Subarnarekha River
- 24 Jun 2025
In News:
A flash flood in the Subarnarekha River affected over 50,000 people in Balasore district, Odisha. The flooding was triggered by heavy rainfall and the release of water from Chandil Dam in Jharkhand.
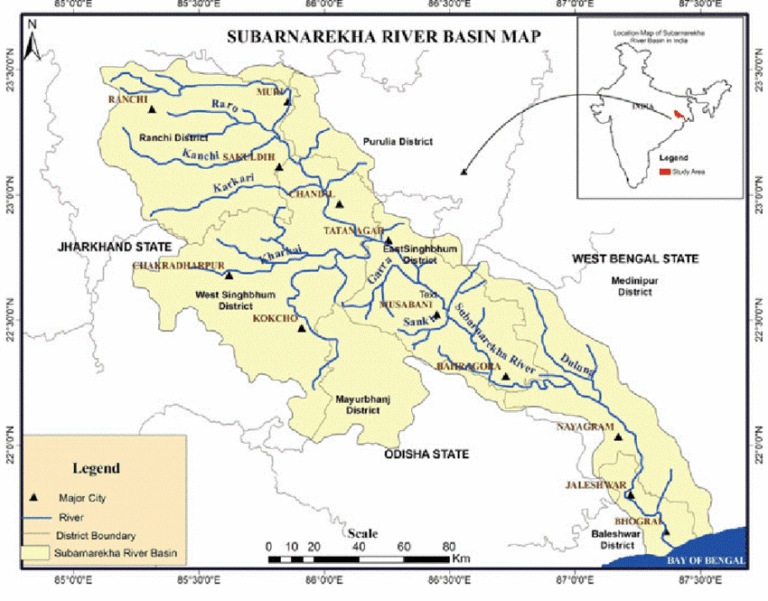
About Subarnarekha River
Origin:
- Arises near Piska/Nagri, close to Ranchi, in Jharkhand.
- The name "Subarnarekha" means “Streak of Gold”, referring to traces of gold once found in the river’s origin area.
Geographical Course:
- States Covered: Jharkhand, West Bengal, Odisha.
- Mouth: Empties into the Bay of Bengal near Talsari, in Odisha.
- Total Length: Approx. 395 km.
- Drainage Basin Area: 18,951 sq. km, making it a relatively small multi-state river basin.
- Course Details: Flows through Paschim Medinipur (WB) and Balasore (Odisha) after originating in Jharkhand.
Key Features:
- Hundru Falls: A well-known waterfall on Subarnarekha, located in Jharkhand, with a drop of 98 metres.
- The river system is independent, not a tributary of any larger river.
- Known for its historical and cultural significance due to gold particles in its sands.
Major Tributaries:
- Kharkai (joins at Jamshedpur)
- Kanchi, Roro, Harmu Nadi, Dulunga, Karru, Karakari, Singaduba, Kodia, Dhamra
About Chandil Dam
Location:
- Situated in Chandil, Seraikela Kharsawan district, Jharkhand.
- Built near the confluence of the Subarnarekha River and Karkori River (originating from Hundru Falls).
Purpose:
- Multi-purpose project serving irrigation, flood control, and tourism.
- Plays a significant role in managing water flow in the Subarnarekha basin.
Estimates Committee

- 24 Jun 2025
In News:
The Lok Sabha Speaker inaugurated the National Conference of Estimates Committees in Mumbai to mark 75 years of the Parliamentary Estimates Committee.
About the Estimates Committee:
- Type: Parliamentary Financial Standing Committee (Lok Sabha).
- Established in: 1950, under the Rules of Procedure of Lok Sabha, after the adoption of the Constitution.
- Purpose: To examine how public funds are allocated and utilized, and recommend improvements in economy, efficiency, and accountability.
Composition:
- Total Members: 30 Lok Sabha MPs.
- Exclusion: Ministers are not eligible to be members.
- Chairperson: Appointed by the Speaker of Lok Sabha.
- Term: One year, renewable annually.
Selection Process:
- Members are elected annually by the Lok Sabha through proportional representation using the single transferable vote system.
Key Functions:
- Examine budget estimates of various ministries and departments.
- Suggest reforms for better economy and efficiency in public expenditure.
- Recommend alternative policies for improved governance and financial management.
- Evaluate effectiveness of spending aligned with policy objectives.
