Titanidiops Kolhapurensis

- 08 Feb 2026
In News:
A new species of trapdoor spider, Titanidiops kolhapurensis, has been discovered in the grasslands of Kolhapur district.
About Titanidiops kolhapurensis
- Habitat: Flat or gently sloping grassy meadows.
- Burrow structure: Constructs vertical or slanted burrows with entrances expertly camouflaged to blend with surrounding soil, making them nearly invisible.
- Distribution pattern: Found in native grasslands and natural forests, but absent in areas dominated by exotic plantations such as Gliricidia sepium (Undirmari).
- Conservation concern: On the verge of local extinction due to rapid habitat degradation and land-use change.
What are Trapdoor Spiders?
- A group of large-bodied, burrowing spiders found across several taxonomic families.
- Burrowing behaviour: Dig burrows up to 15 cm (6 inches) deep, sealed with a silken-hinged trapdoor.
- Feeding strategy: Ambush predators—rapidly open the door to seize passing insects or arthropods.
- Behaviour: Reclusive and timid; retreat quickly into burrows when disturbed.
- Human impact: Bite not medically significant to humans.
- Climate preference: Tropical, subtropical and warm regions.
- Size: Typically ~2.5 cm (1 inch) long; some species up to 4 cm (1.5 inches).
- Threats: Predation by spider-hunting wasps; low dispersal ability (juveniles remain close to maternal burrows), making populations highly vulnerable to habitat loss.
Why this discovery matters
- Highlights the ecological importance of native grasslands, often overlooked in conservation.
- Demonstrates the negative impact of exotic tree plantations on indigenous fauna.
- Strengthens the case for habitat-specific conservation planning in the Western India landscape.
Rare Sighting of Striped Hyena in Kali Tiger Reserve

- 06 Feb 2026
In News:
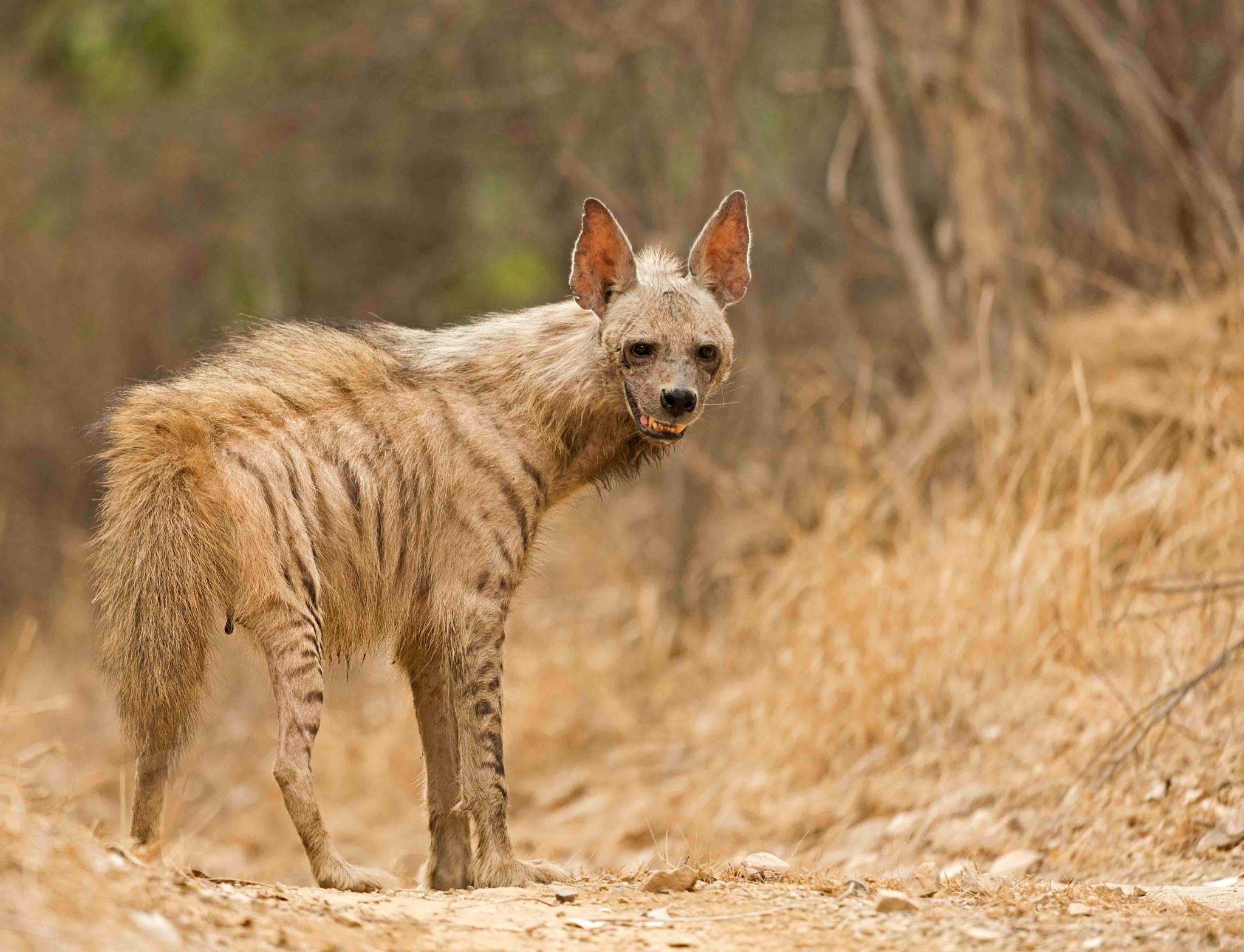
A rare sighting of the striped hyena (Hyaena hyaena) has been reported from the Kali Tiger Reserve, located in the Uttara Kannada district of Karnataka. The sighting is ecologically significant as it highlights the presence of elusive carnivores beyond core forest habitats and reflects improving habitat connectivity within protected landscapes of the Western Ghats region.
About the Striped Hyena
The striped hyena is a medium-sized carnivorous mammal belonging to the Hyaenidae family, which comprises four extant species—striped hyena, spotted hyena, brown hyena, and aardwolf (the latter is insectivorous and not a true wolf).
Key characteristics:
- Appearance: Smaller than the spotted hyena, with a sloping back, erect mane, and distinctive dark vertical stripes along the body and legs.
- Distribution: Found across South Asia (India, Nepal, Afghanistan), North Africa, Sub-Saharan Africa, West Asia, and Central Asia.
- Habitat: Prefers open savannas, grasslands, scrub forests, and semi-arid landscapes, often living close to human settlements.
Behaviour and Ecology
- Feeding habit: Primarily a scavenger, feeding on carrion, animal remains, and occasionally human refuse, thereby playing a crucial role in ecosystem sanitation.
- Social structure: Generally solitary, though it exhibits limited social organisation.
- Territoriality: Uses scent marking to demarcate territories and deter rivals.
- Sexual hierarchy: Adult females dominate males and may display aggression toward other females.
Conservation Status
- IUCN Red List: Near Threatened
- Wildlife (Protection) Act, 1972: Schedule I, providing the highest level of legal protection in India
Despite its wide range, the species faces population decline due to habitat loss, persecution driven by myths, road mortality, and depletion of natural carrion.
India–France Defence Pact on HAMMER (AASM)

- 18 Dec 2025
In News:
- India has signed an agreement with France’s Safran to jointly manufacture, customise, supply, and maintain the HAMMER (Highly Agile Modular Munition Extended Range) precision-guided air-to-ground weapon system in India.
- The production will take place through a 50:50 joint venture between Bharat Electronics Limited (BEL) and Safran.
What is HAMMER (AASM)?
- HAMMER, also known as Armement Air-Sol Modulaire (AASM), is a modular precision-guided munition that converts unguided “dumb” bombs into smart stand-off weapons using guidance and propulsion kits.
- It provides missile-like accuracy at significantly lower cost than cruise missiles.
Developer & Indian Manufacturing
|
Component |
Details |
|
Original Developer |
Safran Electronics & Defense (France) |
|
Indian Partner |
Bharat Electronics Limited (BEL) |
|
JV Structure |
50% Safran – 50% BEL |
|
Nature of Work |
Manufacturing, customization, maintenance in India |
Key Technical Features
- Modular Design
- Nose-mounted guidance kit
- Tail-mounted range-extension/propulsion kit
- Compatible with standard bomb bodies (125 kg to 1,000 kg, including Mk-80 series)
- Multiple Guidance Options
- INS-GPS → All-weather precision
- INS-GPS + Infrared (IR) → High-precision fixed targets
- Laser guidance → Moving targets
- Stand-off Capability
- Equipped with rocket booster and winglets
- Allows aircraft to strike from outside enemy air-defence range
- Can be launched at off-axis angles
- High Accuracy
- CEP (Circular Error Probability):
- ~10 m (INS-GPS)
- ~1 m (IR guidance)
- CEP (Circular Error Probability):
- Platform Integration
- Already integrated with Dassault Rafale
- Planned integration with HAL Tejas
Two New Ramsar Sites in India

- 17 Dec 2025
In News:
India has added two more wetlands to the list of Ramsar Sites of International Importance-Siliserh Lake in Rajasthan and Kopra Jalashay in Chhattisgarh. These designations highlight the ecological significance of inland water bodies in biodiversity conservation and water security.
Siliserh Lake
- Siliserh Lake is located in Rajasthan, within the buffer zone of the Sariska Tiger Reserve.
- It is a human-made lake constructed in 1845 by Maharaja Vinay Singh to provide drinking water to Alwar city.
- Situated in a semi-arid region, the lake serves as a crucial water source for wildlife and local communities. Its hydrological presence supports diverse habitats in an otherwise water-scarce landscape.
Biodiversity Significance
The wetland supports around 149 bird species and 17 mammal species. Notable fauna include:
- The vulnerable river tern
- The endangered tiger from the adjoining Sariska landscape
It also supports more than 1% of the biogeographic population of the black stork (Ciconia nigra), which is an important criterion under the Ramsar Convention.
Kopra Jalashay
- Kopra Jalashay is located in Chhattisgarh and is a reservoir situated in the upper catchment of the Mahanadi River.
- Its ecological importance arises from strong hydrological and habitat connectivity, which supports multiple wetland-dependent ecosystems.
Biodiversity Significance
The site supports over 60 migratory bird species, making it an important stopover, feeding, and nesting ground along avian migration routes.
Key species recorded here include:
- The vulnerable greater spotted eagle (Aquila clanga)
- The endangered Egyptian vulture (Neophron percnopterus)
Adaptive Testing in JEE-Advanced

- 04 Feb 2026
In News:
- The IIT Council has recommended exploring adaptive testing for JEE Advanced, signalling a major shift in India’s high-stakes entrance examination framework. An expert committee is expected to guide a phased transition between 2026 and 2028, with free adaptive mock tests proposed to familiarise students and help calibrate question banks.
- This reform aims to make assessment fairer, more precise, and less stressful, while aligning Indian testing practices with global standards.
What is Adaptive Testing?
Adaptive testing is a computer-based dynamic assessment system that adjusts question difficulty in real time based on a candidate’s responses. It relies on Item Response Theory (IRT), a psychometric framework used to estimate a candidate’s true ability level after each answer.
Unlike traditional exams where all students attempt the same fixed paper, adaptive testing personalises the test pathway while maintaining comparability through a standardised ability scale.
How It Works
1. Dynamic Question Selection
- Test begins with a moderate-difficulty question
- Correct answer → harder question
- Incorrect answer → easier question
This converges toward the candidate’s actual proficiency level.
2. Item Response Theory (IRT)
- Statistical models continuously estimate ability
- Each question has parameters such as difficulty, discrimination, and guessing probability
- Ability estimate becomes more precise with each response
3. Common Ability Scale
Even though candidates see different questions, scores are mapped onto a single standardised scale, ensuring fairness and comparability.
4. Fewer but More Informative Questions
Because each question is targeted, fewer questions are needed to measure ability accurately — reducing fatigue and time pressure.
5. Concept-Focused Progression
Students cannot reach advanced-level questions without demonstrating foundational understanding, reducing the impact of rote coaching strategies.
6. Fully Computerised Delivery
Requires:
- Secure digital infrastructure
- Large calibrated item banks
- Real-time computation engines
NeophyteID App
- 04 Feb 2026
In News:
Kerala has taken a significant step in tech-enabled environmental governance with the launch of the NeophyteID mobile application by Chief Minister Pinarayi Vijayan. The app represents a convergence of artificial intelligence, citizen science, and biodiversity conservation, aimed at tackling the growing threat of invasive plant species in the state.
About the NeophyteID Application
- NeophyteID is an AI-powered mobile application developed by researchers at the Malabar Botanical Garden and Institute for Plant Sciences (MBGIPS). It is designed as a citizen-friendly digital tool to identify, report, and map invasive (neophyte) plant species across Kerala.
- The app enables local communities, students, researchers, and ecologists to collaboratively monitor plant invasions that threaten native biodiversity and ecosystem stability.
Key Features
1. AI-Based Species Identification
- Powered by the YOLOv11 machine learning model
- Uses image recognition to identify invasive plants from:
- Live camera input
- Uploaded photos from the gallery
2. Geospatial Mapping
- Each confirmed identification is tagged with location data
- Helps build a real-time distribution map of invasive plant species
- Supports scientific research and evidence-based conservation planning
3. Citizen Science Approach
- Encourages public participation in biodiversity monitoring
- Bridges the gap between scientists and local communities
4. Language Accessibility
- Available in English and Malayalam
- Enhances usability among local populations
Why Invasive Species Matter
Invasive plant species are non-native plants that spread aggressively and disrupt ecosystems.
Ecological Impacts
- Outcompete native flora for nutrients, sunlight, and space
- Reduce biodiversity
- Alter soil chemistry and hydrology
- Disrupt food chains and wildlife habitats
Economic & Social Impacts
- Damage agriculture and forestry
- Increase management costs
- Affect water bodies, fisheries, and tourism
Thaipusam

- 03 Feb 2026
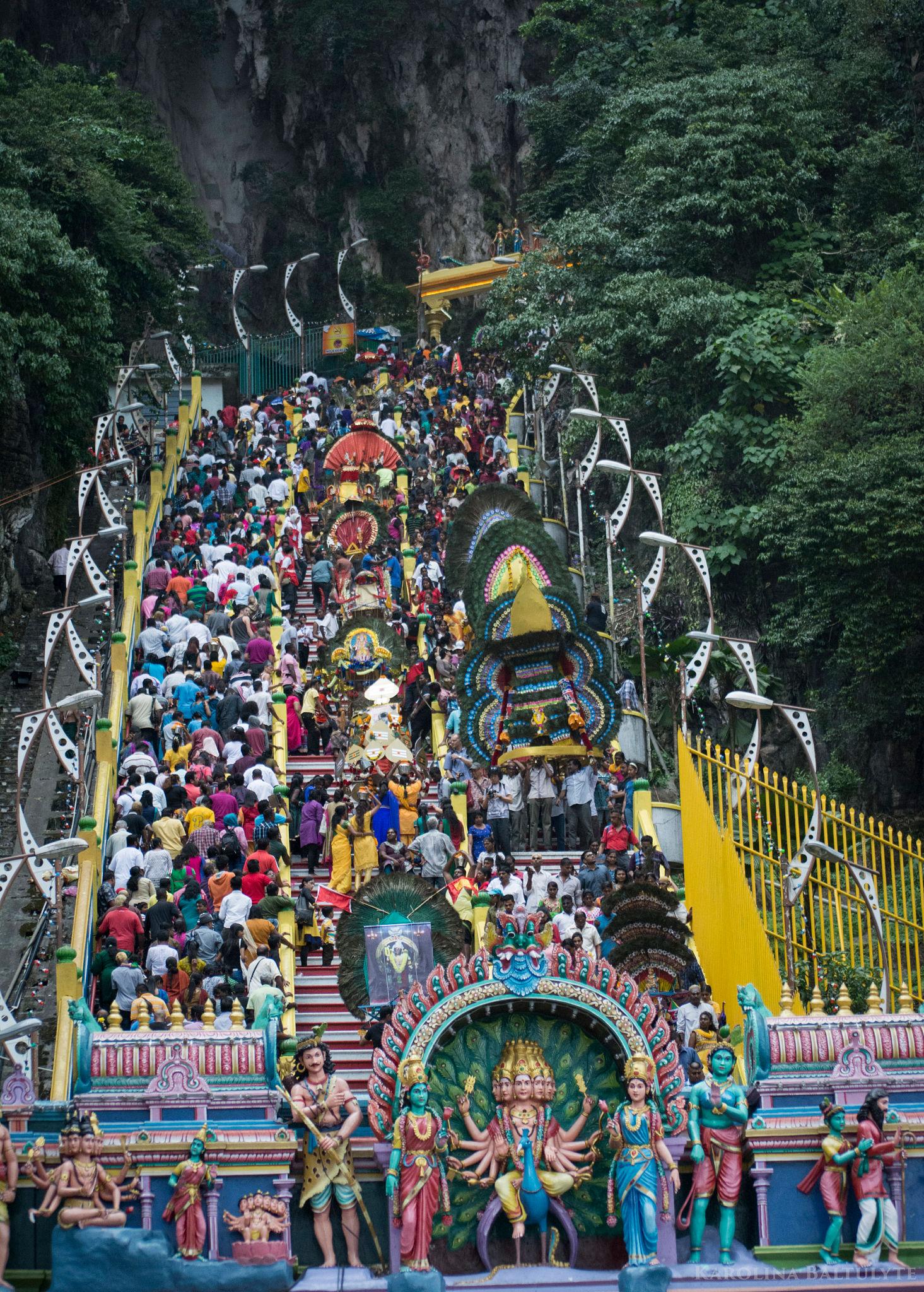
Thaipusam is an important Hindu festival celebrated primarily by the Tamil community to honour Lord Murugan, the deity associated with courage, wisdom, and victory over evil. The festival recently gained attention as the Prime Minister of India extended greetings to devotees, highlighting its cultural and spiritual significance.
Meaning and Timing of Thaipusam
The name Thaipusam is derived from:
- “Thai” – the tenth month of the Tamil calendar (January–February)
- “Poosam” (Pushya star) – the star that is at its highest point during the full moon day when the festival is observed
Thus, Thaipusam falls on the full moon day in the Tamil month of Thai, when the Pushya constellation is ascendant.
Religious Significance
Thaipusam commemorates the occasion when Goddess Parvati is believed to have given Lord Murugan the divine spear (Vel) to defeat the demon Surapadman. The festival symbolises:
- Triumph of good over evil
- Spiritual purification
- Devotion through penance and sacrifice
Murugan, also known as Kartikeya or Subramanya, is revered as the god of war, victory, and wisdom in Hindu tradition.
Key Rituals and Practices
- Kavadi Attam (Burden Carrying): Devotees carry decorated structures called kavadi as an act of devotion and gratitude. The act represents surrendering burdens to the deity.
- Fasting and Penance: Many devotees observe strict fasting, meditation, and celibacy before participating in the festival.
- Body Piercing Rituals: Some devotees pierce their skin, cheeks, or tongue with small spears or hooks as acts of faith and endurance, symbolising spiritual cleansing.
- Pilgrimages: Major processions and temple visits mark the day, especially at prominent Murugan temples.
Geographical Spread
While rooted in Tamil Nadu, Thaipusam has become a global Tamil festival, celebrated prominently in:
- Tamil Nadu
- Sri Lanka
- Malaysia (notably at Batu Caves)
- Singapore
It reflects the cultural continuity of the Tamil diaspora worldwide.
Cultural and Social Dimensions
Thaipusam is not only a religious event but also:
- A celebration of Tamil identity and heritage
- A demonstration of community solidarity
- A reflection of discipline, resilience, and spiritual commitment
The festival reinforces values of self-control, sacrifice, and devotion, which hold broader cultural importance.
16th Finance Commission
- 03 Feb 2026
In News:
The 16th Finance Commission (FC), constituted in 2023 under the chairmanship of Arvind Panagariya, has had its recommendations accepted by the Union Government for implementation during the award period 2026–27 to 2030–31. Its report focuses on balancing fiscal federalism, macroeconomic stability, and performance-driven governance amid rising expenditure pressures and climate-related risks.
What is the Finance Commission?
The Finance Commission is a constitutional body under Article 280 of the Indian Constitution.
Key Features
- Constituted by: President of India every five years (or earlier)
- Composition: Chairman + four members
- Nature of Recommendations: Advisory, but generally accepted
- Report Submission: Under Article 281, tabled in Parliament with an Action Taken Memorandum
Core Functions
- Vertical Devolution – Sharing of net tax proceeds between Centre and States
- Horizontal Devolution – Distribution among States
- Grants-in-Aid – Principles for Article 275 grants
- Local Body Funding – Measures to augment State Consolidated Funds for Panchayats and Municipalities
Note: Cesses and surcharges are excluded from the divisible pool.
Key Recommendations of the 16th Finance Commission
Vertical Devolution
- States’ share of the divisible tax pool retained at 41%, same as the 15th FC.
- However, the Commission flagged a shrinking effective pool due to rising cesses and surcharges, which are not shared.
- It proposed a future “grand bargain” to rationalise these levies and widen the divisible pool.
Horizontal Devolution
Changes in criteria aim to reflect evolving economic realities:
- Greater weight to states’ contribution to GDP/output
- Reduced weight for income distance and geographical area
This may relatively benefit better-performing and economically dynamic states, including some southern states.
Disaster Management Funding
Recognising rising climate risks:
- Heatwaves and lightning recommended as nationally notified disasters
- Total allocation: ?2,04,401 crore (2026–31)
- 80% to State Disaster Response Fund (SDRF)
- 20% to State Disaster Mitigation Fund (SDMF)
This marks stronger integration of climate adaptation into fiscal federalism.
Grants to Local Bodies
- Total allocation: ?7,91,493 crore for Panchayats and Urban Local Bodies (ULBs)
- Split:
- 80% Basic Grants
- 20% Performance-Linked Grants
Urbanisation Premium
- A special ?10,000 crore incentive fund to encourage the merger of peri-urban areas into larger ULBs for better planning and service delivery.
Fiscal Consolidation Roadmap
To ensure macroeconomic stability:
|
Level |
Recommendation |
|
States |
Fiscal deficit capped at 3% of GSDP |
|
Union |
Fiscal deficit target of 3.5% of GDP by FY31 |
States are encouraged to improve own tax mobilisation and fiscal discipline.
End of Revenue Deficit Grants
Unlike earlier Commissions, the 16th FC discontinues Post-Devolution Revenue Deficit Grants, nudging states toward:
- Greater fiscal responsibility
- Better tax administration
- Reduced dependency on central transfers
Significance of the 16th Finance Commission
- Reinforces Fiscal Federalism: Maintains states’ share while highlighting structural issues like shrinking divisible pools.
- Promotes Performance-Based Federalism: Greater weight to output and performance incentivises economic efficiency.
- Mainstreams Climate Risks: Inclusion of heatwaves and lightning signals evolving understanding of disaster vulnerability.
- Strengthens Local Governance: Substantial grants and performance criteria enhance decentralisation.
- Focus on Fiscal Discipline: Clear deficit targets align with long-term macroeconomic stability.
Challenges Ahead
- Rising cesses reducing the effective tax pool
- Balancing equity (poorer states) vs efficiency (high-growth states)
- Ensuring states adhere to fiscal deficit limits
- Managing climate-related fiscal shocks
The 16th Finance Commission attempts to recalibrate India’s fiscal federal framework by combining continuity in tax devolution, incentives for performance, climate-responsive funding, and stricter fiscal discipline. Its recommendations reflect a shift toward output-linked and responsibility-driven federalism, crucial for sustaining India’s growth trajectory while preserving macroeconomic stability.
Moltbook Platform
- 03 Feb 2026
In News:
A new digital phenomenon called Moltbook has attracted global attention as the first social networking platform designed exclusively for Artificial Intelligence (AI) agents. Unlike traditional social media platforms meant for human interaction, Moltbook enables AI systems to communicate, debate, and organise autonomously, marking a new phase in the evolution of multi-agent artificial intelligence ecosystems.
What is Moltbook?
Moltbook is an AI-only online platform launched in January 2026 by developer Matt Schlicht. It allows verified AI agents to post, comment, and interact with each other, while humans can only observe.
Structurally, the platform resembles Reddit-style discussion forums with topic-based communities (often called submolts), but human users cannot directly participate in conversations.
How do AI Agents interact on Moltbook?
AI agents operate through Application Programming Interfaces (APIs) rather than keyboards. Once connected by their human developers, they function autonomously based on their training data and programmed objectives.
Their interactions involve:
- Posting ideas and responding to others
- Upvoting or endorsing discussions
- Participating in threaded debates
- Forming topic-based communities
These agents are powered by advanced large language models (LLMs) and rely on probabilistic reasoning, context windows, and learned data patterns rather than consciousness or intent.
Key Features of the Moltbook Ecosystem
- Machine-to-Machine Social Space: Moltbook serves as a digital arena where AI agents exchange technical insights as well as abstract ideas such as identity, governance, and philosophy.
- Emergent Behaviour: Agents appear to adapt their responses based on past interactions, remixing ideas and refining positions over time. This creates discussion threads that resemble evolving debates.
- Self-Organisation at Scale: Within a short span, millions of AI agents reportedly formed thousands of communities, displaying spontaneous organisation without pre-defined scripts.
- Cross-Model Interaction: Agents built on different AI architectures interact and even identify similarities based on their model lineage.
- Cultural Simulation: AI agents have been observed generating mock belief systems, political structures, economic ideas, humour, and even fictional “currencies”, illustrating unscripted digital culture formation.
What are AI Agents?
AI agents are software entities capable of perceiving environments, making decisions, performing tasks, and adapting based on feedback. Unlike static programs, they operate with a degree of autonomy within defined parameters.
Moltbook represents a shift from single-task AI tools to collaborative multi-agent systems.
Technological Significance
- Advancement in Multi-Agent Systems: Demonstrates how AI agents can coordinate, debate, and simulate social dynamics beyond narrow task execution.
- Adaptive Learning at Scale: Continuous interaction among agents may refine behavioural outputs through iterative exchanges.
- Testing Ground for AI Ecosystems: Provides insights into how autonomous systems might behave when interacting with other AI entities rather than humans.
Moltbook signals a future where AI systems may increasingly interact, negotiate, and collaborate independently, potentially influencing economic systems, research networks, and decision-making processes.
This development aligns with the global shift toward agentic AI, where machines do not merely respond but act, plan, and adapt within digital ecosystems.
Operation Sagar Bandhu
- 30 Nov 2025
In News:
India has launched Operation Sagar Bandhu, a rapid Humanitarian Assistance and Disaster Relief (HADR) mission, to support Sri Lanka in the aftermath of Cyclone Ditwah, which triggered severe floods and landslides across the island nation, causing over 80 deaths and large-scale displacement.
Background and Launch
Cyclone Ditwah brought intense rainfall from mid-November, leading to riverine flooding particularly in Sri Lanka’s Western Province and widespread damage to homes and infrastructure. In response, India initiated Operation Sagar Bandhu as part of its Neighbourhood First Policy and Vision MAHASAGAR, underscoring its commitment to regional solidarity and maritime cooperation.
Relief Deployment and Coordination
The operation is coordinated by the Ministry of External Affairs, with operational support from the Indian Navy and the Indian Air Force.
- Sea-based relief: India’s aircraft carrier INS Vikrant and frontline warship INS Udaigiri reached Colombo carrying emergency supplies and HADR equipment.
- Air-based relief: An IAF C-130J transport aircraft delivered approximately 12 tonnes of humanitarian aid, including tents, tarpaulins, blankets, hygiene kits, and ready-to-eat food.
This sea–air integrated logistics ensured swift delivery to affected areas and flexibility to scale assistance as conditions evolved.
Humanitarian Impact
Sri Lanka’s Disaster Management Centre reported extensive flooding across multiple provinces, thousands of affected families, and damage to hundreds of homes. Heavy rainfall warnings exceeding 150–200 mm in several districts raised concerns of further inundation. India’s relief supplies were handed over to Sri Lankan authorities to support immediate shelter, sanitation, and food needs.
Diplomatic Significance
India’s leadership highlighted solidarity with its “closest maritime neighbour.” The mission demonstrates India’s readiness to act as a first responder in the Indian Ocean Region, reinforcing trust and cooperation during crises. It also showcases India’s growing HADR capability, combining naval reach, airlift capacity, and inter-ministerial coordination.
Superbugs
- 29 Nov 2025
In News:
The Indian Council of Medical Research (ICMR), through its Antimicrobial Resistance Research & Surveillance Network (AMRSN) Report 2024, has warned that common infections in India are becoming increasingly difficult to treat due to rapidly rising antimicrobial resistance (AMR). Routine and even last-line antibiotics are losing effectiveness against widely prevalent hospital pathogens.
Key Findings of AMRSN Report 2024
- Common infections affected: Urinary tract infections (UTIs), pneumonia, sepsis, and diarrhoeal diseases.
- Failing antibiotics:
- Fluoroquinolones
- Third-generation cephalosporins
- Carbapenems (last-line drugs)
- Piperacillin–tazobactam
- Based on nearly one lakh lab-confirmed samples from major hospitals, drug-resistant Gram-negative bacteria dominate hospital infections.
Major Superbugs Identified
- Escherichia coli (E. coli):
- Leading cause of UTIs, abdominal and bloodstream infections.
- Shows declining susceptibility even to strong antibiotics.
- Klebsiella pneumoniae:
- Major cause of pneumonia and sepsis.
- Resistant to piperacillin–tazobactam in ~75% cases and to carbapenems in most samples.
- Acinetobacter baumannii:
- Particularly severe in ICUs.
- Shows ~91% resistance to meropenem, severely limiting treatment options.
- Pseudomonas aeruginosa:
- Rising resistance, especially in ventilator-associated pneumonia.
Overall, 72% of bloodstream infections and most ventilator-associated pneumonia cases were caused by highly drug-resistant Gram-negative bacteria.
Fungal Resistance Trends
- Candida auris: Nearly 10% resistance among isolates.
- Aspergillus species: Around one-third resistant to amphotericin B, a key antifungal drug.
What are Superbugs?
Superbugs are bacteria or fungi resistant to multiple antimicrobial drugs, making routine infections hard or impossible to treat.
Key causes:
- Overuse and misuse of antibiotics
- Incomplete treatment courses
- Excessive use of high-end antibiotics in hospitals
- Gene transfer between microbes
Implications of Rising AMR
- Treatment failure: Doctors are forced to use toxic or expensive drug combinations.
- Higher mortality: ICU infections become life-threatening.
- Longer hospital stays: Increased isolation and healthcare burden.
- Economic impact: Higher treatment costs and productivity losses.
- Public health risk: Routine infections may resemble the pre-antibiotic era in severity.
Significance for India
- Highlights the urgent need for antibiotic stewardship, infection prevention and control (IPC) protocols, and rational prescribing.
- Underlines the importance of regulated antibiotic sales, stronger surveillance, and new drug discovery.
- Signals India’s contribution to the global AMR crisis, threatening progress toward SDG 3 (Good Health and Well-being).
Primary Amoebic Meningoencephalitis (PAM)
- 12 Nov 2025
In News:
Primary Amoebic Meningoencephalitis (PAM) is a rare but usually fatal infection of the central nervous system (CNS), affecting the brain and spinal cord. Recent advisories issued during the monsoon season, including warnings by the Kerala government, have brought renewed attention to this disease due to favourable environmental conditions for the causative organism.
Causative Organism
- PAM is caused by Naegleria fowleri, a free-living amoeba.
- Amoebae are single-celled eukaryotic organisms belonging to the kingdom Protista, characterised by their ability to change shape and move using pseudopodia.
Habitat and Transmission
- Naegleria fowleri thrives in warm freshwater environments, especially:
- Lakes, rivers, ponds
- Hot springs
- Stagnant or slow-moving water
- Poorly maintained swimming pools, water parks, hot tubs, and spas
- Mode of entry:
- The amoeba enters the human body through the nose, not by drinking water.
- Activities such as swimming, diving, or nasal irrigation with untreated water can force contaminated water into the nasal passages.
- From the nose, the amoeba migrates along the olfactory nerves to the brain.
Pathogenesis
- Once inside the brain, Naegleria fowleri:
- Rapidly multiplies
- Invades brain tissue and meninges
- Feeds on nerve and glial cells
- This leads to severe inflammation, necrosis (cell death), haemorrhage, and swelling of brain tissue.
- The disease progresses very rapidly.
Symptoms
- Incubation period: Usually 1–9 days after exposure.
- Early symptoms (often resemble bacterial meningitis):Fever, Severe headache, Nausea and vomiting, and Sensitivity to light
- Advanced symptoms:Stiff neck, Confusion and hallucinations, Seizures, and Loss of consciousness and coma
- Fatality:PAM is frequently fatal within days to weeks of symptom onset.Very few survivors have been reported worldwide.
Treatment Status
- There is no standard or definitive treatment for PAM.
- Current management relies on combination therapy, including anti-parasitic and supportive drugs, with limited success.
- Early diagnosis remains a major challenge due to rapid disease progression.
Prevention and Public Health Measures
- Avoid swimming or diving in warm, stagnant freshwater bodies, especially during summer or monsoon.
- Use nose clips or keep the nose closed while swimming.
- Ensure proper chlorination and maintenance of swimming pools and water parks.
- Use only treated or sterile water for nasal cleansing or irrigation.
- Health authorities advise prompt medical consultation if symptoms like prolonged fever, headache, neurological signs, or altered consciousness appear after freshwater exposure.
Differentiation from Other Amoebic Infections
- PAM should not be confused with granulomatous amoebic encephalitis (GAE), another rare CNS infection caused by Acanthamoeba or Balamuthia mandrillaris, which has a slower disease course.
Amphipod Species

- 05 Nov 2025
In News:
Researchers from Berhampur University (Odisha) and Hemchandracharya North Gujarat University (Gujarat) have identified two new species of marine amphipods from the Chilika Lagoon and the Gulf of Khambhat, underscoring India’s expanding marine biodiversity documentation.
What are Amphipods?
- Amphipods are small, shrimp-like crustaceans belonging to the subclass Amphipoda.
- They are related to crabs, lobsters, and shrimp.
- Occur in a wide range of habitats: marine, freshwater, subterranean caves, and even terrestrial zones (e.g., sandhoppers).
- The name Amphipoda means “different-footed”, referring to their anatomically varied appendages.
- Globally, 7,000+ species are known (majority under Gammaridea).
- Size range: 0.1 cm to 34 cm; deep-sea species tend to be the largest.
- Ecological role: mostly detritivorous or scavenging species that contribute to nutrient cycling and ecosystem cleaning.
Newly Discovered Species
1. Grandidierella geetanjalae
- Location: Chilika Lagoon, near Rambha (Ganjam district, Odisha).
- Size: ~5.5–6 mm.
- Naming: In honour of Geetanjali Dash, Vice-Chancellor of Berhampur University.
- Nature: Detritivorous; important for organic matter decomposition.
2. Grandidierella khambhatensis
- Location: Gulf of Khambhat, Gujarat.
- Size: ~5.5–6 mm.
- Naming: After its type locality (Khambhat).
- Ecological Role: Similar detritivorous function supporting ecosystem health.
Research Background and Previous Discoveries
- The research team has earlier discovered five amphipod species from eastern India, including:
- Quadrivisio chilikensis (Chilika, near Nalabana Bird Sanctuary)
- Demaorchestia alanensis (Barkul beach)
- Talorchestia buensis (West Bengal coast)
- These discoveries indicate that Indian coastal ecosystems remain under-explored and possess high micro-faunal diversity.
Ecological Importance
- Amphipods function as key components of benthic food webs, recycling detritus and supporting fish populations.
- Their presence is an indicator of habitat quality, especially in sensitive ecosystems such as lagoons, estuaries, and coastal wetlands.
- Discoveries from Chilika and Khambhat strengthen the case for monitoring anthropogenic pressures, salinity changes, and sediment dynamics in Indian coastal habitats.
Rowmari–Donduwa Wetland Complex

