AIM4NatuRe
- 02 May 2025
In News:
On Earth Day 2025 (April 22), the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) of the United Nations launched the AIM4NatuRe (Accelerating Innovative Monitoring for Nature Restoration) initiative with funding from the United Kingdom (GBP 7 million / USD 9.38 million).
Key Highlights:
- The programme aims to enhance countries’ capacities to monitor and report ecosystem restoration as part of the Kunming-Montreal Global Biodiversity Framework (GBF).
- Objective: To support Target 2 of the Global Biodiversity Framework:Restore at least 30% of degraded ecosystems globally by 2030.
- Key Features
- Lead Agency: FAO (United Nations)
- Funding:
- GBP 7 million from the UK (approx. USD 9.38 million)
- Project duration: 2025–2028
- Scope of Restoration:
- Forests
- Wetlands
- Grasslands
- Marine ecosystems
- Degraded agricultural lands
- Technology Integration:
- Uses satellite tools, data analysis, and advanced monitoring systems
- Promotes standardized data formats and data interoperability
- Monitoring Support Tools:
- Introduces the Framework for Ecosystem Restoration Monitoring (FERM)
- Provides technical guidance and capacity development training
- Inclusivity & Indigenous Participation:
- Pilot projects in Brazil and Peru
- Supports Indigenous Peoples in biocentric monitoring — respecting traditional knowledge and holistic ecosystem restoration
Why It Matters
- Global Restoration Commitments: Nearly 1 billion hectares pledged for restoration
- Transparency & Accountability:
- Creation of a harmonized global dataset
- Public tracking of progress toward restoration goals
- Bridging Gaps:
- Responds to 80% of countries reporting lack of monitoring capacity (CBD survey)
- Provides tools and training for effective implementation and reporting
- Broader Goals:
- Tackles climate change, biodiversity loss, and land degradation
- Enhances food security and livelihoods
India moves to curb GM Alfalfa Seed imports amid US push for market access
- 02 May 2025
In News:
India is preparing to restrict the import of genetically modified (GM) alfalfa (lucerne) seeds, even as the United States urges a reduction in import duties on the crop. Alfalfa is a high-protein forage crop widely used for animal feed.
Key Highlights
- Alfalfa (Lucerne):
- Botanical Name: Medicago sativa
- Origin of Name: From Arabic al-fasfasa, meaning "the best forage"
- Nutritional Profile: Rich in vitamins A, C, K, B-complex, minerals (calcium, potassium, magnesium), proteins, fiber, and antioxidants
- Uses: Primarily as fodder, also consumed by humans for its health benefits
- Agricultural Benefit: Being a leguminous crop, it helps in nitrogen fixation
India’s Regulatory Stand
- The government plans to bar GM alfalfa seed imports under powers granted by the Environment (Protection) Act, 1986.
- A rapid detection kit may be developed by Indian scientists to identify GM seeds before unloading at ports.
- Phytosanitary Certification: All imported alfalfa seeds must be accompanied by valid certificates meeting India’s plant protection standards.
Current Import Policy & Tariffs
- HS Code: 12092100 (Lucerne seed for sowing)
- Effective Import Duty: 50.045%, broken down as:
- 30% Basic Customs Duty (BCD)
- 30% AIDC (Agri Infrastructure and Development Cess) on BCD
- 10% Social Welfare Surcharge on (BCD + AIDC)
- 5% IGST
- Import Status: Currently, India does not import alfalfa seeds due to high domestic availability and high import duty.
- Domestic Price: ?500–800/kg; imported seeds would cost more.
Other Forage Imports
- Berseem (Trifolium spp.): India imports mainly from Egypt and CIS countries
- Import Drop: From 5,776 tonnes (2023-24) to 618 tonnes (April 2024–Jan 2025) due to increased domestic production
Environmental and Agricultural Considerations
- Water Requirement: Alfalfa is water-intensive, making seed cultivation less viable in water-scarce regions.
