All-India Consumer Price Index for Agricultural and Rural Labourers
- 02 Mar 2025
In News:
The Labour Bureau, Ministry of Labour& Employment released the All-India Consumer Price Index (CPI) for Agricultural Labourers (CPI-AL) and Rural Labourers (CPI-RL) for January 2025.
Key Highlights:
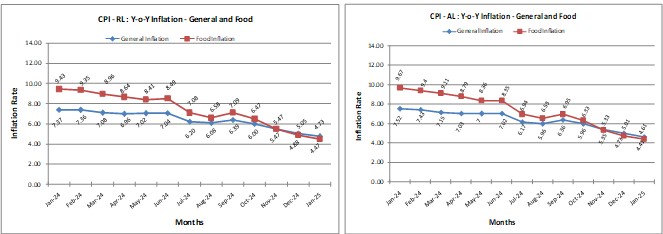
- Inflation Rates:
- CPI-AL: 4.61%
- CPI-RL: 4.73%
- Marked a decline from January 2024, when rates were 7.52% (CPI-AL) and 7.37% (CPI-RL).
- Also lower than December 2024: 5.01% (CPI-AL) and 5.05% (CPI-RL), indicating easing rural inflation.
- Index Levels:
- CPI-AL: 1316 (down by 4 points from 1320 in December 2024)
- CPI-RL: 1328 (down by 3 points from 1331 in December 2024)
Group-wise Index Comparison (Dec 2024 vs Jan 2025):
Group CPI-AL (Dec → Jan) CPI-RL (Dec → Jan)
General Index 1320 → 1316 1331 → 1328
Food 1262 → 1255 1269 → 1261
Pan, Supari, etc. 2093 → 2103 2100 → 2111
Fuel & Light 1382 → 1390 1372 → 1380
Clothing, Bedding, Footwear 1329 → 1332 1392 → 1396
Miscellaneous 1376 → 1385 1377 → 1385
About CPI-AL and CPI-RL:
- CPI-AL: Measures cost-of-living changes for agricultural labourers; used for revising minimum wages in agriculture.
- CPI-RL: Captures cost-of-living changes for rural labourers (includes CPI-AL as a subset).
- Compiled monthly for 20 states and at the All-India level.
- Base Year: 1986–87=100 (used to measure price change over time).
Significance:
- Declining CPI reflects lower rural price pressure, beneficial for wage policy formulation, poverty analysis, and rural development planning.
Ultra-Conserved Elements (UCEs)
- 02 Mar 2025
In News:
A recent study on the Tra2b gene in mice has revealed a potential reason why certain segments of the genome called Ultra-Conserved Elements (UCEs) have remained unchanged for over 80 million years across species like humans, mice, rats, chickens, and even fish.
What are Ultra-Conserved Elements (UCEs)?
- Definition:DNA sequences at least 200 base pairs long that have remained perfectly identical across diverse species for tens of millions of years.
- Number in Human Genome:Around 500 UCEs have been identified in the human genome.
- Location:Found in both coding regions (genes) and non-coding regulatory regions like enhancers and silencers.
- Species Overlap:Identical UCEs are shared by humans, mice, rats, chickens, and fish, reflecting their evolutionary conservation.
Key Findings from the Tra2b Gene Study
- Research Insight:A UCE embedded in the first intron of the Tra2b gene acts as a “poison exon” to regulate production of the Tra2β protein, which is involved in RNA splicing.
- Mechanism:
- When Tra2β levels rise, the UCE is included as an extra exon in the mRNA.
- This exon contains multiple stop codons, halting protein synthesis.
- The mRNA is then degraded, preventing excess Tra2β protein.
- Experimental Result:
- Deleting this UCE in mouse sperm-producing cells led to overproduction of Tra2β, causing cell death and infertility.
- This implies that any mutation in the UCE that disrupts its function would lead to infertility and thus prevent its transmission, explaining its evolutionary stability.
Significance of UCEs
- Evolutionary Importance:Their intolerance to mutation suggests they are critical for basic survival and reproductive success.
- Functional Role:
- Do not typically code for proteins.