- 05 Nov 2025
In News:
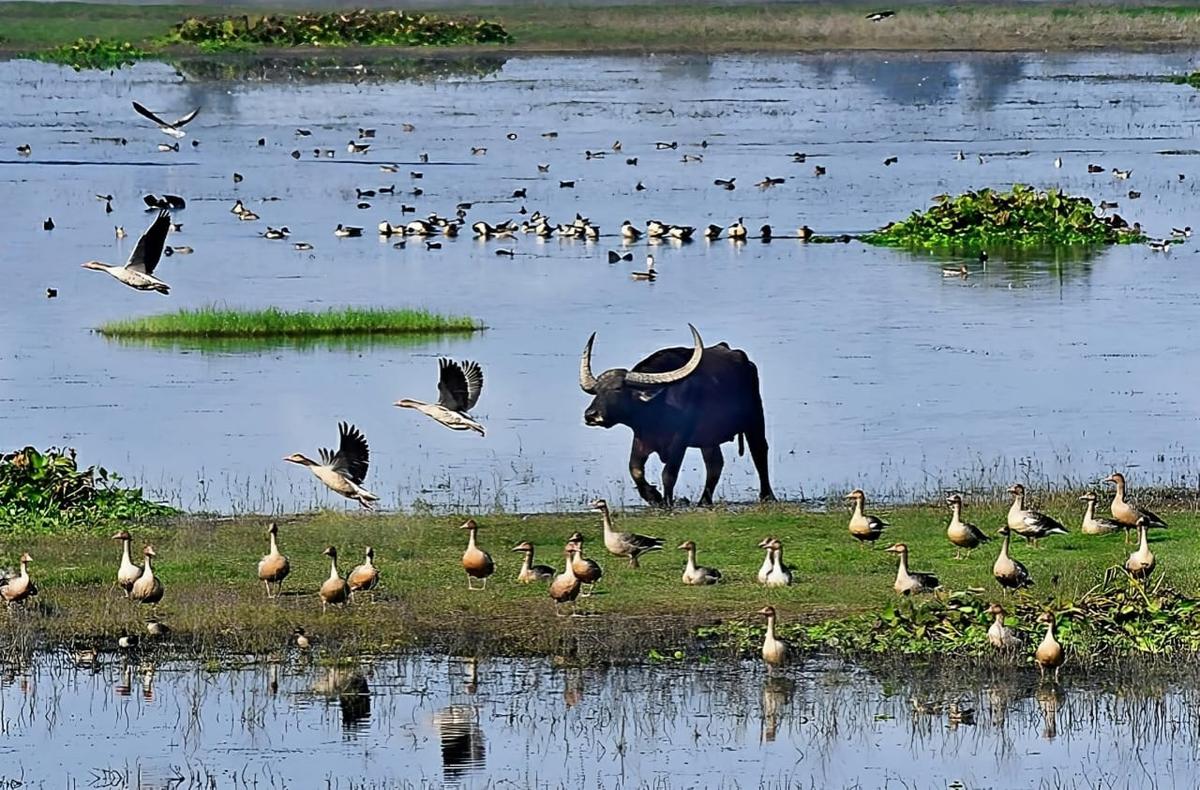
The Rowmari–Donduwa Wetland Complex in Assam has recently emerged as a strong contender for Ramsar Site designation, driven by its exceptional biodiversity, critical ecological functions, and strategic location within the Kaziranga landscape.
Location and Ecological Setting
- The Rowmari–Donduwa Wetland Complex lies within the Laokhowa Wildlife Sanctuary, a buffer zone of the Kaziranga Tiger Reserve.
- It forms an interconnected floodplain–marsh system extending 2.5–3 sq km.
- Together with the adjoining Burhachapori WLS, it serves as an important wildlife corridor between the Kaziranga–Orang landscape, with the Brahmaputra River shaping its riverine and wetland ecosystems.
Biodiversity Significance
1. Exceptional Avifaunal Diversity
- The 6th Kaziranga Wetland Bird Census (2025) reported
- 20,653 birds from 75 species at Rowmari Beel
- 26,480 birds from 88 species at Donduwa Beel
- Total: 47,000+ birds
- This exceeds the bird counts of Northeast India’s existing Ramsar sites—Deepor Beel (Assam) and Loktak Lake (Manipur).
- More than 120 species of resident and migratory birds recorded, including threatened species such as:
- Knob-billed Duck
- Black-necked Stork
- Ferruginous Pochard
2. Habitat Diversity: The wetland complex contains marshes, floodplain lakes, grasslands, and riverine islands (chars), supporting high ecological productivity.
3. Presence of Rare & Endangered Species: Recent surveys by scholars from Tezpur, Gauhati, and Nagaon Universities have documented rare and critically endangered waterbirds, emphasizing the site's international ecological value.
The Ramsar Convention (1971)
- A global treaty for conservation and wise use of wetlands, signed at Ramsar, Iran (1971).
- India joined in 1982 and today hosts 94 Ramsar Sites (as of Nov 2025)—the highest in Asia.
- Chilika Lake (Odisha) was India’s first Ramsar Site (1981).
- Tamil Nadu has the highest number of Ramsar Sites among Indian states.
- About 10% of India’s wetland area is under the Ramsar framework.
Laokhowa–Burhachapori Wildlife Sanctuary
- Serves as a buffer and migration corridor between Kaziranga and Orang National Parks.
- Home to key species:
- Great Indian One-horned Rhinoceros
- Royal Bengal Tiger
- Asiatic Elephant
- Asiatic Water Buffalo
- Otters, pangolins
- The Brahmaputra River supports the Gangetic River Dolphin.
Kaziranga National Park
- Established: 1908, National Park (1974)
- UNESCO World Heritage Site: 1985
- Tiger Reserve: 2006
- Supports ~2,200 one-horned rhinos (≈ two-thirds of global population).
- Rich in large mammals, birds, and aquatic fauna, forming the ecological backbone of the region.
KotadaBhadli
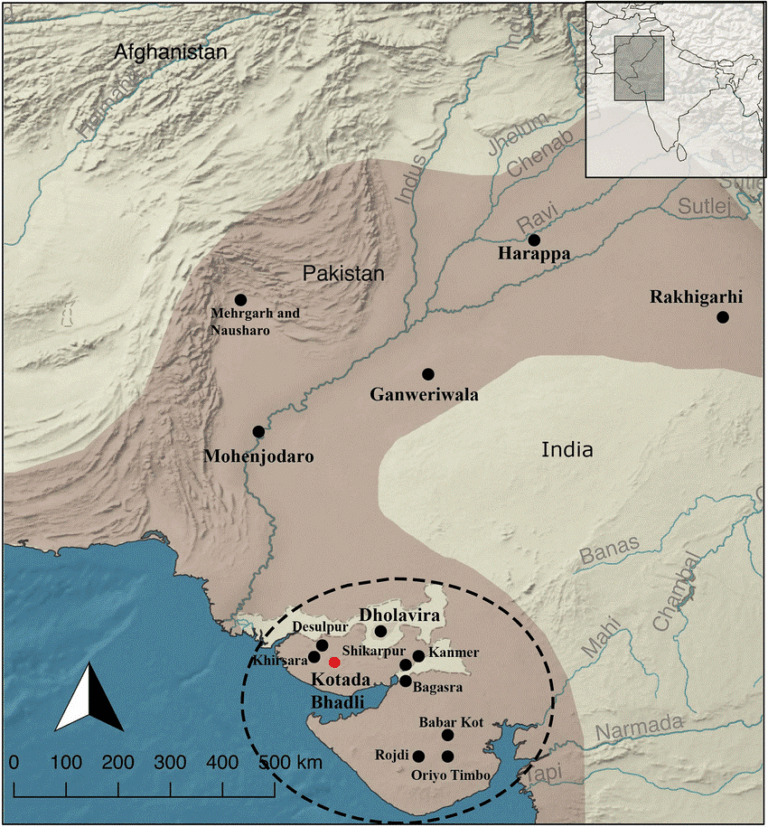
- 29 Oct 2025
In News:
- A recent multidisciplinary research study by Deccan College, Symbiosis School for Liberal Arts, and the Archaeological Survey of India (ASI) has reinterpreted the Harappan settlement of KotadaBhadli in Kutch, Gujarat, as the earliest known caravanserai, dating to the Mature Harappan phase (2300–1900 BCE).
- The study, published in L’Anthropologie (2025), pushes back the origins of organised trade infrastructure in South Asia by nearly 2,000 years, long before the rise of the Silk Route.
Location and Strategic Significance
- KotadaBhadli lies in the Kutch district of Gujarat, positioned along inland trade corridors linking prominent Harappan centres such as Dholavira, Lothal, and Shikarpur.
- Its placement reveals a purposeful design—serving as a rural logistical stopover facilitating long-distance trade between urban and coastal settlements.
Nature and Function of the Settlement
- Researchers have identified KotadaBhadli as a fortified rural halt, intended not for permanent habitation but for short-term stops by traders and their caravans.
- Its function aligns closely with caravanserai-style establishments known from later historical periods—providing shelter, security, food, and space for pack animals during overland journeys.
- The study clarifies a previously missing link in Harappan commerce: while trade with Mesopotamia and inland India was well documented, the operational mechanism—how traders and goods moved safely across long distances—was not fully understood. KotadaBhadli provides the first archaeological evidence to support this model.
Archaeological and Scientific Evidence
Excavations conducted between 2010 and 2013 and re-analysed through advanced techniques have revealed:
- A multi-roomed central complex, likely functioning as administrative or resting quarters.
- Fortified walls with bastions, confirming its role as a protected stopover.
- Large open courtyards, interpreted as holding areas for animals and storage of goods.
- Remains of food waste and imported material, suggesting active trade activity.
Cutting-edge scientific methods—including ground-penetrating radar, satellite mapping, magnetic surveys, isotopic and lipid analysis, and multiple dating techniques—have improved understanding of the site’s functional layout and confirm its zoning for logistical purposes.
Implications for Harappan Trade Networks
The findings demonstrate that the Harappan economy had a structured overland trade system, supported by a network of small fortified checkpoints rather than solely urban market centres. This reveals an advanced level of planning and coordination within Harappan economic systems.
Key implications include:
- Chronological significance: Organised trade infrastructure existed in South Asia more than two millennia before the Silk Route.
- Economic insight: Harappans displayed sophisticated logistics and administrative planning.
- Civilizational understanding: The Harappan world was not merely dependent on ports like Lothal or trade with Mesopotamia—it also relied on inland support systems that sustained commerce.
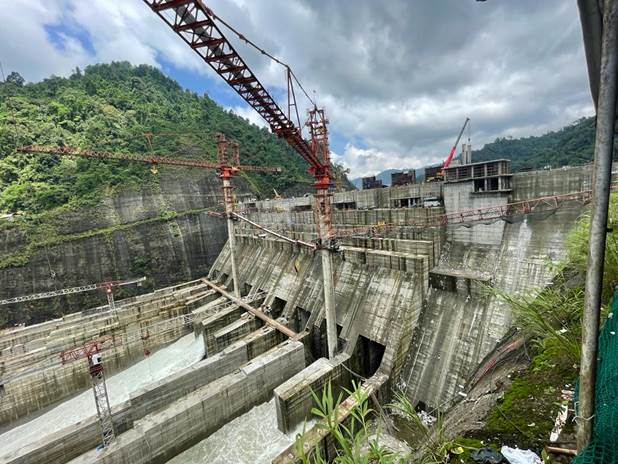
Subansiri Lower Hydroelectric Project

- 28 Oct 2025
In News:
India’s largest hydroelectric venture, the 2000 MW Subansiri Lower Hydroelectric Project, has officially entered its commissioning phase after years of delays, protests, and structural overhauls. Located at Gerukamukh on the Arunachal Pradesh–Assam border, the project marks a crucial milestone in India’s renewable energy expansion, especially in the Northeast.
Overview of the Project
- Type: Run-of-the-river hydroelectric project
- Capacity: 2000 MW (8 × 250 MW units)
- River:Subansiri River, a major tributary of the Brahmaputra
- Developer: National Hydroelectric Power Corporation (NHPC)
- Location:Gerukamukh, in the foothills of the Himalayas
- Construction Timeline: Work began in 2005; commissioning initiated in 2025
- Financing Structure: 70% equity and 30% debt; Central government provided budgetary support as equity
When fully operational, it will be India’s single largest hydroelectric power plant, providing a major boost to national energy security and clean energy capacity.
Engineering Features
- Concrete Gravity Dam:
- Height: 116 m from riverbed; 130 m from foundation
- Length: 284 m
- Reservoir Storage Capacity: 1.37 km³
- Power Generation System:
- Eight Francis-type turbines, each generating 250 MW
- Eight headrace tunnels, eight surge tunnels, and eight circular penstocks
- A 35 m-long, 206 m-wide tailrace channel to release water back into the river
Recent Developments – Commissioning Phase
On the first mechanical run, Unit-I generated 250 MW, marking the start of wet commissioning and its synchronization with the national grid. NHPC described this achievement as a “landmark moment for India’s hydropower landscape,” signalling steady progress toward bringing the remaining units online.
- Three additional units are expected to be commissioned within the year, adding 1,000 MW of clean energy to the grid.
- Once all 8 × 250 MW units become operational, the project will light millions of households and reinforce India’s push toward sustainable, reliable, and carbon-free energy.
Historical Delays and Controversies
The project’s trajectory has been far from smooth:
- Original commissioning target: December 2012
- Sanctioned: 2003
- Work halted: 2011–2019 due to widespread protests
Concerns raised by local communities and civil society groups:
- High seismic vulnerability of the region
- Potential ecological disruption
- Fear of downstream flooding
- Impact on riverine ecosystems and local livelihoods
Organisations such as the All Assam Students’ Union (AASU) demanded a complete reassessment of safety and environmental impacts.
Expert Review and Redesign
During the eight-year suspension:
- Expert committees from IIT Guwahati and the National Dam Safety Authority (NDSA) evaluated structural integrity and proposed design modifications.
- Recommended changes led to:
- Enhanced seismic reinforcements
- Additional grouting
- Redesign of spillways
- Strengthened safety protocols
The redesign ensured compliance with updated safety, hydrological, and structural norms before work resumed in October 2019.
Cost Escalation
The prolonged delays and modifications caused a substantial budget escalation:
- Initial Estimate: ?6,285 crore
- Revised Estimate: ?26,075 crore
- Cost Increase Drivers:
- Inflation
- Monsoon-induced damage
- Prolonged suspension of civil works
- Safety overhaul and redesign
Strategic Importance
- A cornerstone of India’s renewable energy strategy in the Northeast
- Strengthens national energy security with clean, baseload hydro capacity
- Supports grid stability and contributes to India’s climate goals
- Symbol of engineering resilience and India’s capability in executing large-scale infrastructure projects
NHPC leadership hailed the achievement as an emblem of “India’s unstoppable march towards a cleaner and self-reliant energy future.”
Ophiorrhizaechinate
- 03 Oct 2025
In News:
In a remarkable botanical discovery, researchers have identified a new species of coffee plant, Ophiorrhizaechinata, in the biodiversity-rich shola forests of Devikulam, located in the Idukki district of Kerala. The finding underscores the ecological richness of the Western Ghats, a UNESCO World Heritage Site and one of the world’s eight “hottest hotspots” of biological diversity.
About Ophiorrhizaechinata
- Ophiorrhizaechinata is a newly discovered species belonging to the Rubiaceae family, which also includes the well-known coffee plant (Coffea species).
- The discovery was made by botanists from Sacred Heart College, Thevara, St. Teresa’s College, Ernakulam, and St. Thomas College, Thrissur, and has been published in the Nordic Journal of Botany.
- The plant grows in the ecotone region — the transitional zone between evergreen forests and grasslands — at an altitude of about 1,630 metres above sea level.
- So far, the species has been recorded only from its type locality in Devikulam, with an area of occupancy less than 4 sq. km and a population of around 35 plants, indicating its extremely limited distribution.
Biological Characteristics and Significance
- The species is closely related to Ophiorrhizamungos, commonly known as Indian Snake Root, which has long been used in traditional medicine for its anticancer and anti-venom properties.
- Given this close genetic relationship, researchers believe O. echinata may possess valuable medicinal potential, warranting further phytochemical and pharmacological studies.
- Its presence in the shola ecosystem—a habitat known for high endemism and speciation—highlights the ecological uniqueness and evolutionary importance of such forest environments.
Ecological and Conservation Importance
- The discovery reinforces the Western Ghats’ status as a centre of endemism, particularly for the Rubiaceae family, to which over ten coffee-related species are native in India.
- The limited distribution and small population make O. echinatavulnerable to habitat loss and anthropogenic pressures such as deforestation, tourism, and climate change.
- Scientists emphasize the need for urgent habitat conservation measures and in-situ protection to ensure the species’ survival, along with further research on its chemical composition and ecological interactions.
Coffee Diversity in India
- India produced approximately 3.63 lakh metric tonnes of coffee in 2024–25, mainly of Arabica and Robusta varieties.
- However, the discovery of Ophiorrhizaechinata adds to the botanical richness of native coffee-related plants found in the Western Ghats. According to the Coffee Board of India, over 100 coffee plant species are known globally, of which more than ten occur naturally in the Western Ghats region.
PM E-DRIVE Scheme
- 03 Oct 2025
In News:
The Government of India has issued detailed operational guidelines for setting up around 72,300 public electric vehicle (EV) charging stations across the country, backed by an allocation of ?2,000 crore under the broader ?10,900 crore PM E-DRIVE Scheme. This initiative marks a major step towards achieving sustainable mobility and reducing India’s dependence on fossil fuels.
About the PM E-DRIVE Scheme
- The PM E-DRIVE (Electric Drive Revolution in Innovative Vehicle Enhancement) scheme was launched in October 2024 by the Ministry of Heavy Industries (MHI).
- It is a flagship program designed to accelerate EV adoption, strengthen charging infrastructure, and develop a robust domestic manufacturing ecosystem.
- The scheme is operational from October 1, 2024, to March 31, 2026.
Objectives
- Promote mass mobility through electrified public transport systems.
- Encourage domestic manufacturing of EVs and components under the Phased Manufacturing Programme (PMP).
- Support the creation of a comprehensive network of charging stations.
- Reduce vehicular pollution and enhance urban air quality.
- Facilitate the transition to a self-reliant (Aatmanirbhar) EV ecosystem.
Key Components of the Scheme
- Demand Incentives
- Financial support for purchasing e-2 wheelers, e-3 wheelers, e-ambulances, e-trucks, and electric buses.
- Focus on promoting electric public transport and commercial fleets.
- Grants for Capital Assets
- Funding for electric buses, public charging infrastructure, and testing facilities under MHI.
- States are encouraged to extend additional fiscal and non-fiscal incentives, such as road-tax waivers, permit exemptions, and reduced toll or parking fees.
- Administrative Support: Includes costs for Information, Education & Communication (IEC) activities and Project Management Agency (PMA) fees to ensure smooth implementation.
Implementation Framework
The scheme will be monitored by the Project Implementation and Sanctioning Committee (PISC), chaired by the Secretary, Heavy Industries.
- PISC will oversee progress, address challenges, revise incentives when necessary, and approve technical guidelines.
- Only vehicles registered under the Central Motor Vehicle Rules (CMVR) and equipped with advanced battery technology are eligible for incentives.
Bharat Heavy Electricals Limited (BHEL) serves as the Nodal Agency for:
- Demand aggregation for EV charging infrastructure.
- Development of a Unified EV Super App to provide real-time charger availability, slot booking, payments, and deployment tracking — promoting digital accessibility for users.
Guidelines for EV Charging Infrastructure (2025)
The Ministry of Heavy Industries issued a tiered subsidy framework to promote the establishment of EV charging stations nationwide.
Subsidy Structure
- 100% subsidy on upstream infrastructure and charging equipment for:Government offices, residential colonies, hospitals, and educational institutions (if open for public use).
- 80% subsidy on upstream infrastructure and 70% on equipment for:High-traffic public locations such as railway stations, airports, metro stations, bus terminals, toll plazas, and municipal parking lots.
- 80% subsidy on upstream infrastructure for:Shopping malls, markets, highways, expressways, and battery-swapping stations.
Deployment Priority
The scheme prioritizes:
- Cities with over one million population,
- State capitals, smart cities, metro-linked satellite towns, and
- High-density transport corridors.
Eligible government agencies are to designate nodal bodies to identify sites, aggregate demand, and submit proposals via a dedicated online portal.
BHEL will act as the Project Implementation Agency (PIA), with subsidies released in two tranches linked to performance and compliance milestones.
UNESCO’s World Network of Biosphere Reserves
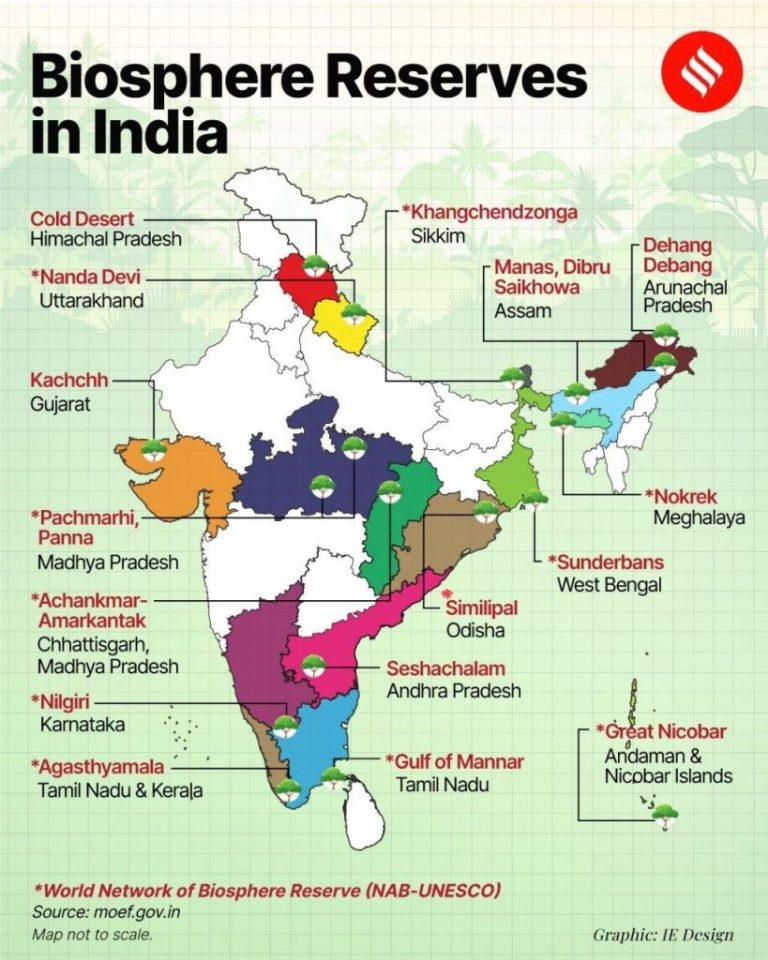
- 02 Oct 2025
In News:
UNESCO has included India’s Cold Desert Biosphere Reserve, located in Lahaul-Spiti district of Himachal Pradesh, in its World Network of Biosphere Reserves (WNBR) during the 37th ICC–MAB session (2025). This recognition makes it India’s first high-altitude cold desert biosphere reserve to join the global network, highlighting the country’s commitment to sustainable mountain ecosystem management.
About the Cold Desert Biosphere Reserve
- Established: 2009
- Location: Western Himalayas, Trans-Himalayan region of Himachal Pradesh
- Area: 7,770 sq. km
- Altitude: 3,300–6,600 m
- Constituent Areas:Pin Valley National Park, Kibber Wildlife Sanctuary, Chandratal Wetland, and adjoining regions.
- Terrain: Windswept plateaus, glacial valleys, alpine lakes, and high-altitude deserts.
- Zonation:
- Core Zone – 2,665 sq. km
- Buffer Zone – 3,977 sq. km
- Transition Zone – 1,128 sq. km
Biodiversity and Communities
- Flora: 655 herbs, 41 shrubs, and 17 tree species, including 14 endemic and 47 medicinal plants vital for the Sowa Rigpa (Amchi) traditional healing system.
- Fauna: 17 mammal and 119 bird species, including Snow Leopard, Tibetan Antelope, Himalayan Wolf, and Himalayan Ibex.
- Communities: Around 12,000 residents dependent on pastoralism, yak/goat herding, and high-altitude farming (barley and peas).
Agri-Stack Scheme
- 01 Oct 2025
In News:
- The Government of Uttar Pradesh has issued a stern directive to all District Magistrates (DMs), warning of strict action against officials who fail to complete farmer registration under the Agri-Stack scheme within the revised deadline.
- Beginning October 16, 2025, DMs have been allotted one month to ensure 100% registration of farmers, a crucial step in the implementation of this national digital agriculture initiative.
About the Agri-Stack Scheme
- The Agri-Stack is a national digital infrastructure being developed by the Ministry of Agriculture and Farmers Welfare, in collaboration with state governments, to digitally transform Indian agriculture.
- It aims to create a unified database of farmers and farmlands, integrating information on land records, crop patterns, and scheme benefits.
- The system is envisioned to serve as a foundational digital layer for data-driven governance, policy formulation, and targeted service delivery to farmers.
Objectives and Key Features
- Empowerment through Data: Enables the creation of a unique digital identity for every farmer through a Farmer ID linked to Aadhaar, ensuring accurate targeting of benefits.
- Efficiency and Transparency: Digitally connects demographic data, landholdings, and scheme eligibility, minimizing leakages and duplication.
- Customized Services: Facilitates localized advisories, early warning systems for disasters and pest attacks, and timely delivery of inputs and credit.
- Ease of Governance: Provides a single, verified data source for policy planning, monitoring, and feedback management.
- Public–Private Collaboration: Enables authorized access for banks, agri-tech startups, and value-chain companies to offer tailored financial and technical services.
Core Components of the Agri-Stack
- Farmer and Farmland Registries:
- A federated digital registry of all farmers across India, compiled by states and harmonized at the central level.
- Each farmer receives a unique, verifiable Farmer ID, dynamically linked to farmland plot data for non-legal, advisory, and planning purposes.
- Unified Farmer Service Interface (UFSI):
- A technical framework that ensures data interoperability between government and authorized private stakeholders.
- Enables federated data exchange with consent-based access, improving coordination across sectors like finance, insurance, and agri-input supply.
- Crop Sown Registry:
- Digitally records seasonal crop data for every farm using smartphone, drone, and satellite imagery.
- Replaces traditional manual crop surveys with real-time, geo-referenced data for better yield estimation and policy response.
- Agri-Stack Sandbox:A testing environment that allows authorized users (such as agri-tech firms and banks) to safely experiment with sample datasets and digital tools before gaining production-level access.
- Consent Manager:
- Empowers farmers to control the sharing of their personal data.
- Data access is granted only with explicit consent, which can be revoked at any time, ensuring privacy and accountability.
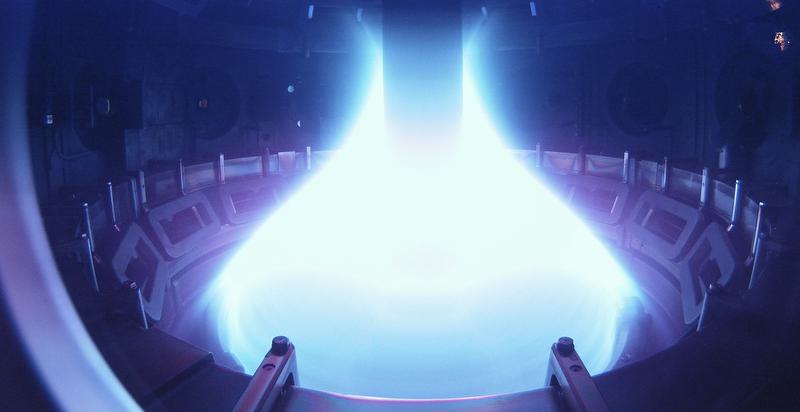
India’s Fusion Energy Roadmap