- Alternative Option: Experts suggest importing direct alfalfa fodder instead of seeds to meet demand while conserving water and preserving agricultural land for oilseeds and pulses.
Global Context
- USA:
- World’s largest alfalfa producer
- Grows both GM and non-GM varieties
- Alfalfa is mostly grown under rainfed conditions, with lower yield compared to irrigated regions
Amazon’s Project Kuiper
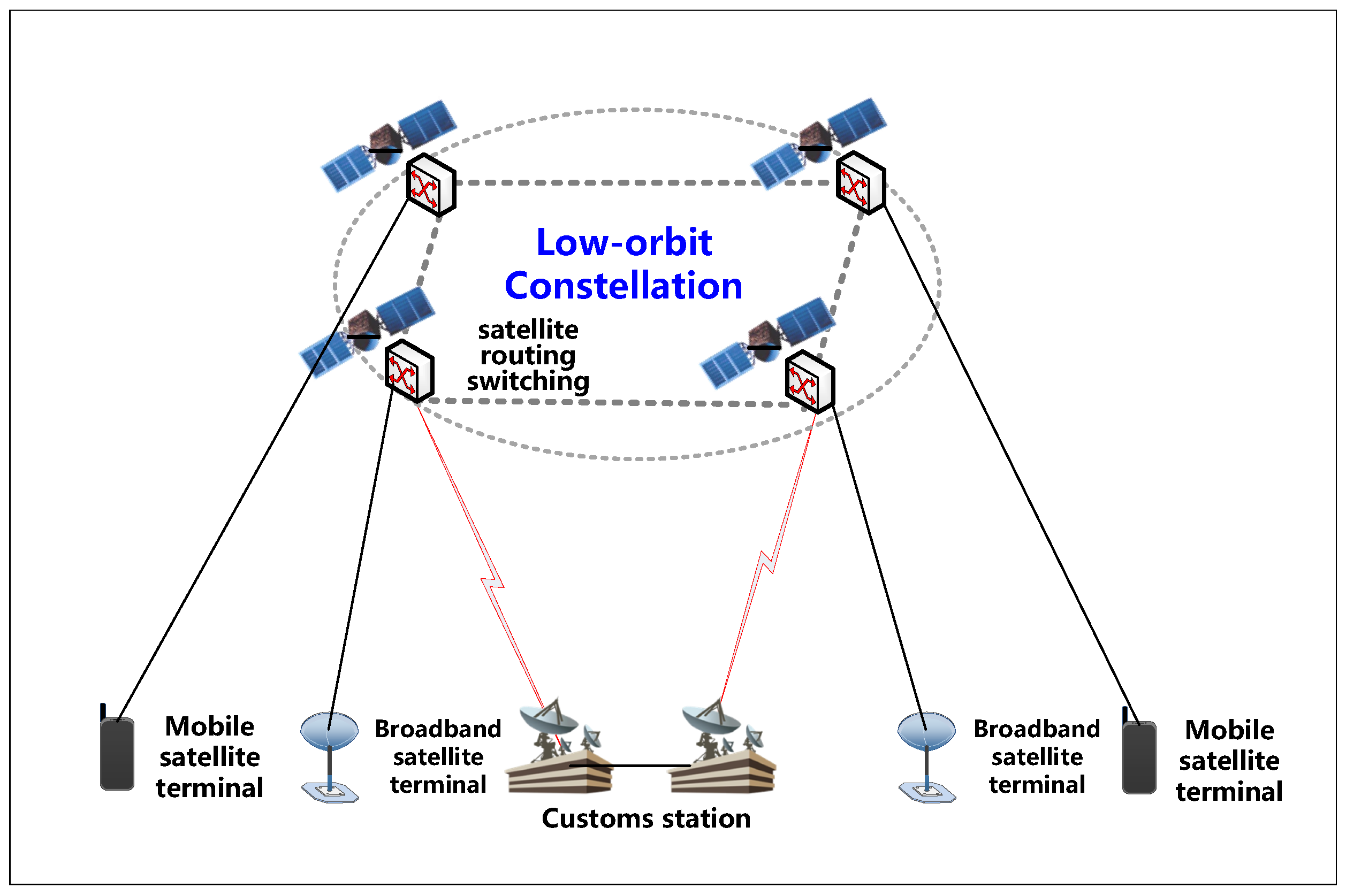
- 02 May 2025
In News:
Amazon successfully launched the first 27 satellites of Project Kuiper aboard an Atlas V rocket from Cape Canaveral Space Force Station, Florida. This marks the beginning of a large-scale effort to deploy a global satellite internet network to compete with SpaceX’s Starlink.
