Bio-based Chemicals and Enzymes

- 16 Feb 2026
In News:
India is prioritising bio-based chemicals and enzymes under the BioE3 policy to reduce petrochemical imports, promote sustainable manufacturing, and strengthen its bioeconomy.
What are Bio-Based Chemicals?
Bio-based chemicals are industrial chemicals produced from renewable biological feedstocks such as sugarcane, corn, starch, and agricultural residues, rather than fossil fuels. They are typically manufactured through fermentation, enzymatic conversion, or microbial processes using biomass.
Examples:
- Organic acids (e.g., lactic acid)
- Bio-alcohols
- Solvents
- Surfactants
- Chemical intermediates used in plastics, cosmetics, pharmaceuticals
These chemicals form a core component of the bioeconomy, which integrates biological resources and biotechnology into industrial production systems to create sustainable alternatives to petrochemicals.
What are Enzymes?
Enzymes are biological catalysts (mainly proteins) that accelerate chemical reactions without being consumed in the process. While enzymes have been used traditionally in brewing and baking for centuries, modern industrial enzyme engineering expanded significantly in the 20th century with advances in biotechnology.
Enzymes are produced via microbial fermentation, followed by purification and formulation for industrial use.
Key Characteristics
- Renewable Feedstock Base – Derived from biomass instead of fossil hydrocarbons.
- Lower Carbon Footprint – Reduced greenhouse gas emissions compared to petrochemical pathways.
- Energy Efficiency – Enzymes operate at lower temperatures and pressures.
- Biodegradability – Many bio-based products are environmentally friendly.
- High Specificity – Enzymes provide targeted catalytic action, improving efficiency and reducing waste.
Applications
1. Chemical Industry
- Organic acids (lactic acid)
- Acetyl intermediates (acetic anhydride, ethyl acetate)
- Solvents and specialty chemicals
2. Pharmaceuticals & Vaccines: Active ingredient synthesis through fermentation technologies.
3. Food & Beverage: Brewing, baking, dairy processing.
4. Textiles & Detergents: Stain removal, fabric treatment.
5. Biomanufacturing & Clean Technology: Sustainable plastics, biofuels, specialty chemicals.
Why Does India Need Bio-Based Chemicals?
India has strong structural advantages:
- Large agricultural base (ample biomass availability)
- Established fermentation expertise (pharmaceuticals and vaccines)
- Expanding manufacturing ecosystem
- Rising demand for sustainable industrial inputs
India imported approximately $479.8 million worth of acetic acid in 2023, reflecting dependence on petrochemical imports. Scaling domestic bio-based chemical production can:
- Reduce import dependence
- Create value-added markets for agricultural produce
- Strengthen climate commitments
- Boost rural and industrial employment
Policy Support: BioE3 Initiative
India has identified bio-based chemicals and enzymes as priority sectors under the Department of Biotechnology’s BioE3 Policy.
BioE3 focuses on:
- Biomanufacturing scale-up
- Shared infrastructure (biofoundries, pilot plants, demonstration facilities)
- Innovation ecosystem development
- Reducing capital risk for emerging firms
Industry Landscape in India
Bio-Based Chemicals
- Praj Industries
- Godrej Industries
- Godavari Biorefineries
- Jubilant Ingrevia
- StringBio
Enzymes Market
The Indian enzyme market is highly consolidated, with top players accounting for over 75% market share.
Key companies:
- Novozymes India
- DuPont
- DSM
- Advance Enzyme Technologies
- BASF SE
- Ultreze Enzymes Private Limited
Global Initiatives
European Union
The EU Bioeconomy Strategy links industrial transformation with:
- Climate mitigation
- Circular economy
- Waste reduction
United States
- The USDA BioPreferred Program mandates federal procurement preference for certified bio-based products, helping create stable demand.
China
- Bioeconomy development plans prioritise high-value bio-based chemicals and enzyme technologies as strategic sectors.
Japan
- Projects supported by METI/NARO integrate research with manufacturing readiness in bio-based chemicals.
African Union
- 16 Feb 2026
In News:
The African Union (AU), launched in 2002 to replace the OAU, is a continental body of 55 African states headquartered in Addis Ababa, Ethiopia.
Recently, the African Union (AU) held its annual summit in Ethiopia amid growing discussions on governance reforms and youth representation within the bloc.
Origin and Evolution
The African Union was officially launched in 2002, replacing the Organization of African Unity (OAU), which had been established in 1963.
Why the Transition?
- The OAU primarily focused on decolonization and anti-apartheid struggles.
- The AU was created with a broader mandate including:
- Political and economic integration
- Conflict resolution
- Sustainable development
- Stronger global representation for Africa
Membership
- Comprises 55 member states (all internationally recognized African countries).
- It represents the entire African continent.
Headquarters
- Located in Addis Ababa, Ethiopia.
Objectives of the African Union
The AU aims to:
- Promote unity and solidarity among African countries.
- Foster peace, security, and stability.
- Advance economic integration and development.
- Protect sovereignty and territorial integrity.
- Enhance Africa’s voice in global governance.
Governance Structure
Assembly
- Highest decision-making body.
- Composed of Heads of State and Government.
- Determines policy direction.
Executive Council
- Consists of Foreign Affairs Ministers.
- Prepares decisions and policies for the Assembly.
AU Commission
- Administrative arm of the AU.
- Implements decisions of the Assembly and Executive Council.
- Headquartered in Addis Ababa.
Peace and Security Council (PSC)
- Responsible for:
- Conflict prevention
- Peacekeeping missions
- Crisis response mechanisms
The PSC functions somewhat similarly to the UN Security Council but at the continental level.
Participatory and Advisory Bodies
To promote democratic participation:
- Pan-African Parliament
- Ensures representation of African peoples.
- Economic, Social and Cultural Council (ECOSOCC)
- Civil society advisory body.
These institutions reflect the AU’s goal of citizen engagement and inclusive governance.
Contemporary Context
Recent summits have witnessed debates over:
- Youth representation in governance
- Leadership renewal within member states
- Democratic accountability
- Economic integration initiatives such as the African Continental Free Trade Area (AfCFTA)
With Africa having one of the world’s youngest populations, youth inclusion has become a prominent theme in AU deliberations.
Removal of the Lok Sabha Speaker
- 16 Feb 2026
In News:
The Lok Sabha Speaker can be removed only by a resolution passed by an Effective Majority (majority of all the then members of the House) under Article 94(c) of the Constitution.
The recent notice seeking the removal of Lok Sabha Speaker Om Birla has revived attention on the constitutional and procedural safeguards governing the office of the Speaker.
Constitutional Basis
The removal of the Speaker is governed primarily by:
Article 94 of the Constitution of India
It lays down the circumstances under which the Speaker or Deputy Speaker vacates office:
- Article 94(a) – If they cease to be a member of the Lok Sabha.
- Article 94(b) – They may resign by writing addressed to the Deputy Speaker (or Speaker, in case of Deputy Speaker).
- Article 94(c) – They may be removed by a resolution of the House passed by a majority of all the then members of the House (Effective Majority).
This provision applies only to the Lok Sabha and not to the Rajya Sabha.
Effective Majority
An Effective Majority means: Majority of all the then members of the House (excluding vacant seats).
It is different from:
- Simple Majority – Majority of members present and voting.
- Absolute Majority – Majority of total membership of the House.
- Special Majority – Required in constitutional amendment cases (Article 368).
Procedural Framework
The detailed procedure is laid down under Rules 200–203 of the Rules of Procedure and Conduct of Business in Lok Sabha.
Notice Requirement
- A written notice must be submitted to the Secretary-General of the Lok Sabha.
- At least 14 days’ prior notice is mandatory.
- It may be signed by one or more members.
Admission of Motion
- The motion is listed in the List of Business.
- The presiding officer reads it to the House.
- At least 50 Members must rise in support.
- If fewer than 50 members stand → Motion fails (no “leave of the House”).
Conditions on the Motion (Rule 200A)
The resolution must:
- Be specific and precise
- Clearly state charges
- Not contain arguments, inferences, defamatory or ironic expressions
Discussion must remain strictly confined to the charges mentioned.
Role of the Speaker During Removal Proceedings
Under Article 96:
- The Speaker cannot preside while the resolution is under consideration.
- They have the right to:
- Speak
- Participate in debate
- Vote in the first instance (as an ordinary member)
- They cannot exercise a casting vote in case of a tie.
Timeline After Admission
If 50 or more members support:
- Leave is granted.
- The resolution must be taken up within 10 days.
- Discussion follows.
- The member moving the motion may speak (maximum 15 minutes, if allowed).
If passed by Effective Majority → The Speaker is removed immediately.
Continuity of Office
- Even after dissolution of the Lok Sabha, the Speaker continues in office until immediately before the first meeting of the new Lok Sabha.
- However, removal by resolution results in immediate vacation of office.
Historical Precedents
No Speaker has ever been removed through this process.
Three motions have been moved:
- 1954 – Against G. V. Mavalankar (First Speaker of Lok Sabha)
- 1966 – Against Hukam Singh
- 1987 – Against Balram Jakhar
All three motions failed.
PerumbiduguMutharaiyar II

- 19 Dec 2025
In News:
A commemorative postage stamp honouringPerumbiduguMutharaiyar II was released by the Vice President of India, recognising his role in early medieval Tamil history.
Who was PerumbiduguMutharaiyar II?
- Period: c. 705–745 CE
- Also known as:Suvaran Maran, Shatrubhayankar
- Lineage: Ruler from the Mutharaiyar dynasty
- Political status: Feudatory of the Pallavas; later exercised near-sovereign authority as Pallava power waned
- Military role: Fought alongside Pallava king Nandivarman
- Reputation: Capable administrator; remembered for stability and governance
Mutharaiyars: Polity & Region
- Territory: Central Tamil Nadu-Thanjavur, Pudukkottai, Perambalur, Tiruchirappalli and adjoining Cauvery basin areas
- Historical trajectory: Rose in prominence as Pallava authority declined
- Cultural legacy: Influential temple builders; active in cave-temple enterprises into the early 9th century
- Architectural significance: Their innovations influenced later Chola temple architecture
Religion & Patronage
- Religious climate: Period of Hindu revival alongside Jain and Buddhist presence
- Patronage: Supported Shaivism and scholarly debates; Jain monk Vimalachandra is recorded to have visited his court for theological discussions
- Inions: Credit him with temple endowments, irrigation works, and Tamil literary patronage
Historical Importance
- Demonstrates the transition from Pallava feudatories to regional rulers
- Bridges Pallava and early Chola phases in Tamil polity and architecture
- Highlights plural religious discourse in early medieval South India
ICGS Sarthak at Chabahar Port

- 21 Dec 2025
In News:
The offshore patrol vessel ICGS Sarthak of the Indian Coast Guard has made its first-ever port call at Chabahar Port, Iran. A port call refers to the period during which a naval or coast guard vessel arrives at, stays in, and departs from a port. This visit marks a notable step in strengthening maritime security cooperation, regional engagement, and strategic outreach in the Indian Ocean Region (IOR).
Strategic Importance of the Visit
- Gateway Role: Chabahar serves as India’s direct maritime gateway to Iran, Afghanistan, and Central Asia, bypassing the Strait of Hormuz.
- Connectivity & Supply Lines: The port call reinforces secure supply chains and India’s access to continental markets.
- Policy Alignment: The engagement aligns with India’s maritime visions of SAGAR (Security and Growth for All in the Region) and MAHASAGAR, underscoring cooperative security and prosperity in the IOR.
Environmental Outreach
Alongside operational engagements, the visit included environmental activities such as a beach walkathon and sports fixtures, supporting Puneet Sagar Abhiyan. Launched in 2021 by the National Cadet Corps, the campaign focuses on cleaning seashores, beaches, rivers, lakes, and other water bodies of plastic and waste—integrating maritime operations with environmental stewardship.
Chabahar Port
- Location:Sistan-Baluchistan province, Iran; on the Gulf of Oman, outside the Strait of Hormuz.
- Uniqueness: Iran’s only deep-sea port with direct ocean access.
- Agreement: Developed under the 2016 Chabahar Agreement between India, Iran, and Afghanistan.
- Connectivity Corridor: Part of the International North-South Transport Corridor (INSTC).
- Terminals:Shahid Beheshti and Shahid Kalantari.
- Indian Role: India developed and actively operates the Shahid Beheshti terminal.
- Management: Since December 2018, operations are managed by India Ports Global Limited (IPGL) through its subsidiary India Ports Global Chabahar Free Zone (IPGCFZ).
India as ‘Country of the Year’ at BIOFACH 2026
- 12 Feb 2026
In News:
- India has been recognised as the ‘Country of the Year’ at BIOFACH 2026, the world’s premier trade fair for organic food and agriculture. The event is held annually at the Nuremberg Messe Exhibition Centre in Germany and is managed by NürnbergMesse GmbH.
- This recognition reflects India’s growing prominence in the global organic sector and its expanding footprint in sustainable agriculture and exports.
About BIOFACH
BIOFACH is widely regarded as the world’s leading international platform for certified organic products.
Key Features:
- Focus on organic food and agriculture
- Promotes global trade in certified organic products
- Facilitates B2B networking among producers, exporters, retailers and policymakers
- Encourages sustainable farming practices and environmentally responsible consumption
- Serves as a hub for innovation in organic farming and processing technologies
Significance for India
1. Strengthening Global Organic Leadership
India’s designation positions it as a major supplier of certified organic produce at a time when global demand for sustainable food systems is rising.
2. Boost to Agricultural Exports
The recognition enhances India’s visibility and market access for organic exports such as:
- Organic rice
- Spices
- Pulses
- Oilseeds
- Cashew
- Turmeric
- Ginger
- Mango puree
- Essential oils
3. Promotion of GI-Tagged Products
India is showcasing five GI-tagged rice varieties, reinforcing the branding of its traditional agricultural heritage and geographical diversity.
4. Empowerment of FPOs and Regional Producers
Participation from over 20 States and Union Territories highlights inclusive growth and the integration of grassroots producers, including Farmer Producer Organisations (FPOs), into global value chains.
5. Soft Power and Culinary Diplomacy
Live tastings and demonstrations, including organic biryani and heritage rice varieties, strengthen India’s cultural outreach and organic brand identity internationally.
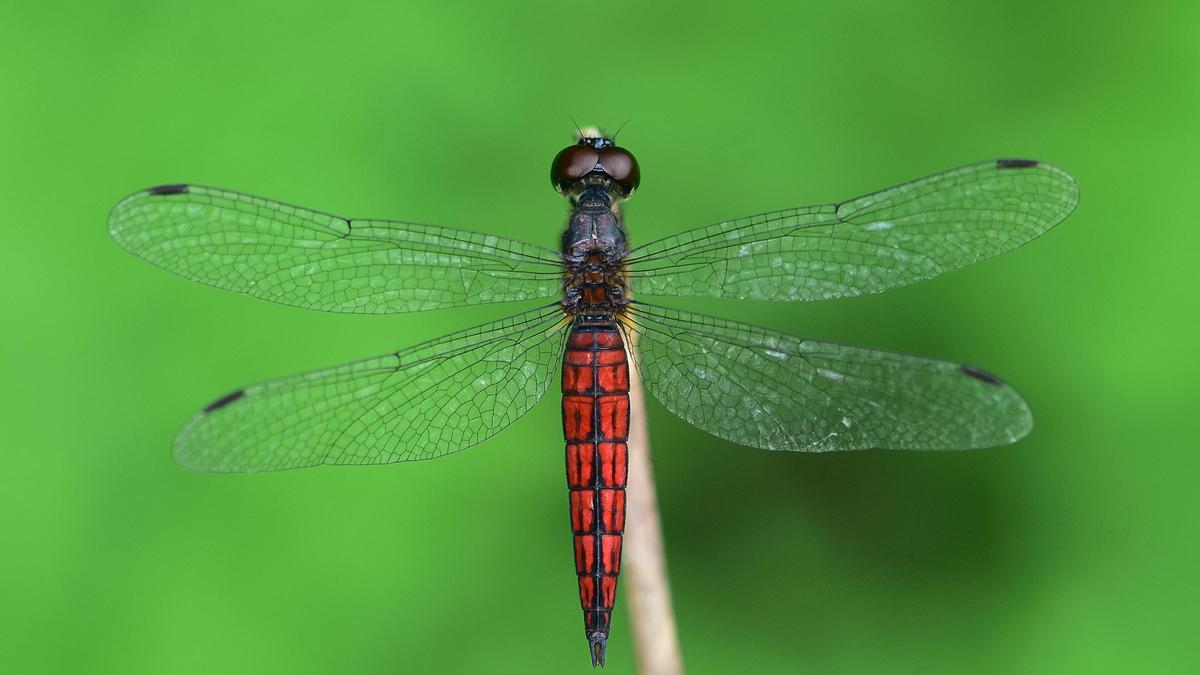
Discovery of Lyriothemis keralensis in Kerala

- 12 Feb 2026
In News:
Researchers have identified a new dragonfly species named Lyriothemis keralensis in Kerala, extending the known geographical range of the genus beyond northeast India. The discovery underscores the rich biodiversity of the Western Ghats and the importance of careful taxonomic studies.
Taxonomic Clarification
Although the species has been present in Kerala since 2013, it was misidentified for over a decade as Lyriothemis acigastra. Detailed morphological examination, including microscopic analysis and comparison with museum specimens, confirmed its distinct identity.
This highlights:
- The importance of systematic taxonomy
- The role of reference collections in biodiversity research
- Potential underestimation of species diversity in India
Key Features
The species exhibits pronounced sexual dimorphism:
- Males: Bright blood-red body with black markings
- Females: Yellow body with black markings
Such colour variation aids in species identification and reproductive behaviour studies.
Habitat and Ecology
Unlike many dragonflies associated with pristine forest ecosystems, Lyriothemis keralensis thrives in human-modified irrigation landscapes, including:
- Pineapple plantations
- Rubber plantations
- Shaded irrigation canals
Most recorded populations occur outside protected areas, indicating that biodiversity conservation must extend beyond national parks and wildlife sanctuaries.
Seasonality and Life Cycle
The species is:
- Seasonally visible during the Southwest Monsoon (late May to August)
- Present as aquatic larvae in water bodies for the remainder of the year
This seasonal emergence aligns with monsoon-driven ecological cycles in Kerala.
Conservation Concerns
The discovery raises important conservation issues:
- Plantation-dominated landscapes may act as secondary habitats
- Changes in irrigation patterns, pesticide use, and land conversion could threaten populations
- Lack of protection outside designated conservation zones may expose species to habitat loss
The finding reinforces the need for biodiversity-sensitive land-use planning, especially in agriculturally modified ecosystems.
Corruption Perceptions Index 2025
- 12 Feb 2026
In News:
- India has climbed to the 91st position in the Corruption Perceptions Index 2025, improving from 96th rank in the previous year. However, its score of 39 out of 100 remains below the global average of 42, indicating that corruption continues to be perceived as a structural challenge in governance.
- The CPI is released annually by Transparency International and ranks 182 countries and territories based on perceived levels of public sector corruption. Scores range from 0 (highly corrupt) to 100 (very clean).
Global Trends in CPI 2025
- The global average score has declined to 42, reflecting stagnation in anti-corruption efforts worldwide.
- More than two-thirds of countries score below 50, indicating widespread governance challenges.
- Denmark (89) remains the cleanest country, while Somalia and South Sudan (9) rank at the bottom.
- Several established democracies, including the United Kingdom (20th) and the United States (29th), have witnessed declines.
- The report highlights risks faced by journalists investigating corruption, noting that 90% of journalist killings occur in countries scoring below 50-a category that includes India.
Reasons for Persistent Corruption in India
Despite incremental improvements, structural factors continue to affect perceptions:
1. Bureaucratic Red Tape: Complex regulatory processes and approval systems create opportunities for rent-seeking behaviour.
2. Political Funding Opacity: Lack of transparency in electoral financing and the influence of money power remain concerns.
3. Weak Whistleblower Protection: Individuals exposing corruption often face harassment or threats, discouraging reporting.
4. Inconsistent Enforcement: Low conviction rates in high-profile cases and delays in judicial processes reduce deterrence.
5. Informal Economy and Black Money: A large unorganised sector facilitates unaccounted transactions and tax evasion.
Anti-Corruption Measures Undertaken
India has adopted several reforms to improve governance and transparency:
- Digitalisation of Governance: Expansion of Direct Benefit Transfer (DBT) systems to reduce middlemen.
- Prevention of Corruption (Amendment) Act, 2024: Strengthened penalties and introduced asset forfeiture provisions.
- Blockchain-based Land Records and E-Tendering: To enhance transparency in public procurement.
- Central Vigilance Commission (CVC) Reforms: Adoption of AI-based financial scrutiny tools.
- Strengthened oversight by institutions such as the Central Vigilance Commission.
Key Challenges
- Overburdened judiciary causing delays in corruption trials
- Cross-border asset recovery challenges
- Technological misuse such as digital fraud and deepfake scams
- Weak local-level oversight in municipal and panchayat institutions
Significance for India
India’s CPI ranking has both economic and governance implications. Perceptions of corruption affect:
- Investor confidence
- Ease of doing business
- Regulatory credibility
- Democratic accountability
While the improvement from 96th to 91st rank signals incremental progress, the low score of 39 underscores the need for deeper institutional reforms, enhanced transparency in political finance, judicial efficiency and stronger protection for whistleblowers.
Strengthening India’s Tsunami Early Warning System

- 11 Feb 2026
implemented by the Indian National Centre for Ocean Information Services (INCOIS), which operates the Indian Tsunami Early Warning Centre (ITEWC).
Location and Regional Role
- Proposed site: Vijaynagar on Swaraj Dweep, Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Project cost: ?300 crore
- First-of-its-kind tsunami coordination centre in India
- Will provide warning services to Indian Ocean countries, including Sri Lanka
The Andaman and Nicobar Islands lie close to major tectonic activity zones, making them strategically important for tsunami detection.
Limitations of the Current System
Currently, tsunami warnings are processed at INCOIS headquarters in Hyderabad. The system relies on:
- Seismic signals
- Tidal gauges along the Indian coast
- Surface buoys deployed in the Indian Ocean
- Satellite data
However, the existing system primarily detects earthquake-triggered tsunamis, which account for about 80% of global tsunamis. Nearly 20% are caused by non-seismic sources such as:
- Submarine landslides
- Volcanic eruptions
- Mudslides
Surface buoys are also vulnerable to vandalism and theft, and satellite data sometimes has gaps.
Next-Generation Capabilities
The new RSC will develop a system capable of detecting both seismic and non-seismic tsunamis, significantly enhancing early warning capacity.
Key Technological Features:
- Laying of 270 km-long sub-sea cables along tectonic subduction zones
- Improved monitoring of acoustic signals, which travel faster than conventional seismic signals
- Reduced data gaps compared to surface buoys
Subduction zones are regions where one tectonic plate moves beneath another, often generating earthquakes and volcanic activity.
Vulnerability of Indian Coasts
While India’s east coast has experienced past tsunamis (notably in 2004), experts highlight emerging risks:
- The west coast of India may be vulnerable to non-seismic tsunamis due to fragile marine geology.
- Presence of underwater mud volcanoes along the Makran coast increases risk potential.
- India’s only active volcano at Barren Island in the Andaman Sea also poses a latent threat.
- If an epicentre is located close to the Andaman and Nicobar Islands, the islands themselves could face severe impact.
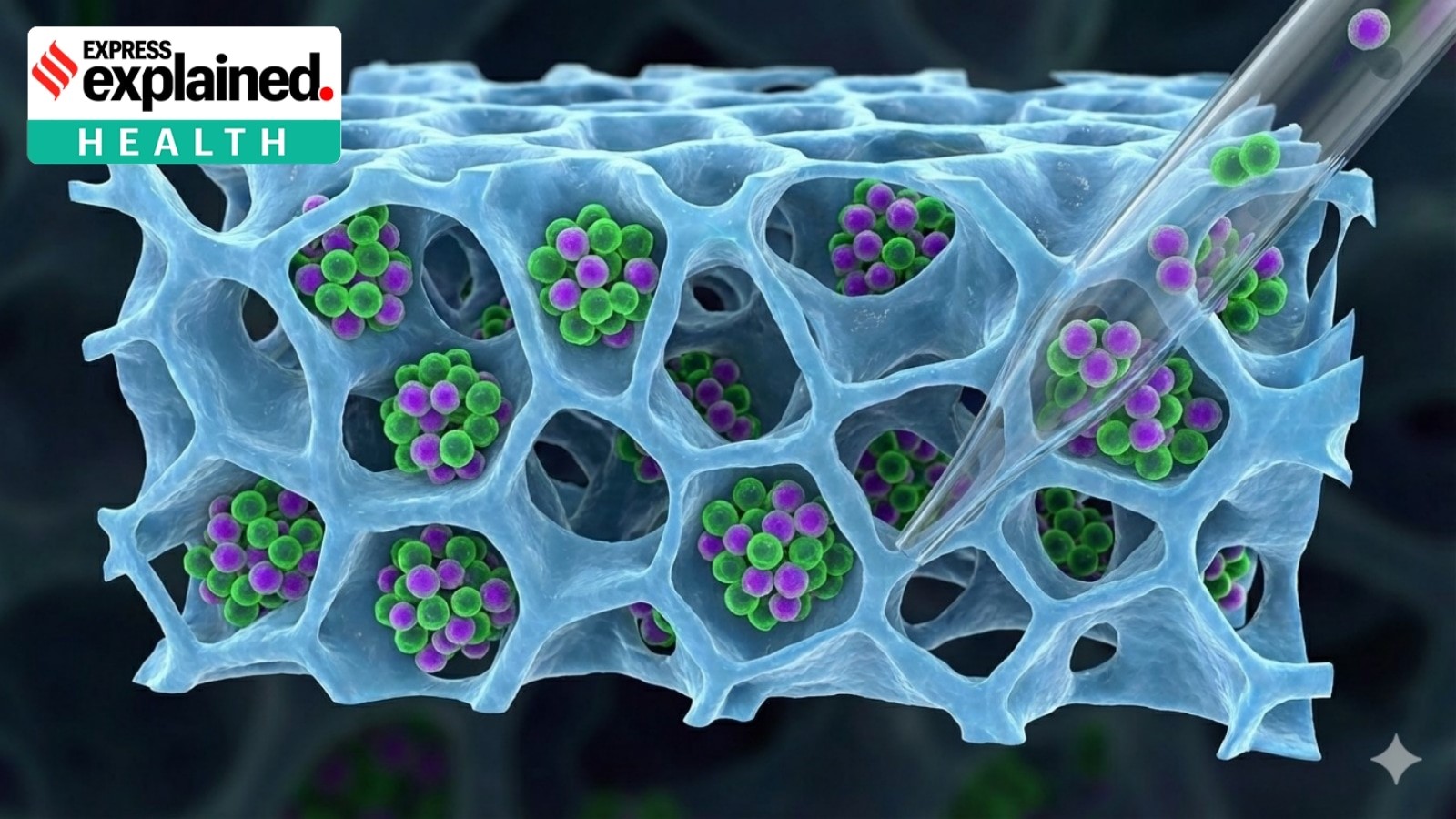
IIT Bombay breakthrough in CAR T-Cell and Adoptive T-Cell Therapies
- 09 Feb 2026
In News:
Researchers at Indian Institute of Technology Bombay (IIT Bombay) have addressed a key technical bottleneck in CAR T-cell and other Adoptive T-cell Transfer (ACT) therapies, safe recovery of lab-grown T-cells without loss of viability or immune function. The study demonstrates that using a gentler enzyme (Accutase) significantly improves therapeutic reliability and may reduce costs of cancer immunotherapy in India.
Basics for Prelims
T-Cells
- A type of white blood cell central to the immune response
- Detect and destroy infected or abnormal (cancerous) cells
- Coordinate other immune cells, making them crucial for immunotherapy
CAR T-Cell Therapy
- A personalised cancer treatment using a patient’s own T-cells
- Process:
- T-cells collected from patient’s blood
- Genetically engineered to express Chimeric Antigen Receptors (CARs)
- CARs act like GPS, guiding T-cells to cancer cells
- Cells are multiplied in the lab and infused back into the patient
- Approved globally for certain blood cancers (leukaemia, lymphoma)
- Indian milestone: NexCAR19, the world’s first humanised CAR-T therapy, developed by ImmunoACT
Key Research Development (IIT Bombay)
The Challenge
- T-cells are grown on 3D fibrous scaffolds to mimic the body’s environment
- These scaffolds improve growth and potency, but cells adhere tightly, making recovery difficult
- Harsh recovery methods damage surface proteins, reducing therapeutic effectiveness
Methods Tested
- Manual flushing
- TrypLE enzyme (harsh)
- Accutase enzyme (gentle)
Findings
- Cell yield: Similar across all methods
- Cell viability & immune function:
- TrypLE → higher cell death, reduced immune activity
- Accutase → preserved viability, clustering ability, and cancer-killing potency
- T-cells grown on scaffolds and recovered with Accutase remained highly effective against cancer cells
Significance of the Study
- Improves reliability of CAR T-cell and ACT therapies
- Potentially reduces production costs of immunotherapy
- Enhances India’s capacity for indigenous, affordable advanced cancer treatments
- Supports expansion of immunotherapy beyond elite centres
Benefits of CAR T-Cell Therapy
- Targeted precision: Spares healthy cells compared to chemotherapy
- Personalised: Uses patient’s own engineered cells
- Long-lasting protection: Engineered T-cells persist in the body
- Reduced hospitalisation and costs (especially with indigenous innovations)
- Expands future possibilities in cancer immunotherapy research
AI-Led Disruption of the Global Software Industry

- 06 Feb 2026
In News:
Global technology markets witnessed sharp volatility following the launch of a new AI-powered workplace automation suite by Anthropic, a San Francisco–based artificial intelligence firm known for developing the Claude large language model. The announcement triggered a reassessment of the long-term viability of traditional software and IT service business models, giving rise to fears of a so-called “SaaSpocalypse”—a potential existential crisis for Software-as-a-Service (SaaS) companies.
What is Anthropic’s AI Workplace Suite?
Anthropic’s new offering is a suite of autonomous AI agent–based tools designed to automate end-to-end white-collar workflows, moving beyond assistive AI towards action-taking AI.
Key characteristics include:
- Claude Cowork agents with 11 specialised plug-ins for tasks such as contract review, NDA analysis, compliance monitoring, sales tracking, and data analytics.
- Platform bypass capability, allowing AI agents to execute tasks directly without relying on conventional enterprise software interfaces such as CRM or IT service management tools.
- Autonomous execution, where AI agents can make decisions and complete workflows with minimal human intervention.
The stated objective is to reduce dependence on traditional SaaS platforms and human intermediaries, thereby fundamentally altering how enterprise work is organised and delivered.
Understanding the “SaaSpocalypse”
The term “SaaSpocalypse”, popularised by analysts including Jefferies, refers to a scenario in which AI agents disintermediate software firms entirely, rather than merely enhancing their products.
Unlike earlier AI tools that complemented existing software, autonomous AI agents threaten to replace entire layers of enterprise software and IT services, undermining subscription-based revenue models.
Impact on Global and Indian Markets
The announcement triggered a broad sell-off in technology stocks:
- In the United States, the S&P 500 fell about 0.8%, while the Nasdaq Composite declined over 1.4%.
- Major technology companies such as Microsoft, Meta Platforms, and Nvidia registered significant losses.
- Enterprise software firms like Salesforce and ServiceNow saw sharp valuation corrections.
The shockwaves were equally visible in India:
- The Nifty IT plunged around 3%.
- Major IT firms such as Infosys, Tata Consultancy Services, HCLTech, Tech Mahindra, and Wipro recorded steep declines, erasing billions in market capitalisation.
Why India’s IT Sector is Particularly Vulnerable
India’s IT industry has historically relied on services such as data processing, compliance monitoring, contract analysis, and customer support, exactly the functions targeted by Anthropic’s AI agents.
The Economic Survey 2025-26 had already warned that:
- Control over AI data and compute is highly concentrated, raising concerns over market power and technological dependence.
- Failure to adapt could “hollow out” India’s core value proposition in global IT services.
The Survey emphasised that sustaining competitiveness would require structural evolution, not incremental adoption of AI tools.
From Opportunity to Threat: A Shift in AI Narrative
Until recently, AI was widely viewed as a productivity enhancer and growth driver for technology firms. Heavy investments were made in AI upskilling and AI-enabled service offerings.
However, the emergence of autonomous AI agents capable of bypassing traditional software platforms has altered investor sentiment. The very technology that firms sought to monetise is now perceived as a direct threat to their core business models.
NDMA’s First-Ever Guidelines on Disaster Victim Identification (DVI)

- 06 Feb 2026
In News:
- India has taken a major institutional step in disaster governance with the release of its first national guidelines and Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs) for Disaster Victim Identification (DVI) by the National Disaster Management Authority (NDMA).
- Titled “National Disaster Management Guidelines on Comprehensive Disaster Victim Identification and Management”, the document was released on Republic Day, marking 25 years of the 2001 Gujarat earthquake, one of India’s worst mass fatality disasters.
Rationale and Context
The guidelines were necessitated by a series of mass fatality incidents in 2025, which exposed serious gaps in India’s ability to scientifically identify victims and ensure dignified management of human remains. These included:
- Air India aircraft crash, Ahmedabad
- Chemical factory explosion, Sangareddy (Telangana)
- Gambhira bridge collapse, Vadodara (Gujarat)
- Flash floods, Dharali (Uttarakhand)
- Delhi car bomb blast (near Red Fort)
In several of these incidents, victims remained unidentified or were identified after long delays, aggravating emotional trauma for families and creating legal and administrative complications. The absence of standard protocols, trained forensic manpower, and modern infrastructure highlighted the urgent need for a comprehensive national framework.
Objectives of the Guidelines
The DVI guidelines aim to:
- Ensure scientific, accurate and coordinated identification of disaster victims
- Enable dignified handling and handover of human remains
- Address forensic, logistical and institutional lacunae
- Standardise roles of multiple agencies across local, state and central levels
- Integrate humanitarian sensitivity with forensic science
Four-Stage Disaster Victim Identification Process
The guidelines prescribe a globally accepted four-stage identification protocol:
- Systematic Recovery – Careful retrieval of human remains from disaster sites
- Post-Mortem Data Collection – Collection of fingerprints, DNA, dental data and physical markers
- Ante-Mortem Data Collection – Gathering medical records, dental history and identifying features from families
- Reconciliation – Scientific matching of ante-mortem and post-mortem data before release of remains
This structured approach minimises errors, duplication, and misidentification.
Key Innovations and Forensic Advances
A landmark recommendation is the creation of a National Dental Data Registry, recognising that teeth and jaws often survive fires, explosions and decomposition, making dental records a reliable identification tool. The guidelines also formally incorporate:
- Forensic odontology (dental identification)
- Forensic archaeology, enabling identification of remains months or years after disasters, especially in landslides and buried sites
The framework draws from INTERPOL Disaster Victim Identification (DVI) standards, suitably adapted to Indian conditions.
Humanitarian Forensics Approach
The guidelines consciously move beyond a purely procedural mindset to adopt a “humanitarian forensics” approach:
- Discourages mass physical autopsies in large-scale disasters
- Emphasises cultural and religious sensitivity
- Mandates emotional support and counselling for families
- Focuses on the dignity of the dead, timely legal closure, and emotional closure for survivors
Institutional and Operational Framework
The document clearly outlines:
- Composition of DVI teams
- Coordination among police, medical, forensic, administrative and disaster-response agencies
- Command and leadership structures at multi-agency disaster sites
It realistically acknowledges challenges arising from overlapping jurisdictions and the presence of hundreds of responders during major disasters.
Challenges Highlighted
The guidelines identify multiple India-specific constraints:
- Rapid decomposition due to hot and humid climate
- Fragmentation, charring and commingling of remains
- Displacement of bodies during floods and landslides
- Severe shortage of mortuary spaces and cold-chain infrastructure
- Lack of trained forensic manpower
- Absence of reliable manifests or centralized data systems
Implementation Roadmap
NDMA has proposed:
- Establishing organisational DVI structures nationwide
- Training experts across forensic disciplines
- Creating specialised state-level DVI teams
- Fast-tracking implementation on a “war footing”
Way Forward and Value Addition
To strengthen the framework further:
- Linking Ayushman Bharat Health Account (ABHA) with optional dental or implant data can make the Dental Registry operational
- Use of digital forensics (smart devices, biometric locks, cloud health data) for rapid preliminary identification
- Deployment of portable Rapid DNA labs at disaster sites to reduce delays
- Adoption of blockchain-based chain-of-custody systems for tamper-proof forensic records
- Development of international DVI cooperation mechanisms for cross-border disasters
Conclusion
NDMA’s first-ever DVI guidelines mark a paradigm shift from ad hoc responses to an institutionalised, scientific and humane disaster response framework. By integrating advanced forensic science with ethical sensitivity and global best practices, the guidelines significantly strengthen India’s disaster governance architecture.
Their success, however, will depend on effective implementation, sustained capacity-building, and technological integration, ensuring dignity for victims and closure for families during future mass fatality events.
Pax Silica Initiative
- 17 Dec 2025
In News:
India’s absence from the U.S.-led Pax Silica Initiative has triggered political debate domestically. The issue gained attention after remarks by opposition leaders questioning India’s exclusion from the grouping, which is aimed at securing high-technology supply chains.
What is the Pax Silica Initiative?
- Pax Silica is a United States–led strategic framework designed to build a secure, resilient, and innovation-driven silicon supply chain.
- The term combines “pax” (Latin for peace and stability) with “silica,” the raw material refined into silicon, which is foundational for semiconductors and AI hardware.
- The initiative focuses on strengthening cooperation among trusted partners across the entire technology value chain fromcritical minerals and energy inputs to chip manufacturing, AI infrastructure, and logistics networks.
- Its broader objective is to reduce coercive dependencies, particularly in sensitive technology sectors, and to ensure that partner nations can develop and deploy advanced technologies such as artificial intelligence at scale.
Member Countries
- The current participants in Pax Silica include:United States, Japan, South Korea, Singapore, Netherlands, United Kingdom, Israel, United Arab Emirates and Australia
- Notably, India is not currently part of the initiative, even though several member countries are key Indo-Pacific technology and security partners.
Areas of Cooperation
Member nations have affirmed cooperation in multiple strategic sectors:
- Securing critical minerals required for semiconductor production
- Semiconductor design, fabrication, and advanced packaging
- Strengthening logistics and transportation networks for tech supply chains
- Expanding compute capacity and AI infrastructure
- Ensuring reliable energy grids and power generation for digital ecosystems
- Developing trusted ICT networks, data centres, fibre-optic connectivity, and AI models
- Encouraging joint ventures and co-investment in emerging technology sectors
- Protecting sensitive technologies and infrastructure from access by countries considered strategic risks
Strategic Significance
Pax Silica reflects the growing geopolitical importance of semiconductor and AI supply chains, which are now seen as central to economic security and national power. The initiative is part of a broader trend where technology alliances are being shaped to reduce overdependence on any single country in high-tech manufacturing.
The grouping also complements other emerging frameworks that aim to create trusted technology ecosystems among like-minded nations.
Project Suncatcher

- 16 Dec 2025
In News:
Google has unveiled Project Suncatcher, a long-term research initiative to explore solar-powered AI data centres in space. The plan envisions orbiting satellites equipped with high-performance AI hardware, potentially launching early prototypes by 2027.
Background: Rising Demand for AI Infrastructure
Artificial Intelligence tools such as ChatGPT and Gemini require enormous computing power, which depends on large data centres. These facilities consume vast quantities of:
- Electricity for processing
- Water for cooling systems
- Land and infrastructure for expansion
Global demand for AI data centres is projected to grow rapidly, raising concerns about energy security, water stress, and carbon emissions.
What is Project Suncatcher?
Project Suncatcher is a “moonshot” research effort to develop constellations of satellites that function as orbiting AI data centres. Instead of storing and processing data on Earth, Google proposes to deploy Tensor Processing Units (TPUs) in space.
These space-based nodes would be connected through free-space optical (laser) communication links, forming a distributed computing network similar in structure to internet satellite constellations, but dedicated to AI processing rather than broadband delivery.
Why put Data Centres in Space?
1. Abundant Solar Energy
In orbit, solar panels can be up to 8 times more productive than on Earth and receive near-continuous sunlight. This could provide a steady, renewable power supply without the intermittency issues of terrestrial solar farms.
2. Reduced Environmental Stress on Earth
Shifting computing loads to space could lower:
- Land use conflicts
- Freshwater consumption for cooling
- Local pollution and noise from massive server farms
3. Infrastructure and Regulatory Flexibility
On Earth, building new data centres often faces delays due to land acquisition, environmental clearances, and local opposition. Space offers fewer regulatory constraints, though governance frameworks are still evolving.
How Would It Work?
Satellites in close formation would host AI accelerators and exchange data using high-speed optical interconnects capable of terabit-per-second transmission. Google suggests satellites may need to remain within hundreds of meters to a kilometre of each other to maintain efficient energy sharing and communication.
The company has also tested the radiation tolerance of its latest TPU chips, reporting encouraging resilience under simulated space radiation conditions.
Major Technical Challenges
1. High-Speed Communication: Maintaining ultra-fast, stable links between rapidly moving satellites is difficult. Current wireless optical technologies are still far from matching fibre-optic speeds used in terrestrial data centres.
2. Cooling in Microgravity: Traditional cooling methods rely on gravity-driven convection. In space, heat dissipation is far more complex and requires advanced thermal management systems.
3. Radiation and Space Weather: Electronics in orbit face constant exposure to cosmic radiation and solar storms, which can damage circuits and reduce hardware lifespan.
4. Orbital Mechanics and Formation Control: Satellites must maintain very tight formations, demanding precise station-keeping and increased fuel consumption.
5. Space Debris Risk: Growing congestion in Earth’s orbit increases the likelihood of collisions, posing a threat to delicate computing infrastructure.
Economic Feasibility
Currently, launch costs make space data centres extremely expensive. However, future reductions in launch prices could improve viability. Google is targeting the mid-2030s as a period when costs may become competitive with Earth-based facilities.
Several private firms are also experimenting with space data storage and processing, indicating growing commercial interest in orbital computing.
Strategic Significance
If successful, space-based AI infrastructure could:
- Transform global computing architecture
- Reduce environmental strain from terrestrial data centres
- Provide resilient, disaster-proof computing networks
However, the concept remains experimental, with major engineering, economic, and regulatory hurdles to overcome.
Sudden Stratospheric Warming (SSW)
- 12 Dec 2025
In News:
Meteorologists have recently warned of a potential Sudden Stratospheric Warming (SSW) event, which may cause below-average temperatures across parts of the United States and other mid-latitude regions later this month.
What is Sudden Stratospheric Warming?
- Sudden Stratospheric Warming (SSW) is a phenomenon marked by a rapid increase in stratospheric temperatures, sometimes by 30–50°C within a few days.
- It results in the weakening, displacement, or splitting of the polar vortex, a cold air system usually confined to the polar regions.
Mechanism of SSW
- SSW events are triggered by large-scale atmospheric (Rossby) waves generated in the troposphere.
- These waves propagate upward into the stratosphere and break over the polar vortex, similar to ocean waves.
- If sufficiently strong:
- The westerly winds of the polar vortex weaken or reverse to easterlies
- The vortex loses its circular symmetry
- This causes descending air to warm adiabatically, leading to sudden temperature rise in the stratosphere.
Impact of SSW
- The weakened or split polar vortex allows cold Arctic air to spill southward into the mid-latitudes.
- This can result in:
- Cold waves
- Severe winter weather
- Below-normal temperatures over regions such as:
- North America
- Europe
- Asia
Polar Vortex: Key Features
- A large, persistent low-pressure system containing cold air around both poles.
- Extends from:
- Tropopause
- Through the stratosphere
- Up to the mesosphere (above ~50 km)
- Seasonal behavior:
- Stronger in winter
- Weaker in summer
- During winter, it can expand and interact with the jet stream, pushing cold air southward.
Role of Jet Streams
- Jet streams are narrow bands of strong winds located in the upper troposphere (~9–12 km altitude).
- They act as a conduit for polar air outbreaks during polar vortex disturbances.
- Such interactions are common during Northern Hemisphere winters.
India International Science Festival (IISF), 2025

- 12 Dec 2025
In News:
The 11th edition of the India International Science Festival (IISF) 2025 commenced in Panchkula, Haryana, reaffirming India’s commitment to science-led national development and public engagement with science.
About IISF
- Launched: 2015
- Vision: Conceived under the guidance of the Hon’ble Prime Minister of India to promote scientific temper, innovation, and public participation in science
- Nature: India’s flagship annual science outreach and collaboration platform
- Aim:
- Strengthen India’s science culture
- Highlight India’s position as a global S&T leader
- Support national goals in research, innovation, and talent development
- Bridge traditional knowledge systems with modern science
IISF 2025: Key Details
- Edition: 11th
- Venue: Panchkula, Haryana
- Dates: 6–9 December 2025
- Theme:“Vigyan Se Samruddhi: for Aatmanirbhar Bharat”
- Organised by: Ministry of Earth Sciences (MoES)
- Coordinating Institution: Indian Institute of Tropical Meteorology (IITM), Pune
Theme Significance
- Emphasisesscience-led prosperity and self-reliance (Aatmanirbharta)
- Aligns science and technology with:
- Economic growth
- Indigenous innovation
- National and global development goals
- Reflects the broader vision: “Innovation. Aatmanirbharta. India for Global Good”
Scale and Participation
- Expected Participants: Over 40,000 from India and abroad
- Sessions: More than 150 technical and thematic sessions
- Stakeholders Involved:
- Scientists and researchers
- Students and educators
- Startups, industry leaders and investors
- Policy-makers (Union & State Governments)
- Science communicators and media professionals
- Women scientists and early-career researchers
Major Thematic Focus Areas (2025)
- Science, Technology & Ecology of North-West India and Himalayan Region
- Science for Society and Education
- Aatmanirbhar Bharat through Science & Technology
- Biotechnology and Bio-Economy
- Integration of Traditional Knowledge with Modern Science
Priority domains include:
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Artificial General Intelligence (AGI)
- Quantum technologies
- Gene editing
- Bio-manufacturing and genomics
- Space science (satellites, launch systems, applications)
- Climate and Himalayan science
Key Components of IISF 2025
- Large-scale science and technology exhibitions
- Business-to-business (B2B) meetings
- Competitions, cultural programmes and outreach activities
- Special sessions for:
- Women in science
- School students
- Young entrepreneurs
- Early-career researchers
Partner Ministries and Institutions
- Department of Science and Technology (DST): Quantum tech, AI, advanced materials
- Department of Biotechnology (DBT): Genomics, health tech, bio-economy
- Council of Scientific & Industrial Research (CSIR): Clean energy, materials, aerospace, sensors
- Department of Space: Satellites, launch vehicles, space applications
- Department of Atomic Energy: Nuclear science, radiation tech, medical isotopes
- Vijnana Bharati (VIBHA): Public outreach and student engagement
Evolution and Significance of IISF (2015–2025)
- Hosted across major Indian cities including Delhi, Kolkata, Lucknow, Chennai, Goa, Bhopal, Faridabad, Assam
- Conducted in virtual and hybrid modes during COVID-19
- Known for:
- Guinness World Records
- Massive public footfall (up to 10 lakh+ visitors in earlier editions)
- Introduction of science villages, innovation expos, and science communication platforms
- Continual emphasis on Swadeshi science, indigenous innovation, and societal relevance
Karnataka Hate Speech and Hate Crimes (Prevention) Bill, 2025

- 12 Dec 2025
In News:
Karnataka has introduced the first state-level legislation in India specifically aimed at tackling hate speech and hate crimes. The move highlights a long-standing legal gap although the term “hate speech” is widely used, Indian criminal law does not formally define it.
What is Hate Speech?
According to the 267th Report of the Law Commission (2017), hate speech includes words, signs, or visible representations intended to incite hatred, discrimination, or violence against individuals or groups based on identity markers such as religion, caste, race, gender, or sexual orientation.
Constitutional Context
- Article 19(1)(a) guarantees freedom of speech and expression.
- Article 19(2) allows reasonable restrictions in the interests of public order, morality, sovereignty, defamation, and incitement to offences.
Thus, hate speech regulation must balance free expression and social harmony.
Existing Legal Framework in India
India currently regulates hate speech through scattered provisions, mainly focused on public order:
Under the Bharatiya Nyaya Sanhita (BNS), 2023
- Section 196 (earlier IPC 153A): Promoting enmity between groups and acts prejudicial to harmony.
- Section 299 (earlier IPC 295A): Deliberate acts intended to outrage religious feelings.
- Section 353: Statements or misinformation inciting offences or disturbing public order.
These offences are cognisable, allowing arrest without warrant, and usually carry punishment up to three years.
Other Relevant Laws
- Representation of the People Act, 1951 – Disqualification for certain hate-related offences.
- SC/ST (Prevention of Atrocities) Act, 1989 – Penalises caste-based insults and humiliation.
- Protection of Civil Rights Act, 1955 – Addresses promotion of untouchability.
Digital Dimension
Section 66A of the IT Act, 2000 was widely used for online speech but was struck down in Shreya Singhal v. Union of India for being vague and unconstitutional.
Supreme Court’s Approach
The Supreme Court of India has increasingly intervened:
- Shaheen Abdulla v. Union of India – Directed police to take suo motu action on hate speech.
- Tehseen S. Poonawalla v. Union of India – Mandated nodal officers to prevent mob violence.
- Later observations stressed that implementation failures, not legal vacuum alone, are the key challenge.
Karnataka Hate Speech and Hate Crimes (Prevention) Bill, 2025
Key Features
- Clear Definition of Hate Speech: Expression causing injury or disharmony against a person or group based on:Religion, Race, Caste, Gender, Sexual orientation, Place of birth and Disability
- Inclusion of gender and sexual orientation expands protection beyond current BNS scope.
- Collective Liability: If hate speech is committed through an organisation, office bearers or responsible persons can also be held liable.
- Online Regulation: State government empowered to block or remove hateful online content, addressing digital propagation.
- Stringent Punishment
- First offence: 1–7 years imprisonment + ?50,000 fine
- Repeat offence: 2–10 years imprisonment + ?1 lakh fine
- Offences are cognisable and non-bailable
- Victim Compensation: Mandates adequate compensation for victims.
- Public Good Exception: Books, art, research, or material published in good faith for public interest may be exempt.
Past Attempts to Define Hate Speech
- Law Commission 267th Report (2017) – Proposed IPC Sections 153C & 505A.
- Private Member’s Bill (2022) in Rajya Sabha sought a comprehensive definition but was not enacted.
- Committees like Viswanathan (2015) and Bezbaruah (2014) also suggested legal reforms.
Significance of the Karnataka Bill
- First dedicated state law on hate speech
- Attempts to shift focus from public order to dignity and equality
- Recognisesdigital hate propagation
- Expands protection to LGBTQ+ communities and persons with disabilities
Hindu Rate of Growth

- 11 Dec 2025
In News:
Prime Minister Narendra Modi recently, denounced attempts to link India's past economic slowdown with the Hindu faith, calling the “Hindu rate of growth” label a deliberate distortion.
What is meant by “Hindu Rate of Growth”?
- The phrase refers to India’s persistently low real GDP growth of about 3–4% per year from the 1950s to late 1970s, before growth accelerated in the 1980s and later reforms. It described long-run macroeconomic performance, not any religion-based economic model.
- Coined by: Economist Raj Krishna (Delhi School of Economics) in the late 1970s (often dated to 1978). He used it as a polemical device to highlight how India’s growth appeared stuck at a low, stable trend.
Key Characteristics of the Period
- Low & Persistent Growth: GDP hovered near 3.5–4%, while population growth ~2% kept per-capita income growth modest.
- Stability Across Shocks: Growth changed little despite wars, droughts, political shifts—suggesting a structural equilibrium.
- Licence–Permit–Quota Raj: Extensive industrial licensing, high tariffs, import substitution, and a dominant public sector curbed competition and productivity.
- State-Led Mixed Economy: Planning, public control of core sectors, and tight trade/FDI policies limited private dynamism.
- East Asia Contrast: Economies like South Korea and Taiwan grew 7–10%, underscoring India’s relative underperformance.
Was it “Cultural”?
Later scholarship clarified that “Hindu” was not a technical or religious category. It reflected Krishna’s rhetorical framing about the embeddedness of low growth across decades, not a claim about faith-based behavior. Contemporary debates have criticized the label as misleading or colonial in tone.
Growth Before and After
- Colonial Benchmark: Estimates place late colonial GDP growth near ~1%; early post-Independence growth rose to ~4% in the 1950s–early 1960s, indicating capacity building in heavy industry, power, transport, and basic chemicals.
- 1980s Acceleration (Pre-1991): Evidence shows growth rose to ~5.6–5.8% in the 1980s, before the 1991 liberalisation.
- Attributed to within-system reforms: selective de-licensing, technology imports, export incentives, and fiscal/credit easing.
- Scholars like Baldev Raj Nayar, Arvind Virmani, and Arvind Panagariya highlight the 1980s as a turning point.
- Post-1991: Broad liberalisation deepened competition, trade openness, and private investment, sustaining higher trend growth.
Policy Drivers of the Low-Growth Phase
- Import Substitution Industrialisation (ISI): Protected domestic industry but reduced export competitiveness.
- High Effective Protection & Quotas: Limited scale and innovation.
- Financial Repression: Directed credit and administered interest rates distorted capital allocation.
- Public Sector Dominance: Efficiency varied; crowding-out and soft budget constraints emerged.
What the Term Does Not Mean
- Not a religious doctrine or a formal macroeconomic theory.
- Not uniform stagnation: agriculture, services, and specific industries saw episodic gains; human capital and infrastructure bases expanded.
Right to Disconnect Bill, 2025

- 09 Dec 2025
In News:
A Private Member’s Bill titled the Right to Disconnect Bill, 2025 has been reintroduced in the Lok Sabha. The Bill seeks to legally recognise employees’ right to disengage from work-related communication beyond official working hours.
What is the Right to Disconnect?
The Right to Disconnect refers to an employee’s right to not respond to work-related calls, emails, or messages outside prescribed working hours without facing disciplinary action. It aims to address the growing problem of constant digital connectivity, protect mental well-being, and promote a healthier work–life balance.
In the era of smartphones, remote work, and global time zones, employees are often expected to remain available beyond office hours, leading to stress, burnout, and reduced productivity.
Key Provisions of the Bill
The Bill proposes a legal and institutional framework to safeguard employees from after-hours work pressure:
- Right to Refuse After-Hours Communication: Employees cannot be penalised for ignoring work-related communication outside official hours.
- Employees’ Welfare Authority: A statutory body will be established to implement and monitor the right to disconnect.
- Baseline Study: The Authority will conduct a nationwide study to assess the burden of digital communication on employees outside work hours.
- Mandatory Negotiations: Companies with more than 10 employees must negotiate with workers or unions to set clear rules for work beyond office hours. Any such work will qualify for overtime wages.
- Mental Health Support: Provision for counselling services and the establishment of digital detox centres in collaboration with the government.
- Penalties for Non-Compliance: Companies violating the provisions may face penalties of up to 1% of their total employee remuneration.
Private Member’s Bill - Key Facts
- A Private Member’s Bill (PMB) is introduced by an MP who is not a Minister.
- Such Bills are generally taken up on Fridays in Parliament.
- PMBs rarely become law -only 14 have been enacted since Independence, with the last passed in 1970.
Global Perspective
Several countries have already recognised the Right to Disconnect in law:
- France (2017) – One of the first countries to implement it.
- Portugal – Employers are restricted from contacting employees after work hours.
- Australia (2024) – Recently introduced similar legal protections.
These examples show a global shift toward prioritising employee well-being in digital workplaces.
Status in India
India currently has no specific law guaranteeing the Right to Disconnect. However, the concept aligns with constitutional principles:
- Article 38 – Promotes welfare of the people.
- Article 39(e) – Directs the State to protect workers’ health and strength.
Existing labour laws focus on working hours and safety but do not address digital overreach beyond work hours.
Significance
- Promotes work–life balance and mental health
- Reduces risks of burnout, stress, and “telepressure”
- Encourages clear workplace boundaries
- Aligns India with emerging global labour welfare standards
Mahatma Gandhi Gram Swaraj Initiative (MGGSI)

- 02 Feb 2026
In News:
The Union Budget 2026–27 introduced the Mahatma Gandhi Gram Swaraj Initiative (MGGSI) as a focused intervention to revitalise India’s traditional rural industries. The programme seeks to strengthen khadi, handloom, and handicrafts by improving competitiveness, market access, and sustainability of artisan livelihoods. In doing so, it draws inspiration from the Gram Swaraj vision of Mahatma Gandhi, which emphasised self-reliant villages built on local production and decentralized economic power.
Objectives and Target Groups
MGGSI is designed to make traditional sectors economically viable in a modern market environment while preserving India’s craft heritage. It focuses on:
- Weavers and artisans in khadi, handloom, and handicrafts
- Village industries and rural micro-enterprises
- Beneficiaries under the One District One Product (ODOP) initiative
- Rural youth, encouraging them to view traditional industries as viable careers
The initiative recognises that these sectors not only sustain livelihoods but also represent cultural capital and employment-intensive growth, particularly in labour-surplus rural regions.
Addressing Structural Challenges
Traditional craft sectors suffer from long-standing bottlenecks:
- Fragmented supply chains that raise costs and reduce efficiency
- Inconsistent quality standards, limiting access to premium and export markets
- Weak branding and marketing, leading to dependence on middlemen
- Limited integration with modern retail and e-commerce platforms
MGGSI aims to address these constraints through institutional support, quality standardisation, design innovation, and better market linkages. It encourages artisans to adopt modern production techniques and tools without compromising traditional craftsmanship.
Market Access and Branding
A core pillar of MGGSI is improving global and domestic market access. The initiative promotes:
- Professional branding and packaging
- Entry into organised retail chains
- Access to export markets
- Integration with digital and online marketplaces
This shift from subsistence production to market-oriented enterprise aligns with the broader “Vocal for Local” philosophy and the push to strengthen MSMEs as engines of inclusive growth.
Link to Gandhi’s Gram Swaraj Vision
Gandhi’s concept of Gram Swaraj envisioned villages as self-sufficient republics, economically independent and socially cohesive. However, contemporary rural India faces challenges such as agrarian distress, migration, inequality, and weak non-farm employment opportunities, which prevent villages from achieving that ideal.
MGGSI attempts to reinterpret Gram Swaraj for the 21st century by:
- Promoting local production for wider markets
- Generating non-farm rural employment
- Reducing distress migration
- Enhancing economic self-reliance through village industries
Thus, instead of isolation, the modern approach combines local production with global connectivity.
Indian Maritime Doctrine 2025

- 06 Dec 2025
In News:
The Indian Maritime Doctrine (IMD) 2025, released by the Chief of the Naval Staff on Indian Navy Day (4 December), is the apex doctrinal publication guiding India’s naval strategy. Navy Day commemorates Operation Trident (1971), when the Indian Navy launched a successful missile attack on Karachi harbour using INS Nipat, Nirghat and Veer, supported by INS Kiltan, Katchall and fleet tanker INS Poshak, crippling Pakistan’s maritime capability.
What is the Indian Maritime Doctrine 2025?
The IMD 2025 defines how India prepares and operates across the full spectrum of maritime conflict, from peacetime presence to warfighting. First issued in 2004 and updated in 2009 and 2015, the 2025 edition reflects India’s evolving maritime environment and Indo-Pacific priorities.
Key Features
1. “No-War, No-Peace” Category:The doctrine formally recognises a grey-zone space between peace and open conflict, where coercion, intimidation, and competition occur without declared war.
2. Multi-Domain and Hybrid Threats:It integrates challenges from cyber, space, electronic and cognitive warfare, along with irregular and hybrid threats.
3. Jointness and Theatre Commands:The document stresses tri-service interoperability and supports India’s move toward theatre command structures.
4. Technology and Modernisation:Emphasis is placed on uncrewed systems, autonomous platforms, AI-enabled surveillance, and network-centric warfare.
5. Maritime Security and Blue Economy:It links naval power to protection of Sea Lanes of Communication (SLOCs), maritime trade, offshore resources, and India’s blue economy ambitions.
Strategic Significance
- The doctrine aligns with national initiatives such as Sagarmala, PM Gati Shakti, Maritime India Vision 2030, Maritime Amrit Kaal Vision 2047, and MAHASAGAR. It positions maritime power as central to achieving Viksit Bharat 2047 and strengthens India’s role as a net security provider in the Indo-Pacific.
Indian Navy: Historical Background
- India’s maritime legacy dates back over 4,000 years, with Harappan ports like Lothal engaged in overseas trade. Ancient Indian navigators influenced Southeast Asia culturally and commercially.
- During the medieval period, powers such as the Cholas, Zamorins, and Marathas developed naval strength. The Maratha Navy under KanhojiAngre resisted European fleets along India’s west coast.
- European dominance began after Vasco da Gama (1498), leading to colonial maritime supremacy. The modern navy evolved from the Royal Indian Navy (RIN), which became the Indian Navy after independence.
Structure and Role Today
The President of India is the Supreme Commander of the Navy. Its motto is “Sam No Varunah” (May Varuna be auspicious to us).
India today maintains a blue-water navy capable of sustained operations across the Indian Ocean Region (IOR) and beyond. Its roles include:
- Maritime security and SLOC protection
- Power projection and deterrence
- Humanitarian assistance and disaster relief (HADR)
- Counter-piracy and anti-terror operations
The Navy’s elite force, MARCOS (Marine Commandos), specialises in amphibious warfare, counter-terrorism, and special operations.
Major Operations
Post-independence milestones include the Liberation of Goa (1961), Operations Trident and Python (1971 war), and ongoing maritime security missions in the IOR.
Alaknanda Galaxy
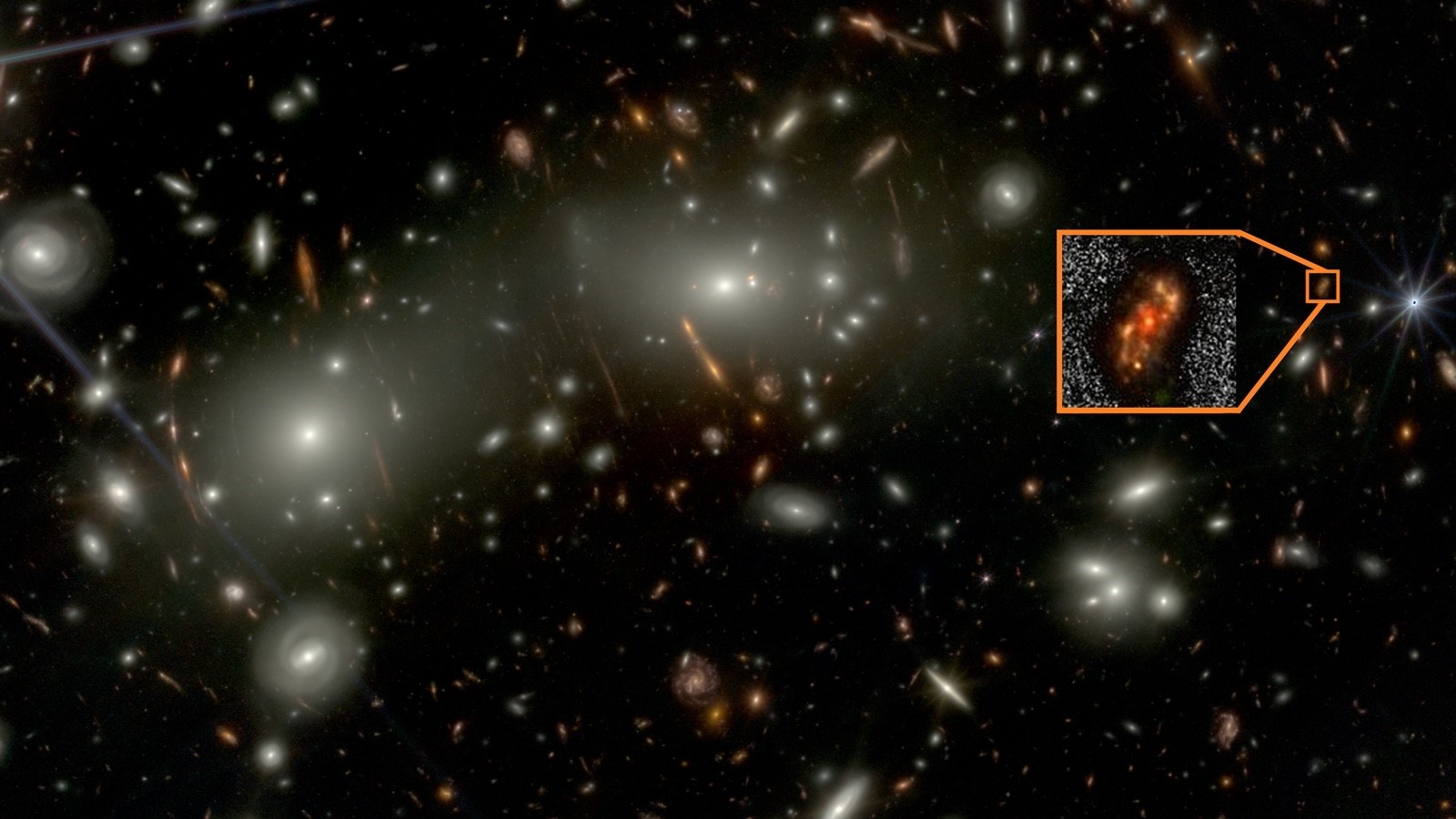

- 05 Dec 2025
In News:
Researchers from the National Centre for Radio Astrophysics (NCRA), Tata Institute of Fundamental Research (TIFR), Pune, have discovered a well-structured spiral galaxy named Alaknanda. This galaxy dates back to just 1.5 billion years after the Big Bang and was identified using NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope (JWST). The finding challenges existing theories about how early galaxies formed.
Why This Discovery is Important
Scientists believed that galaxies in the early universe were generally chaotic, clumpy, and unstable, lacking well-defined structures. Spiral galaxies like the Milky Way were thought to have developed much later. However, Alaknanda shows a mature spiral structure, indicating that complex galactic systems may have evolved far earlier than previously assumed.
Key Facts About the Alaknanda Galaxy
Alaknanda formed when the universe was only about 10 percent of its current age, roughly 1.5 billion years old. It lies approximately 12 billion light-years away from Earth. The galaxy displays a textbook spiral structure with two well-defined spiral arms and a bright central bulge. Its diameter is estimated to be around 30,000 light-years.
The name “Alaknanda” is inspired by the Alaknanda River in the Himalayas, considered the sister river of Mandakini, which is also a Hindi name for the Milky Way galaxy. The naming reflects the idea that this distant galaxy resembles a “sister” of our own galaxy.
Scientific Significance
The discovery adds to growing evidence from JWST that the early universe may have been more mature and structured than earlier models suggested. It challenges current theories of galaxy formation and indicates that organized spiral structures may have emerged earlier in cosmic history.
Future research will focus on studying the motion of gas and stars within Alaknanda to understand how its spiral arms formed. Scientists plan to use further data from JWST and the Atacama Large Millimeter/submillimeter Array (ALMA) in Chile. These studies will help determine whether the galaxy’s disk is dynamically calm or turbulent, which in turn reveals the mechanism behind its structure.
About Galaxies
Galaxies are vast systems made up of stars, planets, gas, dust, dark matter, and usually a supermassive black hole at their centre. They are held together by gravity and vary greatly in size. Some dwarf galaxies contain only a few thousand stars, while giant galaxies can contain trillions of stars and span over a million light-years.
Galaxies are commonly classified into three main types: spiral, elliptical, and irregular.
Galaxies in the Cosmic Web
Galaxies are not randomly scattered. They form groups, which can contain up to about a hundred galaxies, and clusters, which can include thousands. These clusters connect to form superclusters, which are part of the large-scale cosmic web that structures the universe.
Key Processes in Galaxy Evolution
Spiral galaxies often develop stellar bars that influence star formation. Galaxies may collide, causing gas clouds to compress and trigger new star formation. Some collisions lead to mergers, forming a single larger galaxy and altering its structure. Larger galaxies can also grow by absorbing smaller ones, a process sometimes called galactic cannibalism.
Milky Way Galaxy - Important Facts
The Milky Way is a spiral galaxy more than 100,000 light-years across. Earth lies in one of its spiral arms, roughly halfway from the galactic centre. The Milky Way is part of the Local Group, which includes more than 50 galaxies such as the Andromeda Galaxy. This group is located within the vast Laniakea Supercluster. Our solar system takes about 240 million years to complete one orbit around the Milky Way.
WHO Issues First-Ever Guidelines on GLP-1 Weight-Loss Drugs to Tackle Obesity
- 04 Dec 2025
In News:
The World Health Organization (WHO) has for the first time issued guidelines on the use of Glucagon-Like Peptide-1 (GLP-1) receptor agonists as part of a comprehensive strategy to manage obesity a chronic, relapsing disease affecting over 1 billion people worldwide.
Understanding Obesity
- Definition: Obesity in adults is defined as having a Body Mass Index (BMI) ≥ 30.
- Disease Burden: Obesity contributes significantly to morbidity and mortality through increased risk of type 2 diabetes, cardiovascular diseases, kidney disease, and certain cancers. Globally, over 1 billion people are obese, and if current trends continue, the number is expected to double by 2030.
WHO’s Stance on Obesity
WHO classifies obesity as a chronic disease requiring lifelong care. Its guidelines emphasize that treatment must go beyond medication to include early screening, diagnosis, behavioural support, lifestyle modification, and management of comorbidities.
GLP-1 Therapies: Role and Mechanism
- What they are: GLP-1 receptor agonists are medications that mimic the gut hormone GLP-1, which regulates appetite, digestion, and blood sugar.
- Mechanism: These drugs improve satiety, slow gastric emptying, enhance insulin secretion, and suppress glucagon leading to reduced food intake and improved glycemic outcomes.
- Clinical Benefits: GLP-1 therapies have been shown to produce meaningful weight loss (often ≥5% of body weight) and offer metabolic benefits for cardiovascular and kidney health.
WHO Guidelines on GLP-1 Use
Key Recommendations
- Conditional Long-Term Use:WHO recommends that GLP-1 therapies may be used long term (continuous treatment beyond 6 months) for adults with obesity (BMI ≥ 30), except in pregnant women due to lack of safety data.
- Multimodal Care:GLP-1 medications should be prescribed only as part of a broader, lifelong obesity-care plan that includes:
- Intensive behavioural therapy (diet planning, physical activity, counselling)
- Structured lifestyle interventions
- Continued monitoring and follow-up.
- Equity and Access:WHO highlights the global inequity in access to GLP-1 therapies. Current production capacity could cover only ~100 million people, representing <10% of those living with obesity.
Therefore, equitable access, affordable pricing, and support for generic production are essential for broader reach.
Rationale
The recommendations are conditional due to:
- Limited long-term efficacy and safety data
- High treatment costs
- Health system readiness and infrastructure gaps
- Equity concerns across populations.
Adverse Effects of GLP-1 Therapies
Reported side effects include gastrointestinal symptoms such as nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and constipation. Rare but more serious effects, including pancreatitis and possible thyroid tumors, are under evaluation.
Obesity: Global and Indian Context
- Global Trends: Obesity prevalence has been rising across countries of all income levels, with substantial increases in both urban and rural populations.
- India: According to national surveys, nearly 24% of women and ~23% of men aged 15–49 are overweight or obese, reflecting a growing public health concern. Unhealthy diets, sedentary lifestyles, and socio-economic shifts underpin this trend.
National Implications for Health Policy
- Epidemiological Transition: India’s dual burden of communicable and non-communicable diseases (NCDs) emphasizes obesity as a priority area in preventive and primary health strategies.
- Health Systems: Integrating obesity screening and management into primary healthcare, strengthening referral pathways, and building patient registries are recommended to support long-term care models.
Italy Recognises Femicide as a Crime

- 03 Dec 2025
In News:
Recently, Italy passed a landmark law formally recognisingfemicide as a separate criminal offence, making life imprisonment the mandatory punishment for gender-motivated killings of women.
Femicide: Concept, Legal Recognition & Global Context
Femicide refers to the intentional killing of women and girls because of their gender. It is regarded as one of the most extreme forms of gender-based violence (GBV) and reflects deep-rooted patriarchal discrimination and control over women.
What is Femicide?
According to UN frameworks, femicide includes gender-related killings committed by:
- Intimate partners (current or former)
- Family members (including relatives by marriage or adoption)
- Other perpetrators, where gender is a primary motive
Femicide is distinct from general homicide because the victim’s gender is central to the motive, often linked to control, honour, jealousy, or refusal to accept autonomy.
Why Recognise Femicide as a Separate Crime?
Countries that legislate specifically on femicide argue that:
- It highlights systemic gender discrimination
- Helps improve data collection and crime classification
- Enables targeted policy and prevention strategies
- Signals stronger state acknowledgment of gender-based violence
Without separate recognition, such crimes may be treated as ordinary homicide, masking the structural gender dimension.
Italy’s Femicide Law
- Italy recently amended its criminal law to explicitly recognise femicide
- Life imprisonment is mandated for killings proven to be gender-motivated
- The law was passed with broad political support
- It follows public outrage over high-profile murders of women, particularly cases involving:
- Former partners
- Patterns of harassment and coercive control
Italy joins a small group of countries with dedicated femicide laws.
Countries with Specific Femicide Laws
- Examples include:Mexico, Chile, Cyprus, Morocco, North Macedonia, Türkiye, Gabon, and Italy (latest addition)
- Many other countries do not define femicide separately but may treat gender as an aggravating factor during sentencing.
Global Situation
- UN reports indicate that tens of thousands of women each year are killed by intimate partners or family members
- However, data gaps remain because many countries do not classify or report femicide separately
- Researchers link femicide to:
- Patriarchal norms
- Gender inequality
- Weak protection mechanisms
- Social tolerance of domestic violence
Debates Around Femicide Laws
Some legal experts argue that:
- Broad definitions may create challenges in proving gender motive
- Laws must be supported by:
- Strong policing and investigation
- Victim protection systems
- Social awareness campaigns
Legal reform alone may not be sufficient without institutional and cultural change.
India’s Position
India does not recognise femicide as a separate legal category, but has several laws addressing gender-based violence and harmful practices:
- Protection of Women from Domestic Violence Act, 2005
- Dowry Prohibition Act, 1961
- Prohibition of Child Marriage Act, 2006
- National Commission for Women Act, 1990
- Specific provisions under IPC/CrPC related to dowry death, cruelty, and sexual offences
In India, gender may act as a contextual or aggravating factor, but homicide laws are not separately classified as femicide.
Related International Observance
International Day for the Elimination of Violence Against Women
- Observed on 25 November
- Designated by the United Nations General Assembly in 1999
- Aims to raise awareness about violence against women and girls (VAWG)
Supreme Court Clarifies Governor’s Powers on Assent to State Bills

- 24 Nov 2025
In News:
In a landmark constitutional opinion, a five-judge Constitution Bench of the Supreme Court clarified the scope and limits of the powers of Governors and the President regarding assent to State Bills under Articles 200 and 201 of the Constitution. The opinion was delivered in response to a Presidential Reference under Article 143, addressing 14 questions of law, amid complaints by several States that Governors were delaying or withholding assent, causing legislative paralysis.
Constitutional Framework
Article 200 – Governor and State Bills
When a Bill passed by a State Legislature is presented, the Governor has only three constitutionally permissible options:
- Grant assent to the Bill.
- Withhold assent and return the Bill (except Money Bills) to the Legislature with recommendations for reconsideration.
- Reserve the Bill for the President’s consideration.
The Court categorically held that there is no power to “withhold assent simpliciter”. A Governor cannot sit indefinitely on a Bill without taking one of the three actions.
Article 201 – President and Reserved Bills
When a Bill is reserved, the President may:
- Grant assent, or
- Withhold assent.
The President’s discretion here is similar to that of the Governor, but operates only after reservation.
Key Clarifications by the Supreme Court
- No indefinite delay permitted:“Prolonged, unexplained, and indefinite inaction” by a Governor is unconstitutional and subject to judicial review.
- Discretion, but not arbitrariness:Governors are not bound by the aid and advice of the Council of Ministers while exercising powers under Article 200, as this discretion is constitutionally envisaged. However, this discretion cannot be used to obstruct the legislative will of an elected government.
- Judicial review limited to inaction:Courts cannot review the merits or wisdom of a Governor’s or President’s decision to grant or withhold assent. Judicial scrutiny is limited only to cases of constitutional inaction or procedural violation.
- No judicially imposed timelines:The Court held that it cannot prescribe rigid deadlines (such as 1–3 months) for Governors or the President. The phrase “as soon as possible” in Articles 200 and 201 allows flexibility and cannot be judicially converted into fixed timelines.
- Rejection of ‘deemed assent’:The Court firmly rejected the idea that a Bill automatically becomes law if assent is delayed. Article 142 (complete justice) cannot be used to bypass the constitutional requirement of assent.
- Article 361 is not an absolute shield:While Governors and the President enjoy personal immunity, the office itself is not immune from judicial scrutiny where constitutional duties are not discharged.
- Courts cannot examine Bills:Judicial review applies only to laws in force, not to Bills awaiting assent. Courts cannot examine the constitutionality of proposed legislation.
Broader Constitutional Significance
- Reinforces constitutional morality and federal balance.
- Prevents misuse of gubernatorial discretion while respecting constitutional design.
- Protects legislative supremacy of elected assemblies without eroding the discretionary role of constitutional authorities.
- Clarifies limits of Article 142, ensuring it does not override substantive constitutional provisions.
Ultra-Processed Foods (UPFs) in India

- 24 Nov 2025
In News:
A recent series published in The Lancet highlights that India is witnessing the fastest global growth in sales of Ultra-Processed Foods (UPFs)from USD 0.9 billion (2006) to nearly USD 38 billion (2019), representing a ~40-fold increase. This rapid dietary transition is strongly associated with rising obesity, diabetes, and cardiovascular diseases in the country.
What are Ultra-Processed Foods (UPFs)?
- Definition: Industrial formulations designed for convenience, long shelf life, and mass consumption, made largely from manufactured ingredients rather than whole foods.
- Typical Components: Refined starches, protein isolates, added sugars, unhealthy fats, flavour enhancers, colourants, stabilisers, emulsifiers, and preservatives.
- Examples: Soft drinks, chips, chocolates, ice creams, sweetened breakfast cereals, packaged soups, instant noodles, ready-to-heat meals.
Processed vs Ultra-Processed Foods
- Processed foods: Minimally altered (e.g., cooking, fermenting, canning) and retain basic food structure (e.g., pickles, jam, cheese).
- Ultra-processed foods: Contain industrial additives; the presence of emulsifiers or artificial flavours classifies a product as UPF.
Why is UPF Consumption Rising in India?
- Aggressive Marketing: Celebrity endorsements, sports sponsorships, targeted ads (especially for children), discount offers.
- Lifestyle Changes:Urbanisation, time constraints, and preference for ready-to-eat foods.
- Dietary Transition: Shift towards Western-style diets rich in fast foods and sugary snacks.
- Perceived Convenience: Seen as time-saving substitutes for traditional meals.
Health and Nutrition Impacts
- Poor Nutritional Quality: UPFs are high in fat, sugar, and salt (HFSS) but low in fibre and micronutrients.
- Disease Burden: Linked to higher risks of obesity, Type 2 diabetes, hypertension, heart disease, kidney and gastrointestinal disorders, mental health issues, and premature mortality.
- India-Specific Risk: Genetic predisposition to visceral obesity and metabolic disorders amplifies harms.
- Children at High Risk: Childhood obesity increased from 2.1% to 3.4% (NFHS 2016 → 2019–21). Long-term effects include addictive eating behaviours, gut microbiome imbalance, impaired brain development, and early-onset diabetes.
Regulatory and Awareness Gaps
- Weak Regulation: Heavy reliance on self-regulation; absence of mandatory front-of-pack (FOP) warning labels.
- Misleading Packaging: Health claims (e.g., “high protein”) obscure high sugar, salt, or fat content.
- Identification Challenge: Public confusion between processed foods and UPFs.
- The Economic Survey 2024–25 underlines the need for stronger regulatory action.
Existing Indian Initiatives for Healthy Diets
- Eat Right India Movement
- State Food Safety Index
- RUCO (Repurpose Used Cooking Oil)
- Food Safety Mitra
- World Food Safety Day observances
What Measures are Needed?
- Stronger Regulations:
- Mandatory FOP warning labels (“High in Sugar/Salt/Fats”).
- Restrictions on marketing to children.
- Healthy Food Environments:
- UPF-free school canteens; promotion of minimally processed foods (Brazilian model).
- Increased availability of healthy alternatives in public spaces.
- Public Awareness Campaigns:
- Avoid foods with >10% sugar or fat; sodium >1 mg/kcal.
- Prefer whole foods like fruits, vegetables, milk, nuts.
- Monitoring & Research:
- Measure UPF share in diets (especially children and youth).
- Identify consumption patterns to support targeted regulation.
- Global & National Coordination:
- Align with forthcoming World Health Organization guidelines on UPFs.
- Involve FSSAI, health and education sectors, industry, and civil society.
WHO Recommendation: Free sugar intake should be <10% of daily energy, ideally <5% (~25 g/day).
Ratanmahal Wildlife Sanctuary
- 22 Nov 2025
In News:
A wild tiger has established a sustained presence for about nine months in Ratanmahal Wildlife Sanctuary, marking the first long-term tiger residency in Gujarat in decades. The tiger, first sighted in February 2025, is believed to have naturally dispersed from Madhya Pradesh, highlighting improving habitat connectivity and ecosystem health along the inter-state border.
About Ratanmahal Wildlife Sanctuary
- Location:Gujarat; along the Gujarat–Madhya Pradesh border (major portion within Gujarat)
- Established: March 1982
- Also Known As:Ratanmahal Sloth Bear Sanctuary (hosts the highest sloth bear population in Gujarat)
- Hydrology: Forms the catchment of the Panam River, a key river of Central Gujarat
Habitat & Vegetation
- Forest Types:
- Dry teak forests at foothills
- Mixed deciduous forests with dry bamboo brakes on the periphery
- Plateau Vegetation: Dominance of Mahuda (Mahudo) with patches of Sadad and Timru
- Key Flora: Teak, bamboo, amla, dhavdo, kakadiyo, mahuda, tanach, charoli, ber, jamun, khakhro, dudhlo
Faunal Diversity
- Mammals: Leopard, Sloth bear, Palm civet, Indian civet, Four-horned antelope
- Birds:Loten’s sunbird, Large green barbet, Yellow-cheeked tit
- Recent Addition:Tiger (Panthera tigris)
Ecological Significance of the Tiger’s Return
- Indicator Species: Tigers are apex predators; their presence signals healthy prey base, water availability, and habitat quality.
- Natural Dispersal: The tiger was not translocated; it migrated naturally from MP, aided by landscape connectivity and population pressure there.
- Contrast with Past: A tiger that reached Mahisagar (2019) did not survive due to inadequate prey—underscoring the improved conditions now at Ratanmahal.
- Monitoring: Continuous surveillance via camera traps and field teams to track movement and behaviour.
Conservation Implications
- Unique Coexistence: Gujarat now hosts all three big cats—Asiatic lion, Indian leopard, and tiger—within the same broader landscape.
- Management Challenges: Overlapping ranges demand enhanced corridor management, conflict mitigation, and community safety measures.
- Policy Signal: Validates habitat restoration, prey augmentation, and inter-state ecological linkages.
Dugong

- 21 Nov 2025
In News:
A new global report released at the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) Conservation Congress in Abu Dhabi has warned that India’s dugong populations in the Gulf of Kutch, Gulf of Mannar–Palk Bay, and Andaman & Nicobar Islands face serious long-term survival risks due to habitat degradation and human pressures.
About Dugong
- Scientific Name:Dugong dugon
- Type: Large herbivorous marine mammal
- Evolutionary Links: Closely related to manatees; distantly related to elephants
- Common Name: Sea cow (inspired ancient “mermaid” myths due to gentle behaviour)
Distribution & Habitat
- Global: Warm, shallow coastal waters of the Indian and Pacific Oceans; largest stable population near north-western Australia
- India (Major Habitats):
- Gulf of Mannar–Palk Bay
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Gulf of Kutch
- Prefer calm, shallow (<10 m) coastal waters with abundant seagrass meadows
Key Biological Features
- Size: Up to 3 m long; 300–420 kg
- Morphology: Whale-like tail fluke; paddle-shaped flippers
- Diet:Exclusively herbivorous—feeds on seagrass
- Consumption: ~ 30–40 kg of seagrass/day
- Ecological Role:
- Act as “ecosystem engineers”—natural grazing maintains healthy seagrass
- Seagrass meadows function as blue carbon sinks, aiding climate regulation
- Life History: Long-lived (up to 70 years) but very low reproductive rate (calving once every 3–7 years)
Conservation Status
- IUCN Red List:Vulnerable (declining trend since 1982)
- India:Schedule I, Wild Life (Protection) Act, 1972 (highest legal protection)
Population Status in India (Indicative)
- Gulf of Mannar–Palk Bay: ~ 150–200 individuals (largest remaining group)
- Andaman & Nicobar Islands:<50 individuals
- Gulf of Kutch:<20 individuals(Exact estimates are difficult due to turbid waters and elusive behaviour.)
Major Threats
- Habitat Loss & Seagrass Degradation: Coastal pollution, sedimentation, dredging, port development
- Fisheries Bycatch: Accidental entanglement in fishing nets—primary cause of mortality
- Marine Pollution & Heavy Metals: Detection of arsenic, cadmium, chromium, mercury and lead in dugong tissues (linked to industrial discharge, agricultural runoff, untreated wastewater)
- Slow Reproduction: Limits population recovery
Conservation Measures in India
- MoEFCC Task Force (2010) on dugong conservation
- National Dugong Recovery Programme with Tamil Nadu, Gujarat, A&N
- Dugong Conservation Reserve, Palk Bay (2022)—448 sq km to protect seagrass and dugongs
- Ongoing need for stronger enforcement, bycatch reduction, and incentive-based fisheries management
Adam Chini Rice

- 20 Nov 2025
In News:
Agricultural scientists at Banaras Hindu University (BHU) have achieved a major breakthrough in improving the resilience and productivity of the traditional Adam Chini (Adamchini) rice using mutagenesis, making the variety suitable for large-scale cultivation while preserving its unique aroma and grain quality.
About Adam Chini Rice
- Type: Aromatic black rice variety
- Region: Eastern Uttar Pradesh – mainly Chandauli, Varanasi and Vindhya region
- GI Status: Received Geographical Indication (GI) tag in 2023
- Local Branding: Recognised by the state government as “Vindhya Black Rice”
Key Characteristics (Traditional Variety)
- Grain Type: Short-bold, sugar-crystal-like grains
- Aroma & Quality: Renowned for excellent flavour and pleasant fragrance
- Plant Height: Up to 165 cm (tall, prone to lodging)
- Maturity Period: ~ 155 days
- Yield: Low – 20–23 quintals/ha
- Cooking Quality:
- Intermediate amylose content → rice remains fluffy and soft on cooling
- Intermediate alkali digestion value
- Stress Tolerance: Drought tolerance and disease resistance
Scientific Intervention
- Technique Used:Mutagenesis (induced genetic variation without altering core varietal identity)
- Research Duration: Over 14 years by BHU’s Department of Genetics & Plant Breeding
- Output: Development of 23 novel mutant lines retaining aroma and grain type
Improved Mutant Traits
- Reduced Height: ~ 105 cm (e.g., Mutant-14) → less lodging
- Early Maturity: ~ 120 days (e.g., Mutant-19)
- Higher Yield:30–35 quintals/ha (Mutants 14, 15, 19, 20)
- Net Impact: Higher productivity + climate resilience without loss of fragrance, reportedly superior to Basmati in aroma
National Database for Emergency Management (NDEM)
- 16 Nov 2025
In News:
The Ministry of Road Transport and Highways (MoRTH) has made it mandatory to incorporate ISRO’s National Database for Emergency Management (NDEM) analysis in all Detailed Project Reports (DPRs) for highway construction. This marks a shift towards geospatially informed, risk-aware infrastructure planning wherein satellite-based decision support systems become integral to national development.
Key Highlights:
- NDEM is a national-level geospatial platform providing real-time, multi-temporal satellite data for disaster preparedness, mitigation, response, and infrastructure planning.
Institutional Architecture
- Developer: National Remote Sensing Centre (NRSC), ISRO
- Guidance: National Disaster Management Authority (NDMA) & Ministry of Home Affairs (MHA)
- Users: Central and State agencies, NDRF, SDRFs, SDMA, infrastructure planners
Core Functionalities
- Multi-hazard mapping (floods, earthquakes, cyclones, landslides, droughts)
- Digital Elevation Models (DEM) for terrain, slope, and drainage
- Land Use / Land Cover (LULC)
- Decision-support tools for emergency response
- Geospatial analytics for risk modelling and vulnerability assessment
Rationale Behind MoRTH’s Mandate
- Addressing Infrastructure Vulnerability: India’s highways traverse diverse geomorphological zones—floodplains, seismic zones, fragile Himalayan slopes - making them prone to natural hazards. NDEM’s geospatial datasets reduce the probability of faulty alignment, slope failure, and drainage mismanagement.
- Enhancing Project Feasibility and Efficiency: The mandate seeks to:
- Reduce field-level uncertainties
- Prevent cost overruns due to unforeseen terrain constraints
- Align infrastructure with long-term climatic and hydrological trends
- Enabling Evidence-Based Governance: By mandating NDEM analysis, MoRTHinstitutionalises:
- Data-driven DPR preparation
- Accountability in route design
- Standardisation of hazard-informed planning
Key Areas Where NDEM Strengthens Highway Planning
- Route Alignment Optimisation: NDEM helps engineers identify:
- Landslide-prone slopes
- Flood-prone lowlands
- Seismic fault lines
- Ecologically sensitive zones
- This enables selection of safer, cost-optimal corridors.
- Improved Engineering Design
- Hazard zonation supports:
- Slope stabilisation design
- Optimum bridge and culvert placement
- Scientific drainage planning
- Protection structures in vulnerable zones
- Social and Environmental Risk Reduction: NDEM layers assist in:
- Avoiding densely populated risk zones
- Minimising displacement and ecological impact
- Strengthening environmental and social screening
- Strengthening Disaster Resilience: In the context of rising climate-driven hazards, NDEM supports planning that ensures:
- Continuity of road networks during disasters
- Reduced damage to assets
- Better deployment of emergency services
DRISHTI System

- 14 Nov 2025
In News:
The DRISHTI System is a new AI-enabled safety and security initiative of Indian Railways, aimed at strengthening freight train operations by addressing a long-standing challenge-detecting unlocked or tampered wagon doors during transit. The system represents a significant step towardstechnology-driven rail logistics and asset security.
What is the DRISHTI System?
- DRISHTI is an AI-based Freight Wagon Locking Monitoring System.
- It has been developed through a collaboration between Northeast Frontier Railway (NFR) and the IIT Guwahati Technology Innovation and Development Foundation (IITG TIDF).
- The system focuses on real-time monitoring of door locking mechanisms on moving freight wagons.
Why was DRISHTI Needed?
- Freight wagons often face security risks due to unlocked or tampered doors, leading to:
- Theft and pilferage
- Safety hazards during train movement
- Traditional manual inspection methods are:
- Time-consuming
- Impractical for long-haul trains
- Ineffective under dynamic, high-speed conditions
DRISHTI provides an automated, continuous, and non-intrusive solution to this problem.
Key Features
- AI-powered cameras and sensors mounted at strategic locations to capture door positions.
- Use of computer vision and machine learning algorithms to:
- Analyse locking conditions
- Detect anomalies or tampering in real time
- Automated alerts generated instantly without disrupting train operations.
- Continuous surveillance during transit, unlike point-based manual checks.
How the System Works
- Cameras capture live visual data of wagon doors.
- AI algorithms process images to determine whether doors are:
- Properly locked
- Unlocked
- Tampered with
- Any abnormality triggers a data-driven alert, enabling swift corrective action.
Benefits and Significance
- Enhances freight security and reduces pilferage.
- Improves wagon sealing integrity and overall rolling stock reliability.
- Minimises human intervention, lowering operational risks and costs.
- Brings greater transparency and technological assurance to freight operations.
- Supports India’s broader push towards digitalisation and indigenous innovation in transport infrastructure.
Ramman Festival

- 06 Nov 2025
In News:
During a special session of the Uttarakhand Assembly, President of India Droupadi Murmu was presented with a traditional Ramman mask, bringing national attention to this centuries-old ritual festival practiced in the Garhwal region.
About the Ramman Festival
- Type: Annual religious and cultural festival
- Location: Twin villages of Saloor–Dungra, Chamoli district, Uttarakhand
- Time: Celebrated in late April during Baisakhi
- Deity: Dedicated to the tutelary deity Bhumiyal Devta, worshipped at his temple courtyard where the festival is performed.
- UNESCO Status: Inscribed in 2009 on UNESCO’s Intangible Cultural Heritage of Humanity list.
UNESCO recognises Ramman as a multiform cultural event integrating theatre, music, historical reconstruction, and oral tradition—reinforcing the community’s identity and relationship with nature.
Key Features of the Festival
1. Rituals, Recitations & Divine Storytelling
- Begins with an invocation to Lord Ganesha, followed by the dance of the Sun God, and enactments of the birth of Brahma and Ganesha.
- Includes performances of Bur Deva, dances of Krishna and Radhika, and multiple ritual acts.
- Central attraction: Enactment of the local Ramkatha (episodes from the Ramayana), sung to 324 beats and steps.
2. Theatrical Performances & Masked Dances
- Combines narration, ritual drama, masked dances, music, and local legends.
- 18 different types of masks made from Bhojpatra (Himalayan birch) are used.
- Masks are accompanied by natural make-up materials such as sheep’s wool, honey, vermilion, wheat flour, oil, turmeric, soot, and plant-based dyes.
3. Instruments Used
- Dhol, Damau (percussion)
- Manjira, Jhanjhar (cymbals)
- Bhankora (trumpet)
4. Sacred Space & Community Participation
- Performed in the courtyard of Bhumiyal Devta temple.
- The entire village contributes—roles are caste-based:
- Brahmins: lead rituals
- Bhandaris (Rajputs): allowed to wear the sacred Narasimha mask
- Das drummers (lower caste): play percussion
- Jagaris/Bhallas (Rajput caste): act as bards singing epics and legends
- Funding and organisation are managed by village households collectively.
5. Transmission of Knowledge
- Oral transmission of epic songs, ritual lore, dance forms, mask-making, and traditional practices from elders to the younger generation.
Origin and Evolution
- Exact origins are unclear but believed to date back to medieval times.
- Linked to the arrival of Vaishnavite saints who brought the Ramayana tradition to the Central Himalayas.
- Initially a purely religious tradition centered on Ram bhakti, later expanded to include local folklore, social narratives, and community histories.
Examples of Local Narrative Additions
- Mwar–Mwarin dance: depicts the hardships of buffalo herders attacked by a tiger.
- Baniya–Baniyain Nritya: portrays the struggles of a trader-couple attacked by robbers.
These stories localise the Ramayana tradition, connecting mythic narratives to regional realities.
Cultural Significance
- Reinforces ties between humans, nature, and the divine.
- Ritual offerings include sprouted maize and barley seeds symbolising prosperity and agricultural abundance.
- Embodies the environmental, spiritual, and cultural ethos of the Garhwal Himalayan communities.
Burevestnik Missile

