ISRO’s CARTOSAT-3

- 02 Apr 2025
In News:
Recently, a 7.7 magnitude earthquake struck Myanmar near the Sagaing-Mandalay border, causing severe damage in key cities such as Mandalay and Sagaing. The Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) used its advanced Earth observation satellite CARTOSAT-3 to assess the destruction via high-resolution post-disaster imagery.
CARTOSAT-3: An Overview
- Developer: ISRO
- Launched by: PSLV-C47
- Mission Type: Third-generation agile Earth observation satellite
- Successor to: IRS (Indian Remote Sensing) series
Key Specifications:
Feature Details
Resolution Panchromatic: 0.25 metres (sharpest civilian)
Orbit Altitude 509 km (Sun-synchronous orbit)
Inclination 97.5°
Weight 1,625 kg
Technologies Agile cameras, advanced onboard computers, high-speed data transmission
Commercial Use
- First commercial order executed by NewSpace India Ltd (NSIL), ISRO’s commercial arm.
Applications of CARTOSAT-3
- Disaster Management: Monitoring and assessing damage from earthquakes, floods, and landslides
- National Security & Strategic Operations: Surveillance and intelligence (used in 2016 LoC surgical strikes and 2015 Myanmar-Manipur ops)
- Urban & Rural Planning: Infrastructure development, land-use mapping, and road networks
- Environmental Monitoring: Coastal regulation and land-use changes
- Cartography and Remote Sensing: High-precision geospatial mapping and terrain analysis
Cartosat and Other ISRO Satellite Series
Satellite Series Focus Area
Cartosat-1 to 3 High-resolution Earth imaging for urban/rural planning
RISAT Radar-based imaging (all-weather surveillance)
Oceansat Oceanography, weather, and marine research
INSAT &Megha-Tropiques Atmospheric and climate monitoring
NITI NCAER States Economic Forum Portal

- 02 Apr 2025
In News:
The NITI NCAER States Economic Forum portal, jointly developed by NITI Aayog and the National Council of Applied Economic Research (NCAER), was launched on April 1, 2025, by the Union Finance Minister.
Key Highlights:
The portal serves as a comprehensive digital repository offering over 30 years (1990-91 to 2022-23) of state-wise data on social, economic, and fiscal parameters, promoting evidence-based policymaking and fiscal transparency.
Purpose and Significance
- Objective: To enable policymakers, researchers, and academics to access, compare, and analyze long-term trends in State finances and socio-economic indicators.
- Promotes data-driven governance, facilitates inter-State comparisons, and strengthens cooperative federalism.
- Addresses persistent demands for transparent, centralized, and accessible fiscal data, especially amid concerns of fiscal imbalance between Centre and States.
Core Features of the Portal
The portal is structured around four main components:
- State Reports:
- Covers all 28 Indian States.
- Summarizes macroeconomic and fiscal landscapes based on key indicators—demography, economic structure, social indicators, and fiscal metrics.
- Data Repository:
- Offers access to extensive datasets organized into five verticals:
- Demography
- Economic Structure
- Fiscal
- Health
- Education
- Offers access to extensive datasets organized into five verticals:
- Fiscal and Economic Dashboard:
- Interactive dashboards with graphical representations of vital statistics.
- Enables visualization of trends and download of datasets.
- Research and Commentary:Features expert analyses, research papers, and commentary on fiscal policies and State-level financial management.
Benefits and Policy Implications
- Enhances transparency and informed public debate.
- Supports benchmarking of States' performance against national averages and peer States.
- Aids in planning reforms, improving public finance management, and addressing regional disparities.
- A vital tool for academicians, policy analysts, and government officials working on State-level governance and development planning.
