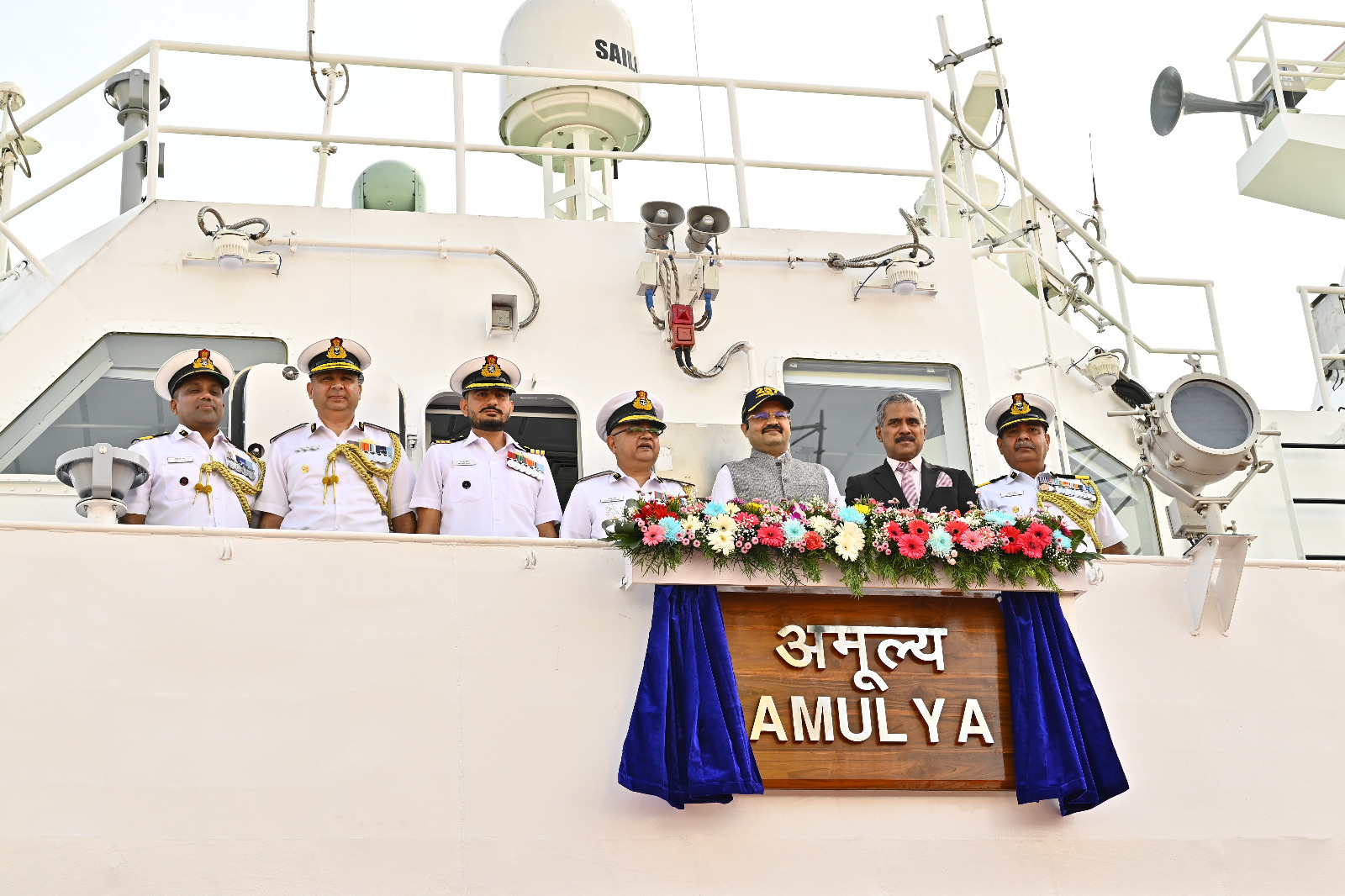
Indian Coast Guard Ship Amulya

- 22 Dec 2025
In News:
The Indian Coast Guard commissioned ICG Ship Amulya in Goa, marking another milestone in India’s efforts to enhance maritime security and indigenous defence capability. Amulya is the third vessel in the series of eight Adamya-class Fast Patrol Vessels (FPVs) being inducted into the Coast Guard fleet.
Design and Indigenous Content
- Amulya is a 51-metre-long Fast Patrol Vessel.
- Designed and built byGoa Shipyard Limited.
- Incorporates over 60% indigenous components, underscoring India’s push for defence self-reliance.
- Reflects the objectives of Aatmanirbhar Bharat and Make in India.
- Built with a modern design philosophy focused on efficiency, endurance, and rapid response.
Propulsion and Performance
- Propulsion: Powered by two 3000 kW advanced diesel engines.
- Top Speed:27 knots.
- Operational Endurance:1,500 nautical miles, enabling extended patrols across India’s maritime zones.
- Equipped with indigenous state-of-the-art weapons and systems, providing enhanced manoeuvrability, flexibility, and operational performance at sea.
Roles and Functions
ICG Ship Amulya is designed to undertake a wide range of coast guard missions, including:
- Maritime surveillance and interdiction
- Search and Rescue (SAR) operations
- Anti-smuggling and law enforcement
- Marine pollution response
These roles are critical for safeguarding India’s coastline, maritime trade routes, and offshore assets.
Operational Deployment
- Home Port: Paradip, Odisha
- Operates under the administrative and operational control of the Commander, Coast Guard Region (North East).
- Its deployment strengthens surveillance and response capabilities along the eastern seaboard.
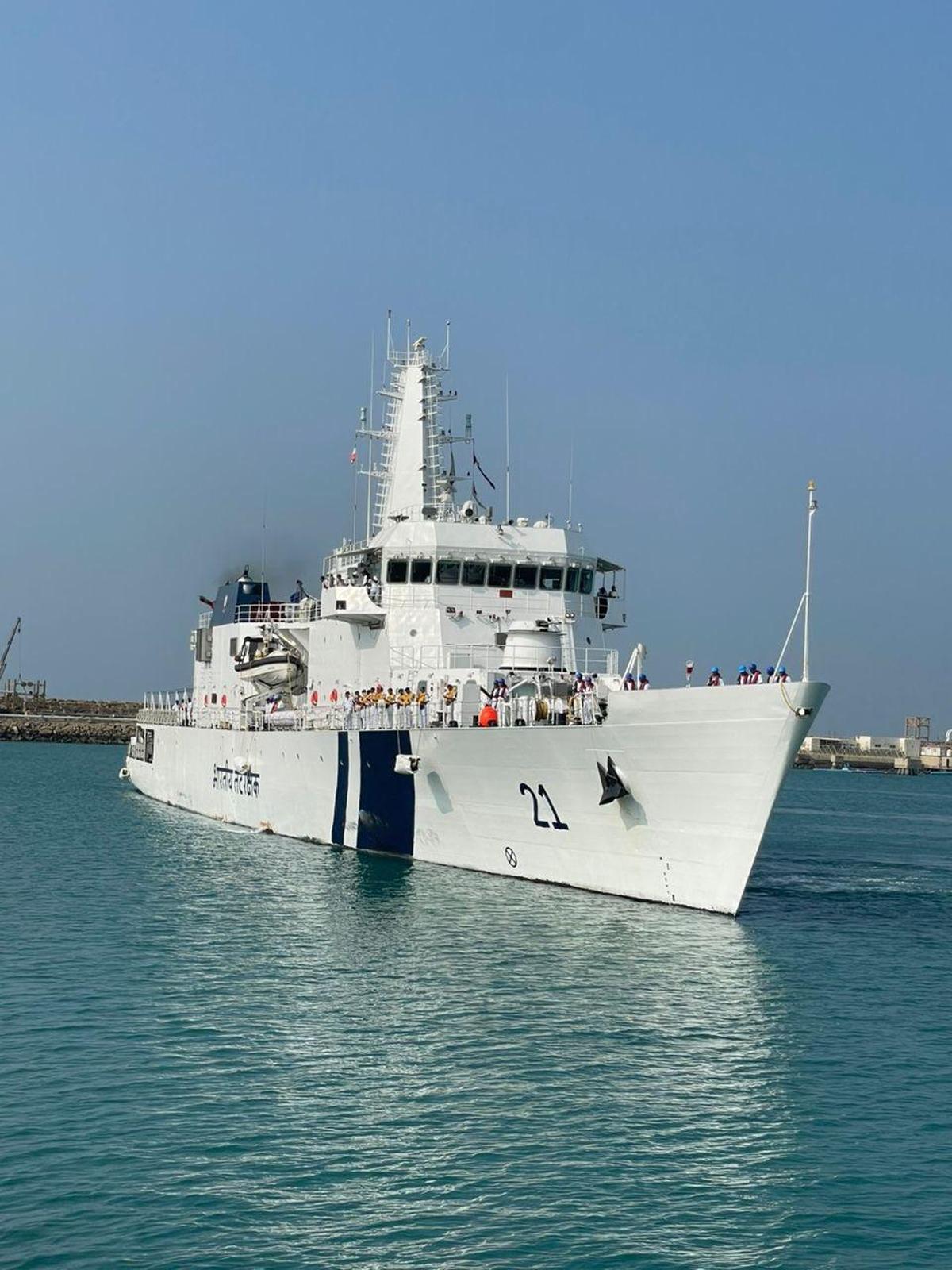
ICGS Sarthak at Chabahar Port

- 21 Dec 2025
In News:
The offshore patrol vessel ICGS Sarthak of the Indian Coast Guard has made its first-ever port call at Chabahar Port, Iran. A port call refers to the period during which a naval or coast guard vessel arrives at, stays in, and departs from a port. This visit marks a notable step in strengthening maritime security cooperation, regional engagement, and strategic outreach in the Indian Ocean Region (IOR).
Strategic Importance of the Visit
- Gateway Role: Chabahar serves as India’s direct maritime gateway to Iran, Afghanistan, and Central Asia, bypassing the Strait of Hormuz.
- Connectivity & Supply Lines: The port call reinforces secure supply chains and India’s access to continental markets.
- Policy Alignment: The engagement aligns with India’s maritime visions of SAGAR (Security and Growth for All in the Region) and MAHASAGAR, underscoring cooperative security and prosperity in the IOR.
Environmental Outreach
Alongside operational engagements, the visit included environmental activities such as a beach walkathon and sports fixtures, supporting Puneet Sagar Abhiyan. Launched in 2021 by the National Cadet Corps, the campaign focuses on cleaning seashores, beaches, rivers, lakes, and other water bodies of plastic and waste—integrating maritime operations with environmental stewardship.
Chabahar Port
- Location:Sistan-Baluchistan province, Iran; on the Gulf of Oman, outside the Strait of Hormuz.
- Uniqueness: Iran’s only deep-sea port with direct ocean access.
- Agreement: Developed under the 2016 Chabahar Agreement between India, Iran, and Afghanistan.
- Connectivity Corridor: Part of the International North-South Transport Corridor (INSTC).
- Terminals:Shahid Beheshti and Shahid Kalantari.
- Indian Role: India developed and actively operates the Shahid Beheshti terminal.
- Management: Since December 2018, operations are managed by India Ports Global Limited (IPGL) through its subsidiary India Ports Global Chabahar Free Zone (IPGCFZ).
Param Vir Chakra (PVC)

- 20 Dec 2025
In News:
On Vijay Diwas 2025, the President of India, Droupadi Murmu, inaugurated the ‘Param Vir Dirgha’ at the Rashtrapati Bhavan, New Delhi.
The gallery showcases portraits of all 21 recipients of the Param Vir Chakra (PVC), India’s highest military gallantry award.
Notably, this display replaced portraits of 96 British Aide-de-Camps (ADCs) from the colonial era, symbolising India’s continued effort to decolonise public memory and national symbols.
Param Vir Chakra (PVC): India’s Highest Gallantry Award
The Param Vir Chakra is the highest military decoration for valour in India, awarded for the most conspicuous bravery, indomitable courage and supreme sacrifice in the presence of the enemy during wartime.
- Instituted: 26 January 1950, coinciding with the enforcement of the Constitution
- Eligibility: Personnel of all ranks from the Army, Navy, Air Force, Territorial Army and other lawfully constituted armed forces
- Nature: Can be awarded posthumously
Key Features
- Awarded only during wartime
- Recognises acts of extraordinary courage against the enemy
- Includes a monthly honorarium of ?3,000, with an additional ?3,000 for every bar
Recipients
- Total awardees: 21
- Posthumous awards: 14
- Conflicts covered: Four major wars fought by India
The high proportion of posthumous awards underlines the supreme sacrifice associated with the honour.
Param Vir Dirgha: Symbolism and National Memory
The establishment of the Param Vir Dirgha serves multiple purposes:
- Institutionalising remembrance of India’s war heroes
- Educating citizens and visitors about acts of exceptional military valour
- Reinforcing national pride and military ethos
According to the Rashtrapati Bhavan, the initiative helps visitors understand the “dauntless resolve and unconquerable spirit” of India’s soldiers and represents a conscious move to replace colonial symbolism with Indian national heroes.
Who are Aide-de-Camps (ADCs)?
An Aide-de-Camp is a personal military officer attached to high constitutional authorities such as the President or Governors.
Key Characteristics
- Typical Rank:
- Major (Army)
- Lieutenant Commander (Navy)
- Squadron Leader (Air Force)
Functions
- Managing official schedules and engagements
- Coordinating ceremonial and protocol duties
- Acting as liaison between the dignitary and civil/military authorities
- Assisting in security and coordination
While ADCs continue to serve an important functional role today, the earlier display of British ADC portraits reflected colonial legacy rather than independent India’s military ethos.
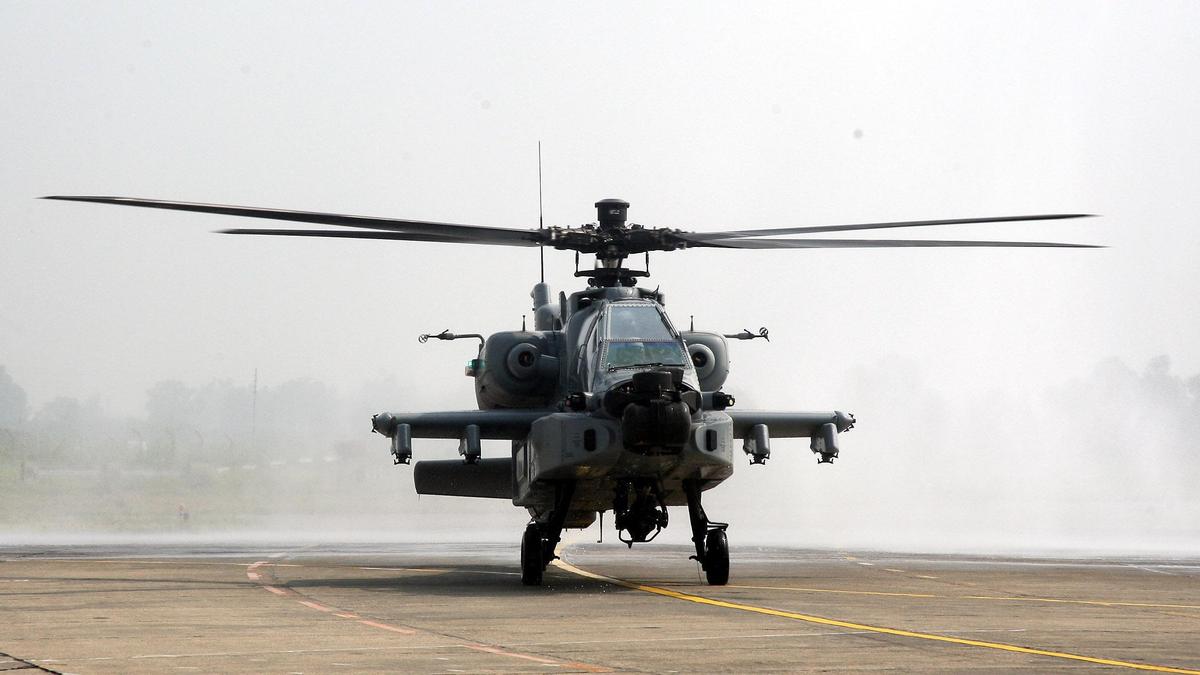
AH-64E Apache Attack Helicopter

- 20 Dec 2025
In News:
The Indian Army has received the final batch of three AH-64E Apache attack helicopters, completing its sanctioned fleet of six helicopters. These platforms have been inducted into the 451 Army Aviation Squadron based at Jodhpur, Rajasthan, marking a key step in enhancing India’s offensive rotary-wing capability.
About the AH-64E Apache Attack Helicopter
The AH-64E Apache, also known as the Apache Guardian, is regarded as the world’s most advanced multi-role combat helicopter. It is designed for advanced reconnaissance, precision strike and close air support (CAS) missions in high-intensity battlefield environments.
- Country of Origin: United States
- Manufacturer: Boeing
- User Nations: United States, India, Israel, Japan, South Korea, UK, UAE, Saudi Arabia, Qatar, Netherlands, among others
- Operational Variant: Latest version currently used by the US Army
Apache in India’s Defence Architecture
India operates the Apache across two services, reflecting a shift towards service-specific combat roles:
- Indian Air Force: Operates 22 AH-64E helicopters, inducted primarily for air force-led strike and support roles
- Indian Army: Inducted 6 AH-64E helicopters (contract signed in 2020) to strengthen Army Aviation Corps’ direct battlefield support
This dual induction enhances jointness, while enabling the Army to independently conduct armoured warfare support and offensive air manoeuvres.
Key Technical and Combat Features
The AH-64E is a twin-engine, heavily armed attack helicopteroptimised for survivability and lethality:
- Length: 17.8 metres
- Maximum Speed: ~300 km/h
- Maximum Operating Weight: 10,432 kg
- Rate of Climb: Over 2,800 feet per minute
Weapons Suite:
- AGM-114 Hellfire missiles (anti-tank and precision strike)
- 70 mm rockets
- 30 mm chain gun (nose-mounted)
- Stinger air-to-air missiles (short-range aerial threats)
Advanced Avionics & Sensors:
- Integrated infrared laser designator
- Enhanced night-fighting capability combining infrared and night vision imagery
- Ability to track up to 128 targets per minute and prioritise threats in real time
These features enable operations in all-weather, day-night and high-threat environments.
Strategic Significance for India
The induction of AH-64E Apaches into the Indian Army has multiple strategic implications:
- Enhanced anti-armour capability, especially in desert and plains sectors
- Improved close air support for mechanised and infantry formations
- Greater operational autonomy for the Army Aviation Corps
- Boost to network-centric warfare, surveillance and precision strike capacity
The deployment at Jodhpur is particularly relevant for western theatre preparedness, including rapid response in desert warfare scenarios.
Agni-3 Intermediate-Range Ballistic Missile (IRBM)

- 08 Feb 2026
In News:
India has successfully test-fired the Intermediate-Range Ballistic Missile (IRBM) Agni-3 from the Integrated Test Range (ITR), Chandipur, Odisha, validating all operational and technical parameters. The launch was conducted under the aegis of the Strategic Forces Command, confirming the missile’s operational readiness.
What is Agni-3?
- Agni-3 is an indigenously developed Intermediate-Range Ballistic Missile (IRBM).
- It is a surface-to-surface missile and a key component of India’s land-based nuclear deterrent.
- Developed by Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO).
- It has already been inducted into the armed forces and is operationally deployed under the Strategic Forces Command.
Key Technical Features
- Type: Intermediate-Range Ballistic Missile (IRBM)
- Range: 3,000–3,500 km
- Propulsion: Two-stage, solid-fuelled
- Payload Capacity: ~1.5 tonnes (1,500 kg)
- Warhead: Conventional or nuclear
- Estimated Nuclear Yield: 200–300 kilotons
- Length: 16.7 metres
- Diameter: 2 metres
- Launch Weight: ~48,300 kg
Guidance & Accuracy
- Uses strap-down inertial navigation system (INS) supported by GPS
- Accuracy: ~40 metres Circular Error Probable (CEP)
- Considered one of the most accurate strategic ballistic missiles in its range class
Structural & Design Highlights
- First Stage: Maraging steel motor case
- Second Stage: Carbon-fibre motor case
- Thrust Vector Control (TVC) in both stages for enhanced stability and precision
Launch & Mobility
- Launch Platforms: Road-mobile and rail-mobile launchers
- Enhances survivability, flexibility and second-strike capability
Strategic Objectives
- Ensures credible minimum deterrence
- Strengthens second-strike capability
- Provides strategic depth beyond short- and medium-range missiles
- Enhances deterrence across extended regional theatres
Agni Missile Series
Conceptualised under the Integrated Guided Missile Development Programme (IGMDP) in the 1980s
- Agni-I: 700–1,250 km
- Agni-II: 2,000–2,500 km
- Agni-III: 3,000–3,500 km
- Agni-IV: 3,000–4,000 km (advanced systems, field trials)
- Agni-V: ~5,000+ km (ICBM-class, canisterised, road-mobile)
- Agni-VI: Under development (expected 8,000–10,000 km; land & sea-based)
- Agni Prime: New-generation, lighter, canisterised missile (1,000–2,000 km)
Miniratna Category-I Status to Yantra India Limited

- 06 Feb 2026
In News:
The Union Defence Minister Rajnath Singh has approved the grant of Miniratna Category-I status to Yantra India Limited (YIL), recognising its rapid transformation into a profit-making Defence Public Sector Undertaking (DPSU) within a short span of about four years.
Background
Yantra India Limited was established on 1 October 2021 following the corporatisation of the erstwhile Ordnance Factory Board (OFB) into seven new DPSUs. The reform aimed to enhance functional autonomy, efficiency, competitiveness, and innovation in India’s defence manufacturing ecosystem.
YIL is a Schedule ‘A’ DPSU functioning under the administrative control of the Department of Defence Production.
Performance Highlights
Since its inception, YIL has demonstrated strong operational and financial performance:
- Sales growth: From ?956.32 crore in FY 2021-22 (H2) to ?3,108.79 crore in FY 2024-25.
- Export growth: From nil in FY 2021-22 (H2) to ?321.77 crore in FY 2024-25, reflecting growing global competitiveness.
Key Products
Yantra India Limited operates in critical defence production segments, manufacturing:
- Carbon fibre composites
- Glass composites
- Aluminium alloys
- Assembly products for medium and large calibre ammunition
- Assembly products for armoured vehicles, artillery guns, and main battle tanks (MBTs)
Significance of Miniratna Category-I Status
The Miniratna-I status empowers YIL’s Board of Directors to:
- Incur capital expenditure up to ?500 crore
- Undertake new projects, modernisation, and equipment procurement
- Make faster commercial and investment decisions without prior government approval
This enhanced autonomy is expected to accelerate growth, modernisation, and export capacity.
Broader Policy Context
The decision aligns with India’s defence sector reforms and the vision of Aatmanirbhar Bharat, which seeks to:
- Reduce import dependence in defence equipment
- Promote indigenous defence production and R&D
- Encourage participation of Indian industry
- Position India as a global defence manufacturing and export hub
Notably, in May 2025, Miniratna-I status was also granted to Munitions India Limited, Armoured Vehicles Nigam Limited, and India Optel Limited, reflecting the government’s phased approach to empowering corporatised DPSUs.
India–France Defence Pact on HAMMER (AASM)

- 18 Dec 2025
In News:
- India has signed an agreement with France’s Safran to jointly manufacture, customise, supply, and maintain the HAMMER (Highly Agile Modular Munition Extended Range) precision-guided air-to-ground weapon system in India.
- The production will take place through a 50:50 joint venture between Bharat Electronics Limited (BEL) and Safran.
What is HAMMER (AASM)?
- HAMMER, also known as Armement Air-Sol Modulaire (AASM), is a modular precision-guided munition that converts unguided “dumb” bombs into smart stand-off weapons using guidance and propulsion kits.
- It provides missile-like accuracy at significantly lower cost than cruise missiles.
Developer & Indian Manufacturing
|
Component |
Details |
|
Original Developer |
Safran Electronics & Defense (France) |
|
Indian Partner |
Bharat Electronics Limited (BEL) |
|
JV Structure |
50% Safran – 50% BEL |
|
Nature of Work |
Manufacturing, customization, maintenance in India |
Key Technical Features
- Modular Design
- Nose-mounted guidance kit
- Tail-mounted range-extension/propulsion kit
- Compatible with standard bomb bodies (125 kg to 1,000 kg, including Mk-80 series)
- Multiple Guidance Options
- INS-GPS → All-weather precision
- INS-GPS + Infrared (IR) → High-precision fixed targets
- Laser guidance → Moving targets
- Stand-off Capability
- Equipped with rocket booster and winglets
- Allows aircraft to strike from outside enemy air-defence range
- Can be launched at off-axis angles
- High Accuracy
- CEP (Circular Error Probability):
- ~10 m (INS-GPS)
- ~1 m (IR guidance)
- CEP (Circular Error Probability):
- Platform Integration
- Already integrated with Dassault Rafale
- Planned integration with HAL Tejas
Solid Fuel Ducted Ramjet (SFDR) Technology
- 05 Feb 2026
In News:
The Defence Research and Development Organisation successfully demonstrated Solid Fuel Ducted Ramjet (SFDR) technology from the Integrated Test Range.
What is SFDR Technology?
- SFDR is an advanced air-breathing missile propulsion system that uses a solid fuel gas generator combined with ramjet propulsion.
- It is being developed by Defence Research and Development Laboratory along with other DRDO labs.
How It Works
- The missile is first accelerated to supersonic speed (Mach 2+) using a nozzle-less solid booster.
- Once at high speed, the ramjet engine takes over.
- The system draws oxygen from the atmosphere instead of carrying an oxidiser.
- A solid fuel ducted ramjet motor then produces sustained and controllable thrust throughout the missile’s flight.
Key Subsystems Tested
- Nozzle-less Booster
- Solid Fuel Ducted Ramjet Motor
- Fuel Flow Controller
All systems performed as expected during the flight test.
What is a Ramjet?
A ramjet is a jet engine that:
- Has no moving compressor parts
- Uses the missile’s forward speed to compress incoming air
- Works efficiently only at high supersonic speeds
Advantages of SFDR Over Conventional Rockets
|
Feature |
Conventional Rocket |
SFDR System |
|
Oxidiser |
Carried onboard |
Not required (air-breathing) |
|
Weight |
Heavier |
Lighter |
|
Thrust Duration |
Short boost phase |
Sustained throughout flight |
|
Maneuverability |
Reduces after boost |
Maintains high agility till end |
|
Range |
Limited by fuel burn |
Significantly extended |
Strategic Significance
- Long-Range Air-to-Air Missiles (LRAAM): SFDR will power advanced missiles such as future variants of Astra Mark-3, potentially enabling engagement ranges beyond 150–300 km.
- Expanded “No-Escape Zone”: Sustained propulsion allows high-G manoeuvres near the target, making evasion extremely difficult.
- Elite Technology Club: Places India among a select group of nations possessing advanced ramjet missile propulsion capability.
- Future Surface-to-Air Systems: Technology may be adapted for next-generation SAM systems to counter high-speed cruise or hypersonic threats.
Diving Support Craft (DSC) A20

- 15 Dec 2025
In News:
The Indian Navy is set to commission Diving Support Craft (DSC) A20 at Kochi under the aegis of the Southern Naval Command. The vessel marks a significant step in enhancing India’s underwater operational preparedness and advancing indigenisation in specialised naval platforms.
About DSC A20
- DSC A20 is the first indigenously designed and constructed Diving Support Craft and serves as the lead ship in a series of five vessels being built by Titagarh Rail Systems Limited (TRSL), Kolkata.
- It is purpose-built to undertake a wide spectrum of diving and underwater missions in coastal waters, supporting naval operations that require specialised diving assistance and underwater technical intervention.
Key Features
- The vessel features a catamaran hull design, which provides superior stability, larger deck space, and improved seakeeping capabilities compared to conventional hull forms.
- It is equipped with advanced, state-of-the-art diving systems, ensuring high standards of operational efficiency and diver safety.
- DSC A20 has an approximate displacement of 390 tonnes, making it suitable for sustained coastal support roles.
- The ship has been designed and constructed in accordance with the Naval Rules and Regulations of the Indian Register of Shipping (IRS).
- Extensive hydrodynamic analysis and model testing were conducted at the Naval Science and Technological Laboratory (NSTL), Visakhapatnam, to ensure optimal performance and reliability.
Operational Role
DSC A20 is intended to support:
- Diving operations for underwater repairs and maintenance
- Underwater inspection of hulls, harbours, and maritime structures
- Salvage and recovery assistance
- Coastal operational deployment, including emergency response
Once commissioned, the vessel will be based at Kochi and operate under the Southern Naval Command, a key formation responsible for training and operational readiness in the southern maritime theatre.
Strategic and Policy Significance
The induction of DSC A20 reflects India’s progress in maritime self-reliance (Aatmanirbharta) and the success of the Make in India initiative in defence manufacturing. The project represents close collaboration between the Navy, domestic shipbuilding industry, and national research institutions.
By enhancing underwater operational capability, the vessel strengthens India’s preparedness for naval maintenance, search and rescue, disaster response, and maritime security operations in coastal regions.
Exercise Harimau Shakti
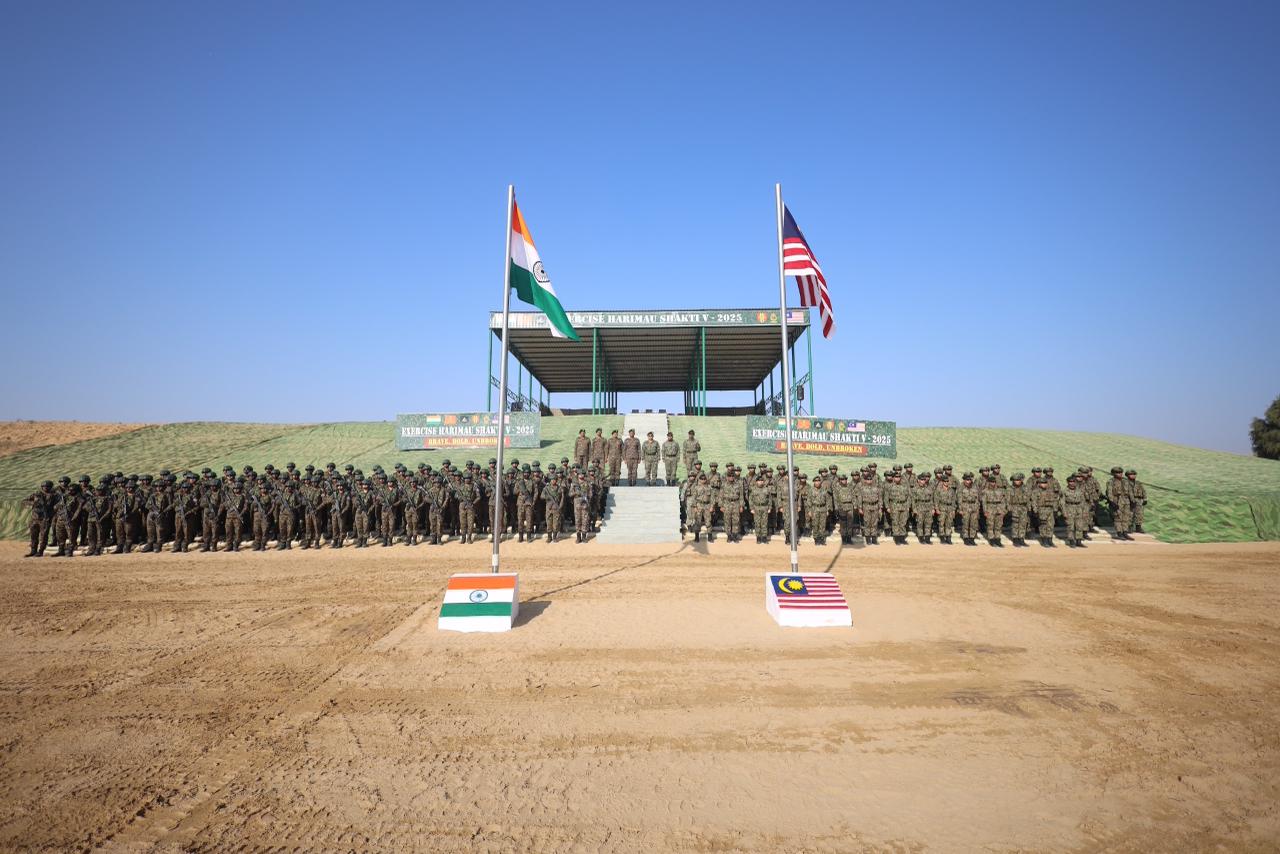

- 08 Dec 2025
In News:
The 5th edition of Exercise Harimau Shakti was conducted at the Mahajan Field Firing Range, Rajasthan. It is a bilateral joint military exercise between India and Malaysia aimed at enhancing operational coordination and interoperability between the two armies.
Participating Forces
- India: Troops primarily from the Dogra Regiment of the Indian Army
- Malaysia: Soldiers from the 25th Battalion, Royal Malaysian Army
Nature of the Exercise
Exercise Harimau Shakti focuses on Sub-Conventional Operations (SCO) under the framework of Chapter VII of the United Nations Charter, which deals with peace enforcement and security operations. The training is designed to simulate counter-terrorism and peacekeeping scenarios in semi-arid and desert terrain.
Key Training Components
The exercise includes joint practice of:
- Cordon and search operations
- Search and destroy missions
- Heliborne operations
- Securing helipads in hostile environments
- Casualty evacuation (CASEVAC) drills during combat
- Combat reflex shooting
- Army Martial Arts Routine (AMAR)
- Yoga sessions for endurance and mental conditioning
These activities aim to improve tactical coordination, combat readiness, and joint response capability during counter-terrorist and UN peacekeeping missions.
Objectives
- Enhance interoperability between the Indian Army and Royal Malaysian Army
- Share best practices, tactics, techniques, and procedures in sub-conventional warfare
- Improve joint planning and execution of operations under a UN peace enforcement mandate
- Reduce risks to life and property during complex operations
Strategic Significance
- Strengthens India–Malaysia defence cooperation
- Supports India’s broader engagement with ASEAN nations
- Contributes to regional stability and collaboration in counter-terrorism and peacekeeping
- Promotes mutual trust and professional military exchanges between the two countries
Exercise GARUDA SHAKTI

- 07 Dec 2025
In News:
The 10th edition of Exercise GARUDA SHAKTI, a joint Special Forces exercise between India and Indonesia, is being conducted at the Special Forces Training School, Bakloh, Himachal Pradesh.
Participating Forces
- India: Troops from The Parachute Regiment (Special Forces) of the Indian Army
- Indonesia: Personnel from the Indonesian Special Forces
This exercise is part of the growing defence engagement between the two Indo-Pacific partners.
Nature of the Exercise
GARUDA SHAKTI is a bilateral Special Forces exercise designed to enhance mutual understanding, cooperation, and interoperability between elite troops of both nations. It focuses on high-intensity combat training and realistic operational scenarios in semi-mountainous terrain.
Key Areas of Training
The exercise includes a range of tactical and operational drills relevant to modern counter-terror and special operations environments:
- Counter-terrorism tactics at the troop level
- Unarmed combat techniques
- Combat shooting and sniping
- Heliborne operations
- Planning and execution of operations involving:
- Drones
- Counter-Unmanned Aerial Systems (Counter-UAS)
- Loitering munitions
The training emphasisesphysical endurance, tactical coordination, and combat readiness.
Exchange of Expertise
A key component of GARUDA SHAKTI is the exchange of knowledge related to:
- Weapons and specialised equipment
- Tactical drills and operational procedures
- Best practices in special operations
Such exchanges help both sides understand each other’s operational doctrines and capabilities.
Validation Phase
The joint training culminates in a validation exercise, simulating a real-world operational scenario. This phase tests:
- Joint planning capabilities
- Coordination under stress
- Tactical response and decision-making
- Endurance and teamwork of both contingents
Strategic Significance
- Strengthens India–Indonesia defence cooperation
- Enhances interoperability between Special Forces
- Contributes to regional security collaboration in the Indo-Pacific
- Reflects India’s broader policy of deepening defence partnerships with ASEAN nations
Indonesia holds strategic importance due to its location near key Sea Lanes of Communication (SLOCs) such as the Malacca Strait, making defence cooperation crucial for maritime and regional stability.
India’s Special Forces
The Parachute Regiment (Special Forces) is among India’s most elite military units, trained for:
- Counter-terrorism
- Special reconnaissance
- Direct action missions
- High-altitude and difficult terrain operations
Indian Maritime Doctrine 2025

- 06 Dec 2025
In News:
The Indian Maritime Doctrine (IMD) 2025, released by the Chief of the Naval Staff on Indian Navy Day (4 December), is the apex doctrinal publication guiding India’s naval strategy. Navy Day commemorates Operation Trident (1971), when the Indian Navy launched a successful missile attack on Karachi harbour using INS Nipat, Nirghat and Veer, supported by INS Kiltan, Katchall and fleet tanker INS Poshak, crippling Pakistan’s maritime capability.
What is the Indian Maritime Doctrine 2025?
The IMD 2025 defines how India prepares and operates across the full spectrum of maritime conflict, from peacetime presence to warfighting. First issued in 2004 and updated in 2009 and 2015, the 2025 edition reflects India’s evolving maritime environment and Indo-Pacific priorities.
Key Features
1. “No-War, No-Peace” Category:The doctrine formally recognises a grey-zone space between peace and open conflict, where coercion, intimidation, and competition occur without declared war.
2. Multi-Domain and Hybrid Threats:It integrates challenges from cyber, space, electronic and cognitive warfare, along with irregular and hybrid threats.
3. Jointness and Theatre Commands:The document stresses tri-service interoperability and supports India’s move toward theatre command structures.
4. Technology and Modernisation:Emphasis is placed on uncrewed systems, autonomous platforms, AI-enabled surveillance, and network-centric warfare.
5. Maritime Security and Blue Economy:It links naval power to protection of Sea Lanes of Communication (SLOCs), maritime trade, offshore resources, and India’s blue economy ambitions.
Strategic Significance
- The doctrine aligns with national initiatives such as Sagarmala, PM Gati Shakti, Maritime India Vision 2030, Maritime Amrit Kaal Vision 2047, and MAHASAGAR. It positions maritime power as central to achieving Viksit Bharat 2047 and strengthens India’s role as a net security provider in the Indo-Pacific.
Indian Navy: Historical Background
- India’s maritime legacy dates back over 4,000 years, with Harappan ports like Lothal engaged in overseas trade. Ancient Indian navigators influenced Southeast Asia culturally and commercially.
- During the medieval period, powers such as the Cholas, Zamorins, and Marathas developed naval strength. The Maratha Navy under KanhojiAngre resisted European fleets along India’s west coast.
- European dominance began after Vasco da Gama (1498), leading to colonial maritime supremacy. The modern navy evolved from the Royal Indian Navy (RIN), which became the Indian Navy after independence.
Structure and Role Today
The President of India is the Supreme Commander of the Navy. Its motto is “Sam No Varunah” (May Varuna be auspicious to us).
India today maintains a blue-water navy capable of sustained operations across the Indian Ocean Region (IOR) and beyond. Its roles include:
- Maritime security and SLOC protection
- Power projection and deterrence
- Humanitarian assistance and disaster relief (HADR)
- Counter-piracy and anti-terror operations
The Navy’s elite force, MARCOS (Marine Commandos), specialises in amphibious warfare, counter-terrorism, and special operations.
Major Operations
Post-independence milestones include the Liberation of Goa (1961), Operations Trident and Python (1971 war), and ongoing maritime security missions in the IOR.
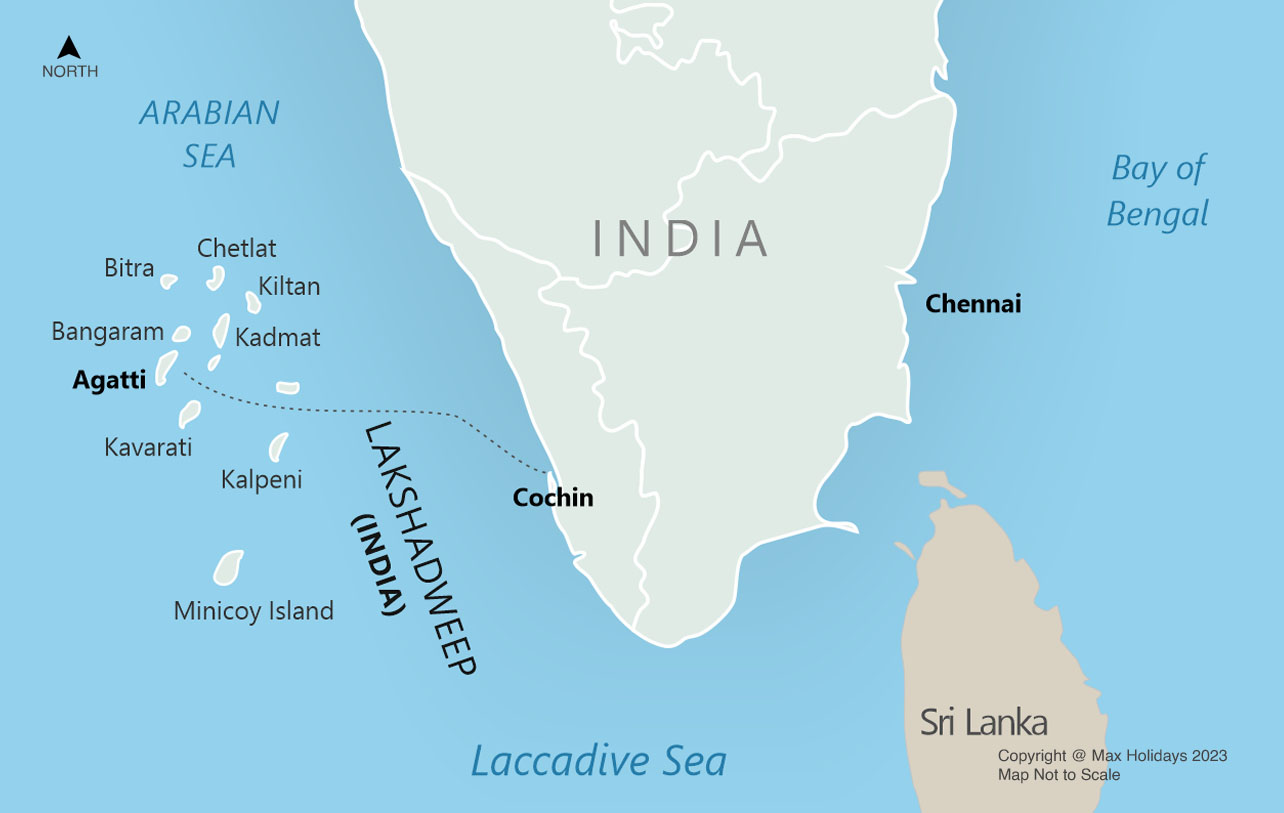
Bitra Island
- 05 Dec 2025
In News:
India is set to strengthen its military footprint in Lakshadweep, with a new naval detachment on Bitra Island expected to become fully operational next year. Simultaneously, the Indian Air Force (IAF) is expanding facilities on Agatti and planning a new air base on Minicoy. These steps are aimed at enhancing India’s maritime security posture in the Arabian Sea amid rising strategic challenges.
Why Lakshadweep Matters Strategically
Lakshadweep’s location gives India a vantage point over critical sea lanes of communication (SLOCs) in the Arabian Sea, through which a significant portion of global energy and trade flows.
Rising shipping traffic, growing Chinese presence in the Indian Ocean Region (IOR), and threats such as piracy and maritime crime have increased the strategic relevance of the islands. Enhanced surveillance and rapid response capabilities from Lakshadweep will strengthen India’s maritime domain awareness.
About Bitra Island
Basic Facts
- Smallest inhabited island of Lakshadweep
- Part of the Amindivi subgroup
- Located about 483 km west of Kochi in the Arabian Sea
Geographical Setting
- Lies north of Perumal Par and southeast of Byramgore Reef
- A coral atoll, formed from reef growth over submerged volcanic structures
- Features a ring-shaped lagoon system
Physical Features
|
Feature |
Detail |
|
Main Island Area |
~0.177 sq km |
|
Southern Cay |
~0.009 sq km |
|
Lagoon Area |
~45–54 sq km |
|
Reef System |
Coral reef barrier protects lagoon waters |
The surrounding reef keeps lagoon waters relatively calm even during monsoon conditions.
Ecological and Cultural Importance
- Bitra is part of Lakshadweep’s fragile coral ecosystem, historically known as a major seabird breeding ground. The island’s small landmass and reef system make it environmentally sensitive.
- Culturally, Bitra houses the shrine of Malik Mulla, an Arab saint, making it a place of local religious significance.
- It was permanently settled only in 1945, making it one of India’s newest inhabited regions.
Military Developments
Naval Expansion
- A new Indian naval detachment is being established on Bitra.
- It will improve maritime surveillance, especially over shipping routes in the Arabian Sea.
- Development is being carried out in a measured manner, considering ecological sensitivity.
Air Force Expansion
- Agatti Airfield is being expanded.
- A new air base on Minicoy is under development.
- Future plans include long-range cargo drones to support logistics and operations across dispersed island territories.
Strategic Significance
The military expansion in Lakshadweep supports:
- Maritime security and surveillance
- Monitoring of strategic sea lanes
- Countering piracy and illegal activities
- Strengthening India’s role as a net security provider in the IOR
Taragiri

- 02 Dec 2025
In News:
The Indian Navy has received INS Taragiri (Yard 12653), the fourth Nilgiri-class frigate under Project 17A and the third P17A ship built by Mazagon Dock Shipbuilders Ltd (MDL). Delivered in November 2025, the induction of Taragiri marks a major milestone in Aatmanirbhar Bharat and India’s quest for indigenous, advanced warship construction.
INS Taragiri: Key Facts
- Type: Advanced stealth frigate (Nilgiri class)
- Project:Project 17A
- Builder:Mazagon Dock Shipbuilders Limited (MDL)
- Legacy: Reincarnation of the earlier INS Taragiri, a Leander-class frigate that served the Indian Navy from 1980 to 2013 (33 years)
- Designer: Warship Design Bureau (WDB)
Project 17A (Nilgiri Class): Overview
- Programme to build seven advanced stealth frigates as successors to the Shivalik-class (Project 17).
- Shipbuilders:
- MDL:Nilgiri, Udaygiri, Taragiri, Mahendragiri
- **Garden Reach Shipbuilders & Engineers (GRSE): Himgiri, Dunagiri, Vindhyagiri
- Construction philosophy:Integrated Construction Method
- Pre-outfitting of blocks to reduce build time and improve quality.
- Indigenisation: ~75% indigenous content, involving 200+ MSMEs.
- Delivery timeline: Remaining P17A ships to be delivered progressively by August 2026.
Design & Propulsion
- Role: Blue-water, multi-mission frontline combatant
- Propulsion:Combined Diesel or Gas (CODOG) system
- Diesel engine + gas turbine
- Each driving a Controllable Pitch Propeller (CPP)
- Automation: Advanced Integrated Platform Management System (IPMS) for efficient monitoring and control.
Weapons & Sensors Suite
- Missiles:
- BrahMos supersonic surface-to-surface missile
- Long Range Surface-to-Air Missiles (LRSAM) / Barak-8 (MRSAM)
- Guns & CIWS:
- 76 mm Super Rapid Gun Mount
- 30 mm and 12.7 mm close-in weapon systems
- Anti-Submarine Warfare:
- Lightweight torpedoes
- Indigenous Rocket Launchers (IRL)
- Sensors & EW:
- Multi-function radar (MF-STAR)
- Shakti Electronic Warfare Suite
- Airborne early-warning radar
- Surface surveillance radar
- Humsa-NG sonar
Operational Significance
- Capable of anti-surface, anti-air, and anti-submarine warfare.
- Enhanced stealth, survivability, firepower, and automation over earlier frigate classes.
- Reduces dependence on imports and strengthens India’s blue-water naval capabilities.
- Employment generation: ~4,000 direct and 10,000 indirect jobs.
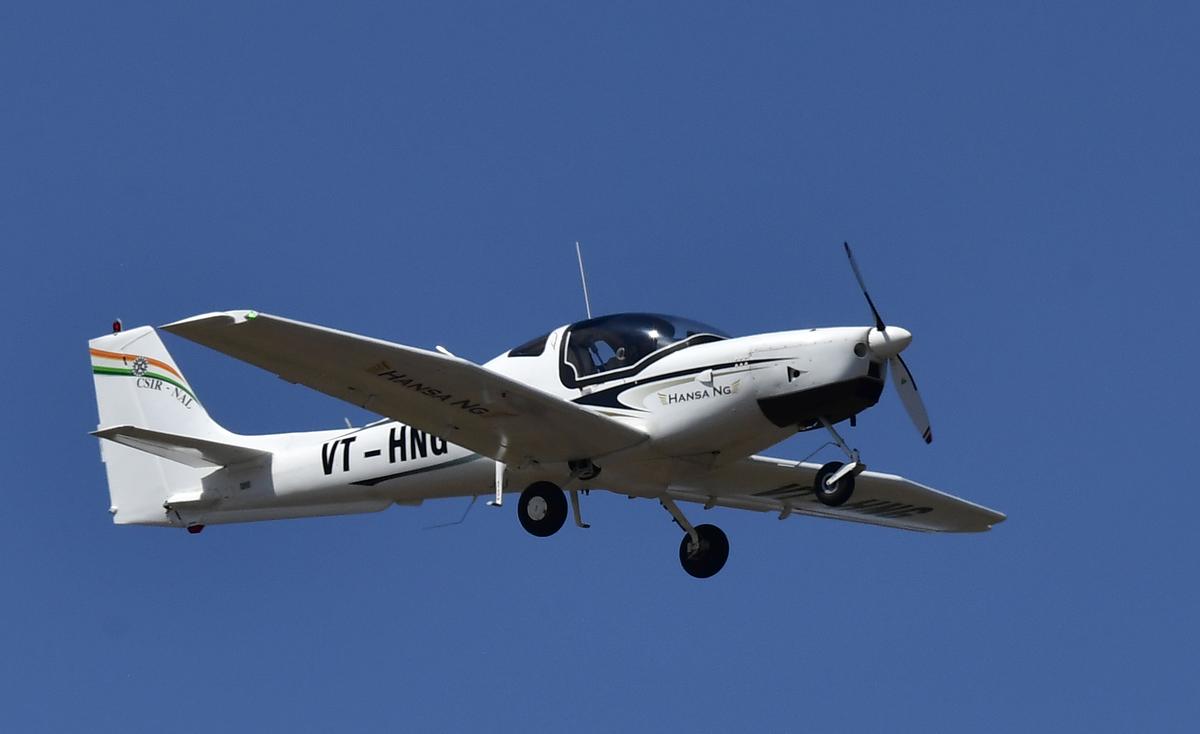
Hansa-3 NG Trainer Aircraft

- 01 Dec 2025
In News:
The CSIR–National Aerospace Laboratories (CSIR-NAL), Bengaluru, has launched the production-version of the indigenous Hansa-3 (NG) trainer aircraft, marking a significant step towards strengthening India’s self-reliance in civil aviation training and indigenous aircraft manufacturing.
About Hansa-3 Aircraft
- Type: Indigenous two-seat trainer aircraft
- Developer: CSIR-NAL
- Purpose: Basic / ab-initio flight training
- Primary Users: Flying clubs, pilot training academies, and civil aviation training institutions
Design & Construction
- Built entirely using fiberglass and carbon composite materials
- Advantages:
- High corrosion resistance
- Better damage tolerance
- Ease of repair and maintenance
- Lightweight airframe suited for repetitive training operations
Hansa-3 (NG – New Generation): Key Upgrades
The Hansa-3 NG is an advanced version of the earlier Hansa-3, incorporating modern avionics and performance improvements:
- Digital Glass Cockpit
- Replaces traditional analogue instruments
- Enhances situational awareness and training efficiency
- Increased Fuel Capacity
- Allows longer training sorties
- Improves aircraft endurance
- Improved Flight Characteristics
- Low stall speed
- Stable and predictable handling
- Ideal for first-time trainee pilots
- Training-Friendly Design
- Simple systems
- Forgiving flight envelope for beginners
Significance of Production-Grade Launch
- Transition from prototype to production-ready aircraft
- Boosts Atmanirbhar Bharat in civil aviation
- Reduces dependence on imported trainer aircraft
- Supports expansion of pilot training capacity in India
- Strengthens the civil aerospace ecosystem led by CSIR laboratories
3rd India-Indonesia Defence Ministers’ Dialogue

- 30 Nov 2025
In News:
India and Indonesia held the third India–Indonesia Defence Ministers’ Dialogue in New Delhi, co-chaired by Rajnath Singh, India’s Defence Minister, and Sjafrie Sjamsoeddin, the Defence Minister of Indonesia. The dialogue marked another step in deepening bilateral defence ties amid evolving regional security dynamics in the Indo-Pacific.
Context and Significance
The Indonesian Defence Minister’s visit reflects growing momentum in India–Indonesia defence engagement. It followed high-level interactions earlier in the year, including the Indonesian President’s visit to India, underscoring the strategic importance both countries attach to defence and security cooperation.
Key Areas of Discussion
1. Regional and Multilateral Security: The two sides reviewed regional security developments and discussed multilateral issues affecting the Indo-Pacific. They reaffirmed commitment to a free, open, inclusive, and rules-based Indo-Pacific, noting convergence between the ASEAN Outlook on the Indo-Pacific and India’s Indo-Pacific Oceans Initiative (IPOI).
2. Maritime Cooperation: Given Indonesia’s strategic geography overseeing key sea lanes such as the Malacca, Sunda, and Lombok Straits both sides agreed to enhance cooperation in maritime domain awareness, naval coordination, and regional maritime security. They also highlighted collaboration through multilateral forums like the Indian Ocean Rim Association.
3. Defence Industry and Technology Collaboration: Indonesia welcomed India’s proposal to establish a Joint Defence Industry Cooperation Committee. This mechanism aims to strengthen technology transfer, joint research and development, harmonisation of certification standards, and defence supply-chain linkages. Prospects such as the BrahMos missile deal and broader defence manufacturing collaboration were also noted.
4. Military-to-Military Engagements: The dialogue reviewed progress in joint exercises across the three services. Key engagements include Super Garuda Shield, Exercise Garuda Shakti (Army), Exercise Samudra Shakti (Navy), participation in MILAN naval exercises, and proposed air manoeuvre exercises, reflecting expanding operational interoperability.
Broader India–Indonesia Relations
Beyond defence, India and Indonesia share strong economic ties, with bilateral trade reaching USD 38.8 billion in 2022–23. Defence cooperation is increasingly viewed as a pillar supporting wider strategic, economic, and people-to-people relations.
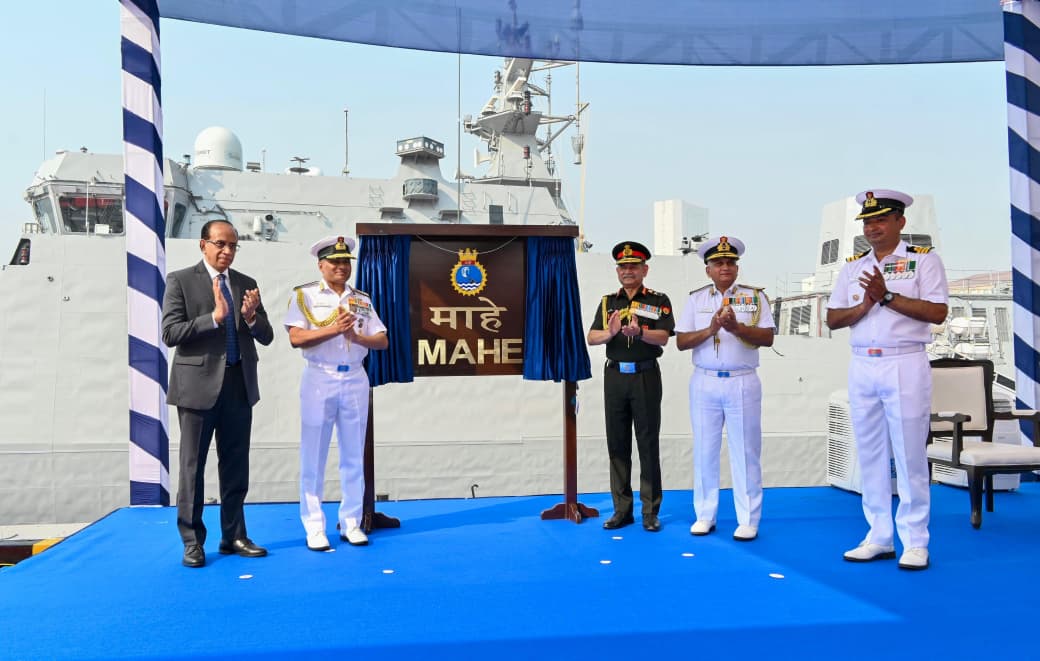
INS Mahe