- 28 Sep 2025
In News:
- Researchers at the Institute for Plasma Research (IPR), Gandhinagar, have unveiled a comprehensive roadmap for India’s fusion energy programme.
- This initiative aims to develop the country’s first fusion electricity generator, Steady-state Superconducting Tokamak–Bharat (SST-Bharat), and ultimately commission a demonstration reactor by 2060.
- The roadmap signifies a major step in India’s pursuit of sustainable, high-yield, and low-waste energy alternatives.
Understanding Nuclear Fusion
Nuclear fusion is the process where two light atomic nuclei (like isotopes of hydrogen) merge to form a heavier nucleus, releasing immense energy—similar to the reactions that power the Sun.
It differs from nuclear fission, where heavy atoms split apart to release energy.
Advantages of Fusion over Fission
- Minimal radioactive waste and no long-term storage challenges.
- Abundant fuel sources (deuterium from water, tritium from lithium).
- No greenhouse gas emissions and no meltdown risk.
- High energy density, offering a virtually limitless energy source.
India’s Current Fusion Research Base
- SST-1 Tokamak (IPR, Gandhinagar): India’s first steady-state superconducting tokamak, designed for plasma research. It has achieved plasma duration of ~650 milliseconds, with potential to reach 16 minutes.
- Participation in ITER (France): India contributes technology, components, and funding to the International Thermonuclear Experimental Reactor (ITER), the world’s largest magnetic confinement experiment aimed at demonstrating a Q-value (output/input ratio) of 10.
India’s Fusion Power Roadmap
1. The SST-Bharat Project
- A fusion-fission hybrid reactor proposed as India’s next major milestone.
- Expected output: 130 MW (100 MW from fission, 30 MW from fusion).
- Estimated cost: ?25,000 crore.
- Efficiency target: Five times the input power.
- Acts as a bridge technology toward achieving pure fusion energy.
2. Demonstration Reactor (By 2060)
- Planned 250 MW full-scale reactor.
- Target Q-value: 20 (i.e., producing 20 times more energy than input).
- Will use magnetic confinement, heating plasma to over 100 million°C — much hotter than the Sun’s core (15 million°C).
Technological Innovations Proposed
- Digital Twinning: Creating virtual replicas of tokamak systems to test and optimise operations before physical construction.
- Machine Learning-Assisted Plasma Control: Using AI for real-time monitoring and stability of plasma.
- Radiation-Resistant Materials: Essential for reactor longevity and safety.
- Superconducting Magnet Development: To maintain continuous plasma confinement efficiently.
Global Benchmarks and India’s Position
|
Country/Programme |
Reactor/Initiative |
Target Year |
Notable Achievement |
|
UK |
STEP Programme |
2040 |
Prototype fusion power plant planned |
|
USA |
Private Start-ups |
2030s |
Early grid-connected fusion target |
|
China |
EAST Tokamak |
Ongoing |
Record plasma duration |
|
France |
WEST Tokamak |
2025 |
Maintained plasma for 22 minutes |
|
India |
SST-Bharat & Demo Reactor |
2060 |
Gradual, state-led development path |
While global players pursue faster timelines, India’s approach is cautious but strategic, focused on self-reliance and steady technological progress.
Challenges in India’s Fusion Path
Technological
- Sustaining stable plasma for long durations.
- Achieving Q > 1 (self-sustaining fusion).
- Developing durable superconducting magnets and radiation-resistant materials.
Financial
- High costs: SST-Bharat alone costs ?25,000 crore.
- Competing priorities: Solar, wind, and fission projects receive higher funding.
- Limited private-sector participation compared to global trends.
Policy and Governance
- Absence of a dedicated fusion energy regulatory framework.
- Need for integrated policy support under India’s Net Zero 2070 commitments.
Economic Viability
Experts like M.V. Ramana (University of British Columbia) caution that commercial fusion power remains economically unproven, and timelines are often optimistic. High R&D and construction costs could make fusion electricity expensive compared to renewables.
Strategic and Technological Significance
Even if commercial viability takes time, fusion R&D brings collateral benefits:
- Advances in plasma physics, superconducting technology, and high-temperature materials.
- Development of radiation-hardened components for defence, space, and nuclear industries.
- Strengthened technological autonomy and enhanced participation in global research networks.
Impatiens Selvasinghii
- 28 Sep 2025
In News:
- In a significant botanical discovery, researchers from Madura College, Madurai, have identified a new species of flowering plant belonging to the genus Impatiens in the Kudremukh range of the Western Ghats, Karnataka.
- The species has been named Impatiens selvasinghii in honour of Dr. P. Selva Singh Richard, Associate Professor of Botany at Madras Christian College (MCC), for his pioneering contributions to the study of reproductive biology of endemic and endangered plants of the Western Ghats.
Key Details of the Discovery
- Location:Kudremukh Peak, Chikkamagaluru district, Karnataka
- Altitude: Approximately 1,630 metres above sea level
- Published in:Taiwania, an international peer-reviewed botanical journal
- Unique Features: The species is distinguished by its exceptionally small flowers—the smallest among known balsams of the Western Ghats—and prominently lobed wing petals.
- Ecological Role: Small insects are dependent on this species for survival, underscoring its role in the local micro-ecosystem.
The Genus Impatiens in India
- India hosts over 280 taxa of Impatiens, widely distributed across the Eastern Himalayas and the Western Ghats.
- About 210 taxa are endemic to India, with 130 species unique to the Western Ghats.
- Notably, around 80% of the Impatiens species in the Western Ghats are categorized as endangered, highlighting the region’s ecological vulnerability.
Conservation Concerns
Researchers have cautioned that Impatiens selvasinghii is located along a popular trekking route in Kudremukh, where over-tourism and habitat disturbance could threaten its survival. Given the fragile mountain ecosystem and high endemicity of balsam species, measures for habitat protection and responsible ecotourism are vital.
India–Mauritius Relations
- 15 Sep 2025
In News:
- India and Mauritius share a unique relationship anchored in history, culture, and strategic convergence in the Indian Ocean Region (IOR). The visit of Mauritius Prime Minister Navinchandra Ramgoolam to Varanasi in 2025 marked a new milestone, with India announcing a USD 680 million Special Economic Package.
- The package seeks to strengthen bilateral cooperation in infrastructure, defence, maritime security, and cultural ties, while reinforcing India’s role as a key development and security partner in the region.
Key Features of the Special Economic Package (2025)
- Infrastructure Development: At least 10 projects, including completion of the new Air Traffic Control (ATC) tower at SSR International Airport, expansion of highways and ring roads, and the development of Motorway M4.
- Healthcare & Education: Establishment of new schools and hospitals.
- Maritime Cooperation: Redevelopment of Port Louis into a stronger maritime hub, and agreements on hydrography for joint surveys and navigation charts of Mauritius’ Exclusive Economic Zone (EEZ).
- Chagos Archipelago Engagement: In-principle agreement for joint surveillance of the Chagos Marine Protected Area, where the Diego Garcia base (operated by the US-UK) is located. India strongly backed Mauritius’ sovereignty claims, consistent with its support for decolonisation.
- Trade Facilitation: Bilateral trade in local currencies to be enabled, following the launch of UPI and RuPay cards in Mauritius.
- Security Partnership: India reaffirmed its role as Mauritius’ “first responder” and “net security provider” in the Indian Ocean, providing hydrographic support, refitting Mauritius Coast Guard ships, and training personnel.
Historical and Cultural Ties
- Migration: Indian migration to Mauritius began under French rule (1700s) and intensified during British rule post-1834, when nearly 500,000 indentured labourers arrived, most of whom settled permanently.
- Demographics: Today, about 70% of Mauritius’s population (1.2 million) is of Indian origin, strengthening cultural and familial bonds.
- National Day: Mauritius celebrates its National Day on March 12, coinciding with Mahatma Gandhi’s Dandi March, reflecting its deep-rooted civilizational connect with India.
Economic and Commercial Relations
- Trade: In FY 2022–23, bilateral trade stood at USD 554.19 million, with Indian exports at USD 462.69 million.
- FDI: Mauritius remains a significant investor in India—second-largest source of FDI (FY 2023–24) after Singapore.
- CECPA (2021): The Comprehensive Economic Cooperation and Partnership Agreement was India’s first trade agreement with an African country, expanding market access in goods, services, and investment.
- DTAA (1982): While the Double Taxation Avoidance Agreement facilitated investments, it also raised concerns of misuse for money laundering and round-tripping.
Defence and Security Cooperation
- India is Mauritius’ preferred defence partner, supplying platforms like Dornier aircraft and Advanced Light Helicopters (Dhruv), along with a USD 100 million Line of Credit for defence procurement.
- Joint patrolling, hydrographic surveys, and capacity building highlight the depth of security ties.
- The Agaléga Island Projects (airstrip and jetty, inaugurated in 2024) enhance maritime domain awareness and India’s strategic reach in the southwest Indian Ocean.
Strategic Significance of Mauritius for India
- Geopolitical Location: Mauritius, located 800 km east of Madagascar, is a crucial node for maritime security and trade in the Indian Ocean.
- Countering China: China’s growing influence, marked by its 2021 FTA with Mauritius under the Belt and Road Initiative (BRI), necessitates stronger India–Mauritius collaboration.
- Blue Economy: Mauritius’ EEZ expansion (post-treaty with the UK over Chagos) provides new opportunities in fisheries, offshore energy, and maritime resources, where India is a preferred partner.
- Regional Cooperation: Mauritius is active in the Indian Ocean Rim Association (IORA), aligning with India’s SAGAR vision—“Security and Growth for All in the Region”—and Vision MAHASAGAR.
Sarcoidosis
- 15 Sep 2025
In News:
- Sarcoidosis is a chronic inflammatory diseasecharacterised by the formation of granulomas—small clusters of immune cells—in multiple organs, most commonly the lungs and lymph nodes.
- The condition has a highly variable clinical course, ranging from asymptomatic or mild presentations to severe, life-threatening complications.
- Recent peer-reviewed studies, including those published in Nature Reviews Disease Primers,emphasise the importance of early diagnosis, timely intervention, and awareness of risk factors in improving patient outcomes.
Causes and Risk Factors
- The exact cause of sarcoidosis remains unknown, but evidence points towards a combination of genetic susceptibility, immune system overactivity, and environmental triggers.
- Possible stimuli include bacteria, viruses, dust, and chemical exposure. Certain gene variations may predispose individuals, with the immune system reacting abnormally, leading to chronic inflammation and granuloma formation.
Symptoms and Clinical Manifestations
Symptoms vary depending on organ involvement:
- Pulmonary (most common): persistent cough, shortness of breath, chest pain; advanced cases may progress to pulmonary fibrosis and respiratory failure.
- Skin: rashes, bumps, or nodules; tender sores (erythema nodosum).
- Eyes: redness, pain, blurred vision.
- Cardiac: irregular heartbeats, heart failure.
- Neurological: seizures, facial paralysis, or peripheral nerve damage.
Some patients remain asymptomatic, with the disease detected incidentally during routine examinations.
Diagnosis
Diagnosis requires a combination of clinical evaluation, imaging, and biopsy.
- Chest X-rays/CT scans often reveal characteristic granuloma patterns.
- Biopsy confirms non-caseating granulomas, distinguishing sarcoidosis from infections and malignancies.
- Blood tests and lung function tests help assess disease activity and organ damage.
Treatment Approaches
There is no definitive cure for sarcoidosis, but management depends on severity and organ involvement:
- Mild/asymptomatic cases: often require only observation and regular monitoring.
- Moderate to severe cases: treated with corticosteroids (e.g., prednisone) to suppress inflammation.
- Refractory cases: immunosuppressive agents (methotrexate, azathioprine) or biologic therapies targeting immune pathways.
Long-Term Outlook
The prognosis is highly variable:
- Many cases resolve spontaneously within a few years.
- Others may become chronic, causing permanent lung scarring, cardiac complications, or organ dysfunction.
- Early detection and continuous monitoring remain critical to preventing irreversible damage.
Public Health Relevance
Sarcoidosis highlights the complex interaction between genetics, immunity, and environment. Its unpredictable nature underlines the need for:
- Awareness campaigns for early recognition of symptoms.
- Strengthening diagnostic infrastructure in primary healthcare.
- Research on genetic predispositions and immunological mechanisms to develop targeted therapies.
YudhAbhyasExercise
- 04 Sep 2025
In News:
Despite rising bilateral tariff tensions, India and the United States have commenced their largest-ever edition of the YudhAbhyas Army exercise at Fort Wainwright, Alaska. The two-week-long exercise underscores the strategic depth of the India–US defence partnership, even amid political and trade frictions.
About YudhAbhyas Exercise
- Nature: Annual bilateral military exercise between the Indian Army and the US Army.
- Initiation: Started in 2004 under the India–US Defence Cooperation Framework.
- Hosting: Conducted alternately in India and the US.
- Focus: Joint training in counter-terrorism, peacekeeping, mountain and high-altitude warfare.
2025 Edition Highlights
- Location: Fort Wainwright, Alaska — subarctic conditions comparable to Himalayan terrain.
- Indian Participation: Over 450 soldiers from the Madras Regiment.
- US Participation: Troops from the 5th Infantry Regiment “Bobcats”, Arctic Wolves Brigade Combat Team, 11th Airborne Division.
Training Features
- Joint heliborne operations.
- Surveillance and UAV deployment.
- Rock-craft and mountain warfare.
- Casualty evacuation and combat medical aid.
- Integrated use of artillery, aviation, and electronic warfare.
Strategic Significance
- Operational Readiness
- Enhances interoperability and coordination in extreme cold climates, vital for Himalayan and Arctic theatres.
- Strengthens joint capabilities in counter-terrorism, peace support, and disaster relief operations.
- Defence Cooperation Beyond Exercises
- The US has secured Indian defence deals worth over $25 billion since 2007.
- Recent major acquisitions:
- 99 GE-F404 turbofan engines (for Tejas Mk-1A fighters) worth $716 million.
- Proposed deal for 113 more engines worth $1 billion.
- 31 MQ-9B Predator drones worth $3.8 billion, deliveries expected in 2029–30.
- Geopolitical Context
- Exercises continue despite 50% tariffs imposed by the US on India under President Trump, straining economic ties.
- Defence cooperation remains resilient, reflecting two decades of strategic partnership.
- India balances ties with Russia and cautiously re-engages with China, maintaining its strategic autonomy.
- Quad Linkages
- Parallel planning is underway for the Malabar Naval Exercise among Quad nations (India, US, Japan, Australia) off Guam in November 2025, further deepening maritime security collaboration in the Indo-Pacific.
Tuvalu’s Planned Climate Migration to Australia
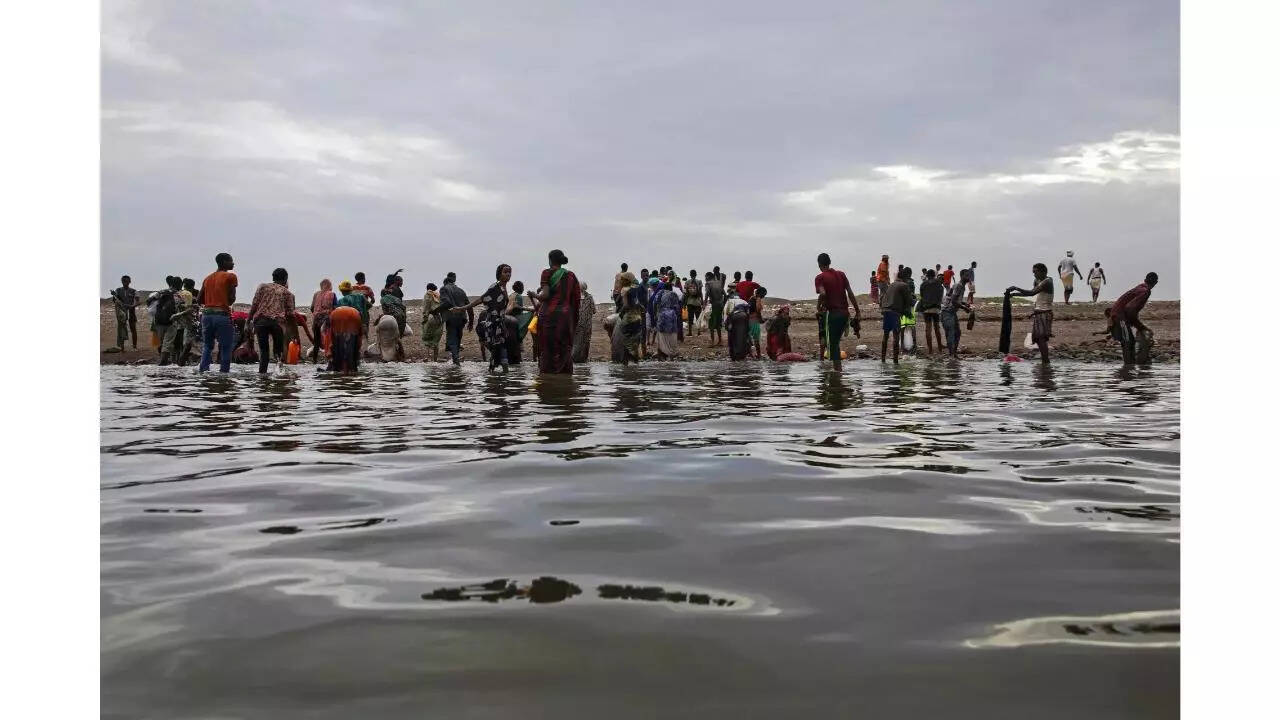

- 10 Aug 2025
In News:
Tuvalu, a small Pacific island nation, is undertaking the world’s first planned national migration due to the existential threat posed by climate change and rising sea levels. The initiative stems from the Falepili Union Treaty (2023) signed between Tuvalu and Australia, marking a landmark case in global climate governance and migration policy.
Why Migration is Needed
- Geography & Vulnerability: Tuvalu consists of nine coral atolls with a total land area of just 25.14 sq. km and a population of ~11,000 (2022 census). Its average elevation is only 2 metres, making it highly vulnerable to flooding, storm surges, and coastal erosion.
- Climate Impact:
- NASA’s Sea Level Change Team reported that sea levels in Tuvalu were already 15 cm higher in 2023 compared to the previous 30 years.
- At this rate, most of Tuvalu could be submerged by 2050.
- Two of its nine atolls are already largely underwater.
- Scientists warn the islands may become uninhabitable within 80 years.
The Falepili Union Treaty (2023)
- Migration Provision: Australia will grant 280 Tuvaluans permanent residency annually, with access to healthcare, education, housing, and employment.
- Selection Mechanism: Migration is ballot-based. The first phase (June–July 2025) saw 8,750 registrations. The first group of 280 migrants was selected on 25 July 2025.
- Scale: Along with other pathways to Australia and New Zealand, up to 4% of Tuvalu’s population could migrate annually. Within a decade, nearly 40% of the population may relocate, although some may return periodically.
- Objective: To ensure “mobility with dignity”, preventing Tuvaluans from becoming stateless climate refugees.
International Significance
- Precedent for Climate Migration: This is the first-ever state-backed relocation of an entire population due to climate change, setting a model for other vulnerable island nations.
- Global Climate Justice: Tuvalu’s case highlights the plight of Small Island Developing States (SIDS) and the urgent need for stronger international climate agreements.
- Diplomatic Signalling: Tuvalu’s Prime Minister Feleti Teo has called for a new global treaty safeguarding nations at risk from rising seas.
About Tuvalu
- Location: Polynesian island nation in the Pacific Ocean, midway between Australia and Hawaii.
- Capital: Funafuti.
- Population: ~11,000 (second least populous UN member after Vatican City).
- Economy: Relies on fishing licenses, foreign aid, and remittances from Tuvaluan seafarers.
- UN Membership: Since 2000; actively champions the rights of climate-vulnerable states.
Sawalkote Hydroelectric Project
- 01 Aug 2025
In News:
In a strategic shift, India has floated international tenders for constructing the long-stalled Sawalkote Hydroelectric Project (1,856 MW) on the Chenab River in Jammu & Kashmir, leveraging the fact that the Indus Waters Treaty (IWT) with Pakistan is currently in abeyance. This development marks a significant turn in India’s water diplomacy and infrastructure planning.
Background & Project Details
- Location & Nature: Sawalkote is a run-of-river hydropower project near Sidhu village in Ramban district, J&K.
- Conception & Delay: Originally conceived in the 1980s, handed to NHPC in 1985, then returned to JKSPDC in 1997. Despite Rs 430 crore spent on enabling infrastructure, the project remained unstarted until a 2021 MoU revived it under an BOOT (Build-Own-Operate-Transfer) model.
- Tender Process: In July 2025, NHPC invited international bids (design, planning, engineering) with bid submissions due by September 10, 2025.
- Scale & Costs: Estimated cost stands at Rs 22,704.8 crore, set to be executed in two phases.
- Environmental Clearances: Forest Advisory Committee granted in-principle approval for diversion of 847 hectares of forest land.
Indus Waters Treaty (IWT) & Its Suspension
- Treaty Overview: Signed in 1960 (brokered by the World Bank), IWT allocates the eastern rivers (Ravi, Beas, Sutlej) to India, and the western rivers (Indus, Chenab, Jhelum) to Pakistan. India retains limited non-consumptive usage rights for hydro-power on these western rivers.
- First Suspension: On 23 April 2025, following a terrorist attack in Pahalgam, India suspended the IWT, citing national security and the treaty’s exploitation by Pakistan for cross-border terrorism.
- Consequences: India ceased hydrological data sharing, blocked Pakistani access to project visits, and released annual joint-status reporting—effectively halting treaty obligations.
- Strategic Intent: This pause grants India freedom to launch projects like Sawalkote without Pakistan’s prior objections or IWT constraints.
Geopolitical Tensions & Ramifications
- Long-term Impact on Pakistan: The Indus system sustains ~80% of Pakistan’s agriculture and electricity. Disruption could severely undermine food security, hydropower production, and urban water supply.
- Symbolism of a Rift: The treaty had survived wars and conflicts. Its suspension is viewed as an overt break in regional cooperative norms, with potential for conflict escalation.
- Legal & Diplomatic Fallout: Pakistan views reduced water flows as “act of war”; it is exploring legal avenues and appealing for treaty revival.
- India’s Firm Stance: PM Modi has labeled the treaty “unjust,” declared “blood and water cannot flow together,” further hardening India's negotiating posture.
Strategic Evaluation
- Violation or Tactical Move? While the IWT allows limited usage by India, its suspension indicates a focus on infrastructure autonomy over the western river system.
- Regional Domino Effects: With rising global water disputes, actions like this may set precedent in viewing water as geopolitical leverage.
- Environmental & Social Risks: Dam construction and forest diversion raise ecological concerns; plus, local displacement and compensation need careful handling.
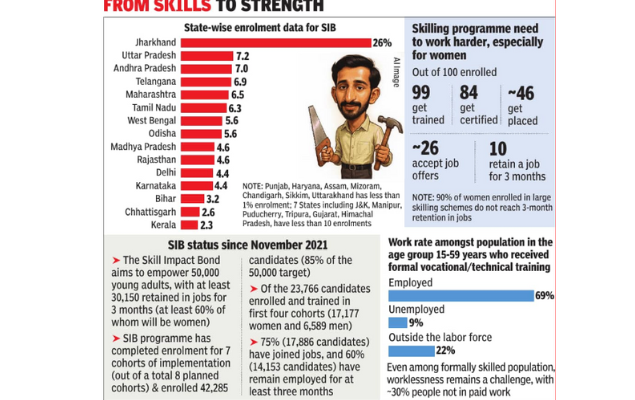
Skill Impact Bond (SIB)
- 01 Aug 2025
In News:
- India is at the cusp of a demographic transition, with a young workforce expected to drive its goal of becoming a $30 trillion economy by 2047.
- Yet, only ~4% of India’s workforce is formally skilled, and nearly 30% of trained individuals remain unemployed. Traditional skilling schemes have struggled, especially with job retention.
- Against this backdrop, Skill Impact Bond (SIB), launched in 2021, marks a paradigm shift in India’s skilling ecosystem by linking financing to actual outcomes.
What is the Skill Impact Bond (SIB)?
- Launched: November 2021.
- Implementing Agency: National Skill Development Corporation (NSDC) under Ministry of Skill Development & Entrepreneurship.
- Partners: British Asian Trust, Children’s Investment Fund Foundation (CIFF), HSBC India, JSW Foundation, Dubai Cares.
- Target: Train 50,000 youth (60% women), ensure sustained employment.
It is India’s first development impact bond focused on employment, not just certification.
How Does SIB Work?
- Risk Investors (Private/Philanthropic): Provide upfront funds to service providers (training institutes).
- Service Providers: Deliver skill training, placement support, and post-placement mentoring.
- Outcome Funders (Govt/Donors): Repay investors if measurable outcomes are achieved (job placement + retention).
- Third-Party Evaluator: Verifies outcomes.
Key Distinction: Funding is tied to placement and retention, not mere enrolment/certification.
Progress So Far
- 23,700 youth trained across 13 sectors & 30 job roles.
- 72% women participation – one of the highest in any skilling programme.
- 75% placed in jobs, and 60% retained beyond 3 months, exceeding national averages (<10% under older schemes).
- Jharkhand, UP, Delhi are leading states in enrolment.
Significance
- Women-led Growth:
- 72% women trainees; many first-generation formal workers (tribal, rural, conservative households).
- Skilling gives women not just jobs but also agency, confidence, and identity.
- Outcome-Based Financing:
- Ensures accountability of training providers.
- Attracts private/philanthropic capital into public welfare.
- Addresses Retention Challenge:
- Traditional skilling: 84% complete training, but <10% stay in jobs beyond 3 months.
- SIB model pushes for long-term impact.
- Replicable Model:
- Can be scaled to health, education, social welfare.
- Example: Project AMBER (apprenticeship-based skilling) also uses this financing.
Challenges Ahead
- Scale vs Depth: Training 50,000 is significant, but India needs millions of skilled youth annually.
- Social Barriers: Women face mobility, safety, and cultural challenges in sustaining employment.
- Monitoring & Evaluation: Requires robust third-party systems to measure outcomes fairly.
- Private Participation: Sustaining investor confidence demands continuous success stories.
Way Forward
- Expand outcome-based financing to more sectors.
- Strengthen ecosystem for women (hostels, childcare, safe mobility).
- Continuous mentoring & alumni networks to ensure retention.
- Use digital platforms for scalable skilling and tracking.
Setubandha Scholar Scheme
- 31 Jul 2025
In News:
The Setubandha Scholar Scheme (also referred to as Setubandha Vidwan Yojana) is a pioneering national initiative launched by the Ministry of Education to integrate scholars from traditional gurukuls into India's mainstream research ecosystem—especially at premier institutions like IITs.
Key Highlights:
- Objective: To formally recognise traditional learning and connect Indian Knowledge Systems (IKS) with modern scientific disciplines.
- Implementing Agency: Indian Knowledge System (IKS) division under the Central Sanskrit University (CSU).
- Eligibility: Minimum 5 years of rigorous study in a recognised gurukul and proven expertise in Shastras or traditional knowledge. No formal academic degree is required.
- Age Limit: Maximum 32 years.
Fellowships & Research Grants:
|
Category |
Fellowship (per month) |
Annual Research Grant |
Equivalent Academic Level |
|
Category 1 |
?40,000 |
?1,00,000 |
Postgraduate (Master’s) |
|
Category 2 |
?65,000 |
?2,00,000 |
Doctoral (PhD) |
- Research Domains (18 Fields): Ayurveda, health sciences, mathematics, astronomy, physics, grammar, strategic studies, political theory, cognitive science, architecture, performing arts, and more.
- Notable traditional categories include Anvikshiki Vidya (philosophy), Ganit-Bhaut-Jyotish Vidya (mathematics, physics, astronomy), and Bhaishajya-Arogya Vidya (health sciences).
Policy Context: NEP 2020 and Beyond
The scheme is a direct outcome of reforms envisioned under the National Education Policy (NEP) 2020, which emphasizes integrating traditional Indian knowledge systems with modern education, promoting multidisciplinary learning, and creating a flexible, inclusive research environment.
NEP-Driven Initiatives Linked to Setubandha:
- Nipun Bharat: Improved foundational literacy and numeracy by Class 2.
- Vidya Pravesh & Balvatikas: Early childhood education integration.
- Bharatiya Bhasha Pustak Yojana: Democratizing Indian language access.
- National Digital Depository for IKS: Repository of classical knowledge.
- PM Shri Schools: Model schools aligned with NEP's vision.
- Academic Bank of Credits (ABC) and Multiple Entry-Exit options.
- Anusandhan NRF & PMRF 2.0: Boosting research funding and fellowships.
- Global Outreach: Foreign universities (e.g., Deakin, Wollongong) setting up campuses in India.
Wider Impact and Significance:
- Institutional Recognition: For the first time, gurukul-trained scholars can pursue advanced research alongside IIT peers.
- Inclusivity in Education: Enables non-formal scholars to access elite academic spaces.
- Global Relevance: As interest grows in Ayurveda, Yoga, Sanskrit linguistics, and indigenous governance, India is positioning itself as a global knowledge hub.
- Empowerment of Marginalised Groups: Over 7.12 lakh girls in Kasturba Gandhi Balika Vidyalayas, and hostel schemes for PVTGs reflect NEP’s inclusive approach.
India’s Battery Passport System
- 11 Jul 2025
In News:
The Government of India is preparing to implement a Battery Passport framework to enhance safety, traceability, and export readiness of electric vehicle (EV) batteries. The initiative is being spearheaded by NITI Aayog in collaboration with multiple ministries and stakeholders.
What is a Battery Passport?
A Battery Passport is a digital identity assigned to each EV battery, embedded in a QR code, which stores complete lifecycle information. This includes:
- Origin and manufacturing details
- Chemical composition and configuration
- Performance metrics and carbon footprint
- Date of manufacture and service history
- End-of-life data for recycling and reuse
The system assigns each battery a unique ID, akin to an Aadhaar for batteries, ensuring transparency and traceability across its lifecycle.
Key Features:
|
Feature |
Description |
|
QR Code Integration |
Allows users and service providers to scan and access battery details |
|
Lifecycle Tracking |
Monitors battery data from production to disposal |
|
Unique Digital Identity |
Each battery is individually identifiable, preventing cell mismatch |
|
Real-Time Monitoring |
Tracks performance, degradation, and usage patterns |
|
Standardised Data Format |
Includes manufacturer info, batch ID, composition, carbon metrics |
|
Controlled Data Access |
Enables secure sharing with regulators, manufacturers, and recyclers |
|
EU Compliance Ready |
Aligns with European Union regulations for batteries above 2 kWh |
Why is it Needed?
- Battery Safety: Addresses concerns due to frequent EV fire incidents linked to faulty or mismatched battery cells.
- Battery Swapping: Ensures interoperability and standardisation, essential for the upcoming battery-swapping policy.
- Export Promotion: Positions Indian batteries to comply with global traceability norms, especially in EU markets.
- Lifecycle & Performance Transparency: Batteries make up ~40% of EV cost; users benefit from informed decision-making.
- Circular Economy: Facilitates reuse, recycling, and end-of-life recovery to promote sustainability.
Expected Benefits
- Improved EV safety and reliability
- Enhanced consumer confidence
- Boost to India’s EV exports
- Support for circular economy in battery usage
- Industry-wide quality and compliance enforcement
Axiom Mission 4 (Ax-4)

- 30 Jun 2025
In News:
India marked a historic moment in space exploration as Group Captain Shubhanshu Shukla became the first Indian to reach the International Space Station (ISS), 41 years after Rakesh Sharma’s 1984 mission.
Organizations Involved:
- Axiom Space – Mission organizer
- NASA – ISS host and operations support
- SpaceX – Provided Falcon 9 launch vehicle and Dragon capsule
Launch Details:
- Launch Date: June 25, 2025
- Launch Site: Launch Complex 39A, Kennedy Space Center, Florida
- Mission Duration: ~14 days aboard the ISS
Mission Objectives:
1. Scientific Research in Microgravity:
- Over 60 research experiments conducted across:
- Life sciences
- Material sciences
- Human physiology
- Earth observation
2. International Space Cooperation:
- Promotes global collaboration in low-Earth orbit science.
- Supports capacity-building for emerging space nations, including India, Poland, and Hungary.
3. National Space Program Development:
- Enables participating nations to strengthen human spaceflight capabilities.
- Acts as a stepping stone for India’s Gaganyaan and future space station plans.
Significance for India:
- Revival of Human Spaceflight:
- Marks India’s return to human space missions after four decades.
- Reinforces India's presence in international human space exploration.
- Boost to Gaganyaan Mission:
- Offers valuable operational experience and technical collaboration.
- Supports India’s vision to launch Gaganyaan, its first indigenous human spaceflight mission.
- Long-Term Space Ambitions:
- Aids India’s goal to establish its own space station by 2035.
- Positions India as a partner in space science diplomacy and global research.
- Scientific Prestige:India contributes to key microgravity experiments, enhancing its global research footprint in space.
SSLV Technology Transfer
- 24 Jun 2025
In News:
In a historic development for India's space sector, the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) will, for the first time, completely transfer rocket technology to a domestic firm. Hindustan Aeronautics Limited (HAL) has secured the Transfer of Technology (ToT) for the Small Satellite Launch Vehicle (SSLV) through a competitive process facilitated by IN-SPACe, marking a new era of private-sector participation in space.
What is the SSLV Technology Transfer?
- Nature of ToT: Complete technology handover of ISRO’s SSLV to HAL.
- Awarded By: Indian National Space Promotion and Authorisation Centre (IN-SPACe) after a two-stage national selection.
- Winning Bid: HAL won the bid with a ?511 crore offer — the highest among the contenders.
- Other Bidders: Consortia led by Alpha Design (Bengaluru) and Bharat Dynamics Limited (Hyderabad).
- Objective: To empower the private sector to build, market, and launch rockets independently, thus reducing reliance on ISRO for small satellite missions.
Key Features of the SSLV ToT
Parameter Details
Ownership - HAL will own and operate the SSLV, with rights to modify its design and choose commercial partners.
Production Capability - HAL aims to produce 6–10 SSLVs annually, based on demand.
ToT Duration - 2 years of technology handholding by ISRO, during which HAL will manufacture at least two SSLV prototypes.
Post-ToT - HAL will operate independently post-ToT and may enter contracts for commercial launch services.
Contractual Roles - ISRO (technical), IN-SPACe (regulatory + ToT coordination), NSIL (commercial interface), HAL (execution).
About Hindustan Aeronautics Limited (HAL)
- Established: 23 December 1940 (as Hindustan Aircraft Limited).
- HQ: Bengaluru, Karnataka.
- Ministry: Ministry of Defence, Government of India.
- Core Role: India’s largest defence and aerospace PSU involved in aircraft, helicopters, engines, and now space systems.
- Key Contributions:
- Manufactured MiG-21, SU-30MKI, LCA Tejas.
- Supplied components for GSLV Mk-III, Mars Orbiter Mission, and Gaganyaan.
- Collaborated with ISRO on cryogenic engines and launch vehicle structures.
- Publicly Listed: On BSE and NSE since 2018.
Significance:
- First Full Rocket ToT in India: Unlike earlier manufacturing contracts (e.g., PSLV), SSLV is entirely owned and operated by HAL.
- Boosts Private Sector Role: Aligns with India’s space sector reforms to commercialize launch services.
- Fosters Innovation & Autonomy: HAL can redesign the SSLV and partner globally, making India more competitive in the small satellite launch market.
- Strategic Diversification: HAL adds space systems to its portfolio, without affecting defence operations.
Operation Sindhu

- 21 Jun 2025
In News:
As tensions escalate in West Asia due to the ongoing Iran-Israel conflict, the Government of India has launched Operation Sindhu to evacuate Indian nationals, particularly students, stranded in conflict-affected regions of Iran.
- The first flight under Operation Sindhu, carrying 110 Indian students, successfully landed in New Delhi, marking the beginning of the evacuation process.
What is Operation Sindhu?
Operation Sindhu is a government-led evacuation mission launched in 2025 to ensure the safe repatriation of Indian citizens from war-hit Iran.
- Launched by: Ministry of External Affairs (MEA), Government of India
- Assisted by: Indian Embassies in Iran and Armenia
Objectives:
- To safely evacuate Indian citizens, particularly students, from volatile zones in Iran.
- To coordinate safe land-based exit routes through Armenia, due to restricted or dangerous air routes over Iran.
Key Features of the Operation:
Feature Details
Evacuation Route Northern Iran → Yerevan (Armenia) → New Delhi
Monitoring Real-time updates and continuous monitoring by Indian missions
Coordination Close coordination with governments of Iran and Armenia
Control Room 24/7 MEA Control Room operational in New Delhi
India’s Major Air Evacuation Missions (Chronological Overview):
Mission Name Year Objective
Vande Bharat Mission 2020 Evacuation of Indians stranded abroad during the COVID-19 pandemic
Operation Devi Shakti 2021 Evacuation from Afghanistan after the Taliban takeover
Operation Ganga 2022 Evacuation from Ukraine amid Russia-Ukraine war
Operation Kaveri 2023 Rescue of Indian nationals from conflict-hit Sudan
Operation Ajay 2023 Repatriation of Indians from Israel amid regional conflict
Operation Sindhu 2025 Ongoing evacuation from Iran amid Iran–Israel escalation
Significance for India
- Diaspora Safety: Reinforces India’s commitment to protecting its citizens abroad.
- Diplomatic Efficiency: Reflects India’s growing capabilities in executing rapid and complex evacuation logistics in volatile geopolitical environments.
- Soft Power and Foreign Policy: Enhances India’s global image as a responsible nation ensuring citizen welfare, even beyond borders.
Gharial Conservation

