SAHI and BODH Initiative

- 18 Feb 2026
In News:
At the India AI Summit held at Bharat Mandapam, the Union Minister of Health and Family Welfare launched two key national initiatives - the Strategy for Artificial Intelligence in Healthcare for India (SAHI) and the Benchmarking Open Data Platform for Health AI (BODH). Together, these initiatives seek to establish a structured, ethical, and technology-driven framework for integrating Artificial Intelligence (AI) into India’s healthcare ecosystem, aligning innovation with public health priorities.
Rationale: The Need for Governance in Health AI
Artificial Intelligence holds transformative potential in areas such as diagnostics, disease surveillance, medical imaging, predictive analytics, and health system management. However, its deployment raises critical concerns related to:
- Data privacy and security
- Algorithmic bias and accountability
- Clinical validation and safety
- Ethical use and regulatory oversight
In a country with diverse health challenges and socio-economic disparities, the integration of AI must be inclusive, evidence-based, and aligned with public welfare objectives. SAHI and BODH aim to address these systemic gaps.
SAHI: Strategy for Artificial Intelligence in Healthcare for India
SAHI serves as a national guidance framework for the responsible adoption of AI in healthcare.
Core Objectives:
- Safe and Ethical Deployment – Establishes principles for transparency, accountability, and fairness in AI systems.
- Evidence-Based Validation – Emphasises scientific testing and performance benchmarking before large-scale adoption.
- Data Stewardship and Governance – Provides direction on responsible data use, storage, and sharing.
- Monitoring and Evaluation – Ensures continuous oversight of AI solutions in real-world settings.
- Support to States and Institutions – Aligns AI adoption with local health priorities and public health objectives.
By offering strategic direction on governance, validation, and deployment, SAHI aims to mainstream AI within India’s health infrastructure while preventing misuse or premature adoption.
BODH: Benchmarking Open Data Platform for Health AI
Complementing SAHI, BODH is a privacy-preserving benchmarking platform developed by the Indian Institute of Technology (IIT) Kanpur in collaboration with the National Health Authority.
Key Features:
- Enables rigorous evaluation of AI models using diverse, real-world health data.
- Operates without sharing underlying datasets, thereby preserving patient privacy.
- Functions as a digital public good under the Ayushman Bharat Digital Mission (ABDM).
- Strengthens transparency and quality assurance in AI-based health solutions.
By creating a standardised benchmarking environment, BODH promotes trust and reliability in AI systems used for clinical or administrative purposes.
Significance
- Institutionalising AI Governance – Moves beyond pilot projects to structured regulation.
- Enhancing Trust – Ensures accountability and public confidence in AI tools.
- Promoting Interoperability – Aligns with ABDM’s digital health ecosystem.
- Global Competitiveness – Positions India as a responsible innovator in health AI.
- Equity in Healthcare Delivery – Supports inclusive and evidence-based adoption across regions.
Samriddh Gram Phygital Services Pilot Project

- 01 Nov 2025
In News:
The Samriddh Gram Phygital Services Pilot Project, launched by the Department of Telecommunications (DoT) through the Telecom Centres of Excellence (TCoE), is a rural digital empowerment initiative aimed at bridging the digital divide by integrating physical infrastructure with digital service delivery (“phygital model”). It leverages BharatNet — India’s flagship rural broadband programme — to ensure seamless access to essential citizen-centric services.
Pilot Locations & Implementation
The pilot is being implemented in three villages, each hosting a Samriddhi Kendra:
- Ari & Umri (Madhya Pradesh) – Partner: Digital Empowerment Foundation
- Narakoduru (Andhra Pradesh) – Partner: Corpus Enterprises Pvt. Ltd.
- Chaurawala (Uttar Pradesh) – Partner: I-Novate Infotech Pvt. Ltd.
These Kendras act as integrated digital service hubs, providing both physical support and digital-enabled services.
Objectives:
- To create a replicable and scalable rural digital service model.
- To deliver last-mile digital access through BharatNet-powered connectivity.