- 28 Nov 2025
In News:
The Indian Navy commissioned INS Mahe, the first Mahe-class Anti-Submarine Warfare Shallow Water Craft (ASW-SWC), at the Naval Dockyard, Mumbai. With this induction, India has taken a significant step in strengthening its coastal and littoral anti-submarine warfare (ASW) capabilities under the Western Naval Command.
About INS Mahe
- Type: Anti-Submarine Warfare Shallow Water Craft (ASW-SWC)
- Class: Mahe-class (lead ship of eight vessels)
- Role: First line of coastal defence, designed to operate in shallow and near-shore waters
- Operational Command: Western Naval Command
INS Mahe is specially optimised to detect, track, and neutralise sub-surface threats in coastal regions where larger surface combatants face manoeuvrability constraints.
Design and Indigenous Content
- Designed & Built by: Cochin Shipyard Limited (CSL), Kochi
- Indigenisation: Over 80% indigenous content
- Industrial Ecosystem: Contributions from Bharat Electronics Limited, L&T Defence, Mahindra Defence Systems, NPOL, and more than 20 MSMEs
- A major milestone under Aatmanirbhar Bharat in naval shipbuilding
Key Features
- ASW Specialisation: Optimised for coastal and shallow water operations
- Advanced Combat Suite:
- Modern weapons
- High-precision sensors
- Secure and integrated communication systems
- Stealth & Endurance: Designed for prolonged operations in littoral waters
- Modern Machinery: Technologically advanced propulsion and integrated control systems
- Motto: “Silent Hunters” - reflecting stealth, vigilance, and readiness
Symbolism and Heritage
- Namesake: Historic coastal town of Mahe on the Malabar Coast
- Crest: Features the Urumi, the flexible sword of Kalaripayattu, symbolising agility and precision
- Mascot: Cheetah, representing speed and focus
Strategic Significance
- Boosts ASW Capability: Enhances India’s ability to counter submarine threats in littoral zones
- Strengthens Coastal Security Grid: Acts as the forward layer of a multi-tiered maritime defence architecture
- Force Multiplier: Integrates seamlessly with larger surface combatants, submarines, and naval aviation assets
- Indigenisation Push: Demonstrates India’s growing capacity to design, construct, and field complex naval combatants using domestic technology
Exercise Suryakiran

- 27 Nov 2025
In News:
India and Nepal are conducting the 19th edition of the bilateral military exercise Suryakiran from 25 November to 8 December in Pithoragarh, Uttarakhand. The exercise reflects the deep-rooted defence cooperation and operational coordination between the Indian Army and the Nepal Army.
About Exercise Suryakiran
- Nature: Bilateral, annual, battalion-level joint military exercise
- Participating Countries: India and Nepal
- Frequency & Venue: Conducted annually, alternately in India and Nepal
- Last Edition: 18th edition held at Saljhandi, Nepal (Dec 2024–Jan 2025)
Objectives
- Enhance operational synergy in jungle warfare and mountain warfare
- Strengthen cooperation in counter-terrorism operations
- Improve interoperability through integration of niche and modern technologies
- Exchange best practices, tactical doctrines, and operational experiences
Key Features
- High-Altitude & Jungle Warfare Training: Joint drills in forested and mountainous terrain, mirroring Himalayan operational conditions.
- Counter-Terrorism Modules: Includes cordon-and-search operations, room intervention, surveillance, and small-team tactics.
- Technology Integration: Use of modern surveillance systems, secure communications, drones, medical evacuation, and battlefield support tools.
- Comprehensive Participation: Battalion-sized contingents (around 300+ personnel) including specialists in aviation, medical, engineering, and high-altitude warfare.
- Professional Exchange: Platform for soldiers to share combat experiences, survival skills, and standard operating procedures.
Strategic Significance
- Reinforces long-standing military ties based on mutual trust, respect, and historical linkages.
- Helps standardise operational procedures and communication protocols for joint missions.
- Enhances preparedness for counter-terrorism, border security, and disaster response in the Himalayan region.
- Contributes to regional stability and shared commitment to peace and security.
HAMMER Precision Weapon System
- 27 Nov 2025
In News:
India and France have taken a major step in defence industrial cooperation with the signing of a Joint Venture Cooperation Agreement (JVCA) between Bharat Electronics Limited (BEL) and Safran Electronics & Defence (SED) for the manufacture of the HAMMER (Highly Agile Modular Munition Extended Range) precision-guided air-to-ground weapon system in India.
Key Highlights of the Joint Venture
- The proposed Joint Venture Company (JVC) will be incorporated in India as a private limited company with 50:50 shareholding between BEL and Safran.
- Manufacturing, supply, and maintenance of HAMMER will be localised to meet the operational requirements of the Indian Air Force and the Indian Navy, including integration with Rafale and Rafale Marine aircraft.
- Indigenisation will progressively rise to about 60%, covering key sub-assemblies, electronics, and mechanical components.
- Technology and production transfer will occur in phases, with BEL leading final assembly, testing, and quality assurance.
About HAMMER Precision Weapon System
- Type: Smart, precision-guided, air-to-surface weapon
- Developer: Originally developed by Safran (France)
- Configuration: Modular system comprising a guidance kit and a range-extension kit, which can be fitted onto standard general-purpose bombs of different weights.
Key Features
- High Precision: Multiple guidance options (GPS/INS, infrared, laser) enable accurate strikes on hardened targets such as bunkers, shelters, airstrips, and enemy infrastructure.
- Stand-off Capability: Effective strike range of up to ~70 km, allowing launch aircraft to remain outside hostile air-defence envelopes.
- High Agility: Optimised for mountainous and high-altitude terrain, making it suitable for areas like Ladakh.
- Platform Flexibility: Currently integrated with Rafale; planned integration with indigenous platforms like LCA Tejas.
Operational Background
- HAMMER was procured by the IAF under emergency procurement powers to quickly operationalise Rafale aircraft amid heightened security challenges, as it filled a capability gap for shorter-range precision strikes against hardened targets.
- Its selection was influenced by quicker availability and suitability for mountain warfare compared to alternative systems that would have required additional time and cost for integration.
Strategic Significance
- Make in India & Aatmanirbharta: The JV strengthens indigenous defence manufacturing and reduces long-term import dependence in critical precision weaponry.
- Enhanced Strike Capability: Improves India’s ability to conduct accurate, stand-off precision strikes in contested and high-risk environments.
- Cost and Time Efficiency: Local production lowers lifecycle costs, ensures faster availability, and supports sustained operational readiness.
- Industrial Ecosystem & Exports: Encourages technology absorption, skill development, and potential future export opportunities.
Coastal Security Exercise ‘Sagar Kavach’
- 24 Nov 2025
In News:
The biannual coastal security exercise ‘Sagar Kavach’ has commenced along the Tamil Nadu coast, covering Cuddalore and Villupuram districts, to test multi-agency preparedness against maritime security threats.
About ‘Sagar Kavach’
- Nature:‘Sagar Kavach’ is a biannual, multi-agency coastal security exercise conducted along India’s coastline.
- Conducted by:Indian Coast Guard (ICG)
Key Objectives
- Validate and refine Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs) for coastal security
- Identify vulnerabilities in coastal surveillance and response mechanisms
- Strengthen inter-agency coordination among maritime, security, and civil authorities
- Enhance readiness of coastal police and local administration
Key Features
- Frequency: Conducted twice a year across coastal States and island territories
- Threat Simulation:
- Deployment of ‘Red Force’ dummy intruders
- Mock infiltration and sabotage scenarios
- Operational Activities:
- Sea and coastal patrolling
- Boat and vessel inspections
- Harbour and port security checks
- Surveillance of vulnerable coastal stretches
- Coverage:
- Coastal villages
- Fishing harbours and ports
- Vital installations
- Railways, bus stations, and sensitive public infrastructure
- Capacity Building:
- Trains coastal police in intelligence gathering, interception, interrogation, and patrolling
- Tests response time and communication efficiency
- Integrated Approach:
- Combines surface assets, aerial surveillance, and communication networks
- Involves coordination between defence forces, paramilitary units, State police, intelligence agencies, and civil administration
Significance
- Strengthens India’s layered coastal security architecture, especially after lessons from past maritime attacks
- Enhances preparedness against non-traditional security threats such as terrorism and smuggling
- Builds local-level resilience by integrating coastal communities and police into national security efforts
- Reinforces India’s commitment to maritime security and coastal surveillance
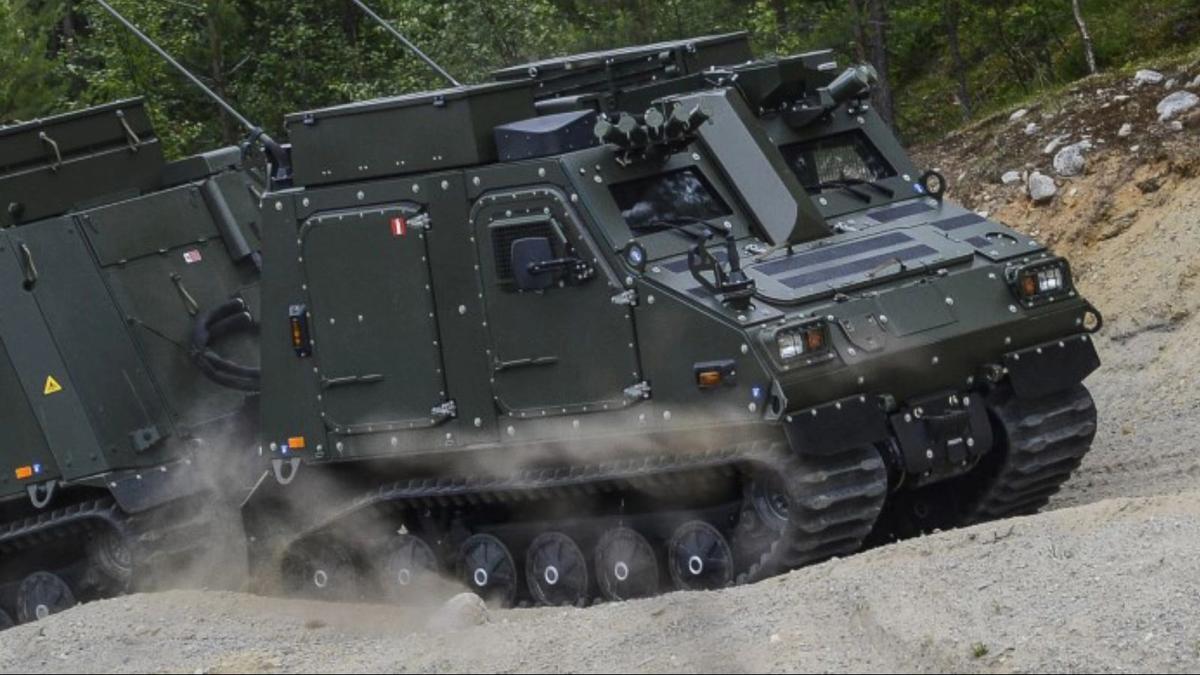
BvS10 Sindhu

- 21 Nov 2025
In News:
Infrastructure major Larsen & Toubro (L&T), in partnership with BAE Systems, has secured a contract from the Indian Army to supply BvS10 Sindhu, a specialised all-terrain armoured vehicle. The platform will be manufactured in India, strengthening indigenous defence production.
About BvS10 Sindhu
- Base Platform: BvS10 (Bandvagn S10), a proven articulated all-terrain vehicle used by several European militaries.
- Sindhu Variant: An upgraded, India-specific version adapted for the country’s terrain and climatic extremes.
- Manufacturing: To be produced by L&T at its Armoured Systems Complex, Hazira (Gujarat), with design and technical support from BAE Systems Hägglunds (Sweden), the original BvS10 manufacturer.
Design & Capabilities
- Articulated Configuration: Two connected vehicle sections improve mobility over terrain where conventional wheeled or tracked vehicles struggle.
- All-Terrain Performance: Optimised for high-altitude areas, deserts, marshlands, snow, and flood-prone regions.
- Amphibious Capability: Can operate in waterlogged and flooded environments, enhancing operational reach.
- Protection & Mobility: Armoured design balances crew protection with high mobility in adverse conditions.
Operational Flexibility
The BvS10 Sindhu can be reconfigured for multiple roles, including:
- Troop transport
- Command post
- Ambulance/medical evacuation
- Recovery and logistics support
- Weapon-armed variants
This modularity suits the diverse mission profiles of the Indian Army across varied theatres.
Global Usage (Base BvS10)
- In Service: Austria, France, Netherlands, Sweden, Ukraine, United Kingdom
- On Order / Selected: Germany; selected for the U.S. Army’s Cold Weather All-Terrain Vehicle (CATV) programme
This underscores the platform’s global acceptance and proven performance.
Industrial & Strategic Significance
- Make in India / Atmanirbhar Bharat: Indigenous manufacturing with global OEM support enhances self-reliance.
- Lifecycle Support: The contract includes integrated logistics support for deployment, maintenance, and sustainment.
- Capability Boost: Addresses mobility gaps in extreme and amphibious terrains, critical for border and disaster-response operations.
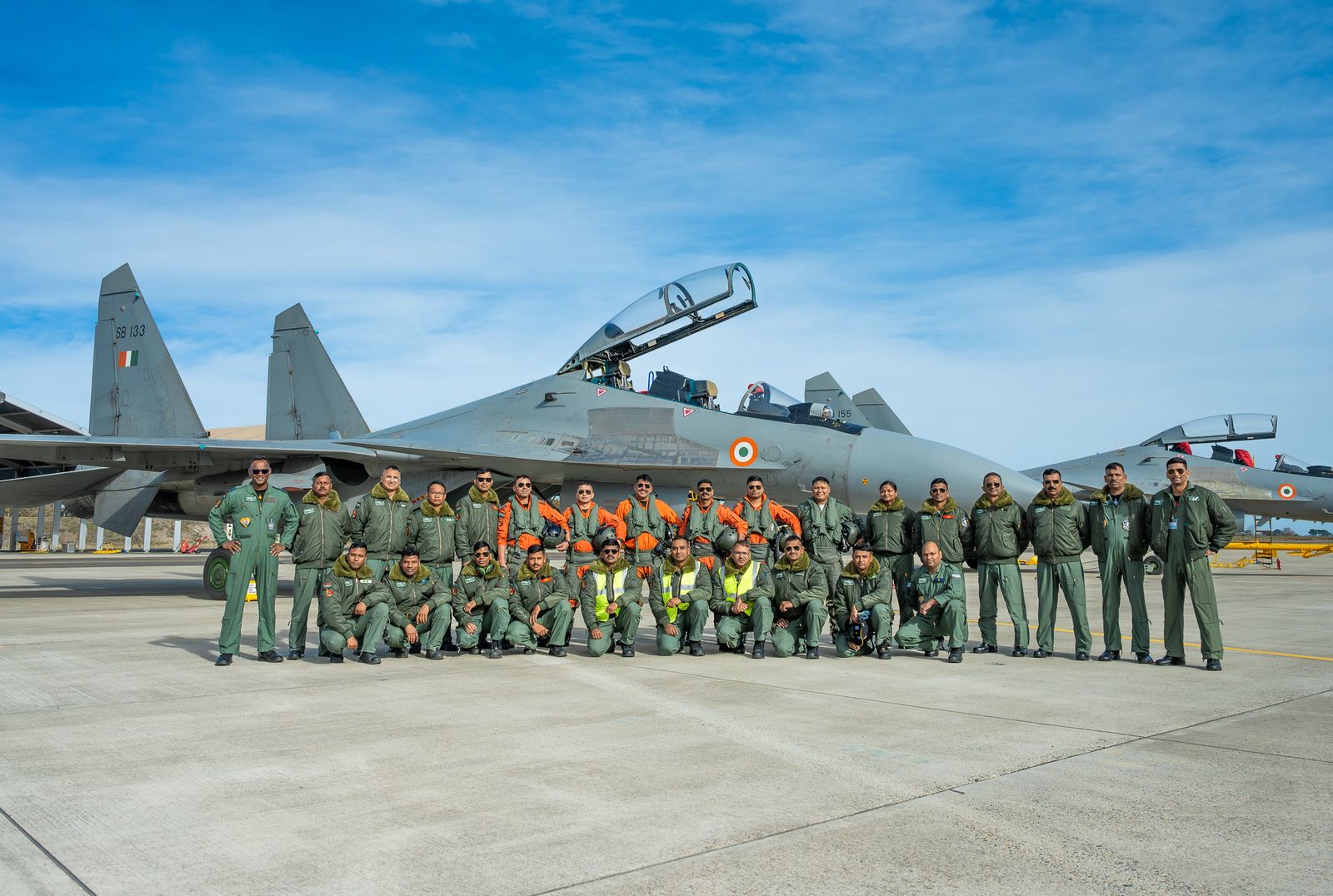
Exercise Garuda 2025

- 18 Nov 2025
In News:
The Indian Air Force (IAF) is participating in the 8th edition of Exercise Garuda, a bilateral air exercise with the French Air and Space Force (FASF), held at Mont-de-Marsan Air Base, France. The engagement reinforces operational cooperation and strategic partnership between India and France in the domain of air power.
About Exercise Garuda
- Type: Bilateral Indo–French Air Exercise
- Started: Early 2000s
- Edition: 8th (2025)
- Location: Mont-de-Marsan, France
Aim
Exercise Garuda aims to:
- Enhance interoperability between the IAF and FASF
- Refine air combat tactics and operational coordination
- Simulate realistic multi-threat scenarios
- Improve understanding of each other’s air operations and procedures
Indian Participation
The IAF has deployed:
- Su-30MKI multirole fighter aircraft
- C-17 Globemaster III for airlift support
- IL-78 mid-air refuelling aircraft for extended-range operations
Exercise Focus Areas
IAF’s Su-30MKI will operate alongside advanced French fighters in:
- Air-to-air combat missions
- Air defence operations
- Joint strike missions
- Large-force engagement scenarios
The training includes complex simulations to assess fighter manoeuvrability, situational awareness, networked operations, and air combat decision-making under realistic combat conditions.
Significance of Exercise Garuda
- Strengthens strategic defence cooperation between India and France
- Enhances interoperability and joint operational capability
- Facilitates exchange of:
- Flight safety and operational practices
- Combat training methodologies
- Best practices for mission planning and execution
Participation reflects the IAF’s ongoing engagement with friendly foreign air forces and highlights India’s commitment to collective security and international military cooperation.
Other Major India–France Military Exercises
|
Service |
Exercise |
Domain |
|
Navy |
Varuna |
Naval warfare |
|
Air Force |
Desert Knight-21 |
Air operations |
|
Army |
Shakti |
Counter-terror and joint ground operations |
Air-Sol Moyenne Portée-Renove (ASMPA-R)
- 18 Nov 2025
In News:
France recently released the first clear official images of its latest-generation ASMPA-R (Air-Sol Moyenne Portée–Renové) missile, following a successful test launch from a Rafale-M carrier-based fighter jet. The test marks the missile’s operational entry into France’s Naval Nuclear Aviation Force (FANu), strengthening the air-based leg of the country’s nuclear deterrent.
What is ASMPA-R?
- The ASMPA-R is a medium-range, supersonic, nuclear-capable air-to-surface cruise missile.
- It is the upgraded version of the ASMPA-A and belongs to the ASMP family developed by France since the 1980s.
- Integral to the Force de Frappe, France’s independent nuclear deterrence structure.
- Used by both France’s Strategic Air Forces (FAS) and Naval Nuclear Aviation Force (FANu).
Key Features of ASMPA-R
1. Propulsion & Speed
- Ramjet-powered missile with dual air intakes.
- Capable of sustained supersonic flight up to Mach 3.
- Uses a solid-fuel booster at launch before ramjet ignition.
2. Range
- Approx. 600 km (extended from 500 km in ASMPA-A).
- Enables stand-off launches beyond enemy air-defense zones.
3. Warhead
- Carries the TNA (Tête NucléaireAéroportée) nuclear warhead.
- A dial-a-yield system, with adjustable yields from:
- 100 kilotons (minimum)
- 300 kilotons (maximum)
4. Design Updates
- Improved aerodynamics and updated tail fin configuration compared to ASMPA-A:
- Larger fins at the rear
- Smaller fins at the front
Evolution of the ASMP Family
|
Variant |
Service Entry |
Range |
Notes |
|
ASMP |
1986 |
300 km |
Replaced older gravity nuclear bombs |
|
ASMPA-A |
2009 |
500 km |
Modernized, improved accuracy |
|
ASMPA-R |
2023–25 |
600 km |
Latest version, improved reliability and range |
The ASMP system was originally developed by MBDA, selected over rival turbojet concepts for superior survivability and penetration capability.
Launch Platforms
- Rafale (Air Force)
- Rafale-M (Carrier-based variant used on Charles de Gaulle aircraft carrier)
Its integration with the Rafale-M enhances France’s ability to deliver nuclear strikes from both land and sea, reinforcing the nuclear dyad.
Geopolitical Significance
- The ASMPA-R strengthens France’s strategic independence within Europe.
- Permits deep-strike capability from aircraft carriers, extending deterrence beyond national borders.
- Aligns with French ambitions to:
- Modernize nuclear capabilities under the Military Programming Law 2024–2030
- Provide a potential “nuclear umbrella” for Europe
- Counter evolving missile and nuclear tests by rival powers (Russia, China, Pakistan)
Man-Portable Autonomous Underwater Vehicles
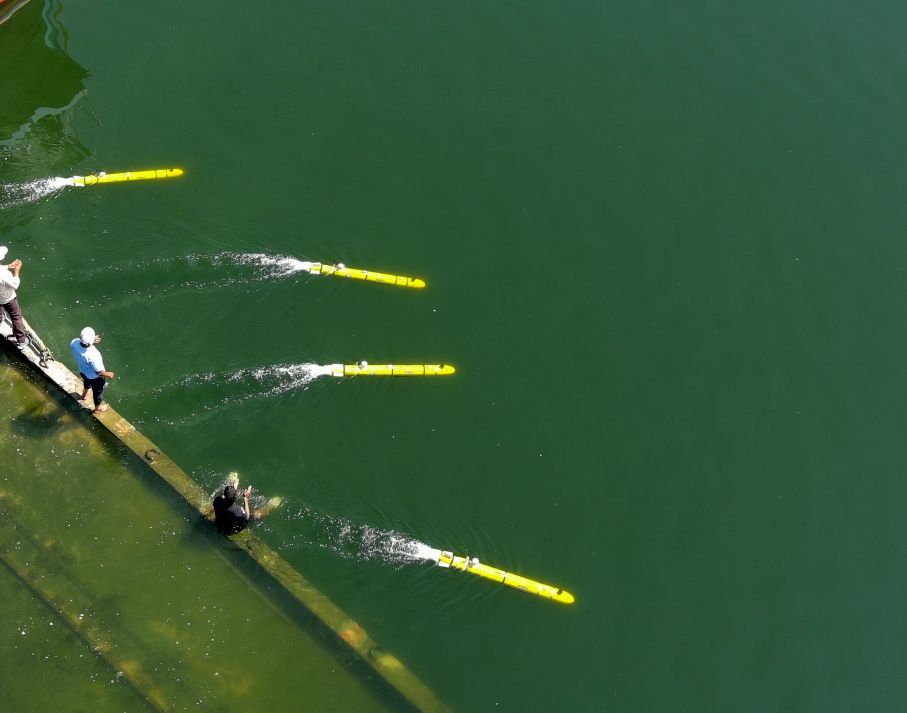

- 17 Nov 2025
In News:
The Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO) has successfully developed a new generation of Man-Portable Autonomous Underwater Vehicles (MP-AUVs) for mine countermeasure missions. These systems have been designed by the Naval Science & Technological Laboratory (NSTL), Visakhapatnam, a premier DRDO establishment responsible for underwater naval systems. MP-AUVs mark a major step in enhancing India’s underwater surveillance and mine-neutralisation capability.
The MP-AUV system comprises multiple autonomous underwater vehicles, each equipped with advanced sensors for underwater mine detection.
Primary payloads include:
- Side Scan Sonar – for seabed mapping and mine-like object detection
- Underwater Cameras – for visual identification and classification
These vehicles incorporate deep learning-based target recognition algorithms, enabling autonomous classification of underwater threats. This reduces operator workload, enhances accuracy, and shortens mission duration. The system also integrates a robust underwater acoustic communication network, allowing AUV-to-AUV data exchange and enabling networked operations. This improves situational awareness and allows coordinated search patterns without direct human control.
The MP-AUV design prioritisesrapid response capability and low logistical footprint, making it suitable for deployment from small naval vessels or shore platforms. Its man-portable nature allows fast mobilisation and reduces operational risk by minimising diver involvement in hazardous minefields. Field trials conducted at NSTL/harbour sites have successfully validated key performance parameters, including detection accuracy, communication reliability and autonomous navigation.
This development aligns closely with India's push for indigenous defence technologies and intelligent autonomous systems. It enhances operational readiness in underwater mine warfare and supports the broader goal of strengthening maritime security. DRDO, headquartered in New Delhi and established in 1958, continues to lead India’s indigenous defence R&D, focusing on strategic capabilities and advanced naval systems.
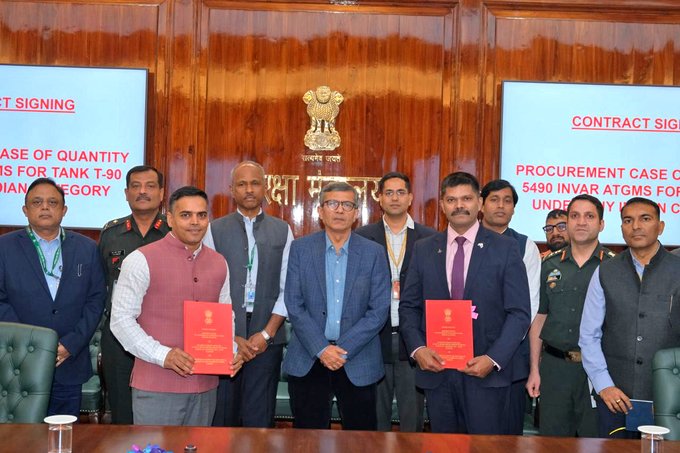
INVAR Missile

- 17 Nov 2025
In News:
The Ministry of Defence has recently signed a ?2,095 crore agreement with Bharat Dynamics Limited (BDL) for the procurement of INVAR Anti-Tank Guided Missiles (ATGMs). The acquisition aims to enhance the lethality and combat effectiveness of T-90 main battle tanks in the Indian Army.
About INVAR Missile
- Type: Laser-guided Anti-Tank Guided Missile (ATGM)
- Launch Platform: Fired from the 125 mm gun barrel of T-90 tanks
- Origin: Developed by Rosoboronexport (Russia); produced in India under licence by BDL
- Category: Procured under the ‘Buy (Indian)’ category to promote domestic defence capability and align with the goal of Aatmanirbhar Bharat.
Key Features
1. Guidance and Accuracy
- Uses semi-automatic laser beam-riding guidance.
- High resistance to electronic jamming.
- Offers high hit probability against fortified armour.
2. Penetration Capability
- Equipped with a tandem warhead designed to defeat:
- Explosive Reactive Armour (ERA) on modern tanks
- Both stationary and moving targets (up to 70 km/hr)
3. Range and Performance
- Effective range: Up to 5 km
- Calibre: 125 mm
- Weight: 17.2 kg
- Length:
- Missile: 695 mm
- Throwing device: 395 mm
4. Operational Integration
- Fired directly through the T-90 tank’s gun tube.
- Guidance and tracking through the tank’s integrated fire-control optics.
Significance of the Procurement
1. Enhanced Mechanised Warfare Capability
- Strengthens India’s ability to neutralise heavily armoured enemy platforms.
- Provides precision strike capability at extended ranges.
2. Boost to Defence Manufacturing
- Encourages utilisation of DPSU expertise, primarily BDL.
- Supports development of niche defence technologies by Indian industry.
3. Strategic Impact
- Improves India’s frontline preparedness along sensitive borders.
- Modernises the equipment profile of mechanised forces.
Omen Drone

- 16 Nov 2025
In News:
The United States and the United Arab Emirates announced a new defence cooperation initiative involving joint capability development during the U.S. President’s visit to Abu Dhabi.As part of this partnership, American defence technology firm Anduril Industries and the UAE’s state-owned EDGE Group are co-developing a new AI-enabled Omen drone at a research facility in Abu Dhabi.
Omen Drone: Overview
- The Omen drone is an advanced, hybrid-electric, tail-sitting vertical takeoff and landing (VTOL) unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV).
- It is being developed under a joint U.S.–UAE defence technology initiative, reflecting deeper bilateral defence ties.
- Development Centre:
- A dedicated 50,000 sq ft (≈4,645 sqm) research and production facility has been established in Abu Dhabi.
- Joint development integrates:
- U.S. high-tech autonomous systems expertise
- UAE’s expanding defence manufacturing ecosystem
Key Features of Omen Drone
- Tail-sitting VTOL Design
- Takes off and lands vertically in a tail-sitting position (approx. 10 feet in height).
- Eliminates the need for runways or large launch infrastructure.
- Enables deployment from rugged terrain or forward operating bases.
- Hybrid-electric Propulsion
- Combines electric and combustion systems for:
- Extended endurance
- Greater operational range
- Quieter operation compared to fully combustion UAVs
- Combines electric and combustion systems for:
- Aerodynamic Configuration
- Long, slender main wings mounted toward the rear.
- Canard foreplanes near the nose for stability.
- Twin-boom tail extending from each wing nacelle.
- Dual Flight Mode: Capable of:
- Hovering like a rotorcraft
- Transitioning to fixed-wing flight for longer and faster missions
This hybrid ability makes it highly versatile across different mission profiles.
- Compact, Modular, and Portable
- Foldable and lightweight design.
- Can be carried and assembled by a two-person team.
- Supports multiple payload options due to open architecture.
Operational Roles and Mission Applications
The Omen drone is designed for both military and civilian use-cases.
Military Roles
- Maritime surveillance
- Border security
- Persistent intelligence, surveillance, and reconnaissance (ISR)
- Monitoring choke points and coastal zones
- Complementing larger UAV systems in tactical operations
Civilian/Non-military Roles
- Critical infrastructure protection
- Search and rescue support
- Communication relay in remote areas
The modular configuration allows integration of:
- Electro-optical (EO) sensors
- Infrared (IR) sensors
- Communication and data-link systems
Geopolitical and Strategic Significance
- Represents deepening US–UAE defence cooperation through co-development, not just arms transfers.
- Shows the UAE’s increasing focus on domestic defence R&D and manufacturing.
- Strengthens U.S. strategic presence and influence in the Gulf region.
- Demonstrates the growing role of AI, autonomy, and hybrid propulsion in next-generation unmanned systems.
- Reflects a broader defence trend of modular, multi-role drones replacing older single-purpose platforms.
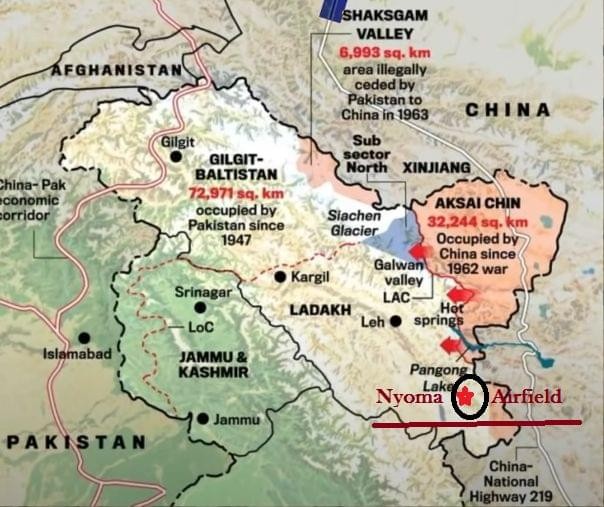
Nyoma Air Base Operationalised in Eastern Ladakh
- 15 Nov 2025
In News:
The Indian Air Force (IAF) has formally operationalised the Nyoma Air Base in Eastern Ladakh after Air Chief Marshal A.P. Singh successfully landed a C-130J aircraft on its newly completed runway. The airbase is now one of the world’s highest fully operational military airfields, marking a major milestone in India’s border infrastructure modernisation along the Line of Actual Control (LAC) with China.
Location and Geography
- Situated at: Mudh-Nyoma, Leh district, Ladakh
- Altitude: ~13,700 feet
- Distance from LAC: About 23-30 km
- Located near:
- Southern bank of Pangong Tso
- Northern bank of the Indus River
- Strategic valleys of Hanle, Chumar, and Demchok
- Terrain:
- High-altitude cold desert
- Harsh temperatures reaching –30°C
- Construction possible only for limited months each year
Historical Background
- Initially built as a mud airstrip in 1962, remained unused for decades.
- Reactivated in 2009 with the landing of an AN-32 aircraft.
- After the 2020 India-China standoff, Nyoma ALG supported:
- C-130J
- AN-32
- Apache
- Chinook
helicopter and aircraft operations.
- In 2023, the BRO began converting the airstrip into a full airbase under Project Himank.
- Completed in 2024 at a cost of ?218 crore, led significantly by women officers of the BRO.
- Fully operationalised in November 2025, after installation of hangars, ATC, hardstanding, and allied facilities.
Infrastructure and Capability
Nyoma Air Base now includes:
- 2.7-km paved runway, capable of handling:
- Fighter aircraft
- Heavy-lift transport aircraft
- Helicopter operations
- Supporting infrastructure:
- Hangars
- Air Traffic Control (ATC)
- Hard surfaces for aircraft parking
- Logistics and troop accommodation
- Its flatter valley location makes operations easier and quicker compared to Leh.
Strategic Importance
- Enhanced Operational Reach
- Enables rapid deployment of troops and equipment near the LAC.
- Allows quicker launch of interdiction strikes if required.
- Strengthens high-altitude air mobility in the Indus–Pangong–Hanle corridor.
- Bolsters Border Infrastructure
- Complements existing airfields at:Leh, Kargil, Thoise, Daulet Beg Oldie, and Fukche
- Part of India’s larger infrastructure push post-2020, including new roads, bridges, tunnels, helipads, and logistics hubs.
- Strategic Deterrence Against China
- Improves surveillance and presence along a sensitive frontier.
- Counters China’s rapid infrastructure development along its side of the LAC, including new airbases, missile sites, bunkers, and underground storage facilities.
- Supports Ground Operations
- Facilitates sustained patrols in areas such as Demchok and Depsang, where the Army resumed patrolling in 2024 after a long pause.
- Helps maintain operational readiness in a “stable but sensitive” LAC environment.
- Strengthens India’s long-term defensive posture and contributes to overall border stability.
Project-76

- 12 Nov 2025
In News:
Project-76 is a flagship indigenous defence initiative under which India aims to design and develop its first fully indigenous conventional diesel-electric attack submarine. The project reflects India’s growing emphasis on self-reliance in defence manufacturing and strengthening undersea warfare capabilities.
What is Project-76?
- Project-76 is being conceptualised by the Warship Design Bureau of the Indian Navy.
- It envisages the construction of 12 conventional submarines in the long term.
- These submarines will be diesel-electric attack submarines equipped with Air Independent Propulsion (AIP) systems.
- Expected submerged displacement: around 3,000 tonnes, placing them in a higher capability class than earlier foreign-designed submarines.
Key Technological Features
- Air Independent Propulsion (AIP): Enhances underwater endurance and stealth by reducing the need to surface frequently.
- Indigenous Weapon Control System: Reduces dependence on foreign Original Equipment Manufacturers (OEMs).
- Lithium-ion batteries: Improve energy density, endurance, and operational efficiency compared to traditional lead-acid batteries.
- Incorporation of design learnings from:
- Project-75 (French Scorpène-class submarines)
- Project-751 (India) (German–Spanish design lineage)
Strategic Significance
- Project-76 is intended to replace and succeed the Sindhughosh (Kilo) class submarines, which form a major part of India’s current conventional submarine fleet.
- It will help the Indian Navy maintain a robust 3,000-ton-class submarine force, critical for:
- Sea denial operations
- Protection of Sea Lines of Communication (SLOCs)
- Deterrence in the Indo-Pacific region
- The project marks a shift from licensed production to indigenous design ownership.
Role of DRDO
- The Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO) has received approval from the Ministry of Defence to undertake a preliminary design study for Project-76.
- This study will define:
- Technical contours
- Feasibility and timelines
- Cost and capability parameters
- The study is expected to take about one year, after which a proposal will be submitted to the Cabinet Committee on Security (CCS) for formal project sanction.
- Project-76 builds upon experience gained from the Advanced Technology Vessel (ATV) programme, under which the Arihant-class nuclear ballistic missile submarines (SSBNs) were developed, and ongoing work on nuclear-powered attack submarines (SSNs).
INS Ikshak

- 10 Nov 2025
In News:
The commissioning of INS Ikshak marks a significant milestone in India’s maritime capability enhancement and defence indigenisation. As the third vessel of the Survey Vessel (Large) – SVL (Sandhayak) class, Ikshak represents a major boost to the Indian Navy’s hydrographic survey and charting infrastructure, which is critical for maritime safety, naval operations, and the blue economy.
Background and Commissioning
INS Ikshak is scheduled to be commissioned into the Indian Navy on 6 November 2025 at Naval Base, Kochi, in the presence of the Chief of Naval Staff, Admiral Dinesh K. Tripathi. Notably, it will be the first SVL-class ship to be based at the Southern Naval Command, enhancing hydrographic coverage in India’s southern maritime domain.
The vessel has been constructed by Garden Reach Shipbuilders and Engineers (GRSE) Ltd., Kolkata, one of India’s premier defence public sector shipyards. With over 80% indigenous content, Ikshak stands as a concrete outcome of the Aatmanirbhar Bharat initiative, achieved through close collaboration between GRSE and a large network of Indian Micro, Small and Medium Enterprises (MSMEs).
The name Ikshak, meaning “Guide” in Sanskrit, symbolically reflects the ship’s role in guiding safe navigation and charting uncharted or poorly mapped waters.
Design, Specifications and Capabilities
INS Ikshak is a technologically advanced hydrographic survey vessel designed for full-scale coastal and deep-water surveys of ports, harbours, and navigational channels. With a length of about 110 metres, a displacement of around 3,300 tonnes, and accommodation for over 230 personnel, the ship is built for long-duration and complex survey missions.
The vessel is equipped with state-of-the-art hydrographic and oceanographic systems, including:
- High-resolution multi-beam echo sounder and side-scan sonar for seabed mapping,
- Autonomous Underwater Vehicle (AUV) capable of operating up to 1,000 m depth with extended endurance,
- Remotely Operated Vehicle (ROV) for underwater inspection,
- Four Survey Motor Boats (SMBs) for shallow-water and near-shore surveys.
In addition, Ikshak features a helicopter deck, enhancing its operational reach for logistics, surveillance, and multi-domain missions. It is powered by diesel engines with an Integrated Platform Management System, bow and stern thrusters for precision manoeuvring, and a maximum speed of about 18 knots.
A unique feature of the SVL class is its dual-use capability. INS Ikshak can be converted into a 40-bed hospital ship, equipped with an operation theatre, laboratory, blood bank, and isolation wards, making it highly valuable for Humanitarian Assistance and Disaster Relief (HADR) operations.
Strategic and Economic Significance
The commissioning of INS Ikshak significantly strengthens India’s hydrographic excellence. Accurate hydrographic data and nautical charts are vital for:
- Safe navigation of commercial and naval vessels,
- Port and harbour development,
- Coastal security and naval planning,
- Seabed mapping for undersea cables, offshore energy, and marine resources.
The data generated by Ikshak will support the National Hydrographic Office and also contribute to India’s role as a regional hydrographic service provider, assisting friendly countries such as Mauritius, Sri Lanka, Bangladesh, and Myanmar.
From a strategic perspective, the ship enhances maritime domain awareness and underpins India’s ability to operate effectively across its vast maritime frontiers. From an economic standpoint, it supports the Blue Economy, facilitating sustainable use of ocean resources, port-led development, and marine infrastructure expansion.
Burevestnik Missile

- 04 Nov 2025
In News:
Russia has announced the successful testing of its Burevestnik nuclear-powered, nuclear-capable cruise missile, significantly escalating global concerns regarding a renewed nuclear arms race. The missile, known in Russia as 9M730 Burevestnik (“Storm Petrel”), is part of a new class of strategic weapons first unveiled in 2018.
About the Burevestnik Missile
- Type: Ground-launched, low-flying cruise missile.
- Capabilities:
- Nuclear-powered propulsion system.
- Nuclear warhead–capable.
- Designed for unlimited range and unpredictable flight trajectory.
- NATO Code Name: SSC-X-9 Skyfall.
- Developer: Russia.
- Introduced: One of six new strategic weapons announced by President Putin in 2018.
Key Features
1. Nuclear Propulsion System
- Powered by a miniaturised nuclear reactor.
- Reactor heats incoming air to generate thrust — replacing traditional chemical fuel.
- Enables theoretically unlimited flight time, constrained only by material durability and guidance systems.
- Offers the ability to loiter for days and strike from unexpected directions.
2. Long Range & Stealth
- Russia claims a test in 2023/2025 achieved:
- 14,000 km travel
- 15 hours of flight
- Low-altitude flight path makes detection by radar extremely difficult.
- Unpredictable trajectory designed to defeat missile defence systems.
3. Strategic Role
- Intended as a second-strike or surprise-attack weapon that can bypass US and NATO missile shields.
- Falls outside current New START definitions, as it is neither an ICBM, SLBM, nor heavy bomber.
Technical Background
- Nuclear-powered missiles were previously explored under the 1960s US Project Pluto (SLAM) but abandoned due to extreme safety risks.
- According to the Nuclear Threat Initiative (NTI), the Burevestnik uses a compact reactor similar in concept to nuclear ramjet technology.
Arms Control Context – New START Treaty
- New START Treaty (effective 2011, extended to 2026) limits deployed strategic nuclear weapons of the US and Russia.
- Russia suspended participation in February 2023.
- The Burevestnik is not restricted under New START, as it represents a new category of strategic cruise missile not covered under existing treaty definitions.
- Russia’s testing signals an attempt to sidestep treaty limits and intensify the nuclear competition.
Exercise 'Poorvi Prachand Prahar

- 04 Nov 2025
In News:
India is set to conduct the tri-service military exercise ‘Poorvi Prachand Prahar’ in the high-altitude terrain of Mechuka, Arunachal Pradesh. The drill represents India’s continued push toward jointness, interoperability, and multi-domain military readiness along the eastern sector.
About the Exercise
- Type: Tri-service exercise involving the Army, Navy, and Air Force.
- Location: Mechuka, a strategically significant forward area in Arunachal Pradesh.
- Nature: Designed as a forward-looking, multi-domain integration exercise.
Objectives
- Enhance warfighting capabilities under realistic operational conditions.
- Promote technological adaptation and the use of emerging platforms.
- Improve interoperability among the three services for integrated operations.
- Strengthen situational awareness and joint command-and-control mechanisms.
- Validate coordinated responses across land, air, and maritime domains.
Key Features
- Employment of:
- Special Forces
- Unmanned systems (UAVs and remote platforms)
- Precision weapon systems
- Networked operations centres
- Execution under rugged, high-altitude, and extreme-climate conditions.
- Testing of revised tactics, techniques, and procedures (TTPs) to improve combat agility and rapid response.
Strategic Importance
- Demonstrates India’s commitment to strengthening joint military preparedness along sensitive border regions.
- Enhances the ability to conduct synchronised, multi-domain operations in future conflicts.
- Integrates modern technologies to support real-time decision-making and network-centric warfare.
Background
‘Poorvi Prachand Prahar’ builds on earlier tri-service drills:
- ‘Bhala Prahar’ – 2023
- ‘Poorvi Prahar’ – 2024
Together, these exercises represent India’s broader drive toward theaterisation, integrated commands, and enhanced mission readiness.
Dhvani Hypersonic Missile
- 03 Nov 2025
In News:
The Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO) is preparing for the first test of Dhvani, India’s next-generation hypersonic missile system. Its development marks a major advancement in India’s indigenous strategic and aerospace capabilities, placing the country among a select group working on Hypersonic Glide Vehicle (HGV) technology.
What is Dhvani?
- Dhvani is an upcoming hypersonic missile being developed by DRDO.
- It is designed as a Hypersonic Glide Vehicle (HGV), enabling high-speed, maneuverable flight at hypersonic speed (greater than Mach 5 or approx. 7,400 km/h).
- The system departs from conventional ballistic or cruise missile trajectories by:
- Being launched to very high altitudes, and
- Then gliding at hypersonic speeds toward the target with significant maneuvering capability.
This flight profile complicates detection and interception by most existing missile defence systems.
Key Technical Features
1. Speed & Range
- Expected to fly at Mach 5–6+.
- Estimated operating range: 6,000–10,000 km (long-range strategic class).
2. Hypersonic Glide Vehicle Design
- Blended wing–body configuration
- Approx. 9 m length
- Approx. 2.5 m width
- Optimized for lift generation and maneuverability during hypersonic glide.
3. Thermal Protection System
- Uses ultra-high-temperature ceramic composites.
- Can withstand 2,000–3,000°C generated during atmospheric re-entry and sustained hypersonic flight.
4. Stealth Features
- Stealth-shaped geometry with:
- Angled surfaces
- Smooth contours
- Intended to reduce radar cross-section (RCS) and enhance survivability against surveillance systems.
5. Guidance & Precision: Designed to strike both land and maritime targets with high accuracy.
Technology Background
- Dhvani builds on technologies proven in the Hypersonic Technology Demonstrator Vehicle (HSTDV), including:
- Scramjet propulsion research
- Thermal shielding systems
- High-temperature material development
The success of HSTDV provided DRDO the platform to develop operational HGV systems such as Dhvani.
Notice to Airmen (NOTAM)

- 27 Oct 2025
In News:
India has recently issued a Notice to Airmen (NOTAM) for a large-scale tri-services military exercise, “Ex Trishul,” scheduled along the Pakistan border. The announcement highlights India’s focus on joint operational preparedness, self-reliance, and technological innovation in defence.
About Notice to Airmen (NOTAM)
- Notice to Airmen (NOTAM), also known as Notice to Air Missions, is an official notification issued by national aviation authorities to inform airspace users about temporary or permanent changes that may affect flight operations.
- Purpose: NOTAMs ensure flight safety by providing timely information about:
- Changes in aeronautical facilities or services
- Temporary airspace restrictions
- Hazards or obstacles along flight paths
- Military activities, such as exercises or missile tests
They are critical for pilots, air traffic controllers, and flight planners, allowing them to modify flight paths or schedules to ensure operational safety.
Common Reasons for Issuing NOTAMs
- Airshows, parachute jumps, or glider operations
- VIP movements (e.g., heads of state)
- Runway or taxiway closures
- Unserviceable navigational aids or airport lighting
- Construction activities or temporary obstacles near airfields
- Military exercises involving restricted or closed airspace
NOTAMs are disseminated rapidly via aeronautical communication systems, online aviation portals, and electronic flight planning tools, enabling real-time updates for all stakeholders.
India’s Recent NOTAM: Context and Significance
The recent NOTAM covers a large segment of India’s western frontier, extending up to 28,000 feet, indicating one of the largest joint operational drills in recent years. Satellite imagery has highlighted the vast scale of the restricted airspace, reflecting India’s intent to conduct multi-domain, tri-service coordination along the Pakistan border.
This development follows Operation Sindoor (May 2025)—a precision air campaign against Pakistan’s terror infrastructure launched in response to the Pahalgam terror attack (April 2025). The operation neutralized over 100 terrorists, marking one of the most intense India–Pakistan military confrontations in decades.
About Exercise Trishul
Exercise Trishul (Ex Trishul) is a tri-services military exercise involving the Indian Army, Navy, and Air Force. It aims to strengthen jointness, operational integration, and technological innovation, aligning with the government’s JAI Vision—Jointness, Aatmanirbharta, and Innovation.
Objectives
- To enhance inter-service coordination in high-tempo, multi-domain operations.
- To test indigenous systems and weapons platforms developed under the Aatmanirbhar Bharat initiative.
- To refine tactics, techniques, and procedures (TTPs) suited to emerging hybrid and asymmetric threats.
Key Operational Components
- Joint Operations:
- Coordinated manoeuvres across desert, creek, and coastal sectors, led by Southern Command.
- Amphibious operations off the Saurashtra coast, integrating Navy and Army assets.
- Air defence missions, reconnaissance, and electronic warfare (EW) exercises by the Air Force.
- Multi-Domain Integration:
- Exercises in Intelligence, Surveillance, and Reconnaissance (ISR) networks.
- Deployment of cyber warfare and space-enabled systems.
- Incorporation of Artificial Intelligence–based decision support and digital command systems.
- Indigenous Focus:
- Use of home-grown technologies in sensors, communication networks, and combat systems.
- Demonstrates the operational maturity of India’s defence manufacturing ecosystem.
Mahe- Anti-Submarine Warfare Shallow Water Craft

- 27 Oct 2025
In News:
The Indian Navy has recently received ‘Mahe’, the first of eight Anti-Submarine Warfare Shallow Water Crafts (ASW SWCs), built indigenously by Cochin Shipyard Limited (CSL), Kochi. The induction marks a major step towards bolstering India’s littoral (coastal) defence capabilities and advancing the vision of Aatmanirbhar Bharat in naval shipbuilding.
About Mahe – ASW Shallow Water Craft
- Builder: Cochin Shipyard Limited (CSL), Kochi
- Delivered to: Indian Navy
- Named after:Mahe, a historic port town in the Union Territory of Puducherry, symbolizing India’s rich maritime heritage.
- Classification: Designed and constructed under the rules of Det Norske Veritas (DNV) classification society.
- Displacement: Around 1,100 tons
- Length: Approximately 78 metres
- Indigenous Content: Over 80%, showcasing India’s growing self-reliance in naval design and shipbuilding.
Design and Features
- Advanced Warfare Capabilities
- Equipped with torpedoes and multi-functional anti-submarine rockets.
- Integrated radar and sonar systems for precise detection and engagement of underwater threats.
- Designed for Anti-Submarine Warfare (ASW) operations in shallow coastal waters.
- Operational Flexibility
- Capable of underwater surveillance, mine-laying operations, and Low Intensity Maritime Operations (LIMO).
- Suitable for coastal defence, escort missions, and search and rescue operations in littoral zones.
- Sustainability and Efficiency
- Compact yet powerful platform for quick maneuverability in shallow regions.
- Built using modern shipbuilding technologies, ensuring durability, stealth, and operational efficiency.
Strategic Significance
- Enhancing ASW Capabilities:The induction of Mahe will significantly strengthen India’s anti-submarine warfare capacity in coastal waters, enabling faster response to sub-surface threats from enemy submarines or unmanned underwater vehicles.
- Maritime Security:Strengthens surveillance and security along India’s vast 7,500 km coastline, ensuring greater control over sea lines of communication (SLOCs) and exclusive economic zones (EEZs).
- Boost to Aatmanirbhar Bharat:The vessel, with more than 80% indigenous components, reflects the Make in India initiative’s success in the defence manufacturing sector. It reinforces India’s ambition to be a net security provider in the Indian Ocean Region (IOR).
- Support to Blue Water Aspirations:While designed for shallow waters, the ASW SWC fleet complements India’s blue-water naval capability by securing coastal zones — the first line of maritime defence.
About Cochin Shipyard Limited (CSL)
- Established: 1972
- Location: Kochi, Kerala
- Ownership: Under the Ministry of Ports, Shipping, and Waterways
- CSL has emerged as one of India’s premier shipbuilding and repair facilities, with successful projects like:
- INS Vikrant (India’s first indigenous aircraft carrier)
- ASW Shallow Water Craft series
Project Arunank

- 27 Oct 2025
In News:
Project Arunank of the Border Roads Organisation (BRO) recently celebrated its 18th Raising Day at Naharlagun, marking over 17 years of sustained infrastructure development in Arunachal Pradesh’s remote and strategic regions.
About Project Arunank
- Launched: 2008
- Implementing Agency: Border Roads Organisation (BRO), under the Ministry of Defence.
- Name Origin: Derived from the state’s name — Arunachal Pradesh.
- Objective:To enhance road connectivity in remote valleys and forward areas of Arunachal Pradesh, supporting both civilian access and the operational needs of the Indian Armed Forces.
Key Achievements
- Strategic Road Development
- Constructed and maintained over 696 km of roads and 1.18 km of major bridges across the state.
- Completed the 278 km Hapoli–Sarli–Huri Road, which was blacktopped for the first time since Independence, connecting the remote KurungKumey district — a major milestone in post-Independence connectivity.
- Technological Innovations
- Adopted modern and sustainable construction technologies, including:
- Steel Slag and GGBFS Concrete for durability.
- Cut-and-Cover Tunnels and Geo Cells for terrain stability.
- Plastic Sheets, Gabion Walls, and Slope Stabilisation Systems to prevent landslides and improve road resilience.
- These innovations promote eco-friendly and climate-resilient infrastructure in fragile Himalayan terrain.
- Adopted modern and sustainable construction technologies, including:
- Green and Welfare Initiatives
- Under the ‘Ek Ped MaaKe Naam’ campaign, over 23,850 trees were planted across Arunachal Pradesh to promote environmental conservation.
- Welfare measures for Casual Paid Labourers (CPLs) included better shelters, protective gear, and regular health camps—acknowledging their crucial contribution to BRO’s success.
- Community and Awareness Programs: Conducted a motorable expedition along the Naharlagun–Joram Top–Sangram–Ziro–Naharlagun route to promote road safety and connectivity awareness among locals and officials.
Future Plans
- Focus on road widening, construction of new bridges and tunnels, and improving all-weather, high-altitude connectivity for both civilian and defence use.
- Integration of digital monitoring tools, geotextiles, and eco-friendly materials to enhance infrastructure sustainability while reducing maintenance costs.
About the Border Roads Organisation (BRO)
- Established: 7 May 1960
- Parent Ministry: Ministry of Defence
- Mandate:To construct and maintain road networks in border areas of India and in friendly neighbouring countries to ensure defence preparedness and socio-economic development.
- The BRO has been pivotal in strategic connectivity across northern and northeastern India, including projects like Arunank (Arunachal Pradesh), Vartak (Assam & Arunachal), Himank (Ladakh), and Sampark (Jammu & Kashmir).
Japan–India Maritime Exercise (JAIMEX) 2025

- 26 Oct 2025
In News:
The Indian Naval Ship (INS) Sahyadri, an indigenously built Shivalik-class guided missile stealth frigate, participated in the Japan–India Maritime Exercise (JAIMEX-25).
About JAIMEX 2025
- Nature of Exercise: JAIMEX is a bilateral maritime exercise conducted between the Indian Navy (IN) and the Japan Maritime Self-Defense Force (JMSDF).
- Objective: It aims to enhance operational interoperability, mutual understanding, and maritime cooperation, reflecting the robust ‘Special Strategic and Global Partnership’ established between India and Japan in 2014.
- Theme: Upholding a free, open, and inclusive Indo-Pacific based on the principles of rules-based order, freedom of navigation, and shared maritime security.
Exercise Structure
JAIMEX 2025 was conducted in two distinct phases — the Sea Phase and the Harbour Phase, each designed to deepen operational synergy and people-to-people interaction between the two navies.
1. Sea Phase:
- Participating vessels included INS Sahyadri, and JMSDF ships Asahi, Oumi, and Submarine Jinryu.
- The drills focused on:
- Advanced Anti-Submarine Warfare (ASW)andmissile defence operations.
- Flying operationsandunderway replenishmentexercises.
- Maritime domain awareness and communication interoperability.
- These activities aimed to enhance tactical coordination, build mutual trust, and improve joint operational readiness between the two navies.
2. Harbour Phase (Yokosuka, Japan)
- Featured professional and cultural exchanges, including:
- Cross-deck visits,
- Collaborative operational planning,
- Sharing of best practices, and
- A combined Yoga session to promote cultural camaraderie.
- The harbour engagement served as a part of INS Sahyadri’s Long Range Deployment (LRD) to the Indo-Pacific, reflecting India’s increasing maritime outreach and strategic presence in the region.
Significance of JAIMEX
- Strengthens Maritime Cooperation: Enhances India–Japan naval interoperability, crucial for coordinated responses to maritime security challenges such as piracy, illegal fishing, and humanitarian assistance.
- Supports the Indo-Pacific Vision: Reinforces the shared commitment to a rules-based maritime order and an inclusive Indo-Pacific, aligning with initiatives like QUAD and Indo-Pacific Oceans Initiative (IPOI).
- Boosts Defence Diplomacy: Builds mutual trust and operational understanding through regular bilateral and multilateral engagements.
- Showcases India’s Indigenous Naval Capability: INS Sahyadri’s participation underscores India’s progress under ‘Aatmanirbhar Bharat’ and its ability to deploy advanced indigenous platforms for extended missions.
INS Sahyadri: Key Facts
|
Feature |
Description |
|
Class & Type |
Shivalik-class Guided Missile Stealth Frigate |
|
Commissioned |
2012 |
|
Built by |
Mazagon Dock Shipbuilders Ltd, Mumbai |
|
Missile Systems |
Barak-1, Shtil-1 (3S90M) SAMs, BrahMos anti-ship missiles |
|
Other Armaments |
Anti-submarine rocket launchers and torpedoes |
|
Capabilities |
Multi-role stealth platform for surface, anti-air, and anti-submarine warfare |
|
Previous Deployments |
Multiple bilateral and multilateral exercises across the Indo-Pacific |
India–Japan Defence and Strategic Cooperation
The India–Japan defence partnership has become a key component of their broader Special Strategic and Global Partnership (2014), rooted in shared democratic values and converging strategic interests in the Indo-Pacific.
Major Bilateral and Multilateral Defence Engagements:
- Malabar Exercise – Multilateral naval exercise (India, Japan, USA, Australia).
- Dharma Guardian – Bilateral Army exercise.
- Veer Guardian – Bilateral Air Force exercise.
- 2+2 Ministerial Dialogue – Institutional mechanism for strategic coordination.
These engagements collectively strengthen maritime domain awareness, supply chain resilience, and defence technology cooperation between the two nations.
Strategic Context
- The JAIMEX exercise aligns with India’s Act East Policy and Japan’s Free and Open Indo-Pacific (FOIP) vision.
- It demonstrates a collective response to maritime challenges such as increasing militarization, territorial disputes, and climate-driven risks in the Indo-Pacific.
- The partnership complements India’s engagement in regional groupings such as the QUAD, ASEAN-led mechanisms, and IORA (Indian Ocean Rim Association).
Hyunmoo-5 Missile
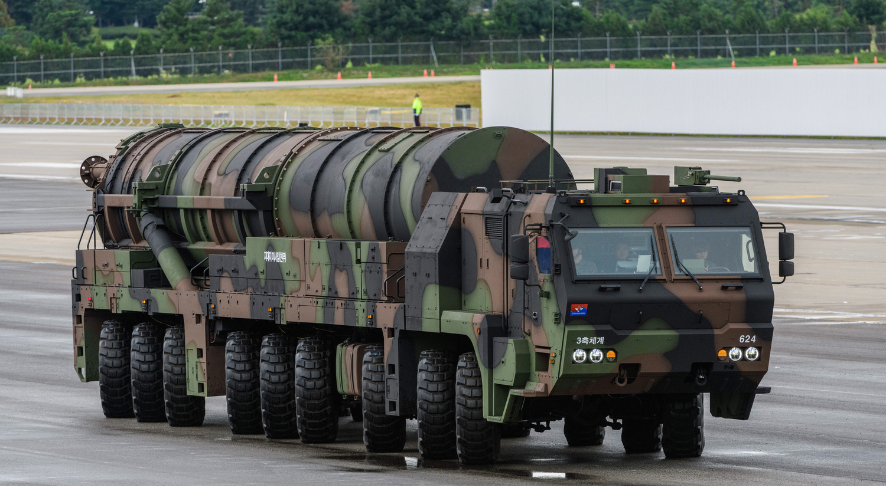

