Prime Minister’s 15-Point Programme for Minorities
- 11 Feb 2025
In News:
The Prime Minister’s New 15 Point Programme for welfare of Minorities is a programme which covers various schemes/initiatives of the participating Ministries/Departments with an aim to ensure that the underprivileged and weaker sections of six centrally notified minority communities have equal opportunities for availing the various Government welfare Schemes and contribute to the overall socio-economic development of the Country.
Key Highlights:
The programme has the following broad objectives:
- Enhancing opportunities for education
- Ensuring an equitable share for minorities in economic activities and employment, through existing and new schemes, enhanced credit support for self-employment, and recruitment to State and Central Government jobs
- Improving the conditions of living of minorities by ensuring an appropriate share for them in infrastructure development schemes
- Prevention and control of communal disharmony and violence.
The schemes of the Ministry of Minority Affairs covered under the Prime Minister’s 15 Point Programme are exclusively meant for notified minorities. However, 15% of the outlays and targets, to the extent possible, of schemes/initiatives implemented by other participating Ministries/Departments are earmarked for notified minorities.
The welfare schemes, including initiatives for education and skill development of minorities, being implemented by Ministry of Minority Affairs and other participating ministries under the programme, are as under:
- Pre-Matric Scholarship Scheme
- Post-Matric Scholarship Scheme
- Merit-cum- Means based Scholarship Scheme
- National Minorities Development Finance Corporation (NMDFC) Loan Schemes
- Samagra Shiksha Abhiyaan (M/o Education)
- DeenDayalAntyodaya Yojana (DAY-NRLM)- (M/o Rural Development)
- DeenDayal Upadhyay – GraminKaushalya Yojana (M/o Rural Development)
- Pradhan Mantri Awaas Yojana (M/o Rural Development)
- DeenDayalAntyodaya Yojana - National Urban Livelihoods Mission (M/o Housing & Urban Affairs)
- Priority Sector Lending by Banks (Department of Financial Services)
- Pradhan Mantri Mudra Yojana (Department of Financial Services)
- POSHAN Abhiyaan (Ministry of Women & Child Development)
- National Health Mission (Department of Health & Family Welfare)
- Ayushman Bharat (Department of Health & Family Welfare)
- National Rural Drinking Water Programme (Jal Jeevan Mission), (Department of Drinking Water & Sanitation)
The Schemes are being implemented by the respective Ministries/Departments under the saturation approach of Government. Under the saturation approach of the Government many of the components have achieved mainstreaming.
SwavalambiniProgramme

- 11 Feb 2025
In News:
The SwavalambiniProgramme, launched by the Ministry of Skill Development and Entrepreneurship (MSDE) in collaboration with NITI Aayog, is a pioneering initiative aimed at empowering women in the Northeast.
This programme targets female students in select Higher Education Institutions (HEIs) in Assam, Meghalaya, and Mizoram, providing them with an entrepreneurial mindset, essential resources, and ongoing mentorship to ensure their success in entrepreneurial ventures.
Programme Structure and Implementation
The programme follows a structured, stage-wise entrepreneurial process to guide participants through the various phases of business creation, from awareness to development, mentorship, and funding. It includes the following key components:
- Entrepreneurship Awareness Programme (EAP): Introduces 600 female students to entrepreneurship as a viable career option. The programme involves a 2-day session covering foundational entrepreneurial concepts and opportunities.
- Women Entrepreneurship Development Programme (EDP): This intensive 40-hour training is offered to 300 selected students, covering crucial aspects of business, including:
- Business training and skilling
- Access to finance and market linkages
- Compliance and legal support
- Networking opportunities
- Mentorship: After completing the training, participants receive six months of mentorship to help them translate their ideas into sustainable business ventures.
- Faculty Development Programme (FDP): A 5-day FDP will upskill faculty members in HEIs, enabling them to effectively mentor students in entrepreneurship. The training focuses on industry insights, business incubation strategies, and coaching techniques.
- Award to Rewards Initiative: Successful ventures will be recognized and awarded, inspiring others and fostering a culture of women-led enterprises.
