Agni-3 Intermediate-Range Ballistic Missile (IRBM)

- 08 Feb 2026
In News:
India has successfully test-fired the Intermediate-Range Ballistic Missile (IRBM) Agni-3 from the Integrated Test Range (ITR), Chandipur, Odisha, validating all operational and technical parameters. The launch was conducted under the aegis of the Strategic Forces Command, confirming the missile’s operational readiness.
What is Agni-3?
- Agni-3 is an indigenously developed Intermediate-Range Ballistic Missile (IRBM).
- It is a surface-to-surface missile and a key component of India’s land-based nuclear deterrent.
- Developed by Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO).
- It has already been inducted into the armed forces and is operationally deployed under the Strategic Forces Command.
Key Technical Features
- Type: Intermediate-Range Ballistic Missile (IRBM)
- Range: 3,000–3,500 km
- Propulsion: Two-stage, solid-fuelled
- Payload Capacity: ~1.5 tonnes (1,500 kg)
- Warhead: Conventional or nuclear
- Estimated Nuclear Yield: 200–300 kilotons
- Length: 16.7 metres
- Diameter: 2 metres
- Launch Weight: ~48,300 kg
Guidance & Accuracy
- Uses strap-down inertial navigation system (INS) supported by GPS
- Accuracy: ~40 metres Circular Error Probable (CEP)
- Considered one of the most accurate strategic ballistic missiles in its range class
Structural & Design Highlights
- First Stage: Maraging steel motor case
- Second Stage: Carbon-fibre motor case
- Thrust Vector Control (TVC) in both stages for enhanced stability and precision
Launch & Mobility
- Launch Platforms: Road-mobile and rail-mobile launchers
- Enhances survivability, flexibility and second-strike capability
Strategic Objectives
- Ensures credible minimum deterrence
- Strengthens second-strike capability
- Provides strategic depth beyond short- and medium-range missiles
- Enhances deterrence across extended regional theatres
Agni Missile Series
Conceptualised under the Integrated Guided Missile Development Programme (IGMDP) in the 1980s
- Agni-I: 700–1,250 km
- Agni-II: 2,000–2,500 km
- Agni-III: 3,000–3,500 km
- Agni-IV: 3,000–4,000 km (advanced systems, field trials)
- Agni-V: ~5,000+ km (ICBM-class, canisterised, road-mobile)
- Agni-VI: Under development (expected 8,000–10,000 km; land & sea-based)
- Agni Prime: New-generation, lighter, canisterised missile (1,000–2,000 km)
Dolomedes indicus
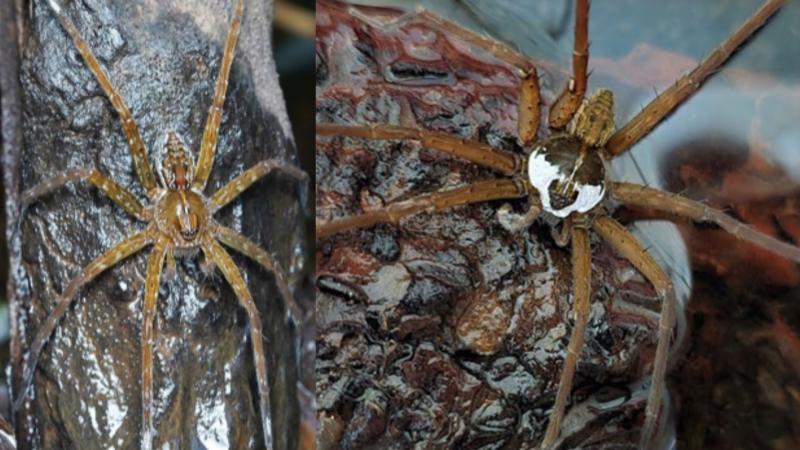

- 10 Dec 2025
In News:
Researchers have discovered a new spider species, Dolomedes indicus, in the evergreen rainforests of the Western Ghats, specifically in Wayanad district, Kerala.
What is Dolomedes indicus?
- Dolomedes indicus is a newly identified species of spider belonging to the genus Dolomedes, commonly known as raft spiders or fishing spiders.
- This discovery marks the first recorded member of the Dolomedes genus in India.
Genus Dolomedes (Raft/Fishing Spiders)
- Members of this genus are known for their semi-aquatic lifestyle.
- Unlike web-building spiders, they are active hunters.
- They are typically found near freshwater streams, ponds, and wetlands.
Habitat
- Found in evergreen forest streams of the Western Ghats, a global biodiversity hotspot.
- Prefers cool, clean, shaded freshwater habitats under dense forest canopies.
- Its presence indicates pristine stream ecosystems with minimal disturbance.
Behaviour and Hunting Strategy
Dolomedes indicus is a semi-aquatic predator that:
- Uses surface tension of water to stand and move on water surfaces
- Detects vibrations caused by insects or small aquatic animals struggling in water
- Swiftly lunges across the water to capture prey
- Is capable of swimming and diving to escape predators or catch prey
This makes it ecologically different from typical web-dependent house spiders.
Physical Characteristics
- Males: Identified by a distinctive snow-white marking extending from the face to the middle of the back
- Females: Larger in size and greenish-brown, helping them camouflage against mossy rocks and streamside vegetation
Sexual dimorphism (difference in appearance between males and females) is clearly visible.
Ecological Importance
- Being highly sensitive to environmental changes, Dolomedes indicus may serve as an indicator species
- Its survival depends on:
- Clean freshwater
- Stable forest canopy cover
- Undisturbed stream ecosystems
Thus, its presence can help scientists monitor freshwater ecosystem health and assess the impact of habitat degradation.
Significance of Discovery
- Highlights the rich but understudied biodiversity of the Western Ghats
- Expands the known geographical range of the Dolomedes genus
- Emphasizes the importance of conserving freshwater habitats within forest ecosystems
Bioremediation
- 03 Dec 2025
In News:
Human waste is leading to a world where access to clean air, water and soil is becoming increasingly difficult. The solution is two-pronged — reduce waste and clean up the waste already made.
What is bioremediation?
Bioremediation refers to the use of living organisms to clean up environmental pollution. The term literally means “restoring life through biology.” It involves harnessing microorganisms such as bacteria, fungi, algae, and plants to degrade, transform, or neutralise harmful contaminants in soil, water, and air.
These organisms use pollutants like oil, pesticides, plastics, and some heavy metals as sources of energy or nutrients. Through natural metabolic processes, they break down toxic substances into less harmful by-products such as water, carbon dioxide, and organic acids. In certain cases, microbes can also convert toxic metals into less mobile or less bioavailable forms, reducing their environmental impact.
Types of Bioremediation
Bioremediation is broadly classified into two types:
- In situ bioremediation involves treating contamination at the original site without removing soil or water. For example, oil-degrading bacteria may be applied directly to an oil spill.
- Ex situ bioremediation involves removing contaminated material to a controlled environment for treatment and returning it once cleaned. This is often used for heavily polluted soil or wastewater.
The effectiveness of bioremediation depends on factors such as temperature, pH, oxygen availability, and nutrient levels, which influence microbial growth and activity.
Modern Advances
Modern bioremediation combines traditional microbiology with advanced biotechnology. Scientists now use genetic and molecular tools to identify microbes with specific pollutant-degrading abilities. In some cases, genetically modified (GM) microorganisms are being designed to break down persistent pollutants like certain plastics or petroleum residues that natural microbes struggle to degrade.
Nanotechnology is also being explored, such as absorbent materials that help collect oil or pollutants before microbial treatment.
Why Bioremediation is important for India
India faces severe environmental challenges due to rapid industrialisation, urbanisation, and poor waste management. Many rivers receive untreated sewage and industrial effluents, while agricultural soils are affected by pesticide residues and heavy metals. Oil spills, landfill leachates, and industrial waste further degrade ecosystems and threaten public health.
Traditional remediation methods are often expensive, energy-intensive, and may generate secondary pollution. Bioremediation offers a cost-effective, scalable, and environmentally friendly alternative, especially for a country with vast contaminated areas and limited remediation resources.
India’s rich biodiversity provides an advantage, as indigenous microbes adapted to local climatic conditions can be more effective than imported strains.
Status of Bioremediation in India
Bioremediation is gradually gaining ground in India, though largely at pilot and project levels. Government-supported research institutions and universities are working on microbial solutions for treating sewage, industrial effluents, oil spills, and contaminated soils.
The Department of Biotechnology (DBT) has supported clean technology initiatives, and research organisations such as CSIR laboratories and IITs have developed microbial formulations and innovative materials for environmental cleanup. Start-ups are also entering the sector with products for wastewater and soil treatment.
Bioremediation aligns with national initiatives such as NamamiGange, Swachh Bharat Mission, and sustainable waste management efforts.
Advantages
Bioremediation is considered environmentally friendly because it relies on natural biological processes rather than harsh chemicals. It is generally cost-effective, requires less heavy infrastructure, and can offer a long-term solution, as pollutants are broken down rather than merely transferred elsewhere. It is particularly useful for treating oil contamination and organic pollutants.
Limitations and Risks
Bioremediation is not universally applicable. It works best for biodegradable pollutants, and some contaminants, particularly certain heavy metals and synthetic chemicals, may not be fully removed. The process can also be slow, sometimes taking months or years.
The use of genetically modified microorganisms raises biosafety concerns. If not properly regulated, their release into open environments could have unintended ecological impacts. There is also a need for site-specific knowledge, regulatory standards, and skilled personnel for large-scale adoption.
Pharmacogenomics: Towards Precision Medicine
- 24 Nov 2025
In News:
Pharmacogenomics is increasingly being highlighted as a transformative approach in healthcare, enabling personalised drug prescriptions based on an individual’s genetic makeup and moving away from the traditional “one-size-fits-all” model of treatment.
What is Pharmacogenomics?
Pharmacogenomics is the study of how genetic variations influence an individual’s response to medicines. It combines pharmacology (study of drugs) with genomics (study of genes) to determine whether a drug will be effective, ineffective, or potentially harmful for a specific person. This approach replaces trial-and-error prescribing with precision medication.
Scientific Basis
- Genetic differences, especially in drug-metabolising enzymes such as the cytochrome P450 (CYP) family, significantly affect drug absorption, metabolism, and clearance.
- Nearly 75% of commonly prescribed drugs are metabolised by CYP enzymes.
- Variations create different metaboliser types:
- Poor metabolisers → drug accumulation and toxicity
- Ultrarapidmetabolisers → reduced drug efficacy
- Studies show that ~90% of individuals carry at least one actionable pharmacogenetic variant, making this clinically relevant at the population level.
Clinical Applications
- Cardiovascular Medicine:
- Warfarin: Variants in CYP2C9 and VKORC1 explain ~50% of dose variability. Genotype-guided dosing reduces bleeding risk and stabilises therapy faster.
- Clopidogrel: Loss-of-function variants in CYP2C19 reduce drug activation, increasing risk of stent thrombosis; guidelines now recommend alternative drugs for poor metabolisers.
- Psychiatry:Antidepressants and antipsychotics metabolised by CYP2D6/CYP2C19 show improved outcomes and fewer side effects with genetic-guided prescribing.
- Oncology:Screening for DPYD variants before using 5-fluorouracil prevents severe, life-threatening toxicity.
- Immunology & Neurology:Testing for HLA-B*57:01 (Abacavir) and HLA-B*15:02 (Carbamazepine) prevents fatal drug reactions such as Stevens–Johnson syndrome.
Economic Relevance
- Cost of genetic testing has declined sharply to USD 200–500 per panel.
- Pharmacogenomics is most cost-effective in chronic diseases requiring long-term medication.
- Preventing even a single serious adverse drug reaction can offset testing costs for multiple patients.
- Pre-emptive panel testing offers lifetime utility, guiding prescriptions for dozens of drugs.
Key Challenges
- Knowledge Gaps: Limited pharmacogenomics training among doctors and pharmacists.
- Infrastructure: Lack of electronic health record–based decision-support systems.
- Regulatory & Reimbursement Issues: Inconsistent insurance coverage and evolving regulatory guidance.
- Research Complexity: Millions of SNPs must be linked accurately to drug response, and drug development for small genetic subgroups can be costly.
Way Forward
- Promote pre-emptive genetic testing integrated with electronic health records.
- Strengthen medical education and clinical guidelines on pharmacogenomics.
- Expand digital clinical decision-support systems.
- Encourage public–private investment to lower costs and widen access.
Batten disease

