Vehicle-to-Grid (V2G) Technology

- 18 Mar 2025
In News:
Vehicle-to-Grid (V2G) is an innovative energy solution that allows Electric Vehicles (EVs) to not only draw power from the grid (charging) but also send excess stored electricity back to the grid (discharging) when not in use. This bi-directional energy flow creates a unique opportunity to support grid stability, especially when renewable energy (RE) sources like solar and wind are intermittent. When connected via bi-directional chargers, EV batteries can act as decentralized storage systems, offering a potential solution to address the challenges posed by renewable energy integration and peak demand periods.
Global Adoption and Benefits of V2G
V2G technology has gained significant traction in developed EV markets like Europe and the U.S., where it is seen as a cost-effective solution for distributed energy storage.
- In the U.K. and the Netherlands, EV owners are compensated for supplying excess energy to the grid, particularly during peak hours.
- In California, EVs are integrated into the ancillary services market, helping improve grid reliability.
- Additionally, V2G technologies have shown promise in offering emergency power during natural disasters and grid failures, proving to be an essential tool for enhancing grid resilience.
V2G in India: Current Status and Challenges
In India, V2G technology is still in its nascent stages. While there is a growing adoption of EVs and charging infrastructure, integrating these vehicles into the national grid remains a challenge. The electricity market in India is not yet fully equipped to support decentralized energy solutions like V2G. The current grid structure, characterized by variable RE generation and mismatches in supply and demand, requires significant regulatory and structural changes for successful V2G integration.
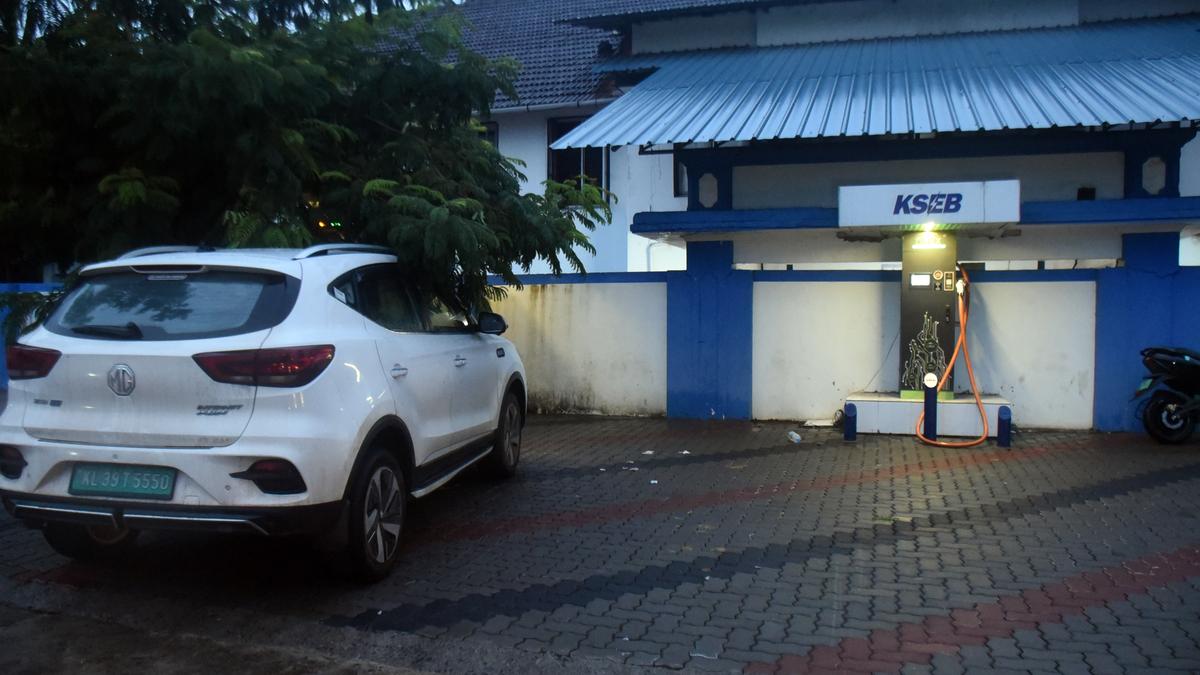
The Kerala State Electricity Board (KSEB) and the Indian Institute of Technology Bombay (IIT Bombay) have launched a pilot V2G project to assess the feasibility of this technology in the state. This project will explore how EVs can help support grid demand during peak hours, particularly when solar energy generation is low, as Kerala experiences both rapid EV adoption and increasing rooftop solar installations.
