Empowered Committee for Animal Health (ECAH)
- 13 Nov 2025
In News:
The Empowered Committee for Animal Health (ECAH) is India’s apex, evidence-driven policy body guiding animal health governance. Established in 2021, it functions as the think tank of the Department of Animal Husbandry and Dairying (DAHD) under the aegis of the Office of the Principal Scientific Adviser (PSA) to the Government of India.
Composition and Mandate
- Chair: Principal Scientific Adviser to the Government of India
- Vice-Chair: Secretary, DAHD
- Members: Experts from Central Drugs Standard Control Organisation (CDSCO), Department of Biotechnology (DBT), Indian Council of Agricultural Research (ICAR), Indian Council of Medical Research (ICMR), Indian Veterinary Research Institute (IVRI), Veterinary Council of India (VCI), academia, and industry.
- Core Role: Provide strategic guidance on national animal health programmes, emerging disease threats, One Health initiatives, and regulatory frameworks for veterinary vaccines, drugs, and biologicals.
Functions
- Act as a national think tank for animal health programmes of importance.
- Streamline regulatory approvals by assessing safety, efficacy, and quality of veterinary products.
- Promote innovation uptake and resilient, farmer-centric animal health systems.
- Assess and advise on emerging animal diseases with epidemic/pandemic potential.
9th ECAH Meeting (July 2025): Key Outcomes
Held in New Delhi under DAHD, the meeting-chaired by the PSA-reviewed progress and charted the roadmap for animal health strengthening. Emphasis areas included farmer awareness, vaccination coverage, antimicrobial resistance (AMR), and regulatory reforms to improve access to quality veterinary products.
Major Milestones Reported
National Disease Control Programmes (Vaccination):
- FMD: 124.10 crore doses
- PPR: 28.89 crore doses
- Brucellosis: 4.77 crore doses
- Classical Swine Fever: 0.88 crore doses
- Vaccination records digitised via Bharat Pashudhan app.
- Animal Vaccine Intelligence Network (AVIN) pilots for real-time cold-chain monitoring.
- All programme vaccines are indigenously developed, reinforcing Atmanirbhar Bharat; India also exports vaccines.
Disease-Free Compartments & International Recognition:
- India’s first Equine Disease-Free Compartment (EDFC) endorsed by World Organisation for Animal Health (WOAH) (July 2025), enabling global movement of Indian sport horses.
- 44 HPAI (Avian Influenza) compartments approved for biosecure, export-ready poultry systems.
- ICAR–NIHSAD, Bhopal recognised as a Category A Rinderpest Holding Facility by WOAH and Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO)-placing India among a small global cohort.
- Additional WOAH reference labs recognised for Equine Piroplasmosis (Hisar) and Epizootic Ulcerative Syndrome in fish (Lucknow).
Laboratory & Surveillance Capacity:
- Under the Pandemic Fund Project:
- Indian Network of Genomic Surveillance (INGeS): 11 labs
- Indian Network on Transboundary Animal Diseases & EIDs: 19 labs
- Push for NABL accreditation of CDDLs/RDDLs and State ADLs; launch of “Rate My Lab” for transparency and benchmarking.
Unified Payments Interface (UPI) Block Mechanism
- 13 Nov 2025
In News:
The Unified Payments Interface (UPI) block mechanism is an emerging reform in India’s capital markets aimed at enhancing investor protection and fund safety in secondary market trading. Recently, the market regulator Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI) proposed making this facility mandatory for Qualified Stock Brokers (QSBs), drawing parallels with the well-established Application Supported by Blocked Amount (ASBA) system used in the primary market.
What is the UPI Block Mechanism?
- It allows investors to trade in the secondary market using funds blocked in their bank accounts, rather than transferring money upfront to the trading member.
- The actual debit occurs only when a trade is executed, while the remaining funds stay safely in the investor’s bank account.
- The mechanism is conceptually similar to ASBA, but extended to secondary market transactions.
Key Features
- Funds remain in the investor’s bank account, with only a lien/block created.
- Reduces the risk of misuse or diversion of client funds by intermediaries.
- Currently optional for investors and not mandatory for trading members, though SEBI has proposed mandatory adoption for QSBs.
- SEBI has also sought feedback on whether a “3-in-1 trading account” (bank + demat + trading) can be allowed as an alternative.