- 11 Nov 2025
In News:
Batten disease refers to a group of rare, inherited neurodegenerative disorders that primarily affect the brain and nervous system. Scientifically, it is known as neuronal ceroid lipofuscinosis (NCL).
Nature of the Disease
- It is a congenital, progressive, and terminal neurological disorder.
- Onset may occur in infancy, childhood (most commonly), or rarely adulthood, often after an initial period of normal development.
- The disease leads to a gradual and irreversible decline in nervous system function.
Genetic Basis
- Batten disease is caused by mutations in a group of genes collectively called CLN genes.
- There are 13–14 recognised forms (CLN1 to CLN14), each linked to a different gene mutation.
- CLN3 disease is the most common form, typically manifesting between 4–7 years of age.
Clinical Features
- Early symptoms often include progressive vision loss, which is usually the first noticeable sign.
- Other major manifestations:
- Seizures
- Cognitive decline
- Loss of motor coordination and speech
- Behavioural and learning difficulties
- In advanced stages, affected individuals may become blind, non-ambulatory, unable to speak or swallow, and require full-time care.
- Life expectancy varies by subtype and age of onset, ranging from early childhood to the second or third decade of life.
Treatment Status
- No curative treatment exists at present.
- Management is symptomatic, including:
- Anti-epileptic drugs for seizures
- Physical and occupational therapy to maintain function and quality of life
- Several gene therapy approaches are currently under advanced research and experimental stages.
Recent Scientific Developments
Recent research has highlighted that sex and age significantly influence disease progression, particularly in CLN3 Batten disease.
- Researchers from the University of Rochester used electroencephalography (EEG) to non-invasively track brain function.
- Studies on mouse models of CLN3 disease revealed:
- Male mice showed early auditory processing deficits that partially improved with age.
- Female mice exhibited persistent auditory and brainwave abnormalities, indicating faster or more sustained progression.
- Similar EEG-based biomarkers had earlier been identified in human CLN3 patients, enabling better disease monitoring.
- The findings were published in the Journal of Neurodevelopmental Disorders.
Significance
- Confirms that Batten disease progression differs by sex, with females often showing later onset but more rapid progression.
- Establishes EEG-based neuromarkers as a reliable tool to track disease progression.
- Provides a translational animal model to test emerging therapies, especially gene-based interventions.
- Supports the future development of personalised and time-sensitive treatment strategies.
MAHA MedTech Mission
- 27 Oct 2025
In News:
The Anusandhan National Research Foundation (ANRF), in collaboration with the Indian Council of Medical Research (ICMR) and the Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation, has launched the Mission for Advancement in High-Impact Areas (MAHA)–Medical Technology (MedTech).This landmark initiative seeks to accelerate innovation in India’s medical technology ecosystem, reduce dependence on costly imports, and ensure affordable, high-quality healthcare technologies for all.
About the MAHA MedTech Mission
- Launched by: ANRF, in partnership with ICMR and Gates Foundation
- Mission Duration: 5 years
- Deadline for Concept Note Submission: 7 November 2025
- Implemented through: ANRF online portal – www.anrfonline.in
The mission represents a strategic push under the government’s Aatmanirbhar Bharat vision to strengthen India’s domestic MedTech sector, which is currently import-heavy and fragmented.
Objectives of the MAHA MedTech Mission
- Public Health Impact:
- Promote technologies addressing priority disease areas such as tuberculosis, cancer, neonatal and maternal care, and primary healthcare.
- Expand access to safe, high-quality medical care across India.
- Affordability and Accessibility:
- Support innovative solutions that reduce healthcare costs while maintaining quality standards.
- Promote equitable access to advanced medical devices, especially in rural and underserved regions.
- Self-Reliance and Competitiveness:
- Catalyze indigenous research, manufacturing, and commercialization in MedTech.
- Foster industry–academia collaboration and boost India’s global competitiveness in medical innovation.
Scope of the Mission
The MAHA MedTech Mission will support a wide range of medical technologies and innovations, including:
- Medical devices and equipment
- In-vitro diagnostics (IVDs) and subcomponents
- Implants and surgical instruments
- Assistive and wearable devices
- Consumables and disposables
- AI/ML-driven software-based medical platforms
- Robotics, imaging, and minimally invasive technologies
- Point-of-care and molecular diagnostics
These innovations will target priority national health areas, promoting early disease detection, efficient treatment delivery, and improved healthcare infrastructure.
Funding Mechanism
- Milestone-linked funding:
- ?5–25 crore per project
- Up to ?50 crore for exceptional projects with transformative potential.
- Eligible Applicants:
- Academic and R&D institutions
- Hospitals and clinical research centers
- Startups and MSMEs
- Established MedTech industries
- Interdisciplinary collaborations between public and private entities
The funding structure encourages translational research, product prototyping, clinical validation, and commercialization of indigenous medical technologies.
Enabling Support Framework
The Mission also provides institutional and regulatory facilitation through several national support programs:
- Patent Mitra:Facilitates intellectual property protection, patent filing, and technology transfer.
- MedTech Mitra:Provides regulatory guidance, helps in obtaining clinical and market approvals, and supports compliance with national and international standards.
- Clinical Trial Network:Offers access to a national network of hospitals and research centers for clinical validation and evidence generation.
- Mentorship and Industry Linkages:Access to industry mentors, market experts, and commercialization partners to support end-to-end product development.
Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine 2025
- 09 Oct 2025
In News:
The 2025 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine was awarded jointly to Mary Brunkow, Fred Ramsdell, and Shimon Sakaguchi for their pioneering work on peripheral immune tolerance. Their research identified the critical role of regulatory T-cells (Tregs) in preventing the immune system from attacking the body’s own tissues.
The Human Immune System
The immune system protects the body against harmful pathogens, including bacteria, viruses, fungi, and parasites. It is composed of:
- Organs: Bone marrow, thymus, spleen, lymph nodes, and tonsils.
- Cells: White blood cells (leukocytes), including lymphocytes, macrophages, and neutrophils.
- Molecules: Antibodies, cytokines, and complement proteins.
Its central challenge is distinguishing between harmful invaders and the body’s own healthy cells, including those altered by mutation or cancer.
B-Cells and T-Cells
Lymphocytes, including B-cells and T-cells, are key players in immune defense.
- B-cells: Produce antibodies to neutralize antigens. Main types include plasma cells and memory cells.
- T-cells: Originate in the bone marrow, mature in the thymus, and migrate to lymphoid tissues and the bloodstream. Types include:
- Cytotoxic T-cells: Destroy virus-infected and tumor cells.
- Helper T-cells: Coordinate immune responses by signaling other immune cells.
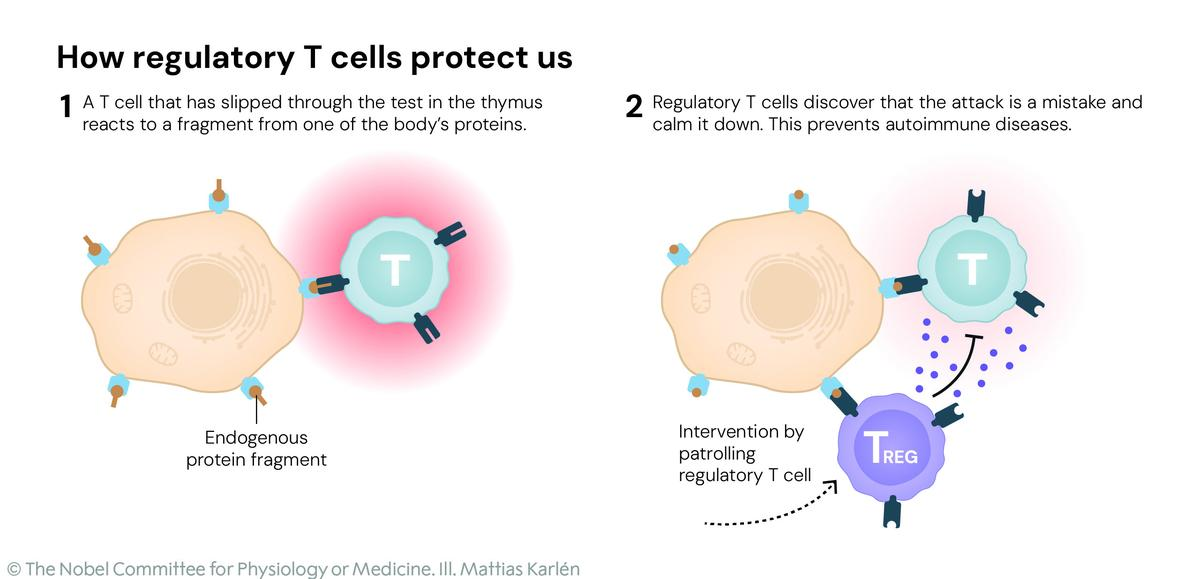
- Regulatory T-cells (Tregs): Suppress excessive immune activity, preventing autoimmune reactions and maintaining self-tolerance.
Discovery and Significance
The laureates’ research revealed regulatory T-cells as the immune system’s “security guards,” preventing it from attacking the body.
Key implications:
- Advanced understanding of peripheral tolerance, the mechanism by which the immune system avoids self-damage.
- Informed the development of therapies for autoimmune diseases, cancer, transplantation, and chronic inflammatory conditions.
- Highlighted that tumors may recruit Tregs to evade immune destruction, providing insights for cancer immunotherapy.
The discovery reshaped immunology by showing that the immune system is not solely attack-oriented, but also self-regulating.
About the Nobel Prize
- Established: 1901, through Alfred Nobel’s will (largest share of his fortune dedicated).
- Fields: Physics, Chemistry, Physiology or Medicine, Literature, Peace; Economics added in 1968.
- Awarding Institutions:
- Karolinska Institute: Physiology or Medicine
- Royal Swedish Academy of Sciences: Physics, Chemistry, Economics
- Swedish Academy: Literature
- Norwegian Nobel Committee: Peace Prize
- Award Venues: Stockholm (all except Peace), Oslo (Peace Prize)
- Administration: Managed by the Nobel Foundation, independent of prize selection.
Selection Process:
- Nominations are invited from qualified individuals (scientists, professors, former laureates).
- Expert committees evaluate candidates and recommend winners.
- Final decisions rest with the respective Nobel institutions.
SarvottamYudhSeva Medals
- 24 Aug 2025
In News:
On the eve of the 79th Independence Day, President DroupadiMurmu approved the awarding of seven SarvottamYudhSeva Medals (SYSM), the nation’s highest wartime distinguished service honour, to the leaders of Operation Sindoor, marking the first such awards since the Kargil War.
About the SarvottamYudhSeva Medal:
- Institution: 26 June 1980, to recognise distinguished service of the highest order during war, conflict, or hostilities.
- Eligibility: All ranks of the Army, Navy, Air Force, including Territorial Army Units, Auxiliary and Reserve Forces, and lawfully constituted Armed Forces when embodied. Nursing officers and members of the Nursing Services are also eligible. Awards can be given posthumously.
- Design: Circular medal, 35 mm in diameter, gold gilt, with the State Emblem and inscription “SARVOTTAM YUDH SEVA MEDAL” on the obverse, and a five-pointed star on the reverse. The ribbon is golden with a red vertical stripe in the centre. Subsequent awards are recognised by a Bar on the ribbon with a miniature insignia.
- Significance: Considered the wartime equivalent of the Param VishishtSeva Medal (PVSM) for exceptional service in peacetime. Previously awarded to three officers for Kargil War leadership: Lt Gen Amarjit Singh Kalkat, Air Marshal Vinod Patney, and Lt Gen Hari Mohan Khanna.
Supreme Court orders immediate removal of stray dogs from Delhi-NCR streets
- 13 Aug 2025
In News:
The Supreme Court of India has directed the immediate removal of all free-ranging dogs from Delhi, Noida, Gurugram, and Ghaziabad. The Court emphasized permanent relocation of these animals to shelters, citing rising incidents of rabies and dog bites, particularly affecting children and vulnerable groups.
Key Features of the Order
- Complete Removal: All stray dogs are to be captured to ensure “stray-free” streets in urban and peri-urban areas.
- No-Release Policy: Unlike the earlier Animal Birth Control (ABC) approach, captured dogs will not be returned to their original localities but retained in shelters.
- Shelter Infrastructure: Authorities must build facilities capable of housing at least 5,000 dogs within eight weeks, prioritizing high-risk localities.
- Emergency Response: A 24×7 helpline with a four-hour response time is mandated to tackle bite incidents.
- Strict Compliance: Interference with the process will attract contempt of court, ensuring accountability.
Rationale Behind the Order
- Public Health Priority: With nearly 5,700 rabies-related deaths annually (95% from dog bites), the order seeks to directly curb a preventable disease.
- Protection of Vulnerable Groups: Children and the elderly face higher risks due to limited self-defence capacity.
- Policy Ineffectiveness: The sterilisation-centric ABC model has not adequately addressed aggressive or rabies-carrying dogs.
- Constitutional Angle: By invoking Article 21 (Right to Life and Liberty), the Court underlined safe mobility and freedom from fear in public spaces.
- Permanent Reform: A structural shift from temporary containment to long-term removal from public areas.
Arguments in Favour
- Public Safety: A direct life-saving intervention against rabies deaths.
- Constitutional Backing: Strengthens the right to security under Article 21.
- Urban Governance: Integrates sanitation and safety into city management.
- Accountability: Surveillance and records ensure transparency in enforcement.
- Policy Gaps Addressed: Closes loopholes of the ABC model by ending return-to-locality practices.
Concerns and Counter-Arguments
- Legal Conflict: The directive may clash with existing ABC Rules framed under the Prevention of Cruelty to Animals Act.
- Animal Welfare: Overcrowded shelters risk inhumane conditions, raising ethical concerns.
- Ecological Impact: Sudden removal could disrupt rodent control and waste management functions performed by strays.
- Risk of Abuse: Lack of monitoring might lead to covert culling under the guise of relocation.
- Rights-Based Critique: May be seen as undermining the intrinsic rights of animals and compassion-based governance.
Way Forward
- Humane Shelter Models: Ensure adequate space, veterinary care, and nutrition.
- Mass Vaccination Drives: Combine removal with preventive health measures to eradicate rabies.
- Adoption and Community Participation: Promote responsible adoption under strict guidelines.
- Policy Harmonisation: Amend ABC Rules to align with SC directions and resolve legal inconsistencies.
- Awareness and Behavioural Change: Community-level campaigns on rabies prevention and civic responsibility.
Conclusion
The Supreme Court’s intervention highlights the tension between public health imperatives and animal welfare ethics. While it seeks to secure citizens’ right to safe public spaces, it also raises concerns of legality, humane treatment, and ecological balance. Going forward, the challenge lies in striking a balance between constitutional morality (right to life) and compassion ethics (animal welfare) through coherent policy design and ethical urban governance.
Agricultural Monitoring and Event Detection (AMED) API
- 15 Jul 2025
In News:
Google has introduced a set of artificial intelligence (AI)-based innovations to advance India’s agricultural practices and enhance the cultural and linguistic relevance of global AI models.
Agricultural Monitoring and Event Detection (AMED) API
- Launched by: Google DeepMind and Google’s Partnerships Innovation Team
- Collaborators: TerraStack, IIT-Kharagpur, and other local partners
- Foundation: Built on the Agricultural Landscape Understanding (ALU) API launched in 2023
- Key Features:
- AI-Based Field Monitoring: Offers field-level insights using satellite imagery and deep learning to monitor crops and agricultural activity.
- Crop-Specific Data: Provides details on crop type, season, field size, and three years of historical cropping and land-use data.
- Event Detection: Detects agricultural changes at individual field levels, improving yield prediction and input management.
- Biweekly Updates: Data refreshed every two weeks to ensure real-time agricultural monitoring.
- Open Access for Innovation: Available for integration by agri-tech startups, financial institutions, and government bodies to support data-backed rural lending, climate adaptation, and sustainable farming practices.
- Objectives and Utility:
- Empower agriculture stakeholders with granular, real-time intelligence.
- Facilitate precision agriculture by tailoring support for soil, water, and climatic needs.
- Strengthen India's resilience to climate-related risks and promote informed policymaking.
- Help financial services design location-specific rural credit systems.
Amplify Initiative: Cultural and Linguistic Localization of AI
Google is also working to enrich AI systems with deeper understanding of India’s diversity through the Amplify Initiative, piloted earlier in Sub-Saharan Africa.
Indian Collaboration:
- Partner Institution: IIT-Kharagpur
- Goal: Create hyperlocal annotated datasets in multiple Indic languages related to healthcare, safety, and social issues.
- Aims to ensure that Large Language Models (LLMs) are better aligned with India’s cultural plurality and linguistic complexity.
Global Impact:
- Builds on success in Africa, where 8,000+ queries in 7 languages were developed by 155 experts to address issues such as chronic illness and misinformation.
Fort William Renamed Vijay Durg

- 08 Feb 2025
In News:
In a significant step towards decolonising the Indian Armed Forces and aligning with indigenous historical consciousness, Fort William, the headquarters of the Eastern Command of the Indian Army in Kolkata, has been renamed Vijay Durg. This renaming is part of a broader initiative to remove colonial-era symbols and practices and restore Indian military heritage.
Historical Background of Fort William
- Construction: The original Fort William was constructed in 1696 by the English East India Company. It was later attacked and captured by Siraj-ud-Daulah, the Nawab of Bengal, in 1756.
- The Black Hole Incident: The original fort had an inner bastion used for imprisoning captives, leading to the infamous “Black Hole of Calcutta” narrative.
- Reconstruction: After the Battle of Plassey (1757) and the defeat of Siraj-ud-Daulah, Robert Clive initiated the construction of a new fort, which was completed in 1773 or 1781 (sources differ).
- Naming: It was named Fort William in honour of King William III of England.
Architectural Features
- Design: The fort is octagonal in shape with a massive structure made of brick and mortar.
- Area: Spread across 70.9 acres on the eastern bank of the Hooghly River, it features hundreds of arched windows and lush green surroundings.
- Aesthetics: Its walls are adorned with intricate stonework, reflecting colonial military architecture.
Recent Changes and Renaming
- New Name: Vijay Durg – Inspired by Vijaydurg Fort in Maharashtra, a prominent naval base of the Marathas under Chhatrapati Shivaji Maharaj.
- Other Changes:
- Kitchener House has been renamed Manekshaw House, after Field Marshal Sam Manekshaw.
- St. George’s Gate has been renamed Shivaji Gate.
- Implementation: According to the Defence Public Relations Office in Kolkata, the name change was decided in mid-December 2024, and internal communications have already adopted the new nomenclature, though an official notification is awaited.
Broader De-Colonisation Drive in Indian Defence
The renaming of Fort William is part of a larger movement initiated by the Government of India to eliminate colonial vestiges in the armed forces. Prime Minister Narendra Modi, in a 2022 speech at Kevadia, Gujarat, urged the forces to discard “legacy systems” and move towards “freedom from the mentality of slavery (gulami ki mansikta se mukti)”.
Key Initiatives:
- Indianisation of military music during the Beating Retreat ceremony.
- Adoption of a new naval ensign (2022) inspired by the seal of Chhatrapati Shivaji Maharaj, moving away from British colonial symbols.
- Renaming of military establishments and symbols rooted in colonial heritage.
- Review publication (2024) titled “Colonial Practices and the Armed Forces – A Review”, released at the Joint Commanders’ Conference in Lucknow by Defence Minister Rajnath Singh.
M23 Armed Group

- 24 Jan 2025
In News:
The March 23 Movement (M23), a rebel group active in eastern Democratic Republic of Congo (DRC), has intensified its insurgency in North Kivu province, capturing key areas like Minova and threatening the provincial capital, Goma.
About M23 Armed Group:
- Full Form: March 23 Movement
- Formation: 2012, by mutineers from the Congolese army protesting a failed 2009 peace deal.
- Base of Operations: Eastern DRC, primarily in North Kivu province.
- Activities: Armed rebellion, territorial control, ethnic conflict, disruption of state authority.
External Support:
- Rwandan Involvement:
- UN Reports (2023): Estimated 3,000–4,000 Rwandan troops operating alongside M23.
- Rwanda alleged to have “de facto control” over M23 operations.
- Kigali denies direct territorial aggression claims.
- International Concerns: The group’s resurgence reflects broader regional instability and transnational military dynamics.
Recent Developments (2024):
- Territorial Gains: Capture of Minova; encroachment on Goma, a strategic and densely populated city.
- Humanitarian Crisis:
- Over 2,30,000 displaced since January 2024.
- Influx of injured civilians in hospitals; risk of further displacement and violence.
- Congolese Military Weakness:
- Internal instability and operational setbacks have contributed to M23’s advances.
- The Congolese army acknowledged a “breakthrough” by M23 with external backing.
Geographical Significance of the Region:
- DRC Capital: Kinshasa
- Strategic Location: Borders 9 countries—Angola, Zambia, Tanzania, Burundi, Rwanda, Uganda, South Sudan, Central African Republic, Republic of Congo.
- Topography:
- Rwenzori & Virunga Mountains: Includes active volcanoes (e.g., Mount Nyiragongo).
- Congo River: Vital for transport, hydroelectric power, and biodiversity.
- Natural Resources:
- Rich in cobalt, coltan, gold, and other rare minerals—critical to the global tech industry.
- The mineral wealth of North Kivu is a major driver of prolonged conflict.
Access to Medicine Index Report 2024

- 25 Nov 2024
In News:
- Recently, Access to Medicine Index Report 2024 was released by the Access to Medicine Foundation. The report evaluates 20 leading pharmaceutical companies on their efforts to expand access to medicines in low- and middle-income countries (LMICs).The biennial report has been published since 2008.
- Key Highlights:
- Key Areas of Evaluation
- Governance of Access: Companies’ leadership in addressing access issues.
- Research & Development (R&D): Focus on innovations for diseases prevalent in LMICs.
- Product Delivery: Efforts to ensure medicines and vaccines are accessible.
- Findings from the 2024 Report
- Gaps in Access for Low-Income Countries:
- Many pharmaceutical companies are adopting ‘inclusive business models,’ but outcomes are mixed, with transparent reporting still lacking.
- 61% of products lack specific access strategies for low-income countries.
- Exclusion from Clinical Trials:Only 43% of clinical trials take place in LMICs, despite these countries representing 80% of the global population.
- Limited Technology Transfers & Local Availability:
- Technology transfers and voluntary licensing are concentrated in countries like Brazil, China, and India.
- Sub-Saharan Africa (excluding South Africa) remains largely overlooked.
- Decline in R&D for Priority Diseases:
- Pharmaceutical companies are moving away from diseases like malaria, tuberculosis, and neglected tropical diseases, which disproportionately affect LMICs.
- Gaps in Access for Low-Income Countries:
- Key Issues in Accessing Medicines in LMICs
- Economic Barriers:
- High costs of essential medicines, including patented drugs, limit access for patients in LMICs with low purchasing power.
- Out-of-pocket expenditures lead to catastrophic financial consequences for families.
- Infrastructure Challenges:
- Poor transportation and cold chain infrastructure hamper the efficient distribution of medicines, especially in rural areas.
- Disruptions in supply chains (e.g., during pandemics) exacerbate medicine shortages.
- Regulatory Issues:Weak enforcement of regulatory frameworks results in the proliferation of substandard and counterfeit medicines, compromising treatment efficacy.
- Workforce Limitations:
- A shortage of trained healthcare professionals restricts appropriate prescription and management of medicines.
- Cultural beliefs and low health literacy further complicate adherence to treatments.
- Economic Barriers:
- Challenges Specific to LMICs
- Dual Burden of Diseases:
- LMICs face both infectious diseases and non-communicable diseases (NCDs), putting strain on fragile healthcare systems.
- 17 million people die from NCDs before age 70 annually, with 86% of these deaths occurring in LMICs.
- Need for Local Manufacturing:
- Strengthening local pharmaceutical manufacturing and distribution networks is crucial to ensure a reliable supply of essential medicines and reduce dependence on imports.
- Dual Burden of Diseases:
- Recommendations for Improving Access
- Companies should scale up efforts to bridge the health equity gap and use innovative approaches and local partnerships to improve access.
- Focus on increasing transparency in access reporting and addressing the lack of strategies for low-income countries.
- Pharmaceutical companies should refocus on diseases prevalent in LMICs, such as malaria and tuberculosis, and ensure that their R&D addresses the needs of these regions.
- Key Areas of Evaluation
Know Your Medicine (KYM) App

