Pradhan Mantri Annadata Aay Sanrakshan Abhiyan (PM-AASHA)

- 21 Feb 2025
In News:
Context:
The Government of India has approved the continuation of the PM-AASHA Scheme till 2025–26, aligning with the 15th Finance Commission cycle, to strengthen farmer income security and achieve self-sufficiency in pulses production.
Overview of PM-AASHA Scheme
- Launched by: Ministry of Agriculture & Farmers’ Welfare
- Objective: To ensure remunerative prices to farmers and stabilize market prices of key crops.
- Type: Umbrella scheme combining various price support mechanisms.
Key Components
- Price Support Scheme (PSS)
- Procurement of pulses, oilseeds, and copra at Minimum Support Prices (MSP) through NAFED and NCCF.
- Covers 25% of national production, except for 100% procurement of Tur, Urad, and Masur during 2024–25 and extended for the next four years.
- Procurement is done from pre-registered farmers through State-level agencies.
- Price Deficiency Payment Scheme (PDPS)
- Farmers receive direct payments for the shortfall between the MSP and market price.
- Covers 40% of oilseed production for a duration of four months.
- Price Stabilization Fund (PSF)
- Maintains buffer stocks of pulses and onions.
- Aims to stabilize prices, prevent hoarding, and ensure affordable supply for consumers.
- Market Intervention Scheme (MIS)
- Provides price support for perishable horticultural crops.
- Covers 25% of production with direct financial transfers to farmers, not physical procurement.
Recent Developments (2025)
- Procurement Commitment:The Union Government announced 100% procurement of Tur (Arhar), Urad, and Masur under PSS for 2024–25, extended for four years, to reduce import dependence and promote self-sufficiency.
- Tur Procurement Approval:Union Agriculture Minister Shivraj Singh Chouhan approved procurement of 13.22 Lakh Metric Tonnes (LMT) of Tur for Kharif 2024–25 in 9 states:
Andhra Pradesh, Chhattisgarh, Gujarat, Haryana, Karnataka, Madhya Pradesh, Maharashtra, Telangana, and Uttar Pradesh. - Procurement Progress(as of 15 Feb 2025):
- 0.15 LMT of Tur procured from Andhra Pradesh, Karnataka, Maharashtra, and Telangana.
- 12,006 farmers have benefited so far.
- Procurement in remaining states will commence shortly.
- Central procurement is conducted by NAFED and NCCF.
UNESCO’s “Imagine a World with More Women in Science” Campaign

- 21 Feb 2025
In News:
On February 11, 2025, to mark the 10th anniversary of the International Day of Women and Girls in Science, UNESCO, with support from Canada’s International Development Centre (IDRC), launched the global campaign titled “Imagine a World with More Women in Science.”
Campaign Highlights
- Objective: Promote gender equality in science and innovation by encouraging the active participation and leadership of women in STEMM (Science, Technology, Engineering, Mathematics, and Medicine).
- Social Media Drive: The campaign uses the hashtag #EveryVoiceInScience to amplify diverse voices and encourage global engagement.
- Focus: Emphasizes the real-world impact of gender disparities in science, including missed innovations, biased artificial intelligence, and inequitable scientific opportunities.
Background
- The UN General Assembly (UNGA) declared February 11 as the International Day of Women and Girls in Science in 2015 to foster female participation in scientific research and innovation globally.
Current Status of Women in Science
Global Trends
- Representation: Women comprise only one-third of the global scientific workforce.
- Leadership Gap: Merely 10% of STEM leadership positions are held by women.
India-Specific Data
- STEMM Enrolment: Women account for 43% of enrolment in STEMM disciplines.
- Women Scientists: Only 18.6% of scientists in India are women.
- R&D Projects: About 25% of R&D projects are led by women researchers.
Challenges Faced by Women in Science
Challenge Description
Restrictive Social Norms Traditional gender roles hinder women’s
scientific pursuits.
Lack of Role Models Few visible female leaders discourage young women from
aspiring to scientific careers.
