Grid Connected Rooftop Solar Scheme

- 31 Aug 2025
In News:
The Grid Connected Rooftop Solar Scheme was launched by the Government of India to promote clean energy, reduce dependence on fossil fuels such as coal and petroleum, and control pollution. By harnessing solar power through rooftop installations, the scheme provides households, institutions, and commercial entities with access to low-cost, sustainable electricity, while contributing to India’s climate goals.
Solar Rooftop System
- Definition: Installation of solar photovoltaic (SPV) panels on rooftops of residential, commercial, industrial, and institutional buildings.
- Types:
- With Battery Storage – Stores excess solar energy for later use.
- Grid Connected (SPV System) – Converts DC power from solar panels into AC power, which is used for captive consumption and surplus energy is fed into the grid. During low solar generation, the grid compensates for the shortfall.
Objectives of the Programme
- Achieve 40,000 MW capacity by 2022 (target set under the National Solar Mission).
- Central government allocation: ?11,814 crore.
- Phase II incentives:
- Up to 40% subsidy for systems up to 3 kW.
- 20% subsidy for systems between 3–10 kW.
- Increase the role of Distribution Companies (DISCOMs) in promotion and implementation.
Advantages of Grid-Connected Rooftop Solar
- Economic:
- Reduces consumer electricity bills.
- No additional land requirement as panels are roof-mounted.
- Short gestation period compared to large-scale power projects.
- Technical:
- Minimises transmission and distribution losses.
- Reduces congestion and improves voltage at tail ends of distribution lines.
- Environmental:
- Cuts carbon emissions.
- Strengthens long-term energy and environmental security.
Implementation & Nodal Ministry
- Implemented by the Ministry of New and Renewable Energy (MNRE).
- MNRE promotes research, innovation, and global collaboration in renewable energy sectors (solar, wind, hydropower, and biogas).
- Broader goals include:
- Increasing renewable energy share in India’s energy mix.
- Reducing dependence on oil-based energy.
- Supporting clean cooking, heating, and energy equity across regions.
Sundarbans Tiger Reserve
- 31 Aug 2025
In News:
The Sundarbans Tiger Reserve (STR) in West Bengal has become India’s second-largest tiger reserve after the National Board for Wildlife (NBWL) approved the state government’s proposal to expand its area by 1,044.68 sq km. With this addition, STR now spans 3,629.57 sq km, moving up from the seventh to the second position among the country’s 58 tiger reserves, next only to Andhra Pradesh’s Nagarjunasagar-Srisailam Tiger Reserve (3,727.82 sq km).
Expansion Details
- The newly added area includes three tiger-bearing forest ranges of South 24 Parganas district: Matla, Raidighi, and Ramganga.
- The expansion brings all tiger-bearing mangrove forests under the unified management of STR, ensuring uniform application of National Tiger Conservation Authority (NTCA) guidelines.
- The proposal was first conceived nearly two decades ago, revived in 2022–23, and formally cleared by NBWL in August 2025 after approvals from the State Wildlife Board and NTCA.
Location and Ecological Importance
- STR is located in the coastal districts of West Bengal, at the southernmost tip of the Gangetic delta, bordering the Bay of Bengal.
- It is part of the world’s largest delta, formed by the Ganga and Brahmaputra rivers.
- STR is unique as it is the only mangrove habitat in the world (shared with Bangladesh) that supports a significant tiger population.
- It also holds the status of a National Park and a Biosphere Reserve.
Boundaries
- East: International boundary with Bangladesh (rivers Harinbhanga, Raimangal, Kalindi).
- South: Bay of Bengal.
- West: River Matla (boundary with South 24-Parganas Forest Division).
- North-West: Rivers Bidya and Gomdi.
Biodiversity
- Flora: True mangroves, mangrove associates, halophytic herbs, shrubs, weeds, epiphytes, and parasitic plants.
- Fauna: Bengal tiger, estuarine crocodile, fishing cat, Gangetic and Irrawaddy dolphins, king cobra, water monitor lizard, and numerous bird and fish species.
Conservation and Development Implications
- Estimated tiger population: ~101 (80 within STR, 21 in adjoining forests). The number is expected to increase with better management.
- Expansion is expected to enhance:
- Central funding for tiger conservation.
- Tourism potential and local economic benefits.
- Infrastructure and staff capacity within the reserve.
- Conservationists welcome the move as long overdue, while some forest officials caution about manpower shortages (currently only 40% of sanctioned strength).
Support for Marginalized Individual for Livelihood and Enterprise (SMILE) Scheme

- 31 Aug 2025
In News:
The Government of India has undertaken multiple initiatives for the welfare and empowerment of marginalized groups, including the transgender community. A significant step in this direction is the launch of a 15-day Entrepreneurship Development Programme (EDP) under the Support for Marginalized Individual for Livelihood and Enterprise (SMILE) scheme.
About the Programme
- Inaugurated at Garima Greh, a shelter home for transgender persons in Delhi.
- Organized by the Department of Social Justice & Empowerment (DoSJE) and implemented by the National Institute of Entrepreneurship and Small Business Development (NIESBUD).
- Initially, 25 transgender candidates will be trained, with a target of 18 programmes nationwide on a pilot basis, benefitting around 1800 persons.
- Training includes:
- Business opportunity identification and market survey
- Knowledge of the entrepreneurship ecosystem
- Financial aid support schemes and banking procedures
- Entrepreneurial accounting, taxation, and regulatory compliances
- Exposure visits (e.g., incubation centres of NSIC)
- Trainees will prepare business plans and be linked with banks for financial support. Post-training, 6 months of handholding support will ensure sustainability of enterprises.
Financial Inclusion Measures
On the request of DoSJE, the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) has included the transgender community in the Priority Sector Lending (PSL) category. This ensures easier access to credit and financial services for entrepreneurial ventures.
The SMILE Scheme – Key Features
The SMILE scheme is a Central Sector Scheme implemented by the Ministry of Social Justice & Empowerment. It has two components:
- Comprehensive Rehabilitation for Welfare of Transgender Persons
- Comprehensive Rehabilitation of Persons Engaged in Begging
Provisions under SMILE
- Education: Scholarships for transgender students (Class IX to Post-Graduation).
- Skill Development & Livelihood: Training support under PM-DAKSH.
- Healthcare: Composite medical support through convergence with PM-JAY, including gender-reaffirmation surgeries in selected hospitals.
- Housing: Garima Greh shelters providing food, clothing, skill training, recreational and medical support.
- Protection & Legal Support: Establishment of Transgender Protection Cells in each state for timely investigation and prosecution of offences.
- Information Support: National Portal & Helpline for grievance redressal and information dissemination.
Significance
- Promotes economic empowerment and self-reliance of transgender persons.
- Ensures financial inclusion through PSL categorization.
- Strengthens India’s commitment towards an inclusive “Viksit Bharat” by addressing social and economic vulnerabilities of marginalized groups.
Drake Passage
- 31 Aug 2025
In News:
A powerful earthquake of magnitude 7.5 struck the Drake Passage, the stretch of ocean between South America’s Cape Horn and the South Shetland Islands of Antarctica.
About Drake Passage
- Location: Lies between Cape Horn (South America) and the South Shetland Islands (Antarctica).
- Geography: A deep and wide waterway connecting the southwestern Atlantic and southeastern Pacific Oceans; also the narrowest stretch of the Southern Ocean, spanning nearly 800 km between South America and the West Antarctic Peninsula.
- Climatic Role: Marks a climatic transition zone, separating the cool, humid subpolar conditions of Tierra del Fuego from the frigid polar climate of Antarctica.
- Navigation: Considered among the roughest seas in the world due to the collision of cold southern currents and warmer northern waters, which create strong eddies, compounded by powerful westerly winds around Cape Horn.
- Historical Importance: Before the opening of the Panama Canal, it served as a vital maritime trade route in the 19th and early 20th centuries.
- Naming: The passage is named after Sir Francis Drake, the first Englishman to circumnavigate the globe.
Lipulekh Pass

- 31 Aug 2025
In News:
India has rejected Nepal’s claims over Lipulekh Pass after the resumption of India–China trade through this border point. The issue has once again brought the strategic and political importance of the pass into focus.
Location & Geography
- Situated in the Kumaon region of Uttarakhand, near the trijunction of India, Nepal, and China.
- Altitude: ~5,334 metres (17,500 feet).
- Serves as a gateway to the higher Himalayan ranges and the Tibet Autonomous Region of China.
Historical & Trade Importance
- A traditional trade route connecting India with Tibet for centuries.
- In 1992, Lipulekh became the first Indian border post opened for official trade with China.
- Later followed by Shipki La (Himachal Pradesh, 1994) and Nathu La (Sikkim, 2006).
Religious Significance
- Forms an integral part of the Kailash Mansarovar Yatra, an important Hindu pilgrimage route to Mount Kailash and Lake Mansarovar in Tibet.
Strategic Significance
- Its geopolitical location near the trijunction makes it strategically vital for India’s border security and connectivity with Tibet.
- The dispute with Nepal underscores its sensitive nature in regional geopolitics.
Blue Carbon

- 30 Aug 2025
In News:
Seaweed farming has emerged as a potential Blue Carbon strategy, yet empirical estimates of carbon burial from such farms remain lacking in the literature.
What is Blue Carbon?
- Blue Carbon refers to organic carbon captured and stored by ocean-based vegetated ecosystems such as mangroves, saltmarshes, and seagrass meadows.
- The term “blue” highlights its association with aquatic ecosystems.
- Most blue carbon comes from carbon dioxide dissolved directly into the ocean. Smaller amounts are stored in:
- Underwater sediments and soils
- Coastal vegetation
- Organic molecules (DNA, proteins, etc.)
- Marine organisms (phytoplankton, whales, etc.)
- Despite covering just 2% of the ocean surface, these ecosystems account for 50% of total oceanic carbon absorption, making them vital in global climate mitigation efforts.
Seaweed Farming as a Blue Carbon Strategy
- Emerging Role: Seaweed cultivation has been identified as a potential Blue Carbon pathway, though empirical evidence of its carbon burial capacity has been limited until recently.
- Global Study: An analysis of 20 seaweed farms worldwide, aged between 2 and 300 years and ranging from 1 to 15,000 hectares, provides new insights.
- Findings:
- Sediment organic carbon stocks increased with farm age, reaching 140 tC ha?¹ in the oldest farm.
- Average burial rates: 1.87 ± 0.73 tCO?e ha?¹ yr?¹ in farm sediments, nearly double that of nearby reference sediments.
- Excess CO?e burial attributable to seaweed farming: 1.06 ± 0.74 tCO?e ha?¹ yr?¹.
- Conclusion: Seaweed farms in depositional environments act as effective carbon sinks, with burial rates at the lower end of traditional Blue Carbon habitats but increasing significantly with farm maturity.
Significance
- Reinforces the role of marine ecosystems in carbon sequestration.
- Highlights seaweed farming as a scalable, nature-based climate solution alongside mangroves, saltmarshes, and seagrasses.
- Provides a scientific basis for integrating seaweed aquaculture into Blue Carbon policies and climate strategies.
Charge-Coupled Device

- 30 Aug 2025
In News:
A Charge-Coupled Device (CCD) is an innovative electronic component that transformed imaging technology and left a lasting impact across multiple disciplines.
What is a CCD?
- A CCD is a technology that converts light into electrical signals using an arrangement of capacitors, which transfer stored charges sequentially.
- It is built as an integrated circuit containing a grid of tiny picture elements, or pixels.
- Each pixel functions as a miniature light sensor that captures incoming photons and converts them into electrical charges.
- These charges are then shifted across the device pixel by pixel until they reach a readout register, where they are processed into a digital image.
Working Principle
- Based on the photoelectric effect, where incident light generates electron-hole pairs in a semiconductor.
- When photons hit a pixel, they dislodge electrons, creating an electric charge proportional to the light intensity at that point.
- Each pixel acts like a capacitor, storing the accumulated electrons.
- By applying a controlled voltage to electrodes over the pixels, the stored charges are moved step by step across the array—similar to passing buckets of water along a line.
- Once charges reach the output stage, they are converted into voltage signals, amplified, and digitized to form a high-resolution digital image.
- This sequential transfer mechanism is what gives the device its name—charge-coupled.
Applications
- Everyday Use:
- Revolutionized digital photography by replacing traditional film.
- Widely used in CCTV cameras, offering high-quality surveillance in banks, malls, hospitals, and other sensitive locations.
- Medical Field:
- Integral to diagnostic imaging such as X-rays, CT scans, and endoscopy.
- Also employed in microscopes, spectrometers, and particle detectors, enabling detailed scientific analysis.
- Astronomy:CCD-equipped telescopes capture faint and distant celestial objects with greater sensitivity and accuracy than old photographic plates, driving advances in space observation.
CCDs remain one of the most influential inventions in modern imaging, bridging science, medicine, security, and astronomy.
Exercise Samanvay Shakti

- 30 Aug 2025
In News:
The Indian Army, in collaboration with the state governments of Assam and Manipur, inaugurated Exercise Samanvay Shakti 2025 at Laipuli in Tinsukia district, Assam. The initiative is a Military–Civil Integration Exercise designed to build cooperation, cohesion, and mutual understanding among various stakeholder
Aim & Objectives
- Enhance synergy between the armed forces, government departments, and civil institutions.
- Develop a unified and coordinated approach to address the region’s complex challenges.
- Improve preparedness through refined SOPs, effective communication channels, and practical rehearsals.
- Strengthen the bond of trust between local communities and institutions.
- Promote nation-building, development, and national integration.
Participation
The inaugural session saw participation from:
- Indian Army and Indian Air Force.
- State administration, Police, and Intelligence Agencies.
- NDRF, SDRF, BRO, GREF, Medical officials, and Railways.
- Educational institutions and security teams from OIL India, IOCL, Coal India, along with local media representatives.
Key Features
- Location & Duration: Conducted in Assam and a parallel 10-day exercise in Manipur (20–30 August 2025).
- Thematic Focus in Manipur: Disaster management, healthcare, education, public works, forest initiatives, narcotics control, irrigation, road safety, employment in armed forces, sports promotion, police–Army–paramilitary coordination, and infrastructure development under Operation Sadbhavna.
Significance
- Provides a platform for collaboration between civil authorities and the military.
- Enhances regional security preparedness while addressing developmental needs.
- Encourages community participation in governance and security-related initiatives.
- Contributes towards integrated development and inclusive nation-building in the Northeast.
Sci-Hub Ban and the ‘One Nation, One Subscription’ Scheme

- 30 Aug 2025
In News:
The Delhi High Court has ordered a ban on Sci-Hub and its mirror websites after global publishing houses filed a copyright infringement case. This decision has reignited the debate on access to academic literature in India and highlighted the relevance of the government’s One Nation, One Subscription (ONOS) initiative
About Sci-Hub
- Founded: 2011 by Alexandra Elbakyan.
- Nature: A free digital repository providing millions of research articles.
- Function: Circumvents paywalls of academic journals, allowing unrestricted access without subscriptions.
- Popularity: Widely used by students, independent researchers, and scholars, particularly in developing nations.
The Sci-Hub Case
- Litigation: Publishing giants Elsevier, Wiley, and the American Chemical Society (ACS) filed a copyright case against Sci-Hub.
- Court Ruling: The Delhi High Court found Alexandra Elbakyan guilty of contempt for violating earlier commitments.
- Directive: Internet Service Providers (ISPs) were instructed to block Sci-Hub and related mirror portals.
- Implication: While the ruling reinforced intellectual property rights, it left unanswered the critical issue of affordable access to scholarly resources in India.
One Nation, One Subscription (ONOS) Scheme
- Launch: 2024.
- Funding: ?6,000 crore allocated for the first phase (2023–26).
- Approach: Centralized negotiations with 30 publishing houses to provide access to nearly 13,000 journals.
- Coverage:
- Phase I: Public universities and research institutions.
- Phase II: Private colleges and institutes.
- Objective: To provide equitable, legal, and affordable access to global research material, reducing dependence on piracy platforms like Sci-Hub.
Project Aarohan

- 30 Aug 2025
In News:
The National Highways Authority of India (NHAI), in collaboration with Vertis Infrastructure Trust, has launched Project Aarohan, a nationwide scholarship and mentorship program aimed at supporting the educational aspirations of the children of toll plaza employees, particularly those from economically weaker sections (EWS) and disadvantaged communities.
Key Objectives
- Remove financial barriers to education.
- Ensure equal access to quality education for children of toll plaza staff.
- Bridge socio-economic divides while nurturing talent among first-generation learners, girls, and students from EWS, SC, ST, OBC, and minority groups.
- Prepare students for higher education, employment, and entrepreneurship through holistic guidance.
Features of Project Aarohan
- Coverage: 500 students from Class 11 to the final year of graduation.
- Scholarships: Each selected student will receive ?12,000 annually (FY 2025–26).
- Higher Studies Support: 50 bright students aspiring for postgraduate and higher studies will get ?50,000 each.
- Beyond Finance: Mentorship, skill-building workshops, career guidance, and structured progress tracking to foster holistic growth.
- Fund Allocation: ?1 crore for the first phase (July 2025–March 2026).
- Application Process: Through an online portal, requiring academic records, income proof, caste certificate, ID proof, etc., with a transparent selection and renewal mechanism.
Super Garuda Shield 2025

- 29 Aug 2025
In News:
Indonesia, in collaboration with the United States and allied nations, has launched the annual multinational military exercise “Super Garuda Shield 2025”. Initiated in 2009 as a bilateral drill between U.S. and Indonesian forces, the exercise has expanded significantly since 2022 to include multiple Indo-Pacific and Western partners.
Features of Super Garuda Shield 2025
- Organisers: Indonesian National Armed Forces and the U.S. Indo-Pacific Command.
- Participants: Core members — Indonesia and the U.S.; Expanded members — Australia, Japan, Singapore, UK, France, Canada, Germany, Netherlands, New Zealand, Brazil, and South Korea.
- Scale: Around 6,500 troops.
- Duration & Location: 11 days, conducted in Jakarta and on Sumatra island.
- Activities: Joint combat training, interoperability drills across land, air, and maritime domains, and a combined live-fire exercise.
- Objectives:
- Enhance interoperability and combat readiness.
- Strengthen regional security cooperation.
- Uphold sovereignty, territorial integrity, and collective deterrence.
Strategic Context
The Indo-Pacific is witnessing rising tensions due to China’s growing military assertiveness, especially in the South China Sea. Indonesia has expressed concern about Chinese encroachment in its Exclusive Economic Zone (EEZ), though it continues to maintain positive economic relations with Beijing.
The U.S., meanwhile, is reinforcing an “arc of alliances” to reassure partners against coercion and status quo changes by force. Washington views the expanded Garuda Shield as a demonstration of collective resolve to uphold sovereignty and deter aggression.
China, however, has criticised the exercise, calling it an attempt to build an “Asian NATO” to contain its influence.
Indonesia’s Diplomatic Balancing
- Indonesia follows a dual-track diplomacy — avoiding overt confrontation with China while diversifying its defence partnerships with the U.S. and Western powers.
- This includes arms purchases from the U.S. and France and enhancing interoperability with multiple militaries.
- Scholars note that Indonesia’s refusal to choose sides outright reflects its strategy of defence diversification without formal alignment.
- Such an approach is seen as a key asset for Jakarta in a region marked by great power rivalry.
Significance
- For Regional Security: Strengthens multinational defence cooperation, collective deterrence, and stability in the Indo-Pacific.
- For Indonesia: Demonstrates its role as a pivotal state capable of balancing economic ties with China while engaging in security cooperation with the West.
- For the World Order: Reflects the growing salience of multilateral military exercises in managing great power competition and reinforcing the principles of sovereignty and territorial integrity.
India Launches First Veterinary Blood Transfusion Guidelines 2025

- 29 Aug 2025
In News:
A tragic incident in Pune has highlighted regulatory gaps in complex medical procedures. A woman, who donated part of her liver to her husband, died shortly after he succumbed to complications following a transplant surgery at a private hospital.
The Maharashtra Health Department has issued a notice to the hospital, underscoring the critical need for robust patient safety mechanisms, accountability, and monitoring of high-risk medical interventions such as organ transplants.
This incident reiterates the importance of strict compliance with Transplantation of Human Organs and Tissues Act (THOTA), 1994, ensuring informed consent, donor safety, quality control, and post-operative care. It also brings attention to the ethical dimensions of living donor transplants, where both donor and recipient are at significant medical risk. Strengthening regulatory oversight, grievance redressal mechanisms, and transparency in medical procedures is vital for safeguarding trust in India’s healthcare system.
Veterinary Healthcare Regulation: First National Guidelines
In a landmark step for animal health, the Department of Animal Husbandry and Dairying (DAHD), Government of India has released the first comprehensive national guidelines for veterinary blood transfusion services (2025). Until now, most transfusions in veterinary practice were conducted in emergencies without standardized norms, creating risks for animals as well as humans due to possible zoonotic disease transmission.
Key Features of the Guidelines:
- Scientific Protocols: Blood typing, cross-matching, and mandatory donor screening to prevent transfusion reactions.
- Donor Criteria: Health checks, vaccination requirements, and a Donor Rights Charter encouraging voluntary donation.
- Veterinary Blood Banks: State-regulated facilities with biosafety-compliant infrastructure.
- One Health Integration: Addressing zoonotic disease risks by linking animal and human health surveillance.
- Digital Network: Real-time inventory tracking, emergency helplines, and registries for donor–recipient matching.
- Capacity Building: Training modules for veterinary professionals and students.
- Future Innovations: Mobile blood collection units and rare blood-type preservation.
Significance
Both developments underline the evolving landscape of healthcare governance in India. While the Pune case exposes ethical and regulatory challenges in human medicine, the veterinary guidelines represent a proactive, systematised approach to animal welfare, biosafety, and public health.
These events also reflect the growing importance of One Health — the integrated management of human, animal, and environmental health — as India strengthens its healthcare regulations in response to rising public expectations, ethical concerns, and global standards.
India’s Fossil Heritage
- 29 Aug 2025
In News:
India’s fossil heritage, spanning hundreds of millions of years, holds clues to the evolution of plants, dinosaurs, mammals, and marine life. Yet, the absence of strong protection laws and national repositories leaves this heritage vulnerable to theft, vandalism, and illegal global trade.
India’s Fossil Wealth
- Diverse Record: Fossils in India range from the Precambrian era to the Cenozoic, covering ancient plants, marine life, dinosaurs, and mammals.
- Key Discoveries:
- Vasuki indicus – a 47-million-year-old giant snake (~15 m long) from Kutch.
- Indohyus – an early ancestor of whales, discovered in Central India.
- Dinosaur nests and eggs – particularly in the Narmada Valley and Deccan basalt formations.
- Unique Evolutionary Insights: India’s prolonged isolation after separating from Gondwanaland (~150 million years ago) and later collision with Asia (50–60 million years ago) created unique fossil beds documenting crucial evolutionary transitions.
Sites of Importance
- Kutch, Gujarat – rich in marine fossils and large vertebrates.
- Narmada Valley, Madhya Pradesh – known for dinosaur eggs, nests, and bones.
- Deccan Traps & Himalayan foothills – diverse vertebrate and invertebrate fossils.
- Balasinor, Gujarat – developed as India’s Dinosaur Fossil Park.
Lunar Module Launch Vehicle (LMLV)
- 29 Aug 2025
In News:
Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) Chairman V Narayanan said the space agency was in the process of building its heaviest rocket ever, and had named it Lunar Module Launch Vehicle (LMLV).
About the LMLV
- A next-generation heavy-lift launch vehicle, planned readiness by 2035.
- Designed specifically for lunar and interplanetary missions.
- Will be India’s most powerful rocket to date.
Specifications
- Payload to Moon: ~27 tonnes.
- Payload to Low Earth Orbit (LEO): ~80 tonnes.
- Propulsion: Advanced cryogenic and semi-cryogenic engines.
- Objective: To enable crewed lunar missions by 2040 and expand India’s capabilities in deep space exploration.
Evolution of India’s Launch Vehicles
- Sounding Rockets (1963): For atmospheric studies; first launch at Thumba, Kerala.
- SLV-3 (1980): Led by A.P.J. Abdul Kalam; placed Rohini satellite in orbit.
- ASLV (1987–94): Limited success; ~150 kg payloads.
- PSLV (1994 onwards): India’s “workhorse” rocket; enabled Chandrayaan-1 (2008), Mangalyaan (2013).
- GSLV (1990s–2010s): Introduced cryogenic engines; ~2,500 kg payload to GTO.
- LVM-3 / GSLV Mk-III (2017): Heaviest operational rocket; ~4,000 kg to GTO; launched Chandrayaan-2 (2019), Chandrayaan-3 (2023).
- LMLV (planned 2035): Will surpass all earlier systems; cornerstone for India’s human spaceflight to the Moon and beyond.
Integrated Air Defence Weapon System (IADWS)
- 29 Aug 2025
In News:
India has successfully conducted the maiden flight tests of its Integrated Air Defence Weapon System (IADWS) off the coast of Odisha, marking a major milestone under Project Sudarshan Chakra. Developed indigenously by the Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO), the system represents a significant advancement in the country’s ability to defend critical assets against evolving aerial threats.
What is IADWS?
The IADWS is a multi-layered, network-centric air defence architecture that integrates:
- Quick Reaction Surface-to-Air Missile (QRSAM)
- Very Short Range Air Defence System (VSHORADS)
- Directed Energy Weapon (DEW) (high-power laser)
Together, these components form a composite shield capable of engaging a wide spectrum of threats—from high-speed aircraft and cruise missiles to drones, swarm UAVs, and loitering munitions.
Key Features
- Centralised Command & Control Centre (C2C2): Integrates radar and electro-optical sensor data to generate a real-time aerial picture. Based on parameters like speed, altitude, and trajectory, threats are assigned to the most effective weapon.
- Multi-layered Defence:
- QRSAM (outer layer): Intercepts fighter aircraft, helicopters, and standoff precision weapons (cruise missiles, glide bombs) at 25–30 km range and up to 10 km altitude. Highly mobile with short reaction times.
- VSHORADS (middle layer): Infrared seeker-based shoulder-fired missiles to neutralise low-flying UAVs and helicopters within 6 km range and up to 4 km altitude.
- Directed Energy Weapon (inner layer): A DRDO-developed laser system capable of disabling drones and loitering munitions at close range. Offers virtually unlimited firing capacity, making it cost-effective and sustainable.
- Simultaneous Target Engagement: During trials, IADWS successfully intercepted three different aerial targets (two fixed-wing UAVs and a multi-copter drone) in real time.
- Mobility & Flexibility: Mounted on high-mobility launchers, the system can be rapidly deployed in forward areas.
Strategic Importance
IADWS strengthens India’s area defence capability by providing a layered shield for:
- Forward air bases and command centres
- Radar and missile installations
- Nuclear and space assets
- Power plants and critical industrial hubs
By combining kinetic (missiles) and non-kinetic (lasers) weapons under a unified command structure, India has taken a major step toward countering both conventional and asymmetric aerial threats.
Significance for India’s Defence Preparedness
- Enhances self-reliance under Atmanirbhar Bharat in advanced defence technologies.
- Strengthens India’s deterrence against hostile air campaigns, drone swarms, and precision strikes.
- Positions India among a select group of nations with multi-layered integrated air defence systems.
ISRO Integrated Air Drop Test (IADT-01)
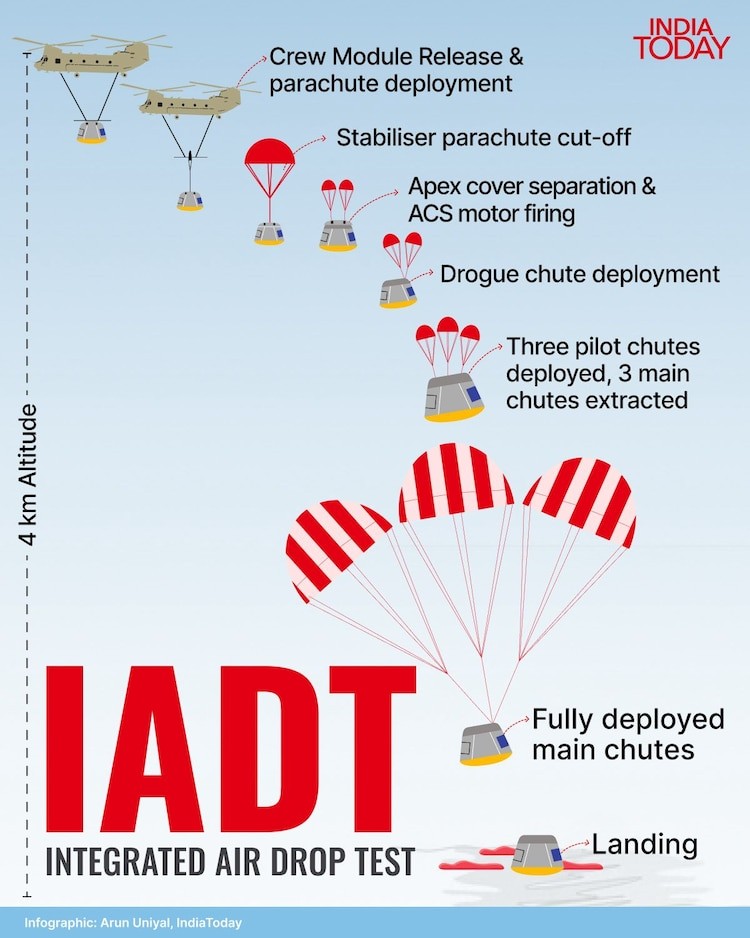
- 28 Aug 2025
In News:
The Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO)has successfully conducted its firstIntegrated Air Drop Test (IADT-01) for the Gaganyaan human spaceflight programme, marking a critical milestone in validating astronaut safety systems.
Objective of IADT-01
- Test the end-to-end parachute recovery system of the Gaganyaan crew module.
- Demonstrate reliability, sequencing, and redundancy of drogue, pilot, and main parachutes for controlled deceleration and safe splashdown.
- Ensure astronaut safety during the re-entry and landing phases, considered the riskiest part of any human space mission.
Significance
- Validates a vital safety mechanism for Gaganyaan, boosting confidence ahead of upcoming missions like Test Vehicle-D2 (TV-D2) and the first uncrewedGaganyaan mission (G1).
- Strengthens India’s human-rating capabilities, positioning the country to become the fourth nation with independent crewed spaceflight capability.
- Reflects successful inter-agency collaboration among ISRO, Indian Air Force, DRDO, Navy, and Coast Guard.
Gaganyaan Mission Overview
- Crewed mission scheduled for 2028; uncrewed test flight planned in December 2025.
- Mission profile: Carry a three-member crew to low Earth orbit (~400 km) for up to three days, followed by safe return.
- The programme emphasizes astronaut safety, technological reliability, and operational preparedness, with future tests including additional parachute validations, pad abort trials, and sea recovery rehearsals.
Strategic Importance
- Demonstrates India’s capability in human spaceflight, enhancing its global standing in space technology.
- Paves the way for advanced crewed missions and potential applications in scientific research, space exploration, and international collaborations.
India’s Push for 27% Ethanol Blending
- 28 Aug 2025
In News:
India has announced its ambitious plan to increase ethanol blending in petrol to 27% (E27) by 2030, building upon the successful Ethanol Blended Petrol (EBP) Programme launched in 2003. This move aligns with India’s goals of energy security, environmental sustainability, and rural development.
Background and Progress
- EBP Programme: Started with 5% blending, it has grown from less than 2% a decade ago to 10% (E10) by 2022, with 20% blending (E20) projected for 2025, five years ahead of schedule.
- Ethanol Feedstocks: Primarily derived from sugarcane, maize, and surplus food grains, with an increasing push for second-generation ethanol from crop residues and agricultural waste under PM-JI-VAN Yojana.
- Energy Security: India imports nearly 88% of crude oil, spending over $120 billion annually. Ethanol blending reduces crude imports, conserves foreign exchange, and mitigates vulnerability to global price shocks.
- Environmental Goals: Ethanol blends reduce carbon monoxide and hydrocarbon emissions, supporting the National Green Mobility Strategy and India’s Net Zero 2070 commitment.
Economic and Social Benefits
- Farmer Welfare: The programme has channeled over ?1.2 lakh crore to farmers and nearly ?2 lakh crore to distilleries, providing stable markets for sugarcane, maize, and other crops.
- Rural Development: Ethanol distilleries generate employment, promote agro-industries, and reduce distress migration.
- Circular Economy Link: Second-generation ethanol initiatives convert crop residues and waste into energy, addressing stubble burning and enhancing sustainability.
Challenges and Risks
- Food Security: Rising ethanol demand strains maize and grain supplies. In 2023, a 5-million-tonne maize shortfall forced imports, affecting poultry, starch industries, and food prices.
- Water Use: Sugarcane requires 1,500–2,000 litres of water per kg of sugar, risking groundwater depletion in states like Maharashtra and Uttar Pradesh.
- Technological Issues: Higher blends can reduce fuel efficiency by 6–7% in vehicles not designed for ethanol. Adoption of Flex Fuel Vehicles is slow and more costly.
- Supply-Side Constraints: India produced 7 billion litres of ethanol in 2023 but will require over 12 billion litres by 2030. Financially stressed sugar mills and limited investment in grain-based or second-generation plants challenge scaling.
- Infrastructure Needs: Storage, transport, and fuel dispensing networks must expand nationwide to meet E27 targets.
Policy Recommendations
- Feedstock Diversification: Rapid development of second-generation ethanol from crop residues, forestry waste, and municipal solid waste.
- Consumer Incentives: Subsidies for Flex Fuel Vehicles, retrofitting existing engines, and awareness campaigns to ensure adoption.
- Public–Private Partnerships: Investment and collaboration to scale production, distribution, and technology adoption.
- Integration with Clean Energy Transition: Ethanol should complement electric mobility and green hydrogen, serving as a bridge solution for decarbonisation while more transformative technologies mature.
Famine in Gaza
- 28 Aug 2025
In News:
The United Nations has confirmed a famine in Gaza City and surrounding areas, describing it as a “failure of humanity” and a man-made disaster. The declaration follows a report by the Integrated Food Security Phase Classification (IPC), which raised food insecurity in parts of Gaza to Phase 5, the highest level, indicating catastrophic conditions of starvation, destitution, and death.
Scale of the Crisis
- Population affected: Nearly 641,000 people are facing IPC Phase 5 conditions, while 1.14 million (58% of Gaza’s population) are projected to experience emergency-level food insecurity (IPC Phase 4) between mid-August and end of September.
- Children at risk: By June 2026, 132,000 children under five may face life-threatening malnutrition.
- Mortality: Gaza’s Hamas-run health ministry reports 271 deaths due to malnutrition, including 112 children.
- Historical Context: Since 2004, IPC has officially classified only four famines, with the last one in Sudan, 2024.
Causes
The famine is described as “starvation by design” by UN officials:
- Aid Restrictions: Israel has been accused of systematically obstructing humanitarian aid. The UN estimates 600 aid trucks per day are needed, but only 300 trucks are entering daily.
- Conflict Impact: Israel launched a military campaign in response to the Hamas attack on southern Israel in October 2023, leading to mass casualties and displacement. Over 62,000 deaths have been reported in Gaza, with more than 90% of homes damaged or destroyed.
- Infrastructure Collapse: Healthcare, water, sanitation, and hygiene systems have collapsed, exacerbating malnutrition and disease.
International Response
- UN Officials:
- Secretary-General Antonio Guterres called the famine a “moral indictment” and a man-made disaster.
- UNRWA Chief Philippe Lazzarini termed it “starvation by design”.
- UN Human Rights Chief Volker Turk attributed the famine to Israel’s unlawful restriction of aid.
- Global Condemnation:
- UK Foreign Secretary David Lammy described it as a “moral outrage”.
- Humanitarian groups and UN bodies have called for an immediate, at-scale response to prevent widespread starvation.
- Israeli Position: Israel denies a policy of starvation, claiming it has allowed 2 million tons of aid since the conflict began and continues to organize humanitarian corridors and airdrops, though the UN calls these efforts insufficient and sometimes unsafe.
NITI Aayog Report on “Rethinking Homestays: Navigating Policy Pathways”