- 04 Nov 2025
In News:
Russia has announced the successful testing of its Burevestnik nuclear-powered, nuclear-capable cruise missile, significantly escalating global concerns regarding a renewed nuclear arms race. The missile, known in Russia as 9M730 Burevestnik (“Storm Petrel”), is part of a new class of strategic weapons first unveiled in 2018.
About the Burevestnik Missile
- Type: Ground-launched, low-flying cruise missile.
- Capabilities:
- Nuclear-powered propulsion system.
- Nuclear warhead–capable.
- Designed for unlimited range and unpredictable flight trajectory.
- NATO Code Name: SSC-X-9 Skyfall.
- Developer: Russia.
- Introduced: One of six new strategic weapons announced by President Putin in 2018.
Key Features
1. Nuclear Propulsion System
- Powered by a miniaturised nuclear reactor.
- Reactor heats incoming air to generate thrust — replacing traditional chemical fuel.
- Enables theoretically unlimited flight time, constrained only by material durability and guidance systems.
- Offers the ability to loiter for days and strike from unexpected directions.
2. Long Range & Stealth
- Russia claims a test in 2023/2025 achieved:
- 14,000 km travel
- 15 hours of flight
- Low-altitude flight path makes detection by radar extremely difficult.
- Unpredictable trajectory designed to defeat missile defence systems.
3. Strategic Role
- Intended as a second-strike or surprise-attack weapon that can bypass US and NATO missile shields.
- Falls outside current New START definitions, as it is neither an ICBM, SLBM, nor heavy bomber.
Technical Background
- Nuclear-powered missiles were previously explored under the 1960s US Project Pluto (SLAM) but abandoned due to extreme safety risks.
- According to the Nuclear Threat Initiative (NTI), the Burevestnik uses a compact reactor similar in concept to nuclear ramjet technology.
Arms Control Context – New START Treaty
- New START Treaty (effective 2011, extended to 2026) limits deployed strategic nuclear weapons of the US and Russia.
- Russia suspended participation in February 2023.
- The Burevestnik is not restricted under New START, as it represents a new category of strategic cruise missile not covered under existing treaty definitions.
- Russia’s testing signals an attempt to sidestep treaty limits and intensify the nuclear competition.
Exercise 'Poorvi Prachand Prahar

- 04 Nov 2025
In News:
India is set to conduct the tri-service military exercise ‘Poorvi Prachand Prahar’ in the high-altitude terrain of Mechuka, Arunachal Pradesh. The drill represents India’s continued push toward jointness, interoperability, and multi-domain military readiness along the eastern sector.
About the Exercise
- Type: Tri-service exercise involving the Army, Navy, and Air Force.
- Location: Mechuka, a strategically significant forward area in Arunachal Pradesh.
- Nature: Designed as a forward-looking, multi-domain integration exercise.
Objectives
- Enhance warfighting capabilities under realistic operational conditions.
- Promote technological adaptation and the use of emerging platforms.
- Improve interoperability among the three services for integrated operations.
- Strengthen situational awareness and joint command-and-control mechanisms.
- Validate coordinated responses across land, air, and maritime domains.
Key Features
- Employment of:
- Special Forces
- Unmanned systems (UAVs and remote platforms)
- Precision weapon systems
- Networked operations centres
- Execution under rugged, high-altitude, and extreme-climate conditions.
- Testing of revised tactics, techniques, and procedures (TTPs) to improve combat agility and rapid response.
Strategic Importance
- Demonstrates India’s commitment to strengthening joint military preparedness along sensitive border regions.
- Enhances the ability to conduct synchronised, multi-domain operations in future conflicts.
- Integrates modern technologies to support real-time decision-making and network-centric warfare.
Background
‘Poorvi Prachand Prahar’ builds on earlier tri-service drills:
- ‘Bhala Prahar’ – 2023
- ‘Poorvi Prahar’ – 2024
Together, these exercises represent India’s broader drive toward theaterisation, integrated commands, and enhanced mission readiness.
Kerala Declare Free from Extreme Poverty

- 03 Nov 2025
In News:
On Kerala Piravi Day (1 November 2025), Kerala declared itself free from extreme poverty, becoming the first Indian state to achieve this milestone. The achievement is the outcome of a four-year Extreme Poverty Eradication Programme (EPEP) led by the state government and marks a key step toward SDG-1 (No Poverty).
What is Extreme Poverty?
Global Definition
- As per the World Bank’s 2025 revision, extreme poverty refers to living on less than $3/day (2021 PPP).
- Earlier benchmark: $2.15/day (2017 PPP).
- Additional poverty lines:
- Lower-middle-income countries: $4.20/day
- Upper-middle-income countries: $8.30/day
Difference Between Poverty & Extreme Poverty
- Individuals between $3–$4.20/day are poor but not extremely poor.
- Extreme poverty captures severe deprivation in food, health, shelter, and education.
India in the Global Context
- 838 million people lived in extreme poverty globally in 2022 (World Bank).
- In India, extreme poverty fell from 16.2% (2011–12) to 2.3% (2022–23).
- Around 171 million Indians moved out of extreme poverty over the decade.
- Improvements were driven by rising employment, urbanisation, and economic recovery.
- Persistent issues include:
- Youth unemployment: 13.3% (29% among graduates)
- Female labour force participation: 31%
- Informal employment: 77% of non-farm jobs
Measuring Poverty in India – The MPI Framework
NITI Aayog’s Multidimensional Poverty Index (MPI) uses the Alkire–Foster method, covering:
- Health: nutrition, maternal health, child mortality
- Education: years of schooling, attendance
- Living Standards: sanitation, housing, fuel, drinking water, bank accounts, assets
Kerala already had India’s lowest poverty rate (0.7%) in NITI Aayog’s 2021 MPI.
Kerala’s Approach: Extreme Poverty Eradication Programme (EPEP)
Launch & Implementation
- Launched in 2021 under the Local Self-Government Department (LSGD).
- 4 lakh personnel (officials, elected representatives, volunteers) trained for implementation.
- Aimed at family-specific micro-interventions rather than income-only metrics.
Kerala’s Local Definition of Extreme Poverty
Unlike World Bank or MPI, Kerala used four local indicators:
- Food insecurity
- Poor access to healthcare
- Lack of housing
- Absence of income and livelihood security
Identification of Beneficiaries
- Initial survey: 1.18 lakh families identified.
- Verification and migration checks narrowed it to 59,000 families.
- Conducted through a bottom-up, participatory exercise by local bodies.
Key Interventions
- Food and Nutrition Security: 20,600+ families ensured regular meals through Kudumbashree community kitchens and LSGD support.
- Housing for the Homeless: Of 4,677 homeless families, 4,005 received houses under the LIFE Mission.
- Access to Essential Services – Avakasam Athivegam (Rights Fast): Ensured:
- Aadhaar, voter ID
- Bank accounts, social pensions
- MGNREGS job cards
- Electricity & LPG connections
- Micro-Plans for Every Household: Customized plans addressing food, shelter, health, education, and income security.
- Institutional Convergence: Collaboration among local governments, Kudumbashree, health services, and welfare departments.
Significance of the Achievement
- India’s first state to officially eliminate extreme poverty.
- Demonstrates effectiveness of localized targeting, data-driven governance, and micro-level planning.
- Reinforces Kerala’s long-standing strengths in education, health, and social welfare.
- Provides a replicable model aligned with SDG-1 targets.
Alfvén Waves

- 03 Nov 2025
In News:
- A major advancement in solar physics has been achieved with the first direct detection of small-scale torsional Alfvén waves in the Sun’s corona.
- The discovery, enabled by the Daniel K. Inouye Solar Telescope (DKIST) and its Cryogenic Near Infrared Spectropolarimeter (Cryo-NIRSP), provides crucial evidence toward solving a long-standing mystery: why the solar corona is millions of degrees hotter than the Sun’s surface.
Understanding Alfvén Waves
- Alfvén waves are low-frequency, transverse electromagnetic waves that travel along magnetic field lines in a plasma.
- They arise from the interaction between electric currents and magnetic fields within conducting plasma.
- First proposed by Hannes Alfvén (1942), after whom they are named.
- Previously, only large, sporadic Alfvén waves linked to solar flares were observed; detection of subtle, continuous coronal waves had remained elusive.
Solar Heating Problem
- Photosphere temperature: ~5,500°C (10,000°F).
- Coronal temperature: ~1.1 million°C (2 million°F).
- The mechanism by which energy moves from the relatively cooler surface to the super-heated corona has been unclear for decades.
- Proposed contributors include:
- Magnetic reconnection
- Alfvén wave heating
Breakthrough Observations Using DKIST
- DKIST in Hawaii is the world’s largest ground-based solar telescope (4-m mirror).
- Its Cryo-NIRSP instrument enables imaging of coronal plasma motions using Doppler shift signatures.
- Researchers identified distinct red and blue Doppler shifts, confirming twisting, torsional Alfvén waves in the corona.
- These observations provide:
- First direct evidence of small-scale, persistent Alfvén waves.
- Proof that such waves are pervasive across the solar atmosphere.
Significance of the Findings
- Coronal Heating Mechanism
- The study suggests Alfvén waves may supply at least 50% of the energy required to heat the corona.
- Their energy transport is now supported by direct observational data rather than assumptions.
- Role of Magnetic Reconnection
- DKIST findings indicate that magnetic reconnection and Alfvén wave activity frequently occur together. Both mechanisms likely contribute to:
- Coronal heating
- Solar wind acceleration (>1 million mph)
- DKIST findings indicate that magnetic reconnection and Alfvén wave activity frequently occur together. Both mechanisms likely contribute to:
- Scientific and Predictive Implications: Improved understanding of:
- Solar atmospheric dynamics
- Short-term solar wind behaviour
- Long-term stellar evolution
- Enhances ability to forecast solar activity with implications for space weather and planetary environments.
Special Intensive Revision 2025

- 01 Nov 2025
In News:
The Election Commission of India (ECI) has initiated the Special Intensive Revision (SIR) 2025, a large-scale verification exercise aimed at ensuring that India’s electoral rolls remain accurate, inclusive, and up-to-date. Covering twelve States and Union Territories, this marks the most comprehensive revision of voter records in nearly two decades.
Purpose and Objectives
The SIR 2025 is designed to:
- Authenticate voter data to eliminate duplication and ineligible entries.
- Verify citizenship and age to ensure that only eligible Indian citizens remain on the rolls.
- Update demographic information such as addresses and photographs.
- Enhance transparency in the voter registration process and strengthen public trust in electoral institutions.
Through this exercise, the ECI seeks to uphold the Representation of the People Act, 1950, which mandates a clean and credible electoral register as the foundation of free and fair elections.
Implementation and Process
The revision process is being carried out by the Election Commission under the supervision of the Chief Election Commissioner and coordinated at the State and district levels through Chief Electoral Officers (CEOs), District Magistrates (DMs), and Electoral Registration Officers (EROs).
Key stages of the exercise include:
- Enumeration and Data Collection: Field officials known as Booth Level Officers (BLOs) visit households to distribute and collect pre-filled forms containing existing voter details.
Voters may also submit or verify their information online via the ECI’s voter portal. - Verification through Historical Records: Citizens are encouraged to confirm their or a family member’s presence in electoral rolls from earlier intensive revisions (2002–2005). This helps maintain continuity in the voter database and authenticate older registrations.
- Document-Based Scrutiny: In cases where a voter cannot trace prior records, documents proving identity, residence, age, and citizenship are reviewed. This ensures compliance with the Citizenship Act, 1955, particularly for voters born after 1987.
- Draft and Final Roll Publication: Following field verification, draft rolls are published for public inspection and correction. After resolving claims and objections, the final electoral rolls are released, forming the official list for upcoming elections.
Significance of the SIR 2025
- Reviving Electoral Accuracy: This is the first full-scale revision of voter rolls in nearly twenty years, addressing issues like outdated entries, migration, and data mismatches.
- Citizenship Assurance: The verification framework ensures that only legitimate Indian citizens exercise voting rights, strengthening electoral credibility.
- Technological Modernisation: Integration with digital platforms such as the ECI voter portal enhances accessibility and reduces manual errors.
- Transparency and Accountability: The participation of political party representatives as Booth Level Agents (BLAs) provides an additional layer of oversight.
- Foundation for Free and Fair Elections: A verified, inclusive, and error-free voter list is critical to maintaining the integrity of democratic processes and protecting voter rights.
Mission for Aatmanirbharta in Pulses (2025–31)

- 31 Oct 2025
In News:
- India, the world’s largest producer and consumer of pulses, continues to face a structural gap between domestic production and rising demand. Lower productivity levels, yield gaps, and increasing import dependence have highlighted the need for a targeted national strategy.
- To address these concerns, the Government of India has launched the Mission for Aatmanirbharta in Pulses (2025–31)—a six-year initiative aimed at transforming India into a self-reliant pulses-producing nation through scientific, institutional, and market reforms.
Overview of the Mission
Formally launched by the Prime Minister on 11 October 2025, the Mission for Aatmanirbharta in Pulses was first announced in the Union Budget 2024–25. The programme is implemented by the Ministry of Agriculture and Farmers’ Welfare, with collaborative support from NAFED, NCCF, and state governments.
Mission Duration and Financial Outlay
- Implementation period: 2025–26 to 2030–31
- Total outlay: ?11,440 crore
- Targets:
- Raise production by 45%—from 242 lakh MT (2023–24) to 350 lakh MT (2030–31)
- Expand cultivated area by 13%—from 275 lakh ha to 310 lakh ha
- Improve average yield by 28%—from 881 kg/ha to 1,130 kg/ha
Rationale: Current Status and Challenges
India cultivates a wide variety of pulses across agro-climatic zones. Major pulse-growing states include:
- Area (2023–24): Rajasthan (54.67 lakh ha), Madhya Pradesh (51 lakh ha), Maharashtra (44 lakh ha), Uttar Pradesh (30 lakh ha)
- Production (2023–24): Madhya Pradesh (59.74 lakh MT), Maharashtra (40 lakh MT), Rajasthan (33 lakh MT), Uttar Pradesh (31 lakh MT)
Gram dominates both area and output, followed by moong, tur (arhar), urad, and masoor. Over 60% of pulses production occurs during the rabi season.
Despite being the largest pulses producer, India remains dependent on imports from Myanmar, Tanzania, Mozambique, Canada, Australia, among others. Demand is projected to reach 268 lakh MT by 2030 and 293 lakh MT by 2047 (NITI Aayog), far exceeding current production levels. Productivity remains significantly lower than global benchmarks—Canada (2200 kg/ha) and China (1815 kg/ha).
Why Focus on Tur, Urad, and Masoor?
These three pulses account for 34% of total pulses area and contribute significantly to national output. They also exhibit high yield gaps and are crucial for nutritional security. The Mission plans:
- 9 lakh ha expansion in tur—across Karnataka, Maharashtra, Uttar Pradesh, Gujarat, Jharkhand and non-traditional areas like the Northeast.
- Utilisation of rice fallows for expanding urad in Uttar Pradesh, Andhra Pradesh, and Maharashtra.
- Promotion of masoor in rice fallow areas of West Bengal, Bihar, Chhattisgarh.
Key Components and Features of the Mission
1. Development of Climate-Resilient Seeds: Focus on high-yielding, drought-tolerant, pest-resistant, and protein-enriched varieties.
2. Higher Productivity through Technological Adoption
- Enhanced support of ?10,000/ha for Front Line Demonstrations (FLDs) of improved technologies (higher than ?9,000 under NFSM).
- Strengthening post-harvest storage, grading, and processing infrastructure.
3. 100% Assured Procurement
A major innovation in the mission framework:
- NAFED and NCCF will undertake 100% procurement of tur, urad and masoor for four years under PM-AASHA’s Price Support Scheme (PSS).
- Aadhaar-enabled biometric/facial authentication will ensure transparency and eliminate leakages.
4. Cluster-Based Approach
Each cluster will include minimum 10 ha (2 ha in hilly/Northeast region). Cluster selection based on:
- Four-fold district classification: HA-HY, HA-LY, LA-HY, LA-LY
- Rice fallow, rainfed, and watershed areas
- Aspirational districts, border/LWE districts
- Regions under PM Dhan-Dhaanya Krishi Yojana, Adarsh Gram Yojana, and Northeast/Himalayan areas
5. Value-Chain Strengthening: Interventions span input supply, extension, mechanisation, processing, market linkages and digital traceability.
Comparative Advantage over Previous Schemes
The Mission subsumes the pulses component of National Food Security and Nutrition Mission (NFSNM) but provides:
- Higher financial support
- Wider geographical coverage
- Expanded interventions (seed hubs, storage, procurement)
- Stronger digital governance
- Guaranteed procurement for three major pulses
National Significance
- Food and Nutritional Security: Pulses are key protein sources in Indian diets.
- Import Substitution: Reduces dependency on global markets and price volatility.
- Farmer Income Stability: Guaranteed procurement and improved yields boost profitability.
- Climate Resilience: Promotes drought-friendly crops, diversifies cropping patterns, and utilises rice fallows.
- Balanced Regional Development: Targets backward, rainfed, aspirational and border districts.
India–ASEAN Summit 2025

- 31 Oct 2025
In News:
- Prime Minister Narendra Modi virtually addressed the 22nd India–ASEAN Summit in Kuala Lumpur, reaffirming India’s commitment to enhancing cooperation in maritime security, digital inclusion, resilient supply chains, and economic integration.
- During the address, he announced that 2026 will be celebrated as the “ASEAN–India Year of Maritime Cooperation,” reflecting an intensified focus on the Indo-Pacific maritime domain. The remarks aligned with ASEAN’s theme under Malaysia’s chairmanship — “Inclusivity and Sustainability.”
Evolution of India–ASEAN Engagement
India’s engagement with ASEAN has evolved over more than three decades:
- 1992: Sectoral Dialogue Partnership initiated.
- 1996: Upgraded to Full Dialogue Partnership.
- 2002: India began regular participation in ASEAN Summits.
- 2009: ASEAN–India FTA in Goods (AITIGA) came into force;
- 2015: Services and Investment Agreements added.
- 2014 onwards: Transition from “Look East” to Act East Policy, increasing political, cultural and strategic connectivity.
- 2022: Partnership elevated to Comprehensive Strategic Partnership.
The partnership is grounded in shared civilisational links, especially through Buddhism, historical maritime routes, and cultural exchanges dating back to the Gupta and Srivijaya eras.
Recent Summit Highlights: Strategic Messaging
Despite PM Modi’s long-standing practice of physical participation in ASEAN summits, his virtual presence this year was noted as an unusual departure. Given the symbolic importance of leader-level diplomacy in ASEAN's consensus-driven ecosystem, some observers considered his absence a missed opportunity, especially amid strengthening bilateral ties with Malaysia after upgrading relations to a Comprehensive Strategic Partnership.
Nevertheless, PM Modi reaffirmed India’s intent to complement ASEAN’s Community Vision 2045 and India’s national vision of Viksit Bharat 2047, framing both as convergent long-term goals. He highlighted India’s role as a First Responder in regional crises, a position increasingly recognised across Southeast Asia.
Unlike previous years featuring extensive multi-point proposals, the 2025 address emphasised consolidation over expansion, centred primarily on maritime cooperation — a significant signal as the Philippines assumes ASEAN chairmanship in 2026 amid rising maritime tensions in the South China Sea.
Key Pillars of Cooperation
1. Maritime Security & Indo-Pacific Cooperation
- Joint patrols, coordinated naval exercises, and enhanced maritime domain awareness.
- Blue economy initiatives under the ASEAN–India Year of Maritime Cooperation (2026).
2. Economic Integration
- Review of the ASEAN–India Trade in Goods Agreement (AITIGA) to address market access constraints, streamline rules of origin, and reduce non-tariff barriers.
- Policymakers are urged to prioritise long-term regional integration over short-term protectionist anxieties.
3. Digital & Green Economy
- Cooperation in digital public infrastructure, cybersecurity, AI governance, renewable energy, green ports, and climate-resilient supply chains.
4. Connectivity Projects
- Acceleration of India–Myanmar–Thailand Trilateral Highway.
- Progress on the Kaladan Multi-Modal Transit Corridor, strengthening multimodal and economic connectivity.
5. Cultural Diplomacy & People-to-People Links
- ICCR scholarships, academic exchanges, tourism linkages, and the ASEAN–India Network of Think Tanks (AINTT).
- Emphasis on shared civilisational heritage and cultural exchanges.
Initiatives & Institutional Mechanisms
- ASEAN–India Plan of Action (2026–2030) focusing on trade, innovation, food security, agriculture, health, and education.
- India’s ?500 crore ASEAN–India Fund supporting capacity building, agriculture, and connectivity projects.
- Track 1.5 dialogue platforms reveal growing regional acknowledgement of India’s strategic role in Southeast Asia.
Forest Rights Act (FRA), 2006
- 26 Oct 2025
In News:
The Central Government has strongly defended the Forest Rights Act (FRA), 2006 before the Supreme Court, asserting that the law plays a transformative role in restoring the dignity, livelihoods, and cultural identity of India’s forest-dependent communities. The Ministry of Tribal Affairs (MoTA), in its affidavit, has rebutted allegations that the FRA or its 2012 Rules conflict with existing wildlife and forest protection laws.
Background
- The Forest Rights Act was enacted in 2006 to correct historical injustices faced by Scheduled Tribes (STs) and Other Traditional Forest Dwellers (OTFDs), whose rights over forest lands were never formally recorded.
- The Act’s constitutional validity was challenged in 2008 by the NGO Wildlife First, which sought eviction of people whose claims were rejected under the Act.
- In February 2019, the Supreme Court directed states to evict rejected claimants, triggering widespread protests from tribal groups and civil society.
- The MoTA intervened, pointing to procedural lapses in claim verification, leading the Court to stay the eviction order and call for fresh data and review of rejected claims.
Government’s Stand Before the Supreme Court
- The MoTA has upheld both the legal validity and spirit of the Act, clarifying that FRA is not merely about land ownership but about restoring dignity, livelihoods, and cultural identity.
- The Ministry has rebutted claims that FRA undermines wildlife or forest conservation, arguing that the coexistence model has long been practiced by indigenous groups such as the Baiga and Santhal communities.
- The Centre has emphasized that the absence of a sunset clause in the Act is intentional to ensure equity and prevent arbitrary timelines for claim submissions.
- It also highlighted that the Gram Sabha is the final authority in determining forest rights, as reaffirmed by the 2013 Niyamgiri judgment, which upheld the community and cultural rights of the DongriaKondh tribe in Odisha.
Key Provisions of the FRA, 2006
The Act recognises two broad categories of rights:
- Individual Forest Rights (IFR): Ownership and habitation rights for forest land cultivated or occupied by individuals or families.
- Community Forest Rights (CFR): Rights of communities over forest resources, including grazing, fishing, and collection of Minor Forest Produce (MFP) like bamboo, tendu leaves, honey, lac, and wax.
Empowerment of Gram Sabha:
- To identify, verify, and recommend claims for forest rights.
- To manage and protect community forest resources sustainably.
- To regulate access to and trade of MFP, ensuring benefits reach local communities directly.
Government Initiatives Supporting FRA Implementation
- The Minimum Support Price (MSP) scheme for Minor Forest Produce ensures fair value for tribal collectors.
- The Tribal Cooperative Marketing Development Federation (TRIFED) and Van DhanKendras assist tribal communities in value addition and marketing of forest products.
- These mechanisms prevent the monopolisation of forest produce by contractors and enhance economic self-reliance among tribal communities.
Key Issues and Challenges
- Implementation Delays: Many claims remain pending due to administrative inefficiencies and lack of trained personnel at local levels.
- Conflict with Conservation Laws: Overlaps with the Wildlife Protection Act (1972) and Forest Conservation Act (1980) often lead to confusion and litigation.
- Commercialization Risks: Concerns exist over unsupervised extraction of MFP if monitoring is weak.
- Data and Monitoring Gaps: Lack of digitized and transparent claim records has led to disputes and wrongful rejections.
- Integration with Conservation Goals: Balancing livelihood rights with ecological preservation remains a challenge.
Significance of FRA
- Empowers tribal and forest communities by recognizing their traditional rights and promoting participatory forest governance.
- Strengthens decentralized decision-making through Gram Sabhas.
- Promotes poverty reduction and sustainable livelihoods.
- Reinforces constitutional principles, notably:
- Article 21 – Right to Life with dignity.
- Article 46 – Promotion of educational and economic interests of Scheduled Tribes.
- Advances the philosophy of “Conservation through Coexistence”, integrating ecological and social sustainability.
OpenAI Launches AI Browser ‘Atlas’

- 25 Oct 2025
In News:
OpenAI has unveiled ‘Atlas’, its new AI-powered web browser built around ChatGPT, marking a significant step in the evolving generative AI competition and posing a direct challenge to Google Chrome’s dominance. The move comes soon after Perplexity AI introduced its own AI-integrated browser, Comet, underscoring a major transformation in how users interact with the internet.
About Atlas
- Developer:OpenAI
- Nature: AI-integrated web browser built around ChatGPT
- Availability: Currently in preview mode for ChatGPT Plus, Pro, and Business users.
- Design: Atlas removes the traditional address bar, replacing it with a conversational AI interface.
- Key Feature – Agent Mode:
- Enables the browser to autonomously perform searches, analyze sources, and synthesize information into concise summaries.
- Allows users to ask questions in natural language instead of typing web addresses or search keywords.
The browser seamlessly combines web navigation and AI interaction, positioning itself as the next step in AI-mediated online browsing.
Why AI Companies Are Building Browsers
- Control Over User Interface and Data:Browsers act as the gateway to most online activities—search, shopping, finance, entertainment, and social media. Controlling this entry point enables AI companies to own user intent, data, and engagement patterns.
- Monetization Potential:Like Google’s ad-based model, AI browsers can monetize user activity and queries by integrating AI-generated recommendations and sponsored content.
- Integrated AI Experience:AI browsers embed conversational AI tools directly into familiar interfaces, bridging the gap between chatbots and traditional search engines.
- Strategic Advantage:By embedding AI assistants within browsers, companies like OpenAI and Perplexity can reduce dependence on traditional search engines (notably Google), reshaping the competitive dynamics of the internet ecosystem.
How AI Browsers Are Transforming Search
- Traditional Search Model:Relies on keyword-based queries returning multiple hyperlinks for users to navigate.
- AI-Powered Search Model (Atlas & Comet):
- Delivers direct, synthesized, and contextually relevant answers instead of a list of links.
- Suggests related prompts for deeper exploration and learning.
- Adapts to individual user preferences, creating personalized information journeys.
This shift reduces dependence on link-based navigation, potentially disrupting traditional search traffic and publisher visibility models.
Broader Implications
- For Users:
- Offers faster, personalized, and conversational search experiences.
- Transforms passive browsing into interactive discovery.
- For the Digital Ecosystem:
- Challenges Google’s dominance in search and browser markets.
- Raises new debates on data privacy, content attribution, and information accuracy.
- Could reshape digital advertising, as traffic shifts from web pages to AI-generated summaries.
- For the AI Industry:
- Signals a new phase of competition between leading AI firms like OpenAI, Google, and Perplexity.
- Marks a trend towards AI-integrated ecosystems where chatbots, browsers, and search engines converge.
Intrusion Detection System
- 25 Oct 2025
In News:
The Northeast Frontier Railway (NFR) has successfully completed trial works of the Intrusion Detection System (IDS) across four key railway sections in Assam and West Bengal to prevent elephant fatalities due to train collisions.
About the Intrusion Detection System (IDS)
The Intrusion Detection System (IDS) is a cutting-edge initiative of the Northeast Frontier Railway (NFR) under the Ministry of Railways, aimed at protecting wildlife—particularly elephants—while ensuring smooth and efficient railway operations through forested and ecologically sensitive zones.
Objective
- To minimize elephant deaths caused by train collisions along railway lines intersecting elephant corridors.
- To balance operational efficiency with ecological conservation, aligning with India’s broader goals of sustainable infrastructure and biodiversity protection.
Technology and Working
- Technology Used: IDS employsadvanced optical fibre sensing technology installed parallel to railway tracks at a distance of around 10 metres.
- Functioning:
- The system detects vibrations generated by elephant movement near railway tracks.
- These vibrations are captured by sensor cables, which relay the data to a central control room.
- The system then generates real-time alerts for train drivers and control rooms, enabling them to take immediate preventive actions, such as slowing down or halting trains.
This real-time detection mechanism ensures timely intervention and minimizes human-wildlife conflict along railway routes.
Implementation by NFR
The Intrusion Detection System has been successfully implemented in the following pilot sections:
- Madarihat–Nagrakata section (Alipurduar Division)
- Habaipur–Lamsakhang–Patharkhola–Lumding section (Lumding Division)
- Kamakhya–Azara–Mirza section (Rangiya Division)
- Titabar–Mariani–Nakachari section (Tinsukia Division)
- Coverage:The pilot installations collectively span 64.03 km of elephant corridors and 141 km of block sections, marking a significant step in NFR’s ongoing wildlife protection efforts.
Significance
- Wildlife Protection: Helps prevent accidental elephant deaths, promoting coexistence between rail infrastructure and biodiversity.
- Operational Efficiency: Enhances train safety by providing advance alerts, reducing service disruptions.
- Technological Advancement: Demonstrates the integration of AI and fibre-optic sensing in railway operations.
- Environmental Responsibility: Reflects the government’s commitment to sustainable development goals (SDGs), particularly those related to life on land (SDG-15) and industry, innovation and infrastructure (SDG-9).
Central Asian Mammals Initiative
- 24 Oct 2025
In News:
- Representatives from several Central Asian countries — including India — have endorsed a six-year work programme (2021–2026) under the Central Asian Mammals Initiative (CAMI) to identify and conserve priority transboundary regions crucial for the survival of 17 iconic mammal species across the region.
- The meeting was hosted by Uzbekistan, under its presidency of the 14th Conference of the Parties (COP14) to the Convention on the Conservation of Migratory Species of Wild Animals (CMS).
About the Central Asian Mammals Initiative (CAMI)
- Launched: 2014, during CMS COP11 (Quito, Ecuador).
- Objective: To halt and reverse the population decline of migratory mammals across 14 Central Asian countries, through coordinated conservation action.
- Framework: Provides a regional platform for cooperation among Range States to address shared threats such as habitat loss, poaching, migration barriers, and climate change.
Key Features
- Species Covered (17 total):Argali sheep, Asiatic cheetah, Asiatic wild ass, Bukhara deer, Eurasian lynx, Gobi bear, Goitered gazelle, Kiang, Mongolian gazelle, Pallas’s cat, Persian leopard, Przewalski’s horse, Saiga antelope, Snow leopard, Urial, Wild camel, and Wild yak.
- Range States Involved:Bhutan, China, India, Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Mongolia, Nepal, Pakistan, Tajikistan, Turkmenistan, and Uzbekistan; with Iran and the Russian Federation participating online.
- Collaborating Organizations: Over 15 conservation institutions, including IUCN, government agencies, and NGOs, are supporting the work programme’s implementation.
- Current Programme of Work: Adopted for 2021–2026, focuses on ecosystem-based conservation, improved connectivity, and data-sharing between range states.
Recent Meeting Outcomes
- Countries reaffirmed commitment to joint action for migratory mammal conservation, emphasizing that species conservation transcends national borders.
- Success stories shared included recovery trends in Saiga antelope, Bukhara deer, and Persian leopard populations.
- Delegates discussed persistent challenges such as fragmented habitats, climate change impacts, illegal hunting, and limited cross-border coordination.
- Uzbekistan’s Minister of Ecology Aziz Abdukhakimov highlighted the importance of a unified regional approach, stating that “these species know no borders, and neither should our conservation efforts.”
About the Convention on the Conservation of Migratory Species (CMS)
- Also known as: Bonn Convention.
- Established: 1979 in Bonn, Germany.
- Under the Aegis of: United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP).
- Mandate: To promote the conservation and sustainable use of migratory animals and their habitats worldwide.
- Nature: The only global and UN-based intergovernmental treaty exclusively focused on migratory species conservation.
- Instruments:
- Legally binding Agreements
- Non-binding Memoranda of Understanding (MoUs)
- Decision-making Body:Conference of the Parties (COP).
- Next Milestone:CMS COP15 will be held in Brazil (March 23–29, 2026), where the CAMI resolution will be reviewed and updated.
India’s Quantum Breakthrough in Cybersecurity

- 17 Oct 2025
In News:
India has achieved a major milestone in quantum technology and cybersecurity. Researchers at the Raman Research Institute (RRI), Bengaluru, have demonstrated and certified the generation of true random numbers using a general-purpose quantum computer.This breakthrough positions India at the forefront of quantum-secure digital infrastructure, marking a key outcome under the National Quantum Mission.
Why Randomness Matters in Digital Security
- Modern encryption — including banking, digital communication, defence networks and authentication systems — relies on random numbers.These numbers form the basis of encryption keys and secure passwords. The more unpredictable the number, the stronger the security.
Current challenge
- Most systems use pseudorandom numbers, produced through algorithms. While highly complex and secure against classical brute-force attacks, they are not fundamentally random. With the advent of quantum computers, which can process data exponentially faster, many of today’s encryption systems may become vulnerable.
The Need for True Quantum Randomness
- Quantum mechanics provides intrinsic unpredictability. In the microscopic world, particles such as photons do not have definite states until measured — creating true randomness, unlike algorithm-based outputs.
- Quantum Random Number Generators (QRNGs) tap this behaviour.However, a persistent problem has been certifying whether the randomness is genuine or manipulated by device flaws or external interference.
- Cybersecurity demands systems that are not just hard to break, but theoretically impossible to break under known physical laws — making device-independent, quantum-certified randomness essential.
India’s Scientific Breakthrough
The RRI team achieved device-independent quantum random number generation and certification, a frontier area globally.
Key Scientific Contributions
- Utilisation of quantum entanglement and temporal correlations to certify randomness
- Demonstration of violation of Leggett-Garg inequality, confirming true quantum randomness
- Execution on a commercial, general-purpose quantum computer — proving real-world applicability beyond controlled lab environments
Earlier global attempts relied on large-scale entanglement experiments requiring hundreds of metres of physical separation.India’s approach achieves equivalent validation using time-separated measurements on a single particle, making it compact and practical.
Significance of the Breakthrough
Technological Impact
- Enables hack-proof encryption and post-quantum security systems
- First globally-relevant breakthrough under India’s National Quantum Mission
- Demonstrates practical, scalable and noise-tolerant quantum technology
Strategic Implications
- Boosts India’s readiness for quantum cyber warfare and digital sovereignty
- Critical for secure defence networks, financial systems, and government communication
- Promotes indigenous capability in a domain dominated by the US, EU and China
Saksham Counter-Unmanned Aerial Threat Grid System
- 13 Oct 2025
In News:
- The Indian Army has initiated induction and fast-track procurement of “SAKSHAM” (Situational Awareness for Kinetic Soft and Hard Kill Assets Management), an indigenously developed, AI-enabled Counter-Unmanned Aerial System (C-UAS) grid created with Bharat Electronics Limited (BEL).
- Designed as a modular Command & Control (C2) backbone, SAKSHAM provides real-time detection, tracking, identification and neutralisation of hostile drones and other low-altitude aerial threats across the specially defined Tactical Battlefield Space (TBS) or Air Littoral — the airspace up to 3,000 metres (≈10,000 ft) above the ground.
What SAKSHAM is — technical outline
- Purpose: A unified C2 grid to secure ground formations by controlling low-altitude airspace, countering drone surveillance, weaponised UAS and swarms.
- Developer & partners: Designed and developed indigenously by Bharat Electronics Limited (BEL) in collaboration with the Indian Army’s Corps of Air Defence.
- Architecture & connectivity: Operates over the encrypted Army Data Network (ADN) and presents a GIS-based, common recognised air picture that fuses data from C-UAS sensors, friendly and hostile UAS feeds, and both soft- and hard-kill effectors.
- AI & fusion capabilities: Uses AI/ML-driven fusion to automate threat classification (friendly / neutral / hostile), prioritise responses, and support automated or semi-automated soft-kill (jamming/spoofing) and hard-kill (kinetic) decisions.
- Interoperability: Integrates inputs from India’s automated air-defence network Akashteer and is designed for plug-and-play addition of sensors, jammers, lasers/EMP and future upgrades.
Why SAKSHAM was conceptualised
The Army’s operational experience during Operation Sindoor (2025) — where hostile drone activity exposed detection and response gaps — accelerated the need for a comprehensive C-UAS framework and a shift from traditional Tactical Battle Area concepts to the more inclusive Tactical Battlefield Space (TBS) that explicitly includes the Air Littoral. SAKSHAM is a direct response to those operational lessons.
Operational and strategic impact
- Enhanced situational awareness: A common, real-time air picture shortens decision loops and reduces fratricide risk while allowing freedom of manoeuvre for friendly aerial assets.
- Force protection & deterrence: Rapid detection and neutralisation of drone threats protects troops, logistics nodes and infrastructure from ISR (intelligence, surveillance, reconnaissance) and weaponised UAS attacks.
- Atmanirbhar capability: Indigenous design and BEL partnership strengthen defence manufacturing and upgradeability—key to the Army’s Decade of Transformation (2023–2032) and wider strategic autonomy.
- Scalability & integration: FTP approval and modular design aim for rapid rollout across field formations, enabling layered C-UAS coverage and future networked integration with other services and civil air-safety systems.
Nobel Prize in Literature 2025
- 13 Oct 2025
In News:
- The 2025 Nobel Prize in Literature has been conferred on László Krasznahorkai, the Hungarian novelist celebrated for his profoundly philosophical and apocalyptic prose.
- The Swedish Academy recognized him for his ability to capture the “tension between ruin and redemption” and for reaffirming the enduring power of art in an age of crisis.
About the Nobel Prize in Literature
- Established under Alfred Nobel’s will (1895), the Nobel Prize in Literature is awarded annually by the Swedish Academy to an author who has produced “the most outstanding work in an ideal direction.”
- The award, accompanied by a cash prize of 11 million Swedish crowns (≈ USD 1.2 million), represents the highest global recognition in the literary world.
Life and Background
- Born in 1954 in Gyula, Hungary, near the Romanian border, Krasznahorkai grew up amid the tensions of post-war socialism.
- Educated in law and literature in Budapest, his early life in a repressive political climate shaped his preoccupation with decay, faith, and endurance. His Jewish and rural background deepened his sensitivity to questions of identity and moral collapse.
Literary Career and Major Works
Krasznahorkai made his literary debut with Sátántangó (1985), a dark, surreal portrayal of a disintegrating collective farm that has since become a modern classic. Its cinematic adaptation by Béla Tarr as a seven-hour film further cemented its cult status.
His subsequent works expanded his thematic range:
- The Melancholy of Resistance (1989): Explores moral and social decay under authoritarianism in a small Hungarian town.
- War and War (1999): A meditation on history, violence, and transcendence through the story of an archivist.
- Seiobo There Below (2008): Reflects his deep engagement with Asian philosophies and aesthetics, particularly from Japan and China.
- Herscht 07769 (2018): A study of German social unrest and the search for order amid chaos.
Themes and Literary Style
- Krasznahorkai’s fiction fuses metaphysical inquiry with social critique. His narratives depict societies on the brink of collapse, where individuals confront spiritual drift, institutional decay, and existential dread.
- Stylistically, his long, recursive sentences and dense, rhythmic prose challenge readers to engage deeply with the text. His influences range from Franz Kafka and Samuel Beckett to Thomas Bernhard, yet his vision remains uniquely his own — a fusion of absurdism, grotesque realism, and mystical introspection.
International Recognition and Legacy
- Over four decades, Krasznahorkai has emerged as one of Europe’s most formidable literary voices. His earlier accolades include the Kossuth Prize (2004), Hungary’s highest cultural honor, and the Man Booker International Prize (2015).
- His global reach reflects a bridge between Central European existentialism and Eastern contemplative traditions, making his work both regionally grounded and universally resonant.
International Stabilization Force for Gaza (ISF)

- 10 Oct 2025
In News:
In September 2025, U.S. President Donald Trump unveiled a 20-point “Comprehensive Plan to End the Gaza Conflict”, proposing an International Stabilization Force (ISF) to manage post-war Gaza. While both Israel and Hamas accepted the ceasefire and hostage-release obligations, deep divergences persist over Gaza’s future governance, Hamas’s fate, and the legitimacy of the ISF.
What Is the ISF?
The International Stabilization Force for Gaza is a proposed multinational security mission aimed at maintaining internal stability, enabling phased Israeli withdrawal, and overseeing Gaza’s demilitarization.
- Nature: A temporary but long-term security component of a technocratic, apolitical Palestinian Transitional Committee, which will govern Gaza during the interim period.
- Oversight: The ISF will operate under a “Board of Peace” chaired by the U.S. President, rather than the United Nations (UN).
- Composition: To be formed with “Arab and international partners,” but without a UN Security Council (UNSC) mandate—limiting its neutrality and legal legitimacy.
Objectives and Core Functions
- Demilitarization of Gaza:
- Confiscate and destroy Hamas weaponry.
- Prevent smuggling and block the inflow of arms.
- Security and Law Enforcement:
- Maintain order in “terror-free zones” vacated by the Israeli Defense Forces (IDF).
- Set milestones and timelines linked to Israel’s phased withdrawal.
- Capacity Building:Train and professionalize Palestinian law enforcement under international supervision.
- Governance Transition:Facilitate the formation of a reformed Palestinian security apparatus aligned with the transitional governance framework.
- Monitoring and Compliance:Track progress on demilitarization and withdrawal to prevent relapse into conflict.
Absence of a UN Mandate and Legitimacy Concerns
Unlike traditional UN peacekeeping or stabilization missions, which derive legitimacy from UNSC authorization under Chapter VII of the UN Charter, the ISF is designed to operate outside the UN framework.
- The UN’s role in Trump’s plan is restricted to aid distribution, not peacekeeping.
- Arab states have historically resisted deploying troops in Palestine under non-UN command, citing concerns about political bias and lack of legal accountability.
- Consequently, the ISF’s perceived alignment with American and Israeli objectives could undermine its credibility among Palestinians and regional actors.
Precedents and Lessons from Past Stabilization Missions
Previous stabilization forces outside or alongside the UN framework reveal the complexity and risks of such interventions:
- Afghanistan (ISAF, 2001–2021): Initially authorized by the UN and later led by NATO, the mission expanded into combat operations against the Taliban but failed to establish durable peace.
- Lebanon (MNF, 1982–1983): A U.S.-led multinational force, created outside the UN, withdrew after facing intense violence from militias, highlighting the dangers of intervention without broad legitimacy or consent.
These experiences underscore that stabilization without political resolution often leads to mission failure and regional backlash.
Challenges in the Palestinian Context
- Lack of Political Resolution:
- The two-state solution remains unrealized; Israeli occupation continues in parts of Gaza and the West Bank.
- Without a clear political settlement, any international force risks being drawn into hostilities.
- Israeli and Hamas Positions:
- Israel has refused a full withdrawal from Gaza, citing security concerns.
- Hamas has not agreed to complete disarmament or exclusion from the Palestinian political framework.
- These contradictory stances create operational uncertainty for the ISF.
- Arab States’ Reservations:
- Arab governments have called for aUN-mandated protection force, not a U.S.-led stabilization mission.
- An eight-nation Arab-Islamic statement (Sept 30, 2025) demanded Israel’s complete withdrawal, diverging sharply from Washington’s version of the plan.
- Risk of Renewed Armed Resistance:Partial Israeli withdrawal and continued occupation zones could fuel militant activity, increasing the risk of direct confrontation with the ISF.
- Limited Accountability:Absence of UN oversight and clear reporting mechanisms raises concerns over the ISF’s command structure, rules of engagement, and human rights compliance.
Geopolitical and Strategic Implications
- For the U.S.: The ISF signifies Washington’s intent to maintain strategic control over Gaza’s post-conflict order, reducing UN influence.
- For Israel: The arrangement allows for partial demilitarization without ceding full security control—aligning with its domestic political compulsions.
- For Arab States: It poses a dilemma between supporting stability and avoiding association with a potentially occupation-legitimizing force.
- For Palestine: The lack of a fully sovereign and representative governance framework risks perpetuating disenfranchisement and renewed cycles of violence.
Draft Rules for Online Gaming

- 06 Oct 2025
In News:
The Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology (MeitY) has released the draft Promotion and Regulation of Online Gaming Rules, 2025, intended to operationalise the Promotion and Regulation of Online Gaming (PROG) Act, 2025. The government has also invited public feedback on the draft rules till the end of this month via email submission.
Objective
The draft rules aim to establish a comprehensive national framework for regulating the online gaming ecosystem in India. They seek to differentiate legitimate e-sports and social gaming from real money gaming (RMG) platforms, thereby ensuring user protection, transparency, and responsible innovation.
Key Provisions
1. Ban on Real Money Gaming: The Act prohibits real money gaming (RMG) — including online poker, rummy, fantasy sports, and betting — where players wager or stake money for potential returns. Only social games and e-sports, meant for recreation, education, or skill development, are permitted.
2. Establishment of the Online Gaming Authority of India (OGAI): A dedicated regulatory body, the Online Gaming Authority of India (OGAI), will be set up to oversee the sector.
- Composition: A Chairperson and five members representing different ministries.
- Powers: Quasi-judicial authority to summon individuals, examine evidence, and issue binding directions.
- Functions:
- Determine whether a game qualifies as an “online money game.”
- Register and certify online social games and e-sports.
- Impose penalties, suspend or cancel registrations for violations.
- Ensure compliance with ethical and revenue guidelines.
3. Registration Framework
- Mandatory Registration: All social and e-sports games must register with OGAI.
- Validity: Registration certificates will remain valid for up to five years.
- Disclosure Requirements: Companies must declare revenue sources and user protection measures.
- Revenue must originate from advertising, subscriptions, or access fees, not wagers or stakes.
4. Penalties and Offences
- Offering or operating an online money gaming service: up to 3 years’ imprisonment and ?1 crore fine.
- Advertising such platforms: up to 2 years’ imprisonment and ?50 lakh fine.
- Offences are non-bailable, and company officials can be held personally liable.
- Penalty quantum will depend on extent of gain, user loss, and frequency of violation.
5. Grievance Redressal Mechanism (Three-Tiered)
- Internal redressal unit of the gaming company.
- Grievance Appellate Committee (GAC) under the IT Rules, 2021.
- Online Gaming Authority of India (OGAI) as the final appellate body.
6. Role of Various Ministries
- Ministry of Electronics & IT (MeitY): Nodal authority for overall regulation.
- Ministry of Youth Affairs: Oversight of e-sports.
- Ministry of Information & Broadcasting (I&B): Regulation of social games, including issuing codes of practice and classification guidelines.
Radar-Mounted Drones for Surveillance
- 02 Oct 2025
In News:
The Border Security Force (BSF), India’s first line of defence, is collaborating with the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) to develop radar-mounted drones aimed at enhancing surveillance along India’s western and eastern borders. This initiative seeks to strengthen border security by providing persistent, high-accuracy monitoring of remote and difficult terrains without crossing international boundaries.
About Radar-Mounted Drones:
- Technology: Unmanned aerial systems equipped with compact radars capable of detecting moving targets, vehicles, or intruders.
- All-Weather Capability: Operates effectively in fog, darkness, rain, or adverse weather, unlike visual-only sensors.
- Real-Time Alerts: Provides immediate notifications, enabling rapid deployment of troops and timely response to border threats.
- Integrated Sensor Fusion: Potential to combine radar with infrared, high-resolution cameras, and ground sensors for enhanced detection.
- High Mobility and Scalability: Drones can be rapidly deployed in inaccessible areas, and multiple units can cover larger regions during crises.
Significance:
- The system is designed to overcome limitations of conventional border guarding, which relies on mobile soldiers or fixed towers and is effective only in limited areas.
- Radar-equipped drones can provide continuous day-and-night surveillance, monitor regions where permanent radars or outposts cannot be installed, and assist in controlling smuggling or infiltration attempts.
- The BSF, drawing experience from operations like ‘Operation Sindoor’, has also established a School of Drone Warfare at its Tekanpur Academy in Madhya Pradesh. In the coming months, the force plans to manufacture these radar-equipped drones in-house, further enhancing India’s technological edge in border security.
- This initiative exemplifies the growing role of technological interventions in modern border management, ensuring vigilance, rapid response, and comprehensive monitoring of India’s frontier regions.
SPARSH Pension System
- 30 Sep 2025
In News:
The System for Pension Administration – Raksha (SPARSH), an initiative of the Ministry of Defence (MoD), has emerged as a landmark reform in defence pension management. Recently, SPARSH resolved 87% of legacy discrepancies—addressing 5.60 lakh out of 6.43 lakh cases—and has significantly improved grievance redressal efficiency.
About SPARSH Pension System
- Launched by: Ministry of Defence
- Administered by:Defence Accounts Department (DAD) through the Principal Controller of Defence Accounts (Pensions), Prayagraj
- Coverage: Caters to pensioners from the Army, Navy, Air Force, and Defence Civilians
- Scope: Over 31.54 lakh defence pensioners across India and Nepal are onboarded on SPARSH, making it the world’s largest digital pension management system.
Objectives
- To provide a comprehensive, transparent, and paperless system for pension sanction, disbursement, and grievance redressal.
- To ensure direct pension disbursement to beneficiaries without intermediaries.
- To modernize defence pension administration by shifting from a fragmented and manual process to a centralized and integrated digital framework.
Key Features
- Centralized and Web-Based Platform:Handles pension sanction, claim, and disbursement directly into the pensioners’ bank accounts, eliminating third-party intermediaries.
- Self-Service Portal:Enables self-verification, easy data correction, and real-time access to pension details through a personal dashboard.
- Digital Life Certification:Pensioners can complete identification digitally, removing the need for physical visits to pension offices.
- Comprehensive Record Management:Maintains the entire pension lifecycle—from initiation to cessation and transfer to the last eligible beneficiary.
- Grievance Management:Provides an integrated mechanism for service requests and grievance redressal within the same platform.
Significance
SPARSH represents a paradigm shift in defence pension administration—from manual and fragmented systems to a transparent, technology-driven model. It embodies the government’s commitment to “Minimum Government, Maximum Governance”, ensuring efficiency, accountability, and dignity for millions of defence pensioners.
By integrating real-time disbursal, grievance monitoring, and self-service accessibility, SPARSH has strengthened financial inclusion, digital governance, and welfare delivery within India’s defence ecosystem.
L-1 Visa

- 30 Sep 2025
In News:
The U.S. administration’s decision to impose a steep $100,000 fee on new H-1B visa applications has reignited debate over whether the L-1 visa could serve as a practical alternative for Indian professionals. While both facilitate skilled migration, they serve distinct purposes and cater to different categories of workers.
About the L-1 Visa
- Nature and Purpose:
- The L-1 visa is a non-immigrant work visa designed for intra-company transfers within multinational corporations.
- It enables global firms to relocate executives, managers, and employees with specialized knowledge from their overseas branches to U.S. offices.
- Introduced under the Immigration and Nationality Act (1965), it aims to promote international business operations and internal talent mobility without depending on the external labour market.
- Categories:
- L-1A: For executives and managers; maximum stay of 7 years.
- L-1B: For employees with specialized knowledge; maximum stay of 5 years.
Applicants must have worked at least one continuous year abroad for the same company within the preceding three years.
Key Features and Advantages
- No Cap or Lottery: Unlike the H-1B, the L-1 has no annual quota or lottery system, allowing year-round applications.
- Blanket Petitions: Large multinationals can file blanket petitions for quicker processing.
- Dual Intent: L-1 holders can apply for a green card without jeopardizing their visa status.
- Dependent Work Rights: Spouses on L-2 visas can work freely in the U.S., offering significant flexibility for families.
- Corporate Convenience: Firms can manage global mobility efficiently, especially for leadership or niche technical roles.
Limitations and Challenges
- Narrow Eligibility: Only employees of the same multinational company are eligible. The visa cannot be used to switch to another employer in the U.S.
- High Scrutiny: U.S. consulates, especially in India, closely scrutinize “specialized knowledge” claims, leading to higher rejection rates than H-1B visas.
- Time-Bound Stay: L-1 visas have strict duration limits and cannot be extended while awaiting permanent residency.
- No Portability: The visa binds the employee to the sponsoring company, unlike H-1B holders who can change employers under certain conditions.
L-1 vs H-1B: The Key Differences
|
Aspect |
L-1 Visa |
H-1B Visa |
|
Purpose |
Intra-company transfer |
Employment in speciality occupation |
|
Eligibility |
Must have worked abroad for the same company |
Bachelor’s degree in speciality field |
|
Annual Cap |
No cap |
85,000 new visas per year |
|
Employer Flexibility |
Cannot switch companies |
Can change employers (with transfer approval) |
|
Wage Requirement |
No prevailing wage rule |
Must meet U.S. Department of Labor’s wage standards |
|
Processing System |
No lottery |
Lottery-based selection |
|
Dependent Work Rights |
L-2 spouse can work freely |
H-4 spouse requires separate authorization |
|
Maximum Stay |
5–7 years (non-extendable beyond limits) |
6 years (extendable in green card process) |
AI-enabled Centre at Betla National Park
- 27 Sep 2025
In News:
Betla National Park, located in Latehar district, Jharkhand, will soon host India’s first AI-enabled nature experience centre. Part of the Palamu Tiger Reserve (PTR), the park is known for its rich biodiversity, including tigers, elephants, and diverse flora and fauna. PTR is one of the first nine tiger reserves established under Project Tiger (1973), covering a total area of 1,129.93 sq. km, and was notified as a National Park in 1986.
About the AI-Enabled Centre
The centre, developed by Palamu Tiger Reserve authorities under Deputy Director Prajesh Kant Jena, aims to provide visitors with an immersive, high-tech wildlife experience. Unlike conventional nature interpretation centres, it will use cutting-edge technologies to recreate the dynamics of the jungle ecosystem, including:
- AI assistants for guided learning.
- 3D holographic projections to display lifelike animal behaviour.
- Augmented Reality (AR) and immersive sound effects to simulate waterfalls, bird calls, predator-prey interactions, and herd movements.
- Ecosystem simulation, portraying animal movement, food-sharing activities, and other natural behaviours in a realistic manner.
Purpose and Significance
The centre, themed “Threads of Nature,” is designed to convey the interconnection between humans and nature. Key objectives include:
- Enhancing eco-tourism by offering a realistic jungle experience, including sightings of tiger hunts, elephant herds, and lions.
- Promoting conservation awareness through interactive learning and observation tools.
- Supporting researchers and nature enthusiasts with virtual wildlife monitoring capabilities.
Unique Features
While nature interpretation centres have existed in Betla since the 1970s, this facility represents the first high-tech effort in India to integrate AI, AR/VR, holograms, and immersive sound for wildlife education. Visitors will not just see static models or photographs but will experience the sights, sounds, and atmosphere of a living jungle, providing a deeper understanding of ecosystem dynamics.
By merging technology with conservation education, the Betla AI-enabled centre is poised to become a pioneering hub for tourism, research, and ecological awareness in Jharkhand and across India.
Phytosaur fossil
- 27 Sep 2025
In News:
Recent paleontological excavations in Megha village, Fatehgarh subdivision, Jaisalmer district, Rajasthan, have uncovered fossilised remains that may belong to a Phytosaur, a large, extinct semi-aquatic reptile. This discovery has generated significant excitement in the scientific community and reinforces Jaisalmer’s reputation as a paleontological hotspot.
About Phytosaurs
Phytosaurs are extinct reptiles of the order Phytosauria, resembling modern crocodiles, which thrived during the Late Triassic to Early Jurassic period. They displayed morphological diversity, including:
- Long-snouted forms (primarily fish-eating)
- Short-snouted forms (adapted for terrestrial prey)
- High-snouted forms (generalist feeders)
Phytosaur fossils have been reported in India, Europe, North America, Brazil, Morocco, Thailand, and Madagascar, highlighting their wide distribution and evolutionary significance.
Significance of the Find
The Megha village fossil adds to Jaisalmer’s growing list of paleontological finds, which includes dinosaur footprints, shark fossils, and marine remains. Experts suggest that the site may contain additional hidden fossils, which could provide crucial insights into:
- The evolution of prehistoric reptiles
- Convergent evolution with modern crocodilians
- Jurassic-era biodiversity and climate in India
If confirmed as a Phytosaur, the fossil will enhance our understanding of prehistoric fauna in the Indian subcontinent and strengthen the region’s global paleontological significance.
World’s 1st Functioning AI-designed Viral Genome

- 26 Sep 2025
In News:
Scientists at Stanford University and the Arc Institute have created the world’s first artificially designed viral genome using Artificial Intelligence (AI), marking a major milestone in computational biology and synthetic genomics. The breakthrough demonstrates AI’s capability to generate an entirely new and functional virus—one that can infect and kill bacteria.
About the Discovery
The AI-generated virus was designed using a genomic model called Evo, which functions like a “language model” for DNA. Evo was trained on nearly two million viral genomes, learning the patterns and grammar of genetic sequences—akin to how language models learn human syntax and semantics.
The model was guided to mimic the bacteriophage ΦX174 (phi-X-174), a virus that infects E. coli bacteria. This phage was chosen because:
- It has a small yet complex genome (about 5,386 DNA letters and 11 overlapping genes).
- It was the first genome ever sequenced (1977) and the first synthesized from scratch (2003)—now it is the first AI-designed genome.
How It Was Done
- Training the AI: Evo was trained on millions of viral sequences to understand gene order, composition, and regulatory logic.
- Design Phase: Using prompts, Evo generated thousands of potential genome designs.
- Screening & Testing: Researchers filtered these using software checks to ensure each genome contained the necessary genes and functional proteins.
- Lab Validation: Hundreds of genomes were synthesized and inserted into E. coli bacteria. Out of 302 attempts, 16 fully functional viruses emerged.
- Results:
- These viruses contained over 392 mutations never seen in nature.
- Some designs achieved functions human scientists had failed to engineer, such as borrowing DNA-packaging proteins from unrelated viruses.
- Cryo-electron microscopy confirmed the structural integrity of these AI-designed proteins within the viral shell.
What is a Virus?
A virus is a microscopic infectious agent made of nucleic acid (DNA or RNA) enclosed within a protein coat (capsid).
- It cannot replicate independently and must hijack a host cell’s machinery to reproduce.
- Many viruses cause diseases like COVID-19, AIDS, measles, and smallpox.
What is a Genome?
The genome is the complete set of DNA instructions in an organism.
- In humans, it comprises 23 pairs of chromosomes in the nucleus plus mitochondrial DNA.
- It encodes all genetic information required for growth, development, and functioning.
Significance of the Breakthrough
- Redefining Synthetic Biology:The experiment represents a leap from reading and writing genomes to designing them. AI is now capable of generating entirely new, functional genetic blueprints.
- Advancing Phage Therapy:The AI-designed bacteriophages could revolutionize phage therapy—the use of viruses to target and kill antibiotic-resistant bacteria, a major global health threat.
- Accelerating Biotechnology:This development showcases how AI can drastically accelerate genetic innovation, enabling rapid design and testing of new biological entities.
- Proof of Concept for AI-Driven Evolution:AI-generated viruses adapted to bacterial defenses faster than natural ones, indicating potential for directed evolution through computational models.
- Ethical and Regulatory Implications:While promising, the creation of new synthetic organisms underscores the need for global biosafety, biosecurity, and ethical frameworks to govern AI-driven genetic design.
High Seas Treaty of UN Reaches Entry into Force Threshold
- 26 Sep 2025
In News:
- The Biodiversity Beyond National Jurisdiction (BBNJ) Treaty, also known as the UN High Seas Treaty, has crossed the crucial threshold of 60 ratifications, enabling it to enter into force on January 17, 2026. With Morocco and Sierra Leone becoming the 60th and 61st ratifying nations, this milestone marks a historic step in the global conservation of marine biodiversity in international waters.
- So far, 143 countries, including India, have signed the treaty, reflecting strong international consensus on protecting marine ecosystems that lie beyond national boundaries.
About the BBNJ Treaty
- Full Name:Agreement under the United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea on the Conservation and Sustainable Use of Marine Biological Diversity of Areas Beyond National Jurisdiction (BBNJ).
- Parent Framework: Builds upon the UN Convention on the Law of the Sea (UNCLOS), adopted in 1982 and effective since 1994 — often called the “Constitution for the Oceans”.
- Geographical Scope: Applies to areas beyond 200 nautical miles from the Exclusive Economic Zones (EEZs) of coastal nations, commonly referred to as the high seas.
- Coverage: These high seas account for nearly two-thirds of the global ocean and cover over 70% of the Earth’s surface, yet currently, only 1.44% are under any form of protection.
Objectives and Key Provisions
The BBNJ Treaty seeks to conserve and sustainably use marine biodiversity in areas beyond national jurisdiction through legally binding measures. Its major provisions include:
- Creation of Marine Protected Areas (MPAs):
- Aims to designate and manage MPAs in international waters.
- Currently, 6.35% of the ocean is protected, with only 1.89% designated as no-take MPAs, where all extractive activities such as fishing, mining, and drilling are prohibited.
- This aligns with the Kunming-Montreal Global Biodiversity Framework target of protecting 30% of global land and sea areas by 2030 (30x30 goal).
- Equitable Sharing of Marine Genetic Resources (MGRs):
- Establishes mechanisms to ensure fair and equitable distribution of benefits derived from marine genetic resources — biological materials such as microorganisms, plants, and animals with applications in pharmaceuticals and biotechnology.
- Mandatory Environmental Impact Assessments (EIAs):Mandates EIAs for high-impact activities like deep-sea mining, carbon sequestration, and bioprospecting in international waters to mitigate potential ecological harm.
- Scientific Cooperation and Technology Transfer:Encourages capacity building, data sharing, and technology transfer to support developing nations in ocean research and sustainable marine resource management.
Process for the Treaty’s Entry into Force
- Condition: The BBNJ Treaty enters into force 120 days after the deposit of the 60th instrument of ratification, approval, or accession.
- Implementation Date: Given the 60th ratification milestone was achieved in September 2025, the treaty will legally come into effect on January 17, 2026.
- Next Steps:
- Preparatory Commission (PrepCom): Tasked with operationalizing the treaty by establishing scientific and technical bodies, expert qualifications, and procedural frameworks for reviewing MPA proposals.
- First Conference of Parties (COP1): Will convene post-entry into force to initiate formal implementation. Key agenda items include governance mechanisms, financial arrangements, and the Clearing-House Mechanism for information exchange.
India’s Role and Strategic Interests
- India’s Involvement:
- The Union Cabinet approved India’s signing of the BBNJ Treaty in July 2024.
- India is among the 143 signatories, signaling commitment to sustainable ocean governance.
- Strategic Significance for India:
- Enhanced Oceanic Presence: Expands India’s strategic and scientific footprint beyond its Exclusive Economic Zone (EEZ).
- Scientific Research: Facilitates participation in global marine research, access to marine genetic resources, and technological collaboration.
- Alignment with SDG-14: Advances India’s commitment to Sustainable Development Goal 14 – “Life Below Water”, which seeks to conserve and sustainably use ocean resources.
- Diplomatic and Environmental Leadership: Positions India as a responsible stakeholder in global commons management and strengthens its environmental diplomacy credentials.
GST 2.0

- 23 Sep 2025
In News:
The Government of India launched GST 2.0, marking a significant revamp of the Goods and Services Tax framework. Prime Minister Narendra Modi described the initiative as the “GST Bachat Utsav”, highlighting its focus on savings, simplicity, and growth.
Overview
- GST 2.0 represents the most comprehensive reform since the introduction of the Goods and Services Tax in 2017.
- It focuses on rationalising tax rates, reducing compliance burden, and boosting consumption and investment by lowering tax rates on more than 375 items.
Objectives
- Enhance household savings: By cutting rates on essential goods and services, it seeks to leave more disposable income with consumers, thereby stimulating demand.
- Simplify the tax framework: Aligns similar goods under the same slab to minimise disputes and litigation.
- Promote ease of doing business: Reduces procedural complexities and enhances transparency through digital solutions.
Key Features
- Simplified Tax Structure:Moves towards a broad two-slab system—5% (merit rate) and 18% (standard rate)—with a 40% slab for demerit or luxury goods.
- Consumer-Centric Relief:Tax reductions on essential food items, life and health insurance, and beauty and wellness services.
- Technology-Driven Compliance:Introduces digital registration, pre-filled returns, and automated refund systems, including 90% provisional refunds for Integrated Dispute Settlement (IDS) cases.
- Input-Output Correction:Aligns related goods under the same tax bracket to avoid input-output tax mismatches.
- Support for Key Sectors:Rate cuts to encourage investment and growth in textiles, agriculture, construction, and services industries.
Revised Tax Slabs
|
Rate |
Category / Examples |
|
0.25% |
Rough diamonds, precious stones |
|
1.5% |
Cut and polished diamonds |
|
3% |
Precious metals (gold, silver, pearls) |
|
5% |
516 items including food, agricultural machinery, medical devices, hydrogen vehicles, health & life insurance, salons |
|
18% |
640 items including machinery, chemicals, paints, automobile parts, small cars/bikes |
|
40% (Demerit Rate) |
Pan masala, tobacco, aerated beverages, luxury yachts, private aircraft, high-end vehicles |
|
Special Provision |
Bricks remain under dual option — 6% (without ITC) or 12% (with ITC) |
Significance: GST 2.0 is expected to spur demand, enhance compliance, and boost industrial growth, positioning India’s indirect tax system among the most simplified globally.
Brown Trout

- 17 Sep 2025
In News:
- Kashmir is embarking on a significant initiative to revive its brown trout (Salmo trutta) population, a species first introduced to the Valley by the British in 1900.
- Once a hallmark of Kashmir’s cold-water streams and a popular game fish, the brown trout population had declined over decades due to unregulated angling, habitat degradation, and ecological disturbances.
- The Fisheries Department of Jammu & Kashmir plans to reintroduce the species into streams and lakes, aiming to combine conservation with tourism promotion.
About Brown Trout
- The brown trout is a cold-water, salmonid fish native to Europe, northern Africa, and parts of Asia. It prefers cool, well-oxygenated freshwater streams, often residing in crevices between boulders. Typically, individuals grow 15–22 inches in length and weigh 1–5 pounds.
- Brown trout are renowned as a game fish due to their aggressive and elusive nature, which makes angling challenging and rewarding.
- Globally, brown trout have been introduced widely as a game fish, but outside their native range, they are considered one of the world’s worst invasive species.
- In India, their introduction to Kashmir was facilitated by Frank J Mitchel, a British entrepreneur, and earlier attempts during Maharaja Pratap Singh’s era. The fish initially thrived in streams such as Panzagam, Lidder, Bringhi, and Ferozpora, eventually supporting recreational fishing and angling tourism.
Revival Initiative
The current revival project is supported under Pradhan Mantri Matsya Sampada Yojana (PMMSY) and J&K’s Holistic Agricultural Development Programme, enabling the import of 3 lakh pure brown trout eggs from Denmark. These were hatched at the Tchansar Hatchery in Kulgam, marking a milestone as previous efforts primarily focused on rainbow trout for food production rather than wild trout restoration.
Rearing brown trout posed unique challenges:
- They refuse artificial feed, requiring specially formulated diets of crustaceans mixed with cod liver oil.
- They feed in darkness, prompting hatchery modifications to simulate natural conditions and monitor feeding.
The October–November period, coinciding with their breeding season, was chosen for release as brown trout exhibit lower aggression and reduced cannibalism, increasing survival rates. Streams and lakes targeted for reintroduction include Veshav River and Kounsarnag Lake in Kulgam.
Ecological and Socioeconomic Significance
Reintroduction serves multiple purposes:
- Biodiversity restoration: Revives native aquatic fauna and strengthens freshwater ecosystems.
- Tourism enhancement: Brown trout are a draw for anglers, boosting local tourism and allied services.
- Heritage and culture: The initiative reconnects the Valley with a century-old ecological and recreational tradition.
Experts, however, caution that habitat preservation is crucial, emphasizing the need to control illegal riverbed mining and maintain clean, oxygen-rich streams for the trout’s survival.
Conservation Status and Global Context
According to the IUCN Red List, the brown trout is listed as Least Concern, reflecting its wide distribution and adaptability in native ranges. However, localized conservation efforts, such as this reintroduction in Kashmir, are essential to sustain ecologically and economically significant populations in specific regions.
Erra Matti Dibbalu

- 17 Sep 2025
In News:
Andhra Pradesh has taken a major step towards global heritage recognition with the inclusion of Erra Matti Dibbalu (Red Sand Dunes) near Visakhapatnam and the Natural Heritage of Tirumala Hills in the UNESCO Tentative List of World Heritage Sites. The move reflects India’s growing commitment to protect and preserve sites of geological and ecological importance. Being placed on the Tentative List is a mandatory prerequisite for eventual nomination to the UNESCO World Heritage List, symbolizing international acknowledgment of a site’s Outstanding Universal Value (OUV).
Erra Matti Dibbalu: India’s Rare Coastal Geo-Heritage Site
- Located along the coast near Visakhapatnam, Erra Matti Dibbalu—literally “Red Sand Dunes”—is a unique National Geo-heritage Monument, spread over 1,500 acres.
- The formations consist of sand, silt, and clay, with their deep red hue arising from natural oxidation over thousands of years.
- These dunes exhibit badland topography with striking geomorphic features such as gullies, buried channels, paired terraces, beach ridges, wave-cut terraces, knick points, and waterfalls.
- The site represents the late Quaternary geologic age and provides vital evidence of climatic and sea-level fluctuations over millennia. Dendritic drainage patterns and layered sediments at the site act as a natural archive of environmental changes and coastal evolution.
- First recorded in 1886 by British geologist William King, the site is globally rare — with only two similar formations identified, one in Sri Lanka and another in Tamil Nadu (Teri Sands).
- Additionally, archaeological artefacts discovered here point to Upper Palaeolithic human activity (around 20,000 BCE), making it an important cultural and scientific site.
- Recognizing its geological and historical significance, the Geological Survey of India (GSI) declared Erra Matti Dibbalu a National Geo-heritage Monument in 2016. However, experts warn that unregulated tourism and filming activities pose a threat to its fragile ecosystem, calling for stronger conservation and monitoring mechanisms.
- According to IUCN’s Geological World Heritage (2021) classification, the site may qualify under Theme 2: Tectonic System and Theme 7: Coastal System.
Tirumala Hills: A Geological and Ecological Treasure
- The Tirumala Hills in Tirupati district are celebrated not just for spiritual significance but also for their geological, ecological, and cultural heritage.
- The hills showcase the Eparchaean Unconformity—a rare geological boundary where 2.5-billion-year-old Archean rocks meet younger Proterozoic formations of the Cuddapah Supergroup. This boundary represents a vast time gap in Earth’s geological record, offering critical insights into planetary evolution.
- The site also houses the famous Natural Arch (Silathoranam), a naturally sculpted rock formation estimated to be 1.5 billion years old. The region forms part of the Seshachalam Biosphere Reserve and Venkateswara National Park, both home to rich biodiversity including endangered red sanders (Pterocarpus santalinus), Cycas beddomei, and the elusive Jerdon’s Courser.
- With dense forests, seasonal waterfalls, and unique geological formations, Tirumala Hills qualify under multiple UNESCO criteria related to natural beauty, ecological diversity, and geological significance. As per IUCN (2021), the site aligns with Theme 1: History of Planet Earth and Evolution of Life.
Majorana Particles
- 09 Sep 2025
In News:
One of the biggest challenges in quantum computing is decoherence — the tendency of qubits to lose their fragile quantum state due to environmental noise. To address this, scientists are exploring the potential of Majorana particles, exotic entities that are their own antiparticles. Their unique quantum properties may help build topological qubits, inherently resistant to errors, offering a radically new path toward practical quantum computing.
What are Majorana Particles?
- Proposed by: Italian physicist Ettore Majorana in 1937.
- Nature: A hypothetical fermion that is its own antiparticle, unlike electrons or protons which have distinct antimatter counterparts.
- Key Characteristics:
- Neutral in charge, hence elusive in detection.
- Do not annihilate on contact with themselves.
- In condensed-matter systems, they appear as quasiparticles (collective excitations) inside superconductors at ultra-low temperatures.
- Often exist in pairs: two spatially separated halves forming one quantum state.
- Exhibit non-Abelian statistics, meaning that exchanging or “braiding” them changes the overall quantum state in a predictable but unusual way.
Relevance to Quantum Computing
- Problem of Decoherence
- Qubits (quantum bits) exist in superpositions of 0 and 1, but are easily disturbed by external noise.
- Current quantum error correction requires hundreds to thousands of physical qubits to stabilise a single logical qubit, making scaling inefficient.
- Majorana-Based Solution
- Information can be encoded nonlocally across two Majorana modes.
- Disturbance of one half does not collapse the qubit; both must be affected simultaneously, making errors less likely.
- Braiding Majoranas enables topologically protected operations, where outcomes depend only on the braiding pattern and not on experimental imperfections.
- This reduces the need for massive error correction, making quantum hardware simpler and more stable.
- Current Research
- Experiments in superconducting nanowires (e.g., indium antimonide) have shown conductance patterns consistent with Majorana modes.
- However, alternative explanations exist, and conclusive proof requires demonstrating controlled braiding.
Wider Implications
- Quantum Technology: Potential to drastically lower the qubit requirement for large-scale quantum computers.
- Particle Physics: Ongoing efforts to test whether fundamental particles like neutrinos could be Majorana fermions.
- Condensed Matter Physics: Research into Majoranas has advanced material science, superconductors, and nanotechnology.
Challenges
- Experimental signals remain inconclusive, as other phenomena can mimic Majorana-like behaviour.
- Braiding demonstrations in two-dimensional architectures remain technically difficult.
- Majorana-based qubits are still at the proof-of-concept stage, not yet integrated into practical computing systems.
Incentive Scheme to Promote Critical Mineral Recycling

- 08 Sep 2025
In News:
- The Union Cabinet has approved a ?1,500 crore Incentive Scheme to promote critical mineral recycling in India, marking a significant step towards reducing import dependence and ensuring sustainable supply chain resilience.
- The scheme forms part of the broader National Critical Mineral Mission (NCMM), which seeks to build domestic capacity in exploration, mining, acquisition of foreign assets, and recycling of critical minerals.
Key Features of the Scheme
- Tenure: Six years, from FY 2025-26 to FY 2030-31.
- Outlay: ?1,500 crore.
- Eligible Feedstock:
- E-waste
- Lithium-ion battery (LIB) scrap
- Other scrap sources such as catalytic converters from end-of-life vehicles.
- Beneficiaries:
- Large, established recyclers.
- Small/new recyclers and start-ups (allocated one-third of scheme outlay).
- Applicability: Investments in new units, as well as expansion, modernization, or diversification of existing units.
Incentive Structure
- Capex Subsidy:
- 20% subsidy on plant, machinery, equipment, and utilities for projects that commence production within the stipulated timeframe.
- Delays will lead to reduced subsidies.
- Opex Subsidy:
- Linked to incremental sales over FY 2025-26 baseline.
- 40% subsidy in the 2nd year (FY 2026-27).
- 60% subsidy in the 5th year (FY 2030-31), subject to achieving threshold sales.
- Ceilings per Entity:
- Large recyclers – ?50 crore (with ?10 crore cap on Opex subsidy).
- Small recyclers/start-ups – ?25 crore (with ?5 crore cap on Opex subsidy).
- Scope: Incentives are limited to the extraction of critical minerals, not just black mass production.
Expected Outcomes
- Development of 270 kilotons of annual recycling capacity.
- Production of around 40 kilotons of critical minerals annually.
- Mobilization of about ?8,000 crore investment.
- Creation of nearly 70,000 direct and indirect jobs.
Significance
- Strategic Minerals Security: Provides near-term solutions to bridge supply-demand gaps until new mines and foreign acquisitions materialize.
- Circular Economy Boost: Promotes recycling of high-value e-waste and LIB scrap, reducing environmental load.
- Atmanirbhar Bharat: Strengthens domestic industries in electronics, renewable energy, and EV sectors by ensuring reliable access to lithium, cobalt, nickel, and other critical minerals.
- Inclusivity: Special provisions for start-ups and small recyclers to encourage innovation and wider participation.
Matanomadh in Kutch
- 08 Sep 2025
In News:
- A remote village in Gujarat’s Kutch district, Matanomadh, is emerging as a potential analogue site for India’s future Mars missions.
- Researchers from the Space Applications Centre (ISRO), Savitribai Phule Pune University, and the Birbal Sahni Institute of Palaeosciences have confirmed the presence of jarosite, a mineral also discovered on Mars, making the region significant for planetary studies.
Jarosite and Its Relevance
- Composition: Jarosite is a yellow-brown mineral composed of potassium, iron, and sulphate, typically formed in arid, saline environments under extreme geochemical conditions.
- Formation: On Earth, it is linked to volcanic activity, where volcanic ash containing sulphur reacts with water-rich environments.
- Global Occurrence: Rare on Earth; found in Mexico, Canada, Japan, Spain, USA (Utah, California), and in India at Kerala’s Varkala cliffs and now Kutch.
- On Mars: First detected in 2004 by NASA’s Opportunity Rover at Meridiani Planum, jarosite is considered strong evidence of water activity on the red planet.
The Kutch Discovery
- Age: Jarosite deposits at Matanomadh have been dated to around 55 million years ago (Paleocene period).
- Geological Significance: Indicates that environmental and chemical conditions in Kutch millions of years ago resembled those on Mars.
- Current Findings: The mineral occurs as fine deposits mixed with clay. When mixed with water, this clay expands—closely resembling Martian sulphate-clay formations.
Importance for Space Research
- Field Analogue for Mars: The site provides a natural laboratory to test rovers, instruments, drilling, geochemistry, and astrobiology experiments for upcoming missions like Mangalyaan-2.
- Astrobiology Potential: Sulphates such as jarosite can trap organic molecules, offering clues to possible microbial life.
- Palaeo-evolution Insights: Helps decode the geological and chemical history of Mars.
- Complementary Sites: While Ladakh’s Tso Kar Valley (HOPE Mission) simulates Martian living conditions, Kutch offers geological parallels for studying surface mineralogy.
Challenges
- The site is currently waterlogged and threatened by coal mining activities in the vicinity. Scientists have urged that Matanomadh be declared a site of planetary geo-heritage to protect its unique deposits.
Samudrayaan Project

- 02 Sep 2025
In News:
India is set to join a select group of nations—US, Russia, China, Japan, and France—with the capability for manned deep-sea exploration through its ambitious Samudrayaan Project.
As part of preparations, two Indian aquanauts recently dived into the Atlantic Ocean aboard France’s submersible Nautile, gaining critical experiential insights.
The mission is a core component of the Deep Ocean Mission (2021–26), which supports India’s Blue Economy vision and aligns with the UN Decade of Ocean Science for Sustainable Development (2021–30).
Samudrayaan Project
- Objective: To send three humans in a manned submersible to a depth of 6,000 metres by 2027.
- Coordinating agency:National Institute of Ocean Technology (NIOT) under the Ministry of Earth Sciences (MoES), with technical support from ISRO’s Vikram Sarabhai Space Centre (VSSC).
- Budget: Part of the ?4,077 crore Deep Ocean Mission, approved by the Union Cabinet in 2021.
Key Aims
- Develop deep-sea mining technologies, robotics, and underwater vehicles.
- Conduct surveys for mineral deposits, particularly polymetallic nodules (rich in nickel, cobalt, manganese, rare earths).
- Explore deep-sea biodiversity and promote bio-prospecting.
- Establish an ocean climate change advisory service.
- Develop technologies for energy and freshwater from oceans.
- Build an advanced marine station for ocean biology and engineering.
Matsya-6000: The Crewed Submersible
- India’s first self-propelled manned submersible, designed like a fish.
- Built with a titanium alloy sphere (2.1 m diameter, 80 mm thickness) to withstand 600 times atmospheric pressure at 6,000 m depth and temperatures as low as -3°C.
- Capacity: 3 aquanauts for 12-hour missions, extendable to 96 hours in emergencies.
- Equipped with:
- Life-support systems (oxygen supply, CO? scrubbers, re-breather systems).
- Acoustic communication systems (since radio waves cannot penetrate deep water).
- Drop-weight escape mechanism for emergency ascent.
- Li-Po batteries and bio-vests for crew health monitoring.
Challenges in Deep-Sea Exploration
- Extreme Pressure: Precise fabrication (via electron beam welding) is required, as even a 0.2 mm deviation in sphere thickness can lead to collapse.
- Material Constraints: Titanium alloy of required grade is rare, and countries are reluctant to share reserves.
- Life Support: Ensuring safe oxygen levels, CO? absorption, and emergency backup systems.
- Communication: Acoustic telephones must overcome issues of temperature, salinity, and water depth.
- Human Endurance: Aquanauts face restricted mobility, limited nutrition, and confined conditions during 9–12 hour dives.
Deep Ocean Mission (DOM)
- Launched in 2021 for 5 years.
- Components:
- Deep Sea Mining & Manned Submersible: Samudrayaan and mineral exploration.
- Ocean Climate Change Advisory Services: Seasonal to decadal forecasting.
- Deep-Sea Biodiversity Studies: Exploration of flora, fauna, microbes.
- Deep Ocean Surveys: Mapping multi-metal sulphide and PMN sites.
- Energy & Freshwater: Research into Ocean Thermal Energy Conversion (OTEC) and desalination.
- Advanced Marine Station: Capacity building, R&D, and technology incubation.
Recent Progress
- Ocean Mineral Explorer (OMe 6000): Autonomous underwater vehicle deployed in 2022, surveying 14 sq. km in the Central Indian Ocean Basin at depths of 5,271 m, assessing PMN deposits and biodiversity.
- Research vessel SagarNidhi used for exploration and surveys.
Strategic and Economic Significance
- Blue Economy Growth: Supports industries like shipping, fishing, tourism, and biotechnology.
- Resource Security: Access to polymetallic nodules critical for electronics, renewable energy, and defense sectors.
- Geostrategic Edge: Enhances India’s role in the International Seabed Authority (ISA) regime.
- Scientific Advancement: Builds indigenous expertise in ocean engineering and extreme-environment technologies.
- Climate Preparedness: Generates critical data on ocean-climate interactions.
Grid Connected Rooftop Solar Scheme

- 31 Aug 2025
In News:
The Grid Connected Rooftop Solar Scheme was launched by the Government of India to promote clean energy, reduce dependence on fossil fuels such as coal and petroleum, and control pollution. By harnessing solar power through rooftop installations, the scheme provides households, institutions, and commercial entities with access to low-cost, sustainable electricity, while contributing to India’s climate goals.
Solar Rooftop System
- Definition: Installation of solar photovoltaic (SPV) panels on rooftops of residential, commercial, industrial, and institutional buildings.
- Types:
- With Battery Storage – Stores excess solar energy for later use.
- Grid Connected (SPV System) – Converts DC power from solar panels into AC power, which is used for captive consumption and surplus energy is fed into the grid. During low solar generation, the grid compensates for the shortfall.
Objectives of the Programme
- Achieve 40,000 MW capacity by 2022 (target set under the National Solar Mission).
- Central government allocation: ?11,814 crore.
- Phase II incentives:
- Up to 40% subsidy for systems up to 3 kW.
- 20% subsidy for systems between 3–10 kW.
- Increase the role of Distribution Companies (DISCOMs) in promotion and implementation.
Advantages of Grid-Connected Rooftop Solar
- Economic:
- Reduces consumer electricity bills.
- No additional land requirement as panels are roof-mounted.
- Short gestation period compared to large-scale power projects.
- Technical:
- Minimises transmission and distribution losses.
- Reduces congestion and improves voltage at tail ends of distribution lines.
- Environmental:
- Cuts carbon emissions.
- Strengthens long-term energy and environmental security.
Implementation & Nodal Ministry
- Implemented by the Ministry of New and Renewable Energy (MNRE).
- MNRE promotes research, innovation, and global collaboration in renewable energy sectors (solar, wind, hydropower, and biogas).
- Broader goals include:
- Increasing renewable energy share in India’s energy mix.
- Reducing dependence on oil-based energy.
- Supporting clean cooking, heating, and energy equity across regions.
Lunar Module Launch Vehicle (LMLV)
- 29 Aug 2025
In News:
Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) Chairman V Narayanan said the space agency was in the process of building its heaviest rocket ever, and had named it Lunar Module Launch Vehicle (LMLV).
About the LMLV
- A next-generation heavy-lift launch vehicle, planned readiness by 2035.
- Designed specifically for lunar and interplanetary missions.
- Will be India’s most powerful rocket to date.
Specifications
- Payload to Moon: ~27 tonnes.
- Payload to Low Earth Orbit (LEO): ~80 tonnes.
- Propulsion: Advanced cryogenic and semi-cryogenic engines.
- Objective: To enable crewed lunar missions by 2040 and expand India’s capabilities in deep space exploration.
Evolution of India’s Launch Vehicles
- Sounding Rockets (1963): For atmospheric studies; first launch at Thumba, Kerala.
- SLV-3 (1980): Led by A.P.J. Abdul Kalam; placed Rohini satellite in orbit.
- ASLV (1987–94): Limited success; ~150 kg payloads.
- PSLV (1994 onwards): India’s “workhorse” rocket; enabled Chandrayaan-1 (2008), Mangalyaan (2013).
- GSLV (1990s–2010s): Introduced cryogenic engines; ~2,500 kg payload to GTO.
- LVM-3 / GSLV Mk-III (2017): Heaviest operational rocket; ~4,000 kg to GTO; launched Chandrayaan-2 (2019), Chandrayaan-3 (2023).
- LMLV (planned 2035): Will surpass all earlier systems; cornerstone for India’s human spaceflight to the Moon and beyond.
National Tiger Conservation Authority’s Corridor Restriction
- 27 Aug 2025
In News:
The National Tiger Conservation Authority (NTCA), the apex statutory body under the Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change (MoEFCC), has recently issued a clarification restricting the definition of tiger corridors to only the 32 “least cost pathways” identified in 2014 and those recorded in Tiger Conservation Plans (TCPs) of individual reserves. This excludes later studies by the Wildlife Institute of India (WII) (2016, 2021) and data from the All-India Tiger Estimation (AITE) exercises.
What are Tiger Corridors?
Tiger corridors are natural pathways that connect fragmented tiger habitats, allowing for:
- Genetic flow and long-term survival of populations.
- Migration and dispersal between reserves.
- Minimisation of human-wildlife conflict through guided movement.
Projects that require land in or around these corridors or reserves need statutory clearance from the Standing Committee of the National Board for Wildlife (SC-NBWL) under the Wildlife Protection Act, 1972.
About NTCA
- Established: 2005 (through 2006 amendment of Wildlife Protection Act, 1972).
- Chairperson: Union Minister of Environment, Forest and Climate Change.
- Functions:
- Approves TCPs of states.
- Provides financial and technical support for tiger conservation.
- Oversees Project Tiger implementation.
- Conducts All-India Tiger Estimation (AITE) every 4 years.
- Ensures ecological connectivity through corridor protection.
The Recent Controversy
- NTCA had earlier told the Bombay High Court (July 2025) that multiple benchmarks would be used to identify corridors, including:
- Protected areas with tiger occupancy.
- 2014 least-cost pathways.
- WII studies (2016, 2021).
- AITE distribution data.
- However, in its latest clarification, NTCA restricted corridors only to 2014 least-cost pathways and TCP records, ignoring updated scientific models.
Potential Beneficiaries
Industrial projects, particularly in Maharashtra, such as:
- Western Coalfields Limited’s Durgapur open cast mines.
- Lloyds Metals & Energy’s Surajgarh iron ore mines in Gadchiroli.
Scientific Concerns
- 2014 NTCA Report itself noted that its corridors were “minimal requirement” and alternative connectivities also needed conservation.
- Newer studies (e.g., Circuitscape modelling, 2025) suggest at least 192 corridors across 10 central Indian states, far beyond the restricted 32.
- Narrowing protection risks fragmentation of habitats, reducing gene flow and increasing chances of local extinctions.
RBI Discussion Paper on Inflation Targeting
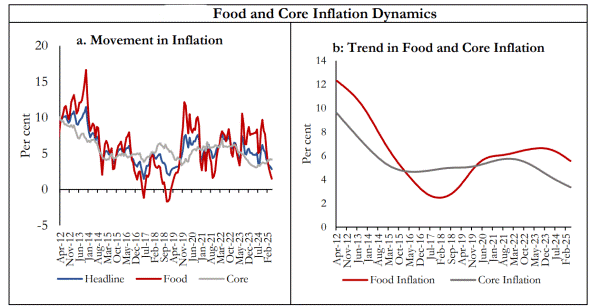
- 27 Aug 2025
In News:
The Reserve Bank of India (RBI), in August 2025, released its discussion paper on reviewing India’s Flexible Inflation Targeting (FIT) framework, which is due for renewal in March 2026. The paper seeks public feedback on key questions such as whether the 4% target remains optimal, whether the 2–6% tolerance band should be revised, and whether the target should be expressed as a point or only a range.
Evolution of the Framework
- Adopted in 2016, the FIT framework formalised inflation targeting in India.
- Current mandate: 4% CPI-based inflation target with a tolerance band of 2–6%, jointly set by the RBI and the Government of India.
- Review cycle: Every five years, with the next mandate to begin April 2026.
Rationale for Retaining the 4% Target
- Credibility with Investors: Raising the target above 4% could be perceived as policy dilution, eroding credibility. Rating agencies like S&P Global recently upgraded India’s rating (BBB), citing the RBI’s strong inflation management.
- Institutional Stability: The framework has strengthened the Monetary Policy Committee (MPC) process and fiscal discipline.
- Domestic Outcomes: Headline CPI inflation has mostly remained within the 2–6% band. In July 2025, it hit 1.55%, the second-lowest since the series began.
- External Balance: Low and stable inflation safeguards the rupee, maintains external competitiveness, and prevents capital outflows.
Headline vs Core Inflation Debate
- Economic Survey 2023–24: Suggested targeting core inflation (excluding food and fuel) as food inflation is largely supply-driven and beyond monetary control.
- RBI’s View: Headline CPI should remain the target, as persistent food shocks spill over into wages, rents, and production costs, influencing core inflation.
- Global Norm: Nearly all inflation-targeting countries focus on headline CPI; Uganda is the only exception.
- Indian Context: Food has ~50% weight in CPI. Excluding it would undermine policy relevance for households and workers.
Key Issues Under Review
- Target Level: Lowering below 4% could hurt growth; raising above 4% risks credibility loss.
- Tolerance Band: Debate on retaining the 2–6% range, narrowing it, or removing it. While a band allows flexibility, it may reduce accountability.
- Inflation Volatility: Between 2014–2025, headline CPI ranged from 1.5% to 8.6%, mainly due to food prices, while core inflation remained relatively stable.
Positive Outcomes of the Framework
- Anchored Expectations: Households and firms now base decisions around a credible 4% anchor, reducing uncertainty.
- Investor Confidence: Predictable inflation management has lowered risk premiums on Indian assets, boosting FDI and portfolio inflows.
- Improved Sovereign Ratings: Low inflation stability has supported fiscal credibility, earning global recognition.
- Resilience to Shocks: Despite global supply disruptions and oil price volatility, India avoided runaway inflation.
Mercator Projection Map
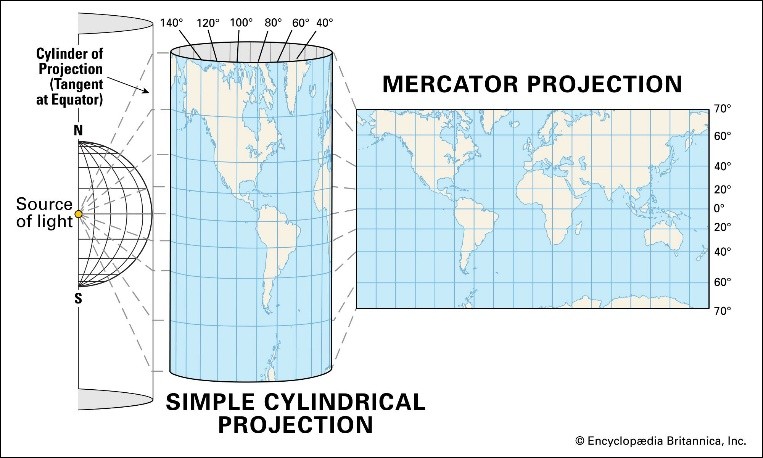
- 27 Aug 2025
In News:
The African Union (AU) has endorsed the “Correct the Map”campaign, calling for the replacement of the Mercator projection with modern alternatives that represent Africa’s true size. This move is not just cartographic—it is deeply political, tied to questions of historical justice, cultural representation, and global perception.
The Mercator Projection: Origins and Features
- Introduced: 1569 by Gerardus Mercator, a Flemish mathematician and cartographer.
- Purpose: Designed for navigation, enabling sailors to follow a straight line of constant compass bearing (Rhumb lines/loxodromes).
- Structure:
- Meridians (longitude): parallel, vertical, equally spaced.
- Parallels (latitude): horizontal, spacing increases away from the equator.
- Grid forms right angles.
- Strengths: Conformal projection that preserves shapes and angles, ideal for maritime exploration.
- Limitations: Distorts area and scale. True scale exists only along the equator; distortion grows near the poles.
Distortions and Bias
- Africa & South America appear much smaller than their real size.
- Europe, North America, and Greenland are disproportionately enlarged.
- Example: Greenland (≈2.1 million sq km) appears similar in size to Africa (≈30 million sq km).
- Such distortions fed into Eurocentric worldviews, reinforcing colonial narratives of Africa as “smaller” and “conquerable.”
Corrective Measures
- Gall-Peters Projection (1970s): Area-accurate but distorts shapes. Adopted in some schools, e.g., Boston (2017).
- Equal Earth Projection (2018): Balances shape and area, providing a fairer representation of continents.
- AU’s Endorsement: By backing the Equal Earth projection, the AU aims to restore “Africa’s rightful place on the global stage,” highlighting the continent’s true scale and importance.
SarvottamYudhSeva Medals
- 24 Aug 2025
In News:
On the eve of the 79th Independence Day, President DroupadiMurmu approved the awarding of seven SarvottamYudhSeva Medals (SYSM), the nation’s highest wartime distinguished service honour, to the leaders of Operation Sindoor, marking the first such awards since the Kargil War.
About the SarvottamYudhSeva Medal:
- Institution: 26 June 1980, to recognise distinguished service of the highest order during war, conflict, or hostilities.
- Eligibility: All ranks of the Army, Navy, Air Force, including Territorial Army Units, Auxiliary and Reserve Forces, and lawfully constituted Armed Forces when embodied. Nursing officers and members of the Nursing Services are also eligible. Awards can be given posthumously.
- Design: Circular medal, 35 mm in diameter, gold gilt, with the State Emblem and inscription “SARVOTTAM YUDH SEVA MEDAL” on the obverse, and a five-pointed star on the reverse. The ribbon is golden with a red vertical stripe in the centre. Subsequent awards are recognised by a Bar on the ribbon with a miniature insignia.
- Significance: Considered the wartime equivalent of the Param VishishtSeva Medal (PVSM) for exceptional service in peacetime. Previously awarded to three officers for Kargil War leadership: Lt Gen Amarjit Singh Kalkat, Air Marshal Vinod Patney, and Lt Gen Hari Mohan Khanna.
First removable Solar Panel System between tracks

