium, Selenium, and Cadmium.
- Mining Permissions: The government amended a key law, allowing for the mining of three critical minerals – lithium, niobium, and REEs.
- New royalty rates for critical minerals, aligning with global benchmarks, were specified to attract bidders.
- Geological Survey of India's Exploration: The Geological Survey of India initiated 125 projects in the current fiscal to explore critical mineral reserves.
- Notably, it estimated 5.9 million tonnes of lithium ore in the Salal-Haimna areas (Reasi district, J&K).
- In the preceding eight fiscal years, a total of 625 mineral exploration projects were undertaken.
- Centre of Excellence for Critical Minerals: The Committee on Identification of Critical Minerals recommended establishing a Centre of Excellence for Critical Minerals to formulate policies and incentives for creating a comprehensive value chain of critical minerals in the country.
- Khanij Bidesh India Ltd. (KABIL): A joint venture company, Khanij Bidesh India Ltd. (KABIL), is mandated to identify and acquire overseas mineral assets of a critical and strategic nature, such as lithium and cobalt, to ensure a secure supply.
- Mineral Security Partnership (MSP): India joined the US-led Mineral Security Partnership (MSP), a collaboration of 14 countries aiming to catalyze public and private investment in critical mineral supply chains globally.
How Google DeepMind’s AI breakthrough could revolutionise chip, and battery development (Indian Express)

- 08 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
Earlier this year, a South Korean laboratory unveiled a significant advancement that holds promise as a potential solution to the energy crisis.
What is Google DeepMind's Project?
- Google has introduced the Graph Networks for Materials Exploration (GNoME), an AI tool developed by DeepMind.
- Leveraging Artificial Intelligence, GNoME successfully predicted the structures of over 2 million new materials.
- The potential applications span diverse sectors, including renewable energy, battery research, semiconductor design, and enhanced computing efficiency.
How does GNoME operate?
- GNoME functions as an advanced graph neural network model (GNN), where input data takes the form of a graph resembling connections between atoms.
- The model employs 'active learning,' initially training on a small specialized dataset and later incorporating new targets for machine learning with human assistance.
- This adaptability suits the algorithm well for material discovery, as it involves identifying patterns not present in the original dataset.
Operational Mechanism of GNoME:
- GNoME employs two pipelines for discovering stable materials with low energy.
- The structural pipeline generates candidates with structures akin to known crystals, while the compositional pipeline follows a more randomized approach based on chemical formulas.
- Outputs from both pipelines undergo evaluation using established Density Functional Theory calculations, contributing to the GNoME database and guiding subsequent rounds of active learning.
- Consequently, the model has significantly improved its precision rate for predicting material stability, reaching around 80%, up from an initial 50%.
- DeepMind's research, encompassing 380,000 stable predictions, is equivalent to nearly 800 years of knowledge, facilitating further breakthroughs in materials discovery for researchers.
What is the Significance of GNoME?
- This breakthrough in artificial intelligence dramatically expands the inventory of 'stable materials,' multiplying it by tenfold in a single stride.
- These materials encompass inorganic crystals crucial for a spectrum of modern technologies, from computer chips to batteries.
- Stability is paramount for these crystals, as any instability could lead to decomposition.
- While the synthesized and tested processes still lie ahead, DeepMind has shared a curated list of 381,000 crystal structures from the predicted 2.2 million, offering a promising foundation for advancing new technologies.
- In comparison, human experimentation over the last decades has revealed the structures of around 28,000 stable materials, catalogued in the Inorganic Crystal Structures Database, representing a noteworthy advancement in material discovery.
Food versus Fuel: What’s happening with Centre’s ethanol blending scheme (Indian Express)

- 13 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
After banning sugar exports, the Centre has taken the next step towards augmenting domestic availability – restricting the diversion of the sweetener for ethanol production.
What is the Ethanol Blended Petrol (EBP) Programme?
- The Ethanol Blended Petrol (EBP) programme was launched in January 2003.
- The programme sought to promote the use of alternative and environment-friendly fuels and to reduce import dependency for energy requirements.
- Effective from April 1, 2019, across the nation (excluding UTs of Andaman Nicobar and Lakshadweep islands), Oil Marketing Companies (OMCs) sell petrol blended with up to 10% ethanol.
- The average ethanol blending in petrol has surged from 1.6% in 2013-14 to 11.8% in 2022-23.
- India targets a 20% ethanol blending ratio by 2025, revised from the initial 2030 deadline per the NITI Aayog's roadmap.
- Benefits of the EBP Programme:
- Reducing India’s import bill.
- Mitigating environmental pollution.
- Augmenting farm income.
- Offering a biofuel option with minimal additional investment for manufacturers.
- Challenges for 20% Ethanol Blending:
- Engine modifications are required to process petrol blended with 20% ethanol.
- Ethanol combustion yields no CO2, yet it doesn't address nitrous oxide emissions.
- Concerns about inefficient land use in ethanol production and the substantial water demand for cultivating crops.
- Food security considerations due to uncertainties about future agricultural output.
Why is the Restriction on Sweetener Diversion for Ethanol Production Imposed?
- Sugar Supply Concerns: Closing the 2022-23 sugar year with stocks slightly exceeding 57 lakh tonnes (lt), the lowest since 2016-17 (39.4 lt), raises apprehensions.
- The stock level falls significantly below the peak of 143.3 lt in 2018-19.
- Uncertainties surround the sugar production for the ongoing 2023-24 year, with Maharashtra and Karnataka anticipating substantial declines due to insufficient rainfall and low reservoir water levels in key cane-growing regions.
- Key Implication of the Decision: The recent decision, coupled with the ban on sugar shipments since May 2023, underscores a clear priority.
- Governments emphasize domestic supply over exports, favouring consumers over producers and prioritizing food over fuel.
Strategies to Boost Ethanol Production without Compromising Food Security:
- Diversification of Feedstocks: The government's ethanol policy, marked by favourable pricing and the incorporation of alternative feedstocks such as 2G ethanol sources, has been instrumental.
- The historical dependence on sugarcane-based feedstocks, which constituted 100% of ethanol sources (reduced to 76% in 2022-23), is no longer the sole reliance of the Ethanol Blended Petrol (EBP) program.
About Ethanol:
- Ethanol, an anhydrous ethyl alcohol having the chemical formula of C2H5OH, can be produced from sugarcane, maize, wheat, etc which have high starch content.
- In India, ethanol is mainly produced from sugarcane molasses by fermentation process.
- Ethanol can be mixed with gasoline to form different blends.
- As the ethanol molecule contains oxygen, it allows the engine to more completely combust the fuel, resulting in fewer emissions and thereby reducing the occurrence of environmental pollution.
- Since ethanol is produced from plants that harness the power of the sun, ethanol is also considered a renewable fuel.
This explosion in space, will now form a new solar system! James Webb Telescope captures Cassiopeia A in its latest discovery (Business Today)

- 13 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
The James Webb Space Telescope by NASA has recently documented a striking image of a star that underwent a supernova explosion within the Cassiopeia A (Cas A) supernova remnant.
What is Cassiopeia A?
- Cassiopeia A is the aftermath of a colossal star's explosion approximately 340 years ago, standing as the most recently formed remnant of its kind in our galaxy.
- Renowned for its status as a prototypical type of supernova remnant, it has been the subject of extensive exploration by various ground- and space-based observatories.
- Encompassing around 10 light-years, this remnant resides 11,000 light-years away in the Cassiopeia constellation, offering valuable insights into the intricate dynamics of supernovae.
What is Supernova?
A supernova is a powerful and catastrophic stellar explosion that occurs during the final stages of a massive star's life cycle. This extraordinary event releases an immense amount of energy, temporarily outshining entire galaxies and producing luminosities that can briefly outshine an entire galaxy.
What happens during a supernova explosion?
- Massive stars: Supernovas typically occur in massive stars, at least 8 times the mass of our sun.
- These stars burn brightly and fiercely, fusing hydrogen into helium in their cores.
- Nuclear fusion: As the star ages, it runs out of hydrogen fuel in its core.
- The core starts to collapse inwards due to gravity, while the outer layers expand and cool.
- This increased pressure and temperature trigger the nuclear fusion of heavier elements, like carbon and oxygen, releasing immense energy.
- Bounce and shockwave: The core's collapse eventually leads to a sudden rebound, called the core bounce.
- This bounce creates a shockwave that rips through the star's outer layers, ejecting them outwards in a violent explosion.
Types of supernovae: There are two main types of supernovae:
- Core-collapse supernovae: The explosion blows away the star's outer layers, leaving behind a neutron star or, if the mass is even greater, a black hole.
- Type Ia supernovae: These occur in binary systems where a white dwarf, the remnant of a low-mass star, siphons material from its companion star.
- This builds up mass on the white dwarf until it reaches a critical point and undergoes thermonuclear runaway, leading to a massive explosion.
Significance of supernovae: Supernovae play a crucial role in the universe's evolution.
- Enrich the interstellar medium with heavy elements: The ejected material from supernovae is rich in elements heavier than hydrogen and helium, which are essential for the formation of new stars and planets.
- Trigger star formation: The shockwaves from supernovae can compress surrounding gas clouds, triggering the formation of new stars.
- Create black holes and neutron stars: The most massive stars leave behind black holes or neutron stars, incredibly dense objects with fascinating properties.
Calling for caution, PM flags need for ethics, democratic values in AI (Indian Express)

- 13 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
India is negotiating with GPAI member countries for a consensus on a declaration document on the proper use of AI, the guardrails for the technology, and how it can be democratised.
Context:
- India is currently hosting the 4th Global Partnership on Artificial Intelligence (GPAI) Summit at Bharat Mandapam in New Delhi, scheduled from December 12-14, 2023.
- The first three GPAI summits were held in Montreal, Paris and Tokyo, respectively.
- Prime Minister Modi emphasized the dual nature of AI, portraying it as a significant development tool for the 21st century but also highlighting potential risks.
- He called for a global framework to ensure responsible AI use and urged caution in deployment.
- Addressing concerns like deepfakes, cybersecurity, and cyber-terrorism, he proposed an audit mechanism categorizing AI tools based on their capabilities.
- PM Modi is negotiating with GPAI member countries for a consensus on a declaration document outlining proper AI use, technology guardrails, and democratization.
- Recognizing AI's role in economic growth, he announced India's upcoming AI mission, focusing on AI computing power for startups and innovators, with applications in agriculture, health, and education.
- The mission aims to extend AI skills to Tier 2 and Tier 3 cities.
- PM Modi stressed ethical AI use as a guiding principle and suggested the inclusion of development and deployment protocols for high-risk AI systems in the global framework.
- He underscored AI's potential for connecting people and envisioned its ethical use in promoting economic growth, equality, and social justice.
About the Global Partnership on Artificial Intelligence (GPAI) Summit:
- The Global Partnership on Artificial Intelligence (GPAI) Summit is a three-day event starting December 12, which will see representatives from 28 member countries and the European Union.
- India is the Lead Chair for the alliance in 2024.
- The founding members of the GPAI: are Australia, Canada, France, Germany, India, Italy, Japan, Mexico, New Zealand, the Republic of Korea, Singapore, Slovenia, the UK, the US, and the EU.
- Prime Minister Narendra Modi inaugurated the summit on December 12.
- The objective of this summit is to bridge the gap between theory and practice on AI by supporting cutting-edge research and applied activities on AI-related priorities.
- It will feature a number of seminars covering a wide range of subjects, including AI and global health, education and skill development, AI and data governance, and machine learning workshops.
- More than 150 speakers from various nations will be present at the summit, including more than fifty GPAI experts.
- Moreover, leading global AI innovators such as Intel, Google, Meta, Microsoft, etc will be taking part in these events.
- Additionally, start-ups and students who win under the YUVA AI programme will present their AI models and solutions.
Missiles from rebel territory in Yemen miss a ship near key Bab el-Mandeb Strait, US official says (TOI)

- 13 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
Two missiles fired by Yemen's Houthi rebels missed a commercial tanker near the Bab el-Mandeb Strait.
Context:
- Two missiles fired from territory held by Yemen's Houthi rebels missed a commercial tanker near the key Bab el-Mandeb Strait on Wednesday.
- An American warship also shot down a suspected Houthi drone flying in its direction during the incident.
- The ship was carrying Indian-manufactured jet fuel and was heading for either Rotterdam in the Netherlands.
- It was coming from Mangalore in southern India and had an armed security crew on board.
- The Houthis have carried out a series of attacks on vessels in the Red Sea and launched drones and missiles targeting Israel.
About Bab el-Mandeb Strait:
- The Bab-el-Mandeb is a strait between Yemen on the Arabian Peninsula, and Djibouti and Eritrea in the Horn of Africa.
- It connects the Red Sea to the Gulf of Aden.
- The Bab el-Mandeb Strait is a chokepoint between the Horn of Africa and the Middle East and is a strategic link between the Mediterranean Sea and the Indian Ocean.
- It is one of the world's most important routes for global seaborne commodity shipments, particularly crude oil and fuel.
- The Perim Island divides the strait into two channels, of which the eastern is known as the Bab Iskender (Alexander's Strait), while the western is known as Dact-el-Mayun.
What is the Horn of Africa?
- The Horn of Africa, the world's fourth-largest peninsula, is located in Northeast Africa, extending eastwards from the African mainland and bordered by the Red Sea, Guardafui Channel, Gulf of Aden, and Indian Ocean.
- Positioned equidistantly from the equator and the Tropic of Cancer, it encompasses diverse landscapes, including the Ethiopian Plateau, Ogaden desert, and Eritrean and Somalian coasts.
- The Horn of Africa includes the countries of Djibouti, Eritrea, Ethiopia, and Somalia.
- This region has experienced historical complexities, including imperialism, neo-colonialism, the Cold War, ethnic tensions, intra-African conflicts, poverty, disease, and famine.
India’s first Pompe disease patient passes away: What is this rare genetic disorder? (Indian Express)

- 13 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
Nidhi Shirol, India’s first Pompe disease patient, passed away last month at the age of 24 years after battling the disease. She spent the last six years in a semi-comatose state.
What is Pompe Disease?
- Pompe disease is a rare genetic disorder caused by a deficiency of the enzyme acid alpha-glucosidase (GAA) and is also known as Glycogen Storage Disease Type II.
- This enzyme is crucial for breaking down glycogen into glucose within the lysosomes of cells.
- Its prevalence estimates range from 1 in 40,000 to 1 in 300,000 births and occur across diverse ethnicities and populations.
- The age of onset and severity can vary, leading to a spectrum of clinical presentations.
How does Pompe disease affect an individual?
The severity of the condition and the progression of symptoms may differ among individuals. Some key symptoms are:
- Muscle weakness: Progressive muscle weakness is a primary feature of Pompe disease.
- It affects both skeletal and smooth muscles, leading to difficulties in mobility and daily activities.
- Weakness in the respiratory muscles can result in breathing difficulties, especially during physical exertion or even while lying down.
- Motor skill delay: Children with the disease may experience delays in achieving motor milestones, such as sitting, crawling, and walking.
- The degree of motor skill delay can vary, and some individuals may never attain certain motor milestones.
- Degenerative impact on bones: Prolonged muscle weakness and reduced mobility can have a degenerative impact on bones, leading to joint contractures and skeletal deformities.
- Respiratory complications: The weakening of respiratory muscles, including the diaphragm, can have an impact.
- Patients may experience shortness of breath, respiratory infections, and in severe cases, respiratory failure.
- Cardiac involvement: In some cases, Pompe disease can affect the heart muscles, leading to complications.
- Symptoms such as heart palpitations, fatigue, and chest pain, may manifest.
- Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy: Pompe disease can cause hypertrophic cardiomyopathy, characterised by the thickening of the heart muscle walls.
- This can lead to impaired heart functions and cardiovascular symptoms.
- Implications for daily living: Patients may face challenges in performing daily activities independently due to muscle weakness and respiratory limitations.
- Assistive devices such as wheelchairs and respiratory support equipment may become necessary.
How is Pompe disease diagnosed?
- Diagnosing Pompe disease involves a multi-faceted approach.
- Enzyme assays are conducted to measure the activity of acid alpha-glucosidase (GAA), the deficient enzyme.
- Genetic testing identifies mutations in the responsible GAA gene.
- Clinical evaluations consider the patient’s symptoms and medical history.
- Enzyme tests, often performed on blood or skin cells, provide crucial insights into GAA deficiency.
- Genetic analysis confirms the presence of specific mutations associated with Pompe Disease.
- The combination of these diagnostic tools enables healthcare professionals to accurately identify and confirm the disease, helping achieve timely intervention and management.
Is Pompe disease curable?
- While there is currently no cure for Pompe disease, treatment options are available to manage symptoms and improve the patient’s quality of life.
- Enzyme Replacement Therapy (ERT) is a standard treatment, involving the infusion of the missing enzyme to alleviate glycogen buildup.
Data | Sharp rise in Indians illegally crossing U.S. northern border from Canada (The Hindu)

- 15 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
In the last ten years, the number of unauthorized Indian migrants entering the U.S. has surged significantly, climbing from a mere 1,500 a decade ago to an astonishing 96,917 in 2023, as reported by the U.S. Customs and Border Protection.
What are the Implications for India Amidst the Surge in Illegal Migrants?
- Bilateral Relations: The surge in illegal migration poses potential challenges to bilateral relations between India and the USA, impacting areas such as trade negotiations, security cooperation, and strategic partnerships.
- Economic Factors: India faces the risk of a brain drain, as skilled individuals seek illegal entry, potentially affecting sectors with a demand for skilled labour and impacting the country's economy.
- The outflow of skilled and educated individuals through illegal migration can have adverse effects on India's economy, leading to a depletion of talent and expertise.
- Labour Market Challenges: The departure of skilled or semi-skilled workers may create labour shortages in specific sectors, affecting India's workforce and economic productivity.
- Policy Repercussions: India may need to institute stringent policies to address the root causes of illegal migration, potentially diverting resources and attention from other developmental priorities.
What are the Causes Behind the Surge in Illegal Indian Migrants to the USA?
- Pull Factors: The USA's reputation for offering improved employment prospects, higher wages, and career advancement acts as a significant attraction for migrants.
- The allure of quality education and prestigious academic institutions in the USA attracts students and families in search of educational opportunities.
- The desire to reunite with family members or relatives already settled in the USA motivates some migrants to seek illegal entry for proximity to loved ones.
- Push Factors: Numerous push factors, including limited job opportunities and economic prospects in India, drive individuals to seek better employment opportunities abroad.
- Social conflicts or a lack of confidence in India's governance structure may prompt some individuals to search for a more stable environment elsewhere.
- Visa Backlogs and Alternative Routes: Smugglers adapt their methods, providing sophisticated services to facilitate illegal entry into America.
- Prolonged visa backlogs prompt individuals to explore alternative, albeit illegal, pathways to enter the USA due to extended waiting times and limited legal entry options.
- Global Migration Trends: The overall increase in global migration post-pandemic contributes to this surge as individuals seek improved opportunities and security in different countries.
- Misinformation: Social media and deceptive travel agencies disseminate misinformation, misleading desperate migrants and encouraging them to embark on perilous journeys guided by multiple facilitators across continents.
- Desperate migrants may undertake complex, multi-leg journeys through various continents and countries, facing numerous risks and challenges along the way.
What can be Done?
Prioritizing economic stability, job creation, and social welfare programs to alleviate distress and offer improved opportunities within India. Initiating diplomatic dialogues to comprehend and address concerns that contribute to migration, fostering collaboration with other nations to safeguard the rights of migrants.
In a monthly report, the IEA projected that India's oil product demand growth would slow to 2.5% next year from 4.1% in 2023. (ET)

- 15 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
The International Energy Agency (IEA) said recently that the "explosive growth" in Indian oil product consumption may be coming to an end.
About International Energy Agency:
- The International Energy Agency (IEA) is an autonomous intergovernmental organization founded in 1974 in Paris, France.
- Its primary focus revolves around energy policies, emphasizing economic development, energy security, and environmental protection, collectively known as the '3 E’s of IEA.'
- The IEA Clean Coal Centre is dedicated to providing independent information and analysis on making coal a cleaner energy source in line with UN Sustainable Development Goals.
- Originating in response to the oil crisis of 1973-1974, the IEA's mandate has evolved to include tracking global energy trends, advocating sound energy policies, and fostering international energy technology cooperation.
- Mission: The IEA's mission is to ensure reliable, affordable, and clean energy for its member countries and beyond.
- Focus Areas: Key focus areas include energy security, economic development, environmental awareness, and global engagement.
- The IEA collaborates closely with non-member countries, particularly major producers and consumers, to find solutions to shared energy and environmental concerns.
- IEA’s Membership: The IEA is made up of 30 member countries.
- It also includes eight association countries. Four countries are seeking accession to full membership, Chile, Colombia, Israel and Lithuania.
- A candidate country to the IEA must be a member country of the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD).
- Membership Criteria:
- Adequate Reserves: Prospective member countries must maintain crude oil and/or product reserves equivalent to 90 days of the previous year's net imports.
- These reserves, accessible to the government even if not directly owned, should be readily deployable to address disruptions in the global oil supply.
- Demand Restraint Program: Candidates are required to implement a demand restraint program aimed at reducing national oil consumption by up to 10%.
- Emergency Response Capability: Member countries must have legislation and organizational frameworks in place to operate Coordinated Emergency Response Measures (CERM) on a national basis.
- Transparent Reporting: Legislation and measures should be established to ensure that all oil companies under the jurisdiction of the candidate country promptly report information upon request.
- Collective Action Capability: Measures must be in place to guarantee the country's capability to contribute its share in collective actions initiated by the International Energy Agency (IEA).
- Adequate Reserves: Prospective member countries must maintain crude oil and/or product reserves equivalent to 90 days of the previous year's net imports.
- India joined this organization in 2017 as an Associate member.
- However, in 2021, the International Energy Agency (IEA) invited India, the world’s third-largest energy consumer, to become its full-time member.
- Major reports published by the IEA include the World Energy Outlook, World Energy Investment Report, World Energy Statistics, World Energy Balances, Energy Technology Perspectives, and the India Energy Outlook Report.
NASA all set to launch of PACE mission to study air quality, key climate factors and more (NASA)

- 15 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
NASA is ready to enhance our understanding of Earth’s atmosphere with the upcoming Plankton, Aerosol, Cloud, Ocean Ecosystem (PACE) mission, scheduled for launch in early 2024.
What is NASA's PACE Mission?
- The mission will leverage advanced polarimeters to investigate the intricate interactions of light, aerosols, and clouds, enhancing our understanding of their impact on both air quality and climate.
- Beyond aerosol analysis, the PACE mission will delve into the study of ocean colour.
- At its core, the Ocean Colour Instrument (OCI) serves as the primary science instrument for PACE, designed to measure the ocean's colour across a spectrum ranging from ultraviolet to shortwave infrared.
- The mission includes two polarimeters:
- The Spectro-polarimeter for Planetary Exploration (SPEXone) and
- The Hyper Angular Research Polarimeter (HARP2)
- Working in tandem, these instruments offer complementary spectral and angular sampling, ensuring polarimetric accuracy and extensive spatial coverage.
- This integrated approach aims to deliver enhanced atmospheric correction and a comprehensive dataset on aerosols and clouds, surpassing the capabilities of OCI alone.
- The collaborative payload of OCI, SPEXone, and HARP2 is poised to achieve significant breakthroughs in aerosol-cloud-ocean research.
What are Aerosols and their Effect?
- Aerosols are comprised of liquid or solid particles suspended in a gaseous or liquid medium.
- In the atmosphere, these particles are predominantly found in the lower layers (< 1.5 km) since aerosol sources are terrestrial.
- However, specific aerosols may extend into the stratosphere, particularly those ejected by volcanoes at high altitudes.
- Sources of Aerosols:
- Natural Sources: Generated from breaking waves (sea salt), wind-blown mineral dust from the surface, and volcanic emissions.
- Anthropogenic Aerosols: These include sulphate, nitrate, and carbonaceous aerosols, primarily originating from fossil fuel combustion.
- Effects of Aerosols:
- Impact on Atmospheric Chemistry.
- Reduction of Visibility.
- Significance for Air Quality and Human Health: Aerosols can adversely affect the heart and lungs.
- Role as Nuclei: Serve as nuclei for cloud droplets or ice crystals in ice clouds.
Mumps outbreak: Worrying symptoms to watch out for, preventive tips (India TV)
- 15 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
A mumps outbreak has recently been reported in several states across the country, causing concern among public health officials.
What is Mumps Disease?
- Mumps is a contagious disease caused by the mumps virus, which belongs to the paramyxovirus family.
- It typically involves painful swelling in the parotid salivary glands, located on the sides of the face below and in front of the ears.
- These swollen glands often give the infected person a characteristic "chipmunk-cheek" appearance.
- Humans are the only known host for the mumps virus, which is spread via direct contact or by airborne droplets from the upper respiratory tract of infected individuals.
- Transmission of mumps: Mumps is spread through contact with the saliva or respiratory droplets of an infected person. This can happen through coughing, sneezing, kissing, sharing utensils, or close contact.
- Symptoms:
- Mumps typically manifest after an incubation period of 2 to 4 weeks, starting with nonspecific symptoms like myalgia, headache, malaise, and low-grade fever.
- Within days, these initial symptoms progress to the swelling of the parotid salivary glands, either unilaterally or bilaterally, with other salivary glands affected in 10% of cases.
- Prevention: The best way to prevent mumps is to get vaccinated with the MMR (measles, mumps, and rubella) vaccine.
- The MMR vaccine is safe and effective for most people.
- Other preventive measures include practising good hand hygiene, avoiding close contact with sick people, and covering your coughs and sneezes.
- Treatment: There is no specific treatment for mumps. Most people recover on their own within a few weeks.
- Treatment focuses on relieving symptoms, such as with pain relievers and fever reducers.
- In general, mumps is a mild, self-limiting disease that resolves without lasting effects.
- However, complications can arise, including encephalitis or sensorineural deafness.
- Orchitis, a painful inflammation of the testes, occurs in approximately 20% of young adult males who contract mumps.
The Hindu Parliament security breach | 14 Opposition MPs suspended from House amid face-off (LiveMint)

- 15 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
Fourteen MPs have been suspended for "unruly conduct" as stormy scenes played out in Parliament in the wake of the massive security breach recently.
Context:
- A total of 14 MPs, 13 from Lok Sabha and one from Rajya Sabha, were suspended from Parliament on Thursday for the remainder of the Winter Session.
- This follows after stormy scenes played out in Parliament on Thursday, December 14, in the wake of the massive security breach a day before.
- Earlier in the day, TMC member Derek O'Brien was suspended from the Rajya Sabha for the remainder of the Winter session for "unruly behaviour" and "misconduct".
Suspension of MPs:
- The Presiding Officer, whether the Speaker of the Lok Sabha or the Chairman of the Rajya Sabha, plays a crucial role in maintaining order for the smooth functioning of the House.
- Empowered to uphold proper proceedings, the Speaker/Chairman has the authority to compel a Member to withdraw from the House, ensuring the orderly conduct of parliamentary affairs.
What are the Rules under which the Presiding Officer/Chairman acts?
- In Lok Sabha: Rule 373 of the Rules of Procedure and Conduct of Business empowers presiding officers to direct an MP to withdraw for disorderly conduct.
- The suspended Member must remain absent for the remainder of the day's sitting.
- Rules 374 and 374A are invoked for more persistent disruptions.
- Rule 374 allows the Speaker to name legislators for continued disruptions, leading to a motion for suspension not exceeding the session's remainder.
- Rule 374A, added in December 2001, facilitates automatic suspension for five days or the remaining session part.
- In Rajya Sabha: Rule 255 grants the Chairman the authority to immediately direct withdrawal for disorderly conduct.
- Rule 256 enables the Chairman to name members persistently disregarding the Chair's authority or abusing Council rules.
- The House may then pass a motion for suspension not exceeding the session's remainder.
- Unlike Lok Sabha, Rajya Sabha cannot suspend members without a formal motion.
Judicial Oversight in MP Suspension Cases:
- While Article 122 of the Indian Constitution shields parliamentary proceedings from judicial review, there are instances of courts intervening in legislative procedures.
- In a case involving the Maharashtra Legislative Assembly's 2021 Monsoon Session, where 12 BJP MLAs were suspended for a year, the Supreme Court stepped in.
The Court ruled that the assembly's resolution had legal limitations and was only applicable for the duration of the Monsoon Session, underscoring the judiciary's role in assessing the legality and effectiveness of legislative actions.
Rashtriya Gokul Mission (RGM) (The Hindu)

- 02 Nov 2023
Why in the News?
The Centre has decided to deploy National Level Monitors (NLM) to oversee the implementation of its livestock schemes including the National Livestock Mission and Rashtriya Gokul Mission.
About Rashtriya Gokul Mission (RGM):
- The Rashtriya Gokul Mission (RGM) has been implemented for the development and conservation of indigenous bovine breeds since December 2014.
- The scheme is important in enhancing milk production and productivity of bovines to meet the growing demand for milk and making dairying more remunerative to the rural farmers of the country.
- The scheme is also continued under the umbrella scheme Rashtriya Pashudhan Vikas Yojna from 2021 to 2026 with a budget outlay of Rs.2400 crore.
- The RGM will result in enhanced productivity and benefit of the programme, percolating to all cattle and buffaloes of India, especially with small and marginal farmers.
- This programme will also benefit women in particular since over 70% of the work involved in livestock farming is undertaken by women.
Objectives:
- To enhance the productivity of bovines and increase milk production in a sustainable manner using advanced technologies.
- To propagate the use of high genetic merit bulls for breeding purposes.
- To enhance Artificial insemination coverage through strengthening the breeding network and delivery of Artificial insemination services at farmer’s doorstep.
- To promote indigenous cattle & buffalo rearing and conservation in a scientific and holistic manner.
India’s First ‘City Of Literature’ (NewsOnAir)

- 02 Nov 2023
Why in the News?
Recently India-born author Nandini Das is the winner of 2023 British Academy Book Prize for Global Cultural Understanding.
About the British Academy Book Prize:
- The British Academy Book Prize, formerly known as the Nayef Al Rodhan Prize for Global Cultural Understanding, is a prestigious annual award given to the best non-fiction book that, in the opinion of the judges, contributes to global cultural understanding for a wider public audience.
- The prize was established in 2013 in partnership with Professor Nayef Al-Rodhan and is worth £25,000.
- The British Academy is the UK's national academy for the humanities and social sciences, and the prize is one of its most prestigious awards.
- It is a testament to the importance of these disciplines in helping us to understand ourselves and the world around us.
- Eligible books must be non-fiction, and come from the subjects that fall within the humanities and social sciences, from archaeology, history and psychology to philosophy, languages and cultural studies.
- Nandini Das who is a Professor in the English faculty at the University of Oxford, won the award for her book ‘Courting India: England, Mughal India and the Origins of Empire’
Debrigarh Wildlife Sanctuary (The Hindu)

- 02 Nov 2023
Why in the News?
Recently, in the Bargarh area of Odisha's Debrigarh Wildlife Sanctuary, two rare and elusive wild dogs, known as Dholes, have been spotted.
About Debrigarh Wildlife Sanctuary:
- Debrigarh Wildlife Sanctuary is Located between the Hirakud Dam (on the Mahanadi River) and the Reservoir in Odisha.
- It was declared a wildlife sanctuary in 1985.
- It's also famous because the freedom fighter Veer Surendra Sai used 'Barapathara' within the sanctuary as his base during his struggle against the British.
- It covers an area of 347 square kilometres and is home to a variety of wildlife, including Indian Bison, Wild Boars, Sambhar, and Peacocks.
- The dry deciduous forest attracts many migratory birds during the winter season.
- The sanctuary also houses the endangered four-horned antelope, known as Chousingha.
- Additionally, it's internationally significant due to its notable population of Leopards, Bisons, and Chousingha.
State Food Safety Index (SFSI) (Indian Express)

- 02 Nov 2023
Why in the News?
Recently, the Food Safety and Standards Authority of India (FSSAI) published the State Food Safety Index in which 15 out of 20 states recorded lower 2023 scores compared to 2019.
About the State Food Safety Index:
- Since 2019, FSSAI has released the State Food Safety Index (SFSI) each year on June 7 on the occasion of World Food Safety Day.
- SFSI scores are given out of a total of 100 points that are calculated based on five parameters with different weightages:
- Human Resources and Institutional Data
- Compliance
- Food Testing Infrastructure
- Training and Capacity Building
- Consumer Empowerment.
- In the 2023 index, a new parameter called ‘Improvement in SFSI Rank’ was added, which assesses improvement in each state’s rank from the year before.
- The primary goal of this index is to ensure that citizens have access to safe and nutritious food.
- This index is a dynamic and comprehensive system that offers an objective way to assess food safety across all states and UTs.
- States and UTs are categorized into three groups: large states, small states, and UTs, for evaluation and comparison.
Key findings from the report:
- 19 out of 20 large states — including Maharashtra, Bihar, Gujarat and Andhra Pradesh — recorded a drop in their 2023 scores from 2019.
- The most substantial drop was observed in the 'Food Testing Infrastructure' category, with states like Maharashtra, Bihar, Andhra Pradesh, and Chhattisgarh receiving lower scores in this aspect.
- Gujarat, Madhya Pradesh, and Jharkhand also had reduced scores in the 'Compliance' category.
- In the 2023 index, the 'Human Resources and Institutional Data' category was given the third-highest importance, accounting for 18% of the evaluation (it was 20% in previous years).
- The only category that showed notable improvement was 'Training and Capacity Building,' which was given the least importance, 8%, in the 2023 index (compared to 10% in previous years).
Future Leaders Scholarship Programme (Indian Express)

- 02 Nov 2023
Why in the News?
Imperial College London recently announced a new scholarship programme for Indian students that aims to nurture the country’s most talented Master’s scholars over the next three years.
About the Future Leaders Scholarship Programme:
- Imperial College London unveils the Future Leaders Scholarship Programme for Indian students.
- It aims to support 30 highly talented Master's students in India for the next three years.
- This scholarship will cover all tuition and living expenses.
- It is available for Master's students in fields such as engineering, natural sciences, business, and medical research.
- Notably, half of the scholarships are set aside for female scholars.
- The program creates an opportunity for India's brightest students to further their education and gain valuable experiences at a top international university.
- In addition to this scholarship, the university has partnered with the UK government's Chevening Scholarships programme to sponsor an extra three Master's scholars from India in the next three years.
One Nation, One Registration Platform (The Hindu)

- 01 Nov 2023
Why in the News?
The National Medical Commission (NMC)will launch its “One Nation, one registration platform’‘ for doctors across the country
About One Nation, One Registration Platform:
- The National Medical Commission (NMC) will launch a patch trial of the National Medical Register (NMR), in which physicians will receive a unique identification number and, based on their location, be able to apply for a license to practice in any State within the next six months.
- The change was announced by the commission in a gazette notification earlier this year under the title "Registration of Medical Practitioners and Licence to Practice Medicine Regulations, 2023."
- The NMR will receive the data of almost 14 lakh doctors who are currently registered in the system.
- Objectives: The goal is to supply undergraduate students on the NMR with a masked ID, and based on when they complete their course, the ID is unmasked and assigned.
- It will eliminate duplication and red tape while also providing the public with access to information on any physician practising in India.
Features of the NMR:
- The public will have access to the NMR via the NMC website, which will take the role of the current Indian Medical Register (IMR). It will provide detailed information about registered doctors, such as:
- Unique Identification Number (UID): Each doctor will be assigned a unique identification number.
- Registration Number: The doctor’s registration number for verification.
- Qualifications: Information about the doctor’s educational qualifications.
- Specialization: The doctor’s area of expertise.
- Name and Place of Work: Details of the doctor’s name and workplace.
- Institute/University: The name of the institution or university where the qualifications were obtained.
Tamil Lambadi Embroidery (The Hindu)

- 01 Nov 2023
Why in the News?
For almost 60 years, the Porgai Artisan Association Society has been producing and distributing embroidered clothing in an effort to raise awareness of the art form and ensure that it is passed down to future generations.
About Tamil Lambadi Embroidery:
- The Lambadi community has a long-standing tradition of practising Lambadi embroidery.
- This craft is used to embellish their clothing and household items and it holds significant cultural and identity value for the Lambadis.
- Traditionally, Lambadi women use colourful cotton threads to create intricate embroidery on cotton and silk fabrics.
- Embroidery Designs: The traditional Lambadi embroidery designs are characterized by geometrical patterns, including squares, rectangles, and circles.
- These designs have also been influenced by elements from the local environment, such as forests, birds, fruits, and flowers.
Facts About the Lambadi Community:
- They are also known as Lambadis or Banjaras.
- Historically they are nomadic tribes, originating from Afghanistan and settling in regions including Rajasthan, Karnataka, Andhra Pradesh, Madhya Pradesh, Gujarat, and Maharashtra.
- They also assisted Mughal Emperor Aurangzeb in transporting goods in the 17th century.
- Speak 'Gor Boli' or 'Lambadi,' which is often written in Devanagari or local languages.
- Many members of the Lambani community are bilingual or multilingual to communicate in the predominant language of their region in India.
- The elderly women within the Lambadi community continue to wear the Petia, a traditional five-piece dress.
- The Petia is made using Mushru silk from Kutch, showcasing the enduring connection to their heritage and craftsmanship.
Black Stork (TOI)

- 01 Nov 2023
Why in the News?
For the first time, a Black Stork, a species rarely seen, has been spotted in the Hastinapur Wildlife Sanctuary in Uttar Pradesh recently.
About Black Stork:
- The black stork (Ciconia nigra) is a large bird in the stork family Ciconiidae.
- It is usually found in marshy areas, rivers or inland waters.
- It is a long-distance migrant, with European populations wintering in tropical Sub-Saharan Africa, and Asian populations in the Indian subcontinent.
- The black stork is considered to be a species of least concern by the International Union for Conservation of Nature, but its actual status is uncertain.
- Despite its large range, it is nowhere abundant, and it appears to be declining in parts of its range, such as in India, China and parts of Western Europe, though increasing in others such as the Iberian Peninsula.
- Various conservation measures have been taken for the black stork, like the Conservation Action Plan for African black storks by Wetlands International.
- It is also protected under the African-Eurasian Waterbird Agreement and the Convention on International Trade in Endangered Species of Wild Fauna and Flora.
Light Combat Helicopter (LCH) 'Prachand' (The Hindu)

- 01 Nov 2023
Why in the News?
The Indian Army's Light Combat Helicopter (LCH) Prachand has conducted the first-ever day-and-night firing of 20 mm turret guns and 70 mm missiles.
About Light Combat Helicopter (LCH) 'Prachand':
- The LCH is the only assault helicopter in the world that has the ability to land and take off at 5,000 meters while carrying a sizable payload of fuel and weaponry.
- The helicopter features a frame and landing gear that are largely crash-proof, and it uses material that absorbs radar waves to reduce its radar signature.
- For protection against nuclear, biological, and chemical (NBC) emergencies, a pressurised compartment is available.
- The helicopter is protected from enemy radars and infrared seekers of enemy missiles by a countermeasure dispensing mechanism.
- LCH is powered by two French-origin Shakti engines manufactured by the HAL.
- The helicopter will be equipped with Helina missiles, the air force version of which is called Dhruvastra.
- It is capable of combat duties such as enemy air defence destruction, counter-insurgency warfare, combat search and rescue, anti-tank, and counter-surface force operations.
India’s First ‘City Of Literature’ (Money Control)

- 01 Nov 2023
Why in the News?
Kozhikode, in Kerala, was named the ‘City of Literature’ by the Unesco Creative Cities Network (UCCN), making it the first such city in India.
About India’s First ‘City Of Literature’:
- Kozhikode (Kerala), has achieved global recognition by joining the UNESCO Creative Cities Network.
- It is now known as the 'City of Literature,' making it the first Indian city to receive this prestigious title.
- This recognition was awarded on World Cities Day, (31 October) along with Gwalior, Madhya Pradesh, which was designated a 'City of Music.'
- Prague was the first city to receive the 'City of Literature' title in 2014.
About UNESCO Creative Cities Network:
- The UNESCO Creative Cities Network is a global initiative established by the United Nations Educational, Scientific, and Cultural Organization (UNESCO) to recognize and promote cities that have made significant contributions to the development of creative industries and culture.
- The UNESCO Creative Cities Network now comprises 350 creative cities from over 100 countries.
- These cities represent seven creative fields, including Crafts and Folk Art, Design, Film, Gastronomy, Literature, Media Arts, and Music.
- Participation in the UNESCO Creative Cities Network provides cities with opportunities for international collaboration, knowledge sharing, and the exchange of best practices in creative and cultural endeavours.
- These cities serve as hubs for artistic expression, cultural preservation, and economic growth, making them vital players in the global creative economy.
- Through this network, cities work together to harness the power of culture and creativity to address common challenges and promote sustainable development, ultimately enhancing their status on the global stage.
Digital Health Incentives Scheme (DHIS) (NewsOnAir)

- 05 Aug 2023
Why in the News?
The National Health Authority (NHA) has recently declared the extension of its Digital Health Incentives Scheme (DHIS) until the 31st of December 2023.
About Digital Health Incentives Scheme (DHIS):
- Launched in December 2022, the DHIS became effective from 1st January 2023.
- The scheme is implemented by the National Health Authority (NHA) under the Ministry of Health and Family Welfare.
- Its primary objectives include giving a further impetus to digital health transactions across the country through the Ayushman Bharat Digital Mission (ABDM).
Salient Features of DHIS:
- The scheme offers incentives of up to four crore rupees, determined by the number of digital health records created and linked to patients' Ayushman Bharat Health Account numbers.
- Incentives are extended to hospitals, diagnostic labs, and providers of digital health solutions, including Hospital/Health Management Information Systems (HMIS) and Laboratory Management Information Systems (LMIS).
- Health facilities (hospitals and diagnostic labs) registered with the Ayushman Bharat Digital Mission's Health Facility Registry (HFR) and meeting the specified eligibility criteria can avail of the incentives.
Benefits of DHIS:
- Incentives for Digitization: Healthcare facilities and Digital Solution Companies participating in the scheme can earn incentives to cover expenses related to digitization.
- Enhanced Efficiency in Healthcare Delivery: DHIS streamlines the healthcare process, eliminating hassles in registration, appointment scheduling, consultations, IPD admission, discharge, and more.
- Robust Digital Health Ecosystem: The scheme contributes to the development of a strong digital health ecosystem, encompassing various levels of healthcare facilities.
- Improved Quality of Care: DHIS facilitates evidence-based, accessible, and high-quality healthcare services, leading to better patient outcomes and satisfaction.
Spike Non-Line of Sight (NLOS) Anti-tank Guided Missiles (TOI)

- 05 Aug 2023
Why in the News?
Israel's Spike Non-Line of Sight (NLOS) anti-tank guided missiles were recently delivered to the Indian Air Force.
About the Spike Non-Line of Sight (NLOS) Anti-tank Guided Missile:
- The Spike Non-Line of Sight (NLOS) Anti-tank Guided Missile (ATGM) is a sophisticated fire-and-forget missile designed for anti-tank and anti-personnel purposes.
- It features a tandem-charge high-explosive warhead.
- Developed by Rafael Advanced Defense Systems, an Israeli defense technology company, the Spike NLOS ATGM comes in man-portable, vehicle-launched, and helicopter-launched variants.
- The missile is currently in use by the defense forces of Israel and 38 other countries, including India, Netherlands, Germany, Italy, Peru, Spain, Belgium, Brazil, Canada, the UK, Philippines, and Singapore.
- Key features of the Spike NLOS ATGM:
- Striking range of up to 30 kilometers
- Weight of 71 kg, and
- An electro-optical seeker that offers superior target visibility compared to radar or infrared-guided missiles.
- The missile's seeker is equipped with a datalink, enabling the launch operator to maintain control over the missile during flight.
- This capability allows for precise targeting, including attacking different parts of a tank or engaging an alternative target, or aborting the strike if necessary.
- The Spike NLOS ATGM can be armed with various types of warheads, making it versatile for destroying tanks, and air defense systems, or for use in urban combat scenarios.
Perucetus colossus (Indian Express)
- 05 Aug 2023
Why in the News?
Perucetus colossus, whose fossils were discovered in Peru, maybe the heaviest discovered animal ever, even heavier than the blue whale.
About Perucetus colossus:
- The whale species Perucetus colossus is known from a recently described fossil dating back over 38 million years.
- Despite potentially being shorter in length, scientists believe that this ancient whale species might have been heavier than the modern blue whale.
- Researchers estimate that the weight of the Perucetus colossus could have ranged from 85 to an astonishing 340 tonnes.
- The fossilized bones of this species exhibited an unusual combination of large volume and extreme density, a characteristic known as pachyosteosclerosis.
- Pachyosteosclerosis is not observed in living whales, dolphins, and porpoises, but it is present in sirenians, a marine mammal group that includes sea cows.
- Unlike deep-diving whales, Perucetus colossus likely lived in shallow coastal areas, suggesting that it might have dived with air in its lungs.
- However, diving with air in the lungs would make it challenging to stay near the seafloor.
- The heavy bones of the Perucetus colossus might have played a crucial role in enabling it to do so.
- The skeletal mass of the Perucetus colossus is estimated to have been between five and eight tons, double that of a modern blue whale.
Study in India (SII) portal (Indian Express)

- 05 Aug 2023
Why in the News?
The Study In India (SII) portal was recently introduced by the Education Ministry, aiming to promote Indian education among international students.
About the Study in India (SII) portal:
- The Study in India (SII) portal serves as a dedicated website offering comprehensive information about higher education institutions (HEIs) in India.
- The main objective of the portal is to establish India as a global education hub and attract students from diverse backgrounds.
- The portal showcases a wide range of academic programs available in the HEIs, including undergraduate, postgraduate, and doctoral courses, along with courses related to the Indian Knowledge System (IKS), such as Yoga, Ayurveda, and classical arts.
- Detailed information about the academic facilities, research support, and other related offerings in the institutes is provided on the portal.
- It acts as a convenient one-stop platform for students, enabling them to register, apply for a visa, select desired courses, and receive offer letters from their chosen institutes.
- The portal allows students to apply to multiple institutes or courses of their preference, simplifying the application process.
- Study in India (SII) offers a streamlined and well-organized application process, providing international students with easy access to higher education opportunities in India.
What is Study in India (SII) Programme?
- The Study in India (SII) program is a prominent initiative initiated by the education ministry in 2018 with the aim of positioning India as a premier education destination for international students.
- The program seeks to attract foreign students to pursue higher education in India, providing them with valuable educational opportunities offered by renowned Indian universities.
Great Nicobar Island Project (DownToEarth)
- 05 Aug 2023
Why in the News?
According to the Union Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change's statement in the Rajya Sabha, approximately 964,000 trees are expected to be cut down for the implementation of the Great Nicobar Island Project.
About Great Nicobar Island Project:
- Ministry:
- The Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change (MoEFCC).
- Implementing Agency:
- The Andaman and Nicobar Islands Integrated Development Corporation (ANIIDCO).
- The project is a massive undertaking with a budget of ?72,000 crore and is spearheaded by NITI Aayog, known as NITI Aayog's Project for Great Nicobar Island.
- Objective:
- The primary goal of the project is to achieve holistic development for the Great Nicobar Island (GNI).
- The project's vision is to transform the Great Nicobar Island, situated in the Bay of Bengal, into a modern, sustainable, and self-sufficient territory, thus facilitating the comprehensive development of Great Nicobar.
The plan comprises four key components:
- A transshipment port at Galathea Bay with an investment of ?35,000 crore.
- Development of a dual-use military-civil international airport.
- Establishment of a power plant.
- Creation of a township to support the overall project.
Indian National Space Promotion and Authorisation Centre (IN-SPACe) (TOI)

- 04 Aug 2023
Why in the News?
The Indian National Space Promotion and Authorisation Centre (IN-SPACe) has reported that three private sector satellite manufacturers plan to launch their earth observation satellites during this fiscal year.
About Indian National Space Promotion and Authorisation Centre (IN-SPACe):
- IN-SPACe serves as a single-window, independent, and autonomous agency within the Department of Space (DOS).
- It was established as part of the Space sector reforms to encourage and facilitate the active involvement of private players in the space industry.
- IN-SPACe's responsibilities include promoting, enabling, authorizing, and supervising various space activities of non-governmental entities, such as manufacturing launch vehicles and satellites, providing space-based services, and utilizing space infrastructure and facilities.
- Acting as an intermediary between ISRO and Non-Governmental Entities (NGEs), the agency assesses opportunities for leveraging India's space resources effectively and enhancing space-based initiatives.
- Also, IN-SPACe addresses the specific needs and demands of private players, including educational and research institutions, while working in collaboration with ISRO.
- The headquarters of IN-SPACe is located in Bopal, (Ahmedabad).
Samudrayaan (IndiaToday)

- 04 Aug 2023
Why in the News?
India's ambitious Samudrayaan project, aimed at exploring the deep ocean and its resources, is set to send three personnel to a depth of 6000 meters in a submersible vehicle.
About Samudrayaan Project:
- India's inaugural manned mission to delve into the depths of the ocean for exploration.
- Its primary objectives include studying deep ocean resources and conducting biodiversity assessments.
- The mission is designed to ensure minimal disturbance to the ecosystem, focusing solely on exploration.
- Part of the comprehensive Deep Ocean Mission aligned with the Central Government's Blue Economy policy.
- The Ministry of Earth Sciences (MoES) leads the implementation of this ambitious, multi-institutional endeavor.
What is the Blue Economy?
- Blue economy refers to the sustainable use of marine resources for exploration, economic growth, improved livelihoods, and transport while preserving the health of marine and coastal ecosystems.
- In India, the blue economy encompasses a wide range of sectors, including shipping, tourism, fisheries, and offshore oil and gas exploration.
Pradhan Mantri JI-VAN (Jaiv Indhan- Vatavaran Anukool fasal awashesh Nivaran) Yojana (PIB)

- 04 Aug 2023
Why in the News?
In the Lok Sabha, the Ministry of Petroleum & Natural Gas provided details about the Pradhan Mantri JI-VAN scheme.
About Pradhan Mantri JI-VAN (Jaiv Indhan- Vatavaran Anukool fasal awashesh Nivaran) Yojana:
- The scheme was officially notified in March 2019.
- Its main objective is to extend financial support to integrated bio-ethanol projects, facilitating the establishment of Second Generation (2G) ethanol projects using lignocellulosic biomass and other renewable feedstocks.
- It has a financial outlay of Rs. 1969.50 crore, spanning the period from 2018-19 to 2023-24.
- Financial assistance of Rs. 150 crore is offered per project for commercial projects, while demonstration projects receive Rs. 15 crore per project.
- The Ministry of Petroleum and Natural Gas serves as the nodal ministry for this scheme.
What is Lignocellulosic Biomass?
- Abundant Source: It is found in agricultural and forestry residues, as well as dedicated energy crops.
- Biofuels and Bio-based Products: Lignocellulosic biomass holds promise as a sustainable feedstock for producing biofuels like second-generation ethanol and various bio-based products.
- Challenges: Efficiently breaking down its complex structure to release sugars for fermentation or chemical conversion is a key challenge.
- Innovative Technologies: Researchers are exploring enzymatic hydrolysis and thermochemical treatments to unlock its energy potential.
- Green and Sustainable Future: Utilizing lignocellulosic biomass can reduce reliance on non-renewable resources and mitigate environmental impacts linked to conventional energy production.
Himalayan vulture bred (The Hindu)

- 04 Aug 2023
Why in the News?
The first-ever instance of captive breeding of the Himalayan vulture in India has been successfully recorded at the Assam State Zoo in Guwahati by researchers.
About Himalayan Vulture:
- Scientific Name: Gyps himalayensis
- It is a rare and the largest bird species native to the Himalayas.
- Habitat:
- The Himalayan vulture primarily inhabits higher regions of the Himalayas and the Tibetan Plateau, typically found at elevations above 1500 meters.
- This species has a distribution range that extends from western China, Kazakhstan, Uzbekistan, Kyrgyzstan, Tajikistan, Afghanistan, and Pakistan to the eastern part of the Himalayan mountain range, including India, Nepal, and Bhutan, and further to central China and Mongolia.
- Description:
- This vulture is impressively large, featuring a sandy brown plumage with a pale, featherless head. In flight, it displays black primaries and a distinctive small-headed, squared-winged appearance.
- Himalayan vultures are usually spotted alone or in small groups, but they gather in large flocks when feeding on a carcass.
- Conservation status:
- The Himalayan vulture is categorized as "Near Threatened" on the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) Red List of Threatened Species.
- To ensure its preservation, the species is covered under the Multi-species Action Plan (MsAP) for the conservation of African-Eurasian vultures and is also included in national Action Plans in India, Bangladesh, Nepal, and Cambodia.
- Threats:
- The most significant potential threat to this vulture species is believed to be mortality resulting from the ingestion of diclofenac and other vulture-toxic non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), commonly used in livestock, particularly in South Asia.
India to launch female robot astronaut 'Vyommitra' ahead of manned mission (IndiaTV News)

- 14 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
The Minister of Science & Technology, Dr Jitendra Singh, announced on Wednesday that India is set to launch Vyommitra, a female robot astronaut, into space as part of the ambitious Gaganyaan project.
What is Vyommitra?
- Vyommitra is an AI-enabled female robot.
- It was introduced at the inaugural session of the "Human Spaceflight and Exploration — Present Challenges and Future Trends" event in January 2020.
- The name is a combination of two Sanskrit words: Vyoma (Space) and Mitra (Friend), and it was created for the unmanned Gaganyaan mission.
- Because she lacks legs, she is described as a half-humanoid robot.
- She may, however, bend to the sides and forward.
- The ISRO Inertial Systems Unit (IISU) designed, developed, and integrated the robot.
- At the same time, Vikram Sarabhai Space Centre (VSSC), a sister Isro facility based in Thumba, built its fingers.
- This robot is designed to ride aboard a rocket and survive stress and vibrations while in flight.
- With the ability to speak, see, and make facial expressions, it has been created to resemble a human.
- Vyommitra will also acquire a digital twin.
- The twin would be built through collaboration with academic institutions such as the IITs.
- Vyommitra will accompany astronauts on manned missions in addition to the unmanned Gaganyaan mission.
- Vyommitra's mission is to perform specific tasks in order to analyse how astronauts might behave.
- She will mimic every action that astronauts are required to take and respond to them in two languages.
- She will monitor via module parameters, alert, carry out life support procedures, carry out tasks like operating switch panels, and imitate other human actions in space throughout the uncrewed flight.
What is the Gaganyaan mission?
- Named after the Sanskrit word for craft or vehicle to the sky, the Gaganyaan project has been developed at the cost of ?90 billion.
- If it succeeds, India will become only the fourth country to send a human into space after the Soviet Union, the US, and China.
- Under the Gaganyaan Mission, ISRO will be sending three humans to an orbit of 400 km for a 3-day mission and bring them back safely to Earth.
- Launch Vehicle: GSLV Mk III, also called the LVM-3 (Launch Vehicle Mark-3,) the three-stage heavy lift launch vehicle, will be used to launch Gaganyaan as it has the necessary payload capability.
- Training Collaboration with Russia: In June 2019, ISRO's Human Space Flight Centre partnered with Russia's Glavkosmos, a government-owned entity, under a contract encompassing comprehensive astronaut training.
- However, four astronauts selected for the Gaganyaan have been undergoing mission-specific training at the Astronaut Training Facility in Bengaluru.
CHD1L gene (DownToEarth)
- 04 Aug 2023
Why in the News?
A new study indicates that some individuals of African descent have a CHD1L gene variant that may be involved in controlling the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV).
What is the CHD1L gene?
- The CHD1L gene encodes proteins that aid in repairing DNA damage within the body.
- A specific variant of the CHD1L gene is found predominantly in the African population and has been associated with a decreased viral load (amount of HIV in the blood) of HIV-1, the most common and severe type of HIV compared to HIV-2.
- Through the analysis of DNA from nearly 4,000 people of African descent living with HIV-1, researchers identified the presence of a gene variant of CHD1L located on chromosome 1.
- Individuals carrying this particular gene variant exhibited a low viral load, reducing their risk of transmitting the virus and slowing the progression of their own HIV-related illness.
- The study suggests that between 4% and 13% of people with African origins could be carrying this specific CHD1L gene variant.
How Google DeepMind’s AI breakthrough could revolutionise chip, and battery development (India Today)
- 14 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
The World Health Organisation (WHO) has reported a significant anthrax outbreak in Zambia, marking an alarming spread of the disease across nine out of the country's ten provinces.
What is anthrax?
- According to Centres for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), anthrax is a highly infectious disease that is caused by the gram-positive, rod-shaped bacteria known as Bacillus anthracis.
- Although it affects animals like cows, sheep, and goats, humans can get sick if they come in contact with infected animals or contaminated animal products.
- Anthrax is not contagious, which means we can't catch it from another person like the cold or flu.
Symptoms of anthrax:
- The disease manifests in three forms depending on the route of infection: cutaneous, gastrointestinal, and inhalational.
- Cutaneous anthrax, the most common form, presents with itchy bumps that develop into black sores, often accompanied by fever and muscle aches.
- Gastrointestinal anthrax resembles food poisoning initially but can escalate to severe abdominal pain and bloody diarrhoea.
- Inhalational anthrax, the deadliest form, starts with cold-like symptoms before progressing to severe respiratory distress and shock.
How is anthrax diagnosed?
- Anthrax can be diagnosed by identifying Bacillus anthracis in blood, skin lesions, or respiratory secretions through laboratory culture, PCR, or ELISA tests.
- While there is no specific test to determine exposure to anthrax, public health investigations play a crucial role in identifying potential cases.
Treatment for anthrax:
- Treatment for anthrax is available and includes antibiotics such as ciprofloxacin, doxycycline, or levofloxacin.
- If diagnosed early, antibiotic treatment can cure most anthrax infections.
- In severe cases, hospitalisation and treatments like continuous fluid drainage and mechanical ventilation may be necessary.
- Vaccines are also available for both livestock and humans, although human vaccines are typically reserved for those at high occupational risk.
How Google DeepMind’s AI breakthrough could revolutionise chip, and battery development (The Hindu)

- 14 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
Road traffic deaths fell by 5% to 1.19 million fatalities annually worldwide between 2010 and 2021, with 108 UN member nations reporting a drop, a report by the World Health Organization (WHO) said. India, however, registered a 15% increase in fatalities.
News Summary:
- The fifth edition of the WHO Global Status Report on Road Safety, released in 2023, serves as a comprehensive assessment of progress in mitigating road traffic deaths.
- This report evaluates advancements made between 2010 and 2021, establishing a foundation for meeting the ambitious target of the United Nations Decade of Action 2021–2030—to cut road traffic fatalities in half by 2030.
- Declared by the United Nations General Assembly in September 2020, the Decade of Action for Road Safety 2021-2030 strives to achieve a 50% reduction in road traffic deaths and injuries by 2030.
- Generous support from Bloomberg Philanthropies has played a crucial role in producing this report.
- Since 2007, Bloomberg Philanthropies has committed $500 million to facilitate road safety initiatives in low- and middle-income countries and cities worldwide
Key Insights from the Global Status Report on Road Safety 2023:
- Countries Achieving Over 50% Reduction in Road Traffic Deaths: Ten countries, including Belarus, Brunei Darussalam, Denmark, Japan, Lithuania, Norway, Russian Federation, Trinidad and Tobago, the United Arab Emirates, and Venezuela, have successfully reduced road traffic deaths by more than 50%.
- Additionally, 35 more countries have made commendable progress, achieving a reduction in road traffic deaths ranging from 30% to 50%.
- Leading Cause of Death for Children and Youth: As of 2019, road traffic crashes have become the primary cause of death for children and youth aged five to 29 years.
- Globally, these crashes rank as the 12th leading cause of death across all age groups.
- 5% Reduction in Road Traffic Fatalities in the Last Decade: Despite a population growth of nearly 14 billion over the last decade, there has been a 5% reduction in the absolute number of road traffic fatalities.
- The road fatality rate has declined from 18 per 1 lakh people in 2010 to 15 per 1 lakh in 2021, marking a 16% decrease in the road traffic death rate since 2010.
- Regional Distribution of Traffic Deaths: The regional breakdown indicates that:
- 28% of global road traffic deaths occurred in the WHO’s South-East Asia Region
- 25% in the Western Pacific Region
- 19% in the African Region
- 12% in the Region of the Americas
- 11% in the Eastern Mediterranean Region, and
- 5% in the European Region.
- The situation in Low- and Middle-Income Countries: Nine out of 10 road traffic deaths transpire in low- and middle-income countries, with fatalities in these nations being disproportionately higher (three times) in comparison to the number of vehicles and roads they possess.
- Countries Meeting WHO Best Practices for Risk Factors: Only six countries have legislation aligning with WHO best practices for all risk factors (speeding, drunk driving, and the use of motorcycle helmets, seatbelts, and child restraints).
- Meanwhile, 140 countries, constituting two-thirds of UN Member States, have such laws governing at least one of these risk factors.
- India-Specific Observation: In India, the reported deaths due to road crashes increased from 1,50,785 in 2018 to 1,53,792 in 2021.
- Notably, the number stood at 1.3 lakh in 2010.
Lunar Codex (The Guardian)

- 03 Aug 2023
Why in the News?
The Lunar Codex program has the potential to bestow immortality upon an assorted collection of human-created art.
About Lunar Codex:
- The Lunar Codex is a remarkable collection of art curated by artists worldwide, intended to endure on the lunar surface as a timeless testament to human creativity, even amid tumultuous times like wars, pandemics, and economic crises.
- At the helm of this endeavor is Samuel Peralta, a semi-retired physicist and art enthusiast from Canada.
- Comprising diverse forms of digitized art, the Lunar Codex will be dispatched to the moon to serve as a permanent record of human ingenuity. Memory cards and NanoFiche, an updated 21st-century version of film-based microfiche, guarantee the safe arrival of these artistic expressions to the lunar surface.
- Carefully assembled from contributions by 30,000 artists, writers, filmmakers, and musicians representing 157 countries, the collection spans an array of art forms, including images, magazines, books, podcasts, movies, and music.
- The art is divided into four capsules:
- The first capsule, the Orion collection, has already encircled the moon after being launched aboard NASA's Artemis 1 mission via the Orion spacecraft last year.
- In the months ahead, multiple lunar landers will transport the Lunar Codex capsules to distinct locations, including craters at the moon's South Pole and the lunar plain known as Sinus Viscositatis, ensuring the enduring legacy of human creativity on Earth's celestial neighbor.
Here to enhance partnership between EFTA, India: Norway's trade minister (Business Standard)

- 14 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
Norway's Minister of Trade and Industry Jan Christian Vestre has said his India visit aims to enhance collaboration between European free trade partners and India and improve framework conditions for job creation, value creation, and investments.
About the European Free Trade Association (EFTA):
- The European Free Trade Association (EFTA) is an intergovernmental organization established in 1960 by the Stockholm Convention.
- Its core objective is to foster free trade and economic integration among its member countries, both within Europe and on a global scale.
- Member Countries: EFTA comprises four member countries: Iceland, Liechtenstein, Norway, and Switzerland.
- These nations are characterized by open, competitive economies, demonstrating a shared commitment to progressively liberalize trade both within multinational forums and through individual free trade agreements.
- Customs Distinction: Unlike the European Union (EU), EFTA operates differently as it is not a customs union.
- This key distinction allows each EFTA State the autonomy to establish its own customs tariffs and formulate foreign trade measures independently concerning non-EFTA States.
- Association Responsibilities:
- EFTA manages various aspects crucial to its objectives, including:
- Facilitating free trade among EFTA countries.
- Overseeing EFTA's engagement in the European Economic Area (EEA), encompassing the European Union and three EFTA countries (Iceland, Liechtenstein, and Norway, excluding Switzerland).
- Managing EFTA's extensive network of free trade agreements globally.
- Free Trade Agreement Network: EFTA member countries boast one of the largest networks of Free Trade Agreements (FTAs) globally.
- This comprehensive network spans over 60 countries and territories, incorporating the European Union among others.
EFTA plays a pivotal role in promoting economic collaboration, free trade, and global engagement, distinguishing itself from the EU through its approach to customs and foreign trade measures.
What is a Free Trade Agreement?
- A Free Trade Agreement (FTA) is an agreement between two or more nations aimed at lowering barriers to imports and exports among them.
- In a free trade scenario, goods and services can move across international borders with minimal government tariffs, quotas, subsidies, or restrictions hindering their exchange.
- The principle of free trade stands in contrast to trade protectionism or economic isolationism.
- FTAs come in various forms, including Preferential Trade Agreements, Comprehensive Economic Cooperation Agreements, and Comprehensive Economic Partnership Agreements (CEPA).
COP28: What was the most important deal short (Indian Express)

- 14 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
COP28: The annual climate conference this year saw some key resolutions on fossil fuels, methane emissions, and funds to fight global warming, among others. However, many concerns remain.
Context:
- The 2023 United Nations Climate Change Conference, also referred to as COP28 took place from November 30 to December 12 at Expo City in Dubai, United Arab Emirates.
- While the event yielded significant outcomes, it, akin to its predecessors, fell short of meeting the anticipated expectations.
Key Outcomes of COP28:
- Fossil Fuel Transition Ambiguity: Acknowledging the role of fossil fuels in global warming for the first time, the agreement calls for countries to contribute to transitioning away from fossil fuels to achieve net-zero emissions by 2050.
- However, the lack of specific time schedules and targets disappointed some nations that expected a more explicit commitment to a "fossil fuel phase-out."
- Renewable Energy Tripling: The agreement calls on countries to contribute to tripling the global installed capacity of renewable energy and doubling annual improvements in energy efficiency.
- This measure is expected to result in emissions avoidance of approximately 7 billion tonnes of carbon dioxide equivalent by 2030.
- However, the global nature of this target raises questions about individual country responsibilities.
- Coal Phase-Down Continuation: The agreement reiterates the commitment to the phase-down of coal, following up on the decision made at COP26.
- While there were considerations to impose restrictions on new coal-fired power plants without carbon capture and storage, these were dropped due to resistance from countries like India, China, and South Africa.
- The agreement lacks specifics on measurement criteria or baseline for this phase-down.
- Methane Emission Challenges: Despite the significance of methane as a greenhouse gas, responsible for nearly 25% of emissions and is 80 times more potent than CO2, the agreement avoids setting targets for methane emission cuts in 2030.
- Countries like India are opposed to mandates due to the agricultural sector's major role in methane emissions.
- Operational Loss & Damage Fund: A significant outcome for vulnerable nations, COP28 operationalized the Loss and Damage Fund, established in COP27.
- Commitments, totaling around US$ 800 million, were made during the conference to assist countries recovering from climate-induced disasters.
- Global Goal on Adaptation Establishment: COP28 adopted a global framework for adaptation, addressing a historic imbalance where adaptation efforts received less attention and resources compared to mitigation activities.
- The framework, though established, lacks financial provisions, necessitating further strengthening in subsequent years.
- Adaptation Challenges: While the global adaptation framework is a positive step, there is still work to be done, particularly in defining indicators for measuring progress on each global goal.
- Adaptation efforts historically focused on local initiatives, and the agreement aims to garner more attention and resources for these endeavours on a global scale.
- Climate Action Acceleration Shortcomings: The final agreement falls short of providing sufficient impetus for the acceleration of climate action in the immediate term.
What is the Conference of the Parties (COP)?
- In 1992, Rio Earth Summit, 154 countries joined an international treaty, the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change, as a framework for international cooperation to combat climate change by limiting average global temperature increases and the resulting climate change, and coping with impacts that were, by then, inevitable.
- The COP is the supreme decision-making body of the Convention.
- All States that are Parties to the Convention are represented at the COP, at which they review the implementation of the Convention and any other legal instruments that the COP adopts and take decisions necessary to promote the effective implementation of the Convention, including institutional and administrative arrangements.
- Currently, there are 198 'parties' or signatories of the Convention.
JALDOST airboat (The Hindu)

- 03 Aug 2023
Why in the News?
The National Aerospace Laboratories (NAL) recently revealed its latest creation, the JALDOST airboat.
What is JALDOST?
- JALDOST is an innovative airboat specifically designed for water operation, aimed at effectively removing excess aquatic weed and floating waste from various water bodies.
- The airboat features a closed, airtight pontoon-type hull, ensuring its inherent unsinkability.
- Notably, the JALDOST incorporates a hybrid propulsion system, combining air propulsion and paddle wheel propulsion, making it versatile and efficient in its movements.
- Operating through weed with ease, JALDOST serves as an ideal platform for collecting and transporting these undesirable aquatic plants to the shore.
- It achieves this through a steel mesh belt conveyor system situated at the front, which gathers the waste and deposits it on the horizontal deck conveyor.
- Upon reaching the shore, the collected waste is efficiently unloaded using a rear conveyor system, facilitating easy transfer to trucks or tractors.
- The National Aerospace Laboratories (NAL) has introduced two versions of the airboat, namely JALDOST Mark-1 and an upgraded version, JALDOST Mark-2, further enhancing its capabilities.
Green Rising initiative launched at RewirEd summit to empower Youth-Led climate solutions (DD News)

- 09 Dec 2023
What is the Green Rising Initiative?
- The "Green Rising" initiative focuses on engaging youth for impactful environmental actions at the grassroots level, aligning with the global effort to address the severe impacts of climate change.
- This initiative encompasses both the global "Green Rising" initiative and the "Green Rising India Alliance," a collaborative endeavor that brings together UNICEF, Generation Unlimited, and a diverse network of public, private, and youth partners.
- The primary objective is to mobilize millions of young individuals globally, encouraging their active engagement in green initiatives aimed at addressing and adapting to the profound impacts of climate change within their communities.
- In India, this effort is channelled through the YuWaah campaign, which specifically focuses on harnessing the energy and commitment of the youth to drive impactful environmental actions at the grassroots level.
About UNICEF:
UNICEF, or the United Nations International Children's Emergency Fund, is a specialized agency of the United Nations committed to promoting the well-being and rights of every child globally.
- Foundation and Establishment: Established in 1946 by the United Nations General Assembly, UNICEF was originally designed to provide emergency food and healthcare to children in countries devastated by World War II.
- Over time, UNICEF's scope evolved to include long-term developmental programs, focusing on education, healthcare, nutrition, clean water, sanitation, and protection for children in need.
- UNICEF is governed by an Executive Board consisting of 36 members who are elected to terms of three years by the United Nations Economic and Social Council.
- Universal Presence: UNICEF operates in over 190 countries and territories worldwide, making it one of the most extensive and widely recognized humanitarian organizations globally.
- Child Rights Advocacy: UNICEF is a leading advocate for children's rights, working to ensure that every child has the right to survive, thrive, and reach their full potential, regardless of their background or circumstances.
- Emergency Response: In times of crises, including natural disasters, conflicts, and pandemics, UNICEF plays a crucial role in providing immediate and life-saving assistance to affected children and communities.
- Partnerships and Collaborations: UNICEF collaborates with governments, non-governmental organizations (NGOs), other UN agencies, and the private sector to implement its programs and maximize its impact.
- Funding Mechanism: UNICEF is funded entirely by voluntary contributions from governments, private donors, businesses, and the general public. It relies on these funds to carry out its programs and respond to emergencies.
- Focus on Equality and Inclusion: UNICEF emphasizes the importance of equality and inclusion, working to address disparities and ensure that the most vulnerable children, including those with disabilities or from marginalized communities, are not left behind.
- Global Campaigns: UNICEF spearheads global campaigns to address critical issues affecting children, such as vaccination drives, education initiatives, and efforts to eliminate child labour and violence against children. These campaigns aim to rally public support and create awareness about the challenges faced by children worldwide.
- It was awarded the Nobel Prize for Peace in 1965 for the “promotion of brotherhood among the nations”.
- Headquarters: New York City
India is expected to withstand global shocks as its current account deficit improves due to falling crude oil prices. (ET)

- 09 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
After two years of battling inflation and growth pangs, the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) was in for a pleasant surprise when the economic growth trumped its expectations to hit 7.2 per cent in the last month.
Context:
- The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) has unveiled its most recent monetary policy report, projecting a robust economic recovery for the country in the current fiscal year.
- Anticipating a significant upswing, the central bank foresees the gross domestic product (GDP) to expand by 7 percent in 2021-22, a notable rebound from the 7.3 percent contraction witnessed in the preceding year.
- However, the RBI issues a cautionary note about the challenges posed by inflation, which has consistently exceeded the target range of 2-6 percent over several months.
- The report attributes inflationary pressures to supply-side disruptions, escalating commodity prices, increased fuel taxes, and demand-related factors.
- The RBI anticipates inflation to remain elevated in the short term before gradually moderating in the latter half of the year.
- The RBI's stance mirrors a delicate equilibrium, emphasizing the intricate balance between fostering economic growth and managing inflation, often characterized as the Goldilocks Effect.
- This effect alludes to a scenario where the economy is neither excessively overheated nor excessively sluggish but rather poised for optimal growth with minimal inflationary pressures.
What is the Goldilocks Effect?
- The Goldilocks Effect, also known as the Goldilocks Principle, posits that individuals have a predisposition to seek an amount that is 'just right' for their specific needs or preferences.
- This concept, derived from the children's story of Goldilocks and the Three Bears, reflects a preference for options that are neither too extreme nor too moderate, falling within an optimal and desirable range.
- This principle finds application across various fields and disciplines, encompassing psychology, hard sciences, economics, marketing, and engineering, each incorporating its unique interpretation of the principle.
- Goldilocks Pricing: One notable application of the Goldilocks Effect is in Goldilocks Pricing, a psychological pricing strategy grounded in concepts such as product differentiation, comparative pricing, and bracketing.
- Product differentiation involves distinguishing certain products from others, a crucial step for businesses looking to leverage the Goldilocks Effect.
- This differentiation is then coupled with comparative pricing, where businesses simultaneously offer multiple versions of a product with varying quality levels attached to corresponding price points.
- The strategy hinges on providing three options: one priced too high for most, one priced too low for most, and one priced just right.
- When executed effectively, this approach enables businesses to appeal to diverse segments of the market, capturing premium buyers, standard consumers, and discount seekers.
What is the Universal Declaration of Human Rights, which is marking its 75th anniversary? (Indian Express)

- 09 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
Seventy-five years ago on Sunday, the UN General Assembly approved the Universal Declaration of Human Rights at a meeting in Paris – laying one of the foundation stones of the international order that emerged following the horrors of World War II.
What is the Universal Declaration of Human Rights (UDHR)?
- On 10 December 1948, during a session in Paris, the United Nations General Assembly unanimously endorsed the Universal Declaration of Human Rights (UDHR), marking a pivotal moment in shaping the post-World War II international order.
- The UDHR emerged as a response to wartime atrocities and aimed to establish a shared understanding of the fundamental rights and freedoms inherent to all individuals.
- A concise yet impactful document, the declaration comprises a preamble and 30 articles that delineate essential rights and freedoms.
- These 30 articles encompass a comprehensive spectrum of civil, political, economic, social, and cultural rights.
- Emphasizing their universality, these rights are deemed applicable to all individuals, irrespective of nationality, ethnicity, gender, religion, or any other status.
- While not legally binding, the UDHR has functioned as a guiding force inspiring the development of international human rights law.
Key Features:
- Preamble: The preamble elucidates the reasons behind adopting the declaration, underscoring the inherent dignity and the equal and inalienable rights of all members of the human family.
- Articles: The UDHR articulates 30 articles outlining a wide array of civil, political, economic, social, and cultural rights. Examples of these rights include:
- The right to life, liberty, and security of person.
- The right to freedom of religion, expression, and assembly.
- The right to work and education.
- The right to an adequate standard of living.
- The declaration asserts that "all are equal before the law" and emphasizes the entitlement of everyone to "a fair and public hearing by an independent and impartial tribunal."
- It also affirms the right of "everyone to seek and to enjoy in other countries asylum from persecution.
Achievements of UNDHR:
- The United Nations Universal Declaration of Human Rights (UNDHR) is acknowledged for its significant impact, having served as the inspiration and foundation for over 70 human rights treaties at both global and regional levels, as noted by the United Nations.
- It played a pivotal role in inspiring movements such as decolonization, the anti-apartheid movement, and various struggles for freedom worldwide, including those related to gender, LGBTIQ+ rights, and opposition against racism.
What is the Current Situation?
- As the 75th anniversary is commemorated, human rights face challenges amid conflicts such as the Israel-Hamas war, Russia's actions in Ukraine, internal strife in Myanmar and Sudan, and numerous other global situations.
- UN Secretary-General Antonio Guterres has remarked that the Universal Declaration has been frequently misused and abused, exploited for political gain, and often ignored by those who should uphold it.
- Contrastingly, Amnesty International asserts that the declaration serves as living proof that a global vision for human rights is attainable and can be realized.
- Despite instances of neglect or exploitation, the declaration remains relevant, and the world is encouraged to recognize its successes while learning from its failures.
Amit Shah to chair 26th meeting of Eastern Zonal Council in Bihar on Sunday (Business Standard)

