150 Years of Vande Mataram

- 09 Nov 2025
In News:
India has commenced a year-long national commemoration marking 150 years of Vande Mataram, with an enthusiastic response across the country and abroad. The celebrations were approved by the Union Cabinet on October 1 and formally inaugurated through a grand national event in New Delhi led by the Prime Minister. The President of India and other constitutional authorities have also extended their greetings, underlining the song’s enduring national significance.
About Vande Mataram
- Author: Bankim Chandra Chattopadhyay
- First Appearance: Serialized in the Bengali journal Bangadarshan and later included in the novel Anandamath (1882)
- Language: Blend of Sanskrit and Bengali
- Status: National Song of India (adopted on 24 January 1950)
Vande Mataram is not merely a song but a symbolic invocation of the motherland, embodying India’s cultural, spiritual, and national identity.
Historical Significance
- First sung publicly by Rabindranath Tagore at the 1896 Indian National Congress session in Calcutta
- Became a political slogan during the Swadeshi Movement (first used as a slogan on 7 August 1905)
- Madam Bhikaji Cama unfurled India’s tricolour in Stuttgart (1907) with the words Vande Mataram inscribed on it
- Served as a rallying cry for freedom fighters, inspiring mass participation in the national movement
The song played a critical role in forging a shared emotional and cultural identity during colonial resistance.
Baliyatra Festival

- 09 Nov 2025
In News:
The President of India, Droupadi Murmu, recently extended greetings to the nation, especially to the people of Odisha, on the occasion of the historic Baliyatra festival and Boita Bandana. She described Baliyatra as a symbol of Odisha’s glorious maritime commercial tradition and rich cultural heritage, inspiring citizens to draw strength from the past to build a developed nation.
About Baliyatra Festival
- Location: Cuttack, Odisha
- Time of Celebration: Annually on Kartika Purnima (full moon day of Kartika month)
- Literal Meaning: Bali Jatra means “Voyage to Bali”
The festival marks the day when ancient Kalingan seafaring traders (Sadhabas) set sail for distant lands across the Bay of Bengal.
Historical Significance
Baliyatra commemorates Odisha’s over 2,000-year-old maritime and trade links between ancient Kalinga (present-day Odisha) and regions of South and Southeast Asia, including:
- Bali
- Java
- Sumatra
- Borneo
- Burma (Myanmar)
- Ceylon (Sri Lanka)
These voyages played a vital role in spreading Indian culture, language, religion, art, and trade networks, making Kalinga one of the most prosperous maritime powers of ancient India.
Cultural Practices and Celebrations
- Boita Bandana: Women float small boats (boitas) made of paper, banana leaf, or sholapith, with lighted lamps, on rivers—especially the Mahanadi—to honour the ancient sailors.
- Festivities:
- Large fairs and exhibitions
- Folk dance and music
- Traditional food and craft stalls
- Cultural performances reflecting Odisha’s heritage
The festival celebrates the courage, navigational expertise, and commercial acumen of Kalinga’s sailors.
National Unity Day

- 31 Oct 2025
In News:
- National Unity Day (Rashtriya Ekta Diwas) is observed annually on 31 October to mark the birth anniversary of Sardar Vallabhbhai Patel, India’s first Deputy Prime Minister and Home Minister.
- Introduced in 2014, the day highlights Patel's pivotal role in consolidating the nation by integrating over 560 princely states into the Indian Union at the time of Independence— a task that earned him the enduring title, the “Iron Man of India.”
- The year 2025 marks the 150th birth anniversary of Sardar Patel, and the commemorative events have been organised on an unprecedented scale at the Statue of Unity in Ekta Nagar, Gujarat, led by Prime Minister Narendra Modi.
- The celebrations highlight the theme “Unity in Diversity”, underscoring India’s multicultural character and the importance of national cohesion.
Historical Significance of Sardar Vallabhbhai Patel
- Born on 31 October 1875 in Nadiad, Gujarat, Patel initially practised law before joining the national movement under Mahatma Gandhi.
- His leadership in the Kheda Satyagraha (1918) and Nagpur Flag Satyagraha (1923) marked his rise as a mass leader.
- As President of the Ahmedabad Municipal Board (1924), he reformed urban infrastructure, sanitation and civic systems.
- The Bardoli Satyagraha (1928) elevated him to national prominence, earning him the honorific “Sardar.”
- At Independence, he was entrusted with unifying the 17 British provinces and integrating the princely states—an immense administrative and diplomatic feat.
- Served as Deputy Prime Minister and Home Minister (1947–1950) and also held charge of the Information and Broadcasting Ministry.
Nafithromycin

- 21 Oct 2025
In News:
India has achieved a major scientific milestone with the development of Nafithromycin, the country's first indigenously conceptualized, developed, and clinically validated antibiotic. Announced by the Union Science and Technology Minister, this breakthrough reflects India's growing self-reliance in the biotechnology and pharmaceutical sector and its commitment to addressing the global challenge of Antimicrobial Resistance (AMR).
About Nafithromycin
- Developed with support from: Biotechnology Industry Research Assistance Council (BIRAC)
- Trade Name:Miqnaf
- Target Use: Community-Acquired Bacterial Pneumonia (CABP)
- Key Beneficiaries: Cancer patients and individuals with poorly controlled diabetes
- Spectrum & Novelty: Effective against both typical and atypical respiratory pathogens; marks the first new antibiotic in its class globally in over 30 years
Nafithromycin is particularly relevant in India where respiratory infections remain a key public-health concern. The antibiotic is designed to combat drug-resistant respiratory infections, providing a potent solution amid rising antimicrobial resistance.
Why It Matters: Tackling AMR
Antimicrobial Resistance (AMR) occurs when microbes such as bacteria, viruses, fungi, or parasites develop the ability to defeat drugs designed to kill them. As a result, common infections become harder to treat, increasing the risk of severe illness, prolonged hospitalization, disability, and death. While AMR is a natural evolutionary process, misuse and overuse of antimicrobials significantly accelerate it. Nafithromycin’s development represents a strategic step in strengthening India's response to AMR.
Related Scientific Milestones Announced
The Minister also highlighted other key achievements underscoring India’s expanding biotech capabilities:
- Indigenous gene-therapy trial success for Hemophilia at Christian Medical College, Vellore — achieving 60–70% correction with zero bleeding episodes
- Human genome sequencing initiative: Over 10,000 genomes already sequenced, target set to reach 1 million
- Deployment of AI-based hybrid mobile clinics to improve healthcare access in rural and remote regions
These advancements reflect India’s push toward a self-sustainable innovation ecosystem, combining science, technology, and healthcare delivery to support the vision of a developed and technology-driven nation.
Blue Flag Certification

