Technology Perspective and Capability Roadmap (TPCR) 2025

- 12 Sep 2025
In News:
- The Ministry of Defence (MoD) recently released the Technology Perspective and Capability Roadmap (TPCR) 2025, a strategic blueprint outlining India’s defence technology and capability requirements over the next 15 years.
- The roadmap aims to guide the Indian Army, Navy, and Air Force in modernisation while providing domestic industry, academia, and research institutions early visibility to align R&D and production with future procurement needs. Indigenisation and self-reliance form the core of TPCR 2025.
Objectives of TPCR 2025
- Early Visibility for Industry: Help domestic manufacturers and research organisations plan development and production of advanced defence systems.
- Indigenisation: Reduce dependence on imports and promote domestic defence manufacturing.
- Future-Ready Armed Forces: Equip the military to face multi-domain warfare challenges, including cyber, space, AI-enabled, and hybrid conflicts.
- Sustainability: Integration of green logistics and energy-efficient systems in defence operations.
Key Features by Service
Navy:
- Nuclear Propulsion: Plans to induct 10 nuclear propulsion systems for aircraft carriers and large surface combatants, providing virtually unlimited endurance at sea.
- Next-Generation Aircraft Carrier: Equipped with Electromagnetic Aircraft Launch System (EMALS) to launch heavy fighters, airborne early warning aircraft, and UAVs in all sea states. Digital twin simulations to enable predictive maintenance.
- Surface Combatants: Induction of 5–10 destroyers, 7 corvettes, 4 Landing Platform Docks (LPDs) (~29,000 tonnes each), and 100 Next Generation Fast Interceptor Craft for coastal security.
- Underwater Warfare: 20 high-endurance Autonomous Underwater Vehicles (AUVs) for long-range surveillance and mine countermeasures.
- Missiles & Weapons: Over 200 surface-to-surface missiles and universal launchers for multi-platform deployment.
Army:
- ArmouredModernisation: Replacement of ageing T-72 fleet with 1,800 Future Ready Combat Vehicles (FRCVs); 300–400 light tanks for high-altitude sectors.
- Anti-Tank and Precision Weapons: Procurement of 50,000 ATGMs with tandem HEAT warheads, along with 600,000 artillery rounds, emphasising precision-guided munitions.
- UAV & Robotic Systems: Deployment of 70 MALE/HALE UAVs, 800 integrated drone-loitering munitions systems, and 400 ultra-light missiles for UAVs; over 700 robotic counter-IED systems.
- Cyber & AI Warfare: AI-enabled detection, classification, and adaptive jammers creating 15 km electronic denial zones; deepfake detection tools for operational security.
Air Force:
- Directed-Energy Weapons: 10–15 Tactical High-Energy Laser (THEL) systems with ranges of 6–15 km; high-power microwave systems to neutralise incoming threats.
- Stealth and UAVs: 150 stealth bomber drones for deep-strike missions; 100+ remotely piloted aircraft for ISR and strike roles.
- Persistent Surveillance: 75 High-Altitude Pseudo-Satellites (HAPS) and 20 stratospheric airships for continuous ISR and communications over extended periods.
Tri-Services (Joint):
- Hypersonic Missiles: Induction of 500+ scramjet-propelled hypersonic missiles capable of Mach 5+ speeds for rapid strike across land, sea, and air.
- Universal Missile Launchers: Platforms for multiple missile types to ensure interoperability.
- Cyber-Space Preparedness: AI-as-a-service platforms for 4,000 users, quantum key distribution networks, satellite hardening, and post-quantum secure communications.
Cross-Cutting Technologies
- AI & ML: Smart, predictive warfare through digital twin simulations and autonomous systems.
- Hybrid Warfare Capability: Integration of unmanned systems, robotic tools, and precision-guided munitions.
- Green & Sustainable Defence: Energy-efficient platforms and logistics aligned with national sustainability goals.
Strategic Significance
TPCR 2025 positions India to:
- Achieve self-reliance in defence technologies.
- Maintain credible deterrence and modernisation across all domains.
- Address emerging threats in cyber, space, and multi-domain warfare environments.
- Strengthen domestic defence industrial base through early technology visibility.
India’s first port-based Green Hydrogen Pilot Project

- 12 Sep 2025
In News:
Union Minister for Ports, Shipping and Waterways, SarbanandaSonowal, inaugurated India’s first port-based Green Hydrogen Pilot Project at V.O. Chidambaranar (VOC) Port, Tuticorin, Tamil Nadu, marking a significant step in India’s clean energy transition and green shipping ambitions.
