India to Receive INS Tamal
- 07 May 2025
In News:
India is set to induct INS Tamal, the second advanced stealth frigate of the Krivak-III class, built in Russia under a bilateral defence contract.
About INS Tamal
- Type & Class:INS Tamal is a 3,900-tonne stealth frigate, part of the Krivak-III class deal signed in 2016 between India and Russia. It is the sister ship of INS Tushil, commissioned in December 2024.
- Builder & Collaboration:Constructed at the Yantar Shipyard in Kaliningrad, Russia, under India-Russia defence cooperation.
The contract includes four frigates: two built in Russia and two under construction at Goa Shipyard with technology transfer.
Key Features
- Stealth Technology:Equipped with advanced suppression systems for radio, infrared, and acoustic signatures to enhance survivability.
- Armaments:
- BrahMos supersonic cruise missiles (range approx. 450 km)
- Shtil surface-to-air missiles
- Anti-submarine torpedoes and rocket launchers
- Performance:
- Speed exceeding 30 knots
- Can deploy Kamov-28 and Kamov-31 helicopters for anti-submarine warfare and airborne early warning.
- Automation: High automation reduces crew workload and improves operational efficiency.
Strategic Importance
- Enhances India’s blue-water naval capabilities across air, surface, underwater, and electromagnetic domains.
- Strengthens naval deterrence and force projection in the Indo-Pacific region, especially amid rising tensions in the Arabian Sea.
- Demonstrates successful Make in India initiative combined with global collaboration, as two of the frigates are being built domestically at Goa Shipyard.
Rare 7th-Century Old Kannada Inscription unearthed at Madapura Lake, Karnataka

- 07 May 2025
In News:
A rare 7th-century Old Kannada inscription from the reign of Vikramaditya I of the Badami Chalukyas has been discovered at Madapura Lake in Davangere, Karnataka. The inscription sheds light on taxation, land grants, and regional governance during his rule.
About the Badami Chalukyas
- Origins: Emerged as a regional Kannada power claiming descent from Ayodhya to establish legitimacy.
- Capital:Vatapi (present-day Badami, Karnataka).
- Notable Rulers and Political History:
- Pulakesin I (543–566 CE): Founder of the dynasty; fortified Badami.
- Pulakesin II (609–642 CE): Most celebrated ruler; defeated Harshavardhana at the Narmada river; established diplomatic contacts with Persia (depicted in Ajanta caves).
- Vikramaditya I (644–681 CE): Son of Pulakesin II; reclaimed Badami from Pallavas and expanded influence over southern kingdoms like the Cholas, Pandyas, and Keralas.
- Administration:
- Centralised monarchy with limited autonomy granted to villages.
- Economy relied on land revenue and military conquests.
- Maintained a naval fleet—Pulakesin II had around 100 ships.
- Religion:Patronised Shaivism, Vaishnavism, Shaktism, and Jainism. Vikramaditya I and others made donations to Jain institutions; Pulakesin I performed Ashvamedha Yajna.
- Art and Architecture:
- Developed the Vesara style, a fusion of northern Nagara and southern Dravida temple architecture.
- Constructed rock-cut and structural temples in Aihole, Badami, and Pattadakal.
About Vikramaditya I
- Background: Son of Pulakesin II; ascended the throne during a period of political turmoil following his father's death and Pallava invasion.
- Military Achievements:
- Defeated Narasimhavarman I of the Pallavas, who had earlier seized Badami.
- Reunited the fractured Chalukya empire, restoring its former prestige.
- Subdued southern powers including the Cholas, Pandyas, and Keralas, consolidating control over the southern Deccan.
- Political Consolidation:
- Re-established central authority across Karnataka and surrounding regions.
- Appointed loyal feudatories, such as Singhavenna (mentioned in the new Davangere inscription), to manage local governance.
- Legacy:
- Known by titles such as Rajamalla (King of Kings) and Yuddhamalla (Warrior King).
- His reign marked a revival of Chalukya power and paved the way for cultural and architectural achievements under his successors Vikramaditya II and Kirtivarman II.
India-Angola Bilateral Talks and Strategic Cooperation
- 07 May 2025
In News:
The Prime Minister of India recently held bilateral talks with Angolan President João Lourenço in New Delhi. During the meeting, India offered Angola a $200 million defence credit line and discussed expanding cooperation in sectors such as infrastructure, defence, and space technology. The visit also commemorates the 40th anniversary of diplomatic relations between India and Angola.
