Chaolung Sukapha

- 05 Dec 2025
In News:
Assam Day (02nd December) celebrations recently paid tribute to Chaolung Sukapha, the founder of the Ahom kingdom and a key figure in Assam’s historical and cultural identity.
Who was Chaolung Sukapha?
- Chaolung Sukapha was a 13th-century ruler who established the Ahom kingdom in Assam, which went on to rule the region for nearly six centuries. He is widely regarded as the architect of “Bor Asom” (Greater Assam) due to his role in unifying diverse communities.
- Sukapha crossed the Patkai hills and established his first principality at Charaideo, which later became an important political and cultural centre of the Ahom rulers.
Administrative System
- Sukapha developed an organised administrative structure that later evolved into the famous Paik system of the Ahoms.
- The kingdom was divided into territorial units called khels (or phoids). Each unit was supervised by an officer responsible for mobilising paiks, able-bodied adult males who provided labour and military service.
- Every adult male between the ages of 16 and 50 was registered as a paik. They served the state in activities such as agriculture, construction, and warfare for a fixed period each year. In return, they were granted land for cultivation.
- Sukapha also emphasised guerrilla warfare tactics suited to Assam’s geography of rivers, forests, and hills, a strategy that later helped the Ahoms resist external invasions.
Policy of Integration and Assimilation
- One of Sukapha’s most significant contributions was his policy of conciliation and assimilation. Instead of conquering local tribes through force, he built alliances and integrated communities into his kingdom.
- He maintained friendly relations with indigenous groups such as the Sutias, Morans, and Kacharis, laying the foundation for a composite Assamese society. His approach fostered social harmony and cultural blending, which became a defining feature of Assam’s identity.
Why Sukapha is Important Today
- Sukapha’s legacy lies in his vision of unity through diversity. His governance model promoted peace, cooperation, and shared prosperity among different ethnic and cultural groups.
- This inclusive approach is often seen as an early example of nation-building through social integration, making his legacy relevant in discussions on cultural harmony and regional identity.
Charaideo and Historical Legacy
- Charaideo, where Sukapha established his initial base, later became the site of the Charaideo Maidams, the burial mounds of Ahom royalty. These maidams have gained global recognition for their historical and cultural importance.
India’s Commitment to Disability Rights and Inclusive Growth

- 05 Dec 2025
In News:
India reaffirmed its commitment to disability inclusion around the International Day of Persons with Disabilities (3 December), with renewed focus on accessibility, digital empowerment, education, livelihoods, and rights-based governance for persons with disabilities (PwDs).
Disability Scenario in India
According to the Census 2011, India has 2.68 crore persons with disabilities, constituting 2.21% of the total population. The Rights of Persons with Disabilities (RPwD) Act, 2016 defines a person with disability as someone with long-term physical, mental, intellectual or sensory impairment which, in interaction with barriers, hinders full and effective participation in society.
Disability and poverty are closely linked, making inclusive growth essential for ensuring dignity, independence, and equal opportunity.
Constitutional and International Commitments
The Indian Constitution supports disability rights through:
- Article 21, which ensures the right to live with dignity
- Article 41 (DPSP), which directs the State to provide assistance in cases of disability
- The State List (Seventh Schedule) includes relief of the disabled
India is also a signatory to the UN Convention on the Rights of Persons with Disabilities (UNCRPD), committing to a rights-based approach to inclusion.
Legal and Policy Framework
- The Rights of Persons with Disabilities Act, 2016 is the cornerstone law. It recognises 21 categories of disabilities, mandates reservations in education and employment, and enforces accessibility, non-discrimination, and inclusive education.
- The National Trust Act, 1999 supports persons with autism, cerebral palsy, intellectual and multiple disabilities.
- The Rehabilitation Council of India (RCI) Act, 1992 regulates training of rehabilitation professionals and maintains a national register.
- The Scheme for Implementation of RPwD Act (SIPDA) supports ministries and states in making infrastructure and services accessible.
Major Government Initiatives
- Sugamya Bharat Abhiyan (Accessible India Campaign), launched in 2015, aims to improve accessibility in public buildings, transport systems, and information and communication technology. The revamped Sugamya Bharat App now serves as a digital accessibility hub with mapping tools, scheme directories, and grievance reporting.
- The Unique Disability ID (UDID) Project creates a national database and provides a universal disability identity card, improving transparency and access to benefits.
- The ADIP Scheme provides assistive devices, including advanced aids like cochlear implants, to support independent living.