Key Features of V2G
- Charging (G2V): When an EV is charged, it functions as a load on the grid. This process can be managed through Time of Use (ToU) electricity tariffs, which incentivize charging during off-peak hours to reduce grid stress.
- Discharging (V2G): When EV batteries discharge power back to the grid, they act as distributed energy resources. This is especially valuable during periods of high demand or when renewable energy generation is insufficient.
- Decentralized Energy Storage: V2G enables EVs to serve as decentralized storage units, reducing the dependency on centralized storage systems and making the grid more resilient and efficient.
Advantages for the Indian Power Sector
- Grid Stability: V2G can help modulate the power flow in the grid by reducing the impact of variable RE generation. It also helps to stabilize grid operations during peak demand periods.
- Support for Renewable Energy: By enabling EVs to store excess solar energy during the day, V2G can assist in using this stored power during nighttime or when renewable energy generation is low, contributing to true decarbonization.
- Smart Charging: Integrating V2G with smart charging systems can help optimize energy use, ensuring that EVs charge during periods of high renewable energy generation and discharge during peak demand.
Potential for Wider Adoption
The Kerala pilot project is expected to pave the way for broader V2G implementation across India. The project aims to test how EVs can provide support during peak demand, particularly when solar power generation is unavailable. The integration of smart charging solutions and V2G will help mitigate concerns about increasing electricity demand due to the growing number of EVs. Additionally, incentives for EV owners to participate in V2G systems can lead to cost-effective solutions for grid management.
The Indian government, through the Central Electricity Authority (CEA), has already initiated steps to frame guidelines for reverse charging (V2G). With the increasing adoption of EVs and solar power, V2G has the potential to become a cornerstone of India's energy future.
Operation ATALANTA

- 18 Mar 2025
In News:
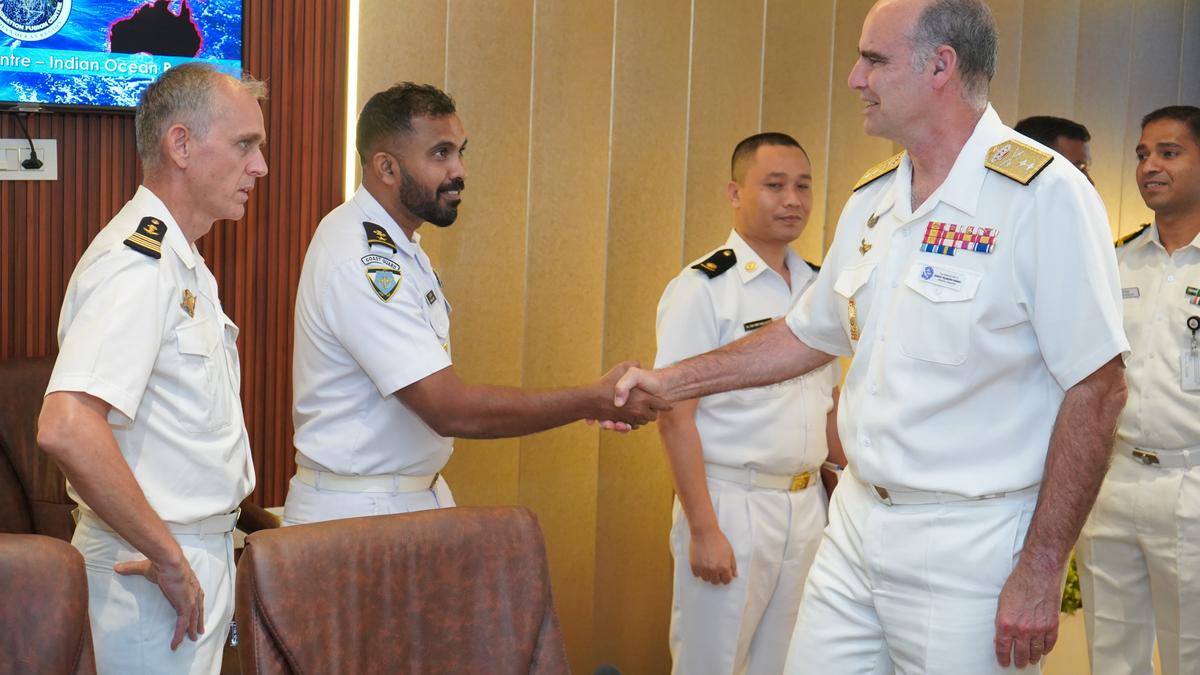
The European Union Naval Force (EUNAVFOR) Operation ATALANTA has proposed a significant joint anti-piracy naval exercise with the Indian Navy, scheduled for the end of May 2025. This initiative reflects the growing strategic cooperation between India and the European Union in maritime security, particularly in the Western Indian Ocean and the Red Sea.