What is Project Kuiper?
Project Kuiper is Amazon’s satellite-based broadband project aimed at delivering high-speed internet across the globe, especially in underserved and remote regions, using Low Earth Orbit (LEO) satellites.
- Implementing Agency: Amazon
- FCC License: Approved in July 2020 by the US Federal Communications Commission
- Launch Name: KA-01 (Kuiper Atlas 1)
- Total Satellites Planned: 3,232 satellites in LEO (~630 km altitude)
- Current Launch: 27 satellites deployed; over 80 launches are planned to build the full constellation.
Objectives
- Provide affordable, high-speed internet to users across the globe.
- Support education, healthcare, disaster response, rural connectivity, and government services.
- Serve sectors requiring resilient communications in low-connectivity areas.
Internet Speed Tiers
Terminal Type Speed
Compact (Home Use) Up to 100 Mbps
Standard (Schools/Hospitals) Up to 400 Mbps
Large (Govt/Enterprise) Up to 1 Gbps
Comparison with Starlink and Other Satellite Internet Systems
Network Organisation Satellites Planned Current Status
Starlink SpaceX 40,000+ ~7,200 operational satellites; 5M+ users
OneWeb UK/India 648 Hundreds in orbit
Telesat Lightspeed Canada 298 In development
Guowang China 13,000+ Under planning
Project Kuiper Amazon 3,232 First 27 launched (May 2025)
How Satellite Internet Works
- Constellation: A network of satellites working in coordination to provide continuous global coverage.
- LEO Orbit: Satellites operate between 500–2,000 km altitude, offering low latency (20–40 ms).
- Ground Stations: Transmit and receive data to and from satellites.
- Inter-satellite Links: Use lasers/radio waves to relay data between satellites.
- AI-based Routing: Manages network traffic and reduces lag.
Technical Features
- Frequency Bands Used:
- Ka-band: High speed, weather-sensitive
- Ku-band: Balanced speed and reliability
- C-band: Slower, good in poor weather
- V-band: Experimental, ultra-fast but obstructed easily
- ACM Technology: Adjusts signal strength dynamically during adverse weather conditions.
Challenges
- High Cost: Satellite launches and user equipment are expensive.
- Weather Sensitivity: Rain and storms disrupt signals, especially in Ka/V bands.
- Space Debris Risk: Dense constellations increase chances of satellite collisions.
- Astronomical Interference: Bright satellite trails obstruct telescopic observations.
Strategic and Commercial Implications
- Project Kuiper marks Amazon’s entry into a growing space-based internet economy, competing with SpaceX’s Starlink.
- Expected to play a commercial and strategic role, including possible defence applications.
- With over 80 launches planned, Amazon will use various launch providers including ULA, Arianespace, Blue Origin, and SpaceX.
