Climate Risk Index 2025
- 19 Feb 2025
In News:
- The Climate Risk Index (CRI) 2025, published by the international environmental think tank Germanwatch, ranks countries based on their vulnerability to extreme weather events, assessing both human and economic losses due to climate-induced disasters.
- The index, which has been released annually since 2006, covers a 30-year period, evaluating the impact of extreme weather events in terms of economic losses, fatalities, and the number of affected people.
Key Findings:
- Global Impact: From 1993 to 2022, more than 9,400 extreme weather events occurred globally, resulting in 765,000 fatalities and USD 4.2 trillion in economic losses. Heatwaves, droughts, and floods were the leading causes of fatalities and displacement, with heatwaves alone claiming 61,778 lives (83% of fatalities) in 2022. Droughts affected the largest number of people, with 59% of the global population impacted during the past three decades.
- India's Position: India ranks as the 6th most affected country in the world by climate change between 1993 and 2022, suffering significant losses. During this period, the country experienced over 400 extreme weather events, including floods, heatwaves, cyclones, and droughts, causing a loss of USD 180 billion in economic damages and leading to at least 80,000 fatalities (10% of global deaths).
Some notable extreme weather events include:
-
- Cyclones: Gujarat (1998), Odisha (1999), Hudhud (2014), and Amphan (2020).
- Floods: Uttarakhand (2013), Jammu and Kashmir (2014), and Kerala (2018).
- Heatwaves: Intense temperatures exceeding 50°C in 1998, 2002, 2003, and 2015.
Methodology of the Climate Risk Index
The CRI assesses the impact of extreme weather events across three hazard categories:
- Hydrological (floods, landslides),
- Meteorological (storms, cyclones),
- Climatological (heatwaves, droughts).
The six key indicators used for the ranking are:
- Economic loss
- Fatalities
- Affecting population, assessed in both absolute and relative terms.
Climate Risk and Its Implications for India
India’s vulnerability to climate change is highlighted by frequent and intense extreme weather events. The country faces risks from:
- Floods: Regular heavy monsoons lead to significant displacement and damage to infrastructure and agriculture.
- Cyclones: Rising sea levels and warming oceans increase the frequency and intensity of cyclones.
- Heatwaves: India experiences rising temperatures, with heatwaves becoming more intense, contributing to health crises.
- Droughts: A growing concern, affecting agriculture and water resources.
Additionally, the Asia-Pacific Climate Report 2024 projects that India may face a 24.7% GDP loss by 2070 due to climate change impacts, driven by rising sea levels and decreasing labor productivity.
Global Challenges in Climate Change Mitigation
- Historical Responsibility vs. Future Emissions: Developed nations, despite having contributed more to global emissions historically, are pressuring emerging economies like India to take greater responsibility for climate action. This has led to tensions over burden-sharing and the need for climate finance.
- Global Temperature Breach: In 2024, the world breached the 1.5°C threshold for a full year, highlighting the inadequacy of current mitigation efforts. Projections indicate a global temperature increase of 2.6-3.1°C by 2100 if current trends continue.
- Weak Commitments and Insufficient Finance: Many countries have not updated their Nationally Determined Contributions (NDCs), and the USD 300 billion annual funding promised for developing nations is insufficient to meet climate adaptation and mitigation needs.
India's Climate Adaptation Challenges and Suggestions
India faces several climate adaptation challenges, including inadequate infrastructure, insufficient funding, and a lack of robust policy frameworks for disaster risk management. To enhance adaptation efforts, the following measures are suggested:
- Enhanced Climate Finance: Developing countries need greater financial and technical support to manage and adapt to climate-induced losses.
- Strengthening Mitigation Efforts: Nations, including India, must scale up their NDCs to restrict global warming to 1.5°C or lower.
- Accountability of High-Income Countries: Developed nations must expedite mitigation actions and increase financial contributions to support climate-vulnerable countries like India.
National Skill Development Corporation (NSDC)

- 19 Feb 2025
In News:
The National Skill Development Corporation (NSDC) has announced plans to establish 50 Future Skills Centres (FSCs) and 10 NSDC International Academies to enhance skill development and improve workforce readiness in India. This initiative aims to address the country's growing demand for skilled professionals, particularly in emerging technologies and international markets.
About NSDC
- NSDC is a not-for-profit public limited company set up to promote skill development across India.
