Special and Differential Treatment (SDT)

- 02 Oct 2025
In News:
China has announced that it will continue to be classified as a developing country within the World Trade Organization (WTO) but will no longer seek Special and Differential Treatment (S&DT) in future negotiations.
About Special and Differential Treatment (S&DT):
- S&DT grants developing and least-developed countries (LDCs) flexibilities in implementing WTO obligations, including longer deadlines, preferential market access, safeguard measures, and technical assistance.
- Introduced under GATT in the 1960s and formalized in WTO agreements (1995) and the Doha Development Agenda (2001).
- LDCs receive additional automatic benefits; other countries self-declare their status, subject to challenge by WTO members.
Significance of China’s Decision:
- China, historically a major beneficiary of S&DT, will forego such benefits while retaining its developing country status.
- The move signals support for multilateral trade and contributes to WTO reform, addressing concerns raised by the United States and others over selective access to S&DT.
- It highlights the tension between economic capabilities and self-declared developing status, especially among major economies.
Implications:
- Encourages balanced WTO negotiations and strengthens the global trading system.
- Marks a step towards aligning development considerations with global economic realities without relinquishing China’s role in the Global South.
India Develops its first indigenous Mechanical Thrombectomy Device for Stroke Treatment
- 02 Jun 2025
In News:
In a significant milestone for India’s medical technology sector, the Technology Development Board (TDB) under the Department of Science and Technology (DST) has extended support for the development of the country’s first indigenously manufactured mechanical thrombectomy device for the treatment of acute ischemic stroke.
What is a Mechanical Thrombectomy Device?
The device is a minimally invasive medical tool designed to treat acute ischemic stroke, which occurs due to a blockage in a large blood vessel in the brain. Unlike conventional thrombolytic drugs that dissolve clots chemically, this device physically extracts the clot, thereby restoring blood flow swiftly and reducing the risk of severe brain damage or paralysis.
Development and Manufacturing
This pathbreaking innovation was developed by S3V Vascular Technologies Ltd, based in Mysuru, with financial backing from the TDB. The manufacturing takes place at an advanced, high-precision production facility within the Medical Devices Park in Oragadam, Tamil Nadu.
Key Features and Technological Highlights
- Indigenous Design: S3V is the first Indian company to conceptualize and produce stroke-intervention tools such as microcatheters, aspiration catheters, guidewires, and stent retrievers.
- R&D and Patents: The company has filed multiple patents, particularly for innovations in clot retriever head design and advanced catheter structures.
- Training and Capacity Building: A simulator-based training program has been initiated to train young medical professionals, with a focus on outreach in Tier-II cities.
- Global Compliance: The device aims to meet CE and USFDA standards, paving the way for international exports and aligning with global quality benchmarks.
Significance for India
- Reduces Import Dependency: The device addresses India’s reliance on expensive, imported stroke-care equipment.
- Cost-Effective Healthcare: By making stroke treatment more affordable, it enhances access to quality care for economically weaker sections.
- Supports Public Health Initiatives: It is expected to be integrated into government schemes like Ayushman Bharat, strengthening the country’s universal healthcare mission.
- Boosts MedTech Ecosystem: This innovation is a major stride in positioning India as a global player in the high-end medical devices sector.
Cashless Treatment of Road Accident Victims Scheme, 2025
- 09 May 2025
In News:
The Government of India has recently introduced the Cashless Treatment of Road Accident Victims Scheme, 2025, aimed at providing immediate, hassle-free medical care to individuals injured in road accidents. This initiative reflects the government's commitment to strengthening the emergency healthcare response system and reducing fatalities due to delays in treatment.
Key Features of the Scheme:
- Universal Eligibility: Any person injured in a road accident involving a motor vehicle on a public road anywhere in India is eligible for cashless treatment.
- Financial Coverage: The scheme offers a maximum coverage of ?1.5 lakh per accident victim, valid for up to seven days from the date of the accident.
- Designated Hospital Network: Victims can avail full cashless treatment only at empanelled hospitals under the scheme. In non-designated hospitals, treatment will be restricted to initial stabilisation, as per official guidelines.
Implementation Mechanism:
- National Health Authority (NHA): The NHA is the central coordinating body for scheme implementation. It will work closely with state health agencies, police, and hospital networks.
- State-Level Execution: In each state and Union Territory, the State Road Safety Council serves as the nodal agency, responsible for:
- Coordinating the onboarding of designated hospitals.
- Managing treatment procedures and claim settlements.
- Facilitating real-time communication through a dedicated online portal.
- Monitoring Framework: A 17-member Steering Committee, chaired by the Secretary, Ministry of Road Transport and Highways, has been constituted to oversee and monitor implementation and address policy-level concerns.