- 25 Oct 2025
In News:
South Korea is set to deploy its most powerful conventional ballistic missile, the Hyunmoo-5, by the end of this year. The move signifies a major step in Seoul’s efforts to enhance its deterrence capabilities amid escalating tensions with nuclear-armed North Korea.
Background and Development
- The Hyunmoo missile series forms the backbone of South Korea’s indigenous missile program, designed for strategic self-reliance under the constraints of the Nuclear Non-Proliferation Treaty (NPT).
- The concept of Hyunmoo-5 emerged after North Korea’s series of provocations in the early 2010s, including deadly border attacks. However, progress was limited by a bilateral missile agreement with the United States, which imposed payload and range restrictions to maintain stability on the Korean Peninsula.
- In 2017, following North Korea’s hydrogen bomb test, the Trump administration lifted these restrictions, enabling South Korea to pursue the development of high-payload, long-range conventional missiles such as Hyunmoo-5.
Technical Features of Hyunmoo-5
- Type: Ground-to-ground ballistic missile
- Weight: Approximately 36 tonnes
- Length: Around 16 metres
- Warhead Capacity: Can carry up to 8 tonnes of conventional explosive payload, including bunker-buster warheads capable of penetrating underground fortifications.
- Range: Estimated between 600 km and 5,000 km, depending on payload configuration.
- Purpose: Designed to neutralize hardened and deeply buried North Korean missile silos, command centres, and nuclear facilities.
Because South Korea does not possess nuclear weapons, the Hyunmoo-5 represents an attempt to achieve a “conventional balance of terror”—a deterrent parity based on precision and power rather than nuclear arms.
Storm Shadow Missile

- 24 Oct 2025
In News:
- Ukraine has reportedly carried out a long-range missile strike on a Russian chemical plant in Bryansk using UK-made Storm Shadow cruise missiles, marking one of the most significant deep-penetration attacks into Russian territory since the beginning of the war.
- The strike, which reportedly bypassed Moscow’s air defence systems, triggered retaliatory drone and missile attacks by Russia on Ukrainian cities, including Kyiv and Dnipropetrovsk, leading to civilian casualties and power outages.
- The episode underscores the escalation in the Ukraine–Russia conflict and highlights the growing strategic role of Western-supplied precision weaponry in modern warfare.
About the Storm Shadow Missile
- Type: Long-range, air-launched stealth cruise missile
- Developed by:United Kingdom and France (known as SCALP EG in France)
- Manufacturer:MBDA Systems
- Operational Since: Early 2000s
- Primary Role: Designed to destroy high-value, well-protected targets such as:
- Airbases
- Radar installations
- Command and control centres
- Port and fuel storage facilities
The missile’s combination of low observability, precision guidance, and deep-penetration warhead makes it one of the most advanced conventional strike weapons in the world.
Technical Specifications and Features
|
Feature |
Details |
|
Length |
~5.1 metres |
|
Wingspan |
~3 metres |
|
Weight |
~1,300 kg |
|
Warhead |
450 kg BROACH (Bomb Royal Ordnance Augmented Charge) — capable of penetrating hardened bunkers |
|
Propulsion |
Turbojet engine |
|
Speed |
Subsonic (~Mach 0.8) |
|
Range |
Over 550 km |
|
Guidance System |
Combination of GPS, Inertial Navigation (INS), Terrain-following radar, and infrared terminal seeker for pinpoint accuracy |
|
Flight Profile |
Low-altitude, terrain-hugging trajectory to evade radar detection |
Stealth and Precision Capabilities
- Designed for “fire and forget” operations, requiring minimal pilot input after launch.
- Terrain-following capability allows the missile to fly under radar coverage, reducing detection probability.
- The infrared imaging seeker enables precise terminal guidance even in adverse weather conditions.
- Known for its “deep-strike capability”, allowing it to destroy hardened and strategic installations from a safe stand-off distance.
Global Operators
The Storm Shadow/SCALP EG is in service with several countries, including:United Kingdom, France, Italy, Greece, Egypt, Saudi Arabia, Qatar, United Arab Emirates and India – where it is integrated with the Rafale fighter jets operated by the Indian Air Force (IAF), enhancing India’s precision-strike capabilities.
Military Combat Parachute System

- 17 Oct 2025
In News:
- India has achieved a major milestone in defenceindigenisation with the successful testing of the Military Combat Parachute System (MCPS) by the Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO).
- The system demonstrated a combat freefall jump from 32,000 feet, making it a significant advancement in India’s aerial delivery capability.
About the Military Combat Parachute System
The MCPS is an indigenous high-altitude parachute system designed to support special operations and military freefall missions in extreme altitudes and hostile environments.
- Developed by:
- Aerial Delivery Research & Development Establishment (ADRDE), Agra
- Defence Bioengineering & Electromedical Laboratory (DEBEL), Bengaluru
Key Features
- Altitude Capability: Successfully tested from 32,000 feet, and the only parachute system in operational use with the capability to be deployed above 25,000 feet by Indian forces.
- Enhanced Tactical Performance:
- Lower rate of descent
- Superior steering and maneuvering abilities
- Allows accurate navigation and landing at designated drop zones
- Navigation Support: Compatible with NavIC (Indian satellite navigation system), ensuring secure and interference-free guidance.
- Mission Capability: Enables safe aircraft exit, controlled descent, and precise landing in complex terrains—critical for special forces operations.
Strategic Significance
- Self-Reliance in Defence:
- Major step towards Aatmanirbhar Bharat in aerial delivery systems
- Reduces dependence on foreign parachute systems and maintenance support
- Operational Advantage:
- Ensures reliability in high-risk environments
- Immune to external interference/denial of service attempts
- Enhances special operations capability against any adversary
- Logistics & Lifecycle Benefits:
- Faster maintenance turnaround compared to imported systems
- Ensures availability during conflicts or war-time contingencies
Astra Mark 2 Missile
- 16 Oct 2025
In News:
- India is set to make a major leap in its air-to-air weapon capability with the Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO) upgrading the Astra Mk-2 air-to-air missile.
- The missile’s range is being extended to beyond 200 kilometres, marking a significant improvement over earlier versions and positioning India among the few nations with such long-range Beyond Visual Range (BVR) missile technology.
- This upgrade is part of India’s broader push towards defenceindigenisation under the Aatmanirbhar Bharat vision.
Importance and Context
- The Astra programme reflects India's commitment to reducing dependence on foreign defence systems, strengthening self-reliance, and enhancing air superiority capabilities.
- The Astra Mk-1, with a range of around 90–110 km, has already been successfully inducted by the Indian Air Force (IAF) and proven operationally, including during Operation Sindoor.
- The Mk-2 variant, now under advanced development, will boost India's long-range interception capability, enabling IAF aircraft to engage enemy targets from well outside hostile air defence zones—an essential capability in modern aerial combat.
Key Features and Technological Advancements
- The Astra Mk-2 will be an extended-range, next-generation BVR missile capable of striking targets over 200 km away.
- It will employ a dual-pulse solid rocket motor, which provides an initial burst of acceleration followed by a second ignition phase for enhanced end-game manoeuvrability and precision. This propulsion design ensures higher terminal speed and greater accuracy compared to single-pulse missiles.
- The missile is expected to fly at speeds close to Mach 4.5 and will be equipped with a fully indigenous Radio Frequency (RF) seeker, fibre-optic gyroscopes, and advanced electronic countermeasure (ECM) resistance, making it highly effective in electronic warfare environments.
- Physically, the missile will be larger and heavier than its predecessor, with an estimated diameter of around 190 mm and a weight of approximately 175 kg. Its enhanced aerodynamic design will allow superior range and altitude engagement.
Operational Deployment and Strategic Impact
- Following successful development and testing, the Astra Mk-2 will be integrated with frontline fighter jets such as the Sukhoi-30MKI and LCA Tejas. The IAF plans to procure an initial stock of nearly 700 missiles, ensuring high operational availability.
- The missile’s extended range capability will serve as a key deterrent against regional adversaries. It is viewed as a counter to China’s PL-15, and it significantly surpasses Pakistan’s PL-15E, which has a maximum range of around 145 km. This enhancement will allow Indian pilots to neutralise hostile aircraft long before they pose a threat.
Saksham Counter-Unmanned Aerial Threat Grid System
- 13 Oct 2025
In News:
- The Indian Army has initiated induction and fast-track procurement of “SAKSHAM” (Situational Awareness for Kinetic Soft and Hard Kill Assets Management), an indigenously developed, AI-enabled Counter-Unmanned Aerial System (C-UAS) grid created with Bharat Electronics Limited (BEL).
- Designed as a modular Command & Control (C2) backbone, SAKSHAM provides real-time detection, tracking, identification and neutralisation of hostile drones and other low-altitude aerial threats across the specially defined Tactical Battlefield Space (TBS) or Air Littoral — the airspace up to 3,000 metres (≈10,000 ft) above the ground.
What SAKSHAM is — technical outline
- Purpose: A unified C2 grid to secure ground formations by controlling low-altitude airspace, countering drone surveillance, weaponised UAS and swarms.
- Developer & partners: Designed and developed indigenously by Bharat Electronics Limited (BEL) in collaboration with the Indian Army’s Corps of Air Defence.
- Architecture & connectivity: Operates over the encrypted Army Data Network (ADN) and presents a GIS-based, common recognised air picture that fuses data from C-UAS sensors, friendly and hostile UAS feeds, and both soft- and hard-kill effectors.
- AI & fusion capabilities: Uses AI/ML-driven fusion to automate threat classification (friendly / neutral / hostile), prioritise responses, and support automated or semi-automated soft-kill (jamming/spoofing) and hard-kill (kinetic) decisions.
- Interoperability: Integrates inputs from India’s automated air-defence network Akashteer and is designed for plug-and-play addition of sensors, jammers, lasers/EMP and future upgrades.
Why SAKSHAM was conceptualised
The Army’s operational experience during Operation Sindoor (2025) — where hostile drone activity exposed detection and response gaps — accelerated the need for a comprehensive C-UAS framework and a shift from traditional Tactical Battle Area concepts to the more inclusive Tactical Battlefield Space (TBS) that explicitly includes the Air Littoral. SAKSHAM is a direct response to those operational lessons.
Operational and strategic impact
- Enhanced situational awareness: A common, real-time air picture shortens decision loops and reduces fratricide risk while allowing freedom of manoeuvre for friendly aerial assets.
- Force protection & deterrence: Rapid detection and neutralisation of drone threats protects troops, logistics nodes and infrastructure from ISR (intelligence, surveillance, reconnaissance) and weaponised UAS attacks.
- Atmanirbhar capability: Indigenous design and BEL partnership strengthen defence manufacturing and upgradeability—key to the Army’s Decade of Transformation (2023–2032) and wider strategic autonomy.
- Scalability & integration: FTP approval and modular design aim for rapid rollout across field formations, enabling layered C-UAS coverage and future networked integration with other services and civil air-safety systems.
IAF to Receive First Tejas Mk1A Fighter Jet

- 11 Oct 2025
In News:
The Indian Air Force (IAF) is set to receive its first Light Combat Aircraft (LCA) Tejas Mk1A by the end of October 2025, marking a major milestone in India’s indigenous defence manufacturing journey under the ‘Atmanirbhar Bharat’ initiative.
Background
- The Tejasprogramme, initiated in 1984 and managed by the Aeronautical Development Agency (ADA) under the Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO), was conceived to replace India’s ageing MiG-21 fighter fleet with an indigenously designed and developed multi-role combat aircraft.
- The delivery of the Tejas Mk1A comes under a ?48,000 crore contract signed in 2021 between the Indian Air Force and HAL for 83 aircraft (73 single-seaters and 10 twin-seaters). The production had been delayed primarily due to slow engine deliveries and global supply chain disruptions.
About Tejas Mk1A
The Tejas Mk1A is an upgraded and advanced variant of the baseline Tejas Mk1, designed to enhance combat capability, survivability, and operational maintainability.
Key Upgrades and Capabilities
- Active Electronically Scanned Array (AESA) Radar:Provides superior target detection, tracking, and engagement capability, improving situational awareness and strike precision.
- Electronic Warfare Suite (EWS):Equipped with radar-warning receivers and self-protection jammers, enhancing survivability against enemy radar and missile threats.
- Digital Flight Control Computer (DFCC Mk1A):Improves flight stability, agility, and maneuverability during high-G operations.
- Weapon Compatibility:Supports a wide range of weapons including:
- Beyond Visual Range (BVR) missiles,
- Air-to-Air and Air-to-Ground missiles, and
- Advanced Short-Range Air-to-Air Missiles (ASRAAM).
- Enhanced Avionics and Network Systems:Planned integration of Combined Interrogator and Transponder (CIT), Software Defined Radio (SDR), and Operational Data Link (ODL) for real-time communication and network-centric warfare.
LCA Tejas: Core Features
- Design: Lightest, smallest, and tailless multi-role supersonic fighter in its class.
- Speed: Capable of reaching Mach 1.8.
- Range: Up to 3,000 km.
- Payload Capacity:4,000 kg, supporting precision-guided and conventional munitions.
- Roles: Capable of air superiority, ground attack, and reconnaissance missions.
Variants of the Tejas Family
- Tejas Mk1: Baseline version currently operational with the IAF.
- Tejas Trainer: Twin-seat variant for advanced pilot training and operational conversion.
- LCA Navy: Carrier-capable single- and twin-seat variants for deck operations.
- Tejas Navy Mk2: Phase-II version with enhanced endurance and payload for naval missions.
- Tejas Mk1A: Improved variant with advanced avionics, weapon systems, and network capabilities.
Dhvani Missile
- 07 Oct 2025
In News:
India is on the verge of a historic breakthrough with the upcoming test of Dhvani, a cutting-edge hypersonic missile developed by the Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO). This missile positions India among an elite group of nations with hypersonic capabilities, including the United States, Russia, and China.
About Dhvani:
- Dhvani is being developed as a Hypersonic Glide Vehicle (HGV), capable of speeds exceeding Mach 5 (over 7,400 km/h).
- Unlike conventional missiles that follow predictable trajectories, Dhvani is launched to extreme altitudes and then glides toward its target with high maneuverability, making detection and interception extremely difficult. It is designed to strike both land-based and maritime targets with precision.
- Estimated ranges are 6,000 to 10,000 kilometers, potentially doubling the reach of India’s current Agni-V intercontinental ballistic missile.
Design and Technology:
- Dimensions: Approximately 9 meters long and 2.5 meters wide with a blended wing-body configuration.
- Heat Protection: Uses ultra-high-temperature ceramic composites to withstand 2,000–3,000°C during atmospheric reentry.
- Stealth Features: Angled surfaces and smooth contours reduce radar visibility.
- Indigenous Development: Built on technologies demonstrated by the Hypersonic Technology Demonstrator Vehicle (HSTDV), including scramjet propulsion and thermal shielding.
Strategic Implications:
The Dhvani missile significantly enhances India’s strategic deterrence, creating a technological edge in South Asia. Its ability to perform unpredictable maneuvers during the terminal phase renders most current missile defense systems ineffective, thereby deterring adversaries.
Global Context:
Dhvani is comparable to China’s DF-ZF, Russia’s Avangard, and U.S. programs such as Dark Eagle and HACM, which face developmental delays. India’s achievement demonstrates self-reliance in critical defense technologies and strengthens its capability for both regional security and global power projection.
Akshar Fast Patrol Vessel
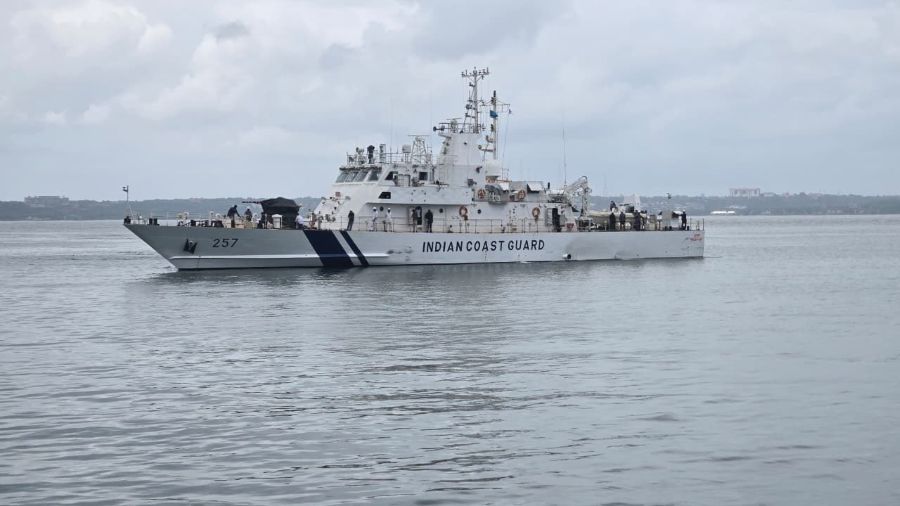

- 06 Oct 2025
In News:
The Indian Coast Guard Ship (ICGS) Akshar, the second vessel in a series of eight Adamya-class Fast Patrol Vessels (FPVs), was commissioned at Karaikal, Puducherry. Built by Goa Shipyard Limited (GSL), this indigenously designed vessel represents a major stride in India’s maritime self-reliance under the ‘Aatmanirbhar Bharat’ and ‘Make in India’ initiatives.
About ICGS Akshar
- Class and Type:Adamya-class Fast Patrol Vessel (FPV)
- Shipbuilder: Goa Shipyard Limited (GSL)
- Indigenous Content: Over 60%
- Length: 51 metres
- Displacement: Approximately 320 tonnes
- Name Significance: ‘Akshar’, meaning imperishable, signifies the Indian Coast Guard’s unwavering resolve to ensure safe, secure, and clean seas.
Key Technical and Operational Features
- Propulsion System:Equipped with two 3,000 kW diesel engines driving indigenously developed Controllable Pitch Propellers (CPP) and gearboxes, the vessel can achieve a maximum speed of 27 knots.
- Endurance:Capable of operating up to 1,500 nautical miles at an economical cruising speed, enabling extended surveillance missions.
- Weapons and Defence Systems:Armed with a 30 mm CRN 91 gun and two 12.7 mm Stabilised Remote-Controlled Guns (SRCG), integrated with an advanced Fire Control System, enhancing accuracy and combat effectiveness.
- Automation and Navigation Systems:Features an Integrated Bridge System (IBS), Integrated Platform Management System (IPMS), and Automated Power Management System (APMS) for high operational efficiency, reduced human intervention, and seamless information integration.
- Deployment:The vessel will be based at Karaikal, Puducherry, under the administrative and operational control of the Commander, Coast Guard Region (East) through District Headquarters No. 13.
Strategic Role and Functions
ICGS Akshar will be deployed for:
- Maritime surveillance and coastal security operations in India’s Exclusive Economic Zone (EEZ).
- Anti-smuggling, anti-poaching, and anti-piracy operations.
- Search and Rescue (SAR) missions, pollution control, and law enforcement duties in the maritime domain.
Its operational flexibility and advanced systems make it a multi-role platform capable of responding swiftly to emerging maritime threats and humanitarian contingencies.
Radar-Mounted Drones for Surveillance
- 02 Oct 2025
In News:
The Border Security Force (BSF), India’s first line of defence, is collaborating with the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) to develop radar-mounted drones aimed at enhancing surveillance along India’s western and eastern borders. This initiative seeks to strengthen border security by providing persistent, high-accuracy monitoring of remote and difficult terrains without crossing international boundaries.
About Radar-Mounted Drones:
- Technology: Unmanned aerial systems equipped with compact radars capable of detecting moving targets, vehicles, or intruders.
- All-Weather Capability: Operates effectively in fog, darkness, rain, or adverse weather, unlike visual-only sensors.
- Real-Time Alerts: Provides immediate notifications, enabling rapid deployment of troops and timely response to border threats.
- Integrated Sensor Fusion: Potential to combine radar with infrared, high-resolution cameras, and ground sensors for enhanced detection.
- High Mobility and Scalability: Drones can be rapidly deployed in inaccessible areas, and multiple units can cover larger regions during crises.
Significance:
- The system is designed to overcome limitations of conventional border guarding, which relies on mobile soldiers or fixed towers and is effective only in limited areas.
- Radar-equipped drones can provide continuous day-and-night surveillance, monitor regions where permanent radars or outposts cannot be installed, and assist in controlling smuggling or infiltration attempts.
- The BSF, drawing experience from operations like ‘Operation Sindoor’, has also established a School of Drone Warfare at its Tekanpur Academy in Madhya Pradesh. In the coming months, the force plans to manufacture these radar-equipped drones in-house, further enhancing India’s technological edge in border security.
- This initiative exemplifies the growing role of technological interventions in modern border management, ensuring vigilance, rapid response, and comprehensive monitoring of India’s frontier regions.
Jal Prahar 2025

- 01 Oct 2025
In News:
The Indian Navy has successfully concluded the biannual joint amphibious exercise ‘Jal Prahar 2025’ along the eastern seaboard, in close coordination with the Indian Army. The exercise aimed to enhance joint operational readiness, inter-service synergy, and maritime security preparedness.
About Jal Prahar 2025
- Nature of Exercise:‘Jal Prahar’ is a biannual joint amphibious exercise conducted by the Indian Navy in collaboration with the Indian Army.
- Objective:To strengthen coordination, interoperability, and integration between the two forces for effective amphibious operations and coastal defence.
Exercise Structure and Key Highlights
The 2025 edition of the exercise was conducted in two phases:
- Harbour Phase (Visakhapatnam):
- Focused on the induction and integration of Army troops onboard naval platforms such as INS Gharial.
- Included onboard training sessions, safety briefings, familiarization with naval operations, and interaction activities to foster inter-service camaraderie.
- Sea Phase (Kakinada):
- Involved the execution of full-scale amphibious operations, including hard beaching, launching of Landing Craft Assaults (LCAs) and infantry combat vehicles (BMPs).
- Validated Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs) and Joint Training Protocols, ensuring seamless coordination during real-world operations.
India test-fires Agni-Prime missile from rail-based mobile launcher
- 30 Sep 2025
In News:
India has successfully test-fired the Agni-Prime (Agni-P) intermediate-range ballistic missile from a rail-based mobile launcher, marking a first-of-its-kind achievement in the nation’s defence history. The test was conducted from a platform integrated with the national railway network. This milestone represents a significant leap in India’s strategic mobility and deterrence capabilities.
About Agni-Prime Missile
- Type: Next-generation, nuclear-capable, intermediate-range ballistic missile (IRBM)
- Range: Up to 2,000 kilometres
- Developed by:Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO) in collaboration with the Strategic Forces Command (SFC)
- Part of: India’s Agni missile series, designed to reinforce the country’s credible minimum deterrence posture.
The Agni-Prime is equipped with advanced guidance and communication systems, featuring a canisterised launch mechanism that enhances storage safety, rapid deployment, and longer shelf life.
Rail-Based Mobile Launcher: A Game-Changing Innovation
The recent test marked the first time India used a rail-based canisterised mobile launcher.
- It can move seamlessly across the national rail network, allowing flexible positioning and quick deployment.
- The launcher enables a short reaction time with low visibility, enhancing operational stealth and survivability.
- This mobility reduces predictability of launch locations, complicating adversarial surveillance and targeting efforts.
Strategic Significance
- Enhanced Strategic Deterrence:The test demonstrates India’s ability to deliver a credible and survivable nuclear deterrent, joining the select group of nations with rail-based canisterised launch systems.
- Improved Survivability and Flexibility:Rail mobility adds a new dimension to India’s nuclear command structure by complementing road-based and silo-based systems, ensuring launch readiness even under high-threat scenarios.
- Operational Stealth and Rapid Response:The ability to launch within minutes from concealed rail positions strengthens India’s second-strike capability under its nuclear doctrine.
- Geopolitical Implications:The development aligns with India’s effort to maintain strategic stability in a complex regional environment, particularly amid evolving threats in South Asia and the Indo-Pacific.
Recent Developments in India’s Missile Programme
- In August 2025, Agni-Prime was successfully tested from Chandipur, Odisha.
- Earlier, in March 2024, under Mission Divyastra, India tested Agni-5 with MIRV (Multiple Independently Targetable Re-entry Vehicle) capability — allowing a single missile to carry and deliver multiple nuclear warheads to different targets.
- The Strategic Forces Command, operational since 2003, currently manages India’s nuclear arsenal and deployment systems.
India’s first overseas defence manufacturing facility

- 29 Sep 2025
In News
- In a major step towards expanding India’s defence industrial footprint globally, Defence Minister Rajnath Singh and his Moroccan counterpart AbdelatifLoudyi jointly inaugurated India’s first overseas defence manufacturing facilityatBerrechid, Morocco.
- Set up by Tata Advanced Systems Limited (TASL) in collaboration with the Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO), the facility marks a historic milestone in India’s defence diplomacy and the growing strategic partnership between India and Morocco.
About the Facility
- Location:Berrechid, Morocco
- Established by: Tata Advanced Systems Limited (TASL) in partnership with DRDO
- Launched in: 2025
- Scale: Spread over 20,000 sq. metres, it is Morocco’s largest defence manufacturing facility and India’s first such overseas plant by a private defence company in Africa.
- Primary Production: The Wheeled Armoured Platform (WhAP) — an indigenously developed 8×8 modular combat vehicle jointly designed by TASL and DRDO.
Key Features
- Product Range: The WhAP will be produced in multiple configurations including:
- Infantry Fighting Vehicle
- Armoured Personnel Carrier
- Reconnaissance Vehicle
- Command Post
- Mortar Carrier
- Armoured Ambulance
- Technical Capabilities:
- Equipped with advanced mobility, armour protection, remote weapon stations, and anti-tank guided missile systems.
- Incorporates indigenous technologies and customised modular design for varied combat roles.
- Local Sourcing:
- Initially, one-third of components will be sourced locally from Morocco.
- This is expected to increase to 50% in later phases, fostering industrial collaboration and technology transfer.
Strategic Objectives
The facility aims to advance India’s Aatmanirbhar Bharat vision beyond domestic production to global partnerships under the theme “Make with Friends, Make for the World.”
Key Goals:
- Strengthen India–Morocco defence cooperation and bilateral industrial partnerships.
- Promote defence exports and technology sharing with friendly nations.
- Support regional security and stability across Africa and Europe through capacity-building.
Significance
1. Strategic and Diplomatic
- Establishes Morocco as a strategic hub for Indian defence manufacturing in North Africa and Europe.
- Deepens India’s defence diplomacy and enhances its global footprint in high-technology sectors.
- Reinforces India’s credibility as a trusted partner in defence collaboration.
2. Economic and Industrial
- Generates direct and indirect employment in Morocco.
- Develops a local supplier ecosystem and supports critical technology capabilities within the host nation.
- Boosts India’s defence exports while contributing to Morocco’s industrial development.
3. Technological and Strategic Autonomy
- Demonstrates India’s growing capability to design, produce, and export advanced defence systems.
- Showcases India’s transition from import dependence to a global exporter of high-end military technologies.
Exercise Cold Start

- 29 Sep 2025
In News:
- India will conduct a major tri-service exercise, ‘Cold Start’, in the first week of October 2025 in Madhya Pradesh.
- The exercise, involving the Army, Navy, and Air Force, will focus on testing drones and counter-drone systems to strengthen the country’s integrated air defence capabilities.
- It is being described as the largest such joint drill since Operation Sindoor.
About Exercise Cold Start
- Nature: A tri-service military exercise designed to simulate aerial threats and defence responses using drones, UAVs, and counter-drone systems.
- Objective:
- To evaluate operational readiness of the armed forces against evolving aerial threats.
- To identify technological and procedural gaps in India’s air defence systems.
- To enhance interoperability and coordination between the three defence services.
- Participants:
- Indian Army, Navy, and Air Force as primary participants.
- Supported by industry partners, research and development (R&D) agencies, and academic institutions, fostering a military–industry–academia partnership.
Key Features
- Live demonstrations of drones and counter-drone systems.
- Integration of GPS jamming, electronic warfare, and surveillance technologies.
- Testing of indigenous technologies developed through collaboration between defence R&D and private industry.
- Conceptual inspiration: The integrated air defence approach draws from the Sudarshan Chakra—symbolising a seamless and multi-layered defensive network against drones, UAVs, and hypersonic weapons.
Significance
- Enhances Jointness: Promotes synergy among the three defence services in technology-driven warfare.
- Technological Edge: Strengthens India’s counter-drone warfare capabilities and electronic warfare resilience.
- Strategic Readiness: Demonstrates India’s preparedness to respond to emerging aerial and cyber threats in the evolving domain of modern warfare.
- Defence Innovation: Encourages indigenous R&D and strengthens public–private collaboration in developing next-generation air defence systems.
Combined Operational Review and Evaluation (CORE) Programme

- 27 Sep 2025
In News:
- The Headquarters Integrated Defence Staff (HQ IDS) is organising the Combined Operational Review and Evaluation (CORE) Programme at the United Service Institution of India, New Delhi.
- The initiative serves as a unique platform for civil-military engagement on national and regional security, bringing together senior officers from the Indian Armed Forces alongside officials from the Ministries of Defence, External Affairs, and Home Affairs.
Objectives and Significance
The CORE Programme aims to:
- Strengthen civil-military synergy in addressing multidimensional security threats.
- Enhance strategic awareness among senior officers and develop their capacity for balanced, pragmatic decision-making.
- Foster leadership development and inter-agency coordination in complex national and international security scenarios.
The programme underscores HQ IDS’s commitment to jointness within the Armed Forces and professional development, preparing participants to navigate dynamic security challenges effectively.
Key Themes and Focus Areas
The CORE Programme covers a spectrum of contemporary security issues, including:
- Regional and global security challenges
- Technological transformation of warfare
- Strategic communication
- Inter-agency collaboration and joint problem-solving
The programme employs a combination of lectures, interactive discussions, and sessions with subject-matter experts and professionals from diverse fields. This approach broadens participants’ outlook, encourages collaborative solutions, and strengthens the intellectual foundations of senior leadership.
Participants
The five-day programme brings together senior civil and military officers, facilitating a holistic understanding of national security from multiple perspectives. By promoting dialogue across the defence and civilian sectors, CORE enhances preparedness to address complex, multidimensional threats at both national and international levels.
Exercise Amogh Fury
- 25 Sep 2025
In News:
The Indian Army’s Sapta Shakti Command recently conducted a major integrated firepower exercise, ‘Amogh Fury’, at the Mahajan Field Firing Ranges in Rajasthan’s Thar Desert. The large-scale drill showcased the Army’s growing emphasis on technology-driven warfare, jointness of combat arms, and preparedness for multi-domain operations.
Objectives and Significance
- The primary aim of Exercise Amogh Fury was to test combat power, coordination, and operational readiness under realistic battlefield conditions.
- The exercise simulated live battle scenarios, enabling forces to validate their capabilities in offensive and defensive operations, while ensuring seamless integration between ground and air platforms.
- The drill reflected the Army’s commitment to operational transformation in line with evolving security dynamics, focusing on rapid decision-making, situational awareness, and integrated command structures.
Key Features of the Exercise
The exercise featured coordinated manoeuvres involving:
- Battle Tanks and Infantry Combat Vehicles – for armoured and mechanised warfare.
- Attack Helicopters and Long-Range Artillery – providing precision firepower support.
- Drones and Unmanned Aerial Systems (UAS) – for real-time reconnaissance, surveillance, and target acquisition.
These diverse platforms operated in unison to demonstrate jointness between air and ground forces, vital for modern high-intensity conflicts.
Integration of Advanced Technologies
A central focus of Amogh Fury was the use of modern technologies such as:
- Network-centric communication systems
- Integrated Command-and-Control (C2) architecture
- Real-time surveillance and targeting systems
These advancements allowed for the creation of a unified operational picture, enhancing situational awareness, rapid coordination, and decision-making across command levels. The integration of these systems reflects the Army’s move toward digitised battlefield management and multi-domain warfare capability.
Training and Outcomes
The exercise provided pragmatic training for personnel across all ranks under realistic combat conditions. It served as a testbed for refining tactical procedures and assessing the synergy between combat arms, support units, and logistic elements.
Through Amogh Fury, the Indian Army strengthened its readiness to counter emerging threats, underscoring its focus on agility, precision, and technological superiority on the modern battlefield.
Androth Anti-Submarine Warfare Ship
- 24 Sep 2025
In News:
- The Indian Navy has commissioned INS Androth, an indigenously built Anti-Submarine Warfare Shallow Water Craft (ASW-SWC), marking a significant milestone in strengthening India’s maritime security and self-reliance in defence production.
- Built by Garden Reach Shipbuilders & Engineers (GRSE), Kolkata, INS Androth is the second vessel in a series of eight ASW-SWCs being developed for the Navy.
Strategic Significance
- Named after Androth Island in the Lakshadweep archipelago, the ship’s designation underscores India’s commitment to safeguarding its maritime frontiers in the Arabian Sea and ensuring the security of critical sea lanes around the island territories.
- The induction comes at a time of growing Chinese naval presence in the Indian Ocean Region (IOR), adding a crucial layer of deterrence and surveillance to India’s coastal defence network.
Design and Capabilities
- INS Androth is designed for anti-submarine operations in shallow waters, coastal security patrols, and escort missions.
- It is 77 metres long and powered by diesel engine–waterjet propulsion, providing superior maneuverability in littoral and near-shore environments.
- Key onboard systems include:
- Advanced indigenous sonar and sensor suites for submarine detection and tracking.
- Lightweight torpedoes and ASW rockets for engaging underwater threats.
- 80% indigenous components, aligning with the ‘Aatmanirbhar Bharat’ initiative to reduce import dependence in defence production.
Operational Role
- The ship will primarily operate along India’s western seaboard, particularly around Lakshadweep, where it will conduct surveillance and deterrence missions against sub-surface threats.
- Its shallow-water design allows it to access areas that larger vessels cannot, enhancing the Navy’s reach in coastal and island territories.
Saudi–Pakistan Strategic Mutual Defence Agreement (SMDA)

- 23 Sep 2025
In News:
- Recently, Saudi Arabia and Pakistan signed a Strategic Mutual Defence Agreement (SMDA) in Riyadh, formalising a long-discussed framework for joint defence and mutual security.
- The agreement, viewed as a landmark in bilateral ties, symbolises a renewed effort to institutionalise their security partnership amid changing regional dynamics and waning U.S. influence in West Asia.
Nature and Scope of the Pact
- The SMDA commits both nations to collective defence, stipulating that any attack on one country will be treated as an attack on both.
- It builds upon the 1982 Bilateral Security Cooperation Agreement, strengthening channels of military coordination, intelligence exchange, training, and arms trade.
- The pact extends across conventional defence cooperation, advisory roles, and — in principle — joint deterrence, though not explicitly nuclear.
Strategic Context
- The timing of the agreement follows rising regional uncertainty, including Israel–Qatar tensions, Yemen conflict spillovers, and Iran–Saudi rivalry.
- By signing the SMDA, Riyadh signals its intent to pursue greater regional self-reliance in defence, moving beyond full dependence on the U.S. security umbrella.
- For Pakistan, it secures much-needed economic and energy support from Saudi Arabia amid a deep fiscal crisis, while reaffirming its role as a key security partner in the Islamic world.
Key Drivers
- Mutual Security Assurance: Establishes a framework for joint deterrence and defence coordination.
- Economic Complementarity: Opens avenues for Saudi financial assistance, arms procurement, and energy trade with Pakistan.
- Symbolic Islamic Solidarity: Positions Pakistan as a pan-Islamic security contributor, enhancing its strategic visibility.
- Regional Rebalancing: Demonstrates Saudi Arabia’s effort to diversify security partnerships beyond Washington and regional blocs.
Implications
1. For India
- Strategic Caution: While the pact theoretically enables Pakistan to seek Saudi backing in a potential India–Pakistan confrontation, Riyadh’s growing ties with India — including $42.9 billion in bilateral trade, defence collaboration, and major investments — make an overt anti-India stance unlikely.
- Diplomatic Opportunity: New Delhi can leverage its energy and economic partnerships to maintain Saudi neutrality in South Asian affairs.
- Policy Imperative: India must sustain strategic dialogue and ensure Arab neutrality in regional crises through proactive diplomacy.
2. Regional and Global Dimension
- Shift in Gulf Security Architecture: Reflects a decline in U.S. dominance and emergence of a multipolar Gulf order, with Riyadh exploring independent alliances.
- Iran–Saudi–Pakistan Equation: Enhances Saudi deterrence posture against Iran, Yemeni Houthis, and potentially Israel’s unilateral actions.
- Nuclear Sensitivities: Raises concerns about possible nuclear collaboration, though the actual transfer of Pakistani nuclear technology to Saudi Arabia remains highly improbable, constrained by global non-proliferation norms and Israeli sensitivities.
Way Forward for India
- Deepen Defence and Security Cooperation: Expand joint training, exercises, and intelligence exchanges with Saudi Arabia.
- Energy Diplomacy: Pursue long-term crude oil and green hydrogen partnerships to consolidate interdependence.
- Strategic Monitoring: Closely track SMDA implementation, including possible Pakistani troop deployments or defence projects.
- Maritime Synergy: Strengthen India’s presence in the Arabian Sea through naval cooperation to protect vital energy routes.
- Economic Leverage: Utilize India’s market potential and diaspora network as stabilising anchors in Indo-Saudi relations.
Adamya Fast Patrol Vessel
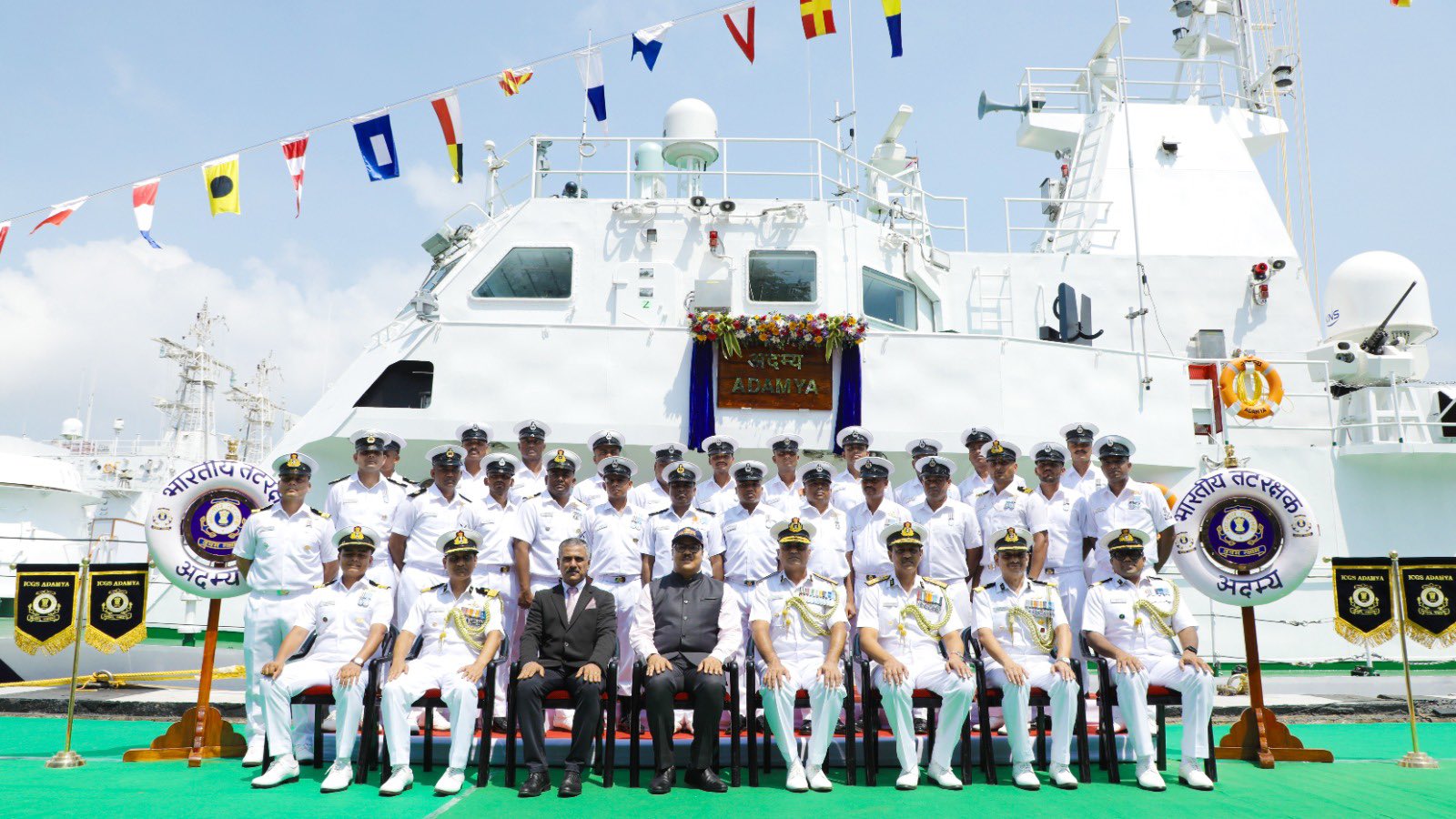

- 22 Sep 2025
In News:
The Indian Coast Guard Ship (ICGS) Adamya, the first in a new series of eight Adamya-class Fast Patrol Vessels (FPVs), was commissioned at Paradip Port, Odisha. The vessel, designed and built indigenously by Goa Shipyard Limited (GSL), marks another step forward in India’s Aatmanirbhar Bharat initiative in the defence sector.
About ICGS Adamya
- Meaning: “Adamya” translates to indomitable, symbolizing the Indian Coast Guard’s (ICG) resolve to safeguard the nation’s maritime interests.
- Operational Base: The ship will be based at Paradip, Odisha, under the administrative control of the Commander, ICG Region (North East).
- Crew Strength: The vessel is manned by five officers and 34 personnel.
- Primary Role: Coastal surveillance, anti-smuggling operations, anti-poaching patrols, and search and rescue missions within India’s maritime zones.
Key Specifications
|
Feature |
Specification |
|
Displacement |
Approx. 320 tons |
|
Speed |
Maximum 28 knots |
|
Endurance |
1500 nautical miles at economical speed |
|
Propulsion |
Two 3000 KW diesel engines |
|
Builder |
Goa Shipyard Limited |
|
Indigenous Content |
Over 60% |
Technological Highlights
- First-of-its-kind Propulsion:The Adamya is the first Indian vessel fitted with indigenously developed Controllable Pitch Propellers (CPPs) and gearboxes, enhancing manoeuvrability and fuel efficiency.
- Advanced Systems:Equipped with an Integrated Bridge System (IBS), Integrated Platform Management System (IPMS), and Automated Power Management System (APMS) to improve operational efficiency and automation.
- Weaponry:Armed with a 30 mm CRN 91 gun and two 12.7 mm stabilized remote-controlled machine guns, supported by advanced fire-control systems.
About Fast Patrol Vessels (FPVs)
Fast Patrol Vessels are medium-sized, high-speed ships used by the Indian Coast Guard for surveillance, policing, and search and rescue operations in coastal areas. They play a vital role in maintaining maritime safety, enforcing laws, and preventing smuggling and infiltration.
INS Rajali
- 21 Sep 2025
In News:
The Indian Navy’s Eastern Naval Command hosted a two-day seminar on Long-Range Maritime Reconnaissance (LRMR) at INS Rajali, Arakkonam. The event underscored India’s growing maritime responsibilities, technological advancements, and strategic commitment to ensuring security in the Indian Ocean Region (IOR).
Objectives and Key Outcomes
The seminar brought together senior naval commanders, operational experts, and industry representatives, including from Boeing Ltd, to deliberate on the evolving role of LRMR platforms in safeguarding India’s maritime interests.
Key highlights included:
- Release of a compendium of scholarly papers on maritime domain awareness and surveillance.
- Discussions on the operational roles of Boeing P-8I Poseidon aircraft and High-Altitude Long Endurance (HALE) drones, such as the MQ-9B Sea Guardian, in anti-submarine warfare (ASW), multi-domain reconnaissance, and long-range surveillance.
- Recognition of the Navy’s drive to build indigenous capacity while maintaining strategic partnerships with global defence leaders to enhance maritime security cooperation.
INS Rajali: Strategic Maritime Aviation Base
INS Rajali, commissioned on March 11, 1992, is a premier Naval Air Station located near Arakkonam, Tamil Nadu, about 80 km west of Chennai.
- It is spread across 2,200 acres and houses over 4,700 personnel.
- Named after ‘Rajali’, a hawk native to Tamil Nadu’s coast, symbolizing vigilance and speed.
- It operates under the Eastern Naval Command and has the longest military runway in Asia, enabling operations of long-range aircraft.
- The station performs dual roles in operations and training, including hosting the Helicopter Training School (HTS).
INS Rajali has emerged as the hub of India’s maritime reconnaissance and surveillance operations, crucial for maintaining real-time situational awareness over the IOR.
INAS 312: A Milestone Achievement
The seminar also celebrated a historic milestone — the completion of 50,000 flying hours by INAS 312, the Navy’s premier Long-Range Maritime Reconnaissance Squadron based at INS Rajali.
- INAS 312 operates the Boeing P-8I Poseidon aircraft, a state-of-the-art platform known for anti-submarine warfare, surveillance, and maritime strike missions.
- The squadron’s operations have enhanced India’s ability to monitor sea lanes, detect hostile submarines, and secure trade routes across the Indo-Pacific.
- This achievement marks a first in Indian Naval Aviation history, reflecting the squadron’s professionalism and pivotal contribution to national security.
Technological Edge: Integration of LRMR Platforms
The integration of P-8I aircraft with MQ-9B Sea Guardian drones represents a transformative leap in India’s maritime surveillance ecosystem.
- These systems enable persistent intelligence gathering, real-time situational awareness, and high-endurance operations across vast oceanic stretches.
- The synergy between manned and unmanned assets significantly enhances Maritime Domain Awareness (MDA), ensuring rapid response to traditional and non-traditional threats, including piracy, smuggling, and humanitarian emergencies.
Strategic Significance
The LRMR initiative aligns with India’s vision of being a “Net Security Provider” in the Indo-Pacific.
By strengthening reconnaissance and surveillance capabilities, India is:
- Expanding its operational reach and deterrence posture.
- Enhancing interoperability with partner navies.
- Supporting Humanitarian Assistance and Disaster Relief (HADR) missions.
- Contributing to a Free, Open, and Rules-Based Indo-Pacific order.
Exercise Pacific Reach 2025

- 19 Sep 2025
In News:
The Indian Navy’s latest indigenously designed and constructed Diving Support Vessel (DSV), INS Nistar, is participating in the multinational Exercise Pacific Reach 2025 in Singapore, marking a key step in strengthening India’s naval cooperation and submarine rescue capabilities.
About Exercise Pacific Reach 2025
- Exercise Pacific Reach is a biennial multinational naval exercise hosted by Singapore, with the 2025 edition witnessing the participation of over 40 nations.
- The exercise focuses on submarine rescue operations, interoperability, and sharing of best practices among participating navies.
- It is conducted in two major phases:
- Harbour Phase:
- Involves in-depth discussions on submarine rescue systems.
- Includes Subject Matter Expert Exchanges (SMEE), a medical symposium, and cross-deck visits among participating nations.
- Aims to enhance coordination in rescue procedures and underwater medical responses.
- Sea Phase:
- Conducted in the South China Sea, featuring multiple intervention and rescue operations.
- INS Nistar and Submarine Rescue Unit (East) will collaborate with other international assets to simulate real-world submarine rescue missions and deep-sea operations.
The exercise underscores the growing importance of multilateral maritime cooperation in ensuring submarine safety, operational interoperability, and humanitarian response readiness in the Indo-Pacific region.
INS Nistar: A Technological Milestone in Naval Capability
- Commissioned on: 18 July 2025
- Built by: Hindustan Shipyard Limited (HSL), Visakhapatnam
- Under: Ministry of Defence’s ‘Aatmanirbhar Bharat’ initiative
- INS Nistar is designed to act as a mothership (MoSHIP) for Deep Submergence Rescue Vehicles (DSRVs) — a critical capability for submarine rescue and deep-sea support operations.
- The vessel exemplifies India’s indigenous shipbuilding prowess and self-reliance in complex maritime technologies.
Key Technical Features and Capabilities:
- Integrated Saturation Diving System (ISDS):Enables diver deployment up to 300 meters depth, facilitating underwater repairs, salvage, and rescue missions.
- Remotely Operated Vehicles (ROVs):Deployed for underwater surveillance and recovery in deep-sea environments.
- Side Scan Sonar:Assists in locating submerged vessels, wreckage, or obstacles on the seabed.
- Integrated Platform Management System (IPMS):Streamlines the operation and monitoring of onboard systems for greater efficiency and safety.
- Submarine Rescue System:A critical asset for submarine emergency response, ensuring timely and safe evacuation of personnel from disabled submarines.
Exercise SiyomPrahar

- 18 Sep 2025
In News:
The Indian Army's Exercise SiyomPrahar, represents a significant step in modernizing the Army’s operational capabilities. This field training exercise focused on validating the integration of unmanned aerial systems (UAS) into tactical operations, with a strong emphasis on surveillance, reconnaissance, target acquisition, and precision strikes. Below are the key highlights and insights from the exercise:
Key Objectives:
- Integration of Drone Technology: The core goal was to test how drone systems can be employed for persistent surveillance, battlefield reconnaissance, and precision strikes, thus enhancing overall combat effectiveness.
- Development of New TTPs (Tactics, Techniques, and Procedures): A key focus was on refining how drone-derived intelligence could be fused with conventional firepower, ensuring rapid decision-making in dynamic and evolving combat scenarios.
- Joint Targeting and Decision-making: The exercise aimed at refining joint targeting processes, highlighting the importance of real-time intelligence to improve targeting accuracy and decision-making speed in the heat of battle.
Key Features of the Exercise:
- Realistic Battlefield Conditions: The exercise was conducted under simulated real-world combat conditions, providing a comprehensive test of UAS capabilities in diverse operational environments.
- Synergy Between Traditional Combat and Emerging Technologies:Exercise SiyomPrahar underscored the importance of blending traditional combat arms with cutting-edge technologies, such as drones, to create a more adaptive and efficient military force.
- Operational Preparedness: The exercise was a significant step toward enhancing the Indian Army’s operational preparedness for future combat scenarios, integrating modern technology to ensure readiness for future battlefields.
Strategic Importance and Key Insights:
- Adaptability and Synergy: The exercise highlighted how the Army is integrating modern warfare tactics with traditional methods to create a more effective, adaptable force that can operate in dynamic and complex environments.
- Real-Time Data Utilization: By using drones to gather real-time intelligence, the Indian Army is significantly improving targeting accuracy, enabling faster, more informed decisions in combat situations.
- Reduced Soldier Risk: The deployment of drones for reconnaissance and strikes minimizes the exposure of ground troops to potential dangers, enhancing both tactical effectiveness and safety on the battlefield.
- Joint Operational Capabilities: Exercise SiyomPrahar demonstrated how drones can be integrated into joint operational structures, improving communication and coordination between various arms of the military.
Broader Implications for Future Warfare:
- Technological Innovation in Combat: The successful integration of drone technology in this exercise indicates a shift towards technology-driven warfare, where drones play a critical role in intelligence gathering, battlefield awareness, and precision targeting.
- India’s Commitment to Modernization: The exercise is a testament to India’s proactive approach to adapting to the changing nature of warfare, ensuring that its forces remain future-ready and capable of responding effectively to emerging security challenges.
STAR Missile
- 16 Sep 2025
In News:
India has developed the Supersonic TARget (STAR) missile — an indigenous, reusable high-speed target system designed to reproduce modern cruise-missile and anti-ship threat profiles for realistic training and validation of sensors, weapons and doctrines. STAR replaces expensive imported target systems and fills a critical gap in live realistic training for the Navy, Air Force and Army.
What STAR does
STAR is not a combat weapon but a high-fidelity aggressor platform that simulates hostile supersonic missiles so air defence systems, shipborne weapons and interceptor pilots can practise time-critical engagements under realistic conditions. It can mimic sea-skimming runs, steep dives and evasive manoeuvres to test detection, tracking and interception chains end-to-end.
Key technical features
- Propulsion: Two-stage system — a solid booster for launch followed by a Liquid Fuel Ramjet (LFRJ) for sustained supersonic cruise. The ramjet experience is also being matured for future systems (e.g., Astra Mk-3 development).
- Speed: Mach 1.8–2.5 (roughly 612–850 m/s).
- Altitude & profiles: Operates from low sea-skimming heights (as low as ~12 feet above water) up to ~10 km, and can execute high-speed dives and complex manoeuvres.
- Range & flight time: Designed for missions between 55–175 km with flight durations of ~50–200 seconds, enabling diverse scenario replication.
- Variants:
- Air-launched STAR (carried by combat aircraft such as LCA Tejas) to emulate air-to-air or air-to-ground supersonic threats and anti-radar/anti-AWACS profiles.
- Ground-launched STAR (truck-mounted) for shore-based or remote launches without extensive infrastructure.
- Operational utility: High manoeuvrability, programmable trajectories and safe recovery/destruction options make it suitable for repeated use in trials.
Operational and strategic significance
- Realism in training: STAR provides time-critical, live target practice that simulations alone cannot offer — particularly valuable against low-altitude, high-speed cruise profiles which compress engagement timelines.
- Atmanirbhar Bharat: Fully indigenous development reduces dependency on foreign target systems, cuts recurring costs, and supports domestic missile-R&D ecosystems. STAR is reusable and cost-effective relative to imported alternatives.
- Force integration: Its modular design serves tri-service needs, helping calibrate ship radars, point-defence systems, interceptor missiles, and fighter tactics in joint exercises.
- R&D multiplier: The ramjet and guidance technologies validated on STAR feed into broader missile-development programs, strengthening long-term indigenous capabilities. Analysts also view STAR as a potential seed technology that could be adapted into tactical offensive roles in the future (e.g., anti-radar or precision suppression platforms), should doctrinal decisions and legal frameworks permit.
Development status and outlook
As of mid-2025, STAR progressed into advanced development and flight validation phases — integrating propulsion, guidance and control subsystems and conducting combat-style trials. Operational induction for routine service trials and training is anticipated as tests mature.
INS Aravali