Arctic Geopolitics
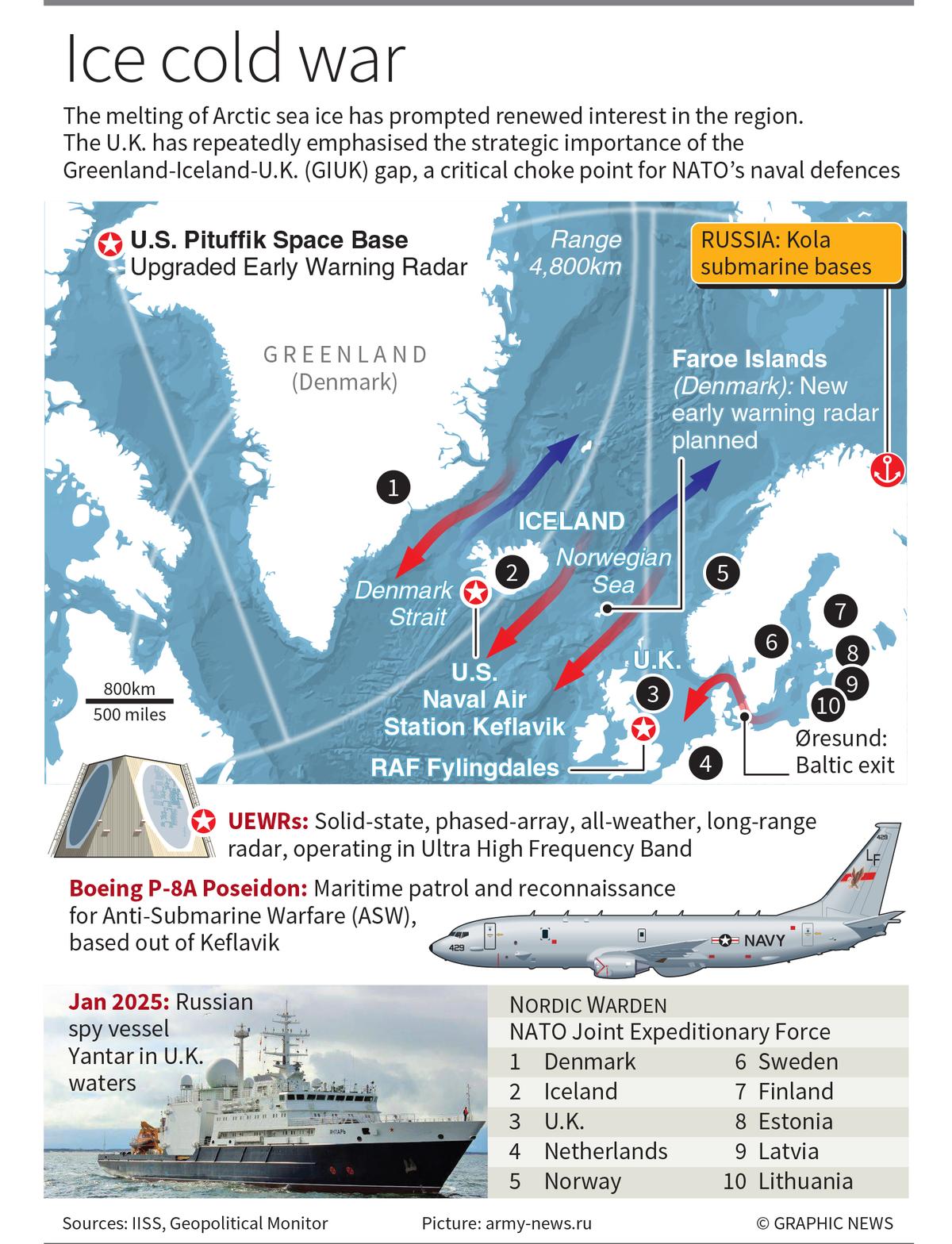
- 02 Apr 2025
In News:
The Arctic region, traditionally isolated due to its extreme climate and thick ice cover, is rapidly emerging as a global geopolitical hotspot. Accelerated melting of ice caps due to climate change has unlocked access to untapped resources and new shipping routes, intensifying competition among major powers.
Resource Wealth and Strategic Significance
- The Arctic holds an estimated 13% of the world’s undiscovered oil and 30% of untapped natural gas (USGS, 2009).
- Rich in rare earth elements, phosphates, and copper, particularly in areas like Greenland.
- Melting ice is opening access to valuable fishing grounds and enabling commercial navigation.
Emerging Shipping Routes
- Northeast Passage (Northern Sea Route): Along Russia’s Arctic coast, connecting Europe and Asia. Reduces distance by ~8,000 km compared to the Suez Canal.
- Northwest Passage: Through Canada’s Arctic Archipelago. Disputed between Canada (claims internal waters) and the U.S. (asserts international strait).
These routes offer significant economic and strategic advantages, including reduced dependency on traditional chokepoints like the Suez Canal.
Governance: The Arctic Council
The Arctic Council, established by the 1996 Ottawa Declaration, is the key intergovernmental forum for Arctic affairs.
Members (8 Arctic States):
- Canada, Denmark (via Greenland), Finland, Iceland, Norway, Russia, Sweden, and the United States
These countries:
- Control Arctic land territories
- Have sovereign rights over resources within their Exclusive Economic Zones (EEZs)
Permanent Participants:
- Six Indigenous groups representing Arctic communities.
Observers:
- Includes India, China, Japan, UK, among others.
- 13 countries, 13 intergovernmental, and 12 non-governmental organisations.
- All decisions require consensus of member states and consultation with Indigenous groups.
Legal Framework and Territorial Claims
- Governed primarily by UNCLOS (United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea).
- Allows Arctic states to extend claims beyond their 200-nautical-mile EEZ if they prove natural extension of the continental shelf.
- Russia, Canada, and Denmark have submitted overlapping claims to the Arctic seabed.
Unlike Antarctica, which is demilitarised under international treaties, the Arctic has no such binding legal framework, allowing military infrastructure and territorial claims.
Geopolitical Tensions in the Arctic
Russia’s Military Build-up:
- Largest fleet of Arctic icebreakers, including nuclear-powered vessels.
- Maintains Soviet-era Arctic military bases.
- Planted a flag on the Arctic seabed at the North Pole in 2007.
- In 2022, conducted naval exercises with China, signaling deepening strategic ties.
U.S. Interests:
- Renewed interest in Greenland, citing national security.
- Operates the Pituffik Air Base in Greenland.
- Dispute with Canada over Northwest Passage navigation rights.