- 09 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
Union Home Minister Amit Shah will chair the 26th meeting of the Eastern Zonal Council in Bihar's capital on Sunday, the Ministry of Home Affairs (MHA) said on Saturday.
What are Zonal Councils?
- The conceptualization of Zonal Councils can be attributed to the visionary initiative of India's first Prime Minister, Pandit Jawahar Lal Nehru, in 1956.
- These councils are statutory bodies established by an Act of Parliament, namely the States Reorganisation Act of 1956.
- The act delineated the country into five zones (Northern, Central, Eastern, Western, and Southern), assigning a Zonal Council to each.
Present Composition of Zonal Councils:
- Northern Zonal Council: Includes Haryana, Himachal Pradesh, Jammu & Kashmir, Punjab, Rajasthan, National Capital Territory of Delhi, and Union Territory of Chandigarh.
- Central Zonal Council: Encompasses Chhattisgarh, Uttarakhand, Uttar Pradesh, and Madhya Pradesh.
- Eastern Zonal Council: Comprises Bihar, Jharkhand, Orissa, and West Bengal.
- Western Zonal Council: Involves Goa, Gujarat, Maharashtra, and the Union Territories of Daman & Diu and Dadra & Nagar Haveli.
- Southern Zonal Council: Consists of Andhra Pradesh, Karnataka, Kerala, Tamil Nadu, and the Union Territory of Puducherry.
- Exclusion and Special Council: The North Eastern States (Assam, Arunachal Pradesh, Manipur, Tripura, Mizoram, Meghalaya, and Nagaland) are not part of Zonal Councils.
- Instead, their unique challenges are addressed by the North Eastern Council, established under the North Eastern Council Act of 1972.
- Sikkim was included in the North Eastern Council in 2002.
Organizational Structure:
- Chairman: The Union Home Minister serves as the Chairman for each Zonal Council.
- Vice Chairman: Chief Ministers of the states in each zone act as Vice-Chairman, rotating annually.
- Members: Chief Minister and two nominated Ministers from each state, along with two members from Union Territories in the zone.
- Advisers: Planning Commission nominees, Chief Secretaries, and another officer/Development Commissioner from each state in the zone.
Objectives:
- The primary objectives of Zonal Councils include promoting national integration and curbing acute State consciousness, regionalism, linguism, and particularistic tendencies.
- Additionally, they aim to facilitate cooperation, idea exchange, and a climate of collaboration among states for the successful execution of development projects.
Functions:
- Zonal Councils function as advisory bodies, empowered to discuss common interests between the Union and represented states.
- They can recommend courses of action to the Central Government and individual state governments.
- Specific areas of discussion may include economic and social planning, border disputes, linguistic minorities, inter-state transport, and matters arising from the reorganization of states under the States Reorganisation Act.
Navy plans to get undersea chariots, made in India, for special operations (Indian Express)

- 09 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
The Indian Navy is planning to acquire indigenously made swimmer delivery vehicles — also known as underwater chariots and midget submarines — as part of efforts to modernise and strengthen the capabilities of its Marine Commandos (MARCOS) for special undersea operations.
News Summary:
- In a strategic move, the Indian Navy set to deploy domestically manufactured undersea chariots for specialized operations.
- These innovative vessels, designed to accommodate a crew of at least six, will be equipped with cutting-edge lithium-ion batteries for enhanced performance.
- The significant size of these undersea chariots opens up new possibilities, allowing divers to transport larger cylinders.
- This advancement translates to extended underwater missions, thereby amplifying operational capabilities in shallow waters.
- Moreover, the spacious design of these chariots facilitates the carriage of extra weaponry, providing the Navy with increased flexibility for diverse and complex operations.
- This development signifies a noteworthy stride in bolstering the Navy's underwater capabilities through indigenous technological advancements.
What are Chariots?
- Nearly all modern navies in the world use chariots, which are extremely specialized platforms.
- These self-propelled vehicles can be deployed from ships or submarines, tailored to their size and designated roles.
- Notably, during World War II, manned human torpedoes were commonly referred to as chariots.
- Functionality: Chariots prove invaluable for naval operations in shallow waters, offering a spectrum of missions.
- These include shallow-water surveillance, targeted assaults on adversary coastal installations, and even engagements with ships in harbours.
- Particularly advantageous is their ability to grant marine commandos access to areas close to adversary harbours—locations that submarines, constrained by shallow waters, may find challenging to reach.
- Furthermore, these chariots facilitate the efficient transportation of weapons and equipment to operational zones.
- Utilization in India: While detailed information on the swimmer delivery vehicles employed by the Indian Navy is not widely available, some sources suggest the utilization of Italian-made chariots for several years.
- Around 2012, recognizing the strategic importance of these platforms, the Ministry of Defence entrusted Hindustan Shipyard Limited with the construction of two such submarines, underscoring India's commitment to enhancing its maritime capabilities.
What are Marine Commandos (MARCOS)?
- The Marine Commandos, known by the acronym MARCOS and formally recognized as the Marine Commando Force (MCF), stand as the specialized forces within the Indian Navy entrusted with the execution of special operations.
- Established in February 1987, MARCOS possesses versatile capabilities to operate effectively across diverse environments, encompassing sea, air, and land.
- Over time, the force has accumulated valuable experience, earning an esteemed international reputation for its high level of professionalism.
- MARCOS routinely engage in specialized maritime operations in regions such as Jammu and Kashmir, navigating the Jhelum River and Wular Lake with precision and expertise.
Iberian wolf (DownToEarth)

- 03 Aug 2023
Why in the News?
As per the regional government, the Iberian wolf (Canis lupus signatus) has been declared extinct in the historical region of Andalusia, located in the southernmost part of Iberia, since the year 2020.
About the Iberian Wolf:
- The Iberian wolf is a subspecies of the Grey wolf, distinguished by its prolonged isolation from other wolf populations for over a century.
- With the largest wolf population in Western Europe, this magnificent species is native to the Iberian Peninsula, encompassing Spain and Portugal.
- Thriving in diverse habitats, Iberian wolves inhabit forests, inland wetlands, shrublands, grasslands, pastures, and mountainous areas.
- These wolves lead a social lifestyle, living, hunting, and traveling in small packs.
- Each pack includes the alpha male and female, along with their young and older offspring.
- The alphas serve as the pack leaders, responsible for establishing territory, selecting den sites, tracking down, and hunting prey.
- Primarily carnivorous, the Iberian wolf's diet comprises various animal species.
- With regard to conservation, the Iberian wolf holds the status of "Vulnerable" according to the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN).
PM Street Vendor’s AtmaNirbhar Nidhi (PM SVANidhi) Schemer (Indian Express)

- 03 Aug 2023
Why in the News?
The Union Housing and Urban Affairs Ministry has recently announced a fresh target for its PM SVANidhi scheme, focusing on empowering street vendors.
About PM Street Vendor’s AtmaNirbhar Nidhi (PM SVANidhi) Scheme:
- Launched on June 01, 2020, by the Ministry of Housing and Urban Affairs, the PM SVANidhi Scheme aims to assist street vendors affected by the Covid-19 lockdown in reviving their livelihoods.
- As a micro-credit initiative, it provides street vendors with a collateral-free loan of Rs. 10,000 at a low-interest rate (below 12%) for one year, facilitating their financial recovery.
- Originally scheduled until March 2022, the scheme has now been extended till December 2024 with a focus on expanding the affordable loan corpus, encouraging digital transactions, and promoting holistic socio-economic development for street vendors and their families.
- Eligibility for the loan requires street vendors who were vending on or before March 24, 2020, and hold a certificate of vending issued by the Town Vending Committees (comprising local authorities and vendors) after conducting a survey.
- The scheme offers several benefits, including an interest subsidy of 7% per annum on timely loan repayment, no penalty on early repayment, cash back incentives up to Rs. 100 per month to promote digital transactions, and the possibility of credit limit escalation for prompt loan repayment.
- The Small Industries Development Bank of India (SIDBI) serves as the implementation agency for the scheme, ensuring efficient delivery and monitoring of financial support to street vendors across the country.
Lumpy Skin Disease (LSD) (Indian Express)
- 03 Aug 2023
Why in the News?
The Telangana High Court's division bench recently conveyed its discontentment over the absence of specific information regarding measures taken to manage the outbreak of Lumpy Skin Disease (LSD) in cattle.
What is Lumpy Skin Disease (LSD):
- Lumpy Skin Disease (LSD) is a highly infectious viral disease that affects cattle, ranging from acute to chronic in nature.
- It is caused by the lumpy skin disease virus (LSDV), belonging to the genus Capripoxvirus within the poxviridae family (related to smallpox and monkeypox viruses), but it is not zoonotic, meaning it does not spread to humans.
- Symptoms of LSD include the enlargement of lymph nodes, resulting in lumps on the cattle's skin, primarily appearing on the head, neck, limbs, udder, genitalia, and perineum.
- The cutaneous nodules, usually 2–5 cm in diameter, may develop into ulcers and scabs over time.
- Other signs of infection include high fever, reduced milk yield, nasal and ocular discharge, salivation, loss of appetite, depression, damaged hides, emaciation, infertility, and abortions.
- Transmission occurs through blood-feeding insects such as certain flies, mosquitoes, and ticks, as well as the movement of affected animals and contaminated equipment.
- Direct animal-to-animal transmission can also occur in some cases.
- While no direct antiviral treatment is available for LSD, supportive care is provided to infected animals, including the use of antibiotics, painkillers, and wound care sprays to alleviate symptoms.
- Vaccines are used to control disease transmission, as there is no specific cure.
- LSD is economically significant as it can lead to temporary reductions in milk production, temporary or permanent sterility in bulls, hide damage, and, in some instances, fatalities among the affected cattle population.
ZARTH App (The Hindu)

- 02 Aug 2023
Why in the News?
The Center for Data-Driven Discovery at the California Institute of Technology has recently unveiled the ZARTH app, enabling smartphone users to actively search for transients.
What is ZARTH App?
ZARTH (ZTF Augmented Reality Transient Hunter) combines the excitement of an augmented reality mobile game with serious scientific pursuits. This innovative app empowers users to engage in real science while enjoying a gaming experience.
Key Features:
- Leveraging the open-source Sky Map, the ZARTH app integrates daily data from the Zwicky Transient Facility (ZTF) at California's Palomar Observatory.
- The Palomar Observatory houses the prestigious 200-inch Hale reflector, one of the world's oldest and most powerful telescopes.
- The ZTF conducts bi-daily scans of the entire northern sky, generating crucial large-area sky maps with applications in tracking near-earth asteroids and studying supernovae.
- Each day, the ZARTH app receives real-time data on transients detected by the ZTF, including flaring stars, white dwarf binaries, active galactic nuclei, and other intriguing types.
- Transients are ranked based on rarity and significance, fostering a competitive environment among players who strive to earn points and daily credits displayed on leaderboards.
Offshore Areas Minerals (Development and Regulation) Amendment Bill, 2023 (Indian Express)

- 02 Aug 2023
Why in the News?
The Offshore Areas Minerals (Development and Regulation) Amendment Bill, 2023, has been successfully passed by the Lok Sabha.
The Offshore Areas Minerals (Development and Regulation) Amendment Bill, 2023:
It seeks to amend the existing Offshore Areas Mineral (Development and Regulation) Act, 2002, to regulate mining activities in India's maritime zones.
The key highlights of the Bill include:
- Reservation of Offshore Areas: The government is empowered to reserve offshore areas not under any operating rights.
- Composite Licence and Production Lease: The administering authority can grant composite licenses or production leases to the government or a government company.
- Fixed Production Lease Period: The provision for renewal of production leases is removed, and a fixed period of fifty years, akin to the Mines and Minerals (Development and Regulation) Act 1957, is introduced.
- Auction-Based Allocation: Private sector entities can acquire production leases through auction by competitive bidding.
- Operating Rights for Government Entities: Operating rights without competitive bidding can be granted to government or government companies or corporations in mineral-bearing areas reserved by the central government.
- Atomic Minerals: For atomic minerals, exploration licenses or production leases can only be granted to the government or government corporations.
- Production Commencement Timeline: A four-year timeline for production commencement and dispatch after the execution of composite licenses or production leases is introduced, with a two-year timeline (extendable by one year) for re-commencement of production and dispatch after discontinuation.
- Framing Rules for Conservation and Environment: The central government is enabled to establish rules for mineral conservation and systematic development in offshore areas, along with measures to protect the environment and control pollution resulting from exploration or production operations.
eSanjeevani (India's Integrated Telemedicine Solution ) (Indian Express)

- 02 Aug 2023
Why in the News?
The Union Health Minister revealed to the Rajya Sabha that the eSanjeevani telemedicine application, introduced by the Centre, has successfully conducted a remarkable 14,17,81,384 teleconsultations.
About eSanjeevani:
- eSanjeevani is an integrated telemedicine solution, hosted on the cloud, developed by the Ministry of Health and Family Welfare, Government of India.
- This telemedicine app facilitates seamless communication between doctors and patients as well as doctor-to-doctor interactions.
- The Centre for Development and Advanced Computing (C-DAC), Mohali, is responsible for the design, development, deployment, and maintenance of this platform.
- The eSanjeevani system consists of two essential modules:
- eSanjeevani AB-HWC:
- This module serves as a doctor-to-doctor telemedicine platform, strategically implemented across all Health and Wellness Centres (HWCs) in the country under the Ayushman Bharat Scheme.
- It operates on a Hub-and-Spoke model, with zonal hubs comprising MBBS/Specialty/Super-Specialty doctors connected to state-level Ayushman Bharat-Health and Wellness Centers.
- eSanjeevani OPD:
- Rolled out in 2020 during the initial Covid-19 lockdown when outpatient departments (OPDs) were closed, this module enables patient-to-doctor remote consultations.
- People can access outpatient services from the comfort of their homes, ensuring healthcare accessibility during challenging times.
- eSanjeevani represents a significant step towards enhancing healthcare accessibility and digital healthcare services across India.
Infrastructure investment trust (InvIT) (Business Standard)

- 02 Aug 2023
Why in the News?
The government is actively developing a proposal to introduce a new Infrastructure Investment Trust (InvIT) dedicated to national highways. This initiative aims to enable domestic retail investors to own units of the trust, expanding opportunities for individual investors to participate in highway infrastructure projects.
What is Infrastructure Investment Trust (InvIT)?
- An Infrastructure Investment Trust (InvIT) functions as a Collective Investment Scheme, offering a pathway for both individual and institutional investors to directly invest in diverse infrastructure projects.
- Operating akin to mutual funds, InvITs are established as trusts and undergo registration with Sebi (Securities and Exchange Board of India).
- InvITs involve four key parties:
- the Trustee, Sponsor(s), Investment Manager, and Project Manager. The Sebi-certified Trustee assumes the crucial role of overseeing the InvIT's performance. Meanwhile, the Sponsor(s) act as the company's promoters responsible for creating and setting up the InvIT.
- Overall, InvITs present an attractive investment option, as they allow investors to participate in the development of vital infrastructure projects while enjoying the benefits of a collective investment structure similar to mutual funds.
What is NHAI InvIT?
- NHAI InvIT is an infrastructure investment trust proudly sponsored by the National Highways Authority of India (NHAI) to bolster the government's National Monetisation Pipeline (NMP) initiative.
- This Trust has been established by NHAI in accordance with the Indian Trusts Act, of 1882, and adheres to the regulations set forth by SEBI (Security and Exchange Board of India).
- The NHAI InvIT plays a vital role in supporting the nation's infrastructure development by providing a platform for investors to participate in highway projects' growth and monetization.
- Through this innovative investment vehicle, NHAI aims to tap into private and institutional investments to enhance the funding and execution of critical infrastructure projects across the country, ultimately contributing to India's overall economic progress.
TransLunar Injection (TLI) (The Hindu)
- 02 Aug 2023
Why in the News?
The TransLunar Injection (TLI) was performed successfully from ISRO Telemetry, Tracking and Command Network (ISTRAC) in Bengaluru recently.
What is the TransLunar Injection (TLI)?
- TransLunar Injection (TLI) is a crucial space mission maneuver, propelling spacecraft from Earth's orbit to a trajectory aimed at reaching the Moon.
- An essential step in lunar missions, TLI allows spacecraft to break free from Earth's gravity and commence their journey toward the Moon.
- TLI is executed when the spacecraft reaches the perigee, the closest point to Earth in its orbit.
- During TLI, the spacecraft's propulsion system ignites its engines, accelerating the craft and providing the necessary speed to escape Earth's gravitational pull.
- The thrust and duration of the TLI burn are determined by factors like spacecraft mass, Earth's orbital velocity, and specific mission objectives.
- Following a successful TLI, the spacecraft is directed onto a lunar trajectory, continuing its autonomous journey to the Moon without further reliance on Earth's propulsion.
- Subsequent to TLI, the spacecraft enters a transfer orbit, an elliptical path that intersects with the Moon's orbit.
- The spacecraft traverses this highly eccentric orbit until it reaches the lunar surface.
- As the spacecraft approaches the Moon, additional maneuvers like lunar orbit insertion (LOI) may be executed to enter lunar orbit or facilitate landing, based on the mission's objectives.
- TLI has been effectively utilized in numerous Moon missions, including Apollo, Chang'e, and Artemis missions.
National Digital Nagrik Forum (Indian Express)

- 01 Aug 2023
Why in the News?
The forum by the Confederation of All India Traders (CAIT) aims to raise awareness about digital regulations and help build the capacities of citizens to engage with innovation via expert sessions and instructional materials.
About the National Digital Nagrik Forum:
- The National Digital Nagrik Forum is an online platform with the primary goal of advancing the rights of traders, consumers, and various sections of society, while also influencing policy to foster the growth of the digital trade economy.
- Through expert sessions and instructional materials, the forum aims to raise awareness about digital regulations and empower citizens to engage with innovation effectively.
- The main objective is to shape policy discourse around the digital economy trade in India, aligning with the Government of India's vision of establishing a trillion-dollar digital economy.
- Simultaneously, it seeks to maintain an open, safe, trusted, and accountable Internet ecosystem.
- The forum will conduct awareness camps, digital and physical dialogues, and training sessions.
- It will also engage in targeted outreach to stakeholders from the government, private sector, and civil society.
- The National Digital Nagrik Forum will concentrate on five core themes:
- The first pillar focuses on consumer protection and online safety, with a central emphasis on efficient grievance redressal mechanisms.
- The second pillar addresses the challenges of digital cartelization, advocating for a level-playing field to discourage discriminatory and anti-competitive practices in the online world.
- The third pillar explores the potential of Indian digital technologies to transform retail and industrial trade, while also contributing to employment growth and expanding investment opportunities.
- The fourth pillar advocates for a first principles-based taxation policy that fosters certainty and productivity, especially for sectors with high growth potential. It simultaneously works to prevent illegal activities like tax evasion and money laundering.
- The fifth pillar conducts research on emerging technologies such as blockchain and artificial intelligence to assess their impact on retail trade and ensure the protection of consumers' interests.
- The National Digital Nagrik Forum aims to make significant contributions towards shaping a vibrant digital economy in India, fostering fair trade practices, and safeguarding the interests of both consumers and traders.
Room-temperature Superconductor (The Hindu)

- 01 Aug 2023
Why in the News?
Korean researchers claim to have developed a superconductor that can operate at room temperature and ambient pressure.
What have the researchers developed?
- The researchers assert that they have created a superconductor named LK-99, which operates at room temperature and under ambient pressure.
- LK-99 is a combination of powdered compounds containing lead, oxygen, sulphur, and phosphorus.
- Upon heating at extremely high temperatures, it transforms into a dark grey solid.
- The potential significance of this discovery is immense, provided other laboratories can replicate these results.
- Nevertheless, some researchers remain skeptical as this study has not undergone peer review, and the results must be independently reproduced by other scientific groups.
What is a Superconductor?
- A superconductor is a material that exhibits superconductivity, a unique state of matter characterized by the absence of electrical resistance and the exclusion of magnetic fields.
- In a superconductor, an electric current can flow indefinitely without any hindrance.
- Superconductors have significant practical applications in our everyday lives.
- In 1933, Walther Meissner and Robert Ochsenfeld discovered that superconductors act as perfect diamagnets, repelling magnetic fields, a phenomenon known as the Meissner effect.
- This property makes them ideal for applications like magnetic resonance imaging (MRI).
- However, achieving superconductivity typically requires extremely low temperatures.
- Currently, researchers are actively exploring and developing superconductors that can operate at room temperature, a groundbreaking advancement that would revolutionize various technologies and industries.
How will the room-temperature superconductors help?
- The use of room-temperature superconductors can offer significant benefits in various applications.
- Typically, the critical temperature of conventional superconductors is below 10 Kelvin (-263 degrees Celsius), whereas room temperature is around 20-22°C.
- By having superconductors that function at room temperature, the cost of electricity grids, computer chips, magnets for maglev trains, energy-storage devices, and fusion reactors can be reduced significantly.
- This is achieved through electricity and cost savings on coolants, as the need for extreme cooling methods is eliminated.
- The widespread adoption of room-temperature superconductors holds the potential to revolutionize multiple industries, making them more efficient and cost-effective.
Nasha Mukt Bharat Abhiyan (NMBA) (The Hindu)

- 01 Aug 2023
Why in the News?
During the Man ki Baat program, the Prime Minister announced that India achieved a remarkable feat by destroying 10 lakh kilograms of drugs worth ?12,000 crore in the previous year.
What is Nasha Mukt Bharat Abhiyan (NMBA)?
- Launched on: The NMBA was launched on 15th August 2020.
- Nodal Ministry: The Ministry of Social Justice & Empowerment oversees the implementation of NMBA.
- Aim: The primary objective of NMBA is to raise awareness about the harmful consequences of substance abuse, with a special focus on youth, women, and children.
- It aims to reach out to higher education institutes, university campuses, schools, and the broader community, encouraging community involvement and ownership of the initiative.
- Implementation: NMBA is implemented in 372 vulnerable districts, identified based on the findings of the first Comprehensive National Survey and inputs from the Narcotics Control Bureau (NCB).
- Significance:
- NMBA targets and engages various stakeholders directly or indirectly affected by substance abuse, as well as those vulnerable to it.
- The major beneficiaries of NMBA include youth, women, children, educational institutions, civil society, and the community at large.
- This approach emphasizes community involvement rather than just organizational participation in addressing the issue of substance abuse.
Cell-free DNA (The Hindu)
- 01 Aug 2023
Why in the News?
Over the past two decades, as genome sequencing technologies have become increasingly accessible, scientists have made significant strides in understanding the applications of Cell-free DNA.
Regarding Cell-free DNA:
- In the human body, a significant portion of the DNA in the genome is safely enclosed within cells, safeguarded by specific proteins to prevent degradation.
- However, in various circumstances, certain DNA fragments are liberated from their confines and can be found outside the cells, circulating in body fluids.
- These minute fragments of nucleic acids are commonly referred to as cell-free DNA (cfDNA).
How Cell-free DNA is generated/released?
- The generation and release of Cell-free DNA (cfDNA) can occur through various mechanisms.
- One such process is when a cell undergoes cell death, leading to the degradation of nucleic acids and subsequent release of cfDNA.
- The degradation of cfDNA is influenced by a diverse set of processes, resulting in variations in the amount, size, and origin of cfDNA.
- Furthermore, this release of cfDNA can be associated with different biological processes, including those essential for normal development, the progression of certain cancers, and various other diseases.
- The generation and release of cfDNA can be triggered by a range of situations and processes, making it a versatile biomarker with potential implications in various health conditions.
Applications of Cell-free DNA (cfDNA):
- One of the most prevalent uses of cfDNA is in non-invasive prenatal testing, where it aids in screening fetuses for specific chromosomal abnormalities.
- Also, cfDNA serves as a valuable tool for comprehending human diseases and leveraging this knowledge to enhance diagnosis, monitoring, and prognosis.
- cfDNA plays a crucial role in understanding the rejection of transplanted organs by the body.
- It shows promise as a potential biomarker for various neurological disorders, including Alzheimer's disease, neuronal tumors, stroke, and traumatic brain injury.
Cocos (Keeling) Islands (The Hindu)
- 01 Aug 2023
Why in the News?
A maritime patrol aircraft from the Indian Navy and a transport aircraft from the Indian Air Force (IAF) made a visit to Australia's Cocos (Keeling) Islands (CKI) recently.
About Cocos (Keeling) Islands:
- Location:
- The Cocos (Keeling) Islands are situated in the eastern Indian Ocean, approximately 2,900 kilometers (1,800 miles) northwest of the Australian city of Perth.
- Geography:
- Comprising coral atolls and islands, the archipelago includes North Keeling Island and the South Keeling Islands.
- Administrative Headquarters:
- The territory's administrative headquarters are located on West Island, situated in the southern atoll.
- Climate:
- The islands experience a warm and humid climate.
- Vegetation:
- The predominant vegetation consists of coconut palms, which were previously cultivated for copra on plantations.
- On North Keeling and Horsburgh islands, coarse grass serves as the primary ground cover.
- National Park:
- The northern atoll is home to Australia's most remote Commonwealth National Park, known as the Pulu Keeling National Park.
- Inhabitants:
- The population of the islands mainly comprises descendants of the original plantation workers, predominantly of Malay origin.
- Administration:
- The Cocos (Keeling) Islands are governed by an administrator appointed by the Australian governor-general. The islands became an Australian territory under the Cocos (Keeling) Islands Act 1955.
Worldcoin Project (The Hindu)

- 31 Jul 2023
Why in the News?
In a recent announcement, the CEO of OpenAI officially reintroduced his Worldcoin project, which had previously taken a backseat to the widespread popularity of ChatGPT.
What is Worldcoin Project?
- The Worldcoin Project aims to establish a digital network that enables everyone to participate and claim some form of stake in the digital economy.
- The project operates on a straightforward model:
- Individuals can prove their uniqueness as humans by allowing their eyes to be scanned, and in return, they receive a cryptocurrency reward and an identification called a "World ID."
- Worldcoin relies on a device called "Orb," which is used by volunteers known as "Orb operators."
- These operators scan a person's iris pattern to collect their biometric data and facilitate the issuance of a World ID through the World app.
- Participants who have been scanned can use the World app to receive the Worldcoin cryptocurrency at regular intervals or engage in transactions using their World ID wherever applicable.
- This process, known as "proof of personhood," ensures that individuals cannot register multiple times to gain more crypto rewards.
Voyager 2 Spacecraft (HT)

- 31 Jul 2023
Why in the News?
NASA’'s Voyager 2 spacecraft, which is venturing through space between stars, faces communication problems due to antenna misalignment. .
About Voyager 2 Spacecraft:
- Voyager 2 is an iconic interplanetary spacecraft launched by NASA on August 20, 1977, with the primary objective of exploring the outer planets of our solar system.
- It is part of the Voyager program, and along with its twin, Voyager 1, it has provided invaluable insights into the distant regions of our cosmic neighborhood.
- The spacecraft is equipped with a suite of scientific instruments to study various aspects of the planets it encounters, including their atmospheres, magnetic fields, and planetary surfaces.
- Voyager 2 successfully conducted close flybys of Jupiter in 1979, Saturn in 1981, Uranus in 1986, and Neptune in 1989, becoming the first and only spacecraft to visit these four giant gas planets.
- Beyond its initial mission, Voyager 2 continues to be operational and remains in communication with Earth, traveling at an impressive speed of approximately 34,000 miles per hour (55,000 kilometers per hour).
- It has since left the heliosphere, the region influenced by the Sun's magnetic field, and entered interstellar space, becoming the second human-made object to do so after Voyager 1.
- Throughout its journey, Voyager 2 has provided a wealth of data and discoveries about the outer planets and their moons, as well as valuable information about the space environment outside the solar system.
- It has captured breathtaking images of planetary systems, revealing the beauty and complexity of the outer planets and their fascinating moons.
- The spacecraft continues to be a remarkable testament to human ingenuity and curiosity as it ventures farther into the cosmos, providing us with an enduring legacy of exploration and knowledge about our celestial neighbors.
GOBARdhan Initiative (PIB)

- 31 Jul 2023
Why in the News?
Recently, Union Minister for Jal Shakti has launched the Unified Registration Portal for GOBARdhan.
About GOBARdhan Initiative:
- GOBARdhan (Galvanizing Organic Bio-Agro Resources Dhan) initiative was launched in 2018.
- Aim:
- The primary goal of the initiative is to convert waste to wealth by promoting a circular economy.
- Nodal Ministry:
- The GOBARdhan Initiative is under the Department of Drinking Water and Sanitation, Ministry of Jal Shakti.
- Gobardhan is an integral part of Swachh Bharat Mission (Gramin) Phase II, focusing on Solid Waste Management.
- Objectives:
- To assist villages in safely managing their cattle and agricultural waste, leading to cleaner villages.
- To help communities convert cattle and organic waste into wealth using treatment systems.
- To transform organic waste, especially cattle waste, into biogas and organic manure for utilization in rural areas.
- To promote environmental sanitation and control vector-borne diseases by effectively disposing of waste in rural regions.
- To create employment and income-generation opportunities in rural areas by involving entrepreneurs, Self-Help Groups (SHGs), and youth groups in setting up, operating, and managing GOBARdhan units.
- Financial Incentive:
- The Government of India provides technical assistance and financial support of up to 50 lakhs for each district to achieve the safe disposal of cattle and organic waste as part of the initiative.
ULLAS Initiative (PIB)

- 31 Jul 2023
Why in the News?
In New Delhi, the logo, slogan "Jan Jan Sakshar," and mobile application of ULLAS were recently unveiled by Shri Dharmendra Pradhan, the Union Minister of Education and Minister of Skill Development and Entrepreneurship.
About the ULLAS Initiative:
- The ULLAS (Understanding Lifelong Learning for All in Society) initiative, holds the potential to revolutionize education and literacy nationwide.
- Its primary objective is to create a learning ecosystem that reaches every individual, bridging the gaps in basic literacy and essential life skills.
- Targeting citizens aged 15 and above who missed the opportunity to attend formal schooling, the initiative imparts basic education, digital and financial literacy, and critical life skills.
- Implementation is driven by volunteerism, emphasizing community participation.
- The slogan of the initiative is "ULLAS: Nav Bharat Saksharta Karyakram."
- To support its goals, the ULLAS app was launched, designed with user-friendliness and interactivity in mind.
- Available on both Android and iOS platforms, the app serves as a digital gateway for learners to access a diverse range of learning resources through the DIKSHA portal of NCERT.
- The ULLAS app facilitates the registration of learners and volunteers, either through self-registration or with the assistance of surveyors.
- Significance:
- This app plays a crucial role in promoting functional literacy, vocational skills, and vital life skills such as financial literacy, legal literacy, digital literacy, and empowering citizens to actively participate in nation-building efforts.
- Furthermore, the ULLAS Initiative nurtures a culture of continuous learning and knowledge-sharing within communities across India, fostering a brighter future for the nation.
Parkachik Glacier (Indian Express)

- 31 Jul 2023
Why in the News?
According to a recent study by scientists from the Wadia Institute of Himalayan Geology, the rapid ice melt of the Parkachik Glacier in Ladakh is anticipated to lead to the formation of three glacial lakes.
Regarding the Parkachik Glacier:
- The Parkachik Glacier, stretching 14 km in length and covering approximately 53 square km, stands as one of the largest glaciers in the Suru River valley.
- This valley is situated within the southern Zanskar Ranges of the western Himalayas.
- The glacier's accelerated melting can be attributed to two primary factors.
- Firstly, the effects of global warming and rising temperatures in the area contribute to this phenomenon.
- Secondly, its lower altitude compared to other glaciers in the Zanskar region also plays a significant role in the rapid melting process.
- Also, its relatively lower altitude compared to other glaciers in the Zanskar region contributes to its vulnerability to melting.
Important details about the Zanskar Ranges:
- Location:
- Zanskar is a high-altitude semi-desert situated on the Northern flank of the Great Himalayan Range.
- Climatic Influence:
- The Zanskar Ranges serve as a climatic barrier, shielding Ladakh and Zanskar from much of the monsoon weather. Consequently, the region experiences a pleasantly warm and dry climate during the summer months.
- Flora:
- The lower reaches of Zanskar's valleys harbor most of its vegetation, primarily consisting of alpine and tundra species.
- Fauna:
- Zanskar is home to diverse wildlife, including marmots, bears, wolves, snow leopards, kiangs (Tibetan wild asses), bharals (Himalayan blue sheep), alpine Ibex, wild sheep and goats, and the impressive lammergeier, also known as the bearded vulture.
National Coal Index (AIR)
- 27 Jul 2023
Why in the News?
The National Coal Index (NCI) has shown a significant decline of 33.8 per cent in May this year at 157.7 points compared to May last when it was at 238.3 points. It indicates a strong supply of coal in the market, with sufficient availability to meet the growing demands.
About National Coal Index:
- Launch Date:
- The National Coal Index was introduced in the year 2020.
- Ministry:
- Developed under the purview of the Ministry of Coal, India.
- The esteemed Indian Statistical Institute, Kolkata, played a key role in creating the index as part of India's transition away from coal.
- Price Index:
- It serves as a price index, reflecting changes in the price level of coal during a specific month relative to the fixed base year.
- Objective:
- The primary objective of the National Coal Index is to offer an accurate reflection of the market price of coal.
- Base Year:
- The base year for the index is 2017-18.
- Inclusive Prices:
- The price index amalgamates coal prices from various sales channels, including Notified Prices, Auction Prices, and Import Prices.
- The National Coal Index combines coal prices from all sales channels, including notified prices, auction prices and import prices.
- It serves as a reliable indicator of market dynamics, providing valuable insights into coal price fluctuations.
- The National Coal Index (NCI) has shown a significant decline of 33.8% in May 2023 compared to May 2022, which suggests significant reduction in coal prices.
- This indicates a strong supply of coal in the market, with sufficient availability to meet the growing demands.
Resource Efficiency and Circular Economy Industry Coalition (RECEIC) (Indian Express)

- 27 Jul 2023
Why in the News?
Union Environment, Forest and Climate Change Minister Bhupender Yadav on Thursday launched a Resource Efficiency Circular Economy Industry Coalition (RECEIC), conceptualised under India’s G20 Presidency, to promote the practices of resource efficiency and circular economy globally.
About Resource Efficiency and Circular Economy Industry Coalition (RECEIC):
- RECEIC was launched in 2023 at Chennai, Tamil Nadu, with the honorable presence of Shri Bhupender Yadav, Minister for Environment, Forest, and Climate Change.
- The launch event witnessed the participation of distinguished guests, including the Commissioner on Environment from the European Union and esteemed Ministers from Canada, France, Italy, Denmark, Mauritius, and the United Arab Emirates.
- Industry-Driven Initiative:
- RECEIC is an industry-led initiative with a primary goal of fostering global resource efficiency and circular economy practices.
- Embracing the circular economy model, RECEIC promotes production and consumption practices involving sharing, leasing, reusing, repairing, refurbishing, and recycling materials and products to maximize their utility.
- Sustainable Impact:
- The coalition is envisioned to be a self-sustaining entity, committed to lasting environmental sustainability, beyond India's G20 Presidency.
- Founding Members:
- With 39 companies headquartered in 11 different countries, the coalition boasts a diverse group of founding members.
- As a collaborative platform, RECEIC fosters knowledge-sharing, best practice exchange, and the adoption of sustainable approaches among participating industries.
Millipede species (India Today)

- 27 Jul 2023
Why in the News?
In a recent discovery, a previously unknown species of millipede was found dwelling beneath the city of Los Angeles, United States.
About Millipede Species:
- The recently discovered species belongs to the category of thread Millipedes.
- It measures approximately the length of a paperclip but is as slim as pencil lead.
- Scientifically identified as Illacme socal, this millipede is translucent and displays sinuous movements akin to a jellyfish tentacle.
- The creature's habitat lies about four inches beneath the ground, where it burrows and secretes distinctive chemicals, exhibiting unique behavior.
- Remarkably, this millipede is blind and relies on hornlike antennas extending from its head to navigate its surroundings.
What are Millipedes?
- Millipedes belong to the arthropod class Diplopoda, placing them in the same group as centipedes.
- These invertebrates exhibit a cylindrical or slightly flattened body structure.
- Despite their name, "millipede," which translates to "a thousand feet," these creatures do not actually have a thousand feet. However, they possess numerous legs on their bodies.
- The millipede's body is segmented, and each segment carries two sets of legs attached to the underside.
- Diet-wise, millipedes are detritivores, subsisting on dead organic matter found in the earth, such as damp wood pieces, decaying leaves, and other materials that are naturally present in their moist underground habitat.
Rare ‘Ureilite’ Meteorite (Weather Channel)

- 27 Jul 2023
Why in the News?
Recently, a team of scientists from Allahabad University and the University of Bern, Switzerland, made an intriguing discovery. They unveiled that the Dhala crater was formed by the impact of an exceedingly uncommon and ancient meteorite called Ureilite.
Key Facts About Ureilite:
- Ureilite is an extraordinary type of meteorite, characterized by its rarity, making up only a minuscule portion of the meteorites found on Earth.
- The name "Ureilite" originates from the location of its first discovery, the Novo Urei village in Russia.
- Composition:
- Ureilites are primarily composed of silicate rock, with olivine and pyroxene being the dominant minerals.
- They also contain a smaller fraction of carbon, which can be in the form of either diamond or graphite, along with metal sulphides and a few fine-grained silicates.
- Elongated cavities are commonly found, typically oriented in the same direction.
- Lack of Chondrules:
- Unlike many other stony meteorites, ureilites do not contain chondrules, which are small, spherical grains that formed in the early solar system.
- Primitive Nature:
- Ureilites are regarded as primitive meteorites because their composition closely resembles the material from which the solar system originated.
- Their unique characteristics offer valuable insights into the early stages of our cosmic environment.
About Dhala Crater:
- Dhala Crater holds significance as India's oldest and largest impact crater, with an estimated formation age of approximately 2500 million years.
- Named after the village Dhala, it remains an eroded remnant of the original impact structure.
- Situated in the Shivpuri district of Madhya Pradesh, the crater boasts an impressive size, spanning a massive 11 km in diameter, making it the largest impact crater in Asia.
Urea Gold (ET)

- 27 Jul 2023
Why in the News?
During a recent event held in Rajasthan's Sikar, the Prime Minister unveiled "Urea Gold," a novel type of Urea fertilizer.
About Urea Gold:
- Urea Gold is an advanced variety of Urea that features a Sulphur coating.
- Its primary purpose is to address soil Sulphur deficiency while also offering cost-saving benefits to farmers.
- In comparison to the existing Neem-coated urea, Urea Gold stands out due to its superior economic viability and efficiency.
- The gradual release of nitrogen facilitated by its Sulphur coating enhances crop uptake, and the inclusion of humic acid extends its fertilizing lifespan.
- Notably, Urea Gold not only acts as a substitute for traditional urea but also contributes to a reduction in overall fertilizer usage.
- According to a report, using 15 kg of Urea Gold can provide comparable benefits to 20 kg of conventional urea, making it a more efficient and effective choice for farmers.
INDIAai (ET)

- 26 Jul 2023
Why in the News?
In a recent development, INDIAai and Meta India entered into a memorandum of understanding (MoU) to create a collaborative framework for cooperation and partnership in the realm of artificial intelligence (AI) and emerging technologies.
About INDIAai:
- INDIAai, the National artificial intelligence Portal of India, was launched on 28th May 2020 as a comprehensive platform.
- It serves as a knowledge portal, research organization, and ecosystem-building initiative.
- Its primary aim is to foster unity and encourage collaborations within India's AI ecosystem by bringing together various entities.
- This joint initiative is supported by the Ministry of Electronics and IT (MeitY), the National e-Governance Division (NeGD), and NASSCOM.
- NeGD, established in 2009 under the Digital India Corporation (a not-for-profit company set up by MeitY), plays a crucial role in this venture.
- NASSCOM, a prominent not-for-profit industry association, serves as the apex body for India's IT and IT-enabled products and services sector.
- INDIAai functions as the central knowledge hub for artificial intelligence and related fields, catering to aspiring entrepreneurs, students, professionals, academics, and all other stakeholders in the domain.
What is Artificial intelligence (AI)?
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) is a branch of computer science: It involves the development of intelligent machines that can perform tasks typically requiring human intelligence.
- Machine Learning and Algorithms: AI systems utilize machine learning algorithms to process vast amounts of data, learn from it, and improve their performance over time without explicit programming.
- Applications in various fields: AI finds applications in diverse domains, including natural language processing, image recognition, robotics, healthcare, finance, and autonomous vehicles, among others. Its goal is to mimic human cognitive abilities, such as problem-solving, reasoning, and decision-making.
Hike in US Federal Reserve Interest and Impact on Indian Economy (Live Mint)
- 26 Jul 2023
Why in the News?
The US Federal Reserve is expected to raise benchmark rates by 25 bps to the 5.25-5.50 percent range on Wednesday. Investors will be watching for cues on inflation and rate hike trajectory.
About US Federal Reserve:
- The US Federal Reserve, also known as the Fed, serves as the central banking system of the United States, offering a secure, adaptable, and steady monetary and financial framework.
- It operates through 12 regional Federal Reserve Banks, each responsible for a designated U.S. geographic area.
- The Fed's primary functions encompass conducting national monetary policy, overseeing and regulating banks, ensuring financial stability, and delivering banking services.
Impacts of US Federal Reserve Interest Hike:
- The US Fed's Significance: As the world's most powerful central bank, the decisions taken by the US Federal Reserve regarding interest rates have significant implications worldwide. These decisions influence both developed and emerging economies across the globe.
- Global Effects: Changes in US interest rates have a ripple effect that extends beyond the nation's borders. The adjustments impact various economies worldwide, leading to shifts in investment patterns and financial flows.
- Appeal of American Assets: When the Federal Reserve raises interest rates, American assets become more attractive to investors seeking higher returns. Consequently, there is a possibility of capital outflows from emerging and riskier markets to the US.
- Impact on Capital-Intensive Sectors: Sectors heavily reliant on Foreign Direct Investments (FDIs) are particularly vulnerable to the consequences of a US interest rate hike. The increased cost of borrowing may affect their growth prospects.
- Global Liquidity Tightening: Higher US interest rates can lead to a tightening of global liquidity. Foreign investors may face challenges in obtaining affordable funds, which could have implications for their investment decisions and overall economic activities.
Potential Impacts on the Indian Economy:
- Interest Rate Differential: Following a rate hike by the US Federal Reserve, the gap between interest rates in the US and India narrows, adversely affecting currency trade and financial flows.
- Foreign Investor Response: With higher returns available in the US due to increased interest rates and attractive Dollar and US Treasury yields, foreign investors may be inclined to withdraw investments from the Indian market, leading to capital outflows.
- Currency and RBI Response: The relative strengthening of the US currency (Dollar) makes the Indian rupee weaker, prompting the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) to consider a rate hike domestically.
- RBI's Action to Curb Outflows: To mitigate the outflows of funds from Foreign Institutional Investors (FIIs) and safeguard the rupee's stability, the RBI may find it necessary to increase interest rates within India.
- Forex Reserve Management: In the event of a significant decline in the rupee's value, the RBI might be compelled to sell some of its Dollar reserves to support the domestic currency. This action, however, depletes the country's foreign exchange reserves.
Conjunctivitis (India Today)
- 26 Jul 2023
Why in the News?
India has been witnessing a sharp increase in eye infections, specifically conjunctivitis. Amid heavy rainfall, Delhi and nearby areas have reported multiple cases of conjunctivitis.
About Conjunctivitis:
Conjunctivitis, commonly known as "pink eye," is an inflammation or infection of the conjunctiva, which is the thin, clear tissue that covers the white part of the eye and lines the inner surface of the eyelids. It can affect one or both eyes and is a highly contagious condition.
Causes of Conjunctivitis:
- Bacterial Infection: Bacteria, such as Staphylococcus aureus or Streptococcus pneumoniae, can cause bacterial conjunctivitis.
- Viral Infection: Viruses, including adenoviruses, can lead to viral conjunctivitis. This form of conjunctivitis is highly contagious and is often associated with colds or respiratory infections.
- Allergies: Allergic conjunctivitis occurs due to an allergic reaction to substances like pollen, pet dander, dust mites, or certain medications.
- Irritants: Exposure to irritants like smoke, chemicals, or foreign objects in the eye can cause irritant conjunctivitis.
Symptoms of Conjunctivitis:
- Redness of the eyes
- Watery or thick, yellowish discharge from the eyes
- Itchiness or burning sensation in the eyes
- Sensitivity to light
- Crusty eyelids or lashes, especially in the morning (more common in bacterial conjunctivitis)
- Swelling of the conjunctiva
- Blurred vision
Treatment:
- The treatment of conjunctivitis depends on its underlying cause:
- Bacterial conjunctivitis: Antibiotic eye drops or ointments are commonly prescribed to treat bacterial infections.
- Viral conjunctivitis: Since it is caused by a virus, antibiotics won't work. The symptoms are often relieved with supportive measures like artificial tears, cold compresses, and good hygiene practices to prevent spreading.
- Allergic conjunctivitis: Avoiding allergens is essential. Antihistamine eye drops or oral medications can help alleviate symptoms.
- Irritant conjunctivitis: Removing the irritant and using artificial tears can help soothe the eyes.
Prevention:
- To prevent the spread of conjunctivitis, one should follow these measures:
- Frequent handwashing.
- Avoid touching or rubbing the eyes.
- Avoid sharing towels, pillowcases, or eye makeup with an infected person.
- Avoid close contact with individuals showing symptoms of conjunctivitis.
Hematene (PIB)
- 26 Jul 2023
Why in the News?
A new and remarkably efficient optical limiter has been developed by researchers, utilizing a novel 2D material known as 'hematene.'
- About Hematene:
- Nanoflakes of a material called hematene extracted from iron ore have been found capable of withstanding and acting as a shield from high laser intensities.
- Hence it could be used to make devices called optical limiters that can protect sensitive optical equipment from light-induced damage.
- Radiation from laser sources is highly concentrated and powerful and can be detrimental to sensitive equipment such as sensors, detectors, and other optical devices.
- When the input intensity increases optical limiters control the amount of light that passes through, thereby preventing damage to the optical component.
- These devices are often useful in laser technologies, military, telecommunications, aircraft, and scientific research in several ways.
- The MESO (Materials for Energy Storage and Optoelectronic Devices) Group of the Department of Physics, Sanatana Dharma College, Alappuzha, in collaboration with the Ultrafast and Nonlinear Optics Lab of the Raman Research Institute, Bangalore, has come up with a new and highly efficient optical limiter using a novel 2D material, ‘hematene’.
- They found that 2D nanoflakes of hematene, a material extracted from iron ore or hematite are capable of withstanding very high laser intensities, and they exhibited excellent optical limiting of green laser light (532 nm) while maintaining a high linear transmission (about 87%) for low-intensity light.
- The nanoflakes of lateral dimensions less than 10 nm, prepared by applying ultrasonic waves to hematite in a liquid medium ( facile exfoliation process) for a definite period to exfoliate the 2D nanoflakes of hematene were also found to be highly stable after year-long storage under ambient conditions, indicating tremendous potential as an optical limiter for futuristic applications.
- This research work carried out at SD College using the instrumentation facility procured through the Fund for Improvement of S&T Infrastructure (FIST) programme of the Department of Science and Technology (DST) programme, was recently published in ACS Applied Optical Materials.
Maitree Super Thermal Power Project (STPP) (ET)

- 26 Jul 2023
Why in the News?
The synchronization of the 660-MW unit-2 of the 1,320-MW Maitree Super Thermal Power Project (STPP) with the electricity grid in Bangladesh was recently announced by the state-owned engineering firm Bharat Heavy Electricals.
- Location:
- It is situated in Rampal, in the Bagerhat district of Bangladesh's Khulna division.
- It will be one of the biggest coal-fired power plants in Bangladesh, along with the Payra Power Plant in Pataukhali, which commenced test production in January 2020.
- Capacity and Cost:
- The power station has a capacity of 1320 MW (2x660 MW) and is estimated to cost around $2 billion.
- Financing Plan:
- The project is being developed under India's tax concessions finance plan, aiming to enhance Bangladesh's national grid by an additional 1320 MW.
- Financed through a £1.3bn ($1.6bn) loan from the Export-Import (EXIM) Bank of India.
- Implementing Entity:
- India’s Bharat Heavy Electricals Limited (BHEL) is responsible for constructing the power plant on behalf of Bangladesh-India Friendship Electricity Company Private Limited (BIFPCL).
- Commercial Operation:
- The first unit of the super thermal power plant is expected to commence commercial operation in early October, representing a significant milestone in the growing cooperation between India and Bangladesh in the power industry.
- Future Expansion:
- In the subsequent year, the power plant's Unit-II, also known as the Rampal coal-fired power project, is scheduled for implementation.
Ichamati River (PIB)

- 06 Oct 2023
Why in the News?
The Minister of State for Ports, Shipping, and Waterways recently launched the dredging project on National Waterways 44 in the Ichamati River of West Bengal.
About the Ichamati River:
- The Ichamati River crosses both India and Bangladesh.
- It serves as a natural boundary between the two nations India and Bangladesh.
- It has three main sections.
- The longest part originates from the Mathabhanga River, a branch of the Padma River, flowing for 208 kilometers before merging with the Kalindi River near Hasnabad in North 24 Parganas and Debhata in the Satkhira District of Bangladesh.
- Additionally, the Ichhamati River and its tributaries together create a large oxbow lake complex in the North 24-Paraganas district, near Bangaon.
NanoPtA (The Hindu)
- 06 Oct 2023
Why in the News?
Scientists at the Indian Institute of Science's Materials Research Centre (MRC) have recently created a novel enzyme mimic known as NanoPtA.
About NanoPtA:
- The research team at the Materials Research Centre (MRC), Indian Institute of Science (IISc), has created a unique platinum-based nanozyme called NanoPtA.
- This nanozyme can be turned into a powder for use in industries.
- When NanoPtA encounters wastewater, the molecule's benzene rings and long alkyl chains engage in multiple non-covalent interactions.
- Individual NanoPtA molecules link together to form tape-like structures that emit light, which is the source of its oxidizing capability.
- In the presence of sunlight, this nanozyme can break down pollutants in wastewater, reducing its toxicity.
- Remarkably, the nanozyme can rapidly degrade even small amounts of common contaminants like phenols and dyes (micromolar levels) within ten minutes when exposed to sunlight.
- The researchers also observed that the NanoPtA complex remained stable for up to 75 days at room temperature.
Applications:
- Besides wastewater treatment, this nanozyme could find applications in healthcare and serve as a valuable diagnostic tool for neurological and neurodegenerative diseases.
BlueWalker 3 Satellite (The Hindu)

- 06 Oct 2023
Why in the News?
An international team of scientists has recently published a paper that explains how the prototype BlueWalker 3 satellite has affected the field of astronomy.
About the BlueWalker 3 satellite:
- The BlueWalker 3 satellite is a prototype that's part of a constellation owned by AST SpaceMobile.
- Launched in September 2022, it's notable for being one of the brightest objects in the night sky, even outshining the brightest stars.
- This satellite represents the largest-ever commercial communications array in low-Earth orbit, specifically designed to directly communicate with cellular devices at 5G speeds using 3GPP standard frequencies.
- Interestingly, the satellite operates at wavelengths close to those observed by radio telescopes, which could potentially interfere with radio astronomy.
Yak Churpi (TOI)

- 06 Oct 2023
Why in the News?
Arunachal Pradesh, a northeastern state, achieved a noteworthy milestone as the distinctive and culturally important yak milk product known as 'Yak Churpi' has received the prestigious Geographical Indication (GI) tag.
About 'Yak Churpi':
- Yak Churpi is a special dairy product crafted from the milk of the indigenous Arunachali yak breed.
- It's produced by Brokpas, tribal yak herders who migrate with their yaks to higher altitudes (above 10,000 ft) during summers and return to mid-altitude mountainous areas in winters.
- These exceptional yaks are primarily found in the West Kameng and Tawang districts of Arunachal Pradesh.
- Churpi is a naturally fermented dairy item with a high protein content.
- It plays a vital role in the diets of tribal communities living in the cold, mountainous regions of the state.
- It's often used as a vegetable substitute and is a common ingredient in vegetable and meat dishes, frequently enjoyed with rice.
- The GI tag for Yak Churpi has significant benefits, including the conservation of yaks and the improvement of the socio-economic status of yak herders.
- Arunachali yaks are unique in terms of their body characteristics, size, strain, and weight, making them the only registered yak breed in India.
National Turmeric Board (NTB) (PIB)

- 06 Oct 2023
Why in the News?
The Government of India recently announced the formation of the National Turmeric Board.
About the National Turmeric Board:
- The National Turmeric Board has a specific focus on developing and expanding turmeric and its products in India.
- It's especially dedicated to helping turmeric growers improve their skills and capabilities to add more value to their products.
- The Board also works to ensure high-quality and safe turmeric products.
- The composition of the Board includes a Chairperson appointed by the Central Government, members from various government departments such as AYUSH, Pharmaceuticals, Agriculture & Farmers Welfare, Commerce & Industry, as well as senior representatives from three states (on a rotational basis).
- Additionally, it includes representatives from national/state research institutions, turmeric farmers, and exporters.
- The Department of Commerce appoints a Secretary for the Board, and this department provides funds and infrastructure support.
- The NTB's main responsibilities include boosting demand, production, research, market connections, and exports related to turmeric.
PM Modi flags off RRTS: What is this mass transport system, and how it can benefit NCR (Indian Express)

- 20 Oct 2023
Why in the News?
The inauguration of the first segment of India's Regional Rapid Transit System (RRTS), the country's inaugural mass rapid transit system designed for regional connectivity, will be officiated by the Prime Minister of India.
About the Regional Rapid Transit System:
- The RRTS is an integrated mass transit network with semi-high-speed rail connectivity at its core.
- It aims to promote "balanced and sustainable urban development" throughout the National Capital Region (NCR) by improving connectivity and access.
- The National Capital Region Transport Corporation (NCRTC), a joint venture of the Central government and the governments of Delhi, Haryana, Rajasthan, and Uttar Pradesh, is building it.
- It is modeled after systems such as Paris' RER, Regional-Express trains in Germany and Austria, and SEPTA Regional Rail in the United States, among others.
- The project will develop eight corridors, three of which are currently under construction:
- the 82-kilometer Delhi-Ghaziabad-Meerut,
- the 164-kilometer Delhi-Gurugram-SNB-Alwar, and
- the 103-kilometer Delhi-Panipat corridors
- The importance of this system:
- The RRTS network is faster when compared to metros
- It will serve commuters who need to cover relatively longer distances across the NCR in a short amount of time.
- When compared to Indian Railways, the RRTS train will cover shorter distances but at a higher frequency and with greater comfort than the average railway coach.
List Niemann-Pick as a rare disease, parents of young patients (TOI)
- 20 Oct 2023
Why in the News?
Recently, parents of children with Niemann-Pick disease urged the Union government to notify the disease under the National Policy for Rare Diseases.
About Niemann-Pick Disease:
Niemann-Pick Disease is a rare genetic disorder characterized by the buildup of harmful substances in the body's cells and organs.
- Genetic Basis: It is inherited in an autosomal recessive manner, meaning that both parents must carry a mutated gene for their child to develop the disease.
- Types: There are several types of Niemann-Pick Disease, with types A and B being more common and types C and D being rarer.
- Lipid Accumulation: The disease is primarily characterized by the abnormal accumulation of lipids, specifically sphingomyelin, in various tissues and organs.
- Symptoms: Symptoms vary depending on the specific type of Niemann-Pick Disease but can include hepatosplenomegaly (enlarged liver and spleen), neurological problems, and lung issues.
- Type A: Niemann-Pick Disease Type A typically presents in infancy and can lead to severe neurological problems, making it a life-limiting condition.
- Type B: Niemann-Pick Disease Type B generally has a later onset and primarily affects the liver and spleen, with milder or absent neurological symptoms.
- Type C and D: Type C and D are characterized by cholesterol metabolism issues and can lead to neurological symptoms.
- Type C, in particular, can present with cognitive decline and movement problems.
- Treatment: There is currently no cure for Niemann-Pick Disease, but treatments aim to manage symptoms and may include enzyme replacement therapy, medications, and supportive care.
Niemann-Pick Disease is a complex condition with various subtypes, and the severity and specific symptoms can differ significantly among affected individuals.
Mangaluru | Archaeologist discovers inscription announcing the death of King KulashekaraAlupendra I at Someshwara (The Hindu)

- 20 Oct 2023
Why in the News?
During a recent archaeological exploration at Someshwara near Mangaluru, Karnataka, archaeologists unearthed a rare inscription related to the Alupa dynasty.
About the Someshwara inscription:
- This inscription holds great importance in understanding Tuluva history and culture.
- It features two panels on top, with the first line carved between them.
- The rest of the inscription, inscribed below the panels in Kannada script and the language of 12th century characters, announces Alupendra I's death.
- The human figures depicted in the inscription are KulashekaraAlupendra.
- He is depicted in the first figure standing in Tribhanga (tri-bent stance).
- He is holding a sword in his right hand and a gurani (shield) in his left.
- The King is represented in a sitting posture on a mound to the left of this panel, separated by a pillar, resting both palms on the center of his legs in dhyana mudra.
About the Alupa dynasty:
- The Alupa dynasty, active from the 2nd to the 15th century CE, ruled over Alvakheda Arusasira in the coastal regions of modern Karnataka.
- Initially independent, they later became vassals to powers like the Kadambas, Chalukyas, Rashtrakutas, and Hoysalas due to shifting politics in Southern India.
- They practiced matrilineal inheritance.
- Their descendants, known as the Bunt, continue to follow this system and bear surnames like Shetty, Rai, Hegde, Alva, and Chowta.
- While most are Hindus, some still follow Jainism.
- The last Alupa king, Kulasekharadeva Alupendradeva, is documented through a 1444 CE inscription in Mudabidri's Jain Basadi.
ISRO’s Gaganyaan TV-D1 test flight tomorrow: Everything you need to know (Indian Express)

- 20 Oct 2023
Why in the News?
The Indian Space Research Organization (ISRO) is preparing to launch its first-ever test flight, TV-D1, for the Gaganyaan mission, marking a watershed moment in the country's pursuit of human spaceflight.
About the TV-D1 Mission:
- Test Vehicle Abort Mission-1 (TV-D1) will assess the crew module's readiness for the Gaganyaan mission.
- It is a single-stage liquid rocket designed specifically for this abort mission.
- The payloads include the Crew Module (CM) and Crew Escape Systems (CES) with their fast-acting solid motors, as well as the CM fairing (CMF) and Interface Adapters.
- This flight will simulate the abort condition encountered during the Gaganyaan mission's ascent trajectory, which corresponds to a Mach number of 1.2.
- The Crew Escape System is designed to operate automatically at various altitudes if the onboard computer detects any problems.
One nation, one student: Educationists apprehensive of APAAR student ID card scheme (Indian Express)

- 20 Oct 2023
Why in the News?
In accordance with the National Education Policy (NEP) 2020, the Union Education Ministry has recently established the concept of 'One Nation, One Student ID,' referred to as APAAR ID.
About Automated Permanent Academic Account Registry (APAAR) ID:
- The Automated Permanent Academic Account Registry, or APAAR ID, is a digital identification system used by students in India.
- Academic qualifications, credit scores, certificates, and other academic data for students from pre-primary to higher education will be digitally stored.
- Students must obtain their parent’s consent to enroll in the APAAR ID system, and states have been directed to begin this process.
- The unique 12-digit APAAR ID will be used for admissions and other academic activities, making it more convenient for students.
- Both new and returning users can register or log in using their mobile number, Aadhar Card, or ID and password.
- This initiative seeks to unify the educational system, improve security, and make academic data more easily accessible to students.
Lok Sabha passes Advocates (Amendment) Bill to weed out touts from court complexes(The Hindu)
- 05 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
The Lok Sabha recently passed a Bill that seeks to regulate the legal profession by targeting “touts”, with Law Minister Arjun Ram Meghwal asserting there should be no role of such persons in courts.
About the Advocates (Amendment) Bill, 2023:
- The Rajya Sabha introduced the Advocates (Amendment) Bill, 2023, in August 2023.
- This bill amends the Advocates Act of 1961, specifically repealing certain sections related to touts under the Legal Practitioners Act of 1879.
- The 1961 Act consolidates laws regarding legal practitioners and establishes Bar Councils and the All-India Bar.
- Having already passed in the Rajya Sabha during the Monsoon Session, the bill aims to regulate the legal profession through a single act with a focus on addressing the issue of touts.
Key Features of the Advocates (Amendment) Bill, 2023:
- Touts: High Courts, district judges, sessions judges, district magistrates, and revenue officers are empowered to create and publish lists of touts.
- A tout is defined as a person who either seeks or secures the employment of a legal practitioner in legal matters for payment or frequents specific locations to obtain such employment.
- The Court or judge has the authority to bar any person listed as a tout from the premises of the Court.
- Preparation of Lists: Authorities with the power to create tout lists may instruct subordinate courts to conduct inquiries into individuals suspected or alleged to be touts.
- If proven, the person's name can be included in the list, ensuring due process is followed before inclusion.
- Penalty: Individuals acting as touts while being listed can face imprisonment up to three months, a fine up to Rs 500, or both.
Will India reassess its position on China-backed Asian trade bloc RCEP? (Business Standard)
- 05 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
India is keeping a watchful eye on its neighbour countries’ recent deliberations to join the China-backed Asian trade bloc, Regional Comprehensive Economic Partnership (RCEP), although the government is yet to “re-evaluate” the position it took four years ago.
What is Regional Comprehensive Economic Partnership (RCEP)?
- RCEP, or the Regional Comprehensive Economic Partnership, is a proposed agreement involving ASEAN member states and their free trade agreement partners.
- Introduced in 2011, negotiations started in 2012, aiming to finalize the deal by November 2019.
- After the withdrawal of India, there are 15 members of RCEP, which includes 10 ASEAN countries and 5 other countries, namely:
- Australia, Brunei, Cambodia, China, Indonesia, Japan, South Korea, Laos, Malaysia, Myanmar, New Zealand, the Philippines, Singapore, Thailand, and Vietnam.
- RCEP's objective is to establish an integrated market, facilitating the availability of products and services across the region.
- The negotiations cover trade, investment, intellectual property, dispute settlement, e-commerce, SMEs, and economic cooperation.
- Initially proposed by Beijing in 2012 to counter the Trans-Pacific Partnership, RCEP became a key tool for China after the U.S. withdrew from the TPP in 2016.
- India chose not to sign the RCEP in 2019 due to concerns about its industries competing with China and potential flooding of Indian markets.
- Despite some sectors anticipating gains, India emphasized the need for a deal favorable to all countries and sectors.
SC pulls up Bhopal municipal corporation for flouting Solid Waste Management Rules (DownToEarth)

- 05 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
There is non-compliance with the provision of the Solid Waste Management Rules, 2016 by the Bhopal Municipal Corporation, the Supreme Court observed December 1, 2023 after going through the affidavit filed by the corporation.
What is About Compensatory Afforestation Fund Management and Planning Authority (CAMPA)?
- The Supreme Court of India, in 2001, mandated the creation of the Compensatory Afforestation Fund and the Compensatory Afforestation Fund Management and Planning Authority (CAMPA).
- Initially, an ad-hoc CAMPA was established in 2006 to manage the Compensatory Afforestation Fund.
- (CAMPA) are meant to promote afforestation and regeneration activities as a way of compensating for forest land diverted to non-forest uses.
- National CAMPA Advisory Council has been established as per orders of The Hon’ble Supreme Court with the following mandate:
- Lay down broad guidelines for State CAMPA.
- Facilitate scientific, technological and other assistance that may be required by State CAMPA.
- Make recommendations to State CAMPA based on a review of their plans and programmes.
- Provide a mechanism to State CAMPA to resolve issues of an inter-state or Centre-State character.
CAMPA Act:
- To address the loss of forest area and ensure sustainability, the Government of India introduced the CAMPA (Compensatory Afforestation Fund Management and Planning Authority) Act.
- This legislation establishes the National Compensatory Afforestation Fund in the Public Account of India and a State Compensatory Afforestation Fund in the Public Account of each state.
- These funds receive payments for compensatory afforestation, net present value of forests (NPV), and other project-specific payments.
- The National Fund gets 10% of these funds, while the State Funds receive the remaining 90%.
- As per the Act, companies diverting forest land must provide alternative land for compensatory afforestation.
- For afforestation purposes, companies are required to pay for planting new trees in the alternative land provided to the state.
Houthi attacks on vessels in Red Sea sound alarm for global trade (Financial Times)
- 05 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
Shipowners have called for more military protection on maritime routes in the Middle East after attacks by Iran-backed rebels in the Red Sea sparked fears of new disruptions to global trade, including of energy supplies.
Key Facts the about Red Sea:
- The Red Sea is a semi-enclosed inlet of the Indian Ocean situated between Africa and Asia.
- It stands out as one of the warmest seas globally.
- Connecting to the Arabian Sea and the Indian Ocean through the Gulf of Aden and Bab El-Mandeb strait to the south, it is divided by the Sinai Peninsula into the Gulf of Aqaba and the Gulf of Suez in the north.
- The Gulf of Suez is linked to the Mediterranean Sea via the famous Suez Canal.
- The Red Sea is bordered by Yemen and Saudi Arabia to the east, while Egypt is to the north and west, and Sudan, Eritrea, and Djibouti are to the west.
- Covering an area of about 438,000 km2, it stretches approximately 2,250 km.
- The sea's maximum width is 355 km, and its deepest point, the central Suakin Trough, reaches 3,040 m, with an estimated average depth of 490 m.
- Notable islands in the Red Sea include Tiran Island near the mouth of the Gulf of Aqaba and Shadwan Island at the entrance of the Gulf of Suez.
Meghalaya’s Lakadong turmeric gets GI Tag (Northeast Live)

- 05 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
Recently, Meghalaya’s Lakadong turmeric has received the Geographical Indication (GI) tag from the Registrar of Geographical Indications in Chennai.
About Lakadong Turmeric:
- Lakadong Turmeric is known as one of the best turmerics in the world and is sourced from a village in Meghalaya’s Jaintia Hills.
- Lakadong, a distinct type of turmeric, is exceptionally abundant in curcumin, with levels ranging from 7-8%, a significant contrast to the typical varieties containing only 2-3% curcumin.
- Curcumin has numerous health benefits, including anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties.
- Under the “One District One Product” scheme, Lakadong turmeric gained recognition in the West Jaintia Hills district.
- India produces 78% of the world’s turmeric.
What is One District One Product (ODOP)?
- One District One Product (ODOP) initiative is aimed at fostering balanced regional development across all districts of the country.
- The initiative aims to select, brand, and promote at least One Product from each District (One District - One Product) of the country for enabling holistic socioeconomic growth across all regions.
- The ODOP Initiative has identified a total of 1102 products from 761 districts across the country.
- Under the ODOP initiative, all products have been selected by States/UTs by taking into consideration the existing ecosystem on the ground, products identified under Districts as Export Hubs (DEH), and GI-tagged products.
- The finalized list is communicated to DPIIT by the relevant Department of States/UTs.
- All activities including exhibitions, capacity building, etc. are undertaken at the State/UT and district level, in consultation and coordination with the States/UTs.
Quantum Dots (QDs) (The Hindu)
- 05 Oct 2023
Why in the News?
Moungi G. Bawendi, Louis E. Brus, and Alexei I. Ekimov were recently honored with the 2023 Nobel Prize in Chemistry for their remarkable contributions to the discovery and synthesis of quantum dots.
About Quantum Dots (QDs):
- Quantum dots, often referred to as "artificial atoms," are tiny semiconductor nanoparticles that possess unique optical and electronic properties because of their minuscule size.
- The concept of quantum dots was first theorized in the 1970s and later successfully synthesized in the early 1980s.
- Various semiconductor materials, including cadmium selenide, cadmium sulfide, or indium arsenide, can be utilized to create quantum dots. These nanoparticles exhibit quantum dot properties.
- During the synthesis process, scientists can precisely control the size and composition of quantum dots, allowing for tailored properties suitable for diverse applications.
- Optical Properties: A standout characteristic of quantum dots is their adjustable emission properties. Researchers can finely adjust the wavelength of emitted or absorbed light by manipulating the size of the quantum dot.
- Quantum dots can emit light across the entire visible spectrum and even into the infrared and ultraviolet ranges, providing a broad spectrum of colors for numerous applications.
- The smallest quantum dots emit high-energy waves, resulting in blue light, while larger dots emit lower-energy waves, producing red light, with intermediate sizes generating colors in between.
Applications:
- Displays: Quantum dots are employed in display technology to enhance color and efficiency in devices like TVs, monitors, and other electronics.
- Photovoltaics: Quantum dots can enhance light absorption and energy conversion efficiency in solar cells.
- Biomedical Applications: Due to their small size, quantum dots have versatile applications in areas such as medical imaging, biosensors, and targeted drug delivery.
- Quantum Computing: Quantum dots are under investigation for their potential role in quantum computing as they can function as qubits, the fundamental units of quantum information.
Swamp Deer (NewsOnAIR)

- 05 Oct 2023
Why in the News?
Manas National Park & Tiger Reserve recently shared some good news: The number of swamp deer in the park has increased.
About Swamp deer:
- Swamp deer, also known as barasingha (scientifically called Rucervus duvaucelii), is a type of deer found in the Indian subcontinent.
- They belong to the Cervidae family and are typically spotted in open forests and grasslands across India and Nepal.
- These deer primarily feed on wetland plants and the herbs commonly found in their natural habitat.
- Unfortunately, their population is now limited to isolated areas in Nepal, Assam, and the northern regions of India.
- Swamp deer used to exist in Bangladesh and Pakistan, but they are now extinct in both of these countries.
In the Indian Subcontinent, there are three subspecies of swamp deer:
- Western swamp deer (Rucervus duvaucelii) found in Nepal.
- Southern swamp deer (Rucervus duvaucelii branderi) found in central and north India.
- Eastern swamp deer (Rucervus duvaucelii ranjitsinhi) found in the Kaziranga and Dudhwa National Parks.
In terms of conservation, swamp deer are classified as follows:
- IUCN Red List: Vulnerable
- CITES: Appendix I
- The Wildlife Protection Act, 1972: Schedule I
Bojjannakonda (The Hindu)

- 05 Oct 2023
Why in the News?
Recently, the Central government allocated 7.30 crore rupees to undertake landscaping and develop tourist amenities at the Bojjannakonda site.
About Bojjannakonda:
- Bojjannakonda is situated in the state of Andhra Pradesh.
- It was excavated by Alexander Rim in 1906.
- Originally known as ‘Buddhuni konda’ (meaning hill of the Buddha), it eventually came to be known as ‘Bojjannakonda’ over time.
- Approximately 2,000 years ago, Buddhist monks used this hill for their practices.
- During excavations, various artifacts were unearthed, including a gold coin from the Samudra Gupta period, copper coins from the Chalukya king Kubja Vishnu Vardhan, coins from the Andhra Satavahanas, and pottery.
- Bojjannakonda is unique as it reflects features of all three phases of Buddhism: Hinayana, Mahayana, and Vajrayana.
- Notable discoveries at the site include a figure of ‘Kalabhairava’ with the head of Lord Ganesha adorned with conch shells and the statue of a Buddhist monk named ‘Harati.’
- There is a large double-storeyed cave on the hill with a rectangular doorway flanked by 'dwarapalakas' on both sides.
- At its center stands a rock-cut stupa on a square platform.
- The northern side of the hill features a series of rock-cut caves and monolithic structures on rock platforms.
- The upper cave has a rectangular doorway, with Buddha figures on either side.
- The prominent attractions for tourists at Bojjannakonda are the imposing figures of the Buddha seated in a meditative posture and the stupa.
- At the hill's summit, there are structural buildings and a vihara (monastery), which are now in ruins.
- To the west of Bojjannakonda lies another hillock called Lingalakonda or Lingalametta, where several monolithic and structural stupas can be found.
- Interestingly, the structures on Lingalametta served as inspiration for the Buddhist temple at Barabodur in Java.
- Similarities between the caves at Bojjannakonda and those in Takshasila suggest Buddhist influences, although the word ‘Sangrama’ was used in Takshasila but not in Andhra Pradesh.
Haploclastus Nilgirinus (The Hindu)

- 05 Oct 2023
Why in the News?
Recently, scientists warned that Haploclastus nilgirinus, a tarantula species, may face endangerment due to habitat loss and the effects of climate change.
About Haploclastus Nilgirinus:
- This tarantula species, known as Haploclastus nilgirinus, is a venomous and rarely seen spider that burrows in the Nilgiri hills of the Western Ghats.
- Notably, there is a significant difference in size between males and females of this species, with the males being considerably smaller.
- The primary threats to Haploclastus nilgirinus are illegal wildlife trade and the impact of climate change.
What is a tarantula?
- Tarantulas are a type of large, hairy spider belonging to the Theraphosidae family.
- They are found all around the world, except for Antarctica.
- These spiders move slowly on their eight hairy legs but are skilled nocturnal predators.
- Adult tarantulas typically measure around five inches (13 centimeters) in length, and when their legs are fully extended, their span can reach up to 11 inches (28 centimeters).
National Investment and Infrastructure Fund (NIIF) (The Hindu)

- 05 Oct 2023
Why in the News?
Recently, the National Investment and Infrastructure Fund collaborated with the Japan Bank for International Cooperation (JBIC) to launch the India-Japan Fund, which amounts to $600 million.
About the National Investment and Infrastructure Fund (NIIF):
- NIIF is a fund manager owned by investors and anchored by the Government of India (GoI).
- It collaborates with both global and domestic institutional investors.
- Established in 2015, NIIF is India's first sovereign wealth fund (SWF).
- NIIF plays a vital role in financing infrastructure projects, including greenfield (new), brownfield (existing), and stalled projects.
- The primary objective of NIIF is to maximize its economic impact by investing in various infrastructure-related projects.
There are three types of NIIF funds:
- Master Fund: This fund primarily invests in infrastructure projects such as roads, ports, airports, and power generation.
- It also invests in well-established enterprises operating under long-term agreements in regulated environments with a strong track record.
- Fund of Funds: This category focuses on investing in funds managed by renowned fund managers with a proven track record.
- It acts as an anchor investor, which encourages fund managers to attract more investments from institutional investors.
- Strategic Fund: Registered as an Alternative Fund II under the Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI), the Strategic Fund primarily invests in equity and equity-linked instruments.
- All these funds are registered as Alternative Investment Funds (AIF) with SEBI.
Basohli Pashmina is Recognized with GI Tag (HT)

- 04 Oct 2023
Why in the News?
Recently, Basohli Pashmina, a traditional craft with over a century of history from the Kathua district in Jammu and Kashmir, has been granted the Geographical Indication (GI) tag.
About Basohli Pashmina:
- Basohli Pashmina is renowned for its exceptional softness, fineness, lightweight quality, insulation, and durability.
- Pashmina products include shawls, mufflers, blankets, and baskets.
- Pashmina is a premium variety of cashmere, obtained from the fine undercoat of the Changthangi mountain goats.
- These goats are found on the Changthang Plateau in Tibet and parts of Ladakh.
- The Changpa people, who are nomads living on the Changthang plateau of Tibet, are traditional producers of pashmina wool.
United Nations Convention against Transnational Organised Crime (PIB)

- 04 Oct 2023
Why in the News?
Minister of State for Home Affairs Shri Nityanand Rai attends the two-day conference to mark the 20th anniversary of the United Nations Convention against Transnational Organised Crimes (UNTOC) at Palermo in Italy.
About the United Nations Convention against Transnational Organized Crime (UNTOC):
- NTOC, established by the United Nations in 2000, is a global treaty targeting transnational organized crime.
- It's often referred to as the Palermo Convention.
- It has 147 signatories and 190 parties to the convention.
- The Convention is complemented by three Protocols:
- Protocol to Prevent, Suppress and Punish Trafficking in Persons, Especially Women, and Children
- Protocol against the Smuggling of Migrants by Land, Sea, and Air
- Protocol against the Illicit Manufacturing of and Trafficking in Firearms, their Parts, and Components, and Ammunition.
- India signed UNTOC and its three Protocols on December 12, 2002.
- The Central Bureau of Investigation (CBI) is the primary agency responsible for all interactions related to UNTOC.
Exercise SAMPRITI (PIB)

- 04 Oct 2023
Why in the News?
On the 3rd of October 2023, India and Bangladesh kicked off the 11th installment of exercise SAMPRITI in Umroi, Meghalaya.
About Exercise SAMPRITI:
- This is an annual joint military exercise that India and Bangladesh hold together.
- It began in Jorhat, Assam, in 2009 and has successfully completed ten editions up to 2022.
- The exercise is organized alternately by both countries, demonstrating their strong bilateral defense cooperation.
- SAMPRITI-XI, which spans 14 days, will involve around 350 personnel from both sides.
- The primary focus of the exercise is to improve interoperability between the two armies, exchange tactical strategies, and promote best practices.
- A wide range of units, including artillery, engineers, and other supporting arms and services, will participate from both sides.
- The exercise centers on the execution of Sub-Conventional Operations in line with Chapter VII of the UN mandate.
- It includes a Command Post Exercise (CPX) and a Field Training Exercise (FTX), concluding with a Validation Exercise.
- SAMPRITI-XI aims to strengthen defense cooperation between India and Bangladesh, fostering deeper bilateral relations, cultural understanding, and mutual benefits through shared experiences in Sub-Conventional Operations.
International Coral Reef Initiative (NewsOnAIR)