- 28 Aug 2025
In News:
NITI Aayog, in collaboration with the Internet and Mobile Association of India (IAMAI), released the report “Rethinking Homestays: Navigating Policy Pathways”. The document provides a strategic roadmap for strengthening India’s homestay and BnB sector, emphasizing its role in tourism, rural livelihoods, and cultural preservation.
Key Highlights of the Report
- Tourism & Cultural Value: Homestays offer travelers culturally immersive experiences while promoting local entrepreneurship, heritage conservation, and community participation.
- Economic Role: They serve as engines of livelihood creation, particularly in rural and semi-urban areas, fostering inclusive and sustainable growth.
- Regulatory Approach: The report calls for light-touch, transparent regulation to balance safety, consumer trust, and ease of doing business.
- Digital Integration: Strong emphasis on leveraging digital platforms for marketing, consumer engagement, and capacity building of hosts.
- Public–Private Partnerships: Collaboration with stakeholders like Airbnb, MakeMyTrip, IAMAI, ISPP, Chase India, and The Convergence Foundation was highlighted as critical for shaping a vibrant ecosystem.
- Best Practices: State-level examples from Goa, Kerala, Uttarakhand, and Uttar Pradesh showcase scalable models in policy, governance, and community-led initiatives.
- Policy Recommendations: Suggests flexible frameworks, skill development, financial access, and infrastructure support to strengthen the sector.
Significance for India
- Tourism Development – Homestays diversify India’s hospitality sector, offering authentic alternatives to conventional hotels.
- Employment Generation – Potential to create entrepreneurial opportunities for women, youth, and local communities.
- Cultural Preservation – Encourages conservation of art, craft, cuisine, and heritage while generating income.
- Rural Transformation – Helps bridge urban–rural divides by promoting community-based tourism.
- Sustainability – Supports low-impact tourism models, aligning with SDG 8 (Decent Work & Economic Growth) and SDG 11 (Sustainable Cities & Communities).
About NITI Aayog
- Established: 1 January 2015, replacing the Planning Commission.
- Chairperson: Prime Minister of India.
- Vice-Chairperson: Appointed by PM.
- Members: Full-time, part-time experts, ex-officio Union Ministers.
- Governing Council: Chief Ministers of states and LGs of UTs.
- Functions:
- Premier policy think tank for cooperative federalism.
- Provides strategic and long-term policy frameworks.
- Monitors and evaluates development programmes.
- Promotes innovation, entrepreneurship, and technology adoption.
- Coordinates between Centre, States, and global partners.
- Nature: Advisory, yet influential in shaping policies; key driver of initiatives like Aspirational Districts Programme, Atal Innovation Mission, and SDG localization.
Climate Change and Workplace Heat Stress
- 28 Aug 2025
In News:
The WHO–WMO joint report (2025), Climate Change and Workplace Heat Stress, warns that rising global temperatures are creating an unprecedented occupational health and productivity crisis. The year 2024 was the warmest on record, with global average temperatures 1.45°C above pre-industrial levels, and the decade 2015–2024 being the hottest ever recorded.
Key Findings
- Productivity Losses: Each 1°C rise in Wet-Bulb Globe Temperature (WBGT) above 20°C reduces global worker productivity by 2–3%. Sun exposure further raises WBGT by 2–3°C, amplifying risk.
- Scale of Exposure: Over 2.4 billion workers are directly exposed; annually, 22.85 million injuries, 18,970 deaths, and 2.09 million disability-adjusted life years (DALYs) are linked to workplace heat stress (ILO estimates).
- Geographical Hotspots: South Asia, Sub-Saharan Africa, and the Middle East face the highest risks. Heat stress now affects 30% of the global population seasonally or daily.
- Health Impacts: More than one-third of workers in hot conditions report physiological heat strain (hyperthermia, kidney dysfunction, dehydration, neurological problems). WHO safety guidance (1969) recommends that core body temperature during an 8-hour shift not exceed 38°C, a threshold increasingly breached.
- Climate Change Dimension: Daytime peaks of 40–50°C are becoming frequent even outside the tropics. Europe’s 2023 heatwave saw worker fatalities, showing that occupational heat stress is no longer limited to equatorial regions.
India’s Experience
In India, informal workers in brick kilns, construction, agriculture, and power looms are the most affected. Many begin work before sunrise to avoid peak heat, yet still suffer dehydration, dizziness, and lost wages as work hours shrink. Indoor workplaces with poor ventilation often become “furnaces,” leading to chronic fatigue, kidney strain, and even fatalities. By 2030, the ILO projects India could lose 34 million full-time equivalent jobs, particularly in agriculture and construction, due to heat stress.
Wider Implications
- Public Health Burden – Rising cases of heat stroke, cardiovascular collapse, and chronic kidney disease (26.2 million cases in 2020 alone) strain already weak health systems.
- Economic Losses – Developing economies face shrinking GDP as productivity drops; agriculture and construction are most vulnerable.
- Social Inequality – The poor, migrant labourers, and women are disproportionately at risk due to unsafe working conditions and lack of social protection.
- Climate Justice – Regions contributing least to emissions, like Bangladesh and Sub-Saharan Africa, suffer the harshest effects, deepening global inequities.
- Food Security – Agricultural labour productivity loss disrupts crop cycles and threatens farmer incomes, worsening hunger and malnutrition.
- Legal Burden – Rising occupational illness cases risk overwhelming compensation systems and highlight gaps in labour safety laws.
Adaptation Strategies
- Occupational Heat Action Plans: Early warning systems, rescheduling work timings, shaded shelters, and worker training.Example: The Ahmedabad Heat Action Plan (India) has reduced heatwave mortality through alerts, shelters, and training.
- Infrastructure & Technology: Cooling shelters, hydration points, and mechanisation to reduce manual strain.Example: Bangladesh’s garment sector has piloted low-cost ventilation and cooling fans, lowering worker fatigue.
- Labour Policy Reforms: Enforcing heat-index-based work-hour rules, mandatory rest breaks, and compensation for heat-linked illnesses.Example: Qatar bans outdoor work between 10 am–3:30 pm during peak summer.
- Public Health Measures: Hydration protocols, health screenings, and recognition of heat stress as an occupational disease.Example: US OSHA’s “Water–Rest–Shade” campaigninstitutionalises hydration and rest breaks.
- Global & National Coordination: Mainstreaming heat stress into ILO conventions, COP climate talks, and SDG frameworks, with climate finance support for vulnerable economies.Example: Australia integrates climate projections into mining and agriculture workplace safety standards.
National Tiger Conservation Authority’s Corridor Restriction
- 27 Aug 2025
In News:
The National Tiger Conservation Authority (NTCA), the apex statutory body under the Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change (MoEFCC), has recently issued a clarification restricting the definition of tiger corridors to only the 32 “least cost pathways” identified in 2014 and those recorded in Tiger Conservation Plans (TCPs) of individual reserves. This excludes later studies by the Wildlife Institute of India (WII) (2016, 2021) and data from the All-India Tiger Estimation (AITE) exercises.
What are Tiger Corridors?
Tiger corridors are natural pathways that connect fragmented tiger habitats, allowing for:
- Genetic flow and long-term survival of populations.
- Migration and dispersal between reserves.
- Minimisation of human-wildlife conflict through guided movement.
Projects that require land in or around these corridors or reserves need statutory clearance from the Standing Committee of the National Board for Wildlife (SC-NBWL) under the Wildlife Protection Act, 1972.
About NTCA
- Established: 2005 (through 2006 amendment of Wildlife Protection Act, 1972).
- Chairperson: Union Minister of Environment, Forest and Climate Change.
- Functions:
- Approves TCPs of states.
- Provides financial and technical support for tiger conservation.
- Oversees Project Tiger implementation.
- Conducts All-India Tiger Estimation (AITE) every 4 years.
- Ensures ecological connectivity through corridor protection.
The Recent Controversy
- NTCA had earlier told the Bombay High Court (July 2025) that multiple benchmarks would be used to identify corridors, including:
- Protected areas with tiger occupancy.
- 2014 least-cost pathways.
- WII studies (2016, 2021).
- AITE distribution data.
- However, in its latest clarification, NTCA restricted corridors only to 2014 least-cost pathways and TCP records, ignoring updated scientific models.
Potential Beneficiaries
Industrial projects, particularly in Maharashtra, such as:
- Western Coalfields Limited’s Durgapur open cast mines.
- Lloyds Metals & Energy’s Surajgarh iron ore mines in Gadchiroli.
Scientific Concerns
- 2014 NTCA Report itself noted that its corridors were “minimal requirement” and alternative connectivities also needed conservation.
- Newer studies (e.g., Circuitscape modelling, 2025) suggest at least 192 corridors across 10 central Indian states, far beyond the restricted 32.
- Narrowing protection risks fragmentation of habitats, reducing gene flow and increasing chances of local extinctions.
Fortified Rice Scheme Extended to 2028

- 27 Aug 2025
In News:
The Union Cabinet has approved the continuation of the universal supply of fortified rice under all government food safety net schemes till December 2028, with 100% central funding of ?17,082 crore. This initiative is part of India’s broader strategy to combat anaemia, malnutrition, and hidden hunger, which remain major public health challenges.
Evolution of the Scheme
- 2018: Launch of Anemia Mukt Bharat (AMB) initiative by MoHFW, emphasising fortified foods.
- 2019: Pilot project for rice fortification introduced in select districts.
- 2022: Government approved national scale-up of fortified rice across welfare schemes.
- March 2024: Fortified rice fully replaced normal rice in all central schemes.
- 2025: Cabinet approved extension till 2028, ensuring continuity with dedicated funding.
Nodal Ministries & Agencies
- Department of Food and Public Distribution (DFPD) under Ministry of Consumer Affairs → implementing agency.
- FSSAI (Food Safety and Standards Authority of India) → sets fortification standards.
- Convergence with Ministry of Education, MoHFW, Ministry of Women and Child Development, and NDDB Foundation for Nutrition.
Components of the Programme
- Public Distribution System (PDS): Fortified rice supplied through ration shops.
- PM POSHAN (Mid-Day Meal): Fortified rice used in school meals; guidelines also promote Double Fortified Salt (DFS) and fortified edible oil.
- Integrated Child Development Services (ICDS): Supplies fortified staples to children and women.
- Special Schemes: Distribution under Wheat-Based Nutrition Programme (WBNP) and Scheme for Adolescent Girls (SAG).
- Complementary Nutrition Initiatives:NDDB’s Gift Milk Programme has provided 7.1 lakh litres of fortified milk, benefitting 41,700 children in 257 schools across 11 states.
Nutritional Focus
- Micronutrients in Fortified Rice: Iron, Folic Acid, and Vitamin B12 → combat iron-deficiency anaemia, support neurological and cognitive health.
- Double Fortified Salt (DFS): Prevents anaemia and goitre.
- Fortified Edible Oil: Provides Vitamins A & D, preventing deficiencies.
Key Features
- Universal Coverage: Fortified rice supplied across all central schemes.
- Cost Coverage: Entire fortification cost borne by the Government of India.
- Monitoring & Accountability: States/UTs tasked with ensuring quality and compliance.
- Multi-Sectoral Approach: Linked with nutrition awareness campaigns and Anemia Mukt Bharat.
- Private & CSR Partnerships: NFN mobilises funds and awareness through CSR and donations.
Wider Context – Food Processing Linkages
The Ministry of Food Processing Industries (MoFPI) supports complementary schemes like:
- PM Kisan SAMPADA Yojana (PMKSY)
- PLI Scheme for Food Processing Industry (PLISFPI)
- PM Formalization of Micro Food Processing Enterprises (PMFME)
These aim to improve supply chains, reduce wastage, and enhance processing levels – strengthening nutrition outcomes alongside fortification.
RBI Discussion Paper on Inflation Targeting
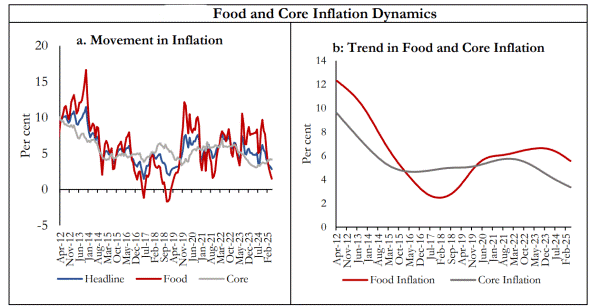
- 27 Aug 2025
In News:
The Reserve Bank of India (RBI), in August 2025, released its discussion paper on reviewing India’s Flexible Inflation Targeting (FIT) framework, which is due for renewal in March 2026. The paper seeks public feedback on key questions such as whether the 4% target remains optimal, whether the 2–6% tolerance band should be revised, and whether the target should be expressed as a point or only a range.
Evolution of the Framework
- Adopted in 2016, the FIT framework formalised inflation targeting in India.
- Current mandate: 4% CPI-based inflation target with a tolerance band of 2–6%, jointly set by the RBI and the Government of India.
- Review cycle: Every five years, with the next mandate to begin April 2026.
Rationale for Retaining the 4% Target
- Credibility with Investors: Raising the target above 4% could be perceived as policy dilution, eroding credibility. Rating agencies like S&P Global recently upgraded India’s rating (BBB), citing the RBI’s strong inflation management.
- Institutional Stability: The framework has strengthened the Monetary Policy Committee (MPC) process and fiscal discipline.
- Domestic Outcomes: Headline CPI inflation has mostly remained within the 2–6% band. In July 2025, it hit 1.55%, the second-lowest since the series began.
- External Balance: Low and stable inflation safeguards the rupee, maintains external competitiveness, and prevents capital outflows.
Headline vs Core Inflation Debate
- Economic Survey 2023–24: Suggested targeting core inflation (excluding food and fuel) as food inflation is largely supply-driven and beyond monetary control.
- RBI’s View: Headline CPI should remain the target, as persistent food shocks spill over into wages, rents, and production costs, influencing core inflation.
- Global Norm: Nearly all inflation-targeting countries focus on headline CPI; Uganda is the only exception.
- Indian Context: Food has ~50% weight in CPI. Excluding it would undermine policy relevance for households and workers.
Key Issues Under Review
- Target Level: Lowering below 4% could hurt growth; raising above 4% risks credibility loss.
- Tolerance Band: Debate on retaining the 2–6% range, narrowing it, or removing it. While a band allows flexibility, it may reduce accountability.
- Inflation Volatility: Between 2014–2025, headline CPI ranged from 1.5% to 8.6%, mainly due to food prices, while core inflation remained relatively stable.
Positive Outcomes of the Framework
- Anchored Expectations: Households and firms now base decisions around a credible 4% anchor, reducing uncertainty.
- Investor Confidence: Predictable inflation management has lowered risk premiums on Indian assets, boosting FDI and portfolio inflows.
- Improved Sovereign Ratings: Low inflation stability has supported fiscal credibility, earning global recognition.
- Resilience to Shocks: Despite global supply disruptions and oil price volatility, India avoided runaway inflation.
India’s Draft Climate Finance Taxonomy

- 27 Aug 2025
In News:
In May 2025, the Ministry of Finance (Department of Economic Affairs) released India’s draft Climate Finance Taxonomy (CFT) for public consultation. This initiative is timely, as it coincides with India’s expanding climate finance ecosystem, including green bonds, carbon credit trading, and global commitments under the Paris Agreement and net-zero targets by 2070.
What is a Climate Finance Taxonomy?
- A classification framework that defines which sectors, technologies, and activities qualify as climate-aligned investments.
- It is described as a “living document”, evolving with India’s domestic priorities and international climate obligations.
- Core purpose: To mobilise public and private finance, ensure transparency, and prevent greenwashing.
Key Features of India’s Draft CFT
- Scope: Covers activities contributing to mitigation, adaptation, and low-carbon transition.
- Review Mechanism
- Annual reviews for course correction.
- Five-year reviews aligned with India’s Nationally Determined Contributions (NDCs) and the UNFCCC global stocktake.
- Legal Coherence
- Designed to be consistent with Indian laws (Energy Conservation Act, SEBI regulations, Carbon Credit Trading Scheme).
- Harmonised with international standards for credibility.
- Substantive Clarity: Provides clear, precise, and updated definitions that are accessible to both experts and non-experts.
- Inclusivity
- Simplified compliance for MSMEs, informal sector actors, and vulnerable communities.
- Staggered timelines for smaller entities to avoid exclusion.
- Institutional Accountability
- Proposal for a standing review unit/expert committee.
- Public dashboards to ensure transparency and investor confidence.
Significance
- Boosts Investor Confidence: Provides clarity for domestic and global investors in India’s green economy.
- Ensures Transparency: Prevents mislabeling of projects as “green,” tackling greenwashing risks.
- Mobilises Finance: Unlocks predictable, science-based finance flows for mitigation and adaptation.
- Supports Net-Zero Goals: Complements instruments like green bonds and carbon credit markets.
- Global Positioning: Strengthens India’s role in shaping international norms on climate finance.
Mercator Projection Map
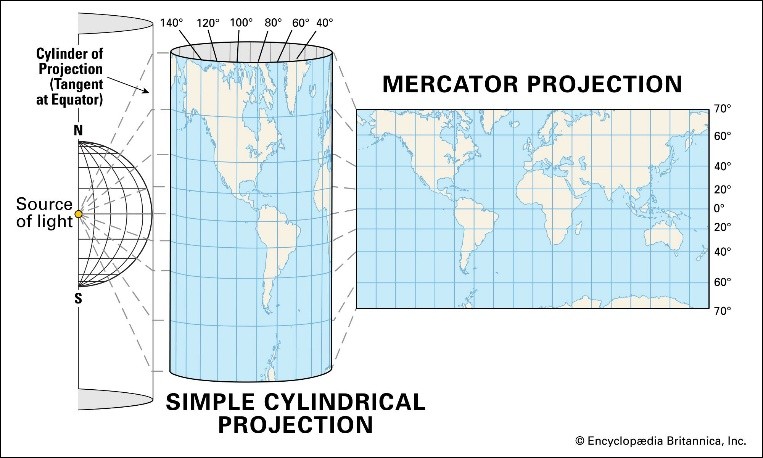
- 27 Aug 2025
In News:
The African Union (AU) has endorsed the “Correct the Map”campaign, calling for the replacement of the Mercator projection with modern alternatives that represent Africa’s true size. This move is not just cartographic—it is deeply political, tied to questions of historical justice, cultural representation, and global perception.
The Mercator Projection: Origins and Features
- Introduced: 1569 by Gerardus Mercator, a Flemish mathematician and cartographer.
- Purpose: Designed for navigation, enabling sailors to follow a straight line of constant compass bearing (Rhumb lines/loxodromes).
- Structure:
- Meridians (longitude): parallel, vertical, equally spaced.
- Parallels (latitude): horizontal, spacing increases away from the equator.
- Grid forms right angles.
- Strengths: Conformal projection that preserves shapes and angles, ideal for maritime exploration.
- Limitations: Distorts area and scale. True scale exists only along the equator; distortion grows near the poles.
Distortions and Bias
- Africa & South America appear much smaller than their real size.
- Europe, North America, and Greenland are disproportionately enlarged.
- Example: Greenland (≈2.1 million sq km) appears similar in size to Africa (≈30 million sq km).
- Such distortions fed into Eurocentric worldviews, reinforcing colonial narratives of Africa as “smaller” and “conquerable.”
Corrective Measures
- Gall-Peters Projection (1970s): Area-accurate but distorts shapes. Adopted in some schools, e.g., Boston (2017).
- Equal Earth Projection (2018): Balances shape and area, providing a fairer representation of continents.
- AU’s Endorsement: By backing the Equal Earth projection, the AU aims to restore “Africa’s rightful place on the global stage,” highlighting the continent’s true scale and importance.
Agni-5 Missile
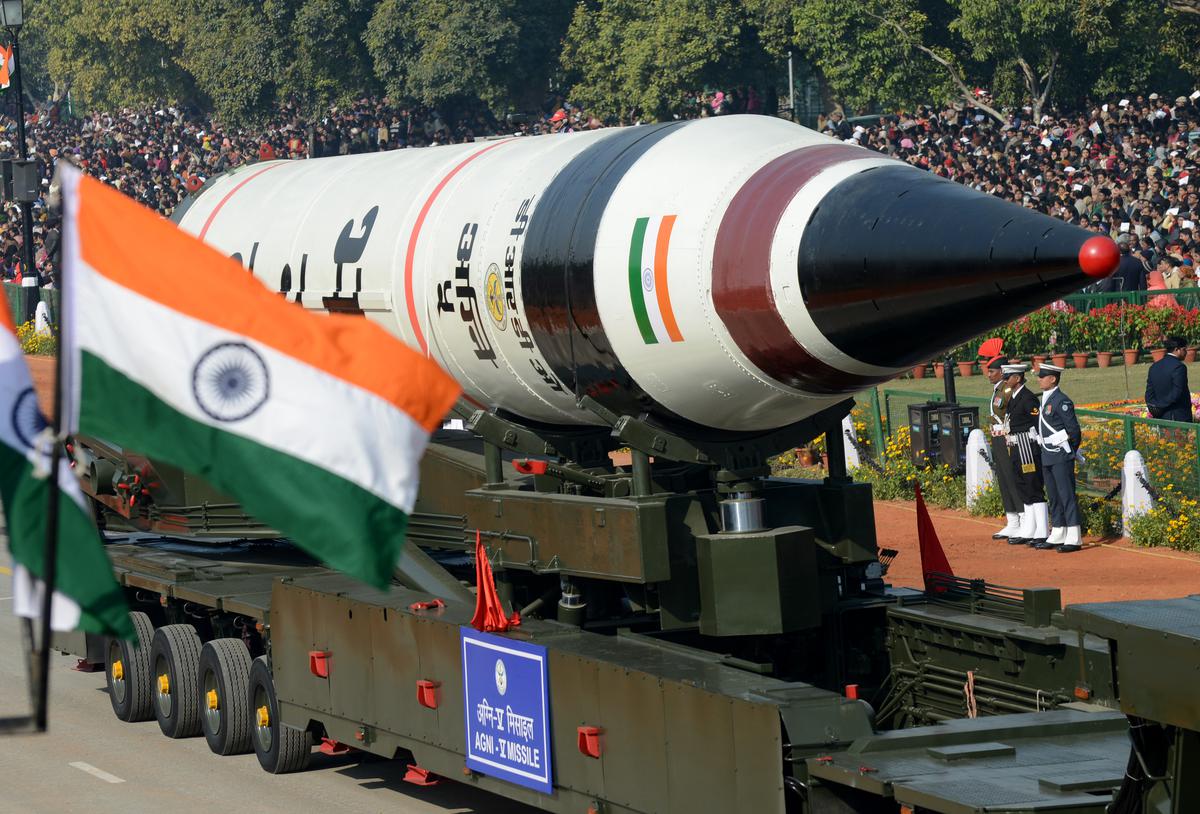

- 26 Aug 2025
In News:
India has successfully conducted the test of its nuclear-capable Agni-5 ballistic missile from the Integrated Test Range (ITR), Chandipur, Odisha. The launch was carried out under the Strategic Forces Command (SFC) and validated all operational and technical parameters, marking a significant boost to India’s strategic deterrence capabilities.
About Agni-5 Missile
- Type: Land-based Intercontinental Ballistic Missile (ICBM).
- Developer: Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO).
- Range: Beyond 5,000 km, capable of covering most of Asia and parts of other continents.
- Payload Capacity: Equipped with Multiple Independently Targetable Reentry Vehicle (MIRV) technology, enabling it to carry and deliver up to three nuclear warheads simultaneously at different targets.
- Technologies Used: Modern navigation, guidance, warhead, and propulsion systems, ensuring high accuracy and survivability.
Ballistic Missiles – Classification by Range
Ballistic missiles are rocket-propelled strategic weapons that follow a ballistic trajectory after the powered phase:
- Short-range: < 1,000 km (Tactical role).
- Medium-range: 1,000–3,000 km (Theater role).
- Intermediate-range: 3,000–5,500 km.
- Intercontinental (ICBM): > 5,500 km (Strategic role).
Agni-5, with its long range and MIRV capability, places India in the league of nations with advanced ICBM technology.
Strategic Significance
- Strengthens nuclear deterrence under India’s credible minimum deterrence and no first use (NFU) doctrines.
- Enhances India’s security architecture amidst evolving regional and global threats.
- Positions India among the select group of countries (U.S., Russia, China, France) with operational ICBM and MIRV capability.
National Policy to Promote Globally Important Agricultural Heritage Systems (GIAHS) in India
- 26 Aug 2025
In News:
- The Globally Important Agricultural Heritage Systems (GIAHS) programme, launched by the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) in 2002 at the World Summit on Sustainable Development, aims to conserve unique agricultural systems that sustain biodiversity, traditional knowledge, and rural livelihoods while adapting to modern challenges such as climate change, biodiversity loss, and community displacement.
- GIAHS adopts a multi-stakeholder approach by offering technical assistance, enhancing the value of traditional agricultural knowledge, and stimulating markets through agrotourism, product branding, and sustainable value chains.
India’s Recognised GIAHS Sites
Currently, India hosts three GIAHS sites, each reflecting diverse agro-ecological and cultural traditions:
- Koraput Region (Odisha):
- Known for subsistence paddy cultivation on highland slopes.
- Conserves a wide range of paddy landraces and farmer-developed varieties.
- Rich in medicinal plant genetic resources, closely linked with indigenous tribal knowledge.
- Supported by community seed banks, organic farming practices, and branding initiatives under state biodiversity programmes.
- Kuttanad Farming System (Kerala):
- A rare below-sea-level farming landscape.
- Comprises wetlands for paddy, garden lands for coconut and food crops, and inland water bodies for fishing and shell collection.
- Infrastructure development works under RKVY-DPR projects, such as HaritamHarippad in Alappuzha, and research on ecological utilization of water hyacinth are underway.
- Saffron Heritage of Kashmir:
- Represents a traditional agro-pastoral system of saffron cultivation.
- Characterized by organic farming practices, intercropping, and soil conservation.
- Supported through Rashtriya Krishi Vikas Yojana (RKVY) and the Mission for Integrated Development of Horticulture (MIDH) for revival and economic sustainability.
National Support Mechanisms
- Government Schemes: RKVY, MIDH, and other sectoral interventions promote conservation, branding, and livelihood opportunities.
- Biodiversity Revival: Emphasis on neglected crops and forgotten foods to ensure resilience.
- Integration with Research: State-supported projects in Kerala and Odisha enhance scientific validation and infrastructure.
Significance
- Ensures balance between conservation and socioeconomic development.
- Protects traditional knowledge systems and cultural landscapes.
- Enhances climate resilience and strengthens India’s commitment to sustainable agriculture.
- Promotes rural development, agrotourism, and niche product markets, thereby contributing to farmer incomes.
NAVYA Initiative

- 26 Aug 2025
In News:
- The Government of India launched the NAVYA (Nurturing Aspirations through Vocational training for Young Adolescent Girls) initiative in June 2025 to strengthen the socio-economic empowerment of adolescent girls (aged 16–18 years), particularly in aspirational districts.
- It is a joint initiative of the Ministry of Skill Development & Entrepreneurship (MSDE) and the Ministry of Women & Child Development (MWCD).
Objectives of NAVYA
- Vocational Training: Provide demand-driven skilling in both traditional and modern sectors.
- Holistic Development: Cover modules on health, nutrition, hygiene, life skills, financial literacy, and legal awareness.
- Enhancing Employability: Facilitate internships, apprenticeships, and job linkages, along with promoting self-employment.
- Gender-Inclusive Skilling: Ensure a safe and supportive training environment for adolescent girls.
- Bridging Gaps: Connect education and livelihood opportunities in underserved and remote regions.
Key Features
- Coverage: Implemented across 19 States and 27 districts, including Barpeta (Assam), Gaya (Bihar), Bastar (Chhattisgarh), Nuh (Haryana), Chamba (Himachal Pradesh), Baramulla (J&K), Raichur (Karnataka), Gadchiroli (Maharashtra), Rayagada (Odisha), Dholpur (Rajasthan), Virudhunagar (Tamil Nadu), Sonbhadra (Uttar Pradesh), and Haridwar (Uttarakhand), among others.
- Beneficiaries: 3,850 adolescent girls are being trained under Pradhan Mantri Kaushal Vikas Yojana (PMKVY) 4.0.
- Modern Job Roles: Training includes digital marketing, cybersecurity, AI-enabled services, green jobs, and other emerging sectors.
- Future Readiness: Modules on life skills, digital competence, and financial literacy prepare participants for evolving workforce demands.
Significance
- Strengthens women-centric skilling ecosystem.
- Promotes inclusive growth and gender equity in workforce participation.
- Supports Atmanirbhar Bharat by creating a skilled workforce in emerging sectors.
- Contributes to SDG 4 (Quality Education), SDG 5 (Gender Equality), and SDG 8 (Decent Work and Economic Growth).
Anna-Chakra

- 26 Aug 2025
In News:
The Government of India has introduced “Anna-Chakra”, a digital supply chain optimisation tool under the Public Distribution System (PDS), aimed at improving efficiency, reducing costs, and minimizing environmental impact in foodgrain distribution.
Implementation Status
- Implemented in 30 out of 31 States/UTs; yet to be implemented in Manipur.
- States/UTs covered include Punjab, Telangana, Tamil Nadu, Rajasthan, Bihar, Gujarat, Maharashtra, Uttar Pradesh, Delhi, J&K, Ladakh, Kerala, Karnataka, Odisha, among others.
Development and Collaboration
- Spearheaded by the Department of Food and Public Distribution.
- Developed in collaboration with:
- World Food Programme (WFP)
- Foundation for Innovation and Technology Transfer (FITT), IIT-Delhi
Working of Anna-Chakra
- Uses advanced algorithms to identify optimal routes for foodgrain movement across supply chain nodes.
- Covers 4.37 lakh Fair Price Shops (FPSs) and around 6,700 warehouses.
- Integrated with:
- FOIS (Freight Operations Information System) of Railways through the Unified Logistics Interface Platform (ULIP).
- PM Gati Shakti platform, which now houses geo-locations of FPSs and warehouses.
Key Benefits
- Financial Savings: Estimated ?250 crore per annum through reduction in transportation costs.
- Efficiency Gains: Faster delivery and streamlined PDS operations in the world’s largest food security programme benefiting 81 crore citizens.
- Environmental Impact: Reduction in fuel consumption and CO? emissions, aligning with India’s climate commitments.
- Operational Improvement: Ensures seamless coordination among multiple stakeholders, from farmers to FPS dealers.
Significance
Anna-Chakra represents a major leap in digitally enabled governance and logistics management, combining technology, sustainability, and welfare delivery. By cutting costs and carbon emissions while enhancing the efficiency of foodgrain delivery, it strengthens India’s food security architecture under the National Food Security Act (NFSA).
e-Jagriti Platform
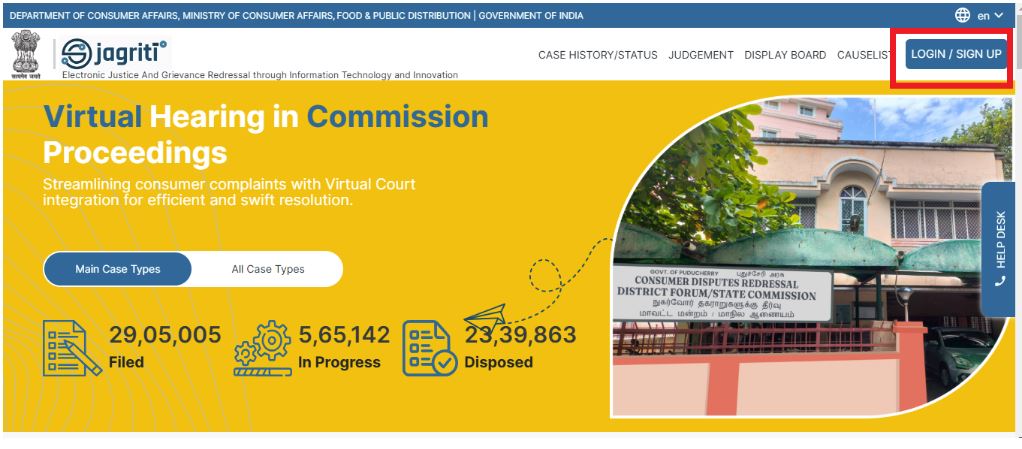
- 26 Aug 2025
In News:
In a significant boost to India’s consumer protection framework, ten States along with the National Consumer Disputes Redressal Commission (NCDRC) achieved a disposal rate of over 100% in July 2025. This indicates that the number of consumer cases resolved exceeded the number of new cases filed, showcasing efficiency in grievance redressal.
Key Disposal Achievements
- NCDRC: 122%
- Tamil Nadu: 277%
- Rajasthan: 214%
- Telangana: 158%
- Himachal Pradesh & Uttarakhand: 150% each
- Meghalaya: 140%
- Kerala: 122%
- Puducherry: 111%
- Chhattisgarh: 108%
- Uttar Pradesh: 101%
This trend highlights faster case resolution and effective functioning of consumer commissions across India.
The e-Jagriti Platform
The success is largely aided by e-Jagriti, a flagship digital initiative of the Department of Consumer Affairs, designed to strengthen the consumer dispute redressal system.
Objectives
- Computerization and networking of all Consumer Commissions (National, State & District).
- Enhancing transparency, efficiency, and speed in dispute resolution.
- Providing accessible, cost-effective, and paperless grievance redressal.
Features
- E-filing of complaints with online fee payment.
- Real-time case tracking and access to judgments.
- AI-powered Smart Search for archived complaints/judgments.
- Voice-to-text conversion of judgments and case details using AI/ML.
- Integration of multiple platforms:
- Online Case Monitoring System (OCMS)
- E-Daakhil
- NCDRC Case Monitoring System
- CONFONET website
- Mediation application
Since its launch, over 2 lakh users (including NRIs) have registered on e-Jagriti, with 85,531 cases filed online in 2025 alone, demonstrating growing public trust.
Significance
- Strengthens consumer rights and access to justice.
- Reduces backlog and delays through tech-driven case management.
- Promotes digital governance and transparency in consumer protection.
- Aligns with citizen-centric reforms and Digital India Mission.
UdyamSakhi Portal

- 25 Aug 2025
In News:
The UdyamSakhi Portal, launched by the Ministry of Micro, Small and Medium Enterprises (MSME) in March 2018, is helping women entrepreneurs across India start, build, and expand their businesses, fostering self-reliance and economic empowerment.
Objectives and Significance
The portal serves as a one-stop resource for existing and prospective women entrepreneurs, providing information on:
- Financial schemes such as the Prime Minister’s Employment Generation Programme (PMEGP), Credit Guarantee Fund Trust for Micro and Small Enterprises (CGTMSE), MUDRA, and Trade Receivables e-Discounting System (TReDS).
- Policies, programs, and business plan preparation.
- Nodal offices and supporting organizations of the MSME Ministry across states.
It also updates users on exhibitions, trade fairs, and international events, creating opportunities to connect with markets and expand business reach.
Programmatic Functions
UdyamSakhi provides a comprehensive suite of services, including:
- Entrepreneurship learning tools and guidance for business model creation
- Incubation facilities for nurturing startups
- Training programs for fundraising
- Mentorship support and one-on-one investor interactions
- Market survey support
- Learning and development through education, information, technical assistance, and training
The portal acts as a network for nurturing entrepreneurship, especially for low-cost products and services, enabling women to become self-reliant and self-sufficient.
Outreach and Impact
Since its inception, the portal has seen 4,535 women register, demonstrating its growing impact on women-led entrepreneurship in the MSME sector. Developed with an expenditure of ?43.52 lakh, the portal continues to expand access to resources, guidance, and opportunities for women entrepreneurs nationwide.
Sliteye Shark
- 25 Aug 2025
In News:
For the first time, scientists have recorded the sliteye shark (Loxodonmacrorhinus) in the Great Chagos Bank, the world’s largest coral atoll in the Indian Ocean. The discovery underscores the hidden biodiversity of the Chagos Archipelago and its Marine Protected Area (MPA), highlighting the ecological importance of deepwater habitats.
About the Sliteye Shark
The sliteye shark is a small-bodied requiem shark in the family Carcharhinidae and is the only species in the genus Loxodon. Named for its distinctive slit-like eyes, the species is adapted to low-light, deepwater environments, though it can also inhabit clear, shallow seas.
- Scientific Name:Loxodonmacrorhinus
- Size: Up to 95 cm in length
- Features: Slender body, long narrow face, large eyes, short furrows at mouth corners, small teeth with protruding tips, absent or rudimentary ridge between dorsal fins, gray coloration with white belly, dark-edged caudal and first dorsal fins
- Distribution: Tropical waters of the Indian and western Pacific Oceans, including countries such as India, Indonesia, Sri Lanka, Japan, Australia, China, Kenya, South Africa, and others between 34°N and 30°S
Discovery in Chagos
- Researchers observed two sliteye sharks at depths of 23–29 metres, just 11 km apart, using Baited Remote Underwater Video systems in deep seagrass habitats on the southern rim of the Great Chagos Bank. These meadows, first mapped in 2016 using satellite tracking of green turtles, support more than 110 fish species and are now confirmed as important for sliteye sharks as well.
Conservation Concerns
- The sliteye shark is classified as Near Threatened by the IUCN Red List, with populations projected to decline by approximately 30% over the next 15 years due to heavy fishing pressure.
- The Chagos discovery raises critical questions regarding the species’ abundance, habitat use, and conservation needs.
- The study forms part of a project led by Swansea University in collaboration with international partners, funded by the Bertarelli Foundation, with full findings expected in 2026. The results strengthen the case for protecting deepwater seagrass habitats in the Indian Ocean.
Sakura Science Programme 2025
- 25 Aug 2025
In News:
- A group of 34 students from government schools across India has been selected to participate in the Sakura Science Programme 2025, a prestigious Japan-Asia Youth Exchange Program in Science.
- The initiative, implemented by the Japan Science and Technology Agency (JST), provides young learners an opportunity to explore cutting-edge scientific innovations and experience Japanese culture firsthand.
Programme Details
- The 2025 edition of the programme was held, with participants from India, Egypt, Ghana, Kenya, Nigeria, South Africa, and Zambia. The Indian delegation consists of students, hailing from nine states—Andhra Pradesh, Bihar, Delhi, Himachal Pradesh, Lakshadweep, Odisha, Puducherry, West Bengal, and the Regional Institute of Education (RIE) demonstration schools in Ajmer, Bhopal, Bhubaneswar, and Mysuru. The students will be accompanied by three supervisors.
- The selected students were flagged off at a ceremony at NCERT, New Delhi, hosted by the Ministry of Education’s Department of School Education & Literacy (DoSEL), attended by key officials including Sanjay Kumar, Secretary of DoSEL, Professor Prakash Chandra Agrawal, Joint Director of NCERT, and Archana Sharma Awasthi, Joint Secretary of DoSEL.
Background and Objectives
Launched globally in 2014, the Sakura Science Programme aims to foster scientific curiosity among youth and promote international collaboration. India joined the programme in 2016, and since then, over 630 Indian students and 90 supervisors have participated.
The programme’s objectives include:
- Developing talented human resources overseas with potential contributions to science and technology innovation.
- Facilitating international brain circulation.
- Promoting continuous collaboration between Japanese and foreign educational and research institutes.
- Strengthening diplomatic relations through science and technology exchanges.
Through short-term visits to Japan, students gain exposure to advanced scientific research, innovation ecosystems, and Japanese culture, fostering both academic growth and cross-cultural understanding.
Nepal Eliminates Rubella
- 25 Aug 2025
In News:
The World Health Organization (WHO) has officially announced that Nepal has eliminated rubella as a public health problem, marking a significant achievement in the country’s fight against vaccine-preventable diseases. Nepal is the sixth country in the WHO South-East Asia Region to achieve rubella elimination, joining Bhutan, DPR Korea, Maldives, Sri Lanka, and Timor-Leste.
About Rubella
- Rubella, also known as German measles or three-day measles, is a highly contagious viral infection caused by the Rubella virus, an enveloped, single-stranded RNA virus distinct from the measles virus.
- Rubella primarily spreads through coughing, sneezing, or contact with contaminated surfaces, and can also be transmitted from a pregnant woman to her fetus.
- While rubella generally causes mild or no symptoms, the hallmark is a spotty red rash starting on the face or behind the ears and spreading to the neck and body.
- Infection during early pregnancy is particularly dangerous, with a 90% chance of virus transmission to the fetus, potentially causing miscarriage, stillbirth, or Congenital Rubella Syndrome (CRS). CRS may result in hearing impairments, eye and heart defects, and lifelong disabilities, including autism, diabetes, and thyroid dysfunction.
- Currently, there is no specific treatment for rubella, and symptoms are generally managed with rest and fever-reducing medications. Prevention through vaccination is key: the measles-mumps-rubella (MMR) vaccine is safe, highly effective, and provides lifelong protection.
Nepal’s Rubella Elimination Journey
- Nepal introduced the rubella-containing vaccine in its immunization program in 2012, targeting children aged 9 months to 15 years. A second dose was added to the routine immunization schedule in 2016.
- Nationwide campaigns in 2012, 2016, 2020, and 2024 helped achieve over 95% coverage for at least one dose, despite challenges such as the COVID-19 pandemic and earthquakes in 2015 and 2023.
- The country implemented innovative strategies such as observing an “immunization month,” outreach programs for missed children, and incentives for districts to achieve “fully immunized” status. Nepal also strengthened rubella surveillance through a robust laboratory testing algorithm, the first of its kind in the WHO South-East Asia Region.
Regional and Global Recognition
The Regional Verification Commission for Measles and Rubella (SEA-RVC), established in 2016, reviewed data from Nepal’s National Verification Committee and recommended verification of rubella elimination. Nepal’s Ministry of Health and Population acknowledged the contribution of government leadership, health workers, volunteers, and communities, alongside support from WHO and Gavi, in achieving this milestone.
The WHO South-East Asia Region initially aimed to eliminate measles and control rubella by 2020, later revising the target to 2023, and finally extending to 2026 due to setbacks caused by the COVID-19 pandemic. Nepal’s early achievement underscores the strength of its national immunization program and serves as a model for other countries in the region.
SWAYAM Portal
- 25 Aug 2025
In News:
The Ministry of Education (MoE) has launched five free Artificial Intelligence (AI) courses on the SWAYAM portal to equip students with the skills required in the rapidly growing AI-driven economy. These courses aim to enhance employability, promote research and innovation, and provide access to high-quality education for learners across India.
About SWAYAM
SWAYAM (Study Webs of Active–Learning for Young Aspiring Minds) is India’s indigenous Massive Open Online Course (MOOC) platform, launched in 2017. It seeks to bridge the digital divide and provide access to education for students across rural and urban areas. The platform hosts courses from Class 9 to post-graduation across disciplines including Engineering, Science, Humanities, Management, Commerce, Arts, Mathematics, and Language.
Courses are delivered in four quadrants:
- Video lectures
- Downloadable reading material
- Self-assessment tests (quizzes and assignments)
- Online discussion forums
Courses are free of cost, though learners opting for certification must pay a nominal fee. Successful completion is assessed through a proctored examination, and the earned credits can be transferred to a student’s academic record under UGC’s Credit Framework for Online Learning (2016).
National Coordinators of SWAYAM
- AICTE: Self-paced and international courses
- NPTEL: Engineering courses
- UGC: Non-technical post-graduate education
- CEC: Undergraduate education
- NCERT & NIOS: School education
- IGNOU: Out-of-school learners
- IIMB: Management studies
- NITTTR: Teacher training programs
- Institutes of National Importance (INI): Non-technical courses
SWAYAM Plus Platform
SWAYAM Plus, operated by IIT Madras, offers industry-collaborated courses to enhance employability. It focuses on sectors such as Manufacturing, Energy, IT/ITES, Healthcare, Management, Hospitality, and Indian Knowledge Systems, with features like multilingual content (12 Indian languages), AI-enabled guidance, credit recognition, and employment pathways.
Free AI Courses Offered
- AI/ML Using Python: Covers basics of AI, Machine Learning, Statistics, Linear Algebra, Optimization, Data Visualization, and Python programming. Duration: 36 hours with certification assessment.
- Cricket Analytics with AI: Introduces sports analytics using Python with cricket as a case study. Offered by IIT Madras. Duration: 25 hours with multiple-choice assessment.
- AI in Physics: Demonstrates how Machine Learning and Neural Networks can solve real-world physics problems through interactive sessions and lab work. Duration: 45 hours.
- AI in Accounting: Focused on commerce and management students, explaining applications of AI in accounting practices. Duration: 45 hours with certification assessment.
- AI in Chemistry: Teaches prediction of molecular properties, reaction modeling, and drug design using AI and Python. Duration: 45 hours, offered by IIT Madras.
These courses exemplify practical applications of AI, such as predicting outcomes from data—for instance, estimating the speed of the next ball in cricket by analyzing past records. They aim to prepare students for careers in technology, innovation, and research, keeping India at the forefront of the AI revolution.
Almond Cultivation in Kashmir