Workplace Inequality Gender biases, hostile work environments, and lack of inclusive
policies create barriers.
Educational Gaps Gender-biased teaching content and insufficient support systems
limit girls’ access to science education.
Recommended Measures
Dismantle Gender Stereotypes
- Remove gender biases from teaching and learning materials.
- Include contributions of female scientists in textbooks with visuals.
- Promote equitable representation of women in boards, panels, and decision-making bodies.
Enhance Visibility of Women Role Models
- Highlight discoveries by female scientists.
- Increase media and curriculum exposure to successful women in science.
Open Educational Pathways
- Promote inclusive teaching practices and gender-neutral curricula.
- Encourage CSR (Corporate Social Responsibility) initiatives to support girls in science education.
Create Inclusive Work Environments
- Enforce policies for diversity, equity, and inclusion.
- Take strong action against gender-based violence, including sexism and harassment in the workplace.
- Advance women into leadership roles in scientific institutions.
mRNA-Based Cancer Vaccine
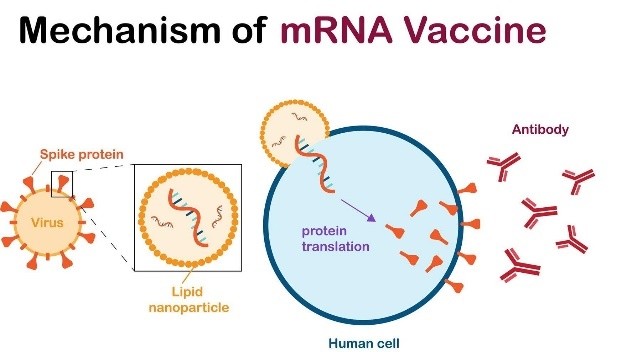
- 21 Feb 2025
In News:
Russia has announced the development of an mRNA-based personalized cancer vaccine, expected to be available free of cost to patients by early 2025. It is being developed under the Russian Ministry of Health, with pre-clinical trials showing promising results in suppressing tumour growth and metastasis.
What is an mRNA-Based Cancer Vaccine?
- mRNA (Messenger RNA) vaccines deliver genetic instructions to the body’s cells to produce antigens—proteins that trigger an immune response.
- In the case of cancer, these vaccines train the immune system to recognize and destroy tumor-specific antigens, thereby attacking cancer cells.
- Unlike conventional vaccines, these are therapeutic, not preventive, and are used in existing cancer patients.
How Does It Work?
- The vaccine prompts the body to produce proteins that mimic tumor markers.
- These markers stimulate the immune system to target and destroy cancer cells.
- The treatment is personalized, with the mRNA sequence tailored to match the unique antigens of a patient’s tumour, enhancing precision and efficacy.
- It can potentially target multiple antigens simultaneously, unlike standard mRNA vaccines such as those for COVID-19.
Advantages Over Conventional Therapies
- Selective Action: Targets only cancer cells, minimizing damage to healthy tissue.
- Fewer Side Effects: Compared to chemotherapy, the side effects are significantly reduced.
- Customizable: Can be adapted to target various cancers through tumor-specific markers.
- Boosts Immunity: Enhances the body’s natural defense mechanisms for long-term protection.
mRNA Technology – Core Concepts
- mRNA is a single-stranded RNA transcribed from DNA.
- It delivers genetic instructions to ribosomes (protein factories) in cells to produce specific proteins.
- In mRNA vaccines, this mechanism is harnessed to make the body generate target antigens, which the immune system learns to combat.
India and mRNA Vaccines
- India has approved two mRNA COVID-19 vaccines developed by Gennova Biopharmaceuticals with DBT-BIRAC support:
- GEMCOVAC-OM(Omicron-specific)
- GEMCOVAC-19
- Features include needle-free delivery and thermostability, marking India’s entry into mRNA-based immunotherapy platforms.
Cautions and Limitations
- Not Preventive: These are not preventive like HPV or Hepatitis B vaccines, which protect against cancers linked to viruses.