- 15 Oct 2025
In News:
- Five beaches in Maharashtra have recently been awarded the prestigious Blue Flag certification, a global eco-label that recognises high standards in environmental management, cleanliness, and sustainable tourism.
- The certified beaches include Shrivardhan and Nagaon (Raigad district), Parnaka (Palghar), and Guhagar and Ladghar (Ratnagiri district). The announcement was made by the state government, marking a significant achievement in coastal conservation and eco-tourism promotion.
About Blue Flag Certification
The Blue Flag is an internationally recognised eco-label awarded by the Foundation for Environment Education (FEE), Denmark. Established in France in 1985 and expanded globally in 2001, it is regarded as one of the world's most prestigious voluntary awards for beaches, marinas, and sustainable tourism boats.
Criteria and Objectives
To receive the Blue Flag, sites must meet 33 stringent criteria across key focus areas:
- Water quality
- Environmental management
- Environmental education and awareness
- Safety and essential services
The certification aims to promote sustainable development in coastal and freshwater ecosystems by ensuring high cleanliness standards, protecting natural habitats, and encouraging responsible tourism practices. Its mission centers on environmental education, conservation, and sustainable tourism development.
Blue Flag Beaches in India
With the addition of the five Maharashtra beaches, India continues to expand its presence on the global sustainable tourism map. Previously recognised Indian Blue Flag beaches include:
- Shivrajpur (Gujarat)
- Ghoghla (Diu)
- Kasarkod and Padubidri (Karnataka)
- Kappad (Kerala)
- Rushikonda (Andhra Pradesh)
- Golden Beach (Odisha)
- Radhanagar (Andaman & Nicobar)
- Kovalam (Tamil Nadu)
- Eden (Puducherry)
- Minicoy Thundi and Kadmat (Lakshadweep)
Significance
This recognition underscores India's ongoing efforts to align coastal tourism with global environmental standards, enhance beach amenities, and promote eco-friendly tourism models. It also strengthens India's initiative to improve coastal governance under programmes like the Integrated Coastal Zone Management Project and the government's broader sustainability mission.
Armenia Joins IUCN

- 15 Oct 2025
In News:
Armenia has recently become the newest State Member of the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN), marking a key milestone in its environmental policy direction. The announcement was made at the IUCN World Conservation Congress in Abu Dhabi, reflecting Armenia’s growing commitment to global biodiversity protection, sustainable development, and alignment with international conservation frameworks.
Significance of Membership
By joining IUCN, Armenia gains access to global research, conservation tools, and international collaborations. This step also supports its preparations to host COP17 of the Convention on Biological Diversity in 2026, signalling its intent to play a leadership role in global biodiversity discussions.
IUCN leadership has welcomed Armenia’s membership, noting that it aligns with the country’s efforts to expand protected areas, restore degraded ecosystems, and bring its environmental laws in line with international standards.
Armenia’s Biodiversity and Conservation Efforts
Situated at the crossroads of Europe and Asia, Armenia hosts varied ecosystems—from alpine meadows and mountain forests to semi-deserts and freshwater bodies. These habitats support several threatened and endemic species, including:
- Caucasian leopard (Critically Endangered)
- Bezoar goat
- Sevan trout, native to Lake Sevan
The country has made progress in environmental governance through initiatives such as its National Biodiversity Strategy and Action Plan and the Red Book of Armenia. Its conservation agenda includes forest restoration across 12.9% of its territory by 2030, strengthening biodiversity monitoring, and expanding protected areas.
Geographical and Environmental Profile of Armenia
- Location: Southern Caucasus; landlocked
- Borders: Georgia (north), Azerbaijan (east), Iran (southeast), Turkey (west)
- Terrain: Dominated by the Lesser Caucasus Mountains; volcanic soils rich in nitrogen, potash, phosphates
- Highest Peak:Mount Aragats (4,090 m)
- Climate: Highland continental — hot summers, cold winters
- Rivers: Aras, Hrazdan, Arpa, Vorotan — key for irrigation and hydropower
- Major Lake:Lake Sevan, Armenia’s largest freshwater body
- Resources: Small deposits of copper, gold, molybdenum, zinc, bauxite
- Capital & Language: Yerevan; Armenian
India Re-elected to the Universal Postal Union’s Governing Bodies

- 23 Sep 2025
In News:
- India has been re-elected to the Council of Administration (CA) and the Postal Operations Council (POC) of the Universal Postal Union (UPU) during the 28th Universal Postal Congress held in Dubai.
- This re-election reaffirms global confidence in India Post’s leadership, digital reforms, and commitment to inclusive postal development, strengthening India’s voice in shaping international postal governance.
About the Universal Postal Union (UPU)
- Founded: 1874 under the Treaty of Bern
- Headquarters: Berne, Switzerland
- Members: 192 countries
- Status: A specialized agency of the United Nations, it is the second-oldest international organization after the International Telecommunication Union (ITU).
Mandate and Objectives
- To promote global postal cooperation and ensure universal connectivity in mail and parcel delivery.
- To establish standards, regulations, and tariffs for international postal exchanges.
- To enhance efficiency, affordability, and reliability of postal services globally.
- To facilitate the growth of e-commerce and cross-border logistics through modern postal systems.
Governance Structure of UPU
The UPU functions through four key organs:
- Congress:
- The supreme decision-making body, convened every four years.
- Sets the long-term strategy, budget, and policy framework for global postal operations.
- Council of Administration (CA):
- Handles policy, legal, administrative, and regulatory issues between Congress sessions.
- Oversees the implementation of Congress decisions and coordinates global postal governance.
- Postal Operations Council (POC):
- The technical and operational body comprising 48 elected member countries.
- Works on service innovation, quality enhancement, digital integration, and modernisation of global postal systems.
- International Bureau:
- The secretariat of the UPU providing logistical, analytical, and technical support to member states and councils.
Significance of India’s Re-election
- Endorsement of Leadership: India’s re-election underscores the international community’s trust in its postal transformation, particularly in digital and financial inclusion.
- Modernisation Initiatives: India Post’s progress in e-commerce facilitation, postal banking, logistics efficiency, and technology-driven governance has positioned it as a model for developing nations.
- Strategic Representation: Through its roles in both CA and POC, India can influence policy formulation, standard setting, and capacity-building initiatives within the UPU.
- Global Collaboration: Reinforces India’s vision of “One World, One Postal Network”, aligning with its broader digital diplomacy and South-South cooperation goals.
India and the UPU: A Historical Perspective
- India joined the UPU in 1876, just two years after its establishment.
- Over the decades, it has played a constructive role in strengthening postal connectivity across the Global South.
- Under the leadership of the Ministry of Communications, India Post has transitioned from traditional mail delivery to offering digital, financial, and logistical services, supporting Digital India and Atmanirbhar Bharat missions.
Exercise Pacific Reach 2025
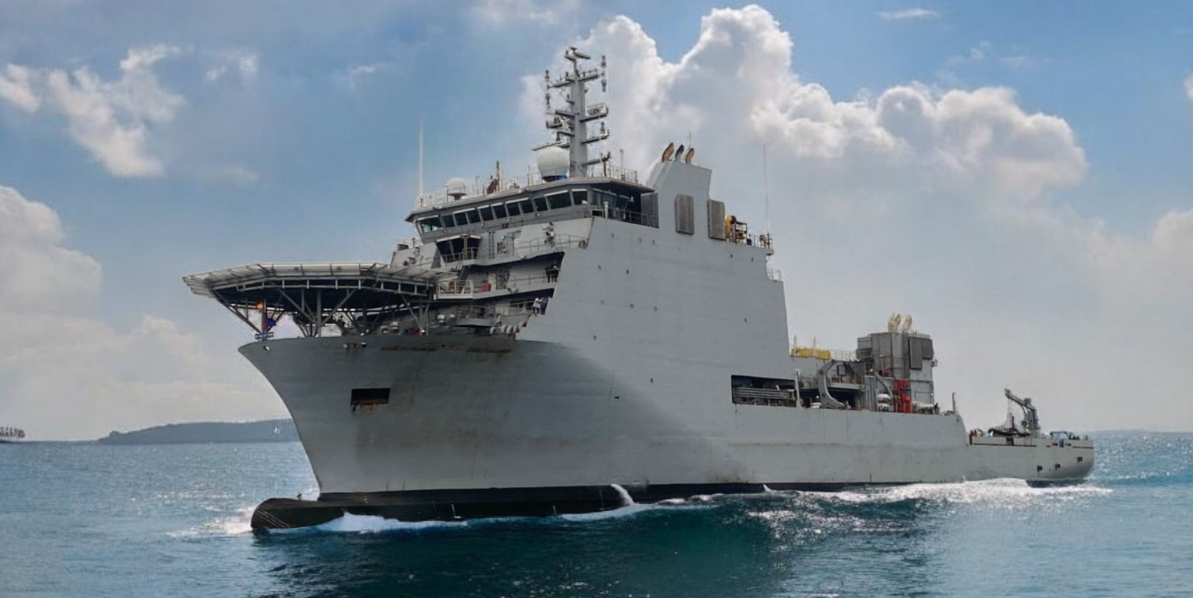