- 22 Aug 2025
In News:
Indian Railways has taken a major step towards achieving its net-zero carbon emission target by 2030 with the commissioning of India’s first removable solar panel system between railway tracks at Banaras Locomotive Works (BLW), Varanasi in August 2025.
About the Project
- Length of Installation: 70 metres
- Number of Panels: 28 removable panels
- Capacity: 15 KWp (Power density: 240 KWp/km; Energy density: 960 units/km/day)
- Special Feature: Panels are removable, enabling easy maintenance, emergency clearance, and seasonal adaptation.
- Design: Indigenously developed to be installed between tracks without disrupting rail traffic.
Technical Specifications of Panels
- Dimensions: 2278 mm × 1133 mm × 30 mm
- Weight: 31.83 kg per panel
- Type: 144 half-cut mono crystalline PERC bifacial collar cells (multi-bus bar)
- Efficiency: 20.15%
- Maximum Voltage: 1500V; Open Circuit Voltage (Voc): 49.71V
Significance
- Green Energy Transition: Promotes sustainable transport by reducing dependency on fossil fuels and cutting carbon footprint.
- Innovative Space Utilisation: Uses the space between tracks, avoiding land acquisition. Potential estimated at 3.5 lakh units/year/km of track. With IR’s 1.2 lakh km track length, the scalability is massive.
- Economic Efficiency: Supports auxiliary energy needs of railway units, lowering operational costs.
- Replicability: Being a pilot project, it serves as a model for adoption across Indian Railways.
Other Recent Railway Developments
- Green Logistics: In August 2025, the first salt-loaded freight rake from Sanosara (Bhuj–Naliya section) to Dahej carried 3,851.2 tonnes of industrial salt over 673.57 km, generating ?31.69 lakh in freight revenue. This initiative boosts regional industry and expands rail freight solutions.
- Electrification Innovation: Western Railway commissioned the country’s first 2×25 kV Electric Traction System at the Nagda–Khachrod section (Ratlam Division). Powered by two Scott-connected 100 MVA transformers, it enhances efficiency in overhead equipment (OHE) supply, marking a leap in electrification infrastructure.
Broader Context
- Indian Railways is rapidly expanding its solar adoption strategy, aligning with the National Solar Mission and Sustainable Development Goal (SDG-7: Affordable and Clean Energy).
- This innovation aligns with India’s climate commitments under the Paris Agreement and helps advance the country’s energy transition pathway.
India Semiconductor Mission
- 20 Aug 2025
In News:
The Union Cabinet has cleared four new semiconductor manufacturing projects worth ?4,600 crore in Odisha, Punjab, and Andhra Pradesh under the India Semiconductor Mission (ISM). With this, the total number of approved projects under ISM has reached ten across six states, attracting cumulative investments of nearly ?1.60 lakh crore.
Details of Newly Approved Units
- SiCSem Pvt. Ltd. (Odisha):
- In partnership with UK-based Clas-SiC Wafer Fab Ltd.
- India’s first commercial compound semiconductor fabrication unit focused on Silicon Carbide (SiC) devices.
- Capacity: 60,000 wafers and 96 million packaged units annually.
- 3D Glass Solutions Inc. (Odisha):
- Will establish a vertically integrated packaging and embedded glass substrate unit.
- Focus: 3D Heterogeneous Integration modules.
- ASIP Technologies (Andhra Pradesh):
- Joint venture with APACT Co. Ltd., South Korea.
- Annual capacity: 96 million units.
- Applications: Mobile phones, set-top boxes, automobiles, and other electronic devices.
- Continental Device India Pvt. Ltd. (Punjab):
- Brownfield expansion of its Mohali facility.
- Focus: High-power discrete devices – MOSFETs, IGBTs, Schottky diodes, and transistors (using both silicon and SiC).
- Capacity: 158.38 million units annually.
Production from these units is expected to commence within the next 2–3 years.
Progress under ISM
- Launch Year: 2021
- Nodal Ministry: Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology (MeitY)
- Objective: Establish a self-reliant semiconductor and display ecosystem in India.
- Support: Incentive package of ?75,000 crore for fabs, ATMP/OSAT, compound semiconductor plants, and display fabs.
- Capacity Building: Target to train 60,000+ skilled professionals.
- Strategic Significance: Reduce import dependency, boost Atmanirbhar Bharat, and make India a global semiconductor hub.
Major Ongoing Projects under ISM
- Tata-PSMC Fab (Dholera, Gujarat): ?91,526 crore investment; capacity of 50,000 wafers/month for automotive and AI; operational by 2026.
- Micron ATMP (Sanand, Gujarat): ?22,900 crore investment; focus on DRAM and NAND packaging; expected by late 2025.
- Tata TSAT OSAT (Jagiroad, Assam): Output of 48 million chips/day.
- Kaynes OSAT (Sanand, Gujarat): Capacity of 6 million chips/day for telecom and industrial use.
- HCL–Foxconn JV (Uttar Pradesh): To produce 36 million display driver chips/month by 2027.
SabhaSaar
- 19 Aug 2025
In News:
The Government of India is set to launch ‘SabhaSaar’, an Artificial Intelligence (AI)-based tool designed to automatically generate structured minutes of gram sabha meetings, thereby enhancing transparency, uniformity, and efficiency in local governance. The tool will be first rolled out in Tripura on Independence Day (August 15) and later extended to other states.
What is SabhaSaar?
- Gram Sabha: It is the primary body of the Panchayati Raj system, consisting of all registered voters of a gram panchayat. Gram sabhas are mandated to meet at least four times a year (January 26, May 1, August 15, and October 2).
- SabhaSaar: An AI tool that converts audio and video recordings of gram sabha meetings into structured minutes, ensuring uniformity across the country.
- Access: Panchayat officials can upload recordings using their e-GramSwaraj login credentials.
Key Features
- AI-driven transcription &summarisation: Generates transcripts, translates into the chosen language, and prepares concise summaries.
- Language inclusivity: Built on Bhashini, the government’s AI-powered language platform, it supports transcription in all major Indian languages (Hindi, Bengali, Tamil, Telugu, Marathi, Gujarati) and English.
- Standardisation: Ensures uniformity of gram sabha documentation nationwide.
- Ease of governance: Facilitates instant access to insights for panchayats, administrative bodies, and rural development projects.
Associated Reforms for Gram Sabhas
- Panchayat NIRNAY Portal: A real-time monitoring system for gram sabha meetings, enabling scheduling, agenda notification to citizens, decision tracking, and transparency in implementation.
- Recent progress: In 2024–25, more than 10,000 gramsabha meetings were held through the NIRNAY platform, with Punjab, Andhra Pradesh, Telangana, and Bihar leading in usage.
Significance
- Governance efficiency: Automates and digitises record-keeping, reducing errors and delays.
- Transparency & accountability: Ensures that decisions of gram sabhas are properly recorded and accessible.
- Public participation: Facilitates better citizen awareness and engagement in local governance.
- Bridging digital divide: Through Bhashini, makes governance accessible across linguistic barriers.
Orbiting Carbon Observatories (OCO)Program

- 17 Aug 2025
In News:
The Trump administration has proposed terminating NASA’s Orbiting Carbon Observatories (OCO) program, a key initiative monitoring global carbon dioxide (CO?) emissions and plant health. The move, part of the 2026 federal budget, has triggered concerns among scientists and lawmakers given its implications for climate monitoring and policy.
About the Orbiting Carbon Observatories (OCO) Program
- Objective: Dedicated Earth remote-sensing satellites designed to observe atmospheric CO? and study its role in climate change.
- Timeline:
- OCO-1 (2009): Failed shortly after launch.
- OCO-2 (2014): Successfully launched, providing high-precision global CO? data.
- OCO-3 (2019): Installed on the International Space Station (ISS) to enhance observations.
- Significance:
- Produced high-resolution maps of plant growth, drought stress, and carbon fluxes.
- Helped discover that the Amazon rainforest emits more CO? than it absorbs, while boreal forests in Canada and Russia are turning into unexpected carbon sinks.
- Tracked photosynthesis rates to forecast crop yields, drought conditions, and food shortages—data crucial for global food security and preventing civil unrest.
- Utilized by the US Department of Agriculture and private agricultural firms for crop yield predictions and rangeland management.
Reasons for Proposed Termination
- The administration claims the missions are “beyond their prime mission” and need to align with new budgetary priorities.
- Funding for OCO missions is excluded from the proposed 2026 budget.
International dimension:
-
- Scientists are exploring partnerships with Japan and Europe to keep OCO-3 operational on the ISS.
- Private or philanthropic funding is also being considered, though experts warn this is unsustainable.
Operation Falcon and Rhino Conservation in Assam
- 14 Aug 2025
In News:
The Assam government has achieved major success in protecting the greater one-horned rhinoceros through Operation Falcon, a joint initiative of the Assam Police and Forest Department launched in 2024. The operation was initiated after the killing of two rhinos prompted a shift in anti-poaching strategy.
Key Outcomes
- 42 poachers arrested across districts including Biswanath (18), Darrang (8), Nagaon (6), Karbi Anglong (5), Sonitpur (2), and one each in Udalguri, Dibrugarh, and Cachar.
- Six major poaching gangs with links to illegal trade through Myanmar dismantled.
- Nine poaching attempts foiled using digital and on-ground intelligence.
- Zero rhino killings reported in 2025 so far.
Conservation Impact
- Rhino poaching in Assam has dropped by 86% since 2016, when the BJP came to power.
- Annual data shows steady decline: one rhino killed in 2021, none in 2022, one in 2023, two in 2024, and none so far in 2025.
- Enhanced coordination, intelligence-driven operations, and rapid response mechanisms have been key factors.
About Assam’s Rhinos (Census 2022)
- Total Rhinos: 2,895 in Assam.
- Distribution:
- Kaziranga National Park & Tiger Reserve – 2,613 (largest habitat, ~1,300 sq km).
- Orang National Park & Tiger Reserve – 125.
- Pobitora Wildlife Sanctuary – 107.
- Manas National Park & Tiger Reserve – 50.
Significance of Operation Falcon
- Biodiversity Protection: Safeguards the greater one-horned rhino, listed as Vulnerable on the IUCN Red List.
- International Recognition: Strengthens India’s image in global wildlife conservation.
- Eco-Tourism Boost: Ensures safety in parks like Kaziranga, enhancing Assam’s tourism appeal.
Sukhna Lake
- 14 Aug 2025
In News:
The Chandigarh Administration recently closed the floodgate of Sukhna Lake after water levels receded from the near-danger mark.
About Sukhna Lake
- Type: Artificial, rain-fed lake at the foothills of the Shivalik Hills, Chandigarh.
- Creation: Built in 1958 by damming the Sukhna Choe, a seasonal stream.
- Size: Originally 188 ha (now ~150 ha); length 1.52 km, width 1.49 km.
- Depth: Originally 18 ft, reduced to ~8.5 ft due to siltation.
- Ecological Importance:
- Declared a National Wetland by the Government of India.
- Habitat for ~30 species of resident and migratory birds, including Siberian ducks, storks, and cranes.
- Part of Sukhna Wildlife Sanctuary.
- Recreational Importance:
- Longest channel for rowing and yachting events in Asia.
- Surrounded by Nek Chand’s Rock Garden (west) and a golf course (south).
Rhisotope Project

- 12 Aug 2025
In News:
South Africa, which shelters the world’s largest rhino population, has lost over 10,000 rhinos in the last decade to poaching driven by the illegal horn trade in Asian markets. To counter this crisis, the University of the Witwatersrand, in collaboration with the International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA), has launched the Rhisotope Project (2024) — a novel initiative using radioactive isotopes to protect rhinos.
What is the Rhisotope Project?
- A non-invasive procedure where rhino horns are injected with low doses of radioisotopes.
- The process is harmless to rhinos but makes horns:
- Detectable through Radiation Portal Monitors (RPMs) and scanners at borders, ports, and airports — even in sealed shipping containers.
- Toxic and unfit for human use, reducing demand in illegal trade.
- Pilot studies (2024–25):
- 20 rhinos in the Waterberg Biosphere Reserve were treated.
- Tests by Ghent University (Belgium) showed no cellular damage or health impact.
- 3D-printed horns used in trials confirmed detectability in container loads.
Why Radioisotopes?
- Radioisotopes are unstable forms of elements that emit ionising radiation (alpha, beta, gamma) to achieve stability.
- They are easily traceable with nuclear detection systems.
- Already widely used in medicine (I-131 for thyroid, Tc-99m for imaging), archaeology (C-14 dating), and industry.
The Scale of the Crisis
- Global rhino numbers: Declined from ~5,00,000 in the early 20th century to ~27,000 today (IUCN).
- South Africa: Lost 103 rhinos to poaching in the first quarter of 2025 alone.
- Conventional measures like dehorning reduce poaching but disrupt rhino social behaviour and habitat use. The Rhisotope Project offers a less disruptive alternative.
Broader Conservation Significance
- If successful, the method could be extended to other endangered species like elephants and pangolins.
- It represents an international collaboration that combines nuclear science with wildlife conservation, redefining the role of technology in biodiversity protection.
Threats Beyond Poaching
- Invasive species: Plants like Parthenium threaten habitats (e.g., Assam’s Pobitora Wildlife Sanctuary, home to the densest one-horned rhino population).
- Climate change: Intensified droughts and monsoons push rhinos into human-dominated landscapes, increasing conflicts.
- Habitat loss due to agricultural expansion and human settlement.
Rhino Conservation Initiatives
- Global/Regional:
- New Delhi Declaration on Asian Rhinos (2019)
- DNA Profiling of all Rhinos for tracking and protection
- India-specific:
- National Rhino Conservation Strategy
- Indian Rhino Vision 2020 (for Assam’s one-horned rhinos)
About the IAEA
- Established in 1957 as the UN’s “Atoms for Peace”organisation.
- Promotes peaceful applications of nuclear technology while preventing misuse for weapons.
- 178 member states; India is a founding member.
- Awarded the 2005 Nobel Peace Prize for contributions to nuclear safety and disarmament.
- HQ: Vienna, Austria. Reports to both UNGA and UNSC.
Diabetes in India
- 11 Aug 2025
In News:
A Lancet Global Health study (2023), based on the Longitudinal Aging Study in India (LASI), has highlighted the alarming rise of diabetes among Indians aged 45 years and above. The findings underscore the urgent need for universal screening, awareness, and improved management strategies to address this public health challenge.
Key Findings of the Study
- Prevalence: One in five Indians aged 45+ (approx. 20%) had diabetes in 2019.
- Undiagnosed Diabetes: Nearly 40% of people with diabetes were unaware of their condition—around 20 million Indians remain undiagnosed.
- Treatment Gaps:
- 5% had untreated diabetes.
- 47% were under-treated.
- Only 36% were adequately treated.
- Awareness and Treatment: Once aware, 94% of patients sought treatment, highlighting the impact of diagnosis.
- Control Rates:
- 46% achieved blood sugar control,
- 59% achieved blood pressure control,
- 6% used lipid-lowering medicines.
- Urban-Rural Divide: Urban prevalence (30%) was nearly double that of rural areas (15%).
- Gender Gap: Prevalence was similar in men (19.6%) and women (20.1%).
- Regional Trends:
- Highest rates: Chandigarh (36.9%), Kerala (36%), Puducherry (36%).
- Largest number of diabetics: Tamil Nadu (6.1 mn), Maharashtra (5.8 mn), Uttar Pradesh (4.7 mn).
- Methodology: Diagnosis based on HbA1c testing (3-month blood sugar average), more accurate than random glucose tests used in earlier surveys.
Understanding Diabetes
- Type 1: Autoimmune; body destroys insulin-producing cells. Requires lifelong insulin.
- Type 2: Accounts for 95%+ of cases; due to insulin resistance or inadequate production; linked to obesity, sedentary lifestyle, and genetics. Preventable via lifestyle changes.
- Gestational Diabetes: Occurs during pregnancy; increases risk of complications and later Type 2 diabetes.
- Type 5 (Newly Recognized): Seen in lean adolescents (BMI < 18.5 kg/m²); caused by malnutrition damaging pancreatic beta cells, leading to insulin deficiency.
India’s Policy and Programmatic Response
- Ayushman Arogya Mandirs (Health and Wellness Centres): Provide population-based diabetes screening.
- Fit India Movement: Encourages preventive health and fitness practices.
- School Interventions: CBSE mandates ‘sugar boards’ to educate students about hidden sugars and health risks.
- National Programme for Prevention and Control of Cancer, Diabetes, Cardiovascular Diseases and Stroke (NPCDCS): Strengthens NCD screening and management across primary healthcare.
Framework Agreement

- 07 Aug 2025
In News:
The Framework Agreement (FA), signed on 3rd August 2015 between the Government of India and the National Socialist Council of Nagalim–Isak-Muivah (NSCN-IM), remains a central element in the ongoing Naga peace process. Its 10th anniversary (2025) witnessed renewed debates over its sanctity and future.
Background
- The Indo-Naga conflict has persisted for over six decades, rooted in demands for sovereignty and recognition of the Nagas’ unique identity.
- The Government of India first acknowledged the “unique history of the Nagas” in 2002 (Amsterdam talks), paving the way for structured peace negotiations.
The Framework Agreement: Key Provisions
- Recognition of Political Identity: India recognized the Nagas’ distinct historical and cultural identity.
- Shared Sovereignty: Proposed a cooperative model of governance, dividing powers between India and Nagalim while ensuring coexistence.
- Political Equality: Both India’s and Nagalim’s political systems to be respected, avoiding a hierarchical relationship.
- People-Centric Governance: Emphasizes sovereignty residing with the people, aiming for inclusive, democratic self-rule.
- Commitment to Peace: Seeks to end armed struggle and establish a roadmap for lasting peace and autonomy.
Political Significance
- The accord symbolically acknowledges the existence of the “Naga nation.”
- It shifted the discourse from an administrative problem to a political conflict requiring negotiated settlement.
- It was signed in New Delhi in the presence of Prime Minister Narendra Modi and interlocutor RN Ravi.
Current Developments
- On the 10th anniversary (2025), NSCN-IM chairman Q Tuccu reaffirmed commitment to the FA, calling it the “torchbearer of Naga sovereignty”.
- He criticized the Naga National Political Groups (NNPGs)—a coalition of other Naga factions—accusing them of aligning too closely with New Delhi by accepting a settlement under the Indian Constitution (“Agreed Position”).
- Tuccu argued that the NNPGs’ stance compromises the Nagas’ historical and political identity, unlike the FA which ensures recognition of sovereign rights.
- NSCN-IM maintains that the Government of India is slow in implementing the FA, but it remains committed despite challenges.
ICJ Ruling on the Kyoto Protocol
- 03 Aug 2025
In News:
In a landmark advisory opinion, the International Court of Justice (ICJ) has clarified that the Kyoto Protocol (1997) remains legally valid and binding, even after the Paris Agreement (2015) came into effect. This ruling has revived the Protocol’s legal relevance and has far-reaching implications for international climate law and global climate governance.
Background: The Kyoto Protocol
- Adopted: 1997; Entered into force: 2005 under the UN Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC).
- Nature: First binding international treaty mandating emission reductions by industrialised nations (Annex-I countries).
- Principle: Based on Common but Differentiated Responsibilities and Respective Capabilities (CBDR–RC), recognising that developed nations bear greater responsibility due to their historical emissions.
- Commitment Periods:
- First: 2008–2012
- Second: 2012–2020
- Obligations:
- Quantified emission reduction targets (from 1990 baseline).
- Provision of finance and technology transfer to developing nations.
- Market-based mechanisms such as the Clean Development Mechanism (CDM).
Why was Kyoto Considered Obsolete?
- US Non-Ratification: The largest historical emitter never joined the Protocol.
- Withdrawals: Countries like Canada and Japan later exited or refused binding targets.
- Rise of New Emitters: China overtook the US as the largest emitter by mid-2000s but, as a “developing country,” had no binding obligations.
- Shift to Paris Agreement (2015):
- Kyoto: Top-down, binding targets for developed countries.
- Paris: Bottom-up, voluntary Nationally Determined Contributions (NDCs) for all states.
- With no third commitment period defined after 2020, Kyoto was widely seen as defunct though never formally repealed.
ICJ’s Key Rulings
- Kyoto Still in Force: The absence of a new commitment period does not terminate the Protocol; it remains part of applicable international law.
- Legal Accountability: Non-compliance with emission reduction targets can constitute an “internationally wrongful act.”
- Retroactive Review: Past obligations (e.g., unfulfilled first commitment period targets) remain open for assessment.
- Advisory but Influential: Though not legally binding, the ruling strengthens grounds for climate litigation and accountability mechanisms.
Significance of the Ruling
- Legal Continuity: Confirms coexistence of Kyoto and Paris, rather than substitution.
- Revival of CBDR–RC: Re-emphasises differentiated responsibilities of developed nations, which Paris had diluted.
- Climate Justice: Opens the door for renewed scrutiny of historical emitters and their unfulfilled obligations.
- Litigation Pathways: Strengthens civil society and state efforts to seek compensation or stronger climate actions through international and domestic courts.
Implications for Global Climate Governance
- Developed countries face renewed legal and moral pressure to honour past commitments and extend finance and technology support.
- Developing nations gain a stronger footing to demand accountability for historical emissions.
- The ruling highlights the layered nature of international climate treaties, with Kyoto, UNFCCC, and Paris coexisting rather than replacing each other.
- It may reshape climate negotiations by reviving unfinished obligations under Kyoto while reinforcing Paris as the ongoing framework.
First-Ever Grassland Bird Census in Kaziranga National Park
- 31 Jul 2025
In News:
The first dedicated Grassland Bird Census was conducted in Kaziranga National Park, Assam, marking a significant step in avian biodiversity monitoring in India. The initiative was widely acknowledged, including by Prime Minister Narendra Modi in his Mann Ki Baat broadcast, for its innovative use of Artificial Intelligence (AI) and acoustic monitoring.
Objective and Significance
- Purpose: To systematically monitor the population, breeding patterns, and habitat health of grassland-dwelling bird species, many of which are rare or threatened.
- Conservation Value: Grassland birds serve as ecological indicators of habitat quality, akin to how BMI reflects human health.
- Highlight Species:
- Documented 43 bird species
- Included 1 Critically Endangered, 2 Endangered, and 6 Vulnerable species (IUCN Red List)
- Notably, over 85 nests of the endangered Finn’s Weaver, endemic to the Brahmaputra floodplains, were discovered.
Methodology & Technological Innovations
- Conducted By: Joint effort of forest officials, Kaziranga National Park authorities, conservationists, and researchers including INSPIRE fellow Chiranjib Bora.
- Sites Covered: 185 grassland locations across the national park.
- Tools Used:
- Passive Acoustic Monitoring: Audio recorders placed atop trees to capture bird calls during the breeding season.
- AI Integration:
- BirdNET Software used to automatically identify bird species by analyzing vocalizations.
- Spectrograms enabled visual analysis of sound frequencies for accurate classification.
Key Innovations and Impact
- First of its Kind: India’s first census focused exclusively on grassland bird species, often overlooked in standard bird surveys.
- Non-Intrusive Monitoring: AI-powered audio analysis allowed species identification without disturbing natural behavior.
- Awareness & Biodiversity Education: The census is a powerful example of how technology and sensitivity can together enhance biodiversity understanding and conservation awareness.
Gavri Festival
- 30 Jul 2025
In News:
Gavri is a unique 40-day ritualistic folk festival celebrated annually by the Bhil tribal community of the Mewar region in Rajasthan. It is a vibrant blend of dance, drama, music, and oral storytelling rooted deeply in the Bhil worldview, spirituality, and socio-cultural expression.
Key Features:
- Duration: 40 days, usually observed during the Hindu months of Shravana and Bhadrapada (July to September), coinciding with the monsoon and early harvest season.
- Form: A fusion of dance, drama (khel), mime, and dialogues.
- Theme: Enacts mythological battles between good and evil, primarily featuring Goddess Gauri/Amba and demons such as Bhasmasur or Bhiamwal, symbolizing the triumph of good.
- Performance Spaces: Villages where the performers' married sisters and daughters reside, reinforcing familial ties and social cohesion.
- Characters: All roles, including female ones, are portrayed by male performers, due to prevailing patriarchal norms.
- Narration: A storyteller called Kutkadiya introduces each scene, enhancing audience immersion.
- Costumes & Music: Colorful attire, energetic drumming, and folk instruments create a lively, theatrical atmosphere.
Cultural and Social Significance
- Spiritual Identity: The Bhil community considers themselves descendants of Lord Shiva and Goddess Parvati, viewing Parvati (Gauri) as their divine sister. Gavri is performed to honour her and ensure the well-being of their married women.
- Oral Heritage: The festival preserves centuries-old oral traditions, possibly dating back to the 3rd or 4th century CE, with references to the era of Siddhraj Jai Singh of Gujarat.
- Carnivalesque Spirit: Gavri subverts caste and class hierarchies through humor, parody, and satire. Authority figures, kings, and even gods may be lampooned in the plays.
- Resistance & Nature Worship: Performances like Badliya Hindwa and Bhilurana reflect themes of nature worship, tribal resistance to invaders (Mughals, British), and warnings against ecological destruction.
- Gender Fluidity: Though patriarchal in nature, the performance of female roles by men adds a layer of gender expression and cultural fluidity during the ritual.
Bhil Tribe: An Overview
- One of India's largest Adivasi groups, found mainly in Rajasthan, Gujarat, Madhya Pradesh, and Maharashtra.
- Speak the Bhili language and practice a syncretic faith combining animism with Hindu mythology.
- Their cultural identity is closely tied to forests, nature, and community-based rituals like Gavri.
Veer Parivar Sahayata Yojana
- 29 Jul 2025
In News:
The National Legal Services Authority (NALSA), in a significant step toward safeguarding the legal rights of India’s uniformed forces, launched the Veer Parivar Sahayata Yojana during the North Zone Regional Conference in Srinagar. Themed “Reaffirming the Constitutional Vision of Justice for Defence Personnel and Tribals,” the event spotlighted the urgent need to institutionalize accessible legal assistance for military personnel and their families.
Rationale and Objectives
- Defence and paramilitary personnel frequently serve in remote, conflict-prone, or high-risk environments, which limits their ability to attend to civilian legal matters. Be it land disputes, family conflicts, service-related claims, or bureaucratic issues, legal hurdles can deeply affect their lives. The scheme acknowledges that a soldier stationed on the border cannot readily leave his post to handle legal proceedings back home.
- The Veer Parivar Sahayata Yojana is designed to bridge this critical gap by providing free, competent, and timely legal aid to serving personnel, veterans, and their families.
Key Features of the Scheme
- Joint Collaboration: The initiative is a joint effort between NALSA, the Kendriya Sainik Board (KSB), Rajya Sainik Boards (RSBs), and Zilla Sainik Boards (ZSBs) under the Department of Ex-Servicemen Welfare, Ministry of Defence.
- Legal Clinics Across Sainik Boards: Legal Services Clinics will be established at the district, state, and central levels of the Sainik Boards across India. These will function as the first point of contact for defence families seeking legal assistance.
- Trained Legal Volunteers: The initiative actively involves panel lawyers and trained paralegal volunteers, including ex-servicemen and defence family members, to offer legal services and counselling.
- Back-end Legal Infrastructure: A robust administrative mechanism will support the on-ground functioning of clinics and ensure prompt resolution of legal grievances.
- Coverage for Paramilitary Forces: The scheme will also extend support to paramilitary personnel from forces such as BSF, CRPF, ITBP, and others, who operate under similar hardships and isolation.
Significance and Constitutional Context
- The scheme upholds Article 39A of the Constitution, which mandates equal justice and free legal aid for all citizens. Defence personnel, who make immense sacrifices for national security, often remain underserved when it comes to civilian entitlements, rights, and dispute resolution.
- By reaffirming the constitutional commitment to access to justice, the scheme aligns with the broader goal of legal empowerment of vulnerable and marginalized communities, including those in service of the nation.
Foot and Mouth Disease (FMD)
- 29 Jul 2025
In News:
- In July 2025, a concerning outbreak of Foot and Mouth Disease (FMD) led to the death of 16 spotted deer (chitals) at the Rajiv Gandhi Zoological Park in Pune, Maharashtra.
About Foot and Mouth Disease (FMD)
Nature of the Disease
- Foot and Mouth Disease (FMD) is a highly contagious viral infection caused by the aphthovirus from the Picornaviridae family.
- It affects cloven-hoofed animals, including cattle, buffaloes, goats, pigs, sheep, deer, and camelids.
- FMD is not zoonotic, i.e., it does not affect humans, and it poses no food safety risk.
Global and National Status
- FMD is classified as a Transboundary Animal Disease (TAD).
- It remains endemic in over 77% of the world’s livestock populations, particularly across Asia, Africa, and the Middle East.
- It severely disrupts livestock productivity, animal trade, and rural livelihoods.
Transmission and Symptoms
Transmission Routes
- Direct contact with infected animals.
- Indirect transmission through contaminated feed, equipment, vehicles, human movement, and airborne particles.
- Incubation period: 2–14 days.
- The virus can enter via inhalation, ingestion, or skin wounds.
Clinical Symptoms
- High fever lasting 2–3 days.
- Blisters and ulcers on the tongue, lips, hooves, teats, and mouth.
- Excessive salivation, lameness, and depression.
- Significant drop in milk production, weight loss, and growth retardation.
- In young animals, the disease can cause high mortality, while adults may suffer debilitating effects, affecting long-term productivity.
Strains and Immunity
- There are seven known strains of the FMD virus: A, O, C, SAT1, SAT2, SAT3, and Asia1.
- Immunity to one strain does not protect against others, making strain-specific vaccination critical.
Diagnosis and Institutional Infrastructure
- Confirmatory diagnosis is conducted through laboratory testing at premier institutes such as:
- ICAR-National Institute on Foot and Mouth Disease (NIFMD), Bhubaneswar
- Indian Veterinary Research Institute (IVRI), Bareilly
- National Institute of High Security Animal Diseases (NIHSAD), Bhopal
Government Interventions and Policies
National Animal Disease Control Programme (NADCP)
- Launched in 2019, the 100% centrally funded programme targets eradication of FMD and Brucellosis by 2030.
- Key components include:
- Mass vaccination
- Ear-tagging for traceability
- Cold chain infrastructure
- Disease surveillance and reporting
- Farmer awareness and community participation
Integrated Disease Management
- NADCP is aligned with the Livestock Health and Disease Control Programme (LHDCP).
- Several institutions like NIVEDI Bengaluru and Regional Disease Investigation Laboratories contribute to monitoring and outbreak control.
Preventive Strategies and Recommendations
To strengthen India's preparedness against FMD and other epizootics, the following measures are vital:
- Expand FMD Vaccination Coverage: Include zoo animals, wildlife reserves, and peri-urban livestock in regular vaccination drives.
- Strengthen Veterinary Surveillance: Ensure round-the-year disease surveillance, especially during weather extremes (monsoon and summer).
- Upgrade Infrastructure
- Expand testing capacity at regional levels.
- Deploy mobile diagnostic labs in remote zones.
- Raise Awareness: Educate livestock owners, zoo staff, and veterinary professionals about early symptoms, hygiene practices, and reporting protocols.
- Develop Strain-Specific Vaccines: Increase funding for R&D in strain identification and rapid-response vaccines.
- Leverage Technology: Use AI, GIS mapping, and data analytics to predict outbreaks and monitor disease spread.
Henley Passport Index 2025
- 26 Jul 2025
In News:
The Henley Passport Index 2025 reveals significant shifts in global mobility, highlighting increased visa-free access for citizens worldwide. India has made notable progress in the latest rankings, climbing eight places to reach the 77th position, up from 85th in 2024. Indian passport holders can now access 59 countries without a prior visa.
What is the Henley Passport Index?
The Henley Passport Index is a global ranking of passports based on the number of destinations their holders can enter without a visa or with visa-on-arrival. It is compiled by Henley & Partners using data from the International Air Transport Association (IATA). The index, started in 2006, now covers 199 passports and 227 travel destinations.
India’s Passport Performance:
- Current Rank (2025): 77th
- Visa-Free Access: 59 countries
- Previous Rank (2024): 85th
- Lowest Rank: 90th in 2021
- Best Rank: 71st in 2006
India's improved standing reflects enhanced global engagement and evolving diplomatic relations. However, it still trails far behind leading Asian and Western nations in terms of travel freedom.
Top 10 Most Powerful Passports (2025):
- Singapore – 193 visa-free destinations
- Japan, South Korea – 190 destinations
- Germany, France, Italy, Spain, Ireland, Denmark, Finland – 189 destinations
- Sweden, Austria, Belgium, Portugal, Netherlands, Luxembourg, Norway – 188 destinations
- Greece, Switzerland, New Zealand – 187 destinations
- United Kingdom – 186 destinations
- Australia, Czechia, Poland, Malta, Hungary – 185 destinations
- Canada, Estonia, United Arab Emirates (UAE) – 184 destinations
- Croatia, Latvia, Slovakia, Slovenia – 183 destinations
- United States, Iceland, Lithuania – 182 destinations
Note: The UAE is the only significant climber in the top 10, jumping from 42nd to 8th over the past decade.
Bottom 10 Least Powerful Passports (2025):
99. Afghanistan – 25 destinations
98. Syria – 27 destinations
97. Iraq – 30 destinations
96. Pakistan, Yemen, Somalia – 32 destinations
95. Libya, Nepal – 38 destinations
94. Bangladesh, Eritrea, Palestinian Territories – 39 destinations
93. North Korea – 40 destinations
92. Sudan – 41 destinations
91. Sri Lanka – 42 destinations
Global Trends in Passport Power:
- The global average of visa-free destinations has risen from 58 in 2006 to 109 in 2025, indicating increasing global mobility.
- Asian dominance continues, with Singapore, Japan, and South Korea topping the list.
- European Union countries maintain strong positions, reflecting widespread bilateral agreements.
- The United States and United Kingdom, once top-ranking, have seen a decline in influence. The US ranks 10th (182 destinations), while the UK stands at 6th (186 destinations).
- Afghanistan remains at the bottom of the list, with access to just 25 countries, highlighting stark global disparities in travel freedom.
Significance:
- The Henley Passport Index reflects soft power, diplomatic ties, and economic standing of nations.
- India's rising passport strength indicates improved bilateral relations, trade diplomacy, and international mobility.
Paika Rebellion (1817)

- 25 Jul 2025
In News:
The recent exclusion of the Paika Rebellion of 1817 from NCERT’s Class VIII history textbook triggered political backlash in Odisha. Former Chief Minister Naveen Patnaik termed the omission a “huge dishonour” to the Paika warriors, prompting NCERT to clarify that the topic would be included in the second volume of the textbook to be released later in 2025.
Who were the Paikas?
- The Paikas (literally "foot soldiers") were military retainers traditionally employed by the Gajapati kings of Odisha since the 16th century.
- In exchange for military service, they were granted hereditary rent-free lands (nish-kar jagirs), which they cultivated during peacetime.
- Under British rule, their privileges eroded, and they faced land dispossession, economic hardship, and social marginalisation.
Background to the Revolt
- In 1803, the British East India Company annexed Odisha. Colonel Harcourt marched from Madras to Cuttack, defeating feeble Maratha opposition.
- A deal with King Mukunda Deva II of Khurda promised ?1 lakh and four parganas (Lembai, Rahanga, Surai, Chabiskud) for safe passage, but the British defaulted.
- Jayee Rajguru, the king’s adviser, mobilised 2,000 Paikas to confront the British. Though part payment was made, the parganas were not returned.
- Rajguru was arrested and executed on 6 December 1806 for waging war against the British. The king was dethroned and exiled, and the Barunei Fort was demolished.
Causes of the Paika Rebellion
- Loss of Traditional Privileges:
- Confiscation of rent-free lands after British land settlements.
- End of royal patronage.
- Land Alienation & Tax Burden:
- Local Odia landowners were forced to sell land to Bengali absentee landlords.
- Revenue demands shifted to rupee payments, affecting marginal farmers and tribal communities.
- Salt Monopoly & Trade Restrictions: British control over salt trade, particularly after 1814, increased hardship for inland hill populations.
- Cultural and Political Suppression: The decline of local leadership and traditions under colonial authority contributed to growing dissent.
Course of the Rebellion (1817)
- In March 1817, approximately 400 Kondh tribal fighters from Ghumusar marched toward Khurda.
- They were joined by Bakshi Jagabandhu Bidyadhar, the former commander-in-chief of Khurda and ex-holder of the Rodanga estate.
- The rebels:
- Attacked the police station at Banpur
- Burned colonial buildings
- Looted the treasury
- Killed several British officials
- The rebellion spread across southern and central Odisha. Despite initial successes, the British suppressed the revolt.
- Jagabandhu evaded capture for years and surrendered in 1825 under negotiated terms.
Contemporary Significance and Political Debate
- The Paika Rebellion is widely regarded in Odisha as an early expression of anti-colonial resistance.
- In 2017, the Odisha government demanded that the uprising be recognised as the “First War of Independence”, predating the 1857 revolt.
- The Union Government, while not granting this status, acknowledged it as one of the early popular uprisings against colonial rule.
- National Recognition Efforts:
- In 2017, PM Narendra Modi felicitated over 200 descendants of Paika rebels.
- In 2019, President Ram Nath Kovind laid the foundation for a Paika Memorial at Barunei foothills, the rebellion’s epicentre.
- In 2024–25, the new BJP-led government in Odisha announced fast-tracked development of the Paika Academy and Memorial.
Stablecoins
- 24 Jul 2025
In News:
In the evolving landscape of digital finance, stablecoins have emerged as a promising innovation. Unlike volatile cryptocurrencies such as Bitcoin, stablecoins are designed to maintain a consistent value by pegging their worth to stable assets like fiat currencies or commodities. Recent legislative and technological developments, particularly in the United States, indicate growing global interest in integrating stablecoins into everyday financial systems.
What are Stablecoins?
Stablecoins are a type of cryptocurrency whose value is anchored to an external asset, commonly a fiat currency like the US dollar, or commodities such as gold. This pegging mechanism aims to minimize price volatility, making them more suitable for routine transactions.
There are three primary categories of stablecoins:
- Fiat-collateralized: Backed by actual reserves of fiat currency.
- Crypto-collateralized: Secured using other cryptocurrencies as collateral.
- Algorithmic (non-collateralized): Use smart contracts to automatically manage the coin’s supply based on demand.
Although designed for stability, these digital assets still carry some risks, especially if reserve management is opaque or unregulated.
Technological Foundation
Stablecoins, like other cryptocurrencies, are built on blockchain technology—a decentralized, distributed ledger system that records transactions in a secure, transparent manner. Blockchains operate through consensus mechanisms without needing a central authority, making stablecoins capable of direct peer-to-peer transactions without traditional banking intermediaries.
Recent Policy Development: The GENIUS Act
In a landmark move, the GENIUS Act (Generating Emergency National Income Using Stablecoins) was recently signed into law by the US President. It provides a regulatory framework specifically for US dollar-pegged stablecoins like USDC (by Circle) and USDT (by Tether). This legislative support is expected to accelerate the mainstream adoption of stablecoins, especially in cross-border payments.
Applications of Stablecoins
- Remittances and Cross-Border Transfers:
- Traditional remittance services like Western Union or MoneyGram charge high fees and delays.
- Stablecoins offer instant, low-cost transactions, benefiting especially those in countries facing hyperinflation or capital controls.
- Companies can also pay overseas workers in stablecoins, bypassing complex financial systems and exchange rate risks.
- E-Commerce and Retail:
- Online merchants can reduce reliance on credit card networks, which collected over $187 billion in fees in the US in 2023 alone.
- Stablecoins eliminate intermediaries, reducing transaction fees and improving profit margins.
- Enterprise and Supply Chain Payments:
- Businesses can benefit from faster and cheaper cross-border payments.
- Chinese conglomerate JD.com suggests stablecoins could cut transaction costs by 90% and reduce settlement time from days to seconds.
- Custom Stablecoins by Corporations:
- Giants like Amazon, Walmart, and JD.com are exploring the issuance of proprietary stablecoins to support in-house payment systems, customer loyalty programs, and even financial services.
- This could potentially shift customer deposits away from traditional banks, affecting their lending capacity.
- Integration with Artificial Intelligence: Emerging AI agents may autonomously execute and manage stablecoin-based transactions, particularly in business-to-business ecosystems, improving operational efficiency.
Opportunities and Challenges
Advantages:
- Faster, cheaper international payments
- Improved financial inclusion
- Enhanced efficiency in e-commerce and global business operations
Concerns:
- Regulatory uncertainty, especially across jurisdictions
- Security risks, including fraud and hacking
- Potential disruption to traditional banking systems
Bima Sakhi Yojana
- 22 Jul 2025
In News:
Life Insurance Corporation of India (LIC) has signed a Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) with the Department of Rural Development, Ministry of Rural Development, to implement the Bima Sakhi Yojana in rural areas. The agreement was formalized during the ‘Anubhuti’ national conclave on financial inclusion held in Goa.
About Bima Sakhi Yojana:
- Implementing Body: Life Insurance Corporation of India (LIC) in collaboration with the Union Ministry of Rural Development.
- Objective: To promote financial inclusion and women empowerment by facilitating their participation in the insurance distribution sector.
- Target Group: Rural women aged 18–70 years, with at least a Class 10 qualification.
Key Features:
- Stipendiary LIC Agency Scheme:
- Women are inducted as LIC agents with all associated privileges.
- The scheme offers a monthly stipend for the initial three agency years:
- ?7,000 in the first year
- ?6,000 in the second year
- ?5,000 in the third year (Subject to performance and terms and conditions)
- Commission Benefits:
- In addition to stipends, Bima Sakhis are eligible for sales commissions.
- A commission of ?48,000 (excluding bonuses) is provided in the first year for qualifying agents.
- Training & Career Path:
- Selected candidates undergo specialized training to build capacity in insurance awareness and financial literacy.
- Post-training, they function as LIC agents.
- Graduates among them may be eligible to become LIC Development Officers.
- Scale of Implementation: The scheme aims to appoint 2 lakh Bima Sakhis over a period of three years, with focus on enhancing rural outreach and insurance penetration.
Eligibility Criteria:
- Age Limit: 18 to 70 years
- Minimum Education: Must have passed Class X
- Preference: Women from rural areas are prioritized
Ineligibility Conditions:
- Women who are:
- Related to existing LIC agents or employees (including spouse, children, siblings, parents, and in-laws)
- Retired LIC employees or ex-agents
- Currently working as LIC agents
Significance:
- Promotes gender empowerment and financial literacy in rural India.
- Part of government’s push for inclusive financial growth through public-private partnerships.
- Illustrates convergence between LIC’s social responsibility and government rural development goals.
Hatti Tribe
- 22 Jul 2025
In News:
Recently, two brothers from the Hatti tribe in the Trans-Giri region of Sirmaur district, Himachal Pradesh, married the same woman under the traditional custom of polyandry. The wedding, held in Shillai village, was conducted openly and witnessed by hundreds, reviving attention to this rare tribal practice.
About the Hatti Tribe
- The Hatti community derives its name from the traditional occupation of selling agricultural produce, meat, and wool in local markets called haats.
- They reside primarily in the Himachal–Uttarakhand border region, especially in the basins of the Giri and Tons rivers, both tributaries of the Yamuna.
- The Hattis are divided into two major groups:
- One in Trans-Giri, Sirmaur district (Himachal Pradesh)
- Another in Jaunsar-Bawar (Uttarakhand)
- They maintain similar cultural practices, and intermarriage between these clans is common.
- The community follows a traditional council system called ‘Khumbli’ for resolving social issues.
- As of 2023, the Hatti tribe in Himachal Pradesh was granted Scheduled Tribe (ST) status, while Jaunsar-Bawar in Uttarakhand received tribal status in 1967.
- Their economy is largely agrarian, with a focus on cash crops due to favorable climatic conditions.
The Tradition of Polyandry ("Jajda")
- Polyandry in the Hatti community is locally called “Jajda” and was historically practiced to prevent division of ancestral land.
- The ritual includes a marriage procession of the bride to the groom’s village and a ceremony called “Seenj”.
- Local priests chant mantras in the native language and conclude the ceremony with blessings and offerings like jaggery.
- This practice has declined in recent decades due to increasing literacy among women, social modernization, and economic shifts.
Legal and Social Acceptance
- Polyandrous marriages are informally recognized under Himachal Pradesh revenue laws, where the practice is referred to as “Jodidara”.
- Though rare, such marriages continue to be socially accepted in some remote villages of Trans-Giri, Kinnaur, and Jaunsar-Bawar.
Demographics
- As per the 2011 Census, the Hatti population was around 2.5 lakh, and estimates now suggest about 3 lakh people across 450 villages in the Trans-Giri region alone.
Cultural and Practical Rationale
According to Hatti elders and community leaders:
- Land Preservation: Prevents fragmentation of ancestral property.
- Joint Family Bonding: Promotes unity and mutual understanding among brothers.
- Labor Sharing: Ensures adequate manpower to manage scattered agricultural lands in hilly terrain.
- Security: A larger family offers greater social and economic protection in tribal settings.
Biostimulants
- 21 Jul 2025
In News:
Union Agriculture Minister Shivraj Singh Chouhan last week wrote to Chief Ministers of all states to immediately stop the “forced tagging” of nano-fertilisers or biostimulants along with conventional fertilisers.
What are Biostimulants?
Biostimulants are substances or microorganisms that enhance nutrient uptake, plant growth, yield, and stress resistance in crops. They are distinct from fertilisers and pesticides, as they do not directly supply nutrients or control pests.
- Composition: Often derived from plant waste, seaweed extracts, or microbes.
- Function: Stimulate physiological processes in plants.
- Not classified as: Fertilisers (under nutrient input) or Pesticides (regulated under Insecticides Act, 1968).
Official Definition (FCO, 1985): A substance or microorganism whose primary function is to stimulate physiological processes in plants, enhancing nutrient uptake, growth, and yield—but not including pesticides or plant growth regulators.
Regulatory Framework
- Governing Law: Fertiliser Control Order (FCO), 1985 – amended in February 2021 to include biostimulants.
- Central Biostimulant Committee (CBC): Established in April 2021 for five years to advise the Ministry on:
- Product approval and specifications
- Sampling/testing methods
- Lab and data standards
Toxicity and Safety Requirements:
To be approved, biostimulants must undergo:
- 5 acute toxicity tests: Oral, dermal, inhalation (rat), skin, and eye irritation (rabbit)
- 4 eco-toxicity tests: Impact on fish, birds, honeybees, and earthworms
- Field trials: At 3 agro-ecological zones, with 3 doses, for one crop season
No biostimulant shall contain pesticide beyond 0.01 ppm.
Why Tightened Regulation?
- Previous Lack of Oversight: Biostimulants operated in a regulatory vacuum for years.
- Market Flooded with Unapproved Products: Over 30,000 unregulated products were in circulation.
- Farmer Complaints: Rising concerns over efficacy and “forced sales” with subsidised fertilisers like urea and DAP.
- Judicial Push: A 2011 Punjab & Haryana HC observation prompted states to monitor biostimulant sales more stringently.
Recent Government Measures
- Provisional Registration (2021–2024): Allowed 2-year sale of products while testing was underway. Deadline extended repeatedly until June 16, 2024. Post-June 2024: Unsold stocks from unregistered firms are no longer permitted for sale.
- Retailer Misuse: Reports of retailers forcing farmers to buy biostimulants with subsidised fertilisers prompted Union Agriculture Minister Shivraj Singh Chouhan to direct states to halt such practices.
- Product Crackdown: From over 8,000 products four years ago, the number of approved products is now down to 650.
- Crop-Specific Specifications (May 2025): Government notified biostimulant standards for crops including tomato, chilli, brinjal, paddy, cotton, potato, soybean, maize, etc.
3I/Atlas: Third Interstellar Object Discovered
- 16 Jul 2025
In News:
Scientists have confirmed the discovery of 3I/Atlas, the third-known interstellar object, which could be over 7 billion years old — predating the Solar System by nearly 3 billion years. It was detected on July 1, 2025, by the Asteroid Terrestrial-impact Last Alert System (ATLAS) telescope in Río Hurtado, Chile.
Key Features:
- Interstellar Origin: 3I/Atlas is not gravitationally bound to the Sun and follows a hyperbolic trajectory, indicating it entered the Solar System from interstellar space.
- High Speed: It is traveling at approximately 60 km/s — too fast to be retained by the Sun’s gravity at a distance of 670 million km from the Sun.
- Current Location: The object is now roughly 917 million km from Earth, close to the orbit of Jupiter.
- Age Estimation: Estimated to be around 7 billion years old, making it potentially the oldest comet ever observed.
Understanding Interstellar Objects
- Definition: Interstellar objects are celestial bodies that originate outside the Solar System and pass through it without being gravitationally bound to the Sun.
- Known Interstellar Objects:
- 1I/?Oumuamua (2017)
- 2I/Borisov (2019)
- 3I/Atlas (2025)
How do scientists confirm Interstellar Origin?
- Trajectory Analysis: Objects within the Solar System follow closed elliptical orbits. Interstellar objects exhibit open hyperbolic orbits — they have a perihelion (closest point to the Sun) but no aphelion (no return).
- Velocity Measurement: A high velocity at a great distance from the Sun, such as with 3I/Atlas, suggests that the object was not accelerated within our Solar System and must have originated externally.
- Example: At 670 million km from the Sun, 3I/Atlas’s speed of 60 km/s indicates a hyperbolic escape path, unaffected significantly by the Sun’s gravitational pull.
Why is it Significant?
- Clues to Alien Planetary Systems: The chemical composition of interstellar objects offers insights into the formation conditions of other star systems.
- Rare Opportunity: These objects provide a direct sample of exoplanetary material, potentially long before space missions can reach other star systems.
- Scientific Value: If rich in ices, as expected in long-distance comets, it implies ejection from a cold, outer region of a distant planetary system—likely influenced by large planets like Jupiter or Neptune analogues.
Roll Cloud
- 06 Jul 2025
In News:
A striking atmospheric event unfolded over Portugal’s coastline during a severe European heatwave, where beachgoers and weather enthusiasts witnessed a rare roll cloud. The phenomenon occurred as cooler Atlantic air met the hot, dry continental air, producing a visually stunning and scientifically intriguing cloud formation.
What is a Roll Cloud?
A roll cloud is an uncommon, tube-shaped, low-altitude cloud formation that appears to rotate horizontally along its axis. Unlike funnel clouds, it is not connected to any thunderstorm base or rotating system.
Typical Occurrence Zones:
- Frequently spotted in coastal areas, particularly where oceanic and continental air masses interact
- Notably seen in regions like:
- U.S. Great Plains
- Gulf of Carpentaria, Australia (famous for “Morning Glory” clouds)
- Atlantic coasts of Europe
Formation Mechanism:
- Air Mass Interaction: Roll clouds develop when cool, moist maritime air confronts hot, dry air from land, creating instability.
- Temperature Inversion: A thermal inversion layer traps cooler air beneath a warmer layer, suppressing vertical air movement.
- Gravity Waves: As dense cool air undercuts warm air, it creates gravity waves—oscillations within the lower atmosphere.
- Adiabatic Cooling: The ascending portion of the wave cools rapidly, leading to condensation and cloud formation.
- Detached Structure: The cloud remains independent of any parent cloud system, often forming a long, horizontal roll.
Cloud Characteristics:
- Shape: Long, tubular, and low-lying—can stretch over hundreds of kilometers
- Motion: Appears to roll horizontally like a barrel
- Timing: Often forms during early morning hours
- Orientation: Aligns with low-level wind flow, sometimes influenced by sea breeze or nocturnal land breeze fronts
Why are Roll Clouds important?
- Serve as visual indicators of atmospheric instability and changing weather conditions
- Though not hazardous, they reflect mesoscale meteorological processes
- May signal localized shifts in temperature or wind that could precede storm activity in some environments
- Their presence also highlights the interplay between land-sea thermal contrasts, especially relevant in the context of climate variability
International Potato Research Center

- 01 Jul 2025
In News:
- On June 25, 2025, the Union Cabinet approved the establishment of the CIP-South Asia Regional Center (CSARC) in Agra, Uttar Pradesh.
- The center will function as a regional wing of the International Potato Center (CIP) headquartered in Lima, Peru.
About CIP
- Founded: 1971
- Headquarters: Lima, Peru
- Focus Crops: Potato, Sweet Potato, and Andean roots & tubers
- Global Presence: South America, Africa, Asia
- India Operations: Since 1975, through partnership with ICAR
About CIP-South Asia Regional Center (CSARC)
- Location: Singna, Agra district, Uttar Pradesh
- Land Provided: 10 hectares (by UP Government)
- Total Project Cost: ?171 crore
- Indian Contribution: ?111.5 crore
- CIP Contribution: ?60 crore
- Implementing Ministry: Ministry of Agriculture & Farmers’ Welfare
Objectives of the Center
- Improve productivity of potato and sweet potato
- Promote climate-resilient, disease-free varieties
- Enhance post-harvest management and value addition
- Boost domestic seed production
- Support exports and food processing industries
- Increase farmer income, employment, and nutritional security
Why is this Significant?
- Potato is the 3rd most consumed crop globally (after rice and wheat)
- Sweet potato ranks 6th globally (after maize and cassava)
- India is the 2nd largest producer and consumer of potato
- Current average yield in India:
- Potato: ~25 tonnes/ha (Potential: >50 tonnes/ha)
- Sweet Potato: ~11.5 tonnes/ha (Potential: ~30 tonnes/ha)
- Establishment of CSARC will:
- Reduce dependency on seed imports
- Improve access to global germplasm
- Help bridge the yield gap
Global and National Context
- China is the largest potato producer (78.24 million tonnes, 2020)
- India is second (51.3 million tonnes, 2020)
- Top Potato-Producing States in India (2020–21):
- Uttar Pradesh (~15 million tonnes)
- West Bengal (~15 million tonnes)
- Bihar (~9 million tonnes)
Related Agricultural Research Institutions in India
- ICAR-CPRI, Shimla – Potato research
- ICAR-CTCRI, Thiruvananthapuram – Sweet potato and tuber crops
- IRRI-SARC, Varanasi – Regional center of International Rice Research Institute
CIP Centers Outside Peru
- China Center for Asia-Pacific (CCCAP) – Established in 2017 in Beijing, China
- India's CSARC (Agra) will be the second major CIP center outside Peru
19th National Statistics Day

- 01 Jul 2025
In News:
MoSPI celebrates 19th Statistics Day honouring Prof. P.C. Mahalanobis and 75 years of National Sample Survey.
Key Highlights:
June 29 is observed as National Statistics Day in India to commemorate the birth anniversary of Prof. Prasanta Chandra Mahalanobis (1893–1972), widely regarded as the Father of Indian Statistics. The 2025 theme is "75 Years of National Sample Survey (NSS)".
The day is dedicated to promoting the role of statistics in nation-building and policy formulation, especially among the youth.
Key Contributions of P.C. Mahalanobis
1. Architect of India’s National Sample Survey (NSS)
- In 1950, Prof. Mahalanobis pioneered the National Sample Survey, India's first scientific and large-scale household data collection system.
- NSS is a large-scale, nationwide socio-economic data collection initiative conducted by the National Sample Survey Office (NSSO) under the Ministry of Statistics and Programme Implementation (MoSPI).
- Key Objectives of the NSS: Generate high-quality data to inform public policy, planning, and developmental programs.Conduct household surveys on:
- Consumption expenditure
- Employment & unemployment
- Health and education
- Migration and the informal sector
- Undertake the Annual Survey of Industries (ASI) to evaluate industrial performance.
- Support the agricultural sector by supervising crop area and yield estimation.
- Provide price statistics for rural and urban India to monitor inflation and cost-of-living changes.
- Key Features of the NSS
- All-India Scientific Coverage: Surveys conducted in both rural and urban areas using stratified multi-stage sampling methods.
- Organizational Structure – Four Major Divisions
Division Function
Survey Design & Research Division (SDRD) Survey planning, design, and methodology (HQ: Kolkata)
Field Operations Division (FOD) Data collection via 170+ regional offices (HQ: Delhi/Faridabad)
Data Processing Division (DPD) Data validation, tabulation, processing for surveys like PLFS & ASI
Survey Coordination Division (SCD) Coordinates survey activities and publishes Sarvekshana journal
- Multi-Thematic and Integrated Surveys
- Consumption patterns
- Employment trends (via Periodic Labour Force Survey - PLFS)
- Health and morbidity
- Education, migration, and social welfare indicators
- Support for Agriculture and Industry: Strengthens crop statistics and supports the ASI Web Portal for industrial data validation.
- Digital Integration & Real-Time Processing:Modernization efforts include urban sampling frame maintenance, tablet-based data collection, and real-time monitoring tools.
2. Mahalanobis Distance (1936)
- A multivariate statistical measure used to identify outliers and data anomalies.
- It quantifies the distance of a data point from a distribution, factoring in correlations between variables.
- Widely applied in fields such as public health, market research, and machine learning.
3. Flood Control and Environmental Planning
- In the 1920s, Mahalanobis used historical data to guide flood mitigation in Bengal and Odisha.
- His studies disproved incorrect assumptions (e.g., rising river beds) and recommended drainage improvements and dam construction.
- His early estimates contributed to the Hirakud Hydroelectric Project, inaugurated in 1957.
4. Institution Building: Founder of ISI & Sankhya Journal
- Founded the Indian Statistical Institute (ISI) in Kolkata in 1931, a premier research institute for statistics and mathematics.
- Launched ‘Sankhya’, India’s first statistical journal, fostering academic and applied research.
5. Role in National Planning & Technology Advocacy
- Chief architect of the Second Five-Year Plan, which introduced the Mahalanobis Model — emphasizing heavy industries and public sector-led growth.
- Advocated for digital computing in India. However, during the Cold War, the U.S. denied India access to the UNIVAC computer, fearing Mahalanobis’s pro-Soviet leanings.
Biographical Snapshot
Attribute Details
Born 29 June 1893, Kolkata (then Calcutta)
Education Presidency College; King's College, Cambridge
Field Statistics, Economic Planning, Data Science
Key Institutions Indian Statistical Institute (ISI), NSS, Planning Commission
Died 28 June 1972
Sree Narayana Guru

- 29 Jun 2025
In News:
The Prime Minister recently attended the centenary celebrations of the historic 1925 conversation between Mahatma Gandhi and Sree Narayana Guru, held at Vigyan Bhawan, New Delhi. The event marked the enduring relevance of Guru's message of social equality, spiritual unity, and reform.
Who was Sree Narayana Guru?
- Born: 20 August 1856, in a backward Ezhava community in Kerala
- Died: 20 September 1928
- Role: Spiritual leader, philosopher, poet, yogi, and one of India’s foremost social reformers from Kerala
Historical Context:
- During the 19th century, Kerala society was deeply caste-ridden, and the Ezhava community was subjected to systemic social exclusion.
- Guru revolted against caste oppression, advocating for spiritual liberation without ritual orthodoxy.
Core Philosophy:
- Message of Universal Unity:“OruJathi, OruMatham, OruDaivam, Manushyanu”
(One Caste, One Religion, One God for Mankind) — a powerful call for social harmony, inclusivity, and humanism. - Non-violent transformation:Unlike many radical reform movements, Guru’s approach was inclusive and reformative, rejecting social division without inciting confrontation.
Key Contributions:
- Religious and Spiritual Reforms:
- Aruvippuram Movement (1888):
- Consecrated a Shiva idol at Aruvippuram — a direct challenge to Brahmanical dominance and the exclusion of lower castes from temple worship.
- Established over 40 temples in Kerala, allowing unrestricted worship by the marginalized.
- Promoted yoga and meditation, and spent years in hermitage to attain spiritual depth.
- Aruvippuram Movement (1888):
- Social Reforms:
- Founded the Sivagiri Mutt (1904) near Varkala — a centre for spiritual and social awakening.
- SNDP Yogam (1903):
-
- Full form: Sri Narayana Guru Dharma ParipalanaYogam
- Aimed at securing education, government access, and political rights for the Ezhavas.
- Guru was the permanent chairman; Kumaran Asan, his disciple, became general secretary.
-
- Vaikom Satyagraha:Played a pivotal role in the anti-untouchability movement, alongside leaders like Mahatma Gandhi and Periyar.
- Promoted free education, ashrams, and vocational training for underprivileged children and communities.
- Sivagiri Foundation and Pilgrimage:
- Founded in 1924 to promote values like:Cleanliness, education, devotion, agriculture, handicrafts, and trade
- SivagiriTheerthadanam (pilgrimage):Initiated by his followers to reinforce values of purity, education, and organization
Literary Contributions:
- Guru was a Vedantic scholar and philosopher-poet. His notable works include:
- Advaitha Deepika
- Atmavilasam
- DaivaDasakam
- BrahmavidyaPanchakam
These texts reflected Advaita (non-dualist) philosophy, spiritual self-realization, and social ethics.
Legacy and Recognition:
- Revered as “Gurudevan”by his followers
- His birth and death anniversaries are observed as public holidays in Kerala and some other states
- Celebrated as Sri Narayana Jayanthi
India’s Coffee Exports

- 28 Jun 2025
In News:
India has emerged as a significant player in the global coffee trade, with its exports witnessing a sharp rise of 125% in the past 11 years, increasing from $800 million in 2014–15 to $1.8 billion in 2023–24, and continuing the momentum with over 25% growth in FY2025–26. This export surge highlights India's expanding footprint in the global premium coffee market, driven by a blend of policy support, sustainable cultivation practices, and global demand for specialty coffee.
Key Drivers of Export Growth
The Coffee Board of India, under the Ministry of Commerce, has played a pivotal role in this transformation through:
- Digitalisation of export permits, RCMC, and certificates of origin.
- Export incentives like freight and transit assistance—?3/kg for value-added exports and ?2/kg for green coffee to distant markets (e.g., US, Canada, Japan, Nordic countries).
- Subsidy support of 40% (up to ?15 lakh) for processing units (roasting, grinding, packaging).
- Global market intelligence and regular industry engagement to remove bottlenecks.
- Promotion via GI tags and digital branding campaigns.
These efforts have enhanced India’s readiness to meet stringent import regulations (e.g., EU deforestation norms) while enabling access to new and emerging markets.
Production and Cultivation
India is the 7th largest producer of coffee globally, accounting for about 3.5% of world production and ranks 5th in global coffee exports with a 5% share. The country produces 3.5–4 lakh tonnes of coffee annually, with Karnataka (70%), Kerala, and Tamil Nadu being major contributors.
- Arabica varieties: Kents, S.795, Cauvery, Selection 9.
- Robusta: High-yielding selections suited to Indian climate.
Climatic Features:
- Grown under two-tier shade canopies with over 50 native tree species.
- Arabica thrives at 1000–1500m, Robusta at 500–1000m altitudes.
- Requires 1600–2500 mm rainfall and 15°C–25°C temperature.
India is unique as the only country that cultivates 100% shade-grown coffee, which promotes biodiversity, soil and water conservation, and ensures a sustainable income for 2 million people, including small and marginal farmers.
Specialty and GI-Tagged Coffee
India’s coffee is known for its mild acidity, full-bodied flavour, and fine aroma. Intercropping with spices like pepper, cardamom, and vanilla further enhances its appeal. The country also boasts five regional and two specialty coffees with Geographical Indication (GI) tags, strengthening brand value in global markets.
The historic legacy of Indian coffee dates back over 400 years to the planting of coffee beans by Baba Budan in Karnataka, making it one of the oldest coffee traditions in Asia.
Dharti AabaJanbhagidari Abhiyan (DAJA)

- 28 Jun 2025
In News:
In a landmark initiative for tribal inclusion, the Government of India has launched the Dharti AabaJanbhagidari Abhiyan (DAJA)—India’s largest-ever tribal outreach and empowerment campaign. The programme aims to ensure saturation of welfare schemes and promote tribal pride and participation, covering over 1 lakh tribal villages and PVTG habitations across 31 States and Union Territories.
What is DAJA?
- Full Name: Dharti AabaJanbhagidari Abhiyan — named in honour of Bhagwan Birsa Munda, a revered tribal freedom fighter.
- Launched by: Ministry of Tribal Affairs, Government of India.
- Nature: A people-centric campaign focused on participatory governance and last-mile delivery of services among Scheduled Tribes (STs) and Particularly Vulnerable Tribal Groups (PVTGs).
Objectives of DAJA
- Saturate government welfare schemes across all tribal settlements.
- Empower over 5.5 crore tribal citizens through Janbhagidari (people’s participation).
- Preserve and promote tribal identity and cultural heritage, invoking the legacy of Birsa Munda.
- Strengthen last-mile governance through technological and administrative convergence.
Key Features:
Feature Description
Geographic Coverage - 1 lakh+ tribal villages, including remote PVTG habitations, across 31 States/UTs.
Scheme Integration - Converges services such as Aadhaar, Ayushman Bharat, PM Kisan, PM
Ujjwala, Jan Dhan, pension schemes, and Forest Rights Act (FRA) claims.
Five Foundational Pillars -
- Janbhagidari (people’s participation)
- Saturation of welfare benefits
- Cultural inclusion
- Convergence of schemes
- Last-mile delivery
Technology-Driven Monitoring - Use of real-time dashboards and data analytics for
transparent tracking and reporting.
Cultural Revival - Celebrates tribal cuisines, folk arts, handicrafts, and oral traditions
during outreach camps to reaffirm cultural identity.
Significance:
- Governance: Represents a shift toward targeted and integrated tribal welfare, reducing administrative fragmentation.
- Inclusion: PrioritisesPVTGs, often the most marginalised and underserved groups.
- Empowerment: Embeds a participatory model, aligning with the spirit of democratic decentralisation.
- Cultural Reaffirmation: Bridges the gap between development and cultural identity, crucial for tribal dignity and preservation.
Total Revolution
- 28 Jun 2025
In News:
India commemorates the 51st anniversary of Jayaprakash Narayan’s (JP) historic call for “Sampoorna Kranti” or Total Revolution, first proclaimed on June 5, 1974, at Gandhi Maidan, Patna. The movement remains a landmark in India's democratic evolution, reflecting enduring concerns over governance, democracy, and civic empowerment.
What is Total Revolution?
- Concept: A holistic, non-violent movement rooted in Gandhian ideals, aimed at comprehensive transformation—political, economic, social, cultural, and spiritual.
- Vision: Building a just and equitable society through decentralised democracy, moral rejuvenation, and participatory governance.
- Leadership: Spearheaded by Jayaprakash Narayan (JP), advocating a “party-less democracy” blending Gandhian ethics, Sarvodaya ideals, and Marxist critique.
Underlying Causes of the Movement
- Electoral Legitimacy Crisis:The 1975 Allahabad High Court judgment disqualified Prime Minister Indira Gandhi for electoral malpractices, eroding her authority and galvanising mass opposition.
- Youth Unrest:Movements like Navnirman Andolan (Gujarat) and Bihar student protests reflected mounting youth dissatisfaction over unemployment and poor governance.
- Economic Distress:The early 1970s saw inflation exceeding 20%, acute unemployment, and food shortages, leading to widespread discontent.
- Democratic Backsliding:Use of draconian laws like MISA, increased centralisation, and suppression of dissent led to civil society mobilisation.
- Charismatic Mobilisation:JP’s appeal for non-violent civic awakening and his ability to unify diverse ideological streams helped launch a broad-based national movement.
Core Components of the Total Revolution
Domain Focus
Political Advocated bottom-up governance, decentralisation, and accountability
to counter bureaucratic authoritarianism.
Economic Promoted land reforms and people-centric development to address inequality.
Social Called for eradication of casteism, gender bias, and dowry to foster egalitarianism.
Educational Suggested reforms emphasisingethics, rural upliftment, and vocational training.
Cultural-Spiritual Encouraged self-discipline, national unity, and moral regeneration.
Impact of Total Revolution
On Society and Citizenry
- Youth Mobilisation: Inspired a generation of political leaders—Lalu Prasad Yadav, Nitish Kumar, Sushil Modi—who reshaped regional politics.
- Civic Engagement: Fostered a deeper culture of public accountability and democratic participation.
- Non-Violent Resistance: Reinforced the efficacy of peaceful protest, a legacy echoed in later movements like Anna Hazare’s anti-corruption crusade.
On Governance and Policy
- Collapse of Congress Monopoly: Led to the formation of the Janata Party, marking a historic electoral defeat for the Congress in 1977.
- Constitutional Safeguards: Triggered the 44th Constitutional Amendment, curbing emergency powers and restoring judicial oversight.
- Democratic Deepening: Inspired Panchayati Raj reforms through the 73rd and 74th Amendments, enhancing grassroots democracy.
Significance and Contemporary Relevance
- Democratic Dissent: Reinvigorated the right to protest as a fundamental democratic tool.
- Leadership Incubation: Nurtured mass-based political leadership, altering India’s political landscape.
- Institutional Vigilance: Exposed systemic vulnerabilities, prompting long-term institutional reforms.
- Civic Awakening: Broadened the role of civil society in governance beyond electoral cycles.
- Modern-Day Lessons: Offers vital insights for addressing centralisation of power, youth alienation, and democratic backsliding in contemporary India.
Ambubachi Mela 2025
- 27 Jun 2025
In News:
Thousands of devotees have congregated at the Kamakhya Temple in Guwahati, Assam, to participate in the annual Ambubachi Mela—one of the largest and most significant religious gatherings in Northeast India.
About Ambubachi Mela
- Timing: Celebrated annually during the monsoon season, typically in June.
- Location: Held at the Kamakhya Temple, situated atop Nilachal Hill in Guwahati, Assam.
- Religious Significance:
- Marks the menstrual cycle of Goddess Kamakhya, symbolising the fertility of Mother Earth.
- During this period, the sanctum sanctorum is closed for three days, after which it is ceremonially reopened for darshan.
- Cultural Symbolism:
- Reflects ancient beliefs that associate the Earth with feminine fertility.
- The word ‘Ambubachi’ translates to ‘water flowing’, indicative of both the monsoon rains and the goddess’s fertility.
Kamakhya Temple: Key Facts
- Spiritual Importance:
- Dedicated to Goddess Kamakhya, an incarnation of Shakti.
- Considered one of the most revered sites of Tantric Shaktism in India.
- Recognised as one of the 51 Shakti Peethas, where the yoni (womb) of Sati is believed to have fallen.
- Geographical Location:Located on Nilachal Hill, overlooking the southern bank of the Brahmaputra River.
Architectural Features of Kamakhya Temple
- Architectural Style:
- Combines traditional Nagara style with Saracenic (Mughal) architectural elements, known as the Nilachala Style of Architecture.
- Temple Layout:
- Only temple in Assam with a fully developed ground plan.
- Comprises five main sections:
- Garbhagriha (sanctum sanctorum)
- Antarala (vestibule)
- Jaganmohan (assembly hall)
- Bhogmandir (offering hall)
- Natmandir (performance hall)
- Distinctive Structural Elements:
- Main dome: Modified Saracenic style.
- Antarala: Features a two-roofed structure.
- Bhogmandir: Crowned with five domes, echoing the central shrine.
- Natmandir: Designed with a shell-shaped roof and apsidal end, similar to the namghars (prayer halls) of Assam.
B-2 Spirit Bomber
- 23 Jun 2025
In News:
In a major escalation of the ongoing US–Iran tensions, the United States deployed the B-2 Spirit stealth bomber to strike Iran’s fortified nuclear infrastructure, including the heavily guarded Fordow enrichment facility, which was described by President Donald Trump as the “crown jewel” of Iran’s nuclear programme. The strikes signal a new phase in the geopolitical standoff, showcasing advanced US airpower and precision capabilities.
What is the B-2 Spirit Bomber?
The B-2 Spirit, developed by Northrop Grumman during the Cold War, is one of the most advanced strategic bombers in the world. Originally built for penetrating heavily defended Soviet airspace, it remains a key asset in the US Air Force due to its stealth capabilities, long range, and precision payload delivery.
Only 21 B-2 bombers were built, each costing an estimated $2.1 billion, making it one of the most expensive aircraft ever developed. Its bat-wing design and radar-absorbent coating significantly reduce its radar cross-section, making it almost invisible to radar and ideal for deep penetration missions in hostile territory. It is operated by a two-person crew and extensively automated to reduce pilot workload.
Why was it used in the Iran strikes?
The B-2 Spirit was chosen for the Iran mission because of its unique combination of stealth, range, and payload capacity. The Fordow facility, built deep within a mountain and protected by sophisticated air defences, required a bomber that could both evade detection and deliver a bunker-busting payload with high precision.
During the mission, the B-2s were reportedly equipped with the GBU-57A/B Massive Ordnance Penetrator (MOP) — a 30,000-pound bomb specifically designed to destroy deeply buried and fortified targets like Fordow. Due to the weapon’s size and weight, a B-2 can carry only one or two MOPs per sortie. Reports indicate that six MOPs were dropped on Fordow, demonstrating the operational effectiveness of the B-2 for such critical missions.
Capabilities and Strategic Role
The B-2 has an unrefueled range of over 6,000 nautical miles (approximately 11,000 km), enabling it to undertake intercontinental missions directly from the United States. Past missions have seen the B-2 operate from Missouri to targets in Afghanistan, Libya, and now Iran, demonstrating its global strike capability.
With a total payload capacity exceeding 40,000 pounds (18,000 kg), the B-2 can carry both conventional and nuclear weapons. It forms a crucial part of the US nuclear triad, capable of delivering up to 16 B83 nuclear bombs. Its ability to carry nuclear and precision-guided munitions gives it unmatched strategic versatility.
Weapon Systems Compatible with the B-2
Beyond the MOP, the B-2 can be armed with a variety of precision and standoff weapons, including:
- JDAMs (Joint Direct Attack Munitions): GPS-guided bombs used for high-accuracy strikes on fixed targets.
- JSOW (Joint Standoff Weapons): Glide bombs launched from a distance, allowing engagement of targets outside enemy air defence range.
- JASSM and JASSM-ER (Joint Air-to-Surface Standoff Missiles): Long-range cruise missiles, with the extended-range variant capable of striking targets up to 500 miles (805 km) away.
This versatility allows the B-2 to adapt to multiple mission profiles, from conventional warfare to nuclear deterrence.
Strategic and Geopolitical Implications
The deployment of the B-2 in this mission has both tactical and symbolic implications. Tactically, it underscores the US military’s ability to deliver precision strikes on highly protected strategic infrastructure. Strategically, it sends a strong signal to adversaries about the technological edge and operational reach of American military power.
From a geopolitical perspective, the strikes could exacerbate tensions in the already volatile West Asian region, heighten concerns about nuclear proliferation, and potentially provoke retaliatory actions by Iran and its regional allies. It also raises questions about the future of US-Iran relations and the fragility of nuclear diplomacy in the region.
Revised Green India Mission (GIM)
- 22 Jun 2025
In News:
Recently, the Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change released the revised roadmap for the National Mission for a Green India (GIM). The updated strategy focuses on restoring degraded ecosystems, enhancing forest cover, and addressing climate impacts, especially in vulnerable landscapes like the Aravallis, Western Ghats, Himalayas, and mangroves.
About Green India Mission (GIM)
- Launched in: 2014
- Under: National Action Plan on Climate Change (NAPCC)
- Nodal Ministry: Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change (MoEFCC)
- Core Objectives:
- Increase forest/tree cover by 5 million hectares.
- Improve the quality of forest cover on another 5 million hectares.
- Restore degraded ecosystems and enhance biodiversity.
- Improve the livelihoods of forest-dependent communities.
Achievements So Far
- Afforestation Activities: 11.22 million hectares covered (2015–16 to 2020–21) through central and state schemes.
- Funding: ?624.71 crore released (2019–24) to 18 states; ?575.55 crore utilized.
- Target Areas: Selected based on ecological vulnerability, sequestration potential, and restoration needs.
Key Features of the Revised Roadmap
- Landscape-Specific Restoration:
- Prioritizes Aravalli ranges, Western Ghats, Himalayas, and mangrove ecosystems.
- Emphasizes regionally adapted best practices for ecosystem restoration.
- Integration with Aravalli Green Wall Project:
- Aims to combat desertification and sandstorm risks in northern India.
- Initial restoration planned across 8 lakh hectares in 29 districts of 4 states.
- Estimated cost: ?16,053 crore.
- Aims to develop a 5 km buffer zone covering 6.45 million hectares around the Aravallis.
- Western Ghats Focus:
- Tackling deforestation, illegal mining, and degradation.
- Measures include afforestation, groundwater recharge, and mining site restoration.
Combating Land Degradation and Climate Change
- Land Degradation (2018–19): Affected 97.85 million hectares (~1/3rd of India’s land), per ISRO data.
- India’s Climate Targets (2030):
- Create an additional carbon sink of 2.5–3 billion tonnes of CO? equivalent via forest/tree cover.
- Restore 26 million hectares of degraded land.
- Carbon Sequestration Potential (FSI Estimates):
- Restoration of open forests can sequester 1.89 billion tonnes of CO? over 15 million hectares.
- With intensified afforestation and aligned schemes, forest cover could reach 24.7 million hectares—achieving a carbon sink of 3.39 billion tonnes CO? equivalent by 2030.
Significance of the Revised Mission
- Aligns with India’s NDCs under the Paris Agreement.
- Supports goals under UNCCD and UNFCCC.
- Helps mitigate climate change impacts by creating natural buffers and carbon sinks.
- Promotes ecological sustainability, biodiversity conservation, and community livelihood enhancement.
Cyber Suraksha Exercise
- 17 Jun 2025
In News:
A comprehensive national-level cyber security exercise, Cyber Suraksha, was launched by the Defence Cyber Agency (DCyA) under the Headquarters Integrated Defence Staff (HQ IDS).
About Cyber Suraksha
- Type: Multi-phased cybersecurity drill.
- Organised by: Defence Cyber Agency (DCyA) under the aegis of HQ IDS.
- Duration: From 17–27 June 2025.
- Participants: Over 100 experts from national agencies and defence domains.
- Environment: High-paced, gamified simulation of real-world cyber threats.
Objectives
- Enhance national cyber resilience.
- Train personnel in handling advanced cyberattacks.
- Promote a security-first culture across defence institutions.
- Integrate technical proficiency with strategic leadership.
Key Features
- Training capsules: Technical + leadership components.
- CISOs Conclave: Sessions by cybersecurity leaders, culminating in a table-top simulation.
- Hands-on exercises: Real-time attack simulations to test response capabilities.
- Focus on joint operations and decision-making under crisis.
About Defence Cyber Agency (DCyA)
Background
- Established: Announced in 2018, operational from November 2019.
- Origin: Recommended by Naresh Chandra Committee (2012).
- Part of India’s tri-service defence transformation, alongside proposed Aerospace and Special Operations Commands.
Role & Mandate
- Parent Ministry: Ministry of Defence (MoD).
- Reports to: Chief of Defence Staff (CDS) through Integrated Defence Staff (IDS).
- Location: Based in New Delhi.
Functions
- Conducts cyber defence operations for the armed forces.
- Coordinates incident response, cyber intelligence, and audits.
- Develops capabilities in cyber warfare, AI-driven cyber tools, and joint operations.
- Supports capacity building, certification, and training within the military.
DNA Identification in Mass Fatality Events
- 17 Jun 2025
In News:
Following the tragic crash of an Air India Boeing 787 Dreamliner from Ahmedabad to London Gatwick (June 2025), authorities have initiated DNA-based identification to match the remains of victims. In mass fatality incidents where bodies are mutilated or decomposed, DNA analysis becomes the gold standard for establishing identity.
What is DNA Identification?
DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid) is a unique genetic code present in almost every cell of the human body, with the exception of identical twins. It is widely used in forensic science for accurate identification, particularly in disasters where visual identification is impossible.
Sample Collection and Preservation:
- DNA begins degrading post-mortem, and the rate of degradation is influenced by:
- Type of tissue (soft vs hard)
- Environmental conditions (humidity, temperature)
- Hard tissues such as bones and teeth are preferred due to better preservation against decomposition.
- Soft tissues (like skin and muscle) degrade faster and, if used, must be stored in 95% ethanol or frozen at -20°C.
- In large-scale accidents, sample collection from wreckage can take weeks or even months (e.g., 9/11 took 10 months).
Reference Samples:
To match unidentified remains, reference DNA is taken from biological relatives—preferably parents or children of the victims, who share about 50% of their DNA.
Methods of DNA Analysis:
1. Short Tandem Repeat (STR) Analysis:
- Evaluates short, repeating DNA sequences that vary among individuals.
- Requires nuclear DNA, hence not suitable if the DNA is highly degraded.
- Analysis of 15+ hyper-variable STR regions can confirm family relationships with high accuracy.
2. Mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) Analysis:
- Used when nuclear DNA is not recoverable.
- mtDNA is inherited exclusively from the mother and is present in multiple copies per cell.
- Effective for matching with maternal relatives (e.g., mother, maternal uncles/aunts, siblings).
3. Y-Chromosome Analysis:
- Targets male-specific genetic material.
- Useful for identifying remains using DNA from paternal male relatives (father, brothers, paternal uncles).
- Helpful when direct relatives are unavailable but male-line relatives exist.
4. Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms (SNPs) Analysis:
- Suitable when DNA is highly degraded.
- Analyzes variations at single base-pair locations in DNA.
- Can also match DNA with personal items like a toothbrush or hairbrush.
- However, less accurate than STR analysis.
Significance for Disaster Management and Forensics:
- DNA-based victim identification ensures scientific accuracy, aiding in closure for families, and upholding legal and humanitarian obligations.
- Modern forensic genetics has become an essential tool in mass disaster response protocols worldwide.
CROPIC: A New AI-Driven Crop Study Scheme
- 13 Jun 2025
In News:
The Ministry of Agriculture and Farmers Welfare plans to launch CROPIC, a study to gather crop information using field photographs and AI-based models.
What is CROPIC?
CROPIC stands for Collection of Real Time Observations & Photo of Crops. It is a new initiative by the Ministry of Agriculture and Farmers’ Welfare aimed at studying crops through photographs and artificial intelligence (AI). The core objective is to monitor crop health and assess mid-season losses using images captured at multiple stages of the crop cycle.
Why is CROPIC significant?
CROPIC plays a pivotal role in modernizing and digitizing crop monitoring under the Pradhan Mantri Fasal Bima Yojana (PMFBY), India’s flagship crop insurance scheme.
Significance:
- Improved Loss Assessment: Traditional methods of crop loss assessment are time-consuming and subjective. CROPIC introduces AI-based analysis for faster and more objective decision-making.
- Automation of Compensation: It will help automate claim processes, ensuring faster payments to farmers in case of crop failure.
- Rich Crop Signature Database: Repeated field observations will build a valuable dataset of crop images over time, useful for future agricultural planning and risk management.
- Farmer Involvement: By crowdsourcing photographs directly from farmers, CROPIC also encourages their direct participation in data collection.
How will CROPIC work on the ground?
- Data Collection via App:
- A mobile app developed by the ministry will be used.
- Farmers and officials will take photos of crops 4–5 times during a crop’s life cycle.
- AI-Based Analysis:
- Photos will be processed on a cloud-based AI platform.
- The model will identify crop type, growth stage, health condition, damage, and loss extent.
- Visualization and Monitoring:
- A web-based dashboard will visualize crop status and damage patterns for stakeholders.
- Use in Insurance Claims:
- The app will also be used by officials to collect photo evidence for PMFBY claims, helping streamline compensation payouts.
Project Timeline:
- Pilot Phase:
- Begins with Kharif 2025 and Rabi 2025-26.
- Will cover at least 50 districts per season, spanning various agro-climatic zones and major crops.
- Full Roll-Out: After initial R&D, nationwide implementation is planned from 2026 onwards.
Funding and Support:
- Funded through the Fund for Innovation and Technology (FIAT) under PMFBY.
- FIAT has a total allocation of ?825 crore for various tech-driven agricultural initiatives.
Rediscovery of the Eurasian Otter in Kashmir
- 12 Jun 2025
In News:
After being presumed extinct in the Kashmir Valley for nearly three decades, the Eurasian otter (Lutra lutra) has been spotted again in the Lidder River in Srigufwara, South Kashmir. This rare sighting rekindles hope for the revival of the Valley’s aquatic biodiversity.
About Eurasian Otter:
- Common Names: Eurasian otter, European otter, Common otter, Old-World otter
- Local Name in Kashmir: Vuder
- Type: Semi-aquatic carnivorous mammal
- Distribution:
- Widely spread across Europe, the Middle East, Northern Africa, and Asia (from Eastern Russia to China).
- In India, found in northern, northeastern, and southern regions.
- In Kashmir, historically abundant in Dal Lake, Dachigam streams, Rambiara stream, and the Lidder River.
Habitat & Features:
- Habitat:
- Occupies diverse freshwater and coastal ecosystems—lakes, rivers, marshes, swamp forests, and mountain streams.
- In the Indian subcontinent, prefers cold hill and mountain waters.
- Physical Traits & Adaptations:
- Sleek brown fur (lighter underneath), long streamlined body, short legs, and thick tail.
- Aquatic adaptations:
- Webbed feet
- Ability to close ears and nostrils underwater
- Dense fur trapping air for insulation
- Excellent vision, hearing, and olfactory senses.
- Behavior: Elusive, solitary, and primarily nocturnal.
Conservation Concerns:
- Primary Threats:
- Water pollution degrading habitats
- Hunting for fur, historically significant in Kashmir
- Conservation Status:
- IUCN Red List: Near Threatened
- Wildlife Protection Act, 1972 (India): Schedule II
- CITES: Appendix I
Sant Kabirdas
- 12 Jun 2025
In News:
11th June 2025 marked the 648th birth anniversary of Sant Kabirdas, one of India’s most revered 15th-century Bhakti saints.
Place of Birth: Varanasi, Uttar Pradesh
Birth Period: Circa 1440 CE, raised in a Muslim weaver family
Philosophy and Teachings
- Nirguna Bhakti: Kabir rejected idol worship and sectarian divisions, instead preaching devotion to a formless, universal God (Nirguna Brahman).
- Social Reform: He denounced casteism, rituals, and blind faith, stressing ethical conduct, humility, and self-realization.
- Inner Divinity: He believed God resides within and taught seekers to seek truth through introspection (Antar-drishti) rather than temple rituals.
- Language and Style:
- Composed in Sant Bhasha, a blend of local dialects understood across religions.
- Created Ulatbansi verses — paradoxical or "upside-down sayings" — challenging conventional wisdom.
Literary Legacy
- Major Works: Bijak, Sakhi Granth, Kabir Granthavali, Anurag Sagar
- Scriptural Inclusion:
- His verses appear prominently in the Adi Granth Sahib compiled by Guru Arjan Dev.
- Adopted by various traditions:
- Kabir Bijak (Kabirpanth, UP)
- Kabir Granthavali (Dadupanth, Rajasthan)
Impact and Influence
- Kabir Panth: A spiritual sect founded on his teachings, still active in North India.
- Sikhism: Deeply influenced Guru Nanak; Kabir’s dohas are integrated into Guru Granth Sahib.
- Cross-Religious Appeal: Respected by both Hindus and Muslims, he is a symbol of India’s syncretic spiritual culture.
- Other Sects: Influenced Dadu Panthis and Nirguna Bhakti traditions across India.
Contemporary Relevance
- Religious Harmony: In a climate of polarization, Kabir’s teachings offer a path of unity and spiritual inclusivity.
- Social Justice: His resistance to caste hierarchy echoes India’s constitutional values of equality and dignity.
- Sustainable Living: His emphasis on simplicity and contentment aligns with ecological and minimalist principles.
- Spiritual Humanism: He stressed conduct over ritual, making his message resonate across belief systems in today’s pluralistic society.
Raja Bhabhut Singh Honoured
- 09 Jun 2025
In News:
In June 2025, the Madhya Pradesh Government held a special Cabinet meeting at Pachmarhi, renaming the Pachmarhi Wildlife Sanctuary after Raja Bhabhut Singh, a lesser-known but formidable tribal freedom fighter of the 1857 revolt.
About Raja Bhabhut Singh
- Lineage: Belonged to the Jagirdar family of Harrakot Raikheri, descended from Thakur Ajit Singh. His grandfather, Thakur Mohan Singh, had allied with Peshwa Appa Saheb Bhonsle of Nagpur during the 1819–20 resistance against the British.
- Role in 1857 Revolt:
- A key Gond tribal leader with control over Jabalpur and the Satpura hills.
- Employed guerrilla warfare tactics in the Satpura forests, using deep geographical knowledge to harass British forces.
- Maintained close ties with Tatya Tope, a prominent national leader.
- Martyrdom:
- British deployed the Madras Infantry to capture him.
- He was executed in 1860, and is remembered in Korku tribal folklore.
- Known as the "Shivaji of Narmadachal" for his resistance strategies.
Pachmarhi Wildlife Sanctuary (Now Raja Bhabhut Singh Sanctuary)
- Located in the Satpura mountain range, central Madhya Pradesh, within the Deccan Peninsula biogeographic zone.
- Highest point: Dhoopgarh (1,352 m).
- Forms part of the Satpura Tiger Reserve, along with:
- Satpura National Park
- Bori Wildlife Sanctuary
- Key Biodiversity Zone in Central India.
Korku Tribe Overview
- Region: Mainly in Madhya Pradesh, Chhattisgarh, and Melghat (Maharashtra).
- Occupation: Traditionally agriculturalists; introduced potato and coffee cultivation.
- Society: Patrilineal communities led by traditional headmen.
- Culture:
- Practice ancestral worship through memorial stones called Munda.
- Rich in oral traditions, which preserve the memory of tribal icons like Raja Bhabhut Singh.
Legionnaires’ Disease
- 13 Apr 2025
In News:
Health authorities in New South Wales (NSW), Australia, have issued a public alert after a spike in Legionnaires’ disease cases in Sydney. The outbreak is suspected to be linked to contaminated air-conditioning systems in the city.
About Legionnaires’ Disease
Aspect Details
Cause Legionella bacteria, found in freshwater and man-made water systems
Type A severe form of pneumonia
Related Disease Pontiac fever – a milder, flu-like respiratory illness caused by the same bacteria
Key Features
- Symptoms:
- High fever, cough, shortness of breath
- Muscle pain, headaches, confusion
- Diarrhoea or nausea in some cases
- Transmission:
- Not person-to-person
- Spread through inhalation of contaminated aerosols (e.g., from cooling towers, air conditioners, hot tubs)
- Risk Factors:
- Elderly individuals
- Smokers
- People with weakened immune systems or chronic lung conditions
Treatment and Prevention
- Treatment: Requires antibiotic therapy
- Vaccine: No vaccine currently available
- Prevention:
- Regular maintenance and disinfection of water systems
- Monitoring air-conditioning and cooling systems
Indian Giant Flying Squirrel
- 13 Apr 2025
In News:
A rare sighting of the Indian Giant Flying Squirrel (Petauristaphilippensis) has been reported in Ranikhet, a hill station in Uttarakhand, highlighting the ecological richness of the region.
About Indian Giant Flying Squirrel
Feature Description
Scientific Name Petauristaphilippensis
Size Body length: 30–45 cm; Tail length: up to 60 cm
Appearance Rufous coat, grey underparts, large eyes, and a gliding membrane from wrist
to ankle
Locomotion Glides up to 60 meters between trees using patagium (gliding membrane)
Habitat and Distribution
- Found in tropical and subtropical forests across central and southern India
- Inhabits evergreen, semi-evergreen, and deciduous forests, especially near forest edges
- Recent sighting in Uttarakhand indicates possible range expansion or overlooked presence
Ecological Role
- Diet: Fruits, nuts, leaves, and bark
- Acts as a seed disperser, supporting forest regeneration
- Considered a keystone species due to its ecological significance
Behavioural Traits
- Nocturnal and arboreal
- Emits alarm calls upon detecting predators like owls
- Active at night, gliding from tree to tree in search of food
Conservation Status
Category Status
IUCN Red List (Global) Least Concern
IUCN Status (India) Near Threatened (due to habitat loss)
Wildlife Protection Act, 1972 Schedule II
Threats
- Habitat loss and fragmentation
- Deforestation and degradation of forest corridors
- Increasing human encroachment in forested landscapes
Blue Washing of Polluting Industries
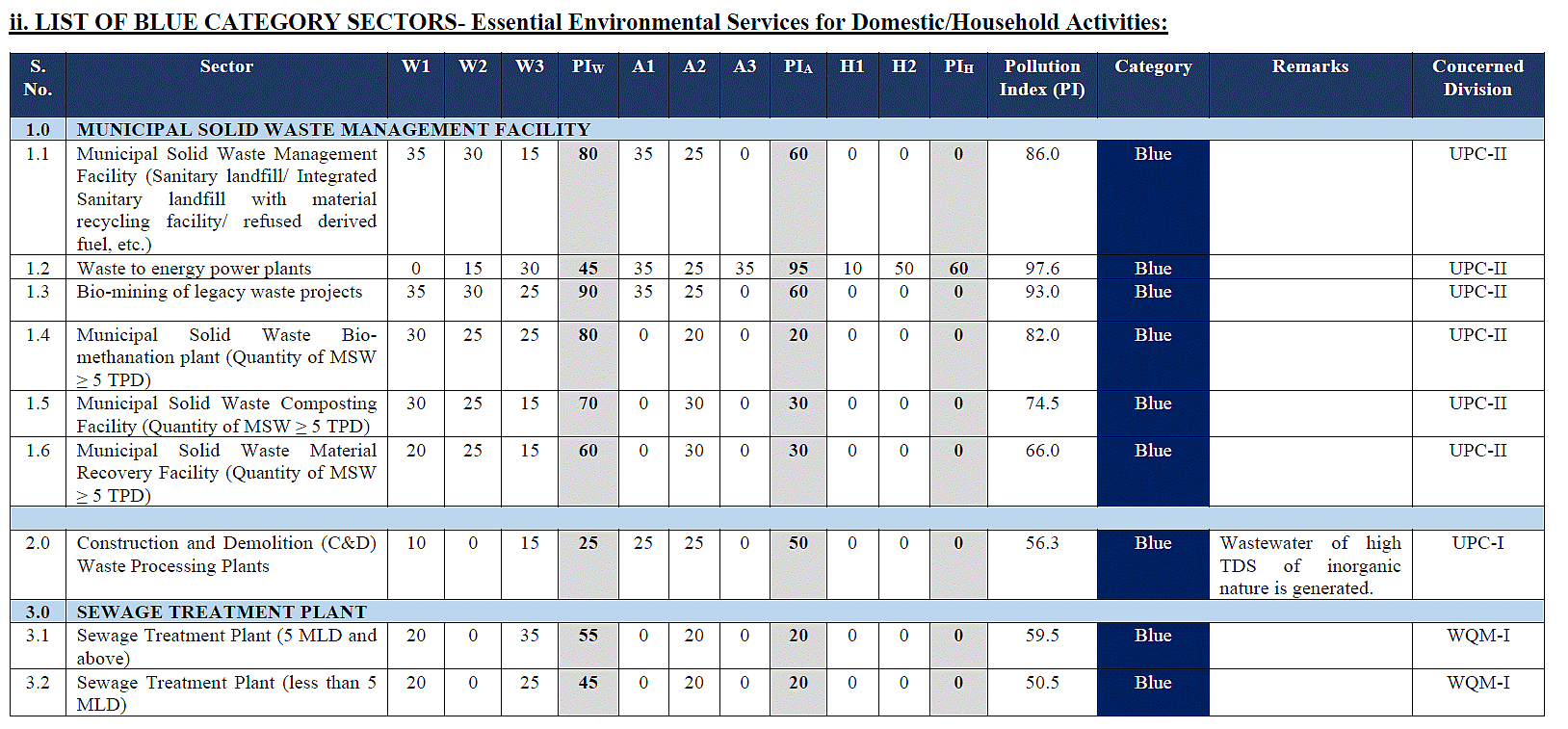
- 12 Apr 2025
In News:
- The Central Pollution Control Board (CPCB) has recently introduced a new ‘Blue Category’ for industries under its Essential Environmental Services (EES) framework.
- Notably, Waste-to-Energy (WTE) incineration plants, previously classified as highly polluting ‘Red Category’ industries, have now been controversially reclassified under this new category.
Background: Pollution Index (PI) and Industry Categorisation
- The Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change (MoEFCC) classifies industries into categories — White, Green, Orange, and Red — based on a Pollution Index (PI) (0–100 scale).
- White (0–20): Least polluting
- Green (21–40)
- Orange (41–59)
- Red (60–100): Most polluting
- WTE plants, with a PI of 97.6, were originally in the Red Category.
What is the new Blue Category?
- Created under Essential Environmental Services (EES) classification.
- Grants 2 additional years of “Consent to Operate” (essentially, consent to pollute).
- Aims to support infrastructure like composting units, biogas plants, material recovery facilities, etc
Controversy: WTE Incineration in the Blue Category
- WTE plants burn unsegregated municipal solid waste (MSW) to generate electricity by producing steam to drive turbines.
- Unlike claimed benefits, WTE plants emit more CO? per unit of electricity than coal-fired plants, contributing to climate change.
- CPCB’s inspection reports found that Delhi’s WTE plants exceeded emission norms, releasing carcinogens and other pollutants such as:
- SOx, NOx, HCL, PM, Dioxins, and Furans
- In FY 2022–23, Delhi’s WTE plants incinerated ~735,840 tons of plastic, contributing significantly to Delhi’s poor air quality.
- These plants also generate hazardous ash, requiring secure landfill disposal.
Issues with Reclassification
- The CPCB’s own guidelines state that:
- Only projects that do not emit hazardous waste or
- Projects that promote the circular economy can be blue-listed.
- However, leading government institute CSIR-NEERI has observed that WTE plants violate the principles of the circular economy and contravene Solid Waste Management Rules, 2016.
- Reclassification undermines environmental safeguards, harms waste pickers’ livelihoods, and imposes financial burdens on Urban Local Bodies (ULBs).
Sunbird