- Suggest improvements in the presentation of budget estimates to Parliament.
Exclusions: Does not examine Public Sector Undertakings — these are dealt with by the Committee on Public Undertakings.
Working Mechanism:
- Selects specific departments or statutory bodies for scrutiny.
- Seeks inputs from government officials and external experts.
- Undertakes study visits and on-ground assessments (with prior approval).
- Holds formal evidence sessions in Parliament.
- Submits findings and recommendations through reports to the Lok Sabha.
- The Government must submit Action Taken Reports (ATR) within six months.
Achievements (as of 2025):
- Total Reports Presented: 1,184
- 656 Original Reports
- 528 Action Taken Reports
- Covered nearly all major ministries and departments.
- Contributed to strengthening Parliamentary financial oversight and ensuring fiscal discipline.
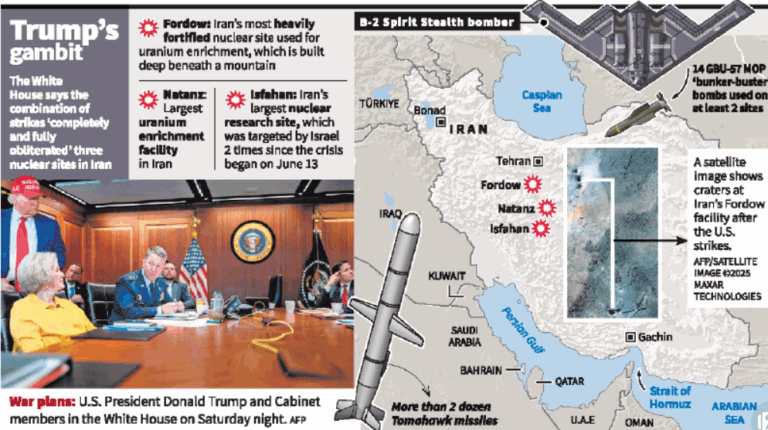
Operation Midnight Hammer
- 24 Jun 2025
In News:
The United States launched a classified military operation named Operation Midnight Hammer, targeting Iran’s major nuclear sites at Fordow, Natanz, and Isfahan, claiming significant damage to its nuclear infrastructure.
About Operation Midnight Hammer:
- A covert US airstrike intended to degrade Iran’s nuclear weapons program.
- Launched by: US Department of Defense.
- Objective: Destruction of fortified nuclear facilities and demonstration of US strategic air power.
Key Assets Deployed:
- B-2 Spirit Stealth Bombers equipped with GBU-57A/B Massive Ordnance Penetrators (MOPs) – “bunker-buster” bombs designed to penetrate over 200 feet of reinforced concrete.
- Tomahawk Land Attack Cruise Missiles launched from US submarines.
- Support aircraft and decoys for air defence suppression.
B-2 Spirit Stealth Bomber:
- Type: Long-range strategic stealth bomber of the US Air Force.
- Developed by: Northrop Grumman (1980s).
- Cost: Approx. $2.1 billion per unit – one of the most expensive aircraft in the world.
- Range: Over 6,000 nautical miles without refuelling.
- Crew: Operated by two pilots.
Weapons and Capabilities:
- Payload Capacity: Over 40,000 pounds.
- Armament Options:
- 2 × GBU-57A/B MOPs
- 16 × B83 nuclear bombs (part of US nuclear triad)
- Precision-guided weapons: JDAM, JSOW, JASSM-ER.
- Stealth Features: Radar cross-section as small as a bird – allows evasion of sophisticated air defences.
Strategic Significance:
- Enhances the US’s global precision strike capabilities.
- Reinforces the deterrence role of the B-2 in both conventional and nuclear domains.
- Capable of targeting heavily fortified underground facilities.
- Proven operational effectiveness in Afghanistan, Libya, and now Iran.
SSLV Technology Transfer
- 24 Jun 2025
In News:
In a historic development for India's space sector, the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) will, for the first time, completely transfer rocket technology to a domestic firm. Hindustan Aeronautics Limited (HAL) has secured the Transfer of Technology (ToT) for the Small Satellite Launch Vehicle (SSLV) through a competitive process facilitated by IN-SPACe, marking a new era of private-sector participation in space.
What is the SSLV Technology Transfer?