- To enhance education, agriculture, health, governance, and financial inclusion in rural areas.
- To enable digital entrepreneurship and strengthen participation in the digital economy.
Key Features & Services
1. Education & Skilling
- Smart classrooms, digital content
- AR/VR-based learning
- Skill development aligned with national skilling schemes
2. Agriculture
- IoT-based soil testing
- Drone-enabled services (monitoring, spraying)
- Smart irrigation solutions
3. Healthcare
- Teleconsultations
- Health ATMs for diagnostics
- Basic emergency care support
4. e-Governance
- Assisted access to government services
- Document facilitation
- Grievance redress mechanisms
5. E-Commerce & Entrepreneurship
- Integration with ONDC
- Digital marketplace access for local products
- Support for rural microenterprises
6. Financial Inclusion
- Digital banking services
- Payment systems & UPI-assisted transactions
7. Connectivity Backbone
- BharatNet FTTH connectivity
- Village Area Network (VAN)
- Public Wi-Fi hotspots
Significance
- Strengthens Digital India at the grassroots.
- Demonstrates a phygital last-mile service delivery model.
- Enhances socio-economic outcomes in rural areas by integrating technology with governance and service delivery.
- Designed as a sustainable and scalable model for nationwide expansion.
Matanomadh in Kutch
- 08 Sep 2025
In News:
- A remote village in Gujarat’s Kutch district, Matanomadh, is emerging as a potential analogue site for India’s future Mars missions.
- Researchers from the Space Applications Centre (ISRO), Savitribai Phule Pune University, and the Birbal Sahni Institute of Palaeosciences have confirmed the presence of jarosite, a mineral also discovered on Mars, making the region significant for planetary studies.
Jarosite and Its Relevance
- Composition: Jarosite is a yellow-brown mineral composed of potassium, iron, and sulphate, typically formed in arid, saline environments under extreme geochemical conditions.
- Formation: On Earth, it is linked to volcanic activity, where volcanic ash containing sulphur reacts with water-rich environments.
- Global Occurrence: Rare on Earth; found in Mexico, Canada, Japan, Spain, USA (Utah, California), and in India at Kerala’s Varkala cliffs and now Kutch.
- On Mars: First detected in 2004 by NASA’s Opportunity Rover at Meridiani Planum, jarosite is considered strong evidence of water activity on the red planet.
The Kutch Discovery
- Age: Jarosite deposits at Matanomadh have been dated to around 55 million years ago (Paleocene period).
- Geological Significance: Indicates that environmental and chemical conditions in Kutch millions of years ago resembled those on Mars.
- Current Findings: The mineral occurs as fine deposits mixed with clay. When mixed with water, this clay expands—closely resembling Martian sulphate-clay formations.
Importance for Space Research
- Field Analogue for Mars: The site provides a natural laboratory to test rovers, instruments, drilling, geochemistry, and astrobiology experiments for upcoming missions like Mangalyaan-2.
- Astrobiology Potential: Sulphates such as jarosite can trap organic molecules, offering clues to possible microbial life.
- Palaeo-evolution Insights: Helps decode the geological and chemical history of Mars.
- Complementary Sites: While Ladakh’s Tso Kar Valley (HOPE Mission) simulates Martian living conditions, Kutch offers geological parallels for studying surface mineralogy.
Challenges
- The site is currently waterlogged and threatened by coal mining activities in the vicinity. Scientists have urged that Matanomadh be declared a site of planetary geo-heritage to protect its unique deposits.
Exercise Yudh Kaushal 3.0
- 06 Sep 2025
In News:
The Indian Army recently conducted Exercise Yudh Kaushal 3.0 in the high-altitude Kameng region of Arunachal Pradesh, reaffirming its preparedness for next-generation warfare in extreme Himalayan terrain.
The exercise underscored the Army’s shift towards multi-domain operations, greater reliance on emerging technologies, and closer engagement with the domestic defence industry.
Key Highlights of the Exercise
- Terrain & Conditions: Conducted in high-altitude, harsh Himalayan conditions, validating combat effectiveness and operational resilience.