Role of Qualified Stock Brokers (QSBs)
- Trading members are classified as QSBs based on:
- Number of active clients
- Total client assets held
- Trading volumes
- End-of-day margins
- Being a QSB entails higher regulatory responsibilities and compliance standards.
- SEBI’s proposal targets QSBs first due to their scale and systemic importance.
Link with ASBA
Application Supported by Blocked Amount (ASBA):
- Introduced by SEBI in 2008.
- Mandatory for IPOs and rights issues.
- Allows investors to apply for issues by blocking funds in their bank account, with debit only after allotment.
- Prevents premature transfer of investor money and improves transparency.
The UPI block mechanism mirrors this principle but applies it to secondary market trading.
Regulatory Background
- UPI, developed by the National Payments Corporation of India (NPCI) and regulated by the Reserve Bank of India (RBI), was launched in 2016.
- SEBI mandated UPI-based payments with fund blocking for IPO applications in 2019.
- In January 2024, SEBI introduced a single-block, multiple-debits UPI mechanism for secondary market use, paving the way for the current proposal.
Significance
- Enhanced investor protection by keeping funds under the investor’s control.
- Improves trust and transparency in secondary market operations.
- Aligns with SEBI’s broader objective of segregation and safety of client funds.
- Reduces settlement risk and strengthens market integrity.
Astrophysical Jets
- 13 Nov 2025
In News:
Astrophysical jets are highly collimated outflows of ionised matter (plasma) ejected at relativistic speeds from extreme celestial environments such as black holes, neutron stars, and pulsars. Understanding their plasma composition is crucial to decoding the physical processes operating near these compact objects.
What are Astrophysical Jets?
- Extended, beam-like streams of plasma emitted along the rotation axes of compact objects.
- Travel vast distances (from parsecs to kiloparsecs) and interact with surrounding interstellar or intergalactic media.
- Powered by strong gravitational and magnetic fields near compact objects.
Why Plasma Composition Matters
- For decades, it has been unclear whether jets are composed of:
- Electron-positron pairs, or
- Electron-proton plasma, or
- A mixture of electrons, positrons, and protons.
- Plasma composition determines the jet’s:
- Internal energy
- Propagation speed
- Shock structure
- Stability and turbulence
- These properties directly affect how jets evolve and how they appear in astronomical observations.
Recent Scientific Findings
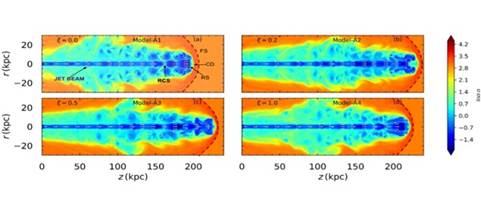
Scientists from the Aryabhatta Research Institute of Observational Sciences (ARIES), an autonomous institute under the Department of Science and Technology, have studied how plasma composition influences jet dynamics.
- The research, used:
- A relativistic equation of state (accounting for plasma composition),
- Advanced numerical simulations of jet propagation.
- The findings were published in the Astrophysical Journal.
Key Results of the Study
- Jets with identical initial conditions (same density, pressure, and Lorentz factor) can behave very differently solely due to plasma composition.
- Electron–positron jets were found to be slowest, despite positrons being much lighter than protons.
- Electron–proton jets propagate faster because plasma composition alters the thermodynamic properties of the jet.
- This result is counter-intuitive, as protons are about 2,000 times heavier than electrons or positrons.
Impact on Jet Structure and Stability
- Plasma composition affects:
- Number and strength of recollimation shocks (shocks formed due to interaction with backflowing material),
- Shape and dynamics of reverse shocks,
- Degree of turbulence within the jet.
- Electron–positron jets develop stronger turbulent structures, leading to:
- Jet deceleration,
- Reduced long-term stability.
Nemaline Myopathy
- 13 Nov 2025
In News:
Nemaline myopathy is a rare, inherited neuromuscular disorder that primarily affects skeletal muscles, leading to muscle weakness and impaired mobility. Recently, the condition drew public attention after D. Y. Chandrachud, the Chief Justice of India, spoke about his foster daughters’ experience with the disease, highlighting the lack of awareness, delayed diagnosis, and need for better support systems for children living with rare genetic disorders.
What is Nemaline Myopathy?
- Also known as rod myopathy, it is characterised by the presence of thread-like (rod-shaped) structures called nemaline bodies within muscle fibres.
- It is a congenital genetic disorder, caused by mutations in genes encoding muscle proteins.