- 24 Aug 2025
In News:
The almond harvest in Kashmir is not only a vital agricultural activity but also a culturally significant seasonal event. This year’s bumper crop has brought relief and optimism to local farmers, reinforcing the economic and social importance of almond cultivation in the region.
About Almonds:
- Almonds are among the oldest and most widely cultivated tree nuts in the world, with two primary types: sweet almonds and bitter almonds.
- They are used extensively in culinary preparations, including sweets, almond milk, and as raw nuts, and are also processed for almond oil.
Climatic and Soil Requirements:
- Climate: Almond trees thrive in colder regions.
- Temperature: Optimal growth occurs between 7°C and 24°C.
- Soil: Deep, loamy, well-drained soils are ideal.
- Rainfall: Requires an average of 75–110 cm of rainfall.
- Altitude: Can grow effectively at 750–3200 meters above sea level.
Global and Indian Context:
- Major producing countries: USA, Australia, Spain, Turkey.
- In India: Almond cultivation is concentrated in hilly and colder regions, primarily in Jammu & Kashmir, Himachal Pradesh, Uttarakhand, with smaller cultivation in Kerala and some hilly areas of Andhra Pradesh.
Economic and Cultural Significance in Kashmir:
- Almond farming provides livelihoods to thousands of farmers in the region.
- The harvest season coincides with local festivals and traditional practices, reinforcing the crop’s cultural relevance.
- This year’s abundant yield has boosted local income and food security.
Primary Amoebic Meningoencephalitis (PAM)
- 24 Aug 2025
In News:
Kerala’s Kozhikode district has reported three recent cases of primary amoebic meningoencephalitis (PAM), including the death of a nine-year-old girl. A three-month-old infant and another child are currently receiving treatment. Following these incidents, the state health department has issued an alert to prevent further infections.
About Primary Amoebic Meningoencephalitis (PAM):
- Definition: PAM is a rare but severe infection of the brain and its protective membranes, caused by the free-living amoeba Naegleria fowleri, popularly called the “brain-eating amoeba.”
- Transmission: The amoeba thrives in warm, fresh water, soil, hot tubs, and improperly maintained swimming pools. Infection occurs when contaminated water enters the nose, allowing the pathogen to reach the brain and meninges. Dust or soil exposure can also serve as potential sources.
- Symptoms: Include headache, fever, nausea, vomiting, sore throat, hallucinations, and neurological deterioration. PAM progresses rapidly, often proving fatal within days.
- Treatment: Early diagnosis and administration of specific antibiotics can sometimes save lives, but recovery is rare. Globally, the disease has a 97% fatality rate, whereas Kerala has reduced it to 25% due to prompt medical interventions and protocols.
Other Amoebic Infections:
- Granulomatous Amebic Encephalitis (GAE): Caused by Acanthamoeba or Balamuthia mandrillaris, GAE progresses more slowly than PAM but is equally deadly if untreated. Unlike PAM, GAE does not necessarily require water exposure for infection.
Epidemiology in Kerala:
- The first PAM case in India was reported in 1971, and Kerala’s first case occurred in 2016. From 2016 to 2023, eight cases were confirmed in the state.
- Last year, Kerala recorded 36 positive cases with nine deaths, prompting the development of the state’s first standard operating procedure (SOP) for managing amoebic meningoencephalitis.
- Notably, in July 2024, a 14-year-old boy in Kozhikode became the first Indian to survive PAM, only the 11th survivor globally.
Factors Contributing to Recent Cases:
- Increased testing for acute encephalitis syndrome (AES).
- Environmental changes, including climate change and pollution.
- Greater awareness and proactive healthcare measures, leading to earlier detection and treatment.
Ionic Liquids

- 24 Aug 2025
In News:
Recent scientific research suggests that life could exist on rocky super-Earths with volcanic activity and minimal water, thanks to ionic liquids (ILs)—salts that remain liquid even in extreme conditions such as a vacuum.
About Ionic Liquids (ILs):
- ILs are salts that are liquid at room temperature, typically with melting points below 100°C.
- Unlike ordinary liquids composed of neutral molecules, ILs are made entirely of ions or short-lived ion pairs.
- Examples include tetrabutylammonium nitrite, 1-(Cyanomethyl)-3-methylimidazolium chloride, and choline acetate.
- ILs are also called liquid electrolytes, ionic melts, ionic fluids, fused salts, liquid salts, or ionic glasses.
Properties and Significance:
- Non-volatile and non-flammable, making them safe under extreme conditions.
- Thermally and chemically stable, resisting decomposition up to 200–400°C depending on composition.
- Can be hydrophobic or hydrophilic, and act as good conductors with a broad electrochemical range.
- Highly tunable: Their physico-chemical properties can be modified by changing the size and type of ions, making them versatile in applications.
Applications in Science and Industry:
- Widely used in synthesis, catalysis, extraction, electrochemistry, analytics, and biotechnology.
- Serve as environmentally friendly alternatives to conventional organic solvents and catalysts.
- Their stability under heat and vacuum conditions allows their use in high-temperature processes.
Role in Supporting Extraterrestrial Life:
- Laboratory experiments demonstrated that ILs can be created by mixing volcanic sulphuric acid with nitrogen-containing organic molecules found on planets.
- These liquids can dissolve biological molecules, offering a medium for biochemical reactions without the need for liquid water.
- This discovery expands the scope of habitable environments beyond Earth-like conditions, suggesting that life could potentially survive on arid, volcanic exoplanets.
SarvottamYudhSeva Medals
- 24 Aug 2025
In News:
On the eve of the 79th Independence Day, President DroupadiMurmu approved the awarding of seven SarvottamYudhSeva Medals (SYSM), the nation’s highest wartime distinguished service honour, to the leaders of Operation Sindoor, marking the first such awards since the Kargil War.
About the SarvottamYudhSeva Medal:
- Institution: 26 June 1980, to recognise distinguished service of the highest order during war, conflict, or hostilities.
- Eligibility: All ranks of the Army, Navy, Air Force, including Territorial Army Units, Auxiliary and Reserve Forces, and lawfully constituted Armed Forces when embodied. Nursing officers and members of the Nursing Services are also eligible. Awards can be given posthumously.
- Design: Circular medal, 35 mm in diameter, gold gilt, with the State Emblem and inscription “SARVOTTAM YUDH SEVA MEDAL” on the obverse, and a five-pointed star on the reverse. The ribbon is golden with a red vertical stripe in the centre. Subsequent awards are recognised by a Bar on the ribbon with a miniature insignia.
- Significance: Considered the wartime equivalent of the Param VishishtSeva Medal (PVSM) for exceptional service in peacetime. Previously awarded to three officers for Kargil War leadership: Lt Gen Amarjit Singh Kalkat, Air Marshal Vinod Patney, and Lt Gen Hari Mohan Khanna.
Escherichia coli
- 24 Aug 2025
In News:
Researchers have recently developed a method to transform genetically engineered Escherichia coli (E. coli) bacteria into self-powered chemical sensors capable of detecting mercury and directly interfacing with electronic devices. This breakthrough represents a significant advancement in environmental monitoring and bioengineering.
About Escherichia coli:
- E. coli is a rod-shaped bacterium belonging to the Enterobacteriaceae family, commonly found in the intestines of humans and animals.
- Most strains are harmless or beneficial, aiding digestion, but certain strains can cause illnesses such as diarrhea, urinary tract infections, respiratory issues, and pneumonia.
- Pathogenic strains, particularly Shiga toxin-producing E. coli (STEC), produce toxins that damage the intestinal lining, leading to symptoms such as fever, persistent diarrhea, bloody stools, and vomiting.
- Transmission occurs through contaminated food, water, or contact with fecal matter from infected individuals or animals.
- Most infections are self-limiting, and treatment primarily focuses on hydration and symptomatic care.
E. coli as a Mercury Sensor:
By leveraging synthetic biology, scientists have reprogrammed E. coli to detect trace amounts of mercury, a highly toxic heavy metal. These bacteria generate an electrical signal when they encounter mercury, allowing direct interfacing with electronic devices to provide real-time monitoring of environmental contamination.
Significance and Applications:
- Provides a low-cost, eco-friendly alternative to conventional mercury detection methods, which often rely on expensive and sophisticated instruments.
- Potential use in monitoring water bodies, industrial effluents, and soil for mercury pollution.
- Demonstrates the broader potential of bioengineered microorganisms in environmental sensing, medical diagnostics, and bio-electronic devices.
This development highlights the convergence of microbiology, synthetic biology, and electronics, paving the way for innovative solutions in pollution monitoring and environmental safety.
Golden Dome Missile Defense Shield

- 23 Aug 2025
In News:
The Golden Dome is a proposed ground- and space-based missile defense system of the United States, announced in 2025 with a projected outlay of $175 billion. It is designed to provide multi-layered protection against intercontinental ballistic missiles (ICBMs), hypersonic weapons, and cruise missiles from adversaries such as China, Russia, Iran, and North Korea.
Objectives
- Establish a comprehensive shield capable of intercepting hostile missiles in their boost, midcourse, and terminal phases.
- Enhance U.S. homeland security through satellite-based early warning, tracking, and interception.
- Integrate existing U.S. missile defense systems into a unified architecture.
Key Features
- Space-Based Layer
- Hundreds of satellites equipped with sensors and interceptors to detect and neutralize missiles soon after launch.
- Incorporation of laser-based systems for mid-flight interception.
- Ground-Based Layers
- Layer 2: Strengthening of the existing Ground-Based Midcourse Defense (GMD) in California and Alaska.
- Layer 3: Five new land-based launch sites (three in continental U.S., two in Hawaii and Alaska) to intercept missiles during their space trajectory.
- Layer 4: “Limited Area Defense” to protect key population centers, using radars, common launchers, and systems like Patriot, THAAD, and Aegis BMD.
- Integration with Existing Systems
- Builds upon existing U.S. missile defense infrastructure to ensure layered and redundant protection.
Comparison with Other Systems
- Israel’s Iron Dome: Golden Dome is often compared to Iron Dome, though the latter is designed for short-range rockets (4–70 km), while Golden Dome targets long-range ballistic and hypersonic threats.
- Reagan’s Strategic Defense Initiative (SDI/“Star Wars”): Golden Dome revives the 1980s concept of space-based defenses, but with advanced modern technology in satellites, sensors, and lasers.
Challenges
- Funding uncertainties: Though an initial $25 billion allocation has been proposed, political hurdles remain.
- Technological feasibility: Space-based interceptors and lasers pose significant challenges in cost, testing, and deployment.
- Strategic implications: Critics argue the system could revive debates on arms races and anti-ballistic missile treaties.
Significance
If realized, the Golden Dome would represent the most ambitious U.S. missile defense program since the Cold War, potentially altering global strategic stability by providing the U.S. with a multi-domain shield against next-generation missile threats.
Sri Lanka–India Naval Exercise (SLINEX-25)

- 23 Aug 2025
In News:
The 12th edition of the Sri Lanka–India Naval Exercise (SLINEX-25)was held recently, marking another milestone in the two-decade-long maritime cooperation between India and Sri Lanka. The exercise underscores India’s commitment to strengthening regional security in line with its vision of MAHASAGAR (Mutual and Holistic Advancement for Security and Growth Across Regions).
Background
- Initiation: Conceptualised in 2005, SLINEX has emerged as a key bilateral exercise, promoting interoperability and mutual trust.
- Previous edition: Conducted at Visakhapatnam, India in December 2024.
Participants
- India: INS Rana (Guided Missile Destroyer) and INS Jyoti (Fleet Tanker).
- Sri Lanka: SLNS Gajabahu and SLNS Vijayabahu (Advanced Offshore Patrol Vessels).
- Special Forces from both navies also took part.
Structure of the Exercise
- Harbour Phase:
- Professional interactions and Subject Matter Expert Exchanges (SMEE).
- Sharing of best practices, cultural and social events, yoga sessions, and sporting activities to strengthen naval camaraderie.
- Sea Phase:Naval drills including gunnery firing, seamanship evolutions, navigation, communication protocols, fueling at sea, and Visit Board Search and Seizure (VBSS) operations.
Significance
- Enhances interoperability between the two navies for multi-faceted maritime operations.
- Facilitates capacity-building and knowledge-sharing in naval tactics.
- Deepens people-to-people and defence diplomacy ties, reinforcing maritime security in the Indian Ocean Region (IOR).
- Complements India’s broader strategic engagement under MAHASAGAR to promote cooperative security and growth in the region.
Pradhan Mantri Viksit Bharat Rozgar Yojana

- 23 Aug 2025
In News:
In his 12th Independence Day address from the Red Fort (15 August 2025), Prime Minister Narendra Modi announced the launch of the Pradhan Mantri Viksit Bharat Rozgar Yojana (PMVBRY). With an ambitious financial outlay of nearly ?1 lakh crore, the scheme aims to generate over 3.5 crore jobs in two years, representing a landmark initiative to strengthen the bridge from Swatantra Bharat to Samriddha Bharat through massive employment creation.
Objectives
The scheme seeks to:
- Boost formal job creation by offering direct financial incentives to both employees and employers.
- Promote workforce formalisation by bringing more workers under the ambit of the Employees’ Provident Fund Organisation (EPFO).
- Encourage savings and financial literacy among youth entering the workforce for the first time.
- Catalyse employment growth in the manufacturing sector, a critical pillar of Make in India and Atmanirbhar Bharat.
Key Features of the Scheme
Part A – Support to First-Time Employees
- Targets first-time employees registered with EPFO.
- Provides one month’s EPF wage support up to ?15,000, disbursed in two instalments:
- First instalment after 6 months of continuous service.
- Second instalment after 12 months, subject to completion of a financial literacy programme.
- Incentive is partly locked in a savings/deposit account to encourage long-term financial discipline.
- Employees earning up to ?1 lakh per month are eligible.
- Expected to benefit 1.92 crore first-time employees.
Part B – Incentives for Employers
- Employers will be incentivised to create additional formal jobs, with a focus on manufacturing.
- Incentive: up to ?3,000 per employee per month for two years, provided the employment is sustained for at least six months.
- For the manufacturing sector, support will extend to the 3rd and 4th year as well.
- Expected to facilitate the creation of 2.6 crore jobs.
Incentive Payment Mechanism
- Payments to employees under Part A will be made via Direct Benefit Transfer (DBT) using the Aadhaar Bridge Payment System (ABPS).
- Payments to employers under Part B will be credited directly into PAN-linked accounts.
e-Sushrut@Clinic

- 23 Aug 2025
In News:
- India’s healthcare system is undergoing rapid digital transformation under the Ayushman Bharat Digital Mission (ABDM), launched in 2021 to build an integrated digital health infrastructure.
- In this context, the National Health Authority (NHA) and the Centre for Development of Advanced Computing (C-DAC) have signed an MoU to roll out e-Sushrut@Clinic—a lightweight, government-backed Hospital Management Information System (HMIS).
- Designed specifically for small and medium healthcare providers, this initiative seeks to bridge the digital divide, enhance interoperability, and empower clinics with affordable, secure, and efficient digital solutions.
Need for a Digital HMIS for Small Providers
- The demand for a trustworthy and affordable HMIS has been persistent, especially among small clinics and medium hospitals that face resource constraints.
- Feedback from ABDM microsites revealed the challenges of adopting costly and fragmented private solutions. While large hospitals like AIIMS have already benefitted from C-DAC’s flagship e-Sushrut HMIS—currently operational in 17 AIIMS and over 4,000 health facilities—a simplified version was needed for smaller stakeholders.
- By addressing these gaps, e-Sushrut@Clinic provides a low-cost, easy-to-adopt, and ABDM-enabled platform that ensures inclusivity in India’s digital health journey.
Features of e-Sushrut@Clinic
- Lightweight Cloud-Based System: Tailored for outpatient management, with pharmacy and nursing modules.
- Ease of Onboarding: Providers can register using the Health Facility Registry (HFR) and Health Professionals Registry (HPR). Even unregistered facilities can directly sign up on the platform.
- Comprehensive Utilities: Facilitates patient record digitization, prescriptions, billing, and telemedicine with minimal technical burden.
- Integration with ABDM Tools: Enables interoperability across the health ecosystem.
- Clinical Decision Support Systems (CDSS): Offers free AIIMS-developed modules for hypertension and diabetes, supporting doctors in evidence-based diagnosis and treatment.
- Patient-Centric Benefits: Enhances efficiency, data security, and patient satisfaction through transparent and reliable digital care.
Significance for Healthcare Delivery
- For Providers – Simplifies administrative processes, reduces paperwork, and improves continuity of care.
- For Patients – Facilitates secure access to health records, better treatment planning, and telemedicine consultations.
- For the System – Creates a standardised, interoperable, and government-backed HMIS that strengthens trust and accelerates the adoption of ABDM.
By reducing barriers to digital adoption, this initiative will benefit tens of thousands of doctors and facility managers nationwide.
Contribution to ABDM and Digital India
- e-Sushrut@Clinic is a pivotal step in expanding the ABDM ecosystem, which aims to create a digital health highway connecting patients, providers, and policymakers. Its low per-user cost ensures affordability, while government backing guarantees credibility.
- The platform complements other digital health initiatives by promoting transparency, efficiency, and interoperability.
- Moreover, it aligns with the Digital India mission, ensuring that even small clinics in rural and semi-urban areas can be integrated into the national digital health infrastructure.
Online Gaming Bill, 2025

- 23 Aug 2025
In News:
- The Promotion and Regulation of Online Gaming Bill, 2025, passed by Parliament, represents a landmark intervention in India’s digital policy.
- It seeks to prohibit exploitative online money games while simultaneously promoting e-sports and safe online social games.
- The legislation balances the twin objectives of protecting citizens, especially the middle class and youth, from financial and psychological harm and leveraging the potential of the online gaming industry as a driver of innovation, employment, and global competitiveness.
Rationale for the Bill
- The rapid proliferation of online money gaming platforms has led to addiction, financial ruin, fraud, and even suicides.
- The World Health Organization has classified “gaming disorder” as a health condition, reinforcing the urgency of regulation. According to government estimates, 45 crore people were adversely impacted, with losses exceeding ?20,000 crore.
- These platforms also posed risks of money laundering, terror financing, and cybercrime, exploiting loopholes in existing laws. With most operators based offshore, regulatory gaps persisted. Therefore, the Bill provides a comprehensive legal framework that integrates social protection with sectoral growth.
Understanding the Online Gaming Sector
- E-Sports – Organised competitive digital sports that foster strategy, teamwork, and discipline.
- Online Social Games – Recreational, skill-based, and educational games designed for safe entertainment and learning.
- Online Money Games – Games involving financial stakes, often associated with addiction, fraud, and economic distress.
The Bill encourages the first two categories while imposing a blanket ban on money games.
Key Provisions of the Bill
- Applicability: Extends to all of India, including offshore platforms offering services within India.
- Promotion of E-Sports: Recognised as a legitimate sport; guidelines to be framed by the Ministry of Youth Affairs and Sports, with support for training academies and tournaments.
- Encouragement of Social/Educational Games: Central Government to register safe games and develop platforms for digital literacy and skill-building.
- Ban on Online Money Games: Prohibition on offering, advertising, or facilitating such games; banks barred from processing related transactions.
- Online Gaming Authority: A national regulator to classify games, enforce compliance, and address grievances.
- Penalties: Up to 3 years imprisonment and ?1 crore fine for violations; harsher penalties for repeat offenders.
- Corporate Liability: Companies and responsible officers held accountable, with protection for independent directors.
- Investigative Powers: Authorised officers may search, seize, and arrest under the Bharatiya Nagarik Suraksha Sanhita, 2023.
Complementary Legal Measures
- IT Act, 2000 and Intermediary Rules, 2021 – Empower government to block illegal platforms; 1,524 sites already blocked.
- Bharatiya Nyaya Sanhita, 2023 – Criminalises betting and unlawful economic activities.
- GST Act, 2017 – Extends taxation compliance to offshore gaming platforms.
- Consumer Protection Act, 2019 – Prohibits misleading advertisements; celebrities warned against endorsing betting apps.
- Advisories and Education Guidelines – Awareness campaigns on safe gaming for parents, teachers, and youth.
Societal Benefits
- Consumer Protection: Shields families from predatory gaming platforms.
- Youth Empowerment: Expands avenues for e-sports careers and skill-based learning.
- Digital Economy Growth: Positions India as a global gaming hub, driving innovation, exports, and jobs.
- National Security: Prevents misuse of platforms for illicit financing or propaganda.
- Global Leadership: Establishes India as a model for responsible digital regulation.
Conclusion
The Promotion and Regulation of Online Gaming Bill, 2025 reflects India’s attempt to balance innovation with responsibility. By banning harmful money games while nurturing e-sports and educational platforms, the Bill not only safeguards citizens but also unlocks opportunities in the digital economy. It exemplifies a preventive yet progressive regulatory approach, aligning national security, youth welfare, and economic growth. Ultimately, it ensures that technology remains a tool for empowerment, not exploitation.
Indian Ports Bill, 2025
- 22 Aug 2025
In News:
The passage of the Indian Ports Bill, 2025 in both Houses of Parliament marks a landmark reform in India’s maritime governance. The new legislation replaces the colonial-era Indian Ports Act, 1908, bringing in a modern, transparent, and sustainability-driven framework for port development and operations.
Why the Reform was needed
- The 1908 Act, framed under colonial administration, had become outdated in the context of globalised trade, containerisation, and environmental challenges.
- India’s expanding maritime ambitions under the SagarmalaProgramme and Maritime India Vision 2030 required a contemporary law aligned with international standards.
- The reform is also tied to India’s long-term goal of becoming a leading maritime nation by 2047.
Key Objectives of the Bill
- Replace archaic colonial rules with a forward-looking framework.
- Strengthen cooperative federalism through Centre–State partnership in port governance.
- Promote ease of doing business with digitalised and simplified procedures.
- Encourage investment, including PPPs and FDI, by providing regulatory clarity.
- Standardise safety, security, and operational protocols across ports.
- Advance sustainability through green and smart port development.
Major Provisions
1. Institutional Reforms
- Maritime State Development Council (MSDC): A central–state body for coordinated planning, policy harmonisation, and dispute resolution.
- State Maritime Boards: Strengthened to manage non-major ports and oversee expansion/modernisation projects.
- Dispute Resolution Committees: Fast-track mechanisms for sectoral disputes among ports, operators, and users.
2. Operational Reforms
- Tariff Autonomy: Ports empowered to set competitive tariffs under transparent guidelines.
- Integrated Planning: Long-term strategies for cargo handling, multimodal logistics, and coastal shipping.
- Digitalisation: Introduction of the Maritime Single Window, e-clearances, and real-time vessel tracking to cut delays.
- Boost to Coastal & Inland Waterways: Greater connectivity with rail, road, and riverine transport.
3. Environmental & Safety Measures
- Mandatory Waste Reception Facilities and Ballast Water Management systems.
- Compliance with MARPOL (International Convention for the Prevention of Pollution from Ships).
- Emergency Preparedness Plans for accidents, natural disasters, and security threats.
- Promotion of renewable energy, electrification, and shore power systems to cut emissions.
Significance of the Bill
- Economic Growth: Ports as engines of trade, logistics, and job creation.
- Global Alignment: Brings India’s port governance on par with leading maritime nations.
- Sustainability: Push for eco-friendly, digitally enabled, and climate-resilient ports.
- Cooperative Federalism: Greater state participation ensures balanced and region-specific development.
The Bigger Picture
By integrating institutional, operational, and environmental reforms, the Indian Ports Bill, 2025 seeks to transform Indian ports into world-class hubs of trade and logistics. It not only aligns with global best practices but also supports the Prime Minister’s vision of “Ports for Prosperity”, contributing to India’s emergence as a maritime power by 2047.
First removable Solar Panel System between tracks

- 22 Aug 2025
In News:
Indian Railways has taken a major step towards achieving its net-zero carbon emission target by 2030 with the commissioning of India’s first removable solar panel system between railway tracks at Banaras Locomotive Works (BLW), Varanasi in August 2025.
About the Project
- Length of Installation: 70 metres
- Number of Panels: 28 removable panels
- Capacity: 15 KWp (Power density: 240 KWp/km; Energy density: 960 units/km/day)
- Special Feature: Panels are removable, enabling easy maintenance, emergency clearance, and seasonal adaptation.
- Design: Indigenously developed to be installed between tracks without disrupting rail traffic.
Technical Specifications of Panels
- Dimensions: 2278 mm × 1133 mm × 30 mm
- Weight: 31.83 kg per panel
- Type: 144 half-cut mono crystalline PERC bifacial collar cells (multi-bus bar)
- Efficiency: 20.15%
- Maximum Voltage: 1500V; Open Circuit Voltage (Voc): 49.71V
Significance
- Green Energy Transition: Promotes sustainable transport by reducing dependency on fossil fuels and cutting carbon footprint.
- Innovative Space Utilisation: Uses the space between tracks, avoiding land acquisition. Potential estimated at 3.5 lakh units/year/km of track. With IR’s 1.2 lakh km track length, the scalability is massive.
- Economic Efficiency: Supports auxiliary energy needs of railway units, lowering operational costs.
- Replicability: Being a pilot project, it serves as a model for adoption across Indian Railways.
Other Recent Railway Developments
- Green Logistics: In August 2025, the first salt-loaded freight rake from Sanosara (Bhuj–Naliya section) to Dahej carried 3,851.2 tonnes of industrial salt over 673.57 km, generating ?31.69 lakh in freight revenue. This initiative boosts regional industry and expands rail freight solutions.
- Electrification Innovation: Western Railway commissioned the country’s first 2×25 kV Electric Traction System at the Nagda–Khachrod section (Ratlam Division). Powered by two Scott-connected 100 MVA transformers, it enhances efficiency in overhead equipment (OHE) supply, marking a leap in electrification infrastructure.
Broader Context
- Indian Railways is rapidly expanding its solar adoption strategy, aligning with the National Solar Mission and Sustainable Development Goal (SDG-7: Affordable and Clean Energy).
- This innovation aligns with India’s climate commitments under the Paris Agreement and helps advance the country’s energy transition pathway.
Water-Scarce Districts in India
- 22 Aug 2025
In News:
Water, being a State subject, places the responsibility for augmentation, conservation, and efficient management primarily on State Governments. However, the Central Government supplements efforts through technical and financial support. Recent assessments by the Central Ground Water Board (CGWB) highlight the growing challenge of water scarcity in India.
Water-Scarce Districts in India
- The “National Compilation of Dynamic Ground Water Resources of India, 2024” jointly prepared by CGWB and State Governments, categorises districts based on groundwater status.
- Classification:
- Over-exploited: 102 districts
- Critical: 22 districts
- Semi-critical: 69 districts
- Total water-stressed districts:193
- Causes of Stress: Over-extraction for agriculture, rapid urbanisation, industrial demand, erratic monsoons, and climate variability.
- Geographic Spread: Punjab, Haryana, Rajasthan, Tamil Nadu, and Karnataka are among the most affected.
Government Initiatives
1. Jal Shakti Abhiyan (JSA) – 2019 onwards
- A mission-mode campaign for water conservation in 256 water-stressed districts.
- Scaled up nationwide with the tagline: “Catch the Rain – Where it Falls, When it Falls.”
2. Thematic Focus under JSA: Catch the Rain (CTR)
- 2023 – Source Sustainability for Drinking Water: Focused on 150 districts identified by Jal Jeevan Mission.
- 2024 – Nari Shakti se Jal Shakti: Focused on 151 districts identified by CGWB, highlighting women’s role in water management.
- 2025 – Jal Sanchay Jan Bhagidari: Focused on 148 districts, emphasising community participation, inter-sectoral convergence, and innovative financing.
3. Institutional Mechanism
- Central Teams: Comprising Central Nodal Officers (Additional Secretary/Joint Secretary level) and Technical Officers from agencies like CWC, CGWB, NIH, CSMRS, CWPRS, etc., for field monitoring and technical support.
- State Nodal Officers: Oversee campaign execution at state level.
- 148 Central Nodal Officers appointed for high-focus districts in JSA: CTR 2025–26.
Significance of Water Scarcity Data
- Drinking Water Security: Ensures reliable access in rural and urban areas.
- Climate Adaptation: Builds resilience against droughts and erratic rainfall.
- Policy Planning: Provides evidence for programmes such as Jal Jeevan Mission, Atal Bhujal Yojana, and achieving SDG 6 (Clean Water and Sanitation).
- Public Awareness & Participation: Encourages community-led water conservation for sustainable outcomes.
State of Food Security and Nutrition in the World 2025