- 04 Oct 2023
Why in the News?
Recently, the International Coral Reef Initiative (ICRI) announced its commitment to obtain both public and private investments to support the conservation and restoration of coral ecosystems.
About the International Coral Reef Initiative:
- It was established in 1994 with founding members including Australia, France, Japan, Jamaica, the Philippines, Sweden, Britain, and the United States.
- It now boasts a membership of 45 countries, collectively representing three-quarters of the world's coral reefs.
- India is one of these member countries.
- This initiative serves as a global partnership between nations and organizations dedicated to preserving coral reefs and their related ecosystems worldwide.
- It's important to note that the decisions made by ICRI are not legally binding on its members.
- ICRI's work is frequently recognized in United Nations documents, emphasizing its significant role in cooperation, collaboration, and advocacy on the international stage.
Objectives of ICRI include:
- Promoting the adoption of best practices for sustainable management of coral reefs and associated ecosystems.
- Building capacity to effectively manage and protect these ecosystems.
- Raising awareness at all levels about the challenges faced by coral reefs worldwide.
R21/Matrix-M vaccine (The Hindu)
- 04 Oct 2023
Why in the News?
The WHO has given its thumbs-up to the R21 vaccine, the second malaria vaccine they've recommended, following the RTS, S/AS01 vaccine, which got their approval in 2021. Right now, the WHO is closely examining this vaccine for prequalification, which is like their gold seal of approval. Once it's prequalified, organizations like GAVI (a global vaccine alliance) and UNICEF can purchase the vaccine from the manufacturers.
About the R21/Matrix-M Vaccine:
- It's a new vaccine designed to protect children from malaria.
- The University of Oxford and the Serum Institute of India developed it, with support from the European and Developing Countries Clinical Trials Partnership (EDCTP), the Wellcome Trust, and the European Investment Bank (EIB).
- This vaccine is a game-changer as it's the first one to meet the WHO's target of 75% effectiveness.
- Burkina Faso, Ghana, and Nigeria have already given the green light for its use.
- In early 2024, these African countries will start administering the vaccine, and by mid-2024, it will be available in other countries too.
Intelligent Grievance Monitoring System (IGMS) 2.0 (PIB)

- 03 Oct 2023
Why in the News?
Recently, the Minister of State (Independent Charge) for Science & Technology, MoS Personnel, Public Grievances, and Pensions introduced the upgraded version of the Intelligent Grievance Monitoring System (IGMS 2.0).
About the Intelligent Grievance Monitoring System (IGMS) 2.0:
- IGMS 2.0 is a digital platform and Automated Analysis in Tree Dashboard portal, under the purview of the Department of Administrative Reforms and Public Grievances (DARPG).
- Implementation of this system has been entrusted to IIT Kanpur.
Key Objectives:
- The Dashboard provides real-time tabulated analysis of both filed and resolved grievances, offering insights at state, district, and ministry levels.
- It assists in identifying the underlying causes of grievances.
- Additionally, this portal streamlines the creation of draft letters for specific schemes or ministries, expediting the grievance resolution process within the respective ministries and departments.
- IGMS 2.0 is equipped with Artificial Intelligence (AI) capabilities, enhancing its functionality.
Sanwariya Seth Temple (PIB)

- 03 Oct 2023
Why in the News?
The Prime Minister recently visited and paid his respects at the Sanwariya Seth Temple located in Chittorgarh, Rajasthan.
About Sanwariya Seth Temple:
- Sanwariya Seth Temple is a Hindu place of worship dedicated to Lord Krishna, particularly in his cherished child form known as “Sanwariya Seth” or “Shyam Seth."
- Location: Situated in the village of Mandaphia, Chittorgarh district, Rajasthan.
- Historical Origin: The temple dates back to its construction in the year 1840 A.D.
- Architectural Marvel:
- The temple embodies the quintessential Rajasthan architectural style, renowned for its intricate carvings, distinctive domes, and vivid color palette.
- The primary temple structure is crafted from pristine white marble.
- Elaborate carvings grace the walls, pillars, and ceilings, illustrating scenes from Hindu mythology and an array of motifs.
- Multiple ornate domes adorn the temple, enhancing its aesthetic appeal.
- The temple boasts a prominent spire, or 'shikhar,' which soars above the central sanctum.
- Sanctum Sanctorum: Inside the temple's innermost chamber rests a black stone idol of Lord Krishna.
- Welcoming Spaces: The temple offers expansive, pillared halls that serve as communal gathering areas for devotees and visitors alike.
United Nations Conference on Trade and Development (UNCTAD) (DownToEarth)

- 03 Oct 2023
Why in the News?
As per the United Nations Conference on Trade and Development's Review of Maritime Transport 2023, international shipping witnessed a notable increase of 20 percent in greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions in 2023 compared to the previous decade.
Key Highlights from the Review:
- The shipping industry plays a pivotal role, accounting for over 80 percent of global trade volume, yet contributes nearly three percent of total global greenhouse gas emissions.
- Containerized trade, after a 3.7 percent decline in 2022, is projected to grow by 1.2 percent in 2023 and is expected to further expand by three percent from 2024 to 2028.
- Oil and gas trade exhibited robust growth in 2022, with tanker freight rates experiencing a significant resurgence driven by geopolitical developments.
About the United Nations Conference on Trade and Development (UNCTAD):
- UNCTAD serves as the United Nations' primary institution addressing trade and development matters.
- Established in 1964 by the United Nations General Assembly, it functions as a permanent intergovernmental body.
- UNCTAD's mission is to promote equitable and effective access to the benefits of a globalized economy for developing countries.
- It offers economic and trade analysis, fosters consensus-building, and provides technical assistance to assist developing nations in leveraging trade, investment, finance, and technology for inclusive and sustainable development.
- Headquartered in Geneva, Switzerland, UNCTAD publishes influential reports, including the Trade and Development Report, the World Investment Report, and The Least Developed Countries Report.
National Service Scheme Awards (PIB)

- 03 Oct 2023
Why in the News?
Recently, the President of India conferred the National Service Scheme Awards for the period 2021-2022 at Rashtrapati Bhavan.
About the National Service Scheme Awards:
- Established in 1993-1994, the National Service Scheme Awards have been an annual tradition since their inception.
- These awards are bestowed by the Ministry of Youth Affairs & Sports, Department of Youth Affairs.
- Objectives:
- Acknowledge exceptional contributions of NSS student volunteers, NSS Programme Officers, and Programme Coordinators in community service.
- Encourage young NSS student volunteers to develop their personalities through community engagement.
- Applaud the efforts of Programme Officers and Programme Coordinators in fulfilling the goals of the National Service Scheme through NSS volunteers.
- Motivate NSS Volunteers to continue their selfless service in community work.
What is the National Service Scheme?
- The National Service Scheme is a Central Sector Scheme initiated by the Government of India.
- It provides students in the 11th & 12th grade at the +2 Board level, as well as students at technical institutions, colleges, and universities, the opportunity to participate in government-led community service activities and programs.
- Motto: The guiding motto of the National Service Scheme is 'NOT ME BUT YOU.'
- Nodal Ministry: The Ministry responsible for overseeing the National Service Scheme is the Ministry of Youth Affairs & Sports.
Sastra Ramanujan Prize (The Hindu)

- 03 Oct 2023
Why in the News?
Ruixiang Zhang, an Assistant Professor at the University of California, Berkeley, USA, will receive the prestigious 2023 SASTRA Ramanujan Prize in recognition of his exceptional achievements in the field of mathematics.
About the SASTRA Ramanujan Prize:
- Established in 2005, the SASTRA Ramanujan Prize is an esteemed mathematical award.
- It is annually presented by SASTRA University, located near Kumbakonam in Tamil Nadu, on December 22, Ramanujan's birth anniversary.
- This accolade is reserved for mathematicians worldwide who are under the age of 32 and are engaged in research influenced by the legendary Srinivasa Ramanujan.
- The age limit of 32 is a tribute to Ramanujan's remarkable achievements within a short lifespan.
- The prize includes a cash award of $10,000 along with a citation.
- It has earned global recognition and prestige since its inception.
- Notable past recipients of the prize include mathematicians Manjul Bhargava and Akshay Venkatesh.
Ruixiang Zhang's Contributions:
- Ruixiang Zhang, a young mathematician, has made significant contributions across various mathematical domains, including analytic number theory, combinatorics, and Euclidean Harmonic Analysis, among others.
- Based on his doctoral work at Princeton, Zhang, in collaboration with Shaoming Guo, successfully demonstrated a multivariable extension of Vinogradov's Mean Value Theorem.
- This groundbreaking work, published in Inventiones Mathematicae in 2019, is celebrated as a major milestone in the field.
Sycamore tree (Indian Express)

- 02 Oct 2023
Why in the News?
Recently, a 300-year-old sycamore tree in England, renowned for its beauty and exceptional location, was felled by a teenager.
About Sycamore Tree:
- Location: Situated within a hollow between two hills, at a break in the Hadrian Wall, an ancient stone structure near the border of England and Scotland in Northumberland, northern England.
- These 'breaks' are essentially channels that were naturally carved by extensive meltwater flows beneath ancient ice sheets, thousands of years ago.
- As they mature, sycamore trees can grow impressively tall, reaching heights of up to 35 meters.
- They are commonly found in the UK and feature leaves reminiscent of maple trees.
- Initially, the bark is dark pink-grey and smooth when young, but over time, it becomes textured, developing small plates.
- Sycamores have a remarkable lifespan and can survive for as long as 400 years.
- Distribution: Native to central, eastern, and southern Europe, it's believed that the introduction of sycamore trees to the UK occurred either during the Roman era or in the Tudor period around the 1500s.
Greater sand-plover (The Hindu)

- 02 Oct 2023
Why in the News?
A Greater sand-plover (Charadrius leschenaultii), typically found along seashores, was recently observed in an urban reservoir within Coimbatore.
About Greater Sand-Plover:
- Known for its impressive long-distance migrations.
- Physical Characteristics:
- A medium-sized plover featuring a lengthy and robust bill.
- Breeding adults display a dark mask and an orange chest, neck, and forehead, with females being somewhat less vibrant than males.
- Non-breeding birds and juveniles exhibit sandy brown plumage on top and white underneath, including a white throat and 'eyebrows.'
- Notably, unlike some Lesser Sand-Plovers, the Greater Sand-Plover never sports a black boundary around the throat.
- Breeding habitat includes high-elevation regions, favoring arid, open environments, often near water sources.
- During winters, it can be found along coastal mudflats and estuaries.
- Breeding season typically spans from April to May in central Asia, late March to late May in Turkey, and up to late June in Armenia.
- During the non-breeding season, it migrates to the shores of the Indian and Australian Oceans.
- The bird sustains itself on a diet comprising beetles, worms, crustaceans, mollusks, other insects, and their larvae.
- Preferred Habitat: Mudflats and sandy shores.
- Behavior/Ecology: Tends to associate with other shorebirds, particularly the Lesser Sand Plover.
- Conservation Status: IUCN: Least Concern
Pygmy hog (The Hindu)

- 02 Oct 2023
Why in the News?
Recently, a total of eighteen pygmy hogs, which were bred in captivity, were set free within the Manas National Park and Tiger Reserve located in western Assam.
About Pygmy Hog:
- It holds the distinction of being the world's smallest and rarest wild pig species.
- Remarkably, it's among the few mammals that construct their own dwellings, complete with a 'roof.'
- Considered an indicator species, its presence serves as a barometer for the well-being of its primary habitat, which consists of tall and moist grasslands.
- Habitat: Pygmy hogs thrive in untouched expanses of grassland dominated by early-stage riverine ecosystems.
- These areas typically feature dense tall grass interspersed with a rich variety of herbs, shrubs, and young trees.
- Currently, the only viable population of these hogs in the wild resides in the Manas Tiger Reserve in Assam.
- Conservation Status: IUCN: Critically Endangered
- Wildlife Protection Act, 1972: Listed under Schedule I
Kalakkad-Mundanthurai Tiger Reserve (Indian Express)

- 02 Oct 2023
Why in the News?
The Madurai Bench of the Madras High Court has recently issued a notice to the State regarding a public interest litigation petition. This petition aims to request a directive to limit the access of individuals and vehicles into the Kalakkad-Mundanthurai Tiger Reserve.
About Kalakkad-Mundanthurai Tiger Reserve:
- Location: Situated in the Southern Western Ghats within the Tirunelveli and Kanyakumari districts of Tamil Nadu.
- Established as a Tiger Reserve in 1988.
- Comprises three primary sanctuaries:
- Kalakad Sanctuary
- Mundanthurai Sanctuary, and
- A portion of Kanyakumari Sanctuary.
- The core area of the sanctuary is the Agastya Malai Hill Range, nestled between Kerala and Tamil Nadu.
- This range is part of one of the world's 18 biodiversity hotspots.
- Often referred to as the 'River Sanctuary,' it serves as the source for as many as 14 rivers.
- Terrain: Characterized by undulating landscapes with numerous valleys and porous rock formations.
- Vegetation:
- Varies from thorny shrub jungles to lush evergreen forests.
- Apart from forests, the reserve also includes savannah woodlands, grasslands, and even tea and coffee plantations.
- Flora: Notable species encompass Sarcandra, Paphiopedulum druryi, Hopea parviflora, Hopea utilis, Calophylum elatum, Cullenia exarillata, and more.
- Fauna: Home to a diverse range of wildlife, including tigers, leopards, rusty spotted cats, wild dogs, sloth bears, elephants, gaurs, sambar deer, spotted deer, mouse deer, Nilgiri langurs, slender lorises, bonnet macaques, lion-tailed macaques, among others.
FINANCIAL ACTION TASK FORCE (FATF) (Business Standard)
- 31 Oct 2023
What is the News ?
The Financial Action Task Force (FATF), an inter-governmental body that sets anti-money laundering standards, has removed the offshore tax haven Cayman Islands from its ‘grey list’.
Facts About:
- The Financial Action Task Force (FATF) is an intergovernmental organization that was founded in 1989 as part of the G7's effort to develop laws to combat money laundering.
- Its directive was extended to cover financing of terrorism in 2001.
- Only a few nations are listed in the grey and black lists that the FATF releases.
- To monitor the country's progress in combating money laundering and terrorism financing, a grey list is established.
- Non-cooperative nations are included on a blacklist in an effort to combat money laundering and financing of terrorism.
About the Cayman Islands:
- The Cayman Islands are situated in the Western Caribbean Sea and are a British Overseas Territory.
- Grand Cayman, Cayman Brac, and Little Cayman are the three islands that make up the territory; they are situated northwest of Jamaica and south of Cuba.
- Its topography is low-lying, with coral reefs.
- Economy: The islands are a thriving offshore financial hub, with a mixed economic system.
ARALAM WILDLIFE SANCTUARY (The Hindu)
- 31 Oct 2023
What is the News ?
Recently, individuals suspected to be associated with Maoist groups allegedly engaged in a gunfire exchange with Forest Department watchers in the Aralam Wildlife Sanctuary located in Kannur, Kerala.
Facts About:
- It's situated on the Western Ghats' western slopes.
- Founded in 1984, it is the northernmost wildlife sanctuary in Kerala.
- It shares borders with Wayanad-Brahmagiri, the northern slopes of Wayanad, and the Karnataka State Protected Areas, which include the Coorg forests and the Brahmagiri Wildlife Sanctuary.
- Katti Betta is the sanctuary's highest peak.
- In terms of vegetation, West Coast semievergreen forests and tropical evergreen forests predominate here.
It is the only protected area of the West Coast Tropical Evergreen Forest of Dipterocarpus-Mesua- Palaquium type.
- This wildlife sanctuary is traversed by the Cheenkani River.
- Flora: Cinnamomum Zeylanicum, Hopea parviflora, Largestroemia lanceolata, Xyliaxylocarpa, Mallotus, and Philippinensis are common trees in the semievergreen regions.
- Fauna: Bison, deer, boar, and elephants are fairly common. Here, one can see leopards, jungle cats, and a variety of squirrel species.
CRAB PLOVER (The Hindu)
- 31 Oct 2023
What is the News ?
Recently, for the first time, breeding nests of crab plovers were spotted at Great Vedaranyam Swamp near Point Calimere, Tamil Nadu.
Facts About:
The Crab-Plover is a distinctive bird found along the coasts of the Indian Ocean.
- It stands out with its long legs and striking black-and-white colouration.
This bird belongs to the plover family and is closely related to other shorebird species.
Unlike most shorebirds, the Crab-Plover lays white eggs.
- Their chicks stay inside burrows until they are ready to fledge, which sets them apart from other shorebirds.
Distribution: They can spotted in various places around the Indian Ocean, as they are residents in these regions.
- They breed in places like the Arabian Sea in Pakistan, the Gulf of Oman, the Persian Gulf, the Red Sea, Somalia, the Andaman Islands, Sri Lanka, Tanzania, and Madagascar.
Habitat: Crab Plovers make their homes in a variety of coastal environments, including sandy coastlines, mudflats, estuaries, lagoons, exposed coral reefs, and rocky shorelines. During the breeding season, they can also be found in sand dunes.
Conservation Status: The Crab-Plover is categorized as 'Least Concern' by the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN).
- Additionally, it falls under the protection of the Agreement on the Conservation of African-Eurasian Migratory Waterbirds (AEWA).
CARBON NANOFLORETS (The Hindu)
- 31 Oct 2023
What is the News ?
Carbon nanoflorets made by IIT Bombay researchers can convert incident sunlight to heat with 87% efficiency.
Facts About:
Carbon nanoflorets (NCFs) are a newly discovered type of carbon nanostructure that resembles tiny marigold flowers.
- They are made up of a network of carbon nanotubes arranged in a conical microcavity structure. NCFs have a number of unusual properties, including:
Broadband absorption: NCFs can absorb sunlight at all wavelengths, from ultraviolet to infrared.
- This is because their conical microcavity structure traps light for a longer period of time, allowing it to be absorbed by the carbon nanotubes.
- They are also extremely black, absorbing more than 95% of sunlight across a broad spectrum of wavelengths.
High light-heat conversion efficiency: NCFs can convert sunlight to heat with an efficiency of up to 87%.
- This is much higher than the efficiency of other solar-thermal materials, such as photovoltaic cells.
Low thermal conductivity: NCFs have a very low thermal conductivity, which means that they can efficiently convert sunlight to heat without losing much of the energy to conduction.
A team of researchers at the Indian Institute of Technology Bombay (IIT Bombay) reported that NCFs could convert incident sunlight to heat with an efficiency of 87%.
- This is significantly higher than the efficiency of other solar thermal materials, such as black carbon.
- It effectively absorbs over 97 per cent of sunlight's ultraviolet, visible, and infrared components, converting them into thermal energy.
- The resulting heat can be efficiently transferred to either air or water for practical applications.
- Research reveals that NCFs can raise the temperature of the surrounding air from room temperature to 60 degrees Celsius, providing smoke-free space-heating solutions.
AGARTALA-AKHAURA RAIL LINK PROJECT (Indian Express)
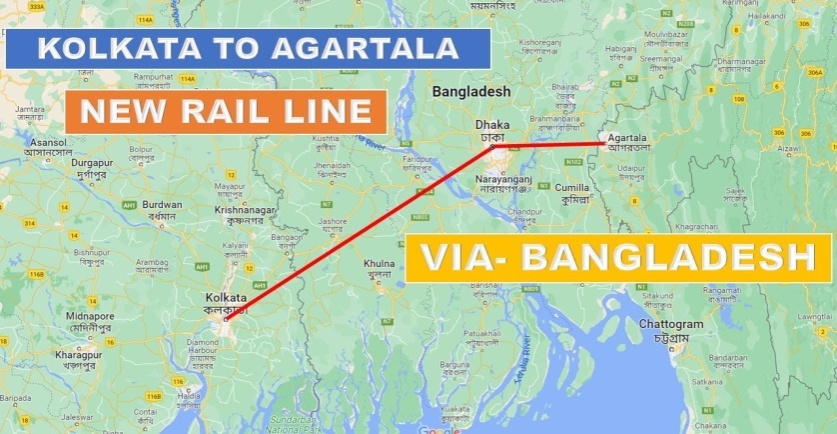
- 31 Oct 2023
What is the News ?
Prime Minister Narendra Modi and his Bangladesh counterpart Sheikh Hasina will jointly inaugurate the Agartala-Akhaura cross-border rail link project on Wednesday.
Facts About:
- The rail line between Agartala in Tripura and Akhaura in Bangladesh would pave the way for the first train to run from the northeastern region of India to Bangladesh.
- The project is significant from an international as well as from a domestic point of view.
- At present, the rail route from Agartala to Kolkata is around 1600 kilometres and takes about 38 hours.
- The footfall of passengers from Agartala to Kolkata is significantly very high due to the linguistic similarity between the two states.
Both states also share age-old cultural and business relations and Agartala depends on Kolkata from the medical tourism point of view as well.
- Upon operationalisation of the Agartala-Akhaura Rail link project the distance will be reduced by around 500 kilometres and the travel time will be 16 hours between Agartala and Kolkata.
- In addition, this rail link will also provide direct access between landlocked northeastern India and the Chittagong port of Bangladesh.
- The Ministry for Development of North Eastern Region (DoNER) has funded the railway line from Agartala to Nischintpur;
whereas the Ministry of External Affairs has funded the rail line from Nischintpur to Gangasagar which is in Bangladesh.
- The project is part of India's 'Act East Policy', which aims to promote economic cooperation and develop strategic ties with countries in the Asia-Pacific region.
AMANGARH TIGER RESERVE (TOI)
- 30 Oct 2023
What is the News ?
The tiger population at the Amangarh Tiger Reserve has increased from 21 mature tigers and six cubs in 2021 to 28 mature tigers and four cubs now.
Facts About:
Amangarh Tiger Reserve is situated in Amangarh, Bijnor district, Uttar Pradesh, covering an area of approximately 97 square kilometres.
- It shares its boundaries with Uttarakhand's Jim Corbett National Park.
Originally a part of Jim Corbett National Park, Amangarh became a separate reserve in Uttar Pradesh when Uttarakhand was carved out of UP..
- It received the status of a tiger reserve in 2012.
The reserve features diverse ecosystems, including grasslands, wetlands, and dense forests.
Wildlife: The reserve is home to a variety of wildlife.
- Among the mammals present are tigers, elephants, swamp deer, sambar, cheetal, hog deer, kakar, langur, sloth bear, porcupine, and otter.
- The bird population includes hornbills, red jungle fowl, pea fowl, Bengal floricans, fishing eagles, serpent eagles, ospreys, woodpeckers, shamas, Indian pittas, paradise flycatchers, orioles, and emerald doves.
- Additionally, the reserve is inhabited by reptiles such as monitor lizards, turtles, pythons, Gangetic dolphins, muggers, and gharial.
BRU REFUGEES (The Hindu)
- 30 Oct 2023
What is the News ?
The Bru refugees have been granted permanent settlement in Tripura as part of a centrally sponsored rehabilitation arrangement, which means they won't be taking part in Mizoram elections for the first time.
Facts About:
- The Bru refugees, also known as Reang, are an indigenous community primarily residing in the Northeast of India, particularly in Tripura, Mizoram, and Assam.
In Tripura, they hold the status of a Particularly Vulnerable Tribal Group, recognized by the government.
- Ethnically, they can be classified into two main clans, Meska and Molsoi, and they belong to the Indo-Mongoloid racial stock.
Their languages are affiliated with the Austro-Asiatic groups within the Tibeto-Burman family.
- They speak a language called "Kaubru," which shares some tonal features with the Kuki language, although it broadly falls under the Kok-Borok dialect.
- Occupation-wise, they continue to maintain their nomadic traditions, with a significant number of them engaged in Hilltop Jhum Cultivation and various food-gathering activities.
- Their beliefs encompass a belief in spirits and the existence of the soul.
- Religiously, they follow Hinduism, with most of their deities being akin to gods and goddesses of the Hindu faith.
Traditionally, they practice endogamy, not marrying outside their community.
- In their cultural tradition, the village council chief, known as "RAI," has the authority to approve divorce and widow marriages.
MAHABALI TUG (PIB)
- 30 Oct 2023
What is the News ?
Indian Navy launches 'Mahabali', a 25-ton BP Tug, showcasing India's self-reliance in shipbuilding.
Facts About:
- ‘Mahabali’ is a 25-ton Bollard Pull (BP) tug.
- It is one of three tugs of its kind that the Ministry of Defence and the Shipyard jointly commissioned.
It was built at the Shoft Shipyard in Bharuch, Gujarat.
- It has been built in compliance with the Indian Register of Shipping's (IRS) classification guidelines.
- It will become indispensable in supporting naval vessels and submarines in berthing and unberthing procedures and in manoeuvring through restricted waters.
- It has the capability to improve a ship's ability to put out fires while anchored and while cruising at port.
- Additionally, it has limited search and rescue capabilities.
THE SUBSURFACE WATER ICE MAPPING (SWIM) PROJECT (TOI)
- 30 Oct 2023
What is the News ?
The Subsurface Water Ice Mapping (SWIM) project, funded by NASA, has released its fourth map pinpointing potential subsurface water ice locations on Mars.
Facts About:
The Subsurface Water Ice Mapping (SWIM) project goal is to find the best locations to access water ice buried beneath the Mars' surface.
Recently, they released their fourth set of maps, which are the most detailed and accurate maps so far since the project began in 2017.
This project is led by the Planetary Science Institute in Tucson, Arizona, and managed by NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Southern California.
- They gather data from various NASA missions like the Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO), the 2001 Mars Odyssey, and the now-inactive Mars Global Surveyor.
To create these maps, SWIM utilized two high-resolution cameras on the MRO.
- They used Context Camera data to make better maps of the Northern Hemisphere.
- For the first time, they used HiRISE (High-Resolution Imaging Science Experiment) data to get the closest, most detailed view of the ice's edge near the equator.
The SWIM project was done in two phases.
- The first phase, finished in 2019, focused on the northern hemisphere, and
- The second phase, completed in 2020, included the southern hemisphere.
One exciting thing about the new map is that it shows 'polygon terrain,' where the ice beneath the surface causes the ground to crack into polygonal shapes.
- This suggests there's more ice hidden below.
EJECTA HALO (Indian Express)
- 30 Oct 2023
What is the News ?
The Chandrarayaan-3 Lander Module produced an amazing 'ejecta halo' of lunar material, according to recent information released by the Indian Space Research Organization (ISRO).
Facts About:
An ejecta halo is a bright, irregular patch of lunar material that surrounds a lander after it has landed on the Moon.
- It is caused by the thrust from the lander's engines and the impact of the lander on the lunar surface, which displaces and ejects lunar regolith (soil) and dust.
- The ejecta halo can be several meters in diameter and can extend tens of meters from the lander.
The Vikram lander of the Chandrayaan-3 mission created a spectacular ejecta halo when it landed on the Moon in August 2023.
- Scientists from the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) estimate that about 2.06 tonnes of lunar regolith were ejected and displaced over an area of 108.4 square meters around the landing site.
Ejecta halos can be studied to learn more about the composition and structure of the lunar regolith.
- They can also be used to calibrate remote sensing instruments and to develop new methods for landing spacecraft on the Moon.
NATIONAL TIGER CONSERVATION AUTHORITY (NTCA) (PIB)
- 29 Oct 2023
What is the News ?
The National Tiger Conservation Authority (NTCA) is holding an art exhibition in New Delhi from November 3–5, 2023, titled "Silent Conversation: From Margins to the Center."
Facts About:
- The National Tiger Conservation Authority (NTCA) has been constituted under section 38 L (1) of the Wildlife (Protection) Act, 1972.
- It is a statutory body, established in 2006 under the Ministry of Environment, Forest, and Climate Change (MoEFCC).
Objectives:
- Providing statutory authority to Project Tiger so that compliance with its directives becomes legal.
- Fostering Center-State accountability in Tiger Reserve management by providing a foundation for MoUs with states within the federal structure.
- Including a provision for parliamentary oversight.
- Addressing the livelihood interests of local residents in areas surrounding Tiger Reserves.
- Members of NTCA:
Minister in charge of MoEFCC (as Chairperson),
Minister of State in MoEFCC (as Vice-Chairperson),
Three members of Parliament, the Secretary (MoEFCC), and other members.
LOWER SUBANSIRI HYDROELECTRIC POWER PROJECT (HT)
- 29 Oct 2023
What is the News ?
The Lower Subansiri Hydro Electric Power project in Assam encountered a major problem when a significant landslide completely blocked its sole operational diversion tunnel, causing a substantial interruption in water flow through the river.
Facts About:
- This is the country's biggest hydroelectric project to date.
It is a run-of-river project on the Subansiri River.
- The Project is situated close to North Lakhimpur, which marks the boundary between Arunachal Pradesh and Assam.
- Capacity: 2000 MW.
- Up to 7.4 billion kWh of electricity will be produced there each year.
- Along with building a concrete gravity dam rising 116 meters above the riverbed, the project also entails building a surface powerhouse.
The dam will be 284 meters in length.
- The powerhouse is situated in the Subansiri district of Arunachal Pradesh, whereas the dam is situated in the Dhemaji district of Assam.
- It is being developed by the state-owned National Hydro Power Corporation (NHPC).
- Finance: A term loan was used to finance 30% of the project's debt in addition to 70% equity.
- The budgetary support provided by the central government is a component of the equity component.
NASA-ISRO SYNTHETIC APERTURE RADAR (NISAR) (TOI)
- 29 Oct 2023
What is the News ?
The 'NASA-ISRO Synthetic Aperture Radar' (NISAR) is set to enable the investigation of how changes in Earth's forest and wetland ecosystems affect the worldwide carbon cycle and exert an influence on climate change.
Facts About:
- NASA and ISRO collaborated to develop the Low Earth Orbit (LEO) observatory known as NISAR.
It's about the size of an SUV and weighs 2,800 kilograms.
- It is a dual-frequency imaging radar satellite, having both L-band and S-band synthetic aperture radar (SAR) instruments.
- The first satellite mission to measure variations in the surface of our planet will be NISAR, which will use two distinct radar frequencies (L-band and S-band).
No matter the weather, SAR can gather data day or night and penetrate clouds to gather information.
- NASA has contributed GPS, an L-band radar, a payload data subsystem, and a high-capacity solid-state recorder for data storage.
ISRO on the other hand supplied the S-band radar, as well as the GSLV launch system and spacecraft.
- Additionally, it has a sizable 39-foot stationary antenna reflector with an upward-facing feed on the instrument structure that will be used to focus "the radar signals emitted and received."
The reflector is constructed of gold-plated wire mesh.
- The mission's objectives are to measure the dynamic surfaces, ice masses, and changing ecosystems of Earth in order to gather data on groundwater, biomass, natural hazards, and sea level rise.
- NISAR is going to perform global 12-day regular observations of Earth's land and ice-covered surfaces during ascending and descending passes.
SEISMIC SWARM/EARTHQUAKE SWARM (The Hindu)
- 29 Oct 2023
What is the News ?
A seismic swarm has hit the Reykjanes peninsula in southwest Iceland with more than 5,500 small earthquakes in the last three days, raising the prospect of a volcanic eruption.
Facts About:
An earthquake swarm is a sequence of earthquakes that occur in a relatively short period, typically days or weeks, with no clear mainshock.
- It can occur anywhere in the world, but they are most common in volcanic regions and areas with active faults.
There are a number of different possible causes of earthquake swarms, but the most common cause is thought to be the movement of fluids through the Earth's crust.
- Fluids can weaken the rocks along faults, making them more likely to slip and generate earthquakes.
- Fluids can also move heat around, which can trigger earthquakes in some cases.
Reasons for swarm sequences:
Fluid migration: When fluids, such as water or magma, move through the Earth's crust, they can lubricate faults and make them more likely to slip.
- This can lead to a swarm of earthquakes as the fault ruptures in multiple places.
Magmatic activity: Earthquake swarms are often associated with volcanic regions.
- This suggests that magma moving underground can also trigger swarms.
Slow fault slip: When a fault slips slowly, the stress on the fault can build up over time until it is released in a series of small earthquakes.
- This can also lead to a swarm.
About the Reykjanes Peninsula:
- The Reykjanes Peninsula, located in southwestern Iceland, is a captivating region known for its dramatic and otherworldly landscapes.
- This geologically active area is characterized by rugged coastlines, extensive lava fields, and numerous geothermal features, including the famous Blue Lagoon.
- As part of the Mid-Atlantic Ridge, it showcases a bridge between the North American and Eurasian tectonic plates, making it a site of significant geological events such as earthquakes and volcanoes.
TALAGIRISVARA TEMPLE (The Hindu)
- 29 Oct 2023
What is the News ?
The ancient Pallava period paintings at Talagirishwara temple in Panamalai, Villupuram district, have suffered greatly due to neglect. The painting that showed Lord Shiva's dance has nearly disappeared, leaving only the face of goddess Parvathi and a few small sections remaining.
Facts About:
Talagirishwara Temple is situated in Panamalai village, Viluppuram district, Tamil Nadu, India.
- It is built on a small hill overlooking Panamalai Lake.
The temple was constructed by Pallava king Narasimhavarman II, also known as Rajasimha, during the Seventh Century.
Notable features of the temple include a Vimana similar to the one at Kailasanatha temple in Kanchipuram.
- The Vimana has three layers, with the highest tier being reconstructed.
Inside the temple's garbhagriha, there's a Dharalingam, and a Somaskanda section on the rear wall.
The temple has an Ardhamandapam (partial Mandapam) with walls featuring depictions of divinities like Brahma with Saraswati and Vishnu with Lakshmi.
- It faces east and is surrounded on three sides by sub-shrines.
- Additional sub-shrines and a large Mandapam called Mahamandapam were added at a later date.
The typical Pallava-style pillars with crouching lions can be found in the temple.
The temple houses paintings that resemble those in Ajantha and Chithannavasal.
- These paintings are on the walls of a sub-temple on the northern side of Talagirishwara (Shiva) temple.
- Notable among the paintings is one of Lord Shiva with eight hands dancing, known as Latathilagabhani, watched by Goddess Parvathi.
These paintings are older than the ones in Chithannavasal and were created by covering the stonewalls with a paste made of limestone and sand.
MELGHAT TIGER RESERVE (TOI)
- 28 Oct 2023
What is the News ?
Recently, a tiger was found dead in the Susarda range within the buffer zone of Melghat Tiger Reserve's Paratwada division.
Facts About:
The name "Melghat" signifies the confluence of various 'ghats' or valleys, reflecting the landscape of the reserve.
Location: Melghat Tiger Reserve is situated in the Amaravati district of Maharashtra.
- It's positioned on the southern offshoot of the Satpura Hill Range known as Gavilgarh Hill, approximately 225 km west of Nagpur.
Establishment: It was initially designated as a wildlife sanctuary in 1967 and later declared a tiger reserve in 1974.
- Melghat was one of the first nine tiger reserves established under Project Tiger in 1973-74, an initiative for the conservation of Bengal tigers in India.
- It is one of the largest tiger reserves in India in terms of its area.
Rivers: Melghat Tiger Reserve serves as the catchment area for five significant rivers: Khandu, Khapra, Sipna, Gadga, and Dolar.
Vegetation: The forest primarily consists of tropical dry deciduous trees, with teak being the dominant species.
Wildlife: Apart from Bengal tigers, the reserve is home to a variety of wildlife, including Sloth Bears, Indian Gaur, Sambar deer, Leopards, Nilgais, and more.
- Notably, the endangered Forest Owlet, once believed to be extinct, has been found in various areas of Melghat.
Tribal Communities: The largest tribal community in Melghat is the Korkus.
SARAS AAJEEVIKA MELA (PIB)
- 28 Oct 2023
What is the News ?
The popular SARAS Mela Gurugram was recently inaugurated by the Union Minister of State for Rural Development, Consumer Affairs, Food, and Public Distribution.
Facts About:
- SARAS Mela is a women empowerment initiative by the Deendayal Antyodaya Yojana National Rural Livelihoods Mission of the Ministry of Rural Development (MoRD)
- It’s aim is to bring the rural women self-help group members under one platform where they can showcase their skills, sell their products and build connections with potential market players at fair prices.
- The organisation trains women in different livelihood craftsmanship skills and gives them a platform to market their products.
- Their stalls are entirely free, and all their expenses, including their stay, are borne by the Mela organising committee.
- The SARAS Mela is organised by the National Institute of Rural Development and Panchayati Raj (NIRDPR).
- Saras Melas are regularly organised across India throughout the year.
RASHTRIYA GOKUL MISSION (Down to Earth)
- 28 Oct 2023
What is the News ?
The Rashtriya Gokul Mission is actively supporting the promotion of the Gir indigenous cow breed.
Facts About:
- It is being implemented for the development and conservation of indigenous bovine breeds since December 2014.
- With a budget of Rs. 2400 crore, the program is also carried out under the general Rashtriya Pashudhan Vikas Yojna from 2021 to 2026.
- The Ministry of Fisheries, Animal Husbandry, and Dairying is the nodal ministry.
Mission Objectives:
- To use cutting-edge technologies to raise milk production and sustainably improve the productivity of cows.
- To spread the practice of breeding bulls with high genetic merit.
- To increase the breeding network's strength and provide farmers with doorstep artificial insemination services to increase the coverage of artificial insemination.
- To encourage the scientific, all-encompassing rearing of native cattle and buffalo as well as conservation.
WHAT IS THALLIUM? (The Hindu)
- 28 Oct 2023
What is the News ?
A woman uses Thallium to seek revenge from in-laws in Gadchiroli, Maharashtra
Facts About:
- Thallium is a chemical element with the symbol "Tl" and atomic number 81 on the periodic table.
- It is a rare and heavy metal that is often considered a post-transition metal.
It is a soft, malleable metal that can easily be cut with a knife.
- Historical Use: In the past, thallium compounds were used in rat poisons and insecticides, but their use has been largely discontinued due to their toxicity.
- Electrical Conductivity: It has good electrical conductivity and is sometimes used in the manufacturing of electrical conductors.
- Radioactive Isotope: Thallium has a radioactive isotope, thallium-201, which is used in medical imaging as a radioactive tracer in cardiac stress tests.
- Chemical Properties: Thallium is chemically similar to lead and is often found in association with lead and zinc ores.
- Applications: Despite its toxicity, thallium has some limited applications in industries, including the manufacture of electronics, optical glasses, and low-melting thermometers.
- It is highly toxic to humans and is sometimes referred to as "the poisoner's poison" due to its extreme toxicity.
Exposure to thallium can cause a variety of health problems, including hair loss, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, abdominal pain, peripheral neuropathy, and seizures.
In severe cases, thallium poisoning can be fatal.
- Due to its toxicity, thallium is a highly regulated substance and its use is restricted to a limited number of industrial applications, and it is not available to consumers.
SATELLITE INTERNET TECHNOLOGY (Indian Express)
- 28 Oct 2023
What is the News ?
Reliance Jio recently declared that it had effectively tested the first gigabit internet service in India, based on satellite technology.
Facts About:
- Satellite Internet operates in a way similar to satellite TV.
- It begins with an internet service provider launching satellites into space to orbit the Earth.
These satellites, placed in low- or high-Earth orbit, transmit a signal.
- A receiver dish, positioned in your home or business, captures this signal.
It should have an unobstructed view of the sky.
- You connect a modem to this dish to convert the received signal into usable internet connectivity.
- High-speed satellite internet is typically delivered through constellations of low-Earth orbit (LEO) satellites.
- LEO satellites orbit the planet at altitudes ranging from 250 to 2,000 kilometers.
- Communication between these satellites and Earth occurs using radio waves.
Advantages of Satellite Internet:
- Satellite Internet is ideal for users residing in rural or remote areas, far from urban centers or cable/phone offices.
- It relies on a satellite dish for two-way communication and doesn't require telephone cables or lines.
- When compared to other internet options, satellite internet experiences fewer or minimal network outages.
MANAGEMENT & ENTREPRENEURSHIP AND PROFESSIONAL SKILLS COUNCIL (Business Standard)

- 27 Oct 2023
What is the News ?
A Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) was recently signed by the Management & Entrepreneurship and Professional Skills Council (MEPSC) and Magic Bus India Foundation, a prominent non-profit in the education and skilling sector.
Facts About:
MEPSC is a horizontal Sector Skill Council (SSC) that was established using a unique Public-Private Partnership (PPP) model in 2013 and registered as a Section-8 (Not for Profit Company) under the Companies Act.
The Ministry of Skill Development has been providing guidance to the Council during its operations.
The only organization promoting it is the All India Management Association (AIMA), which is the highest authority for the management profession in India.
MEPSC receives support from the National Skill Development Corporation (NSDC) and is acknowledged as an awarding body by the National Council for Vocational Education and Training (NCVET), the skills regulator.
Over the next ten years, MEPSC aims to train and certify about 4.75 lakh trainees, create and develop 50 Qualifications Packs (QPs)/National Occupational Standards (NOS), and train over 550 trainers.
It will take the lead on skill development programs in five major areas, including:
- Assessment and training
- Professional skills (including Security)
- Non-Teaching job roles in the education sector
- Entrepreneurship
The MEPSC Board of Directors is made up of several well-known and experienced business leaders, academics, NSDC, AIMA, and Ministry officials.
HANLE DARK SKY RESERVE (the Hindu)

- 27 Oct 2023
Facts About:
- The Hanle Dark Sky Reserve (HDSR) is India’s first dark sky region, and is centered at Hanle in Eastern Ladakh, around the Indian Astronomical Observatory.
- HDSR preserves the dark skies by reducing light pollution in the surrounding areas, and uses these dark skies to promote astrotourism as a means to further enhance socio-economic development in the area.
What is the Indian Astronomical Observatory?
- The Indian Astronomical Observatory (IAO) is one of the highest observatories in the world.
- It is situated in Hanle, Ladakh, at an elevation of 14.8 kilometers.
- Within the Changthang Wildlife Sanctuary, it will surface.
- Ladakh's vast arid region, high elevation, and sparse population make it an excellent choice for long-term observatories and dark-sky locations.
- The facility is supported by the Indian Institute of Astrophysics (IIA) in Bengaluru and the Department of Science and Technology.
GUDAVI BIRD SANCTUARY (The Hindu)
- 27 Oct 2023
What is the News ?
The Forest Department officials are concerned about the sudden deaths of multiple birds at the Gudavi Bird Sanctuary in the Shivamogga district of Karnataka.
Facts About:
- Gudavi Bird Sanctuary is located in the state of Karnataka.
It is situated on the banks of Gudavi Lake.
- It covers an area of about 0.74 square kilometers, making it a small but important sanctuary.
- Travelers from all over the world come here because of its rich biodiversity and surrounding natural beauty.
- During the winter months, the sanctuary attracts a large number of migratory birds, such as the beautiful Demoiselle Cranes.
- Fauna: The Bird Sanctuary is proud to be home to over 217 different bird species, including migratory and resident birds such as White-Headed Crane, Grey Heron, Little Cormorant, and Little Grebe.
- Flora: There are patches of grass mixed in with moist deciduous forest.
- The microphyte biota and marshy plants make up this type of wetland vegetation.
PM-SHRI SCHOOL (NDTV)
- 27 Oct 2023
What is the News ?
Union Minister for Education and Skill Development and Entrepreneurship, Dharmendra Pradhan, along with Haryana Chief Minister Manohar Lal Khattar, launched 124 PM-Shri schools in the state.
Facts About:
- PM SHRI School is a scheme sponsored by the Government of India.
- Objective: The initiative aims to establish over 14,500 PM SHRI Schools, managed by various government bodies, to provide a welcoming and caring environment for students.
These schools will offer a wide range of learning experiences, have good infrastructure, and ensure that all students have access to appropriate resources.
- National Education Policy 2020: The goal is to nurture students to become engaged, productive, and contributing citizens, in alignment with the vision of the National Education Policy 2020.
- Beneficiaries: More than 20 lakh students are expected to benefit directly from this scheme.
- Quality of School Education: The scheme will promote an understanding of various dimensions of the quality of school education and will inform policy, practice, and implementation in the education sector.
- Scaling Up: The lessons and best practices from these schools will be scaled up and implemented in other schools across the country.
- Implementation Period: The scheme is planned to be executed over a 5-year period from 2022-23 to 2026-27.
- Exemplar Schools: PM SHRI Schools are expected to showcase the implementation of the National Education Policy 2020 and become exemplary schools over time.
- This initiative aims to enhance the quality of education in India and create an inclusive and equitable society as envisioned in the National Education Policy.
REFERENCE FUELS (PIB)
- 27 Oct 2023
What is the News ?
Recently, Indian Oil's "Reference Gasoline and Diesel Fuels" was introduced for the first time in India by the Union Minister of Petroleum & Natural Gas.
Facts About:
- Reference fuels (Gasoline and Diesel) are premium, high-value products used for calibration and testing of vehicles by auto Original Equipment Manufacturers (OEMs) and organisations involved in testing and certification in the automotive field.
- These fuels are used for calibration and testing of vehicles by automobile manufacturers and testing agencies like ICAT (International Centre for Automotive Technology) and ARAI (Automotive Research Association of India).
- These indigenously developed products will lead to import substitution at better prices and a shorter lead time for the vehicle manufacturers.
- Reference Gasoline fuels will be available in E0, E5, E10, E20, E85, and E100 from Flagship Paradip Refinery.
Reference diesel fuel shall be available in B7 grade from Panipat Refinery.
- The indigenously developed product by Indian Oil meets Automotive Industry Standard (AIS) specifications, substitutes imports, and is available at better prices with reduced lead time.
- Indian Oil Corporation Limited has established facilities for the production of Reference Gasoline Fuels (E-5, E-10, and E-20) at its Paradip Refinery and Reference Diesel Fuel (B-7) at its Panipat refinery.
- The demand for Reference Fuels in India is currently met by imports from other countries.
- Indian Oil has successfully commenced the production of Reference Gasoline and Diesel Fuels for the first time in India.
UNITED NATIONS FORUM ON FORESTS (PIB)

- 26 Oct 2023
What is the News ?
The United Nations Forum on Forests (UNFF) will organise a Country-Led Initiative (CLI) event hosted by the Ministry of Environment, Forests, and Climate Change from October 26–28, 2023, at the Forest Research Institute (FRI), Dehradun, Uttarakhand.
Facts About:
- It encourages the sustainable development, preservation, and management of all kinds of forests.
- The UNEconomic and Social Council of the United Nations (ECOSOC) was founded it in 2000.
- Every year, the Forum gathers at the UN Headquarters in New York to discuss high-level policy issues in even years and technical issues in odd years, bringing together representatives of all member states and agencies with an interest in forests.
- All United Nations members as well as specialized agencies make up the forum, which has universal membership.
- India is one of UNFF's founding members.
JAMRANI DAM MULTIPURPOSE PROJECT (PTI)

- 26 Oct 2023
What is the News ?
The Pradhan Mantri Krishi Sinchayee Yojana-Accelerated Irrigation Benefit Programme (PMKSY-AIBP) now includes the Jamrani Dam Multipurpose Project, as approved by the Government of India recently.
Facts About:
The Pradhan Mantri Krishi Sinchayee Yojana-Accelerated Irrigation Benefit Programme (PMKSY-AIBP) now includes the Jamrani Dam Multipurpose Project, as approved by the Government of India recently.
About the Jamrani Dam Multipurpose Project:
- According to the project, a dam will be built in the Uttarakhand district of Nainital, close to Jamrani village, across the Gola River, a tributary of the Ram Ganga.
- The neighboring state of Uttar Pradesh would receive a sizable portion of the project's irrigation benefits.
- This is the seventh project to be added to the PMKSY-AIBP list.
Facts about the Pradhan Mantri Krishi Sinchayee Yojana:
It was introduced in 2015–16.
Aim: To improve physical access to water on farms, increase cultivable land under assured irrigation, increase on-farm water use efficiency, and implement sustainable water conservation practices.
Through the Accelerated Irrigation Benefit Programme (AIBP), ongoing major and medium irrigation projects, including national projects, will be completed more quickly.
Har Khet Ko Pani: It is divided into four smaller components:
- Ground Water (GW) Development component,
- Surface Minor Irrigation (SMI),
- Repair, Renovation and Restoration (RRR) of Water Bodies, and
- Command Area Development & Water Management (CAD&WM).
The Department of Agriculture and Farmers Welfare, Ministry of Agriculture and Farmers Welfare, is the nodal ministry.
NANCY GRACE ROMAN SPACE TELESCOPE (NASA)
- 26 Oct 2023
What is the News ?
NASA is preparing to use its Nancy Grace Roman Space Telescope to take humanity's deepest-ever look into the heart of our Milky Way Galaxy.
Facts About:
- The Nancy Grace Roman Space Telescope will offer one of the deepest views into the heart of the Milky Way galaxy.
Its mission includes monitoring hundreds of millions of stars to detect various celestial objects like planets, distant stars, icy objects in our solar system, black holes, and more.
- It will likely discover the farthest-known exoplanet, opening up new possibilities in the search for other worlds.
- Time-domain astronomy is a significant focus, studying how the universe changes over time, and Roman contributes to this field.
- The Galactic Bulge Time-Domain Survey will concentrate on the Milky Way, using infrared vision to see through dust clouds in the galaxy's central region.
The survey will involve taking images every 15 minutes around the clock for about two months, repeated six times over Roman's five-year primary mission.
- Astronomers anticipate finding over a thousand planets, including some within their host stars' habitable zones.
- It can detect "rogue" worlds that don't orbit stars, providing insights into planetary system formation.
- The mission will also identify brown dwarfs and help explore the boundary between planet and star formation.
- It is expected to spot neutron stars, stellar-mass black holes, Kuiper belt objects, and conduct stellar seismology studies on a million giant stars.
The telescope's broad view of space allows for a new view of an ever-changing universe.
- The Nancy Grace Roman Space Telescope is managed by NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center with participation from several other institutions and partners.
ANCIENT LANDSCAPE UNEARTHED BENEATH ANTARCTIC ICE SHEET (Space.com)
- 26 Oct 2023
What is the News ?
A new study finds that beneath East Antarctica's undulating ice sheet lies an ancient, river-carved landscape that provides a perfect snapshot of the region before glaciers covered the continent.
Facts About:
- In a groundbreaking discovery, scientists have unveiled an ancient, hidden world beneath the East Antarctic Ice Sheet, offering a correction to the traditional perception of a frozen wasteland.
This revelation reshapes our understanding of Antarctica's history and environmental conditions.
- This newly discovered landscape, believed to have been shaped by rivers over 14 million years ago, predates the initial formation of the East Antarctic ice around 34 million years ago.
- This ancient terrain comprises valleys and ridges that are strikingly reminiscent of the glacially-altered landscape in North Wales, UK, signifying the long-term temperature stability of the ice sheet in the studied region.
- The recent discovery builds upon the team's prior work, which revealed concealed mountain ranges, canyons, and lakes beneath the Antarctic ice.
The researchers suggest that additional undiscovered ancient landscapes may remain hidden under the East Antarctic Ice Sheet.
- This discovery underscores the significance of ongoing exploration and research in this largely uncharted territory, emphasizing that there is much more to uncover beneath the ice.
- This revelation prompts a re-evaluation of the conventional perception of Antarctica, demonstrating that it has a rich geological history dating back millions of years.
PRAGATI PLATFORM (News On Air)
- 26 Oct 2023
What is the News ?
Prime Minister Narendra Modi chaired the meeting of the 43rd edition of PRAGATI involving Centre and State governments recently.
Facts About:
- PRAGATI, which stands for Pro-Active Governance and Timely Implementation, is a multi-purpose and multi-modal platform.
- Its primary purpose is to address public grievances and concurrently oversee significant government programs and projects at both the national and state levels.
- It was officially launched on March 25, 2015.
- Developed in-house by the Prime Minister's Office (PMO) team in collaboration with the National Informatics Center (NIC), it is a robust system.
- This platform promotes e-transparency and e-accountability by facilitating real-time communication among key stakeholders.
- It integrates three cutting-edge technologies, video conferencing, digital data management, and geo-spatial technology.
- It fosters cooperative federalism by uniting Chief Secretaries of states and Government of India Secretaries on a common platform.
- The Prime Minister can engage in ground-level discussions with this platform, enabling communication with state and central officials while having access to up-to-date visuals on the screen.
- The three objectives of PRAGATI are:
Grievance Redressal
Programme Implementation
Project Monitoring
CYCLONE HAMOON (Indian Express)
- 25 Oct 2023
What is the News ?
The severe cyclonic storm “Hamoon” weakened into a deep depression and is likely to weaken further into a depression in the next six hours, the India Meteorological Department (IMD) said Wednesday.
Facts About:
- Presently situated over the west-central Bay of Bengal, it is anticipated to intensify shortly and proceed north and northeastward towards the coastal regions of Bangladesh and West Bengal.
- Named by: Iran gave the cyclonic storm its name after it formed.
Inland desert lakes and marshlands are referred to as "hamoon" in Persian.
They developed as yearly natural reservoirs in regions that border the Helmand basin.
- Projected Landfall: After weakening into a deep depression, it is predicted to make landfall between Khepupara and Chittagong on the coast of Bangladesh.
- Potential Effects: Parts of India are predicted to receive rainfall from the Hamoon, despite its decreased intensity.
- The northeastern states of Nagaland, Manipur, Mizoram, Tripura, south Assam, and Meghalaya are expected to experience light to moderate rainfall, with isolated heavy rains (64.5 mm-115.5 mm) according to the India Meteorological Department (IMD).
- Because of the anticipated effects of the cyclone, the (IMD) has also issued a yellow alert for coastal districts in West Bengal and Odisha.
How are Cyclones Given Their Names?
- Cyclones receive their names through a process managed by regional specialized meteorological centers (RSMCs) and Tropical Cyclone Warning Centers (TCWCs).
- There are a total of six RSMCs and five regional Tropical Cyclone Warning Centers responsible for this naming process.
- The Indian Meteorological Department (IMD) serves as an RSMC and is responsible for naming cyclones that form over the north Indian Ocean, encompassing the Bay of Bengal and the Arabian Sea.
- Additionally, the IMD is tasked with issuing advisories to 12 other countries in the region regarding cyclone and storm development.
NANO DAP FERTILIZER (PIB)
- 25 Oct 2023
What is the News ?
Recently, India's first liquid nano di-ammonia phosphate (DAP) fertilizer plant was inaugurated by Union Home Minister Amit Shah.
Facts About:
- Established in 2023 by Indian Farmers Fertiliser Cooperative Limited (IFFCO).
- Location: Gandhinagar, Gujarat's Kalol.
- It is the nation's first plant-producing liquid nano-ammonia phosphate (DAP).
What is Nano DAP fertilizer?
- Nano DAP is a nanotechnology-based fertilizer that contains di-ammonium phosphate (DAP) in the form of nanoparticles.
This means that the particles of DAP are much smaller than those in conventional DAP fertilizer.
It is more bioavailable to plants than conventional DAP because the smaller particles have a larger surface area, which allows them to be absorbed more easily by plant roots and leaves.
- It can be applied to crops through a variety of methods, including foliar application, soil application, and seed treatment.
- Nano DAP has been shown to increase crop yields by up to 20%. It can also improve crop quality and reduce the need for pesticides.
- It is more efficient than conventional DAP, meaning that less fertilizer is needed to achieve the same results.
This can save farmers money and reduce the environmental impact of agriculture.
- After urea, DAP is the second most popular fertilizer in the country.
DUST SUPPRESSANT (Indian Express)
- 25 Oct 2023
What is the News ?
Dust suppressants will be used in Delhi to mitigate pollution from dust. This, however, is not the first time it has been used in the Capital and parts of NCR.
Facts About:
- Magnesium or calcium salts with moisture-absorbing properties can act as dust suppressants.
- For longer-lasting dust control, water and dust suppressant powder are combined and sprayed on roads.
- Efficacy: In 2019, the Central Pollution Control Board (CPCB) advised using them, citing a study that discovered a 30% decrease in dust concentration, including PM10, PM2.5, and PM1, when dust suppressants were used in conjunction with water.
- Dust suppressants combined with water are significantly more effective at reducing particulate matter emissions than plain water sprinkling, according to a 2019 advisory from the Delhi Public Works Department (PWD).
- Magnesium chloride and bio-additives have been found to be particularly effective as a dust suppressant.
- To reduce dust emissions, the Delhi Pollution Control Committee and the CPCB both released guidelines recommending the use of dust suppressants during construction and in areas with high levels of dust.
The Central Consumer Protection AuthoRITY (CCPA) (The Hindu)
- 25 Oct 2023
What is the News ?
The Central Consumer Protection Authority (CCPA), has sent notices to 20 IAS coaching institutes across the country for issuing “misleading” advertisements.
Facts About:
CCPA is a regulatory authority set up under Section 10(1) of the Consumer Protection Act, 2019 and came into force on 20th July, 2020.
The Ministry of Consumer Affairs is the nodal ministry.
Composition:
- It will be led by a Chief Commissioner, with only two other commissioners as members, one of whom will deal with goods cases and the other with services cases.
- There will be a Director General in charge of the CCPA's Investigation Wing.
- Additionally, District Collectors will have the authority to look into claims of consumer rights abuses, unfair business practices, and deceptive or false advertising.
The goal is to promote, protect, and enforce the rights of consumers as a group.
- It will be given the authority to: conduct investigations into violations of consumer rights and file complaints/prosecute violators.
- Order the recall of dangerous goods and services, the cessation of unfair trade practices and misleading advertisements, and the imposition of penalties on manufacturers, endorsers, and publishers of misleading advertisements.
INTERNATIONAL MIGRATION OUTLOOK 2023 (Down to Earth)
- 25 Oct 2023
What is the News ?
Recently, the Organization for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD), published the "International Migration Outlook 2023."
Facts About:
- In 2021 and 2022, India had the largest migration flows to nations that are members of the Organization for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD).
- In terms of citizenship, 0.13 million Indians became citizens of an OECD nation in 2021.
- The ongoing conflict between Russia and Ukraine has caused the greatest level of internal displacement and refugee inflows into the OECD, with over 10 million people becoming internally displaced or refugees.
- In terms of workers, migration flows from India (+172 percent), Uzbekistan (+122 percent), and Turkey (+240 percent) increased dramatically, making them the primary countries of origin after Ukraine.
About the Organization for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD):
- The OECD is an international group of 38 countries that aims to foster economic development, and cooperation, and combat poverty by promoting economic stability.
- It was founded in 1961, by 18 European nations, the United States, and Canada.
Its headquarters are in Paris, France.
- Primary Goal: The primary goal of the OECD is to create policies that promote prosperity, equality, opportunity, and well-being for everyone.
- They produce economic reports, data, and predictions about global economic growth.
- The OECD also works to combat bribery and financial crimes worldwide, maintaining a list of uncooperative tax havens.
- India is not a member of the OECD, but a key economic partner.
PRADHAN MANTRI ANUSUCHIT JAATI ABHUYDAY YOJANA (PM-AJAY) (PIB)
- 24 Oct 2023
What is the News ?
Authorities have implemented the Pradhan Mantri Anusuchit Jaati Abhuyday Yojana (PM-AJAY) since 2021-22.
Facts About:
Pradhan Mantri Anusuchit Jaati Abhuyday Yojana, or PM-AJAY, is a combination of three government schemes:
- Pradhan Mantri Adarsh Gram Yojana (PMAGY),
- Special Central Assistance to Scheduled Castes Sub Plan (SCA to SCSP), and
- Babu Jagjivan Ram Chhatrawas Yojana (BJRCY).
The main goals of PM-AJAY are:
- To reduce poverty among Scheduled Caste (SC) communities by creating more jobs through skill development, income-generating programs, and other initiatives.
- To improve the overall development of SC-dominated villages by providing necessary infrastructure and essential services.
The scheme has three parts:
- Developing SC-dominated villages into model villages with proper infrastructure for socio-economic progress.
- Providing grants for projects at the district or state level that aim to better the socio-economic conditions of SCs, including building infrastructure in SC-dominated villages.
- Implementing comprehensive livelihood projects, including skill development, improving infrastructure, and offering financial assistance for assets needed to generate income.
Additionally, the scheme involves constructing hostels in higher educational institutions that are highly ranked according to the National Institutional Ranking Framework (NIRF) of the Government of India, and these hostels are funded by the Central, State, or Union Territory governments.
PAINTBRUSH SWIFT BUTTERFLY (The Hindu)
- 24 Oct 2023
What is the News ?
The paintbrush swift was recently photographed and documented for the first time in the Chamba district of Himachal Pradesh.
Facts About:
- The Paintbrush Swift butterfly, a rare species in the western Himalayas, was recently photographed and documented in Himachal Pradesh's Chamba district.
- Himachal Pradesh supports approximately 430 butterfly species, which make up about 25% of all butterfly species found in India.
- The Paintbrush Swift (Baoris farri) belongs to the Hesperiidae family and was discovered during a field survey under the Wild Bhattiyat Project in 2022.
It had never been photographed in Himachal Pradesh since its initial discovery in 1878.
- The project, initiated by the Bhattiyat Forest Range of the Dalhousie Forest Division, has documented 120 butterfly species, including the Paintbrush Swift.
- The butterfly's habitat distribution is common in northeast, central, and south India but rare in Uttarakhand.
- The Paintbrush Swift can be identified by two separated spots in the upper forewing cell.
- Conservation efforts are urgently needed to protect butterflies, including creating butterfly parks, rearing centers, and awareness campaigns, especially for high-altitude species facing habitat destruction and declining numbers.
DOGRA ARCHITECTURE (The Hindu)
- 24 Oct 2023
What is the News ?
Srinagar Smart City Limited and the Kashmir chapter of INTACH have joined hands to conserve vernacular elements of Kashmiri architecture, including colonnaded walkways, decorative pilasters, and exposed moulded brickwork.
Facts About:
- The buildings and structures that were built by the Dogra Hindu kings, who ruled over Jammu and Kashmir from 1846 to 1947, are known as "Dogra architecture."
- Maharaja Gulab Singh, a vassal of the Sikh Empire who later joined the British, established the Dogra dynasty.
- The Dogra kings were patrons of the arts and introduced a new architectural style that blended elements of Hindu, Islamic, and Sikh traditions.
- The interiors are richly decorated with frescoes, stucco work, and intricate wooden carvings that evoke both Rajput and Mughal architectural styles.
- European architectural features like arches, columns, and ornamental brackets were incorporated into Dogra architecture.
During the British colonial era, when interactions between European architects and local builders increased, this influence became more pronounced.
- Dogra architecture frequently uses symbolic elements taken from Hindu mythology and religious texts to express the people's spiritual beliefs.
PROJECT UDBHAV (TOI)
- 24 Oct 2023
What is the News ?
The Indian Army has launched a new project called 'Udbhav' to integrate ancient strategic knowledge with modern military practices.
Facts About:
- The Indian Army launched the Project Udbhav initiative to re-discover the rich Indian heritage of statecraft and strategic ideas drawn from ancient Indian texts on diplomacy, warcraft, and grand strategy.
It concentrates on a wide range of topics, such as indigenous military systems, historical texts, regional texts and kingdoms, thematic studies, and complex Kautilya studies.
Project Udbhav's main goal is to build a link between the past and the present.
- The project aims to create an indigenous strategic vocabulary that is deeply rooted in India's rich philosophical and cultural heritage, going beyond simply rediscovering historical narratives.
- The ultimate goal is to incorporate traditional knowledge into contemporary military education so that the Indian Army can use age-old principles in the complex strategic environment of today.
AADI MAHOTSAV (PIB)
- 24 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
Aadi Mahotsav, the National Tribal Festival will be inaguarted by the Union Minister for Tribal Affairs on 25th October, at Ahmedabad (Gujarat).
Facts About:
- The Tribal Cooperative Marketing Development Federation of India Limited (TRIFED), is organizing this mega event.
- It acts as a one-of-a-kind, mutually beneficial bridge to begin a journey through the tapestry of India's indigenous heritage.
- At this event, more than 100 stalls would present a wide range of Indian tribal culture, handicrafts, culinary artistry, and entrepreneurial endeavors.
- 'Millets grown by Tribals' will be featured at this Aadi Mahotsav in addition to other handicrafts, handloom, pottery, and jewelry attractions.
What is the Tribal Cooperative Marketing Development Federation of India Limited (TRIFED)?
- It is a national-level apex organization that operates under the administrative control of the Ministry of Tribal Affairs.
It facilitates and provides services to help tribes sell their products.
- In order for tribal people to carry out their operations in a more organized and scientific way, it aims to equip them with the necessary knowledge, resources, and tools.
- Its goal is to promote the socioeconomic development of the nation's indigenous populations through the sale of products made by them, such as pottery, metalwork, textiles, paintings, and pottery, on which they heavily rely for a significant portion of their income.
OPTOELECTRONICS (PIB)
- 23 Oct 2023
What is the News ?
For the investigation of opto-electronic properties in a variety of materials, a new Laboratory of Advance Synthesis and Characterization (LASC) in Gujarat is creating LASC probe stations for universities in India and abroad.
Facts About:
Optoelectronics is typically regarded as a sub-field of photonics and is the study and application of electronic devices and systems that source, detect, and control light.
The term "light" in this context frequently refers to both visible light and invisible radiation, such as gamma rays, X-rays, ultraviolet, and infrared.
For their opto-electronic properties, materials like tungsten diselenide (WSe2) and molybdenum diselenide are being closely examined.
The ability of these materials to absorb light and reemit it as a spectrum is known as photoluminescence.
- Quantum LEDs, which can be used for computation and communication, are one example of a device that can make use of photoluminescence properties.
TRIBAL COOPERATIVE MARKETING DEVELOPMENT FEDERATION (TRIFED) (PTI)
- 23 Oct 2023
What is the News ?
The Union Tribal Affairs Ministry on Saturday declared "null and void" the suspension of the managing director of TRIFED.
Facts About:
The Tribal Cooperative Marketing Development Federation (TRIFED) is a national-level organization operating under the Ministry of Tribal Affairs.
Its primary focus is on the development and marketing of tribal handicrafts and natural products.
Established in 1987, it became registered under the Multi-State Cooperative Societies Act, 1984 (now the Multi-State Cooperative Societies Act, 2002).
TRIFED's main objectives include enhancing the capabilities of tribal communities, promoting their products, and creating marketing opportunities to ensure better prices for tribal products, ultimately improving their income sustainably.
Some of its key goals are:
- Enhancing the socio-economic welfare of tribal communities.
- Facilitating and providing services to improve production within tribal communities.
- Offering training to enhance artistic skills using modern technology, making tribal products more competitive in the global market.
- Promoting tribal art and crafts to provide a stable livelihood.
- Identifying target groups, monitoring activities, and providing input to the Ministry.
Under retail marketing, TRIFED is responsible for marketing of tribal products under the brand name "TRIBES INDIA."
It promotes and establishes a sustainable market through retail outlets, exhibitions like Aadishilp, Aadichitra, and OCTAVE, international fairs, and e-marketing.
The Government of India has also entrusted TRIFED with the implementation of the Minimum Support Price Scheme for Minor Forest Produce.
Headquarter: New Delhi
It continues to operate a system of Regional Offices throughout India and a collection of TRIBES INDIA Retail Outlets.
GLOBAL COOLING COALITION (The Hindu)
- 23 Oct 2023
What is the News ?
The United Arab Emirates is leading the Global Cooling Pledge alongside the United Nations Environment Programme's (UNEP) Cool Coalition during the COP28 Presidency.
Facts About:
- The Global Cool Coalition is a unified front that connects action across the Kigali Amendment, Paris Agreement, and Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs).
- The aim is to increase aspiration, find solutions, and mobilize action to hasten the transition to clean and effective cooling.
- In addition to the UN, the Kigali Cooling Efficiency Program, the Climate and Clean Air Coalition, and Sustainable Energy for All (SEforALL) all support it.
- It is composed of leaders from civil society, academia, and government from countries like Chile, Rwanda, and Denmark.
Why is it necessary?
- 2020 was the hottest year on record for the entire planet, after 2019, 2018, 2017, and 2015.
- By 2050, there will be 4.5 billion air conditioning units installed worldwide as a result of rising incomes and urbanization; India may account for one billion of those units.
- India's cooling demand will more than double in the next 20 years, with air conditioners alone consuming more than half of the total energy required for cooling in the country by 2037-38.
- The Union Environment Ministry in India has already launched a national cooling action plan on March 8, 2019.
LITTLE ICE AGE (The Hindu)
- 23 Oct 2023
What is the News ?
During the Little Ice Age (LIA), the Western Ghats in India bore the hallmark of moist conditions, according to a recent study.
Facts About:
- It revealed significant variations in rainfall patterns during that time period, challenging the conventional view of the Little Ice Age (LIA) as a uniformly cold and dry climate with reduced monsoon rainfall.
- It was proposed that the Inter Tropical Convergence Zone's (ITCZ) northward motion, positive temperature anomalies, an increase in the number of sunspots, and high solar activity may be responsible for climate change and an accelerated South West Monsoon.
- In general, they believed that the southward shift of the ITCZ, which was brought on by increased northward energy flux across the equator during a cold northern hemisphere, was to blame for the weakest phase of the Indian Summer Monsoon (ISM) across the Indian subcontinent during the Little Ice Age.
- The high-resolution palaeoclimatic records produced in the current study may be useful in developing paleoclimatic models for future climatic predictions as well as for scientifically sound policy planning.
- In order to better understand the current Indian Summer Monsoon (ISM)-influenced climatic conditions as well as potential future climatic trends and projections, knowledge and understanding of climate change and Indian Summer Monsoon (ISM) variability during the Holocene could be of immense interest.
About the Little Ice Age:
- The Little Ice Age, which began in the late 19th and early 20th centuries, came after the Mediaeval Warming Period (roughly 900–1300 CE) and came before the current warming period.
- It was one of the coldest times in the last 10,000 years, with the North Atlantic region experiencing the greatest cooling.
- Millions of people suffered and died as a result of this cold spell, whose precise timing scholars debate but which appears to have begun around 600 years ago.
It is thought to have been the cause of crop failures, famines, and pandemics throughout Europe.
EDAKKAL CAVES (The Hindu)
- 23 Oct 2023
What is the News ?
Kerala Tourism has initiated a ?2.9-crore project to enhance civic amenities around Edakkal caves in Wayanad.
Facts About:
- These caves are situated on the magnificent Ambukuthi hills, 3,900 feet above sea level. The name Edakkal translates as "a stone in between."
- The ancient intricate stone carvings that are one-of-a-kind and come from the Neolithic and Mesolithic periods.
- The caves are two naturally occurring structures that are thought to have been created by a significant rock split.
- These include Neolithic-era pictorial writings that are thought to have been created at least 6,000 BCE.
Features:
- The Edakkal Caves are not actually caves, despite their name, as they also feature human and animal figures in addition to symbols and letters.
- They are a piece of a prehistoric rock shelter that naturally developed when one enormous boulder got wedged between two larger ones.
These include human figures, animals, tools, vehicles, everyday objects, and scripts in various language scripts.
- The Muniyaras, or ancient burial sites, that have been discovered in these hills have yielded a rich collection of ancient earthenware and pottery.
- The variety of the engravings suggest that the Edakkal caves were inhabited several times at different points in history.
EXERCISE 'MILAN' (TOI)
- 21 Oct 2023
What is the News ?
The Indian Navy will host the Mid Planning Conference (MPC) of the MILAN 24 Exercise in Visakhapatnam from February 19 to February 27, 2024.
Facts About:
- ‘MILAN’ is a multilateral naval exercise held every two years.
- It was established in 1995 by the Indian Navy.
- MILAN was originally conceived in accordance with India's 'Look East Policy,' but has since grown to include participation from other Friendly Foreign Countries (FFCs) in conjunction with the Government of India's 'Act East Policy' and Security and Growth for All in the Region (SAGAR) initiative.
- The harbor phase of MILAN 24 will include a City Parade at RK Beach, an International Maritime Seminar, a Swavlamban Exhibition, a Subject Matter Expert Exchange, and a Milan of Young Officers.
Friendly foreign country ships, maritime patrol aircraft, and submarines would take part in the sea phase alongside Indian Navy units.
- The operations will include large-force maneuvers, sophisticated air defense operations, anti-submarine warfare, and anti-surface warfare.
- MILAN 22 was held in/around Visakhapatnam from February 25th to March 4th, with 39 countries taking part.
UNITED NATIONS WORLD TOURISM ORGANISATION (UNWTO) (PIB)

- 21 Oct 2023
What is the News ?
The Dhordo village in Gujarat's Kutch district was recently recognized as the Best Tourism Village by the United Nations World Tourism Organization (UNWTO), which was praised by India's Prime Minister.
Facts About:
- The United Nations World Tourism Organization (UNWTO) is a specialized agency of the United Nations responsible for promoting sustainable and responsible tourism on a global scale.
- Its functions include acting as a global forum for tourism policy issues and encouraging the adoption of the Global Code of Ethics for Tourism.
It was founded in 1975.
- Members: 159 countries are members of the UNWTO.
- Arabic, Chinese, English, French, Russian, and Spanish are the UNWTO's official languages.
- Structure of the organization:
The World Tourism Organization's General Assembly is the organization's main meeting.
It is made up of full members and associate members. It convenes every two years.
- The Executive Council serves as the UNWTO's governing body.
It is made up of 35 members, one for every five full members, who are elected by the General Assembly. It holds at least two meetings per year.
- Headquarters are in Madrid, (Spain).
GREEN ENERGY CORRIDOR (GEC) (PIB)

