Satellite Internet
- 17 Aug 2025
In News:
The advent of satellite internet, spearheaded by mega-constellations like Elon Musk’s Starlink, is set to transform global connectivity. With Starlink’s expected entry into India, this technology carries vast implications for bridging the digital divide, disaster resilience, national security, and economic development.
Why Satellite Internet?
Conventional internet networks rely on cables and towers, which are efficient in urban areas but face limitations:
- Economically unviable in sparsely populated or remote regions.
- Vulnerable to disruptions from floods, earthquakes, or cyclones.
- Restricted mobility, failing to meet connectivity needs for ships, aircraft, or defence units in rugged terrains.
Satellite internet addresses these gaps by providing global, resilient, and mobile coverage, independent of terrestrial infrastructure. It can be rapidly deployed in emergencies and enables connectivity in conflict zones or offshore locations.
How Satellite Internet Works
A satellite internet network has two key segments:
- Space Segment: Satellites orbiting Earth, carrying communication payloads (antennas, transponders, onboard processors).
- Ground Segment: User terminals, antennas, and ground stations that link devices to satellites.
Data flow: When a user sends a request, the signal goes to the satellite → routed to a ground station connected to the internet backbone → response sent back via satellite to the user.
Seamless handover: Especially in Low Earth Orbit (LEO), satellites move fast (~27,000 km/hr) and stay over a region only for minutes. Smart handovers between satellites ensure uninterrupted connectivity.
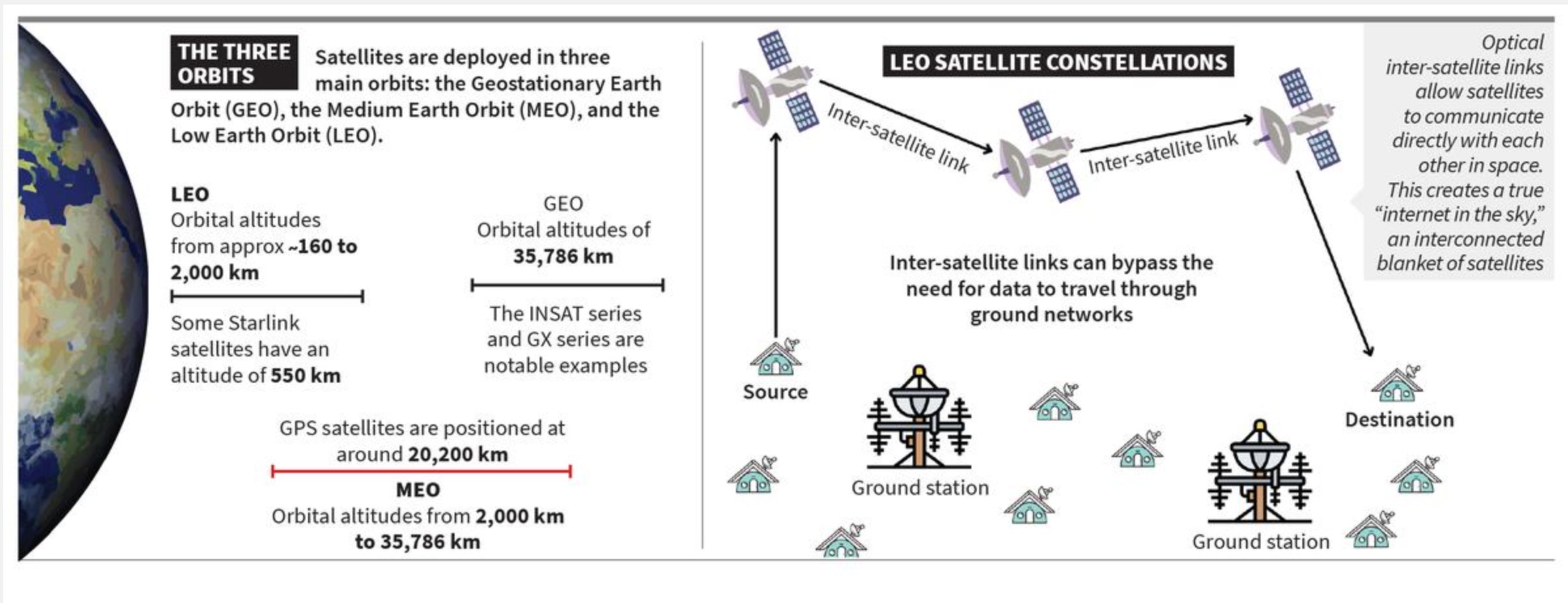
Types of Orbits
|
Orbit Type |
Altitude |
Advantages |
Limitations |
Example |
|
Geostationary Earth Orbit (GEO) |
~35,786 km |
Covers ~? of Earth; stable position |
High latency, no polar coverage |
Viasat Global Xpress |
|
Medium Earth Orbit (MEO) |
2,000–35,786 km |
Balanced coverage & latency |
Needs constellations; still moderate latency |
O3b Network |
|
Low Earth Orbit (LEO) |
<2,000 km |
Very low latency; smaller, cheaper satellites |
Small footprint; requires mega-constellations |
Starlink (7,000+ satellites, plans for 42,000) |
Key Features of Satellite Internet
- Global Coverage: Works across oceans, mountains, deserts, and polar regions.