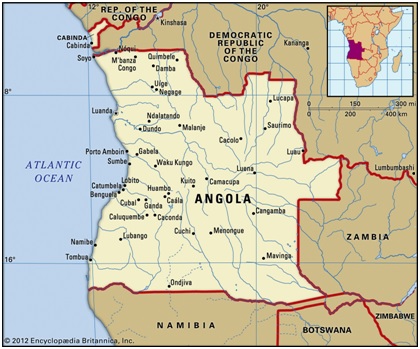
About Angola
- Location: Southwestern Africa, bordered by the Atlantic Ocean to the west.
- Capital: Luanda, a major coastal port city.
- Neighbouring countries: Republic of the Congo, Democratic Republic of the Congo, Zambia, Namibia, and the Atlantic Ocean.
- Special territory: Includes the exclave of Cabinda, located north of the main territory.
Geographical Features
- Major Plateaus:Bié Plateau (~2,600 m), Huíla Plateau (~2,300 m), Malanje Highlands.
- Highest Point: Mount Moco (2,620 m or 8,596 ft) near Huambo.
- Rivers:
- Cuanza (Kwanza): Largest river entirely within Angola.
- Cunene River: Forms part of the border with Namibia.
- Cuango River: Tributary of the Congo River.
- Other rivers drain into the Zambezi and Okavango river systems.
- Desert: Southwest Angola forms part of the Namib Desert.
- Climate: Tropical with distinct rainy and dry seasons, influenced by the cold Benguela ocean current.
Demographics and Economy
- Ethnic groups: Predominantly Bantu-speaking, including Ovimbundu, Kimbundu, and Bakongo communities.
- Economic importance:
- One of Africa’s leading oil producers.
- Rich mineral resources including diamonds, iron ore, copper, and gold.
- The northeast is notable for diamond deposits found in river gravels.
ECINET: India’s Unified Digital Platform for Elections

- 07 May 2025
In News:
The Election Commission of India (ECI) is set to launch ECINET, a single, unified digital platform aimed at consolidating and simplifying election-related services for voters, officials, political parties, and civil society organizations.
About ECINET:
ECINET will merge over 40 existing mobile and web applications—including the Voter Helpline, cVIGIL, Suvidha 2.0, ESMS, Saksham, KYC App, Voter Turnout app, Know Your Candidate app, and election results app—into one integrated system. This platform will also serve election officials such as Electoral Registration Officers and Booth Level Officers by providing a comprehensive interface.
Objectives:
- Simplify access to electoral services through a single window and one login (single sign-on).
- Eliminate the redundancy of multiple applications and multiple logins.
- Provide real-time access to verified and authenticated election data for all stakeholders.
- Strengthen electoral infrastructure by fostering digital innovation and integration.
- Enhance cybersecurity through robust testing and protocols.
Key Features:
- Unified Platform: Consolidates all election-related apps into one.
- Single Sign-On: One login credential for all services reduces confusion.
- Cross-Device Compatibility: Accessible on smartphones and desktops alike.
- Modern User Interface: Intuitive and user-friendly design.
- Data Integrity: Only authorized ECI officials can enter data, with statutory forms prevailing in case of discrepancies.
- Robust Cybersecurity: Rigorous trials to ensure safety and performance.
- Nationwide Coverage: Designed to serve nearly 100 crore voters and the entire electoral administration.
Timeline:
The ECINET platform is in advanced stages of development and testing and is expected to be launched before the Bihar Assembly elections later this year.