Key Features of the Project
- Capacity: 10 Nm³ per hour.
- Cost: ?3.87 crore.
- Uses: The green hydrogen produced will power streetlights and an EV charging station in the port colony.
- Significance: VOC Port becomes the first Indian port to generate green hydrogen, aligning with India’s vision of Viksit Bharat 2047 and clean energy leadership.
Associated Green Initiatives at VOC Port
- Green Methanol Bunkering and Refuelling Facility
- Capacity: 750 m³, at a cost of ?35.34 crore.
- Expected to make VOC Port a green bunkering hub in South India.
- Linked to the proposed Coastal Green Shipping Corridor (Kandla–Tuticorin).
- Renewable Energy and Infrastructure Projects
- 400 KW rooftop solar plant, raising total capacity to 1.04 MW (highest among Indian ports).
- Foundation for a 6 MW wind farm.
- ?24.5 crore link conveyor to improve coal handling efficiency.
- ?90 crore multi-cargo berth and 3.37 km four-lane road for port connectivity.
- Upcoming Tamil Nadu Maritime Heritage Museum to showcase maritime history.
Strategic Importance
- Port Modernisation: Chennai, Kamarajar, and VOC ports have seen rapid expansion under the SagarmalaProgramme.
- 98 projects worth ?93,715 crore initiated in Tamil Nadu’s ports in the past 11 years.
- 50 projects completed; ?16,000 crore invested in modernisation and capacity building.
- Economic Impact:
- Expected to generate thousands of jobs.
- Attract global investments in green shipping and clean fuels.
- Strengthen India’s ambition of becoming a top 10 shipbuilding nation by 2030 and top 5 by 2047.
About V.O. Chidambaranar (VOC) Port
- Location: Tuticorin, Tamil Nadu, on the Coromandel Coast.
- Status: One of India’s 13 major ports, serving as a key maritime hub for South India.
- History: Formerly Tuticorin Port, renamed in 2011 after freedom fighter V.O. Chidambaranar (KappalottiyaTamizhan).
- Role: Major centre for coal handling, container trade, and now emerging as a green energy hub.
Angikaar 2025 Campaign
- 12 Sep 2025
In News:
The Ministry of Housing and Urban Affairs (MoHUA) has launched Angikaar 2025, a nationwide outreach campaign under the Pradhan Mantri Awas Yojana – Urban 2.0 (PMAY-U 2.0). The initiative seeks to bridge last-mile implementation gaps, accelerate housing delivery, and ensure that welfare benefits reach vulnerable urban families.
Objectives of Angikaar 2025
- Awareness Generation: Create widespread awareness of PMAY-U 2.0 across urban India.
- Housing Delivery: Fast-track verification of applications and completion of sanctioned houses.
- Beneficiary Support: Facilitate access to financial assistance, credit-linked support, and convergence with other welfare schemes.
- Inclusion: Prioritise housing needs of Special Focus Groups identified under PMAY-U 2.0.
Key Features
- Coverage: Over 5,000 Urban Local Bodies (ULBs) across India.
- Activities: Door-to-door campaigns, awareness drives, loan melas, cultural events, and anchor events under PM Awas Mela – Shehri.
- Convergence: Linkage with schemes such as the Credit Risk Guarantee Fund Trust for Low Income Housing (CRGFTLIH) and PM Surya Ghar: Muft Bijli Yojana.
PMAY-U Progress So Far
- Sanctioned Houses: 120 lakh.
- Completed & Delivered: 94.11 lakh pucca houses.
- Pending: Angikaar 2025 will focus on expediting completion of remaining sanctioned houses.
- Future Target under PMAY-U 2.0: Provide financial support (up to ?2.5 lakh per family) to an additional one crore urban families for constructing or purchasing pucca houses.
Significance
- Last-Mile Outreach: Brings government schemes closer to beneficiaries through direct engagement.
- Community Mobilisation: Promotes Jan Bhagidari (people’s participation) via awareness camps and cultural events.
- Holistic Development: Integrates housing with access to electricity, financial inclusion, and basic services.
- Housing for All: Reaffirms the government’s commitment to inclusive and sustainable urban development.
Vulture Network Portal

- 12 Sep 2025
In News:
- Vultures, once abundant across India, have faced catastrophic population declines over the past three decades due to carcass poisoning, harmful veterinary drugs (notably diclofenac), and negative social perceptions.
- Recognizing the urgency of conservation, an Assam-based foundation has launched India’s first dedicated vulture conservation portal to create a knowledge-sharing and awareness-driven network for their protection.