Expected Outcomes and Impact
- The SwavalambiniProgramme aims to promote entrepreneurship among women, with an expectation that 10% of EDP trainees will successfully launch their businesses.
- It strives to establish a clear framework for nurturing and scaling women-led enterprises in India.
- The initiative contributes to economic transformation by making entrepreneurship a viable career path for women, particularly in the Northeast, a region brimming with untapped entrepreneurial potential.
Alignment with National Policies
The SwavalambiniProgramme aligns with several national initiatives and policies aimed at promoting women entrepreneurship:
- National Education Policy (NEP) 2020: The programme complements the NEP’s vision by integrating skill development, industry collaboration, and entrepreneurship-driven education within HEIs.
- Women Entrepreneurship Schemes: It strengthens existing initiatives like Start-Up India, Stand-Up India, PM Mudra Yojana, and the Women Entrepreneurship Platform, providing financial and mentorship support to emerging women entrepreneurs.
- Union Budget 2025: The ?10,000 crore start-up fund and the extension of the 100% tax exemption on start-up profits for five years in the Union Budget 2025 offer crucial financial backing for women-led enterprises.
Launch and Regional Focus
The programme was officially launched across nine colleges and universities in the Northeast, including Gauhati University, North-Eastern Hill University (NEHU), Mizoram University, and others.
National Commission for SafaiKaramcharis (NCSK)

- 11 Feb 2025
In News:
The Union Cabinet, on February 7, 2025, approved the extension of the tenure of the National Commission for SafaiKaramcharis (NCSK) for three years beyond March 31, 2025, i.e., up to March 31, 2028.
The move is aimed at sustaining efforts to eradicate manual scavenging, improve the welfare of sanitation workers, and achieve zero fatalities in hazardous cleaning activities. The extension involves a financial outlay of ?50.91 crore.
Background and Legal Status
- Constitution: NCSK was established in August 1994 under the National Commission for SafaiKaramcharis Act, 1993 as a statutory body.
- Post-2004 Status: The statutory Act lapsed in 2004, and since then, NCSK has functioned as a non-statutory body under the Ministry of Social Justice and Empowerment, with periodic extensions.
- Current Demand: The current Chairperson, M. Venkatesan, has welcomed the extension but stressed the need for granting statutory status to the commission to enhance its authority and effectiveness.
Mandate and Functions
As per Government Notification and MS Act, 2013:
- Policy Recommendations:Recommend specific programmes of action to eliminate inequalities in the status, facilities, and opportunities of SafaiKaramcharis.
- Monitoring and Evaluation:
- Study and evaluate implementation of welfare schemes and programmes.
- Monitor working conditions, including health, safety, and wages of sanitation workers.
- Grievance Redressal:
- Investigate specific complaints and take suomotu cognizance of non-implementation of policies or schemes related to SafaiKaramcharis.
- Report to governments on issues affecting SafaiKaramcharis.
- Role under the Prohibition of Employment as Manual Scavengers and their Rehabilitation Act, 2013:
- Monitor the implementation of the Act.
- Enquire into violations, and convey findings with recommendations to authorities.
- Advise the Centre and States on effective implementation.
- Take suomotu notice of non-compliance.
- Data Collection:
- NCSK remains the only national body tracking sewer and septic tank deaths.
Significance of the Extension
- Aims to improve working conditions in the sanitation sector.
- Supports the socio-economic upliftment of one of the most marginalized communities in India.
- Enhances implementation of manual scavenging prohibition laws.
- Facilitates rehabilitation and dignity for sanitation workers.
- Aligns with the broader vision of inclusive development and social justice.