NATO’s Arctic Response:
- All Arctic Council members except Russia are NATO allies.
- NATO has increased its Arctic presence post-Ukraine conflict.
- Strategic focus on GIUK (Greenland-Iceland-UK) Gap, a critical naval chokepoint for Russian submarines.
China’s Arctic Aspirations:
- Declared itself a "Near-Arctic State" in 2018.
- Investing in Arctic research and building its first nuclear-powered icebreaker.
- Interested in Russia’s Northeast Passage for trade under the proposed “Polar Silk Road”.
India and the Arctic
India, an observer in the Arctic Council, is closely monitoring developments. It has an Arctic Policy focusing on:
- Scientific research
- Climate and environmental protection
- International cooperation
Understanding "Vibe Coding"
- 02 Apr 2025
In News:
The concept of “vibe coding” gained traction after an OpenAI co-founder demonstrated how modern AI tools can translate intuitive prompts into working code—eliminating the need for in-depth technical expertise.
What is Vibe Coding?
Vibe coding is an intuition-driven, casual approach to programming where users describe what they want to build, and AI generates the code accordingly. Instead of relying on traditional programming logic, this method focuses on the user’s "feel" or intent—making it well-suited for low-stakes, creative, or personal projects.
How It Works:
- Users give natural language prompts describing their desired output (e.g., a simple game, utility, or web page).
- AI models like ChatGPT, Cursor, or Sonnet generate the corresponding code.
- The user then runs or copies the code without necessarily understanding its structure or logic.
Key Features of Vibe Coding:
- Prompt-first, logic-second: Relies on describing functionality rather than coding step-by-step.
- Low technical barrier: No deep knowledge of syntax, algorithms, or frameworks required.
- Trial-and-error approach: Users often accept AI-generated suggestions without critical review.
- Heavy dependence on AI: Debugging and improvements rely primarily on AI assistance.
- Limited focus on performance/security: Generated code may lack optimization or safeguards.
Why Vibe Coding Matters:
- Democratizes coding: Makes programming accessible to those without formal training.
- Fuels creativity: Encourages playful experimentation and rapid prototyping.
- Saves time for developers: Ideal for automating small, repetitive tasks.
- Inspires new learners: Attracts non-traditional audiences into tech through approachable tools.
- Useful for quick builds: Ideal for weekend hacks, personal utilities, or mock-ups.
Alzheimer’s Disease
- 02 Apr 2025
In News:
A new drug, Gantenerumab, has shown potential in slowing the progression of early-onset Alzheimer’s by significantly reducing the accumulation of amyloid plaques, a major indicator of the disease.
Alzheimer’s Disease Overview
- Alzheimer’s disease is a progressive neurodegenerative disorder, primarily impairing memory, thinking, and reasoning.
- It is the most common cause of dementia, accounting for 60–80% of all dementia cases globally.
- The disease is marked by the accumulation of amyloid beta plaques, which interfere with neuronal communication and trigger brain inflammation, eventually leading to cell death.
What is Early-Onset Alzheimer’s Disease (EOAD)?
- EOAD affects individuals below 65 years of age, comprising 5–10% of total Alzheimer’s cases.
- It progresses more rapidly and often strikes during a person’s prime working years.
- EOAD is strongly linked to genetic mutations in three genes: APP, PSEN1, and PSEN2, which result in overproduction of amyloid beta proteins.
Amyloid Plaques: The Disease Hallmark
- Amyloid plaques are clusters of misfolded amyloid beta proteins.
- These plaques disrupt brain function, contribute to inflammation, and kill neurons.
- They are central to the amyloid hypothesis, which posits that amyloid accumulation is a primary cause of Alzheimer’s progression.
Gantenerumab: A Potential Breakthrough
- Gantenerumab is a monoclonal antibody developed to target and eliminate amyloid beta plaques in the brain.
- It can cross the blood-brain barrier, a key obstacle in neurological drug delivery.
- The drug binds to amyloid plaques, signaling microglial cells (brain's immune cells) to break down and clear these plaques.
- This action may slow cognitive decline in early stages of the disease.
Recent Clinical Trial Findings
- A randomized, placebo-controlled trial involved 73 participants with rare inherited EOAD mutations.
- A subgroup of 22 asymptomatic participants showed reduced risk of symptom development from nearly 100% to 50% over eight years.
- Brain imaging confirmed a significant reduction in amyloid buildup.
Limitations and Risks
- Amyloid-related imaging abnormalities (ARIA) were observed in 53% of trial participants:
- Brain swelling in 30%
- Microbleeds in 27%
- Iron deposits in 6%
- No major hemorrhages or deaths occurred, but side effects necessitate regular monitoring.
- The cognitive benefits were modest, and the drug is costly to produce, raising affordability concerns.
- The study had a small sample size and focused only on a rare genetic subset of EOAD.
Significance and Future Prospects
- Gantenerumab supports the amyloid hypothesis, alongside other drugs like lecanemab and donanemab.
- Despite its discontinuation in 2022 due to limited efficacy, new findings may revive interest in its development.
- The trial highlights the critical importance of early diagnosis and biomarker testing for timely therapeutic intervention.