- 15 Nov 2024
In News:
Union Minister for Youth Affairs & Sports, Dr. Mansukh Mandaviya, has launched a nationwide appeal to strengthen the fight against doping in sports, urging athletes, coaches, and the entire sporting community to embrace the National Anti-Doping Agency (NADA) India's ‘Know Your Medicine (KYM)’ app.
Introduction to KYM App
- Launch: The app was launched by Dr. Mansukh Mandaviya, Union Minister for Youth Affairs and Sports, to combat doping in sports.
- Developer: National Anti-Doping Agency (NADA) India.
- Purpose: To prevent inadvertent doping by allowing athletes to check whether a medicine contains substances prohibited by the World Anti-Doping Agency (WADA).
Key Features of the KYM App
- Medicine Verification: The app enables athletes to verify if any medicine or its ingredients contain banned substances listed by WADA.
- Image and Audio Search: Unique search features help users easily search for specific sport-related information.
- Customizable Search: Users can select their sport category and receive relevant, sport-specific information.
- User-Friendly: Designed for athletes, coaches, and sports professionals to quickly verify medicines and ensure clean competition.
Importance of KYM App
- Supporting Clean Sports: The app promotes a fair and ethical sporting culture by reducing the risk of inadvertent doping.
- Integrity of Sports: Helps athletes avoid penalties or bans due to accidental doping, maintaining the integrity of the competition.
- Accessible Information: Provides easy access to information regarding medicines that may contain banned substances, which is crucial for athletes' health and careers.
NADA India's Mission
- Anti-Doping Awareness: The KYM app is part of NADA India’s broader initiative to educate athletes and raise awareness about the dangers of doping.
- Goal: To promote dope-free sports and ensure that athletes and coaches are equipped with the tools needed for compliance with anti-doping regulations.
NADA India: Background and Functions
- Established: NADA India was set up in November 2005 under the Societies Registration Act, 1860.
- Mission: To serve as the independent Anti-Doping Organization for India, aiming to create a doping-free sporting environment.
- Key Functions:
- Implementing Anti-Doping Code: Ensuring compliance with the World Anti-Doping Code among all sports organizations in India.
- Dope Testing Program: Coordinating a national dope testing program with stakeholders across various sports.
- Promoting Research and Education: Encouraging research on anti-doping and educating athletes on the importance of staying clean.
- Adopting Best Practices: Ensuring the implementation of high-quality standards for anti-doping programs.
Impact and Significance
- Preventing Doping: The KYM app helps prevent inadvertent doping incidents by providing athletes with the necessary tools to check their medicines.
- Supporting Athletes: It provides athletes with a reliable way to avoid banned substances in over-the-counter medications, thus safeguarding their careers.
- National and International Compliance: Supports India’s commitment to complying with international anti-doping norms, contributing to a global effort to maintain fairness in sports.
Precision Medicine, Biobanks, and Regulatory Challenges in India
- 26 Oct 2024
In News:
Precision medicine is bringing in a new era of personalised healthcare. The field began to take concrete shape when scientists were wrapping up the Human Genome Project.
Introduction to Precision Medicine:
- Precision Medicine is a novel approach to healthcare that tailors treatments and preventive strategies based on an individual’s genetics, environment, and lifestyle, instead of using a one-size-fits-all approach.
- It leverages technologies like genomics, gene editing (CRISPR), and mRNA therapeutics to address various diseases such as cancer, chronic diseases, and genetic disorders.
- Recent breakthroughs include gene therapy for restoring vision and stem cell transplants for reversing diabetes, demonstrating the transformative potential of precision medicine.
Role of Biobanks in Precision Medicine:
- Biobanks are repositories storing biological samples (blood, DNA, tissues) along with associated health data. These samples are crucial for research and development of personalized treatments.
- Large and diverse biobanks are essential for ensuring that precision medicine benefits a wide demographic, as data from homogenous groups could limit the applicability of findings.
- Recent studies using biobank data have led to breakthroughs, such as identifying rare genetic disorders and developing organoid models for high-throughput drug screening.
Precision Medicine and Biobanks in India:
- Market Growth: India’s precision medicine market is growing at a CAGR of 16%, expected to surpass USD 5 billion by 2030, contributing 36% to the national bioeconomy.
- Policy Framework: The government’s BioE3 policy aims to promote biomanufacturing, with a focus on precision therapeutics and related technologies like gene editing and cancer immunotherapy.
- Biobank Initiatives:
- Genome India Programme: Completed sequencing of 10,000 genomes from 99 ethnic groups, aimed at identifying treatments for rare genetic diseases.
- Phenome India Project: Focused on collecting 10,000 samples for improving prediction models for cardio-metabolic diseases.
- Paediatric Rare Genetic Disorders (PRaGeD) Mission: Aiming to identify genes that could help develop targeted therapies for genetic diseases in children.
Regulatory and Ethical Challenges in Biobanking:
- India’s biobanking regulations are inconsistent, hindering the full potential of precision medicine. Unlike countries like the U.K., U.S., and Japan, which have comprehensive laws addressing issues like informed consent, data protection, and privacy, India lacks a cohesive regulatory framework.
- Informed Consent Issues: In India, participants provide samples without full knowledge of how their data will be used, who will have access to it, and for how long it will be stored. This lack of transparency undermines public trust in biobank research.
- Ethical Concerns: Without a clear regulatory framework, there is a risk of misuse of biological samples, such as non-consensual data sharing and sample mishandling.
- International Implications: The absence of robust laws allows foreign pharmaceutical companies to access Indian biobank data and samples without ensuring that the Indian population benefits from the resulting research or profits.
Global Comparison of Biobank Regulations:
- International Standards: Countries like the U.K., U.S., and Japan have established comprehensive biobank regulations, addressing:
- Informed consent for sample collection and data usage.
- Privacy protection and secure storage of genetic information.
- Withdrawal rights for participants at any stage of research.
- India’s biobank regulations lack clear provisions for data protection and participant rights, limiting the effectiveness of research and undermining public confidence in biobanks.
Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine 2024: MicroRNA Research
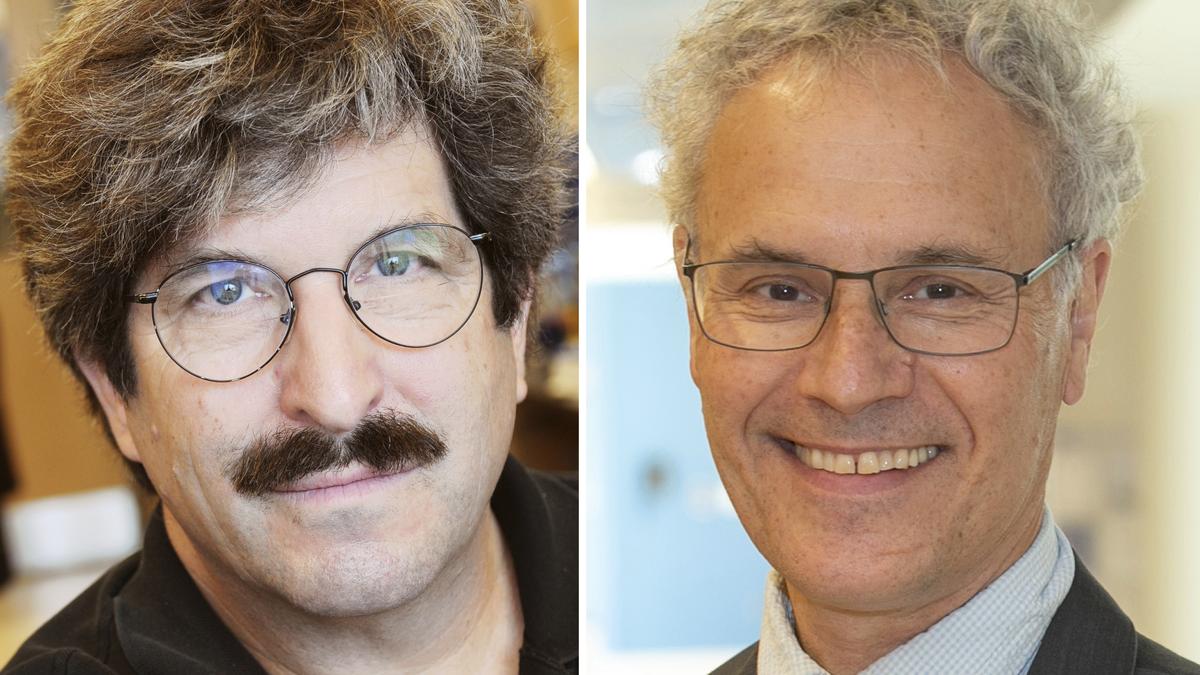

- 08 Oct 2024
Overview
The 2024 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine was awarded to Victor Ambros and Gary Ruvkun for their groundbreaking discovery of microRNA and its crucial role in post-transcriptional gene regulation. This award highlights their individual contributions to understanding how microRNAs influence gene expression, significantly advancing the field of molecular biology.
What are MicroRNAs?
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are small, non-coding RNA molecules typically 19-24 nucleotides long. They regulate protein production by interacting with messenger RNA (mRNA), ultimately influencing how much protein is synthesized from genetic information.
The Process of Gene Regulation
Gene expression involves two primary steps:
- Transcription: DNA is copied into mRNA in the nucleus.
- Translation: mRNA is translated into proteins by ribosomes with the help of transfer RNA (tRNA).
MicroRNAs play a critical role in regulating this process, particularly after transcription, by silencing mRNA and thereby controlling protein production.
Pioneering Research
Background
In the late 1980s, Ambros and Ruvkun utilized the model organism Caenorhabditis elegans, a small roundworm, to explore developmental processes. They focused on mutant strains, lin-4 and lin-14, which displayed abnormal development.
Key Discoveries
- Victor Ambros: Ambros cloned the lin-4 gene and discovered that it produced a short RNA molecule that did not code for proteins. This finding suggested that lin-4 could inhibit lin-14’s activity.
- Gary Ruvkun: Ruvkun investigated the regulation of the lin-14 gene and determined that lin-4 did not prevent the production of lin-14 mRNA. Instead, it inhibited protein production later in the gene expression process. He identified crucial segments in lin-14 mRNA essential for its inhibition by lin-4.
Collaborative Findings
Their subsequent experiments demonstrated that lin-4 microRNA binds to lin-14 mRNA, effectively blocking the production of lin-14 protein. Their findings were published in 1993 and laid the foundation for the understanding of microRNA.
Impact and Recognition
Initially, the significance of their discoveries was not widely recognized, as it was thought that microRNA regulation was specific to C. elegans. However, Ruvkun’s later identification of the let-7 gene, a microRNA found in various animal species, broadened the understanding of microRNAs' universal role in gene regulation.
Current Understanding
Today, it is known that humans possess over a thousand genes that code for different microRNAs. These molecules are crucial in regulating gene expression across multicellular organisms.
Applications and Future Directions
MicroRNAs can fine-tune gene expression, influencing various cellular functions despite similar genetic backgrounds. Abnormal microRNA regulation has been linked to diseases such as cancer and genetic disorders. While the Nobel Committee acknowledged that practical applications of miRNA research are still developing, understanding these molecules is vital for future research and therapeutic advancements.
Armed Forces (Special Powers) Act (AFSPA)

