Khelo India Youth Games 2025

- 06 May 2025
In News:
- Prime Minister Narendra Modi virtually inaugurated the 7th edition of the Khelo India Youth Games (KIYG) on May 4, 2025, marking Bihar’s first time hosting a national-level multi-sport event.
- The event will be held across five cities in Bihar: Patna, Rajgir, Gaya, Bhagalpur, and Begusarai from May 4–15, 2025.
About Khelo India Youth Games (KIYG)
Feature Details
Launch Year 2018
Nodal Ministry Ministry of Youth Affairs and Sports
Target Group Youth athletes under 17 and 21 years of age
Objective Promote grassroots sports, mass participation, and talent
development for global competition
Host Cities in 2025 Patna, Rajgir, Gaya, Bhagalpur, Begusarai
Total Athletes (2025) Over 6,000 participants
Special Highlights of KIYG 2025
- Medal Events: Competitions held in 27 sporting disciplines.
- New Inclusions:
- Sepaktakraw included as a medal sport for the first time.
- Esports introduced as a demonstration event, reflecting the rise of digital-age sports.
- Support for Athletes: Winners eligible for scholarships under the Khelo India Scheme to pursue professional training.
Significance
- PM Modi emphasized the role of regular tournaments like KIYG in shaping India’s sports ecosystem.
- Cited Vaibhav Suryavanshi, a 14-year-old cricketer who scored a 38-ball century in IPL 2025, as a symbol of emerging youth talent.
- Highlighted that platforms like Khelo India events (youth, para, winter, and senior levels) help identify, nurture and promote talent, building confidence among young athletes.
Previous Editions of KIYG
Edition Host City
1st (2018) New Delhi
2nd (2019) Pune
3rd (2020) Guwahati
4th (2021) Panchkula
5th (2022) Bhopal
6th (2023) Chennai
7th (2025) Bihar (multiple cities)
DRR Dhan 100 (Kamala) &Pusa DST Rice 1
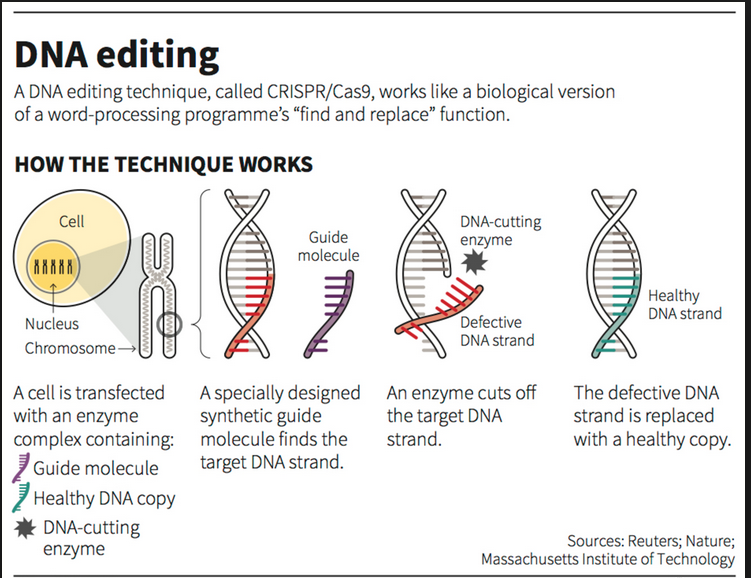
- 06 May 2025
In News:
- Recently, the Union Ministry of Agriculture and Farmers’ Welfare launched India’s first genome-edited rice varieties—DRR Dhan 100 (Kamala) and Pusa DST Rice 1.
- Developed by ICAR-IIRR (Hyderabad) and ICAR-IARI (New Delhi) using CRISPR-Cas9 technology under SDN1/SDN2 methods.
About the Varieties
DRR Dhan 100 (Kamala)
- Developed by: ICAR-Indian Institute of Rice Research (IIRR), Hyderabad
- Parent variety: Samba Mahsuri (BPT 5204)
- Features:
- 19% increase in yield
- Matures in ~130 days (20 days earlier than parent)
- Stronger stem – reduces lodging
- Saves ~7,500 million cubic meters of irrigation water
- Lower methane emissions
- Edited gene: CKX2 (Gn1a) – increases grain number per panicle
Pusa DST Rice 1
- Developed by: ICAR-Indian Agricultural Research Institute (IARI), New Delhi
- Parent variety: MTU 1010 (Cotton Dora Sannalu)
- Features:
- Improved tolerance to drought and salinity
- Yield increase: Up to 30.4% in saline/alkaline soils
- Edited gene: DST gene
- Developed using SDN1 genome editing – no foreign DNA inserted
Technology Used
- CRISPR-Cas9 genome editing system:
- Enables precise editing of native genes without inserting foreign DNA
- SDN1/SDN2 methods approved by India’s biosafety regulations
- Genome editing vs GMOs:
- Genome editing makes internal gene alterations
- GMOs involve insertion of foreign genetic material
- GM crops are banned for cultivation/import in India (except Bt cotton)
Benefits Claimed
- Increased agricultural productivity:
- 19% increase in yield (DRR Dhan 100)
- Up to 30.4% increase in saline soils (Pusa DST Rice 1)
- Environmental benefits:
- Reduced greenhouse gas emissions (~20%)
- Lower methane release due to early maturation
- Major water conservation
- Target states: Andhra Pradesh, Telangana, Tamil Nadu, Kerala, Karnataka, Chhattisgarh, Maharashtra, Madhya Pradesh, Odisha, Jharkhand, Bihar, Uttar Pradesh, West Bengal, and Puducherry
Concerns and Criticisms
Biosafety and Unintended Effects
- Unintended mutations: CRISPR-Cas enzymes may cause off-target gene edits, potentially resulting in unknown protein formations.
