Katchatheevu Island
- 01 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
Prime Minister Narendra Modi once again attacked the Congress about its decision to “callously give away” the island of Katchatheevu.
About the Island of Katchatheevu:
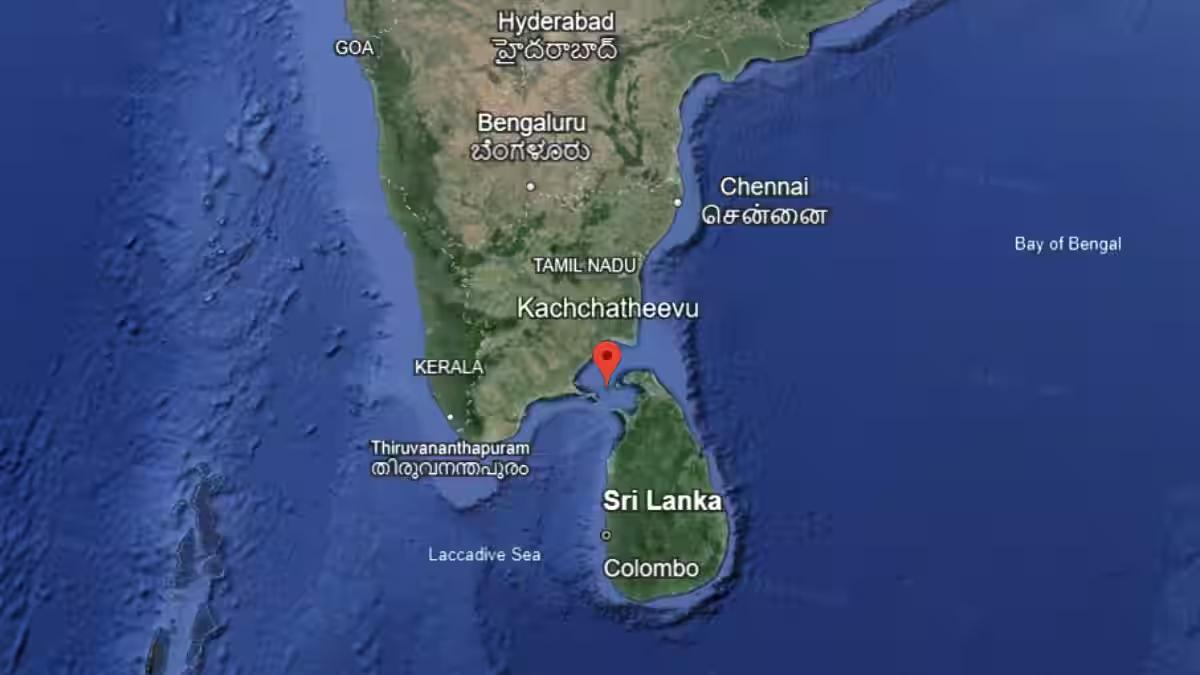
- Katchatheevu is an uninhabited area located between India and Sri Lanka in the Palk Strait.
- It measures around 1.6 km in length and slightly over 300 m wide at its broadest point.
- Situated northeast of Rameswaram, it is approximately 33 km away from the Indian coast.
- Moreover, it is positioned about 62 km southwest of Jaffna, at the northern tip of Sri Lanka, and 24 km from the inhabited Delft Island, which is a part of Sri Lanka.
- Katchatheevu is not suited for permanent settlement as there is no source of drinking water on the island.
History of the island:
- Being the product of a 14-century volcanic eruption, Katchatheevu is relatively new in the geological timescale.
- In the early medieval period, it was controlled by the Jaffna kingdom of Sri Lanka.
- In the 17th century, control passed to the Ramnad zamindari based out of Ramanathapuram, about 55 km northwest of Rameswaram.
What is the dispute?
- The island became part of the Madras Presidency during the British Raj.