- Regulate gene expression, often during early development, fertility, and immune response.
- Act as enhancers, silencers, or splice regulators (as in the case of poison exons).
- Medical Relevance:
- Help understand gene regulation and disease mechanisms.
- Their conservation across species makes them valuable for comparative genomics and biomedical research.
- Mice are used as model organisms due to ~85% genetic similarity with humans.
Aditya-L1 Mission
- 02 Mar 2025
In News:
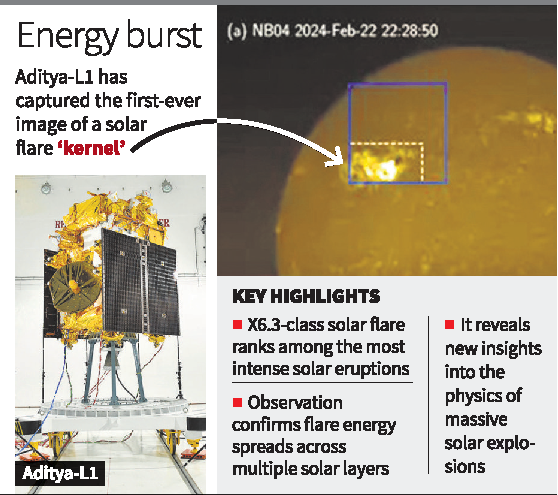
ISRO’s Aditya-L1 mission has made a significant breakthrough by capturing the first-ever image of a solar flare 'kernel' using the Solar Ultraviolet Imaging Telescope (SUIT) payload.
Key Highlights:
- Captured Phenomenon:
- An X6.3-class solar flare (among the most intense categories) was observed on February 22, 2024.
- SUIT detected localized brightening in the Near Ultraviolet (NUV) wavelength (200–400 nm), a range never before observed in such detail.
- Scientific Significance:
- Observation occurred in the lower solar atmosphere (photosphere and chromosphere).
- Confirmed energy transmission from the flare through multiple solar atmospheric layers.
- Demonstrated a direct link between flare energy deposition and plasma temperature increase in the solar corona.
- Validated longstanding theories while offering new insights into solar flare physics.
About Aditya-L1 Mission:
- Launch Date: September 2, 2023
- Orbit: Placed in a halo orbit around the first Earth-Sun Lagrange Point (L1) on January 6, 2024.
- Objective: Study solar activities and their impact on space weather.
- Significance: India’s first space-based solar observatory, and ISRO’s second astronomy mission after AstroSat (2015).
Solar Flares – Quick Facts:
- Solar flares are massive explosions on the Sun's surface that release energy, light, and high-speed charged particles.
- Often associated with Coronal Mass Ejections (CMEs) that can affect Earth's magnetosphere and satellites.
- Classification: A, B, C, M, and X — with X-class being the most powerful, increasing tenfold in energy per class.
Amazon’s Ocelot Quantum Chip
- 02 Mar 2025
In News:
Amazon Web Services (AWS) has unveiled its first in-house quantum computing chip, Ocelot, aimed at significantly reducing the development time for commercially viable quantum computers.
Key Highlights:
- Developed By: AWS Center for Quantum Computing at the California Institute of Technology.
- Objective: To accelerate the development of scalable and error-resilient quantum computers using novel architecture.
What is Ocelot?
- Type: Prototype quantum computing chip.
- Technology: Utilizes “cat” qubits—named after Schrödinger’s cat paradox—to suppress certain types of quantum errors intrinsically.
- Efficiency: Achieves 1 logical qubit using only 9 physical qubits, compared to the industry norm of ~1 million physical qubits for similar output.
Technical Features:
- Chip Design:
- Dual silicon microchips (~1 sq. cm each) stacked together.
- 14 core components:
- 5 cat qubits (for data storage),
- 5 buffer circuits (for qubit stabilization),
- 4 ancillary qubits (for error detection).
- Material Used: Standard chip fabrication techniques with tantalum.
Significance:
- Developmental Impact:
- Expected to reduce quantum computer development timelines by 5–10 years.
