Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO)

- 08 Apr 2025
In News:
The Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) has launched two major global initiatives to advance inclusive and sustainable agrifood systems:
- “Four Betters Courses” Initiative – To revolutionize agrifood systems education
- “Commit to Grow Equality” Initiative – To bridge the gender gap in agrifood sectors
1. Four Betters Courses Initiative
- Launched: October 2024 during the World Food Forum
- Objective: To integrate FAO’s expertise into global agrifood systems education through partnerships with universities and academic networks.
- Alignment: Anchored in the FAO Strategic Framework 2022–2031
Core Philosophy – The “Four Betters” Approach:
- Better Production – Promote efficient, inclusive, and resilient food systems
- Better Nutrition – Ensure access to safe, nutritious, and affordable diets
- Better Environment – Address climate change and protect ecosystems
- Better Life – Improve rural livelihoods and reduce inequalities
- Delivery Platform: Implemented through the FAO eLearning Academy, which provides over 600 multilingual, certified courses.
2. Commit to Grow Equality (CGE) Initiative
- Launched: 2024 on the platform of the United Nations General Assembly (UNGA)
- Objective: To narrow the gender gap in agrifood systems and enhance women’s empowerment, especially in rural areas.
Key Highlights:
- Aims to benefit over 54 million women worldwide
- Mobilizes $1 billion in investments toward gender-responsive agrifood initiatives
- Provides strategic tools for tracking gender equality outcomes in public and private sectors
- Promotes gender-aligned national agricultural policies
- Facilitates evidence-based policymaking and fosters collaboration across governments, NGOs, and the private sector
Pradhan Mantri MUDRA Yojana (PMMY)

- 08 Apr 2025
In News:
The Pradhan Mantri MUDRA Yojana (PMMY), a flagship initiative aimed at providing financial support to unfunded micro and small enterprises, has completed 10 years since its launch in 2015.
Overview of PMMY
- Objective: To offer collateral-free institutional credit to non-corporate, non-farm micro and small enterprises.
- Loan Limit: Up to ?20 lakh without any collateral.
- Implementing Institutions (MLIs):
- Scheduled Commercial Banks
- Regional Rural Banks (RRBs)
- Non-Banking Financial Companies (NBFCs)
- Micro Finance Institutions (MFIs)
Categories of MUDRA Loans
Loan Category Loan Amount Range
Shishu Up to ?50,000
Kishor ?50,000 to ?5 lakh
Tarun ?5 lakh to ?10 lakh
Tarun Plus ?10 lakh to ?20 lakh
Key Achievements (2015–2025)
- Boost to Entrepreneurship: PMMY has sanctioned over 52 crore loans amounting to ?32.61 lakh crore, catalyzing a grassroots entrepreneurship revolution.
- MSME Sector Financing: Lending to MSMEs increased significantly:
- From ?8.51 lakh crore in FY14
- To ?27.25 lakh crore in FY24
- Projected to exceed ?30 lakh crore in FY25
- Women Empowerment: 68% of Mudra beneficiaries are women, highlighting the scheme’s impact in fostering women-led enterprises.
- Social Inclusion:
- 50% of loan accounts are held by SC, ST, and OBC entrepreneurs.
- 11% of beneficiaries belong to minority communities, showcasing PMMY’s contribution to inclusive growth.
Woolly Flying Squirrel
- 08 Apr 2025
In News:
The Wildlife Wing of the Himachal Pradesh Forest Department (HPFD) has recently documented the first-ever photographic evidence of the Woolly Flying Squirrel in Miyar Valley, located in the Lahaul and Spiti district. This marks a significant discovery, as the species is extremely elusive and rarely sighted.
About Woolly Flying Squirrel
- Common Name: Woolly Flying Squirrel / Western Woolly Flying Squirrel
- Scientific Name: Eupetaurus cinereus
- Taxonomy: The only known species under the genus Eupetaurus
- Conservation Status: Listed as Endangered on the IUCN Red List
Habitat and Distribution
- Endemism: Confined to the northwestern Himalayas
- Countries Found: Northern Pakistan and northwestern India
- Habitat Type: Inhabits a narrow elevational range within dry coniferous forests, typically in fragmented habitats
- Historical Records:
- Rediscovered in 1994, nearly 70 years after it was presumed extinct
- Since then, reported from Sai Valley, Gorabad, and Balti Gali in northern Pakistan
Key Characteristics
- Equipped with patagium (elastic skin membrane) that connects the forelimbs and hind limbs, enabling gliding—typical of flying squirrels
- Fur: Dense, straight, and silky
- Dorsal side: Blue-gray
- Ventral side: Pale gray
- Throat and ears: Covered in creamy white hairs
- Feet soles: Dense black fur, except for bare pinkish-brown toe pads
World Health Day 2025
- 08 Apr 2025
In News:
World Health Day, observed annually on 7 April, highlights pressing global health issues and mobilises action to improve public health outcomes.