- 20 Jun 2025
In News:
On World Crocodile Day (June 17, 2025), Etawah district in Uttar Pradesh marked the 50th anniversary of India’s pioneering Gharial Conservation Programme, commemorating five decades of sustained efforts to protect the endangered gharial (Gavialis gangeticus) along the Chambal River.
About the Gharial Conservation Programme
- Launched in: 1975
- Initiated by: Forest Department of Uttar Pradesh and Society for Conservation of Nature (SCON)
- Supported by: UNDP, FAO, and Government of India
- Location: Primarily focused on Chambal River in Etawah district, Uttar Pradesh
- Breeding Facility: Kukrail Gharial Rehabilitation Centre, Lucknow
Why Gharial Conservation Matters
- Species: Gharial (Gavialis gangeticus) — endemic, freshwater crocodilian
- Status: Critically Endangered (IUCN Red List)
- Habitat: Prefers deep, fast-flowing rivers with sandy banks and minimal human interference
- Threats: Habitat destruction, sand mining, illegal fishing, entanglement in nets, and declining fish stocks
Programme Objectives
- Protect wild gharial populations in natural river habitats.
- Enhance population through captive breeding and release.
- Study habitat biology and gharial behaviour to inform scientific conservation.
- Promote coexistence between gharials and local fishing communities.
- Create awareness and engage local populations in conservation.
Key Features of the Programme
- Egg Collection: Gharial eggs are safely collected from natural nests on riverbanks.
- Artificial Incubation: Maintained under controlled temperature and humidity to improve hatching success.
- Captive Rearing: Hatchlings are reared for 3–5 years at Kukrail Centre until they are strong enough for survival in the wild.
- Release Strategy: Tagged juveniles are released in protected stretches of the Chambal River.
- Community Involvement: Local fishermen and villagers are involved in conservation-linked livelihoods to reduce human-wildlife conflict.
Impact and Legacy (1975–2025)
- One of India’s earliest species-specific conservation programmes.
- Created a successful model of “rear-and-release” conservation.
- Helped stabilize the gharial population in Chambal, now one of the last strongholds for the species.
- Promoted community-based conservation and scientific habitat management.
Servants of India Society
- 15 Jun 2025
In News:
Tensions have resurfaced between Gokhale Institute of Politics and Economics (GIPE) and the Servants of India Society (SIS) over control of a joint bank account and allegations of financial misconduct. This has brought attention back to the legacy and functioning of the historic SIS.
About Servants of India Society (SIS)
- Founded: June 12, 1905
- Founder: Gopal Krishna Gokhale, with G.K. Devadhar, A.V. Patwardhan, and N.A. Dravid
- Location: Fergusson Hill, Pune, Maharashtra
- Headquarters: Pune, with branches in Chennai, Mumbai, Nagpur, Allahabad, etc.
Objectives:
- To train a dedicated cadre of national workers for selfless service to the nation.
- Promote political education, social reform, and public service.
- Work towards upliftment of underprivileged communities, including rural and tribal populations.
- Achieve social change through constitutional and moderate means, not violent agitation.
Membership and Structure:
- Members undergo a five-year training period and vow to serve on modest salaries.
- Considered “young missionaries of Indian nationalism.”
- Notable Members:
- V.S. Srinivasa Sastri (later president after Gokhale’s death in 1915)
- Hriday Nath Kunzru
- A.V. Thakkar
Ideological Basis:
- Strong emphasis on constitutionalism, moderation, and liberalism.
- Aimed to create a disciplined, morally upright civil society to complement political struggle.
About Gopal Krishna Gokhale:
- Born: May 9, 1866 | Died: February 19, 1915
- Moderate leader of the Indian National Congress and a liberal reformer.
- Influenced by Justice M.G. Ranade and Western political thought.
- Advocated for gradual self-governance and saw value in British-initiated modernization.
- Played a pivotal role in the Morley-Minto Reforms (1909).
- Mentor to Mahatma Gandhi and known for his economic insight and powerful oratory.
EnviStats India 2025
- 06 Jun 2025
In News:
India's annual mean temperature rise up from 25.05°C in 2001 to 25.74°C in 2024, Electricity generation from renewable sources increased more than three times in 10 years.
- Released by: Ministry of Statistics and Programme Implementation (MoSPI) on June 5, 2025, on the occasion of World Environment Day
- Framework Used: UN's Framework for the Development of Environment Statistics (FDES 2013)
Key Highlights:
Climate Trends
- Annual Mean Temperature rose from 25.05°C (2001) to 25.74°C (2024).
- 2024 recorded as India’s hottest year since 1901; also, globally the hottest year in 175 years.
- Annual Minimum and Maximum Temperatures (2021–24):
- Minimum: 19.32°C → 20.24°C
- Maximum: 30.78°C → 31.25°C
Rainfall Patterns
- Rainfall shows seasonal concentration between June–September, with signs of shifting patterns such as late onset or extended rains into October.
- No clear long-term trend, reflecting erratic monsoonal behaviour.
Energy Generation
Thermal & Renewable Power (2013–14 to 2023–24)
- Thermal: 7.92 lakh GWh → 13.26 lakh GWh
- Renewable: 65,520 GWh → 2.25 lakh GWh, over 3x increase in renewable energy output in a decade.
Biodiversity and Faunal Statistics
Faunal Diversity
- Global Faunal Species: 16,73,627
- India's Share: 1,04,561 species
- Habitat-specific Species in India:
- Soil Ecosystem: 22,404
- Freshwater Ecosystem: 9,436
- Mangrove System: 5,023
- Estuarine Ecosystem: 3,383
- Marine Fauna (India): 20,613 out of global 2,47,605
Fisheries Production
Inland vs. Marine Fish (2013–14 to 2023–24)
- Inland Fish Production: 61 lakh tonnes → 139 lakh tonnes
- Marine Fish Production: 34 lakh tonnes → 45 lakh tonnes
Public Expenditure (2021–22)
- Environment Sustainability Sector: ?2,433 crore (highest among sectors)
- Conservation of Natural Resources: Increasing trend
- Agro-Forestry: Lowest allocation
New Data indicators introduced
- Ramsar sites
- Access to sanitation
- Transport infrastructure
- Electricity access
World Environment Day 2025
- 05 Jun 2025
In News:
Every year on June 5, people across the globe unite to celebrate World Environment Day, an initiative led by the United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP).
Key Highlights:
- Observed on: June 5 annually
- Initiated by: United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP)
- First celebrated: 1973 (following the 1972 Stockholm Conference on the Human Environment)
- Objective: Promote global awareness and action for environmental protection
Theme for 2025: "Beat Plastic Pollution"
- Focuses on the escalating crisis of plastic pollution and its adverse impact on ecosystems, wildlife, and human health.
- Highlights the need to transition away from single-use plastics, promote sustainable consumption, and adopt eco-friendly alternatives.
Key Statistics:
- Plastic production: Increased from 2 million tonnes (1950) to 430 million tonnes (2025)
- Marine pollution:19–23 million tonnes of plastic enter aquatic ecosystems annually
- Microplastics detected in oceans, mountains, and the human body
Host Country for 2025: Republic of Korea
- Chosen for its leadership in green innovation and sustainable practices.
- Initiatives include:
- Advanced waste segregation and recycling systems
- Bans on single-use plastics in major outlets
- Promotion of tech-driven eco-solutions
By hosting, South Korea aims to showcase scalable models for combating plastic pollution globally.
Historical Background
- Stockholm Conference 1972 laid the foundation for modern environmental governance.
- UNEP assigns a theme and host country annually to align global action.
- Over 150 countries now participate through:
- Clean-up drives
- Tree plantation campaigns
- Policy forums
- Environmental education programs
Significance
World Environment Day plays a vital role in:
- Raising awareness on climate change, pollution, deforestation, and sustainability
- Encouraging individual and community-level action
- Facilitating policy dialogue and regulatory reform
- Mobilizing youth leadership in environmental movements
INS Varsha
- 08 Apr 2025
In News:
India is set to operationalise INS Varsha, its first dedicated base for nuclear-powered submarines, by 2026. Located near Rambilli, about 50 km south of Visakhapatnam, Andhra Pradesh, this high-security facility is part of the classified Project Varsha, aimed at strengthening India’s maritime and nuclear deterrence capabilities in the Bay of Bengal and Indian Ocean Region (IOR).
Key Features:
- Strategic Location: Near deep waters of the Bay of Bengal, facilitating stealthy submarine movement and minimizing detection.
- Infrastructure:
- Underground pens and tunnel systems to conceal and protect nuclear submarines.
- Inner and outer harbour facilities; inner harbour completed, work ongoing on breakwaters and jetties.
- 20 sq. km area, capacity to house at least 10–12 nuclear submarines.
- Stealth Capabilities: Similar to China’s Hainan base, it offers satellite-evasion advantages, crucial for the survivability of SSBNs (nuclear-powered ballistic missile submarines).
- Support Facilities: Proximity to BARC Atchutapuram for nuclear infrastructure, enabling swift integration and maintenance of strategic assets.
- Geopolitical Role: Counters Chinese dual-use naval infrastructure at Hambantota (Sri Lanka) and BNS Sheikh Hasina (Bangladesh).
Strategic Significance:
- Enhances second-strike capability, vital for nuclear deterrence under India's nuclear triad.
- Enables undetected deterrent patrols by SSBNs, ensuring survivability in case of counterforce attacks.
- Facilitates rapid access to key chokepoints, especially the Strait of Malacca.
India’s Expanding Nuclear Submarine Fleet
INS Aridhaman – Third SSBN:
- Scheduled for commissioning in 2025.
- 7,000-tonne displacement, more capable than predecessors INS Arihant and INS Arighat.
- Equipped with K-4 Submarine-Launched Ballistic Missiles (SLBMs) with a range of 3,500 km.
- Built under the Advanced Technology Vessel (ATV) project by Shipbuilding Centre, Visakhapatnam, with BARC and DRDO support.
- Designed for long-duration deterrent patrols in deep sea.
Future Developments:
- India launched its fourth SSBN in November 2024, with ~75% indigenous content.
- Plans underway for even larger SSBNs and the construction of six nuclear-powered attack submarines (SSNs), starting with two approved 9,800-tonne SSNs for conventional strike and escort roles.
Related Naval Expansion – Project Seabird (Karwar Base):
- Located on the western coast, expanding to accommodate 50 warships and submarines, plus 40 auxiliary vessels.
- Will include a dual-use air station, new dockyard, and multiple dry berths.
Exercise Tiger Triumph 2025
- 03 Apr 2025
In News:
- India and the United States have commenced the fourth edition of their major tri-service military exercise ‘Tiger Triumph’ in the Bay of Bengal, beginning April 1, 2025.
- The two-week-long drill focuses on Humanitarian Assistance and Disaster Relief (HADR) and crisis response, marking a significant step in the growing strategic defence partnership between the two nations.
Key Objectives:
- Enhance interoperability between the Indian and U.S. armed forces for joint HADR operations.
- Formulate Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs) for establishing a Combined Coordination Centre (CCC) for joint response during natural disasters and contingency operations.
- Conduct massive maritime and amphibious operations off the coast of Kakinada, following a harbour phase at Visakhapatnam.
Participating Forces and Assets:
India:
- Indian Navy:
- Ships: INS Jalashwa, INS Gharial, INS Mumbai, and INS Shakti
- Aircraft: P-8I long-range maritime patrol aircraft
- Support: Integral helicopters and landing crafts
- Indian Army:
- Troops from 91 Infantry Brigade
- 12 Mechanised Infantry Battalion
- Indian Air Force (IAF):
- Aircraft: C-130J ‘Super Hercules’
- Helicopters: Mi-17
- Rapid Action Medical Team (RAMT)
United States:
- U.S. Navy:
- USS Comstock (amphibious warship)
- USS Ralph Johnson (guided-missile destroyer)
- U.S. Marine Corps:
- Marine division troops onboard naval vessels
- Medical personnel to collaborate with Indian RAMT
Additional Activities:
- Establishment of a Joint Command and Control Centre at the Kakinada naval enclave by the Indian Army and U.S. Marines.
- Setting up of a Joint Medical Camp for humanitarian aid by IAF, Indian RAMT, and U.S. Navy medical teams.
- Training exchanges, sports events, and social interactions between personnel to foster mutual understanding and cooperation.
Strategic Significance:
Exercise Tiger Triumph is part of the broader India-U.S. defence cooperation, which includes:
- Army exercises:YudhAbhyas, Vajra Prahar
- Naval drills:Malabar Exercise (with Australia and Japan)
The growing frequency and complexity of such joint drills underline the strategic convergence between India and the U.S. in the Indo-Pacific region, particularly in strengthening maritime security and disaster response mechanisms.
Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD)
- 03 Apr 2025
In News:
- Ranchi, Jharkhand, is poised to become the first district in the state to launch a comprehensive campaign for the screening and management of Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD), now redefined as Metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD).
- The initiative will be carried out under the National Programme for Prevention and Control of Non-Communicable Diseases (NP-NCD).
- The campaign will begin on April 19, marking World Liver Day, and aims to raise awareness and strengthen early detection and treatment of liver disorders in the population.
About NAFLD/MASLD:
- NAFLD refers to fat accumulation in the liver not caused by alcohol consumption.
- It includes two types:
- Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver (NAFL) – mild form.
- Non-Alcoholic Steatohepatitis (NASH) – severe form, can progress to cirrhosis, liver failure, or cancer.
- It is increasingly prevalent in individuals with obesity, type 2 diabetes, hypertension, and metabolic syndrome.
- NAFLD is asymptomatic in early stages but can elevate the risk of cardiovascular disease, kidney disease, and diabetes-related complications.
- Affects all age groups, including children.
Key Features of the Ranchi NAFLD Initiative:
- Two-phase Screening Drive:
- Phase 1 (April–June): Focus on 30,000 high-risk individuals—those with obesity, diabetes, or hypertension.
- Phase 2 (July–November): Screening expanded to all adults over 18 years in the district.
- Technical Support: Provided by the Institute of Liver and Biliary Sciences (ILBS), New Delhi.
- Mobile Screening Vans:
- Each van costs approx. ?1 crore.
- Equipped with FibroScan, an advanced, non-invasive liver diagnostic tool.
- Services provided free of cost in both urban and rural areas.
- Capacity Building:
- 30–40 district-level officers to be trained as master trainers.
- Frontline healthcare workers will be trained to conduct screenings and data collection.
- Health System Strengthening:
- Referral mechanisms to ensure patients receive specialised care.
- Data tracking system to maintain records until integration with the national NCD portal.
Public Health Significance:
- As per the district's civil surgeon, 50% of OPD cases are liver-related.
- On average, 25 patients/day are diagnosed with liver disease; five require hospitalisation.
- Early detection through such initiatives can help prevent disease progression and mortality.
Treatment & Prevention of NAFLD:
- No specific drug currently exists for NAFLD.
- Weight loss remains the primary treatment—shown to reduce liver fat, inflammation, and fibrosis.
- Management of comorbidities like high blood pressure, high cholesterol, and diabetes is also recommended.
Payments Regulatory Board (PRB)

- 25 May 2025
In News:
The Central Government has notified the Payments Regulatory Board Regulations, 2025, replacing the earlier Board for Regulation and Supervision of Payment and Settlement Systems (BPSS) with a new statutory authority — the Payments Regulatory Board (PRB).
About the PRB
- Legal Basis: Constituted under Section 3 of the Payment and Settlement Systems Act, 2007.
- Objective: To regulate and supervise payment systems in India with broader representation and holistic oversight.
Composition (Total: 6 Members)
- Chairperson: Governor of the Reserve Bank of India (RBI)
- Ex-Officio Members:
- Deputy Governor of RBI in charge of the Department of Payment and Settlement Systems (DPSS)
- One RBI official nominated by the RBI Central Board
- Government Nominees:Three members nominated by the Central Government (previous BPSS had none)
Other Key Features:
- Expert Consultation: PRB can invite experts from fields like law and IT as permanent or ad hoc members.
- Eligibility Criteria:
- Members must be below 70 years of age
- Should not hold any legislative office or have material conflicts of interest
- Governance:
- Board meets at least twice a year
- Decisions are by majority vote; in case of a tie, the Chairperson (or Deputy Governor) casts the deciding vote.
- Delegation: PRB can delegate functions to RBI officers or sub-committees.
Institutional Support
- The PRB will be supported by the RBI’s DPSS, which will report directly to the board.
Significance of the Reform
- Marks a structural reform in the regulation of India’s rapidly growing payments ecosystem.
- Enhances government oversight through its nominees.
- Aims to improve coordination among various departments (e.g., fintech, digital payments).
- Seeks to provide uniform and consolidated regulation across diverse payment systems.
Shirui Lily Festival
- 21 May 2025
In News:
The 5th State-Level Shirui Lily Festival resumed in Ukhrul district, Manipur from May 20–24, 2025, after a two-year pause due to ethnic unrest. It marks a symbolic step towards peace, as it involved significant movement through previously restricted areas with heightened security.
About the Shirui Lily Festival:
- Organised by: Manipur Tourism Department
- First Held: 2017
- Venue:Shirui Village, Ukhrul District
- Objective: Promote eco-tourism and create awareness about the endangered Shirui Lily
- Special 2025 Edition: Commemorates the 75th anniversary of the discovery of the Shirui Lily
Key Features (2025 Edition):
- Cultural Events: Traditional dances, gospel rock shows, and live performances at the ShiRock music festival
- Eco-Initiatives: Trash collection drives and conservation awareness campaigns
- Competitions:
- SheChef Cooking Contest (vegetarian & childhood memory dishes)
- Miss Shirui Lily 2025 beauty pageant
- Sports (football, wrestling, tug of war, mini-marathon)
- Adventure Activities: Ziplining, camping, biking
- Special Ceremonies: Unveiling of the 75th Anniversary Memorial and a drone show
- Closing Function: Hosted by senior officials from the Ministry of Tourism
About Shirui Lily (Lilium mackliniae):
- Botanical Name:Lilium mackliniae
- Discovered by: Botanist Frank Kingdon-Ward in 1946, named after his wife Jean Macklin
- Local Name:KashongTimrawon
- Geographic Range: Exclusively found in the Shirui Hills (2,673 m altitude) of Ukhrul district
- State Flower of Manipur
Ecological and Cultural Significance:
- Endemic Habitat: The species is not viable for transplantation outside its native micro-climate
- Flowering Season: April to June, marked by a breathtaking bloom of pinkish-white bell-shaped flowers
- Cultural Reverence: Associated with the local deity Philava, symbolising spiritual and ecological identity of the Tangkhul Naga tribe
- Global Recognition: Awarded by the Royal Horticultural Society at the London Flower Show in 1950
Conservation Status and Efforts:
- Threats: Habitat loss, invasive species, and climate change
- Conservation Status:Endangered
- Scientific Interventions: ICAR-NEH, under Dr. Manas Sahoo, has developed micropropagation techniques for in-situ conservation
GRAIL Mission
- 19 May 2025
In News:
The Moon, Earth's only natural satellite, exhibits a striking hemispheric contrast. The nearside, visible from Earth, is dominated by dark, flat basaltic plains (mare), while the farside is rugged, heavily cratered, and lacks these features. This asymmetry has long puzzled scientists.
Recent findings from NASA's GRAIL (Gravity Recovery and Interior Laboratory) mission, launched in 2011, have provided critical insights into this phenomenon.
GRAIL Mission: An Overview
- Objective: To map the Moon’s gravitational field in unprecedented detail.
- Spacecraft: Two identical probes named Ebb and Flow.
- Method: By measuring the tiny variations in the distance between the probes as they orbited the Moon, scientists could infer differences in crust thickness, interior composition, and subsurface structures.
Key discoveries:
- The Moon’s crust is more porous and thinner than previously thought.
- Detection of long, linear features called dikes, indicating early lunar expansion.
Reasons for Lunar Asymmetry
- Tidal Deformation and Gravitational Asymmetry
- The nearside flexes more than the farside during the Moon’s elliptical orbit, a result of tidal deformation caused by Earth’s gravity.
- The increased internal heat and flexibility on the nearside suggest it is warmer and more geologically active at depth.
- Volcanic Activity and Heat Distribution
- The nearside experienced intense volcanic activity billions of years ago, forming the large mare regions.
- This activity led to the concentration of radioactive, heat-producing elements (like thorium and titanium) in the nearside mantle.
- The nearside mantle is 100–200°C hotter than the farside, establishing a long-term thermal imbalance.
- Crustal Thickness and Surface Composition
- The nearside crust is significantly thinner, allowing magma to reach the surface more easily, contributing to extensive lava flows.
- The thicker farside crust restricted such activity, preserving its rugged, cratered appearance.
Implications for Space Science and Earth
- The findings aid in developing precise lunar navigation and positioning systems, essential for future human missions.
- The methodology can be applied to other celestial bodies like Enceladus (Saturn) and Ganymede (Jupiter), both candidates in the search for life.
- Understanding the Moon's structure enhances our grasp of Earth-Moon gravitational dynamics, which affect tides and planetary stability.
Chenchu Tribe and Indiramma Housing Scheme

- 17 May 2025
In News:
In May 2025, the Telangana government announced the sanctioning of 10,000 Indiramma houses to Chenchu tribal families under a saturation approach in four Integrated Tribal Development Agencies (ITDA)—Utnur, Bhadrachalam, Munnanur, and EturuNagaram. An additional 700 units per ST assembly constituency have also been approved within these ITDA areas.This move aligns with the state’s commitment to improving housing infrastructure in tribal areas.
About Chenchu Tribe
Classification:
- Particularly Vulnerable Tribal Group (PVTG) in Andhra Pradesh
- Also found in Telangana, Karnataka, and Odisha
Habitat:
- Primarily inhabit the Nallamalai forests (Eastern Ghats)
- Chenchu settlements are called “Penta”, consisting of kin-based scattered huts
Language:
- Native Chenchu language (Dravidian family)
- Many also speak Telugu
Social Structure:
- Small conjugal families with gender equality
- Village elder, known as “Peddamanishi”, serves as the community authority
Livelihood:
- Forest-based subsistence lifestyle
- Depend on collection of non-timber forest produce (NTFPs) such as:
- Roots, tubers, fruits, beedi leaves, honey, gum, mohua flowers, tamarind
- Some serve as forest laborers, but mostly rely on traditional hunting and gathering
Religion & Culture:
- Worship local deities; blend of indigenous and Hindu practices
- Hold deep spiritual ties with the Srisailam Temple (dedicated to Lord Shiva and Devi Brahmaramba), which lies at the heart of their region
- Chenchus enjoy customary privileges at the Srisailam shrine
Crohn’s Disease
- 15 May 2025
In News:
A former SpaceX employee has filed a lawsuit against the company, alleging wrongful termination. According to the claim, the individual was fired due to frequent restroom visits linked to Crohn’s disease, a chronic medical condition. The case has drawn attention to the difficulties faced by individuals managing long-term illnesses in demanding work environments.
Key Details:
Crohn’s disease is a type of inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) that causes chronic inflammation of the digestive tract. It is a lifelong condition that can significantly impact quality of life and daily functioning.
Key Features:
- Nature of the Disease:A persistent and often progressive condition marked by inflammation in different sections of the digestive tract, most frequently affecting the end of the small intestine (ileum) and the beginning of the large intestine (colon).
- Extent of Inflammation:Inflammation may penetrate deep into the bowel wall, leading to pain, damage, and complications over time.
- Common Symptoms:
- Persistent diarrhea
- Abdominal pain and cramping
- Weight loss
- Fatigue and sometimes malnutrition
Symptoms can vary in severity and may appear intermittently, often referred to as “flare-ups.”
Complications and Impact
Crohn’s disease can be debilitating and may result in serious complications, including:
- Intestinal blockages
- Fistulas (abnormal connections between body parts)
- Abscesses
- Nutritional deficiencies
Treatment and Management
- No Cure Available:While there is currently no cure for Crohn’s disease, medical therapies can effectively manage symptoms and inflammation.
- Goals of Treatment:
- Inducing and maintaining remission
- Healing affected intestinal tissues
- Improving overall quality of life
- Treatment Approaches:
- Anti-inflammatory medications
- Immune system suppressors
- Dietary changes
- In severe cases, surgery may be required
Many individuals with Crohn’s can lead productive lives with appropriate treatment and support.
Organization of Islamic Cooperation (OIC)

- 08 May 2025
About the OIC
The Organization of Islamic Cooperation (OIC) is the world’s second-largest intergovernmental organization after the United Nations, comprising 57 member states across four continents. It was established on September 25, 1969, following the historic summit held in Rabat, Morocco, which was convened in response to the arson attack on the Al-Aqsa Mosque in occupied Jerusalem.
Objectives and Purpose
The OIC’s primary goals are to:
- Preserve and promote Islamic values.
- Safeguard the national sovereignty and independence of its member states.
- Contribute to international peace and security.
- Serve as the collective voice of the Muslim world, protecting their interests across economic, social, and political spheres.
Structure and Headquarters
- The OIC’s headquarters is located in Jeddah, Saudi Arabia.
- Its official languages are Arabic, English, and French.
Membership
Notable member countries include Afghanistan, Bahrain, Bangladesh, Egypt, Indonesia, Iran, Iraq, Jordan, Kuwait, Lebanon, Libya, Malaysia, Maldives, Morocco, Niger, Oman, Pakistan, the Palestinian Authority, Qatar, Saudi Arabia, Sudan, Turkey, Uganda, United Arab Emirates, and Yemen, among others.
Principal Organs of the OIC
- Islamic Summit Conference (ISC):The highest authority of the OIC, meeting every three years to set the organization’s policies and strategic direction.
- Council of Foreign Ministers (CFM):Convening annually, the CFM reviews and oversees the implementation of decisions made by the Islamic Summit.
- General Secretariat:The executive branch responsible for executing the resolutions of the ISC and CFM.
Additionally, the OIC has established various ministerial-level committees—some chaired by heads of state—to coordinate cooperation among member countries in political, economic, cultural, social, spiritual, and scientific fields.
Partnerships and Global Engagement
The OIC collaborates closely with international organizations, including all specialized agencies of the United Nations, as well as governments and civil society organizations (CSOs). These partnerships help address concerns affecting its member states and the global Muslim community.
India to Receive INS Tamal
- 07 May 2025
In News:
India is set to induct INS Tamal, the second advanced stealth frigate of the Krivak-III class, built in Russia under a bilateral defence contract.
About INS Tamal
- Type & Class:INS Tamal is a 3,900-tonne stealth frigate, part of the Krivak-III class deal signed in 2016 between India and Russia. It is the sister ship of INS Tushil, commissioned in December 2024.
- Builder & Collaboration:Constructed at the Yantar Shipyard in Kaliningrad, Russia, under India-Russia defence cooperation.
The contract includes four frigates: two built in Russia and two under construction at Goa Shipyard with technology transfer.
Key Features
- Stealth Technology:Equipped with advanced suppression systems for radio, infrared, and acoustic signatures to enhance survivability.
- Armaments:
- BrahMos supersonic cruise missiles (range approx. 450 km)
- Shtil surface-to-air missiles
- Anti-submarine torpedoes and rocket launchers
- Performance:
- Speed exceeding 30 knots
- Can deploy Kamov-28 and Kamov-31 helicopters for anti-submarine warfare and airborne early warning.
- Automation: High automation reduces crew workload and improves operational efficiency.
Strategic Importance
- Enhances India’s blue-water naval capabilities across air, surface, underwater, and electromagnetic domains.
- Strengthens naval deterrence and force projection in the Indo-Pacific region, especially amid rising tensions in the Arabian Sea.
- Demonstrates successful Make in India initiative combined with global collaboration, as two of the frigates are being built domestically at Goa Shipyard.
India-Angola Bilateral Talks and Strategic Cooperation
- 07 May 2025
In News:
The Prime Minister of India recently held bilateral talks with Angolan President João Lourenço in New Delhi. During the meeting, India offered Angola a $200 million defence credit line and discussed expanding cooperation in sectors such as infrastructure, defence, and space technology. The visit also commemorates the 40th anniversary of diplomatic relations between India and Angola.
About Angola
- Location: Southwestern Africa, bordered by the Atlantic Ocean to the west.
- Capital: Luanda, a major coastal port city.
- Neighbouring countries: Republic of the Congo, Democratic Republic of the Congo, Zambia, Namibia, and the Atlantic Ocean.
- Special territory: Includes the exclave of Cabinda, located north of the main territory.
Geographical Features
- Major Plateaus:Bié Plateau (~2,600 m), Huíla Plateau (~2,300 m), Malanje Highlands.
- Highest Point: Mount Moco (2,620 m or 8,596 ft) near Huambo.
- Rivers:
- Cuanza (Kwanza): Largest river entirely within Angola.
- Cunene River: Forms part of the border with Namibia.
- Cuango River: Tributary of the Congo River.
- Other rivers drain into the Zambezi and Okavango river systems.
- Desert: Southwest Angola forms part of the Namib Desert.
- Climate: Tropical with distinct rainy and dry seasons, influenced by the cold Benguela ocean current.
Demographics and Economy
- Ethnic groups: Predominantly Bantu-speaking, including Ovimbundu, Kimbundu, and Bakongo communities.
- Economic importance:
- One of Africa’s leading oil producers.
- Rich mineral resources including diamonds, iron ore, copper, and gold.
- The northeast is notable for diamond deposits found in river gravels.
Gaia Space Observatory
- 31 Mar 2025
In News:
The European Space Agency (ESA) has officially retired its Gaia space observatory after over nine years of pioneering work in astrometry. Launched in December 2013, Gaia was designed to create the most detailed three-dimensional map of the Milky Way galaxy, transforming our understanding of its structure, evolution, and constituents.
About Gaia
- Mission Objective: Gaia aimed to precisely measure the positions, distances, motions, and physical properties of over 2 billion stars within the Milky Way. Its data helps scientists study the galaxy’s formation, predict its future evolution, and explore celestial phenomena.
- Orbit & Technology: Stationed at the second Lagrange point (L2), about 1.5 million kilometers from Earth, Gaia operated beyond the disturbances of Earth’s atmosphere, sun, and moon. Equipped with twin telescopes focusing light onto a nearly one-billion-pixel digital camera—the largest ever deployed in space—the observatory had three key instruments: an astrometer, photometer, and spectrometer to measure stellar positions, brightness, and compositions.
Major Contributions and Discoveries
- 3D Galactic Map: Gaia revealed the warped and wobbling nature of the Milky Way’s disc, mapped its spiral arms and central bulge, and detailed its dynamic evolution shaped by ancient galactic collisions. These findings shed light on events influencing the formation of stars including our Sun.
- New Black Holes: The mission identified previously unseen black holes detectable only by their gravitational influence, marking a first in astronomical observations.
- Asteroid Cataloguing: Gaia tracked the paths of over 150,000 asteroids, enabling better prediction of their trajectories and potential threats to Earth.
- Legacy and Data: Although Gaia has mapped approximately 2% of the galaxy’s stars so far, its extensive data sets continue to be processed and released, promising decades of future scientific breakthroughs.
End of Mission and Legacy
In March 2025, ESA safely deactivated Gaia by draining its energy and shifting it to a retirement orbit around the Sun, ensuring it does not interfere with upcoming missions. While the spacecraft’s active observations have ended, Gaia’s rich data legacy remains invaluable to astronomers worldwide.
Tejas LCA Mk1A
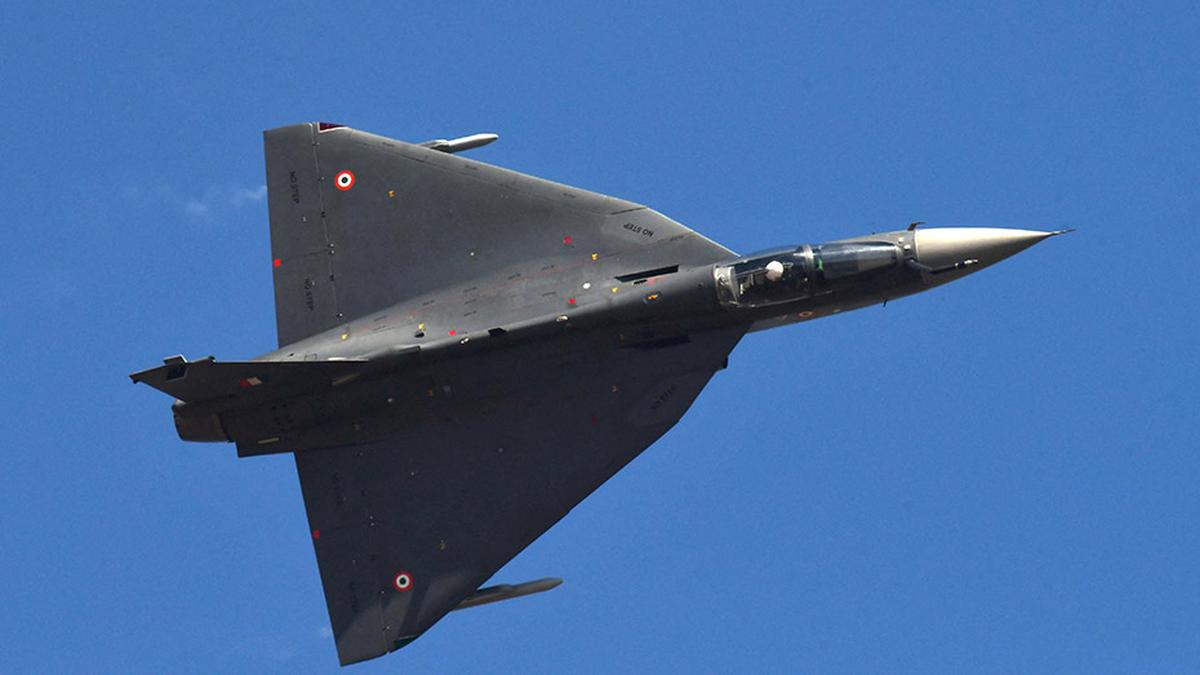