- Enables building practical quantum systems with around 100,000 qubits instead of the previously assumed 1 million.
- Potential Applications:
- Advanced drug discovery,
- New material development (e.g., batteries),
- Financial modeling, and
- Climate simulations.
- Strategic Implication: Strengthens Amazon’s position in the global quantum computing race alongside rivals like Google, Microsoft, and PsiQuantum.
Understanding Quantum Chips:
- Qubits vs Classical Bits:
- Classical bits = 0 or 1;
- Qubits = 0 and 1 simultaneously (superposition).
- Entanglement:Interlinked qubits can influence each other instantly, enhancing computational capacity.
- Quantum Gates:Operations are performed via gates like Hadamard, CNOT, and Pauli.
- Error Correction:Quantum systems are fragile; Ocelot’s built-in cat qubit architecture enhances stability and reliability.
One Nation-One Port Initiative

- 02 Mar 2025
In News:
The Ministry of Ports, Shipping and Waterways (MoPSW) has launched the ‘One Nation, One Port Process (ONOP)’, a transformative initiative aimed at standardizing port operations across India to improve efficiency, reduce costs, and bolster India’s position in global trade. This move aligns with PM Gati Shakti, the National Logistics Policy, and India’s ambition to become a leading maritime and logistics hub under Viksit Bharat@2047.
Key Components of the Maritime Reform Package:
1. One Nation, One Port Process (ONOP):
- Seeks uniform documentation and standardized customs procedures across all Indian ports.
- Reduced container operation documents by 33% (from 143 to 96) and bulk cargo documentation by 29% (from 150 to 106).
- Aims to eliminate procedural inconsistencies, boost ease of doing business, and cut logistics delays.
2. Sagar Ankalan – Logistics Port Performance Index (LPPI):
- Evaluates performance of major and non-major ports under Bulk (Dry & Liquid) and Container categories.
- Assesses indicators like cargo handling, turnaround time, berth idle time, and container dwell time.
- Encourages data-driven port benchmarking and fosters transparency in maritime logistics.
- Supports India’s improvement in the World Bank’s LPI (International Shipments) – from rank 44 to 22 in 2023.
3. MAITRI (Master Application for International Trade and Regulatory Interface):
- A digital platform using AI and Blockchain to automate trade clearances and enable Virtual Trade Corridors (VTC).
- Initial linkage with UAE, to expand towards BIMSTEC and ASEAN nations.
- Reduces bureaucratic redundancies, improves supply chain integration, and enhances trade resilience.
4. Bharat Ports Global Consortium:
- A collaborative body combining IPGL (operations), SDCL (finance), and IPRCL (infrastructure).
- Focuses on port development, global trade connectivity, and supporting the Make in India initiative.
- Strengthens India's presence in global logistics networks.
5. Financial and Policy Support:
- Launch of a ?25,000 crore Maritime Development Fund to facilitate long-term port and shipping investments.
- Shipbuilding Financial Assistance Policy 2.0 to aid Indian shipyards in competing globally.
- Customs duty exemptions on shipbuilding inputs extended for 10 years.
- Inclusion of large ships in the Infrastructure Harmonised Master List (HML) to ease access to funding.
6. Sustainability and Green Shipping:
- Launch of the National Centre of Excellence in Green Port and Shipping (NCoEGPS).
- Focus on carbon footprint reduction, cleaner fuels, and eco-friendly port operations.
7. Promotion and Maritime Diplomacy:
- Announcement of India Maritime Week (Oct 27–31, 2025) in Mumbai to showcase India’s Maritime Virasat (Heritage) and Vikaas (Development).
- Will host the 4th Global Maritime India Summit and the 2nd Sagarmanthan Dialogue, with representation from 100 countries and over 1 lakh delegates.
Strategic Significance:
- Aligns with Atmanirbhar Bharat, Blue Economy, and India-Middle East-Europe Economic Corridor (IMEEC).
- Boosts domestic manufacturing and export potential through better port infrastructure and trade facilitation.
- Reflects India’s push toward a digital, green, and globally competitive maritime sector.