- 19 Sep 2025
In News:
The Indian Navy’s latest indigenously designed and constructed Diving Support Vessel (DSV), INS Nistar, is participating in the multinational Exercise Pacific Reach 2025 in Singapore, marking a key step in strengthening India’s naval cooperation and submarine rescue capabilities.
About Exercise Pacific Reach 2025
- Exercise Pacific Reach is a biennial multinational naval exercise hosted by Singapore, with the 2025 edition witnessing the participation of over 40 nations.
- The exercise focuses on submarine rescue operations, interoperability, and sharing of best practices among participating navies.
- It is conducted in two major phases:
- Harbour Phase:
- Involves in-depth discussions on submarine rescue systems.
- Includes Subject Matter Expert Exchanges (SMEE), a medical symposium, and cross-deck visits among participating nations.
- Aims to enhance coordination in rescue procedures and underwater medical responses.
- Sea Phase:
- Conducted in the South China Sea, featuring multiple intervention and rescue operations.
- INS Nistar and Submarine Rescue Unit (East) will collaborate with other international assets to simulate real-world submarine rescue missions and deep-sea operations.
The exercise underscores the growing importance of multilateral maritime cooperation in ensuring submarine safety, operational interoperability, and humanitarian response readiness in the Indo-Pacific region.
INS Nistar: A Technological Milestone in Naval Capability
- Commissioned on: 18 July 2025
- Built by: Hindustan Shipyard Limited (HSL), Visakhapatnam
- Under: Ministry of Defence’s ‘Aatmanirbhar Bharat’ initiative
- INS Nistar is designed to act as a mothership (MoSHIP) for Deep Submergence Rescue Vehicles (DSRVs) — a critical capability for submarine rescue and deep-sea support operations.
- The vessel exemplifies India’s indigenous shipbuilding prowess and self-reliance in complex maritime technologies.
Key Technical Features and Capabilities:
- Integrated Saturation Diving System (ISDS):Enables diver deployment up to 300 meters depth, facilitating underwater repairs, salvage, and rescue missions.
- Remotely Operated Vehicles (ROVs):Deployed for underwater surveillance and recovery in deep-sea environments.
- Side Scan Sonar:Assists in locating submerged vessels, wreckage, or obstacles on the seabed.
- Integrated Platform Management System (IPMS):Streamlines the operation and monitoring of onboard systems for greater efficiency and safety.
- Submarine Rescue System:A critical asset for submarine emergency response, ensuring timely and safe evacuation of personnel from disabled submarines.
Amrit Sarovar Mission
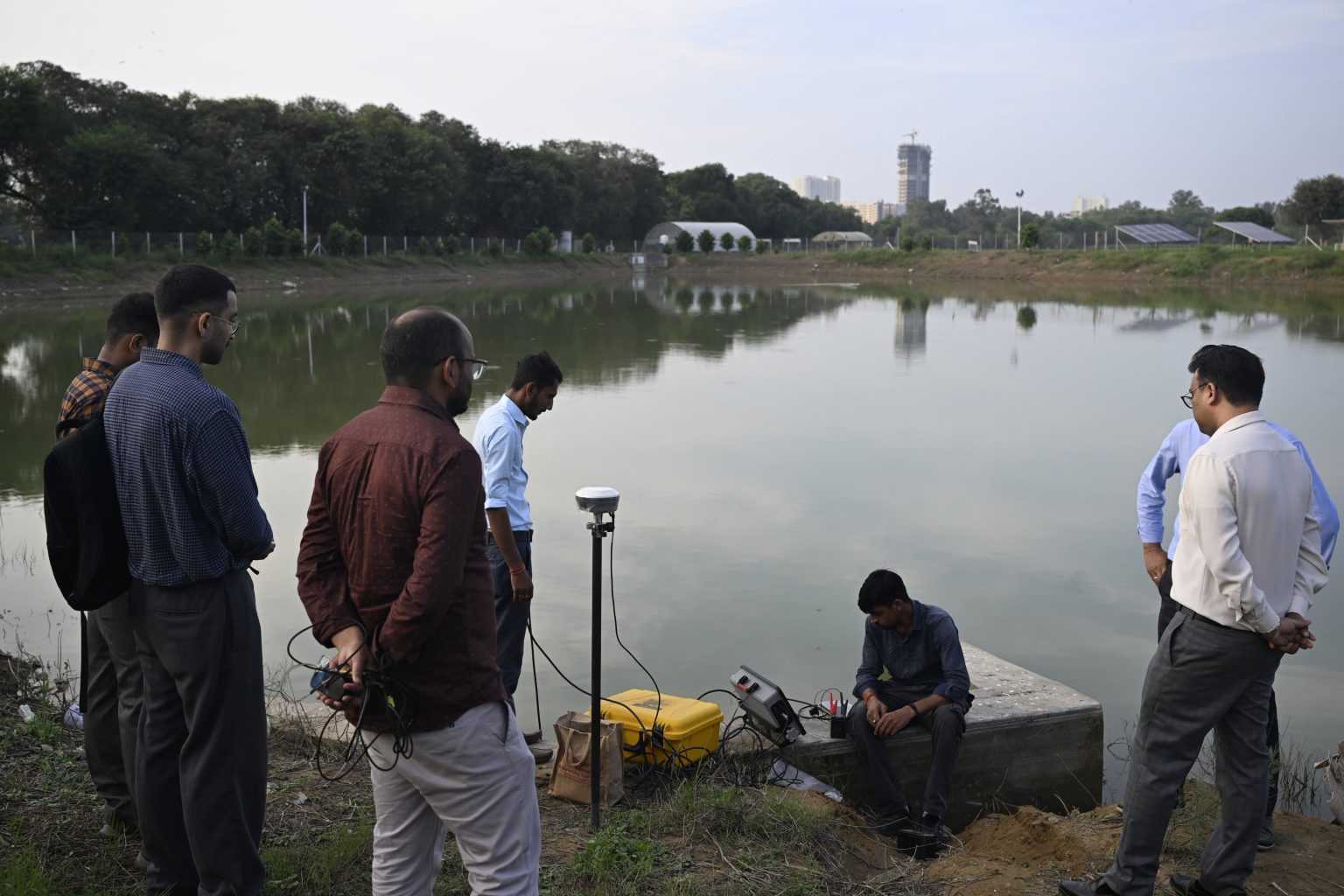