- Technological Integration: Featured drone surveillance, precision strikes, real-time target acquisition, air–littoral operations, and synchronized battlefield tactics, reflecting the Army’s technological adaptation.
- Debut of ASHNI Platoons: Marked the first operational deployment of the newly raised ASHNI platoons, designed to combine advanced technology with traditional combat expertise for decisive battlefield advantage.
- Indigenous Defence Industry Participation: Reflected India’s emphasis on Atmanirbhar Bharat and the “Decade of Transformation,” with active involvement of the domestic defence sector.
Strategic Significance
- Demonstrated India’s ability to conduct large-scale, coordinated operations in sensitive border regions.
- Validated the Army’s preparedness for multi-domain conflicts involving land, air, cyber, and unmanned systems.
- Reinforced the importance of self-reliance in defence technology by incorporating indigenous systems in live combat simulations.
- Showcased India’s resolve to maintain combat superiority in high-altitude operational theatres along the Line of Actual Control (LAC).
Riyadh Design Law Treaty (DLT)

- 27 Nov 2024
In News:
- India reaffirms its commitment to inclusive growth and strengthening its intellectual property (IP) ecosystem.The signing of the treaty comes after nearly two decades of negotiations.
Key Highlights:
Purpose of the DLT:
- Aims to harmonize industrial design protection frameworks across multiple jurisdictions.
- Improves efficiency and accessibility of design registration processes.
Key Features of the DLT:
- Grace Period: A 12-month grace period after the first disclosure of the design, ensuring its validity for registration.
- Flexibility for Applicants: Provides relief measures such as relaxed deadlines, reinstatement of lost rights, and flexibility in adding priority claims.
- Simplified Processes: Includes simplified procedures for design renewals, assignment, and license recording.
- E-Filing Systems: Promotes the adoption of electronic filing systems and exchange of priority documents.
Benefits of DLT:
- Empowering SMEs and Startups: Helps small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) and startups protect designs globally, enhancing competitiveness and market growth.
- Reduced Administrative Burden: Standardizes procedures, making the design protection process less complex, more predictable, and affordable.
- Support for Developing Countries: Offers technical assistance for implementation in developing and least-developed countries.
Significance for India:
- India’s rich heritage of design and craftsmanship underscores the importance of design protection for sustainable economic growth.
- Design registrations in India have surged, with a 120% increase in domestic filings over the last two years.
Supporting Programs:
- The treaty’s provisions align with India’s initiatives like Startup India and the Startups Intellectual Property Protection (SIPP) Scheme to boost the protection and commercialization of designs for Indian innovators.
Broader Impact:
- DLT aims to integrate design protection with traditional knowledge and cultural expressions, further enhancing protection for India’s diverse creative sectors.
About WIPO:
- The World Intellectual Property Organization (WIPO), headquartered in Geneva, Switzerland, is a specialized UN agency established in 1967, promoting IP rights globally.
- India is a member of WIPO, which has 193 member countries.
Overview of Intellectual Property (IP):
- IP includes creations like inventions, industrial designs, literary and artistic works, symbols, and more, which are used in commerce.
- IP rights protect creators, allowing them to benefit from their work when commercially exploited.