Key Highlights
Proposed Exercise:
- The exercise, if approved, will involve two European warships and the Indian Navy practicing advanced counter-piracy operations, tactical manoeuvres, and inter-naval communications.
- This drill goes beyond the routine Passage Exercises (PASSEX) and aims to enhance interoperability, coordination, and mutual confidence between the two navies.
Strategic Objectives:
- Strengthen maritime security in the Indian Ocean, ensuring it remains a free, open, sustainable, and inclusive area.
- Address resurgent piracy threats, especially off the Horn of Africa, amid ongoing instability in the Red Sea due to Houthi rebel activity.
- Build operational synergy to respond swiftly to piracy incidents-EUNAVFOR claims the capability to tackle pirate cases within 48–72 hours.
Recent Developments:
- Piracy incidents near the Horn of Africa have declined recently, but the threat persists, necessitating continued vigilance and cooperation.
- In 2024, joint anti-piracy efforts led to the apprehension of 70 suspected pirates, with the Indian Navy responsible for 44 captures.
- The Indian Navy is recognized as a major actor in the region, with both sides regularly coordinating through maritime information fusion centers.
Operation ATALANTA: Overview
Aspect Details
Launch Year 2008
Initial Focus Preventing piracy and armed robbery off the Somali coast
Expanded Mandate - Protecting World Food Programme (WFP) vessels
- Enforcing UN arms embargo on Somalia
- Monitoring drug and arms trafficking
- Combating Illegal, Unreported, and Unregulated (IUU) fishing
- Disrupting illicit charcoal trade
Area of Operations Western Indian Ocean and Red Sea
Recent Activities - Joint drills with Indian Navy
- Successful coordination in anti-piracy operations, e.g., MV Ruen hijacking
India–EU Maritime Engagement: Significance
- Geopolitical Context:
- The Indian Ocean is a critical global trade route, and its security is vital for international commerce.
- The resurgence of piracy and instability in the Red Sea has heightened the need for robust maritime partnerships.
- Strategic Partnerships:
- The EU and India share a vision of maintaining maritime order and security.
- The vastness of the Indian Ocean requires significant assets and robust logistics, making cooperation essential.
- Professional Interactions:Encounters with other navies, including China, are described as professional, underscoring the importance of multilateral engagement.