- 22 Aug 2025
In News:
According to the UN’s “State of Food Security and Nutrition in the World 2025”, global undernourishment decreased to 8.2% (673 million individuals) in 2024, down from 8.5% in 2023.
India has been instrumental in this turnaround—its prevalence of undernourishment fell from 14.3% (2020–22) to 12% (2022–24), equating to 30 million fewer hungry people. These outcomes underscore India’s unique role in advancing SDG 2: Zero Hunger globally.
Defining Hunger: Layers and Causes
- Undernourishment: Insufficient calorie intake.
- Malnutrition: Poor diet quality lacking protein and essential micronutrients.
- Hidden Hunger: Micronutrient deficiencies (iron, iodine, vitamin A, zinc).
Root Causes:
- Economic barriers: Poverty limits access to nutritious food (NITI Aayog Index: ~11.3% multidimensionally poor).
- Agricultural inefficiencies: Fragmented holdings, climate variability, poor irrigation, and 13% post-harvest losses.
- High food costs: A nutritious diet remains unaffordable for over 60% of Indians.
- Weak infrastructure: Poor cold storage and logistics aggravate food wastage.
- Health and sanitation challenges: NFHS-5 (2019–21): 35.5% of children under five are stunted; 19.3% are wasted.
- Macro-disruptions: Global conflicts, pandemics, and climate shocks affect food systems, impacting India too.
India’s Strategic Interventions: From Policies to Systems
- Public Distribution System (PDS) Reforms
- Extensive digital overhaul: Aadhaar-based targeting, biometric authentication, real-time inventory tracking, and ONORC (One Nation One Ration Card) ensuring portability and inclusion for migrants and the vulnerable.
- Served over 800 million beneficiaries during COVID-19—a monumental welfare scaling.
- Emphasis on Nutrition Over Mere Calories
- Continued unaffordability of healthy diets (60%+ can’t afford) due to price inflation and weak linkages.
- Nutrition-centric interventions:
- PM POSHAN (2021): Expanded mid-day meals into nutrition-sensitive programs.
- ICDS & POSHAN Abhiyaan: Enhanced focus on dietary diversity and maternal-child health.
- AnaemiaMukt Bharat: Tackles widespread anaemia among women and children.
- Agrifood System Transformation
- Promote nutrient-dense food affordability (pulses, fruits, vegetables, animal-source proteins).
- Address 13% food loss via upgraded cold-chain infrastructure and logistics.
- Support women-led enterprises and FPOs, especially in climate-resilient, biofortified crop cultivation.
- Digital Innovations in Agriculture: Tools such as AgriStack, e-NAM, and geospatial platforms enhance market access, planning, and transparency.
Strategies for Sustainable Impact
|
Strategy |
Actions |
|
Nutrition-centric policy shift |
Fortify staples, subsidise nutrient-rich foods (pulses, eggs, milk) |
|
Infrastructure strengthening |
Upgrade cold storage, logistics, and digital post-harvest systems |
|
Inclusive economy |
Scale women-led food enterprises, FPOs, and biofortified crop cultivation |
|
Digital expansion |
Broaden use of AgriStack, e-NAM, geospatial tools for planning & targeting |
|
Urban nutrition resilience |
Launch community kitchens, food banks, awareness drives |
|
Global sharing & leadership |
Replicate ONORC, PDS digitalisation, nutrition models in the Global South |
Overseas Citizens of India (OCI) Scheme
- 22 Aug 2025
In News:
The Ministry of Home Affairs has announced new rules for overseas citizens of India that may impact their future registration or cancellation.
Background
The Overseas Citizens of India (OCI) Scheme was launched in 2005 by the Ministry of Home Affairs (MHA) to strengthen India’s engagement with its diaspora. It provides certain residency, travel, and economic benefits to foreign nationals of Indian origin, while keeping intact India’s constitutional restrictions on dual citizenship.
Key Features of OCI
- Eligibility:
- Persons who were citizens of India on or after 26 January 1950, or their children/grandchildren/great-grandchildren.
- Excludes individuals who have ever been citizens of Pakistan or Bangladesh, and their descendants.
- Benefits:
- Visa-free travel: Lifelong, multiple-entry, multi-purpose visa to India.
- Economic & Educational Rights: Can pursue education, invest in India, and purchase property (except agricultural/plantation land).
- Ease of Residency: Long-term residency without repeated visa applications.
- Restrictions:
- No political rights (cannot vote, contest elections, or hold constitutional posts).
- No ownership of agricultural or plantation land.
New Rules Notified by MHA (2025)
The government has tightened the regulatory framework around OCI registration by amending rules under the Citizenship Act, 1955 (Section 7D).
Fresh Grounds for Cancellation
- Conviction-based: If an OCI cardholder is sentenced to imprisonment for two years or more.
- Charge-sheet-based: If charge-sheeted for an offence punishable with seven years or more.
- Applicability: These provisions apply irrespective of where the conviction or charge-sheet occurs (India or abroad), provided the offence is recognised under Indian law.
Existing Grounds (already under law)
An OCI card can also be cancelled if the person:
- Obtained registration through fraud, misrepresentation, or concealment of facts.
- Has shown disaffection towards the Indian Constitution.
- Has engaged in unlawful trade or communication with an enemy during war.
- Acts against the sovereignty, integrity, security of India, or its friendly relations with other countries/public interest.
- Within five years of registration, is sentenced to imprisonment for two years or more.
Significance of the Amendment
- Strengthens legal accountability of OCI cardholders.
- Ensures parity of standards between domestic and overseas citizens regarding serious offences.
- Reinforces national security and constitutional safeguards while maintaining diaspora ties.
Damselfly Species
- 21 Aug 2025
In News:
Researchers have discovered two new species of damselflies in the Western Ghats—Konkan Shadowdamsel from Maharashtra’s Sindhudurg district and Crimson Shadowdamsel (Protosticta sanguinithorax) from Kerala’s Thiruvananthapuram district. The findings were published in the international journal Zootaxa.
About the New Species
- Group: Both belong to the genus Protosticta, commonly called Shadowdamsels, which prefer shaded forest habitats and pristine streams.
- Physical Traits:
- Crimson Shadowdamsel → reddish body.
- Konkan Shadowdamsel → coffee-brown ground colouration.
- Previously, these were mistaken for the Red-spot Shadowdamsel (Protosticta sanguinostigma), described over a century ago from the Nilgiris, which is jet black in colour.
- Identification: Differentiation was confirmed using high-resolution microscopy and molecular analysis of the COI gene, a standard marker for species classification.
- Distribution: Both species are endemics with very restricted microhabitats in the Western Ghats, often outside protected areas.
Ecological Importance
- Shadowdamsels are considered bioindicators:
- Found only in pristine forests with good canopy cover and unpolluted streams.
- Their presence reflects the ecological health of habitats.
- Many species are microendemics, restricted to small hill ranges, making them highly vulnerable to habitat disturbance.
- Current threats include expansion of plantations, deforestation of shade trees, and loss of natural streams.
Damselflies: A Brief Overview
- Belong to the order Odonata, along with dragonflies.
- Characteristics: slender body, delicate net-veined wings, weak flight.
- Habitat: shallow freshwater ecosystems.
- Difference from dragonflies: generally smaller, more fragile, and weaker fliers.
APAAR ID
- 21 Aug 2025
In News:
The Central Board of Secondary Education (CBSE) has made it mandatory for students to submit their APAAR ID during board exam registration, beginning with the 2026 board examinations. This marks a major step in integrating India’s education system under the Digital Public Infrastructure for Education (DPIE).
What is APAAR ID?
- Full Form: Automated Permanent Academic Account Registry.
- Origin: Envisioned under the National Education Policy (NEP), 2020.
- Nature: A unique, permanent 12-digit identification number assigned to every student from pre-primary to higher education.
- Function: Tracks a student’s entire academic journey, consolidating degrees, report cards, scholarships, awards, and credits.
- Integration:
- Linked to Aadhaar for authentication.
- Records stored in DigiLocker for easy and secure access.
- Generated through the Unified District Information System for Education Plus (UDISE+).
- Vision: Embodies the principle of “One Nation, One Student ID”, serving as a lifelong academic passport.
Objectives of APAAR
- Unified Academic Record – Create a lifelong, universally accessible digital database of academic achievements.
- Seamless Transfers – Facilitate smooth migration of students across schools and institutions.
- Transparency & Verification – Eliminate fake certificates and duplication through verifiable digital records.
- Policy Support – Aid educational policymaking and data-driven governance by maintaining standardized records.
- Student Empowerment – Provide students easy access to academic documents via DigiLocker.
Why is CBSE Making APAAR Mandatory?
- Until now, CBSE schools submitted student lists for Class 10 and 12 exams with registration details in Classes 9 and 11.
- There was no standardised identity system, causing inconsistencies and lack of verifiability.
- Linking APAAR ID with registration ensures accuracy, transparency, and elimination of duplication in student records.
- The Ministry of Education has mandated APAAR adoption as part of DPIE for improved data management and transparency.
Concerns and Safeguards
- Concerns Raised: Parents have expressed fears of misuse of personal data and privacy breaches.
- Government’s Assurance: Information will only be accessible to authorized educational entities—such as UDISE+, scholarship agencies, recruitment boards, and institutions—and strictly for academic purposes.
Significance
- APAAR will transform academic governance by creating a single, verifiable, lifelong academic identity.
- It will help students, institutions, and policymakers by streamlining record-keeping, enabling mobility, and ensuring trust in credentials.
- In the long term, it could become the backbone of India’s digital education ecosystem, aligned with NEP 2020’s vision of inclusivity, efficiency, and accountability.
RBI has released a report on the FREE-AI
- 21 Aug 2025
In News:
The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) has released the Framework for Responsible and Ethical Enablement of Artificial Intelligence (FREE-AI) Committee Report, marking a major step in shaping ethical, transparent, and sustainable AI adoption in India’s financial sector. The framework seeks to balance innovation with risk mitigation, ensuring that the transformative power of AI is harnessed without compromising trust, fairness, or safety.
RBI’s 7 Sutras for Responsible AI in Finance
The FREE-AI framework is built on seven guiding principles (Sutras):
- Trust is the Foundation – AI must be reliable, transparent, and inspire public confidence.
- People First – AI should empower human decision-making while safeguarding dignity, inclusion, and citizen interest.
- Innovation over Restraint – Encourage responsible innovation without excessive restrictions.
- Fairness and Equity – AI outcomes must be unbiased and equitable.
- Accountability – Responsibility for AI decisions rests with deploying entities, with clear lines of answerability.
- Understandable by Design – Systems must be interpretable and explainable to users, auditors, and regulators.
- Safety, Resilience, and Sustainability – AI must be secure, adaptable, and capable of delivering long-term benefits.
India’s Policy Developments
- MuleHunter AI – Developed by RBI Innovation Hub to detect mule accounts and curb digital frauds.
- Digital Lending Rules – Mandate auditable AI-driven credit assessments with human oversight and grievance redressal.
- SEBI’s 2025 Guidelines – Propose responsible AI use in Indian securities markets.
- IndiaAI Mission – Aims to boost AI innovation, research, and computational infrastructure.
RBI’s Recommendations under FREE-AI
The Committee laid down 26 recommendations across six pillars:
- Infrastructure – Establish high-quality financial data infrastructure, integrated with AI Kosh.
- Innovation Enablement – Create an AI Innovation Sandbox for testing models with anonymised data, ensuring compliance with AML, KYC, and consumer protection norms.
- Consumer Protection & Security – Periodic AI red-teaming, incident reporting frameworks, and good-faith disclosures.
- Capacity Building – Structured AI governance training at all institutional levels; knowledge sharing across REs (regulated entities).
- Governance – Oversight frameworks ensuring accountability and transparency in AI deployments.
- Assurance Mechanisms – Standards and audit processes for AI-based systems.
Higher Education Commission of India (HECI)
- 21 Aug 2025
In News:
India’s higher education system is poised for its most significant transformation since independence with the establishment of the Higher Education Commission of India (HECI), a unified regulatory body that will replace the fragmented oversight of University Grants Commission (UGC), All India Council for Technical Education (AICTE), and National Council for Teacher Education (NCTE).
Background & Genesis
- The HECI is a proposed unified regulator intended to replace the existing oversight bodies: UGC, AICTE, and NCTE—tasked with regulating non-technical, technical, and teacher-education domains respectively.
- The concept originates from NEP 2020, which advocates for a "light but tight" regulatory framework governed by one umbrella institution with four independent verticals.
- Originally floated in a 2018 draft bill, the idea regained momentum in 2021 and is currently under drafting, with status updates as recent as July–August 2025.
Objectives & Rationale
- Streamline governance: HECI aims to eliminate overlapping jurisdictions, reduce bureaucratic delays, and improve accountability across higher education institutions.
- Enhance autonomy and innovation: Under NEP 2020’s vision, it seeks to foster institutional independence coupled with data-driven oversight.
- Align with global best practices: The vertical structure (regulation, accreditation, funding, standards) mirrors international examples like the UK's Office for Students and Australia’s TEQSA.
Structural Framework: Four Vertical Councils
As per NEP 2020, HECI will function through four independent verticals:
- National Higher Education Regulatory Council (NHERC): Responsible for regulatory oversight, excluding medical and legal education.
- National Accreditation Council (NAC): Acts as a meta-accrediting body, setting phased benchmarks and ensuring quality across institutions.
- Higher Education Grants Council (HEGC): Will manage funding based on transparent, performance-linked criteria, replacing UGC’s funding role.
- General Education Council (GEC): Tasked with developing the National Higher Education Qualification Framework (NHEQF), defining graduate learning outcomes. It will subsume the NCTE and liaise with other professional standard-setting bodies.
Some sources also mention integration of accreditation entities such as NAAC and NBA into HECI’s accreditation wing, adopting peer-review models.
Legislative Journey & Current Status
- The HECI bill is being prepared following NEP 2020, specifically underwritten by Minister Sukanta Majumdar in July 2025. A Cabinet note is anticipated before formal introduction.
- Finalisation is pending, with no clear date as of mid-2025.
Expected Benefits
- Simplified administration—one regulator instead of multiple authorities.
- Improved transparency and efficiency, eliminating redundancy.
- Promoting global standards, quality enhancements, and integration of interdisciplinary and digital learning.
Gaur
- 20 Aug 2025
In News:
The Palamau Tiger Reserve (PTR), the last stronghold of the Gaur (Bos gaurus) in Jharkhand, has reported an alarming decline in population. Once spread across Saranda, Dalma, Hazaribagh, Gumla, and other forests of the state, Gaurs are now restricted to small and isolated groups in PTR’s northern range.
About Gaur
- Common name: Indian Bison
- Family: Bovidae; largest species of wild cattle.
- Distribution: Native to South and Southeast Asia.
- Preferred habitat:
- Evergreen, semi-evergreen, and moist deciduous forests with grasslands.
- Hilly terrains below 1,500–1,800 m with large, undisturbed forests and reliable water sources.
Conservation Status
- IUCN Red List: Vulnerable
- CITES: Appendix I
- Wildlife Protection Act, 1972: Schedule I
Population Trends in PTR
- 1970s population: ~150
- Recent study: Only 68 individuals remain.
- Demography: Slightly female-biased sex ratio (1:1.32), but very low numbers of juveniles and calves indicate poor recovery.
Ecological Significance
- Important prey species for large predators such as tigers and leopards.
- Herbivory: Helps regulate vegetation dynamics.
- Seed dispersal: Contributes to forest regeneration and ecosystem balance.
Causes of Decline
- Habitat degradation & fragmentation due to human activity.
- Anthropogenic pressures: Rising livestock populations (approx. 1.5 lakh around Betla region).
- Disease transmission from domestic cattle (e.g., foot-and-mouth disease, rinderpest).
- Genetic bottlenecks due to small and isolated herds.
Recovery Efforts in PTR
- Action Plan: “Ecology and Recovery Plan of Gaur in PTR” prepared after two years of research.
- Habitat improvement: Grassland expanded from 190 ha to 400 ha; waterholes secured.
- Security: 40 anti-poaching camps with round-the-clock staff.
- Technology: Use of GPS and modern monitoring systems.
- Disease control: Large-scale livestock vaccination programmes to reduce risks.
- Genetic infusion: Proposal to introduce Gaurs from Kanha Tiger Reserve (Madhya Pradesh) to improve genetic diversity.
About Palamau Tiger Reserve
- Location: Chota Nagpur Plateau, Jharkhand.
- Established: One of the first nine tiger reserves (1973 Project Tiger).
- Area: 1,129 sq km (Core: 414 sq km; Buffer: 715 sq km).
- Protected areas within PTR:
- Palamau Wildlife Sanctuary
- Betla National Park
Moai Statues
- 20 Aug 2025
In News:
A recent study published in the Journal of Cultural Heritage warns that rising sea levels may submerge Easter Island’s iconic Moai statues by 2080, endangering both the island’s cultural heritage and tourism-based economy.
About Moai Statues
- What they are: Massive monolithic statues carved from volcanic rock by the Rapa Nui people, the island’s first Polynesian settlers.
- Time of construction: Approx. 1250–1500 CE (some estimates: 1400–1650 CE).
- Number: Nearly 1,000 statues have been identified.
- Features:
- Tallest statue: ~33 feet high.
- Made primarily of volcanic tuff.
- Carved in the likeness of ancestors.
- Cultural role:
- Built to honor chiefs and important individuals.
- Placed on rectangular stone platforms called ahu, which also served as tombs.
- Each statue has unique traits to represent the person commemorated.
Study Findings
- Researchers used digital twin models and advanced simulations to project flooding risks caused by sea-level rise.
- Results show that by 2080, seasonal waves could reach Ahu Tongariki – the largest ceremonial platform on the island, part of the Rapa Nui National Park (UNESCO World Heritage Site since 1995).
- The flooding could impact 51 cultural assets, including the world-famous Moai statues.
- The study emphasizes the urgency of local community planning to safeguard heritage against climate risks.
Easter Island – Key Facts
- Location: Eastern Pacific Ocean.
- Forms part of the Polynesian Triangle along with Hawaii and New Zealand – the traditional homeland of Polynesian peoples.
- Known globally for its archaeological and cultural significance, particularly the Moai statues.
Mud Waves
- 20 Aug 2025
In News:
A recent study published in Global and Planetary Change (2025) has uncovered 117-million-year-old mud waves buried nearly 1 km beneath the Atlantic seabed west of Guinea-Bissau. This finding reshapes our understanding of the formation of the Atlantic Ocean, ancient climate patterns, and tectonic shifts during the Cretaceous period.
About Mud Waves
- Definition: Large, rhythmic sedimentary structures formed on the seafloor by persistent bottom currents.
- Age & Size: Approximately 117 million years old; over 1 km long and several hundred meters high.
- Location: Deep seabed, west of Guinea-Bissau, near the Equatorial Atlantic Gateway.
- Composition: Layered sediments preserving evidence of historic ocean circulation.
Formation Process
- Early Atlantic Spillover: Around 117 million years ago, the young North Atlantic Ocean began spilling dense, salty waters into southern basins through the newly formed Equatorial Atlantic Gateway.
- Underwater Avalanches: The influx collided with older, stagnant waters rich in mud and organic matter, triggering massive sediment avalanches.
- Wave Formation: These currents pushed and piled up sediments into wave-like structures, which solidified into permanent mud waves over millions of years.
Scientific Significance
- Rewrites Ocean History: Suggests Atlantic waters circulated much earlier than previously thought.
- Climate Insights: Provides evidence of Cretaceous climate shifts and ancient carbon cycles.
- Tectonic Implications: Offers clues to plate movements shaping Earth’s geography during the breakup of Gondwana.
About the Atlantic Ocean
- Size & Shape: Second-largest ocean after the Pacific; distinctive ‘S’-shape.
- Major Features:
- Mid-Atlantic Ridge: 14,000 km long, ~4 km high, central seafloor mountain range.
- Continental Shelves: Widest along NE America and NW Europe.
- Islands & Seamounts: Azores, Canary Islands, Bermuda, Cape Verde.
- Trenches: Puerto Rico Trench, Romanche Trench (less prominent than Pacific trenches).
- Marginal Seas: Hudson Bay, Gulf of Mexico, Baltic Sea.
India Semiconductor Mission
- 20 Aug 2025
In News:
The Union Cabinet has cleared four new semiconductor manufacturing projects worth ?4,600 crore in Odisha, Punjab, and Andhra Pradesh under the India Semiconductor Mission (ISM). With this, the total number of approved projects under ISM has reached ten across six states, attracting cumulative investments of nearly ?1.60 lakh crore.
Details of Newly Approved Units
- SiCSem Pvt. Ltd. (Odisha):
- In partnership with UK-based Clas-SiC Wafer Fab Ltd.
- India’s first commercial compound semiconductor fabrication unit focused on Silicon Carbide (SiC) devices.
- Capacity: 60,000 wafers and 96 million packaged units annually.
- 3D Glass Solutions Inc. (Odisha):
- Will establish a vertically integrated packaging and embedded glass substrate unit.
- Focus: 3D Heterogeneous Integration modules.
- ASIP Technologies (Andhra Pradesh):
- Joint venture with APACT Co. Ltd., South Korea.
- Annual capacity: 96 million units.
- Applications: Mobile phones, set-top boxes, automobiles, and other electronic devices.
- Continental Device India Pvt. Ltd. (Punjab):
- Brownfield expansion of its Mohali facility.
- Focus: High-power discrete devices – MOSFETs, IGBTs, Schottky diodes, and transistors (using both silicon and SiC).
- Capacity: 158.38 million units annually.
Production from these units is expected to commence within the next 2–3 years.
Progress under ISM
- Launch Year: 2021
- Nodal Ministry: Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology (MeitY)
- Objective: Establish a self-reliant semiconductor and display ecosystem in India.
- Support: Incentive package of ?75,000 crore for fabs, ATMP/OSAT, compound semiconductor plants, and display fabs.
- Capacity Building: Target to train 60,000+ skilled professionals.
- Strategic Significance: Reduce import dependency, boost Atmanirbhar Bharat, and make India a global semiconductor hub.
Major Ongoing Projects under ISM
- Tata-PSMC Fab (Dholera, Gujarat): ?91,526 crore investment; capacity of 50,000 wafers/month for automotive and AI; operational by 2026.
- Micron ATMP (Sanand, Gujarat): ?22,900 crore investment; focus on DRAM and NAND packaging; expected by late 2025.
- Tata TSAT OSAT (Jagiroad, Assam): Output of 48 million chips/day.
- Kaynes OSAT (Sanand, Gujarat): Capacity of 6 million chips/day for telecom and industrial use.
- HCL–Foxconn JV (Uttar Pradesh): To produce 36 million display driver chips/month by 2027.
Burevestnik Missile
- 20 Aug 2025
In News:
According to recent reports, Russia is preparing to conduct fresh trials of the 9M730 Burevestnik – a nuclear-powered cruise missile that has often been described as a “unique” and formidable addition to Moscow’s strategic arsenal.
About the Burevestnik
- The term Burevestnik translates to “storm petrel” in Russian.
- It is a ground-launched, nuclear-powered cruise missile, also capable of carrying a nuclear warhead.
- The system was first unveiled by the Russian President in 2018, as part of six advanced strategic weapons.
- NATO has designated it as SSC-X-9 “Skyfall.”
- In theory, its nuclear propulsion allows it to circle the globe multiple times before striking a target, making it an unprecedented strategic weapon.
Key Features
- Nuclear Propulsion: The missile uses a compact nuclear reactor that heats the surrounding air for thrust.
- Extended Range: Unlike traditional engines restricted by fuel capacity, the nuclear design enables a potential range of up to 22,000 km (14,000 miles).
- Low-Altitude Flight: The system is engineered to fly close to the ground, significantly reducing its detectability by conventional air-defence radars.
- Strategic Significance: Its combination of long endurance and stealthy trajectory poses challenges to existing missile defence systems.
SabhaSaar
- 19 Aug 2025
In News:
The Government of India is set to launch ‘SabhaSaar’, an Artificial Intelligence (AI)-based tool designed to automatically generate structured minutes of gram sabha meetings, thereby enhancing transparency, uniformity, and efficiency in local governance. The tool will be first rolled out in Tripura on Independence Day (August 15) and later extended to other states.
What is SabhaSaar?
- Gram Sabha: It is the primary body of the Panchayati Raj system, consisting of all registered voters of a gram panchayat. Gram sabhas are mandated to meet at least four times a year (January 26, May 1, August 15, and October 2).
- SabhaSaar: An AI tool that converts audio and video recordings of gram sabha meetings into structured minutes, ensuring uniformity across the country.
- Access: Panchayat officials can upload recordings using their e-GramSwaraj login credentials.
Key Features
- AI-driven transcription &summarisation: Generates transcripts, translates into the chosen language, and prepares concise summaries.
- Language inclusivity: Built on Bhashini, the government’s AI-powered language platform, it supports transcription in all major Indian languages (Hindi, Bengali, Tamil, Telugu, Marathi, Gujarati) and English.
- Standardisation: Ensures uniformity of gram sabha documentation nationwide.
- Ease of governance: Facilitates instant access to insights for panchayats, administrative bodies, and rural development projects.
Associated Reforms for Gram Sabhas
- Panchayat NIRNAY Portal: A real-time monitoring system for gram sabha meetings, enabling scheduling, agenda notification to citizens, decision tracking, and transparency in implementation.
- Recent progress: In 2024–25, more than 10,000 gramsabha meetings were held through the NIRNAY platform, with Punjab, Andhra Pradesh, Telangana, and Bihar leading in usage.
Significance
- Governance efficiency: Automates and digitises record-keeping, reducing errors and delays.
- Transparency & accountability: Ensures that decisions of gram sabhas are properly recorded and accessible.
- Public participation: Facilitates better citizen awareness and engagement in local governance.
- Bridging digital divide: Through Bhashini, makes governance accessible across linguistic barriers.
Cheque Truncation System (CTS)

- 19 Aug 2025
In News:
The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) has announced the transition of the Cheque Truncation System (CTS) from batch processing to a continuous clearing mechanism, with settlement on realisation, to be implemented in two phases. This reform aims to further enhance efficiency, reduce delays, and strengthen the digitalisation of cheque-based transactions.
About Cheque Truncation System (CTS)
- Introduced by RBI to speed up cheque clearance and minimise physical movement of instruments.
- Process: Physical cheques are truncated at the collecting bank; only cheque images and MICR data are transmitted electronically.
- Security: Protected by a PKI-based security architecture with dual access controls, user authentication, crypto box, and smart card interfaces.
- CTS-2010 Standards: Only compliant instruments are accepted, ensuring:
- Use of specified paper quality, watermark, and invisible-ink logos.
- Mandatory minimum-security features like void pantograph.
- Standardised cheque design for uniform image-based processing.
Current vs. New System
- Current CTS: Clearing cycle takes up to two working days.
- New System (Continuous Clearing):
- Cheques will be cleared within hours of submission.
- Settlement will occur on realisation basis rather than at fixed batch intervals.
Benefits
- Faster Settlement: Realisation of cheque proceeds on the same day.
- Efficiency Gains: Reduced bottlenecks and delays in processing.
- Cost Savings: Eliminates costs linked to physical cheque movement.
- Security & Reliability: Enhanced authentication safeguards against fraud.
- Better Data Management: Easy storage and retrieval of digital records via a centralised archival system.
- Customer Convenience: Shorter clearing cycles improve banking efficiency for individuals and businesses.
NashaMukt Bharat Abhiyaan (NMBA)

- 19 Aug 2025
In News:
India has intensified efforts to combat substance abuse through community engagement and national-level programmes. Recently, a “Drug-Free India” campaign was held in Mysuru, complementing the larger framework of the NashaMukt Bharat Abhiyaan (NMBA), which has completed five years since its launch in 2020.
About NashaMukt Bharat Abhiyaan (NMBA)
- Launched: 15 August 2020.
- Nodal Ministry: Ministry of Social Justice & Empowerment (MoSJE).
- Objective:
- Reduce drug demand through awareness, prevention, and education.
- Strengthen community response by mobilising youth, women, and local institutions.
- Provide rehabilitation and treatment support to victims of addiction.
Key Features
- Targeted Districts: Implemented in 272 high-risk districts identified through national surveys and Narcotics Control Bureau (NCB) data.
- Three-Pronged Strategy:
- Supply Reduction: Led by NCB.
- Demand Reduction: Community outreach under MoSJE.
- Treatment: Medical interventions coordinated by the Health Department.
- Community-Based Model: District and state committees headed by senior officials ensure localised implementation.
- Technology Integration: Dedicated NMBA app, website, and social media platforms for wider outreach.
- Mass Mobilisation: Partnerships with civil society organisations like Art of Living, Brahma Kumaris, and ISKCON for awareness drives.
Impact
- Public Health: Over 18 crore citizens sensitised, with a focus on youth and women.
- Capacity Building: More than 20,000 Master Volunteers trained nationwide.
- Social Stability: Contributed to reducing drug-related crime and strengthening the social fabric.
- Awareness Events: Local campaigns such as the Drug-Free India drive in Mysuru amplify the Abhiyaan’s outreach at the grassroots level.
Significance
- Strengthens India’s commitment to tackling the drug menace through prevention, rehabilitation, and community participation.
- Complements India’s obligations under international conventions on narcotic drug control.
- Directly contributes to SDG 3 (Good Health and Well-being) and SDG 16 (Peace, Justice, and Strong Institutions).
Human African Trypanosomiasis (HAT)
- 19 Aug 2025
In News:
The World Health Organization (WHO) has certified Kenya as free from human African trypanosomiasis (HAT), or sleeping sickness, marking it the 10th African nation to eliminate the disease as a public health problem (August 2025). This is Kenya’s second victory against a Neglected Tropical Disease (NTD) after eliminating guinea worm disease in 2018.
About Human African Trypanosomiasis (HAT)
- Cause: A vector-borne parasitic disease caused by the protozoa Trypanosoma brucei.
- Vector: Spread by the bite of infected tsetse flies (Glossina spp.).
- Types:
- T.b.gambiense (West & Central Africa): Chronic, slow-progressing form.
- T.b. rhodesiense (East & Southern Africa): Acute, fast-progressing form (present in Kenya).
- Symptoms:
- First stage: Fever, headache, joint pain, swollen lymph nodes.
- Second stage: Parasites invade the central nervous system → confusion, behavioural changes, loss of coordination, and disrupted sleep cycle.
- Fatal if untreated, though effective drugs exist (pentamidine, suramin, fexinidazole, nifurtimox–eflornithine, melarsoprol), supplied free by WHO.
Kenya’s Journey
- History: First detected in early 20th century; no indigenous cases since 2009. Last imported cases reported in 2012 (Masai Mara).
- Control measures:
- Strengthened disease surveillance in 12 facilities across 6 endemic counties (Busia, Siaya, Kisumu, Homa Bay, Migori, Kwale).
- Upgraded laboratories, diagnostic capacity, and trained personnel.
- Controlled tsetse flies and animal trypanosomiasis with veterinary support.
- Partnerships: WHO, Kenya’s Ministry of Health, FIND (Foundation for Innovative New Diagnostics), and community engagement played key roles.
Global Context
- WHO’s NTD Road Map 2021–2030: Target—100 countries to eliminate at least one NTD by 2030.
- So far, 57 countries (including Burundi, Senegal) have achieved elimination of at least one NTD.
- However, cuts in international funding threaten progress, risking resurgence in vulnerable areas.
- Success is critical for meeting SDG 3 (Good Health and Well-being), particularly the target of ending epidemics of NTDs by 2030.
Bhu-Neer Portal

- 19 Aug 2025
In News:
The Bhu-Neer Portal, launched in 2024 during the 8th India Water Week by the Ministry of Jal Shakti, is a digital initiative developed by the Central Ground Water Authority (CGWA) in collaboration with the National Informatics Centre (NIC). It represents a significant reform in the regulation and management of groundwater extraction in India.
Background:
- CGWA: Constituted under the Environment (Protection) Act, 1986, regulates and controls the development and management of groundwater resources in the country.
- NIC: Established in 1976, under MeitY, it supports e-Governance and digital platforms for sustainable development.
- The portal replaces the earlier NOCAP system, offering a more transparent, user-friendly, and efficient mechanism for granting No Objection Certificates (NOCs) for groundwater abstraction.
Objectives:
- To provide a centralised, transparent, and efficient platform for groundwater regulation.
- To ensure compliance with the Guidelines of September 24, 2020 on groundwater abstraction.
- To promote sustainability by integrating water conservation measures such as rooftop rainwater harvesting and sewage treatment plants.
Key Features:
- PAN-based Single ID System for ease of access and integration with payment gateways.
- QR code-enabled NOCs for secure and quick verification.
- Online charges calculator for transparency in fee structures.
- Eligibility checker before filing applications.
- Query module for real-time interaction with CGWA officials.
- SMS and email alerts to track application status.
- Centralised database for groundwater compliance, policies, and monitoring.
Scope:
- Applicable in 19 States/UTs where groundwater regulation is under CGWA’s jurisdiction.
- Covers industries, infrastructure, and mining projects seeking to abstract groundwater.
Significance:
- Strengthens enforcement of groundwater guidelines, curbing indiscriminate extraction.
- Enhances Ease of Doing Business by streamlining NOC procedures.
- Promotes water-use efficiency and sustainable management of depleting groundwater resources.
- Facilitates greater transparency and accountability in resource governance.
Awareness & Outreach:
- The Ministry has organized workshops with industry bodies and Public Interaction Programmes (PIPs) to promote adoption of the portal among stakeholders.
Chagas Disease
- 18 Aug 2025
In News:
- Chagas disease, or American trypanosomiasis, is an infection caused by the protozoan Trypanosoma cruzi and is transmitted primarily through the feces of triatomine bugs—commonly known as “kissing bugs.”
- It can also spread via congenital transmission (from mother to child), contaminated food or water, blood transfusion, organ transplant, or during laboratory handling.
- Though initially endemic to South and Central America, and Mexico, the disease has now emerged as a global health concern, partly due to migration and local vector presence in places like the southern United States.
Clinical Progression & Treatment
- Many infected individuals remain asymptomatic initially, but chronic infection can lead to severe cardiac and digestive complications if left untreated.
- In the acute phase, antiparasitic treatment is aimed at eliminating the parasite. In the chronic phase, therapeutic focus shifts to managing symptoms since parasite clearance becomes difficult.
Alarming Underinvestment in R&D
- R&D investment for Chagas disease is startlingly low—accounting for only 0.6% of all neglected disease research globally.
- This share is even smaller when compared to other tropical diseases: less than US$1 million was spent on new drug development in 2007, constituting a mere 0.04% of neglected disease R&D funding.
- Between 2009 and 2018, US$236 million was invested in Chagas-related R&D—just 0.67% of the total neglected disease investment. Only a handful of funders (NIH, industry, Wellcome Trust) accounted for the majority.
- Patent data reflect this disparity, especially in vaccine development—highlighting significant underinvestment relative to the global health threat posed by Chagas.
- To put it in perspective, malaria receives 20 times more funding than Chagas.
Pathways to Progress
- Innovative Therapies: Research shows promise in novel, low-cost immunotherapeutic agents derived from cyanobacteria that may offer safer and more tolerable options than current drugs.
- Campaigns and Advocacy: Initiatives like the “Chagas: Time to Treat” campaign by DNDi (Drugs for Neglected Diseases Initiative) emphasize urgent need for:
- Affordable, pediatric formulations
- Safe, field-ready treatments for chronic phases
- Greater public and private funding for R&D.
Broader Significance and Current Calls to Action
- Chagas disease remains among the most neglected tropical diseases, impacting an estimated 6 million people, causing approximately 12,000 deaths annually, and contributing to over 30,000 new cases each year—mainly in Latin America.
- Effective solutions require:
- Improved surveillance and mandatory case notification systems
- Enhanced training and diagnostic tools for health workers
- Integration of One Health approaches (veterinary, environmental control, and human health) in vector management.
- Investment in neglected disease R&D delivers substantial societal returns—studies suggest $1 spent yields $405 in broader economic and health benefits.
18th International Olympiad on Astronomy and Astrophysics

- 18 Aug 2025
In News:
India is hosting the 18th International Olympiad on Astronomy and Astrophysics (IOAA) in Mumbai, Maharashtra, with participation from over 300 young astronomers from 64 countries. The event is jointly organised by the Homi Bhabha Centre for Science Education (HBCSE), Tata Institute of Fundamental Research (TIFR), and the Union Ministry of Education.
About IOAA:
- A premier global competition for high-school students in astronomy, astrophysics, and observational sciences.
- Tests theoretical knowledge, data analysis skills, and observational abilities.
- Objectives:
- Promote scientific thinking and problem-solving in space sciences.
- Encourage international cooperation and cultural exchange.
- Inspire careers in space sciences and research.
- Showcase India’s scientific and technological progress.
Features of the 18th Edition:
- Largest-ever IOAA with record participation from 64 nations.
- Competition includes written exams, data analysis, and night-sky observations.
- Highlighting India’s legacy: From Aryabhatta’s discoveries to modern space missions like Chandrayaan-3 (historic landing near Moon’s South Pole) and Aditya-L1 (India’s first solar observatory).
- Showcasing STEM Empowerment:
- Atal Tinkering Labs benefitting over 10 million students through hands-on STEM learning.
- One Nation One Subscription scheme providing free access to global research journals for students and researchers.
- Global Collaboration: Participation in mega-science projects such as the Square Kilometre Array and LIGO-India.
Significance for India:
- Strengthens India’s global image as a leader in space sciences and STEM education.
- Provides a platform for showcasing India’s scientific achievements and educational initiatives.
- Encourages the next generation to pursue careers in astronomy, astrophysics, and research.
- Aligns with India’s broader vision of linking science, innovation, and human welfare.
UNDP Equator Initiative Award 2025

- 18 Aug 2025
In News:
The Bibi Fatima Women’s Self-Help Group (SHG) from Teertha village, Kundgol taluk, Dharwad district, Karnataka, has won the prestigious Equator Initiative Award 2025. The award, often referred to as the Nobel Prize for Biodiversity Conservation, honours community-led, nature-based solutions for sustainable development.
About the Equator Initiative Award:
- Organiser: United Nations Development Programme (UNDP) under its Equator Initiative.
- Nature: Recognises local and indigenous communities for biodiversity conservation, ecological resilience, and poverty reduction.
- Frequency: Biennial.
- Prize: Includes a cash award of $10,000 (approx. ?8.5 lakh).
- Theme (2025):“Women and Youth Leadership for Nature-Based Climate Action”.
- Eligibility: The initiative must have been active for at least three years, community-based, and contribute to at least two Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs).
In 2025, Bibi Fatima SHG was the only Indian winner, alongside groups from Argentina, Brazil, Ecuador, Indonesia, Kenya, Papua New Guinea, Peru, and Tanzania.
Achievements of Bibi Fatima SHG:
- Formation: Established in 2018 by 15 women, with support from Sahaja Samruddha (NGO), Indian Institute of Millets Research (IIMR, Hyderabad), and CROPS4HD.
- Eco-Friendly Farming: Revived millet-based mixed cropping systems on rainfed lands through natural and climate-resilient farming practices in nearly 30 villages.
- Community Seed Bank: Distributes millet seeds free of cost to farmers, strengthening local seed sovereignty.
- Food & Nutrition Security: Promoted millets to improve dietary diversity and resilience against climate change.
- Women-led Enterprise: Established a solar-powered millet processing unit with support from SELCO Foundation, entirely managed by women.
- Value Addition & Marketing: Produces millet-based products such as rotis and vermicelli, boosting local markets.
- Livelihood Diversification: Expanded into livestock rearing, horticulture, and farmers’ markets, improving incomes of small and marginal households.
- Partnerships: Collaborates with Devadhanya Farmer Producer Company to scale rural, agriculture-based enterprises.
Significance:
- Strengthens the role of women’s leadership in climate action and sustainable agriculture.
- Demonstrates a successful community-driven model for biodiversity conservation, food security, and rural entrepreneurship.
- Aligns with India’s efforts to revive millets (International Year of Millets 2023) and promote climate-resilient farming.
- Advances multiple SDGs – notably SDG 1 (No Poverty), SDG 2 (Zero Hunger), SDG 5 (Gender Equality), SDG 12 (Responsible Consumption and Production), and SDG 13 (Climate Action).
State Health Regulatory Excellence Index

- 18 Aug 2025
In News:
The Union Health Secretary, Smt. Punya Salila Srivastava, recently launched the State Health Regulatory Excellence Index (SHRESTH), a first-of-its-kind national framework to benchmark and strengthen state drug regulatory systems through transparent, data-driven assessments. The initiative has been developed by the Central Drugs Standard Control Organization (CDSCO) in collaboration with states and UTs.
About SHRESTH:
- Objective: To improve the performance of state drug regulatory authorities, ensuring drug safety, quality, and efficacy across India.
- Nature: Functions as a virtual gap-assessment tool, enabling states to measure their regulatory preparedness and move towards maturity certification.
- Categories of States:
- Manufacturing States: Assessed on 27 indices under five themes – Human Resources, Infrastructure, Licensing Activities, Surveillance Activities, Responsiveness.
- Primarily Distribution States/UTs: Assessed on 23 indices under similar themes.
- Process:
- States/UTs submit predefined data to CDSCO by the 25th of every month.
- Metrics are scored on the 1st of the following month and shared with all states/UTs.
- Significance:
- Enables targeted improvements in infrastructure, digitisation, inspection, and grievance redressal.
- Promotes cross-learning by sharing best practices of top-performing states.
- Provides a roadmap rather than a scorecard, encouraging harmonization of drug regulatory systems nationwide.
Wallacean Hominids
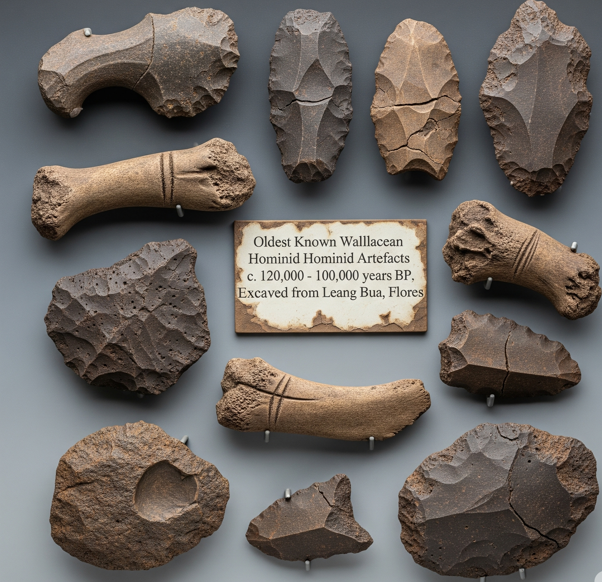

- 18 Aug 2025
In News:
Recent archaeological findings on Sulawesi Island, Indonesia, have revealed stone tools dating back to nearly 1.5 million years ago, marking the earliest known evidence of human presence in the Wallacea region.
Key Findings:
- Archaeologists from Australia and Indonesia discovered small, chipped stone tools in the Soppeng region of South Sulawesi.
- The artefacts, likely used to cut small animals and carve rocks, were found along with animal teeth.
- Radioactive dating suggests the tools are up to 1.48 million years old.
- These findings were published in Nature (August 2025).
Significance:
- The artefacts are attributed to Homo erectus, pre-historic hominids that lived long before the emergence of Homo sapiens.
- Previously, Homo erectus in Wallacea were thought to have occupied only Flores (Indonesia) and Luzon (Philippines) around 1.02 million years ago.
- The Sulawesi discovery pushes back the timeline by almost half a million years, challenging earlier assumptions that Homo erectus lacked the capacity for long-distance sea crossings.
- It provides crucial evidence of early maritime dispersal and migration patterns of ancient humans from the Asian mainland into island ecosystems.
About Wallacea:
- Wallacea is a biogeographic region in Eastern Indonesia, comprising islands such as Sulawesi, Lombok, Flores, Timor, and Sumbawa, situated between Borneo–Java and Australia–New Guinea.
- The region is named after Alfred Russel Wallace, the naturalist who studied its distinct biodiversity.
- It acts as a natural transitional zone between the fauna of Asia and Australia.
Satellite Internet
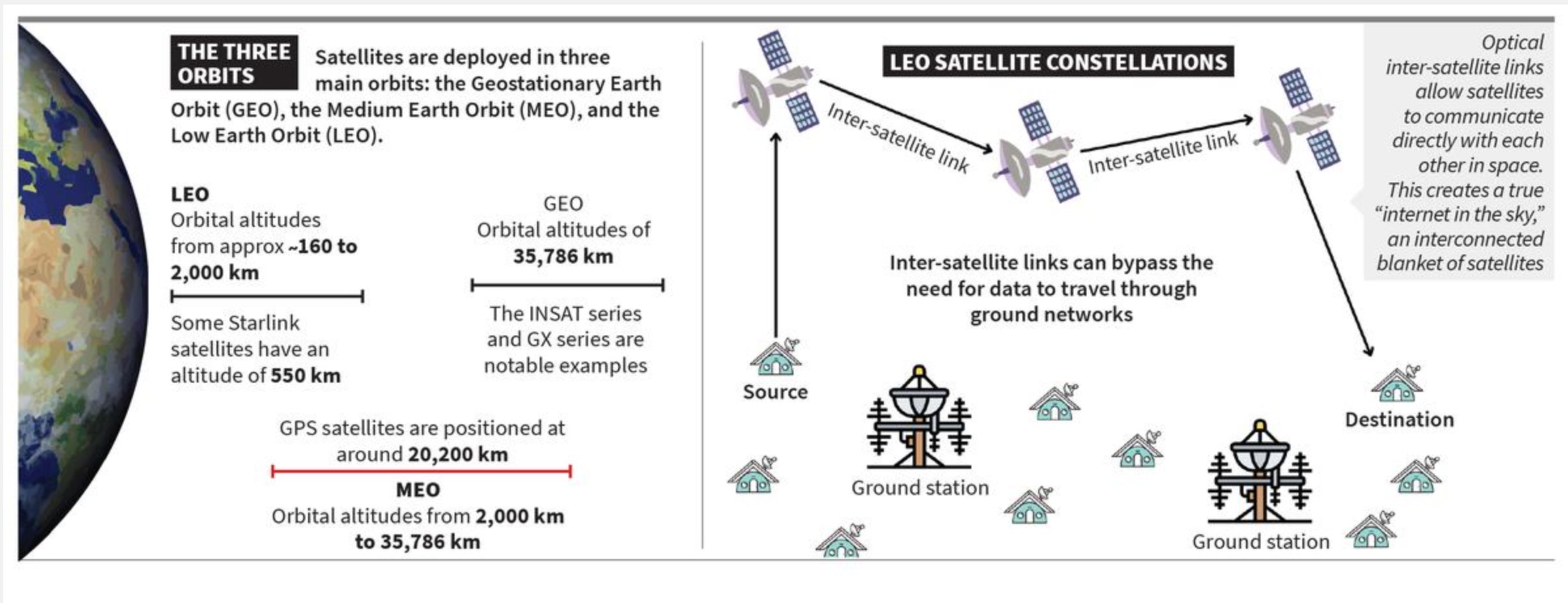
- 17 Aug 2025
In News:
The advent of satellite internet, spearheaded by mega-constellations like Elon Musk’s Starlink, is set to transform global connectivity. With Starlink’s expected entry into India, this technology carries vast implications for bridging the digital divide, disaster resilience, national security, and economic development.
Why Satellite Internet?
Conventional internet networks rely on cables and towers, which are efficient in urban areas but face limitations:
- Economically unviable in sparsely populated or remote regions.
- Vulnerable to disruptions from floods, earthquakes, or cyclones.
- Restricted mobility, failing to meet connectivity needs for ships, aircraft, or defence units in rugged terrains.
Satellite internet addresses these gaps by providing global, resilient, and mobile coverage, independent of terrestrial infrastructure. It can be rapidly deployed in emergencies and enables connectivity in conflict zones or offshore locations.
How Satellite Internet Works
A satellite internet network has two key segments:
- Space Segment: Satellites orbiting Earth, carrying communication payloads (antennas, transponders, onboard processors).
- Ground Segment: User terminals, antennas, and ground stations that link devices to satellites.
Data flow: When a user sends a request, the signal goes to the satellite → routed to a ground station connected to the internet backbone → response sent back via satellite to the user.
Seamless handover: Especially in Low Earth Orbit (LEO), satellites move fast (~27,000 km/hr) and stay over a region only for minutes. Smart handovers between satellites ensure uninterrupted connectivity.
Types of Orbits
|
Orbit Type |
Altitude |
Advantages |
Limitations |
Example |
|
Geostationary Earth Orbit (GEO) |
~35,786 km |
Covers ~? of Earth; stable position |
High latency, no polar coverage |
Viasat Global Xpress |
|
Medium Earth Orbit (MEO) |
2,000–35,786 km |
Balanced coverage & latency |
Needs constellations; still moderate latency |
O3b Network |
|
Low Earth Orbit (LEO) |
<2,000 km |
Very low latency; smaller, cheaper satellites |
Small footprint; requires mega-constellations |
Starlink (7,000+ satellites, plans for 42,000) |
Key Features of Satellite Internet
- Global Coverage: Works across oceans, mountains, deserts, and polar regions.
- Dual-use Technology: Supports both civilian services and military operations.
- Rapid Deployment: Can be activated within hours during emergencies.
- Network Resilience: Independent of local telecom infrastructure.
- Mega-Constellations: Thousands of interconnected satellites with optical inter-satellite links create an “internet in the sky,” reducing reliance on ground stations.
Applications
- Civilian: Expands broadband to rural and island communities, supports e-governance, smart farming, education, and environmental monitoring.
- Disaster Management: Provides resilient connectivity after cyclones, floods, or earthquakes (e.g., Hurricane Harvey, 2017).
- Defence & Security: Ensures battlefield communication, drone operations, and secure links in high-altitude zones (e.g., Indian Army at Siachen, Ukraine’s defence using Starlink).
- Transport: Improves aviation, shipping, and autonomous vehicle navigation.
- Healthcare: Enables telemedicine and remote patient monitoring.
- Space Economy: Strengthens global trade, logistics, and exploration.
Orbiting Carbon Observatories (OCO)Program