- 01 Oct 2024
In News:
- The Manipur government has extended the Armed Forces (Special Powers) Act (AFSPA) in the hill districts of the State for another six months.
- Effective October 1, the provisions of the Act will be extended to the whole State, except 19 police station limits in seven valley districts, thus maintaining the status quo, since three such notifications were passed since March 2023.
- It added that the “disturbed area” status could not be reviewed and a detailed ground assessment could not be done as “the sister security agencies are preoccupied with maintenance of law and order” and “it will be premature to arrive at any conclusion or decision on such sensitive matter without detailed assessment.”
Overview of the Armed Forces (Special Powers) Act (AFSPA)
- Enactment: The AFSPA was passed by Parliament and approved by the President on September 11, 1958.
- Context: It was introduced in response to rising violence in the North-eastern States, which state governments struggled to control.
Key Provisions of AFSPA
- Powers Granted:
- The Act empowers armed forces and Central Armed Police Forces in "disturbed areas" to:
- Kill anyone acting against the law.
- Arrest and search premises without a warrant.
- Receive protection from prosecution and legal action without Central government sanction.
- The Act empowers armed forces and Central Armed Police Forces in "disturbed areas" to:
- Issuance of Notifications:
- Both State and Union governments can issue notifications regarding AFSPA.
- The Ministry of Home Affairs issues "disturbed area" notifications for Arunachal Pradesh and Nagaland.
Definition of Disturbed Areas
- Criteria:
- A disturbed area is declared under Section 3 of AFSPA, indicating the need for armed forces' assistance in maintaining civil order.
- Factors leading to the declaration can include:
- Conflicts among different religious, racial, linguistic, or regional groups.
- Authority to Declare:
- The Central Government, the Governor of the State, or the administrator of a Union Territory can declare an area as disturbed.
- Duration:
- Once designated as disturbed, the area remains classified as such for three months, as per The Disturbed Areas (Special Courts) Act, 1976.
- State Government Input:
- State governments can recommend whether AFSPA should continue in their region.
India-Middle East-Europe Economic Corridor (IMEC)
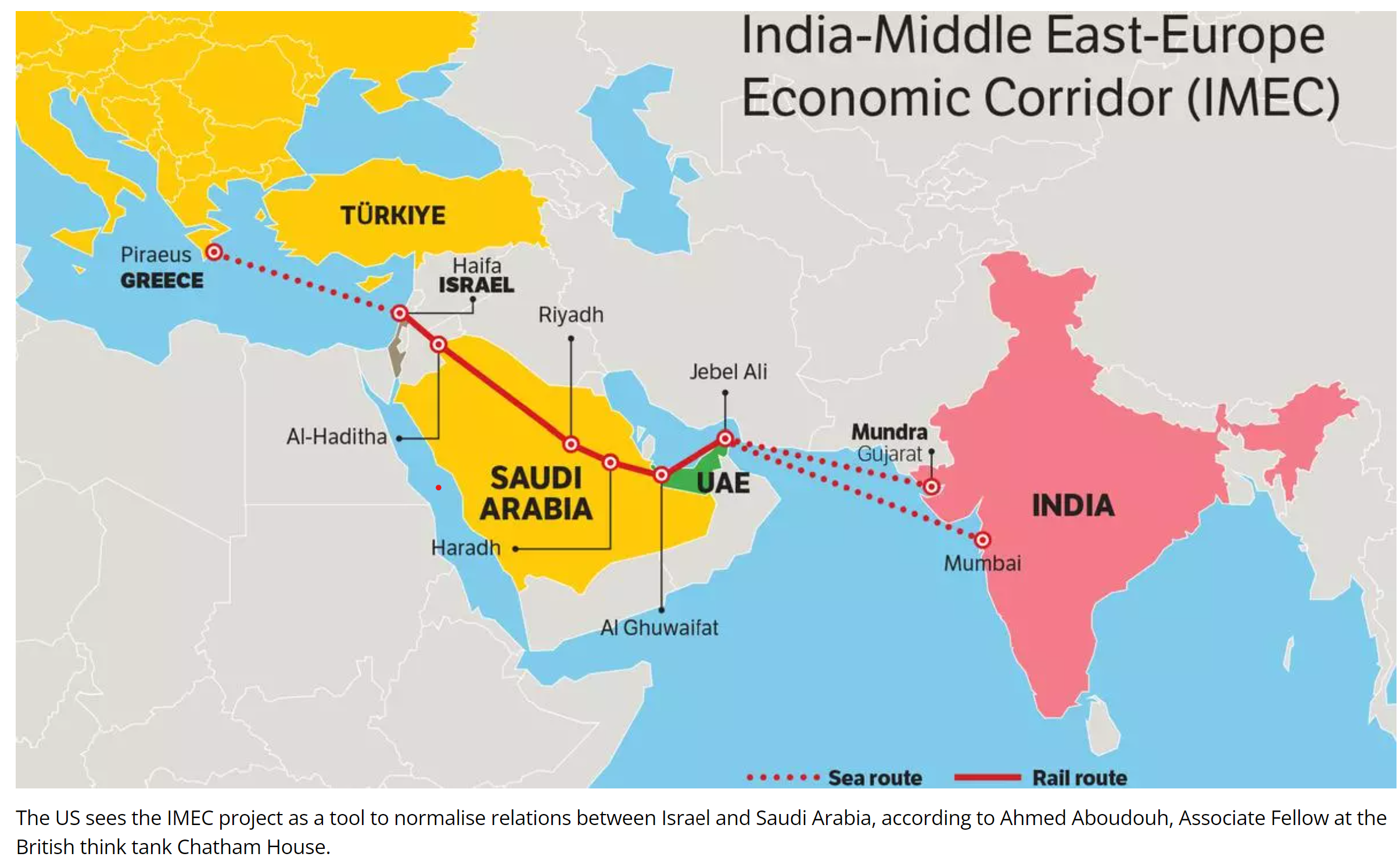
- 07 Sep 2024
In News:
IMEC is an important initiative that can add to India's maritime security and faster movement of goods between Europe and Asia, said Union Minister of Commerce & Industry at the Confederation of Indian Industry (CII) India-Mediterranean Business Conclave 2024 in New Delhi.
Key Details:
- Corridors:
- East Corridor: Connects India to the Gulf.
- Northern Corridor: Links the Gulf to Europe.
- Components:
- Railroad: Provides a reliable and cost-effective cross-border ship-to-rail transit network.
- Ship-to-Rail Networks: Integrates road, sea, and rail transport routes.
- Road Transport: Complements the overall transport infrastructure.
- Expected Benefits:
- Increased Efficiency: Enhances transit efficiency and reduces costs.
- Economic Unity: Promotes economic integration and job creation.
- Environmental Impact: Lowers greenhouse gas emissions.
- Transformative Integration: Connects Asia, Europe, and the Middle East.
- Additional Features:
- Infrastructure: Includes laying cables for electricity and digital connectivity, and pipes for clean hydrogen export.
- Implementation:
- MoU Commitments: Participants will collaboratively address technical design, financing, legal, and regulatory aspects.
- Action Plan: A meeting is planned within 60 days to develop an action plan with specific timetables.
Geoeconomic Perspective
- Economic Integration and Interdependence:
- Prosperity Through Integration: IMEC aims to foster trade and investment among India, the Middle East, and Europe, potentially leading to mutual prosperity and regional stability.
- Building Bridges: Aligns with the liberal international order by promoting economic interdependence to reduce tensions and create shared interests.
- Support from Major Powers: Backed by the US, Europe, and India, signaling a strong commitment to economic ties and regional stability.
- Economic Potential:
- Infrastructure and Trade Routes: Enhances infrastructure and trade routes, boosting economic activity, trade volumes, and investment opportunities.
- Regional Development: Promotes job creation and development in economically disadvantaged areas along the corridor.
Geopolitical Perspective
- Strategic Rivalry with China:
- Countering the BRI: IMEC is seen as a strategic counterbalance to China's Belt and Road Initiative (BRI), offering an alternative aligned with US, European, and Indian interests.
- Regional Influence: Aims to limit China’s influence in the Middle East and South Asia by establishing a competing corridor.
- Geopolitical Alliances:
- Aligning Interests: Involves strategic partnerships among the US, Europe, and India, reflecting concerns about China’s global strategy and shifting power dynamics.
- Rivalry and Competition: The IMEC could be viewed as a global positioning move, responding to China’s growing influence and securing strategic interests.
Reasons for Joining the IMEC
- Economic Enhancement:
- Boosts Indo-Gulf Relations: Enhances trade and economic ties with the Arab Gulf, addressing infrastructure gaps.
- Regional Connectivity: Links India with key partners like Israel and Jordan, boosting economic opportunities.
- Strategic Trade Routes:
- Alternative Routes: Complements existing routes like Chabahar Port and INSTC, connecting India to southern Eurasia.
- Bypassing Choke Points: Offers a shorter route to Eastern Mediterranean and Western Europe, avoiding strategic choke points.
- Energy and Trade Opportunities:
- Access to Resources: Provides potential access to Eastern Mediterranean gas fields.
- Trade Bloc Connectivity: Links India with the EU and GCC, opening up growth opportunities.
- Geopolitical Aspirations:
- Global Power Ambitions: Supports India’s goal to enhance global influence and integrate with eastern and western neighbors.
- Economic Growth: Leverages economic integration to support development and influence.
- Infrastructure Development:
- Economic Integration: Facilitates infrastructure creation for increased trade volumes and regional stability.
Dag Hammarskjold Medal
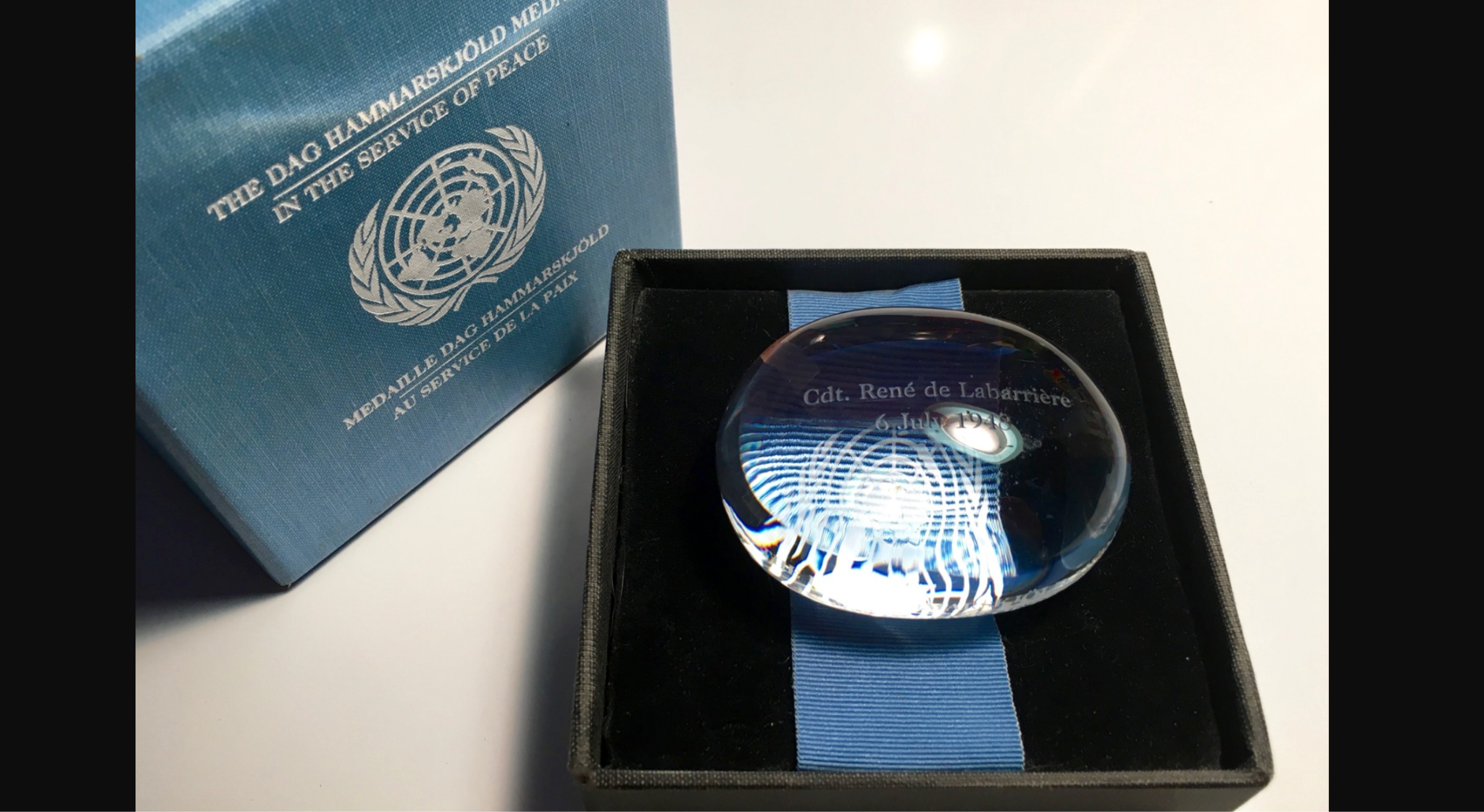

- 30 May 2024
Why is it in the News?
An Indian peacekeeper who lost his life serving under the UN flag is among over 60 military, police and civilian peacekeepers to be honoured posthumously with a prestigious medal for their service and supreme sacrifice in the line of duty.
What is Dag Hammarskjold Medal?
- The Dag Hammarskjold medal is a prestigious honour commemorating the ultimate sacrifice made by United Nations peacekeepers.
- Established in 1997, it pays tribute to those who have lost their lives while serving in UN peacekeeping missions under the organization's operational control and authority.
- This posthumous award is presented annually on Peacekeeper's Day at a solemn ceremony held at the United Nations headquarters in New York.
- Each member state that has had military or police personnel perish during peacekeeping duties receives the medal in recognition of their fallen compatriots.
- The medal bears the name of Dag Hammarskjold, the second Secretary-General of the United Nations, whose own life was tragically cut short in 1961 while working to resolve the Congo crisis.
- In naming this honour after him, the UN commemorates both his exceptional leadership and the courageous individuals who have followed in his footsteps by making the ultimate sacrifice for the cause of global peace and security.
India’s Role in Peacekeeping:
- India is currently the second largest contributor of uniformed personnel to UN Peacekeeping after Nepal.
- India is followed by Uganda with 5,764 personnel, and Bangladesh with 5,393.
- These personnel are deployed across 12 UN peacekeeping missions across the world.
- Traditionally, India has always been among the biggest contributors of UN peacekeepers.
- Since 1950, approximately 2, 86,000 Indian soldiers have served in the UN across the globe.
- UN peacekeeping missions are mandated under Article 99 by which the Secretary-General is granted the authority to independently address potential global conflicts or threats.
- Also seen as a very robust diplomatic tool, it is also a way in which the Secretary-General flags the issue to the UN Security Council.
- The functions of UN peacekeeping operations range from maintaining peace and security to escorting humanitarian relief, upholding human rights, supporting the fight against gender-based violence to assist in the restoration of the rule of law and facing the complex crises of today from climate change to pandemic.
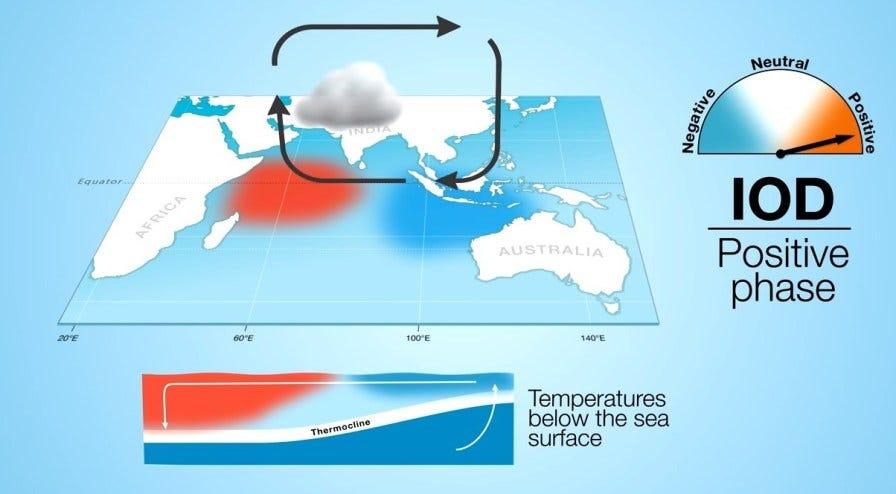
Indian Ocean Dipole (IOD)
- 08 May 2024
Why is it in the News?
The Positive Indian Ocean Dipole (IOD), also known as the Indian Nino, could potentially resurface for the second consecutive year during the latter part of 2024.
What is the Indian Ocean Dipole (IOD)?
- The Indian Ocean Dipole (IOD) is defined by the difference in the sea surface temperature between the two equatorial areas of the Indian Ocean – a western pole near the Arabian Sea (in western Indian Ocean) and an eastern pole closer to the Bay of Bengal (in eastern Indian Ocean).
- The IOD affects the climate of Southeast Asia, Australia and other countries that surround the Indian Ocean Basin.
- The Indian Monsoon is invariably influenced by the IOD.
- IOD is simply the periodic oscillation of sea surface temperatures, from ‘positive’ to ‘neutral’ and then ‘negative’ phases.
- If the sea surface temperature of the western end rises above normal (0.4°C) and becomes warmer than the eastern end, it leads to a positive IOD.
- This condition is favourable for the Indian Monsoon as it causes a kind of barrier in the eastern Indian Ocean and all the southwesterly winds blow towards the Indian sub-continent.
- Accordingly, the waters in the eastern Indian Ocean cool down, which tends to cause droughts in adjacent land areas of Indonesia and Australia.
- Conversely, during a negative IOD period, the waters of the tropical eastern Indian Ocean are warmer than water in the tropical western Indian Ocean.
- This results in increased rainfall over parts of southern Australia.
Effects on India:
- A positive IOD can boost India's southwest monsoon performance depending on its development timing.
- Example: In 2019, a strong IOD event improved a 30% rainfall deficit during the late monsoon season.
- Benefits for agriculture through recharging water sources and reservoirs.
- The development of IOD likely benefits India's agricultural sector, particularly in areas with precarious water storage levels.
Difference between El Nino and IOD:
- The Indian Ocean Dipole (IOD) and the El Nino are independent climatic phenomena but often co-occur.
- Both IOD and El Nino result in changes in global wind patterns. To know about the change of wind patterns, click here.
- However, the cycle of IOD is shorter, while El Nino condition could last for even two years.
- IOD commences in the month of May and ends with the withdrawal of the Southwest Monsoon in the Indian sub-continent.
Five Eyes Intelligence-sharing Network

- 03 May 2024
Why is it in the News?
Recently, the Australian Broadcasting Corporation (ABC) reported that “Indian spies” had been “kicked out of Australia” after being caught trying to steal secrets about sensitive defence projects and airport security, as well as classified information on Australia’s trade relationships”.
What is the Five Eyes?
- The Five Eyes is an intelligence alliance comprising Australia, Canada, New Zealand, the United Kingdom and the United States, formed in 1946.
- The alliance is based on a series of bilateral agreements on surveillance and intelligence-sharing.
- These arrangements are commonly known as the United Kingdom-United States Communication Intelligence Act (UKUSA) agreement.
- The UKUSA agreement is a secret pact that, since 1946, has allowed the two countries to share intelligence with each other.
- The UKUSA agreement was so secret that its existence wasn't even acknowledged until 2005.
- Each of the Five Eyes states pursues interception, collection, and decryption activities and shares all intelligence information obtained with the others by default.
- These countries share information with each other through the ultra-sensitive STONEGHOST network, which has been claimed to contain "some of the Western world's most closely guarded secrets".
- The Five Eyes states share integrated programmes, staff, and bases.
Origins of the Five Eyes
- During World War II, informal secret meetings between British and American code-breakers laid the groundwork for establishing the FE alliance.
- After the Cold War, the information-sharing arrangement became formalised under the ECHELON surveillance system in the 1960s.
How does the Five Eyes Alliance operate?
- The alliance facilitates the sharing of signals intelligence among the five countries.
- The countries agree to exchange by default all signals intelligence they gather.
- The bedrock of the Five Eyes Alliance is based on the joint abilities of the United Kingdom's Government Communications Headquarters (GCHQ) and the USA's National Security Agency (NSA) to intercept intelligence.
- These agencies collect and decrypt signal intelligence, called SigInt, which involves internet, telephone, radio and satellite data from across the world.
- The UKUSA Agreement, which was made public in 2010, states:
- "It will be contrary to this agreement to reveal its existence to any third party whatsoever" and "each party will seek the agreement of the other to any action with third parties and will take no action until its advisability is agreed upon."
'Egg Shell Skull' Rule

- 30 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
Underlining that the state and central consumer courts incorrectly applied the ‘eggshell skull’ legal principle, the Supreme Court recently restored the compensation of Rs 5 lakhs awarded by the district consumer forum in a medical negligence case.
What is the ‘Eggshell Skull’ Rule?
- The eggshell skull rule is a common law principle applied in civil litigation.
- Essentially, when the offender would be liable for all injuries that might be intensified due to the peculiar conditions of the injured person that the offender might not have known.
- Simply put, the defendant would be held responsible for injuries caused to a person when he hit him on the head, even if the victim had a particularly delicate skull or an ‘eggshell’ for a skull.
- A person who has an eggshell skull would be more severely impacted by an act, which an otherwise “normal person” would be able to withstand.
- The rule is applied for claiming an enhanced compensation, for damage that is more than what could have been ordinarily anticipated to be caused by the defendant.
Origin of the ‘Eggshell Skull’ Rule:
- The 'eggshell skull' rule, also known as the 'thin skull rule,' is a legal doctrine that holds a defendant liable for all consequences resulting from their negligent or intentional actions, even if the victim's pre-existing vulnerability worsens the outcome.
- The rule's origins can be traced back to an 1891 US case, Vosburg v. Putney, in which a boy kicked another's shin without knowing about his prior injury, leading to complications.
- The Wisconsin Supreme Court held that the defendant was responsible for the subsequent harm, even though he did not intend to cause such severe damage.
- A similar case in England a decade later involved a pregnant woman who experienced severe shock and gave birth to a disabled child after a horse van was negligently driven into a public house where she worked.
- The King's Bench upheld the principle that defendants are liable for the harm caused to victims, regardless of pre-existing vulnerabilities.
- The eggshell skull rule has been applied in various legal cases across different jurisdictions, emphasizing that defendants are accountable for the consequences of their actions, even when victims' unique vulnerabilities contribute to more significant harm.
What was the Jyoti Devi Medical Negligence Case?
- In 2005, Jyoti Devi underwent an appendix removal surgery in Himachal Pradesh, India.
- However, her abdominal pain persisted, leading to a four-year ordeal and multiple hospital visits.
- Eventually, doctors discovered that a 2.5 cm needle had been left in her abdomen during the initial surgery, requiring another operation to remove it.
- Jyoti sought compensation for medical negligence and was initially awarded Rs 5 lakhs by the district consumer forum.
- The hospital appealed, leading to the state consumer forum reducing the compensation to Rs. 1 lakh, and the National Consumer Disputes Redressal Commission (NCDRC) increasing it to Rs. 2 lakhs.
What did the SC Rule?
- The Supreme Court (SC) restored the original Rs 5 lakh compensation, criticizing the lower compensation amounts as "paltry" and "unjust."
- The SC ruled that the 'eggshell skull' rule did not apply in Jyoti's case since there was no evidence of a pre-existing vulnerability or medical condition that contributed to her suffering.
- The court cited two factors for increasing the compensation: Jyoti's prolonged pain over five years and the decade-long legal battle she endured.
Sulthan Bathery