SAMRIDH Scheme
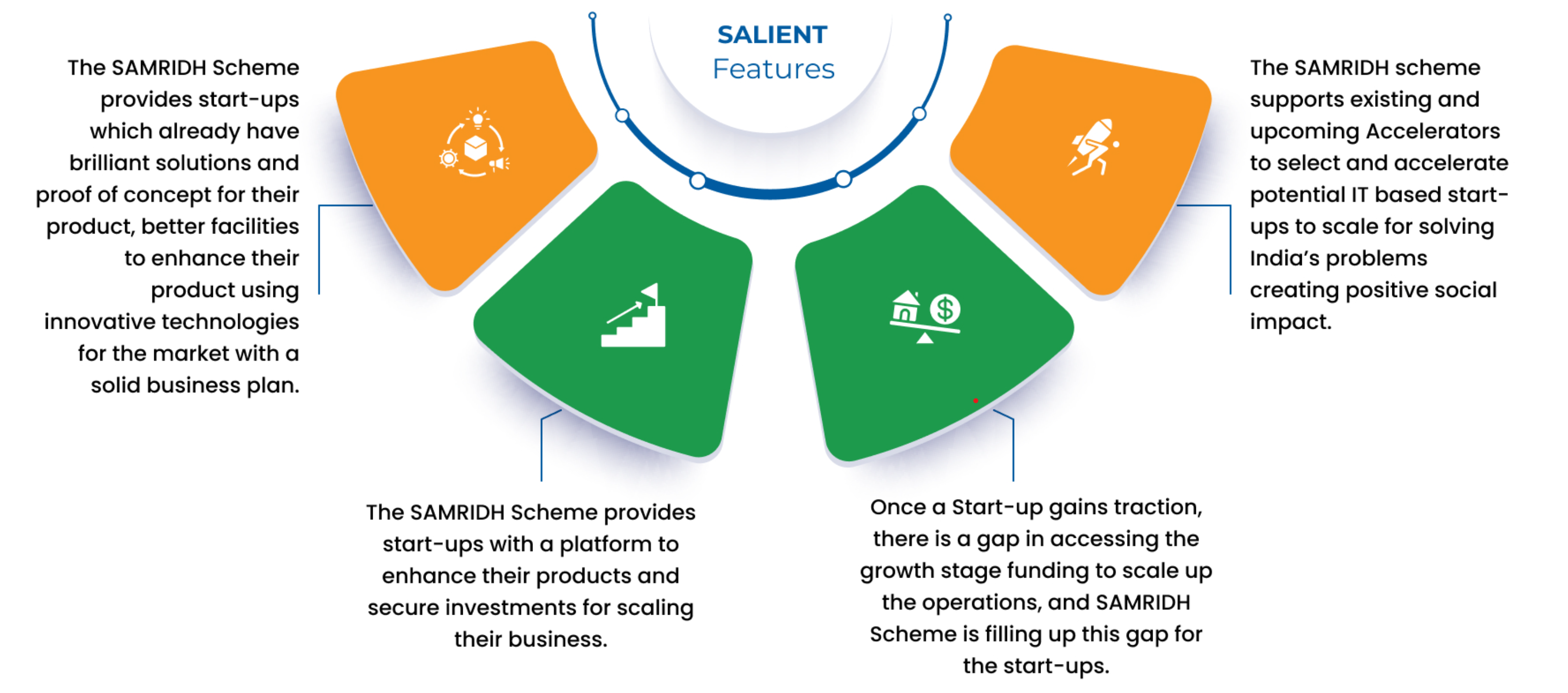
- 06 Sep 2024
In News:
- Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology (MeitY) launches 2nd Cohort of Startup Accelerators of MeitY for Product Innovation, Development and Growth (SAMRIDH).
About SAMRIDH Scheme:
- SAMRIDH is a flagship programme of MeitY for startups acceleration under National Policy on Software Products – 2019.
- The SAMRIDH programme, launched in August 2021 aims to support 300 software product startups with outlay of ?99 crore over a period of 4 years.
- SAMRIDH is being implemented through potential and established accelerators across India which provide services like making products market fit, business plan, investor connect and international expansion to startups plus matching funding upto ?40 lakh by MeitY.
- The scheme is being implemented by MeitY Start-up Hub (MSH), Digital India Corporation (DIC).
- In the first round of cohort, 22 Accelerators spread across 12 states are supporting 175 startups, selected through a multilevel screening process.
- Major Objective:
- The SAMRIDH scheme aims to support existing and upcoming Accelerators to select and accelerate potential IT-based startups to scale.
- Among others, the program focuses on accelerating the startups by providing customer connect, investors connect and connect to international markets
- Eligibility of Accelerator:
- Should be a registered Section-8/Society, [Not-for-Profit Company (eligible to hold equity)] having operations in India.