- It operates under the Ministry of Skill Development & Entrepreneurship (MSDE).
- Established on July 31, 2008, NSDC was founded as a Public-Private Partnership (PPP) under Section 25 of the Companies Act, 1956 (now Section 8 under the 2013 Act).
- The corporation operates with a 49% government stake and 51% private sector participation, ensuring a balanced approach to skill development through public and private sector collaboration.
Key Objectives of NSDC
- Bridging the Skill Gap: NSDC aims to fill the gap between industry requirements and the available workforce by providing industry-relevant training. This enhances workforce employability and supports the growth of the Indian economy.
- Financial Support for Enterprises: NSDC provides funding and concessional loans to enterprises, start-ups, and training organizations to expand their operations and develop a skilled workforce.
- Skilling the Workforce for Emerging Technologies: The corporation focuses on upskilling individuals in emerging technologies to make them market-ready.
Key Functions of NSDC
- Skill Development & Training: NSDC provides vocational training and certification across emerging technologies to align the workforce with current industry needs, ensuring that individuals are equipped with the necessary skills to succeed in the job market.
- Apprenticeship & Job Training: Under the National Apprenticeship Promotion Scheme (NAPS), NSDC trains around 5 million apprentices by disbursing ?100,250 million for skill-based learning, giving them hands-on experience and industry exposure.
- Digital & Remote Skilling: Through the Skill India Digital Hub (SIDH), NSDC offers over 7,100 courses in 23 languages, catering to 30 crore candidates. These online courses provide accessibility to skill development programs across the country, particularly for individuals in remote and rural areas.
- Job & Career Support: NSDC runs JobX, a platform that connects job seekers with potential employers. This platform offers services such as resume building, career coaching, and placement assistance, having already supported 4 million candidates in securing jobs.
New Initiatives by NSDC
To further strengthen India’s skill ecosystem, NSDC is establishing 50 Future Skills Centres (FSCs) and 10 NSDC International Academies. These initiatives will focus on:
- Future Skills Centres: These centers will offer training in emerging fields such as artificial intelligence, data science, cybersecurity, and robotics, ensuring that India's workforce is prepared for future job markets.
- International Academies: The academies will focus on global skill standards and international certifications, enhancing the employability of Indian workers in global markets.
Gulf of Eilat
- 19 Feb 2025
In News:
A new study has revealed that the coral reefs in the Gulf of Eilat (also known as the Gulf of Aqaba) faced a 3,000-year growth shutdown due to global cooling. However, these reefs later recovered naturally from deeper waters, demonstrating resilience in the face of environmental changes.
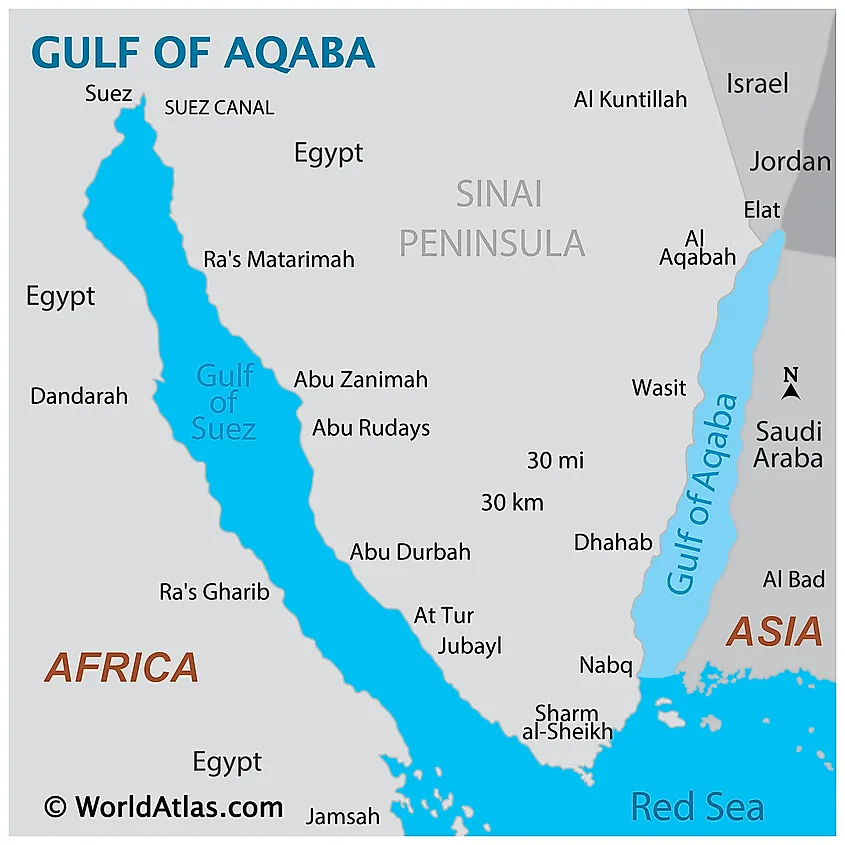
About the Gulf of Eilat (Gulf of Aqaba)
- Location: The Gulf of Eilat is a northern extension of the Red Sea, positioned east of the Sinai Peninsula and west of the Arabian Peninsula. It is strategically significant and is also known as the Gulf of Aqaba.