- 15 Sep 2025
In News:
The Indian Navy has recently commissioned INS Aravali, its latest naval base, at Gurugram, Haryana. Named after the ancient Aravali mountain range, the establishment is envisaged as a nerve centre for command, control, and Maritime Domain Awareness (MDA) operations, marking a significant stride in India’s maritime security architecture.
Strategic Importance
INS Aravali is designed to enhance the Navy’s information and communication infrastructure, which is central to modern maritime operations. Located in Gurugram—close to the national capital—it will support real-time decision-making, inter-agency coordination, and domain awareness across the vast Indian Ocean Region (IOR). This reflects India’s aspiration to position itself as the Preferred Security Partner in the IOR amidst evolving geopolitical challenges.
Motto and Vision
Guided by the motto “Maritime Security through Collaboration”, INS Aravali embodies a cooperative approach to maritime defence. It seeks synergy between naval information centres, maritime agencies, and allied stakeholders. The base also aligns with India’s broader strategic vision of MAHASAGAR (Mutual and Holistic Advancement for Security and Growth Across Regions), which underlines collaborative security and regional growth.
Symbolism and Identity
The crest of INS Aravali carries deep symbolism:
- A central mountain signifies the resilience and enduring strength of the Aravali Range.
- A rising sun reflects eternal vigilance, renewal, and the dawn of technological advancement in naval communications.
Together, they highlight the base’s mission to combine steadfastness with innovation in safeguarding India’s maritime interests.
Role in Maritime Domain Awareness (MDA)
MDA has become indispensable in an era of increasing threats, including piracy, illegal fishing, smuggling, cyber vulnerabilities, and grey-zone conflicts. INS Aravali’s role is to integrate satellite-based monitoring, coastal radar networks, information fusion, and real-time communication to ensure seamless surveillance of India’s maritime domain. It also supports the Navy’s partnerships with regional navies, reflecting the Indo-Pacific emphasis on collaborative security.
Broader Significance
- National Security: Enhances India’s capability to respond rapidly to maritime threats and secure sea lanes of communication, vital for trade and energy security.
- Regional Diplomacy: Strengthens India’s profile as a net security provider in the Indian Ocean, reinforcing strategic trust among neighbouring littoral states.
- Technological Edge: Demonstrates the Navy’s focus on modern information infrastructure and cyber-resilient systems to address multi-dimensional security challenges.
- Civil-Military Integration: Showcases participatory security governance by working with other agencies, reflecting a whole-of-government approach.
Technology Perspective and Capability Roadmap (TPCR) 2025

- 12 Sep 2025
In News:
- The Ministry of Defence (MoD) recently released the Technology Perspective and Capability Roadmap (TPCR) 2025, a strategic blueprint outlining India’s defence technology and capability requirements over the next 15 years.
- The roadmap aims to guide the Indian Army, Navy, and Air Force in modernisation while providing domestic industry, academia, and research institutions early visibility to align R&D and production with future procurement needs. Indigenisation and self-reliance form the core of TPCR 2025.
Objectives of TPCR 2025
- Early Visibility for Industry: Help domestic manufacturers and research organisations plan development and production of advanced defence systems.
- Indigenisation: Reduce dependence on imports and promote domestic defence manufacturing.
- Future-Ready Armed Forces: Equip the military to face multi-domain warfare challenges, including cyber, space, AI-enabled, and hybrid conflicts.
- Sustainability: Integration of green logistics and energy-efficient systems in defence operations.
Key Features by Service
Navy:
- Nuclear Propulsion: Plans to induct 10 nuclear propulsion systems for aircraft carriers and large surface combatants, providing virtually unlimited endurance at sea.
- Next-Generation Aircraft Carrier: Equipped with Electromagnetic Aircraft Launch System (EMALS) to launch heavy fighters, airborne early warning aircraft, and UAVs in all sea states. Digital twin simulations to enable predictive maintenance.
- Surface Combatants: Induction of 5–10 destroyers, 7 corvettes, 4 Landing Platform Docks (LPDs) (~29,000 tonnes each), and 100 Next Generation Fast Interceptor Craft for coastal security.
- Underwater Warfare: 20 high-endurance Autonomous Underwater Vehicles (AUVs) for long-range surveillance and mine countermeasures.
- Missiles & Weapons: Over 200 surface-to-surface missiles and universal launchers for multi-platform deployment.
Army:
- ArmouredModernisation: Replacement of ageing T-72 fleet with 1,800 Future Ready Combat Vehicles (FRCVs); 300–400 light tanks for high-altitude sectors.
- Anti-Tank and Precision Weapons: Procurement of 50,000 ATGMs with tandem HEAT warheads, along with 600,000 artillery rounds, emphasising precision-guided munitions.
- UAV & Robotic Systems: Deployment of 70 MALE/HALE UAVs, 800 integrated drone-loitering munitions systems, and 400 ultra-light missiles for UAVs; over 700 robotic counter-IED systems.
- Cyber & AI Warfare: AI-enabled detection, classification, and adaptive jammers creating 15 km electronic denial zones; deepfake detection tools for operational security.
Air Force:
- Directed-Energy Weapons: 10–15 Tactical High-Energy Laser (THEL) systems with ranges of 6–15 km; high-power microwave systems to neutralise incoming threats.
- Stealth and UAVs: 150 stealth bomber drones for deep-strike missions; 100+ remotely piloted aircraft for ISR and strike roles.
- Persistent Surveillance: 75 High-Altitude Pseudo-Satellites (HAPS) and 20 stratospheric airships for continuous ISR and communications over extended periods.
Tri-Services (Joint):
- Hypersonic Missiles: Induction of 500+ scramjet-propelled hypersonic missiles capable of Mach 5+ speeds for rapid strike across land, sea, and air.
- Universal Missile Launchers: Platforms for multiple missile types to ensure interoperability.
- Cyber-Space Preparedness: AI-as-a-service platforms for 4,000 users, quantum key distribution networks, satellite hardening, and post-quantum secure communications.
Cross-Cutting Technologies
- AI & ML: Smart, predictive warfare through digital twin simulations and autonomous systems.
- Hybrid Warfare Capability: Integration of unmanned systems, robotic tools, and precision-guided munitions.
- Green & Sustainable Defence: Energy-efficient platforms and logistics aligned with national sustainability goals.
Strategic Significance
TPCR 2025 positions India to:
- Achieve self-reliance in defence technologies.
- Maintain credible deterrence and modernisation across all domains.
- Address emerging threats in cyber, space, and multi-domain warfare environments.
- Strengthen domestic defence industrial base through early technology visibility.
Exercise Yudh Kaushal 3.0
- 06 Sep 2025
In News:
The Indian Army recently conducted Exercise Yudh Kaushal 3.0 in the high-altitude Kameng region of Arunachal Pradesh, reaffirming its preparedness for next-generation warfare in extreme Himalayan terrain.
The exercise underscored the Army’s shift towards multi-domain operations, greater reliance on emerging technologies, and closer engagement with the domestic defence industry.
Key Highlights of the Exercise
- Terrain & Conditions: Conducted in high-altitude, harsh Himalayan conditions, validating combat effectiveness and operational resilience.
- Technological Integration: Featured drone surveillance, precision strikes, real-time target acquisition, air–littoral operations, and synchronized battlefield tactics, reflecting the Army’s technological adaptation.
- Debut of ASHNI Platoons: Marked the first operational deployment of the newly raised ASHNI platoons, designed to combine advanced technology with traditional combat expertise for decisive battlefield advantage.
- Indigenous Defence Industry Participation: Reflected India’s emphasis on Atmanirbhar Bharat and the “Decade of Transformation,” with active involvement of the domestic defence sector.
Strategic Significance
- Demonstrated India’s ability to conduct large-scale, coordinated operations in sensitive border regions.
- Validated the Army’s preparedness for multi-domain conflicts involving land, air, cyber, and unmanned systems.
- Reinforced the importance of self-reliance in defence technology by incorporating indigenous systems in live combat simulations.
- Showcased India’s resolve to maintain combat superiority in high-altitude operational theatres along the Line of Actual Control (LAC).
Exercise Samanvay Shakti

- 30 Aug 2025
In News:
The Indian Army, in collaboration with the state governments of Assam and Manipur, inaugurated Exercise Samanvay Shakti 2025 at Laipuli in Tinsukia district, Assam. The initiative is a Military–Civil Integration Exercise designed to build cooperation, cohesion, and mutual understanding among various stakeholder
Aim & Objectives
- Enhance synergy between the armed forces, government departments, and civil institutions.
- Develop a unified and coordinated approach to address the region’s complex challenges.
- Improve preparedness through refined SOPs, effective communication channels, and practical rehearsals.
- Strengthen the bond of trust between local communities and institutions.
- Promote nation-building, development, and national integration.
Participation
The inaugural session saw participation from:
- Indian Army and Indian Air Force.
- State administration, Police, and Intelligence Agencies.
- NDRF, SDRF, BRO, GREF, Medical officials, and Railways.
- Educational institutions and security teams from OIL India, IOCL, Coal India, along with local media representatives.
Key Features
- Location & Duration: Conducted in Assam and a parallel 10-day exercise in Manipur (20–30 August 2025).
- Thematic Focus in Manipur: Disaster management, healthcare, education, public works, forest initiatives, narcotics control, irrigation, road safety, employment in armed forces, sports promotion, police–Army–paramilitary coordination, and infrastructure development under Operation Sadbhavna.
Significance
- Provides a platform for collaboration between civil authorities and the military.
- Enhances regional security preparedness while addressing developmental needs.
- Encourages community participation in governance and security-related initiatives.
- Contributes towards integrated development and inclusive nation-building in the Northeast.
Integrated Air Defence Weapon System (IADWS)
- 29 Aug 2025
In News:
India has successfully conducted the maiden flight tests of its Integrated Air Defence Weapon System (IADWS) off the coast of Odisha, marking a major milestone under Project Sudarshan Chakra. Developed indigenously by the Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO), the system represents a significant advancement in the country’s ability to defend critical assets against evolving aerial threats.
What is IADWS?
The IADWS is a multi-layered, network-centric air defence architecture that integrates:
- Quick Reaction Surface-to-Air Missile (QRSAM)
- Very Short Range Air Defence System (VSHORADS)
- Directed Energy Weapon (DEW) (high-power laser)
Together, these components form a composite shield capable of engaging a wide spectrum of threats—from high-speed aircraft and cruise missiles to drones, swarm UAVs, and loitering munitions.
Key Features
- Centralised Command & Control Centre (C2C2): Integrates radar and electro-optical sensor data to generate a real-time aerial picture. Based on parameters like speed, altitude, and trajectory, threats are assigned to the most effective weapon.
- Multi-layered Defence:
- QRSAM (outer layer): Intercepts fighter aircraft, helicopters, and standoff precision weapons (cruise missiles, glide bombs) at 25–30 km range and up to 10 km altitude. Highly mobile with short reaction times.
- VSHORADS (middle layer): Infrared seeker-based shoulder-fired missiles to neutralise low-flying UAVs and helicopters within 6 km range and up to 4 km altitude.
- Directed Energy Weapon (inner layer): A DRDO-developed laser system capable of disabling drones and loitering munitions at close range. Offers virtually unlimited firing capacity, making it cost-effective and sustainable.
- Simultaneous Target Engagement: During trials, IADWS successfully intercepted three different aerial targets (two fixed-wing UAVs and a multi-copter drone) in real time.
- Mobility & Flexibility: Mounted on high-mobility launchers, the system can be rapidly deployed in forward areas.
Strategic Importance
IADWS strengthens India’s area defence capability by providing a layered shield for:
- Forward air bases and command centres
- Radar and missile installations
- Nuclear and space assets
- Power plants and critical industrial hubs
By combining kinetic (missiles) and non-kinetic (lasers) weapons under a unified command structure, India has taken a major step toward countering both conventional and asymmetric aerial threats.
Significance for India’s Defence Preparedness
- Enhances self-reliance under Atmanirbhar Bharat in advanced defence technologies.
- Strengthens India’s deterrence against hostile air campaigns, drone swarms, and precision strikes.
- Positions India among a select group of nations with multi-layered integrated air defence systems.
Agni-5 Missile
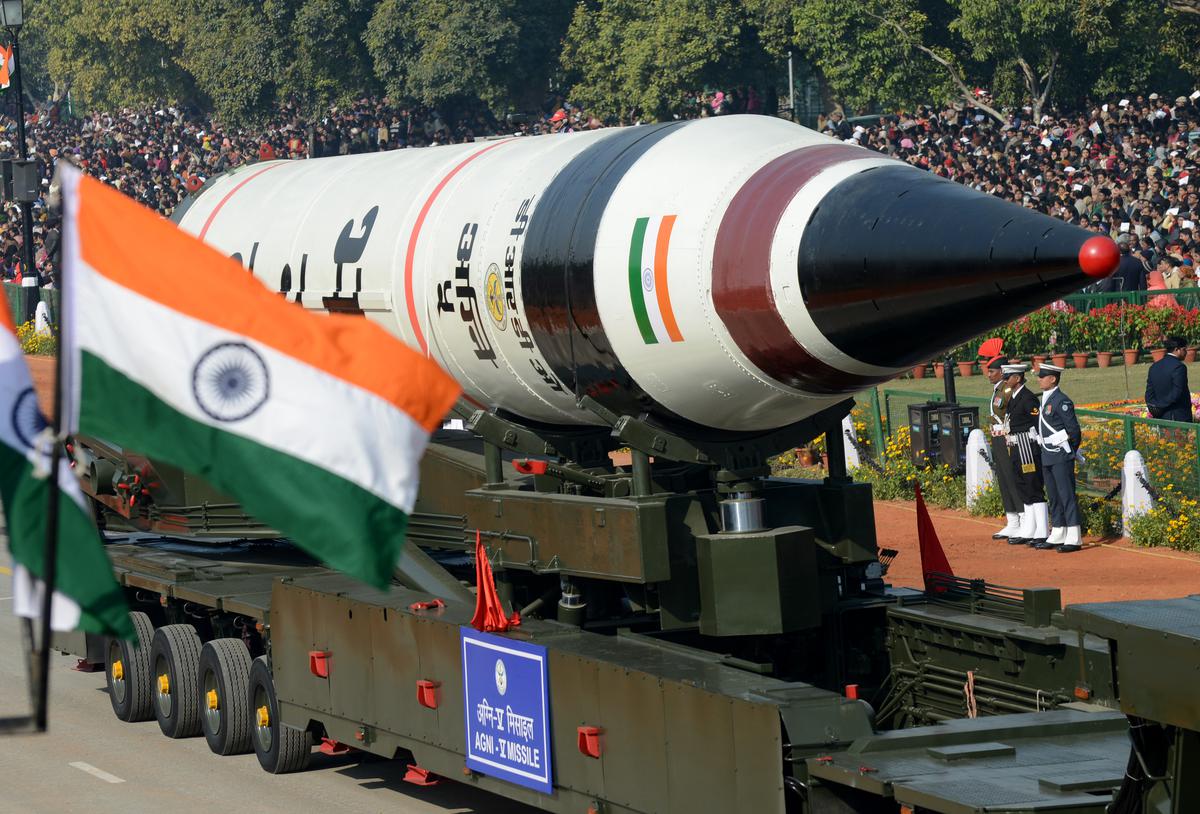

- 26 Aug 2025
In News:
India has successfully conducted the test of its nuclear-capable Agni-5 ballistic missile from the Integrated Test Range (ITR), Chandipur, Odisha. The launch was carried out under the Strategic Forces Command (SFC) and validated all operational and technical parameters, marking a significant boost to India’s strategic deterrence capabilities.
About Agni-5 Missile
- Type: Land-based Intercontinental Ballistic Missile (ICBM).
- Developer: Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO).
- Range: Beyond 5,000 km, capable of covering most of Asia and parts of other continents.
- Payload Capacity: Equipped with Multiple Independently Targetable Reentry Vehicle (MIRV) technology, enabling it to carry and deliver up to three nuclear warheads simultaneously at different targets.
- Technologies Used: Modern navigation, guidance, warhead, and propulsion systems, ensuring high accuracy and survivability.
Ballistic Missiles – Classification by Range
Ballistic missiles are rocket-propelled strategic weapons that follow a ballistic trajectory after the powered phase:
- Short-range: < 1,000 km (Tactical role).
- Medium-range: 1,000–3,000 km (Theater role).
- Intermediate-range: 3,000–5,500 km.
- Intercontinental (ICBM): > 5,500 km (Strategic role).
Agni-5, with its long range and MIRV capability, places India in the league of nations with advanced ICBM technology.
Strategic Significance
- Strengthens nuclear deterrence under India’s credible minimum deterrence and no first use (NFU) doctrines.
- Enhances India’s security architecture amidst evolving regional and global threats.
- Positions India among the select group of countries (U.S., Russia, China, France) with operational ICBM and MIRV capability.
Burevestnik Missile
- 20 Aug 2025
In News:
According to recent reports, Russia is preparing to conduct fresh trials of the 9M730 Burevestnik – a nuclear-powered cruise missile that has often been described as a “unique” and formidable addition to Moscow’s strategic arsenal.
About the Burevestnik
- The term Burevestnik translates to “storm petrel” in Russian.
- It is a ground-launched, nuclear-powered cruise missile, also capable of carrying a nuclear warhead.
- The system was first unveiled by the Russian President in 2018, as part of six advanced strategic weapons.
- NATO has designated it as SSC-X-9 “Skyfall.”
- In theory, its nuclear propulsion allows it to circle the globe multiple times before striking a target, making it an unprecedented strategic weapon.
Key Features
- Nuclear Propulsion: The missile uses a compact nuclear reactor that heats the surrounding air for thrust.
- Extended Range: Unlike traditional engines restricted by fuel capacity, the nuclear design enables a potential range of up to 22,000 km (14,000 miles).
- Low-Altitude Flight: The system is engineered to fly close to the ground, significantly reducing its detectability by conventional air-defence radars.
- Strategic Significance: Its combination of long endurance and stealthy trajectory poses challenges to existing missile defence systems.
Dark Eagle Hypersonic Missile

- 09 Aug 2025
In News:
The United States has achieved a major milestone by deploying its Long-Range Hypersonic Weapon (LRHW), known as Dark Eagle, to Australia’s Northern Territory during the Talisman Sabre 2025 multinational military exercise. This marks the system’s first-ever overseas deployment and represents a critical step in strengthening U.S. deterrence capabilities in the Indo-Pacific.
Features:
- Range & Speed: Approximately 2,700–2,776 km with a reported velocity of up to Mach 17.
- Design: A land-based, road-mobile system comprising four trailer-mounted launchers, each with two missile canisters.
- Warhead: Equipped with the Common Hypersonic Glide Body (C-HGB), an unpowered yet maneuverable glide vehicle capable of evading interception.
- Deployment Capability: Road-mobile, air-transportable (C-17), and integrated with the U.S. Army’s Integrated Air and Missile Defense Battle Command System (IBCS).
- Developers: Jointly developed by Lockheed Martin and Northrop Grumman, with collaboration from the U.S. Navy on the glide body and boosters.
- Mission Role: Designed to penetrate anti-access/area-denial (A2/AD) networks, suppress enemy defenses, and engage time-sensitive, high-value targets.
Exercise Talisman Sabre
For the first time, India participated in the 11th edition of Exercise Talisman Sabre 2025, a large-scale Australia-led multinational military exercise. This reflects India’s growing role in the Indo-Pacific security architecture and deepening defense cooperation with like-minded partners.
- Launch & Evolution: Initiated in 2005 as a bilateral drill between Australia and the United States, it has expanded into a premier multinational warfighting exercise.
- Scale: The 2025 edition is the largest-ever, involving over 35,000 personnel from 19 nations including Australia, U.S., India, Japan, France, U.K., and others.
- Geographical Spread: Conducted across Queensland, Northern Territory, Western Australia, New South Wales, and Christmas Island, with a first-ever extension to Papua New Guinea, underscoring wider regional engagement.
- Objective:
- To uphold a free, open, and inclusive Indo-Pacific.
- Enhance military readiness, interoperability, and joint operational capabilities.
- Reinforce regional security cooperation among allies and partners.
- Activities: Includes live-fire drills, amphibious landings, ground maneuvers, air combat, maritime operations, and force preparation exercises, testing joint warfighting capabilities.
Key India-Australia Military Exercises
- AUSINDEX – Naval exercise.
- Pitch Black – Multinational air exercise.
- AustraHind – Bilateral military exercise.
Key India-U.S. Military Exercises
- YudhAbhyas – Joint military training.
- Vajra Prahar – Special Forces exercise.
- Cope India – Air combat exercise.
- Tiger Triumph – Tri-services amphibious exercise.
Oreshnik Hypersonic Missile
- 04 Aug 2025
In News:
In August 2025, Russian President Vladimir Putin announced that the Oreshnik hypersonic missile—a new-generation intermediate-range ballistic missile—has entered production and military service. Plans are underway to deploy the system in Belarus by the end of 2025, signalling a major escalation in Russia’s standoff with NATO amid the Ukraine conflict.
Key Features
- Type: Intermediate-range, solid-fuel, mobile, hypersonic ballistic missile
- First Operational Use: November 2024, in a strike on Ukraine’s Pivdenmashdefence facility at Dnipro
- Speed: Capable of reaching Mach 10 (10 times the speed of sound)
- Range: Approx. 5,000 km (3,100 miles), bringing the entirety of Europe within its strike zone
- Warhead Capability:
- Carries conventional or nuclear warheads
- Equipped with Multiple Independently Targetable Re-entry Vehicles (MIRVs), allowing simultaneous strikes on multiple targets
- Strategic Advantage: Hypersonic speed, mid-flight manoeuvrability, and MIRV capability make it virtually immune to interception by current Western missile defence systems
Strategic Context
- Belarus as a Forward Base:
- Belarus shares a 673-mile border with Ukraine, making it strategically vital.
- It already hosts Russian troops and tactical nuclear weapons.
- Deployment of Oreshnik here allows Moscow to project power deeper into Europe.
- Nuclear Security Pact (2023):
- Russia and Belarus signed an agreement placing Belarus under Russia’s nuclear umbrella.
- Russia retains the right to use nuclear weapons stationed in Belarus if “aggression” is perceived.
- Belarus has reportedly hosted “several dozen” Russian nuclear weapons since late 2024.
- Geopolitical Implications:
- Russia warned NATO against supplying Ukraine with long-range weapons capable of striking inside Russia.
- Putin cautioned that Russia could retaliate with systems like Oreshnik “even beyond Ukraine.”
- By suggesting that conventional Oreshnik strikes could be as devastating as nuclear attacks, Moscow is raising deterrence levels against the West.
Implications for Global Security
- Erosion of Arms Control: With the collapse of Cold War-era treaties like the INF Treaty (1987), weapons such as Oreshnik operate in a largely unregulated environment.
- Escalation of NATO–Russia Rivalry: The missile’s deployment in Belarus expands Russia’s strike capability across Europe, heightening NATO security concerns.
- Nuclear Threshold Ambiguity: Oreshnik’s dual capability (conventional and nuclear) blurs the line between conventional warfare and nuclear escalation.
- Arms Race in Hypersonics: The U.S., China, and other powers are also developing hypersonic weapons, intensifying competition in next-generation strategic arms.
Exercise Divya Drishti
- 31 Jul 2025
In News:
In July 2025, the Indian Army conducted Exercise Divya Drishti in East Sikkim, showcasing next-generation warfare technologies under high-altitude conditions.
Organised by the Trishakti Corps, the exercise focused on integrating Artificial Intelligence (AI) with battlefield surveillance and decision-making systems, in alignment with the Atmanirbhar Bharat initiative and the Army’s Decade of Transformation roadmap.
Key Features:
- AI-Enabled Battlefield Awareness: The Army deployed AI-integrated sensors capable of real-time surveillance, terrain mapping, and threat detection.
- Sensor-to-Shooter Linkage: Real-time data was transmitted from UAVs, drones, and ground-based sensors to command centres and firepower units, ensuring rapid response capability.
- UAV-Drone-Ground Synergy: Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAVs) and drones operated in coordination with ground platforms to simulate operational combat scenarios.
- Secured Communication Networks: Robust digital communication systems enabled seamless and secure data sharing across units.
- High-Altitude Readiness: The technologies were tested in the Himalayan terrain to assess their effectiveness in extreme operational environments.
Strategic Significance:
- Enhanced Situational Awareness: The exercise aimed to improve the Army’s capacity to observe, interpret, and act swiftly on the modern battlefield.
- Faster Decision-Making: AI integration minimizes command delays, improving response speed and operational precision.
- Indigenisation Drive: Demonstrates the Indian Army’s push for self-reliance in defence technology under Make in India.
- Future Warfare Doctrines: The insights will inform new operational strategies for multi-domain and hybrid warfare.
Veer Parivar Sahayata Yojana
- 29 Jul 2025
In News:
The National Legal Services Authority (NALSA), in a significant step toward safeguarding the legal rights of India’s uniformed forces, launched the Veer Parivar Sahayata Yojana during the North Zone Regional Conference in Srinagar. Themed “Reaffirming the Constitutional Vision of Justice for Defence Personnel and Tribals,” the event spotlighted the urgent need to institutionalize accessible legal assistance for military personnel and their families.
Rationale and Objectives
- Defence and paramilitary personnel frequently serve in remote, conflict-prone, or high-risk environments, which limits their ability to attend to civilian legal matters. Be it land disputes, family conflicts, service-related claims, or bureaucratic issues, legal hurdles can deeply affect their lives. The scheme acknowledges that a soldier stationed on the border cannot readily leave his post to handle legal proceedings back home.
- The Veer Parivar Sahayata Yojana is designed to bridge this critical gap by providing free, competent, and timely legal aid to serving personnel, veterans, and their families.
Key Features of the Scheme
- Joint Collaboration: The initiative is a joint effort between NALSA, the Kendriya Sainik Board (KSB), Rajya Sainik Boards (RSBs), and Zilla Sainik Boards (ZSBs) under the Department of Ex-Servicemen Welfare, Ministry of Defence.
- Legal Clinics Across Sainik Boards: Legal Services Clinics will be established at the district, state, and central levels of the Sainik Boards across India. These will function as the first point of contact for defence families seeking legal assistance.
- Trained Legal Volunteers: The initiative actively involves panel lawyers and trained paralegal volunteers, including ex-servicemen and defence family members, to offer legal services and counselling.
- Back-end Legal Infrastructure: A robust administrative mechanism will support the on-ground functioning of clinics and ensure prompt resolution of legal grievances.
- Coverage for Paramilitary Forces: The scheme will also extend support to paramilitary personnel from forces such as BSF, CRPF, ITBP, and others, who operate under similar hardships and isolation.
Significance and Constitutional Context
- The scheme upholds Article 39A of the Constitution, which mandates equal justice and free legal aid for all citizens. Defence personnel, who make immense sacrifices for national security, often remain underserved when it comes to civilian entitlements, rights, and dispute resolution.
- By reaffirming the constitutional commitment to access to justice, the scheme aligns with the broader goal of legal empowerment of vulnerable and marginalized communities, including those in service of the nation.
MiG-21 Fighter Jets
- 24 Jul 2025
In News:
- The Indian Air Force (IAF) is set to retire its final two squadrons of the iconic MiG-21 Bison fighter jets in September 2025, marking the end of an era that spanned over six decades.
- First inducted in 1963, the MiG-21 played a pivotal role in shaping India's aerial combat capabilities and remains a symbol of India's early steps toward defence self-reliance.
MiG-21: An Overview
- Origin: Designed by the Mikoyan-Gurevich Design Bureau of the Soviet Union in the 1950s.
- Type: Single-engine, supersonic jet fighter.
- Speed: Capable of speeds over Mach 2.0, making it one of the fastest jets of its time.
- Induction in India: Entered IAF service in 1963; licensed production began in the 1960s by Hindustan Aeronautics Limited (HAL).
- Significance: India’s first combat aircraft of non-Western origin and a key asset for air superiority during the Cold War and beyond.
Operational Legacy
The MiG-21 became the backbone of the IAF from the 1970s until the early 2000s, remaining in service even after the induction of more advanced aircraft like the Su-30MKI.
Wars and Combat Contributions
- 1965 & 1971 Indo-Pak Wars: Played a crucial role in establishing air superiority.
- During the 1971 war, MiG-21s conducted multiple successful bombing missions, including attacks on Pakistani airbases, contributing significantly to India’s decisive victory and the creation of Bangladesh.
- The aircraft famously outmatched Pakistan’s F-104 Starfighters in dogfights.
Strengths
- All-weather operations capability.
- Versatility in roles: air-to-air combat, ground attacks, and reconnaissance.
- Compatibility with a variety of air-to-ground and air-to-air weapons.
Limitations and Controversy
Despite its legendary status, the MiG-21's later years were marked by increasing technical limitations and a poor safety record:
- Nicknamed "Flying Coffin" due to over 400 crashes since the 1970s.
- Resulted in the deaths of over 200 pilots and 50 civilians.
- Upgraded variants like the MiG-21 Bison included radar and avionics improvements but could not overcome structural and safety limitations.
- Retirement was delayed multiple times due to shortages in the IAF’s squadron strength.
Retirement and Replacement
- The last two MiG-21 Bison squadrons will be phased out by September 2025.
- India had produced over 600 MiG-21s under license.
- Replacement underway with indigenously developed Tejas Mk-1A fighter jets, part of India’s push for self-reliance under Atmanirbhar Bharat.
- The IAF currently operates 29 squadrons—well below the sanctioned strength of 42.5 squadrons.
Exercise SIMBEX
- 20 Jul 2025
In News:
The Indian Navy is participating in the 32nd edition of the Singapore-India Maritime Bilateral Exercise (SIMBEX) in Singapore in July 2025. It marks one of the longest uninterrupted bilateral naval exercises India has with any country.
What is SIMBEX?
- SIMBEX stands for Singapore-India Maritime Bilateral Exercise
- It is an annual naval exercise conducted between the Indian Navy and the Republic of Singapore Navy (RSN)
- Origin: Initiated in 1994 as Exercise Lion King
- It has evolved into a complex maritime engagement, showcasing interoperability in surface, subsurface, and air operations
Significance
- It supports India’s Vision SAGAR (Security and Growth for All in the Region) and the Act East Policy
- Promotes regional maritime security cooperation and ensures the safety of sea lanes of communication (SLOCs)
- Reinforces commitment to a rules-based international maritime order, especially amidst rising piracy and threats from non-state actors
Indian Navy’s Participation (2025 Edition)
- The Indian naval contingent includes:
- INS Delhi – Guided missile destroyer
- INS Satpura – Stealth frigate
- INS Shakti – Fleet replenishment tanker
- INS Kiltan – Anti-submarine corvette
- These vessels are indigenously designed and equipped with advanced systems for high-seas operations
Strategic Engagement Highlights
- SIMBEX is a critical part of India’s expanding maritime diplomacy in the Indo-Pacific
- The naval exercise is conducted alongside a goodwill visit to Singapore, coinciding with the 60th anniversary of India-Singapore diplomatic ties
- Following Singapore, the Indian Navy’s Eastern Fleet is also scheduled to visit the Philippines and Vietnam
Broader Defence Cooperation with Singapore
In addition to SIMBEX, India and Singapore engage in:
- Exercise Agni Warrior (Army)
- Joint Military Training (JMT) (Air Force)
India also engages with ASEAN through:
- ASEAN-India Maritime Exercise (First held in 2023, co-hosted by Singapore)
- Participation in ASEAN-led forums like:
- ADMM-Plus
- ASEAN Regional Forum
- East Asia Summit
Vision SAGAR & Maritime Security
India’s Vision SAGAR emphasizes:
- Collaborative maritime partnerships
- Combating common maritime threats (e.g., piracy, trafficking, and disasters)
- Securing economic and strategic interests in the Indian Ocean Region (IOR)
Prithvi-II and Agni-I Ballistic Missiles
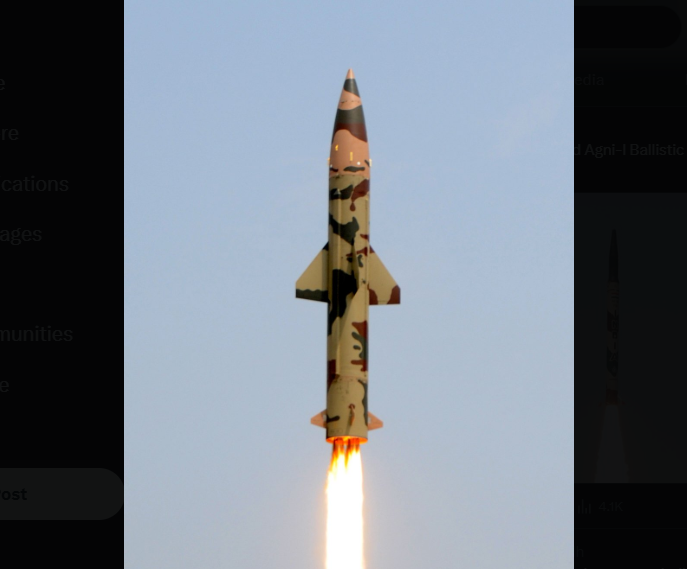

- 19 Jul 2025
In News:
India recently conducted successful test-firings of its nuclear-capable short-range ballistic missiles Prithvi-II and Agni-I from the Integrated Test Range (ITR), Chandipur, Odisha. The trials aimed to validate operational readiness and technical reliability of India’s strategic missile systems.
These tests follow closely on the heels of the Indian Army's successful high-altitude test of the Akash Prime air defence system in Ladakh, underscoring India’s advancing indigenous defence capabilities.
Strategic Significance
- Conducted by: Strategic Forces Command (SFC) under routine training and validation exercises.
- Developed by: Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO) under the Integrated Guided Missile Development Programme (IGMDP).
- Purpose:
- To validate accuracy, technical parameters, and combat readiness.
- To reinforce India’s nuclear deterrence and second-strike capability.
- To ensure strategic preparedness post the May 2025 Indo-Pak conflict.
Prithvi-II Missile: Key Features
|
Parameter |
Details |
|
Type |
Short-range, surface-to-surface ballistic missile |
|
Range |
~350 km |
|
Propulsion |
Liquid-fuelled |
|
Payload Capacity |
Up to 500 kg |
|
Warhead Type |
Conventional and nuclear |
|
Navigation |
Advanced inertial navigation system |
|
Deployment |
Road-mobile launcher |
|
Speed |
Above Mach 1 |
|
Role |
Part of India’s tactical nuclear strike capability |
Agni-I Missile: Key Features
|
Parameter |
Details |
|
Type |
Short-range, single-stage ballistic missile |
|
Range |
700–900 km |
|
Propulsion |
Solid-fuelled |
|
Payload Capacity |
Up to 1,000 kg |
|
Warhead Type |
Conventional and nuclear |
|
Accuracy |
High precision with advanced guidance |
|
Induction |
Early 2000s, operational with Indian Army |
|
Strategic Role |
Integral to India’s minimum credible deterrence posture |
Akash Prime Missile System

- 19 Jul 2025
In News:
India has successfully conducted a high-altitude trial of the Akash Prime surface-to-air missile system in Ladakh, marking a major step in strengthening indigenous air defence capabilities, particularly for mountainous and high-altitude terrains.
What is Akash Prime?
Akash Prime is an upgraded variant of the Akash Surface-to-Air Missile (SAM) system, developed by the Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO). It is designed to operate efficiently in high-altitude, low-oxygen environments—ideal for India’s sensitive border regions like Ladakh and Sikkim.
Developers
- DRDO – Lead developer
- In collaboration with:
- Bharat Dynamics Limited (BDL)
- Bharat Electronics Limited (BEL)
Key Features
|
Feature |
Description |
|
Purpose |
Neutralizes aerial threats like enemy aircraft, drones, and cruise missiles |
|
Altitude Performance |
Successfully tested at 15,000 ft; engineered for deployment above 4,500 metres |
|
Seeker Technology |
Equipped with an indigenous Radio Frequency (RF) seeker for precise target acquisition during terminal phase |
|
Guidance System |
Hybrid: Command guidance + terminal active homing |
|
Range & Speed |
Operates within 25–30 km range; travels at Mach 2.5 |
|
Mobility |
Mounted on mobile platforms for rapid deployment across terrains |
|
All-Weather Capability |
Functions in extreme cold and low-density atmospheric conditions |
|
Kill Probability |
88% (single missile); up to 98.5% in dual-salvo mode |
Operational Significance
- High-Altitude Readiness: Specifically tailored for mountainous regions such as the Line of Actual Control (LAC).
- Versatile Deployment: Protects mobile, semi-mobile, and fixed military installations.
- Strategic Feedback Integration: Incorporates enhancements based on feedback from armed forces for use in vital installations.
Strategic Importance
- Aatmanirbhar Bharat: Fully indigenous system contributing to self-reliance in defence manufacturing.
- Cost Efficiency: Reduces dependency on imported air defence systems.
- Force Multiplier: Strengthens India’s layered air defence network against modern aerial threats.
Exercise Talisman Sabre 2025

- 16 Jul 2025
In News:
India is participating in Exercise Talisman Sabre 2025, a major multinational military exercise led by Australia and the United States, now in its 11th edition. The exercise commenced on July 13, 2025, and includes over 35,000 military personnel from 19 nations.
About Exercise Talisman Sabre:
- Origin & Nature:
- A biennial bilateral military exercise between Australia and the United States since 2005.
- Designed to promote a free and open Indo-Pacific and strengthen interoperability and strategic partnerships among allies.
- Multinational Participation (2025):
- Participants: Australia, United States, India, Canada, Fiji, France, Germany, Indonesia, Japan, Netherlands, New Zealand, Norway, Papua New Guinea, Philippines, Republic of Korea, Singapore, Thailand, Tonga, United Kingdom.
- Observers: Malaysia and Vietnam.
- Geographical Scope: Exercises are being conducted across Queensland, Northern Territory, Western Australia, New South Wales, Christmas Island, and for the first time, in Papua New Guinea (outside Australian territory).
Significance for India and the Indo-Pacific:
- Strengthens India's defence diplomacy and military interoperability with Indo-Pacific allies.
- Reinforces commitment to collective security and rules-based international order.
- Enhances India's operational exposure in multidomain warfighting scenarios alongside major powers.
Astra Missile
- 15 Jul 2025
In News:
The Astra missile, developed by the Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO), is India’s first indigenous Beyond-Visual-Range Air-to-Air Missile (BVRAAM). Recently, the Indian Air Force (IAF) and DRDO successfully flight-tested the missile from a Sukhoi-30 MKI fighter jet off the coast of Odisha.
Key Features:
- Range: Over 100 km, enabling engagement of distant aerial targets.
- Speed: Capable of flying at speeds exceeding Mach 4.
- Operational Ceiling: Effective up to 20 km altitude.
- Seeker: Equipped with a fully indigenous Radio Frequency (RF) Seeker, enhancing precision targeting.
- Guidance System: State-of-the-art navigation and guidance technologies ensure high accuracy.
- All-weather Capability: Operable in day and night across diverse weather conditions.
Recent Tests:
- Conducted against high-speed unmanned aerial targets at varying ranges and conditions.
- Achieved pinpoint accuracy in both launches.
- All subsystems, including the RF seeker and tracking systems, functioned flawlessly.
- Tests were conducted at the Integrated Test Range (ITR), Chandipur.
Strategic Significance:
- Boosts India’s air-to-air combat capability.
- Reduces dependency on foreign missile systems.
- Supports the vision of Aatmanirbhar Bharat in defence technology.
- Over 50 Indian public and private sector industries, including Hindustan Aeronautics Limited (HAL), contributed to its development.
INS Nistar

- 14 Jul 2025
In News:
In a significant stride towards self-reliance in defence manufacturing under the Aatmanirbhar Bharat initiative, the Indian Navy has inducted INS Nistar, its first indigenously designed and built Diving Support Vessel (DSV). Developed by Hindustan Shipyard Limited (HSL), Visakhapatnam, INS Nistar enhances India’s capabilities in deep-sea rescue, submarine emergency response, and underwater operations, placing India among a select group of nations with such advanced maritime assets.
Key Features and Capabilities
- Size and Endurance:
- Length: ~118–120 meters
- Displacement: Over 10,000 tonnes
- Endurance: Capable of operating for over 60 days at sea
- Diving and Rescue Capabilities:
- Equipped for saturation diving up to 300 meters and side diving stage operations up to 75 meters
- Integrated with Remotely Operated Vehicles (ROVs) for diver monitoring and salvage missions up to 1000 meters below sea level
- Serves as the Mother Ship for the Deep Submergence Rescue Vehicle (DSRV), crucial for submarine crew evacuation in emergencies
- Medical and Operational Infrastructure:
- Includes an 8-bed hospital, ICU, operation theatre, and hyperbaric chambers for diver treatment and recovery
- Fitted with a 15-tonne subsea crane, helicopter landing deck, and Side Scan SONAR for multi-role logistics and salvage operations
- Navigation and Control: Integrated Dynamic Positioning System (DPS) ensures precision during complex underwater missions
Indigenous Content and Industrial Participation
- Indigenous Content: Approximately 75–80%
- Over 120 Indian MSMEs contributed to the vessel’s construction
- Compliant with Indian Register of Shipping (IRS) classification standards
Strategic and Symbolic Significance
- Bridges critical capability gaps in submarine rescue, deep-sea salvage, and maritime disaster response
- Strengthens India’s strategic posture in the Indian Ocean Region (IOR), ensuring rapid and self-reliant response to undersea emergencies
- Reinforces India’s position as an emerging blue water navy
- Symbolically revives the legacy of the erstwhile Soviet-origin INS Nistar (commissioned in 1971), reaffirming continuity and progress in naval capabilities
MALE Drone Procurement

- 14 Jul 2025
In News:
In a significant stride towards self-reliance in defence technology, India has expedited the procurement of 87 Medium Altitude Long Endurance (MALE) drones from domestic manufacturers under the ?20,000 crore initiative, marking a major step in strengthening border surveillance and operational readiness.
What are MALE Drones?
MALE (Medium Altitude Long Endurance) drones are unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) capable of flying at altitudes of up to 35,000 feet and sustaining flight for over 30 hours. These drones are equipped for Intelligence, Surveillance, and Reconnaissance (ISR) and can undertake limited combat missions.
Key Features
- Endurance: Operational capacity exceeds 30 hours.
- Altitude Range: Effective at 35,000 feet or higher.
- Payload: Equipped with Electro-Optical/Infrared (EO/IR) cameras, radar systems, and combat modules.
- Real-time ISR: Provides persistent surveillance over diverse terrain.
- Remote Operations: Ground stations with secure communication links manage operations.
- Indigenous Content: Over 60% of components are locally manufactured, promoting import substitution.
Strategic Applications
- Border and Maritime Surveillance: Enhances India’s ability to monitor land borders with Pakistan and China, and maritime boundaries in the Indian Ocean Region.
- Tri-Service Integration: These drones will be deployed across the Army, Navy, and Air Force, improving joint situational awareness.
- Counter-Insurgency Support: Useful in operations in Naxal-affected and insurgency-prone areas, providing tactical aerial intelligence.
- Disaster Relief and Mapping: Can aid in real-time mapping and coordination during natural disasters and humanitarian crises.
Strategic Importance
- Fills the capability gap between smaller tactical UAVs and high-altitude surveillance drones like the MQ-9B Sea/ Sky Guardians.
- Replaces India’s earlier dependence on Israeli UAVs (e.g., Heron drones), boosting the ‘Make in India’ initiative in defence manufacturing.
- Enhances 24×7 real-time surveillance, thereby strengthening national security architecture.
Extended Range Anti-Submarine Rocket (ERASR)

- 13 Jul 2025
In News:
India recently conducted successful user trials of the Extended Range Anti-Submarine Rocket (ERASR) from INS Kavaratti, marking a significant milestone in strengthening the country’s anti-submarine warfare (ASW) capabilities through indigenously developed technologies.
What is ERASR?
The ERASR is a state-of-the-art anti-submarine rocket system designed to neutralize hostile submarines from Indian naval warships. It is specifically intended for launch from Indigenous Rocket Launchers (IRLs) onboard Indian Navy ships.
- Developed by: Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO), specifically the Armament Research & Development Establishment (ARDE), Pune, in collaboration with the High Energy Materials Research Laboratory and Naval Science & Technological Laboratory.
- Production partners: Bharat Dynamics Limited (Hyderabad) and Solar Defence & Aerospace Ltd. (Nagpur).
Key Features
- Twin Rocket Motor System: Enables engagement of both short- and long-range submarine targets with high accuracy and consistency.
- Electronic Time Fuze: Fully indigenously developed to ensure precise detonation near underwater threats.
- High Operational Reliability: Demonstrated through consistent warhead detonation and fuze performance.
- Launch Compatibility: Designed to be fired from frontline warships equipped with Indian-made rocket launchers.
Highlights of User Trials
- Conducted from: INS Kavaratti under simulated maritime combat conditions.
- Number of Rockets Tested: 17
- Parameters Evaluated:
- Range performance
- Fuze timing reliability
- Warhead detonation effectiveness
- Outcome: All trial objectives were met; system demonstrated full battlefield readiness.
Significance
- Strengthens India’s ASW capabilities in the Indian Ocean Region, a vital strategic space.
- Boosts Atmanirbharta in defence by reducing reliance on foreign imports.
- Economically efficient, as the scalable domestic production replaces high-cost foreign systems.
- Reflects DRDO’s technological maturity in delivering mission-ready, indigenous defence solutions.
Advanced Towed Artillery Gun System (ATAGS)
- 12 Jul 2025
In News:
The Advanced Towed Artillery Gun System (ATAGS) marks a significant milestone in India’s defence modernization. Developed indigenously under the ‘Make in India’ initiative, the system is poised to replace the Indian Army’s ageing artillery with cutting-edge, high-performance firepower.
Key Facts:
- Calibre: 155 mm / 52 calibre
- Maximum Range: Up to 48 km, among the longest for towed artillery globally
- Developer: Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO) through ARDE (Pune)
- Production Partners: Bharat Forge Ltd and Tata Advanced Systems Ltd
Project Timeline & Cost:
- Project initiated in 2012 and completed within 12 years
- In March 2025, the Defence Ministry signed contracts worth ?6,900 crore for procurement of 307 ATAGS units and associated 6×6 towing vehicles
- Delivery scheduled over five years
Salient Features of ATAGS:
- Firing Modes: Burst, Intense, and Sustained fire
- Firing Capacity: Up to five rounds per minute, 60 rounds per hour
- Automation: Fully electric gun-laying and ammunition handling, replacing conventional hydraulics for enhanced reliability and reduced maintenance
- Shoot-and-Scoot Capability: Quick repositioning post firing to avoid counter-battery fire
- Rapid Deployment: Becomes operational within 90 seconds
- Mobility: Towed by a 6×6 high mobility vehicle, suitable for desert and mountainous terrain
- Ammunition Compatibility: Supports all 155 mm ammunition types including high-explosive, smoke, illumination, and precision-guided shells
- Minimum Range Advantage: Capable of achieving shortest minimum range at high elevation angles
- Operating Conditions: Designed for extreme climates
Strategic Significance:
- Artillery Modernization: Replaces vintage, smaller-calibre guns, enhancing range, accuracy, and tactical mobility
- Indigenous Content: Over 80% components sourced domestically, contributing to Aatmanirbhar Bharat
- Mission Mode Achievement: Described as an "exemplary mission-mode success" by the Ministry of Defence
- Multi-Sector Collaboration: Joint effort between DRDO, Indian Army, public and private sector manufacturers
National Maritime Domain Awareness (NMDA) Project

- 11 Jul 2025
In News:
The Indian Navy has signed a significant contract with Bharat Electronics Limited (BEL), Bengaluru for the implementation of the National Maritime Domain Awareness (NMDA) Project, a strategic initiative to strengthen India’s maritime and coastal security infrastructure.
Key Objectives and Scope
- Purpose: The NMDA Project aims to create a unified, real-time maritime surveillance and information-sharing framework to safeguard India's vast coastline and maritime interests.
- It seeks to enhance coordination among maritime stakeholders, including national agencies, coastal states, and union territories.
Major Components of the Project
- Upgrade of NC3I Network: The existing National Command, Control, Communication and Intelligence (NC3I) Network will be upgraded to a more advanced NMDA Network.
- AI Integration: Artificial Intelligence-enabled software will be deployed to enable smart surveillance, automated threat detection, and informed decision-making.
Multi-Agency NMDA Centre
- The Information Management and Analysis Centre (IMAC) at Gurugram — currently the nodal agency of the NC3I Network — will be transformed into a Multi-Agency NMDA Centre.
- The upgraded centre will include representatives from 15 national agencies across seven key ministries, such as Defence, Shipping, Petroleum, and Fisheries, ensuring seamless inter-agency coordination.
Operational and Strategic Benefits
- Integrated Maritime Picture: The system will link various stakeholders to provide a comprehensive operational view of India’s maritime domain.
- Enhanced Response: It will improve response mechanisms to maritime threats, search and rescue operations, environmental incidents, and other contingencies.
- Data Integration: Inputs from sectors such as commercial shipping and fisheries will be integrated into the system for improved situational awareness.
Execution and Administration
- The project will be implemented on a turnkey basis and administered by the Indian Navy.
- BEL will act as the lead system integrator, delivering both hardware and AI-enabled software solutions for the project.
AIR LORA
- 08 Jul 2025
In News:
The Indian Air Force (IAF) is reportedly exploring the procurement of AIR LORA, an advanced air-launched ballistic missile system, aimed at strengthening its long-range precision strike capability.
About AIR LORA Missile System:
- Origin: Developed by Israel Aerospace Industries (IAI), AIR LORA (Long-Range Artillery) is a next-generation air-to-surface ballistic missile designed for high-impact strike missions.
- Role: Optimized to target high-value and fortified enemy assets, such as:
- Military command centers
- Airbases
- Critical infrastructure
- Naval vessels, especially in coastal and contested maritime zones
Key Features and Specifications:
|
Parameter |
Details |
|
Length |
5.2 meters |
|
Diameter |
0.624 meters |
|
Launch Weight |
~1,600 kg |
|
Payload Capacity |
Up to 600 kg |
|
Warhead Types |
High Explosive (HE) or submunitions |
|
Maximum Range |
~400 km |
|
Speed |
Supersonic |
Technological Capabilities:
- Autonomous Fire-and-Forget System:
- Post-launch, the missile requires no further guidance from the aircraft.
- Supports mid-course re-targeting, allowing dynamic adaptation to battlefield changes.
- Navigation and Guidance:
- Employs advanced INS/GNSS (Inertial Navigation System/Global Navigation Satellite System).
- Features robust anti-jamming systems, ensuring operability in highly contested electronic warfare environments.
- Operational Versatility:
- All-weather, 24/7 deployable
- Can be integrated as a standalone weapon or via an aircraft’s avionics.
- Terminal trajectory shaping and 90° steep-attack profile enhance target precision and survivability against air defences.
- Combat Proven: Boasts high mission success rates due to its supersonic speed, GNSS immunity, and precision terminal guidance system.
Strategic Relevance for India:
- Enhances the IAF’s standoff strike capabilities, allowing engagements beyond the reach of enemy air defences.
- Provides the ability to strike deep targets with minimal risk to pilots or aircraft.
- Strengthens India's deterrence posture, especially in regions with highly fortified enemy positions or naval assets.
INS Nilgiri
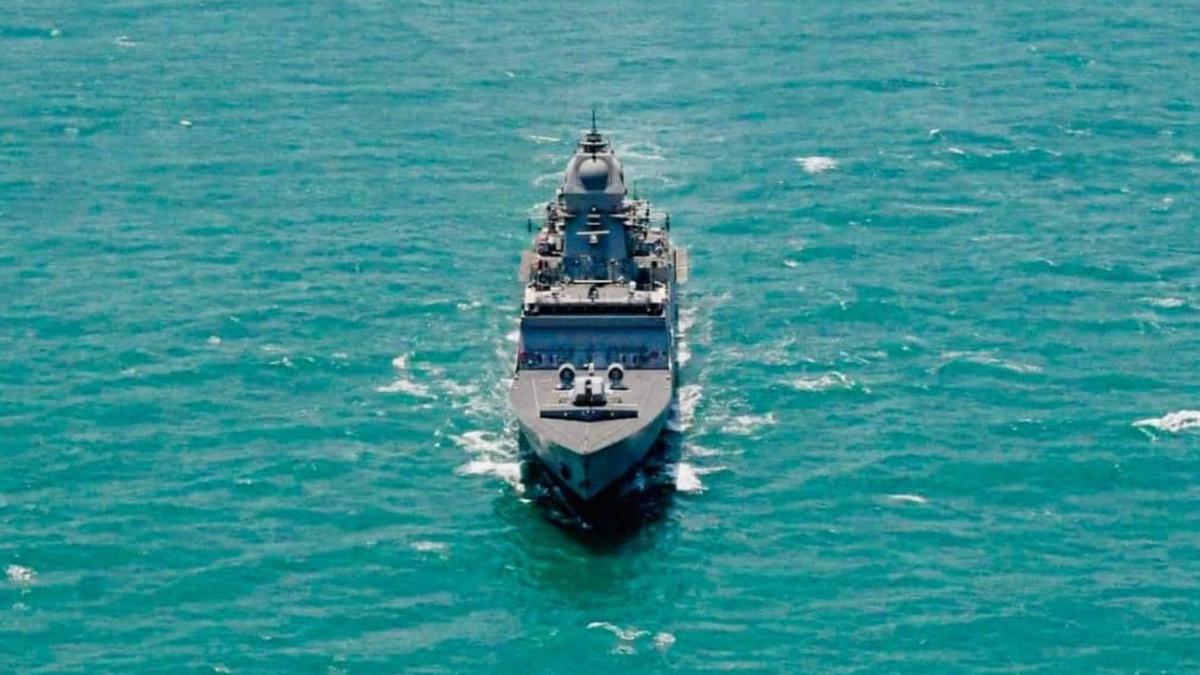

- 26 Jun 2025
In News:
INS Nilgiri, the first stealth frigate of the indigenously developed Project 17A series, has recently been inducted into the Eastern Naval Command. It will play a crucial role in the Eastern Sword-Sunrise Fleet.
Key Facts:
- Class and Design:INS Nilgiri belongs to the Nilgiri-class frigates under Project 17A, an advanced stealth warship initiative. It is an improved version of the earlier Shivalik-class (Project 17) frigates.
- Design and Construction:The vessel has been designed by the Indian Navy’s Warship Design Bureau and constructed by Mazagon Dock Shipbuilders Limited (MDL) in Mumbai.
- Sister Ships Under Construction:Six other frigates of the same class—Himgiri, Taragiri, Udaygiri, Dunagiri, Vindhyagiri, and Mahendragiri—are currently being built at MDL, Mumbai and Garden Reach Shipbuilders and Engineers (GRSE), Kolkata.
Technical Specifications & Capabilities:
- Dimensions & Displacement:
- Length: 149 meters
- Displacement: Approximately 6,670 tonnes
- Propulsion:
- Equipped with a CODAG (Combined Diesel and Gas) propulsion system
- Maximum speed: Up to 28 knots
- Combat Capability:
- Anti-Air Warfare: Armed with 16 Barak-8 surface-to-air missiles
- Surface Warfare: Equipped with 8 BrahMos supersonic cruise missiles for anti-ship and land-attack roles
- Surveillance & Targeting Systems:
- MF-STAR Radar: Offers 360-degree situational awareness
- 3D AESA Radar: Enables tracking of multiple targets simultaneously
- Nishant Radar: Enhances fire control and targeting precision
- Network-Centric Warfare:The onboard Combat Management System (CMS) seamlessly integrates various sensors and weapons, allowing for coordinated operations with other naval platforms.
Significance:
The induction of INS Nilgiri marks a major milestone in India’s pursuit of a modern, self-reliant naval fleet. It enhances the Indian Navy’s blue-water capabilities, contributing to maritime dominance and regional security in the Indo-Pacific.
Tomahawk Missiles
- 25 Jun 2025
In News:
In a major escalation of the Iran-Israel conflict, the United States has reportedly launched precision strikes on Iran’s nuclear infrastructure, targeting key sites at Fordow, Natanz, and Esfahan. These attacks were carried out using Tomahawk cruise missiles and GBU-57 bunker busters, marking a critical intervention by the US in the unfolding regional crisis. President Donald Trump termed the strikes a “clear warning” to Iran, signalling the potential for intensified military action if diplomatic overtures are rejected.
What Are Tomahawk Missiles?
The Tomahawk missile is a long-range, subsonic, all-weather cruise missile primarily operated by the United States Navy and Royal Navy. It is designed for precision strikes on high-value or heavily defended targets, including hardened or buried infrastructure such as nuclear sites.
- Launch platforms: Ships and submarines
- Flight path: Low-altitude terrain-following flight to evade radar
- Use case: Strategic, surgical strikes in contested or defended environments
Design and Capabilities
- Length: ~5.6 meters (without booster)
- Weight: Up to 1,600 kg
- Speed: ~880 km/h (subsonic)
- Range: Over 1,600 km (varies by variant)
- Flight altitude: As low as 30–50 meters
- Warheads:
- Unitary high-explosive
- Cluster munitions
- Nuclear warheads (retired from use)
Navigation and Guidance Systems
Tomahawk missiles are known for pinpoint accuracy, achieved through a multi-layered guidance system:
- GPS (Global Positioning System) and INS (Inertial Navigation System) for real-time course tracking
- TERCOM (Terrain Contour Matching): Compares terrain under flight path with stored maps
- DSMAC (Digital Scene Matching Area Correlation): Matches live terrain imagery with onboard target data
- Data-link capability: Allows for in-flight re-targeting, mission abort, or loitering over areas
Variants and Modern Upgrades
- Tomahawk Block IV (TLAM-E): Most modern variant, featuring:
- In-flight reprogramming
- Target loitering
- Real-time battle damage assessment
- Two-way satellite communication
Historical Combat Usage
Tomahawk missiles have been extensively used in US military operations:
- Gulf War (1991): ~280 missiles used in the opening strikes
- Operation Infinite Reach (1998): Targeted terrorist camps in Sudan and Afghanistan
- Iraq War (2003): Hundreds used during the initial “shock and awe” campaign
- Libya Intervention (2011): Destroyed air defence infrastructure
- Syria (2017): 59 Tomahawks used against Shayrat Airbase in retaliation for chemical attacks
INS Tamal

