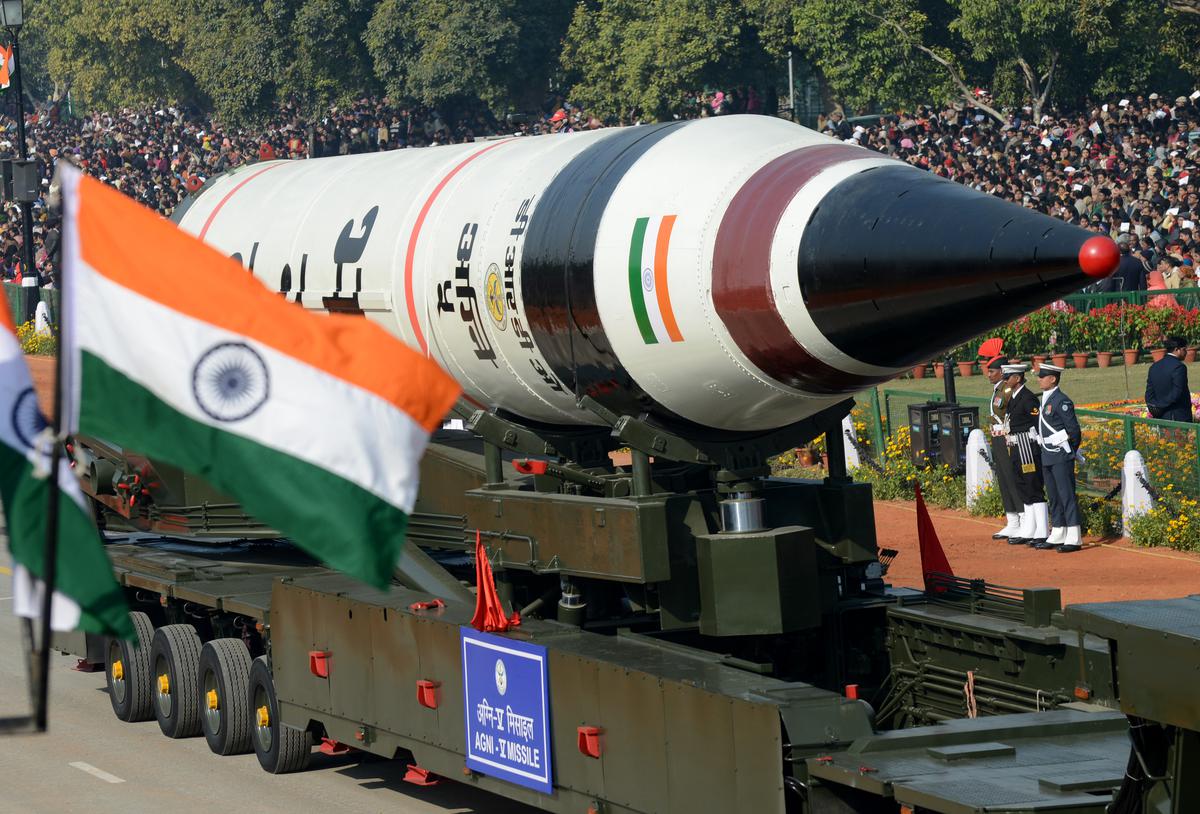
Agni-5 Missile

- 26 Aug 2025
In News:
India has successfully conducted the test of its nuclear-capable Agni-5 ballistic missile from the Integrated Test Range (ITR), Chandipur, Odisha. The launch was carried out under the Strategic Forces Command (SFC) and validated all operational and technical parameters, marking a significant boost to India’s strategic deterrence capabilities.
About Agni-5 Missile
- Type: Land-based Intercontinental Ballistic Missile (ICBM).
- Developer: Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO).
- Range: Beyond 5,000 km, capable of covering most of Asia and parts of other continents.
- Payload Capacity: Equipped with Multiple Independently Targetable Reentry Vehicle (MIRV) technology, enabling it to carry and deliver up to three nuclear warheads simultaneously at different targets.
- Technologies Used: Modern navigation, guidance, warhead, and propulsion systems, ensuring high accuracy and survivability.
Ballistic Missiles – Classification by Range
Ballistic missiles are rocket-propelled strategic weapons that follow a ballistic trajectory after the powered phase:
- Short-range: < 1,000 km (Tactical role).
- Medium-range: 1,000–3,000 km (Theater role).
- Intermediate-range: 3,000–5,500 km.
- Intercontinental (ICBM): > 5,500 km (Strategic role).