Red-Crowned Roofed Turtle

- 02 May 2025
In News:
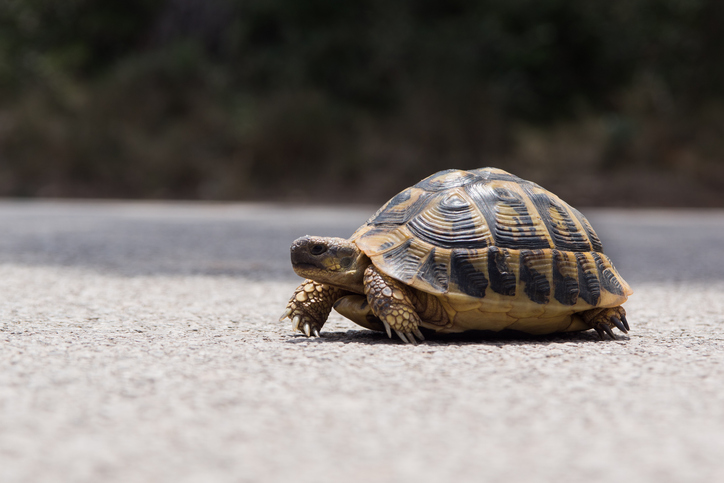
After nearly 30 years of absence, the Red-Crowned Roofed Turtle (Batagurkachuga) has been rediscovered in the Ganga River — a significant success for conservation efforts aimed at reviving endangered freshwater species.
Overview
- Commonly known as the Bengal Roof Turtle, it is a rare species of freshwater turtle found only in South Asia.
- Scientific Name: Batagurkachuga
Geographical Distribution
- Native Range: India, Nepal, and Bangladesh.
- Historical Presence: Widely distributed across the Ganga River system in India and Bangladesh, with additional presence in the Brahmaputra River basin.
- Current Habitat in India: The most viable population is now confined to the National Chambal Sanctuary, a protected riverine stretch for species like gharials and turtles.
Distinctive Features
- Size: Medium-sized species, females can grow up to 56 cm in length and weigh up to 25 kg, while males are significantly smaller.
- Coloration: Notable for their reddish-orange head marked with a black crown, and a greenish-brown carapace patterned with yellow streaks.
- Plastron (under-shell): Yellow with distinctive black markings.
- Adaptations: Possess a broad head, strong jaws, and webbed feet, suited for an aquatic lifestyle.
- Diet: Omnivorous — consumes both plant material and small aquatic organisms.
Conservation Status
- IUCN Red List: Critically Endangered
- Wildlife (Protection) Act, 1972: Listed under Schedule I – providing the highest level of legal protection in India.
- CITES: Included in Appendix II, regulating international trade.
International Labour Day (May Day)
- 02 May 2025
In News:
International Labour Day, also known as May Day, is observed annually on May 1 to honor the dedication and contributions of workers across the globe.
Key Highlights:
- Observed On: May 1
- Also Known As: International Workers’ Day, May Day
- Purpose: To commemorate the contributions of workers and honor the global labor movement's struggles and achievements.
Historical Background
- Origin: The roots of International Labour Day trace back to Chicago, USA, where on May 1, 1886, workers launched a strike demanding an 8-hour workday.
- The protest culminated in the Haymarket Affair on May 4, 1886, when a bomb explosion led to the deaths of six police officers and several civilians, marking a major milestone in labor rights activism.
- In 1889, the Second International (Paris) declared May 1 as a day of international workers’ solidarity.
Global Observance
- Observed in over 160 countries, including India, China, Cuba, France, Germany, Brazil, South Africa, Russia, Vietnam, among others.
- Celebrated through parades, union meetings, and public demonstrations advocating workers’ rights and social justice.
Country-wise Observance Differences
- India: First observed in 1923 in Chennai by the LabourKisan Party of Hindustan. It is a public holiday, widely recognized across the country.
- United States: Despite its historical origin, the U.S. celebrates Labor Day on the first Monday of September, officially declared in 1894 after the Pullman Strike. The shift was made to distance the holiday from socialist and communist affiliations.
- Canada: Also celebrates Labor Day on the first Monday of September, following U.S. traditions, though May 1 has some informal recognition by trade unions.
- United Kingdom: Celebrates a related holiday called the Early May Bank Holiday on the first Monday of May, which may or may not fall on May 1. It is not explicitly labor-themed like in other countries.
Significance
- Serves as a global reminder of workers’ rights, the historical fight for humane working conditions, and the ongoing struggles of labor communities.
- Symbolizes solidarity among workers across nations, cutting across political ideologies and economic systems.