- The Deendayal Divyangjan Rehabilitation Scheme (DDRS) funds NGOs working in rehabilitation and education.
- The National Divyangjan Finance and Development Corporation (NDFDC) provides concessional loans for self-employment under schemes such as Divyangjan Swavalamban Yojana.
- ALIMCO, a government-owned enterprise, manufactures and distributes assistive devices nationwide.
Digital and Educational Inclusion
- The PM-DAKSH DEPwD portal links PwDs to skill training and employment opportunities.
- The Indian Sign Language Research and Training Centre (ISLRTC) promotes Indian Sign Language (ISL). The launch of PM e-Vidya Channel 31 provides dedicated ISL training. ISLRTC has also created the world’s largest ISL digital repository and expanded the ISL dictionary to over 10,000 terms.
- The PRASHAST App enables early screening of disabilities in schoolchildren.
Inclusion Through Culture and Enterprise
- The Divya Kala Mela provides market linkages to Divyang artisans and entrepreneurs under the “Vocal for Local” initiative.
- The Purple Fest celebrates inclusion, assistive technologies, and accessibility innovations.
Key Challenges
- Despite progress, barriers remain in accessibility, employment, healthcare costs, awareness, and last-mile delivery. Digital divides and social stigma continue to hinder full participation.
India’s disability framework is shifting toward rights-based, technology-enabled, and inclusion-driven governance. Strengthening awareness, enforcing accessibility standards, expanding financial support, and improving implementation will be crucial for achieving the goal of “inclusive growth with dignity”.
Alaknanda Galaxy

- 05 Dec 2025
In News:
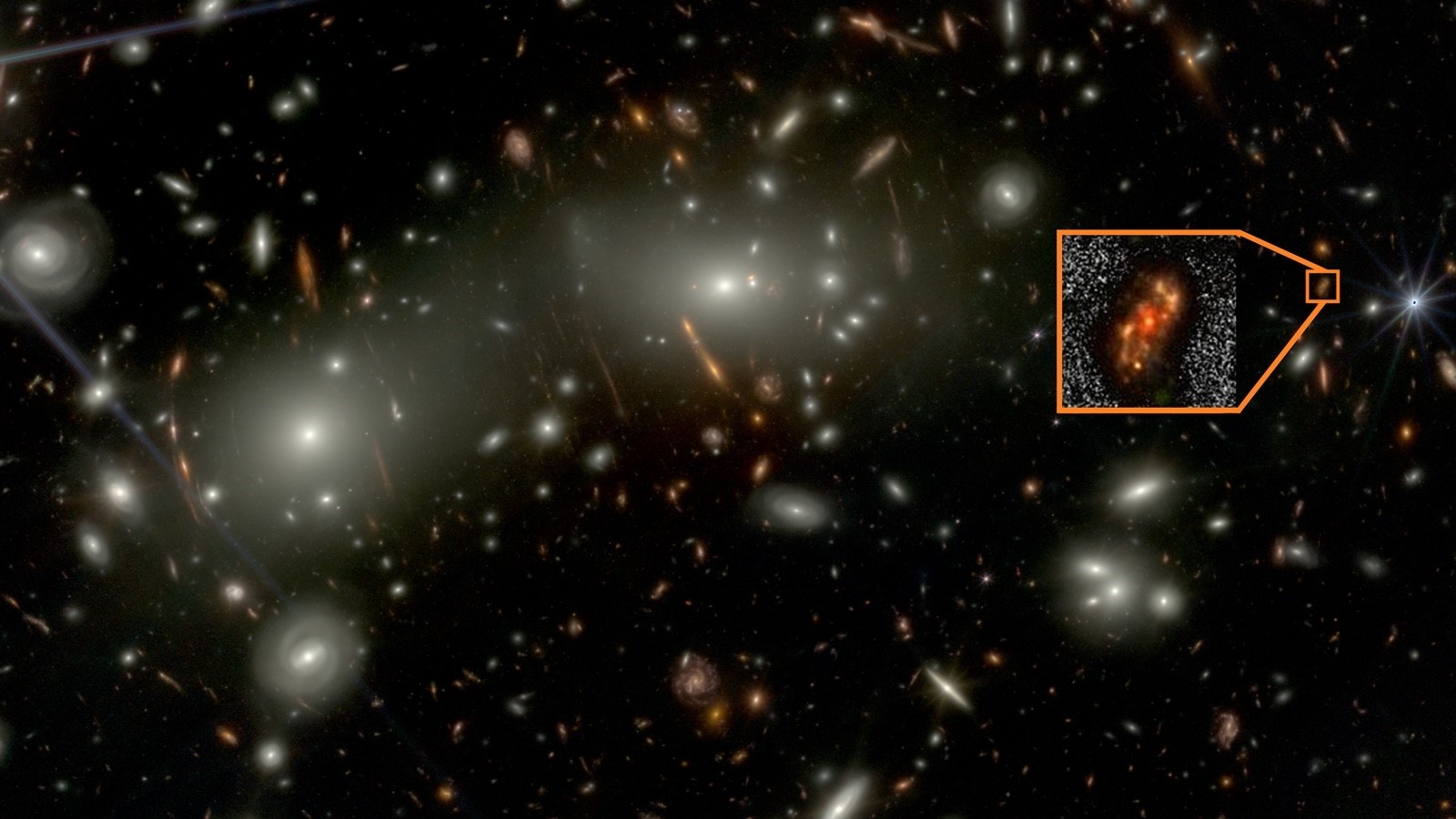
Researchers from the National Centre for Radio Astrophysics (NCRA), Tata Institute of Fundamental Research (TIFR), Pune, have discovered a well-structured spiral galaxy named Alaknanda. This galaxy dates back to just 1.5 billion years after the Big Bang and was identified using NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope (JWST). The finding challenges existing theories about how early galaxies formed.
