India’s Social Security coverage reaches 64.3% in 2025
- 13 Jun 2025
In News:
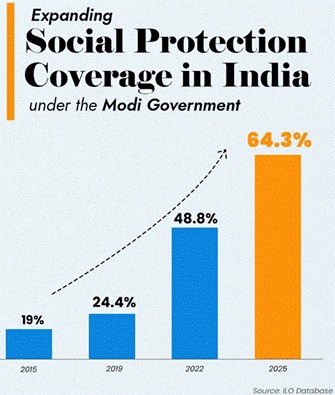
According to the latest data from the International Labour Organization’s (ILO) ILOSTAT database, India’s social security coverage has increased from 19% in 2015 to 64.3% in 2025, an unprecedented 45 percentage point surge over the past decade.
What is Social Security?
Social security (or social protection) refers to systems and policies that protect individuals and households from:
- Income loss (e.g. old age, unemployment, disability)
- High healthcare costs
- Social vulnerability (e.g. poverty, maternity, sickness)
It is built on three pillars:
- Social Assistance – Non-contributory support (e.g. food, housing)
- Social Insurance – Contributory programs (e.g. pensions, health insurance)
- Labour Market Programs – Employment schemes to build self-reliance
Key Highlights from ILOSTAT 2025
- India’s social security coverage jumped to 64.3%, up from 19% in 2015 – a 45 percentage point increase in 10 years.
- This means over 94 crore (940 million) people are now covered under at least one form of social protection.
- India now ranks 2nd globally in terms of population covered by social security.
- It is also the first country to update its 2025 social protection data in the ILOSTAT global database, showcasing its progress in digital governance and transparency.
Major Social Protection Initiatives Driving the Surge
India’s massive expansion in social coverage is due to a wide range of targeted schemes, including:
Pension & Insurance Schemes
- Atal Pension Yojana (APY): Pension of ?1,000–?5,000/month for informal workers aged 18–40.
- PM Shram Yogi Maan-Dhan Yojana (PM-SYM): Contributory pension for unorganized workers with 50% government support.
- PM Jeevan Jyoti Bima Yojana (PMJJBY): ?2 lakh life insurance for people aged 18–50.
- PM Suraksha Bima Yojana (PMSBY): Accident insurance of ?2 lakh for ages 18–70.
Healthcare & Nutrition
- Ayushman Bharat – PMJAY: ?5 lakh health cover for low-income families.
- Janani Suraksha Yojana: Maternity care for pregnant women.
- PM POSHAN (formerly Mid-Day Meal Scheme): Nutritional support to schoolchildren.
Income, Housing & Food Security
- MGNREGA: Guaranteed 100 days of wage employment annually in rural areas.
- PM Kisan Samman Nidhi: ?6,000/year income support to small and marginal farmers.
- Public Distribution System (PDS) under NFSA: Subsidized food grains to eligible households.
- PM Awaas Yojana – Gramin (PMAY-G): Pucca homes with basic amenities for rural poor.
Significance
- Poverty Reduction: Enhanced safety net for vulnerable populations.
- Inclusive Growth: Formal inclusion of informal sector workers.
- Digital Governance: Use of technology for efficient delivery (e.g., Aadhaar, DBT).
- Resilience Building: Helps households withstand economic shocks (e.g., pandemics, job loss).
