Bharat Taxi

- 22 Dec 2025
In News:
India is set to launch Bharat Taxi, the country’s first cooperative-run taxi service, in Delhi from 2027. Operated by Sahakar Taxi Cooperative Limited, the initiative aims to provide a homegrown, driver-first alternative to private cab aggregators such as Uber and Rapido, aligning with India’s broader push for cooperative-led growth and digital public infrastructure.
Key Features of Bharat Taxi
1. Cooperative Ownership & Governance
- Bharat Taxi is structured as a cooperative platform, ensuring drivers are stakeholders rather than gig workers.
- It seeks to curb profit extraction by intermediaries and promote equitable income distribution among drivers.
2. Commission Model
- Zero-commission model initially: 100% of ride payments go directly to drivers.
- A proposed ~20% cooperative fee may be introduced later, which will be redistributed back to drivers as incentives, unlike conventional aggregator commissions.
3. Institutional Collaboration
The platform is being developed through collaboration among:
- National e-Governance Division (NeGD)
- Digital India Corporation
- Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology (MeitY)
- Sahakar Taxi Cooperative Limited
This ensures integration with India’s Digital Public Infrastructure (DPI).
4. Digital Integration
Bharat Taxi will be integrated with:
- DigiLocker
- UMANG
- API Setu
These integrations will streamline driver onboarding, document verification, and service delivery.
5. Pricing Policy
- No surge pricing under normal conditions, enhancing affordability and predictability for commuters.
- Dynamic pricing permitted only under specific, clearly defined circumstances, unlike algorithm-driven surge pricing models.
6. Safety and Consumer Protection
- Driver verification and background checks.
- Integration with Delhi Police systems.
- Real-time ride tracking and 24×7 customer care, enhancing passenger safety and trust.
Significance
- Promotes the cooperative movement in the digital platform economy.
- Supports driver welfare, income stability, and transparency.
- Demonstrates the use of government-backed digital infrastructure for service delivery.
- Offers a public-interest alternative to profit-driven ride-hailing platforms.
Global Environment Outlook–7 (GEO-7), 2025

- 13 Dec 2025
In News:
The 7th edition of the Global Environment Outlook (GEO-7) was released by the United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP) during its session in Nairobi, warning that the world is far off track in meeting climate and environmental goals.
About Global Environment Outlook (GEO)
- The Global Environment Outlook is UNEP’s flagship assessment of the state of the global environment, future risks, and policy solutions. It provides scientific evidence for international environmental decision-making.
Key Findings of GEO-7
Rising Greenhouse Gas Emissions
- Global GHG emissions have grown ~1.5% annually since 1990
- 2024 recorded temperatures around 1.55°C above pre-industrial levels
- Intensifying heatwaves, floods, droughts, and extreme events
Biodiversity Loss
- 1 million species (out of ~8 million) face extinction
- 20–40% of global land is degraded
- Over 3 billion people are affected by land degradation
Economic Costs of Environmental Damage
- Climate-related disasters cost ~USD 143 billion annually
- Air pollution caused USD 8.1 trillion in health damages in 2019 (≈6% of global GDP)
- 9 million deaths per year linked to pollution
Plastic Pollution Crisis
- About 8 billion tonnes of plastic waste pollute ecosystems
- Toxic chemical exposure leads to ~USD 1.5 trillion annual health losses
Projected Impacts if Current Trends Continue
- Temperature thresholds: Likely to exceed 1.5°C in early 2030s and 2°C by 2040s
- Economic decline: Global GDP may fall 4% by 2050 and 20% by 2100
- Loss of fertile land: Equivalent to losing a country-sized fertile area annually
- Food insecurity: Per capita food availability may drop 3.4% by 2050
- Rising hunger, poverty, displacement, and conflict risks
GEO-7 Recommended Transformative Actions
Economy & Finance
- Move beyond GDP to wealth-based indicators
- Price environmental externalities
- Invest in decarbonization, ecosystem restoration, sustainable agriculture
- USD 8 trillion/year investment needed till 2050
- Could generate USD 20 trillion annual benefits by 2070
Materials & Waste
- Promote circular economy models
- Transparent product design and recycling chains
- Shift from linear consumption to regenerative systems
Energy Transition
- Rapid decarbonization of energy
- Improve energy efficiency
- Secure sustainable critical mineral supply chains
- Reduce air pollution → 9 million premature deaths avoidable by 2050
Food Systems
- Promote sustainable diets
- Reduce food loss and waste
- Improve agricultural efficiency
- Could reduce undernourishment by ~200 million people
Ecosystem Protection
- Scale up ecosystem restoration
- Use Nature-based Solutions (NbS) for adaptation
- Stronger mitigation and biodiversity conservation policies
Collaborative & Integrated Governance
- Solutions must involve governments, private sector, civil society, academia, Indigenous communities
- Policies across sectors must be implemented together, not in isolation
About UNEP
- Established in 1972 after the Stockholm Conference
- Headquarters: Nairobi, Kenya
- Leading global authority on environmental issues
- Major reports include:
- Emissions Gap Report
- Adaptation Gap Report
- Global Environment Outlook
- Frontiers Report
Directorate General of Civil Aviation (DGCA)

- 09 Dec 2025
In News:
Recent large-scale flight cancellations by a major Indian airline led the Directorate General of Civil Aviation (DGCA) to grant a one-time exemption from the newly implemented Flight Duty Time Limitations (FDTL) rules. These rules are designed to reduce pilot fatigue by regulating maximum duty hours and ensuring mandatory rest periods. The decision has highlighted DGCA’s critical role in balancing aviation safety with operational realities.
About DGCA
The Directorate General of Civil Aviation (DGCA) is India’s statutory civil aviation regulator responsible for ensuring aviation safety, airworthiness, and regulatory compliance in line with international standards.
- Established: 1927 (as a government organisation)
- Statutory Status: Granted under the Aircraft (Amendment) Act, 2020
- Administrative Ministry: Ministry of Civil Aviation (MoCA)
- Mandate: Promote safe, efficient, and reliable air transport through regulatory oversight and alignment with International Civil Aviation Organization (ICAO) standards.
Key Functions of DGCA
1. Safety Regulation & Oversight
- Frames and enforces Civil Aviation Requirements (CARs)
- Conducts surveillance, audits, and inspections of airlines, airports, MROs, and training institutes
2. Aircraft & Aerodrome Certification
- Registers civil aircraft
- Issues Certificates of Airworthiness
- Certifies aerodromes for operational safety
3. Licensing & Training
- Issues licences to pilots, Aircraft Maintenance Engineers (AMEs), Air Traffic Controllers (ATCOs), cabin crew, and flight dispatchers
- Approves flying schools, AME institutes, and simulator training centres
4. Accident & Incident Investigation
- Investigates incidents and serious incidents (aircraft up to 2,250 kg All-Up Weight)
- Implements aviation safety programmes
5. Air Transport Regulation
- Grants Air Operator Certificates (AOCs)
- Regulates scheduled and non-scheduled domestic and international operations
6. ICAO Coordination
- Aligns Indian aviation standards with ICAO norms
- Participates in global aviation safety audits (USOAP)
7. Dangerous Goods & Air Navigation Oversight
- Certifies operators transporting dangerous goods
- Coordinates civil–military airspace usage
Flight Duty Time Limitations (FDTL)
FDTL rules regulate:
- Maximum flying and duty hours for pilots
- Minimum mandatory rest periods
- Fatigue risk management
These are crucial for aviation safety, as pilot fatigue is a significant risk factor in accidents.
Significance of DGCA
- Ensures Passenger Safety: Through strict oversight of aircraft airworthiness, pilot training, and crew rest norms
- Maintains Operational Discipline: Enforces compliance with technical and safety regulations
- Balances Safety & Industry Needs: The recent FDTL exemption shows DGCA’s role in managing real-time operational disruptions while upholding safety standards
- Global Compliance: Ensures India meets international aviation obligations under ICAO
8th Economic Census (EC) in 2027

- 06 Dec 2025
In News:
India will conduct its 8th Economic Census (EC) in 2027, following the completion of the Population Census (2026–27). The announcement was made by the Ministry of Statistics and Programme Implementation (MoSPI). Data from the upcoming Economic Census will be used to establish a Statistical Business Register (SBR), a comprehensive database of enterprises across the country.
Economic Census (EC)
The Economic Census is a complete count of all establishments engaged in the production and/or distribution of goods and services (excluding those for sole household consumption) within India’s geographical boundaries.
Key Facts
- First conducted: 1977
- Conducting authority: Ministry of Statistics &Programme Implementation (MoSPI) through the National Statistics Office (NSO)
- Implemented in collaboration with Directorates of Economics and Statistics (DES) of States and UTs
- Covers both organised and unorganised sector establishments
Purpose
The EC provides disaggregated data on the number, type, location, ownership, and operational characteristics of establishments. This data supports:
- Evidence-based economic planning
- Employment and enterprise mapping
- Sectoral and regional policy formulation
Statistical Business Register (SBR)
The 8th EC data will be used to build India’s Statistical Business Register, which will:
- Create a unified list of all enterprises in the country
- Track whether enterprises are active, dormant, or closed
- Improve the quality and consistency of national economic statistics
- Enable better sampling frames for future surveys
The government is also working on harmonisation and standardisation of data across ministries and states to improve statistical reliability.
Population Census (2026–27)
The Population Census will precede the Economic Census and will be conducted in two phases:
- House-listing and housing census: April–September 2026
- Population enumeration: February 2027
Key Facts
- Conducted under the Census Act, 1948 and Census Rules, 1990
- Led by the Registrar General and Census Commissioner of India
- The upcoming exercise will be India’s 16th decennial Census (first synchronous census in 1872)
Importance
The Census is the largest source of primary data at village, town, and ward levels. It provides information on:
- Population size and distribution
- Housing and amenities
- Literacy and education
- Work and economic activity
- Migration, fertility, and demographic trends
- Social composition (SC/ST), religion, and language
Significance of Sequencing EC After Census
Conducting the Economic Census after the Population Census allows for:
- Updated administrative and geographical frames
- Improved sampling accuracy
- Better alignment of demographic and economic data
IMF to Alter Classification of India’s Forex Framework