Why This Discovery is Important
Scientists believed that galaxies in the early universe were generally chaotic, clumpy, and unstable, lacking well-defined structures. Spiral galaxies like the Milky Way were thought to have developed much later. However, Alaknanda shows a mature spiral structure, indicating that complex galactic systems may have evolved far earlier than previously assumed.
Key Facts About the Alaknanda Galaxy
Alaknanda formed when the universe was only about 10 percent of its current age, roughly 1.5 billion years old. It lies approximately 12 billion light-years away from Earth. The galaxy displays a textbook spiral structure with two well-defined spiral arms and a bright central bulge. Its diameter is estimated to be around 30,000 light-years.
The name “Alaknanda” is inspired by the Alaknanda River in the Himalayas, considered the sister river of Mandakini, which is also a Hindi name for the Milky Way galaxy. The naming reflects the idea that this distant galaxy resembles a “sister” of our own galaxy.
Scientific Significance
The discovery adds to growing evidence from JWST that the early universe may have been more mature and structured than earlier models suggested. It challenges current theories of galaxy formation and indicates that organized spiral structures may have emerged earlier in cosmic history.
Future research will focus on studying the motion of gas and stars within Alaknanda to understand how its spiral arms formed. Scientists plan to use further data from JWST and the Atacama Large Millimeter/submillimeter Array (ALMA) in Chile. These studies will help determine whether the galaxy’s disk is dynamically calm or turbulent, which in turn reveals the mechanism behind its structure.
About Galaxies
Galaxies are vast systems made up of stars, planets, gas, dust, dark matter, and usually a supermassive black hole at their centre. They are held together by gravity and vary greatly in size. Some dwarf galaxies contain only a few thousand stars, while giant galaxies can contain trillions of stars and span over a million light-years.
Galaxies are commonly classified into three main types: spiral, elliptical, and irregular.
Galaxies in the Cosmic Web
Galaxies are not randomly scattered. They form groups, which can contain up to about a hundred galaxies, and clusters, which can include thousands. These clusters connect to form superclusters, which are part of the large-scale cosmic web that structures the universe.
Key Processes in Galaxy Evolution
Spiral galaxies often develop stellar bars that influence star formation. Galaxies may collide, causing gas clouds to compress and trigger new star formation. Some collisions lead to mergers, forming a single larger galaxy and altering its structure. Larger galaxies can also grow by absorbing smaller ones, a process sometimes called galactic cannibalism.
Milky Way Galaxy - Important Facts
The Milky Way is a spiral galaxy more than 100,000 light-years across. Earth lies in one of its spiral arms, roughly halfway from the galactic centre. The Milky Way is part of the Local Group, which includes more than 50 galaxies such as the Andromeda Galaxy. This group is located within the vast Laniakea Supercluster. Our solar system takes about 240 million years to complete one orbit around the Milky Way.
SC Tasks CBI to Tackle ‘Digital Arrest’ Scams

- 05 Dec 2025
In News:
The Supreme Court of India has directed the Central Bureau of Investigation (CBI) to lead a pan-India probe into rising cases of “digital arrest” scams, a form of cyber fraud involving impersonation of law-enforcement agencies. The Union government informed the Court that fraudsters have siphoned off thousands of crores of rupees, with senior citizens being frequent victims.
