Lokpal of India adopts new motto

- 13 Jun 2025
In News:
The Full Bench of the Lokpal of India has officially adopted a new motto — “Empower Citizens, Expose Corruption” — replacing the earlier Sanskrit phrase:
Old Motto: Ma Gridhah Kasyasvid Dhanam (Do not be greedy for anyone’s wealth)
The change aims to improve institutional visibility, enhance public engagement, and reaffirm the Lokpal’s mission to fight corruption by empowering the people.
About Lokpal of India
- Established under: Lokpal and Lokayuktas Act, 2013
- Came into force: 16 January 2014
- Headquarters: Vasant Kunj, New Delhi
- Nature: Independent statutory anti-corruption body
Composition
- Chairperson: Former Chief Justice of India or SC Judge
- Members: Up to 8 members
- 4 Judicial
- 4 Non-Judicial
- Appointed by: President of India on recommendation of a high-level Selection Committee
Jurisdiction
Lokpal can investigate allegations of corruption against:
- Prime Minister, Union Ministers, and Members of Parliament
- Central Government employees (Group A to D)
- Officials of organizations receiving govt. funding (full/partial)
- Entities receiving foreign donations over ?1 crore annually
Functions & Powers
- Investigates complaints under the Prevention of Corruption Act, 1988
- Can:
- Sanction prosecution
- Order attachment of properties
- Recommend suspension or transfer of officials
- Possesses powers of a civil court:
- Summon witnesses
- Seize documents
- Can supervise the CBI in referred cases
- Collaborates with other investigative and enforcement agencies
Why the New Motto Matters
The new motto, “Empower Citizens, Expose Corruption”, reflects:
- A citizen-centric approach to governance
- A renewed commitment to transparency, accountability, and institutional trust
- The evolving role of Lokpal in aligning public participation with anti-corruption efforts
Exercise KHAAN QUEST 2025

- 13 Jun 2025
In News:
The Indian Army contingent has arrived in Ulaanbaatar, Mongolia, to take part in the 22nd edition of the Multinational Peacekeeping Exercise KHAAN QUEST, scheduled from 14 to 28 June 2025.
About Exercise KHAAN QUEST
- Origin: Launched in 2003 as a bilateral exercise between the USA and Mongolian Armed Forces.
- Multinational Format: Expanded in 2006 to include multiple countries, now recognized as a major UN peacekeeping readiness exercise.
- 2024 Edition: Held from 27 July to 9 August in Mongolia.
- India’s Participation: Contingent Strength: 40 personnel, primarily from a Battalion of the Kumaon Regiment, supported by members from other arms and services.
Aim and Objectives
- Enhance readiness for UN peacekeeping operations under Chapter VII of the UN Charter.
- Promote interoperability, joint tactical planning, and multinational cooperation.
- Share best practices in peace support operations.
Key Tactical Drills
- Static and Mobile Checkpoint Setup
- Cordon and Search Operations
- Patrolling and Evacuation of Civilians from conflict zones
- Counter-IED procedures
- Combat First Aid and Casualty Evacuation
Significance
Exercise KHAAN QUEST serves as a critical platform for building military-to-military cooperation, strengthening international partnerships, and improving operational cohesion among troops from around the world.
International Organization for Marine Aids to Navigation (IALA)