- Prevalence: Approximately 1 in 50,000 births.
- The disease shows wide variability in severity, ranging from mild muscle weakness to severe, life-threatening forms.
Genetic Basis
- The disorder is hereditary, arising due to genetic mutations—permanent changes in a gene’s DNA sequence.
- These mutations disrupt the structure and function of muscle proteins, impairing muscle contraction.
- Nemaline myopathy is classified into six types, based on age of onset and severity:
- Severe congenital
- Intermediate congenital
- Typical congenital (most common)
- Childhood-onset
- Adult-onset (mildest form)
- Amish type (rare)
Clinical Features
- Muscle weakness, especially in:
- Face and neck
- Trunk and proximal muscles (near the body’s centre)
- Feeding and swallowing difficulties, particularly in infants.
- Respiratory muscle involvement in severe cases, leading to breathing difficulties and risk of respiratory failure.
- Orthopaedic complications:
- Foot deformities
- Abnormal curvature of the spine (scoliosis)
- Joint stiffness or deformities (contractures)
- Motor development may be delayed; many individuals can walk initially, but wheelchair support may be required later in progressive cases.
Prognosis
- Severity-dependent:Severe congenital type is often life-threatening, with early childhood mortality due to respiratory failure.
- Typical congenital type presents in infancy with muscle weakness and feeding issues.
- Adult-onset type is usually mild, with symptoms appearing between 20–50 years.
Treatment and Management
- No definitive cure exists at present.
- Management is supportive and symptomatic, focusing on:
- Physiotherapy and muscle-strengthening exercises
- Respiratory support when required
- Nutritional and feeding support
- Early diagnosis and multidisciplinary care can significantly improve quality of life.
Current Significance
- The recent public discussion by the CJI has underlined:
- Low awareness among doctors and caregivers
- Painful and delayed diagnostic processes
- The need for better genetic testing, counselling, and disability support systems in India
World Craft City Programme

- 13 Nov 2025
In News:
The World Craft City (WCC) Programme is a global initiative aimed at recognising and strengthening cities with a rich living craft heritage, while integrating traditional skills into the modern creative economy. Recently, Srinagar was conferred the World Craft City tag, marking a significant milestone for Kashmir’s artisanal legacy and its global cultural linkages.
What is the World Craft City Programme?
- Launched in 2014 by the World Crafts Council (WCC-International).
- Recognises cities where crafts play a pivotal role in cultural identity, livelihoods, and local development.
- Establishes a global network of craft cities, aligned with the principles of the creative economy.
- Emphasises the role of local authorities, artisans, and communities in sustaining traditional crafts.
Indian Cities under the World Craft City Programme
India has several cities recognised under the WCC Programme:
- Jaipur – traditional jewellery, blue pottery, block printing
- Mamallapuram – stone carving and sculpture
- Mysore – silk, wood carving, painting
- Srinagar – diverse and historic handicrafts
The inclusion of Srinagar highlights the global recognition of Kashmir’s craft ecosystem and is expected to revive its traditional links with Central Asia and Iran.
Major Crafts of Srinagar (Kashmir)
- Papier-mâché: Objects made from mashed paper pulp, hand-painted and finished with lacquer or varnish.
- Pashmina: Fine hand-spun and hand-woven shawls originating from Kashmir’s unique geography.
- Sozni embroidery: Delicate needlework (from Persian soz meaning needle); artisans are known as sozankar.
- Kani shawls (associated with pashmina tradition): Intricate weaving using wooden spools.
These crafts are not only cultural symbols but also key sources of artisan livelihoods.
About the World Crafts Council
- Founded in 1964 by Aileen O. Webb, Margaret M. Patch, and Kamaladevi Chattopadhyay.
- A non-governmental, non-profit organisation.
- Objectives:
- Strengthen the status of crafts in cultural and economic life.
- Promote fellowship among craftspeople.
- Facilitate cultural exchange through conferences, workshops, exhibitions, research, and international collaboration.
UNESCO Creative Cities Network (UCCN)
- The UNESCO Creative Cities Network (UCCN) was launched in 2004.
- Promotes cooperation among cities that use creativity as a driver of sustainable urban development.
- Includes over 350 cities worldwide across creative fields such as crafts, design, music, and literature.
- While UCCN is a UNESCO initiative, the WCC Programme is led by the World Crafts Council (NGO).