- 17 Sep 2025
In News:
- The Amrit Sarovar Mission, launched by Prime Minister Narendra Modi in April 2022, is a flagship initiative aimed at addressing water scarcity and promoting sustainable rural development across India.
- The mission seeks to construct or rejuvenate 75 Amrit Sarovars (ponds) in each district, as part of the celebrations of Azadi ka Amrit Mahotsav.
- As of 2025, the government has reported the creation of over 68,000 Amrit Sarovars nationwide, marking a significant milestone in water conservation and community engagement.
Objectives and Significance
The mission’s primary objectives include:
- Water conservation and management in rural areas.
- Enhancement of local livelihoods through irrigation, fisheries, duckery, cultivation of water chestnut, and water-based tourism.
- Promotion of social cohesion by establishing Amrit Sarovars as community gathering points.
- Integration of government initiatives through a “Whole of Government” approach, ensuring convergence of resources and expertise.
Each Amrit Sarovar is designed to have a minimum pondage area of one acre with a water-holding capacity of about 10,000 cubic metres. Surrounding vegetation typically includes trees such as Neem, Peepal, and Banyan, contributing to ecological sustainability and enhancing biodiversity.
Participatory and Institutional Framework
The site selection and supervision of Amrit Sarovars are conducted by Gram Sabhas, with Panchayat representatives overseeing the development. This participatory approach ensures that local communities have ownership and accountability for the maintenance and sustainable use of water resources.
The mission operates on convergence principles, utilizing funds and resources from multiple sources including:
- Mahatma Gandhi NREGS
- 15th Finance Commission Grants
- Pradhan Mantri Krishi Sinchai Yojana (PMKSY) sub-schemes, such as Watershed Development and Har Khet Ko Pani
- State government schemes
There is no separate financial allocation for the mission; rather, it leverages ongoing programs for maximum impact.
Technology and Monitoring
To ensure efficient implementation and progress tracking, the Bhaskaracharya National Institute for Space Applications and Geo-informatics (BISAG-N) has been engaged as a technical partner. The institute has developed the Amrit Sarovar Portal and Mobile App, which enables real-time monitoring, reporting, and evaluation of district-level activities.
Workshops and Capacity Building
The Ministry of Rural Development organized a national workshop in New Delhi to reinforce the mission’s technical foundations and promote community-driven sustainable practices. Officials from states and Union Territories discussed strategies to enhance technical capacity, innovation, and inter-departmental collaboration, paving the way for the next phase of the mission.
Impact and Prospects
The Amrit Sarovar Mission exemplifies integrated rural development, linking water security, ecological sustainability, and livelihood generation. By reviving traditional water bodies and creating new ponds, it contributes to groundwater recharge, climate resilience, and rural prosperity. The initiative also strengthens people’s participation in natural resource management, ensuring that water resources are used efficiently and sustainably.
As the mission progresses, it is expected to play a critical role in mitigating rural water crises, enhancing agricultural productivity, and fostering inclusive growth in India’s villages.
Mela Patt Festival
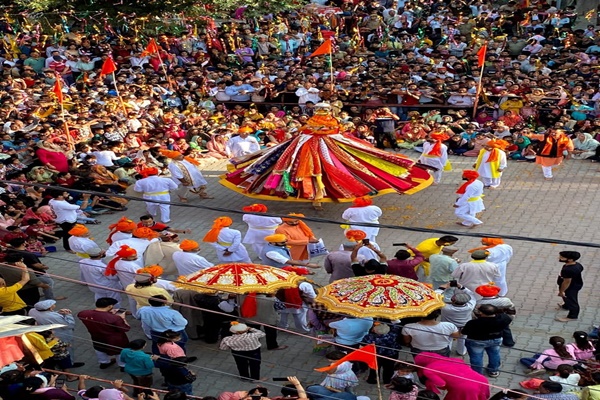

- 03 Sep 2025
In News:
The Mela Patt Festival, celebrated annually in Bhaderwah (Doda district, Jammu & Kashmir), is one of the most prominent cultural and religious events of the region. Rooted in Nag culture, the festival honors Lord Vasuki Nag, the presiding deity of Bhaderwah Valley, and reflects the valley’s rich legacy of syncretic traditions and communal harmony.
Historical Background
- The origins of the festival date back to the 16th century, when it was first celebrated by King Nag Pal during the era when Bhaderwah was known as Bhadarkashi.
- The festival commemorates the historic meeting between Mughal Emperor Akbar and King Nag Pal of Bhaderwah, highlighting its integration into broader Indian history.
- Over the centuries, the event has remained a symbol of unity, with no reported communal discord in its nearly 600-year-long history.
Rituals and Celebrations
- Timing: The festival is observed on Nag Panchami, seven days after the conclusion of the sacred Kailash Yatra.
- Cultural Expressions:
- The unique ‘Dikko Dance’ features participation from men and women across communities, symbolizing peace and pride.
- The ‘Dhakku Dance’, a traditional Dogra folk performance, is also showcased, underscoring its importance in the cultural mosaic of India.
- Inclusivity: Devotees and visitors from across Jammu & Kashmir, irrespective of caste or religion, gather to pay homage to Raja Nag Pal’s bravery and spiritual power.
Paithani Sarees
- 30 Jul 2025
In News:
The Prime Minister recently highlighted the cultural and artisanal significance of Paithani sarees during the monthly ‘Mann Ki Baat’ radio programme, bringing national attention to this traditional Maharashtrian textile.
Historical Background
- Origin: Paithani sarees derive their name from Paithan, an ancient town on the banks of the Godavari River in Maharashtra.
- Antiquity: The tradition of Paithani weaving dates back over 2,000 years, with its roots in the Satavahana dynasty (2nd century BCE).
- Royal Patronage: These sarees were patronized by several royal courts, including the Satavahanas, Peshwas of Pune, Nizams of Hyderabad, and Mughal emperors.
Key Features
|
Attribute |
Description |
|
Material |
Woven using pure silk and gold/silver zari |
|
Technique |
Crafted using the tapestry weaving method, all handwoven |
|
Designs |
Intricate motifs like peacocks, parrots, lotuses, and floral vines |
|
Border & Pallu |
Known for distinctive kath (border) and padar (pallu) designs |
|
Size |
Typically six- or nine-yard sarees |
|
Cultural Significance |
Regarded as the ‘Mahavastra’ (great garment) of Maharashtra, traditionally worn by Maharashtrian brides |
Recognition and Cultural Value
- Symbol of Heritage: Paithani sarees are considered a symbol of Maharashtrian cultural identity and artisanal excellence.
- GI Tag: Granted the Geographical Indication (GI) tag in 2010, acknowledging their unique regional origin and craftsmanship.
- Artistic Value: Among the most exquisite and expensive sarees in India, valued for their aesthetic finesse and traditional techniques.
Bhashini