- 12 Apr 2025
In News:
British startup Pulsar Fusion is developing Sunbird, a nuclear fusion-powered rocket that could significantly reduce travel time to outer planets like Mars and Pluto. An orbital demonstration is planned for 2027.
Key Features of Sunbird
- Maximum Speed: Up to 805,000 km/h, surpassing the Parker Solar Probe (692,000 km/h), the fastest human-made object to date.
- Travel Efficiency: Could enable missions to Pluto in just 4 years, and cut travel time to Mars by nearly 50%.
- Payload Capacity: Capable of delivering up to 2,000 kg to Mars in six months.
- Functionality: Unlike chemical rockets like SpaceX’s Starship, Sunbird would act as an interplanetary booster, attaching to spacecraft and possibly operating between charging stations in Low Earth Orbit (LEO) and Mars orbit.
About Nuclear Fusion Propulsion
Nuclear Fusion aims to replicate the process that powers stars — the fusion of atomic nuclei to release energy. Unlike nuclear fission, fusion is cleaner, offers higher energy output, and produces minimal radioactive waste.
Types of Nuclear Propulsion Systems
Propulsion Type Description
Nuclear Thermal Propulsion (NTP) Uses a nuclear reactor to heat liquid hydrogen which
turns to plasma and produces thrust. Provides high exhaust
velocity and can increase payload efficiency 2–3 times
over chemical rockets. Ground tests began in the 1950s.
Nuclear Electric Propulsion (NEP) Converts reactor heat into electricity to power ion thrusters,
which gradually reach high speeds. Components include a
compact reactor core, electric generator, heat rejection
system, and electric propulsion system. Unlike solar power,
nuclear sources ensure consistent energy beyond Mars.
Challenges in Fusion Rocket Development
- Fusion systems are currently large and heavy, posing difficulties in miniaturisation for spaceflight.
- Fusion on Earth is hard to replicate due to atmospheric constraints; space offers a more natural environment for fusion reactions.
Global Efforts and Timeline
Apart from Pulsar Fusion, companies like Helicity Space and General Atomics (backed by NASA and Lockheed Martin) are also advancing fusion-powered space propulsion systems, with testing planned around 2027.
UMEED Portal and Waqf (Amendment) Act, 2025
- 04 Jun 2025
In News:
The Government of India will launch the UMEED Portal to digitize and streamline the registration and management of Waqf properties under the Waqf (Amendment) Act, 2025.
What is the UMEED Portal?
- Full Form: Unified Waqf Management, Empowerment, Efficiency, and Development
- Purpose: A centralized digital platform to register, regulate, and monitor Waqf properties nationwide.
- Nodal Ministry: Ministry of Minority Affairs, in collaboration with State Waqf Boards and judicial authorities.
Objectives:
- Ensure transparent, efficient, and time-bound registration of Waqf assets.
- Digitally empower stakeholders with access to legal rights, obligations, and procedural information.
- Resolve long-pending disputes and enhance accountability in Waqf administration.
- Provide real-time data, including geo-tagged property mapping, to support policymaking.
Key Features:
- Time-Bound Registration:All Waqf properties must be registered within six months of the portal's launch.
- Geo-Tagging and Digital Mapping:Properties must be geo-tagged and include precise dimensions for registration.
- Dispute Resolution Mechanism:Properties not registered by the deadline will be automatically flagged as disputed and referred to Waqf Tribunals for adjudication.
- Legal Support Services:The portal offers awareness tools regarding the amended Act and clarifies legal entitlements.
- Women-Centric Provision:Properties solely in women’s names cannot be declared as Waqf. However, women, children, and the economically weaker sections (EWS) remain eligible beneficiaries.
About Waqf and Recent Legal Reforms:
- What is Waqf?
A Waqf is a permanent charitable endowment under Islamic law, where assets (usually land) are donated for religious or public welfare purposes. Such property is inalienable and cannot be sold, inherited, or transferred.
- Waqf (Amendment) Act, 2025:
- Digital Mandate: Mandatory online registration of all Waqf properties within 6 months.
- Judicial Oversight:Introduced provision for appealing Waqf Tribunal decisions in the High Court within 90 days.
- Tribunal Empowerment:Unregistered properties after the deadline will be treated as disputed and decided by Waqf Tribunals.
- Government Monitoring:Enhanced role of State Waqf Boards in ensuring compliance, registration, and dispute handling.
Significance:
- Aims to reduce litigation, encroachments, and opacity in Waqf land management.
- Bridges the gap between community welfare and digital governance.
- Strengthens institutional mechanisms for protecting religious endowments and improves access to justice.
First-Person View (FPV) Drones
- 03 Jun 2025
In News:
Recently, Ukraine conducted a major drone strike on Russia, reportedly destroying over 40 aircraft using First-Person View (FPV) drones—marking one of the deepest strikes into Russian territory since the start of the conflict in 2022. This highlights the growing role of FPV drones in modern asymmetric warfare.
What are FPV Drones?
First-Person View (FPV) drones are unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) that allow remote pilots to view the drone’s surroundings through a camera mounted on the drone. The live feed can be transmitted to:
- Specialized goggles
- Smartphones
- Other display screens
This immersive view enables highly precise navigation and control.
Key Features and Technologies
- GPS-Independent Navigation: Operates effectively even when GPS signals are jammed or unavailable.
- SmartPilot System: Uses visual-inertial navigation by interpreting camera data to assess the drone's position and orientation.
- LiDAR Integration: Enhances terrain mapping and obstacle detection in complex environments.
- Low Cost: A functional FPV drone can cost as little as $500, making them highly affordable compared to traditional weapon systems.
Operational Use in Combat
- Reconnaissance First: Typically, a long-range reconnaissance drone is used to identify the target area before deploying FPV drones for strikes.
- Deep Strike Capability: Despite having a short range (a few kilometres), FPV drones offer stealth and precision to strike deeply into enemy territory.
- Combat Strategy: Their agility and affordability make FPV drones a key component of attrition warfare, especially for resource-constrained nations.
Advantages in Warfare
- Cost-effectiveness: Offers high-impact capability at a fraction of the cost of conventional weapons.
- Reduced Human Risk: Limits the need for manned missions in hostile territory.
- Stealth: Smaller size and low acoustic footprint make them harder to detect and intercept.
- High Destructiveness: Able to carry payloads such as explosives, effectively targeting tanks, aircraft, and installations.
Challenges and Limitations
- Limited Range: Operates within a few kilometres, requiring deployment close to target zones.
- Reduced Situational Awareness: Pilots rely solely on camera feed, which may not provide full spatial context.
- Need for Visual Observers: In complex environments, an additional observer may be needed to guide the operator safely.
Ukraine’s Use of FPV Drones
Ukraine has effectively integrated FPV drones into its military strategy:
- In November 2023, FPVs were credited as a low-cost, high-impact method of resisting Russian advances.
- NATO sources indicated that over two-thirds of Russian tanks destroyed recently were hit by FPV drones.
- Ukrainian drone manufacturer Vyriy Drone delivered 1,000 indigenous FPVs in March 2025.
- Ukraine is projected to produce over 4 million drones in 2025, reflecting a significant scaling of domestic capabilities.
Geopolitical and Strategic Implications
- Technological Self-Reliance: Domestic production protects nations from geopolitical supply chain disruptions (e.g., China’s chip exports).
- Global Proliferation: Countries like Israel and Iran have also developed drone systems, including HAROP and Shahed drones respectively.
India’s Provisional GDP Estimates for FY 2024–25
- 01 Jun 2025
In News:
The Ministry of Statistics and Programme Implementation (MoSPI) released the Provisional Estimates (PEs) of India’s Gross Domestic Product (GDP) and Gross Value Added (GVA) for the financial year 2024–25 (FY25), providing a comprehensive picture of the country's economic performance.
Understanding GDP and GVA
- GDP (Gross Domestic Product) measures the total expenditure in the economy, including consumption, investment, government spending, and net exports — representing the demand side.
- GVA (Gross Value Added) evaluates the income generated from the production of goods and services in different sectors — representing the supply side.
- The two are related by the formula:GDP = GVA + Taxes – Subsidies
- Both are reported in nominal terms (current prices) and real terms (adjusted for inflation).
Nature of Provisional Estimates
- The estimates are termed provisional because they include data from all four quarters but are subject to revision:
- First Advance Estimates (FAE): January
- Second Advance Estimates (SAE): February
- Provisional Estimates (PE): May
- Revised Estimates: Finalized over the next two years (in 2026 and 2027 for FY25)
Key Economic Indicators for FY 2024–25
- Nominal GDP
- Estimated at ?330.68 lakh crore, showing a 9.8% growth over FY24.
- In dollar terms (?85.559/USD), India’s economy reached $3.87 trillion.
- However, this 9.8% nominal growth marks the third-slowest since 2014.
- Real GDP
- Rose by 6.5%, reaching ?187.97 lakh crore.
- The real GDP growth slowed from 9.2% in FY24, indicating reduced economic momentum.
- Sectoral GVA Performance
- Overall GVA grew by 6.4%, down from 8.6% in FY24.
- Sector-wise real GVA growth:
- Agriculture & Allied Activities: 4.4% (up from 2.7% last year)
- Industry (including Manufacturing & Construction): 6.1%
- Services: 7.5% (notable growth in public admin, trade, and finance)
- Q4 FY25 Trends
- Real GDP growth: 7.4%
- Nominal GDP growth: 10.8%
- Indicates a strong end-of-year performance.
Structural Insights and Concerns
- Manufacturing Weakness:Since FY20, manufacturing GVA CAGR (4.04%) lags behind agriculture (4.72%), signaling industrial stagnation.
- Employment Implications:Manufacturing’s sluggishness contributes to high urban unemployment and labour migration to rural/agricultural sectors.
- Consumption and Investment Revival:
- Private Final Consumption Expenditure (PFCE) grew by 7.2%.
- Gross Fixed Capital Formation (GFCF) increased by 7.1%, indicating investment momentum.
Significance for Policymaking
- The GDP data serves as a basis for fiscal planning, monetary policy decisions, and public investment.
- It highlights India’s position as one of the fastest-growing major economies, while also revealing structural vulnerabilities — particularly in manufacturing.
- For international comparison, real GDP is crucial as it neutralizes inflationary differences across countries.
Stromatolites in India
- 30 May 2025
In News:
600-million-year-old stromatolites in the Himalayas tell the story of an ocean lost and Earth’s first breath.
What are Stromatolites?
Stromatolites are organo-sedimentary structures formed by the entrapment of calcium carbonate precipitates by cyanobacteria (blue-green algae) in shallow marine environments. These layered, dome-shaped mounds represent some of the earliest evidence of life on Earth, with their formation driven by photosynthetic microbial mats.
- Composition: Typically found in limestone, shale, and sandstone.
- Structure: Characterized by laminated layers that may appear flat, dome-shaped, or columnar.
- Habitat (Ancient & Modern): Mostly marine; some ancient forms inhabited freshwater and intertidal zones. Today, living stromatolites survive in limited saline lagoons and bays.
Latest Discovery: Chambaghat, Himachal Pradesh
A major stromatolite outcrop, dating back 600 million years, was recently found in Chambaghat, Solan district, Himachal Pradesh. These structures lie within the Krol Group of sedimentary rocks — a part of the ancient Tethys Sea that existed before the Indian plate collided with Eurasia.
- Elevation: Found at 5,000–6,000 ft above sea level, showcasing tectonic uplift.
- Age Significance: Though not the oldest globally or in India, these are among the younger but well-preserved stromatolites, possibly from the Precambrian-Cambrian boundary (~543–548 million years ago).
Scientific Importance
- Geological Record: Stromatolites document Earth's atmospheric shift from a greenhouse gas-rich to an oxygen-rich environment — a transformation driven by photosynthetic cyanobacteria.
- The Great Oxidation Event (GOE): Occurred ~2.4 billion years ago, when oxygen produced by cyanobacteria began accumulating in the atmosphere, enabling the evolution of multicellular life.
- Tectonic History: Their presence in the Himalayas illustrates the story of the Gondwana supercontinent, India’s northward drift, and the closure of the Tethys Sea.
Global and Indian Context
- Oldest Stromatolites (Global): ~3.6 billion years old from Western Australia.
- Oldest in India: ~2.5 billion years old in the Dharwar Supergroup, Karnataka.
Prominent Stromatolite Sites in India:
Region Geological Feature
Chitrakoot, Uttar Pradesh Columnar stromatolites in Vindhyan limestones
Morni Hills, Haryana Preserved stromatolites in dolomite
Mussoorie & Nainital, Uttarakhand Precambrian marine stromatolites in Krol Belt
Jaisalmer Fossil Park, Rajasthan Protected Mesozoic marine fossil site
Dharwar Supergroup, Karnataka Neoarchean stromatolites (~2.6 billion years old)
Bhima Basin, Karnataka Precambrian stromatolites in shallow marine limestones
Preservation and Geoheritage
Geologists and experts advocate for declaring Chambaghat as a Geoheritage Park, involving local communities and schools to foster awareness. The goal is to integrate science with tourism, conservation, and education.
- Challenge: Many stromatolitic sites across India face neglect or risk from mining and construction, despite their scientific and educational potential.
- Appeal: Proposal for UNESCO Geoheritage status to protect and promote this prehistoric legacy.
India’s First Gene-Edited Sheep

- 30 May 2025
In News:
Sher-e-Kashmir University of Agricultural Sciences and Technology (SKUAST-Kashmir) has successfully developed India’s first gene-edited sheep, marking a significant breakthrough in the field of animal biotechnology.
Key Highlights:
- Institution Involved: Sher-e-Kashmir University of Agricultural Sciences and Technology (SKUAST), Srinagar.
- Technology Used:
- CRISPR-Cas9 gene editing — a precision genome editing tool that won the 2020 Nobel Prize in Chemistry.
- Gene editing was conducted without insertion of foreign DNA, thus the sheep is non-transgenic and differs from traditional GMOs.
- Gene Targeted: The myostatin gene, which regulates muscle growth, was edited to enhance muscle mass.
- Result: Muscle mass increased by 30%, a trait absent in Indian sheep breeds but seen in select European breeds like the Texel.
- Significance:
- Improved meat yield and quality in sheep.
- Potential for disease-resistant and higher-reproduction-rate livestock in the future.
- Supports India’s evolving biotech policy by promoting non-transgenic, gene-edited organisms that are more likely to receive regulatory acceptance.
- Aligns with goals of sustainability and food security by enhancing productivity per animal.
- Regulatory & Safety Aspects:
- Research adhered to international biosafety protocols.
- Sponsored by the Indian Council of Agricultural Research (ICAR).
- Legacy & Research Background:
- Developed after 4 years of dedicated research.
- Led by Prof. Riaz Ahmad Shah, also known for creating India’s first cloned Pashmina goat, Noori, in 2012, and contributing to the world’s first cloned buffalo at NDRI, Karnal.
Implications for the Future:
- Opens doors for precision breeding in livestock to boost India’s animal husbandry sector.
- Strengthens India’s position in advanced genomic research and supports the vision of Atmanirbhar Bharat in biotechnology.
- Awaits comprehensive regulatory framework for gene-edited animals, currently under government consideration.
India’s Sharp Decline in Poverty
- 29 May 2025
In News:
Recent Household Consumption Expenditure Surveys (2022–23 and 2023–24) by the National Statistical Office (NSO), alongside a World Bank Poverty & Equity Brief, highlight a historic decline in poverty in India. This achievement is largely attributed to sustained GDP growth and declining inequality.
Key Findings:
Poverty Reduction Trends (2011–12 to 2023–24)
- All-India Poverty Ratio: Fell from 29.5% (2011–12) → 9.5% (2022–23) → 4.9% (2023–24).
- Extreme Poverty (<$2.15/day, PPP): Declined from 16.2% → 2.3% (2011–12 to 2022–23).
- Lower-Middle Income Poverty (<$3.65/day): Declined from 61.8% → 28.1%.
Updated Poverty Lines (Rangarajan Committee Methodology):
Area 2011–12 2022–23 2023–24
Rural ?972 ?1,837 ?1,940
Urban ?1,407 ?2,603 ?2,736
- For a 5-member urban household, the 2023–24 poverty threshold is ?13,680/month.
Factors Driving Poverty Reduction:
- High GDP Growth: Rose from 7.6% (2022–23) to 9.2% (2023–24).
- Moderating Inflation: Consumer Price Index (CPI) inflation dropped from 6.7% to 5.4%, enhancing real incomes. However, food inflation rose to 7.5%, affecting poor households disproportionately.
- Inequality Decline:
- Gini Coefficient fell from 0.310 (2011–12) → 0.282 (2022–23) → 0.253 (2023–24).
- Urban areas saw faster decline in consumption inequality.
Nature and Depth of Poverty:
- Poverty Near the Threshold:
- Over 50% of the poor lie between 75–100% of the poverty line.
- Large share of non-poor lie just above the line (115–125%), making them vulnerable.
- Depth Analysis (Raised Cut-Offs): Even at 125% of the poverty line, poverty fell by 34.2 percentage points (2011–24), showing broad-based gains.
Regional & Structural Challenges:
- Persisting Regional Disparities: States like Bihar, Jharkhand, Odisha still report higher poverty levels.
- Urban Informality & Data Gaps: Recent surveys underrepresent informal workers and migrants, skewing urban poverty estimates.
- Vulnerability to Shocks: Health crises, climate events, or inflation could push the near-poor back into poverty.
- Gaps in Welfare Coverage: Urban poor and migrant populations face limited access to PDS and safety nets.
Policy Imperatives:
- Targeted Cash Transfers: Scale up schemes like PM-GKAY, DBT for LPG, and tailor transfers to those just above the poverty line.
- Strengthen Rural Employment: Enhance MGNREGA funding and integrate climate-resilient jobs.
- Build Urban Safety Nets: Develop a comprehensive urban social protection framework for gig and informal sector workers.
- Education & Nutrition Investments: Bridge human capital gaps via PM POSHAN, Saksham Anganwadi.
- Continuous Poverty Monitoring: Institutionalize annual poverty tracking using real-time and multidimensional indicators.
Landmine and Cluster Munition Treaties
- 07 Apr 2025
In News:
In a major shift that challenges global disarmament efforts, NATO members Poland, Finland, and the three Baltic states—Estonia, Latvia, and Lithuania—have announced their withdrawal from the 1997 Ottawa Convention banning anti-personnel landmines. These countries cite growing security threats from Russia amidst the ongoing Russia-Ukraine war as the primary reason for exiting the treaty.
Ottawa Convention (1997)
- Objective: To prohibit the use, stockpiling, production, and transfer of anti-personnel landmines, and to mandate the destruction of existing stockpiles within four years.
- Adoption and Enforcement: Finalized in Oslo on 18 September 1997, it came into force on 1 March 1999.
- Scope: The treaty bans anti-personnel mines but not anti-vehicle mines.
- Membership: 164 states are party to the convention. However, major powers like the US, Russia, China, and India have not signed or ratified it.
- Humanitarian Impact:
- Over 80% of landmine victims are civilians (ICRC).
- Ukraine has been declared the most mined country in the world (UN, October 2024), with 1,286 civilian victims reported as of August 2024.
- Victim Assistance: The Convention includes obligations to assist mine victims, many of whom suffer permanent disabilities.
Motivations Behind Withdrawals
- The withdrawing countries argue that their security environment has fundamentally changed, especially with the threat of Russian aggression.
- They fear that any ceasefire in Ukraine might allow Russia to regroup and pose a direct threat to bordering nations.
- By exiting the convention, these states aim to achieve military parity with Russia, which is not a party to the treaty.
- Poland has already indicated interest in resuming landmine production.
Impact on Global Demining and Humanitarian Efforts
- The move risks reversing decades of global advocacy and humanitarian work.
- Compounding the problem, global demining efforts are under stress due to sharp US funding cuts. The US had been the largest donor, contributing over $300 million annually, or 40% of global demining funds (Landmine Monitor 2024).
- Though the US has resumed some humanitarian demining programs (March 2024), specific details remain limited.
Convention on Cluster Munitions (2008)
- Purpose: Bans the use, production, transfer, and stockpiling of cluster munitions.
- Mechanism: These weapons disperse bomblets over large areas, posing serious risks to civilians long after deployment.
- Membership: 112 state parties and 12 signatories.
- Recent Withdrawal: Lithuania has signaled its withdrawal from this treaty.
- Non-Signatories: India, the US, Russia, China, Ukraine, and Israel have not joined the convention due to strategic and military considerations.
- Recent Usage: In 2023, the US supplied cluster munitions to Ukraine as part of its defense against Russian invasion.
6th BIMSTEC Summit

- 07 Apr 2025
In News:
The 6th BIMSTEC Summit was recently held in Bangkok, Thailand, under the theme “BIMSTEC: Prosperous, Resilient, and Open.”The Indian Prime Minister participated in the Summit, emphasizing regional connectivity, economic integration, and collective resilience.
About BIMSTEC
- Full Form: Bay of Bengal Initiative for Multi-Sectoral Technical and Economic Cooperation
- Members: Bangladesh, Bhutan, India, Myanmar, Nepal, Sri Lanka, and Thailand
- Founded: 1997 (Bangkok Declaration)
- Initial Name: BIST-EC (later BIMST-EC, and finally BIMSTEC in 2004)
- Population & Economy: Covers 1.7 billion people (~22% of world population) with a combined GDP of USD 5.2 trillion (2023)
Key Outcomes:
- Summit Declarations and Documents
- Bangkok Vision 2030: Adopted as a roadmap for regional economic integration, technological collaboration, and resilience against global challenges.
- 21-point Action Plan: Proposed by India to revitalize BIMSTEC as a dynamic platform for regional cooperation, especially in light of SAARC’s dormancy.
- Institutional and Governance Reforms
- Enforcement of the BIMSTEC Charter.
- Institutionalization of the Home Ministers' Mechanism, with India offering to host the first meeting.
- Strengthening mechanisms to counter terrorism, cybercrime, and human trafficking.
India’s Key Announcements and Initiatives
A. Centres of Excellence
India announced the establishment of BIMSTEC Centres of Excellence in:
- Disaster Management
- Sustainable Maritime Transport
- Traditional Medicine
- Agricultural Research and Training
B. Connectivity and Digital Infrastructure
- Operationalization of the BIMSTEC Energy Centre in Bengaluru.
- Proposal to link India’s UPI with BIMSTEC payment systems.
- Launch of a pilot study on Digital Public Infrastructure (DPI) for governance and service delivery.
C. Trade and Economic Integration
- Proposal to create a BIMSTEC Chamber of Commerce.
- Plan for an Annual Business Summit.
- Suggestion for a feasibility study on trade in local currencies.
D. Maritime and Space Cooperation
- Proposal for a Sustainable Maritime Transport Centre in India.
- Support for electric grid interconnection across member states.
- Space cooperation: development of nano-satellites, remote sensing data sharing, and training via a dedicated ground station.
Human Development and Cultural Engagement
- BIMSTEC for Organized Development of Human Resource Infrastructure (BODHI):
- Training for 300 youth annually.
- Scholarships (e.g., Nalanda University, Forestry Research Institute).
- Diplomatic training programs.
Health Sector
- Cancer Care Capacity Building Program for BIMSTEC countries.
Youth and Cultural Initiatives
- BIMSTEC Traditional Music Festival
- Young Leaders’ SummitandHackathon
- Young Professional Visitors Program
- BIMSTEC Athletics Meet (2025)
- BIMSTEC Games (2027)– to mark the 30th anniversary
India–Thailand Strategic Partnership (Announced on Sidelines)
Maritime and Regional Cooperation
- Strengthening ties via Indo-Pacific Oceans Initiative (IPOI) and ASEAN Outlook on Indo-Pacific (AOIP).
- Boosting connectivity via the India–Myanmar–Thailand Trilateral Highway.
Defence and Security
- Expansion of defence dialogues and joint military exercises (e.g., Exercise Maitree).
- Cooperation in cybersecurity, counter-terrorism, and intelligence sharing.
Economic and Trade Engagement
- Enhancing supply chain resilience, boosting bilateral trade, and exploring FTA upgradation.
Science and Innovation
- Joint ventures in renewable energy, space technology, and biotech innovation.
- Cooperation on digital public infrastructure.
Cultural Relations
- Promotion of Buddhist heritage, education exchanges, and tourism.
- Engagement with the Indian diaspora in Thailand.
Artificial Rain to combat Delhi’s Air Pollution
- 06 Apr 2025
In News:
With the national capital grappling with chronic air pollution every winter, the Delhi Government is exploring artificial rain (cloud seeding) as a potential mitigation strategy. In a recent high-level meeting chaired by Environment Minister Manjinder Singh Sirsa, experts and representatives from key institutions brainstormed the feasibility and logistics of implementing cloud seeding in Delhi's airspace.
What is Artificial Rain (Cloud Seeding)?
- Cloud seeding is a form of weather modification aimed at inducing rainfall.
- It involves spraying chemical agents such as silver iodide or salt particles into clouds to stimulate condensation and precipitation.
- Requires favourable meteorological conditions, especially adequate moisture and cloud density.
- Usually conducted using aircraft or ground-based dispersal systems.
Significance for Delhi:
- Rainfall helps settle airborne particulate matter (PM2.5 and PM10), thereby reducing pollution levels.
- Delhi’s air quality worsens in winter due to a combination of low wind speeds, crop residue burning, vehicular and industrial emissions, and construction dust.
- Artificial rain could serve as an emergency intervention to improve air quality during severe pollution episodes.
Key Highlights of the Meeting:
- Convened by Delhi Environment Department with participation from:
- CPCB, DPCC
- Ministry of Defence, MoEFCC
- IIT-Kanpur, India Meteorological Department (IMD)
- Directorate General of Civil Aviation (DGCA), AAI
- IIT-Kanpur scientists shared results from previous successful cloud seeding trials in Kanpur (2023), demonstrating its potential under ideal conditions.
- Past trials in 2018 also showed partial success, with rainfall occurring in 5 out of 6 attempts during pre-monsoon months.
Challenges Identified:
- Weather-dependence: Effectiveness relies heavily on cloud presence and moisture levels, which are limited in Delhi during winters.
- Airspace clearance and coordination among multiple agencies (civil aviation, defence).
- High costs and uncertain outcomes make it a supplementary, not primary, solution.
Complementary Measures Underway:
- Delhi’s 14-point action plan to curb dust pollution includes:
- Anti-smog guns, covering construction sites, cleaning of construction vehicles, andregulated debris disposal.
- Exploring static ionisation systems as an alternative to cloud seeding for artificial precipitation.
Heard and McDonald Islands
- 05 Apr 2025
In News:
Donald Trump has imposed a 10% tariff on imports from the Heard and McDonald Islands.
Geographical Context
- Heard Island and McDonald Islands (HIMI) are remote, sub-Antarctic volcanic islands in the southern Indian Ocean, situated:
- ~4,100 km southwest of Perth (Australia),
- ~1,600 km north of the Antarctic coast.
- They are one of Australia’s seven external territories, administered directly by the Australian government.
Physical and Ecological Significance
- Volcanically active: Home to Big Ben (2,745 m, Mawson Peak), Australia’s highest mountain outside the mainland and Tasmania.
- McDonald Island has expanded due to recent eruptions in the 1990s and 2000s.
- Only volcanically active sub-Antarctic islands, making them valuable for studying:
- Earth’s crustal processes,
- Glacial dynamics,
- Oceanic and atmospheric changes.
- Designated as a UNESCO World Heritage Site (1997) and classified under IUCN Category Ia (Strict Nature Reserve).
Biodiversity
- Inhabited by marine birds and mammals like:Penguins, elephant seals, and seabirds.
- Notable for being free from invasive species, aiding biodiversity and evolutionary research.
- Largely uninhabited by humans; no known permanent population.
US Tariff Controversy
- The US President (Donald Trump) imposed a 10% tariff on imports from HIMI—despite the islands having no known exports or trade with the US.
- The islands have no recent human presence and are mainly home to wildlife.
- Other Australian external territories targeted by similar tariffs include:
- Norfolk Island – 29% tariff despite limited economic activity.
- Cocos (Keeling) Islands and Christmas Island – 10% tariff.
- The British Indian Ocean Territory (BIOT), including Diego Garcia, also faced a 10% tariff. Diego Garcia hosts a US-UK military base, with no civilian population.
Mitathal and Tighrana: Newly Protected Harappan Sites in Haryana

- 05 Apr 2025
In News:
The Haryana Government has declared Mitathal and Tighrana, two historically significant Harappan civilisation sites in Bhiwani district, as protected archaeological sites under the Haryana Ancient and Historical Monuments and Archaeological Sites and Remains Act, 1964.
Location and Legal Status
- Both sites are located in Mitathal and Tighrana villages of Bhiwani district, Haryana.
- The notification was issued on March 13, 2025, designating a 10-acre area at Mitathal for protection.
- The Heritage and Tourism Department will ensure preservation through site fencing and deployment of guards.
Mitathal Site: Key Highlights
- Period: Dates to the Copper-Bronze Age, roughly 3rd to 2nd millennium BCE.
- Archaeological Finds:
- Well-baked red pottery with black painted motifs like pipal leaves and fish scales.
- Beads, copper tools, bangles, terracotta, and bone artefacts.
- Historical Timeline:
- First identified in 1913 through Samudragupta coins.
- Systematic excavations began in 1965–68 and continued post-2016 by the Central University of Haryana.
- Cultural Features:
- Reflects urban planning and craftsmanship typical of the Harappan Civilization.
Tighrana Site: Cultural Significance
- Chronology: Rich in pre-Harappan, Harappan, and post-Harappan layers.
- Inhabitants: Associated with Sothian culture – early Chalcolithic farming communities (~2400 BCE).
- Settlement Traits:
- Mud-brick houses, some possibly fortified.
- Use of bichrome wheel-made pottery (black and white designs).
- Artefacts:Green carnelian bangles, beads, and tools suggest a thriving bead and jewellery industry.
Archaeological and Cultural Importance
- Continuity of Settlement: Offers insight into continuous human occupation from Pre-Siswal to Post-Harappan periods.
- Socio-economic Insights:Demonstrates early agricultural practices, urban planning, and craft traditions in the Indo-Gangetic divide.
Background: Harappan Civilization
- Also known as the Indus Valley Civilization (IVC); flourished around 2500 BCE.
- One of the world’s oldest urban civilizations, alongside Mesopotamia, Egypt, and China.
- Classified as Bronze Age due to artefacts made from copper-based alloys.
- Key excavations:
- Harappa (1921–22) by Daya Ram Sahni.
- Mohenjo-daro (1922) by R.D. Banerji, under supervision of Sir John Marshall (ASI).
Protection of Interests in Aircraft Objects Bill, 2025

- 04 Apr 2025
In News:
The Protection of Interests in Aircraft Objects Bill, 2025, recently passed by the Rajya Sabha, aims to implement two key international agreements in India’s legal framework:
- Cape Town Convention on International Interests in Mobile Equipment (2001)
- Protocol to the Convention on Matters Specific to Aircraft Equipment
Objective:
To provide legal clarity and security to stakeholders in the aviation leasing industry by integrating global standards into Indian law.
Background:
- India became a signatory in 2008 after Cabinet ratification in 2007.
- The Cape Town Convention addresses complex issues of cross-border leasing and financing of high-value mobile assets like aircraft, helicopters, and engines.
- With over 86.4% of India's 840 commercial aircraft under leasing arrangements, there was an urgent need for a dedicated legal framework.
Key Provisions:
- Directorate General of Civil Aviation (DGCA) is designated as the registry authority.
- Responsible for registration and deregistration of aircraft.
- Creditors must notify the DGCA prior to initiating recovery actions in case of defaults.
- In case of default by airlines:
- Creditors can reclaim aircraft or related equipment within two months, or as per a mutually agreed period.
- Lessors and airlines are required to regularly inform the DGCA about dues and lease activities.
- The central government is empowered to make rules for the implementation of the convention and protocol.
Expected Benefits:
- Enhances legal protection for creditors and lessors.
- Reduces leasing costs by an estimated 8–10%, potentially lowering airfares for consumers.
- Encourages the growth of a domestic aircraft leasing industry, reducing dependence on foreign jurisdictions like Ireland, Singapore, and Dubai.
Civil Aviation Minister’s Remarks:
- The Bill addresses a long-standing legislative vacuum.
- It will bolster investor confidence and attract leasing businesses to India.
- Airfare regulation remains complex and is influenced by multiple factors including fuel prices, leasing charges, and maintenance costs.
India’s Agricultural Trade Dilemma
- 04 Apr 2025
In News:
India faces growing global pressure to liberalise its agricultural markets amidst trade negotiations, FTAs, and WTO commitments. At the same time, ensuring food security and protecting rural livelihoods remains a domestic priority.
Benefits of Global Trade Integration
- Export Revenue Growth: Enhanced access to global markets has increased agri-exports.E.g., India’s agricultural exports to the US were worth $8.4 billion.
- Technology & Investment Inflow: FTAs can attract agri-tech innovations and cold-chain infrastructure.E.g., partnerships with developed nations enable modernisation of storage and logistics.
- Market Efficiency: Global competition improves price discovery and benefits quality producers.
- Geopolitical Leverage: Trade agreements strengthen India’s role in forums like the WTO and BRICS.
- Input Security via Diversified Imports: Import of essentials like palm oil and fertilisers protects supply chains. E.g., Indonesia’s 2022 palm oil export ban highlighted India’s vulnerability.
Importance of Domestic Food Security
- Rural Livelihoods: Agriculture employs ~42% of the workforce, primarily small and marginal farmers.Over 100 million dairy farmers depend on protective tariffs.
- Nutrition and Price Stability: Domestic self-sufficiency guards against global price shocks.
- Reduced Import Dependence: A strong domestic base cushions India during crises.E.g., Ukraine war caused a spike in fertiliser prices, exposing dependency.
- Political and Strategic Stability: Ensures rural harmony and policy autonomy.
Challenges of Trade Liberalisation
- Subsidy Imbalances: Developed nations offer massive farm subsidies.E.g., US farm aid of $10 billion distorts global price competitiveness.
- FTA Pressures: Demands from countries like New Zealand to lower dairy tariffs threaten Indian farmers.
- WTO Constraints: India’s MSP system faces scrutiny under global trade rules.
- Illegal Imports: Despite bans, cheap imports like Chinese garlic infiltrate markets, undermining domestic prices.
- Retaliatory Tariffs: India’s high tariffs invite reciprocal duties.E.g., the US “reciprocal tariff” policy under Trump era.
Macroeconomic Risks
- Rural Unemployment: Liberalisation could displace small-scale farmers.
- Trade Deficit Worsening: Import liberalisation without export flexibility can widen the deficit.
- Revenue Loss: Tariff cuts may reduce fiscal space for welfare schemes.
- Exposure to Global Shocks:E.g., Ukraine war disrupted fertiliser supply; Indonesia’s ban hiked edible oil prices by 27% in India.
Way Forward
India must adopt a calibrated, strategic approach:
- Selective Liberalisation: Lower tariffs only in non-sensitive sectors while safeguarding essential crops.
- Investment-Oriented FTAs: Prioritise infrastructure, tech transfer, and rural development over tariff cuts.
- Domestic Strengthening: Boost agri-logistics, seed innovation, and food processing capabilities.
- Trade Vigilance: Strengthen customs and surveillance to prevent substandard or banned imports.
- WTO Reforms: Advocate for fair subsidy norms and transparent trade rules.
Naini Lake
- 04 Apr 2025
In News:
Naini Lake record-low water levels in 2025.
Geographical and Environmental Significance
- Location: Heart of Nainital, Uttarakhand.
- Type: Natural, kidney-shaped freshwater lake.
- Surroundings: Enclosed by seven hills.
- Deepest Point: 89 feet.
- Gauge Level: 12 feet (normal level).
- Water Level (2025): 4.7 feet – lowest in 5 years, nearing “zero level”.
- Zero Level Meaning: Water level below normal gauge, not fully dry.
Ecological & Civic Importance
- Water Source: Supplies 10 million litres/day of drinking water.
- 2024 Dependence: Met 76% of Nainital’s water demand.
- Aquifer Recharge:Sukhatal Lake is a major recharge zone.
Factors Behind Depletion
1. Climate Variability
- Rising Temperatures: +1.5°C rise in Uttarakhand (1970–2022).
- Rainfall Data:
- 2022: 2400 mm (good year).
- 2024: Dropped to 2000 mm.
- Winter Rainfall (Jan–Mar 2025): 107 mm.
- Snowfall Days:
- 2022: Four.
- 2025: None.
2. Anthropogenic Pressures
- Urbanisation& Encroachment:
- Concrete construction → low rainwater infiltration.
- Encroachments on wetlands and recharge zones.
- Pollution Issues:
- Untreated wastewater discharge.
- Improper solid waste disposal.
- Overflowing sewage into stormwater drains.
- Tourism & Homestays:
- High tourist influx.
- Rise in homestays; ~1 in 3 houses converted.
Institutional & Governance Challenges
- Overlapping Jurisdictions:
- Inadequate coordination among agencies.
- Aging Infrastructure:
- Old water distribution system, unable to meet demand.
- Reports Highlighting Issues:
- USCST 2017:Naini Lake most manipulated among Kumaon lakes.
- 2024 Research (CEDAR): Faulty water governance exacerbating stress.
Legal and Civic Interventions
- SC Intervention (1993): Ban on commercial complex projects.
- Uttarakhand HC (2022): Stay on Sukhatal beautification project.
- Petitions Filed: Alleging degradation due to construction on recharge areas.
Way Forward
- Ecosystem-Based Approach: Recognize catchment area, slope vulnerability, and recharge zones.
- Rejuvenation Focus:Prioritisenatural hydrological restoration over tourism promotion.
- Sustainable Urban Planning: Regulation of construction, homestays, and infrastructure development.
Tribhuvandas Patel
- 03 Apr 2025
In News:
The Lok Sabha recently approved a bill to establish the Tribhuvan Sahkari University in Anand, Gujarat, named in honour of TribhuvandasKishibhai Patel, a seminal figure in India’s cooperative movement and a founding architect behind Amul.
Who was Tribhuvandas Patel?
- Born in 1903 in a farming family in Gujarat, Tribhuvandas Patel was an Indian freedom fighter, lawyer, and social reformer.
- A dedicated follower of Mahatma Gandhi, he actively participated in the civil disobedience movement, anti-untouchability campaigns, and rural development initiatives.
- He was first arrested during the Salt Satyagraha in 1930 at Nasik and later in Visapur, where he resolved to commit his life to public service.
- Between 1948 and 1983, he served as the President of Harijan Sevak Sangh, an organisation founded by Gandhi to uplift marginalized communities.
Role in India's Cooperative Movement
- In 1946, with encouragement from Morarji Desai and Sardar Vallabhbhai Patel, Tribhuvandas spearheaded the formation of the Kaira District Cooperative Milk Producers’ Union Ltd. (KDCMPUL) to counter exploitative practices by private dairies such as Polson Dairy.
- His strategy began with organizing village-level milk cooperatives, where membership was inclusive, cutting across caste, class, and religion.
- Recognizing the need for professional management, he brought in Dr. VergheseKurien, who later led India’s White Revolution.
Institution Building and Legacy
Tribhuvandas Patel played a pivotal role in laying the foundations of several key institutions that transformed India’s dairy sector:
- Gujarat Cooperative Milk Marketing Federation (GCMMF)
- National Dairy Development Board (NDDB)
- Institute of Rural Management, Anand (IRMA)
His lifelong efforts significantly empowered rural milk producers and contributed to India’s emergence as a dairy powerhouse.
Recognitions and Awards
- Ramon Magsaysay Award (1963) for Community Leadership
- Padma Bhushan (1964) from the Government of India for his services to society
Weather Balloons and Global Forecasting Concerns
- 24 May 2025
Background:
Weather balloons, crucial for upper atmospheric observations, are facing reduced deployment in the United States due to recent budget cuts. The National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) has significantly scaled back balloon launches since March 2025 following a 25% budget reduction. This has raised global concerns among meteorologists over the potential decline in forecast accuracy.
What are Weather Balloons?
- Inventor: Léon Teisserenc de Bort (France), first launched them in 1896; discovered the tropopause and stratosphere.
- Composition: Latex balloons filled with helium or hydrogen.
- Altitude: Can ascend up to 1,15,000 feet (35 km) in approximately 2 hours.
- Instrument Carried: Radiosonde – a small device suspended ~66 feet below the balloon that transmits real-time atmospheric data (temperature, pressure, humidity, wind) via radio signals.
- Technology: Modern radiosondes are lightweight, GPS-enabled, and energy-efficient.
Historical Context:
- Initial upper-air measurements in the 18th century used kites with meteorographs.
- Weather balloons replaced kites due to higher altitude capability and improved data reliability.
- The introduction of radiosondes in the 1930s revolutionized weather forecasting by enabling real-time data transmission.
Importance of Upper Air Observations
- Upper atmosphere (>5,000 feet) plays a vital role in generating surface-level weather conditions like rain, storms, and drought.
- Weather balloons help bridge the data gap between surface stations and satellites by offering vertical atmospheric profiles.
- Twice-daily launches at 0000 UTC and 1200 UTC (~5:30 AM and 5:30 PM IST) are globally coordinated at over 900 stations, including 56 in India.
India’s Scenario
- The India Meteorological Department (IMD) conducts routine balloon launches for weather forecasting.
- The National Balloon Facility (NBF) in Hyderabad, jointly managed by ISRO and TIFR, supports high-altitude atmospheric research.
Impact of Reduced Launches
- NOAA’s scaling down has sparked fears of reduced forecast accuracy globally.
- A similar move by Russia in 2015 led to a measurable decline in forecast quality across Europe, highlighting the critical role radiosondes play.
- NOAA plans to replace some balloon data with AI-powered alternatives developed by private firms to reduce costs.
Why Weather Balloons Still Matter in the Satellite Era
- Satellites provide large-scale imagery but lack the granularity of vertical atmospheric data.
- Weather balloons offer crucial insights into lower- and mid-atmospheric layers where storms and climate dynamics form.
- Radiosonde data is essential for calibrating satellite measurements, ensuring reliability in climate modeling and forecasting systems.
Mizoram Becomes India’s First Fully Literate State
- 22 May 2025
In News:
Mizoram has officially become India’s first fully literate state, attaining a literacy rate of 98.2% according to the Periodic Labour Force Survey (PLFS) 2023–24. This achievement surpasses the 95% threshold defined by the Ministry of Education to classify a region as fully literate.
Definition of Literacy
- As per the Office of the Registrar General of India, a literate person is someone aged 7 years or above who can read and write with understanding in any language.
- Under NEP 2020 and in alignment with SDG 4.6, the definition has expanded to include the ability to read, write, and compute with comprehension, and includes digital and financial literacy and critical life skills.
India’s Literacy Landscape (2023–24)
- National Literacy Rate: 80.9% (age 7+)
- Mizoram: 98.2% (Highest; now declared fully literate)
- Ladakh: First UT to achieve full functional literacy under ULLAS
- Lowest Literacy Rates: Andhra Pradesh (72.6%), Bihar (74.3%)
ULLAS – Nav Bharat SaakshartaKaryakram
The achievement is attributed to the ULLAS (Understanding Lifelong Learning for All in Society)programme, a centrally sponsored scheme running from 2022 to 2027, aligned with the National Education Policy (NEP) 2020.
Key Features:
- Target Group: Adults aged 15 years and above who missed formal education.
- Implementation: Based on volunteerism and the principle of Kartavya Bodh (sense of duty).
- Components:
- Foundational Literacy and Numeracy
- Critical Life Skills (including digital, legal, financial literacy)
- Basic Education
- Vocational Skills Development
- Continuing Education
- Assessment: Foundational Literacy and Numeracy Assessment Test (FLNAT) is conducted periodically for certification.
- Digital Tools: Resources provided through the DIKSHA platform and the ULLAS mobile/web portal in regional languages.
What is Functional Literacy?
Functional literacy refers to an individual's ability to apply reading, writing, and numeracy in daily tasks, enabling personal development and community participation.
Other Key Educational Initiatives
- PM SHRI Schools
- Sarva Shiksha Abhiyan
- PRAGYATA (Digital Education)
- Mid-Day Meal Scheme
- BetiBachaoBetiPadhao
- National Programme on Technology Enhanced Learning (NPTEL)
Asiatic Lion Census 2025

- 22 May 2025
In News:
According to the 16th Asiatic Lion Census (2025) conducted by the Gujarat Forest Department, the Asiatic lion (Panthera leopersica) population has grown from 674 in 2020 to 891 in 2025, marking a 32.2% increase in five years.
Key Highlights:
- Core Areas (Protected Forests & Sanctuaries): 384 lions
- Non-Forest Areas: 507 lions (up from 340 in 2020)
- 44.22% of the total population now lives outside traditional protected zones.
- Gir National Park, along with Gir Wildlife Sanctuary and Pania Wildlife Sanctuary, holds 394 lions—the core population.
- Amreli district leads with 257 lions, while Mitiyala Wildlife Sanctuary has seen its count double to 32.
- Barda Wildlife Sanctuary near Porbandar recorded 17 lions, marking a population return since 1879.
- New satellite populations identified near Jetpur and Babra-Jasdan.
- Adult Females: 330 recorded—a 27% increase since 2020, indicating strong reproductive potential.
Census Methodology
The 2025 census employed direct beat verification, a statistically rigorous method:
- The landscape was divided into zones and sub-zones.
- Personnel included officials, enumerators, supervisors, and volunteers.
- Unlike the tiger census (which spans 2 years), the lion census was completed in just 3 days.
Project Lion (Launched in 2020)
Aimed at ensuring the long-term conservation of Asiatic lions, Project Lion focuses on:
- Habitat restoration
- Strengthening the prey base
- Human-wildlife conflict mitigation
- Monitoring via advanced technology, including:
- Radio-collars
- Camera traps
- Global Positioning System (GPS) tracking
- GIS-based real-time surveillance
- AI-driven tools likeSIMBA, e-GujForest, andAlert Generation System
- Automated sensor grids (magnetic, motion, infrared)
Habitat and Legal Status
- Natural Habitat: Grasslands, open woodlands, savannas, and scrublands.
- Main Range: Gir Forests in Gujarat; Barda Wildlife Sanctuary emerging as a second habitat.
- Legal Protection:
- Schedule I and IV of the Wildlife (Protection) Act, 1972
- Appendix I of CITES
- IUCN Status: Vulnerable
Distinctive Traits
- Smaller in size compared to African lions.
- Males have a moderate mane allowing visible ears.
- A distinct belly fold—rare in African lions.
- No fixed breeding season.
Global Conservation Context
India is a founding member of the International Big Cats Alliance (IBCA), launched in 2023 to enhance global cooperation on big cat conservation, including lions.
Additionally, the IUCN’s Green Status of Species (2025) introduced a recovery-based conservation framework. Lions are currently classified as "Largely Depleted", highlighting the need for sustained and collaborative conservation actions.
Supreme Court Strikes Down Retrospective Environmental Clearances

- 20 May 2025
In News:
In a significant verdict for environmental governance, the Supreme Court of India, in the case Vanashakti v. Union of India (May 2025), struck down the 2017 notification and 2021 Standard Operating Procedure (SOP) issued by the Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change (MoEF&CC). These instruments allowed retrospective (ex-post facto) environmental clearances—i.e., granting environmental approval to industries after they had begun operations without prior clearance.
What are Retrospective Environmental Clearances?
- Definition: Ex-post facto clearances permit projects to start operations without prior Environmental Impact Assessment (EIA) approval and seek clearance later.
- Contradiction: These violate the EIA Notification, 2006, issued under the Environment (Protection) Act, 1986, which mandates prior approval before beginning any project impacting the environment.
Details of the 2017 Notification & 2021 SOP
- 2017 Notification:
- Provided a one-time 6-month window for industries that violated clearance norms to regularize operations.
- Central-level appraisal for all cases, regardless of project size or category.
- Violators remained subject to action by State Pollution Control Boards.
- Intended to bring violators under regulatory oversight and ensure remediation costs.
- 2021 SOP:
- Issued to standardize processing of violation cases following an NGT directive.
- Did not use the term “ex-post facto”, but allowed project appraisals after operations began—effectively regularising violations.
- Appraisal Committee: A committee led by NEERI’s former director S.R. Wate appraised such cases over 47 meetings between 2017–2021.
Supreme Court’s Rationale
- Violation of Fundamental Rights:
- Held the 2017 Notification and 2021 SOP unconstitutional as they violate:
- Article 21 – Right to a clean and pollution-free environment.
- Article 14 – Equality before law; violators were unjustly protected.
- Held the 2017 Notification and 2021 SOP unconstitutional as they violate:
- Against Environmental Jurisprudence:
- Reaffirmed past rulings:
- Common Cause v. Union of India (2017)
- Alembic Pharmaceuticals v. Rohit Prajapati (2020)
- These had declared ex-post facto clearances illegal and anathema to environmental law.
- Reaffirmed past rulings:
- On “One-Time” Justification:
- Rejected the Centre’s argument that the 2017 measure was a one-time exception.
- Even a one-time relaxation, the Court said, undermines environmental protections and encourages illegal practices.
- Criticized Centre's Intent:
- Noted that the SOP was a disguised attempt to bring back ex-post facto clearances.
- Warned against such “clever drafting” to bypass the law.
Implications of the Verdict
- Reinforces EIA Norms: Upholds the mandatory prior environmental clearance process under EIA 2006.
- Strengthens Environmental Rule of Law: Emphasizes precautionary principle and polluter pays principle.
- Curtails Regulatory Evasion: Sends a clear message that industries cannot bypass environmental safeguards.
- Protects Public Health: Highlights link between environmental damage and issues like pollution in Delhi.
- Judicial Oversight: Asserts constitutional checks on executive actions that dilute environmental protections.
Extended Fund Facility (EFF)

- 16 May 2025
In News:
Recently, the IMF Executive Board approved a $1 billion disbursement to Pakistan under the Extended Fund Facility (EFF). This brings total disbursements under the current EFF arrangement to $2.1 billion out of a total planned support of $7 billion.
What is the Extended Fund Facility (EFF)?
- Governed by: International Monetary Fund (IMF), part of the Bretton Woods Institutions.
- Purpose: To support countries facing medium-term balance of payments problems caused by structural economic weaknesses.
- Nature of Support:Loan (not a grant or aid), with extended repayment periods.
- Tenure: Typically spans over three or more years, with phased disbursements.
- Objective: Enables countries to implement structural reforms such as:
- Broadening the tax base
- Strengthening financial institutions
- Reducing fiscal deficits
- Managing inflation
Eligibility for EFF:
To qualify, countries must:
- Exhibit persistent balance of payments stress
- Have deep-rooted economic weaknesses (e.g., poor governance, low investment, weak tax systems)
- Show a willingness to undertake IMF-monitored reforms
Pakistan’s Economic Situation:
- Stagnant GDP: Estimated at $338 billion in 2023, lower than in 2017.
- High Inflation: Averaging over 20% between 2020–2024.
- Frequent Borrowing: Pakistan has received 28 IMF loans in 35 years, and also borrows from:
- China
- UAE and Saudi Arabia
- ADB, IDB, Paris Club, Nordic Development Fund
Key Challenges:
- Economic mismanagement
- Low savings and investment
- Infrastructure gaps
- Low female workforce participation
- High population growth
Why Did IMF Approve the 2025 Tranche?
The IMF approved the tranche based on positive macroeconomic developments:
- Reduced inflation: Down to 0.3% in April 2025
- Improved forex reserves
- Fiscal reforms: Implementation of the FY2025 budget and Agricultural Income Tax
- Credible reform measures: IMF noted Pakistan’s “significant progress” in restoring economic stability.
SCALP Missile
- 11 May 2025
In News:
During Operation Sindoor, the Indian Air Force reportedly employed SCALP missiles launched from Rafale fighter jets to target high-value terror infrastructure in Pakistan and Pakistan-occupied Kashmir (PoK).
What is the SCALP Missile?
- The SCALP (Système de CroisièreAutonome à Longue Portée) is a long-range, air-launched cruise missile designed for deep-strike missions.
- It is also known by its British designation, Storm Shadow.
- Developed jointly by France and the United Kingdom, it is built for precision attacks on strategic, fixed, and fortified targets.
- Global Operators: The missile is in operational use by the air forces of:India, France, United Kingdom, Egypt, Italy, Greece, Saudi Arabia, Qatar, and UAE.
- Indian Integration: The Indian Air Force has integrated the SCALP missile with its Rafale fleet, enhancing India's capacity to conduct long-range precision strikes with minimal collateral damage.
Key Features:
Feature Description
Range Approximately 500 km
Warhead 450 kg high-explosive, designed to penetrate hardened structures
Weight Around 1,300 kg
Dimensions Length: ~5 metres; Wingspan: ~3 metres
Speed Subsonic (around Mach 0.8)
Guidance Systems Combined GPS/INS navigation, terrain-following radar, and
infrared homing for terminal precision
Stealth Capability Optimized for low-altitude flight to evade radar detection
Accuracy Uses image-based terminal guidance to match
preloaded target images
All-weather Capability Can operate under diverse weather conditions
Kosmos 482
- 11 May 2025
In News:
A 500-kg fragment of the Soviet-era Kosmos 482 spacecraft, launched in 1972 as part of the Venera programme, is expected to make an uncontrolled re-entry into Earth’s atmosphere around May 10, 2025, after over 53 years in orbit.
What was the Kosmos 482 Mission?
- Launched: March 31, 1972, by the Soviet Union.
- Objective: To land a probe on Venus and collect atmospheric and surface data.
- Programme: Part of the Venera series (1961–1984), which launched 28 probes to Venus.
- 13 entered the Venusian atmosphere.
- 10 successfully landed on the surface.
- Twin Mission:Venera 8, launched on March 27, 1972, successfully landed on Venus and transmitted data for 50 minutes.
Mission Failure and Orbit Status
- The mission failed due to a timer malfunction in the rocket's upper stage, which shut down prematurely, leaving the spacecraft stranded in low Earth orbit instead of heading to Venus.
- The main spacecraft eventually burned up in the atmosphere, but a lander module (approx. 500 kg) remained in orbit.
Expected Re-entry (May 2025)
- The lander module is currently being dragged down by atmospheric friction.
- No precise location or time of impact is known due to the uncontrolled nature of its descent.
- Expected re-entry corridor lies between 52° North and 52° South latitude, covering:
- Africa, Australia
- Most of the Americas
- Much of southern and mid-latitude Europe and Asia
Is it a risk to Earth?
- The lander is made of titanium, with a melting point of ~1,700°C, higher than typical atmospheric re-entry temperatures (~1,600°C).
- This increases the likelihood of survival through re-entry.
- Possible outcomes as per space debris experts:
- “A splash” (ocean impact) — least dangerous
- “A thud” — impact on uninhabited land
- “An ouch” — impact on populated area (least desired scenario)
- If intact, the object could impact Earth at a speed of ~242 km/h, similar to a high-speed train.
HAROP Drone
- 11 May 2025
In News:
On May 8, 2025, as part of Operation Sindoor, India reportedly used Israeli-made HAROP loitering munitions to destroy a Pakistani air defence system in Lahore, in response to Pakistan’s attempted attacks on Indian military installations.
What is HAROP?
- HAROP is an advanced loitering munition, also known as a suicide drone or kamikaze drone.
- Developed by Israel Aerospace Industries (IAI), it combines features of a UAV and a missile.
- It is designed to loiter over an area, search for high-value targets, and crash into the target with an explosive payload.
Key Characteristics and Capabilities
Feature Description
Function Combines surveillance and attack roles; can loiter, identify, and
strike autonomously or manually
Targets Designed to hit air defence systems, radars, command posts,
tanks, and moving military assets
Sensor Equipped with an Electro-Optical (EO) sensor for real-time
target tracking and acquisition
Endurance Up to 9 hours of loitering capability for deep-target missions
Launch Platforms Can be launched from truck-mounted canisters,
naval vessels, or ground stations
Navigation Resistance GNSS (GPS)-jam resistant, effective in communication-
denied environments
Strike Profile Executes attacks from various angles using
steep or shallow dive maneuvers
Evolution and Operational Use
- HAROP is an evolution of the earlier HARPY system, which was radio-frequency (RF) guided.
- Unlike the HARPY, HAROP uses EO sensors for improved visual target identification.
- HAROPs are "fire-and-forget" weapons, meaning they do not require active control after launch.
- The system has been described by IAI as the “King of the Battlefield”, with a claimed mission success rate of 98%.
- Proven effective in multiple combat scenarios, including suppression of enemy air defences (SEAD).
Carbon Border Adjustment Mechanism (CBAM)
- 11 May 2025
In News:
India has warned it will retaliate if the United Kingdom implements its proposed Carbon Border Adjustment Mechanism (CBAM) from January 1, 2027, calling it a violation of the Common But Differentiated Responsibilities (CBDR) principle of international climate agreements.
What is Carbon Border Adjustment Mechanism (CBAM)?
- It is a carbon tax on imports based on their carbon intensity of production.
- Aim: Prevent carbon leakage by aligning the cost of carbon between domestic and foreign producers.
- Sectors likely to be initially targeted include steel, cement, aluminium, and energy-intensive products.
- The UK is expected to implement its version of CBAM in 2027, following a similar approach by the European Union.
India’s Concerns
- Violation of CBDR Principle
- CBAM undermines the UNFCCC and Paris Agreement, which recognize that developing countries require flexibility and support for decarbonization.
- India’s per capita emissions are low, but its carbon intensity is higher due to developmental needs.
- Unfair Trade Practice
- CBAM could nullify tariff concessions negotiated under the India–UK Free Trade Agreement (FTA).
- Finance Minister Nirmala Sitharaman and Commerce Minister Piyush Goyal have labelled CBAM “unfair” and discriminatory.
- Double Taxation and Export Losses
- Indian exporters may face double taxation—domestic environmental levies and UK’s border tax.
- India proposed a ‘rebalancing mechanism’ and MSME carve-out, both of which the UK declined.
- Export-heavy sectors like textiles, leather, ceramics, engineering goods, and steel may be hit hard due to sustainability compliance burdens.
- MSME Vulnerability
- Labour-intensive MSMEs lack the capacity to meet expensive ESG norms and carbon tracking requirements.
- India's request for exemption or compensation for MSMEs was not accepted.
India’s Response Strategy
- India reserves the right to retaliate if CBAM is imposed.
- Potential responses include:
- Domestic carbon taxation to offset UK’s CBAM and use revenue for green transition.
- Invoking a rebalancing clause under the FTA’s “general exceptions” (similar to GATT), allowing trade countermeasures for environmental or public interest.
Strategic Implications for India
- Non-tariff barriers like CBAM can undermine market access gained through FTAs.
- India must stay alert to evolving trade conditions involving environment, labour, IPR, and gender standards, which often require policy adjustments.
- Calls for India to strengthen its carbon tracking, ESG frameworks, and climate-compliant production systems to remain globally competitive.
Saola Genome Mapping
- 11 May 2025
In News:
An international team of scientists has successfully mapped the genome of the saola (Pseudoryxnghetinhensis), the world’s rarest large land mammal, providing critical insights for conservation through genetic rescue and captive breeding.
About Saola
- Common Name: Asian Unicorn
- Scientific Name: Pseudoryxnghetinhensis
- First Described: 1993 (based on a skull found in Vietnam in 1992)
- Classification: Bovine species, closely related to cattle but resembling an antelope
- Habitat: Endemic to the Annamite Mountains along the Laos–Vietnam border; prefers humid evergreen forests
- IUCN Status: Critically Endangered
- Estimated Population (2015): 50–300 individuals
- Physical Traits:
- Height: ~33 inches at shoulder
- Both sexes possess straight, parallel horns (~20 inches)
- Distinct white facial markings and muzzle scent glands
Major Threats
- Habitat loss, primarily due to agricultural expansion and forest degradation
- Poaching and indiscriminate snaring, including by-catch in traps set for other animals
- Lack of successful captive care: Over 20 captured saolas died in the 1990s due to inadequate professional care
Genome Mapping and Key Findings
- Sample Base: Genomes of 26 individuals sequenced using remains sourced from hunter households
- Population Divergence: Two genetically distinct populations emerged 5,000–20,000 years ago, likely due to:
- Forest fragmentation during/after the Last Glacial Maximum
- Expansion of human activities such as agriculture, burning, and hunting around 4,000 years ago
- Genetic Complementarity: Each population retains different genetic variants, offering potential for enhanced genetic diversity if combined
- Scientific Importance:
- Confirms historical population isolation and genetic loss
- Provides a genetic foundation for targeted conservation efforts
Conservation Implications
- Captive Breeding Program: Plans underway in Vietnam to establish a well-equipped breeding center
- Goal: Capture at least a dozen individuals from both genetic lineages to create a genetically resilient population
- Long-term Vision: Reintroduction into protected forest areas with strict anti-poaching measures
Mission Sankalp
- 10 May 2025
In News:
Mission Sankalp is a large-scale counter-insurgency operation launched jointly by security forces of Chhattisgarh Police, Telangana Police, CRPF, and the elite CoBRA unit. The operation targets the dense forested Karregutta hills along the Chhattisgarh–Telangana border, focusing on dismantling Maoist strongholds and disrupting their operational capabilities.
Key Objectives and Area of Operation
- Primary Aim: Neutralize senior Maoist leaders, especially targeting Battalion 1 of the People’s Liberation Guerrilla Army (PLGA), the armed wing of the CPI-Maoist.
- Geographical Focus: Forested, hilly terrain covering parts of Bijapur district (Chhattisgarh) and Mulugu district (Telangana).
- Goals: Destroy Maoist hideouts, bunkers, arms caches, and logistics networks to cripple the insurgency infrastructure.
Forces Involved and Operational Scale
- Personnel: Over 28,000 personnel including District Reserve Guard (DRG), Bastar Fighters, Special Task Force (STF), CRPF, CoBRA, and support from the Indian Air Force.
- Tactics: Precision strikes guided by aerial surveillance and intelligence inputs in challenging forest terrain.
- Scope: The operation spans approximately 800 square kilometres across the inter-state border area.
Achievements and Impact
- Casualties and Encounters: Since its launch on April 21, around 35 encounters have taken place. At least 26 Maoists, including several senior cadres and three women cadres with bounties of ?8 lakh each, have been killed. Approximately 168 Maoists have been eliminated across Chhattisgarh in 2025, with 151 in the Bastar region.
- Seizures: Security forces have recovered over 2 tonnes of explosives, 400+ improvised explosive devices (IEDs), around 40 firearms, and more than 6 tonnes of ration, medicines, and daily essentials. Hundreds of Maoist hideouts and bunkers have been destroyed.
- Casualties Among Security Forces: Six personnel, including a CoBRA officer, were injured in IED blasts but are now stable.
- Strategic Outcome: The operation has dealt a severe blow to the Maoist command structure, disrupted logistics, and restored state authority in previously inaccessible tribal areas.
Strategic Importance
- Inter-State Cooperation: Mission Sankalp marks one of the largest coordinated anti-Naxal operations in recent years, reflecting enhanced synergy between central and state security forces.
- National Security: It aligns with the Centre’s zero-tolerance policy towards Left Wing Extremism, aiming to weaken the Maoists’ influence and support the restoration of governance and development in affected tribal regions.
- Long-Term Goals: By neutralizing the insurgency's core military units, the operation seeks to create conditions for improved infrastructure, welfare delivery, and civilian confidence in law enforcement.
Persian Gulf vs Arabian Gulf
- 10 May 2025
In News:
The United States, under then-President Donald Trump, proposed a shift in terminology by referring to the Persian Gulf as the “Arabian Gulf” during a state visit to Saudi Arabia, aligning with the preferences of some Arab Gulf countries.
Historical and Geopolitical Background
- The name “Persian Gulf” has been historically documented since the 16th century, appearing in treaties, maps, and international references.
- Arab countries such as Saudi Arabia, UAE, and Bahrain use the term “Arabian Gulf” in national documents and cartography.
- The proposal by Trump faced criticism from Iran, which regards the renaming as a politically motivated act aimed at undermining its historical and cultural identity.
Iran’s Response
- Iran’s leadership, including Foreign Minister Abbas Araghchi, has condemned any attempt to alter the name, calling it a hostile and invalid act with no legal or geographical legitimacy.
- In 2012, Iran had threatened to sue Google for omitting the name "Persian Gulf" from its maps.
International Standards
- The International Hydrographic Organisation (IHO), responsible for standardizing maritime names, continues to officially recognise the name “Persian Gulf.”
- While countries can adopt different terms domestically, they cannot enforce global changes unilaterally.
Geographical Features of the Persian Gulf
- Type: Marginal sea of the Indian Ocean, located in Western Asia.
- Size: ~251,000 km²
- Depth: Average ~50 m; Maximum ~90 m
- Coastline: ~5,117 km; Iran has the longest stretch (~1,536 km)
- Borders:
- North: Iran
- Southwest: Saudi Arabia, UAE, Qatar
- Northwest: Iraq, Kuwait, Bahrain
- Islands:
- Qeshm Island (Iran): Largest in the Gulf (~1,491 km²)
- Bahrain: Sovereign island nation with over 50 islands and a key US naval base
Strategic and Economic Significance
- The Strait of Hormuz, linking the Persian Gulf to the Arabian Sea, is a critical chokepoint for global energy, with ~30% of global oil exports passing through.
- The region is a theatre of military presence, with navies of the US, Iran, and Gulf countries asserting control and influence.
- Strategic islands like Qeshm and Bahrain hold economic and military importance.
Operation Sindoor

- 10 May 2025
In News:
On May 7, 2025, the Indian Armed Forces launched Operation Sindoor, a coordinated precision strike on terrorist camps located in Pakistan and Pakistan-occupied Kashmir (PoK). The operation was a response to the killing of civilians in Pahalgam by Pakistan-backed terrorists.
Key Facts:
- 21 terror camps across 9 locations were targeted.
- Advanced niche-technology weapons were employed to ensure minimal collateral damage.
- The operation highlights India's evolving capability in long-range, precision-guided weaponry.
Major Precision-Guided Weapons in India’s Arsenal
1. HAMMER (Highly Agile and Manoeuvrable Munition Extended Range)
- Origin: France (by Safran)
- Platform: Integrated with Rafale fighter jets
- Range: Up to 70 km
- Features:
- All-weather precision
- Autonomous guidance
- Jamming-resistant
- Operable at low altitude over rough terrains
- Role in Operation: Likely used for air-to-ground strikes on tactical targets.
2. SCALP (Storm Shadow in UK)
- Type: Air-launched stealth cruise missile
- Origin: Europe (by MBDA)
- Range: Up to 450 km
- Navigation: Uses INS, GPS, and terrain referencing
- Capabilities:
- Bunker-penetration
- Low radar signature
- All-weather and night operable
- Relevance: Designed for deep precision strikes, ideal for hardened terrorist infrastructure.
3. METEOR
- Type: Beyond Visual Range Air-to-Air Missile (BVRAAM)
- Origin: MBDA (Europe)
- Propulsion: Solid-fuel ramjet for sustained high-speed interception
- Special Feature: Large No-Escape Zone, effective in electronic warfare conditions
- Use Case: Enhances air superiority and can neutralize enemy aircraft before visual contact.
4. BRAHMOS Supersonic Cruise Missile
- Developed by: DRDO (India) and NPOM (Russia) under BrahMos Aerospace
- Speed: Mach 2.8–3.0
- Range: Initially 290 km, now extended to 450–500 km after India’s MTCR entry
- Warhead: 200–300 kg
- Platforms: Compatible with land, sea, and air platforms
- Features:
- Fire-and-Forget
- Precision strike at low terminal altitude (~10 m)
- Strategic Role: Provides rapid, stealthy, and accurate strikes across the services.
5. Loitering Munitions ("Kamikaze Drones")
- Function: Combines surveillance and strike capabilities
- Features:
- Can loiter over target zones
- Autonomous or semi-autonomous targeting
- High precision against time-sensitive or mobile targets
- Adoption: Increasing induction across the Army, Navy, and Air Force
ECINET: India’s Unified Digital Platform for Elections

- 07 May 2025
In News:
The Election Commission of India (ECI) is set to launch ECINET, a single, unified digital platform aimed at consolidating and simplifying election-related services for voters, officials, political parties, and civil society organizations.
About ECINET:
ECINET will merge over 40 existing mobile and web applications—including the Voter Helpline, cVIGIL, Suvidha 2.0, ESMS, Saksham, KYC App, Voter Turnout app, Know Your Candidate app, and election results app—into one integrated system. This platform will also serve election officials such as Electoral Registration Officers and Booth Level Officers by providing a comprehensive interface.
Objectives:
- Simplify access to electoral services through a single window and one login (single sign-on).
- Eliminate the redundancy of multiple applications and multiple logins.
- Provide real-time access to verified and authenticated election data for all stakeholders.
- Strengthen electoral infrastructure by fostering digital innovation and integration.
- Enhance cybersecurity through robust testing and protocols.
Key Features:
- Unified Platform: Consolidates all election-related apps into one.
- Single Sign-On: One login credential for all services reduces confusion.
- Cross-Device Compatibility: Accessible on smartphones and desktops alike.
- Modern User Interface: Intuitive and user-friendly design.
- Data Integrity: Only authorized ECI officials can enter data, with statutory forms prevailing in case of discrepancies.
- Robust Cybersecurity: Rigorous trials to ensure safety and performance.
- Nationwide Coverage: Designed to serve nearly 100 crore voters and the entire electoral administration.
Timeline:
The ECINET platform is in advanced stages of development and testing and is expected to be launched before the Bihar Assembly elections later this year.
India’s First Inter-State Cheetah Conservation Corridor
- 04 May 2025
In News:
Rajasthan has joined hands with Madhya Pradesh to develop India’s first inter-state cheetah conservation corridor, a landmark initiative under the Cheetah Reintroduction Project. The corridor will facilitate the safe movement of cheetahs across a 17,000 sq. km protected landscape, enhancing conservation and habitat connectivity.
Key Features of the Cheetah Conservation Corridor
Aspect Details
Total Area 17,000 sq. km (MP: 10,500 sq. km; Rajasthan: 6,500 sq. km)
States Involved Madhya Pradesh and Rajasthan
Supported by National Tiger Conservation Authority (NTCA), Wildlife Institute of India (WII)
MoU Status In progress between Chief Ministers of MP and Rajasthan
Geographical Scope and Key Sites
- PalpurKuno National Park (MP):Core site for cheetah reintroduction; located in Sheopur district.
- Gandhi Sagar Sanctuary (MP):Being developed as a second habitat for cheetahs; located in Mandsaur district along the Chambal River.
- Mukundara Hills Tiger Reserve (Rajasthan):Proposed extension site; comprises parts of Darrah, Jawahar Sagar, and Chambal sanctuaries in Kota division.
- Rajasthan Districts Involved:Kota, Bundi, Baran, Jhalawar, Sawai Madhopur, Karauli, Chittorgarh
- Proposed Future Expansion:Forest regions of Jhansi and Lalitpur in Uttar Pradesh
Objectives and Benefits
- Inter-State Wildlife Connectivity:India’s first corridor linking cheetah habitats across state borders.
- Seamless Migration:Enables cheetahs to roam freely between reserves, mimicking natural ecological patterns.
- Ecological Restoration:Aims to revive and conserve India’s arid grassland ecosystems, which are essential habitats for cheetahs.
- Federal Conservation Model:Demonstrates cooperative federalism in wildlife management and biodiversity conservation.
- Global Recognition:Touted as a unique conservation model in Asia, aligning with Convention on Biological Diversity (CBD) targets.
India’s Green Hydrogen Push
- 04 May 2025
In News:
India has signed agreements to supply 4.12 lakh tonnes of green hydrogen derivatives to Japan and Singapore, signaling its emergence as a global leader in green hydrogen. Simultaneously, the Green Hydrogen Certification Scheme of India (GHCI) was launched to ensure transparent and credible verification of green hydrogen production.
Green Hydrogen Certification Scheme of India (GHCI)
- Launched by: Ministry of New and Renewable Energy (MNRE)
- Nodal Agency: Bureau of Energy Efficiency (BEE)
- Support: National Green Hydrogen Mission (2023; outlay ?19,744 crore)
- Certification by: Accredited Carbon Verification (ACV) Agencies
- Operational Basis: Evaluated annually, aligned with the financial year
- Objective:
- Certify hydrogen produced exclusively using renewable energy (e.g., solar, wind, biomass) as "green."
- Promote transparency, traceability, and market credibility.
- Align with India’s target of 5 million metric tonnes (MMT) of green hydrogen production by 2030.
- Enable integration with India’s Carbon Credit Trading Scheme from 2026.
- Key Features:
- Scope: Applies at the project level up to hydrogen purification (excludes transport/storage).
- Eligibility: Applies to hydrogen produced via electrolysis and biomass conversion; additional methods subject to BEE approval.
- Compliance: Mandatory for domestic producers; exempt for export-only units.
- Verification: Annual third-party audits with data logging via the Green Hydrogen Portal.
- GHG Measurement: Emissions calculated in kg CO? equivalent per kg of H?.
- Guarantee of Origin (GO): Validates green hydrogen claims, crucial for global markets.
Significance and Impact
- Credibility Boost: Certified hydrogen gains international recognition and competitive advantage.
- Export Readiness: Facilitates global trade through verified green hydrogen standards.
- Investment Attraction: Defined certification process encourages private and foreign investment.
- Carbon Market Linkage: Future integration with India's carbon trading market allows certificates to become tradable assets.
- Fossil Fuel Reduction: Supports India’s long-term goal of energy transition and emission reduction.
International Agreements
- India to supply 4.12 lakh tonnes of green hydrogen derivatives to Japan and Singapore, enhancing strategic energy ties and export potential.
- Discussions ongoing with state governments to facilitate Power Purchase Agreements (PPAs) for renewable energy sourcing.
- Coordination underway with Ministry of Power and Central Electricity Regulatory Commission (CERC) to address regulatory barriers.
USCIRF’s 2025 Report

- 30 Mar 2025
In News:
In its 2025 Annual Report, the United States Commission on International Religious Freedom (USCIRF) recommended designating India as a "Country of Particular Concern" (CPC), citing alleged systemic violations of religious freedom.
Key USCIRF Recommendations:
- Label India as a CPC under the International Religious Freedom Act (IRFA), 1998.
- Impose targeted sanctions on Indian institutions, including the Research and Analysis Wing (RAW), and individuals such as Vikash Yadav.
- Review bilateral defence agreements, including drone deals.
- Prioritise religious freedom in diplomatic dialogues with India.
- Reintroduce the Transnational Repression Reporting Act, 2024 to monitor global religious freedom violations.
About USCIRF:
- Established by: U.S. Congress (1998) under IRFA.
- Nature: Independent, bipartisan federal agency.
- Not affiliated with: U.S. State Department (but works in coordination).
- Structure: 9 Commissioners appointed by the U.S. President and Congressional leaders.
- Mandate: Monitor global religious freedom (FoRB), advise U.S. leadership, recommend sanctions, and publish annual reports.
Core Functions:
- Track global trends in freedom of religion or belief.
- Recommend policy actions including CPC designation.
- Advocate for religious prisoners of conscience.
- Maintain a FoRB Victims List and issue thematic reports.
India’s Official Response:
The Ministry of External Affairs (MEA) firmly rejected USCIRF’s report, calling it “biased and politically motivated.”
- MEA Spokesperson Randhir Jaiswal criticized the report for misrepresenting isolated incidents and ignoring India’s multicultural and pluralistic society.
- Highlighted India’s 1.4 billion diverse population, representing all major religions.
- Emphasized that USCIRF’s assessments reflect a deliberate narrative rather than genuine concern for religious rights.
- Asserted that such reports would not affect India’s image as a democratic and tolerant nation.
- Called for USCIRF itself to be recognized as an “entity of concern.”
Vertically-Launched Short-Range Surface-to-Air Missile (VL-SRSAM)
- 30 Mar 2025
In News:
India successfully conducted a flight test of the VL-SRSAM from a defence testing range off the Odisha coast.
Overview:
- Type: Indigenous short-range surface-to-air missile (SRSAM)
- Developed by: Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO)
- Purpose: Designed for quick reaction air defence, capable of intercepting a variety of aerial threats including low-altitude sea-skimming targets.
- Users:Originally developed for the Indian Navy, with applications now extending to the Indian Air Force for safeguarding air bases.
Performance Parameters:
- Initial range: 40 km (Navy version)
- Extended range: Up to 80 km
- Maximum altitude: 16 km
- Top speed: Mach 4.5
Technical Specifications:
- Length: 3.93 meters
- Diameter: 178 mm
- Wingspan: 508 mm
- Weight: ~170 kg
- Propulsion: Solid fuel
- Guidance System:
- Mid-course: Inertial navigation based on fibre-optic gyroscope
- Terminal phase: Active radar homing
- Launcher Configuration: Twin quad-pack canisters integrated with weapon control systems (WCS) for multiple missile launches.
Significance:
- Enhances India's self-reliant air defence capability.
- Supports indigenous development under the Aatmanirbhar Bharat initiative.
- Strengthens India's maritime and aerial defensive posture through versatile deployment.
Gold Monetisation Scheme (GMS)

- 28 Mar 2025
In News:
The Government of India discontinued the Medium-Term and Long-Term Government Deposits (MLTGD) under the Gold Monetisation Scheme (GMS) with effect from March 26, 2025. Earlier, the Sovereign Gold Bond (SGB) scheme was also discontinued.
What is the Gold Monetisation Scheme (GMS)?
- Launched: 15th September 2015 (improved version of earlier Gold Deposit Scheme and Gold Metal Loan Scheme).
- Objective:
- Mobilize idle gold held by households and institutions.
- Bring privately held gold into the formal economy.
- Reduce the country's dependence on gold imports.
- Help lower the Current Account Deficit (CAD).
- Eligibility: Individuals, institutions, and government entities could deposit their idle gold in banks.
- Redemption:
- Gold is not returned in the same form (e.g., jewellery).
- Maturity proceeds are redeemed in the form of cash, gold bars, or coins (depending on the type of deposit).
Types of Deposits under GMS (Before Discontinuation of MLTGD):
- Short-Term Bank Deposit (STBD):
- Tenure: 1–3 years
- Interest Rate: Variable; decided by banks
- Redemption: Gold or cash
- Use: Lending by banks for domestic needs
- Medium-Term Government Deposit (MTGD):
- Tenure: 5–7 years
- Interest Rate: 2.25%; decided by Govt. in consultation with RBI
- Redemption: Cash only
- Use: Government and RBI reserves
- Long-Term Government Deposit (LTGD):
- Tenure: 12–15 years
- Interest Rate: 2.5%; decided by Govt. in consultation with RBI
- Redemption: Cash only
- Use: Monetary policy operations and reserves
Note: As of 2025, only the Short-Term Bank Deposit remains operational.
Sovereign Gold Bond (SGB) Scheme – Overview:
- Launched: 2015
- Objective:
- Reduce demand for physical gold.
- Promote investment in financial gold instruments.
- Channel household savings into productive financial assets.
- Key Features:
- Issued in denominations of 5g, 10g, 50g, and 100g.
- Tenure: 8 years (with exit option after 5 years).
- Interest Rate: 2.5% per annum (paid semi-annually).
- Capital gains tax exemption on maturity.
- Backed by the Government of India.
- Status: Discontinued as of 2025, alongside MLTGD and LTGD under GMS.
Other Gold-Related Initiative:
- Indian Gold Coin Scheme (2015):
- First-ever national gold coin with the Ashoka Chakra emblem.
- Launched alongside GMS and SGB to promote domestically branded gold and reduce reliance on imported gold bars/coins.
Parker Solar Probe

- 28 Mar 2025
In News:
Recently, the NASA’s Parker Solar Probe made another close approach to the Sun, reaching within 6 million km of its surface. It continues to break records as the closest any human-made object has come to the Sun, aiming to improve our understanding of solar activity and space weather.
Key Highlights:
- Background:Launched on August 12, 2018, by NASA from Cape Canaveral, Florida, the Parker Solar Probe is designed for in-situ study of the Sun's outer atmosphere (corona), solar wind, and magnetic field. It was named after physicist Eugene Parker, who first theorized the existence of the solar wind in the late 1950s.
- Mission Objectives:
- Investigate the structure and dynamics of the solar corona
- Understand the origin and evolution of solar wind
- Study energetic particles responsible for solar storms
- Examine the mechanisms that heat the corona to over a million degrees Celsius while the Sun’s surface remains relatively cooler at ~6,000°C
- Orbital Details & Speed:The Parker Probe moves in a highly elliptical orbit using Venus' gravity for repeated assists to get closer to the Sun. It is the fastest human-made object, reaching speeds of up to 692,000 km/hr. Its closest planned approach is 6.16 million km (3.83 million miles) from the Sun—about seven times closer than any previous spacecraft.
- Heat Protection Technology:To withstand extreme solar radiation, the probe uses an 8-foot-wide, 4.5-inch-thick carbon-carbon composite heat shield capable of resisting temperatures up to 1,377°C. The shield’s sun-facing side is coated with white ceramic paint to reflect sunlight, and its design ensures that just behind the shield, temperatures drop to a manageable 29°C, protecting the onboard instruments.
- Scientific Instruments Onboard:
- FIELDS – Measures electric and magnetic fields in the corona.
- ISoIS (Integrated Science Investigation of the Sun) – Studies high-energy solar particles.
- SWEAP (Solar Wind Electrons, Alphas, and Protons) – Captures data on solar wind particles.
- WISPR (Wide-Field Imager) – Takes images of the solar corona and heliosphere.
- Faraday Cup – An external device made of molybdenum alloy (melting point: 2,349°C), measures ion and electron densities in solar wind.
- Key Discoveries:
- First ‘Touch’ of the Sun (April 2021): The probe crossed the Sun’s Alfvén surface — the boundary where solar wind escapes the Sun’s influence — thus officially entering the solar corona.
- Magnetic Switchbacks: Detected sudden reversals in the Sun’s magnetic field direction, providing clues about how solar wind accelerates.
- Dust-Free Zones: Found regions near the Sun unexpectedly devoid of dust, challenging earlier theories about uniform dust distribution in the solar system.
- Corona Heating Mystery: Parker’s data, especially on Alfvén waves and magnetic switchbacks, may help solve why the corona is vastly hotter than the Sun’s surface
- Challenges Overcome:Contrary to expectations, the Sun’s gravity, not heat, posed a significant challenge. High speeds needed careful navigation to avoid crashing into the Sun. The mission used Earth and Venus flybys to gradually spiral inward for closer approaches rather than the initial, longer route via Jupiter.
- Mission Timeline:The Parker Solar Probe is scheduled to make 24 close passes of the Sun, continuing into the 2030s. Each pass provides new insights into solar activity and its potential impacts on Earth.
- Comparison with India’s Aditya-L1 Mission:While the Parker Solar Probe performs in-situ analysis by flying into the corona, ISRO’s Aditya-L1, launched in 2023, is stationed at the Lagrange Point 1 (L1), 1.5 million km from Earth. Aditya-L1 remotely observes solar flares, coronal mass ejections (CMEs), and magnetic storms using seven payloads, including a coronagraph.
Permafrost Degradation in the Kashmir Himalayas

- 26 Mar 2025
In News:
Permafrost, the ground that remains frozen for at least two years, has long been a critical feature in high-altitude regions like the Kashmir Himalayas. Recent studies have highlighted that melting permafrost is emerging as a significant environmental threat, with the potential to disrupt both ecological systems and infrastructure in the region.
Key Findings of Recent Studies
- Extent of Permafrost: Permafrost covers 64.8% of Jammu & Kashmir (J&K) and Ladakh, with 26.7% being continuous, 23.8% discontinuous, and 14.3% sporadic.
- Regional Distribution: Ladakh has the highest concentration of permafrost (87%), while areas like the Shigar Valley and Siwaliks have no permafrost.
- Impact on Infrastructure: Permafrost degradation threatens key infrastructure, including roads, settlements, and hydropower projects. Approximately 193 km of roads, 2,415 households, and eight hydropower projects are at risk due to thawing permafrost.
- Glacial Lake Outburst Floods (GLOFs): Permafrost thaw increases the likelihood of GLOFs, as seen in recent events like the 2021 Chamoli disaster and the 2023 South Lhonak GLOF. These floods, triggered by the instability of glacial lakes formed by melting ice, can cause significant destruction.
Environmental Impacts of Permafrost Thawing
- Carbon Release: As permafrost melts, it releases stored organic carbon, including methane, a potent greenhouse gas that exacerbates climate change.
- Hydrological Changes: Thawing permafrost can alter river flow and groundwater availability, impacting water resources for local communities and ecosystems.
- Geological Instability: The breakdown of permafrost leads to landslides and slope instability, posing risks to both natural landscapes and human settlements.
Factors Contributing to Permafrost Degradation
- Global Warming: Rising surface temperatures are the primary driver of permafrost thaw.
- Human Activities: Construction activities, including road-building, dam construction, and real estate development, disturb the stability of permafrost. Additionally, deforestation and land-use changes increase the exposure of permafrost to solar radiation, accelerating its degradation.
- Natural Events: Earthquakes and natural processes, like rock-ice avalanches, also contribute to the destabilization of permafrost.
Risks to Local Communities and Infrastructure
- Vulnerable Regions: Thousands of households and critical infrastructure in permafrost-rich areas, such as Ladakh, are at risk due to permafrost thawing. Military and strategic infrastructure, including roads vital for connectivity, may face serious disruptions, compromising national security.
- Glacial Lake Outburst Floods (GLOFs): The melting of glaciers can lead to the formation of proglacial lakes, increasing the risk of GLOFs. In J&K, 332 such lakes have been identified, with 65 showing significant flood risks. GLOFs are a major threat to downstream communities and infrastructure.
Way Forward: Mitigating Risks
- Integrated Planning: Future infrastructure development, especially roads and hydropower projects, should incorporate data on permafrost zones. Risk-sensitive land-use planning and construction methods must be adopted to minimize environmental damage.
- Enhanced Monitoring: Remote sensing technologies, including satellite-based monitoring and ground-based LiDAR systems, should be employed to track permafrost degradation and associated environmental changes more effectively.
- Comprehensive Environmental Assessments: Environmental Impact Assessments (EIAs) must be strengthened to include the risks of permafrost thawing, particularly in relation to GLOFs, landslides, and groundwater depletion. This is crucial for ensuring that development projects in these regions do not exacerbate the environmental risks posed by permafrost degradation.
Revival of Vikramshila University

- 26 Mar 2025
In News:
Following the revival of Nalanda University, another historic centre of learning—Vikramshila University in Bihar—is now set for rejuvenation. The Archaeological Survey of India (ASI) began developing the site in December 2023 to boost heritage tourism. Simultaneously, the Bihar government has earmarked 202.14 acres of land in Antichak village, Bhagalpur district, for setting up a Central University at the ancient site.
The revival project was approved by the Central Government in 2015 with a sanctioned budget of ?500 crore. However, work was delayed due to issues in land acquisition. With recent approval of ?87.99 crore for land procurement and the identification of suitable land, the project has regained momentum. The site is located about 3 km from the ancient ruins of the original university.
Historical Background:
- Vikramshila University was founded in the late 8th or early 9th century AD by King Dharmapala of the Pala Dynasty as a response to declining academic standards at Nalanda.
- Situated along the banks of the Ganges in eastern India, Vikramshila emerged as a major hub of Tantric Buddhism (Vajrayana) and occult studies, distinguishing itself from the broader curriculum of Nalanda.
- During its peak, Vikramshila housed over 1,000 students and 100 teachers, many of whom came from other parts of India and abroad.
- The university became renowned for its scholarship in theology, logic, metaphysics, grammar, philosophy, and especially tantric studies, which were popular in both Buddhism and Hinduism during that era. Among its most prominent scholars was AtisaDipankara, who played a key role in the spread of Buddhism to Tibet.
- The university featured a central cruciform brick stupa surrounded by 208 monk cells, arranged symmetrically on all four sides. A major architectural marvel of the site is its library, which had an innovative cooling system where water from a nearby reservoir was used to preserve manuscripts. This reflects the advanced engineering and scholarly focus of the institution.
- Although Nalanda and Vikramshila were separate entities, they often collaborated and shared scholars under the patronage of King Dharmapala. At one point, Vikramshila even held administrative authority over Nalanda.
Decline:
Vikramshila flourished for nearly four centuries before being destroyed around 1203 AD during the invasions of Muhammad Bin Bakhtiyar Khalji, the same event that marked the end of Nalanda University. The decline was also contributed to by the waning influence of Buddhism in India and the rise of Hinduism.
Recent Initiatives:
The ASI has divided the Vikramshila ruins into grids for careful excavation and preservation. A museum at the site displays several important antiquities, including sculptures of Buddhist and Hindu deities like Avalokiteshvara, Loknath, Surya, Vishnu, Ganesh, and more. Restoration work is also underway on NH-80, which connects Vikramshila to Bhagalpur city, about 50 km away.
Inner Line Permit (ILP)