- Limited Data: Russian vaccine data is not yet publicly available; clinical validation is pending.
- Not Universally Effective: Immunotherapy may not work for all types or stages of cancer.
- Time-Consuming Trials: New treatments must undergo phased trials, often spanning years, before general approval.
AI-Powered Surveillance in Similipal Tiger Reserve

- 21 Feb 2025
In News:
The Similipal Tiger Reserve in Odisha has seen a significant drop in poaching activities following the deployment of TrailGuard AI-enabled surveillance cameras. These advanced systems are helping protect both forest personnel and wildlife by providing real-time alerts and enhancing enforcement actions.
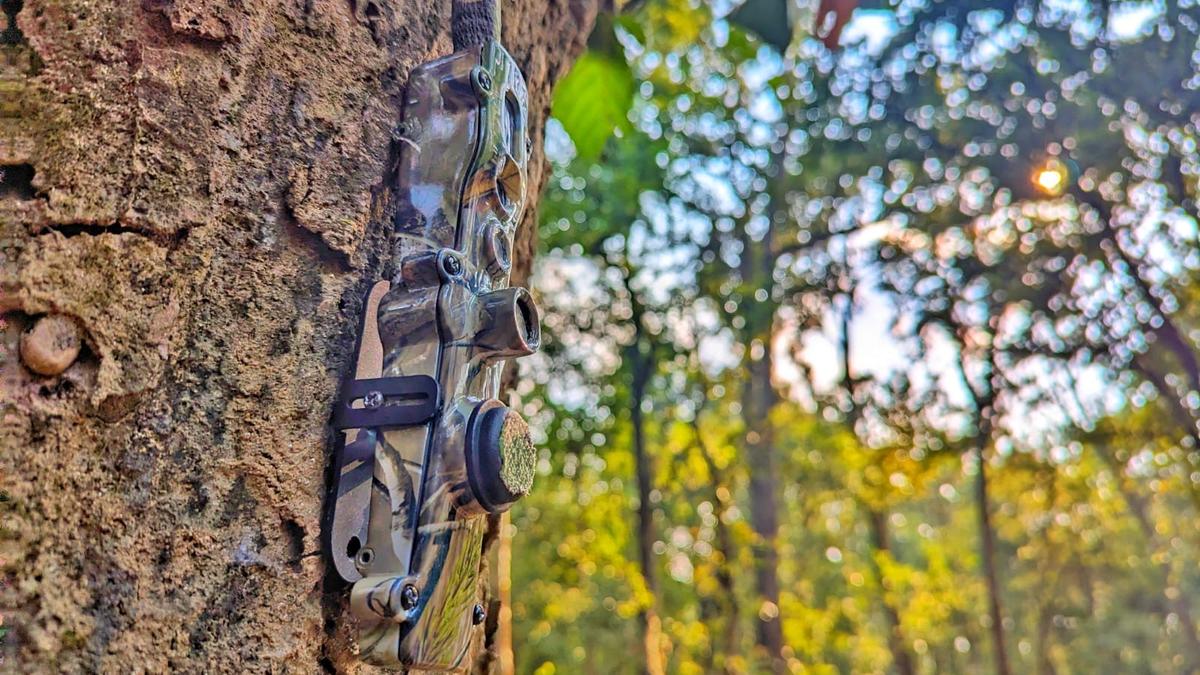
About TrailGuard AI System
- Developed by: Nightjar Technologies, Gurgaon.
- Design:
- Two-part system: a pen-sized camera unit and a notepad-sized battery/communication unit connected via a 2-metre cable.
- Camouflaged and compact, reducing chances of being detected or stolen.
- Operation:
- Operates in low-power mode by default, switches to high-power mode upon sensing movement.
- Uses on-device AI inference to identify object classes (e.g., humans, animals, vehicles).
- Sends alerts via cellular network within 30–40 seconds to a central control room.
- Battery life: 6 months to 1 year.
