BIRSA 101 Gene Therapy
- 21 Nov 2025
In News:
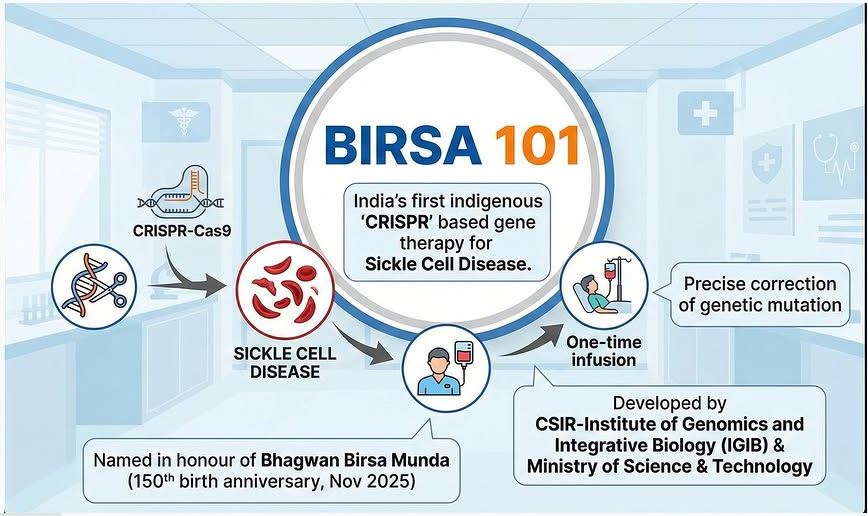
India has launched its first indigenously developed CRISPR-based gene therapy for Sickle Cell Disease (SCD), named BIRSA 101. The therapy marks a major milestone in affordable genomic medicine and aligns with the national goal of a Sickle Cell–Free India by 2047.
What is BIRSA 101?
- BIRSA 101 is a CRISPR gene-editing therapy designed to correct the genetic mutation responsible for Sickle Cell Disease.
- Developed by: CSIR–Institute of Genomics & Integrative Biology (CSIR-IGIB)
- Industry Partner:Serum Institute of India (for technology transfer, scale-up and affordable deployment)
- Named after:Birsa Munda, commemorating his 150th birth anniversary
- Target Group: Populations with high SCD prevalence, especially tribal communities such as Gond, Munda, Bhil and Santal.
How Does It Work?
- Uses CRISPR technology as a form of “precise genetic surgery”.
- The therapy edits the defective gene in a patient’s hematopoietic stem cells, correcting the mutation that causes sickle-shaped red blood cells.
- The corrected stem cells are infused back into the patient, enabling normal haemoglobin production.
- Designed as a potential one-time, lifelong cure, unlike lifelong symptomatic management.
Key Features
- Fully Indigenous CRISPR Platform: Uses enFnCas9, engineered by CSIR-IGIB.
- Affordable Innovation: Intended to replace global gene therapies costing ?20–25 crore with a low-cost Indian alternative.
- Atmanirbhar Bharat: Strengthens India’s self-reliance in frontline biomedical technologies.
- Public–Private Partnership (PPP): Ensures scalability, regulatory readiness and global-standard manufacturing.
- Research Ecosystem: Supported by a new advanced translational research facility at CSIR-IGIB.
Why is it Significant?
- Public Health Impact: SCD is a severe hereditary blood disorder with a disproportionate burden among tribal populations in central and eastern India.
- Global Positioning: Places India among global leaders in advanced gene-editing therapies.
- Cost Disruption: Demonstrates India’s ability to deliver world-class therapies at a fraction of international prices.
- Future Potential: Opens pathways for CRISPR-based cures for other inherited genetic disorders.
