Gyan Post

- 15 Jun 2025
In News:
The Department of Posts, under the Ministry of Communications, launched a new service called ‘Gyan Post’ to facilitate affordable delivery of educational and cultural books across India.
Key Highlights:
Objective:
- To bridge the educational divide by improving access to printed educational materials, especially in rural and remote regions.
- Aligned with the goals of the National Education Policy (NEP) to promote inclusive education.
Salient Features:
- Service Availability: All Departmental Post Offices across India.
- Type of Material:
- Only non-commercial printed educational, cultural, social, and religious books.
- Books must not contain advertisements or promotional content.
- Must bear the name of the printer or publisher.
- Delivery Mode: Surface mail (traceable) – enhances transparency and reliability.
- Tariff Structure:
- ?20 for packets up to 300 grams
- ?100 for packets up to 5 kilograms (excluding applicable taxes)
- Tracking: Available to ensure accountability and customer confidence.
Significance:
- Promotes educational equity by supporting learners in under-served areas.
- Complements Digital India and NEP 2020 by reinforcing multi-modal education access (print + digital).
- Encourages the circulation of knowledge, especially in regions with poor digital penetration.
Servants of India Society
- 15 Jun 2025
In News:
Tensions have resurfaced between Gokhale Institute of Politics and Economics (GIPE) and the Servants of India Society (SIS) over control of a joint bank account and allegations of financial misconduct. This has brought attention back to the legacy and functioning of the historic SIS.
About Servants of India Society (SIS)
- Founded: June 12, 1905
- Founder: Gopal Krishna Gokhale, with G.K. Devadhar, A.V. Patwardhan, and N.A. Dravid
- Location: Fergusson Hill, Pune, Maharashtra
- Headquarters: Pune, with branches in Chennai, Mumbai, Nagpur, Allahabad, etc.
Objectives:
- To train a dedicated cadre of national workers for selfless service to the nation.
- Promote political education, social reform, and public service.
- Work towards upliftment of underprivileged communities, including rural and tribal populations.
- Achieve social change through constitutional and moderate means, not violent agitation.
Membership and Structure:
- Members undergo a five-year training period and vow to serve on modest salaries.
- Considered “young missionaries of Indian nationalism.”
- Notable Members:
- V.S. Srinivasa Sastri (later president after Gokhale’s death in 1915)
- Hriday Nath Kunzru
- A.V. Thakkar
Ideological Basis:
- Strong emphasis on constitutionalism, moderation, and liberalism.
- Aimed to create a disciplined, morally upright civil society to complement political struggle.
About Gopal Krishna Gokhale:
- Born: May 9, 1866 | Died: February 19, 1915
- Moderate leader of the Indian National Congress and a liberal reformer.
- Influenced by Justice M.G. Ranade and Western political thought.
- Advocated for gradual self-governance and saw value in British-initiated modernization.
- Played a pivotal role in the Morley-Minto Reforms (1909).
- Mentor to Mahatma Gandhi and known for his economic insight and powerful oratory.
Step-and-Shoot Spot-Scanning Proton Arc Therapy (SPArc)
- 15 Jun 2025
In News:
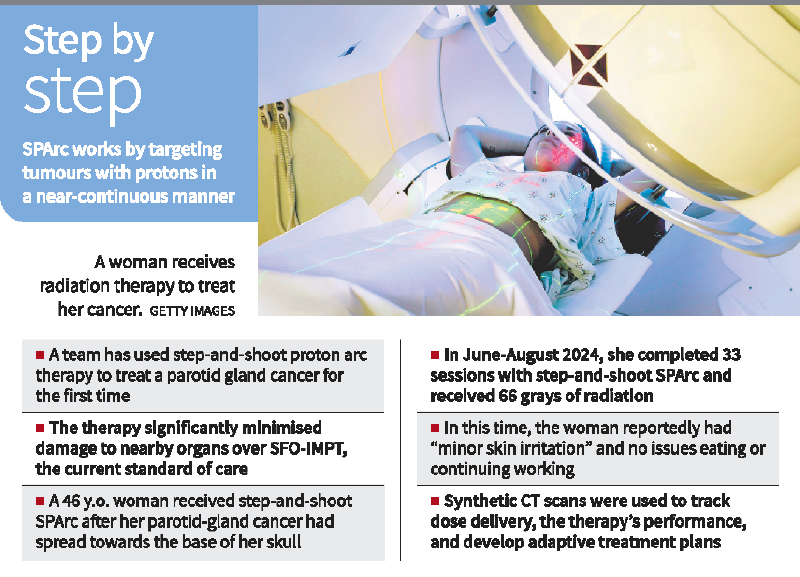
In a significant medical advancement, a team at the Corewell Health William Beaumont University Hospital in the U.S. has successfully administered Step-and-Shoot Spot-Scanning Proton Arc Therapy (SPArc) to treat adenoid cystic carcinoma—a cancer originating in the parotid gland. This marked the first-ever clinical application of this technology. The findings were published in the International Journal of Particle Therapy in June 2025.
What is SPArc Therapy?
SPArc (Spot-Scanning Proton Arc Therapy) is an advanced form of proton beam therapy where proton particles are delivered in a controlled arc across the tumor. It includes two primary modalities:
- Step-and-Shoot SPArc: Follows a pre-programmed dose delivery path.
