Viksit Bharat Buildathon 2025
- 13 Oct 2025
In News:
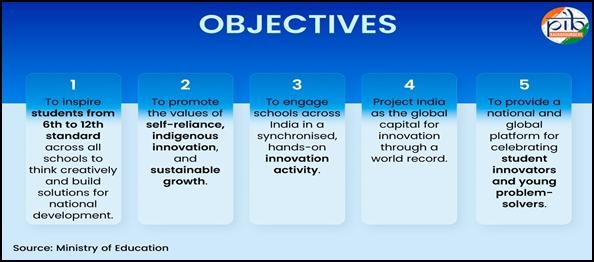
The Viksit Bharat Buildathon 2025 is a nationwide innovation movement being organised by the Department of School Education & Literacy (DoSEL), Ministry of Education, in collaboration with Atal Innovation Mission, NITI Aayog.
- This largest-ever school hackathon aims to strengthen the culture of innovation at the school level by encouraging students to ideate or build prototypes on four themes: Atmanirbhar Bharat, Swadeshi, Vocal for Local, and Samriddh Bharat.
- The Buildathon aims to foster innovation, creativity, and problem-solving among our youth so that they become key drivers of a prosperous, developed, and self-reliant India.
The Buildathon will provide hands-on, experiential learning in line with the National Education Policy (NEP) 2020. Participation is inclusive with special focus on Aspirational Districts, Tribal and Remote Regions.
Key Features
- Dedicated Portal: There is a national portal for registration and submission of final entries (ideas or prototypes)
- Mode of Participation: A team of 3-5 students will participate in the Buildathon and submit entries (ideas/prototypes) in the form of videos. There will be no limit on the number of teams from a school.
- Mentorship Support: Dedicated support will be provided by volunteers and mentors from Incubation Centres, Mentor of Change Network, Higher Education Institutions, and Corporates to help students build their projects at the school level.
- National Live Event: National level virtual live streaming session will be organised, which shall be joined by all schools (6th to 12th standard).
- Global Streaming: The event will be streamed on nationwide news and media channels.
- Inclusive Spotlight: A Special spotlight will be given to schools from Aspirational Blocks, Tribal Regions, Frontier Villages, and Remote Areas.
- District & State-Level Events: Schools will conduct Innovation activities. States are encouraged to organise community level innovation events inviting multiple schools and dignitaries.
- Submission of Entries: Post-event, schools will submit videos of their innovation entries (Ideas or Prototypes).
How to Participate
- Eligibility: Participation is open to all school students from class 6-12, across India. Students must form a team of 3-5 members from same schools. Students can register with the help of their teachers. There is no restriction on the number of teams per school.
- Registration of Team: Schools/teachers have to encourage students to form teams and then register their teams on the official Buildathon portal after which a unique registration ID will be generated for each team. The Registration Link for schools for Viksit Bharat Buildathon is - vbb.mic.gov.in
- Selection of Theme: Each team will need to choose one out of the four Buildathon themes and identify any problem statement.
- Brainstorm & Build: The team will ideate to solve community problems.
- Prepare for Submission: Teams will be required to create a 2–5 minute video explaining the problem it is solving, the innovative solution/prototype they have created, how it works and its possible impact.
- Submission: The project video/ summaries have to be submitted on the Portal within the submission window of Oct. 13 to Oct. 31, 2025
Awards
- A panel of experts will evaluate the entries, and the top student teams will be awarded prizes. These schools and students will receive long-term support through corporate adoption, mentorship, and resources to further strengthen their innovations.
- There will be an Awards Pool of Rs. 1 Crore, with 10 National Level winners, 100 State level winners and 1000 District level winners.
AI for Inclusive Societal Development
- 13 Oct 2025
In News:
- NITI Aayog has released a landmark study titled “AI for Inclusive Societal Development”, shifting India’s artificial intelligence discourse toward the informal workforce, which constitutes the backbone of the national economy. This first-of-its-kind framework seeks to harness AI and frontier technologies to formalise and uplift nearly 490 million informal workers, who contribute around 45% of India’s GDP but remain largely excluded from institutional protections and productivity systems.
- At the core of this initiative is the proposed National Mission “Digital ShramSetu”, conceptualised as a technology-enabled bridge connecting informal workers to formal systems of work, finance, skilling, and social protection — a critical step for achieving the Viksit Bharat 2047 vision.
Mission Digital ShramSetu: Vision & Framework
Objective:To drive large-scale socio-economic inclusion by integrating AI, blockchain, robotics, IoT, AR/VR, and immersive learning into workforce development.