- Cost: ?50,000–53,000 per unit.
Impact and Achievements
- Installed: 100–150 AI-enabled cameras in Similipal.
- In 10 months, led to:
- 96 poachers arrested
- 86+ country-made guns seized
- 40+ arrests in December 2024 alone
- Enabled quick house raids and identifications using photographic evidence.
- Enabled one conviction within six months, with more expected.
Integrated Enforcement System
- Real-time alerts displayed on a central control room screen.
- Information shared swiftly via WhatsApp groups and VHF radio.
- Ground teams rely on human intelligence sources (including undercover staff) to identify suspects.
- Raids and arrests are executed only after 100% identity confirmation, ensuring due process.
Advantages of the System
- Enhances forest ranger safety.
- Enables targeted and proactive patrolling.
- Effective in challenging terrains with minimal maintenance.
- Also used to monitor wildlife, including profiling of tuskers.
- Functions as an anti-poaching as well as human-wildlife conflict mitigation tool.
Wider Adoption and Future Plans
- Apart from Similipal, TrailGuard AI has been deployed at:
- Kanha Tiger Reserve, Madhya Pradesh (20 cameras)
- Dudhwa National Park, Uttar Pradesh (10 cameras)
- Total: Active in 14+ sites across five states
- Planned expansion to other protected areas in Odisha.
Community Sensitivity and Tribal Engagement
- Similipal is surrounded by tribal communities, where hunting has traditional roots.
- Increased surveillance has caused concerns over restricted forest access for collecting firewood and non-timber forest products.
- The forest department is:
- Holding awareness meetings in local languages.
- Exploring safe and non-intrusive access solutions for villagers.
- Ensuring that enforcement doesn’t indiscriminately impact local livelihoods.
Conservation Significance
- Demonstrates the fusion of technology with conservation.
- Aligns with India’s broader environmental goals under:
- Project Tiger
- National Wildlife Action Plan
- Digital India initiatives in conservation.
Exercise Komodo

