UNESCO’s World Network of Biosphere Reserves
- 02 Oct 2025
In News:
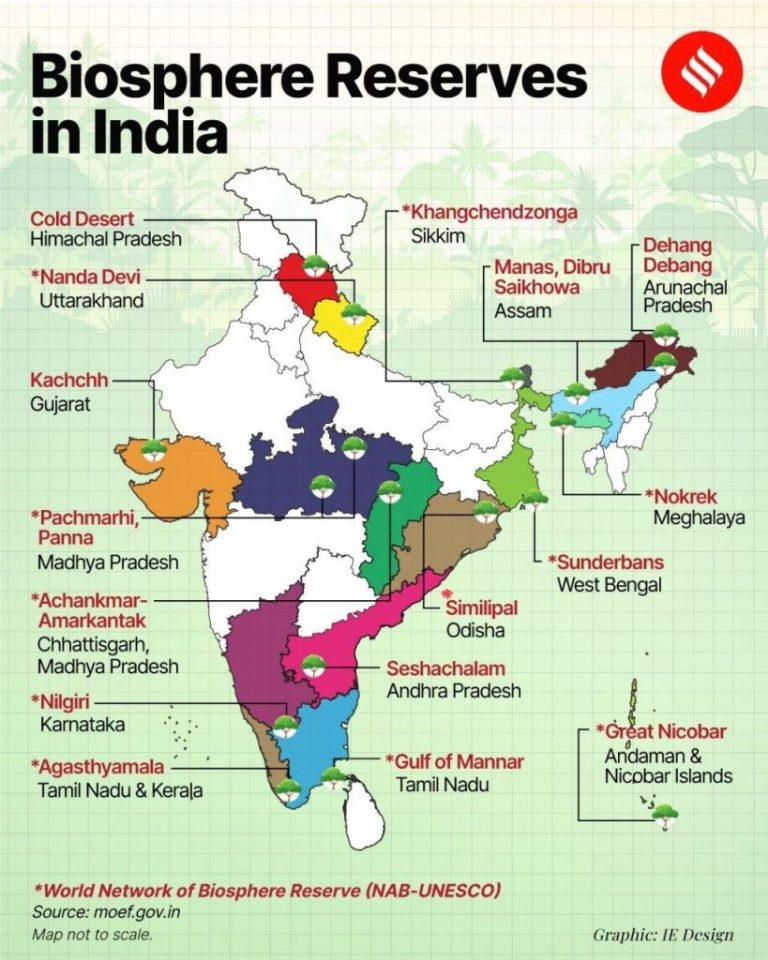
UNESCO has included India’s Cold Desert Biosphere Reserve, located in Lahaul-Spiti district of Himachal Pradesh, in its World Network of Biosphere Reserves (WNBR) during the 37th ICC–MAB session (2025). This recognition makes it India’s first high-altitude cold desert biosphere reserve to join the global network, highlighting the country’s commitment to sustainable mountain ecosystem management.
About the Cold Desert Biosphere Reserve
- Established: 2009
- Location: Western Himalayas, Trans-Himalayan region of Himachal Pradesh
- Area: 7,770 sq. km
- Altitude: 3,300–6,600 m
- Constituent Areas:Pin Valley National Park, Kibber Wildlife Sanctuary, Chandratal Wetland, and adjoining regions.
- Terrain: Windswept plateaus, glacial valleys, alpine lakes, and high-altitude deserts.
- Zonation:
- Core Zone – 2,665 sq. km
- Buffer Zone – 3,977 sq. km
- Transition Zone – 1,128 sq. km
Biodiversity and Communities
- Flora: 655 herbs, 41 shrubs, and 17 tree species, including 14 endemic and 47 medicinal plants vital for the Sowa Rigpa (Amchi) traditional healing system.
- Fauna: 17 mammal and 119 bird species, including Snow Leopard, Tibetan Antelope, Himalayan Wolf, and Himalayan Ibex.
- Communities: Around 12,000 residents dependent on pastoralism, yak/goat herding, and high-altitude farming (barley and peas).