- 21 Oct 2023
What is the News ?
The 13 GW Renewable Energy Project in Ladakh's Green Energy Corridor (GEC) Phase-II - Inter-State Transmission System (ISTS) has received approval from the Cabinet Committee on Economic Affairs.
Facts About:
- The Green Energy Corridor (GEC) is an initiative that aims to integrate and evacuate renewable energy into India's power grid, promote sustainable growth, and improve energy security. It is divided into two stages.
- Power Grid Corporation of India Limited (POWERGRID) is the implementation agency.
- Implementation of GEC-1 is already underway in Gujarat, Andhra Pradesh, Karnataka, Himachal Pradesh, Maharashtra, Madhya Pradesh, Tamil Nadu, and Rajasthan, with the goal of integrating and evacuating 24GW of Renewable Energy (RE).
- For GEC-2, Gujarat, Himachal Pradesh, Karnataka, Kerala, Rajasthan, Tamil Nadu, and Uttar Pradesh will be the first states to implement.
Grid integration and power evacuation of approximately 20 GW of renewable energy projects over a five-year period (FY 2021-22 to 2025-26).
Objectives:
- Synchronize renewable energy sources (wind and solar) with traditional power sources.
- Non-fossil fuel installed capacity should reach 500 GW by 2030..
- 20,000 MW of large-scale renewable energy should be evacuated.
- Importance: Improve India's long-term energy security; Promote environmentally friendly growth by reducing carbon footprint; Create employment opportunities for both skilled and unskilled workers.
WHITE PHOSPHOROUS BOMBS (Indian Express)
- 21 Oct 2023
What is the News ?
According to recent reports, Israeli forces have been using white phosphorous against the civilian population of Gaza.
Facts About:
It is a waxy solid that is colorless, white, or yellow.
Occurrence:
- It does not occur naturally. Phosphate rocks are used to make it.
- It is a highly flammable substance that reacts with oxygen in the atmosphere.
- As little as 10 to 15 degrees above room temperature can cause it to catch fire.
Every country has strict regulations regarding its manufacturing and handling due to its combustible nature.
Applications:
- It is primarily used in the military, but it may also be used as a component in fertilizers, food additives, and cleaning compounds.
- It was originally used in pesticides and fireworks, but many countries have banned its use in a variety of industries.
The Organisation for the Prohibition of Chemical Weapons (OPCW), an intergovernmental organization and the implementing body for the Chemical Weapons Convention, has not included White Phosphorus in any of the three Chemical Weapons Schedules.
YARD 12706 (IMPHAL) (PIB)
- 21 Oct 2023
What is the News ?
Mazagon Dock Shipbuilders Limited (MDL) recently delivered to the Indian Navy the third Stealth Destroyer of the Project 15B Class Guided Missile Destroyer, Yard 12706 (IMPHAL).
Facts About:
- The ship is made of indigenous steel DMR 249A and is one of India's largest destroyers, with an overall length of 164 meters and a displacement of over 7500 tonnes.
- The ship is propelled by a powerful Combined Gas and Gas Propulsion Plant (COGAG), which consists of four reversible Gas Turbines and allows her to reach speeds of more than 30 knots (approximately 55 Kmph).
- The ship is a powerful tool that can be used for a wide range of operations and missions, covering every aspect of maritime warfare.
- It is equipped with medium range Surface to Air Missiles ('Barak-8') and supersonic Surface to Surface Missiles ('Brahmos').
- The Destroyer is equipped with indigenously made anti-submarine weapons and sensors, including the Hull-mounted Sonar Humsa NG, Heavy Weight Torpedo Tube Launchers, and ASW Rocket Launchers.
- Compared to earlier classes of naval destroyers and frigates, it is more adaptable.
- It can operate independently without supporting vessels and can also serve as the flagship of a naval task force thanks to its all-around capability against enemy submarines, surface warships, anti-ship missiles, and fighter aircraft.
Toto language (The Hindu)
- 30 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
Recently, a dictionary called Toto Shabda Sangraha has been created with the aim of preserving a language from becoming extinct.
Facts About:
- It belongs to the Sino-Tibetan language family and is the native language of the Toto tribal community. Toto is typically written using the Bengali script.
- Remarkably, a script for Toto was developed by a prominent community member named Dhaniram Toto as recently as 2015.
- Toto is spoken by a relatively small population of around 1,600 individuals residing in parts of West Bengal that border Bhutan.
Key Highlights of the Toto Shabda Sangraha:
- This dictionary has been meticulously compiled by Bhakta Toto, who serves as both a bank employee and a poet. It has been jointly published by a trust and Bhasha Samsad.
- The dictionary serves as a significant step towards preserving the Toto language, which has primarily been an oral tradition, by documenting its vocabulary in written form.
- To facilitate wider understanding, Toto words will be translated into Bengali and English and presented using the Bengali script, as the Toto script is still in its early stages of development, and community members are more familiar with the Bengali script.
Naganathaswamy Temple (The Hindu)
- 30 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
The Tamil Nadu Department of Archaeology is preparing to initiate the restoration of the ancient Naganathaswamy Temple, which has stood for a millennium in Manambadi, located within the Thanjavur district.
Facts About:
- This temple was commissioned by Rajendra Chola I, reigning from 1012 to 1044 CE.
- In historical inscriptions, it is also known as the Kailasamudaiyar Temple.
- Key Features:
- Renowned for its intricate stone carvings and significant inscriptions.
- Comprises a single-tiered vimana (sanctum) and a mukha mandapa (front hall).
- The walls of both structures are divided into three sections.
- Within the central bays of the vimana, niches are dedicated to Dakshinamurthi in the south, Lingodhbava in the west, and Brahma in the north.
- The mukha mandapa features three niches each on the south and north sides.
- Notable sculptures in the southern niches include Bikshatana, Adavallan, and Ganapathi, while the northern niches feature Gangadarara, Durga, and Ammaiappar.
- All these niches exhibit finely crafted and distinctive makara thoranas (decorative arches) with central relief sculptures.
- Inscriptions: The temple boasts important inscriptions dating back to the reigns of Rajendra Chola I and Kulothunga I (1070-1120 CE).
- A total of nine informative inscriptions have been documented within the temple premises.
- The earliest of these inscriptions dates to the fourth year of Rajendra Chola I's rule and pertains to a tax-free land grant by the nagaratthar of Ilaichikkudi for establishing a flower garden in honor of the king for the temple's benefit.
CRIIIO 4 GOOD Initiative (PIB)
- 30 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
Recently, the Union Minister for Education, Skill Development, and Entrepreneurship unveiled a program called 'CRIIIO 4 GOOD'.
Facts About:
- This is a novel online module designed to impart essential life skills.
- Comprising a series of eight cricket-themed animated films, its primary objectives are to promote gender equality, empower girls with valuable life skills, and foster their active engagement in sports.
- Leveraging the immense popularity and enthusiasm for cricket among young audiences, the ICC (International Cricket Council) and UNICEF collaborated to introduce these modules, aiming to inspire children and youth to embrace crucial life skills and appreciate the significance of gender parity.
- The program is available in three languages: English, Hindi, and Gujarati.
- The eight modules revolve around key themes such as leadership, problem-solving, self-assurance, decision-making, negotiation, empathy, teamwork, and goal-setting, all depicted through cutting-edge animations using cricket-related examples.
- This initiative was launched in partnership with the International Cricket Council, UNICEF, and the Board of Control for Cricket in India.
Sankalp Saptaah (News On Air)
- 30 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
The Prime Minister will launch a special week-long program called 'Sankalp Saptaah' at Bharat Mandapam in New Delhi.
Facts About:
- This initiative is closely tied to the successful execution of the Aspirational Blocks Programme (ABP).
- In order to implement the ABP effectively and devise a robust strategy for block development, 'chintan shivirs' or brainstorming sessions were conducted at the village and block levels across the nation. The Sankalp Saptah marks the culmination of these brainstorming sessions.
- Sankalp Saptah will be observed in all 500 aspirational blocks.
- Each day during Sankalp Saptah will be dedicated to a specific development theme that all aspirational blocks will focus on.
- The themes for the initial six days include 'Comprehensive Health', 'Nourished Families', 'Cleanliness', 'Agriculture', 'Education', and 'Prosperity Day'.
- The final day of the week will be a celebration of the collective efforts undertaken throughout the week, known as 'Sankalp Saptah – Inclusive Conclave.'
- The inaugural event will see the participation of approximately 3,000 representatives from panchayats and block-level officials from across the country at Bharat Mandapam.
CALIPSO Mission (Indian Express)
- 30 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
Recently, NASA declared the conclusion of the CALIPSO mission, which conducted assessments of climate, weather, and air quality.
Facts About:
- CALIPSO (Cloud-Aerosol LIDAR and Infrared Pathfinder Satellite Observations), is a dedicated mission aimed at understanding the influence of clouds and aerosols on Earth's climate.
- A collaborative endeavor between NASA (National Aeronautics and Space Administration) and CNES (Centre National d'Études Spatiales), the French space agency, CALIPSO took to the skies in 2006 as a satellite-based observatory.
- Scientists have harnessed CALIPSO's data to construct three-dimensional atmospheric models, enhancing our capacity to forecast future climate changes.
- CALIPSO has been an integral part of the "A-Train" constellation of spacecraft, which includes Aqua, Aura, and PARASOL, all dedicated to the study of Earth's weather and environment.
Key Instrumentation:
- The mission is equipped with CALIOP, a lidar system that operates at two wavelengths and is sensitive to polarization.
Additionally, it carries two passive sensors functioning in the visible and thermal infrared spectral ranges.
- CALIOP emits laser pulses and measures the light scattered back by clouds and aerosols, enabling the creation of vertical profiles detailing properties such as height, thickness, and optical depth.
- Notably, CALIOP is the first lidar to provide continuous atmospheric measurements from Earth's orbit.
- This invaluable data aids scientists in generating comprehensive three-dimensional profiles of cloud and aerosol distributions.
- Throughout its 17 years of operation, the mission amassed over 10 billion LIDAR measurements and contributed to the creation of numerous scientific reports.
Global Innovation Index 2023 (PIB)
- 29 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
India maintains its position at the 40th rank among 132 economies in the Global Innovation Index for the year 2023..
Facts About:
- Published by the World Intellectual Property Organization (WIPO).
- Serves as a valuable tool for governments worldwide to evaluate the impact of innovation on social and economic development in their nations.
- The India Launch of GII 2023 is being virtually hosted on September 29, 2023, by NITI Aayog in collaboration with the Confederation of Indian Industry (CII) and WIPO.
Key Insights:
- The Global Innovation Index relies on a diverse dataset, incorporating 80 indicators from international public and private sources, offering a comprehensive view of innovation beyond conventional measures.
- Top 5 countries in the ranking include Switzerland, Sweden, the United States, the United Kingdom (4th), and Singapore (5th).
- India is recognized among the 21 economies that have consistently outperformed in innovation relative to their level of development for the 13th consecutive year.
- The report highlights India, Iran, the Philippines, Turkey, Vietnam, and Indonesia as economies within the GII top 65 that have made significant ranking improvements over the last decade.
- Within the Central and Southern Asia region, India secures top positions in categories such as Human capital and research (48th), Business sophistication (57th), and Knowledge and technology outputs (22nd).
- Prominent indicators for India encompass ICT services exports (5th), Venture capital received (6th), Graduates in science and engineering (11th), and Global corporate R&D investors (13th).
e-Cabinet System (Indian Express)
- 29 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
Recently, the Chief Minister of Tripura inaugurated an e-cabinet system in Agartala, aimed at advancing digital infrastructure and enhancing the digitization of government services and information.
Facts About:
- The e-Cabinet system is a robust software portal designed for State Governments to facilitate electronic and online Cabinet meetings.
- It has been developed by the National Information Centre (NIC), Ministry of Electronics & Information Technology (MeitY).
- Tripura is now the fourth state, and the second in the Northeast region, to implement the e-cabinet system, following in the footsteps of Uttarakhand, Uttar Pradesh, and Arunachal Pradesh.
Key Features:
- Enhances the utilization of technology in meetings and reduces paper consumption.
- Streamlines workflow activities for meetings, covering pre-meeting, during the meeting, and post-meeting phases.
- Offers a user-friendly interface designed for smart tablets, ensuring a smooth user experience.
- Incorporates a secure push and pull mechanism to safeguard sensitive Cabinet matters.
- Establishes an institutional memory and knowledge repository, facilitating quick searches and retrieval of information.
- For virtual meetings, eCabinet seamlessly integrates with the Bharat VC solution of NIC.
Benefits and Impact of eCabinet:
- Substantial savings in paper, fuel, and manpower resources.
- Real-time data updates.
- Enhanced information accessibility, promoting coordinated actions.
- Improved decision-making processes and swift retrieval of meeting decisions and action taken.
- Enables virtual participation of Ministers in Cabinet proceedings.
Five Eyes’ Intelligence Alliance (The Hindu)
- 29 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
The recent claims made by Canadian Prime Minister Justin Trudeau, connecting the murder of Hardeep Singh Nijjar on Canadian territory to the Indian government, have drawn attention to the intelligence-sharing coalition known as the 'Five Eyes' (FVEY).
Facts About:
- This multilateral intelligence-sharing network involves more than 20 agencies from five predominantly English-speaking nations:
Australia, Canada, New Zealand, the United Kingdom, and the United States.
- It encompasses both surveillance-based activities and signals intelligence (SIGINT).
- The intelligence documents shared among member countries are labeled as 'Secret—AUS/CAN/NZ/UK/US Eyes Only,' which gives rise to the group's name, 'Five Eyes.'
Background of the Alliance:
- The origins of this alliance between the U.S. and the U.K. date back to the Second World War when they collaborated to counter the Cold War Soviet threat.
- These two nations, renowned for their code-breaking achievements during World War II, established cooperation in sharing intelligence related to various forms of signals, including radio, satellite, and internet communications.
- Following the war, in 1946, the alliance formalized through an agreement focused on signals intelligence.
This agreement, originally named the British-U.S. Communication Intelligence Agreement (BRUSA) and now known as the UKUSA Agreement, was signed between the U.S. State-Army-Navy Communication Intelligence Board (STANCIB) and the British London Signal Intelligence Board (SIGINT).
- Initially, its scope was limited to 'communication intelligence matters only,' involving the unrestricted exchange of intelligence products across six areas: traffic collection, acquisition of communication documents and equipment, traffic analysis, cryptanalysis, decryption and translation, and the acquisition of information regarding communication organizations, practices, procedures, and equipment.
- Over time, the alliance expanded to include 'second party' countries, with Canada joining in 1948, and Australia and New Zealand becoming part of the alliance in 1956.
Conocarpus Tree (Indian Express)
- 29 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
Recently, the government of Gujarat has instituted a prohibition on the planting of Conocarpus trees in both forested and non-forested areas, citing concerns regarding their detrimental effects on the environment and human well-being.
Facts About:
- The Conocarpus tree is a flowering plant belonging to the Combretaceae family.
- It is categorized as an invasive mangrove species.
- These trees bloom during the winter season, releasing pollen into their surroundings.
- In India, public authorities have commonly used Conocarpus for landscaping purposes, including road medians, roadsides, and public gardens.
- In the Arabian Peninsula, it has been employed to combat desert storms and pollution.
- This tree is renowned for its year-round dark green leaves and its ability to thrive in harsh environmental conditions, including extreme temperatures.
- It exhibits adaptability, even in areas with high salinity.
- The Conocarpus tree absorbs a significant amount of water from the soil, posing a threat to groundwater levels.
- Its extensive root system can damage communication cables, drainage lines, and drinking water pipelines.
- This species is native to various regions in North and South America, as well as parts of Africa.
Gems and Jewellery Export Promotion Council (GJEPC) (Indian Express)
- 29 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
The Gems and Jewellery Export Promotion Council (GJEPC) has made a plea to the diamond industry, urging them to halt the importation of rough diamonds.
Facts About:
- GJEPC serves as the apex organization representing India's Gem and Jewellery industry, operating under the sponsorship of the Ministry of Commerce & Industry, Government of India.
- Primary Role: The Council's primary mission is to introduce Indian gem and jewellery products to global markets and facilitate their exports.
It achieves this by furnishing its members with crucial information on foreign trade inquiries, trade regulations, tariff rates, and updates on jewellery fairs and exhibitions.
- Location: Headquartered in Mumbai, Maharashtra, GJEPC maintains a presence through regional offices nationwide, boasting a membership exceeding 7,500.
Additional Functions:
- Collaborating in international jewellery showcases.
- Encouraging countries to explore opportunities for cooperation in the supply of rough diamonds, colored gemstones, and finished jewellery.
- Identifying potential partners and buyers in international markets through buyer-seller meetings.
- Administering the Kimberly Process Certification Scheme as India's Nodal Agency.
- Advocating for export-related matters with the Government, Ministries, Regulatory Authorities, and Agencies.
- Conducting image-building campaigns via international advertisements, publications, and audio-visuals.
- Establishing training institutes across six cities (Mumbai, Delhi, Surat, Jaipur, Varanasi, and Udupi) to impart manufacturing skills and promote technical and design excellence.
- Initiating the establishment of Jewellery Parks throughout the country.
Balsams (Genus Impatiens) (The Hindu)
- 28 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
Balsams, belonging to the genus Impatiens, are currently putting on a vibrant display of blooms in Munnar, offering a captivating visual treat to tourists.
Facts About:
- Locally referred to as Kasithumba and Onappovu.
- Commonly known as 'touch-me-not' due to its seed dispersal mechanism.
- Various names used for these plants include balsams, touch-me-nots, and jewel weeds.
Distribution:
- Natively found in tropical, sub-tropical, and northern temperate regions worldwide.
- Predominantly present in India, China, Africa, and scattered regions of Europe and North America.
- India boasts 220 balsam species, with 135 of them thriving in the southern Western Ghats.
- The Western Ghats, including Anamudi, its highest peak, host diverse wild balsam varieties.
- Typically, balsams complete their life cycle between June and December.
- These fleshy, herbaceous plants are often found in pockets within forested areas.
- They thrive in humid habitats and complete their life cycle during the rainy season.
- Balsams are recognized as significant indicators of climate change.
Manis Mysteria (The Hindu)
- 28 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
In addition to the eight previously identified pangolin species, researchers have recently found a ninth variety, which is currently given the temporary name "Manis mysteria.
Facts About:
Scientists have recently made a significant discovery in the world of wildlife by identifying a previously unknown ninth species of pangolin.
- This newly found pangolin variety has been tentatively named "Manis mysteria."
Origins from Confiscated Scales: The origins of this remarkable discovery trace back to the examination of pangolin scales that were seized in China's Yunnan province during the years 2015 and 2019.
- These scales provided vital clues leading to the identification of the new species.
Ancient Divergence: Research indicates that "Manis mysteria" took a distinct evolutionary path around five million years ago, separating from its Philippine and Malayan pangolin relatives.
- This long separation in the evolutionary timeline highlights its unique characteristics.
Distinctive Features of Pangolins: Pangolins are known for their distinctive characteristics, including protective keratin scales that cover their bodies and a diet primarily consisting of ants and termites.
- They hold the distinction of being the only mammals with such specialized scales.
Defensive Behavior: One of the most intriguing aspects of pangolins is their ability to curl up into a tight, defensive ball when they feel threatened.
- This remarkable behavior helps protect them from potential predators.
- Grave Threats to Pangolins: Unfortunately, all species of pangolins face severe threats to their survival.
- Each species is currently listed on the IUCN Red List of Threatened Species, a concerning designation that highlights their vulnerable status.
- For instance, the Indian pangolin is specifically categorized as "Endangered," underlining the urgent need for conservation efforts to safeguard these unique creatures.
Social Bonds (The Hindu)
- 28 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
The National Bank for Agriculture and Rural Development (NABARD) has just released its first-ever social bonds, amounting to a total of Rs 1,040.50 crore.
Facts About:
- Social bonds, or social impact bonds (SIBs), are a type of bond used to raise funds for projects with positive social outcomes.
- These projects tackle various societal issues like healthcare, education, affordable housing, poverty reduction, and environmental sustainability.
Notable Example in India:
- In 2020, the Pimpri Chinchwad Municipal Corporation (PCMC) in Pune, Maharashtra, partnered with the United Nations Development Programme (UNDP) to create India's first Social Impact Bond (SIB).
Key Features of NABARD's Social Bonds:
- NABARD's social bonds are the first externally certified AAA-rated Indian Rupee-denominated SIBs. They have received 'AAA' ratings from CRISIL and ICRA.
- The initial bond size was ?1,000 crore, with the option to accept oversubscriptions up to ?2,000 crore, totaling up to ?3,000 crore.
- Each bond has a face value of ?1 lakh.
- Maturity period: 5 years
- Coupon Rate: 7.63 percent
Sustainability Bond Framework:
- NABARD has introduced a Sustainability Bond Framework to finance and refinance green and social projects.
- Eligible social projects include basic infrastructure, essential services, affordable housing, job creation, food security, socioeconomic advancement, and empowerment.
- Projects focused on energy efficiency, such as green buildings, energy storage, and smart grids, are also eligible for funding through these bonds.
Foreign Contribution Regulation Act (FCRA) (Indian Express)
- 28 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
The Ministry of Home Affairs (MHA) has made changes to the regulations for Non-Governmental Organizations (NGOs) registered under the Foreign Contribution Regulation Act (FCRA). They now require these NGOs to furnish information about assets, both movable and immovable, that have been established using foreign funds in their annual returns.
Facts About:
- FCRA is a law governing foreign contributions, especially monetary donations, to NGOs and entities in India.
- Originally passed in 1976 and significantly amended in 2010.
- Aims to prevent foreign organizations from influencing India's politics, society, economy, or religion for harmful purposes.
- Administered by the Ministry of Home Affairs (MHA).
- Defines 'foreign contribution' as donations, currency, or securities from foreign sources.
- Allows individuals, associations, companies, and others to receive foreign contributions with FCRA registration.
- Funds must be used for the intended purpose, with a maximum of 20% for administrative expenses.
- Requires NGOs to open a designated bank account with the State Bank of India, Delhi.
- Registration is mandatory for NGOs and can be renewed if they meet requirements.
- Cancellation is possible for false statements or illegal activities.
- Suspension and fund-freezing authority were also granted to the Ministry.
- Challenges to government orders can be filed in the High Court.
Scheme for Remission of Duties and Taxes on Exported Products (LiveMint)
- 28 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
The RoDTEP scheme, which initially lasted until September 30, 2023, will now continue until June 30, 2024, with the same rates for products that are already being exported.
Facts About:
- The RoDTEP Scheme, officially known as the Scheme for Remission of Duties and Taxes on Exported Products, plays a crucial role in helping Indian exporters.
- It became operational on January 1, 2021, replacing the earlier export incentive program called Merchandise Exports from India (MEIS).
- This change was necessary because the World Trade Organization (WTO) found that the MEIS scheme violated WTO rules by providing export subsidies for a wide range of goods.
- How it Works: Under the RoDTEP Scheme, exporters receive a rebate based on a percentage of the value of their exports (known as FOB or Freight On Board value).
This rebate is given in the form of a transferable duty credit/electronic scrip (e-scrip), and the details of these credits are maintained digitally by the Central Board of Indirect Taxes and Customs (CBIC).
The RoDTEP Committee, which operates within the Department of Revenue, is responsible for reviewing and recommending the maximum rates for different export sectors under this scheme.
- Main Objective: The primary goal of the RoDTEP Scheme is to offer comprehensive support to exporters by refunding the duties and taxes incurred during the production and distribution of exported products.
Importantly, it covers taxes, duties, and levies imposed at the central, state, and local levels, which are not reimbursed through other existing mechanisms.
- Financial Support: In the fiscal year 2023-24, the Indian Government has allocated a substantial budget of Rs. 15,070 crores to support the RoDTEP Scheme.
- Engaging with Stakeholders: The RoDTEP Committee has recently started its work by collaborating with Export Promotion Councils (EPCs) and Chambers of Commerce.
Armed Forces Tribunal (Indian Express)
- 27 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
The Armed Forces Tribunal (AFT) Chandigarh Bench Bar Association has taken the step of going on an unlimited strike. This strike is a response to the decision made by the AFT chairperson to move a judicial member from Chandigarh to Kolkata.
Facts About:
- The Armed Forces Tribunal (AFT) is like a special court in India for military matters, and it started in 2009 under the Armed Forces Tribunal Act, 2007.
- What it does: It deals with arguments and complaints about things like appointments, jobs, and the rules for people who are part of the Army, Navy, and Air Force.
- It handles appeals when someone disagrees with the decisions made by military courts.
- If the military court's decision seems right, the Tribunal can say so.
But if it's not right, the Tribunal can change it.
- If someone doesn't agree with what the Tribunal says, they can only go to the Supreme Court to argue their case.
- The AFT has its main office in New Delhi, and there are eight other offices in different cities.
- Each office has two important people:
A Judicial Member who is a retired High Court Judge and
An Administrative Member who is a retired Armed Forces officer with a high rank.
- Sometimes, a Judge Advocate General (JAG) who has been in the job for at least a year can also be an Administrative Member.
- How it works:
The Tribunal follows certain rules for how they do things, and they use English for all their work.
They usually do things the way High Courts in India do them.
Dadasaheb Phalke Award (PIB)
- 27 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
The Union Minister of Information & Broadcasting has just revealed some exciting news. The renowned actress, Ms. Waheeda Rehman, is set to receive the Dadasaheb Phalke Lifetime Achievement Award for the year 2021.
Facts About:
- The Dadasaheb Phalke Award is India's top honor in the world of cinema.
- Every year, it's given out at the National Film Awards ceremony, organized by the Directorate of Film Festivals, part of the Ministry of Information and Broadcasting.
- This award is for people who have made a really big and important contribution to Indian cinema.
- When someone gets this award, they receive a special Golden Lotus medal, a shawl, and 10 lakh rupees in cash.
- The award was created by the Government of India to remember Dadasaheb Phalke, who's often called "the father of Indian cinema."
- It all began in 1969, and the first person to receive it was the famous actress Devika Rani, known as "the first lady of Indian cinema.
Chincholi Wildlife Sanctuary (The Hindu)
- 27 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
The Chincholi Wildlife Sanctuary is like a lush oasis in a large, dry area that covers seven districts in the northeastern part of Kalyana Karnataka, Karnataka.
Facts About:
- It's located near the Chandrampalli Dam in Karnataka's Kalaburagi district.
- This sanctuary was officially established in 2011.
- It's special because it's the first dry land Wildlife Sanctuary in South India.
- This area in the Hyderabad Karnataka Region is known for having a lot of different plant species.
- You can find a mix of forests, including dry and moist deciduous areas, with Acacia and Teak trees on the edges.
- Some important plants include medicinal herbs, Red Sanders, and Sandalwood.
- As for animals, it's home to Black Bucks, Common Foxes, Four-horned Antelopes, Hyenas, Indian Wolves, and more.
There are also 35 different types of birds here.
- A special mention goes to the Lambani Tandas, a protected tribal community that lives in harmony with nature in this area.
World Coffee Conference (The Hindu)
- 27 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
The 5th World Coffee Conference (WCC) is happening in Bengaluru, and it's a joint effort by the International Coffee Organization (ICO), the Coffee Board of India, and the Ministry of Commerce and Industry, Government of India, along with the Government of Karnataka.
Facts About:
- This is the first time India is hosting this conference.
- In the past, the conference has been held in London (2001), Brazil (2005), Guatemala (2010), and Ethiopia (2016).
- The event is a collaboration between the Coffee Board, the Ministry of Commerce and Industry, and the International Coffee Organization.
- The conference's mascot is Coffee Swami.
- The main theme of the conference is "Sustainability through Circular Economy and Regenerative Agriculture.
About the International Coffee Organization:
- The organization was created in 1963 with support from the United Nations after the first International Coffee Agreement was approved in 1962.
- The ICO is a special international group that brings together countries that export and import coffee.
- Right now, it represents a big part of the world's coffee - 93% of coffee production and 63% of coffee consumption.
- Their mission is to make the coffee business better all around the world in a way that's good for everyone involved.
- There are 49 countries in this group, with 42 of them exporting coffee and 7 of them importing it. India is one of these member countries.
Promotion of Research and Innovation in Pharma (PRIP) scheme (PIB)
- 27 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
The Indian Government, led by the Minister of Chemicals and Fertilizers and the Minister of Health & Family Welfare, has just introduced a new program called PRIP. This program aims to support and encourage research and innovation in the Pharma and MedTech sectors.
Facts About:
- The PRIP scheme has a clear goal: to shift the Indian pharmaceutical sector from being focused on costs to being driven by innovation.
This means we want to encourage more research and new ideas in the country.
- Aim: We want to create stronger connections between industries and educational institutions to do research in important areas.
This will help us build a culture of high-quality research and support our scientists.
- By doing this, we hope India will be more competitive on the global stage, and it will also create better job opportunities.
- How Long It Will Last: This program will run for five years, from 2023-24 to 2027-28.
- The Scheme Has Two Parts:
Part A: We will invest Rs 700 Crores to set up 7 Centers of Excellence (CoEs) at the National Institutes of Pharmaceutical Education and Research (NIPERs). These will focus on specific areas of research.
Part B: We will support research in six important areas like new medicines, complex generics, medical devices, stem cell therapy, rare disease drugs, and fighting against drug resistance. This will also include helping industries, small businesses, startups, and academic research.
- Total Budget: The program has a total budget of Rs. 4250 Crores.
- This scheme is all about making pharmaceutical research in India stronger and more innovative.
- It will support researchers and industries working on important health-related projects.
Brent Crude (LiveMint)
- 26 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
Brent crude oil has recently surged to its highest point in 10 months, exceeding $93 per barrel.
Facts About:
- Brent Crude is the primary benchmark used to determine oil prices globally.
- The name "Brent" originates from the Brent oil field, which was discovered in the 1970s and became a major source of oil production.
- Roughly two-thirds of all internationally traded crude oil is priced relative to Brent, making it the most widely recognized benchmark.
- It's a type of light, sweet crude oil extracted from oil fields in the North Sea.
- Brent crude's special characteristics, such as its low density and low sulfur content, make it easier to refine into products like gasoline.
- Since it's transported by sea, it's convenient to move Brent crude oil to distant locations.
- The price of Brent Crude is influenced by several factors, including shifts in supply and demand, geopolitical events, production interruptions, and economic conditions.
Emerging Markets Bond Index (Down to Earth)
- 26 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
Recently, scientists at the Indian Institute of Science Education and Research Bhopal (IISER Bhopal) pinpointed a particular circular RNA (circRNA) named 'ciTRAN.' This circRNA plays a vital role in the replication of the HIV-1 virus, which causes AIDS, inside the human body.
Facts About:
- Ribonucleic acid (RNA) is a molecule found in living cells that carries genetic instructions and aids in protein production.
- Most RNAs have a linear, open-end structure, but circular RNA, known as 'circRNA,' forms a closed loop.
- CircRNA plays a crucial role in regulating gene expression and is essential for various biological processes.
- Its involvement in the replication of HIV-1 was not well understood for a long time.
- Identifying circular RNA can be challenging because it is typically present in lower amounts, making it harder to detect in its natural form.
- During viral infections, the abundance of viral genetic material can make it difficult to isolate less common components like circular RNA.
Bolson tortoises (The Hindu)
- 26 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
Biologists are working slowly and steadily to assist North America's biggest and most uncommon tortoise species.
Facts About:
- Bolson tortoises are the biggest and rarest land reptiles in North America.
They are also the rarest among the six Gopherus species that are found on this continent.
- Among Bolson tortoises, adult females are generally larger than males.
- These tortoises are land-dwellers and spend over 95% of their time in burrows they dig using their shovel-like front feet.
- They are most active from around April to October when they do everything like searching for food, nesting, and mating.
- While we don't know their exact lifespan, Bolson tortoises can live for more than a century.
- Currently, Bolson tortoises are found in a small area in north-central Mexico, specifically in the states of Chihuahua, Coahuila, and Durango.
However, they exist in separate groups within this region.
- In terms of conservation, Bolson tortoises are Critically Endangered according to the IUCN (International Union for Conservation of Nature).
Mukurthi National Park (The Hindu)
- 26 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
The Tamil Nadu Forest Department carried out thorough operations in Mukurthi National Park and the nearby forest areas to prevent any unlawful entry of individuals and deter poaching activities.
Facts About:
- Mukurthi National Park is situated in the western part of the Nilgiris Plateau, in the northwest corner of Tamil Nadu.
- This park was established primarily to safeguard its key species, the Nilgiri tahr.
- The park is crossed by the Pykara and Kundah rivers, and it's home to several streams that originate within the park and flow into the Bhavani Puzha River.
- It holds the prestigious status of being a UNESCO World Heritage Site.
- In terms of its vegetation, the park features high-altitude montane grasslands and shrublands with shola forests, in an area with ample rainfall.
- You can find various plants in the park, including fragrant shrubs like Gaultheria fragrantissima, Helichrysum, and Berberis. Other notable plants include Rhododendrons, Cinnamon, Mahonia, Satyrium, and Raspberries.
- As for wildlife, Mukurthi National Park is a sanctuary for endangered species such as the Nilgiri tahr, Indian elephants, Nilgiri Langur, Bengal tiger, and bonnet macaque, among others.
Galactic Tides (The Hindu)
- 26 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
Similar to how the oceans on Earth have tides at their shores, galaxies in the universe also go through tides, but on a much grander scale.
Facts About:
- Galactic tides are like gravitational pulls that objects within a galaxy, like our Milky Way, experience due to the galaxy's gravitational field.
- These tidal forces happen because of the gravitational interactions between celestial objects, such as stars and gas clouds, within the galaxy.
- Galactic tides have several effects on a galaxy's evolution.
They can change the shape of a galaxy by creating tidal tails and bridges, encouraging the birth of new stars, and disrupting smaller star systems.
- They also alter the paths that stars follow in their orbits, causing long-term changes in a galaxy's structure.
- Galactic tides even play a role in how nearby galaxies interact or don't interact with each other.
For example, when studying Andromeda, the closest galaxy to the Milky Way, researchers have noticed tidal streams near its edges.
- These streams may be signs of dwarf galaxies that were swallowed by Andromeda over time.
- Galactic tides also impact the supermassive black holes at the centers of galaxies, leading to events that change how these cosmic giants interact with nearby stars.
India-UN Capacity Building Initiative (News On Air)
- 25 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
India and the United Nations have introduced a collaborative capacity-building effort known as the 'India-UN Capacity Building Initiative.' Its goal is to promote progress and prosperity in the Global South.
Facts About:
What is the Global South?
- The Global South encompasses countries in regions such as Africa, Latin America and the Caribbean, Asia (excluding Israel, Japan, and South Korea), and Oceania (excluding Australia and New Zealand).
- These regions are generally characterized by lower levels of economic and industrial development.
About the India-UN Capacity Building Initiative:
- This initiative aims to enhance the capabilities of countries in the Global South.
- Its objective is to facilitate the sharing of India's development experiences, best practices, and expertise through capacity-building programs and training.
- The initiative extends the achievements of India's G20 Presidency, which emphasized the inclusion of perspectives from the Global South in the G20 agenda.
- It builds upon India's existing bilateral cooperation in development and capacity-building with partner countries.
- As part of this endeavor, the UN India team will collaborate with the Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation to leverage India's Technical and Economic Cooperation platform. This partnership will enable the dissemination of India's development experiences and best practices worldwide.
- Furthermore, it will translate the development objectives outlined during India's G20 Presidency into action.
- This includes the implementation of the G20 Action Plan for advancing the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) and enhancing technology and digital infrastructure.
Exercise Yudh Abhyas (PIB)
- 25 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
The 19th iteration of 'EXERCISE YUDH ABHYAS' is scheduled to take place from September 25th to October 8th, 2023, at Fort Wainwright, Alaska, USA
Facts About:
- Exercise Yudh Abhyas is an annual collaborative military exercise carried out jointly by the Indian Army and the United States Army.
- In this edition, the Indian Army contingent, consisting of 350 personnel, will participate. The lead battalion from the Indian side is associated with the MARATHA Light Infantry Regiment.
- The primary focus of the exercise is to practice a series of tactical drills aimed at improving the ability to work together effectively during United Nations peacekeeping operations.
- The exercise's theme centers on the 'Employment of an Integrated Battle Group in Mountain/ Extreme Climatic Conditions,' as outlined in Chapter VII of the United Nations mandate.
- The Field Training Exercise will encompass various elements, including the validation of Integrated Battle Groups in confronting hostile forces at the Brigade level, the establishment of an Integrated Surveillance Grid at the Brigade/ Battalion level, and the utilization of Heliborne/ Airborne units and Force Multipliers, among others.
- Additionally, the exercise will facilitate the exchange of ideas and best practices in a wide range of combat skills, encompassing combat engineering, obstruction clearance, and tactics for dealing with mines and Improvised Explosive Devices.
Other Exercises involving India and the USA:
- Army: Vajra Prahar
- Navy: MALABAR (Multilateral)
- Air Force: Cope India, Red Flag (Multilateral)
Free Movement Regime (Indian Express)
- 25 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
The Chief Minister of Manipur recently stated that his government has requested the Union Home Ministry to discontinue the free movement arrangement along the India-Myanmar border and finalize the border fencing.
Facts About:
- The Free Movement Regime (FMR) allows all hill tribes, whether they hold citizenship in India or Myanmar, to travel within a 16 km radius on either side of the Indo-Myanmar Border (IMB).
- To cross the border, they need to present a border pass with a one-year validity issued by the relevant authority.
Each visit can last for up to two weeks.
- The FMR was put into effect in 2018 as part of the Central government's Act East policy.
- Both governments, India and Myanmar, implement the FMR for the benefit of the people residing along the IMB.
- This arrangement facilitates greater cultural integration among residents of trans-border villages.
They engage in activities like weddings, joint celebrations of festivals, and cross-border trade.
- The FMR underscores the physical, ethnic, linguistic, cultural, and fraternal connections among communities living across the border.
- Indo-Myanmar Border (IMB):
The IMB stretches over 1,643 km, traversing four states: Mizoram, Manipur, Nagaland, and Arunachal Pradesh.
It extends from the northern tripoint with China to the southern tripoint with Bangladesh.
The responsibility of guarding the IMB falls on the Assam Rifles.
I2U2 Group (TOI)
- 25 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
The I2U2 group has just unveiled a new collaborative space project with the goal of developing a one-of-a-kind space tool designed for use by policymakers, organizations, and business innovators.
Facts About:
- The I2U2 Group comprises India, Israel, the United Arab Emirates, and the United States.
- Formation:
This alliance was originally established in October 2021 with the primary objective of addressing infrastructure, transportation, and maritime security issues in the region.
Originally, it was named the "International Forum for Economic Cooperation" and was also referred to as the "West Asian Quad."
- First Virtual Summit: In July 2022, the group conducted its inaugural virtual summit.
- This unique coalition of nations identifies viable projects and initiatives aimed at addressing significant challenges.
- It places special emphasis on collaborative investments and new endeavors in areas such as water, energy, transportation, space, health, food security, and technology.
- The group's objectives encompass mobilizing private sector resources and expertise to achieve various goals, including the modernization of infrastructure, the promotion of low-carbon development pathways, and enhancements in public health.
Emerging Markets Bond Index (Indian Express)
- 25 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
JP Morgan Chase & Co will add Indian government bonds to its emerging markets bond index starting in June 2024.
Facts About:
- This index serves as a benchmark for measuring how well international government and corporate bonds from emerging market countries perform.
These countries must meet specific liquidity and structural requirements.
- Emerging market bonds are debt instruments issued by developing nations.
They usually offer higher yields compared to bonds from developed countries.
- A total of 23 Indian Government Bonds (IGBs) with a combined notional value of $330 billion are eligible for inclusion.
They are all categorized as "fully accessible" for non-residents.
- Advantages of this inclusion:
This development is expected to lead to higher demand for the Indian rupee, potentially protecting it from depreciation.
Lower borrowing costs could support important infrastructure projects.
Increased liquidity may result in more efficient trading conditions.
- India's local bonds will become part of JP Morgan's Government Bond Index-Emerging Markets (GBI-EM) index.
- They are expected to make up a maximum of 10 percent of the GBI-EM Global Diversified Index (GBI-EM GD).
Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (The Hindu)
- 23 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
A recent study has shown that Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) is becoming more prevalent among contemporary women in India.
Facts About:
- PCOS is a prevalent hormonal issue that primarily affects women in their childbearing years.
- Symptoms: PCOS is associated with irregular ovulation, elevated androgen (male hormone) levels, and the presence of numerous small ovarian cysts.
It can result in missed or irregular menstrual cycles, excess hair growth, acne, fertility challenges, and weight gain.
- Causes: PCOS often has a genetic component, with a family history of diabetes or obesity being common.
Environmental factors that promote an unhealthy diet, lack of exercise, and high stress levels can also contribute.
- Treatment: Managing PCOS involves lifestyle adjustments, medications, and fertility treatments to address its symptoms and complications.
- PCOS is a concern for one out of every five women in India, and 60% of those seeking infertility treatments are doing so because of issues related to PCOS.
Tasmanian Tiger (The Hindu)
- 23 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
Researchers have recently extracted Ribonucleic acid (RNA) from the desiccated skin and muscle of a Tasmanian tiger that had been stored at a museum in Stockholm since 1891.
Facts About:
- The Tasmanian tiger had a wolf-like appearance, distinguished by tiger-like stripes along its back.
- Regrettably, the last known Tasmanian tiger passed away in a Tasmanian zoo in 1936.
- This large carnivorous marsupial is now considered extinct.
- Among the family Thylacinidae, it stood as the sole survivor into modern times.
- Its habitat once spanned across continental Australia, reaching as far north as New Guinea and as far south as Tasmania.
- As an apex predator, it hunted kangaroos and various other prey.
What is RNA?
- RNA, short for Ribonucleic acid, is a complex compound with a high molecular weight, and it plays a crucial role in cellular protein synthesis.
- In some viruses, RNA takes on the role of carrying genetic codes, replacing DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid).
- RNA is composed of ribose nucleotides, which are nitrogenous bases attached to a ribose sugar via phosphodiester bonds.
- The nitrogenous bases found in RNA include adenine, guanine, cytosine, and uracil.
- Unlike DNA, RNA is a single-stranded molecule responsible for carrying genetic information.
- RNA's primary function is to synthesize the diverse array of proteins required by an organism for survival, while also regulating cell metabolism.
World Federation for Medical Education (WFME) (Indian Express)
- 23 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
The National Medical Commission (NMC) of India has recently earned a 10-year recognition status from the World Federation for Medical Education (WFME).
Facts About:
WFME is a worldwide organization dedicated to the training and education of medical doctors.
Their mission is to work towards better healthcare for all people.
WFME's primary goal is to elevate the quality of medical education on a global scale by promoting the highest scientific and ethical standards.
They achieve this goal through several means, including:
- Establishing standards in medical education
- Advocating for the accreditation of medical schools
- Developing databases related to medical education
- Initiating projects focused on the future of medicine and medical education
- Publishing informative materials and forming partnerships
WFME was established in 1972 and has its headquarters in Ferney-Voltaire, France.
Notably, WFME is the organization that officially represents medical teachers and medical teaching institutions on a global scale, serving as their voice before the World Health Organization (WHO).
WFME's accreditation program plays a crucial role in ensuring that medical institutions meet and uphold the highest international standards in education and training.
General Crop Estimation Survey Portal (PIB)
- 23 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
The Secretary of the Department of Agriculture and Farmers Welfare (DA&FW) recently launched the mobile application and web portal for the General Crop Estimation Survey (GCES).
Facts About:
- This innovative portal and mobile application aim to revolutionize agricultural practices across the nation.
- The Department of Agriculture and Farmers' Welfare has developed this technology-driven solution to expand the reach, scope, and effectiveness of government initiatives in the development process.
- Automating the GCES process ensures timely reporting of crop statistics and data accuracy.
Key Features:
- Comprehensive Information: The portal and app serve as a complete repository of yield estimates, encompassing village-specific GCES plans, plot details where crop cutting experiments occur, and post-harvest crop and driage weights.
- Geo-referencing: The mobile app offers a crucial feature that allows field workers to define the boundaries of experimental plots and upload photos of both the plots and the crops within them.
- This feature enhances data transparency and accuracy.
Adi Shankaracharya (IndianExpress)
- 23 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
The Chief Minister of Madhya Pradesh recently revealed a 108-feet tall statue of Adi Shankaracharya, an ancient Vedic scholar and teacher from the 8th century, in Omkareshwar.
Facts About:
- Adi Shankaracharya, also known as Shankara, was an ancient Indian philosopher and theologian who lived around the 8th century CE.
- Birthplace: He was born in Kalady, a village in what is now Kerala.
His Philosophical Contributions:
- His most famous achievement was his role in developing and spreading Advaita Vedanta, a school of Hindu philosophy that emphasizes non-duality.
- He brought together the ideas of 'Advaita Vedanta' and explained the core concepts of the Upanishads.
- Shankaracharya's significant work involved uniting six sub-sects known as 'Shanmata,' which translates to 'six religions.' This concept recognized six supreme deities, all part of one divine power.
- He also established the 'Dashanami Sampradaya,' which promotes a monastic way of life.
- While he strongly believed in ancient Hinduism, he criticized the 'Mimamsa school of Hinduism,' which focused primarily on rituals.
- Founding of Four Mathas: He founded four important monastic centers in India, each associated with one of the cardinal directions:
Sringeri in the south
Dwarka in the west
Puri in the east, and
Badrinath in the north.
Asia Pacific Forum (PIB)
- 22 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
The President of India recently opened the Annual General Meeting and Biennial Conference of the Asia Pacific Forum on Human Rights in New Delhi.
Facts About:
- Established in 1996, the Asia Pacific Forum is a unified platform that brings together National Human Rights Institutions (NHRIs) from across the Asia Pacific.
- It focuses on addressing significant human rights challenges in the region.
- The forum consists of 17 full members and eight associate members, with India being a full member since its inception.
- To become a full member, an NHRI must fully adhere to the international standards outlined in the Paris Principles. NHRI's that partially comply are granted associate membership.
- Decisions regarding new member admissions are made by the Forum Council.
- A primary objective of the APF is to encourage the establishment of independent NHRIs in the Asia Pacific and support its members in their effective work.
Promotion of Tribal Products for North East Region’ (PTP-NER 2.0) scheme (PIB)
- 22 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
The Tribal Cooperative Marketing Development Federation of India Ltd. (TRIFED), under the Union Ministry of Tribal Affairs, is set to launch the second phase of the 'Promotion of Tribal Products for the North East Region' (PTP-NER 2.0) scheme, running from September 21 to November 10, 2023.
Facts About:
This scheme, launched by the Ministry of Tribal Affairs, aims to enhance the livelihoods of tribal artisans by improving the procurement, logistics, and marketing of their products.
It covers the states of Arunachal Pradesh, Assam, Manipur, Meghalaya, Mizoram, Nagaland, Tripura, and Sikkim.
The scheme has two phases:
- Phase 1 included 8 states and 38 districts, with 64 Tribal Artisans Empanelment Melas (TAeM) organized by TRIFED and NEHHDC.
- Phase 2 will cover 29 districts, continuing the effort to support tribal artisans and showcase their cultural heritage.
Implementing partners include the North Eastern Handicrafts and Handlooms Development Corporation (NEHHDC), India Post, and various North Eastern State Government Departments and Agencies.
India Post will provide logistical support to achieve the scheme's objectives.
SIMBEX 23 (PIB)
- 22 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
Indian Naval Ships Ranvijay and Kavaratti, along with the submarine INS Sindhukesari, have reached Singapore to take part in the 30th Singapore-India Maritime Bilateral Exercise (SIMBEX).
Facts About:
- SIMBEX 23 is an annual naval exercise between the Indian Navy and the Republic of Singapore Navy (RSN).
- It's been held every year since 1994 and is the longest continuous naval exercise India has with any country.
- The exercise has two phases: a harbor phase in Singapore from September 21 to 24, 2023, and a sea phase.
- In addition to Indian Naval Ships Ranvijay, Kavaratti, and INS Sindhukesari, the Long-Range Maritime Patrol Aircraft P8I is also participating.
- During the harbor phase, there will be professional interactions, cross-deck visits, knowledge exchanges, and sports events to improve cooperation and understanding between the two navies.
- The sea phase will involve advanced exercises like air defense, gunnery, tactical maneuvers, anti-submarine drills, and other maritime operations.
- Both navies aim to enhance their skills for joint maritime operations.
Digital Personal Data Protection Act, 2023 (The Hindu)
- 22 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
The Central Government has announced that companies and entities may have approximately one year to comply with the regulations outlined in the Digital Personal Data Protection (DPDP) Act, 2023. Smaller organizations or startups might be granted even more time for compliance.
Facts About:
The DPDP Act is a legal framework in India designed to protect individuals' personal data and ensure it's only shared with their consent. It governs the processing of digital personal data to safeguard privacy in the digital age.
Applicability:
- It applies to digital personal data processed within India, regardless of its origin (online or offline).
- It also applies to data processing outside India if it involves offering goods or services to Indian data subjects.
Evolution:
- It originates from the recommendations of the Justice BN Srikrishna-led Expert Committee, leading to the introduction of the Personal Data Protection Act in 2019.
- After consultations and revisions, the Digital Personal Data Protection Act, 2023, was enacted by both houses of Parliament.
Key Stakeholders:
- Data Principal (DP): The data owner who must give consent for data generation and processing.
- Data Fiduciary: The entity collecting, storing, and sharing data, acting as a "Consent Manager."
- Data Processor: The entity processing data on behalf of a data fiduciary.
- Data Protection Officer (DPO): An individual appointed by a data fiduciary to oversee data protection compliance.
Individuals have rights such as the right to information, correction, erasure, grievance redressal, and the right to nominate someone to exercise these rights in case of incapacity or death.
Rashtriya Vigyan Puraskar (PIB)
- 22 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
The Indian Government recently introduced a new set of National Awards for achievements in science, technology, and innovation called the "Rashtriya Vigyan Puraskar."
Facts About:
The Rashtriya Vigyan Puraskar is an award that recognizes outstanding contributions in the fields of science, technology, and innovation in India.
It's one of the highest honors in these fields.
Who can receive the awards?
- Scientists, technologists, and innovators, whether in government or private sectors, who have made significant breakthroughs in their respective fields.
- People of Indian origin living abroad who have made exceptional contributions benefiting Indian communities.
The awards are given in four categories:
- Vigyan Ratna (VR): Lifetime achievements in science and technology.
- Vigyan Shri (VS): Distinguished contributions in science and technology.
- Vigyan Yuva-Shanti Swarup Bhatnagar (VY-SSB): Young scientists under 45 years old who've made exceptional contributions.
- Vigyan Team (VT): Teams of three or more scientists, researchers, or innovators who've excelled in their field.
The awards cover 13 domains, including Physics, Chemistry, Biology, Mathematics & Computer Science, Earth Science, Medicine, Engineering, Agriculture, Environment, Technology & Innovation, Atomic Energy, Space Science, and more.
Nuakhai Juhar Festival (PIB)
- 21 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
Recently, the Prime Minister of India actively conveyed greetings to the people on the auspicious occasion of Nuakhai Juhar.
Facts About:
- Nuakhai Juhar is a significant social festival celebrated in Western Odisha and parts of Simdega in Jharkhand.
- The term 'Nuakhai' combines 'nua,' meaning 'new,' and 'khai,' signifying 'food.'
- This agricultural festival marks the welcoming of the fresh rice harvest of the season.
- It falls on the fifth day of the lunar fortnight in the month of Bhadrapada or Bhadra (August-September), following the Ganesh Chaturthi festival.
- Rituals:
- Nuakhai is associated with nine colors, leading to nine sets of pre-celebration rituals.
- People offer the newly harvested crop, known as Nabanha, to their respective deities.
- Following the Nabanha offering, individuals savor various delicacies made from the freshly harvested produce.
- A central ritual of the Nuakhai Juhar is a significant highlight of the festival.
Vanadium (TOI)
- 21 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
Vanadium, a critical raw material for many industrial applications, has been found in sediment samples collected from Gulf of Khambhat, which opens into the Arabian Sea off Alang in Gujarat.
Facts About:
- Vanadium is a chemical element with the symbol "V" and atomic number 23.
- Vanadium is a naturally occurring element found in minerals and ores.
It was first discovered in the early 19th century.
- It is a transition metal known for its various applications in science and industry.
Applications:
- Strengthens Steel: One of its primary uses is as an alloying agent in steel production.
Vanadium steel is renowned for its exceptional strength, durability, and resistance to corrosion.
It is commonly used in manufacturing tools, knives, and structural components in construction.
- Aerospace Alloys: Vanadium alloys are utilized in aerospace applications, such as jet engines and rocket frames, due to their high-temperature resistance and lightweight properties.
- Batteries: Vanadium redox flow batteries (VRFBs) are emerging as a promising energy storage technology.
They offer scalability and long cycle life, making them suitable for grid-level energy storage.
- Catalysts: Vanadium compounds act as catalysts in chemical reactions, particularly in the production of sulfuric acid and maleic anhydride.
- Medical Applications: Vanadium has potential health benefits and is being studied for its role in managing diabetes and its antioxidant properties.
- Dye and Pigment Production: Vanadium compounds are used in the manufacture of dyes, pigments, and ceramics.
- Metallurgy: Vanadium is employed in the refining of certain metals like aluminum and titanium.
- Nuclear Applications: In nuclear reactors, vanadium serves as a structural material due to its neutron-absorbing properties.
- Research and Development: Vanadium's unique properties make it valuable for scientific research, including studies in material science and chemistry.
Vanadium's versatility and strength-enhancing properties find application in various industries, from steel manufacturing to energy storage and even potential health-related uses, making it a vital element in modern technology and innovation.
Bharatkosh Portal (PIB)
- 21 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
Recently, the Union Minister of Civil Aviation actively launched an e-wallet payment option on the Bharatkosh portal.
Facts About:
- The Bharatkosh portal is an initiative led by the Controller General of Accounts under the Ministry of Finance, Government of India.
- It serves as a unified platform for depositing various fees, fines, and other payments directly into the government's account.
- The portal integrates all Civil Ministries and Departments of the Government of India for streamlined financial transactions.
- Its primary objective is to offer round-the-clock, year-round electronic payment services, enabling users to deposit funds into the government's account through internet-based payment technologies from the convenience of their location via the web-based portal.
- In doing so, it aligns with the government's commitment to e-Governance, ensuring efficient, effective, and excellent government services accessible anytime and anywhere.
Batillipes Kalami (The Hindu)
- 21 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
Recently, researchers at Cochin University of Science and Technology (Cusat) named a new species of marine tardigrade after the late former President and scientist A.P.J. Abdul Kalam.
Facts About:
- Batillipes Kalami, the newly discovered species found in Mandapam, southeast Tamil Nadu, belongs to the Batillipes genus.
- Notably, it's the second marine tardigrade discovered in Indian waters and the first from the east coast.
- This species is also the first of its kind taxonomically described from India and is the 37th species within the Batillipes genus.
Physical characteristics:
- It typically measures around 170 micrometres (0.17 mm) in length and approximately 50 micrometres (0.05 mm) in width.
- Its head has a trapezoid shape with sharp-tipped filament-like appendages (cirri) extending from it.
- Each of its four pairs of legs features sensory spines of varying lengths.
- Females are slightly larger than males.
Pandit Deendayal Upadhyay National Welfare Fund For Sportspersons (PDUNWFS) (PIB)
- 21 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
The Union Minister for Youth Affairs & Sports honored athletes supported by the Pandit Deendayal Upadhyay National Welfare Fund for Sportspersons (PDUNWFS) in New Delhi.
Facts About:
- The Pandit Deendayal Upadhyay National Welfare Fund for Sportspersons (PDUNWFS) was established in March 1982.
- Its primary goal is to support former exceptional athletes who are now facing financial hardship but had previously brought honor to India through their sporting achievements.
- In May 2016, the scheme underwent revisions, enabling it to provide one-time financial assistance to former exceptional athletes.
- This scheme covers athletes across the entire nation and is designed to enhance the well-being of sportspersons and their families by alleviating financial distress.
- The scheme can be applied to individual athletes or groups of active sportspersons.
Red-necked Phalarope (The Hindu)
- 20 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
A Red-necked phalarope (Phalaropus lobatus) was recently spotted by a group of birders who visited Kurichi Tank in Coimbatore.
Facts About:
- This is a relatively small shorebird renowned for its energetic spinning on the water surface to stir up small invertebrates.
- With a circumpolar distribution, it inhabits both boreal and tundra zones within the 60 to 70-degree latitude range.
- These phalaropes are commonly found along the coastlines of the Arctic Ocean, extending southward to the Aleutian Islands and northwestward to Britain.
- During the winter months, they predominantly reside in oceanic environments.
- In their non-breeding season, Red-Necked Phalaropes can be observed in areas ranging from central-west South America to the Arabian Sea, and from central Indonesia to western Melanesia.
- Conservation Status: IUCN Classification: Least Concern
Sacred Ensembles of the Hoysala (The Hindu)
- 20 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
UNESCO recently included the Sacred Ensembles of the Hoysalas, consisting of three temples in Karnataka, on its World Heritage List.
Facts About:
The Sacred Ensembles of the Hoysalas consist of a collection of temples crafted by the Hoysala dynasty in the 12th-13th centuries.
- This ensemble includes three significant components: Belur, Halebid, and Somnathapura.
These three temples are as follows:
- The Chennakeshava Temple: Located at the heart of Belur in the Hassan district, it serves as the main temple in the complex. It is surrounded by the remnants of a mud fort and a moat.
- The Hoysaleswara Temple: Situated on the banks of the Dwarasamudra tank in Halebidu, the Hassan district, this temple is part of a town with numerous protected and unprotected temples, archaeological ruins, and mounds.
- The Keshava Temple: Found in the center of Somanathapura village in the Mysore district.
- These temples are primarily dedicated to Hindu deities like Shiva and Vishnu, with some also honoring the Jain faith.
- The architecture of the Hoysala temples reflects a blend of Dravidian design with influences from the Bhumija style prevalent in Central India, the Nagara traditions of northern and western India, and the Karntata-Dravida styles favored by the Kalyani Chalukyas.
Bima Sugam Platform (Indian Express)
- 20 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
Recently, the Insurance Regulatory and Development Authority of India (IRDAI) has established a steering committee, which will serve as the highest authority responsible for developing its ambitious Bima Sugam platform.
Facts About:
- This platform will empower individuals to purchase life, health, motor, or property insurance policies online, providing a convenient digital solution.
- It aims to offer a one-stop destination for insurance companies, agents, brokers, banks, and aggregators, streamlining accessibility.
- Serving as a centralized database, it will assist consumers with all their insurance-related needs, ensuring efficiency.
- The platform will facilitate the swift introduction of new or experimental insurance products.
- Cyril Amarchand Mangaldas (CAM) has been appointed as the legal counsel for this project, responsible for establishing a Section 8 not-for-profit company that will own the Bima Sugam platform.
- It will cater to both personal and commercial/business insurance needs, aiding users in identifying and comparing the best-suited products within specified timelines.
- The platform will encompass a comprehensive range of insurance offerings, including life insurance and its various forms such as term plans, savings (Par and Non-Par), annuities, pension plans, and more.
- Furthermore, it will showcase a fully digital onboarding process for all insurance products, eliminating manual interventions.
Operation Sajag (PIB)
- 20 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
The Indian Coast Guard has recently carried out 'Operation Sajag,' a Coastal Security Exercise along the Western Coast.
Facts About:
- Operation Sajag is a coastal security exercise conducted by the Indian Coast Guard along the western coastline.
- It involves the participation of all stakeholders responsible for Indian coastal security.
- A total of 118 ships, including vessels from Customs, Marine Police, Ports, and the Indian Navy, took part in this exercise.
- The primary goals of this drill are to reassess and strengthen the coastal security system and raise awareness among fishermen operating at sea.
- During the exercise, there was extensive checking and verification of documents and crew passes for all fishing boats, barges, and crafts at sea.
- Additionally, biometric card readers have been provided to security agencies to enhance security measures.
- Apart from monitoring dhows, the coastal security construct also includes initiatives related to island security and community interaction programs.
Kisan Rin Portal (News On Air)
- 20 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
The Finance Minister and Agriculture Minister are going to start the 'Kisan Rin Portal' on September 19.
Facts About:
- This portal assists farmers in obtaining reduced-rate loans through the Kisan Credit Card (KCC).
- Several government departments worked together to create it.
- It provides a clear picture of farmer information, loan distribution details, interest subsidy requests, and progress in scheme usage.
- It seamlessly connects with banks to enhance the accessibility and efficiency of agricultural credit.
Brief Overview About Kisan Credit Card (KCC):
- Introduced in 1998, the Kisan Credit Card (KCC) scheme provides farmers with a convenient way to access loans for buying agricultural supplies like seeds and fertilizers and for cash withdrawals.
- Developed by NABARD (the National Bank for Agriculture and Rural Development), the scheme was later expanded in 2004 to cover investment needs in farming and related activities.
- In 2012, the scheme was simplified to facilitate Electronic Kisan Credit Cards.
- Applicable to Commercial Banks, RRBs, Small Finance Banks, and Cooperatives.
Anamudi Shola National Park (The Hindu)
- 19 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
The Pazhathottam region within Anamudi Shola National Park, close to Munnar in Idukki, has blossomed into a lush paradise bustling with vibrant life.
Facts About:
- Location: Situated in Kerala, India.
- Surrounded by Eravikulam National Park, Pampadum Shola National Park, Chinnar Wildlife Sanctuary, and Mathikettan Shola Park.
- Vegetation: Encompasses southern subtropical hill forests, southern montane wet temperate forests, and moist deciduous forests.
- Unique Features: The dense shola woods here contain stunted trees and are adorned with lush lichen, mosses, and climbers.
- Flora: Houses approximately 174 species of herbs and shrubs, 62 tree species, and around 40 species of climbers, some of which are unique to the region.
- Fauna: Abode to diverse wildlife, including leopards, civet cats, wolves, Indian bison, wild boars, elephants, tigers, panthers, and sloth bears.
Gold Exchange-traded Funds (Indian Express)
- 19 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
In August, Gold exchange-traded funds (ETFs) saw an impressive inflow of Rs 1,028 crore, marking the highest influx in the past 16 months.
Facts About:
- These are investment funds linked to the value of gold.
- Gold ETFs are passive investments that track the price of gold and invest in physical gold bullion.
- They represent gold in a form that can be paper-based or dematerialized.
- Each unit of a Gold ETF is equivalent to 1 gram of highly pure physical gold.
- Gold ETFs are listed and traded on the National Stock Exchange of India (NSE) and the Bombay Stock Exchange Ltd. (BSE).
- They offer complete transparency regarding their gold holdings, thanks to direct gold pricing.
SHREYAS Scheme (PIB)
- 19 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
Through the comprehensive SHREYAS program, a total of 1,628.89 crore rupees have been disbursed from 2014-15 to 2022-23, benefiting 21,326 recipients.
Facts About:
- The Ministry of Human Resource and Development has introduced the Scheme for Higher Education Youth for Apprenticeship and Skills (SHREYAS) to align educational programs with the needs of industries and service sectors.
- It also encourages students to gain practical experience while studying.
Objectives:
- Enhance Students' Employability: By providing on-the-job work exposure through the National Apprenticeship Promotional Scheme (NAPS) and the National Career Service (NCS), SHREYAS aims to improve students' employability.
- Bridge the Gap Between Education and Industry: The scheme establishes a strong connection between education and industry.
- Dynamic Skill Development: SHREYAS offers students the opportunity to acquire skills in a dynamic manner.
- arn While You Learn": It introduces an "earn while you learn" system into higher education.
- Facilitate Quality Manpower: The scheme assists industries in recruiting high-quality manpower.
- Connect Students with Employment Opportunities: It links students with the government's employment facilitation efforts.
Pralay Ballistic Missiles (Financial Express)
- 19 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
The Defense Ministry has recently approved the purchase of a regiment of Pralay tactical ballistic missiles for the Indian Army.
Facts About:
- Pralay is a quasi-ballistic surface-to-surface missile.
- It can strike targets at distances ranging from 150 to 500 kilometers.
- The missile can carry between 350 and 700 kilograms of high-grade explosives.
- Pralay is developed by the Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO).
- It uses a solid propellant rocket motor and incorporates advanced technologies.
- The missile features a state-of-the-art navigation and integrated avionics system.
- Pralay can alter its trajectory during mid-flight.
Yashobhoomi (Indian Express)
- 19 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
The Prime Minister recently opened the first part of the India International Convention and Expo Centre (IICC) called Yashobhoomi in New Delhi's Dwarka.
Facts About:
- YashoBhoomi,' also known as the India International Convention and Expo Centre (IICC), is a modern and advanced convention center located in Dwarka, New Delhi.
- It's one of the largest places in the world for meetings, incentives, conferences, and exhibitions (MICE).
Key features:
- The project covers an area of over 8.9 lakh square meters and costs about Rs 5400 crores.
- The Convention Center is huge, with 15 convention rooms, including the Main Auditorium, the Grand Ballroom, and 13 meeting rooms. It can hold up to 11,000 delegates.
- It has the country's biggest LED media facade.
- The plenary hall in the Convention Center can seat about 6,000 guests.
- There are also large exhibition halls covering over 1.07 lakh square meters for exhibitions, trade fairs, and business events.
- The center is environmentally friendly, with a state-of-the-art wastewater treatment system that recycles 100% of the wastewater and provisions for rainwater harvesting.
India-Middle East-Europe Economic Corridor (Financial Express)
- 18 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
Presently, the Indian Coast Guard Ship (ICGS) Samudra Prahari is on an international mission covering ASEAN countries.
Facts About:
- Samudra Prahari is an Indian Coast Guard Ship (ICGS) specifically designed for pollution control purposes.
Key Highlights:
- It holds the distinction of being Southeast Asia's pioneering pollution control vessel.
- Equipped with cutting-edge Pollution Response and Control equipment for effectively managing oil spills within the Exclusive Economic Zone.
- Features tanks and inflatable barges for the storage of oil spills.
- Capable of seamless oil recovery operations with a substantial storage capacity of 500 KL.
- Designed to accommodate and operate a twin-engine Advanced Light Helicopter, along with the capability to handle and embark Chetak helicopters.
- Notable features encompass an integrated platform management system, power management system, high-powered external firefighting system, and an indigenous gun mount with firefighting capabilities.
- The vessel possesses unmanned machinery operation capabilities for enhanced efficiency.
TrailGuard AI camera (The Hindu)
- 18 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
The wildlife officials have found the TrailGuard AI camera-alert system very useful in the Kanha-Pench corridor in Madhya Pradesh.
Facts About:
- These cameras are thin and can be discreetly placed in trees.
- They look like a pen, measuring 13.8 cm long and 1.4 cm wide. They are connected to another unit, about the size of a notepad.
- These cameras have special software that can be told to take pictures of specific animals or people.
- They are really small, about the size of a person's index finger when you consider the camera head and the infrared sensor.
- You can set them to capture specific things like humans or certain animals like lions, tigers, or cheetahs.
- If the camera is near a cellphone tower, it can send pictures in just 30 seconds. If it's far from a tower, it might take 3-10 minutes using a longer method.
- The 'AI' part of this system means that it doesn't send every picture it takes. Instead, it only sends pictures that are interesting to the forest officials.
- This camera was created by RESOLVE, a non-profit organization. The brain of this camera is Intel's Myriad chip.
Gandhi Sagar Wildlife Sanctuary (TOI)
- 18 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
India is getting ready to bring in a new group of cheetahs from South Africa and release them into the Gandhi Sagar Wildlife Sanctuary in Madhya Pradesh.
Facts About:
- Location: Situated at the northern border of Madhya Pradesh's Mandsaur and Nimach districts, adjacent to Rajasthan.
- Area: Covers 368.62 km2 (142.32 sq mi) and is part of the Khathiar-Gir dry deciduous forest ecoregion.
- Establishment: Established in 1974 and officially designated as a sanctuary in 1984.
- River Chambal: Divides the sanctuary into two sections and adds to its unique landscape.
- Terrain: Features diverse topography, including hills, plateaus, and the catchment area of the Gandhi Sagar Dam on the Chambal River.
- Cultural Significance: Houses historical, archaeological, and religious sites like Chaurasigarh, Chaturbhujnath temple, Bhadkaji rock paintings, Narsinghjhar Hinglajgarh fort, and Taxakeshwar temple.
- Flora: Dominated by tree species like Khair, Salai, Kardhai, Dhawda, Tendu, and Palash.
- Fauna: Home to herbivores such as Chinkara, Nilgai, and Spotted Deer, as well as carnivores like the Indian Leopard, Striped Hyena, and Jackal. The sanctuary also hosts a variety of aquatic life, including crocodiles, fish, otters, and turtles.
Scrub Typhus and Leptospirosisa (Financial Express)
- 18 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
Scrub Typhus claims 5 lives, while Leptospirosis spreads in Odisha; health authorities remain vigilant.
Facts About:
- Scrub typhus, caused by Orientia tsutsugamushi bacteria, is prevalent in Asia-Pacific regions, including India.
- It spreads via chigger mites in rural areas. Symptoms include high fever, headaches, muscle pain, and a distinctive rash, often leading to swollen lymph nodes.
- If untreated, it can cause severe complications affecting vital organs.
- Diagnosis relies on clinical symptoms and blood tests.
- Timely antibiotics like doxycycline or azithromycin are effective treatments.
- Preventive measures include protective clothing, insect repellent, and avoiding dense vegetation.
- Recent cases in Odisha, have prompted heightened health alerts and emphasize the importance of early detection and treatment, alongside public awareness efforts.
About Leptospirosis:
- Leptospirosis caused by the bacterium Leptospira interrogans, is a potentially fatal zoonotic disease and is common in warm, humid regions worldwide.
- Humans can contract it from infected animal urine, particularly rodents, cattle, pigs, and dogs.
- Symptoms include fever, chills, headache, muscle aches, vomiting, and diarrhea.
- Leptospirosis may occur in two phases, with the second phase being more severe and potentially causing kidney or liver failure, or meningitis.
- Antibiotics are effective in treating the disease, particularly when administered early.
- It's prevalent in both urban and rural areas, emphasizing the importance of preventive measures and public health awareness.
Antlion species in Kerala (The Hindu)
- 18 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
Recently, a group of researchers in Kerala found two brand new antlion species. They're called Nemoleon ghoshi and Nemoleon madayiensis.
Facts About:
- These two new antlion species are part of the Myrmeleontidae family in the Neuroptera order.
- Antlions are well-known for their habit of building pits.
- Some antlion types, during their larval stages, create cone-shaped pits in loose, dry soil to catch their prey.
- However, the larvae of Nemoleon don't build pits. They live beneath the surface in loose soil, which provides them protection from sunlight, wind, and rain.
- You can easily recognize antlions by their long, distinct antennae.
- This is the first time that the Nemoleon genus has been spotted in the Oriental region.
- In Kerala, these are the 5th and 6th antlion species to be discovered, and they are the 125th and 126th species found in India.
- Antlions are found all around the world, mainly in dry, sandy areas.
- The research was made possible with financial support from the Council of Scientific and Industrial Research (CSIR).
Monoclonal Antibodies (The Hindu)
- 16 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
India has made a request to Australia for a replenishment of monoclonal antibody doses to fight against the Nipah virus.
Facts About:
Monoclonal antibodies, often abbreviated as moAbs or mAbs, are artificially created proteins in laboratories that mimic the function of natural antibodies found in our immune system.
- These antibodies play a crucial role in identifying foreign substances called antigens and attaching to them to neutralize or eliminate them.
The term "monoclonal" indicates that these laboratory-made antibodies are exact copies of a single antibody.
- They are produced by replicating a specific type of immune cell known as a B cell, resulting in large quantities of identical antibodies.
This process leads to the development of highly specialized antibodies that can precisely target specific antigens, which might include viruses, bacteria, cancer cells, or other disease-related molecules.
- Their remarkable specificity reduces the risk of unintended side effects.
Monoclonal antibodies find applications in various medical fields, including the treatment of cancer, autoimmune disorders, and infectious diseases.
Unified Portal for Agricultural Statistics (UPAg) (PIB)
- 16 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
The Ministry of Agriculture and Farmers' Welfare (DA & FW) recently introduced the Unified Portal for Agricultural Statistics, and its launch was attended by members of NITI Aayog.
Facts About:
- This innovative platform is specifically designed to improve the management of data within the agricultural sector.
- It represents a significant stride towards a more efficient and responsive framework for agricultural policies.
- As a vital part of the Digital Public Infrastructure for Agriculture, it's an initiative led by the Department of Agriculture and Farmers' Welfare to streamline data management in agriculture.
- The primary goal is to offer real-time, standardized, and verified data about agricultural commodities, simplifying data-driven decision-making for policymakers, researchers, and stakeholders.
- This initiative is in line with the principles of e-governance, introducing intelligence, transparency, and flexibility to India's agricultural sector.
World Spice Congress (WSC) (NewsOnAir)
- 16 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
The 14th World Spice Congress (WSC) recently kicked off in Vashi, Navi Mumbai.
Facts About:
- The World Spice Congress (WSC) was originally conceived in 1990 as a platform for discussions and interactions between spice importers and exporters.
Over its three decades of existence, it has evolved into a vital gathering for the global spice industry.
- Since its inception, the Spices Board under the Ministry of Commerce and Industry, Government of India, has organized the WSC.
The theme for WSC 2023 is "VISION 2030: S-P-I-C-E-S," which stands for sustainability, productivity, innovation, collaboration, excellence, and safety.
About the Spices Board of India:
- The Spices Board of India was established on February 26, 1987, through the Spices Board Act of 1986. It was formed by merging the former Cardamom Board (1968) and the Spices Export Promotion Council (1960).
- It operates under the jurisdiction of the Ministry of Commerce & Industry.
- The board has the responsibility of promoting the export of 52 scheduled spices and facilitating the development of both small and large cardamom.
- It serves as a crucial link connecting Indian exporters with foreign importers.
Main Functions:
- Conducting research, development, and regulation related to the domestic marketing of small and large cardamom.
- Enhancing post-harvest practices for all spices.
- Promoting the production, processing, and certification of organic spices.
- Supporting the development of spices in the North East region.
- Providing quality evaluation services.
Digital birth certificates (The Hindu)
- 16 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
The government has announced that starting from October 1, all births and deaths in the country will be registered digitally on the Centre's portal.
Facts About:
- Digital birth certificates are set to become a single, versatile document thanks to the 2023 Registration of Births and Deaths (Amendment) Act.
- This document will serve various purposes such as admission to schools, applying for driver's licenses, government jobs, passports, Aadhaar, voter registration, and even marriage registration.
- The central database will also keep the National Population Register (NPR), ration cards, property records, and electoral rolls up to date.
- All states will be required to use the Centre's Civil Registration System (CRS) portal to register births and deaths and share this data with the Registrar General of India (RGI).
International Organisation of Legal Metrology (OIML) (Indian Express)
- 16 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
Recently, the Secretary of the Union Ministry of Consumer Affairs announced that India has achieved the status of being an OIML certificate-issuing authority.
Facts About:
- OIML, short for the International Organisation of Legal Metrology, was established in 1955 as an international body.
- Its primary role is to develop model regulations, standards, and related documents that are used by legal metrology authorities and industry worldwide.
- OIML plays a vital part in aligning national laws and regulations concerning the accuracy of measuring instruments such as clinical thermometers, alcohol breath analyzers, radar speed measuring devices, ship tanks at ports, and petrol dispensing units.
- India joined the OIML in 1956 and simultaneously signed the metric convention.
- Headquartered in Paris, France.
National Judicial Data Grid (NJDG) portal (PIB)
- 15 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
Recently, the Chief Justice of India declared the inclusion of the Supreme Court in the National Judicial Data Grid (NJDG) during a public court session.
Facts About:
- The National Judicial Data Grid (NJDG) portal serves as a comprehensive national database for tracking cases in courts throughout India.
- It provides access to case-related information and statistics, including the number of cases filed, pending, and resolved, as well as case types and year-wise data for the Supreme Court of India.
- The NJDG portal is part of the e-Courts Project and covers 18,735 District & Subordinate Courts and High Courts.
- Developed by the National Informatics Centre (NIC) in collaboration with the Computer Cell, Registry's software development team, the NJDG portal features an interactive interface and analytics dashboard.
- It is regularly updated with current case data and serves as a valuable tool for monitoring and managing case backlogs, supporting policy decisions to expedite case resolution, and improving overall court performance.
- Additionally, it aids in tracking land dispute cases.
Data-driven Innovations in Agriculture (PTI)
- 15 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
The National Bank for Agriculture and Rural Development (Nabard) has teamed up with the United Nations Development Programme (UNDP) in India to jointly develop data-driven innovations for the benefit of smallholder farmers in agriculture and food systems.
Facts About:
- This partnership aims to improve the well-being of smallholder farmers by jointly using open-source data for product development, technology transfer, and policy formulation.
- It focuses on enhancing climate resilience in agriculture and involves sharing collaborative digital resources like DiCRA (Data in Climate Resilient Agriculture).
- DiCRA offers access to essential geospatial data related to climate-resilient agriculture and is curated by UNDP and partner organizations.
- This collaboration represents a significant opportunity to harness data and present it as a digital public infrastructure for India's rural farming community.
- Such open data innovations can promote best practices, optimize agricultural investments, and bolster the resilience of smallholder farmers, including women, against various challenges.
C-295 MW Aircraft (Indian Express)
- 15 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
Recently, Airbus delivered the first C-295MW transport aircraft to the Indian Air Force in Seville, Spain.
Facts About:
- C-295 MW Aircraft a versatile transport aircraft with a capacity of 5-10 tonnes.
- Replacing the 1960s Avro aircraft in the Indian Air Force (IAF).
- Suitable for various missions.
- Contract includes 16 fly-away aircraft from Seville and 40 to be jointly manufactured with Tata Advanced Systems Ltd. (TASL).
Key Features:
- Up to 11-hour flight endurance.
- All-weather, day and night operations.
- Short Take-off and Landing (STOL) capability.
- Rear ramp door for troop and cargo drops.
- Air tanker conversion with a detachable refueling kit.
- Airborne Early Warning (AEW) variant with 360-degree radar coverage.
- Water bomber capability (7,000 liters).
- Close-air support and Intelligence Surveillance and Reconnaissance (ISR).
- Suitable for medical evacuation, airdropping, and special missions.
Skill India Digital (SID) Platform (Indian Express)
- 15 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
The Ministry of Skill Development has just introduced the Skill India Digital (SID) platform.
Facts About:
- Skill India Digital (SID) is India’s Digital Public Infrastructure (DPI) for skill development, education, employment, and entrepreneurship.
- It consolidates various skilling initiatives, offering over 264 courses from 42,623 centers nationwide.
- Developed by the National Skill Development Corporation (NSDC) in partnership with industry players.
- Part of the World Bank-assisted Skill Acquisition and Knowledge Awareness for Livelihood Promotion (SANKALP) program.
- Supports multiple Indian languages and uses Aadhaar-based eKYC for secure access.
- Features user-friendly interface, adaptable to various devices.
- Utilizes AI and facial recognition for personalized course recommendations.
- Integrates government training programs from Central and State governments.
- Introduces Digitally Verified Credentials (DVCs) for secure skill showcasing.
- Offers Digital CVs with personalized QR Codes for easy access to qualifications and skills.
eCourts Project (Indian Express)
- 15 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
The Union Cabinet recently gave the green light to the third phase of the eCourts Projects, allocating a budget of ?7,210 crore for it.
Facts About:
- The eCourts Project is a nationwide initiative aimed at modernizing the Indian judiciary by using technology.
- It all began with the 'National Policy and Action Plan for Implementation of Information and Communication Technology (ICT) in the Indian Judiciary – 2005,' proposed by the eCommittee of the Supreme Court of India.
- This committee was formed by the Government of India in response to a suggestion from the Chief Justice of India.
- Its purpose is to develop a national strategy for computerizing the Indian judiciary and advise on technological and management-related improvements.
- This project covers all District Courts across India and is overseen and funded by the Department of Justice under the Ministry of Law and Justice, Government of India
The eCourts Project has several key goals:
- Providing efficient and citizen-centric services in a timely manner.
- Implementing decision support systems in courts.
- Automating processes to increase transparency and access to information.
- Boosting judicial productivity to make the justice system affordable, accessible, cost-effective, predictable, reliable, and transparent.
- Phase I of the eCourts Project was completed in 2015, computerizing 14,249 court sites. Phase II expanded this effort, computerizing 18,735 District and Subordinate courts.
Shanti Swarup Bhatnagar Award (The Hindu)
- 14 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
Rajnish Kumar, professor at the Indian Institute of Technology Madras (IIT-M) has won the Shanti Swarup Bhatnagar prize for science and technology.
Facts About:
- Named after the founder Director of CSIR India, Shanti Swarup Bhatnagar.
- Given annually for outstanding contributions in science and technology.
- Prize amount: Rs 5,00,000.
- Awarded in various disciplines including Biological, Chemical, Earth, Engineering, Mathematical, Medical, and Physical Sciences.
- Eligible for Indian citizens up to age 45, including OCI and PIO working in India.
- Recognizes work primarily conducted in India during the five years prior.
- Awardees selected based on recommendations from CSIR Advisory Committees.
West Coast Refinery Project (Business Standard)
- 14 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
India and Saudi Arabia have recently decided to accelerate the progress of the $50 billion West Coast refinery project.
Facts About:
- The West Coast refinery project, also known as Ratnagiri Refinery and Petrochemicals Ltd. (RRPCL), was initially conceived in 2014.
It is intended to be India's largest greenfield refinery, boasting a massive capacity of 60 million tonnes per annum.
This project is set to become the world's largest integrated refinery and petrochemical facility.
- Location-wise, the project is planned to be situated on India's western coast, specifically in Ratnagiri, Maharashtra.
- Upon completion, the refinery is anticipated to produce approximately 1.2 million barrels of oil daily, in addition to various petroleum products generated by the attached petrochemical facilities.
- Three prominent government-owned enterprises in the Indian oil and gas sector came together to establish a joint venture named RRPCL.
- RRPCL is a joint venture in which India's three national oil companies, namely Indian Oil Corporation Limited (IOCL), Bharat Petroleum Corporation Limited (BPCL), and Hindustan Petroleum Corporation Limited (HPCL), hold stakes of 50%, 25%, and 25%, respectively.
- In 2019, Saudi Aramco and the Abu Dhabi National Oil Company (ADNOC) also joined the project by acquiring a collective 50 percent stake.
This investment is estimated to be valued at around Rs 3 lakh crore, covering the setup costs.
Overnight Index Swap )Business Standard)
- 14 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
Recently, Indian overnight index swap (OIS) rates have surged to their highest levels in a span of 10 months. This increase has been attributed to offshore payments and the triggering of stop-loss orders.
Facts About:
- An Overnight Index Swap (OIS) is a financial tool that involves exchanging returns from a fixed-rate asset for a predetermined daily overnight reference rate index for an agreed-upon duration.
- The primary goal of OIS is to mitigate interest rate risk, specifically the risk linked to changes in the overnight lending rate.
- An OIS rate is computed daily, and it is based on the average interest rate that institutions with loans tied to the overnight rate have paid for that particular day.
How does an OIS Operate:
- OIS instruments enable financial institutions to exchange the interest rates they are currently paying, all without the need to refinance or alter the terms of their existing loans.
- In a typical overnight index swap arrangement, one financial institution swaps an overnight (floating) interest rate, while the other swaps a fixed short-term interest rate.
- To initiate the swap, both institutions agree to maintain their loan obligations as usual.
- However, at the end of an agreed-upon timeframe, the institution that ends up paying less interest will compensate the other institution for the difference.
Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy (PIB)
- 14 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
The Department of Empowerment of Persons with Disabilities (DEPwD) recently marked World Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy Day.
Facts About:
- Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy (DMD) is a rare and severe genetic disorder that primarily affects muscles.
- Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy (DMD) is a condition passed down through families, which means it's in your genes.
- It mainly affects the muscles, the body's moving parts, making them weaker and less effective as time goes on.
- DMD often begins in childhood, more commonly in boys than girls.
- Signs typically appear when children are about 3 to 5 years old, with noticeable difficulties in walking and getting around.
- Children with DMD may also struggle with breathing and using their arms and legs.
- Unfortunately, DMD worsens as time passes, making everyday tasks more challenging.
- Although there is no cure, there are treatments and therapies available that can help manage the symptoms and enhance the quality of life for those with DMD.
About World Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy Day:
- World Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy Day falls on 7th September annually.
- The aim of this day is to increase awareness about Duchenne muscular dystrophy and to encourage initiatives that enhance the lives of individuals with dystrophinopathies through education, advocacy, and promoting social inclusion.
Eastern Maritime Corridor (EMC) (Business Standard)
- 14 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
The Indian shipping Minister recently mentioned that India and Russia want to start working on the Eastern Maritime Corridor (EMC).
Facts About:
- The EMC is like a new sea road that connects the Indian port of Chennai with the Russian port of Vladivostok.
- This new road is expected to make it much faster to move things between Indian and Russian ports in the Far East. It could be up to 40 percent faster, which means instead of taking 40 days, it might only take 24 days.
- Right now, when things are shipped from Mumbai, India, to St. Petersburg, Russia, it's a really long trip of 8,675 nautical miles.
- The EMC, on the other hand, is a shorter route, only about 5,600 nautical miles, which is way quicker than the current path through the Suez Canal.
- So, when the EMC is ready, it will be a faster way to send stuff from India to Far East Russia.
- It's great for India, because it's a quicker and better route to reach places in the Far East like China and Japan.
New Spider Species (HT)
- 13 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
In recent discoveries, two new spider species, named Palpimanus Godawan and Palpimanus Maldhok, were identified within the conservation areas of Rajasthan Desert National Park and Solapur.
Facts About:
- These two spider species, Godawan and Maldhok, have been named in tribute to the local name of the Great Indian Bustard.
Features of these Spiders:
- These spiders are quite reserved and tend to seek shelter under rocks or in crevices when they feel disturbed.
- They exhibit a maroon coloration, a distinctive characteristic shared with the other two recognized species within the Palpimanidae genus.
- Being ground-dwelling creatures, they possess relatively robust bodies, which restricts their ability to disperse in the typical spider fashion through ballooning or shooting webs to move from place to place.
- They tend to remain within a limited area.
Megalithic Dolmen Site Near Moodbidri (The Hindu)
- 13 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
During recent archaeological excavations at the megalithic dolmen site near Moodbidri in Dakshina Kannada, researchers discovered terracotta figurines in various states of preservation that are quite distinct.
Facts About:
The Megalithic culture in India is renowned for its various burial practices and the use of iron.
- One of these practices involves the construction of dolmens.
Characteristics:
- Dolmens consisted of large stone slabs, known as orthostats, placed in a clockwise arrangement, forming a square chamber.
- This square chamber was sealed by another massive stone slab acting as a capstone.
- Typically, an entrance, often circular or U-shaped, known as a port hole, was created on the Eastern slab.
In South India, it was known by various names such as Kalmane, Pandavara Mane, Moriyara Mane, and Moriyara Betta, highlighting its popularity among the local population.
Significance:
- The presence of cow bovines in these dolmens assists in establishing their historical timeline.
The discovery of terracotta artifacts within megalithic burials provides valuable insights into the Bhoota cult or Daiva Aradhane in coastal Karnataka.
Similarities with cow goddess figures are observed in the megalithic terracotta figurines of Malampuzha in Kerala and even in Egypt.
Kisan Credit Card (KCC) (PIB)
- 13 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
Union Minister of Fisheries, Animal Husbandry and Dairying, Shri Parshottam Rupala chaired a National KCC Conference in Mumbai on 4th September 2023 to boost Kisan Credit Card (KCC) saturation among animal husbandry and dairy farmers.
Facts About:
Ministry: Ministry of Fisheries, Animal Husbandry and Dairying.
Historical Background: Introduced in 1998 to simplify and streamline access to timely credit support for farmers. Expanded in 2004 to include allied and non-farm activities. Extended to fisheries and animal husbandry in the Budget-2018-19.
Objectives:
- Meet short-term credit needs for cultivation.
- Cover post-harvest expenses.
- Fulfill household consumption needs.
- Implementing Agencies: Commercial Banks, Regional Rural Banks (RRBs), Small Finance Banks, Cooperatives.
Salient Features:
- Offers an ATM-enabled RuPay Card.
- Requires one-time documentation.
- Allows for cost escalation in the limit.
- Permits multiple withdrawals within the limit.
- Covers post-harvest expenses, produce marketing loans, and household consumption.
- Repayment period aligned with crop harvesting and marketing.
- Maximum short-term loan tenure: 1 year, long-term loan: 5 years.
- Interest subvention scheme of 2% for short-term crop loans up to Rs. 3 lakh.
- Additional 2% interest subvention and 3% prompt repayment incentive.
- Simple interest for prompt payments; compound interest for delays.
Benefits:
- Interest rates as low as 2.00%.
- No security required for loans up to Rs. 1.60 lakh.
- Crop insurance coverage against various calamities.
- Insurance coverage for permanent disability, death, and other risks provided to farmers.
Global Symposium on Farmers' Rights (NewsOnAir)
- 13 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
President Droupadi Murmu recently launched the First Global Symposium on Farmers' Rights in New Delhi.
Facts About:
- Location: ICAR Convention Centre, National Agricultural Science Centre, New Delhi. from September 12 to 15, 2023.
- Historical Background: The concept of hosting the inaugural GFSR was proposed by the Government of India during the Ninth Session of the Governing Body (GB9) of the International Treaty on Plant Genetic Resources for Food and Agriculture (International Treaty) in September 2022.
This proposal received approval from the FAO (Food and Agriculture Organization).
- Organized by: The Secretariat of the International Treaty on Plant Genetic Resources for Food and Agriculture (International Treaty) under the umbrella of the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) based in Rome.
- Hosted by: The Ministry of Agriculture and Farmers Welfare, Government of India, in collaboration with the Protection of Plant Varieties and Farmers’ Rights (PPVFR) Authority, Indian Council of Agricultural Research (ICAR), ICAR-Indian Agricultural Research Institute (IARI), and ICAR-National Bureau of Plant Genetic Resources (NBPGR).
- Objective: The primary aim is to address crucial issues concerning farmers' rights and their pivotal role in global food security and agriculture.
- Distinguished scientists and experts from 59 countries around the world will participate.
- They will engage in discussions on how to acknowledge and compensate the significant contributions made by local and indigenous communities, as well as farmers from all corners of the world, in preserving and advancing plant genetic resources (PGR).
Nipah Virus (The Hindu)
- 13 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
The Kerala health department sent out a warning in Kozhikode because they suspected that two individuals who passed away from unusual causes in the district might have contracted the Nipah virus (NiV).
Facts About:
Nipah virus infection is an illness that can be passed from animals to humans.
- The virus responsible for Nipah Virus encephalitis is an RNA virus belonging to the Paramyxoviridae family and Henipavirus genus.
- It is closely related to the Hendra virus.
This virus first emerged in Malaysia and Singapore in 1998 and 1999.
- Initially, it was detected in domestic pigs but has since been found in various domestic animals, including dogs, cats, goats, horses, and sheep.
Transmission:
The disease is transmitted through fruit bats, often referred to as 'flying foxes,' specifically those belonging to the Pteropus genus.
- These bats are natural hosts for both Nipah and Hendra viruses.
- The virus is present in bat urine and, potentially, in bat feces, saliva, and birthing fluids.
Symptoms:
- Typically, when humans become infected, they experience symptoms resembling encephalitis, which include fever, headaches, drowsiness, confusion, disorientation, coma, and sometimes even death.
Treatment: Currently, there is no specific treatment available for this virus.
Vidya Samiksha Kendra (Indian Express)
- 12 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
As part of the National Digital Education Architecture (NDEAR), the Ministry of Education is encouraging states to establish Vidya Samiksha Kendras (VSKs).
Facts About:
- Vidya Samiksha Kendra, abbreviated as VSKs, serves as a comprehensive data repository housing information from all Ministry of Education (MoE) initiatives.
- These Kendras operate control rooms responsible for collecting data, monitoring key performance indicators, and employing AI and machine learning to analyze data sourced from government schemes.
This repository regularly updates data from various sources, including:
- The PM-POSHAN mid-day meal programs.
- Teacher training data sourced from the National Initiative for School Heads' and Teachers' Holistic Advancement portal.
- Textbook content originating from Digital Infrastructure for Knowledge Sharing.
- School attendance and dropout statistics accessible through the Unified District Information System for Education (UDISE+).
- Students' learning outcomes as determined by the National Achievement Survey.
- The Performance Grading Index, evaluating the state and union territory-level school education systems.
Funding for this initiative includes a central allocation ranging from 2 to 5 crore rupees to each state for the adoption and establishment of VSKs.
Phanigiri Artefacts (The Hindu)
- 12 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
The Phanigiri artefacts, which were found in 1942 and date back to 200 BCE-400 CE, are currently showcased at the New York Metropolitan Museum of Art.
Facts About:
- The Phanigiri Buddhist site is a significant discovery in Buddhist iconography in this era.
- Phanigiri, a small village located in Telangana, is where these artefacts were unearthed.
Key Discoveries:
- The thoranas found at Phanigiri hold great importance, especially because they are some of the earliest ones discovered south of Sanchi.
- One particular thorana has a panel that depicts both Mahayana and Hinayana schools of Buddhist thought.
- Evidence from Phanigiri indicates the transformation of Buddha's status, marking a transition from a historical and spiritual figure to canonization and ritualization.
- In the monograph of this discovery, you can find an image of Buddha wearing what appears to be a Roman toga, carved in limestone.
Gene-drive Technology (The Hindu)
- 12 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
Gene-drive technology has been employed in India, Brazil, and Panama under carefully controlled outdoor conditions to genetically modify mosquitoes.
Facts About:
- Gene-drive technology is a form of genetic engineering that involves the modification of genes.
- This groundbreaking technique was conceptualized by Professor Austin Burt from Imperial College London.
- Its potential lies in effectively addressing issues posed by pest species, such as malaria-transmitting mosquitoes.
- Rather than adhering strictly to Mendelian genetics principles, this method ensures the selective inheritance of specific genes by mosquitoes.
Here's how it works:
- A protein precisely cleaves the mosquito's DNA at a specific location that doesn't encode a particular sequence in the genome.
- This action triggers a natural cellular mechanism to repair the DNA, compelling the incorporation of a designated sequence known as the 'drive sequence' into the repaired region.
Self Regulatory Organisation for Fintech (Indian Express)
- 12 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
Recently, the Governor of the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) has requested fintech organizations to establish a Self-Regulatory Organization (SRO).
Facts About:
- A Self-Regulatory Organization is an independent entity, not affiliated with the government, responsible for formulating and enforcing industry-specific rules and standards that govern the behavior of its member entities.
- The primary objectives are safeguarding customers' interests and fostering a culture of ethics, fairness, and professionalism within the industry.
Key Functions of an SRO:
- Facilitating Communication: A recognized SRO serves as a vital bridge for communication between its members and the Reserve Bank of India (RBI).
This ensures a seamless flow of information and feedback.
- Setting Standards: SROs play a pivotal role in establishing and upholding minimum benchmarks and standards.
This helps in cultivating professional and ethical conduct among their member entities.
- Education and Awareness: SROs contribute to enhancing industry expertise by providing training to the staff of their members and other relevant stakeholders.
They also organize awareness programs to disseminate knowledge.
- Grievance Resolution: An important function of an SRO is to create a uniform framework for addressing grievances and managing disputes across its member organizations, promoting fairness and transparency.
Eastern Economic Forum (PIB)
- 12 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
The Eastern Economic Forum, taking place in the Russian port city of Vladivostok, will be graced by the presence of the Union Minister of Ports, Shipping & Waterways.
Facts About:
The EEF, established in 2015, serves as a catalyst for attracting foreign investments into the Russian Far East (RFE). It effectively showcases the economic potential of the region, favorable business conditions, and enticing investment opportunities.
- The significance of the EEF is underlined by the remarkable increase in agreements signed during the forum, surging from 217 in 2017 to a staggering 380 agreements in 2021, valued at 3.6 trillion roubles.
These agreements span various sectors, including infrastructure, transportation, mineral exploration, construction, industry, and agriculture.
Key Players:
- In the RFE, China, South Korea, Japan, and India emerge as pivotal players, with China leading the pack as the largest investor.
- China recognizes the potential for advancing its Belt and Road Initiative (BRI) and the Polar Sea Route in the RFE, accounting for a substantial 90% of total investments in the region.
Objectives:
- Russia's strategic vision for the RFE involves linking the nation to the bustling Asian trade routes.
- Through rapid modernization efforts in cities such as Vladivostok, Khabarovsk, Ulan-Ude, Chita, and more, Russia aims to attract increased investments to fortify its economic resilience amidst challenges like economic crises and sanctions, with support from China and other Asian powers.
Interbank Call Money Market (ET)
- 11 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
The RBI is considering launching a pilot program for a central bank digital currency (CBDC) specifically designed for interbank borrowing or the call money market.
Facts About:
- The Interbank Call Money Market is a short-term financial market where big institutions borrow and lend money to each other at interbank rates, which are the interest rates banks charge when they borrow from one another.
- The loans in this market are very short, typically lasting only a week or less.
- These loans are often used by banks to meet their reserve requirements.
- It's not just banks that use this market; other participants can include financial institutions, mutual funds, large corporations, and insurance companies.
One Sun, One World, One Grid (OSOWOG) (PIB)
- 11 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
New Delhi recently hosted a full-day conference discussing "Transnational Grid Interconnections for One Sun, One World, One Grid (OSOWOG).
Facts About:
The OSOWOG initiative was introduced by the Prime Minister of India during the First Assembly of the International Solar Alliance (ISA) in October 2018.
Its goal is to link energy supply across international borders.
Vision:
- The initiative plans to connect various regional power grids using a common grid to transmit renewable energy, especially solar power.
The project is a collaboration between the governments of India and the UK, along with the International Solar Alliance (ISA) and the World Bank Group.
It will bring together governments, financial organizations, legislators, power operators, and experts to speed up the development of the infrastructure needed for a world powered by clean energy.
Completion timeline:
- The ISA is expected to establish this grid in the next few years.
- Once operational, it will transmit solar power to different countries.
Global Biofuels Alliance (The Hindu)
- 11 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
The Prime Minister of India recently declared the establishment of the Global Biofuels Alliance.
Facts About:
- The Global Biofuels Alliance is an initiative led by India that aims to bring together governments, international organizations, and industry to promote the use of biofuels.
- So far, 19 countries and 12 international organizations, including G20 members and non-members, have joined this alliance.
India, Brazil, and the US are its founding members.
- The alliance's main goal is to encourage the use of sustainable biofuels, especially in transportation.
Why it matters:
- The alliance will focus on strengthening markets, promoting global biofuels trade, sharing practical policy lessons, and providing technical support for national biofuels programs worldwide.
- It will support the development and use of sustainable biofuels through capacity-building, technical assistance, and knowledge sharing.
- The alliance will create a virtual marketplace to connect industries, countries, and technology providers involved in biofuels.
- Additionally, it will work on establishing internationally recognized standards and regulations to promote biofuels adoption and trade.
Konark Temple Wheel (Indian Express)
- 11 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
At the G20 summit venue, Bharat Mandapam, the Prime Minister of India greeted the leaders with a backdrop featuring a replica of the Konark Wheel from Odisha's Sun Temple in Puri.
Facts About:
- The Konark Wheel was created in the 13th century when King Narasimhadeva-I ruled.
- This wheel, with 24 spokes, is also seen on India's national flag.
- It represents India's ancient knowledge, advanced civilization, and great architecture.
- The spinning motion of the Konark Wheel represents time, Kalachakra, and the idea of constant progress and change.
- It's a strong symbol of democracy, reflecting the endurance of democratic values and dedication to societal progress.
India-Middle East-Europe Economic Corridor (Indian EXpress)
- 11 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
The Prime Minister of India recently declared the start of a massive economic corridor connecting India, the Middle East, and Europe.
Facts About:
- The project involves India, the UAE, Saudi Arabia, the European Union, France, Italy, Germany, and the US.
- Its goal is to boost trade between these countries, especially in energy products.
- The IMEC has two parts:
An Eastern Corridor linking India to the Gulf region and
A Northern Corridor connecting the Gulf region to Europe.
- It includes railways, ship-rail transit, and road routes.
- This corridor will have a railway, an electricity cable, a hydrogen pipeline, and a high-speed data cable.
- In the future, it will play a big role in connecting India, West Asia, and Europe economically.
- This rail and shipping corridor is part of the Partnership for Global Infrastructure Investment (PGII).
- Why is it important?
- It will increase prosperity by enhancing energy and digital communications flow among these nations.
- The project will also address the infrastructure needs of developing countries in terms of growth.
Schizostachyum Andamanicum (The Hindu)
- 09 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
The Government of India's patent office recently awarded a patent to the Botanical Survey of India for a reusable straw made from bamboo (Schizostachyum andamanicum).
Facts About:
- This bamboo is pretty rare and can only be found in certain forests in the Andaman Islands.
- It likes to grow in wet tropical areas.
- This type of bamboo has tall, skinny stems that are hollow inside. It's perfect for making straws.
- It has little white flowers that grow together in groups. The seeds are small and black, and the baby plants have thin, light green leaves.
NAVAL EXERCISE ‘VARUNA’ – 2023 (PIB)
- 09 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
The Indian and French Navies recently conducted Phase II of the Varuna naval exercise in the Arabian Sea.
Facts About:
- This is a naval exercise that India and France have been doing together since 1993.
- In this exercise, they use guided missile frigates, tankers, Maritime Patrol Aircraft, and helicopters from both sides.
- The goal is to make their fighting skills better, work together smoothly, and show that they can keep the peace, security, and stability in the region.
- This exercise also helps the two navies work together and cooperate to keep the seas safe and free for everyone around the world.
Central Empowered Committee (Indian Express)
- 09 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
The Supreme Court of India has transferred its environmental oversight committee, the Central Empowered Committee, to the Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change.
Facts About:
- The Supreme Court created this committee in 2002, and it was restructured in 2008.
- Its main job was to keep an eye on environmental issues and make sure everyone followed the rules.
- Now, there have been some changes. The Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change says the CEC shouldn't be a temporary group anymore; it should become a permanent team that deals with environmental stuff.
Here's how the new CEC will be set up:
- It will have a chairperson who has 25 years of experience in environment, forests, and wildlife or 25 years of big-time government work.
- They can't be older than 66 years and should be at least an additional secretary in rank.
- The member secretary will be a full-time government officer, at least a Deputy Inspector General of forests or a director in the Government of India.
- They need to know a lot about the environment, forests, or wildlife and have 12 years of experience.
- There will be three expert members, one each for environment, forests, and wildlife. They should have 20 years of experience.
- The central government will pick these members for a three-year term.
Dark Patterns (The Hindu)
- 09 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
The Central Government recently asked the public to share their thoughts on the draft rules for stopping and controlling deceptive tactics on the Internet.
Facts About:
- Dark patterns are sneaky and tricky design tricks that websites, apps, and digital platforms use to fool or manipulate users into doing things they might not want to do or making choices that aren't good for them.
- The term "dark patterns" was coined back in 2010 by Harry Brignull, a specialist in making sure user experiences are good.
- These tricky tricks are often used to get users to sign up for things, buy stuff, or share their personal info, among other stuff.
- Dark patterns work by using the way our brains work and making us do things we might not mean to do. They can be just a little misleading or really pushy and aggressive.
- There are 12 types of dark patterns including, Friend spam, Forced continuity, Disguised ads, Confirm shaming, Bait and switch, Hidden costs, Roach motel, Privacy zuckering, Misdirection, Price comparison prevention, Trick questions, Sneak into basket
For example, "confirm shaming" is when they use words, videos, sounds, or anything else to make you feel bad or embarrassed so you'll do what they want you to do.
Varicella Zoster Virus (Indian Express)
- 09 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
Scientists from the Indian Council of Medical Research-National Institute of Virology have made a historic discovery in India. They have identified the Clade 9 variant of the varicella-zoster virus (VZV) here for the first time.
Facts About:
- Varicella-zoster is a type of herpes virus that gives you chickenpox, which is a common illness when you're a kid.
- This virus only infects humans and belongs to the α-herpesvirus family.
- It's found all over the world and spreads easily.
- When you first get infected with this virus, you get chickenpox, which is also called acute varicella.
- In some cases, this virus can even affect your central nervous system and lead to serious problems.
Zero Draft Plastic Pollution Treaty (Down to Earth)
- 08 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
The second session of the Intergovernmental Negotiating Committee (INC) concluded with member states instructing the INC secretariat to create an initial draft aimed at putting an end to plastic pollution, including in marine ecosystems.
Facts About:
- This is a globally binding agreement designed to put an end to plastic pollution, especially in marine ecosystems.
- The zero draft consists of ten sections covering topics such as the preamble, definitions, principles, scope, institutional arrangements, and final provisions.
- During INC-2, member states like Saudi Arabia, Iran, China, and India emphasized the significance of clearly defining the scope of this legally binding instrument.
Competition Commission of India (CCI) (TOI)
- 08 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
The Competition Commission of India has recently unveiled preliminary rules for overseeing mergers and acquisitions involving significant India-based operations, particularly those in the technology sector, thereby extending the authority of the antitrust regulator.
Facts About:
- CCI is a government-established statutory body founded in March 2009 under the Competition Act, 2002.
- The primary objective of CCI is to foster fair competition in the economy, ensuring a level playing field for producers and promoting market dynamics that benefit consumers.
- The Commission's key focus areas include eradicating practices detrimental to competition, fostering and maintaining competitive environments, safeguarding consumer interests, and upholding the freedom of trade in India's markets.
Mandate: CCI enforces the provisions of The Competition Act, 2002, which:
- Prohibits anti-competitive agreements and the abuse of dominant positions by enterprises.
- Regulates mergers and acquisitions (M&A) that could potentially harm competition within India. Hence, deals exceeding certain thresholds require clearance from CCI.
- Monitors the activities of large enterprises to ensure they do not misuse their 'dominant position' by controlling supply, setting high purchase prices, or engaging in unethical practices that may harm emerging businesses.
Composition: CCI functions as a quasi-judicial body, consisting of one chairperson and six additional members, all appointed by the Central Government.
Headquarters: The Commission is headquartered in New Delhi.
Wide Field Survey Telescope (HT)
- 08 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
In September, China plans to launch the Wide Field Survey Telescope (WFST).
Facts About:
This telescope is the largest time-domain survey facility in the Northern Hemisphere.
Its main goals are as follows:
- To explore and continuously monitor dynamic astronomical events and conduct research in the field of time-domain astronomy.
- To detect faint and distant celestial signals, including those from galaxies beyond our Milky Way and galaxy clusters.
- To search for planets or their moons in the Kuiper Belt and beyond.
- To track and study a comprehensive list of one million solar system objects, providing a detailed view of the solar system's history and evolution.
The WFST is positioned at the Lenghu astronomical observation base in Qinghai Province, northwest China.
- This location, with an average altitude of approximately 4,000 meters, offers ideal conditions for observing the night sky, thanks to its clear skies, stable atmosphere, dry climate, and minimal artificial light pollution.
- It's widely recognized as one of the finest observatory sites across the Eurasian continent.
The WFST project commenced in July 2019, a result of collaboration between the University of Science and Technology of China and the Purple Mountain Observatory under the Chinese Academy of Sciences.
Sambar Deer (The Hindu)
- 08 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
Researchers recently spotted a rare sambar deer with leucism (partial white coloring) in the Cauvery Wildlife Sanctuary.
Facts About:
- Sambar deer, scientifically known as Rusa unicolor, are large deer native to the Indian subcontinent and Southeast Asia.
- They prefer to stay hidden and are most active during the evening and night.
- These deer can be found in a wide range of forest environments, including dry deciduous forests, rainforests, and mixed forests.
- One of their crucial roles in the ecosystem is seed dispersal within their natural habitats.
Distribution:
- They inhabit areas stretching from the foothills of the Himalayan Mountains across southern Asia, extending to the islands of Taiwan, Sumatra, and Borneo.
Threats they face:
- The main threats to Sambar deer are hunting and the encroachment of their natural habitat.
- In response to human hunting, they have adapted by becoming more active at night to avoid being hunted for trade and food.
Conservation status:
- According to the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN), they are classified as 'Vulnerable.'
Under the Wildlife (Protection) Act of 1972, they are listed in Schedule-III for protection.
Nation First Transit Card (The Hindu)
- 08 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
The State Bank of India has introduced the 'Nation First Transit Card.' It's a prepaid RuPay card that falls under the National Common Mobility Card (NCMC) program, allowing you to use it anywhere in the country.
Facts About:
- This card is designed to make your commuting experience smooth and convenient.
- You can use it to pay for tickets on metros, buses, water ferries, and even parking with just one card.
- Plus, it's not just for transportation; you can also use it for shopping online and in stores.
- What makes it work is the technology behind it. It's powered by RuPay and National Common Mobility Card (NCMC) tech.
Important Facts About National Common Mobility Card (NCMC):
- With NCMC, you can use your Bank's Debit Cards as travel cards for Metro Rail and Buses in places where it's available.
- The idea for NCMC came from a committee led by Nandan Nilekani, set up by the Reserve Bank of India (RBI).
- NCMC is an initiative by the Ministry of Housing and Urban Affairs in India. Its goal is to promote cashless transactions and provide a single payment platform for commuters. It was launched on March 4, 2019.
- It offers a unified contactless transport solution through the RuPay platform, which is developed by the National Payments Corporation of India (NPCI).
- NCMC is like a magic card that can turn your smartphone into a transport card. You can use it to pay for Metro, bus, and suburban railway services.
Malaviya Mission (PIB)
- 07 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
The Malaviya Mission - Teachers Training Programme, initiated by the University Grants Commission, was recently unveiled at Kaushal Bhawan in New Delhi by the Union Minister for Education and Skill Development & Entrepreneurship.
Facts About:
- The primary objective is to offer customized training programs for educators.
- This initiative is focused on enhancing the capabilities of faculty members in higher education institutions (HEI).
- It is dedicated to achieving continuous professional development and strengthening the skills of 15 lakh HEI teachers across India through 111 Malaviya Mission centers within a specific timeframe.
- The program is designed to elevate the quality of teacher training, foster leadership qualities among educators, and align with the objectives of the National Education Policy (NEP).
- Capacity building activities under this Mission will be aligned with a credit framework to facilitate career advancement opportunities for teachers.
- Notably, the Indian Knowledge System has been incorporated into the program's modules.
- As part of this initiative, Human Resource Development Centers will undergo a transformation and be renamed as Madan Mohan Malaviya Teachers Training Centers.
Satkosia Tiger Reserve (New Indian Express)
- 07 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
Recently, the Satkosia Tiger Reserve made a distressing discovery of two elephants' severely decomposed remains.
Facts About:
- Location: Situated in the heart of Odisha, this reserve spans across four districts: Angul, Cuttack, Boudh, and Nayagarh. The Mahanadi River flows through the valleys within the reserve.
- Size: Covering an area of 1136.70 sq km, with 523.61 sq km designated as the core area, Satkosia Tiger Reserve is also part of the Mahanadi Elephant Reserve.
- Unique Geography: Satkosia serves as the convergence point of two distinctive bio-geographic regions in India: the Deccan Peninsula and the Eastern Ghats.
- Landscape: The terrain here is characterized by hills, featuring moderate to steep slopes and narrow valleys.
- Vegetation: The forest primarily consists of North Indian tropical moist deciduous forests and moist peninsular low-level sal.
- Flora: The dominant tree species is sal, forming dense stands. Other associated species include Asan (Terminalia alata), Dhaura (Anogeissus latifolia), Bamboo (Dendrocalamus strictus), and Simal (Bombax ceiba).
- Fauna: The reserve is home to a diverse range of wildlife, including tigers, leopards, elephants, spotted deer, sambar deer, chowsingha, barking deer, bison, wild dogs, sloth bears, jackals, giant squirrels, and porcupines. Additionally, it provides a natural habitat for two endangered species: the freshwater crocodile and the gharial.
One-hour Trade Settlement (Indian Express)
- 07 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
The Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI), which previously stated its intention to introduce real-time settlement of trades in July, is now considering implementing one-hour settlement of trades as the initial step.
Facts About:
In a one-hour settlement, when an investor sells a share, the money will be deposited into their account within an hour, and the buyer will have the shares in their demat account within an hour.
Trade settlement is a process that involves the transfer of funds and securities on the settlement date.
- It's considered complete when the purchased securities from a listed company are delivered to the buyer, and the seller receives the money.
- Previously, trade settlements followed the T+1 cycle, meaning they occurred within one day or 24 hours of the actual transactions.
This changed in January 2023 when India shifted to the T+1 settlement cycle, making it the second country globally, after China, to adopt this cycle for top-listed securities.
Chitala Fish (TOI)
- 07 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
The Union Minister for Fisheries, Livestock, and Dairying has just revealed plans to boost the population of the Uttar Pradesh state fish Chitala by introducing it into natural water sources like the Ganga through river ranching.
Facts About:
Chitala Fish is a type of predator fish that primarily hunts at night and preys on smaller fish.
Distribution:
- Although it's often reported to inhabit various parts of southern Asia, this species is mainly found in the Indian subcontinent, including Pakistan, India (particularly in states like Manipur, Uttaranchal, West Bengal, Assam, Tripura, Uttar Pradesh, and Bihar), Nepal, and Bangladesh.
Habitat:
- Chitala Fish is commonly found in major river channels and freshwater lakes but has also been observed in swamps.
- Its primary habitat includes the Indus, Ganges-Brahmaputra, and Mahanadi river basins in India.
Conservation Status:
- According to the IUCN, Chitala Fish is classified as "Near Threatened."
Significance of Chitala’s River Ranching:
- The river ranching initiative has multiple aims, including restoring the aquatic ecosystem's balance, boosting the income of fish farmers, and providing the public with a protein-rich diet.
Additionally, Uttar Pradesh has ongoing projects worth over 1000 crore under the Pradhan Mantri Matsya Sampada Yojana.
Indian Green Building Council (The Hindu)
- 07 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
The Indian Green Building Council (IGBC) gave the highest Platinum rating to Vijayawada Railway Station, certifying it as a 'Green Railway Station.
Facts About:
- The Indian Green Building Council (IGBC) is part of the Confederation of Indian Industry (CII) and started in 2001.
- It's India's top certification organization.
- They offer various services like creating new green building rating systems, certification services, and green building training programs.
- IGBC also hosts the Green Building Congress, their main yearly event on green buildings.
- Additionally, it's one of the five countries on the board of the World Green Building Council, where global issues are discussed at events like COP.
- The rating is based on six environmental categories: sustainable station facility, health, hygiene, and sanitation, energy efficiency, water efficiency, smart and green initiatives, and innovation and development.
- Their headquarters is in Hyderabad.
Project Naman (India Today)
- 06 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
The Indian Army has initiated 'Project Naman,' which involves setting up centers to provide support and address concerns for veterans and the families of personnel who have made the ultimate sacrifice.
Facts About:
- Project Naman aims to create centers for veterans and the families of fallen personnel to provide assistance and address their concerns.
- The first center will be located in Delhi Cantonment.
- Named 'Naman,' these centers will include a Common Service Centre, offering various government-to-customer services.
- Additionally, they will assist in updating pensioners' accounts on the SPARSH portal for veterans, next of kin, and dependents.
Gramodyog Vikas Yojana (PIB)
- 06 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
Recently, the Chairman of the Khadi and Village Industries Commission (KVIC), a part of the Ministry of Micro, Small and Medium Enterprises, provided artisans with tool-kits and machinery as part of the 'Gramodyog Vikas Yojna' program.
Facts About:
- Gramodyog Vikas Yojana is a vital part of the Khadi Gramodyog Vikas Yojana and has a mission to advance and enhance village industries through various means such as shared facilities, technological upgrades, training, and more.
- It encompasses a range of activities associated with different village industries.
Components of the Yojana:
- Research & Development and Product Innovation: This component supports institutions engaged in product development, innovations, design improvements, and diversification processes.
- Capacity Building: It focuses on enhancing the skills and knowledge of staff and artisans through the existing MDTCs (Management Development and Training Centers) and excellence institutions.
- Marketing & Publicity: The Yojana assists village industry institutions in various ways, including preparing product catalogs, industry directories, conducting market research, introducing new marketing techniques, organizing buyer-seller meetings, and arranging exhibitions.
- Target beneficiaries of this program are artisans, unemployed youth, and self-help groups (SHGs).
- To be eligible, individuals must be traditional artisans with skill and experience in art and craft.
Tilapia fish (Down to Earth)
- 06 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
The report about invasive alien species highlighted that the proliferation of water hyacinth (scientifically known as Pontederia crassipes) in Lake Victoria has had a negative impact on the tilapia fish population.
Facts About:
- It is a common name for some fish species in the family Cichlidae (order Perciformes), which includes a large number of predominantly freshwater species endemic to Africa.
- These fish are primarily found in freshwater environments, such as shallow streams, ponds, rivers, and lakes. They are less commonly found in brackish water.
- In some cases, Tilapia can become problematic invasive species in warm-water habitats like Australia, whether introduced intentionally or accidentally.
- However, they generally can't survive in cold temperate climates.
- It has emerged as one of the world's most productive and internationally traded food fish.
- Tilapia culture has become economically successful in many parts of the world, and fishery experts have termed tilapia "aquatic chicken" because to its rapid growth and minimal maintenance cultivation.
Nagarahole Tiger Reserve (The Hindu)
- 06 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
A 10-year-old boy was recently killed by a tiger in Nagarahole Tiger Reserve's Metikuppe wildlife region.
Facts About:
Nagarahole Tiger Reserve is located in the Mysore and Kodagu districts of Karnataka.
- Its name, "Nagarahole," means "snake stream" in Kannada, and it's named after a small river that flows through the area, eventually joining the Kabini River.
The reserve is bordered by the Bandipur Tiger Reserve to the southeast and the Wayanad Wildlife Sanctuary in Kerala to the southwest.
- It's also a part of the Nilgiri Biosphere Reserve.
Its history dates back to the time of the Wodeyar dynasty, the former rulers of the Kingdom of Mysore, who used it as an exclusive hunting ground.
- It was established as a wildlife sanctuary in 1955 by Coorg State, later becoming a national park in 1988.
- In 1999, it was designated as a Tiger Reserve under Project Tiger.
Nagarahole's forests consist mainly of deciduous trees.
The eastern part of the reserve has dry deciduous forests, while the western areas, with higher rainfall, feature tropical moist and semi-evergreen forests.
Throughout the reserve, you'll find swampy areas called 'hadlu,' rich in grasses and sedges, which are favored by herbivores.
The region is known for commercially valuable trees like rosewood, teak, sandalwood, and silver oak.
In terms of wildlife, Nagarahole is home to a diverse range of species, including tigers, leopards, wild dogs, sloth bears, Asiatic elephants, gaurs, sambar deer, chital deer, muntjacs, and four-horned antelopes, among others.
Tharosaurus indicus (The Hindu)
- 06 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
Recently, scientists from IIT Roorkee studied dinosaur fossils from the Middle Jurassic period. These fossils were discovered in the Thar desert near the Jaisalmer Basin by the Geological Survey of India.
Facts About:
- It is a member of the Dicraeosauridae family and the Diplodocoidea superfamily.
- These are the earliest dicraeosaurid sauropod fossils discovered in India.
- It is the world's oldest known diplodocoid fossil, dating back 167 million years.
- The dinosaur was named Tharosaurus indicus, with Tharo originating from the Thar desert, Saurus from the Greek'sauros', meaning lizard, and indicus from its Indian provenance.
- This family was distinct in that its members were smaller and had shorter necks and tails than other long-necked sauropods.
- Sauropods originally arrived on Earth some 200 million years ago, during the Jurassic period.
- They were one of the most dominating dinosaur clades, surviving until the late Cretaceous period 65 million years ago, when dinosaurs became extinct.
- According to the experts, dicraeosaurid dinosaur fossils have previously been discovered in North and South America, Africa, and China, but such fossils were unknown from India.
Urban Infrastructure Development Fund (Indian Express)
- 05 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
Authorities from the Ministry of Union Housing and Urban Affairs have indicated that the initial installment of loans for supporting ongoing projects in tier-2 and tier-3 cities through the Urban Infrastructure Development Fund (UIDF) is expected to be released shortly.
Facts About:
The UIDF is created by utilizing the priority sector lending shortfall.
Objective:
- This fund serves as a resource for public agencies to develop urban infrastructure in tier-2 and tier-3 cities.
Emphasis is placed on essential services such as sewage and solid waste management, water supply, sanitation, construction, and improvement of drainage systems, with a priority on projects that have a significant impact.
The National Housing Bank manages this fund.
It initially has a corpus of ?10,000 crore and is modeled after the Rural Infrastructure Development Fund (RIDF).
States are encouraged to harness resources from the 15th Finance Commission's grants and existing schemes, while also considering user charges when accessing the UIDF.
Currently, it covers 459 tier-2 cities and 580 tier-3 cities.
UIDF Loans:
- nterest rate: Bank Rate minus 1.5%
- The loan principal is repayable in five equal annual installments within seven years from the draw date, including a two-year moratorium period.
- Interest payments are made on a quarterly basis.
Stump-tailed Macaque (Indian Express)
- 05 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
The Delhi Zoo has recently welcomed eight stump-tailed macaques, which were transferred from the Aizawl Zoological Park in Mizoram.
Facts About:
The stump-tailed macaque, also known as the bear macaque, is an Old-World monkey species native to South Asia.
Scientific Name: Macaca arctoides
Natural Habitat: These monkeys inhabit tropical and subtropical evergreen forests.
Geographic Range:
- They are indigenous to regions including Cambodia, southwest China, northeast India, Laos, Myanmar, northwest Peninsular Malaysia, Thailand, and Vietnam.
- In India, they are predominantly found south of the Brahmaputra River, primarily in the northeastern states.
Their Indian range extends from Assam and Meghalaya to eastern Arunachal Pradesh, Nagaland, Manipur, Mizoram, and Tripura.
Conservation Status:
- IUCN Red List: Vulnerable
- Wildlife (Protection) Act, 1972: Schedule II
Gilbert Hill (Indian Express)
- 05 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
The Maharashtra Government has recently put forward a plan to transform Gilbert Hill into a tourist attraction, drawing inspiration from the iconic Burj Khalifa in Dubai.
Facts About:
- Situated in Andheri, Mumbai, Gilbert Hill is a remarkable 200-foot tall monolithic column made of black basalt rock.
- This unique geological formation was created approximately 66 million years ago during the Mesozoic Era when molten lava erupted from the Earth's crevices and solidified.
- In 1952, it received National Park status, and in 2007, the Brihan Mumbai Municipal Corporation recognized it as a Grade II heritage structure.
- Notably, Gilbert Hill is one of only three volcanic rock outcrops worldwide.
- As one of the oldest heritage sites in its original condition, it features a collection of temples and a small garden perched atop, accessible via a steep staircase carved into the rock.
PM-DAKSH Yojana (PIB)
- 05 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
From 2020 to 2023, the PM-DAKSH Yojana has provided training to a total of 107,156 beneficiaries.
Facts About:
The Pradhan Mantri Dakshata Aur Kushalata Sampanna Hitgrahi (PM-DAKSH) Yojana is a Central Sector Scheme launched in the fiscal year 2020-21.
Its primary goal is to boost the skills and competency of specific target groups, making them capable of finding employment, either through self-employment or wage-employment, to improve their socio-economic status.
This Yojana serves as a National Action Plan for training marginalized individuals, including Scheduled Castes (SCs), Other Backward Classes (OBCs), Economically Backward Classes (EBCs), Denotified Tribes (DNTs), sanitation workers, and waste pickers.
Target Groups:
- Artisans: Those looking to enhance their income within their current vocations.
- Women: Empowering them to engage in self-employment while managing domestic responsibilities.
- Youth: Providing them with long-term training and specialization in employable fields to improve their job prospects.
Eligibility:
- Age range: 18-45 years.
- No income limit for SCs, Safai Karamcharis (sanitation workers), and waste pickers.
- Annual family income below Rs. 3 lakh for OBCs.
- Annual family income below Rs. 1 lakh for EBCs (Economically Backward Classes).
- Nodal Ministry: Ministry of Social Justice & Empowerment (MoSJ&E).
GRIHA-IV Norms (The Hindu)
- 05 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
The Indian Army is building a new Thal Sena Bhawan (TSB) using GRIHA-IV (Green Rating for Integrated Habitat Assessment) standards.
Facts About:
GRIHA stands for Green Rating for Integrated Habitat Assessment, and the word 'GRIHA' means 'Abode' in Sanskrit.
It's a tool that helps us measure how well a building performs compared to national standards.
GRIHA looks at a building's environmental impact throughout its entire life cycle, setting a clear standard for what qualifies as a 'green building.'
This rating system is based on accepted energy and environmental principles, balancing established practices with new ideas, both nationally and internationally.
TERI (The Energy and Resources Institute) developed GRIHA, and it's been adopted by the Ministry of New and Renewable Energy.
Criteria:
- GRIHA assesses a building using 34 criteria and awards points on a scale of 100.
- To get GRIHA certification, a project needs at least 50 points.
- Some criteria are mandatory, and the project must meet them to be eligible for any rating.
Project Ratings:
- 50-60 points: 1-star GRIHA rating
- 61-70 points: 2-star GRIHA rating
- 71-80 points: 3-star GRIHA rating
- 81-90 points: 4-star GRIHA rating
- 91-100 points: 5-star GRIHA rating
What is Preeclampsia? (The HIndu)
- 04 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
A recent research study has shown that utilizing a liquid-biopsy method to assess DNA-methylation levels in the blood could enhance the early detection of pregnancies at risk of developing preeclampsia.
Facts About:
Preeclampsia is a severe condition characterized by elevated blood pressure that typically emerges during pregnancy, usually after the 20th week.
- This condition can have adverse effects on multiple organs in the body and poses risks to both the mother and the developing fetus.
Symptoms:
- Individuals with preeclampsia commonly experience high blood pressure (hypertension) and elevated levels of protein in their urine (proteinuria).
- Additional symptoms may include vision changes such as temporary loss of vision, blurred vision, or heightened sensitivity to light.
Prevention:
- The primary clinical recommendation for preventing preeclampsia is the use of low-dose aspirin, supported by strong clinical evidence.
Additionally, adopting a healthy lifestyle and making prudent choices is advisable, especially for individuals who have previously experienced preeclampsia.
Aatmanirbhar Bharat Rozgar Yojana (ABRY) (PIB)
- 04 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
The Aatmanirbhar Bharat Rozgar Yojana (ABRY), an inventive employment incentive scheme introduced by the Central Government, has surpassed its initial objectives for generating employment. This achievement highlights its effectiveness in promoting job creation and supporting economic recovery amidst the challenges posed by the COVID-19 pandemic.
Facts About:
- Launched in 2020, the Aatmanirbhar Bharat Rozgar Yojana (ABRY) was created to stimulate the creation of new job opportunities.
- It achieves this by providing financial support to employers who are part of the Employees' Provident Fund Organization (EPFO).
- The primary objective of this scheme is to incentivize the employment of individuals, including those who lost their jobs due to the pandemic.
- It does so by covering both the employee and employer contributions, which amounts to 24% of wages, for establishments with up to 1000 employees.
- For larger establishments with over 1000 employees, the scheme covers only the employee's EPF contributions, which is 12% of wages, in relation to new employees.
- As of July 31, 2023, the ABRY has successfully enrolled more than 7.58 million new employees, surpassing its initial target for employment generation.
- This achievement underscores its significant contribution to revitalizing the job market and supporting economic recovery during these challenging times.
Umiam Lake (ET)
- 04 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
The Meghalaya government has just started using advanced AI-powered robots to ensure that Umiam Lake, a popular tourist destination, remains clean and free from pollution.
Facts About:
Umiam Lake, also known as Barapani Lake, is located 15 kilometers (9.3 miles) north of Shillong, the capital of Meghalaya.
- This beautiful lake is surrounded by the lush green hills of East Khasi and covers an expansive 10 square kilometers.
The history of Umiam Lake dates back to 1965 when a dam was built to generate hydroelectric power as part of the Umiam Umtru Hydroelectric Power Project, marking the lake's inception.
The primary source of water for the lake is the confluence of two streams, Umkhrah and Umshvrpi, which merge to form the Wah Ro-ro stream in the northwest of the town.
- This stream then joins the River Umiam, ensuring a steady flow of water into the lake.
The catchment area for the lake and dam extends over 220 square kilometers, encompassing not only Shillong but also its neighboring regions.
- Umiam Lake has gained popularity as a hub for water sports and adventure activities, making it a favorite destination for thrill-seekers and nature enthusiasts alike.
C-TAP initiative (WHO)
- 04 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
Recently, the COVID-19 Technology Access Pool (C-TAP) has revealed three fresh licensing agreements obtained via the Medicines Patent Pool (MPP).
Facts About:
- In May 2020, the World Health Organization (WHO) and the Government of Costa Rica, in collaboration with 44 Member States, the UN Development Programme, Unitaid, UNAIDS, and implementing partners like the Medicines Patent Pool (MPP), launched C-TAP.
- C-TAP operates based on the principles outlined in the Solidarity call to action.
- Its primary objective is to provide a platform where developers of COVID-19 treatments, diagnostics, vaccines, and other health products can voluntarily share their intellectual property, knowledge, and data.
- This sharing is aimed at expediting technological advancements and increasing global production capabilities in the fight against the pandemic.
DIKSHA Platform (The Hindu)
- 04 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
The National eGovernance Division (NeGD) within the Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology (MeitY) is gearing up to incorporate Personalised Adaptive Learning (PAL) into its established Digital Infrastructure for Knowledge Sharing (DIKSHA) platform.
Facts About:
DIKSHA is a national education platform initiated by the National Council for Education Research and Training (NCERT) under the Ministry of Education.
- Its primary purpose is to deliver educational content to schools through both an online portal and a mobile application.
The platform was developed with a strong emphasis on key principles such as open architecture, open access, open licensing, choice, and autonomy.
- It relies on open-source technology tailored to India, featuring internet-scale capabilities that accommodate various teaching and learning needs.
Key Features:
- DIKSHA incorporates many essential components of the National Digital Education Architecture (NDEAR), enabling successful use-cases like interactive textbooks, online courses, content creation, content sourcing, interactive quizzes, question banks, chatbots, analytics, and dashboards.
To support the learning needs of Children With Special Needs (CWSN), DIKSHA offers a substantial collection of resources, including audiobooks, Indian Sign Language (ISL) videos, and a comprehensive dictionary.
DIKSHA Platform (The Hindu)
- 04 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
The National eGovernance Division (NeGD) within the Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology (MeitY) is gearing up to incorporate Personalised Adaptive Learning (PAL) into its established Digital Infrastructure for Knowledge Sharing (DIKSHA) platform.
Facts About:
DIKSHA is a national education platform initiated by the National Council for Education Research and Training (NCERT) under the Ministry of Education.
- Its primary purpose is to deliver educational content to schools through both an online portal and a mobile application.
The platform was developed with a strong emphasis on key principles such as open architecture, open access, open licensing, choice, and autonomy.
- It relies on open-source technology tailored to India, featuring internet-scale capabilities that accommodate various teaching and learning needs.
Key Features:
- DIKSHA incorporates many essential components of the National Digital Education Architecture (NDEAR), enabling successful use-cases like interactive textbooks, online courses, content creation, content sourcing, interactive quizzes, question banks, chatbots, analytics, and dashboards.
To support the learning needs of Children With Special Needs (CWSN), DIKSHA offers a substantial collection of resources, including audiobooks, Indian Sign Language (ISL) videos, and a comprehensive dictionary.
The Global Fund (The Hindu)
- 02 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
Recently, the Global Fund unveiled an agreement with generic pharmaceutical companies to substantially reduce the cost of a state-of-the-art HIV medication.
Facts About:
The Global Fund represents a global initiative aimed at conquering HIV, TB, and malaria, striving for a healthier, safer, and more equitable future for everyone.
Established in 2002, this movement unites governments, civil society, healthcare professionals, and the private sector.
Funding:
- The Global Fund operates on a three-year funding cycle, providing more extended-term stability in the fight against AIDS, TB, and malaria.
Funding primarily originates from the public sector, with 92% of total contributions originating from donor governments.
- Additional funding sources encompass the private sector, foundations, and innovative financial initiatives.
In 2006, India became a donor to the Global Fund, committing $25 million for the Seventh Replenishment period spanning 2023-2025.
Adopt a Heritage 2.0 Scheme (Indian Express)
- 02 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
The Archaeological Survey of India is ready to introduce its new and innovative program called "Adopt a Heritage 2.0.
Facts About:
- This initiative is a joint effort of the Ministry of Tourism in partnership with the Ministry of Culture and the Archaeological Survey of India.
- It was inaugurated on World Tourism Day in September 2017.
- Under this program, the government invites various entities, including public and private sector companies, as well as individuals, to undertake the development of selected historical monuments and tourist sites throughout India.
- The primary goal is to encourage these entities to become 'Monument Mitras' and assume the responsibility of enhancing both basic and advanced tourist facilities at these locations.
- The corporate sector is encouraged to utilize corporate social responsibility (CSR) funds for site maintenance.
- In return, Monument Mitras receive limited visibility on-site and on the official Incredible India website.
Meningococcal Disease (HT)
- 02 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
The state of Virginia in the United States has issued a caution regarding a widespread outbreak of meningococcal disease.
Facts About:
Meningococcal disease is a rare but severe bacterial infection that causes inflammation of the membranes covering the brain and spinal cord.
The two primary forms are meningitis and septicemia, both potentially life-threatening within hours.
Causes:
- This disease is caused by Neisseria meningitidis bacteria. Approximately 1 in 10 people carry these bacteria in their nose and throat without illness, but sometimes they can cause meningococcal disease.
Transmission:
- Transmission occurs through respiratory and throat secretions, like saliva, but usually requires close or prolonged contact. It's less contagious than the common cold or flu.
Symptoms:
- Common symptoms include fever, headache, stiff neck, photophobia (sensitivity to light), nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and a distinctive rash.
Treatment:
- Meningococcal disease is treated with antibiotics, and additional therapies may be necessary, such as oxygen therapy, medications for low blood pressure, and skin treatments, including surgery.
Strategic Disinvestment (The Hindu Business Line)
- 02 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
The government has recently issued a Request for Proposal (RFP) to hire an asset appraiser for the Strategic Disinvestment of IDBI Bank.
Facts About:
Strategic disinvestment involves the sale of a significant portion of the government's ownership in a central public sector enterprise (CPSE), which can be up to 50% or a higher percentage as decided by the competent authority.
- This process also includes the transfer of management control.
It essentially means transferring both ownership and control of a public sector entity to another entity, which can be either private or public.
Distinguishing Strategic Disinvestment/Sale from Disinvestment:
- Disinvestment refers to the sale of minority shares of public enterprises to another entity, whether it's public or private.
- In this case, the government still maintains ownership of the enterprise.
In contrast, strategic disinvestment/sale occurs when the government sells a majority share in an enterprise, relinquishing not only ownership but also control of the entity.
What are the objectives of Strategic Disinvestment:
- Reduce Government Ownership
- Raise Capital
- Enhance Efficiency
- Foster Competition
- Attract Private Investment
- Focus on Core Functions
- Alleviate Fiscal Burden
Financial Action Task Force (Deccan Herald)
- 02 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
India has suggested to all G20 nations to actively cooperate to deal comprehensively and efficiently with fugitive economic offenders as part of the action against them and recovery of the assets.
Facts About:
- The FATF is an international organization made up of governments that focuses on creating policies and standards to combat money laundering and terrorist financing.
- Objective: Its main goal is to establish global standards and encourage the development of policies at both national and international levels to prevent money laundering and the financing of terrorism.
- The FATF provides recommendations to combat financial crimes, assesses its member countries' policies and procedures, and strives to promote the adoption of anti-money laundering regulations worldwide.
- Formation: The FATF was established in 1989 during the G7 Summit in Paris with the initial aim of addressing money laundering. In 2001, its scope expanded to include combating terrorism financing.
- Headquarters: Its headquarters are located in Paris, France.
- Membership: The FATF comprises 39 member countries, including the United States, India, China, Saudi Arabia, Britain, Germany, France, and the European Union.
- India became a member in 2010.
- As part of its efforts, the FATF maintains two lists: the blacklist and the greylist.
Black List:
- The blacklist contains countries referred to as Non-Cooperative Countries or Territories (NCCTs). These are countries known for supporting terrorism funding and money laundering activities.
- The FATF regularly updates this list, adding or removing countries as needed.
Grey List:
- The grey list includes countries considered to be safe havens for supporting terrorism funding and money laundering. Placement on this list serves as a warning that a country may eventually be placed on the blacklist.
- Currently, three countries on the FATF blacklist are North Korea, Iran, and Myanmar.
Consequences of Being on the FATF Blacklist:
- Countries on the FATF blacklist do not receive financial aid from organizations such as the International Monetary Fund (IMF), the World Bank, the Asian Development Bank (ADB), and the European Union (EU).
- Additionally, they face various international economic and financial restrictions and sanctions.
Invasive Alien Species (Down to Earth)
- 01 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
Report on invasive species & their control to be approved at the plenary was developed over four years by 86 leading experts from 49 countries
Facts About:
An alien species is one that has been introduced outside its native habitat.
According to experts, these are whether intentionally or accidentally, find their way outside their natural environments.
- Once there, they often outcompete local species, disrupting the delicate ecological balance.
These invasive species typically possess specific traits that aid their success, including the ability to adapt to new conditions (known as phenotypic plasticity).
- Other characteristics include rapid reproduction, high dispersal capabilities, versatility in diet and environmental adaptation, and a propensity for quick reproduction.
It's crucial to note that invasive alien species are not a natural part of their new ecosystems, and their presence can lead to severe harm to the economy, the environment, and even human health.
In developing countries, where agriculture, forestry, fisheries, and natural systems play a pivotal role in people's livelihoods, invasive alien species exacerbate poverty and pose a significant threat to development.
- This situation is further compounded by factors like climate change, pollution, habitat loss, and human-induced disturbances.
Liquid Apogee Motor (LAM) (The Hindu)
- 01 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
In the Aditya-L1 mission, ISRO will utilize a Liquid Apogee Motor (LAM) identical to the one employed in previous missions to Mars and the Moon.
Facts About:
- This compact yet potent engine, referred to as 'LAM,' assumes a pivotal role in ISRO's upcoming Aditya-L1 mission, designed for the study of the sun.
- The effective functioning of the LAM holds significant importance as it enables ISRO to position the Aditya spacecraft in a halo orbit at Lagrangian point L1.
- These engines are commonly employed for making precise orbital adjustments to satellites and spacecraft while they are in orbit.
- The Liquid Apogee Motor is the product of the Liquid Propulsion Systems Centre (LPSC), an ISRO facility specializing in Liquid and Cryogenic Propulsion, located in Thiruvananthapuram.
Bhoramdev Wildlife Sanctuary (BWS) (TOI)
- 01 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
The Chhattisgarh High Court has recently rejected a public interest litigation (PIL) seeking the designation of the Bhoramdeo Wildlife Sanctuary (BWS) as a tiger reserve.
Facts About:
- Location: Situated in the Kawardha district of Chhattisgarh, this sanctuary takes its name from the renowned 11th-century Bhoramdeo Temple located nearby.
-
- It shares its boundary with Kanha National Park in Madhya Pradesh, making it a significant tiger habitat in central India.
- Covering an expanse of around 325 square kilometres (125 square miles), it boasts a diverse landscape.
- The sanctuary serves as the origin of the Fen and Sankari rivers.
- Characterized by lush green forests, undulating hills, and the Maikal Range of the Satpura Hills, it presents a picturesque setting.
- Vegetation: Comprising a blend of dense forests and open grasslands, it offers a rich variety of flora.
- Flora Highlights: Notable plant species within the sanctuary include sal, saja, tinsa, kara, and haldu.
- Diverse Fauna: Bhoramdeo Wildlife Sanctuary is home to a wide range of wildlife, including tigers, leopards, wild dogs, sloth bears, sambar deer, barking deer, chital (spotted deer), gaur (Indian bison), as well as numerous bird and reptile species.
Third Rail Current Collector (PIB)
- 01 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
The Kolkata Metro of Indian Railways intends to substitute the steel third rail with a composite Aluminum third rail Current Collector.
Facts About:
- The third rail system serves as a method of supplying electrical power to trains via a conductor positioned beside the railway tracks.
- Kolkata Metro Railway has relied on steel Third Rails for the past four decades.
- It has now opted for composite Aluminium Third Rails in all forthcoming construction projects, as well as retrofitting existing corridors that currently employ steel Third Rails.
- By making this transition, Kolkata Metro Railway joins a select group of metro systems, including those in London, Moscow, Berlin, Munich, and Istanbul, that have also shifted from steel Third Rails to Aluminium Third Rails.
Advantages of Aluminum Composite Third Rail compared to Steel Third Rail include:
- Reduced resistive current loss leading to improved traction voltage levels.
- Lower maintenance and life cycle costs.
- Enhanced efficiency of train operations.
- Significant improvements in energy efficiency.
- Decreased carbon footprint.
JAIS Language Model (NewsOnAir)
- 01 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
Recently, a division of the Abu Dhabi-based AI company G42 has unveiled 'Jais,' the most cutting-edge Arabic large language model globally.
Facts About:
- Jais is a bilingual Arabic-English model meticulously trained on an extensive dataset of text and code.
- Its versatility makes it suitable for a wide range of tasks, including machine translation, text summarization, and question-answering.
- Trained on the world's largest AI supercomputer, the Condor Galaxy, Jais has been exposed to a vast dataset, encompassing 116 billion Arabic tokens and 279 billion English tokens.
- Being open-source means that Jais is accessible for anyone to use and contribute to its development, and it is available for download on the Hugging Face machine learning platform.
- The introduction of Jais represents a significant milestone in advancing AI within the Arabic-speaking community.
Applications:
- Jais finds potential applications in machine translation, bridging the language gap between Arabic and English, thereby enhancing information accessibility and cross-lingual communication.
- This versatile model excels at condensing extensive text content, from news articles to research papers, into concise and comprehensible summaries, facilitating improved accessibility and comprehension.
- Furthermore, Jais is adept at responding to text-based queries, making it a valuable tool for educational purposes, such as interactive chatbots for students, and enhancing customer service applications for effective client inquiries.
US – India Strategic Clean Energy Partnership (Indian Express)
- 31 Aug 2023
What is the News ?
Renewable Energy Technology Action Platform under the US – India Strategic Clean Energy Partnership.
Facts About:
In August 2023, the U.S.-India Renewable Energy Technology Action Platform (RETAP) was launched under the Strategic Clean Energy Partnership.
RETAP was established to take bilateral collaboration further with a result-oriented, time-bound technology focus.
It is intended to advance new and emerging renewable technologies with a view toward deployment and scaling.
RETAP’s initial focus is to be on green/clean hydrogen, wind energy, long long-duration energy storage, and to explore geothermal energy, ocean/tidal energy and other emerging technologies as mutually determined in the future.
The initial work plan is guided by the following five themes:
- Research & Development
- Piloting & Testing of Innovative Technologies
- Advanced Training & Skill Development
- Policy and Planning for Advancing RET and Enabling Technologies
- Investment, Incubation and Outreach programmes
Source: https://pib.gov.in/PressReleaseIframePage.aspx?PRID=1940523
Air Quality Life Index (AQLI) report (Economic Times)
- 31 Aug 2023
What is the News ?
Annual update of the Air Quality Life Index (AQLI) 2023 has been released.
Facts About:
India ranked second among the countries worst hit by air pollution with Bangladesh topping the list.
- Nepal ranked third followed by Pakistan and Mongolia.
PMI in South Asia: Particulate pollution has increased9.7 percent from 2013 to 2021 in South Asia.
- In India, PM2.5 levels rose 9.5 percent; in Pakistan 8.8 percent; and in Bangladesh, levels rose by 12.4 percent over this same time interval.
Life Expectancy: An average Indian citizen loses around 5.3 years of life expectancy due to air pollution.
- While an average citizen in Bangladesh loses 6.8 years of their life to air pollution
- An average Chinese citizen has seen an improvement — from 4.7 years of life expectancy being lost in 2013 to 2.5 now, an improvement of 2.2 years,
Pollution in India: Pollution in India has increased from 56.2 µg/m3 in 2020 to 58.7 µg/m3 in 2021.
- This is more than 10 times the WHO guideline of 5 µg/m3.
Health Risk: Pollution is biggest threat to human health in India in terms of lowering life expectancy, beating cardiovascular diseases and child and maternal malnutrition.
- While particulate pollution takes 5.3 years off the life of the average Indian, cardiovascular diseases reduce life expectancy by about 4.5 years, and child and maternal malnutrition reduces life expectancy by 1.8 years.
Poor AIr in Delhi: It is the most polluted city in the world.
- Delhi’s annual average PM2.5 level in 2021 was found to be 126.5 µg/m3, which is more than 25 times the World Health Organization (WHO) guideline of 5 µg/m3.
- Delhi residents are on track to lose 11.9 years of life expectancy on average relative to the WHO limit and 8.5 years relative to the national guideline if the current pollution levels persist.
About Air Quality Life Index (AQLI)
- AQLI measures the impact of particulate pollution on life expectancy.
- It is released by Energy Policy Institute at University of Chicago (EPIC).
Source: https://economictimes.indiatimes.com/news/india/your-life-is-getting-short-by-5-years-due-to-air-pollution-chicago-university-report-reavels-scary-numbers/articleshow/103198930.cms?from=mdr
State of Food Security and Nutrition in the World-2023 (FAO)
- 31 Aug 2023
What is the News ?
A recently published report, ‘State of Food Security and Nutrition in the World’ (SOFI) 2023, shows that the cost of a healthy diet has increased in India in recent years, but it is still lowest among the BRICS countries (including the newly added six countries) and India’s neighbours.
Facts About:
- The ‘State of Food Security and Nutrition in the World’ (SOFI) 2023 report prepared by FAO and United States agencies has been released with the theme of “Urbanisation, agrifood systems transformation, and healthy diets across the rural-urban continuum”.
- According to a UN agency report 74% of people in India can’t afford a healthy diet because of increasing costs.
‘State of Food Security and Nutrition in the World’ (SOFI) 2023 :-
The report is published by the partnership of Food and Agriculture Organisation(FAO) of the United Nations with the United States agencies i.e International Fund for Agricultural Development (IFAD), United Nations Children’s Fund (UNICEF), World Food Programme (WFP) and World Health Organisation (WHO).
The aim of the report is
- ending hunger
- achieving food security
- improving nutrition
- to provide an in-depth analysis for achieving this goal in the context of the SDG.
FAO:-Each year, FAO’s most deeply scrutinised report presents the leading numbers of undernourished people worldwide, while advocating for strategies against hunger and malnutrition.
SOFI 2023 related to India:-
PPP report:-
- The concept of PPP is 1ppp dollar in the United States should be able to buy the same amount of goods in either India or Brazil or in other countries.
- xPPP dollar per day means how much would it cost to buy a very simple healthy diet in every country.
- According to this data India compared to its other countries or other regional countries of the world itself has the lowest PPP dollar for a healthy diet.
According to another data which shows the share of the population that is unable to afford a healthy diet in 2021, for instance 74% of the Indian population cannot afford a healthy diet and the fourth highest share in the country itself .
So when it comes to afford a healthy diet, India comes fourth.
Because of stagnation, poor income levels, General stagnation, people of India are not able to afford the cheapest healthy diet in the world.
According to Above two report
- India doesn’t have to spend too much to get a healthy diet.
- 74% of our population cannot afford a healthy diet.
Conclusion:-
The share of people able to afford such a healthy diet is still low: India is at the bottom of that list because income levels are stagnant or going down.
- For example, while in mumbai the cost of meals have risen by 65% in last 5 years wages and salaries have only risen by 28% to 37% , so it shows that prices are rising but our incomes are not rising therefore though India have the cheapest food in the world there is most of people of india can’t afford it.It is not about the can’t afford food it’s a about a nutritional healthy diet divided by FAO and the UN.
Source: https://www.fao.org/documents/card/en?details=cc3017en
Meghalaya Shawl and Chhattisgarh’s Dhokra Art and Telangana Bidri Art vases (Times now)
- 31 Aug 2023
What is the News ?
Prime Minister presented Meghalaya Shawl and Chhattisgarh Dhokra Art and Telangana Bidri Art vases to Greek President and Prime Minister.
Facts About:
Meghalaya shawls
Meghalaya shawls were originally woven for Khasi and Jaintia royalty who considered them a symbol of their power and status.
Shawls were worn at formal events and festivals, and their intricate designs and vibrant colors reflected the wealth and prestige of the royal family.
The designs used in Meghalaya shawls were very symbolic.
- For example, the use of animal motifs such as tigers and elephants was a symbol of strength and power, while the use of floral motifs was a symbol of beauty and grace.
- The weavers, mostly women, spend hours weaving intricate designs and patterns using traditional weaving techniques.
- The shawls are made from local wool and natural colors.
- Shawls are highly valued for their fine workmanship and intricate designs.
Dhokra Art of Chhattisgarh
One of the earliest manifestations of this ancient art is the dancing girl object found in the excavations at Mohenjo-Daro and Harappa.
Traditionally, the Gadwads, Gonds and Dhurwas tribes of Chhattisgarh practice the art of Dhokra using the lost wax technique or hollow casting.
It is named after the Dhokar Damar, an Indian tribe in the central and eastern part of the country.
Common themes in Dhokra art revolve around Hindu gods and goddesses and various animal figures.
Dhokra Art is a non-ferrous metal casting art that uses wax casting technology.
This type of metal casting has been used in India for over 4000 years and is still used today.
There are two main processes involved in lost wax casting: solid casting and hollow casting.
Bidri Art vases
It originated from the city of Bidar in Karnataka in the 14th century.
Bidar in Karnataka and Hyderabad in Telangana are the most active centers of the art form.
Bidri Work handicraft is the art of inlaying metal alloys.
The soil of Bidar Fort magically gives black color to the base metals and the art form has been given the prestigious GI status.
Technique: For smelting, a new mold must be made, into which molten metal, an alloy of zinc and copper, is poured.
- Patterns are drawn on them and carved with a chisel and hammer.
- The engravings are attached with silver wire.
- This contrast of shiny silver with black metal is unique in Bidri art.
Source: https://www.timesnownews.com/india/meghalaya-shawl-to-telangana-vase-what-pm-modi-gifted-to-his-greek-counterpart-article-103065689
Hollongapar Gibbon Sanctuary (The Hindu)
- 30 Aug 2023
What is the News ?
Recently, scientists suggested rerouting the railway track running through the Hollongapar Gibbon Sanctuary.
Facts About:
The Hoollongapar Gibbon Sanctuary was renamed on 25 May 2004, formerly known as the Gibbon Wildlife Sanctuary or Hollongapar Reserve Forest.
It is an isolated protected area of evergreen forest located in the Jorhat district of Assam.
Vegetation: The upper canopy of the forest is dominated by the Hollong tree, while the Nahar dominates the middle canopy. The lower canopy consists of evergreen shrubs and herbs.
Fauna:
- The sanctuary has a rich biodiversity and is home to the only apes in India, the western Hoolock, as well as the only nocturnal primate found in the northeast Indian states, the Bengal slow loris.
- Also it is home to Stump-tailed macaque, northern pig-tailed macaque, eastern Assamese macaque, rhesus macaque, and capped langur etc
Key facts about Hoolock Gibbon
It is the only ape found in India.
It is native to eastern Bangladesh, Northeast India, Myanmar, and Southwest China.
Gibbons, the smallest and fastest of all apes, live in tropical and subtropical forests in the southeastern part of Asia.
The Hoolock gibbon, unique to India’s northeast, is one of 20 species of gibbons on Earth.
It is categorised into Western Hoolock Gibbon and Eastern Hoolock Gibbon.
Like all apes, they are extremely intelligent, with distinct personalities and strong family bonds.
Western Hoolock Gibbon
- It has a much wider range, as it is found in all the states of the northeast, restricted between the south of the Brahmaputra River and east of the Dibang River.
- It is listed as Endangered on the IUCN Red List.
Eastern Hoolock gibbon
- It inhabits specific pockets of Arunachal Pradesh and Assam in India, and southern China and northeast Myanmar.
- It is listed as Vulnerable in the IUCN Red list.
Source: https://www.thehindu.com/news/national/reroute-railway-track-running-through-assam-gibbon-sanctuary-suggest-scientists/article67247555.ece
Cauvery Water dispute (Indian Express)
- 30 Aug 2023
What is the News ?
Cauvery Water Authority fixes quantum to be released by Karnataka.
Facts About:
- The current outflow rate into the river is 4,398 cubic feet per second (cusecs), whereas the inflow stands at 2,300 cusecs as of Wednesday.
- The outflow rate was 2,292 cusecs on Tuesday at 8 p.m. but was increased after 11 p.m.
- The Kabini Reservoir in Mysuru district also contributes to the outflow, currently standing at 2,000 cusecs.
- Cumulatively, both reservoirs will release around 6,398 cusecs of water.
Cauvery Water Sharing Dispute: Historical Background
- 1892 Onset: The water dispute originates from 1892 between British-ruled Madras Presidency and the princely state of Mysore (now Karnataka).
- 1924 Agreement: A 50-year agreement mediated by the British aimed to ease tensions but set the stage for future conflicts.
- Post-Independence Battles: Karnataka’s dam constructions in the 1960s-80s triggered Tamil Nadu’s Supreme Court appeal, leading to the Cauvery Water Disputes Tribunal (CWDT).
- Interim Measures: The Cauvery River Authority (CRA) implemented interim orders in 1998. Contentious issues persisted despite CWDT’s 2013 award.
- Final Award: CWDT’s 2013 award allocated water quantities for Tamil Nadu (419 TMC), Karnataka (270 TMC), Kerala (30 TMC), and Puducherry (7 TMC).
Water Sharing Criteria
- Monthly Schedule: Karnataka, the upper riparian state, must provide Tamil Nadu a specified monthly water quantity.
- Annual Allocation: In a “normal” year, Karnataka provides 177.25 TMC to Tamil Nadu, with 123.14 TMC during the southwest monsoon.
- Challenges: Monsoon disagreements arise due to varying rainfall during this period.
Constitutional Provisions for Water Sharing
- Article 262: Empowers Parliament to address inter-State river disputes; IRWD Act, 1956 enacted under this article.
- Seventh Schedule: Defines legislative authority over water resources in Entry 17 (State List) and Entry 56 (Union List).
Resolving Cauvery Water Sharing
(A) Supreme Court’s 2018 Verdict:
- Cauvery as National Asset: The Supreme Court declared Cauvery a “national asset,” upholding inter-State river water equality.
- Allocation Adjustments: The Court noted deficiencies in CWDT’s assessment, resulting in marginal relief for Karnataka and reduced allocation for Tamil Nadu.
- Formation of CMB: The Court directed the establishment of the Cauvery Management Board (CMB) for effective implementation.
(B) Cauvery Water Management Scheme:
- CWMA Establishment: Formed to regulate water releases with CWRC’s assistance.
- Permanent and Technical Bodies: CWMA oversees regulation, while CWRC ensures data collection and award implementation.
Current Status and Future Implications:
- Ongoing Challenge: The Cauvery water dispute remains a historical and legal challenge.
- Resource Management: CWMA and CWRC aim to address the dispute through effective water management.
- Continued Struggle: The dispute underscores the complexity of water sharing in a federal system and the need for equitable solutions.
Tamil Nadu’s Contention
- CWMA’s Decision: CWMA sought 10,000 cusecs for 15 days from Karnataka, but Karnataka proposed 8,000 cusecs up to August 22.
- Previous Agreement: Karnataka’s refusal to adhere to the earlier agreement of 15,000 cusecs for 15 days at the CWRC meeting angered Tamil Nadu.
- Distress-sharing Formula: Tamil Nadu supports distress-sharing, but Karnataka hasn’t embraced it.
Karnataka’s Perspective
- Rainfall Deficit: Karnataka claims lower rainfall in Cauvery’s catchment areas, including Kerala, leading to reduced inflow.
- Challenging Situation: Karnataka cites reduced reservoir inflow as the reason for not releasing water this year.
- Lack of Consistency: Despite endorsing distress-sharing, Karnataka declined to accept the formula.
Future Scenario
- Tamil Nadu’s Concerns: Mettur reservoir’s critically low storage affects farmers and upcoming kuruvai crop.
- Water Shortage: Current water availability may last only 10 days, considering dead storage and drinking water needs.
- Awaiting Supreme Court: The case’s outcome depends on the Supreme Court’s interpretation and decision.
- Need for Resolution: The need for a mutually acceptable distress-sharing formula is evident.
Ongoing Challenges and Factors Prolonging the Dispute:
- Erratic Water Levels: Flood-drought cycles, pollution, and groundwater depletion cause unpredictable water levels.
- Idealistic Calculations: SC’s verdict relies on favorable conditions often misaligned with reality.
- Dependency and Population: Both states heavily rely on the river, causing conflicting urban and agricultural water needs.
- Inefficient Water Use: Inefficient irrigation methods lead to low crop productivity per unit of water used.
- Hydropolitics and Delays: Water disputes are used for political mobilization. Prolonged tribunal processes contribute to delays.
Source: https://indianexpress.com/article/cities/bangalore/cauvery-water-dispute-siddaramaiah-says-tn-causing-unnecessary-nuisance-8934747/
Kampala Declaration (Down to Earth)
- 30 Aug 2023
What is the News ?
A total of 48 African countries have now agreed to adopt the Kampala Ministerial Declarationon Migration, Environment and Climate Change (KDMECC) to address the nexus of human mobility and climate change in the continent.
Facts About:
Background: KDMECC was originally signed and agreed upon by 15 African states in Kampala, Uganda in July 2022.
The Declaration is the first comprehensive, action-oriented framework led by Member States to address climate-induced mobility in a practical and effective manner.
The KDMECC-AFRICA is expected to be signed by Member States during the Africa Climate Summit in Nairobi on September 4, 2023.
Need:
- Africa is one of the world's most vulnerable continents to the impacts of climate change.
- Climate change, which leads to an increased frequency and intensity of extreme weather events, has a direct impact on migration.
Significance:
- The Kampala Ministerial Declaration on Migration, Environment and Climate Change gives us the unprecedented opportunity to support Member State priorities in addressing the challenges while also leveraging migration for sustainable development.
- It will ensure that all voices, including those of youth, women and persons in vulnerable situations are the priority of the expanded declaration.
Linkage between Climate change and Human Rights:
- Climate change has indisputable long-term consequences on the environment, which, in turn, seriously undermine the enjoyment of human rights.
- The African continent is projected to be one of the hardest hit by the negative effects of climate change.
- The consequences of climate change are not only disproportionately felt by the most vulnerable and poorest populations; there are also disparities along gender lines.
- The connections between climate change, gender equality, and women’s rightsare complicated and multidimensional.
- In contrast, most existing studies on gender and climate change action offer a narrow conception of what gender equality and women’s rights mean in the context of climate change action.
Other similar declarations:
The Maputo Convention on the Conservation of Nature and Natural Resources: This Convention shall apply;
- To all areas which are within the limits of national jurisdiction of any Party; and
- To the activities carried out under the jurisdiction or control of any Partywithin the area of its national jurisdiction or beyond the limits of its national jurisdiction.
The Parties shall adopt and implement all measures necessary to achieve the objectives of this Convention, in particular through preventive measures and the application of the precautionary principle, and with due regard to ethical and traditional values as well as scientific knowledge in the interest of present and future generations.
Source: https://www.downtoearth.org.in/news/climate-change/kampala-declaration-on-climate-change-human-mobility-now-has-48-african-countries-as-members-91393
Sequencing the Y Chromosome (The Hindu)
- 30 Aug 2023
What is the News ?
Scientists have fully sequenced the Y chromosome for the first time, uncovering information that could have implications for the study of male infertility and other health problems.
Facts About:
- In the nucleus of a human cell, each DNA molecule is packaged into a long thread like structure called chromosome.
- Most human cells contains 23 pairs of chromosomes. One half of each pair of chromosomes from one parent, while other half comes from other parent.
- The 23rd pair are X and Y chromosomes, often called as sex chromosomes. The other 22 pairs called as autosomes.
- Females have a pair of X chromosomes, whereas males have X and Y chromosome.
- The Y chromosome is male-determining because it bears a gene called SRY, which directs the development of a ridge of cells into a testis in the embryo.
- The embryonic testes make male hormones, and these hormones direct the development of male features in a baby boy.
What is the difficulty in sequencing Y chromosome?
- Repetition - The Y chromosome was a particularly hard nut to crack because it is unusually repetitive.
- While all human chromosomes contain repeats, more than 30 million letters of the Y chromosome — out of 62.5 million — are repetitive sequences, sometimes called satellite DNA or junk DNA.
- Repetitive DNA complicates the assembling of data from genetic sequencing.
- Palindromes - The Y chromosome also contains palindromes — sequences of letters that are the same backward and forward, like radar.
- Degeneration of Proto- Y - The proto-Y is degenerating at a faster pace, losing about 10 active genes per million years, reducing the number from its original 1,000 to just 27.
- There has been great debate about whether this degradation continues, because at this rate the whole human Y would disappear in a few million years
How the scientists unravelled the complex Y chromosome?
- Sequencing - Advanced "long-read" sequencing technology and computational methods enabled researchers to achieve a complete reading of the Y chromosome.
- This accomplishment added over 30 million repetitive base pairs to the human reference genome.
- The new technology has allowed sequencing of bases along individual long DNA molecules, producing long-reads of thousands of bases.
- It effectively dealt with repetitive sequences and transformed raw sequencing data into a usable resource.
- These longer reads are easier to distinguish and can therefore be assembled more easily.
- Findings- Overall, the combined research determined that the Y chromosome has 106 protein-coding genes.
- 42 were found that were new, but many still appear to be repeats.
What is the importance of the study?
- Advanced diagnostics- The study empowers future sequencing endeavours to explore into health and disease aspects through comprehensive Y chromosome inclusion.
- To study whether loss of the Y chromosome is a biomarker of biological aging or has a direct effect on the health of men.
- Infertility- It will help to study conditions and disorders linked to the chromosome, such as lack of sperm production that leads to infertility.
- Health- Genes have been identified on the Y chromosomes that have been shown to be required for the prevention of cancer and cardiovascular disease.
- Dark matter- It represents the ‘dark matter’ of the genome. This analysis will allow us to better understand the regions of the Y chromosome that have regulatory functions and may encode mRNA and proteins.
- Human evolution- Assembling complete sequences of Y chromosomes across space and time not only helps to investigate sex chromosome evolution but also human evolution.
- Gene therapy- It will open up avenues to treat diseases that may linked to Y chromosomes.
- Future studies- The findings provide a solid base to explore how genes for sex and sperm work, how the Y chromosome evolved, and whether as predicted will disappear in a few million years.
Source: https://www.thehindu.com/sci-tech/science/y-male-chromosome-gene-sequencing-sry-gene-sequencing-evolution/article67230274.ece
Food Inflation & Challenges of Malnutrition (Down to Earth)
- 30 Aug 2023
What is the News ?
According to recent data, the cost of meals rose by 65% in five years, wages by just 37% in the last five years.
Facts About:
- In Mumbai, the cost of a vegetarian thali surged 65% in five years, while income for laborers and salaried workers in urban Maharashtra increased only 37% and 28%, respectively. This discrepancy is making essential food items unaffordable, leading to compromised meals.
What is Thalinomics?
- Thalinomics is a term coined by an Indian economist and former Chief Economic Adviser to the Government of India, Arvind Subramanian.
- It refers to a concept that involves analyzing changes in the cost of a vegetarian thali (a meal consisting of a variety of dishes served on a single plate) to gain insights into the trends and dynamics of food inflation and affordability.
- It involves tracking the prices of key ingredients that constitute a thali, such as cereals, pulses, vegetables, and other essential items.
- This concept is particularly relevant in countries like India, where food affordability and inflation are significant concerns for a large population.
Key insights: A case study of Mumbai and urban Maharashtra
- Rising Cost of Thali: The cost of preparing a home-cooked vegetarian thali in Mumbai has increased significantly by 65% over the past five years. This increase is attributed to rising prices of essential ingredients like rice, dal, vegetables, and other items that constitute a thali.
- Income Growth: Over the same five-year period, the average wage earned by casual laborers in urban Maharashtra increased by 37%, while the average salary of regular salaried workers increased by 28%. These income growth rates reflect the changes in earnings for these two categories of workers.
- Disparity Between Costs and Income: While the cost of a thali increased by 65%, income growth for casual laborers and salaried workers was significantly lower, at 37% and 28%, respectively.
- Affordability Challenge: The disparity between rising costs and income growth has resulted in essential food items becoming increasingly unaffordable for households. This affordability challenge can lead to reduced portion sizes or a compromise in the variety and nutritional quality of meals.
- Impact on Budget Share: The study also analyzes the portion of monthly wages or salaries required to afford two thalis every day for a month. This share increased from 22.5% of a casual laborer’s monthly earnings in 2018 to 27.2% in 2023. For salaried employees, it increased from 9.9% to 12.8% over the same period.
- Incomplete Data: Data limitations, particularly regarding the absence of certain ingredients like spices and ghee in the analysis, This suggests that the actual cost of making a thali could be even higher than the calculated figures.
Key aspects of the relationship between thali prices and inflation
- Inflation and Ingredient Prices: The prices of ingredients like rice, dal, vegetables, and oil can be affected by inflation. If the prices of these essential ingredients rise due to inflationary pressures, the overall cost of preparing a thali would increase.
- Food Inflation: The cost of a thali, which is composed of various food items, is directly influenced by food inflation. If there’s high food inflation, it can significantly impact the affordability of thalis and other meals.
- Supply and Demand Dynamics: Inflation can be driven by supply and demand imbalances. If there’s a shortage of certain ingredients due to supply disruptions (e.g., poor harvests or transportation issues), prices can rise. Similarly, changes in consumer demand patterns can affect the prices of specific ingredients, further impacting thali costs.
- Monetary Policy: Central banks often use monetary policy tools to control inflation. Interest rate adjustments, money supply regulation, and other measures can impact inflation rates. High inflation rates can lead to increased production costs for farmers and manufacturers, which may trickle down to the prices of thali ingredients.
- Income Effects: Inflation can impact consumers’ purchasing power. When inflation outpaces income growth, households might need to allocate a larger portion of their income to cover basic expenses like food. This can particularly affect lower-income households, leading to affordability challenges for items like thalis.
- Regional Variation: Inflation rates can vary regionally and even locally. Different regions might experience different rates of inflation due to factors like supply chain disruptions, local economic conditions, and government policies.
- Government Policies: Government policies such as subsidies, import/export regulations, and agricultural policies can influence ingredient prices and, consequently, the cost of preparing a thali. These policies can impact the supply and availability of key ingredients.
Implications of the higher cost of a thali
- Nutritional Impact: The rising cost of thali ingredients can lead to compromised nutritional intake as households might cut back on certain items to manage expenses. This can result in inadequate diets and potential health implications.
- Affordability Strain: As thali prices escalate, households may face financial strain by allocating a larger portion of their income to food expenses. This can limit their ability to save, invest, and engage in non-essential expenditures.
- Dietary Diversity: Increased thali costs can potentially lead to reduced dietary diversity as households might opt for cheaper, less nutritious alternatives, affecting overall dietary quality.
- Balanced Meals: Higher thali costs might lead to smaller portions or fewer items in the thali, disrupting the balance of a typical meal and potentially impacting satiety and nutritional completeness.
- Quality of Life: Reduced dietary quality due to affordability challenges can have broader implications for individuals’ quality of life, health, and overall well-being.
- Economic Struggles: For households with limited disposable income, the burden of increased thali costs can exacerbate economic struggles and hinder progress.
Way forward
- Policy Interventions: Implement policies to address the widening gap between thali costs and income growth, ensuring that essential food remains affordable.
- Income Enhancement: Focus on raising wages for casual laborers and salaried workers to match the rising cost of thalis.
- Affordability Measures: Establish measures to mitigate the impact of expensive thalis on households, considering subsidies or targeted assistance.
- Nutrition Awareness: Launch campaigns to educate households about maintaining nutritious diets even when faced with affordability challenges.
- Gender-Inclusive Approach: Address gender disparities by formulating policies that empower women economically.
- Data-Driven Approach: Base policies on accurate and up-to-date data on food prices, wages, and consumption patterns.
- Food Security Initiatives: Strengthen food security programs to ensure access to nutritious food despite thali cost increases.
- Policy Evaluation: Continuously assess the effectiveness of policies in addressing thali affordability and overall well-being.
Conclusion
- The shifting dynamics between escalating costs and relatively stagnant income pose a serious challenge to maintaining a nutritionally balanced diet. As prices continue to rise, a more comprehensive approach is crucial to ensuring that affordable nutrition remains within reach for all strata of society.
Source: https://www.downtoearth.org.in/blog/price-of-food-inflation-42483
Exercise BRIGHT STAR-23 (PIB)
- 29 Aug 2023
What is the News ?
Recently, an Indian Air Force (IAF) contingent departed to participate in Exercise BRIGHT STAR-23, scheduled to be held at Cairo (West) Air Base, Egypt, from 27 August to 16 September 2023.
Facts About:
- It is a biennial multilateral tri-service exercise.
- This multinational exercise was launched in 1980 as part of the US-brokered peace treaty between Egypt and Israel.
- This is the first time that IAF is participating in Ex BRIGHT STAR-23.
- Participating countries: United States of America, Saudi Arabia, Greece and Qatar.
- The Indian Air Force contingent will consist of five MiG-29, two IL-78, two C-130 and two C-17 aircraft.
- Personnel from the IAF's Garud Special Forces, as well as those from the Numbers 28, 77, 78 and 81 Squadrons, will be participating in the exercise.
- Objective: To practice planning and execution of joint operations. Besides leading to the formation of bonding across borders, such interactions also provide a means to further strategic relations between participating nations.
- India and Egypt have had an exceptional relationship and deep cooperation wherein the two jointly undertook the development of aero-engine and aircraft in the 1960s, and training of Egyptian pilots was done by Indian counterparts.
Source: https://pib.gov.in/PressReleaseIframePage.aspx?PRID=1955399
LK-99 (The Hindu)
- 29 Aug 2023
What is the News ?
Independent scientists have found that LK-99 is not a superconductor.
Facts About:
- LK-99 has been claimed by South Korean scientists as a superconductor at room temperature and atmospheric pressure. However, currently scientists have discarded their claims.
What are the reasons behind discarding LK-99 as a superconductor?
- First, when superconductors get cold, they push away magnets, causing repulsion below their transition temperature. The South Korean video showed LK-99 partly repelling a magnet. However, independent researchers found that the material was an insulator whose impurities could be magnetized.
- Second, the South Korean scientists saw less resistance in LK-99 around 104°C, which could mean it’s a superconductor. However, researchers found that this drop occurred due to the copper sulphide impurities present in the material.
- Hence, as per the scientists, no formal confirmation aligns with the initial declarationthat this material can conduct electricity without resistance in regular conditions.
What lies ahead?
- The LK-99 case raises concerns over misunderstandings caused in the open science competition. However, this misunderstanding shouldn’t stop open collaboration.
- Moreover, now, the burden lies on South Korean group to show evidence for their claim
Source: https://www.thehindu.com/sci-tech/science/lk-99-room-temperature-superconductor-hype/article67233834.ece
Moody’s Report on Demographic Dividend (Economic Times)
- 29 Aug 2023
What is the News ?
Alongwith the population growth, strong education and quality infrastructure are key to reap economic gains in India: Moody
Facts About:
Relation between population growth and economic growth:
Population Growth as a Driver of Economic Growth (Early Stages)
- A larger population means a larger labor force, which can lead to increased production, consumption, and innovation. This phenomenon is often referred to as the demographic dividend. When the ratio of working-age individuals to dependents (children and elderly) is high, it can create a favorable environment for economic expansion.
Labor Force and Human Capital:
- A growing population can provide a larger labor force, which, if properly educated and skilled, can contribute to higher productivity and economic growth. However, for population growth to positively impact economic growth, there must be adequate investments in education, healthcare, and skill development to ensure that the workforce is productive and capable of contributing to economic activities.
Consumption and Demand:
- A larger population can lead to increased consumption and demand for goods and services, which can stimulate economic growth. Businesses may expand to meet this increased demand, leading to higher levels of investment and production.
Urbanization and Productivity:
- Population growth often leads to urbanization, as people move from rural areas to cities in search of better opportunities. Urbanization can lead to increased productivity due to factors like economies of scale, improved infrastructure, and better access to markets and resources.
Resource Constraints and Negative Impacts:
- Rapid population growth without corresponding economic development and resource management can lead to resource constraints, environmental degradation, and increased competition for limited resources. This can have negative effects on economic growth in the long run.
Demographic Transition:
- As economies develop and standards of living improve, birth rates tend to decline. This results in a shift from high population growth rates to lower ones. During this demographic transition, countries can experience a period of accelerated economic growth due to a relatively smaller dependent population.
Aging Population:
- In more advanced economies, declining birth rates and increased life expectancy can lead to an aging population. While this may result in a decline in the working-age population, it can also create opportunities for innovation and growth in industries related to healthcare, elderly care, and technology.
Quality of Institutions and Policies:
- The relationship between population growth and economic growth is influenced by the quality of institutions and policies in place. Good governance, effective healthcare systems, education policies, and infrastructure development play a crucial role in determining how population growth impacts economic growth.
In summary, the relationship between population growth and economic growth is not deterministic, and its effects can vary widely based on numerous factors. While a growing population can potentially provide a demographic dividend and contribute to economic growth, this positive outcome depends on factors such as investments in human capital, infrastructure, and sound governance.
Additionally, as countries progress in their development, the relationship often becomes more nuanced, with demographic transitions and changingpopulation structures influencing economic dynamics.
Factors responsible for India’s population growth
- Falling mortality: The IMR has decreased from 40.7 in 2015-16 to 35.3 in 2019-21.
- Increasing Life expectancy at birth: It reached to 69.7 years in the 2015-19 period from 31 in 1947.
- Unintended pregnancies: 1 in every 7 unintended pregnancies of world occur in India.
- Lack of female education, child marriage and early marriages, etc.
Challenges caused by growing population
- Pressure on resources: As India has only 2.45% of the global surface area and 4% of the water resources.
- Pandemic outbreaks: Due to increasing urbanization and expansion of humans in wild habitats.
- Disruption and Conflicts: Due to rise in struggle for finite resource.
- Decline in social indicators: Due to suboptimal public expenditures on health and education may not be possible.
- Pressure on economy: Due to low skilled workforce, stagnant economy, unemployment, etc.
- Widening gender gap: If expenditure on health and education decline, women would suffer the most.
Way ahead to harness the benefits of population growth
- Supporting Reproductive Justice: Provisions of safe and effective methods of family planning and freedom to make the best reproductive choice.
- Education for all: Educational attainment, particularly of girls, enhances intergenerational formation of human capital and has a positive impact on demographic behaviour with respect to nuptiality, fertility, health, etc.
- Foster Inclusive Growth developing democratic institutions to facilitate equity in the society.
- Facilitate migration to bridge the demand and supply of the workforce.
- Investment in green technology and social innovations to adapt to and mitigate climate and environmental changes.
- Better geriatric care, health insurance and pension facilities for 65+ age category.
Source: https://economictimes.indiatimes.com/news/economy/indicators/india-must-focus-on-education-and-infra-for-growth-moodys-report/articleshow/103147127.cms?from=mdr
Care Protocol for Babies in India (The Hindu)
- 29 Aug 2023
What is the News ?
British nurse was sentenced to life in prison after being found guilty in the worst child serial killer case in the history of the U.K.
Facts About:
What are patient safety provisions in India?
National Patient safety Implementation Framework - It was launched for the period 2018-25 by the Ministry of Health and Family Welfare.
Patient safety - It is the fundamental element of public healthcare, defined as the freedom for a patient from unnecessary harm.
Hippocratic Oath - It is an oath of ethics historically taken by physician which is one of the most widely known of Greek medical texts.
Consumer Protection Act,1986 - It deals with medical negligence and deficiency of services
Clinical Establishment Act, 2010 - It sets out the legal rights of the patients.
Institutional Mechanism - To see the patients’ rights in terms of medication and devices are protected and that they are not overcharged.
- National Pharmaceutical Pricing Authority
- Drugs Controller General of India
Charter of patients’ rights - It is adopted by the National Human Rights Commission.
It act as a guidance document for the Union Government and State Governments to formulate concrete mechanisms for Patients’ Rights.
Charter of Patients’ Rights and Responsibilities - It is approved by National Council for Clinical Establishments.
Responsibilities of Patients’ -
- Provide all health related information.
- Cooperate with Doctors during examination and treatment.
- Pay hospitals agreed fees on time.
- Respect dignity of doctors and other hospital staff.
- Never resort to violence
How is neonatal safety maintained?
- Rules - There are no exclusive rules for neonatal care and safety, or protection against external harm in Indian hospitals.
- However, there are provisions and checks against issues like inadvertent mix-up of babies at birth and abduction.
- Training - The healthcare staff is also trained to counsel parents and provide emotional support, contributing to the safety and development of neonates.
- Adequate manpower - Trained healthcare is fostered by adequate staffing which can closely monitor each baby’s condition and respond swiftly to any concerns.
- Equipment - Neonates are typically kept in controlled environments to avoid exposure to external infections and temperature fluctuations.
What lies ahead?
- Regular training and continuing medical education for healthcare staff are essential to maintain high-quality neonatal care and uphold safety standards.
- The global organisation has also advised families that prompt medical care should be sought in case of danger signs.
- These include feeding problems, reduced activity, difficult breathing, fever, fits or convulsions, jaundice in the first 24 hours after birth.
- Families are also required to register the birth and bring the baby for timely vaccination, according to national schedules.
Source: https://www.thehindu.com/sci-tech/health/explained-what-is-the-care-protocol-for-babies-in-india/article67239285.ece
Seethakali folk art (Indian Express)
- 28 Aug 2023
What is the News ?
The 20-member group is going to perform Seethakali folk art, outside Kerala for the first time as to revive one of the fading dance forms of Kerala.
Facts About:
- In the early times, Seethakali was performed as part of the harvest festival Onam.
- From Atham star till the 28th day after Onam, the performers who belong to the subaltern communities go from one house to another performing this art.
Key Features of Seethakali:
- Folk Dance Drama: Seethakali is a traditional folk dance drama that was once performed during the festival days in erstwhile Desinganad (Kollam, Kerala), primarily during the Onam festivities.
- Dalit Artists: The performance was carried out by Dalit artists belonging to the Veda and Pulaya communities, focusing on presenting episodes from the Ramayana from Sita’s perspective.
- Vanayatra to Andardhanam: Seethakali portrays the journey from “vanayatra” (exile to the forest) to “andardhanam” (descend into the earth) of Sita, featuring a blend of songs, storytelling, and fast movements.
- Instruments: The dance drama is accompanied by instruments such as ganjira, manikatta, chiratta, and kaimani.
- Narrative through Songs: Seethakali’s story is conveyed through songs, with 28 collected over three years, featuring a folk style influenced by Vallappaattu, Kuthirappaattu, and Rakshasappattu.
- Oral Tradition: Seethakali songs were orally transmitted from one generation to the next, which led to a pause in the tradition.
- Basic Movements: The dance involves basic steps, striving to preserve the original essence of the art form.
- Character Ensemble: The performance includes key characters such as Sita, Ram, Lakshman, Ravan, and Hanuman.
Source: https://www.thehindu.com/news/national/kerala/artistes-breathe-a-new-life-into-seethakali-folk-art/article67234768.ece
Terai-Arc Landscape (TAL) (Times of India)
- 28 Aug 2023
What is the News ?
Recently, the poop of tigers has helped a team of scientists at the Wildlife Institute of India (WII) understand the prey selection patterns of the striped feline in the Indian part of the Terai-Arc Landscape.
Facts About:
- It is an 810km stretch between the river Yamuna in the west and the river Bhagmati in the east.
- It comprises the Shivalik hills, the adjoining bhabhar areas and the Terai flood plains.
- It is spread across the Indian states of Uttarakhand, Uttar Pradesh, Bihar, and the low-lying hills of Nepal.
- About 22% of the wild tiger population in India is found across the TAL, living amidst some of the highest human and livestock densities on the subcontinent.
- The landscape boasts of some of India’s most well-known Tiger Reserves and Protected Areas, such as Corbett Tiger Reserve, Rajaji National Park, Dudhwa Tiger Reserve, Valmiki Tiger Reserve and Nepal’s Bardia Wildlife Sanctuary, Chitwan National Park, Sukhla Phanta Wildlife Sanctuary.
- These forests are home to three flagship species: the Bengal tiger(Panthera tigris), the greater one-hornedrhino (Rhinoceros unicornis) and the Asian elephant (Elephas maximus).
Key Facts about the Wildlife Institute of India
- It is an autonomous Institution of the Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change, Government of India.
- It was established in 1982.
- It offers training programs, academic courses and advisory in wildlife research and management.
- The Institute is actively engaged in research across the breadth of the country on biodiversity-related issues.
Source: https://timesofindia.indiatimes.com/city/dehradun/10-tiger-corridors-across-india-need-attention-experts/articleshow/95518729.cms
The State of India’s Birds Report (The Hindu)
- 28 Aug 2023
What is the News ?
The State of India’s Birds Report has been released recently.
Facts About:
- The State of India’s Birds (SoIB) report based on data collected from approximately 30,000 birdwatchers has unveiled concerning trends regarding India’s bird population.
- The study highlights a substantial decline in numerous bird species, attributing this decline to a range of factors.
About SoIB Report
- The SoIB report aims to evaluate the conservation status of a wide range of species regularly present in India.
- It is published by a partnership involving 13 governmental and non-governmental organizations, including SACON, WII, and ZSI.
- The report extensively employs data from over 30 million observations on eBird by more than 30,000 birdwatchers.
- The report assesses distribution range size, abundance trends over the long term and since 2015, and information from the IUCN Red List to categorize Indian species into Low, Moderate, and High Conservation Priority tiers.
Key Highlights of the Report
- Widespread Decline: Among the species analyzed, 60% of those assessed for long-term trends show decline, while 40% exhibit a decline in current annual trends.
- Raptors and Vultures: Birds consuming vertebrates and carrion, including raptors and vultures, have significantly declined, possibly due to pollutants or prey availability reduction.
- Endemics and Biodiversity Hotspots: Endemic species in the Western Ghats and Sri Lanka biodiversity hotspot have experienced rapid declines over the past decades.
- Positive Outlook: Certain generalist species, exemplified by the Indian peafowl, demonstrate remarkable increases in abundance, with a 150% rise observed over the past decades.
- Conservation Priority: The report classifies species into High, Moderate, and Low Conservation Priority, with 178 species as High Priority, 323 as Moderate, and 441 as Low Priority. Noteworthy species include the Ruddy shelduck, Indian courser, Narcondam hornbill, and Nicobar megapode.
Identified Threats to Bird Species
- The report underscores threats encompassing forest degradation, urbanization, energy infrastructure.
- Birds are highly impacted by environmental pollutants like Nimesulide affecting vulture populations, climate change’s impacts on migratory species, avian diseases, and illegal hunting and trade.
Actions and Research Implications
- Targeted Conservation: The report advocates for the conservation of specific groups, such as grassland specialists that have suffered a more than 50% decline, highlighting the importance of protecting and preserving grassland ecosystems.
- Long-Term Monitoring: The significance of continuous, systematic bird population monitoring is emphasized to comprehend subtle fluctuations in bird numbers.
- In-Depth Research: Further research is needed to understand the causes behind both declines and increases in bird populations.
- Synergy among Policies: The report calls for the harmonization of policies related to river, water, and wasteland development, recognizing the multifaceted role of abundant, widespread bird species.
- Citizen Participation: Citizen Engagement plays a pivotal role in biodiversity conservation, warranting an essential role in the action plan for bird population and habitat preservation.
Source: https://www.thehindu.com/news/national/kerala/state-of-indias-birds-report-lists-20-species-of-highest-conservation-priority-for-kerala/article67241741.ece
RIGHT TO REPAIR (Indian Express)
- 28 Aug 2023
What is the News ?
In recent years, several states in the U.S. have enacted ‘right to repair’ laws.
Facts About:
- It refers to government measures that forbid manufacturers to impose barriers that deny consumers the ability to repair consumer products.
- The sectors identified for the right to repair include farming equipment, mobile phones/tablets, consumer durables, and automobiles/automobile equipment.
- Government has launched a unified portal, https://righttorepairindia.gov.in, to onboard leading brands and reliable third-party technicians to provide easy access to overhauling services.
- The portal has on boarded leading brands such as Apple, Samsung, Honda, Kent RO Systems, Havells, Hewlett Packard, and Hero MotoCorp.
- The portal seeks to streamline trade between original equipment manufacturers and third-party sellers.
- The right to repair has been recognized in many countries across the globe, including the USA, UK, and European Union.
Significance of Right to repair for India:
- Lowering costs for consumers: By providing access to third-party technicians, the right to repair can reduce costs for consumers who may not be able to afford expensive repairs or replacement devices.
- Reducing electronic waste: India is one of the largest generators of electronic waste in the world, and the right to repair can help reduce e-waste by extending the lifespan of electronic devices and appliances.
- Supporting small businesses: The right to repair can also support small businesses that provide repair services, by creating a level playing field with manufacturers who may have previously had a monopoly on repairs.
- Empowering consumers: By giving consumers the ability to repair their own devices or choose where to have them repaired, the right to repair empowers consumers to make informed choices and take control of their own devices.
- Promoting transparency and collaboration: The right to repair framework aims to build a consumer-centric ecosystem that promotes transparency and collaboration between manufacturers, sellers, and consumers.
Challenges associated with implementing right to repair in India
- Limited Access to Information: Many manufacturers do not provide adequate information to consumers about repair options or how to repair devices, which can make it difficult for consumers to exercise their right to repair.
- Lack of Awareness: Consumers lack awareness about their rights to repair and the benefits of repairing their devices leading to a lack of demand for repair services, limiting the growth of the repair industry.
- Opposition from manufacturers: Some manufacturers may oppose the right to repair, arguing that it could compromise their intellectual property rights or lead to safety concerns making it difficult to pass legislation or regulations to support the right to repair.
- Limited availability of spare parts: The availability of spare parts is often limited in India, particularly for older or less common models of devices makes it difficult for repair technicians to perform repairs or for consumers to find reliable repair services.
- Lack of regulatory mechanism: Currently, there is no comprehensive regulation in India that governs the right to repair which can lead to confusion among consumers and repair technicians about their rights and responsibilities, and may limit the growth of the repair industry.
Way Forward:
Many countries around the world have been attempting to pass effective ‘right to repair’ laws. But the movement has faced tremendous resistance from tech giants such as Apple and Microsoft over the years.
The New York legislation is a reminder that it is time to not only acknowledge the right to repair of consumers but also respond to the corresponding rights of the manufacturers. This warrants some expedited policy changes to recognise the ‘right to repair’, be it through amendments in the Consumer Protection Act, 2019 or through a separate law.
Source: https://indianexpress.com/article/explained/explained-what-is-the-right-to-repair-movement-7400287/
Scholarship Schemes for Religious Minorities (PIB)
- 28 Aug 2023
What is the News ?
There is a shift in Centre’s policy towards minority education in the past few years. It has discontinued two key educational schemes for religious minorities and gradually cut down on the expenditure incurred on the programmes of the Ministry of Minority Affairs.
Facts About:
Minority Educational Schemes: Overview
- Pre-Matric Scholarship Scheme: Initially covering classes 1 to 10, now limited to classes 9 and 10.
- Post-Matric Scholarship Scheme: Supports class 11 and above students, with increased funding this fiscal year.
- Merit-cum-Means based Scholarship Scheme: Aided professional and technical courses, underwent significant funding reduction.
- Maulana Azad National Fellowship (MANF): Provided financial assistance for research scholars but discontinued in 2022.
- Padho Pardesh: Discontinued interest subsidy scheme for higher education abroad.
- Begum Hazrat Mahal National Scholarship: Scholarship for meritorious girls discontinued.
Policy Shift and Consequences
- Change in Focus: Despite acknowledging the importance of education for religious minorities and inclusive growth, the government has discontinued two key educational schemes, narrowed the scope of another, and reduced expenditure on multiple programs by the Ministry of Minority Affairs.
- Beneficiary Drop: Between 2019 and 2022, the number of beneficiaries under six educational schemes for religious minorities decreased by 7%, while government spending on these programs declined by around 12.5%.
- Budget Cuts: The Ministry of Minority Affairs faced a budgetary reduction of 38.3% for the fiscal year 2023-24, from Rs 5,020.5 crore in 2022-23 to Rs 3,097 crore. Additionally, a significant portion of funds allocated in the previous year went unutilized.
Importance of Strengthening Educational Aid
- Diverse Religious Minorities: India encompasses over 30 crore people from religious minority communities, including Muslims (14.2%), Christians (2.3%), Sikhs (1.7%), Buddhists (0.7%), Jains (0.4%), and Zoroastrians.
- Challenges Faced by Muslims: Muslims, the largest religious minority, confront challenges in areas like economics, health, and education. Their participation in formal employment remains low, with many working in the informal sector under poor conditions.
- Sachar Committee Report: The Sachar Committee highlighted the deprivation and neglect faced by Muslims across various development dimensions, underscoring the need for affirmative action.
- Formation of Ministry of Minority Affairs: Responding to these challenges, the UPA government established this Ministry in 2006 to ensure focused attention on the issues affecting minority communities.
Challenges and Impact
- Reduction in beneficiaries and funding has impacted the implementation of schemes, resulting in a widening gap in education and economic parameters.
- Poor coverage of beneficiaries and unchanged low unit costs remain hurdles in scheme implementation.
- Muslim students’ enrolment in higher education is lagging behind other communities, worsening the existing disparities.
Way Forward
- Strengthen educational aid through enhancing scholarships, such as pre-matric, post-matric, merit-cum-means, and national overseas scholarships.
- Implement targeted schemes based on the 15-Point Programme to address development gaps in minority-concentrated localities.
- Make scholarships demand-driven and provide additional financial resources to improve unit costs.
- Increase the total budget allocation for the Ministry of Minority Affairs to address the deprivation in educational attainment for minorities.
Source: https://static.pib.gov.in/WriteReadData/specificdocs/documents/2022/mar/doc202231626301.pdf
G20 ministers agree to map global value chains, link MSMEs (Indian Express)
- 26 Aug 2023
What is the News ?
Trade and Investment Ministers of G20 nations agreed recently to map global value chains, integrate small businesses with them and ease trade documentation.
Facts About:
What are important parts of outcome document from Trade and Investment Ministers of G20 nations?
- Comprehensive framework within the G20 context for the purpose of mapping out global value chains is suggested.
The objective is to comprehend the existing issues and identify the necessary actions to enhance the inclusivity, sustainability, and resilience of these value chains.
- It focuses on MSMEs. The declaration from Jaipur emphasizes the imperative of reinforcing the capabilities of MSMEs.
Due to their small scale, MSMEs face limitations in accessing critical information, financial resources, and market-related data points.
A worldwide trade assistance platform, overseen by theInternational Trade Centre, will be consistently upgraded through consultation with UNCTAD and the World Trade Organisation (WTO).
This evolution aims to make the platform more inclusive and to offer comprehensive data to MSMEs.
- The principles associated with the digitization of trade documents is important part of outcome document. The aim is to minimize the reliance on paper documents and remove obstacles that hinder the seamless movement of goods and services.
Source: https://indianexpress.com/article/business/g20-trade-meet-ends-ministers-priority-areas-value-chains-msmes-8909647/
China-Bhutan boundary dispute and its impacts on India (The Hindu)
- 26 Aug 2023
What is the News ?
The 13th Expert Group Meeting (EGM) on the China-Bhutan boundary issues was held recently.
Facts About:
- A joint press release from Beijing and Thimphu said the 13th Expert Group Meeting (EGM) was held in Beijing
- It described as an “important outcome” the setting up of a Joint Technical Team on the Delimitation of the China-Bhutan Boundary, which held its first meeting along the sidelines of the EGM.
- The two sides had talks on
- continuously implementing the MOU on the Three-Step Road Map for Expediting the China-Bhutan Boundary Negotiations
- agreed to expedite and take simultaneous steps to implement the Three-Step Road Map
- agreed upon keeping the positive momentum of frequent Expert Group Meetings
- holding the 14th Expert Group Meeting on the China-Bhutan Boundary Issues as soon as possible
- maintaining communication on holding the 25th Round of China-Bhutan Boundary Talk
- It did not, however, announce a date for the already much delayed 25th round of boundary talks, which have not been held since 2016.
- In recent months, both sides have portrayed the long-running talks as picking up speed and nearing a possible solution, which would have ramifications for India.
- While there was a two-year gap between the 10th round of the EGM held in April 2021 and the 11th round of the EGM held in January 2023, the last two rounds have been held in relatively quick succession.
Impact on India
- Experts in India have said any deal between Beijing and Thimphu that accedes to a “swap arrangement” between areas to the North (Jamparlung and Pasamlung valleys) with Doklam to the West would be of concern to India, given the proximity to India’s narrow “Siliguri corridor” that connects northeastern States with the rest of India.
- India and China were involved in a stand-off in Doklam near the India-China-Bhutan trijunction in 2017.
- In March, the Bhutanese Prime Minister said in an interview that the process of “demarcating territories” and “drawing a line” could be completed “after one or two more meetings”.
Conclusion
The boundary talks between Bhutan and China began in 1984, and the 24th round was held in 2016.
The talks have largely focused on disputed areas to Bhutan’s north, and to its west, abutting the Doklam plateau.
However, these have been stalled since 2016, especially after the 2017 Doklam stand-off.
Source: https://www.thehindu.com/opinion/interview/post-covid-necessary-for-neighbours-to-work-together-bhutan-fm-on-china-bhutan-boundary-talks/article65646740.ece
7th Global Environment Facility (GEF) Assembly (Down to Earth)
- 26 Aug 2023
What is the News ?
As per the chief executive of the Global Environment Facility (GEF) in a plenary session, it will likely to work more closely with civil society organisations in the future.
Facts About:
About: Environmental leaders from 185 countries will gather in Vancouver, Canada for the Seventh Assembly of the Global Environment Facility from August 22-26, 2023.
Global Environment Facility (GEF): The GEF Assembly, which meets every 4 years, is the global body that coordinates financing for international efforts to address climate change, biodiversity loss, pollution, and factors inhibiting land and ocean health.
Points of discussion:
- Building on recent diplomatic breakthroughs on biodiversity loss, toxic chemicals, and the high seas, the GEF Assembly will be a critical stocktaking for 2030 goals to end pollution and nature loss, combat climate change, and propel inclusive, locally-led conservation.
- GEF would work directly with non-governmental organisations that work at the convention level.
- It is set to include the launch of the Global Biodiversity Framework Fund, a new source of funding for protecting species and ecosystems globally.
- The fund will open new avenues for private sector and philanthropic support to enable rapid implementation of the historic Global Biodiversity Framework agreed at COP15 in Montreal, December 2022, and of the high seas treaty adopted in New York City, in June 2023.
Need of such an initiative:
- Biodiversity funding needs differ between recipient countries, for example between countries with key areas for biodiversity (often large emerging countries such as Brazil and Indonesia) and the least developed countries (LDCs) or Small Island Developing States (SIDS), for which it is more difficult to access funds.
Global Biodiversity Framework:
- It contains goals to be achieved by 2050 focus on ecosystem and specieshealth including;
- To halt human-induced species extinction,
- The sustainable use of biodiversity,
- Equitable sharing of benefits, and
- On implementation and finance to include closing the biodiversity finance gap of $700 billion per year.
Source: https://update-mac.com/?tid=103&tag_id=1528a5df-4f9e-4046-9232-3361bc5f2c12&cnv_id=e891de8lpg6sc0b4c&placement=20427977&sub1=726006&clickcost=0
India-Iran drop Foreign Arbitration clause in Chabahar Port Issue (The Hindu)
- 26 Aug 2023
What is the News ?
India and Iran have agreed to pursue arbitration under rules framed by the UN Commission on International Trade Law (UNCITRAL) and will not go for commercial arbitration in foreign courts.
Facts About:
UN Commission on International Trade Law (UNCITRAL):
It is a subsidiary body of the UN General Assembly, established in 1966.
Mandate: To further the progressive harmonisation and unification of the law of international trade.
Membership:
- The Commission is composed of 60 member States elected by the General Assembly.
- The 60 member States include 14 African States, 14 Asian States, 8 Eastern European States, 10 Latin American and Caribbean States and 14 Western European and other States.
- The General Assembly elects members for terms of six years; every three years, the terms of half of the members expire.
- India is a founding member of this organisation.
Key facts about Chabahar Port
- It is a seaport in the Sistan-Balochistan province of Iran, on the Gulf of Oman, at the mouth of the Strait of Hormuz.
- It is a deep-water port with direct access to the Indian Ocean that is outside the Hormuz Strait.
- Its geographic proximity to countries such as Afghanistan, Pakistan, and India, as well as its status as a key transit centre on the burgeoning International North-South Transport Corridor.
Source: https://www.thehindu.com/news/national/india-and-iran-drop-foreign-court-arbitration-for-chabahar-port/article67234071.ece
Insurance Surety Bonds (PIB)
- 25 Aug 2023
What is the News ?
The National Highways Authority of India (NHAI)is advocating for the adoption of surety bond insurance products for highway projects
Facts About:
These bonds can be defined in their simplest form as a written agreement to guarantee compliance, payment, or performance of an act.
These are instruments where insurance companies act as ‘Surety’ and provide the financial guarantee that the contractor will fulfil its obligation as per the agreed terms.
Surety is a unique type of insurance because it involves a three-party agreement.
The three parties in a surety agreement are:
- Principal: The party that purchases the bond and undertakes an obligation to perform an act as promised.
- Surety: The insurance company or surety company that guarantees the obligation will be performed. If the principal fails to perform the act as promised, the surety is contractually liable for losses sustained.
- Obligee: The party who requires and often receives the benefit of the surety bond. For most surety bonds, the obligee is a local, state or federal government organisation.
What are the advantages?
- It will act as a security arrangement for infrastructure projects and will insulate the contractor as well as the principal.
- The product will cater to the requirements of a diversified group of contractors, many of whom are operating in today’s increasingly volatile environment.
- The product gives the principal a contract of guarantee that contractual terms and other business deals will be concluded in accordance with the mutually agreed terms.
- In case the contractor doesn’t fulfil the contractual terms, the Principal can raise a claim on the surety bond and recover the losses they have incurred.
- Unlike a bank guarantee, the Surety Bond Insurance does not require large collateral from the contractor, thus freeing up significant funds for the contractor, which they can utilise for the growth of the business.
- The product will also help in reducing the contractors’ debts to a large extent, thus addressing their financial worries.
Source: https://pib.gov.in/PressReleasePage.aspx?PRID=1951715
National Medical Commission (Indian Express)
- 25 Aug 2023
What is the News ?
The National Medical Commission (NMC) has put on hold the regulations that make it mandatory for doctors to prescribe generic drugs.
Facts About:
- In light of the criticism received by the Indian Medical Association (IMA) as well as the as the Indian Pharmaceutical Alliance (IPA), the National Medical Commission put on hold the Medical Practitioner (Professional Conduct) Regulations, 2023.
- Even the country’s apex drug regulator, the Central Drugs Standard Drug Control Organisation (CDSCO), questioned the language in the notification.
- The participating bodies suggested that the guidelines be kept in abeyance until the WHO’s good manufacturing practices are implemented.
- The participants said that prescribing only generic drugs will prompt pharmacies to sell generic drugs at high-profit margins, disincentivising firms that manufacture quality branded generics
National Medical Commission:
- The National Medical Commission is a statutory body established under the National Medical Commission Act, 2019.
- The NMC replaced the erstwhile Medical Council of India (MCI) which was established in 1934.
Objectives of NMC –
- Improve access to quality and affordable medical education;
- Ensure availability of adequate and high-quality medical professionals in all parts of the country;
- Promote equitable and universal healthcare that encourages community health perspective and makes services of medical professionals accessible to all the citizens;
- Encourages medical professionals to adopt latest medical research in their work and to contribute to research;
- Objectively assess medical institutions periodically in a transparent manner;
- Maintain a medical register for India;
- Enforce high ethical standards in all aspects of medical services;
- Have an effective grievance redressal mechanism.
Composition of NMC –
- NMC is a 25-member body, majority of them being nominated by the Central government.
- Tenure of NMC members is four years (except for part-time members whose tenure is two years).
- The NMC has 11 part-time members representing states or state medical councils.
- The NMC chairpersons and other members, nominated by the Central government, cannot be renominated.
- Any decision requires approval of the majority (minimum 13 out of 25) of the Commission.
Medical Practitioner (Professional Conduct) Regulations, 2023:
- On August 2nd, the National Medical Commission had published the Medical Practitioner (Professional Conduct) Regulations, 2023 aimed at reshaping prescription practices.
- It mandated that registered medical practitioners prescribe medications using “generic”, “non-proprietary”, or “pharmacological” names.
- The guidelines define a generic drug as a “drug product that is comparable to brand/reference listed product in dosage form, strength, route of administration, quality and performance characteristics, and intended use.”
- It says branded generic drug is one which has come off patent and is manufactured by drug companies and sold under different companies’ brand names.
- The guidelines say, “Every RMP (Registered Medical Practitioner) should prescribe drugs using generic names written legibly and prescribe drugs rationally, avoiding unnecessary medications and irrational fixed-dose combination tablets.”
- The guidelines have also talked about punitive measures against those violating the directive.
- Besides the instructions on generic drugs, the NMC guidelines included directives on issues ranging from continued medical education, usage of social media platforms and maintaining a dynamic register of doctors.
- It also barred doctors from attending events sponsored by pharmaceutical companies.
- However, the NMC guidelines have not gone down well with the Indian Medical Association (IMA).
Issued Raised by the Indian Medical Association (IMA):
- The IMA issued a statement in response to the regulations introduced by the NMC.
- The IMA says the biggest impediment to generic drugs is the uncertainty about its quality.
- IMA said that the quality control in the nation being very weak, there’s practically no guarantee of the quality of drugs and prescribing drugs without assured quality would be detrimental to patient health.
- The statement added that less than 0.1% of the drugs manufactured in India are tested for quality.
- The IMA said that step should be deferred till the Government can assure the quality of all the drugs released into the market.
- The statement says patient care and safety are not negotiable.
- The IMA says it has been demanding for long that only good quality drugs should be made available in the country and prices should be uniform and affordable.
- It urges the Government to have ‘one drug, one quality, one price’ system whereby all brands should either be sold at the same price or banned and only generics allowed while ensuring highest quality of these drugs.
Source: https://indianexpress.com/article/india/nmc-hold-regulations-mandating-doctors-prescribe-generic-drugs-bar-them-endorsing-drug-brand-8907964/
Gene-Edited Mustard (Indian Express)
- 25 Aug 2023
What is the News ?
Indian scientists have developed the first ever low-pungent mustard that is pest and disease-resistant. It is based on CRISPR/Cas9 gene editing.
Facts About:
- Among India’s domestically grown oilseeds, rapeseed-mustard stands out.
- However, its pungent oil and unpalatable meal have posed challenges for both consumers and livestock.
- Scientists have undertaken breeding efforts to create Canola-quality (white) mustard with reduced pungency and improved meal quality.
About Rapeseed-Mustard
- Rapeseed-Mustard: India’s significant oilseed is rapeseed-mustard, contributing significantly to vegetable oil production and meal availability.
- Pungency: Mustard seeds contain glucosinolates, compounds that give the oil and meal their pungent flavor and odor.
Quest for Canola-Quality Mustard
- Canola-Quality Pursuit: Scientists aimed to breed mustard lines with low glucosinolate content similar to Canola.
- Reducing Pungency: Efforts to create low-pungency oil and meal have faced challenges due to the necessity of glucosinolates in plant defense.
- Vulnerability to Pests and Diseases: Canola-quality mustard lines have not been cultivated extensively due to their susceptibility to pests and diseases.
Role of Gene Editing
- Innovative Research: Gene editing emerges as a solution to balance glucosinolate levels for improved quality and plant defence.
- CRISPR/Cas9 Approach: Researchers used CRISPR/Cas9 gene editing tool to target and modify 10 out of 12 GTR genes in Indian mustard.
- Achieving Desired Changes: Editing GTR genes led to lower glucosinolate content in seeds while preserving higher levels in leaves and pod walls.
Benefits of GE Mustard
- Easy Synthesis: Glucosinolates are synthesized in mustard leaves and pod walls before translocation to seeds.
- Dual Benefit of Glucosinolates: The study revealed that edited mustard lines with low-seed glucosinolates exhibited improved defence against pests and diseases.
Distinction between GE and GM
- GE Mustard: The new mustard lines are genome-edited (GE), not genetically modified (GM).
- Transgene-Free Solution: Unlike GM crops with foreign genes, GE lines have no foreign DNA and no residual gene-editing tools.
Regulatory Considerations and Future Prospects
- Regulation Changes: India’s regulatory environment is shifting, exempting GE plants free of exogenous introduced DNA from stringent approval requirements.
- Potential Field Trials: Scientists are preparing for open field trials of GE mustard, with expectations to conduct them in the upcoming planting season.
- Importance of Self-Reliance: With massive edible oil imports, domestic oilseed production through breeding advancements like GE mustard becomes vital for self-reliance.
Economic Implications and Self-Sufficiency
- Importance of Oilseeds: India’s substantial edible oil imports highlight the need for boosting domestic oilseed production.
- Mustard’s Role: Mustard’s high oil content and protein-rich meal position it as a significant oilseed crop.
- Potential Benefits: Both GE mustard and GM hybrid mustard have the potential to reduce dependence on imported vegetable oils.
Conclusion
- The journey of rapeseed mustard from its pungent state to a potentially improved, self-sufficient crop demonstrates the power of innovative breeding techniques.
- The breakthrough in gene editing opens doors to balancing quality and plant defence.
Source: https://indianexpress.com/article/explained/explained-economics/gene-edited-mustard-less-pungent-more-useful-8901549/
India and the Northern Sea Route (NSR) (The Hindu)
- 25 Aug 2023
What is the News ?
Murmansk, the beginning point of the Northern Sea Route (NSR), is witnessing the rising trend of Indian involvement in cargo traffic.
Facts About:
What is Northern Sea Route?
- It is the shortest shipping route for freight transportation between Europe and countries of the Asia-Pacific region, straddles four seas of the Arctic Ocean.
- Coverage- It runs around 5,600 km, the Route begins at the boundary between the Barents and the Kara seas (Kara Strait) and ends in the Bering Strait (Provideniya Bay).
- Save distance- Distance savings along the NSR can be as high as 50% compared to the currently used shipping lanes via Suez or Panama.
- The traditional Suez Canal route is 8000 km longer than Northern Sea passage.
- 2021 blockage- The 2021 blockage of the Suez Canal, which forms part of the widely-used maritime route involving Europe and Asia, has led to greater attention on the NSR.
- Navigability- Arctic Ocean remain icebound during most of the year, the icebreaking assistance is organised to ensure safe navigation along the NSR.
What are the advantages of Northern Sea Route?
- Profitable-It is a strategically important transport artery; it is economically profitable when comapared with Suez Canal.
- Save fuel- It will save fuel due to reduced distance.
- Cost effective- The shorter distance reduces the cost of staff labor and chartering vessels.
- The route does not charge payments for the passage unlike Suez Canal.
- Time saving-There are no queues (unlike, for example, the Suez Canal);
- Safety- There is no risk of a pirate attack.
Why Arctic region is so significant for India?
- Impact on India-The vulnerability of the Arctic region leads to unprecedented changes in the climate.
- This may have an impact on India in terms of economic security, water security and sustainabilit
- Svalbard Treaty- India’s engagement with the Arctic can be traced to the signing of the Svalbard Treaty in 1920.
- Conduct studies: Indian conducts studies regarding atmospheric, biological, marine, hydrological, glaciological events.
- Arctic Council- Arctic Council addresses the issues faced by governments in the region and the indigenous people of the Arctic.
- India is an observer state in Arctic Council including China.
- Himadri research station- India's first permanent Arctic research station located at Spitsbergen, Svalbard, Norway.
- It is located at the International Arctic Research base, Ny-Alesund.
- Infrastructural base-
- Multi-sensor moored observatory was inaugurated in 2014
- Northernmost atmospheric lab was launched in 2016
- Successful expeditions- India conducted around 13 successful expeditions to Arctic till 2022.
- Arctic Policy of 2022- It mentions that the country’s approach to economic development of the region is guided by UN Sustainable Development Goals.
- Potential for minerals- The region constitutes the largest unexplored prospective area for hydrocarbons remaining on the earth.
- There may be significant reserves of coal, zinc, and silver.
- Institutional support- In 2018 India renamed National Centre for Antarctic and Ocean Research to National Centre for Polar and Ocean Research.
- It shows India’s refocusing priorities in Arctic region.
What are the driving factors for India to participate in the NSR development?
- Growth in cargo traffic- India engagement in NSR is on the constant rise and during 2018-2022, the growth rate was around 73%.
- Last year, the volume of cargo traffic was 34.117 million tonnes.
- India-Russia trade- India increasingly imports crude oil and coal from Russia in recent years.
- The record supplies of energy resources for the Indian economy are possible due to such a reliable and safe transport artery as the NSR.
- Transit route- NSR assumes importance, given India’s geographical position and the major share of its trade associated with sea transportation.
- East meets East- In 2019 India and Russia signed Chennai-Vladivostok Maritime Corridor (CVMC) project.
- It is signed as one linking with another organise international container transit through the NSR.
- Reduce travel time-The 10,500 km-long CVMC, passing through the Sea of Japan, the South China Sea and Malacca Strait, will bring down transport time to 12 days.
- This is almost a third of what is taken under the existing St. Petersburg-Mumbai route of 16,000 km.
- Chennai Port Trust study- Fuel and fertilisers are some of the cargo that can be imported from Russia to India through CVMC.
What lies ahead?
- NSR development plan- It is approved until 2035 by Russia, this sets the cargo traffic target as 80 million tonnes and 150 million tonnes for 2024 and 2030.
- The plan approval took place amid economic sanctions imposed by the West against Russia following the latter’s war with Ukraine.
- Chennai-Vladivostok Maritime Corridor project-Workshop featuring stakeholders from the two countries, is expected to be held in the second half of October.
Source: https://www.thehindu.com/news/international/explained-india-and-the-northern-sea-route/article67230900.ece
ASTRA air-to-air Missile (PIB)
- 24 Aug 2023
What is the News ?
The Light Combat Aircraft(LCA) Tejas successfully test-fired an ASTRA beyond visual range (BVR) air-to-air missile off the coast of Goa.
Facts About:
- The ASTRA BVR missile is designed to engage and destroy highly maneuvering supersonic aerial targets. It has a range of over 100 kilometers.
BVR missiles are capable of engaging beyond the range of 20 nautical miles or 37 kilometres.
- This missile has all weather day and night capability. The system is being developed to meet specific requirements.
- It is jointly designed and developed by the Defence Research and Development Laboratory (DRDL), Research Centre Imarat (RCI) and other laboratories of DRDO.
- ASTRA missile would significantly enhance the combat prowess of Tejas and reduce the dependency on imported weapons.
Tejas is a single-engine multi-role fighter aircraft capable of operating in high-threat air environments. It has been designed to undertake the air defence, maritime reconnaissance and strike roles.
- The ASTRA Mk-I Weapon System integrated with SU-30 Mk-I aircraft is being inducted into the Indian Air Force (IAF).
Fujiwhara Effect (Indian Express)
- 24 Aug 2023
What is the News ?
Recently, powerful winds tormented the Bay Area and other parts of Central and Southern California, uprooting trees and disrupting the power supply due to Fujiwhara effect.
Facts About:
- It was identified by a Japanese meteorologist Sakuhei Fujiwhara.
- It was observed for the first time over the western Pacific Ocean, when typhoons Marie and Kathy merged in 1964.
What is it?
- When two hurricanes (or cyclones, depending on where you live), spinning in the same direction, are brought close together, they begin ‘an intense dance around their common center’ – this interaction between two cyclones is called the Fujiwhara effect.
When it Occur?
- If one hurricane’s intensity overpowers the other, then the smaller one will orbit it and eventually crash into its vortex to be absorbed.
- On the other hand, if two storms of similar strengths pass by each other, they may gravitate towards each other until they reach a common center and merge, or merely spin each other around for a while before shooting off on their own paths.
- In rare instances, the two ‘dancing’ cyclones, if they are intense enough, may merge with one another, leading to the formation of a mega cyclone capable of wreaking havoc along coastlines.
Experts have noted the rising frequency of this unusual effect, attributing it to a rapidly warming world and the subsequent heating of ocean waters.
Source: https://www.google.com/url?sa=t&rct=j&q=&esrc=s&source=web&cd=&ved=2ahUKEwia1b_gj6OBAxXpSmwGHVb_DTQQFnoECBUQAQ&url=https%3A%2F%2Findianexpress.com%2Farticle%2Fexplained%2Fexplained-climate%2Ffujiwhara-effect-cyclones-dance-8905398%2F&usg=AOvVaw0_moE3dRI3IZbhz8XqmBkl&opi=89978449
CHANDRAYAAN 3 MAKES SOFT LANDING (The Hindu)
- 24 Aug 2023
What is the News ?
Launched on 14 July 2023, Chandrayaan-3 etched its place in history when the lander and rover touched down near the lunar south pole region on 23 August 2023 at 18:02 IST.
Facts About:
- Chandrayaan-3, part of the Indian Space Research Organisation's (ISRO) Chandrayaan program, signifies a remarkable feat in lunar exploration.
- Comprising a lander named Vikram and a rover named Pragyan, akin to the Chandrayaan-2 mission, this mission focuses on achieving a controlled landing and rover mobility on the lunar surface.
- With the propulsion module transporting the lander-rover configuration to lunar orbit, a powered descent by the lander was the critical phase of the operation.
- The mission encompasses a Lander and Rover configuration, propelled by LVM3 from SDSC SHAR, Sriharikota. The propulsion module carries the Lander and Rover until the lunar orbit's 100 km mark.
Origins and Progression: Chandrayaan-2's Influence
- Chandrayaan-2's launch in July 2019, which featured an orbiter, lander, and rover, set the stage for Chandrayaan-3.
- While the initial lander's trajectory went awry during a landing attempt in September 2019, ISRO's spirit remained unbroken, leading to the conception of Chandrayaan-3 and other future lunar missions.
Global Collaboration: ESA's Involvement
- The European Space Tracking network (ESTRACK), operated by the European Space Agency (ESA), provided support for the mission.
- A mutual support agreement emerged, where ESA's tracking assistance for ISRO missions, including Gaganyaan (India's human spaceflight program) and the Aditya-L1 solar research mission, was reciprocated by ISRO's support for future ESA missions.
- This collaboration underlines the global nature of space exploration.
Mission Aims
- ISRO laid out three primary objectives for Chandrayaan-3:
- Achieve a safe and soft lunar landing.
- Demonstrate the rover's mobility capabilities.
- Conduct experiments on lunar surface materials to enhance understanding of lunar composition.
Spacecraft Configuration
Propulsion Module
- Carries the lander-rover to a 100 km lunar orbit.
- Features a solar panel and mounting structure for the lander.
Lander (Vikram)
- Executes the soft landing on the Moon.
- It had four landing legs and four landing thrusters capable of producing 800 newtons of thrust each
- Accommodates the rover and scientific instruments.
Rover (Pragyan)
- A six-wheeled, 26 kg vehicle.
- Conducts diverse measurements, contributing to lunar research.
- Investigates lunar surface composition, presence of water ice, lunar impact history, and atmosphere evolution.
Payloads
Lander Payloads
Chandra’s Surface Thermophysical Experiment (ChaSTE)
- Objective: Measure thermal conductivity and temperature of the lunar surface.
- Information gleaned aids in comprehending lunar surface properties near polar regions.
Instrument for Lunar Seismic Activity (ILSA)
- Objective: Measure seismic activity around the landing site, revealing the lunar crust and mantle's structure.
Langmuir Probe (LP)
- Objective: Estimate plasma density variations in the vicinity of the landing site.
- Langmuir probe plays a crucial role in studying ionosphere and atmospheric phenomena.
Laser Retroreflector Array (LRA)
- Objective: Passive experiment for lunar laser ranging studies.
- LRA aids in comprehending the dynamics of the Moon system.
Additional Payload: Collaboration with NASA
- Passive Laser Retroreflector Array from NASA contributes to lunar laser ranging studies.
Rover Payloads
Alpha Particle X-ray Spectrometer (APXS)
- Objective: Determine elemental composition (e.g., Mg, Al, Si, K, Ca, Ti, Fe) of lunar soil and rocks around the landing site.
- APXS provides insights into the chemical makeup of lunar materials.
Laser Induced Breakdown Spectroscope (LIBS)
- Objective: Conduct qualitative and quantitative elemental analysis.
- LIBS aids in deciphering chemical and mineralogical composition for a deeper understanding of the lunar surface.
Propulsion Module Payload
Spectro-polarimetry of Habitable Planet Earth (SHAPE)
- Objective: To make future discoveries of smaller planets through reflected light, potentially identifying habitable exoplanets.
- SHAPE payload enhances India's contribution to the study of exoplanets.
Mission Progress
The mission progressed through several stages, including launch, Earth and lunar orbit maneuvers, and descent. Notable milestones include:
- Launch on 14 July 2023.
- Lunar orbit insertion on 5 August 2023.
- Lander separation from the propulsion module on 17 August 2023.
- Successful soft landing on 23 August 2023, making India the fourth nation to land on the Moon.
Technological Innovations
- Advanced Altimeters: Laser and RF-based altimeters for precise altitude measurements.
- Velocimeters: Laser Doppler Velocimeter and Lander Horizontal Velocity Camera for speed monitoring.
- Inertial Measurement: Laser Gyro-based Inertial referencing and Accelerometer package for navigation.
- Navigation, Guidance & Control (NGC): Software elements for powered descent trajectory design.
- Hazard Detection and Avoidance: Lander Hazard Detection & Avoidance Camera and Processing Algorithm.
- Landing Leg Mechanism: Enhanced landing leg design for secure touchdown.
Mission Life
- Propulsion Module: Carried lander and rover to lunar orbit, with operation of experimental payload for up to 6 months.
- Lander Module: 1 Lunar Day (14 Earth Days).
- Rover Module: 1 Lunar Day (14 Earth Days).
Key Team Members and Funding:
- ISRO Chairperson: Somanath.
- Mission Director: Mohanakumar.
- Associate Mission Director: Narayanan.
- Project Director: Veeramuthuvel.
- Deputy Project Director: K.
- Vehicle Director: Biju C. Thomas.
- Estimated cost: Around ?615 crore.
Source: https://www.thehindu.com/sci-tech/science/isro-chandrayaan-3-vikram-lander-touch-down-live-updates/article67219323.ece
National Curriculum Framework for school Education 2023 (PIB)
- 24 Aug 2023
What is the News ?
Recently, the final National Curriculum Framework (NCF) has been released by the National Council of Educational Research and Training (NCERT).
Facts About:
- Framed by: The NCF was drafted by the National steering committee headed by former Chairman of the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO), K. Kasturirangan.
- Key points:
- For languages:
- From now, Students in Classes 9 and 10 will need to learn three languages, of which at least two will be native to India.
- Classes 11 and 12, students will learn two languages, including one of Indian origin.
- Board Exams: The NCF states that all students will be allowed to take Board exams on at least two occasions during any given school year, with only the best score being retained.
- New Text books: It follows the lead of the National Education Policy (NEP) 2020, and gives assent for formulating new textbooks from Grades 3 to 12 under the Central Board of Secondary Education (CBSE).
- Number of Subjects: For students from Classes 9 to 12 has to study five mandatory subjects, with an option of adding one more subject.
- Now, the number of mandatory subjects for Classes 9 and 10 is seven and six for Classes 11 and 12.
- Optional subjects have been grouped in three parts in the NCF.
- The first optional group includes art education, physical education and vocational education.
- The second group includes Social Science, the Humanities, and interdisciplinary areas.
- The third group includes Science, Mathematics, and computational thinking.
- Shift to semester-based term: The NCF has recommended that in the long term, all Boards should change to semester or term-based systems.
- Now, there is no hard separation between academic and vocational subjects, or between Science, Social Science, Art, and Physical Education.
- For languages:
NCF from NEP 2020:
The NCF brings the aims and commitments of the NEP:
- This includes the full range of human capacities, values and dispositions that are aimed to be developed in school education.
- Pedagogy, practices, and culture must work in tandem to develop these, and move away from an overemphasis on memorization and content accumulation; in fact, content reduction is required to create space for such development.
- The 5+3+3+4 Curricular and Pedagogical structure of school education is reflected in the learning standards, the content, the pedagogy, and the assessment approaches.
- It is integrative and holistic with equal status to all subjects and learning domains from Math to Sports.
- It integrates vocational education in all schools, and there is integration across subjects while developing rigorous subject understanding and capacities.
National Council of Educational Research and Training (NCERT):
- The National Council of Educational Research and Training (NCERT) is an autonomous organisation set up in 1961 by the Government of India to assist and advise the Central and State Governments on policies and programmes for qualitative improvement in school education.
- The major objectives of NCERT and its constituent units are to:
- Undertake, promote and coordinate research in areas related to school education
- Prepare and publish model textbooks, supplementary material, newsletters, and journals and develops educational kits, multimedia digital materials, etc.
- organize pre-service and in-service training of teachers
- develop and disseminate innovative educational techniques and practices
- Collaborate and network with state educational departments, universities, NGOs and other educational institutions
Source: https://pib.gov.in/PressReleaseIframePage.aspx?PRID=1951485
Prime Minister’s Development Initiative for North East Region (PM-DevINE) (PIB)
- 23 Aug 2023
What is the News ?
The revised guidelines were issued for the Prime Minister’s Development Initiative for the North East Region (PM-DevINE).
Facts About:
- PM-DevINE, was announced in the Union Budget 2022-23 to address development gaps in the North Eastern Region (NER).It was approved by the Cabinet for the remaining four years of the 15th Finance Commission from 2022-23 to 2025-26.
- The new Scheme is a Central Sector Scheme and will be implemented by the Ministry of Development of North Eastern Region (DoNER).
- The PM-DevINE Scheme will have an outlay of Rs.6,600 crore for the four year period from 2022-23 to 2025-26.
- An Empowered Inter-Ministerial Committee (EIMC) will be established, tasked with various functions under the scheme.
Objectives of PM-DevINE
- Fund infrastructure convergently, in the spirit of PM Gati Shakti;
- Support social development projects based on felt needs of the NER;
- Enable livelihood activities for youth and women;
- Fill the development gaps in various sectors.
Functions of Empowered Inter-Ministerial Committee (EIMC)
- It assesses initial project proposals based on quality, viability, and socio-economic impact, working alongside representatives from relevant Indian Government Ministries/Departments and State Governments.It then recommends project selection from among these proposals.
- The EIMC proposes effective monitoring and evaluation methods, which may involve on-site inspections through third-party agencies.
- The committee also devises mechanisms for the operation and maintenance of PM-DevINEprojects, aiming to ensure their sustainability.
Source: https://pib.gov.in/PressReleasePage.aspx?PRID=194206
Debt-Fossil Fuel Trap (Indian Express)
- 23 Aug 2023
What is the News ?
Recently, a new report ‘The Debt-Fossil Fuel Trap’, was published by the anti-debt campaigners Debt Justice and partners.
Facts About:
Key Takeaways from ‘The Debt-Fossil Fuel Trap’ report:
- Debt-Reliant Economies and Fossil Fuel Dependence:Poor countries burdened with heavy debts are compelled to rely on fossil fuel revenue to repay loans borrowed from wealthier nations, multilateral creditors like the World Bank and IMF, or private lenders.
For Example: Argentina has been supporting fracking projects in the Vaca Muerta oil and gas field in Northern Patagonia to generate revenues to ease the country’s debt crisis. Notably, the IMF has also backed these projects.
- Surging External Debt Payments in Global South:The external debt payments of Global South countries have surged by 150% between 2011 and 2023, reaching the highest levels in 25 years.
- Debt Crisis and Constrained Public Spending:Around 54 countries are facing a debt crisis, resulting in reduced public spending during the pandemic to meet loan repayment obligations.
- Climate Challenges Amplify Borrowing in Global South:Many of these indebted countries lack adequate resources for climate adaptation, mitigation, and addressing loss and damage, forcing them to borrow more money.
- Natural Disasters Escalate Debt-to-GDP Ratio:After events like natural disasters, countries can see their debt as a percentage of GDP rise significantly, such as Dominica’s experience after Hurricane Maria in 2017.
- Unfulfilled Pledges: Despite promises to discontinue investing in fossil fuels in Global South countries, richer nations and lenders continue to finance fossil fuel projects through loans, perpetuating fossil fuel production.
- Resource Backed Loans (RBLs):Resource backed loans (RBLs) are a mechanism through which repayment is tied to natural resources or future income streams derived from those resources.
Recommendations for a Sustainable Path Forward:
- Implementing ambitious debt cancellation for countries in need without economic conditions
- Rejecting repayments from fossil fuel projects.
- Aligning bilateral and multilateral finance with a 1.5-degree warming scenario while avoiding fossil fuel financing.
Source: https://indianexpress.com/article/explained/explained-global/rich-countries-force-poor-nations-rely-fossil-fuels-8904371/
20th ASEAN India Economic Ministers’ Meeting (PIB)
- 23 Aug 2023
What is the News ?
India participated in the 20th ASEAN-India Economic Ministers’ Meeting.
Facts About:
- The 20th ASEAN-India Economic Ministers’ meeting was held in Semarang, Indonesia.
- The Economic Ministers or their representatives from all the 10 ASEAN countries viz. Brunei, Cambodia, Indonesia, Laos, Malaysia, Myanmar, Philippines, Singapore, Thailand and Vietnam participated in the meeting.
- The Democratic Republic of Timor-Leste also joined the Meeting as an observer.
- The Ministers reviewed the bilateral trade and investment relations between India and ASEAN and underscored their commitment to strengthen and enhance the economic partnership between India and ASEAN to ensure that the ASEAN-India Comprehensive Strategic Partnership delivers meaningful benefits for both sides, particularly in the post-pandemic era.
- The Ministers also interacted with the ASEAN-India Business Council (AIBC).
- The main agenda of this year’s meeting was the timely review of the ASEAN-India Trade in Goods Agreement (AITIGA) which was signed in 2009.
- India and ASEAN registered a bilateral trade of USD 131.5 billion in 2022-23. The trade with ASEAN accounted for 11.3% of India’s global trade in 2022-23.
ASEAN-India Trade in Goods Agreement (AITIGA):
- AITIGA is a trade deal between the ten member states of ASEAN and India.
- ASEAN and India signed the Agreement at the 7th ASEAN Economic Ministers-India Consultations in Bangkok, Thailand in 2009. The Agreement, which came into effect in 2010, is sometimes referred to as the ASEAN-India Free Trade Agreement.
- The Agreement has led to steadily increasing trade between ASEAN and India since its signing.
- The Agreement originated out of the Framework Agreement on Comprehensive Economic Cooperation between India and ASEAN created in 2003.
- It covers trade in physical goods and products and not services trade.
ASEAN and India signed a separate ASEAN-India Trade in Services Agreement in 2014.
Along with the ASEAN-India Investment Agreement, the three agreements collectively form the ASEAN-India Free Trade Area.
- Under the Agreement, ASEAN and India have committed to progressively eliminating duties on 76.4 percent of goods and to liberalize tariffs on over 90 percent of goods.
Source: https://pib.gov.in/PressReleaseIframePage.aspx?PRID=1950902#:~:text=Shri%20Rajesh%20Agrawal%2C%20Additional%20Secretary,%2C%20Minister%20of%20Trade%2C%20Indonesia.
Strong case to restore Section 8(4) of the RP Act (The Hindu)
- 23 Aug 2023
What is the News ?
The recent disqualification of Rahul Gandhi, based on his conviction and imprisonment in a defamation case, has brought attention to the legal complexities and implications associated with the disqualification of sitting legislators in India. The focus is on the Supreme Court's decision to strike down Section 8(4) of the Representation of People Act 1951.
Facts About:
Disqualification and Legal Framework:
- Instant Disqualification and Lily Thomas Case: The disqualification of Rahul Gandhi based on his conviction in a defamation case raised questions about the legal basis of instant disqualification for sitting legislators. The Supreme Court's judgment in Lily Thomas vs Union of India (2013) invalidated Section 8(4) of the Representation of People Act 1951, removing the three-month appeal window before disqualification took effect.
- Section 8(3) and Disqualification: With the removal of Section 8(4), only Section 8(3) remains, which stipulates that a person convicted and sentenced to imprisonment for at least two years shall be disqualified from the date of conviction. The wording does not explicitly indicate an immediate disqualification upon the court's pronouncement of guilt.
- Disqualification Authority and Presidential Role: The authority to declare a sitting legislator disqualified might lie with the President of India under Article 103. While the Supreme Court rejected this proposition in Lily Thomas, the Consumer Education & Research ... vs Union Of India & Ors (2009) held that the President's declaration is necessary for disqualification.
Legal Implications and Challenges:
- Staying of Sentence and Conviction: The question arises whether the stay of only sentence or the stay of conviction itself is required to lift the disqualification. Different High Courts have held differing views on this issue, adding complexity to the interpretation of disqualification.
- Quantum of Sentence and Disqualification: Disqualification hinges on the imprisonment term being two years or more. The recent case of Rahul Gandhi emphasized this connection, highlighting that the disqualification's trigger is the sentence length, not just the conviction itself.
- Career Impact and Urgent Attention: Instant disqualification can significantly affect legislators' careers, especially given the slow pace of appeals and legal proceedings. There's a need to address this issue urgently to ensure the stability of legislators' careers and prevent abrupt disqualifications.
Source: https://www.thehindu.com/opinion/lead/a-strong-case-to-restore-section-84-of-the-rp-act/article67224103.ece
New Scheme Guidelines for North Eastern Region (PIB)
- 22 Aug 2023
What is the News ?
The Ministry of Development of North Eastern Region (MDoNER) releases new Scheme Guidelines for implementing Cabinet-approved Schemes during 15th Finance Commission's balance period (2022-2026).
Facts About:
- The Cabinet approved Continuation of the North East Special Infrastructure Development Scheme (NESIDS) with an outlay of Rs.8139.50 crore for the period from 2022-23 to 2025-26.
- The scheme is a central sector scheme.It has two components viz. NESIDS-Road and NESIDS-Other Than Road Infrastructure (OTRI).
- The objective of the NESIDS is to support infrastructure development in identified sectors including connectivity in the North Eastern States.
- The Union Cabinet had also approved continuation of the ‘Schemes of North Eastern Council (NEC)’ for the period from 2022-23 to 2025-26 with a total outlay of Rs.3202.7 crore.
- The MDoNER Schemes help provide gap-filling support to the eight North Eastern States as per their felt needs, by taking up projects – e.g., for developing infrastructure to mitigate connectivity and social sector deficits and enhancing livelihood and employment opportunities in the region.
Source: https://pib.gov.in/PressReleasePage.aspx?PRID=195088
ICMR study on post COVID mortality (Indian Express)
- 22 Aug 2023
What is the News ?
Recently, an Indian Council of Medical Research (ICMR) study reported that 17.1% of those hospitalized since September 2020 experience post-Covid conditions.
Facts About:
What were the main findings of the ICMR study?
- The study, encompassing 14,419 Covid-19 patients hospitalized since September 2020, revealed a 6.5% mortality rate within a year after hospitalization. Around 17.1% experienced post-Covid-19 conditions. It also highlighted the increased mortality risk associated with comorbidities, age, and gender.
How did the study define “post-Covid-19 conditions”?
- The study defined “post-Covid-19 conditions” as the persistence or new onset of fatigue, breathlessness, or cognitive abnormalities, due to the lack of established definitions from organizations like the World Health Organization or the CDC during patient enrollment.
What impact did a single vaccine dose have on mortality?
- The study indicated that a single vaccine dose prior to Covid-19 infection reduced one-year mortality by 60%, emphasizing the importance of vaccination even before exposure.
Who faced a higher risk of mortality according to the study?
- The study revealed that individuals with comorbid conditions were at the highest risk of mortality, being more than 9 times likely to die within a year. Men were 1.3 times more likely to die, while those above 60 years were 2.6 times more likely.
What risk did children face in terms of mortality?
- Children between 0 and 18 years had a 5.6-fold higher risk of death in the year following infection, with a 1.7-fold increase in the immediate four weeks post-hospitalization. Severe comorbidities among admitted children were hypothesized as a reason for the higher odds of death.
Can mild Covid-19 variants lead to long Covid?
- The long Covid might occur even in individuals with mild Covid-19. While symptoms improve with therapy, over-diagnosis of long Covid may be occurring, warranting consideration of alternative causes for reported symptoms.
Source: https://www.thehindu.com/business/Industry/explained-the-debate-over-indias-smartphone-manufacturing-dreams/article67220769.ece
PLI Scheme for Smartphone Manufacturing Industry & Its Effectiveness (The Hindu)
- 22 Aug 2023
What is the News ?
Over the last few months, former RBI governor Raghuram Rajan and the Minister of State for Electronics Rajeev Chandrasekhar have sparred over how well a Central government scheme to boost electronics manufacturing has been faring.
Facts About:
- Former RBI governor Raghuram Rajan, along with two other economists, had released a brief discussion paper arguing that the Production-Linked Incentive (PLI) programme isn’t really pushing India towards becoming a self-sufficient manufacturing powerhouse.
- They argued that the government is using taxpayer money to create an ecosystem of low-level assembly jobs that will still depend heavily on imports.
What is the Production-Linked Incentive (PLI) Programme?
- Around five years ago, the Government of India decided it wanted more companies to make things in India.
- Manufacturing is a key ingredient to economic growth and also comes with what economists call a multiplier effect — every job created and every rupee invested in manufacturing has a positive cascading effect on other sectors in the economy.
- To boost manufacturing in India, the Government introduced the production-linked incentive (PLI) scheme.
- Under PLI, the government gives money to foreign or domestic companies that manufacture goods here.
- The annual pay-out is based on a percentage of revenue generated for up to five years.
PLI Programme for Smartphone Manufacturing Industry:
- The industry that has shown the most enthusiasm for the scheme is smartphone manufacturing.
- Companies like Micromax, Samsung, and Foxconn (which makes phones for Apple) can get up to 6% of their incremental sales income through the PLI programme.
- With the scheme, mobile phone exports jumped from $300 million in FY2018 to an astounding $11 billion in FY23.
- Imports – while India imported mobile phones worth $3.6 billion in FY2018, it dropped to $1.6 billion in FY23.
- Central government Ministers, including Mr. Chandrasekhar, have regularly cited this data as proof of the PLI’s scheme’s success.
Former RBI Governor Raghuram Rajan’s Argument:
- In his paper, the former Central bank governor argued that while imports of fully put-together mobile phones have come down, the imports of mobile phone components — including display screens, cameras, batteries, printed circuit boards — shot up between FY21 and FY23.
- Incidentally, these are the same two years when mobile phone exports jumped the most.
- He said that manufacturers aren’t really making mobile phones in India in the traditional sense which would involve their supply chain also moving to India and making most of the components here as well.
- All that the companies are doing is importing all of the necessary parts and assembling them in India to create a ‘Made in India’ product.
- Another criticism is that low-level assembly work doesn’t produce well-paying jobs and doesn’t nearly have anywhere the same multiplier effect that actual manufacturing might provide.
Union Government’s Response:
- Minister of State for Electronics Rajeev Chandrasekhar’s argument is two-fold.
- First, he said, Mr. Rajan wrongly assumed that all imports of screens, batteries, etc. are used to make mobile phones.
- It is possible these items are used also for computer monitors, DSLR cameras, electric vehicles etc.
- He also argued that not all mobile phone production in India is supported by the PLI scheme, only around 22% so far.
- The Minister’s overarching point is that the import dependency isn’t as bad as Mr. Rajan says it is.
Conclusion:
- Former RBI Governor argued that even if only 60% of imports are used for production, India’s net exports will still be negative.
- That is, even if only 60% of screens, batteries, etc. are used to make mobile phones, the final import tally would still beat the final export tally.
- The main divide is over whether the PLI programme will be able to create long-lasting jobs and firmly establish India as a manufacturing and supply hub that adds value to the production process.
- The Union Government believes that it will take time for the PLI Scheme’s results to show.
Source: https://www.thehindu.com/business/Industry/explained-the-debate-over-indias-smartphone-manufacturing-dreams/article67220769.ece
Marine Heat Waves (Indian Express)
- 22 Aug 2023
What is the News ?
Extreme Heat waves are harming marine life in the Mediterranean Sea.
Facts About:
Why are high sea temperatures a problem?
- Lesser dissolution of gases: Gases like oxygen and carbon dioxide dissolve better at colder temperatures, so that means the warmer the water; the less oxygen is available to breathe.
- Higher rate of respiration in marine organism: Higher temperatures also cause an increase in metabolism, which in turn means animals have to breathe even more than usual.
- The rise in temperature accelerates metabolism, and the organisms need more food to maintain this metabolic rate.
- More Algal blooms: They are more common in hotter waters. Such blooms can further deplete oxygen levels and produce toxins harmful for fish, marine mammals and birds.
What species and ecosystems are worst hit by marine heat waves?
- High water temperatures are most harmful for animals living at the bottom of oceans, lakes or rivers.
- These benthic species include corals, mussels, sponges, starfish and plants like sea grasses, and are often attached to rock or solid ground.
- Scientists observed mass deaths of benthic species along thousands of kilometers of Mediterranean coastline between 2015 and 2019.
What does extreme heat in the Mediterranean mean for people?
- Affecting fishing activities in the area: Fishermen are catching fewer familiar species and instead are finding more invasive fish which they have difficulty selling.
- Increase in invasive fishes: Some are even poisonous, like the puffer fish migration is seen in the region.
- Habitat loss: It could also lead to an overall decline in fish populations, while disappearing seagrass.
What is the phenomenon behind heat trap in oceans?
- Ocean Heat Content (OHC): It is the amount of energy absorbed by and stored in the oceans. It is measured in joules.
- When sunlight reaches the earth, oceans absorb this energy and store it as heat.
- While the heat is first absorbed at the surface of the water body, some of it is eventually disbursed throughout.
- Water has a higher heat capacity than air, which means that it can store much larger amounts of heat.
- GHG emissions - These gases trap heat in a blanket around the earth, not allowing it to escape, thus raising the temperature of the earth’s surface and leading to global warming.
Why Mediterranean Sea is significant for global temperatures?
The Mediterranean Sea has significant implications for global temperatures due to its role as a "climate amplifier." This phenomenon is referred to as the "Mediterranean Effect" or "Mediterranean Climate Amplification." Here are the reasons:
- Heat Absorption and Release: The Mediterranean Sea has a lower heat capacity compared to the vast oceans, such as the Atlantic or Pacific.
- As a result, it heats up and cools down more quickly. During the summer months, the Mediterranean Sea absorbs heat from the sun, leading to warming of the surrounding land areas.
- In winter, it releases the stored heat, moderating temperatures in nearby regions.
- Warm and Dry Summers: The Mediterranean region experiences warm and dry summers, which are conducive to high evaporation rates from the sea's surface.
- This process results in the release of latent heat into the atmosphere, contributing to the warming of the air.
- Atmospheric Circulation: The temperature contrast between the relatively warm Mediterranean Sea and the cooler landmasses during summer leads to the development of low-pressure systems over land.
- This creates a pressure gradient that drives winds from the sea to the land, bringing warm, moist air with it. This warm air can further increase temperatures over land areas.
- Feedback Loops: The warming effect of the Mediterranean Sea can lead to feedback loops. Warmer land areas result in higher evaporation rates, which in turn contribute to the amplification of temperature rise.
- This cycle of heat absorption, release, and evaporation intensifies the Mediterranean Climate Amplification.
Source: https://indianexpress.com/article/explained/explained-climate/extreme-heatwaves-mediterranean-sea-8901948/
Vegetated Canopies (Indian Express)
- 22 Aug 2023
What is the News ?
In a recent development in Spain, tensioned sail-like vegetated awnings or canopies known as “Greenshades” have been strategically installed on the facades of buildings.
Facts About:
- Vegetated canopies are innovative structures designed to reintroduce greenery into urban landscapes.
- Inspired by the natural canopies found in forests and diverse plant ecosystems, these canopies play a crucial role in mitigating the urban heat island effect and enhancing the overall environmental quality of urban areas.
- This installation approach not only adds an aesthetic dimension to the urban architecture but also serves as a practical solution for reintroducing green elements in areas where traditional planting is challenging.
Emulating Nature’s Canopies:
- Mimicking the canopy formations observed in forest ecosystems, these vegetated awnings recreate a semblance of natural green cover.
- By doing so, they provide shade, reduce direct sunlight exposure, and create a more pleasant atmosphere in commercial streets and public spaces.
- This is particularly valuable in areas where the presence of trees and vegetation is limited.
Hydroponic Growth System:
- The vegetation integrated within these awnings grows using a hydroponic growth system.
- This method utilises a water supply point to provide the plants with the necessary moisture and nutrients. Additionally, a water outlet is incorporated into the design to facilitate efficient drainage.
- This innovative approach ensures that the greenery thrives even in non-traditional planting environments.
BENEFITS OF VEGETATED CANOPIES
Cooling Effects via Evapotranspiration
- Singular Green’s innovative canopy design efficiently reduces temperatures in both immediate areas and beneath the awnings.
- Achieved through evapotranspiration, where plants transfer water to the atmosphere, this cooling process enhances comfort.
Air Quality Improvement through Plant Selection
- Carefully chosen plants possess a special ability to absorb gases, including pollutants like carbon monoxide and nitrogen oxide.
- This contributes to better urban air quality and healthier living conditions.
Noise Reduction with Sound Wave Absorption
- Vegetated canopies excel at absorbing sound waves, minimising noise pollution and creating a more serene urban environment.
- Incorporating sound-absorbing substrates enhances the auditory experience.
Oxygen Generation and Gas Filtration
- Surprisingly, a single square metre of these canopies produces a year’s worth of oxygen for an individual.
- Moreover, they serve as natural filters, removing harmful gases from the air and thus improving overall air quality.
Efficient Water and Lighting Integration
- Beyond their green benefits, these canopies facilitate centralised water and lighting installations.
- Integrated lights equipped with motion sensors respond to real-time needs, promoting energy-efficient urban infrastructure.
Promoting Biodiversity and Ecosystem Health
- Introducing these canopies into urban spaces fosters biodiversity by creating habitats for diverse wildlife.
- This initiative aligns with the vision of sustainable, nature-friendly cities, nurturing a harmonious urban ecosystem.
In the face of climate change-induced challenges, our response must be proactive, multifaceted, and holistic. The success of vegetated canopies as a means to combat extreme heat waves demonstrates that nature-inspired solutions have the power to transform urban environments into havens of sustainability, resilience, and well-being. By embracing such strategies and embarking on a collective journey, we can build cities that thrive in harmony with the planet.
Source: https://indianexpress.com/article/explained/explained-climate/vegetated-canopies-green-spaces-urban-spain-8893918/
Concerns about Drilling in the North Sea (The Hindu)
- 22 Aug 2023
What is the News ?
The Prime Minister of the U.K. recently backed plans for new fossil fuel drilling off Britain’s coast.
Facts About:
Evolution of North Sea Drilling
- Origins and Legislation: The North Sea drilling history dates back to the 1958 Geneva Convention on the Continental Shelf, which set the stage for exploration in the region.
- Continental Shelf Act: The U.K. Parliament’s enactment of the Continental Shelf Act in 1964 established the country’s jurisdiction over oil and gas resources beneath its seabed.
Milestones and Concerns in Drilling
- Early Exploration and Challenges: British Petroleum (BP) was granted the first exploration license in 1964, leading to natural gas discovery the following year.
- Forties Field Discovery: BP’s breakthrough commercial oil discovery in the Forties Field in 1970 marked a significant milestone.
- Expanding Operations and Safety Revamp: The following years witnessed increased exploration activities and installation of oil platforms. The Piper Alpha disaster in 1988 prompted crucial safety reforms.
Rationale and Concerns
- Government’s Position: In an official statement, the government justified the move as a strategy to enhance Britain’s energy independence.
- Environmental Alarm: However, environmental experts express apprehension, especially given the global push towards averting irreversible climate change.
North Sea Transition Authority and Offshore Licensing
- NTSA’s Role: The North Sea Transition Authority (NTSA) is responsible for regulating the oil, gas, and carbon storage sectors.
- Offshore Licensing Round: The NTSA is currently conducting the 33rd offshore oil and gas licensing round, aiming to award more than 100 licenses.
- Timing and Awards: The first licenses are expected to be granted in the autumn, furthering the expansion of drilling operations.
Shaping Geopolitical Energy Dependence
- Energy Security Concerns: The Prime Minister emphasized the necessity of domestic oil and gas sources, even as the country aims to reach net-zero emissions by 2050.
- Strategic Implications: The decision is portrayed as an effort to reduce reliance on oil and gas imports, which could originate from potentially unfavourable sources.
Ecological Concerns and Climate Impact
- Adverse Environmental Effects: Offshore drilling poses risks to workers, marine ecosystems, and climate health. It contributes to ocean warming, rising sea levels, and threatens marine biodiversity.
- Carbon Pollution Impact: Carbon pollution settling into oceans contributes to acidification, endangering coral reefs and shellfish.
Evaluating UK’s Climate Commitments
- Climate Change Committee Report: The Climate Change Committee (CCC) pointed out deficiencies in the U.K.’s preparations for climate change under the National Adaptation Programme.
- Adaptation Implementation: The CCC’s assessment highlighted a lack of substantial implementation of adaptation measures to address climate risks.
- Inconsistent with Paris Agreement: The Climate Action Tracker assesses the U.K.’s climate action as not fully aligned with the Paris Agreement.
- Long-Term Targets: The U.K.’s Nationally Determined Contributions (NDCs) and long-term targets do not reflect a fair share of global efforts to mitigate climate change.
- Incompatibility with Limits: Licensing new oil and gas extraction plans contradicts the 1.5°C temperature rise limit set by the Paris Agreement.
Conclusion
- The UK’s endorsement of offshore drilling reflects a complex balancing act between energy security, economic considerations, and environmental stewardship.
- As the world grapples with the imperative of combating climate change, the decisions made today hold the potential to shape the course of a sustainable future.
Evolution of North Sea Drilling
- Origins and Legislation: The North Sea drilling history dates back to the 1958 Geneva Convention on the Continental Shelf, which set the stage for exploration in the region.
- Continental Shelf Act: The U.K. Parliament’s enactment of the Continental Shelf Act in 1964 established the country’s jurisdiction over oil and gas resources beneath its seabed.
Milestones and Concerns in Drilling
- Early Exploration and Challenges: British Petroleum (BP) was granted the first exploration license in 1964, leading to natural gas discovery the following year.
- Forties Field Discovery: BP’s breakthrough commercial oil discovery in the Forties Field in 1970 marked a significant milestone.
- Expanding Operations and Safety Revamp: The following years witnessed increased exploration activities and installation of oil platforms. The Piper Alpha disaster in 1988 prompted crucial safety reforms.
Rationale and Concerns
- Government’s Position: In an official statement, the government justified the move as a strategy to enhance Britain’s energy independence.
- Environmental Alarm: However, environmental experts express apprehension, especially given the global push towards averting irreversible climate change.
North Sea Transition Authority and Offshore Licensing
- NTSA’s Role: The North Sea Transition Authority (NTSA) is responsible for regulating the oil, gas, and carbon storage sectors.
- Offshore Licensing Round: The NTSA is currently conducting the 33rd offshore oil and gas licensing round, aiming to award more than 100 licenses.
- Timing and Awards: The first licenses are expected to be granted in the autumn, furthering the expansion of drilling operations.
Shaping Geopolitical Energy Dependence
- Energy Security Concerns: The Prime Minister emphasized the necessity of domestic oil and gas sources, even as the country aims to reach net-zero emissions by 2050.
- Strategic Implications: The decision is portrayed as an effort to reduce reliance on oil and gas imports, which could originate from potentially unfavourable sources.
Ecological Concerns and Climate Impact
- Adverse Environmental Effects: Offshore drilling poses risks to workers, marine ecosystems, and climate health. It contributes to ocean warming, rising sea levels, and threatens marine biodiversity.
- Carbon Pollution Impact: Carbon pollution settling into oceans contributes to acidification, endangering coral reefs and shellfish.
Evaluating UK’s Climate Commitments
- Climate Change Committee Report: The Climate Change Committee (CCC) pointed out deficiencies in the U.K.’s preparations for climate change under the National Adaptation Programme.
- Adaptation Implementation: The CCC’s assessment highlighted a lack of substantial implementation of adaptation measures to address climate risks.
- Inconsistent with Paris Agreement: The Climate Action Tracker assesses the U.K.’s climate action as not fully aligned with the Paris Agreement.
- Long-Term Targets: The U.K.’s Nationally Determined Contributions (NDCs) and long-term targets do not reflect a fair share of global efforts to mitigate climate change.
- Incompatibility with Limits: Licensing new oil and gas extraction plans contradicts the 1.5°C temperature rise limit set by the Paris Agreement.
Conclusion
- The UK’s endorsement of offshore drilling reflects a complex balancing act between energy security, economic considerations, and environmental stewardship.
- As the world grapples with the imperative of combating climate change, the decisions made today hold the potential to shape the course of a sustainable future.
Source: https://www.thehindu.com/news/international/explained-drilling-in-the-north-sea-history-and-environmental-concerns/article67204792.ece
Turmeric Supplements (The Hindu)
- 21 Aug 2023
What is the News ?
Australia’s Therapeutic Goods Administration (TGA) issued a medical advisory warning Australians of the risk of liver injury from using medicines and herbal supplements containing turmeric or its active ingredient, curcumin.
Facts About:
Health benefits of turmeric:
- The risk of liver injury did not appear to relate to curcuma longa consumed in typical dietary amounts as a food.
- As a staple ingredient in South and South East Asian cuisine, turmeric is also used in Ayurvedic and Chinese-medicine concoctions.
- Several studies report it to have anti-oxidant properties that can help with inflammation.
- These include arthritis and infections.
- A research have reported that curcumin used along with the drug Artemisininwas effective in treating malaria when tested on mice.
- There have also been studies investigating the drug as an adjuvant in chemotherapy based on results in mice and animal studies.
- However, their effect in human trials have been inconclusive.
Adverse effects of turmeric:
- The French Agency for Food reported various adverse effects, including reports of hepatitis, potentially related to the consumption of food supplements containing turmeric or curcumin.
- The ANSES report underlines that turmeric has “choleretic” properties, which means it stimulates the secretion of bile to improve digestion, and therefore, it is advisable that those with bile duct disease should avoidturmeric.
- Curcumin could also interact with medications such as anticoagulants, cancer drugs and immunosuppressants, reducing their safety and effectiveness.
Why is curcumin being used in supplements?
- One of the challenges of turmeric and by extension curcumin is that very little of it is absorbed, or made ‘bioavailable’, by the body.
- To improve its bioavailability, a popular approach is to use piperine, the major active component of black pepper, which improves bioavailability by 2000.
- However, whether increasing the bioavailability of curcumin and packaging them in supplements makes them effective and safe for use in medicines is still being debated with no conclusive evidence emerging from trials.
Safe limit on consumption of turmeric:
- The European Food Safety Authority has set an acceptable daily intake of 180 mg of curcumin per day for a 60 kg adult as the safe level of consumption.
- A World Health Organization/Food and Agricultural Organisationadvisoryrecommends 3 mg/kg of body weight.
- India’s Food Safety and Standards Authority of India has standards that packaged turmeric must comply with but nothing on the recommended dietary allowance.
- Statistically, on an average about 200 to 500mgs is consumed on a daily basis in Indian households.
Source: https://www.thehindu.com/sci-tech/health/explained-are-turmeric-supplements-advisable/article67214093.ece
Expansion of BRICS (Indian Express)
- 21 Aug 2023
What is the News ?
Recently there have been internal conflicts about the nature and scope of the potential expansion of BRICS.
Facts About:
- BRICS is an acronym for five regional economies: Brazil, Russia, India, China and South Africa.
- The first four were initially grouped as “BRIC” in 2001 by an economist Jim O’Neill, who coined the term to describe fast-growing economies that would collectively dominate the global economy by 2050.
- Summits: The governments of the BRICS states have met annually at formal summits since 2009.
- India hosted the 13th BRICS summit in 2021 virtually.
- China hosted the 14th BRICS summit in 2022.
- South Africa will host the 15th summit 2023.
- BRICS is an important grouping bringing together the major emerging economies from the world, comprising:
- 41% of the world population,
- 24% of the world GDP
- Over 16% share in world trade.
- Total combined area of 29.3% of the total land surface of the world
- Over a period of time, BRICS countries have come together to deliberate on important issues under the three pillars of:
- political and security,
- economic and financial and
- Cultural and people-to-people exchanges.
- New Development Bank and BRICS: Formerly referred to as the BRICS Development Bank, is a multilateral development bank established by the BRICS states.
- The Bank shall support public or private projects through loans, guarantees, equity participation and other financial instruments.
The need for BRICS expansion
- Economic strength: The economic strength of the five members of the grouping is not as promising as it was when the platform was first announced in 2009.
- Though the BRICS nations certainly represent 43% of the world’s population and around 30% of the global economy, their economic weaknesses are certain.
- China’s anti-western orientation: China is focused on a quick expansion of BRICS with the aim of giving the platform a distinctly anti-western orientation.
- Prevailing Anti-Western sentiment: Many realize that the doors of other groupings are closed to them.
- The clamour reflects prevailing anti-western sentiments and a pervasive desire to create a sizeable forum of the Global South.
- Global challenges: Russia is being marginalised in the global economy, while China is facing a difficult economic environment with the west turning against it.
Challenges with expanding BRICS grouping:
- An increase in membership is likely to weigh the group in favour of Chinabecause some countries waiting to join are also part of the Chinese Belt and Road Initiative.
- This raise concerns that an expanded BRICS could be seen as a Chinese-led anti-American bloc.
- India, which has been strengthening its bilateral relationship with the US, has been concerned about expansion.
- India views China’s role in driving these countries for membership of BRICS along with the support of Russia.
- India also raised its concern in last year’s BRICS that any addition of new members must follow the carefully thought-out objective criteria for membership.
- This should be mutually discussed among the present members, so that all are of the same view regarding expansion.
- Further, at the BRICS foreign ministers’ meeting last month, India’s External Affairs Minister S Jaishankar emphasized the need to consider the ways in which existing BRICS countries collaborate with each other and engages with non-BRICS countries.
Way Forward:
The 15th BRICS summit holds multifaceted importance for India, offering a platform for addressing geopolitical concerns, facilitating bilateral talks, and advancing economic collaborations. As the global landscape continues to evolve, BRICS remains a critical forum for emerging economies to engage and collaborate on key global challenges. The outcomes of this summit will not only affect the member nations but also shape the broader trajectory of international relations and cooperation.
Source: https://indianexpress.com/article/explained/explained-global/brics-expansion-significance-for-india-8907925/
Megalithic Site In Kerala (The Hindu)
- 21 Aug 2023
What is the News ?
A large number of megalithic hat stones were found during a recent archaeological salvage excavation conducted by the Kerala Archaeology Department at Nagaparamba in Kuttippuram village, near Tirunavaya.
Facts About:
- Hat stones, popularly called Thoppikkallu in Malayalam, are hemispherical laterite stones used as lid on burial urns during the megalithic period.
What is Salvage excavation?
- Salvage excavation also known as rescue archaeology or emergency archaeology, refers to a type of archaeological excavation that is conducted in response to a situation where archaeological remains are threatened by construction, development, or other activities
Megaliths
- Megaliths were constructed either as burial sites or commemorative (non-sepulchral) memorials.
- Origin: As megalithic societies were preliterate, the racial or ethnic origins of the megalithic people are thus difficult to pin down.
- Significance: Megaliths were not built for commoners. They signify the emergence of a ruling class or elite who presided over a surplus economy.
- Time – Period: In India, archaeologists trace the majority of the megaliths to the Iron Age (1500 BC to 500 BC), though some sites precede the Iron Age, extending up to 2000 BC.
Geographical Spread: Megaliths are spread across the Indian subcontinent, though the bulk of them are found in peninsular India, concentrated in the states of Maharashtra (mainly in Vidarbha), Karnataka, Tamil Nadu, Kerala, Andhra Pradesh and Telangana.
- Even today, a living megalithic culture endures among some tribes such as the Gonds of central India and the Khasis of Meghalaya.
- Different Types of Megalithic Structure include: Stone Circles, Dolmen, Cist, Monolith and Capstone style.
Source: https://www.thehindu.com/sci-tech/science/hat-stones-in-abundance-at-archaeology-site-near-tirunavaya/article67210231.ece
RBI allows switch from ‘floating to fixed rate’ regime (Indian Express)
- 19 Aug 2023
What is the News ?
The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) asked all regulated entities (REs), including banks and NBFCs, to give personal loan borrowers an option to switch over from a floating rate to a fixed rate regime at the time of resetting interest rates.
Facts About:
- When a customer takes a loan, the interest rate reset clause in the loan agreement allows the lender to review the interest rate after a certain period, as per the occurrence of a scheduled reset date of the loan.
- The reset rate is the new interest rate that a borrower must pay effective from the scheduled reset date.
- EMI of a floating rate loan changes with periodical changes in reset interest rates.
- These rates and the calculation are not uniform for all the banks as the cost of funds differs from banks.
Changes made by RBI:
The RBI asked banks to implement the following regulations:
- For Regulated entities (RE) :
- At the time of sanction, REs will have to clearly communicate to the borrowers about the possible impact of a change in benchmark interest rate on the loan leading to changes in EMI and/or tenor or both.
- Any increase in the EMI/ tenor or both will have to be communicated to the borrower immediately through appropriate channels.
- At the time of reset of interest rates, REs will have to give the option to borrowers to switch over to a fixed rate as per their board-approved policy.
- The policy will also specify the number of times a borrower will be allowed to switch during the tenor of the loan.
- REs will have to disclose all applicable charges for switching loans from floating to fixed rate and any other service charges/ administrative costs in the sanction letter and also at the time of revision of charges or costs from time to time.
- For EMI or Elongation of tenor:
- The borrowers will also be given the choice to opt for enhancement in EMI or elongation of tenor or for a combination of both options, and to prepay, either in part or in full, at any point during the tenor of the loan, with foreclosure charges.
- The RBI said REs will have to ensure that these instructions are extended to the existing as well as new loans by December 31, 2023.
Why has RBI issued new regulations?
- RBI's Supervisory Reviews: The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) has conducted supervisory reviews and received feedback from the public.
- Unreasonable Tenor Elongation: Instances of banks significantly extending tenors of floating rate loans without proper borrower consent and communication have been identified.
- Interest Rate Changes: Banks can alter interest rates by adjusting the internal benchmark rate and spread during the loan term, potentially harming borrowers' interests and monetary transmission.
- Arbitrary EMI Resets: Borrowers complain of banks arbitrarily resetting Equated Monthly Installments (EMIs) and extending tenors without adequate notification.
- Hidden Foreclosure Charges: Borrowers are often unaware of foreclosure charges, adding to borrower dissatisfaction.
- Stress Concealment: RBI notes that prolonged tenor elongation may obscure underlying stress in banks' financial health.
- Refinancing Challenges: While theoretically possible, refinancing floating rate loans across different banks with distinct internal benchmarks is complex due to varying benchmark adjustment methods.
- Limited Borrower Options: Borrowers might feel compelled to stay with their original bank, paying higher charges, as refinancing is often impractical due to benchmark disparities.
Possible impacts:
- Interest rate of borrowers: Banks can change the interest rate by changing the internal benchmark rate and the spread during the term of the loan which could harm the interest of the borrower and also impair monetary transmission.
Benefits of Fixed rate regime:
- For borrowers:
- Protection from Rate Hikes: Shifting to a fixed rate provides protection against potential future increases in interest rates. This can be particularly beneficial if interest rates are expected to rise in the near future.
- Budgeting and Financial Planning: Fixed payments make it easier for borrowers to budget and plan their finances since they know exactly how much they need to allocate for their loan payments.
- Potential Cost: Fixed interest rates tend to be initially higher than prevailing floating rates. Borrowers opting for a fixed rate might end up paying more initially compared to what they would have paid with a floating rate if rates remain relatively stable or decrease.
- For lenders:
- Interest Rate Risk Mitigation: Lenders are less exposed to interest rate risks when borrowers opt for fixed rates. They can better manage their own interest rate risk since they know the interest income they'll receive remains constant.
- Lending Profitability: Fixed-rate loans typically come with higher initial interest rates compared to floating-rate loans. This can lead to increased lending profitability for lenders, especially if rates remain stable or decline.
- Potential Lower Loan Demand: Higher initial fixed rates might deter some potential borrowers who are attracted to lower initial payments offered by floating rates.
- Limited Flexibility: Lenders might have less flexibility in adjusting loan terms for borrowers with fixed-rate loans, as the interest rate remains constant regardless of market conditions.
Source: https://indianexpress.com/article/explained/explained-economics/rbi-fixed-rate-regime-personal-loan-8898445/
Bio-Trace Minerals Project (PIB)
- 19 Aug 2023
What is the News ?
Recently, the Technology Development Board under Department of Science and Technology (TDB-DST) collaborated with M/s Chemlife Innovations pvt ltd. for innovation in the Bio-Trace Minerals Project.
Facts About:
How does the collaboration between TDB and Chemlife Innovations align with India’s strategic framework for livestock development?
- The collaboration between TDB and Chemlife Innovations aligns with India’s strategic framework, including the National Livestock Mission, which seeks to enhance livestock productivity, optimize feed resources, and infuse technology into livestock management. By developing bio-trace minerals for animal feed, the project addresses crucial aspects of animal nutrition, aligning seamlessly with the mission’s objectives.
What innovative technology does Chemlife Innovations employ in their project, and how does it contribute to sustainability?
- Chemlife Innovations employs the “Accelerated Natural Bio Transformation” (ANBioT) technology, which facilitates chelation reactions using a proprietary nutrient medium. This technology operates under milder conditions and is eco-friendly, aligning with principles of sustainability by reducing environmental impact and resource consumption.
How does the use of pupa proteins contribute to the project’s eco-friendly approach?
- Pupa proteins, rich in hydroxy amino acids, are utilized in the project as an alternative to imported ligands. This economical alternative not only enhances the project’s economic viability but also aligns with India’s goal of self-sufficiency, reducing reliance on imported resources and promoting sustainable practices.
What certifications does Chemlife Innovations hold, and how do they attest to the company’s commitment to quality?
- Chemlife Innovations holds Global Certification for Animal Feed Additive Quality and Feed Safety, as well as the esteemed FAMI-QS certification. These certifications validate the company’s commitment to producing high-quality and safe products, maintaining global standards in their operations.
How does the project contribute to the circular economy, and what role does repurposing silk worm pupae meal play?
- The project contributes to the circular economy by repurposing silk worm pupae meal, reducing waste generated by the silk industry. By using locally available by-products, the project aligns with principles of sustainability, economic viability, and import substitution goals.
How does the project’s innovative product “MinBioZen” address livestock health and sustainability?
- “MinBioZen” is an innovative bio-trace mineral product developed by Chemlife Innovations. It integrates bioavailability and stability, optimizing livestock health and growth. This product showcases the company’s dedication to innovation and environmental stewardship, aligning with the goals of sustainable resource utilization.
Source: https://www.google.co.in/url?sa=t&rct=j&q=&esrc=s&source=web&cd=&ved=2ahUKEwjUsaL43aGBAxVEwjgGHU5XAs8QFnoECBQQAQ&url=https%3A%2F%2Fpib.gov.in%2FPressReleaseIframePage.aspx%3FPRID%3D1950125&usg=AOvVaw16iXZ25GRw2ND9aklzZ5ri&opi=89978449
Agnibaan SOrTeD rocket (Economic Times)
- 19 Aug 2023
What is the News ?
A Chennai-based start-up AgniKul Cosmos, has commenced the process of integrating its cutting-edge Agnibaan SOrTeD rocket at its private Launchpad in Sriharikota.
Facts About:
- The integration process was initiated on Independence Day on August 15, 2023.
- A successful launch would make AgniKul the second Indian space tech start-up to send its launch vehicle into space after Skyroot Aerospace.
- AgniKul: Established in 2017, by aerospace engineers Srinath Ravichandran and Moin SPM, along with IIT-Madras faculty member Prof. Sathyanarayan R Chakravarthy.
About Agnibaan SOrTeD (SubOrbital Technological Demonstrator):-
Type: single-stage launch vehicle.
Powered by: AgniKul’s patented Agnilet engine.
- Agnilet engine: It is the world’s sole single-piece 3D-printed engine.
- It is a single-piece, 6 kilonewton (kN) semi-cryogenic engine.
- Initial trial: early 2021.
- Verified at the Vikram Sarabhai Space Centre (VSSC) in Thiruvananthapuram.
- 3D printing: uses materials such as plastics and metals to convert products envisaged on computer-aided design to real three-dimensional items.
Payloads: up to 100 kg.
Altitude: 700 km
- It can carry payloads in five different configurations. (LVM3-M2 rocket)
Stages: It is a customizable launch vehicle that could be launched in one or two stages.
Unique feature: unlike traditional sounding rockets that launch from guide rails, it will lift off vertically and follow a predetermined trajectory to perform a precisely orchestrated set of maneuvers during flight.
The rocket’s first stage could have up to seven Agnilet engines, depending on the mission, which are powered by Liquid Oxygen and Kerosene.
The rocket is also designed for launch from more than 10 different launch ports.
To ensure its compatibility with multiple launch ports, AgniKul has built a launch pedestal named ‘Dhanush’.
- It will support the rocket’s mobility across all its configurations.
Source: https://economictimes.indiatimes.com/news/science/chennai-based-agnikul-prepares-for-maiden-sub-orbital-flight-of-agnibaan-rocket/articleshow/102805834.cms?from=mdr
3D Printing (The Hindu)
- 19 Aug 2023
What is the News ?
India’s first 3D printed Post Office was inaugurated in Bengaluru’s Cambridge Layout.
Facts About:
- India’s pioneering 3D-printed post office located in Bengaluru’s Cambridge Layout was recently inaugurated.
3D Printed Post Office
- Swift Build: The 3D-printed post office was constructed in just 43 days, surpassing the original deadline by two days.
- Construction Team: Larsen & Toubro Limited undertook the project in collaboration with IIT Madras.
Technological Process
- Spatial Dimension: The post office covers an area of 1,021 square feet and was created using advanced 3D concrete printing.
- Automated Procedure: Robotic printers used an automated process to layer concrete according to the approved design.
- Strong Bonding: A specially formulated quick-hardening concrete ensured strong bonding between layers.
- Rapid Construction: With robotic precision and pre-embedded designs, the project was completed in just 43 days, far shorter than the conventional 6 to 8 months.
Advantages of 3D Printing
- Cost-Effective: The project cost ?23 lakhs, indicating a 30-40% cost reduction compared to traditional methods.
- Showcasing Technology: The project highlighted concrete 3D printing technology using indigenous machinery and robots, showcasing its scalability.
Distinctive Features
- Continuous Perimeter: The project boasted continuous perimeter construction without vertical joints.
- Flexibility: The 3D printing accommodated curved surfaces and different site dimensions, overcoming flat wall limitations.
- Structural Innovation: Continuous reinforced concrete footing and three-layer walls were created, enhancing structural integrity.
- Reduced Timeline: The innovative technique drastically reduced the construction timeline to 43 days, minimizing material wastage.
Source: https://www.google.co.in/url?sa=t&rct=j&q=&esrc=s&source=web&cd=&ved=2ahUKEwi88OSW3aGBAxVDTWwGHafnBzMQFnoECB8QAQ&url=https%3A%2F%2Fwww.thehindu.com%2Fnews%2Fcities%2Fbangalore%2Findia-first-3d-printed-post-office-is-now-open-for-business-in-bengaluru%2Farticle67208897.ece&usg=AOvVaw1xcvOgM9Z66xFGFeSZ-7W_&opi=89978449
Aqueduct Water Risk Atlas (Indian Express)
- 19 Aug 2023
What is the News ?
New data from the Aqueduct Water Risk Atlas of World Resources Institute (WRI) has been released.
Facts About:
What does it mean for a country to be exposed to extreme water stress?
- Extreme water stress signifies that a country uses more than 80% of its renewable water supply for activities such as irrigation, livestock, industry, and domestic needs. This reliance makes them vulnerable to water scarcity during periods of drought.
How does the WRI define the term ‘water stress’?
- A region is deemed ‘water stressed’ when the demand for water surpasses the available volume or when water quality limitations restrict its use for various purposes.
Which regions and countries are the most water-stressed according to the report?
- The most water-stressed regions are West Asia, North Africa, and South Asia. Notable water-stressed countries include Bahrain, Cyprus, Kuwait, Lebanon, Oman, Qatar, and others.
How is global water demand projected to change by 2050?
- Global water demand is estimated to increase by 20-25% by 2050. Additionally, watersheds facing unpredictable water supplies are expected to rise by 19%. This could result in 100% of West Asia and North Africa’s population facing extreme water stress by 2050.
What are the implications of high water stress beyond immediate concerns?
- The report emphasizes that extreme water stress affects not only consumers and industries but also has far-reaching political implications. Water stress can impact political stability, making it a critical issue to address for global leaders.
What are the economic implications of solving global water challenges?
- According to WRI’s findings, addressing global water challenges would cost around 1% of the global GDP or 29 cents per person per day from 2015 to 2030. Despite the costs, the potential economic benefits and stability improvements make it a worthwhile investment.
Source: https://chinawaterrisk.org/useful-links/aquaduct-water-risk-atlas/
INS Vindhyagiri' (PIB)
- 18 Aug 2023
What is the News ?
President Droupadi Murmu launched the 'INS Vindhyagiri' in Kolkata at Garden Reach Shipbuilders and Engineers Limited (GRSE).
Facts About:
- Project 17A – Vindhyagiri, named after the mountain range in Karnataka, is the sixth ship of the Project 17A program, as per PTI reports.
- Vindhyagiri, a technologically advanced Frigate, and a tribute to the erstwhile INS Vindhyagiri, the Leander Class ASW Frigate.
- Old Vindhyagiri – It is nearly 31 years of service from July 1981 to June 2012, had witnessed various challenging operations and multinational exercises.
- Under the Project 17A program, a total of 4 ships by Mazagon Dock Ltd (MDL) and 3 ships by GRSE are under construction.
- The project's first 5 ships have been launched by the MDL and GRSE between 2019 and 2022.
- Project 17A ships have been designed in-house by the Indian Navy's Warship Design Bureau, the pioneer organization for all warship design activities.
- A substantial 75% of the orders for equipment and systems of Project 17A ships are from indigenous firms.
Source: https://pib.gov.in/PressReleaseIframePage.aspx?PRID=1949974
Artificial Intelligence Index 2023 (Indian Express)
- 18 Aug 2023
What is the News ?
India ranked fifth in Artificial Intelligence (AI)-based investments according to Stanford University’s annual AI Index report 2023.
Facts About:
- AI Index is an independent project at Stanford Institute for Human-Centered Artificial Intelligence (HAI).
Purpose:
- The annual report compiles, analyzes, and visually presents AI-related data to empower responsible and ethical AI advancements in collaboration with human interests
Global AI Investment Rankings
- United States
- China
- United Kingdom
- Israel
- India
India's Remarkable Growth
- India secured the fifth position in AI investments received by startups worldwide in 2022.
- AI startups in India attracted $3.24 billion in funding, surpassing countries like South Korea, Germany, Canada, and Australia.
Investment Revival amidst Recession
- Despite a global AI investment dip since 2021 due to economic challenges, a resurgence in Venture Capital (VC) funding is anticipated this year.
- Enterprises and consumers' heightened interest in generative AI products like Open AI's ChatGPT is expected to drive this revival.
Global Contribution to LLM Development
- 54% of researchers involved in advancing large language models (LLMs) hail from American institutions.
- Significant progress observed as researchers from Canada, Germany, and India joined the LLM development landscape in the past year.
Source: https://indianexpress.com/article/technology/artificial-intelligence/key-takeaways-from-stanford-ai-index-report-2023-8539812/
PM Vishwakarma (Economic Times)
- 17 Aug 2023
What is the News ?
The Cabinet Committee on Economic Affairs has approved a new Scheme named “PM Vishwakarma”
Facts About:
Type: Central Sector Scheme
Aim: To strengthen and nurture the Guru-Shishyaparampara or family-based practice of traditional skills by artisans and craftspeople working with their hands and tools.
– To improve the quality, as well as the reach of products and services of artisans and craftspeople and to ensure that the Vishwakarmas are integrated with the domestic and global value chains.
Coverage: The scheme will provide support to artisans and craftspeople of rural and urban areas across India.
– Eighteen traditional trades will be covered under the scheme. These include carpenter, boat maker, armourer, blacksmith, hammer and tool kit maker, locksmith, goldsmith, potter, sculptor, stone breaker, cobbler, mason, basket/mat/broom maker/coir weaver, traditional doll and toy maker, barber, garland maker, washerman, tailor and fishing net maker.
Duration of the scheme: Five years (FY 2023-24 to FY 2027-28).
Key Features of the scheme: Artisans and craftspeople will be provided a recognition through PM Vishwakarma certificate and ID card.
– The scheme has a provision of credit support of up to ?1 lakh (first tranche) and ?2 lakh (second tranche) with a concessional interest rate of 5%.
– It also has a provision to provide skill upgradation, incentive for toolkit as well as digital transactions and marketing support.
– Skilling programmes will take place at both basic and advanced types. Participants will get a stipend of ?500 per day while undergoing training.
– Beneficiaries will also receive up to ?15,000 to buy modern tools.
Source: https://economictimes.indiatimes.com/news/politics-and-nation/pms-vishwakarma-scheme-launch-on-sept-17-70-ministers-to-attend-event-at-70-locations/articleshow/103559849.cms?from=mdr
The first-ever Global Summit on Traditional Medicine (The Hindu)
- 17 Aug 2023
What is the News ?
The first WHO Traditional Medicine Global Summit will take place in Gandhinagar, Gujarat.
Facts About:
First WHO Traditional Medicine Global Summit:
Organized by: World Health Organization (WHO) and co-hosted by the Ministry of Ayush.
Aim: To bring together various stakeholders, such as traditional medicine practitioners, policymakers, academics, and others on a common platform to share best practices, evidence and innovation related to how traditional medicine contributes to health and sustainable development.
Significance: Traditional and complementary medicine has been vital for health in communities for centuries and has influenced modern medical knowledge.
– About 40% of today’s medicines have natural origins, including well-known drugs like aspirin and artemisinin.
– Currently, 170 countries have informed WHO about their use of traditional medicine, seeking evidence and data to guide safe, cost-effective, and fair policies and regulations.
About WHO Global Centre for Traditional Medicine:
In 2022, WHO with the support of the Government of India established the Global Centre for Traditional Medicine in Jamnagar, Gujarat.
Mandate: The centre provides leadership on all global health matters related to traditional medicine as well as extending support to member countries in shaping various policies related to traditional medicine research, practices and public health.
Significance: It is the first and only global outpost for traditional medicine across the globe.
Source: https://www.thehindu.com/news/national/who-director-general-to-inaugurate-first-ever-global-summit-on-traditional-medicine/article67193778.ece
Removing gender stereotypes from the law (The Hindu)
- 17 Aug 2023
What is the News ?
The Supreme Court has recently launched a ‘Handbook on Combating Gender Stereotypes’.
Facts About:
What is the significance?
- Combats Gender Stereotypes: It aims to combat gender stereotypes in language used within the judiciary and legal community.
- For instance, terms like "career woman," "fallen woman," "faithful or obedient wife," "eve-teasing," and "hermaphrodite" have been identified as gender-unjust terms.
- The Supreme Court suggests using more neutral and respectful terms like "woman," "wife," "street sexual harassment," and "intersex" instead.
- Promoting Equity and Justice: Promoting a more just and equitable society. He mentioned that relying on predetermined stereotypes in judicial decision-making goes against the duty of judges to decide cases impartially, based on their merits.
- Addresses false assumptions: The handbook addresses false assumptions about women's characteristics, such as the stereotype that women are overly emotional, illogical, and unable to make rational decisions.
- It emphasizes that a person's gender should not determine their capacity for rational thought.
- Addresses Prejudices: The handbook discusses assumptions made about a woman's character based on her clothing choices and sexual history.
- These assumptions can influence how the court assesses her actions, particularly in cases involving sexual violence, and may undermine the importance of consent in such cases.
- Significance of language: The Chief Justice pointed out that language used by judges reflects not only their interpretation of the law but also their perception of society.
- The example of changing the term "pauper" to "indigent" in the Code of Civil Procedure, 1908 was cited to demonstrate how language can impact the dignity and humanity attributed to individuals.
- The handbook aims to raise awareness about the role of language in perpetuating gender stereotypes within the legal system and provides guidance on using more respectful and neutral terms to promote fairness and equality.
Source: https://www.thehindu.com/news/national/to-remove-gender-stereotypes-from-the-law-a-new-supreme-court-handbook/article67201169.ece
Legalising Cannabis : Good or Bad for India (The Hindu)
- 17 Aug 2023
What is the News ?
Himachal Pradesh CM has announced that the state government is considering legalizing the cultivation of cannabis.
Facts About:
What is Cannabis?
- Cannabis, also known as marijuana among other names, is a psychoactive drug from the Cannabis plant used primarily for medical or recreational purposes.
- The main psychoactive component of cannabis is tetrahydrocannabinol (THC), which is one of the 483 known compounds in the plant, including at least 65 other cannabinoids, including cannabidiol (CBD).
- It is used by smoking, vaporizing, within the food, or as an extract.
Prospects of legalizing Marijuana
(1) Health benefits
- The cannabinoids found in Cannabis is a great healer and has found mentioned in Ayurveda.
- It can be used to treat a number of medical conditions like multiple sclerosis, arthritis, epilepsy, insomnia, HIV/AIDS treatment, and cancer.
(2) Ecological benefits
- The cannabis plant and seeds apart from being labelled a ‘super-foods’ as per studies is also a super-industrial carbon-negative raw material.
- Each part of the plant can be used for some industry. Hemp currently is also being used to make bio-fuel, bio-plastics and even construction material in certain countries. The cosmetic industry has also embraced Hemp seeds.
(3) Marijuana is addiction-free
- An epidemiological study showed that only 9% of those who use marijuana end up being clinically dependent on it.
- The ‘comparable rates’ for tobacco, alcohol and cocaine stood at 32%, 15% and 16% respectively.
(4) Good source of Revenue
- By legalizing and taxing marijuana, the government will stand to earn huge amounts of revenue that will otherwise go to the Italian and Israeli drug cartels.
- In an open letter to US President George Bush, around 500 economists, led by Nobel Prize winner Milton Friedman, called for marijuana to be “legal but taxed and regulated like other goods”.
(5) A potential cash crop
- The cannabis plant is something natural to India, especially the northern hilly regions. It has the potential of becoming a cash crop for poor marginal farmers.
- If proper research is done and the cultivation of marijuana encouraged at an official level, it can gradually become a source of income for poor people with small landholdings.
(6) Prohibition was ineffective
- In India, the consumption of synthetic drugs like cocaine has increased since marijuana was banned, while it has decreased in the US since it was legalized in certain states.
- Moreover, these days, it is pretty easy to buy marijuana in India and its consumption is widespread among the youth. So it is fair to say that prohibition has failed to curb the ‘problem’.
(7) Marijuana is less harmful
- Marijuana consumption was never regarded as a socially deviant behaviour any more than drinking alcohol was. In fact, keeping it legal was considered as an ‘enlightened view’.
- It is now medically proven that marijuana is less harmful than alcohol.
Risks of Legalizing Cannabis
(1) Health risks continue to persist
- There are many misconceptions about cannabis. First, it is not accurate that cannabis is harmless.
- Its immediate effects include impairments in memory and in mental processes, including ones that are critical for driving.
- Long-term use of cannabis may lead to the development of addiction of the substance, persistent cognitive deficits, and of mental health problems like schizophrenia, depression and anxiety.
- Exposure to cannabis in adolescence can alter brain development.
(2) A new ‘tobacco’ under casualization
- A second myth is that if cannabis is legalized and regulated, its harms can be minimized.
- With legalization comes commercialization. Cannabis is often incorrectly advertised as being “natural” and “healthier than alcohol and tobacco”.
- Tobacco, too, was initially touted as a natural and harmless plant that had been “safely” used in religious ceremonies for centuries.
(3) Unconvincing Advocacy
- Advocates for legalization rarely make a convincing case. To hear some supporters tell it, the drug cures all diseases while promoting creativity, open-mindedness, moral progression.
- Too much trivialization of Cannabis use could lead to its mass cultivation and a silent economy wreaking havoc through a new culture of substance abuse in India.
Legalization status elsewhere in India
- Several states in India have already legalized cannabis cultivation, including neighboring Uttarakhand, which became the first state in the country to do so in 2017.
- Controlled cultivation is being done in some districts of Gujarat, Madhya Pradesh, and Uttar Pradesh.
Legal Framework for Cannabis Cultivation
- Definition of Cannabis: The Parliament has defined cannabis in the Narcotic Drugs and Psychotropic Substances Act (NDPS), 1985.
- Ban on extracting resin and flowers: While a complete ban has been imposed on extracting the resin and flowers of the cannabis plant, the law determines the method and extent of cultivation of cannabis for medicinal and scientific purposes.
- Authorities to States: Section 10 (a) (iii) of the Act empowers States to make rules regarding the cultivation of any cannabis plant, production, possession, transport, consumption, use, purchase, sale, and consumption of cannabis (except charas).
- Cultivation of hemp: States are also empowered to permit, by general or special order, the cultivation of hemp, only for obtaining fibber or seeds or for horticultural purposes.
Source: https://www.thehindu.com/opinion/op-ed/the-risks-of-legalising-cannabis/article29216035.ece
Talwar-class Stealth Frigates (PIB)
- 16 Aug 2023
What is the News ?
- Two Krivak- or Talwar-class stealth frigates are now expected to be delivered by May and October in 2024
- The ship is in the final stages of development; in two months time, it will go for sea trials.
Facts About:
The Talwar class of frigates of the Indian Navy have been built in Russia under an Indo-Russian joint production.
The Talwar class guided missile frigates are modifiedKrivak III class frigates from Russia.
- In October 2016, India and Russia signed an Inter-Governmental Agreement for four stealth frigates, after which a $1-billion deal was signed for direct purchase.
The Talwar Class has a displacement of 4,000 tons and speed of 30 knots and is capable of accomplishing a wide variety of naval missions, primarily, finding and eliminating enemy submarines and large surface ships.
Due to the use of stealth technologies and a special hull design, the resulting frigate features reduced radar cross section (RCS) as well as electromagnetic, acoustic and infrared signatures.
Source: https://swarajyamag.com/defence/russia-delays-advanced-talwar-class-stealth-frigates-delivery-yet-again-now-projected-to-join-navy-by-may-and-october-2024
Graphene-Aurora program (PIB)
- 16 Aug 2023
What is the News ?
Recently, the Ministry of Electronics & Information Technology (MeitY) Secretary launched the ‘Graphene-Aurora program’ at a function in Maker Village Kochi, Kerala.
Facts About:
- The program shall be implemented by Digital University Kerala with joint funding from Ministry of Electronics & Information Technology (MeitY), and Government of Kerala and Industry partners, Carborundum PvtLimitedjoined as one of the main industry partners.
- It shall nurture the deep/emerging Graphene technology & innovation ecosystem that can guide, develop, implement, and support SMEs and startups to commercialize developed graphene technologies for scale adoption.
- Creation of a commercialization eco-system for graphene as an emerging technology would help India take a pole position in the world’s new material market.
Key facts about Graphene
- Graphene is a material that is extracted from graphite and is made up of pure carbon.
- It is one of the most important elements in nature which we find in daily objects like the lead of a pencil.
- It is the world’s thinnest, strongest, and most conductive material of both electricity and heat.
- It conducts electricity better than copper.
- It is 200 times stronger than steel but six times lighter.
- It is almost perfectly transparent as it absorbs only 2% of light.
- It is impermeable to gases, even those as light as hydrogen and helium.
Source: https://pib.gov.in/PressReleasePage.aspx?PRID=1948661
Deemed Forest (The Hindu)
- 16 Aug 2023
What is the News ?
Odisha has no ‘deemed forest’ as per the amended Forest (Conservation) Act, 1980.
Facts About:
What are deemed forests?
Deemed forest refers to land that resembles forests but has not been recognized as such by either the Union or the States.
They account for about 1% of the total forest land in the country.
In 1996, the Supreme Court expanded the remit of the Van (SanrakshanEvamSamvardhan) Act to areas that weren’t notified as forests but conformed to the “dictionary” definition of forests i.e. deemed forests.
- The Godavarman verdict stated that the states must identify and categorize such land.
- The SC directed the states to establish Expert committees to determine deemed forests in order to clarify the area that may be protected under the Forest (Conservation) Act.
According to the Forest Act, land cannot be diverted without the consent of the Centre as well as gram panchayats in the regions.
- It serves as a deterrent to deforestation by directing the parties responsible for diverting forest land to grow trees on a plot of land equivalent to twice the razed area and imposing a significant monetary penalty.
What does the Odisha government directive mention?
All district collectors must ensure that the diversion of forest land for infrastructure projects, particularly state development projects, should follow provisions of the new law.
Any survey or exploration will also not be treated as a non-forestry activity.
Expert Committees
Although all the states were expected to form expert committees to identify deemed forests, not all States submitted their reports.
- This has left states with enough leeway in defining or omitting large parcels of land as forests.
According to the Union Ministry of Environment, the amendments to the 1980 Act were necessary to remove ambiguities and clarify the application of the laws.
According to the amended act, the Forest Conservation Act would not apply to notified forest land that was legally diverted for non-forest uses between 1980 and 1996.
- As a result, forest land that was not specifically notified as such would cease to be protected under the provisions of the Act.
The Union Environment Ministry had earlier stated that deemed forests would continue to be protected.
- The amendments made to the FCA recognized deemed forest lands, which had been identified by the Expert Committee of the State. Therefore the provisions of the Act will be applicable in such lands also.
Future unclear
According to the latest Forest Survey of India, Odisha has approximately 52,156 square km or 130 lakh acres of forest coverage.
- This amounts to 33.50% of the State’s geographical area, which is much higher than the national level of forest cover - 21.71%.
Since 1996, around 66 lakh acres have been identified as deemed forests in Odisha.
- However, a majority of this land has not been officially notified in the government records.
This amounts to about 40-50% of Odisha’s forest land.
In addition, there are several community forests that are managed by tribal and forest-dependent groups while several have land title rights under the provisions of the separate Forest Rights Act.
- The decision of the Odisha government that deemed forests have ceased to exist means that these will face an uncertain future.
One consequence of the new amendments is that there will be no check on forest diversion, making it easier to divert forest land.
- According to data from the Union Coal and Mining Ministry, of the 19,200 hectares of forest land that have been diverted nationally for mining between 2017-2022, around 8,000 hectares was from Odisha.
The reality on the ground is that most of the forest officer bureaucracy isn’t too keen on protecting forest rights
Impact
The Adivasi communities of Odisha depend on the deemed forests for their livelihood.
- These include some of the community-protected forests and bio-cultural habitats of vulnerable tribal groups such as the Dongria Kondhs in Niyamgiri.
- The removal of deemed forest areas from the Act could adversely affect the statutory rights of these communities which have claimed community forest rights and habitat rights on such forests
Around 46% of Odisha’s geographical area is notified as fifth schedule area under the Constitution, where thePanchayat Extension to Scheduled Areas (PESA) Act applies.
Boundary disputes: In Karnataka, people have alleged that large amounts of agriculture and non-forest land are “unscientifically” classified as deemed forest land.
- This was found to have caused undue hardship to farmers in the region and restricted industrial development.
Criticism
Deemed forests already identified as forests in records ‘held’ by any department or administration should be considered as ‘forest’ even by the new amendment.
- However, the directive of the Odisha government violates this.
It is uncertain if the amendment is yet to be considered to be law as the date of enforcement is yet to be notified.
- The government has temporarily withdrawn the notification until the Union Government establishes the rules and guidelines of the new act.
The amendment narrows down the definition of forests.
- As a result, vast tracts of forests are excluded which leaves them vulnerable to destruction.
Source: https://www.thehindu.com/news/national/other-states/no-more-deemed-forests-says-odisha-government/article67198187.ece
Pradhan Mantri Uchchatar Shiksha Abhiyan (PM-USHA) (PIB)
- 14 Aug 2023
What is the News ?
14 States and Union Territories are yet to sign a crucial Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) with the Union Education Ministry.
Facts About:
Higher education Institutions (HEIs) in India
Statistics
As per the AISHE report 2020-21, there are 1,113 Universities, 43,796 Colleges, and 11,296 Stand Alone Institutions.
- There are 422 State Public Universities that have 41,836 affiliated colleges.
- 446 Universities are privately managed and 475 Universities are located in rural areas, 17 are women-centric universities.
Total enrolment in higher education has been estimated to be 4.13 crores with 2.12 crores boys and 2.01 crores females.
- Females constitute 48.7% of the total enrolment.
There are 2,255 students enrolled in Integrated Ph.D. in addition to 2.11 lakh students enrolled in Ph.D. Level.
Major problems currently faced by the higher education system in India – As identified by National Education Policy 2020:
- A severely fragmented higher educational ecosystem; less emphasis on the development of cognitive skills and learning outcomes;
- A rigid separation of disciplines, early specialization, and streaming of students into narrow areas of study;
- Limited access particularly in socio-economically disadvantaged areas, with few HEIs that teach in local languages;
- Limited teacher and institutional autonomy;
- Inadequate mechanisms for merit-based career management and progression of faculty and institutional leaders;
- Lesser emphasis on research at most universities and colleges, and lack of competitive peer-reviewed research funding across disciplines;
- Suboptimal governance and leadership of HEIs;
- An ineffective regulatory system; and large affiliating universities result in low standards of undergraduate education.
- PM-USHA aims to address the key gaps and issues identified by NEP 2020.
What is Pradhan Mantri Uchchatar Shiksha Abhiyan (PM-USHA)?
Background
- Rashtriya Uchchatar Shiksha Abhiyan (RUSA) was a Centrally Sponsored Scheme to fund States/UTs institutions.
- It was launched with the vision to attain higher levels of access, equity, and excellence in the State higher education system with greater efficiency, transparency, accountability, and responsiveness.
- The first phase of the scheme was launched in 2013 and the second phase was launched in 2018.
- Now, in the light of the National Education Policy, RUSA scheme has been launched as Pradhan Mantri Uchchatar Shiksha Abhiyan (PM-USHA).
About
- It is a centrally sponsored scheme of the Government of India executed through the Ministry of Education.
- The scheme aims to work with over 300 HEIs including the state universities, its affiliated colleges to raise the quality of education.
Key Objectives of Pradhan Mantri Uchchatar Shiksha Abhiyan
The key objectives of PM-USHA are to improve access, equity and quality in higher education through planned development of higher education at the state level.
The objectives also include:
- creating new academic institutions,
- expanding and upgrading the existing ones,
- developing institutions that are self-reliant in terms of quality education, professionally managed, and characterized by greater inclination towards research.
Funding
- The PM-USHA aims at providing strategic funding to eligible state higher educational institutions.
- The central funding is based on norms and is outcome dependent.
- Funds flow from the central ministry through the state governments/union territories before reaching the identified institutions.
- Funding to states is made on the basis of the critical appraisal of State Higher Education Plans, which enlist each state’s strategy to address issues of equity, access and excellence in higher education.
Source: https://www.education.gov.in/sites/upload_files/mhrd/files/upload_document/pm-usha_guidelines.pdf
National Medical Commission’s New Guidelines (Indian Express)
- 14 Aug 2023
What is the News ?
According to the National Medical Commission’s Registered Medical Practitioner (Professional Conduct) Regulations or NMC RMP Regulations 2023, doctors can now refuse treatment to the unruly and violent patients.
Facts About:
The National Medical Commission Act, 2019:
- It was introduced to address various issues and challenges in the medical field, including improving the quality of medical education, enhancing access to healthcare services, and ensuring ethical and transparent practices.
- Key Provisions include:
- Ethical and Professional Conduct: The Act emphasizes maintaining ethical and professional conduct among medical practitioners and includes provisions to address any deviations from these standards.
- Community Health Providers: The Act introduces the concept of Community Health Providers who are allowed to practice limited medicine in underserved rural areas to address the shortage of doctors.
- Formation of the National Medical Commission (NMC): NMC is an regulatory body which regulates medical education and medical professionals.
- Establishment of Medical Advisory Council.
- Reforms in Medical Education.
Refusing treatment is a complex issue that involves various stakeholders viz. doctors and healthcare professionals, patients and their families, healthcare institutions, medical associations and regulatory bodies, legal authorities, ethics committees, public opinion and media, religious and cultural communities, etc.
Arguments in Favour of the Regulation:
- Unruly Behaviour
- Justice: If an unruly patient’s behaviour poses a threat to their own safety, the safety of healthcare staff, or the safety of other patients, refusing treatment might be justified as a means to mitigate these risks.
- For example, a 21-year-old patient attacked a doctor with a knife during consultation at Delhi’s Sir Ganga Ram Hospital.
- Dignity and Integrity: Unruly behaviour can sometimes cross ethical boundaries, leading to disrespectful or abusive treatment of healthcare staff. Doctors have a right to work in an environment that respects their dignity and professional integrity.
- For example, a 40-year-old doctor on duty in a hospital in Faridabad was assaulted by attendants of a patient as the doctor was attending to another patient, he could not immediately attend to the patient.
- Brings Deterrence: Allowing unruly behaviour to go unchecked might enable a cycle of disruptive or non-compliant behaviour, which could negatively impact the patient’s overall health outcomes. By refusing treatment, the doctor may communicate that certain standards of behaviour are expected for a therapeutic relationship to proceed.
- Right to Freedom to practise any profession: The regulations give the doctors the right to choose whom they will serve, except in case of a life-threatening emergency.
- Justice: If an unruly patient’s behaviour poses a threat to their own safety, the safety of healthcare staff, or the safety of other patients, refusing treatment might be justified as a means to mitigate these risks.
- Financial Constraints
- Autonomy and Consent: Doctors are ethically obligated to provide patients with accurate information about their treatment options,including potential costs.
- If a patient cannot afford the treatment, the doctor might argue that proceeding with treatment without full financial transparency could undermine the patient’s autonomy and informed consent.
- In extreme cases, relatives of patients have been known to hold doctors or hospital staff hostage, demanding treatment.
- Professional Boundaries: Some proponents of this perspective argue that doctors have a professional duty to provide medical care and expertise, but they are not obligated to address broader societal issues such as patients’ financial difficulties.
- Autonomy and Consent: Doctors are ethically obligated to provide patients with accurate information about their treatment options,including potential costs.
- Ethical Boundaries: Doctors have ethical responsibilities not only toward their patients but also toward themselves, their families and the healthcare community.
- For example, potential threats and violence have long-lasting impacts which manifests in the degradation of personal and professional relations.
- Objectivity: Taking decisions which are free from subjectivity caused by emotions, perceptions and individual bias is necessary for long term sustainability.
- For example, Free medical care for a desperate patient may be ethical, but providing it to many patients may not be feasible for one provider.
- Selfless Duty: Medical practitioners often prioritize the well-being of their patients above their own comfort, personal time and space. However, the job can be thankless at times.
- For example, During COVID-19 despite their selfless dedication, medical professionals were subjected to regular assaults and verbal abuse throughout the country.
Arguments against the Regulation
- Dedication and the Duty of Care: Dedication is the sense of deep rooted commitment to devote oneself to a cause.. This includes a duty to provide care to those in need, regardless of their financial status.
-
- In India, out-of-pocket health expenditure accounts for more than half of total health expenditure pushing many households into poverty. This shows the dire need for empathy and compassion towards those in need.For example, Dr Ramanand Singh has been treating his patients for just Rs 50 for the past 35 years in Bihar. He even waives off his fees in cases where the patients cannot afford medical treatment.
- Justice and Equity: The principle of justice requires that healthcare be distributed fairly and equitably.Denying treatment to a patient solely based on their inability to pay could be seen as unjust, perpetuating disparities in healthcare access.
- Hippocratic Oath: Physicians pledge to do what is in the best interest of their patients and to avoid causing harm.
- Physicians promise to treat all patients fairly, regardless of their background, and to provide care to the best of their abilities without bias.
- Unholy Nexuses: Many doctors form nexuses with drugmakers to prescribe specific drugs from their brand instead of generic drugs leads to considerable rise in treatment costs for patients.
- For example, freebies given to doctors including travel expenses, gifts etc. by drugmakers is a common practice.Beneficence: It means kindness or generosity and this principle refers to the moral obligation to act in a manner that will benefit others.The principle of beneficence obligates doctors to act in the best interests of their patients and to promote their well-being.
- Compassion: It is the desire to end someone’s suffering which forms the core principle of a medical practitioner. Refusing treatment to individuals on certain grounds could lead to the possibility of crisis of conscience among several practitioners.
- Loss of Trust and Credibility: The medical profession relies on public trust, and denying treatment to those in need could erode that trust and damage the reputation of the medical community.
- Responsibility: Some argue that healthcare professionals have a broader social responsibility to address systemic issues in healthcare, including affordability and access. Refusing treatment might be seen as abdicating this responsibility.
- Undermining Right to Life: Providing a legal caveat for the registered physicians to refuse treatment is against the fundamental right guaranteed under Article 21 of the Constitution.
- Further, there is no specific definition of “abusive” in law as it is purely a subjective interpretation that may depend on the personal opinion of any individual.
- Subjective interpretation may further lead to exclusion on the basis of race, religion, caste, sex etc.
What Should be Done?
- Persuasion: Influencing patients to follow prescribed norms for behaviour and ensuring smooth functioning.
- For example, during COVID-19 pandemic, voice messages were circulated using caller tune to make people aware of the importance of vaccination and prevent attacks on health workers.
- Emotional Intelligence: Equipping and training medical personnel with necessary skills so that they can manage their emotions and try to avoid escalation of situation and providing practical solutions to the given problems.
- Transparent Approaches: Consider alternative approaches before refusing treatment. This might involve social workers, mental health professionals, or conflict resolution experts to address the underlying issues contributing to the unruly behaviour.
- For example, Doctors in San Diego (USA)refer patients to low-cost family health centersthat provide caring, affordable, high-quality health care and supportive services to everyone.
- Ethical Principles Balancing: Weigh the principles of patient autonomy, duty of care, patient safety, and respect for healthcare personnel’s well-being. Consider how refusing treatment aligns with these principles and what potential consequences might arise from the decision.
- For example, Doctors Without Borders is a Nobel Peace Prize receiver charity that provides humanitarian medical care in conflict zones to all those in need of medical care, irrespective of the role played by them in the conflict.
- Tolerance: Accepting actions and practices which may be considered to be incorrect but still tolerable to some extent that they should not be prohibited or penalised heavily.
- For example, a significant number of the cases of unruly behaviour arises in situations which may not be considered as “common” and even the most well-behaved might behave in a way which is not acceptable in society due to the shock or intensity of the moment which one may not be able to handle.
- Consent: Communicating the decision clearly to the patient, and explaining the reasons behind it thus ensuring that the patient understands the potential consequences of their behaviour on their health and the doctor-patient relationship.
- Offering Continuity of Care: If possible, provide recommendations for alternative sources of care, whether within your healthcare institution or elsewhere. Ensure the patient’s ongoing health needs are addressed.
Conclusion
We must protect those who heal. Ethical decisions in healthcare are rarely black and white. It’s important to approach each situation with sensitivity, professionalism, and a commitment to upholding the well-being of patients, healthcare staff, and the broader community. Consulting with colleagues, supervisors, and ethics committees can provide valuable guidance in making these difficult decisions
Source: https://indianexpress.com/article/explained/explained-health/doctors-new-national-medical-commission-guidelines-8890632/#:~:text=The%20guidelines%20say%20that%20doctors,but%20at%20least%20three%20credits.
Urea Gold (Indian Express)
- 14 Aug 2023
What is the News ?
Prime Minister Narendra Modi officially launched Urea Gold fertiliser.
Facts About:
- In a significant development, Prime Minister Narendra Modi unveiled Urea Gold, a novel fertiliser product, created by Rashtriya Chemicals and Fertilizers Ltd (RCF), a state-owned entity. This pioneering formulation involves enhancing urea with sulphur to address crucial agricultural challenges.
What is Urea Gold?
- Traditional urea primarily consists of 46% nitrogen (N). Urea Gold represents a leap forward by combining 37% nitrogen and 17% sulphur.
- This innovative composition serves two primary purposes: bolstering soil quality and boosting nitrogen utilization efficiency.
Soil Deficiencies Nitrogen Utilization Efficiency (NUE)
- Soil Deficiencies in India
- Indian soils suffer from deficiencies, particularly in key nutrients like sulphur (S).
- This deficiency is particularly crucial for certain crops such as oilseeds and pulses, which play a significant role in India’s agricultural output. These crops require adequate sulphur for healthy growth and optimal yield.
- The deficiency in sulphur can hinder their productivity and affect the overall agricultural landscape.
- Nitrogen Utilization Efficiency (NUE) Challenge
- NUE refers to the proportion of applied nitrogen fertilisers that is effectively taken up by crops for growth and yield production.
- Only about 35% of the nitrogen from urea, a commonly used fertiliser, is utilized by crops in India.
- The rest, roughly 65%, is lost through various processes, including ammonia volatilisation into the atmosphere and leaching into the ground as nitrate.
Challenges in Urea Consumption in India
- Import Dependency: India heavily relies on imported urea due to insufficient domestic production. Around 7.6 million tonnes of urea were imported out of the total 35.7 million tonnes sold last fiscal year.
- Feedstock Dependency: The feedstock for domestic urea production, natural gas, is predominantly imported. This adds to the overall import dependence for the fertiliser.
- High Consumption: Urea is India’s most widely used fertiliser, with consumption rising from 26.7 million tonnes to 35.7 million tonnes between 2009-10 and 2022-23.
- Environmental Impact: Excessive urea usage contributes to environmental problems such as air and water pollution. Ammonia emissions and nitrate leaching are associated with these environmental challenges.
- Higher Input Costs: Inefficient fertiliser use due to low NUE leads to higher input costs for farmers. They need to apply more fertiliser to achieve desired yields.
Significance of Urea Gold
- Nutrient Enrichment: Urea Gold is a novel fertiliser fortified with sulphur (S). It contains 37% nitrogen (N) and 17% sulphur, addressing soil deficiencies that are critical for crops like oilseeds and pulses.
- Targeted Improvement: The sulphur content in Urea Gold addresses the specific nutrient requirements of oilseeds and pulses, which are crucial components of Indian agriculture and are significantly import-dependent.
- Packaging and Pricing Shift: Urea Gold’s introduction might entail packaging in 40-kg bags, adapting to the preferences of farmers.While exact pricing remains undisclosed, market trends suggest Urea Gold could be priced between Rs 400 to Rs 500 per 40-kg bag.
- Enhanced NUE: The sulphur-coated urea granules in Urea Gold facilitate a controlled and gradual release of nitrogen. This extended nutrient availability improves NUE, leading to reduced fertiliser application frequency and better crop health.
- Sustainable Agriculture: Urea Gold’s dual focus on addressing soil deficiencies and improving NUE contributes to more sustainable agricultural practices. It reduces excessive fertiliser use and associated environmental impact.
- Economic Benefit: The improved NUE offered by Urea Gold has the potential to reduce input costs for farmers, as they can achieve similar or better yields with lower fertiliser quantities.
- Potential Yield Boost: The sustained nitrogen release mechanism of Urea Gold can potentially lead to increased crop yields due to longer periods of vibrant foliage and enhanced nutrient availability.
Potential Hurdles
- Pricing Uncertainty: Lack of clear pricing details for Urea Gold could impact its adoption among farmers.
- Subsidy Disparity: The current additional rates offered by the government may not sufficiently incentivize companies to promote fortified fertilisers like Urea Gold.
- Limited Farmer Incentives: Farmers might perceive fortified fertilisers as more expensive compared to traditional options, leading to reluctance in adoption.
- Distribution Challenges: Ensuring uniform distribution and application of fortified fertilisers presents logistical complexities.
- Regulatory Influence: Regulatory aspects, such as pricing controls and subsidy structures, can affect the feasibility of fortified fertiliser products.
- Awareness Gap: Limited farmer awareness regarding the benefits and correct usage of fortified fertilisers might hinder their willingness to switch.
- Production Scalability: Scaling up fortified fertiliser production to meet demand and ensure availability poses a significant hurdle.
Way Forward
- Price Rationalization: The government could consider revisiting subsidy rates to make fortified fertilisers economically attractive for both companies and farmers. This would encourage the adoption of innovative products like Urea Gold.
- Subsidy Structure: Tailoring subsidies to reflect the enhanced benefits of fortified fertilisers, such as improved NUE and reduced environmental impact, could encourage their adoption.
- Education Campaigns: Launching awareness campaigns about the advantages of fortified fertilisers, like Urea Gold, can educate farmers and dispel misconceptions about their higher costs.
- Field Demonstrations: Organizing on-field demonstrations of the benefits of fortified fertilisers could provide tangible evidence to farmers, boosting their confidence in making the switch.
- Long-Term Perspective: Encouraging farmers to consider the long-term economic and environmental benefits of fortified fertilisers could shift their focus from initial cost concerns.
- Market Diversification: Exploring partnerships with private sector players and agribusinesses to promote fortified fertilisers could enhance market penetration.
- Gradual Transition: Gradually phasing in fortified fertilisers while continuing to offer traditional options at subsidized rates can ease farmers into adopting the new products.
Source: https://indianexpress.com/article/explained/explained-economics/how-to-make-urea-more-efficient-as-a-fertiliser-and-why-thats-needed-8891183/
Indian judicial data on bail appeals (The Hindu)
- 14 Aug 2023
What is the News ?
The number of bail appeals filed in India’s High Courts surged post 2020, according to the ‘High Court dashboard’ by DAKSH, a think-tank focussed on law and justice system reforms.
Facts About:
- Bail appeals went up from around 3.2 lakh to 3.5 lakh each year before 2020, to 4 lakh to 4.3 lakh thereafter.
- Consequently, the number of pending bail appeals in High Courts also surged from around 50,000 to 65,000 to between 1.25 lakh to 1.3 lakh.
Reasons for rise in bail appeals post 2020
- One possible reason could be the sharp increase in cases related to the flouting of COVID-19-related lockdown norms during the pandemic.
- At the same time, pending bail cases piled up as the functioning of the courts was compromised during this time.
- The DAKSH ‘High Court dashboard’ explains that in 77% of regular bail cases, it was not possible to ascertain the Act under which the person seeking bail was imprisoned.
- It was not mentioned in the e-courts data of various High Courts. An analysis of 23% of cases in which the Act was mentioned shows that the Epidemic Diseases Act, 1897, was ranked fourth, hinting at the possibility of cases surging under this Act as the reason for more bail appeals.
- The database also reveals that the median number of days taken from the filing date to the decision date for regular bail applications was 23. However, for some High Courts, the median days taken for disposal were much higher.
Conclusion
- Delays in resolution have the same effect as denying bail as the accused remains in prison for the duration of their trial,” the DAKSH database argues.
- Finally, data regarding the outcome of bail appeals in High Courts were also missing in many cases. In close to 80% of the disposed bail cases in all High Courts, the outcome of the bail appeal — whether it was granted or rejected — was either unclear, or the outcome was missing.
Source: https://www.thehindu.com/data/data-indian-judicial-data-hides-more-than-it-reveals-in-bail-cases/article67198313.ece
What is Luna-25? (The Hindu)
- 12 Aug 2023
What is the News ?
Russia is set to launch its first lunar landing spacecraft in nearly half a century on August 11
Facts About:
- It is also designated as the Luna-Glob-Lander which is a Russian lunar lander mission.
- It is targeted to the south polar region of the Moon.
- There are two primary scientific objectives of the mission: to study composition of the polar regolith, and to study the plasma and dust components of the lunar polar exosphere.
- It will take off from the Vostochny cosmodrome.
- Lander structure:
- Luna 25's lander features a four-legged base housing landing rockets and propellant tanks.
- An upper compartment contains solar panels, communication equipment, onboard computers, and scientific instruments.
- Payloads:
- It carries eight science instruments, including gamma-ray and neutron spectrometers, infrared spectrometers, mass spectrometers, and imaging systems.
- Landing Site:
- The primary landing site for Luna 25 is near the lunar south pole, with a reserve site located southwest of the Manzini crater.
- Mission duration:
- It is expected to operate on the lunar surface, studying regolith and exospheric dust and particles, for approximately one year.
Source: https://www.thehindu.com/sci-tech/science/luna-25-failure-roscosmos-implications-moon-base-china/article67218643.ece
MALABAR-2023 (PIB)
- 11 Aug 2023
What is the News ?
Indian Navy's indigenous frontline warships INS Sahyadri and INS Kolkata will participate in Exercise MALABAR 2023.
Facts About:
- The MALABAR series of maritime exercises commenced in 1992 as a bilateral exercise between the Indian Navy and US Navy.
- Japan joined the Naval Exercises in 2015. Malabar 2020 saw the participation of the Australian Navy.
- This year marks the 27th edition of MALABAR which is being hosted by Royal Australian Navy (RAN) and will see participation from the US Navy (USN), Japan Maritime Self Defence Force (JMSDF) and the Royal Australian Navy (RAN).
- INS Sahyadri is the third ship of the indigenously designed and built Project-17 class multi-role stealth frigates.
- INS Kolkata is the first ship of the indigenously designed and built Project-15A class destroyers.
- Both ships have been built at Mazagon Dock Ltd, Mumbai and are fitted with a state-of-the-art array of weapons and sensors to detect and neutralise threats in surface, air and underwater domains.
Source: https://pib.gov.in/PressReleaseIframePage.aspx?PRID=1947436
China’s economy slides into deflation (Economic Times)
- 11 Aug 2023
What is the News ?
Facts About:
China’s recent bout of deflation, marked by a decline in consumer prices for the first time in over two years, has sparked debates about its implications and causes.
- This article delves into the intricacies of deflation, its potential impact on economic growth, and the unique circumstances driving deflation in China.
Understanding Deflation
- Deflation Defined: Deflation refers to a sustained decrease in the general price level of goods and services within an economy.
- Historical Context: Historically, the terms “inflation” and “deflation” were linked to changes in the money supply, with “inflation” representing a rise and “deflation” a fall in money supply.
Concerns Associated with Deflation
- Economic Slowdown: Many economists view deflation as an indicator of dwindling demand for goods and services, potentially leading to an economic slowdown.
- Demand-Supply Dynamics: Falling prices may prompt consumers to delay purchases, hampering demand and triggering a ripple effect throughout the economy.
- Resource Utilization: A certain level of inflation is deemed necessary for optimal resource utilization, ensuring full economic potential is realized.
Varied Perspectives on Deflation
- Positive Instances: Some economies have experienced deflation during periods of robust growth. Japan witnessed increased real income levels despite persistent deflation.
- Economic Crises: Deflation can arise during economic crises when cautious spending and resource reallocation occur.
- Consumer Demand and Prices: Some economists argue that consumer demand dictates prices, rather than the other way around.
China’s Deflation Scenario
- Policy Measures: China’s central bank maintained low interest rates to stimulate demand amid the post-pandemic recovery.
- Property Sector Turmoil: China’s pre-pandemic property sector challenges, affecting GDP contribution, may be a root cause of the current deflationary trend.
- Complex Factors: While liquidity may not be the core issue, comprehensive analysis of money supply and monetary transmission is necessary to determine the underlying cause.
Repercussions of Chinese Deflation
[A] Positive Impacts:
- Cheaper Imports: If Chinese goods become cheaper due to deflation, it could lead to lower import costs for India, benefiting consumers and businesses that rely on Chinese imports.
- Lower Input Costs: Reduced prices for raw materials and intermediate goods from China could lower production costs for Indian industries that depend on these inputs.
- Global Supply Chains: If Chinese deflation reduces the cost of production within global supply chains, Indian businesses integrated into these chains might experience cost savings.
- Improved Trade Balance: Cheaper Chinese imports can contribute to a more favorable trade balance for India, especially if it leads to reduced import bills.
[B] Negative Impacts:
- Export Competition: Cheaper Chinese exports due to deflation could increase competition for Indian exports in international markets, potentially affecting certain Indian industries.
- Import Dumping: A flood of cheap Chinese goods into the Indian market could harm domestic producers, leading to job losses and economic strain.
- Investment Flows: A slowdown in China’s economy caused by deflation might lead to reduced investor confidence and affect foreign direct investment (FDI) flows to India.
- Currency Effects: If China’s central bank devalues its currency to boost exports in response to deflation, it could lead to a stronger Indian rupee, impacting India’s export competitiveness.
- Commodity Prices: Reduced demand for commodities from China due to deflation could lead to lower global commodity prices, affecting Indian exporters of raw materials.
Conclusion
- China’s encounter with deflation amidst efforts to boost demand and stabilize its economy presents a multi-faceted challenge.
- Understanding the nuances of deflation, its interaction with demand dynamics, and China’s unique economic landscape are vital.
- As China navigates its path forward, policymakers must consider the interplay of factors, including the property sector’s impact and broader economic goals.
Source: https://www.google.com/url?sa=t&rct=j&q=&esrc=s&source=web&cd=&ved=2ahUKEwidya2w1qGBAxVcd2wGHTEWAzQQFnoECC0QAQ&url=https%3A%2F%2Fm.economictimes.com%2Fopinion%2Fet-editorial%2Fwhy-chinas-economy-is-down-not-out%2Farticleshow%2F102731901.cms&usg=AOvVaw1udWdqudtF2oR3qve57xGB&opi=89978449
NavIC to link to Aadhaar enrolment devices (The Hindu)
- 11 Aug 2023
What is the News ?
The Department of Space (DoS) has told the Parliamentary Committee of Science and Technology that the Navigation with Indian Constellation or (NavIC) is going to be integrated into Aadhaar enrolment devices.
Facts About:
About the merger:
- Need: Currently the Aadhaar enrolment kits that are used to collect and verify personal details are linked to Global Positioning system (GPS).
- The DoS has conducted successful field trials and is providing technical expertise for the finalisation of procurement specifications for the devices.
- Overall, the integration of NavIC into Aadhaar enrolment devices will enhance navigation accuracy and provide better disaster management capabilities.
- Significance:
- NavIC’s integration will enhance the accuracy and reliability of these devices.
Aadhaar authentication process:
- The Unique Identification Authority of India (UIDAI) has been created, with the mandate of providing a Unique Identity (Aadhaar) to all Indian residents.
- The UIDAI provides online authentication using demographic and biometric data.
- Aadhaar authentication is the process involves Aadhaar Number, along with other attributes, including biometrics, is submitted online to the Aadhaar system for its verification on the basis of information or data or documents available with it.
- During the authentication transaction, the resident’s record is first selected using the Aadhaar Number and then the demographic/biometric inputs are matched against the stored data which was provided by the resident during enrolment/update process.
How NavIC will ensure data protection?
- NavIC offers two services:
- Standard Position Service (SPS) for civilian users and;
- Restricted Service (RS) for strategic users.
- These two services are provided in both L5 (1176.45 MHz) and S band (2498.028 MHz).
- NavIC coverage area includes India and a region up to 1,500 km beyond the Indian boundary.
- Newer satellites will have an additional band called L1 that will be compatible with civilian use.
Present NavIC uses:
- The National Disaster Management Agency (NDMA) was already utilising NavIC as an alert dissemination system for major natural disasters like landslips, earthquakes, floods, and avalanches.
- The Indian National Centre for Ocean Information System (INCOIS) relies on NavIC to broadcast cyclones, high waves, and tsunamis alert messages to fishermen venturing into the deep sea.
Organizations working with NavIC data:
- NavIC standards were set by the Bureau of Indian Standards (BIS), Telecom Standards Development Society, India (TSDSI), Telecom Engineering Centre (TEC), Third Generation Partnership Project (3GPP), and Radio Technical Commission for Maritime Services (RTCM), International Electrotechnical Committee (IEC), and International Standards Organisation (ISO).
Concerns with GPS or other global systems:
- Threat to data security and sovereignty: System like GPS and GLONASS are operated by defence agencies of the respective nations.
- Breach of personal information: It is possible that the civilian service can be degraded or denied.
Source: https://www.thehindu.com/sci-tech/technology/indian-gps-navic-to-link-to-aadhaar-enrolment-devices/article67181022.ece
India, Japan to restart trilateral cooperation with Sri Lanka (The Hindu)
- 11 Aug 2023
What is the News ?
Sri Lanka, India and Japan are studying ways of restarting trilateral cooperation on the East Container Terminal (ECT) project in Colombo.
Facts About:
Exploring New Avenues of Collaboration
- Shared Vision for Indo-Pacific Stability: India and Japan share a vision of a Free Open and Inclusive Indo-Pacific (FOIIP), which they believe benefits all nations in the region. This common vision has provided a basis for renewed cooperation and joint initiatives.
- Potential Areas for Collaboration: The Pathfinder Foundation's paper highlights potential areas of collaboration, including renewable energy projects, grid connectivity, development of Trincomalee as an oil pipeline hub, and people-centric initiatives like tourism and education.
- Joint Economic Vision Statement: Leaders from India and Sri Lanka have issued a Joint Economic Vision Statement, setting the stage for collaborative efforts to catalyze economic growth.
- While governments will play a role in kickstarting projects, they intend to involve the private sector in investment and execution.
- Debt restructuring process:India, Japan, and France's collaborative effort in co-chairing a committee for Sri Lanka's debt restructuring process demonstrates the commitment to stabilizing the country's financial situation. This initiative aims to address debt-related challenges and foster economic recovery.
Challenges and Future Prospects
- Balancing Interests and Lessons from the Past: Officials acknowledge the challenges faced in executing joint projects, given past setbacks. The need to align interests and strategies between India, Japan, and Sri Lanka remains a crucial factor in determining the success of future collaborations.
- Toward a Resilient Indo-Pacific Partnership: Japan underscores the significance of Japan's partnership with India and Sri Lanka in realizing a Free and Open Indo-Pacific.
- Japan emphasizes creditor parity, transparency, and debt sustainability in Sri Lanka's debt restructuring process.
- Role of China: China's involvement in Sri Lanka's infrastructure projects and its status as the country's largest bilateral lender add complexity to the trilateral dynamics. China's investments in Sri Lanka have prompted concerns about debt sustainability and transparency.
- While India and Japan aim to include China in the creditors' platform for Sri Lanka's debt restructuring process, China's decision to remain an observer highlights the complexities of fostering inclusive cooperation.
Conclusion
The revival of trilateral cooperation marks a crucial step toward promoting stability and development in the Indo-Pacific region. By overcoming challenges and leveraging their collective strengths, India, Japan, and Sri Lanka have the potential to contribute to a more interconnected and prosperous future for the region.
Source: https://www.thehindu.com/news/national/india-japan-look-to-restart-trilateral-cooperation-with-sri-lanka-but-with-caution/article67180586.ece
Uniform Civil Code (Indian Express)
- 11 Aug 2023
What is the News ?
The Kerala Legislative Assembly has unanimously adopted a resolution expressing its concern over the Union Government move to impose a Uniform civil code (UCC).
Facts About:
- The Kerala Assembly resolution essentially strikes a cautious note that a proposed “UCC could harm the secular nature of the country. “
- The resolution also talks about federalism – that the Centre could make a unilateral move on the contentious issue without consulting states.
- The resolution also argued that, it is critical to note that the Uniform Civil Code was limited to Directive Principles.
What does Constitution say about UCC?
- The Constitution refers to civil code only in its Directive Principles.
- Implementation of Directive Principles is not mandatory.
- The court may order to enforce Fundamental rights. But the Directive Principles of Article 44 of the Constitution cannot be enforced even by the courts.
Can the state legislate on UCC?
- Article 162 of the Constitution:
- The issue of personal laws falls in List III —the Concurrent List of the Seventh Schedule to the Constitution.
- While subjects in the Union lists fall within the purview of the Parliament, states can legislate on subjects in the State List.
- For entries in the ‘Concurrent List’, Article 162 of the Constitution gives state governments the power to legislate on subjects where a central law does not occupy the field.
- If there is a central law, it automatically gains precedence over the state law on the subject.
- Entry 5 of Concurrent List:
- Also the Entry 5 of the Concurrent lists “Marriage and divorce; infants and minors; adoption; wills, intestacy and succession; joint family and partition; all matters in respect of which parties in judicial proceedings were immediately before the commencement of this Constitution subject to their personal law.
- This allows states the power to legislate on the subject but only in the absence of a central law.
Do states can bring their own personal laws again?
The answer to it is NO, due to following cases;
- State laws on the issues mentioned in Entry 5 of the Concurrent List will not have precedence over central legislation.
- On specific areas not covered by central legislation, states can legislate.
- But central legislation already covers all aspects of marriage, divorce, inheritance and succession.
Supreme Court’s stand:
- The Court mentioned that Article 162 of the Constitution indicates that the executive power of a State extends to matters with respect to which the Legislature of the State has power to make laws.
- In view of the provisions of Entry 5 of the Concurrent List of the Seventh Schedule, the constitution of a Committee per se cannot be challenged as ultra vires.
Source: https://indianexpress.com/article/explained/explained-law/kerala-assembly-resolution-against-uniform-civil-code-8885558/#:~:text=The%20Kerala%20Legislative%20Assembly%20on,a%20common%20personal%20law%20code.
Bill on Election Commission members’ Appointments (Indian Express)
- 11 Aug 2023
What is the News ?
A Bill is set to be introduced in the Rajya Sabha with the view of overturning the effect of the Supreme Court’s (SC) verdict on the appointment of the Chief Election Commissioner (CEC) and Election Commissioners (ECs).
Facts About:
- The Bill seeks to establish a committee of the Prime Minister, the Leader of Opposition in the Lok Sabha and a Cabinet Minister nominated by the PM for selecting members of the Election Commission of India (ECI).
- Current Procedure: Currently, the Law Minister suggests a pool of suitable candidates to the Prime Minister for consideration.
- The President makes the appointment on the advice of the PM.
- As per the Bill, a Search Committee headed by the Cabinet Secretary and comprising two other members, not below the rank of Secretary to the government, having knowledge and experience in matters relating to elections, shall prepare a panel of five persons who can be considered for appointment.
- Then, as per the Bill, a Selection Committee consisting of the Prime Minister, the Leader of Opposition in the Lok Sabha, and a Union Cabinet Minister to be nominated by the Prime Minister will appoint the CEC and other ECs.
Present structure to appoint CEC and ECs:
- Under Article 324 (2), the President appoints the CEC and other ECs.
- The President makes the appointment on the advice of the Union Council of Ministers headed by the Prime Minister.
- The Constitution does not prescribe any qualifications, academic or otherwise, for appointment to these offices.
- Tenure:
- The tenure of office and the conditions of service of all the commissioners is determined by the President.
- The tenure of commissioners is 6 years or up to the age of 65, whichever is earlier.
- The CEC and the two other ECs have the same powers and emoluments, including salaries, which are the same as a Supreme Court judge.
- All three commissioners have the same right of taking a decision. In case of a difference of opinion amongst the three members, the matter is decided by the Commission by a majority.
Process of removal:
- Article 324 of the Constitution of India mentions the provisions to safeguard and ensure the independent and impartial functioning of the Election Commission.
- The CEC is provided with security of tenure. He cannot be removed from his office except in the same manner and on the same grounds as a judge of the Supreme Court.
- Any other election commissioner or a regional commissioner cannot be removed from office except on the recommendation of the CEC.
Supreme Courts’ Judgment:
- On March 2, a five-judge bench of the Supreme Court unanimously ruled that a high-power committee consisting of the Prime Minister, Leader of Opposition in Lok Sabha, and the Chief Justice of India must pick the CEC and ECs.
- The judgement by a bench came in 2015, challenging the constitutional validity of the practice of the Centre-appointed members of the Election Commission.
- According to the judgement, the SC has now given the Opposition and the judiciary a say in the matter, ruling that the CEC and ECs must be appointed by the President on the advice of a committee comprising the PM, Leader of Opposition in Lok Sabha, and the Chief Justice of India.
- Also, in 2018, a two-judge bench of the SC referred the case to a larger bench since it required a close examination of Article 324 of the Constitution, which deals with the role of a Chief Election Commissioner.
Debate around appointment of CEC and ECs:
- Article 324(2) reads that “The Election Commission shall consist of the Chief Election Commissioner and such number of other Election Commissioners, if any, as the President may from time-to-time fix and the appointment of the Chief Election Commissioner and other Election Commissioners shall, subject to the provisions of any law made in that behalf by Parliament, be made by the President.”
- The Parliament has the power to nullify the effect of a Court ruling by addressing the concerns flagged in the judgment.
- In this case, the arrangement prescribed by the Supreme Court was specifically because the Court noted that there was a “legislative vacuum.” Filling that vacuum is well within the purview of the Parliament.
- However, the idea of an independent body that conducts elections permeates through the judgement.
- The Court repeatedly stated that to be the objective of the framers of the Constitution.
- The composition of the Selection Committee in the Bill raises questions on whether the process is now independent or still rigged in favour of the Executive.
Source: https://indianexpress.com/article/explained/explained-law/bill-election-commission-members-appointment-process-explained-8885676/#:~:text=The%20Centre%27s%20Bill%20seeks%20to,Commission%20of%20India%20(ECI).
Consultative Committees (PIB)
- 10 Aug 2023
What is the News ?
Recently, the government was asked about the constitution of consultative committees for the year 2023-24.
Facts About:
Consultative Committees.
- These committees are constituted by the Ministry of Parliamentary Affairs. Consultative Committees of different ministries are not constituted year wise.
- As per Guidelines on Constitution, Functions and Procedures of Consultative Committees, Consultative Committees shall be constituted upon constitution of each Lok Sabha.
- For 17th Lok Sabha, 40 Consultative Committees have so far been constituted.
- The maximum membership of a Consultative Committee should be limited to forty. In addition, a maximum of four Members from both Houses can also be nominated as Permanent Special Invitees. The minimum membership of the Consultative Committee shall be ten.
- There is no requirement of presence of a minimum number of Members to constitute the quorum for holding meetings of Consultative Committees.
- The Minister concerned with each Ministry/Department shall preside over the meeting of the Consultative Committee attached to his/her Ministry.
- Functions: Consultative committees provide a forum for informal discussions between the ministers and the members of Parliament on policies and programmes of the government and the manner of their implementation
Source: https://pib.gov.in/PressReleaseIframePage.aspx?PRID=1947060
Small modular nuclear reactors (SMRs) (The Hindu)
- 10 Aug 2023
What is the News ?
The recent increase in coal consumption, despite the increase in solar and wind power, suggests that reliable and low-carbon electricity resources are critical to ensure the deep decarbonisation of power generation, along with grid stability and energy security.
Small modular reactors – a type of nuclear reactor – can be helpful to India in this regard.
Facts About:
Sources of Energy Production:
- India’s Energy sector is one of the most diversified in the world. Sources of power generation range from conventional sources such as coal, lignite, natural gas, oil, hydro and nuclear power, to viable non-conventional sources such as wind, solar, agricultural and domestic waste.
- India was ranked fourth in wind power, fifth in solar power and fourth in renewable power installed capacity, as of 2020.
- Near-universal household access to electricity was achieved in 2019, meaning that over 900 million citizens have gained an electrical connection in less than two decades.
- But, the per capita electricity consumption in India is only one-third of the global average, even though the demand for energy has doubled.
- So, to catch up with the increasing demand for energy, there is a need to make arrangements for a secure and sustainable form of self-reliance in the energy sector.
What are Small Modular Nuclear reactors (SMRs)?
- Small modular reactors (SMRs) are advanced nuclear reactors that have a power capacity of up to 300 MW (e) per unit, which is about one-third of the generating capacity of traditional nuclear power reactors.
- SMRs, which can produce a large amount of low-carbon electricity using:
- Small– physically a fraction of the size of a conventional nuclear power reactor.
- Modular – making it possible for systems and components to be factory-assembled and transported as a unit to a location for installation.
- Reactors – harnessing nuclear fission to generate heat to produce energy.
Conventional Nuclear power plants vs. Small modular reactors:
- Nuclear Power Plants (NPPs) are efficient users of land and their grid integration costs are lower than those associated with variable renewable energy (VRE) sources because NPPs generate power 24x7 in all kinds of weather.
- As an alternative, several countries are developing small modular reactors (SMRs) – nuclear reactors with a maximum capacity of 300 MW – to complement conventional NPPs.
- SMRs can be installed in decommissioned thermal power plant sites by repurposing existing infrastructure, thus sparing countries from having to acquire more land and/or displace people beyond the existing site boundary.
- SMRs can be safely installed and operated at several brownfield sites that may not meet the more stringent zoning requirements for conventional NPPs.
Need for SMRs:
- According to the International Energy Agency, the demand for critical minerals like lithium, nickel, cobalt, and rare earth elements, required for clean-energy production technologies, is likely to increase by up to 3.5x by 2030.
- This jump poses several global challenges, including the large capital investments to develop new mines and processing facilities.
- The environmental and social impacts of developing several new mines and plants in China, Indonesia, Africa, and South America within a short time span, coupled with the fact that the top three mineral-producing and -processing nations control 50-100% of the current global extraction and processing capacities, pose geopolitical and other risks.
Advantages of SMRs:
- SMRs are designed with a smaller core damage frequency (the likelihood that an accident will damage the nuclear fuel) and source term (a measure of radioactive contamination) compared to conventional NPPs.
- They also include enhanced seismic isolation for more safety.
- SMR designs are also simpler than those of conventional NPPs and include several passive safety features, resulting in a lower potential for the uncontrolled release of radioactive materials into the environment.
How nuclear reactors can lead to sustainable energy generation?
- Accelerating the deployment of SMRs under appropriate international safeguards, by implementing a coal-to-nuclear transition at existing thermal power-plant sites, will take India closer to net-zero and improve energy security because uranium resources are not as concentrated as reserves of critical minerals.
- Most land-based SMR designs require low-enriched uranium, which can be supplied by all countries that possess uranium mines and facilities for such enrichment if the recipient facility is operating according to international standards.
- Further, serial manufacture of SMRs can reduce costs by simplifying plant design to facilitate more efficient regulatory approvals and experiential learning with serial manufacturing.
What are the initiatives to Achieve Self-reliance in the Energy Sector?
- Gas Based Economy
- Blending of Ethanol in Petrol
- Prime Minister UjjwalaYojana
- Renewable Energy Initiatives
- National Hydrogen Mission
Way forward:
- The aspects like investment, infrastructure development, private-public partnership, green financing, policy framework need to be strengthened both at the national level and regional level to cater to inclusiveness in the development process.
- Green energy has tremendous potential in contributing to income, employment, and entrepreneurship and undoubtedly fosters sustainable development.
- In addition to job and income generation, it opens up opportunities/avenues for investment and markets for new products and services. So, India should focus on achieving green energy and self-reliance in the Energy Sector together.
Source: https://www.thehindu.com/sci-tech/science/small-modular-reactors-india-nuclear-power-net-zero/article67175626.ece
Asian Elephant Population and Demography Estimates (The Hindu)
- 10 Aug 2023
What is the News ?
The number of elephants in Karnataka has increased according to an interim report on Asian Elephant Population and Demography Estimates, 2023.
Facts About:
- It was reported by “Asian Elephant Population and Demography Estimates, 2023”.
- The population range for elephants in Karnataka is estimated to bebetween (5,914 - 6,877).
- The report was officially released by Karnataka’s Forest Minister, ahead of World Elephant Day, which is observed on August 12 to raise awareness about the importance of protecting these endangered animals.
- The report was the result of a synchronised elephant census conducted from May 17 to 19, involving the Forest Department of Karnataka and neighbouring states including Kerala, Tamil Nadu, Andhra Pradesh, Maharashtra, and Goa.
- Among the different regions, the Bandipur Tiger Reserve stands out with the highest elephant density of 1,116 elephants and a density of 0.96 elephants per square kilometre.
The Nagarahole Tiger Reserve follows closely with 831 elephants and a density of 0.93 elephants per square kilometre.
Source: https://www.thehindu.com/news/national/karnataka/number-of-elephants-in-state-goes-up-by-364-from-last-census-touching-6395/article67176333.ece
Belem Declaration (Down to Earth)
- 10 Aug 2023
What is the News ?
The eight countries that make up the Amazon Cooperation Treaty Organization (ACTO) signed the Belém Declaration during the Amazon Summit.
Facts About:
- The leaders focused on initiating a dialogue about the sustainability of mining and fossil fuel-related activities but failed to commit to stopping oil drilling in the region.
- This lack of consensus has implications for global biodiversity goals, including those set under the Convention on Biological Diversity’s Global Biodiversity Framework in 2022, where countries agreed to protect 30% of land and sea by 2030.
About Belem Declaration:
The Belem Declaration is a statement released during the Amazon Summit, involving leaders from Amazon countries.
- It emphasizes the importance of Indigenous knowledge for biodiversity conservation and calls for Indigenous Peoples’ participation in decision-making.
- The declaration promotes sustainable forest use and diverse economic solutions, addressing concerns about deforestation and degradation in the Amazon region.
- It also underlines the need to protect land rights to prevent deforestation and preserve biodiversity within Indigenous territories.
Source: https://www.downtoearth.org.in/news/forests/belem-declaration-amazon-countries-fail-to-agree-on-protection-goals-91095
Bharat New Car Assessment Programme (The Hindu)
- 10 Aug 2023
What is the News ?
India is all set to get its own car crash safety star rating from Oct 1, 2023
Facts About:
What is Bharat NCAP?
- Bharat NCAP is a new car safety assessment programme which proposes a mechanism of awarding ‘Star Ratings’ to automobiles based upon their performance in crash tests.
- BNCAP standard is aligned with global benchmarks and it is beyond minimum regulatory requirements.
- The proposed Bharat NCAP assessment will allocate Star Ratings from 1 to 5 stars.
- The testing of vehicles for this programme will be carried out at testing agencies, with the necessary infrastructure.
Its implementation
- BNCAP will be rolled out from April 1, 2023.
- It will be applicable on type-approved motor vehicles of category M1 with gross vehicle weight less than 3.5 tonnes, manufactured or imported in the country.
- M1 category motor vehicles are used for the carriage of passengers, comprising eight seats, in addition to driver’s seat.
Significance of Bharat NCAP
- BNCAP rating will provide consumers an indication of the level of protection offered to occupants by evaluating the vehicle in the areas of:
- Adult occupant protection
- Child occupant protection
- Safety assist technologies
- It will serve as a consumer-centric platform, allowing customers to opt for safer cars based upon their Star-Ratings.
- It will also promote a healthy competition among original equipment manufacturers (OEMs) in India to manufacture safer vehicles.
- It will ensure structural and passenger safety in cars, along with increasing the export-worthiness of Indian automobiles.
- It will prove to be a critical instrument in making our automobile industry Aatmanirbhar.
Why does India need to crash-test vehicles?
- Indian vehicles have historically not been crash-tested in the country.
- Despite being home to only 1% of the world’s vehicles, India shoulders 11% of the global road crash fatality burden.
What about existing testing standards?
- India’s Central Motor Vehicle Rules (CMVR) mandate a safety and performance assessment, including a basic conformity crash test by agencies like the ARAI and ICAT when vehicles go in for type approvals.
- However, this does not involve a crash test rating.
- Many international automakers have been found to sell products in India which score much lower on safety and structural performance parameters.
- This is done to reduce costs in the price-sensitive Indian market.
- However, safety is moving up nowadays the list of key purchase criteria in India as well.
How will a homegrown NCAP help?
- Global NCAP (GNCAP) crash tests for many best-selling Indian vehicles have dismal ratings, many of them rated zero in a bias.
- The government hopes that by facilitating these tests by in-house agencies, more automakers will voluntarily undergo safety assessments and build vehicles that hold up to global standards.
How will it compare with GNCAP?
- The government wants the two tests to be in congruence with each other.
- It intends to design the?BNCAP?to?resemble?the GNCAP, the global gold standard, as closely as possible, including the speed for crash testing at 64kmph.
- Central Motor Vehicle rules encompass standards with?respect?to pedestrian protection and seat belt reminders among others and will be retained in the testing under the BNCAP.
- The government hopes the move will increase the export-worthiness of Indian automobiles.
Source: https://www.thehindu.com/news/national/explained-what-is-the-bharat-new-car-assessment-programme/article67228536.ece
India takes first step to remove animals from Drug-testing (Indian Express)
- 10 Aug 2023
What is the News ?
Recently, an amendment to the New Drugs and Clinical Trial Rules (2023) passed by the Government of India, aims to replace the use of animals in research, especially in drug testing.
Facts About:
What is the reason behind shifting to Alternative testing modes?
- The drug development journey involves rigorous testing to assess the efficacy and unintended effects.
- The first step of this process has been to test the candidate molecule in at least two animal species: a rodent (mouse or rat) and a non-rodent, such as canines and primates
- Lack of accuracy: Human response is influenced by factors like genetics and diet, leading to a significant mismatch between animal models and human responses.
- This mismatch contributes to the high failure rate during human clinical trials, highlighting the need for more accurate testing methods.
- Animals cannot consent to their own participation in research.
- Welfare of animals: Critics argue that animal testing can cause suffering and harm to animals. Animals are held in sterile, isolated cages, forced to suffer disease and injury, and typically euthanized at the end of each study.
What are Alternative testing modes?
- Organoids: These technologies encompass three-dimensional cellular structures, known as "organoids" or "mini-organs," which closely replicate the functions of specific body organs at a miniature scale.
- Organ-on-a-chip: The "organ-on-a-chip" technology employs small chips with human cells and microchannels to simulate physiological processes.
- organ-on-a-chip are AA-battery-sized chips lined with human cells connected to microchannels, to mimic blood flow inside the body.
- Additive manufacturing: 3D bioprinters use human cells as 'bio-ink' to build tissues. This could help make personalized drug tests and change how we create drugs.
What are Global regulatory frameworks that have adopted non-animal methods to test the effect and potential side-effects of new drug candidates?
- European Union: In 2021, the European Union adopted a resolution for an action plan promoting non-animal technologies in research, regulatory testing, and education.
- USA: The U.S. passed the FDA Modernization Act 2.0 in December 2022, permitting the use of these methods for drug safety and efficacy testing.
- South Korea: South Korea introduced a Bill for advancing alternatives to animal testing in December 2022.
- Canada: In June 2023, Canada amended its Environmental Protection Act to minimize vertebrate animal use in toxicity testing.
India
- In March 2023, the Indian government incorporated non-animal alternatives for drug testing and development into the drug development process by modifying the New Drugs and Clinical Trials Rules 2019.
- This step followed public input and consultation with the Drug Technical Advisory Board, which advises governments on drug-related technical issues at both the Central and State levels.
What are the challenges with these alternate methods?
- Multidisciplinary: Developing an organ-on-a-chip system requires multidisciplinary knowledge in the fields of cell biology, materials science, fluid dynamics, electronics, engineering, and pharmacology/toxicology to accurately replicate organ behavior and assess drug effects.
- At present there is a lack of focused training and expertise in India.
- Dependence of Imports: Most of the reagents, cell-culture related materials, and instruments for these technologies are currently imported from the U.S., Europe, and Japan.
- Managing Complexity: Researchers simplify recreating human tissues in the lab by minimizing components for disease simulation.
- No universal approach due to disease-specific variations; for example, a liver-on-a-chip won't fit all liver diseases.
- Variability arises from differences in lab protocols, expertise, and specific research goals. Regulators express concerns about data consistency due to these variations.
Suggestions
- Establishment of specialized institutes: Recently, a meeting organized by the Centre for Predictive Human Model Systems and Humane Society International India called for the need of specialized institutes similar to the Wyss Institute.
- WyssInsitute in Boston is a dedicated center that focuses on innovations that emulate human biology.
- The dedicated institute will facilitate effective communication and collaboration across various fields.
- Promoting innovation: Developing a comprehensive and self-sustaining ecosystem in India to address this gap in the fields of cell culture, material science, and electronics.
- Guidelines: Urgent need for guidelines establishing minimal quality criteria and standards for these systems.
- Existing guidelines on animal testing requirements need re-evaluation and updating to accommodate advancements in cell-based and gene-editing therapies.
Source: https://www.thehindu.com/sci-tech/science/animal-trials-drug-development-india-amendment-2019-rules/article67019288.ece
ECOWAS and Niger Coup: Challenges and Potential Responses (Indian Express)
- 09 Aug 2023
What is the News ?
Context: Recently there was apprehension of intervention by the ECOWAS( Economic Community of West African States) in Niger following a military coup in the country.
Facts About:
- The recent coup in Niger has brought the Economic Community of West African States (ECOWAS) into the spotlight as it grapples with responding to the political crisis in the region.
- As Niger faces economic hardships and military intervention by regional players looms, the role of ECOWAS is under scrutiny.
Understanding ECOWAS
- Formation and Membership: Established in 1975, ECOWAS aims to foster economic integration among its 15 member countries, including Benin, Burkina Faso, Ghana, Nigeria, and more.
- Objective: The organization envisions a borderless region based on democratic principles and good governance.
- Economic Goals: ECOWAS seeks to create a unified trading bloc, single currency, and enhanced cooperation in sectors such as industry, energy, and telecommunications.
ECOWAS in Conflict Resolution
- Regional Peacekeeping: ECOWAS has played a role in resolving conflicts by deploying peacekeeping missions. Notable examples include ECOMOG’s involvement in Liberia and Sierra Leone during the 1990s and early 2000s.
- Gambia Crisis: In 2017, ECOWAS intervened in Gambia, ensuring the peaceful transfer of power after then-President Yahya Jammeh refused to step down following an election defeat.
- Challenges and Successes: While ECOWAS has effectively resolved conflicts in some cases, it faces challenges due to differing interests among member countries and evolving security threats.
ECOWAS’s Response to Niger Coup
- Potential Military Intervention: ECOWAS has hinted at possible military intervention in Niger. However, regional challenges, including shared borders with other military-led nations, could complicate intervention plans.
- Support for Coups: Some military coups in West Africa have been justified by leaders citing terrorism and security challenges, accusing civilian governments of inadequacy.
- Security Situation: The ECOWAS Commission President reported a significant rise in terrorist attacks in the region, with a substantial death toll and refugees fleeing the violence.
Economic Measures and Sanctions
- Economic Sanctions: ECOWAS has previously imposed economic sanctions on countries undergoing political turmoil. However, the efficacy of these measures is questionable, especially when nations are grappling with economic difficulties.
- France’s Role: France’s historical ties to Niger and the presence of foreign troops have fueled local sentiments against foreign involvement, creating complexities for potential interventions.
Challenges and Dilemmas
- Leadership Dynamics: The current chairman of ECOWAS, Nigerian President Bola Ahmed Tinubu, advocates for military intervention in Niger. However, internal opposition and conflicting interests within ECOWAS member states complicate decision-making.
- Complexity of the Situation: The unique circumstances of each nation undergoing turmoil require tailored responses. The Niger coup’s leader, Gen. Abdourahmane Tchiani, has a history with ECOWAS peacekeeping missions.
Conclusion
- ECOWAS’s response to the Niger coup underscores the complexity of regional dynamics, the challenges of military intervention, and the delicate balance between security and democratic governance.
- As the organization grapples with finding an effective solution, its role as a mediator and peacekeeping force in West Africa continues to evolve in response to the changing geopolitical landscape.
Source: https://indianexpress.com/article/explained/explained-global/ecowas-west-africa-niger-coup-explained-8882492/
State of Elementary Education in Rural India Report (Indian Express)
- 09 Aug 2023
What is the News ?
Recently, Union Education Minister Dharmendra Pradhan launched the first State of Elementary Education in Rural India report.
Facts About:
Key Highlight of the Report:
Pan-India survey was conducted by the Development Intelligence Unit (DIU), across 6,229 rural households in 20 states, focussing on 6 to 16-year-old children in rural communities.
Equality Among Gender: Parents from rural communities believe that a child’s gender, whether a boy or a girl, should not hinder their educational aspirations.
- Total of 78 percent of parents of girls and 82 per cent of parents of boys wanted to educate their children to graduation and above.
Parental participation: About 84 percent of parentsregularly attend parent-teacher meetings, demonstrating their active involvement in their children’s education.
Role of Parents: Majority of children (62.5 per cent) are under the supervision of their mothers when it comes to their studies, while 49 per cent are supervised by their fathers.
- Over 38 per cent of parents opt for private tutors to further enhance their children’s education.
- About 26 per cent of the children study under the supervision of a private tutor.
Drop Outs: Out of the total dropped-out children, around one-fourth of male children discontinued their education during primary schooling, due tolack of interest in studies.
- Dropout rate for female children is high at 35 per cent, due to the need to contribute to the family’s earnings.
- A higher proportion of both boys and girls dropped out of school after completing the primary school education (75 per cent for boys and 65 per cent for girls).
Increased access to smartphones: Nearly half, 49.3 percent of students in rural India have access to smartphones.
- 76.7 percent of these students primarily use their phones for entertainment purposes, such as playing video games and watching movies.
- Only 34 percent of smartphone-accessible students use their devices for study-related downloads, while 18 percent access online learning through tutorials.
Learning Environment at Home: 40 percent of parents have age-appropriate reading materials available at home, beyond school books.
- Only 40 percent of parents engage in daily conversations with their children about their school learning, while 32 percent have such discussions a few days a week.
Source: https://indianexpress.com/article/education/78-parents-in-rural-india-want-their-daughters-to-study-till-graduation-and-beyond-report-8885528/#:~:text=in%20family's%20earnings.- ,According%20to%20the%20survey%2C%20one%2Dfourth%20of%20male%20children%20dropped,after%20completing%20primary%20school%20education.
Gita Mittal Committee (The Hindu)
- 08 Aug 2023
What is the News ?
Supreme Court panel flags reconstruction of lost essential documents of victims as the first healing step in Manipur.
Facts About:
The Committee
- The committee was constituted to supervise, intervene and monitor relief and rehabilitation, restoration of homesteads, religious places of worships, better relief work, etc. in Manipur.
- The committee is led by former Jammu & Kashmir High Court Chief Justice Gita Mittal, the committee includes Justices (retd) Shalini P Joshi and Asha Menon.
- This move aims to oversee various aspects beyond the investigation, such as relief, rehabilitation, and compensation for those affected by the violence.
- The committee's role extends beyond investigation, encompassing vital aspects of recovery and rebuilding.
- The primary goal behind the committee is to restore public confidence, reinforce faith in the rule of law, and rebuild trust within the affected community.
- The committee has filed three separate reports in the Supreme Court after meeting stakeholders on August 19.
The Reports
- First report – The first of the three reports submitted by the committee highlights the loss of essential documentation of the residents of Manipur who have been dis-housed.
- The committee suggests the appointment of a nodal officer to take charge of the reconstruction of these documents.
- Second report – The committee’s second report raised concerns on the Manipur Victim Compensation Scheme (MVCS).
- The committee says the MVCS needs to be substantially improved.
- The MVCS should be in the same league as the schemes framed by the National Legal Services Authority (NLSA).
- Third Report – The committee submitted a proposal for appointment of domain experts to facilitate its work.
Manipur Victim Compensation Scheme (MVCS)
- Victim Compensation Scheme (VCS) – Compensation to persons groundlessly arrested is under Section-358.
- The Government introduced the Central Victim Compensation Fund (CVCF) Scheme to enable support to victims of rape, acid attacks, human trafficking, women killed or injured in cross border firing.
- The Manipur scheme – It provides that if a victim of violence has received benefits under any other scheme, then they would not receive any compensation under the state victim compensation scheme.
- NALSA scheme – The benefit received under other schemes would be taken into consideration while determining the extent of benefits that would be additionally provided to the victims of violence.
Source:
https://www.thehindu.com/news/national/manipur-violence-supreme-court-to-pass-orders-on-august-25-to-facilitate-proper-functioning-of-justice-mittal-panel/article67218800.ece#:~:text=A%20Supreme%20Court%2Dappointed%20committee,taken%20to%20nurse%20the%20Stat
Mines and Minerals (Development and Regulation) Amendment Bill, 2023 (PIB)
- 08 Aug 2023
What is the News ?
The Rajya Sabha approved the Mines and Minerals (Development and Regulation Amendment) Bill, 2023 which seeks larger participation of the private sector in mineral exploration and production, including that for sought-after lithium.
Facts About:
Key-highlights of the Bill
The Bill amends the Mines and Minerals (Development and Regulation) Act, 1957. The Act regulates the mining sector.
Out of restrictions: The reform initiative in the Bill brings lithium out from the list of restrictive atomic minerals where permission to mine could only be granted by the Centre to government companies.
Welcomed private players: The change would allow auction of this critical mineral, used extensively for making batteries for electric vehicles, by the private sector.
Forestry clearance process: The amendment Bill will also dispense with the cumbersome forestry clearance process for mine reconnaissance and prospecting operations, making it easier for the private sector to participate in exploration of the country’s mineral resources.
Auction power: The Bill empowers the central government to exclusively auction mining lease and composite exploration licence for certain critical high value minerals such as gold, silver, platinum and copper.
Exploration licence: One of the major reforms proposed in the Bill is to introduce exploration licence for deep-seated and critical minerals. The exploration licence granted through auction will allow the licencee from private sectors to undertake “reconnaissance” and prospecting operations for critical and deep-seated minerals.
Composite mineral licence: The reform proposals in the amendment legislation also include allowing states to grant composite mineral licence without having to get central nod.
Fixing mineral-wise maximum area: It will also raise and fix mineral-wise maximum area limits for mineral concessions to provide larger and economically viable mines to investors.
- For prime minerals such as iron ore, the maximum area for prospecting licence and mining lease has been doubled to 50 sq. km and 20 sq. km respectively.
- This would allow private entries to get same land area for mining as was earlier being given to government companies and that also by the state governments itself without any need for central approval.
What are Critical Minerals?
- Critical minerals are elements that are the building blocks of essential modern-day technologies, and are at risk of supply chain disruptions.
- These minerals are now used everywhere from making mobile phones, computers to batteries, electric vehicles and green technologies like solar panels and wind turbines.
- Based on their individual needs and strategic considerations, different countries create their own lists.
Recent government interventions
Mineral Security Partnership (MSP): India joined Mineral Security Partnership (MSP),a US-led collaboration that aims to catalyse public and private investment in critical mineral supply chains globally.
- The MSP includes Australia, Canada, Finland, France, Germany, Japan, the Republic of Korea, Sweden, UK, the European Commission, Italy, and now India.
Identification of critical minerals: Recently, the Centre has identified ‘30 critical minerals’, which are essential for the country’s economic development and national security.
Source: https://pib.gov.in/PressReleaseIframePage.aspx?PRID=1947213
The Coastal Aquaculture Authority (Amendment) Bill 2023 (PIB)
- 08 Aug 2023
What is the News ?
The Government has recently introduced the Coastal Aquaculture Authority (Amendment) Bill 2023 to promote ease of doing business.
Facts About:
What is Coastal Aquaculture?
- Coastal aquaculture refers to culturing or cultivating, under controlled conditions in ponds, pens and enclosures or in coastal areas of shrimp, prawn, fish or any other aquatic life in saline or brackish water.
- Coastal aquaculture does not include freshwater aquaculture.
What is the Coastal Aquaculture Authority Act 2005?
- Coastal Aquaculture Authority - The Act introduced the Coastal Aquaculture Authority (CAA).
- The main objective of the Authority is to regulate coastal aquaculture activities in coastal areas in order to endure sustainable development without causing damage to the coastal environment.
- The authority consists of a Chairperson who is a current or former HC judge being an expert in coastal aquaculture.
- The members will be nominated by the
- Central Department of Ocean Development
- Ministry of Environment and Forests
- Ministry of Agriculture
- Ministry of Commerce
- 4 members representing coastal States on a rotation basis and one member secretary.
- Coastal area - It refers to the area declared as the Coastal Regulation Zone (CRZ), and includes such other area as the Central Government may notify under Environment Protection Act 1986.
What are the new provisions of the amendment bill 2023?
- Definition - It broadens the definition of coastal to include rearing and cultivation of any life stages of fish including crustacean, mollusc, finfish, seaweed or any other aquatic life.
- Environment friendly - It encourages environment friendly aquaculture such as cage culture, seaweed culture, bi-valve culture, marine ornamental fish culture and pearl oyster culture.
- It has the potential for creating employment opportunitiesfor coastal fisher communities especially fisherwomen.
- Brood stocks - It encourages the establishment of facilities in areas having direct access to seawater to produce genetically improved and disease-free brood stocks and seeds for use in coastal aquaculture.
- Brood stock or brood fish are a group of mature individuals used in aquaculture for breeding purposes.
- Brood Stock Multiplication Centre - The center will be used to rear marine organisms under strict biosecurity and disease surveillance.
- Usage of antibiotics - The Bill seeks to prevent the use of antibiotics and pharmacologically active substances which are harmful to human health in coastal aquaculture.
- Biosecurity - It introduces measures for analyzing and preventing the risk of introducing or spreading harmful organisms like viruses and bacteria within the coastal aquaculture unit.
Source: https://pib.gov.in/PressReleaseIframePage.aspx?PRID=1947213
Mediation Bill, 2023 (Live law)