- 25 Jun 2025
In News:
In a landmark development for India's maritime defence, the Indian Navy is set to commission its latest stealth multi-role frigate, INS Tamal, on 1st July 2025 at Yantar Shipyard, Kaliningrad, Russia
Overview:
- Class & Series: INS Tamal is the second ship of the Tushil-class, an upgraded variant of the Talwar and Teg class frigates, forming part of the Krivak class series built under Indo-Russian cooperation.
- Total Induction: With Tamal’s addition, India will operate ten ships with common capabilities across four related classes.
- Construction: Built at Yantar Shipyard with oversight from Indian specialists under the Warship Overseeing Team (WOT), Kaliningrad, under the Embassy of India, Moscow.
Symbolism and Identity
- The name ‘Tamal’ represents the mythical sword of Indra, the King of Gods.
- The ship’s mascot blends India’s Jambavant, the immortal bear king of mythology, with Russia’s Eurasian Brown Bear, symbolising Indo-Russian defence cooperation.
- The ship’s motto: ‘Sarvada Sarvatra Vijaya’ (Victorious Always Everywhere).
Make in India & Indigenous Content
- INS Tamal is the last warship to be inducted from a foreign source, aligning with Aatmanirbhar Bharat and Make in India initiatives.
- 26% indigenous content, including:
- BrahMos supersonic cruise missiles (anti-ship & land attack roles)
- HUMSA NG Mk II sonar, Indian radars, and communication systems
- Indian OEMs involved: BrahMos Aerospace, BEL, Keltron, Nova Integrated Systems (Tata), Elcome Marine, Johnson Controls India, among others.
- Indigenous components have more than doubled to 33 systems compared to previous imports.
Key Features & Capabilities
- Displacement: 3,900 tonnes | Length: 125 metres
- Top speed: Over 30 knots
- Armament & Combat Systems:
- Vertically Launched Surface-to-Air Missiles (VL-SAM)
- Improved 100 mm main gun, 30 mm CIWS
- Heavyweight torpedoes, anti-submarine rockets
- EO/IR system, fire control radars
- Aviation Support: Flight deck for Air Early Warning & Multi-Role helicopters
- Sensors & Network:
- Surface Surveillance Radar
- Advanced Electronic Warfare suite
- Network Centric Warfare capabilities
- Trials: Successfully completed 3-month sea trials, validating systems and weapons in challenging winter conditions (St. Petersburg & Kaliningrad).
Strategic Importance
- Upon commissioning, INS Tamal will join the Indian Navy’s Western Fleet—the 'Sword Arm' of the Navy under Western Naval Command.
- Reinforces India’s blue water naval ambitions, enhancing operational readiness in multi-threat maritime environments.
- Embodies two decades of Indo-Russian naval cooperation and represents a transition towards domestic warship production.
B-2 Spirit Bomber
- 23 Jun 2025
In News:
In a major escalation of the ongoing US–Iran tensions, the United States deployed the B-2 Spirit stealth bomber to strike Iran’s fortified nuclear infrastructure, including the heavily guarded Fordow enrichment facility, which was described by President Donald Trump as the “crown jewel” of Iran’s nuclear programme. The strikes signal a new phase in the geopolitical standoff, showcasing advanced US airpower and precision capabilities.
What is the B-2 Spirit Bomber?
The B-2 Spirit, developed by Northrop Grumman during the Cold War, is one of the most advanced strategic bombers in the world. Originally built for penetrating heavily defended Soviet airspace, it remains a key asset in the US Air Force due to its stealth capabilities, long range, and precision payload delivery.
Only 21 B-2 bombers were built, each costing an estimated $2.1 billion, making it one of the most expensive aircraft ever developed. Its bat-wing design and radar-absorbent coating significantly reduce its radar cross-section, making it almost invisible to radar and ideal for deep penetration missions in hostile territory. It is operated by a two-person crew and extensively automated to reduce pilot workload.
Why was it used in the Iran strikes?
The B-2 Spirit was chosen for the Iran mission because of its unique combination of stealth, range, and payload capacity. The Fordow facility, built deep within a mountain and protected by sophisticated air defences, required a bomber that could both evade detection and deliver a bunker-busting payload with high precision.
During the mission, the B-2s were reportedly equipped with the GBU-57A/B Massive Ordnance Penetrator (MOP) — a 30,000-pound bomb specifically designed to destroy deeply buried and fortified targets like Fordow. Due to the weapon’s size and weight, a B-2 can carry only one or two MOPs per sortie. Reports indicate that six MOPs were dropped on Fordow, demonstrating the operational effectiveness of the B-2 for such critical missions.
Capabilities and Strategic Role
The B-2 has an unrefueled range of over 6,000 nautical miles (approximately 11,000 km), enabling it to undertake intercontinental missions directly from the United States. Past missions have seen the B-2 operate from Missouri to targets in Afghanistan, Libya, and now Iran, demonstrating its global strike capability.
With a total payload capacity exceeding 40,000 pounds (18,000 kg), the B-2 can carry both conventional and nuclear weapons. It forms a crucial part of the US nuclear triad, capable of delivering up to 16 B83 nuclear bombs. Its ability to carry nuclear and precision-guided munitions gives it unmatched strategic versatility.
Weapon Systems Compatible with the B-2
Beyond the MOP, the B-2 can be armed with a variety of precision and standoff weapons, including:
- JDAMs (Joint Direct Attack Munitions): GPS-guided bombs used for high-accuracy strikes on fixed targets.
- JSOW (Joint Standoff Weapons): Glide bombs launched from a distance, allowing engagement of targets outside enemy air defence range.
- JASSM and JASSM-ER (Joint Air-to-Surface Standoff Missiles): Long-range cruise missiles, with the extended-range variant capable of striking targets up to 500 miles (805 km) away.
This versatility allows the B-2 to adapt to multiple mission profiles, from conventional warfare to nuclear deterrence.
Strategic and Geopolitical Implications
The deployment of the B-2 in this mission has both tactical and symbolic implications. Tactically, it underscores the US military’s ability to deliver precision strikes on highly protected strategic infrastructure. Strategically, it sends a strong signal to adversaries about the technological edge and operational reach of American military power.
From a geopolitical perspective, the strikes could exacerbate tensions in the already volatile West Asian region, heighten concerns about nuclear proliferation, and potentially provoke retaliatory actions by Iran and its regional allies. It also raises questions about the future of US-Iran relations and the fragility of nuclear diplomacy in the region.
Fattah Hypersonic Missile

- 21 Jun 2025
In News:
In light of intensifying hostilities between Iran and Israel, Iran has deployed its advanced Fattah hypersonic ballistic missile, marking a significant shift in regional military capabilities and raising concerns over existing air defence systems such as Israel’s Iron Dome.
About Fattah Hypersonic Missile
- Developed by: Aerospace Force of the Islamic Revolutionary Guard Corps (IRGC), Iran
- Unveiled: November 2022 (on the 11th death anniversary of missile scientist Hassan Tehrani Moghaddam)
- Inducted: 2023
- Name Meaning: “Fattah” translates to “victor” or “conqueror”
Key Capabilities:
Feature Specification
Speed Mach 13–15 (approx. 15,000 km/h)
Range 1,400 km (planned upgrade to 2,000 km)
Mobility Capable of mid-air directional changes
Stealth Forms a plasma shield that blinds radar & blocks radio signals
Deployment Used in attacks against Israeli territory
- A more advanced version, Fattah-2, with a range of 1,500 km, is reportedly under development.
Strategic Significance
- The missile’s ability to evade modern air defence systems—such as Iron Dome and David’s Sling—makes it a potential game-changer.
- Iran claims Fattah is capable of operating within the upper atmosphere with unpredictable trajectory, making interception extremely difficult.
- This hypersonic manoeuvrability marks a leap over traditional ballistic missiles that follow a predictable parabolic trajectory.
Comparative Global Context
Iran claims to be the fourth country globally to possess operational hypersonic missiles, after:
- Russia
- China
- India
Other nations like the USA and North Korea are developing or testing hypersonic systems but have not fielded them in combat as Iran reportedly has.
Operational History
- October 2024: Fattah missiles were reportedly used by Iran in a prior attack on Israeli targets.
- 2025 Escalation: The missile was deployed during “Operation Honest Promise 3,” marking the 11th wave of retaliatory attacks by Iran on Israeli territory.
Iran’s Broader Ballistic Missile Arsenal
In addition to Fattah, Iran possesses a wide range of short-to-long range missiles, including:
- Fateh Series: Short-range solid-fuel missiles (Fateh-110, Fateh-313)
- Zolfaghar and Qasem: Extended versions of Fateh series
- Emad: Long-range liquid-fuel missile with 1,700 km range
- Sejjil: Solid-fuel missile with 2,500 km range, speeds up to 17,000 km/h
- Others: Kheibar, Ghadr-110, Fajr-3, Shahab-3, Ashoura, Haj Qasem, Basir
Implications for India and the Region
- Regional Arms Race: Iran’s hypersonic capability may trigger further military build-up in the Middle East.
- India’s Position: As one of the few nations with hypersonic R&D, India must monitor evolving doctrines and maintain strategic balance.
- Global Security: The usage of such missiles in conflict zones raises concerns over escalation, proliferation, and undermining of existing missile defence systems.
Rudrastra
- 15 Jun 2025
In News:
India's Rudrastra, a homegrown VTOL drone, has been successfully tested by the Indian Army, marking a significant advancement in battlefield technology. Developed by Solar Aerospace and Defence Limited, this drone can perform precision strikes across borders without endangering soldiers.
Overview:
- Rudrastra is a hybrid Vertical Take-Off and Landing (VTOL) combat drone developed indigenously by Solar Aerospace and Defence Limited (SDAL).
- Successfully tested by the Indian Army in June 2025.
Key Features:
- Hybrid VTOL Capability:
- Takes off like a helicopter and cruises like a fixed-wing aircraft.
- Increases versatility, maneuverability, and stealth.
- Combat Role:
- Equipped with smart anti-personnel warheads.
- Capable of deep-strike missions against targets like artillery guns or terrorist hideouts.
- Deployed as a “stand-off weapon”—engages targets from a safe distance.
- Performance Parameters:
- Range: Full range of 170 km.
- Strike Capability: Targets more than 50 km away.
- Flight Endurance: Nearly 90 minutes.
- Navigation: Autonomous return capability.
- Surveillance: Real-time video feed for reconnaissance.
- Payload: Capable of deploying airburst munitions—detonates low to the ground to cause area damage.
Strategic Importance:
- Reduces risk to soldiers in hostile territory.
- Enhances India's unmanned combat aerial vehicle (UCAV) arsenal.
Useful in anti-terror operations, border surveillance, and precision strikes.
INS Arnala
- 08 Jun 2025
In News:
The Indian Navy is set to commission 'Arnala', the first warship under the Anti-Submarine Warfare Shallow Water Craft (ASW-SWC) series at the Naval Dockyard in Visakhapatnam. The commissioning will be presided over by Chief of Defence Staff, General Anil Chauhan.
About INS Arnala
- Type: First in the series of 16 Anti-Submarine Warfare Shallow Water Crafts (ASW-SWC)
- Builder:
- Primary: Garden Reach Shipbuilders & Engineers (GRSE), Kolkata
- Partner: L&T Shipbuilders
- Delivery Date: May 8, 2025
- Indigenous Content: Over 80%
- Partners Involved:
- BEL, L&T, Mahindra Defence, MEIL
- 55+ MSMEs involved in the supply chain
Capabilities & Features
- Length: 77 meters
- Displacement: 1,490+ tonnes
- Propulsion: Diesel engine-waterjet system (a first for a warship of this size in India)
- Roles:
- Anti-submarine operations in coastal/shallow waters
- Subsurface surveillance
- Search and Rescue (SAR)
- Low-intensity maritime operations
Significance
- Aatmanirbhar Bharat Milestone: Highlights indigenous shipbuilding and defence manufacturing capabilities
- Boost to Coastal Defence: Enhances the Navy’s reach in shallow and strategic coastal zones
- Employment & Industrial Growth: Significant MSME and domestic defence industry involvement
Heritage & Symbolism
- Name Origin: Inspired by Arnala Fort, near Vasai, Maharashtra
- Built by the Marathas in 1737 under Chimaji Appa
- Historically guarded the Vaitarna River mouth and northern Konkan coast
- Design Symbolism:
- Armoured hull reflects the resilient walls of Arnala Fort
- Advanced sensors and weapons echo the fort’s cannons
- Crest:
- Stylised auger shell – precision, strength, vigilance
- Motto: Arnave Shauryam — “Valour in the Ocean”
DRDO’s Long-Range Glide Bomb (LRGB) ‘Gaurav’

- 13 Apr 2025
In News:
The Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO) successfully conducted release trials of the indigenously developed Long-Range Glide Bomb (LRGB) ‘Gaurav’ from a Su-30 MKI aircraft.
About LRGB ‘Gaurav’
- Type: Air-launched, precision-guided munition.
- Purpose: Designed for accurate strikes on land targets from stand-off distances, i.e., beyond enemy air defence range.
- Indigenously developed by DRDO under the Ministry of Defence.
Key Features
- Range:
- Demonstrated precision strike at nearly 100 km.
- Operational range: 30–150 km.
- Variants by Weight:
- Gaurav (winged): 1,000 kg
- Gautham (non-winged): 550 kg
- Guidance Systems:
- Inertial Navigation System (INS)
- Satellite-based navigation (e.g., GPS/IRNSS)
- Digital control for enhanced accuracy
Significance
- Boosts India’s precision strike capability.
- Promotes self-reliance in defence technology under the Atmanirbhar Bharat initiative.
Related Concepts
Glide Bomb:
- A precision-guided munition that travels significant distances without powered propulsion.
- Uses aerodynamic lift to glide toward the target.
- Navigation via INS, GPS, or laser guidance.
Su-30 MKI Aircraft:
- A twin-engine, multirole fighter aircraft.
- Developed jointly by Sukhoi Design Bureau (Russia) and Hindustan Aeronautics Limited (HAL).
- Backbone of the Indian Air Force (IAF) combat fleet.
BM-04 Missile
- 12 Apr 2025
In News:
India recently introduced the BM-04, a new-generation Short-Range Ballistic Missile (SRBM), during the Vigyan Vaibhav 2025 defence exhibition in Hyderabad. Developed by the Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO), the missile underscores India’s commitment to enhancing its conventional precision strike and counterforce capabilities.
Key Specifications and Features:
- Length: 10.2 metres
- Diameter: 1.2 metres
- Weight: Approximately 11,500 kg
- Propulsion: Dual-stage, solid-fuel system
- Range: Capable of striking targets up to 1,500 km away
- Warhead: Equipped with a 500 kg conventional payload
- Accuracy: Features a 30-metre Circular Error Probability (CEP)
Advanced Capabilities:
- Canisterized Launch System: Like other strategic missiles in India’s arsenal, the BM-04 is canisterized, enabling quicker launch readiness by pre-mating the warhead and delivery system.
- Mobile Deployment: Transported and launched via an indigenous six-wheeled Transport Erector Launcher (TEL), offering enhanced mobility and operational flexibility.
- Hypersonic Glide Body (C-HGB): The missile incorporates a Common Hypersonic Glide Body, allowing it to maneuver mid-flight, making its trajectory less predictable and improving its ability to evade missile defence systems, particularly in contested A2/AD environments.
- Modular Design: The BM-04 platform is designed for upgradability, supporting integration of advanced warheads, sensors, and propulsion technologies as threat perceptions evolve.
Strategic Significance:The induction of the BM-04 marks a leap in India’s tactical missile capability, bolstering its credible conventional deterrence posture. With precision targeting, improved survivability, and adaptability for future upgrades, the BM-04 is poised to play a vital role in India’s defence architecture.
First-Person View (FPV) Drones
- 03 Jun 2025
In News:
Recently, Ukraine conducted a major drone strike on Russia, reportedly destroying over 40 aircraft using First-Person View (FPV) drones—marking one of the deepest strikes into Russian territory since the start of the conflict in 2022. This highlights the growing role of FPV drones in modern asymmetric warfare.
What are FPV Drones?
First-Person View (FPV) drones are unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) that allow remote pilots to view the drone’s surroundings through a camera mounted on the drone. The live feed can be transmitted to:
- Specialized goggles
- Smartphones
- Other display screens
This immersive view enables highly precise navigation and control.
Key Features and Technologies
- GPS-Independent Navigation: Operates effectively even when GPS signals are jammed or unavailable.
- SmartPilot System: Uses visual-inertial navigation by interpreting camera data to assess the drone's position and orientation.
- LiDAR Integration: Enhances terrain mapping and obstacle detection in complex environments.
- Low Cost: A functional FPV drone can cost as little as $500, making them highly affordable compared to traditional weapon systems.
Operational Use in Combat
- Reconnaissance First: Typically, a long-range reconnaissance drone is used to identify the target area before deploying FPV drones for strikes.
- Deep Strike Capability: Despite having a short range (a few kilometres), FPV drones offer stealth and precision to strike deeply into enemy territory.
- Combat Strategy: Their agility and affordability make FPV drones a key component of attrition warfare, especially for resource-constrained nations.
Advantages in Warfare
- Cost-effectiveness: Offers high-impact capability at a fraction of the cost of conventional weapons.
- Reduced Human Risk: Limits the need for manned missions in hostile territory.
- Stealth: Smaller size and low acoustic footprint make them harder to detect and intercept.
- High Destructiveness: Able to carry payloads such as explosives, effectively targeting tanks, aircraft, and installations.
Challenges and Limitations
- Limited Range: Operates within a few kilometres, requiring deployment close to target zones.
- Reduced Situational Awareness: Pilots rely solely on camera feed, which may not provide full spatial context.
- Need for Visual Observers: In complex environments, an additional observer may be needed to guide the operator safely.
Ukraine’s Use of FPV Drones
Ukraine has effectively integrated FPV drones into its military strategy:
- In November 2023, FPVs were credited as a low-cost, high-impact method of resisting Russian advances.
- NATO sources indicated that over two-thirds of Russian tanks destroyed recently were hit by FPV drones.
- Ukrainian drone manufacturer Vyriy Drone delivered 1,000 indigenous FPVs in March 2025.
- Ukraine is projected to produce over 4 million drones in 2025, reflecting a significant scaling of domestic capabilities.
Geopolitical and Strategic Implications
- Technological Self-Reliance: Domestic production protects nations from geopolitical supply chain disruptions (e.g., China’s chip exports).
- Global Proliferation: Countries like Israel and Iran have also developed drone systems, including HAROP and Shahed drones respectively.
INS Varsha
- 08 Apr 2025
In News:
India is set to operationalise INS Varsha, its first dedicated base for nuclear-powered submarines, by 2026. Located near Rambilli, about 50 km south of Visakhapatnam, Andhra Pradesh, this high-security facility is part of the classified Project Varsha, aimed at strengthening India’s maritime and nuclear deterrence capabilities in the Bay of Bengal and Indian Ocean Region (IOR).
Key Features:
- Strategic Location: Near deep waters of the Bay of Bengal, facilitating stealthy submarine movement and minimizing detection.
- Infrastructure:
- Underground pens and tunnel systems to conceal and protect nuclear submarines.
- Inner and outer harbour facilities; inner harbour completed, work ongoing on breakwaters and jetties.
- 20 sq. km area, capacity to house at least 10–12 nuclear submarines.
- Stealth Capabilities: Similar to China’s Hainan base, it offers satellite-evasion advantages, crucial for the survivability of SSBNs (nuclear-powered ballistic missile submarines).
- Support Facilities: Proximity to BARC Atchutapuram for nuclear infrastructure, enabling swift integration and maintenance of strategic assets.
- Geopolitical Role: Counters Chinese dual-use naval infrastructure at Hambantota (Sri Lanka) and BNS Sheikh Hasina (Bangladesh).
Strategic Significance:
- Enhances second-strike capability, vital for nuclear deterrence under India's nuclear triad.
- Enables undetected deterrent patrols by SSBNs, ensuring survivability in case of counterforce attacks.
- Facilitates rapid access to key chokepoints, especially the Strait of Malacca.
India’s Expanding Nuclear Submarine Fleet
INS Aridhaman – Third SSBN:
- Scheduled for commissioning in 2025.
- 7,000-tonne displacement, more capable than predecessors INS Arihant and INS Arighat.
- Equipped with K-4 Submarine-Launched Ballistic Missiles (SLBMs) with a range of 3,500 km.
- Built under the Advanced Technology Vessel (ATV) project by Shipbuilding Centre, Visakhapatnam, with BARC and DRDO support.
- Designed for long-duration deterrent patrols in deep sea.
Future Developments:
- India launched its fourth SSBN in November 2024, with ~75% indigenous content.
- Plans underway for even larger SSBNs and the construction of six nuclear-powered attack submarines (SSNs), starting with two approved 9,800-tonne SSNs for conventional strike and escort roles.
Related Naval Expansion – Project Seabird (Karwar Base):
- Located on the western coast, expanding to accommodate 50 warships and submarines, plus 40 auxiliary vessels.
- Will include a dual-use air station, new dockyard, and multiple dry berths.
INSV Tarini at Cape Town

- 04 Apr 2025
In News:
The Indian Naval Sailing Vessel (INSV) Tarini, crewed by women officers Lt CdrDilna K. and Lt Cdr Roopa A., reached Cape Town, South Africa, marking the final international port in the Navika Sagar Parikrama II — a global circumnavigation mission by the Indian Navy.
About INSV Tarini:
- Type: 56-foot indigenously built sailing vessel.
- Commissioned: February 2017.
- Builder:Aquarius Shipyard Ltd., Goa, under the Make in India initiative.
- Features:
- Equipped with Raymarine navigation suite, satellite communication systems, and emergency steering.
- Designed to operate in extreme maritime conditions.
- Name Origin: Named after the Tara-Tarini hill shrine in Odisha; ‘Tarini’ in Sanskrit means “boat” and “saviour.”
Navika Sagar Parikrama II:
- Flagged off from Goa: October 2, 2024, by Admiral Dinesh K. Tripathi, Chief of the Naval Staff.
- Duration: ~8 months.
- Total distance: Approx. 23,400 nautical miles (43,300 km).
- Route across three oceans, rounding three major capes.
- Ports of call before Cape Town:
- Fremantle (Australia)
- Lyttelton (New Zealand)
- Port Stanley (Falkland Islands, UK)
Challenges Faced:
- Extreme weather: Winds > 50 knots (93 km/h), waves up to 7 metres.
- Rough seas and cold temperatures posed significant navigational challenges.
Significance:
- Demonstrates India’s commitment to women-led maritime expeditions.
- Strengthens India–South Africa naval cooperation:
- October 2024: INS Talwar participated in Exercise IBSAMAR.
- January 2025: INS Tushil made a port call at Durban.
Exercise PrachandPrahar (2025)
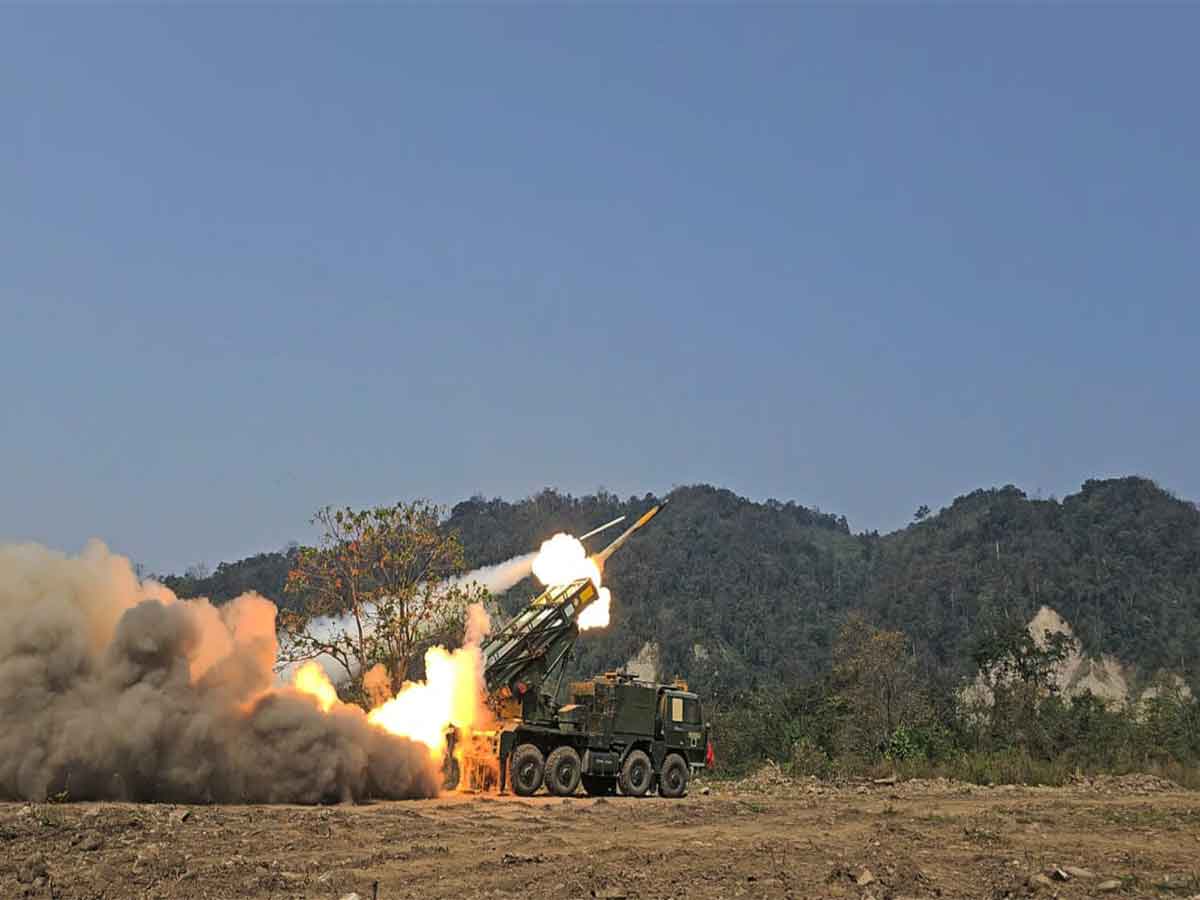

- 01 Apr 2025
In News:
Exercise PrachandPrahar was a tri-service integrated multi-domain military exercise conducted by the Indian Armed Forces in the high-altitude terrain of Arunachal Pradesh, along the Northern Borders, specifically under the Eastern Army Command.
Timeline:
- Held: March 25–27, 2025
- Preceded by:Exercise PoorviPrahar (November 2024), which focused on integrated aviation asset application.
Objective:
To validate integrated operational capabilities of the Army, Navy, and Air Force, and enhance India's preparedness for future warfare scenarios along the 3,488-km long Line of Actual Control (LAC) with China.
Key Highlights:
- Location: High-altitude Himalayan terrain, eastern sector of the LAC in Arunachal Pradesh.
- Forces Involved:
- Indian Army (including Special Forces)
- Indian Air Force (IAF)
- Indian Navy
Major Components:
- Surveillance and Domain Awareness:
- Long-range surveillance aircraft (IAF)
- Maritime domain awareness aircraft (Navy)
- Helicopters and UAVs
- Space-based assets
- Precision Strike Capabilities:
- Fighter aircrafts
- Long-range rocket systems
- Medium artillery
- Armed helicopters
- Swarm drones
- Loitering munitions
- Kamikaze drones
- Operational Environment:
- Simulated electronic warfare and contested conditions.
- Focus on jointness, precision, and rapid response.
Strategic Importance:
- Demonstrated seamless command, control, and coordination among the three services.
- Validated the ability to conduct multi-domain operations (MDO) in challenging terrain.
- Reinforced India’s technological edge and combat readiness along strategic frontiers.
BrahMos-NG and Extended Range BrahMos

- 23 May 2025
In News:
India is advancing its supersonic missile capabilities with the development of two significant assets:
- The BrahMos-NG (Next Generation) missile—lighter, stealthier, and more versatile.
- The extended-range BrahMos, which pushes the missile’s reach up to 800 km, enhancing India’s strategic depth.
About BrahMos:
- Joint Venture: BrahMos Aerospace (DRDO of India and Russia’s NPO Mashinostroyenia).
- First Induction: 2005 (anti-ship version).
- Name Origin: Combines names of Brahmaputra (India) and Moskva (Russia) rivers.
- Capabilities: Launch from land, sea, sub-sea, and air against land and sea targets.
BrahMos-NG (Next Generation):
A miniaturized, next-gen supersonic cruise missile designed for enhanced operational flexibility and platform compatibility.
Key Features:
- Size & Weight: ~1.33–1.5 tonnes, nearly half the current air-launched BrahMos (2.5–2.65 tonnes).
- Speed: Mach 2.8.
- Range: ~400–450 km; potential for 800 km with future trials.
- Stealth: Lower radar cross-section and advanced stealth design.
- Platforms: Compatible with Su-30MKI, LCA Tejas, Rafale, MiG-29, naval ships, and submarines.
- Launch Options: From air, land vehicles, surface warships, and submarine torpedo tubes.
- Advanced ECCM: Improved resistance against electronic warfare/jamming.
- Precision Targeting: Ideal for land-attack, anti-ship, and underwater combat scenarios.
Strategic Benefits:
- Higher platform density: E.g., a Su-30MKI can carry up to 4 BrahMos-NG missiles; Tejas can carry 2.
- Faster deployment and reload cycles due to reduced size and logistics burden.
- Future-ready design: Modular, stealthy, and agile—ideal for modern warfare.
Extended-Range BrahMos:
- Background: Initial range capped at 290 km under Missile Technology Control Regime (MTCR).
- Post-MTCR Membership: India joined MTCR in 2016, enabling range extension.
- Current Status: Successfully extended to 450 km; testing ongoing for 800 km version.
- Trial Update: Initial flight trial of the 800 km version conducted; more planned.
Operational Highlights:
- Combat Proven: BrahMos was used by the IAF for precision strikes on Pakistani airbases during the 2024 confrontation, demonstrating effective penetration of enemy air defence.
- Deterrence Capability: Former Air Chief Marshal V.R. Chaudhari called BrahMos-NG the IAF’s "primary deterrent weapon".
- Squadron Integration: 222 ‘Tiger Sharks’ squadron in Thanjavur equipped with BrahMos-armed Su-30MKIs.
INSV Kaundinya

- 22 May 2025
In News:
The Indian Navy formally inducted and named an ‘ancient stitched sail ship’ as the INSV Kaundinya at a ceremonial event held at the Naval Base in Karwar. INSV Kaundinya has been built based on a 5th century ship depicted in paintings seen in the Ajanta Caves.
What is INSV Kaundinya?
The INSV Kaundinya is a reconstructed ancient stitched ship, modeled after maritime imagery found in the Ajanta Cave murals. It represents India’s historical naval engineering capabilities and cultural exchanges across the Indian Ocean.
Construction and Origins
- The project was initiated in July 2023 as a collaborative effort between the Ministry of Culture, the Indian Navy, and Hodi Innovations.
- The ship was built using traditional stitched shipbuilding methods, where wooden planks are lashed with coir ropes and coconut fibre, sealed with natural resin—a method that avoids the use of nails or metal fasteners.
- The design took inspiration from 5th-century depictions in the Ajanta caves, interpreted through archaeological analysis, hydrodynamics, and naval architecture, as no original ship designs from that era have survived.
Planned Expedition
- INSV Kaundinya is slated to retrace an ancient maritime trade route in 2025, sailing from Gujarat to Oman, highlighting India's historical seafaring ties with West Asia.
Cultural Symbolism
- The ship’s sails are embellished with traditional motifs such as the Gandabherunda (a two-headed mythical eagle) and Sun iconography, symbolizing resilience and energy.
- A SimhaYali (lion-dragon hybrid) figure adorns the bow, a nod to Dravidian maritime symbolism.
- The deck features a Harappan-style stone anchor, linking the vessel to India’s ancient Indus Valley maritime practices.
- Named after Kaundinya, an ancient Indian voyager known for establishing early trade and cultural links with Southeast Asia, the ship reflects India's historic role in transoceanic interaction.
Ajanta Cave Paintings: Artistic Reference
- Located in Maharashtra, the Ajanta Caves date from the 2nd century BCE to the 6th century CE, renowned for some of the oldest surviving Indian mural art.
- These murals use the tempera technique—painting on dry plaster with natural dyes such as red ochre and black.
- They largely portray Buddhist narratives, including Jataka Tales, and scenes from the Buddha’s life, interwoven with nature and decorative elements.
- The paintings emphasize emotional expression, spiritual depth, and distinctive anatomical stylization.
Bhargavastra: India’s Indigenous Anti-Drone Weapon System
- 18 May 2025
In News:
India has developed 'Bhargavastra', a cutting-edge indigenous weapon system designed to neutraliseenemy drones, including drone swarms. It has been developed by Solar Defence and Aerospace Limited (SDAL), marking a major advancement in India’s drone warfare capabilities.
Key Features:
- Type:A multi-layered anti-drone system using micro-rockets and guided micro-missiles.
- Detection & Destruction Range:
- Detects drones from 6–10 km using radar.
- Destroys drones up to 2.5 km away.
How It Works:
- Layer 1:
- Unguided micro-rockets target drone swarms.
- Each rocket has an effective kill radius of 20 meters.
- Layer 2:Guided micro-missiles provide precision strikes on individual drones.
- Additional Features:Jammers and spoofers to confuse and disable drones electronically.
Successful Testing:
- Date & Location:Conducted on May 13, 2025, at the Seaward Firing Range, Gopalpur, Odisha.
- Results:
- Three tests: two with single rockets, one with two rockets fired within two seconds.
- All rockets hit their intended targets successfully.
Technological Components:
- Integrated Command and Control Centre
- High-resolution cameras and infrared sensors
- Real-time battlefield awareness system
Operational Versatility:
- All-Terrain Capability:Effective even in high-altitude zones above 5,000 metres.
- User Base:Can be deployed by Indian Army, Air Force, and Navy.
- Modularity:System components such as radars and launchers can be configured based on operational requirements.
Significance:
- Strategic Defence Tool:Counters rising threats from low-cost drones and UAV swarms.
- Indigenous Development:Boosts the Make in India initiative in defence manufacturing.
- First-of-its-kind in India:Among the few operational drone defence systems globally with successful tests.
Raika Tribe
- 14 May 2025
In News:
The Raika community's deep-rooted knowledge of pasture cycles, animal health, and biodiversity continues to play a vital role in sustaining the delicate ecological balance of Rajasthan’s arid regions.
Who are the Raikas?
The Raika tribe, also known as Rabaris, is an indigenous pastoralist community predominantly residing in the arid and semi-arid landscapes of Rajasthan, especially around Kumbhalgarh in Rajsamand district.
Their identity is intricately linked to camel herding, particularly the breeding of the hardy Marwari camel—a breed renowned for its strength, endurance, and adaptability to desert conditions.
Cultural and Ecological Significance
For the Raikas, camel herding is more than just a livelihood—it is a way of life. Their cultural practices, seasonal migrations, and oral traditions are closely tied to their pastoral role.
Over generations, they have cultivated extensive traditional knowledge about:
- Pasture Cycles: Insight into optimal grazing periods and routes to maintain vegetation health.
- Animal Health: Natural methods to ensure the well-being of livestock, particularly camels.
- Biodiversity Management: Sustainable herding practices that promote ecological resilience.
Their traditional migratory routes enable camels to graze on medicinal desert plants, which not only improve animal health but also contribute to preserving the region’s unique biodiversity and ecological stability.
PL-15 Missile
- 14 May 2025
In News:
Amid rising tensions between India and Pakistan, a fully intact Chinese-made PL-15 long-range air-to-air missile has reportedly been recovered in Hoshiarpur, Punjab. The incident has sparked security and strategic concerns, given the missile's advanced capabilities and origin.
Overview of the PL-15 Missile
Also known as the "Thunderbolt-15," the PL-15 is a cutting-edge beyond-visual-range air-to-air missile (BVRAAM) developed by China’s 607 Institute and produced by the China Aerospace Science and Industry Corporation (CASIC). It is specifically designed to engage enemy aircraft at extended distances, far beyond the visual range of the launching platform.
Key Features:
- Propulsion and Speed:The missile is powered by a dual-pulse solid-propellant rocket motor, enabling it to reach speeds of over Mach 5.
- Range Capabilities:The domestic Chinese version has an estimated operational range of 200 to 300 km. The export version, the PL-15E, is officially rated for a maximum range of 145 km, though in practice this may be limited to 100–120 km depending on the launch conditions and platform.
- Warhead:It carries a high-explosive fragmentation warhead weighing between 20 and 25 kg, engineered to effectively neutralize maneuvering aerial targets.
- Guidance System:The PL-15 is equipped with an advanced guidance package that includes:
- Inertial navigation
- Beidou satellite updates
- Two-way datalink for real-time mid-course adjustments
- Terminal active radar homing with an AESA (Active Electronically Scanned Array) radar seeker
Arnala

- 13 May 2025
In News:
Recently, the Indian Navy received Arnala, the first of eight indigenously designed and built Anti-Submarine Warfare Shallow Water Crafts (ASW SWCs). The vessel was constructed by Garden Reach Shipbuilders and Engineers (GRSE), Kolkata, in partnership with M/s L&T Shipyard, Kattupalli, under a Public-Private Partnership (PPP), exemplifying the growing collaboration in India’s defence manufacturing sector.
Key Features and Significance
- Arnala is named after the historic Arnala Fort located off Vasai, Maharashtra, symbolizing India’s rich maritime heritage.
- The ship measures 77 metres in length and is the largest Indian Naval warship powered by a Diesel Engine-Waterjet propulsion system.
- Designed and built according to the Indian Register of Shipping (IRS) classification rules, the vessel adheres to domestic naval architecture standards.
- Over 80% of the ship’s components are sourced indigenously, marking a significant stride toward the Government’s vision of ‘Aatmanirbhar Bharat’ in defence production.
Operational Roles
The Arnala class ASW SWCs are specialized for:
- Underwater surveillance in coastal and littoral zones
- Conducting search and rescue (SAR) operations
- Engaging in Low Intensity Maritime Operations (LIMO)
- Performing coastal Anti-Submarine Warfare (ASW) missions
- Advanced mine-laying activities
The induction of these vessels enhances India’s capabilities in shallow water ASW, critical for safeguarding maritime security in near-shore environments and ensuring dominance in the strategically vital littoral areas.
Strategic Importance
The delivery of Arnala signifies a major milestone in the Indian Navy’s ongoing efforts to promote indigenous shipbuilding and strengthen domestic defence manufacturing. It highlights successful public-private collaboration in advanced warship construction and contributes directly to India’s broader strategic goal of self-reliance in defence technology.
SCALP Missile
- 11 May 2025
In News:
During Operation Sindoor, the Indian Air Force reportedly employed SCALP missiles launched from Rafale fighter jets to target high-value terror infrastructure in Pakistan and Pakistan-occupied Kashmir (PoK).
What is the SCALP Missile?
- The SCALP (Système de CroisièreAutonome à Longue Portée) is a long-range, air-launched cruise missile designed for deep-strike missions.
- It is also known by its British designation, Storm Shadow.
- Developed jointly by France and the United Kingdom, it is built for precision attacks on strategic, fixed, and fortified targets.
- Global Operators: The missile is in operational use by the air forces of:India, France, United Kingdom, Egypt, Italy, Greece, Saudi Arabia, Qatar, and UAE.
- Indian Integration: The Indian Air Force has integrated the SCALP missile with its Rafale fleet, enhancing India's capacity to conduct long-range precision strikes with minimal collateral damage.
Key Features:
Feature Description
Range Approximately 500 km
Warhead 450 kg high-explosive, designed to penetrate hardened structures
Weight Around 1,300 kg
Dimensions Length: ~5 metres; Wingspan: ~3 metres
Speed Subsonic (around Mach 0.8)
Guidance Systems Combined GPS/INS navigation, terrain-following radar, and
infrared homing for terminal precision
Stealth Capability Optimized for low-altitude flight to evade radar detection
Accuracy Uses image-based terminal guidance to match
preloaded target images
All-weather Capability Can operate under diverse weather conditions
HAROP Drone
- 11 May 2025
In News:
On May 8, 2025, as part of Operation Sindoor, India reportedly used Israeli-made HAROP loitering munitions to destroy a Pakistani air defence system in Lahore, in response to Pakistan’s attempted attacks on Indian military installations.
What is HAROP?
- HAROP is an advanced loitering munition, also known as a suicide drone or kamikaze drone.
- Developed by Israel Aerospace Industries (IAI), it combines features of a UAV and a missile.
- It is designed to loiter over an area, search for high-value targets, and crash into the target with an explosive payload.
Key Characteristics and Capabilities
Feature Description
Function Combines surveillance and attack roles; can loiter, identify, and
strike autonomously or manually
Targets Designed to hit air defence systems, radars, command posts,
tanks, and moving military assets
Sensor Equipped with an Electro-Optical (EO) sensor for real-time
target tracking and acquisition
Endurance Up to 9 hours of loitering capability for deep-target missions
Launch Platforms Can be launched from truck-mounted canisters,
naval vessels, or ground stations
Navigation Resistance GNSS (GPS)-jam resistant, effective in communication-
denied environments
Strike Profile Executes attacks from various angles using
steep or shallow dive maneuvers
Evolution and Operational Use
- HAROP is an evolution of the earlier HARPY system, which was radio-frequency (RF) guided.
- Unlike the HARPY, HAROP uses EO sensors for improved visual target identification.
- HAROPs are "fire-and-forget" weapons, meaning they do not require active control after launch.
- The system has been described by IAI as the “King of the Battlefield”, with a claimed mission success rate of 98%.
- Proven effective in multiple combat scenarios, including suppression of enemy air defences (SEAD).
International Maritime Defence Exhibition (IMDEX) Asia 2025
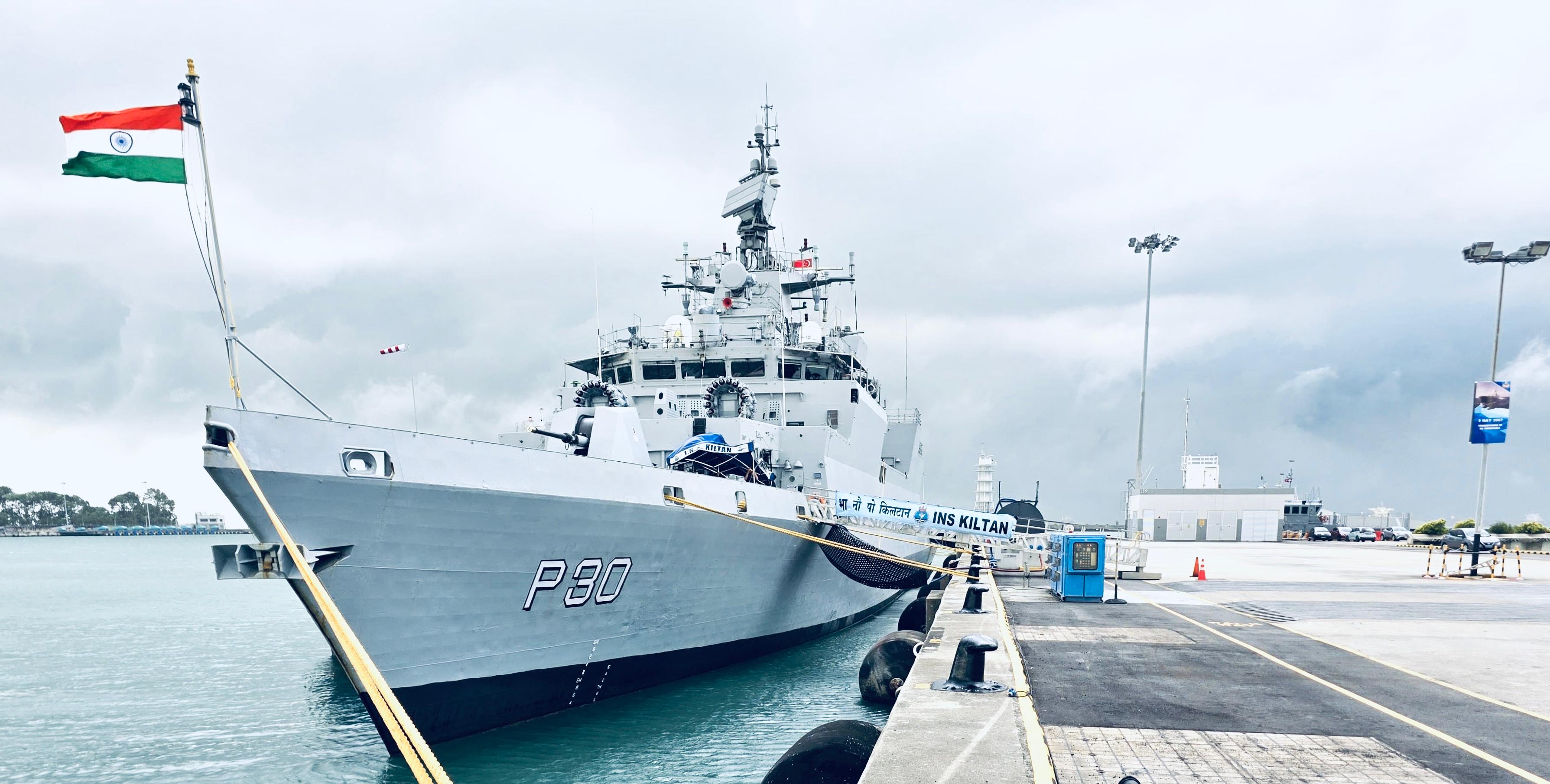

- 10 May 2025
In News:
The International Maritime Defence Exhibition (IMDEX) Asia is a leading biennial maritime and defence event in the Asia-Pacific region, held since 1997 in Singapore at the Changi Exhibition Centre. It serves as a key global platform for navies, coast guards, and maritime defence industries to showcase advanced naval platforms, cutting-edge technologies, and engage in strategic dialogue.
Indian Navy’s Participation
- In May 2025, the Indian Naval Ship INS Kiltan arrived in Singapore to participate in IMDEX Asia 2025.
- This deployment forms part of the Indian Navy’s operational commitments and highlights the strong maritime partnership between India and Singapore.
- During the exhibition, the Indian Navy crew engaged in multiple bilateral and multilateral activities, including professional exchanges with the Republic of Singapore Navy (RSN) and other participating navies.
- Activities included guided tours for schoolchildren, cross-deck visits with other navies, and curated visits for defence industry representatives to promote awareness of maritime security and India’s naval heritage.
Key Features of IMDEX Asia
- Platform for Defence Collaboration: IMDEX Asia facilitates showcasing of naval systems and debut of advanced maritime technologies.
- Strategic Dialogue: The event hosts high-level policy discussions and strategic dialogues on maritime security.
- International Maritime Security Conference (IMSC):
- Established in 2009, IMSC is a crucial component of IMDEX.
- Jointly organised by the Republic of Singapore Navy and the S. Rajaratnam School of International Studies (RSIS).
- It convenes navy chiefs, coast guard leaders, policymakers, and strategic analysts.
- The conference aims to enhance mutual maritime security, improve maritime domain awareness, and foster cooperative responses to challenges in the global maritime commons.
Significance
- The Indian Navy’s participation in IMDEX Asia underlines its commitment to regional maritime security and stability.
- It also reinforces the longstanding friendly ties between India and Singapore and highlights the importance of naval interoperability and defence cooperation in the Indo-Pacific region.
GhassemBasir Missile unveiled by Iran

- 08 May 2025
In News:
Iran has recently introduced a new solid-fuel medium-range ballistic missile (MRBM) named GhassemBasir.
About the GhassemBasir Missile
The missile is designed to engage targets at distances exceeding 1,200 kilometers, enhancing Iran’s strategic strike capabilities.
Key Features:
- Size and Weight: The missile measures approximately 11 meters in length and weighs around 7 tons.
- Advanced Materials: Its airframe is reportedly constructed using carbon fiber composite materials, which reduce structural weight and lower its radar signature.
- Warhead: The missile carries a warhead estimated to weigh about 500 kilograms.
- Propulsion: Powered by a solid-fuel system, the missile benefits from quicker launch readiness and improved storage stability compared to liquid-fuel missiles.
- Speed: Capable of reaching speeds up to Mach 12.
- Guidance System: Equipped with a thermal imaging sensor that enables the missile to detect and home in on targets by sensing heat signatures during the final flight phase.
- Maneuverable Reentry Vehicle (MaRV): The missile features a MaRV that separates from the booster, reducing aerodynamic drag, decreasing radar detectability, and enhancing ballistic performance.
- Mobility: It can be launched from mobile transporter-erector-launchers (TELs), including vehicles resembling civilian trucks, increasing its operational flexibility and survivability.
India to Receive INS Tamal
- 07 May 2025
In News:
India is set to induct INS Tamal, the second advanced stealth frigate of the Krivak-III class, built in Russia under a bilateral defence contract.
About INS Tamal
- Type & Class:INS Tamal is a 3,900-tonne stealth frigate, part of the Krivak-III class deal signed in 2016 between India and Russia. It is the sister ship of INS Tushil, commissioned in December 2024.
- Builder & Collaboration:Constructed at the Yantar Shipyard in Kaliningrad, Russia, under India-Russia defence cooperation.
The contract includes four frigates: two built in Russia and two under construction at Goa Shipyard with technology transfer.
Key Features
- Stealth Technology:Equipped with advanced suppression systems for radio, infrared, and acoustic signatures to enhance survivability.
- Armaments:
- BrahMos supersonic cruise missiles (range approx. 450 km)
- Shtil surface-to-air missiles
- Anti-submarine torpedoes and rocket launchers
- Performance:
- Speed exceeding 30 knots
- Can deploy Kamov-28 and Kamov-31 helicopters for anti-submarine warfare and airborne early warning.
- Automation: High automation reduces crew workload and improves operational efficiency.
Strategic Importance
- Enhances India’s blue-water naval capabilities across air, surface, underwater, and electromagnetic domains.
- Strengthens naval deterrence and force projection in the Indo-Pacific region, especially amid rising tensions in the Arabian Sea.
- Demonstrates successful Make in India initiative combined with global collaboration, as two of the frigates are being built domestically at Goa Shipyard.
Stratospheric Airship Platform by DRDO

- 07 May 2025
In News:
India successfully conducted the maiden flight trial of its indigenous Stratospheric Airship Platform, developed by the Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO). The trial took place at Sheopur, Madhya Pradesh, and marked a significant milestone in India’s pursuit of advanced high-altitude surveillance technologies.
About the Stratospheric Airship Platform
- Nature: A lighter-than-air, high-altitude airship designed to operate at stratospheric heights (~17 km altitude).
- Developer: Aerial Delivery Research and Development Establishment (ADRDE), Agra under DRDO.
- Purpose: To provide extended surveillance and real-time observation capabilities for military and civilian applications.
Key Features and Flight Trial Details
- Successfully reached an altitude of about 17 km (stratosphere).
- Carried an instrumental payload for Intelligence, Surveillance, and Reconnaissance (ISR) tasks.
- Flight duration: Approximately 62 minutes.
- Tested crucial systems such as envelope pressure control and emergency deflation mechanisms.
- Data from onboard sensors will aid in developing simulation models for future flights.
- The platform was recovered post-mission for further analysis.
Strategic and Operational Significance
- Enhanced ISR: Boosts India’s military surveillance over borders, coastal regions, and conflict zones.
- Earth Observation: Supports disaster management, environmental monitoring, and communication relays.
- Cost-Effective: Provides persistent coverage at a fraction of the cost of satellite launches.
- Technological Edge: Places India among a select group of nations with indigenous high-altitude airship capabilities, crucial amid rising regional security challenges.
- Dual-Use Potential: Suitable for both defence and civilian applications, including atmospheric sensing.
National Security Advisory Board (NSAB)
- 03 May 2025
In News:
The Government of India has reconstituted the National Security Advisory Board (NSAB) with former R&AW chief Alok Joshi appointed as its Chairman. The move comes in the backdrop of increasing national security threats, including the recent terrorist attack in Pahalgam, which prompted a series of high-level security meetings chaired by Prime Minister Narendra Modi.
What is NSAB?
The NSAB is an advisory body functioning under the National Security Council (NSC). It offers independent, long-term strategic assessments and policy recommendations on national security issues.
- Established: December 1998, under NSA Brajesh Mishra
- Parent Body: National Security Council Secretariat (NSCS)
- Associated Bodies:
- National Information Board (NIB)
- Technology Coordination Group (TCG)
Composition of the Newly Reconstituted Board (2025)
- Chairman: Alok Joshi (Former R&AW Chief)
- New Members Include:
- Military:
- Air Marshal P.M. Sinha (ex-Western Air Commander)
- Lt Gen A.K. Singh (ex-Southern Army Commander)
- Rear Admiral Monty Khanna
- Police:
- Rajiv Ranjan Verma (Retd IPS)
- Manmohan Singh (Retd IPS)
- Diplomacy:
- B. Venkatesh Varma (Retd IFS, ex-Ambassador to Russia)
- Military:
Current NSAB Strength: 16 members, including military veterans, diplomats, academics, and civil society experts.
Functions and Objectives
- Provide non-partisan, long-term strategic inputs to the National Security Council.
- Recommend policy measures on defence, diplomacy, cyber security, and internal security.
- Assist in drafting key national security documents:
- Nuclear Doctrine (2001)
- National Security Review (2007)
- Hold monthly or emergency meetings to assess national and global threats.
- Submit independent reports to the NSA for evidence-based policy making.
- Act as a bridge between the strategic community and the government.
Nag Anti-Tank Missile System (NAMIS)

- 31 Mar 2025
In News:
The Ministry of Defence (MoD) signed contracts worth approximately ?2,500 crore for procuring advanced anti-tank missile systems and light vehicles to enhance the Indian Army's operational capabilities.
Nag Anti-Tank Missile System (NAMIS)
- Development and Production:Developed by the Defence Research and Development Laboratory (DRDL) under the Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO) and produced by Bharat Dynamics Limited (BDL).
- System Overview:NAMIS is a tracked, third-generation anti-tank guided missile (ATGM) system mounted on a BMP-2 chassis (Nag Missile Carrier or NAMICA). It features a ‘fire-and-forget’ capability, employing an Imaging Infrared (IIR) seeker to lock on to heavily armored targets before launch.
- Key Features:
- Range: 500 meters to 4 kilometers.
- Attack Modes:
- Top Attack Mode: Missile climbs and strikes the target from above to penetrate weaker top armor.
- Direct Attack Mode: Missile flies directly to strike the target.
- Night Capability: Operates effectively under low visibility.
- Mobility: Based on the amphibious BMP-2, NAMIS can operate across varied terrains.
- Significance:The tracked NAMIS enhances the anti-tank capabilities of mechanized infantry, marking a crucial step in modernizing the Indian Army’s battlefield readiness.
- Other Nag Variants:The Helina is a helicopter-launched version designed for deployment on Rudra and Light Combat Helicopters (LCH), successfully tested in 2018.
Light Vehicles Procurement
- The MoD signed contracts with Force Motors Limited and Mahindra & Mahindra Limited for around 5,000 light vehicles.
- These vehicles are equipped with enhanced engine power and designed to carry payloads of up to 800 kg, ensuring mobility across diverse terrains and operational conditions.
Additional Defence Contract
- Zen Technologies Limited secured a contract worth approximately ?152 crore for supplying Integrated Air Defence Combat Simulators (IADCS) for the Army’s L70 air defence guns.
- The IADCS is a virtual training system developed under the Make-II category to provide realistic simulation-based training for air defence operations.
Vertically-Launched Short-Range Surface-to-Air Missile (VL-SRSAM)
- 30 Mar 2025
In News:
India successfully conducted a flight test of the VL-SRSAM from a defence testing range off the Odisha coast.
Overview:
- Type: Indigenous short-range surface-to-air missile (SRSAM)
- Developed by: Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO)
- Purpose: Designed for quick reaction air defence, capable of intercepting a variety of aerial threats including low-altitude sea-skimming targets.
- Users:Originally developed for the Indian Navy, with applications now extending to the Indian Air Force for safeguarding air bases.
Performance Parameters:
- Initial range: 40 km (Navy version)
- Extended range: Up to 80 km
- Maximum altitude: 16 km
- Top speed: Mach 4.5
Technical Specifications:
- Length: 3.93 meters
- Diameter: 178 mm
- Wingspan: 508 mm
- Weight: ~170 kg
- Propulsion: Solid fuel
- Guidance System:
- Mid-course: Inertial navigation based on fibre-optic gyroscope
- Terminal phase: Active radar homing
- Launcher Configuration: Twin quad-pack canisters integrated with weapon control systems (WCS) for multiple missile launches.
Significance:
- Enhances India's self-reliant air defence capability.
- Supports indigenous development under the Aatmanirbhar Bharat initiative.
- Strengthens India's maritime and aerial defensive posture through versatile deployment.
Tejas LCA Mk1A