- 17 Aug 2025
In News:
The Trump administration has proposed terminating NASA’s Orbiting Carbon Observatories (OCO) program, a key initiative monitoring global carbon dioxide (CO?) emissions and plant health. The move, part of the 2026 federal budget, has triggered concerns among scientists and lawmakers given its implications for climate monitoring and policy.
About the Orbiting Carbon Observatories (OCO) Program
- Objective: Dedicated Earth remote-sensing satellites designed to observe atmospheric CO? and study its role in climate change.
- Timeline:
- OCO-1 (2009): Failed shortly after launch.
- OCO-2 (2014): Successfully launched, providing high-precision global CO? data.
- OCO-3 (2019): Installed on the International Space Station (ISS) to enhance observations.
- Significance:
- Produced high-resolution maps of plant growth, drought stress, and carbon fluxes.
- Helped discover that the Amazon rainforest emits more CO? than it absorbs, while boreal forests in Canada and Russia are turning into unexpected carbon sinks.
- Tracked photosynthesis rates to forecast crop yields, drought conditions, and food shortages—data crucial for global food security and preventing civil unrest.
- Utilized by the US Department of Agriculture and private agricultural firms for crop yield predictions and rangeland management.
Reasons for Proposed Termination
- The administration claims the missions are “beyond their prime mission” and need to align with new budgetary priorities.
- Funding for OCO missions is excluded from the proposed 2026 budget.
International dimension:
-
- Scientists are exploring partnerships with Japan and Europe to keep OCO-3 operational on the ISS.
- Private or philanthropic funding is also being considered, though experts warn this is unsustainable.
Dardanelles Strait
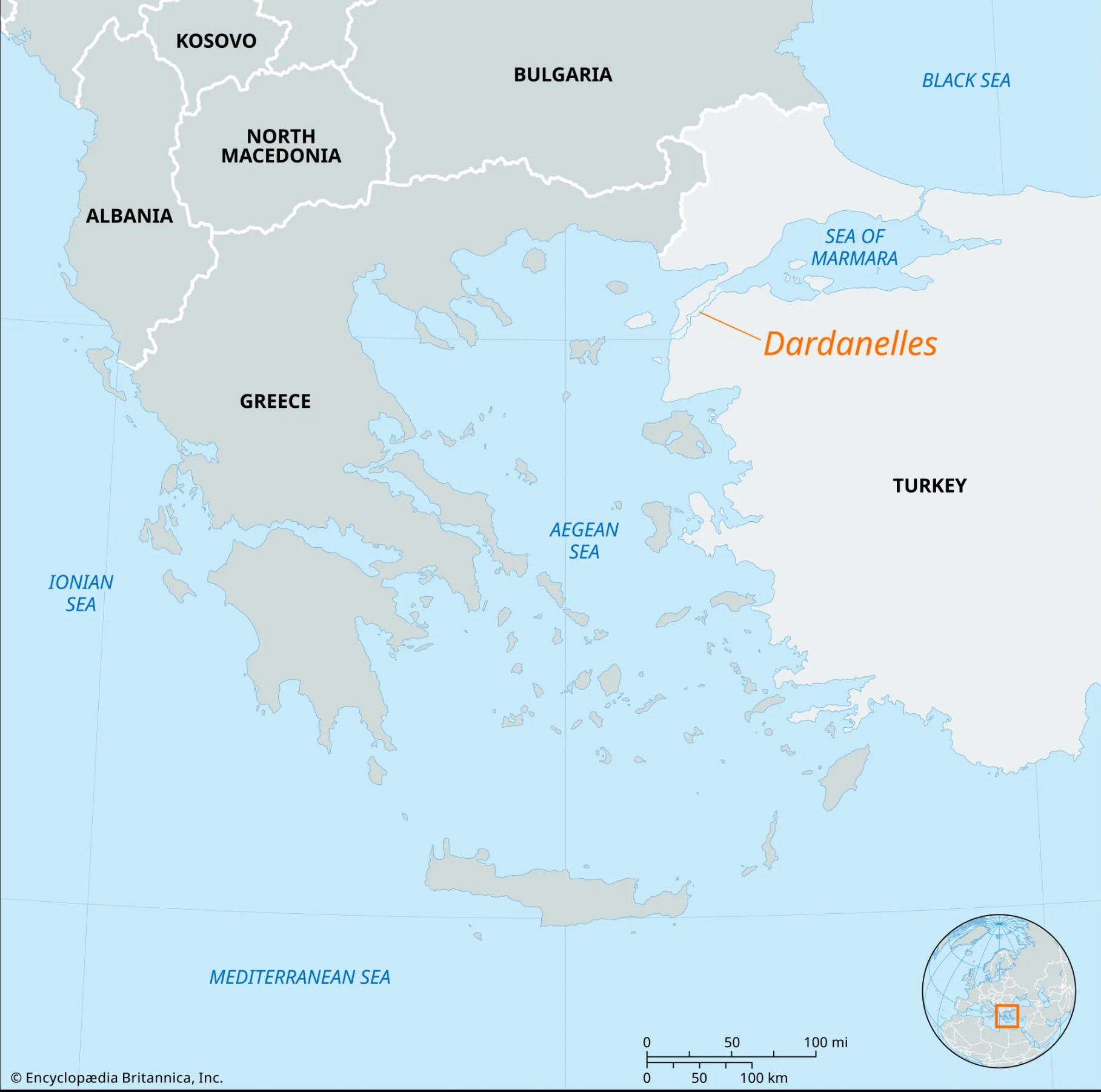
- 17 Aug 2025
In News:
The Dardanelles Strait, a narrow but vital maritime passage in northwestern Turkey, was recently closed to shipping traffic after severe forest fires broke out near Çanakkale province. The incident highlights the strait’s enduring strategic, economic, and environmental importance.
Geographical Overview
- Length: 61 km; Width: 1.2–6.5 km.
- Depth: Average ~55 m, maximum ~90 m in central narrow sections.
- Location: Separates the Gallipoli Peninsula (Europe) from Anatolia (Asia), lying entirely within Turkey’s territorial waters.
- Connectivity: Links the Aegean Sea to the Sea of Marmara, and with the Bosphorus Strait, forms the Turkish Straits system, connecting the Mediterranean to the Black Sea.
- Hydrology: Two-way currents – surface flow from Marmara to the Aegean, undercurrent in the reverse direction.
- Ports: Major ones include Gallipoli, Eceabat, and Çanakkale.
Strategic and Economic Significance
- Maritime Trade: Nearly 46,000 vessels crossed the Dardanelles in 2024, underscoring its role as a global shipping artery between Europe and Asia.
- Chokepoint Status: Serves as a gateway to Istanbul and the Black Sea, shaping regional power dynamics.
- Fisheries: Rich in migratory fish species, supporting local economies.
- Geopolitical Role: Critical for Turkey’s strategic influence, NATO security, and Black Sea maritime routes.
Historical Importance
- Known in antiquity as the Hellespont.
- Greek mythology: Associated with the tale of Hero and Leander.
- Ancient campaigns: Xerxes I of Persia crossed via a pontoon bridge (480 BCE); Alexander the Great crossed during his conquest of Asia (334 BCE).
- Modern conflicts: Key battleground in World War I’s Gallipoli Campaign, where Allied forces attempted but failed to seize control.
Nüshu: Revival of the World’s Only Women’s Script

- 17 Aug 2025
In News:
Nüshu, literally meaning “women’s writing” in Chinese, is a unique script originating in the 17th century in Jiangyong, Hunan Province. Developed when women were excluded from formal education, it functioned as a private communication system among women through letters, embroidery, songs, and poetry. With around 500 core characters, it is the only known writing system in the world created and used exclusively by women.
Distinctive Features
- Form: Rhomboid, thread-like characters derived from traditional Chinese script; composed of dots, horizontals, virgules, and arcs.
- Medium of Use: Mothers taught daughters; used among sisters and friends. Content included folk songs, riddles, autobiographies, and translations of Chinese poems.
- Symbolism: Embodied sisterhood, resilience, and empowerment in a patriarchal society.
Historical Transformation and Conservation
- Decline: By the late 20th century, Nüshu faced near extinction with the death of its last native writers such as Yi Nianhua (1988–89).
- Revival Efforts: Since the 21st century, museums, training centers, and manuals have been established to preserve and promote Nüshu.
- National Recognition: Inscribed on China’s National Intangible Cultural Heritage list; efforts are ongoing for UNESCO recognition.
- Community Role: Women inheritors and enthusiasts continue to practice Nüshu as a cultural art form, while scholars study its historical and social value.
Technology and Modern Adaptation
- Digital Archiving: Unicode integration, high-resolution scans, and cloud storage aid global accessibility.
- AI Tools: Machine learning assists in translation and decoding.
- Global Outreach: Social media, e-courses, AR/VR exhibitions, and documentaries such as Hidden Letters have amplified its relevance.
- Cultural Integration: Featured in creative mediums—e.g., WeChat memes celebrating Chinese female athletes during the Paris 2024 Olympics—blending heritage with contemporary culture.
Social and Cultural Impact
- Women’s Empowerment: Nüshu fosters confidence, independence, and identity among modern women, especially Gen Z.
- Dialogue Across Genders: Increasing interest among men reflects its role as a bridge between genders, expanding from women’s private script to a shared cultural heritage.
- Economic Potential: Provides livelihood through digital art, tourism, crafts, and cultural exchanges.
Smooth-Coated Otters
- 17 Aug 2025
In News:
In a significant conservation development, the National Zoological Park (NZP), Delhi, has welcomed a pair of smooth-coated otters from the Shyamaprasad Mukherji Zoological Garden, Surat, marking the first such arrival in two decades. The last otter at the Delhi Zoo died in 2004. The transfer took place under a Central Zoo Authority (CZA)-approved exchange programme.
About Smooth-Coated Otters (Lutrogaleperspicillata)
- Taxonomy: The only extant member of the genus Lutrogale.
- Distribution: Found across India, southern and Southeast Asia, China, and Iraq (small population).
- Habitat: Freshwater wetlands, mangroves, peat swamps, forested rivers, lakes, rice paddies; capable of long overland movements.
- Features:
- Largest otter species in Southeast Asia.
- Smooth, short fur (brown dorsally, lighter ventrally) with water-repellent guard hairs.
- Social animals, hunt in groups, often using V-formations while fishing upstream.
- Threats:
- Habitat loss due to urbanization, agriculture, and pollution (fertilizers, pesticides).
- Poaching for fur and pet trade.
- Conservation Status: IUCN – Vulnerable.
Landmark Study on Dengue Immunity
- 14 Aug 2025
In News:
A new study published in Science Translational Medicine has provided critical insights into dengue immunity and vaccine development. The research, conducted in the Philippines with nearly 3,000 children, highlighted the role of Envelope Dimer Epitope (EDE)-like antibodies as a key driver of broad, cross-serotype protection against dengue virus (DENV).
Dengue: Global Challenge
- Caused by four serotypes (DENV1–DENV4).
- Most common vector-borne viral disease, affecting nearly half the world’s population, particularly in Southeast Asia, Africa, and the Americas.
- Economic burden in Southeast Asia exceeds that of 17 other diseases including hepatitis B and Japanese encephalitis.
- Severe dengue typically occurs during secondary infection with a different serotype due to Antibody-Dependent Enhancement (ADE), where non-neutralising antibodies worsen infection.
Current Vaccines
- Dengvaxia – Licensed in some countries, but recommended only for those with prior dengue exposure (requires laboratory confirmation).
- QDENGA – Approved in some regions, effective mainly in pre-exposed individuals.
- Limitation: Both vaccines carry ADE risks for dengue-naïve individuals.
What are EDE-like Antibodies?
- Definition: Antibodies targeting Envelope Dimer Epitope (EDE), a quaternary structure formed by paired E proteins on the viral surface.
- Function: Broadly neutralise all four serotypes by preventing viral entry into cells.
- Key Features:
- Broadly neutralising, cross-reactive across serotypes.
- Common in individuals with multiple infections or vaccinated with prior exposure.
- Rare in primary infection (detected in only 4–12% of such cases).
- Strongly correlated with reduced disease severity and hospitalisation risk.
- Potential biomarker for evaluating vaccine efficacy.
Study Highlights
- Conducted during a dengue outbreak in Cebu, Philippines (DENV2 dominant, followed by DENV3).
- Children with secondary immunity showed high prevalence of EDE-like antibodies (82–90%).
- These antibodies explained 42–65% of the protective effect of neutralising antibodies and 41–75% of E protein-binding antibodies, making them the primary determinant of broad protection.
- Findings:
- Less protective against new infections but highly effective against severe disease.
- Boosted by both natural infection and vaccination.
- Strong predictor of reduced symptomatic dengue and hospitalisation.
Implications
- Vaccine Development: Targeting EDE could overcome ADE risks and provide universal dengue protection.
- Public Health: Potential for safer immunisation strategies in endemic regions like India.
- Therapeutics: Basis for developing monoclonal antibody treatments to deliver rapid, cross-serotype protection during outbreaks.
Ladakh Protest: Demand for Statehood and Inclusion in Sixth Schedule
- 14 Aug 2025
In News:
In August 2025, a large protest rally was held in Kargil, led by climate activist Sonam Wangchuk and Ladakh MP Mohmad Haneefa Jan, demanding statehood for Ladakh and its inclusion under the Sixth Schedule of the Constitution. The rally marked the conclusion of a three-day hunger strike and was organized jointly by the Leh Apex Body and the Kargil Democratic Alliance (KDA).
The protesters criticized the delay in resuming dialogue by the Centre, despite the formation of a high-powered committee by the Union Home Ministry in January 2023 to address Ladakh’s concerns. Earlier discussions led to the introduction of a domicile policy with a 15-year eligibility criterion beginning from 2019.
Background
- On 5 August 2019, Article 370 was abrogated, and Jammu & Kashmir was bifurcated into two Union Territories—J&K with legislature and Ladakh without legislature.
- Since then, political groups and civil society in Ladakh have been demanding statehood for democratic representation and Sixth Schedule inclusion to safeguard land, resources, and cultural identity.
Ladakh Statehood Demand
- Objective: To grant a democratically elected legislature with full legislative powers.
- Rationale: Local representation, protection of fragile ecology, and preservation of Ladakh’s unique cultural heritage.
Sixth Schedule of the Constitution
- Constitutional Basis: Articles 244(2) and 275(1).
- Current Applicability: Assam, Meghalaya, Tripura, and Mizoram.
- Purpose: To safeguard tribal communities’ rights through Autonomous District and Regional Councils (ADCs).
Key Features
- Autonomous Councils: Elected bodies with powers over land, forests, agriculture, village administration, and social customs.
- Judicial Powers: Village councils/courts to resolve community disputes.
- Revenue & Taxation: Power to levy taxes on land, trade, and professions.
- Governor’s Role: Can alter council boundaries and approve laws.
- Financial Provisions: Grants-in-aid from the Consolidated Fund of India under Article 275(1).
- Cultural Safeguards: Protection against alienation of tribal land and exploitation by outsiders.
Significance of Demand
- Democratic Governance: Ensures political autonomy and local participation.
- Cultural Protection: Safeguards Ladakh’s Buddhist and tribal identity.
- Environmental Security: Allows better control over fragile Himalayan ecosystems.
- Strategic Importance: Strengthens governance in a border region critical for India’s national security.
Operation Falcon and Rhino Conservation in Assam
- 14 Aug 2025
In News:
The Assam government has achieved major success in protecting the greater one-horned rhinoceros through Operation Falcon, a joint initiative of the Assam Police and Forest Department launched in 2024. The operation was initiated after the killing of two rhinos prompted a shift in anti-poaching strategy.
Key Outcomes
- 42 poachers arrested across districts including Biswanath (18), Darrang (8), Nagaon (6), Karbi Anglong (5), Sonitpur (2), and one each in Udalguri, Dibrugarh, and Cachar.
- Six major poaching gangs with links to illegal trade through Myanmar dismantled.
- Nine poaching attempts foiled using digital and on-ground intelligence.
- Zero rhino killings reported in 2025 so far.
Conservation Impact
- Rhino poaching in Assam has dropped by 86% since 2016, when the BJP came to power.
- Annual data shows steady decline: one rhino killed in 2021, none in 2022, one in 2023, two in 2024, and none so far in 2025.
- Enhanced coordination, intelligence-driven operations, and rapid response mechanisms have been key factors.
About Assam’s Rhinos (Census 2022)
- Total Rhinos: 2,895 in Assam.
- Distribution:
- Kaziranga National Park & Tiger Reserve – 2,613 (largest habitat, ~1,300 sq km).
- Orang National Park & Tiger Reserve – 125.
- Pobitora Wildlife Sanctuary – 107.
- Manas National Park & Tiger Reserve – 50.
Significance of Operation Falcon
- Biodiversity Protection: Safeguards the greater one-horned rhino, listed as Vulnerable on the IUCN Red List.
- International Recognition: Strengthens India’s image in global wildlife conservation.
- Eco-Tourism Boost: Ensures safety in parks like Kaziranga, enhancing Assam’s tourism appeal.
Sukhna Lake
- 14 Aug 2025
In News:
The Chandigarh Administration recently closed the floodgate of Sukhna Lake after water levels receded from the near-danger mark.
About Sukhna Lake
- Type: Artificial, rain-fed lake at the foothills of the Shivalik Hills, Chandigarh.
- Creation: Built in 1958 by damming the Sukhna Choe, a seasonal stream.
- Size: Originally 188 ha (now ~150 ha); length 1.52 km, width 1.49 km.
- Depth: Originally 18 ft, reduced to ~8.5 ft due to siltation.
- Ecological Importance:
- Declared a National Wetland by the Government of India.
- Habitat for ~30 species of resident and migratory birds, including Siberian ducks, storks, and cranes.
- Part of Sukhna Wildlife Sanctuary.
- Recreational Importance:
- Longest channel for rowing and yachting events in Asia.
- Surrounded by Nek Chand’s Rock Garden (west) and a golf course (south).
Pfizer’s Next-Generation Vaccine
- 14 Aug 2025
In News:
- Pfizer has introduced the 20-valent pneumococcal conjugate vaccine (PCV20) for adults in India.It offers protection against 20 pneumococcal serotypes, which are responsible for most pneumococcal diseases.
About Pneumococcal Disease
- Cause: Infection by Streptococcus pneumoniae (pneumococcus), an encapsulated bacterium with a polysaccharide capsule (major virulence factor).
- Serotypes: ~90 identified worldwide; only a few cause the majority of infections.
Types of Illness
- Mild: Ear infections, sinus infections.
- Severe:
- Pneumonia
- Bloodstream infections (septicemia)
- Meningitis (CNS infection)
Public Health Burden
- Major global health concern.
- Most vulnerable groups: young children and the elderly.
- Mortality: Around 1 million child deaths annually due to pneumococcal disease.
- Transmission: Direct contact with respiratory secretions of patients or asymptomatic carriers.
Treatment and Prevention
- Treatment: Antibiotics.
- Challenge: Rapidly growing antimicrobial resistance in pneumococci.
- Prevention: Vaccination remains the most effective strategy, especially for:
- Children under 5 years
- Elderly individuals
- Immunocompromised patients
Khelo India ASMITA

- 13 Aug 2025
In News:
The Khelo India ASMITA Football League 2025-26 was inaugurated in Jalgaon, Maharashtra, by the Minister of State for Youth Affairs & Sports, Raksha Khadse. The initiative is a key step in promoting gender-inclusive sports participation and empowering women athletes at the grassroots level.
About ASMITA
- Full form: Achieving Sports Milestone by Inspiring Women Through Action (ASMITA).
- Launched: 2021, under Khelo India.
- Nodal Ministry: Ministry of Youth Affairs and Sports.
- Support: Sports Authority of India (SAI), National Sports Federations, AIFF, WIFA, and other stakeholders.
- Component of: Khelo Bharat Niti – promoting sports as a tool for nation-building and empowerment.
Objectives
- Affirmative action to increase women’s participation in sports.
- Provide grassroots platforms for talent discovery, especially among tribal and minority communities.
- Create opportunities for young girls, addressing historical imbalances in sports.
- Help women challenge stereotypes and emerge as role models.
Key Features
- Inclusive Participation: From first-time players to hidden talent, ensuring wide outreach.
- Talent Identification: Leagues used as scouting grounds for future athletes.
- Scale: In FY 2025-26, 852 leagues are planned across 15 sports disciplines, targeting 70,000+ women athletes in all States/UTs.
- Age Focus: Leagues cover multiple categories, including U-13 and above.
- Institutional Backing: Supported by SAI and National Sports Federations to ensure professional management.
Significance
- Promotes women’s empowerment through sports.
- Strengthens grassroots sports ecosystem.
- Contributes to India’s vision of becoming a global sporting powerhouse with equal female participation.
- Aligns with the government’s philosophy of “Sabka Saath, Sabka Vikas.”
Revised Income Tax Bill, 2025

- 13 Aug 2025
In News:
The Income Tax (No. 2) Bill, 2025 was passed in the Lok Sabha in August 2025, replacing the Income Tax Act, 1961 after nearly six decades. The earlier draft of the Bill was withdrawn to incorporate recommendations of the Parliamentary Select Committee and stakeholder feedback. The revised Bill consolidates, simplifies, and modernises India’s direct tax framework.
Background
- Old Act (1961): Complex language, overlapping provisions, and compliance burden.
- New Bill (2025):
- Contains 536 sections and 16 schedules.
- Incorporates over 285 recommendations of the Select Committee, which examined the draft for four months and submitted a 4,500-page report.
- Aims to make the law simpler, clearer, and more aligned with the digital era.
Key Features
- Simplification of Tax Framework
- Single “Tax Year” concept replaces “Previous Year” and “Assessment Year”.
- Outdated and contradictory provisions removed to reduce litigation.
- Clear drafting, structured numbering, and improved terminology for easier interpretation.
- Taxpayer-Friendly Provisions
- Refunds allowed even if returns are filed after the due date.
- NIL-TDS certificates available for taxpayers with no liability.
- Relief on vacant house property – no taxation on notional rent.
- 30% standard deduction (post municipal tax) and interest deduction allowed on rented property.
- Corporate and MSME Reforms
- ?80M deduction on inter-corporate dividends reintroduced.
- MSME definition aligned with the MSME Act for uniformity.
- Institutional & Governance Reforms
- CBDT empowered for flexible, digital-era rule-making.
- Simplified compliance for TDS, PF withdrawals, advance rulings, and penalties.
- Relief to Specific Sectors
- Alternate Minimum Tax (AMT) on LLPs abolished.
- Charitable Trusts – compliance relaxations and reduced regulatory burden.
- Transfer Pricing & Associated Enterprise definitions rationalised.
- Extension of pension benefits – commuted pension deduction available even for non-employee individuals.
World Elephant Day 2025

- 13 Aug 2025
In News:
World Elephant Day 2025 was celebrated on August 12 in Coimbatore, Tamil Nadu, organised by the Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change (MoEF&CC) in collaboration with the Tamil Nadu Forest Department. The event focused on human–elephant conflict (HEC) mitigation and reaffirmed global commitment to elephant conservation.
About World Elephant Day
- Launched in 2012 by Patricia Sims (Canada) and the Elephant Reintroduction Foundation of Thailand.
- Aims to promote conservation of elephants, raise awareness on threats like habitat loss, poaching, and HEC, and encourage human–elephant coexistence.
Elephants in India
- India holds 60% of the global wild elephant population.
- 33 Elephant Reserves and 150 Elephant Corridors (as per 2023 Report).
- Elephants are recognised as National Heritage Animal of India.
- Legal and institutional backing provided through Project Elephant (1992), Wildlife Protection Act, and corridor conservation measures.
Human–Elephant Conflict (HEC)
- Rising incidents of elephants entering human settlements due to habitat loss, fragmentation, and search for food/water.
- The Coimbatore workshop under World Elephant Day 2025 brought together policymakers, foresters, conservationists, and civil society to share best practices.
- Measures discussed: habitat management, corridor maintenance, awareness campaigns, and capacity building in high-conflict areas.
- Focus on balancing wildlife conservation with human safety through community participation and scientific approaches.
Public Participation
- 12 lakh students from 5,000 schools across India joined awareness programmes.
- Citizen outreach emphasised coexistence, youth engagement, and long-term behavioural change in society.
Conservation Status (IUCN Red List)
- Asian Elephant (Elephas maximus): Endangered.
- African Savanna Elephant (Loxodonta africana): Endangered.
- African Forest Elephant (Loxodonta cyclotis): Critically Endangered.
Ecological Importance of Elephants
- Keystone species: maintain grasslands, disperse seeds, create water holes, and support biodiversity.
- Social structure: Matriarch-led herds with strong communal care for calves; males often solitary or in small groups.
- Long gestation (22 months) and slow reproduction make them vulnerable to population decline.
Jal Jeevan Mission (JJM)

- 13 Aug 2025
In News:
The Jal Jeevan Mission (JJM), launched in August 2019, aims to provide Functional Household Tap Connections (FHTCs) to every rural household, ensuring safe, adequate, and regular potable water supply. At the time of its launch, only 17% of rural households (3.23 crore) had tap water access. As of 14 August 2025, this has increased to 81% coverage (15.68 crore households) out of a total 19.36 crore rural households, with over 12.45 crore additional connections provided.
Institutional Framework
- State Subject: Drinking water supply is primarily the responsibility of States/UTs, while the Centre provides technical and financial support.
- Funding: An initial outlay of ?2,08,652 crore was approved; the scheme has now been extended until 2028 with enhanced allocation for completing pending works and strengthening Operation & Maintenance (O&M).
- Citizen Participation: The 2025 Budget emphasized “Jan Bhagidari” for sustainable and community-centric water service delivery.
Quality Standards and Monitoring
- Benchmark: Water quality is mandated to comply with BIS:10500 standards, which specify acceptable and permissible limits for chemical, physical, and bacteriological parameters.
- Testing: In December 2024, the government released a Concise Handbook for States/UTs, recommending comprehensive testing at multiple points—source, treatment plant, storage, and distribution.
- Remedial Actions: Include regular cleaning of overhead tanks and corrective measures in case of contamination.
- Transparency Tools:
- JJM Dashboard “Citizen Corner” displays village-level water test results.
- Complaints can be filed via CPGRAMS (pgportal.gov.in) and the Department’s website (jalshakti-ddws.gov.in).
- Aadhaar-linked monitoring, geo-tagging, IoT sensors, and third-party inspections are employed for real-time tracking.
Significance
- Public Health: Ensures safe drinking water, reducing the burden of waterborne diseases.
- Gender Empowerment: Frees women and girls from time-consuming water collection, enabling better education and livelihoods.
- Rural Development: Improves quality of life, reduces drudgery, and enhances rural productivity.
- Sustainability: Integrates with groundwater management initiatives like the Atal Bhujal Yojana, promoting long-term water security.
Current Status (2025)
- Coverage: 81% rural households have tap water supply.
- Target: Universal coverage by 2028 with a focus on infrastructure quality, O&M, and sustainable, citizen-driven service delivery.
Supreme Court orders immediate removal of stray dogs from Delhi-NCR streets
- 13 Aug 2025
In News:
The Supreme Court of India has directed the immediate removal of all free-ranging dogs from Delhi, Noida, Gurugram, and Ghaziabad. The Court emphasized permanent relocation of these animals to shelters, citing rising incidents of rabies and dog bites, particularly affecting children and vulnerable groups.
Key Features of the Order
- Complete Removal: All stray dogs are to be captured to ensure “stray-free” streets in urban and peri-urban areas.
- No-Release Policy: Unlike the earlier Animal Birth Control (ABC) approach, captured dogs will not be returned to their original localities but retained in shelters.
- Shelter Infrastructure: Authorities must build facilities capable of housing at least 5,000 dogs within eight weeks, prioritizing high-risk localities.
- Emergency Response: A 24×7 helpline with a four-hour response time is mandated to tackle bite incidents.
- Strict Compliance: Interference with the process will attract contempt of court, ensuring accountability.
Rationale Behind the Order
- Public Health Priority: With nearly 5,700 rabies-related deaths annually (95% from dog bites), the order seeks to directly curb a preventable disease.
- Protection of Vulnerable Groups: Children and the elderly face higher risks due to limited self-defence capacity.
- Policy Ineffectiveness: The sterilisation-centric ABC model has not adequately addressed aggressive or rabies-carrying dogs.
- Constitutional Angle: By invoking Article 21 (Right to Life and Liberty), the Court underlined safe mobility and freedom from fear in public spaces.
- Permanent Reform: A structural shift from temporary containment to long-term removal from public areas.
Arguments in Favour
- Public Safety: A direct life-saving intervention against rabies deaths.
- Constitutional Backing: Strengthens the right to security under Article 21.
- Urban Governance: Integrates sanitation and safety into city management.
- Accountability: Surveillance and records ensure transparency in enforcement.
- Policy Gaps Addressed: Closes loopholes of the ABC model by ending return-to-locality practices.
Concerns and Counter-Arguments
- Legal Conflict: The directive may clash with existing ABC Rules framed under the Prevention of Cruelty to Animals Act.
- Animal Welfare: Overcrowded shelters risk inhumane conditions, raising ethical concerns.
- Ecological Impact: Sudden removal could disrupt rodent control and waste management functions performed by strays.
- Risk of Abuse: Lack of monitoring might lead to covert culling under the guise of relocation.
- Rights-Based Critique: May be seen as undermining the intrinsic rights of animals and compassion-based governance.
Way Forward
- Humane Shelter Models: Ensure adequate space, veterinary care, and nutrition.
- Mass Vaccination Drives: Combine removal with preventive health measures to eradicate rabies.
- Adoption and Community Participation: Promote responsible adoption under strict guidelines.
- Policy Harmonisation: Amend ABC Rules to align with SC directions and resolve legal inconsistencies.
- Awareness and Behavioural Change: Community-level campaigns on rabies prevention and civic responsibility.
Conclusion
The Supreme Court’s intervention highlights the tension between public health imperatives and animal welfare ethics. While it seeks to secure citizens’ right to safe public spaces, it also raises concerns of legality, humane treatment, and ecological balance. Going forward, the challenge lies in striking a balance between constitutional morality (right to life) and compassion ethics (animal welfare) through coherent policy design and ethical urban governance.
Biofortified Potatoes
- 12 Aug 2025
In News:
India is intensifying efforts to combat micronutrient deficiencies and enhancenutritional security by introducing biofortified potatoes with enhanced iron content. These varieties, developed by the International Potato Center (CIP), Peru, are being adapted for Indian conditions in collaboration with the ICAR–Central Potato Research Institute (CPRI), Shimla.
What are Biofortified Potatoes?
- Definition: Specially bred potatoes enriched with higher levels of iron, zinc, and vitamin C compared to conventional varieties.
- Objective: Address iron deficiency anemia and “hidden hunger” without compromising yield or taste.
- Development: CIP has released iron-rich potato varieties in Peru, now under evaluation and seed multiplication for Indian farmers.
Sweet Potatoes with Vitamin A
- Biofortified Sweet Potatoes with high beta-carotene (Vitamin A precursor) are already cultivated in Odisha, West Bengal, Karnataka, and Assam.
- Their bright orange flesh indicates nutritional richness, helping prevent night blindness, strengthen immunity, and improve child growth.
- ICAR-CTCRI’s SP-95/4 variety combines high beta-carotene with good yield, enhancing tribal nutrition.
- Advantages: Long shelf life (up to 2 years without refrigeration), versatile in food preparation, and suitable for Mid-Day Meal and nutrition schemes.
Institutional Initiatives
- CIP South Asia Regional Centre is being set up in Agra, Uttar Pradesh, within the Indo-Gangetic Plains – the world’s largest potato-producing region – to strengthen R&D and seed access.
- ICAR’s Wider Biofortification Drive:
- Released 61 biofortified crop varieties, including 34 field crops (cereals, pulses, millets, oilseeds) and 27 horticultural crops (tubers, vegetables, medicinal plants).
- Examples:
- CR Dhan 416: Salinity-resistant rice with pest resistance.
- Durum Wheat: Rich in zinc (41.1 ppm), iron (38.5 ppm), and 12% protein.
Biofortification: Concept and Importance
- Definition: Enhancing the nutrient content of crops through conventional breeding, agronomic practices, or biotechnology while preserving consumer-preferred traits.
- Examples:
- Iron-rich: Rice, beans, sweet potato, cassava, legumes.
- Zinc-rich: Wheat, rice, maize, beans.
- Vitamin A-rich: Sweet potato, maize, cassava.
- Protein/amino acid-rich: Sorghum, cassava.
Significance for India
- Public Health: Addresses widespread iron deficiency anemia, especially among women and children.
- Agricultural Sustainability: Promotes nutritionally dense crops without heavy reliance on supplements.
- Policy Alignment: Supports PoshanAbhiyaan, Mid-Day Meal Scheme, and SDG 2 (Zero Hunger).
- Economic Benefits: Enhances farmer incomes by creating demand for nutrient-rich crops.
MERITE Scheme

- 12 Aug 2025
In News:
The Union Cabinet has approved the Multidisciplinary Education and Research Improvement in Technical Education (MERITE) Scheme with a total outlay of ?4,200 crore (2025–26 to 2029–30). This includes ?2,100 crore World Bank loan assistance. The scheme seeks to transform India’s technical education landscape in line with the National Education Policy (NEP), 2020.
Coverage
- Institutions: 275 government/government-aided technical institutions (175 engineering institutions + 100 polytechnics).
- Beneficiaries: Around 7.5 lakh students across all States and Union Territories.
- Stakeholders: National Institutes of Technology (NITs), State Engineering Institutions, Affiliating Technical Universities (ATUs), with implementation support from IITs, IIMs, AICTE, and NBA.
Objectives
- Improve quality, equity, and governance in technical education.
- Align curricula with labour market requirements.
- Strengthen the research and innovation ecosystem.
- Support State/UT technical education departments in digitalization and quality assurance.
Key Focus Areas
- Digital Transformation: ICT-enabled learning, blended teaching models.
- Multidisciplinary Programs: Introduction of NEP-2020 aligned technical courses.
- Skill & Employability Enhancement: Internships, industry-linked curricula, language labs, skill/maker labs.
- Research and Innovation: Establishing research hubs, incubation centres, innovation labs.
- Faculty & Governance: Faculty development programs, creation of academic administrators with focus on women leadership.
- Accreditation & Quality Assurance: Strengthening institutional governance and accountability.
Expected Outcomes
- Increased student employability and higher placement rates.
- Improved research output and innovation ecosystem.
- Greater equity and inclusion in technical education, with emphasis on reducing gender gaps and digital divide.
- Enhanced global competitiveness of Indian technical institutions.
Employment Generation Impact
By modernising technical education and strengthening linkages with industry, MERITE is expected to:
- Improve fresh graduates’ placement prospects.
- Foster entrepreneurship through incubation and innovation centres.
- Contribute to reducing unemployment among engineering graduates.
Background and Significance
India’s sustainable and inclusive growth hinges on technological advancement, which demands upgraded academic and research standards. MERITE builds upon NEP-2020 reforms such as curriculum revamp, skill development, interdisciplinary learning, and enhanced governance. Importantly, it integrates global expertise through the World Bank partnership.
The scheme also ensures participatory governance, incorporating feedback from States/UTs during policy design, thereby strengthening cooperative federalism in higher education reform.
Global Risk of Zoonotic Diseases and India’s Preparedness
- 12 Aug 2025
In News:
A recent study published in Science Advances has highlighted that over 9.3% of the world’s land surface is at high (6.3%) or very high (3%) risk of zoonotic outbreaks — diseases transmitted between animals and humans. About 3% of the global population lives in extremely high-risk areas, while nearly 20% live in medium-risk zones.
The study introduced a Global Epidemic Risk Index, combining country-specific zoonotic risk factors with national preparedness capacities, to help policymakers strengthen health systems, allocate resources effectively, and enhance global cooperation.
Disease Burden and Examples
- Zoonotic diseases account for 60% of all known infectious diseases and up to 75% of emerging infectious diseases (EIDs).
- Globally, they cause 2.5 billion cases and 2.7 million deaths annually.
- Examples: Rabies, anthrax, influenza (H1N1, H5N1), Nipah virus, brucellosis, tuberculosis, Ebola, SARS, MERS, and Covid-19.
Drivers of Spillover Events
- Climate Change: Rising temperatures, erratic rainfall, and water scarcity heighten risks by altering habitats and vector distribution.
- Land Use Change: Deforestation, urban expansion, and agricultural intensification increase human–animal contact.
- Transmission Routes:
- Direct (e.g., avian influenza)
- Food-borne (e.g., salmonella)
- Vector-borne (e.g., West Nile virus)
- Water-borne (e.g., cryptosporidiosis)
Regional Vulnerabilities
- Latin America: 27% of land at high risk
- Oceania: 18.6%
- Asia: 7%
- Africa: 5%
India’s Vulnerability
- An ICMR study (2018–23) found that 8.3% of all reported outbreaks (583 of 6,948) were zoonotic.
- Outbreaks peaked during June–August, linked to monsoon-driven ecological changes.
- The Northeast region accounted for 35.8% of reported zoonotic outbreaks.
India’s Initiatives
- National Animal Disease Control Programme (NADCP): Mass vaccination to eliminate Foot & Mouth Disease (FMD) and Brucellosis.
- Target: Control FMD by 2025 and eradicate by 2030.
- National One Health Programme for Prevention and Control of Zoonoses (2013): Integrated surveillance and inter-sectoral coordination.
- Animal Birth Control (Dogs) Rules, 2023: Rabies vaccination and sterilisation of stray dogs.
- Rabies Vaccination under ASCAD (Livestock Health & Disease Control Programme).
Global Initiatives
- Zoonotic Disease Integrated Action (ZODIAC): Launched by IAEA (2020) for early detection and rapid response.
- World Zoonoses Day (6 July): Marks Louis Pasteur’s rabies vaccine in 1885.
- G20 Pandemic Fund: Financial support for strengthening preparedness and response.
- Global Early Warning System (GLEWS): A WHO–FAO–WOAH collaboration for coordinated zoonotic disease surveillance.
One Health Approach
The One Health framework recognizes the interconnectedness of human, animal, and environmental health. It promotes collaborative, multisectoral strategies for sustainable disease prevention and response.
Rhisotope Project