- 08 Aug 2023
What is the News ?
The Parliament has passed the Mediation Bill 2023 to reduce pendency of court cases.
Facts About:
The Mediation Bill, 2021
- It was introduced in the Rajya Sabha in December, 2021, with the Parliamentary Standing Committee being tasked with a review of the Bill.
- The Bill aims at institutionalising mediation and establishing the Mediation Council of India.
Key Features of the Bill
Pre-litigation mediation
- Parties must attempt to settle civil or commercial disputes by mediation before approaching any court or certain tribunals.
- Even if they fail to reach a settlement through pre-litigation mediation, the court or tribunal may at any stage refer the parties to mediation if they request for the same.
Disputes not fit for mediation
- The Bill contains a list of disputes which are not fit for mediation.
- These include disputesrelating to claims against minors or persons of unsound mind, involving criminal prosecution, and affecting the rights of third parties. The central government may amend this list.
Applicability
- The Bill will apply to mediations conducted in India:
involving only domestic parties
involving at least one foreign party and relating to a commercial dispute (i.e., international mediation)
if the mediation agreement states that mediation will be as per this Bill.
- If the central or state government is a party, the Bill will apply to commercial disputes, and other disputes as notified.
Mediation process
- Mediation proceedings will be confidential, and must be completed within 180 days (may be extended by 180 days by the parties).
- A party may withdraw from mediation after two sessions.
- Court annexed mediation must be conducted as per the rules framed by the Supreme Court or High Courts.
Mediators
- Mediators may be appointed bythe parties by agreement, a mediation service provider (an institution administering mediation).
- They must disclose any conflict of interest that may raise doubts on their independence.
- Parties may then choose to replace the mediator.
Concerns Highlighted by the Parliamentary Standing Committee
Pre-Litigation
- The panel highlighted many key issues including mandatory and coercive nature of pre-litigation mediation.
- Making pre-litigation mediation necessary may result in case delays and provide another instrument in the hands of truant litigants to prolong case disposition.
Clause 26: The panel was against Clause 26of the draft which gives power to the SC or the High court to make laws of pre-litigation according to them.
Non-Applicability to Non-Commercial Disputes: The members questioned the non-applicability of the provisions of the Bill to disputes/matters of non-commercial nature involving the Government and its agencies.
Appointments: The panel had discussions about the qualifications and appointment of the Chairperson and Members of the proposed Mediation Council.
Recommendations Accepted by the Union Cabinet
Reducing the Time for Concluding a Mediation
- The Union cabinet has accepted the recommendations of the standing committee by reducing the time for concluding a mediation from 180 to 90 days.
Making Pre-Litigation Mediation Voluntary
- The recommendation for making pre-litigation mediation voluntary instead of mandatory was also much needed as voluntariness is an essential principle of mediation.
Recognition and Enforcement of Agreements
- Recognition and enforcement of settlement agreements arising out of mediation is a welcome move.
- This is also in line with India’s commitment as a signatory to the United Nations Convention on International Settlement Agreements Resulting from Mediation (Singapore Convention).
Provisions of the Final Bill that Require a Relook
Limited Grounds to Challenge a Settlement Agreement
- The limited grounds listed to challenge the enforcement of a settlement agreement and the fact that a period of 90 days is given to raise the challenge need a relook.
- The fact that a settlement agreement is essentially a contract between the parties; there are several instances where grounds for challenge such as fraud and impersonation are detected at a later stage.
Technical Flaws in Clause 8
- Clause 8 of the Bill entitles a party to move the Court before the commencement or during mediation for interim relief but only in “exceptional circumstances”.
- The term “exceptional circumstances”is not only undefined in the Bill but is also abnormal to the settled principles of seeking interim relief before the civil courts.
- Moreover, there is no remedy of appeal available against an order passed under this proposed section.
The Concept of Online and Community Mediation
- A recent Niti Aayog report reveals that only 55 per cent of India have access to the internet and only 27 per cent possess compatible devices.
- For online mediation to be a success, the government will have to scale the bandwidth accessibility to remote parts of the country.
- As for community mediation, the Bill makes it mandatory to have a panel of three mediators.This requirement is unnecessary and impinges on the flexibility that mediation brings.
Restricting the Government’s Participation in Mediation to only Commercial Disputes
- The real issue is that the government is the biggest litigant in the country.
- Restricting the ability of the government to participate in mediation proceedings arising only out of commercial disputes goes against the objective of enacting the legislation.
Way Forward
Legal Aid Setup: Setting up legal aid or access to justice clinics with adequate IT infrastructure could address the issue of online mediation.
Inclusion of Government Related Disputes in the Bill
- The standing committee had also recommended that government-related disputes be included in the Bill.
- The common litigant sees the government as an adversary before the court of law. The Bill provided a golden opportunity to the government to change that perception.
- This will inspire confidence amongst all stakeholders but would also help in reducing pendency backlog.
Conclusion
Mediation should be promoted as a preferred and voluntary mode of securing justice.
Although the legislature may have intended to lighten the load on the judiciary, the law needs to be improved because it may cause a delay in the administration of justice and raise the cost of litigation.
Source: https://www.livelaw.in/news-updates/parliament-passes-mediation-bill-234671
River Devika Rejuvenation Project (PIB)