Hyperloop Project
- 18 Mar 2025
In News:
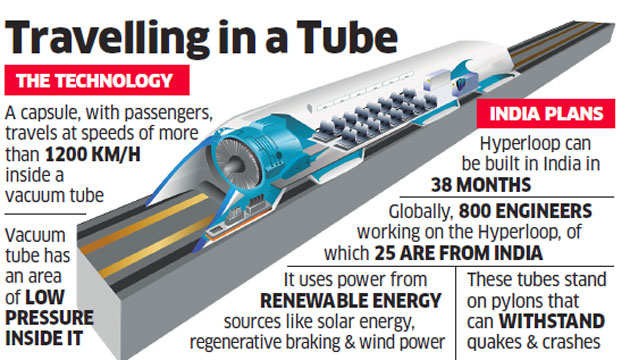
India is moving closer to realizing ultra-high-speed transportation with the development of indigenous Hyperloop technology. The Ministry of Railways, has announced that Integral Coach Factory (ICF), Chennai will develop the electronics component for the country’s Hyperloop initiative. This decision follows promising test results at IIT Madras, which hosts the longest Hyperloop testing facility in Asia.
What is Hyperloop?
Hyperloop is a next-generation, ultra-fast transportation system that combines magnetic levitation (maglev) and near-vacuum tubes to enable passenger pods to travel at speeds up to 1,220 km/h. It was first proposed by Elon Musk in 2013 through the Hyperloop Alpha white paper and has since evolved into a global open-source research initiative.
Working Mechanism:
- Low-pressure tubes drastically reduce air resistance.
- Magnetic levitation allows pods to float without touching surfaces, minimizing friction.
- Electromagnetic propulsion moves pods forward efficiently.
Key Features:
- Highly energy-efficient and sustainable, with low emissions.
- Can surpass air travel speeds on shorter routes.
- Reduces road congestion, travel time, and noise pollution.
India’s Hyperloop Developments:
- Institutions Involved:
- IIT Madras – Developed the 410-meter test facility.
- Avishkar Hyperloop Team – Leading design and innovation.
- ICF Chennai – To develop electronics and technical components.
- Government Support:
- The Railway Ministry has provided financial and technical support.
- The testing system uses fully indigenous technology.
Challenges Ahead:
Despite its promise, Hyperloop faces significant hurdles:
- High infrastructure costs.
- Technical challenges in maintaining vacuum conditions.
- Safety concerns due to the high speed and pressure system.
Sarthi and Pravaah Initiatives
- 18 Mar 2025
In News:
The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) was awarded the Digital Transformation Award 2025 by Central Banking (UK) for its in-house digital innovations — Sarthi and Pravaah — marking a significant step in the digitization of internal and external regulatory processes.
Sarthi System (Launched January 2023)
- Objective: Digitize RBI’s internal workflows and reduce reliance on paper-based systems.
- Key Features:
- Secure document storage and sharing for over 13,500 employees across 40+ locations.
- Enhanced record management and data analysis through dashboards and reports.
- Automation of internal tasks such as approvals, tracking, and documentation.
- Support Infrastructure:
- SarthiPathshala: Online and in-person training module for staff.
- SarthiMitras: Designated personnel in each office to provide user assistance.
Pravaah System (Launched May 2024)
- Objective: Facilitate external submission of regulatory applications digitally.
- Key Features:
- Integration with Sarthi for streamlined processing.
- Supports 70+ regulatory application types across 9 departments.
- Enhanced efficiency, transparency, and real-time tracking.
- Centralized cybersecurity and monitoring framework.
- Impact:
- 80% increase in monthly application submissions.
- Major reduction in delays caused by manual and paper-based procedures.
Significance
- Reflects India’s push toward governance digitization and institutional efficiency.
- Demonstrates how indigenous technology solutions can modernize financial regulation and public administration.