- But in 1921, both India and Sri Lanka, at the time British colonies, claimed Katchatheevu to determine fishing boundaries.
- A survey marked Katchatheevu in Sri Lanka, but a British delegation from India challenged this, citing ownership of the island by the Ramnad kingdom.
- This dispute was not settled until 1974.
What is the Agreement on Katchatheevu Island?
- In 1974, Indira Gandhi made attempts to settle the maritime border between India and Sri Lanka, once and for all.
- As a part of this settlement, known as the ‘Indo-Sri Lankan Maritime Agreement’, Indira Gandhi ‘ceded’ Katchatheevu to Sri Lanka.
- At the time, she thought the island had little strategic value and that ceasing India’s claim over the island would deepen its ties with its southern neighbor.
- Moreover, as per the agreement, Indian fishermen were still allowed to access Katchatheevu “hitherto”.
- Unfortunately, the issue of fishing rights was not ironed out by the agreement.
- Sri Lanka interpreted Indian fishermen’s right to access Katchatheevu to be limited to “rest, drying nets and for visit to the Catholic shrine without a visa”.
- Another agreement in 1976, during the period of Emergency in India, barred either country from fishing in the other’s Exclusive Economic Zone.
- Again, Katchatheevu lay right at the edge of the EEZs of either country, retaining a degree of uncertainty about fishing rights.
How did the Sri Lankan Civil War Impact Katchatheevu?
- Between 1983 and 2009, the border dispute remained on the back burner as a bloody civil war raged in Sri Lanka.
- With the Sri Lankan naval forces preoccupied with their task of cutting off supply lines of the LTTE based out of Jaffna, incursions by Indian fishermen well into Sri Lankan waters were commonplace.
- Bigger Indian trawlers were especially resented as they would not only tend to overfish but also damage Sri Lankan fishing nets and boats.
- In 2009, the war with the LTTE ended, and things dramatically changed. Colombo beefed up its maritime defenses and turned its focus to Indian fishermen.
- Facing a depletion of marine resources on the Indian side, they would frequently enter Sri Lankan waters as they had been doing for years, but finally began facing consequences.
- To date, the Sri Lankan navy routinely arrests Indian fishermen and there have been many allegations of custodial torture and death.
- The demand for Katchatheevu is revived each time such an incident happens.
Indian Government Stance on Katchatheevu Island:
- The Union government’s position on Katchatheevu has largely remained unchanged.
- It has argued that since the island had always been under dispute, “no territory belonging to India was ceded nor sovereignty relinquished.”
Kodaikanal Solar Observatory (KOSO)

- 01 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
Since ancient times, seafarers, mathematicians, astronomers, and physicists have all diligently studied and tracked the Sun and its phenomena, with the establishment of the Madras Observatory by the British East India Company in 1792 marking a pioneering effort in this region.
About Kodaikanal Solar Observatory:
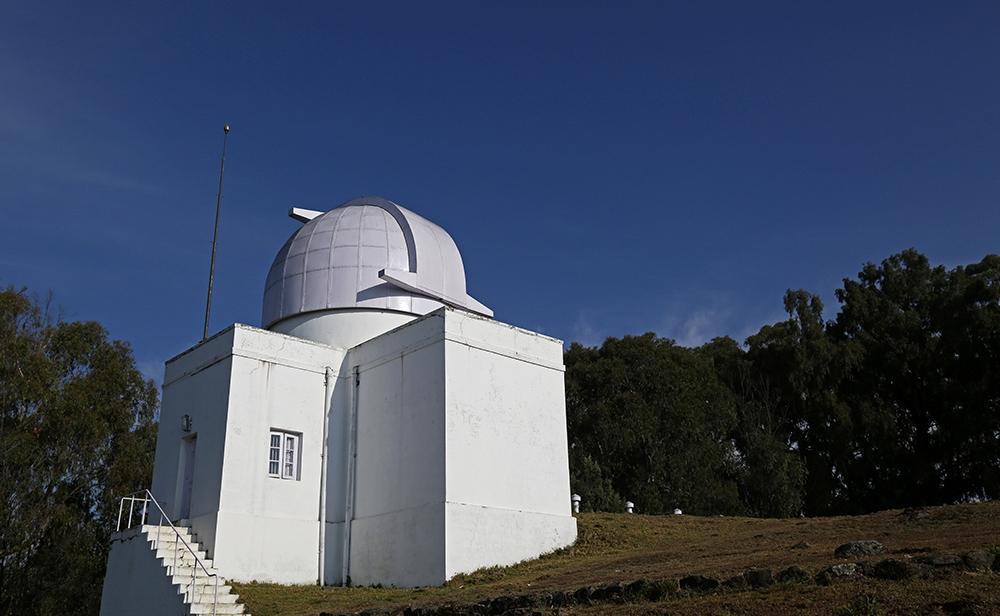
- The Kodaikanal Solar Observatory is a solar observatory owned and operated by the Indian Institute of Astrophysics (IIA), Bengaluru.