- 07 Aug 2023
What is the News ?
Recently, Union Minister of State (Independent Charge) Science & Technology sheds light on the progress of the River Rejuvenation Project, Devika. This initiative, inspired by the Namami Ganga campaign, aims to safeguard the sacred Devika River’s purity and health.
Facts About:
Comprehensive Waste Management:
- Focus on Liquid Waste Management.
- Creation of a network of pipes and manholes connecting households.
- Objective: Efficient disposal of liquid waste, preventing pollution, and preserving the sanctity of the river.
Complementary Solid Waste Management:
- Encompasses responsible collection, disposal, and management of solid waste.
- Essential to prevent environmental degradation and maintain river and surrounding health.
Financial Allocation Breakdown:
- Project investment exceeds Rs 190 crores.
- Allocation shared between Central and Union Territory (UT) at a 90:10 ratio.
Empowering Communities through PRIs:
- Panchayati Raj Institutions (PRIs) pivotal for grassroots project success.
- PRIs’ involvement enhances community engagement, fosters ownership, and promotes sustainable development practices.
Devika River:
- Originates from Suddha Mahadev temple in Jammu and Kashmir’s Udhampur district.
- Flows through western Punjab (now Pakistan) where it merges with the Ravi River.
Cultural Significance:
- Revered by Hindus as sister of the Ganga River.
- Devika River believed to be a manifestation of Goddess Parwati, benefiting the people of MaderDesha (areas between river Ravi and Chenab).
Source: https://pib.gov.in/PressReleaseIframePage.aspx?PRID=1946187
Revised manufacturing rules for drug firms (Indian Express)
- 07 Aug 2023
What is the News ?
Recently the center government directed all pharmaceutical companies in the country to implement the revised Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP).
Facts About:
Directions by the Government:
- Larger companies with a turnover of over Rs 250 crore have been asked to implement the changes within six months.
- The medium and small-scale enterprises with turnover of less than Rs 250 crore have been asked to do so within a year.
About Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP):
- Quality Management: It is a set of guidelines and quality management principles which ensure pharmaceutical products, as well as other products in the food and healthcare industries, are consistently produced and controlled to meet quality standards appropriate for their intended use.
- Aspects Include: It covers all aspects of the manufacturing process, including the premises, equipment, personnel, materials, production, quality control, documentation, and storage of finished products.
Need for the Improved Standards:
- To match up with the Global Standards: Implementation of the new norms will bring the Indian industry on par with global standards.
- Only 2,000 of the 10,500 drug manufacturing units in the country at present meet global standards, being WHO-GMP certified.
- The improved standards will ensure that pharmaceutical companies follow standard processes, quality control measures, and do not cut corners, improving the quality of medicines available in India as well as sold in the global market.
- To improve Indian Products Image: There have been a string of incidents where other countries have reported alleged contamination in India-manufactured syrups, eye-drops, and eye ointments.
- The deaths of 70 children in the Gambia, 18 children in Uzbekistan, three persons in the United States, and six deaths in Cameroon have been linked to these products.
- To rectify the Deficiencies: A risk-based inspection of 162 manufacturing units by the government found several deficiencies — incoming raw materials not being tested before use, product quality not being reviewed , absence of quality failure investigation, infrastructure deficiency to prevent cross-contamination, faulty design of manufacturing and testing areas, missing qualified professionals, and poor documentation.
- To Provide a Structure to the Draft: Implementation of the revised good manufacturing practices (GMP) as listed in the 2018 draft schedule M of the drugs and cosmetics rules.
Major Changes & Significance:
- Standard & Reliable Quality: The revised GMP guidelines focus on quality control measures, proper documentation, and IT backing to maintain quality of medicines produced.
- Review & Validation: It introduces pharmaceutical quality systems, quality risk management, product quality review and validation of equipment.
- Thorough Investigation: Carrying regular quality reviews of all its products, verify consistency of the quality and the processes, thorough investigation of any deviation or suspected defect and implementation of any preventive actions.
- Evaluation of Changes: It also suggests a change control system to evaluate all changes that may affect the production or quality of the product.
- Maintenance of Stability & Required Conditions:The companies will also be needed to mandatorily maintain the drugs in a stability chamber, set the proper temperature and humidity, and carry out an accelerated stability test as well.
- Data Safety & Security: The guidelines also state that companies should have GMP-related computerized systems, which ensure that there is no tampering of data related to the processes.
- In case sensitive data is entered manually to the system, there will be additional checks to validate the accuracy of the data. Backups would also be created to ensure there is no loss of data.
Conclusion:
The step taken is a required and desirable one. Instituting the same quality across the industry will give confidence to regulators from other countries and will improve the quality of drugs in the domestic markets.
Source: https://indianexpress.com/article/explained/explained-health/revised-manufacturing-rules-for-drug-firms-what-changes-and-why-8879305/
5% of birds in India are endemic (The Hindu)