Key Components
|
Pillar |
Purpose |
|
Digital Identity & Trust |
Verifiable worker IDs and credentials for payments, loans, and welfare access |
|
Tech-Enabled Skilling |
Multilingual, adaptive, offline-enabled training for real-world tasks |
|
Blockchain-Based Smart Contracts |
Automated, transparent, dispute-free wage payments |
|
Federated Credentialing |
Real-time validation of skills by government, employers, institutions |
|
Grassroots Outreach |
Collaboration with state bodies and civil society to improve digital literacy and adoption |
|
Apex Governance |
Mission chaired at PM-level with sectoral task forces (agri, healthcare, retail, construction) and state units |
India’s Informal Workforce: Current Realities
- Size: ~490 million workers (≈85% of labour force)
- GDP Share: ~45%
- Productivity: ~USD 5/hour vs national avg. USD 11/hour
- Annual Per Capita Income: ~USD 1,800 (projected USD 6,000 by 2047 if status quo continues; target ≈ USD 14,500)
- Women’s Informal Sector Participation: ~15% (ex-agriculture) vs 37% national avg & 47% global avg
- Social Security Access: ~48%
- Formalisation Vision: Reduce informal sector to 40% by 2047; formalise73.2% of current informal enterprises
Existing Support Tools:e-Shram Portal, PM-JJBY, PM-SYM, Atal Pension Yojana, Micro-lending schemes, Skill India programmes
Challenges Confronting Informal Workers
- Income Instability & Wage Delays: No contracts; reliance on informal credit
- Limited Market Access: Fragmented, unorganised demand; lack of digital presence
- Low Skilling & Tech Adoption: Traditional workflows; language & literacy barriers
- Poor Social Security Coverage: Non-portable records and scheme awareness gaps
- Migrant Vulnerability: No portable credentials or employment networks
- Safety Risks: Hazardous work environments without monitoring support
Institutional & Policy Architecture
- Apex Mission Leadership: PM-level council for policy, funding & coordination
- Sector-Specific Task Forces: Agriculture, construction, healthcare, retail etc.
- State Coordination Units: Local deployment, innovation hubs, adoption drives
- Partnership Ecosystem: Government, industry coalitions (CII, NASSCOM), World Bank, global philanthropies & academia
Why It Matters
The roadmap stresses that technology alone is insufficient; success depends on human-centric deployment, affordability, and multi-stakeholder collaboration. With proactive adoption, India can multiply informal productivity, enhance incomes, reduce vulnerability, and transition toward a high-productivity, high-trust labour economy. Delay, however, could lock millions into low-income traps, weakening India's development trajectory.
Saksham Counter-Unmanned Aerial Threat Grid System
- 13 Oct 2025
In News:
- The Indian Army has initiated induction and fast-track procurement of “SAKSHAM” (Situational Awareness for Kinetic Soft and Hard Kill Assets Management), an indigenously developed, AI-enabled Counter-Unmanned Aerial System (C-UAS) grid created with Bharat Electronics Limited (BEL).
- Designed as a modular Command & Control (C2) backbone, SAKSHAM provides real-time detection, tracking, identification and neutralisation of hostile drones and other low-altitude aerial threats across the specially defined Tactical Battlefield Space (TBS) or Air Littoral — the airspace up to 3,000 metres (≈10,000 ft) above the ground.
What SAKSHAM is — technical outline
- Purpose: A unified C2 grid to secure ground formations by controlling low-altitude airspace, countering drone surveillance, weaponised UAS and swarms.
- Developer & partners: Designed and developed indigenously by Bharat Electronics Limited (BEL) in collaboration with the Indian Army’s Corps of Air Defence.
- Architecture & connectivity: Operates over the encrypted Army Data Network (ADN) and presents a GIS-based, common recognised air picture that fuses data from C-UAS sensors, friendly and hostile UAS feeds, and both soft- and hard-kill effectors.
- AI & fusion capabilities: Uses AI/ML-driven fusion to automate threat classification (friendly / neutral / hostile), prioritise responses, and support automated or semi-automated soft-kill (jamming/spoofing) and hard-kill (kinetic) decisions.
- Interoperability: Integrates inputs from India’s automated air-defence network Akashteer and is designed for plug-and-play addition of sensors, jammers, lasers/EMP and future upgrades.
Why SAKSHAM was conceptualised
The Army’s operational experience during Operation Sindoor (2025) — where hostile drone activity exposed detection and response gaps — accelerated the need for a comprehensive C-UAS framework and a shift from traditional Tactical Battle Area concepts to the more inclusive Tactical Battlefield Space (TBS) that explicitly includes the Air Littoral. SAKSHAM is a direct response to those operational lessons.
Operational and strategic impact
- Enhanced situational awareness: A common, real-time air picture shortens decision loops and reduces fratricide risk while allowing freedom of manoeuvre for friendly aerial assets.
- Force protection & deterrence: Rapid detection and neutralisation of drone threats protects troops, logistics nodes and infrastructure from ISR (intelligence, surveillance, reconnaissance) and weaponised UAS attacks.
- Atmanirbhar capability: Indigenous design and BEL partnership strengthen defence manufacturing and upgradeability—key to the Army’s Decade of Transformation (2023–2032) and wider strategic autonomy.