- 24 Mar 2025
In News:
The Inner Line Permit (ILP) system plays a significant role in regulating entry into certain states of India's Northeast. Originally derived from the Bengal Eastern Frontier Regulation (BEFR) of 1873, the ILP aims to protect indigenous communities and preserve their cultural identity by regulating the movement of non-residents into restricted areas. This system requires Indian citizens who are not permanent residents of these states to obtain an ILP to enter and stay in these areas for a limited period.
Currently, four states—Arunachal Pradesh, Nagaland, Mizoram, and Manipur—require an ILP for entry. In recent years, the ILP system has become a topic of contention in Meghalaya, where local opposition to developmental projects, particularly railway expansion, has intensified.
What is the Inner Line Permit (ILP)?
The ILP is an official travel document issued by the respective state governments and regulates the entry of Indian citizens into restricted tribal areas. The system's primary aim is to safeguard indigenous communities from exploitation and prevent land alienation.
- Legal Basis: The Bengal Eastern Frontier Regulation (BEFR), 1873, introduced by the British, created an "Inner Line" to restrict the movement of outsiders. The Foreigners (Protected Areas) Order, 1958 and Foreigners (Restricted Areas) Order, 1963 further delineated areas where foreigners and Indian citizens from other states require special permits to enter.
- Difference Between ILP and PAP: The Inner Line Permit (ILP) applies to Indian citizens in certain northeastern states, while the Protected Area Permit (PAP) is for foreigners wishing to enter restricted areas, including parts of Arunachal Pradesh, Sikkim, Himachal Pradesh, J&K, and Rajasthan.
Current Status of Rail Connectivity in Meghalaya
Meghalaya has limited rail connectivity, with Mendipathar in North Garo Hills being the only operational railway station since 2014. Passenger services run daily between Mendipathar and Guwahati, and the station recently received its first freight shipment. However, several proposed railway projects in the state face significant opposition from local groups, particularly in the Khasi and Jaintia Hills.
The Northeast Frontier Railways (NFR) had planned three key projects in Meghalaya:
- Tetelia-Byrnihat Railway Line (21.5 km connecting Assam to Meghalaya)
- Byrnihat-Shillong Railway Line (108.76 km)
- Chandranathpur-Jowai Railway Line (connecting Assam to Jowai)
These projects are now at risk of being shelved due to local resistance, particularly from Khasi pressure groups such as the Khasi Students' Union (KSU).
Opposition to Railway Projects in Meghalaya
The opposition to these railway projects stems from fears of an influx of “outsiders” into the state, potentially threatening the cultural identity and livelihood of indigenous communities. The Khasi Students' Union (KSU) has been opposed to the extension of railway lines into the Khasi Hills since the 1980s, arguing that such projects would facilitate large-scale migration and overwhelm local populations. The group's concerns have now expanded to include other regions, such as the Jaintia Hills, where protests have emerged against the proposed Chandranathpur-Jowai line.
The KSU has long advocated for the introduction of the ILP system in Meghalaya to prevent non-residents from settling in the state. They argue that the ILP would serve as a safeguard against uncontrolled migration, offering a mechanism to regulate entry, especially at railway stations, where people can be monitored and restricted from staying beyond their designated period.
The KSUemphasized that while the group does not oppose railway development in principle, it seeks safeguards like the ILP to ensure that the state's indigenous communities do not become minorities.
Economic Considerations and Government Response
While the local opposition is strong, there is also significant support for railway connectivity, particularly from economic perspectives. Chief Minister Conrad Sangma has argued that improved rail connectivity would reduce logistical costs and facilitate the movement of goods, benefiting both the state's economy and its local entrepreneurs. Toki Blah, a political commentator, noted that railway expansion could lower the cost of goods, particularly in a state where much of the population depends on small-scale agriculture and service-based industries.
Additionally, representatives from the Garo Hills, another major tribal region in Meghalaya, have advocated for expanding existing rail links from Mendipathar to Baghamara in the South Garo Hills, citing the need for better transportation infrastructure.
World Happiness Report 2025
- 23 Mar 2025
In News:
The World Happiness Report (WHR) 2025 was released on 20th March (World Happiness Day) by the Wellbeing Research Centre at the University of Oxford, in collaboration with Gallup and the UN Sustainable Development Solutions Network (UNSDSN).
India’s Performance:
- India’s Rank (2025):118th out of 147 countries (Improved from 126th in 2024).
- Sub-Indicator Performance:
- Donations: 57th
- Volunteering: 10th
- Helping a Stranger: 74th
- Wallet Return Probability:
- 115th (by neighbor)
- 86th (by stranger)
- 93rd (by police)
- Sub-Indicator Performance:
- Happiness Score: Increased from 4.054 (2021–23) to 4.389 (2022–24).
- Rank among Neighbors:
- Nepal: 92nd
- Pakistan: 109th
- Myanmar: 126th
- Sri Lanka: 133rd
- Bangladesh: 134th
Top 10 Happiest Countries (2025):
- Finland (8th consecutive year)
- Denmark
- Iceland
- Sweden
- Israel
- Costa Rica (new entrant)
- Netherlands
- Norway
- Luxembourg
- Mexico(new entrant)
Least Happy Countries (Bottom 5):
- 147th: Afghanistan (4th consecutive year as lowest)
- 146th: Sierra Leone
- 145th: Lebanon
- 144th: Malawi
- 143rd: Zimbabwe
About the Report:
- Purpose: Measures global well-being through life evaluations and promotes policy focus on happiness, mental health, and quality of life over mere economic growth.
- Methodology:
- Based on Gallup World Poll (2022–2024 data).
- Uses Cantril Ladder Scale (0–10) for life evaluation.
- Six Key Indicators:
- GDP per capita
- Healthy life expectancy
- Social support
- Freedom to make life choices
- Generosity
- Perception of corruption
Global Trends in Happiness (2025):
- Nordic Dominance: Finland, Denmark, Iceland, and Sweden occupy top ranks.
- Decline in Western Countries:
- USA: 24th (down from 11th in 2012)
- UK: 23rd (lowest since 2017)
- Rising loneliness and social isolation major causes.
- Israel (5th): Maintained high rank despite ongoing conflict.
- Social Support Decline: 19% of young adults globally report having no one to rely on.
Special Focus: India vs Pakistan – The Paradox
Despite India’s:
- Higher GDP per capita ($2,480.8 vs Pakistan’s $1,365.3),
- Better health indicators (life expectancy: 58.1 vs 56.9),
- Better corruption perception rank (India: 96th, Pakistan: 135th),
India still ranks lower in happiness.
Reason: Low scores in perceived freedom and individual life satisfaction.
World Happiness Day:
- Observed on: 20th March
- Initiated by: Bhutan, which pioneered the concept of Gross National Happiness (GNH).
- Adopted by UNGA: July 2012
- Theme 2025:"Caring and Sharing"
AFSPA in the Northeast

- 22 Mar 2025
In News:
The Union Ministry of Home Affairs (MHA) is reviewing the scope of the Armed Forces (Special Powers) Act, 1958 (AFSPA) in the Northeast, especially in light of ongoing ethnic violence in Manipur and security reviews in Nagaland, Arunachal Pradesh, and Assam.
What is AFSPA?
- AFSPA (1958) empowers the armed forces to maintain public order in ‘disturbed areas’.
- It authorizes armed forces to:
- Use force or open fire after due warning.
- Arrest without a warrant.
- Conduct searches without a warrant.
- Enjoy legal immunity from prosecution without prior sanction of the Central Government.
Declaration of Disturbed Area
- A region is declared ‘disturbed’ through a notification in the Official Gazette.
- The declaration can be made by:
- Governor of a State, or
- Central Government.
- Duration: Notifications are valid for 6 months, reviewed periodically for extension or withdrawal.
AFSPA in Manipur: Recent Developments
- AFSPA was withdrawn from all valley police stations between April 2022–April 2023 due to improved law and order.
- However, after ethnic violence erupted on May 3, 2023, the Act was reimposed in 6 police stations across 5 districts (mostly in valley areas) as of November 14, 2024.
- At a review meeting on March 20, 2025, the Indian Army proposed re-imposition of AFSPA in 12 more police station limits in Manipur Valley for operational efficiency.
- President’s Rule has been in force in Manipur since February 13, 2025.
- The final decision on AFSPA expansion in Manipur will be taken by the MHA.
Status in Other Northeastern States
- The MHA held a multi-agency review on March 19, 2025, regarding AFSPA coverage in Nagaland, Arunachal Pradesh, Assam, and Manipur.
- Current Authority to Notify Disturbed Areas:
- MHA: Nagaland and Arunachal Pradesh.
- State Governments: Manipur and Assam.
- Possible De-Notification: One district in Assam may be removed from AFSPA coverage based on the latest review.
Legal and Administrative Background
- AFSPA came into force in Manipur in 1981.
- Manipur attained Statehood in 1972, earlier being a Union Territory.
- The Imphal Municipality area has remained outside AFSPA since 2004.
- The most recent “disturbed area” notification for hill districts in Manipur was issued on September 26, 2024.
States Under AFSPA (as of February 2025)
- Manipur
- Nagaland
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Jammu and Kashmir
PEPSU Muzhara Movement

- 22 Mar 2025
In News:
The PEPSU Muzhara Movement, commemorated annually on March 19, was a significant agrarian uprising by landless tenant farmers (muzharas) in Punjab demanding ownership rights over the land they cultivated. It stands as a historic resistance against feudal and colonial exploitation.
Background & Region
- Initiation: Started in the 1930s in the Patiala princely state.
- Expanded Across: 784 villages in present-day Patiala, Barnala, Mansa, Sangrur, Bathinda, Mohali, Fatehgarh Sahib, Faridkot (Punjab), and Jind (now in Haryana).
- After independence, the region was reorganized into the Patiala and East Punjab States Union (PEPSU), where the movement intensified.
Who Were the Muzharas?
- Muzharas were landless tenant farmers who cultivated land owned by biswedars (feudal landlords).
- They were forced to give one-third of their produce to landlords, who further paid a share to princely rulers, who in turn paid the British.
- Even after Independence (1947), landlords continued this exploitative practice, leading to widespread unrest.
Causes of the Movement
- Feudal oppression and loss of ancestral land.
- Colonial revenue structure perpetuated peasant poverty.
- Post-independence continuation of feudal demands.
- Denial of land ownership despite generations of cultivation.
Key Leaders
- Jagir Singh Joga – Organised and united tenant farmers.
- Buta Singh – Advocate for land redistribution.
- Teja Singh Sutantar – Linked the struggle with broader peasant movements.
- Sewa Singh Thikriwala – Anti-feudal ideologue and early inspiration.
- Bhai Jodh Singh – Strengthened the movement through grassroots mobilisation.
Phases and Nature of the Movement
- Peaceful Protests: Initial petitions and mobilisations.
- Armed Resistance: Tenant farmers took up arms for self-defense as repression increased.
- Mass Mobilisation: Conferences, rallies, and united action across villages.
Significance of March 19
- In March 1949, landlords attempted to reclaim cultivated lands in Kishangarh (Mansa district).
- The muzharas resisted by harvesting crops themselves, leading to a violent standoff.
- On March 17, a police officer was killed, resulting in the arrest of 35 muzharas—all acquitted by 1950.
- On March 19, 1949, the army surrounded the village, and four muzharas were killed.
- Since 1953, March 19 has been observed as “Muzhara Shaheedi Diwas”, honouring martyrs of the movement.
Outcome
- Land Reforms (1952): The movement culminated in reforms granting ownership rights to tenant farmers.
- Became a symbol of peasant resistance against exploitation and injustice.
Tren de Aragua

- 20 Mar 2025
In News:
In March 2025, the United States deported 261 Venezuelans, including alleged members of the violent Venezuelan gang Tren de Aragua (TdA). The deportation invoked the Alien Enemies Act of 1798, used for the first time since World War II.
What is the Tren de Aragua (TdA)?
- Origin: Formed in 2014 inside Tocorón Prison in Aragua state, Venezuela.
- Evolution: Began as a prison gang under the “pran” system—where incarcerated crime bosses operated external criminal networks.
- Operations: Expanded amid Venezuela's economic crisis (post-2017) to Colombia, Peru, Chile, and later the United States, exploiting Venezuelan migrants.
- Criminal Activities: Drug trafficking, human trafficking, extortion, murder, and kidnapping.
- International Links: Chile accused the Venezuelan regime of facilitating the murder of a former opposition officer in 2023 via TdA operatives.
Presence in the United States
- Size: Estimated 5,000 global members; only a few hundred suspected in the U.S.
- Incidents: Linked to violent crimes in New York, Florida, Texas, Pennsylvania, California, and a high-profile case in Aurora, Denver.
- Designation: Labeled a "Transnational Criminal Organization" in 2023 by the Biden administration. Assets in the U.S. frozen and a $12 million reward announced for its leaders.
Alien Enemies Act (1798):
- Purpose: Allows the U.S. President to detain, deport, or restrict foreign nationals from hostile nations during war or invasion.
- Historic Use:
- War of 1812: Used against British citizens.
- WWI & WWII: Used for surveillance, restrictions, and internment of citizens from enemy nations (Japanese, Germans, Italians).
- Post-War: Used in 1948 to deport a Nazi operative; upheld by the U.S. Supreme Court.
Controversial Invocation in 2025
- First use since WWII to target non-state criminal actors (TdA).
- The White House termed TdA a "terrorist gang" and a "direct threat to national security".
- Claimed that illegal immigration and cartel activity constituted a modern “invasion”, thereby justifying use of the Act.
- Legal Backing: The Act remains constitutional and in force unless revoked.
- Criticism: Civil rights advocates argue its use may violate due process; calls for repeal by some lawmakers due to historical misuse.
Identification of Gang Members
- Criteria (ICE Directive, 2017): Gang tattoos, prior convictions, confessions, or identification by reliable sources.
- Due Process Concerns: Migrants can be deported even if gang membership is unproven before a judge.
National Wildlife Health Policy (NWHP)

- 20 Mar 2025
In News:
In the aftermath of the COVID-19 pandemic, the Government of India is formulating the National Wildlife Health Policy (NWHP) to address the growing threat of zoonotic diseases through integrated wildlife health management. Over 60% of emerging infectious diseases in humans originate from animals, underscoring the importance of a "One Health" approach—integrating human, animal, and environmental health.
Key Objectives of NWHP
- Establish a comprehensive wildlife disease surveillance system.
- Strengthen diagnostic infrastructure and research capacity.
- Facilitate cross-sectoral collaboration among environment, agriculture, and animal husbandry ministries.
- Integrate existing animal and human health data systems with wildlife health information.
Institutional Framework & Implementation
- National Referral Centre for Wildlife (NRC-W):
- Inaugurated in Junagadh, Gujarat (March 2024).
- India’s first wildlife disease diagnostic and research centre.
- Will serve as a referral hub for investigating wildlife mortality and outbreak events.
- Wildlife Health Information System (WHIS):
- Proposed digital system for real-time disease data collection, reporting, and analysis.
- Will integrate with National Animal Disease Reporting System (NADRS) and National Animal Disease Referral Expert System (NADRES).
- Satellite Diagnostic Labs:To be established near important forest zones for timely wildlife disease detection and diagnosis.
- Community Engagement:Involves measures like cattle vaccination near national parks to reduce disease transmission risks.
Key Agencies Involved
- Central Zoo Authority (CZA): Nodal agency under the Wildlife Protection Act, 1972; responsible for policy coordination and implementation.
- Office of the Principal Scientific Adviser and IIT-Bombay: Supporting technical and policy formulation.
- Ernst & Young: Consultancy support.
- Ministry of Environment, Forest & Climate Change (MoEF&CC): Policy oversight.
Alignment with Existing Conservation Frameworks
- National Wildlife Action Plan (2017–31):
- Provides for 103 actions and 250 projects.
- Includes protocols for disease surveillance in protected areas and tiger reserves.
- Wildlife Protection Act, 1972: Provides legal basis for wildlife health regulation and zoonotic disease control.
Chhareda Panchayat Water Conservation Model

- 19 Mar 2025
In News:
Rajasthan’s Chhareda Panchayat in Dausa district has emerged as a leading example of effective water conservation, driven by a community-driven initiative that has significantly transformed agricultural practices and farmer livelihoods. The project, led by Vipra Goyal, an alumnus of IIT-Kharagpur, has revolutionized water usage in the region through the construction of 250 farm ponds.
Key Aspects:
- Objective:The model aims to address water scarcity and groundwater depletion through rainwater harvesting and the construction of farm ponds, reducing dependence on overexploited groundwater sources.
How Farm Ponds are Contributing to Water Conservation in Rajasthan
- Rainwater Harvesting:Farm ponds serve as storage systems for rainwater, minimizing reliance on deep, contaminated groundwater sources. This helps prevent the further depletion of underground water reserves.
- Year-Round Water Availability:The ponds provide consistent water supply for both kharif and rabi crops, ensuring that farmers can grow crops throughout the year without facing water shortages.
- Groundwater Conservation:By reducing the need to extract groundwater, this initiative has helped conserve approximately 30 crore litres of water annually, easing the pressure on local aquifers.
- Boosting Agricultural Productivity and Income:With reliable water sources, farmers have shifted from subsistence farming to growing cash crops, which has resulted in a collective increase of about ?5 crore in household incomes.
- Reduced Water Pollution:The initiative avoids the use of groundwater contaminated with harmful substances like arsenic and fluoride, which are prevalent in many areas of Rajasthan.
- Sustainability and Climate Resilience:The farm ponds offer a climate-resilient solution, ensuring that agriculture in water-scarce regions is sustainable even in the face of erratic rainfall patterns.
- Cost-Free Construction:The construction of the ponds has been facilitated through CSR funds and government schemes, making the project cost-free for farmers.
International Big Cat Alliance (IBCA)
- 19 Mar 2025
In News:
The International Big Cat Alliance (IBCA), a treaty-based intergovernmental organisation dedicated to the conservation of seven major big cat species, has officially signed an agreement with the Government of India, establishing India as the permanent host of its headquarters and secretariat.
Background and Launch
- Launched: April 2023 by Prime Minister Narendra Modi during the 50th anniversary celebrations of Project Tiger.
- Objective: To facilitate global cooperation for the conservation of seven big cats:Tiger, Lion, Leopard, Snow Leopard, Cheetah, Puma, andJaguar.
- The IBCA is implemented through the National Tiger Conservation Authority (NTCA) under the Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change (MoEFCC).
International Status and Membership
- The IBCA became a treaty-based intergovernmental alliance after five countries ratified the framework agreement:India, Liberia, Eswatini, Somalia, andNicaragua.
- India formally joined the IBCA in September 2023.
- The alliance is open to all UN Member States, including:
- Range countries (where big cats are native), and
- Non-range countries that wish to support conservation efforts globally.
Headquarters and Agreement
- On March 28, 2024, the Union Cabinet approved the establishment of the IBCA headquarters in India.
- An agreement was signed in May 2024 between the IBCA and the Indian government, outlining:
- Privileges and immunities for IBCA personnel,
- Visa facilitation, and
- Operational and legal provisions for the headquarters.
Funding and Support
- India has committed a total of ?150 crore (2023–2028) for:
- Creating a corpus fund,
- Building infrastructure, and
- Meeting recurring expenditures over five years.
Operation ATALANTA

- 18 Mar 2025
In News:
The European Union Naval Force (EUNAVFOR) Operation ATALANTA has proposed a significant joint anti-piracy naval exercise with the Indian Navy, scheduled for the end of May 2025. This initiative reflects the growing strategic cooperation between India and the European Union in maritime security, particularly in the Western Indian Ocean and the Red Sea.
Key Highlights
Proposed Exercise:
- The exercise, if approved, will involve two European warships and the Indian Navy practicing advanced counter-piracy operations, tactical manoeuvres, and inter-naval communications.
- This drill goes beyond the routine Passage Exercises (PASSEX) and aims to enhance interoperability, coordination, and mutual confidence between the two navies.
Strategic Objectives:
- Strengthen maritime security in the Indian Ocean, ensuring it remains a free, open, sustainable, and inclusive area.
- Address resurgent piracy threats, especially off the Horn of Africa, amid ongoing instability in the Red Sea due to Houthi rebel activity.
- Build operational synergy to respond swiftly to piracy incidents-EUNAVFOR claims the capability to tackle pirate cases within 48–72 hours.
Recent Developments:
- Piracy incidents near the Horn of Africa have declined recently, but the threat persists, necessitating continued vigilance and cooperation.
- In 2024, joint anti-piracy efforts led to the apprehension of 70 suspected pirates, with the Indian Navy responsible for 44 captures.
- The Indian Navy is recognized as a major actor in the region, with both sides regularly coordinating through maritime information fusion centers.
Operation ATALANTA: Overview
Aspect Details
Launch Year 2008
Initial Focus Preventing piracy and armed robbery off the Somali coast
Expanded Mandate - Protecting World Food Programme (WFP) vessels
- Enforcing UN arms embargo on Somalia
- Monitoring drug and arms trafficking
- Combating Illegal, Unreported, and Unregulated (IUU) fishing
- Disrupting illicit charcoal trade
Area of Operations Western Indian Ocean and Red Sea
Recent Activities - Joint drills with Indian Navy
- Successful coordination in anti-piracy operations, e.g., MV Ruen hijacking
India–EU Maritime Engagement: Significance
- Geopolitical Context:
- The Indian Ocean is a critical global trade route, and its security is vital for international commerce.
- The resurgence of piracy and instability in the Red Sea has heightened the need for robust maritime partnerships.
- Strategic Partnerships:
- The EU and India share a vision of maintaining maritime order and security.
- The vastness of the Indian Ocean requires significant assets and robust logistics, making cooperation essential.
- Professional Interactions:Encounters with other navies, including China, are described as professional, underscoring the importance of multilateral engagement.
Hyperloop Project
- 18 Mar 2025
In News:
India is moving closer to realizing ultra-high-speed transportation with the development of indigenous Hyperloop technology. The Ministry of Railways, has announced that Integral Coach Factory (ICF), Chennai will develop the electronics component for the country’s Hyperloop initiative. This decision follows promising test results at IIT Madras, which hosts the longest Hyperloop testing facility in Asia.
What is Hyperloop?
Hyperloop is a next-generation, ultra-fast transportation system that combines magnetic levitation (maglev) and near-vacuum tubes to enable passenger pods to travel at speeds up to 1,220 km/h. It was first proposed by Elon Musk in 2013 through the Hyperloop Alpha white paper and has since evolved into a global open-source research initiative.
Working Mechanism:
- Low-pressure tubes drastically reduce air resistance.
- Magnetic levitation allows pods to float without touching surfaces, minimizing friction.
- Electromagnetic propulsion moves pods forward efficiently.
Key Features:
- Highly energy-efficient and sustainable, with low emissions.
- Can surpass air travel speeds on shorter routes.
- Reduces road congestion, travel time, and noise pollution.
India’s Hyperloop Developments:
- Institutions Involved:
- IIT Madras – Developed the 410-meter test facility.
- Avishkar Hyperloop Team – Leading design and innovation.
- ICF Chennai – To develop electronics and technical components.
- Government Support:
- The Railway Ministry has provided financial and technical support.
- The testing system uses fully indigenous technology.
Challenges Ahead:
Despite its promise, Hyperloop faces significant hurdles:
- High infrastructure costs.
- Technical challenges in maintaining vacuum conditions.
- Safety concerns due to the high speed and pressure system.
India’s Space Docking Capability

- 17 Mar 2025
In News:
Recently, ISRO successfully demonstrated autonomous space docking and undocking with its Space Docking Experiment (SpaDEx), making India the fourth country—after the USA, Russia, and China—to achieve this advanced space capability.
Two satellites, SDX01 (Chaser) and SDX02 (Target), were launched into a 470 km orbit. From a starting separation of 20 km, they were autonomously maneuvered, docked using an indigenous androgynous docking mechanism, and later undocked after two months of in-orbit operation.
What is Space Docking and Why It Matters?
Docking is the process where two spacecraft in orbit are brought together and joined. Undocking is the controlled separation of these joined vehicles. These procedures are vital for:
- Assembling large structures (e.g., space stations) in orbit, bypassing launch weight limits.
- Orbital servicing of satellites (repairs, refueling).
- Interplanetary missions requiring in-space assembly and resupply.
- Crewed missions to space stations and planetary bodies (e.g., Moon, Mars).
Historical Context
- 1966 (USA): First manual docking by NASA’s Gemini VIII (Neil Armstrong with Agena).
- 1967 (USSR): First autonomous docking using Kosmos 186 & 188.
- 2011–12 (China): First unmanned and then crewed docking.
- 2025 (India): Successful autonomous docking and undocking via SpaDEx.
Strategic and Technological Significance for India
Future Missions:
- BharatiyaAntariksh Station (BAS) by 2035 and Human Moon Mission by 2040 will rely heavily on in-orbit docking and assembly.
- Chandrayaan-4, aiming to return lunar samples, will use docking systems for orbital rendezvous and return modules.
Global Space Economy
- Positions ISRO as a leader in modular satellite design, orbital assembly, and international collaborations.
- Enables NewSpace India Ltd. (NSIL) to attract commercial contracts for space stations, satellite servicing, and deep-space ventures.
Domestic Technological Advancements
- Promotes indigenous innovation in docking systems, AI-driven autonomous navigation, robotics, and in-space power sharing.
- Supports R&D in microgravity, space manufacturing, and even space agriculture (e.g., orbital seed germination experiments).
Strategic and Diplomatic Impact
- Enhances India’s soft power and strengthens ties with space agencies like NASA and ESA.
- Contributes to space security by enabling orbital refueling and satellite servicing during emergencies.
- Offers collaborative platforms for BRICS and developing countries through BAS.
Capacity Building
- Encourages STEM education and youth engagement via initiatives like YUVIKA.
- Expands India’s aerospace industrial base, creating skilled jobs and fostering innovation.
Mudumal Megalithic Menhirs

- 17 Mar 2025
In News:
The Mudumal Megalithic Menhirs of Narayanpet district, Telangana have been included in India’s UNESCO Tentative World Heritage Sites list in 2025, highlighting their archaeological, cultural, and astronomical significance. Telangana now has two tentative UNESCO heritage sites, the first being the Ramappa Temple (inscribed in 2021).
What are Menhirs and Megaliths?
- Menhirs are large, upright standing stones, often tapered at the top, used by prehistoric communities.
- They served ritual, memorial, or astronomical purposes and are found globally, with prominent examples in Europe such as Stonehenge (UK) and Carnac (France).
- Megaliths refer broadly to prehistoric stone structures, used for burials (like dolmens, cairns, cists) or as commemorative monuments (like menhirs).
- In India, megalithic culture thrived during the Iron Age (c. 1500 BCE–500 BCE), especially in the Deccan Plateau (Maharashtra, Karnataka, Tamil Nadu, Kerala, Andhra Pradesh, Telangana).
Significance of the MudumalMenhirs
- Age: Estimated to date back 3,500–4,000 years (1000 BCE–300 BCE).
- Site extent: Spread across 80 acres near the Krishna River, the site comprises:
- Around 80 large menhirs (10–14 feet tall).
- Nearly 3,000 alignment stones set in rows, believed to represent funerary rites and astronomical alignments.
- Astronomical importance: The alignments correspond with solar events such as solstices and equinoxes.
- A unique cup-marked stone represents the Ursa Major (Saptarshi) constellation—South Asia’s earliest known star depiction.
- Suggests advanced prehistoric knowledge of celestial navigation and calendar calculation.
Cultural and Living Traditions
- The site continues to hold spiritual value among locals.
- Menhirs are revered as "NilurallaThimmappa" (Thimmappa of the Standing Stones).
- One stone is worshipped as Goddess Yellamma, blending ancient heritage with living cultural practices.
Path Toward UNESCO World Heritage Status
- The MudumalMenhirs are among six sites added to India’s Tentative List in 2025, alongside:
- Kanger Valley National Park (Chhattisgarh)
- Ashokan Edict Sites (Multiple States)
- Chausath Yogini Temples (MP & Odisha)
- Gupta Temples (Multiple States)
- Palace-Fortresses of the Bundelas (MP & UP)
- India now has 62 sites on the Tentative List, a prerequisite for UNESCO nomination.
Maritime Security Belt 2025

- 16 Mar 2025
In News:
Amid rising tensions over Iran’s expanding nuclear program and threats from Yemen's Houthi rebels, China, Iran, and Russia conducted the Maritime Security Belt 2025 naval exercise in the Gulf of Oman, strategically located near the Strait of Hormuz. This region is of global significance as it serves as a major maritime route, through which a fifth of the world’s crude oil is transported daily.
Key Highlights of the Exercise
- Location: Gulf of Oman, near the Strait of Hormuz, connecting the Persian Gulf to the open seas. This waterway is crucial for global energy supplies and trade.
- Participating Navies:
- Iran: State-run media highlighted the drills as a show of strength, particularly after Israeli strikes targeted Iran’s defense and missile programs.
- Russia: Participated with corvettes Rezky and Aldar Tsydenzhapov as well as the tanker Pechenega. Russia continues to rely on Iran for drone supplies, particularly in the ongoing war in Ukraine.
- China: Sent guided-missile destroyer Baotou and supply ship Gaoyouhu. China maintains deep ties with Iran, especially in the oil sector, despite facing Western sanctions.
- Operational Objectives:
- The exercise aimed to enhance coordination and operational synergy between the three nations, with a focus on maritime security, countering threats to shipping lanes, and addressing global security challenges.
- It featured live-fire drills, night operations, and complex naval maneuvers, ensuring the readiness of all three navies to respond to maritime threats.
- Regional Significance: The Gulf of Oman serves as the only maritime access for Iran to the open seas, making it critical for global trade. The Strait of Hormuz is particularly significant as it handles a significant portion of the world’s oil trade.
Strategic Context and Implications
- Nuclear Tensions: Iran's nuclear program, which has drawn concerns from both Israel and the U.S., remains a central issue in the region. The exercises coincide with the growing concerns over Iran’s stockpiling of uranium enriched to near weapons-grade levels, despite Tehran's assertions that its nuclear ambitions are peaceful.
- Impact of Drills: These joint naval exercises highlight the growing influence of China and Russia in the Middle East, both of which have strategic ties with Iran. While these countries do not patrol the wider Middle East region, their naval presence in the Gulf signals their deepening involvement in the region’s security dynamics, particularly in opposition to the U.S.-led presence.
- Yemen's Role: The Houthi rebels in Yemen have previously targeted international shipping in the Red Sea and Bab el-Mandeb Strait, and have threatened to resume attacks unless humanitarian aid is allowed into Gaza. The instability in the region further complicates security, as seen in the potential for maritime disruptions.
Geopolitical Dimensions
- China’s Interests: China, as a major consumer of Iranian crude oil, continues to engage with Iran despite facing Western sanctions. These drills serve as a symbol of China’s increasing military presence and its growing role in the Middle East, particularly in energy security.
- Russia’s Involvement: Russia's reliance on Iran for bomb-carrying drones in the Ukraine conflict further deepens the military relationship between the two nations. The maritime drills highlight Russia’s interest in securing its position in the Middle East amidst growing tensions with the West.
- U.S. Interests: The U.S., which monitors the region through its 5th Fleet based in Bahrain, remains cautious of the growing military cooperation between China, Russia, and Iran. The drills, especially the interference with GPS systems, have raised concerns about regional stability and the ability to ensure free navigation through critical maritime chokepoints.
Bongosagar 2025 Naval Exercise

- 16 Mar 2025
In News:
India and Bangladesh conducted the Bongosagar 2025 naval exercise in the Bay of Bengal, aimed at enhancing maritime cooperation, operational interoperability, and regional security. This joint exercise aligns with India's maritime foreign policy doctrine — SAGAR (Security and Growth for All in the Region).
Key Highlights
- Participants:
- Indian Navy: INS Ranvir, a Rajput-class guided missile destroyer, commissioned in 1986.
- Bangladesh Navy: BNS Abu Ubaidah.
- Objectives:
- Strengthen tactical planning, information sharing, and coordinated response capabilities.
- Enhance interoperability for seamless maritime operations.
- Reinforce regional trust and cooperation under the SAGAR framework.
- Exercise Components:
- Surface firing drills
- Tactical manoeuvres
- Underway replenishment
- VBSS (Visit, Board, Search and Seizure) operations
- Cross-deck boarding exercises
- Communication drills
- Professional knowledge quizzes and steam past ceremonies
Strategic Significance
- Supports India’s SAGAR initiative (2015), promoting security and growth in the Indian Ocean region.
- Aligns with the broader MAHASAGAR (2025) vision — Mutual and Holistic Advancement for Security and Growth Across Regions — targeting deeper engagement with the Global South.
- Enhances the ability of both navies to counter maritime threats, uphold freedom of navigation, and ensure regional maritime stability.
India-Bangladesh Defence Cooperation
- Army-level: Exercise Sampriti
- Navy-level: Exercises Bongosagar and Coordinated Patrol (CORPAT)
India’s First CAR T-Cell Therapy
- 16 Mar 2025
In News:
India has achieved a significant milestone in cancer treatment with the successful clinical trials of its first CAR T-cell therapy, marking a crucial step in indigenous biomedical innovation. The findings were recently published in The Lancet, making it the first CAR T-cell clinical trial from India to appear in an international journal.
What is CAR T-Cell Therapy?
- CAR T-cell therapy (Chimeric Antigen Receptor T-cell therapy) is a form of immunotherapy where a patient’s own T-cells are genetically modified to identify and destroy cancer cells.
- Primarily used for blood cancers, especially those unresponsive to first-line treatments, such as:
- Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia (ALL)
- Large B-cell Lymphoma
Indian Breakthrough
- Developed by ImmunoAct, a start-up incubated at IIT Bombay.
- 73% response rate recorded in Phase I and II clinical trials.
- Approved by India’s drug regulator in 2023, bypassing Phase III trials under conditional approval due to the urgent need and novelty.
- Therapy is now available in major hospitals like Apollo, Fortis, Max, and Amrita.
Key Findings (Lancet Report)
- Median progression-free survival:
- 6 months for ALL patients
- 4 months for lymphoma patients
- Therapy costs approx. ?25 lakh, about 1/20th of global CAR T-cell therapy prices (?8–10 crore abroad).
Side Effects
- Severe immune reaction (Haemophagocyticlymphohistiocytosis) in 12% patients, leading to at least one death.
- Other adverse effects:
- Neutropenia (96%) – Low white blood cells
- Thrombocytopenia (65%) – Low platelet count
- Anemia (61%) – Low red blood cell count
- Febrile neutropenia (47%) – Infection risk due to low immunity
Significance
- Makes advanced cancer care more accessible and affordable within India.
- Positions India among a select group of countries with indigenous CAR T-cell therapy capabilities.
- Marks progress towards self-reliance in high-end medical technologies.
Supersolid Light
- 14 Mar 2025
In News:
In a groundbreaking achievement, Italian scientists have successfully created the world’s first ‘supersolid’ made from light, marking a new milestone in quantum physics. This discovery demonstrates that light, traditionally understood as pure energy, can be manipulated into a rare state of matter that combines the order of a solid with the frictionless flow of a superfluid.
What Is a Supersolid?
A supersolid is an exotic quantum phase of matter exhibiting dual characteristics:
- Solid-like structure: Maintains a periodic, lattice-like spatial arrangement.
- Liquid-like behavior: Flows without internal resistance (zero viscosity), like a superfluid.
Previously, supersolidity was observed in Bose-Einstein condensates (BECs)—ultracold atomic systems cooled near absolute zero (–273.15°C), where quantum effects dominate.
How was Supersolid Light created?
Researchers used semiconductor nanostructures (gallium arsenide with micro-ridges) to create polaritons—hybrid quasiparticles formed by coupling photons (light) with excitons (matter).
- When cooled and stimulated with a laser, these polaritons condensed into a coherent quantum fluid arranged in a regular pattern, exhibiting both superfluid and solid-like properties.
Key Features of Supersolid Light:
- Quantum Coherence: Particles move in a synchronized, wave-like manner due to shared quantum states.
- Frictionless Flow: Can move through obstacles without energy loss.
- Crystalline Order: Particles maintain a rigid spatial configuration.
- Symmetry Breaking: Demonstrates both spatial order and dynamic fluidity.
Significance and Applications:
- Quantum Computing: Enhances qubit stability and coherence, essential for error-free quantum operations.
- Photonics and Optical Devices: Enables development of light-based circuits with high efficiency.
- Energy Technologies: Potential applications in superconductors and frictionless systems.
- Fundamental Research: Offers insights into non-equilibrium quantum systems and phase transitions.
Why it matters for Science & Technology?
This marks the first time light has been shown to form a supersolid, expanding the boundaries of material science. It provides a new experimental platform for studying quantum behavior in light-matter systems, bridging the gap between theoretical physics and practical innovation.
PM-ABHIM

- 14 Mar 2025
In News:
The Pradhan Mantri Ayushman Bharat Health Infrastructure Mission (PM-ABHIM) is a major Centrally Sponsored Scheme launched in 2021 to strengthen public health systems across India, with a focus on pandemic preparedness and infrastructure development at all levels of healthcare.
In March 2025, the Delhi government agreed to sign a Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) with the Ministry of Health and Family Welfare to implement PM-ABHIM, marking a policy shift after earlier resistance. Under the agreement:
- 553 existing Mohalla Clinics will be upgraded to Urban Ayushman Arogya Mandirs (U-AAMs).
- 413 new U-AAMs will be established.
- A total of 1,139 Urban AAMs will cater to Delhi’s primary healthcare needs.
Key Features of PM-ABHIM (2021–26):
- Total outlay: ?64,180 crore.
- Goal: Strengthen health infrastructure for effective response to future pandemics and disasters, and improve public health systems at primary, secondary, and tertiary levels.
- Scope: Combines Central Sector and Centrally Sponsored Scheme (CSS) components.
Major Components:
- 17,788 Sub-Centres asAyushman Arogya Mandirs (AAMs)in rural areas.
- 11,024 Urban AAMs, focusing onslum areas.
- 3,382 Block Public Health Units (BPHUs).
- 730 Integrated Public Health Labs (IPHLs)—one per district.
- 602 Critical Care Hospital Blocks (CCBs)in districts with populations above 5 lakh.
Governance & Implementation:
- Health being a State subject, implementation is carried out by State/UT governments.
- The MoHFW provides technical and financial assistance.
- Awareness and IEC (Information, Education, Communication) activities are integrated with other National Health Mission programs.
Nagorno-Karabakh Conflict
- 14 Mar 2025
In News:
In a landmark development, Armenia and Azerbaijan have finalized a peace agreement in 2024, aiming to end decades of hostilities over the Nagorno-Karabakh region—a flashpoint in the South Caucasus with deep-rooted ethnic and geopolitical tensions.
About Nagorno-Karabakh:
- A landlocked, mountainous region in the South Caucasus, referred to as Artsakh by Armenians.
- Located within internationally recognized Azerbaijani territory, but historically inhabited by ethnic Armenians.
- Features diverse geography: steppe lowlands, dense forests, and alpine meadows.
Historical Background:
- Soviet Era (1920s): USSR established Nagorno-Karabakh as an autonomous region within Muslim-majority Azerbaijan, despite its Armenian Christian majority.
- Post-USSR Collapse (1991): Karabakh declared independence; First Nagorno-Karabakh War (1988–1994) broke out.
- Result: Armenian forces took control of Nagorno-Karabakh and surrounding Azerbaijani districts.
- 2017: A referendum in Karabakh changed the government to a fully presidential system and renamed the region from Nagorno-Karabakh Republic to Republic of Artsakh.
- Second War (2020): Azerbaijan regained significant territory; thousands of soldiers were killed on both sides.
- 2023 Azerbaijani Offensive: In a swift one-day operation, Azerbaijan reasserted full control over the region.
- The Republic of Artsakh (unrecognized government) was officially dissolved in 2024.
- Over 1 lakh ethnic Armenians fled to Armenia.
India’s Position:
- India maintains a neutral stance, supports a peaceful diplomatic resolution under the aegis of the OSCE Minsk Group.
- Both Armenia and Azerbaijan are part of the International North-South Transport Corridor (INSTC), critical for India’s strategic connectivity and trade with Central Asia and Russia.
U.S. Strategic Bitcoin Reserve

- 13 Mar 2025
In News:
In March 2025, U.S. President Donald Trump signed an executive order establishing a Strategic Bitcoin Reserve, positioning the United States as a frontrunner in digital asset storage and long-term crypto strategy.
What is the Strategic Bitcoin Reserve?
- A government-backed stockpile of Bitcoin and select other cryptocurrencies, managed by the U.S. Department of Treasury and Department of Commerce.
- Intended to serve as a digital financial reserve, akin to the U.S. Strategic Petroleum Reserve or gold reserves (e.g., Fort Knox).
- Aims to enhance U.S. leadership in digital currency markets, provide a hedge against inflation, and integrate digital assets into national reserve strategy.
Key Features:
Aspect Details
Establishment By executive order of President Trump, March 2025
Management U.S. Treasury & Commerce Departments
Funding Source Bitcoin and other digital assets seized in criminal and civil forfeiture
proceedings
Assets Held Bitcoin (BTC), Ethereum (ETH), XRP, Solana (SOL), Cardano (ADA)
Ownership As of 2025, U.S. government reportedly holds 200,000 BTC ($18.1 billion)
Policy No short-term sales; assets to be held long-term
Cost to Taxpayers Budget-neutral – funded through seized assets only
Audit Directive Full accounting of federal digital asset holdings mandated
Strategic Rationale:
- Limited Supply Advantage: Bitcoin’s capped supply of 21 million gives it value retention properties similar to gold.
- Inflation Hedge: Cryptocurrencies offer resistance to fiat currency inflation.
- Diversification: Adds a new asset class to U.S. strategic reserves.
- Legitimacy Boost: Government backing may encourage broader adoption of digital currencies.
Concerns & Criticisms:
- Volatility: High market risk; value of crypto assets can fluctuate rapidly.
- Speculation Risk: Critics argue buying crypto at peak prices (BTC ~$109,000) may backfire.
- Ideological Contradiction: Centralized crypto reserve contradicts the decentralized ethos of cryptocurrencies.
- Market Manipulation Potential: Large-scale government holdings could distort free market dynamics.
- Public Benefit Questioned: Critics argue early investors may benefit more than the general public.
Global Context:
- El Salvador: First nation to adopt Bitcoin as legal tender and build a crypto reserve.
- Gold Reserves Trend: Countries like India, China, Turkey, Poland have increased gold holdings—crypto reserves may reflect a similar diversification strategy.
Woolly Mice

- 12 Mar 2025
In News:
Scientists at Colossal Biosciences, a US-based biotechnology company, have genetically engineered mice with mammoth-like traits, dubbed “woolly mice”, as part of a broader project aiming to revive the extinct woolly mammoth.
What are Woolly Mice?
Woolly mice are genetically modified laboratory mice that express specific traits observed in woolly mammoths, such as thick, wavy fur and cold adaptation features. These traits were introduced to validate the feasibility of editing multiple genes for the potential de-extinction of the woolly mammoth.
How Were Woolly Mice Created?
- Methodology:
- Scientists compared ancient DNA of woolly mammoths with modern Asian elephants (their closest living relatives) to identify unique cold-adaptation genetic variants.
- Selected 10 mammoth-associated gene variants related to hair length, thickness, color, and fat metabolism were mapped to their equivalents in lab mice.
- Using CRISPR gene-editing technology, seven key genes were edited across eight changes in mouse embryos.
- Key Gene Edits:
- FGF5: Regulated hair cycle, producing hair three times longer than normal.
- MC1R: Altered coat color to golden, similar to mammoths.
- FABP2: Modified lipid metabolism for potential cold resistance.
- Additional genes affected hair texture, follicle structure, and whisker curling.
Significance of the Experiment
- Proof of Concept: Demonstrates that mammoth-like traits can be recreated in living organisms through targeted gene editing.
- Model for Cold Adaptation Studies: Offers insights into thermoregulation and climate resilience, useful for biodiversity research.
- Potential for Conservation: Highlights the emerging role of gene editing in preventing extinctions and enhancing species’ adaptability.
Scientific and Ethical Concerns
- Some experts argue that the research lacks conclusive evidence that the mice are truly cold-adapted.
- Critics note that while physical traits were achieved, this does not equate to reviving a mammoth, but rather mimicking select features in a different organism.
- There are broader debates on whether such de-extinction efforts are beneficial or divert resources from conserving existing endangered species.
PashuAushadhi Initiative

- 12 Mar 2025
In News:
The Government of India has launched the PashuAushadhi initiative to establish dedicated stores across the country offering affordable, high-quality generic veterinary medicines. This move aims to reduce the out-of-pocket expenditure of farmers and enhance animal health and productivity, especially in the livestock and dairy sectors.
Key Features:
- Modelled on PMBJK: Inspired by the success of the Pradhan Mantri BharatiyaJanaushadhiKendras (PMBJK) that provide generic human medicines, the PashuAushadhiKendras will serve the same purpose for animals.
- Affordable Veterinary Drugs: These Kendras will provide non-branded (generic) veterinary medicines at significantly lower prices.
- Ethnoveterinary Medicines: Alongside allopathic drugs, they will also stock traditional remedies based on indigenous knowledge, compiled by the National Dairy Development Board (NDDB). These include formulations for fever, diarrhoea, indigestion, mastitis, and more.
Implementation Framework
- The initiative is part of the revised Livestock Health and Disease Control Programme (LHDCP), approved by the Union Cabinet.
- Run by Co-operative Societies & PM-KisanSamriddhiKendras (PMKSKs).
- An initial budget of ?75 crore has been allocated under the LHDCP for veterinary medicine access and sales incentives.
Livestock Health and Disease Control Programme (LHDCP)
- With an outlay of ?3,880 crore for 2024–25 and 2025–26, the LHDCP focuses on:
- Prophylactic vaccination against major animal diseases (e.g., FMD, Brucellosis, CSF, PPR, Lumpy Skin Disease).
- Disease surveillance and veterinary infrastructure strengthening.
- Capacity building of veterinary services across India.
Need and Significance
- As per the 20th Livestock Census (2019), India has 535.78 million livestock, including over 302 million bovines.
- Livestock productivity is often hampered by preventable diseases.
- Farmers bear significant expenses on veterinary care, highlighting the need for cost-effective treatment options.
AI Kosha

- 12 Mar 2025
In News
The Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology (MeitY) has launched AI Kosha, a secure platform to catalyze Artificial Intelligence (AI) innovation by providing centralized access to high-quality datasets, models, and development tools. This initiative is part of the broader IndiaAI Mission, which has an outlay of ?10,371 crore and aims to democratize AI access and boost research and governance applications.
Key Features and Infrastructure
- Datasets & Models: AI Kosha hosts 316 datasets and over 80 AI models, covering areas such as Indian language translation, health, census, meteorology, pollution, and satellite imagery.
- AI Sandbox Environment: Offers integrated development tools, tutorials, and an IDE for training AI models.
- Security Protocols: Implements encryption, secure API-based access, real-time threat filtering, and tiered permissions for users (researchers, startups, government bodies).
- AI-readiness Scoring: Aids users in selecting relevant and usable datasets.
Compute Capacity Boost
Under the Compute Capacity pillar of the IndiaAI Mission, the government has commissioned 14,000 GPUs (up from 10,000 announced earlier in 2025) to support shared access for startups and academic institutions. This infrastructure is vital for training large AI models, particularly foundational models tailored for Indian needs.
Policy and Data Governance Background
- AI Kosha complements earlier government efforts like data.gov.in, which already hosts 12,000+ public datasets.
- A 2018 committee, led by Infosys co-founder Kris Gopalakrishnan, proposed access to non-personal data from private firms to promote innovation—a proposal that faced resistance from industry stakeholders.
- The platform promotes ethically sourced and consent-based datasets, aligning with responsible AI practices.
Challenges
- Limited Dataset Diversity: Current datasets are mostly government or research-based, limiting private-sector applicability.
- Access Barriers: Strong security protocols, while crucial, may hinder ease of access for some innovators.
- Early Stage Evolution: Wider participation from industry is essential to expand dataset variety and utility.
Ayushman Arogya Mandirs

- 11 Mar 2025
In News:
The Government of India has operationalisedAyushman Arogya Mandirs (AAMs) across the country, marking a transformative step towards holistic, accessible, and preventive health care. As of January 31, 2025, a total of 1,76,141 Ayushman Arogya Mandirs have been established nationwide.
Recent Development in Delhi:
Recently three Primary Health Centres (PHCs) in Najafgarh, Palam, and Ujwa were converted into Ayushman Arogya Mandirs. These are among the first AAMs in Delhi, focused on:
- Preventive and promotive healthcare, beyond clinical and immunisation services.
- Free access to 172 medicines and 63 diagnostic tests.
- Dissemination of health awareness via health talks and educational displays (e.g., ear health, lifestyle diseases).
- Community outreach through ASHA and ANM workers under IEC and BCC programmes.
These centres operate under the Rural Health Training Centre, Najafgarh, affiliated with the Union Ministry of Health and Family Welfare. The Najafgarh PHC, one of Delhi’s oldest (established in 1937), is undergoing certification under National Quality Assurance Standards (NQAS) and Indian Public Health Standards (IPHS).
Key Features of Ayushman Arogya Mandirs:
- Comprehensive Primary Health Care (CPHC): Includes preventive, promotive, curative, rehabilitative, and palliative services.
- Staff trained in yoga, lifestyle counselling, diabetes and blood pressure screening.
- Universal, free healthcare services located closer to communities.
Institutional Framework:
Ayushman Arogya Mandir is a rebranded initiative under the broader Ayushman Bharat scheme, launched as per the National Health Policy 2017 to achieve Universal Health Coverage (UHC).
It consists of two major components:
- Ayushman Arogya Mandirs – Delivering comprehensive primary healthcare services.
- Pradhan Mantri Jan Arogya Yojana (PM-JAY) – Providing health insurance coverage of ?5 lakh per family/year for secondary and tertiary hospitalization to over 12 crore poor and vulnerable families (covering approximately 55 crore individuals).
Bollgard-3

- 10 Mar 2025
In News:
Punjab's cotton sector is facing a severe crisis due to increasing pest infestations and declining yields. In response, there is a rising demand for advanced genetically modified (GM) cotton varieties, particularly Bollgard-3, ahead of the 2025 sowing season.
Key Facts:
Decline in Cotton Cultivation in Punjab:
- Cotton acreage in Punjab has drastically declined from ~8 lakh hectares (1990s) to just 1 lakh hectares (2024).
- The ginning industry has also shrunk — only 22 ginning units remain functional, down from 422 in 2004.
- The main causes are whitefly (2015–16) and pink bollworm (2018–19) infestations.
About Bollgard Series of Bt Cotton:
Version Introduced in India Features
Bollgard-1 2002 Contains Cry1Ac gene — limited pest resistance
Bollgard-2 2006 Added Cry2Ab gene — wider pest control, still ineffective against
whiteflies and pink bollworms
Bollgard-3 Not approved in India Contains Cry1Ac, Cry2Ab, and Vip3A — effective against
lepidopteran pests like pink bollworm
- Bollgard-3, developed by Monsanto, offers enhanced pest resistance, but remains unapproved in India despite global usage.
- Bt (Bacillus thuringiensis) is a soil-dwelling bacterium used in GM crops for pest resistance by producing insecticidal proteins.
Alternative in Pipeline – BG-2RRF:
- Bollgard-2 Roundup Ready Flex (BG-2RRF) is aherbicide-tolerant GM cotton variety pending final regulatory approval in India.
- Enables better weed control and potentially reduces pest hosts, boosting yield.
- Field trials for BG-2RRF were conducted in 2012–13, but commercial approval remains pending.
- Experts argue that regulatory hurdles are delaying the adoption of next-generation GM seed technologies, affecting India's cotton competitiveness.
Current Agronomic Recommendations:
- In absence of new GM varieties, experts suggest:
- High-density planting
- Drip fertigation
- Proper seeding and mulching
- However, pest management remains a critical issue under current practices.
Comparative Global Context:
- Countries like Brazil are using Bollgard-5, achieving yields of 2400 kg/ha, compared to 450 kg/ha in India.
- India's profit margin from cotton is just 15%, whereas Brazil enjoys 85% margins due to advanced biotech adoption.
Dragon Copilot

- 10 Mar 2025
In News:
Microsoft has launched Dragon Copilot, a voice-activated AI assistant designed specifically for the healthcare sector. It aims to reduce administrative burdens on clinicians by automating documentation and providing quick access to medical information.
Key Features and Functionalities:
- Platform Integration: Part of Microsoft Cloud for Healthcare, Dragon Copilot integrates with Electronic Health Records (EHR) and is accessible via desktop, browser, or mobile app.
- Technology Base: Built on Nuance’s Dragon Medical One (DMO) and DAX (Dragon Ambient eXperience) platforms, which have supported transcription of billions of patient records and over 3 million ambient patient interactions.
- Voice & AI Capabilities:
- Uses natural language dictation and ambient listening technologies.
- Enhanced with generative AI and healthcare-specific safeguards.
- Allows drafting of memos, referral letters, clinical summaries, and after-visit notes in personalized formats.
- Facilitates real-time voice-to-text transcription and AI-generated notes via user prompts or templates.
- Supports automated search for verified medical information.
Benefits:
- Reduces clinician paperwork and burnout, enhancing focus on patient care.
- Survey Data (Microsoft Findings):
- Saves ~5 minutes per patient interaction.
- 70% clinicians reported reduced fatigue.
- 62% were less likely to leave their organizations.
- 93% patients reported improved experiences.
Concerns and Risks of Healthcare AI:
- AI Hallucinations: Tools like OpenAI’s Whisper have produced fictitious content, including inappropriate or incorrect medical information.
- Regulatory Caution:
- The US FDA warns of risks from generative AI in healthcare, including false diagnoses or biased outputs.
- Emphasizes the need for transparent and accountable development practices.
- Microsoft’s Response:
- Claims to have integrated “clinical, chat, and compliance safeguards” into Dragon Copilot.
- Built in alignment with Microsoft’s Responsible AI principles, although technical specifics remain undisclosed.
Broader AI Healthcare Landscape:
- Companies like Google Cloud, Abridge, and Suki are developing similar AI-based healthcare assistants.
- Growing interest in generative AI for reducing clinician workload and improving patient outcomes is driving innovation and investment across the sector.
U.S. Reciprocal Tariffs
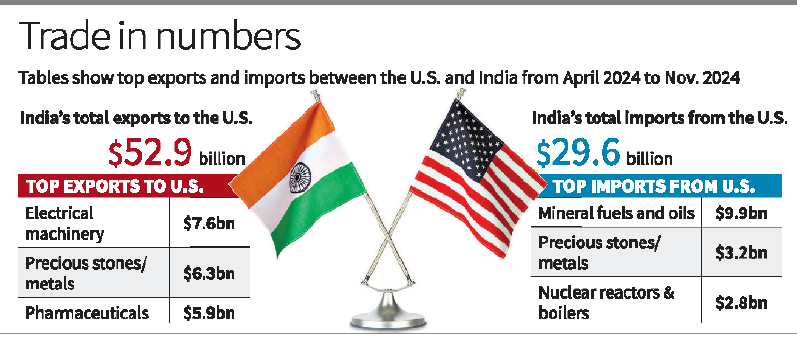
- 09 Mar 2025
In News:
On April 2, 2025, the United States is set to implement reciprocal tariffs as announced by President Donald Trump during his address to a joint session of the U.S. Congress. The move targets major trade partners including India, China, the European Union, Canada, and Mexico.
What Are Reciprocal Tariffs?
- Definition: A reciprocal tariff is a trade measure in which a country imposes import duties equal to the tariffs its exports face in other nations.
- Objective: To establish a level playing field, correct trade imbalances, and respond to unfair tariff structures by trading partners.
- Application:
- If a foreign nation imposes high tariffs on U.S. goods, the U.S. will match that rate on goods imported from that country.
- Applies to goods, services, and even non-tariff barriers limiting U.S. market access.
Why Now? Trump’s Trade Strategy
- President Trump cited India’s high tariffs on automobile imports (reportedly over 100%) as an example of unfair trade.
- The U.S. also flagged China, EU, Brazil, and Mexico for imposing higher duties on U.S. exports.
- Trump emphasized that the U.S. has been “taken advantage of for too long” and that reciprocal tariffs are necessary to protect American jobs and industry.
WTO Implications
- May violate WTO's Most-Favoured-Nation (MFN) rule, which mandates equal treatment of trade partners.
- The U.S. could invoke Article XX (general exceptions) or Article XXI (national security exception) of the WTO Agreement to justify its policy.
Potential Impacts of Reciprocal Tariffs
Positive Impacts Negative Impacts
Boosts U.S. manufacturing by reducing import dependency May trigger retaliatory tariffs,
escalating trade wars
Encourages tariff reductions by partner nations Leads to higher import prices and
consumer inflation
Aims to reduce the trade deficit Causes economic uncertainty
and hurts investor confidence
Promotes domestic job creation May lead to WTO disputes and
strain diplomatic relations
PUNCH Mission

- 09 Mar 2025
In News:
NASA is set to launch the PUNCH (Polarimeter to Unify the Corona and Heliosphere) mission on March 6, 2025, from Vandenberg Space Force Base, California. It will be the third major solar mission launched globally in the past 18 months.
About the PUNCH Mission:
Aspect Details
Agency NASA (National Aeronautics and Space Administration)
Launch Date March 6, 2025
Mission Objective Study the Sun’s corona (outer atmosphere) and how solar wind evolves as it moves
into the heliosphere
Unique Features - First dedicated mission to image the transition from the corona to the heliosphere
- Will use four identical suitcase-sized satellites for continuous imaging of the inner corona
Importance - Improves understanding of space weather
- Helps predict solar storms, safeguarding satellites, astronauts, and
communication networks
What is the Solar Cycle?
- The solar cycle is an ~11-year periodic change in the Sun’s magnetic field, where the north and south poles flip positions.
- This cycle governs the level of solar activity, including sunspots, solar flares, and coronal mass ejections (CMEs).
- Solar Maximum: Period of peak activity with increased sunspots and solar eruptions.
- Solar Minimum: Period of least activity.
The current solar cycle began gaining momentum around May 2022, and solar activity remained above normal through 2024. The solar maximum is anticipated around 2025, offering an ideal window for solar observation.
Why the Surge in Solar Missions?
- Solar maximum periods offer the best conditions to observe high-energy events like flares and CMEs.
- Scientists aim to maximize data collection before the next solar minimum (next solar max expected ~2035–36).
- Monitoring solar activity is crucial because solar storms can disrupt satellite communications, navigation systems, and power grids on Earth.
Recent Major Solar Missions (2023–25):
Mission Agency Launch Date Purpose
Aditya-L1 ISRO (India) Sept 2, 2023 India’s first solar observatory; studies solar flares, solar winds, and magnetic fields
Proba-3 ESA (Europe) Dec 4, 2024 Dual-satellite mission to study solar corona and space weather
PUNCH NASA (USA) Mar 6, 2025 First mission to study continuous evolution from solar corona to heliosphere
IRCTC and IRFC Granted ‘Navratna’ Status
- 07 Mar 2025
In News:
The Indian Railway Catering and Tourism Corporation (IRCTC) and Indian Railway Finance Corporation (IRFC) have been granted Navratna status by the Government of India, becoming the 25th and 26thNavratna CPSEs (Central Public Sector Enterprises) in India. This recognition enhances their operational autonomy and positions them for further growth and expansion.
What is Navratna Status?
Navratna status is a prestigious classification granted by the Department of Public Enterprises (DPE) under the Ministry of Finance to select CPSEs that demonstrate exceptional financial and operational performance. The status provides these enterprises with enhanced autonomy, empowering them to make decisions independently and engage in significant investments without needing government approval.
Eligibility Criteria for Navratna Status:
- Must be a Miniratna-I CPSE with a positive net worth.
- Must secure an Excellent or Very Good MoU rating for three of the last five years.
- Must score 60+ points on key financial indicators, such as net profit, net worth, and manpower cost.
- The board must have at least four independent directors.
Benefits of Navratna Status:
- Investment Autonomy: Ability to invest up to ?1,000 crore or 15% of net worth without government approval.
- Global Expansion: Freedom to form joint ventures, subsidiaries, and alliances globally.
- Increased Market Credibility: Attracts strategic partnerships and enhances business growth.
About IRCTC and IRFC
- Indian Railway Catering and Tourism Corporation (IRCTC):
- Establishment: 1999
- Ministry: Ministry of Railways, Government of India
- Key Functions:
- E-Ticketing: Manages online train reservations through portals and mobile apps.
- Catering Services: Operates onboard catering and manages railway food plazas.
- Tourism Services: Offers rail-based tourism packages, including luxury trains like Maharajas’ Express.
- Rail Neer: Supplies packaged drinking water for railway passengers.
- Indian Railway Finance Corporation (IRFC):
- Establishment: 12 December 1986
- Ministry: Ministry of Railways, Government of India
- Key Functions:
- Funding Indian Railways: Provides low-cost capital for railway expansion and modernization.
- Market Borrowings: Raises funds through bonds, external borrowings, and public offerings.
- Rolling Stock Leasing: Finances the procurement of locomotives, coaches, and wagons.
- Infrastructure Development: Supports the modernization and electrification of railway networks.
Performance of IRCTC and IRFC for FY 2023-24:
- IRCTC:
- Annual Turnover: ?4,270.18 crore
- Profit After Tax (PAT): ?1,111.26 crore
- Net Worth: ?3,229.97 crore
- IRFC:
- Annual Turnover: ?26,644 crore
- Profit After Tax (PAT): ?6,412 crore
- Net Worth: ?49,178 crore
Implications of Navratna Status for IRCTC and IRFC
The grant of Navratna status is a significant milestone for both IRCTC and IRFC, offering them several advantages:
- Operational Autonomy: Both entities can now make larger investments independently, enhancing their capabilities to drive further growth and development.
- Business Expansion: The status will facilitate the ability to enter into joint ventures, partnerships, and alliances, both within India and internationally.
- Enhanced Market Credibility: This recognition will likely attract more investors and strategic partners, boosting the financial health and market standing of IRCTC and IRFC.
Harpoon Missile
- 07 Mar 2025
In News:
The U.S. Air Force is exploring a new approach to naval warfare by integrating the Harpoon anti-ship missile onto its F-16 fighter aircraft. This development signifies a shift in operational capabilities and enhances the U.S. Air Force’s ability to conduct anti-surface warfare.
Overview of the Harpoon Missile:
The Harpoon missile is a subsonic anti-ship cruise missile developed by Boeing for the U.S. Navy, first introduced in 1977. It is designed to strike surface targets, such as ships and land-based structures, and is currently in service with over 30 countries, including India.
Key features:
- Length: 4.5 meters
- Weight: 526 kilograms
- Range: 90 to 240 kilometers
- Speed: Mach 0.85 (approximately 647 mph or 1,041 km/h)
- Guidance System: GPS-assisted inertial navigation and active radar seeker, enabling both anti-ship and land-strike capabilities
- Warhead: 221-kilogram blast warhead
- Launch Platforms: The Harpoon can be launched from various platforms including ships, submarines, aircraft, and shore batteries
- All-Weather Operations: Designed to perform under various environmental conditions, Harpoon can execute both over-the-horizon and sea-skimming maneuvers for high survivability.
U.S. Air Force Integration with F-16 Aircraft:
The integration of the Harpoon missile onto F-16 aircraft represents a strategic shift for the U.S. Air Force, as traditionally, the missile has been used exclusively by naval platforms. The 53rd Test and Evaluation Group demonstrated a new gateway system that allows for rapid integration of the Harpoon with the F-16, significantly enhancing its anti-surface capabilities.
This integration system enables communication between the missile and aircraft without requiring extensive modifications, potentially shortening the deployment timeline for advanced weaponry. The F-16 fighter aircraft, traditionally designed for air-to-air combat, would now also have the capability to engage surface targets, improving the Air Force’s combat readiness and operational versatility.
Implications for Naval Warfare:
The potential for deploying the Harpoon missile from F-16s would mark a shift in the U.S. Air Force’s role in naval warfare. Traditionally, the Air Force has not employed anti-ship missiles, relying instead on the Navy for such capabilities. The integration of Harpoon onto F-16s would diversify the operational roles of the aircraft, adding flexibility to U.S. military strategies and improving overall effectiveness in anti-surface warfare.
This move would also enable the Air Force to act more autonomously in surface combat scenarios, without relying solely on naval assets. The introduction of this capability could prove critical in multi-domain operations, where air, land, and sea forces must be seamlessly integrated to respond to evolving threats.
Future Developments:
The success of integrating the Harpoon missile onto the F-16 could pave the way for future projects involving the integration of other advanced weapon systems across various military platforms. The flexibility to adapt quickly and innovate beyond bureaucratic constraints is crucial in maintaining a strategic advantage and responding effectively to emerging threats.
The U.S. military’s ongoing commitment to technological advancements and interoperability across its branches signals its readiness to maintain supremacy in naval and aerial warfare. The integration of Harpoon onto F-16s is an example of this evolving capability, with potential implications for future military operations worldwide.
Payodhi Milk Bank at AIIMS

- 07 Mar 2025
In News:
Payodhi, a human milk bank and lactation management centre at AIIMS, New Delhi, has emerged as a critical facility for premature and critically ill newborns in the Neonatal Intensive Care Unit (NICU). Launched in September 2024, it provides pasteurised donor breast milk to newborns who require it due to medical conditions or where the mother cannot breastfeed.
Objectives:
- Provide Safe and Processed Human Milk: Ensures critically ill or premature infants receive the essential nutrients they need for survival, brain development, and immune system strengthening.
- Support Lactating Mothers: Provides counselling, milk donation, and storage facilities to lactating mothers, helping them contribute to milk banks if they have excess milk or cannot breastfeed.
- Free-of-Cost Service: The milk bank offers these services free of charge, ensuring equitable access to life-saving nutrition for vulnerable newborns.
- Global Standards: Payodhi follows guidelines set by the World Health Organization (WHO) and the Government of India on infant nutrition.
Significance:
- Lifesaving Nutrition: The use of donor milk reduces mortality risks in preterm babies, helping to prevent conditions like sepsis, necrotising enterocolitis (NEC), and retinopathy—common complications faced by premature infants.
- Prevents Milk Wastage: By utilising excess milk from donor mothers, Payodhi prevents the wastage of breast milk, which could otherwise be discarded.
- Support for Medical Conditions: The milk bank is crucial for infants whose mothers cannot produce sufficient milk due to medical reasons, such as pulmonary hypertension or those undergoing surgery.
Medical and Health Benefits of Donor Milk:
- Sepsis Reduction: Donor breast milk reduces the risk of sepsis by 19%, compared to formula feeding.
- Reduction in NEC: It significantly lowers the risk of necrotising enterocolitis (NEC) by 79%, a severe infection with a high mortality rate in premature infants.
- Improved Health Outcomes: Early initiation of breast milk within an hour of birth can reduce neonatal deaths by 22%. It also reduces feeding intolerance, vomiting, and shortens NICU stays.
Expansion and Reach:
Payodhi is one of around 90 milk banks in India, contributing to the nationwide effort to reduce neonatal deaths. AIIMS is working to expand its donor pool by reaching out to mothers whose babies have undergone surgery or those whose infants are in long-term NICU care. The milk bank also plans to reach out to working mothers, encouraging them to express and donate excess milk, benefiting both the infants and their own health.
Why Donating Milk is Beneficial:
Donating milk not only helps save newborns but also benefits the donor mothers by stimulating lactation and preventing milk suppression. The act of expressing milk helps maintain milk production, which is essential for the health of both the baby and the mother.
World Wildlife Day 2025

- 05 Mar 2025
In News:
World Wildlife Day is observed on March 3 every year, and in 2025, it will be observed under the theme of “Wildlife Conservation Finance: Investing in People and Planet.”
Key Details:
- Declared by: United Nations General Assembly (UNGA)
- First Observed: 2014
- Occasion: Commemorates the signing of CITES (Convention on International Trade in Endangered Species of Wild Fauna and Flora) in 1973.
- Theme 2025:“Wildlife Conservation Finance: Investing in People and Planet”
Purpose and Significance
World Wildlife Day is an annual UN-recognized global event aimed at:
- Raising awareness about wild fauna and flora.
- Highlighting threats such as climate change, poaching, habitat destruction, and illegal wildlife trade.
- Encouraging global cooperation for wildlife protection.
- Promoting innovative financing models to bridge the estimated $824 billion global biodiversity funding gap.
2025 Theme Focus: Conservation Finance
The 2025 theme calls for sustainable financial strategies, emphasizing:
- Wildlife Conservation Bonds
- Debt-for-Nature Swaps
- Green Bonds and Carbon Credits
- Payments for Ecosystem Services (PES)
- Public-Private Partnerships
These mechanisms aim to support conservation while fostering economic opportunities for local communities.
Timeline of Key Events
- 1973: CITES adopted.
- 2013: UNGA designates March 3 as World Wildlife Day.
- 2014: First official celebration.
- 2021: Theme – Forests and Livelihoods.
- 2025: Theme – Finance for Conservation.
Wildlife Status in India
- Protected Areas: 1,014 total (as of 2024), including:
- 106 National Parks
- 573 Wildlife Sanctuaries
- 115 Conservation Reserves
- 220 Community Reserves
(Covers ~5.32% of India’s total area)
- Tiger Population (2022): 3,682 – ~75% of global wild tigers
- Asiatic Lion Population (2020): ~674 (only in Gujarat's Gir Forest)
- India's Biodiversity Share:
- 7.6% of global mammal species
- 14.7% of amphibians
- 6% of birds and reptiles
- 6% of flowering plants
Major Causes of Wildlife Decline
- Habitat loss & fragmentation
- Illegal wildlife trade and poaching
- Climate change and pollution
- Invasive species
- Industrialization & urban expansion
Conservation Measures in India
- Project Tiger (1973): Boosted tiger numbers significantly.
- Project Elephant (1992): Focuses on elephant corridors and human-wildlife conflict mitigation.
- Wildlife Protection Act (1972): Key legal framework to safeguard endangered species.
- Eco-Sensitive Zones (ESZs): Buffer areas around protected habitats.
- Community Initiatives: Ecotourism, local participation in conservation.
Dramatic Performances Act, 1876

- 05 Mar 2025
In News:
Prime Minister Narendra Modi, at the NXT Conclave, highlighted the Dramatic Performances Act, 1876, as an example of outdated colonial legislation that continued in India long after independence. Though declared unconstitutional in 1956, the Act was formally repealed in 2017 as part of the government's initiative to eliminate obsolete laws and improve ease of doing business.
About the Dramatic Performances Act, 1876
Purpose and Background:
- Enacted by the British colonial government to suppress nationalist sentiments expressed through theatre and performance arts.
- Followed the 1875–76 visit of Prince of Wales (Albert Edward) to India, a period that saw increased resistance against colonial rule.
- Part of a broader strategy alongside other repressive laws such as the Vernacular Press Act (1878) and the Sedition Law (1870).
Key Provisions:
- Wide Banning Powers: Authorities could prohibit any play, pantomime, or public performance deemed seditious, defamatory, scandalous, or obscene.
- Search and Seizure: Magistrates had the authority to raid venues, seize performance materials, and cancel licenses.
- Punishment: Violations could lead to up to 3 months' imprisonment, fines, or both.
- Covered theatre groups, performers, and venues hosting dramatic works.
Post-Independence Status:
Continued Operation:
- Article 372 of the Indian Constitution allowed pre-existing colonial laws to remain valid until repealed or declared unconstitutional.
- The Act was adopted in some states like Madhya Pradesh, Karnataka, Delhi, and Tamil Nadu.
Judicial Rejection:
- In 1956, the Allahabad High Court, in State vs. Baboo Lal &Ors., ruled the Act unconstitutional, citing violation of Article 19(1)(a) (Freedom of Speech and Expression).
- The Court found the Act’s procedural provisions ultra vires and beyond the permissible limits under Article 19(2).
Notable Case:
- In 1953, the Indian People’s Theatre Association (IPTA) attempted to stage ‘Idgah’, based on Munshi Premchand's story.
- The performance was abruptly banned mid-show by the local magistrate. The theatre group defied the order, leading to the court case that triggered the judicial review.
Final Repeal:
- Although unused since 1956, the law remained on the statute books until its formal repeal through the Repealing and Amending (Second) Act, 2017.
- This repeal was part of a larger reform initiative launched by the Modi government in 2014, which has repealed over 2,000 obsolete laws to streamline the legal system and boost administrative efficiency.
MISHTI Scheme

- 03 Mar 2025
In News:
Gujarat has emerged as the national leader in mangrove afforestation, covering 19,020 hectares in just two years under the Centre’s ‘MISHTI’ scheme.
Key Highlights:
- The Mangrove Initiative for Shoreline Habitats and Tangible Incomes (MISHTI) scheme was launched in 2023 under the Union Budget for 2023-24.
- The scheme aims to restore degraded mangrove ecosystems and increase India’s mangrove cover, enhancing coastal resilience while fostering sustainable livelihoods for coastal communities.
- Implemented from 2023 to 2028, the scheme is funded through various channels, including the CAMPA Fund (Compensatory Afforestation Fund Management and Planning Authority), MGNREGS (Mahatma Gandhi National Rural Employment Guarantee Scheme), and other governmental and private funding sources.
- The initiative also supports India’s participation in the global Mangrove Alliance for Climate (MAC) launched at COP27.
Key Objectives of MISHTI
- Ecological Restoration: To restore degraded mangrove ecosystems and expand mangrove cover across coastal areas.
- Coastal Resilience: To strengthen coastal resilience against climate change, such as coastal erosion and rising sea levels.
- Livelihood Generation: To promote ecotourism, sustainable livelihoods, and fishing opportunities for coastal communities.
- Climate Change Mitigation: The scheme plays a crucial role in protecting shorelines from storms, supporting India's commitments under the Paris Agreement and the UN Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs).
Gujarat’s Role in MISHTI Scheme
- Gujarat has emerged as the national leader in mangrove afforestation under the MISHTI scheme, planting over 19,000 hectares of mangroves in just two years.
- The state is spearheading the mangrove expansion efforts, with its coastline covering diverse ecosystems such as mangroves, coral reefs, and seagrasses.
- Gujarat has surpassed the Central Government’s target of planting 540 sq. km of mangroves in five years, completing plantation across 190 sq. km in the initial two years of the scheme.
Mangrove Distribution in Gujarat
- Gujarat's mangrove cover is distributed strategically across different coastal regions:
- Kutch: 799 sq. km, including the Gulf of Kutch, home to the Marine National Park and Wildlife Sanctuary.
- Other Coastal Districts: Jamnagar, Rajkot (Morbi), Porbandar, DevbhoomiDwarka (236 sq. km).
- Central and Southern Belt: Includes Bhavnagar, Ahmedabad, Anand, Bharuch, Surat, Navsari, and Valsad, covering 134 sq. km, with important areas like the Gulf of Khambhat and Dumas-Ubhrat.
- Saurashtra Region: Amreli, Junagadh, and Gir-Somnath maintain 6 sq. km of mangrove cover.
Significance of Mangroves
- Erosion Prevention: Mangroves act as a natural barrier, protecting coastal regions from erosion caused by waves and storms.
- Biodiversity Support: They provide vital breeding grounds for fish and other marine species, supporting coastal livelihoods.
- Climate Resilience: Mangroves help mitigate the effects of climate change by shielding vulnerable coastal communities from cyclones, reducing salinity, and preserving agricultural lands.
Global and National Mangrove Status
- Global Mangrove Distribution: Mangroves are found in tropical and subtropical regions worldwide, providing critical ecosystem services.
- India’s Mangrove Cover: According to the India State of Forest Report 2023, India has a total mangrove cover of 4,991.68 km², which accounts for 15% of the country’s total geographical area. The MISHTI scheme plays a pivotal role in further expanding this cover.
Zagros Mountains and Iraq’s Tectonic Subsidence

- 27 Feb 2025
In News:
Recent geological studies have found that the hilly region around the Zagros Mountains in northern Iraq is slowly sinking into the Earth, a process attributed to ancient tectonic dynamics. This discovery has implications for earthquake prediction and geothermal energy potential.
Zagros Mountains
- Location: Stretches ~1,500 km from eastern Turkey and northern Iraq across the Iranian Plateau to the Strait of Hormuz.
- Highest Peak: Mount Dena (4,409 m / 14,465 ft).
- Geological Composition: Primarily limestone and shale from the Mesozoic Era and Paleogene Period.
- Climate: Semi-arid temperate – cold winters and dry, arid summers.
- Vegetation: Dominated by oak and pistachio trees with steppe vegetation.
Geological Process Behind Iraq’s Sinking
- The Zagros region is influenced by the tectonic collision between the Arabian and Eurasian Plates.
- A sinking oceanic slab, part of the ancient Neotethys Ocean floor (over 66 million years old), is pulling the region down.
- This slab is subducting beneath the Eurasian Plate, a process occurring over tens of millions of years, making it imperceptible in human timescales.
Research Insights
- The studyused rock records, sediment analysis, and deep-earth imaging to understand the tectonic architecture of the region.
- The findings explain why the depressions around the Zagros Mountains are deeper than the current topography would suggest.
Significance of the Study
- Helps develop precise geological models critical for:
- Earthquake prediction – by understanding fault depths and configurations.
- Geothermal energy exploration – estimating areas with high geothermal gradients.
- Especially relevant in a region prone to seismic activity (e.g., 2023 Turkey-Syria earthquakes).
Three-Language Formula and NEP 2020

- 27 Feb 2025
In News:
The Three-Language Formula (TLF) under the National Education Policy (NEP) 2020 has sparked controversy, particularly with Tamil Nadu opposing its implementation. The Union government’s withholding of ?573 crore under the Samagra Shiksha Abhiyan (SSA) for non-compliance has intensified the Centre-State standoff.
What is the Three-Language Formula?
- NEP 2020 mandates students learn three languages, of which at least two must be Indian languages.
- States, schools, and students have flexibility to choose the languages, with no imposition from the Centre.
- The medium of instruction should be the home language, mother tongue, or regional language at least until Grade 5, preferably till Grade 8 and beyond.
- Foreign languages like French, German, and Japanese can be offered at the secondary level.
Historical Background:
- Kothari Commission (1964–66) proposed the Three-Language Formula to promote national unity and linguistic diversity.
- Formally adopted in the NPE 1968 under PM Indira Gandhi, reaffirmed in 1986 (Rajiv Gandhi), and revised in 1992 (Narasimha Rao).
- Article 351 of the Constitution mandates the Union to promote the spread of Hindi.
- Tamil Nadu has historically rejected Hindi imposition, favoring a two-language policy (Tamil and English) since CM C.N. Annadurai’s tenure.
Benefits of the Three-Language Formula (UNESCO-backed):
- Improved Learning:
- Multilingual students show better cognitive development and academic performance.
- Education in the mother tongue improves comprehension and parental engagement.
- Social Inclusion:
- Helps include marginalized communities and preserve indigenous languages.
- Promotes unity in diversity and national integration.
- Economic & Environmental Gains:
- Preserves traditional ecological knowledge.
- Example: Switzerland attributes 10% of its GDP to its multilingual heritage.
Challenges and Criticisms:
- Politicization: Language policies can fuel regionalism and identity politics.
- Educational Burden: Students, especially from monolingual or low-literacy households, may struggle with an extra language.
- Infrastructure Gaps: There’s a shortage of trained language teachers.
- Diverse States: Linguistically complex states like Nagaland may face logistical issues.
- Technological Alternatives: Tools like AI translators reduce the need for multilingual proficiency.
Way Forward:
- Focus on quality of education before adding languages.
- Promote cooperative federalism—respecting state autonomy while aligning with NEP goals.
- UNESCO-aligned implementation:
- Use sociolinguistic data for planning.
- Develop learning materials in regional languages.
- Train bilingual teachers.
- Encourage community participation in language education.
Ancient Tea Horse Road
- 27 Feb 2025
In News:
The Tea Horse Road, also known as the Southern Silk Road, was an ancient trade network connecting China, Tibet, and India. It played a pivotal role in economic, cultural, and strategic exchanges between these regions for over a millennium. Though less popular than the Silk Road, it was vital for the tea-horse trade and strategic logistics.
Geography and Route
- Length: Over 2,000 km
- Route Type: Not a single path, but a network of caravan routes
- Regions Covered:
- Originated in Southwest China (Yunnan & Sichuan)
- Passed through Tibet, Nepal, Bhutan
- Extended into India via Himalayan passes, reaching Kalimpong and Kolkata
- Key Nodes:
- Dali & Lijiang (Yunnan): Tea production centers
- Lhasa (Tibet): Central convergence point for trade
- Kalimpong& Kolkata (India): Export destinations to Europe and Asia
- Elevation: Reached up to 10,000 feet in the Himalayas
- Terrain: Extremely challenging — cold, steep, and remote
Historical Evolution
- Tang Dynasty (618–907 CE): Early mentions by Buddhist monk Yijing; trade included sugar, textiles, rice noodles, gold, saffron, and medicinal herbs
- Song Dynasty (960–1279 CE): Institutionalized the tea-for-horse exchange; established official markets for regulated trade
- Mongol Period (13th century): Heightened need for horses for military use against nomadic tribes
- Qing Dynasty's Fall (1912): Political instability weakened trade, but the road was used for global tea exports
- World War II: Gained renewed importance as a logistical route after Japanese blockade of China’s coastline
Tea and Horses – The Core Trade
- Tea: Essential in Tibetan climate; popularized due to practicality and possibly a royal dowry tradition
- Tibetan staple: Yak butter tea
- Pressed tea bricks used as currency in medieval Tibet
- Horses: Sourced from Tibet and Yunnan, vital for China’s cavalry
- Tibetan horses were prized for battles against Mongolian tribes
Decline and Modern Legacy
- Post-1949 (PRC Formation):
- Land reforms and modern infrastructure reduced reliance on traditional portering
- Mechanized transport replaced mule and porter-based systems
- Modern Times:
- Revival through tourism and heritage promotion
- Lijiang declared UNESCO World Heritage Site (1997) for its trade history and cultural legacy
Significance for India-China Relations
- Demonstrates centuries-old economic and cultural exchanges
- Reflects shared heritage through trade, Buddhism, and ethnic interactions
- Ambassador Xu Feihong recently invoked the Tea Horse Road to highlight historical Indo-China links, reinforcing its symbolic role in bilateral diplomacy
Quality of Public Expenditure (QPE) Index
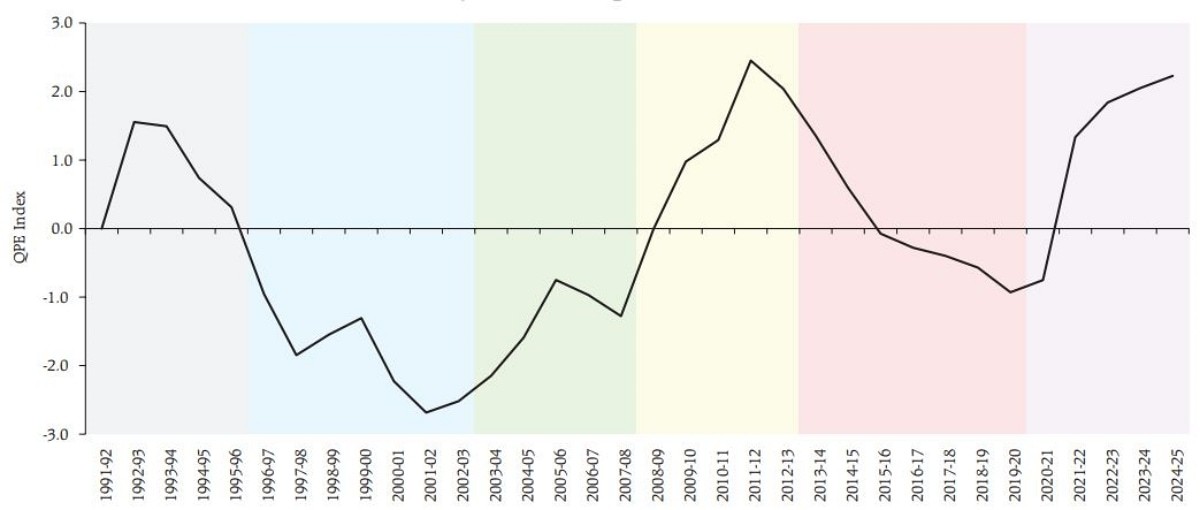
- 25 Feb 2025
In News:
The Quality of Public Expenditure (QPE) Index, developed by the Reserve Bank of India (RBI), measures how efficiently public funds are allocated and utilized by the Central and State governments. Unlike traditional fiscal measures that focus on total expenditure, the QPE Index assesses the composition and developmental impact of government spending, emphasizing long-term economic growth and social development.
Key Components of the QPE Index
Indicator What it Measures Significance
Capital Outlay to GDP Ratio - Share of GDP spent on physical infrastructure - Higher ratio = better quality of expenditure
Revenue Expenditure to Capital Outlay Ratio - Relative spending on salaries, pensions vs. asset creation - Lower ratio = better efficiency
Development Expenditure to GDP Ratio - Spending on education, healthcare, R&D, infrastructure - Higher ratio = enhanced productivity
Development Expenditure as % of Total Expenditure - Proportion of total expenditure directed to development sectors - Higher share = improved allocation
Interest Payments to Total Expenditure Ratio - Financial burden from past borrowings - Lower ratio = better fiscal health
Evolution of Public Expenditure (1991–2025)
- 1991–1997(Early liberalization):
- Slight improvement at Centre; states faced fiscal pressure.
- Public investment declined due to focus on fiscal deficit reduction.
- 1997–2003:Decline in QPE due to Fifth Pay Commission, rising interest burden, dominance of revenue expenditure.
- 2003–2008(FRBM Era):
- Fiscal Responsibility and Budget Management (FRBM) Act, 2003 improved fiscal discipline.
- States gained from higher tax devolution; capital spending rose.
- Growth momentum sustained until the 2008 Global Financial Crisis (GFC).
- 2008–2013(GFC response):
- Stimulus spending initially boosted development but later widened fiscal deficits.
- Spending quality eroded over time.
- 2013–2019(GST & 14th Finance Commission):
- 14th Finance Commission (2015) increased states' tax share to 42%, improving state-level development spending.
- GST rollout (2017) benefited states more than Centre initially, stressing Centre’s finances.
- 2019–2025(COVID-19 & Recovery):
- Pandemic-induced fiscal stimulus reduced QPE temporarily.
- Post-pandemic recovery led by record capital expenditure boosted infrastructure, improving QPE.
- By FY 2024–25, India's QPE reached its highest level since 1991 reforms.
Recent Trends in Public Expenditure (as per Economic Survey 2024–25 & Budget 2025–26)
- Capital expenditure (Capex) rose 8.2% YoY.
- Revenue expenditure (primarily by states) increased 12% YoY.
- FY 2025–26 Budget allocated ?11.21 lakh crore for Capex (3.1% of GDP).
- Capex to GDP ratio increased from 1.5% in 2000 to 2.5% in 2023.
- Revenue expenditure to Capex ratio improved from 8:1 in 2000 to 5:1 in 2023.
- Development expenditure rose from 6% to 8% of GDP between 2000–2023.
- Interest payments declined from 25% to 20% of total expenditure in the same period.
Why Quality of Public Expenditure Matters
- Governments use citizens’ money (via taxes or borrowing). Efficient use ensures better socio-economic outcomes.
- High QPE means greater focus on productive investment over populist spending (freebies, subsidies).
- Better QPE leads to:
- Higher GDP growth (average 6.5% annually since 2000).
- Improved infrastructure and service delivery.
- Enhanced social indicators like literacy (77.7% in 2023) and life expectancy (70 years).
Challenges Affecting Public Expenditure Quality
- Persistent revenue deficits (3.3% of GDP in 2023) limit fiscal space for Capex.
- Rising populism: Loan waivers, cash handouts, free electricity.
- Welfare scheme inefficiencies: Leakages in MGNREGA, PDS.
- Debt servicing: High interest payments constrain spending.
- Inter-state disparities: Unequal fiscal capacity hampers balanced development.
Way Forward
- Boost Capex to over 3% of GDP to enhance infrastructure-led growth.
- Rationalize subsidies via Direct Benefit Transfers (DBT).
- Strengthen fiscal federalism through equitable devolution and performance-based grants.
- Leverage technology for transparent and outcome-based expenditure tracking.
- Reform FRBM Act:
- Focus on debt-to-GDP targets.
- Introduce flexibility in deficit norms during crises.
Dr. Purnima Devi Barman

- 24 Feb 2025
In News:
Indian wildlife biologist Dr. Purnima Devi Barman has been named among TIME Magazine’s Women of the Year 2025, recognizing her as one of 13 global leaders working toward a more equitable and sustainable world. She is the only Indian woman on the list.
Key Contributions:
- Known for her pioneering conservation work with the greater adjutant stork (locally called Hargila), once critically endangered and culturally stigmatized in Assam.
- Founded the Hargila Army, a women-led grassroots movement focused on protecting the stork’s habitat and changing negative local perceptions.
- Her model uniquely blends wildlife conservation with women’s empowerment, engaging thousands of rural women in ecological and livelihood activities.
Impact:
- Due to her efforts, the greater adjutant stork’s population in Assam has significantly recovered, leading to its status being upgraded from “endangered” to “near threatened” by IUCN.
- The Hargila Army, with over 10,000 members, participates in bird rescue, awareness campaigns, tree planting, and embroidery-based income generation.
- Her approach has become a global model for community-based conservation.
Background:
- Hails from the Kamrup region of Assam.
- Holds a Master’s degree in Zoology from Gauhati University.
- Inspired by her early life near the Brahmaputra and her grandmother’s teachings on biodiversity.
Awards & Recognition:
- Nari Shakti Puraskar (2017) – India’s highest civilian award for women.
- UN Champions of the Earth Award (2022) – For entrepreneurial vision in conservation.
- Whitley Gold Award (2017, 2024) – Often called the "Green Oscar".
Other Roles:
- Director of Women in Nature Network (YNN) – India chapter.
- Member of IUCN’s Stork, Ibis, and Spoonbill Specialist Group.
About TIME Magazine:
- Founded in 1923, USA.
- Known for its global recognitions like Person of the Year and Women of the Year.
- Now operates as a multimedia platform covering politics, science, and culture.
Remission and the Supreme Court’s 2025 Ruling

- 24 Feb 2025
In News:
Recently, the Supreme Court directed states with remission policies to consider the premature release of prisoners even if they don’t apply for remission beforehand.
What is Remission?
- Remission refers to the reduction of a convict's sentence by the government before the term is completed. It does not nullify the conviction, but shortens imprisonment.
- It is governed by:
- Section 473 of BNSS, 2023 (earlier Section 432 of CrPC, 1973) – empowers state governments to grant remission.
- Articles 72 and 161 of the Constitution – empower the President and Governors respectively to remit sentences.
- Section 475 of BNSS (earlier Section 433A CrPC) – restricts remission for life convicts found guilty of offences punishable by death until 14 years of imprisonment are completed.
Background: SC’s Suo Motu Intervention
- The Supreme Court in 2025, in the suomotu case In Re: Policy Strategy for Grant of Bail, altered the interpretation of remission rules to address prison overcrowding.
- The Court held that states must consider remission for eligible convicts even without a formal application, if a remission policy exists.
Shift in Judicial Interpretation
- Earlier rulings (Sangeet v. Haryana and Mohinder Singh v. Punjab, 2013) required a convict's application for remission.
- The 2025 judgment acknowledges that many state prison manuals already mandate prison authorities to initiate remission review.
- It recognized that failing to consider remission proactively could lead to arbitrary discrimination, violating Article 14 (Right to Equality).
Key Guidelines Issued by the Supreme Court
- Suo motu Remission:States must automatically assess eligibility under remission policies—no application needed.
- Mandatory Remission Policy:States without existing remission policies must formulate a comprehensive one within two months.
- Conditions for Remission Must Be:
- Reasonable, non-oppressive, and clearly defined.
- Based on factors like motive, criminal background, and public safety.
- Aimed at rehabilitation and prevention of recurrence.
- Safeguards Against Arbitrary Cancellation:
- Minor breaches shouldn’t lead to automatic cancellation.
- Notice and hearing must be given before cancellation.
- Transparency:
- Legal aid bodies must monitor remission cases.
- States to maintain real-time digital data on remission.
Significance and Implications
- The ruling helps streamline remission processes and could contribute to decongesting Indian prisons, which are heavily overcrowded.
- It ensures uniformity and fairness in the exercise of executive powers related to sentencing.
- Reinforces constitutional values of equality and procedural fairness for prisoners.
Note:
- Remission ≠ Pardon: Remission reduces sentence, doesn’t erase conviction.
- Articles 72 & 161: Concern constitutional remission powers (President & Governor).
- BNSS Sections 473 & 475: Replace CrPC Sections 432 & 433A, relevant for state remission powers.
- Suo motu action by SC: Taken to address systemic prison overcrowding.
- Article 14 invoked: To ensure equitable treatment of eligible prisoners.
Meta’s Project Waterworth
- 22 Feb 2025
In News:
Meta has launched Project Waterworth, its most ambitious subsea cable initiative to date, aimed at enhancing global digital connectivity. The project involves the deployment of AI-driven subsea cable infrastructure, with India being a key beneficiary.
Key Features:
- Massive Scale:A multi-billion dollar, multi-year global initiative, the project will lay over 50,000 km of undersea cables, connecting five continents, including India, the USA, Brazil, South Africa, and others.
- AI Integration:The project leverages advanced machine learning models to predict and mitigate network disruptions, ensuring greater resilience and reliability of global internet infrastructure.
- Deep Water Deployment:The cable will operate at depths reaching 7,000 meters, using enhanced burial techniques in high-risk areas to prevent damage from ship anchors and other maritime hazards.
- Digital Backbone:Subsea cables like those in Project Waterworth currently carry over 95% of global internet traffic, forming the backbone of international digital communication, video streaming, e-commerce, and cloud-based AI services.
Strategic Relevance for India:
- India’s Digital Push:The project supports India’s growing digital economy by ensuring faster, more reliable internet connectivity and fostering digital inclusion and innovation.
- AI and Infrastructure Synergy:With AI-driven maintenance and deployment, the initiative complements India's vision of becoming a global hub for AI, data centers, and digital services.
- Economic and Strategic Benefits:Enhanced connectivity is expected to boost economic cooperation, cross-border trade, and participation in global digital platforms.
Kaveri 2.0 Cyberattack

