Hygrocybe Pellucida
- 21 Oct 2025
In News:
In a significant biodiversity finding, Hygrocybe pellucida, a rare and recently identified fungus species, has been recorded for the first time in Telangana at the Kawal Tiger Reserve. The species, known for its vivid waxy appearance, was first described in Kerala in 2024 and belongs to the Hygrophoraceae family. This sighting expands its known range in southern India and highlights the ecological richness of the reserve.
About Hygrocybe pellucida
- Part of the Hygrocybe (waxcap) genus, containing ~350 species globally
- Distinguished by bright, translucent, waxy fruit bodies
- Prefers nutrient-poor, moss-rich forest floors and unimproved grasslands
- Indicator of undisturbed and pristine microhabitats
- Newly documented fungus species in India, reinforcing fungal diversity in tropical ecosystems
Ecological Significance
The discovery underscores the value of fungi as bioindicators of healthy ecosystems. It reflects the presence of intact microhabitats—moist, shaded forest floors with moss and low human interference—and complements ongoing biodiversity documentation in the region. Researchers have identified over 80 fungal species in Kawal, including several first records for Telangana, such as Marasmiushaematocephalus and Dacryopinaxspathularia.
Kawal Tiger Reserve: Key Facts
- Location: Telangana, along the Godavari River in the Deccan Peninsula–Central Highlands
- Declared Tiger Reserve: 2012 (originally a Wildlife Sanctuary)
- Landscape Linkages: Connects to Tadoba–Andhari (Maharashtra) and Indravati (Chhattisgarh) Tiger Reserves
- Topography: Part of the Sahyadri mountain ranges
- Rivers: Catchment area for Godavari and Kadam
- Vegetation:Southern Tropical Dry Deciduous Forests
- Flora: Teak, bamboo, Anogeissuslatifolia, Mitragyna parviflora, etc.
- Fauna: Tiger, leopard, sambar, blackbuck, nilgai, chinkara, chousingha, spotted deer
Conservation Perspective
While tiger conservation often takes center stage, this discovery emphasizes that forest floor biodiversity —including fungi and microfauna—plays a critical ecological role and requires equal attention. The finding strengthens the case for protecting microhabitats and maintaining minimal human disturbance in core forest areas.
We Rise Initiative

- 21 Oct 2025
In News:
India has launched a major initiative to strengthen women-led entrepreneurship and boost their participation in global trade. NITI Aayog’s Women Entrepreneurship Platform (WEP), in partnership with DP World, has introduced the ‘We Rise’ – Women Entrepreneurs Reimagining Inclusive and Sustainable Enterprisesprogramme. This initiative aligns with the Government of India’s vision of women-led development and is a part of WEP’s Award to Reward (ATR) framework.
Key Objectives and Features
- Purpose: To support women entrepreneurs in scaling their businesses globally
- Focus Areas:
- Trade facilitation
- Mentorship and business capacity-building
- Strategic partnerships and global market access
- Target Group: High-potential women-led MSMEs, particularly product-centric enterprises
- Coverage:100 women entrepreneurs will be selected for export-readiness programmes
- Global Exposure: Participants will showcase products at Bharat Mart in Dubai (Jebel Ali Free Zone), gaining access to international B2B and B2C markets
DP World will leverage its global supply chain expertise and logistics network to build export capabilities for women-led businesses, ensuring they meet international trade standards.
Strategic Significance
This initiative strengthens India’s women entrepreneurship ecosystem by providing:
- Access to finance and global markets
- Training, skill development, and compliance support
- Mentorship, networking, and business development services
It reinforces the importance of public-private collaboration in accelerating women's economic empowerment and building a more inclusive trade ecosystem.
Women Entrepreneurship Platform (WEP) Overview
- Established: 2018 by NITI Aayog; transitioned to PPP mode in 2022
- Engagement: Over 90,000 women entrepreneurs and 47 partners
- Mandate: Acts as a national aggregator and enabler to strengthen women-led businesses
- Core Functions: Addresses six ecosystem needs —
- Access to finance
- Market linkages
- Training & skilling
- Mentorship & networking
- Legal & compliance assistance
- Business development services
ATR Initiative
Launched in 2023, the Award to Reward (ATR) model institutionalises partnerships by celebrating women entrepreneurs and fostering scalable, outcome-driven collaborations.
Nafithromycin

- 21 Oct 2025
In News:
India has achieved a major scientific milestone with the development of Nafithromycin, the country's first indigenously conceptualized, developed, and clinically validated antibiotic. Announced by the Union Science and Technology Minister, this breakthrough reflects India's growing self-reliance in the biotechnology and pharmaceutical sector and its commitment to addressing the global challenge of Antimicrobial Resistance (AMR).
About Nafithromycin
- Developed with support from: Biotechnology Industry Research Assistance Council (BIRAC)
- Trade Name:Miqnaf
- Target Use: Community-Acquired Bacterial Pneumonia (CABP)
- Key Beneficiaries: Cancer patients and individuals with poorly controlled diabetes
- Spectrum & Novelty: Effective against both typical and atypical respiratory pathogens; marks the first new antibiotic in its class globally in over 30 years
Nafithromycin is particularly relevant in India where respiratory infections remain a key public-health concern. The antibiotic is designed to combat drug-resistant respiratory infections, providing a potent solution amid rising antimicrobial resistance.