The Vulture Network Portal
- Nature: A cloud-based, first-of-its-kind portal in India dedicated to vulture conservation.
- Developer: We Foundation India, in collaboration with partners like the Assam Bird Monitoring Network and other organizations.
- Functions:
- Compiles scientific information on vultures.
- Provides freely downloadable outreach materials for awareness campaigns.
- Disseminates conservation material in local languages (beginning with Assamese) to ensure community participation.
- Focuses on addressing key threats to vultures, including:
- Carcass poisoning.
- Harmful veterinary drugs such as diclofenac.
- Myths and negative social perceptions around scavenger birds.
Significance
- Community Engagement: Builds a network of individuals and organizations working for vulture conservation.
- Policy & Awareness: Offers a centralized platform to support awareness drives, education, and grassroots campaigns.
- Localized Impact: By promoting information in regional languages, it enhances outreach among rural communities, where interaction with vultures is most direct.
Vultures of India
India hosts several species of vultures, many of which are critically endangered:
- Slender-billed vulture – ~800 mature individuals left.
- White-rumped vulture.
- Red-headed vulture.
- Himalayan griffon.
- Indian vulture.
- Cinereous vulture.
- Eurasian griffon.
- Egyptian vulture.
- Bearded vulture.
Conservation Context
- India has already banned the veterinary use of diclofenac (a major cause of vulture deaths) and promoted safer alternatives like meloxicam.
- Initiatives such as Vulture Safe Zones, breeding centres, and now this digital portal strengthen the country’s commitment to vulture conservation.
- As vultures play a critical ecological role as scavengers, their survival is linked to disease control and overall ecosystem health.
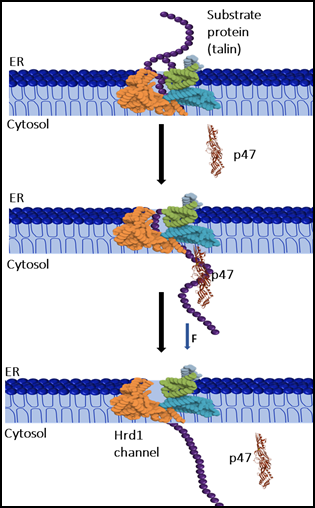
P-47 Protein
- 12 Sep 2025
In News:
Proteins within living cells constantly face mechanical stress during processes such as intracellular transport, cytoskeletal remodeling, and degradation. These stresses can compromise protein folding and stability, leading to cellular dysfunction.
Traditionally, specialized proteins called canonical chaperones were considered the primary agents guiding protein folding and stability. However, recent research has uncovered a surprising player in this landscape—p47, a cofactor protein with previously underestimated roles.
Discovery by SNBNCBS
A study conducted by the S. N. Bose National Centre for Basic Sciences (SNBNCBS), an autonomous institute under the Department of Science & Technology (DST), revealed that p47 functions as a “mechanical chaperone.” Using single-molecule magnetic tweezers, researchers applied controlled mechanical forces to mimic stresses faced by proteins inside cells.
The experiments demonstrated that:
- p47 stabilizes mechanically stretched proteins, enabling them to refold even under constant pulling forces.
- It enhances the mechanical efficiency of protein extraction from the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) lumen to the cytoplasm.
- It facilitates polypeptide translocation through narrow pores, reducing misfolding risks and improving protein quality control.
About p47 Protein
- Nature: A cofactor protein traditionally associated with the p97 complex, a major cellular machine responsible for protein trafficking, degradation, and membrane fusion.
- Revised Role: Beyond being a passive assistant, p47 exhibits autonomous, force-dependent protective activity, extending the functional repertoire of accessory proteins.
Significance of the Findings
- Scientific Breakthrough
- This is the first direct, single-molecule evidence that cofactors can act as mechanical chaperones.
- It challenges the existing view of accessory proteins as mere helpers and redefines their role in protein mechanics.
- Therapeutic Potential
- Targeting p47 or similar cofactors may provide new treatment avenues for diseases where protein stability under stress is compromised, such as:
- Cardiomyopathies (heart muscle diseases).
- Laminopathies (genetic disorders linked to nuclear protein instability).
- This could lead to precision medicine strategies focusing on mechanical resilience of proteins.
- Targeting p47 or similar cofactors may provide new treatment avenues for diseases where protein stability under stress is compromised, such as:
- Broader Implications
- Enhances understanding of cellular stress response mechanisms.
- Opens possibilities for drug development aimed at modulating protein folding under force.
- Strengthens India’s contributions to cutting-edge biophysical research with global relevance.