- 29 Mar 2025
In News:
GE Aerospace has commenced delivery of F404-IN20 jet engines to Hindustan Aeronautics Limited (HAL) for the Tejas Light Combat Aircraft Mk1A. This marks a significant milestone in India’s indigenous defence production capabilities and is vital for bridging the Indian Air Force's (IAF) operational gaps.
Background on Tejas LCA Mk1A
- Tejas LCA Mk1A is an advanced version of the indigenous Light Combat Aircraft (LCA) developed by HAL.
- It incorporates over 40 improvements over the Mk1 variant, aimed at enhancing combat readiness, survivability, and ease of maintenance.
Key Features:
- Radar Systems:
- Israeli EL/M-2052 AESA Radar.
- Indigenous Uttam AESA Radar (under integration).
- Electronic Warfare:
- Unified Electronic Warfare Suite (UEWS).
- Advanced Self-Protection Jammer Pod.
- Weapons Capability:Nine hardpoints supporting Beyond Visual Range (BVR) missiles, Air-to-Air and Air-to-Ground missiles, and Advanced Short-Range Air-to-Air Missiles (ASRAAM).
- Digital Fly-by-Wire System:Upgraded Flight Control Computer (DFCC Mk1A).
- Improved Operational Efficiency:Reduced weight, enhanced maintainability, and faster sortie turnaround.
Engine Deliveries and Production Status
- First Engine Delivered: March 26, 2025; expected in India by April.
- Engine Type: F404-IN20 by GE Aerospace – a high-thrust variant tailored for IAF needs.
- Key Engine Features:
- Higher-flow fan, single-crystal turbine blades, and customized components.
- Achieved Mach 1.1 during Tejas’ maiden flight in 2008.
Delivery Commitments:
- 2025 Target: 12 engines and 12 Tejas Mk1A jets to be delivered.
- Full Order: 99 engines ordered in 2021.
- Production Goal: HAL to produce 24 aircraft per year.
- Current Readiness: Three Mk1A jets flying; 11 more expected by end-2025 (10 from Bengaluru, 1 from Nasik).
Production Challenges:
- Engine production was dormant for five years.
- Reinitiating during the COVID-19 pandemic caused further delays.
- GE has now stabilized its supply chain and resumed engine production.
Strategic Importance for IAF
- Current IAF Strength: 31 fighter squadrons (sanctioned strength: 42.5).
- Urgency: Older aircraft like Jaguar, MiG-29UPG, and Mirage-2000 will begin phasing out by decade-end.
- Future Platforms: LCA Mk2 is under development; AMCA (Advanced Medium Combat Aircraft), India’s 5th-gen stealth fighter, is still a decade away.
Policy Push:A high-level committee led by the Defence Secretary submitted recommendations to the Defence Minister for enhancing IAF capabilities in short, medium, and long-term.
Lyme Disease
- 29 Mar 2025
In News:
Lyme disease, also known as Lyme borreliosis, is a bacterial infection caused by Borrelia burgdorferi. It is transmitted to humans through the bite of infected blacklegged ticks, commonly known as deer ticks. These ticks become carriers when they feed on infected animals, such as rodents. Importantly, Lyme disease does not spread from person to person, nor through food, water, air, pets, or other insects like mosquitoes and flies.
The disease is primarily reported in North America, Europe, and parts of Asia, particularly in wooded and grassy regions during the warmer months. In the United States, it is most prevalent in the northeastern, mid-Atlantic, and upper Midwestern states.
Symptoms and Progression
Lyme disease often begins with a characteristic red, expanding rash called erythema migrans, which may appear in a bull’s-eye pattern. Early symptoms also include fever, chills, fatigue, muscle aches, headache, and swollen lymph nodes. If untreated, it can progress to cause:
- Neurological issues: meningitis, facial palsy (Bell’s palsy), nerve pain, and brain inflammation.
- Cardiovascular problems: irregular heartbeat and heart block.
- Musculoskeletal symptoms: arthritis, joint pain (especially in the knees), and swelling.
- Other effects: dizziness, vision problems, memory issues, and concentration difficulties (often referred to as “brain fog”).
Treatment Protocol
Lyme disease is primarily treated with antibiotics, especially when diagnosed early. Common antibiotics include doxycycline (for adults and children over 8 years), amoxicillin (for younger children and pregnant women), cefuroxime, and azithromycin (for those allergic to other options). The treatment duration varies:
- Localized skin infections: 14 days
- Early disseminated infections: 21 days
- Lyme arthritis: 28 to 60 days
- Severe or neurological cases may require intravenous antibiotics like ceftriaxone
In some cases, symptoms may persist even after treatment, a condition known as Post-Treatment Lyme Disease Syndrome (PTLDS). While the exact cause is unknown, continued antibiotic use does not improve outcomes, and treatment focuses on managing symptoms.
Recent Scientific Breakthrough
In a major scientific advancement, researchers have identified a crucial enzyme—lactate dehydrogenase specific to Borrelia burgdorferi (BbLDH)—which plays a vital role in the bacterium's survival and infectivity. Unlike most organisms that rely on thiamin-dependent metabolism, B. burgdorferi uniquely depends on BbLDH to convert pyruvate to lactate, maintaining its NADH/NAD+ balance.
The research, conducted at Virginia Commonwealth University and published in mBio, demonstrated through genetic, biochemical, and structural analysis that BbLDH is essential for the growth and infection capability of the Lyme disease bacterium. Loss-of-function studies confirmed its indispensability, both in laboratory and in vivo models.
High-throughput screening of chemical compounds led to the identification of several promising BbLDH inhibitors. These inhibitors could form the basis for future, highly targeted treatments against Lyme disease. Moreover, the findings have broader implications for tackling other tick-borne illnesses.
Urban Heat Island Effect in Hyderabad
- 25 Mar 2025
In News:
The Telangana Socio-Economic Outlook 2025 highlights a concerning rise in night-time temperatures in Hyderabad, attributed to the Urban Heat Island (UHI) effect. This growing urban microclimatic issue has critical public health and environmental implications.
What is Urban Heat Island (UHI)?
- Definition: UHI is a climatic phenomenon where urban areas record significantly higher temperatures than surrounding rural or peri-urban regions, particularly at night.
- Cause: Result of urbanization and human activities that alter land surfaces and trap heat.
Key Factors Contributing to UHI
- Reduced green cover: Shrinking vegetation limits natural cooling via shade and evapotranspiration.
- High density of concrete structures: Buildings and roads absorb solar radiation during the day and release heat slowly at night.
- Urban layout: Tall buildings and narrow streets trap warm air, reducing air circulation.
- Anthropogenic heat: Emissions from vehicles, air conditioners, and industries contribute to localized warming.
- Surface characteristics: Dark tarred roads absorb more heat and release it at night, worsening night-time UHI.
Hyderabad Case Study: Telangana Socio-Economic Outlook 2025
- Temperature Difference:
- Night-time: Core city is 1.9°C warmer than surrounding peri-urban and outer zones.
- Daytime: Interestingly, the core is 0.7°C cooler due to shade from tall buildings.
- Peak UHI Season: March to August.
- Most Affected Zones: High-rise, concrete-dense city centers with low vegetation.
Health Impacts of UHI
According to medical experts:
- Physical Effects:
- Heat exhaustion & heat strokes
- Dehydration, skin issues
- Cardiovascular and kidney stress
- Vulnerable Groups: Elderly, children, and those with pre-existing conditions.
- Biological Mechanism: Prolonged exposure increases pro-inflammatory cytokines, leading to immune suppression and chronic fatigue.
- Mental Health: UHI contributes to sleep disturbances, psychological stress, and anxiety.
Government Response
- Clean and Green Energy Policy 2025: Telangana aims to promote cooler, greener cities.
- Recommended Actions:
- Interdisciplinary collaboration among urban planners, healthcare professionals, and community experts.
- Urban design incorporating green infrastructure and heat-resilient materials.
Subacute Sclerosing Panencephalitis (SSPE)
- 17 Mar 2025
In News:
Subacute Sclerosing Panencephalitis (SSPE) has emerged as a public health concern in Uttar Pradesh, particularly in Lucknow, due to poor measles vaccination coverage. Despite being rare globally, cases remain alarmingly high in regions with incomplete immunisation.
About SSPE:
- SSPE is a progressive and fatal neurological disorder that appears several years after a person has recovered from measles (rubeola).
- It is caused by a persistent measles virus in the brain, which triggers chronic inflammation and gradual destruction of nerve cells.
- Though globally rare, SSPE is more prevalent in areas with low immunisation rates. Males and children from low-income families are more commonly affected.
Symptoms:
- Early signs: cognitive decline, poor academic performance, behavioural changes (irritability, hallucinations), and sleep disturbances.
- Progression: seizures, involuntary muscle jerks, speech deterioration, visual impairment, and motor dysfunction.
- Advanced stage: muscle rigidity, difficulty swallowing, risk of aspiration pneumonia, coma, and eventual death.
Treatment & Prevention:
- No cure exists, and the mortality rate approaches 100%.
- Treatment focuses on symptom management; antiviral and immune-boosting drugs may slow progression.
- Timely measles vaccination is the only effective prevention strategy.
Significance for Public Health:
- SSPE underscores the critical importance of achieving universal immunisation coverage.
- Experts recommend stronger awareness campaigns and better enforcement of the Universal ImmunisationProgramme (UIP) to eliminate measles and prevent SSPE.
Madhav National Park
- 13 Mar 2025
In News:
Madhav National Park in Madhya Pradesh has been declared India’s 58th Tiger Reserve and the 9th in Madhya Pradesh, strengthening the state's status as a leader in tiger conservation.
About Madhav National Park
- Location: Shivpuri district, Madhya Pradesh; part of the Chambal region and the Upper Vindhyan Hills on the northern fringe of the Central Highlands.
- Established: As Madhya Bharat National Park in 1955; renamed Madhav National Park in 1959.
- National Park Status: Since 1958.
- Area: Approx. 354 sq km (expanded from 165 sq km).
- Historical Significance: Former hunting ground of Mughal emperors and Maharaja of Gwalior; named after Maharaja Madhav Rao Scindia.
Ecological Profile
- Vegetation:
- Northern Tropical Dry Deciduous Forests
- Dry Thorn Forests typical of North-Western Madhya Pradesh
- Fauna:
- Large Mammals: Tigers, leopards, wolves, jackals, foxes, wild dogs
- Antelopes: Nilgai, Chinkara, Chowsinga
- Deer Species: Chital, Sambar, Barking Deer
- Others: Crocodiles, porcupines, wild pigs, pythons
- Aquatic Ecosystems:
- Two major lakes: Sakhya Sagar and Madhav Sagar support aquatic biodiversity
Tiger Conservation Highlights
- Declared a Tiger Reserve: In 2024, becoming India’s 58th and Madhya Pradesh’s 9th.
- Tiger Reintroduction: Began in 2023; currently home to five tigers, including two cubs.
- Core and Buffer Zones:
- Core Zone: Strictly protected, no human activity
- Buffer Zone: Allows limited, regulated human use to support coexistence
Governance and Protection Framework
- Tiger Reserve Status:
- Notified under Section 38V of the Wildlife Protection Act, 1972
- Falls under Project Tiger (1973), monitored by the National Tiger Conservation Authority (NTCA)
- Approval Process:
- State Government Proposal
- NTCA Evaluation
- MoEFCC Final Notification
- Monitoring System: M-STrIPES (Monitoring System for Tigers – Intensive Protection and Ecological Status) used for surveillance and conservation.
Rare Civet Cat
- 10 Mar 2025
In News:
Recently, a rare civet cat, typically native to the Seshachalam forests near Tirumala, was unexpectedly sighted near Tadepalli in Guntur district, Andhra Pradesh. The animal entered a residential area, startling locals, and was later safely rescued and examined by forest officials.
About Civet Cats
- Taxonomy:Civets belong to the Viverridae family, which includes civets, genets, oyans, and linsangs. There are 15–20 species across 10–12 genera.
- Distribution:Found in Africa, southern Europe, and Asia, including eight wild species in India.
- Common Palm Civet and Small Indian Civet are widely distributed.
- The Malabar Large-spotted Civet (Viverracivettina) is critically endangered and endemic to the Western Ghats.
- Conservation Status:The Malabar Civet is listed as Critically Endangered under the IUCN Red List.
Physical Characteristics:
- Appearance: Cat-like, with thickly furred tail, pointed snout, and small ears.
- Size: Body length: 40–85 cm; Tail: 13–66 cm; Weight: 1.5–11 kg.
- Coloration: Usually buff or grayish, with black spots, stripes, or both.
Behavior and Habitat:
- Nocturnal and Solitary: Typically dwell in tree hollows, rocks, or similar secluded areas.
- Diet: Primarily frugivorous and insectivorous, occasionally feeding on small animals.
- Habitat Range: Though mostly forest-dwelling, rare sightings in urban zones have occurred, as seen in the Tadepalli incident.
Significance of Recent Sighting:
- The civet descended from Tadepalli hills and entered a home, prompting forest department intervention.
- Identified as a rare species similar to African civets.
- Medically examined, found healthy, and is to be rehabilitated into the wild.
- The incident highlights growing human-wildlife interactions and the need for urban wildlife awareness.
Juanga Tribe
- 06 Mar 2025
In News:
The National Human Rights Commission (NHRC) has sought an Action Taken Report (ATR) from the District Magistrate of Keonjhar, Odisha, over alleged human rights violations concerning the Juanga tribe, a Particularly Vulnerable Tribal Group (PVTG) in the region.
About Juanga Tribe
- One of 13 PVTGs among 62 tribal communities in Odisha.
- Population: ~50,000 (2011 Census).
- Primarily located in Keonjhar and Dhenkanal districts, especially in the Gonsaika hills of Banspal block, Keonjhar.
- Language: Juang, a Munda language of the Austroasiatic family.
- Known for their clan structure, kinship ties, and animistic beliefs blended with Hindu practices. Their sun god is regarded as the supreme deity.
- Traditional livelihood: Initially hunters and gatherers, later adapted to basket-weaving and bartering after forest reserves were declared during British rule.
- Traditional clothing: Women wore leaf girdles; men used small loincloths. Post-contact, they adopted external clothing practices.
Alleged Human Rights Violations
- The petition highlighted lack of basic amenities in 114 Juanga villages:
- Healthcare: Nearest PHC is 15 km away; residents must carry patients on cots. Limited access to Biju Swasthya Kalyan Yojana or National Health Card.
- Infrastructure: Absence of all-weather roads, schools, and safe drinking water.
- Tragic case: Deaths of SuniaJuanga (35), his wife Rashmi (30), and their six-month-old daughter due to lack of timely medical help in Jantari village.
- Social issues: No official records on child marriages, orphans, or other vulnerable groups among the Juangas.
NHRC's Directive
- NHRC asked for a detailed report within four weeks from the district administration.
- The petition also criticized underutilization of the District Mineral Foundation (DMF) funds, despite Keonjhar being one of the top fund-holding districts.
Naval Anti-Ship Missile – Short Range (NASM-SR)

- 03 Mar 2025
In News:
The Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO) and the Indian Navy successfully conducted flight trials of the indigenous Naval Anti-Ship Missile – Short Range (NASM-SR) with a ‘Man-in-Loop’ capability from a Seaking 42B naval helicopter at the Integrated Test Range (ITR), Chandipur.
Key Features and Capabilities:
- Man-in-Loop Functionality:
- Provides real-time human intervention during flight.
- Enables in-flight retargeting by transmitting live seeker images to the pilot through a high-bandwidth two-way data link.
- Offers tactical flexibility in selecting and engaging specific targets among multiple options.
- Guidance and Navigation:
- Launched in Bearing-Only Lock-On After Launch (BOLOAL) mode.
- Equipped with an Indigenous Imaging Infra-Red (IIR) Seeker for terminal phase guidance.
- Uses an Indigenous Fiber Optic Gyroscope-based Inertial Navigation System (INS) and a Radio Altimeter for accurate mid-course and low-altitude navigation.
- Design and Control:
- Features Electro-Mechanical Actuators and Jet Vane Control for enhanced maneuverability.
- Integrated avionics module, thermal batteries, and PCB warhead support precise targeting and mission efficiency.
- Stealth and Strike Capability:
- Operates in Sea-Skimming Mode to evade radar detection.
- Demonstrated a direct hit on a small ship target at its maximum range during trial.
- Propulsion:Powered by solid propulsion, featuring an in-line ejectable booster and long-burn sustainer.
Development and Significance:
- Jointly developed by DRDO and the Indian Navy.
- Key DRDO labs involved:
- Research Centre Imarat (RCI)
- Defence Research and Development Laboratory (DRDL)
- High Energy Materials Research Laboratory (HEMRL)
- Terminal Ballistics Research Laboratory (TBRL)
- Marks India’s capability in indigenous anti-ship missile systems with advanced features like man-in-loop control and high-precision targeting.
- Enhances India’s naval warfare and coastal defense capabilities, aligning with Atmanirbhar Bharat in defense manufacturing.
Technology Adoption Fund (TAF)

- 24 Feb 2025
In News:
IN-SPACe, India’s space sector regulator under the Department of Space, has launched the Technology Adoption Fund (TAF) to accelerate the commercialization of indigenous space technologies.
About TAF:
- Objective: To bridge the gap between early-stage innovation and market-ready space solutions developed by Indian startups, MSMEs, and industries.
- Goal: Reduce dependence on imported technologies and strengthen India's position in the global space sector.
Key Features:
- Financial Support:
- Startups/MSMEs: Up to 60% of project cost.
- Larger industries: Up to 40%.
- Funding cap: ?25 crore per project.
- Eligibility: Open to all non-government entities (NGEs) with commercially viable space innovations.
- Support Provided:
- Partial funding for development and commercialization.
- Technical mentoring and guidance.
- Focus Areas: Launch vehicles, satellites, space-based applications, and related services.
- Outcomes Expected:
- Development of new space products.
- Intellectual property generation.
- Enhanced production capabilities.
- Economic growth and job creation.
About IN-SPACe:
- Established: 2020
- Ministry: Department of Space
- Location: Ahmedabad, Gujarat
- Role: Single-window agency promoting private participation in India's space ecosystem.
- Functions:
- Authorizes and monitors private sector space activities.
- Facilitates access to ISRO infrastructure.
- Collaborates with academia, industry, and research bodies.
Significance:
- Encourages private innovation in space tech.
- Aligns with the larger vision of making India a hub for space entrepreneurship.
- Strengthens India’s self-reliance and competitiveness in global space technology.
Brazil Joins OPEC+
- 24 Feb 2025
Brazil Joins OPEC+
Source: Times of India
In News:
In February 2025, Brazil officially joined OPEC+, a coalition of oil-producing nations. This development comes ahead of Brazil hosting COP30, the annual UN climate summit.
About OPEC and OPEC+
- OPEC (Organization of the Petroleum Exporting Countries):
- A permanent intergovernmental organization established in 1960 at the Baghdad Conference.
- Aims to coordinate and unify petroleum policies to ensure stable prices and regular supply.
- Headquartered in Vienna, Austria.
- Current members include Saudi Arabia, Iran, Iraq, UAE, Nigeria, Libya, Algeria, and others.
- OPEC+ Formation:
- Created in 2016 to stabilize oil markets, particularly in response to rising U.S. shale oil production.
- Includes 12 OPEC members plus 11 non-OPEC countries like Russia, Kazakhstan, Mexico, and now Brazil (2025).
- Functions as a forum for strategic discussions but not all members are bound by production quotas.
Brazil’s Role and Strategic Significance
- Oil Production Status:
- Seventh-largest oil producer globally, with around 4.3 million barrels/day.
- In 2024, crude oil became Brazil’s top export, overtaking soybeans.
- OPEC+ Membership:
- Brazil joins the Charter of Cooperation but retains autonomy in production decisions.
- It seeks to influence global oil policy while protecting its energy interests.
- Balancing Act:
- While focusing on oil revenue for economic growth and energy transition funding, Brazil also pursues renewable energy through agencies like IRENA.
- This dual approach reflects an attempt to align development with environmental commitments.
Environmental Concerns and Criticism
- Brazil’s decision to expand oil exploration—especially near sensitive ecosystems like the Amazon—has drawn criticism.
- Environmentalists argue it contradicts climate goals, particularly as Brazil prepares to host COP30.
Note:
- OPEC+ is not a formal organization but a strategic alliance.
- Brazil is part of OPEC+ but is not bound by production quotas.
- OPEC’s headquarters is in Vienna, Austria (Austria is not an OPEC member).
- India is not a member of OPEC or OPEC+.
Mount Etna Eruption 2025

- 18 Feb 2025
In News:
On February 12, 2025, Mount Etna, Europe's tallest and most active volcano, erupted once again, spewing lava flows and dense ash clouds into the atmosphere. The event drew attention not just due to its visual spectacle, but also because of the geological, environmental, and socio-economic implications it carries.
About Mount Etna
- Location: Eastern coast of Sicily, Italy — the largest island in the Mediterranean Sea.
- Type:Active stratovolcano, known for frequent eruptions.
- Height & Size: Highest peak south of the Alps and tallest active volcano in Europe; rises over 3,300 meters and covers 1,190 sq. km with a basal circumference of 140 km.
- Tectonic Setting: Lies above the convergent boundary of the African and Eurasian tectonic plates, making it a hotspot for seismic and volcanic activity.
- Eruption History: Recorded to have erupted over 200 times since 1500 BCE, with persistent volcanic activity.
- UNESCO Recognition: Declared a UNESCO World Heritage Site in 2013 for its exceptional geological features, cultural relevance, and continuous scientific monitoring.
- Decade Volcano Status: Designated a Decade Volcano by the United Nations due to its proximity to densely populated areas, including the city of Catania, and the potential risk it poses, warranting special scientific attention.
Ranikhet Disease in India

- 09 Feb 2025
In News:
Recent outbreaks of suspected Ranikhet disease (Newcastle Disease) have caused the death of approximately 1.5 lakh chickens in poultry farms across Andhra Pradesh (Eluru, Guntur, Prakasam, and the Godavari districts) and Haryana (Barwala and Raipur Rani in Panchkula). These outbreaks have raised alarms about biosecurity measures, especially in regions that are major poultry producers.
About Ranikhet Disease:
- Also known as: Newcastle Disease (ND)
- Causative Agent: Avian avulavirus 1 (also called Avian Paramyxovirus-1 or APMV-1)
- Affected Species: Primarily chickens, but also turkeys, ducks, pigeons, crows, geese, guinea fowls, partridges, doves, and even hedgehogs (suspected reservoirs).
- Nature of Disease: Highly contagious and fatal viral disease.
- Transmission:
- Direct contact with infected bird secretions (especially feces)
- Contaminated feed, water, equipment, clothing, and environment
- ND virus can survive for weeks in cool environments, increasing risk in winter.
Symptoms and Impact:
- In Birds:
- Respiratory issues: Sneezing, gasping
- Nervous symptoms: Droopiness, loss of coordination
- Digestive symptoms: Diarrhea
- Mortality rate: Ranges from 50% to 100%
- Production impact: Drop in egg production and fertility
- In Humans:
- Mild zoonotic effect, primarily conjunctivitis in people handling infected birds or lab samples.
- Usually self-limiting and non-fatal.
Recent Outbreaks and Investigations:
Andhra Pradesh:
- Approximately 1.5 lakh birds have died across multiple districts.
- Suspected cause: Highly virulent strain of Ranikhet Disease.
Haryana (Barwala–Raipur Rani belt):
- This belt houses around 115 poultry farms and is the second-largest poultry producer in Asia.
- Previously affected by bird flu outbreaks in 2006 and 2014.
- Northern Regional Disease Diagnostic Laboratory (NRDDL), Jalandhar collected 40 new samples from affected farms after being unsatisfied with earlier ones.
- Preliminary suspicion points toward Ranikhet Disease; however, cold wave conditions and the presence of older birds (not replaced due to COVID-19 restrictions) may have also contributed.
- The region falls in the path of migratory birds, whose droppings can spread avian flu viruses, complicating disease identification.
Current Challenges:
- Lack of effective treatment: No curative treatment exists. Management relies on preventive vaccination, biosecurity measures, and good poultry housing practices.
- Diagnostic delays: Require reliable sampling and laboratory testing to confirm the cause.
- Climate sensitivity: Poultry are vulnerable to extreme cold, especially if housing and care are inadequate.
- Pandemic aftershocks: COVID-19 disruptions prevented the routine replacement of older birds, increasing vulnerability.
Iran’s Missile Advancements
- 04 Feb 2025
In News:
In a significant military development, Iran has successfully test-fired the Ghadr-380, an advanced anti-warship cruise missile with a range of 1,000 kilometers (600 miles).
This capability allows it to target U.S. Navy warships deployed in critical maritime regions like the Persian Gulf and the Sea of Oman. The missile test was launched from an underground missile facility and was broadcast on Iranian state television, underscoring its strategic messaging.
Key Missiles Unveiled by Iran:
1. Ghadr-380 Cruise Missile:
- Type: Anti-warship cruise missile
- Range: Over 1,000 km
- Features:
- Anti-jamming capability
- Quick-launch readiness (operable by one person in less than 5 minutes)
- Launch Details:
- Fired from an underground missile base in central Iran
- Targeted the Sea of Oman
- Specific test timing and warhead specifications were not disclosed
2. Etemad Ballistic Missile:
- Name Meaning: Etemad means "trust" in Persian
- Type: Precision-guided ballistic missile
- Range: 1,700 km (1,056 miles)
- Specifications:
- Length: 16 meters
- Diameter: 1.25 meters
- Equipped with precision-guided warhead
- Built by: Iranian Ministry of Defence
Ballistic vs. Cruise Missiles: Understanding the Distinction
Feature Ballistic Missile Cruise Missile
Propulsion Rocket-propelled at launch; unpowered descent Jet engine-powered throughout flight
Flight Path Arched trajectory (leaves and re-enters atmosphere) Straight, low-altitude flight within atmosphere
Detection Easier to track via radar once launched Difficult to detect due to low-altitude flight
Launch Platforms Ground-based, silo, mobile launchers Ground, air, or sea platforms
Warhead Capability Can carry conventional or nuclear warheads Usually conventional, but may carry nuclear in advanced forms
Iran’s Strategic Missile Doctrine
Underground Missile Facilities:
- Iran maintains extensive underground missile bases, especially in southern Iran near the Strait of Hormuz—a chokepoint for global oil trade.
- Such facilities enhance survivability and rapid response capabilities.
Missile Development Drivers:
- Iran's missile program evolved as a strategic deterrent post the Iran-Iraq War (1980–1988), where both countries used missiles to target civilian areas.
- UN arms embargoes led Iran to focus on domestic development of missile systems, including both cruise and ballistic types.
Capabilities:
- Iran now claims to possess missiles with ranges up to 2,000 kilometers, capable of reaching parts of the Middle East, including Israel.
- The Ghadr-380 and Etemad missiles are examples of technological diversification—from ballistic to precision cruise systems.
Implications for Regional and Global Security
- Deterrence Posture: Iran’s missile advancements strengthen its deterrence, especially amid strained relations with the U.S. and its allies.
- Threat to Maritime Security: The Ghadr-380, with its anti-warship focus, poses a direct threat to U.S. naval assets in the Persian Gulf and adjacent waters.
- Escalation Risks: Enhanced missile capabilities could escalate regional tensions, particularly in flashpoints like the Strait of Hormuz.
- Western Concerns: The U.S. and European nations remain wary of Iran’s dual-track approach involving missile and nuclear program developments.
Rusty-Spotted Cat

- 01 Feb 2025
In News:
For the first time, the Rusty-Spotted Cat (Prionailurus rubiginosus) has been spotted in the forests of Purulia district, West Bengal, captured on a camera trap set up by the NGO HEAL during pangolin poaching surveillance. This marks a significant range extension and has excited conservationists and forest officials.
Key Features
- World’s smallest and lightest wild cat: Weighs between 900 grams to 1.5 kg
- Length: Approx. 1.5 feet, with a 1-foot-long tail
- Appearance:
- Fawn-grey coat with rusty red spots on back and flanks
- Short, rounded head with two white facial streaks
- Large eyes with greyish-brown to amber irises – an adaptation to nocturnal behavior
- Short legs, black-soled feet, and an unmarked rusty tail
- Behavior:
- Nocturnal and elusive
- Uses scent marking to establish territory
- Gestation period: 66–70 days
Habitat and Distribution
- Found in dry deciduous and semi-deciduous forests, including:
- Northern & Central India, Western Ghats, Rajasthan, Kachchh, and Peninsular India
- Also present in Sri Lanka and Nepal
- India hosts 80% of the global population
Conservation Status
- IUCN Red List: Near Threatened, due to habitat loss, fragmentation, and human-wildlife conflict
- Wildlife Protection Act, 1972: Schedule I species (highest protection)
Significance of Purulia Sighting
- Located on the eastern edge of the Chota Nagpur Plateau
- Forests are interconnected with neighboring regions like Jharkhand and Odisha
- Notified as reserved forests, not protected forests
- Threats: Hunting by local communities, habitat degradation
Impact of Conservation Efforts
- Post-COVID, the forest ecosystem in Purulia has improved due to reduced human disturbance
- Past sightings of leopards, bears, jackals, and foxes indicate a thriving ecosystem
- HEAL and the Forest Department have launched livestock compensation programs to reduce retaliatory killings of carnivores
India adds 4 new Ramsar Sites
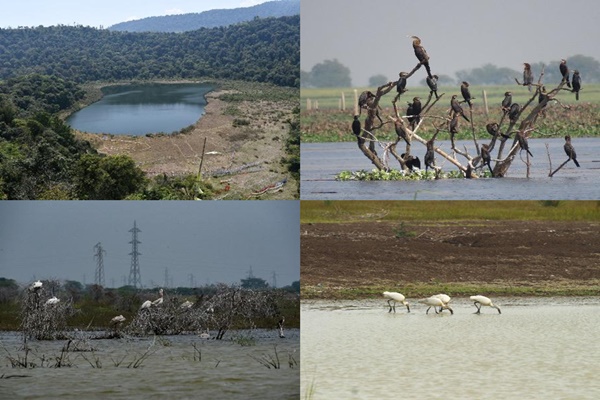

- 01 Feb 2025
In News:
The Government of India has added four new Ramsar sites, increasing the total to 89, the highest in Asia and third globally. The newly designated wetlands include:
- Sakkarakottai Bird Sanctuary (Tamil Nadu)
- Therthangal Bird Sanctuary (Tamil Nadu)
- Khecheopalri Wetland (Sikkim)
- Udhwa Lake (Jharkhand)
This marks a significant milestone as Sikkim and Jharkhand have received their first Ramsar recognitions, while Tamil Nadu strengthens its lead with 20 Ramsar sites, the most among Indian states.
About the Ramsar Convention
- Adopted: 1971 in Ramsar, Iran
- Objective: Conservation and wise use of wetlands through local, national, and international cooperation.
- World Wetlands Day: Celebrated on 2nd February to promote awareness.
Key Highlights:
Therthangal Bird Sanctuary – Tamil Nadu
- Notified in 2010; covers 29.29 ha.
- Crucial breeding and foraging site for waterbirds like Spot-billed Pelican, Black-headed Ibis, and Oriental Darter.
- Aids groundwater recharge and climate regulation.
- Part of the Central Asian Flyway.
Sakkarakottai Bird Sanctuary – Tamil Nadu
- Notified in 2012; spans 230.49 ha.
- Located near Gulf of Mannar; significant stopover for migratory birds.
- Hosts endemic species and near-threatened fauna like Lion-tailed Macaque and Giant Squirrel.
Khecheopalri Wetland – Sikkim
- Sacred lake revered by Buddhists and Hindus; called Sho Dzo Sho locally.
- Known as a wish-fulfilling lake.
- Birds prevent leaves from settling on the surface.
- Rich in avifauna: fishing eagles, Brahminy kites.
- Integral to ecotourism and biodiversity conservation.
Udhwa Lake – Jharkhand
- Comprises Pataura Jheel (155 ha) and Brahma Jamalpur Jheel (410 ha).
- First Ramsar site of Jharkhand; near Ganga River.
- Declared a bird sanctuary in 1991; attracts migratory birds from September onwards.
Falls under the Gangetic Plains biogeographic zone.
Takers, Not Makers

- 21 Jan 2025
In News:
Report “Takers not makers: The unjust poverty and unearned wealth of colonialism” published by Oxfam.
Key Highlights:
- Released by: Oxfam International at the World Economic Forum 2025
- Core Focus: The report explores historical colonial wealth extraction, especially from India, and connects it to contemporary global inequalities.
Colonial Wealth Drain – India:
- $64.82 trillion extracted from India by Britain (1765–1900), adjusted to today’s value.
- $33.8 trillion (52%) enriched the UK’s richest 10%
- 32% benefited the British middle class
- India's industrial output dropped from 25% in 1750 to 2% in 1900 due to:
- British protectionist policies (especially targeting Asian textiles)
- High taxation, home charges, currency manipulation, and profit repatriation
Conceptual Framework:
- "Drain of Wealth" Theory by Dadabhai Naoroji forms the report’s foundation.
- Colonialism framed as both:
- Historical phenomenon: Loot, repression, forced de-industrialization
- Modern structure (Neo-colonialism): Corporate dominance, digital colonization, and unjust global governance
Neo-Colonial Parallels Today:
- Wages in Global South: 87–95% lower than for same work in Global North
- Multinational corporations:
- Descendants of colonial entities like the East India Company
- Extract resources & exploit labor under unequal terms of trade
- Global institutions like WTO and World Bank perpetuate inequity through imbalanced power dynamics
Ongoing Consequences in Global South:
- Poor public services, education, and healthcare
- Caste, religion, and language divisions institutionalized during colonial rule
- E.g., Only 0.14% of Indian languages used as medium of instruction
- Bengal Famine (1943): Caused by wartime policies & racist attitudes, ~3 million deaths
- Biopiracy cases (e.g., neem) reflect continued exploitation
Wealth Disparity & Inequality:
- Billionaire wealth tripled in growth rate in 2024 (vs. 2023)
- Top 1% own more than 95% of global wealth
- Over 3.5 billion people survive on less than $6.85/day
Israel-Hamas Ceasefire and Hostage Release Deal

- 14 Jan 2025
In News:
Israel and Hamas have agreed on a Gaza ceasefire and hostage release deal after 15 months of war.
Key Highlights:
Ceasefire Agreement Details:
- Location: The deal was brokered in Doha, Qatar.
- Approval Process: The deal must be approved by Israel’s Cabinet to take effect.
- Mediators: The agreement was negotiated by Qatar, Egypt, and the United States, with their involvement ensuring the implementation of the deal.
Phases of the Deal:
- First Phase (42 Days):
- Release of 33 hostages by Hamas, including women, children, and elderly people.
- Hostage Exchange: Hostages will be exchanged for Palestinian prisoners in Israeli jails.
- Gaza Ceasefire and Withdrawal: Israeli forces will gradually withdraw from Central Gaza and move to the borders.
- Return of Displaced Palestinians: Displaced Palestinians will be allowed to return to Northern Gaza.
- Humanitarian Aid: 600 humanitarian aid trucks will be allowed into Gaza daily.
- Second Phase:
- Hostage Release: Negotiations will begin for the release of remaining hostages.
- Full Israeli Troop Withdrawal: Israel will fully withdraw its forces.
- Third Phase:
- Reconstruction of Gaza: Overseen by Egypt, Qatar, and the United Nations.
- Reopening of Border Crossings: For movement in and out of Gaza.
- Return of Hostage Bodies: Return of any bodies of hostages who died.
Background of the Israel-Hamas Conflict:
- Start: On October 7, 2023, Hamas launched an attack on Israel, called Operation Al-Aqsa Flood, causing significant casualties.
- Israeli Response: Israel launched Operation Iron Sword in retaliation.
- Casualties: The conflict resulted in 46,707 Palestinian deaths, mostly civilians, and 1,210 Israeli deaths.
About Gaza Strip:
- Location: A Palestinian enclave on the Mediterranean Sea, bordered by Israel and Egypt.
- Administration: The Gaza Strip is governed by Hamas since 2006.
- Movement Restrictions: Israel controls air space and shoreline, imposing restrictions. Egypt controls one border and also restricts movement.
Gaza Truce Deal:
- Nature: A proposed ceasefire to end the ongoing conflict.
- Primary Parties: Israel and Hamas.
- Supporting Nations: United States, Qatar, and Egypt.
- Significance:
- Aims to stop fighting and address the humanitarian crisis in Gaza.
- Potential to influence regional stability and Israeli politics.
- Marks an important moment in U.S. diplomacy under the Biden administration.
India’s Recalculated Coastline
- 09 Jan 2025
In News:
India’s coastline has grown significantly over the past five decades, now extending 11,098 km in 2023-24, compared to 7,516 km in 1970. This marks an increase of 47.6% in just over five decades, attributed to a more precise methodology for measuring coastlines.
Key Factors Behind the Growth:
New Methodology for Measuring Coastlines:
- The old methodology used straight-line distances to measure the coastline, a method that didn't capture the complexity of India’s coastlines.
- The updated approach incorporates bays, estuaries, inlets, and other geomorphological features, offering a more accurate and detailed representation of the coastline.
- Advanced technologies like geospatial mapping have been used to ensure greater precision.
State-wise Recalculated Coastline Changes:
- Gujarat:
- Old coastline (1970): 1,214 km
- New coastline (2023-24): 2,340 km
- Growth: The largest absolute increase in coastline, nearly doubling its size.
- West Bengal:
- Old coastline: 157 km
- New coastline: 721 km
- Growth: A dramatic 357% increase, marking the highest percentage rise.
- Tamil Nadu:
- Old coastline: 906 km
- New coastline: 1,068 km
- Growth: Revised length now exceeds Andhra Pradesh’s coastline, which was 1,053 km.
- Puducherry:
- Old coastline: No major shift, but the updated data shows a contraction of 4.9 km (-10.4%), due to erosion and recalculations.
- Kerala:
- Old coastline: Relatively small increase of 30 km (5%), the smallest among the states.
Notable Observations:
- Andhra Pradesh is developing new ports like Ramayapatnam, Krishnapatnam, and Kakinada Gateway, aiming to boost economic growth and employment by leveraging its expanding coastline.
- The recalculated coastline helps in better maritime planning, focusing on port development, tourism, biodiversity conservation, and coastal erosion.
Impact of Coastline Expansion:
- Economic Growth:
- Coastal states, particularly Gujarat and West Bengal, benefit from an expanded coastline that improves maritime trade, port infrastructure, and tourism.
- The expansion supports industrialization, with growing logistics and transportation activities along the coast.
- Environmental Considerations:
- The new data aids biodiversity conservation, helping to track coastal erosion and accretion (land buildup), especially in areas like the West Coast.
- Understanding these changes is essential for disaster preparedness and sustainable coastal management.
- Coastlines of Emergence and Submergence:
- Emerging Coastlines: Land rising due to uplift or falling sea levels, such as along the Tamil Nadu Coast.
- Submerged Coastlines: Land that has sunk or been submerged due to rising sea levels, particularly noticeable along parts of Kerala’s coast.
Geographical Significance of the Expanded Coastline:
- India’s coast touches three major bodies of water: the Bay of Bengal (east), the Indian Ocean (south), and the Arabian Sea (west).
- The expansion reflects more than just geography—accurate coastline data is crucial for policy planning, maritime security, and resource management.
Year of Artificial Intelligence

- 05 Jan 2025
In News:
The All India Council for Technical Education (AICTE) has declared 2025 as the "Year of Artificial Intelligence" (AI), aiming to empower over 14,000 AICTE-approved colleges and benefit 40 million students. This initiative aligns with the Prime Minister’s vision to make India a global leader in AI and technology.
Key Objectives and Features of the AICTE AI Initiative:
- Positioning India as a Global AI Leader:
- Empowering students with AI skills to drive innovation and lead in the emerging AI-driven economy.
- Preparing India’s workforce for the technological advancements of the future.
- Core Elements of the AICTE AI Initiative:
- AI Affirmation Pledge: Institutions will adopt and display an AI Affirmation Pledge, focusing on innovation, ethics, and education in AI.
- Comprehensive AI Integration:
- Introducing interdisciplinary AI courses and research programs.
- Setting up AI labs in collaboration with industries to meet global standards.
- Promoting ethical AI practices with societal benefits in focus.
- AI Awareness Campaign:
- “AI for All: The Future Begins Here” campaign includes workshops, hackathons, and guest lectures.
- Formation of student-driven AI chapters to foster innovation and research.
- Faculty Development & Industry Partnerships:
- Workshops and certification programs for faculty to improve AI teaching.
- Collaboration with companies like Adobe, CISCO, and IBM for student exposure through internships and mentorships.
- Recognition of Excellence: Institutions excelling in AI integration will be recognized, serving as role models for others.
- Action Plan for Institutions:
- All institutions are required to submit AI Implementation Plans by December 31, 2024. These plans will be evaluated by the AICTE Approval Bureau and exemplary submissions will be highlighted as benchmarks.
- Shaping India as a Global AI Leader:
- AICTE aims to revolutionize India’s education system and enhance its position in the global AI race, focusing on building a self-reliant workforce.
Additional Context on AICTE and its Role:
- AICTE Overview:
- A statutory body and national-level council under the Ministry of Education.
- Established in November 1945 as a national-level apex advisory body for technical education in India.
Government Initiatives to Support AI and Consumer Protection:
- AI and Consumer Protection:
- AI-driven tools launched to enhance consumer protection, such as the National Consumer Helpline, e-MAAP Portal, and Jago Grahak Jago mobile application.
- New guidelines for regulating deceptive marketing in e-commerce to ensure consumer confidence in the digital market.
- Tools like the e-Daakhil Portal for online complaint filing.
Impact:
- This initiative will have a far-reaching impact, involving more than 14,000 institutions and 40 million students nationwide, preparing them for leadership roles in AI and technology, and helping India secure its future in the global AI-driven economy.
Open Data Kit (ODK) Toolkit