- 28 Nov 2025
In News:
The International Monetary Fund (IMF) has reclassified India’s de facto exchange rate regime from a “stabilised arrangement” to a “crawl-like arrangement”, reflecting the actual behaviour of the Indian rupee in the foreign exchange market rather than India’s official policy description.
What Has Changed?
- Earlier, India’s exchange rate was classified as stabilised, implying limited movement around a reference rate.
- The IMF now categorises it as crawl-like, meaning:
- The exchange rate remains within a ±2% band around a trend for at least six months.
- The currency is not fully market-determined, even though there is no formally announced crawl.
India’s Existing Exchange Rate Framework
- India officially follows a managed float system:
- The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) allows market forces to determine the broad trend of the rupee.
- RBI intervenes selectively to curb excessive volatility, maintain financial stability, and manage external sector risks.
- This differs from:
- Floating exchange rate: Fully market-determined with minimal intervention.
- Fixed exchange rate: Officially pegged and defended by the government/central bank.
Crawl-like Arrangement vs Crawling Peg
- Crawling Peg:
- Involves pre-announced, periodic adjustments in the exchange rate.
- Adjustments are often linked to indicators like inflation differentials.
- Crawl-like Arrangement (IMF classification):
- Based on observed currency behaviour, not on a declared policy.
- Indicates gradual and controlled movement of the currency, even without formal commitments.
How Does the IMF Classify Exchange Rate Regimes?
- Based on:
- IMF Articles of Agreement (foundational charter adopted in 1944 at the UN Monetary and Financial Conference).
- Article IV surveillance, under which IMF assesses:
- Actual exchange rate movements
- Scale and pattern of central bank intervention
- Degree of policy commitment to any exchange rate path
- The methodology is uniform across countries and focuses on de facto practices rather than de jure claims.
Bharat NCAP 2.0
- 26 Nov 2025
In News:
The Ministry of Road Transport and Highways (MoRTH) has released the draft Bharat NCAP 2.0, significantly upgrading India’s vehicle safety assessment framework by introducing new crash-test categories, higher benchmarks, and pedestrian safety norms.
What is Bharat NCAP 2.0?
- Nature: Revised vehicle safety rating programme for passenger cars sold in India.
- Background: Updates the Bharat NCAP guidelines notified in 2023.
- Objective:
- Align India’s crash-safety standards with global NCAP norms.
- Protect vehicle occupants as well as pedestrians and other vulnerable road users (VRUs).
- Push manufacturers to adopt advanced safety technologies.
Implementing & Testing Agency
- Certification & Testing: Central Institute of Road Transport (CIRT), Pune
- Nodal Ministry: MoRTH
Key Features of Bharat NCAP 2.0
1. Five Safety Assessment Verticals
- Safe Driving
- Accident Avoidance
- Crash Protection
- Vulnerable Road User (VRU) Protection (New)
- Post-Crash Safety (New)
2. Expanded Crash-Test Regime
- Existing Tests:
- Frontal impact
- Side impact
- Oblique pole impact
- New Tests Added:
- Full-width frontal crash test
- Rear impact test
3. Advanced Injury Evaluation: Use of Advanced Test Dummies (ATDs) to assess injury risks to different body regions under multiple crash scenarios.
4. Vulnerable Road User (VRU) Protection
- Pedestrian Safety Tests:
- Legform impact test
- Adult and child head impact tests
- Optional Safety Tech: Autonomous Emergency Braking (AEB) for pedestrians and motorcyclists earns additional points.
5. Accident-Avoidance Technologies
- Mandatory: Electronic Stability Control (ESC)
- Optional (Extra Score): Autonomous Emergency Braking System (AEBS)
6. Post-Crash Safety Assessment
- Fire and electrical safety checks
- Ease of occupant escape (functioning doors, seat-belt buckles after crash)
Revised Star Rating System
- Stricter thresholds for higher star ratings.
- A vehicle cannot receive a 5-star rating if:
- Any assessment vertical scores zero, or
- There is evidence of severe or life-threatening injury risk.
Significance of Bharat NCAP 2.0
- Moves India closer to global vehicle safety benchmarks.
- Addresses pedestrian safety—pedestrians account for over 20% of road accident deaths in India.
- Supports India’s target to reduce road fatalities by 50% by 2030.
- Encourages safety-led competition among automobile manufacturers.
Individual Entitlement Survey for Particularly Vulnerable Tribal Groups (PVTGs)
- 23 Nov 2025
In News:
The Union Government will conduct India’s first-ever ‘Individual Entitlement Survey’ covering 10 lakh households of Particularly Vulnerable Tribal Groups (PVTGs) to assess whether benefits of 39 central government schemes are reaching the most vulnerable tribal communities at the grassroots level.
What is the Individual Entitlement Survey?
- Nodal Ministry: Ministry of Tribal Affairs
- Objective:
- To map scheme-wise coverage gaps among PVTG households
- To identify eligible beneficiaries who remain uncovered and enable corrective action by line ministries
- Schemes Covered:
- 39 schemes across 18 central ministries/departments, including:
- Mahatma Gandhi National Rural Employment Guarantee Scheme (MGNREGS)
- Social security schemes for unorganised workers
- Old-age and social pensions
- Financial assistance for meritorious Scheduled Tribe students
- Flagship welfare schemes such as LPG connections
- 39 schemes across 18 central ministries/departments, including:
Scope & Coverage
- Households: ~ 10 lakh PVTG households
- Population Covered: ~ 48 lakh individuals
- Geographical Spread:
- 1,000 blocks dominated by PVTGs
- 75 recognised PVTGs across 18 States and Andaman & Nicobar Islands (UT)
Methodology & Implementation
- Execution: Through State Governments
- Ground Support:States may engage NGOs, panchayat officials, or local functionaries
- Digital Tool:A mobile application developed by the National e-Governance Division (NeGD)
- Data Collection Features:
- House-to-house survey
- Scheme-wise eligibility and benefit status
- Geo-tagging (latitude & longitude) and household photographs
- Post-Survey Outcome:
- Issuance of a ‘Universal Entitlement Card’ to every PVTG household/member
- Card will clearly mention entitlements and coverage status under tracked schemes
What are Particularly Vulnerable Tribal Groups (PVTGs)?
- Definition:A sub-classification of Scheduled Tribes that are more vulnerable due to extreme socio-economic backwardness
- Constitutional Basis:Article 342(1) empowers the President to notify Scheduled Tribes
- Historical Evolution:
- 1973:Dhebar Commission identified Primitive Tribal Groups (PTGs)
- 1975: First list of 52 PTGs notified
- 1993: 23 more groups added
- 2006: Renamed as PVTGs
- Total:75 PVTGs out of 705 Scheduled Tribes
- Key Characteristics:
- Small, isolated and homogeneous populations
- Pre-agricultural or simple subsistence economy
- Low literacy and poor health indicators
- Lack of written language and limited access to infrastructure
- Stagnant or declining population growth
- State-wise Concentration:
- Odisha: Highest number (13)
- Andhra Pradesh & Telangana: 12
- Jharkhand & Bihar: ~9
Major Government Initiatives for PVTGs
- PM-JANMAN (Pradhan Mantri Janjati Adivasi Nyaya Maha Abhiyan):
- Covers 75 PVTGs across 18 States/UTs, 22,544 villages, 220 districts
- Focus on connectivity, services and protection of near-extinct tribes
- PM-PVTG Development Mission:Aims to improve housing, drinking water, sanitation, health, nutrition, education and road access
- Janjatiya Gaurav Divas:
- Celebrated on Birsa Munda’s birth anniversary
- Recognises tribal contributions to India’s cultural heritage and freedom struggle
ARISE Program
- 16 Nov 2025
In News:
At the COP30 Climate Summit in Belém, Brazil, the Climate Investment Funds (CIF) launched a new climate-resilience initiative -ARISE (Accelerating Resilience Investments and Innovations for Sustainable Economies).Germany and Spain jointly committed USD 100 million as the program’s initial funding.
About ARISE Program
- ARISE is a next-generation climate resilience initiative aimed at enabling developing nations to withstand and adapt to increasing climate shocks such as floods, droughts, storms, and economic disruptions.
- Objectives
- Integrate climate resilience into national economic planning.
- Strengthen the adaptive capacity of vulnerable economies.
- Mobilisecatalytic finance for adaptation.
- Convert climate risks into opportunities for sustainable and inclusive growth.
- Facilitate investments from:
- Multilateral Development Banks (MDBs)
- Climate funds
- Private sector
- Key Functions
- Support countries in embedding resilience into development strategies.
- Unlock new financing channels and reduce investment risks.
- Enhance institutional and community-level preparedness.
About Climate Investment Funds (CIF)
- A $13 billion multilateral climate finance mechanism established in 2008, housed within the World Bank Group.
- Purpose: To provide concessional finance to developing countries for:
- Low-carbon development
- Climate resilience
- Clean technology deployment
- Nature-based solutions
- Coverage: Supports climate action in 70+ low- and middle-income countries.
- Institutional Framework: CIF is implemented through six Multilateral Development Banks (MDBs) including:
- World Bank
- IFC
- Asian Development Bank (ADB)
- African Development Bank (AfDB)
- European Bank for Reconstruction and Development (EBRD)
- Inter-American Development Bank (IDB)
This MDB-based structure ensures country-led implementation and strong international coordination.
Structure of CIF
CIF consists of two core funding windows:
1. Clean Technology Fund (CTF)
Focus:
- Renewable energy
- Clean transportation
- Energy efficiency
2. Strategic Climate Fund (SCF)
Focuses on innovative pilot initiatives such as:
- Pilot Program for Climate Resilience (PPCR)
- Forest Investment Program (FIP)
- Smart Cities Program
Finance Model
CIF operates on a blended finance approach:
- Combines concessional funding with MDB and private investments.
- Reduces financial risks to attract large-scale commercial capital.
- Catalyses transformational climate investments.
Rationalisation of Royalty Rates for Critical Minerals
- 15 Nov 2025
In News:
The Union Cabinet has approved revised royalty rates for four critical minerals-Graphite, Caesium, Rubidium, and Zirconiumto promote domestic mining, reduce imports, and strengthen India’s position in the global clean-tech and strategic minerals sector.
What are Royalty Rates?
- A government levy charged on mineral producers for extracting natural resources.
- Calculated either as:
- A percentage of the Average Sale Price (ASP), or
- A fixed per-tonne rate.
- Legal Basis:
- Governed under the Mines and Minerals (Development and Regulation) Act, 1957 (MMDR Act).
- Empowered through the Mineral Concession Rules, 1960 to fix and revise rates.
Aim of Rationalisation
- Ensure fair value capture for the state.
- Encourage exploration and auction of new mineral blocks.
- Support availability of critical minerals essential for:
- Electric vehicles (EVs)
- Renewable and nuclear energy systems
- Electronics and defence applications
- Align India’s royalty structure with global benchmarks (typically 2–4%).
New Royalty Structure for Critical Minerals
- Graphite
- ≥80% fixed carbon:2% royalty on ASP (ad valorem)
- <80% fixed carbon:4% royalty on ASP
- Earlier: Flat per-tonne rate; now linked to quality and market price.
- Caesium: 2%of ASP based on the metal contained in ore.
- Rubidium: 2%of ASP on the metal value.
- Zirconium: 1%royalty on the metal value.
Additional Feature: Revised rates will improveauction viabilityof mineral blocks and facilitate discovery of associated strategic minerals such as lithium and rare earth elements.
Significance of the Cabinet Decision
- Reduces Import Dependency
- India imports nearly 60% of its graphite needs.
- Revised rates incentivise domestic exploration, mining, and value addition.
- Boosts Clean-Energy Transition
- These minerals are crucial for:
- EV battery anodes (graphite)
- Nuclear reactor components (zirconium)
- Atomic clocks and energy storage (caesium, rubidium)
- High-tech electronics and fiber optics
- Enhances ‘Atmanirbhar Bharat’
- Strengthens resource security and supply chain stability.
- Opens opportunities for investment and job creation in the mining sector.
- Encourages Global Competitiveness
- Royalty rates aligned with international norms improve investor confidence.
- Facilitates geological exploration to identify deeper reserves and critical co-located minerals.
Interstellar Comet 3I/ATLAS
- 06 Nov 2025
In News:
NASA astronomers have confirmed the chemical fingerprint of water on the interstellar comet 3I/ATLAS using ultraviolet data from the Neil Gehrels Swift Observatory. This marks a major advance in understanding the chemistry of planetary systems beyond the Sun.
What is 3I/ATLAS?
- Designation: 3I/ATLAS
- Discovery: 1 July 2025 by the Asteroid Terrestrial-impact Last Alert System (ATLAS) in Hawaii.
- Category: Third confirmed interstellar object after 1I/‘Oumuamua (2017) and 2I/Borisov (2019).
- Origin: Formed in another planetary system, possibly 7 billion years old, older than Earth.
Trajectory & Motion
- Travels on a hyperbolic orbit—meaning it is not gravitationally bound to the Sun and will exit the Solar System permanently.
- Speed relative to Sun: 57–68 km/s.
Physical Characteristics
- An active comet with a visible coma of dust and icy particles.
- Expected to form a cometary tail as it approaches the Sun.
- Surface hue: Slightly reddish, indicating the presence of complex organics or water ice.
- Nucleus size: Estimated 10–30 km wide.
- Age: Nearly twice as old as Earth, making it one of the oldest comets ever observed.
Breakthrough Discovery: Water Signature Detected
How was it detected?
- Swift Observatory captured faint ultraviolet emissions from hydroxyl (OH).
- OH forms when sunlight breaks apart water molecules → indirect but strong evidence of water ice sublimation.
Why is it important?
- First chemical confirmation of water activity on an interstellar comet at such a large distance from the Sun.
- Indicates that protoplanetary systems outside the Solar System may share similar chemical building blocks.
Unusual Behaviour
- 3I/ATLAS was losing water at ~40 kg per second even when far beyond the usual frost line where comets become active.
- Suggests:
- Presence of small icy grains being heated by sunlight,
- Complex physical and chemical processes not seen in typical comets.
Scientists noted its activity “defies our models”, indicating new insights into comet evolution.
Significance for Planetary Science & Astrobiology
- Strengthens the idea that organic chemistry and water—key ingredients for life—are common across the Galaxy.
- Provides clues on:
- Composition of ancient planetary systems,
- How water and organics travel between stars,
- Early stages of planet formation.
3I/ATLAS acts as a “messenger” from another star, preserving primordial material from its home system.
Interstellar Objects:
- Formed outside the Solar System and travel through it.
- Not gravitationally bound → follow open-ended hyperbolic trajectories.
- Have a perihelion (closest approach to Sun) but no aphelion.
- Often ejected from their home systems due to collisions or gravitational slingshot events.
Port of Pasni
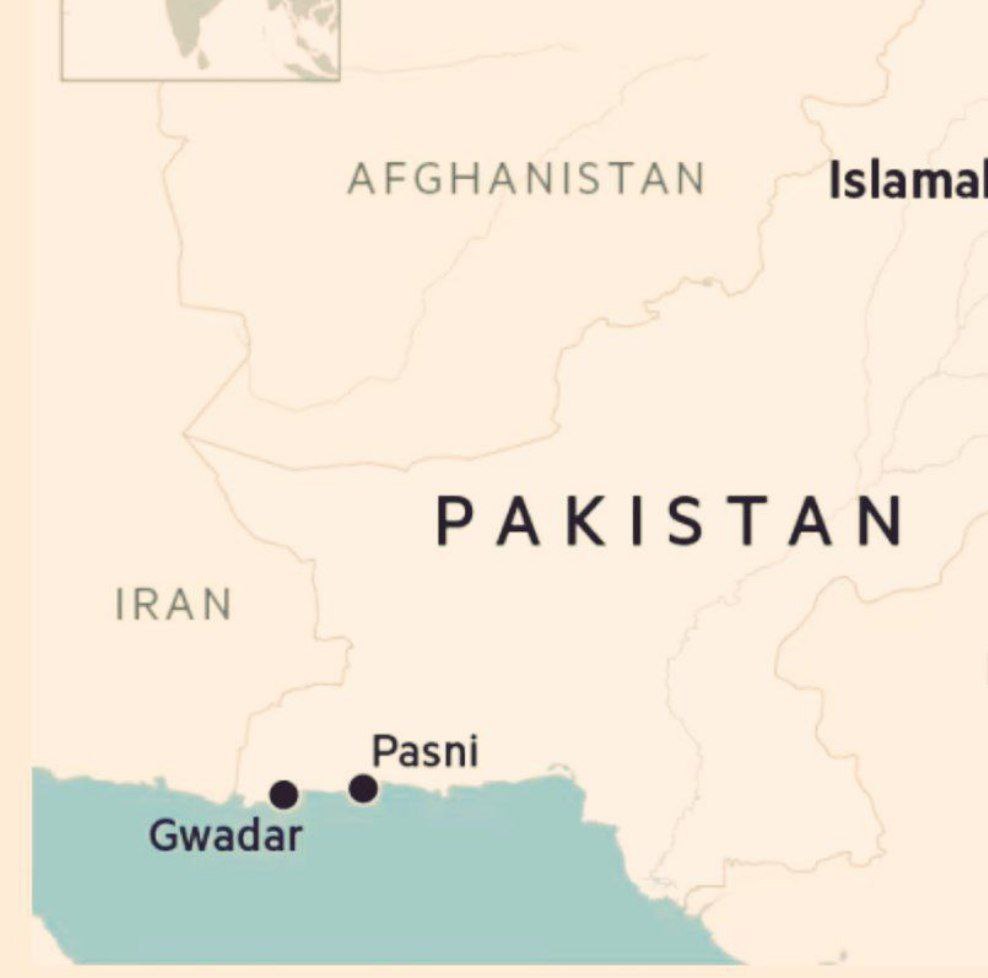
- 12 Oct 2025
In News:
Pakistan’s recent diplomatic engagements indicate a marked shift in its foreign policy priorities. The country, traditionally aligned with China under the China–Pakistan Economic Corridor (CPEC) framework, is now attempting to re-engage with the United States. Central to this emerging realignment is Islamabad’s reported proposal to allow the US to develop a new port at Pasni in Balochistan — a move that carries significant geopolitical and strategic ramifications.
The Pasni Port Proposal: Redefining Strategic Partnerships
Pakistan has reportedly offered the United States the opportunity to build and operate a port at Pasni, a deep-water harbour located on the Arabian Sea in Balochistan’s Gwadar district.
- The proposed port is around 70 miles east of China-operated Gwadar Port and approximately 100 miles from Iran’s border.
- The initiative aims to reduce Pakistan’s dependence on China’s Belt and Road Initiative (BRI), attract American investment, and open access to critical mineral exports from Balochistan.
- Plans for a railway linkage between Pasni and the hinterland have also been discussed to enhance trade connectivity.
If realised, this project would grant Washington a strategic maritime foothold in the region — an area of growing competition among global powers.
The Emerging Maritime Triangle: Pasni–Gwadar–Chabahar
Pasni’s location gives rise to a new maritime triangle involving:
- Gwadar Port – a China–Pakistan venture central to the CPEC framework;
- Chabahar Port – a joint India–Iran initiative providing access to Afghanistan and Central Asia; and
- Pasni Port – potentially linked to US–Pakistan cooperation.
This triad places China, the US, and India in close operational proximity, turning the northern Arabian Sea into a strategic hotspot where economic corridors overlap with geopolitical rivalries.
Economic Drivers: The Mineral Dimension
Balochistan is rich in rare earth elements and critical minerals, crucial for high-tech manufacturing and green technologies.
- During recent engagements in Washington, Pakistan’s leadership reportedly showcased samples of these minerals to US officials in an attempt to secure American investment.
- The proposal reflects a shift in Pakistan’s economic diplomacy — reoffering projects once promised to China now to the United States.
This “resource diplomacy” underlines Islamabad’s efforts to diversify partnerships amid economic distress and debt dependence on China.
Domestic Political Motivations
The overtures toward Washington also have domestic political undertones.
- The civil–military establishment, led by Prime Minister Shehbaz Sharif and Army Chief General Asim Munir, faces questions of legitimacy and stability at home.
- Closer ties with the US are seen as a way to gain international backing and financial relief.
- However, the leadership’s willingness to reconsider Pakistan’s stance on issues like recognition of Israel under the Abraham Accords has invited domestic criticism for allegedly compromising national principles and Palestinian solidarity without parliamentary approval.
Regional Reactions and Strategic Fallout
China’s Concerns
- Beijing views the Pasni initiative as undermining CPEC and encroaching upon its sphere of influence.
- A potential US presence near Gwadar and close to Xinjiang’s western frontier could be perceived as a strategic encirclement.
Iran’s Apprehensions
- Pasni’s proximity to the Iranian border raises concerns in Tehran, which already faces tensions with the US.
- The project could alter the regional balance and complicate Iran’s trade interests via Chabahar.
India’s Calculations
- India’s Chabahar Port project could lose strategic relevance if the Pasni initiative attracts significant US investment and attention.
- The US’s ambiguous stance on the Chabahar sanctions waiver further limits India’s operational space in the region.
Afghanistan’s Position
- The Taliban government may cautiously welcome US economic engagement but will resist any renewed American military presence, such as at Bagram Airbase.
Security Implications: Risk of Regional Instability
Balochistan already faces persistent challenges, including:
- Baloch insurgency,
- Militant violence in Khyber Pakhtunkhwa, and
- Ethnic and sectarian tensions.
Introducing American infrastructure and personnel into this volatile setting could exacerbate local grievances and trigger a new phase of proxy competition between the US and China.
Such dynamics risk turning Balochistan into a geostrategic flashpoint and further destabilising Pakistan’s internal security landscape
Super Typhoon Ragasa
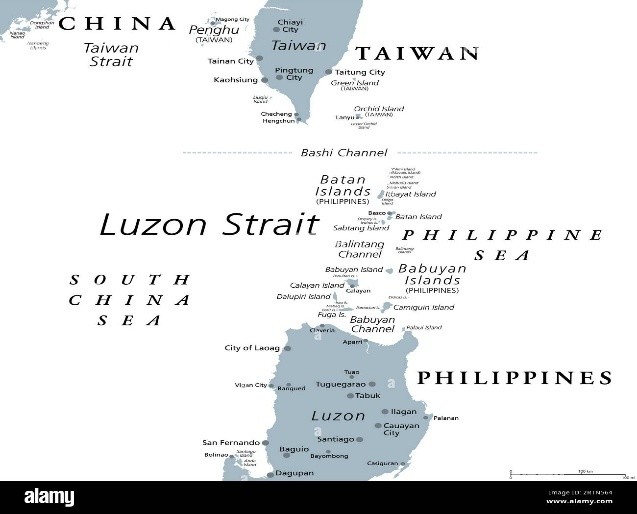
- 26 Sep 2025
In News:
Super Typhoon Ragasa—locally known as Nando—has emerged as one of the most powerful storms to strike Southeast Asia in recent years. With sustained winds exceeding 200 km/h and gusts up to 250 km/h, it has prompted large-scale shutdowns across the Philippines and Hong Kong, highlighting the region’s vulnerability to climate-induced extreme weather events.
About Super Typhoon Ragasa
- Category: 5 (the highest on the Saffir-Simpson scale)
- Wind Speed: Sustained winds of around 205 km/h, gusting up to 250 km/h.
- Origin: Formed over the western Pacific Ocean, where warm sea surface temperatures and low wind shear facilitated rapid intensification.
- Track: Moving northwestward across the Luzon Strait, impacting the Babuyan Islands in northern Philippines before heading toward southern China, including Hong Kong.
Regional and Environmental Significance
- The increasing intensity of storms like Ragasa reflects the broader pattern of climate change-driven extreme weather in the western Pacific region.
- Rising sea surface temperatures and shifting atmospheric circulation patterns have led to more frequent and severe typhoons, posing long-term challenges to disaster preparedness and coastal infrastructure resilience in densely populated regions like Luzon and Hong Kong.
Way Forward
- Strengthening Early Warning Systems: Enhanced forecasting and community-based alert dissemination can save lives in coastal and island regions.
- Climate Adaptation Infrastructure: Investment in storm-resilient housing, flood barriers, and sustainable urban planning is critical for mitigating recurring damage.
- Regional Cooperation: Shared meteorological data and coordinated disaster response among ASEAN nations, China, and Pacific island states can improve resilience.
Dongsha Islands
- 18 Sep 2025
In News:
Taiwan’s Coast Guard Administration (CGA) recently repelled both a Chinese coast guard ship and a Chinese fishing boat near the Dongsha Islands (Pratas Islands), highlighting escalating tensions in the South China Sea and the strategic significance of the region.
Key Highlights:
These confrontations coincided with China’s announcement of a national nature reserve at Scarborough Shoal, a territory also claimed by Taiwan and the Philippines. While Beijing described it as a conservation initiative, analysts view it as part of China’s broader strategy to assert control over disputed areas.
Taiwan condemned the repeated incursions, labeling them “grey zone tactics”—persistent, low-intensity actions aimed at exerting pressure without provoking direct military conflict. The CGA reaffirmed its commitment to defend Taiwan’s sovereignty, pledging ongoing patrols and surveillance in the Dongsha region.
About the Dongsha Islands:
- Located in the northern South China Sea, ~445 km southwest of Kaohsiung, Taiwan, and 320 km southeast of Hong Kong.
- Governed by Taiwan and staffed by marines, with no permanent civilian residents.
- Comprised of three formations: Dongsha Island (above sea level) and Northern and Southern Vereker atolls (below sea level).
- Circular coral atoll structure: reef flats span 24 km in diameter, enclosing a 16 km lagoon; Dongsha Island itself is ~1.6 km long and 0.8 km wide.
The incidents underscore the fragile security balance in the South China Sea, where overlapping territorial claims, strategic maritime routes, and China’s assertive posture pose ongoing regional challenges. Taiwan’s proactive coastal defense measures reflect its determination to safeguard administered territories.
High Performance Biomanufacturing Platforms
- 05 Sep 2025
In News:
- India has taken a significant step towards strengthening its bioeconomy with the launch of High-Performance Biomanufacturing Platforms by the Department of Biotechnology (DBT) and the Biotechnology Industry Research Assistance Council (BIRAC) under the BioE3 Policy (Biotechnology for Environment, Economy & Employment).
- The initiative aims to provide world-class infrastructure, tools, and expertise to start-ups, SMEs, industry, and academia, enabling the transition of bio-based innovations from laboratories to production scale.
Key Features of the Platforms
- National Network: 21 bio-enablers comprising advanced biofoundries and biomanufacturing hubs.
- Focus Areas:
- Microbial strains & smart proteins
- Probiotics & bio-based chemicals
- Next-generation cell therapies & mRNA medicines
- Marine bio-innovations
- Sustainable biofuels
- Support System: Offers integrated facilities for R&D, innovation, and commercialization.
- Alignment: Consistent with Atmanirbhar Bharat vision and India’s climate commitments.
Objectives
- Economic: Position India as a global bioeconomy leader and build a multi-trillion-dollar bioeconomy by 2047.
- Strategic: Reduce dependence on imports by strengthening indigenous capabilities.
- Social: Generate employment, build capacity, and support youth-led innovations.
- Environmental: Promote green growth and sustainable production systems.
Significance of the Initiative
- Economic Potential
- India now accounts for ~20% of global biomanufacturing capacity.
- Bio-industrial sector contributes 47.2%, bio-farmers 35.2%, bio-services 9.4%, and bio-agri8.1% to the bioeconomy.
- Reinforces India’s status as the world’s fourth-largest economy and a rising biotech powerhouse.
- Employment and Innovation
- Creates an enabling ecosystem for start-ups and SMEs, boosting entrepreneurship.
- Generates skilled jobs in cutting-edge sectors like synthetic biology, bioenergy, and therapeutics.
- Strategic Autonomy
- Enhances self-reliance in critical biomanufacturing domains such as vaccines, smart proteins, and biofuels.
- Reduces vulnerability to global supply chain disruptions.
- Sustainability and Viksit Bharat 2047
- Supports green growth through bio-based, low-carbon solutions.
- Anchors India’s long-term development vision of Viksit Bharat by 2047.
Pfizer’s Next-Generation Vaccine
- 14 Aug 2025
In News:
- Pfizer has introduced the 20-valent pneumococcal conjugate vaccine (PCV20) for adults in India.It offers protection against 20 pneumococcal serotypes, which are responsible for most pneumococcal diseases.
About Pneumococcal Disease
- Cause: Infection by Streptococcus pneumoniae (pneumococcus), an encapsulated bacterium with a polysaccharide capsule (major virulence factor).
- Serotypes: ~90 identified worldwide; only a few cause the majority of infections.
Types of Illness
- Mild: Ear infections, sinus infections.
- Severe:
- Pneumonia
- Bloodstream infections (septicemia)
- Meningitis (CNS infection)
Public Health Burden
- Major global health concern.
- Most vulnerable groups: young children and the elderly.
- Mortality: Around 1 million child deaths annually due to pneumococcal disease.
- Transmission: Direct contact with respiratory secretions of patients or asymptomatic carriers.
Treatment and Prevention
- Treatment: Antibiotics.
- Challenge: Rapidly growing antimicrobial resistance in pneumococci.
- Prevention: Vaccination remains the most effective strategy, especially for:
- Children under 5 years
- Elderly individuals
- Immunocompromised patients
MERITE Scheme

- 12 Aug 2025
In News:
The Union Cabinet has approved the Multidisciplinary Education and Research Improvement in Technical Education (MERITE) Scheme with a total outlay of ?4,200 crore (2025–26 to 2029–30). This includes ?2,100 crore World Bank loan assistance. The scheme seeks to transform India’s technical education landscape in line with the National Education Policy (NEP), 2020.
Coverage
- Institutions: 275 government/government-aided technical institutions (175 engineering institutions + 100 polytechnics).
- Beneficiaries: Around 7.5 lakh students across all States and Union Territories.
- Stakeholders: National Institutes of Technology (NITs), State Engineering Institutions, Affiliating Technical Universities (ATUs), with implementation support from IITs, IIMs, AICTE, and NBA.
Objectives
- Improve quality, equity, and governance in technical education.
- Align curricula with labour market requirements.
- Strengthen the research and innovation ecosystem.
- Support State/UT technical education departments in digitalization and quality assurance.
Key Focus Areas
- Digital Transformation: ICT-enabled learning, blended teaching models.
- Multidisciplinary Programs: Introduction of NEP-2020 aligned technical courses.
- Skill & Employability Enhancement: Internships, industry-linked curricula, language labs, skill/maker labs.
- Research and Innovation: Establishing research hubs, incubation centres, innovation labs.
- Faculty & Governance: Faculty development programs, creation of academic administrators with focus on women leadership.
- Accreditation & Quality Assurance: Strengthening institutional governance and accountability.
Expected Outcomes
- Increased student employability and higher placement rates.
- Improved research output and innovation ecosystem.
- Greater equity and inclusion in technical education, with emphasis on reducing gender gaps and digital divide.
- Enhanced global competitiveness of Indian technical institutions.
Employment Generation Impact
By modernising technical education and strengthening linkages with industry, MERITE is expected to:
- Improve fresh graduates’ placement prospects.
- Foster entrepreneurship through incubation and innovation centres.
- Contribute to reducing unemployment among engineering graduates.
Background and Significance
India’s sustainable and inclusive growth hinges on technological advancement, which demands upgraded academic and research standards. MERITE builds upon NEP-2020 reforms such as curriculum revamp, skill development, interdisciplinary learning, and enhanced governance. Importantly, it integrates global expertise through the World Bank partnership.
The scheme also ensures participatory governance, incorporating feedback from States/UTs during policy design, thereby strengthening cooperative federalism in higher education reform.
Global Risk of Zoonotic Diseases and India’s Preparedness
- 12 Aug 2025
In News:
A recent study published in Science Advances has highlighted that over 9.3% of the world’s land surface is at high (6.3%) or very high (3%) risk of zoonotic outbreaks — diseases transmitted between animals and humans. About 3% of the global population lives in extremely high-risk areas, while nearly 20% live in medium-risk zones.
The study introduced a Global Epidemic Risk Index, combining country-specific zoonotic risk factors with national preparedness capacities, to help policymakers strengthen health systems, allocate resources effectively, and enhance global cooperation.
Disease Burden and Examples
- Zoonotic diseases account for 60% of all known infectious diseases and up to 75% of emerging infectious diseases (EIDs).
- Globally, they cause 2.5 billion cases and 2.7 million deaths annually.
- Examples: Rabies, anthrax, influenza (H1N1, H5N1), Nipah virus, brucellosis, tuberculosis, Ebola, SARS, MERS, and Covid-19.
Drivers of Spillover Events
- Climate Change: Rising temperatures, erratic rainfall, and water scarcity heighten risks by altering habitats and vector distribution.
- Land Use Change: Deforestation, urban expansion, and agricultural intensification increase human–animal contact.
- Transmission Routes:
- Direct (e.g., avian influenza)
- Food-borne (e.g., salmonella)
- Vector-borne (e.g., West Nile virus)
- Water-borne (e.g., cryptosporidiosis)
Regional Vulnerabilities
- Latin America: 27% of land at high risk
- Oceania: 18.6%
- Asia: 7%
- Africa: 5%
India’s Vulnerability
- An ICMR study (2018–23) found that 8.3% of all reported outbreaks (583 of 6,948) were zoonotic.
- Outbreaks peaked during June–August, linked to monsoon-driven ecological changes.
- The Northeast region accounted for 35.8% of reported zoonotic outbreaks.
India’s Initiatives
- National Animal Disease Control Programme (NADCP): Mass vaccination to eliminate Foot & Mouth Disease (FMD) and Brucellosis.
- Target: Control FMD by 2025 and eradicate by 2030.
- National One Health Programme for Prevention and Control of Zoonoses (2013): Integrated surveillance and inter-sectoral coordination.
- Animal Birth Control (Dogs) Rules, 2023: Rabies vaccination and sterilisation of stray dogs.
- Rabies Vaccination under ASCAD (Livestock Health & Disease Control Programme).
Global Initiatives
- Zoonotic Disease Integrated Action (ZODIAC): Launched by IAEA (2020) for early detection and rapid response.
- World Zoonoses Day (6 July): Marks Louis Pasteur’s rabies vaccine in 1885.
- G20 Pandemic Fund: Financial support for strengthening preparedness and response.
- Global Early Warning System (GLEWS): A WHO–FAO–WOAH collaboration for coordinated zoonotic disease surveillance.
One Health Approach
The One Health framework recognizes the interconnectedness of human, animal, and environmental health. It promotes collaborative, multisectoral strategies for sustainable disease prevention and response.
Strategic Interventions for Green Hydrogen Transition (SIGHT) Scheme

