Gravity Energy Storage
- 08 Nov 2025
In News:
As climate change intensifies and the global transition towards low-carbon energy accelerates, the integration of renewable energy into power grids has become a major policy and technological challenge. Solar and wind energy, though abundant and clean, are intermittent in nature, creating mismatches between electricity generation and demand. In this context, Gravity Energy Storage (GES) is emerging as a promising long-duration, grid-scale energy storage technology, offering a viable alternative to conventional battery-based systems.
What is Gravity Energy Storage?
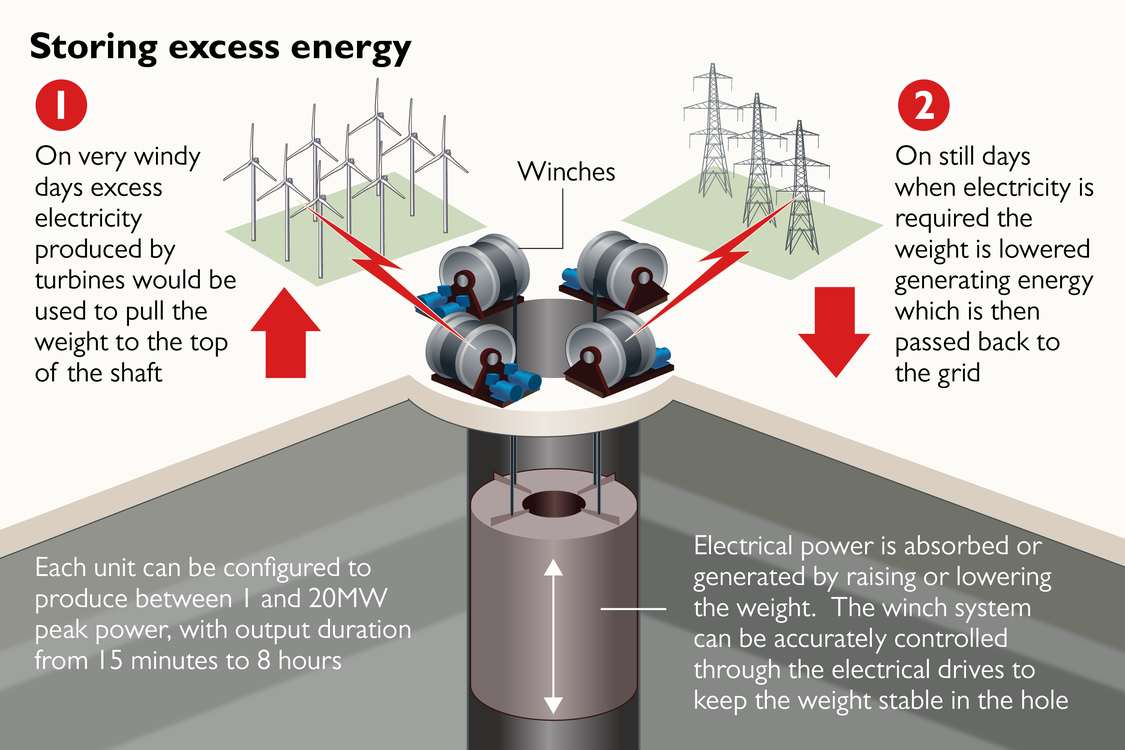
Gravity Energy Storage is an innovative energy storage technology that harnesses gravitational potential energy to store and release electricity. It involves lifting a heavy mass during periods of surplus electricity generation and allowing it to descend when demand rises, thereby converting stored energy back into electricity. The technology is particularly suited for renewable-dominated power systems, where supply fluctuations are frequent.
Working Mechanism
The basic principle of gravity energy storage is simple yet effective:
- During periods of excess renewable energy generation, such as peak solar output, surplus electricity is used to lift a heavy mass—commonly water, concrete blocks, or compressed earth blocks.
- This process converts electrical energy into stored gravitational potential energy.
- When electricity demand exceeds supply or renewable generation falls, the mass is released to descend under gravity.
- The downward motion drives water or mechanical systems through a turbine, generating electricity that is fed back into the grid.
A typical configuration may involve a heavy piston within a fluid-filled cylindrical container, where the piston’s vertical movement enables controlled energy storage and release. Unlike pumped-hydro storage, gravity energy storage systems offer greater flexibility in site selection and do not require large reservoirs or specific topographical features.
Advantages of Gravity Energy Storage
Gravity energy storage offers several strategic advantages that make it attractive for long-term energy planning:
- Long operational life: These systems can operate for several decades with minimal maintenance, unlike batteries which degrade chemically over time.
- Environmentally benign: The absence of toxic chemicals eliminates risks related to pollution, recycling, and disposal, aligning with sustainability goals.
- Cost-effective at scale: Lower lifetime costs of energy and storage make it suitable for large-scale grid applications.
- Flexible deployment: Can be installed in urban, space-constrained, or environmentally sensitive areas where pumped-hydro or large battery systems are not feasible.
- Grid stability: Provides reliable energy during peak demand and enhances grid resilience in renewable-heavy energy systems.
Limitations and Challenges
Despite its potential, gravity energy storage faces certain constraints:
- Early stage of development: High initial capital costs and limited commercial deployment pose adoption challenges.
- Regulatory and infrastructure hurdles: Large-scale installations require regulatory approvals and long-term planning.
- Geographical constraints: Although more flexible than pumped hydro, suitable locations are still required for large infrastructure.
- Lower energy density: Compared to batteries, gravity energy storage is less suitable for compact or small-scale applications.
Significance for Energy Transition
Gravity energy storage represents an important step towards clean, reliable, and sustainable energy systems. By addressing the intermittency of renewable sources, it supports grid stability, energy security, and decarbonisation goals. For countries like India, which are rapidly expanding solar and wind capacity, such storage technologies can play a vital role in achieving energy transition targets, reducing dependence on fossil-fuel-based peaking power, and strengthening climate resilience.