- Scalability & integration: FTP approval and modular design aim for rapid rollout across field formations, enabling layered C-UAS coverage and future networked integration with other services and civil air-safety systems.
DRAVYA Portal
- 13 Oct 2025
In News:
The Ministry of Ayush has launched the DRAVYA (Digitised Retrieval Application for Versatile Yardstick of Ayush) portal, developed by the Central Council for Research in Ayurvedic Sciences (CCRAS), marking a major step towards the digital transformation of traditional medicine systems in India. Announced during the 10th Ayurveda Day celebrations in Goa (23 September 2025), the initiative aligns with India's vision of integrating ancient medical wisdom with contemporary scientific tools.
Objective and Vision
DRAVYA aims to create a scientifically validated, AI-enabled knowledge repository that consolidates data on medicinal substances used across Ayush systems. In its first phase, the platform will document 100 key medicinal substances, with scope for continuous expansion.
The portal seeks to:
- Digitise and unify classical and modern knowledge on medicinal substances
- Enable evidence-based research and innovation
- Support cross-disciplinary collaboration across Ayurveda, botany, chemistry, and pharmacology
- Standardise and globally disseminate authentic Ayush data
Key Features
|
Feature |
Details |
|
AI-ready architecture |
Supports advanced analytics, research mapping, future tech integration |
|
Open-access platform |
Makes verified data globally accessible |
|
QR-code integration |
Enables standardised medicinal plant identification in gardens and repositories |
|
Comprehensive dataset |
Pharmacotherapeutics, botany, chemistry, pharmacy, pharmacology & safety profiles |
|
User-friendly design |
Intuitive search system covering classical texts and modern scientific references |
|
Ayush Grid linkage |
Facilitates interoperability with other digital health systems and policy platforms |
Impact and Significance
- Knowledge Modernisation:DRAVYA bridges traditional Ayurvedic knowledge with contemporary scientific validation, enhancing credibility and global acceptance of Indian medical systems.
- Research Advancement:Supports scholars, practitioners, and policymakers with standardised, authentic, real-time updated data, strengthening evidence-based drug development and pharmacopoeialstandardisation.
- Global Accessibility & Innovation:By making curated research internationally accessible, DRAVYA promotes collaborative innovation, pharmaceutical research, and knowledge-driven growth of the Ayush sector.
Nobel Prize in Literature 2025
- 13 Oct 2025
In News:
- The 2025 Nobel Prize in Literature has been conferred on László Krasznahorkai, the Hungarian novelist celebrated for his profoundly philosophical and apocalyptic prose.
- The Swedish Academy recognized him for his ability to capture the “tension between ruin and redemption” and for reaffirming the enduring power of art in an age of crisis.
About the Nobel Prize in Literature
- Established under Alfred Nobel’s will (1895), the Nobel Prize in Literature is awarded annually by the Swedish Academy to an author who has produced “the most outstanding work in an ideal direction.”
- The award, accompanied by a cash prize of 11 million Swedish crowns (≈ USD 1.2 million), represents the highest global recognition in the literary world.
Life and Background
- Born in 1954 in Gyula, Hungary, near the Romanian border, Krasznahorkai grew up amid the tensions of post-war socialism.
- Educated in law and literature in Budapest, his early life in a repressive political climate shaped his preoccupation with decay, faith, and endurance. His Jewish and rural background deepened his sensitivity to questions of identity and moral collapse.
Literary Career and Major Works
Krasznahorkai made his literary debut with Sátántangó (1985), a dark, surreal portrayal of a disintegrating collective farm that has since become a modern classic. Its cinematic adaptation by Béla Tarr as a seven-hour film further cemented its cult status.
His subsequent works expanded his thematic range:
- The Melancholy of Resistance (1989): Explores moral and social decay under authoritarianism in a small Hungarian town.
- War and War (1999): A meditation on history, violence, and transcendence through the story of an archivist.
- Seiobo There Below (2008): Reflects his deep engagement with Asian philosophies and aesthetics, particularly from Japan and China.
- Herscht 07769 (2018): A study of German social unrest and the search for order amid chaos.
Themes and Literary Style
- Krasznahorkai’s fiction fuses metaphysical inquiry with social critique. His narratives depict societies on the brink of collapse, where individuals confront spiritual drift, institutional decay, and existential dread.
- Stylistically, his long, recursive sentences and dense, rhythmic prose challenge readers to engage deeply with the text. His influences range from Franz Kafka and Samuel Beckett to Thomas Bernhard, yet his vision remains uniquely his own — a fusion of absurdism, grotesque realism, and mystical introspection.
International Recognition and Legacy
- Over four decades, Krasznahorkai has emerged as one of Europe’s most formidable literary voices. His earlier accolades include the Kossuth Prize (2004), Hungary’s highest cultural honor, and the Man Booker International Prize (2015).
- His global reach reflects a bridge between Central European existentialism and Eastern contemplative traditions, making his work both regionally grounded and universally resonant.