What is a Digital Arrest Scam?
A digital arrest is a cyber fraud where scammers pose as officials from agencies such as the police, CBI, ED, or customs authorities.
Modus Operandi
- Victims receive calls about a fake parcel, KYC issue, or alleged criminal link.
- Fraudsters use spoofed phone numbers, forged documents, and even video calls to appear official.
- Victims are threatened with arrest, passport cancellation, or frozen bank accounts.
- Under psychological pressure, victims are forced to transfer money as a “security deposit” or “fine”.
This scam combines cybercrime and psychological coercion, making it particularly dangerous.
Reasons for the Rise
- Fear-based social engineering exploiting public trust in law enforcement
- Easy access to SIM cards, mule bank accounts, and spoofing tools
- Cross-border cybercrime syndicates operating in organised networks
- Widespread adoption of digital payments (UPI, QR codes, online banking)
- Low digital awareness among vulnerable groups such as elderly citizens
Supreme Court Directions
The Court issued several key directives:
Investigation & Coordination
- CBI given nationwide jurisdiction to probe digital arrest scams.
- States directed to grant consent under Section 6 of the Delhi Special Police Establishment (DSPE) Act, 1946.
- CBI to coordinate with States, Interpol, RBI, telecom authorities, and digital platforms.
Financial Tracking
- RBI asked to explore AI and Machine Learning tools to detect suspicious money “layering” through multiple accounts.
- Banks and financial institutions to assist in identifying mule accounts.
Telecom Accountability
- The Department of Telecommunications (DoT) directed to tighten SIM issuance norms and KYC processes.
- Action sought against negligent telecom operators enabling misuse of SIMs.
Platform Responsibility
- Online intermediaries must comply with IT Rules, 2021 and provide data to investigators.
Institutional Strengthening
- States to operationalise Regional Cybercrime Coordination Centres and integrate them with the Indian Cybercrime Coordination Centre (I4C).
Scale of the Problem
- I4C has blocked over 59,000 WhatsApp accounts linked to such scams.
- Financial cyber fraud reporting systems have saved thousands of crores of rupees through timely intervention.
Challenges in Tackling Digital Arrests
- Use of advanced technologies like deepfakes, encrypted apps, and AI-generated documents
- Dark web networks supplying scam tools
- Cross-border jurisdictional hurdles
- Delayed reporting by victims due to stigma or fear
- Limited cyber forensic and policing capacity
Government Initiatives
|
Initiative |
Purpose |
|
Indian Cyber Crime Coordination Centre (I4C) |
National coordination against cybercrime |
|
National Cyber Crime Reporting Portal |
Public reporting of cyber offences |
|
Helpline 1930 |
Immediate reporting of financial fraud |
|
Anti-spoofing measures by DoT |
Blocking fake international calls masked as Indian numbers |