- Dynamic SPArc: Simulated version where energy levels and targeting points are adjusted in real-time. (Still under regulatory review)
Comparison with Existing Techniques
The study compared three techniques:
- SFO-IMPT (Single-Field Optimized Intensity-Modulated Proton Therapy – current standard)
- Step-and-Shoot SPArc (clinical)
- Dynamic SPArc (simulated)
SPArc showed reduced radiation exposure to key organs when compared with SFO-IMPT:
- Brainstem: ↓ 10%
- Optical chiasm: ↓ 56%
- Oral cavity: ↓ 72%
- Spinal canal: ↓ 90%
Treatment Case Study
The first patient treated was a 46-year-old woman with a tumor extending from her parotid gland to the base of her skull. She underwent 33 sessions of SPArc therapy from June to August 2024, reporting only minor skin irritation and no disruptions to eating or daily functioning.
Process & Technology Used:
- Cone-Beam CT (CBCT) was used for real-time imaging before each session.
- A machine learning model converted CBCT to synthetic CT, allowing accurate dose tracking.
- As the patient lost weight, the dose plan was adjusted after two weeks to maintain precision.
- Nine beam angles spanning a 180º arc were used, delivering radiation at 20º intervals.
Each session lasted about 15–18 minutes, enabling nearly continuous dose delivery.
Working Mechanism
- The therapy operates by 'painting' the tumor in energy layers.
- Each energy level targets a specific tissue depth, ensuring maximum precision.
- The system scans dozens of spots in each layer before moving to the next one with increased penetration.
Advantages
- High precision in delivering radiation to deep and complex anatomical regions like the skull base.
- Limits collateral damage to vital organs.
- Effective in large or invasive tumours.
- Better quality of life during treatment (reduced side effects such as fatigue or swallowing issues).
Limitations & Concerns
- Geographical miss risk: Tiny tumors may be missed due to breathing motion or tumor shrinkage over time.
- Cost: High installation and operational costs, making it suitable for a limited patient base.
- Potential for overuse in non-indicated cases, leading to inequitable healthcare delivery.
- Dynamic SPArc still awaits regulatory clearance and integration into oncology systems.
Significance for India
SPArc therapy can be transformative for cancers in anatomically intricate regions and may serve as a benchmark for future precision cancer therapies. However, adoption in India requires cost-reduction, infrastructure investment, and regulatory frameworks.
Spartaeus karigiri
- 15 Jun 2025
In News:
A team of researchers has identified a new species of jumping spiders of the Spartaeinae subfamily in southern India, known for their intelligent hunting skills and web-invasion tactics.
Source: European Journal of Taxonomy (June 2025)
Key Facts:
- Species Name: Spartaeus karigiri
- Taxonomy:
- Family: Salticidae (Jumping Spiders)
- Subfamily: Spartaeinae
- Genus: Spartaeus
- Named After: Karigiri (Elephant Hill) in Devarayanadurga, Karnataka.
Significance:
- First recorded presence of Spartaeus and Sonoita genera in India.
- These genera were previously known only from Southeast Asia and Africa.
- Discovery expands India’s Spartaeinae spider fauna to 15 species across 10 genera.
Features of Spartaeus karigiri:
- Noted for intelligent hunting and web-invasion tactics.
- Possesses keen eyesight and mimics prey to deceive other spiders.
- Males were found in rocky crevices; females guarding egg clutches.
- Found in Karnataka and Villupuram, Tamil Nadu.
Other Findings:
- Sonoita cf. lightfooti, previously known from Africa, was also found in Karnataka.
- A taxonomic correction: Marpissa gangasagarensis (2005) is the same as Phaeacius fimbriatus (1900).
Conservation and Research Insight:
- India's arachnid diversity remains under-studied.
- New discoveries indicate rich but undocumented biodiversity in Indian terrains.
Rudrastra
- 15 Jun 2025
In News:
India's Rudrastra, a homegrown VTOL drone, has been successfully tested by the Indian Army, marking a significant advancement in battlefield technology. Developed by Solar Aerospace and Defence Limited, this drone can perform precision strikes across borders without endangering soldiers.
Overview:
- Rudrastra is a hybrid Vertical Take-Off and Landing (VTOL) combat drone developed indigenously by Solar Aerospace and Defence Limited (SDAL).
- Successfully tested by the Indian Army in June 2025.
Key Features:
- Hybrid VTOL Capability:
- Takes off like a helicopter and cruises like a fixed-wing aircraft.
- Increases versatility, maneuverability, and stealth.
- Combat Role:
- Equipped with smart anti-personnel warheads.
- Capable of deep-strike missions against targets like artillery guns or terrorist hideouts.
- Deployed as a “stand-off weapon”—engages targets from a safe distance.
- Performance Parameters:
- Range: Full range of 170 km.
- Strike Capability: Targets more than 50 km away.
- Flight Endurance: Nearly 90 minutes.
- Navigation: Autonomous return capability.
- Surveillance: Real-time video feed for reconnaissance.
- Payload: Capable of deploying airburst munitions—detonates low to the ground to cause area damage.
Strategic Importance:
- Reduces risk to soldiers in hostile territory.
- Enhances India's unmanned combat aerial vehicle (UCAV) arsenal.
Useful in anti-terror operations, border surveillance, and precision strikes.