- 22 Feb 2025
In News:
In January–February 2025, Karnataka's property registration portal, Kaveri 2.0, faced major disruptions due to a Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attack, severely affecting property registrations and revenue generation. The portal, launched in 2023, is a key component of the state's e-governance infrastructure.
What is a DDoS Attack?
A Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attack aims to disrupt a server, service, or network by flooding it with excessive traffic, rendering it inaccessible to legitimate users.
How it works:
- Botnet Formation: Hackers compromise multiple devices using malware, turning them into bots.
- Traffic Overload: These bots generate huge volumes of fake traffic directed at the target system.
- Service Disruption: The targeted service slows down or crashes, affecting user access.
Types of DDoS Attacks:
- Bandwidth Saturation – Exhausting the target's internet capacity.
- Protocol Exploitation – Abusing vulnerabilities in network protocols.
- Application Targeting – Crashing specific applications or services.
Kaveri 2.0 Case: AI-Based DDoS Attack
- The Stamps and Registration Department (SRD) of Karnataka confirmed that the portal was targeted using AI tools that generated over 20 lakh fake search queries per day—far beyond its capacity of 2.5 lakh.
- These queries mainly targeted services like Encumbrance Certificate (EC) searches, causing widespread slowdown and outages.
- On February 1, only 556 property registrations occurred, compared to the usual 8,000–9,000 daily, with revenue dipping to ?15.18 crore from an average of over ?62 crore.
- After mitigation, services were restored by February 7, returning to normal levels of 7,225 registrations and ?62.59 crore in revenue.
Impact of DDoS Attacks on Public Services
- Operational Disruption: Essential citizen services are halted, creating public inconvenience.
- Financial Loss: Delayed transactions and reduced revenue, as seen in the Kaveri 2.0 case.
- Reputational Damage: Public trust in digital governance platforms may erode.
- Cybersecurity Risks: DDoS attacks can mask more sophisticated intrusions.
Preventive Measures
- Traffic Filtering: Using AI tools to detect and block abnormal traffic.
- Rate Limiting: Restricting the number of queries per user/IP.
- Bot Detection: Implementing CAPTCHAs and behavior analysis.
- Robust Authentication: Enhancing security for administrative access.
- Incident Response Teams: Dedicated cybersecurity units to respond to threats promptly.
India introduces HS Code for GI-Tagged Rice Exports

- 13 Feb 2025
In News:
India has amended the Customs Tariff Act, 1975, becoming the first country in the world to introduce a Harmonised System (HS) code for Geographical Indication (GI)-tagged rice varieties. This was announced in the Union Budget 2025–26.
Key Features of the Amendment
- HS Code Introduced For:
- 1006-30-11 – GI-tagged parboiled rice
- 1006-30-91 – GI-tagged white rice
- Objective:
- To enable uninterrupted exports of GI rice even during general export restrictions or bans.
- GI rice exports will not require special government notification during such bans.
About Harmonised System (HS) Code
- Full Form: Harmonised System Code
- Developed by: World Customs Organization (WCO)
- Structure: 6-digit global standard; India uses an 8-digit extension for more specific classification.
- Purpose: Classification of traded goods for customs, tariffs, and trade statistics.
- HS Code Hierarchy:
- First 2 digits: Chapter (e.g., “10” for cereals)
- Next 2 digits: Heading (e.g., “06” for rice)
- Last 2 digits: Subheading (e.g., “30” for semi-milled or wholly milled rice)
Impact on GI Rice Exports
- Facilitates global market access for Indian specialty rice varieties.
- Differentiates GI-tagged rice from conventional rice in trade documents.
- Prevents mislabeling and misuse of India’s GI rice identity.
- Allows exports of GI rice even under export bans, without fresh government clearance.
GI-Tagged Rice Varieties in India
- 20 GI-recognized rice varieties, including:Navara, Palakkadan Matta, Pokkali, Wayanad Jeerakasala, etc.
- 20 pending GI applications, including:Seeraga Samba, Jammu & Kashmir Red Rice, Wada Kolam Paddy, etc.
About the World Customs Organization (WCO)
- Established in 1952 as the Customs Co-operation Council; renamed WCO in 1994.
- Headquarters: Brussels, Belgium.
- Membership: 183 customs administrations, including India, covering 98% of global trade.
- Key Functions:
- Maintains and updates the HS Code every 5 years.
- Drives customs modernization through instruments like the Revised Kyoto Convention (RKC).
- Coordinates anti-smuggling, anti-counterfeiting, and trade enforcement efforts.
- Collaborates with global institutions like the WTO and UN to enhance trade efficiency.
Pong Dam Lake Wildlife Sanctuary
- 11 Feb 2025
In News:
Pong Dam Lake Wildlife Sanctuary, located in the Kangra district of Himachal Pradesh, has witnessed a record-breaking influx of migratory birds in 2025, according to the latest annual bird census conducted on February 1, 2025.
The sanctuary, a designated Ramsar Site (since 2002) and a Wetland of National Importance (1994), recorded a total of 1,53,719 birds across 97 species, indicating a sharp rise in avifaunal population and reaffirming its ecological significance.
Key Highlights from the 2025 Census
- Migratory birds recorded: 1,44,371 individuals from 55 species.
- Total bird count: 1,53,719 birds from 97 species.
- Increase from 2024: 83,555 more birds.
- Bar-headed Goose population: 90,959 (up from 37,501 in 2024) — highest ever recorded since the census began in 2004.
Other dominant waterfowl included:
- Eurasian Coots – 10,785
- Common Pochards – 9,692
- Common Teals – 8,497
- Northern Pintails – 8,053
Lesser-spotted species included the Greater and Lesser White-fronted Goose, Red Crested Pochard, and Northern Lapwing.
Reasons Behind the Surge
- Experts attribute the significant increase in bird numbers to a decline in the water level of Pong Dam Lake, which exposed additional lakebed areas, creating new feeding grounds. This has made the sanctuary increasingly attractive to birds migrating from Tibet, Central Asia, Russia, Siberia, and the Trans-Himalayan region.
Survey and Conservation Collaboration
- The census was conducted by over 100 participants, including officials from the Himachal Pradesh Forest Department, experts from the Bombay Natural History Society, Wildlife Institute of India, and local birdwatchers. The sanctuary was divided into 25 zones for comprehensive coverage.
- To further conservation efforts, a new Interpretation Centre was inaugurated on January 18, 2025, aimed at promoting awareness about the wetland's role in sustaining biodiversity and supporting migratory birds.
Ecological and Geographical Profile
Pong Dam Lake (Maharana Pratap Sagar)
- Type: Manmade reservoir formed by construction of Pong Dam on the Beas River.
- Location: Wetland zone of the Shivalik hills, Kangra district, Himachal Pradesh.
- Area: Approx. 307 sq. km — among the largest man-made wetlands in northern India.
- Importance: Key stopover on the Trans-Himalayan flyway for migratory birds.
Flora
- Vegetation types: Submerged aquatic vegetation, grasslands, forests.
- Dominant species:Eucalyptus, Acacia, Shisham.
Fauna
- Avifauna: Over 220 bird species recorded; 54 waterfowl species.
- Notable birds: Bar-headed Geese, Pintails, Pochards, Coots, Grebes, Cormorants, Herons, Storks, Grey Partridge, Peafowl.
- Mammals: Sambar, Barking Deer, Nilgai, Wild Boar, Clawless Otter, Leopard.
Makhana Board

- 06 Feb 2025
In News:
In the Union Budget 2025–26, Finance Minister announced the establishment of a Makhana Board in Bihar with a dedicated budget of ?100 crore to boost the production, processing, and export of Makhana (Fox Nuts).
About Makhana (Fox Nuts):
- Botanical Name: Euryale ferox
- Family: Nymphaeaceae (Water lily family)
- Description:
- Makhana is the dried edible seed of the prickly water lily.
- Grown in freshwater bodies across South and East Asia.
- The plant is known for its violet and white flowers and large, round, prickly leaves.
- Due to its black outer covering, Makhana is nicknamed the "Black Diamond."
Nutritional and Medicinal Value:
- Low in fat, rich in carbohydrates, and a good source of protein and minerals.
- Widely used in:
- Traditional medicine
- Health and wellness products
- Culinary preparations such as popped Makhana (‘Lava’)
Major Producing Regions:
- India:
- Bihar produces 90% of India’s total Makhana, especially in the Mithilanchal region.
- Key districts: Darbhanga, Madhubani, Purnea, Katihar, Saharsa, Supaul, Araria, Kishanganj, Sitamarhi.
- The first four districts contribute 80% of Bihar’s Makhana output.
- Bihar produces 90% of India’s total Makhana, especially in the Mithilanchal region.
- Other Indian states: Assam, Manipur, West Bengal, Tripura, Odisha.
- Other countries: Nepal, Bangladesh, China, Japan, Korea.
- GI Tag: Mithila Makhana received the Geographical Indication (GI) tag in 2022.
Climatic Conditions for Cultivation:
- Type: Aquatic crop; grows in stagnant water bodies (ponds, lakes, wetlands).
- Ideal Conditions:
- Water Depth: 4–6 feet
- Temperature: 20°C – 35°C
- Relative Humidity: 50% – 90%
- Annual Rainfall: 100 – 250 cm
About the Makhana Board:
- Allocated Budget: ?100 crore
- Objectives:
- Train farmers in advanced cultivation techniques.
- Support processing and value addition in the Makhana supply chain.
- Facilitate financial aid and access to government schemes.
- Develop export infrastructure and promote branding and marketing.
Makhana under ODOP Scheme:
- Recognized as a One District One Product (ODOP) commodity for Bihar.
- Under ODOP, the Union Government provides subsidies to processors for:
- Infrastructure development
- Branding and marketing
About ODOP Scheme:
- Launched by: Ministry of Food Processing Industries (MoFPI)
- Objective: Promote district-level economic specialization and turn each district into an export hub.
- Origin: First launched in Uttar Pradesh (2018); adopted as a national initiative under the Atmanirbhar Bharat vision.
- Implementation:
- In coordination with the ‘Districts as Export Hubs’ (DEH) initiative.
- Managed by DGFT, Department of Commerce, and DPIIT.
- Significance:
- Encourages rural entrepreneurship, local employment, and global trade linkages.
- Strengthens district economies by scaling up traditional and unique products.
Extra-Long Staple (ELS) Cotton

- 06 Feb 2025
In News:
In the Union Budget 2025–26, the Union Finance Minister announced a five-year Cotton Mission to boost productivity, sustainability, and promotion of Extra-Long Staple (ELS) cotton in India, aiming to reduce import dependency and strengthen the high-end textile sector.
What is Extra-Long Staple (ELS) Cotton?
- Definition: ELS cotton refers to cotton varieties with fibre lengths of 30 mm or more, renowned for their superior softness, strength, durability, and premium quality.
- Botanical Origin: Derived primarily from the species Gossypium barbadense, commonly known as Egyptian or Pima cotton.
Distinguishing Cotton Types by Fibre Length
Type Fibre Length Species Quality Uses Yield per Acre
Short Staple < 25 mm Gossypium hirsutum Coarser Low-cost textiles High
Medium Staple 25–28.6 mm Gossypium hirsutum Moderate Everyday fabrics 10–12 quintals
Extra-Long 30 mm & above Gossypium barbadense Superior Luxury textiles 7–8 quintals
Staple (ELS)
Special Characteristics of ELS Cotton
- Softer & Smoother: Ideal for premium, luxury clothing.
- Stronger & More Durable: Resistant to wear and tear.
- Resistant to Pilling: Maintains smoothness over time.
- Luxurious Finish: Produces fine yarns with a natural sheen.
- Minimal Finishing Required: Retains natural texture and quality.
Global and Indian Production Landscape
- Origin: Native to South America.
- Globally Grown In:
- Egypt, China, Australia, Peru – leading producers.
- In India:
- Cultivated in Atpadi Taluka (Sangli, Maharashtra), around Coimbatore (Tamil Nadu), and in parts of Karnataka and Madhya Pradesh.
- Grown mostly in rain-fed areas with warm climates and fertile soil, aiding fibre quality.
Challenges in ELS Cotton Cultivation in India
- Low Yield: ELS cotton yields 7–8 quintals/acre, significantly lower than medium staple varieties (10–12 quintals/acre).
- Market Linkage Deficit: Farmers struggle to fetch premium prices for ELS cotton due to weak market access and lack of dedicated procurement infrastructure.
- Technological Gaps: Limited access to improved seed varieties, agronomic practices, and technologies like HtBT (Herbicide-tolerant Bt) cotton.
- Import Dependency: India imports 20–25 lakh bales annually, accounting for ~90% of its ELS cotton requirements, to meet demand from the premium textile industry.
Significance of the Five-Year Cotton Mission
- Aimed at:
- Enhancing productivity and sustainability of ELS cotton.
- Reducing import dependence through indigenous development.
- Strengthening high-value textile exports by ensuring reliable ELS supply.
- Supports:
- Farmer income enhancement through value-added cultivation.
- Research and development in ELS cotton seed technology.
- Improved extension services, supply chain development, and market support mechanisms.
Guneri Inland Mangrove

- 03 Feb 2025
In News:
In 2024, the Gujarat government declared the Inland Mangrove of Guneri, located in Kutch district, as the first Biodiversity Heritage Site (BHS) of the state under the Biological Diversity Act, 2002. The declaration followed a recommendation by the Gujarat Biodiversity Board.
Key Features of Guneri Inland Mangroves:
- Location: Guneri village, Lakhtar tehsil, Kutch district, Gujarat.
- Area: 32.78 hectares.
- Distance from Sea: ~45 km from the Arabian Sea; ~4 km from Kori Creek.
- Nature: Inland (non-coastal) mangrove ecosystem — one of only eight such sites globally and the last remaining in India.
- Terrain: Flat land resembling a forest; no tidal influence or sludge typically seen in coastal mangroves.
- Water Source: Sustained by groundwater retained in limestone deposits; no direct contact with seawater.
Ecological and Geological Significance:
- Possibly originated from:
- Miocene marine transgression, or
- Along the ancient Saraswati River, believed to have flowed in the Great Rann of Kutch around 3000–4000 BCE.
- Limestone formations in western Kutch provide continuous subsurface water flow, enabling survival of this unique mangrove system.
Biodiversity:
- Habitat to:
- 20 migratory bird species
- 25 resident migratory avifaunal species
- Acts as a vital ecosystem for local and seasonal wildlife.
Mangroves in India – 2024 Snapshot:
- As per the “Red List of Mangrove Ecosystems” (May 22, 2024):
- India has 3% of South Asia’s mangrove cover.
- Total mangrove area: 4,975 sq km (0.15% of India's land area).
- Increase: 54 sq km (1.10%) since last assessment.
- State-wise share:
- West Bengal: 42.45% (notably South 24 Parganas & Sundarbans)
- Gujarat: 23.66% (with highest increase: 37 sq km)
- Andaman & Nicobar Islands: 12.39%
Legal Framework:
- Declared under the Biological Diversity Act, 2002, which empowers state governments to notify BHS after consulting local self-government bodies.
- A local Biodiversity Management Committee (BMC), including representatives from self-governance institutions, will oversee protection and conservation.
- This provides a formal structure for site management, previously absent.
Conservation Measures:
- Training programs for local and tribal communities along with forest officials.
- A management plan will be implemented to preserve the unique flora and fauna.
National Bank for Financing Infrastructure and Development (NaBFID)

- 03 Feb 2025
In News:
In the Union Budget 2025, Finance Minister Nirmala Sitharaman announced that the National Bank for Financing Infrastructure and Development (NaBFID) will set up a partial credit enhancement facility to promote corporate bond issuance in the infrastructure sector.
Need for Credit Enhancement:
- Pension and insurance funds in India, as per regulatory norms, can invest only in AA-rated or higher securities.
- Most infrastructure firms issue bonds rated below this threshold (often "A" rated).
- Partial credit enhancement will elevate such bonds to AA ratings, enabling large-scale participation from long-term institutional investors.
Significance:
- Currently, pension and insurance funds prefer government bonds. However, with the government's ongoing fiscal consolidation, sovereign bond issuance is expected to decline.
- This measure provides alternative, long-term investment avenues for these funds.
- Enhances liquidity in the corporate bond market, especially for infrastructure players.
- Helps in reducing infrastructure companies' dependence on banks for funding.
About NaBFID:
- Established: 2021 under The National Bank for Financing Infrastructure and Development Act, 2021.
- Type: Development Finance Institution (DFI).
- Regulator: Reserve Bank of India (RBI) as an All-India Financial Institution (AIFI).
- Purpose: Bridge gaps in long-term, non-recourse infrastructure financing and promote bond and derivatives markets in India.
Development Finance Institutions (DFIs):
- Government-owned or public sector-backed institutions that finance large-scale, long-gestation projects.
- Provide medium (1–5 years) and long-term (>5 years) financing.
- Raise funds via sovereign borrowings, insurance companies, pension funds, and sovereign wealth funds.
- Offer both financial support (loans, guarantees) and technical support (project viability, consultancy).
- Do not accept public deposits.
Benefits of Partial Credit Enhancement:
- Democratizes access to the corporate bond market for sub-AA-rated firms.
- Attracts long-term capital into infrastructure through safer, credit-enhanced instruments.
- Promotes diversification and deepening of India's debt markets.
- Makes infrastructure financing more cost-efficient and sustainable over the long term.
Challenges Ahead:
- Regulatory streamlining is essential.
- Guarantee fees need optimization to ensure cost competitiveness against traditional bank lending.
Kurdistan Region
- 01 Feb 2025
In News:
India recently dispatched a humanitarian shipment of medical supplies to the Kurdistan Region in Iraq, reflecting its commitment to global cooperation and humanitarian diplomacy.
About the Kurdistan Region
- Geographical Spread: The Kurdistan Region is a culturally and geographically distinct area predominantly inhabited by ethnic Kurds, spread across:
- Northern Iraq (Erbil, Sulaymaniyah, Dohuk, Halabja)
- Eastern Turkey
- Western Iran
- Northern Syria and parts of Armenia
- Capital: Erbil (Iraq)
- Terrain: Dominated by the Zagros and Taurus mountain systems
- Major Rivers: Tigris River and Greater Zab River, crucial for agriculture and settlement
Ethnic and Political Context
- Kurds: An ethnic group of 25–30 million people, mostly Sunni Muslims, with no official nation-state. They seek autonomy or independence through the Kurdish nationalist movement.
- Kurdistan Regional Government (KRG): An autonomous administration in northern Iraq, managing the Kurd-majority areas with limited sovereignty under Iraq’s federal system.
- Geopolitical Significance:
- Rich in oil and natural gas, especially in Iraqi Kurdistan
- Strategically located, controlling key border regions and trade routes
- Kurdish militia (Peshmerga) played a critical role in the fight against ISIS
Ongoing Political Disputes
- Kurdish Independence Movement:
- The 2017 independence referendum in Iraqi Kurdistan was rejected by Baghdad, followed by economic and military backlash.
- Kurds face resistance from Iraq, Turkey, Iran, and Syria, which fear territorial fragmentation.
- Turkey regularly conducts military operations against Kurdish groups, labeling them as threats to national security.
India-Kurdistan Relations
- Diplomatic Presence: India established a Consulate in Erbil in August 2016 to deepen ties with the Kurdistan Region and Iraq.
- Economic and Workforce Engagement:
- Indian companies have participated in trade fairs in Erbil and Sulaymaniyah.
- A growing number of Indian workers are employed in sectors like:
- Steel mills
- Oil companies
- Construction projects
- Indian workers are valued for their skills and reliability in these industries.
Financialisation
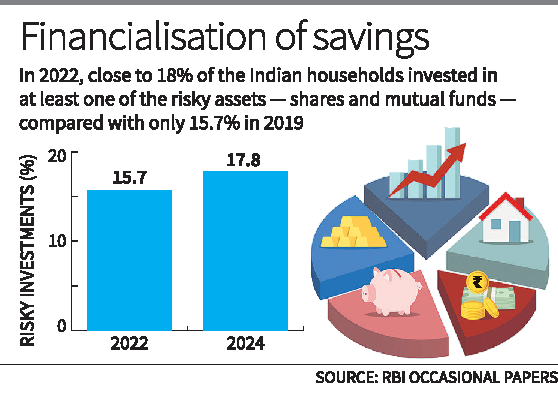
- 01 Feb 2025
In News:
The Economic Survey 2024–25 cautions against the risks of excessive financialisation in India, emphasizing that while finance is a crucial enabler of economic growth, unchecked expansion of the financial sector can pose systemic risks, increase inequality, and divert resources from the real economy.
What is Financialisation?
Financialisation refers to the growing dominance of financial markets, institutions, and motives in shaping economic policies, business decisions, and resource allocation. It involves:
- A shift from productive (real sector) activities like manufacturing to financial activities, including trading, speculation, and asset management.
- Increasing reliance on asset price growth (e.g., stocks, real estate) to stimulate the economy.
- Deep influence of financial motives in corporate governance, economic policies, and household behavior.
Key Drivers of Financialisation in India
- Increased household savings funneled into stock markets.
- Growing retail investor participation in equities and mutual funds.
- Policy and regulation increasingly influenced by financial market considerations.
- Rising public and private sector debt to leverage economic growth.
Risks Highlighted by the Economic Survey
- Real Sector Crowding Out: Over-expansion of the financial sector may compete with the real economy for scarce resources like skilled labour and capital, potentially depriving productive sectors.
- Unsustainable Booms: Rapid financial growth often favours high-collateral, low-productivity investments (e.g., construction) over innovation and manufacturing, creating unsustainable financial booms.
- Complex Financial Products: Proliferation of opaque and complex financial instruments can increase consumer risk exposure and the probability of a financial crisis, as seen during the 2008 global financial meltdown.
- Increased Inequality: Financialisation tends to transfer income from the real sector to the financial sector, worsening income inequality and contributing to wage stagnation.
- Debt Dependency: Over-reliance on financial leverage (debt) increases macro-financial vulnerabilities, especially if credit growth outpaces productive investment.
Global Lessons and Historical Context
- 2008 Global Financial Crisis: Reckless lending and financial engineering, including mortgage-backed securities, led to a global economic collapse. India was impacted indirectly, prompting RBI intervention to stabilise the economy.
- Examples from Ireland & Thailand: Rapid growth of private credit in these countries led to reduced productivity and economic distortions, serving as cautionary tales.
Balanced View on Finance
The Survey recognizes that a well-regulated financial system plays a vital role in:
- Channeling capital to innovative and high-risk ventures.
- Reducing transaction costs and improving price discovery.
- Alleviating poverty and inequality by enabling shock absorption for households and firms.
- Smoothing consumption across economic cycles.
However, the Survey emphasizes that there is a tipping point beyond which financial development becomes counterproductive.
Ultra-Processed Foods (UPFs)

- 01 Feb 2025
In News:
The Economic Survey 2024–25 underscores the adverse impact of Ultra-Processed Foods (UPFs) on public health, particularly among children and youth, and calls for urgent regulatory intervention.
Key Recommendations
- Stringent Front-of-the-Pack Labelling (FOPL): The Survey advocates for clear, enforceable FOPL rules to inform consumers, curb misleading nutrition claims, and restrict aggressive marketing, especially those targeted at children and adolescents.
- Stronger Role for FSSAI: The Food Safety and Standards Authority of India (FSSAI) is advised to:
- Define UPFs clearly in regulation.
- Establish labelling standards.
- Monitor compliance of branded products.
- ‘Health Tax’ Proposal: The Survey proposes higher taxes on UPFs, especially brands engaging in excessive advertising, to act as a deterrent and promote healthier food choices.
- Awareness and Education: It recommends targeted awareness campaigns in schools and colleges, integrated with broader health and lifestyle campaigns, to reduce the rising consumption of UPFs.
Why this matter
- Rising Consumption: According to a 2023 WHO report, India’s UPF consumption grew from $900 million (2006) to over $37.9 billion (2019).
- Long-term National Impact: India's ?2,50,000 crore UPF industry is built on hyper-palatability and is a threat to India’s demographic dividend, productivity, and future economic growth.
Health Risks of UPFs
- Directly linked to:
- Obesity
- Cardiovascular diseases
- Colorectal cancer
- Respiratory and gastrointestinal disorders
- Mental health issues, especially among youth
- Poor dietary intake due to UPFs contributes to micronutrient deficiencies, while synthetic additives may have long-term biological impacts.
What are Ultra-Processed Foods?
UPFs are industrial formulations that undergo extensive processing and typically include:
- Artificial flavours, colours, preservatives, emulsifiers, sweeteners, and other cosmetic additives.
- High sugar, salt, and fat content for taste enhancement.
- Low in essential nutrients such as vitamins, minerals, and fibre.
- Designed for convenience and high palatability, often leading to overconsumption.
Examples of Ultra-Processed Foods
(As per Indian Council of Medical Research - ICMR):
- Commercial bakery items: bread, cakes, biscuits, breakfast cereals
- Snack foods: chips, fries
- Condiments: sauces, jams, mayonnaise
- Dairy & protein products: processed cheese, butter, protein powders, soy chunks, tofu
- Frozen and ready-to-eat foods with additives
- Beverages: energy drinks, health drinks, sweetened fruit juices
- Refined flours of cereals, millets, legumes
- Culinary ingredients containing cosmetic additives like artificial colours or emulsifiers
Contract Farming in India

- 31 Jan 2025
In News:
Contract farming has emerged as a significant model in India's agricultural landscape, especially with its success in processed potato cultivation and the recent rise in French fry exports. As the country transitions from being an importer to a major exporter in sectors like frozen French fries, the contract farming model underpins the structural transformation of Indian agriculture.
Understanding Contract Farming
Contract farming is an agricultural production system where farmers and buyers (agribusinesses, processors, exporters, or retailers) enter into a pre-harvest agreement. This contract outlines key parameters including price, quality, quantity, delivery schedules, and in many cases, input provision and technical assistance.
Types of Contract Farming Arrangements
- Direct Input Provision by the Company: Firms supply seeds, fertilizers, and support services, deducting costs from the final payment to farmers.
- Partnership with Local Input Dealers: A hybrid model balancing company control with third-party services, chosen based on crop complexity, local support availability, and firm capabilities.
Advantages of Contract Farming
- Stable and Enhanced Income: Contracts assure farmers of a fixed price and market access, shielding them from volatile markets. RBI data shows farmers typically receive only 31%–43% of consumer prices; contract farming can significantly improve this share.
- Access to Inputs and Technology: Companies provide high-quality seeds, fertilizers, training, and modern farming practices, leading to improved yields and quality.
- Post-Harvest Efficiency: Streamlined procurement reduces wastage of perishables and post-harvest losses, ensuring efficient supply chain management.
- Credit and Financial Support: Assured incomes help farmers access institutional credit, reducing dependency on informal lenders.
- Food Safety and Export Standards: Training on pesticide use and residue limits ensures compliance with international standards like Maximum Residue Limits (MRLs), boosting export potential.
- Consumer Benefits: Direct procurement reduces intermediaries, enabling competitive pricing and higher quality products.
- Technology Transfer: Farmers benefit from the introduction of new, high-efficiency production techniques.
Concerns and Challenges
- Power Imbalance: Small and marginal farmers often lack bargaining power. This dependency may lead to exploitative contracts or one-sided terms, especially where firms demand investments in crop-specific infrastructure.
- Market Risk and Default: Price volatility can lead to side-selling by farmers or contract breaches by firms when market prices crash.
- Delayed Payments and Inputs: Contractual delays in payment or input delivery can severely affect crop cycles and farmer finances.
- Exclusion of Marginal Farmers: For economies of scale, firms often prefer large landholders, sidelining smallholders.
- Environmental Impact: Monocropping, overuse of water and agrochemicals, and soil degradation threaten long-term sustainability.
- Food Security Trade-offs: A shift to high-value crops under contracts may reduce acreage for food crops, impacting local food security.
- Loss of Autonomy: Farmers may lose control over farming decisions, with firms determining most aspects of cultivation, leading to indirect control over land use.
Case Study: Contract Farming in Potato Sector
India is the second-largest potato producer globally, with Uttar Pradesh, West Bengal, and Bihar as leading states. The Central Potato Research Institute (CPRI), Shimla developed several high-yielding Kufri varieties to support commercial cultivation.
The success of processed potato farming is best illustrated by India’s emergence as an exporter of frozen French fries, driven by contract-based procurement from farmers. However, issues such as the PepsiCo vs. Indian farmers legal dispute over unauthorized cultivation of the FL 2027 variety underline ongoing concerns around intellectual property rights and farmers’ autonomy.
Policy and Legal Framework
- Model APMC Act, 2003: Introduced contract registration, dispute resolution, and exempted market fees while protecting land ownership.
- Model Agricultural Produce and Livestock Contract Farming Act, 2018: Proposed institutional frameworks, insurance provisions, and promotion of Farmer Producer Organizations (FPOs).
- e-NAM Integration: Supports transparent pricing and contract enforcement.
- National Agriculture Policy: Endorses contract farming as a tool for enhancing productivity and rural incomes.
Resumption of Kailash Mansarovar Yatra
- 29 Jan 2025
In News:
After a four-year hiatus due to the COVID-19 pandemic and the 2020 Galwan Valley clash, India and China have agreed to resume the Kailash Mansarovar Yatra in June 2025, along with other confidence-building measures.
This decision aligns with the 75th anniversary of India-China diplomatic relations, symbolizing an attempt to stabilize and recalibrate bilateral ties through people-centric initiatives.
Key Highlights:
Key announcements include:
- Resumption of the Kailash Mansarovar Yatra
- Restoration of direct air services
- Visa issuance for journalists and think tanks
- Hydrological data sharing and cooperation on trans-border rivers
- Enhanced people-to-people exchanges and academic/media dialogues
About the Yatra
- The Yatra involves a pilgrimage to Mount Kailash and Lake Mansarovar in the Tibetan Autonomous Region (Xizang).
- Organised by India’s Ministry of External Affairs between June–September, via two routes:
- Lipulekh Pass (Uttarakhand)
- Nathu La Pass (Sikkim)
- Supported by the state governments of Uttarakhand, Sikkim, and Delhi, and coordinated with the Indo-Tibetan Border Police.
- Open only to Indian citizens with valid passports; no financial subsidy is provided by the Government of India.
Geographical and Religious Significance:
- Mount Kailash, located in the Kailash Range (Transhimalaya), is the source of four major rivers: Sutlej, Brahmaputra, Indus, and Karnali.
- Revered across religions:
- Hindus consider it the abode of Lord Shiva; Mansarovar is one of the 51 Shaktipeeths.
- Buddhists and Tibetans regard it as the ‘Stairway to Heaven’.
- Jains believe Rishabhanatha attained enlightenment here—referred to as Ashtapada.
Diplomatic Interpretations and Differences
- India’s Position: Emphasized a step-by-step, cautious approach focusing on rebuilding trust and resolving contentious issues, particularly the border situation. India sought policy predictability and transparency in trade, and reaffirmed the importance of mutual respect and interests.
- China’s Position: Took a more optimistic and strategic stance, stressing the need to avoid "mutual suspicion" and to advance cooperation based on long-term national interests. It emphasized early action, including the swift resumption of the Yatra and flights.
Ongoing Concerns in Bilateral Relations
- Unresolved Border Disputes:
- Tensions persist along the Line of Actual Control (LAC)—notably in Galwan (2020) and Tawang (2022).
- India and China have made limited progress in resolving issues in Depsang and Demchok.
- Trade Imbalance:
- Bilateral trade in 2023–24 stood at USD 118.4 billion, with India facing a trade deficit of USD 85 billion.
- India raised concerns on market access and non-tariff barriers.
- China-Pakistan Axis:
- The China-Pakistan Economic Corridor (CPEC) runs through Pakistan-occupied Kashmir, violating India’s territorial sovereignty.
- China’s support for Pakistan in multilateral forums remains a thorn in bilateral ties.
- China’s Regional Assertiveness:
- Expanding influence in South Asia and the Indian Ocean through the String of Pearls, strategic presence in Maldives, Sri Lanka, and strong claims in the South China Sea, contribute to regional unease.
Significance of the Current Diplomatic Thaw
- The resumption of the Kailash Mansarovar Yatra reflects a symbolic softening in ties, emphasizing religious diplomacy and people-to-people connection.
- Restoration of direct flights and journalistic presence can aid in reducing mistrust.
- Hydrological cooperation, particularly over the Brahmaputra River, is essential for India’s water security, especially with China constructing mega-dams upstream.
Way Forward
- Rebuild Trust Through Engagement: Maintain diplomatic dialogues via platforms like BRICS, SCO, and G20, while holding to core national interests.
- Resolve Border Disputes: Pursue early finalization of the LAC through confidence-building agreements and military disengagement.
- Diversify Economic Strategy: Reduce dependency on Chinese imports by strengthening domestic manufacturing and regional trade alternatives.
- Enhance Cultural Diplomacy: Use platforms like the Kailash Yatra to foster mutual understanding rooted in shared civilizational values.
- Promote Transparency and Reciprocity: Especially in media, trade, and information sharing, to ensure balanced bilateral engagement.
Libia Lobo Sardesai

- 28 Jan 2025
In News:
In 2024, at the age of 100, Libia Lobo Sardesai was awarded the Padma Shri for her pivotal role in Goa’s liberation struggle from Portuguese colonial rule.
About Libia Lobo Sardesai
- Born: 25 May 1924, in Portuguese-ruled Goa; raised in Mumbai.
- Profession: Freedom fighter, broadcaster, and Goa’s first Director of Tourism post-liberation.
- Legacy: Symbol of courage and resistance, known as the “voice of Goa’s liberation.”
Role in Goa’s Liberation Movement
- Involvement: Joined the Goan nationalist movement during her college years.
- Underground Radio:
- From 1955 to 1961, Libia, along with her husband Vaman Sardesai and Nicolau Menezes, ran an underground radio station – initially called ‘Q’, later named:
- Goenche Sodvonecho Awaz (Voice of Freedom of Goa) – Konkani
- Voz de Liberdade – Portuguese
- Operated from Amboli (Maharashtra) and Castle Rock (Karnataka) in the Western Ghats.
- Purpose: Counter Portuguese censorship and propaganda; broadcast news, updates, and morale-boosting messages to Goans.
- From 1955 to 1961, Libia, along with her husband Vaman Sardesai and Nicolau Menezes, ran an underground radio station – initially called ‘Q’, later named:
- Final Broadcast:
- On 19 December 1961, Libia flew over Panaji in an IAF plane, announcing Goa’s liberation with the message:
“Rejoice brothers and sisters, Rejoice! Today, after 451 years of alien rule, Goa is free and united with the Motherland.”
Goa Liberation Movement: Background
- Colonial Rule: Goa was under Portuguese rule for over 451 years (from 1510 to 1961).
- Key Phases:
- 1954: India imposed an economic blockade after Portuguese crackdown on satyagrahis.
- August 1955: Mass satyagraha met with violent repression by Portuguese forces.
- Censorship: Portuguese regime enforced total censorship; only official Portuguese narratives were allowed.
- 1961 – Operation Vijay:
- Initiated on 17 December 1961 by the Indian Army under Lt. Gen. J.N. Chaudhuri.
- Portuguese forces surrendered by 19 December 1961, marking Goa’s official liberation.
Notable Leaders of the Movement
- Dr. Ram Manohar Lohia: Sparked initial resistance against Portuguese rule.
- Libia Lobo Sardesai: Voice of the resistance via underground broadcasting.
- Lt. Gen. J.N. Chaudhuri: Led military operations during Operation Vijay.
Significance
- Libia Lobo Sardesai represents the unsung contributions of civil resistance and communication warfare in India’s decolonization.
- Her work sustained nationalist morale, informed citizens under censorship, and shaped the narrative of a liberated Goa.
Aero India 2025
- 28 Jan 2025
In News:
Aero India 2025, the 15th edition of India’s premier aerospace and defence exhibition, is scheduled from February 10–14, 2025, at the Yelahanka Air Force Station, Bengaluru.
Organised by the Ministry of Defence and the Defence Exhibition Organisation (DEO), the event continues to be a vital forum for promoting India's indigenous defence capabilities and fostering international collaboration.
Evolution of Aero India: From Showcase to Strategic Asset
- Inception (1996): Launched as a modest exhibition to attract foreign investments and highlight India’s aerospace potential.
- Growth Phase (2005–2015): Marked by the entry of global giants like Boeing, Airbus, Lockheed Martin, and Dassault Aviation. Indigenous platforms like LCA Tejas began gaining prominence.
- Current Phase (2015–Present): Aligned with ‘Make in India’ and ‘Aatmanirbhar Bharat’, Aero India has become a symbol of India's defence self-reliance and a magnet for global partnerships.
Aero India 2025 Highlights
1. International Participation and Strategic Displays
- Participation from 15+ countries and major OEMs.
- Russia’s Su-57 and USA’s F-35—two of the world’s most advanced 5th-generation fighters—will be showcased together, reflecting India’s growing strategic importance.
- Other prominent platforms: KC-135 Stratotanker, Embraer C-390, and Light Combat Helicopter Prachand.
2. Indigenous Innovation
- Advanced Medium Combat Aircraft (AMCA): India’s 5th-generation stealth fighter, developed by HAL and ADA, will be unveiled.
- Indigenous platforms like LCA Mk2, LUH, HTT-40, ALH, and Naval Twin-Engine Deck-Based Fighter will also be featured.
3. Start-Up Integration via 'Manthan'
- Through the iDEX initiative, Aero India is promoting start-ups working in AI, unmanned systems, cybersecurity, and electronic warfare.
- Start-ups will showcase innovations including jetpack suits, robotics, and defence software tools.
4. Business & Public Engagement
- Business Days: February 10–12, 2025
- Public Days: February 13–14, 2025
- Over 7 lakh visitors expected; the event offers aerial displays, seminars, tech expos, and networking forums.
5. Defence Diplomacy and Deals
- Aero India 2023 had seen over ?80,000 crore worth of MoUs. A similar or higher scale of defence agreements is expected in 2025.
- High-level participation from defence ministers, air chiefs, and CEOs of OEMs, signalling deepening international defence cooperation.
Strategic Significance for India
- Geopolitical Leverage: Participation of both US and Russian defence firms signals India’s strategic autonomy and balanced defence diplomacy.
- Self-Reliance Boost: The event enhances domestic manufacturing by integrating MSMEs, promoting co-development and co-production with foreign partners.
- Global Recognition: Positions India as an emerging aerospace hub in the Indo-Pacific.
- Technological Edge: Demonstrates advancements in stealth technology, avionics, and unmanned systems.
Theme of Aero India 2025: “The Runway to a Billion Opportunities” — highlighting India’s expanding defence manufacturing capabilities and its aim to integrate with the global supply chain.
Uniform Civil Code (UCC) in Uttarakhand

- 28 Jan 2025
In News:
On January 27, 2025, Uttarakhand became the first Indian state to formally implement the Uniform Civil Code (UCC) after Independence. The legislation was passed by the State Assembly on February 7, 2024, and received Presidential assent on March 12, 2024.
Historical Background:
- A five-member expert committee chaired by Justice (Retd.) Ranjana Prakash Desai was constituted to draft the UCC report.
- The committee submitted its report on October 18, 2023.
- Though initially scheduled for implementation by November 9, 2024 (Uttarakhand's Foundation Day), the rollout was delayed due to administrative preparedness and staff training.
Scope and Applicability:
- Applicable to all residents of Uttarakhand, including those in live-in relationships outside the state.
- Scheduled Tribes (as per Article 342) and migrated natives have been exempted to safeguard cultural rights.
Key Provisions of the UCC:
1. Marriage, Divorce & Live-in Relationships
- Legal marriage age: 21 years (men), 18 years (women).
- Mandatory registration of marriages, divorces, and live-in relationships.
- Prohibited practices: Triple talaq, halala, iddat, polygamy, and child marriage.
- Live-in Relationships:
- Mandatory registration for couples aged 21 and above.
- Parental consent required if under 21.
- Termination of live-in relationships requires mutual consent.
- Mandatory reporting of pregnancy within 30 days of childbirth.
- Landlords cannot deny housing to registered live-in couples.
2. Inheritance & Property Rights
- Equal inheritance rights for sons and daughters.
- Children born to live-in couples recognized as legitimate, eligible for inheritance.
3. Wills and Succession
- Wills can be:
- Submitted online.
- Uploaded as handwritten/typed documents.
- Recorded as a 3-minute video.
Digital Infrastructure – UCC Portal (ucc.uk.gov.in):
- Aadhaar-based verification for authenticity.
- AI-based multilingual translation in 22 Indian languages.
- Tatkal service for expedited registrations with a nominal fee.
- Integrated with 13+ departments, including police, civic bodies, and courts.
- Disaster recovery systems and cloud-based architecture ensure secure data management.
- Access to:
- Online registration of marriages, divorces, live-in relationships.
- Upload and registration of wills.
- Grievance redressal and appeal mechanisms.
Administrative Framework:
- Village Panchayat Development Officers appointed as sub-registrars in rural areas.
- Common Service Centres (CSCs) enabled to facilitate registration, especially in remote and mountainous areas.
- Registration applications processed within 15 days, or 3 days in emergencies.
- Appeals must be filed within 30 days of rejection, resolved within 60 days.
Penalties:
- Initial warnings for non-compliance.
- Fines imposed for repeated violations.
Significance:
- The UCC aims to promote gender equality, legal uniformity, and women's empowerment.
- Represents a constitutional vision under Article 44, reinforcing the idea of a common civil law for all citizens.
- Seen as a potential model for other states in India.
Paraquat Poisoning

- 27 Jan 2025
In News:
- In a landmark ruling, a Thiruvananthapuram court sentenced a 24-year-old woman to death for the murder of her boyfriend by poisoning him with paraquat, a highly toxic herbicide.
- The incident, which occurred in 2022, has brought the spotlight back on paraquat's widespread availability, extreme toxicity, and the lack of regulatory enforcement in India.
What is Paraquat?
- Paraquat, chemically known as paraquat dichloride or methyl viologen, is one of the most widely used herbicides globally.
- It is primarily used for:
- Weed control
- Crop desiccation, especially in crops like cotton before harvest
- Despite its toxicity, India and the United States continue to permit its usage, unlike over 70 countries, including China, Brazil, and the European Union, which have banned it.
WHO Classification
- The World Health Organization (WHO) classifies paraquat as a Category 2 chemical, meaning it is moderately hazardous and irritating to the skin and eyes.
- It has a narrow margin between a safe and lethal dose, making accidental or intentional poisoning common and often fatal.
Routes and Effects of Exposure
- Ingestion is the most common method of poisoning.
- It may also occur through inhalation or skin contact, especially if the exposure is prolonged or the skin is broken.
Symptoms Vary by Dosage and Exposure Time:
Exposure Level Symptoms and Organ Damage
Small Quantity Gradual damage to lungs, liver, kidneys, and heart over days/weeks
Large Quantity Immediate symptoms such as:
- Acute kidney failure
- Liver and heart failure
- Seizures
- Respiratory failure
- Severe abdominal pain
- Bloody diarrhea
- Nausea
- Mouth and throat swelling |
Treatment and Challenges
- No known antidote exists for paraquat poisoning.
- Treatment options include:
- Immunosuppressive therapy
- Charcoal hemoperfusion (a blood-purification technique)
- However, these treatments offer limited efficacy, especially in cases of large-dose ingestion.
Regulatory and Public Health Implications in India
- Despite paraquat’s well-documented toxicity, it remains:
- Legally available in India
- Easily accessible in rural markets
- The lack of regulation increases the risks of:
- Occupational exposure
- Accidental poisoning
- Use in crimes or suicides
ISRO’s NVS-02 Satellite Launch

- 25 Jan 2025
In News:
ISRO successfully launched the NVS-02 satellite aboard GSLV-F15, placing it into a Geosynchronous Transfer Orbit (GTO). This marks ISRO’s 100th mission, reinforcing India’s space and navigation capabilities under the NavIC (Navigation with Indian Constellation) program.
What is NavIC?
- NavIC is India’s indigenous regional satellite navigation system, developed for both civilian and strategic use.
- Offers accurate positioning over India and up to 1,500 km beyond its borders.
- Comparable to GPS (USA), GLONASS (Russia), Galileo (EU), and BeiDou (China).
About NVS-02 Satellite:
Feature Description
Series Second satellite in the next-gen NVS series (after NVS-01 in 2023)
Mission Role Replaces aging IRNSS-1E satellite
Mass 2,250 kg
Power Capacity ~3 kW
Orbit Final orbital slot at 111.75°E in geosynchronous orbit (~36,000 km)
Life Span 12 years
Developed by URSC (U R Rao Satellite Centre), Bengaluru
Technological Advancements:
- Equipped with navigation payloads across L1, L5, and S-bands for enhanced accuracy and broader coverage.
- Features the Rubidium Atomic Frequency Standard (RAFS) – an indigenously developed atomic clock for precision timekeeping.
- Includes C-band ranging payload, similar to NVS-01.
Significance of NVS-02:
- Enhances NavIC’s positioning accuracy for civilian, commercial, and strategic applications:
- Disaster management
- Fleet tracking
- Precision agriculture
- Emergency response
- Mobile navigation
- L1 signal inclusion makes NavIC-compatible with international GNSS systems, improving global device integration.
- Demonstrates India’s technological self-reliance, particularly in atomic clock development.
ISRO’s Launch Vehicles
Vehicle First Flight Notable Use
SLV 1980 Launched Rohini satellite
ASLV 1987 Five-stage solid rocket, retired in 1990s
PSLV 1994 Reliable, used for Mars Orbiter, LEO missions
GSLV 2001 Used for heavier payloads, INSAT/GSAT
GSLV 2014 Heavy-lift, Chandrayaan-2/3, Gaganyaan crew module
Mk III (LVM3)
SSLV 2022 Affordable launches for nano/micro satellites
SEBI’s Sachetisation of Mutual Funds
- 25 Jan 2025
In News:
In January 2025, the Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI) proposed the “sachetisation” of mutual fund investments to promote financial inclusion, especially among low-income and first-time investors.
What is Sachetisation?
- Originating from the FMCG sector (e.g., shampoo sachets), sachetisation refers to offering financial products in small, affordable units, enhancing accessibility and affordability.
- In capital markets, it implies micro-level investment options, particularly through low-ticket SIPs (Systematic Investment Plans).
Objectives:
- Promote financial inclusion and empower economically underserved sections.
- Expand mutual fund penetration to semi-urban and rural areas.
- Encourage long-term savings and wealth creation among new investors.
- Reduce dependency on large institutional or foreign investors by broadening the domestic retail base.
Key Features of SEBI’s Sachet SIP Proposal:
Feature Details
Minimum SIP Amount ?250 per month
Eligibility Only for new mutual fund investors
Investment Limit Up to 3 sachet SIPs across different AMCs
Excluded Schemes Debt funds, sectoral/thematic, small-cap, mid-cap equity funds (due to higher risk)
Commitment Period Encouraged to commit for 5 years (60 SIPs), but premature withdrawal allowed
Payment Modes Only via auto-pay mechanisms such as UPI Autopay and NACH
Cost Incentives AMCs to receive subsidies from SEBI’s Investor Education and Awareness Fund
Distributor Incentive ?500 per investor after completion of 24 monthly SIPs
Significance:
- Democratizes investment access by lowering the entry barrier for mutual funds.
- Encourages behavioral shift towards long-term financial planning and discipline.
- Stabilizes domestic markets by broadening and diversifying the retail investor base.
Supports SEBI’s vision of making capital markets inclusive, tech-enabled, and accessible.
Sanjay Battlefield Surveillance System

- 25 Jan 2025
In News:
Defence Minister Rajnath Singh recently flagged off Sanjay, an indigenously developed Battlefield Surveillance System (BSS), to be inducted into the Indian Army in phased manner from March to October 2025, designated as the ‘Year of Reforms’ by the Ministry of Defence.
Overview:
- Nature: Automated surveillance system
- Purpose: To integrate real-time data from ground and aerial sensors, enabling swift, informed decision-making in conventional and sub-conventional warfare scenarios.
Key Features:
- Common Surveillance Picture (CSP): Fuses verified sensor data to generate a real-time surveillance image of the battlefield.
- Real-time Integration & Analytics: Processes inputs using advanced analytics to eliminate duplication and enhance situational awareness.
- Secure Networks: Operates over the Indian Army’s Data Network and Satellite Communication Network, ensuring reliable and secure data flow.
- Centralized Web Application: Provides integrated inputs to Command Headquarters and Army HQ through a unified platform, supporting the Indian Army's Decision Support System.
- Indigenous Development: Jointly developed by the Indian Army and Bharat Electronics Limited (BEL) under the Buy (Indian) category, promoting Aatmanirbharta in defense.
Operational Significance:
- Enhances battlefield transparency, situational awareness, and surveillance capabilities along vast and sensitive land borders.
- Functions as a force multiplier in Intelligence, Surveillance & Reconnaissance (ISR) operations.
- Enables network-centric warfare, marking a shift towards data-driven military operations.
Deployment:
- To be inducted into all Brigades, Divisions, and Corps of the Army in three phases (March–October 2025).
Ad Hoc High Court Judges

- 24 Jan 2025
In News:
To address the mounting pendency of criminal cases in several High Courts, the Supreme Court of India has suggested invoking Article 224A of the Constitution, which allows the appointment of retired High Court judges on an ad hoc basis.
Constitutional Provision: Article 224A
- Title: Appointment of Retired Judges at Sittings of High Courts.
- Key Provision: The Chief Justice of a High Court, with the consent of the President, may invite retired judges of the same or other High Courts to act as judges temporarily.
- Status: These judges enjoy the powers, jurisdiction, and privileges of regular High Court judges, but are not deemed permanent judges.
Why the Provision is Being Invoked Now:
- Backlog of Cases: Over 40% vacancy rate in High Courts; huge pendency, especially of criminal cases.
- Delays in Regular Appointments: Slow process of regular judicial appointments prompted the Supreme Court to consider alternative mechanisms.
- Underuse of Article 224A: Only three recorded instances of ad hoc appointments since Independence:
- Justice Suraj Bhan – MP High Court (1972)
- Justice P. Venugopal – Madras High Court (1982–83)
- Justice O.P. Srivastava – Allahabad High Court (2007, Ayodhya case)
Judicial Interpretation – Lok Prahari v. Union of India (2021):
- The Supreme Court laid down guidelines for invoking Article 224A.
- The process must be routed through the SC collegium (CJI + 2 senior-most judges).
- Trigger Point for Appointment:
- High Court vacancies exceed 20% of sanctioned strength (excluding pending proposals).
- More than 10% of pending cases are over 5 years old.
Procedure for Appointment:
- Consent: Retired judge must agree to serve again.
- Initiation: Chief Justice of the High Court forwards the name.
- State and Centre: Proposal routed through State CM → Union Law Ministry.
- SC Collegium: Must review and approve the name.
- Executive Clearance: Law Ministry → PM → President for final approval.
Term & Allowances:
- Duration: Typically 2–3 years, renewable if required.
- Number of Judges: Suggested 2–5 ad hoc judges per High Court.
- Remuneration: Entitled to allowances as per Presidential order.
- Status: Have full judicial powers during tenure.
Concerns & Safeguards:
- Fear of using ad hoc appointments as a substitute for regular appointments.
- Therefore, SC mandates that regular appointment process must be underway before invoking Article 224A.
- Periodic review and panel creation of eligible retired judges recommended.
Mission SCOT

- 23 Jan 2025
In News:
The Prime Minister of India praised Indian space startup Digantara for the successful launch of Mission SCOT (Space Camera for Object Tracking) — the world’s first commercial SSA satellite, launched via SpaceX’s Transporter-12 rideshare mission.
What is Mission SCOT?
Feature Description
Developer Digantara (Indian space startup), supported by Aditya Birla Ventures & SIDBI
Launched on SpaceX Transporter-12 mission (rideshare platform)
Type First commercial Space Situational Awareness (SSA) satellite
Orbit Sun-Synchronous Orbit – ideal for consistent Earth observation
Function Tracks Resident Space Objects (RSOs) as small as 5 cm in Low Earth Orbit (LEO)
What is Space Situational Awareness (SSA)?
- SSA involves the detection, tracking, cataloging, and prediction of natural and man-made objects in Earth's orbit (like satellites, debris, etc.).
- Ensures safe and sustainable operations by minimizing collision risks.
- Critical due to increasing congestion in LEO, especially with rising numbers of small satellites and mega-constellations.
Key Features of Mission SCOT
Feature Advantage
High Revisit Rate More frequent observations of objects in orbit
Precision Tracking Can track debris ≥ 5 cm in size
All-Weather Monitoring Overcomes limitations of ground-based systems like cloud cover, FoV
Space-based System Unhindered by geography, providing continuous global surveillance
Supports SSA Infrastructure Aids in collision avoidance, space traffic management, and defence preparedness
???????? India’s SSA Ecosystem
Initiative Role
ISRO’s IS4OM Provides Indian Space Situational Assessment Report (ISSAR); enables safe & sustainable space operations
NETRA Project Network for Space Objects Tracking & Analysis – aims to build a dedicated SST (Space Surveillance & Tracking) network using radars & optical telescopes
Multi-Object Tracking Radar Operated at Sriharikota – limited range, being augmented
Collision Avoidance Manoeuvres (CAMs) Regularly performed by ISRO to protect its satellites from debris threats
Global Context: Transporter-12 Rideshare
- A SpaceX program providing low-cost access to space by allowing multiple customers to launch small payloads on a single rocket.
- Enhances global commercial space activity, democratizes space access.
Significance for India
Strategic:
- Strengthens national space defence by enabling indigenous tracking of space threats.
- Reduces reliance on foreign SSA data (e.g., NORAD/US Space Command).
Technological:
- Demonstrates India’s capability in space-based surveillance tech.
- Positions India as a global contributor in the emerging SSA domain.
Economic:
- Boosts private sector space innovation aligned with India’s NewSpace Policy.
- Attracts venture capital and international collaboration.
Mount McKinley

- 22 Jan 2025
In News:
In a controversial move, President Donald Trump (2025) signed an executive order to rename Denali (North America’s highest peak) back to Mount McKinley, and also proposed renaming the Gulf of Mexico to the Gulf of America, citing the need to "honor American greatness."
About Denali / Mount McKinley:
Feature Description
Location Alaska Range, South-Central Alaska, USA
Height 20,310 feet (6,190 meters) – Highest in North America
Geology Giant granite block uplifted by tectonic activity ~60 million years ago
Glaciers Feeds major glaciers: Kahiltna, Muldrow, Peters, Ruth, Traleika
Tectonics Lies along the Denali Fault, a major right-lateral strike-slip fault
National Park Forms the core of Denali National Park and Preserve
Historical Background of the Name:
- Original Name: Denali, meaning “The High One” in the Athabascan language of the Koyukon people.
- 1897: Renamed Mount McKinley by a gold prospector in honor of President William McKinley (1897–1901).
- 1917: Official federal recognition with the creation of Mount McKinley National Park.
- 1980: Park renamed Denali National Park and Preserve; mountain's name remained McKinley federally.
- 2015: Obama administration officially renamed the peak Denali through the U.S. Department of the Interior.
- 2025: Trump issued executive order to revert the name to Mount McKinley, stating McKinley “deserves” the honor.
Rationale Behind Trump’s Renaming Order:
- Claims it honors McKinley’s legacy: economic growth, leadership in Spanish-American War, and tariff reforms.
- Declares Obama’s 2015 decision an “affront” to American heritage.
- Connects the move to his broader theme of “Restoring Names that Honor American Greatness.”
Opposition & Cultural Sensitivity:
- Alaska’s bipartisan leadership, including Senators Lisa Murkowski (R) and Scott Kawasaki (D), oppose the move.
- Indigenous groups maintain that Denali is the rightful and culturally authentic name.
- Critics argue it undermines native heritage and local identity.
Renaming the Gulf of Mexico to “Gulf of America”:
- Also part of Trump’s 2025 executive order.
- Geographic Facts:
- Borders the US, Mexico, and Cuba.
- Crucial to the US energy sector:
- 14% of US crude oil
- 5% of US natural gas
- 48% of refining capacity
- International Validity: The International Hydrographic Organization (IHO) allows local name usage but retains “Gulf of Mexico” in global records.
- Not binding on Mexico or Cuba.
International & Historical Parallels in Naming Disputes:
- Persian Gulf vs. Arabian Gulf (Iran vs. Arab states)
- Sea of Japan vs. East Sea (Japan vs. South Korea)
- South China Sea: Multiple nations claim different names and areas.
About the Denali Fault:
- Major strike-slip fault running through Alaska.
- Responsible for extensive tectonic movement and uplift of Denali.
- Evidence of horizontal displacement (~483 km) over millions of years.
- Marked the final suturing of tectonic plates in North American geological history.
Chinar Trees

- 22 Jan 2025
In News:
The J&K Forest Department, in collaboration with the J&K Forest Research Institute (JKFRI), has launched a pioneering conservation initiative to digitally preserve the iconic Chinar trees (Platanus orientalis)—a vital part of Kashmir’s ecological and cultural heritage.
Significance of Chinar Trees:
- Locally known as Boonyi or Boueen, Chinar trees are deeply embedded in Kashmir’s cultural identity.
- These deciduous trees can grow up to 30 meters tall with a girth of 10–15 meters, and can live for over 600 years.
- They are known for their seasonal leaf color transformation—from green in summer to red, amber, and yellow in autumn.
- Notable specimens include Asia’s largest Chinar in Ganderbal and the oldest known Chinar (647 years) in Chattergam, Budgam.
Challenges to Chinar Survival:
- Urban expansion and habitat encroachment.
- Climate change, altering precipitation and temperature patterns.
- Illegal felling and timber exploitation.
- Increased susceptibility to pests and diseases.
Tree Aadhaar & Geo-Tagging Initiative:
- Over 28,500 Chinar trees have been geo-tagged and assigned unique Tree Aadhaar numbers from 2021 to 2023.
- Each tree is fitted with a QR-coded digital plate, enabling real-time access to:
- Tree location, height, girth, canopy dimensions
- Health status, ecological threats, and pest presence
- These plates are spring-mounted metal tags to prevent damage to the trees.
Conservation Goals & Future Plans:
- Digital Protection: Enables proactive monitoring and protection through a centralized database.
- Chinar Atlas: A comprehensive mapping of all Chinar trees in the region.
- Public Access Website: A dedicated digital portal is planned for broader access to Chinar data.
- Risk Assessment: Use of USG-based, non-invasive surveys to identify trees at risk without human interference.
- Emphasis on covering remote and restricted areas in future phases to ensure inclusivity in conservation.
ILO Global Estimates on International Migrant Workers – 2022

- 21 Jan 2025
In New:
By addressing labour market shortages in host nations and contributing remittances to home countries, International Migrants (IM) continue to make contributions to world economic growth, the fourth edition of ‘Global Estimates on International Migrant Workers’, released by the International Labour Organization (ILO), stated.
Key Findings:
Global Representation:
- International Migrants (IMs) = 4.7% of global labour force - 167.7 million total:
- Employed: 155.6 million
- Unemployed (but seeking work): 12.1 million
- Increase of 30+ million migrant workers since 2013
- Growth rate dropped below 1% annually (2019–2022) due to COVID-19
Gender Composition:
- Male IMs: 61.3% (102.7 million)
- Female IMs: 38.7% (64.9 million)
- Lower female participation attributed to:
- Lower female migration rates globally
- Gender-based barriers in labour markets
- Over-representation in informal and unpaid sectors
Age Distribution:
- Prime working age (25–54 yrs): 74.9%
- Youth (15–24 yrs): 9.3%
- Older adults (55–64 yrs): 12.5%
- Seniors (65+ yrs): 3.4%
Sector-wise Employment:
Sector Share of IMs Notes
Services 68.4% Highest; women dominate (80.7%)
Industry 24.3% On par with non-migrants
Agriculture 7.4% Far lower than non-migrants (24.3%)
Care economy in high-income countries is a major pull for female migrants.
Host Country Distribution:
Region/Income Group % of IMs Notes
High-income countries 68.4% (114 million) Majorly Europe & North America
Upper-middle-income 17.4% (29.2 million)
Arab States 13.3% Declined since 2013
Europe (23.3%) and North America (22.6%) are top destinations. Arab states saw a 3% decline over the decade.
Definition: International Migrants (IMs)
As per the UN: Persons residing in a country different from their place of usual residence for at least one year, regardless of reason or legal status. Includes refugees, asylum seekers, etc.
Role & Contributions of IMs:
- Economic Drivers: Fill labour shortages (healthcare, construction, care work).
- Remittances: Boost home country economies.
- Demographic Support: Help address aging populations in developed nations.
Cultural Exchange: Promote diversity and global connectivity.
Ratnagiri Buddhist Site

- 19 Jan 2025
In News:
The Archaeological Survey of India (ASI) has resumed excavations at the ancient Buddhist site of Ratnagiri in Odisha’s Jajpur district, unveiling monumental discoveries that underline its rich religious, cultural, and maritime legacy. This renewed effort comes more than 60 years after the site was first excavated between 1958 and 1961.
About Ratnagiri
- Meaning: Ratnagiri translates to “Hill of Jewels.”
- Location: Situated on a hill between the Brahmani and Birupa rivers, northeast of Bhubaneswar.
- Part of the Diamond Triangle: Along with Lalitgiri and Udaygiri, Ratnagiri forms Odisha’s famed “Diamond Triangle” of Buddhist heritage sites.
- Historical Period: Flourished between the 5th and 13th centuries CE, peaking under the Bhauma-Kara dynasty (8th–10th century CE).
- Buddhist School: An important centre for Mahayana and especially Vajrayana (Tantrayana) Buddhism.
- It possibly rivalled Nalanda in prominence as a Buddhist learning centre.
- The monastery complex at Ratnagiri is the only one in India with a curvilinear roof, once housing about 500 monks.
Recent Discoveries by ASI
- Three colossal Buddha heads, each measuring 3–4 feet.
- A massive palm sculpture, 5 feet in size.
- Hundreds of votive stupas, sculptures of Buddhist deities.
- A monolithic elephant statue, 5 feet long and 3.5 feet tall.
- Pottery, inscribed stones, beads, stone pillars, and a brick wall believed to be part of a larger structure.
- Rich ceramic assemblages, which may shed light on the region’s cultural and technological evolution.
These artefacts are estimated to date back to the 8th and 9th centuries CE and are believed to enhance understanding of Buddhism’s evolution in Odisha and its linkages with other cultures.
Buddhism in Odisha & Southeast Asian Links
- Buddhism gained a strong foothold in Odisha after Emperor Ashoka’s conquest of Kalinga (modern-day Odisha) in 261 BCE, a turning point that led him to embrace Buddhism.
- Though Buddha never visited Odisha, the region became instrumental in spreading Buddhism to Southeast Asia, especially during the Bhauma-Kara period.
- The state maintained robust maritime trade and cultural links with regions like Java, Bali, Sumatra, Borneo, Myanmar, and Sri Lanka.
- Baliyatra Festival: A vibrant annual event held in Cuttack, commemorating Odisha’s ancient seafaring ties with Bali and other Southeast Asian regions.
- According to some studies, Chinese monk Hiuen Tsang may have visited Ratnagiri during his travels in India (638–639 CE).
Significance of the Renewed Excavations
- The ASI aims to uncover partially visible structures, complete the site’s mapping, and contextualize the findings within the broader Buddhist history of India and Southeast Asia.
- Researchers hope to discover signs of foreign architectural or cultural influences, further confirming ancient Odisha’s global Buddhist and trade connections.
- The discoveries reaffirm Ratnagiri’s importance as a cornerstone of Buddhist learning and art, potentially on par with other renowned ancient centres like Nalanda and Vikramashila.
Interest Equalisation Scheme (IES)

- 19 Jan 2025
In News:
- Launched in April 2015, the Interest Equalisation Scheme (IES) offers subsidised interest rates on pre- and post-shipment export credit to Indian exporters, particularly MSMEs.
- The Commerce Ministry has sought a Rs 3,000 crore extension of the scheme beyond December 2024, with emphasis on supporting MSME exporters amidst global economic challenges.
Objectives of IES:
- Reduce Cost of Credit: Offers 3% to 5% interest subvention to make export credit affordable.
- Boost Export Competitiveness: Enables Indian exporters, especially MSMEs, to match international pricing.
- Encourage Export Diversification: Supports MSMEs in exploring new markets and products.
- Enhance Financial Inclusion: Promotes access to formal credit systems for small exporters.
Key Features:
- Interest Subsidy:
- 3% for MSME manufacturer exporters.
- 2% for merchant and manufacturer exporters of 410 specified tariff lines.
- Coverage: Initially limited to select products, later extended to all MSME exporters.
- Implementation:
- Managed by the RBI, in coordination with DGFT and authorized banks.
- Subsidy reimbursed to banks offering export credit at reduced rates.
- Banks exceeding Repo Rate + 4% are excluded.
Need for Extension:
- The scheme expired in December 2024, but exporters are demanding continuation due to:
- Rising global inflation and logistics disruptions (e.g., Red Sea crisis).
- Increase in credit duration demands from foreign buyers (120–150 days).
- Decline in export credit availability despite higher demand.
- FIEO reports a drop in outstanding export credit from ?2.27 lakh crore (2023) to ?2.17 lakh crore (2024).
- MSMEs operate on thin margins, and the subvention can make or break deals.
Significance for MSMEs:
- MSMEs contribute ~45% to India’s total exports and often struggle with high borrowing costs and limited financial access.
- Affordable credit via IES allows MSMEs to:
- Remain price competitive.
- Take larger and longer-term orders.
- Invest in product innovation and value addition.
- Improve market diversification and resilience.
Challenges in Accessing Credit:
- Stringent eligibility norms and collateral requirements.
- Complex administrative procedures for availing benefits.
- Limited awareness among small enterprises about the scheme.
- Slow disbursal and inconsistent application by banks.
Policy Implications and the Way Forward:
- A revamped, MSME-focused IES can ensure inclusive growth and boost India’s export-led development.
- Calls for:
- Simplification of procedural norms.
- Higher interest subvention limits or removal of caps (e.g., ?50 lakh per IEC holder).
- Longer validity (multi-year horizon) for predictability and planning.
- Aligns with the broader goals of Atmanirbhar Bharat, Make in India, and achieving $1 trillion in exports by 2030.
Kuka Rebellion and Namdhari Sect

- 18 Jan 2025
In News:
On January 17, Punjab Chief Minister Bhagwant Mann paid tribute at the Namdhari Shaheed Smarak in Malerkotla to commemorate Kuka Martyrs’ Day. The event marks the execution of 66 Namdhari Sikhs by the British in January 1872.
Kuka Rebellion: An Overview
The Kuka Rebellion was an anti-British movement led by the Namdhari sect in Punjab. It combined religious reform with resistance to colonial rule, reaching its peak in January 1872.
Key Events:
- January 13, 1872: Kukas, led by Hira Singh and Lehna Singh, protested against cow slaughter in Malerkotla.
- January 15, 1872: Clashes occurred between Kukas and government officials. A contingent attacked Malaudh Fort but was repulsed.
- January 17-18, 1872: 66 Kukas were executed by being blown up with cannons under orders of British official John Lambert Cowan.
Reasons Behind the Movement:
- Religious Reform: Opposed meat consumption, alcohol, and social vices.
- Colonial Oppression: Protested against British rule and native collaborators.
- Cow Protection: Strongly opposed cow slaughter, leading to confrontations with British authorities.
Impact and Aftermath:
- Suppression: The British crushed the movement with extreme brutality.
- Exile of Leaders: Satguru Ram Singh and other key leaders were exiled to Rangoon, Burma.
- Legacy of Martyrdom: The sacrifice of young Namdharis like 12-year-old Bishan Singh and Waryam Singh inspired future resistance movements in India.
Who are the Namdharis?
The Namdharis, also called Kukas, are a Sikh sect founded by Satguru Ram Singh in 1857 in Ludhiana. Their distinctive practices include:
- High-pitched recitation of Gurbani (hence the name ‘Kuka’ meaning ‘crying’ or ‘screaming’ in Punjabi).
- Wearing white attire as a sign of mourning for their exiled leader.
- Early adoption of Swadeshi principles, boycotting British goods and services.
Current Status of Namdhari Sect:
- The Namdharis, numbering around 2 lakh in Punjab today, have faced internal divisions since the death of Satguru Jagjit Singh in 2012.
- Two major factions exist:
- One led by Thakur Dilip Singh, headquartered in Sirsa, Haryana.
- Another led by Sangrur Uday Singh, headquartered at Bhaini Sahib, Ludhiana.
- A core belief remains that Satguru Ram Singh is still alive and will return one day.
Significance:
The Kuka Rebellion, though localized, was an important precursor to later national movements against British rule. It showcased the early spirit of resistance, long before organized freedom movements gained momentum in the 20th century.
QS World Future Skills Index 2025

- 17 Jan 2025
In News:
The QS World Future Skills Index 2025, released by Quacquarelli Symonds (QS), evaluates countries' readiness to meet the evolving demands of the global job market. It assesses nations based on skill development, education, and economic transformation, highlighting their preparedness for emerging technologies, artificial intelligence (AI), and sustainability.
India’s Performance in the Index:
- Overall Ranking: India is ranked 25th globally, categorizing it as a “Future Skills Contender.”
- Future of Work Category: India ranked 2nd, only behind the United States, reflecting its preparedness for AI, digital, and green jobs.
- Economic Transformation: India scored 58.3, the lowest among the top 30 countries, reflecting challenges in innovation and sustainability.
- Skills Fit: India received a score of 59.1, the weakest among the top 30 nations, indicating a gap between workforce skills and industry requirements.
- Academic Readiness: India’s education system is struggling to keep pace with employer demands, necessitating curriculum reforms and stronger academia-industry collaboration.
Key Findings from the Report:
Strengths:
- Digital Readiness: India has demonstrated strong capabilities in integrating digital talent into the workforce.
- Youth Advantage: A large, young population provides a demographic dividend for sustained economic growth.
- Startup Ecosystem: India’s startup culture and government initiatives support technological advancement and innovation.
Weaknesses:
- Higher Education-Industry Gap: Mismatch between education and employer requirements, particularly in AI, green skills, and entrepreneurship.
- Limited R&D Investment: India’s research and development spending is 0.6% of GDP, far below the global average of 2.7%.
- Low Innovation in Sustainability: India scored 15.6 out of 100, ranking poorly in future-oriented innovation for sustainability.
Challenges and Concerns:
- Skilled Workforce Shortage: The National Skill Development Corporation (NSDC) estimates a 29 million skilled workforce gap in critical sectors such as healthcare, semiconductor manufacturing, and AI.
- Low Employability Rates: Only 25% of management professionals, 20% of engineers, and 10% of graduates meet global employability standards.
- Higher Education Accessibility: Many students face difficulties in accessing quality tertiary education, particularly in skill-intensive fields.
Opportunities for Growth:
- Leverage Demographic Dividend: India can capitalize on its young workforce to dominate skill-based industries while other nations struggle with aging populations.
- Policy Support:
- National Education Policy (NEP) 2020: Focuses on modular education and reskilling initiatives.
- ULLAS Program: Aims to expand lifelong learning and skill development.
- Technological Integration: Advancements in AI and digital learning can help modernize academic curricula and improve job readiness.
Recommendations for Improvement:
- Enhancing Academia-Industry Collaboration: Universities should prioritize problem-solving, entrepreneurship, and creativity to align education with employer needs.
- Increasing R&D Investment: Raising spending on research and development to promote innovation and sustainability.
- Expanding Access to Education: Bridging regional disparities in tertiary education through flexible and modular learning.
- Strengthening Policy Implementation: Ensuring effective execution of skilling programs to reduce the workforce-employability gap.
Human Papillomavirus (HPV)

- 16 Jan 2025
In News:
January is Cervical Cancer Awareness Month, and the focus on this month underscores the critical importance of preventing cervical cancer, a disease responsible for significant mortality among women in India. At the heart of this prevention is the Human Papillomavirus (HPV) vaccine, which is recognized as the most effective measure to prevent cervical cancer and other HPV-related cancers. Despite its potential, the HPV vaccine remains out of reach for many due to its high cost and the need for greater awareness.
HPV and its Impact in India
HPV is responsible for 99.7% of cervical cancers worldwide, making it one of the primary causes of cancer in women. In India, cervical cancer is the third most common cancer among women, accounting for about 6-29% of all cancers in women. As of GLOBOCAN 2020, India alone has 20% of the global burden of cervical cancer, with over 123,000 cases and a 9.1% mortality rate.
Additionally, HPV can lead to several other cancers, including anal, vulvar, vaginal, penile, and throat cancers, making its vaccination vital for overall cancer prevention.
The HPV Vaccine: A Game-Changer
The HPV vaccine is the most effective tool to prevent infections caused by the virus and reduce the incidence of associated cancers. The vaccine works by stimulating the immune system to produce antibodies that neutralize the virus before it can cause damage. There are different types of vaccines authorized in India, including:
- Gardasil (protects against HPV types 6, 11, 16, and 18)
- Cervarix (a bivalent vaccine targeting HPV 16 and 18)
- Cervavac (India's first HPV vaccine, developed by the Serum Institute of India)
The vaccine is recommended for both males and females between 9 and 26 years, with a special focus on children aged 12 to 13 years, as the vaccine is most effective when administered before exposure to the virus. It’s also suitable for people who are immunocompromised or HIV-infected.
Challenges to HPV Vaccination in India
Despite the obvious benefits, the uptake of the HPV vaccine in India faces several barriers:
- High Costs: The price of the vaccine remains prohibitively high. For example:
- Gardasil 9 costs ?10,850 per dose.
- Gardasil 4 is priced between ?2,000 to ?4,000 per dose.
- Cervavac, the Indian-made vaccine, costs around ?2,000 per dose, which is more affordable but still out of reach for many.
- Awareness and Cultural Perceptions: There is a lack of awareness about HPV and its link to cervical cancer. Cultural factors, particularly around reproductive health, can also create reluctance to vaccinate, especially in rural or conservative areas.
- Limited Access: Currently, the vaccine is available through private practitioners and is not part of the National Immunisation Programme (NIP), limiting access to the broader population.
The Way Forward: National Immunisation and Awareness Campaigns
The National Technical Advisory Group on Immunisation (NTAGI) has recommended that the HPV vaccine be included in India’s National Immunisation Programme (NIP). This would enable broader access and affordability, especially for girls aged 9–14 years and ensure that a routine vaccination schedule is implemented at the age of 9 years. Some states like Punjab and Sikkim have already taken steps to introduce the vaccine in their state-level immunization programs.
Additionally, a nationwide HPV vaccination campaign could raise awareness about the vaccine and its benefits, helping to overcome the challenges of cost, safety concerns, and cultural perceptions. Regular cervical cancer screenings (such as Pap smears and HPV tests) should also be encouraged to identify precancerous changes early.
Cabinet Approves Establishment of ‘Third Launch Pad’ at ISRO's Sriharikota Facility

- 16 Jan 2025
In News:
The Union Cabinet, has approved the establishment of a Third Launch Pad (TLP) at the Satish Dhawan Space Centre (SDSC), located at Sriharikota, Andhra Pradesh. This project marks a significant step in enhancing India’s space capabilities and will support the Next Generation Launch Vehicles (NGLV) for ISRO’s evolving space exploration programs.
Key Features of the Third Launch Pad
The TLP will be built with an adaptable design, capable of supporting NGLV and LVM3 vehicles with semi-cryogenic propulsion. The launch pad will also serve as a standby for the Second Launch Pad (SLP) at Sriharikota. This addition will help ISRO meet its growing launch capacity needs, particularly for future human spaceflight missions and space exploration projects. It will facilitate higher launch frequencies, thus boosting the Indian space ecosystem.
Implementation Strategy and Timeline
The Third Launch Pad is planned to be developed within 48 months (4 years), with the total cost pegged at ?3984.86 Crore. The development will involve maximized industry participation and will utilize existing infrastructure at the launch complex. The project will also leverage ISRO’s experience gained from establishing the earlier launch pads.
The Importance of the Third Launch Pad
The TLP is designed to support the Next Generation Launch Vehicles (NGLV), a key part of ISRO’s vision for space exploration. The facility will not only accommodate heavier vehicles but will also ensure standby capacity for the Second Launch Pad (SLP). Its strategic location at Sriharikota ensures several advantages:
- Proximity to the Equator: This offers a substantial increase in payload capacity due to the additional push provided by the Earth's rotation.
- Safety and Accessibility: The site is free from major international maritime or airline routes, ensuring a safe flight path.
- Geographical Advantage: The launch pad is situated on the eastern coast, enabling launches in an easterly direction, maximizing the benefits of Earth’s rotational speed.
Future Plans for Indian Space Exploration
The establishment of the Third Launch Pad is crucial for the expanded vision of India’s space program, particularly in line with the Amrit Kaal period. ISRO aims to achieve ambitious milestones, such as the Bharatiya Antariksh Station (BAS) by 2035 and an Indian Crewed Lunar Landing by 2040. The NGLV will play a pivotal role in these plans, with features like:
- A three-stage vehicle and reusable first stage.
- Semi-cryogenic propulsion, using refined kerosene and liquid oxygen, which will increase payload capacity by three times at 1.5 times the cost of current vehicles.
The Role of Sriharikota in India’s Space Program
Sriharikota, the hub of ISRO’s launch operations, has been integral to India’s space exploration. Currently, the Indian Space Transportation Systems rely on two operational launch pads:
- First Launch Pad (FLP): Established over 30 years ago for PSLV and SSLV missions, FLP continues to support Polar Satellite Launch Vehicle (PSLV) and Small Satellite Launch Vehicle (SSLV) launches.
- Second Launch Pad (SLP): Built primarily for GSLV and LVM3 vehicles, SLP also serves as a standby for PSLV. Over its 20 years of operation, SLP has supported several national missions, including Chandrayaan-3, and is preparing for the Gaganyaan missions.
US AI Hardware Export Restrictions and Impact on India

- 16 Jan 2025
In News:
Days before demitting office, the Joe Biden administration has released an expansive regulatory framework on the export of artificial intelligence (AI) hardware such as graphics processing units (GPUs), which could have far-reaching consequences for India’s AI ambitions.
Three-Tier Framework for AI Hardware Export Restrictions
- Tier 1: Closest US Allies
- Countries: Australia, Belgium, Canada, South Korea, UK, etc.
- No restrictions on computing power deployment.
- Minimal security requirements.
- Impact: Free access to AI technology for these nations.
- Tier 2: Majority of Countries (Including India)
- Countries: India, Brazil, South Africa, etc.
- Restrictions: Limited to importing approximately 50,000 advanced AI chips (around $1 billion) through 2027.
- Potential to Double Cap: If countries sign agreements to uphold strict security standards.
- Impact on India:
- Short-Term: Likely to fulfill current demand for 10,000 GPUs for the IndiaAI Mission.
- Long-Term: Challenges in scaling AI infrastructure, with possible delays in large AI data centers and difficulty acquiring large-scale GPUs.
- Tier 3: Countries of Concern (Restricted Nations)
- Countries: Russia, China, North Korea, Iran, etc.
- No Access to US AI Technology: Nearly total prohibition of AI tech exports.
Special Provisions for India and China
- General Validated End User (GVEU) status for India and China:
- India: Authorisation for civilian and military use, excluding nuclear applications.
- China: Only civilian use permitted under similar conditions.
Why the US Imposed These Restrictions?
- National Security: Prevent adversaries (China, Iran, Russia) from acquiring advanced AI technologies.
- US Technological Leadership: To protect US AI leadership and prevent loss of competitive edge.
- Trusted Ecosystem: Build secure and trusted AI environments for allied nations.
Impact on India
- Short-Term:
- IndiaAI Mission: Current procurement of 10,000 GPUs unlikely to be affected.
- Subsidized GPUs: Available for startups, academia, and researchers.
- Long-Term Concerns:
- Licensing Uncertainties: Possible delays in large-scale AI deployments and AI data centers.
- Impact on Large Firms: Companies like Reliance and Yotta may face challenges scaling up AI compute infrastructure.
- National AI Mission Challenges: Difficulty in acquiring enough GPUs for large-scale AI projects beyond 2027.
- Strategic Leverage: US could use AI export restrictions to negotiate trade deals or tariff adjustments.
Nvidia’s Criticism of the AI Diffusion Rules
- Overreach and Bureaucratic: Nvidia criticized the 200+ page regulatory framework as excessive, secretive, and bureaucratic.
- Harming US Competitiveness: Claims that the rules would hinder US innovation and global leadership, weakening the competitiveness of the US semiconductor and software industries.
- Contrast with Trump’s Approach: Praises the earlier Trump administration for fostering AI growth through industry competition without compromising national security.
Enforcement of the Rules
- Regulatory Control: Managed by the US Bureau of Industry and Security (BIS) under the Department of Commerce.
- Technology Access: Ensures AI chips and models do not reach adversaries or nations posing security risks.
Potential Impact on India’s AI Strategy
- AI Hardware Infrastructure: Challenges in large-scale AI hardware deployment.
- Competitive Disadvantage: Potential delays or downsizing of AI data centers could affect India’s competitiveness in AI technology.
- Strategic Partnerships: India may need to secure General National Validated End User authorizations to ensure uninterrupted access to advanced chips.
- AI Market Growth: India’s AI market projected to grow to $17 billion by 2027, with an annual growth rate of 25%-35%.
Commissioning of Three Indian Naval Combatants

- 15 Jan 2025
In News:
In a major boost to India’s maritime defense capabilities, three frontline warships—INS Nilgiri, INS Surat, and INS Vaghsheer—were commissioned into the Indian Navy at the Naval Dockyard in Mumbai. This marks a significant step in India's self-reliance in defense manufacturing and strengthens its presence in the Indian Ocean Region (IOR).
INS Nilgiri: Project 17A Stealth Frigate
INS Nilgiri is the lead ship of the Project 17A class, an advanced version of the Shivalik-class frigates, designed for multi-mission capabilities in blue-water operations.
Key Features:
- Advanced stealth technology reducing radar and infrared signatures.
- Equipped with supersonic surface-to-surface missiles, Medium Range Surface-to-Air Missiles (MRSAM), upgraded 76 mm guns, and rapid-fire close-in weapon systems.
- Versatile roles in anti-surface, anti-air, and anti-submarine warfare.
- Constructed using integrated modular design for faster assembly.
- Other ships in this class—Himgiri, Taragiri, Udaygiri, Dunagiri, and Vindhyagiri—are under construction at Mazagon Dock Shipbuilders Limited (MDL) and Garden Reach Shipbuilders and Engineers (GRSE).
INS Surat: Project 15B Stealth Destroyer
INS Surat is the fourth and final guided missile destroyer under Project 15B, following INS Visakhapatnam, INS Mormugao, and INS Imphal. It represents an upgraded version of the Kolkata-class destroyers.
Key Features:
- AI-Enabled Operations: First Indian warship integrated with artificial intelligence solutions for enhanced combat efficiency.
- High-Speed Capability: Can exceed speeds of 30 knots (56 km/h).
- Advanced Armament: Equipped with modern surface-to-air and anti-ship missiles, torpedoes, and sophisticated network-centric warfare sensors.
- Strategic Role: Acts as a high-speed, maneuverable warship with increased strike capability and endurance.
Project 15B was initiated in 2011, with ships named after major Indian cities to symbolize national unity. These destroyers serve as critical assets in naval operations, ensuring dominance in maritime warfare.
INS Vaghsheer: Project 75 Scorpene-Class Submarine
INS Vaghsheer is the sixth and final Kalvari-class submarine built under Project 75, designed for stealth and versatile naval operations.
Key Features:
- Scorpene-Class Design: Developed in collaboration with the French Naval Group.
- Diesel-Electric Propulsion: Silent and highly maneuverable, making it one of the world’s most advanced attack submarines.
- Mission Capabilities: Specializes in anti-surface warfare, anti-submarine warfare, intelligence gathering, and special operations.
- Weapons Systems: Armed with wire-guided torpedoes, anti-ship missiles, and state-of-the-art sonar systems.
The Kalvari-class submarines continue India's legacy of submarine warfare, named after decommissioned Soviet-origin Foxtrot-class submarines post-Independence.
World’s First Cryo-Born Baby Corals

- 13 Jan 2025
In News:
World’s First Cryo-Born Baby Corals Successfully Settled on the Great Barrier Reef.
Introduction to Cryo-Born Corals
- Cryo-born corals are created using cryopreservation techniques, which involve freezing coral cells and tissues at very low temperatures.
- The process preserves coral cells by preventing the formation of ice crystals that would otherwise damage them.
- Cryopreservation involves adding cryoprotectants to remove water from cells, enabling their survival during freezing and thawing.
Significance of the Breakthrough
- Climate Change Resilience: The initiative aims to create heat-tolerant corals, which are crucial in combating the impact of rising ocean temperatures due to climate change.
- Selective Breeding Advantage: Cryopreservation allows for controlled breeding and bypasses the limitations of natural coral spawning, which occurs only once a year. This enables multiple reproduction cycles without disturbing wild populations.
The Process of Cryo-Born Coral Production
- Sperm Collection: During coral spawning events, sperm from various coral species is collected and frozen at -196°C using liquid nitrogen, halting metabolic processes.
- Coral Egg Fertilization: Cryopreserved sperm is used to fertilize fresh coral eggs, which are grown in a specialized research facility called the National Sea Simulator.
- Coral Cradles: After growth, the cryo-born corals are carefully transported and settled into specially designed "coral cradles" placed in the Great Barrier Reef, where their growth is monitored during their critical first year.
Importance of Cryo-Born Corals in Reef Restoration
- The primary aim is to introduce millions of heat-tolerant corals annually to restore reefs affected by climate change.
- The Taronga CryoDiversity Bank houses the world’s largest frozen coral sperm collection from 32 coral species, collected annually since 2011, providing a resource for future restoration efforts.
Coral Reefs: An Overview
- Corals are marine invertebrates from the class Anthozoa, phylum Cnidaria.
- Reefs are built by colonies of coral polyps that secrete limestone skeletons and rely on symbiotic algae (zooxanthellae) for nutrition.
- Coral reefs are typically found in shallow, sunlit waters with a temperature range of 16-32°C and depths less than 50 meters.
Global and Indian Coral Conservation Efforts
- India:
- The National Committee on Wetlands, Mangroves, and Coral Reefs (1986) advises on conservation measures.
- The Environment (Protection) Act (1986) prohibits the use of coral and sand in construction.
- Zoological Survey of India (ZSI) uses Biorock technology for coral restoration.
- Global Efforts:
- CITES lists coral species in Appendix II, regulating coral trade.
- The World Heritage Convention designates coral reefs as protected sites.
Global Impact and Future Directions
- The innovative work by Australian scientists opens the door for large-scale restoration efforts by allowing more controlled breeding and genetic diversity, making corals more resilient to climate change.
- This breakthrough could revolutionize coral restoration, scaling up efforts to introduce millions of resilient corals to reefs worldwide, building long-term resilience against climate change.
Pink Fire Retardant

- 13 Jan 2025
In News:
As wildfires continue to rage across Southern California, authorities are deploying pink fire retardant from aircraft to help combat the blazes. Despite its widespread use, concerns over its effectiveness and environmental risks have surfaced in recent years.
What is Pink Fire Retardant?
- Fire retardant is a chemical mixture designed to slow down or extinguish wildfires. The most commonly used product in the U.S. is Phos-Chek, a brand of retardant.
- Phos-Chek primarily contains ammonium phosphate-based slurry (salts like ammonium polyphosphate), which helps the retardant stay longer and resist evaporation, unlike water.
Purpose and Visibility
- Fire retardants are sprayed ahead of fires to coat vegetation, reducing oxygen and preventing flames from spreading.
- Color is added to the fire retardant, often bright pink, to improve visibility. This ensures firefighters can track its spread and create effective fire lines, helping protect lives and property.
Manufacturer
- Perimeter Solutions manufactures Phos-Chek, which is used for aerial fire suppression efforts.
Effectiveness of Pink Fire Retardant
Limited Effectiveness
- The use of fire retardants like Phos-Chek is not always effective across different wildfire conditions.
- Aerial retardants depend on environmental conditions like terrain, slope, and weather for optimal effectiveness.
- Researchers, including Forest Service scientists, suggest that retardant effectiveness is more limited under changing climate conditions.
- Climate change is narrowing the window of opportunity for using aerial retardants, reducing their impact.
Uncertainty in Impact
- The effectiveness of fire retardants is hard to quantify. Multiple firefighting methods are used simultaneously, making it difficult to attribute wildfire suppression success solely to the retardant.
Environmental Concerns of Pink Fire Retardant
Toxicity and Pollution
- Phos-Chek contains toxic metals such as chromium and cadmium, both of which are harmful to humans and the environment.
- Chromium and cadmium are linked to serious health issues, including cancer and liver/kidney diseases.
- Aquatic life is particularly vulnerable to these toxins, as the chemicals can enter waterways, causing extensive damage to ecosystems.
Impact on Rivers and Streams
- The use of pink fire retardant has raised concerns regarding the contamination of rivers and streams.
- A study by the University of Southern California (USC) in 2024 estimated that 850,000 pounds of toxic chemicals have been released into the environment since 2009 due to fire retardant use.
Growing Use and Pollution
- From 2009 to 2021, over 440 million gallons of retardant were applied across U.S. lands.
- During this period, an estimated 400 tons of heavy metals were introduced into the environment, further exacerbating the pollution levels.
Financial and Practical Concerns
High Cost and Inefficiency
- The cost of deploying fire retardant is significant. Aerial firefighting operations require substantial resources, including planes, helicopters, and large quantities of retardant.
- Environmental experts argue that using fire retardant from planes is ineffective and expensive, especially in light of the growing environmental concerns.
Dr. V. Narayanan Takes Over as ISRO Chairman