- 21 Feb 2025
In News:
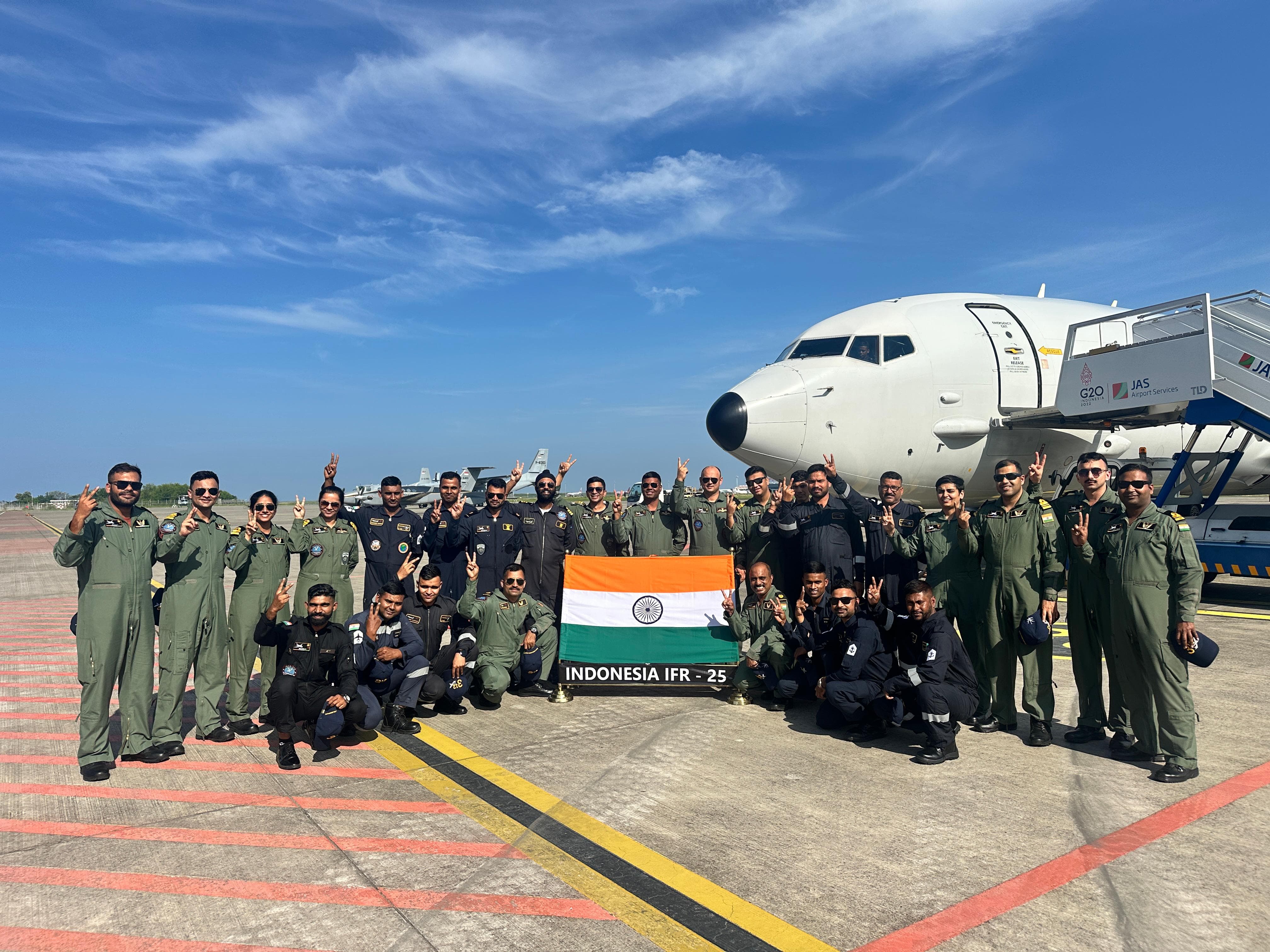
The Indian Navy's platforms—INS Shardul, an amphibious warfare ship, and the P-8I Long Range Maritime Surveillance Aircraft—participated in the International Fleet Review (IFR) 2025 and the 5th edition of the Multilateral Naval Exercise Komodo held in Bali, Indonesia, from 15 to 22 February 2025.
International Fleet Review (IFR) 2025
- IFR 2025 is a prestigious multinational naval event reviewed by the President of Indonesia.
- Participating nations showcased naval assets including warships, helicopters, and maritime aircraft.
- The Indian Navy took part in:
- International Maritime Security Symposium
- Tactical floor games
- City parade
- Coral and mangrove plantation
- Beach cleaning activities
- Baby turtle release, promoting environmental and maritime sustainability.
Exercise Komodo 2025
- Initiated in 2014, Exercise Komodo is a non-combat multilateral naval exercise hosted by the Indonesian Navy.
- The 2025 edition had the theme: "Maritime Partnership for Peace and Stability".
- Objectives:
- Promote maritime cooperation
- Enhance interoperability
- Foster regional security cooperation
- Key Features:
- Participation from 39 countries
- Involvement of 34 foreign and 18 Indonesian Navy warships
- Included:
- Naval exercises
- Officer exchange forums
- Bilateral naval meetings
- Defense exhibition
- Cultural parades
Strategic Context and Bilateral Engagements
- The participation builds upon the Indian Navy’s involvement in the La Pérouse exercises in Indonesia (January 2025) involving INS Mumbai and a P-8I aircraft.
- It coincided with the visit of Admiral Muhammad Ali, Chief of Staff of the Indonesian Navy, to India during the Republic Day 2025, accompanying President Prabowo Subianto as the Chief Guest.
Significance for India
- The participation reaffirms India’s commitment to SAGAR (Security and Growth for All in the Region).
- It strengthens India-Indonesia defense ties and underscores India's proactive role in regional maritime diplomacy and environmental stewardship.