- 11 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
BJP suggests renaming Sulthan Bathery to Ganapathivattam due to historical identity alteration by Tipu Sultan.
Where Does the Name Ganapathyvattam Come From?
- Sulthan Bathery, one of the three municipal towns in Wayanad has a stone temple that was once known as Ganapathyvattam.
- The temple, built in the prevalent architectural style of the Vijayanagar dynasty, was constructed by Jains who migrated to Wayanad from areas in present-day Tamil Nadu and Karnataka in the 13th century.
- The temple was partly destroyed during the invasions of Tipu Sultan, the ruler of Mysuru in the second half of the 18th century.
- Between 1750 and 1790, today’s northern Kerala was invaded several times by the rulers of Mysuru, Hyder Ali and his son Tipu.
- It remained abandoned for nearly 150 years.
- Later, it was taken over by the Archaeological Survey of India, which declared it as a monument of national importance.
- The town of Ganapathyvattam, on the route between Mysore and the ports of the Arabian Sea, also gained prominence as a trading center and a stopover.
The History of Sultan Bathery:
- The armies of Tipu destroyed temples and churches and forced many in the path of the invasion to flee to escape forced religious conversion.
- Tipu Sultan used the Maha Ganapathy temple in Sulthan Bathery as a battery or store for weapons for his army in the Malabar region (today’s North Kerala, including Wayanad).
- This led to the British recording Ganapathyvattam as “[Tipu] Sultan’s Battery”, and the name survived as Sulthan Bathery.
Presence of Ozone on Jupiter's Moon Callisto

- 02 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
An international team of scientists, including from India, has discovered strong evidence indicating the presence of ozone on Jupiter’s moon Callisto, shedding light on the complex chemical processes taking place on icy celestial bodies in the Solar System.
Study on the Formation of Ozone in Callisto's Icy Environment:
- A recent study examined the chemical evolution of sulfur dioxide (SO2)-rich astrochemical ice found on Callisto's surface when exposed to ultraviolet (UV) radiation.
- The investigation revealed a unique signature indicating the formation of ozone, which could have implications for the potential habitability of the Jovian moon.
- Callisto is Jupiter's second-largest moon and the third-largest moon in our solar system.
- It has a relatively stable surface, which could play a vital role in preserving subsurface oceans or potential habitats beneath its icy crust.
- The study analyzed UV absorption spectra data from ice samples containing SO2, a primary component of Callisto's surface ice, and observed the generation of ozone under UV irradiation.
- Ozone formation on Callisto could have implications for the moon's astrobiological potential, as ozone can protect the surface from harmful radiation.
- Further research is needed to better understand the implications of this discovery on Callisto's habitability and the potential for future exploration missions.
Callisto's Distinctive Environment:
- Following Saturn, Jupiter boasts the second-highest number of moons in the Solar System, with Callisto ranking among its largest moons and holding the position of the third-largest moon overall, after Ganymede and Titan.
- Comprised predominantly of water ice, rocky elements, sulfur dioxide, and traces of organic compounds, Callisto presents a compelling potential for harboring life beyond Earth within the Solar System.
- The moon's extensively cratered surface bears witness to a lengthy history of impacts from asteroids and comets.
Importance of the Research:
- The identification of ozone on Callisto hints at the existence of oxygen, a crucial component essential for the development of intricate molecules vital for life, including amino acids, thus prompting inquiries into the moon's potential for sustaining life.
- This finding also has implications for other icy moons within our Solar System, offering insights that could broaden our comprehension of habitable environments beyond Earth.
Significance of Ozone:
- Consisting of three oxygen atoms bonded together, the ozone molecule plays a pivotal role in shielding life on Earth.
- Situated in the lower region of the Earth's stratosphere, approximately 15-35 kilometers above the surface, the ozone layer acts as a protective barrier.
- Without this layer, ultraviolet radiation would intensify, posing significant threats to various species and disrupting ecosystems.
- Ultraviolet-B and ultraviolet-C, with wavelengths ranging from 290 to 320 nanometers and 100 to 280 nanometers respectively, can cause DNA damage, and mutations, and elevate the risk of skin cancer and cataracts in humans.
- Furthermore, ultraviolet light can impede plant growth and adversely affect diverse organisms.
Cannabis

- 26 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
During the celebration of Holi across India, Bhang, derived from the Cannabis sativa plant or true hemp, is widely favored for consumption.
What is Cannabis?
- Cannabis is found mainly in the Indo-Gangetic plains – in Himachal Pradesh, Punjab, Haryana, Uttar Pradesh, Bihar, and West Bengal – along with the Deccan region.
- Cannabis is termed Ganzai in Telugu, Ganja in Tamil, and Bangi in Kannada.
- The cannabis plant can be 4 to 10 feet tall at maturity.
- Its plant also grows on wastelands and can easily be spotted on roadsides.
- Three products can be obtained from the plant – fiber, oil, and narcotics.
- Bhang is obtained from the seeds and leaves of the plant, which are reduced to powder.
- Then, the powder is filtered and prepared for drinking, mixed often with cold, flavored milk or thandai on Holi.
Additional Uses and Benefits of Cannabis:
- According to the Indian Council of Agricultural Research (ICAR), cannabis ash can be applied to animals' skin in cases of hematoma, a condition characterized by blood clotting outside of blood vessels.
- Hemp-seed oil is employed in varnish industries as a substitute for linseed oil and in soft soap manufacturing, as well as possessing numerous medicinal properties.
- In Himachal Pradesh, cannabis cultivation is concentrated in Chhota/Bada Bhangal of Kangra and the Karsog area of Mandi district.
- While cultivating cannabis for addictive narcotics is illegal, states permit regulated cultivation for industrial or horticultural purposes, focusing on fiber and seed extraction.
- Cannabis-based treatments, such as bhang application on paddy seeds, can enhance germination and control threadworms in paddy nurseries, particularly in the temperate regions of Jammu and Kashmir.
- Heated and crushed cannabis leaves are often transformed into a paste to alleviate pain from a honey bee or wasp stings.
Pusa Basmati Rice

- 21 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
Even as basmati rice exports from the country are poised to scale a new high, scientists at the Indian Agricultural Research Institute (IARI) have red-flagged the “illegal” cultivation of its blockbuster varieties in Pakistan.
Unauthorized Cultivation and Export of Pusa Basmati Rice Varieties in Pakistan:
- Despite being officially registered and protected Indian varieties, several IARI-bred Basmati rice varieties, such as Pusa Basmati 1121, Pusa Basmati-6, and Pusa Basmati 1509, are being illegally cultivated and marketed in Pakistan.
- Recent YouTube videos even feature newer IARI varieties like Pusa Basmati-1847, PB-1885, and PB-1886, released in late 2021.
- Pakistan's unauthorized Basmati exports have been substantial, with 7.58 lt ($694.55 million) in 2021-22 and 5.95 lt ($650.42 million) in 2022-23 (July-June).
- This growth is partly due to the depreciation of the Pakistani rupee, allowing the country to offer lower export prices than India.
- The proliferation of these protected varieties in Pakistan can be attributed to the ease of seed multiplication.
- With just a small quantity of seeds, large-scale cultivation can be established within two years of the variety's release in India.
- This unauthorized cultivation not only undermines India's intellectual property rights but also impacts the competitiveness of India's Basmati rice exports in the global market.
What is the Basmati Crop Improvement Program?
- The Basmati Crop Improvement Program focuses on refining the unique qualities of Basmati rice, such as its distinct grain characteristics, cooking properties, and pleasing aroma.
- IARI has played a crucial role in the genetic enhancement, leading to the development of high-yielding, semi-dwarf, and photo-insensitive Basmati varieties like Pusa Basmati 1.
- These improvements have significantly reduced the crop duration from 160 to 120 days and increased productivity from 2.5 to 6-8 tons per hectare.
- As a result, these advanced Basmati varieties account for approximately 90% of India's projected $5.5 billion exports in 2023-24.
- This achievement contributes to substantial foreign exchange earnings and economic growth for the country.
Key Features of IARI-Developed Basmati Rice Varieties:
- IARI has cultivated various Basmati rice varieties with distinct characteristics, including:
- Pusa Basmati 1121: Known as the world's longest Basmati rice, it matures in 145 days with an average yield of 45 q/ha.
- Pusa Basmati 1509: Derived from Pusa 1121 x Pusa 1301, this variety addresses Pusa Basmati 1121's weaknesses, matures in 115 days, and yields 5 tons/ha.
- Improved Pusa Basmati 1 (Pusa 1460): This variety, the first product of molecular breeding in Indian rice, is an enhanced Pusa Basmati 1 with bacterial leaf blight resistance.
- Pusa Basmati 6 (Pusa 1401): Offering superior grain quality, this variety improves upon Pusa 1121's yielding ability, agronomy, and cooking quality.
- Pusa RH10: The world's first superfine grain aromatic rice hybrid, it was released in 2001 for commercial cultivation in specific irrigated ecosystems.
Registration and Cultivation Areas of Pusa Basmati Rice in India:
- All Pusa Basmati rice varieties are officially recognized under the Seeds Act 1966 and can be cultivated within the designated Geographical Indication (GI) area of Basmati rice in India, encompassing seven northern states.
- These varieties are further registered under the Protection of Plant Varieties and Farmers' Rights Act 2001, which permits only Indian farmers to sow, save, re-sow, exchange, or share the seeds of protected/registered varieties.
India’s indigenous fifth-gen fighter jet AMCA

- 09 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
The Cabinet Committee on Security (CCS) this week cleared a Rs 15,000 crore project to design and develop the Advanced Medium Combat Aircraft (AMCA), India’s fifth-generation fighter multirole fighter jet.
About Advanced Medium Combat Aircraft (AMCA)?
- The AMCA will be India’s indigenous fifth-generation fighter aircraft.
- The indigenous Light Combat Aircraft (LCA) Tejas is a 4.5-generation single-engine multirole aircraft.
- The Aeronautical Development Agency (ADA) under the Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO) will be the nodal agency for executing the programme and designing the aircraft.
- It will be manufactured by state-owned Hindustan Aeronautics Limited (HAL).
- The aircraft will put India in a select group of nations that have their own fifth-generation fighter aircraft.
- Discussions for developing the AMCA started in 2007.
- The initial plan was to jointly develop the aircraft with Russia under a Fifth Generation Fighter Aircraft (FGFA) programme.
- However, India withdrew from the FGFA project in 2018.
Features of AMCA:
- Stealth: The 25-tonne twin-engine aircraft, which will be bigger that other fighters in the Indian Air Force inventory, will have advanced stealth features to avoid detection by enemy radar.
- With stealth features, this aircraft (AMCA) would be able to compete with other stealth fighters in the world.
- Fuel & Weapons: The aircraft will have a large, concealed internal fuel tank of 6.5-tonne capacity, and an internal weapons bay for a range of weapons, including indigenous weapons, to be buried in its belly.
- Engine: The AMCA Mk1 variant will have the US-built GE414 engine of the 90 kilonewton (kN) class, while the more advanced AMCA Mk2 will fly on the more powerful 110kN engine, which will be developed indigenously by DRDO’s Gas Turbine Research Establishment (GTRE) in collaboration with a foreign defense major.
- India has been talking with Safran SA of France, one of the world’s largest manufacturers of aircraft engines and related equipment, in order to finalize the roadmap for the development of the combat aircraft engine
- Another important aspect would be to ensure a higher utilization time and smaller serviceability or maintenance periods for the aircraft.
- This will be aided by the inclusion of a comprehensive Integrated Vehicle Health Management (IVHM) system to keep track of multiple structural components, and to assess the condition of the aircraft in real time.
- Other features such as a diverterless supersonic inlet for controlling air flow into the engines, and a serpentine air intake duct to shield the engines from radar emissions, are likely to be part of the AMCA.
Other Fifth-generation Fighters:
- Only a few countries have built a fifth-generation stealth fighter aircraft.
- The list of the aircraft currently in service includes:
- The F-22 Raptor and F-35A Lightning II of the US
- The Chinese J-20 Mighty Dragon, and
- The Russian Sukhoi Su-57.
Supreme Court’s ban on Patanjali ads

- 04 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
Recently, the Supreme Court restrained Patanjali Ayurved from discrediting allopathy in its campaigns, and from advertising products that claim to cure chronic conditions.
What is the Magic Remedies Act?
- The Drugs and Magic Remedies (Objectionable Advertisements) Act of 1954 is a legislative framework to control the advertisement of drugs and prohibit claims of magical qualities in remedies.
- The Act encompasses various forms of advertisements, including written, oral, and visual mediums.
What does the Magic Remedies Act entail?
- Under the Act, “drug” refers to medicines intended for human or animal use, substances for diagnosis or treatment of diseases, and articles affecting the body’s functions.
- Other than articles meant for consumption, the definition of “magic remedy” under this Act also extends to talismans, mantras, and charms that allegedly possess miraculous healing powers or influence bodily functions.
Regulations on advertisements under the Magic Remedies Act:
- The Act imposes strict regulations on the publication of advertisements related to drugs.
- It prohibits advertisements that give false impressions, make false claims, or are otherwise misleading.
- The term “advertisement,” under the Act, extends to all notices, labels, wrappers, and oral announcements.
- Violations of these provisions can result in penalties upon conviction, including imprisonment or fines.
Punishment:
- Violating the Act can result in imprisonment, fines, or both.
- If this is the first conviction for the violator, they may face up to six months in prison, fines, or both.
- For a subsequent conviction, imprisonment may extend to one year, a fine, or both.
- The Act does not include any limits for the fines that may be imposed on individuals or organizations.
Who comes under the Magic Remedies Act?
- The Act applies to all individuals and entities involved in the publication of advertisements, including manufacturers, distributors, and advertisers.
- The Act can hold both individuals and companies accountable for contraventions.
Earth’s early evolution: Fresh insights from rocks formed 3.5 billion years ago

- 23 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
Exploring ancient cratons such as the Singhbhum Craton in India, alongside similar formations in South Africa and Australia, provides unparalleled insights into the early stages of our planet's development, reaching back approximately 3.5 billion years.
What is Singhbhum Craton?
- The Singhbhum Craton encompasses a vast expanse of rugged terrain, primarily spanning regions in Jharkhand and Odisha, situated between the Chhota Nagpur plateau and the Eastern Ghats.
- Dating back approximately 3.5 billion years, this ancient segment of the Earth's crust offers valuable insights into early geological processes.
- Its oldest rock formations consist predominantly of volcanic and sedimentary rocks, referred to as greenstone successions.
- Greenstones are characterised by submarine volcanic rocks with minor sedimentary components.
- Geologically akin to greenstone belts in South Africa's Barberton and Nondweni regions and the Pilbara Craton in Western Australia, these areas experienced extensive submarine mafic volcanic activity, rich in magnesium oxide, between 3.5 and 3.3 billion years ago, with preserved features like pillowed lava and komatiites.
Significance:
- The Singhbhum Craton sheds light on early tectonic activities during the Archaean era, enhancing our understanding of the Earth's formative stages.
- Its distinctive geological characteristics, particularly the presence of greenstone belts, yield invaluable data on surface and atmospheric processes crucial for theorising about early habitable conditions and the emergence of life on Earth.
What are Cratons?
- A craton is a stable and ancient part of Earth's lithosphere that has experienced long-term tectonic and geomorphic stability.
- It is considered to be the nucleus of a continent and is characterised by its thick and cold lithosphere.
- Cratons can undergo destruction, which is defined as a geological process resulting in the loss of craton stability due to changes in its physical and chemical properties.
- The mechanisms responsible for craton destruction include oceanic plate subduction, rollback and retreat of subducting plates, stagnation and dehydration of subducting plates in the mantle transition zone, melting of the mantle caused by dehydration of stagnant slabs, non-steady flow in the upper mantle induced by melting, and changes like the lithospheric mantle.
- Craton destruction can lead to crustal thinning, surface uplift, and the concentration of mineral deposits.
Israel discovers 6-million-year-old giant underwater canyon of Messinian Event (TOI)

- 06 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
The Israel Geological Survey announced recently that Israeli geologists discovered a huge underwater canyon on the bottom of the Eastern Mediterranean that was formed about 6 million years ago.
What is Messinian Event?
- The Messinian Event, also referred to as the Messinian Salinity Crisis (MSC).
- It marks a significant geological occurrence during which the Mediterranean Sea experienced a cycle of partial or near-complete desiccation, making it one of the most severe ecological crises in Earth's history.
- This event unfolded approximately 6 million years ago (MYA) and persisted until around 5.3 MYA.
- The process began with the severance of the connection between the Atlantic Ocean and the Mediterranean Sea.
- This disconnection resulted from a combination of reduced sea levels globally and the collision of the European and African plates, causing the land to rise.
- Consequently, the Mediterranean experienced significant evaporation, as its evaporation rate exceeded its precipitation rate.
- Without a substantial influx of water from the Atlantic, the sea began to evaporate rapidly.
- During this period, a vast underground canyon formed, with rivers cutting deep into the basin floor, creating a canyon much larger than the Grand Canyon, reaching depths of up to 2,000 meters (6562 feet).
- As the Mediterranean water evaporated, salt deposits, primarily composed of Halite and Gypsum, accumulated on the basin floor, some reaching depths of 800 meters (2,500 feet).
- Despite the rapid evaporation, salt deposition did not keep pace, resulting in an increase in water salinity.
- The heightened salinity levels made the Mediterranean inhospitable to marine life, leading to a decline in biodiversity.
- Eventually, the sea dried up almost entirely, culminating in the Zanclean flood when the Atlantic Ocean reclaimed the basin.
What is Deep-sea Canyon?
- Deep-sea canyons, such as those formed during the Messinian Event, are steep valleys carved into the seafloor of the continental slope, extending onto the continental shelf.
- These canyons vary in size and shape and have been sculpted by various erosional processes, including river flows during periods of low sea levels, mudslides, debris flows, and turbidity currents.
US Approved Sale of 31 Predator Drones to India (India Today)