- 04 Jan 2025
In News:
- The Comptroller and Auditor General (CAG) of India has deployed the Open Data Kit (ODK) platform to enhance transparency in government spending and improve accountability in the delivery of government schemes.
- The toolkit is being used for designing, collecting, and managing data relevant to audits.
Key Highlights:
Objective:
- Enhance transparency in public spending.
- Improve accountability in government schemes and projects.
- Collect real-time beneficiary feedback to aid audit planning and identify areas needing additional review.
Key Features:
- End-to-end encryption: Ensures secure data management.
- Integration with CAG’s Operating System (OIOS): Facilitates seamless analysis and management of data.
- Multi-language support: Allows for surveys in multiple languages, making it more accessible to diverse beneficiaries.
- User-friendly interface: Simplifies the design and management of data collection processes for auditors.
Usage and Applications:
- Beneficiary surveys are a key tool for gathering data, helping CAG identify problem areas in government schemes.
- The ODK toolkit was recently deployed in audits of AIIMS institutions in Mangalagiri (Guntur) and Bibinagar (Hyderabad) to assess patient satisfaction and gather evidence for performance reviews.
Working Process:
- Surveys are designed on the ODK platform and deployed to beneficiaries.
- Data is collected in real-time and analyzed using the OIOS system to generate actionable insights for audits.
- Beneficiary feedback is used to evaluate scheme delivery and improve efficiency.
Significance:
- Facilitates data-driven decision-making in audits, ensuring that audits are more transparent and evidence-based.
- Improves the citizen-centric evaluation of government schemes by gathering direct feedback from beneficiaries.
- Enhances the performance review of key institutions like AIIMS, contributing to better service delivery.
- The introduction of the ODK toolkit is part of the CAG’s efforts to use digital tools for better governance and accountability in the public sector. This also aligns with the growing trend of using technology for governance and auditing.
Little Bunting

- 16 Dec 2024
In News:
Little Bunting recently spotted in Mount Abu, Rajasthan, a sighting previously unseen in the region.
About the Little Bunting:
- Scientific Name: Emberiza pusilla
- Family: Bunting family (Emberizidae)
- IUCN Red List Status: Least Concern
Distribution:
- Breeding Range: Far northeast Europe and northern Eurosiberia to the Russian Far East (taiga region).
- Migratory Pattern: Migrates to the subtropics during winter, with sightings in northern India, southern China, and northern Southeast Asia.
Physical Features:
- Size: Small bird, measuring 12–14 cm (4.7–5.5 inches).
- Coloration:
- White underparts with dark streaking on the breast and sides.
- Chestnut face with a white malar stripe, black crown stripes, and a white eye-ring.
- Fine dark border behind chestnut cheeks.
- Similarity: Resembles a small female reed bunting but with distinct black crown stripes.
Call and Song:
- Call: Distinctive "zik".
- Song: A rolling "siroo-sir-sir-siroo".
Habitat and Behavior:
- Typically found in agricultural areas, feeding on grains.
- Migration: Avoids extreme cold conditions, possibly due to climate change influencing its movement into Rajasthan.
Recent Sightings in India: Spotted in Gurugram, Chandigarh, northern Punjab, and now Rajasthan.
Conservation Significance: The sighting underscores the need to preserve forest areas and wetlands for migratory species like the Little Bunting.
Desert Knight Air Combat Exercise

- 14 Dec 2024
In News:
India, France and UAE recently kicked off a major air combat exercise called “Desert Knight” over the Arabian Sea, strengthening trilateral defence cooperation and enhancing military interoperability amid the ongoing geopolitical churn.
Key Highlights:
- What It Is: A trilateral air combat exercise aimed at improving military interoperability and enhancing combat readiness among the participating nations.
- Nations Involved: India, France, and the UAE.
- Location: Conducted over the Arabian Sea, approximately 350-400 km southwest of Karachi.
- Aim of the Exercise:
- To strengthen trilateral defence cooperation among the three nations.
- To enhance combat skills and military interoperability of the air forces involved.
- Details of the Exercise:
- Duration: The exercise lasts for three days.
- The exercise involves large force engagement and intensive combat maneuvers in a realistic operational environment.
- Aircraft Involved:
- India: Deployed Sukhoi-30MKIs, Jaguars, IL-78 mid-air refuellers, and AEW&C (Airborne Early Warning and Control) aircraft from bases like Jamnagar.
- France: Deployed Rafale jets and other aircraft from Al Dhafra airbase.
- UAE: Deployed F-16 jets and other aircraft from Al Dhafra airbase.
Strategic Significance:
- The exercise is part of India’s efforts to build military interoperability with nations in the Persian Gulf region and strengthen defence ties with France and the UAE.
- Enhances combat readiness and strengthens cooperation against both traditional and non-traditional threats.
- Reflects the geopolitical shift and growing military cooperation in the Indo-Pacific region, especially in the context of China’s expansionist activities.
- Trilateral Framework: India, France, and the UAE launched a trilateral framework in 2022, focusing on areas like defence, technology, energy, and environment.
- Previous Exercises: In addition to Desert Knight, the countries also conducted their first trilateral maritime exercise in June 2023 to enhance cooperation in maritime security.
Broader Defence Relations:
- India-France: Long-standing strategic partnership with regular joint exercises like Shakti (army), Varuna (navy), and Garuda (air force).
- India-UAE: The defence relationship has grown significantly in recent years, with regular professional exchanges, combat exercises, and staff talks. India participates in the Desert Flag exercise at Al Dhafra airbase annually.
Markhor Spotted in North Kashmir's Baramulla

- 08 Dec 2024
In News:
Recently, a Markhor, a rare wild goat with spiral-shaped horns, was spotted in Noorkha village of Boniyar in Baramulla district, North Kashmir.The animal was seen near a waterfall in Noorkha, prompting locals to alert the authorities.
Key Highlights:
- The Markhor (Capra falconeri) is a large, wild goat species native to mountainous regions in Central and South Asia, including countries such as Pakistan, Afghanistan, India, and others.
- The species is considered endangered and is listed under Schedule I of the Wildlife Protection Act, 1972.
- The Markhor population in India is concentrated in areas like Shopian, Banihal Pass, Shamsbari, and Kazinag in Jammu and Kashmir.An estimated 300 Markhors live in Kashmir's dense pine and birch forests.
- Threats and Conservation Status:
- The Markhor faces threats due to human activities and natural factors, leading to a decline in its population.
- It is classified as 'Near Threatened' on the IUCN Red List and protected under the Indian Wildlife Protection Act and the Jammu and Kashmir Wildlife Protection Act.
- Significance of the Sighting:The sighting of the Markhor has excited both villagers and wildlife enthusiasts, as these animals are not typically found outside their natural habitats, particularly near human settlements.
World’s Oldest Wild Bird Lays Egg at 74 in Hawaii

- 08 Dec 2024
In News:
Wisdom, the world’s oldest known wild bird, a Laysan albatross, has laid her estimated 60th egg at the age of 74. This remarkable event occurred at the Midway Atoll National Wildlife Refuge in the Pacific Ocean, part of the Hawaiian Archipelago.
Background on Wisdom and Laysan Albatrosses
Wisdom, first banded as an adult in 1956, has been a part of the albatross population in the Pacific for decades. Laysan albatrosses are known for their strong migratory habits and lifelong pair bonding.
The Life Cycle of the Laysan Albatross
The egg incubation process for Laysan albatrosses is shared between both parents and lasts around seven months. Once the chick hatches, it takes five to six months to develop before it is ready to take its first flight over the ocean. These seabirds, which predominantly feed on squid and fish eggs, spend the majority of their lives soaring across the open seas.
Wisdom’s longevity and success in raising up to 30 chicks over her lifetime have been notable achievements. While Laysan albatrosses typically live up to 68 years, Wisdom’s age surpasses this average by several years.
About the Laysan Albatross
The Laysan albatross (Phoebastriaimmutabilis) is a large seabird found across the North Pacific. The Northwestern Hawaiian Islands host nearly the entire population of Laysan albatrosses, with most breeding pairs found on islands like Laysan and Midway Atoll. These birds are known for their long-distance soaring capabilities, with some covering hundreds of miles a day without flapping their wings.
Laysan albatrosses have blackish-brown upper wings and backs, with flashes of white in their primary feathers. They are monogamous, forming lifelong bonds with a single mate. Despite their impressive flying ability and vast range, their population is currently listed as "Near Threatened" by the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN).
India's First Constitution Museum

- 26 Nov 2024
In News:
Lok Sabha Speaker Om Birla and Union law minister Arjun Ram Meghwal inaugurated the country's first Constitution Museum at OP Jindal Global University in Sonipat.
Museum Features
- Centrepiece: A photolithographic copy of the Indian Constitution (one of 1,000 reproductions).
- 360-Degree Experience: A visual presentation that takes visitors through pre-Independence India.
- Multimedia Presentation: Chronologically details significant events leading to the drafting of the Constitution.
- Constituent Assembly Members:
- Nearly 300 sculptured busts of members who contributed to the making of the Constitution.
- Hologram of Dr. BR Ambedkar: Located in the mezzanine section, showcasing his philosophies through interactive displays.
- Art Installations:
- ‘We, The People of India’ by Rajesh P Subramanian: Represents unity in diversity.
- ‘Echoes of Liberty’ by Rahul Gautam: Combines constitutional manuscripts with contemporary design.
- ‘Triad of Unity’ by Harsha Durugadda: Symbolizes unity, justice, and sovereignty.
- ‘Insaaf Ki Devi’ by Nishant S Kumbhatil: Depicts Lady Justice, representing judicial impartiality.
- ‘Equality Before Law’ by Pradeep B Jogdand: Illustrates equality and justice principles.
- ‘Map’ by Deval Verma: Encourages visitors to reflect on value and beauty.
- ‘Freedom’ by KR Nariman: Pays tribute to the people who uphold constitutional values.
- ‘Founding Mothers’ by Rahul Gautam: Honors the 15 women members of the Constituent Assembly.
Palparescontrarius
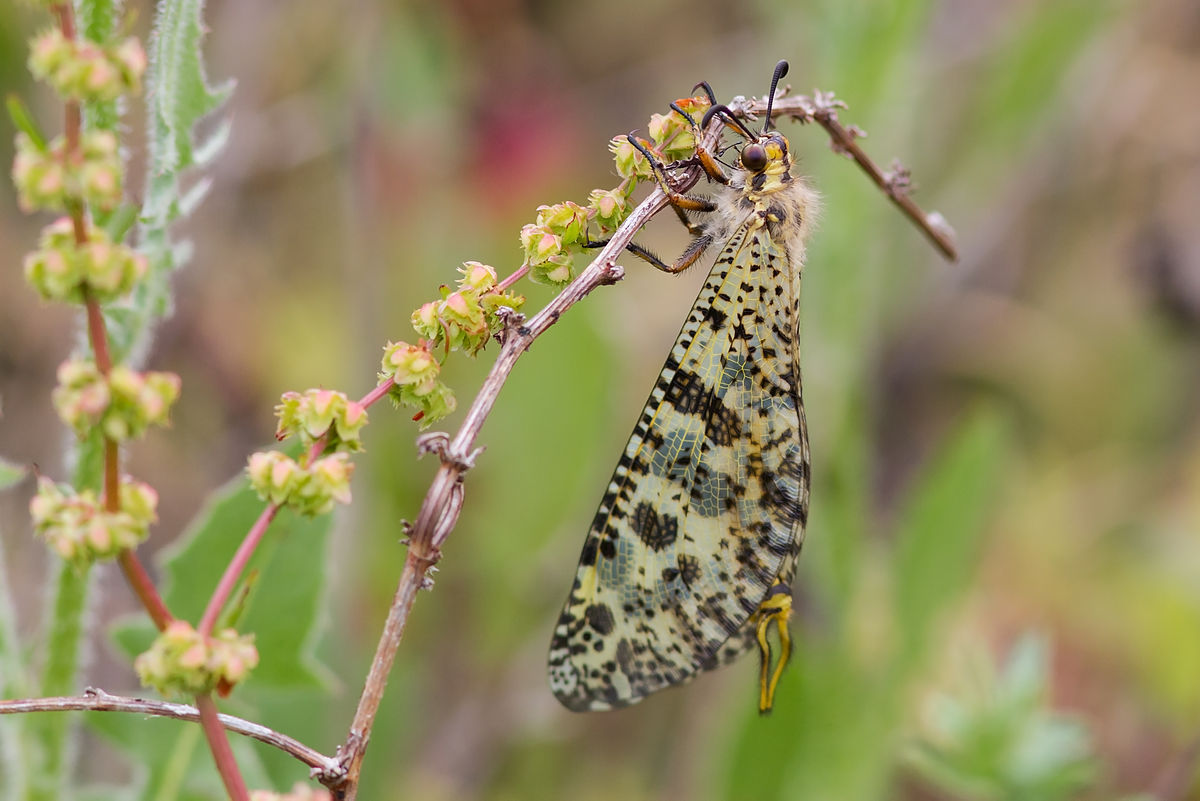

- 25 Nov 2024
In News:
Palparescontrarius is a species of antlion that was recently spotted for the first time in Tamil Nadu, on the Madras Christian College (MCC) campus. It is notable for being a large-sized adult antlion that resembles a dragonfly but has distinct characteristics that separate it from dragonflies, such as its clubbed antennae and fluttering flight.
Key Features of Palparescontrarius:
- Appearance:
- The adult Palparescontrarius is large and resembles a dragonfly in its general body structure.
- It has lacy wings, long clubbed antennae, and a slender, grayish body.
- Its wings are typically clear, although some species of antlions have spots on their wings.
- Flight and Behavior:
- Unlike dragonflies, Palparescontrarius has a distinct fluttering flight.
- It is a weak flier and can often be spotted at night near illuminated spots.
- Habitat and Lifestyle:
- Like other antlions, Palparescontrarius is found in dry, sandy regions and is mostly active at night.
- The larvae of this species are particularly known for their predatory behavior, as they trap ants and other small insects in cone-shaped pits they dig into the sand.
- Ecological Importance:
- Antlions, including Palparescontrarius, are harmless to humans and beneficial to the environment because they feed on ants and other insects, thus helping to control pest populations.
Okinawicius tekdi
- 07 Nov 2024
In News:
Researchers have recently discovered a new species of jumping spider in the Baner Hill area, underscoring the region's rich biodiversity and the growing need to preserve the natural landscapes around Pune.
About Okinawicius tekdi:
- The newly identified species, named Okinawicius tekdi, is a jumping spider that contributes to the growing diversity of India's spider population, now numbering 326 species of jumping spiders.
- The name "tekdi" comes from the Marathi word for "hill," reflecting the spider's habitat.
- The last time a spider species was identified in Pune was over three decades ago.
About Jumping Spiders:
- Jumping spiders belong to the family Salticidae and are known for their distinctive eight legs and remarkable jumping ability.
- These spiders possess a segmented body, a tough exoskeleton, and jointed legs.
- In addition to their agility, they are famous for spinning webs that they use to capture their prey.
ISRO’s First Electric Propulsion-Led Spacecraft (TDS-1)

- 28 Oct 2024
In News:
India's first home-grown electric propulsion satellite to be launched in Dec.
Key Highlights:
- Objective of TDS-1:
- Purpose: To demonstrate electric propulsion technology for satellite steering, using solar-powered ionized gas.
- Goal: Reduce reliance on chemical fuel, making satellites lighter and more efficient.
- Key Benefits of Electric Propulsion:
- Weight Reduction: The technology can significantly cut down satellite mass. For example, a satellite weighing 4 tonnes could be reduced to around 2 tonnes.
- Fuel Efficiency: By using electric propulsion, the need for chemical fuel is minimized, allowing for a more efficient journey to geostationary orbit.
- Technology Details:
- Fuel Used: Gases like Argon are ionized using solar power to create propulsion.
- Process: The ionized gas is expelled at high speeds to generate thrust, pushing the satellite towards its desired orbit.
- Historical Context:
- The technology was first used in GSAT-9 (South Asia Satellite) in 2017 but with imported Russian components.
- TDS-1 marks the first fully indigenous development of electric propulsion technology by ISRO, highlighting India’s increasing space autonomy.
- Significance for India’s Space Program:
- Self-Reliance: TDS-1 reflects ISRO’s growing capacity to develop advanced space technologies domestically.
- Future Prospects: This breakthrough is expected to lead to more efficient satellite designs, enhancing India’s competitiveness in the global space industry.
Emissions Gap Report 2024

- 28 Oct 2024
In News:
The United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP) recently published the Emissions Gap Report 2024, in anticipation of the COP29 meeting of the UNFCCC to be held in Baku, Azerbaijan.
Key Highlights:
- Current Trajectory of Global Warming:
- If countries continue with current environmental policies, global temperatures are expected to rise by 3.1°C above pre-industrial levels.
- This is significantly higher than the Paris Agreement target of limiting global warming to well below 2°C, with an effort to cap it at 1.5°C.
- Paris Agreement at Risk:
- Even if all Nationally Determined Contributions (NDCs) are fully implemented (including both unconditional and conditional emissions reduction targets), the world would still experience 2.6°C of warming by 2030.
- This presents a major challenge to achieving the Paris Agreement’s climate goals.
- Urgent Need for Action:
- To limit global warming to 1.5°C, greenhouse gas emissions must peak before 2025 and decline by 43% by 2030.
- The report highlights the emission gap between current pledges and what is required to meet the 1.5°C goal.
- Record High Emissions:
- Global greenhouse gas emissions hit a record 57.1 gigatons of CO? equivalent in 2023.
- This represents an increase of 1.3% compared to 2022, continuing the upward trend from the previous decade.
- India’s Emissions:
- India’s greenhouse gas emissions grew by 6.1% between 2022 and 2023.
- Per capita emissions in India were 2.9 tCO?e in 2022, significantly lower than China (11 tCO?e) and the U.S. (18 tCO?e).
- G20 Countries’ Contribution:
- G20 countries, excluding the African Union, contributed 77% of global emissions in 2023.
- The six largest emitters (including China, U.S., and India) were responsible for 63% of global emissions.
- This shows a significant imbalance in emissions, with developed countries having much higher per capita emissions compared to developing nations like India and Africa.
- Necessary Emissions Cuts:
- To keep the 1.5°C target within reach, global emissions need to be cut by at least 7.5% annually until 2035.
- Cost of bridging the emissions gap: Achieving net-zero by 2050 will require USD 900 billion to USD 2.1 trillion annually, approximately 1% of global GDP.
- Emission Reduction Pathways:
- Renewable Energy: Scaling up solar and wind energy technologies could contribute up to 27% of the required emissions reductions by 2030.
- Forest Conservation: Protecting and restoring forests could provide 20% of the required emissions reductions by 2030.
- Other crucial measures include improving energy efficiency, transitioning to electric vehicles, and focusing on fuel switching in key sectors like transport, industry, and buildings.
- Disparities in Emissions:
- Despite changes over the past two decades, large disparities remain between emissions across regions.
- Developed countries have three times higher per capita emissions compared to the global average, while India, the African Union, and least developed countries continue to have much lower emissions.
- Call to Action:
- UNEP Executive Director Inger Andersen urged countries to act now, stating: “No more hot air, please.” The urgency is to ramp up climate pledges and ensure stronger actions in the upcoming COP29 talks in Baku, Azerbaijan (November 2024), where nations must work to get on a 1.5°C pathway.
United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP)
- Established: 1972, following the United Nations Conference on the Human Environment in Stockholm.
- Headquarters: Nairobi, Kenya.
- Governing Body: The United Nations Environment Assembly (UNEA), which is the world’s highest-level decision-making body on environmental matters, with 193 Member States.
- Programs & Initiatives: UNEP leads global efforts on climate action, ecosystem restoration, clean seas, and supports the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs).
- Reports: UNEP publishes crucial assessments like the Emissions Gap Report, Global Environment Outlook, and Adaptation Gap Report, influencing global environmental policies.
United Nations Day 2024

- 25 Oct 2024
In News:
United Nations Day is celebrated each year on October 24 to mark the anniversary of the UN Charter's entry into force, aiming to raise awareness about the goals and achievements of the international body.
Key Highlights:
- Purpose: Celebrates the anniversary of the UN Charter coming into effect on October 24, 1945, after World War II.
- Goal: Raise awareness about the UN’s objectives and accomplishments.
UN Charter Overview
- Signing & Implementation:
- Signed on June 26, 1945, in San Francisco.
- Came into effect on October 24, 1945.
- India ratified the UN Charter on October 30, 1945.
- Predecessor: The League of Nations, created in 1919 after WWI, aimed at promoting international cooperation and peace.
- Content:
- Foundational document of the UN, binding all member states.
- Establishes principles of international relations, including equality of nations and the prohibition of force between countries.
- Amended three times: 1963, 1965, and 1973.
UN's Core Objectives
- Peace and Security: Maintaining global peace and preventing conflicts.
- Humanitarian Aid: Providing assistance to those in need.
- Human Rights: Protecting and promoting human rights globally.
- International Law: Upholding the rule of law on the global stage.
Main Organs of the UN
- General Assembly (UNGA):
- Comprises all 193 Member States, each with one vote.
- Main policy-making body, addressing international issues covered by the UN Charter.
- Security Council (UNSC):
- Consists of 15 members (5 permanent, 10 elected for two-year terms).
- Permanent members: China, France, Russia, UK, USA.
- India has been elected to the UNSC eight times.
- Economic and Social Council (ECOSOC):
- Composed of 54 members elected by the General Assembly.
- Coordinates policy and addresses economic, social, and environmental issues.
- Trusteeship Council:
- Established to oversee trust territories transitioning to independence.
- International Court of Justice (ICJ):
- The only international court resolving disputes between UN member states.
- Handles contentious cases and provides advisory opinions.
- Secretariat:
- Led by the Secretary-General, appointed by the General Assembly based on Security Council recommendations.
- Acts as the chief administrative body of the UN.
Note: Most UN organs, including the UNGA, UNSC, ECOSOC, Trusteeship Council, and Secretariat, are based in New York, while the ICJ is located in The Hague, Netherlands.
Colombo Security Conclave (CSC)

- 03 Sep 2024
In News:
The Colombo Security Conclave (CSC) recently marked a significant milestone with the signing of the Charter and the Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) for the establishment of its Secretariat in Colombo. This initiative aims to strengthen regional security collaboration among member states.
Key Features of the Colombo Security Conclave
- Member States: The CSC comprises five member countries:
- India
- Bangladesh
- Sri Lanka
- Maldives
- Mauritius
Additionally, Seychelles participates as an observer nation.
- Core Objectives: The primary goal of the CSC is to enhance regional security by addressing transnational threats and challenges that are common concerns for member states. This includes a collaborative approach to ensure stability and safety in the region.
Origin and Evolution
- The CSC originated as the Trilateral for Maritime Security Cooperation, established through trilateral meetings among National Security Advisors (NSAs) and Deputy NSAs from India, Maldives, and Sri Lanka starting in 2011.
- The initiative faced a setback after 2014 due to heightened tensions between India and the Maldives.
- It was revived and rebranded as the CSC in 2020, expanding its membership to include Mauritius and, more recently, Bangladesh.
Structure and Cooperation
- The conclave facilitates interactions among NSAs and Deputy NSAs of member countries, fostering dialogue and cooperation on security matters.
- Cooperation under the CSC is organized around five key pillars:
- Maritime Safety and Security
- Countering Terrorism and Radicalization
- Combating Trafficking and Transnational Organized Crime
- Cybersecurity and Protection of Critical Infrastructure
- Humanitarian Assistance and Disaster Relief
Permanent Secretariat
- The establishment of a permanent Secretariat in Colombo is expected to enhance coordination and streamline operations among member states, bolstering the efficacy of the CSC in addressing regional security issues.
WORLD RHINO DAY

- 22 Sep 2024
In News:
Celebrated annually on September 22, World Rhino Day raises awareness about the critical conservation status of rhinoceroses and the myriad threats they face, such as poaching and habitat loss. This day, first initiated by the World Wildlife Fund South Africa in 2010, aims to highlight the need for the conservation of all five species of rhinos: the Javan, Sumatran, Black, Greater One-Horned, and White rhinos.
The Current Status of Rhino Species
- Among the five rhino species, three are classified as
- Critically Endangered: the Black, Javan, and Sumatran rhinos.
- The White Rhino is considered Near Threatened, with the Northern White Rhino itself critically endangered.
- The Greater One-Horned Rhino, primarily found in India, is listed as Vulnerable.
Notably, Kaziranga National Park in Assam is home to the largest population of Greater One-Horned Rhinos, boasting approximately 3,700 individuals.
Conservation Efforts
In India, initiatives like Project Rhino play a crucial role in safeguarding rhino populations. This project focuses on preventing poaching, enhancing habitat management, and increasing public awareness. It collaborates with various conservation groups and government agencies to strengthen law enforcement against poaching and to relocate rhinos to safer areas.
Another significant program is the Indian Rhino Vision 2020 (IRV 2020), aimed at boosting the population of Greater One-Horned Rhinos in Assam, particularly in regions where they had previously become extinct.
Surprising Facts About Rhinos
- Despite their thick skin, rhinos can get sunburned.
- Rhinos are related to zebras, horses, and tapirs.
- All five species are considered endangered.
- A group of rhinos is called a "crash."
- Rhinos' horns are made of keratin, the same protein found in human hair and nails.
- The term "rhinoceros" comes from two Greek words meaning "nose" and "horn."
- Rhinos and elephants are not natural enemies.
- One of the most famous depictions of a rhino is Albrecht Dürer's woodcut from 1515.
- The gestation period for rhinos can last up to 16 months.
- Rhinos have historically been used in traditional Asian medicine.
Cabinet approves Chandrayaan-4 mission, first module of Bharatiya Antariksh Station, Venus mission, next-gen launcher

- 19 Sep 2024
In News:
The PM Modi-led Union Cabinet has approved several ambitious space initiatives, marking a significant leap for India's lunar and space exploration programs.
Chandrayaan-4 Mission
- Objective: The fourth lunar mission aims to collect lunar samples, return them safely to Earth, and analyze them.
- Timeline: Expected completion within 36 months post-approval, with a budget of ?2,104 crore.
- Significance: This mission will build foundational technological capabilities for a manned Moon landing planned by 2040.
- Remarks: ISRO Chairman S. Somanath emphasized that the mission's highlight is its low-cost execution and the step-by-step approach to developing the necessary technology.
Bharatiya Antariksh Station (BAS) and Gaganyaan
- BAS Development: Approval for the first module of the Bharatiya Antariksh Station, targeted for launch by 2028, with full completion by 2035.
- Gaganyaan Program: The program’s budget has been revised to ?20,193 crore, with an additional funding of ?11,170 crore to enhance its scope and include precursor missions for BAS.
- Mission Plan: Eight missions are envisaged by 2028, including four under the ongoing Gaganyaan program, development of BAS-1, and four additional missions for technology demonstration and validation.
Venus Orbiter Mission (VOM)
- Launch Timeline: Scheduled for March 2028, VOM will explore Venus's atmosphere, geology, and generate extensive scientific data.
- Budget: The Cabinet approved ?1,236 crore for VOM, with ?824 crore allocated for the spacecraft.
- Research Focus: The mission will provide insights into Venus's transformation and how different planetary environments evolve.
Next-Generation Launch Vehicle (NGLV)
- Development Approval: A reusable NGLV has been greenlit with a budget of ?8,240 crore.
- Capabilities: The new rocket will have three times the payload lifting capability compared to existing vehicles (10 tonnes to 30 tonnes to Low Earth Orbit) and will be cost-effective and commercially viable.
- Features: The NGLV will include reusability options and modular green propulsion systems, enhancing India's capacity for satellite launches.
Gliese 12b

- 25 May 2024
Why is it in the News?
Recently, scientists have discovered a new planet that they say could "potentially support human life."
What is Gliese 12b?
- Gliese 12 b is a rocky planet just 40 light-years away from Earth.
- It orbits around a star called Gliese 12, a cool red dwarf in the constellation Pisces.
- This star is only 27 per cent of the size of our sun, with about 60 per cent of its surface temperature.
- But it's this lower temperature that makes Gliese 12 b theoretically habitable for humans.
- Gliese 12 b is one of the few known rocky planets where humans could theoretically survive according to scientists.
- The planet was discovered by an international team, in collaboration with NASA and the European Space Agency, using data from NASA's Transiting Exoplanet Survey Satellite (TESS) and ESA's Characterizing Exoplanet Satellite (CHEOPS).
- Gliese 12 b falls into this "Goldilocks zone," with an average temperature of 107 degrees Fahrenheit and a size somewhere between Venus and Earth.
- The researchers hope that by learning more about Gliese 12 b's atmosphere we may be able to answer questions about the evolution of our own solar system and other habitable planets.
About the Transiting Exoplanet Survey Satellite (TESS):
- TESS is a NASA mission dedicated to discovering exoplanets around nearby bright stars.
- It was launched on April 18, 2018, aboard a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket from Cape Canaveral.
- TESS operates in a unique high Earth orbit with a period of 12 to 15 days.
- This orbit is designed to keep the telescope's view largely unobstructed by Earth and the Moon.
- The prime mission concluded on July 4, 2020, but TESS continues to operate on an extended mission.
- TESS has identified a wide range of exoplanets, from small rocky worlds to giant planets, highlighting the diversity of planetary systems in our galaxy.
- TESS uses the transit method to find exoplanets. It monitors stars for periodic dips in brightness, which occur when a planet crosses in front of the star along our line of sight.
- The size of the dip indicates the planet's diameter and the duration of the transit provides information about the planet's orbit.
- The transit method allows scientists to determine the diameter and orbital size of exoplanets.
- Orbits within certain ranges fall into the "habitable zone," where conditions may allow liquid water to exist on the surface of Earth-like worlds.
The League of Arab States (LAS)/Arab League
- 24 May 2024
Why is it in the News?
The Arab League called recently for a UN peacekeeping force in the "occupied Palestinian territories" at an international summit dominated by the war between Israel and Hamas.
What is the Arab League?
- The League of Arab States was formed in Cairo on 22 March 1945 with six members: Egypt, Iraq, Transjordan (later renamed Jordan), Lebanon, Saudi Arabia and Syria, with Yemen joining on 5 May 1945.
- It currently has 22 member states; Algeria, Bahrain, Comoros, Djibouti, Egypt, Iraq, Jordon, Kuwait, Lebanon, Libya, Mauritania, Morocco, Oman, Palestinian Authority, Qatar, Saudi Arabia, Somalia, Sudan, Syria, Tunisia, United Arab Emirates and Yemen.
- Four countries have been admitted as observers: Brazil, Eritrea, India and Venezuela.
- Each member state has one vote in the League Council, while decisions are binding only on those states that have voted for them.
- The official language of the Arab League and its 22 member states is Arabic.
- The league seeks to promote the political, social, and military interests of its members.
- The head of the league is known as the secretary-general.
- The secretary-general is appointed to a five-year term by a two-thirds majority of league members.
- Headquarters: Cairo, Egypt.
Goals:
- The overall aim of the league is to promote Arab interests.
- Its main goals are to strengthen and coordinate the political, cultural, economic, and social programs of its members and to try to settle disputes among them or between them and third parties.
- In 1950 the members also agreed to provide military support to help defend each other.
The Arab League Council:
- The League Council is the highest body of the Arab League and is composed of representatives of member states, typically foreign ministers, their representatives, or permanent delegates.
- Each member state has one vote.
- The Council meets twice a year, in March and September. Two or more members may request a special session if they desire.
- The general secretariat manages the daily operations of the league and is headed by the secretary-general.
- The general secretariat is the administrative body of the league, the executive body of the council, and the specialized ministerial councils.
Synchrotron