- It is on the southern tip of the Palani Hills 4 kilometers from Kodaikanal (Tamil Nadu).
- The Government of India separated Astrophysics from the India Meteorological Department (IMD) in April 1971.
- From solar data recorded on basic photographic plates or films, the 125-year-old KoSO boasts a mammoth digital repository containing 1.48 lakh digitized solar images of 10 terabytes.
- These include 33,500 white-light images (showing sunspots) and thousands of other images of the Sun recorded every day since the start of the 20th century.
- KoSO is the only observatory offering high-resolution digitized images for such a long period (with coverage of more than 75 percent).
- Today, it houses a spectrum of advanced instruments like the H-alpha telescope to perform full disc imaging, a White light Active Region Monitor (WARM) with calcium and sodium filters to make full disc simultaneous observations of the photosphere and chromosphere layers of the Sun, a solar tunnel telescope and more.
Links to the Great Drought:
- Scanty rainfall over south India during the winter monsoon of 1875 triggered one of the worst droughts the country had experienced till then.
- Multiple failed crops over the famine-stricken peninsular India killed 12.2 to 29.3 million people across the Madras and Mysore Provinces during 1875-1877.
- India, along with China, Egypt, Morocco, Ethiopia, southern Africa, Brazil, Columbia, and Venezuela, suffered concurrent multi-year droughts during 1876-1878, later named the Great Drought, and an associated global famine that killed nearly 50 million.
- The drought was thought to be due to multiple reasons:
- Solar activity
- Cool Pacific Ocean conditions followed by a record-breaking El Nino (1877-1878)
- Strong Indian Ocean Dipole and
- Warm North Atlantic Ocean conditions.
Solar Physics Observatory in Palani Hills:
- Established in response to the British Raj's acknowledgment of solar activity's link to India's weather patterns, the Palani Hills Solar Physics Observatory, also known as the Indian Solar Observatory, was founded to conduct systematic studies on solar phenomena and their correlation with Indian meteorology.
- Located in Kodaikanal, selected for its favorable atmospheric conditions after careful consideration by Charles Michie Smith (a Professor of Physics at the Madras Christian College), the observatory was officially sanctioned by the Government of India in August 1893 and inaugurated by Lord Wenlock (the then Governor of Madras) in 1895.
- Commencing systematic observations in 1901, it merged with the Madras Observatory, enriching its instrumentation.
- Notable discoveries ensued, including the identification of the Evershed Effect.
- Over time, the observatory expanded its research domains to encompass cosmic rays, radio astronomy, and ionospheric physics, among others, solidifying its status as a pioneering institution in the field of astrophysics.
- Notably, it initiated solar radio observations in 1952, marking a significant milestone in Indian solar research.
- Despite the closure of contemporaneous observatories, the Palani Hills Solar Physics Observatory has endured, continuing to contribute to our understanding of the Sun and its effects on Earth's climate and space weather.