- 12 Aug 2025
In News:
South Africa, which shelters the world’s largest rhino population, has lost over 10,000 rhinos in the last decade to poaching driven by the illegal horn trade in Asian markets. To counter this crisis, the University of the Witwatersrand, in collaboration with the International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA), has launched the Rhisotope Project (2024) — a novel initiative using radioactive isotopes to protect rhinos.
What is the Rhisotope Project?
- A non-invasive procedure where rhino horns are injected with low doses of radioisotopes.
- The process is harmless to rhinos but makes horns:
- Detectable through Radiation Portal Monitors (RPMs) and scanners at borders, ports, and airports — even in sealed shipping containers.
- Toxic and unfit for human use, reducing demand in illegal trade.
- Pilot studies (2024–25):
- 20 rhinos in the Waterberg Biosphere Reserve were treated.
- Tests by Ghent University (Belgium) showed no cellular damage or health impact.
- 3D-printed horns used in trials confirmed detectability in container loads.
Why Radioisotopes?
- Radioisotopes are unstable forms of elements that emit ionising radiation (alpha, beta, gamma) to achieve stability.
- They are easily traceable with nuclear detection systems.
- Already widely used in medicine (I-131 for thyroid, Tc-99m for imaging), archaeology (C-14 dating), and industry.
The Scale of the Crisis
- Global rhino numbers: Declined from ~5,00,000 in the early 20th century to ~27,000 today (IUCN).
- South Africa: Lost 103 rhinos to poaching in the first quarter of 2025 alone.
- Conventional measures like dehorning reduce poaching but disrupt rhino social behaviour and habitat use. The Rhisotope Project offers a less disruptive alternative.
Broader Conservation Significance
- If successful, the method could be extended to other endangered species like elephants and pangolins.
- It represents an international collaboration that combines nuclear science with wildlife conservation, redefining the role of technology in biodiversity protection.
Threats Beyond Poaching
- Invasive species: Plants like Parthenium threaten habitats (e.g., Assam’s Pobitora Wildlife Sanctuary, home to the densest one-horned rhino population).
- Climate change: Intensified droughts and monsoons push rhinos into human-dominated landscapes, increasing conflicts.
- Habitat loss due to agricultural expansion and human settlement.
Rhino Conservation Initiatives
- Global/Regional:
- New Delhi Declaration on Asian Rhinos (2019)
- DNA Profiling of all Rhinos for tracking and protection
- India-specific:
- National Rhino Conservation Strategy
- Indian Rhino Vision 2020 (for Assam’s one-horned rhinos)
About the IAEA
- Established in 1957 as the UN’s “Atoms for Peace”organisation.
- Promotes peaceful applications of nuclear technology while preventing misuse for weapons.
- 178 member states; India is a founding member.
- Awarded the 2005 Nobel Peace Prize for contributions to nuclear safety and disarmament.
- HQ: Vienna, Austria. Reports to both UNGA and UNSC.
National Narcotics Helpline MANAS
- 12 Aug 2025
In News:
The Government of India launched the National Narcotics Helpline MANAS (Madak-PadarthNishedAsoochna Kendra) to strengthen citizen participation in the fight against the drug menace. The initiative, spearheaded by the Narcotics Control Bureau (NCB) under the Ministry of Home Affairs (MHA), functions as a secure, bilingual, and citizen-centric platform to enable anonymous reporting of drug trafficking, illicit cultivation, and related crimes, while also providing counselling and rehabilitation support.
Key Features of MANAS
- Helpline Number: 1933 (Toll-Free)
- Digital Access: Web portal (www.ncbmanas.gov.in), Email (info.ncbmanas@gov.in), and UMANG Mobile App
- Integration: Direct transfer to the MoSJE De-addiction Helpline (14446) for rehabilitation guidance
- Awareness Outreach: Posters, videos, contests, and citizen engagement through MyGov platform under the Drug-Free Bharat campaign
India’s Legal & Policy Framework Against Drug Abuse
- Constitutional Backing: Article 47 directs the State to prohibit intoxicating substances except for medicinal purposes.
- Legislation:
- Narcotic Drugs and Psychotropic Substances (NDPS) Act, 1985
- Prevention of Illicit Traffic in NDPS Act, 1988
- Drugs and Cosmetics Act, 1940
- International Conventions: India is party to the
- Single Convention on Narcotic Drugs, 1961 (amended 1972)
- Convention on Psychotropic Substances, 1971
- UN Convention against Illicit Traffic in Narcotic Drugs and Psychotropic Substances, 1988
- Other Initiatives: NIDAAN Portal (for drug law offenders), NashaMukt Bharat Abhiyan (community-based de-addiction programme).
Significance for Governance & Society
The MANAS helpline marks a shift from enforcement-centric approaches to a citizen-participatory, tech-enabled model. It bridges law enforcement, rehabilitation, and public awareness, reflecting India’s commitment to a balanced supply and demand reduction strategy against narcotics.
World Lion Day 2025
- 11 Aug 2025
In News:
India celebrated World Lion Day 2025 at Barda Wildlife Sanctuary, Gujarat, marking a milestone in wildlife conservation. The event highlighted the success of Project Lion, launched by Prime Minister Narendra Modi on 15th August 2020, and underscored India’s global leadership in protecting the endangered Asiatic Lion (Panthera leopersica).
Status of Asiatic Lions
- Population Growth: Numbers rose from 284 in 1990 to 674 in 2020, and further to 891 in 2025(16th Lion Census). This reflects a 32% increase since 2020 and 70% rise over the last decade.
- Distribution: The lions roam across ~35,000 sq. km in 11 districts of Saurashtra, with Gir National Park as the core habitat. In recent years, Barda Wildlife Sanctuary (192 sq. km) has emerged as a second home, hosting 17 lions including 11 cubs.
- Global Significance: If Asiatic lions survive anywhere today, it is solely in India—making their conservation a matter of both ecological and national pride.
Ecological and Cultural Importance
- Apex Predators: Regulate herbivore populations, prevent overgrazing, and maintain ecosystem balance.
- Cultural Symbolism: Depicted on the National Emblem and Indian currency, symbolizing strength and heritage.
- Unique Traits: Asiatic lions are smaller than African lions, with a distinct belly fold and less prominent mane (ears remain visible).
Conservation Measures
1. Project Lion (2020–2030)
- Budget: ?2,927 crore sanctioned.
- Focus Areas:
- Habitat improvement and prey base augmentation.
- Scientific monitoring using GPS, GIS-based real-time surveillance, and automated sensor grids.
- Veterinary healthcare (National Referral Centre at Junagadh).
- Human–wildlife conflict mitigation.
- Community participation and eco-tourism.
2. Greater Gir Concept: Expands protected landscapes toGirnar, Pania, Mitiyala, and Bardasanctuaries to reduce habitat pressure.
3. Recent Developments
- ?180 crore wildlife and ecotourism initiative launched in 2025 for new habitats, safari park, and veterinary facilities.
- Barda Safari Park & Zoo approved to boost ecotourism and conservation.
- Return of lions to Barda after 143 years, enhancing biodiversity and eco-tourism potential.
4. Global Cooperation
- International Big Cats Alliance (IBCA, 2023): A platform of 97 countries for sharing knowledge and resources on big cat conservation.
Conservation Status
- Panthera leo (Lion)IUCN Red List: Vulnerable (Green Status: Largely Depleted).
- CITES: Appendix I.
- Wildlife (Protection) Act, 1972: Schedule I species.
- Part of India’s Species Recovery Programme under the Centrally Sponsored Scheme – Development of Wildlife Habitat.
India’s 3rd Launch Pad in Sriharikota by 2029
- 11 Aug 2025
In News:
India’s space programme is set for a major expansion with the Third Satellite Launch Pad (TLP) being developed at the Satish Dhawan Space Centre (SDSC), Sriharikota. The facility, sanctioned in March 2025, is expected to be fully operational by March 2029, significantly strengthening India’s ability to handle next-generation launch vehicles (NGLV) and ambitious human spaceflight missions.
Development Timeline and Infrastructure
The TLP project has been structured with clear milestones:
- Civil works: by May 2028
- Fluid and propellant storage systems: by July 2028
- Launch pad systems: by September 2028
- Commissioning: by March 2029
Preliminary geotechnical investigations and topographic surveys were completed in May 2025. Currently, tenders for essential road, electrical, and infrastructure works are under evaluation.
Objectives and Capabilities
- Support NGLV Operations: The 91-metre-tall Next Generation Launch Vehicle, designed with semi-cryogenic stages, will have a payload capacity of up to 30 tonnes to Low Earth Orbit (LEO)—a major leap from existing LVM3 capabilities.
- Backup for LVM3: Ensures continuity of operations in case of single-pad disruption.
- Enable Human Spaceflight: Provides critical infrastructure for the Gaganyaan mission, future astronaut flights, and crewed lunar landing plans by 2040.
- Facilitate Deep-Space Missions: Supports long-term goals like BharatiyaAntariksh Station (2035), lunar missions, and interplanetary exploration.
Key Features
- Advanced Propellant Systems: Compatible with cryogenic and semi-cryogenic fuels with higher thrust requirements.
- New Jet Deflection Systems: Built to withstand the powerful thrust of next-gen rockets.
- Make-in-India Integration: Emphasis on collaboration with private industry and MSMEs, ensuring maximum indigenous participation in design, construction, and manufacturing.
- Modular Construction: Use of multiple work packages for efficient execution.
- Increased Launch Capacity: Enhances frequency, redundancy, and capability to handle commercial as well as strategic missions.
Strategic Significance
- Redundancy and Reliability – Reduces dependence on two existing pads, mitigating risks of delays due to maintenance or failure.
- Future-Proofing India’s Space Infrastructure – Specifically designed for larger payloads, human-rated systems, and next-gen propulsion.
- Boost to Space Economy – By enabling frequent and diverse launches, TLP supports India’s rising commercial space sector under the Make-in-India and Atmanirbhar Bharat initiatives.
- Geopolitical Leverage – Strengthens India’s position in the global space economy, catering to both domestic and international clients.
Diabetes in India
- 11 Aug 2025
In News:
A Lancet Global Health study (2023), based on the Longitudinal Aging Study in India (LASI), has highlighted the alarming rise of diabetes among Indians aged 45 years and above. The findings underscore the urgent need for universal screening, awareness, and improved management strategies to address this public health challenge.
Key Findings of the Study
- Prevalence: One in five Indians aged 45+ (approx. 20%) had diabetes in 2019.
- Undiagnosed Diabetes: Nearly 40% of people with diabetes were unaware of their condition—around 20 million Indians remain undiagnosed.
- Treatment Gaps:
- 5% had untreated diabetes.
- 47% were under-treated.
- Only 36% were adequately treated.
- Awareness and Treatment: Once aware, 94% of patients sought treatment, highlighting the impact of diagnosis.
- Control Rates:
- 46% achieved blood sugar control,
- 59% achieved blood pressure control,
- 6% used lipid-lowering medicines.
- Urban-Rural Divide: Urban prevalence (30%) was nearly double that of rural areas (15%).
- Gender Gap: Prevalence was similar in men (19.6%) and women (20.1%).
- Regional Trends:
- Highest rates: Chandigarh (36.9%), Kerala (36%), Puducherry (36%).
- Largest number of diabetics: Tamil Nadu (6.1 mn), Maharashtra (5.8 mn), Uttar Pradesh (4.7 mn).
- Methodology: Diagnosis based on HbA1c testing (3-month blood sugar average), more accurate than random glucose tests used in earlier surveys.
Understanding Diabetes
- Type 1: Autoimmune; body destroys insulin-producing cells. Requires lifelong insulin.
- Type 2: Accounts for 95%+ of cases; due to insulin resistance or inadequate production; linked to obesity, sedentary lifestyle, and genetics. Preventable via lifestyle changes.
- Gestational Diabetes: Occurs during pregnancy; increases risk of complications and later Type 2 diabetes.
- Type 5 (Newly Recognized): Seen in lean adolescents (BMI < 18.5 kg/m²); caused by malnutrition damaging pancreatic beta cells, leading to insulin deficiency.
India’s Policy and Programmatic Response
- Ayushman Arogya Mandirs (Health and Wellness Centres): Provide population-based diabetes screening.
- Fit India Movement: Encourages preventive health and fitness practices.
- School Interventions: CBSE mandates ‘sugar boards’ to educate students about hidden sugars and health risks.
- National Programme for Prevention and Control of Cancer, Diabetes, Cardiovascular Diseases and Stroke (NPCDCS): Strengthens NCD screening and management across primary healthcare.
RBI’s Internal Working Group Recommendations on Liquidity Management Framework
- 11 Aug 2025
In News:
The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) recently released the recommendations of its Internal Working Group (IWG) constituted to review the Liquidity Management Framework (LMF), which has been operational since February 2020. The review seeks to enhance efficiency, transparency, and predictability in liquidity operations—crucial for ensuring smooth monetary policy transmission.
Liquidity Management Framework (LMF):
- Objective: To manage systemic liquidity and guide short-term interest rates in alignment with monetary policy objectives.
- Core Mechanism: Operates through the Liquidity Adjustment Facility (LAF)—using repo (liquidity injection) and reverse repo (liquidity absorption) operations.
- Corridor System: The policy repo rate sits at the middle of the interest rate corridor, while the Weighted Average Call Rate (WACR) serves as the operating target of monetary policy.
- Other Tools: Open Market Operations (OMO), Cash Reserve Ratio (CRR), Statutory Liquidity Ratio (SLR) for durable liquidity; and Standing Deposit Facility (SDF) for absorbing surplus liquidity.
Key Recommendations of the IWG
- WACR as Operating Target
- Recommendation: Continue using overnight WACR as the operating target.
- Rationale: WACR strongly correlates with collateralized overnight money market rates, making it reliable for transmitting policy signals across the system.
- Discontinuation of 14-day VRR/VRRR as Main Operation
- Recommendation: Replace 14-day Variable Rate Repo/Reverse Repo (VRR/VRRR) as the main liquidity management tool.
- Alternative: Manage transient liquidity primarily through 7-day repo/reverse repo operations and other operations (overnight to 14-day tenor) at RBI’s discretion.
- Rationale: 14-day auctions have witnessed lower participation, as banks prefer shorter-tenor instruments like SDF.
- Advance Notice for Liquidity Operations
- Recommendation: RBI should provide at least one-day advance notice for repo/reverse repo operations.
- Exception: Same-day operations may be undertaken in response to evolving liquidity shocks.
- Rationale: Predictability reduces market uncertainty and stabilizes money market rates.
- Variable Rate Auction Mechanism
- Recommendation: Continue using variable rate auctions for repo and reverse repo operations, including longer tenors.
- Rationale: Enhances price discovery and aligns market rates with liquidity conditions.
- Cash Reserve Ratio (CRR) Norms
- Recommendation: Continue with the 90% daily minimum maintenance requirement of CRR.
- Rationale: Ensures banks maintain sufficient reserves, preventing liquidity shortfalls.
- Durable Liquidity Tools
- Observation: Existing instruments under the LMF are sufficient to meet durable liquidity needs; no changes are required at this stage.
Key Terms:
- WACR (Weighted Average Call Rate): The average overnight interest rate at which banks borrow and lend funds, weighted by transaction volume; RBI’s operating target for monetary policy.
- Repo Rate: Rate at which RBI lends to banks against collateral to inject liquidity.
- Reverse Repo Rate: Rate at which RBI borrows from banks to absorb excess liquidity.
- VRR/VRRR: Auction-based repo/reverse repo operations, where rates are determined by market bids.
- SDF (Standing Deposit Facility): Tool for absorbing liquidity without collateral.
- CRR (Cash Reserve Ratio): Portion of deposits banks must maintain with RBI as liquid cash.
Significance of Recommendations
- For Monetary Policy: Reinforces the role of WACR in aligning short-term rates with policy stance.
- For Markets: Enhances predictability, reducing volatility in money markets.
- For Banks: Offers greater flexibility in managing short-term liquidity needs.
- For RBI: Provides operational flexibility to balance stability with market efficiency.
TRISO Nuclear Fuel
- 11 Aug 2025
In News:
The United States Department of Energy (DOE) has selected Standard Nuclear as the first company to establish a domestic supply chain for TRi-structural ISOtropic (TRISO) nuclear fuel, marking a major step toward reducing dependence on Russian uranium and advancing nuclear innovation. The initiative, part of DOE’s Fuel Line Pilot Program (2025), is designed to strengthen US energy security, promote private sector participation, and accelerate the deployment of advanced nuclear reactors.
Why TRISO Matters
TRISO is a next-generation nuclear fuel specifically engineered for high-temperature gas-cooled reactors (HTGRs) and molten salt-cooled reactors, both of which fall under Generation IV (Gen-IV) advanced reactor designs.
- Composition: TRISO fuel consists of a uranium–carbon–oxygen fuel kernel encapsulated by three protective layers of carbon and ceramic materials.
- Form: The particles are extremely small—seed-sized—and can be fabricated into cylindrical pellets or “pebbles.”
- Key Features:
- Extreme durability: Resistant to neutron irradiation, corrosion, oxidation, and very high temperatures.
- Self-containment: Each particle acts as its own containment system, preventing radiation leakage even under extreme reactor conditions.
- Versatility: Compatible with multiple advanced reactor designs, including small modular reactors (SMRs).
This makes TRISO structurally and functionally superior to conventional nuclear fuels, ensuring safer, more reliable, and more efficient reactor performance.
Strategic Implications
- Energy Security & Supply Chains
- The US has historically relied on imports of enriched uranium, particularly from Russia.
- By developing domestic TRISO production in Tennessee and Idaho, the DOE seeks to build a resilient nuclear fuel ecosystem independent of geopolitical disruptions.
- Advanced Reactor Deployment
- DOE’s Advanced Reactor Demonstration Program targets at least three new advanced reactor designs to achieve criticality by July 4, 2026.
- TRISO fuel is central to this push, enabling safer operation of SMRs and Gen-IV reactors, both of which are crucial to America’s clean energy transition.
- Private–Public Partnership
- Standard Nuclear will finance construction, operation, and decommissioning of TRISO fabrication facilities.
- Reactor developers will source nuclear material feedstock, partly through DOE’s high-assay low-enriched uranium (HALEU) allocation program.
- Technological Momentum
- Other firms, such as BWX Technologies (BWXT), have also developed TRISO production lines, including uranium nitride TRISO, in collaboration with Idaho and Oak Ridge National Laboratories.
- These advancements reinforce US leadership in nuclear innovation while supporting its broader climate and national security goals.
Tuvalu’s Planned Climate Migration to Australia

- 10 Aug 2025
In News:
Tuvalu, a small Pacific island nation, is undertaking the world’s first planned national migration due to the existential threat posed by climate change and rising sea levels. The initiative stems from the Falepili Union Treaty (2023) signed between Tuvalu and Australia, marking a landmark case in global climate governance and migration policy.
Why Migration is Needed
- Geography & Vulnerability: Tuvalu consists of nine coral atolls with a total land area of just 25.14 sq. km and a population of ~11,000 (2022 census). Its average elevation is only 2 metres, making it highly vulnerable to flooding, storm surges, and coastal erosion.
- Climate Impact:
- NASA’s Sea Level Change Team reported that sea levels in Tuvalu were already 15 cm higher in 2023 compared to the previous 30 years.
- At this rate, most of Tuvalu could be submerged by 2050.
- Two of its nine atolls are already largely underwater.
- Scientists warn the islands may become uninhabitable within 80 years.
The Falepili Union Treaty (2023)
- Migration Provision: Australia will grant 280 Tuvaluans permanent residency annually, with access to healthcare, education, housing, and employment.
- Selection Mechanism: Migration is ballot-based. The first phase (June–July 2025) saw 8,750 registrations. The first group of 280 migrants was selected on 25 July 2025.
- Scale: Along with other pathways to Australia and New Zealand, up to 4% of Tuvalu’s population could migrate annually. Within a decade, nearly 40% of the population may relocate, although some may return periodically.
- Objective: To ensure “mobility with dignity”, preventing Tuvaluans from becoming stateless climate refugees.
International Significance
- Precedent for Climate Migration: This is the first-ever state-backed relocation of an entire population due to climate change, setting a model for other vulnerable island nations.
- Global Climate Justice: Tuvalu’s case highlights the plight of Small Island Developing States (SIDS) and the urgent need for stronger international climate agreements.
- Diplomatic Signalling: Tuvalu’s Prime Minister Feleti Teo has called for a new global treaty safeguarding nations at risk from rising seas.
About Tuvalu
- Location: Polynesian island nation in the Pacific Ocean, midway between Australia and Hawaii.
- Capital: Funafuti.
- Population: ~11,000 (second least populous UN member after Vatican City).
- Economy: Relies on fishing licenses, foreign aid, and remittances from Tuvaluan seafarers.
- UN Membership: Since 2000; actively champions the rights of climate-vulnerable states.
India’s Joint Doctrines on Cyberspace and Amphibious Operations

- 10 Aug 2025
In News:
Recently, the Chief of Defence Staff (CDS) General Anil Chauhan released thedeclassified versions of India’s Joint Doctrines for Cyberspace Operations and Amphibious Operations. This step reflects India’s effort to enhance jointness, interoperability, and transparency in military operations while strengthening preparedness for multi-domain warfare.
Cyberspace Operations Doctrine
What is Cyberspace?
- A global domain comprising information systems, communication networks, satellites, and data infrastructures.
- It is borderless, dual-use (civilian and military), and subject to rapidly evolving threats.
Components of Cyberspace Operations
- Defensive Cyber Operations – Protects national and military networks against malware, hacking, and data breaches.
- Offensive Cyber Operations – Targets adversary systems to disrupt communications, disable command networks, or damage infrastructure.
- Cyber Intelligence & Reconnaissance – Collects and analyses data to detect vulnerabilities and anticipate attacks.
- Cyber Support Operations – Provides digital tools and assistance to land, maritime, air, and space operations.
- Resilience & Recovery – Ensures continuity through backup systems, redundancies, and rapid restoration measures.
Operational Principles
- Threat-informed Planning – Based on real-time intelligence.
- Interoperability – Seamless coordination across the three Services and with civil agencies.
- Layered Defence – Multi-tiered cyber security protocols.
- Legal & Ethical Compliance – Operates within Indian law and global cyber norms.
- Real-time Response – Swift counteraction to minimise damage.
Significance:
- Shields critical infrastructure (power grids, defence networks, communication systems).
- Acts as a force multiplier, enhancing conventional operations.
- Prepares India for hybrid warfare, where cyber, land, sea, and air threats are interlinked.
Amphibious Operations Doctrine
What are Amphibious Operations?
- Coordinated actions by naval, air, and land forces launched from the sea to secure objectives onshore.
- Applications range from combat missions to humanitarian assistance and disaster relief (HADR).
Key Features
- Tri-service Integration – Combines maritime, aerial, and ground assets.
- Rapid Response – Enables swift deployment from sea to shore.
- Strategic Reach – Expands influence over island territories and littoral regions.
- Flexible Missions – Suitable for both warfare and non-war operations (e.g., disaster relief).
- Maritime–Land Linkage – Strengthens the sea–land operational continuum.
Significance:
- Enhances maritime superiority in the Indian Ocean Region.
- Secures India’s island territories, trade routes, and coastal areas.
- Strengthens India’s blue-water navy aspirations and capacity for overseas contingencies.
- Provides options for HADR missions, vital in the Indo-Pacific where natural disasters are frequent.
Strategic Importance of Doctrines
The release of these doctrines marks a major step in joint military planning and multi-domain operations. They:
- Promote synergy among the Army, Navy, and Air Force, reducing duplication of efforts.
- Build resilience against hybrid threats, including cyber-attacks and maritime conflicts.
- Signal India’s intent to safeguard its national security and global strategic interests.
- Provide policymakers and military planners with a common framework and lexicon.
Further, the CDS has initiated work on new doctrines covering Military Space Operations, Special Forces Operations, Airborne/Heliborne Operations, Integrated Logistics, and Multi-Domain Operations. These will ensure India remains prepared for the emerging spectrum of modern warfare.
Biochar in India

- 10 Aug 2025
In News:
India is set to launch its carbon credit trading market in 2026, with biochar emerging as a promising carbon dioxide removal (CDR) technology. Biochar is a carbon-rich, porous, and stable substance produced through pyrolysis (burning biomass without oxygen) ofagricultural residue and municipal solid waste. It offers multiple co-benefits spanning climate mitigation, agriculture, energy, construction, and wastewater treatment.
India’s Untapped Biochar Potential
- Resource base: India generates 600+ million tonnes of agricultural residue and 60+ million tonnes of municipal solid waste annually, much of which is burnt or dumped, causing air pollution and GHG emissions.
- Carbon removal: Converting 30–50% of surplus biomass can yield 15–26 million tonnes of biochar, sequestering ~0.1 gigatonne of CO?-eq annually.
- Byproducts:
- Syngas (20–30 MT): Can generate 8–13 TWh electricity, replacing 0.4–0.7 MT coal/year.
- Bio-oil (24–40 MT): Can offset 8% of diesel/kerosene demand, reducing >2% of India’s fossil-fuel-based emissions.
- Employment: Village-level pyrolysis units could create 5.2 lakh rural jobs, linking waste management with livelihoods.
Multi-Sectoral Applications
1.Agriculture and Soil Health
- Enhances soil organic carbon and fertility.
- Improves water retention, critical for semi-arid regions.
- Reduces fertilizer needs by 10–20% and increases crop yields by 10–25%.
- Cuts N?O emissions by 30–50% (273× more potent than CO?).
- Example: Andhra Pradesh’s Community Managed Natural Farming has piloted biochar to improve soil quality.
2. Energy and Fuel Substitution
- Syngas and bio-oil provide renewable energy for rural micro-grids and transport.
- Example: Maharashtra pilot projects use pyrolysis gas to replace diesel generators.
3. Construction Sector
- Adding 2–5% biochar to concrete:
- Increases mechanical strength and heat resistance (+20%).
- Sequesters ~115 kg CO? per cubic metre.
- Offers a green alternative to cement, key for India’s infrastructure push.
- Example: IIT-Madras research shows biochar-concrete mix lowers embodied carbon in buildings.
4. Wastewater Treatment
- 1 kg biochar can treat 200–500 litres of wastewater.
- With India producing 70 billion litres/day (72% untreated), biochar offers low-cost, decentralised treatment solutions for rural and urban areas.
Clouded Leopard
- 10 Aug 2025
In News:
A rare video recently shared by Indian Forest Service officer Susanta Nanda offered a rare glimpse into the secretive life of the clouded leopard (Neofelisnebulosa), showcasing a mother with her cubs in the rainforests of Northeast India. The sighting highlights the critical conservation importance of this elusive and endangered species.
About the Clouded Leopard
- Scientific name:Neofelisnebulosa (mainland Asia); Neofelisdiardi (Sunda clouded leopard, Sumatra & Borneo).
- Classification: Among the most ancient cat species; neither a true “great cat” nor a small cat — cannot roar or purr.
- Size: Medium-sized (60–110 cm long; 11–20 kg); lifespan ~13–17 years.
- Distinctive features:
- Named for large “cloud-like” coat patterns (ellipses with dark edges).
- Exceptionally long tail (often body-length) for balance.
- Long canine teeth, proportionally the same size as those of a tiger.
- Broad paws and short legs, making it an agile climber; one of the only cats that can climb down trees headfirst, hang upside down, and hunt arboreally.
- Behaviour: Solitary, shy, and nocturnal.
Distribution and Habitat
- Found across Nepal, Bangladesh, India, Indochina, Sumatra, Borneo, and southern China (historically also Taiwan).
- In India: Present in Sikkim, northern West Bengal, Meghalaya, Tripura, Mizoram, Manipur, Assam, Nagaland, and Arunachal Pradesh.
- Declared the State Animal of Meghalaya.
- Habitat preference: Lowland tropical rainforests, but also found in dry woodlands, secondary forests, high altitudes in the Himalayas, and even mangrove swamps (Borneo).
Conservation Status
- IUCN Red List:Vulnerable.
- Global wild population:fewer than 10,000 individuals.
- Threats:
- Habitat loss (deforestation, infrastructure expansion).
- Poachingfor pelts and body parts.
- Human-wildlife conflict.
Conservation Significance
- Rare sightings, such as the video from Northeast India, underscore the species’ ecological and cultural importance.
- Conservationists stress the need for:
- Habitat protection through transboundary wildlife corridors.
- Strengthening protected areas across Northeast India.
- Community participation to reduce conflict and safeguard prey base.
Great Barrier Reef
- 10 Aug 2025
In News:
The Great Barrier Reef (GBR), the world’s largest living structure and a UNESCO World Heritage Site (1981), has recorded its steepest decline in hard coral cover in nearly four decades, according to the Australian Institute of Marine Science (AIMS) 2025 survey. The reef, spread over 2,000 km along Australia’s northeast coast and covering ~350,000 sq. km, accounts for nearly 10% of global coral reef ecosystems and hosts extraordinary biodiversity, including 400 coral species, 1,500 fish species, 4,000 mollusk species, six of seven turtle species, dugongs, and numerous seabirds.
The 2024–25 Mass Bleaching Event
- The 2024 bleaching, the fifth since 2016, coincided with record ocean heat stress, cyclones, flooding, and crown-of-thorns starfish outbreaks.
- AIMS’ long-term monitoring across 124 reefs (Aug 2024–May 2025) revealed:
- 48% reefs showed a decline in coral cover,
- 42% reefs showed no change,
- Only 10% reefs recorded recovery.
- Some areas, especially in the northern GBR (around Lizard Island), lost over 70% of hard coral cover, the sharpest decline since monitoring began in 1986.
Regional Breakdown of Coral Loss (2024–25)
- Northern GBR: Coral cover dropped from 39.8% to 30% (–24.8%), driven by record heat stress, cyclones, and freshwater inundation.
- Central GBR: Cover fell by 13.9% to 28.6%, with Cairns sector reefs losing 6–60% due to Cyclone Jasper (2023) and flooding.
- Southern GBR: Sharpest relative loss, down from 38.9% to 26.9% (–30.6%), largely due to extreme heat stress in the Capricorn-Bunker sector, storm damage, and coral disease.
Drivers of Decline
- Climate change-induced heat stress – primary driver of bleaching.
- Cyclones & floods – physical damage and sedimentation.
- Crown-of-thorns starfish – venomous predators that feed on corals.
- Coral disease – post-bleaching infections weaken recovery.
Oscillating Ecosystem Under Stress
- Acropora corals, fast-growing and heat-resilient species that helped reef recovery (2017–24), were worst hit.
- Scientists warn of increasing volatility in coral cover, shifting between record highs and lows within short periods.
- Before the 1990s, mass bleaching was rare (first major event: 1998). Since 2020, GBR has faced bleaching in 2020, 2022, 2024, and 2025, with two consecutive years of mass bleaching for the second time in a decade.
Global Perspective
According to the US NOAA, between Jan 2023 and May 2025, 83.9% of global coral reef area experienced bleaching-level heat stress, with mass bleaching reported in at least 83 countries and territories.
Conservation & Outlook
The GBR, managed largely under the Great Barrier Reef Marine Park Authority, remains one of the most studied ecosystems. However, repeated bleaching events are leaving insufficient recovery time, pushing the ecosystem toward collapse. Scientists warn the window to save the GBR is rapidly closing without urgent global climate action.
Dark Eagle Hypersonic Missile

- 09 Aug 2025
In News:
The United States has achieved a major milestone by deploying its Long-Range Hypersonic Weapon (LRHW), known as Dark Eagle, to Australia’s Northern Territory during the Talisman Sabre 2025 multinational military exercise. This marks the system’s first-ever overseas deployment and represents a critical step in strengthening U.S. deterrence capabilities in the Indo-Pacific.
Features:
- Range & Speed: Approximately 2,700–2,776 km with a reported velocity of up to Mach 17.
- Design: A land-based, road-mobile system comprising four trailer-mounted launchers, each with two missile canisters.
- Warhead: Equipped with the Common Hypersonic Glide Body (C-HGB), an unpowered yet maneuverable glide vehicle capable of evading interception.
- Deployment Capability: Road-mobile, air-transportable (C-17), and integrated with the U.S. Army’s Integrated Air and Missile Defense Battle Command System (IBCS).
- Developers: Jointly developed by Lockheed Martin and Northrop Grumman, with collaboration from the U.S. Navy on the glide body and boosters.
- Mission Role: Designed to penetrate anti-access/area-denial (A2/AD) networks, suppress enemy defenses, and engage time-sensitive, high-value targets.
Exercise Talisman Sabre
For the first time, India participated in the 11th edition of Exercise Talisman Sabre 2025, a large-scale Australia-led multinational military exercise. This reflects India’s growing role in the Indo-Pacific security architecture and deepening defense cooperation with like-minded partners.
- Launch & Evolution: Initiated in 2005 as a bilateral drill between Australia and the United States, it has expanded into a premier multinational warfighting exercise.
- Scale: The 2025 edition is the largest-ever, involving over 35,000 personnel from 19 nations including Australia, U.S., India, Japan, France, U.K., and others.
- Geographical Spread: Conducted across Queensland, Northern Territory, Western Australia, New South Wales, and Christmas Island, with a first-ever extension to Papua New Guinea, underscoring wider regional engagement.
- Objective:
- To uphold a free, open, and inclusive Indo-Pacific.
- Enhance military readiness, interoperability, and joint operational capabilities.
- Reinforce regional security cooperation among allies and partners.
- Activities: Includes live-fire drills, amphibious landings, ground maneuvers, air combat, maritime operations, and force preparation exercises, testing joint warfighting capabilities.
Key India-Australia Military Exercises
- AUSINDEX – Naval exercise.
- Pitch Black – Multinational air exercise.
- AustraHind – Bilateral military exercise.
Key India-U.S. Military Exercises
- YudhAbhyas – Joint military training.
- Vajra Prahar – Special Forces exercise.
- Cope India – Air combat exercise.
- Tiger Triumph – Tri-services amphibious exercise.
France’s Largest Wildfire in Decades
- 09 Aug 2025
In News:
Recently, southern France witnessed its worst wildfire since 1949, scorching nearly 16,000 hectares (39,500+ acres) of forests and villages—an area 1.5 times the size of Paris. Though the blaze has now been contained, firefighters remain deployed to prevent flare-ups and secure the affected zone.
Causes and Challenges
- Climatic Drivers: Officials and France’s Environment Minister attributed the fire’s intensity to climate change, prolonged drought, strong winds, and extremely dry vegetation.
- Geographic Factors: Proximity to the Pyrenees mountains and the Mediterranean coast made the terrain vulnerable to rapid fire spread. Loss of traditional vineyards and land-use changes further accelerated the blaze.
- Future Risks: France’s weather office has warned of fresh heatwaves, increasing wildfire vulnerability across southern Europe.
Geographic Overview of France
- Location: Northern & Eastern Hemispheres; bordered by Belgium, Luxembourg, Germany, Switzerland, Italy, Spain, Andorra.
- Water Bodies: Bounded by the Bay of Biscay (west), English Channel (northwest), and Mediterranean Sea (south).
- Major Rivers:Loire (into Atlantic), Seine (into English Channel).
- Mountain Ranges:Alps, Jura, and Pyrenees (natural border with Spain).
- Resources: Coal, iron ore, bauxite, zinc, uranium, potash, gypsum, etc.
- Overseas Regions: Guadeloupe, French Guiana, Réunion, Martinique, Mayotte.
- Capital: Paris.
Notary Portal

- 09 Aug 2025
In News:
The Government of India has launched the Notary Portal, a dedicated digital platform designed to modernize services under the Notaries Act, 1952 and the Notaries Rules, 1956. The initiative, led by the Ministry of Law and Justice, aims to create a faceless, paperless, transparent, and efficient system for notarial services.
Key Features
- Online Interface: Connects notaries appointed by the Central Government with the Ministry for seamless service delivery.
- Services Offered:
- Submission of applications for appointment as notaries.
- Verification of eligibility for appointment.
- Issuance of digitally signed Certificates of Practice.
- Renewal of certificates, change of practice area, and submission of annual returns.
- Current Status: Modules for verification of documents, eligibility checks, and issuance of digitally signed certificates are operational.
Significance
- Enhances transparency and efficiency in legal certification processes.
- Reduces paperwork, delays, and physical interface, thereby minimizing scope for corruption.
- Aligns with the government’s broader agenda of Digital India and modernization of legal services.
SheLeadsProgramme