- 13 Jun 2025
In News:
India, as the Vice President of the International Organization for Marine Aids to Navigation (IALA), actively participated in the 2nd Session of the IALA Council, held in Nice, France.
What is IALA?
The International Organization for Marine Aids to Navigation (IALA) is a global intergovernmental technical body responsible for:
- Standardizing marine navigation aids (AtoN)
- Enhancing maritime safety
- Promoting environmental protection in marine navigation
Key Facts:
- Established: 1957 (as an NGO; became an IGO in 2024)
- Headquarters: Saint-Germain-en-Laye, near Paris, France
- Members: 39 countries
- Status: Transitioned to an Intergovernmental Organization in August 2024 after ratification by 30 states
India’s Role in IALA
India has been a Council Member since 1980, and was elected Vice President (2023–2027) during the 1st General Assembly in Singapore in 2023 — a significant recognition of India’s leadership in maritime affairs.
Major Indian Contributions:
- Development of Vessel Traffic Services (VTS) across 12 major ports
- Leadership in digital navigation aids and maritime innovation
- Promoting lighthouse heritage tourism
- Launching global training programs at the Kolkata Marine Navigation Training Institute
Highlights from the 2nd IALA Council Session
- Keynote: Outlined India’s achievements in integrating marine AtoN and future roadmap
- Technical Discussions:
- Standardization of AtoN and VTS systems
- Harmonized IoT protocols for visual AtoN
- Maritime Service Registry development
- Lighthouse heritage conservation
- Planning IALA’s global activity schedule for 2025–2026
India to Host Key IALA Events
- 3rd IALA General Assembly – December 2025, Mumbai
- 21st IALA Conference – 2027, Mumbai
This reflects global confidence in India’s technical capabilities and strategic importance in the maritime domain.
Significance:
- Strategic Leadership: Reinforces India’s influence in international maritime governance.
- Digital Maritime Innovation: India is contributing to cutting-edge technologies like IoT protocols and digital AtoN.
- Global Capacity Building: Hosting and training initiatives bolster the global maritime workforce.
- Cultural Diplomacy: Lighthouse tourism and heritage preservation align technology with history.
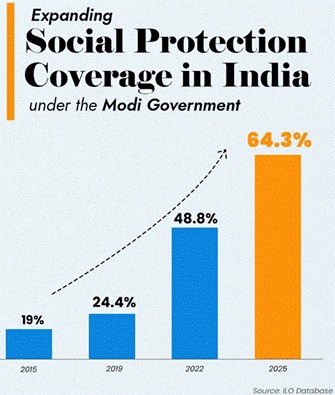
India’s Social Security coverage reaches 64.3% in 2025
- 13 Jun 2025
In News:
According to the latest data from the International Labour Organization’s (ILO) ILOSTAT database, India’s social security coverage has increased from 19% in 2015 to 64.3% in 2025, an unprecedented 45 percentage point surge over the past decade.
What is Social Security?
Social security (or social protection) refers to systems and policies that protect individuals and households from:
- Income loss (e.g. old age, unemployment, disability)
- High healthcare costs
- Social vulnerability (e.g. poverty, maternity, sickness)
It is built on three pillars:
- Social Assistance – Non-contributory support (e.g. food, housing)
- Social Insurance – Contributory programs (e.g. pensions, health insurance)
- Labour Market Programs – Employment schemes to build self-reliance
Key Highlights from ILOSTAT 2025
- India’s social security coverage jumped to 64.3%, up from 19% in 2015 – a 45 percentage point increase in 10 years.
- This means over 94 crore (940 million) people are now covered under at least one form of social protection.
- India now ranks 2nd globally in terms of population covered by social security.
- It is also the first country to update its 2025 social protection data in the ILOSTAT global database, showcasing its progress in digital governance and transparency.
Major Social Protection Initiatives Driving the Surge
India’s massive expansion in social coverage is due to a wide range of targeted schemes, including:
Pension & Insurance Schemes
- Atal Pension Yojana (APY): Pension of ?1,000–?5,000/month for informal workers aged 18–40.
- PM Shram Yogi Maan-Dhan Yojana (PM-SYM): Contributory pension for unorganized workers with 50% government support.
- PM Jeevan Jyoti Bima Yojana (PMJJBY): ?2 lakh life insurance for people aged 18–50.
- PM Suraksha Bima Yojana (PMSBY): Accident insurance of ?2 lakh for ages 18–70.
Healthcare & Nutrition
- Ayushman Bharat – PMJAY: ?5 lakh health cover for low-income families.
- Janani Suraksha Yojana: Maternity care for pregnant women.
- PM POSHAN (formerly Mid-Day Meal Scheme): Nutritional support to schoolchildren.
Income, Housing & Food Security
- MGNREGA: Guaranteed 100 days of wage employment annually in rural areas.
- PM Kisan Samman Nidhi: ?6,000/year income support to small and marginal farmers.
- Public Distribution System (PDS) under NFSA: Subsidized food grains to eligible households.
- PM Awaas Yojana – Gramin (PMAY-G): Pucca homes with basic amenities for rural poor.
Significance
- Poverty Reduction: Enhanced safety net for vulnerable populations.
- Inclusive Growth: Formal inclusion of informal sector workers.
- Digital Governance: Use of technology for efficient delivery (e.g., Aadhaar, DBT).
- Resilience Building: Helps households withstand economic shocks (e.g., pandemics, job loss).
CROPIC: A New AI-Driven Crop Study Scheme
- 13 Jun 2025
In News:
The Ministry of Agriculture and Farmers Welfare plans to launch CROPIC, a study to gather crop information using field photographs and AI-based models.
What is CROPIC?
CROPIC stands for Collection of Real Time Observations & Photo of Crops. It is a new initiative by the Ministry of Agriculture and Farmers’ Welfare aimed at studying crops through photographs and artificial intelligence (AI). The core objective is to monitor crop health and assess mid-season losses using images captured at multiple stages of the crop cycle.
Why is CROPIC significant?
CROPIC plays a pivotal role in modernizing and digitizing crop monitoring under the Pradhan Mantri Fasal Bima Yojana (PMFBY), India’s flagship crop insurance scheme.
Significance:
- Improved Loss Assessment: Traditional methods of crop loss assessment are time-consuming and subjective. CROPIC introduces AI-based analysis for faster and more objective decision-making.
- Automation of Compensation: It will help automate claim processes, ensuring faster payments to farmers in case of crop failure.
- Rich Crop Signature Database: Repeated field observations will build a valuable dataset of crop images over time, useful for future agricultural planning and risk management.
- Farmer Involvement: By crowdsourcing photographs directly from farmers, CROPIC also encourages their direct participation in data collection.
How will CROPIC work on the ground?
- Data Collection via App:
- A mobile app developed by the ministry will be used.
- Farmers and officials will take photos of crops 4–5 times during a crop’s life cycle.
- AI-Based Analysis:
- Photos will be processed on a cloud-based AI platform.
- The model will identify crop type, growth stage, health condition, damage, and loss extent.
- Visualization and Monitoring:
- A web-based dashboard will visualize crop status and damage patterns for stakeholders.
- Use in Insurance Claims:
- The app will also be used by officials to collect photo evidence for PMFBY claims, helping streamline compensation payouts.
Project Timeline:
- Pilot Phase:
- Begins with Kharif 2025 and Rabi 2025-26.
- Will cover at least 50 districts per season, spanning various agro-climatic zones and major crops.
- Full Roll-Out: After initial R&D, nationwide implementation is planned from 2026 onwards.
Funding and Support:
- Funded through the Fund for Innovation and Technology (FIAT) under PMFBY.
- FIAT has a total allocation of ?825 crore for various tech-driven agricultural initiatives.