Agni-5, with its long range and MIRV capability, places India in the league of nations with advanced ICBM technology.
Strategic Significance
- Strengthens nuclear deterrence under India’s credible minimum deterrence and no first use (NFU) doctrines.
- Enhances India’s security architecture amidst evolving regional and global threats.
- Positions India among the select group of countries (U.S., Russia, China, France) with operational ICBM and MIRV capability.
National Policy to Promote Globally Important Agricultural Heritage Systems (GIAHS) in India
- 26 Aug 2025
In News:
- The Globally Important Agricultural Heritage Systems (GIAHS) programme, launched by the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) in 2002 at the World Summit on Sustainable Development, aims to conserve unique agricultural systems that sustain biodiversity, traditional knowledge, and rural livelihoods while adapting to modern challenges such as climate change, biodiversity loss, and community displacement.
- GIAHS adopts a multi-stakeholder approach by offering technical assistance, enhancing the value of traditional agricultural knowledge, and stimulating markets through agrotourism, product branding, and sustainable value chains.
India’s Recognised GIAHS Sites
Currently, India hosts three GIAHS sites, each reflecting diverse agro-ecological and cultural traditions:
- Koraput Region (Odisha):
- Known for subsistence paddy cultivation on highland slopes.
- Conserves a wide range of paddy landraces and farmer-developed varieties.
- Rich in medicinal plant genetic resources, closely linked with indigenous tribal knowledge.
- Supported by community seed banks, organic farming practices, and branding initiatives under state biodiversity programmes.
- Kuttanad Farming System (Kerala):
- A rare below-sea-level farming landscape.
- Comprises wetlands for paddy, garden lands for coconut and food crops, and inland water bodies for fishing and shell collection.
- Infrastructure development works under RKVY-DPR projects, such as HaritamHarippad in Alappuzha, and research on ecological utilization of water hyacinth are underway.
- Saffron Heritage of Kashmir:
- Represents a traditional agro-pastoral system of saffron cultivation.
- Characterized by organic farming practices, intercropping, and soil conservation.
- Supported through Rashtriya Krishi Vikas Yojana (RKVY) and the Mission for Integrated Development of Horticulture (MIDH) for revival and economic sustainability.
National Support Mechanisms
- Government Schemes: RKVY, MIDH, and other sectoral interventions promote conservation, branding, and livelihood opportunities.
- Biodiversity Revival: Emphasis on neglected crops and forgotten foods to ensure resilience.
- Integration with Research: State-supported projects in Kerala and Odisha enhance scientific validation and infrastructure.
Significance
- Ensures balance between conservation and socioeconomic development.
- Protects traditional knowledge systems and cultural landscapes.
- Enhances climate resilience and strengthens India’s commitment to sustainable agriculture.
- Promotes rural development, agrotourism, and niche product markets, thereby contributing to farmer incomes.
NAVYA Initiative

- 26 Aug 2025
In News:
- The Government of India launched the NAVYA (Nurturing Aspirations through Vocational training for Young Adolescent Girls) initiative in June 2025 to strengthen the socio-economic empowerment of adolescent girls (aged 16–18 years), particularly in aspirational districts.
- It is a joint initiative of the Ministry of Skill Development & Entrepreneurship (MSDE) and the Ministry of Women & Child Development (MWCD).
Objectives of NAVYA
- Vocational Training: Provide demand-driven skilling in both traditional and modern sectors.
- Holistic Development: Cover modules on health, nutrition, hygiene, life skills, financial literacy, and legal awareness.
- Enhancing Employability: Facilitate internships, apprenticeships, and job linkages, along with promoting self-employment.
- Gender-Inclusive Skilling: Ensure a safe and supportive training environment for adolescent girls.
- Bridging Gaps: Connect education and livelihood opportunities in underserved and remote regions.
Key Features
- Coverage: Implemented across 19 States and 27 districts, including Barpeta (Assam), Gaya (Bihar), Bastar (Chhattisgarh), Nuh (Haryana), Chamba (Himachal Pradesh), Baramulla (J&K), Raichur (Karnataka), Gadchiroli (Maharashtra), Rayagada (Odisha), Dholpur (Rajasthan), Virudhunagar (Tamil Nadu), Sonbhadra (Uttar Pradesh), and Haridwar (Uttarakhand), among others.
- Beneficiaries: 3,850 adolescent girls are being trained under Pradhan Mantri Kaushal Vikas Yojana (PMKVY) 4.0.