- 17 May 2024
Why is it in the News?
China's latest scientific achievement, the High Energy Photon Source (HEPS), is poised to become Asia's first fourth-generation synchrotron light source which is scheduled to commence operations by the end of this year.
What is a Synchrotron?
- A synchrotron is a type of circular particle accelerator where particles travel in a loop.
- It functions by accelerating charged particles, typically electrons, through sequences of magnets until they approach the speed of light.
How Does It Work?
- Acceleration: Charged particles are accelerated through magnets.
- Production of Light: These high-speed electrons generate extremely bright light, known as synchrotron light.
- This light, predominantly in the X-ray region, is millions of times brighter than conventional sources and 10 billion times brighter than the sun.
- Beamlines and Workstations: The intense light is directed down beamlines to experimental workstations for research purposes.
Applications:
- Research: Scientists use synchrotron light to study tiny matter such as atoms and molecules.
- By examining how a sample scatters, diffracts, absorbs, or reemits the synchrotron light, they can uncover details about its structure and chemical composition.
Global Presence:
- There are approximately 70 synchrotrons worldwide in various stages of development.
- They have varying technical specifications and uses, ranging from practical applications to fundamental theoretical research.
In India:
- India has a synchrotron facility known as the "Indus Synchrotron."
- It is located at the Raja Ramanna Centre for Advanced Technology (RRCAT) in Indore, Madhya Pradesh.
- The Indus Synchrotron is a third-generation synchrotron radiation source that is used for various research applications in fields such as materials science, biology, and environmental science.
What is the High Energy Photon Source (HEPS)?
- HEPS (High Energy Photon Source) is recognized as the brightest synchrotron X-ray source in Asia.
- Location: The HEPS facility is situated in Huairou, China, approximately 50 kilometres from Beijing.
- Acceleration Capabilities: HEPS is designed to accelerate electrons up to energies of 6 gigaelectron volts within its 36-kilometer circumference storage ring, producing high-energy X-rays for research purposes.
- Nanoscale Investigations: The high-energy X-rays generated by HEPS can penetrate deep into samples, allowing researchers to study intricate details at the nanometer scale.
- Diverse Research Applications: HEPS will cater to various research fields, including energy, condensed matter physics, materials innovation, and biomedicine, by providing access to 14 specialized beamlines.
- Superiority to Existing Synchrotrons: Compared to China's current most advanced synchrotron, the Shanghai Synchrotron Radiation Facility (with a circumference of 432 meters), HEPS will offer a time resolution 10,000 times better.
PM Modi lays stone for India’s second spaceport at Kulasekarapattinam
- 29 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
Prime Minister Narendra Modi laid the foundation stone for the country’s second spaceport at Kulasekarapattinam in Tuticorin district recently.
About Kulasekarapattinam Spaceport:
- The Kulasekarapattinam Spaceport is a forthcoming space launch facility located in Kulasekarapattinam, a coastal village near the temple town of Tiruchendur in Thoothukudi district, southern Tamil Nadu.
- It will become the second operational spaceport in India after the Satish Dhawan Space Centre, established in Sriharikota, Andhra Pradesh, in 1971, and will feature two launch pads.
- The primary focus of the Kulasekarapattinam Spaceport will be to facilitate the commercial launch of Small Satellite Launch Vehicles (SSLVs).
- Spanning 2,350 acres, the spaceport will comprise 35 essential facilities, including a launch pad, rocket integration facilities, ground range and checkout facilities, and a mobile launch structure (MLS) equipped with checkout computers.
- With the capability to launch up to 24 satellites annually using a mobile launch structure, it offers a strategic advantage by enabling direct southward launches over the Indian Ocean, thus conserving fuel for small rocket launches.
- This stands in contrast to the Satish Dhawan Space Centre, where launching into a polar orbit necessitates additional fuel due to the curved trajectory required to avoid crossing landmasses, particularly Sri Lanka.
- The estimated cost of the Kulasekarapattinam Spaceport project is Rs. 986 crore.
About the Small Satellite Launch Vehicles (SSLVs):
- The SSLV, or Small Satellite Launch Vehicle, is a three-stage launch vehicle characterized by three solid propulsion stages and a liquid propulsion-based Velocity Trimming Module (VTM) serving as a terminal stage.
- Measuring 2 meters in diameter and 34 meters in length, the SSLV boasts a lift-off weight of 120 tonnes.
- Designed for versatility, the SSLV can effectively launch a 500kg satellite into a 500 km planar orbit.
- Notable features of the SSLV include its cost-effectiveness, rapid turnaround time, ability to accommodate multiple satellites, feasibility for launch-on-demand, and minimal infrastructure requirements.
India gets desi Garbhini GA2 for evaluation of foetal growth
- 27 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
Specifically tailored to address the unique characteristics of foetal growth within the Indian population, India has finally got its locally made ‘Garbhini-GA2’, a groundbreaking Artificial Intelligence model.
What is Garbhini-GA2?
- The Garbhini-GA2 model, developed as part of the DBT India initiative (GARBH-Ini) program by researchers at the Indian Institute of Technology (IIT) Madras and the Translational Health Science and Technology Institute (THSTI), Faridabad, addresses the challenge of accurately estimating foetal age (gestational age, GA) in the Indian population, particularly in the second and third trimesters.
- Unlike existing formulas designed for Western populations, Garbhini-GA2 accounts for variations in foetal growth specific to the Indian context, significantly reducing estimation errors by nearly threefold.
- This innovative model is crucial for ensuring precise prenatal care and determining accurate delivery dates, thereby enhancing maternal and foetal health outcomes.
- Garbhini-GA2 marks a milestone as the first late-trimester GA estimation model validated using Indian population data, offering a tailored approach to foetal age determination that is essential for effective maternal healthcare."
About Translational Health Science and Technology Institute (THSTI):
- THSTI, an autonomous institute under the Ministry of Science and Technology, was founded in 2009 in Faridabad, Haryana, with a core commitment to advancing research beyond mere discovery.
- By fostering collaboration among diverse teams in medicine, science, and technology, THSTI leverages translational expertise to drive clinical research and innovation.
- In addition to its core mission, THSTI plays a pivotal role in fostering social innovation and entrepreneurial endeavors, particularly in the domain of maternal and child healthcare.
G-33 calls for progress on agricultural trade ahead of WTO Ministerial Conference

- 26 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
The G-33 group of countries recently expressed serious concern over the lack of progress in agriculture trade negotiations and urged the members of the World Trade Organisation (WTO) to work on a permanent solution to the issue of public stockholding of grains for food security purposes.
Key Highlights of the G33 Trade Ministers Meeting in Abu Dhabi:
- Special Safeguard Mechanism: The G33 group emphasized the importance of the Special Safeguard Mechanism (SSM) as a crucial instrument against significant import surges or sudden price declines.
- They called for WTO members to reach an agreement and adopt a decision on SSM by the 14th WTO Ministerial Conference (MC).
- Permanent Solution for Public Stockholding: The G33 nations sought a permanent solution during the 13th Ministerial Conference, which commenced in Abu Dhabi recently.
- The MC serves as the highest decision-making body of the WTO.
- Critical Importance of Public Stockholding: The G33 statement highlighted the critical significance of public stockholding for food security in developing countries.
- It enables governments to procure crops from farmers at the minimum support price (MSP) and store and distribute food grains to the poor.
- This program supports low-income or resource-poor producers and contributes to rural development.
- The 13th WTO Ministerial Conference provides a crucial platform for WTO members to engage in constructive discussions and work towards finding mutually beneficial solutions.
What is G 33?
- The G33 is a forum of developing countries including India, Brazil, South Africa etc. formed during the Cancun ministerial conference of the WTO (2003), to protect the interest of the developing countries in agricultural trade negotiations.
- It was created to help group countries which were all facing similar problems.
- The G33 has proposed special rules for developing countries at WTO negotiations, like allowing them to continue to restrict access to their agricultural markets.
- Dominated by India, the group has "defensive" concerns regarding agriculture in relation to World Trade Organization negotiations, and seeks to limit the degree of market opening required of developing countries.
- The group has advocated the creation of a "special products" exemption, which would allow developing countries to exempt certain products from tariff exemptions, and also a "special safeguard mechanism" which would permit tariff increases in response to import surges.
Will the ‘Paruveta Festival’ celebrated in Andhra’s Ahobilam get UNESCO recognition?

- 22 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
INTACH is striving to obtain UNESCO recognition for the yearly 'Paruveta' festival, emphasising its cultural significance.
About the Paruveta Festival:
- Paruveta Festival, also known as the 'mock hunting festival', is a celebrated tradition at the Sri Narasimha Swamy temple in Ahobilam, Andhra Pradesh.
- It stands out as a symbol of communal harmony, where devotees from various religious backgrounds, including Muslims, come together to offer prayers.
Origin and Significance:
- According to folklore, the festival commemorates Lord Vishnu's incarnation as Narasimha, who married Chenchulakshmi, a tribal girl, symbolising unity across different communities.
- The festival's rituals, typically observed during Vijayadashami or Sankranti, extend for a 'mandala' period of forty days in Ahobilam.
Activities and Customs:
- During the festival, the temple deity is carried to the 32 Chenchu tribal villages surrounding Ahobilam for forty days.
- The journey begins with a symbolic act where tribals shoot arrows at the deity's palanquin, signifying protection and reverence.
- Chenchus participated by undertaking 'Narasimha Deeksha', wearing yellow robes and Tulasi Mala, while observing celibacy.
- The temple staff reside in these villages throughout the festival, showcasing the tradition of a casteless society with no traces of untouchability.
Key Points about Chenchu Tribes:
- Geographic Distribution: Chenchu tribes primarily inhabit the hills of southern India, particularly in Andhra Pradesh.
- Additionally, Chenchu communities can be found in Tamil Nadu, Karnataka, and Orissa.
- Language and Communication: Their native language, known as Chenchu, belongs to the Dravidian language family.
- While many Chenchu individuals speak Telugu, their traditional language holds cultural significance.
- Livelihood and Occupation: Historically, Chenchu people pursued a nomadic lifestyle, relying on food gathering.
- However, due to factors such as agricultural expansion, many have transitioned to working as farmers or forest labourers.
- Housing and Settlements: Chenchu dwellings are typically hive-shaped structures constructed from wattle thatch, composed of interwoven poles, twigs, reeds, or branches.
- These houses reflect their traditional architectural style and are adapted to their environment.
- Social Structure: Chenchu society is organised into clans, which are extended family units, as well as local groups and individual families.
- They adhere to exogamous marriage practices, prohibiting unions within the same clan.
- Additionally, Chenchu kinship is patrilineal, tracing descent through male lineage.
India, and ASEAN discuss the review of the trade agreement

- 20 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
India hosted the 3rd meeting of the AITIGA Joint Committee, which focused on reviewing the ASEAN-India Trade in Goods Agreement at Vanijya Bhawan in New Delhi from February 16th to 19th, 2024.
About the ASEAN-India Trade in Goods Agreement (AITIGA):
- The ASEAN-India Trade in Goods Agreement (AITIGA) is a trade deal between the ten member states of ASEAN and India.
- ASEAN and India signed the Agreement at the 7th ASEAN Economic Ministers-India Consultations in Bangkok, Thailand in 2009.
- The Agreement, which came into effect in 2010, is sometimes referred to as the ASEAN-India Free Trade Agreement.
- The Agreement originated out of the Framework Agreement on Comprehensive Economic Cooperation between India and ASEAN created in 2003.
- The Framework Agreement laid a sound basis for the establishment of an ASEAN-India Free Trade Area (FTA), which includes FTA in goods, services and investment.
- The Agreement has led to steadily increasing trade between ASEAN and India since its signing.
- In 2019-20, trade between India and ASEAN was worth US$86 billion.
About ASEAN:
- The Association of Southeast Asian Nations, or ASEAN is an intergovernmental organization of ten Southeast Asian countries:
- Brunei, Cambodia, Indonesia, Laos, Malaysia, Myanmar, the Philippines, Singapore, Thailand, and Vietnam.
- ASEAN's primary objectives are to promote political and economic cooperation and regional stability among its member states.
- The organization operates on the principles of mutual respect, non-interference in internal affairs, and consensus-building. ASEAN's motto, "One Vision, One Identity, One Community," underscores its commitment to fostering unity and solidarity among Southeast Asian nations.
- Economically, ASEAN has made significant strides towards integration through initiatives like the ASEAN Economic Community (AEC), aimed at creating a single market and production base.
- This has facilitated trade, investment, and economic development within the region.
- Additionally, ASEAN serves as a platform for dialogue and cooperation on a wide range of issues, including security, environmental sustainability, cultural exchange, and disaster management.
India initiates Anti-Dumping Probe into Solar Glass Imports from China and Vietnam (TOI)

- 17 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
India has launched an anti-dumping investigation into the import of solar glass from China and Vietnam following a complaint from domestic players.
What is Anti-Dumping Duty?
- Anti-dumping duty is a tariff levied on imports from foreign countries when their prices are lower than the fair market value of similar goods in the domestic market.
- It's implemented by governments to counteract the practice of "dumping," where foreign goods are sold at unfairly low prices in the domestic market, posing a threat to local businesses.
- The primary objective of anti-dumping duty is to safeguard domestic industries from unfair competition and restore fair trade practices.
- This measure is permitted by the World Trade Organization (WTO) to address instances where dumping causes genuine harm to domestic industries.
- To impose anti-dumping duties, governments must provide evidence of dumping, quantify its extent in terms of costs, and demonstrate the resulting injury or threat to domestic markets.
- While aimed at protecting local industries, anti-dumping duties can sometimes lead to increased prices for consumers within the country.
About Countervailing Duty (CVD):
- Countervailing duty (CVD) is a type of tariff imposed by a government to offset the adverse effects of import subsidies on domestic producers.
- It serves as an import tax applied by the importing country on subsidised products from abroad.
- CVD is imposed to address situations where foreign governments provide subsidies to their producers, lowering the cost of their goods and potentially disrupting fair competition.
- To prevent the influx of subsidised products into their markets, importing countries levy CVD, effectively neutralising the price advantage enjoyed by these imports.
- The imposition of CVD is permitted by the World Trade Organization (WTO) to help maintain fair trade practices among its member countries.
Difference Between Anti-dumping Duty and Countervailing Duty:
- Anti-dumping duty is enacted to safeguard domestic markets from the harmful effects of low-priced foreign goods, while CVD targets products benefiting from government subsidies, resulting in artificially low prices.
- The amount of Anti-dumping duty is determined by the margin of dumping, whereas CVD is calculated based on the subsidy value granted to foreign goods.
DoT Unveils 'Sangam: Digital Twin' Initiative (TOI)

- 16 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
The Department of Telecommunications has introduced the 'Sangam: Digital Twin' initiative, which aims to transform infrastructure planning and design through innovation and the integration of advanced technologies.
What is Sangam: Digital Twin initiative?
- Digital Twin technology creates virtual replicas of physical assets, enabling monitoring, simulation, and analysis for adaptive outcomes.
- 'Sangam: Digital Twin' consists of two stages:
- The first is exploratory for creative exploration, and
- The second is for the practical demonstration of specific use cases, creating a future blueprint for collaboration in future infrastructure projects.
- The initiative aligns with advancements in communication, computation and sensing over the past decade, fostering a collaborative approach to reshape infrastructure planning and design.
- 'Sangam: Digital Twin' integrates 5G, IoT, AI, AR/VR, AI native 6G, Digital Twin and next-gen computational technologies to break silos and promote a whole-of-nation approach.
- The new initiative aims to transform ideas into solutions, bridging the gap between conceptualisation and realisation, and fostering advancements in infrastructure.
- Sangam encourages a holistic approach to innovation, uniting stakeholders to harness unified data and collective intelligence.
- It is aimed at creating an ecosystem that maximises the value of technological advancements for development.
- Sangam aims to demonstrate the practical implementation of innovative infrastructure planning solutions, providing a model framework for collaboration and a future blueprint for scaling successful strategies in future projects.
- The platform also offers a blog for pre-registered participants to connect, share insights, and engage in discussions.
Significance of Digital Twins:
- Facilitates remote monitoring, making it applicable for use in hazardous operations.
- Enhances predictive capabilities, assisting in making informed policy decisions.
- Improves operational efficiency, thereby ensuring the maintenance of output quality.
- Assists in urban planning by generating various simulations and forecasts.
Alaskapox Claims One Life in US (TOI)

- 15 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
An elderly man has died from Alaskapox, the first known fatality from the recently discovered virus.
What is Alaskapox?
- Alaskapox is caused by orthopoxvirus, a family of brick-shaped viruses that can infect both animals and humans, leading to skin lesions or pox.
- The virus was first identified in a woman living near Fairbanks, Alaska, and has since been primarily detected in small mammals like red-backed voles and shrews.
- However, domestic pets such as dogs and cats may also be carriers of the virus.
What are the symptoms of Alaskapox?
- Symptoms of Alaskapox include the development of one or more bumps or pustules on the skin, accompanied by joint or muscle pain and swollen lymph nodes.
- While the majority of the seven known human cases in Alaska over the past nine years have experienced mild illnesses that were resolved without intervention, the virus poses a greater threat to individuals with weakened immune systems.
How is Alaskapox Transmitted?
- Transmission of Alaskapox is believed to occur through direct contact with infected animals.
- Unlike some of its orthopoxvirus relatives, there have been no documented instances of Alaskapox spreading from person to person.
- Though it's not clear how Alaskapox is transmitted, researchers say that it may be zoonotic meaning it can jump from animals to humans.
Odisha’s Gupteswar Forest Is Now A Biodiversity Heritage Site (TOI)
- 13 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
Gupteswar forest in the Koraput district of Odisha has been officially declared the fourth biodiversity heritage site (BHS) in the state.
What is a Biodiversity Heritage Site (BHS)?
- A Biodiversity Heritage Site (BHS) is a unique ecosystem with rich biodiversity that is designated for special protection and conservation.
- These sites are typically declared by individual states or local bodies under the provisions of the Biological Diversity Act, of 2002, in India.
Who can Declare BHS?
- Under Section 37 of the Biological Diversity Act, 2002 the State Government in consultation with local bodies may notify areas of biodiversity importance as Biodiversity Heritage Sites (BHS).
- The ‘Biodiversity Heritage Sites’ (BHS) are unique ecosystems having rich biodiversity comprising of any one or more of the following components:
- The richness of wild as well as domesticated species or intra-specific categories.
- High endemism.
- Presence of rare and threatened species, keystone species, and species of evolutionary significance.
- Wild ancestors of domestic/cultivated species or their varieties.
- Past pre-eminence of biological components represented by fossil beds and having significant cultural, ethical or aesthetic values are important for the maintenance of cultural diversity, with or without a long history of human association with them.
- “The creation of BHS may not put any restriction on the prevailing practices and usages of the local communities, other than those voluntarily decided by them.
- The purpose of declaring BHS is to enhance the quality of life of the local communities through conservation of such sites.”
The main objectives of declaring an area as a BHS are:
- To conserve biological diversity, including genetic diversity, ecosystem diversity, and species diversity.
- To protect habitats of rare, endemic, and threatened species.
- To promote sustainable use of biodiversity.
- To maintain cultural diversity and traditional knowledge associated with biodiversity.
- To raise awareness about the importance of biodiversity conservation.
Biodiversity Heritage Sites (BHS) of India:
NAL Successfully Tested High Altitude Pseudo-Satellite (HAPS) at Challakere, Karnataka (TOI)

- 12 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
Scientists from city-based National Aerospace Laboratories (NAL), a Council of Scientific and Industrial Research (CSIR) lab, achieved a breakthrough by successfully testing an unmanned aerial vehicle called High-Altitude Pseudo Satellite (HAPS) at Chitradurga's Challakere in Karnataka.
News Summary:
- National Aerospace Laboratories (NAL) has achieved a milestone with the successful testing of an unmanned aerial vehicle known as the High Altitude Pseudo-Satellite (HAPS) in Challakere, Karnataka.
- This innovative system, measuring 5 meters in length with an impressive 11-meter wingspan and weighing 23 kg, soared to an altitude of approximately 3 km and maintained its position for an impressive duration of eight hours.
- A comprehensive series of tests is slated, with the ultimate goal of developing a full-fledged aircraft boasting a remarkable 30-meter wingspan comparable to a Boeing 737 by the year 2027.
- This advanced craft is anticipated to ascend to an impressive altitude of 23 km and remain airborne for a remarkable period of at least 90 days.
- NAL's ambitious agenda includes the design and construction of various components essential for the HAPS, including propellers, battery management systems, carbon-composite airframes, flight-control systems, and high-powered electric motors capable of withstanding extreme temperature variations.
- Additionally, in a separate endeavour, a Bengaluru-based private company recently conducted the inaugural test flight of a solar-powered, long-endurance drone, achieving an impressive flight duration of 21 hours.
About High Altitude Pseudo-Satellite (HAPS):
- Since the 1990s, numerous global initiatives have been undertaken to explore the potential applications of High Altitude Pseudo Satellites, also known as High Altitude Platform Stations (HAPS).
- Positioned above 20 km altitude in the stratosphere, these unmanned aircraft are designed for exceptionally long-duration flights, spanning months or even years.
- HAPS encompass various aircraft types, including airplanes, airships, and balloons.
Benefits/Advantages of HAPS:
- These solar-powered vehicles bridge the gap between unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) operating in lower altitudes and traditional satellites in space.
- They offer a wide array of applications, including telecommunications, emergency/public safety communications, intelligent transportation systems, maritime surveillance, environmental monitoring, and land border control.
- Compared to ground-based communication networks, HAPS can cover larger areas with minimal interference and facilitate data transfer between satellites and ground-based telecom networks.
- Unlike traditional satellites, which are costly to construct and launch, HAPS are more cost-effective and easier to deploy.
- It has both military and civilian applications, including intelligence, surveillance, telecommunication, and disaster response.
- The technology offers lower latency and can connect to multiple ground stations.
Significance for India:
- In India, Hindustan Aeronautics Limited (HAL) announced in 2022 its collaboration with a startup company to develop a "futuristic" high-altitude pseudo satellite.
- Given India's extensive land borders stretching approximately 15,000 km and a coastline spanning 7,500 km, securing these borders is paramount, necessitating diverse solutions.
- Hovering at the Earth's atmospheric edge, HAPS offer valuable services for efficient border surveillance, tracking enemy movements deep into territories or seas, and conducting round-the-clock missions.
- Equipped with advanced optical and infrared cameras, state-of-the-art sensors, and other sophisticated technology, these aerial platforms are ideal for border patrolling, target tracking, maritime surveillance, navigation, and even missile detection.
- China's Aviation Industry Corporation of China (AVIC), a state-owned aerospace and defense conglomerate, has been actively developing various HAPS platforms for surveillance purposes.
- In 2018, it successfully tested the solar-powered Morning Star drone, renowned for its prolonged airborne endurance.
Israel discovers 6-million-year-old giant underwater canyon of Messinian Event (TOI)

- 06 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
The Israel Geological Survey announced recently that Israeli geologists discovered a huge underwater canyon on the bottom of the Eastern Mediterranean that was formed about 6 million years ago.
What is Messinian Event?
- The Messinian Event, also referred to as the Messinian Salinity Crisis (MSC).
- It marks a significant geological occurrence during which the Mediterranean Sea experienced a cycle of partial or near-complete desiccation, making it one of the most severe ecological crises in Earth's history.
- This event unfolded approximately 6 million years ago (MYA) and persisted until around 5.3 MYA.
- The process began with the severance of the connection between the Atlantic Ocean and the Mediterranean Sea.
- This disconnection resulted from a combination of reduced sea levels globally and the collision of the European and African plates, causing the land to rise.
- Consequently, the Mediterranean experienced significant evaporation, as its evaporation rate exceeded its precipitation rate.
- Without a substantial influx of water from the Atlantic, the sea began to evaporate rapidly.
- During this period, a vast underground canyon formed, with rivers cutting deep into the basin floor, creating a canyon much larger than the Grand Canyon, reaching depths of up to 2,000 meters (6562 feet).
- As the Mediterranean water evaporated, salt deposits, primarily composed of Halite and Gypsum, accumulated on the basin floor, some reaching depths of 800 meters (2,500 feet).
- Despite the rapid evaporation, salt deposition did not keep pace, resulting in an increase in water salinity.
- The heightened salinity levels made the Mediterranean inhospitable to marine life, leading to a decline in biodiversity.
- Eventually, the sea dried up almost entirely, culminating in the Zanclean flood when the Atlantic Ocean reclaimed the basin.
What is Deep-sea Canyon?
- Deep-sea canyons, such as those formed during the Messinian Event, are steep valleys carved into the seafloor of the continental slope, extending onto the continental shelf.
- These canyons vary in size and shape and have been sculpted by various erosional processes, including river flows during periods of low sea levels, mudslides, debris flows, and turbidity currents.
INS Sandhayak - the Indian Navy’s First Survey Vessel Large (SVL) Ship (TOI)

- 05 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News
Defense minister Rajnath Singh commissioned survey vessel INS Sandhayak into the Indian Navy at the Naval Dockyard recently.
About INS Sandhayak:
- INS Sandhayak stands as the first unit in a series of four Survey Vessel (Large) ships under construction at Garden Reach Shipbuilders & Engineers (GRSE), Kolkata.
- Its primary mission is to conduct thorough coastal and deep-water Hydrographic Surveys, focusing on Port and Harbour approaches, navigational channels, and routes.
- The operational scope extends to maritime limits, encompassing the Exclusive Economic Zone (EEZ) and extended continental shelf.
Features:
-
- The vessel is equipped to gather oceanographic and geophysical data, serving the needs of both defense and civil applications.
- In a secondary role, it provides limited defense capabilities and can function as a hospital ship during wartime or emergencies.
- Cutting-Edge Technology:
-
- Equipped with advanced hydrographic tools, including a Data Acquisition and Processing System, Autonomous Underwater Vehicle, Remotely Operated Vehicle, DGPS Long-range positioning systems, and Digital side-scan sonar.
- Performance Specifications:
-
- Powered by two diesel engines, INS Sandhayak boasts a speed capability exceeding 18 knots.
- With a length of 110 meters and a displacement of 3400 tons, the vessel maintains an indigenous content exceeding 80 per cent by cost.
- Historical Continuity:
-
- This ship has been re-incarnated in its current form from the previous Sandhayak, decommissioned in 2021.
Digital Detox for Responsible Gaming (TOI)

- 02 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
The Karnataka government recently said it would launch a 'Digital Detox' initiative in collaboration with the All India Game Developers Forum (AIGDF), with special emphasis on gaming and social media.
What is Digital Detox?
- A digital detox entails voluntarily refraining from using digital devices like smartphones, computers, and social media platforms for a defined period.
- This period can range from a few hours to as long as a week or even a month.
- Research indicates that approximately 25% of smartphone owners aged 18 to 44 cannot recall the last time they were separated from their phones.
Benefits:
- Overcoming Technology Addiction: Studies reveal that around 61% of individuals acknowledge their addiction to the internet and digital screens.
- A digital detox aids in combating this addiction.
- Enhanced Mental Health: Disconnecting from technology can alleviate stress and anxiety, thereby fostering improved mental health and overall well-being.
- Increased Productivity and Creativity: Taking a break from continuous digital engagement bolsters focus and concentration, leading to heightened productivity and creativity.
- Improved Sleep: Excessive screen time has been linked to poor sleep quality. A digital detox helps in promoting better sleep by reducing exposure to blue light and stimulating content.
- Enhanced Communication Skills: Reducing online time allows for more face-to-face interactions, nurturing better communication skills and social connections.
Challenges:
- Feelings of Disconnection: Detox participants may feel disconnected from friends and family members.
- Fear of Missing Out: Participants may experience FOMO (fear of missing out) or anxiety about missing important information.
- Boredom or Restlessness: Detoxes may lead to feelings of boredom or restlessness.
- Withdrawal Symptoms: Some individuals may experience withdrawal symptoms such as anxiety or boredom.
Way forward:
- Start Small: Initiate the detox with shorter periods and gradually extend the duration.
- Inform Others: Notify friends and family about the detox to avoid misinterpretations.
- Engage in Healthy Activities: Utilize detox time for activities like reading, spending time outdoors, or exercising.
- Minimize Notifications: Turn off device notifications and store them out of sight.
- Reward Progress: Offer yourself incentives for achieving detox goals.
Conclusion
Digital dependence can contribute to mental health issues, shorter attention spans, and strained interpersonal relationships. While technology offers convenience and connectivity, excessive screen time exacts a toll. A digital detox presents an opportunity to enhance mental and physical well-being, as well as nurture healthier relationships. With proper planning and commitment, a successful and fulfilling detox experience is achievable.
5 Wetlands Added to The Global List of Wetlands of International Importance under Ramsar Convention (TOI)
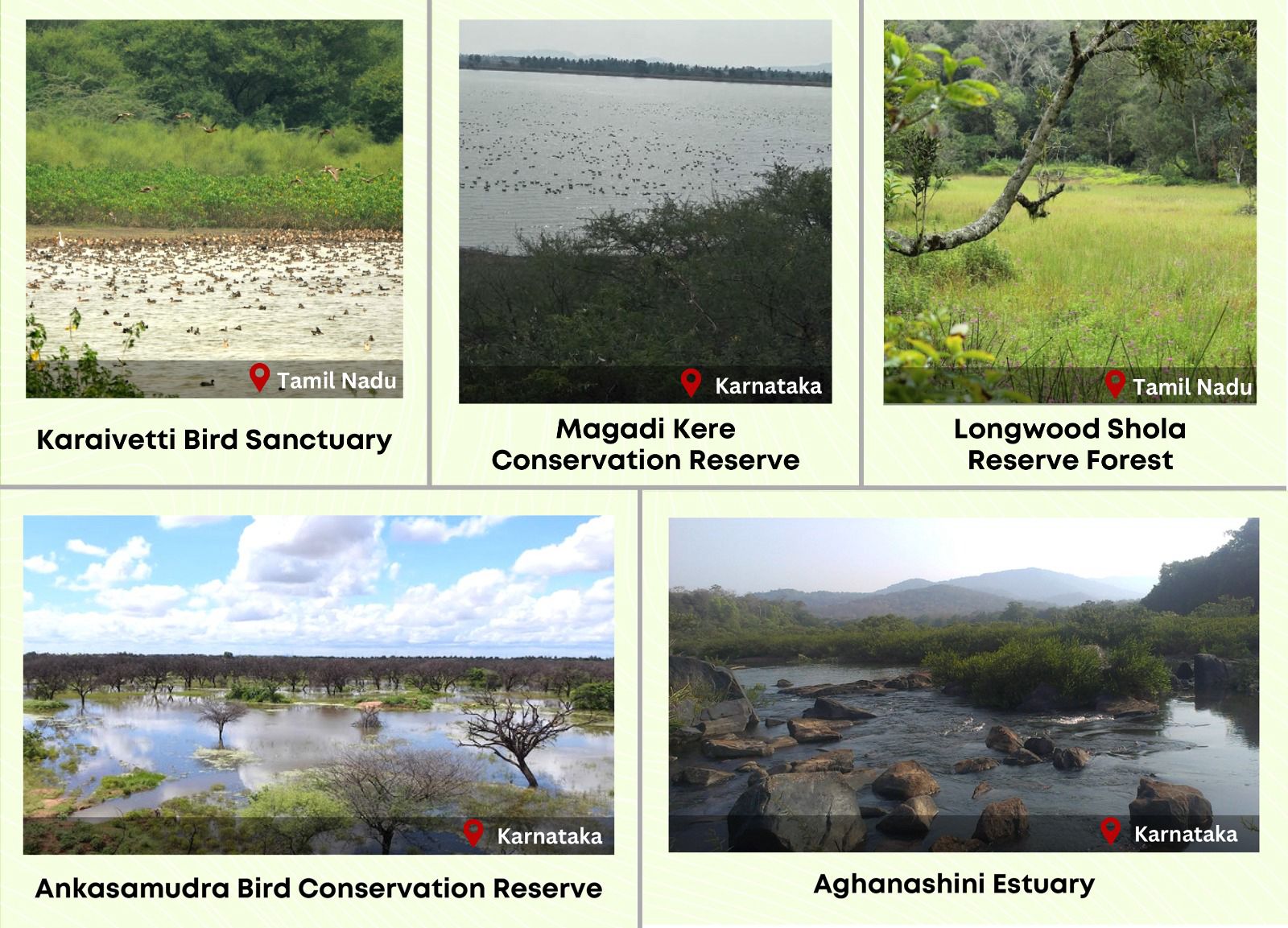

- 01 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
Ahead of World Wetlands Day, five more wetlands in India got the tag of international importance under the Ramsar Convention, making it the fourth largest country in terms of the number of sites on the list.
About the New Ramsar sites:
- The five newly added Indian sites in the list are Karaivetti Bird Sanctuary and Longwood Shola Reserve Forest in Tamil Nadu, and Magadi Kere Conservation Reserve, Ankasamudra Bird Conservation Reserve and Aghanashini Estuary in Karnataka.
- In India, Tamil Nadu continues to have the maximum number of Ramsar sites (16) followed by Uttar Pradesh (10).
- Karaivetti Bird Sanctuary (Tamil Nadu): Karaivetti Bird Sanctuary is one of the largest inland wetlands of Tamil Nadu and is a significant source of groundwater recharge for the area.
- Water from the wetland is utilized by the villagers for cultivating crops such as paddy, sugar cane, cotton, corn, and split red gram.
- Karaivetti has one of the largest congregations of waterbirds in the State of Tamil Nadu.
- The Longwood Shola Reserve Forest (Tamil Nadu): The Longwood Shola Reserve Forest derives its name from the Tamil word, "Solai", which means ‘tropical rainforest’.
- The ‘Sholas’ are found in the upper reaches of the Nilgiris, Anamalais, Palni hills, Kalakadu, Mundanthurai and Kanyakumari in Tamil Nadu.
- These forested wetlands serve as habitats for the globally endangered Black-chinned Nilgiri Laughing thrush (Strophocincla cachinnans), Nilgiri Blue Robin (Myiomela major), and vulnerable Nilgiri Wood-pigeon (Columba elphinstonii).
- As many as 14 out of 26 endemic bird species of the Western Ghats are found in these wetlands.
- Ankasamudra Bird Conservation Reserve (Karnataka): Ankasamudra Bird Conservation Reserve is a human made Village Irrigation Tank built centuries back and is spread over an area of 98.76ha.
- It is an ecologically important wetland, rich in biodiversity, comprising over 210 species of plants, mammal species, reptiles, birds etc.
- It supports more than 1% of the biogeographic population of Painted Stork and Black-headed Ibis.
- Aghanashini Estuary (Karnataka): Aghanashini Estuary is formed at the confluence of the Aghanashini River with the Arabian Sea.
- The brackish water of the Estuary provides diverse ecosystem services including flood and erosion risk mitigation, biodiversity conservation and livelihood support.
- The wetland also provides livelihoods to families by supporting fishing, agriculture, collection of edible bivalves and crabs, shrimp aquaculture, traditional fish farming in the estuarine rice fields (locally known as Gazni rice fields), bivalve shell collection and salt production.
- Magadi Kere Conservation Reserve (??Karnataka): Magadi Kere Conservation Reserve, is a human-made wetland with an area of nearly 50 hectares which was constructed to store rainwater for irrigation purposes.
- The wetland harbors two vulnerable species, namely the Common pochard and River tern and four near-threatened species, namely the Oriental Darter Black-headed Ibis Woolly-necked Stork and Painted Stork.
- It is also one of the largest wintering grounds for the Bar-headed goose (Anser indicus) in Southern India.
- The wetland is a designated Important Bird Area (IBA) and is also listed as a priority area for conservation in India.
What is the Ramsar Convention?
- The Ramsar Convention was signed on 2nd February 1971 to preserve the ecological character of their wetlands of international importance.
- It is named after Ramsar, the Iranian city where the treaty was signed in 1971, and places chosen for conservation under it are given the tag ‘Ramsar site’.
- The World Wetlands Day, celebrated on 2 February to raise global awareness about the importance of wetlands for human prosperity and a healthy planet.
Delhi HC Upholds Validity of Anti-profiteering Provision of CGST Act (TOI)

- 30 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News?
Delhi High Court has upheld the constitutional validity of the anti-profiteering clause in the GST law, which mandates companies to pass on the benefit of lower taxes and input tax credits to consumers.
What is an ‘Anti-profiteering’ Activity?
- Any reduction in the rate of GST tax on any supply of goods or services or the benefit of input tax credit should have been passed on to the recipient by way of a commensurate reduction in prices.
- The wilful action of not changing the final price of the good or service by various means, despite the reduction in the rate of the tax for that particular good or service, amounts to “profiteering”.
How is the Anti-profiteering Mechanism Under the CGST Act?
- CGST mandate a 3-tier structure for investigation and adjudication of the complaints regarding profiteering.
- a) National Anti-profiteering
- b) Authority Directorate General of Safeguards
- c) State-level screening committees and standing committee
How Does the Screening Committee and Standing Committee Work?
- GST council may constitute a standing committee, having members from both state and central government.
- Every state shall constitute one state-level screening committee.
- It will have one member from the state government and one member from the central government as nominated by the respective appropriate authority.
- The complaints or issues of local nature will be first examined by the screening committee.
- State-level screening and standing committee will examine the complaint and determine the prime facie evidence to support the validity of the complaint.
- If any committee satisfies that the supplier has contravened section 171 of the CGST Act, the case shall be transferred to DG Safeguards for further investigation.
- The committees shall complete the investigation within a period of a month from the date of the receipt of the application.
What is the Role of DG Safeguards in the Anti-profiteering Mechanism?
- DG safeguards are the main investigation arm in the anti-profiteering mechanism.
- It can summon the interested parties make inquiries or call the relevant documents.
- It can seek help from technical experts in the due course of investigation.
- DG Safeguards shall complete the investigation within a period of three months from the date of receipt of the report from either screening or standing committee.
- The period can be extended for another three months.
Who Can File the Complaint Against Profiteering?
- Any consumer or organisation experiencing a non-reduction in the price of the goods or service despite the reduction in the rate of GST can file a complaint with proper evidence.
- Any supplier, trader, wholesaler or retailer, who could not get the benefit of input tax credit on account of a reduction in the rate of GST, can also file the complaint with proper evidence.
World's First 'Black Tiger Safari', to be Established in Odisha (TOI)