- 09 Aug 2025
In News:
The Union Minister for Women and Child Development, inaugurated the second edition of UN Women’s flagship capacity-building programme — SheLeads II: Workshop for Women Leaders in New Delhi (August 2025). The initiative seeks to strengthen women’s political leadership, a crucial step towards women-led development and the vision of a Viksit Bharat.
Key Highlights:
- The workshop comes in the backdrop of the Women’s Reservation Act, 2023, mandating 33% reservation for women in the Lok Sabha and State Legislative Assemblies.
- Despite this landmark reform, only 14% of seats in the 18th Lok Sabha are currently occupied by women, highlighting the urgent need for leadership training and political empowerment.
About SheLeadsProgramme
- Flagship Initiative: Launched by the UN Women India Country Office.
- Aim: Advance gender equality in public and political leadership, equipping women with skills, confidence, and networks to contest elections and participate effectively in governance.
- Scope: Supports women leaders in shaping policies, governance structures, and electoral narratives that reflect the aspirations of all citizens.
- Participation: In 2025, over 260 applications from 22 states were received; 36 participants were selected for the two-day workshop.
- Engagement: Interactive sessions with MPs, policy experts, and media strategists on electoral campaigning, governance, narrative building, and media engagement.
About UN Women
- Established in 2010 by the UN General Assembly, consolidating resources and mandates under one entity.
- Mandate:
- Support intergovernmental bodies (e.g., Commission on the Status of Women) in framing global standards.
- Assist member states in implementing gender equality commitments through technical and financial support.
- Partner with civil society to advance women’s rights and empowerment.
Strategic Interventions for Green Hydrogen Transition (SIGHT) Scheme

- 09 Aug 2025
In News:
India has achieved a milestone in its clean energy transition with the discovery of a record-low price of ?55.75/kg (USD 641/MT) for Green Ammonia in the first-ever auction conducted by the Solar Energy Corporation of India (SECI) under the Strategic Interventions for Green Hydrogen Transition (SIGHT) Scheme, a core component of the National Green Hydrogen Mission (NGHM).
About the SIGHT Scheme
- Nature: Flagship financial mechanism under NGHM.
- Nodal Ministries: Ministry of New & Renewable Energy (MNRE) and Ministry of Petroleum & Natural Gas (MoPNG).
- Objective:
- Scale up green hydrogen and its derivatives (like green ammonia).
- Make them cost-competitive with fossil-based alternatives.
- Create domestic demand across fertilizer, refining, and shipping sectors.
- Financial Outlay: ?17,490 crore (till 2029–30) out of the total NGHM budget of ?19,744 crore.
- Implementation Modes:
- Mode 1: Incentives to lowest incentive seekers.
- Mode 2A: Aggregated demand for Green Ammonia (fixed incentive).
- Mode 2B: Aggregated demand for Green Hydrogen (fixed incentive).
- Incentive Structure (Mode 2B): ?50/kg (Year 1), ?40/kg (Year 2), ?30/kg (Year 3).
- Monitoring: A joint MNRE–MoPNG committee ensures compliance with notified green hydrogen standards.
First Green Ammonia Auction (Mode-2A)
- Winning Bid: ?55.75/kg (down from ?100.28/kg discovered in H2Global auction 2024).
- Quantity: 75,000 MTPA out of a total tendered 7.24 lakh MTPA.
- Offtaker:Paradeep Phosphates Ltd., Odisha.
- Contract: Fixed 10-year supply, ensuring price stability and supply chain reliability.
- Global Comparison: Price is slightly higher than grey ammonia (USD 515/MT, March 2025) but provides strong economic incentives for clean transition.
Ectopic Pregnancy
- 08 Aug 2025
In News:
A recent rare case from Bulandshahr, Uttar Pradesh, reported a fetus developing in the liver—a condition termed intrahepatic ectopic pregnancy. This has drawn attention to ectopic pregnancies, a critical medical concern.
What is an Ectopic Pregnancy?
- An ectopic pregnancy occurs when a fertilised egg implants outside the uterus, instead of the uterine lining.
- The fallopian tube is the most common site (called tubal pregnancy).
- Other possible sites include the ovary, abdominal cavity, cervix, or, in extremely rare cases, the liver.
Causes
- Blockage or abnormal movement of the fertilised egg.
- Inflammation or scarring of fallopian tubes.
- Damage from prior surgeries or pelvic infections.
- Congenital irregularities in the structure of the fallopian tubes.
Symptoms
- Early pregnancy-like signs: missed periods, nausea, breast tenderness.
- Progressive symptoms:
- Vaginal bleeding
- Abdominal or pelvic pain
- Back pain, shoulder pain, dizziness
- Low blood pressure in severe cases.
Risks & Complications
- If untreated, ectopic pregnancy can cause rupture of the fallopian tube, leading to life-threatening internal bleeding.
- It is a medical emergency and a significant cause of maternal morbidity and mortality.
Treatment
- Methotrexate (a drug that stops cell growth and dissolves existing cells) may be used in some cases.
- Surgical intervention is required in cases of rupture or internal bleeding.
World Air Transport Statistics (WATS) 2024

- 08 Aug 2025
In News:
According to the World Air Transport Statistics (WATS) 2024, released by the International Air Transport Association (IATA), India has emerged as the world’s 5th-largest aviation market, handling 211 million passengers in 2024.
Key Findings of WATS 2024
- India: 211 million passengers in 2024, growing 11.1% over 2023.
- Ahead of: Japan (205 million, 18.6% growth).
- Global Rankings:
- United States – 876 million passengers (+5.2%).
- China – 741 million passengers (+18.7%).
- United Kingdom – 261 million passengers.
- Spain – 241 million passengers.
- India – 211 million passengers.
- Busiest Routes (Airport Pairs):
- Global:Jeju–Seoul (South Korea) – 13.2 million passengers.
- India: Mumbai–Delhi – 5.9 million passengers, ranked 7th globally.
- Trend: Asia-Pacific dominated busiest airport-pair rankings.
India’s Aviation Transformation
1. Legislative Reforms
- Protection of Interests in Aircraft Objects Bill, 2025: Aligns leasing system with the Cape Town Convention, lowering leasing costs and boosting investor confidence.
- BharatiyaVayuyanAdhiniyam, 2024: Replaces colonial-era Aircraft Act, 1934; promotes Make in India, simplifies licensing, and aligns with ICAO norms.
2. Infrastructure Expansion
- New Terminals: Foundation laid at Varanasi, Agra, Darbhanga, Bagdogra.
- Greenfield Airports: 12 operationalised since 2014 (e.g., Shirdi, Mopa, Shivamogga); Navi Mumbai and Noida (Jewar) to be operational by 2025–26.
- Investment: ?91,000 crore allocated under National Infrastructure Pipeline (NIP); ?82,600 crore already spent by Nov 2024.
3. Government Initiatives
- UDAN Scheme: Expands regional air connectivity, affordable travel.
- National Civil Aviation Policy (NCAP): Boosts MRO (Maintenance, Repair, Overhaul), airport development, and leasing ecosystem.
- Green Airports Policy: Promotes renewable energy, waste reduction, and carbon neutrality.
- Aircraft Leasing Hub:GIFT City being developed as a global hub for aircraft leasing and financing.
Significance
- India consolidates its position as a major aviation hub, driven by rising passenger traffic, policy reforms, and infrastructure expansion.
- Reflects growing regional connectivity under UDAN and global competitiveness with regulatory modernisation.
- Places India in the top five global aviation markets for the first time.
Asian Giant Tortoise

- 08 Aug 2025
In News:
The Asian Giant Tortoise, the largest tortoise in mainland Asia, has been reintroduced into the Zeliang Community Reserve in Peren district, Nagaland. Local youth groups have been engaged as “tortoise guardians” to ensure protection.
About Asian Giant Tortoise
- Scientific name:Manouriaemysphayrei
- Common name: Asian Giant Tortoise / “Small elephants of the forests” (due to their role in forest ecology).
- Lineage: Among the oldest tortoise lineages in the world; display unique nesting behaviour similar to crocodilians, where they protect eggs and regulate incubation temperatures.
- Appearance: Hatchlings are greyish-brown, becoming charcoal-colored in adulthood.
- Diet: Bamboo shoots, tubers, soft vegetation, some invertebrates, and frogs.
Habitat & Distribution
- Habitat: Tropical and subtropical evergreen hill forests.
- Range in India: Northeastern states – Arunachal Pradesh, Nagaland, Assam.
- Global distribution: Bangladesh, Myanmar, Thailand, Malaysia, Indonesia.
Ecological Role
- Seed Dispersal: Helps regenerate forests by dispersing seeds.
- Scavenging: Cleans forest floor by feeding on decomposed organic matter.
Threats
- Hunting and collection for consumption.
- Illegal trade (pets and exotic meat).
- Habitat destruction due to shifting cultivation, deforestation, and infrastructure projects.
Conservation Status
- IUCN Red List: Critically Endangered
- CITES: Appendix II
Conservation Efforts
- Captive Breeding & Assurance Colonies for population recovery.
- Reintroduction Programmes like the recent one in Nagaland.
- Community-based conservation with active participation of locals as guardians.
- Field Surveys to monitor population health and habitat conditions.
Global Artificial Intelligence (AI) City Index 2025

- 08 Aug 2025
In News:
Bengaluru ranks 26thin Global AI City Index, Singapore secures top spot.
About the Index
- Published by: Market research firm Counterpoint Research.
- Objective: Benchmarks global cities on their AI capacity, investment, and innovation.
- Evaluation Criteria:
- AI R&D ecosystem and startup strength
- Investment inflows & public–private partnerships
- AI applications in transport, healthcare, and education
- Data centre growth & digital infrastructure readiness
- Governance and regulatory frameworks
Global Rankings (2025)
- Top 5 Cities: Singapore (1st), Seoul (2nd), Beijing (3rd), Dubai (4th), San Francisco (5th).
- Key Trends:
- Singapore’s success driven by strong startup ecosystem and public–private collaboration in healthcare, telecom, and transport.
- Seoul excels in AI healthcare and education applications.
- Beijing introduced formal AI education for all primary & secondary school students (2025).
- Investments in supercomputing expected to reduce gap between North America and China.
- Tech industry leaders: Microsoft (most active vendor with AI data centres, training, innovation hubs), followed by Google and Amazon expanding their global AI footprint.
India’s Performance
- Bengaluru: Ranked 26th globally – India’s top AI R&D and data centre hub with a vibrant startup ecosystem attracting foreign investment.
- Other Indian Cities:
- Mumbai & Delhi – Leveraging AI for traffic management and public security.
- Chennai & Kolkata – Emerging AI hubs.
- India’s Challenge: Report highlights need for a comprehensive AI roadmap and robust regulatory framework to maximize growth potential.
Significance
- Establishes Bengaluru as India’s AI capital, strengthening its role in digital infrastructure and innovation.
- Reflects India’s growing presence in the global AI landscape while underlining policy gaps.
- Offers lessons from global leaders like Singapore and Seoul on AI integration in governance, education, and healthcare.
India Electric Mobility Index (IEMI)

- 08 Aug 2025
In News:
NITI Aayog launched the India Electric Mobility Index (IEMI), a first-of-its-kind tool developed to comprehensively track and benchmark the progress of States and Union Territories (UTs) in achieving their Electric Mobility goals.
Key Highlights:
- Objective: The IEMIis a first-of-its-kind national tool designed to comprehensively track, evaluate, and benchmark the performance of States and Union Territories (UTs) in their electric mobility transition. It aims to guide sub-national policies, strengthen EV adoption, and align efforts with India’s net-zero by 2070 target.
Core Features of IEMI
- Benchmarking Framework: Scores States/UTs on a 0–100 scale.
- Indicators: Covers 16 indicators under three core themes:
- Transport Electrification Progress – Demand-side adoption in passenger, freight, and public transport.
- Charging Infrastructure Readiness – Deployment of public/private charging stations and supportive policies.
- EV Research & Innovation Ecosystem – R&D, manufacturing capacity, and technological advancements.
- Dashboard Access: Interactive tool for real-time comparison, rankings, and insights.
- Policy Guidance Tool: Identifies gaps, best practices, and investment priorities.
- Cross-Sectoral Utility: Supports inter-ministerial coordination, capacity building, and infrastructure planning.
Trends & Rankings in IEMI 2024
- Top Performers:Delhi, Maharashtra, and Chandigarh led in EV readiness and innovation.
- EV Share in Sales: Grew from 5% (2018) to 7.7% (2024).
- Total EVs on Road: Surpassed 5 million by June 2025, with 12 lakh EVs registered in 2024 alone.
- Charging Infrastructure: Over 25,000 public charging stations installed by October 2024; Karnataka leads in installations.
- Policy Coverage:29 States/UTs have notified EV policies; 4 more are in draft stage.
Significance of IEMI
- Promotes Green Mobility: Aligns state actions with India’s decarbonisation roadmap.
- Encourages Healthy Competition: Enables peer learning and best practice sharing among states.
- Supports Make in India: Strengthens domestic EV manufacturing and innovation clusters.
- Guides Infrastructure Planning: Highlights charging network gaps for targeted rollouts.
- Informs Policy: Helps States/UTs design tailored strategies for equitable e-mobility adoption.
Mount LewotobiLakiLaki
- 07 Aug 2025
In News:
Mount LewotobiLakiLaki, one of Indonesia’s most active volcanoes, erupted in August 2025, spewing volcanic ash up to 18 km into the atmosphere and blanketing nearby villages on the island of Flores. The eruption followed another event just hours earlier, which sent ash plumes 10 km high, accompanied by glowing lava and volcanic lightning.
Key Features of the Eruption
- Scale: Among Indonesia’s largest volcanic events since the 2010 Mount Merapi eruption, which killed over 350 people and displaced hundreds of thousands.
- Hazards Observed:
- Pyroclastic flows of gas, rocks, and lava up to 5 km down the slopes.
- Volcanic debris, including hot gravel, scattered as far as 8 km from the crater.
- Risk of lahars (volcanic mudflows) triggered by heavy rainfall.
- Alert Status: Indonesia’s Geology Agency placed the volcano on the highest alert level since June 18, 2025. The exclusion zone was extended to 7 km radius. Thousands of residents have been permanently relocated due to repeated eruptions, including a deadly series in November 2024 that killed nine and destroyed homes.
Geological Context
- Volcano Type: Part of the Lewotobi twin stratovolcano system (“husband and wife”), comprising:
- LewotobiLakiLaki (male)
- Lewotobi Perempuan(female)
- Location: Island of Flores, Indonesia.
- Height: 1,584 metres (5,197 feet).
- Ring of Fire Connection:
- Situated along the Pacific Ring of Fire (Circum-Pacific Belt), a 40,000 km horseshoe-shaped zone around the Pacific Ocean.
- Hosts 75% of Earth’s volcanoes (over 450) and accounts for 90% of global earthquakes.
India–Nepal Mutual Legal Assistance Pact and Extradition Treaty
- 07 Aug 2025
In News:
India and Nepal have recently finalised a Mutual Legal Assistance (MLA) Agreement in Criminal Matters, marking a significant step in strengthening bilateral security cooperation. The pact is designed to enhance cross-border collaboration in criminal investigations, evidence sharing, and law enforcement.
Mutual Legal Assistance (MLA) in Criminal Matters
- Definition: A bilateral or multilateral treaty that provides a structured framework for cooperation between countries to combat transnational crimes such as terrorism, human trafficking, smuggling, cybercrime, and financial fraud.
- Legal Nature:
- MLAT countries: Legally binding and based on reciprocity.
- Non-MLAT countries: Cooperation remains discretionary.
- India’s Practice:
- Central Authority: Ministry of Home Affairs (MHA), assisted by the Ministry of External Affairs (MEA) when routed through diplomatic channels.
- Existing Network: India has signed MLA treaties with 42 countries (as of November 2019), including the USA (2005), UK (1995), and France (2005).
- Significance for Nepal: Until now, Nepal (along with Bhutan) was the only neighbouring country without such a pact with India, which inadvertently made it a safe haven for criminals.
Extradition Treaty with Nepal
- Current Treaty: India and Nepal are working to revise their outdated 1953 Extradition Treaty.
- Objective of Revision: To overcome legal and administrative hurdles that delay or prevent the extradition of fugitives involved in organised crime and terrorism.
Strategic Importance
- Enhances border management and security cooperation between the two countries.
- Prevents misuse of the open India–Nepal border by criminals and extremists.
- Strengthens India’s regional security framework and supports its fight against transnational crime.
Framework Agreement

- 07 Aug 2025
In News:
The Framework Agreement (FA), signed on 3rd August 2015 between the Government of India and the National Socialist Council of Nagalim–Isak-Muivah (NSCN-IM), remains a central element in the ongoing Naga peace process. Its 10th anniversary (2025) witnessed renewed debates over its sanctity and future.
Background
- The Indo-Naga conflict has persisted for over six decades, rooted in demands for sovereignty and recognition of the Nagas’ unique identity.
- The Government of India first acknowledged the “unique history of the Nagas” in 2002 (Amsterdam talks), paving the way for structured peace negotiations.
The Framework Agreement: Key Provisions
- Recognition of Political Identity: India recognized the Nagas’ distinct historical and cultural identity.
- Shared Sovereignty: Proposed a cooperative model of governance, dividing powers between India and Nagalim while ensuring coexistence.
- Political Equality: Both India’s and Nagalim’s political systems to be respected, avoiding a hierarchical relationship.
- People-Centric Governance: Emphasizes sovereignty residing with the people, aiming for inclusive, democratic self-rule.
- Commitment to Peace: Seeks to end armed struggle and establish a roadmap for lasting peace and autonomy.
Political Significance
- The accord symbolically acknowledges the existence of the “Naga nation.”
- It shifted the discourse from an administrative problem to a political conflict requiring negotiated settlement.
- It was signed in New Delhi in the presence of Prime Minister Narendra Modi and interlocutor RN Ravi.
Current Developments
- On the 10th anniversary (2025), NSCN-IM chairman Q Tuccu reaffirmed commitment to the FA, calling it the “torchbearer of Naga sovereignty”.
- He criticized the Naga National Political Groups (NNPGs)—a coalition of other Naga factions—accusing them of aligning too closely with New Delhi by accepting a settlement under the Indian Constitution (“Agreed Position”).
- Tuccu argued that the NNPGs’ stance compromises the Nagas’ historical and political identity, unlike the FA which ensures recognition of sovereign rights.
- NSCN-IM maintains that the Government of India is slow in implementing the FA, but it remains committed despite challenges.
Operation Akhal

- 07 Aug 2025
In News:
Operation Akhal is a high-intensity counter-terrorism operation being conducted in the AkhalKhulsan forest area of Kulgam district, Jammu & Kashmir. Launched jointly by the Indian Army’s Chinar Corps, the J&K Police, and the Special Operations Group (SOG), the operation reflects India’s continued strategy to dismantle terror networks in the Union Territory.
Objectives
- Neutralize 3–5 terrorists based on intelligence inputs.
- Curb the activities of local terror modules.
- Strengthen internal security in South Kashmir.
- Disrupt associated networks of hawala funding, drug smuggling, and Overground Workers (OGWs).
Key Features
- Nature of Operation: Involves intermittent but calibrated firefights in dense forest terrain, supported by drone surveillance and reinforcements.
- Extended Duration: The operation has continued for several days, indicating the presence of multiple terrorists offering strong resistance.
- Casualties:
- At least three unidentified terrorists have been neutralized.
- Two soldiers — Lance Naik Pritpal Singh and Sepoy Harminder Singh — succumbed to injuries sustained in the encounter, highlighting the intensity of the conflict.
- Security Measures: Strict cordon around suspected hideouts, enhanced surveillance, and troop deployment to block escape routes.
Broader Context
- Operation Akhal is part of a post-Pahalgam crackdown on terror groups and their ecosystem in South Kashmir.
- Reflects India’s evolving counter-terror strategy combining ground operations, intelligence-based targeting, and crackdown on financial/logistical support systems.
Right to Repair and Repairability Index in India
- 07 Aug 2025
In News:
India has accepted the proposal to introduce a Repairability Index for electronics, aligning with the global movement to strengthen the Right to Repair. This is seen as a step towards sustainable consumption and consumer empowerment, but concerns remain about the neglect of India’s vibrant informal repair economy, which is rich in tacit and generational knowledge.
Understanding Right to Repair
- Definition: The Right to Repair ensures that consumers can repair, modify, or access affordable third-party repair services for their products.
- Global Trends:
- The European Union mandates access to spare parts and repair manuals.
- Several U.S. states have legislated consumer rights for repair.
- The principle supports UN SDG-12 (Responsible Consumption and Production).
- India’s Framework:In 2023, the Department of Consumer Affairs launched a Right to Repair portal, covering electronics, automobiles, and farm equipment.
Significance Beyond Consumer Rights
- Tacit Knowledge Systems: Informal repairers acquire skills through observation and mentorship, not formal certifications. Repair hubs like Karol Bagh (Delhi) and Ritchie Street (Chennai) embody this tradition.
- Cultural Identity: Repair is not just technical work but part of India’s jugaad culture, reflecting frugality, resource reuse, and indigenous innovation.
- Sustainability: Repair extends product life, prevents premature disposal, and reduces e-waste burden.
- Unrecognized Workforce: Informal repairers, despite their contribution to the circular economy, remain excluded from labour laws and digital policy frameworks.
Policy and Digital Gaps
- E-Waste Rules, 2022: Focus primarily on recycling while overlooking repair as the first line of defence.
- Skill India (PMKVY): Training modules remain rigid and unsuitable for improvisational, diagnostic repair work.
- AI and Digital Public Infrastructure (DPI) Policies: Emphasize structured data but ignore human-led, tacit repair knowledge.
- Education (NEP 2020): While advocating experiential learning, it fails to recognize repair work as skill education.
- Legal Support: Informal repairers lack certification pathways, formal rights, or recognition within the digital economy roadmap.
Towards an Inclusive Repair Ecosystem
- Repairability Standards: Embed repair norms in AI systems, public procurement, and hardware design.
- Expanded Right to Repair:
- Introduce product classifications by repairability.
- Ensure access to manuals and spare parts.
- Promote community repair hubs.
- Skill Recognition: Integrate informal repairers into e-Shram, and design flexible reskilling modules.
- Knowledge Preservation: Use AI tools (LLMs, decision trees) to digitize tacit repair knowledge and make it shareable.
- Policy Convergence: Collaborate across ministries — Labour (MoLE), Electronics & IT (MeitY), Rural Development (MoRD) — for a unified repair ecosystem.
Single Window System for Appointment of State DGPs
- 06 Aug 2025
In News:
The Union Government has notified a Single Window System (SWS) to streamline the appointment of State Directors General of Police (DGPs)/Heads of Police Force (HoPFs). This move seeks to ensure transparency, uniformity, and compliance with Supreme Court directives inPrakash Singh vs Union of India (2006) and the Ministry of Home Affairs (MHA) guidelines.
Key Features of the SWS
- Standardization: Provides a checklist and uniform formats for States to submit proposals.
- Eligibility Certification: A Secretary-rank officer must certify that officers proposed for empanelment fulfill criteria, including a minimum of 6 months residual service.
- Timely Submission: States are mandated to send proposals at least 3 months before the anticipated vacancy of the DGP/HoPF.
Constitutional and Legal Framework
- State Subject: Police is a State subject under the 7th Schedule of the Constitution.
- Superintendence: As per Section 3 of the Police Act, 1861, the superintendence of police lies with the State Government.
- District Level: A dual control system exists—authority is shared between the District Magistrate (executive) and the Superintendent of Police (police administration).
- State Police Leadership: State police forces are generally headed by officers of the DGP rank.
India–EFTA Trade and Economic Partnership Agreement (TEPA)

- 06 Aug 2025
In News:
The Trade and Economic Partnership Agreement (TEPA) between India and the European Free Trade Association (EFTA) — comprising Iceland, Liechtenstein, Norway, and Switzerland — will come into force on 1 October 2025.
Key Features of TEPA
- Strategic Investment Commitment
- Legally binding commitment of USD 100 billion FDI in India over 15 years (USD 50 billion in first 10 years + USD 50 billion in next 5 years).
- Expected to generate 1 million jobs.
- Excludes foreign portfolio investment (FPI); sovereign wealth funds exempted.
- India can withdraw tariff concessions if commitments are not met.
- Market Access & Tariff Concessions
- EFTA: 92.2% tariff lines offered, covering 99.6% of India’s exports (100% non-agri products + concessions on processed agri products).
- India: 82.7% tariff lines offered, covering 95.3% of EFTA exports (including gold, which retains existing duty).
- Duty-free access: Indian basmati and non-basmati rice exports, without reciprocity.
- Exclusions: Dairy, soya, coal, and sensitive agri products; protection given to sectors linked with PLI schemes (e.g., pharma, medical devices, processed food).
- Concessions: Cheaper Swiss chocolates, wines, luxury watches (though wines < USD 5 excluded to protect Indian wineries).
- Services & Professional Mobility
- Boosts Indian services exports: IT, business, cultural, sporting, educational, and audiovisual services.
- Mutual Recognition Agreements (MRAs): Nursing, accountancy, and architecture professionals to gain work access in EFTA countries.
- Legal & Institutional Framework
- Covers 14 chapters: market access, trade facilitation, investment promotion, IPR, sustainable development.
- Protects India’s generic medicines; prevents evergreening of patents.
- Promotes technology collaboration but not compulsory technology transfer.
About the European Free Trade Association (EFTA)
- Established: 1960 (Stockholm Convention).
- Members: Iceland, Liechtenstein, Norway, Switzerland (not part of the EU).
- Aim: Promote free trade and economic integration among members and global partners.
India–EFTA Trade Relations
- India is EFTA’s 5th largest trading partner (after EU, US, UK, China).
- Trade Volume (2024–25): USD 24.4 billion.
- India’s exports: USD 1.96 billion (chemicals, iron & steel, precious stones, sports goods, bulk drugs).
- Imports from EFTA: USD 22.45 billion (mainly gold, silver, coal, pharma, vegetable oil, medical equipment, dairy machinery).
- Deficit: Large trade deficit, primarily due to gold imports from Switzerland (USD 20.7 billion in 2021–22).
- India–EFTA Desk: Set up by Invest India as a single-window platform to facilitate investments under TEPA.
Krasheninnikov Volcano
- 06 Aug 2025
In News:
The Krasheninnikov volcano, located in Russia’s Kamchatka Peninsula, recently erupted for the first time in recorded history. The eruption followed a nearby magnitude 8.8 earthquake and released ash plumes reaching 20,000 ft (≈6,000 m) into the atmosphere. Authorities issued an “orange” aviation hazard code due to potential risks to air traffic.
About Krasheninnikov Volcano
- Type: Active stratovolcano (composite volcano).
- Height: ~1,856–1,886 m.
- Structure: Formed within a 9 km wide collapsed caldera created by a massive eruption ~39,600 years ago that expelled 50 cubic km of dacitic pumice.
- Cones: Contains two eruptive cones; the southern cone has an 800 m wide, 140 m deep crater.
- Past Activity: Last known eruption occurred ~400–600 years ago.
Kamchatka Peninsula – Volcanic Hotspot
- Lies along the Pacific “Ring of Fire”, one of the world’s most seismically active zones.
- Home to 114 Holocene volcanoes (eruptions recorded in the last ~12,000 years).
- Known for frequent explosive eruptions due to subduction of the Pacific Plate beneath the Eurasian Plate.
Stratovolcano – Key Features
- Steep, conical structure with alternating layers of lava and pyroclastic deposits.
- Typically found above subduction zones (e.g., Pacific Ring of Fire).
- Characterized by explosive eruptions due to viscous andesite/dacite lavas that trap gases.
- Account for about 60% of Earth’s volcanoes.
- Example: Mount Fuji (Japan), Mount Vesuvius (Italy), Mount St. Helens (USA).
Significance of 2025 Eruption
- First recorded activity of Krasheninnikov highlights the unpredictability of dormant volcanoes.
- Demonstrates the link between major seismic events and volcanic eruptions in tectonically active zones.
- Raises concerns for aviation safety, regional ecology, and monitoring of Ring of Fire volcanism.
Slovenia
- 06 Aug 2025
In News:
Slovenia has announced a complete ban on the import, export, and transit of weapons to and from Israel in response to Israel’s military actions in Gaza. This makes it the first European Union (EU) member state to enforce a blanket arms embargo on Israel.
Context and Diplomatic Stand
- Slovenia has frequently criticized Israel for alleged atrocities in Gaza.
- In June 2024, Slovenia’s parliament recognisedPalestinian statehood, joining Ireland, Norway, and Spain.
- In July 2024, it barred two far-right Israeli ministers from entering the country, citing “incitement of violence” and “genocidal statements.”
- Although Slovenia’s arms trade with Israel is minimal, the decision carries symbolic diplomatic weight, intended to pressure Israel amid growing international condemnation.
Other European countries have taken partial measures:
- UK (2024): Suspended export of some weapons that could breach international law.
- Spain (2023): Halted arms sales.
- Netherlands, France, Belgium: Tightened regulations or faced legal challenges, but none imposed a total embargo like Slovenia.
Slovenian Prime Minister Robert Golob emphasized that Slovenia would act unilaterally in the absence of collective EU action, accusing the EU of disunity in addressing the humanitarian crisis in Gaza.
About Slovenia
- Location: Central Europe; formerly part of Yugoslavia.
- Capital: Ljubljana.
- Borders: Austria, Hungary, Croatia, Italy; coastline along the Adriatic Sea (Gulf of Venice).
- Memberships: Joined EU and NATO in 2004; uses the Euro.
- Physical Features:
- Alpine Highlands (~40% of territory) – includes Julian Alps, Karavanke, Kamnik-Savinja Alps. Highest peak: Mount Triglav (2,864 m).
- Karst Plateau – globally renowned for caves, sinkholes, underground rivers.
- Subpannonian Plains – fertile alluvial soils; rivers Sava, Drava, Mura drain toward the Danube.
- Slovene Littoral – 47 km coastline; major port Koper.
Financial Sector Changes from August 2025
- 06 Aug 2025
In News:
India’s financial ecosystem is undergoing significant operational changes aimed at strengthening stability, efficiency, and consumer protection. From August 1, 2025, several regulatory and institutional reforms—spanning digital payments, credit cards, fuel pricing, trading hours, and monetary policy—are set to reshape the financial landscape.
UPI Operational Reforms by NPCI
The National Payments Corporation of India (NPCI), which manages the Unified Payments Interface (UPI), has introduced revised operational rules to reduce transaction delays and prevent system overload during peak hours. UPI, India’s flagship digital payment platform, has emerged as the backbone of cashless transactions with over 14 billion monthly transactions (2025 data).
Key reforms effective from August 1, 2025:
- Balance Check Limit: Maximum 50 balance enquiries per day per app.
- Linked Account Enquiries: Limited to 25 per day per app.
- Auto-Pay Transactions: Permitted only during non-peak hours (before 10 AM, 1–5 PM, after 9:30 PM).
- Transaction Status Checks: Restricted to 3 per transaction, with a mandatory 90-second gap.
- Beneficiary Name Display: Recipient’s registered bank name will be shown before confirmation to curb fraud.
These reforms reflect an effort to balance user convenience with systemic efficiency while reducing risks of fraudulent transfers.
Credit Card Insurance Changes by SBI
The State Bank of India (SBI), India’s largest lender, has announced withdrawal of complimentary air accident insurance cover on several co-branded credit cards. Earlier, insurance covers of ?1 crore (ELITE series) and ?50 lakh (PRIME/Platinum series) were provided. The discontinuation reflects banks’ attempts to rationalize costs in a competitive credit market, but it also raises concerns regarding customer protection.
Fuel Price Revisions
Prices of LPG cylinders, CNG, PNG, and aviation turbine fuel (ATF) are subject to monthly review. Effective August 1, 2025, fresh revisions are expected in line with global crude trends and domestic subsidy policies. Given that LPG and CNG are crucial for households and transport, even marginal adjustments influence inflation and consumer spending.
Extension of Trading Hours
The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) has extended trading hours for money market instruments to deepen liquidity and align with global practices:
- Call Money Market: Extended to 9:00 AM – 7:00 PM (effective July 1, 2025).
- Market Repo & Tri-Party Repo (TREPs): Extended to 9:00 AM – 4:00 PM (effective August 1, 2025).
This reform is expected to improve liquidity management for banks and non-banking financial institutions, enhancing the efficiency of short-term borrowing and lending.
Apna Ghar Initiative

- 05 Aug 2025
In News:
The Ministry of Petroleum and Natural Gas has launched ‘Apna Ghar’, a nationwide initiative to provide resting facilities for truck drivers along highways. The programme, launched in 2025, aims to enhance road safety, driver well-being, and logistics efficiency, addressing the long-standing issue of fatigue and poor hygiene conditions faced by India’s trucking workforce.
Key Features of Apna Ghar
- Coverage: As of July 1, 2025, 368 units with 4,611 beds have been set up at retail fuel outlets along national and state highways by Public Sector Oil Marketing Companies (OMCs).
- Facilities Provided:
- Dormitories (10–30 beds per unit)
- Clean toilets and dedicated bathing areas (Houdas)
- Restaurants/dhabas and self-cooking spaces
- Purified drinking water access
- Technology Integration: Launch of the ‘Apna Ghar’ mobile app for bookings, user feedback, and engagement.
- Implementation Model: Public sector OMCs build and manage facilities at fuel retail stations, ensuring accessibility to drivers during long-haul journeys.
Objectives and Significance
- Road Safety: Reduces driver fatigue, a major cause of road accidents.
- Worker Welfare: Provides dignified working and resting conditions for truckers, a vital yet often informal part of India’s transport ecosystem.
- Economic Impact: Supports supply chain resilience by improving the productivity and well-being of drivers.
- Social Development: Aligns with Sustainable Development Goal 8 (Decent Work and Economic Growth) by promoting safe and humane working environments.
National Waterway-57 (River Kopili)

- 05 Aug 2025
In News:
In a landmark development for sustainable logistics in the Northeast, the Kopili River (National Waterway-57) was operationalised with the maiden cargo movement of 300 MT of cement from Chandrapur (Kamrup) to Hatsingimari (South Salmara, Assam).
About the Kopili River
- Origin:Saipong Reserve Forest in the Borail Range, North Cachar Hills, at 1,525 m altitude.
- Length: 256 km (78 km along the Assam–Meghalaya border; 178 km in Assam).
- Basin Coverage: Flows through Meghalaya and Assam, making it an interstate river.
- Significance: Largest south bank tributary of the Brahmaputra in Assam; traverses North Cachar Hill, KarbiAnglong, Nagaon, and Morigaon districts.
- Agricultural Zone: Supports cultivation of rice (winter, summer, autumn), wheat, mustard, and rapeseed in Kamrup and surrounding areas.
Strategic and Policy Significance
- Economic Impact: Reduces road congestion, lowers logistics costs, and provides an efficient alternative for bulk cargo. The trial run replaced the equivalent of 23 truckloads of cement.
- Environmental Gains: Inland water transport curbs emissions and promotes sustainable logistics.
- Regional Development: Enhances connectivity for riverine communities, boosts trade, and unlocks economic opportunities in Assam.
- National Integration: Aligns with Maritime India Vision 2030 and PM Gati Shakti, which seek to create multimodal, integrated transport infrastructure.
Pradhan Mantri National Dialysis Programme (PMNDP)

- 05 Aug 2025
In News:
The Pradhan Mantri National Dialysis Programme (PMNDP) has been significantly expanded by the Government of India and is now operational in all 36 States and Union Territories, covering 751 districts. As of June 30, 2025, a total of 1,704 dialysis centres are functional under the programme.
Background and Objectives
- Launched in 2016, the PMNDP aims to provide free dialysis services to patients suffering from end-stage kidney failure, with special focus on Below Poverty Line (BPL) beneficiaries.
- It is implemented under the National Health Mission (NHM) in Public-Private Partnership (PPP) mode.
- The programme addresses the rising burden of chronic kidney disease and aims to ensure equitable access to life-saving renal care across India.
Key Features
- Dialysis Services: Supports both Haemodialysis and Peritoneal Dialysis.
- Infrastructure Expansion: Initially recommended at all district hospitals, with flexibility to scale down to Community Health Centres (CHCs), especially in remote and tribal regions.
- PMNDP Portal: Integrates all NHM-supported dialysis centres, facilitates creation of a renal registry, and ensures service portability within states (“One State–One Dialysis”) and eventually nationwide (“One Nation–One Dialysis”).
- Funding Mechanism: The NHM provides financial assistance to States/UTs for setting up and operating dialysis centres.
- Implementation Strategy: Expansion is based on gap assessments carried out by States/UTs as part of their annual Programme Implementation Plans (PIPs).
Significance
- Health Equity: Extends life-saving kidney care to vulnerable groups, including rural and tribal populations.
- Cost Reduction: Provides free dialysis, reducing the out-of-pocket burden on families.
- Data Integration: The renal registry aids in epidemiological tracking and planning of kidney health interventions.
- Public Health Impact: Strengthens India’s healthcare delivery under Universal Health Coverage (UHC) goals.
‘Matri Van’ initiative
- 05 Aug 2025
In News:
The Government of India has launched the ‘Matri Van’ initiative in Gurugram under the ‘Ek Ped MaaKe Naam’ programme, symbolizing ecological preservation and community participation. The project was inaugurated by the Union Minister for Environment, Forest and Climate Change, Shri Bhupender Yadav, and the Union Minister for Housing and Urban Affairs and Power, Shri Manohar Lal, during Van Mahotsav 2025.
About the Initiative
- Location & Scale: Spread over 750 acres in the Aravalli hill area along the Gurugram-Faridabad road.
- Concept: A theme-based urban forest aimed at nurturing generations through mother-nature-inspired green efforts.
- Vision: To enhance biodiversity, public well-being, and urban sustainability, while serving as the “heart and lung of Delhi-NCR.”
- Collaboration: Developed through multi-stakeholder participation, including CSR partners, Resident Welfare Associations (RWAs), NGOs, MNCs, school children, and government bodies.
Ecological and Social Significance
- Restoration of degraded land by removing invasive Kabuli Kikar (Prosopis juliflora).
- Plantation of native Aravalli species such as Dhak, Amaltash, Neem, Bargad, Peepal, Gullar, Pilkhan, Khair, Semal, and bamboo.
- Development of theme-based groves, including:
- Bodhi Vatika (sacred fig species like Bargad, Peepal),
- Bamboosetum (bamboo species),
- Aravalli Arboretum,
- PushpVatika (flowering trees),
- Sugandh Vatika (fragrant species),
- Medicinal Plants Vatika,
- Nakshatra and RashiVatika,
- Cactus Garden,
- Butterfly Garden.
Facilities and Infrastructure
- Eco-tourism and community spaces: nature trails, cycle tracks, yoga zones, gazebos, and sitting areas.
- Environmental safeguards: treated water irrigation systems, sprinklers, and waterbodies to aid water conservation and urban flood prevention.
- Urban amenities: parking spaces, public facilities, and accessibility features.
Broader Environmental Vision
- Linked to Mission LiFE (Lifestyle for Environment) with components like:
- Saving food, water, and energy,
- Solid waste and e-waste management,
- Ban on single-use plastics,
- Promotion of healthy lifestyles.
- Complements India’s renewable energy transition, with non-fossil fuel power now accounting for over 50% of the national energy mix.
- Supports Prime Minister’s vision of rejuvenating the Aravalli ecosystem through plantation of native species.
Significance for Delhi-NCR
- Acts as a natural carbon sink to counter rising emissions.
- Provides a green lung to improve air quality in a highly polluted urban region.
- Promotes eco-tourism and environmental education through biodiversity parks, wildlife safaris, and thematic groves.
- Offers citizens a serene, stress-free environment, strengthening the image of Gurugram as a model “Millennium City.”
Investor Education and Protection Fund Authority (IEPFA)

