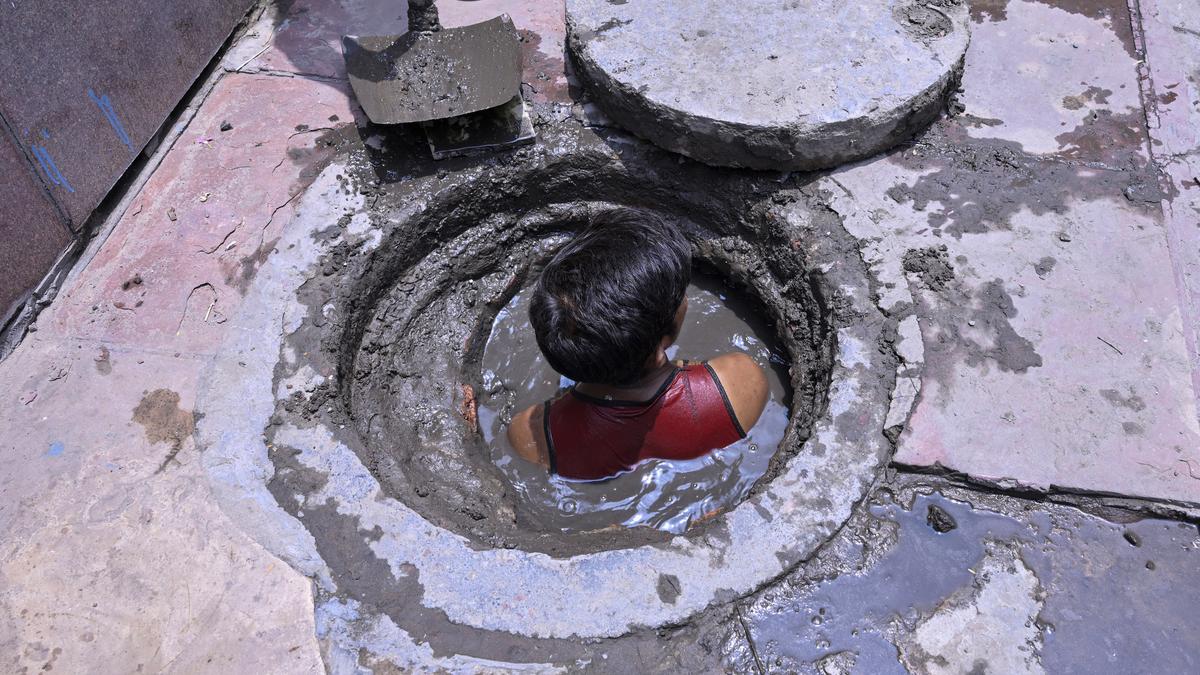
Manual Scavenging

- 24 Jul 2025
In News:
A recent social audit conducted by the Ministry of Social Justice and Empowerment has exposed alarming lapses in the safety and legal safeguards meant to protect sanitation workers. The study, which examined 54 sewer-related deaths across 17 districts in eight States and Union Territories during 2022 and 2023, found that over 90% of the workers who died had no access to basic safety gear or mechanised equipment. Despite legal bans and policy interventions, manual scavenging and hazardous sewer cleaning continue, often resulting in fatalities, primarily among marginalized communities.
What is Manual Scavenging?
Manual scavenging involves the manual handling of human excreta from dry latrines, open drains, sewers, and septic tanks. Although officially prohibited under the 2013 Act, the practice continues under different forms, particularly through hazardous sewer and septic tank cleaning.
Key Findings from the Social Audit (2022–2023)
- 150 deaths from hazardous cleaning were recorded nationally during the two-year period.
- In 49 of the 54 deaths audited, no safety equipment was provided.
- In only five cases, the deceased had gloves; just one worker had both gloves and gumboots.
- No mechanised equipment was available in 47 cases; training was provided in only one instance.
- Informed consent was missing in 27 cases; in the 18 cases where consent was obtained, no counselling on risks was given.
- Most workers were individually contracted and not hired through government channels, evading institutional accountability.
- Post-death awareness drives were conducted in only seven locations, and even these were only partially executed.
Constitutional and Legal Safeguards
Constitutional Provisions:
- Article 21: Ensures the right to life with dignity, including safe working conditions.
- Article 23: Prohibits forced labour, applicable when workers are compelled into hazardous tasks.
- Article 42: Calls for humane working conditions and maternity relief.
Legal Framework:
- Prohibition of Employment as Manual Scavengers and their Rehabilitation Act, 2013:
- Bans manual scavenging.
- Mandates rehabilitation of identified workers.