- 02 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
In a significant development that underscores the deepening strategic partnership between India and the United States, the US State Department has approved a landmark Foreign Military Sale to the Indian government.
News Summary:
- The US Defense Security Cooperation Agency has formally notified the US Congress regarding a potential military sale of MQ-9B SkyGuardian drones and associated equipment to the Government of India.
What is a Drone?
- Drones are aerial vehicles powered by various means, capable of autonomous flight or remote piloting, and can carry payloads, lethal or nonlethal, depending on the mission.
Key Features of MQ-9B SkyGuardian Drones:
- Designed for extended over-the-horizon flights lasting over 30 hours, facilitated by satellite connectivity.
- Incorporates advanced capabilities to safely operate in civilian airspace, facilitating joint operations with civil authorities for real-time situational awareness.
- Equipped with sophisticated maritime intelligence, surveillance, and reconnaissance (ISR) systems, enabling real-time monitoring and patrolling both above and below the ocean's surface.
Significance of Drone Technology in Defense:
- Strategic Importance: Drones offer valuable intelligence, surveillance, and reconnaissance (ISR) capabilities, providing real-time visuals and data to support decision-making processes.
- They also reduce risks to personnel and offer cost-effective alternatives to conventional manned aircraft.
- Tactical Advantages: Drones enable precision strikes with minimal collateral damage, enhance coordination and logistics in challenging terrains, and facilitate operations in remote or hostile environments.
Challenges Associated with Drones:
- Complex Airspace Management: The integration of drones into India's airspace necessitates a robust management framework to ensure safe and efficient operations.
- Adverse Weather Conditions: Factors like strong winds can affect drone operations, highlighting the need for resilient systems capable of operating in varied environmental conditions.
- Privacy and Safety Concerns: There are concerns regarding the potential misuse of drones for breaching privacy and safety regulations, emphasizing the importance of stringent regulations and oversight mechanisms.
Medical care on India’s trains is running late, with passengers at risk (The Hindu)

- 15 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News?
The Balasore train accident in June 2023 raised important concerns about rail safety, but it was largely about accident-related safety.
Provision of Medical Care in Railway:
- In 1995, a ‘Special first aid box’ was provided in long-distance superfast trains, Shatabdi and Rajdhani trains.
- In 1996, as part of a pilot project, Railways stationed a medical team in two long-distance trains.
- This team consisted of a medical officer, a male nurse, and an attendant.
- The Railways subsequently discontinued the service – but to make healthcare accessible, it decided to give doctors travelling on trains a 10% discount if they were willing to provide medical services en route.
- In 2017, the Supreme Court directed the Railways to set up a committee consisting of experts from the All India Institute of Medical Sciences (AIIMS) to recommend further measures.
- Based on the committee’s recommendations, the Railways decided to modify the contents of the first aid boxes and provide them at all railway stations and in all passenger-carrying trains.
- It also mandated first-aid training for railway staff at the time of joining and once every three years.
- In 2021, the Railways launched an integrated helpline number – 139 – for all queries concerning the railways, including medical assistance.
Way Forward
- Railways should ensure the updated 88-item first-aid list is in place on all trains and that passengers are aware of these services.
- Periodic inspections are necessary to maintain the quality of care as well.
- Finally, the Railways need to install a system to capture data on the healthcare needs of people travelling on trains and use that to inform policy.
Modi’s Visit to Gunji Irks Nepal Opposition (Indian Express)

- 13 Oct 2023
Why is it in the News?
Prime Minister Narendra Modi’s visit to Gunji near Kalapani, Uttarakhand has triggered an uproar in Nepal.
About Gunji Village:
- Gunji Village, situated in the Dharchula tehsil of Pithoragarh district in northern Uttarakhand, holds a strategic location near the borders of Tibet and Nepal.
- Nestled at an altitude of 3500 meters, it marks the confluence of the Kuthi Yankti and Kalapani Rivers at the eastern end of the Kuthi Valley, offering stunning views of Mount Api in Nepal.
- Covering a geographical area of 188.9 hectares, Gunji is a seasonal abode for its inhabitants.
- During winters, the residents, totalling 335 people in 194 households as per the 2011 census, migrate to lower altitudes, primarily to Dharchula within the same district.
- The village is under the administration of a Sarpanch, the elected head.
- Renowned for its connection to the traditional Indian/Nepalese route to Kailas–Manasarovar, Gunji attracts visitors seeking its breathtaking vistas.
- To embark on a journey to Gunji, obtaining an Inner Line permit is a prerequisite.
What is an Inner line permit (ILP)?
- An Inner Line Permit (ILP) is an official travel document issued by the Government of India, facilitating the inward travel of Indian citizens into a protected area for a limited duration.
- It is mandatory for Indian citizens residing outside these specific states to secure a permit before entering the designated state.
- This document serves as a regulatory measure by the government to manage and monitor the movement of individuals into areas located in proximity to India's international borders.
- The concept originates from the Bengal Eastern Frontier Regulations of 1873, designed to safeguard the Crown's interests in trades such as tea, oil, and elephants by restricting the entry of "British subjects" into these designated "Protected Areas.
- In 1950, the term "British subjects" was replaced by "Citizen of India."
- ILPs come in various types, including those for tourists and others intended for individuals planning extended stays, often for employment purposes.
ICRISAT Joins One CGIAR Global Initiative (The Hindu BusinessLine)

- 12 Oct 2023
Why in the News?
The International Crops Research Institute for the Semi-Arid Tropics (ICRISAT), a Hyderabad-based international research institute with a focus on tropical dryland agrifood system innovation, has joined the One CGIAR integrated partnership.
What is One CGIAR Global Initiative?
- The One CGIAR global initiative is designed to establish a cohesive approach to transform food, land, and water systems in response to the challenges posed by the climate crisis.
- This collaborative effort involves the CGIAR System Organisation and 12 research centres operating under the umbrella of One CGIAR.
- CGIAR is a publicly-funded network of research centres focused on agrifood systems, operating in over 80 countries.
Key Facts about ICRISAT:
- ICRISAT, a non-profit, non-political international research organization, is dedicated to agricultural research for development in Asia and sub-Saharan Africa.
- Its mission is to support farmers by providing improved crop varieties and hybrids, particularly aiding smallholder farmers in arid regions to combat climate change.
- The organization specializes in research on five highly nutritious, drought-tolerant crops: chickpea, pigeonpea, pearl millet, sorghum, and groundnut.
- Recognized for its impactful work, ICRISAT was awarded the 2021 Africa Food Prize for the Tropical Legumes Project, contributing to improved food security across 13 countries in sub-Saharan Africa.
- ICRISAT is headquartered in Hyderabad, Telangana State, India, with two regional hubs in Nairobi, Kenya, and Bamako, Mali.
- Through its research and initiatives, ICRISAT plays a crucial role in addressing agricultural challenges and promoting sustainable development in diverse regions.
Union Health Minister Launches MedTech Mitra Platform to Empower Medical Technology Innovators (NewsOnAir)

- 26 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
Union Health Minister Dr Mansukh Mandaviya has launched MedTech Mitra - a strategic initiative to empower MedTech innovators and advance healthcare solutions.
What is the MedTech Mitra Portal?
- The MedTech Mitra portal is an online platform designed to support medtech innovators by assisting in clinical evaluation, regulatory facilitation, and the adoption of new products in the medical technology sector.
- This collaborative initiative is overseen by the Indian Council of Medical Research (ICMR) and the Central Drugs Standard Control Organisation (CDSCO), operating under the direction/guidance of NITI Aayog’s Atal Innovation Mission.
Significance:
- In conjunction with recent policies and incentive schemes, such as the medical devices policy and the production-linked incentive scheme, the MedTech Mitra platform aims to catalyze growth in the medical devices sector and promote domestic manufacturing.
- These initiatives seek to foster the indigenous development of affordable and high-quality MedTech devices and diagnostics, thereby significantly reducing the sector's reliance on imports.
- The platform is envisioned to streamline the innovation process and facilitate research and development for emerging start-ups, ensuring a smoother journey from concept to product.
- By offering comprehensive guidance, including support for animal and clinical trials, the platform aims to bridge gaps for startups and promote ease of innovation.
- The MedTech Mitra portal is poised to foster collaborations between engineers, scientists, and clinicians, addressing a previously existing gap in partnerships within the sector.
About the Indian Council of Medical Research (ICMR):
- The Indian Council of Medical Research (ICMR) serves as the apex institution in India responsible for formulating, coordinating, and advancing biomedical research.
- With a primary mandate to conduct, coordinate, and implement medical research for societal benefit, ICMR is dedicated to translating medical innovations into tangible products and processes, subsequently integrating them into the public health system.
- Financial support for ICMR is provided by the Government of India through the Department of Health Research, Ministry of Health & Family Welfare.
New Species of Bagworm Moth discovered From Idukki (The Hindu)

- 10 Oct 2023
Why in the News?
Researchers from the Zoology Department at St. Thomas College (Autonomous), Thrissur, have discovered a new species of bagworm moth, Wizard Bagworm, from near the Nariyampara Falls in the Idukki district.
What is a Bagworm Moth?
- Belonging to the family of moths in the order Lepidoptera, bagworm moths are recognized for their protective larval cases.
- These moths are distributed globally, with notable populations in North America and Africa.
- In their larval stage, these perennial moths inhabit various evergreen trees and junipers.
- They derive their name from the bag-like cases constructed by the larvae around themselves.
- The larvae can pose a threat to trees, particularly evergreens.
About Eumasia Venefica:
- This recently identified species earned its name due to the unique shape of its bag, resembling a wizard's hat.
- It is the fourth species within this genus to be documented in India.
- Distinctive Features:
- The species exhibits effective camouflage techniques to evade predators.
- Larval cases of Eumasia venefica are discovered attached to rocks adorned with lichens.
- These cases join together, forming a colony covered with lichens.
- The larval bags bear a resemblance to a 'witch's hat,' featuring a disc-like anterior and a tubular posterior part.
- Unlike polyphagous pests, the larvae of this species exclusively feed on algae and mosses present on rocks.
Ayushman Arogya Mandir (The Hindu)

- 30 Nov 2023
Why is it in the News?
Recently, the Union Government has decided to rename the current Ayushman Bharat Health and Wellness Centres (AB-HWCs) as 'Ayushman Arogya Mandir.'
About Ayushman Arogya Mandir:
- The government has decided to rename the Ayushman Bharat-Health and Wellness Centres as 'Ayushman Arogya Mandir'
- The rebranded AB-HWCs will also have a new tagline -- 'Arogyam Parmam Dhanam'.
- Under the Government of India's flagship Ayushman Bharat Yojana, more than 1.6 lakhs AB- HWCs have been successfully established across states and UTs over the last five years with 219 crore footfalls so far.
- Ayushman Arogya Mandir is an attempt to move from a selective approach to health care to deliver a comprehensive range of services spanning preventive, promotive, curative, rehabilitative, and palliative care.
- It has two components which are complementary to each other.
- Under its first component, 1,50,000 Ayushman Arogya Mandir will be created to deliver Comprehensive Primary Health Care, that is universal and free to users, with a focus on wellness and the delivery of an expanded range of services closer to the community.
- The second component is the Pradhan Mantri Jan Arogya Yojana (PM-JAY) which provides health insurance cover of Rs. 5 lakhs per year to over 10 crore poor and vulnerable families seeking secondary and tertiary care.
- Ayushman Arogya Mandirs are envisaged to deliver an expanded range of services that go beyond Maternal and child health care services.
- It includes care for non-communicable diseases, palliative and rehabilitative care, Oral, Eye, and ENT care, mental health, and first-level care for emergencies and trauma , including free essential drugs and diagnostic services
- More than 2.71 crore wellness sessions have been held at these centers.
Rythu Bandhu Scheme (The Hindu)

- 28 Nov 2023
Why is it in the News?
The Election Commission recently canceled the Telangana government's approval to give money to farmers through the Rythu Bandhu Scheme.
About Rythu Bandhu Scheme:
- Rythu Bandhu Scheme, also known as the Farmer's Investment Support Scheme (FISS), was initiated by the Telangana government in 2018.
- Objectives:
- Provide timely cash grants for the initial investment needs of farmers.
- Prevent farmers from falling into the debt trap.
- Financial Assistance: Rs 5,000 per acre per farmer per season directly transferred to their accounts.
- Distribution: Biannual support for both kharif and rabi harvests.
- Usage: Farmers can use funds for purchasing seeds, fertilizers, pesticides, labor, and other field operations of their choice.
- Eligibility: Open to all resident land-owning farmers, including those in forest areas with a Record of Forest Rights (ROFR).
- Special Inclusion: Farmers in forest areas, mainly from Scheduled Tribe communities, with a ROFR document, are eligible for benefits.
- It’s India's first direct farmer investment support scheme, providing cash directly to beneficiaries.
Iran has threatened to close the Strait of Gibraltar linking the Mediterranean and the Atlantic for shipping (The Hindu)
- 25 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
Recently, Iran has threatened to close the Strait of Gibraltar and the Mediterranean Sea unless Israel stops bombing Gaza.
About the Strait of Gibraltar:
- The Strait of Gibraltar is a narrow water passage that serves as a crucial link connecting Europe and Africa, facilitating the connection between the Mediterranean Sea and the Atlantic Ocean.
- Historical Significance: Prior to the inauguration of the Suez Canal in 1869, the Strait of Gibraltar held exclusive prominence as the sole gateway to the Mediterranean Sea.
- Geographical Borders: Positioned between Spain and the British Overseas Territory of Gibraltar in the north, and Morocco and the Spanish exclave of Ceuta in the south, the strait spans approximately 58 km and reaches a width of about 13 km at its narrowest point.
- Depth and Geological Formation: With depths ranging from 300 to 900 meters, the strait constitutes a significant divide between the elevated plateau of Spain and the Atlas Mountains of Northern Africa.
- Geological studies indicate that the strait originated from the northward movement of the African Plate towards the European Plate.
- High Maritime Activity: Recognized as one of the world's busiest waterways, the Strait of Gibraltar witnesses the daily transit of around 300 ships, equivalent to approximately one ship every 5 minutes.
- The Moroccan port of Tanger-Med, situated near Tangier, is a prominent port along the strait.
- Pillars of Heracles: Marking the eastern extremity of the strait, the area between the Rock of Gibraltar in the north and Mount Hacho or Jebel Moussa in the south spans approximately 23 km.
- These two land features referred to as the Pillars of Heracles, hold historical and geographical significance.
About the Mediterranean Sea:
- The Mediterranean Sea, an intercontinental body of water, is flanked by Europe to the north, Asia to the east, and Africa to the south.
- In the western expanse, it connects to the Atlantic Ocean through the narrow Strait of Gibraltar.
- To the extreme northeast, it links to the Black Sea via the Dardanelles Strait, the Sea of Marmara, and the Bosporus Strait.
- In the southeast, the Mediterranean Sea is connected to the Red Sea through the Suez Canal.
- Historical Significance: Recognized as the cradle of Western civilization, the Mediterranean Sea has played a pivotal role in the development of ancient cultures.
- Notable civilizations, including the Phoenicians, Ancient Greece, and the Roman Empire, flourished along its shores.
- Countries and Territories Along the Coast: A total of 22 countries, along with one territory (Gibraltar, a British Overseas Territory), have coastlines along the Mediterranean Sea.
- European nations with Mediterranean coastlines include Spain, France, Italy, Malta, Monaco, Slovenia, Croatia, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Montenegro, Albania, and Greece.
- Countries from the West Asian (Middle Eastern) region bordering the Mediterranean Sea include Turkey, Syria, Lebanon, Israel, Palestine (Gaza Strip), and the divided island of Cyprus.
- Additionally, five North African nations, namely Morocco, Algeria, Tunisia, Libya, and Egypt, have coastlines along the Mediterranean.
Real Estate Investment Trusts (REITs) (Indian Express)

- 27 Nov 2023
Why is it in the News?
SEBI on Saturday decided to bring entities facilitating fractional investment in real estate under a regulatory framework, whereby they will be required to operate as Small and Medium Real Estate Investment Trusts.
About Real Estate Investment Trusts (REITs):
- A Real Estate Investment Trusts (REITs) is a company that owns and typically operates income-generating real estate or related assets.
- It pools funds from investors, directing them into various commercial real estate ventures, including office buildings, shopping malls, apartments, hotels, resorts, self-storage facilities, warehouses, and mortgages or loans.
- In contrast to conventional real estate firms, REITs don't develop properties for resale; rather, they acquire and develop properties primarily for inclusion in their investment portfolio.
- REITs offer individual investors an opportunity to share in the income generated by commercial real estate without the need to directly purchase such properties.
- Typically specializing in specific real estate sectors, REITs may focus on diversified or specialty portfolios, encompassing various property types like office and retail spaces.
- Most REITs are publicly traded on stock exchanges, similar to stocks, providing high liquidity compared to physical real estate investments.
- This stock-like nature allows investors to buy or sell REIT shares on the exchange at any time.
Deepfakes (TOI)

- 25 Nov 2023
Why is it in the News?
The government has warned top social media and internet companies that their platforms may be temporarily suspended and even be ordered blocked in case they are unable to tackle the menace of deepfakes.
What are Deepfakes?
- The term "deepfake" combines the concepts of deep learning with the fabrication of content.
- Deepfakes involve the creation of synthetic images and audio using machine-learning algorithms, intending to disseminate misleading content by replacing a real person's appearance, voice, or both with artificially generated likenesses or voices.
- These manipulated creations can either depict nonexistent individuals or simulate real people engaging in actions or utterances they never did.
- Originating in 2017, the word "deepfake" emerged when a Reddit user named "deepfakes" shared explicit videos featuring celebrities.
- The process of crafting deepfakes utilizes machine learning models employing neural networks to manipulate visual and auditory elements.
- To generate a convincing deepfake video, creators train the neural network on extensive real footage of the targeted person, facilitating a realistic understanding of their appearance from various angles and lighting conditions.
- This trained network is then combined with computer graphics to overlay the person onto a different actor.
- Regrettably, this technology is increasingly exploited for malicious purposes, including scams, celebrity impersonation, election interference, social engineering, disinformation attacks, identity theft, and financial fraud.
- The distinguishing factor of deepfakes lies in their challenging detection due to their sophisticated nature.
Tantalum (NewsOnAir)