Why Study the Sun?
- Being the primary source of energy, life on Earth is supported by the Sun.
- Any change on the solar surface or its periphery could significantly affect the Earth’s atmosphere.
- Powerful solar storms and solar flares can be potentially harmful to Earth’s satellite-based operations, power grids, and navigational networks.
- The KoSO (Kodaikanal Solar Observatory), which has been imaging the Sun for over a century now, has a rich repository of data.
- This is extremely useful not only to reconstruct the Sun’s historic past but also to link its behavioral changes to better understand and predict its future and its impact on life on Earth and Space weather.
Fukushima Water Issue

- 01 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
Recently, Japan announced that its experts have engaged in discussions with their Chinese counterparts to address Beijing's concerns regarding the release of treated radioactive wastewater from the damaged Fukushima Daiichi nuclear power plant into the sea.
What is the Fukushima Water Issue?
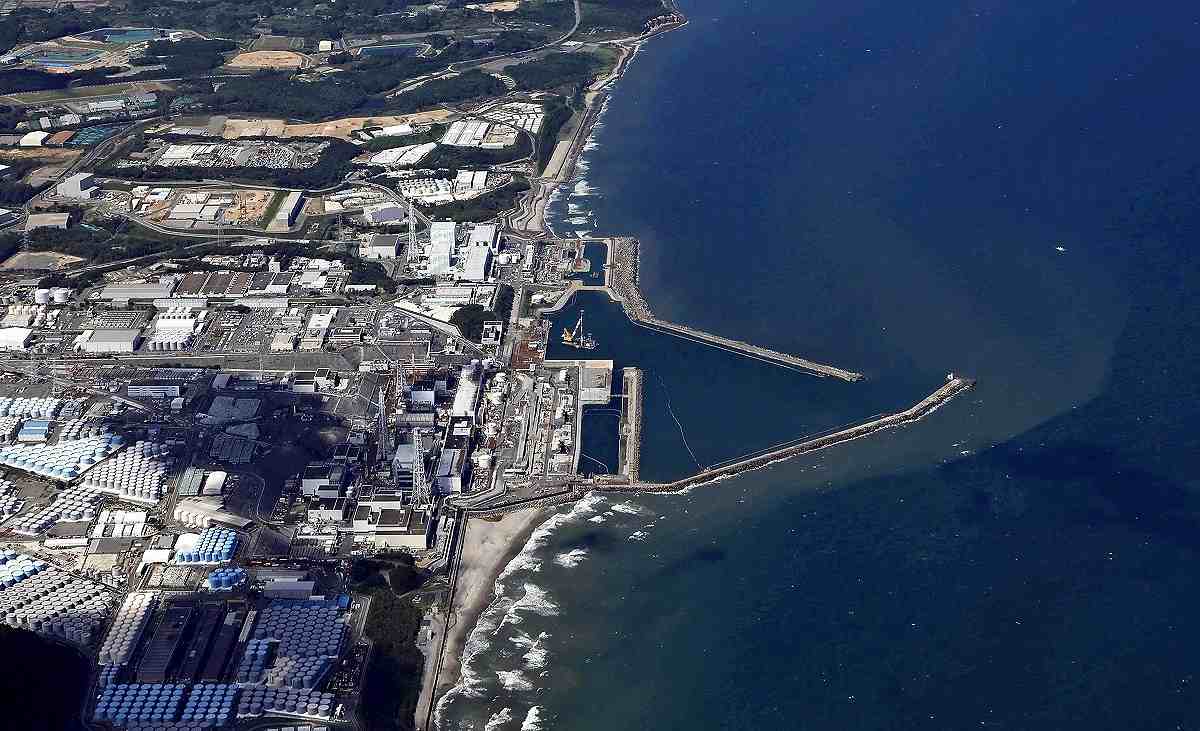
- In 2021, the Japanese government unveiled plans to gradually discharge over one million tonnes of contaminated water from the Fukushima nuclear plant into the ocean over the next three decades.