- 07 Aug 2023
What is the News ?
A publication, titled ‘75 Endemic Birds of India’, which was released on the 108th foundation day of the Zoological Survey of India (ZSI), points out that about 5% of birds found in the country are endemic and are not reported in other parts of the world.
Facts About:
India’s bird species:
- India is home to 1,353 bird species, which represents approximately 40% of global bird diversity.
- Of these 1,353 bird species, 78 species, which is around 5%, are endemic to the country.
About the Publication:
- The publication highlights the importance of endemic bird species in the country.
- The details of endemic bird species contained in the publication include etymology (meanings of scientific names) and their historical relevance along with vital facts such as subspecies’ differences, distinguishing traits, preferred habitats, breeding habits, and food preferences.
- Objective: The publication is aimed at making information about endemic birds of the country available to everyone, and highlighting the efforts to conserve species that are found only in restricted areas.
Highlights from the Publication:
- Around 75 bird species belong to 11 different orders, 31 families, and 55 genera, and exhibit remarkable distribution patterns across various regions in India.
- The highest number of endemic species has been recorded in the Western Ghats, with 28 bird species.
- Some of the rare species recorded in the country’s bio-geographic hotspot are;
- The Malabar Grey Hornbill (Ocycerosgriseus)
- Malabar Parakeet (Psittaculacolumboides
- Ashambu Laughing Thrush (Montecinclameridionalis)
- The White-bellied Sholakili (Sholicolaalbiventris)
- Amongst them 25 bird species are endemic to the Andaman and Nicobar Islands. Bird species which are only found in the Andaman and Nicobar Islands are;
- Nicobar Megapode (Megapodiusnicobariensis);
- Nicobar Serpent Eagle (Spilornisklossi);
- Andaman Crake (Rallinacanningi); and
- Andaman Barn Owl (Tytoderoepstorffi).
- Four species of birds are endemic to the Eastern Himalayas, and one each to the Southern Deccan plateau and central Indian forest.
- Of the 78 endemic species, 25 are classified as ‘Threatened’ by the IUCN.
- Three species are listed as ‘Critically Endangered’.
- Five of the endemic birds in India are categorised as ‘Endangered’, and
- 17 as ‘Vulnerable’,
- While 11 are categorised as ‘Near Threatened’ on the IUCN Red List.
Source: https://www.thehindu.com/sci-tech/energy-and-environment/5-of-birds-in-india-are-endemic-reveals-zoological-survey-of-india-publication/article67162268.ece#:~:text=India%20is%20home%20to%201%2C353,are%20endemic%20to%20the%20country
India's Sugar Surplus and its Impact on Agriculture (The Hindu)