- Dual-use Technology: Supports both civilian services and military operations.
- Rapid Deployment: Can be activated within hours during emergencies.
- Network Resilience: Independent of local telecom infrastructure.
- Mega-Constellations: Thousands of interconnected satellites with optical inter-satellite links create an “internet in the sky,” reducing reliance on ground stations.
Applications
- Civilian: Expands broadband to rural and island communities, supports e-governance, smart farming, education, and environmental monitoring.
- Disaster Management: Provides resilient connectivity after cyclones, floods, or earthquakes (e.g., Hurricane Harvey, 2017).
- Defence & Security: Ensures battlefield communication, drone operations, and secure links in high-altitude zones (e.g., Indian Army at Siachen, Ukraine’s defence using Starlink).
- Transport: Improves aviation, shipping, and autonomous vehicle navigation.
- Healthcare: Enables telemedicine and remote patient monitoring.
- Space Economy: Strengthens global trade, logistics, and exploration.
Starlink receives DoT licence to launch Satellite Internet in India

- 09 Jun 2025
In News:
- The Department of Telecommunications (DoT) has granted a licence to Elon Musk’s Starlink to provide satellite-based internet services in India.
- Starlink becomes the third company, after Eutelsat OneWeb and Jio Satellite Communications, to receive such approval. A fourth contender, Amazon’s Kuiper, is still awaiting clearance.
What is Starlink?
- Developer: Starlink is a satellite internet system by SpaceX, founded by Elon Musk in 2002.
- Objective: Deliver high-speed, low-latency broadband globally, especially targeting rural and remote areas with limited connectivity.
- Technology:
- Operates a constellation of Low Earth Orbit (LEO) satellites (~550 km altitude).
- Satellites communicate via laser links for inter-satellite data relay, forming a global mesh.
- Ground stations transmit data to satellites, which then beam it to user terminals.
Key Features of Starlink
- Speed: Up to 150 Mbps, with future plans to increase it.
- Latency: As low as 20–25 milliseconds — ideal for video calls and streaming.
- Tech Stack:
- Flat-panel antennas for easy user access.
- Argon-powered ion thrusters for satellite positioning.
- Space lasers for fast inter-satellite communication.
- Deployment: Satellites launched via Falcon 9 rockets with regular updates.
- Scale: Plans to deploy up to 42,000 satellites globally.
Significance for India
- Bridging the Digital Divide: Ensures internet access in rural, remote, and disaster-prone regions.
- Reduced Infrastructure Dependency: Less reliance on fibre optics and mobile towers in hard-to-reach areas.
- Boost to Digital Economy: Enhances competition in India’s broadband sector, especially in Tier 2 and Tier 3 cities.
- Security Compliance: Starlink must adhere to India’s security norms, including lawful interception requirements, before commercial rollout.
- Next Steps: Will receive trial spectrum within 15–20 days post-application.
SATELLITE INTERNET TECHNOLOGY (Indian Express)
- 28 Oct 2023
What is the News ?
Reliance Jio recently declared that it had effectively tested the first gigabit internet service in India, based on satellite technology.
Facts About:
- Satellite Internet operates in a way similar to satellite TV.
- It begins with an internet service provider launching satellites into space to orbit the Earth.
These satellites, placed in low- or high-Earth orbit, transmit a signal.
- A receiver dish, positioned in your home or business, captures this signal.
It should have an unobstructed view of the sky.
- You connect a modem to this dish to convert the received signal into usable internet connectivity.
- High-speed satellite internet is typically delivered through constellations of low-Earth orbit (LEO) satellites.
- LEO satellites orbit the planet at altitudes ranging from 250 to 2,000 kilometers.
- Communication between these satellites and Earth occurs using radio waves.
Advantages of Satellite Internet:
- Satellite Internet is ideal for users residing in rural or remote areas, far from urban centers or cable/phone offices.
- It relies on a satellite dish for two-way communication and doesn't require telephone cables or lines.
- When compared to other internet options, satellite internet experiences fewer or minimal network outages.