Shishtachar Squads

- 18 Mar 2025
In News:
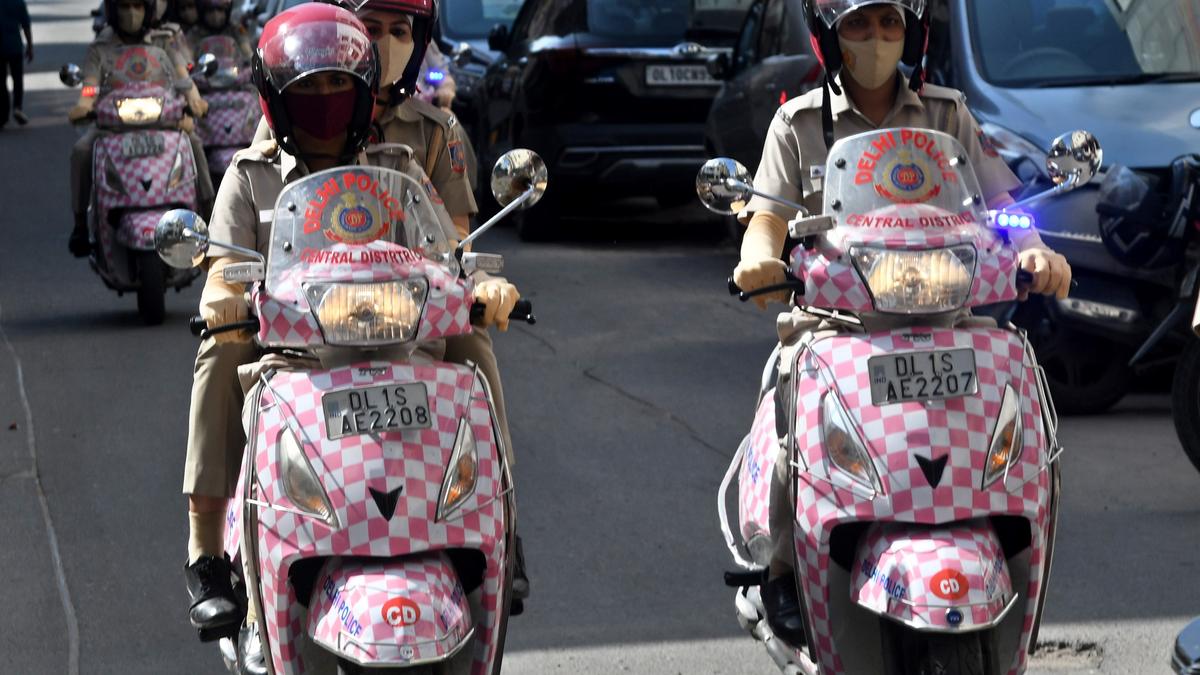
To enhance women's safety in public spaces, Delhi Police has launched district-wise Shishtachar Squads, a dedicated initiative to curb eve-teasing and harassment. The move comes in line with the Bharatiya Janata Party’s pre-poll promise and is inspired by Uttar Pradesh’s Anti-Romeo Squads.
Key Features:
- Purpose: To prevent, intervene, and assist in cases of sexual harassment against women in public areas.
- Deployment: 30 squads have been formed across Delhi, with at least two squads in each district.
- Composition: Each 12-member squad includes:
- 1 Inspector (Head)
- 1 Sub-Inspector
- 4 Female Constables
- 5 Male Constables
- 1 Constable from the Anti-Auto Theft Squad (technical support)
- Supervision: Squads function under the ACP of the district's Crime Against Women (CAW) Cell.
Operational Strategy:
- Patrolling: Daily drives in at least two vulnerable spots identified by District DCPs.
- Surprise Checks: Plainclothes officers inspect public transport and engage with DTC staff, market associations, and RWAs.
- Victim-Centric Approach: Emphasis on sensitive handling of cases, ensuring swift action under relevant provisions of the Bharatiya Nyaya Sanhita (e.g., Sections 74 for molestation and 78 for stalking).
- Monitoring:
- Weekly Reports by ACP-CAW submitted to the DCP of the Special Police Unit for Women and Children (SPUWAC).
- Monthly Evaluations based on feedback from schools, RWAs, MWAs, and control rooms.