- 07 Aug 2023
What is the News ?
India became the world’s top sugar producer in 2021-2022, surpassing Brazil, but the extensive use of resources in sugar production is depleting rapidly, leading to a potential crisis in the future.
Facts About:
The Factors Behind Excessive Sugar Production
- The phenomenon of India's excess sugar production can be attributed to a confluence of factors, including government policies and measures aimed at promoting sugarcane cultivation. At the heart of this lies the fair and remunerative price (FRP) scheme, a government initiative ensuring that sugar mills pay sugarcane farmers a minimum price, thereby ensuring their fair profits
- State governments have further incentivized sugarcane cultivation through substantial subsidies, which some critics argue are aimed at securing the votes of farmers in politically influential rural regions.
- The repercussions of these policies have led to a significant sugar surplus, driving up exports to record levels. However, this expansionary approach has not escaped global scrutiny. Brazil, Australia, and Guatemala raised objections with the World Trade Organization (WTO), alleging that India's excessive export subsidies and domestic support violate international trade rules. The subsequent ruling against India by the WTO underscored the global ramifications of this sugar surplus.
Addressing the Excess Sugar Production: Ethanol as a Solution
- To mitigate the challenges posed by surplus sugar production, the Indian government has explored alternative avenues, with a focus on diverting excess sugar to ethanol production. Ethanol, a versatile organic compound derived from fermenting sugarcane molasses or sugar, has a range of applications in various industries, from alcoholic beverages to chemicals and cosmetics.
- In the realm of transportation, ethanol-blended petrol (EBP) has emerged as an effective strategy to reduce harmful emissions from vehicles, contributing to reduced crude oil imports and greenhouse gas emissions.
- The government's Ethanol Blended Petrol (EBP) program, initiated in 2003, has made significant strides, aiming to achieve a blending rate of 20% by 2025. Reductions in the Goods and Services Tax (GST) on ethanol have further supported this transition.
- Efforts to channel a substantial portion of sugar towards ethanol production have yielded positive results, highlighting a potential solution to the problem of excess sugar.
Groundwater Depletion and Environmental Consequences
- While India's EBP program has succeeded in reducing certain imports and emissions, it has also unearthed environmental concerns associated with sugarcane cultivation. The intensive water requirements of sugarcane, coupled with over-cultivation, have significantly impacted groundwater resources. This trend is particularly pronounced in India's top sugarcane-growing states, which rely heavily on groundwater for irrigation.
- With sugarcane demanding approximately 3,000 mm of rainfall for optimal growth, regions that typically receive 1,000-1,200 mm of rainfall resort to excessive groundwater extraction from confined aquifers. A startling statistic emerges – the cultivation of 100 kg of sugar necessitates a staggering two lakh liters of groundwater for irrigation. This alarming scenario has escalated concerns, particularly in drought-prone and groundwater-stressed areas, threatening the availability of this vital resource.
Sustainable Solutions and the Path Forward
- To safeguard India's agricultural sector from a looming crisis and ensure its long-term sustainability, a multifaceted approach is imperative. While the allure of financial gains from sugar surplus and exports is undeniable, a shift towards balanced and sustainable agricultural practices is essential.
Diversified Subsidy Schemes
- A crucial step involves reevaluating incentive structures that disproportionately favor sugarcane cultivation over other crops. By introducing comprehensive and fair subsidy schemes for a variety of crops, farmers can be encouraged to diversify their cultivation practices. Such measures can prevent monocultures, promote equitable income distribution, and contribute to more efficient resource utilization.
Environmentally Responsible Cultivation
- The adoption of environmentally conscious cultivation practices holds the key to mitigating the groundwater depletion crisis. Implementing methods such as drip irrigation, which directs water directly to the roots of sugarcane plants, can significantly reduce water consumption compared to traditional flood irrigation techniques. Government support through subsidies for setting up drip irrigation systems can accelerate this transition.
Integrated Water Management
- India's agricultural landscape requires a comprehensive approach to water management, encompassing rainwater harvesting, wastewater treatment, and improved canal irrigation networks. By minimising stress on groundwater reservoirs and exploring alternative water sources for irrigation, the strain on vital resources can be alleviated.
Investment in Research
- Despite significant strides, gaps remain in understanding groundwater availability and distribution. Investing in comprehensive groundwater research and data collection is essential for informed decision-making and sustainable resource management.
Conclusion:
As India assumes a prominent role in the global agricultural arena, the imperative for sustainability becomes increasingly apparent. While the achievements in sugar production are commendable, the nation must navigate the delicate balance between economic gains and environmental responsibility. By reassessing subsidy structures, promoting diversified cultivation practices, and embracing environmentally conscious techniques, India can pave the way for a resilient agricultural sector that not only based on the article: meets domestic demands but also ensures the well-being of future generations.
Source: https://www.thehindu.com/sci-tech/energy-and-environment/india-excess-sugar-production-guzzling-groundwater/article67157121.ece
Organ shortage continues to cost lives (The Hindu)
- 07 Aug 2023
What is the News ?
According to recent data, around three lakh patients wait for organ donation in the country.
About:
- the number of donors (including cadavers) grew from 6,916 in 2014 to only 16,041 in 2022.
- The country registered 1,589 kidney, 761 liver and 250 heart transplants in the deceased category that year.
- Kidney and pancreas transplants grew from 3 in 2014 to 22 in 2022.
- In contrast, living donor kidney transplants rose from 4,884 in 2014 to 9,834 in 2022.
- Liver transplants in this category grew from 1,002 to 2,957
- one person is added to the waitlist every 10 minutes in the country
Ministry’s steps to enhance organ donations
- doing away with the domicile rule
- removal of age bar for registration of recipients
- removal of fee for registration for transplant
- easing rules on withdrawal of life support (passive euthanasia)
- facilitation of organ transport across the country
- giving special casual leave for employed organ donors
The annual need for 2,00,000 kidney transplants highlights the pressing urgency of the situation.
- However, a mere 10,000 transplants are performed each year, revealing a staggering gap.
- The demand for deceased donors is substantial because many families lack suitable living donors.
- Therefore, relying on deceased donors can help partially meet this demand
- statistics indicate around 70%-75% of donors are women. Wives, mothers, and sisters have emerged as the most prevalent sources of donatio
Organ donation pledges in India need to translate into actual donations and for that, medical staff need to be educated.
- They must be able to recognise, identify, inform, and counsel familiesabout brain death and the importance of organ donation.
- The gap between demand and supply continues to be tremendous. So, there is a need to equip our ICU staff with knowledge and awareness, the sooner the gap will close.
Greater awareness will improve in following way
- One cadaver can save up to eight lives.
- Two donated kidneys can free two patients from dialysis treatment.
- One donated liver can be split among two patients on the waitlist.
- Two donated lungs mean two other patients are given a second chance, and a donated pancreas and donated heart translate to two more patients receiving the gift of life.
- One tissue donor — someone who can donate bone, tendons, cartilage, connective tissue, skin, corneas, sclera, and heart valves and vessels — can save the lives of as many as 75 people.
Source: https://www.thehindu.com/sci-tech/health/indias-poor-organ-donation-record-continues-to-cost-lives/article67161978.ece#:~:text=Three%20lakh%20patients%20wait%20for,donor%20can%20save%20several%20lives
STARFIRE Algorithm (PIB)

- 25 Jul 2023
Why in the News?
Researchers at Raman Research Institute (RRI) have recently successfully created an algorithm named STARFIRE.
Facts About STARFIRE Algorithm:
- The STARFIRE Algorithm, also referred to as the Simulation of TerrestriAl Radio Frequency Interference in oRbits around Earth (STARFIRE) algorithm, is designed for its specific application in modeling and analyzing terrestrial radio frequency interference within Earth's orbits.
- The model possesses several advantages, including its capability to estimate Radio Frequency Interference (RFI) emitted by various sources such as FM radio stations, Wi-Fi networks, mobile towers, radar, satellites, and communication devices.
This estimation aids in designing and fine-tuning antennas for optimal performance.
- The algorithm can effectively estimate and map unwanted RFI signals in space, providing valuable insights for enhancing data quality from future space-based Astronomy missions.
- By facilitating the design of instruments capable of operating optimally in the presence of RFI, the algorithm significantly enriches the data obtained from future space missions.
- Another noteworthy advantage of the STARFIRE Algorithm is its usefulness in orbit selection for upcoming missions, contributing to better planning and execution.
- To develop this model, scientists utilized data from FM transmitter stations in six countries worldwide, including Canada (8,443 stations), USA (28,072 stations), Japan (Tokyo - 21 stations), Australia (2,664 stations), Germany (2,500 stations), and South Africa (1,731 stations), making the model comprehensive and robust.
Biological Diversity Amendment Bill (The Hindu)

- 25 Jul 2023
Why in the News?
The Lok Sabha recently passed the Biological Diversity (Amendment) Bill, 2021, aimed at modifying the provisions of the Biological Diversity Act, 2002.
About Biological Diversity Act, 2002:
The act was enacted in 2002, it aims at the conservation of biological resources, managing its sustainable use and enabling fair and equitable sharing benefits arising out of the use and knowledge of biological resources with the local communities.
Regulatory Structure: The act envisaged a three-tier structure to regulate the access to biological resources:
- The National Biodiversity Authority (NBA) at the national level.
- State Biodiversity Boards(SBB) at the state level.
- Biodiversity Management Committees at the local body level.
- Under the Biological Diversity Act of 2002, provisions are made to share benefits with biodiversity conservers, holders, and creators of associated knowledge. These benefits encompass monetary compensation, sharing of Intellectual Property Rights (IPRs), and technology transfer.
Amendments Made in Biodiversity Bill 2021:
- Regarding Access to biological resources and associated knowledge, It amends the classification of entities, list of activities requiring intimation, and adds exemptions.
- Approval for Intellectual Property Rights (IPR) will be required before the grant of IPR instead of before the application itself.
- SBB will determine benefit sharing while granting approvals to domestic entities as per the regulations by NBA.
- The Bill decriminalises the offences and makes offences punishable with a penalty between one lakh rupees and Rs 50 lakh.
Significance of the Biological Diversity (Amendment) Bill 2021:
The Bill seeks to amend the 2002 Act to:
- Simplify compliance requirements for domestic companies.
- Encourage the Indian system of medicine and cultivation of wild medicinal plants,
- Facilitate fast-tracking of processes for research, patent application, and transfer of research results,
- Decriminalise offences, and
- Encourage foreign investment in the sector.
Asset Reconstruction Companies (ARCs) (LiveMint)

- 25 Jul 2023
Why in the News?
Taking advantage of the substantial number of written-off loans held by lenders and the government's recovery endeavors, ARCs are seizing the opportunity to acquire these loans.
About Asset Reconstruction Companies (ARCs):
- The Asset Reconstruction Company (ARC) functions as a distinct financial institution that acquires Non Performing Assets (NPAs) from banks and financial institutions, facilitating the process of cleansing their balance sheets.
- This enables banks to focus on their core banking activities. Instead of expending time and effort pursuing defaulters, banks can opt to sell the troubled assets to ARCs at a mutually agreed-upon value.
Legal Basis:
- The establishment of ARCs in India is supported by the Securitization and Reconstruction of Financial Assets and Enforcement of Security Interest (SARFAESI) Act, 2002.
- The SARFAESI Act streamlines the reconstruction of bad assets, avoiding the need for court intervention.
- Subsequently, numerous ARCs were established and registered with the Reserve Bank of India (RBI), which holds regulatory authority over these institutions.
Capital Needs for ARCs:
- Following the 2016 amendment to the SARFAESI Act, ARCs were mandated to possess a minimum Net Owned Fund of Rs. 2 crores. However, in 2017, the RBI increased this threshold to Rs. 100 crores.
- ARCs must maintain a Capital Adequacy Ratio (CAR) equivalent to 15% of their risk-weighted assets.
Krishnaraja Sagar (KRS) Dam (The Hindu)
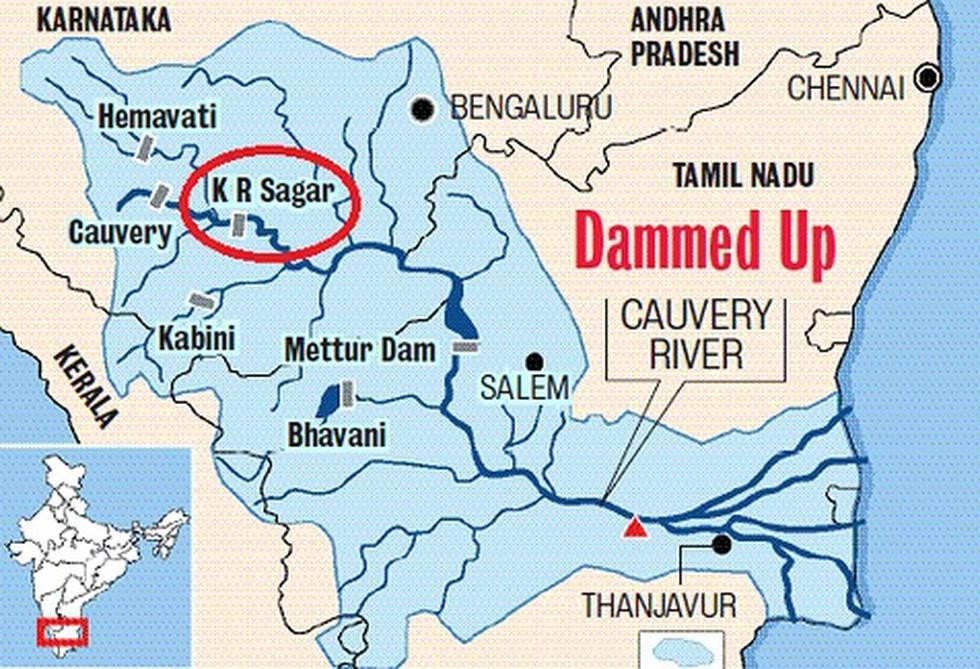
- 25 Jul 2023
Why in the News?
Due to heavy rainfall in the river's catchment area, the water level in the Krishnaraja Sagar (KRS) across the Cauvery recently surpassed the 100-ft mark, although its capacity reaches 124.80 feet.
About Krishnaraja Sagar (KRS) Dam:
- Situated in Karnataka's Mandya district, it lies beneath the merging point of the Kaveri river with its tributaries, Hemavati and Lakshmana Tirtha.
- It is a type of gravity dam.
- The dam is named for the then ruler of the Mysore Kingdom, Krishnaraja Wodeyar IV.
- The dam was designed by Sir M. Visvesvaraya, a famous Indian engineer.
- The reservoir is also the main source of drinking water for all of Mysore city and almost the whole of Bangalore.
- The water released from this dam is further used as an important source of water in the state of Tamil Nadu.
- An ornamental garden named “Brindavan Gardens” is attached to the dam.
Kaveri River:
- Kaveri or Cauvery is a sacred river of southern India. It is known as the Ganga of South India.
- It rises on Brahmagiri Hill of the Western Ghats in southwestern Karnataka state.
Drainage Basin:
- It flows in a southeasterly direction through the states of Karnataka and Tamil Nadu, and descends the Eastern Ghats in a series of great falls.
- Before emptying into the Bay of Bengal south of Cuddalore, Tamil Nadu, the river breaks into a large number of distributaries forming a wide delta called the “garden of southern India.”
Tributaries of Kaveri:
- Arkavathi, Hemavathi, Lakshmana Theertha, Shimsa, Kabini and Harangi.
National Commission for Protection of Child Rights (NCPCR) (Indian Express)

- 25 Jul 2023
Why in the News?
The National Commission for Protection of Child Rights (NCPCR) recently addressed the Manipur DGP, urging the filing of an FIR against three individuals.
About the National Commission for Protection of Child Rights (NCPCR):
- NCPCR is a statutory body set up in March 2007 under the Commissions for Protection of Child Rights (CPCR) Act, 2005.
- It is under the administrative control of the Ministry of Women & Child Development.
- The Commission's mandate is to ensure that all laws, policies, programmes, and administrative mechanisms are in consonance with the child rights perspective as enshrined in the Constitution of India and also the UN Convention on the Rights of the Child.
- It inquires into complaints relating to a child's right to free and compulsory education under the Right to Education Act, 2009.
- It monitors the implementation of Protection of Children from Sexual Offences (POCSO) Act, 2012.
Composition of NCPCR:
- This commission has a chairperson and six members of which at least two should be women.
- All of them are appointed by Central Government for three years.
- The maximum age to serve in commission is 65 years for Chairman and 60 years for members.
Functions and responsibilities of NCPCR:
- Examine and assess current safeguards for child rights and propose effective implementation strategies.
- Submit periodic reports to the central government on the efficacy of these safeguards.
- Conduct investigations into child rights violations and recommend legal action when appropriate.
- Raise awareness about child rights and available safeguards through diverse channels, such as publications, media, and seminars.
- Conduct inspections of institutions housing children, including juvenile homes, and suggest remedial measures if required.
- Investigate complaints and proactively address issues related to child rights deprivation, violation, and non-implementation of protective laws.
National Dental Commission Bill, 2023 (TIO)
- 24 Jul 2023
Why in the News?
The Lok Sabha recently witnessed the introduction of the National Dental Commission Bill, 2023, by the government.
About National Dental Commission Bill, 2023:
- The primary objective of the Bill is to revoke the Dentists Act of 1948, ushering in new regulations and reforms.
- With a focus on affordability, the bill strives to enhance dental education accessibility and ensure quality oral healthcare services.
- In place of the existing Dental Council of India, the Bill proposes the establishment of the National Dental Commission (NDC) to oversee dental education and related matters effectively.
What is National Dental Commission (NDC)?
- The establishment of the new commission entails the formulation of policies and the maintenance of quality standards in dental education and the dental profession.
- A key responsibility of the commission will be to regulate fees for 50% of seats in private dental colleges.
Composition of NDC:
- The structure of the NDC will mirror that of the National Medical Commission (NMC), which replaced the Medical Council of India.
- The head office of the National Dental Commission will be located in New Delhi, consisting of a chairperson, eight ex officio members, and 24 part-time members and the appointment of members will be done by the central government.
- The Bill mandates that all members of the commission must declare their assets and liabilities upon entering and leaving office, along with disclosing any professional and commercial engagements they are involved in.
ISRO's PSLV-C56 (The Hindu)

- 24 Jul 2023
Why in the News?
ISRO recently declared that the launch of the PSLV-C56, carrying Singapore's DS-SAR satellite, is scheduled for July 30th.
Facts About PSLV-C56:
- From the Satish Dhawan Space Centre in Sriharikota, the PSLV-C56 is all set to embark on its mission, carrying the DS-SAR satellite and six additional co-passengers.
- Just like C55, the PSLV-C56 will be configured in its core-alone mode, ensuring a streamlined and efficient launch process.
- The primary objective of the mission is to deploy the DS-SAR satellite, weighing 360 kg, into a Near-equatorial Orbit (NEO) with a precise inclination of 5 degrees and an altitude of 535 km.
What is The DS-SAR satellite?
- The DS-SAR satellite is a collaborative effort between DSTA, representing the Government of Singapore, and ST Engineering.
- Its primary purpose is to cater to the satellite imagery needs of diverse governmental agencies within Singapore.
- ST Engineering intends to utilize the satellite for multi-modal and more responsive imagery and geospatial services, serving their commercial clientele effectively.
- The DS-SAR is equipped with a sophisticated Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) payload, developed by Israel Aerospace Industries (IAI).
- This advanced technology enables the DS-SAR to offer all-weather day and night coverage, providing imaging capabilities at an impressive 1m resolution with full polarimetry.
Silver cockscomb (Down To Earth)

- 24 Jul 2023
Why in the News?
The silver cockscomb plant, which is typically thought of as a weed but has been shown to have benefits, is used by the Soliga tribal community.
About Silver cockscomb:
- This plant is a short-lived, reaching a height of 50-60 cm, often considered a weed, displaying simple, spirally arranged leaves with pinkish or silky white flowers.
- In Karnataka's Chamarajanagara district, it is locally known as "anne soppu," while in other regions, it is referred to as "lagos spinach."
- It belongs to the Amaranthaceae family, which includes economically significant plants like spinach (Spinacia oleracea), beetroot, and quinoa.
- Scientifically named Celosia argentea, it goes by the names "kurdu" in Marathi and "pannai keerai" in Tamil.
- The plant thrives even on fallow land and in drought-like conditions, displaying resilience and adaptability.
- Notably, its leaves have lower levels of oxalic acid and phytic acid, making it nutritionally beneficial for consumption.
Soliga Tribe:
- They are an indigenous tribe of Karnataka.
- Their settlements are located in the outskirts of Biligiri Rangana Hills and Male Mahadeshwara in the Chamarajnagar district of Karnataka, amidst the surrounding forest areas.
- Notably, they hold the distinction of being the first tribal community residing within a tiger reserve in India to have their forest rights formally acknowledged and recognized by a court of law.
Mhadei Wildlife Sanctuary (The Hindu)
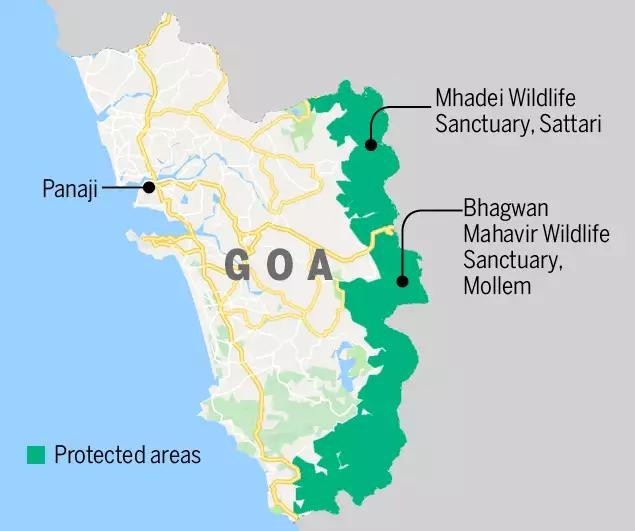
- 24 Jul 2023
Why in the News?
In a recent development, the Government of Goa has been directed by the Goa Bench of the Bombay High Court to take action within the next three months. Specifically, they are required to officially designate the 208 sq. km. Mhadei Wildlife Sanctuary (WLS) along with its adjoining areas as a tiger reserve, as per the court's decision.
Key Facts About Mhadei Wildlife Sanctuary:
Location:
- It is located in the Northern Part of Goa, Sanguem taluka, near Valpoi town.
- The sanctuary is named after the Mhadei River (also known as Mandovi River), which originates from the Sahyadri range of mountains in Karnataka (Belgaum district) and falls in the Arabian Sea at Panaji crossing Goa.
- There are a number of picturesque waterfalls, including Vazra Sakla Falls and Virdi Falls.
- It is known for its nesting grounds of critically endangered Long-billed vultures near Vazra Falls.
Flora and Fauna
- The sanctuary is abundant with lush vegetation, characterized by a dense cover of moist deciduous trees, interspersed with pockets of evergreen species.
- t is particularly well-known for its sacred groves that protect rare and indigenous trees.
- Faunas like Indian gaur, Barking deer, Sambar deer, Asian palm civet, small Indian civet, Wild boar, Indian hare etc. found here.
- The sanctuary holds immense allure for herpetologists due to its impressive diversity of snakes, encompassing all four of India's notorious venomous species - the Indian krait, Russell's viper, Saw-scaled viper, and Spectacled cobra.
Meri Maati Mera Desh campaign

- 24 Jul 2023
Why in the News?
The 'Meri Maati Mera Desh' campaign has been recently launched by the Union government of India, as a culminating event of the 'Azadi Ka Amrit Mahotsav' celebration, commemorating 75 years of Indian Independence.
About Meri Maati Mera Desh campaign:
- Soil collected from various parts of the country during August will be utilized to create a garden along the Kartavya Path in Delhi.
- Events have been planned at different levels including panchayat, village, block, urban local bodies, and state and national levels, respectively.
- The five-point agenda includes the installation of a shilaphalakam (memorial plaque) bearing the names of those who made the supreme sacrifice, following specific specifications.
- Execution of the shilaphalakam project can be undertaken through the Mahatma Gandhi National Rural Employment Guarantee Act (MGNREGA) by leveraging local materials and resources.
- 'Vasudha Vandhan' aims at every gram panchayat or village renewing Mother Earth by planting 75 saplings of indigenous species and creating an Amrit Vatika.
- 'Veeron Ka Vandan' will honor freedom fighters and the families of deceased freedom fighters.
- Young volunteers and others will collect soil from each panchayat/village and bring it to the block, from where the 'Mitti Kalash' will be transported to Delhi.
- Urban areas will organize events at local bodies, notified area councils, Cantonment Boards, and town panchayats from August 9 to 15, and in larger municipalities and municipal corporations from August 16 to 20.
- The 'Mitti Kalash' will be ceremoniously brought to the larger municipalities/corporations and then transported to Kartavya Path.