- 22 Jun 2025
In News:
The Ministry of Panchayati Raj (MoPR) has signed a Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) with Bhashini, the National Language Translation Mission (NLTM), to integrate AI-enabled multilingual tools into rural e-governance platforms.
About Bhashini
- Developed by: Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology (MeitY)
- Purpose: Acts as a digital public infrastructure for real-time, AI-powered translation across Indian languages.
Objective of the MoU
- To build an inclusive, multilingual e-governance ecosystem for Panchayati Raj Institutions (PRIs).
- To bridge language barriers in rural governance and foster participatory democracy.
Key Features of the Initiative
- AI-Driven Language Translation: Offers real-time speech-to-text and text-to-text translation in major Indian languages.
- Platform Integration: Bhashini tools to be integrated with MoPR’s digital platforms like eGramSwaraj, ensuring multilingual access to rural governance services.
- Citizen-Centric Approach: Enables rural citizens to interact with digital governance platforms in their native language, enhancing accessibility and inclusion.
- Promotes Digital Inclusion: Supports rural digital literacy by making digital interfaces linguistically accessible.
- Enhances Transparency and Trust: Facilitates better information dissemination, increasing trust and engagement in local self-governance.
Significance
- Aligns with Digital India goals.
- Empowers Gram Panchayats by ensuring language is not a barrier to governance.
- Sets a precedent for AI-driven, citizen-centric governance reforms.
Panchayat Advancement Index (PAI) 2.0

- 28 May 2025
In News:
The Ministry of Panchayati Raj recently held a two-day national write-shop in New Delhi to roll out the Panchayat Advancement Index (PAI) Version 2.0 for the financial year 2023–24. This updated version marks a significant stride toward enabling evidence-based, participatory local governance in India.
What is Panchayat Advancement Index (PAI)?
The PAI is a multi-domain, multi-sectoral index designed to assess the developmental progress, performance, and governance efficiency of Gram Panchayats. It aligns with the Localization of Sustainable Development Goals (LSDGs) and India's broader commitment to the 2030 SDG Agenda.
Key Features of PAI 2.0
- Framework: Based on 435 unique local indicators (331 mandatory, 104 optional), drawn from 566 data points across 9 LSDG themes, aligned with the National Indicator Framework (NIF) of the Ministry of Statistics and Programme Implementation (MoSPI).
- Purpose:
- Measures holistic development and well-being at the grassroots level.
- Helps identify developmental gaps and supports data-driven planning for Panchayats.
- Encourages bottom-up planning and governance.
- Performance Classification:
- Achiever: 90 and above
- Front Runner: 75 to <90
- Performer: 60 to <75
- Aspirant: 40 to <60
- Beginner: Below 40
Evolution from PAI 1.0 to 2.0
- PAI 1.0 established the baseline, covering 2.16 lakh Gram Panchayats across 29 States/UTs.
- PAI 2.0 offers enhanced functionality, efficiency, and user-friendliness, with refined indicators and improved data usability, while maintaining thematic comprehensiveness.
Recent Developments
- Launch of the PAI 2.0 Portal and a comprehensive PAI 2.0 Booklet for FY 2023–24 to guide implementation.
- According to the Ministry, PAI 2.0 now contains over 100 indicators that collectively offer a robust picture of social and economic development at the Panchayat level.
Asian Productivity Organization (APO)
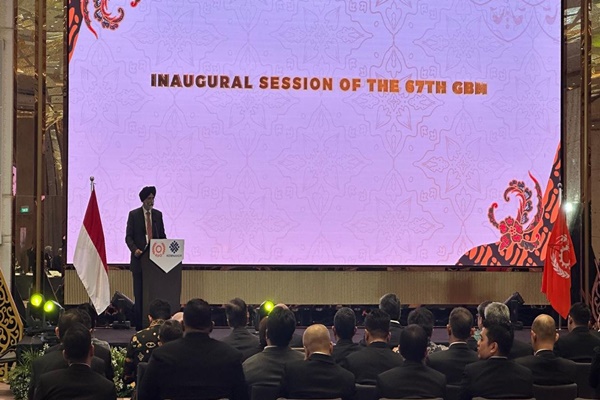

- 25 May 2025
In News:
India has officially taken over the Chairmanship of the Asian Productivity Organization (APO) for the 2025–26 term during the 67th Governing Body Meeting.
About APO:
- Type: Regional intergovernmental organization.
- Established:1961.
- Headquarters:Tokyo, Japan.
- Membership: 21 member economies from the Asia-Pacific region, including India, Japan, Iran, Indonesia, Vietnam, Philippines, South Korea, Singapore, and others.
- India:Founding member of the APO.
Key Objectives:
- Enhance productivity in member countries through mutual cooperation.
- Foster sustainable and inclusive socioeconomic development.
- Promote innovation-led growth across industry, agriculture, services, and public sectors.
Core Functions:
- Policy Advisory:Assists governments in designing national productivity strategies.
- Capacity Building:Conducts training programs, workshops, and research initiatives to boost productivity skills.
- Centres of Excellence:Facilitates innovation and best practices sharing among members.
- Green Productivity:Promotes environmentally sustainable growth models.
- Digital & Innovation Ecosystem:Encourages digital transformation and entrepreneurship through regional collaboration.
Organizational Structure:
- Governing Body:The apex decision-making entity; sets strategic direction and reviews performance annually.
- National Productivity Organizations (NPOs):Act as nodal agencies coordinating with the APO at the national level.
- Secretariat:Based in Tokyo, headed by a Secretary-General, manages daily operations.
Significance for India:
- India’s chairmanship marks a step forward in shaping regional productivity policies and highlights India’s commitment to sustainable development and economic cooperation in the Asia-Pacific.
New Framework for Regulation Formulation and Public Consultation