- The Accelerator and the team are recommended to have more than 3 years of startup experience and should have supported more than 50 start-ups of which at least 10 startups should have received investment from external Investors
- The Accelerator should have an experience of running startup program cohorts with activities listed as desirable under SAMRIDH program.
Six Heritage Sites on Tentative UNESCO List

- 20 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
In a significant boost to its rich cultural and historical legacy, 6 new sites from Madhya Pradesh have found a place in the tentative UNESCO list of World Heritage Sites (WHS).
Six New Sites From MP In the UNESCO Tentative List:
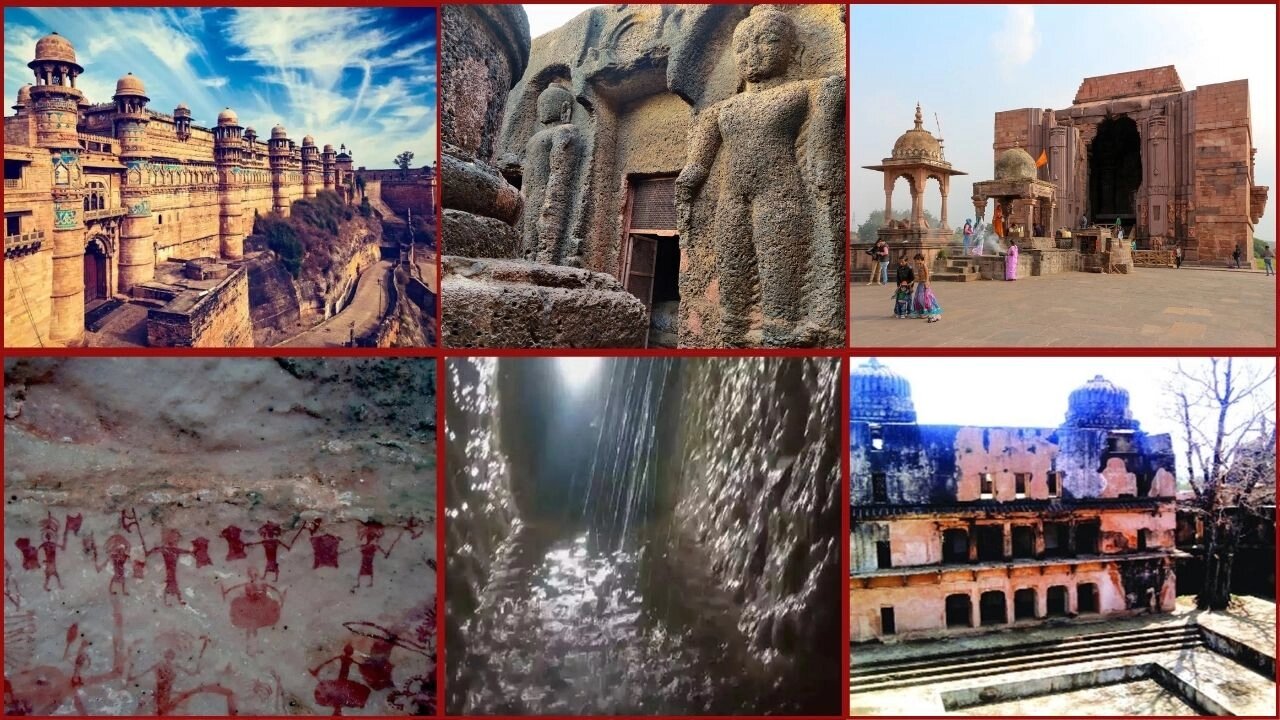
- The sites included in the tentative list are Gwalior Fort, the Historical Group of Dhamnar, Bhojeshwar Mahadev Temple, Rock Art Sites of Chambal Valley, Khooni Bhandara, Burhanpur, and God Memorial of Ramnagar, Mandla.
- The UNESCO tentative list includes those that provide a forecast of the properties that a State Party may decide to submit for inscription in the next five to ten years.