- 09 Aug 2025
In News:
India has achieved a milestone in its clean energy transition with the discovery of a record-low price of ?55.75/kg (USD 641/MT) for Green Ammonia in the first-ever auction conducted by the Solar Energy Corporation of India (SECI) under the Strategic Interventions for Green Hydrogen Transition (SIGHT) Scheme, a core component of the National Green Hydrogen Mission (NGHM).
About the SIGHT Scheme
- Nature: Flagship financial mechanism under NGHM.
- Nodal Ministries: Ministry of New & Renewable Energy (MNRE) and Ministry of Petroleum & Natural Gas (MoPNG).
- Objective:
- Scale up green hydrogen and its derivatives (like green ammonia).
- Make them cost-competitive with fossil-based alternatives.
- Create domestic demand across fertilizer, refining, and shipping sectors.
- Financial Outlay: ?17,490 crore (till 2029–30) out of the total NGHM budget of ?19,744 crore.
- Implementation Modes:
- Mode 1: Incentives to lowest incentive seekers.
- Mode 2A: Aggregated demand for Green Ammonia (fixed incentive).
- Mode 2B: Aggregated demand for Green Hydrogen (fixed incentive).
- Incentive Structure (Mode 2B): ?50/kg (Year 1), ?40/kg (Year 2), ?30/kg (Year 3).
- Monitoring: A joint MNRE–MoPNG committee ensures compliance with notified green hydrogen standards.
First Green Ammonia Auction (Mode-2A)
- Winning Bid: ?55.75/kg (down from ?100.28/kg discovered in H2Global auction 2024).
- Quantity: 75,000 MTPA out of a total tendered 7.24 lakh MTPA.
- Offtaker:Paradeep Phosphates Ltd., Odisha.
- Contract: Fixed 10-year supply, ensuring price stability and supply chain reliability.
- Global Comparison: Price is slightly higher than grey ammonia (USD 515/MT, March 2025) but provides strong economic incentives for clean transition.
Variable Rate Reverse Repo (VRRR)

- 07 Jul 2025
In News:
The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) recently carried out a 7-day Variable Rate Reverse Repo (VRRR) auction worth ?1 lakh crore. This measure was taken to manage the surplus liquidity in the banking system, which had surged to approximately ?3.75 lakh crore.
What is VRRR?
The Variable Rate Reverse Repo (VRRR) is a liquidity management tool employed by the RBI to absorb excess funds from commercial banks for a specified period. Unlike the fixed reverse repo rate, the VRRR rate is determined through an auction mechanism, allowing market forces to decide the interest rate.
Key Characteristics:
- Auction-Based Interest Rate: Interest is not fixed but discovered through competitive bidding.
- Time-Bound Operation: Typically conducted for durations like 7, 14, or 28 days.
- Liquidity Management Tool: Helps the RBI withdraw excess liquidity from the financial system.
- Repo Rate Ceiling: The interest rate in VRRR operations cannot exceed the current repo rate.
- Flexible Tenor: RBI may modify the duration of VRRR auctions based on prevailing liquidity conditions.
Objective of VRRR
- To mop up surplus liquidity from the banking system.
- To help regulate short-term interest rates and support effective transmission of monetary policy.
- To foster a market-driven interest rate environment in the short-term interbank market.
How VRRR Functions
- Auction Announcement: RBI declares the amount and duration of the VRRR operation.
- Bid Submission: Banks submit bids with the amount and the interest rate at which they are willing to park funds with RBI.
- Rate Determination: RBI accepts bids at or above the cut-off rate, determined by the auction.
- Interest Earnings: Banks earn interest at the accepted rate over the auction tenure.
Implications of VRRR Operations
- On the Money Market: Tightens liquidity, leading to an uptick in short-term rates such as the call money rate and TREPS.
- On the Bond Market: May cause short-term government and corporate bond yields to rise, increasing borrowing costs.
- On Banks:
- Offers an avenue to earn returns on idle funds, improving short-term profitability.
- Temporarily locks up funds, which may reduce immediate availability for lending or investment.
This mechanism is a vital part of the RBI's toolkit to maintain financial stability and ensure efficient transmission of monetary policy.
Digital Public Infrastructure for Fraud Risk Management
- 29 Jun 2025
In News:
The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) is set to develop a Digital Public Infrastructure for Fraud Risk Management (DPIP) under its supervision to curb rising instances of banking frauds in India. This aligns with broader efforts to enhance security and transparency in India’s financial ecosystem.
What is Digital Public Infrastructure (DPI)?
- Definition: DPI refers to foundational digital systems that are accessible, secure, interoperable, and designed to deliver essential public services.
- Examples in India:
- Aadhaar (Digital ID)
- Unified Payments Interface (UPI)
- DigiLocker, CoWIN, etc.
About DPIP
- Objective:To enhance fraud risk management through real-time intelligence sharing, data gathering, and interbank coordination using advanced technologies.
- Key Features:
- Will strengthen existing fraud detection systems in the banking ecosystem.
- Enables interoperable intelligence sharing between banks and financial institutions.
- Leverages AI/ML tools and data analytics for better predictive fraud detection.
- Institutional Mechanism:
- A committee under Shri A.P. Hota has been constituted to examine various aspects of DPIP’s implementation.
- RBI Innovation Hub (RBIH) is tasked with developing a prototype, in consultation with 5–10 public and private sector banks.
Need for DPIP
- Rise in Bank Frauds:
- As per RBI’s Annual Report:
- FY 2024: ?12,230 crore in frauds
- FY 2025: ?36,014 crore — almost 3x increase
- Increasing sophistication of cyber threats and fraud techniques necessitates robust preventive digital infrastructure.
- As per RBI’s Annual Report:
Other RBI Initiatives to Combat Bank Frauds
Initiative Description
Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) Mandatory for all digital/electronic payments to ensure
secure transactions.
Zero Liability Framework Customers are not liable for losses arising from bank’s
negligence or third-party breaches.
bank.in and fin.in domains Reserved for verified bank websites to help customers
avoid phishing and fake sites.
Haemophilia A
- 27 Jun 2025
In News:
The National Institute of Immunohaematology (NIIH) has indigenously developed a simple, affordable, and rapid point-of-care test kit for the early diagnosis of Haemophilia A and Von Willebrand Disease (VWD). This development marks a significant step in improving accessible healthcare diagnostics for genetic bleeding disorders in India.
Significance of the Innovation:
- Affordable and accessible: Enables early diagnosis at primary health centres and in low-resource settings.
- Supports Universal Health Coverage: Improves detection and timely treatment, reducing morbidity.
- Make in India in Health Sector: A boost to indigenous biomedical research and diagnostics.
About Haemophilia A
What is it?
- A hereditary bleeding disorder caused by insufficient levels of Factor VIII, a protein essential for blood clotting.
- Part of the broader group of genetic conditions known as inherited coagulopathies.
Causes:
- Deficiency or dysfunction of coagulation Factor VIII in the coagulation cascade.
- Usually inherited through an altered gene passed from parents.
Genetic Transmission:
- X-linked recessive inheritance:
- Males with the defective gene express the disease.
- Females are typically carriers, though they may show mild symptoms.
Symptoms:
- Prolonged bleeding, often seen after circumcision or minor injuries.
- Internal bleeding, particularly into joints, causing pain and swelling.
- Other signs include:
- Nosebleeds
- Blood in stool/urine
- Bruising
- Bleeding after surgery or dental procedures
Treatment:
- Factor VIII replacement therapy: Intravenous infusion of the missing clotting factor.
- Preventive therapy (prophylaxis) to reduce the frequency of bleeding episodes.
About Von Willebrand Disease (VWD)
What is it?
- A genetic bleeding disorder caused by a deficiency or dysfunction of von Willebrand factor (VWF), which helps platelets stick together to form blood clots.
Causes:
- Inherited from one or both parents.
- People with VWD have:
- Low levels of VWF, or
- VWF that does not function properly.
Symptoms:
- Often asymptomatic unless triggered by injury or surgery.
- Common symptoms include:
- Easy bruising
- Frequent nosebleeds
- Bleeding gums
- Heavy or prolonged menstruation (menorrhagia)
- Post-operative bleeding
- Severe cases may show:
- Internal joint bleeding
- Blood in urine (hematuria)
- Blood in stool (melena)
Treatment:
- No cure, but manageable with:
- Desmopressin (DDAVP) to release stored VWF.
- VWF and Factor VIII concentrates.
- Self-care measures to reduce bleeding risks.
Household Income Survey in 2026

- 27 Jun 2025
In News:
The Ministry of Statistics and Programme Implementation (MoSPI) has announced that India will conduct its first nationwide Household Income Survey in 2026, marking a major milestone in the country’s data-driven policymaking framework.
What is the Household Income Survey?
- A comprehensive, nationwide survey aimed at collecting reliable and robust data on household income distribution across India.
- It is the first standalone survey focused specifically on income estimation, unlike earlier efforts that focused primarily on consumption and employment.
Key Implementing Bodies:
- Ministry of Statistics and Programme Implementation (MoSPI)
- National Sample Survey (NSS)
- Technical Expert Group (TEG)
Historical Background:
- 1950: National Sample Survey (NSS) established to conduct large-scale household surveys.
- 1955–1970: Income data attempted in the 9th, 14th, 19th, and 24th NSS rounds but faced challenges such as underreporting.
- 1983–84: A pilot income study failed to produce scalable data due to low income estimates relative to consumption and savings.
- Past difficulties deterred the launch of a dedicated income survey—until now.
Key Features of the 2026 Survey:
- First of its kind: India’s first survey exclusively focused on household income distribution.
- Methodologically robust: Designed by the TEG, incorporating international best practices in conceptual design, sampling, and estimation.
- Use of digital tools: Integration of technology-driven data collection methods to improve precision, timeliness, and reflect the role of digital economy in income generation.
- Built on recent statistical reforms by MoSPI in areas like:
- Unincorporated enterprise surveys
- Services sector data
- Private capital expenditure
- Tourism satellite accounts
Significance of the Survey:
- Addresses a critical data gap in understanding income inequality, disparities, and growth trends.
- Supports evidence-based welfare policies, including targeted subsidies, social protection, and fiscal redistribution.
- Enhances India’s capacity for inclusive growth assessment and SDG tracking.
- Strengthens the country's statistical infrastructure, aligning it with global standards.
Training of Trainers (ToT)Programme

- 27 Jun 2025
In News:
In a significant move to strengthen grassroots governance and fiscal autonomy, the Ministry of Panchayati Raj (MoPR) has launched a Training of Trainers (ToT)programme in collaboration with the Indian Institute of Management (IIM) Ahmedabad and the Indian Institute of Public Administration (IIPA). The initiative aims to enhance the capacity of Panchayats to generate Own Source Revenue (OSR) under the Rashtriya Gram Swaraj Abhiyan (RGSA).
Key Objectives:
- Enhance financial self-reliance of Panchayati Raj Institutions (PRIs).
- Build a cadre of Master Trainers equipped to train Panchayat-level functionaries.
- Shift local governance from a compliance-based model to proactive planning, innovation, and community engagement.
- Promote a culture of fiscal accountability, transparency, and efficient public service delivery at the grassroots level.
Core Focus Areas of Training
- Fundamentals of Own Source Revenue (OSR)
- Revenue enhancement strategiestailored to rural contexts
- Behavioural insights in tax collectionand compliance
- Revenue utilization for development and service delivery
- Village-level financial planningand Gram Panchayat Development Plans (GPDPs)
- Innovative financing mechanisms
- Project management and accountability tools
The training emphasized field orientation, peer learning, and evidence-based practices to ensure real-world applicability and long-term impact.
Institutional Reforms and Digital Integration
As part of the broader reform agenda:
- Model OSR Rules Framework is under development based on state-level legislative reviews.
- A Digital Tax Collection Portal is being created to facilitate:
- Simplified and accountable revenue collection,
- Digital integration with Panchayat-level financial systems.
Case Studies & Best Practices
The training showcased successful Panchayat-level revenue generation models from:Odisha, Gujarat, Goa, Uttar Pradesh, Maharashtra, and the Andaman & Nicobar Islands, highlighting scalable models of local innovation.
Rashtriya Gram Swaraj Abhiyan (RGSA): Background
A Centrally Sponsored Scheme (CSS) launched in 2018 and revamped for 2022–2026, aimed at developing and strengthening the Panchayati Raj System across rural India.
Key Objectives:
- Build governance capacity of PRIs to achieve Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs).
- Empower Panchayat representatives for effective leadership and participatory governance.
- Enhance OSR generation and financial planning at the Panchayat level.
- Promote inclusive development and convergence of schemes.
- Strengthen Gram Sabhas as platforms for citizen engagement.
Salient Features:
- Emphasis on capacity-building and leadership training.
- Promotes decentralisation and compliance with the PESA Act, 1996.
- Encourages use of technology-driven solutions for governance.
- Recognises and incentiviseshigh-performing Panchayats.
- Facilitates collaboration with international and national institutions.
Strengthening Inclusive Education for Children with Disabilities in India

- 21 Jun 2025
In News:
In a major step towards inclusive education, the Government of India signed a tripartite Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) in 2025 between the Department of Empowerment of Persons with Disabilities (DEPwD), National Institute of Open Schooling (NIOS), and National Council of Educational Research and Training (NCERT). The MoU aims to enhance curriculum reform, institutional coordination, and accessibility for children with disabilities across India’s education system.
What is Inclusive Education?
Inclusive education refers to a model where children with and without disabilities learn together in mainstream classrooms. It is supported by adapted curricula, accessible infrastructure, and individualised support mechanisms. The Rights of Persons with Disabilities (RPWD) Act, 2016 legally mandates inclusive education environments in India.
Why Inclusive Education Matters
Inclusive education is not merely a policy choice but a constitutional, social, and developmental imperative:
- Right to Education: Under Article 21A of the Constitution and the RTE Act, 2009, every child aged 6–14 has the right to free and compulsory education. This includes children with special needs (CWSN).
- Equity and Access: Reports by UNESCO highlight that 29 million children are out of school in South Asia, many of them with disabilities. Ensuring their inclusion addresses systemic exclusion.
- Social Transformation: Inclusive classrooms reduce stigma, promote empathy, and facilitate social acceptance of persons with disabilities.
- Human Capital Development: Educating CWSN enhances their ability to participate in the economy, contributing to innovation, productivity, and nation-building.
- Global Commitments: India has ratified the UN Convention on the Rights of Persons with Disabilities (CRPD, 2007) and is committed to SDG 4, which seeks inclusive and equitable quality education for all by 2030. The National Education Policy (NEP) 2020 also stresses disability inclusion at all education levels.
Key Data Points Highlighting the Need for Intervention
- According to the 2011 Census, around 7% of Indian children (0–19 years) have disabilities. However, data from UDISE+ 2019–20 reveals that less than 1% of children enrolled at the primary level are children with disabilities.
- In 2018–19, around 21 lakh CWSN were covered under Samagra Shiksha, supported by only 27,774 special/resource teachers across the country. This highlights the urgent need for both greater coverage and trained human resources.
Government Initiatives Promoting Inclusive Education
- The 2025 MoU between DEPwD, NIOS, and NCERT is aimed at reforming the curriculum to accommodate diverse learners. It also recognises special schools run under the Deendayal Disabled Rehabilitation Scheme (DDRS) as SAIEDs (Schools for Accessible and Inclusive Education for Disabled), expanding academic options for CWSN.
- The National Education Policy 2020 mandates the integration of children with disabilities in regular classrooms and promotes universal access and equity.
- Under Samagra Shiksha, the government provides financial support of ?3,500 per CWSN annually. Additional provisions include stipends for girls (up to Class XII), appointment of special educators, resource rooms, and home-based education for children with severe disabilities.
- NCERT’s Barkha Series, based on the Universal Design for Learning (UDL) framework, offers accessible reading materials in both print and digital formats, tailored to the diverse needs of learners.
- The RPWD Act 2016 mandates the creation of inclusive learning environments, with accessible buildings, assistive devices, and necessary support services.
Rudrastra
- 15 Jun 2025
In News:
India's Rudrastra, a homegrown VTOL drone, has been successfully tested by the Indian Army, marking a significant advancement in battlefield technology. Developed by Solar Aerospace and Defence Limited, this drone can perform precision strikes across borders without endangering soldiers.
Overview:
- Rudrastra is a hybrid Vertical Take-Off and Landing (VTOL) combat drone developed indigenously by Solar Aerospace and Defence Limited (SDAL).
- Successfully tested by the Indian Army in June 2025.
Key Features:
- Hybrid VTOL Capability:
- Takes off like a helicopter and cruises like a fixed-wing aircraft.
- Increases versatility, maneuverability, and stealth.
- Combat Role:
- Equipped with smart anti-personnel warheads.
- Capable of deep-strike missions against targets like artillery guns or terrorist hideouts.
- Deployed as a “stand-off weapon”—engages targets from a safe distance.
- Performance Parameters:
- Range: Full range of 170 km.
- Strike Capability: Targets more than 50 km away.
- Flight Endurance: Nearly 90 minutes.
- Navigation: Autonomous return capability.
- Surveillance: Real-time video feed for reconnaissance.
- Payload: Capable of deploying airburst munitions—detonates low to the ground to cause area damage.
Strategic Importance:
- Reduces risk to soldiers in hostile territory.
- Enhances India's unmanned combat aerial vehicle (UCAV) arsenal.
Useful in anti-terror operations, border surveillance, and precision strikes.
4th India–Central Asia Dialogue (2024)
- 08 Jun 2025
In News:
India hosted the 4th edition of the India–Central Asia Dialogue in New Delhi, chaired by External Affairs Minister Dr. S. Jaishankar. The event emphasized regional security, connectivity, critical minerals, counter-terrorism, and economic integration.
What is the India–Central Asia Dialogue?
- Type: Multilateral forum for structured engagement between India and Central Asian republics.
- Initiated in: 2019, Samarkand (Uzbekistan).
- Participants: India, Kazakhstan, Kyrgyz Republic, Tajikistan, Turkmenistan, Uzbekistan.
Key Objectives:
- Strengthen cooperation in trade, connectivity, security, energy, health, and technology.
- Promote regional stability, counter-terrorism collaboration, and sustainable development.
- Enhance people-to-people ties and institutional coordination.
Major Outcomes of the 4th Dialogue:
- Security Cooperation:
- Condemned terror attacks (e.g., Pahalgam).
- Called for early adoption of the UN Comprehensive Convention on International Terrorism.
- Critical Minerals & Rare Earths:
- Joint intent for collaboration in exploration and investment.
- Decision to hold the 2nd India–Central Asia Rare Earth Forum soon.
- Connectivity & Trade:
- Focus on using the International North-South Transport Corridor (INSTC) and Chabahar Port.
- Supported Uzbekistan and Turkmenistan's inclusion in INSTC.
- Digital & Financial Integration: Agreement to boost digital payments, interbank ties, and trade in local currencies.
- Health and Traditional Medicine: Shared commitment to Universal Health Coverage, medical tourism, and integration of AYUSH systems.
- Clean Energy & Technology: Cooperation on platforms like India Stack, International Solar Alliance, and biofuels.
- Multilateral Support: Reiterated support for India’s permanent seat in UNSC and active role in SCO and UN.
Amrit Bharat Scheme
- 14 Apr 2025
In News:
The Amrit Bharat Station Scheme (ABSS), launched to transform railway stations across India into world-class travel hubs, has achieved a key milestone. Railway Minister Ashwini Vaishnaw announced the completion of redevelopment work at 104 stations out of the planned 1,300 stations under the scheme.
About the Amrit Bharat Station Scheme
- Launched: 2023
- Objective: Comprehensive redevelopment of railway stations to:
- Upgrade passenger amenities
- Enhance multi-modal connectivity
- Modernize infrastructure with sustainable and accessible design
Key Updates (As of April 2025)
- Total stations under ABSS: 1,300
- Stations with completed redevelopment: 104
- Stations in Maharashtra: 132 (significant progress reported)
Major Highlights
Feature Details
Notable Station Project Chhatrapati Shivaji Maharaj Terminus (CSMT), Mumbai
CSMT Redevelopment Cost ?1,800 crore
Modern Facilities Planned Waiting lounges, food courts, clean restrooms, lifts, escalators,
digital signage
International Comparison CSMT post-redevelopment projected to surpass
London’s Kings Cross station
Additional Infrastructure Developments in Maharashtra
- Gondia–Ballarshah Railway Line Doubling:
- Length: 240 km
- Region: Vidarbha
- Approved Investment: ?4,819 crore
- Strategic Importance: Enhances connectivity and freight movement
Centre–State Collaboration
- A Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) was signed between the Government of India and Government of Maharashtra for railway project implementation and coordination.
SEBI’s Operational Framework for ESG Debt Securities
- 07 Jun 2025
In News:
The Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI) has introduced a comprehensive operational framework for the issuance of Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) debt securities. This includes instruments such as social bonds, sustainability bonds, and sustainability-linked bonds, aiming to boost responsible financing in India.
Understanding ESG Debt Securities
Definition:
ESG debt securities are financial tools designed to raise capital specifically for projects that yield positive environmental, social, or governance (ESG) outcomes. These instruments are a key part of sustainable finance, with categories including:
- Social Bonds: Focused on projects with direct social impact (e.g., affordable housing, education).
- Sustainability Bonds: Target projects with both environmental and social objectives.
- Sustainability-Linked Bonds: Tied to specific ESG performance indicators or targets.
Salient Features:
- Funds raised must be used exclusively for eligible ESG-aligned projects.
- Bonds must be clearly labelled in line with the project's primary focus.
- Compliance with global ESG norms and standards is mandatory.
- Verification or certification by an independent third-party is required.
- The framework applies to both public and private debt offerings.
Highlights of SEBI’s Framework
1. Classification Guidelines: Issuers are required to categorize their bonds—green, social, or sustainability—based on the core objective of the projects being financed. This ensures transparent communication of the bond's intended impact.
2. Disclosure Norms:
- At the Issuance Stage: Offer documents must detail project eligibility, selection methodology, and a tentative allocation between financing new initiatives and refinancing existing ones.
- Post-Issuance: Issuers must provide annual updates on fund deployment and report impact metrics to demonstrate accountability and transparency.
3. Independent Assurance: Issuers must engage accredited third-party entities to validate the alignment of bonds with ESG principles, thereby enhancing investor confidence and market integrity.
4. Monitoring and Evaluation: There is an obligation for ongoing impact assessment. Issuers must ensure the projects funded effectively contribute to reducing environmental degradation or addressing social challenges.
5. Scope and Enforcement: The framework will come into effect from June 5, 2025, and is aligned with international ESG standards to facilitate greater inflow of sustainable and ethical investments.
Significance for India: This move marks a significant step in mainstreaming ESG finance in India. It aims to improve transparency, attract climate-conscious capital, and reinforce India’s commitment to sustainable development.
C CARES Version 2.0
- 05 Jun 2025
In News:
The Ministry of Coal recently launched C CARES Version 2.0, a significant upgrade to the Coal Mines Provident Fund Organization’s (CMPFO) digital platform. The new system aims to enhance transparency, efficiency, and accessibility in provident fund (PF) and pension disbursement for coal sector workers.
Key Features of C CARES Version 2.0
- Developed by the Centre for Development of Advanced Computing (C-DAC) in collaboration with the State Bank of India (SBI).
- Provides a unified digital interface for coal workers, coal companies, and CMPFO.
- Enables real-time claim tracking, automated ledger updates, and direct benefit transfers to workers’ bank accounts.
- Includes a mobile application for CMPF members, offering:
- PF balance checks
- Profile viewing
- Grievance redressal
- Claim status tracking
- A chatbot assistant for easy navigation
Benefits to Stakeholders
- For Workers: Faster claim settlement, improved access, and reduced delays in PF/pension disbursement.
- For Coal Companies and CMPFO:
- A prescriptive dashboard to generate custom reports.
- Analytics to track settlement trends.
- Support for data-driven decision-making.
About CMPFO
- Full Form: Coal Mines Provident Fund Organization
- Established: 1948
- Parent Ministry: Ministry of Coal
- Function: Administration of PF and pension schemes for coal sector employees.
- Coverage:
- Serves around 3.3 lakh PF subscribers
- Supports over 6.3 lakh pensioners
Significance
Union Minister for Coal and Mines G. Kishan Reddy launched the portal on June 4, 2025, stating that it aligns with the Government's vision of “Minimum Government, Maximum Governance” under the Digital India initiative. The platform strengthens social security delivery for coal workers and brings administrative reform to a critical sector of the economy.
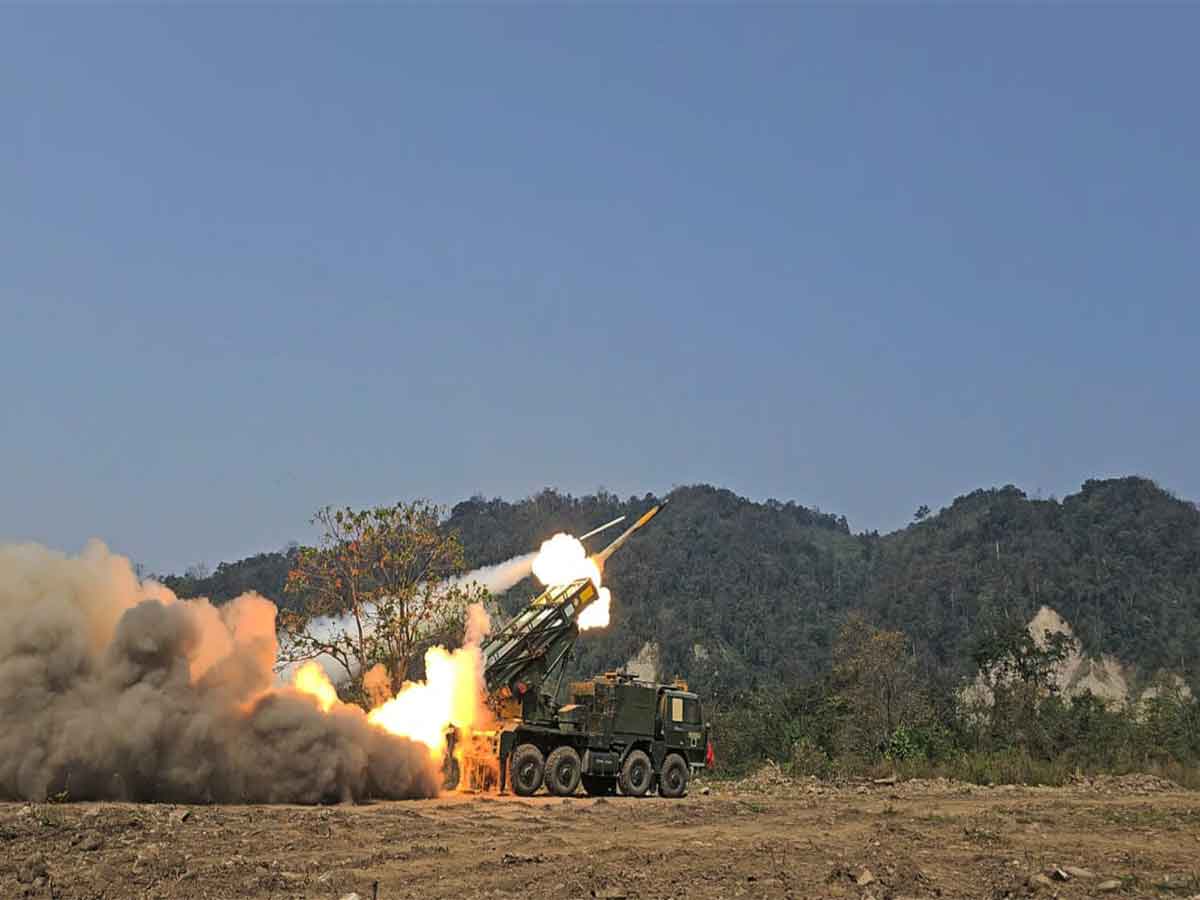
Exercise PrachandPrahar (2025)

