India AI Stack
- 07 Feb 2026
In News:
The India AI Stack is a five-layer integrated framework designed to democratise Artificial Intelligence and enable reliable, affordable and sovereign AI deployment at population scale.
Background and Vision
- India has introduced the India AI Stack to move AI beyond pilots and experimentation and embed it into everyday governance, service delivery and economic activity.
- Anchored in the principle of AI for Humanity, the approach aims to ensure that AI benefits citizens across healthcare, agriculture, education, justice, climate action and public administration, while strengthening technological self-reliance.
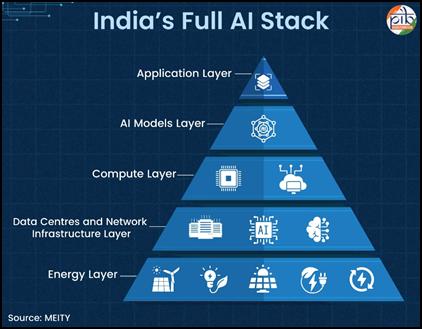
- An AI stack refers to the complete set of applications, models, compute, infrastructure and energy systems required to build, deploy and operate AI solutions seamlessly at scale.
Five Layers of the India AI Stack
1. Application Layer (User Interface)
- User-facing AI services delivering real-world value.
- Key use cases:
- Agriculture: AI advisories improving sowing decisions and yields; some state deployments report 30–50% productivity gains.
- Healthcare: Early detection of TB, cancer, neurological disorders.
- Education: AI integration under NEP 2020 via CBSE, DIKSHA, YUVAi.
- Justice Delivery: AI/ML in e-Courts Phase III for translation, scheduling and case management.
- Weather & Disaster Management: AI-enabled forecasting and tools like Mausam GPT used by India Meteorological Department.
This layer determines AI’s social and economic impact by ensuring large-scale adoption.
2. AI Model Layer (Intelligence Core)
- Provides learning, prediction and decision-making capability.
- Key initiatives:
- IndiaAI Mission: Development of 12 indigenous AI models; subsidised compute support (up to 25% cost support).
- BharatGen: India-centric foundation and multimodal models.
- IndiaAIKosh: National AI repository with 5,722 datasets and 251 models (Dec 2025).
- Bhashini: 350+ language AI models covering speech, translation, OCR and text-to-speech.
Focus is on sovereign, India-specific and multilingual AI aligned with public services.
3. Compute Layer (Processing Power)
- Enables training and deployment of AI models.
- Key facts:
- ?10,300+ crore allocation under IndiaAI Mission (5 years).
- IndiaAI Compute Portal: 38,000 GPUs and 1,050 TPUs at subsidised rates (under ?100/hour).
- National secure GPU cluster: 3,000 next-generation GPUs.
- India Semiconductor Mission: ?76,000 crore, 10 approved semiconductor projects.
- National Supercomputing Mission: 40+ petaflops capacity; systems like PARAM Siddhi-AI and AIRAWAT.
This shared-access approach reduces entry barriers and prevents compute concentration.
4. Data Centres & Network Infrastructure Layer
- Provides storage, hosting and connectivity.
- Key data:
- Nationwide optical fibre network.
- 5G coverage in 99.9% districts, ~85% population.
- Installed data centre capacity: ~960 MW (~3% of global capacity).
- Projected growth to 9.2 GW by 2030.
- Major hubs: Mumbai–Navi Mumbai (25%+), Bengaluru, Hyderabad, Chennai, Delhi-NCR.
- Large investments by global firms (Microsoft, Amazon, Google).
Ensures low-latency, secure and domestic hosting of AI systems.
5. Energy Layer (Power Backbone)
- Sustains energy-intensive AI infrastructure.
- Key facts:
- Peak demand met: 242.49 GW (FY 2025–26); shortage reduced to 0.03%.
- Total installed capacity: 509.7 GW (Nov 2025).
- Non-fossil capacity: 256.09 GW (>51%).
- Targets: 57 GW pumped storage by 2031–32; 43,220 MWh battery storage.
- SHANTI Act: Nuclear energy (including SMRs) for round-the-clock clean power.
Aligns AI growth with sustainability and grid stability.