- Nature of ToT: Complete technology handover of ISRO’s SSLV to HAL.
- Awarded By: Indian National Space Promotion and Authorisation Centre (IN-SPACe) after a two-stage national selection.
- Winning Bid: HAL won the bid with a ?511 crore offer — the highest among the contenders.
- Other Bidders: Consortia led by Alpha Design (Bengaluru) and Bharat Dynamics Limited (Hyderabad).
- Objective: To empower the private sector to build, market, and launch rockets independently, thus reducing reliance on ISRO for small satellite missions.
Key Features of the SSLV ToT
Parameter Details
Ownership - HAL will own and operate the SSLV, with rights to modify its design and choose commercial partners.
Production Capability - HAL aims to produce 6–10 SSLVs annually, based on demand.
ToT Duration - 2 years of technology handholding by ISRO, during which HAL will manufacture at least two SSLV prototypes.
Post-ToT - HAL will operate independently post-ToT and may enter contracts for commercial launch services.
Contractual Roles - ISRO (technical), IN-SPACe (regulatory + ToT coordination), NSIL (commercial interface), HAL (execution).
About Hindustan Aeronautics Limited (HAL)
- Established: 23 December 1940 (as Hindustan Aircraft Limited).
- HQ: Bengaluru, Karnataka.
- Ministry: Ministry of Defence, Government of India.
- Core Role: India’s largest defence and aerospace PSU involved in aircraft, helicopters, engines, and now space systems.
- Key Contributions:
- Manufactured MiG-21, SU-30MKI, LCA Tejas.
- Supplied components for GSLV Mk-III, Mars Orbiter Mission, and Gaganyaan.
- Collaborated with ISRO on cryogenic engines and launch vehicle structures.
- Publicly Listed: On BSE and NSE since 2018.
Significance:
- First Full Rocket ToT in India: Unlike earlier manufacturing contracts (e.g., PSLV), SSLV is entirely owned and operated by HAL.
- Boosts Private Sector Role: Aligns with India’s space sector reforms to commercialize launch services.
- Fosters Innovation & Autonomy: HAL can redesign the SSLV and partner globally, making India more competitive in the small satellite launch market.
- Strategic Diversification: HAL adds space systems to its portfolio, without affecting defence operations.
Green Hydrogen Production
- 24 Jun 2025
In News:
In a significant scientific milestone, Indian researchers have developed a next-generation, scalable solar-driven device for producing green hydrogen—offering a major boost to clean energy innovation and India’s energy transition goals.
Key Highlights:
- Developed By: Centre for Nano and Soft Matter Sciences (CeNS), Bengaluru — an autonomous institute under the Department of Science and Technology (DST).
- Publication: The findings were published in the Journal of Materials Chemistry A (Royal Society of Chemistry).
What Is Green Hydrogen?
Green hydrogen is produced by splitting water molecules using renewable energy sources, especially solar and wind, without any greenhouse gas emissions. It is a clean energy carrier with the potential to decarbonize heavy industries, power vehicles, and store energy.
The Innovation: Solar-Driven Water Splitting Device
- The device uses only solar energy to split water and produce hydrogen.
- It employs a silicon-based photoanode with an n-i-p heterojunction structure:
- n-type TiO?, intrinsic (undoped) Si, and p-type NiO layers.
- This structure enhances charge separation and transport efficiency.
- Fabrication via magnetron sputtering, a scalable, industry-compatible process.
Key Performance Metrics
- Surface photovoltage: 600 millivolts (mV)
- Low onset potential: ~0.11 VRHE
- Stability: Operated continuously for over 10 hours in alkaline medium with only ~4% performance degradation.
- Successfully scaled to a 25 cm² photoanode, showing strong solar-to-hydrogen conversion.
Advantages of the Device
Feature Benefit
Pure solar operation No external power or fossil fuel input
High energy efficiency Better light absorption, reduced recombination loss
Material use Low-cost, earth-abundant materials
Durability Stable under alkaline conditions
Scalability Demonstrated potential for industrial-scale production
Strategic Significance
- Accelerates India’s National Green Hydrogen Mission and hydrogen-based economy.
- Supports India’s net-zero emission commitments and climate action.
- Offers a cost-effective, clean energy alternative to fossil fuels in:
- Hard-to-abate sectors like steel and cement
- Clean transport solutions
- Renewable energy storage systems