- 01 Apr 2025
In News:
Exercise PrachandPrahar was a tri-service integrated multi-domain military exercise conducted by the Indian Armed Forces in the high-altitude terrain of Arunachal Pradesh, along the Northern Borders, specifically under the Eastern Army Command.
Timeline:
- Held: March 25–27, 2025
- Preceded by:Exercise PoorviPrahar (November 2024), which focused on integrated aviation asset application.
Objective:
To validate integrated operational capabilities of the Army, Navy, and Air Force, and enhance India's preparedness for future warfare scenarios along the 3,488-km long Line of Actual Control (LAC) with China.
Key Highlights:
- Location: High-altitude Himalayan terrain, eastern sector of the LAC in Arunachal Pradesh.
- Forces Involved:
- Indian Army (including Special Forces)
- Indian Air Force (IAF)
- Indian Navy
Major Components:
- Surveillance and Domain Awareness:
- Long-range surveillance aircraft (IAF)
- Maritime domain awareness aircraft (Navy)
- Helicopters and UAVs
- Space-based assets
- Precision Strike Capabilities:
- Fighter aircrafts
- Long-range rocket systems
- Medium artillery
- Armed helicopters
- Swarm drones
- Loitering munitions
- Kamikaze drones
- Operational Environment:
- Simulated electronic warfare and contested conditions.
- Focus on jointness, precision, and rapid response.
Strategic Importance:
- Demonstrated seamless command, control, and coordination among the three services.
- Validated the ability to conduct multi-domain operations (MDO) in challenging terrain.
- Reinforced India’s technological edge and combat readiness along strategic frontiers.
Ayurveda Day

- 18 May 2025
In News:
The Government of India has officially fixed September 23 as Ayurveda Day, replacing the earlier practice of celebrating it on Dhanteras, which follows a variable lunar calendar. This change, notified through a Gazette notification in March 2025, aims to bring uniformity and global visibility to Ayurveda observance.
About Ayurveda Day:
- Purpose:Ayurveda Day is observed to honour India’s ancient medicinal heritage and promote Ayurveda as a scientific, evidence-based, and holistic healthcare system rooted in preventive and sustainable wellness practices.
- New Fixed Date:Starting 2025, Ayurveda Day will be celebrated every year on 23rd September, coinciding with the autumnal equinox, a day when day and night are nearly equal, symbolizing balance—a core concept in Ayurvedic philosophy.
- Why the Shift?The previous observance on Dhanteras created logistical challenges due to its annual date fluctuation (between mid-October and mid-November). The new fixed date allows for better planning and consistent global celebrations.
- Symbolism of Autumnal Equinox:The equinox represents cosmic balance and harmony, aligning with Ayurveda’s emphasis on equilibrium between mind, body, spirit, and environment.
Ayurveda: Key Facts for UPSC
- Definition:Ayurveda, meaning the “Science of Life” (from Sanskrit Ayu = life, Veda = knowledge), is a traditional Indian medical system dating back over 5,000 years, with roots in the Atharva Veda.
- Core Principles:
- SwasthasyaSwasthyaRakshanam: Maintaining the health of the healthy
- AturasyaVikaraPrashamanam: Treating diseases in the sick
- Emphasis on natural healing, diet, seasonal routines, and mind-body balance
- Key Features:
- Focus on preventive healthcare
- Use of herbal medicines, detox therapies, yoga, and meditation
- Personalised treatment based on individual constitution (Prakriti)
Significance for Global Health:
The Ministry of AYUSH envisions Ayurveda Day as a global platform to promote India’s traditional knowledge system as a part of the international wellness movement. Health professionals, researchers, academic institutions, and global partners are encouraged to participate in its observance to integrate Ayurveda into broader healthcare dialogues.
India’s First Geothermal Production Well in Northeast

- 18 May 2025
In News:
In a significant advancement for clean energy in Northeast India, Dirang in Arunachal Pradesh has become the site of the region’s first operational geothermal production well. This marks a pivotal step in utilizing Earth’s internal heat for sustainable energy generation in the eastern Himalayas.
Project Details
- Location:Dirang, West Kameng district, Arunachal Pradesh
- Terrain: Eastern Himalayan region
Technology Used
- The project employs a closed-loop binary Organic Rankine Cycle (ORC) system, which captures subsurface geothermal heat for applications such as:
- Electricity generation
- Space heating
- Agricultural processing
- Reservoir Temperature: Approx. 115°C — optimal for direct-use geothermal systems.
- Drilling Approach: Low-impact precision drilling aimed at fault zones between quartzite and schist rock formations.
Institutional Collaboration
- Implementing Agency:Centre for Earth Sciences and Himalayan Studies (CESHS), Itanagar
- Supported by:
- Ministry of Earth Sciences, Government of India
- Government of Arunachal Pradesh
- International partners from Norway, Iceland, and Guwahati research institutes
Significance
- First-of-its-kind in the entire Northeast region
- Potential to make Dirang energy self-reliant through clean geothermal power
- Helps replace diesel and firewood in cold climates, reducing emissions
- Can enhance agricultural productivity and living standards in high-altitude areas
- Strengthens India’s geothermal potential (~10,600 MW), offering reliable base-load renewable energy unlike solar or wind
Stagflation and Banking Sector Risks in the U.S.

- 18 May 2025
In News:
In 2025, economic analysts are raising alarms over growing signs of stagflation in the United States and its potential to trigger a renewed banking crisis similar to the collapse of Silicon Valley Bank (SVB) in 2023.
Unrealized Losses in U.S. Banks
As of early 2025, U.S. banks are grappling with $482.4 billion in unrealized losses from securities investments, according to the Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation (FDIC). This marks a 32.5% rise from the previous quarter. The figure is approaching the $515 billion mark observed during the SVB crisis and could rise to $600–700 billion if interest rates hit 5%.
These losses are primarily linked to long-term securities like government bonds, whose prices have fallen due to rising benchmark 10-year Treasury yields, now exceeding 4.5%.
What is Stagflation?
Stagflation is a rare and difficult economic condition marked by:
- High inflation
- Stagnant or negative economic growth
- High unemployment
It complicates policymaking because:
- Tightening monetary policy (raising interest rates) to control inflation can worsen unemployment and slow growth.
- Loosening policy to boost growth can further fuel inflation.
Causes of Stagflation in 2025:
- Supply Shocks – Rising input costs (e.g., energy or tariffs).
- Tariff Hikes – New U.S. tariffs on imports have raised production costs.
- Policy Missteps – Uncoordinated fiscal and monetary measures.
Impacts on the Financial Sector
- Reduced Bond Values: High interest rates lower the market value of banks’ bond holdings.
- Risk of Bank Runs: Diminished asset values can trigger depositor panic.
- Credit Losses: Particularly in sectors like tech and venture capital where firms have weak earnings and poor debt coverage.
- Liquidity Crisis: A sudden negative news cycle could lead to another SVB-like collapse.
Experts warn that continued high interest rates could deepen banking stress and prolonged stagflation could amplify credit defaults.
Balochistan
- 12 May 2025
In News:
On May 9, 2025, Mir Yar Baloch announced the unilateral declaration of independence for Balochistan from Pakistan. In a public appeal, he urged India to formally recognize Balochistan as a sovereign state and open an embassy in New Delhi. He also called upon the United Nations to deploy peacekeeping forces and demanded the withdrawal of the Pakistani military from the region.
Geographical Profile
- Location: Balochistan lies in the southwestern part of Pakistan and is the country’s largest province by area, comprising nearly 44% of its total territory.
- Area: Approximately 347,190 square kilometers
- Capital: Quetta, situated near the Afghanistan border
- Borders:
- East: Sindh and Punjab provinces
- West: Iran
- Northwest: Afghanistan (across the Durand Line)
- South: Arabian Sea, with a coastline of around 770 km
Topography and Climate
- Characterized by rugged, mountainous terrain (notably the Sulaiman and Makran ranges)
- Arid and semi-arid climate zones, including desert and dry steppe regions
- Low population density, yet abundant in untapped mineral wealth
Demographics and Ethnicity
- Major Ethnic Group: The Baloch, who trace their ancestry to Iranian origins
- Other Communities: Pashtuns in the northern areas, and the Brahui ethnic group
- Languages Spoken: Balochi, Pashto, Brahui, and Urdu
- Religion: Predominantly followers of Sunni Islam
Strategic and Geopolitical Significance
Natural Resource Wealth
- Balochistan is rich in natural gas, coal, copper, and gold.
- The RekoDiq mining site is among the world’s largest undeveloped gold and copper reserves.
- The province contributes about 40% of Pakistan’s natural gas production, yet remains economically underdeveloped and politically marginalized.
China-Pakistan Economic Corridor (CPEC)
- Gwadar Port, located in southern Balochistan, is a critical node in China’s Belt and Road Initiative (BRI).
- It provides China with direct maritime access to the Arabian Sea and strategic connectivity to West Asia, bypassing the Strait of Malacca.
India’s Strategic Perspective
- India has consistently highlighted human rights violations in Balochistan at international forums.
- The region’s geostrategic position intersects with India’s Indo-Pacific vision, and is relevant in India’s efforts to counter China’s growing footprint through CPEC.
Insurgency and Security Dynamics
- Balochistan has long witnessed separatist movements led by Baloch nationalist groups seeking either enhanced autonomy or full independence from Pakistan.
- These groups frequently target Pakistani military convoys, CPEC infrastructure projects, and Chinese nationals working in the region, signaling strong opposition to external control and resource exploitation.
International Labour Day (May Day)
- 02 May 2025
In News:
International Labour Day, also known as May Day, is observed annually on May 1 to honor the dedication and contributions of workers across the globe.
Key Highlights:
- Observed On: May 1
- Also Known As: International Workers’ Day, May Day
- Purpose: To commemorate the contributions of workers and honor the global labor movement's struggles and achievements.
Historical Background
- Origin: The roots of International Labour Day trace back to Chicago, USA, where on May 1, 1886, workers launched a strike demanding an 8-hour workday.
- The protest culminated in the Haymarket Affair on May 4, 1886, when a bomb explosion led to the deaths of six police officers and several civilians, marking a major milestone in labor rights activism.
- In 1889, the Second International (Paris) declared May 1 as a day of international workers’ solidarity.
Global Observance
- Observed in over 160 countries, including India, China, Cuba, France, Germany, Brazil, South Africa, Russia, Vietnam, among others.
- Celebrated through parades, union meetings, and public demonstrations advocating workers’ rights and social justice.
Country-wise Observance Differences
- India: First observed in 1923 in Chennai by the LabourKisan Party of Hindustan. It is a public holiday, widely recognized across the country.
- United States: Despite its historical origin, the U.S. celebrates Labor Day on the first Monday of September, officially declared in 1894 after the Pullman Strike. The shift was made to distance the holiday from socialist and communist affiliations.
- Canada: Also celebrates Labor Day on the first Monday of September, following U.S. traditions, though May 1 has some informal recognition by trade unions.
- United Kingdom: Celebrates a related holiday called the Early May Bank Holiday on the first Monday of May, which may or may not fall on May 1. It is not explicitly labor-themed like in other countries.
Significance
- Serves as a global reminder of workers’ rights, the historical fight for humane working conditions, and the ongoing struggles of labor communities.
- Symbolizes solidarity among workers across nations, cutting across political ideologies and economic systems.
Sahkar Taxi