Stratospheric Airship Platform by DRDO

- 07 May 2025
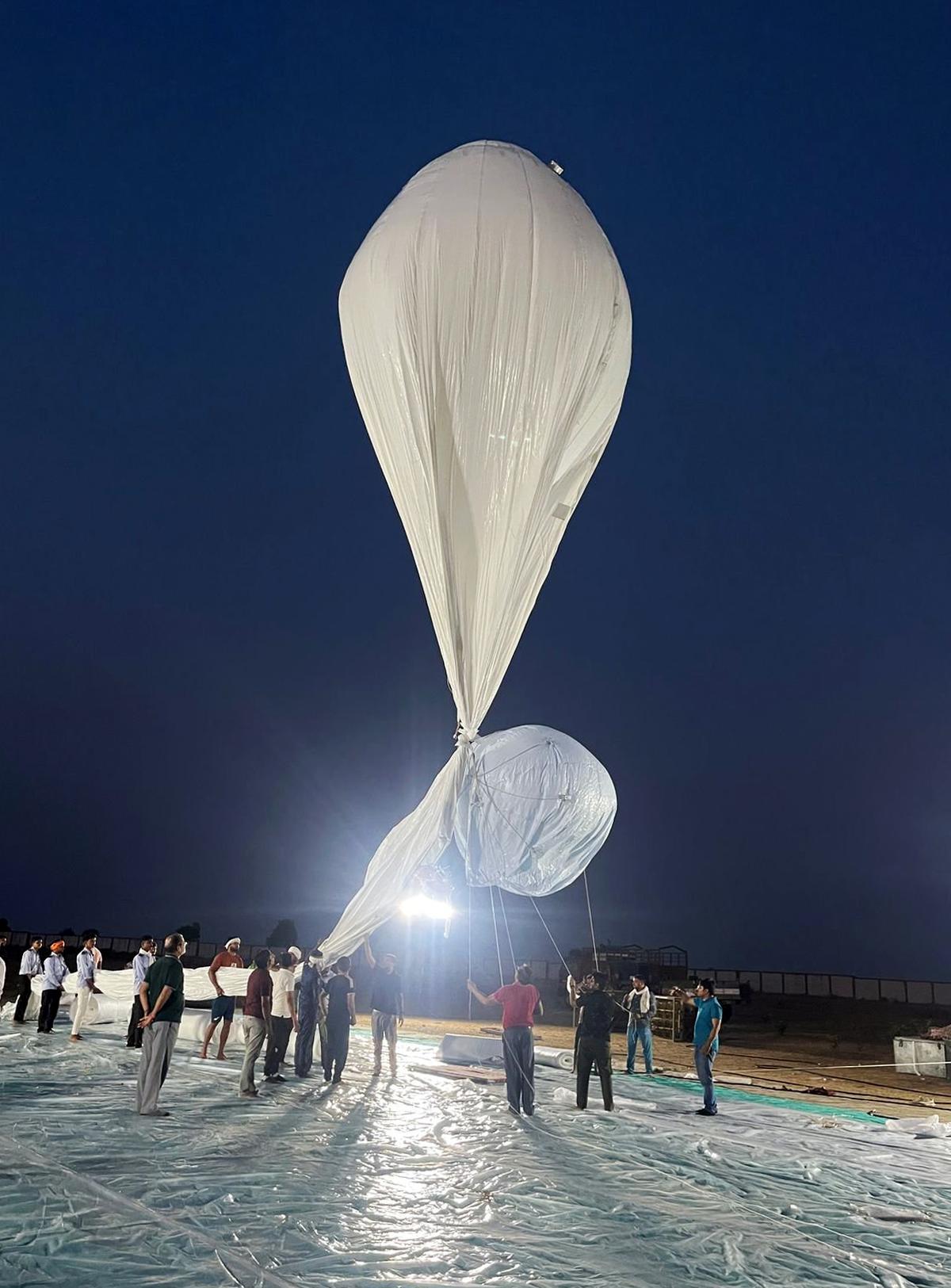
In News:
India successfully conducted the maiden flight trial of its indigenous Stratospheric Airship Platform, developed by the Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO). The trial took place at Sheopur, Madhya Pradesh, and marked a significant milestone in India’s pursuit of advanced high-altitude surveillance technologies.
About the Stratospheric Airship Platform
- Nature: A lighter-than-air, high-altitude airship designed to operate at stratospheric heights (~17 km altitude).
- Developer: Aerial Delivery Research and Development Establishment (ADRDE), Agra under DRDO.
- Purpose: To provide extended surveillance and real-time observation capabilities for military and civilian applications.
Key Features and Flight Trial Details
- Successfully reached an altitude of about 17 km (stratosphere).
- Carried an instrumental payload for Intelligence, Surveillance, and Reconnaissance (ISR) tasks.
- Flight duration: Approximately 62 minutes.
- Tested crucial systems such as envelope pressure control and emergency deflation mechanisms.
- Data from onboard sensors will aid in developing simulation models for future flights.
- The platform was recovered post-mission for further analysis.
Strategic and Operational Significance
- Enhanced ISR: Boosts India’s military surveillance over borders, coastal regions, and conflict zones.
- Earth Observation: Supports disaster management, environmental monitoring, and communication relays.
- Cost-Effective: Provides persistent coverage at a fraction of the cost of satellite launches.
- Technological Edge: Places India among a select group of nations with indigenous high-altitude airship capabilities, crucial amid rising regional security challenges.
- Dual-Use Potential: Suitable for both defence and civilian applications, including atmospheric sensing.
