IISc Develops Nanozyme to Prevent Excessive Blood Clotting

- 07 Jun 2025
In News:
Researchers at the Indian Institute of Science (IISc), Bengaluru have developed a novel vanadium-based nanozyme that effectively controls abnormal blood clotting by reducing reactive oxygen species (ROS). This innovation holds promise for managing life-threatening conditions like pulmonary thromboembolism (PTE) and ischemic stroke.
Scientific Background:
- Normal Blood Clotting: Platelets are specialized blood cells that form clots at injury sites through a process called haemostasis, involving activation by physiological chemicals like collagen and thrombin.
- Problem of Abnormal Clotting: In conditions like COVID-19 and PTE, oxidative stress increases, leading to elevated ROS levels. This causes hyperactivation of platelets, resulting in excessive clot formation (thrombosis) — a leading cause of death globally.
Nanozyme Innovation by IISc:
- What is a Nanozyme?
An engineered nanomaterial that mimics the action of natural enzymes, in this case, glutathione peroxidase, which neutralizes ROS.
- Material Used: Vanadium pentoxide (V?O?) nanozymes, particularly those with spherical morphology, were found to be the most efficient.
- Mechanism: The redox-active surface of vanadium nanozymes catalytically reduces ROS, preventing unwanted platelet aggregation.
Testing and Results:
- In vitro testing: Human blood platelets were activated with physiological agonists. Nanozymes were tested for their ability to curb excessive aggregation.
- In vivo testing (mouse model of PTE):
- Nanozyme injection led to reduced thrombosis.
- Improved survival rates without observable toxicity.
- Animals were monitored for 5 days post-treatment for health parameters.
Future Prospects:
- Researchers aim to test the nanozyme's potential against ischemic strokes, which also result from vascular blockages.
- Encouraging results with human platelets indicate the possibility of clinical trials in the near future.
Kerch Strait and Recent Developments
- 07 Jun 2025
In News:
Ukraine has claimed responsibility for a recent underwater explosion that damaged the Kerch Bridge, a critical transport link connecting mainland Russia to occupied Crimea. The attack underscores the strategic importance of the Kerch Strait in the ongoing Russia-Ukraine conflict.
Kerch Strait: Geographical and Strategic Overview
- Location: The Kerch Strait forms the only maritime passage between the Black Sea and the Sea of Azov.
- Geographical Boundaries:
- West: Kerch Peninsula (Crimea)
- East: Taman Peninsula (Russia)
- Width: Narrows to 3–5 km at its tightest point near the Chushka Spit.
- Nearby City: Kerch, located on the Crimean side, lies near the strait’s midsection.
- Strategic Importance:
- A vital shipping lane for transporting goods and military supplies.
- Gained heightened geopolitical importance after Russia's annexation of Crimea in 2014.
- Frequently features in Russia–Ukraine maritime tensions.
Kerch Strait Bridge (Crimean Bridge)
- Length: 19 km, making it the longest bridge in Europe.
- Completed: In 2018
- Connectivity: Includes dual road and railway tracks, linking the Russian mainland to Crimea.
- Symbolism: Considered a symbol of Russia’s control over Crimea post-2014 annexation.
- Strategic Use: Facilitates military logistics and civilian transit; crucial for sustaining Russian presence in Crimea.
Diphtheria Outbreak in Western Europe – 2022 Onwards
- 07 Jun 2025
In News:
Western Europe is experiencing its largest diphtheria outbreak in 70 years, with cases predominantly among vulnerable groups such as migrants and the homeless. The outbreak, which began in 2022, has raised concerns over disease surveillance, migrant healthcare, and immunisation coverage.
Key Facts from the Outbreak
- As per a study in the New England Journal of Medicine, 536 cases and three deaths have been reported across Europe since 2022.
- Most cases were found among young males (average age: 18) who had recently migrated, particularly from Afghanistan and Syria.
- 98% of strains exhibited close genetic similarities, suggesting a common transmission point during migration journeys or in accommodation facilities, not in the countries of origin.
- A genetic match between the 2022 strains and a recent 2025 case in Germany indicates that the bacteria is still circulating silently in the region.
Recommendations from Health Experts
- Enhance vaccination drives, particularly among high-risk and underserved populations.
- Improve awareness among healthcare providers, especially those working with migrants and the homeless.
- Ensure better access to antibiotics and diphtheria antitoxins.
- Strengthen disease surveillance and contact tracing mechanisms.