- 31 Mar 2025
In News:
The government has announced the upcoming introduction of ‘Sahkar Taxi’, a cooperative-based ride-hailing platform designed to directly benefit drivers by eliminating intermediary commissions.
What is ‘Sahkar Taxi’?
‘Sahkar Taxi’ is a ride-hailing service supported by the government, operated through cooperative societies. Unlike conventional app-based services such as Ola and Uber, this platform allows drivers to retain their full earnings, without deductions by middlemen or aggregators. It draws inspiration from existing app-based models but is fundamentally driven by cooperative principles.
Why is ‘Sahkar Taxi’ Needed?
- Concerns Over Commission Charges: Leading ride-hailing apps have faced criticism for imposing high commission fees, reducing the take-home earnings of drivers.
- Pricing Transparency Issues: Allegations of differential pricing based on the type of user device (e.g., iPhone versus Android) have sparked doubts regarding fairness and transparency.
- Driver Challenges: Centralized control by large platforms often leaves drivers with limited negotiation power and inadequate income security.
Importance and Impact of ‘Sahkar Taxi’
- Driver Empowerment: By establishing a cooperative ownership model, drivers gain a stronger stake in the business, leading to improved financial stability.
- Decentralized Economic Participation: The initiative encourages local involvement and collective growth, aligning with the government’s vision of ‘Sahkar Se Samriddhi’ (Prosperity through Cooperation).
- Sustainable Alternative: It presents a viable, inclusive option to the dominant profit-driven ride aggregator market, focusing on equitable benefit sharing.
- Enhanced Consumer Confidence: The cooperative framework promotes transparent pricing and greater accountability in digital service delivery, fostering trust among users.
India’s First Indigenous MRI Scanner Installed at AIIMS
- 27 Mar 2025
In News:
AIIMS New Delhi is set to install India’s first indigenously developed MRI scanner for clinical evaluation by October 2025. This marks a major milestone under the government's push for import substitution and promotion of ‘Make in India’ in the medical device sector.
Key Highlights:
- MRI Type: 1.5 Tesla Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) system.
- Developed by: SAMEER (Society for Applied Microwave Electronics Engineering and Research), an autonomous R&D institution under the Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology (MeitY).
- Initiative under: National Mission SCAN-ERA (Swadeshi Chumbakiya Anu-naadChitran – EkRashtriyaAbhiyaan), launched in December 2014.
- Purpose: Clinical evaluation and performance feedback at AIIMS to refine the system for wide-scale clinical use.
- Objective: Reduce dependence on imported diagnostic equipment and lower treatment costs.
Significance:
- Currently, 80–85% of India's medical devices are imported.
- In FY 2023–24, India’s medical device import bill rose by 13% to ?69,000 crore.
- The initiative aligns with the Production-Linked Incentive (PLI) Scheme for medical devices, under which 7 critical devices (including MRI machines, CT scanners, LINACs, heart valves, etc.) are now being domestically manufactured.
- 19 PLI-supported projects have been commissioned to manufacture 46 medical devices.
MRI: How It Works
- Principle: Uses strong magnetic fields and radiofrequency pulses to align protons in tissues. As protons return to their original alignment, they emit signals that are captured to create detailed 3D anatomical images.
- Applications:
- Imaging soft tissues, brain, spinal cord, joints, and internal organs.
- Detecting tumors, strokes, neurological disorders, and musculoskeletal injuries.
- Functional MRI (fMRI) maps brain activity during cognitive tasks.
Safety & Limitations:
- Magnetic interference: Risky for patients with implants (e.g., pacemakers).
- Noise: Loud clicking sounds may cause discomfort.
- Claustrophobia: May cause anxiety in closed spaces; open MRI designs mitigate this.
- Contrast agents: Use of gadolinium-based agents can pose risks to dialysis patients.
India to Host FATF Private Sector Collaborative Forum 2025 in Mumbai
- 25 Mar 2025
In News:
- India will host the FATF Private Sector Collaborative Forum (PSCF) 2025 in Mumbai from March 25-27, 2025. This event will focus on global priorities such as payment transparency, financial inclusion, and the digital transformation of financial systems.
- The forum will be a critical platform for addressing the evolving challenges of money laundering and terrorist financing through the use of digital tools and enhanced transparency.
Key Agenda
The discussions at PSCF 2025 will revolve around tackling contemporary financial crimes, including those linked to cryptocurrency-related laundering. Key topics will include:
- Strengthening Anti-Money Laundering (AML) and Counter-Terrorist Financing (CFT) compliance mechanisms.
- Promoting financial inclusion through risk-based supervision of regulated entities.
- Enhancing transparency in beneficial ownership and using digital tools to bolster AML/CFT measures.
- Addressing emerging risks, including terrorist financing and proliferation financing.
The forum will also assess how the private sector can enhance information-sharing practices to address these threats more effectively.
About FATF
The Financial Action Task Force (FATF), established in 1989 during the G7 Summit in Paris, is an intergovernmental body that sets international standards to combat money laundering and terrorist financing. The FATF’s mission is to develop policies, establish guidelines, and promote global cooperation to mitigate the financial risks associated with these crimes.
- Headquarters: Paris, France.
- Membership: FATF has 39 member countries, including major economies such as the United States, India, China, Saudi Arabia, Germany, and theEuropean Union.
- Regional Bodies: In addition to its direct members, FATF affiliates over 180 countries through FATF-Style Regional Bodies (FSRBs) like the Asia Pacific Group (APG) and the Eurasian Group.
- FATF Recommendations are recognized as the global standard for AML/CFT measures.
FATF evaluates countries' efforts to comply with these standards, providing assessments and promoting policy changes to counteract financial crimes. Countries that fail to comply may be placed on the grey list or blacklist.
FATF Grey and Black Lists
Countries that fail to meet FATF standards are placed on one of two lists:
- Black List: Countries known as Non-Cooperative Countries or Territories (NCCTs), which directly support terrorist financing and money laundering. North Korea, Iran, and Myanmar are currently on this list.
- Grey List: Countries considered at risk of supporting financial crimes but not yet fully engaging in those activities. Being on the grey list serves as a warning, with the risk of moving to the blacklist if improvements are not made.
Countries on the blacklist face severe international sanctions, including restrictions on financial aid and economic interactions from organizations like the IMF, World Bank, and Asian Development Bank.
India's Role in FATF
India became a member of FATF in 2010 and has made significant strides in improving its AML/CFT frameworks. In 2024, FATF acknowledged India’s efforts towards anti-money laundering and countering terrorist financing, placing it in the "regular follow-up" category for continued compliance.
The upcoming PSCF 2025 will be a milestone in India’s ongoing commitment to global financial security, as it seeks to enhance international collaboration and discuss innovative ways to address evolving threats in financial crimes.
Gandiva (Astra MK-III) Missile
- 11 Mar 2025
In News:
India’s cutting-edge air-to-air missile, previously known as Astra MK-III, has been officially renamed Gandiva, inspired by the mythical bow wielded by Arjuna in the epic Mahabharata. This rebranding marks a symbolic nod to India's cultural legacy while highlighting its growing defence capabilities.
Overview of the Gandiva (Astra MK-III) Missile
Developed by the Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO), Gandiva is a beyond-visual-range (BVR) missile currently undergoing final stages of development. It is designed to be equipped on frontline fighter aircraft such as the Sukhoi Su-30MKI and LCA Tejas of the Indian Air Force (IAF).
Upon induction, Gandiva is set to become one of the longest-range air-to-air BVR missiles globally, significantly enhancing India's aerial combat capabilities.
Key Capabilities and Features
- Engagement Range:
- Up to 340 km when the target is flying at 20 km altitude.
- Around 190 km if the target is at an altitude of 8 km.
- Propulsion System: Powered by a dual-fuel ducted ramjet engine, allowing high-speed performance across various altitudes—from sea level to 20 km.
- Speed and Maneuverability:
- Launch speed: Between Mach 0.8 and 2.2.
- Target engagement speed: Between Mach 2.0 and 3.6.
- Can engage agile aerial targets with an angle of attack up to 20 degrees.
- Altitude Adaptability: Features a ±10 km snap-up/snap-down capability, enabling it to intercept targets that are significantly above or below the altitude of the launching aircraft.
Strategic Importance
Gandiva is designed to neutralize a wide spectrum of aerial threats, including:
- Enemy fighter jets
- Bombers and transport aircraft
- Aerial refueling planes
- AWACS (Airborne Warning and Control Systems)
Open Market Operations
- 11 Mar 2025
In News:
The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) has announced a liquidity injection of ?1.9 lakh crore into the banking system through Open Market Operations (OMOs) and USD/INR forex swaps, in response to tightening liquidity conditions observed since December 2024.
What are Open Market Operations (OMOs)?
- Open Market Operations refer to the buying and selling of government securities in the open market by the central bank to regulate liquidity in the banking system.
- It is a monetary policy tool used to manage inflation and ensure financial stability.
How OMOs Work:
- To inject liquidity: RBI purchases government securities from banks, increasing their cash reserves, which lowers interest rates, encourages lending, and boosts economic activity.
- To absorb liquidity: RBI sells government securities, reducing cash reserves in the system, which raises interest rates, discourages excessive lending, and cools inflation.
RBI’s Recent Measures (March 2025):
- OMO Purchase Auctions:Government securities worth ?1 lakh crore to be bought in two tranches of ?50,000 crore each on March 12 and March 18.
- Forex Swap Auction:
- A USD/INR Buy/Sell Swap worth $10 billion with a 36-month tenor, scheduled for March 24, to inject long-term dollar liquidity.
- A similar $10 billion swap was conducted on February 28, which saw strong demand.
T-72 Tanks

- 08 Mar 2025
In News:
India has signed a $248 million contract with Russia’s Rosoboronexport for the procurement of 1,000 horsepower (HP) engines to upgrade its fleet of T-72 main battle tanks (MBTs). This marks a significant step in enhancing the Indian Army's offensive and mobility capabilities.
Key Features of the Deal
- Engines to replace existing 780 HP ones in T-72 tanks.
- Delivered in fully formed, completely knocked down (CKD), and semi-knocked down (SKD) formats.
- Includes Transfer of Technology (ToT) to Armoured Vehicles Nigam Limited (AVNL) at the Heavy Vehicles Factory, Avadi (Chennai).
- Boosts the ‘Make in India’ initiative in the defence sector through local assembly and licensed production.
About T-72 Tanks
- Origin: Developed by the Soviet Union in the 1970s; designed by Uralvagonzavod.
- India’s Usage: Operates over 2,400 units, making it the backbone of India’s armored forces.
- Manufacturing in India: Locally produced and upgraded at the Heavy Vehicles Factory, Avadi.
Specifications
- Armament:
- 125 mm smoothbore main gun
- 7.62 mm coaxial machine gun
- 12.7 mm anti-aircraft machine gun
- Mobility: With new 1,000 HP engines, improves maneuverability and combat speed.
- Protection: Equipped with composite and reactive armour.
- Night Capability: Advanced thermal imaging systems.
- Operational Range:
- ~460 km on-road
- ~300 km off-road (with auxiliary fuel)
Strategic Significance
- Combat Readiness: Enhances battlefield performance in high-altitude and desert environments like Ladakh.
- Cost Efficiency: Upgrading older platforms is more economical than procuring new MBTs.
- India-Russia Defence Ties: Reinforces long-standing military cooperation between the two countries.
Electronic Personnel License (EPL) for Pilots
- 25 Feb 2025
In News:
India has launched the Electronic Personnel License (EPL) for pilots, becoming the second country globally, after China, to implement this advanced digital licensing system.
What is EPL?
- Electronic Personnel License (EPL) is a digital version of pilot licenses, replacing the traditional physical cards.
- Pilots can securely access their EPL via the eGCA Mobile Application developed by the Directorate General of Civil Aviation (DGCA).
- It ensures real-time verification, enhancing efficiency, transparency, and security in licensing procedures.
Significance of EPL
- Aligns with:
- Digital India and Ease of Doing Business initiatives.
- ICAO’s Amendment 178 to Annex 1 on Personnel Licensing, promoting digital transformation.
- Enhances:
- Safety and efficiency in civil aviation operations.
- Environmental sustainability by reducing the use of plastic and paper.
- Global employability of Indian pilots through instant international credential verification.
Implementation & Governance
- Ministry: Ministry of Civil Aviation, Government of India.
- Executing Agency: Directorate General of Civil Aviation (DGCA).
- EPL implementation positions India as a leader in aviation innovation and modern governance.
International Civil Aviation Organization (ICAO):
- Established: 1947 under the Chicago Convention (1944).
- Headquarters: Montreal, Canada.
- Nature: A specialized intergovernmental agency affiliated with the United Nations (UN).
- Functions:
- Sets standards and regulations for aviation safety, security, efficiency, and environmental performance.
- Promotes peaceful and efficient international air transport.
- Facilitates global cooperation and market liberalization in aviation.
Gravehawk Hybrid Air Defense System

- 20 Feb 2025
In News:
The Gravehawk is a newly developed mobile surface-to-air missile (SAM) system, introduced by the United Kingdom in collaboration with Denmark, to bolster Ukraine's defenses against Russian aerial threats. This innovative hybrid system exemplifies the modern trend in NATO of repurposing existing missile technology to build flexible, cost-effective, and rapidly deployable air defense platforms.
Overview and Development
- The Gravehawk system is designed to counter short-range aerial threats such as drones, cruise missiles, and low-flying aircraft.
- It combines Western and Soviet-era missile technologies, providing Ukraine with a unique edge in a contested aerial environment.
- The United Kingdom, in partnership with Denmark, is actively delivering these systems to Ukraine, with 15 additional units expected in the coming months.
- The cost per system is approximately USD 1.25 million, with Denmark covering 50% of the expense.
Key Features and Technical Capabilities
- Missiles Used: The system utilizes infrared-guided missiles including the AIM-132 ASRAAM (Advanced Short Range Air-to-Air Missile) and the Soviet-origin R-73 (AA-11 Archer).
- Guidance System: Both missiles employ passive infrared (IR) seekers, allowing them to track heat signatures of targets without emitting radar signals, thereby reducing vulnerability to electronic warfare (EW) detection.
- Speed and Range: Missiles can reach speeds of up to Mach 2.5 and engage targets at distances of approximately 12 miles (about 19 km).
- R-73 Specifics: Originally developed for close-range dogfights, the R-73 is highly maneuverable, capable of tracking targets up to 40 km ahead and 300 meters behind, with off-boresight targeting up to 40 degrees.
- Mobility: Mounted on all-terrain Drops vehicles, the system offers rapid ground mobility and deployment flexibility.
- Containerized Launch Platform: Housed in ISO-standard shipping containers, the system’s roof rolls back to expose two missile rails—repurposed from Soviet-era fighters like the Sukhoi Su-27.
- Crew and Operation: Operated by a five-member crew, the system incorporates electro-optical and infrared targeting cameras, enabling remote operation and safe standoff missile launches.
Strategic Relevance for Ukraine
- Ukraine’s acquisition of the Gravehawk system marks a significant advancement in its air defense capabilities, particularly in the face of persistent Russian air and missile attacks.
- It enhances short-range interception capacity, allows for quick reaction deployment, and reduces dependence on continuous NATO resupplies. Additionally, the system’s use of widely available R-73 missiles ensures operational sustainability.
- The Gravehawk is part of a broader effort to field "hybrid systems", where older missile stocks are integrated into modern platforms.
- Other such initiatives include FrankenSAM programs developed by the U.S. and UK, where systems like ASRAAM have been adapted to ground-based launchers.
- Ukraine has also employed R-73 missiles on drone boats and unmanned surface vessels to target Russian air assets, showcasing the multi-domain applicability of these munitions.
Pradhan Mantri AnusuchitJaatiAbhyuday Yojana (PM-AJAY)

- 14 Feb 2025
In News:
It is a 100% Centrally Sponsored Scheme initiated by the Ministry of Social Justice and Empowerment. The scheme aims at the socio-economic upliftment of the Scheduled Caste (SC) communities, particularly targeting the reduction of poverty through various initiatives that focus on skill development, infrastructure, and income-generating projects.
Key Highlights:
- Launch and Funding: Launched in 2021, the scheme is fully funded by the central government, though states and Union Territories (UTs) have the option to contribute additional funds from their own resources. PM-AJAY is the consolidation of three pre-existing schemes:
- Pradhan Mantri Adarsh Gram Yojana (PMAGY)
- Special Central Assistance to Scheduled Castes Sub Plan (SCA to SCSP)
- BabuJagjivan Ram Chhatrawas Yojana (BJRCY)
- Objectives of PM-AJAY: The scheme is focused on improving the overall well-being of SC communities by:
- Reducing poverty through income-generating schemes, skill development, and infrastructure projects.
- Promoting social and economic development by improving literacy rates, educational enrolment, and providing better livelihood opportunities.
- Transforming SC-majority villages into model villages with integrated development, enhancing socio-economic indicators like education, healthcare, and financial inclusion.
- Eligibility Criteria
- Scheduled Caste (SC) persons living below the poverty line (BPL) are eligible for benefits.
- For infrastructure development, villages with 50% or more SC population are prioritized for grants.
- Key Components of PM-AJAY: The scheme comprises three core components:
- Adarsh Gram Development (formerly PMAGY): Aims to develop SC-majority villages into model villages with holistic improvements in education, healthcare, infrastructure, and skill development.
- Grants-in-Aid for District/State-Level Projects (formerly SCA to SCSP): Financial assistance is provided for livelihood development projects, including skill development programs and infrastructure projects, to generate sustainable income for SC communities.
- Construction of Hostels in Higher Educational Institutions (formerly BJRCY): Focuses on promoting higher education among SC students by constructing hostels in top-ranked institutions according to the National Institutional Ranking Framework (NIRF). This aims to reduce dropout rates and enhance access to quality education.
Special Provisions under the Grants-in-Aid Component
- 15% of the total grants are exclusively allocated for income-generating schemes for SC women.
- 30% of the grants are allocated for infrastructure development in SC-dominated areas.
- 10% of funds are reserved for skill development programs.
- The scheme encourages the formation of SC women cooperatives for producing and marketing consumer goods and services.
Achievements (2022-23)
- 1,260 villages were declared as Adarsh Gram in the financial year 2023-24 under the Adarsh Gram component.
- Nine new hostels were sanctioned under the Hostel Construction component.
- Perspective plans for seven states were approved under the Grants-in-Aid component.
Diamond Imprest Authorization (DIA) Scheme

- 22 Jan 2025
In News:
The Union Government, under the Foreign Trade Policy 2023, has introduced the Diamond Imprest Authorization (DIA) Scheme to enhance India’s competitiveness in the global diamond trade, promote exports, and protect employment, especially in the MSME sector.
Key Highlights:
Objectives:
- Boost value addition and export growth in the diamond sector.
- Support MSME exporters to compete globally.
- Retain India’s position as a global hub for diamond processing and exports.
- Mitigate recent challenges like export decline, job losses, and global demand shifts.
Key Features of the Scheme:
Feature Details
Type of Diamonds Allowed Natural cut and polished diamonds less than ¼ carat (25 cents)
Eligibility Exporters with Two Star Export House status and minimum $15 million annual exports
Export Obligation 10% value addition on imported diamonds
Duty Exemptions Exempts Basic Customs Duty, Anti-dumping Duty, Countervailing Duty, etc.
Effective Date April 1, 2025
Exclusion Lab-Grown Diamonds (LGDs) not covered
Monitoring Agency Gems and Jewellery Export Promotion Council (GJEPC)
Why the Scheme Was Introduced:
Challenges in the Diamond Sector:
- Global: Falling demand in US, Europe, China; rise in lab-grown diamonds.
- Domestic: High unsold inventory, rising operational costs, reduced credit flow, and high corporate tax.
- Employment Impact: Job losses in the diamond cutting and polishing segment.
International Context:
- Inspired by beneficiation policies in diamond-producing countries like Botswana and Namibia, which mandate local value addition.
Significance:
- Enhances India’s role in the global diamond value chain.
- Provides ease of doing business through duty relief.
- Promotes employment generation, especially for diamond assorters and processors.
- Facilitates inclusive growth by supporting MSMEs in a traditionally export-driven industry.
Way Forward:
- Regulate Lab-Grown Diamonds to prevent market distortion.
- Extend export credit period and consider tax exemptions for foreign diamond sellers.
- Ensure technology upgradation and skill training to sustain global leadership.
UJALA Scheme

- 10 Jan 2025
In News:
UJALA scheme completes 10 years, saves ?19,153 crore annually
UJALA Scheme (Unnat Jyoti by Affordable LEDs for All)
- Launch Date: 5th January 2015 by PM Narendra Modi
- Objective:
- To promote energy-efficient LED lighting across India
- To reduce energy consumption, lower electricity bills, and decrease carbon emissions
- Implementing Body: Energy Efficiency Services Limited (EESL), Ministry of Power
- Scheme Relevance: Aims to provide affordable LED bulbs, tube lights, and fans to every household
- Global Recognition: World’s largest zero-subsidy domestic lighting scheme
Key Features:
- Affordability: Subsidized LED bulbs (?70-80), reducing the cost of electricity for households
- Energy Efficiency: LEDs consume 90% less energy than incandescent bulbs, 50% less than CFLs
- Environmental Impact: Significant reduction in CO? emissions by avoiding millions of tonnes annually
- Market Transformation: Over 36.87 crore LED bulbs distributed, saving approximately ?19,153 crore on electricity bills each year
- Consumer Benefit:
- On-Bill Financing: LED bulbs available for purchase through deferred payment via electricity bills
- Targeted low-income communities through Self-Help Groups (SHGs)
Achievements:
- Energy Savings: 47.9 billion kWh annually
- Cost Savings: ?19,153 crore saved on electricity bills
- Carbon Emission Reduction: 38.7 million tonnes of CO? avoided per year
- Peak Demand Reduction: 9,586 MW reduction in peak electricity demand
- Street Lighting: Over 1.34 crore LED streetlights installed, saving 9,001 million units annually
Key Initiatives:
- GRAM UJALA Scheme (March 2021): Aimed at rural households, providing LED bulbs at ?10 each
- Street Lighting National Programme (SLNP): Aimed at reducing public lighting costs with energy-efficient streetlights
- Encouraging Domestic Manufacturing: Stimulated local LED production, aligning with the "Make in India" mission
- E-Procurement Transparency: Real-time procurement ensuring price reductions and maintaining quality
Impact on Environment:
- Energy Savings & Carbon Footprint: The scheme significantly reduced the carbon footprint by promoting energy-efficient appliances
- Reduction in Household Consumption: Consumers benefit from reduced energy consumption and lower utility bills
Centralized Pension Payments System (CPPS)

- 04 Jan 2025
In News:
- The CPPS aims to enhance pension accessibility and simplify the disbursement process for over 7.85 million pensioners in India.
- Key Benefit: Pensioners can now receive their pension from any bank or branch across India, eliminating the need for physical verifications and providing seamless nationwide pension disbursement.
Key Highlights:
- Key Features:
- No need for physical verification: Pensioners do not have to visit the bank for verification at the time of pension commencement.
- Seamless pension disbursement: Upon release, the pension amount is credited immediately.
- Nationwide access: Pensioners can withdraw their pension from any bank or branch, without needing to transfer Pension Payment Orders (PPO) when relocating or changing banks.
- Significance:
- Eliminates the decentralised pension system, where each regional office maintained separate agreements with a few banks.
- Ensures pension portability, especially for pensioners who move or change banks.
Employees’ Provident Fund Organisation (EPFO):
- Overview:
- EPFO is a statutory body under the Employees' Provident Funds and Miscellaneous Act, 1952, and works under the Ministry of Labour and Employment.
- Structure:
- Administered by a tripartite board called the Central Board of Trustees, consisting of representatives from:
- Government (Central & State)
- Employers
- Employees
- The Central Board of Trustees is chaired by the Union Minister of Labour and Employment.
- Administered by a tripartite board called the Central Board of Trustees, consisting of representatives from:
- Key Schemes Operated by EPFO:
- Employees’ Provident Funds Scheme, 1952 (EPF): A savings scheme for workers.
- Employees’ Pension Scheme, 1995 (EPS): A pension scheme for employees after retirement.
- Employees’ Deposit Linked Insurance Scheme, 1976 (EDLI): Provides life insurance coverage to workers.
- Global Coverage: EPFO is also the nodal agency for implementing Bilateral Social Security Agreements with other countries, offering reciprocal social security benefits to international workers from countries with such agreements.
- Impact: The EPFO schemes cover Indian workers and international workers from countries with which EPFO has signed bilateral agreements.
Key Facts:
- CPPS improves the convenience and accessibility of pension services for millions of pensioners across India by simplifying the pension disbursement process and providing nationwide access without the need for physical verifications.
- EPFO, a statutory body under the Ministry of Labour and Employment, plays a crucial role in managing provident funds, pensions, and insurance schemes for both domestic and international workers, fostering social security across India.
World’s First CO? to Methanol Plant