- Established by: World Health Organization (WHO)
- First celebrated: 1950
Overview and Significance
World Health Day is commemorated to mark the founding of the WHO in 1948. It serves to raise awareness about global health issues and mobilize efforts to improve public health outcomes.
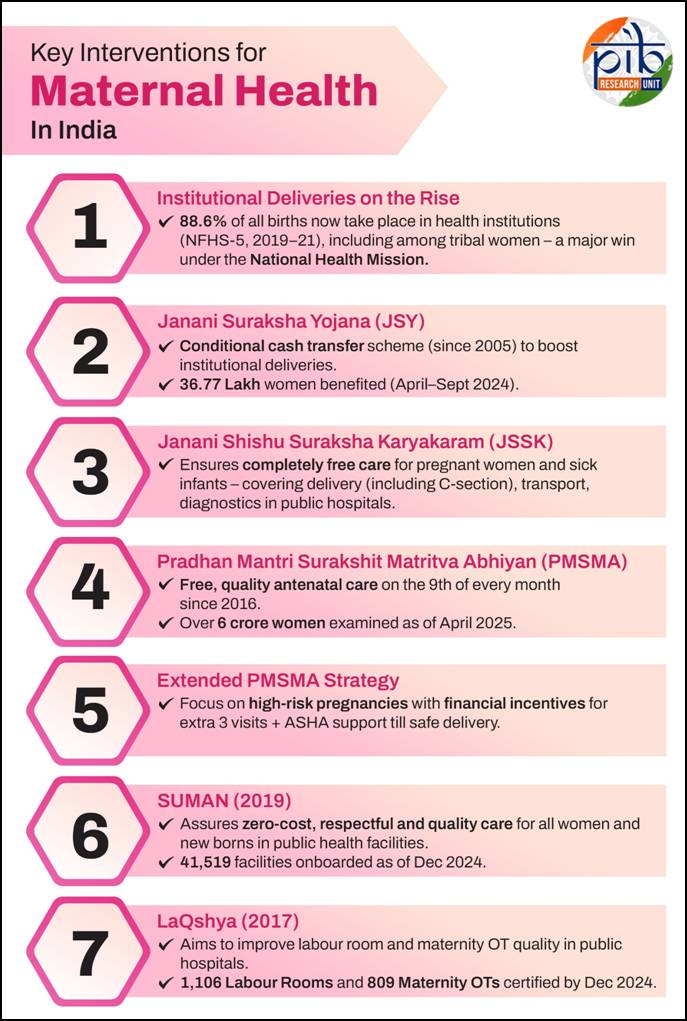
The 2025 theme, Healthy Beginnings, Hopeful Futures, emphasizes maternal and newborn health, calling for coordinated efforts to eliminate preventable deaths and support long-term well-being of women and children.
This year’s observance launches a year-long global campaign aimed at:
- Promoting safe pregnancies and institutional deliveries
- Supporting maternal nutrition and postnatal care
- Encouraging healthcare equity for women and newborns
India’s Progress in Maternal and Child Health
India has made significant strides through initiatives under the Ministry of Health and Family Welfare, particularly via Ayushman Bharat and the National Health Mission (NHM).
Key Health Indicators (India vs Global, 1990–2020)
Indicator India Reduction (%) Global Reduction (%)
Maternal Mortality Ratio 83% 42%
Neonatal Mortality Rate 65% 51%
Infant Mortality Rate 69% 55%
Under-5 Mortality Rate 75% 58%
Recent National Data:
- MMR reduced from 130 (2014–16) to 97 (2018–20) per 1,00,000 live births
- IMR dropped from 39 (2014) to 28 (2020)
- NMR reduced from 26 (2014) to 20 (2020)
- U5MR declined from 45 (2014) to 32 (2020)
Major Initiatives for Maternal and Child Health
- Maternal Death Surveillance and Response (MDSR): Tracks maternal deaths and implements corrective measures.
- Mother and Child Protection (MCP) Card: Educates women on nutrition, rest, and health entitlements.
- Reproductive and Child Health (RCH) Portal: Tracks maternal and child health services.
- Anaemia Mukt Bharat: Focuses on anaemia reduction under POSHAN Abhiyan.
- Birth Waiting Homes: Ensures institutional deliveries in remote areas.
- VHSNDs and Outreach Camps: Deliver maternal and child services in rural and tribal areas.