- Supreme Court Judgment (2014 – Safai Karamchari Andolan v. Union of India):
- Ordered ?10 lakh compensation for each sewer/septic tank death.
- Held the State responsible for implementation failures.
Government Initiatives
NAMASTE Scheme (2023)
The National Action Plan for Mechanised Sanitation Ecosystem (NAMASTE) aims to eliminate hazardous cleaning practices.
- 84,902 workers have been identified across 36 States/UTs.
- Around 50% of them have been provided with PPE kits.
- In Odisha, 100% of identified workers (1,295) have received PPE kits, supported by the Garima Scheme.
- ?20 crore in capital subsidies distributed to 707 sanitation workers.
- 1,000 awareness workshops conducted.
- The scheme has also identified 37,800 waste pickers for support.
Other Key Initiatives:
- Swachh Bharat Abhiyan: Aims to reduce dependence on manual scavenging through sanitation infrastructure.
- Rashtriya Garima Abhiyaan: Campaign to eliminate manual scavenging and ensure rehabilitation.
- Bandicoot Robot: India’s first manhole-cleaning robot, developed in Kerala, which became the first fully robotised state for manhole cleaning in 2023.
Financial Inclusion Index (FI-Index)
- 24 Jul 2025
In News:
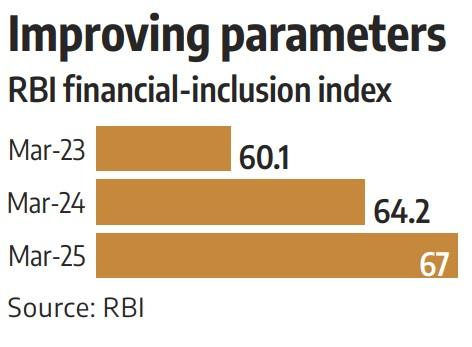
The Reserve Bank of India’s Financial Inclusion Index (FI-Index) saw a 4.3% rise in FY2024-25, climbing from 64.2 in March 2024 to 67 in March 2025. This growth signals India’s ongoing success in expanding access to financial services, particularly in underserved regions, and enhancing the depth and quality of financial inclusion.
Understanding Financial Inclusion
- Financial inclusion refers to ensuring that individuals and businesses have accessible, affordable, and appropriate financial services such as banking, insurance, pensions, and investments. These services should be delivered responsibly and sustainably, supporting long-term economic empowerment.
What is the Financial Inclusion Index (FI-Index)?
- Developed by the RBI, the FI-Index offers a comprehensive measure of financial inclusion in India. It was formulated in consultation with the government and relevant financial sector regulators and captures progress across diverse financial domains—including banking, insurance, postal services, investments, and pensions.
- The Index is expressed as a single score between 0 and 100, where 0 denotes complete exclusion and 100 indicates full financial inclusion.
Components of the FI-Index
- Access (35% weight): Availability of financial services to the public.
- Usage (45% weight): Frequency and extent of usage of financial services.
- Quality (20% weight): Incorporates factors such as financial literacy, consumer protection, and equality in service delivery.
Key Insights from FY2024–25
- The FI-Index rose to 67 in March 2025, indicating broader and deeper financial engagement.
- All three sub-indices—access, usage, and quality—showed improvement.
- Notably, the rise was primarily driven by enhanced usage and service quality, reflecting the success of financial literacy campaigns and improved consumer trust in financial systems.
Importance of Financial Inclusion
Financial inclusion is not just an economic tool—it is a developmental imperative. It:
- Fuels entrepreneurship and employment generation.
- Advances gender empowerment, especially among women-led households.
- Helps in poverty alleviation and the resilience of vulnerable groups against financial and climate-related shocks.
- Supports at least seven of the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), including reducing inequalities and promoting inclusive economic growth.
Major Government Initiatives Driving Financial Inclusion
India's focused efforts have resulted in widespread access to formal financial services:
- Pradhan Mantri Jan Dhan Yojana (PMJDY): Over 54.58 crore bank accounts opened; deposits crossed ?2.46 lakh crore by January 2025.
- Atal Pension Yojana (APY): Enrolments surged to 7.33 crore, with 89.95 lakh new subscribers in FY25 alone.
- Pradhan Mantri Jeevan Jyoti Bima Yojana (PMJJBY): Covered 22.52 crore people, disbursing over ?17,600 crore for 8.8 lakh claims.
- Pradhan Mantri Suraksha Bima Yojana (PMSBY): Provided insurance to 49.12 crore individuals, settling claims worth ?2,994.75 crore.