- 10 Nov 2024
In News:
- NTPC has achieved the first-ever synthesis of CO? (captured from flue gas) and hydrogen (produced via a PEM electrolyzer) into methanol at its Vindhyachal plant.
- This marks a significant step in carbon management technology, aimed at advancing sustainable fuel production.
About CO?-to-Methanol Conversion:
- Carbon Dioxide Capture:
- CO? is captured from industrial sources, such as power plants, or directly from the atmosphere.
- Hydrogen Production:
- Renewable energy sources like solar or wind power are used to produce hydrogen through water electrolysis.
- Methanol Synthesis:
- The captured CO? is combined with hydrogen in the presence of a catalyst to produce methanol, typically under high pressure and temperature conditions.
Benefits of CO?-to-Methanol Conversion:
- Carbon Capture and Utilization (CCU):
- This technology reduces the impact of CO? on the atmosphere by converting it into useful products.
- Renewable Fuel Source:
- Methanol produced through this process can be used as a fuel for transportation, power generation, or as a feedstock for chemicals.
- Energy Storage:
- Methanol offers a more practical storage and transportation option than hydrogen, making it a potential energy storage solution and aiding the transition to hydrogen-based energy systems.
- Versatile Feedstock:
- Methanol is widely used in producing chemicals, solvents, and plastics, supporting various industrial applications.
What is Methanol?
- Brief: Methanol, also known as methyl alcohol or wood alcohol, is the simplest form of alcohol. It is a clear, colorless, and flammable liquid with a distinctive odor.
- Key Properties:
- Colorless, miscible with water, toxic if ingested, flammable.
One Sun One World One Grid (OSOWOG) Initiative

- 10 Nov 2024
In News:
- India is in talks with Oman, UAE, Saudi Arabia, Maldives, and Singapore to establish cross-border electricity transmission lines.
- This is part of the ambitious OSOWOG initiative to create a global renewable energy grid.
Key Points:
- Proposed by the Prime Minister of India at the 2018 International Solar Alliance (ISA) Assembly.
- Aims to create a transnational electricity grid that delivers power worldwide.
- Led by India and the UK, in collaboration with ISA and the World Bank Group.
Vision of OSOWOG:
- Connect regional grids through a common infrastructure for the transfer of renewable energy, focusing on solar power.
- Harness solar and other renewable energy from regions where the sun is shining and efficiently transmit it to areas of need.
- Aim to provide power to 140 countries using clean and efficient solar energy.
Phases of OSOWOG:
- Phase 1:
- Connect the Indian grid with grids in the Middle East, South Asia, and South-East Asia.
- Share solar and other renewable energy resources.
- Phase 2:
- Expand the interconnected grid to include renewable resources from Africa.
- Phase 3:
- Achieve a global interconnection aiming for 2,600 GW by 2050.
- Integrate as many countries as possible into a single renewable energy grid.
Global Collaboration:
- Involves national governments, international organizations, legislators, power operators, and experts.
- Focus on accelerating infrastructure development for a clean energy-powered world.
e-Migrate Portal

- 15 Oct 2024
In News:
Recently, the Union Ministers for External Affairs and Labour and Employment launched the upgraded e-Migrate portal and mobile app, aimed at enhancing the migration experience for Indian workers seeking employment abroad. This initiative reflects the Indian government's commitment to ensuring the safety and welfare of its migrant workforce, aligning with global migration goals under the 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development.
About e-Migrate Portal
The e-Migrate portal is an online platform designed to facilitate and manage the migration of Indian workers. It promotes safe and legal mobility channels by providing a transparent framework for migrant workers, including:
- Information Access: Comprehensive resources to help migrants understand the migration process.
- Documentation Support: Tools to assist with necessary paperwork.
- Helpline Support: A 24/7 multilingual helpline that addresses issues faced by workers, particularly in the Gulf region.
- Awareness Campaigns: Initiatives to educate workers about their rights and responsibilities abroad.
The upgraded version of the portal, launched in October 2024, features enhanced functionality to better serve Indian migrants.
Key Features of e-Migrate v2.0
- Multilingual Helpline: Offers real-time support in multiple languages, ensuring that urgent issues are resolved efficiently.
- Integration with Digilocker: Facilitates secure, paperless submission of essential documents, such as passports and employment contracts.
- Social Security Net: Enhances social security measures for migrants, including insurance policies and partnerships with the State Bank of India for fee-free digital payment services.
- Mobile App: Introduced for the first time, this app provides easy access to services, including a job search marketplace for overseas employment opportunities.
- Rural Accessibility: Collaboration with Common Service Centres (CSCs) aims to expand immigration services to rural areas in local languages, making the platform more accessible to diverse populations.
Significance
The e-Migrate portal aligns with the United Nations' Sustainable Development Goal 10, which promotes orderly and responsible migration. By fostering safe migration practices, this initiative seeks to empower Indian workers and protect their rights while contributing to the country's international workforce.
National Maritime Heritage Complex (NMHC)

- 10 Oct 2024
In News:
The Union Cabinet has approved the development of NMHC in Lothal, Gujarat, under the Sagarmala programme.
- Purpose and Vision Aimed at showcasing India’s 4,500-year-old maritime heritage using an edutainment approach with modern technology.
Employment Generation
- Expected to create approximately 22,000 jobs: 15,000 direct and 7,000 indirect.
Project Phases
- Phase 1A
- Features a museum with 6 galleries, including:
- A large Indian Navy & Coast Guard gallery with external naval artifacts.
- Replica of Lothal township surrounded by an open aquatic gallery.
- A jetty walkway.
- Phase 1B
- Expansion includes:
- 8 additional galleries.
- The world's tallest Light House Museum.
- Bagicha complex with facilities for 1,500 cars, a food hall, and a medical center.
- Phase 2
- Development of Coastal States Pavilions by respective states and union territories.
- Hospitality zone featuring maritime-themed eco-resorts and museuotels.
- Recreation of ancient Lothal City and establishment of a Maritime Institute with hostel.
- Creation of four theme-based parks:
- Maritime & Naval Theme Park
- Climate Change Theme Park
- Monuments Park
- Adventure & Amusement Park
Governance and Management
- Governing Council
- Chaired by the Minister of Ports, Shipping & Waterways, overseeing project implementation and operation.
- Separate Society
- A dedicated society will manage future phases, governed under the Societies Registration Act, 1860.
Benefits and Funding
- Beneficiaries
- Local communities, tourists, researchers, government bodies, educational institutions, cultural organizations, conservation groups, and businesses.
- Funding
- Construction of the Light House Museum in Phase 1B will be financed by the Directorate General of Lighthouses and Lightships (DGLL).
Sagarmala Programme
- Objective
- A flagship initiative aiming to transform India’s maritime sector by enhancing logistics performance and fostering port-led development and coastal community upliftment.
- Background
- Approved in March 2015, the programme focuses on utilizing India’s extensive coastline and waterways for economic growth.
Pradhan Mantri Awas Yojana-Gramin (PMAY-G)

- 09 Oct 2024
Recent Initiatives:
- The Indian government has launched a nationwide survey of kutcha houses.
- Introduction of the Awas Sakhi mobile app to streamline housing assistance.
Purpose of the Kutcha House Survey
- Identify Housing Needs: The survey aims to collect data on families living in kutcha (temporary) houses, enabling targeted support for those in need.
- Support for Awas Sakhi App: The survey will enhance the functionality of the Awas Sakhi app, facilitating the application process and providing beneficiaries with vital housing information.
Overview of PMAY-G
- Launch: Initiated in 2016, PMAY-G aims to provide secure housing for the poorest communities.
- Beneficiary Selection Process: A comprehensive three-stage validation, including the Socio-Economic Caste Census 2011, Gram Sabha approvals, and geo-tagging, ensures that aid reaches those most deserving.
Benefits for PMAY-G Beneficiaries
- Financial Assistance:
- ?1.20 lakh for families in plain areas.
- ?1.30 lakh for families in hilly regions, including northeastern states and union territories.
- Support for Sanitation:
- An additional ?12,000 for toilet construction, aligned with the Swachh Bharat Mission – Gramin or MGNREGS.
- Employment Opportunities:
- Provision of 90/95 days of unskilled wage employment through MGNREGA for house construction.
- Access to Basic Amenities:
- Connections for water, LPG, and electricity facilitated through relevant schemes.
- Cost Sharing Structure:
- Expenses are shared in a 60:40 ratio for plain areas and a 90:10 ratio for northeastern states and selected Himalayan states. The Centre covers 100% of costs for other Union Territories.
Progress Under PMAY-G
- Targets: The government aims to construct 2.95 crore houses.
- Current Status: As of August 2024, 2.94 crore houses have been sanctioned, with 2.64 crore completed, enhancing living conditions for millions in rural areas.
Recent Developments
- In August 2024, the Union Cabinet approved funding for two crore additional houses at existing assistance rates.
- Eligibility Criteria Changes:
- Individuals owning bikes or scooters are now eligible.
- The income limit for eligibility has been raised from ?10,000 to ?15,000 per month.
Future Goals
- This initiative, spanning FY 2024-2029, aims to address ongoing housing demands, benefiting approximately 10 crore individuals by providing safe, hygienic, and socially inclusive housing.
MARBURG VIRUS OUTBREAK IN RWANDA
- 30 Sep 2024
In News:
Rwanda is currently facing an outbreak of Marburg virus disease (MVD), leading to six fatalities, primarily among healthcare workers.
What is Marburg Virus Disease?
Marburg virus disease is a severe and often fatal illness first identified in 1967 in Germany. It is caused by the Marburg virus, which is primarily transmitted to humans through contact with infected animals, particularly fruit bats.
Current Situation in Rwanda
The ongoing outbreak has claimed six lives, most of whom were healthcare professionals. The Minister of Health has emphasized the need for heightened preventive measures and community vigilance.
Symptoms and Transmission
Common symptoms of MVD include high fever, severe headache, watery diarrhea, abdominal pain, and vomiting. The virus spreads through direct contact with the blood, secretions, and bodily fluids of infected individuals.
Available Treatments and Supportive Care
There is currently no specific treatment for Marburg virus disease. Supportive care, including symptom management and hydration, is critical, and early medical attention is essential for those exhibiting symptoms.
Preventive Measures and Recommendations
To prevent the spread of MVD, individuals should:
- Practice good hygiene.
- Avoid contact with infected persons.
- Ensure thorough cooking of animal products.
- Use protective equipment when caring for sick patients.
Global Context and Pandemic Risk
While Marburg virus disease poses a significant mortality risk and can spread between humans, its pandemic potential is lower than that of more contagious viruses. Rapid containment efforts are essential to prevent wider outbreaks.
NIDHI Companies

- 16 Sep 2024
In News:
The Registrar of Companies has imposed penalties on over two dozen Nidhi companies for breaches of the Companies Act, such as delayed financial filings and share allotment issues. Fines range from ?20,000 to ?12.5 lakh, with Sri Sathuragiri Nidhi receiving the highest penalty.
What is Nidhi Company?
A Nidhi Company is a unique NBFC regulated under the Companies Act, 2013, and the Nidhi Rules, 2014. Nidhi company signifies that these companies promote thrift and savings habits among their members by accepting deposits and providing loans. They primarily cater to their local communities and operate within a defined geographical area.
Requirements for Obtaining Nidhi Company Status:
Within One Year of Registration:
- Minimum Membership: A Nidhi company must have at least 200 members within one year of starting operations.
- Financial Strength: The company's net owned funds (equity share capital + free reserves - accumulated losses - intangible assets) must be ?10 lakh or more.
- Deposit Security: Unencumbered term deposits (deposits not pledged as security) must be at least 10% of the total outstanding deposits.
- Healthy Debt Ratio: The ratio of net owned funds to deposits should not exceed 1:20. This ensures the company has sufficient capital to back its deposit liabilities.
Compliance Filing:
If a Nidhi company meets all the above conditions within the first year, it must file form NDH-1 along with the prescribed fees within 90 days from the end of that financial year. The form needs to be certified by a practicing Chartered Accountant (CA), Company Secretary (CS), or Cost and Works Accountant (CWA).
Extension Option:
Companies that are unable to meet the requirements within the first year can apply for an extension of one additional financial year. To do so, they need to submit form NDH-2 to the Regional Director within 30 days from the end of the first financial year.
Strict Enforcement:
If a Nidhi company fails to meet the requirements even after the second financial year, it will be prohibited from accepting new deposits until it complies with the regulations. Additionally, it may face penalties for non-compliance.
Benefits of Nidhi Company Registration
Nidhi companies offer several advantages for entrepreneurs:
- Tax benefits: They can enjoy tax exemptions on their profits under certain conditions.
- Reduced regulatory burden: Compared to other NBFCs, Nidhi companies face less stringent regulations.
- Local focus: They cater to the specific financial needs of their communities, fostering local economic development.
- Enhanced credibility: Registration brings legitimacy and builds trust among members.
Eligibility for Nidhi Company Registration
For registration of Nidhi company, the following requirements must be met:
- Minimum members: A minimum of seven members are required at the time of incorporation.
- Minimum capital: The minimum paid-up capital must be Rs. 5 lakh.
- Business restrictions: Nidhi companies cannot undertake activities like issuing debentures or underwriting insurance.
- Profit distribution: They can only distribute a maximum of 20% of their net profit as dividend.
Shanghai Cooperation Organisation (SCO) Startup Forum

- 22 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
India will host the fifth meeting of the Shanghai Cooperation Organisation startup forum in January next year according to the commerce and industry ministry.
About the Shanghai Cooperation Organisation Startup Forum:
- The SCO Startup Forum is a platform for the stakeholders from the startup ecosystems from all SCO Member States to interact and collaborate.
- The entrepreneurial activities aim to empower the local startup communities in the SCO Member States.
- The SCO Startup Forum aims to create multilateral cooperation and engagement for startups among the SCO Member States.
- This engagement will empower the local startup ecosystems in the SCO Member States.
The following are the objectives of the engagement:
- Sharing of best practices to promote entrepreneurship and innovation to build knowledge-exchange systems
- Bringing Corporations and Investors across to work closely with startups and provide local entrepreneurs with much-needed support and market access
- Increasing scaling opportunities for startups by providing solutions in the field of social innovation and providing Governments with a plethora of innovative solutions
- Creating open procurement channels to enable matchmaking for procuring innovative solutions from startups
- Facilitating cross-border incubation and acceleration programs that will enable the startups to explore international markets and get focused mentorship.
Upcoming Events:
- India is set to host the second meeting of the Special Working Group for Startups and Innovation (SWG) in November 2024 and the SCO Startup Forum 5.0 in January 2025.
Past Initiatives:
- SCO Startup Forum 1.0: Established in 2020, laying the groundwork for multilateral cooperation among SCO Member States' startups.
- SCO Startup Forum 2.0: Held virtually in 2021, introducing the SCO Startup Hub, a centralized platform for the SCO startup ecosystem.
- SCO Startup Forum 3.0: Organized physically in 2023 by the Department for Promotion of Industry and Internal Trade (DPIIT), marking a significant milestone for SCO Member States' startup collaboration.
- 1st Meeting of the SWG: Led by India, the first meeting of the SCO Special Working Group on Startups and Innovation in 2023 focused on the theme 'Growing from Roots', emphasizing foundational growth within the startup ecosystem.
'ETHANOL 100' hits the road at 183 Indian Oil stations in five states

- 16 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
In a strategic advance towards cleaner fuel alternatives, India commenced the sale of ETHANOL 100 across 183 Indian Oil outlets in Maharashtra, Karnataka, Uttar Pradesh, New Delhi, and Tamil Nadu.
What is ETHANOL 100 Fuel?
- ETHANOL 100 fuel represents a significant advancement in automotive technology, offering a high-octane rating ranging from 100 to 105.
- This elevated octane level is particularly advantageous for high-performance engines, delivering improved efficiency and power output while simultaneously reducing environmental impact.
- One of the key features of ETHANOL 100 is its remarkable versatility, making it suitable for a diverse range of vehicles, including flex-fuel vehicles (FFVs) designed to accommodate various fuel types such as gasoline, ethanol, or any blend thereof.
- This adaptability ensures that ETHANOL 100 can seamlessly integrate into existing automotive fleets without requiring extensive modifications or infrastructure upgrades.
- The composition of ETHANOL 100 consists of approximately 93 to 93.5 percent ethanol blended with 5 percent petrol and 1.5 percent co-solvent acting as a binder.
- This well-balanced formulation not only enhances fuel performance but also contributes to its practicality as a mainstream fuel option.
- In addition to its performance benefits, ETHANOL 100 stands out as a cleaner and greener alternative to traditional gasoline.
- By emitting lower levels of greenhouse gases and pollutants, such as carbon dioxide and particulate matter, ETHANOL 100 plays a crucial role in mitigating climate change and improving air quality in our communities.
- With the right infrastructure and support mechanisms in place, ETHANOL 100 has the potential to revolutionize the automotive industry by offering a sustainable and eco-friendly fuel solution that aligns with the global efforts to combat environmental degradation and promote sustainable development.
What are Flex-fuel Vehicles?
- Flex-fuel vehicles are engineered to operate on a diverse range of fuels, offering consumers the flexibility to choose between petrol, ethanol, or methanol at the point of refueling.
- Equipped with an internal combustion engine (ICE), these vehicles can seamlessly switch between different fuel types, providing versatility and convenience to drivers.
- While possessing similarities to conventional petrol-only cars, flex-fuel vehicles undergo minor modifications to accommodate the use of alternative fuels, ensuring compatibility and optimal performance across various fuel options.
India launches revamped scheme to help advance pharma industry's tech capabilities

- 12 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
India's Department of Pharmaceuticals recently unveiled the Revamped Pharmaceuticals Technology Upgradation Assistance Scheme (RPTUAS) to help advance the technological capabilities of India's pharmaceutical industry and align it with global standards.
What is the Pharmaceuticals Technology Upgradation Assistance Scheme?
- In an effort to support pharma companies aligned with global quality standards, the Department of Pharmaceuticals (DoP) has announced a revamped Pharmaceuticals Technology Upgradation Assistance (RPTUAS) Scheme.
- It has been incorporated as a sub-scheme under the Scheme - Strengthening of Pharmaceutical Industry (SPI), which was launched in July 2022.
Objective:
- To facilitate Micro, Small and Medium Pharma Enterprises (MSME) of proven track record to upgrade their technology to meet WHO-GMP or Schedule M standards.
Intended Beneficiaries:
- Micro, Small and Medium Enterprises of the pharma sector.
Key Features of the Revised Scheme:
- Broadened Eligibility Criteria: Reflecting a more inclusive approach, eligibility for the PTUAS has been expanded beyond Micro, Small and Medium Enterprises to include any pharmaceutical manufacturing unit with a turnover of less than 500 crores that requires technology and quality upgradation.
- Preference remains for MSMEs, supporting smaller players in achieving high-quality manufacturing standards.
- Flexible Financing Options: The scheme introduces more flexible financing options, emphasizing subsidies on reimbursement basis, over traditional credit-linked approaches.
- Comprehensive Support for Compliance with New Standards: In alignment with revised Schedule-M and WHO- Good Manufacturing Practice (GMP) standards, the scheme now supports a broader range of technological upgrades.
- Eligible activities include improvements such as HVAC systems, water and steam utilities, testing laboratories etc.
- State Government Scheme Integration: The revised scheme allows integration with state government schemes, enabling units to benefit from additional top-up assistance. This collaborative approach aims to maximize support for the pharmaceutical industry in their technology upgradation efforts.
- The new benefit limit is based on turnover of the company. Units with less than Rs 5 crore turnover will get an incentive of 20 percent of investment under eligible activities.
- The units with turnover ranging from Rs 50 crore to less than Rs 250 crore will get an incentive of 15 percent of investment, while for those with turnover ranging from Rs 250 crore to less than Rs 500 crore, it will be 10 percent of investment under eligible expenses.
India ranks 113 out of 190 countries in the World Bank’s legal gender gap index

- 05 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
India's ranked improved to 113 out of 190 countries in the World Bank’s Women, Business and Law index, according to the 10th edition of the report released Monday.
About Women, Business and Law Index:
- The "Women, Business and the Law (WBL)" index is a project of the World Bank Group, specifically designed to measure the legal environment for women's economic opportunities across 190 economies.
- It's distinct from a general "Gender Equality Index" as it focuses specifically on legal frameworks and their impact on women's involvement in business and professional life.
What does it Measure?
- The WBL index assesses legal frameworks across eight indicators:
- Mobility (freedom of movement)
- Workplace (discrimination, maternity leave, etc.)
- Pay (equal pay for equal work)
- Marriage (property rights, domestic violence)
- Parenthood (parental leave, child custody)
- Entrepreneurship (starting and running a business)
- Assets (ownership and inheritance)
- Pension (access to and benefits)
- Scoring: Each indicator is scored on a scale of 0 to 100, with 100 representing the highest level of legal rights and protections for women.
- The overall score for a country is the average of these eight indicators.
- Latest version: The latest edition is "Women, Business and the Law 2024", released in October 2023.
- This version also introduces two new indicators:
- Safety (addressing violence against women)
- Childcare (availability, affordability, and quality)
Highlights of the Report:
- Women spend an average of 2.4 more hours a day on unpaid care work than men—much of it on the care of children.
- Only 62 economies—fewer than a third—have quality standards governing childcare services, which has an adverse impact on the employment opportunity of women as mothers with young children have their battles to pick.
- Women face hindrances in areas such as entrepreneurship as just one in every five economies mandate gender-sensitive criteria for public procurement processes, meaning women are deprived of significant economic opportunities.
About India:
- According to the 10th edition of the Women, Business and Law index, India ranks 113 out of 190 countries in the Index.
- The addition of Safety and childcare as indicators in the new index is believed to have improved India’s ranking slightly.
- The index shows that in India, women enjoy 60% of the legal rights compared to men, which is lower than the global average of 64.2%, but much higher than the 45.9% of the legal protections compared to men.
- Over the years, India’s score has remained constant at 74.4%, whereas a total of 14 countries around the world, including Denmark, Canada, and Finland, score a perfect 100 in the legal framework score.
- Some of the less developed countries like Ethiopia, Namibia, and even Burundi have better scores than India.
- India’s performance is much lower in providing supportive frameworks, such as programs, services, budgets, procedures, inspections, and sanctions for non-compliance with quality standards.
- Only 54.2% of the supportive frameworks needed were established in the country.
DoT launches Digital Intelligence Portal, ‘Chakshu’ facility to curb cyber crimes, financial frauds