- Neighbouring Nations: The Gulf shares its coastline with four countries: Egypt, Israel, Jordan, and Saudi Arabia.
- Geographical Features:
- The Gulf includes important cities like Taba (Egypt), Eilat (Israel), and Aqaba (Jordan), all located at the Gulf’s northernmost point.
- It has a maximum depth of 1,850 meters, making it much deeper than the adjacent Gulf of Suez.
- The Gulf forms the southern end of the Dead Sea Transform, a significant tectonic fault zone, contributing to its unique geological and environmental features.
- Coral Ecosystem: The Gulf of Eilat is home to the world’s northernmost coral reefs. Despite facing various environmental challenges, these reefs have shown remarkable resilience over the years, highlighting their ability to adapt to changing conditions.
Environmental Challenges and Recovery
- The 3,000-year growth shutdown of the coral reefs in the Gulf of Eilat was primarily driven by global cooling. This climatic phenomenon significantly impacted the growth of the reefs, causing a temporary halt in their development. However, the coral ecosystems in the Gulf have since recovered naturally, drawing from deeper waters to rebuild and thrive once again.
- This recovery underscores the resilience of coral ecosystems despite adverse environmental conditions. It also provides valuable insights into how these ecosystems can recover when given the opportunity, even after significant disruptions caused by global climate changes.
Implications for Coral Reef Conservation
- The study's findings emphasize the importance of understanding the adaptive capacity of coral reefs, which are among the most vulnerable ecosystems to climate change.
- The ability of coral reefs in the Gulf of Eilat to recover after a prolonged period of cooling demonstrates that marine ecosystems can endure long-term environmental stress if they are allowed to regenerate naturally.
- This has significant implications for global coral conservation efforts, which must focus on creating conditions that allow reefs to adapt and recover from environmental stresses, including global warming, ocean acidification, and pollution.
- The Gulf of Eilat’s coral reefs provide an important case study for understanding ecological resilience and the potential for natural recovery in marine ecosystems.
NAMASTE Scheme

- 19 Feb 2025
In News:
The National Action for Mechanized Sanitation Ecosystem (NAMASTE) scheme, launched by the Government of India, aims to empower sanitation workers, particularly Sewer and Septic Tank Workers (SSWs), also known as SafaiMitras.
Key Highlights:
- It focuses on ensuring their dignity, safety, and economic empowerment, while promoting the mechanization of sanitation processes.
- The scheme is designed to address the challenges faced by these workers, who are often exposed to hazardous conditions.
Objectives of the NAMASTE Scheme
The primary objectives of the NAMASTE scheme include:
- Formalization of sanitation work and enhancing occupational safety.
- Promotion of mechanized cleaning techniques to reduce manual interventions.
- Providing personal protective equipment (PPE) and other safety devices to workers.
- Ensuring economic and social empowerment of sanitation workers.
Implementing Agencies and Timeline
- The NAMASTE Scheme is implemented by the Ministry of Social Justice and Empowerment (MoSJE) and the Ministry of Housing and Urban Affairs (MoHUA).
- The scheme is executed by the National SafaiKaramcharis Finance and Development Corporation (NSKFDC), under MoSJE.
- The scheme is scheduled for implementation from FY 2023-24 to 2025-26, with a target group comprising sewer workers, septic tank workers, and waste pickers (the latter being added in 2024).