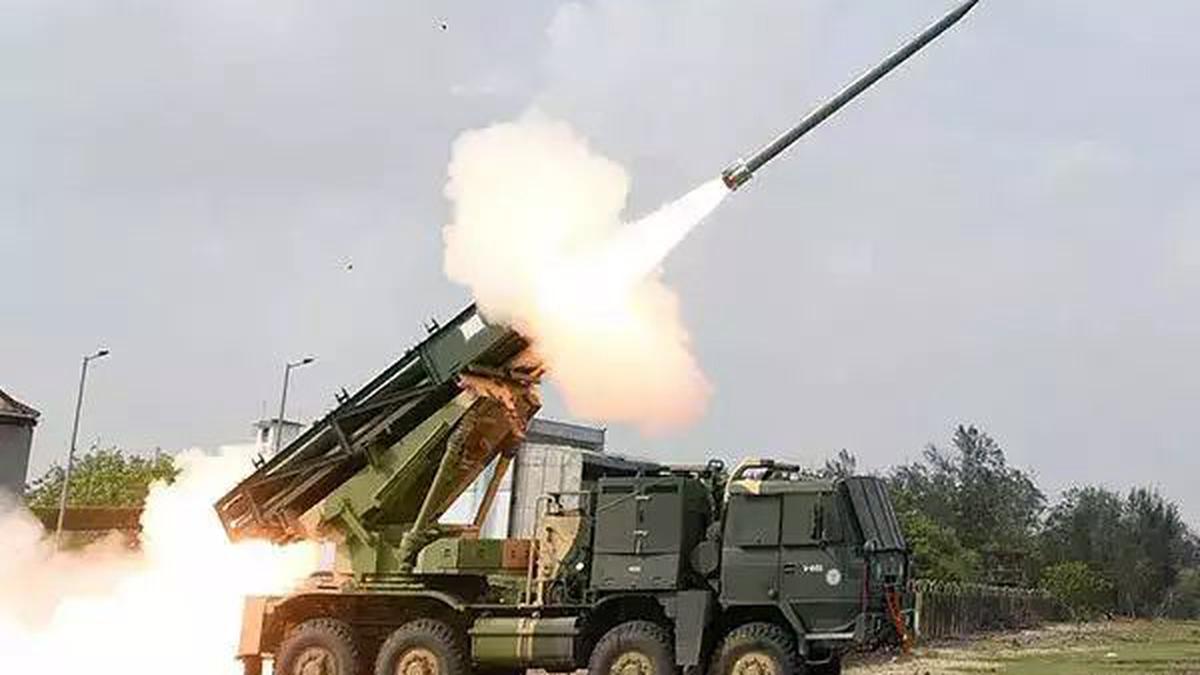
Pinaka Multiple Rocket Launch System (MRLS)

- 11 Feb 2025
In News:
In a significant step towards modernizing India's artillery capabilities, the Union Ministry of Defence signed contracts worth ?10,147 crore on February 6, 2025, for the procurement of advanced ammunition for the Pinaka Multiple Rocket Launch System (MRLS).
These agreements were concluded with Economic Explosives Limited (EEL) and Munitions India Limited (MIL) for the acquisition of Area Denial Munition (ADM) Type-1 and High Explosive Pre-Fragmented (HEPF)-Mk-1 (enhanced) rockets, respectively.
Pinaka MRLS: An Overview
- Type: All-weather, battle-proven, indirect fire Artillery Weapon System.
- Developer: Armament Research and Development Establishment (ARDE) of DRDO.
- Combat History: First used effectively during the Kargil War, neutralising enemy positions on mountain tops.
- Mobility: Mounted on Tatra trucks, providing high mobility and quick deployment.
- Payload & Firing Capacity:
- Each launcher: 12 rockets.
- Each battery: 6 launchers = 72 rockets.
- Capable of delivering a full salvo in 44 seconds.
- Range:
- Initial range: 60–75 km.
- Guided Pinaka (Pinaka-G) extends range to 75 km, with future plans to extend up to 120 km and eventually 300 km.
- Precision: The guided version uses INS/GPS navigation, allowing high accuracy against critical and time-sensitive targets.
- Warhead Types: High-explosive and submunitions, suitable for a wide variety of targets.
New Ammunition Contracts: Enhancing Lethality
The contracts include the procurement of:
- ADM Type-1: Equipped with specialised warheads designed to disperse sub-munitions over wide areas. These are effective in targeting mechanised formations, vehicles, and personnel, thereby denying area access to the enemy. These are similar to Dual Purpose Improved Conventional Munitions (DPICM).