|
Cyber awareness campaigns (CyberDost, SMS alerts) |
Public education on digital safety |
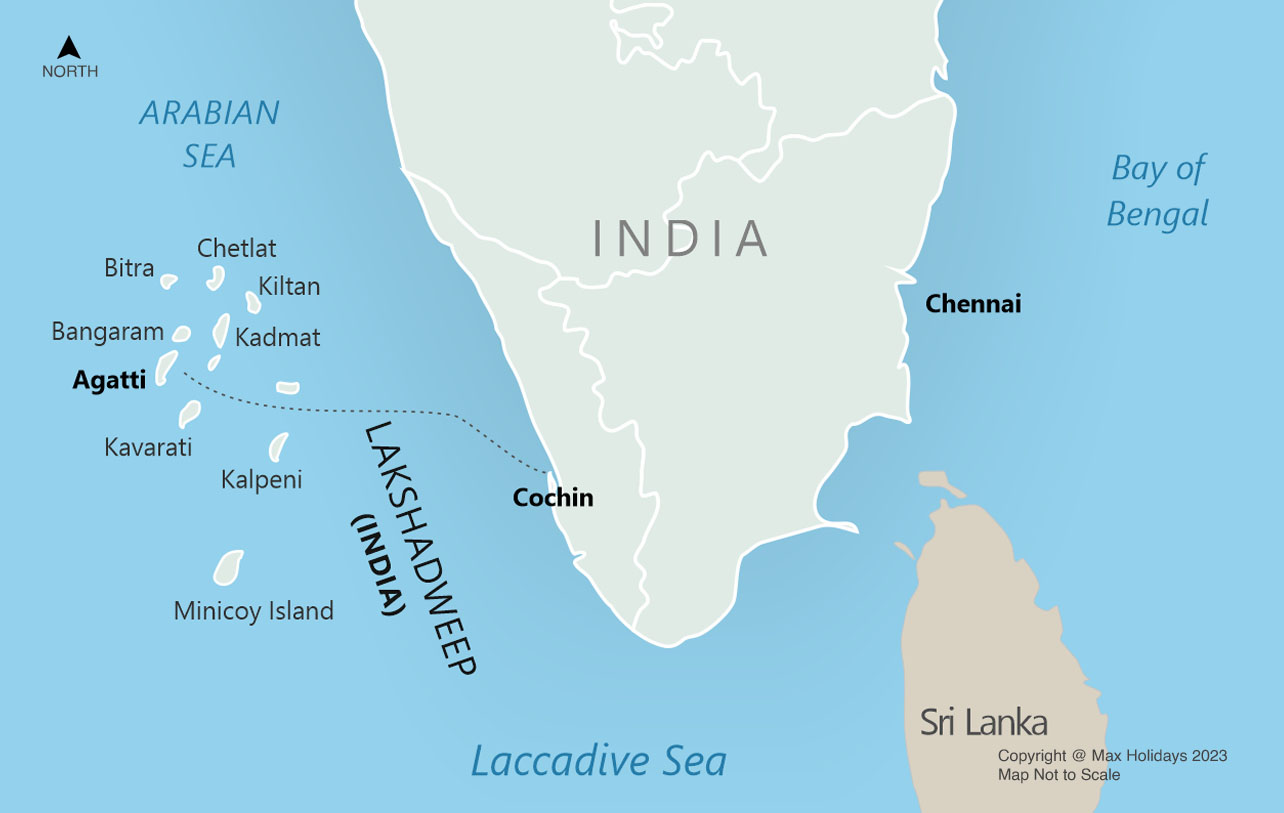
Bitra Island
- 05 Dec 2025
In News:
India is set to strengthen its military footprint in Lakshadweep, with a new naval detachment on Bitra Island expected to become fully operational next year. Simultaneously, the Indian Air Force (IAF) is expanding facilities on Agatti and planning a new air base on Minicoy. These steps are aimed at enhancing India’s maritime security posture in the Arabian Sea amid rising strategic challenges.
Why Lakshadweep Matters Strategically
Lakshadweep’s location gives India a vantage point over critical sea lanes of communication (SLOCs) in the Arabian Sea, through which a significant portion of global energy and trade flows.
Rising shipping traffic, growing Chinese presence in the Indian Ocean Region (IOR), and threats such as piracy and maritime crime have increased the strategic relevance of the islands. Enhanced surveillance and rapid response capabilities from Lakshadweep will strengthen India’s maritime domain awareness.
About Bitra Island
Basic Facts
- Smallest inhabited island of Lakshadweep
- Part of the Amindivi subgroup
- Located about 483 km west of Kochi in the Arabian Sea
Geographical Setting
- Lies north of Perumal Par and southeast of Byramgore Reef
- A coral atoll, formed from reef growth over submerged volcanic structures
- Features a ring-shaped lagoon system
Physical Features
|
Feature |
Detail |
|
Main Island Area |
~0.177 sq km |
|
Southern Cay |
~0.009 sq km |
|
Lagoon Area |
~45–54 sq km |
|
Reef System |
Coral reef barrier protects lagoon waters |
The surrounding reef keeps lagoon waters relatively calm even during monsoon conditions.
Ecological and Cultural Importance
- Bitra is part of Lakshadweep’s fragile coral ecosystem, historically known as a major seabird breeding ground. The island’s small landmass and reef system make it environmentally sensitive.
- Culturally, Bitra houses the shrine of Malik Mulla, an Arab saint, making it a place of local religious significance.
- It was permanently settled only in 1945, making it one of India’s newest inhabited regions.
Military Developments
Naval Expansion
- A new Indian naval detachment is being established on Bitra.
- It will improve maritime surveillance, especially over shipping routes in the Arabian Sea.
- Development is being carried out in a measured manner, considering ecological sensitivity.
Air Force Expansion
- Agatti Airfield is being expanded.
- A new air base on Minicoy is under development.
- Future plans include long-range cargo drones to support logistics and operations across dispersed island territories.
Strategic Significance
The military expansion in Lakshadweep supports:
- Maritime security and surveillance
- Monitoring of strategic sea lanes
- Countering piracy and illegal activities
- Strengthening India’s role as a net security provider in the IOR