- The contaminated water is a residual product of the devastating 2011 earthquake and tsunami that incapacitated the Fukushima Daiichi nuclear power plant, resulting in the release of radioactive materials.
- After more than ten years of storing this wastewater, Japan asserts that they are facing storage space limitations and contends that the treated water is now safe for release.
Concerns Surrounding the Fukushima Water Discharge:
- Tritium and Carbon-14: The water from Fukushima undergoes filtration via the Advanced Liquid Processing System (ALPS), effectively reducing most radioactive contaminants to acceptable safety levels, except tritium and carbon-14.
- While both emit low levels of radiation, consumption in large quantities could potentially pose risks.
- Insufficient Research: Scientists emphasize the need for further investigation into the potential impact of the water discharge on the ocean bed and marine ecosystems.
- The Pacific Islands Forum regional group has labeled the proposed plan as "another significant nuclear contamination disaster," citing ongoing challenges faced by its member nations due to past US nuclear testing.
Pacific Islands Forum (PIF):
- The Pacific Islands Forum (PIF) is an inter-governmental organization that aims to enhance cooperation among countries and territories of Oceania, including the formation of a trade bloc and regional peacekeeping operations.
- It was founded in 1971 as the South Pacific Forum (SPF), and changed its name in 1999 to "Pacific Islands Forum", to be more inclusive of the Forum's Oceania-spanning membership of both north and south Pacific island countries, including Australia.
- It is a United Nations General Assembly observer.
- The PIF secretariat is located in Suva, the capital of Fiji.
Nuclear Incidents:
- A nuclear and radiation incident denotes an occurrence that has resulted in significant repercussions for individuals, the environment, or the facility involved.
- These may entail fatal consequences for individuals, substantial releases of radioactivity into the environment, or reactor core meltdowns.
- Globally, there have been a total of 99 incidents at nuclear power plants.
- Fifty-seven of these incidents have transpired since the Chornobyl disaster, with the United States accounting for 57% of all nuclear-related incidents.
- Noteworthy nuclear power plant mishaps encompass:
- Fukushima Daiichi nuclear disaster (2011)
- Chernobyl disaster (1986)
- Three Mile Island accident (1979), and
- The SL-1 accident (1961).
Real Estate (Regulation and Development) Act, 2016

- 01 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
Eight years after Parliament passed the Real Estate (Regulation and Development) Act, 2016, the Union Ministry of Housing and Urban Affairs is in the process of reviewing the functioning of the Act, including by holding regular meetings with homebuyers and setting up a data collection unit within the Ministry.
What Is Real Estate (Regulation & Development) Act, 2016 (RERA)?
- The Real Estate (Regulation & Development) Act, 2016 is an act of the Parliament of India that strives to protect home buyers and helps escalate the investment made in the real estate industry.
- It was established under this Act to regulate the real estate sector.
- Additionally, it acts as the adjudicating body for faster dispute resolution related to the real estate industry.
The Primary Objectives of the Act:
- Ensuring Transparency: Promoting transparency in the real estate sector regarding the sale of flats, apartments, plots, buildings, or any real estate project.
- Establishing Dispute Resolution: Setting up an adjudicating mechanism to swiftly resolve disputes.
- Protecting Buyer Interests: Safeguarding the interests of buyers/allottees in the real estate domain.
- Building Trust: Fostering trust between buyers and promoters by leveraging regulatory authority.
- Furthermore, the Act mandates that Real Estate Regulatory Authorities establish and maintain a web portal containing pertinent details of all registered real estate projects for public access.
Reasons for RERA Implementation:
- The introduction of RERA was necessitated by challenges faced by the Indian real estate sector since 2012, including factors such as unemployment, recession, low rental yield, inventory pile-up, and ambiguous tax and arbitration frameworks.