About Diphtheria
Feature Details
Cause Corynebacterium diphtheriae (produces a potent toxin)
Mode of Spread Respiratory droplets, contact with infected sores or ulcers
Affected Areas Primarily the respiratory tract, but also the skin in some cases
Symptoms Sore throat, fever, swollen lymph nodes, weakness; grey membrane in throat
Severe Impact Can lead to breathing difficulties, heart and kidney damage, and neurological issues if untreated
Treatment Diphtheria Antitoxin (DAT), antibiotics, and supportive care
Fatality Rate Up to 30% in unvaccinated individuals; higher in children
Prevention Vaccination (DPT/DTP) is the most effective preventive measure
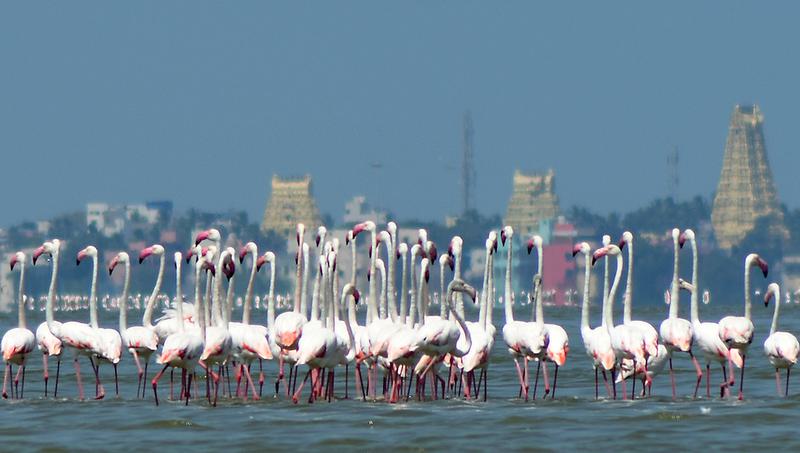
Greater Flamingo Sanctuary

- 07 Jun 2025
In News:
On the occasion of World Environment Day 2025, the Tamil Nadu government officially declared the Greater Flamingo Sanctuary at Dhanushkodi, Ramanathapuram district, aiming to protect a vital stopover site for migratory birds along the Central Asian Flyway.
Key Highlights
What is it?
A newly notified wildlife sanctuary dedicated to safeguarding migratory wetland birds, especially the greater flamingo (Phoenicopterus roseus), in their natural resting and breeding habitat.
Location and Area:
- Located in Rameshwaram taluk, Ramanathapuram district, Tamil Nadu.
- Covers approximately 524.7 hectares of revenue and forest land.
- Lies within the Gulf of Mannar Biosphere Reserve, a globally recognized marine ecosystem.
Ecological Significance
- Functions as a critical site along the Central Asian Flyway, one of the key migratory bird routes.
- As per the 2023–24 Wetland Bird Survey, the region hosts 10,700+ wetland birds representing 128 species, including:
- Flamingos (greater and lesser)
- Herons, egrets, sandpipers, etc.
- The sanctuary harbours diverse ecosystems, such as:
- Mangroves (Avicennia, Rhizophora)
- Mudflats, marshes, sand dunes, and lagoons
- Nesting grounds for sea turtles and marine biodiversity
Conservation and Socioeconomic Benefits
- Strengthens coastal resilience by preventing erosion through natural mangrove buffers.
- Promotes responsible ecotourism, raising awareness of wetland and avian conservation.
- Supports local livelihoods via employment in conservation and tourism activities.
About the Greater Flamingo (Phoenicopterus roseus)
Attribute Details
Size 90–150 cm tall, long necks and legs
Coloration Pink hue from carotenoid-rich diet
Feeding Uses specialized downward-curved bill for filter feeding in shallow waters
Reproduction Builds cone-shaped mud nests, lays 1–2 eggs, both parents incubate
Chick Rearing Chicks are white and fed through regurgitation
Social Traits Highly gregarious, breeds in large colonies and flies in V-formations
Behavioral Note Often seen standing on one leg, possibly to conserve body heat
SEBI’s Operational Framework for ESG Debt Securities
- 07 Jun 2025
In News:
The Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI) has introduced a comprehensive operational framework for the issuance of Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) debt securities. This includes instruments such as social bonds, sustainability bonds, and sustainability-linked bonds, aiming to boost responsible financing in India.
Understanding ESG Debt Securities
Definition:
ESG debt securities are financial tools designed to raise capital specifically for projects that yield positive environmental, social, or governance (ESG) outcomes. These instruments are a key part of sustainable finance, with categories including:
- Social Bonds: Focused on projects with direct social impact (e.g., affordable housing, education).
- Sustainability Bonds: Target projects with both environmental and social objectives.
- Sustainability-Linked Bonds: Tied to specific ESG performance indicators or targets.
Salient Features:
- Funds raised must be used exclusively for eligible ESG-aligned projects.
- Bonds must be clearly labelled in line with the project's primary focus.
- Compliance with global ESG norms and standards is mandatory.
- Verification or certification by an independent third-party is required.
- The framework applies to both public and private debt offerings.
Highlights of SEBI’s Framework
1. Classification Guidelines: Issuers are required to categorize their bonds—green, social, or sustainability—based on the core objective of the projects being financed. This ensures transparent communication of the bond's intended impact.
2. Disclosure Norms:
- At the Issuance Stage: Offer documents must detail project eligibility, selection methodology, and a tentative allocation between financing new initiatives and refinancing existing ones.
- Post-Issuance: Issuers must provide annual updates on fund deployment and report impact metrics to demonstrate accountability and transparency.
3. Independent Assurance: Issuers must engage accredited third-party entities to validate the alignment of bonds with ESG principles, thereby enhancing investor confidence and market integrity.
4. Monitoring and Evaluation: There is an obligation for ongoing impact assessment. Issuers must ensure the projects funded effectively contribute to reducing environmental degradation or addressing social challenges.
5. Scope and Enforcement: The framework will come into effect from June 5, 2025, and is aligned with international ESG standards to facilitate greater inflow of sustainable and ethical investments.
Significance for India: This move marks a significant step in mainstreaming ESG finance in India. It aims to improve transparency, attract climate-conscious capital, and reinforce India’s commitment to sustainable development.