- 10 May 2025
In News:
The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) has introduced a structured framework designed to standardize the creation and revision of its regulatory policies. This initiative aims to enhance transparency, consistency, and public engagement throughout the regulatory process.
Key Aspects of the Framework
- Unified Application:The framework covers all forms of RBI regulations, including directions, guidelines, notifications, policies, and standards.
- Mandatory Public Consultation:Draft regulations are required to be published on the RBI’s official website along with a detailed Statement of Particulars. These drafts will remain open for public comments for a minimum period of 21 days, allowing stakeholders to provide their inputs.
- Impact Evaluation:Each draft must clearly outline its objectives, conduct an impact assessment, and reference relevant international best practices and global standards to ensure comprehensive evaluation.
- Response to Feedback:After considering public comments, the RBI will release a summary addressing the feedback alongside the final version of the regulations.
- Regular Review:Existing regulations will undergo periodic reassessment based on supervisory insights, alignment with global developments, and their continued applicability in a dynamic environment.
Significance of the Framework
- Enhances Transparency and Inclusiveness:By inviting public participation, the framework ensures a more open and accountable regulatory process.
- Encourages Evidence-Based Policy:The incorporation of impact analysis and stakeholder feedback supports more informed and effective policymaking.
- Aligns with Global Standards:The framework positions India’s regulatory governance in harmony with international best practices.
- Boosts Regulatory Efficiency:Continuous review and rationalization help in eliminating redundant regulations and improving overall governance.
Quantum Computing

- 08 Mar 2025
In News:
NITI Ayog releases strategic paper on implication of quantum computing on national security.
What is Quantum Computing?
Quantum computing utilizes quantum bits (qubits), which leverage the principles of superposition and entanglement, enabling them to exist in multiple states simultaneously. Unlike classical bits (0 or 1), qubits can perform parallel computations, exponentially increasing processing power.
Global Landscape and India's Position
- Global Investments: Over $40 billion invested by 30+ nations.
- China: $15 billion (leader)
- USA and EU: Close followers
- India: Launched the National Quantum Mission (NQM) in 2023 with a budget of ?6,003 crore (~USD 750 million) to boost indigenous capabilities in computing, cryptography, communication, and sensing.
National Quantum Mission (NQM): Key Highlights
- Timeframe: 2023–2031
- Quantum Computers: Build systems with 50–1000 physical qubits using superconducting, photonic, and other platforms
- Secure Communication: Satellite-based secure quantum links over 2000 km within India and long-distance secure communication with other nations
- Quantum Sensing & Metrology: Development of precision navigation tools like atomic clocks and magnetometers
- Thematic Hubs (T-Hubs): To be established in premier R&D institutes in four domains:
- Quantum Computing
- Quantum Communication
- Quantum Sensing & Metrology
- Quantum Materials & Devices
Quantum Technology in Defence& National Security
- Cybersecurity
- Existing encryption standards will become obsolete.
- Urgent need for Post-Quantum Cryptography (PQC) to protect critical digital infrastructure.
- Signals Intelligence (SIGINT) & Espionage
- Quantum computers can decrypt communications at scale, risking exposure of classified diplomatic and military data.
- Enables real-time data processing for advanced surveillance.
- Military Applications
- Quantum materials improve stealth detection and weapon precision.
- Enhances autonomous weapons and navigation in GPS-denied environments.
- Logistics & Planning: Quantum AI can optimize defence logistics, battlefield resource allocation, and strategic decision-making.
- Economic Security: Quantum computing can protect or exploit vulnerabilities in financial systems, posing potential risks to economic stability.
Challenges for India
- Funding Gap: India’s allocation is modest compared to global peers.
- Hardware Dependence: Relies on imports for cryogenic systems, high-purity materials, and specialized lasers.
- Limited Industry Participation: India's ecosystem is academia-driven, with limited private sector engagement.
- Cybersecurity Risk: Legacy systems vulnerable to quantum attacks.
- Talent Shortage: Lack of trained quantum scientists and engineers.
- Geopolitical Race: Export restrictions by advanced countries can limit India’s access to key technologies.
Recent Advances in Quantum Technology
- Atom Computing/ColdQuanta: Improved qubit coherence for stable computations.
- IBM/Quantinuum: Enhanced qubit control and error reduction.
- Google Willow Chip: Introduced self-correcting qubit system.
- Microsoft Majorana-1: Developed topological qubits to improve fault tolerance.
Recommendations by NITI Aayog
- Policy & Preparedness:
- Form a National Quantum Task Force to monitor global trends and threats.
- Develop an Early Warning System for quantum vulnerabilities.
- Implement a PQC Transition Plan across critical sectors.
- R&D & Startups:
- Increase funding to scale quantum startups and indigenous hardware.
- Promote public-private partnerships to commercialize academic research.
- Supply Chain Development:Invest in domestic manufacturing for quantum components like chips and lasers.
- Global Engagements:
- Strengthen partnerships with the US, EU, and Japan.
- Advocate for easing export controls to access vital technologies.
African-Asian Rural Development Organization (AARDO)

- 26 Feb 2025
In News:
The 21st AARDO Conference recently concluded in New Delhi, reaffirming the commitment to community-led rural development, local knowledge sharing, and South-South cooperation.
About AARDO
- Full Form: African-Asian Rural Development Organization
- Nature: Intergovernmental, autonomous organization
- Established:March 31, 1962
- Headquarters:New Delhi, India
- Origin:
- Conceptualized at the 1955 East Asian Rural Reconstruction Conference (Tokyo)
- Formalized after the 1961 Afro-Asian Conference on Rural Reconstruction (New Delhi)
- Permanent HQ established in 1966 in India
Membership
- Full Members:32 countries from Asia and Africa (e.g., India, Bangladesh, Egypt, Zambia, Malaysia)
- Associate Members:3 entities (e.g., Korea Rural Community Corporation, Agricultural Bank of Sudan)
- Eligibility: Open to Afro-Asian countries that are full or associate members of the UN or its specialized agencies focused on rural development
Observer Status with International Organizations
AARDO has observer status with:
- FAO – Food and Agriculture Organization
- IFAD – International Fund for Agricultural Development
- UNDP – United Nations Development Programme
- UNESCO – United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization
- UNCTAD – United Nations Conference on Trade and Development
Objectives & Aims
- South-South Cooperation: Enhance technical and economic collaboration in rural development between Asia and Africa
- Sustainable Rural Development: Promote poverty alleviation, food security, and climate-resilient agriculture
- Capacity Building & Knowledge Sharing: Encourage exchange of best practices, innovations, and research
Functions
- Policy & Dialogue Platform: Facilitates discussions among member countries on rural development strategies
- Training & Capacity Building: Organizes international, regional, and national training programs to strengthen rural institutions
- Research & Action Studies: Initiates and disseminates research on shared challenges in agriculture and rural livelihoods
- Pilot Projects: Offers technical and financial assistance for pilot projects to serve as replicable models
- International Collaboration: Partners with UN agencies, regional bodies, and NGOs for integrated rural development
- Data Sharing: Provides members with disaggregated statistics and information for informed decision-making
Mahabodhi Mahotsav at Sanchi