Significance and Impact:
- Addresses Financial Barriers: By offering cashless access to emergency care, the scheme reduces the out-of-pocket burden on accident victims and their families.
- Improves Emergency Response: Ensures timely medical intervention, a critical factor in saving lives during the "golden hour" after a road accident.
- Promotes Inter-Agency Coordination: Brings together multiple stakeholders—healthcare, law enforcement, and road safety agencies—on a unified digital platform for better service delivery.
- Nationwide Coverage: Marks a paradigm shift in accident response policy, aiming to make quality trauma care accessible across both urban and rural India.
West Nile Fever

- 08 May 2024
Why is it in the News?
The Kerala health department has issued an alert after cases of West Nile fever were reported in Malappuram, Kozhikode and Thrissur districts.
What is West Nile Fever?
- West Nile Fever is a viral infection transmitted primarily by mosquitoes, caused by the West Nile virus (WNV).
- The virus is commonly found in Africa, Europe, the Middle East, North America, and West Asia.
- Most people infected with the West Nile virus don’t experience any symptoms.
- About 20% of people who become infected with WNV will develop West Nile fever.
- However, for some, particularly the elderly or those with weakened immune systems, symptoms can range from mild flu-like symptoms such as fever, headache, body aches, fatigue etc.
- Transmission occurs when mosquitoes become infected after feeding on infected birds, and then bite humans.
Why is it named West Nile Fever?
- West Nile Virus was first isolated in a woman in the West Nile district of Uganda in 1937.
- According to the World Health Organisation (WHO), It was identified in birds in the Nile Delta region in 1953,
Symptoms:
- West Nile Fever can manifest with a range of symptoms, although the majority of individuals infected with the West Nile virus (WNV) remain asymptomatic.
- For those who do exhibit symptoms, they typically appear within 2 to 14 days after being bitten by an infected mosquito.
- Common symptoms include fever, headache, body aches, and fatigue, which are similar to those of the flu.
- Additionally, individuals may experience nausea, vomiting, diarrhoea, and swollen lymph glands.
- Skin rash and swollen joints are also reported in some cases.
- In more severe instances, West Nile Fever can lead to neurological complications.
- These may include meningitis (inflammation of the membranes surrounding the brain and spinal cord) or encephalitis (inflammation of the brain).
- Signs of neurological involvement may include severe headache, high fever, neck stiffness, disorientation, tremors, seizures, paralysis, and coma.
Treatment:
- While there is no specific treatment for West Nile Fever, supportive care such as pain management, fluids, and rest can help alleviate symptoms and aid recovery.
- Prompt medical attention is crucial, especially for those experiencing neurological symptoms, as these can be life-threatening.
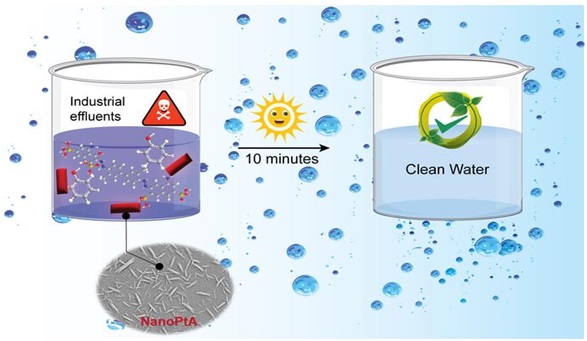
NanoPtA (The Hindu)
- 06 Oct 2023
Why in the News?
Scientists at the Indian Institute of Science's Materials Research Centre (MRC) have recently created a novel enzyme mimic known as NanoPtA.
About NanoPtA:
- The research team at the Materials Research Centre (MRC), Indian Institute of Science (IISc), has created a unique platinum-based nanozyme called NanoPtA.
- This nanozyme can be turned into a powder for use in industries.
- When NanoPtA encounters wastewater, the molecule's benzene rings and long alkyl chains engage in multiple non-covalent interactions.
- Individual NanoPtA molecules link together to form tape-like structures that emit light, which is the source of its oxidizing capability.
- In the presence of sunlight, this nanozyme can break down pollutants in wastewater, reducing its toxicity.
- Remarkably, the nanozyme can rapidly degrade even small amounts of common contaminants like phenols and dyes (micromolar levels) within ten minutes when exposed to sunlight.
- The researchers also observed that the NanoPtA complex remained stable for up to 75 days at room temperature.
Applications:
- Besides wastewater treatment, this nanozyme could find applications in healthcare and serve as a valuable diagnostic tool for neurological and neurodegenerative diseases.