- Pradhan Mantri Mudra Yojana (PMMY): Sanctioned loans worth ?32.36 lakh crore across 51.41 crore accounts; 68% to women and 50% to SC/ST/OBC beneficiaries.
- Stand-Up India Scheme: Loans worth ?53,609 crore sanctioned to 2.36 lakh entrepreneurs, promoting SC/ST and women entrepreneurship.
MiG-21 Fighter Jets
- 24 Jul 2025
In News:
- The Indian Air Force (IAF) is set to retire its final two squadrons of the iconic MiG-21 Bison fighter jets in September 2025, marking the end of an era that spanned over six decades.
- First inducted in 1963, the MiG-21 played a pivotal role in shaping India's aerial combat capabilities and remains a symbol of India's early steps toward defence self-reliance.
MiG-21: An Overview
- Origin: Designed by the Mikoyan-Gurevich Design Bureau of the Soviet Union in the 1950s.
- Type: Single-engine, supersonic jet fighter.
- Speed: Capable of speeds over Mach 2.0, making it one of the fastest jets of its time.
- Induction in India: Entered IAF service in 1963; licensed production began in the 1960s by Hindustan Aeronautics Limited (HAL).
- Significance: India’s first combat aircraft of non-Western origin and a key asset for air superiority during the Cold War and beyond.
Operational Legacy
The MiG-21 became the backbone of the IAF from the 1970s until the early 2000s, remaining in service even after the induction of more advanced aircraft like the Su-30MKI.
Wars and Combat Contributions
- 1965 & 1971 Indo-Pak Wars: Played a crucial role in establishing air superiority.
- During the 1971 war, MiG-21s conducted multiple successful bombing missions, including attacks on Pakistani airbases, contributing significantly to India’s decisive victory and the creation of Bangladesh.
- The aircraft famously outmatched Pakistan’s F-104 Starfighters in dogfights.
Strengths
- All-weather operations capability.
- Versatility in roles: air-to-air combat, ground attacks, and reconnaissance.
- Compatibility with a variety of air-to-ground and air-to-air weapons.
Limitations and Controversy
Despite its legendary status, the MiG-21's later years were marked by increasing technical limitations and a poor safety record:
- Nicknamed "Flying Coffin" due to over 400 crashes since the 1970s.
- Resulted in the deaths of over 200 pilots and 50 civilians.
- Upgraded variants like the MiG-21 Bison included radar and avionics improvements but could not overcome structural and safety limitations.
- Retirement was delayed multiple times due to shortages in the IAF’s squadron strength.
Retirement and Replacement
- The last two MiG-21 Bison squadrons will be phased out by September 2025.
- India had produced over 600 MiG-21s under license.
- Replacement underway with indigenously developed Tejas Mk-1A fighter jets, part of India’s push for self-reliance under Atmanirbhar Bharat.
- The IAF currently operates 29 squadrons—well below the sanctioned strength of 42.5 squadrons.
Fungus-Resistant Pineapple
- 24 Jul 2025
In News:
- Pineapple (Ananas comosus L. Merr.), the most economically significant fruit of the Bromeliaceae family, plays a crucial role in nutrition and agriculture across tropical regions.
- In India, pineapple cultivation contributes significantly to rural livelihoods, particularly in northeastern and southern states. However, the productivity of this high-value fruit is severely impacted by Fusariosis, a destructive fungal disease caused by Fusarium moniliforme.
- A recent breakthrough by Indian scientists promises a potential game-changer in combating this challenge using indigenous genetic innovation.
Fusariosis
- Fusariosis is a devastating fungal infection that warps the stem, blackens the leaves, and rots the fruit internally, leading to heavy crop losses.
- Traditional breeding methods have struggled to provide effective resistance due to the rapid evolution of fungal pathogens. For farmers, this translates into unreliable harvests and financial instability.
The Biotechnological Solution: AcSERK3 Gene Overexpression
Researchers from the Bose Institute, an autonomous body under the Department of Science and Technology (DST), have successfully identified and overexpressed a gene in pineapple that significantly enhances resistance to Fusariosis.
- The gene, AcSERK3 (Somatic Embryogenesis Receptor Kinase 3), is part of the pineapple’s natural genome.
- It is known to regulate somatic embryogenesis and strengthen plant responses to biotic and abiotic stress.
- By genetically overexpressing this gene in pineapple plants, the researchers were able to trigger enhanced internal defence mechanisms.
- The transgenic lines exhibited increased production of stress-associated metabolites and antioxidant enzyme activity, enabling them to survive fungal attacks that severely damaged wild-type plants.