- 29 Mar 2025
In News:
GE Aerospace has commenced delivery of F404-IN20 jet engines to Hindustan Aeronautics Limited (HAL) for the Tejas Light Combat Aircraft Mk1A. This marks a significant milestone in India’s indigenous defence production capabilities and is vital for bridging the Indian Air Force's (IAF) operational gaps.
Background on Tejas LCA Mk1A
- Tejas LCA Mk1A is an advanced version of the indigenous Light Combat Aircraft (LCA) developed by HAL.
- It incorporates over 40 improvements over the Mk1 variant, aimed at enhancing combat readiness, survivability, and ease of maintenance.
Key Features:
- Radar Systems:
- Israeli EL/M-2052 AESA Radar.
- Indigenous Uttam AESA Radar (under integration).
- Electronic Warfare:
- Unified Electronic Warfare Suite (UEWS).
- Advanced Self-Protection Jammer Pod.
- Weapons Capability:Nine hardpoints supporting Beyond Visual Range (BVR) missiles, Air-to-Air and Air-to-Ground missiles, and Advanced Short-Range Air-to-Air Missiles (ASRAAM).
- Digital Fly-by-Wire System:Upgraded Flight Control Computer (DFCC Mk1A).
- Improved Operational Efficiency:Reduced weight, enhanced maintainability, and faster sortie turnaround.
Engine Deliveries and Production Status
- First Engine Delivered: March 26, 2025; expected in India by April.
- Engine Type: F404-IN20 by GE Aerospace – a high-thrust variant tailored for IAF needs.
- Key Engine Features:
- Higher-flow fan, single-crystal turbine blades, and customized components.
- Achieved Mach 1.1 during Tejas’ maiden flight in 2008.
Delivery Commitments:
- 2025 Target: 12 engines and 12 Tejas Mk1A jets to be delivered.
- Full Order: 99 engines ordered in 2021.
- Production Goal: HAL to produce 24 aircraft per year.
- Current Readiness: Three Mk1A jets flying; 11 more expected by end-2025 (10 from Bengaluru, 1 from Nasik).
Production Challenges:
- Engine production was dormant for five years.
- Reinitiating during the COVID-19 pandemic caused further delays.
- GE has now stabilized its supply chain and resumed engine production.
Strategic Importance for IAF
- Current IAF Strength: 31 fighter squadrons (sanctioned strength: 42.5).
- Urgency: Older aircraft like Jaguar, MiG-29UPG, and Mirage-2000 will begin phasing out by decade-end.
- Future Platforms: LCA Mk2 is under development; AMCA (Advanced Medium Combat Aircraft), India’s 5th-gen stealth fighter, is still a decade away.
Policy Push:A high-level committee led by the Defence Secretary submitted recommendations to the Defence Minister for enhancing IAF capabilities in short, medium, and long-term.
Brahmastra Hypersonic Missile
- 13 Mar 2025
In News:
Indian scientists, under the Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO), have successfully developed and tested a hypersonic missile named Brahmastra, officially called the Long Range Anti-Ship Missile (LRAShM). It represents a major milestone in indigenous defence technology.
Key Features of Brahmastra (LRAShM)
- Type: Hypersonic glide missile
- Developer: DRDO
- Speed: Mach 10 (≈12,144 km/h) — 10 times the speed of sound
- Range: 1,500 km
- Flight Time to Target: Can destroy enemy warships within 7–8 minutes of launch
- Launch Platforms: Compatible with both land and naval platforms
- Technology:
- Scramjet propulsion and glide vehicle technology
- Advanced heat-resistant materials to withstand extreme thermal conditions
- Radar evasion and trajectory maneuverability, making interception extremely difficult
Strategic Significance
- Naval Superiority: Enhances India’s maritime strike capabilities, especially in the Indian Ocean Region (IOR).
- Counter to China: Outperforms China’s DF-17 missile, which has a shorter range (1,000 km).
- Quick Response: For instance, a warship near Pakistan’s Karachi port could be neutralized within 4–5 minutes from India’s western coastline.
- Technological Benchmark: Establishes India’s lead in scramjet and hypersonic glide vehicle technology.
Comparative Edge Over Global Counterparts
- China's DF-17: Also hypersonic (Mach 10) but limited to a 1,000 km range.
- U.S. Programs: Still under testing; India’s successful deployment marks it as a front-runner in this emerging domain.
- Strategic Camouflage: Experts speculate India may have publicly understated the missile's actual capabilities for security reasons.
Gandiva (Astra MK-III) Missile
- 11 Mar 2025
In News:
India’s cutting-edge air-to-air missile, previously known as Astra MK-III, has been officially renamed Gandiva, inspired by the mythical bow wielded by Arjuna in the epic Mahabharata. This rebranding marks a symbolic nod to India's cultural legacy while highlighting its growing defence capabilities.
Overview of the Gandiva (Astra MK-III) Missile
Developed by the Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO), Gandiva is a beyond-visual-range (BVR) missile currently undergoing final stages of development. It is designed to be equipped on frontline fighter aircraft such as the Sukhoi Su-30MKI and LCA Tejas of the Indian Air Force (IAF).
Upon induction, Gandiva is set to become one of the longest-range air-to-air BVR missiles globally, significantly enhancing India's aerial combat capabilities.
Key Capabilities and Features
- Engagement Range:
- Up to 340 km when the target is flying at 20 km altitude.
- Around 190 km if the target is at an altitude of 8 km.
- Propulsion System: Powered by a dual-fuel ducted ramjet engine, allowing high-speed performance across various altitudes—from sea level to 20 km.
- Speed and Maneuverability:
- Launch speed: Between Mach 0.8 and 2.2.
- Target engagement speed: Between Mach 2.0 and 3.6.
- Can engage agile aerial targets with an angle of attack up to 20 degrees.
- Altitude Adaptability: Features a ±10 km snap-up/snap-down capability, enabling it to intercept targets that are significantly above or below the altitude of the launching aircraft.
Strategic Importance
Gandiva is designed to neutralize a wide spectrum of aerial threats, including:
- Enemy fighter jets
- Bombers and transport aircraft
- Aerial refueling planes
- AWACS (Airborne Warning and Control Systems)
Mount Erebus
- 10 Mar 2025
In News:
- Volcanic ice caves beneath Mount Erebus host thriving microbial life, offering insights into extremophile survival and potential life on alien planets.
About Mount Erebus:
- Location: Ross Island, Antarctica, in the Ross Sea.
- Type:Glaciated intraplate stratovolcano; part of the Pacific Ring of Fire.
- Altitude:3,794 meters (12,448 feet) above sea level.
- Rank:Second tallest volcano in Antarctica (after Mount Sidley).
- Discovered: In 1841 by British explorer Sir James Clark Ross.
- Name Origin: Named after Ross’s ship, HMS Erebus.
Volcanic Activity:
- Southernmost active volcano on Earth.
- Continuously active since 1972.
- Eruptions are Strombolian in nature — small, explosive, with lava bombs ejected onto crater rim.
- Contains a persistent lava lake with alkalic lava, typical of rift volcanoes.
Proximity to Human Activity:
- Near McMurdo Station, the largest Antarctic research base, just ~40 km away.
Scientific Significance:
- The microbial ecosystems in volcanic ice caves could help understand:
- Life in extreme environments
- Astrobiological prospects on Mars or Europa
T-72 Tanks

- 08 Mar 2025
In News:
India has signed a $248 million contract with Russia’s Rosoboronexport for the procurement of 1,000 horsepower (HP) engines to upgrade its fleet of T-72 main battle tanks (MBTs). This marks a significant step in enhancing the Indian Army's offensive and mobility capabilities.
Key Features of the Deal
- Engines to replace existing 780 HP ones in T-72 tanks.
- Delivered in fully formed, completely knocked down (CKD), and semi-knocked down (SKD) formats.
- Includes Transfer of Technology (ToT) to Armoured Vehicles Nigam Limited (AVNL) at the Heavy Vehicles Factory, Avadi (Chennai).
- Boosts the ‘Make in India’ initiative in the defence sector through local assembly and licensed production.
About T-72 Tanks
- Origin: Developed by the Soviet Union in the 1970s; designed by Uralvagonzavod.
- India’s Usage: Operates over 2,400 units, making it the backbone of India’s armored forces.
- Manufacturing in India: Locally produced and upgraded at the Heavy Vehicles Factory, Avadi.
Specifications
- Armament:
- 125 mm smoothbore main gun
- 7.62 mm coaxial machine gun
- 12.7 mm anti-aircraft machine gun
- Mobility: With new 1,000 HP engines, improves maneuverability and combat speed.
- Protection: Equipped with composite and reactive armour.
- Night Capability: Advanced thermal imaging systems.
- Operational Range:
- ~460 km on-road
- ~300 km off-road (with auxiliary fuel)
Strategic Significance
- Combat Readiness: Enhances battlefield performance in high-altitude and desert environments like Ladakh.
- Cost Efficiency: Upgrading older platforms is more economical than procuring new MBTs.
- India-Russia Defence Ties: Reinforces long-standing military cooperation between the two countries.
Harpoon Missile
- 07 Mar 2025
In News:
The U.S. Air Force is exploring a new approach to naval warfare by integrating the Harpoon anti-ship missile onto its F-16 fighter aircraft. This development signifies a shift in operational capabilities and enhances the U.S. Air Force’s ability to conduct anti-surface warfare.
Overview of the Harpoon Missile:
The Harpoon missile is a subsonic anti-ship cruise missile developed by Boeing for the U.S. Navy, first introduced in 1977. It is designed to strike surface targets, such as ships and land-based structures, and is currently in service with over 30 countries, including India.
Key features:
- Length: 4.5 meters
- Weight: 526 kilograms
- Range: 90 to 240 kilometers
- Speed: Mach 0.85 (approximately 647 mph or 1,041 km/h)
- Guidance System: GPS-assisted inertial navigation and active radar seeker, enabling both anti-ship and land-strike capabilities
- Warhead: 221-kilogram blast warhead
- Launch Platforms: The Harpoon can be launched from various platforms including ships, submarines, aircraft, and shore batteries
- All-Weather Operations: Designed to perform under various environmental conditions, Harpoon can execute both over-the-horizon and sea-skimming maneuvers for high survivability.
U.S. Air Force Integration with F-16 Aircraft:
The integration of the Harpoon missile onto F-16 aircraft represents a strategic shift for the U.S. Air Force, as traditionally, the missile has been used exclusively by naval platforms. The 53rd Test and Evaluation Group demonstrated a new gateway system that allows for rapid integration of the Harpoon with the F-16, significantly enhancing its anti-surface capabilities.
This integration system enables communication between the missile and aircraft without requiring extensive modifications, potentially shortening the deployment timeline for advanced weaponry. The F-16 fighter aircraft, traditionally designed for air-to-air combat, would now also have the capability to engage surface targets, improving the Air Force’s combat readiness and operational versatility.
Implications for Naval Warfare:
The potential for deploying the Harpoon missile from F-16s would mark a shift in the U.S. Air Force’s role in naval warfare. Traditionally, the Air Force has not employed anti-ship missiles, relying instead on the Navy for such capabilities. The integration of Harpoon onto F-16s would diversify the operational roles of the aircraft, adding flexibility to U.S. military strategies and improving overall effectiveness in anti-surface warfare.
This move would also enable the Air Force to act more autonomously in surface combat scenarios, without relying solely on naval assets. The introduction of this capability could prove critical in multi-domain operations, where air, land, and sea forces must be seamlessly integrated to respond to evolving threats.
Future Developments:
The success of integrating the Harpoon missile onto the F-16 could pave the way for future projects involving the integration of other advanced weapon systems across various military platforms. The flexibility to adapt quickly and innovate beyond bureaucratic constraints is crucial in maintaining a strategic advantage and responding effectively to emerging threats.
The U.S. military’s ongoing commitment to technological advancements and interoperability across its branches signals its readiness to maintain supremacy in naval and aerial warfare. The integration of Harpoon onto F-16s is an example of this evolving capability, with potential implications for future military operations worldwide.
Exercise Desert Hunt 2025

- 04 Mar 2025
In News:
Exercise Desert Hunt 2025 was a high-intensity Tri-Service Special Forces military drill conducted by the Indian Air Force at Air Force Station Jodhpur, Rajasthan, from 24 to 28 February 2025.
Participating Forces
- Indian Army: Para (Special Forces)
- Indian Navy: Marine Commandos (MARCOS)
- Indian Air Force: Garud Special Forces
Objective
- To enhance interoperability, coordination, and operational synergy among the Special Forces of the three services.
- To ensure swift and effective responses to emerging security threats through joint operations.
Key Activities
- Airborne insertion and combat free-fall
- Precision strikes and counter-terrorism drills
- Hostage rescue operations
- Urban warfare simulations
- Validation of joint operational doctrines under realistic combat conditions
Significance
- Strengthens tri-service integration and fosters inter-service cooperation.
- Reinforces the commitment of the Indian Armed Forces to national security.
- Provides a platform for doctrinal validation and operational readiness.
Naval Anti-Ship Missile – Short Range (NASM-SR)

- 03 Mar 2025
In News:
The Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO) and the Indian Navy successfully conducted flight trials of the indigenous Naval Anti-Ship Missile – Short Range (NASM-SR) with a ‘Man-in-Loop’ capability from a Seaking 42B naval helicopter at the Integrated Test Range (ITR), Chandipur.
Key Features and Capabilities:
- Man-in-Loop Functionality:
- Provides real-time human intervention during flight.
- Enables in-flight retargeting by transmitting live seeker images to the pilot through a high-bandwidth two-way data link.
- Offers tactical flexibility in selecting and engaging specific targets among multiple options.
- Guidance and Navigation:
- Launched in Bearing-Only Lock-On After Launch (BOLOAL) mode.
- Equipped with an Indigenous Imaging Infra-Red (IIR) Seeker for terminal phase guidance.
- Uses an Indigenous Fiber Optic Gyroscope-based Inertial Navigation System (INS) and a Radio Altimeter for accurate mid-course and low-altitude navigation.
- Design and Control:
- Features Electro-Mechanical Actuators and Jet Vane Control for enhanced maneuverability.
- Integrated avionics module, thermal batteries, and PCB warhead support precise targeting and mission efficiency.
- Stealth and Strike Capability:
- Operates in Sea-Skimming Mode to evade radar detection.
- Demonstrated a direct hit on a small ship target at its maximum range during trial.
- Propulsion:Powered by solid propulsion, featuring an in-line ejectable booster and long-burn sustainer.
Development and Significance:
- Jointly developed by DRDO and the Indian Navy.
- Key DRDO labs involved:
- Research Centre Imarat (RCI)
- Defence Research and Development Laboratory (DRDL)
- High Energy Materials Research Laboratory (HEMRL)
- Terminal Ballistics Research Laboratory (TBRL)
- Marks India’s capability in indigenous anti-ship missile systems with advanced features like man-in-loop control and high-precision targeting.
- Enhances India’s naval warfare and coastal defense capabilities, aligning with Atmanirbhar Bharat in defense manufacturing.
Mount Fentale
- 28 Feb 2025
In News:
Mount Fentale, a stratovolcano located in Awash National Park in northern Ethiopia, has recently gained global attention due to its unprecedented release of massive methane plumes. This rare and unusual volcanic event, has raised significant concerns about its potential impacts on climate change and the necessity for better global methane tracking.
About Mount Fentale
Mount Fentale, standing 600 meters above the Rift Valley floor, is known for its elliptical caldera, approximately 6 km in diameter. The volcano's eruptions, historically infrequent, have typically involved the release of lava and ash.
The Methane "Burp" and Its Unusual Nature
What distinguishes this event from typical volcanic activity is the massive emission of methane—58 metric tonnes per hour. Volcanic eruptions are generally associated with carbon dioxide (CO?) and sulfur dioxide (SO?), not methane. Methane, however, is significantly more effective at trapping heat than CO?, being 28 times more potent over a 100-year period. The scale of the methane release is far greater than what is typically associated with volcanic activity, prompting scientific investigations into the cause and potential implications for the global climate.
The methane release is believed to result from deep magma movements that opened underground gas pockets, allowing the methane to escape through newly formed fissures. Unlike a surface eruption, which would involve molten lava, this "burp" suggests that magma at depth caused the gas to surface without the typical visual eruption.
Scientific and Environmental Concerns
Methane is the second-largest contributor to global warming, responsible for around 11% of total greenhouse gas emissions worldwide. Even short-term spikes in methane levels can have a significant impact on global temperature rise. This phenomenon underscores the urgency for enhanced global methane monitoring systems, particularly from natural sources like volcanic eruptions.
While Mount Fentale is not a frequent eruptor, the discovery of massive methane emissions from the volcano highlights the need for comprehensive tracking of both natural and human-driven sources of greenhouse gases. The event suggests that volcanic activity may be a more significant contributor to climate change than previously understood, particularly in the context of methane.
Recent Developments and Earthquake Activity
Following the methane release, Mount Fentale experienced a magnitude 6.0 earthquake the strongest to hit Ethiopia since 1989. This earthquake, likely associated with tectonic movements beneath the volcano, adds a layer of complexity to the ongoing geological activity in the region.
The volcano's stratovolcanic nature, characterized by steep sides built up by alternating layers of lava and pyroclastic material, makes it particularly prone to explosive events. Stratovolcanoes like Fentale are among the most active types of volcanoes on Earth, and their eruptions can have far-reaching environmental impacts.
Global Significance and the Role of Satellite Monitoring
The unexpected methane release from Mount Fentale is not just a local environmental concern but has global implications. As a powerful greenhouse gas, methane's release into the atmosphere accelerates global warming, making it a key target in climate change mitigation efforts. The event highlights the importance of satellite monitoring programs, like those operated by the European Space Agency’s Copernicus program, which detected thermal anomalies in January, and GHGSat, which later confirmed the methane emissions.
Exercise Komodo

- 21 Feb 2025
In News:
The Indian Navy's platforms—INS Shardul, an amphibious warfare ship, and the P-8I Long Range Maritime Surveillance Aircraft—participated in the International Fleet Review (IFR) 2025 and the 5th edition of the Multilateral Naval Exercise Komodo held in Bali, Indonesia, from 15 to 22 February 2025.
International Fleet Review (IFR) 2025
- IFR 2025 is a prestigious multinational naval event reviewed by the President of Indonesia.
- Participating nations showcased naval assets including warships, helicopters, and maritime aircraft.
- The Indian Navy took part in:
- International Maritime Security Symposium
- Tactical floor games
- City parade
- Coral and mangrove plantation
- Beach cleaning activities
- Baby turtle release, promoting environmental and maritime sustainability.
Exercise Komodo 2025
- Initiated in 2014, Exercise Komodo is a non-combat multilateral naval exercise hosted by the Indonesian Navy.
- The 2025 edition had the theme: "Maritime Partnership for Peace and Stability".
- Objectives:
- Promote maritime cooperation
- Enhance interoperability
- Foster regional security cooperation
- Key Features:
- Participation from 39 countries
- Involvement of 34 foreign and 18 Indonesian Navy warships
- Included:
- Naval exercises
- Officer exchange forums
- Bilateral naval meetings
- Defense exhibition
- Cultural parades
Strategic Context and Bilateral Engagements
- The participation builds upon the Indian Navy’s involvement in the La Pérouse exercises in Indonesia (January 2025) involving INS Mumbai and a P-8I aircraft.
- It coincided with the visit of Admiral Muhammad Ali, Chief of Staff of the Indonesian Navy, to India during the Republic Day 2025, accompanying President Prabowo Subianto as the Chief Guest.
Significance for India
- The participation reaffirms India’s commitment to SAGAR (Security and Growth for All in the Region).
- It strengthens India-Indonesia defense ties and underscores India's proactive role in regional maritime diplomacy and environmental stewardship.
Exercise Dharma Guardian 2025

- 20 Feb 2025
In News:
The 6th edition of Exercise Dharma Guardian, a joint annual military exercisealternately hosted in India and Japan since 2018is scheduled from February 25 to March 9, 2025, at Mount Fuji, Japan.
Key Highlights:
Objectives:
- Strengthen Bilateral Defence Relations: Enhances military diplomacy under the India–Japan Special Strategic and Global Partnership.
- Promote Interoperability: Develops joint operational capabilities and tactical synergy in line with UN peacekeeping mandates (Chapter VII).
- Urban and Semi-Desert Warfare: Trains troops in counter-terrorism operations and urban combat scenarios.
- Regional Stability: Supports the Indo-Pacific security architecture and complements Quad defence objectives (India, Japan, US, Australia).
Key Features of Dharma Guardian 2025
- Advanced Tactical Training: Close-quarter battle drills, live-fire exercises, battlefield medical evacuation.
- Joint Counter-Terror Operations: Conducted under UN charter guidelines for multinational cooperation.
- 48-hour Validation Exercise: Simulated real-time combat for assessing operational readiness and coordination.
- ISR and Tactical Mobility Drills: Involves establishing temporary operating bases, ISR (Intelligence, Surveillance, Reconnaissance) grids, mobile vehicle checkpoints, and heliborne insertions.
- House Intervention & Search Operations: Practical training for securing urban areas against militant threats.
- Weapons & Equipment Display: Demonstrates India’s growing defence manufacturing under the Atmanirbhar Bharat initiative.
Mount Fuji – Host Site
- Geographical Significance: Japan’s highest peak at 3,776.24 meters, located 100 km southwest of Tokyo.
- Cultural Importance: Recognized as a UNESCO World Heritage Site (2013) and revered as one of Japan’s “Three Holy Mountains.”
- Training Terrain: Its stratovolcanic landscape provides a realistic backdrop for high-altitude and rugged terrain operations.
Related India-Japan Military Exercises
India and Japan conduct a wide spectrum of bilateral and multilateral defense exercises across all services:
Exercise Name Service Branch Focus Area
Dharma Guardian Army Land-based counter-terror and urban warfare
JIMEX Navy Naval interoperability and maritime security
Malabar (Quad) Navy (Multilateral) Naval drills with US and Australia
Veer Guardian Air Force Air combat tactics and coordination
ShinyuuMaitri Air Force Air mobility and humanitarian operations
Aero India 2025

- 20 Feb 2025
In News:
Aero India 2025, the 15th edition of Asia's largest biennial airshow, is scheduled to take place from February 10 to 14, 2025, at the Air Force Station, Yelahanka, in Bengaluru, Karnataka.
Organized by the Defence Exhibition Organisation under the Ministry of Defence, with support from HAL, DRDO, and the Indian Air Force, the event showcases India's growing prowess in aerospace, aviation, and defense technologies.
Key Highlights:
Edition: 15th (First held in 1996; originally Avia India in 1993)
Theme: “The Runway to a Billion Opportunities”
Conclave Theme: “BRIDGE – Building Resilience through International Defence and Global Engagement”
Objectives and Significance
- Promote Indigenous Manufacturing: In alignment with ‘Make in India’ and ‘Atmanirbhar Bharat’, the show promotes domestic aerospace and defense production.
- Showcase Technological Advancements: Cutting-edge systems including fighter jets, helicopters, UAVs, and AI-integrated defense solutions will be exhibited.
- Encourage Global Partnerships: Facilitates joint ventures, MoUs, and technology transfers between Indian and foreign defense firms.
- Boost Strategic Diplomacy: A platform for global defense ministers, CEOs, and military leaders to foster bilateral and multilateral defense ties.
- Stimulate Investment: Attracts FDI and international contracts in India’s defense sector.
Key Events
- Live Aerial Displays: Aerobatic performances by combat aircraft, helicopters, and elite teams like Surya Kiran.
- Defense Ministers’ Conclave: Deliberations on enhancing international defense cooperation.
- CEO Roundtable: Industry leaders discuss emerging trends and investment prospects.
- Manthan/iDEX Pavilion: Showcasing start-up innovations in defense and aerospace.
- India Pavilion: A dedicated zone for indigenous defense production and capabilities.
- International Seminar (Feb 8–9): Focused on Futuristic Aerospace Technologies and related R&D challenges.
Strategic Role of Aero India
Aero India plays a pivotal role in:
- Supporting Medium Multi-Role Combat Aircraft (MMRCA) procurements.
- Demonstrating India's readiness as a global defense manufacturing hub.
- Enhancing India’s geopolitical standing by fostering defense diplomacy through multilateral engagement.
R-37M Missile

- 13 Feb 2025
In News:
Russia has recently offered the R-37M missile, a state-of-the-art, long-range air-to-air missile, to India. This missile, one of the world’s most advanced, has the potential to transform India's aerial defense capabilities. The offer also comes with the opportunity for India to license the production of this missile domestically. However, the acquisition of such a potent weapon is raising tensions in the region, particularly with Pakistan, China, and Bangladesh, and has broader strategic implications.
Overview of R-37M Missile:
The R-37M, also known by its NATO reporting name AA-13 Axehead, is a hypersonic, long-range air-to-air missile developed by Russia.
It is designed to target high-value assets, such as AWACS (Airborne Warning and Control Systems), tanker aircraft, and other support platforms, beyond visual range (BVR).
Evolved from the R-33 missile, the R-37M significantly enhances air combat capabilities due to its range, speed, and precision.
- Speed and Range: The missile can travel at speeds of up to Mach 6 (approximately 7,400 km/h), enabling it to intercept fast-moving aerial threats. It has an operational range of 300-400 km (160-220 nautical miles), making it one of the longest-reaching air-to-air missiles.
- Weight: The missile weighs 510 kg, with a 60 kg warhead.
- Guidance System: It uses an advanced combination of inertial navigation with mid-course updates, active radar homing, and semi-active radar guidance for the terminal phase.
- Combat Advantage: The R-37M can target beyond visual range, enabling the launching aircraft to engage enemy targets while remaining outside the reach of enemy missiles.
Impact on the Indian Air Force (IAF):
The R-37M missile could replace the current R-77 missile used by India’s Sukhoi Su-30MKI fighter jets. This acquisition will bolster India's air defense by providing enhanced capabilities to intercept aerial threats at greater distances. Additionally, the offer to license the local production of the missile is a significant step toward strengthening India’s defense industry and reducing its dependence on foreign weapon systems. This move can also contribute to India's strategic autonomy in military engagements.
Strategic Implications for Pakistan:
Pakistan’s Air Force (PAF) primarily relies on F-16 fighter jets for its aerial superiority. However, these aircraft are vulnerable to interception beyond the Line of Control (LoC) by the R-37M, which has an engagement range of up to 400 kilometers. This could significantly alter Pakistan's defense posture, as its aircraft would be exposed to threats from Indian aircraft even before crossing the LoC.
Potential Effects on China:
China, which already possesses advanced air-to-air missiles such as the PL-15 and PL-21, will closely monitor India’s acquisition of the R-37M missile. While China is not directly threatened by the missile due to its own advanced defense systems, India’s missile capabilities could alter the balance of air superiority in the region. The acquisition could prompt China to accelerate the development of counter-hypersonic technologies, potentially altering the trajectory of military developments in the region.
Impact on Bangladesh:
Bangladesh, which shares friendly relations with India, could find itself caught in the strategic competition between India and Pakistan, despite its own military capabilities not directly challenging India. The regional military dynamics, influenced by India’s acquisition of advanced weapons like the R-37M, may push Bangladesh to enhance its defense capabilities, either through regional alliances or by procuring advanced defense technologies.
India-Russia Defense Relations:
India’s defense cooperation with Russia has been longstanding and substantial. Between 2015 and 2020, India’s defense imports from Russia were valued at approximately $10 billion, making Russia one of India’s largest defense suppliers. Around 70% of India's defense equipment is of Russian origin. Key joint defense projects include:
- BrahMos Missile: A joint venture to develop a supersonic cruise missile.
- S-400 Triumph: A $5.4 billion deal for five S-400 air defense systems.
- AK-203 Assault Rifles: A project for the local manufacturing of over 700,000 rifles.
- Military Exercises: India and Russia conduct joint military exercises, such as the INDRA (focused on counter-terrorism) and AVIAINDRA (aerial exercises between the Indian Air Force and Russian Aerospace Forces).
Exercise Cyclone 2025

- 13 Feb 2025
In News:
- The third edition of the India-Egypt Joint Special Forces Exercise CYCLONE is being conducted from February 10–23, 2025 at the Mahajan Field Firing Range, Rajasthan.
- The previous edition (2nd) was held in Egypt in January 2024, and the first edition was conducted in India in 2023.
About Exercise CYCLONE
- It is a bilateral joint special forces military exercise between India and Egypt.
- Annual exercise, held alternatively in India and Egypt.
- The 2025 edition is focused on:
- Counter-terrorism operations
- High-intensity combat training
- Survival techniques in desert/semi-desert terrain
- Tactical drills and real-world combat scenarios
- Motto of the exercise: “Together we train, together we excel.”
Objectives
- Enhance military-to-military cooperation.
- Strengthen interoperability and joint operational capabilities.
- Exchange of special warfare tactics and combat strategies.
- Operate under frameworks aligned with Chapter VII of the UN Charter (pertaining to threats to peace, breaches of peace, and acts of aggression).
Strategic Importance
- The exercise reflects deepening India-Egypt defence cooperation.
- Aimed at enhancing readiness for evolving security challenges in the region.
- Enables both forces to operate together in simulated combat situations, improving coordination and adaptability.
India-Egypt Relations: Defence and Beyond
- Strategic Partnership established in 2023, covering:
- Political, defence, security, energy, and economic cooperation.
- Bilateral Trade Agreement (1978): Based on Most Favored Nation (MFN) clause.
- India is one of Egypt’s key trading partners in Africa.
Pinaka Multiple Rocket Launch System (MRLS)

- 11 Feb 2025
In News:
In a significant step towards modernizing India's artillery capabilities, the Union Ministry of Defence signed contracts worth ?10,147 crore on February 6, 2025, for the procurement of advanced ammunition for the Pinaka Multiple Rocket Launch System (MRLS).
These agreements were concluded with Economic Explosives Limited (EEL) and Munitions India Limited (MIL) for the acquisition of Area Denial Munition (ADM) Type-1 and High Explosive Pre-Fragmented (HEPF)-Mk-1 (enhanced) rockets, respectively.
Pinaka MRLS: An Overview
- Type: All-weather, battle-proven, indirect fire Artillery Weapon System.
- Developer: Armament Research and Development Establishment (ARDE) of DRDO.
- Combat History: First used effectively during the Kargil War, neutralising enemy positions on mountain tops.
- Mobility: Mounted on Tatra trucks, providing high mobility and quick deployment.
- Payload & Firing Capacity:
- Each launcher: 12 rockets.
- Each battery: 6 launchers = 72 rockets.
- Capable of delivering a full salvo in 44 seconds.
- Range:
- Initial range: 60–75 km.
- Guided Pinaka (Pinaka-G) extends range to 75 km, with future plans to extend up to 120 km and eventually 300 km.
- Precision: The guided version uses INS/GPS navigation, allowing high accuracy against critical and time-sensitive targets.
- Warhead Types: High-explosive and submunitions, suitable for a wide variety of targets.
New Ammunition Contracts: Enhancing Lethality
The contracts include the procurement of:
- ADM Type-1: Equipped with specialised warheads designed to disperse sub-munitions over wide areas. These are effective in targeting mechanised formations, vehicles, and personnel, thereby denying area access to the enemy. These are similar to Dual Purpose Improved Conventional Munitions (DPICM).
- HEPF-Mk-1 (Enhanced): An advanced variant of the currently used HEPF rockets with extended range and improved lethality, capable of deep precision strikes in enemy territory.
In addition, a contract was signed with Bharat Electronics Limited (BEL) for upgrades to the Shakti software, which supports artillery operations.
Operational & Strategic Significance
- The upgraded Pinaka system will be the mainstay of long-range rocket artillery in the Indian Army.
- Four Pinaka regiments are already operational, with six more on order.
- The system’s development and expansion are a testament to India’s defenceindigenisation drive.
- The DRDO successfully completed flight tests of the guided Pinaka rocket with a range of 75 km, doubling its earlier reach. Future versions aim for up to 120 km and 300 km range.
Employment and MSME Impact
Besides enhancing strategic deterrence, the ?10,147 crore investment is expected to:
- Generate direct and indirect employment, particularly in the defence manufacturing ecosystem.
- Promote the Indian MSME sector, which contributes components and subsystems for the rockets and launchers.
- Support the vision of Atmanirbhar Bharat by reducing dependency on imported artillery systems.
Stryker Infantry Combat Vehicle

- 09 Feb 2025
In News:
India-U.S. defence cooperation is advancing with the proposed co-production of the Stryker Infantry Combat Vehicle (ICV). This deal represents a significant leap in bilateral defence industrial collaboration and aligns with India's strategic goal of military modernization and indigenisation under the ‘Make in India’ initiative.
About Stryker Infantry Combat Vehicle (ICV):
- Origin: Jointly developed by General Dynamics Land Systems (GDLS) Canada and U.S., it is the first new military vehicle inducted into U.S. Army service since the 1980s.
- Type: Eight-wheeled armoured infantry combat vehicle designed for rapid deployment and battlefield mobility.
- Variants: Includes Infantry Carrier Vehicle (ICV), Mobile Gun System (MGS), reconnaissance vehicle, medical evacuation vehicle, fire support vehicle, and Anti-Tank Guided Missile (ATGM) carrier.
Key Features:
- Mobility: Top speed of ~100 km/h and an operational range of 483 km. Can be airlifted using C-17 and C-130 aircraft (both in IAF’s fleet) or Chinook helicopters, enhancing deployment in remote terrains.
- Firepower: Equipped with a 30 mm cannon and a 105 mm mobile gun.
- Protection: V-hull structure for blast protection; composite armour reinforced with ceramic tiles offers increased survivability against IEDs and small arms.
- Capacity: Operated by a 2-member crew and can transport a 9-member infantry squad.
Operational Evaluation in India:
- High-Altitude Trials: Conducted in Ladakh (13,000–18,000 feet) during September–October 2024. Evaluation reports were shared with Army Headquarters for further review.
- Javelin ATGM Demonstration: Conducted alongside Stryker trials; however, the performance was sub-optimal due to the vintage system used. Repeat trials have been requested by India.
Strategic Importance for India:
- Tactical Advantage: Enhanced mobility and survivability in high-altitude warfare make it suitable for regions like Ladakh and Arunachal Pradesh.
- Border Security: Bolsters India's defence posture along sensitive frontiers with China and Pakistan.
- Force Modernization: Meets the Indian Army’s requirement for ICVs with integrated ATGM capabilities.
- Aatmanirbhar Bharat Push: The proposed model includes initial direct imports followed by large-scale license production in India, potentially by Bharat Earth Movers Limited (BEML).
Defence Diplomacy and Industrial Cooperation:
- The deal is being advanced under the India-U.S. Defence Industrial Cooperation Roadmap, focusing on co-development and co-production.
- In November 2023, Indian Defence Secretary confirmed discussions under this framework.
- The U.S. has reiterated the importance of India enhancing procurement of U.S.-made defence equipment, aiming at a balanced trade partnership.
- The Stryker deal is expected to feature in high-level bilateral dialogues, including the visit of Prime Minister Narendra Modi to Washington DC and during engagements at Aero India.
Challenges and Reservations:
- Some Indian defence officials have flagged concerns, noting that similar ICVs have been developed by Indian private companies.
- Delays in previous U.S. defence exports (e.g., F-404 jet engines for LCA-Mk1A) have also raised caution regarding timelines and reliability.
Iskander-M

- 08 Feb 2025
In News:
In a significant defense development with wide-ranging geopolitical implications, the Russian Federation is preparing to mass-produce the Iskander-M tactical ballistic missile, a new-generation weapon system with enhanced range and destructive capabilities. This move is part of Russia’s broader strategy to upgrade its missile arsenal amid ongoing tensions with NATO, especially in the context of the Ukraine conflict.
Key Features and Strategic Purpose
The 9K720 Iskander-M, developed by the Machine-Building Design Bureau (Kolomna), is a medium-range tactical ballistic missile with an effective range of up to 1,000 kilometers. It is capable of delivering both conventional and nuclear warheads, making it a versatile and high-impact weapon in regional conflict scenarios.
- The missile is precision-targeted and designed to neutralize high-value enemy assets, including NATO’s military infrastructure in Eastern Europe, especially in Ukraine.
- The production of the upgraded missile, unofficially referred to as the Iskander-1000, is expected to begin in full swing by 2025.
- The missile is reported to be highly destructive, with the ability to conduct deep strikes with minimal detection, offering Russia a tactical advantage in asymmetric warfare.
Deployment of Oreshnik Missile Systems in Belarus
In a parallel development, Russia has confirmed the deployment of Oreshnik medium-range ballistic missile systems in Belarus, a strategic ally. This decision follows agreements between the Russian and Belarusian leadership, reinforcing the military integration under their collective defense pact.
- The Oreshnik system, though less publicly detailed than the Iskander, is designed for tactical use and contributes to enhancing Russia’s regional defense shield.
- According to Russian foreign ministry officials, Belarus already hosts a joint Regional Forces Group, non-strategic nuclear weapons, and modern Russian defense systems.
- The positioning of these systems near NATO’s eastern borders heightens tensions with Western powers, particularly the United States, Poland, the Baltic States, and the European Union.
Geopolitical Ramifications
The Iskander-M and Oreshnik missile programs are part of Russia’s strategic doctrine to deter NATO's influence and reassert its military dominance in Eastern Europe. These deployments are:
- Likely to escalate NATO-Russia tensions, increasing the risk of a regional arms race.
- Expected to complicate European security dynamics, especially in Poland, Ukraine, and the Baltic states, which are seen as potential frontlines.
- Raising the prospect of further military escalation in the ongoing Russia-Ukraine conflict.
- Prompting NATO countermeasures, including deployment of missile defense systems and increased troop presence near Eastern borders.
India-Maldives Joint Military Exercise ‘Ekuverin’

- 05 Feb 2025
In News:
The 13th edition of Exercise Ekuverin, a bilateral joint military exercise between the Indian Army and the Maldives National Defence Force (MNDF), commenced in the Maldives on February 4, 2025. The exercise continues to reinforce defence and strategic ties between the two nations.
About Exercise Ekuverin
- Name Meaning: “Ekuverin” means ‘Friends’ in Dhivehi, the official language of the Maldives—symbolizing the deep and friendly defence partnership between India and the Maldives.
- First Conducted: The exercise was initiated in 2009 as part of annual bilateral defence cooperation.
- Venue Alternation: It is held alternatively in India and the Maldives every year.
- 2023 Edition: Conducted at Chaubatia, Uttarakhand from June 11 to 24.
- 2025 Edition: Being hosted in the Maldives.
Key Objectives and Features
- Military Interoperability: Enhances coordination and operational synergy between Indian and Maldivian armed forces.
- Counter-Insurgency and Counter-Terrorism (CI/CT): Focuses on joint tactical drills to counter modern asymmetric threats.
- Humanitarian Assistance and Disaster Relief (HADR): Equips forces to respond effectively to natural disasters and humanitarian crises.
- Strengthening IOR Security: Reinforces regional maritime and strategic stability in the Indian Ocean Region (IOR), a key area of India’s strategic interest.
Significance for India-Maldives Relations
- Strategic Partnership: Builds mutual trust and defence preparedness, aligning with India’s “Neighbourhood First” policy.
- Capacity Building: Helps enhance the capability of the MNDF through joint training with a larger and more experienced Indian Army.
- Regional Security Cooperation: Plays a crucial role in maintaining peace, security, and freedom of navigation in the IOR.
India’s Defence Engagement with Southeast Asia
India actively conducts multiple bilateral and multilateral defence exercises with Southeast Asian countries to enhance defence diplomacy and promote a free, open, and secure Indo-Pacific.
Key Defence Exercises with Southeast Asian Nations:
- Garuda Shakti: Special Forces exercise with Indonesia (Nov 2022, Sangga Buana Training Area).
- Mitra Shakti: Annual exercise with Sri Lanka, last held in 2022.
- VINBAX: India-Vietnam bilateral exercise; 3rd edition held in 2022.
- IMBEX: India-Myanmar bilateral exercise (last noted in 2017–18).
- Maitree: Joint annual military exercise with Thailand, conducted since 2006.
- CORPAT: Coordinated Patrols with Indonesia, Thailand, and Malaysia for maritime domain awareness and security.
- AIME 2023: The first ASEAN-India Maritime Exercise, conducted in May 2023, involving navies from India and ASEAN nations (Brunei, Indonesia, Malaysia, Philippines, Singapore, Thailand, Vietnam).
Aero India 2025
- 28 Jan 2025
In News:
Aero India 2025, the 15th edition of India’s premier aerospace and defence exhibition, is scheduled from February 10–14, 2025, at the Yelahanka Air Force Station, Bengaluru.
Organised by the Ministry of Defence and the Defence Exhibition Organisation (DEO), the event continues to be a vital forum for promoting India's indigenous defence capabilities and fostering international collaboration.
Evolution of Aero India: From Showcase to Strategic Asset
- Inception (1996): Launched as a modest exhibition to attract foreign investments and highlight India’s aerospace potential.
- Growth Phase (2005–2015): Marked by the entry of global giants like Boeing, Airbus, Lockheed Martin, and Dassault Aviation. Indigenous platforms like LCA Tejas began gaining prominence.
- Current Phase (2015–Present): Aligned with ‘Make in India’ and ‘Aatmanirbhar Bharat’, Aero India has become a symbol of India's defence self-reliance and a magnet for global partnerships.
Aero India 2025 Highlights
1. International Participation and Strategic Displays
- Participation from 15+ countries and major OEMs.
- Russia’s Su-57 and USA’s F-35—two of the world’s most advanced 5th-generation fighters—will be showcased together, reflecting India’s growing strategic importance.
- Other prominent platforms: KC-135 Stratotanker, Embraer C-390, and Light Combat Helicopter Prachand.
2. Indigenous Innovation
- Advanced Medium Combat Aircraft (AMCA): India’s 5th-generation stealth fighter, developed by HAL and ADA, will be unveiled.
- Indigenous platforms like LCA Mk2, LUH, HTT-40, ALH, and Naval Twin-Engine Deck-Based Fighter will also be featured.
3. Start-Up Integration via 'Manthan'
- Through the iDEX initiative, Aero India is promoting start-ups working in AI, unmanned systems, cybersecurity, and electronic warfare.
- Start-ups will showcase innovations including jetpack suits, robotics, and defence software tools.
4. Business & Public Engagement
- Business Days: February 10–12, 2025
- Public Days: February 13–14, 2025
- Over 7 lakh visitors expected; the event offers aerial displays, seminars, tech expos, and networking forums.
5. Defence Diplomacy and Deals
- Aero India 2023 had seen over ?80,000 crore worth of MoUs. A similar or higher scale of defence agreements is expected in 2025.
- High-level participation from defence ministers, air chiefs, and CEOs of OEMs, signalling deepening international defence cooperation.
Strategic Significance for India
- Geopolitical Leverage: Participation of both US and Russian defence firms signals India’s strategic autonomy and balanced defence diplomacy.
- Self-Reliance Boost: The event enhances domestic manufacturing by integrating MSMEs, promoting co-development and co-production with foreign partners.
- Global Recognition: Positions India as an emerging aerospace hub in the Indo-Pacific.
- Technological Edge: Demonstrates advancements in stealth technology, avionics, and unmanned systems.
Theme of Aero India 2025: “The Runway to a Billion Opportunities” — highlighting India’s expanding defence manufacturing capabilities and its aim to integrate with the global supply chain.
Sanjay Battlefield Surveillance System

- 25 Jan 2025
In News:
Defence Minister Rajnath Singh recently flagged off Sanjay, an indigenously developed Battlefield Surveillance System (BSS), to be inducted into the Indian Army in phased manner from March to October 2025, designated as the ‘Year of Reforms’ by the Ministry of Defence.
Overview:
- Nature: Automated surveillance system
- Purpose: To integrate real-time data from ground and aerial sensors, enabling swift, informed decision-making in conventional and sub-conventional warfare scenarios.
Key Features:
- Common Surveillance Picture (CSP): Fuses verified sensor data to generate a real-time surveillance image of the battlefield.
- Real-time Integration & Analytics: Processes inputs using advanced analytics to eliminate duplication and enhance situational awareness.
- Secure Networks: Operates over the Indian Army’s Data Network and Satellite Communication Network, ensuring reliable and secure data flow.
- Centralized Web Application: Provides integrated inputs to Command Headquarters and Army HQ through a unified platform, supporting the Indian Army's Decision Support System.
- Indigenous Development: Jointly developed by the Indian Army and Bharat Electronics Limited (BEL) under the Buy (Indian) category, promoting Aatmanirbharta in defense.
Operational Significance:
- Enhances battlefield transparency, situational awareness, and surveillance capabilities along vast and sensitive land borders.
- Functions as a force multiplier in Intelligence, Surveillance & Reconnaissance (ISR) operations.
- Enables network-centric warfare, marking a shift towards data-driven military operations.
Deployment:
- To be inducted into all Brigades, Divisions, and Corps of the Army in three phases (March–October 2025).
Scramjet & Hypersonic Technology
- 23 Jan 2025
In News:
On 21 January 2025, DRDO’s Defence Research & Development Laboratory (DRDL) successfully conducted a 120-second ground test of an indigenously developed Scramjet (Supersonic Combustion Ramjet) engine, marking a major milestone in India’s journey towards hypersonic missile technology.
What is Scramjet Technology?
Definition
A Scramjet is an air-breathing engine that sustains combustion at supersonic speeds—optimized for speeds above Mach 5 (hypersonic range).
Working Principle
- Utilizes vehicle’s forward motion to compress incoming air—no onboard oxidizer needed.
- Injects fuel into the compressed supersonic airflow → ignition → high-speed thrust.
- Operates without moving parts, making it lightweight, efficient, and reliable.
Key Indigenous Innovations
Feature Description
Active-Cooled Combustor Stable combustion achieved at 1.5 km/s airflow, comparable to "keeping a candle lit in a hurricane."
Endothermic Scramjet Fuel First-time development in India; offers cooling + ignition efficiency.
Thermal Barrier Coating (TBC) Jointly developed with DST; withstands temperatures beyond melting point of steel using advanced ceramic coating.
CFD Simulations Used for design optimization and performance validation of flame-holding techniques.
Significance of Scramjet Test
- Stable Combustion: A major challenge in hypersonic propulsion, now successfully demonstrated.
- Hypersonic Missiles:
- Speeds >Mach 5 (~5400 km/h).
- Bypass air defence systems due to speed and maneuverability.
- Enable rapid, high-impact delivery.
- Reusable Launch Vehicles:
- Cuts satellite launch costs via air-breathing propulsion.
- Strategic Edge:
- India joins elite group: USA, Russia, China.
- Strengthens defence deterrence & technological sovereignty.
- Technology Spillover: Advancements in CFD, materials science, flame stabilization, and fuel chemistry.
Global Hypersonic Race
- China (2021): Tested nuclear-capable hypersonic glide vehicle (HGV) that orbited Earth before hitting target.
- USA & Russia: Advanced programs with operational hypersonic systems (e.g., Avangard, Zircon, ARRW).
- India: Now developing indigenous hypersonic missile platform.
Scramjet & Hypersonic Technology

- 23 Jan 2025
In News:
On 21 January 2025, DRDO’s Defence Research & Development Laboratory (DRDL) successfully conducted a 120-second ground test of an indigenously developed Scramjet (Supersonic Combustion Ramjet) engine, marking a major milestone in India’s journey towards hypersonic missile technology.
What is Scramjet Technology?
Definition
A Scramjet is an air-breathing engine that sustains combustion at supersonic speeds—optimized for speeds above Mach 5 (hypersonic range).
Working Principle
- Utilizes vehicle’s forward motion to compress incoming air—no onboard oxidizer needed.
- Injects fuel into the compressed supersonic airflow → ignition → high-speed thrust.
- Operates without moving parts, making it lightweight, efficient, and reliable.
Key Indigenous Innovations
Feature Description
Active-Cooled Combustor Stable combustion achieved at 1.5 km/s airflow, comparable to "keeping a candle lit in a hurricane."
Endothermic Scramjet Fuel First-time development in India; offers cooling + ignition efficiency.
Thermal Barrier Coating (TBC) Jointly developed with DST; withstands temperatures beyond melting point of steel using advanced ceramic coating.
CFD Simulations Used for design optimization and performance validation of flame-holding techniques.
Significance of Scramjet Test
- Stable Combustion: A major challenge in hypersonic propulsion, now successfully demonstrated.
- Hypersonic Missiles:
- Speeds >Mach 5 (~5400 km/h).
- Bypass air defence systems due to speed and maneuverability.
- Enable rapid, high-impact delivery.
- Reusable Launch Vehicles:
- Cuts satellite launch costs via air-breathing propulsion.
- Strategic Edge:
- India joins elite group: USA, Russia, China.
- Strengthens defence deterrence & technological sovereignty.
- Technology Spillover: Advancements in CFD, materials science, flame stabilization, and fuel chemistry.
Global Hypersonic Race
- China (2021): Tested nuclear-capable hypersonic glide vehicle (HGV) that orbited Earth before hitting target.
- USA & Russia: Advanced programs with operational hypersonic systems (e.g., Avangard, Zircon, ARRW).
- India: Now developing indigenous hypersonic missile platform.
Exercise La Perouse 2025
- 19 Jan 2025
In News:
India is participating in the fourth edition of the multinational naval exercise La Perouse, hosted by France in key maritime straits—Malacca, Sunda, and Lombok. The Indian Navy's INS Mumbai, an indigenously built guided-missile destroyer, represents India.
Key Highlights:
- Participating Countries: Navies from India, France, Australia, USA, UK, Indonesia, Malaysia, Singapore, and Canada.
- Objectives:
- Enhance maritime situational awareness.
- Promote tactical interoperability through joint training.
- Conduct surface warfare, anti-air warfare, air defence, and VBSS (Visit, Board, Search and Seizure) operations.
- Strengthen cooperation on maritime surveillance, air operations, and information sharing.
- Significance:
- Demonstrates commitment to a rules-based international order in the Indo-Pacific.
- Reflects India’s vision of SAGAR (Security and Growth for All in the Region).
- Counters increasing presence of Chinese naval forces in the Indo-Pacific.
Strategic Location: Key Straits in Focus
- Strait of Malacca
- Connects: Andaman Sea (Indian Ocean) to South China Sea (Pacific Ocean).
- Geography: Lies between Peninsular Malaysia and Sumatra, near Singapore.
- Significance: One of the world’s busiest trade routes.
- Choke Point: Narrowest part (Philips Channel) is only 2.8 km wide.
- Sunda Strait
- Connects: Java Sea (Pacific) to the Indian Ocean.
- Between: Java and Sumatra (Indonesia).
- Challenges: Volcanic islands (e.g., Krakatoa), shallow depths (20–100 m).
- Importance: Secondary maritime route, strategic in times of congestion in Malacca.
- Lombok Strait
- Connects: Java Sea to the Indian Ocean.
- Between: Bali and Lombok islands.
- Depth: 250–1,300 meters – suitable for large vessels.
- Unique Feature: Part of the Wallace Line, a major ecological boundary.
Bharat Ranbhoomi Darshan

- 17 Jan 2025
In News:
The Bharat Ranbhoomi Darshan initiative, launched by Defence Minister coinciding with the 77th Army Day celebrations, is a collaborative effort between the Ministry of Defence and the Ministry of Tourism.
Key Highlights:
- This initiative is designed to promote battlefield and border tourism by providing citizens with access to historically significant battlefields and military sites.
Objectives
- Promote Battlefield and Border Tourism: Encourage citizens and tourists to explore India's military history.
- Enhance Awareness: Educate visitors about India’s historic battles and military valor.
- Socio-Economic Development: Boost infrastructure, connectivity, and local economies in border regions.
Features of Bharat Ranbhoomi Darshan
- Virtual Tours and Interactive Content: The platform offers historical narratives, virtual tours, and interactive multimedia to provide a detailed account of each battlefield.
- Travel Planning Assistance: Visitors can access information regarding permits, travel routes, and accommodations.
- Integration with the Incredible India Campaign: The initiative is part of the government’s broader tourism strategy, ensuring widespread promotion.
- Collaborative Infrastructure Development: The Indian Army is working with local civil authorities to facilitate safe tourism without compromising operational preparedness.
Key Locations Covered
- Galwan Valley (Ladakh): Site of the 2020 India-China clash.
- Doklam: A tri-junction between India, Bhutan, and China.
- Line of Control (LoC) and Line of Actual Control (LAC) Sites:
- Nathu La Pass (Sikkim): Significant in the 1967 Indo-China clashes.
- Longewala (Rajasthan): Site of a key battle during the 1971 Indo-Pak war.
- Other Sites: Locations of the 1962 war with China and various Indo-Pak conflicts.
Significance
- Historical and Patriotic Engagement: Provides citizens firsthand insights into the challenges faced by soldiers in remote, strategic locations.
- Tourism Development in Border Areas: Previously restricted areas now open for visitors, leading to economic benefits for local communities.
- National Security Awareness: Encourages greater appreciation of India's defense forces and their contributions.
Implementation
The first phase of the Bharat Ranbhoomi Darshan project includes key battlefields and border sites across seven major regions. Future phases will expand coverage to additional historical military locations.
Nag Mark-2

- 14 Jan 2025
In News:
The Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO) successfully conducted field evaluation trials of India's indigenous Anti-Tank Missile - Nag Mark 2 at the Pokhran Field Range in Rajasthan.
Overview of Nag Mk-2:
- Type: Third-generation, fire-and-forget anti-tank guided missile (ATGM).
- Development: Indigenous development by Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO) under the Integrated Guided Missile Development Programme (IGMDP).
- Functionality: Designed to neutralize modern armored threats, including those with Explosive Reactive Armour (ERA), using advanced fire-and-forget technology.
Technological Features:
- Fire-and-Forget Technology: Operators lock onto targets before launch, allowing the missile to autonomously track and engage targets, ensuring precision strikes.
- Lock-on After Launch: The missile can lock onto the target post-launch, providing flexibility in complex battlefield environments.
- Advanced Guidance System: Equipped with Imaging Infrared (IIR) seekers for enhanced accuracy, both during the day and at night.
Performance and Range:
- Effective Range: The missile has a range of 7 to 10 kilometers, a significant improvement over its predecessor, Nag Mk-1, which had a range of only 4 kilometers.
- Test Trials: Successfully destroyed all targets at both maximum and minimum ranges during the field evaluation trials at Pokhran Field Range, Rajasthan.
- Attack Mode: Includes a top-attack capability to target the vulnerable upper surfaces of armored vehicles, enhancing its effectiveness.
Platform and Integration:
- Launch Platform: The missile is launched from the NAMICA (Nag Missile Carrier) Version 2, a tank destroyer vehicle used by the Indian Army to launch anti-tank missiles.
- Versatility: Designed for integration with multiple platforms, enhancing operational flexibility in different combat scenarios.
Strategic and Operational Significance:
- Indigenous Defence Capability: Reduces India's dependence on foreign weapons systems, strengthening self-reliance in defense technology.
- Enhanced Battlefield Readiness: Provides the Indian Army with a cutting-edge weapon to counter modern armored vehicles, improving tactical advantages.
- Operational Effectiveness: The missile’s precision and ability to neutralize targets with minimal collateral damage make it an essential tool in modern warfare.
- Strategic Deterrence: Demonstrates India’s technological advancements in missile systems, signaling strength and deterrence to adversaries.
Sonobuoys