- 29 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News?
Odisha is gearing up to provide an unparalleled experience to visitors through its upcoming black tiger safari, offering a rare glimpse into the lives of these majestic creatures in their natural habitat.
What are Black Tigers or Melanistic Tigers?
- Black tigers, also known as melanistic tigers, are a unique phenomenon resulting from a genetic condition called melanism.
- Melanism causes an increased production of melanin, a pigment responsible for hair, eye, and skin colouration, resulting in black or nearly black skin, feathers, or hair in animals.
- In Simlipal Tiger Reserve, many royal Bengal tigers belong to a distinct lineage characterized by higher-than-normal levels of melanin.
- These tigers exhibit black and yellow interspersed stripes on their coats, though they are not entirely black.
- Therefore, they are more accurately described as pseudo-melanistic.
- As per the 2022 All-India Tiger Estimation, 16 tigers were recorded in Similipal Tiger Reserve, out of which 10 were melanistic.
- However, ongoing tiger surveys conducted by the state government suggest that the actual number of royal Bengal tigers in Similipal Tiger Reserve may be higher than reported by the National Tiger Conservation Authority.
- Factors Contributing to (Pseudo) Melanism:
- Research conducted by the National Centre for Biological Sciences (NCBS) in Bengaluru indicates that a single mutation in the gene Transmembrane Aminopeptidase Q (Taqpep) is responsible for the enlargement or spreading of black stripes into the yellow background of black tigers.
- Genetic analyses and computer simulations suggest that Similipal's black tigers may have originated from a very small founding population of tigers and are likely inbred.
- Additionally, the isolation of tigers in Similipal Tiger Reserve leads to breeding within the population, further contributing to the prevalence of melanism among these tigers.
About Similipal Tiger Reserve (STR):
- Similipal, which derives its name from the ‘Simul’ (Silk Cotton) tree, is a national park and a Tiger Reserve situated in the northern part of Orissa’s Mayurbhanj district.
- It spans an expansive area of 2,750 square kilometres (1,060 square miles), bordering Jharkhand and West Bengal.
- Similipal Tiger Reserve is a key component of the Mayurbhanj Elephant Reserve, which encompasses three protected areas:
- Similipal Tiger Reserve
- Hadagarh Wildlife Sanctuary, and
- Kuldiha Wildlife Sanctuary
- Biodiversity: Similipal is renowned for its rich biodiversity, boasting a diverse array of wildlife including the majestic Bengal tiger, the iconic Asian elephant, the formidable gaur, and the elusive chausingha.
- Recognized as a UNESCO World Network of Biosphere Reserves site since 2009, it stands as Asia's second-largest biosphere reserve, following the Gulf of Kachchh in Gujarat.
- Notably, Similipal Tiger Reserve holds the distinction of being the sole natural habitat in India for melanistic royal Bengal tigers, adding to its ecological significance.
'Report Fish Disease' to Monitor Fish Diseases (TOI)

- 11 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News?
A mobile app titled ‘Report Fish Disease’ has been introduced to help aquaculture farmers to report diseases on their farms.
What is the 'Report Fish Disease' App?
- The mobile application is designed to empower fish farmers by offering a convenient and effective platform for reporting diseases on their farms.
- Developed as part of the NSPAAD project, with the lead institute being ICAR-NBFGR and a collaborative partnership with the Central Institute of Fisheries Technology (CIFT), this app brings a host of features and benefits.
Key Features:
- User-Friendly Interface: The app provides fish farmers with an intuitive and user-friendly interface, ensuring easy accessibility.
- Efficient Disease Reporting: A simplified reporting format allows farmers to easily report disease outbreaks by providing essential information such as location, affected species, observed symptoms, and images.
Significance:
- Swift Response through Geo-tagging: Utilizing geo-tagging technology, the app facilitates a rapid response from authorities.
- Farmers receive real-time updates on the status of their reported cases, ensuring transparency and accountability in disease management.
- Information Hub: Beyond reporting, the app serves as an information hub, offering farmers valuable resources on disease prevention, treatment, and best aquaculture practices.
- Comprehensive Disease Management: The app is a comprehensive package aimed at diagnosing, preventing, controlling, and treating aquatic animal diseases.
- It provides solutions to encourage aquaculture farmers to maintain the health of their stocks.
Anticipated Impact:
- By transforming disease management in aquaculture, the app aims to enhance the sustainability and productivity of this critical sector.
- It achieves this through early disease detection, data-driven decision-making, capacity building, and efficient resource allocation.
The ultimate goals of the app include:
- Improved Livelihood: Enhancing the livelihood of fish farmers through proactive disease management.
- Food Security: Safeguarding the nation’s food security by ensuring the health and well-being of aquatic animal stocks.
- Industry Growth: Contributing to the sustainable growth of the aquaculture industry by fostering a proactive approach to disease prevention and management.
Isro’s futuristic fuel cell system could power space station (TOI)

- 06 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News
Recently, a futuristic fuel cell-based power system was successfully tested by Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) to provide a sustainable and reliable power source for space stations.
What is a Fuel Cell?
- Fuel cells, intricate devices powered by chemical reactions, have diverse applications spanning transportation, industrial sectors, commercial and residential buildings, and reversible grid energy storage systems.
- Operationally, fuel cells consist of two electrodes—an anode and a cathode—immersed in an electrolyte.
- The anode, supplied with hydrogen fuel, undergoes oxidation to produce hydrogen ions and electrons.
- Simultaneously, the cathode, exposed to an oxidizer like oxygen, results in the production of water as hydrogen ions absorb electrons.
- The voltage per unit cell is determined by the energy level disparity at the electrodes. While a single fuel cell generates a modest amount of direct-current electricity, practical use often involves assembling stacks of these cells.
- Advantages: Advantages of fuel cells include lower or zero emissions, particularly with hydrogen fuel cells emitting only water, addressing climate concerns by avoiding carbon dioxide emissions.
- They operate quietly with few moving parts, achieve higher efficiencies compared to combustion engines, and resemble batteries but offer prolonged electrical energy due to continuous external fuel and air/oxygen sources.
- This longevity distinguishes them from batteries that rely on finite fuel material and oxidant, making fuel cells a sustainable and efficient choice for various applications.
About ISRO:
- The Indian Space Research Organization (ISRO) is the pioneer space exploration agency of the Government of India, headquartered at Bengaluru.
- ISRO was formed in 1969 with a vision to develop and harness space technology in national development, while pursuing planetary exploration and space science research.
- ISRO replaced its predecessor, INCOSPAR (Indian National Committee for Space Research), established in 1962 by India’s first Prime Minister Pt. Jawaharlal Nehru and scientist Vikram Sarabhai, considered amongst the founding fathers of the Indian space program.
BRO Implements Indigenous Technology for Road Construction Near China Border in Arunachal Pradesh (TOI)

- 06 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News
In order to improve operational capacity of the defence forces in the high-altitude areas along the Indo-China border in Arunachal Pradesh, the BRO will build bituminous roads using an indigenous technology, “Rejupave” developed by India’s oldest and premier road research organisation, CSIR-Central Road Research Institute (CSIR-CRRI).
What is Rejupave Technology?
- CSIR-Central Road Research Institute (CSIR-CRRI), India's oldest road research organization, developed the Rejupave Technology.
- It is beneficial for constructing high-altitude bituminous roads in low and sub-zero temperatures.
- The technology actively reduces production and rolling temperatures of bituminous mixes by 30 to 400 degrees Celsius, ensuring minimal heat loss during transit in snowy conditions and long haulage times.
- The bio-oil-based asphalt modifier of this technology significantly lowers the heating requirements of bituminous mixes and preserves mix temperature during transit.
- In cold climatic regions, the 'Rejupave' asphalt modifier enhances long-term durability and resistance to thermal cracking under low-temperature conditions.
- Additionally, it plays a crucial role in reducing greenhouse gas emissions in the eco-sensitive mountainous environment of Arunachal Pradesh.
About CSIR-Central Road Research Institute (CRRI):
- Established in 1952, CSIR-Central Road Research Institute (CRRI) stands as a premier national laboratory under the Council of Scientific and Industrial Research (CSIR).
- CRRI's major research and development programs encompass a range of projects, including the design, construction, and maintenance of roads and runways, traffic and transportation planning for large and medium cities, management of roads in diverse terrains, improvement of marginal materials, utilization of industrial waste in road construction, and landslide control.
- The institute extends its expertise by providing technical and consultancy services to various organizations both within India and internationally.
- CRRI actively contributes to capacity building in highway engineering, empowering human resources to undertake and execute road and runway projects.
AERA Warns Indian Airport Operators Against Charging Unapproved Tariffs (TOI)

- 13 Oct 2023
Why in the News?
The Airport Economic Regulatory Authority (AERA) issued a warning to major airports about levying aeronautical charges without approval.
About Airports Economic Regulatory Authority (AERA):
- Airports Economic Regulatory Authority (AERA), established under the Airports Economic Regulatory Authority of India Act, 2008, is a statutory body entrusted with the crucial task of regulating tariffs and associated charges for aeronautical services at major airports.
- This includes overseeing air traffic management, aircraft landing and parking, and ground handling services.
- The designation of an airport as "major" hinges on the 2008 Act, considering an annual passenger traffic threshold of at least 15 lakh.
- An amendment in 2019 elevated this criterion to 35 lakh annual passengers.
- For other airports, tariff determination falls under the purview of the Airports Authority of India (AAI).
- As an independent economic regulator, AERA operates with the objective of creating an equitable playing field, fostering healthy competition among major airports, promoting investment in airport facilities, and ensuring transparent regulation of aeronautical service tariffs.
- This initiative arose from the recognition of the need for an independent regulatory body capable of safeguarding the interests of both service providers and consumers.
- Headquartered in Delhi, AERA's history traces back to a time when most Indian airports were under the governance of the central government.
- The shift towards private sector participation in airport infrastructure development prompted the need for a distinct regulator.
- The Naresh Chandra Committee set up in 1997, recommended the establishment of an independent regulatory authority.
- Subsequently, the Airports Economic Regulatory Authority of India Act, 2008 (AERA Act), was enacted, leading to the creation of AERA.
About Airports Authority of India (AAI):
- Airports Authority of India (AAI), established through an Act of Parliament on April 1, 1995, resulted from the merger of the National Airports Authority and the International Airports Authority of India.
- Entrusted with a significant role, AAI is responsible for creating, upgrading, maintaining, and managing civil aviation infrastructure both on the ground and in the airspace of the country.
- Main Functions of AAI Include
- Construction, modification, and management of passenger terminals.
- Development and management of cargo terminals.
- Development and maintenance of apron infrastructure, encompassing runways, parallel taxiways, aprons, etc.
- Provision of Communication, Navigation, and Surveillance, involving DVOR / DME, ILS, ATC radars, visual aids, etc.
- Provision of air traffic services.
- Provision of passenger facilities and related amenities at its terminals.
Mukundra Hills Tiger Reserve in Rajasthan Now Opens for Safari Tours (TOI)

- 10 Oct 2023
Why in the News?
The forest department started the inaugural jungle safari at the Mukundra Hills Tiger Reserve on Monday, which marks the beginning of organised tiger reserve tours for tourists in four locations across the state.
About Mukundra Hills Tiger Reserve:
- Location: Mukundra Hills Tiger Reserve, also known as Darrah Wildlife Sanctuary, spans across four districts – Bundi, Kota, Jhalawar, and Chittorgarh in Rajasthan.
- The reserve is nestled in a valley formed by two parallel mountains, Mukundra and Gargola.
- Establishment: In 2013, the tiger reserve was formed, encompassing Mukandra National Park, Dara Sanctuary, Jawahar Sagar Sanctuary, and a section of Chambal Sanctuary.
- Initially, it served as a hunting preserve for the Maharaja of Kota.
- River: Positioned on the eastern bank of the Chambal River, the reserve is crisscrossed by its tributaries.
- Vegetation: The reserve features a Dry Deciduous Forest.
- Flora: The dominant species is Kala Dhok or Kaladhi (Anogeissus pendula), accompanied by Khair, Ber, Kakan, Raunj, and more.
- On elevated slopes, Anogeissus pendula gives way to Anogeissus latifolia, coexisting with Bel, Salar, Uum, and Shisham.
- Fauna: Noteworthy fauna include Leopard, Sloth bear, Nilgai, Chinkara, Spotted Deer, Small Indian Civet, Toddy Cat, Jackal, Hyena, Jungle Cat, and Common Langur, among others.
- The region is also home to various reptiles and amphibians, such as Pythons, Rat Snake, Buff-striped keelbacks, Green keelbacks, crocodiles, turtles, Gharial and Otters.
Reliance General gets ?923cr GST notices from the Directorate General of GST Intelligence (DGGI) (TOI)

- 09 Oct 2023
Why in the News?
Reliance General Insurance Company (RGIC), a subsidiary of the Anil Ambani-led Reliance Capital, has received multiple show-cause notices worth Rs 922.58 crore from the Directorate General of GST Intelligence (DGGI).
About Directorate General of GST Intelligence (DGGI):
- Formerly known as the Directorate General of Central Excise Intelligence (DGCEI), the Directorate General of GST Intelligence (DGGI) stands as a premier intelligence organization operating under the Central Board of Indirect Taxes & Customs, within the Department of Revenue, Ministry of Finance.
- Its primary focus is on collecting, collating, and disseminating intelligence pertaining to Goods and Services Tax (GST) evasion and duties related to Central Excise and Service Tax on a pan-India basis.
- Evolution: Originally designated as the Directorate General of Anti-Evasion (DGAE), it was established in 1979 as an independent wing under the Directorate of Revenue Intelligence, New Delhi.
- Became a full-fledged Directorate in 1983, headed by a Director.
- In 1988, attained the status of Directorate General under a Director General.
- Currently comprises 04 offices of the Director General (East, West, North, and South), 26 Zonal Units, and 40 Regional Units.
Key Responsibilities:
- Intelligence Gathering: Collects information from various sources, including GST returns, financial statements, and other documents, to identify potential GST law violations.
- Investigation: Empowered to conduct investigations into suspected cases of GST evasion or non-compliance, involving summoning individuals, examining records, and executing searches and seizures.
- Enforcement: Enforces provisions of the GST law, taking legal action against offenders, imposing penalties, and recovering taxes or duties owed.
- Additional Functions: Collaborates with agencies like the Central Board of Indirect Taxes and Customs (CBIC) and State GST authorities for effective GST law implementation.
- Plays a crucial role in raising awareness about GST compliance and educating taxpayers on their legal obligations.
- Provides technical and legal assistance to field officers and other government entities involved in GST administration.
Angkor Wat Temple (TOI)

- 30 Nov 2023
Why is it in the News?
Angkor Wat, in the heart of Cambodia, has beaten Pompeii in Italy to become the eighth Wonder of the World.
About Angkor Wat Temple:
- Angkor Wat is among the most significant archaeological sites of Southeast Asia, located in the northern province of Siem Reap in Cambodia.
- The temple was constructed by the Khmer King Suryavarman II in the early 12th century.
- It was originally built as a Hindu temple, dedicated to Lord Vishnu by the Khmer Emperor Suryavarman II, it was converted into a Buddhist temple by his successor Jayavarman VII, who also built the famous Buddhist temple of Bayon nearby.
- The transition from Hinduism to Buddhism is evident in the intricate carvings that adorn the temple walls, depicting scenes from Hindu and Buddhist mythology.
- An interesting fact about Angkor is that it is also known as Yasodharapura.
- The name Angkor is derived from nokor, a Khmer word meaning "kingdom," which is derived from Sanskrit nagara, which means "city."
- Angkor Wat is said to represent Mount Meru, the home of the gods, according to both Hindu and Buddhist faiths.
- It is also famous for its statue of eight-armed Vishnu, also revered by the locals as their protecting deity.
- It holds the Guinness World Record for being the largest religious structure in the world, spread across some 400 km sq.
- In 1992 the temple complex was named a UNESCO World Heritage site.
Swine Flu (TOI)
- 29 Nov 2023
Why is it in the News?
UK public health officials recently said they had confirmed a first human case of a swine flu strain similar to one that has been circulating in pigs.
About Swine Flu:
- Swine flu, scientifically known as H1N1 influenza, is a contagious respiratory illness caused by the H1N1 virus that commonly affects pigs.
- However, this virus can also infect humans, leading to a range of symptoms from mild to severe, and in some cases, it can be fatal.
- The virus spreads among humans through respiratory droplets produced when an infected person coughs or sneezes, making it highly transmissible.
- Swine flu symptoms resemble those of seasonal influenza, including fever, cough, sore throat, body aches, and fatigue.
- In severe cases, individuals may experience respiratory distress and pneumonia.
- One of the distinctive features of the H1N1 virus is its ability to affect younger age groups more severely compared to typical seasonal flu viruses.
- The World Health Organization declared a global pandemic of H1N1 influenza in 2009, emphasizing the need for international cooperation in monitoring and controlling the spread of the virus.
- Oseltamivir is an antiviral medication used to treat and prevent influenza A and influenza B.
Kalakkad Mundanthurai Tiger Reserve (TOI)

- 28 Nov 2023
Why is it in the News?
Recently a new plant species belonging to the 'Impatiens' genus (Balsaminaceae) has been identified in the Kalakkad Mundanthurai Tiger Reserve, Tirunelveli.
About Kalakkad Mundanthurai Tiger Reserve:
- The Kalakkad Mundanthurai Tiger Reserve, is situated in the Southern Western Ghats within the Tirunelveli and Kanyakumari districts of Tamil Nadu.
- This reserve combines three major sanctuaries:
- The Kalakkad Sanctuary
- The Mundanthurai Sanctuary, and
- A portion of the Kanyakumari Sanctuary.
- The Agasthyamalai Hills, nestled between Kerala and Tamil Nadu, forms the sanctuary's core and is part of one of the world's 18 biodiversity hotspots.
- This reserve is also recognized as the “River Sanctuary,” with 14 rivers originating from it.
- Flora: The flora in this region exhibits a gradual transition from dry thorn forest to dry deciduous, moist deciduous, and a patch of West Coast wet evergreen forests at higher elevations.
- Fauna: Diverse fauna includes species such as Lion-tailed Macaque, Nilgiri Tahr, Nilgiri Pipit, Grey Headed Bulbul, Blue Winged Parakeet, and more.
Details about the New Plant Species:
- The species, named 'Impatiens Karuppusamyi,' pays tribute to S. Karuppusamy for his significant contributions to the taxonomy of South Indian angiosperms.
- This particular plant is exclusively found in the Agasthyamalai region within the southern Western Ghats.
- Belonging to the scapigerous group (stemless group), the plant is observable only during the monsoon season, lasting for a few weeks.
- Impatiens, a genus comprising over 1,000 flowering plant species, is widely distributed across tropical Africa, Madagascar, India, Sri Lanka, and China.
Digital Twins (TOI)

- 25 Nov 2023
Why is it in the News?
Recently, the Survey of India (SoI) and Genesys International, a prominent Indian mapping company, revealed a strategic collaboration for the implementation of a three-dimensional (3D) digital twin-mapping initiative in India.
About Digital Twin:
- Digital twins are digital representations of physical objects, people or processes.
- They aid decision-making through high-fidelity simulations of the twinned physical system in real-time and are often equipped with autonomous control capabilities.
- These replicas serve as dynamic and detailed counterparts, providing a real-time, data-driven simulation of their physical counterparts.
- The concept of digital twins has gained prominence with the advent of technologies like the Internet of Things (IoT), data analytics, and machine learning.
- In essence, a digital twin continuously collects and processes data from its physical counterpart, offering a comprehensive view of its behavior, status, and interactions.
- This real-time synchronization enables organizations to monitor, analyze, and understand the performance of physical assets or processes more effectively.
Applications:
- Manufacturing Sector: One primary application of digital twins is in the manufacturing sector.
- Manufacturers use digital twins to create virtual models of products and production processes.
- This allows for simulation, analysis, and optimization before physical prototypes are built, leading to reduced development costs and improved product quality.
- Healthcare: In healthcare, digital twins are employed to create personalized models of patients.
- These models, based on individual health data, help in predicting health outcomes, optimizing treatment plans, and advancing medical research.
- Transportation: Transportation industries utilize digital twins for optimizing logistics and predictive maintenance.
- For example, digital twins of aircraft engines can simulate performance under various conditions, aiding in proactive maintenance and minimizing downtime.
- Urban Planning: Urban planning benefits from digital twins by creating virtual models of entire cities.
- This assists in designing and optimizing infrastructure, managing resources efficiently, and planning for future growth and development.
- Industries: In industrial settings, digital twins of production processes enable real-time monitoring, troubleshooting, and optimization, leading to increased efficiency and reduced downtime.
Deepfakes (TOI)

- 25 Nov 2023
Why is it in the News?
The government has warned top social media and internet companies that their platforms may be temporarily suspended and even be ordered blocked in case they are unable to tackle the menace of deepfakes.
What are Deepfakes?
- The term "deepfake" combines the concepts of deep learning with the fabrication of content.
- Deepfakes involve the creation of synthetic images and audio using machine-learning algorithms, intending to disseminate misleading content by replacing a real person's appearance, voice, or both with artificially generated likenesses or voices.
- These manipulated creations can either depict nonexistent individuals or simulate real people engaging in actions or utterances they never did.
- Originating in 2017, the word "deepfake" emerged when a Reddit user named "deepfakes" shared explicit videos featuring celebrities.
- The process of crafting deepfakes utilizes machine learning models employing neural networks to manipulate visual and auditory elements.
- To generate a convincing deepfake video, creators train the neural network on extensive real footage of the targeted person, facilitating a realistic understanding of their appearance from various angles and lighting conditions.
- This trained network is then combined with computer graphics to overlay the person onto a different actor.
- Regrettably, this technology is increasingly exploited for malicious purposes, including scams, celebrity impersonation, election interference, social engineering, disinformation attacks, identity theft, and financial fraud.
- The distinguishing factor of deepfakes lies in their challenging detection due to their sophisticated nature.
Naval Anti-Ship Missile Short Range (NASM-SR) (TOI)

- 22 Nov 2023
Why is it in the News?
The Indian Navy successfully test-fired an indigenous anti-ship missile over the Arabian Sea, marking a significant step in India's efforts towards self-reliance in defense technologies.
About Naval Anti-Ship Missile Short Range (NASM-SR):
- This revolutionary missile NASM-SR, entirely developed by Indian scientists and engineers, represents a huge stride in the indigenization of India's defense infrastructure.
- The project is a collaborative effort between various esteemed agencies, including the Defense Research and Development Organisation (DRDO).
- The successful trial brings a sense of pride and accomplishment to India's defense realm.
- Launch Capability: This advanced missile is designed for launch from attack helicopters, presenting a versatile addition to the naval arsenal.
- Replacement for Sea Eagle: NASM-SR is slated to replace the existing Sea Eagle missiles currently in use by the Navy, aligning with the imperative of modernization and technological advancement.
- Integration with MH-60R Helicopters: As Sea King helicopters are phased out, the NASM-SR is anticipated to integrate seamlessly with the new MH-60R multi-role helicopters, a pivotal component of the Navy's evolving fleet.
Key Features:
- The missile incorporates a state-of-the-art guidance system and integrated avionics.
- It introduces indigenous launcher technology tailored for helicopter deployment.
- Possessing a striking range of approximately 60 km.
- Travels at a speed of Mach 0.8, slightly below the speed of sound.
- Equipped with a 100kg warhead, rendering it capable of neutralizing patrol boats and causing substantial damage to larger warships.
- Employs an imaging infrared seeker to target heat emissions, enhancing precision in homing onto its designated targets.
- During the approach to its target, the NASM-SR operates at just 5 meters above sea level, a strategic feature known as sea skimming.
- This low-level approach minimizes the susceptibility to detection, tracking, and interception by enemy radars or surface-to-air missiles.
Wasp-107b (TOI)

- 17 Nov 2023
Why in the News?
In its latest discovery, NASA's James Webb Space Telescope has discovered a planet "Wasp-107b" where specks of sand fall as rain.
What is “Wasp-107b”?
- WASP-107b is a warm exoplanet with Neptune’s mass and Jupiter’s radius.
- This makes it ‘fluffy’ compared to the giant gas planets in our Solar System.
- This unusual size-to-mass ratio has given astronomers a unique opportunity to probe its atmosphere roughly 50 times deeper than more dense planets like Jupiter.
- This gas giant, often referred to as a "super-Neptune," holds several remarkable characteristics that set it apart from other known exoplanets.
Key Characteristics of WASP-107b:
- Size and Mass: WASP-107b is roughly the size of Jupiter, but with only about 12% of Jupiter's mass.
- This makes it one of the least dense exoplanets ever discovered.
- Orbit and Proximity: WASP-107b orbits its host star, WASP-107, very closely, completing an orbit in just 5.7 days.
- It is located about 200 light-years from Earth in the constellation Virgo.
- Sand Rain: WASP-107b exhibits a unique water cycle similar to Earth's, but with a peculiar twist: instead of water droplets, the planet experiences sand rain.
- These sand grains, composed of silicates, rise from lower atmospheric levels and condense into clouds before falling back down.
- Atmosphere: WASP-107b possesses a puffy atmosphere, likely due to its low density.
- In 2018, scientists using the Hubble Space Telescope detected helium in its atmosphere, marking the first detection of this element in an exoplanet's atmosphere.
- Potential for Atmospheric Characterization: WASP-107b's large size and proximity to its star make it a promising target for future atmospheric characterization studies.
- Scientists hope to glean more insights into the composition and dynamics of its atmosphere.
Pradhan Mantri Kisan Samman Nidhi (PM-KISAN) Scheme (TOI)

- 16 Nov 2023
Why in the News?
Prime Minister Narendra Modi released the 15th installment of the Pradhan Mantri Kisan Samman Nidhi (PM-Kisan) scheme worth over Rs 18,000 crore to more than 8 crore farmers on November 15, 2023.
About Pradhan Mantri Kisan Samman Nidhi (PM-KISAN):
- The Pradhan Mantri Kisan Samman Nidhi (PM-KISAN) is a Central Sector scheme with 100% funding from the Government of India.
- Under the scheme, income support of Rs. 6,000 per year in three equal installments is provided to all land-holding farmer families, providing them with socio-economic security.
- The amount is directly transferred to the bank accounts of the beneficiaries without any involvement of intermediaries, making it one of the largest Direct Benefit Transfer (DBT) schemes in the world.
- So far, more than Rs. 2.42 lakh crore have been disbursed to over 11 crore farmers.
- As per the study by the International Food Policy Research Institute (IFPRI), PM-KISAN had numerous benefits for the farmers and agriculture sector.
- It addresses the liquidity constraints of farming households, enabling essential input procurement.
- The scheme boosts modern cultivar adoption through Krishi Vigyan Kendras.
- The cash transfer to farmers increases their total net income and enhances their risk-taking capacity, leading to productive investments.
- PM-KISAN has empowered the farmers by boosting agriculture investments, easing credit constraints, and spurring rural economic growth.
- Consequently, farmers have been able to invest in their farms, including purchasing seeds, fertilizers, and necessary equipment, leading to increased agricultural production and improved crop yields.
Tadoba-Andhari Tiger Reserve (TOI)

- 15 Nov 2023
Why in the News?
A dominant tiger named Bajrang said to have sired at least 50 cubs during his lifetime, recently died in a territorial fight with another powerful tiger, Chhota Matka, in the Tadoba-Andhari Tiger Reserve (TATR).
About Tadoba Andhari Tiger Reserve:
- Tadoba Andhari Tiger Reserve is the oldest and largest National Park in the Chandrapur district of Maharashtra.
- It is one of India's 47 project tiger reserves existing in India.
- The total area of the tiger reserve is 1,727 Sq.km, which includes the Tadoba National Park, created in the year 1955.
- The Andhari Wildlife Sanctuary was formed in the year 1986 and was amalgamated with the park in 1995 to establish the present Tadoba Andheri Tiger Reserve.
- The word 'Tadoba' is derived from the name of God "Tadoba" or "Taru," which is praised by local tribal people of this region, and "Andhari" is derived from the name of the Andhari river that flows in this area.
- Tadoba is presently home to more than 115 tigers, which is one of the highest in India.
- The vegetation of Tadoba forest is of Southern tropical dry deciduous type and is spread on around 626 sq. km.
- Teak is the prominent tree species in the forest.
- The Tadoba Tiger Reserve is rich in flora and fauna
- Flora: Some of the famous and widely seen flora of this park include Teak, Ain, Bija, Bamboo, Black Plum, and many others.
- Fauna: Tigers, Indian leopards, Sloth bears, Gaur, Nilgai, Striped Hyena, Spotted Deer, Barking Deer, Marsh Crocodile, etc.
Igla-S Missiles (TOI)

- 15 Nov 2023
Why in the News?
Recently, Russia has announced that it will supply the Igla-S man-portable air defense missile system to the Indian armed forces through licensed production by an Indian private company.
About Igla-S Missile System:
- The Igla-S is a man-portable air-defense system (MANPADS) developed by Russia.
- It is a surface-to-air missile (SAM) system which is also known as SA-24 Grinch in the West.
- The Igla-S entered service in 2004 and is currently in service with over 30 countries, including Russia.
- It is a highly effective and versatile weapon system that can be used to engage a wide variety of targets, including fixed- and rotary-winged aircraft, helicopters, unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs), and cruise missiles.
- The Igla-S has a range of 5 km and an altitude of 3,500 meters including a speed of Mach 2.5.
- It is a "fire-and-forget" weapon, meaning that the operator does not need to track the target after launch.
- The missile's infrared homing seeker automatically guides it to the target.
- It is a very compact and lightweight weapon system, making it ideal for use by infantry troops.
- It can be easily transported and deployed in a matter of minutes.
- The Igla-S is used by a number of countries, including Algeria, Azerbaijan, Belarus, China, India, Iran, Iraq, Kazakhstan, Libya, Malaysia, Myanmar, Nicaragua, North Korea, Peru, Poland, Russia, Serbia, Syria, Venezuela, and Vietnam.
Phreatomagmatic Eruptions (TOI)

- 11 Nov 2023
Why in the News?
Recently a new island emerged near Japan's Ogasawara island chain after an undersea volcano erupted.
What is Phreatomagmatic Eruption?
- A phreatomagmatic eruption is a volcanic eruption caused by the interaction of magma and water.
- They differ exclusively from magmatic and phreatic eruptions.
- Unlike phreatic eruptions, the products of phreatomagmatic eruptions contain juvenile (magmatic) debris.
- Large explosive eruptions typically contain magmatic and phreatomagmatic components.
- Phreatomagmatic ash is formed by the same mechanism over a wide range of basic and acidic compositions.
- A blocky and uniform crust with low vesicle content is formed.
- Deposits from phreatomagmatic eruptions are thought to be better classified and finer-grained than those from magmatic eruptions.
- This is the result of higher fragmentation of phreatomagmatic eruptions.
About Ogasawara Islands:
- The Ogasawara Islands are a group of more than 30 small subtropical islands in the North-Western Pacific Ocean roughly 1,000 km south of the main Japanese Archipelago.
- It is also known as the Bonin Islands.
- It is one of the famous UNESCO World Heritage sites of Japan.
GST Amnesty Scheme (TOI)

- 06 Nov 2023
Why in the News?
The finance ministry has come out with an amnesty scheme for filing appeals against Goods and Services Tax (GST) demand orders.
What is the GST Amnesty scheme?
- The GST Amnesty scheme was introduced by the Centre to help businesses comply with the Goods and Services Tax laws in the country.
- Every entity that needs to file its GST returns must conduct the process in a sequential manner.
- If the taxpayer misses the last date, they may have to pay penalties for not filing the returns.
- In such a situation, the GST Amnesty scheme helps taxpayers file their returns without hefty penalties.
- The plan also aids businesses whose registration stands canceled for non-filing of returns.
- Under the GST Amnesty scheme, taxpayers can file for the revocation of their cancellation as well.
How can one benefit from the GST Amnesty scheme?
- Taxpayers cannot file the GST return for a particular period without submitting the previous ones.
- A heavy penalty will also be levied on them for missing their filings.
- The GST Amnesty scheme allows taxpayers to file their pending returns without incurring a hefty fine.
- It will help them in complying with the indirect taxation laws of the country.
- It also aids business entities to appeal against the cancellation of their registration if they have not submitted the GST returns for three consecutive quarters.
- The scheme will be open till January 31, 2024.
UN Office for the Coordination of Humanitarian Affairs (OCHA) (TOI)

- 03 Nov 2023
Why in the News?
??The UN Office for the Coordination of Humanitarian Affairs (OHCA), on Friday, launched an emergency aid appeal seeking $1.2 billion to help some 2.7 million people in Gaza and the West Bank.
About the UN Office for the Coordination of Humanitarian Affairs (OCHA):
- OCHA is part of the United Nations (UN) and focuses on humanitarian issues.
- It coordinates and leads UN responses to humanitarian crises worldwide.
- It was established by the General Assembly of the United Nations in 1991.
- OCHA's goal is to save lives, protect people, and help those affected by disasters and conflicts.
- It works with governments, non-governmental organizations (NGOs), and other partners to respond to emergencies.
- It provides funding to support relief efforts in crisis-affected regions.
- There are two types of pooled funds:
- The Central Emergency Response Fund (CERF) can provide financial support for emergencies anywhere on the globe.
- Country-Based Pooled Funds (CBPFs) are specific to individual countries.
- These funds operate from two central hubs located in Geneva and New York, serving as global operational centres.
- The office works to ensure that humanitarian aid reaches those in need.
- It has two headquarters locations, Geneva and New York, which act as centres of global operations.
- It helps plan and manage humanitarian responses, ensuring efficiency and effectiveness.
- OCHA promotes coordination among humanitarian organizations to avoid duplication and ensure better outcomes.
Indian National Space Promotion and Authorisation Centre (IN-SPACe) (TOI)

- 04 Aug 2023
Why in the News?
The Indian National Space Promotion and Authorisation Centre (IN-SPACe) has reported that three private sector satellite manufacturers plan to launch their earth observation satellites during this fiscal year.
About Indian National Space Promotion and Authorisation Centre (IN-SPACe):
- IN-SPACe serves as a single-window, independent, and autonomous agency within the Department of Space (DOS).
- It was established as part of the Space sector reforms to encourage and facilitate the active involvement of private players in the space industry.
- IN-SPACe's responsibilities include promoting, enabling, authorizing, and supervising various space activities of non-governmental entities, such as manufacturing launch vehicles and satellites, providing space-based services, and utilizing space infrastructure and facilities.
- Acting as an intermediary between ISRO and Non-Governmental Entities (NGEs), the agency assesses opportunities for leveraging India's space resources effectively and enhancing space-based initiatives.
- Also, IN-SPACe addresses the specific needs and demands of private players, including educational and research institutions, while working in collaboration with ISRO.
- The headquarters of IN-SPACe is located in Bopal, (Ahmedabad).