- Lack of global standardisation on enzyme concentration and specificity.
- Some scientists warn of genetic instability in SDN1-based edits.
Seed Sovereignty & Intellectual Property Rights (IPR)
- Genome editing tools are IPR-protected, raising concerns over farmers' seed sovereignty.
- Activist groups like Coalition for a GM-Free India demand transparency on IPR ownership and oppose reliance on proprietary technologies.
- Risk of monoculture, loss of rice genetic diversity, and trade barriers for India’s non-GM rice exports.
Policy and Regulatory Framework
- India’s biosafety guidelines (2022) permit SDN1 and SDN2 genome editing for general crops.
- The Union Budget 2023–24 allocated ?500 crore for advancing genome editing in agriculture.
- ICAR expanding genome editing to oilseeds and pulses.
Neanderthal Spear Tip Discovery
- 06 May 2025
In News:
Ancient bone spear tip found in Russia is oldest in Europe and made by Neanderthals.
What Was Discovered?
- Oldest known spear tip in Europe, crafted by Neanderthals, not Homo sapiens.
- Found in a cave in the North Caucasus region, Russia.
- Dated to 70,000–80,000 years ago, prior to modern human arrival in Europe (~45,000 years ago).
- Study published in the Journal of Archaeological Science.
Artefact Features
- Length: ~9 cm
- Material: Bone (likely from bison)
- Construction:
- Shaped using stone tools
- Attached to a wooden shaft with natural tar (early adhesive use)
- Function:
- Micro-cracks indicate impact with a hard target – used in hunting or combat
- Minimal wear, suggesting it was used shortly after construction
Excavation Details
- Excavated in 2003, thoroughly analyzed recently.
- Found with animal bones and campfire remains – evidence of Neanderthal habitation.
- Analytical techniques used: Spectroscopy, CT scans, Microscopy
Shear-Wave Splitting
- 06 May 2025
In News:
Scientists from the University of Oxford have proposed a new method to monitor volcanic eruptions by using the seismic phenomenon of shear-wave splitting, demonstrated at Mount Ontake in Japan.
What is Shear-Wave Splitting?
- Shear-wave splitting is a seismic phenomenon where shear (S) waves split into two components that travel at different speeds based on their polarisation.
- Occurs when waves pass through aligned cracks or fractures in subsurface rocks.
- Movement of magma and volcanic fluids changes stress conditions, causing rock cracks to open or close.
- These changes influence the speed and direction of shear waves.
- Increased shear-wave splitting can indicate rising internal pressure, serving as a potential early warning for volcanic eruptions.
Mount Ontake – Key Facts
- Type: Active stratovolcano
- Location: Honsh? Island, Central Japan, near Tokyo
- Status: Japan’s second-highest volcano
- Part of the Pacific Ring of Fire
- Major Eruption:
- Year: 2014
- Type: Phreatic eruption (steam-driven)
- Casualties: 60+ people, mainly hikers
- Notably occurred without significant seismic warning
- Phreatic Eruptions:
- Caused by steam pressure from heated underground water
- Do not involve new magma
- Difficult to predict using conventional methods
Pulsar G359 and Galactic ‘Bone’
- 06 May 2025
In News:
Astronomers have discovered a likely explanation for a fracture in a huge cosmic "bone" in the Milky Way galaxy, using NASA's Chandra X-ray Observatory and radio telescopes.
About G359.13-0.20005 ("The Snake")
- G359.13 is a non-thermal filament in the Milky Way, resembling a "galactic bone."
- It stretches about 230 light-years and is located ~26,000 light-years from Earth, near the Galactic Center.
- These filaments are visible primarily in radio waves and aligned with galactic magnetic field lines.
- Emissions result from charged particles spiraling along magnetic fields, producing synchrotron radiation.
Key Discovery
- A fracture has been observed in the continuous structure of G359.13.
- This fracture aligns with the location of a pulsar, identified using:
- Chandra X-ray Observatory (X-ray data)
- MeerKAT and VLA (radio data)
About the Pulsar
- A highly magnetized, fast-moving neutron star formed by a supernova explosion.
- Estimated speed: 1–2 million miles per hour.
- The pulsar likely collided with G359.13, causing:
- Distortion in the magnetic field
- Fracture in the radio filament
- Chandra data revealed blue-colored X-ray emissions from the pulsar.
- Nearby X-ray sources may be from electrons and positrons accelerated to high energies.
Scientific Significance
- Provides insights into:
- High-energy astrophysical processes
- Pulsar interactions with galactic magnetic structures
Chandra X-ray Observatory – Key Facts
- Launched: July 23, 1999, aboard Space Shuttle Columbia (STS-93)
- Function: Detects X-ray emissions from hot cosmic objects (e.g., black holes, supernova remnants)
- Orbit: High Earth orbit (~139,000 km altitude) to avoid atmospheric X-ray absorption
- Part of NASA’s “Great Observatories” (with Hubble, Spitzer, Compton)
- Capabilities:
- 8x better resolution than previous X-ray missions
- Detects X-ray sources 20 times fainter than predecessors
- Managed by: NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center