- 08 Jan 2025
In News:
India and the U.S. have announced cooperation on the co-production of U.S. sonobuoys to enhance Undersea Domain Awareness (UDA) for the Indian Navy. This technology is vital for tracking submarines and strengthening defense capabilities, particularly in the Indian Ocean region amidst growing Chinese naval presence.
This partnership is a key step in deepening defense cooperation under the U.S.-India Initiative on Critical and Emerging Technologies (iCET), launched in May 2022, and will contribute to strengthening both countries’ defense industrial bases.
About Sonobuoys
- What They Are:
- Sonobuoys are expendable sonar devices used for anti-submarine warfare and underwater acoustic research.
- Typically, small (13 cm in diameter and 91 cm in length), they are designed for deployment from aircraft or ships to detect submarines in deep waters.
- Working Principles:
- Deployment: Dropped from aircraft or ships, they activate upon water impact.
- Surface Float: Equipped with inflatable floats and radio transmitters to communicate with tracking platforms on the surface.
- Sensors: Hydrophones descend to selected depths, capturing underwater acoustic signals.
- Data Communication: Transmit acoustic data via Very High Frequency (VHF) or Ultra High Frequency (UHF) radios to operators on aircraft or ships.
- Types of Sonobuoys:
- Active Sonobuoys: Emit sound energy and receive echoes, transmitting the data back to operators.
- Passive Sonobuoys: Only listen for underwater sounds from submarines or ships and relay the information back.
- Special Purpose Sonobuoys: Measure environmental data like water temperature and ambient noise.
- Other Applications:
- Beyond anti-submarine warfare, sonobuoys are used for environmental research, including studying marine life such as whales.
Co-production of Sonobuoys: India-U.S. Collaboration
- Manufacturing Agreement:
- Ultra Maritime (U.S.) and Bharat Dynamics Ltd. (BDL) have entered into discussions to co-produce U.S. sonobuoys, in line with India’s "Make in India" initiative.
- The production will follow U.S. Navy standards, with manufacturing split between the U.S. and India.
- The focus will also be on developing bespoke technologies to optimize sonobuoy performance in the unique acoustic environment of the Indian Ocean.
- Interoperability:
- The sonobuoys co-produced in India will be interoperable between U.S. Navy, Indian Navy, and allied aircraft such as P-8, MH-60R, and MQ-9B Sea Guardian.
- This ensures seamless integration and compatibility with naval assets from the U.S., India, Japan, and Australia, especially given the Quad's strategic naval exercises like Malabar.
- Production Location:
- The sonobuoys will be manufactured at BDL's facilities in Visakhapatnam, with a focus on meeting the Indian Navy’s operational demands.
Strategic and Defense Context
- U.S. and Indian Naval Cooperation:
- India has increasingly acquired military platforms from the U.S., such as the P-8I maritime patrol aircraft, MH-60R helicopters, and MQ-9 drones. These assets are also used by other Quad nations like Australia and Japan, highlighting the importance of interoperability and shared defense capabilities in the region.
- Enhanced Maritime Domain Awareness:
- With China’s growing naval presence in the Indian Ocean, the cooperation on sonobuoys aligns with India’s strategic priority of enhancing maritime domain awareness (MDA) and Undersea Domain Awareness (UDA), which are critical for national security.
- Future Plans:
- India has also signed a $3.5 billion contract for 31 MQ-9B drones, enhancing its surveillance capabilities for maritime and other defense applications. Deliveries of these drones will begin in 2029, further boosting India’s defense readiness in the region.
Exercise SURYA KIRAN

- 28 Dec 2024
In News:
Indian Army Contingent Departs for 18th Edition of Exercise SURYA KIRAN (India-Nepal Joint Military Exercise).
Key Highlights:
- Event Overview:
- Name: 18th Edition of Battalion-Level Joint Military Exercise SURYA KIRAN.
- Dates: 31st December 2024 to 13th January 2025.
- Location: Saljhandi, Nepal.
- Participants: Indian Army (334 personnel, led by a Battalion from the 11th Gorkha Rifles) and Nepal Army (Srijung Battalion).
- Objective of Exercise:
- Enhance interoperability in jungle warfare, counter-terrorism operations in mountainous terrain, and Humanitarian Assistance and Disaster Relief (HADR) under the UN Charter.
- Focus on operational preparedness, aviation training, medical aspects, and environmental conservation.
- Key Features:
- Training Focus: Improving combat skills and coordination to operate together in challenging situations.
- Exchange of Ideas: Soldiers from both nations will share best practices, enhance mutual understanding of operational procedures.
- Strengthening Bilateral Relations: Reinforces strong bonds of friendship, cultural linkages, and defense cooperation between India and Nepal.
- Significance:
- Historical Context: Exercise held alternately in India and Nepal since 2011.
- Enhances Combat Readiness: Prepares both armies to address shared security challenges and improve operational capabilities.
- Diplomatic Engagement: Fosters a productive professional environment between India and Nepal.
- Recent Developments:
- The exercise follows visits by General Upendra Dwivedi (Indian Army Chief) to Nepal and General Ashok Raj Sigdel (Nepali Army Chief) to India, strengthening military ties.
- Previous Editions:
- 17th Edition: Conducted in Pithoragarh, Uttarakhand (24th Nov - 7th Dec 2023).
INS Tushil Commissioned into the Indian Navy in Russia

- 10 Dec 2024
In News:
Recently, the Indian Navy officially commissioned INS Tushil, a multi-role stealth guided missile frigate, at Kaliningrad, Russia. This marks a significant milestone in India-Russia defense cooperation and strengthens India’s maritime capabilities.
About INS Tushil:
- Class & Design: INS Tushil is the seventh ship in the Krivak III class (Project 1135.6) of frigates. It is part of an upgraded series, following the Talwar-class and Teg-class frigates, and was built at the Yantar Shipyard in Kaliningrad, Russia.
- Development & Contract: The construction was initiated under a 2016 contract between the Indian Government, JSC Rosoboronexport (a Russian defense company), and the Indian Navy. The ship incorporates 26% indigenous technology, highlighting growing cooperation between Indian and Russian industries.
- Key Features:
- Stealth Design: With advanced radar-absorbing features, it is less detectable by enemy radar.
- Weaponry: Equipped with BrahMos supersonic cruise missiles, Shtil Surface-to-Air Missiles, anti-submarine torpedoes, electronic warfare systems, and more.
- Versatility: Designed for blue-water operations, the ship can engage in air, surface, underwater, and electromagnetic warfare.
- Helicopter Deck: Supports operations of upgraded Kamov 28 and Kamov 31 helicopters.
- Speed: Capable of exceeding 30 knots.
Significance:
- Enhanced Naval Capabilities: The commissioning of INS Tushil boosts India’s defense strength in the Indian Ocean Region (IOR), a vital area for global maritime trade and security.
- Maritime Security: INS Tushil is designed to support India’s vision of maintaining stability in the IOR and to act as a deterrent against piracy and other maritime threats.
- Defense Cooperation: This commissioning exemplifies the growing defense ties between India and Russia, underscored by joint development, technology transfer, and shared expertise. The ship reflects a major step in India's self-reliance in defense, in line with the “Aatmanirbhar Bharat” initiative.
- Strategic Role in Global Defense: The ship is a key asset in the Indian Navy's efforts to secure maritime trade routes, enhance regional security, and provide humanitarian assistance in times of need.
Key Events & Facts:
- Construction Timeline: The keel of INS Tushil was laid in 2013, and it launched in 2021. After completing extensive sea and weapon trials in 2024, it was formally commissioned into the Navy.
- Collaborative Effort: The ship is a product of collaborative efforts between Indian and Russian industries, marking a significant achievement in joint defense manufacturing.
26 Rafale-Marine Jets

- 03 Dec 2024
In News:
- Deal for 26 Rafale-M jets nearing completion, with final formalities expected to be completed by January 2025.
- These jets are designed for naval operations and will be deployed on INS Vikrant and INS Vikramaditya.
- Rafale-M Features: Multi-role, advanced avionics, AESA radar, and armaments like Meteor, MICA, SCALP, EXOCET.
- Three Scorpene Submarines: Additional three Scorpene-class submarines to be procured from France.
- These are part of a repeat order to Mazagon Dock Shipbuilders Limited (MDL), with five of the earlier six already inducted into service.
Nuclear Capabilities:
- INS Arighaat: Successfully fired a Submarine-Launched Ballistic Missile (SLBM), marking a significant milestone for India's nuclear deterrence.
- Indigenous Nuclear Attack Submarine (SSN): India’s first indigenous SSN expected by 2036-37.
Strategic Maritime Engagement:
- Indian Ocean Region (IOR): Active monitoring of maritime activities, especially of China's PLA Navy and Chinese research vessels.
- Pakistan Navy Expansion: Acknowledged Pakistan’s efforts to become a 50-ship Navy, including the acquisition of 8 Chinese submarines. Indian Navy is adapting its plans to address this.
Nuclear Submarine Program (SSBN):
- INS Arihant: Conducted multiple deterrence patrols.
- INS Arighaat: Ongoing trials including the recent K4 SLBM test, with a range of 3,500 km.
Naval Vision 2047:
- Navy Chief released Vision 2047 document, outlining the future direction and growth of the Indian Navy.
Bilateral and Multilateral Engagements:
- Participation in various bilateral and multilateral exercises, including RIMPAC 2024 (Hawaii) and Russian Federation Navy’s Raising Day (St. Petersburg).
Eklavya Digital Platform
- 29 Nov 2024
In News:
- The Indian Army launched the “Eklavya” online learning platformnmunder the leadership of General Upendra Dwivedi, Chief of the Army Staff (COAS).
- It is part of the Army’s “Decade of Transformation” initiative and aligns with the theme for 2024, “Year of Technology Absorption.”
Platform Development:
- Developed by the Army Training Command (ATC) and sponsored by the Army War College.
- Created at zero cost in collaboration with the Bhaskaracharya National Institute of Space Applications and Geoinformatics (BISAG-N), Gandhinagar.
- Hosted on the Army Data Network with scalable architecture to integrate various training establishments.
Key Features:
- Supports multiple courses from 17Category ‘A’ Training Establishments of the Army.
- Allows student officers to register for several courses simultaneously.
- Aims to decongest physical courses and integrate contemporary, application-focused content.
Categories of Courses:
- Pre-Course Preparatory Capsules: Online study material for physical courses, allowing focus on contemporary topics during offline training.
- Appointment-Specific Courses: Online courses for officers appointed to specialized roles (e.g., information warfare, financial planning, etc.), helping them gain domain-specific expertise before posting.
- Professional Development Suite: Includes courses on strategy, leadership, operational art, finance, emerging technologies, etc., focusing on holistic officer development.
Knowledge Highway:
- A searchable database featuring journals, research papers, and articles to support continuous professional education and development.
Impact:
- Promotes continuous professional military education.
- Enhances the efficiency and specialization of officers, particularly in emerging domains.
- Streamlines training processes and integrates modern technology in the Army’s educational system.
11th ASEAN Defence Ministers’ Meeting-Plus (ADMM-Plus)

- 23 Nov 2024
In News:
The 11th ADMM-Plus held in Vientiane, Laos saw Union Defence Minister Rajnath Singh engage in discussions with his counterparts from the United States, Japan, and the Philippines.
Focus: The talks centered on strengthening defence partnerships, regional security, and enhancing cooperation among Indo-Pacific nations.
ASEAN Defence Ministers’ Meeting-Plus (ADMM-Plus):
- Platform for Dialogue: The ADMM-Plus is a key platform for ASEAN and its eight Dialogue Partners—Australia, China, India, Japan, New Zealand, Republic of Korea, Russia, and the United States.
- Establishment: The inaugural ADMM-Plus was held in HàN?i, Vietnam on 12 October 2010.
- Annual Meetings: Since 2017, the ADMM-Plus has met annually to enhance dialogue and cooperation amidst an increasingly complex regional security environment.
Objectives:
- Capacity Building: To aid ASEAN members in addressing shared security challenges.
- Promote Trust and Transparency: Enhance mutual trust and confidence between ASEAN and partner nations.
- Regional Peace and Stability: Focus on cooperation in defence and security to counter transnational security challenges.
- ASEAN Security Community: Contribute to realizing the ASEAN Security Community, as per the Bali Concord II, aiming for peace, stability, democracy, and prosperity in the region.
- Vientiane Action Programme: Facilitate ASEAN's efforts towards a peaceful, secure, and prosperous ASEAN with outward-looking relations with Dialogue Partners.
Guided Pinaka Weapon System
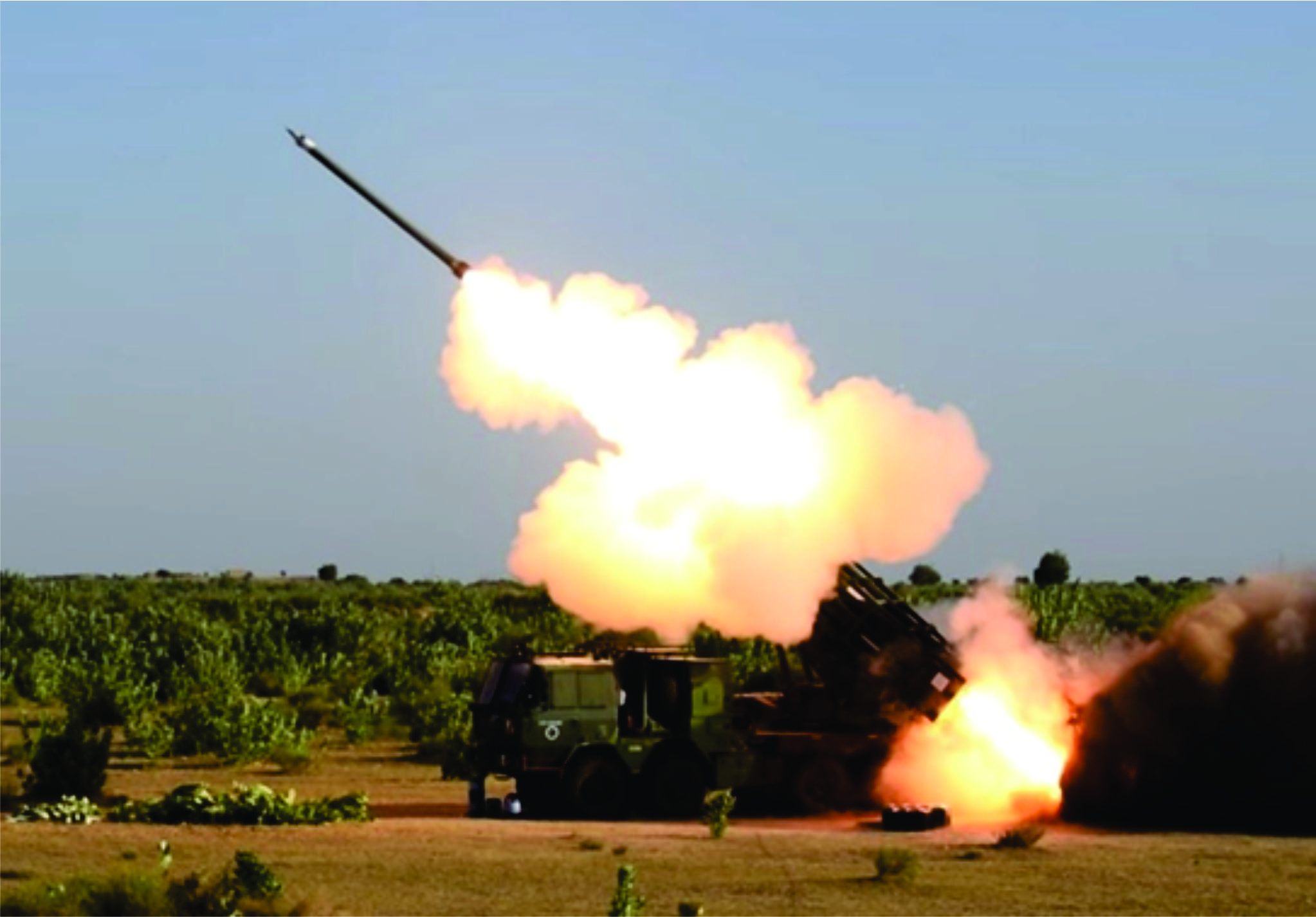

- 22 Nov 2024
In News:
Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO) has successfully completed the Flight Tests of Guided Pinaka Weapon System.
Key Details of the Flight Tests:
- Conducted as part of Provisional Staff Qualitative Requirements (PSQR) Validation Trials.
- Tests Phases: Flight tests were carried out in three phases at different field firing ranges.
- Parameters Assessed:
- Ranging (the distance the weapon can accurately target).
- Accuracy (precision of hits).
- Consistency (performance over multiple trials).
- Rate of Fire (ability to fire multiple rockets simultaneously in salvo mode).
Guided Pinaka Weapon System:
- Design and Development:
- Developed by Armament Research and Development Establishment (ARDE) in association with other DRDO labs and production agencies, including:
- Research Centre Imarat,
- Defence Research and Development Laboratory,
- High Energy Materials Research Laboratory,
- Proof & Experimental Establishment.
- Production Agencies: Munitions India Limited, Economic Explosives Limited, Tata Advanced Systems Limited, and Larsen & Toubro.
- Developed by Armament Research and Development Establishment (ARDE) in association with other DRDO labs and production agencies, including:
- Key Features:
- Pinaka: A multi-barrel rocket launcher system named after Lord Shiva’s bow.
- Mobility: Highly mobile, providing quick deployment in battlefield scenarios.
- Firepower: Capable of delivering concentrated firepower on enemy targets.
- Upgraded Version (Pinaka Mark II):
- Extended range: 70 to 80 km.
- Future range targets: 120 km and 300 km.
- Salvo Mode: Tested for the ability to launch 12 rockets simultaneously.
- Significance:
- Strategic Importance: The successful trials enhance the artillery firepower of the Indian Armed Forces.
- Completion of Pre-requisite Trials: The system has successfully completed all flight trials before its induction into the Indian Army.
Army Tactical Missile System (ATACMS)

- 20 Nov 2024
In News:
- Russia reported that Ukraine fired six US-made Army Tactical Missile System (ATACMS) missiles at Bryansk, Russia, marking a significant escalation in the ongoing conflict.
- This came after US President Joe Biden authorized Ukraine to use long-range missiles to strike deeper inside Russian territory, easing previous restrictions on such weapons
About the Army Tactical Missile System (ATACMS)
- Overview:
- ATACMS is a surface-to-surface artillery weapon system designed to strike targets at much greater ranges than conventional artillery, rockets, or missiles.
- Manufacturer: Produced by Lockheed Martin, a leading US defense contractor.
- First Use: It was first used during the 1991 Persian Gulf War.
- Key Features:
- Guidance: ATACMS missiles are inertially guided ballistic missiles, capable of operating in all weather conditions.
- Range: Approximately 190 miles (305 km).
- Propulsion: It uses a single-stage, solid propellant for propulsion.
- Launch Platforms: Fired from platforms like the High Mobility Artillery Rocket System (HIMARS) and the M270 Multiple Launch Rocket System (MLRS).
- Payload: ATACMS missiles can carry cluster munitions, releasing hundreds of smaller bomblets over a targeted area, increasing their destructive power.
- Global Operators:Besides the US, ATACMS is also operated by countries such as Bahrain, Greece, South Korea, Taiwan, and the United Arab Emirates.
India Successfully Tests Long-Range Hypersonic Missile

- 18 Nov 2024
In News:
- India has made a major advancement in its defense capabilities with the successful flight test of its first long-range hypersonic missile, marking a historic moment in the country's defense technology.
- The test was conducted, by the Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO), took place off the coast of Odisha from the Dr. A.P.J. Abdul Kalam Island.
- The missile has a range of over 1,500 km and is capable of carrying various payloads for all branches of the armed forces.
Key Highlights of the Test:
- Successful Trial: The missile successfully completed its flight test with high accuracy, confirmed by the data gathered from down-range ship stations. It performed a series of terminal maneuvers, validating its precision targeting capabilities.
- Speed and Range: The missile achieved hypersonic speeds (Mach 6), or six times the speed of sound, and is designed for a range of more than 1,500 km, far exceeding the capabilities of many conventional missiles.
- Indigenous Development: This missile is a product of DRDO's indigenous efforts, developed with contributions from the Dr. APJ Abdul Kalam Missile Complex in Hyderabad, as well as other DRDO laboratories and industry partners.
What are Hypersonic Missiles?
- Definition: Hypersonic missiles are defined as weapons that travel at speeds greater than Mach 5 (five times the speed of sound), or about 3,836 miles per hour (6,174 km/h). At such speeds, they are incredibly difficult to track and intercept, posing a challenge for traditional missile defense systems.
- Types:
- Hypersonic Glide Vehicles (HGVs): These are launched from rockets and glide towards their target.
- Hypersonic Cruise Missiles (HCMs): These missiles use air-breathing engines like scramjets for sustained flight at hypersonic speeds.
- Advantages: Hypersonic missiles offer several advantages, including:
- Responsive strike capability: They can target time-sensitive threats quickly and with high precision.
- Manoeuvrability: Unlike ballistic missiles, which follow a predictable parabolic trajectory, hypersonic missiles can change course mid-flight, making them harder to defend against.
- Challenges:
- Heat and air resistance: Traveling at such high speeds generates tremendous heat due to friction, presenting engineering challenges.
- Tracking and interception: Their low-altitude flight and high speeds make them harder to detect and intercept with existing missile defense systems.
- High costs: Developing and deploying hypersonic weapons comes at a higher cost than traditional missile systems.
Global Context of Hypersonic Weaponry
- Russia and China: Both Russia and China are leaders in hypersonic missile technology. Russia has already deployed the Kinzhal hypersonic missile in Ukraine, demonstrating its effectiveness in combat situations.
- United States: The U.S. is also making significant advancements, with contracts like the Long Range Hypersonic Weapon (LRHW), awarded to Lockheed Martin for continued development.
- Other Nations: Countries such as France, Germany, Australia, Japan, and Israel are also actively working on developing hypersonic missile systems.
e-Tarang System
- 18 Nov 2024
In News:
Recently, the Ministry of Defence launched the AI-enabled e-Tarang System.
Key Highlights:
- Development Collaboration: Created in partnership with Bhaskaracharya National Institute for Space Applications and Geo-informatics (BISAG-N).
- Purpose:
- Improve planning for interference-free operation of defence equipment during both wartime and peacetime.
- Enable automated, efficient planning and management of Defence Spectrum.
- Support the development of newer technologies in higher frequency bands.
- Facilitate rapid decision-making and integration of critical modern defence technologies.
BISAG-N Overview:
- Status: Autonomous Scientific Society under the Ministry of Electronics & Information Technology (MeitY), Government of India.
- Key Roles:
- Technology development and management.
- Research and development in geo-spatial technologies.
- National and international cooperation in geo-spatial fields.
- Capacity building and entrepreneurship development in geo-spatial technology.
- Core Domains:
- Satellite Communication
- Geo-informatics
- Geo-spatial Technology
Joint Electromagnetic Board (JEMB) – Annual Meeting Highlights:
- Chairperson: Air Marshal Jeetendra Mishra, Deputy Chief of Integrated Defence Staff (Operations).
- Attendees: Senior officers from the Indian Army, Navy, Air Force, DRDO, DDP, and industry.
- Agenda: Focused on joint operations and integration in several areas:
- Electronic Warfare (EW)
- Signature Management
- Emerging Technologies
- Electromagnetic Interference/Compatibility (EMI/EMC)
- Spectrum Management
- Human Resource Management
- Key Outcome:
- Introduction of the AI-enabled e-Tarang System to enhance Defence Spectrum management.
- Release of the Technical News Letter (TNL) 2024, outlining future technologies for modern warfare.
- Development of a roadmap to enhance Spectrum Warfare capabilities and integration of EW assets across the three Services.
- Successful joint EW exercise conducted in September 2024, promoting the principle of “Victory through Jointness”.
Objective of the Meeting:
- Goal: Achieve synergy in joint electronic warfare operations across the Services.
- Focus: Establish technology development and training priorities for the future.
Exercise PoorviPrahar

- 17 Nov 2024
In News:
- From November 10 to 18, 2024, the Indian Army is conducting a high-intensity tri-services exercise named PoorviPrahar in the forward areas of Arunachal Pradesh.
- The exercise aims to enhance the combat effectiveness and coordination between the Indian Army, Navy, and Air Force, focusing on integrated joint operations in the challenging mountainous terrain of the region.
About Exercise PoorviPrahar
Objective: The primary goal of Exercise PoorviPrahar is to hone the combat readiness and synergy across the three branches of the Indian Armed Forces. It is designed to improve their ability to conduct integrated joint operations, especially in the difficult terrain of Arunachal Pradesh, which is crucial due to the region's strategic location along India's eastern frontier.
Key Features of the Exercise:
- Multidomain Integration:The exercise involves land, air, and sea operations, demonstrating India's capability to conduct multi-domain operations. This showcases the Indian Armed Forces' preparedness to tackle threats across all three domains simultaneously.
- Advanced Military Platforms:
- Aircraft: Advanced fighter jets, reconnaissance aircraft.
- Helicopters: Including Chinook heavy-lift helicopters and Advanced Light Helicopters (ALH Rudra).
- Artillery: The exercise makes use of the M777 Ultra-Light Howitzers, which provide mobility and precision firepower in rugged terrains.
- Swarm Drones and Loitering Munitions: These cutting-edge technologies enable precision strikes and enhanced situational awareness, contributing to more flexible and adaptive operations.
- Technological Integration:
- The exercise integrates next-generation technologies like Swarm Drones, Loitering Munitions, and First-Person View (FPV) Drones. These tools enhance operational flexibility, improve situational awareness, and enable precision in strike capabilities, marking a significant advancement in India's military technology.
- Operational Coordination:A core component of the exercise is the development of a Common Operating Picture (COP). This system integrates real-time data from land, air, and sea operations, improving coordination and decision-making. The system relies on AI-driven analytics and satellite communications, enabling rapid information sharing and quicker response times.
- Tactical Focus on Mountain Warfare:Arunachal Pradesh, with its mountainous and rugged terrain, is the perfect setting for honing skills required for mountain warfare. The region’s proximity to India’s border with China makes it a critical area for India’s defense strategy.
Key Takeaways:
- Integrated Joint Operations: The exercise focuses on improving the coordination between the Army, Navy, and Air Force to execute seamless operations across land, air, and sea.
- Advanced Technology Integration: The exercise features the use of Swarm Drones, Loitering Munitions, and AI-driven systems to enhance precision, situational awareness, and overall operational flexibility.
- Mountain Warfare Expertise: Conducted in the mountainous terrain of Arunachal Pradesh, the exercise is crucial for preparing the Indian Armed Forces to operate effectively in such challenging landscapes.
- Strategic Posture: The exercise reaffirms India’s ability to defend its Eastern frontier and maintain a robust defense posture in the face of potential threats in the region.
India’s Vision of ‘Adaptive Defence’

- 13 Nov 2024
In News:
- Defence Minister Shri Rajnath Singh introduced the concept of ‘Adaptive Defence’ at the inaugural Delhi Defence Dialogue (DDD).
- Adaptive Defence aims to prepare India's military for the rapidly changing landscape of modern warfare, with evolving threats and technologies shaping global security.
Key Aspects of Adaptive Defence:
- Strategic Approach:
- Adaptive Defence is an evolving strategy where military and defence systems continuously adjust to emerging threats, focusing on proactive preparedness rather than reactive responses.
- It is based on anticipating future threats, fostering flexibility, resilience, and agility in both strategic and tactical responses.
- Core Elements:
- Situational Awareness: The ability to understand and respond to dynamic, often unpredictable environments.
- Flexibility & Agility: At both the strategic and tactical levels to ensure swift and effective responses.
- Resilience: The capacity to recover and adapt quickly to unforeseen circumstances.
- Integration with Emerging Technologies: Emphasis on adopting cutting-edge technologies like AI, drones, and cybersecurity to stay ahead of adversaries.
The Changing Nature of Warfare:
- Grey Zone & Hybrid Warfare:
- Modern conflicts now often occur in the grey zone and involve hybrid warfare, blending traditional and non-traditional threats like cyber-attacks, terrorism, and psychological warfare.
- These new threats demand continuous adaptation in strategies, doctrines, and military operations.
- Technological Transformation:
- Drones and swarm technologies are reshaping warfare. India aspires to become a global hub for drones, leveraging these technologies for both economic and military growth.
- The increasing significance of Artificial Intelligence (AI), cyber capabilities, and quantum technologies in defence highlights the need for international collaboration in research and innovation.
- Psychological Warfare:
- The rise of information overload and psychological warfare challenges traditional defence paradigms. Manipulation of information to influence public opinion and disrupt decision-making processes is now a key threat.
Government Initiatives for Adaptive Defence:
- Institutional Strengthening:
- Establishment of the Chief of Defence Staff (CDS) and initiatives to enhance jointness among the three armed services (Army, Navy, Air Force) to create a unified strategic force.
- Reform of training curricula and emphasis on integrated operations to ensure readiness for new-age warfare.
- Focus on Self-Reliance:
- Strengthening the indigenous defence sector through initiatives like Make in India and the Aatmanirbhar Bharat campaign.
- Increasing foreign direct investment (FDI) in defence and promoting defence exports, with India currently exporting to over 100 nations.
- Drone Hub Vision:
- India aims to become the world’s drone hub, supporting R&D and fostering innovation to develop reliable certification mechanisms and enhance Indian intellectual property in the drone sector.
- Programs like iDEX (Innovations for Defence Excellence) and ADITI are rewarding innovation and driving India's defence sector towards greater self-sufficiency.
- Technology and Innovation:
- Focus on cybersecurity, AI, and quantum technologies to develop solutions that address both national and global security challenges.
- India is also working on Theaterisation, integrating the three services into a unified force structure for enhanced coordination and joint operations.
- Defence Acquisition and Export:
- Introduction of the Defence Acquisition Procedure 2020, establishment of Defence Industrial Corridors in Uttar Pradesh and Tamil Nadu, and a Positive Indigenisation List to boost self-reliance.
- India is actively increasing defence exports, aiming for Rs 50,000 crore worth of exports by 2029, with key export destinations including the USA, France, and Armenia.
Strategic Vision for the Future:
- Collaborative Approach:
- Given the interconnectedness of global security, the defence minister emphasized the importance of a collaborative approach in dealing with transnational threats.
- Cross-border issues, cyberspace threats, and the potential of quantum and nanotechnologies demand the sharing of knowledge and strategies across borders.
- Joint Military Vision:
- Jointness in defence strategy should go beyond national borders and should involve international cooperation in response to global security challenges.
- The need for interconnected solutions in the face of transnational threats underscores the importance of multilateral cooperation.
Indian Military Heritage Festival 2024

- 10 Nov 2024
In News:
- Chief of Defence Staff General Anil Chauhan inaugurated the 2nd edition of the Indian Military Heritage Festival (IMHF) on November 8, 2024, in New Delhi.
- The two-day festival engages global and Indian experts, corporations, academicians, and non-profits focusing on India’s national security, foreign policy, military history, and military heritage.
Launch of Project Shaurya Gatha:
- Project ‘Shaurya Gatha’ was launched to conserve and promote India’s military heritage.
- The initiative, spearheaded by the Department of Military Affairs and USI of India, focuses on education and tourism to highlight India’s military history and valor.
- Publications Released:
- General Chauhan released important military publications:
- "Because of this: A History of the Indo-Pak Air War December 1971" by Air Marshal Vikram Singh (Retd).
- "Valour and Honour", a joint publication by the Indian Army and USI of India.
- "War-wounded, Disabled Soldiers, and Cadets", a joint publication by USI and the War Wounded Federation.
- General Chauhan released important military publications:
- Festival's Significance:
- The festival addresses the gap in public awareness regarding India’s military heritage and security concerns.
- It aims to enhance understanding of India’s military traditions, security issues, and the country’s efforts toward self-reliance in military capabilities under the Aatmanirbhar Bharat initiative.
India-Algeria Strengthen Defence Ties

- 06 Nov 2024
In News:
- The Chief of Defence Staff (CDS) of India recently visited Algeria, culminating in the signing of a significant Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) on defence cooperation.
- Objective: The MoU aims to strengthen the strategic and military ties between India and Algeria.
Recent Developments in India-Algeria Relations
- Important Visit: The CDS’s visit coincided with Algeria’s 70th anniversary of its revolution, celebrated on November 1st, with military parades and ceremonies highlighting Algeria’s historical and political legacy.
- Defence Cooperation:
- India re-established its defence wing in Algeria, and Algeria reciprocated by considering the establishment of its defence wing in India.
- India emphasized its role as a “Vishwa Bandhu” (global partner) and offered to share defence expertise and experiences with Algeria.
- Strategic Discussion: The MoU aims to enhance mutual understanding, laying the foundation for long-term defence collaboration across multiple sectors, including manufacturing under India’s 'Make in India' and 'Make for the World' initiatives.
- Global Peace Support: CDS reiterated India’s commitment to peaceful conflict resolution and expressed support for Algeria’s defence interests.
Significant Areas of India-Algeria Relationship
- Diplomatic Relations:
- India and Algeria established diplomatic ties in July 1962, the same year Algeria gained independence from French colonial rule.
- India supported Algeria's liberation movement and both countries have maintained close ties as part of the Non-Aligned Movement.
- Bilateral Trade:
- Trade peaked at USD 2.9 billion in 2018 but dropped to USD 1.5 billion by 2021 due to COVID-19 and Algeria’s import restrictions.
- Trade rebounded in 2022, increasing by 24% to USD 2.1 billion.
- Exports from India (2023-24): Rice, pharmaceuticals, granite.
- Imports from Algeria: Petroleum oils, LNG, calcium phosphates.
- Bilateral Agreements:
- 2015 MoU: Between All India Radio (AIR) and Algerian National Radio for cooperation in broadcasting.
- 2018 Space Cooperation Agreement: Focuses on satellite technology for applications like crop forecasting and disaster management.
- Visa Waiver Agreement (2021): Diplomatic and official passport holders are exempt from visa requirements.
- Cultural Engagement:
- International Day of Yoga (2024): Celebrated in Algeria at the Jardin d’Essai du Hamma, attracting over 300 participants.
- Space Cooperation:
- The 2018 India-Algeria Space Cooperation Agreement focuses on joint space science, technology, and applications.
- India has launched four Algerian satellites (2016), and the 2022 Joint Committee Meeting expanded satellite capacity building efforts.
- Algeria’s space agency has engaged with ISRO on satellite applications like crop forecasting and disaster management.
- Indian Community in Algeria:
- Approximately 3,800 Indians live in Algeria, working in various sectors, including technical and semi-skilled roles.
- The community includes 13 Overseas Citizens of India (OCI), 10 Persons of Indian Origin (PIOs), and 15 Indian students.
VINBAX 2024 Exercise

- 06 Nov 2024
In News:
The 5th Edition of Vietnam Indian Bilateral Army Exercise “VINBAX 2024” had commenced at Ambala.
Key Participants
- Indian Army: A contingent of 47 personnel from the Corps of Engineers, along with personnel from other arms and services.
- Vietnam People's Army: A similar-sized contingent representing Vietnam's military forces.
- Bi-Service Participation: For the first time, personnel from both Army and Air Force of India and Vietnam are participating.
Objectives of VINBAX 2024
- Joint Military Capability Enhancement:
- Focus on enhancing joint military capabilities of both countries, specifically in the deployment of Engineer Companies and Medical Teams.
- Peacekeeping Operations (UN Context):
- The exercise prepares both sides for United Nations Peacekeeping Operations (PKO), under Chapter VII of the UN Charter, which deals with peace enforcement actions.
- Humanitarian Assistance & Disaster Relief (HADR):
- The exercise includes a 48-hour validation exercise with demonstrations of Humanitarian Assistance and Disaster Relief (HADR) operations.
- The HADR component will include equipment displays to assess the technical standards of both contingents while executing disaster relief and humanitarian missions in peacekeeping contexts.
Key Activities & Events
- Field Training Exercise: The exercise includes a field training component, with a larger scope than previous editions, focusing on:
- Engineer Tasks.
- Medical Support.
- Disaster Relief Operations.
- Validation Exercise: A critical 48-hour validation exercise to test the preparedness of the two forces in providing HADR, including:
- Demonstrations of disaster relief operations.
- Equipment displays to showcase capabilities in managing and executing peacekeeping and humanitarian operations.
- Cultural Exchange: The exercise will also provide an opportunity for cultural exchange, where the troops will learn about the social and cultural heritage of each other.
Background of VINBAX
- Inception: VINBAX was first conducted in 2018 as part of the growing defense cooperation between India and Vietnam. The inaugural edition took place in Jabalpur, Madhya Pradesh.
- Alternating Locations: The exercise alternates between India and Vietnam every year.
- Previous Editions:
- 2023 Edition: Held in Vietnam.
- Current Edition: This is the 5th edition, conducted in India (Ambala and Chandimandir).
Indian Defense Engagements in Southeast Asia
- India-Indonesia Joint Special Forces Exercise (Garud Shakti 2024): Held from November 1-12, 2024, in Cijantung, Jakarta, strengthening ties with Indonesian special forces.
- Singapore-India Maritime Bilateral Exercise (SIMBEX 2024): Held from October 23-29, 2024, in Visakhapatnam, focusing on maritime security cooperation in the Indo-Pacific.
Bob Khathing

- 05 Nov 2024
In News:
- Defence Minister Rajnath Singh inaugurated the Major Ralengnao 'Bob' Khathing Museum of Valour in Tawang, Arunachal Pradesh, on October 31, 2023, coinciding with National Unity Day (Sardar Vallabhbhai Patel's birth anniversary).
- Significance: The museum honours Bob Khathing's contributions to India's security and the integration of Tawang into India.
Role in the Integration of Tawang:
- Tawang Expedition (1951): In January 1951, Major Bob Khathing, an officer of the Indian Frontier Administrative Service, led the expedition to peacefully integrate Tawang into India.
- Strategic Importance: At the time, there were concerns over Chinese intentions to enter Tibet and realign boundaries. Khathing's mission was crucial to prevent Chinese advances into the area.
- Expedition Details: Khathing set off with Assam Rifles troops from Charduar, Assam, and after overcoming extreme terrain and weather, he reached Tawang. On February 14, 1951, he hoisted the Indian flag, marking Tawang's official integration into India.
- Administrative Setup: Khathing established an administrative framework, including appointing Gaon Buras (village elders) to manage local governance.
Military Service and Recognition:
- World War II Service: Bob Khathing joined the Indian Army in 1939 and earned recognition for his role in the Second World War. He was awarded the Member of the British Empire (MBE) and the Military Cross (MC) for his bravery and leadership.
- Guerrilla Warfare: Khathing was part of the Victor Force, a British-led guerrilla unit tasked with countering the Japanese in Burma and India during WWII. Later, he became the adviser to SANCOL, a force set up to track Japanese forces in the region.
- Military Cross Citation: Khathing was praised for his tireless efforts in organizing local Naga support, gathering intelligence, and participating in successful ambushes, which played a critical role in defeating the Japanese.
Post-War Career and Civil Service:
- Ministerial Role in Manipur: After WWII, Khathing was demobilized and joined the interim government of Manipur, where he served as a minister in charge of the hill areas.
- Integration of Manipur: Following Manipur's merger with India in 1949, Khathing joined the Assam Rifles and served for two years before moving into civil administration.
- Key Positions: He served as Deputy Commissioner of Mokokchung (Nagaland), Development Commissioner in Sikkim, and Chief Secretary of Nagaland.
- Ambassadorship: In 1975, Khathing became India's ambassador to Burma, possibly the first person of tribal origin to hold such a position in independent India.
The Importance of His Contributions:
- Integration of Border Areas: Khathing’s role in integrating Tawang and securing India's northeastern frontier was pivotal in preventing further territorial disputes, especially with China.
- Institutional Development: He helped establish military and security institutions, including the Sashastra Seema Bal, Nagaland Armed Police, and the Naga Regiment, which played important roles in maintaining peace and security in the region.
- Heroic Leadership: Khathing's leadership, both as a soldier and civil servant, continues to be celebrated, symbolized by the Major Bob Khathing Museum of Valour.
C-295 Aircraft
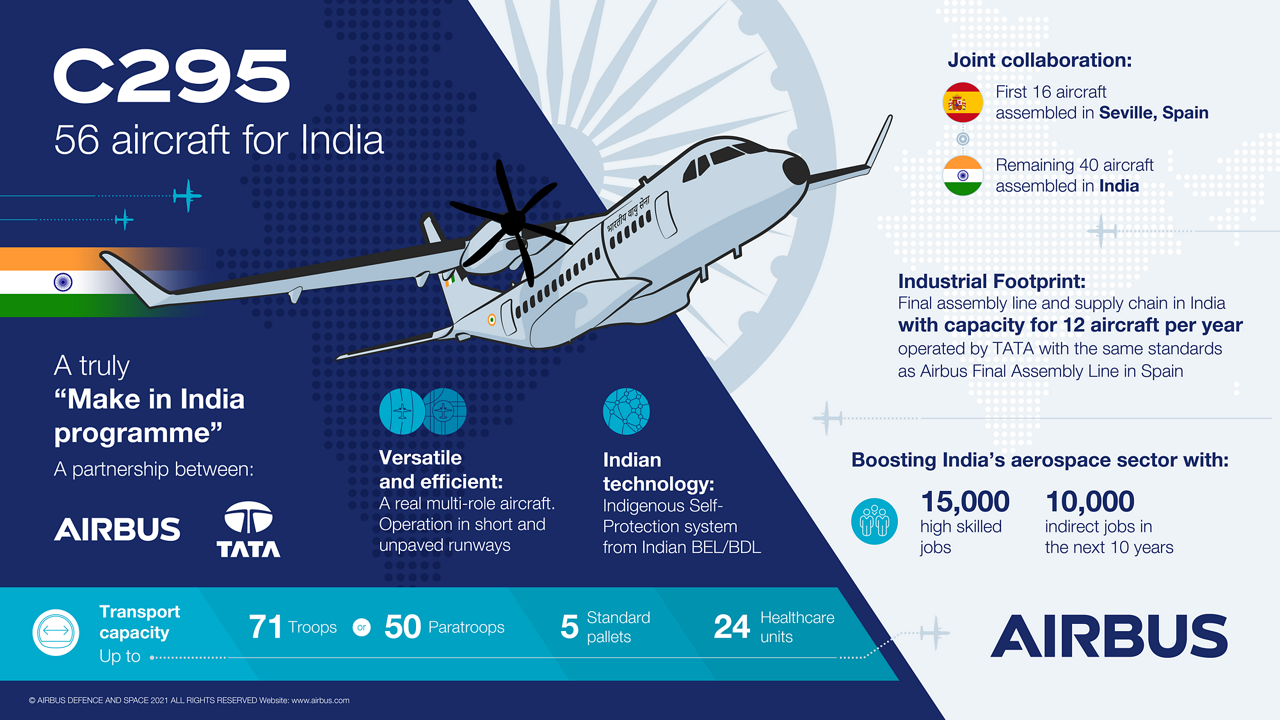
- 29 Oct 2024
In News:
- Recently, PM Narendra Modi inaugurated the Final Assembly Line (FAL) plant in Vadodara, Gujarat, for the manufacturing of the C-295 aircraft.
- The plant is a joint venture between Tata Advanced Systems Ltd (TASL) and Airbus.
- This is the first private sector final assembly line for military aircraft in India.
Key Details:
- Manufacturing Timeline
- Contract: In September 2021, India signed a ?21,935 crore deal with Airbus Defence and Space to procure 56 C-295 aircraft to replace the IAF’s ageing Avro-748 fleet.
- Production Plan:
- The first 16 aircraft will be delivered from Airbus’s plant in Seville, Spain, between September 2023 and August 2025.
- The remaining 40 aircraft will be produced in India by TASL, with the first “Made-in-India” C-295 rolling out in September 2026.
- The entire fleet (56 aircraft) is expected to be delivered by August 2031.
- Key Features and Specifications
- Type: Tactical transport aircraft with a capacity of 5 to 10 tonnes.
- Maximum Speed: 480 km/h.
- Cabin Dimensions: 12.7 meters (41 feet 8 inches), the longest unobstructed cabin in its class.
- Passenger Capacity: Can accommodate up to 71 seats.
- Cargo Handling: Rear ramp door for quick loading/unloading and para-dropping.
- Short Take-off and Landing (STOL): Capable of operating from airstrips as short as 2,200 feet.
- Significance for the Indian Air Force (IAF)
- The C-295 will enhance the medium-lift tactical capability of the IAF.
- It will replace the ageing Soviet-origin AN-32 aircraft, which are nearing the end of their operational life.
- The C-295 will bridge the capability gap in troop and cargo transport over short and medium distances.
- Indigenous Content
- Indigenous Electronic Warfare Suite: All 56 aircraft will be equipped with an indigenous electronic warfare suite, developed by Bharat Electronics Ltd (BEL) and Bharat Dynamics Limited (BDL).
- Made-in-India Components: 96% of the work that Airbus does in Spain will be done at the Vadodara plant, making it one of the highest-ever indigenous contributions for an aircraft in India.
- Global Operations of the C-295
- The C-295 is operational in various challenging terrains worldwide, including:
- Brazilian jungles, Colombian mountains (South America)
- Deserts of Algeria and Jordan (Middle East)
- Cold climates of Poland and Finland (Europe)
- Military operations in Chad, Iraq, and Afghanistan.
- The C-295 is operational in various challenging terrains worldwide, including:
- Roles and Capabilities
- Tactical Transport: Can transport troops and supplies from main airfields to forward operating airfields.
- Short Take-off and Landing (STOL): Capable of operating from short, unprepared airstrips.
- Low-level Operations: Can conduct low-speed, low-level missions at 110 knots.
- Other Missions: Suitable for casualty evacuation, special missions, disaster relief, and maritime patrol.
Launch of 'Abhay'

- 27 Oct 2024
In News:
Recently, ‘Abhay’, the seventh ship in the Anti-Submarine Warfare Shallow Water Craft (ASW SWC) series was launched.
Key Details:
Project Background
- Contract Details: The Ministry of Defence (MoD) signed a contract with Garden Reach Shipbuilders & Engineers (GRSE), Kolkata, in April 2019 for the construction of eight ASW SWC ships.
- Class of Ships: The Arnala-class ships are intended to replace the older Abhay-class ASW Corvettes currently in service with the Indian Navy.
- Purpose: These ships are designed for anti-submarine warfare (ASW) operations in coastal waters and to conduct Low-Intensity Maritime Operations (LIMO) and mine-laying activities.
Design and Features of 'Abhay'
- Dimensions:
- Length: 77 meters
- Width: 10 meters
- Speed and Endurance:
- Maximum speed: 25 knots
- Endurance: 1800 nautical miles (NM).
- Propulsion: Waterjet-propelled, offering agility and swift response in tactical situations.
- Indigenous Content: Over 80% indigenous content, supporting India’s Aatmanirbhar Bharat (self-reliant India) initiative in defence manufacturing.
Capabilities of the ASW SWC
- Anti-Submarine Warfare:
- Designed to conduct subsurface surveillance and anti-submarine operations in coastal waters.
- Equipped with advanced sonar systems, including Hull-Mounted Sonar and Low-Frequency Variable Depth Sonar for enhanced underwater surveillance.
- Armament and Equipment:
- Torpedoes and ASW rockets for anti-submarine operations.
- Mines for mine-laying operations.
- Close-in Weapon System (CIWS): 30 mm for close-range defence against aerial and surface threats.
- 12.7 mm Stabilized Remote-Control Guns for additional defensive capability.
Strategic Importance
- Coastal Defence: The ASW SWC ships enhance the Navy’s capability to defend India’s extensive coastline and exclusive economic zone (EEZ) against submarine threats.
- Operational Role:
- In addition to anti-submarine warfare, these ships can conduct Low-Intensity Maritime Operations (LIMO), which include operations against non-traditional threats.
- Mine-laying capability to disrupt enemy naval operations.
- Advanced Detection: These ships are equipped to track both surface and underwater targets, enabling them to coordinate operations with aircraft, strengthening maritime security.
Chanakya Defence Dialogue 2024

- 26 Oct 2024
In News:
- Recently, the Chanakya Defence Dialogue (CDD) 2024, second edition, was held at the Manekshaw Centre, New Delhi.
- Theme: "Drivers in Nation Building: Fueling Growth Through Comprehensive Security."
- Focus: Discussions on integrating national security into India's development trajectory and global strategy for a Viksit Bharat by 2047.
Key Objectives:
- The dialogue aimed to explore India’s strategic directions and development priorities by fostering discussions between policymakers, strategic thinkers, defence experts, and academia.
- Highlighted the link between national security and economic growth, stressing how security frameworks are vital for national progress.
Key Sessions and Discussions:
- Session 1: Social Cohesion and Inclusive Growth: Pillars of a Secure Nation:
- Focused on internal security, social unity, and inclusive development.
- Panelists discussed the role of community engagement, countering terrorism, and law enforcement reforms.
- Emphasized the need for integrating social progress and addressing challenges like separatism and terrorist narratives.
- Panelists called for evidence-based policies for equitable growth and stronger security frameworks to protect the country from internal threats.
- Session 2: Blurring Frontiers: The Convergence of Technology & Security:
- Addressed the intersection of technology and national security.
- Topics included AI, quantum computing, IoT, and blockchain for improving cyber resilience and data protection.
- Panelists emphasized the need to balance technological innovation with strong security measures, particularly in cybersecurity and critical infrastructure protection.
- Session 3: Ground-breakers: Shaping Land Warfare, Reflections for the Indian Army:
- Explored the integration of emerging technologies like AI, unmanned systems, and cyber warfare tools in enhancing military readiness.
- Focused on indigenous defense technologies under the Atmanirbhar Bharat initiative, promoting self-reliance and reducing dependency on foreign technologies.
- Emphasized multi-domain operations and the challenges of adapting to evolving security threats, especially from advanced cyber and space warfare.
Strategic Insights:
- Economic Growth & Security: The dialogue highlighted that national security and economic growth are interlinked, with a strong military infrastructure crucial for sustaining development.
- Role of Technology: Technological advancements like AI, space technology, and cybersecurity are pivotal for enhancing India's defense capabilities and strategic posture in a rapidly evolving global security landscape.
- Inclusive Security: Emphasized social cohesion and inclusive growth as key components of national security, acknowledging that a unified society contributes significantly to national resilience.
- Global Diplomacy: India’s global leadership in multilateral forums, its stance on peacekeeping, and its role in promoting sustainable development were discussed as part of the country’s soft power strategy.
Russia's Izdeliye 305 (LMUR) Missile

- 21 Oct 2024
In News:
Russian state corporation Rostec has claimed that its Light Multipurpose Guided Rocket, also known as Izdeliye 305 or “Product 305,” has demonstrated remarkable resistance to jamming and interference on the battlefield in Ukraine.
Missile Overview
- Name: Izdeliye 305 (Product 305), also known as LMUR (Light Multipurpose Guided Rocket)
- Primary Use: Deployed by Russia’s Mi-28NM and Ka-52M attack helicopters.
- Function: Designed to target and destroy armored vehicles, fortifications, pillboxes, and watercraft with high precision.
Key Features
- Sniper-Like Accuracy: The missile is touted for its exceptional precision in targeting, making it one of Russia’s most successful guided weapons.
- Resistance to Jamming: The missile’s control channel has shown remarkable resistance to enemy electronic warfare (EW) systems, making it effective even in contested environments.
- No instances of the missile's control channel being suppressed during the ongoing Ukraine conflict.
- Versatile Guidance Systems: The missile operates in several modes:
- Fire-and-Forget: The missile locks onto the target before launch and operates autonomously post-launch.
- Remote Control Mode: The operator guides the missile to the target after it locks onto coordinates and transmits live imagery to the operator’s screen.
- Inertial + Homing Mode: The missile initially flies inertially toward target coordinates, then activates its homing system for final target guidance.
- High Explosive Warhead: Equipped with a 25-kg high-explosive fragmentation warhead, the LMUR is effective against a variety of targets.
Technical Specifications
- Weight: 105 kg (231 lbs)
- Range: Up to 9 miles, double the range of traditional Russian anti-tank missiles, providing the tactical advantage of engaging from beyond line-of-sight.
- Warhead: 25 kg high-explosive fragmentation for effective target destruction.
- Guidance: A combination of inertial navigation, satellite positioning, thermal imaging, and a two-way communication channel for real-time control.
Deployment and Use
- Helicopter Integration: Primarily used on Mi-28NM and Ka-52M attack helicopters, and also on the Mi-8MNP-2 for special operations.
- Combat Experience:
- The missile was actively used in Ukraine where it played a key role in countering Ukraine’s NATO-backed counteroffensive operations.
- It was previously tested in Syria against various targets, showcasing its capabilities before full operational deployment in 2022.
Significance in Ukraine Conflict
- Impact on Ukrainian Forces: The missile’s long range and resistance to EW have made it a critical component of Russia’s aerial operations, hampering Ukraine’s battlefield progress, particularly against heavily fortified positions and NATO-backed counteroffensive efforts.
Strategic Advantage: The missile’s ability to engage targets from a distance while evading jamming attempts gives it a significant edge in modern warfare.
Naseem-Al-Bahr 2024

- 20 Oct 2024
In News:
Indo-Oman bilateral naval exercise Naseem-Al-Bahr was held in Goa from October 2024.
Naseem-Al-Bahr Exercise Overview
- Indian and Omani Participants:
- Indian Navy: INS Trikand (warship) and Dornier Maritime Patrol Aircraft.
- Royal Navy of Oman: Vessel Al Seeb.
- Initiation: Launched in 1993, marking a long-standing strategic partnership between India and Oman.
- Structure: The exercise is conducted in two phases:
- Harbour Phase:
- Professional Interactions: Subject Matter Expert Exchanges (SMEE), planning conferences.
- Social & Sports Engagements: Informal activities to foster mutual understanding.
- Sea Phase:
- Naval Operations:
- Gun firings at surface inflatable targets.
- Close-range anti-aircraft firings.
- Replenishment at Sea Approaches (RASAPS).
- Helicopter Operations: INS Trikand’s helicopter performed cross-deck landings and Vertical Replenishment (VERTREP) with RNOV Al Seeb.
- Aircraft Support: Dornier aircraft provided Over-the-Horizon Targeting (OTHT) data to enhance operational coordination.
- Naval Operations:
- Harbour Phase:
Key Highlights of the 2024 Exercise
- Interoperability: The exercise focused on improving operational coordination and enhancing mutual understanding of naval practices.
- Cohesion: The Indian Navy Sea Riders embarked on RNOV Al Seeb to further strengthen the bilateral relationship.
Strategic Significance
- Strengthening Ties: Naseem-Al-Bahr reaffirms the strong strategic relationship between India and Oman.
- Regional Collaboration: This exercise exemplifies India's growing collaboration with like-minded nations in the Indian Ocean Region (IOR).
- Broader Defence Relations:
- Oman is the first GCC country to conduct such bilateral naval exercises with India.
- Both countries also engage in other defence exercises:
- Army: Al Najah.
- Air Force: Eastern Bridge.
Trade Relations Between India and Oman (2022):
- Oil: India is the second-largest market for Oman's crude oil exports, following China.
- Non-oil Exports: India is Oman's fourth-largest market for non-oil exports, after UAE, US, and Saudi Arabia.
- Imports: India is the second-largest source of Oman's imports, following the UAE.
- Ongoing Trade Agreement: Both nations are currently negotiating a trade agreement to further boost bilateral economic cooperation.
Next Generation Missile Vessels (NGMV)

- 19 Oct 2024
In News:
GE’s LM2500 Marine Engines to Power Indian Navy’s Next Generation Missile Vessels (NGMV)
Key Highlights:
- Engine Selection:
- General Electric’s LM2500 marine gas turbines have been chosen to power the Indian Navy's Next Generation Missile Vessels (NGMV), currently being built by Cochin Shipyard Limited (CSL).
- Project Details:
- Number of Vessels: Six NGMVs are under construction.
- Contract Value: ?9,805 crore, awarded by the Defence Ministry.
- Delivery Schedule: The first deliveries are expected to commence in March 2027.
- Key Components and Suppliers:
- GE Aerospace will deliver six LM2500 engine kits to Hindustan Aeronautics Limited (HAL) for assembly and testing at their Industrial and Marine Gas Turbine Division in Bengaluru.
- GE will also supply the composite base, enclosure, and a full set of auxiliary systems for the gas turbines.
- LM2500 Marine Gas Turbine:
- The LM2500 turbine is known for its reliability and high power output, making it ideal for the NGMV mission.
- Top Speed: 35 knots (64 km/h).
- It is central to the propulsion system, meeting the stealth and power demands of the new missile vessels.
- Capabilities of NGMVs:
- Role: Designed for offensive missions, the NGMVs will be equipped for anti-surface warfare, maritime strike operations, and sea denial.
- Speed & Stealth: Capable of speeds up to 35 knots while maintaining stealth, these vessels will be difficult for enemy ships to detect.
- Weapons: They will carry a variety of anti-surface weapons, including the BrahMos supersonic cruise missile, loitering munitions, unmanned vehicles, and other guided weapons.
- Operational Roles:
- Offensive: The NGMVs will engage in attacking enemy warships, merchant ships, and land-based targets.
- Defensive: They will also be used for local naval defense operations, including the seaward defense of offshore development areas and defending choke points.
- Strategic Importance:
- The NGMVs will significantly enhance India’s maritime strike capability and provide a formidable presence in strategic sea routes, especially in regions like choke points and offshore development areas.
- Cochin Shipyard’s Role:
- After successfully constructing INS Vikrant, India’s first indigenous aircraft carrier, CSL is now focusing on the NGMV project, along with building anti-submarine warfare shallow water crafts for the Indian Navy, currently in various stages of construction.
- Partnerships:
- In 2023, GE Aerospace and HAL signed a Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) to expand their collaboration on marine gas turbines, including assembly, inspection, and testing (AIT) of the LM500 turbines.
- To date, GE Aerospace has delivered 24 marine gas turbine kits to HAL, supporting India’s Make-In-India initiative.
- Global Impact:
- The LM2500 gas turbine is used by 714 vessels globally, reinforcing its reputation for reliability and availability in critical maritime defense systems.
THAAD Missile Defence System