- 10 Jan 2025
In News:
Dr. V. Narayanan has been appointed as the new Chairman of ISRO and Secretary of the Department of Space (DoS), effective from January 14, 2025, succeeding Dr. S. Somanath.
Background and Career of Dr. V. Narayanan:
Dr. Narayanan, currently the Director of Liquid Propulsion Systems Centre (LPSC) in Thiruvananthapuram, has been a key figure in ISRO since joining in 1984. With a focus on cryogenic propulsion, he has played an instrumental role in developing critical technologies for ISRO's launch vehicles. Notably, his work has contributed to India becoming the sixth country globally capable of building and operationalizing cryogenic engines.
Dr. Narayanan’s career highlights include:
- Cryogenic Technology: Leading the development of cryogenic engines for LVM3 (India's heaviest launch vehicle) and PSLV, which are central to missions like Chandrayaan and Gaganyaan.
- Chandrayaan-2 & Chandrayaan-3: As part of ISRO’s missions to the moon, his contributions were pivotal in rectifying the propulsion system issues post-Chandrayaan-2's hard landing, leading to the successful soft landing of Chandrayaan-3 in August 2023.
- Gaganyaan Mission: Overseeing the development of the propulsion systems for crew and service modules, critical for India’s ambitious human spaceflight program.
Dr. S. Somanath's Legacy:
Dr. S. Somanath, who served as ISRO Chairman and DoS Secretary spearheaded multiple landmark missions, including:
- Chandrayaan-3, Aditya-L1, and INSAT missions.
- The Small Satellite Launch Vehicle (SSLV), Re-usable Launch Vehicle (RLV-LEX), and Gaganyaan abort missions.
- National Space Policy 2023 and fostering partnerships between ISRO and private ventures.
Dr. Somanath’s tenure significantly elevated India’s space capabilities, with Chandrayaan-3 marking a historic milestone in India’s lunar exploration.
Dr. Narayanan’s Role in Upcoming ISRO Missions:
As ISRO Chairman, Dr. Narayanan will oversee several ambitious space missions, including:
- NVS-02: The launch of India's navigation satellite as part of the IRNSS constellation.
- Unmanned Gaganyaan Mission: Leading the uncrewed G-1 flight, a precursor to India's first human spaceflight.
- Indo-US NISAR Satellite: A significant collaborative launch with NASA for earth observation.
Additionally, high-profile projects such as Chandrayaan-4, India’s own space station, and future missions to Mars and Venus are in the pipeline, although not all may occur during his tenure.
Vision for ISRO Under Dr. Narayanan:
Dr. Narayanan aims to expand India’s presence in space, targeting increased global market share, particularly in the space economy, which currently holds 2% of the global space sector. His leadership will focus on:
- Increasing Satellite Capacity: Expanding India’s satellite fleet, which currently stands at 53, to meet growing demands for communication, navigation, and earth observation.
- Private Sector Involvement: Leveraging space sector reforms and collaborating with private players to drive innovation and meet burgeoning satellite needs.
- Global Collaboration: Strengthening ties with other space agencies, as ISRO continues to build respect on the global stage.
Upcoming Space Missions and ISRO's Agenda for 2025:
Under Dr. Narayanan's leadership, ISRO has a packed agenda for 2025:
- GSLV Mk-II/IRNSS-1K Mission
- Gaganyaan G-1 Mission (uncrewed flight)
- Chandrayaan-4, Bharatiya Antariksha Station, and Venus Orbiter Mission (VOM) preparations.
Dr. Narayanan’s vision aligns with India's broader goals of becoming a dominant player in the global space economy, aspiring to increase its space market share from 2% to 10%.
Indonesia Becomes 10th Member of BRICS
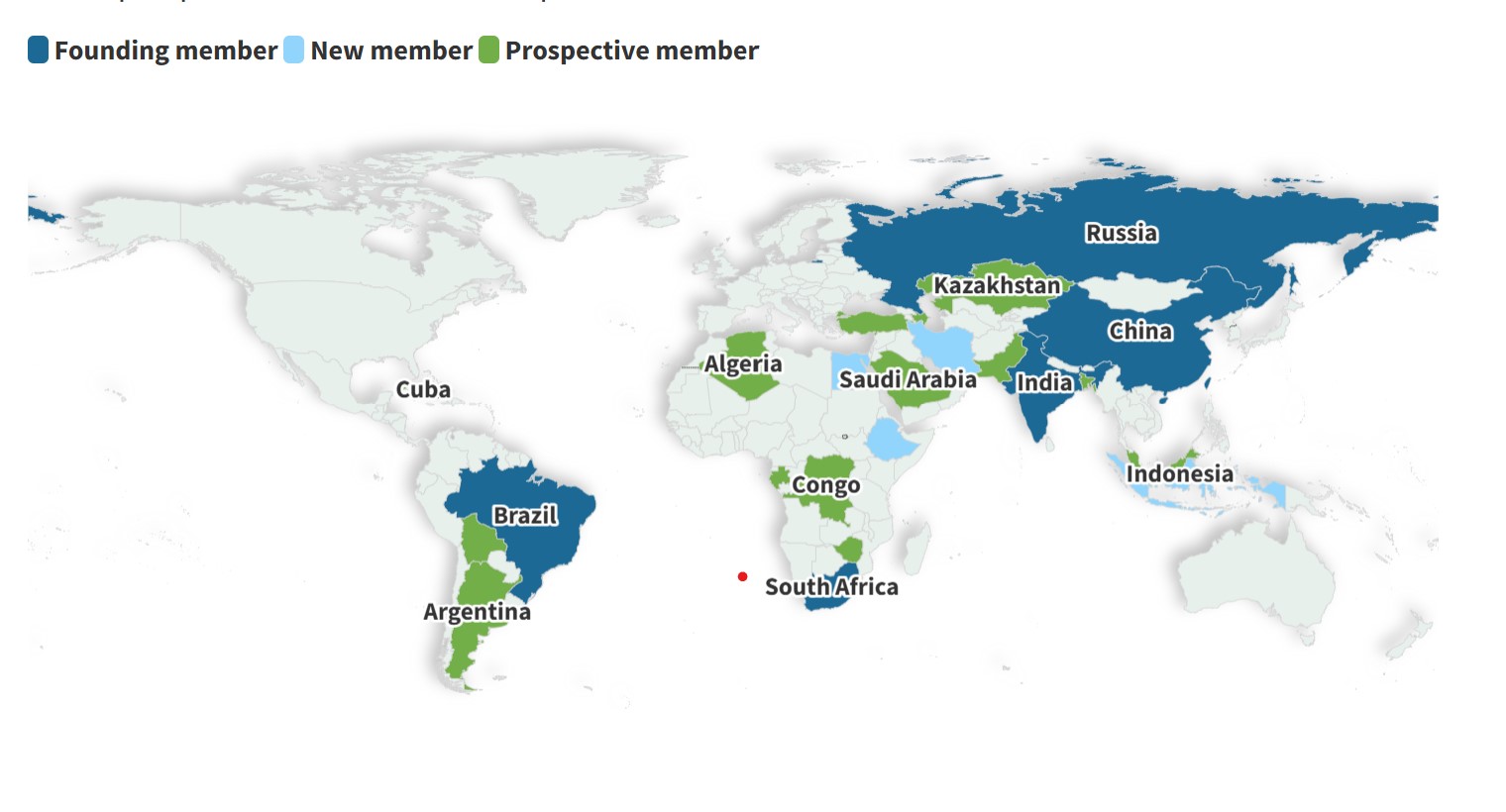
- 10 Jan 2025
In News:
In January 2025, Indonesia officially joined the BRICS group as its 10th member, signaling the expansion of this influential coalition of emerging economies. The addition of Indonesia, a Southeast Asian powerhouse, strengthens BRICS' global position and highlights the group's evolving dynamics.
BRICS Overview:
BRICS (Brazil, Russia, India, China, South Africa) is an informal intergovernmental group that fosters cooperation among major emerging economies. Initially coined as BRIC by economist Jim O'Neill in 2001, the group became BRICS in 2010 with the inclusion of South Africa. The bloc has grown steadily, with Indonesia now joining as its 10th member.
Recent Expansion:
- In 2023, invitations were extended to Saudi Arabia, Iran, UAE, Egypt, Ethiopia, and Argentina.
- By 2024, Iran, Egypt, Ethiopia, and UAE had joined as permanent members.
- Indonesia's membership was finalized in 2025, following its presidential elections and government formation.
Key Objectives of BRICS:
- Economic Growth: Promote trade, investment, and infrastructure development.
- Global Governance Reform: Advocate for equitable representation in global institutions like the UN and IMF.
- Cultural Exchange: Strengthen people-to-people connections and cultural ties.
- South-South Cooperation: Foster collaboration among developing nations.
BRICS Structure and Mechanisms:
- New Development Bank (NDB): Established in 2014, the NDB finances sustainable development projects in BRICS countries.
- Contingent Reserve Arrangement (CRA): A $100 billion safety net for financial crises.
- BRICS Academic Forum: Encourages academic collaboration across member states.
Global Influence and Economic Impact:
- Global Share: BRICS+ represents over 45% of the world’s population and 35% of global GDP (PPP-based).
- Strategic Position: The group acts as a counterbalance to the G7, challenging Western-dominated global financial systems.
- Financial Independence: BRICS aims to reduce dependence on the US dollar by facilitating local currency transactions and exploring a common currency.
- Technology Collaboration: Member countries, such as India and China, collaborate on digital payments and renewable energy technologies.
Indonesia’s Entry into BRICS:
Indonesia, the world’s fourth-most populous nation, strengthens BRICS’ representation in Southeast Asia. The country brings a robust economy and extensive trade networks, boosting the group's negotiating power. Indonesia’s membership was approved during the 2023 BRICS Summit and finalized in January 2025.
- Strategic Importance for Indonesia: The membership aligns with Indonesia's goals to enhance global cooperation, particularly with the Global South. It also reflects Indonesia's growing influence in international trade and geopolitics.
BRICS Challenges:
- Diverse Interests: Differences in economic priorities, such as India's ties with the US and Russia-China’s geopolitical rivalry, complicate consensus-building.
- Geopolitical Tensions: Disputes like the China-India border issue and Russia’s sanctions limit BRICS' ability to present a unified stance.
- Economic Sanctions and Internal Challenges: Countries like Russia face Western sanctions, while domestic issues in Brazil and South Africa divert attention from regional collaboration.
Significance of BRICS’ Expansion:
The expansion of BRICS marks a pivotal shift in global power dynamics, with a focus on South-South cooperation and equitable global governance. Indonesia’s membership further solidifies the group’s influence in Southeast Asia and adds to its efforts to challenge the dominance of Western-led financial institutions.
- Local Currency Use: The group promotes the use of local currencies for trade to reduce reliance on the US dollar.
- Global South Advocacy: BRICS champions the cause of developing nations, ensuring that emerging economies have a voice in global governance.
Recent and Upcoming BRICS Summits:
- 16th BRICS Summit (2024): Held in Kazan, Russia, with a focus on strengthening local currencies and promoting non-dollar transactions.
- 17th BRICS Summit (2025): Scheduled for July 2025 in Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, under the theme "Global South," with an emphasis on payment gateways to facilitate intra-BRICS trade.
Bharatpol

- 11 Jan 2025
In News:
Union Home Minister Amit Shah inaugurated the ‘Bharatpol’ portal, which aims to streamline international cooperation for law investigating agencies.
Key Highlights:
Bharatpol is a newly launched portal developed by the Central Bureau of Investigation (CBI) in India to facilitate faster and more efficient international cooperation between Indian law enforcement agencies and Interpol. It was inaugurated by Union Home Minister Amit Shah, to streamline the process of sharing criminal intelligence and coordinating efforts in transnational crimes like cybercrime, human trafficking, drug trafficking, financial fraud, and organized crime.
The portal aims to address the current challenges in international collaboration, which previously relied on slower communication methods such as letters, emails, and faxes, often leading to delays in investigations.
Key Features and Functions of Bharatpol:
- Unified Platform: Bharatpol integrates CBI as the National Central Bureau (NCB-New Delhi) with all Indian law enforcement agencies, from state police forces to higher authorities. This allows better coordination and quicker access to international resources.
- Simplified Request Mechanism: The portal provides a standardized method for frontline police officers to request international assistance from Interpol member countries, using templates for efficiency.
- Rapid Information Dissemination: Bharatpol enables the CBI to quickly share criminal intelligence and other pertinent information with law enforcement agencies across India, helping to tackle international criminal activities in real-time.
- Increase in Utilization of Interpol Notices: The portal makes it easier for Indian law enforcement agencies to issue and manage Red Corner Notices and other Interpol notices, which are essential tools in tracking criminals globally.
- Capacity Building and Training: Bharatpol includes resources for training law enforcement personnel, improving their ability to conduct investigations abroad and seek foreign assistance via Interpol.
How Bharatpol Works:
- Key Modules of Bharatpol:
- Connect: Facilitates the integration of Indian agencies with the Interpol NCB-New Delhi, creating a seamless communication channel.
- INTERPOL Notices: Supports the rapid issuance and processing of Interpol Notices like Red Corner Notices to locate criminals globally.
- References: Enables Indian agencies to seek and offer international assistance for investigations.
- Broadcast: Ensures quick availability of assistance requests from Interpol member countries, facilitating faster responses.
- Resources: Manages document exchanges and training materials to support the capacity-building efforts of law enforcement agencies.
Potential Benefits of Bharatpol:
- Enhanced Coordination: Bharatpol facilitates better collaboration between central, state, and Union Territory agencies, allowing for a more structured and efficient approach to international crime investigations.
- Faster Investigation: Real-time sharing of information and the use of Interpol notices will help in tracking criminals and criminal activities both in India and abroad.
- Simplified Extradition Process: By streamlining international communication, Bharatpol will assist in expediting the extradition of criminals to India for prosecution.
- Support for Transnational Crime Prevention: It will help address growing threats such as cybercrime, human trafficking, and organized crime by improving the ability of Indian law enforcement to collaborate globally.
Emergency Declared in Trinidad and Tobago
- 11 Jan 2025
In News:
- Trinidad and Tobago declared a state of emergency, in response to a surge in gang violence, which raised the annual death toll to the highest since 2013.
Trinidad and Tobago:
- Location: An island nation in the southern Caribbean, near Venezuela and Guyana.
- Capital: Port of Spain.
- Population: Approximately 1.5 million.
- Ethnic Composition: African (36.3%), Indian (35.4%), Mixed (22.8%), and others.
- Religions: Christianity (64%), Hinduism (18%), Islam (5%), and others.
- Independence: Gained from the UK on August 31, 1962, and became a republic in 1976.
- Member of: Caribbean Community (CARICOM), Commonwealth of Nations, and the United Nations.
- Major Rivers: Ortoire and Caroni.
- Geography:
- Total Land Area: 5,128 sq. km (Trinidad: 4,768 sq. km, Tobago: 300 sq. km).
- Climate: Tropical, with dry and rainy seasons.
- Highest Point: Mount Aripo.
- Natural Resource: Pitch Lake, the world’s largest asphalt reservoir.
- Mountain Range: Northern Range, part of the Andes extension.
Economic and Cultural Significance
- Exports: Major exporter of liquefied natural gas (LNG), methanol, ammonia, and petrochemicals.
- Culture: Known for Carnival, Calypso music, Soca, and the Steelpan (the only musical instrument invented in the 20th century).
- Infrastructure:
- Ports: Port of Spain, Point Lisas, Scarborough.
- Airports: Piarco International Airport (Trinidad) and A.N.R. Robinson International Airport (Tobago).
Engagement with India
- Trinidad and Tobago became the first Caribbean country to adopt India’s UPI platform.
- Both countries granted each other Most Favored Nation (MFN) status in 1997.
- Bilateral trade reached USD 368.96 million in FY 2023-24.
- The Indian diaspora constitutes about 42% of the population.
Past Emergency Declarations:
- 2014: State of emergency declared in response to gang violence.
- 2021: Emergency declared for Covid-19 restrictions.
- 2011: Limited state of emergency for drug-related crimes.
Z-Morh Tunnel
- 11 Jan 2025
In News:
Recently, Prime Minister Narendra Modi inaugurated the Z-Morh Tunnel at Sonamarg, which has now been renamed the Sonamarg Tunnel.
Key Takeaways:
- A 6.4-km bi-directional tunnel with an approach road of 5.6 km, Z-Morh connects the Sonamarg health resort with Kangan town in the Ganderbal district of central Kashmir.
- The tunnel has acquired its name for the Z-shaped road stretch that was previously at the place where the tunnel is being constructed.
- The Z-Morh project was initiated by the Border Roads Organisation in 2012. Although the BRO awarded the construction contract to Tunnelway Ltd, the project was subsequently taken over by National Highways and Infrastructure Development Corporation Limited (NHIDCL).
Significance
Strategic Importance
- Connectivity: Provides all-weather connectivity from Srinagar to Ladakh, ensuring year-round access.
- Military Significance:
- Critical for rapid deployment of Indian Armed Forces to Ladakh’s border areas, particularly in the context of tensions with Pakistan and China.
- Reduces dependence on air transport, lowering costs and increasing the longevity of the Indian Air Force’s aircraft.
- Adjacent Projects:
- Zojila Tunnel: An even more crucial project connecting Sonamarg to Drass in Ladakh, with an expected completion by December 2026 (extended to 2030). This will bypass the avalanche-prone Zojila Pass.
- Srinagar-Leh Highway: The Z-Morh Tunnel supports the key Srinagar-Leh route, which is important for defence logistics and trade.
Economic Significance
- Tourism:
- Sonamarg, known as the "Meadow of Gold," will benefit from year-round accessibility, boosting tourism.
- Local businesses that rely on seasonal tourist traffic will have consistent revenue flow.
- Trade and Agriculture:
- Reduced travel time and improved road safety will benefit farmers and traders, especially for those transporting goods between Kashmir and Ladakh.
- Facilitates increased investment and economic growth in the region.
Broader Infrastructure Projects in Jammu & Kashmir
Several key infrastructure projects are contributing to regional development:
- Zojila Tunnel
- Cost: ?6,800 crore
- Length: 13 km tunnel, bypassing Zojila Pass.
- Completion: Expected by 2030.
- Strategic Importance: Provides all-weather connectivity to Ladakh.
- Srinagar Semi-Ring Road
- Cost: ?2,919 crore
- Objective: Relieve traffic congestion in five districts, including Srinagar.
- Delay: New completion date is June 2025.
- Hydroelectric Power Projects:
- Ratle HE Project: 850 MW, on Chenab River, Kishtwar district.
- Kwar HE Project: 540 MW, in Kishtwar.
- Pakal Dul HE Project: 1,000 MW, on the Marusudar River, Kishtwar.
- Kiru HE Project: 624 MW, on Chenab River, Kishtwar.
- Strategic Relevance: These projects will enhance energy security and contribute to the region’s power grid.
Chhattisgarh’s Link between Forest Ecosystem and Green GDP

- 06 Jan 2025
In News:
In a first, the Chhattisgarh state has introduced an innovative plan that connects the ecosystem services of its forests with the Green Gross Domestic Product (Green GDP).
Key Highlights:
Chhattisgarh's Green GDP Initiative:
- First State in India to link forest ecosystem services with Green GDP.
- Forests cover 44% of Chhattisgarh's land area, playing a vital role in climate change mitigation.
- Key forest products (tendu leaves, lac, honey, medicinal plants) contribute significantly to the rural economy.
Green GDP:
- Definition: An adjustment of traditional GDP that accounts for environmental costs like resource depletion and ecosystem degradation.
- Formula:
- Green GDP = Net Domestic Product (NDP) − (Cost of Resource Depletion + Ecosystem Degradation)
- NDP = GDP − Depreciation of Produced Assets.
Importance of Green GDP:
- Traditional GDP overlooks the environmental cost, treating activities like deforestation as economic gains.
- Green GDP adjusts for sustainability, ensuring long-term economic growth aligns with environmental preservation.
Global Context & Initiatives:
- SEEA (System of Environmental-Economic Accounting): Developed by the UN to track economic-environment relationships.
- WAVES: World Bank initiative integrating natural capital into national economic accounts.
- Bhutan’s GNH: Emphasizes ecological sustainability in development.
Benefits of Green GDP for Chhattisgarh:
- Promotes sustainable development by integrating economic and environmental goals.
- Climate Change Mitigation: Forests help absorb CO2, playing a key role in carbon sequestration.
- Biodiversity Conservation: Supports sustainable use of resources, preserving ecosystems.
- Cultural Integration: Acknowledges forests' cultural and spiritual importance to local tribal communities (e.g., sacred groves).
Key Features of the Initiative:
- Valuing Ecosystem Services: Includes clean air (CO? absorption), water conservation, and biodiversity.
- Eco-tourism Promotion: Developing jungle safaris and national parks, boosting local employment.
- Scientific Assessments: Employing experts to quantify forest contributions to the economy.
Challenges of Green GDP Framework:
- Valuation Complexity: Difficult to assign monetary value to non-market environmental benefits like biodiversity.
- Data Gaps: Lack of comprehensive data on environmental degradation and resource usage.
- Implementation: Requires significant changes in accounting systems and policymaking.
- Forest Definition: Plantations like oil palm may be counted as forests, misleading environmental assessments.
- Political Resistance: States may manipulate data to secure funding, prioritizing plantations over natural forests.
- Local Integration: Difficulties in involving local bodies like Panchayats due to literacy and awareness gaps.
Future of Green GDP:
- Sustainable Resource Use: Encourages responsible consumption and production, aligning with SDG 12.
- Climate Action: Contributes to the reduction of fossil fuel reliance and promotes renewable energy, aligning with SDG 13.
- Green Investments: Stimulates green technologies and industries, fostering sustainable economic growth (SDG 8).
Air India In-Flight Wi-Fi Connectivity
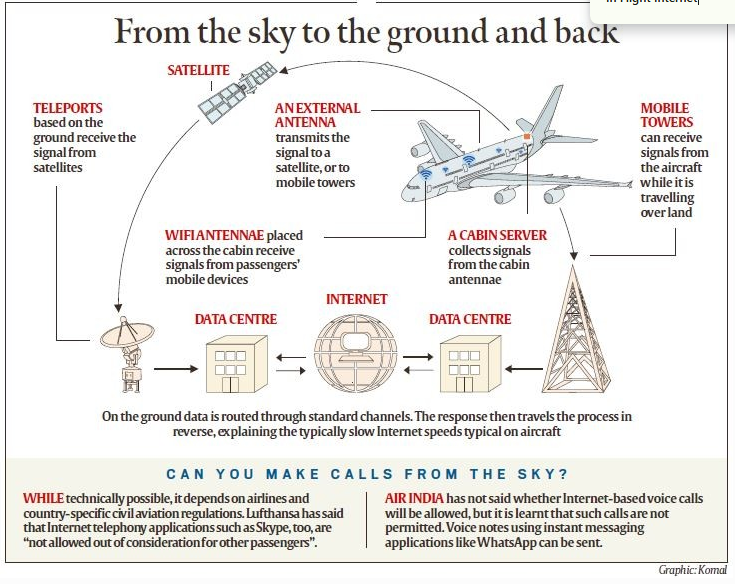
- 04 Jan 2025
In News:
- Tata Group’s Air India launched free Wi-Fi connectivity on select domestic and international flights.
- First Indian airline to offer Internet connectivity on domestic flights.
- The service is free for a limited introductory period on select domestic flights.
- Gradual expansion of Wi-Fi availability to more aircraft in the fleet.
Key Highlights:
Aircraft with Wi-Fi:
- Available on Airbus A350, Boeing 787-9, and select Airbus A321neo aircraft.
- Aircraft equipped with special hardware for Internet connectivity.
- Some aircraft, previously operated by Vistara, now part of Air India after the merger in November.
Technology Partner:
- Vistara’s in-flight Wi-Fi was facilitated by Tata Group’s Nelco, in collaboration with Panasonic Avionics.
- This service is now extended to select Air India domestic flights.
How to Access Wi-Fi:
- Passengers enable Wi-Fi on their devices and connect to the "Air India Wi-Fi" network.
- Redirected to an Air India portal where they enter details (PNR and last name) for access.
Connectivity Technologies:
- Air-to-Ground (ATG) Technology:
- Uses ground-based cellular towers to provide internet.
- Antenna on the aircraft’s belly picks up signals from nearby towers.
- Limited by tower availability, works best over land with dense coverage.
- Satellite-Based Connectivity:
- Uses satellites to provide internet by transmitting signals from ground stations to the aircraft.
- Provides wider coverage, particularly effective over oceans and sparsely populated areas.
In-Flight Wi-Fi Operation:
- Multiple in-cabin antennas collect signals from passengers’ devices.
- Signals are sent to an onboard server.
- For satellite-based systems, signals are transmitted via an antenna to satellites and then relayed to ground stations.
- For ATG systems, signals are sent directly to ground towers.
- In-flight Wi-Fi is slower compared to ground-based internet, though newer technologies are improving speed.
Cost Considerations:
- Airlines incur high initial costs for equipping aircraft with Wi-Fi technology (antennas and hardware).
- Air India is investing in a $400 million retrofit program for its fleet, which could include installing internet connectivity.
- Some airlines install Wi-Fi on new planes, while others retro-fit older models.
Revenue Model:
- Airlines often charge for Wi-Fi after offering a small volume of free internet.
- Some airlines provide free Wi-Fi for loyalty program members or premium passengers (business/first class).
- Air India is offering free Wi-Fi for now, but plans to introduce charges at a later date.
Future Outlook:
- In-flight internet is expected to become a significant source of ancillary revenue.
- Complimentary Wi-Fi for economy class passengers is unlikely in the near-to-medium term due to high costs involved in installation and operation.
Global Context:
- In-flight connectivity is becoming standard on major full-service carriers (FSCs) worldwide.
- Air India's move aligns with global trends, as it aims to be among the world’s leading airlines.
Rapid Chess Championship

- 02 Jan 2025
In News:
In a monumental achievement, Koneru Humpy from Vijayawada, India, claimed the 2024 FIDE Women’s World Rapid Chess Championship in New York. This victory marks her second World Rapid Chess title, five years after her first win in 2019 in Georgia, making her the first Indian and only the second player after China’s Ju Wenjun to win the title multiple times.
Key Highlights of Humpy’s Victory:
- Final Score: Humpy finished with an impressive 8.5 points from 11 rounds, securing the top spot by defeating Irene Sukandar of Indonesia in the final round.
- Strong Finish: Humpy surged ahead of the other joint leaders to clinch the title, with D. Harika, another Indian chess star, securing 5th place with 8 points.
World Rapid Chess Championship
- The World Rapid Chess Championship is a chess tournament that determines the world's top rapid chess player. The tournament is held annually by FIDE, the International Chess Federation.
- How it works
- The tournament uses a Swiss system, where players are paired with opponents of similar scores in each round.
- Players are not eliminated after losses.
- The player with the highest score at the end of the tournament wins.
- Time controls
- Players are given a set amount of time per move, plus an increment for each move.
- In the World Rapid Championship, players have 15 minutes per move, plus a 10-second increment for each move.
A Historic Year for Indian Chess:
- 2024 has been a remarkable year for Indian chess, with D. Gukesh becoming the youngest-ever World Chess Champion after his victory over Ding Liren (China) at the World Chess Championship in Singapore.
- India also made history by winning both the open and women’s sections at the 2024 Chess Olympiad in Budapest.
Smart Cities Mission (SCM)

- 31 Dec 2024
In News:
The introduction of smart classrooms as part of the Smart Cities Mission (SCM) has had a significant impact on education, leading to a 22% increase in enrolment across 19 cities, according to a report from the Indian Institute of Management, Bangalore (IIM-B). The study covers the period from 2015-16 to 2023-24 and highlights several key benefits of this initiative, which aims to improve the overall learning environment in government schools.
Key Findings:
- Increased Enrolment: The introduction of smart classrooms has been linked to a 22% increase in student enrolment across 19 cities, suggesting that the initiative has made education more appealing and accessible.
- Smart Classroom Development: By 2023-24, 71 cities had developed 9,433 smart classrooms in 2,398 government schools. The states with the most smart classrooms are:
- Karnataka (80 classrooms)
- Rajasthan (53 classrooms)
- Tamil Nadu (23 classrooms)
- Delhi (12 classrooms)
- West Bengal has a very limited number, with just two classrooms.
- Improved Learning Experience: Teachers have expressed positive feedback, agreeing that the smart classrooms have improved learning experiences and attendance among students. Additionally, the smart classroom setup has contributed to increased comfort for teachers and higher preference for these modern facilities.
- Teacher Training: Special training provided to teachers has enhanced their comfort with using the smart classroom tools, with senior secondary teachers showing the highest comfort levels.
- Digital Libraries: The study also found that 41 cities have developed Digital Libraries with 7,809 seating capacity, offering essential resources for students. Cities like Raipur (Chhattisgarh) and Tumakuru (Karnataka) have seen positive outcomes from these libraries, particularly in supporting students preparing for competitive exams.
Smart Cities Mission (SCM)
- Launched in June 2015, the Smart Cities Mission aims to promote cities that offer core infrastructure, a decent quality of life, a sustainable environment, and the application of smart solutions. As of November 2024, 91% of the projects under the mission have been completed.
SAAR Platform and Research
- In 2022, the Smart Cities Mission introduced the SAAR (Smart Cities and Academia towards Action and Research) platform to bridge the gap between academia and the government. Under this platform, 50 impact assessment studies have been initiated by 29 premier institutions, including six Indian Institutes of Management (IIMs), eight Indian Institutes of Technology (IITs), and 12 specialized research institutes.
PM CARES Fund Contributions and Utilization (2022-23)
- 30 Dec 2024
In News:
The Prime Minister’s Citizen Assistance and Relief in Emergency Situations Fund (PM CARES Fund) received Rs 912 crore in contributions during the financial year 2022-23 as donations continued to pour in even after the Covid pandemic.
Key Highlights:
Contributions Received:
- Total contributions in 2022-23: Rs 912 crore.
- Voluntary contributions: Rs 909.64 crore.
- Foreign contributions: Rs 2.57 crore.
Interest Income:
- Total interest income for 2022-23: Rs 170.38 crore.
- From regular accounts: Rs 154 crore.
- From foreign contributions account: Rs 16.07 crore.
Refunds and Additional Inflows:
- Rs 225 crore in refunds, including:
- Rs 202 crore refund from procurement of 50,000 ventilators for government hospitals.
Disbursements:
- Total disbursed in 2022-23: Rs 439 crore:
- Rs 346 crore for PM CARES for Children.
- Rs 91.87 crore for procurement of 99,986 oxygen concentrators.
- Rs 1.51 crore for refunds.
- Rs 24,000 for legal charges, and Rs 278 for bank and SMS charges.
Cumulative Contributions (2019-23):
- Rs 13,605 crore received from 2019-20 to 2022-23.
- Voluntary contributions: Rs 13,067 crore.
- Foreign contributions: Rs 538 crore.
- Interest income over these years: Rs 565 crore.
About PM CARES Fund:
Formation and Purpose:
- Established: March 27, 2020, as a Public Charitable Trust under the Registration Act, 1908.
- Purpose: To address emergencies like COVID-19, natural disasters, and man-made calamities. It also supports healthcare infrastructure and essential facilities.
Governance and Structure:
- Chairperson: The Prime Minister (ex-officio).
- Trustees: Defence, Home, and Finance Ministers (ex-officio).
- Additional Trustees: Appointed by the PM, serving on a non-profit basis (e.g., Justice K T Thomas (retd.) and Kariya Munda).
Tax Exemptions:
- Donations are eligible for 100% tax exemption under Section 80G of the Income Tax Act, 1961.
- Donations qualify as Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) expenditure under the Companies Act, 2013.
- The fund is exempt under the Foreign Contribution Regulation Act (FCRA), allowing it to receive foreign donations.
Parker Solar Probe’s Closest-Ever Approach to the Sun

- 28 Dec 2024
In News:
NASA scientists announced that the Parker Solar Probe survived the closest-ever approach to the Sun. The craft was operating normally after it passed just 6.1 million km from the solar surface.
About the Parker Solar Probe:
- Launched: August 12, 2018, as part of NASA’s Living With a Star program.
- Named After: Eugene Newman Parker, a solar astrophysicist, marking the first NASA mission named after a living researcher.
- Mission Objectives:
- To study the Sun’s corona and the solar wind, investigating why the corona is hotter than the Sun’s surface.
- To explore the origins of solar winds and high-energy particles that impact space weather.
- To understand the structure and dynamics of plasma and magnetic fields around the Sun.
- To examine the mechanisms behind the acceleration and transportation of energetic particles.
Technological Feats:
- Heat Shield: Equipped with a 4.5-inch carbon-composite shield that withstands temperatures up to 1,377°C (2,500°F) while keeping the instruments cool at about 29.4°C (85°F).
- Speed: Travels at a speed of 692,000 km/h (430,000 mph), making it the fastest human-made object.
- Venus Flybys: Uses gravitational assists from Venus to gradually reduce its orbit and get closer to the Sun.
Historic Milestone:
- Closest Approach: On December 24, 2024, Parker Solar Probe reached a historic distance of 6.1 million km from the Sun's surface, the closest any human-made object has ever been.
- Comparison: If the Earth and Sun were 1 meter apart, Parker Solar Probe would be just 4 cm from the Sun.
- Temperature: At its closest, it endured temperatures up to 1,377°C.
Significance of the Mission:
- Scientific Contributions:
- Solar Wind: Helps scientists understand the origins of solar winds, which affect space weather and Earth’s technological systems.
- Corona Heating: Investigates why the Sun's corona is much hotter than its surface (a long-standing astrophysical mystery).
- Space Weather: Provides critical data for predicting space weather events that can impact satellites, communication systems, and power grids on Earth.
- Practical Implications:
- Improves understanding of space weather, potentially aiding in the protection of Earth’s infrastructure from solar storms.
- Technological and Engineering Marvel:
- Demonstrates advanced spacecraft technology that can withstand extreme conditions close to the Sun.
Recent Developments:
- Data Collection: As the probe passed through the Sun’s outer atmosphere (the corona), it collected valuable data expected to answer fundamental questions about solar behavior.
- Communication: Despite the extreme proximity to the Sun, the probe sent back a signal on December 26, confirming its status.
Key Dates:
- Launch: August 12, 2018.
- Closest Approach: December 24, 2024.
- Data Expected: Detailed telemetry data on January 1, 2025.
The ‘No-Detention’ Policy and Its Evolution

- 24 Dec 2024
In News:
The ‘no-detention’ policy was a significant part of India’s education reforms under the Right to Education (RTE) Act of 2009. This policy aimed to prevent the detention or expulsion of students until the completion of elementary education (Classes 1-8), with a focus on reducing dropout rates and ensuring every child receives at least basic education. However, the policy has been contentious, with arguments both for and against its implementation.
What was the ‘No-Detention’ Policy and Why Was It Introduced?
The RTE Act (2009) made education free and compulsory for children aged 6 to 14, under Article 21A of the Constitution. Section 16 of the Act specifically prohibited the detention or expulsion of students in elementary education (Classes 1-8). The rationale was to prevent the demotivation and fear of failure that might cause children to drop out of school, especially those from marginalized backgrounds. By promoting automatic progression through grades, the policy aimed to ensure that no child was left behind due to academic struggles.
Key to this system was Continuous and Comprehensive Evaluation (CCE), which assessed students on a holistic basis, beyond just formal exams, encouraging learning through regular feedback and assessments.
Amendments to the RTE Act (2017 and 2019)
In 2017, a Bill was introduced to amend the RTE Act, following concerns about the effectiveness of the ‘no-detention’ policy. The amended policy allowed for regular exams in Classes 5 and 8. If students failed, they would be given a re-examination within two months. If they still did not meet promotion criteria, detention could be enforced. This amendment empowered the Centre and states to decide whether to detain students in these grades.
The amendment came after criticism of the original policy for promoting students without sufficient learning progress. States like Madhya Pradesh and Punjab argued that no-detention was leading to poor academic performance, and called for a return to the traditional system of promoting students based on examination results.
Arguments for and Against the No-Detention Policy
Arguments for No-Detention:
- Reduced Dropout Rates: The policy helped ensure students, especially from disadvantaged backgrounds, continued in school without the fear of failure, leading to a drop in dropout rates.
- Holistic Development: It encouraged a child-centric learning approach where students were assessed on their overall development rather than just exam performance.
- Social Inclusivity: By promoting students regardless of performance, it was hoped that education would be more inclusive, preventing marginalization of students from lower socio-economic backgrounds.
Arguments Against No-Detention:
- Decline in Learning Outcomes: The policy led to a lack of motivation for students to perform academically. Without the accountability of exams, many students became less serious about their studies.
- Low Teacher Accountability: With automatic promotion, teachers had less incentive to ensure quality learning, leading to an overall dip in teaching standards.
- Impact on Educational Standards: Data indicated a decline in learning levels in government schools, as students were passed through the system without mastering the required skills.
In 2015, the Central Advisory Board of Education (CABE) conducted a study suggesting that more flexibility was needed in the policy, allowing schools to retain students who were significantly behind. However, there were differing views within the committee. Some members argued that detention had no proven benefits, and that the real issue was the poor quality of the education system itself.
In 2016, the TSR Subramanian Committee on the New Education Policy suggested continuing the no-detention policy until Class 5, citing evidence of reduced dropout rates and increased enrollment. However, other states pushed for scrapping it due to concerns over declining educational standards.
The Shift Toward Scrapping the No-Detention Policy
By 2019, the RTE Act was amended to give states the discretion to hold back students in Classes 5 and 8, if they failed to meet the promotion criteria. This change came after state feedback that the no-detention policy was having adverse effects on learning outcomes and teacher accountability.
In 2024, the Ministry of Education took further steps to formalize this shift by introducing new rules under the RTE Act Amendment. Students failing to meet the promotion criteria in Classes 5 and 8 will be given additional instruction and an opportunity for a re-examination. If they still fail, they can be detained, with specialized guidance provided to help them catch up.
Which States Continue or Scrapped the No-Detention Policy?
The decision to maintain or scrap the policy varies across states and union territories:
- States Retaining No-Detention Policy: Andhra Pradesh, Arunachal Pradesh, Goa, Karnataka, Kerala, Maharashtra, Odisha, Telangana, Uttar Pradesh, among others, continue to implement the no-detention policy, citing its role in minimizing dropouts and promoting inclusivity.
- States That Have Scrapped the Policy: Delhi, Punjab, Madhya Pradesh, Rajasthan, West Bengal, and Gujarat have already discarded the policy, opting for examinations and re-examinations in Classes 5 and 8 to ensure better academic accountability.
Why the Controversy?
The debate over the no-detention policy hinges on balancing academic accountability with social inclusivity. Supporters argue that it ensures children from marginalized communities receive their full elementary education, while opponents point to the decline in learning standards, especially in government schools, as a major issue.
In summary, while the no-detention policy was introduced with the noble aim of reducing school dropouts and ensuring every child completed at least elementary education, its effectiveness has been questioned due to concerns over declining learning outcomes. The recent changes represent a shift towards better accountability and quality in education, while still ensuring that children receive additional support before being detained.
IPBES Nexus Report

- 22 Dec 2024
In News:
The IPBES Nexus Report, formally titled The Assessment Report on the Interlinkages Among Biodiversity, Water, Food, and Health, was released to address the interconnected global challenges of climate change, biodiversity loss, food insecurity, water scarcity, and health risks. The report stresses that these challenges are deeply intertwined and cannot be solved separately; doing so would lead to ineffective or even counterproductive results.
Key Highlights of the Nexus Report
- Interconnections Between Global Challenges: The report emphasizes the strong interlinkages between the five major global challenges:
- Biodiversity Loss
- Water Scarcity
- Food Insecurity
- Health Risks
- Climate Change
It argues that efforts to address these challenges independently are ineffective and often exacerbate the problems. For example, scaling up food production to combat hunger can put more pressure on land, water, and biodiversity.
- Economic Cost of Biodiversity Loss:
- Global GDP Dependency: Over half of the global GDP (approximately $58 trillion annually) depends on nature. Biodiversity degradation significantly undermines productivity and economic output.
- Unaccounted Costs: The neglect of biodiversity in economic activities contributes to a loss of $10-25 trillion annually.
- Delayed Action: Delaying action on biodiversity conservation could double the costs within the next decade, potentially incurring $500 billion per year in additional costs.
- Synergistic Approach: The report identifies over 70 response options that promote synergistic outcomes across the five challenges. These include:
- Restoring Carbon-Rich Ecosystems: Such as forests, soils, and mangroves to address climate change and biodiversity loss.
- Managing Biodiversity to Prevent Disease Transmission: Effective biodiversity management reduces risks of diseases passing from animals to humans (zoonotic diseases).
- Sustainable Diets: Promoting diets that are both healthy and environmentally sustainable.
- Nature-Based Solutions: Implementing solutions that rely on natural processes to mitigate challenges like water scarcity and climate change.
- Inequality and Vulnerability: The report highlights how inequality exacerbates the challenges. Vulnerable populations, especially those living in areas where biodiversity has sharply declined, face increased health risks, malnutrition, and economic instability. 41% of people live in regions where biodiversity loss has been particularly severe, and 9% face high health burdens due to these declines.
- Principles for Transformative Change: The report outlines principles for achieving transformative change:
- Equity and Justice: Ensuring fair distribution of resources and opportunities for all.
- Pluralism and Inclusion: Embracing diverse perspectives and voices in policy-making.
- Respectful Human-Nature Relationships: Recognizing and nurturing reciprocal relationships between humans and nature.
- Adaptive Learning and Action: Continuously evolving policies and strategies based on feedback and new evidence.
- Urgency for Immediate Action: The report stresses that immediate action is critical. If the world continues to neglect biodiversity, it will face not only environmental collapse but also a missed opportunity for economic growth. Immediate implementation of nature-positive strategies could unlock $10 trillion in business opportunities and create 400 million jobs by 2030.
The IPBES Transformative Change Assessment Report
- This report builds upon the 2019 IPBES Global Assessment Report and advocates for transformative change to halt biodiversity loss and achieve global development goals. It defines transformative change as a system-wide shift in:
- Views: Changing how we think about nature and its value.
- Structures: Reforming systems of governance and organization.
- Practices: Changing behaviors and practices that harm nature.
Key Challenges to Transformative Change:
- Disconnection from Nature: Human societies' disconnection from nature, often rooted in historical domination, is a major cause of biodiversity loss.
- Economic Inequality: The concentration of power and wealth exacerbates environmental degradation.
- Unsustainable Consumption: Unsustainable patterns of consumption and production are significant drivers of environmental harm.
Synergistic Strategies for Transformation:
- Conserve and Regenerate: Restore ecosystems that have both ecological and cultural value.
- Mainstream Biodiversity: Integrate biodiversity considerations into sectors like agriculture, forestry, and infrastructure development.
- Transform Economic Systems: Adopt policies such as true cost accounting and sustainability-based tax principles to internalize the environmental costs of economic activities.
- Inclusive Governance: Promote governance systems that involve all stakeholders, especially local communities, in decision-making.
Specialised Investment Fund (SIF)
- 20 Dec 2024
In News:
SEBI has introduced a new asset class called Specialised Investment Fund (SIF), designed to bridge the gap between Mutual Funds (MFs) and Portfolio Management Services (PMS). This new asset class is targeted at informed investors who are willing to take on higher risks.
SIFs offer a blend of the flexibility seen in PMS and the regulatory framework governing MFs, making them suitable for investors seeking more customized and riskier investment strategies.
Key Features of SIF:
- Minimum Investment: The minimum investment threshold for SIFs is Rs. 10 lakh. However, accredited investors (who meet specific eligibility criteria) can invest with lower amounts.
- Expense Structure: SIFs will follow the same expense structure as mutual funds. For equity schemes up to Rs 500 crore in size, the maximum allowable fee is 2.25% of assets under management (AUM), with the cap decreasing as the fund size grows. This ensures transparency and keeps management fees in line with existing mutual fund norms.
- Investment Strategies: SIFs can offer a mix of open-ended, close-ended, and interval investment strategies. Specific details on permissible strategies will be released by SEBI in the future.
- Investment Restrictions:
- For debt instruments, a single issuer's exposure is capped at 20% of the total AUM. However, this can be raised to 25% with approval from the Asset Management Company (AMC)’s trustees and board of directors. Government securities are exempt from this limit.
- For equities, the exposure is capped at 10% of the total AUM, in line with the norms for mutual funds.
- Ownership in Companies: The maximum permissible ownership in any company is raised to 15%, including the MF exposure.
- REITs and InvITs: SIFs can invest a maximum of 20% of their AUM in Real Estate Investment Trusts (REITs) and Infrastructure Investment Trusts (InvITs). However, the exposure to a single issuer in these areas is limited to 10%.
- Branding and Marketing: SEBI mandates AMCs to distinguish SIFs clearly from MFs through distinct branding, advertising, and website presence. This helps in creating a clear differentiation between the two products for investors.
- Risk Management and Compliance: AMCs managing SIFs are required to have robust risk management systems, internal control systems, and expertise to handle the investments effectively. Trustees are responsible for ensuring that the AMC complies with all risk management, investor protection, and disclosure norms.
Regulatory Context:
- The regulations on SIFs are similar to those governing mutual funds, including taxation and other compliance requirements.
- SEBI also introduced the Mutual Fund Lite regulations to encourage the growth of passively managed funds, such as exchange-traded funds (ETFs) and index funds. These regulations are designed to reduce compliance burdens and lower the barriers to entry for new players in the mutual fund industry.
Significance of SIFs:
- Targeted Audience: SIFs cater to investors who are knowledgeable and willing to take on riskier investments, thereby filling a gap between traditional MFs (which are more conservative) and PMS (which offer highly customized solutions).
- Higher Flexibility: While SIFs maintain some regulations of MFs, they offer more flexibility in investment choices, allowing AMCs to explore more dynamic strategies.
- Investor Protection: By maintaining the same expense structure as mutual funds and ensuring compliance with regulatory frameworks, SEBI aims to protect investor interests while allowing for higher returns that come with riskier investments.
Eastern Maritime Corridor (EMC)
- 19 Dec 2024
In News:
In mid-2024, India surpassed China as the largest importer of Russian oil. This milestone has been accompanied by the operationalization of a new maritime route, the Eastern Maritime Corridor (EMC), which connects Chennai in India to Vladivostok in Russia. The new sea route is significantly reducing both shipping times and costs, facilitating smoother commodity trade between the two countries, particularly crude oil shipments.
The Eastern Maritime Corridor (EMC)
The EMC, covering a distance of about 5,600 nautical miles, has reduced the shipping time between India and Russia’s Far East by up to 16 days. The Chennai-Vladivostok route now takes just 24 days, compared to over 40 days using the traditional St. Petersburg-Mumbai route. This reduction in transit time makes it a highly efficient route for transporting goods such as crude oil, coal, LNG, fertilizers, and other commodities. Additionally, this new corridor supports India’s maritime sector and aligns with the country’s broader vision for maritime growth and regional strategic engagement.
Key Features of the EMC:
- Efficiency and Cost Savings: The route cuts shipping time and distance, reducing costs associated with longer transit periods. For example, a ship traveling between Vladivostok and Chennai now takes only about 12 days at cruising speed, compared to the traditional route's 40+ days.
- Strategic Importance: Vladivostok is Russia’s largest Pacific port, and the corridor strengthens India's strategic presence in the region. This maritime route bypasses traditional chokepoints like the Suez Canal, offering faster, more direct access to key markets.
- Diversification of Trade: Besides crude oil, the EMC facilitates the transportation of coal, LNG, fertilizers, and metals, diversifying India's trade portfolio with Russia. It also helps maintain supply chains for essential goods.
- Boosting India’s Maritime Sector: The corridor supports India’s Maritime Vision 2030, which aims to enhance the efficiency and reach of India's maritime trade, a sector responsible for over 70% of the country’s trade value.
Economic and Strategic Impact:
- The new Eastern Maritime Corridor is particularly significant for India’s energy needs. As the world’s third-largest consumer of crude oil, India imports over 85% of its crude oil demand. The growing imports of Russian crude, especially the Urals grade, are crucial for securing India’s energy future. Additionally, Russia’s competitive pricing on crude, coupled with the savings on shipping costs through the EMC, makes Russian oil even more attractive.
- Beyond the economic benefits, the EMC also supports India’s broader strategic goals, including strengthening ties with Russia, a key partner in defense, nuclear cooperation, and regional geopolitics. The closer maritime links also help counterbalance China's growing dominance in the Pacific region, aligning with India's Act Far East Policy and enhancing trade and diplomatic engagement with East Asia and Russia.
Other Key Maritime Corridors Relevant to India:
- International North-South Transport Corridor (INSTC): A 7,200 km multimodal route linking the Indian Ocean with Russia, offering alternative trade routes to Europe and Central Asia.
- India-Middle East-Europe Economic Corridor (IMEC): A recent project announced at the G20 Summit, which connects India, the Middle East, and Europe via rail, road, and maritime links, fostering greater regional integration.
- Northern Sea Route (NSR): A 5,600 km Arctic route offering shorter transit times between the Barents and Kara Seas and the Bering Strait, gaining importance due to growing imports of Russian energy resources.
In conclusion, the Eastern Maritime Corridor is reshaping India-Russia trade dynamics, boosting economic ties and strategic cooperation between the two nations. By facilitating faster and cheaper transportation, the EMC is not only beneficial for trade in crude oil but also for a range of other commodities, positioning India as a key player in the evolving global trade network.
Wroughton’s Free-Tailed Bat

- 19 Dec 2024
In News:
Wroughton’s free-tailed bat, a highly rare species of molossus bat, has been spotted at the Delhi Development Authority (DDA)’s Yamuna Biodiversity Park, marking a unique sighting.
Key Highlights:
- Species Overview: Wroughton’s free-tailed bat (Otomops wroughtoni) is a rare species of molossus bat, notable for its powerful flight and ecological importance in controlling insect populations and assisting in pollination.
- Conservation Status:
- IUCN: Listed as "Data Deficient".
- Protection: Listed under Schedule I of the Wildlife (Protection) Act, 1972.
- Geographical Distribution:
- Primarily found in the Western Ghats, with a single known breeding colony.
- Small colonies in Jaintia Hills, Meghalaya, and a solitary individual sighted in Cambodia.
- Physical Characteristics:
- Large in size, with huge ears extending beyond the muzzle.
- Bicoloured velvet fur.
- Noted for powerful flying capabilities, enabling long-distance foraging.
- Ecological Role:
- Regulates insect populations.
- Known for assisting in pollination.
- Habitat:
- Roosts in caves, or dark, damp, and slightly warm places, typically in moderate-sized colonies.
- Significance of the Delhi Sighting:
- The sighting at Yamuna Biodiversity Park is significant for Delhi, marking a rare occurrence in the region.
- Delhi's bat species: The city is home to about 14 bat species, with four species, including the Indian false vampire and Egyptian free-tailed bat, considered locally extinct.
- Conservation Efforts:
- Two decades of ecological restoration have created specialized niches in the area, aiding species rewilding and ecological balance.
- The Aravalli Biodiversity Park in Gurugram now serves as the only known roosting site for the Blyth’s horseshoe bat in Delhi NCR.
- Additional Notes:
- Wroughton’s free-tailed bat was considered critically endangered until 2000 due to its limited known population. However, the discovery of populations in other regions has led to a reclassification to "Data Deficient".
- Despite being discovered over a century ago, much about the bat's feeding ecology remains unknown.
Santa Ana Winds

- 15 Dec 2024
In News:
The ongoing Franklin Fire in Malibu, California, has burned over 4,000 acres and affected around 22,000 people. Although the exact cause of the fire is still under investigation, experts point to two key factors contributing to the intensity of the blaze: Santa Ana winds and climate change.
Santa Ana Winds
- Santa Ana winds are powerful, dry winds that typically occur in Southern California from October to January.
- They are caused when high-pressure systems over the Great Basin (the area between the Rocky Mountains and Sierra Nevada) push air toward low-pressure areas over California’s coast.
- As the air moves downhill through mountain passes, it compresses and heats up, which significantly lowers the humidity—sometimes to levels below 10%—creating dry conditions. This extremely low moisture content dehydrates vegetation, making it highly susceptible to combustion.
- These winds have been a natural feature of California's weather, contributing to wildfires for years. However, when combined with other factors like climate change, their impact has become more severe.
The Role of Climate Change
While Santa Ana winds have long played a role in California's wildfires, climate change has exacerbated the situation in recent years. The state's wildfire season has lengthened due to rising global temperatures, which have led to:
- Warmer springs and summers.
- Earlier snowmelt in spring, which leaves vegetation drier for longer periods.
- Longer and more intense dry seasons, which cause increased moisture stress on vegetation.
As a result, forests and brushlands are now more vulnerable to fires. Climate change has also contributed to more extreme weather events, including heatwaves, which further dry out vegetation and create favorable conditions for wildfires.
Intensification of Wildfire Seasons
Recent studies have shown that California's wildfire season has grown longer over the past two decades. For example, a 2021 study in Nature Scientific Reports found that the state's annual burn season has shifted, with the peak fire season now occurring earlier in the year, from August to July. Additionally, research published in PNAS (Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences) in 2023 indicated that the largest wildfires in California history have occurred in the past 20 years, with five of the top 10 largest fires taking place in 2020 alone.
Looking Ahead
The situation is expected to worsen as climate change continues. If global temperatures rise by more than 3°C by the end of the century, as predicted by the United Nations, California’s wildfire risk will likely intensify. The combination of Santa Ana winds and increasingly dry conditions will continue to make areas like Malibu, and much of California, more prone to destructive wildfires.
In conclusion, while Santa Ana winds remain a natural contributor to California's wildfires, the influence of climate change has significantly lengthened the wildfire season, making wildfires more frequent, intense, and harder to control. The continued rise in global temperatures only accelerates these trends, posing a growing challenge for fire management and public safety in California.
Switzerland Suspends MFN Clause in Tax Treaty with India

- 14 Dec 2024
In News:
Switzerland scraps MFN status to India, dividend income to face higher tax
Key Highlights:
- Reason for Suspension:
- The suspension follows a 2023 Supreme Court ruling in India, which clarified that the MFN clause in tax treaties is not automatically triggered when a country joins the OECD if the tax treaty with that country was signed before its OECD membership.
- The Court ruled that the Double Taxation Avoidance Agreement (DTAA) cannot be enforced unless it is notified under the Income-Tax Act, 1961.
- Details of the Suspension:
- Starting January 1, 2025, Switzerland will suspend the Most Favoured Nation (MFN) clause in its DTAA with India.
- The MFN clause was part of the India-Switzerland DTAA signed in 1994.
Impact of the Suspension:
- Higher Tax Liabilities for Indian Companies: Withholding tax on dividends from Switzerland will increase from 5% to 10% for Indian companies.
- Effects on Swiss Investments in India: Swiss companies will continue to face a 10% withholding tax on dividends from India, as per the India-Switzerland DTAA.
- Potential Re-evaluation of MFN Clauses by Other Countries: Other countries may reconsider how the MFN clause is applied in their tax treaties with India, following this development.
- No Change for Other Benefits: Other DTAA benefits and investments related to the European Free Trade Association (EFTA) will remain unaffected.
Most Favoured Nation (MFN) Clause Overview:
- Definition: The MFN principle ensures that favorable trading terms given by one WTO member country to another are extended to all other WTO members, promoting non-discrimination.
- Purpose: To ensure equal treatment among trading nations by preventing discrimination, and to promote fair trade and equitable market access.
- Key Features:
- Equal treatment in tariffs, quotas, and trade barriers.
- Members must extend the best terms to all other WTO members.
- Origin: The MFN principle was established after World War II as a cornerstone of the multilateral trading system under the WTO.
- Exceptions:
- Bilateral or regional trade agreements.
- Special access granted to developing countries.
- Non-WTO members (e.g., Iran, North Korea) are not bound by MFN rules.
- Removal of MFN:
- There is no formal procedure under the WTO to suspend MFN status.
- Countries are not obligated to notify the WTO when suspending or removing MFN treatment.
Recent Development:
- From January 1, 2025, Indian companies will face higher withholding tax (10%) on income sourced from Switzerland, as a result of the MFN clause suspension.
Smuggling in India Report 2023-24
- 12 Dec 2024
In News:
The annual ‘Smuggling in India - Report 2023-24’ report, which highlights DRI’s performance and experience over the last financial year as well as trends in the field of anti-smuggling and commercial fraud, will be released during the celebration.
Major Narcotics Hubs and Routes:
- Afghanistan, Iran, and Pakistan (The Death Crescent):
- Primary source of heroin trafficked into India.
- Routes via Africa, the Gulf, and India-Pakistan border.
- Myanmar, Laos, and Thailand (The Death Triangle):
- Significant source of synthetic drugs and heroin.
- Drugs often enter India through porous northeastern borders (e.g., Assam, Mizoram).
- Vulnerable regions: Moreh, Churachandpur, Zokhawthar.
- Maritime Routes:
- India’s vast coastline provides opportunities for drug trafficking, often through concealed shipping containers and fishing vessels.
- Air Routes:
- Increased trafficking due to international air traffic.
- Smuggled drugs often concealed in luggage, courier packages, or ingested by mules.
Major Narcotics Trends and Seizures (FY24):
- Cocaine:
- Significant increase in trafficking, particularly from South America and Africa.
- 47 seizures, up from 21 in the previous year.
- Seized quantity: 107 kg.
- Methamphetamine:
- Spiked in northeastern states like Assam and Mizoram.
- Seized quantity in FY24: 136 kg; increased in the first half of FY25 with 123 kg.
- Hydroponic Marijuana:
- Increasing smuggling from the US, Thailand, and other countries.
- Black Cocaine:
- New form of cocaine coated with substances like charcoal or iron oxide to evade detection.
- Contraband Cigarettes:
- Smuggling through sea routes, especially from Southeast Asia and the Middle East.
- Seizures increased by 19% in FY25, reaching 3.95 crore sticks.
- Illicit Gold:
- Significant destination for gold smuggling from West Asia (UAE, Saudi Arabia).
- Seized quantity fell slightly (1,319 kg in FY24), with land and air routes being primary methods.
- Wildlife Smuggling:
- Seizures included 53.5 kg of elephant tusks, leopard skins, live pangolins, and more.
Challenges and Issues:
- Porous Borders:
- Smuggling across eastern borders with Bangladesh, Myanmar, and Nepal remains a significant challenge.
- Difficult terrain in these regions aids traffickers.
- Air and Sea Routes:
- Growing use of air and maritime routes due to faster movement of goods.
- Technology and Detection:
- Emergence of “black cocaine” challenges traditional detection methods.
Anti-Smuggling and Drug Control Efforts:
- International Cooperation:
- United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime (UNODC) and the International Narcotics Control Board (INCB) lead global efforts.
- Paris Pact Initiative targets Afghan opiate trafficking.
- Indian Initiatives:
- Narcotic Drugs and Psychotropic Substances Act (1985) provides legal framework.
- Narcotics Control Bureau (NCB) and Anti-Narcotics Task Force (ANTF) work together for enforcement.
- National Action Plan for Drug Demand Reduction and Nasha Mukt Bharat Abhiyaan focus on awareness and rehabilitation.
ABOUT DRI
- The Directorate of Revenue Intelligence (DRI) is the premier intelligence and enforcement agency on anti-smuggling matters under the aegis of Central Board of Indirect Taxes & Customs (CBIC), Government of India.
- It came into existence on 4th December 1957.
- With its Headquarters at New Delhi, 12 Zonal Units, 35 Regional Units and 15 Sub-Regional Units, DRI has been carrying out its mandate of preventing and detecting cases of smuggling of narcotic drugs & psychotropic substances, gold, diamonds, precious metals, wildlife products, cigarettes, arms, ammunitions & explosives, counterfeit currency notes, foreign currency, SCOMET Special Chemicals, Organisms, Materials, Equipment and Technologies) items, hazardous & environmentally sensitive materials, antiques etc. and taking punitive action against the organised crime groups engaged therein.
- DRI is also engaged in unearthing commercial frauds and instances of customs duty evasion.
Human Rights Day 2024

- 11 Dec 2024
In News:
Human Rights Day 2024 celebrated every year on 10th December is dedicated to promote protection of fundamental rights and freedom of all individuals.
Key Highlights:
- Purpose: Promote and protect human rights and freedoms worldwide.
- Theme (2024): “Our Rights, Our Future, Right Now” – highlights the importance of immediate action to protect and uphold human rights globally.
Historical Significance:
- Commemorates: The adoption of the Universal Declaration of Human Rights (UDHR) by the UN General Assembly in 1948.
- UN Resolution: Established by UN Resolution 423 (V) in 1950.
- First Observance: December 10, 1950.
- Father of Human Rights Day: Eleanor Roosevelt, for her pivotal role in drafting the UDHR.
Key Highlights:
- The UDHR:
- Adopted in 1948, it defines fundamental human rights for all individuals.
- Comprises 30 articles, addressing rights such as freedom, equality, and access to education, healthcare, and fair employment.
- Role of the UN: UN Human Rights Council (UNHRC): A body under the UN responsible for monitoring and promoting human rights worldwide, comprising 47 member states.
- Human Rights Day Focus in 2024:
- Emphasizes human rights education, particularly among the youth.
- Addresses emerging challenges like cybercrimes, AI impacts, and climate change.
- Reaffirms the importance of safeguarding human dignity globally.
Human Rights Declared by UDHR:
- Right to freedom and equality
- Right to life, liberty, and security
- Freedom from slavery and torture
- Right to recognition before the law
- Equal protection under the law
- Right to a fair trial
- Right to privacy and protection from attacks
- Right to work and fair employment
- Right to rest and leisure
- Right to education
- Right to an adequate standard of living
- Right to participate in government and cultural activities
INS Tushil Commissioned into the Indian Navy in Russia

- 10 Dec 2024
In News:
Recently, the Indian Navy officially commissioned INS Tushil, a multi-role stealth guided missile frigate, at Kaliningrad, Russia. This marks a significant milestone in India-Russia defense cooperation and strengthens India’s maritime capabilities.
About INS Tushil:
- Class & Design: INS Tushil is the seventh ship in the Krivak III class (Project 1135.6) of frigates. It is part of an upgraded series, following the Talwar-class and Teg-class frigates, and was built at the Yantar Shipyard in Kaliningrad, Russia.
- Development & Contract: The construction was initiated under a 2016 contract between the Indian Government, JSC Rosoboronexport (a Russian defense company), and the Indian Navy. The ship incorporates 26% indigenous technology, highlighting growing cooperation between Indian and Russian industries.
- Key Features:
- Stealth Design: With advanced radar-absorbing features, it is less detectable by enemy radar.
- Weaponry: Equipped with BrahMos supersonic cruise missiles, Shtil Surface-to-Air Missiles, anti-submarine torpedoes, electronic warfare systems, and more.
- Versatility: Designed for blue-water operations, the ship can engage in air, surface, underwater, and electromagnetic warfare.
- Helicopter Deck: Supports operations of upgraded Kamov 28 and Kamov 31 helicopters.
- Speed: Capable of exceeding 30 knots.
Significance:
- Enhanced Naval Capabilities: The commissioning of INS Tushil boosts India’s defense strength in the Indian Ocean Region (IOR), a vital area for global maritime trade and security.
- Maritime Security: INS Tushil is designed to support India’s vision of maintaining stability in the IOR and to act as a deterrent against piracy and other maritime threats.
- Defense Cooperation: This commissioning exemplifies the growing defense ties between India and Russia, underscored by joint development, technology transfer, and shared expertise. The ship reflects a major step in India's self-reliance in defense, in line with the “Aatmanirbhar Bharat” initiative.
- Strategic Role in Global Defense: The ship is a key asset in the Indian Navy's efforts to secure maritime trade routes, enhance regional security, and provide humanitarian assistance in times of need.
Key Events & Facts:
- Construction Timeline: The keel of INS Tushil was laid in 2013, and it launched in 2021. After completing extensive sea and weapon trials in 2024, it was formally commissioned into the Navy.
- Collaborative Effort: The ship is a product of collaborative efforts between Indian and Russian industries, marking a significant achievement in joint defense manufacturing.
Black holes in Webb data allay threat to cosmology’s standard model

- 09 Dec 2024
In News:
The James Webb Space Telescope (JWST), launched almost three years ago, has provided unprecedented insights into the early universe. Astronomers were surprised to find large, fully-developed galaxies when the universe was only 400-650 million years old, a timeframe previously thought to be too early for such structures.
The Challenge to the Standard Model:
- Cosmological Expectations: According to the standard model of cosmology, the first stars formed around 100-200 million years after the Big Bang, and galaxies began to form within the first billion years.
- Unexpected Findings: JWST observations seemed to show that galaxies were already large and well-formed much earlier than expected, raising questions about the timeline of galaxy formation.
New Study's Contribution:
- The Study: A study published in the Astrophysical Journal in August 2024, examined JWST data from the Cosmic Evolution Early Release Science (CEERS) Survey. They focused on galaxies from 650 to 1,500 million years after the Big Bang.
- Key Findings: One explanation for the unexpected size and number of early galaxies is that these galaxies formed stars much more efficiently than those in the modern universe. This could account for the larger-than-expected galaxies.
The Role of Black Holes:
- Impact of Black Holes: The study also explored the presence of black holes at the centers of early galaxies. These black holes, which emit significant light, were previously unaccounted for in the star mass estimations of galaxies. When the researchers removed the light from black holes (referred to as "little red dots"), they found that the galaxies were not as massive as initially thought.
- Correction to Previous Estimates: This adjustment in calculations helped align the data with the standard model of cosmology, sparing it from a major revision.
Implications for the Standard Model:
- Star Formation Efficiency: The study suggests that extreme conditions in the early universe, including abundant gas and less disruptive stellar events, could explain the higher efficiency of star formation.
- Cosmology's Stability: Despite earlier challenges to the standard model, the new findings support its predictions, showing that more efficient star formation and the role of black holes could explain the rapid growth of galaxies in the early universe.
Future Research Directions:
- Expanding Data Sets: The team plans to incorporate more data from JWST to study even earlier galaxies, which could help refine our understanding of galaxy formation in the early universe.
- Further Observations: As the team continues to explore galaxies from even earlier periods (around 400 million years after the Big Bang), they aim to strengthen their findings and provide further evidence to either support or challenge the current cosmological models.
Moths' Reproductive Choices Based on Plant Acoustic Emissions

- 09 Dec 2024
In News:
A new study, "Female Moths Incorporate Plant Acoustic Emissions into Their Oviposition Decision-Making Process," published last month, explores how female moths use sounds emitted by plants to choose where to lay their eggs.
Key Highlights:
Significance of Plant Emitted Sounds:
- Background: Last year, it was discovered that plants emit ultrasonic clicks or pops when stressed (e.g., dehydration). These sounds, although inaudible to humans, can be detected by animals, including insects.
- Moths’ Sensitivity: Moths, particularly the Egyptian cotton leafworm, are shown to be sensitive to these plant sounds, which they use as cues for laying eggs on plants.
Methodology:
- Experimental Setup: Researchers placed a hydrated tomato plant in an experimental arena with another hydrated plant that emitted distress sounds. They observed the behavior of female Egyptian cotton leafworms to understand how these sounds influenced their oviposition choices.
- Initial Finding: Moths typically choose healthy, thriving plants to lay eggs, as they provide better food sources for the larvae.
Study Findings:
- Moths’ Response to Sounds: The moths preferred to lay eggs on the “silent” plant rather than the one emitting distress sounds. This indicates that moths can not only detect the presence of a plant but also interpret acoustic signals to inform their egg-laying decisions.
- Implications: This behavior suggests that moths use a complex set of sensory inputs, including plant-emitted sounds, to select the most suitable plant for offspring development.
Broader Ecological Context:
- Moths as Insects: Moths belong to the order Lepidoptera and are found in diverse environments globally, except polar regions. With around 160,000 species, they are highly adapted and often nocturnal, though some species are diurnal.
- Impact on Agriculture: Certain moth species, especially during their caterpillar stage, are major agricultural pests (e.g., corn borers, bollworms), making understanding their behavior crucial for pest management strategies.
- Climate Change Considerations: Moths, like other species, are impacted by climate change, which can alter the timing and growth of plants they depend on, potentially influencing their reproductive strategies.
Conclusion:
- Innovative Findings: The study reveals a previously unknown aspect of moth behavior, showing that they incorporate plant acoustic emissions into their oviposition decisions.
- Future Implications: This discovery opens avenues for further studies on how environmental signals, like sound, affect the behavior of insects, and how these behaviors could be impacted by changing environmental conditions.
Oilfields Amendment Bill, 2024

- 09 Dec 2024
In News:
To encourage domestic production of petroleum and other mineral oils, along with private investment in these sectors to reduce import dependence, the Rajya Sabha passed the Oilfields (Regulation and Development) Amendment Bill, 2024.
Key Details:
- Objective:
- Encourage domestic petroleum production.
- Reduce import dependence by promoting private investment in the oil sector.
- Key Amendments:
- Delinking petroleum from mining:
- The Bill separates petroleum and mineral oil production from mining activities.
- The Oilfields (Regulation and Development) Act, 1948, is amended to focus on mineral oils, distinct from the Mines and Minerals (Development and Regulation) Act, 1957.
- Expanded Definition of Mineral Oils:
- Includes hydrocarbons in various forms (natural gas, crude oil, petroleum, coal bed methane, and shale gas/oil).
- Excludes coal, lignite, and helium from the definition (falling under the Mines and Minerals Act).
- Petroleum Lease:
- Replaces the term "mining lease" with "petroleum lease."
- Covers activities such as exploration, development, production, and transportation of mineral oils.
- Private Investment:
- Provisions to attract private investment by clarifying rules for petroleum leases.
- Current mining leases remain valid without altering terms to the lessee's disadvantage.
- Decriminalization and Penalties:
- Replaces criminal punishment with financial penalties.
- Fines can go up to Rs. 25 Lakh, with additional penalties for ongoing violations.
- Rule-making Power of Central Government:
- Expands the Centre's authority over petroleum lease regulations, conservation, royalties, mergers, facility sharing, environmental protection, and dispute resolution.
- Delinking petroleum from mining:
- Significance of the Bill:
- Energy Access and Security: Ensures energy security by boosting domestic production.
- Attracting Investment: Creates a conducive environment for private sector investment.
- Environmental Safeguards: Provisions to control carbon emissions and promote renewable energy in oilfields.
- Opposition Criticism:
- State Rights on Mining: Concerns raised by opposition parties, particularly the DMK, about the reduction of state control over resource taxation (taxing mineral rights).
- Impact on Federal Balance: States traditionally manage mining rights under the Constitution’s State List (Entry 50). The Bill may shift control to the Union List (Entry 53), creating constitutional concerns.
- Environmental Concerns:
- Opposition figures like P.P. Suneer (CPI) argue for prioritizing public companies like ONGC, fearing privatization may worsen environmental governance.
- Adjudication of Disputes:
- Appeals against penalty decisions will be handled by the Appellate Tribunal, as per the Petroleum and Natural Gas Regulatory Board Act, 2006.
- Broader Significance:
- Energy Independence: Reduces reliance on fuel imports, fostering energy security and economic stability.
- Regulation: Strengthens the enforcement mechanism for petroleum operations while encouraging private participation.
Petroleum and Natural Gas Regulatory Board (PNGRB):
- Formation: Established under the Petroleum and Natural Gas Regulatory Board Act, 2006.
- Functions: Regulates refining, transportation, distribution, storage, marketing, and sale of petroleum products and natural gas.
- Role in the Bill: Ensures competitive markets for gas and handles appeals regarding regulatory decisions.
China Plus OneStrategy

- 07 Dec 2024
In News:
India had ‘limited success’ in capturing ‘China Plus One’ opportunity.
Limited Success in ‘China Plus One’ Strategy:
- India has had limited success in attracting multinational companies looking to diversify their supply chains under the ‘China Plus One’ strategy, aimed at reducing dependence on China.
- Vietnam, Thailand, Cambodia, and Malaysia have been more successful in benefiting from this shift due to factors like lower labor costs, simplified tax laws, and proactive Free Trade Agreements (FTAs).
Geopolitical Context - US-China Trade Conflict:
- The fresh US-China trade conflict involves tit-for-tat restrictions, with the US imposing export controls on Chinese high-tech goods and China retaliating by banning key materials.
- India's Position: As a "connecting economy" not directly aligned with the US or China, India stands to benefit from trade diversions arising from this conflict.
Opportunities for India Amid Trade Diversion:
- NITI Aayog CEO BVR Subrahmanyam highlighted opportunities arising from trade diversion, particularly due to US trade policies under President-elect Donald Trump, which could potentially create an economic boom for India.
- India has opportunities to capture a larger share of the global trade, especially in sectors where it currently holds a small market share (less than 1% of world trade in many areas).
Trade Policy Challenges:
- Steel Import Duty Proposal: NITI Aayog Vice Chairperson cautioned against imposing high duties on steel imports, arguing that it could reduce India’s competitiveness and lead to negative consequences for domestic industries reliant on steel.
- The global steel market has been affected by oversupply from China, with India’s iron and steel exports experiencing a sharp decline in Q1 FY25 due to weak domestic demand.
Impact of US Tariffs:
- A general 10% tariff on all imports by the US would not have a major negative impact on India.
- However, a 60% tariff on China could open significant opportunities for India, especially in sectors where it competes directly with China. There might be short-term shocks but long-term benefits.
Ongoing Trade Fragmentation:
- The report noted that trade fragmentation is driven by strict export controls on Chinese goods, implemented by the US to curb China’s growth, particularly in high-tech sectors.
Sectoral Competitiveness:
- While China remains India's key competitor across most export sectors, countries like Brazil, Indonesia, and South Africa generally lag behind India.
- Malaysia and Thailand outperform India in select sectors such as electrical machinery.
Challenges in the EU Market - Carbon Border Adjustment Mechanism (CBAM):
- Iron and steel industry facehigh exposure under the CBAM for EU exports, with tariffs potentially rising by 20-35% due to carbon emissions-related regulations.
- Indian firms could experience higher compliance costs due to the requirement for detailed emissions reporting, impacting competitiveness in the European market.
RBI Cuts CRR, Keeps Repo Rate Unchanged

- 07 Dec 2024
In News:
The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) has recently made significant monetary policy decisions that could have a broad impact on the economy.
Key Highlights:
Cut in Cash Reserve Ratio (CRR)
- CRR Reduction: The RBI has reduced the CRR by 50 basis points (bps), from 4.5% to 4%.
- Impact on Banks: This move will free up ?1.16 lakh crore in liquidity, which banks can use to lend, boosting the credit flow in the economy.
- Objective: The CRR cut is aimed at easing the liquidity stress in the financial system, which has been tightening due to RBI's foreign exchange interventions.
- Bank Benefits: Banks will benefit as they don’t earn interest on the CRR, and the extra liquidity may help them reduce deposit rates. Additionally, it may encourage banks to pass on benefits to borrowers, particularly in terms of lending rates.
Repo Rate Kept Unchanged at 6.5%
- Decision: The MPC decided to keep the key policy rate, the Repo rate, unchanged at 6.5%, continuing its stance for the 11th consecutive meeting.
- Reasons for Keeping Repo Rate Steady:
- Persistent inflation, particularly food prices, is a key concern. Despite strong growth in sectors like rural consumption, inflation remains high and continues to affect disposable income.
- RBI Governor emphasized that durable price stability is essential for strong, sustained economic growth.
Impact on Borrowers
- Borrowing Costs: With the Repo rate unchanged, external benchmark lending rates (EBLR) linked to the Repo rate will not rise, providing relief to borrowers by keeping Equated Monthly Installments (EMIs) stable.
- Deposit Rates: However, the CRR cut may lead to a marginal reduction in deposit rates due to increased liquidity in the system.
Economic Growth Forecast Adjusted
- Reduced GDP Growth Estimate: The RBI has downgraded the GDP growth forecast for FY25 to 6.6%, down from the earlier estimate of 7.2%. This revision comes after the economy showed signs of slowdown in the second quarter of FY25.
- Growth Outlook: Despite the downgrade, the RBI remains cautiously optimistic about recovery driven by festive demand and rural consumption. Governor Das indicated that the slowdown had likely bottomed out and the economy is set to recover in the coming quarters.
Inflation Forecast Raised
- Inflation Outlook: The inflation estimate for FY25 has been revised upward to 4.8%, compared to the earlier forecast of 4.5%. This is largely due to rising food prices, which surged to a 14-month high of 6.21% in October.
- Inflationary Pressures: The MPC noted that inflation has remained above the RBI’s target of 4%, primarily driven by food inflation. As inflation impacts consumption, the RBI aims to balance growth support with inflation management.
Monetary Policy Stance
- Neutral Stance Retained: The RBI has maintained a ‘neutral’ stance, meaning it is neither tightening nor easing monetary policy drastically, focusing instead on bringing inflation closer to its target of 4%.
- Inflation Control: While the RBI is aware of the economic slowdown, it continues to prioritize inflation control to ensure price stability and support sustainable growth.
Global and Domestic Economic Context
- Global Factors: The RBI has also been cautious about global developments, including capital outflows and the impact of U.S. monetary policy on the Indian economy. A rate cut could have further weakened the rupee by narrowing the interest rate differential with the U.S.
- Domestic Concerns: Domestically, the economy faces challenges such as weak manufacturing growth and high inflation. The GDP growth in Q2 FY25 dropped to 5.4%, a seven-quarter low, highlighting concerns over demand and inflationary pressures.
Donald Trump's Threat on BRICS and US Dollar

- 05 Dec 2024
In News:
- US President-elect Donald Trump threatens BRICS countries (Brazil, Russia, India, China, South Africa) with 100% import tariffs if they create a new currency or support an alternative to the US dollar as the global reserve currency.
- Trump emphasizes that attempts to undermine the US dollar’s dominance will face economic retaliation, asserting the US economy won’t tolerate such moves.
Background
- Weaponization of the Dollar: The US has increasingly used its financial influence to impose sanctions (e.g., Russia, Iran) and cut off countries from systems like SWIFT (Society for Worldwide Interbank Financial Telecommunication).
- Concerns: Countries are concerned about their vulnerability to US monetary policies, which can have global impacts (e.g., rising US interest rates causing economic instability in other countries).
Efforts to Reduce Dependence on the US Dollar
- BRICS Countries’ Initiatives:
- Russian President Putin criticizes the weaponization of the dollar.
- Brazil's President Lula advocates for a new BRICS currency to increase payment options and reduce vulnerabilities.
- India's Steps:
- The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) allows invoicing and payments in Indian rupees for international trade (since 2022), particularly with Russia.
- Prime Minister Modi supports increasing financial integration and cross-border trade in local currencies within BRICS.
- External Affairs Minister Jaishankar emphasizes the importance of mutual trade settlements in national currencies.
- China-Russia Trade: Over 90% of trade between Russia and China is settled in rubles and yuan due to their more balanced trade relations.
Internationalization of the Indian Rupee
- RBI's Role:
- In July 2022, RBI allowed export/import settlements in rupees, starting with Russia in December 2022.
- More than 19 countries, including the UK and UAE, have agreed to settle trade in rupees.
- Challenges:
- The Indian rupee currently accounts for only 1.6% of global forex turnover.
- India’s trade imbalance with Russia limits the effective use of rupee reserves.
- Indian banks are cautious due to the risk of US sanctions.
Global Trends in Currency Diversification
- Multipolarity in Finance: Emerging economies like China, India, and Brazil are advocating for a more decentralized financial system, moving away from US dominance.
- Declining Dollar Share: The US dollar’s share of global reserves is gradually decreasing, with non-traditional currencies like the Chinese yuan gaining ground.
Risks of Moving Away from the US Dollar
- Chinese Dominance: Concerns about increasing Chinese economic influence, especially within BRICS, as China pushes for more use of the yuan in trade.
- Liquidity and Volatility Issues: Alternatives to the dollar may face challenges like lower liquidity and increased exchange rate volatility.
- Implementation Challenges: Countries, especially those with trade imbalances, find it difficult to adopt local currencies for international trade.
Potential Impact of 100% US Tariff on BRICS Imports
- Global Trade Dynamics: A blanket tariff would likely encourage deeper intra-BRICS trade and accelerate the move towards de-dollarization.
- Impact on the US: Higher import costs for American consumers and potential trade diversification to third countries could hurt the US economy without revitalizing domestic manufacturing.
- Retaliation: BRICS countries might retaliate with tariffs on US goods, escalating trade tensions.
India’s Strategic Approach
- Diplomatic Engagement: India should clarify to the US that diversifying trade mechanisms is not anti-American but seeks financial stability and multipolarity.
- Leadership Role in BRICS: India should support financial reforms within BRICS that align with its interests while maintaining strong ties with the US.
- Promotion of Digital Currency: India should accelerate its Central Bank Digital Currency (CBDC) and strengthen international platforms like UPI to enhance its global financial presence.
Overview of Global Plastic Treaty Negotiations

- 05 Dec 2024
In News:
The recent negotiations for a global treaty aimed at curbing plastic pollution, held in Busan, South Korea, concluded without reaching a legally binding agreement. This marked the fifth round of discussions since the United Nations Environment Assembly (UNEA) initiated the process in March 2022, with the goal of finalizing a treaty by the end of 2024. The failure to adopt a treaty was primarily due to disagreements over production cap goals and the elimination of specific plastic chemicals and products.
Key Points of Dispute
- Production Cap Goals: A coalition of over 100 countries, including many from Africa, Latin America, and the European Union, pushed for clear production cap goals in the treaty. They argued that such measures are essential for effective regulation of plastic pollution.
- Opposition from Oil-Producing Nations: Conversely, a group of “like-minded countries” such as Saudi Arabia, Kuwait, Russia, and Iran opposed these provisions. They contended that regulating production cuts exceeded the original mandate set by UNEA and could lead to trade restrictions disguised as environmental measures. India and China aligned with this coalition, emphasizing their concerns regarding economic impacts.
Draft Treaty Highlights
Despite the failure to finalize an agreement, discussions produced a draft text that included both consensus points and contentious issues:
- Consensus Points:
- Proposals for banning open dumping and burning of plastics.
- Definitions for various plastic types were suggested but lacked clarity on contentious terms like microplastics.
- Contentious Issues:
-
- The draft did not adequately address definitions for microplastics or recycling standards.
- References to single-use plastics were included but faced pushback from certain nations.
India’s Position
India articulated its stance focusing on several key areas:
- Development Rights: Emphasized the need for recognizing varying responsibilities among countries in managing plastic pollution while considering their developmental rights.
- Technical and Financial Support: Advocated for provisions ensuring technical assistance and financial support for developing nations to manage plastic waste effectively.
- Opposition to Production Caps: India opposed any articles that would impose caps on polymer production, arguing that such measures were not directly linked to reducing plastic pollution.
Future Steps
The negotiations will continue with plans to reconvene in 2025. In the meantime, global plastic production is projected to rise significantly, potentially tripling by 2050 if no urgent action is taken. The ongoing dialogue will need to address both environmental concerns and developmental needs to create a balanced approach toward managing plastic pollution globally.
Global Context and Initiatives
The need for a global treaty is underscored by alarming statistics:
- Over 462 million tons of plastic are produced annually, with a significant portion contributing to pollution.
- Microplastics have infiltrated ecosystems worldwide, affecting biodiversity and human health.
Countries like Rwanda and Austria have implemented successful measures to reduce plastic waste, serving as models for global efforts. Initiatives such as the UNDP Plastic Waste Management Program in India aim to enhance waste management practices while addressing environmental impacts.
Notre-Dame Cathedral

- 03 Dec 2024
In News:
The Notre-Dame Cathedral in Paris, a landmark symbol of French Gothic architecture, is set to reopen on after undergoing extensive renovations following a devastating fire in April 2019.
Historical and Architectural Significance:
- Location: Situated on Île de la Cité in the Seine River, Paris.
- Construction: Began in 1163 under Bishop Maurice de Sully and completed in 1260, showcasing a blend of early Gothic to Rayonnant Gothic styles.
- Key Features: The cathedral is renowned for its rib vaults, flying buttresses, stained-glass windows, and sculpted gargoyles.
- Cultural Importance: It has been a stage for significant historical events, including Napoleon Bonaparte's coronation in 1804. It also houses the Holy Crown of Thorns and relics from the crucifixion of Jesus.
- Literary Legacy: Featured in Victor Hugo's "The Hunchback of Notre-Dame" (1831), which drew attention to its architectural and historical significance.
Modern History and Renovation:
- The cathedral endured historical events such as the French Revolution, World War II, and attacks during the Protestant Reformation.
- In April 2019, a fire severely damaged the roof and spire, sparking an international outpouring of support for its restoration.
- Renovation efforts began soon after, involving more than 1,000 craftspeople, with President Emmanuel Macron calling it “the project of the century.”
Construction and Modifications Over Centuries:
- The Notre-Dame was a model for early Gothic architecture and has undergone multiple renovations, including the addition of flying buttresses and other structural changes during the 13th and 14th centuries.
- Modifications continued through the Renaissance and Classical periods, reflecting changing artistic styles and the political moods of the time.
Significance in French History:
- Witness to History: The cathedral has been central to 800 years of French history, serving as a backdrop for both brilliant and tumultuous events.
- Religious and Political Symbolism: It was the heart of Paris' religious and political life, acting as a symbol of the intertwined relationship between the church and the monarchy.
Madhya Pradesh’s 8th Tiger Reserve: Ratapani

- 03 Dec 2024
In News:
Recently, the Ratapani Wildlife Sanctuary in Madhya Pradesh was officially declared a Tiger Reserve, making it the 8th such reserve in the state. This declaration follows approval from the Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change through the National Tiger Conservation Authority (NTCA).
Key Details:
- Core Area: 763.8 sq. km
- Buffer Area: 507.6 sq. km
- Total Area: 1,271.4 sq. km
- Ratapani Tiger Reserve is located in the Raisen and Sehore districts, within the Vindhya hills, and is home to approximately 90 tigers.
- It also forms a crucial part of Madhya Pradesh’s tiger habitat and serves as a migration corridor from the Satpura ranges.
Economic and Ecotourism Benefits:
- The designation will boost ecotourism, generating employment and improving livelihoods for local communities.
- Eco-development programs will support residents, providing new opportunities and addressing the balance between conservation and human interests.
Wildlife Conservation and Management:
- The reserve will focus on habitat management, wildlife protection, and community engagement.
- The core area has been recognized as a critical tiger habitat under the Wildlife Protection Act, 1972.
- Efforts will include strengthening anti-poaching measures, improving surveillance, and enhancing prey base restoration.
Significance for Madhya Pradesh:
- This move places Madhya Pradesh as the "Tiger State of India", with significant conservation focus on the Ratapani and Madhav National Park (also in the process of becoming a tiger reserve).
- Madhya Pradesh now hosts 8 tiger reserves, contributing significantly to the country's overall tiger conservation efforts.
MahaKumbh Mela 2025

- 03 Dec 2024
In News:
- On December 1, 2024, the Uttar Pradesh government declared the MahaKumbh Mela area as a temporary district for four months.
- The new district will be known as the MahaKumbh Mela District, to streamline management for the 2025 MahaKumbh.
- Over 5,000 hectares of land will be part of this district, including 66 revenue villages from four tehsils: Sadar, Sorav, Phulpur, and Karchana.
Key Administrative Changes:
- Mela Adhikari (Kumbh Mela Officer) will act as the District Magistrate (DM) and will hold powers of Executive Magistrate, District Magistrate, and Additional District Magistrate.
- The Mela Adhikari will have authority under the Indian Civil Defense Code, 2023, and the Uttar Pradesh Revenue Code, 2006.
- The Mela Adhikari can appoint an Additional Collector for the district.
MahaKumbh Mela Overview:
- The Kumbh Mela is recognized by UNESCO as an Intangible Cultural Heritage of Humanity.
- It is the largest peaceful congregation of pilgrims, with participants bathing in sacred rivers at locations including Prayagraj, Haridwar, Ujjain, and Nashik.
- The PrayagrajKumbh takes place at the Sangam, the confluence of the Ganges, Yamuna, and the mythical Saraswati rivers.
- The event spans over a month and includes religious, cultural, and social activities, along with massive infrastructural setup including tented townships, civic facilities, and security measures.
Shahi Jama Masjid in Sambhal

- 01 Dec 2024
In News:
The controversy surrounding the Shahi Jama Masjid in Sambhal, Uttar Pradesh, has intensified following claims that the mosque, built during the Mughal Emperor Babur's reign (1526–1530), was constructed over a Hindu temple, the Hari Har Mandir. This claim has led to legal battles and violent clashes, making it part of a broader series of disputes involving mosques built during the Mughal era, such as the Gyanvapi mosque in Varanasi and the Eidgah Masjid in Mathura.
Background and Legal Context:
The dispute began when a petition was filed in Sambhal's district court on November 19, 2024, claiming the Jama Masjid was built on the site of an ancient temple. The petitioners, led by Hari Shanker Jain, demanded a survey to ascertain the religious character of the site. This petition follows a pattern seen in similar cases in Varanasi, Mathura, and Dhar, where Hindu groups have raised similar claims about mosque sites. The court ordered a photographic and videographic survey of the mosque, which, initially carried out peacefully, later sparked violence on November 24 when the survey was accompanied by chanting crowds. This led to protests, stone pelting, and allegations of police firing, resulting in several deaths.
The Jama Masjid is a protected monument under the Ancient Monuments Preservation Act, 1904, and is listed as a Monument of National Importance by the Archaeological Survey of India (ASI). This gives the case legal and cultural sensitivity, as it involves both national heritage and religious sentiments.
Historical and Architectural Context:
The Shahi Jama Masjid in Sambhal was constructed by Mir Hindu Beg, a general under Babur, in the early 16th century. It is one of three mosques commissioned by Babur, alongside those in Panipat and Ayodhya. The mosque is noted for its architectural style, which includes a large square mihrab hall, a dome, and arches, constructed using stone masonry and plaster. Some historians argue that the mosque might be a Tughlaq-era structure modified during Babur's reign. Locally, Hindu tradition holds that the mosque incorporates elements of a Vishnu temple, believed to be the site of Kalki, the tenth avatar of Vishnu.
The Places of Worship Act, 1991:
The dispute has reignited debates about the Places of Worship (Special Provisions) Act, 1991, which mandates that the religious character of any place of worship as it existed on August 15, 1947, should be maintained, with the exception of the ongoing Babri Masjid dispute. The Act aims to prevent any further contests regarding religious sites, and Section 3 of the Act explicitly prohibits converting a place of worship into a site of a different religious denomination.
The petition filed in Sambhal seeks to alter the religious character of the mosque, directly contravening the Places of Worship Act. The petitioners have cited remarks by Supreme Court Justice D.Y. Chandrachud in 2022, suggesting that a survey to ascertain the religious character of a place might not violate the Act. This has led to petitions challenging the Act in the Supreme Court, including cases from Varanasi, Mathura, Dhar, and now Sambhal.
The Legal and Social Implications:
The ongoing dispute over the Shahi Jama Masjid highlights the tension between historical narratives, legal frameworks, and communal harmony. The Supreme Court has intervened in the matter, temporarily halting further proceedings in the trial court, urging that the mosque's management committee approach the Allahabad High Court. The Court emphasized the importance of maintaining peace and harmony and cautioned against any actions that could escalate tensions.
The case underscores the challenges of balancing India's rich historical heritage with its diverse religious communities. As the legal process unfolds, the outcome of the Sambhal dispute could set significant precedents for how similar cases are handled in the future.
Conclusion:
The Sambhal mosque dispute, much like the Gyanvapi and Ayodhya cases, brings to the forefront the complex intersections of history, religion, and law. It also raises critical questions about the application of the Places of Worship Act and its implications for preserving India's pluralistic society. The outcome of this case, alongside the pending petitions in other states, will be crucial in shaping the future of religious site disputes in India.
SASCI Scheme for Tourism Development
- 01 Dec 2024
In News:
Centre clears scheme for development of 40 tourist destinations across 23 States at a cost of ?3,295 crore.
Key Details:
- Focus Areas: The scheme encourages the development of lesser-known destinations such as Bateshwar (Uttar Pradesh), Ponda (Goa), Gandikota (Andhra Pradesh), and Porbandar (Gujarat) to reduce overcrowding at popular sites.
- Implementation Timeline: Projects must be completed within two years, with funding released in stages until March 2026.
- Key Features:
- Long-term interest-free loans for 50 years.
- States responsible for project execution and maintenance, often through public-private partnerships (PPP).
- The Ministry of Tourism will monitor progress, and 66% of the funds have already been released.
- Emphasis on sustainability and boosting local economies by creating jobs through tourism.
- States must provide land at no cost and ensure proper infrastructure like safety, connectivity, and utilities.
Selection Criteria for Projects:
- Consultation Process: Detailed regional consultations led to the selection of 40 projects from 87 proposals received by the Ministry of Tourism. West Bengal was the only state not submitting proposals.
- Evaluation Criteria: Projects were evaluated based on:
- Connectivity, tourism potential, and ecosystem.
- Financial viability and sustainability.
- Impact on local economy and job creation.
- Funding Pattern:
- A maximum of ?100 crore for each project, with higher funding considered for exceptional projects.
- Total funding capped at ?250 crore per state, allocated on a first-come, first-served basis.
Importance of the Scheme:
- Economic Growth & Employment: Projects are designed to stimulate local economies, create employment, and promote sustainable tourism.
- Global Branding: The scheme aims to brand and market tourist destinations on a global scale.
- Tourism Infrastructure Growth: It aims to improve the entire tourism value chain, including transportation, accommodation, activities, and services.
Tourism Sector Overview:
- Current Status:
- India ranks 39th among 119 countries in the Travel and Tourism Development Index (TTDI) 2024.
- Foreign Tourist Arrivals (FTAs) increased by 47.9% in 2023, with 9.52 million tourists.
- Tourism contributed 5% to India’s GDP in 2022-23 and created 76.17 million direct and indirect jobs.
- India earned ?2.3 lakh crore in foreign exchange in 2023 through tourism.
- Projected revenue from tourism to exceed $59 billion by 2028.
- Initiatives for Promotion:
- Swadesh Darshan Scheme: To develop theme-based circuits.
- Dekho Apna Desh Initiative (2020): Promotes domestic tourism.
- PRASHAD & HRIDAY Schemes: Focus on pilgrimage and heritage city development.
MGNREGA Job Card Deletions Issue:
- Context: A significant surge in deletions of job cards under MGNREGA (Mahatma Gandhi National Rural Employment Guarantee Act) raised concerns over transparency and workers’ rights.
- Reasons for Deletion:
- Permanent migration, duplicate cards, forged documents, and refusal to work.
- Aadhaar-based payment system (ABPS) implementation led to deletions for non-linked cards.
- Implications:
- Violation of workers’ legal right to employment, especially when deletions were made without due process.
- The "Not willing to work" designation undermines livelihood opportunities, especially in high unemployment rural areas.
- Recommendations for Reform:
- Strengthening verification processes and ensuring deletions follow due procedure.
- Empowering Gram Sabhas to review and approve deletions.
- Regular audits and better grievance redressal mechanisms.
Other Government Initiatives in Tourism:
- National Mission on Pilgrimage Rejuvenation and Spiritual, Heritage Augmentation Drive (PRASHAD): For holistic and sustainable development of pilgrimage tourism.
- Incredible India & E-Visa Initiatives: To attract more foreign tourists.
- Regional Connectivity Scheme (UDAN): Enhances air connectivity to remote tourist destinations.
- National Heritage City Development and Augmentation Yojana (HRIDAY): Preserves and rejuvenates heritage sites.
Flexible UG Degree Completion Norms

- 30 Nov 2024
In News:
- The University Grants Commission (UGC) has approved new guidelines for undergraduate (UG) degree completion, offering flexibility in the duration of academic programs.
Key Details:
- Two Options for Degree Completion:
- Accelerated Degree Programme:Students with exceptional academic performance or those completing additional credits can graduate earlier than the standard duration.
- Extended Degree Programme:Students facing personal, financial, or academic challenges can extend the time for degree completion without facing penalties.
- Objective:
- Enhance flexibility and a student-centric approach to higher education.
- Address challenges like balancing education with personal or professional commitments.
- Institutional Autonomy:Higher Education Institutions (HEIs) can implement these options based on available infrastructure and academic resources.
- Recognition of Flexibility:Degrees completed earlier or later will be treated on par with those completed within the standard duration.
- Alignment with Global Trends:This initiative aligns with global educational trends towards flexible learning paths.
- Support for Interdisciplinary Studies:The new regulations are expected to benefit students pursuing interdisciplinary studies or professional courses.
- NEP 2020 Alignment:The move is in line with the National Education Policy (NEP) 2020, which promotes learner-centric education and skill development.
- Impact:The decision is likely to provide more options for students, making higher education more accessible and tailored to individual needs.
Supreme Court Ruling on EVMs