Key Initiatives Under NAMASTE
- Distribution of PPE Kits: Under the scheme, PPE kits are provided to sanitation workers to safeguard them from health hazards, especially while working in unsafe environments like sewer lines and septic tanks. These kits include masks, gloves, goggles, face shields, gowns, and shoe covers.
- Ayushman Health Cards: Ayushman Bharat Pradhan Mantri Jan Arogya Yojana (AB-PMJAY) health cards are distributed to SSWs under the scheme. These cards enable workers to access cashless healthcare at empaneled hospitals, ensuring that sanitation workers receive timely medical attention without financial burden.
- Capacity Building and Training: The scheme promotes capacity building for SSWs through training programs on safety protocols, mechanized cleaning processes, and the use of modern sanitation technologies. This helps improve the efficiency and safety of their work, while also reducing manual handling.
- Promoting Mechanization: To reduce the hazardous practice of manual scavenging, the scheme focuses on providing mechanized equipment to enhance sanitation operations and create safer working conditions for workers.
Surge in Colorectal Diseases in India
- 19 Feb 2025
In News:
In recent years, India has witnessed a marked increase in colorectal diseases, including colorectal cancer, Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD), Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS), and other related disorders. This surge is closely linked to urbanization, dietary transitions, sedentary lifestyles, and improved diagnostic practices.
What are Colorectal Diseases?
Colorectal diseases affect the colon and rectum and encompass a spectrum of conditions:
- Colorectal Cancer: Originates from polyps in the colon or rectum. If untreated, these polyps can turn malignant. The incidence of colorectal cancer is rising rapidly in Indian urban centers, now ranking among the top cancers in cities.
- Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD): A chronic condition involving inflammation of the digestive tract, especially the colon and small intestine. Subtypes include Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis. Once rare in India, IBD is now on the rise due to industrialization, Western diets, and enhanced medical diagnostics.
- Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS): A non-inflammatory, functional bowel disorder marked by abdominal pain, bloating, and altered bowel habits (constipation or diarrhea) without visible bowel damage. IBS is highly prevalent in India.
- Diverticular Disease: Characterized by the formation of small pouches (diverticula) in the colon wall. Inflammation or infection of these pouches leads to complications and discomfort.
- Hemorrhoids and Anal Fissures: Swollen veins or tears in the rectal region, leading to pain, bleeding, and itching—often caused by hard stools or chronic constipation.
Why are these diseases increasing?
- Dietary Shifts: Increased intake of processed foods, red meat, and low-fiber diets (lacking fruits and vegetables) have significantly raised the risk of colorectal cancer and other digestive disorders.
- Physical Inactivity: Sedentary behavior, especially in urban populations, heightens susceptibility to these conditions.
- Rising Obesity: Obesity, closely associated with lifestyle disorders, is a contributing factor for colorectal cancer and IBS.
- Ageing Population: Risk increases with age, and India’s growing elderly demographic intensifies disease burden.
- Genetic and Lifestyle Factors: A family history of colorectal conditions, coupled with habits like smoking and alcohol consumption, further elevate risk levels.
- Gut Microbiota Disruption: Imbalance in gut bacteria and possible infections are emerging as factors in the etiology of IBD; ongoing research aims to establish clearer links.
Common Symptoms
- Persistent changes in bowel habits: constipation, diarrhea, or narrow stools.
- Rectal bleeding: presence of bright red or dark blood in the stool.
- Abdominal pain, bloating, or cramps.
- Unexplained weight loss.
- Chronic fatigue and weakness.
- Sensation of incomplete bowel emptying.
Diagnosis
- Physical Examination and clinical history evaluation.
- Stool Tests for blood, infections, or abnormalities.
- Colonoscopy (gold-standard diagnostic tool) to inspect the colon and collect biopsies.
- Sigmoidoscopy for lower colon and rectum.
- Imaging: CT, MRI, or X-rays to detect abnormalities.
- Blood Tests to assess inflammation and exclude other conditions.
Treatment Modalities
- Medication: Anti-inflammatory drugs (for IBD), antibiotics, pain relief, and symptom-specific treatments.
- Lifestyle Interventions: High-fiber diets (for IBS, diverticulitis), regular physical activity, and stress reduction.
- Surgery: Required in advanced cases of colorectal cancer or severe IBD/diverticular disease.
- Chemotherapy and Radiation Therapy: Used post-operatively or in advanced malignancies.
- Targeted Biological Therapies: Including monoclonal antibodies for immune modulation in IBD.