- Gwalior Fort: An imposing fortress atop a hill, featuring impenetrable walls, exquisite sculptures, and stunning architecture.
- Built-in the 6th century AD by Rajput warrior Suraj Sen and expanded by Tomar ruler Maan Singh in 1398.
- Dhamnar Caves: Rock-cut temple site in Mandsaur district, constructed in the 7th century AD.
- It comprises 51 caves, stupas, chaityas, and dwellings, with a colossal Gautam Buddha statue.
- Bhojeshwar Mahadev Temple: Located near Bhopal, this temple is dedicated to Lord Shiva, with a huge Linga carved from a single stone.
- Built between 1010 and 1053 AD by Raja Bhoj but was never completed.
- Chambal Valley Rock Art Sites: The world's largest concentration of rock art sites across MP, Rajasthan, and Uttar Pradesh, depicting ancient daily life, rituals, and hunting scenes.
- Khooni Bhandara: A unique water supply system built in Burhanpur in 1615 by ruler Abdurrahim Khankhana, still operational today.
- Gond Statue, Mandla: Moti Mahal, a five-storied palace built in Mandla in 1667 by Gond king Hriday Shah, showcasing the strong willpower of the king despite limited resources.
What is UNESCO’s Tentative List?
- A World Heritage Site is a site with outstanding universal value.
- It also denotes cultural and natural significance that transcends national boundaries and is of common importance for current and future generations of all humanity.
- According to UNESCO, a tentative list lists the properties each State Party intends to consider for nomination.
- The government of any nation must have a nomination document ready for the UNESCO World Heritage Committee to review once as soon as UNESCO includes it in a location on the Tentative List.
- After this, a UNESCO representative will evaluate the situation and inspect it.
What is the Tentative List Process?
- The States Parties are encouraged to submit their Tentative Lists of properties that they consider cultural and natural heritage of outstanding universal value and, therefore, suitable for inscription on the World Heritage List.
- The States Parties are encouraged to prepare their Tentative Lists with the participation of stakeholders such as site managers, local and regional governments, local communities, NGOs, and other interested parties and partners.
- The States Parties should submit the Tentative Lists to the World Heritage Centre at least one year before submitting any nomination.
- The list should not be exhaustive.
- The States Parties can re-examine and re-submit their list at least every ten years.
- The States Parties are also requested to submit their lists using a submission format (English or French) that should contain the name of the properties, geographical location, a brief description of the properties, and why the property is of outstanding universal value.
- Nomination will only be considered once the property is added to the State Party's Tentative List.
Exercise Yudh Abhyas (PIB)
- 25 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
The 19th iteration of 'EXERCISE YUDH ABHYAS' is scheduled to take place from September 25th to October 8th, 2023, at Fort Wainwright, Alaska, USA
Facts About:
- Exercise Yudh Abhyas is an annual collaborative military exercise carried out jointly by the Indian Army and the United States Army.
- In this edition, the Indian Army contingent, consisting of 350 personnel, will participate. The lead battalion from the Indian side is associated with the MARATHA Light Infantry Regiment.
- The primary focus of the exercise is to practice a series of tactical drills aimed at improving the ability to work together effectively during United Nations peacekeeping operations.
- The exercise's theme centers on the 'Employment of an Integrated Battle Group in Mountain/ Extreme Climatic Conditions,' as outlined in Chapter VII of the United Nations mandate.
- The Field Training Exercise will encompass various elements, including the validation of Integrated Battle Groups in confronting hostile forces at the Brigade level, the establishment of an Integrated Surveillance Grid at the Brigade/ Battalion level, and the utilization of Heliborne/ Airborne units and Force Multipliers, among others.
- Additionally, the exercise will facilitate the exchange of ideas and best practices in a wide range of combat skills, encompassing combat engineering, obstruction clearance, and tactics for dealing with mines and Improvised Explosive Devices.
Other Exercises involving India and the USA:
- Army: Vajra Prahar
- Navy: MALABAR (Multilateral)
- Air Force: Cope India, Red Flag (Multilateral)