- 05 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
The Department of Telecommunications (DoT) recently launched its ‘Digital Intelligence Platform (DIP)’ to curb the misuse of telecom resources in cybercrimes and financial frauds, and the ‘Chakshu’ facility on the Sanchar Saathi portal to enable citizens to report suspected fraud communication.
About Digital Intelligence Platform (DIP):
- Digital Intelligence Platform (DIP) is developed by the Department of Telecommunications.
- It is a secure and integrated platform for real time intelligence sharing, information exchange and coordination among the stakeholders i.e. Telecom Service Providers (TSPs), law enforcement agencies (LEAs), banks and financial institutions (FIs), social media platforms, identity document issuing authorities etc.
- The portal also contains information regarding the cases detected as misuse of telecom resources. The shared information could be useful to the stakeholders in their respective domains.
- It also works as a backend repository for the citizen-initiated requests on the Sanchar Saathi portal for action by the stakeholders.
- The DIP is accessible to the stakeholders over secure connectivity and the relevant information is shared based on their respective roles.
- The said platform is not accessible to citizens.
What is the Chakshu Facility?
- Chakshu is the latest addition to the citizen centric facilities already available on the Sanchar Saathi portal of DoT.
- It facilitates citizens to report suspected fraud communication received over call, SMS or WhatsApp with the intention of defrauding like KYC expiry or update of bank account / payment wallet / SIM / gas connection / electricity connection, sextortion, impersonation as government official / relative for sending money, disconnection of all mobile numbers by Department of Telecommunications etc.
- In case, a citizen is already a victim of cyber-crime or financial fraud, it is advised to report at cyber-crime helpline number 1930 or website https://www.cybercrime.gov.in of Government of India.
Malta becomes the 119th member of the International Solar Alliance

- 21 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
Malta became the 119th country to join the International Solar Alliance recently.
About the International Solar Alliance (ISA):
- The International Solar Alliance (ISA) is an alliance of more than 120 signatory countries that aims to reduce the dependence on non-renewable sources of energy like fossil fuels.
- Currently, 118 countries are signatories to the ISA Framework Agreement.
- The ISA is an action-oriented, member-driven, collaborative platform for increased deployment of solar energy technologies as a means for bringing energy access, ensuring energy security, and driving energy transition in its member countries.
- The platform strives to develop and deploy cost-effective and transformational energy solutions powered by the sun to help member countries develop low-carbon growth trajectories, with a particular focus on delivering impact in countries categorised as Least Developed Countries (LDCs) and the Small Island Developing States (SIDS).
- The ISA was conceived as a joint effort by India and France to mobilise efforts against climate change through the deployment of solar energy solutions.
- It was conceptualised on the sidelines of the 21st Conference of Parties (COP21) to the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC) held in Paris in 2015.
Role of India:
- As a founding member, India holds a pivotal position within the alliance, serving both as a host nation and a major contributor to achieving its objectives.
- The ISA marks a historic milestone as the first international organisation to establish its secretariat in India.
- With a target of generating 100 GW of solar energy by 2022, India's commitment represents a significant portion of the ISA's overall goal.
Recent Developments:
- The ISA was granted Observer Status by the UN General Assembly, fostering closer collaboration between the alliance and the United Nations to advance global energy growth and development.
- The approval of the 'Solar Facility' by the ISA introduces a payment guarantee mechanism aimed at incentivizing investments in solar projects, further driving progress towards sustainable energy initiatives.
Coal Ministry Hosts Industry Interaction on Coal Gasification (ET)
- 16 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
The Ministry of Coal has announced it will host an Industry Interaction on February 16, 2024, in Hyderabad to discuss the development of coal and lignite gasification projects across India.
What is Coal Gasification?
- Coal gasification is a process where coal undergoes partial oxidation with air, oxygen, steam, or carbon dioxide to produce a fuel gas.
- This gas serves as an alternative to piped natural gas or methane for energy generation.
- Underground Coal Gasification (UCG) is a technique involving the conversion of coal into gas within the seam, extracted through wells.
- Production of Syngas: This process yields Syngas, a mixture primarily comprising methane (CH4), carbon monoxide (CO), hydrogen (H2), carbon dioxide (CO2), and water vapour (H2O).
- Syngas finds applications in producing fertilisers, fuels, solvents, and synthetic materials.
- Significance: In manufacturing, steel companies traditionally rely on costly imported coking coal. Syngas derived from coal gasification offers a cost-effective alternative.
- It is utilized in electricity generation, chemical feedstock production, and hydrogen-based applications like ammonia production and fueling a hydrogen economy.
Advantages of Coal Gasification:
- Coal gasification offers a solution to local pollution issues.
- It is deemed environmentally cleaner than direct coal combustion.
- Decreasing dependence on imported natural gas, methanol, ammonia, and other vital commodities, enhances energy security.
- This technology has the potential to mitigate environmental impacts by curbing carbon emissions and promoting sustainable approaches, aligning with India's global objectives for a more environmentally sustainable future.
Concerns Associated with Coal Gasification Plants?
- The main disadvantage of coal gasification is that it is an expensive process.
- The process can produce a number of harmful emissions, including carbon dioxide, sulphur dioxide, nitrogen oxides, and mercury.
- The process produces a lot of ash, which can pollute the environment.
- The process uses a lot of water, which can lead to water shortages in areas where it is used.
Revised Guidelines for Community Radio Stations (ET)

- 14 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
With a view to ensuring the growth of the community radio sector, the Union government on Tuesday increased the advertising time for community radio stations as well as the tariff rate for advertisements.
What are Community Radio Stations (CRSs?
- Community radio stations (CRSs) are low-power radio stations with a coverage area of approximately a 10-15 km radius, depending on the area’s geography, which is meant to be set up and operated by local communities.
- They offer a platform where content is disseminated in localized dialects and regional languages.
- Local, context-specific issues are raised and discussed in these stations in local idioms.
- India's first community radio station (CRS) was inaugurated on the campus of Anna University in 2004.
- Currently, there are 481 CRSs in India.
About the Revised Policy Guidelines:
- Under the revised policy, the government has permitted any eligible organisation functional in multiple districts to set up a maximum of six community radio stations in different districts.
- The advertising time for community radio stations has been increased from seven minutes per hour to 12 minutes per hour, while the rate of advertisement has been hiked from Rs 52 to Rs 74 per 10 seconds, the guidelines stated.
- The policy also fixed the validity of the letter of intent issued to an organisation to one year, with a buffer of three months to the applicant for any unforeseen circumstances.
- The revised policy guidelines are expected to fuel the growth of the community radio sector.
- The guidelines stated that the licensee would set up an advisory and content committee comprising members of the local community, with 50 per cent representation for women.
First meeting of Social Audit Advisory Body reviews social justice schemes (ET)

- 23 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News?
The first meeting of the Social Audit Advisory Body (SAAB) was held last week at the conference hall, Dr Ambedkar International Centre, New Delhi.
What is the Social Audit Advisory Body (SAAB)?
- Social Audit Advisory Body (SAAB) is a first-of-its-kind advisory body in India.
- It is set up under the National Institute of Social Defence (NISD), which functions under the Department of Social Justice & Empowerment (DoSJE), Ministry of Social Justice and Empowerment.
- It will guide the Ministry as it institutionalizes social audits for each of its programs.
- It will support the Social Justice Cell of the Social Audit Unit members in developing their abilities.
What is a Social Audit:?
- A social audit is a procedure that involves looking over and evaluating a plan or program.
- People actively participate in the process, which involves comparing government data with actual ground realities.
- Important tenets of SA include:
- Protection of citizens (Suraksha)
- Participation (Bhagidari), and
- Information access (Jaankari).
Implementation of Social Audit:
- The Mahatma Gandhi National Rural Employment Guarantee Act (MGNREGA), among other hallmark programs, now include the provision of Social Audit (SA) with the efforts of the Union Government.
- In order to guarantee SA through specialized Social Audit Units at the state level, DoSJE developed the National Resource Cell for Social Audit (NRCSA).
- The first state to put a social audit statute into effect was Meghalaya.
Significance: Promote transparency and accountability,
-
- strengthen institutions at the grassroots level etc.
Challenges: Lack of awareness among stakeholders, apathetic attitude of implementing agency etc.
Steps for SocialAudit:
- Orientation and Sensitization:: Conducted by the implementing agency.
- Presentation: Creating a social audit team.
- Verification: Verifying information with beneficiaries, inmates, stakeholders, and institution staff.
- Validation: Presenting the initial report for validation.
- Presentation and Action: Sharing findings at the district level with all stakeholders present.
MeitY signs MoU with Cuba for cooperation on digital public infrastructure (ET)

- 22 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News?
India and Cuba have signed an MoU for cooperation in the field of sharing successful digital solutions implemented at the population scale for digital transformation.
India and Cuba Bilateral Relations:
- India and Cuba share a robust and longstanding diplomatic camaraderie, marked by warmth and amity.
- In a gesture of early support, India was among the first nations to acknowledge and establish relations with the new Cuban government post the revolutionary events in January 1959.
- Trade Dynamics: The bilateral trade engagement, while moderate, exhibits a diverse array of commodities.
- India exports pharmaceutical products, organic chemicals, plastic goods, medical equipment, engineering items, textiles, metal products, mineral oil products, and tools to Cuba.
- Conversely, Cuba primarily imports pharmaceuticals and tobacco products from India.
- Energy Partnership: A pivotal facet of India-Cuba relations is their collaboration in the energy sector.
- As a member country and Vice-President of the Latin America & the Caribbean region at the International Solar Alliance (ISA), Cuba plays a significant role in fostering energy cooperation between the two nations.
- Advancements in Science & Technology, Biotechnology, and Health: The bilateral relations in the domains of science, technology, and health have been fortified through ministerial-level visits from both nations.Development Collaboration: Prioritizing development assistance has been a cornerstone of their bilateral ties.
- India has extended disaster relief assistance to Cuba in the aftermath of hurricanes that have afflicted the region over the years.
- Cultural Relations: Cuban appreciation for Indian culture and civilization is evident, with figures like Mahatma Gandhi, Jawaharlal Nehru, and Rabindranath Tagore holding a special place in Cuban hearts.
- Indian Diaspora: Although the Indian community in Cuba is relatively small, it includes descendants of Indians who migrated to Cuba in the early twentieth century from Jamaica and other parts of the West Indies to contribute to sugarcane plantations.
What is Digital Public Infrastructure (DPI)?
- DPI is a digital network that enables countries to safely and efficiently deliver economic opportunities and social services to all residents.
- DPI can be compared to roads, which form a physical network that connects people and provides access to a huge range of goods and services.??
- DPI allows people to open bank accounts and receive wages faster and more easily.
- It allows governments to support citizens more quickly and efficiently, especially during emergencies.
- And it enables entrepreneurs to reach customers far and wide.??
- A strong DPI has three foundational systems—identity, payments, and data exchange—that together can make life easier in important ways.?
- When the three core systems—identity, payments, and data exchange—exist simultaneously and can talk to one another, people, businesses, and governments can reap the full benefits of DPI.
- Over time, safe and inclusive DPI creates vibrant and competitive economies.?
iDEX innovators to exhibit futuristic technologies at Vibrant Gujarat summit (ET)

- 08 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News
The Ministry of Defence on Sunday said that Innovations for Defence Excellence-Defence Innovation Organization (iDEX-DIO) will participate in the 10th edition of the Vibrant Gujarat Summit from January 10 to 12 in Gandhinagar.
About iDEX:
- iDEX (Innovations for Defence Excellence), the flagship scheme of the Ministry of Defence, Govt of India launched by Prime Minister Modi in 2018.
- The objective of the scheme is to cultivate an innovation ecosystem in the Defence and Aerospace sector by collaborating with startups, innovators, MSMEs, incubators, and academia.
- iDEX offers grants and support for R&D with significant potential for future adoption in Indian defense and aerospace.
- It is currently engaged with around 400+ Startups and MSMEs, till now procurement of 31 items worth over Rs 2000 Cr. has been cleared.
- Recognized as a game-changer in the defense ecosystem, iDEX has received the PM Award for Innovation in the defense sector.
What is the Vibrant Gujarat Summit?
- The Government of Gujarat organizes the Vibrant Gujarat Global Summit, also known as Vibrant Gujarat, a biennial global business event held in the state of Gujarat, India.
- It attracts business leaders, investors, corporations, thought leaders, and policymakers, serving as a platform to understand and explore business opportunities in Gujarat.
- Launched in 2003 and now held every two years, the summit aims to promote Gujarat as an attractive investment destination, fostering partnerships and collaborations across various sectors.
- Industry associations, both nationally and internationally, support the summit, making it one of Gujarat's crucial economic forums.
- The event creates a platform for business leaders, policymakers, and investors to explore opportunities for investment, collaboration, and partnership in sectors such as energy, manufacturing, infrastructure, information technology, agriculture, healthcare, and more.
- It facilitates discussions, negotiations, and agreements in these key sectors.
- The Tenth edition of Vibrant Gujarat Global Summit is being held from 10 to 12 January 2024 in Gandhinagar, Gujarat.
- Its theme is 'Gateway to the Future'.
- This Tenth Edition of the Summit will celebrate “20 Years of Vibrant Gujarat as the Summit of Success”.
- There are 34 Partner countries and 16 Partner organizations for this year’s Summit.
- Further, the Ministry of Development of North-Eastern Region will utilize the Vibrant Gujarat platform to showcase investment opportunities in the North-Eastern regions.
India, Pakistan exchange list of nuclear installations and facilities (ET)

- 02 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News?
India and Pakistan exchanged the list of nuclear installations and facilities, covered under the Agreement on the Prohibition of Attack against Nuclear Installations and Facilities between the two countries.
About the Prohibition of Attack against Nuclear Installations and Facilities:
- The Agreement on the Prohibition of Attack against Nuclear Installations and Facilities, also known as the India-Pakistan Non-Attack Agreement, was signed on 31 December 1988 and became effective on 27 January 1991.
- It was signed by the then Pakistani PM Benazir Bhutto and Indian PM Rajiv Gandhi.
- According to this agreement, both India and Pakistan are required to annually communicate the list of nuclear installations and facilities covered by the agreement on the first of January of each calendar year.
- The agreement stipulates that neither party shall engage, directly or indirectly, in any actions aimed at causing destruction or damage to any nuclear installation or facility in the other country.
- The term 'nuclear installation or facility' encompasses nuclear power and research reactors, fuel fabrication, uranium enrichment, isotopes separation, reprocessing facilities, as well as any other installations involving fresh or irradiated nuclear fuel and materials in any form, along with establishments storing significant quantities of radioactive materials.
Need for the Agreement:
- In 1986, heightened concerns arose when the Indian army conducted a large-scale exercise named 'Brasstacks,' prompting fears of a potential assault on nuclear facilities.
- Subsequently, negotiations ensued between the two nations aimed at fostering an understanding regarding the management of nuclear weapons, ultimately leading to the formulation of the treaty.
Importance of the Agreement:
- Both nations reiterate their dedication to enduring peace and the cultivation of amicable and harmonious bilateral relations.
- They recognize the significance of confidence-building measures in fostering such relations built on mutual trust and goodwill.
- The potential consequences of even a limited nuclear exchange between India and Pakistan are grave, with the potential to cause the loss of 20 million lives within a week.
Mandarin-Trained Territorial Army Inducted At LAC (ET)

- 09 Oct 2023
Why in the News?
Recently the Territorial Army (TA) has inducted its first batch of Mandarin-trained officers to support the regular Army's efforts to enhance expertise in the Chinese language.
What is the Territorial Army (TA)?
- The Indian Territorial Army (TA) acts as the second line of defence, complementing the regular Indian Army.
- It is distinct in its role, being neither a profession, occupation, nor a source of employment.
- Reserved for individuals engaged in mainstay civilian professions, gainful employment or self-employment in a civil field is a prerequisite for joining the TA.
Key Roles:
- Relieving Regular Army: Primarily tasked with relieving the Regular Army from static duties.
- Assistance in Emergencies: Provides crucial assistance to civil authorities during natural calamities and tragedies.
- Essential Services: Aids civil administration in delivering essential services, particularly in areas facing stretched state machinery or security threats.
Service Commitment:
- Part-Time Service: TA volunteers typically serve in uniform for a few days annually, ensuring their readiness to bear arms for national defence during emergencies.
Historical Background:
- Established by the British in 1920 through the Indian Territorial Act, organized into 'The Auxiliary Force' for Europeans & Anglo-Indians and 'The Indian Territorial Force' for Indian Volunteers.
- The Territorial Army Act of 1948 formalized the TA, inaugurated by the first Indian Governor General, Shri C Rajagopalachari, on 9th October 1949.
- Motto: Savdhani Va Shoorta (Vigilance and Valour).
Eligibility Criteria:
- Nationality: Open to Indian citizens (Men & Women).
- Age: 18 to 42 years.
- Education: Graduate from any recognized university.
- Physical Standards: Must be physically and medically fit.
- Employment: Gainful employment in civilian professions.
- Exclusions: Serving members of the Regular Army/Navy/Air Force/Police/GREF/Para Military and similar forces are ineligible.
Govt Mulling Incentives for ASHA Workers (ET)

- 09 Oct 2023
Why in the News?
The government is planning to give incentives to ASHA health activists for mobilising eligible individuals for sickle cell disease screening and distribution of sickle cell cards for prevention and early detection of the disease.
About Accredited Social Health Activist (ASHA):
- ASHA serves as a trained female community health activist integral to the National Rural Health Mission initiated by the Government of India.
- Selected from the community and accountable to it, ASHA is trained to bridge the gap between the community and the public health system.
Key Functions:
- Acts as a care provider at the community level.
- Facilitates access to healthcare, medicine, and sanitation services.
- Health Awareness: Raises awareness of health issues among marginalized sections within the community.
- Advocate for Women's Health: Champions female health and hygiene standards.
- Advocates for a health-conscious approach to livelihood.
Implementation:
- The ASHA scheme is operational in all States/UTs, except Goa.
- States are mandated to employ at least one ASHA worker per every 1000 people.
- Inclusive Selection Process: The selection process involves various community groups, self-help groups, Anganwadi Institutions, and local committees.
Selection Criteria:
- Rural ASHA: Preferably a literate woman resident, married/widowed/divorced, aged 25 to 45 years, and preferably educated up to the 10th standard.
- Urban ASHA: Identified from vulnerable clusters, belonging to specific vulnerable groups, with good communication and leadership skills.
Compensation:
- Primarily an honorary volunteer compensated for specific situations.
- Ranges from Rs 2,000 to Rs 7,000, depending on the state.
- Incentives: Eligible for incentives under various national health programs.
Adani Ports' Flagship Mundra Port Completes 25 Years (ET)

- 09 Oct 2023
Why in the News?
Mundra Port in Gujarat has completed 25 years of its operations, highlighting its expansion and evolution as one of the largest ports globally.
About Mundra Port:
- Mundra Port stands as India's largest private and container port, situated on the north shores of the Gulf of Kutch near Mundra in the Kutch district of Gujarat.
- As a deep-draft, all-weather port, it holds the distinction of being a Special Economic Zone (SEZ).
- Managed by Adani Ports and Special Economic Zone Limited (APSEZ), the port is a pivotal player in India's cargo movement, accounting for nearly one-fourth of the nation's total.
- Mundra Port plays a crucial role in managing 33% of the country's container traffic.
- Key Features: Strategic Location: Positioned on the Gulf of Kutch, Gujarat.
- Handling Capacity: With an impressive capacity of 260 MMT, the port efficiently manages over 155 MMT (FY 2022-23), contributing to almost 11% of India's maritime cargo.
- Infrastructure: Boasting 26 berths and two single-point moorings, the port accommodates diverse vessels and handles various cargo types, including containers, dry bulk, break bulk, liquid cargo, and automobiles.
- Coal Import Terminal: Home to the nation's largest coal import terminal, Mundra facilitates swift cargo evacuation with minimal turnaround time.
- Rail Connectivity: The port's rail network is seamlessly integrated into the national rail network, ensuring efficient cargo handling for destinations across India.
'World's Largest Meditation Centre': PM Modi inaugurates Swarved Mahamandir in Varanasi (ET)