- 14 Oct 2024
In News:
The US pledged its THAAD missile defence system as well as several troops to Israel after Iran warned the country to not get involved.
In a new boost to Israeli forces, the United States will send a Terminal High Altitude Area Defence battery (THAAD) and troops to Israel amid its ongoing offensive against the Hezbollah.
THAAD battery:
- The Terminal High Altitude Area Defence system (THAAD) is an American anti-ballistic missile defence system. It can shoot down short, medium and intermediate range missiles in it's sphere.
- The THAAD has a “hit to kill” approach which blasts missiles as they before they enter their target zone during their descent.
- The THAAD was developed by the US after their experience of Iraq's Scud missile attacks during the Persian Gulf War in 1991. Out of a total of 88 Scud missiles, Iraq fired 42 into Israel and 46 into Saudi Arabia, killing many American soldiers in barracks as well.
- The first proposal for the THAAD was submitted to the US Defence Ministry in 1987 and a series of tests resulting in failures, finally led to a successful version in 1999.
- In 2008, the US deployed an early missile warning radar, a part of the THAAD system to Israel. Similar deployments were also made in 2012 and 2019, aiding Israel's ability to emerge as a military power in the Middle East.
Maritime Exercise Malabar 2024

- 07 Oct 2024
In News:
Maritime Exercise Malabar 2024, Commencing at Visakhapatnam on 08 Oct Hosted by India, USA, Australia and Japan in Participation.
Background
- Origins: Initiated in 1992 as a bilateral naval drill between the United States and Indian Navy.
- Evolution: Has grown into a key multilateral exercise aimed at enhancing interoperability and addressing maritime challenges in the Indian Ocean and Indo-Pacific region.
Participating Naval Assets
- India: Various platforms, including:
- Guided missile destroyers
- Multi-purpose frigates
- Submarines
- Fixed-wing maritime reconnaissance aircraft
- Fighter aircraft and helicopters
- Australia:
- HMAS Stuart (Anzac Class Frigate)
- MH-60R helicopter
- P-8 Maritime Patrol Aircraft
- United States:
- USS Dewey (Arleigh Burke-Class Destroyer)
- Integral helicopter
- P-8 Maritime Patrol Aircraft
- Japan:
- JS Ariake (Murasame-class Destroyer)
Focus Areas of the Exercise
- Operational Enhancements:
- Discussions on special operations
- Surface, air, and anti-submarine warfare
- Subject Matter Expert Exchange (SMEE)
- Maritime Operations:
- Anti-submarine warfare
- Surface warfare
- Air defense exercises
- Emphasis: Improving situational awareness in the maritime domain.
Special Events
- Distinguished Visitors’ Day: Scheduled for October 9, 2024.
- Hosted by Vice Admiral Rajesh Pendharkar, Flag Officer Commanding-in-Chief, Eastern Naval Command.
- Joint Press Conference: Co-chaired by heads of delegations from all participating nations during the Harbour Phase.
Significance
- Comprehensive Exercise: Malabar 2024 is expected to be the most detailed edition to date, featuring complex operational scenarios and enhanced cooperation among the naval forces of the participating countries.GS Paper
DefConnect 4.0

- 07 Oct 2024
In News:
- DefConnect 4.0 was inaugurated by Union Defence Minister Rajnath Singh on October 7, 2024, at Manekshaw Centre, Delhi Cantonment.
- Organizer: Hosted by Innovations for Defence Excellence - Defence Innovation Organisation (iDEX-DIO) under the Department of Defence Production, Ministry of Defence.
Purpose and Focus
- Advancing Indigenous Innovation: Aims to enhance India’s defense ecosystem by promoting self-reliant defense technologies.
- Participants: Involves Armed Forces, Defence Public Sector Undertakings (DPSUs), start-ups, MSMEs, academia, incubators, investors, and policymakers.
Technology Showcase
- Exhibitions: iDEX innovators showcased cutting-edge technologies, products, and capabilities.
- Collaboration and Dialogue: Encourages partnerships and discussions to drive defense innovation and long-term collaborations.
Special Sessions
- Budget Insights: Focused on key takeaways from recent budget announcements impacting the defense innovation ecosystem.
- Semiconductor Domain: Highlighted initiatives and opportunities within the semiconductor sector.
Path Forward: Vision for 2047
- Viksit Bharat Goal: Aligns with India’s vision of becoming a global leader in defense innovation by 2047.
- Government Initiatives: Supports local talent and indigenous solutions through programs like iDEX.
iDEX Impact
- Defence India Start-up Challenges: 11 editions launched, garnering over 9,000 applications.
- Collaborations: Engages with over 450 start-ups/MSMEs on significant defense projects.
- Contribution to Self-Reliance: Supports the goal of achieving self-reliance in the defense and aerospace sectors.
Very Short Range Air Defence System (VSHORAD)

- 06 Oct 2024
In News:
DRDO completed development trials of the 4th Generation miniaturised Very Short Range Air Defence System (VSHORAD).
Key Details:
- Trial Location: Conducted at Pokhran Field Firing Ranges, Rajasthan.
- Importance: VSHORAD addresses the Indian Army's need to replace legacy Igla systems, with past efforts making little progress.
- Recent Procurement: Army acquired small volumes of Igla-S through emergency procurement.
- Production Collaboration: Two production agencies involved in Development cum Production Partner (DcPP) mode for VSHORAD missiles.
- Trial Dates: Successful tests held on October 3 and 4, 2024.
Key Performance Metrics:
- Maximum Range and Altitude: Interception against high-speed aerial targets.
- Hit-to-Kill Capability: Demonstrated success in engaging targets in various scenarios (approaching, receding, crossing).
System Overview:
- Type: Fourth generation man-portable air defence system (MANPADS).
- Developer: Research Centre Imarat (RCI) in collaboration with other DRDO labs and industry partners.
Capabilities:
- Designed to neutralise low altitude aerial threats at short ranges.
- Features include Dual-band IIR Seeker, miniaturised Reaction Control System, and integrated avionics.
- More portable and lightweight than existing missile systems in the Army's arsenal.
Joint Military Exercise KAZIND-2024

- 01 Oct 2024
In News:
The 8th edition of the India-Kazakhstan Joint Military Exercise, KAZIND-2024, has commenced in Auli, Uttarakhand, running from September 30 to October 13, 2024.
Key Details:
- Joint Exercise KAZIND-2024 has been held annually since 2016.
- Last edition of the Joint Exercise was held at Otar, Kazakhstan from 30th October to 11th November 2023.
Participants:
- India:
- 120 personnel from KUMAON Regiment of the Indian Army
- Additional support from other arms and Indian Air Force
- Kazakhstan:
- Personnel primarily from Land Forces and Airborne Assault Troopers
Aim:
- Enhance joint military capability for counter-terrorism operations
- Focus on sub-conventional scenarios under Chapter VII of the UN Charter
Focus Areas:
- Operations in semi-urban and mountainous terrains
- High physical fitness levels
- Rehearsal and refinement of tactical drills
- Sharing best practices
Tactical Drills:
- Joint response to terrorist actions
- Establishment of a Joint Command Post
- Creation of an Intelligence and Surveillance Centre
- Securing helipad/landing sites
- Combat free fall and Special Heliborne Operations
- Cordon and Search operations
- Employment of drones and counter-drone systems
Outcomes Expected:
- Sharing of tactics, techniques, and procedures for joint operations
- Development of interoperability between the two armies
- Strengthening of bonhomie and camaraderie
- Enhancement of defense cooperation and bilateral relations between India and Kazakhstan.
Samudra Pratap

- 02 Sep 2024
In News
Recently, the Indian Coast Guard (ICG) proudly launched the first indigenously built Pollution Control Vessel, ‘Samudra Pratap’, in Goa.
Key Highlights of the Launch
- Vessel Details:
- Built by Goa Shipyard Limited (GSL), the vessel is specifically designed to combat oil spills along India’s coastlines.
- Dimensions: Length: 114.5m, Breadth: 16.5m, Displacement: 4170 T.
- The keel laying ceremony took place on November 21, 2022.
- Contract and Construction: GSL signed a contract worth Rs 583 crores for the construction of two Pollution Control Vessels for the ICG. This marks the first instance of such vessels being designed and built entirely in India.
- Significance of the Vessel: ‘Samudra Pratap’ stands as a testament to India's shipbuilding capabilities, showcasing GSL's expertise in producing advanced Pollution Control Vessels and reinforcing India's commitment to indigenization in defense manufacturing.
Project NAMAN

- 02 Sep 2024
In News:
- The Indian Army launched the first phase of Project NAMAN, aimed at supporting Defence Pensioners, Veterans, and their families.
- Key Features of Project NAMAN:
- Implements the SPARSH (System for Pension Administration Raksha) digital pension system.
- Streamlines pension processes and provides accessible facilitation points for Veterans and Next of Kin (NOK).
- Importance:
- Ensures care and support for veterans and their families.
- Services extended to residents of military stations and surrounding localities.
- Establishment of Common Service Centres (CSCs):
- Tripartite MoU signed between:
- Indian Army’s Directorate of Indian Army Veterans
- CSC e-Governance India Limited
- HDFC Bank Limited
- CSCs provide:
- SPARSH-enabled pension services
- Government to Citizen (G2C) services
- Business to Consumer (B2C) services
- Tripartite MoU signed between:
- Phase One Deployment:
- 14 CSCs established in key locations: New Delhi, Jalandhar, Leh, Dehradun, Lucknow, Jodhpur, Bengdubi, Gorakhpur, Jhansi, Secunderabad, Saugor, Guntur, Ahmedabad, Bangalore.
- Future expansion plans for approximately 200 centres nationwide in the next 2-3 years.
- Infrastructure Support:
- HDFC Bank provided necessary IT infrastructure.
- Local military stations contributed physical facilities.
- Community Engagement:
- Concept developed based on feedback from the Defence community.
- Promotes camaraderie among serving and retired Armed Forces personnel.
- Management of CSCs:
- Each CSC managed by a Village Level Entrepreneur (VLE) selected from veterans or NOKs by Local Military Authorities (LMAs).
- VLEs receive training from CSC e-Governance India Limited.
- HDFC Bank offers monthly grants of ?20,000 for the first 12 months to support VLEs.
- Conclusion:
- Project NAMAN reflects the Indian Army's commitment to veteran welfare.
- Offers SPARSH-centric services and entrepreneurial opportunities for Veterans and NOKs, empowering them to contribute to their communities.
ROBOTIC MULES AND HIGH-ALTITUDE INNOVATIONS IN THE ARMY

- 24 Sep 2024
In News:
The Army has inducted 100 robotic mules, known as Multi-Utility Legged Equipment (MULE), under the fourth tranche of emergency procurements (EP).
- Purpose: These robotic mules are designed for surveillance and transporting light loads across challenging terrains, especially in high-altitude areas.
- Specifications:
- Endurance: Capable of operating for up to three years.
- Temperature Range: Functions effectively in extreme temperatures from -40°C to +55°C.
- Payload Capacity: Can carry up to 15 kg.
- Mobility: Can climb stairs, steep hills, and traverse obstacles; waterproof and able to cross rivers.
- Sensing Abilities: Equipped with electro-optics and infrared capabilities for object recognition.
- Control Mechanisms: Operable via an easy-to-use remote control, Wi-Fi, or Long-Term Evolution (LTE) connections.
- Mission Programming: Can be programmed for specific missions using waypoints or pre-recorded tasks.
- Combat Integration: Capable of integration with small arms for military applications.
- Logistics Drones: Logistics drones are currently undergoing trials to enhance support and movement in forward areas, particularly in high-altitude conditions.
- High-Altitude Habitat Evaluation: A new tent designed for extreme cold environments (operating at temperatures down to -40°C) is under evaluation. This tent, called Peak Pods, is intended for use in sub-zero conditions.
- Evaluation Locations: The tent has been tested in three high-altitude sites:
- Leh (11,500 feet)
- Daulat Beg Oldie (16,700 feet)
- Durbuk (12,500 feet)
- Significance: These advancements reflect the Army's focus on technological innovations to enhance operational capabilities in high-altitude areas, especially following the 2020 stand-off with China in Eastern Ladakh.
- Funding and Timelines: The EP process allows contracts up to ?300 crore, with a requirement for delivery within one year.
Chamran-1 satellite

- 15 Sep 2024
In News:
Iran successfully launched its Chamran-1 research satellite into orbit, utilising the Qaem-100 rocket developed by the paramilitary Revolutionary Guard.
Key Highlights:
- Satellite Details: Chamran-1, a research satellite, was designed and manufactured by Iranian engineers at Iran Electronics Industries (SAIran) in collaboration with the Aerospace Research Institute and private firms. It weighs approximately 60 kilograms.
- Launch Vehicle: The satellite was launched into orbit using the Ghaem-100, Iran's first three-stage solid-fuel space launch vehicle (SLV), developed by the Aerospace Force of the Islamic Revolutionary Guard Corps (IRGC).
- Mission Objectives: The primary mission of Chamran-1 is to test hardware and software systems for validating orbital maneuver technology. Additionally, it aims to assess the performance of cold gas propulsion subsystems and evaluate navigation and attitude control subsystems.
- Orbit Details: The satellite was placed into a 550-kilometer (341 miles) orbit above Earth.
What are Intercontinental ballistic missiles?
- Intercontinental ballistic missiles (ICBMs) are a type of ballistic missile with a range greater than 5,500 kilometers and are primarily designed to deliver nuclear warheads.
- They can carry conventional, chemical, and biological weapons, although the latter types have rarely been deployed on ICBMs.
- The United States, Russia, China, France, India, the United Kingdom, Israel, and North Korea are known to possess operational ICBMs, with Pakistan being the only nuclear-armed state that does not have them.
India-Maldives Defence Talks

- 07 Sep 2024
In News:
- India and the Maldives held their first defence talks since India withdrew its military personnel early this year.
Significance of Talks:
- The dialogue is notable given recent tensions in bilateral relations. Relations soured after President Mohamed Muizzu's election on an "India Out" platform, leading to the withdrawal of Indian troops. The last defence cooperation dialogue was held in March 2023 under President Ibrahim Solih.
Discussion Topics:
-
- Expediting ongoing defence cooperation projects.
- Planning forthcoming bilateral military exercises.
- Enhancing high-level exchanges and capability development.
Context of Tensions:
-
- Mohamed Muizzu, who took office in November 2023, had called for the removal of Indian military personnel, a significant shift from the previous administration’s stance.
- India agreed to withdraw 80 military personnel between March and May 2024. Indian technical personnel now operate key equipment like helicopters and a Dornier aircraft in the Maldives.
Recent Developments:
-
- Maldives Foreign Minister Moosa Zameer visited India in May.
- President Muizzu attended PM Narendra Modi’s swearing-in ceremony in June.
- In August, Indian External Affairs Minister S. Jaishankar visited the Maldives to reaffirm bilateral ties.
Historical Defence Cooperation:
-
- India gifted a Dornier aircraft to the Maldives in 2020 and a patrol vessel in 2019.
- India provided a coastal radar system last year and laid the foundation for the 'Ekatha Harbour' project, enhancing Maldivian Coast Guard capabilities.
Ongoing Projects:
-
- Greater Male Connectivity Project (GMCP) - a $500 million initiative financed by India.
- Building a new Coast Guard base at Uthuru Thilafalhu (UTF) atoll.
- India’s grant for High Impact Community Development Projects (HICDPs).
Strategic Importance:
-
- For Maldives: India is a key security partner and crisis responder, with historical assistance during emergencies (Operation Neer, Vaccine Maitri). Maldives seeks to restore Indian tourist numbers, vital for its economy.
- For India: The Maldives is crucial to India's Neighbourhood First Policy and Vision SAGAR. Its strategic location between major Indian Ocean chokepoints makes it a vital partner for maritime security and countering China's influence.
Recent Changes:
-
- The Muizzu government decided not to renew a 2019 MoU for hydrographic surveying with India, ending joint hydrographic surveys conducted under the pact.
Travel and Trade:
-
- Both countries benefit from an open skies arrangement and visa-free access for tourism, medical, and business purposes
Exercise AL NAJAH

- 13 Sep 2024
In News:
- Indian Army contingent departed for the 5th edition of the India-Oman Joint Military Exercise AL NAJAH on September 12, 2024.
Key Details:
- Location: Rabkoot Training Area, Salalah, Oman.
- Frequency: Exercise AL NAJAH has been held biennially since 2015, alternating between India and Oman. Last edition was conducted at Mahajan, Rajasthan.
- Indian Army Contingent:
- Size: 60 personnel
- Composition: Battalion of the Mechanised Infantry Regiment, along with personnel from other arms and services.
- Royal Army of Oman Contingent:
- Size: 60 personnel
- Composition: Troops of the Frontier Force.
- Objective:
- Enhance joint military capability for counter-terrorism operations under Chapter VII of the United Nations Charter.
- Focus on operations in a desert environment.
- Tactical Drills:
- Joint Planning
- Cordon and Search Operation
- Fighting in Built-Up Areas
- Establishment of Mobile Vehicle Check Posts
- Counter Drone Operations
- Room Intervention
- Training Exercises:
- Combined field training exercises simulating real-world counter-terrorism missions.
- Outcomes Expected:
- Exchange of best practices in tactics, techniques, and procedures for joint operations.
- Foster interoperability, goodwill, and camaraderie between the two armies.
- Strengthen defense cooperation and enhance bilateral relations between India and Oman.
INDUS-X Summit 2024

- 14 Sep 2024
The third edition of the INDUS-X Summit, held on September 9-10, 2024, in California, marked a significant advancement in the collaborative defence innovation ecosystem between India and the USA. Co-organized by the U.S.-India Strategic Partnership Forum (USISPF) and Stanford University, the summit emphasized the deepening of defence cooperation through innovation, joint research, and investment.
Key Outcomes
A major highlight of the summit was the signing of a Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) between India’s Innovations for Defence Excellence (iDEX) and the US Department of Defense’s Defence Innovation Unit (DIU). This agreement aims to enhance collaboration in defence innovation. The summit also saw the release of the INDUS-X Impact Report and the launch of a dedicated webpage for the initiative on both iDEX and DIU platforms.
Technological Showcase and Expert Dialogue
The summit provided a platform for startups and MSMEs to present cutting-edge technologies. Additionally, two advisory forums—the Senior Advisory Group and the Senior Leaders Forum—facilitated in-depth discussions on future technology trends, defence supply chain resilience, and funding opportunities for defence innovation. The discussions included contributions from experts across the defence industry, investment sectors, academia, and think tanks from both countries.
Leadership and Commitment
The Indian delegation was led by Amit Satija, Joint Secretary (Defence Industries Promotion), who underscored the commitment of both India and the USA to advancing defence technology through strategic collaboration. Since its launch in June 2023 during the Indian Prime Minister’s visit to the US, INDUS-X has achieved significant milestones, reinforcing its role in strengthening the US-India defence innovation partnership.
Agni-4 ballistic missile successfully test-fired in Odisha
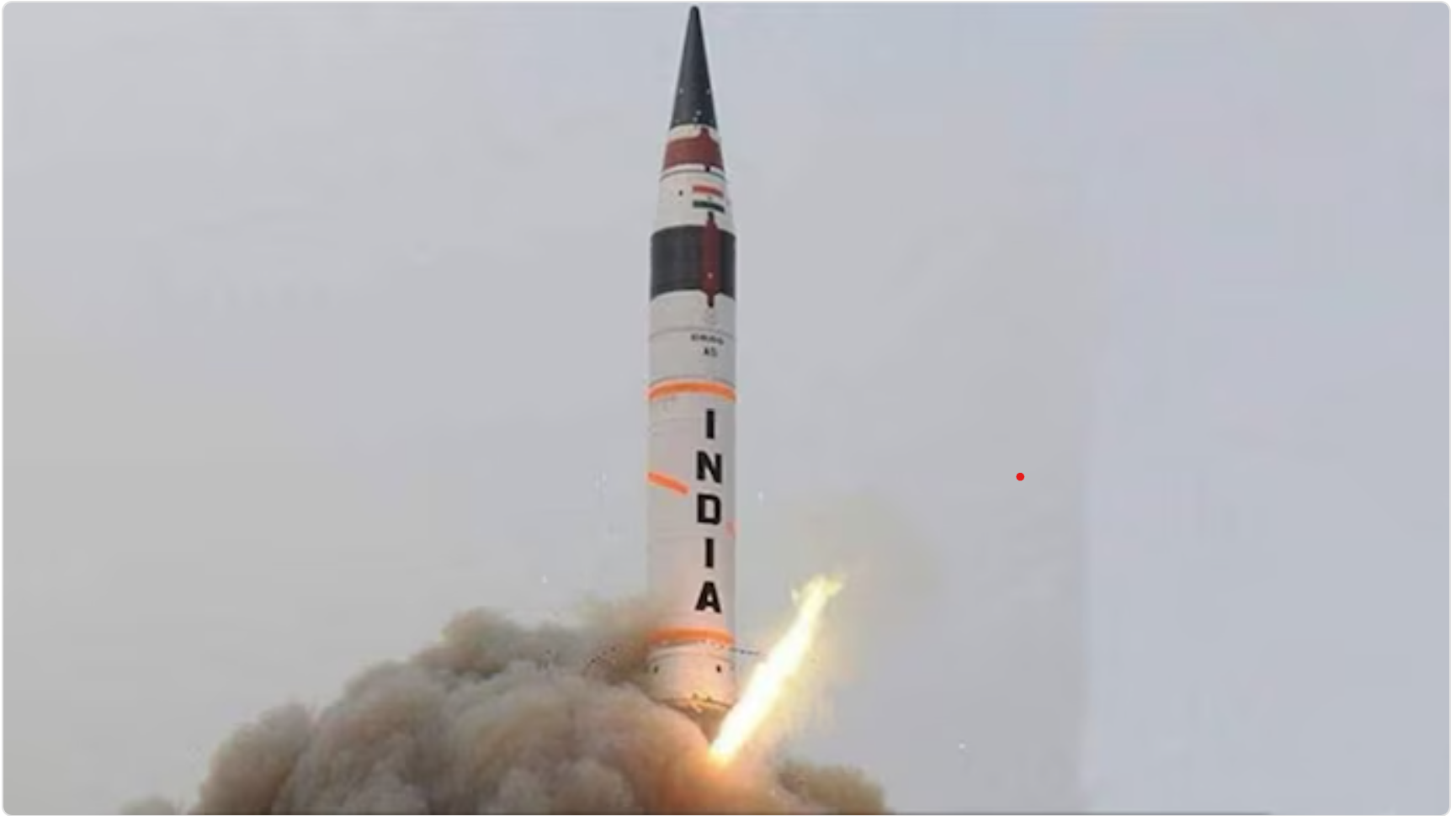

- 09 Sep 2024
In News:
India successfully test-fired the Agni-4 ballistic missile from the Integrated Test Range in Chandipur, Odisha. The test, conducted by the Strategic Forces Command (SFC) under India's Nuclear Command Authority (NCA), demonstrated the missile's operational and technical capabilities.
Key Details:
- Missile Specifications:
- Range: The Agni-4 missile has a maximum range of 4,000 kilometers.
- Payload: It can carry a payload of up to 1,000 kilograms.
- Length: The missile is approximately 20 meters long.
- Launch Platform: It is designed for deployment on a road-mobile launcher, enhancing its flexibility and mobility.
- Historical Context:
- Previous Test (2012): In its earlier test in 2012, Agni-4 successfully covered over 3,000 kilometers within 20 minutes. This was noted as the longest-range mission achieved by the Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO) at that time.
- Name Change: The Agni-4 was previously known as Agni-2 Prime.
- Development and Capabilities:
- Development: The Agni missiles, including the Agni-4, are developed by the DRDO, showcasing India's advancements in missile technology and strategic capabilities.
- Comparison with Agni-5: The Agni-4 is part of a series of Agni missiles that have progressively enhanced India's missile range and strike capabilities. The Agni-5 represents an even more advanced development in this series.
The successful test of Agni-4 underscores India's commitment to strengthening its strategic defense capabilities and maintaining its deterrence posture.
Inter-Services Organisations (ISOs) (Command, Control, and Discipline) Act

- 11 May 2024
Why is it in the News?
The Inter-Services Organisations (Command, Control and Discipline) Act has been notified in a gazette and has been enforced with effect from May 10, the Defence Ministry said recently.
About Inter-Services Organisations (ISOs) (Command, Control, and Discipline) Act:
- During the Monsoon Session of 2023, both houses of Parliament passed a bill aimed at enhancing the operational efficiency and coordination of Inter-Services Organisations (ISOs).
- These organisations comprise personnel from the Army, Air Force, and Navy, such as joint training institutions like the National Defence Academy, National Defence College (NDC), Defence Services Staff College (DSSC), and the Andaman and Nicobar Command (ANC).
Key Provisions of the ACT:
- Inter-Services Organisation Establishment: Existing Inter-Services Organisations will be considered constituted under the Act.
- The central government may establish an Inter-Services Organisation comprising personnel from at least two of the following services: the Army, Navy, and Air Force.
- Control of Inter-Services Organisations: The Act empowers the Commander-in-Chief or Officer-in-Command of an Inter-Services Organisation to exercise command and control over its personnel.
- They are responsible for maintaining discipline and ensuring the proper discharge of duties by service personnel.
- Supervision of an Inter-Services Organisation will be under the purview of the central government.
- Commander-in-Chief Eligibility: Officers eligible for appointment as Commander-in-Chief or Officer-in-Command include:
- A General Officer of the regular Army (rank above Brigadier),
- A Flag Officer of the Navy (rank of Admiral of the Fleet, Admiral, Vice-Admiral, or Rear-Admiral), or
- An Air Officer of the Air Force (a rank above Group Captain).
- Commanding Officer Appointment: The Act establishes a Commanding Officer responsible for leading a unit, ship, or establishment within the Inter-Services Organisation.
- The Commanding Officer carries out duties assigned by the Commander-in-Chief or Officer-in-Command.
- They have the authority to initiate disciplinary or administrative actions for personnel within the Inter-Services Organisation.
Need for the Act:
- Theaterisation Drive: The enactment aligns with the ongoing push for theaterisation, a vital military reform aimed at optimizing resources for future combat scenarios.
- Existing Framework Challenges: Currently, armed forces personnel are governed by separate laws— the Air Force Act, 1950, the Army Act, 1950, and the Navy Act, 1957—resulting in disjointed disciplinary powers.
- Under the current setup, only officers from the same service possess disciplinary authority over personnel governed by the respective Act, leading to command, control, and discipline challenges.
- Financial Implications: The present framework entails time-consuming processes and financial expenditures for personnel transfers.
- The proposed legislation seeks to remedy these challenges by enhancing discipline enforcement, expediting case resolutions, and potentially saving public funds.
Netzah Yehuda Battalion

- 23 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
The US government may soon sanction a battalion of the Israeli Defence Forces (IDF) over alleged human rights violations, marking the first such move in the history of the two countries’ relations.
What is the Netzah Yehuda Battalion?
- The Netzah Yehuda battalion was set up in 1999 to accommodate the religious beliefs of ultra-Orthodox Jews and other religious nationalist recruits in the army.
- It was established to facilitate military service for these communities, accommodating their religious observances by scheduling prayer and study times, and restricting their interactions with female soldiers.
- The battalion is historically stationed in the occupied West Bank region and faces intense scrutiny for allegedly committing human rights violations against Palestinians.
- Netzah Yehuda came on the radar of United States agencies after the death of an elderly Palestinian-American man, who was detained by the battalion.
What is the Unit Accused Of?
- The United States called for a criminal investigation after Netzah Yehuda soldiers were accused of being involved in the death of a 78-year-old Palestinian-American, Omar Assad, who died of a heart attack in 2022 after he was detained and was later found abandoned at a building site.
- A Palestinian autopsy found Assad died from a stress-induced heart attack brought on by being manhandled.
- The case attracted unusual attention because of his dual nationality, his age, and a demand by the U.S. State Department for an investigation into his death.
- There have been several other incidents in recent years, some captured on video, in which Netzah Yehuda soldiers were accused of, or charged with, abusing Palestinian detainees.
- The battalion primarily operated in the West Bank before it was moved out of the territory in late 2022 after U.S. criticism.
- The unit has recently been serving in Gaza.
Defence Attaché (DA)

- 13 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
As India expands its presence in defense diplomacy and plans to deploy Defense Attachés to Indian missions in Africa, Armenia, and the Philippines, experts and experienced diplomats advise against simply "rationalizing" their numbers.
What’s a Defense Attaché?
- According to the Geneva Centre for the Democratic Control of Armed Forces (DCAF), a defence attaché is a member of the armed forces serving at an embassy as a “representative of his/her country’s defence establishment abroad and in this capacity enjoys the diplomatic status and immunity.
- The defence attaché’s work usually concerns bilateral military and defence relations.
- Some countries send attachés for security issues, such as migration or matters relating to police and justice.
- The defence attachés are also responsible for facilitating communication and cooperation between their home nation’s armed forces and the host country’s military.
- They act as military and/or security advisors to their country’s ambassador and embassy staff.
- They can also promote their home nation’s military weapons industry.
- Defence attachés collect and examine military intelligence, facilitate military cooperation pacts, and give an evaluation of security issues to their home country’s government.
- They also act as a link between diplomats and the military.
India to Send Defence Attachés to New Countries:
- India has started dispatching defence attachés to many new countries, while reportedly downsizing the military personnel at its missions in some other nations.
- 15-16 new attaches from the Indian Navy, the Indian Air Force (IAF), and the Indian Army are being posted to Poland, the Philippines, Armenia, and the African countries of Tanzania, Mozambique, Djibouti, Ethiopia, and Ivory Coast.
- In the next phase, 10 entirely new defence wings will be created in different countries, with a particular focus on nations to which arms can be exported.
Why the Other Countries Matter?
- India dispatching a defense attaché to Poland, which is a part of the European Union (EU) and has emerged as an important security partner in Europe in recent years, is also significant.
- The EU posted a military attaché to its mission in India for the first time last year. India’s move to do the same in Poland is “reflective of the desire to expand two-way defence ties.
- Armenia has become a major exporter of India’s arms.
- India has already inked deals with the Asian country for Pinaka rockets, Akash missiles, ammunition, and multi-barrel rocket launchers, with some of them coming amid Armenia’s clash with Azerbaijan over Nagorno-Karabakh.
- Armenia has shown interest in expanding its defence ties with India.
- China’s military assertiveness in the South China Sea has prompted India to grow military ties with ASEAN countries.
- India’s decision to send defence attachés for the first time to the Philippines comes in the wake of the sale of Indian arms to Manila.
- India signed a $375 million deal with the Philippines in 2022 to supply three batteries of the BrahMos missile and will soon start the delivery of the missiles to the Southeast Asian country.
Black Swan Event

- 09 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
Army Chief Gen Manoj Pande on Monday called upon the force to be always prepared for 'black swan' events and "expect the unexpected" even as he identified technology as the new area for strategic competition among nations.
What is the Black Swan Event?
- A black swan is a rare, unpredictable event that comes as a surprise and has a significant impact on society or the world.
- These events are said to have three distinguishing characteristics:
- They are extremely rare and outside the realm of regular expectations
- They have a severe impact after they hit; and
- They seem probable in hindsight when plausible explanations appear.
When did the Term Originate?
- The black swan theory was put forward by author and investor Nassim Nicholas Taleb in 2001 and later popularised in his 2007 book – The Black Swan: The Impact of the Highly Improbable.
- In his book, Taleb does not try to lay out a method to predict such events but instead stresses building “robustness” in systems and strategies to deal with black swan occurrences and withstand their impact.
- The term itself is linked to the discovery of black swans.
- Europeans believed all swans to be white until 1697 when a Dutch explorer spotted the first black swan in Australia.
- The metaphor ‘black swan event’ is derived from this unprecedented spotting from the 17th century, and how it upended the West’s understanding of swans.
Implications of Black Swan Events:
- Black Swan events are characterized by their extreme rarity, severe impact, and widespread implications across various sectors.
- These unanticipated occurrences can trigger substantial disruptions, unveiling vulnerabilities in systems once thought resilient and prompting reassessments of risk management practices.
- Disruption: Black Swan events have the potential to disrupt economies, industries, and societies on a global scale.
- Their unforeseen nature can cause sudden shifts in financial markets, business operations, and everyday life, leaving lasting effects on the overall landscape.
- Uncertainty: The inability to predict Black Swan events using traditional methods injects considerable uncertainty into decision-making and planning for individuals, organizations, and governments.
- Navigating through such unpredictable circumstances can pose significant challenges for all affected parties.
- Vulnerability: These rare events can expose vulnerabilities in systems that were previously thought to be impervious or resilient.
- By doing so, Black Swan events emphasize the importance of preparedness and encourage the development of more robust risk management practices.
- Reassessment of Risk: In the aftermath of a Black Swan event, there is often a renewed focus on identifying and mitigating previously overlooked risks.
- This heightened awareness can lead to changes in investment strategies, regulatory policies, and overall risk management practices.
- Regulatory and Policy Responses: Governments and regulatory bodies may implement new regulations or policies in response to Black Swan events.
- These measures are designed to prevent or mitigate the impact of similar occurrences in the future, ultimately shaping the economic and social landscape.
- Behavioral and Attitude Changes: Black Swan events can significantly alter behaviors and attitudes as individuals and organizations adapt to the new reality.
- These shifts may include changes in consumer behavior, investment strategies, and approaches to risk management.
Examples of Black Swan Events:
- The Dot-com Bubble: In 2000, the valuation of many internet-based companies plummeted after a period of rapid growth.
- The 9/11 Terrorist Attacks: The events of September 11, 2001, had far-reaching consequences on global security, politics, and economies.
- The 2008 Financial Crisis: A series of shocks to Wall Street due to the unraveling of subprime lending practices caused significant economic turmoil.
- Brexit: The unexpected decision of the United Kingdom to leave the European Union in June 2016 caught many by surprise and caused the British pound to plummet against the US dollar.
- COVID-19 Pandemic: The ongoing global health crisis continues to significantly affect economies and markets worldwide.
- These instances illustrate the profound and widespread implications of Black Swan events, underscoring the importance of adaptability and resilience in an ever-changing global landscape.
Agni-Prime Ballistic Missile

- 05 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
India has successfully flight-tested the new generation ballistic missile Agni-Prime from the APJ Abdul Kalam Island off the coast of Odisha.
About Agni-Prime Missile:
- Agni-P or Agni-Prime is a new generation nuclear-capable medium-range ballistic missile (MRBM) developed by the DRDO that incorporates technological advances from Agni-IV and Agni-V and is considered a successor for Agni-I and Agni-II missiles in the operational service of the SFC.
- Agni-Prime, with a strike range of 1,000 to 2,000 km, has significant upgrades, which include composite motor casing, maneuverable reentry vehicle (MaRV), improved propellants, and navigation and guidance systems.
- It is a two-stage, surface-to-surface, road-mobile, and solid-fueled missile that is transported by a truck and launched via a canister.
- It is a ballistic missile with a dual redundant navigation and guidance system.
Features:
- Although Agni-Prime looks similar to Agni-III, the weight is reduced by half.
- Agni-P will replace older generation missiles such as Prithvi-II (350 km), Agni-II (2,000 km), Agni-III (3,000 km), and Agni-4 (4,000 km) ballistic missiles.
- Agni-Prime incorporates upgrades such as propulsion systems, composite rocket motor casings, and advanced navigation and guidance systems.
- Along with Agni-V, Agni-P will provide India with stronger deterrence against countries such as China and Pakistan.
- While Agni-V brings all of China within its strike range, Agni-P seems to have been developed to counter Pakistan's forces.
- Agni-P is developed to achieve maximum maneuverability against missile defense systems and higher accuracy for precision strikes.
What is a Ballistic Missile and why is it named so?
- A Ballistic missile follows a ballistic flight path - which comprises three phases of flight.
- In the first phase or the boost phase, the solid-fuel rocket engine propels the missile upwards and it has to rapidly gain velocity and altitude, by knifing through the densest parts of the earth's atmosphere.
- The second and unpowered phase of flight happens in the upper reaches of the earth's atmosphere or in space, where the missile travels along its pre-determined path, but without the power of its engines.
- It is known as the coast phase or mid-course phase and during this time, it travels along a horizontal path.
- During the coasting, the missile is either in space or the upper atmosphere, where it faces minimal resistance or drag.
- In the third and final phase or the terminal phase, the missile descends and gets back into the earth's atmosphere and flies towards its target, while being guided by its on-board systems.
India’s indigenous fifth-gen fighter jet AMCA

- 09 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
The Cabinet Committee on Security (CCS) this week cleared a Rs 15,000 crore project to design and develop the Advanced Medium Combat Aircraft (AMCA), India’s fifth-generation fighter multirole fighter jet.
About Advanced Medium Combat Aircraft (AMCA)?
- The AMCA will be India’s indigenous fifth-generation fighter aircraft.
- The indigenous Light Combat Aircraft (LCA) Tejas is a 4.5-generation single-engine multirole aircraft.
- The Aeronautical Development Agency (ADA) under the Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO) will be the nodal agency for executing the programme and designing the aircraft.
- It will be manufactured by state-owned Hindustan Aeronautics Limited (HAL).
- The aircraft will put India in a select group of nations that have their own fifth-generation fighter aircraft.
- Discussions for developing the AMCA started in 2007.
- The initial plan was to jointly develop the aircraft with Russia under a Fifth Generation Fighter Aircraft (FGFA) programme.
- However, India withdrew from the FGFA project in 2018.
Features of AMCA:
- Stealth: The 25-tonne twin-engine aircraft, which will be bigger that other fighters in the Indian Air Force inventory, will have advanced stealth features to avoid detection by enemy radar.
- With stealth features, this aircraft (AMCA) would be able to compete with other stealth fighters in the world.
- Fuel & Weapons: The aircraft will have a large, concealed internal fuel tank of 6.5-tonne capacity, and an internal weapons bay for a range of weapons, including indigenous weapons, to be buried in its belly.
- Engine: The AMCA Mk1 variant will have the US-built GE414 engine of the 90 kilonewton (kN) class, while the more advanced AMCA Mk2 will fly on the more powerful 110kN engine, which will be developed indigenously by DRDO’s Gas Turbine Research Establishment (GTRE) in collaboration with a foreign defense major.
- India has been talking with Safran SA of France, one of the world’s largest manufacturers of aircraft engines and related equipment, in order to finalize the roadmap for the development of the combat aircraft engine
- Another important aspect would be to ensure a higher utilization time and smaller serviceability or maintenance periods for the aircraft.
- This will be aided by the inclusion of a comprehensive Integrated Vehicle Health Management (IVHM) system to keep track of multiple structural components, and to assess the condition of the aircraft in real time.
- Other features such as a diverterless supersonic inlet for controlling air flow into the engines, and a serpentine air intake duct to shield the engines from radar emissions, are likely to be part of the AMCA.
Other Fifth-generation Fighters:
- Only a few countries have built a fifth-generation stealth fighter aircraft.
- The list of the aircraft currently in service includes:
- The F-22 Raptor and F-35A Lightning II of the US
- The Chinese J-20 Mighty Dragon, and
- The Russian Sukhoi Su-57.
INS Jatayu, India’s new naval base in Lakshadweep

- 06 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
On Wednesday (March 6), Naval Detachment Minicoy will be commissioned as INS Jatayu, an upgraded naval base, marking an important milestone in the Indian Navy’s resolve to incrementally augment security infrastructure at the strategic Lakshadweep Islands.
About INS Jatayu Naval Base:
- The existing Naval Detachment Minicoy, which is under the operational command of the Naval Officer-in-Charge (Lakshadweep), will be commissioned as INS Jatayu.
- A naval detachment has administrative, logistics, and medical facilities.
- INS Jatayu will be upgraded to a naval base with additional infrastructure such as an airfield, housing, and personnel, after obtaining the requisite environmental and other clearances.
- The fragile ecology of the island may pose challenges for the construction but there are plans to construct a new airfield that will be capable of operating both military and civil aircraft.
Significance of INS Jatayu?
- The basing of an independent naval unit with requisite infrastructure and resources will enhance its overall operational capability in the islands.
- The establishment of the base is in line with the government’s focus on comprehensive development of the islands.
- The base will enhance its operational reach, facilitate its anti-piracy and anti-narcotics operations in the western Arabian Sea, and augment its capability as the first responder in the region.
- With the commissioning of INS Jatayu, the Indian Navy will add to its strength on the western seaboard.
- The proposed airfield will allow operations for a range of aircraft, including P8I maritime reconnaissance aircraft and fighter jets, and extend the Navy’s reach and operational surveillance capabilities at a time when India is seeking to counter the growing Chinese influence in the Indian Ocean Region.
- This has an immediate bearing at a time when India’s relations with the Maldives have come under strain since the election of the pro-China President Mohamed Muizzu.
About the Lakshadweep Islands:
- Lakshadweep, ‘a hundred thousand islands’ in Sanskrit and Malayalam, is an archipelago of 36 islands located between 220 km and 440 km from Kochi.
- The islands, only 11 of which are inhabited, have a total area of only 32 sq km.
- The Lakshadweep are part of a chain of coralline islands in the Indian Ocean that includes Maldives to the south, and the Chagos archipelago farther beyond, to the south of the equator.
- Given their location in the Indian Ocean, the Lakshadweep are of huge strategic importance to India.
- Minicoy straddles vital Sea Lines of Communications (SLOCs) — the world’s main maritime highways — including the Eight Degree Channel (between Minicoy and Maldives) and the Nine Degree Channel (between Minicoy and the main cluster of Lakshadweep islands).
- In consequence, the Lakshadweep Islands are also vulnerable to marine pollution.
Grey-zone Warfare Latest Entry in Lexicon of Warfare

- 04 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
On the last day of the 2024 Raisina Dialogue (February 24), India’s Chief of Defence Staff General Anil Chauhan said that “grey zone warfare” is the latest in informal warfare.
What is the Grey Zone Warfare?
- Grey zone warfare refers to a strategic approach where a nation seeks to gain advantages over others without engaging in overt conflict.
- It involves a series of tactics, including cyberattacks, disinformation campaigns, and economic pressures, aimed at subtly undermining or destabilizing adversaries.
- China has notably employed this strategy against India and neighboring countries.
What are the China's Grey Zone Tactics Against India?
- South China Sea Activities: China asserts its dominance in the South China Sea using naval and civilian vessels, raising tensions with neighboring countries like India.
- Infrastructure Near Borders: China constructs infrastructure and settlements near India's borders, bolstering territorial claims and strategic positioning.
- Digital Investments: China invests in Indian digital platforms and media, influencing public narratives and perceptions.
India's Counter-Measures:
- Inter-Agency Collaboration: India promotes collaboration among defense, intelligence, and law enforcement agencies to devise comprehensive strategies to counter grey zone threats.
- Enhanced Vigilance: India increases surveillance and presence in border areas and strategic locations to detect and respond to covert Chinese activities.
- Regulating Foreign Investments: India scrutinizes foreign investments in critical sectors, particularly technology, to safeguard national security interests.
Long-Term Implications for India:
- Information Warfare: Grey zone conflicts often involve digital misinformation, influencing public opinion and perceptions.
- Economic Leverage: Dependency on foreign investments poses vulnerabilities if used as leverage by investing nations.
- Technology Dependency: Heavy reliance on foreign technology exposes India to risks, emphasizing the need to bolster indigenous technological capabilities.
Conclusion
Grey zone warfare encompasses a multifaceted strategic landscape, blending digital, economic, and geopolitical tactics. India recognizes these challenges and is actively devising strategies to navigate this complex terrain.
China Moves its Nationals into its Vacant ‘Defence Villages’ Along LAC (Indian Express)

- 15 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
Chinese nationals have started occupying several of their model “Xiaokang” border defence villages across India’s north-eastern borders which the country has been building along the Line of Actual Control (LAC) since 2019.
News Summary:
- Chinese activity has been observed in several villages situated on its side of the Line of Actual Control (LAC) opposite the Lohit Valley and the Tawang sector of Arunachal Pradesh.
- Over the past five years, China has been undertaking the construction of 628 "well-off villages" along India's borders with the Tibet Autonomous Region, encompassing regions like Ladakh and Arunachal Pradesh.
- The precise purpose of these villages remains ambiguous, although the structures are believed to serve as "dual-use infrastructure," serving both civilian and military functions.
What is the Line of Actual Control (LAC)?
- The LAC serves as the boundary separating areas under Indian administration from those under Chinese administration.
- However, it is not a formally agreed-upon boundary, lacking delineation on maps or physical demarcation on the ground.
- India views the LAC as approximately 3,488 km in length, while China's perspective estimates it to be around 2,000 km.
- The LAC is segmented into three sectors: the eastern sector covering Arunachal Pradesh and Sikkim, the middle sector spanning Uttarakhand and Himachal Pradesh, and the western sector in Ladakh.
- India's official boundary line, as depicted on maps released by the Survey of India, encompasses both Aksai Chin and Gilgit-Baltistan, diverging from the LAC.
- Consequently, the LAC does not coincide with India's claim line.
- For China, the LAC generally aligns with its claim line, except in the eastern sector, where it asserts control over the entire territory of Arunachal Pradesh, which it regards as South Tibet.
Dispute over the LAC and Controversy Surrounding Claim Lines in Ladakh:
- India disputes the validity of the Line of Actual Control (LAC), asserting that it is a construct devised by China.
- The Chinese demarcation appears as a series of disconnected points on a map, lacking a clear and consistent delineation.
- India contends that the line should exclude territorial gains made through aggression in 1962 and instead reflect the positions as of September 8, 1962, before the Chinese incursion.
- This ambiguity in the Chinese definition of the LAC leaves room for China to pursue incremental changes on the ground through military actions, as evidenced by the clash in the Galwan Valley between the Indian Army and the Chinese PLA in 2020.
- Aksai Chin, located in the Ladakh region of the princely state of Jammu and Kashmir, was not part of British India, despite being under British Empire control.
- As a result, while the eastern boundary was clearly defined in 1914 with the signing of the Shimla Agreement on the McMahon Line by British India, the western boundary in Ladakh remained unresolved.
- These historical maps, still officially recognized today, formed the basis of engagements with China, ultimately culminating in the 1962 War.
Infrastructure Development along the LAC:
- Consistently, China has enhanced its existing infrastructure along the Line of Actual Control (LAC), focusing on improving connectivity through mountain passes, constructing roads, bridges, and model villages.
- Additionally, China has been constructing infrastructure, including border villages, within Bhutanese territory.
- Over the past three to four years, India has intensified efforts to bolster its border infrastructure, encompassing initiatives to enhance forward connectivity, establish alternative routes to the LAC, and connect remote areas.
- India's Vibrant Villages program aims to modernise 663 border villages, providing them with essential amenities in the initial phase.
- Notably, 17 of these villages located along the borders with China in Ladakh, Himachal Pradesh, Uttarakhand, Sikkim, and Arunachal Pradesh have been earmarked for development as pilot projects under this program.
- Moreover, significant progress is underway on three major highways in Arunachal Pradesh:
- The Trans-Arunachal Highway
- The Frontier Highway, and
- The East-West Industrial Corridor Highway.
Defence upgrade roadmap: Apex body led by Prime Minister, MoD sci-tech unit (Indian Express)
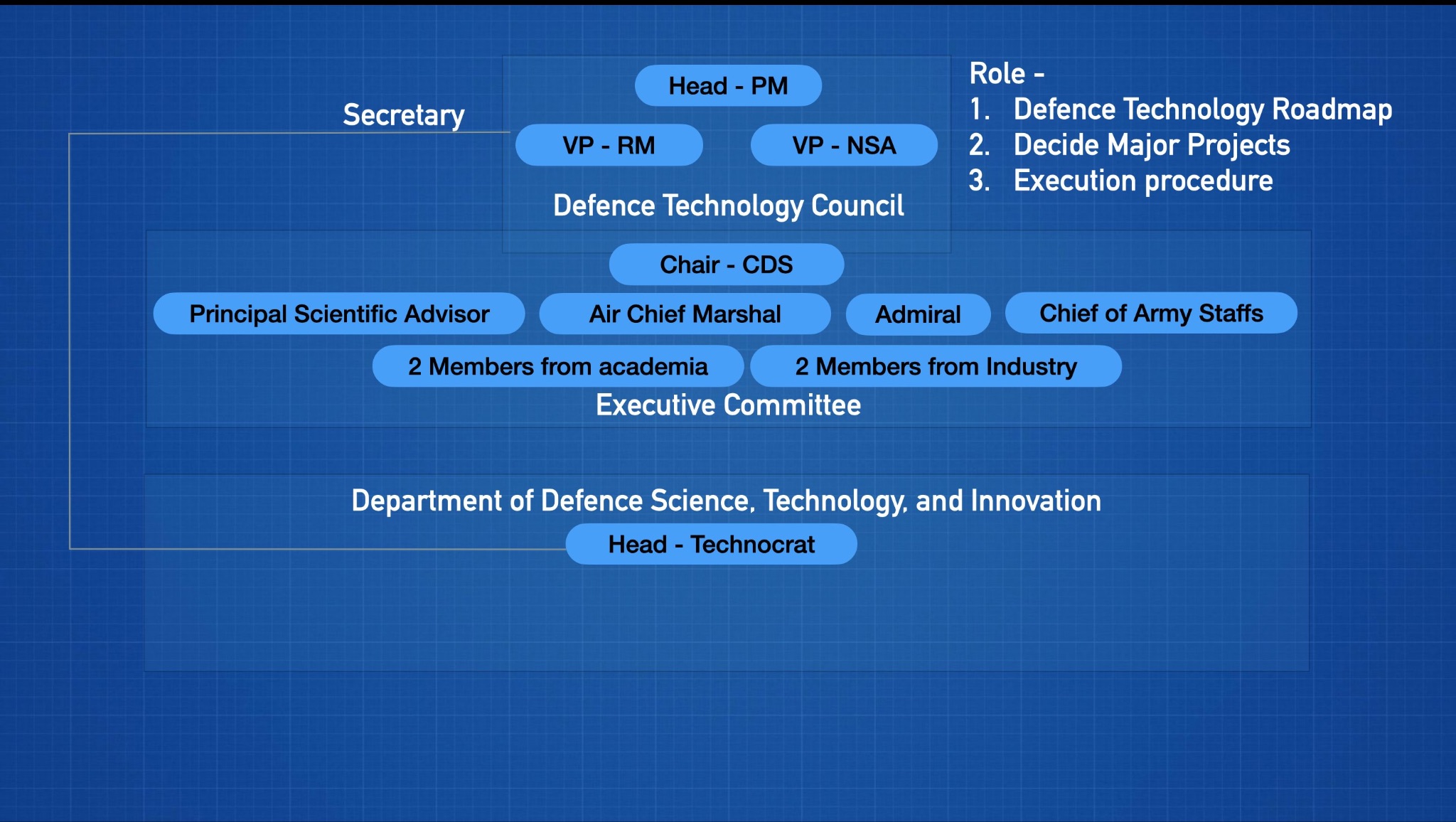
- 17 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News?
The expert committee, led by Vijay Raghavan, the former principal scientific advisor, proposed that the country's defence technology roadmap be overseen by an apex body called the Defence Technology Council, with the Prime Minister serving as its chair.
The context in which the Vijay Raghavan Committee was Established:
- Formed by the government last year, the committee was tasked with assessing the functioning of the Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO).
- The committee's report, submitted this month, follows the government's initiative to address significant delays in various DRDO projects.
- This scrutiny comes in response to concerns raised by the Parliamentary Standing Committee on Defence, which noted that 23 out of 55 mission mode projects faced substantial delays.
- In 2022, the Comptroller and Auditor General (CAG) highlighted that 67% of the 178 scrutinized projects failed to meet their initially proposed timelines.
- The CAG attributed these delays to factors such as persistent alterations in design specifications, delays in completing user trials, and delays in placing supply orders.
- The prevalent practice of seeking multiple extensions for projects, particularly those designated under the Mission Mode category, has been identified as undermining the intended purpose of these initiatives.
Major Recommendations of the Vijay Raghavan Committee:
- Establishment of the Defence Technology Council: Headed by the Prime Minister, with the Defence Minister and the National Security Advisor serving as Vice Presidents.
- This council is envisioned to play a pivotal role in charting the nation's defence technology roadmap, deciding on significant projects, and overseeing their execution.
- An executive committee, led by the Chief of Defence Staff, is proposed, featuring members such as the Principal Scientific Advisor, the three service chiefs, their vice chiefs, and representation from academia and industry.
- Creation of the Department of Defence Science, Technology, and Innovation: To be led by a technocrat, this department aims to foster defence research and development within the academic and startup ecosystem.
- Additionally, it is designated as the secretariat for the Defence Tech Council chaired by the Prime Minister.
- Drawing expertise from scientists in the Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO) and academia, it will compile a knowledge repository on production expertise, conduct background research for the Defence Tech Council, and contribute to informed decisions on technology production.
- Restructuring of DRDO's Focus: Recommends that DRDO concentrate on its original mission of research and development for defence purposes.
- The suggestion is for DRDO to abstain from involvement in productization, production cycles, and product management, tasks deemed more suitable for the private sector.
- Currently, DRDO is engaged in all aspects of its projects, spanning from research and development to production.
iDEX innovators to exhibit futuristic technologies at Vibrant Gujarat summit (ET)

- 08 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News
The Ministry of Defence on Sunday said that Innovations for Defence Excellence-Defence Innovation Organization (iDEX-DIO) will participate in the 10th edition of the Vibrant Gujarat Summit from January 10 to 12 in Gandhinagar.
About iDEX:
- iDEX (Innovations for Defence Excellence), the flagship scheme of the Ministry of Defence, Govt of India launched by Prime Minister Modi in 2018.
- The objective of the scheme is to cultivate an innovation ecosystem in the Defence and Aerospace sector by collaborating with startups, innovators, MSMEs, incubators, and academia.
- iDEX offers grants and support for R&D with significant potential for future adoption in Indian defense and aerospace.
- It is currently engaged with around 400+ Startups and MSMEs, till now procurement of 31 items worth over Rs 2000 Cr. has been cleared.
- Recognized as a game-changer in the defense ecosystem, iDEX has received the PM Award for Innovation in the defense sector.
What is the Vibrant Gujarat Summit?
- The Government of Gujarat organizes the Vibrant Gujarat Global Summit, also known as Vibrant Gujarat, a biennial global business event held in the state of Gujarat, India.
- It attracts business leaders, investors, corporations, thought leaders, and policymakers, serving as a platform to understand and explore business opportunities in Gujarat.
- Launched in 2003 and now held every two years, the summit aims to promote Gujarat as an attractive investment destination, fostering partnerships and collaborations across various sectors.
- Industry associations, both nationally and internationally, support the summit, making it one of Gujarat's crucial economic forums.
- The event creates a platform for business leaders, policymakers, and investors to explore opportunities for investment, collaboration, and partnership in sectors such as energy, manufacturing, infrastructure, information technology, agriculture, healthcare, and more.
- It facilitates discussions, negotiations, and agreements in these key sectors.
- The Tenth edition of Vibrant Gujarat Global Summit is being held from 10 to 12 January 2024 in Gandhinagar, Gujarat.
- Its theme is 'Gateway to the Future'.
- This Tenth Edition of the Summit will celebrate “20 Years of Vibrant Gujarat as the Summit of Success”.
- There are 34 Partner countries and 16 Partner organizations for this year’s Summit.
- Further, the Ministry of Development of North-Eastern Region will utilize the Vibrant Gujarat platform to showcase investment opportunities in the North-Eastern regions.
INS Beas to Be Upgraded (PIB)

- 16 Oct 2023
Why in the News?
The Ministry of Defence signed a contract on October 16, 2023, in New Delhi for the life Upgrade and Re-Powering of "INS Beas" with Kochi-based M/S Cochin Shipyard Limited (CSL) at an overall cost of Rs. 313.42 Cr.
Context:
- The INS Beas is gaining attention as the first Brahmaputra Class Frigate to undergo a transition from steam to diesel propulsion.
- The completion of its Mid-Life Upgrade and Re-Powering in 2026 is expected to result in the INS Beas joining the active fleet of the Indian Navy, equipped with a modernized weapon suite and upgraded combat capabilities.
About INS Beas:
- INS Beas (F37) stands as a Brahmaputra-class frigate within the Indian Navy, constructed at the Garden Reach Shipbuilders and Engineers (GRSE) in Kolkata.
- Commissioned on July 11, 2005, it is the second ship in the Indian Navy to carry this name, with the first being a Leopard-class frigate commissioned in 1960 and decommissioned in 1992.
- Role: Functioning as a versatile warship, INS Beas is proficient in various missions, encompassing anti-aircraft, anti-submarine, and anti-ship warfare.
- Additionally, it plays a crucial role in patrolling, surveillance, and safeguarding India's maritime interests.
- Features: The ship's design and construction are wholly Indian, derived from the modification of the Godavari-class frigate.
- With a displacement of about 3,850 tonnes, INS Beas boasts a length of 126 meters (413 feet) and a beam width of 14.5 meters (48 feet).
- Propulsion: Powered by 2 steam turbines, INS Beas demonstrates remarkable agility, capable of reaching speeds exceeding 30 knots during naval operations.
- Technology: Equipped with modern sensor suites and matching weapon systems, the ship embodies cutting-edge technology to enhance its operational capabilities.
