Kawal Tiger Reserve and KumramBheem Conservation Reserve
- 02 Jun 2025
In News:
In a recent development, the Telangana government has designated the tiger corridor connecting the Kawal Tiger Reserve (Telangana) with the Tadoba-Andhari Tiger Reserve (Maharashtra) as the KumramBheem Conservation Reserve, under Section 36(A) of the Wildlife Protection Act, 1972. This move is aimed at preserving critical wildlife corridors in the Central Indian Landscape.
Kawal Tiger Reserve:
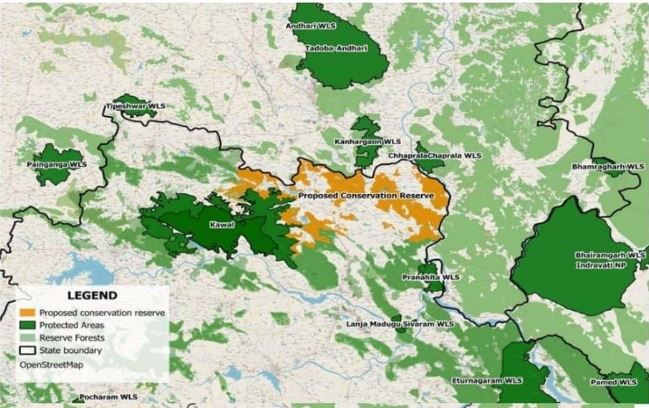
- Location: Situated in Telangana, along the Godavari River, forming part of the Deccan Peninsula – Central Highlands.
- Biogeographic Zone: Lies at the southern tip of the Central Indian Tiger Landscape.
- Connectivity: Links with Tadoba-Andhari (Maharashtra), Indravati (Chhattisgarh), and other reserves like Tipeshwar, Chaprala, and Kanhargaon.
- Vegetation Type: Southern Tropical Dry Deciduous Forests.
- Flora: Dominated by teak, bamboo, and species like Anogeissuslatifolia, Terminalia arjuna, Boswellia serrata, etc.
- Fauna: Hosts tiger, leopard, nilgai, chinkara, sambar, blackbuck, wild dog, wolf, and jungle cat.
KumramBheem Conservation Reserve: Newly Notified Area
- Legal Basis: Declared under Section 36(A), Wildlife Protection Act, 1972, which allows states to notify government-owned land adjacent to or connecting protected areas as conservation reserves.
- Total Area: 1,492.88 sq km (149,288.48 hectares)
- District &Mandals Covered: Spread across KumramBheemAsifabad district, covering parts of Kerameri, Wankidi, Asifabad, Sirpur, Koutala, Bejjur, Kagaznagar, Rebbana, Dahegaon, and Tiryanimandals.
- Forest Blocks Included: 78 blocks including Garlapet, Ada, Manikgarh East & West, Danora, Gudem, Bejjur, Kadamba, and Girali.
Ecological Significance
- Tiger Movement: Over the last decade, more than 45 unique tigers (mostly transient) have been documented in this corridor through camera trapping and surveys.
- Breeding Evidence: Since 2015, 17 tiger cubs born from 3 tigresses have been recorded. The 2022 Tiger Census confirmed 4 adult tigers and 3 cubs in the area.
- Leopard Presence: 8 leopards were recorded during the All India Leopard Estimation, 2022.
- Other Carnivores: Includes sloth bear, hyena, wild dog, wolf, honey badger, and jungle cat.
- Herbivore Diversity: Rich prey base such as gaur, sambar, nilgai, chital, muntjac, four-horned antelope, and Indian gazelle.
- Avifauna: Home to 240+ bird species, including rare species like the Malabar Pied Hornbill and Long-billed Vulture, the latter using the reserve as a nesting site.
- Elephant Movement: Occasional elephant presence has also been reported.
Governance
A Conservation Reserve Management Committee has been established. Members include:
- District Forest Officer (DFO) of KumramBheemAsifabad (Convenor)
- Sarpanches of local panchayats (e.g., Karji, Motlaguda, Murliguda)
- Representatives from NGOs like Hyderabad Tiger Conservation Society, WWF-India, and Wildlife Conservation Trust
- Officials from Veterinary, Agriculture, and Forest Divisions