- 19 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
Prime Minister Narendra Modi inaugurated the world’s largest meditation centre, Swarved Mahamandir, in Varanasi on December 18.
About the Swarved Mahamandir:
- The Swarved Mahamandir stands as the world's largest meditation centre, accommodating 20,000 individuals in collective contemplation.
- Situated in Varanasi, Uttar Pradesh, this spiritual haven aspires to cast a luminous spiritual aura, enveloping the globe in a state of tranquil attentiveness.
- Named after the Swarved, a profound spiritual text penned by Sadguru Shri Sadafal Deoji Maharaj, the visionary behind Vihangam Yoga and an enduring yogi, the temple serves as a bastion for disseminating Swarveda teachings.
- Emphasizing Brahma Vidya, a profound body of knowledge, it guides spiritual seekers toward sustaining an unwavering equilibrium of peace and happiness.
- Architecturally, the Mahamandir is an imposing seven-floor superstructure, adorned with a captivating design featuring 125-petal lotus domes.
- Crafted from teakwood, the intricate carvings embellishing the ceiling and doors add to its allure.
- Pink sandstone envelops the temple walls, complemented by an enchanting garden featuring medicinal herbs.
- Imprinted on the Mahamandir's walls are verses from the Swarveda, serving as an enduring testament to the spiritual wisdom that resonates within its sacred confines.
What is Vihangam Yoga?
- Vihangam Yoga, an indigenous form of Yoga and meditation, was established by Sadguru Sadafal Deo Ji Maharaj in 1924.
- The nomenclature of this practice is derived from two foundational words: "Vihag," signifying bird, and "Yog," denoting union.
- The name encapsulates the profound concept of a bird ascending from the terrestrial realm, soaring high and unbounded in the sky.
- This symbolism mirrors the ultimate aim of Vihangam Yoga – the liberation of the soul from attachments to the material world, allowing it to recognize and embrace its innate, unshackled essence.
- Only through this liberation can an individual's consciousness seamlessly merge with the universal consciousness, often referred to as the Supreme Being, leading to a state of enduring tranquillity and bliss.
India's Akash missile engages four targets at once at 25km, a global first (ET)
- 18 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
India demonstrated the capability of the Akash missile system to engage four aerial targets simultaneously at a range of 25 kilometres, the Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO) said on Sunday.
Context:
- During the recent Exercise Astrashakti 2023, a solitary unit of the Akash weapon system demonstrated its capability by effectively engaging and eliminating four unmanned targets simultaneously.
- This showcase positions India as the pioneer, being the first country to showcase the proficiency of engaging multiple targets at considerable distances concurrently through command guidance from a single firing unit.
About the Akash Surface-to-Air Missile (SAM) Defence System:
- The Akash Surface-to-Air Missile (SAM) Defence System is a Short-Range Surface-to-Air Missile (SRSAM) designed to safeguard vulnerable areas and points from airborne threats.
- Developed indigenously by the Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO), it boasts several notable features:
- Versatility: Capable of simultaneously engaging multiple targets and effectively neutralizing manoeuvring threats, including unmanned aerial vehicles, fighter aircraft, cruise missiles, and helicopter-launched missiles.
- Electronic Counter-Counter Measures (ECCM): Equipped with built-in ECCM features, enhancing its resilience against electronic countermeasures.
- Flexible Deployment: The entire system is configured for launch from both static and mobile platforms such as battle tanks and wheeled trucks, ensuring adaptable deployment options.
- Transportability: Road and rail transportable, with swift mobilization and deployment capabilities, facilitating rapid response scenarios.
- Range: Capable of engaging aerial targets at a distance of approximately 25 km.
- Altitude of Operation: Ranging from 100 meters up to 20 km.
- Weight: 710 kg.
- Guidance System: Command Guidance.
- Automation: Fully automatic with a quick response time from target detection to neutralization.
- Open-System Architecture: Designed with an open-system architecture, ensuring adaptability to current and future air defence environments.
Saint Lucia’s Tax Inspectors without Borders (TIWB) programme launched in partnership with India (ET)

- 16 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
India will help Saint Lucia in strengthening its tax administration by transferring technical knowledge and skills to its tax administration, and sharing best practices under the ‘Tax Inspectors Without Borders (TIWB) programme’.
Key Highlights:
- India has been chosen as the Partner Administration and will provide Tax Experts for this programme.
- This programme is expected to be of 12-18 months’ duration in which India, in collaboration with the TIWB Secretariat and support of the UNDP Country Office, Barbados and the Eastern Caribbean, aims to aid Saint Lucia in strengthening its tax administration by transferring technical knowledge and skills to its tax administration, and through sharing of best practices.
- The focus of the programme will be on the effective use of automatic exchange of information under the Common Reporting Standard (CRS) framework.
What is Tax Inspectors without Borders programme?
- Tax Inspectors Without Borders (TIWB) is a joint initiative of the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD) and the United Nations Development Programme (UNDP).
- It is designed to support developing countries to build tax audit capacity.
- TIWB facilitates well-targeted, specialised tax audit assistance in developing countries around the world.
- Under TIWB, tax audit experts work alongside local officials of developing country tax administrations on tax audit and tax audit-related issues.
- TIWB aims to transfer technical know-how and skills to developing countries’ tax auditors, as well as share general audit practices.
- The host administrations of developing countries are the lead partners in TIWB programmes, clearly specifying their needs and scope of work.
- A dedicated central unit (TIWB Secretariat) jointly managed by OECD and UNDP operates as a clearing house to match the demand for auditing assistance with appropriate expertise.
- TIWB is a capacity-building programme.
Urea Gold (ET)

- 27 Jul 2023
Why in the News?
During a recent event held in Rajasthan's Sikar, the Prime Minister unveiled "Urea Gold," a novel type of Urea fertilizer.
About Urea Gold:
- Urea Gold is an advanced variety of Urea that features a Sulphur coating.
- Its primary purpose is to address soil Sulphur deficiency while also offering cost-saving benefits to farmers.
- In comparison to the existing Neem-coated urea, Urea Gold stands out due to its superior economic viability and efficiency.
- The gradual release of nitrogen facilitated by its Sulphur coating enhances crop uptake, and the inclusion of humic acid extends its fertilizing lifespan.
- Notably, Urea Gold not only acts as a substitute for traditional urea but also contributes to a reduction in overall fertilizer usage.
- According to a report, using 15 kg of Urea Gold can provide comparable benefits to 20 kg of conventional urea, making it a more efficient and effective choice for farmers.
INDIAai (ET)

- 26 Jul 2023
Why in the News?
In a recent development, INDIAai and Meta India entered into a memorandum of understanding (MoU) to create a collaborative framework for cooperation and partnership in the realm of artificial intelligence (AI) and emerging technologies.
About INDIAai:
- INDIAai, the National artificial intelligence Portal of India, was launched on 28th May 2020 as a comprehensive platform.
- It serves as a knowledge portal, research organization, and ecosystem-building initiative.
- Its primary aim is to foster unity and encourage collaborations within India's AI ecosystem by bringing together various entities.
- This joint initiative is supported by the Ministry of Electronics and IT (MeitY), the National e-Governance Division (NeGD), and NASSCOM.
- NeGD, established in 2009 under the Digital India Corporation (a not-for-profit company set up by MeitY), plays a crucial role in this venture.
- NASSCOM, a prominent not-for-profit industry association, serves as the apex body for India's IT and IT-enabled products and services sector.
- INDIAai functions as the central knowledge hub for artificial intelligence and related fields, catering to aspiring entrepreneurs, students, professionals, academics, and all other stakeholders in the domain.
What is Artificial intelligence (AI)?
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) is a branch of computer science: It involves the development of intelligent machines that can perform tasks typically requiring human intelligence.
- Machine Learning and Algorithms: AI systems utilize machine learning algorithms to process vast amounts of data, learn from it, and improve their performance over time without explicit programming.
- Applications in various fields: AI finds applications in diverse domains, including natural language processing, image recognition, robotics, healthcare, finance, and autonomous vehicles, among others. Its goal is to mimic human cognitive abilities, such as problem-solving, reasoning, and decision-making.
Maitree Super Thermal Power Project (STPP) (ET)

- 26 Jul 2023
Why in the News?
The synchronization of the 660-MW unit-2 of the 1,320-MW Maitree Super Thermal Power Project (STPP) with the electricity grid in Bangladesh was recently announced by the state-owned engineering firm Bharat Heavy Electricals.
- Location:
- It is situated in Rampal, in the Bagerhat district of Bangladesh's Khulna division.
- It will be one of the biggest coal-fired power plants in Bangladesh, along with the Payra Power Plant in Pataukhali, which commenced test production in January 2020.
- Capacity and Cost:
- The power station has a capacity of 1320 MW (2x660 MW) and is estimated to cost around $2 billion.
- Financing Plan:
- The project is being developed under India's tax concessions finance plan, aiming to enhance Bangladesh's national grid by an additional 1320 MW.
- Financed through a £1.3bn ($1.6bn) loan from the Export-Import (EXIM) Bank of India.
- Implementing Entity:
- India’s Bharat Heavy Electricals Limited (BHEL) is responsible for constructing the power plant on behalf of Bangladesh-India Friendship Electricity Company Private Limited (BIFPCL).
- Commercial Operation:
- The first unit of the super thermal power plant is expected to commence commercial operation in early October, representing a significant milestone in the growing cooperation between India and Bangladesh in the power industry.
- Future Expansion:
- In the subsequent year, the power plant's Unit-II, also known as the Rampal coal-fired power project, is scheduled for implementation.
Air Quality Life Index (AQLI) report (Economic Times)
- 31 Aug 2023
What is the News ?
Annual update of the Air Quality Life Index (AQLI) 2023 has been released.
Facts About:
India ranked second among the countries worst hit by air pollution with Bangladesh topping the list.
- Nepal ranked third followed by Pakistan and Mongolia.
PMI in South Asia: Particulate pollution has increased9.7 percent from 2013 to 2021 in South Asia.
- In India, PM2.5 levels rose 9.5 percent; in Pakistan 8.8 percent; and in Bangladesh, levels rose by 12.4 percent over this same time interval.
Life Expectancy: An average Indian citizen loses around 5.3 years of life expectancy due to air pollution.
- While an average citizen in Bangladesh loses 6.8 years of their life to air pollution
- An average Chinese citizen has seen an improvement — from 4.7 years of life expectancy being lost in 2013 to 2.5 now, an improvement of 2.2 years,
Pollution in India: Pollution in India has increased from 56.2 µg/m3 in 2020 to 58.7 µg/m3 in 2021.
- This is more than 10 times the WHO guideline of 5 µg/m3.
Health Risk: Pollution is biggest threat to human health in India in terms of lowering life expectancy, beating cardiovascular diseases and child and maternal malnutrition.
- While particulate pollution takes 5.3 years off the life of the average Indian, cardiovascular diseases reduce life expectancy by about 4.5 years, and child and maternal malnutrition reduces life expectancy by 1.8 years.
Poor AIr in Delhi: It is the most polluted city in the world.
- Delhi’s annual average PM2.5 level in 2021 was found to be 126.5 µg/m3, which is more than 25 times the World Health Organization (WHO) guideline of 5 µg/m3.
- Delhi residents are on track to lose 11.9 years of life expectancy on average relative to the WHO limit and 8.5 years relative to the national guideline if the current pollution levels persist.
About Air Quality Life Index (AQLI)
- AQLI measures the impact of particulate pollution on life expectancy.
- It is released by Energy Policy Institute at University of Chicago (EPIC).
Source: https://economictimes.indiatimes.com/news/india/your-life-is-getting-short-by-5-years-due-to-air-pollution-chicago-university-report-reavels-scary-numbers/articleshow/103198930.cms?from=mdr
Moody’s Report on Demographic Dividend (Economic Times)
- 29 Aug 2023
What is the News ?
Alongwith the population growth, strong education and quality infrastructure are key to reap economic gains in India: Moody
Facts About:
Relation between population growth and economic growth:
Population Growth as a Driver of Economic Growth (Early Stages)
- A larger population means a larger labor force, which can lead to increased production, consumption, and innovation. This phenomenon is often referred to as the demographic dividend. When the ratio of working-age individuals to dependents (children and elderly) is high, it can create a favorable environment for economic expansion.
Labor Force and Human Capital:
- A growing population can provide a larger labor force, which, if properly educated and skilled, can contribute to higher productivity and economic growth. However, for population growth to positively impact economic growth, there must be adequate investments in education, healthcare, and skill development to ensure that the workforce is productive and capable of contributing to economic activities.
Consumption and Demand:
- A larger population can lead to increased consumption and demand for goods and services, which can stimulate economic growth. Businesses may expand to meet this increased demand, leading to higher levels of investment and production.
Urbanization and Productivity:
- Population growth often leads to urbanization, as people move from rural areas to cities in search of better opportunities. Urbanization can lead to increased productivity due to factors like economies of scale, improved infrastructure, and better access to markets and resources.
Resource Constraints and Negative Impacts:
- Rapid population growth without corresponding economic development and resource management can lead to resource constraints, environmental degradation, and increased competition for limited resources. This can have negative effects on economic growth in the long run.
Demographic Transition:
- As economies develop and standards of living improve, birth rates tend to decline. This results in a shift from high population growth rates to lower ones. During this demographic transition, countries can experience a period of accelerated economic growth due to a relatively smaller dependent population.
Aging Population:
- In more advanced economies, declining birth rates and increased life expectancy can lead to an aging population. While this may result in a decline in the working-age population, it can also create opportunities for innovation and growth in industries related to healthcare, elderly care, and technology.
Quality of Institutions and Policies:
- The relationship between population growth and economic growth is influenced by the quality of institutions and policies in place. Good governance, effective healthcare systems, education policies, and infrastructure development play a crucial role in determining how population growth impacts economic growth.
In summary, the relationship between population growth and economic growth is not deterministic, and its effects can vary widely based on numerous factors. While a growing population can potentially provide a demographic dividend and contribute to economic growth, this positive outcome depends on factors such as investments in human capital, infrastructure, and sound governance.
Additionally, as countries progress in their development, the relationship often becomes more nuanced, with demographic transitions and changingpopulation structures influencing economic dynamics.
Factors responsible for India’s population growth
- Falling mortality: The IMR has decreased from 40.7 in 2015-16 to 35.3 in 2019-21.
- Increasing Life expectancy at birth: It reached to 69.7 years in the 2015-19 period from 31 in 1947.
- Unintended pregnancies: 1 in every 7 unintended pregnancies of world occur in India.
- Lack of female education, child marriage and early marriages, etc.
Challenges caused by growing population
- Pressure on resources: As India has only 2.45% of the global surface area and 4% of the water resources.
- Pandemic outbreaks: Due to increasing urbanization and expansion of humans in wild habitats.
- Disruption and Conflicts: Due to rise in struggle for finite resource.
- Decline in social indicators: Due to suboptimal public expenditures on health and education may not be possible.
- Pressure on economy: Due to low skilled workforce, stagnant economy, unemployment, etc.
- Widening gender gap: If expenditure on health and education decline, women would suffer the most.
Way ahead to harness the benefits of population growth
- Supporting Reproductive Justice: Provisions of safe and effective methods of family planning and freedom to make the best reproductive choice.
- Education for all: Educational attainment, particularly of girls, enhances intergenerational formation of human capital and has a positive impact on demographic behaviour with respect to nuptiality, fertility, health, etc.
- Foster Inclusive Growth developing democratic institutions to facilitate equity in the society.
- Facilitate migration to bridge the demand and supply of the workforce.
- Investment in green technology and social innovations to adapt to and mitigate climate and environmental changes.
- Better geriatric care, health insurance and pension facilities for 65+ age category.
Source: https://economictimes.indiatimes.com/news/economy/indicators/india-must-focus-on-education-and-infra-for-growth-moodys-report/articleshow/103147127.cms?from=mdr
Agnibaan SOrTeD rocket (Economic Times)
- 19 Aug 2023
What is the News ?
A Chennai-based start-up AgniKul Cosmos, has commenced the process of integrating its cutting-edge Agnibaan SOrTeD rocket at its private Launchpad in Sriharikota.
Facts About:
- The integration process was initiated on Independence Day on August 15, 2023.
- A successful launch would make AgniKul the second Indian space tech start-up to send its launch vehicle into space after Skyroot Aerospace.
- AgniKul: Established in 2017, by aerospace engineers Srinath Ravichandran and Moin SPM, along with IIT-Madras faculty member Prof. Sathyanarayan R Chakravarthy.
About Agnibaan SOrTeD (SubOrbital Technological Demonstrator):-
Type: single-stage launch vehicle.
Powered by: AgniKul’s patented Agnilet engine.
- Agnilet engine: It is the world’s sole single-piece 3D-printed engine.
- It is a single-piece, 6 kilonewton (kN) semi-cryogenic engine.
- Initial trial: early 2021.
- Verified at the Vikram Sarabhai Space Centre (VSSC) in Thiruvananthapuram.
- 3D printing: uses materials such as plastics and metals to convert products envisaged on computer-aided design to real three-dimensional items.
Payloads: up to 100 kg.
Altitude: 700 km
- It can carry payloads in five different configurations. (LVM3-M2 rocket)
Stages: It is a customizable launch vehicle that could be launched in one or two stages.
Unique feature: unlike traditional sounding rockets that launch from guide rails, it will lift off vertically and follow a predetermined trajectory to perform a precisely orchestrated set of maneuvers during flight.
The rocket’s first stage could have up to seven Agnilet engines, depending on the mission, which are powered by Liquid Oxygen and Kerosene.
The rocket is also designed for launch from more than 10 different launch ports.
To ensure its compatibility with multiple launch ports, AgniKul has built a launch pedestal named ‘Dhanush’.
- It will support the rocket’s mobility across all its configurations.
Source: https://economictimes.indiatimes.com/news/science/chennai-based-agnikul-prepares-for-maiden-sub-orbital-flight-of-agnibaan-rocket/articleshow/102805834.cms?from=mdr
PM Vishwakarma (Economic Times)
- 17 Aug 2023
What is the News ?
The Cabinet Committee on Economic Affairs has approved a new Scheme named “PM Vishwakarma”
Facts About:
Type: Central Sector Scheme
Aim: To strengthen and nurture the Guru-Shishyaparampara or family-based practice of traditional skills by artisans and craftspeople working with their hands and tools.
– To improve the quality, as well as the reach of products and services of artisans and craftspeople and to ensure that the Vishwakarmas are integrated with the domestic and global value chains.
Coverage: The scheme will provide support to artisans and craftspeople of rural and urban areas across India.
– Eighteen traditional trades will be covered under the scheme. These include carpenter, boat maker, armourer, blacksmith, hammer and tool kit maker, locksmith, goldsmith, potter, sculptor, stone breaker, cobbler, mason, basket/mat/broom maker/coir weaver, traditional doll and toy maker, barber, garland maker, washerman, tailor and fishing net maker.
Duration of the scheme: Five years (FY 2023-24 to FY 2027-28).
Key Features of the scheme: Artisans and craftspeople will be provided a recognition through PM Vishwakarma certificate and ID card.
– The scheme has a provision of credit support of up to ?1 lakh (first tranche) and ?2 lakh (second tranche) with a concessional interest rate of 5%.
– It also has a provision to provide skill upgradation, incentive for toolkit as well as digital transactions and marketing support.
– Skilling programmes will take place at both basic and advanced types. Participants will get a stipend of ?500 per day while undergoing training.
– Beneficiaries will also receive up to ?15,000 to buy modern tools.
Source: https://economictimes.indiatimes.com/news/politics-and-nation/pms-vishwakarma-scheme-launch-on-sept-17-70-ministers-to-attend-event-at-70-locations/articleshow/103559849.cms?from=mdr
China’s economy slides into deflation (Economic Times)
- 11 Aug 2023
What is the News ?
Facts About:
China’s recent bout of deflation, marked by a decline in consumer prices for the first time in over two years, has sparked debates about its implications and causes.
- This article delves into the intricacies of deflation, its potential impact on economic growth, and the unique circumstances driving deflation in China.
Understanding Deflation
- Deflation Defined: Deflation refers to a sustained decrease in the general price level of goods and services within an economy.
- Historical Context: Historically, the terms “inflation” and “deflation” were linked to changes in the money supply, with “inflation” representing a rise and “deflation” a fall in money supply.
Concerns Associated with Deflation
- Economic Slowdown: Many economists view deflation as an indicator of dwindling demand for goods and services, potentially leading to an economic slowdown.
- Demand-Supply Dynamics: Falling prices may prompt consumers to delay purchases, hampering demand and triggering a ripple effect throughout the economy.
- Resource Utilization: A certain level of inflation is deemed necessary for optimal resource utilization, ensuring full economic potential is realized.
Varied Perspectives on Deflation
- Positive Instances: Some economies have experienced deflation during periods of robust growth. Japan witnessed increased real income levels despite persistent deflation.
- Economic Crises: Deflation can arise during economic crises when cautious spending and resource reallocation occur.
- Consumer Demand and Prices: Some economists argue that consumer demand dictates prices, rather than the other way around.
China’s Deflation Scenario
- Policy Measures: China’s central bank maintained low interest rates to stimulate demand amid the post-pandemic recovery.
- Property Sector Turmoil: China’s pre-pandemic property sector challenges, affecting GDP contribution, may be a root cause of the current deflationary trend.
- Complex Factors: While liquidity may not be the core issue, comprehensive analysis of money supply and monetary transmission is necessary to determine the underlying cause.
Repercussions of Chinese Deflation
[A] Positive Impacts:
- Cheaper Imports: If Chinese goods become cheaper due to deflation, it could lead to lower import costs for India, benefiting consumers and businesses that rely on Chinese imports.
- Lower Input Costs: Reduced prices for raw materials and intermediate goods from China could lower production costs for Indian industries that depend on these inputs.
- Global Supply Chains: If Chinese deflation reduces the cost of production within global supply chains, Indian businesses integrated into these chains might experience cost savings.
- Improved Trade Balance: Cheaper Chinese imports can contribute to a more favorable trade balance for India, especially if it leads to reduced import bills.
[B] Negative Impacts:
- Export Competition: Cheaper Chinese exports due to deflation could increase competition for Indian exports in international markets, potentially affecting certain Indian industries.
- Import Dumping: A flood of cheap Chinese goods into the Indian market could harm domestic producers, leading to job losses and economic strain.
- Investment Flows: A slowdown in China’s economy caused by deflation might lead to reduced investor confidence and affect foreign direct investment (FDI) flows to India.
- Currency Effects: If China’s central bank devalues its currency to boost exports in response to deflation, it could lead to a stronger Indian rupee, impacting India’s export competitiveness.
- Commodity Prices: Reduced demand for commodities from China due to deflation could lead to lower global commodity prices, affecting Indian exporters of raw materials.
Conclusion
- China’s encounter with deflation amidst efforts to boost demand and stabilize its economy presents a multi-faceted challenge.
- Understanding the nuances of deflation, its interaction with demand dynamics, and China’s unique economic landscape are vital.
- As China navigates its path forward, policymakers must consider the interplay of factors, including the property sector’s impact and broader economic goals.
Source: https://www.google.com/url?sa=t&rct=j&q=&esrc=s&source=web&cd=&ved=2ahUKEwidya2w1qGBAxVcd2wGHTEWAzQQFnoECC0QAQ&url=https%3A%2F%2Fm.economictimes.com%2Fopinion%2Fet-editorial%2Fwhy-chinas-economy-is-down-not-out%2Farticleshow%2F102731901.cms&usg=AOvVaw1udWdqudtF2oR3qve57xGB&opi=89978449