Healthcare Access and Infrastructure
- Ayushman Arogya Mandirs (HWCs): 1.76 lakh active centers
- 107.10 crore screenings for hypertension
- 94.56 crore screenings for diabetes
- 5.06 crore wellness sessions (e.g., yoga) conducted
- 17,000+ health facilities certified under National Quality Assurance Standards (NQAS)
Digital Health Ecosystem
- Ayushman Bharat Digital Mission (ABDM):
- 76+ crore ABHA IDs
- 5.95 lakh verified healthcare professionals
- 52+ crore linked health records
- U-WIN Platform:
- 7.90 crore beneficiaries
- 1.32 crore vaccination sessions
- 29.22 crore vaccine doses administered
- eSanjeevani Telemedicine:
- Over 36 crore consultations
- World's largest primary telehealth platform
- 130+ specialities, 131,793 spokes, and 17,051 hubs
Disease Elimination Success
- The WHO World Malaria Report 2024 highlights India’s major strides in malaria elimination, with a 69% drop in cases and 68% reduction in deaths between 2017 and 2023.
- Contributing just 0.8% of global cases in 2023, India’s exit from WHO's High Burden to High Impact (HBHI) group in 2024 marks a significant public health achievement.
- The Government of India has eliminated Trachoma as a public health problem in 2024, a feat recognised by the WHO.
- The Government of India’s proactive Measles-Rubella vaccination drive, strong surveillance, and public awareness efforts have greatly improved public health.
- According to WHO’s Global TB Report, India has made strong progress in tuberculosis control.
- Under the National Tuberculosis Elimination Programme (NTEP), TB incidence fell by 17.7%, from 237 to 195 cases per lakh population between 2015 and 2023.
- TB-related deaths also declined from 28 to 22 per lakh.
- Notably, missing TB cases dropped by 83%, from 15 lakh in 2015 to 2.5 lakh in 2023.
- As of 6th April, 2025, the Pradhan Mantri TB Mukt Bharat Abhiyaan, launched in September 2022, has registered over 2.5 lakh Ni-kshay Mitra volunteers supporting over 15 lakh TB patients. This initiative has further been expanded to include family members of TB patients.
- Kala-azar Elimination: India has successfully achieved Kala-azar elimination as of October 2024, with 100% of endemic blocks reaching the target of less than one case per 10,000 population by the end of 2023.
INS Varsha
- 08 Apr 2025
In News:
India is set to operationalise INS Varsha, its first dedicated base for nuclear-powered submarines, by 2026. Located near Rambilli, about 50 km south of Visakhapatnam, Andhra Pradesh, this high-security facility is part of the classified Project Varsha, aimed at strengthening India’s maritime and nuclear deterrence capabilities in the Bay of Bengal and Indian Ocean Region (IOR).
Key Features:
- Strategic Location: Near deep waters of the Bay of Bengal, facilitating stealthy submarine movement and minimizing detection.
- Infrastructure:
- Underground pens and tunnel systems to conceal and protect nuclear submarines.
- Inner and outer harbour facilities; inner harbour completed, work ongoing on breakwaters and jetties.
- 20 sq. km area, capacity to house at least 10–12 nuclear submarines.
- Stealth Capabilities: Similar to China’s Hainan base, it offers satellite-evasion advantages, crucial for the survivability of SSBNs (nuclear-powered ballistic missile submarines).
- Support Facilities: Proximity to BARC Atchutapuram for nuclear infrastructure, enabling swift integration and maintenance of strategic assets.
- Geopolitical Role: Counters Chinese dual-use naval infrastructure at Hambantota (Sri Lanka) and BNS Sheikh Hasina (Bangladesh).
Strategic Significance:
- Enhances second-strike capability, vital for nuclear deterrence under India's nuclear triad.
- Enables undetected deterrent patrols by SSBNs, ensuring survivability in case of counterforce attacks.
- Facilitates rapid access to key chokepoints, especially the Strait of Malacca.
India’s Expanding Nuclear Submarine Fleet
INS Aridhaman – Third SSBN:
- Scheduled for commissioning in 2025.
- 7,000-tonne displacement, more capable than predecessors INS Arihant and INS Arighat.
- Equipped with K-4 Submarine-Launched Ballistic Missiles (SLBMs) with a range of 3,500 km.
- Built under the Advanced Technology Vessel (ATV) project by Shipbuilding Centre, Visakhapatnam, with BARC and DRDO support.
- Designed for long-duration deterrent patrols in deep sea.
Future Developments:
- India launched its fourth SSBN in November 2024, with ~75% indigenous content.
- Plans underway for even larger SSBNs and the construction of six nuclear-powered attack submarines (SSNs), starting with two approved 9,800-tonne SSNs for conventional strike and escort roles.
Related Naval Expansion – Project Seabird (Karwar Base):
- Located on the western coast, expanding to accommodate 50 warships and submarines, plus 40 auxiliary vessels.
- Will include a dual-use air station, new dockyard, and multiple dry berths.