- HEPF-Mk-1 (Enhanced): An advanced variant of the currently used HEPF rockets with extended range and improved lethality, capable of deep precision strikes in enemy territory.
In addition, a contract was signed with Bharat Electronics Limited (BEL) for upgrades to the Shakti software, which supports artillery operations.
Operational & Strategic Significance
- The upgraded Pinaka system will be the mainstay of long-range rocket artillery in the Indian Army.
- Four Pinaka regiments are already operational, with six more on order.
- The system’s development and expansion are a testament to India’s defenceindigenisation drive.
- The DRDO successfully completed flight tests of the guided Pinaka rocket with a range of 75 km, doubling its earlier reach. Future versions aim for up to 120 km and 300 km range.
Employment and MSME Impact
Besides enhancing strategic deterrence, the ?10,147 crore investment is expected to:
- Generate direct and indirect employment, particularly in the defence manufacturing ecosystem.
- Promote the Indian MSME sector, which contributes components and subsystems for the rockets and launchers.
- Support the vision of Atmanirbhar Bharat by reducing dependency on imported artillery systems.
Pong Dam Lake Wildlife Sanctuary
- 11 Feb 2025
In News:
Pong Dam Lake Wildlife Sanctuary, located in the Kangra district of Himachal Pradesh, has witnessed a record-breaking influx of migratory birds in 2025, according to the latest annual bird census conducted on February 1, 2025.
The sanctuary, a designated Ramsar Site (since 2002) and a Wetland of National Importance (1994), recorded a total of 1,53,719 birds across 97 species, indicating a sharp rise in avifaunal population and reaffirming its ecological significance.
Key Highlights from the 2025 Census
- Migratory birds recorded: 1,44,371 individuals from 55 species.
- Total bird count: 1,53,719 birds from 97 species.
- Increase from 2024: 83,555 more birds.
- Bar-headed Goose population: 90,959 (up from 37,501 in 2024) — highest ever recorded since the census began in 2004.
Other dominant waterfowl included:
- Eurasian Coots – 10,785
- Common Pochards – 9,692
- Common Teals – 8,497
- Northern Pintails – 8,053
Lesser-spotted species included the Greater and Lesser White-fronted Goose, Red Crested Pochard, and Northern Lapwing.
Reasons Behind the Surge
- Experts attribute the significant increase in bird numbers to a decline in the water level of Pong Dam Lake, which exposed additional lakebed areas, creating new feeding grounds. This has made the sanctuary increasingly attractive to birds migrating from Tibet, Central Asia, Russia, Siberia, and the Trans-Himalayan region.
Survey and Conservation Collaboration
- The census was conducted by over 100 participants, including officials from the Himachal Pradesh Forest Department, experts from the Bombay Natural History Society, Wildlife Institute of India, and local birdwatchers. The sanctuary was divided into 25 zones for comprehensive coverage.
- To further conservation efforts, a new Interpretation Centre was inaugurated on January 18, 2025, aimed at promoting awareness about the wetland's role in sustaining biodiversity and supporting migratory birds.
Ecological and Geographical Profile
Pong Dam Lake (Maharana Pratap Sagar)
- Type: Manmade reservoir formed by construction of Pong Dam on the Beas River.
- Location: Wetland zone of the Shivalik hills, Kangra district, Himachal Pradesh.
- Area: Approx. 307 sq. km — among the largest man-made wetlands in northern India.
- Importance: Key stopover on the Trans-Himalayan flyway for migratory birds.
Flora
- Vegetation types: Submerged aquatic vegetation, grasslands, forests.
- Dominant species:Eucalyptus, Acacia, Shisham.
Fauna
- Avifauna: Over 220 bird species recorded; 54 waterfowl species.
- Notable birds: Bar-headed Geese, Pintails, Pochards, Coots, Grebes, Cormorants, Herons, Storks, Grey Partridge, Peafowl.
- Mammals: Sambar, Barking Deer, Nilgai, Wild Boar, Clawless Otter, Leopard.