- 28 Nov 2024
In News:
The Supreme Court dismissed the PIL, remarking that EVMs are only questioned after electoral losses, not when elections are won. It emphasized that no evidence of tampering was found.
What Are EVMs and VVPATs?:
- EVMs: Electronic Voting Machines are used for conducting elections to the Parliament, state legislatures, and local bodies. They consist of two units: theControl Unit (operated by the polling officer) and the Ballot Unit (where voters cast their votes).
- VVPAT: The Voter Verifiable Paper Audit Trail enables voters to verify that their vote is recorded as cast. A slip is printed showing the candidate’s name, symbol, and serial number, visible for 7 seconds before being cut and stored in a sealed box.
Safeguards to Ensure EVM Integrity:
- Technical Safeguards:
- Microcontroller Security: EVMs use one-time programmable (OTP) microcontrollers, which cannot be altered after manufacturing.
- Standalone Operation: EVMs do not have wired or wireless connectivity, eliminating risks of remote tampering.
- Post-2013 Features: Advanced EVMs (M3) include tamper detection and mutual authentication protocols.
- Administrative Protocols:
- Randomized EVM Allocation: EVMs are randomly allocated to polling stations to avoid predetermined assignments.
- Mock Polls: Multiple mock polls are conducted to test the functionality of EVMs.
- Counting Procedures: EVMs are brought to counting tables under CCTV surveillance, and VVPAT slips are randomly cross-verified.
- Secure Storage: EVMs are stored under strict protocols, including double-lock systems, CCTV surveillance, and GPS-tracked transport.
Advantages of EVMs Over Ballot Papers:
- Elimination of Invalid Votes: EVMs ensure no invalid votes, a common problem with torn or mis-marked ballot papers.
- Prevention of Booth Capturing: EVMs restrict vote casting to 4 votes per minute, preventing fraudulent vote insertion.
- Accurate and Fast Counting: EVMs enable quick, error-free vote counting, reducing delays and human errors.
- Transparency: Voters can verify their votes through the VVPAT, and the vote count is displayed transparently without revealing candidate-wise results prematurely.
Evolution of EVMs in India:
- 1977: Concept of EVMs conceived.
- 1990: The Dinesh Goswami Committee recommended the use of EVMs.
- 2004: EVMs used nationwide in Lok Sabha elections.
- 2013: VVPAT was introduced to improve transparency.
- 2019: First nationwide use of EVMs backed by VVPAT.
National Mission on Natural Farming (NMNF)
- 27 Nov 2024
In News:
The Union Cabinet approved the launching of the National Mission on Natural Farming (NMNF) as a standalone Centrally Sponsored Scheme under the Ministry of Agriculture & Farmers' Welfare.
Key Highlights
Objective & Focus:
- Launch of NMNF by the Union Cabinet to promote chemical-free farming in India.
- Aim to improve soil health, reduce input costs, and produce nutritious food.
- Support the shift to natural farming (NF), emphasizing local knowledge and agro-ecological principles.
Financial Allocation:
- Total Outlay: ?2481 crore (Government of India share ?1584 crore, State share ?897 crore) until FY 2025-26.
Key Features of NMNF:
- Coverage: Targeting 15,000 clusters in Gram Panchayats, covering 7.5 lakh hectares and impacting 1 crore farmers.
- Bio-Input Resource Centres (BRCs): 10,000 BRCs to supply ready-to-use natural farming inputs.
- Krishi Vigyan Kendras (KVKs) and Agricultural Universities (AUs): Establishment of 2,000 model demonstration farms for hands-on training in natural farming techniques.
- Farmer Training: 18.75 lakh farmers to be trained in NF practices such as preparation of organic inputs like Jeevamrit and Beejamrit.
- Krishi Sakhis/CRPs: Deployment of 30,000 workers for farmer mobilization and awareness.
Implementation Strategy:
- Farmer Certification System: Providing easy, simple certification for marketing natural farming produce with dedicated branding.
- Monitoring: Real-time, geo-tagged monitoring of implementation through an online portal.
- Convergence with other government schemes and organizations for market linkages and support.
Natural Farming Practices:
- Zero Budget Natural Farming (ZBNF): Promote sustainable farming by using local livestock and diverse crop systems.
- Benefits: Reduce dependence on external inputs like chemical fertilizers and pesticides, rejuvenate soil quality, and increase resilience to climate risks (e.g., drought, floods).
- Encourage biodiversity, and improve soil carbon content and water-use efficiency.
Targeted Areas and Farmer Support:
- Focus on areas where NF practices are already being followed or where farmer producer organizations (FPOs) or self-help groups (SHGs) are active.
- Training through model demonstration farms will focus on practical, location-specific NF techniques tailored to regional agro-ecologies.
Impact on Agriculture and Environment:
- Environmental Impact: Encourages sustainable farming by reducing chemical exposure, improving soil health, and promoting climate resilience.
- Farmer Well-being: By reducing input costs and promoting nutritious food, it aims to improve farmer incomes and family health.
- Contributing to the long-term health of the environment, ensuring a healthy Mother Earth for future generations.
Challenges and Concerns:
- Soil Nutrient Compromise: Concerns that some crops, like rice, might require chemical fertilizers (e.g., NPK) for optimal growth, which may not be sufficiently replaced by organic manure alone.
- The shift to natural farming requires significant awareness and training to ensure sustainable and productive yields.
Institutional Framework:
- Ministry of Agriculture and Farmers’ Welfare is the implementing body.
- Collaboration with KVKs, AUs, and farmer organizations ensures grassroots level support and knowledge dissemination.
Extension of Ban on ULFA

- 27 Nov 2024
In News:
- The Ministry of Home Affairs (MHA) extended the ban on United Liberation Front of Asom (ULFA) for five years under the Unlawful Activities Prevention Act (UAPA), 1967.
- The notification specifically includes all factions, wings, and front organizations associated with ULFA.
Reason for Extension:
- ULFA continues to pursue secessionist objectives (separation of Assam from India).
- The group is involved in criminal activities such as extortion, intimidation, and violent actions.
- ULFA has maintained links with other insurgent groups and continues to engage in illegal activities like the possession of arms and ammunition.
Peace Process:
- Pro-talks faction of ULFA, led by Arabinda Rajkhowa, signed a peace agreement with the central and Assam governments in December 2023.
- This faction has agreed to renounce violence, disband the organization, and join the democratic process.
- However, the hardline faction of ULFA, led by Paresh Baruah, remains active and continues its militant activities.
ULFA’s Formation and Objectives:
- ULFA was founded in 1979 with the goal of achieving the "restoration of Assam's sovereignty" through armed struggle.
- It has been a key player in the Assamese separatist movement for several decades.
Legal Framework:
- The UAPA (1967) empowers the government to declare an organization as unlawful or label individuals as terrorists if they engage in activities threatening India’s sovereignty, integrity, or promote terrorism and secession.
- The latest extension of the ban was made under Section 3(1) of UAPA.
Significance for Internal Security:
- This development is important for understanding insurgency and separatism in the Northeast and the government’s approach to national security and counterinsurgency.
- The ULFA issue highlights challenges in addressing regional insurgencies and the role of the UAPA in maintaining national integrity.
Proba-3 mission

- 26 Nov 2024
In News:
The Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) will launch the European Space Agency’s Proba-3 mission on its PSLV rocket to study the solar corona, the outermost and hottest part of the Sun’s atmosphere, from Sriharikota on December 4.
Key Highlights:
- Mission Objective:The mission will study the Sun’s outermost and hottest atmosphere, the solar corona. The mission will also demonstrate the first-ever precision formation flying with two satellites working in tandem.
- Satellite Formation:Proba-3 consists of two satellites that will fly together, maintaining a fixed formation to study the Sun's corona.
What is Proba-3?
- Proba-3 is a solar mission developed by ESA, with an estimated cost of 200 million euros. The mission involves launching two satellites that will separate after launch, but fly in precise formation. The satellites will create a solar coronagraph, which blocks the Sun’s bright light to observe the solar corona, the Sun’s outermost atmosphere.
- Orbit: Proba-3 will orbit in a highly elliptical path (600 x 60,530 km) with an orbital period of 19.7 hours.
- Mission Duration: The expected mission life is two years.
What will Proba-3 Study?
The Sun's corona is extremely hot (up to 2 million degrees Fahrenheit), making it difficult to observe with conventional instruments. However, studying the corona is essential because it generates space weather phenomena such as solar storms and solar winds, which can impact satellite communications, navigation systems, and power grids on Earth.
Proba-3 will use three main instruments for its mission:
- ASPIICS (Association of Spacecraft for Polarimetric and Imaging Investigation of the Corona of the Sun):This coronagraph will observe the Sun’s outer and inner corona, similar to how the corona is visible during a solar eclipse. It features a 1.4-meter occulting disk to block the Sun’s light and facilitate close-up observations.
- DARA (Digital Absolute Radiometer):This instrument will measure the Sun’s total energy output (total solar irradiance).
- 3DEES (3D Energetic Electron Spectrometer):It will study electron fluxes as they pass through Earth's radiation belts, providing valuable data on space weather.
Why is Proba-3 Unique?
- Proba-3 is designed to mimic a natural solar eclipse, allowing continuous study of the Sun’s corona. Typically, solar scientists observe the corona for only about 10 minutes during an eclipse, occurring around 1.5 times a year. Proba-3 will provide up to six hours of data per day, equivalent to 50 eclipse events annually.
- The two satellites will maintain a precise formation, with one acting as an occulting spacecraft to cast a shadow, while the other (the coronagraph) stays in the shadow and observes the Sun’s corona. They will be positioned 150 meters apart, maintaining their formation autonomously.
- This artificial eclipse will enable scientists to study the corona and its less-understood features more effectively.
Mobility Arrangement for Talented Early-professionals Scheme (MATES)
- 15 Nov 2024
In News:
Australia has come up with a new scheme that allows talented young people from India to work in the country for some time.
What is the MATES Scheme?
- Full Name: Mobility Arrangement for Talented Early-professionals Scheme (MATES).
- Objective: To provide Indian university graduates and early-career professionals with an opportunity to live and work in Australia for up to two years.
- Establishment: The scheme is part of the Migration and Mobility Partnership Arrangement (MMPA) between Australia and India, signed on May 23, 2023.
- Launch Date: MATES will open for applicants in December 2024.
Eligibility Criteria
- Age: Applicants must be 30 years or younger at the time of application.
- Educational Qualifications: Must have graduated within the last two years from an eligible institution with a Bachelor’s degree or higher in one of the following fields:
- Renewable Energy
- Mining
- Engineering
- Information Communications Technology (ICT)
- Artificial Intelligence (AI)
- Financial Technology (FinTech)
- Agricultural Technology (AgriTech)
- English Proficiency: A minimum score of 6 overall in IELTS (or equivalent), with at least 5 in each module.
- Institutional Criteria: Graduates must be from the top 100 Indian universities as per the NIRF Ranking 2024 (e.g., Panjab University, Chandigarh University, Thapar Institute of Engineering, Lovely Professional University).
- Previous Participation: Applicants must not have previously participated in the MATES scheme.
Key Features of the MATES Scheme
- No Employer Sponsorship Required: Applicants are not required to have sponsorship from an Australian employer.
- Visa Duration: The visa allows a stay of up to 2 years in Australia, with multiple entries permitted.
- Dependents: Visa holders can bring dependents (spouse and children). Dependents will have work rights in Australia but will not count towards the annual cap.
- Visa Application Process:
- The visa will be granted through a ballot system (random selection).
- Application Fee: AUD 25.
- Shortlisted candidates will proceed to further formalities.
Program Features
- Targeted Sectors: MATES focuses on key sectors such as renewable energy, mining, engineering, ICT, AI, FinTech, and AgriTech, aligning with Australia’s demand for skilled professionals in these areas.
- Pilot Program: Initially, the scheme will offer 3,000 places per year for primary applicants.
- Work Flexibility: While the visa does not require applicants to work in their nominated field, it is designed to help young professionals expand their skills and network in Australia’s key industries.
Additional Benefits
- Career Development: Participants will gain international work experience, expanding their professional network and skills.
- Cultural Exchange: The scheme also promotes cultural exchange between India and Australia, fostering stronger bilateral relations.
- Pathway for Future Opportunities: Participants may apply for further temporary or permanent residence in Australia, provided they meet the eligibility requirements.
Impact and Significance
- Bilateral Cooperation: The MMPA, under which MATES is established, enhances migration and mobility between India and Australia while addressing concerns related to illegal migration.
- Youth Empowerment: The scheme offers young professionals a platform to develop their careers internationally, particularly in sectors of global relevance like AI, FinTech, and renewable energy.
- Skill Development: MATES aims to bridge skill gaps in Australia by attracting Indian professionals to key sectors where expertise is in high demand.
- Global Talent Mobility: This scheme supports the global mobility of young talent and strengthens the India-Australia economic and educational partnership.
Operation Kawach

- 15 Nov 2024
In News:
The Delhi Police recently initiated Operation Kawach, arresting and detaining around 1,000 people in an attempt to crack down on various gangs and their operations in the wake of the recent incidents of shootings reported in the city.
Overview of Operation Kawach
- Objective: A crackdown on gang-related violence, drug trafficking, and other illegal activities like possession of firearms, banned drugs, and liquor.
- Agencies Involved:Delhi Police (Local Police, Special Cell, and Crime Branch)
- Duration: Initiated on November 12, 2024 (5 PM) and continued until November 13, 2024 (5 PM).
Key Details of the Operation
- Arrests and Detentions:
- Around 1,000 people detained.
- 486 people apprehended in Outer North Delhi (20% juveniles).
- Arrests made in Dwarka, Southwest, and North Delhi.
- Key Gangs Targeted:
- Associated with notorious gangs led by Lawrence Bishnoi, Neeraj Bawana, Kaushal Chaudhary, TilluTajpuria, Kala Jatheri, Manjeet Mahal, and Nandu gangs.
- Charges: Involvement in activities like:
- Possession of illegal firearms.
- Trafficking of liquor and banned drugs (NDPS Act).
- Theft and other criminal activities.
Significance of Operation Kawach
- Public Safety: Aimed at dismantling organized crime networks to enhance safety and reduce violence in Delhi.
- Impact on Gangs: Directly targets high-profile criminals, including those involved in gang wars and drug trafficking.
- Strategic Law Enforcement: Strengthens law enforcement capabilities, working in coordination across multiple police units.
Domestic Systemically Important Banks (D-SIBs)

- 15 Nov 2024
In News:
The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) retained the State Bank of India, HDFC Bank and ICICI Bank as Domestic Systemically Important Banks (D-SIBs).
Overview of D-SIBs
- Definition: D-SIBs are banks that are 'Too Big to Fail' (TBTF) and their failure could significantly disrupt essential banking services, affecting the economy.
- RBI Classification: The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) has designated SBI, HDFC Bank, and ICICI Bank as D-SIBs.
- Bucketing System: These banks are classified into different buckets based on their systemic importance.
Importance of D-SIBs
- Systemic Importance: Banks are considered systemically important due to their:
- Size
- Cross-jurisdictional activities
- Complexity
- Interconnectedness with the economy
- Impact of Failure: Failure of a D-SIB could cause significant disruption in the banking system and economy, impacting services like payments, loans, etc.
Why D-SIBs are Created
- Risk of Disruption: The failure of a large bank can disrupt essential services and lead to a broader economic crisis.
- TBTF Perception: These banks are often perceived as Too Big to Fail, leading to an expectation of government support during crises. This creates moral hazard, encouraging riskier behavior.
Assessment and Selection of D-SIBs
- Two-Step Process:
- Step 1: Selection of banks based on their size, complexity, and interconnectedness. Only banks with systemic importance are assessed (e.g., banks with assets > 2% of GDP).
- Step 2: Calculation of systemic importance score based on a range of indicators. Banks above a certain threshold are classified as D-SIBs.
- Indicators: Size (measured by Basel III Leverage Ratio Exposure Measure), interconnectedness, substitutability, and complexity are key factors.
Bucket Allocation and Capital Requirements
- D-SIBs are assigned to five buckets based on their systemic importance score:
- Bucket 1: Lowest capital surcharge (e.g., ICICI Bank).
- Bucket 5: Highest capital surcharge.
- Additional Capital Requirements:
- SBI: Additional 0.80% CET1 (Common Equity Tier 1) on Risk-Weighted Assets (RWAs).
- HDFC Bank: Additional 0.40% CET1.
- ICICI Bank: Additional 0.20% CET1.
- The higher the bucket, the higher the capital surcharge.
Global Systemically Important Banks (G-SIBs)
- Global List: Identified by the Financial Stability Board (FSB) based on data from the previous year.
- 2023 G-SIB List includes banks like JP Morgan Chase, Bank of America, HSBC, etc.
- Capital Requirement for G-SIBs in India: Foreign G-SIBs with branch presence in India must meet additional CET1 requirements, proportional to their operations in India.
Key Terms
- Risk-Weighted Assets (RWAs): These are used to calculate the minimum capital a bank must hold. It accounts for the risk level of a bank’s assets.
- Common Equity Tier 1 (CET1): The highest quality of capital a bank can hold, primarily made up of common stock, to absorb losses in times of distress.
RBI's New Framework for Reclassification of FPI to FDI
- 13 Nov 2024
In News:
The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) directed foreign portfolio investors (FPIs) to obtain necessary approvals from the government and concurrence from the investee companies when their equity holdings go beyond the prescribed limits and they reclassify the holdings as foreign direct investment (FDI).
- Approval Requirement:
- FPIs (Foreign Portfolio Investors) must obtain necessary government approvals when reclassifying their foreign portfolio investments (FPIs) into Foreign Direct Investment (FDI).
- Approvals are mandatory, including those related to investments from countries sharing a land border with India.
- Investment Limits:
- According to FEMA (NDI) Rules, 2019, an FPI’s investment in an Indian company should not exceed 10% of the total paid-up equity capital (on a fully diluted basis).
- If the FPI exceeds this limit, it has 5 trading days from the settlement of trades to either divest or reclassify the excess holdings as FDI.
- Restrictions on Reclassification:
- Reclassification to FDI is not allowed in sectors where FDI is prohibited.
- FPIs must ensure compliance with FDI norms, such as entry routes, sectoral caps, investment limits, pricing guidelines, and other related conditions.
- Concurrence from Investee Companies:
- The FPI must obtain the concurrence of the investee company for reclassifying the investment into FDI.
- This ensures that the company adheres to conditions related to prohibited sectors, sectoral caps, and government approvals.
- Reclassification Procedure:
- The FPI must clearly state its intent to reclassify the investment to FDI and provide the necessary approvals and concurrence to its custodian.
- The custodian is responsible for freezing the FPI's purchase transactions in the investee company’s equity instruments until the reclassification is complete.
- Regulatory Adherence:
- The reclassification must follow the relevant provisions for FDI, including compliance with the Foreign Exchange Management Act (FEMA) and FDI guidelines.
Spraying Diamond Dust to cool the Earth

- 06 Nov 2024
In News:
- A new study in Geophysical Research Letters suggests that diamond dust could be more effective than any other material in reflecting solar radiation.
- Objective: The goal is to reduce global temperatures by 1.6°C by spraying approximately 5 million tonnes of diamonds annually into the atmosphere.
Background of Geoengineering Solutions:
- Geoengineering refers to large-scale interventions aimed at altering Earth's natural climate system to counteract global warming.
- One proposed solution involves spraying diamond dust in the Earth's upper atmosphere to cool the planet.
- This approach is part of Solar Radiation Management (SRM), which seeks to reflect sunlight away from Earth, thereby reducing global temperatures.
- Previous Materials Considered: Sulphur, calcium, aluminium, silicon, and other compounds have been studied to perform a similar function.
Context of Geoengineering and Climate Crisis:
- Inadequate Progress: Current efforts to mitigate global warming, such as reducing greenhouse gas emissions, have been insufficient. Global temperatures have continued to rise, and targets like the Paris Agreement's 1.5°C are increasingly out of reach.
- Rising Global Temperatures:
- 2023: Global temperatures were approximately 1.45°C higher than pre-industrial levels.
- Projected Challenge: To meet the Paris goal, global emissions must be reduced by at least 43% by 2030. However, current actions will likely result in only a 2% reduction by 2030.
Geoengineering Technologies:
- Geoengineering Methods:
- Solar Radiation Management (SRM): Reflects sunlight to cool Earth.
- Carbon Dioxide Removal (CDR): Involves capturing and storing CO?.
- SRM Techniques:
- SRM draws inspiration from natural events like volcanic eruptions, where large amounts of sulphur dioxide form particles that reflect sunlight.
- Mount Pinatubo (1991): One of the largest eruptions, which temporarily reduced global temperatures by 0.5°C due to the sulphur dioxide released.
Diamond Dust vs Other Materials:
- Study Comparison: Diamonds were found to be the most effective material compared to other compounds (sulphur, calcium, etc.) for reflecting solar radiation.
- Quantity Needed: To achieve a cooling of 1.6°C, 5 million tonnes of diamonds would need to be dispersed into the upper atmosphere each year.
Broader Geoengineering Context:
- Carbon Capture and Storage (CCS):
- CCS is already in practice, where CO? emissions from industries are captured and stored underground to reduce atmospheric carbon.
- However, CCS faces high costs and scalability issues, and safe storage sites for CO? are limited.
- Direct Air Capture (DAC): A more advanced method where CO? is directly removed from ambient air, but it faces even greater challenges in terms of infrastructure and cost.
Bob Khathing

- 05 Nov 2024
In News:
- Defence Minister Rajnath Singh inaugurated the Major Ralengnao 'Bob' Khathing Museum of Valour in Tawang, Arunachal Pradesh, on October 31, 2023, coinciding with National Unity Day (Sardar Vallabhbhai Patel's birth anniversary).
- Significance: The museum honours Bob Khathing's contributions to India's security and the integration of Tawang into India.
Role in the Integration of Tawang:
- Tawang Expedition (1951): In January 1951, Major Bob Khathing, an officer of the Indian Frontier Administrative Service, led the expedition to peacefully integrate Tawang into India.
- Strategic Importance: At the time, there were concerns over Chinese intentions to enter Tibet and realign boundaries. Khathing's mission was crucial to prevent Chinese advances into the area.
- Expedition Details: Khathing set off with Assam Rifles troops from Charduar, Assam, and after overcoming extreme terrain and weather, he reached Tawang. On February 14, 1951, he hoisted the Indian flag, marking Tawang's official integration into India.
- Administrative Setup: Khathing established an administrative framework, including appointing Gaon Buras (village elders) to manage local governance.
Military Service and Recognition:
- World War II Service: Bob Khathing joined the Indian Army in 1939 and earned recognition for his role in the Second World War. He was awarded the Member of the British Empire (MBE) and the Military Cross (MC) for his bravery and leadership.
- Guerrilla Warfare: Khathing was part of the Victor Force, a British-led guerrilla unit tasked with countering the Japanese in Burma and India during WWII. Later, he became the adviser to SANCOL, a force set up to track Japanese forces in the region.
- Military Cross Citation: Khathing was praised for his tireless efforts in organizing local Naga support, gathering intelligence, and participating in successful ambushes, which played a critical role in defeating the Japanese.
Post-War Career and Civil Service:
- Ministerial Role in Manipur: After WWII, Khathing was demobilized and joined the interim government of Manipur, where he served as a minister in charge of the hill areas.
- Integration of Manipur: Following Manipur's merger with India in 1949, Khathing joined the Assam Rifles and served for two years before moving into civil administration.
- Key Positions: He served as Deputy Commissioner of Mokokchung (Nagaland), Development Commissioner in Sikkim, and Chief Secretary of Nagaland.
- Ambassadorship: In 1975, Khathing became India's ambassador to Burma, possibly the first person of tribal origin to hold such a position in independent India.
The Importance of His Contributions:
- Integration of Border Areas: Khathing’s role in integrating Tawang and securing India's northeastern frontier was pivotal in preventing further territorial disputes, especially with China.
- Institutional Development: He helped establish military and security institutions, including the Sashastra Seema Bal, Nagaland Armed Police, and the Naga Regiment, which played important roles in maintaining peace and security in the region.
- Heroic Leadership: Khathing's leadership, both as a soldier and civil servant, continues to be celebrated, symbolized by the Major Bob Khathing Museum of Valour.
Kodo Millet

- 03 Nov 2024
In News:
Kodo millet is a staple food for many tribal and economically weaker sections in India. It is one of the 'hardiest crops, drought tolerant with high yield potential and excellent storage properties,' according to researchers
Background on Kodo Millet:
- Kodo millet (Paspalum scrobiculatum), also known as Kodra or Varagu, is a hardy, drought-tolerant crop widely grown in India, especially in Madhya Pradesh.
- It is a staple food for many tribal and economically weaker sections of India and is used to make various dishes like idli, dosa, and rotis.
- Kodo millet is valued for its high yield, nutritional benefits (rich in vitamins, minerals, antioxidants), and storage properties.
Incident in Bandhavgarh Tiger Reserve:
- 10 elephants from a herd of 13 died over three days in Madhya Pradesh’s Bandhavgarh Tiger Reserve.
- The cause of death was suspected to be mycotoxins associated with kodo millet, particularly Cyclopiazonic Acid (CPA), which is toxic to animals.
Historical Cases of Kodo Poisoning:
- The first human cases of kodo poisoning were reported in 1922 in the Indian Medical Gazette.
- Animals, including elephants, have also been affected by kodo millet consumption, with documented deaths as early as 1983.
- Cyclopiazonic Acid (CPA), a mycotoxin, was identified as the cause of kodo poisoning in the 1980s.
Why Does Kodo Millet Become Poisonous?
- Kodo millet is grown in dry and semi-arid regions and is vulnerable to fungal infections, particularly Ergot fungus, which produces CPA.
- When the crop encounters rainfall during maturing and harvesting, fungal infection can lead to "poisoned kodo," known locally as 'Matawna Kodoo' or 'Matona Kodo'.
- The mycotoxins in the infected millet are stable and resistant to standard food processing techniques.
Impact of Mycotoxins on Animals:
- Symptoms of poisoning: Vomiting, giddiness, unconsciousness, rapid pulse, cold extremities, limb tremors.
- Nervous and cardiovascular systems are primarily affected, causing liver dysfunction, heart damage, and gastrointestinal issues.
- In severe cases, consumption of infected kodo millet can cause death due to cardiovascular collapse and organ failure.
- Similar symptoms of depression and loss of mobility were observed in animal studies, including in mice.
Solution to Kodo Toxicity:
- Biocontrol agents (organisms that fight harmful pathogens) can help reduce fungal growth and mycotoxin production in kodo millet.
- Good agricultural practices: Sorting, proper storage in airtight containers, and avoiding moisture exposure during threshing can minimize contamination.
- Post-harvest management: Removing infected grains is crucial to preventing the spread of the disease.
Detection of Mycotoxins in Kodo Millet:
- Challenges: Mycotoxins are often undetectable by sight, and traditional methods like chromatography are time-consuming.
- Rapid detection tools: Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays (ELISA), lateral flow assays (LFAs), and biosensors offer faster, on-site methods for detecting mycotoxins in kodo millet.
PARAKH RashtriyaSarvekshan 2024

- 02 Nov 2024
In News:
The National Achievement Survey (NAS), a nationwide survey meant to assess students’ learning progress, will be held on December 4 this year under a new name – PARAKH RashtriyaSarvekshan 2024. This year’s assessment involves a few changes from the last round in 2021.
Overview of PARAKH RashtriyaSarvekshan 2024:
- New Name: The National Achievement Survey (NAS) is now rebranded as the PARAKH RashtriyaSarvekshan 2024.
- Date: The survey will be held on December 4, 2024.
- Purpose: To assess students’ learning achievements across India.
- Organizing Bodies: Spearheaded by NCERT and CBSE.
What Does the Survey Assess?
- Assessment Focus: Evaluates students’ learning outcomes in various subjects.
- Survey Methodology: Uses multiple-choice questions to assess a sample of students.
- Target Groups: Students from government, government-aided, and private schools across every district in India.
History of NAS and PARAKH:
- NAS History: Conducted every three years since 2001 to capture learning progress.
- Involvement of Classes:
- 2001-2014: Included Classes 3, 5, and 8.
- 2014-15: Class 10 was introduced.
- 2017 and 2021: Covered Classes 3, 5, 8, and 10.
- Report Cards: Provides national, state, and district-level performance data.
Changes in 2024 Survey (PARAKH RashtriyaSarvekshan):
- Targeted Classes:
- Class 3 (End of foundational stage)
- Class 6 (End of preparatory stage)
- Class 9 (End of middle stage)
- Exclusion of Class 10: Unlike previous years, Class 10 students are not part of this year's assessment.
- Subjects Assessed:
- Class 3 & 6: Language, Mathematics, and The World Around Us (Concepts of Science, Social Science, and Environmental Education).
- Class 9: Language, Mathematics, Science, and Social Science.
Alignment with National Education Policy (NEP) 2020:
- NEP Structure: Aligns with the NEP 2020 framework, categorizing educational stages:
- Class 1-2: Foundational stage
- Class 3-5: Preparatory stage
- Class 6-8: Middle stage
- Class 9-12: Secondary stage
- The shift to Class 6 and 9 for this year’s survey matches the NEP's stage-wise educational framework.
Key Differences in 2024 Assessment:
- Survey Scale: In 2024, 75,565 schools and 22.9 lakh students from 782 districts will participate.
- 2021 Assessment Data:
- The 2021 survey revealed a drop in learning outcomes post-COVID-19.
- Class 3 students showed a performance below the national average in all states.
- Class 5: Only Punjab and Rajasthan had scores above the national average.
PARAKH's Role:
- PARAKH (Performance Assessment, Review, and Analysis of Knowledge for Holistic Development) was established in 2023 as the National Assessment Centre to oversee such achievement surveys.
- Mandate: One of PARAKH’s primary roles is to organize national surveys like the PARAKH RashtriyaSarvekshan.
Significance of the Survey:
- Data Utilization: The survey helps in shaping educational policies based on real-time data on student learning levels.
- Competency-Based Assessment: This year’s survey is focused on competency-based assessments, aligning with the goals of NEP 2020.
- Policy and Planning: The data helps in designing interventions to address regional or subject-wise disparities in education quality.
Discovery of the First "Black Hole Triple" System

- 02 Nov 2024
In News:
Scientists have discovered a "black hole triple" system, which is a rare configuration in space involving one black hole and two stars.
Overview of the Discovery:
- Location: The system is located 8,000 light years away from Earth, in the constellation Cygnus.
- Key Features:
- A black hole at the center, currently consuming a star that is spiraling very close to it.
- A second, more distant star that orbits the black hole every 70,000 years, and another star that orbits it every 6.5 days.
What is a Black Hole Triple System?
- Black Hole and Two Stars: Unlike typical binary systems (comprising a black hole and one other object), this system contains a black hole surrounded by two stars, one nearby and one far away.
- V404 Cygni: The central black hole in the system is the V404 Cygni, one of the oldest known black holes, roughly 9 times the mass of the Sun.
Significance of the Discovery:
- Questions on Black Hole Formation: The discovery raises new questions about how black holes are formed. Traditionally, black holes are thought to form after the explosion of a massive star (supernova), but this system does not follow that model.
- New Formation Theory: Researchers suggest the black hole may have formed via a "direct collapse" process, where a star collapses into a black hole without undergoing a supernova explosion. This is referred to as a "failed supernova".
- In a failed supernova, the star's collapse happens too quickly for the explosive outer layers to be ejected, leading to the formation of a black hole without the typical violent explosion.
Implications for Other Binary Systems:
- The black hole’s gradual consumption of one of its stars may imply that some binary black hole systems could have originally been triple systems, with one star eventually being consumed by the black hole.
Research and Collaboration:
- Study: The discovery was made by researchers at California Institute of Technology (Caltech) and Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT).
- Published in: The findings were published in Nature in October 2024.
Additional Context:
- Distance: The system is about 8,000 light years away, which is vast but still observable with advanced telescopes.
- Mystery of the "Failed Supernova": The concept of a failed supernova offers new insights into the life cycle of massive stars and their transformation into black holes.
PM rolls out Ayushman Bharat for Citizens aged 70 and above

- 01 Nov 2024
In News:
Prime Minister Narendra Modi has expanded the Ayushman Bharat Pradhan Mantri Jan Arogya Yojana (PM-JAY) to provide health coverage to citizens aged 70 years and above, regardless of their income or economic status. This move is aimed at addressing the healthcare challenges faced by India's elderly population, which has been growing rapidly.
Key Highlights of the Ayushman Bharat Expansion:
- Health Coverage for Elderly:
- Ayushman Vaya Vandana Card: This new health card offers Rs 5 lakh annually for individuals aged 70 and above. The coverage is shared within the family, so if there are multiple elderly beneficiaries in one household, the total cover will be split.
- Scope: This initiative is designed to provide a safety net for elderly people, many of whom had previously been unable to access treatment due to high costs.
- Significance of the Scheme:
- India’s elderly population is rapidly growing, with the number of people over 60 expected to reach 319 million by 2050, up from 103 million in 2011.
- The expansion of PM-JAY to include those aged 70+ is a critical step in making universal health coverage more inclusive as India’s population ages.
- Eligibility and Registration:
- Individuals aged 70 years and above must register on the PM-JAY portal or through the Ayushman app. Those who already have an Ayushman Bharat card must complete an eKYC process to receive the new card and coverage.
- Exclusions: The scheme is not available in Delhi and West Bengal, as these states have not adopted the Ayushman Bharat scheme.
- Financial Details:
- The initial outlay for this expansion will be Rs 3,437 crore, covering the remainder of the current financial year and the next year.
- Cover for Overlapping Health Schemes: Elderly individuals who are already covered under other government schemes (e.g., CGHS, Ex-Servicemen Contributory Health Scheme) will have the option to either continue with their current coverage or choose Ayushman Bharat. Those with ESIC or private insurance can access both Ayushman Bharat and their existing cover.
- Coverage Scope:
- The expansion is expected to benefit approximately 6 crore individuals across 4.5 crore families.
- Existing Coverage: Around 1.78 crore elderly people are already covered under the scheme. Additional coverage will be provided to those not currently included in the scheme.
- Interoperability with Other Schemes:
- Those under the Central Government Health Scheme (CGHS), Ex-Servicemen Contributory Health Scheme (ECHS), or other similar schemes will need to choose between their current insurance and the Ayushman Bharat scheme.
- However, individuals enrolled in Employees' State Insurance Corporation (ESIC) can have both their existing cover and the Ayushman Bharat coverage.
- Rollout and Reach:
- The scheme will be implemented across 33 states and Union Territories, except Delhi, Odisha, and West Bengal.
- Over 29,600 hospitals, including more than 12,600 private facilities, are empanelled to provide treatment under PM-JAY.
Other Key Announcements:
- U-WIN Portal: A pan-India digital platform for routine vaccinations, aimed at enhancing the efficiency of vaccination programs.
- Critical Care Facilities: The Prime Minister also launched critical care infrastructure, including new facilities in AIIMS Bhubaneswar, Kalyani, and super-specialty units in Himachal Pradesh and Madhya Pradesh.
LiDAR (Light Detection and Ranging)
- 01 Nov 2024
In News:
LiDAR (Light Detection and Ranging) is a cutting-edge remote sensing technology that uses laser pulses to measure distances and create detailed 3D maps of Earth's surface. This technology has recently played a crucial role in discovering a lost Mayan city hidden under the dense Mexican jungle.
What is LiDAR?
- Definition: LiDAR is a remote sensing technology that uses pulsed laser light to measure distances and generate precise 3D models of Earth’s surface.
- Components: The system includes a laser, a scanner, and a GPS receiver. It is usually mounted on an aircraft to map large areas of terrain.
- Data Accuracy: LiDAR can create high-resolution 3D models with vertical accuracy up to 10 cm, making it highly precise for mapping ground elevation.
How LiDAR Works
- Laser Emission: LiDAR sends out rapid laser pulses toward the ground.
- Reflection: These pulses hit the Earth’s surface, reflecting off features like vegetation, buildings, and terrain.
- Measurement: The time it takes for the laser light to travel to the ground and back is measured, allowing the system to calculate the distance between the sensor and the surface.
- Point Cloud Data: The reflected light data is collected as a "point cloud", representing all the surfaces it hits, including trees, buildings, and other features.
- Refinement: This point cloud can be processed into a Digital Elevation Model (DEM), stripping away vegetation and structures to reveal the “bare earth,” which highlights features like roads, buildings, and hidden settlements.
Why LiDAR is Useful for Archaeologists
- Large-Scale Surveying: Traditional archaeological methods often involve labor-intensive fieldwork, such as walking over every square meter and manually cutting through thick vegetation. LiDAR, however, allows researchers to quickly survey vast areas of land, even through dense jungle, from the comfort of a lab.
- Visibility Under Vegetation: LiDAR’s ability to penetrate dense foliage and reveal features beneath the surface is a game changer. Even thick tree canopies that obscure the ground are no match for the laser pulses, which can pass through gaps to illuminate hidden structures.
The Discovery of the Lost Mayan City
- The City of Valeriana: Using publicly available LiDAR data from a forest monitoring project in 2013, archaeologist Luke Auld-Thomas discovered a lost Mayan city in Mexico’s Campeche region. The city, named Valeriana, had been hidden for centuries by the thick jungle.
- City Features: The city has all the hallmarks of a Classic Maya political capital, including:
- Multiple enclosed plazas
- Broad causeways
- Temple pyramids
- A ball court
- A reservoir formed by damming a seasonal watercourse
- Historical Significance: Valeriana is believed to date back before 150 CE and may have been a key political and cultural center in the Maya civilization.
Applications of LiDAR Beyond Archaeology
- Geography and Mapping: LiDAR is widely used to generate precise, three-dimensional data about the Earth’s surface, helping geographers and planners.
- Environmental Monitoring: It is also used in forest monitoring, flood risk assessment, and environmental conservation.
- Urban Planning and Engineering: Engineers use LiDAR for creating highly accurate topographical maps and planning infrastructure projects.
Ayurveda Day 2024

- 30 Oct 2024
In News:
Celebrated on 29th October 2024, marking the 9th Ayurveda Day, with the theme “Ayurveda Innovations for Global Health”.
- Global Participation: Over 150 countries participating, reflecting Ayurveda's growing global influence.
- Venue: Major events held at the All India Institute of Ayurveda (AIIA), New Delhi.
Key Highlights:
Significance of Ayurveda and its Global Outreach
- Ancient System: Ayurveda is one of the oldest healthcare systems, focusing on holistic well-being, rooted in Vedic traditions, and dating back over 5,000 years.
- Global Recognition: Recognized in 24 countries and Ayurveda products exported to over 100 countries.
- International Cooperation: Collaborative efforts through forums like BRICS, SCO, BIMSTEC, and WHO to integrate Ayurveda into global health policies.
Role of Dhanvantri in Ayurveda Day
- Dhanvantari Jayanti: Ayurveda Day coincides with Dhanteras, marking the birth anniversary of Lord Dhanvantri, considered the divine physician.
- Cultural & Religious Significance: Worshiped for promoting health and longevity, Dhanvantri symbolizes the healing powers of Ayurveda.
Innovations and Relevance of Ayurveda
- Research and Innovation: The theme emphasizes scientific advancements in Ayurveda to address global health challenges such as non-communicable diseases (NCDs), mental health, antimicrobial resistance (AMR), and geriatric care.
- Startup Ecosystem: Focus on fostering innovation through Ayurveda startups, particularly in the North Eastern states and across India.
Ayurveda’s Role in Addressing Global Health Issues
- Non-Communicable Diseases (NCDs): Ayurveda offers preventive and holistic treatment for diseases like diabetes, hypertension, and cardiovascular conditions.
- Mental Health: Ayurveda promotes balance in the mind, body, and spirit, with methods addressing stress, anxiety, and depression.
- Antimicrobial Resistance (AMR): Emphasizing traditional medicinal plants and natural remedies to combat resistance to antibiotics.
- Geriatric Health: Ayurveda's role in managing aging and enhancing quality of life through rejuvenation therapies.
Focus Areas for Ayurveda Innovation
- Women’s Health: Developing Ayurvedic solutions tailored for women's health issues, including reproductive health and hormonal balance.
- Workplace Wellness: Integrating Ayurveda in workplace settings to improve mental and physical health.
- School Wellness Programs: Promoting Ayurvedic practices in schools to boost immunity and overall health of children.
- Food Innovation: Modernizing Ayurvedic dietary concepts, focusing on nutritional balance and preventive health.
Government Initiatives and Digital Transformation
- Ayush Digital Platforms: Initiatives like Ayush Grid, Ayurgyan Scheme, Ayush Research Portal, and Namaste Portal are enhancing accessibility to Ayurvedic knowledge.
- WHO Integration: Ayurveda's inclusion in the WHO ICD-11 Traditional Medicine Module facilitates global standardization and recognition.
- I Support Ayurveda Campaign: A public awareness campaign aiming to garner over 250 million votes in support of Ayurveda.
Ayurvedic Education and Research
- Research Centers: Government-supported centers like the Research Centre for Innovation in Ayurveda Biology and WHO Global Traditional Medicine Centre advancing Ayurveda's global integration.
- Academic Contributions: Institutes like National Institute of Ayurveda, Institute of Teaching and Research in Ayurveda, and North Eastern Institute of Ayurveda and Homeopathy are leading innovation and education in Ayurveda.
Ayurveda and Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs)
- SDG 3 (Good Health and Well-being): Ayurveda contributes significantly to public health, with a focus on preventive care and holistic health.
- Universal Health Coverage (UHC): Ayurveda supports affordable, accessible healthcare solutions, complementing the global health agenda.
'Act4Dyslexia' Campaign

- 29 Oct 2024
In News:
- On October 27, 2024, prominent landmarks such as Rashtrapati Bhawan, Parliament House, India Gate, and the North and South Blocks in Delhi were illuminated in red to raise awareness for Dyslexia and other learning disabilities.
- Similar illuminations took place in major cities like Patna, Ranchi, Jaipur, Kohima, Shimla, and Mumbai, highlighting the importance of dyslexia awareness.
Key Highlights:
- Collaboration for Awareness:
- The campaign is organized in collaboration with UNESCO Mahatma Gandhi Institute of Education for Peace and Sustainable Development (MGIEP) and the ChangeInkk Foundation.
- Its goal is to remove stigma and foster understanding of dyslexia and other learning disabilities, which affect 20% of India’s population—around 35 million students.
- Flagging off the ‘Walk4Dyslexia’:
- The ‘Walk4Dyslexia’ event, aimed at promoting collective action for dyslexia awareness, was flagged off by Shri Rajesh Aggarwal, Secretary of the Department of Empowerment of Persons with Disabilities (DEPwD), along with Mr. Shombi Sharp, UN Resident Coordinator in India.
- The walk was organized by ChangeInkk Foundation, UNESCO MGIEP, Orkids Foundation, and Soch Foundation.
- Growth of the Campaign:
- The Act4Dyslexia campaign saw a significant expansion in 2024, with over 1,600 walks held across the country, from state capitals to villages, engaging over 4 lakh participants.
- The campaign mobilized 2 billion steps in support of dyslexia awareness, with 150+ organizations joining forces.
- Focus on Equal Rights and Opportunities:
- Dyslexia and other specific learning disabilities (SLDs) were officially recognized under the Rights of Persons with Disabilities Act, 2016. This law mandates equal educational and employment opportunities for individuals with disabilities.
- The National Education Policy (NEP) 2020 further emphasizes inclusive education, calling for early identification, teacher capacity building, and necessary support and accommodations.
- Understanding Dyslexia:
- Dyslexia is often misunderstood as a sign of being a "slow learner", but people with dyslexia often excel in areas like logical reasoning, problem-solving, and innovation.
- Notably, 40% of self-made millionaires have dyslexia, and historical figures like Albert Einstein were also dyslexic.
- Global Impact:
- The campaign aligns with the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), aiming to unlock the untapped potential of individuals with learning disabilities, thereby contributing to societal development at a global level.
New Disability Certificate Rules (RPwD Rules, 2024)

- 29 Oct 2024
In News:
- The Rights of Persons with Disabilities (RPwD) Rules, 2024, were amended by the Union Government in the wake of the Puja Khedkar controversy, where an IAS probationer was dismissed for alleged forgery in her disability and caste certificates.
- National Platform for the Rights of the Disabled (NPRD) has called for a rollback of the new rules, citing that they make the process of obtaining disability certificates more stringent and cumbersome.
Key Changes Under the New RPwD Rules, 2024
- Authority for Issuing Disability Certificates:
- Only a designated medical authority or a notified competent medical authority at the district level can issue disability certificates.
- NPRD had proposed that experts from non-profits also be authorized to carry out checks, but this suggestion was not accepted.
- Colour-Coded UDID Cards:
- The new rules introduce colour-coded UDID cards to represent levels of disability:
- White (general disability)
- Yellow (moderate disability)
- Blue (severe disability with 80% or higher).
- The new rules introduce colour-coded UDID cards to represent levels of disability:
- Mandatory Online Applications:
- Applicants are now required to apply for disability certificates online, which could be problematic for individuals who lack access to the internet, smartphones, or are digitally illiterate.
- The NPRD has urged the government to retain the option for in-person applications.
- Extended Time for Certificate Issuance:
- The new rules extend the time for issuing disability certificates from one month to three months.
- Reapplication Requirement:
- If there is no action taken on an application for two years, the applicant will have to reapply, which the NPRD considers unacceptable, as it punishes disabled individuals for system failures.
NPRD's Concerns
- Regressive and Burdensome:NPRD believes the amendments are regressive, adding more hurdles for genuine persons with disabilities to access certificates, which are crucial for identification and entitlement to services.
- Lack of Accountability:The NPRD argues that the rules do not address the systemic issues highlighted by the Puja Khedkar case, such as the lack of accountability at various levels in the certification process.
- Online Application Issues:Many people from the disabled community may struggle with technical jargon used in online applications and may not have the resources to complete the process digitally.
- Delay in Issuance:Extending the time for issuing certificates to three months could create delays for those in urgent need of certification for services or entitlements.
Mission for Integrated Development of Horticulture (MIDH)

- 29 Oct 2024
In News:
- The Union Government has decided to introduce four new components under the Mission for Integrated Development of Horticulture (MIDH), aimed at promoting modern farming techniques:Hydroponics, Aquaponics, Vertical Farming&Precision Agriculture
Key Features of MIDH:
- MIDH is a Central Sponsored Scheme (CSS) aimed at the integrated development of various horticulture crops, including:
- Fruits, vegetables, root and tuber crops, mushrooms, spices, flowers, aromatic plants, coconut, cashew, cocoa, and bamboo.
- The scheme focuses on pre-production, production, post-harvest management, processing, and marketing activities.
Revision of Operational Guidelines and Cost Norms:
- The Ministry of Agriculture and Farmers' Welfare is revising the MIDH operational guidelines and cost norms, which were last updated in April 2014.
- The revised guidelines are expected to be released within one month.
- Cost norms are likely to increase by 20% compared to the existing rates, addressing concerns from various states about outdated guidelines.
Reason for Revision:
- Several states, including Odisha, have raised concerns over the old rates under MIDH. For example, Odisha’s Agriculture Minister highlighted that the state was still using 10-year-old rates.
- The Union Cabinet had already approved the rationalization of all CSS operating under the Ministry into two umbrella schemes:
- Pradhan Mantri Rashtriya Krishi Vikas Yojana (PM-RKVY)
- Krishonnati Yojana (KY)
Growth in India's Horticulture Sector:
- India’s horticulture production has significantly increased in recent years:
- Total production reached 334.60 million metric tonnes in 2020-21, up from 240.53 million metric tonnes in 2010-11.
- India is now the second largest producer of fruits and vegetables globally, surpassing food grain production.
- MIDH Annual Budget:The annual allocation for MIDH in the current financial year (2024-25) is ?2,000 crore.
Greenhouse Gas Levels Hit Record High in 2023: World Meteorological Organization (WMO)

- 29 Oct 2024
In News:
According to the WMO, the last time the earth had a similar CO2 concentration was 3-5 million years ago, when temperatures were 2-3°C higher and sea levels were 10-20 metres higher than they are now
Key Highlights:
- Record High Greenhouse Gas (GHG) Levels:
- In 2023, annual mean carbon dioxide (CO2) levels rose by 2.3 parts per million (ppm), reaching a new record of 420 ppm.
- This marks the 12th consecutive year with an increase of over 2 ppm in CO2 levels.
- Historical Context:
- CO2 levels not seen in 3-5 million years, when temperatures were 2-3°C higher, and sea levels were 10-20 meters higher than they are today.
- Key GHGs at Record Highs:
- The globally averaged surface concentrations of CO2, methane, and nitrous oxide all reached new highs in 2023.
- Contributors to the Increase in CO2:
- Natural Variability: Natural factors such as large vegetation fires and reduced carbon absorption by forests contributed to higher CO2 levels.
- Human Activity: High fossil fuel emissions from human and industrial activities also played a major role.
- El Niño Phenomenon: The El Niño event led to higher temperatures and drier conditions, exacerbating the rise in GHG levels through increased wildfires and reduced carbon absorption by land sinks.
- Climate Feedback Loop Concerns:
- The WMO warned of a vicious cycle:
- Climate change could cause ecosystems to become larger sources of GHGs.
- Wildfires could release more carbon, and warmer oceans may absorb less CO2, leading to more CO2 remaining in the atmosphere, accelerating global warming.
- The WMO warned of a vicious cycle:
- Radiative Forcing:
- Radiative forcing (the warming effect on climate) from long-lived GHGs has increased by 51.5% from 1990 to 2023, with CO2 contributing 81% of this increase.
- Methane Concerns:
- Methane saw its largest three-year increase between 2020 and 2022.
- This increase was linked to warmer temperatures and wetter land conditions during the 2020-2022 La Niña conditions, which caused an uptick in methane emissions from natural wetlands.
- Long-Term Impact of CO2:
- Given CO2's long atmospheric lifetime, even with rapid emissions reductions, the warming effect will persist for several decades.
C-295 Aircraft
- 29 Oct 2024
In News:
- Recently, PM Narendra Modi inaugurated the Final Assembly Line (FAL) plant in Vadodara, Gujarat, for the manufacturing of the C-295 aircraft.
- The plant is a joint venture between Tata Advanced Systems Ltd (TASL) and Airbus.
- This is the first private sector final assembly line for military aircraft in India.
Key Details:
- Manufacturing Timeline
- Contract: In September 2021, India signed a ?21,935 crore deal with Airbus Defence and Space to procure 56 C-295 aircraft to replace the IAF’s ageing Avro-748 fleet.
- Production Plan:
- The first 16 aircraft will be delivered from Airbus’s plant in Seville, Spain, between September 2023 and August 2025.
- The remaining 40 aircraft will be produced in India by TASL, with the first “Made-in-India” C-295 rolling out in September 2026.
- The entire fleet (56 aircraft) is expected to be delivered by August 2031.
- Key Features and Specifications
- Type: Tactical transport aircraft with a capacity of 5 to 10 tonnes.
- Maximum Speed: 480 km/h.
- Cabin Dimensions: 12.7 meters (41 feet 8 inches), the longest unobstructed cabin in its class.
- Passenger Capacity: Can accommodate up to 71 seats.
- Cargo Handling: Rear ramp door for quick loading/unloading and para-dropping.
- Short Take-off and Landing (STOL): Capable of operating from airstrips as short as 2,200 feet.
- Significance for the Indian Air Force (IAF)
- The C-295 will enhance the medium-lift tactical capability of the IAF.
- It will replace the ageing Soviet-origin AN-32 aircraft, which are nearing the end of their operational life.
- The C-295 will bridge the capability gap in troop and cargo transport over short and medium distances.
- Indigenous Content
- Indigenous Electronic Warfare Suite: All 56 aircraft will be equipped with an indigenous electronic warfare suite, developed by Bharat Electronics Ltd (BEL) and Bharat Dynamics Limited (BDL).
- Made-in-India Components: 96% of the work that Airbus does in Spain will be done at the Vadodara plant, making it one of the highest-ever indigenous contributions for an aircraft in India.
- Global Operations of the C-295
- The C-295 is operational in various challenging terrains worldwide, including:
- Brazilian jungles, Colombian mountains (South America)
- Deserts of Algeria and Jordan (Middle East)
- Cold climates of Poland and Finland (Europe)
- Military operations in Chad, Iraq, and Afghanistan.
- The C-295 is operational in various challenging terrains worldwide, including:
- Roles and Capabilities
- Tactical Transport: Can transport troops and supplies from main airfields to forward operating airfields.
- Short Take-off and Landing (STOL): Capable of operating from short, unprepared airstrips.
- Low-level Operations: Can conduct low-speed, low-level missions at 110 knots.
- Other Missions: Suitable for casualty evacuation, special missions, disaster relief, and maritime patrol.
Hong Kong Discovers Dinosaur Fossils

- 28 Oct 2024
In News:
Hong Kong discovers dinosaur fossils for the first time
Key Details:
-
- Significance: This marks the first-ever discovery of dinosaur fossils in Hong Kong.
- Time Period:The fossils date back to the Cretaceous Period, approximately 145 million to 66 million years ago.
- Fossil Details:The fossils belong to a large dinosaur, but further studies are required to determine the exact species.Initial analysis suggests the dinosaur may have been buried by sand and gravel after death, later being washed to the surface by a flood before being buried again.
- Site and Protection:Port Island, part of a geopark, is closed to the public to facilitate ongoing fossil investigations and excavation work.
- Geological and Archaeological Importance:The discovery underscores the significance of Hong Kong's geoparks and its role in preserving and showcasing natural history.This finding contributes to global understanding of prehistoric life, especially in the Cretaceous period.
21st Livestock Census

- 27 Oct 2024
In News:
The Livestock Census is a crucial tool for understanding the current status of India’s livestock sector and its contribution to the economy and society.
What is the Livestock Census?
- The Livestock Census is a nationwide survey conducted every five years to assess the number, species, breed, age, sex, and ownership status of domesticated animals and poultry, including stray animals.
- Purpose: It helps in collecting comprehensive data about the livestock population and their role in the economy and society.
- First Census: The first livestock census was conducted in 1919, and this is the 21st edition.
- Next Census: The 21st Livestock Census will be conducted between October 2024 and February 2025 by approximately 87,000 enumerators across 30 crore households in India.
Animals Covered in the Census
- The census will account for 16 species of animals, including:
- Cattle, Buffalo, Mithun, Yak, Sheep, Goat, Pig, Camel, Horse, Ponies, Mule, Donkey
- Dog, Rabbit, Elephant
- Poultry: Fowl, Chicken, Duck, Turkey, Geese, Quail, Ostrich, and Emu
- The census will also collect data on 219 indigenous breeds of these species recognized by the ICAR-National Bureau of Animal Genetic Resources (NBAGR).
Objectives of the Livestock Census
- Economic Contribution: The livestock sector contributes approximately:
- 30% of the Gross Value Added (GVA) of the agricultural sector
- 4.7% of India's overall GVA
- It plays a crucial role in rural employment, particularly in poultry and animal husbandry.
- Policy Formulation and Planning:
- The data from the census is critical for formulating and implementing policies related to livestock, ensuring sustainable growth in the sector.
- It helps in monitoring and estimating GVA from livestock.
- Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs):
- Provides vital data for tracking the progress towards Goal 2 of SDGs (Zero Hunger) and Target 2.5, which focuses on maintaining genetic diversity in livestock, particularly addressing local breeds at risk of extinction (Indicator 2.5.2).
- Sectoral Monitoring:
- The census helps in monitoring the performance and health of India’s livestock sector, which is vital for ensuring food security, rural livelihoods, and economic growth.
Key Features of the 21st Livestock Census
- Digitization:
- Like the 2019 Census, this year’s census will be fully digitized, with data collected via a mobile application.
- Digital Monitoring: A dashboard will monitor progress at various levels, and the latitude and longitude of the data collection locations will be recorded.
- A software-based livestock census report will be generated to streamline analysis.
- New Data Points:
- For the first time, data on pastoral animals and pastoralists will be collected, focusing on their socio-economic status and livestock holdings.
- Granular Data: The census will gather information on:
- Proportions of households that rely on livestock for major income.
- Gender-based data on stray cattle.
- Extended Scope:
- In addition to animal population statistics, the census will also focus on the socio-economic contributions of the livestock sector, gender inclusion, and employment.
Significance of the Livestock Census
- A Comprehensive Livestock Profile:
- Provides a holistic view of livestock population and the interlinkages between animal husbandry, agriculture, and rural economies.
- Assists in the management and preservation of indigenous animal breeds.
- Informed Decision-Making:
- Helps policymakers, researchers, and development organizations in formulating strategies for sectoral growth, genetic diversity preservation, and livelihood enhancement for rural communities.
- Monitoring Livestock Health:
- The census helps in tracking the health and sustainability of India’s livestock population, which is essential for ensuring food security and preventing animal diseases.
Findings of the 2019 Livestock Census
- Total Livestock Population: 535.78 million
- Cattle: 192.9 million
- Goats: 148.88 million
- Buffaloes: 109.85 million
- Sheep: 74.26 million
- Pigs: 9.06 million
- Other species contributed a small fraction to the total livestock population (0.23%).
Nobel Peace Prize 2024

- 24 Oct 2024
In News:
The Nobel Peace Prize has been awarded to Nihon Hidankyo, an organisation of survivors of the Hiroshima-Nagasaki bombings. In doing so, the Nobel Committee has highlighted the power of their testimonies and the need for disarmament.
Key Points about Nihon Hidankyo and the Hibakusha Movement
- Nihon Hidankyo:
- Established on August 10, 1956, as the nation-wide organization for survivors of the Hiroshima and Nagasaki bombings.
- Focuses on the welfare of Hibakusha (A-bomb survivors), promoting nuclear disarmament, and advocating for compensation for victims.
- Works to share the stories and experiences of Hibakusha, both within Japan and globally.
- Hibakusha (Bomb-affected People):
- Survivors of the atomic bombings of Hiroshima and Nagasaki in 1945.
- Played a pivotal role in the global nuclear disarmament movement.
- Their testimonies have helped create the "nuclear taboo," ensuring nuclear weapons have not been used since 1945.
Role of Hibakusha in Nuclear Disarmament
- Global Impact:
- The bombings ignited a global movement for nuclear disarmament.
- Hibakusha's advocacy has highlighted the human cost of nuclear weapons, shaping international policy and promoting the nuclear taboo.
- Nihon Hidankyo’s Advocacy:
- The organization has been instrumental in documenting the effects of nuclear weapons and advocating for their abolition.
- Testimonies from Hibakusha have been key in raising awareness about the catastrophic humanitarian consequences of nuclear warfare.
Nobel Committee's Recognition and Current Nuclear Challenges
- Recognition of Hibakusha's Work:
- The Nobel Committee awarded the Peace Prize to Nihon Hidankyo for its role in promoting nuclear disarmament and for contributing to the nuclear taboo.
- The nuclear taboo is under increasing pressure as new countries seek nuclear weapons and existing powers modernize their arsenals.
- Current Nuclear Landscape:
- The US and Russia continue to maintain large nuclear stockpiles, with the US planning to spend over $1 trillion on upgrading its nuclear capabilities by the 2040s.
- New Threats: Geopolitical tensions, including regional conflicts, raise concerns about the resurgence of nuclear arms races.
Previous Nobel Peace Prizes for Disarmament
- Past Laureates:
- 1974: Former Japanese Prime Minister Eisaku Sato awarded for Japan's commitment to non-nuclear weapons policy.
- 2017: International Campaign to Abolish Nuclear Weapons (ICAN) awarded for its efforts to draw attention to the humanitarian consequences of nuclear weapons and push for a nuclear ban treaty.
- Link with Alfred Nobel’s Vision:
- Alfred Nobel, the founder of the Peace Prize, made his fortune with the invention of dynamite and sought to use his wealth to promote peace, especially through disarmament.
E. coli Outbreak Linked to McDonald's Burgers

- 24 Oct 2024
In News:
- An E. coli outbreak has been linked to McDonald's burgers in the United States. The infection has affected at least 10 states.
E. coli in India:
- Prevalence: E. coli infections are common in India, especially during the summer and rainy seasons, when there is an increase in gastrointestinal infections.
- Transmission: E. coli spreads mainly through contaminated food and water.
- National statistics: Over 500 outbreaks of diarrhoeal diseases were reported in India in 2023. E. coli is one of the most common pathogens causing gastrointestinal infections in India.
- ICMR data: According to the latest report from the Indian Council of Medical Research (ICMR), E. coli was found in 23.19% of patient samples from tertiary care hospitals across India.
- FSSAI's Role: The Food Safety and Standards Authority of India (FSSAI) is establishing a network of 34 microbiology labs to test food for pathogens like E. coli, salmonella, and listeria.
Symptoms of E. coli Infection:
- Common symptoms include:
- High fever (over 102°F)
- Persistent diarrhoea, sometimes bloody
- Vomiting
- Dehydration due to fluid loss
- Severe cases may lead to acute kidney injury.
Treatment of E. coli Infections:
- E. coli is treated with antibiotics, but medical consultation is necessary before taking any medication.
- Antimicrobial resistance is a growing concern, as E. coli's susceptibility to antibiotics, including carbapenem, has declined from 81.4% in 2017 to 62.7% in 2023.
When to Seek Medical Attention:
- Consult a doctor if:
- Diarrhoea lasts more than a couple of days.
- Frequent visits to the toilet (every half hour to an hour).
- Bloody diarrhoea.
- Vomiting frequently or inability to retain fluids.
Food Safety Measures:
- The FSSAI is working to improve food safety by implementing better testing protocols for microbial contamination in food products across India.
India's Mission Mausam and the Cloud Chamber

- 23 Oct 2024
In News:
Mission Mausamaims to not just improve weather forecasting in the country but also ‘manage’ certain weather events, and on demand, enhance or suppress rainfall, hail, fog and, later, lightning strikes.
- Focus Areas:
- Enhancing or suppressing rainfall, hail, fog, and later, lightning strikes on demand.
- Strengthening cloud physics research to better understand and modify weather conditions.
- Establishment of Cloud Chamber:
- Location: The cloud chamber is being built at the Indian Institute of Tropical Meteorology (IITM) in Pune.
- Purpose: To study cloud physics in detail and develop methods for weather modification.
- Key Feature: It will be a convective cloud chamber, capable of simulating conditions specific to Indian monsoon clouds.
What is a Cloud Chamber?
- A scientific apparatus that mimics the conditions required for cloud formation.
- Function: Water vapour, aerosols, and other particles are injected into the chamber, and under controlled temperature and humidity conditions, clouds can be formed.
- Global Context: While many countries have cloud chambers, India is building one with convection properties, which are essential for studying monsoon clouds. Only a few such chambers exist globally.
Why India Needs a Convective Cloud Chamber?
- Cloud Physics: The chamber will allow scientists to study various phenomena such as:
- Cloud behaviour under normal and extreme conditions.
- Formation of rain droplets and ice particles.
- Influence of moisture from cyclones or low-pressure systems.
- Interactions between different cloud layers.
- Objective: To gain insights into cloud formation specific to the Indian monsoon and develop strategies for weather modification.
Applications for Weather Modification:
- The cloud chamber will help scientists simulate and understand how to influence weather events like rain and fog, particularly in monsoon systems.
- It will allow testing of new ideas and theories under controlled conditions, adjusting temperature, humidity, and convection parameters to suit Indian weather conditions.
India’s Experience with Cloud Seeding:
- Cloud Seeding: A technique tested in India to enhance rainfall by introducing particles (seeds) into clouds.
- CAIPEEX Program: India conducted the Cloud Aerosol Interaction and Precipitation Enhancement Experiment (CAIPEEX) over a decade to study cloud seeding's effectiveness.
- Findings: Cloud seeding increased rainfall by up to 46% in some regions, showing its potential under specific conditions.
- Limitations: Cloud seeding is not a one-size-fits-all solution and is effective only under certain conditions.
Significance for India’s Weather Forecasting:
- Improved Weather Modification: The cloud chamber and insights from it could lead to better management of weather events, especially in regions affected by monsoon rains, cyclones, and droughts.
- Tailored Strategies: India will be able to implement targeted weather interventions, especially in agricultural regions, to reduce the negative impacts of extreme weather.
???????Global and Regional Relevance:
- Cloud Chamber: The Pune facility will be one of the few globally with the specific focus on convective properties needed to study Indian monsoon systems.
- Role in Climate Science: India’s investment in cloud physics research positions it at the forefront of developing technologies to manage climate variability and extreme weather events.
Psychoanalysis
- 24 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
Sudhir Kakar, a pioneering Indian psychoanalyst, author, and cultural critic, passed away on Monday at the age of 85.
What is Psychoanalysis?
- Psychoanalysis is a set of psychological theories and therapeutic methods that focus on the unconscious mind, as well as the role of repressed emotions and desires in shaping behavior and mental health.
- Developed by Sigmund Freud in the late 19th and early 20th centuries, psychoanalysis is based on the idea that many of our thoughts, feelings, and actions are influenced by unconscious motives and conflicts, often rooted in childhood experiences.
- Psychoanalysis has three core components:
- A method of investigation of the mind and the way one thinks.
- A systematized set of theories about human behavior.
- A method of treatment for psychological and emotional issues.
- Key concepts in psychoanalysis include the id, ego, and superego (the structural model of the psyche), the Oedipus complex, defense mechanisms (such as repression, denial, and projection), and dream interpretation.
- During psychoanalysis therapy, a patient works closely with a therapist to explore and understand unconscious thoughts and feelings, often by discussing dreams, memories, and other experiences.
- The goal is to bring repressed emotions to the surface and address any underlying conflicts in order to alleviate mental distress and improve overall well-being.
- While psychoanalysis has had a significant influence on psychology and mental health treatment, it remains a controversial approach due to its lack of scientific rigor and emphasis on subjective interpretation.
- Nevertheless, many of its concepts have been adapted or integrated into other forms of therapy, and psychoanalysis remains an important part of the history and development of psychology.
Significance:
- It has profoundly impacted the fields of psychology and mental health treatment, as well as culture, literature, and the arts. Its significance can be understood through the following points:
- Foundational Role: Psychoanalysis provided a groundbreaking approach to understanding the human mind and behavior, shifting the focus from conscious experiences to unconscious mental processes.
- Influence on Psychology: Many concepts introduced by psychoanalysis, such as the unconscious mind, defense mechanisms, and the influence of early childhood experiences, have been adopted and adapted by various schools of psychology, including cognitive-behavioral, humanistic, and psychodynamic approaches.
- Therapeutic Approach: Psychoanalysis revolutionized the way mental health issues were treated, moving away from a purely medical model and emphasizing the importance of talking therapy in addressing psychological problems.
- Cultural Impact: The ideas of psychoanalysis have permeated culture, literature, and the arts, influencing our understanding of human motivations, relationships, and emotions. Concepts like Freudian slips, dream interpretation, and the Oedipus complex have become part of everyday language.
- Interdisciplinary Applications: The principles of psychoanalysis have been applied in fields beyond psychology, including sociology, anthropology, literature, and film studies.
- Despite criticisms and revisions, psychoanalysis remains a significant and influential theory that has shaped our understanding of the human mind and behavior.
- It continues to contribute to the development of psychological theories and therapeutic approaches, enriching our comprehension of mental health and human nature.
Gujarat Freedom of Religion Act

- 13 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
The Gujarat government recently clarified that Buddhism and Hinduism must be considered as two separate religions for religious conversions in the state.
Why did the Gujarat Government Issue the Circular?
- The Gujarat government issued the circular to address an issue regarding the application process for converting from Hinduism to Buddhism.
- The circular, issued by the Home Department highlights that the proper procedures outlined in the Gujarat Freedom of Religion Act (GFR Act) are not being followed.
- The circular points out that some offices are rejecting these conversion applications, arguing that under Article 25(2) of the Constitution, Sikhism, Jainism, and Buddhism are considered part of Hinduism.
- Therefore, applicants are told they don't need permission for religious conversion.
- This interpretation refers to Article 25, which guarantees religious freedom.
- Article 25(2)(b) allows laws for social welfare or reform for Hindus, which includes Sikhs, Jains, and Buddhists.
- Notably, the circular contrasts with a proposed 2006 amendment to the GFR Act, which suggested considering Jainism and Buddhism as part of Hinduism.
- However, the circular clarifies that, according to the GFR Act, Buddhism must be seen as a separate religion.
How does the GFR Act Govern Religious Conversions in Gujarat?
- The Gujarat Freedom of Religion Act (GFR Act) controls how people change their religion in Gujarat.
- According to the state government, this law aims to stop religious conversion by offering rewards, using force, lying, or tricking people.
- One part of the law, Section 3, makes it a crime to force or persuade someone to change their religion, whether by using force, offering rewards, trickery, or arranging marriages.
- Another part, Section 3A, added in 2021, lets anyone who feels harmed or their relatives report these crimes to the police.
- People who break Section 3 can be sent to jail for up to three years and fined up to Rs 50,000.
- If the person affected is a woman, a child, or from certain communities, the punishment is harsher – up to four years in jail and a fine of Rs 1 lakh.
- For a religious conversion to be legal, Section 5 says the person leading the ceremony must get permission from the District Magistrate beforehand.
- And the person who changes their religion must tell the District Magistrate afterward.
- Not doing this can result in a one-year jail term or a fine of up to Rs 1,000.
- In 2021, the GFR Act was changed to include more rules.
- It now makes it a crime to change religion through marriage (Section 4A) and says marriages are void if one person converts before or after getting married (Section 4B).
- It also punishes people involved in organizations that unlawfully convert others (Section 4C). The accused now have to prove that the conversion was legal (Section 6A).
SC directs UOI to frame a policy to phase out heavy-duty diesel vehicles & replace them with BS VI (The New Indian Express)
- 13 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News?
The Supreme Court has directed the Centre to frame a policy within six months to replace heavy-duty diesel vehicles and replace them with BS VI vehicles, observing that the right to clean air is not the entitlement of people living in Delhi alone.
What are BS-VI Norms?
- Bharat stage (BS) emission standards are laid down by the government to regulate the output of air pollutants from internal combustion engines and spark-ignition engine equipment, including motor vehicles.
- The central government has mandated that vehicle makers must manufacture, sell and register only BS-VI (BS6) vehicles from April 1, 2020.
- The first emission norms were introduced in India in 1991 for petrol and in 1992 for diesel vehicles.
- Following this, the catalytic converter became mandatory for petrol vehicles and unleaded petrol was introduced in the market.
What is the Difference Between BS4 and BS6?
- Both BS-IV and BS-VI are unit emission norms that set the maximum permissible levels for pollutants that an automotive or a two-wheeler exhaust can emit.
- Compared to the BS4, BS6 emission standards are stricter
- Whereas makers use this variation to update their vehicles with new options and safety standards, the biggest modification comes in the permissible emission norms.
What area unit BSI, BSII, BSIII, BSIV, and BSVI emission norms?
- The abbreviation BS refers to ‘Bharat Stage’.
- It is prefixed to the iteration of the actual emission norms.
- The primary rules with the soubriquet Asian nation 2000 were introduced in the year 2000, with the second and third iterations being introduced in 2001 and 2005 with the soubriquet BSII (BS2) and BSIII (BS3), respectively.
- The fourth iteration, BSIV, was introduced in 2017 and therefore the delay between the introduction of BS3 and BS4 resulted in fast-tracking the BSVI or BS6 emission norms rather than BSV (BS5) norms.
- On 29 April 1999, the Supreme Court of India ruled that all vehicles in the country had to meet Euro I or India 2000 norms by June 1, 1999, and Euro II would be mandatory in the National Capital Region (NCR) from April 2000.
- Carmakers were not prepared for this transition and in a subsequent judgment, the implementation of Euro II was deferred.
- On 29 April 1999, the Supreme Court of India ruled that all vehicles in the country had to meet Euro I or India 2000 norms by June 1, 1999, and Euro II would be mandatory in the National Capital Region (NCR) from April 2000.
- In 2002, the government accepted the report submitted by the Mashelkar committee, which proposed a road map for the rollout of Euro-based emission norms in India.
- It also recommended a phased implementation of future norms, with regulations being implemented in major cities first and extended to the rest of the country after a few years.
- Based on the recommendations of the committee, the National Auto Fuel policy was announced officially in 2003.
- The road map for the implementation of the BS norms was laid out in 2010.
- The policy also created guidelines for auto fuels, reduction of pollution from older vehicles and R&D for air quality data creation and health administration.
- The standards and the timeline for implementation are set by the Central Pollution Control Board under the Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change.
- Since October 2010, Bharat Stage (BS) III norms have been enforced across the country.
- BS-IV emission norms were put in place in 13 major cities from April 2010, and the entire country from April 2017.
- In 2016, the government announced that the country would skip the BS-V norms altogether and adopt BS-VI norms by 2020.
Ministry of Environment, Forest, and Climate Change submits proposals for Wetland City Accreditation under the Ramsar Convention on Wetlands for cities of Indore, Bhopal and Udaipur (The New Indian Express)

- 05 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News
MoEF&CC has submitted three nominations from India for Wetland City Accreditation (WCA) of Indore (Madhya Pradesh), Bhopal (Madhya Pradesh) & Udaipur (Rajasthan) under the Ramsar Convention on Wetlands.
What is Wetland City Accreditation (WCA)?
- Recognizing the importance of wetlands in urban and peri-urban environments and to take appropriate measures to conserve and protect these wetlands, the Ramsar Convention during COP12 held in the year 2015 approved a voluntary Wetland City Accreditation system under Resolution XII.10.
- It recognizes cities which have taken exceptional steps to safeguard their urban wetlands.
- The Wetland City Accreditation scheme aims to further promote the conservation and wise use of urban and peri-urban wetlands, as well as sustainable socio-economic benefits for local populations.
- Additionally, the Accreditation seeks to encourage cities that are close to and dependent on wetlands.
- Primarily Wetlands of International Importance, but also wetlands with other conservation category status, to develop and strengthen a positive relationship with these valuable ecosystems.
- To be formally accredited, a candidate for the Wetland City Accreditation should satisfy the standards used to implement each of the six international criteria mentioned Operational Guidance for WCA of the Ramsar Convention on Wetlands.
- This voluntary scheme provides an opportunity for cities that value their natural or human-made wetlands to gain international recognition and positive branding opportunities for their efforts in demonstrating strong positive relationships with wetlands.
- The ongoing Amrit Dharohar initiative of the MoEF&CC announced as part of this year’s budget also aims to achieve similar goals by promoting unique conservation values of Ramsar Sites.
- In this context, WCA will not only generate public awareness about conservation of urban and peri-urban wetlands but will also help in implementation of Amrit Dharohar across the country.
The Three Nominated Cities Include:
- Indore: Founded by Holkars, Indore is the cleanest city in India and the recipient of India’s Smart City Award 2023 for its best sanitation, water and urban environment.
- Sirpur Lake, a Ramsar Site in the city, has been recognised as an important site for water bird congregation and is being developed as a Bird Sanctuary.
- A strong network of more than 200 wetland mitras is engaged in bird conservation and sensitising local community to protect Sarus Crane.
- Bhopal: One of the cleanest cities in India that has proposed conservation zones around the wetlands in its draft City Development Plan 2031.
- Bhoj Wetland, Ramsar Site is the city’s lifeline, equipped with the world-class wetlands interpretation centre, Jal Tarang.
- Additionally, the Bhopal Municipal Corporation has a dedicated Lake Conservation Cell.
- A network of more than 300 wetland mitras is engaged in wetland management and conservation of Sarus Crane.
- Udaipur: Located in Rajasthan, the city is surrounded by five major wetlands, namely, Pichola, Fateh Sagar, Rang Sagar, Swaroop Sagar, and Doodh Talai.
These wetlands are an integral part of the city’s culture and identity, help maintain the city’s microclimate, and provide a buffer from extreme events.
Gajraj Suraksha (Elephant Safety) System (New Indian Express)

- 01 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
"In a first", through cutting-edge indigenous technology, the Indian Railways has successfully developed a system, preliminarily called as ‘Gajraj Suraksha (Elephant safety) system’ to prevent elephant–train collisions in the forest areas.
About Gajraj Suraksha:
- Gajraj Suraksha uses an AI-based algorithm and a network of sensitive optical fiber cables to detect elephants approaching railway tracks, aiming to address elephant fatalities resulting from train accidents.
- How this will work?
- The system functions by sensing pressure waves generated by elephant movements along the tracks.
- As elephants move, the optical fibers detect vibrations from their footsteps, triggering signals within the fiber network.
- This enables the system to identify elephants up to 200 meters ahead of their arrival on the track.
- The Optical Fibre Cable (OFC)-based Intrusion Detection System sends alarms to station masters upon detecting movement along the tracks.
- The network is designed to accurately track elephant movement, allowing prompt communication to nearby station masters.
- This ensures timely information to locomotive drivers, facilitating the slowing down or stopping of trains to prevent potential collisions with elephants.
- The Indian Railway plans to introduce this system in West Bengal, Odisha, Jharkhand, Assam, Kerala, certain parts of Chhattisgarh, and Tamil Nadu.
Manipur to Conduct Census of Amur Ffalcon (The New Indian Express)

- 14 Oct 2023
Why in the News?
The Manipur Forest Department will conduct the first-ever Amur falcon census. This initiative in India is one of the several programs the agency is running to safeguard migrating birds.
About Amur Falcon:
- The Amur Falcon, a diminutive member of the falcon family locally known as Akhuipuina, predominantly frequents Manipur and Nagaland.
- Originating from southeastern Siberia and northern China, these birds embark on extensive migrations in vast formations to winter in Southern and East Africa, covering a one-way journey of approximately 20,000 km through India twice a year.
- In terms of conservation, the Amur Falcon is safeguarded by the Wildlife Protection Act of 1972, listed under Schedule IV.
- Hunting or possession of its meat is subject to legal repercussions, including imprisonment for up to three years, a fine of up to 25,000, or bonds.
- Initiating a conservation effort in 2018, the forest department employed radio tagging to study the birds' migratory routes.
- As per the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN), the Amur Falcon is categorized as "Least Concern."
- Despite this, the species faces threats such as illegal trapping and killing during migration, along with habitat loss due to agricultural practices and land reclamation.
Six armed poachers, timber mafia held by forest officials at Similipal National Park (New Indian Express)

- 26 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
In a significant breakthrough, forest officials at Similipal National Park apprehended four armed poachers and two members of the timber mafia in separate locations on Saturday night.
About Similipal Tiger Reserve (STR):
- Similipal Tiger Reserve is located within the Mayurbhanj District, in the Northernmost part of Odisha.
- Declared a 'Tiger Reserve' in 1956, STR became a part of the national conservation initiative 'Project Tiger' in 1973.
- Recognized by UNESCO in 2009, STR, along with a transitional area covering 2250 sq. km, was included in the World Network of Biosphere Reserves.
- Terrain: Surrounded by high plateaus and hills, STR boasts the twin peaks of Khairiburu and Meghashini, reaching 1515m above mean sea level.
- The undulating and hilly terrain features open grasslands and wooded areas, with the inclined plateau rising abruptly from the low coastal plains.
- Hydrography: The region is crisscrossed with perennial water sources, contributing to rivers like Budhabalanga, Salandi, and various tributaries of the Baitarani River.
- Vegetation: STR encompasses a diverse mix of forest types and habitats, with Northern tropical moist deciduous dominating alongside semi-evergreen patches.
- Notably, it hosts the world's only landscape with melanistic tigers.
- Tribes: The vicinity of STR is inhabited by various tribes, including Kolha, Santhala, Bhumija, Bhatudi, Gondas, Khadia, Mankadia, and Sahara.
- Flora: Home to an impressive 1078 plant species, including 94 orchid species, STR is characterized by the dominance of Sal trees.
- Fauna: The reserve is home to a variety of wildlife, including leopard, gaur, elephant, langur, barking and spotted deer, sloth bear, mongoose, flying squirrel, porcupine, turtle, monitor lizard, python, sambar, pangolin, and more.
What is the Special Tiger Protection Force (STPF)?
- Realizing the importance of ‘tiger protection’ in biodiversity conservation, the Finance Minister announced policy initiatives in February 2008, for constituting the ‘Special Tiger Protection Force’ (STPF).
- Based on the one-time grant of Rs. 50 crore was provided to the National Tiger Conservation Authority (NTCA) for raising, arming and deploying a Special Tiger Protection Force, the proposal for the said force has been approved by the competent authority for 13 tiger reserves.
- The STPF has been made operational in the States of Karnataka (Bandipur), Maharashtra (Pench, Tadoba-Andhari, Nawegaon-Nagzira, Melghat), Rajasthan (Ranthambhore), Odisha (Similipal) and Assam (Kaziranga), out of 13 initially selected tiger reserves, with 60% central assistance under the ongoing Centrally Sponsored Scheme of Project Tiger (CSS-PT).
Odisha Government has declared Leprosy as a 'Reportable Disease' in the State (New Indian Express)
- 25 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
The Odisha government on Friday declared leprosy a reportable disease in the state and asked hospitals and persons dealing with diagnosis and treatment, institutions imparting medical education and providing diagnostic services to report all cases to the respective district health authorities.
What is Leprosy?
- Leprosy, often referred to as Hansen's disease, is a persistent infectious illness brought on by the bacteria Mycobacterium leprae.
- The skin, eyes, mucosal surfaces of the upper respiratory tract, and peripheral nerves are the main areas affected by this condition.
- If left untreated, the condition has the potential to produce gradual and irreversible impairments.
- Prevalent in tropical and subtropical regions, leprosy qualifies as a neglected tropical disease (NTD) found in over 120 countries.
- Its occurrence spans all age groups, encompassing early childhood to advanced age.
- Transmission of Disease: Transmission of leprosy transpires through droplets from the nose and mouth, necessitating prolonged, close contact with an untreated individual.
- Contrary to misconceptions, casual interactions such as handshakes, hugs, shared meals, or proximity do not facilitate transmission.
- Symptoms: Symptoms usually manifest 3 to 5 years post-exposure to the leprosy-causing bacteria.
- Red patches on the skin.
- Skin Lesion
- Numbness in arms, hands, and legs.
- Ulcers on the soles of feet.
- Muscle Weakness and excessive weight loss.
- Nerve damage can result in loss of sensation in limbs and potential mucous membrane complications like a stuffy nose or nosebleeds.
- Treatment: Leprosy is curable through Multi-Drug Therapy (MDT), with early intervention crucial in preventing disability.
- Importantly, the commencement of treatment not only aids in recovery but also halts the transmission of the disease.
About the National Leprosy Eradication Programme (NLEP):
- The National Leprosy Eradication Programme is a centrally sponsored Health Scheme under the National Health Mission of the Ministry of Health and Family Welfare, Govt. of India.
- The Programme is headed by the Deputy Director of Health Services (Leprosy ) under the administrative control of the Directorate General Health Services, Govt. of India.
- While the NLEP strategies and plans are formulated centrally, the programme is implemented by the States/UTs.
- The major concern of the Programme is to detect cases of leprosy at an early stage and provide complete treatment, free of cost, in order to prevent the occurrence of Grade II Disability (G2D) in affected persons.
- India has achieved the elimination of leprosy as a public health problem as per WHO criteria of less than 1 case per 10,000 population at the National level in 2005.
- However, there are few districts within States where leprosy is still endemic.
Rating agencies too subjective, loaded against India, need reform: CEA (Indian Express)

- 22 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
Credit rating agencies need to reform their sovereign rating process to correctly reflect the default risk of developing economies, saving billions in funding costs, the government’s chief economic adviser, V Anantha Nageswaran, said recently.
What is a Sovereign Credit Rating?
- A Sovereign Credit Rating serves as an assessment of a government's ability to meet its debt obligations, with a lower rating reflecting higher credit risk.
- Rating agencies typically consider multiple factors such as growth rate, inflation, government debt, short-term external debt as a percentage of GDP, and political stability.
- A positive credit rating not only boosts credibility but also indicates a history of timely loan repayments, aiding banks and investors in evaluating loan applications and determining appropriate interest rates.
- The global credit rating industry is dominated by three major agencies: Moody's, Standard & Poor's, and Fitch.
- Despite India's ascent from the 12th to the 5th largest economy globally in 2023, with the second-highest growth rate among comparable economies, its credit ratings from S&P and Fitch stand at BBB, while Moody's rates it at Baa3—indicating the lowest investment-grade level.
Concerns Regarding Credit Rating Methodology:
- A quantitative examination revealed that more than 50% of credit ratings rely on qualitative components.
- Institutional Quality, predominantly gauged through the World Bank’s Worldwide Governance Indicators (WGIs), emerges as the primary factor influencing the credit rating of a developing economy.
- This poses a challenge as these metrics are often non-transparent, perception-driven, and derived from a limited group of experts, making them inadequate in representing the sovereign's willingness to meet its financial obligations.
- The non-trivial impact of these indicators on ratings implies that developing economies must exhibit progress along subjective indicators to secure a credit rating upgrade.
CEA's Suggestions for Credit Rating Reform:
- The Chief Economic Advisor (CEA) proposed a shift towards primarily considering a country's historical debt repayment record as a key determinant of its 'willingness to pay,' in contrast to relying on potentially suboptimal qualitative information.
- Embracing such a model would significantly enhance the credibility of Credit Rating Agencies (CRAs).
- The use of qualitative information and judgment should only be a last resort when genuine, verifiable data options are unavailable.
- If governance indicators are to be employed, they should be grounded in clear, well-defined, and measurable principles, steering away from subjective assessments by CRAs.
- CRAs possess a comprehensive database of global best practices, influencing their judgments.
- Sharing this knowledge with the countries they assess would empower sovereigns to take targeted actions to enhance their creditworthiness.
One Station One Product’ scheme (New Indian Express)

- 15 Nov 2023
Why in the News?
The Indian Railway has established more than a thousand outlets in railway stations across the nation under its ‘One Station One Product’ (OSOP) initiative which aimed at providing a platform for skilled artisans to sell their indigenous products.
About One Station One Product’ (OSOP):
- The OSOP scheme is a unique initiative by the Indian Railways and aims to provide livelihood opportunities through skill development to local artisans, potters, weavers, and craftsmen.
- It was announced in the Union Budget 2022-23.
- The scheme, designed by the National Institute of Design, Ahmedabad, provides distinctive outlets that give high visibility to indigenous products, benefiting local craftsmen.
- Railways allot the outlets at its stations through a tendering process.
- The scheme’s outreach measures include advertising, social media, public announcements, press notifications, and personal visits to artisans.
- The products at these outlets range from artifacts and handicrafts to textiles and traditional appliances, indigenous to the region, and are crafted by local artisans or tribals.
- They also include locally made or grown food products in processed or semi-processed forms.
- It provides uniquely designed sale outlets for locals to sell indigenous products, and is now operational at 1,037 stations nationwide.
Birsa Munda (New Indian Express)

- 14 Nov 2023
Why in the News?
On Birsa Munday's birthday on Nov. 15th, PM Modi is scheduled to visit Ulihatu village, where the great leader's descendants live in an asbestos house.
About Birsa Munda:
- Birsa Munda was a tribal leader and folk hero who belonged to the Munda tribe.
- He was born on November 15, 1875, in the village of Ulihatu in the present-day Khunti district of Jharkhand.
- Birsa Munda is known for leading a rebellion against British colonial rule and the exploitation of tribal communities in the late 19th century.
- He was a charismatic leader and a devout Hindu.
- He preached a message of social and religious reform and advocated for the revival of traditional Munda culture and values.
- He also led a campaign against the conversion activities of Christian missionaries.
- In 1895, Birsa Munda launched a rebellion against the British.
- He and his followers attacked police stations, government buildings, and the homes of zamindars (landlords).
- The British responded with a heavy crackdown, and Birsa Munda was arrested in 1897.
- He was released from prison in 1898 but was rearrested in 1900 after he resumed his rebellion.
- Birsa Munda died in prison on June 9, 1900, at the age of 25.
- Birsa Munda's rebellion was a watershed moment in the history of the Indian independence movement.
- It inspired other tribal leaders to rise up against the British, and it helped to raise awareness of the plight of tribal communities in India.
- Birsa Munda is revered as a hero by tribal communities across India, and he is considered to be one of the pioneers of the Indian independence movement.
- In addition to his political activism, Birsa Munda was also a religious reformer.
- He founded a new religious movement called Birsait, which combined elements of Hinduism and tribal animism.
- Birsaitism is still practiced by some tribal communities in Jharkhand today.
- Birsa Munda's legacy continues to inspire people today, and he is remembered as one of the greatest heroes of the Indian independence movement.
- To honor Birsa Munda's significant influence on the national movement, the state of Jharkhand was established on his birthday in 2000.
- Recognizing his contributions, the Central Government declared November 15 as 'Janjatiya Gaurav Divas' in 2021.
Bioluminescent Fungi 'Mycena Chlorophos' (The New Indian Express)

- 10 Nov 2023
Why in the News?
A team of researchers and the forest department have found a rare bioluminescent mushroom in the Kanyakumari Wildlife Sanctuary (KKWLS).
About Mycena chlorophos:
- Mycena chlorophos is a species of bioluminescent fungus, meaning that it can produce its light.
- It is primarily found in subtropical Asia, including India, Japan, Taiwan, Polynesia, Indonesia, and Sri Lanka, as well as in Australia and Brazil.
- The bioluminescence is produced through a chemical reaction that involves luciferin, a light-emitting molecule, and the enzyme luciferase.
- Luciferase catalyzes the oxidation of luciferin, which produces light.
- The luciferin in Mycena chlorophos is a compound called trans-3-hydroxyhispidin.
- This compound is also found in other bioluminescent fungi, such as Neonothopanus nambi and N. gardneri.
- The bioluminescence of Mycena chlorophos is thought to serve several functions.
- It may help the fungus to attract insects, which can help to disperse its spores.
- It may also help the fungus to ward off predators.
What is Bioluminescence?
- It is the ability of living organisms to emit light.
- It occurs due to a biochemical reaction between luciferins, oxygen, and the enzyme luciferase.
- The benefit of bioluminescence in fungi is to attract insects to facilitate their spore dispersal.
Stable Auroral Arc (SAR) (New Indian Express)

- 09 Nov 2023
Why in the News?
In a rare phenomenon, researchers from the Indian Institute of Astrophysics (IIA) have recorded the auroral activity that is normally witnessed over the North Pole- at Hanle and Merak in Ladakh through the all-sky cameras recently.
What is Stable Auroral Arc (SAR)?
- An aurora is a glorious curtain of light that is usually seen at high latitudes like in the Scandinavian countries, and they are not expected to occur at lower latitudes.
- They occur due to the interaction between the Earth’s magnetosphere and the incoming solar wind that carries charged particles and magnetic fields.
- They are typically several hundred kilometers wide and can extend for thousands of kilometers.
- A Stable Auroral Arc (SAR) is red in colour as opposed to the usual green-blue curtains of light seen from high latitudes.
- It is a rare phenomenon and it was not exactly an aurora-like one witnessed from close to the North Pole.
- SAR arcs are typically subvisual, meaning that they cannot be seen with the naked eye.
- However, they can be detected using specialized instruments, such as photometers and spectrographs.
- It was observed in Ladakh during a strong G3-class geomagnetic storm and this event was registered in many parts of the world.
Gundla Brahmeswaram Wildlife Sanctuary (New Indian Express)

- 03 Nov 2023
Why in the News?
In a first-of-its-kind, over 50 grass species were identified during a two-day workshop and survey on ‘Grasses Identification and Grassland Management’ at the Gundla Brahmeswaram Wildlife Sanctuary in the Nagarjunasagar-Srisailam Tiger Reserve (NSTR).
About Gundla Brahmeswaram Wildlife Sanctuary:
- Location: It is located in the Kurnool & Prakasam of Andhra Pradesh with an area of 1194 sq km.
- Located between two important hill passes known as "Mantralamma kanuma" and "Nandi kanuma".
- The Northern part of this Sanctuary forms a major part of the Southern boundary for Nagarjunasagar-Srisailam Tiger Reserve.
- River: The Gundlakamma River stretches across the sanctuary.
- It also has many, mesic sites and ancient rock formations.
- Indicator Species: Tiger, Panther, Wild dog, Bats, Fig trees.
- It was declared a wildlife sanctuary on September 18, 1990.
- Forest Type: Dry mixed deciduous forest, moist dry deciduous, semi-evergreen, dry deciduous scrub forest and dry savannahs.
- Flora: The forest is an adobe to medicinal plants of which 10 are critically endangered, 21 are Endangered and 27 species are vulnerable.
- The plants like Madhuca longifolia, Dellenia pentagyna, Aristolochia indica, Terminalia arjuna, Pithecolobium ducle, Adina cordifolia, Vanda spp; etc; thrive here.
- Fauna: Wildlife like Tiger, Leopard, Flying squirre. angur, jungle cat, panther, tiger, mouse deer, hyena, bonnet monkey etc; are found here.
INCOIS wave rider buoy washes ashore in Gopalpur (New Indian Express)

- 04 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
A wave rider buoy, equipped belonging to the Indian National Centre for Ocean Information Services (INCOIS), with GPS and various weather-related instruments, was found ashore at the Gopalpur Military Station in Ganjam district on Saturday.
About Indian National Centre for Ocean Information Services (INCOIS):
- INCOIS is an autonomous organization under the Ministry of Earth Sciences (MoES).
- It is a unit of the Earth System Science Organization (ESSO), New Delhi.
- It is located in Hyderabad & was established in 1999.
- The ESSO operates as an executive arm of the Ministry of Earth Sciences (MoES) for its policies and programmes.
- It is mandated to provide the best possible ocean information and advisory services to society, industry, government agencies and the scientific community through sustained ocean observations and constant improvement through systematic and focused research.
What is the Earth System Science Organisation (ESSO)?
- Earth System Science Organisation (ESSO) is a virtual organisation set up by the Ministry of Earth Sciences GOI in 2007 and it is the executive arm of MoES.
- It has three major branches of earth sciences viz.,
- Ocean Science & Technology
- Atmospheric Science & Technology
- Geosciences and Technology.
- The overall vision of the ESSO is to excel in knowledge and technology enterprise for the earth system science realm towards the socio-economic benefit of the Indian sub-continent and in the Indian Ocean region.
- The ESSO contributes to the areas of Weather (General) and Weather advisories specific to agriculture, aviation, shipping, sports, etc. Monsoon, Disasters (cyclones, earthquakes, tsunamis, sea level rise), Living and non-living resources (fishery advisory, poly-metallic nodules, gas hydrates, freshwater etc), Coastal and Marine Ecosystems and Climate Change, Underwater Technology.
Satkosia Tiger Reserve (New Indian Express)
- 07 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
Recently, the Satkosia Tiger Reserve made a distressing discovery of two elephants' severely decomposed remains.
Facts About:
- Location: Situated in the heart of Odisha, this reserve spans across four districts: Angul, Cuttack, Boudh, and Nayagarh. The Mahanadi River flows through the valleys within the reserve.
- Size: Covering an area of 1136.70 sq km, with 523.61 sq km designated as the core area, Satkosia Tiger Reserve is also part of the Mahanadi Elephant Reserve.
- Unique Geography: Satkosia serves as the convergence point of two distinctive bio-geographic regions in India: the Deccan Peninsula and the Eastern Ghats.
- Landscape: The terrain here is characterized by hills, featuring moderate to steep slopes and narrow valleys.
- Vegetation: The forest primarily consists of North Indian tropical moist deciduous forests and moist peninsular low-level sal.
- Flora: The dominant tree species is sal, forming dense stands. Other associated species include Asan (Terminalia alata), Dhaura (Anogeissus latifolia), Bamboo (Dendrocalamus strictus), and Simal (Bombax ceiba).
- Fauna: The reserve is home to a diverse range of wildlife, including tigers, leopards, elephants, spotted deer, sambar deer, chowsingha, barking deer, bison, wild dogs, sloth bears, jackals, giant squirrels, and porcupines. Additionally, it provides a natural habitat for two endangered species: the freshwater crocodile and the gharial.