- 30 Nov 2024
In News:
A two-day Mahabodhi Mahotsav is currently being held at the Great Stupa in Sanchi, Madhya Pradesh, a UNESCO World Heritage Site.
Key Highlights:
- The festival will include religious ceremonies and cultural activities centered around the relics of Lord Buddha’s chief disciples, Sariputra and Maudgalyayana.
- Cultural Significance: The Mahotsav serves as a platform for celebrating and reaffirming the cultural and spiritual heritage of the region, with a focus on the teachings of Lord Buddha.
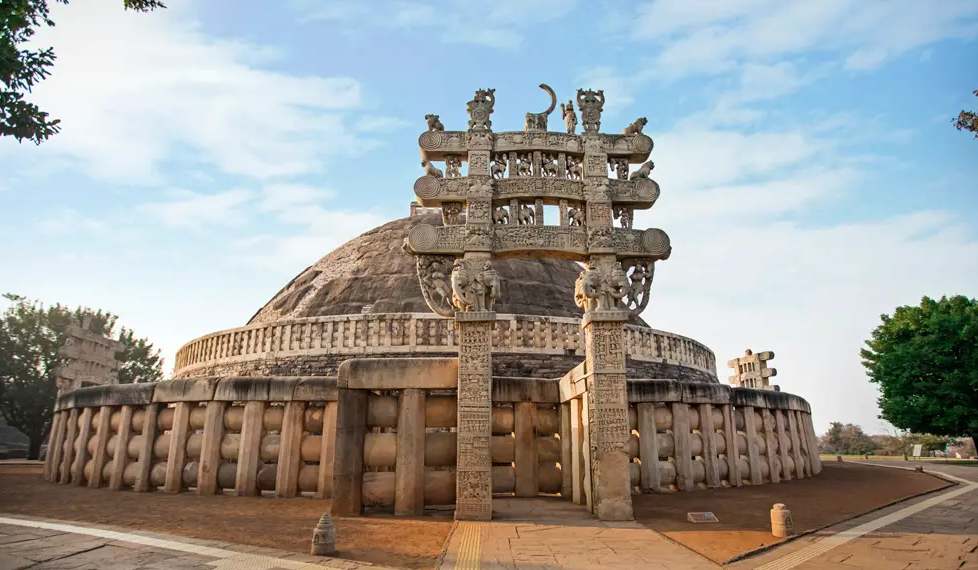
About Sanchi Stupa:
Sanchi Stupa is one of the oldest and most significant monuments of Buddhist architecture in India. It has stood as a symbol of Buddhist history, spirituality, and culture for over two millennia.
- Historical Importance:Commissioned by Emperor Ashoka in the 3rd century BCE, the stupa was later expanded by the Shunga and Satavahana rulers. It stands as a testament to the spread of Buddhism across India and beyond.
- Architectural Features:
- Hemispherical Dome (Anda): The large dome represents the universe, encapsulating the essence of Buddhist cosmology.
- Chatras: The umbrella-like structures on top of the dome symbolize divine protection and royalty.
- Harmika: A small balcony on the dome, which is considered the abode of the gods.
- Medhi: The base of the stupa, which stores sacred relics.
- Toranas: Four intricately carved gateways that depict scenes from the life of Buddha and various Jataka tales. These gateways point to the four cardinal directions, symbolizing the universality of Buddha’s teachings.
- Vedica: The railings surrounding the stupa serve as sacred enclosures.
- Paradakshinapatha: Pathways for circumambulation, allowing devotees to walk around the stupa as a sign of respect.
- Symbolism:The stupa’s architecture is an example of early Buddhist aniconism, where the Buddha is not directly depicted but is represented symbolically through footprints, wheels, or empty thrones.
- Inscriptions:The stupa contains important inscriptions, including the Ashokan Lion Capital and inscriptions in Brahmi and Kharosthi scripts, reflecting the historical significance of the site.
- UNESCO World Heritage Status:In 1989, Sanchi Stupa was declared a UNESCO World Heritage Site, recognizing its exceptional historical and cultural importance as a center for Buddhist art, architecture, and philosophy.
Significance of the Mahabodhi Mahotsav:
The Mahabodhi Mahotsav at Sanchi not only provides a spiritual experience but also highlights the historical and cultural legacy of Buddhism in India. The event brings attention to the preservation and promotion of Buddhist heritage, reflecting India’s rich diversity and commitment to maintaining its ancient traditions. Through this festival, Sanchi continues to be a center of pilgrimage and learning, attracting visitors from around the world who seek to understand and experience the teachings of Lord Buddha.
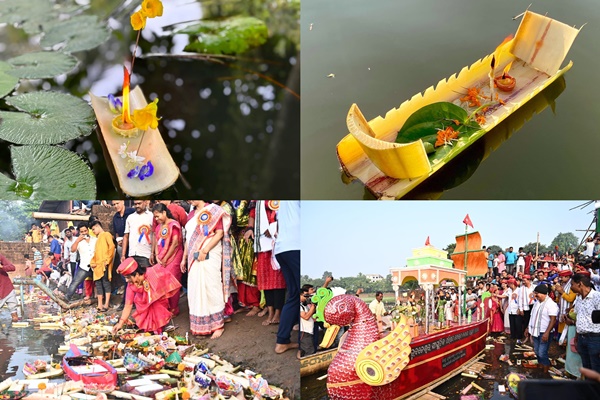
Bali Jatra Cuttack Utsav 2024