- 23 Nov 2023
Why is it in the News?
The Indian Armed Forces contingent comprising 81 personnel departed for Australia on Wednesday to take part in the second edition of Joint Military Exercise AUSTRAHIND-23.
About Exercise AUSTRAHIND-23:
- Exercise AUSTRAHIND-23 was established in 2022, with its first edition held in Mahajan, Rajasthan.
- It is planned as an annual training event, alternating between India and Australia.
- The primary goal of the exercise is to cultivate collaborative partnerships and share best practices between the two sides.
- This year, the exercise is scheduled to take place in Perth, Australia, spanning from November 22nd to December 6th, 2023.
- The Indian Army contingent, consisting of 60 personnel from a Gorkha Rifles battalion, will actively participate in this exercise.
- A key focus is on promoting interoperability during multi-domain operations in urban and semi-urban terrain, aligned with Chapter VII of the United Nations on peacekeeping operations.
- The joint exercise serves as a platform for exchanging ideas and collectively rehearsing tactics, techniques, and procedures for conducting tactical operations.
- Additionally, the exercise contributes to fostering understanding between the two militaries, further strengthening defense cooperation between the two friendly nations.
Other Exercises between India and the Aus:
- AUSINDEX - Naval exercise between India and Australia
- Exercise Pitch Black - It is a biennial warfare exercise hosted by the Royal Australian Air Force (RAAF).
The E Prime Layer (HT)
- 21 Nov 2023
Why is it in the News?
Recently, an international team of scientists found a new mysterious layer called the E prime layer on the outer part of the Earth's core.
About the E Prime Layer:
- Before, it was thought that there's only a small exchange of materials between the Earth's core and mantle.
- However, experiments showed that when water reaches the boundary between the core and mantle, it reacts with silicon in the core and creates silica.
Development of this Layer:
- New research proposes that over billions of years, tectonic plates carrying surface water transported it deep into the Earth.
- When this water reaches about 1,800 miles below the surface at the core-mantle boundary, it triggers significant chemical changes, affecting the core's structure.
- Scientists observed that under high pressure, subducted water chemically reacts with core materials.
- This reaction forms a hydrogen-rich, silicon-depleted layer on the outer core, resembling a film.
- Silica crystals produced in this process rise and mix into the mantle, impacting the overall composition.
- Changes in the liquid metallic layer could potentially lead to reduced density and altered seismic characteristics, consistent with anomalies detected by seismologists.
Importance of this Discovery:
- This finding deepens researchers' understanding of the Earth's internal workings, revealing a more extensive and complex global water cycle than previously known.
- The altered core layer has significant implications for the interconnected geochemical processes that link surface water cycles with the deep metallic core.
INS Sumedha (Financial Express)

- 15 Nov 2023
Why in the News?
In a strategic move as part of the Indian Navy’s mission-based deployment to West Africa and the Atlantic, INS Sumedha conducted a port call at Walvis Bay, Namibia recently.
About INS Sumedha:
- INS Sumedha is a Saryu-class, Naval Offshore Patrol Vessel (NOPV) of the Indian Navy.
- It is the third ship of the class to be commissioned and was built by Goa Shipyard Limited in India.
- The ship was commissioned in March 2014.
- INS Sumedha is designed to undertake a variety of missions, including fleet support operations, coastal and offshore patrolling, ocean surveillance, and monitoring of sea lines of communication and offshore assets.
- The ship is also capable of carrying out humanitarian assistance and disaster relief (HADR) operations.
- INS Sumedha has been deployed on a number of operational missions, including:
- Operation Kaveri, the evacuation of Indian citizens from Sudan in April 2023.
- The ship has also participated in a number of international exercises, including Exercise Bright Star 2023 in Egypt.
About Walvis Bay:
- Walvis Bay is a city on the coast of Namibia, in the Erongo Region.
- It is the second-largest city in Namibia, after Windhoek, and is the capital of the Erongo Region.
- It is a major port city, and is the main port for Namibia.
- The port is home to a number of shipping companies and is a major export center for Namibian goods, such as fish, minerals, and diamonds.
- Originally a German enclave during the colonial era, Walvis Bay became a vital part of Namibia after gaining independence in 1990.
- The official language of the city is English, but Afrikaans, German, and Portuguese are also spoken.
Hermes 900 Star Liner (The Hindu)

- 09 Nov 2023
Why in the News?
Adani Aerospace and Defence in partnership with Elbit Systems manufactures the complete carbon composite aerostructures for Hermes 900 and Hermes 450 in Hyderabad.
About Hermes 900 Starliner:
- The Hermes 900 StarLiner is an Israeli-made, medium-size, multi-payload, medium-altitude long-endurance (MALE) unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) designed for tactical missions.
- It is also known as the Hermes 900 Heavy-Fuel Engine (HFE).
- It is developed by Elbit Systems.
- It is a successor to the Hermes 450 series of drones, one of the most widely used military drones in the world.
- The aircraft has a service ceiling of 30,000ft and offers a flight endurance of up to 36 hours.
- The Hermes 900 has a wingspan of 15 m (49 ft) and can carry a range of multi-sensor payloads weighing up to 450kg for multiple applications.
- Payload options include electro-optical/infrared sensors, synthetic-aperture radar/ground-moving target indication, communications and electronic intelligence, electronic warfare, and hyperspectral sensors.
- The drone has direct and indirect lighting strike capability and can perform missions under instrument flight rules (IFR) in all weather conditions.
'World's Largest Meditation Centre': PM Modi inaugurates Swarved Mahamandir in Varanasi (ET)

- 19 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
Prime Minister Narendra Modi inaugurated the world’s largest meditation centre, Swarved Mahamandir, in Varanasi on December 18.
About the Swarved Mahamandir:
- The Swarved Mahamandir stands as the world's largest meditation centre, accommodating 20,000 individuals in collective contemplation.
- Situated in Varanasi, Uttar Pradesh, this spiritual haven aspires to cast a luminous spiritual aura, enveloping the globe in a state of tranquil attentiveness.
- Named after the Swarved, a profound spiritual text penned by Sadguru Shri Sadafal Deoji Maharaj, the visionary behind Vihangam Yoga and an enduring yogi, the temple serves as a bastion for disseminating Swarveda teachings.
- Emphasizing Brahma Vidya, a profound body of knowledge, it guides spiritual seekers toward sustaining an unwavering equilibrium of peace and happiness.
- Architecturally, the Mahamandir is an imposing seven-floor superstructure, adorned with a captivating design featuring 125-petal lotus domes.
- Crafted from teakwood, the intricate carvings embellishing the ceiling and doors add to its allure.
- Pink sandstone envelops the temple walls, complemented by an enchanting garden featuring medicinal herbs.
- Imprinted on the Mahamandir's walls are verses from the Swarveda, serving as an enduring testament to the spiritual wisdom that resonates within its sacred confines.
What is Vihangam Yoga?
- Vihangam Yoga, an indigenous form of Yoga and meditation, was established by Sadguru Sadafal Deo Ji Maharaj in 1924.
- The nomenclature of this practice is derived from two foundational words: "Vihag," signifying bird, and "Yog," denoting union.
- The name encapsulates the profound concept of a bird ascending from the terrestrial realm, soaring high and unbounded in the sky.
- This symbolism mirrors the ultimate aim of Vihangam Yoga – the liberation of the soul from attachments to the material world, allowing it to recognize and embrace its innate, unshackled essence.
- Only through this liberation can an individual's consciousness seamlessly merge with the universal consciousness, often referred to as the Supreme Being, leading to a state of enduring tranquillity and bliss.
India’s First ‘City Of Literature’ (Money Control)

- 01 Nov 2023
Why in the News?
Kozhikode, in Kerala, was named the ‘City of Literature’ by the Unesco Creative Cities Network (UCCN), making it the first such city in India.
About India’s First ‘City Of Literature’:
- Kozhikode (Kerala), has achieved global recognition by joining the UNESCO Creative Cities Network.
- It is now known as the 'City of Literature,' making it the first Indian city to receive this prestigious title.
- This recognition was awarded on World Cities Day, (31 October) along with Gwalior, Madhya Pradesh, which was designated a 'City of Music.'
- Prague was the first city to receive the 'City of Literature' title in 2014.
About UNESCO Creative Cities Network:
- The UNESCO Creative Cities Network is a global initiative established by the United Nations Educational, Scientific, and Cultural Organization (UNESCO) to recognize and promote cities that have made significant contributions to the development of creative industries and culture.
- The UNESCO Creative Cities Network now comprises 350 creative cities from over 100 countries.
- These cities represent seven creative fields, including Crafts and Folk Art, Design, Film, Gastronomy, Literature, Media Arts, and Music.
- Participation in the UNESCO Creative Cities Network provides cities with opportunities for international collaboration, knowledge sharing, and the exchange of best practices in creative and cultural endeavours.
- These cities serve as hubs for artistic expression, cultural preservation, and economic growth, making them vital players in the global creative economy.
- Through this network, cities work together to harness the power of culture and creativity to address common challenges and promote sustainable development, ultimately enhancing their status on the global stage.
Basohli Pashmina is Recognized with GI Tag (HT)

