Antimony Discovery in Balochistan, Pakistan
- 07 Apr 2025
In News:
In a recent geopolitical development, Pakistan has reportedly discovered a significant deposit of Antimony in the Balochistan region — an area marred by conflict and instability. This finding holds both economic and strategic significance, given the growing global demand for rare and critical minerals.
About Antimony
- Chemical Element: Antimony (Symbol: Sb, Atomic Number: 51) is a metalloid, meaning it exhibits properties of both metals and non-metals.
- Physical Properties:
- Solid at room temperature.
- Poor conductor of heat and electricity.
- Found in commercial forms such as ingots, broken pieces, granules, and cast cakes.
Geological Occurrence
- Primary Ore: The chief ore of Antimony is Stibnite (Sb?S?).
- Mode of Occurrence: Found in volcanic-associated deposits and deep-seated veins, formed under moderate to high temperature and pressure.
- Also commonly obtained as a byproduct from lead-zinc-silver mining operations.
Global Production Landscape
- China is the dominant global producer, accounting for over 88% of world production.
- Other notable producers include Russia, Bolivia, and Tajikistan.
- India currently does not have significant reserves or production of Antimony, making it dependent on imports for industrial use.
Key Industrial and Strategic Uses
- Electronics Industry:Used in manufacturing semiconductors, infrared detectors, and diodes.
- Alloys:
- Alloyed with lead and other metals to increase hardness and strength.
- Lead-antimony alloys are extensively used in lead-acid batteries.
- Defense and Printing:Utilized in the production of bullets, type metal for printing, and cable sheathing.
- Flame-Retardants and Ceramics:Antimony compounds are key ingredients in flame-retardant materials, as well as in paints, enamels, glass, and pottery.
Balochistan
- 12 May 2025
In News:
On May 9, 2025, Mir Yar Baloch announced the unilateral declaration of independence for Balochistan from Pakistan. In a public appeal, he urged India to formally recognize Balochistan as a sovereign state and open an embassy in New Delhi. He also called upon the United Nations to deploy peacekeeping forces and demanded the withdrawal of the Pakistani military from the region.
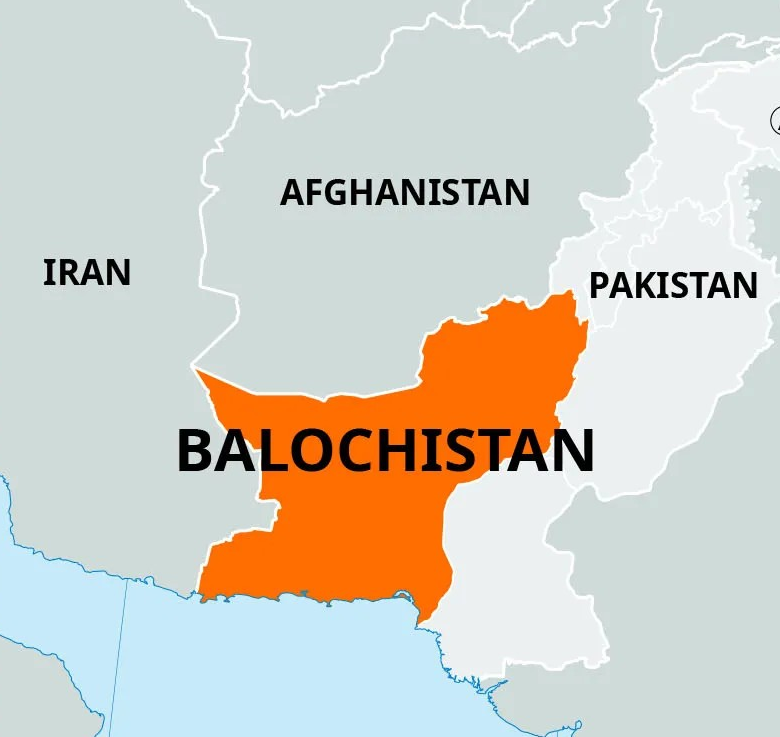
Geographical Profile
- Location: Balochistan lies in the southwestern part of Pakistan and is the country’s largest province by area, comprising nearly 44% of its total territory.
- Area: Approximately 347,190 square kilometers
- Capital: Quetta, situated near the Afghanistan border
- Borders:
- East: Sindh and Punjab provinces
- West: Iran
- Northwest: Afghanistan (across the Durand Line)
- South: Arabian Sea, with a coastline of around 770 km
Topography and Climate
- Characterized by rugged, mountainous terrain (notably the Sulaiman and Makran ranges)
- Arid and semi-arid climate zones, including desert and dry steppe regions
- Low population density, yet abundant in untapped mineral wealth
Demographics and Ethnicity
- Major Ethnic Group: The Baloch, who trace their ancestry to Iranian origins
- Other Communities: Pashtuns in the northern areas, and the Brahui ethnic group
- Languages Spoken: Balochi, Pashto, Brahui, and Urdu
- Religion: Predominantly followers of Sunni Islam
Strategic and Geopolitical Significance
Natural Resource Wealth
- Balochistan is rich in natural gas, coal, copper, and gold.
- The RekoDiq mining site is among the world’s largest undeveloped gold and copper reserves.
- The province contributes about 40% of Pakistan’s natural gas production, yet remains economically underdeveloped and politically marginalized.
China-Pakistan Economic Corridor (CPEC)
- Gwadar Port, located in southern Balochistan, is a critical node in China’s Belt and Road Initiative (BRI).
- It provides China with direct maritime access to the Arabian Sea and strategic connectivity to West Asia, bypassing the Strait of Malacca.
India’s Strategic Perspective
- India has consistently highlighted human rights violations in Balochistan at international forums.
- The region’s geostrategic position intersects with India’s Indo-Pacific vision, and is relevant in India’s efforts to counter China’s growing footprint through CPEC.
Insurgency and Security Dynamics
- Balochistan has long witnessed separatist movements led by Baloch nationalist groups seeking either enhanced autonomy or full independence from Pakistan.
- These groups frequently target Pakistani military convoys, CPEC infrastructure projects, and Chinese nationals working in the region, signaling strong opposition to external control and resource exploitation.