- 17 Nov 2024
In News:
- Bali Jatra 2024 is being held from November 15 to November 22 in Cuttack, Odisha.
- The festival celebrates Odisha’s ancient maritime history and its cultural and trade links with Southeast Asia.
- The event has gained international attention due to the participation of diplomats and cultural troupes from ASEAN, BIMSTEC, and Pacific Island countries.
Historical and Cultural Significance:
- Bali Jatra ("Voyage to Bali") commemorates the 2,000-year-old maritime trade routes between ancient Kalinga (modern-day Odisha) and Southeast Asia, including regions like Bali, Java, Sumatra, Borneo, Burma (Myanmar), and Sri Lanka.
- The festival honors the skills of Kalinga sailors who contributed to the prosperity of the region through trade, including commodities like pepper, cinnamon, cardamom, silk, camphor, gold, and jewelry.
- It highlights Odisha’s maritime legacy and the cultural exchanges between India and Southeast Asia, particularly the cultural influence of Odia merchants on Bali.
Commercial and Economic Aspects:
- Bali Jatra is Asia’s largest open-air trade fair, featuring over 2,500 stalls selling a variety of products including artisanal crafts, household items, and food.
- The event is a major commercial activity with business transactions estimated to exceed ?100 crore over the course of the festival.
- The festival provides an opportunity for both local and national traders to exhibit products at competitive prices.
Cultural Performances and International Participation:
- The festival includes daily cultural performances showcasing Odissi dance, Chhau dance, Bihu, Mahari, Gotipua, Sambalpuri, and Santali folk dances.
- This year, cultural troupes from countries like Indonesia, Thailand, and Sri Lanka have participated, enhancing the international profile of the festival.
- Diplomats, including Ambassadors, High Commissioners, and Heads of Mission from 14 countries attended the inaugural ceremony.
Historical Background of Bali Jatra:
- The festival is linked to Kartika Purnima, the full moon night of the month of Kartika, marking the annual migration of traders from Odisha to Southeast Asia.
- Traders used boats called Boitas to travel to distant lands, which is now symbolically represented in the festival.
- The event’s cultural significance extends to the recognition of Odisha’s historic maritime routes, with ports like Tamralipti, Manikpatna, Chelitalo, Palur, and Pithunda playing key roles in global trade from as early as the 4th century BC.
Kalinga's Maritime Influence:
- The Kalinga Empire (present-day Odisha) had significant influence over the Bay of Bengal, referred to as the Kalinga Sea.
- Kalinga’s dominance in maritime trade is reflected in Kalidasa's Raghuvamsa, where the King of Kalinga is called "Lord of the Sea."
- Kalinga's Boitas (ships) were instrumental in connecting India with the Southeast Asian archipelago, including Bali.
Cultural Linkages with Bali:
- Odisha's trade with Bali influenced the culture, religion, and architecture of the region.
- Balinese Hinduism today still reflects Indian influences, with worship of Hindu deities like Shiva, Vishnu, Brahma, and Ganesha.
- The MasakapankeTukad festival in Bali, similar to Bali Jatra in Odisha, is a tribute to the maritime ancestors of Bali and commemorates the long-standing cultural ties.
Recognition and Milestones:
- Bali Jatra 2022 achieved a Guinness World Record for creating the largest collection of origami sculptures.
- The festival has evolved from a traditional trade fair to an international cultural event that highlights Odisha’s historical role in global trade and cultural exchanges.
Zhurong Rover
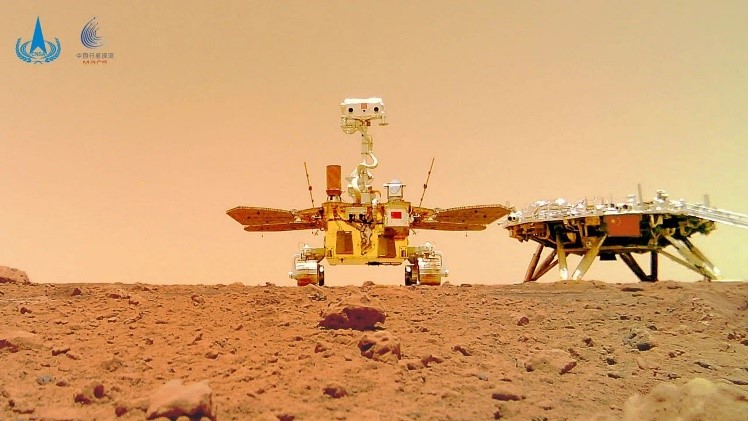

- 10 Nov 2024
In News:
Chinese rover helps find evidence of ancient Martian shoreline.
Mission Overview:
- Rover: Zhurong, part of China’s Tianwen-1 Mars exploration program.
- Mission Launch: Zhurong landed in 2021 in the Utopia Planitia region of Mars' northern hemisphere.
- Key Discovery: Evidence of an ancient ocean on Mars, suggesting a habitable past for the planet.
Key Findings:
- Geological Features Indicating a Coastline:
- Data from Zhurong and orbiting spacecraft (Tianwen-1 Orbiter, NASA's Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter) revealed geological features such as troughs, sediment channels, and mud volcano formations, suggesting the existence of a Martian coastline.
- Features indicate both shallow and deeper marine environments, supporting the idea of a past ocean.
- Age of the Ocean:
- The ocean likely existed around 3.68 billion years ago, with its surface potentially frozen in a geologically short period.
- The ocean is thought to have disappeared by 3.42 billion years ago.
Evolutionary Scenario of Mars:
- At the time of the ocean, Mars might have already begun transitioning away from a habitable planet, losing much of its atmosphere and becoming cold and dry.
- The ocean may have formed after Mars' climate began to change, suggesting that it was once more hospitable, possibly capable of supporting microbial life.
Implications for Life on Mars:
- The presence of water, a key ingredient for life, raises the possibility that Mars could have supported microbial life in its early history.
- When Mars had a thick, warm atmosphere, conditions might have been favorable for life, as microbial life would have been more likely to exist.
Significance of Zhurong's Contribution:
- Zhurong exceeded its original mission duration of three months, operating until May 2022, helping provide key data to understand Mars' ancient water history.
- The discovery adds to ongoing efforts to study the disappearance of water on Mars and its implications for the planet's habitability.
Future Exploration:
- Other studies, including seismic data from NASA’s InSight lander, suggest that liquid water might still exist deep beneath the Martian surface, hinting at the possibility of finding water in the planet's subsurface in the future.
PyPIM platform
- 09 Nov 2024
In News:
Israeli researchers from the Israel Institute of Technology have developed the PyPIM platform, which allows computers to process data directly in memory, eliminating the need for a central processing unit (CPU). This breakthrough aims to address key challenges in modern computing, particularly in terms of energy consumption and processing efficiency.
Key Features of the PyPIM Platform:
- Integration with Python and PIM Technology:
- The PyPIM platform merges Python programming with digital processing-in-memory (PIM) technology, facilitating in-memory computing where computations occur directly within memory instead of transferring data to and from the CPU.
- Functionality and Innovations:
- Direct In-Memory Computations: PyPIM uses specialized instructions that enable computations to take place directly in memory, reducing the need for data movement between the CPU and memory.
- Developer-Friendly: It allows developers to use familiar languages like Python to write software for in-memory computing systems.
- Solving the "Memory Wall" Issue:
- The platform addresses the memory wall problem, where the speed of the CPU and memory exceeds the data transfer rates, creating bottlenecks that lead to inefficiencies.
- By performing calculations directly in memory, PyPIM reduces time and energy spent on data transfer, optimizing performance.
- Performance Improvements:
- Energy and Time Efficiency: By minimizing energy-intensive data transfers, PyPIM leads to significant energy and time savings.
- Simulation Tools: The platform includes tools that allow developers to simulate potential performance improvements from in-memory processing.
- Real-World Benefits:
- Faster Processing: Tasks performed using PyPIM have demonstrated faster processing speeds, with minimal code changes, particularly in mathematical and algorithmic tasks.
- The platform delivers a significant performance boost in areas like data analysis and algorithmic operations.
The PyPIM platform marks a pivotal advancement in computing architecture, providing a more energy-efficient and faster alternative to traditional CPU-dependent systems by reducing reliance on external memory processing and cutting down on data transfer delays.