- 04 Oct 2023
Why in the News?
Recently, Basohli Pashmina, a traditional craft with over a century of history from the Kathua district in Jammu and Kashmir, has been granted the Geographical Indication (GI) tag.
About Basohli Pashmina:
- Basohli Pashmina is renowned for its exceptional softness, fineness, lightweight quality, insulation, and durability.
- Pashmina products include shawls, mufflers, blankets, and baskets.
- Pashmina is a premium variety of cashmere, obtained from the fine undercoat of the Changthangi mountain goats.
- These goats are found on the Changthang Plateau in Tibet and parts of Ladakh.
- The Changpa people, who are nomads living on the Changthang plateau of Tibet, are traditional producers of pashmina wool.
Armed Forces Tribunal (Indian Express)
- 27 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
The Armed Forces Tribunal (AFT) Chandigarh Bench Bar Association has taken the step of going on an unlimited strike. This strike is a response to the decision made by the AFT chairperson to move a judicial member from Chandigarh to Kolkata.
Facts About:
- The Armed Forces Tribunal (AFT) is like a special court in India for military matters, and it started in 2009 under the Armed Forces Tribunal Act, 2007.
- What it does: It deals with arguments and complaints about things like appointments, jobs, and the rules for people who are part of the Army, Navy, and Air Force.
- It handles appeals when someone disagrees with the decisions made by military courts.
- If the military court's decision seems right, the Tribunal can say so.
But if it's not right, the Tribunal can change it.
- If someone doesn't agree with what the Tribunal says, they can only go to the Supreme Court to argue their case.
- The AFT has its main office in New Delhi, and there are eight other offices in different cities.
- Each office has two important people:
A Judicial Member who is a retired High Court Judge and
An Administrative Member who is a retired Armed Forces officer with a high rank.
- Sometimes, a Judge Advocate General (JAG) who has been in the job for at least a year can also be an Administrative Member.
- How it works:
The Tribunal follows certain rules for how they do things, and they use English for all their work.
They usually do things the way High Courts in India do them.
World Federation for Medical Education (WFME) (Indian Express)
- 23 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
The National Medical Commission (NMC) of India has recently earned a 10-year recognition status from the World Federation for Medical Education (WFME).
Facts About:
WFME is a worldwide organization dedicated to the training and education of medical doctors.
Their mission is to work towards better healthcare for all people.
WFME's primary goal is to elevate the quality of medical education on a global scale by promoting the highest scientific and ethical standards.
They achieve this goal through several means, including:
- Establishing standards in medical education
- Advocating for the accreditation of medical schools
- Developing databases related to medical education
- Initiating projects focused on the future of medicine and medical education
- Publishing informative materials and forming partnerships
WFME was established in 1972 and has its headquarters in Ferney-Voltaire, France.
Notably, WFME is the organization that officially represents medical teachers and medical teaching institutions on a global scale, serving as their voice before the World Health Organization (WHO).
WFME's accreditation program plays a crucial role in ensuring that medical institutions meet and uphold the highest international standards in education and training.
National Medical Commission (Indian Express)
- 25 Aug 2023
What is the News ?
The National Medical Commission (NMC) has put on hold the regulations that make it mandatory for doctors to prescribe generic drugs.
Facts About:
- In light of the criticism received by the Indian Medical Association (IMA) as well as the as the Indian Pharmaceutical Alliance (IPA), the National Medical Commission put on hold the Medical Practitioner (Professional Conduct) Regulations, 2023.
- Even the country’s apex drug regulator, the Central Drugs Standard Drug Control Organisation (CDSCO), questioned the language in the notification.
- The participating bodies suggested that the guidelines be kept in abeyance until the WHO’s good manufacturing practices are implemented.
- The participants said that prescribing only generic drugs will prompt pharmacies to sell generic drugs at high-profit margins, disincentivising firms that manufacture quality branded generics
National Medical Commission:
- The National Medical Commission is a statutory body established under the National Medical Commission Act, 2019.
- The NMC replaced the erstwhile Medical Council of India (MCI) which was established in 1934.
Objectives of NMC –
- Improve access to quality and affordable medical education;
- Ensure availability of adequate and high-quality medical professionals in all parts of the country;
- Promote equitable and universal healthcare that encourages community health perspective and makes services of medical professionals accessible to all the citizens;
- Encourages medical professionals to adopt latest medical research in their work and to contribute to research;
- Objectively assess medical institutions periodically in a transparent manner;
- Maintain a medical register for India;
- Enforce high ethical standards in all aspects of medical services;
- Have an effective grievance redressal mechanism.
Composition of NMC –
- NMC is a 25-member body, majority of them being nominated by the Central government.
- Tenure of NMC members is four years (except for part-time members whose tenure is two years).
- The NMC has 11 part-time members representing states or state medical councils.
- The NMC chairpersons and other members, nominated by the Central government, cannot be renominated.
- Any decision requires approval of the majority (minimum 13 out of 25) of the Commission.
Medical Practitioner (Professional Conduct) Regulations, 2023:
- On August 2nd, the National Medical Commission had published the Medical Practitioner (Professional Conduct) Regulations, 2023 aimed at reshaping prescription practices.
- It mandated that registered medical practitioners prescribe medications using “generic”, “non-proprietary”, or “pharmacological” names.
- The guidelines define a generic drug as a “drug product that is comparable to brand/reference listed product in dosage form, strength, route of administration, quality and performance characteristics, and intended use.”
- It says branded generic drug is one which has come off patent and is manufactured by drug companies and sold under different companies’ brand names.
- The guidelines say, “Every RMP (Registered Medical Practitioner) should prescribe drugs using generic names written legibly and prescribe drugs rationally, avoiding unnecessary medications and irrational fixed-dose combination tablets.”
- The guidelines have also talked about punitive measures against those violating the directive.
- Besides the instructions on generic drugs, the NMC guidelines included directives on issues ranging from continued medical education, usage of social media platforms and maintaining a dynamic register of doctors.
- It also barred doctors from attending events sponsored by pharmaceutical companies.
- However, the NMC guidelines have not gone down well with the Indian Medical Association (IMA).
Issued Raised by the Indian Medical Association (IMA):
- The IMA issued a statement in response to the regulations introduced by the NMC.
- The IMA says the biggest impediment to generic drugs is the uncertainty about its quality.
- IMA said that the quality control in the nation being very weak, there’s practically no guarantee of the quality of drugs and prescribing drugs without assured quality would be detrimental to patient health.
- The statement added that less than 0.1% of the drugs manufactured in India are tested for quality.
- The IMA said that step should be deferred till the Government can assure the quality of all the drugs released into the market.
- The statement says patient care and safety are not negotiable.
- The IMA says it has been demanding for long that only good quality drugs should be made available in the country and prices should be uniform and affordable.
- It urges the Government to have ‘one drug, one quality, one price’ system whereby all brands should either be sold at the same price or banned and only generics allowed while ensuring highest quality of these drugs.
Source: https://indianexpress.com/article/india/nmc-hold-regulations-mandating-doctors-prescribe-generic-drugs-bar-them-endorsing-drug-brand-8907964/
The first-ever Global Summit on Traditional Medicine (The Hindu)
- 17 Aug 2023
What is the News ?
The first WHO Traditional Medicine Global Summit will take place in Gandhinagar, Gujarat.
Facts About:
First WHO Traditional Medicine Global Summit:
Organized by: World Health Organization (WHO) and co-hosted by the Ministry of Ayush.
Aim: To bring together various stakeholders, such as traditional medicine practitioners, policymakers, academics, and others on a common platform to share best practices, evidence and innovation related to how traditional medicine contributes to health and sustainable development.
Significance: Traditional and complementary medicine has been vital for health in communities for centuries and has influenced modern medical knowledge.
– About 40% of today’s medicines have natural origins, including well-known drugs like aspirin and artemisinin.
– Currently, 170 countries have informed WHO about their use of traditional medicine, seeking evidence and data to guide safe, cost-effective, and fair policies and regulations.
About WHO Global Centre for Traditional Medicine:
In 2022, WHO with the support of the Government of India established the Global Centre for Traditional Medicine in Jamnagar, Gujarat.
Mandate: The centre provides leadership on all global health matters related to traditional medicine as well as extending support to member countries in shaping various policies related to traditional medicine research, practices and public health.
Significance: It is the first and only global outpost for traditional medicine across the globe.
Source: https://www.thehindu.com/news/national/who-director-general-to-inaugurate-first-ever-global-summit-on-traditional-medicine/article67193778.ece
Deemed Forest (The Hindu)
- 16 Aug 2023
What is the News ?
Odisha has no ‘deemed forest’ as per the amended Forest (Conservation) Act, 1980.
Facts About:
What are deemed forests?
Deemed forest refers to land that resembles forests but has not been recognized as such by either the Union or the States.
They account for about 1% of the total forest land in the country.
In 1996, the Supreme Court expanded the remit of the Van (SanrakshanEvamSamvardhan) Act to areas that weren’t notified as forests but conformed to the “dictionary” definition of forests i.e. deemed forests.
- The Godavarman verdict stated that the states must identify and categorize such land.
- The SC directed the states to establish Expert committees to determine deemed forests in order to clarify the area that may be protected under the Forest (Conservation) Act.
According to the Forest Act, land cannot be diverted without the consent of the Centre as well as gram panchayats in the regions.
- It serves as a deterrent to deforestation by directing the parties responsible for diverting forest land to grow trees on a plot of land equivalent to twice the razed area and imposing a significant monetary penalty.
What does the Odisha government directive mention?
All district collectors must ensure that the diversion of forest land for infrastructure projects, particularly state development projects, should follow provisions of the new law.
Any survey or exploration will also not be treated as a non-forestry activity.
Expert Committees
Although all the states were expected to form expert committees to identify deemed forests, not all States submitted their reports.
- This has left states with enough leeway in defining or omitting large parcels of land as forests.
According to the Union Ministry of Environment, the amendments to the 1980 Act were necessary to remove ambiguities and clarify the application of the laws.
According to the amended act, the Forest Conservation Act would not apply to notified forest land that was legally diverted for non-forest uses between 1980 and 1996.
- As a result, forest land that was not specifically notified as such would cease to be protected under the provisions of the Act.
The Union Environment Ministry had earlier stated that deemed forests would continue to be protected.
- The amendments made to the FCA recognized deemed forest lands, which had been identified by the Expert Committee of the State. Therefore the provisions of the Act will be applicable in such lands also.
Future unclear
According to the latest Forest Survey of India, Odisha has approximately 52,156 square km or 130 lakh acres of forest coverage.
- This amounts to 33.50% of the State’s geographical area, which is much higher than the national level of forest cover - 21.71%.
Since 1996, around 66 lakh acres have been identified as deemed forests in Odisha.
- However, a majority of this land has not been officially notified in the government records.
This amounts to about 40-50% of Odisha’s forest land.
In addition, there are several community forests that are managed by tribal and forest-dependent groups while several have land title rights under the provisions of the separate Forest Rights Act.
- The decision of the Odisha government that deemed forests have ceased to exist means that these will face an uncertain future.
One consequence of the new amendments is that there will be no check on forest diversion, making it easier to divert forest land.
- According to data from the Union Coal and Mining Ministry, of the 19,200 hectares of forest land that have been diverted nationally for mining between 2017-2022, around 8,000 hectares was from Odisha.
The reality on the ground is that most of the forest officer bureaucracy isn’t too keen on protecting forest rights
Impact
The Adivasi communities of Odisha depend on the deemed forests for their livelihood.
- These include some of the community-protected forests and bio-cultural habitats of vulnerable tribal groups such as the Dongria Kondhs in Niyamgiri.
- The removal of deemed forest areas from the Act could adversely affect the statutory rights of these communities which have claimed community forest rights and habitat rights on such forests
Around 46% of Odisha’s geographical area is notified as fifth schedule area under the Constitution, where thePanchayat Extension to Scheduled Areas (PESA) Act applies.
Boundary disputes: In Karnataka, people have alleged that large amounts of agriculture and non-forest land are “unscientifically” classified as deemed forest land.
- This was found to have caused undue hardship to farmers in the region and restricted industrial development.
Criticism
Deemed forests already identified as forests in records ‘held’ by any department or administration should be considered as ‘forest’ even by the new amendment.
- However, the directive of the Odisha government violates this.
It is uncertain if the amendment is yet to be considered to be law as the date of enforcement is yet to be notified.
- The government has temporarily withdrawn the notification until the Union Government establishes the rules and guidelines of the new act.
The amendment narrows down the definition of forests.
- As a result, vast tracts of forests are excluded which leaves them vulnerable to destruction.
Source: https://www.thehindu.com/news/national/other-states/no-more-deemed-forests-says-odisha-government/article67198187.ece
National Medical Commission’s New Guidelines (Indian Express)
- 14 Aug 2023
What is the News ?
According to the National Medical Commission’s Registered Medical Practitioner (Professional Conduct) Regulations or NMC RMP Regulations 2023, doctors can now refuse treatment to the unruly and violent patients.
Facts About:
The National Medical Commission Act, 2019:
- It was introduced to address various issues and challenges in the medical field, including improving the quality of medical education, enhancing access to healthcare services, and ensuring ethical and transparent practices.
- Key Provisions include:
- Ethical and Professional Conduct: The Act emphasizes maintaining ethical and professional conduct among medical practitioners and includes provisions to address any deviations from these standards.
- Community Health Providers: The Act introduces the concept of Community Health Providers who are allowed to practice limited medicine in underserved rural areas to address the shortage of doctors.
- Formation of the National Medical Commission (NMC): NMC is an regulatory body which regulates medical education and medical professionals.
- Establishment of Medical Advisory Council.
- Reforms in Medical Education.
Refusing treatment is a complex issue that involves various stakeholders viz. doctors and healthcare professionals, patients and their families, healthcare institutions, medical associations and regulatory bodies, legal authorities, ethics committees, public opinion and media, religious and cultural communities, etc.
Arguments in Favour of the Regulation:
- Unruly Behaviour
- Justice: If an unruly patient’s behaviour poses a threat to their own safety, the safety of healthcare staff, or the safety of other patients, refusing treatment might be justified as a means to mitigate these risks.
- For example, a 21-year-old patient attacked a doctor with a knife during consultation at Delhi’s Sir Ganga Ram Hospital.
- Dignity and Integrity: Unruly behaviour can sometimes cross ethical boundaries, leading to disrespectful or abusive treatment of healthcare staff. Doctors have a right to work in an environment that respects their dignity and professional integrity.
- For example, a 40-year-old doctor on duty in a hospital in Faridabad was assaulted by attendants of a patient as the doctor was attending to another patient, he could not immediately attend to the patient.
- Brings Deterrence: Allowing unruly behaviour to go unchecked might enable a cycle of disruptive or non-compliant behaviour, which could negatively impact the patient’s overall health outcomes. By refusing treatment, the doctor may communicate that certain standards of behaviour are expected for a therapeutic relationship to proceed.
- Right to Freedom to practise any profession: The regulations give the doctors the right to choose whom they will serve, except in case of a life-threatening emergency.
- Justice: If an unruly patient’s behaviour poses a threat to their own safety, the safety of healthcare staff, or the safety of other patients, refusing treatment might be justified as a means to mitigate these risks.
- Financial Constraints
- Autonomy and Consent: Doctors are ethically obligated to provide patients with accurate information about their treatment options,including potential costs.
- If a patient cannot afford the treatment, the doctor might argue that proceeding with treatment without full financial transparency could undermine the patient’s autonomy and informed consent.
- In extreme cases, relatives of patients have been known to hold doctors or hospital staff hostage, demanding treatment.
- Professional Boundaries: Some proponents of this perspective argue that doctors have a professional duty to provide medical care and expertise, but they are not obligated to address broader societal issues such as patients’ financial difficulties.
- Autonomy and Consent: Doctors are ethically obligated to provide patients with accurate information about their treatment options,including potential costs.
- Ethical Boundaries: Doctors have ethical responsibilities not only toward their patients but also toward themselves, their families and the healthcare community.
- For example, potential threats and violence have long-lasting impacts which manifests in the degradation of personal and professional relations.
- Objectivity: Taking decisions which are free from subjectivity caused by emotions, perceptions and individual bias is necessary for long term sustainability.
- For example, Free medical care for a desperate patient may be ethical, but providing it to many patients may not be feasible for one provider.
- Selfless Duty: Medical practitioners often prioritize the well-being of their patients above their own comfort, personal time and space. However, the job can be thankless at times.
- For example, During COVID-19 despite their selfless dedication, medical professionals were subjected to regular assaults and verbal abuse throughout the country.
Arguments against the Regulation
- Dedication and the Duty of Care: Dedication is the sense of deep rooted commitment to devote oneself to a cause.. This includes a duty to provide care to those in need, regardless of their financial status.
-
- In India, out-of-pocket health expenditure accounts for more than half of total health expenditure pushing many households into poverty. This shows the dire need for empathy and compassion towards those in need.For example, Dr Ramanand Singh has been treating his patients for just Rs 50 for the past 35 years in Bihar. He even waives off his fees in cases where the patients cannot afford medical treatment.
- Justice and Equity: The principle of justice requires that healthcare be distributed fairly and equitably.Denying treatment to a patient solely based on their inability to pay could be seen as unjust, perpetuating disparities in healthcare access.
- Hippocratic Oath: Physicians pledge to do what is in the best interest of their patients and to avoid causing harm.
- Physicians promise to treat all patients fairly, regardless of their background, and to provide care to the best of their abilities without bias.
- Unholy Nexuses: Many doctors form nexuses with drugmakers to prescribe specific drugs from their brand instead of generic drugs leads to considerable rise in treatment costs for patients.
- For example, freebies given to doctors including travel expenses, gifts etc. by drugmakers is a common practice.Beneficence: It means kindness or generosity and this principle refers to the moral obligation to act in a manner that will benefit others.The principle of beneficence obligates doctors to act in the best interests of their patients and to promote their well-being.
- Compassion: It is the desire to end someone’s suffering which forms the core principle of a medical practitioner. Refusing treatment to individuals on certain grounds could lead to the possibility of crisis of conscience among several practitioners.
- Loss of Trust and Credibility: The medical profession relies on public trust, and denying treatment to those in need could erode that trust and damage the reputation of the medical community.
- Responsibility: Some argue that healthcare professionals have a broader social responsibility to address systemic issues in healthcare, including affordability and access. Refusing treatment might be seen as abdicating this responsibility.
- Undermining Right to Life: Providing a legal caveat for the registered physicians to refuse treatment is against the fundamental right guaranteed under Article 21 of the Constitution.
- Further, there is no specific definition of “abusive” in law as it is purely a subjective interpretation that may depend on the personal opinion of any individual.
- Subjective interpretation may further lead to exclusion on the basis of race, religion, caste, sex etc.
What Should be Done?
- Persuasion: Influencing patients to follow prescribed norms for behaviour and ensuring smooth functioning.
- For example, during COVID-19 pandemic, voice messages were circulated using caller tune to make people aware of the importance of vaccination and prevent attacks on health workers.
- Emotional Intelligence: Equipping and training medical personnel with necessary skills so that they can manage their emotions and try to avoid escalation of situation and providing practical solutions to the given problems.
- Transparent Approaches: Consider alternative approaches before refusing treatment. This might involve social workers, mental health professionals, or conflict resolution experts to address the underlying issues contributing to the unruly behaviour.
- For example, Doctors in San Diego (USA)refer patients to low-cost family health centersthat provide caring, affordable, high-quality health care and supportive services to everyone.
- Ethical Principles Balancing: Weigh the principles of patient autonomy, duty of care, patient safety, and respect for healthcare personnel’s well-being. Consider how refusing treatment aligns with these principles and what potential consequences might arise from the decision.
- For example, Doctors Without Borders is a Nobel Peace Prize receiver charity that provides humanitarian medical care in conflict zones to all those in need of medical care, irrespective of the role played by them in the conflict.
- Tolerance: Accepting actions and practices which may be considered to be incorrect but still tolerable to some extent that they should not be prohibited or penalised heavily.
- For example, a significant number of the cases of unruly behaviour arises in situations which may not be considered as “common” and even the most well-behaved might behave in a way which is not acceptable in society due to the shock or intensity of the moment which one may not be able to handle.
- Consent: Communicating the decision clearly to the patient, and explaining the reasons behind it thus ensuring that the patient understands the potential consequences of their behaviour on their health and the doctor-patient relationship.
- Offering Continuity of Care: If possible, provide recommendations for alternative sources of care, whether within your healthcare institution or elsewhere. Ensure the patient’s ongoing health needs are addressed.
Conclusion
We must protect those who heal. Ethical decisions in healthcare are rarely black and white. It’s important to approach each situation with sensitivity, professionalism, and a commitment to upholding the well-being of patients, healthcare staff, and the broader community. Consulting with colleagues, supervisors, and ethics committees can provide valuable guidance in making these difficult decisions
Source: https://indianexpress.com/article/explained/explained-health/doctors-new-national-medical-commission-guidelines-8890632/#:~:text=The%20guidelines%20say%20that%20doctors,but%20at%20least%20three%20credits.
Mediation Bill, 2023 (Live law)

- 08 Aug 2023
What is the News ?
The Parliament has passed the Mediation Bill 2023 to reduce pendency of court cases.
Facts About:
The Mediation Bill, 2021
- It was introduced in the Rajya Sabha in December, 2021, with the Parliamentary Standing Committee being tasked with a review of the Bill.
- The Bill aims at institutionalising mediation and establishing the Mediation Council of India.
Key Features of the Bill
Pre-litigation mediation
- Parties must attempt to settle civil or commercial disputes by mediation before approaching any court or certain tribunals.
- Even if they fail to reach a settlement through pre-litigation mediation, the court or tribunal may at any stage refer the parties to mediation if they request for the same.
Disputes not fit for mediation
- The Bill contains a list of disputes which are not fit for mediation.
- These include disputesrelating to claims against minors or persons of unsound mind, involving criminal prosecution, and affecting the rights of third parties. The central government may amend this list.
Applicability
- The Bill will apply to mediations conducted in India:
involving only domestic parties
involving at least one foreign party and relating to a commercial dispute (i.e., international mediation)
if the mediation agreement states that mediation will be as per this Bill.
- If the central or state government is a party, the Bill will apply to commercial disputes, and other disputes as notified.
Mediation process
- Mediation proceedings will be confidential, and must be completed within 180 days (may be extended by 180 days by the parties).
- A party may withdraw from mediation after two sessions.
- Court annexed mediation must be conducted as per the rules framed by the Supreme Court or High Courts.
Mediators
- Mediators may be appointed bythe parties by agreement, a mediation service provider (an institution administering mediation).
- They must disclose any conflict of interest that may raise doubts on their independence.
- Parties may then choose to replace the mediator.
Concerns Highlighted by the Parliamentary Standing Committee
Pre-Litigation
- The panel highlighted many key issues including mandatory and coercive nature of pre-litigation mediation.
- Making pre-litigation mediation necessary may result in case delays and provide another instrument in the hands of truant litigants to prolong case disposition.
Clause 26: The panel was against Clause 26of the draft which gives power to the SC or the High court to make laws of pre-litigation according to them.
Non-Applicability to Non-Commercial Disputes: The members questioned the non-applicability of the provisions of the Bill to disputes/matters of non-commercial nature involving the Government and its agencies.
Appointments: The panel had discussions about the qualifications and appointment of the Chairperson and Members of the proposed Mediation Council.
Recommendations Accepted by the Union Cabinet
Reducing the Time for Concluding a Mediation
- The Union cabinet has accepted the recommendations of the standing committee by reducing the time for concluding a mediation from 180 to 90 days.
Making Pre-Litigation Mediation Voluntary
- The recommendation for making pre-litigation mediation voluntary instead of mandatory was also much needed as voluntariness is an essential principle of mediation.
Recognition and Enforcement of Agreements
- Recognition and enforcement of settlement agreements arising out of mediation is a welcome move.
- This is also in line with India’s commitment as a signatory to the United Nations Convention on International Settlement Agreements Resulting from Mediation (Singapore Convention).
Provisions of the Final Bill that Require a Relook
Limited Grounds to Challenge a Settlement Agreement
- The limited grounds listed to challenge the enforcement of a settlement agreement and the fact that a period of 90 days is given to raise the challenge need a relook.
- The fact that a settlement agreement is essentially a contract between the parties; there are several instances where grounds for challenge such as fraud and impersonation are detected at a later stage.
Technical Flaws in Clause 8
- Clause 8 of the Bill entitles a party to move the Court before the commencement or during mediation for interim relief but only in “exceptional circumstances”.
- The term “exceptional circumstances”is not only undefined in the Bill but is also abnormal to the settled principles of seeking interim relief before the civil courts.
- Moreover, there is no remedy of appeal available against an order passed under this proposed section.
The Concept of Online and Community Mediation
- A recent Niti Aayog report reveals that only 55 per cent of India have access to the internet and only 27 per cent possess compatible devices.
- For online mediation to be a success, the government will have to scale the bandwidth accessibility to remote parts of the country.
- As for community mediation, the Bill makes it mandatory to have a panel of three mediators.This requirement is unnecessary and impinges on the flexibility that mediation brings.
Restricting the Government’s Participation in Mediation to only Commercial Disputes
- The real issue is that the government is the biggest litigant in the country.
- Restricting the ability of the government to participate in mediation proceedings arising only out of commercial disputes goes against the objective of enacting the legislation.
Way Forward
Legal Aid Setup: Setting up legal aid or access to justice clinics with adequate IT infrastructure could address the issue of online mediation.
Inclusion of Government Related Disputes in the Bill
- The standing committee had also recommended that government-related disputes be included in the Bill.
- The common litigant sees the government as an adversary before the court of law. The Bill provided a golden opportunity to the government to change that perception.
- This will inspire confidence amongst all stakeholders but would also help in reducing pendency backlog.
Conclusion
Mediation should be promoted as a preferred and voluntary mode of securing justice.
Although the legislature may have intended to lighten the load on the judiciary, the law needs to be improved because it may cause a delay in the administration of justice and raise the cost of litigation.
Source: https://www.livelaw.in/news-updates/parliament-passes-mediation-bill-234671