Why It Matters: Tackling AMR
Antimicrobial Resistance (AMR) occurs when microbes such as bacteria, viruses, fungi, or parasites develop the ability to defeat drugs designed to kill them. As a result, common infections become harder to treat, increasing the risk of severe illness, prolonged hospitalization, disability, and death. While AMR is a natural evolutionary process, misuse and overuse of antimicrobials significantly accelerate it. Nafithromycin’s development represents a strategic step in strengthening India's response to AMR.
Related Scientific Milestones Announced
The Minister also highlighted other key achievements underscoring India’s expanding biotech capabilities:
- Indigenous gene-therapy trial success for Hemophilia at Christian Medical College, Vellore — achieving 60–70% correction with zero bleeding episodes
- Human genome sequencing initiative: Over 10,000 genomes already sequenced, target set to reach 1 million
- Deployment of AI-based hybrid mobile clinics to improve healthcare access in rural and remote regions
These advancements reflect India’s push toward a self-sustainable innovation ecosystem, combining science, technology, and healthcare delivery to support the vision of a developed and technology-driven nation.
Zombie Deer Disease
- 21 Oct 2025
In News:
Florida has recently confirmed new cases of Chronic Wasting Disease (CWD), commonly referred to as “Zombie Deer Disease,” heightening concerns among wildlife authorities in the United States. This marks the second confirmed case in wild deer in the state since the first detection in June 2023, triggering an emergency response and surveillance measures in affected regions.
What is Chronic Wasting Disease (CWD)?
CWD is a progressive, fatal neurodegenerative disease affecting deer, elk, moose, and reindeer. It damages the central nervous system, causing:
- Severe weight loss
- Disorientation and loss of awareness
- Abnormal behavior, including reduced fear of humans
- Excessive salivation, increased drinking and urination
- Progressive debilitation and death
The incubation period ranges from 18–24 months, during which animals may appear healthy before showing symptoms.
Cause
- CWD is caused by prions — infectious misfolded proteins that trigger abnormal protein folding in the brain.
- Unlike bacteria or viruses, prions contain no DNA or RNA.
- Prions create spongy holes in brain tissue, leading to neurological failure.
Transmission
CWD spreads through:
- Direct contact among animals
- Contaminated saliva, urine, blood, and feces
- Environmental persistence — prions survive for years in soil, plants, and water
- Movement of infected animals
- Scavengers dispersing prion material
- Use of natural deer urine lures by hunters
Prions are extremely resilient, making eradication difficult.
Threat to Humans
- No confirmed human cases have been reported so far.
- However, health experts advise caution due to similarities with Bovine Spongiform Encephalopathy (mad cow disease), a prion disorder linked to human deaths in the past.
- There is no cure or vaccine for CWD.
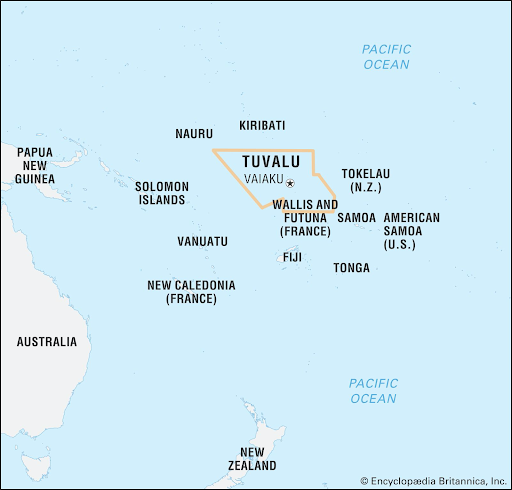
Tuvalu Island
- 21 Oct 2025
In News:
Tuvalu has formally become the 90th State Member of the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN), marking a major step in strengthening its global environmental engagement. This development aligns with the nation’s growing efforts to protect its fragile ecosystems and advocate for climate-vulnerable island states.
About Tuvalu
- Located in the west-central Pacific Ocean between Australia and Hawaii, Tuvalu (formerly the Ellice Islands) comprises nine low-lying atolls and coral islands spanning just 26 sq km—making it the fourth-smallest country in the world.
- With no point higher than 4.5 m above sea level, the country faces existential threats from sea-level rise, coastal erosion and climate change.
- It has an Exclusive Economic Zone (EEZ) of around 900,000 sq km, rich in marine biodiversity, coral reefs, fisheries and migratory seabirds.
- Tuvalu operates as a parliamentary democracy under a constitutional monarchy within the Commonwealth, recognizing King Charles III as head of state. Funafuti is the capital, and Tuvaluan and English are widely spoken. Its economy relies on subsistence activities, remittances, limited copra production, sale of postage stamps, and fisheries licensing revenues.
Significance of IUCN Membership
By joining IUCN, Tuvalu gains access to a global network of conservation experts, funding avenues and policy platforms. This membership strengthens its capacity to pursue:
- Climate change adaptation and resilience strategies
- Sustainable fisheries and marine resource management
- Community-driven conservation initiatives
- Partnerships with bodies such as the Green Climate Fund and Global Environment Facility
The move comes at a time when Pacific Island nations are pushing for stronger global action on climate change, adaptation financing and protection of ocean ecosystems.
Why It Matters
Tuvalu’s participation in IUCN brings heightened international focus on the plight of small island developing states (SIDS) facing climate-induced challenges. It enhances the country's voice in shaping global environmental governance and reinforces the need to safeguard vulnerable ecosystems and cultures deeply connected to the ocean.