This is the first documented instance of overexpression of an indigenous pineapple gene to impart fungal disease tolerance while simultaneously improving regenerative capacity.
Significance of the Research
- The study, published in In Vitro Cellular & Developmental Biology – Plants, lays the foundation for developing multi-fungal tolerant pineapple varieties.
- These genetically enhanced lines are not dependent on foreign genes, thereby addressing biosafety concerns.
- Field trials, if successful, could lead to the commercial deployment of these varieties using conventional propagation methods like slips and suckers.
- This offers a sustainable, farmer-friendly solution, especially for smallholder pineapple growers in India.
Pineapple Cultivation in India: Key Facts
- Climatic Conditions: Grows well in 15–30°C temperature range and 600–2500 mm annual rainfall (optimum: 1000–1500 mm).
- Soil: Requires well-drained soils; intolerant to waterlogging.
- Tolerant to Drought: Possesses water-storing tissues making it suitable for rainfed cultivation.
- Cultivation Pattern: Can be grown as a monocrop or intercropped with coconut.
- Major Producing States: Assam, Meghalaya, Tripura, Manipur, West Bengal, Kerala, Karnataka, and Goa.
- Global Producers: Thailand, Philippines, Brazil, China, Nigeria, Mexico, Indonesia, Colombia, and the USA.
Stablecoins
- 24 Jul 2025
In News:
In the evolving landscape of digital finance, stablecoins have emerged as a promising innovation. Unlike volatile cryptocurrencies such as Bitcoin, stablecoins are designed to maintain a consistent value by pegging their worth to stable assets like fiat currencies or commodities. Recent legislative and technological developments, particularly in the United States, indicate growing global interest in integrating stablecoins into everyday financial systems.
What are Stablecoins?
Stablecoins are a type of cryptocurrency whose value is anchored to an external asset, commonly a fiat currency like the US dollar, or commodities such as gold. This pegging mechanism aims to minimize price volatility, making them more suitable for routine transactions.
There are three primary categories of stablecoins:
- Fiat-collateralized: Backed by actual reserves of fiat currency.
- Crypto-collateralized: Secured using other cryptocurrencies as collateral.
- Algorithmic (non-collateralized): Use smart contracts to automatically manage the coin’s supply based on demand.
Although designed for stability, these digital assets still carry some risks, especially if reserve management is opaque or unregulated.
Technological Foundation
Stablecoins, like other cryptocurrencies, are built on blockchain technology—a decentralized, distributed ledger system that records transactions in a secure, transparent manner. Blockchains operate through consensus mechanisms without needing a central authority, making stablecoins capable of direct peer-to-peer transactions without traditional banking intermediaries.
Recent Policy Development: The GENIUS Act
In a landmark move, the GENIUS Act (Generating Emergency National Income Using Stablecoins) was recently signed into law by the US President. It provides a regulatory framework specifically for US dollar-pegged stablecoins like USDC (by Circle) and USDT (by Tether). This legislative support is expected to accelerate the mainstream adoption of stablecoins, especially in cross-border payments.
Applications of Stablecoins
- Remittances and Cross-Border Transfers:
- Traditional remittance services like Western Union or MoneyGram charge high fees and delays.
- Stablecoins offer instant, low-cost transactions, benefiting especially those in countries facing hyperinflation or capital controls.
- Companies can also pay overseas workers in stablecoins, bypassing complex financial systems and exchange rate risks.
- E-Commerce and Retail:
- Online merchants can reduce reliance on credit card networks, which collected over $187 billion in fees in the US in 2023 alone.
- Stablecoins eliminate intermediaries, reducing transaction fees and improving profit margins.
- Enterprise and Supply Chain Payments:
- Businesses can benefit from faster and cheaper cross-border payments.
- Chinese conglomerate JD.com suggests stablecoins could cut transaction costs by 90% and reduce settlement time from days to seconds.
- Custom Stablecoins by Corporations:
- Giants like Amazon, Walmart, and JD.com are exploring the issuance of proprietary stablecoins to support in-house payment systems, customer loyalty programs, and even financial services.
- This could potentially shift customer deposits away from traditional banks, affecting their lending capacity.
- Integration with Artificial Intelligence: Emerging AI agents may autonomously execute and manage stablecoin-based transactions, particularly in business-to-business ecosystems, improving operational efficiency.
Opportunities and Challenges
Advantages:
- Faster, cheaper international payments
- Improved financial inclusion
- Enhanced efficiency in e-commerce and global business operations
Concerns:
- Regulatory uncertainty, especially across jurisdictions
- Security risks, including fraud and hacking
- Potential disruption to traditional banking systems