- Modern Job Roles: Training includes digital marketing, cybersecurity, AI-enabled services, green jobs, and other emerging sectors.
- Future Readiness: Modules on life skills, digital competence, and financial literacy prepare participants for evolving workforce demands.
Significance
- Strengthens women-centric skilling ecosystem.
- Promotes inclusive growth and gender equity in workforce participation.
- Supports Atmanirbhar Bharat by creating a skilled workforce in emerging sectors.
- Contributes to SDG 4 (Quality Education), SDG 5 (Gender Equality), and SDG 8 (Decent Work and Economic Growth).
Anna-Chakra

- 26 Aug 2025
In News:
The Government of India has introduced “Anna-Chakra”, a digital supply chain optimisation tool under the Public Distribution System (PDS), aimed at improving efficiency, reducing costs, and minimizing environmental impact in foodgrain distribution.
Implementation Status
- Implemented in 30 out of 31 States/UTs; yet to be implemented in Manipur.
- States/UTs covered include Punjab, Telangana, Tamil Nadu, Rajasthan, Bihar, Gujarat, Maharashtra, Uttar Pradesh, Delhi, J&K, Ladakh, Kerala, Karnataka, Odisha, among others.
Development and Collaboration
- Spearheaded by the Department of Food and Public Distribution.
- Developed in collaboration with:
- World Food Programme (WFP)
- Foundation for Innovation and Technology Transfer (FITT), IIT-Delhi
Working of Anna-Chakra
- Uses advanced algorithms to identify optimal routes for foodgrain movement across supply chain nodes.
- Covers 4.37 lakh Fair Price Shops (FPSs) and around 6,700 warehouses.
- Integrated with:
- FOIS (Freight Operations Information System) of Railways through the Unified Logistics Interface Platform (ULIP).
- PM Gati Shakti platform, which now houses geo-locations of FPSs and warehouses.
Key Benefits
- Financial Savings: Estimated ?250 crore per annum through reduction in transportation costs.
- Efficiency Gains: Faster delivery and streamlined PDS operations in the world’s largest food security programme benefiting 81 crore citizens.
- Environmental Impact: Reduction in fuel consumption and CO? emissions, aligning with India’s climate commitments.
- Operational Improvement: Ensures seamless coordination among multiple stakeholders, from farmers to FPS dealers.
Significance
Anna-Chakra represents a major leap in digitally enabled governance and logistics management, combining technology, sustainability, and welfare delivery. By cutting costs and carbon emissions while enhancing the efficiency of foodgrain delivery, it strengthens India’s food security architecture under the National Food Security Act (NFSA).
e-Jagriti Platform
- 26 Aug 2025
In News:
In a significant boost to India’s consumer protection framework, ten States along with the National Consumer Disputes Redressal Commission (NCDRC) achieved a disposal rate of over 100% in July 2025. This indicates that the number of consumer cases resolved exceeded the number of new cases filed, showcasing efficiency in grievance redressal.
Key Disposal Achievements
- NCDRC: 122%
- Tamil Nadu: 277%
- Rajasthan: 214%
- Telangana: 158%
- Himachal Pradesh & Uttarakhand: 150% each
- Meghalaya: 140%
- Kerala: 122%
- Puducherry: 111%
- Chhattisgarh: 108%
- Uttar Pradesh: 101%
This trend highlights faster case resolution and effective functioning of consumer commissions across India.
The e-Jagriti Platform
The success is largely aided by e-Jagriti, a flagship digital initiative of the Department of Consumer Affairs, designed to strengthen the consumer dispute redressal system.
Objectives
- Computerization and networking of all Consumer Commissions (National, State & District).
- Enhancing transparency, efficiency, and speed in dispute resolution.
- Providing accessible, cost-effective, and paperless grievance redressal.
Features
- E-filing of complaints with online fee payment.
- Real-time case tracking and access to judgments.
- AI-powered Smart Search for archived complaints/judgments.
- Voice-to-text conversion of judgments and case details using AI/ML.
- Integration of multiple platforms:
- Online Case Monitoring System (OCMS)
- E-Daakhil
- NCDRC Case Monitoring System
- CONFONET website
- Mediation application
Since its launch, over 2 lakh users (including NRIs) have registered on e-Jagriti, with 85,531 cases filed online in 2025 alone, demonstrating growing public trust.
Significance
- Strengthens consumer rights and access to justice.
- Reduces backlog and delays through tech-driven case management.
- Promotes digital governance and transparency in consumer protection.
- Aligns with citizen-centric reforms and Digital India Mission.