Projects Covered by RERA:
- RERA covers commercial and residential projects, including plotted developments, that exceed 500 square meters or comprise more than 8 units.
- Additionally, projects lacking a Completion Certificate prior to the Act's commencement are subject to its provisions.
Benefits of RERA Implementation:
- Standardization: RERA ensures uniformity in the real estate sector concerning aspects like carpet areas and common areas, thereby preventing malpractices such as alterations in layout, area, agreements, and specifications.
- It also mandates disclosure of details regarding brokers, architects, and contractors.
- Timely Delivery: Developers are obligated to adhere to scheduled delivery timelines for office spaces or homes.
- Failure to comply may result in stringent penalties or imprisonment for the developer.
- Regulatory Compliance: RERA mandates obtaining clearance from government departments before the sale of any residential or commercial property.
- Financial Transparency: Developers are required to maintain separate bank accounts for each project, enhancing financial transparency and accountability.
- Warranty Protection: Buyers are empowered to report any structural defects in the building to the developer within one year of possession, with the developer obligated to rectify them free of charge.
Challenges Associated with RERA:
- Limited Scope: The regulations of RERA do not extend to ongoing projects or those stalled due to clearance issues, potentially leaving certain projects outside its jurisdiction.
- Approval Delays: Delays in approval and clearance from government agencies may impede the timely completion and delivery of real estate projects, affecting both developers and buyers.
- Exemption for Small Developers: Small-scale developers overseeing projects smaller than 500 square meters are exempt from RERA's provisions, and registration with the regulatory authority is not compulsory for them.
- Project Launch Delays: Projects cannot be launched without necessary clearances, which may result in delays in the commencement of new projects.
International Network for Terrestrial Research and Monitoring in the Arctic (INTERACT)

- 01 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
In a recent development, Arctic research stations under INTERACT reported a significant loss of over 1,000 billion tonnes of ice over the past four decades.
About the International Network for Terrestrial Research and Monitoring in the Arctic (INTERACT):
- The International Network for Terrestrial Research and Monitoring in the Arctic (INTERACT) is an infrastructure project under the auspices of SCANNET.
- INTERACT specifically seeks to build capacity for research and monitoring in the European Arctic and beyond and is offering access to numerous research stations through the Transnational Access program.
- It aims to build capacity for identifying, understanding, predicting, and responding to diverse environmental changes throughout the wide environmental and land-use envelopes of the Arctic.
- The project, which is funded by the EU, has the main objective of building capacity for identifying, understanding, predicting, and responding to diverse environmental changes throughout the wide environmental and land-use envelopes of the Arctic.
- INTERACT is a multidisciplinary initiative; collectively, its stations host thousands of scientists worldwide who collaborate on projects spanning glaciology, permafrost studies, climate research, ecology, biodiversity, and biogeochemical cycling.
About the Scandinavian Network for Coordinated Observation of the Atmosphere and Terrestrial Environment (SCANNET):
- SCANNET is a circum-Arctic network of currently 77 terrestrial field bases in northern Europe, Russia, the US, Canada, Greenland, Iceland, the Faroe Islands, and Scotland as well as stations in northern alpine areas.
- The primary aim of SCANNET is to facilitate coordinated observations and research activities focused on the atmosphere and terrestrial environment in the Arctic region.
- These observations cover a wide range of scientific disciplines, including meteorology, climatology, ecology, geology, and environmental science.
- By leveraging the diverse geographical locations of its field bases, SCANNET enables scientists to study various environmental phenomena, such as changes in weather patterns, shifts in ecosystems, permafrost dynamics, and the impact of climate change on Arctic landscapes.
- Moreover, SCANNET serves as a platform for collaboration and information sharing among researchers from different institutions and countries.
- It fosters partnerships and promotes the exchange of data, methodologies, and best practices, thereby enhancing our understanding of Arctic processes and their global implications.