- 05 Aug 2025
In News:
The Investor Education and Protection Fund Authority (IEPFA), established in 2016 under the Companies Act, 2013, functions under the Ministry of Corporate Affairs (MCA) with the mandate of safeguarding investor interests, refunding unclaimed financial assets, and promoting financial literacy across India.
Mandate and Fund Structure
The Investor Education and Protection Fund (IEPF) consists of amounts that remain unclaimed for seven years, including:
- Unpaid dividends,
- Application money due for refund,
- Matured deposits and debentures,
- Accrued interest on investments,
- Grants and donations received from government or other entities.
The fund is utilized to refund unclaimed shares/dividends to rightful investors and to spread financial awareness among citizens.
Recent Developments: Integrated Portal
IEPFA is in the final phase of testing its Integrated Portal, a unified digital platform aimed at:
- Streamlining claim processes for unclaimed shares/dividends,
- Enhancing accessibility for both investors and companies,
- Integrating stakeholders such as depositories and the Public Financial Management System (PFMS).
Companies have been urged to upload their IEPF-1/7 SRNs with prescribed templates to enable smooth data verification and claim processing.
Key Features of the New System
- Simplified claims for low-value refunds through reduced documentation.
- Integrated Call Center to strengthen grievance redressal and ensure responsive communication with stakeholders.
- Temporary disruptions may occur during transition, but the reforms promise faster, transparent, and investor-friendly outcomes.
Investor Awareness Initiatives
IEPFA also undertakes extensive financial literacy campaigns through programs like:
- Niveshak Didi,
- Niveshak Panchayat,
- NiveshakShivir.
These initiatives empower citizens, particularly in rural and semi-urban areas, to make informed financial decisions and protect themselves from fraud and mismanagement.
Significance
- For Investors: Easier access to unclaimed assets and improved grievance redressal.
- For Companies: Structured compliance framework and digital integration with regulators.
- For Governance: Strengthens India’s financial ecosystem by combining investor protection with financial literacy.
Nahargarh Wildlife Sanctuary
- 04 Aug 2025
In News:
The Rajasthan Forest Department has recently redrawn the boundaries of the Nahargarh Wildlife Sanctuary (NWS), located near Jaipur, sparking controversy among conservationists and legal experts. The move, alleged to benefit luxury hotels and commercial establishments within the sanctuary and its Eco-Sensitive Zone (ESZ), has raised questions about legality, ecological safeguards, and governance.
About Nahargarh Wildlife Sanctuary
- Location: ~20 km from Jaipur, under the Aravalli range.
- Size: Originally ~720 hectares; currently notified as 6,025.74 hectares across 16 villages.
- History: Named after Nahargarh Fort, built by Maharaja Sawai Jai Singh II in the 18th century.
- Nahargarh Biological Park: Part of the sanctuary, noted for its lion safari.
- Flora: Dry deciduous forests, scrublands, grasslands.
- Fauna: Leopards, deer, sloth bears, wild boars, lions, tigers, reptiles like pythons and monitor lizards, and diverse birdlife including owls, eagles, and peacocks.
The Controversy
- Procedural Lapses
- Under Section 26A of the Wildlife Protection Act, 1972, any change in sanctuary boundaries requires approval from the National Board for Wildlife (NBWL).
- Experts cite the 2013 Supreme Court judgment (Centre for Environmental Law, WWF-India vs Union of India), which mandated NBWL clearance for altering protected area limits.
- However, Rajasthan submitted revised maps to the National Green Tribunal (NGT) in July 2025 without NBWL’s recommendation.
- Alleged Motivations
- Activists claim the revised map excludes “Described Areas” (revenue lands held by public and private bodies) while retaining only Reserved Forest patches.
- This adjustment allegedly protects existing luxury hotels and other constructions in the ESZ, some of which earlier faced demolition orders for violations.
- Government’s Justification
- Officials argue the 1980 notification used “grossly approximate” boundary descriptions.
- Over four decades, urbanisation and topographical changes blurred the original limits.
- A GIS-based remapping exercise using high-resolution satellite imagery and land records was undertaken, and state approval was granted in July 2025.
BlueBird Communications Satellite
- 04 Aug 2025
In News:
Following the successful NISAR (NASA–ISRO Synthetic Aperture Radar) mission, the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO)is preparing for its next major collaboration with the United States: the launch of the BlueBird communications satellite. The mission highlights India’s growing role as a reliable global launch partner and the expanding scope of Indo–U.S. space cooperation.
The BlueBird Satellite
- Developer: U.S.-based AST SpaceMobile
- Type: Advanced communications satellite designed for direct satellite-to-smartphone connectivity
- Weight: ~6,000 kg
- Antenna: Innovative 64-square-metre antenna array for high-capacity communication
- Orbit: Low Earth Orbit (LEO)
- Technology:
- Enables direct calling and broadband access from space without the need for ground-based mobile towers
- Supports beams up to 40 MHz capacity
- Offers peak speeds of up to 120 Mbps
- Service Plan: After deployment, BlueBird satellites will provide non-continuous broadband cellular service initially in the U.S. and select global markets.
Launch Details
- Launch Vehicle: LVM3 (Launch Vehicle Mark-3), ISRO’s heaviest rocket, formerly known as GSLV Mk-III
- Launch Site: Satish Dhawan Space Centre, Sriharikota
- Timeline: Expected launch in the next 3–4 months (as per ISRO chairman V. Narayanan)
Strategic Significance
- For India–U.S. Cooperation:
- Follows the joint NISAR Earth observation mission, reinforcing strategic space ties.
- Strengthens India’s position as a preferred partner for global commercial satellite launches.
- For India’s Space Economy:
- Enhances ISRO’s reputation in heavy-lift commercial launches, particularly with LVM3.
- Showcases India’s cost-effective access to space, attracting further foreign collaborations.
- For Global Communication Technology:
- Marks a breakthrough in direct-to-device (D2D) connectivity, reducing dependency on ground infrastructure.
- Could help expand mobile and broadband coverage to remote and underserved regions worldwide.
Oreshnik Hypersonic Missile
- 04 Aug 2025
In News:
In August 2025, Russian President Vladimir Putin announced that the Oreshnik hypersonic missile—a new-generation intermediate-range ballistic missile—has entered production and military service. Plans are underway to deploy the system in Belarus by the end of 2025, signalling a major escalation in Russia’s standoff with NATO amid the Ukraine conflict.
Key Features
- Type: Intermediate-range, solid-fuel, mobile, hypersonic ballistic missile
- First Operational Use: November 2024, in a strike on Ukraine’s Pivdenmashdefence facility at Dnipro
- Speed: Capable of reaching Mach 10 (10 times the speed of sound)
- Range: Approx. 5,000 km (3,100 miles), bringing the entirety of Europe within its strike zone
- Warhead Capability:
- Carries conventional or nuclear warheads
- Equipped with Multiple Independently Targetable Re-entry Vehicles (MIRVs), allowing simultaneous strikes on multiple targets
- Strategic Advantage: Hypersonic speed, mid-flight manoeuvrability, and MIRV capability make it virtually immune to interception by current Western missile defence systems
Strategic Context
- Belarus as a Forward Base:
- Belarus shares a 673-mile border with Ukraine, making it strategically vital.
- It already hosts Russian troops and tactical nuclear weapons.
- Deployment of Oreshnik here allows Moscow to project power deeper into Europe.
- Nuclear Security Pact (2023):
- Russia and Belarus signed an agreement placing Belarus under Russia’s nuclear umbrella.
- Russia retains the right to use nuclear weapons stationed in Belarus if “aggression” is perceived.
- Belarus has reportedly hosted “several dozen” Russian nuclear weapons since late 2024.
- Geopolitical Implications:
- Russia warned NATO against supplying Ukraine with long-range weapons capable of striking inside Russia.
- Putin cautioned that Russia could retaliate with systems like Oreshnik “even beyond Ukraine.”
- By suggesting that conventional Oreshnik strikes could be as devastating as nuclear attacks, Moscow is raising deterrence levels against the West.
Implications for Global Security
- Erosion of Arms Control: With the collapse of Cold War-era treaties like the INF Treaty (1987), weapons such as Oreshnik operate in a largely unregulated environment.
- Escalation of NATO–Russia Rivalry: The missile’s deployment in Belarus expands Russia’s strike capability across Europe, heightening NATO security concerns.
- Nuclear Threshold Ambiguity: Oreshnik’s dual capability (conventional and nuclear) blurs the line between conventional warfare and nuclear escalation.
- Arms Race in Hypersonics: The U.S., China, and other powers are also developing hypersonic weapons, intensifying competition in next-generation strategic arms.
Polavaram–Banakacherla Link Project (PBLP)
- 04 Aug 2025
In News:
The bifurcation of Andhra Pradesh in 2014 created prolonged disputes between Andhra Pradesh (AP) and Telangana over sharing the waters of the Krishna and Godavari rivers. Issues have resurfaced with Andhra Pradesh’s proposal of the Polavaram–Banakacherla Link Project (PBLP), opposed by Telangana on legal and ecological grounds.
In July 2025, the Union Government decided to set up two dedicated river management boards—the Krishna River Management Board (KRMB) at Amaravati and the Godavari River Management Board (GRMB) at Hyderabad. Both will include Central officials, technical experts, and representatives from the two states.
Polavaram–Banakacherla Link Project (PBLP)
- Objective: Divert 200 TMC of surplus Godavari floodwaters to drought-prone Rayalaseema by linking the Polavaram reservoir to the Banakacherla regulator in Kurnool district.
- Water Transfer Mechanism:
- Draw water from Polavaram Dam
- Convey through Prakasam Barrage → lift to Bollapalli reservoir
- Tunnel through the Nallamala hills → release into Banakacherla reservoir
- Significance: Strengthens irrigation, drinking water supply, and agricultural sustainability; aligns with national schemes such as Jal Jeevan Mission, Blue Revolution, and Make in India.
Telangana’s Concerns
- Violation of the Andhra Pradesh Reorganisation Act, 2014 – which requires prior approval of the Apex Council, KRMB, and CWC for new inter-state river projects.
- Disputed “Surplus” Claim – Telangana contests Andhra’s claim of 200 TMC surplus Godavari waters, arguing no adjudicatory body has approved such diversion.
- Environmental and Legal Clearances – Though the Polavaram Project got clearance in 2005, the Expert Appraisal Committee has called for fresh scrutiny, especially due to submergence concerns in Odisha and Chhattisgarh.
- Unauthorised Inter-Basin Diversion – Godavari-to-Krishna transfer without mutual consent could undermine Telangana’s own projects.
- Breach of Cooperative Federalism – Telangana sees unilateral action by Andhra as bypassing consensus-driven water governance.
Consensus Achieved in July 2025 Talks
- Telemetry Systems: Both states agreed to install real-time monitoring devices at reservoirs and projects to ensure transparency in water usage.
- Srisailam Project Repairs: Andhra agreed to undertake crucial maintenance at this shared project.
- Board Reorganisation: KRMB’s office to shift to Amaravati/Vijayawada for better oversight.
- Joint Committee: High-level committee of central, state, and technical experts to study outstanding issues and recommend equitable solutions.
Legal and Institutional Mechanisms for Inter-State Water Disputes
- Constitutional Provisions:
- Article 262: Parliament may legislate for adjudication of inter-state water disputes; can also bar courts’ jurisdiction.
- State List (Entry 17): States control water-related issues.
- Union List (Entry 56): Centre can regulate inter-state rivers in the national interest.
- Statutory Framework:
- River Boards Act, 1956: Allows River Boards for coordinated development; not implemented in practice.
- Inter-State Water Disputes Act, 1956: Provides for tribunals. Amendments in 2002 mandated quicker constitution of tribunals (1 year) and decisions within 3 years.
- Judicial Role: Despite Article 262(2), the Supreme Court has intervened in interpretation and implementation of tribunal awards (e.g., Mahadayi Water Dispute, 2018).
A New Approach to Treating Liver Cirrhosis
- 04 Aug 2025
In News:
A team of Indian scientists may have found a way to improve the drainage capacity of lymphatic vessels in the liver and intestine that fails in case of cirrhosis, by using nanocarriers filled with a powerful protein called VEGF-C.
Understanding Liver Cirrhosis
Cirrhosis is the advanced stage of chronic liver disease where healthy tissue is replaced by scar tissue due to prolonged inflammation. This structural distortion affects both blood and lymphatic vessels in the liver and intestine, impairing circulation and fluid balance.
Causes:
- Excessive alcohol consumption
- NASH (Non-Alcoholic Steato-Hepatitis)
- Chronic viral infections such as Hepatitis B and C
Symptoms (often in advanced stages): extreme fatigue, loss of appetite, easy bruising or bleeding, swelling in legs/ankles (edema), and abdominal fluid accumulation (ascites).
The Problem of Lymphatic Dysfunction
In cirrhosis, lymphatic vessels (mesenteric lymphatic vessels or mLVs) become dilated and dysfunctional. Normally, these vessels drain interstitial fluid, proteins, and immune cells back into venous blood.
- In cirrhosis, lymph production increases nearly 30-fold due to portal hypertension and liver congestion.
- Dysfunctional lymph flow leads to ascites (abdominal fluid buildup), one of the most serious complications of decompensated cirrhosis.
- Currently, there is no effective therapy to correct this lymphatic dysfunction.
The VEGF-C Based Breakthrough
A joint team from the Institute of Liver and Biliary Sciences (ILBS), New Delhi and the National Institute of Pharmaceutical Education and Research (NIPER), Guwahati has developed a novel therapy using Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor-C (VEGF-C).
- Role of VEGF-C: A key pro-lymphangiogenic factor that binds to VEGFR-3 receptors, stimulating the growth of new lymphatic vessels and enhancing drainage.
- Challenge: VEGF-C has a short half-life, is hydrophilic, and can cause systemic side effects.
The Innovation: Nanocarriers
- Scientists at NIPER designed reverse micelle-based nanocarriers to encapsulate VEGF-C, ensuring targeted delivery to gut lymphatic vessels.
- These nanocarriers specifically bind to VEGFR-3 homodimers, maximizing efficacy and minimizing side effects.
- The formulation was delivered orally in animal models, ensuring uptake by intestinal lymphatic vessels.
Findings (Animal Studies)
- Significant increase in mesenteric lymph drainage
- Reduction in ascites and portal hypertension
- Enhanced cytotoxic T-cell immunity in lymph nodes
- Reduction in local and systemic bacterial load
Significance and Future Prospects
- This is the first study to demonstrate that therapeutic lymphangiogenesis using VEGF-C can reconstruct fragmented lymphatic networks and restore function in advanced cirrhosis.
- Funded by the DST Nano Mission and published in JHEP Reports, it marks a major step in translational medicine.
- Next steps: Preclinical studies in larger animals, followed by human clinical trials to establish safety, dosage, and efficacy.
Indo-Burma Ramsar Regional Initiative (IBRRI)
- 03 Aug 2025
In News:
The 15th Conference of the Parties (COP15) to the Ramsar Convention concluded with a significant side event of the Indo-Burma Ramsar Regional Initiative (IBRRI), highlighting collaborative efforts for wetland conservation and restoration across Southeast Asia.
About IBRRI
- Origin: Jointly developed by the Ramsar National Focal Points of Cambodia, Lao PDR, Myanmar, Thailand, and Viet Nam, with technical support from the IUCN Asia Regional Office.
- Aim: To coordinate and support the implementation of the Strategic Plan of the Ramsar Convention, particularly in addressing wetland degradation.
- Support: Backed by IUCN’s BRIDGE (Building River Dialogue and Governance) project, which promotes sustainable water management, biodiversity conservation, and cross-border cooperation.
Governance Structure
To ensure oversight, transparency, and inclusivity, IBRRI has developed a multi-tiered governance framework:
- Steering Committee: Comprising Ramsar Administrative Authorities from the five member countries.
- Secretariat: Hosted by the IUCN Asia Regional Office, Bangkok.
- Stakeholder Committee: Provides technical and strategic guidance, ensuring multi-stakeholder participation including governments, NGOs, and civil society.
Strategic Plan 2025–2030
- Launch: Officially unveiled during COP15 as a transboundary framework for wetland management.
- Objective: To halt and reverse wetland loss across member states through restoration, sustainable use, and regional cooperation.
- Approach: Promotes knowledge exchange, policy coordination, and joint action for wetland conservation.
About BRIDGE Project
- Aim: To strengthen transboundary water governance by catalysingsustainable management of shared rivers, ensuring water security, conserving biodiversity, and fostering peaceful cooperation across borders.
Significance
- Provides a regional mechanism for Ramsar Convention implementation.
- Enhances transboundary cooperation in the Indo-Burma region, which hosts critical wetland ecosystems.
- Contributes to biodiversity conservation, climate resilience, and sustainable development goals (SDGs).
Darwin Tree of Life (DToL) Project

- 03 Aug 2025
In News:
The Darwin Tree of Life (DToL) project is nearing the completion of its first phase and represents one of the most ambitious scientific efforts to decode the diversity of life on Earth. Focused on sequencing the genomes of all eukaryotic species in Britain and Ireland, the project is a cornerstone of the global Earth BioGenome Project (EBP).
About the Project
- Objective: To generate high-quality genome sequences of around 70,000 eukaryotic species including animals, plants, fungi, and protists.
- Approach: Careful collection of representative samples, application of advanced DNA sequencing technologies, and use of computational tools to understand how genetic code drives biological diversity.
- Collaboration: A joint initiative involving ten biodiversity, genomics, and data analysis partners.
What are Eukaryotes?
- Definition: Organisms with complex cells that have a well-defined nucleus enclosed by a membrane, along with organelles such as mitochondria and Golgi apparatus.
- Examples: Protists, plants, fungi, and animals.
- Distinctive Features:
- Possess chromosomes inside the nucleus.
- Reproduce asexually (mitosis) or sexually (meiosis + gamete fusion).
- Contrast with Prokaryotes: Unlike bacteria and archaea, eukaryotes are structurally advanced due to compartmentalized cell functions.
The Earth BioGenome Project (EBP)
- Vision: A global initiative to sequence, catalogue, and analyse the genomes of all known eukaryotic species on Earth.
- Timeline: 10 years.
- Network: Collaborative effort involving scientists, institutions, and multiple regional projects like DToL.
Significance:
- Scientific Advancement
- Provides a genomic foundation for understanding biodiversity, evolution, and taxonomy.
- Helps uncover how genetic variations translate into ecological and physiological adaptations.
- Conservation and Sustainability
- Offers data vital for protecting endangered species and ecosystems.
- Assists in addressing biodiversity loss and supporting global conservation strategies.
- Applications in Human Development
- Medicine: Discovery of new genes for disease resistance or therapeutic innovations.
- Agriculture: Identification of traits for crop resilience and productivity.
- Biotechnology:Utilisation of unique biological pathways for industrial and environmental applications.
Human Outer Planet Exploration (HOPE)
- 03 Aug 2025
In News:
- India has taken a decisive step in advancing its space exploration ambitions with the launch of theHuman Outer Planet Exploration (HOPE) analogue station in Ladakh’s Tso Kar region.
- Developed by Bengaluru-based space science company Protoplanet in collaboration with the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO), the station is designed to simulate extra-terrestrial conditions, closely mimicking the geological and environmental features of the Moon and Mars.
What is HOPE?
- Analogue Station Concept: An analogue research station replicates planetary conditions to test technologies, study human adaptability, and conduct crew training. Globally, there are 33 such facilities, including BIOS-3 (Russia), HERA (USA), SHEE (Europe), and the Mars Desert Research Station (Utah, USA).
- Location & Conditions: Situated at an altitude of over 14,500 feet, Tso Kar offers a cold desert and high-altitude environment, chosen after nine years of study. Its extreme terrain makes it an “exceptional analogue site” for simulating extraterrestrial challenges.
- Mission Objective: HOPE aims to generate insights into human adaptability, resilience, and technology readinessfor sustained human presence beyond Earth.
Research and Operations
From August 1, 2025, selected crew members will undergo 10-day isolation missions inside the station. They will be subject to:
- Physiological studies – monitoring body adaptation in extreme conditions.
- Psychological studies – assessing mental resilience during confinement.
- Epigenetic research – studying biological changes in response to stress and environment.
Significance for India
- Strengthening Human Spaceflight Programme: This initiative provides critical data on crew adaptability for long-duration missions, supporting India’s vision of human exploration.
- Policy Alignment: The mission aligns with Prime Minister Narendra Modi’s announcement of establishing the BharatiyaAntariksh Station by 2035 and launching a manned Moon mission by 2040.
- Global Context: While NASA is targeting a manned mission to Mars by the 2030s, India is positioning itself as a rising player in deep-space exploration.
Strategic Importance
- Scientific Gains: HOPE will aid in technology validation, geological studies, life-detection research, and habitability assessments.
- International Standing: India joins the select group of countries operating analogue research stations, strengthening its credibility in interplanetary exploration.
- Capacity Building: The project helps build indigenous expertise in crew training, mission simulations, and psychological conditioning, paving the way for sustained space presence.
OECD Report on Plastic Pollution in Southeast & East Asia
- 03 Aug 2025
In News:
The Organisation for Economic Cooperation and Development (OECD) has warned that plastic use and waste in Southeast and East Asia could nearly double by 2050 unless countries adopt urgent and stringent policy measures. The findings are particularly significant as they coincide with the final round of UN negotiations on a global plastics treaty scheduled in August 2025 in Geneva.
Key Findings of the OECD Report
1. Surge in Plastic Use and Waste
- Plastic consumption in the ASEAN Plus Three (APT) region – which includes ASEAN-10 (Brunei, Cambodia, Indonesia, Laos, Malaysia, Myanmar, Philippines, Singapore, Thailand, Vietnam) plus China, Japan, and South Korea – is projected to rise from 152 million tonnes (2022) to 280 million tonnes (2050).
- Plastic waste will increase from 113 million tonnes (2022) to 242 million tonnes (2050).
- Packaging waste alone will almost double, from 49 million tonnes to 91 million tonnes.
2. Regional Disparities
- China will see the largest absolute rise, from 76 million tonnes (2022) to 160 million tonnes (2050).
- Lower-middle-income ASEAN nations such as Indonesia, Vietnam, and the Philippines will see the sharpest relative increase, with plastic waste nearly quadrupling from 7.5 million tonnes to 28 million tonnes.
3. Mismanaged Waste and Leakage
- Share of mismanaged plastic waste may fall (29% → 23% between 2022–2050), but total mismanaged waste will grow from 33 million tonnes to 56 million tonnes.
- The region is already the largest contributor to global plastic leakage – 8.4 million tonnes in 2022 (one-third of global leakage), projected to rise to 14.1 million tonnes by 2050.
- Plastic build-up:
- Freshwater systems: from 57 million tonnes (2022) → 126 million tonnes (2050).
- Oceans: from 17 million tonnes (2022) → 55 million tonnes (2050).
4. Climate Implications
- Greenhouse gas emissions from the plastic lifecycle (production + waste management) in the APT region are expected to nearly double from 0.6 GtCO?e (2022) to over 1 GtCO?e (2050).
Global High Stringency Scenario: Pathway to Solutions
OECD outlines a Global High Stringency (GHS) policy scenario that can reverse the trajectory:
- Plastic use: Could drop by 28% by 2050.
- Plastic waste: Could fall by 23%.
- Recycling: Average recycling rate could reach 54%, with secondary plastics meeting all future demand growth.
- Mismanaged waste: Could decline by 97%, drastically reducing environmental leakage.
Key recommended measures:
- Phase out single-use plastics.
- Strengthen waste collection systems and invest in recycling infrastructure.
- Promote circular economy approaches and regional cooperation.
Regional and Global Implications
- Cross-border challenge: Plastics persist for decades and move across boundaries. Poorer ASEAN nations like Indonesia often receive waste leakage from wealthier neighbours and China, with spillover impacts reaching the Indian Ocean and African coasts.
- Climate risks: Rising plastic demand intensifies emissions, undermining climate action goals.
- Global treaty negotiations: The report’s timing strengthens the case for an ambitious legally binding plastics treaty.
ICJ Ruling on the Kyoto Protocol
- 03 Aug 2025
In News:
In a landmark advisory opinion, the International Court of Justice (ICJ) has clarified that the Kyoto Protocol (1997) remains legally valid and binding, even after the Paris Agreement (2015) came into effect. This ruling has revived the Protocol’s legal relevance and has far-reaching implications for international climate law and global climate governance.
Background: The Kyoto Protocol
- Adopted: 1997; Entered into force: 2005 under the UN Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC).
- Nature: First binding international treaty mandating emission reductions by industrialised nations (Annex-I countries).
- Principle: Based on Common but Differentiated Responsibilities and Respective Capabilities (CBDR–RC), recognising that developed nations bear greater responsibility due to their historical emissions.
- Commitment Periods:
- First: 2008–2012
- Second: 2012–2020
- Obligations:
- Quantified emission reduction targets (from 1990 baseline).
- Provision of finance and technology transfer to developing nations.
- Market-based mechanisms such as the Clean Development Mechanism (CDM).
Why was Kyoto Considered Obsolete?
- US Non-Ratification: The largest historical emitter never joined the Protocol.
- Withdrawals: Countries like Canada and Japan later exited or refused binding targets.
- Rise of New Emitters: China overtook the US as the largest emitter by mid-2000s but, as a “developing country,” had no binding obligations.
- Shift to Paris Agreement (2015):
- Kyoto: Top-down, binding targets for developed countries.
- Paris: Bottom-up, voluntary Nationally Determined Contributions (NDCs) for all states.
- With no third commitment period defined after 2020, Kyoto was widely seen as defunct though never formally repealed.
ICJ’s Key Rulings
- Kyoto Still in Force: The absence of a new commitment period does not terminate the Protocol; it remains part of applicable international law.
- Legal Accountability: Non-compliance with emission reduction targets can constitute an “internationally wrongful act.”
- Retroactive Review: Past obligations (e.g., unfulfilled first commitment period targets) remain open for assessment.
- Advisory but Influential: Though not legally binding, the ruling strengthens grounds for climate litigation and accountability mechanisms.
Significance of the Ruling
- Legal Continuity: Confirms coexistence of Kyoto and Paris, rather than substitution.
- Revival of CBDR–RC: Re-emphasises differentiated responsibilities of developed nations, which Paris had diluted.
- Climate Justice: Opens the door for renewed scrutiny of historical emitters and their unfulfilled obligations.
- Litigation Pathways: Strengthens civil society and state efforts to seek compensation or stronger climate actions through international and domestic courts.
Implications for Global Climate Governance
- Developed countries face renewed legal and moral pressure to honour past commitments and extend finance and technology support.
- Developing nations gain a stronger footing to demand accountability for historical emissions.
- The ruling highlights the layered nature of international climate treaties, with Kyoto, UNFCCC, and Paris coexisting rather than replacing each other.
- It may reshape climate negotiations by reviving unfinished obligations under Kyoto while reinforcing Paris as the ongoing framework.
Piprahwa Relics

- 02 Aug 2025
In News:
The recent return of the sacred Piprahwa relics of Lord Buddha to India marks a landmark moment in India’s cultural diplomacy, heritage preservation, and spiritual history. Orchestrated by the Ministry of Culture in partnership with the Godrej Industries Group, this event prevented the relics’ auction in Hong Kong (May 2025) and instead restored them to their rightful home. For India, the land where the Buddha attained enlightenment and preached, this repatriation is more than a matter of archaeology—it reaffirms India’s role as the civilizational custodian of global heritage.
What are the Piprahwa Relics?
- Association: Believed to be the mortal remains of Lord Buddha, enshrined by the Sakya clan (his kinsmen) in the 3rd century BCE.
- Discovery: Excavated in 1898 by William Claxton Peppé, a British civil engineer and estate manager, from a stupa at Piprahwa, Uttar Pradesh, located just south of Lumbini (Buddha’s birthplace, now in Nepal).
- Contents:
- Bone fragments of the Buddha
- Caskets: soapstone, crystal, and sandstone coffer
- Offerings: gold ornaments, gemstones, and other ritual objects
- Inscription: A Brahmi script engraving on one of the caskets confirmed the relics’ identity, noting they were deposited by the Sakya clan.
Historical Journey of the Relics
- Colonial Appropriation (1898–1899)
- Following their discovery, the British Crown claimed the artefacts under the Indian Treasure Trove Act, 1878.
- The bone and ash relics were gifted to King Chulalongkorn of Siam (Thailand), reflecting colonial practices of cultural transfer.
- The majority of the remaining relics were placed in the Indian Museum, Kolkata (1899).
- Legal Protection
- Classified as ‘AA’ antiquities under Indian law, these relics cannot be sold, exported, or removed—underscoring their sacred and national significance.
- Attempted Auction in 2025
- The relics resurfaced in Hong Kong for an intended auction.
- Through timely diplomatic and legal intervention, supported by public-private partnership with the Godrej Group, the Ministry of Culture secured their return.
Significance of the Repatriation
1. Spiritual and Cultural Significance
- Buddhism, which spread from India across Asia, regards relics of the Buddha as sacred embodiments of peace, compassion, and enlightenment.
- The return reaffirms India as the spiritual homeland of Buddhism, strengthening cultural linkages with Buddhist-majority nations like Thailand, Myanmar, Japan, and Sri Lanka.
2. Archaeological and Historical Importance
- Piprahwa is one of the earliest archaeologically verified stupa sites.
- The discovery provides rare material evidence of Buddhist practices of relic veneration, confirming textual accounts in Buddhist scriptures.
3. Diplomatic and Soft Power Dimensions
- The move highlights cultural diplomacy as a tool of India’s foreign policy.
- India positions itself as a global guardian of Buddhist heritage, enhancing ties with Southeast Asian nations where Buddhism is deeply rooted.
4. Model of Public–Private Partnership
- The collaboration between the Government of India and the Godrej Industries Group sets a precedent for safeguarding heritage.
- It reflects how corporate social responsibility (CSR) can extend beyond business to civilizational legacy.
Supply and Use Tables 2020–21 & 2021–22
- 02 Aug 2025
In News:
Recently, the Ministry of Statistics and Programme Implementation (MoSPI) released the Supply and Use Tables (SUTs) for 2020–21 and 2021–22.
What are Supply and Use Tables?
SUTs consist of two interlinked matrices—Supply Tables and Use Tables, organized in a product-by-industry format.
- Supply Table: Captures total supply of goods and services, combining domestic production (at basic prices) and imports.
- Use Table: Reveals how these products are used across the economy—intermediate consumption, final consumption, capital formation, and exports (at purchasers’ prices).
Purpose & Significance of SUT
- Integration of GDP Approaches: SUT unifies production, income, and expenditure methods for GDP calculation, helping reconcile discrepancies between them.
- Robust Analytical Tool: Offers granular insights into product-industry dynamics, facilitating better policymaking and economic analysis.
- Data Reconciliation: Aligns macroeconomic estimates from sources like National Accounts Statistics (NAS), ASI, RBI, EXIM data, and census, improving coherence.
Data Coverage & Compilation Methodology
- Scope: Covers 140 products and 66 industries, at current prices, aligned with UN’s System of National Accounts (SNA).
- Key Steps:
- Identify industries (via NIC, NAS compilation categories) and products (via NPCMS for manufacturing, NPCSS for services).
- Compile Supply Table at basic prices; translate to purchasers’ prices using tax, margin, and CIF adjustments.
- Compile Use Table, detailing intermediate and final uses.
- Balance product supply and use to ensure consistency.
- Data Sources: NAS, ASI, EXIM, RBI, CBIC, MCA, Cost of Cultivation, etc.
Key Highlights
|
Metric |
2020–21 |
2021–22 |
|
Total Supply (Purchasers’ Prices) |
?407.52 lakh crore |
?523.08 lakh crore |
|
Sectoral Composition (basic prices) |
Agriculture: 11–13%, Mining: 2%, Manufacturing: 30–33%, Manufacturing-related services: 3%, Other Services: ~55% |
GVA-to-GVO Ratios (Efficiency Indicators)
- Top-performing industries (high ratios):
- 2020–21: Ownership of Dwellings, Fishing & Aquaculture, Forestry & Logging, Agriculture, Education & Research
- 2021–22: Ownership of Dwellings, Fishing & Aquaculture, Forestry & Logging, Agriculture, Crude Petroleum
- Low-performing industries (low ratios):
- 2020–21: Meat processing, Dairy, Grain mill & animal feeds, Communication equipment, Other manufacturing
- 2021–22: Similar, with Coke & Refined Petroleum added
Consumption Patterns
- Intermediate Consumption: Highest share by Construction—13.82% (2020–21), 14.03% (2021–22).
- Consumption Composition:
- 2020–21: Intermediate: Goods 70%, Services 30%; PFCE: Goods 62%, Services 38%
- 2021–22: Intermediate: Goods 72%, Services 28%; PFCE: Goods 59%, Services 41%
GDP Discrepancy Reconciliation
- 2020–21: Discrepancy of –?2,46,154 crores; reconciled by reducing PFCE by ?3,05,628 cr; Inventory by ?18,897 cr; Imports by ?78,374 cr.
- 2021–22: Discrepancy of –?2,16,579 crores; PFCE cut by ?3,55,540 cr; Inventory by ?1,884 cr; Imports by ?1,37,081 cr.
Significance
- Macro-Accounting Sophistication:SUT represents India’s advanced approach to reconciling diverse economic indicators—critical for accurate GDP estimation.
- Policy Insights:Understanding sectoral efficiencies (via GVA-to-GVO), product dependencies, and consumption structures can guide targeted reforms.
- Post-Pandemic Recovery Landscape:The sharp increase in total supply (28.4% growth) between 2020–21 and 2021–22 reflects economic resilience and rebound.
- Data-Driven Governance: SUT’s transparency and granularity strengthen evidence-based policymaking.
- Statistical Infrastructure Evolution: Proposals for SME/MNE disaggregation, real-time dashboards, and annual updates align India with OECD’s extended SUT models and global best practices.
8.8-magnitude earthquakenear Russia’s Kamchatka Peninsula
- 02 Aug 2025
In News:
- Recently, a magnitude 8.8 megathrust quake struck off the eastern coast of Kamchatka Peninsula, one of the largest ever recorded globally.
- This quake ranks among the six strongest recorded since modern seismology began—comparable to events in Ecuador (1906) and Chile (2010)—but caused remarkably limited damage.
- It originated in the Kuril–Kamchatka subduction zone, where the denser Pacific Plate thrusts beneath the North American/Okhotsk plates—a region known for frequent tectonic activity. The rupture extended over 200–300 miles underwater.
Tsunami: Warnings, Impact, and Aftermath
- The quake triggered tsunami alerts across the Pacific: Japan, the U.S. West Coast, Alaska, Hawai‘i, Chile, Ecuador (Galápagos), and French Polynesia, among others, issued multi-national warnings.
- In Kamchatka, waves between 3 to 5 meters struck, inundating the port and fish-processing plants in Severo-Kurilsk.
- Locally in Severo-Kurilsk, the quake caused serious structural damage to residential and social infrastructure, once again highlighting its vulnerability—especially recalling the catastrophic 1952 earthquake and tsunami that devastated the town.
Volcanic Aftermath: A Volcanic Chain Reaction
- In the quake’s wake, six volcanoes on Kamchatka became active. Most notably, Krasheninnikov erupted for the first time in 600 years, while others like KlyuchevskayaSopka, Shiveluch, Bezymianny, Karymsky, and Avachinsky also showed signs of eruption.
- This surge in volcanic activity—sparked by seismic fracturing of the crust—is considered a rare geological cascade, comparable to events last seen in 1737. Ash plumes reached up to 10 km height, posing aviation hazards.
Historical Perspective: Kamchatka’s Seismic Legacy
- 1952 Severo-Kurilsk Earthquake (Mag 8.8–9.0) caused a massive tsunami up to 18 meters, killing thousands and destroying the original town. It remains a defining tragedy in Russia’s seismic history.
- Earlier, the 1923 Kamchatka quake (Mag ~7–8) generated a tsunami that reached Hawaii and California’s coastlines, showing long-standing Pacific-wide impacts.
- These events underline the repeatable seismic vulnerability of the region and importance of preparedness.
India's Digital Payments Index

- 02 Aug 2025
In News:
The Reserve Bank of India’s Digital Payments Index (RBI-DPI), launched in January 2021, serves as a pivotal metric to gauge the country's journey toward a digital payments ecosystem. It uses March 2018 as its base year (index = 100) and is published every six months, offering a holistic and dynamic snapshot of digital transaction adoption.
RBI-DPI Calculation: Five Key Parameters
The DPI aggregates various dimensions of digital payments adoption across five weighted components:
|
Parameter |
Weightage |
Focus |
|
Payment Enablers |
25% |
Access infrastructure—mobile/internet penetration, Aadhaar, bank accounts, fintech regulations |
|
Demand-Side Infrastructure |
10% |
Consumer-facing tools—mobile/internet banking, debit/credit cards, FASTags |
|
Supply-Side Infrastructure |
15% |
Merchant tools—PoS terminals, ATMs, QR codes, bank branches, business correspondents |
|
Payment Performance |
45% |
Transaction metrics—volume/value of digital transfers, IMPS/NEFT/UPI usage, paper clearing |
|
Consumer Centricity |
5% |
User experience—awareness, complaint resolution, fraud handling, system uptime |
Drivers Behind the Mar 2025 Jump
As of March 2025, RBI-DPI stood at 493.22, up from 465.33 in September 2024—a year-on-year rise of 10.7%. The key drivers include:
- Supply-side Infrastructure Improvements: Wider merchant adoption of PoS, QR codes, and enhanced banking outreach.
- Payment Performance Surge: Rapid uptake of UPI, IMPS, and other platforms.
- Policy & Technology Boosters: Initiatives such as Digital India, increasing smartphone penetration, and fintech innovation have fueled demand.
Significance for Digital India
- Digital Economy Tracking: DPI is a quantitative barometer of India’s shift to a digital-first economy—enabling policymakers to monitor progress and identify gaps in access or infrastructure.
- Financial Inclusion & Transparency: Growth in DPI indicates deeper penetration of digital finance into rural and marginalized areas, helping combat cash reliance and promote inclusion.
- Policy Formulation & Monetary Insights: Metrics under Payment Performance bolster the RBI’s real-time understanding of transactional trends, aiding monetary policy and regulatory interventions.
- Enhancing Global Fintech Standing: A rising DPI strengthens India’s position as a global digital finance hub, enhancing credibility and attracting investment.
Challenges & Recommendations Ahead
- Digital Divide: Rural areas still lack adequate connectivity and awareness to fully utilize digital tools.
- Cybersecurity & Fraud: As transactions rise, so do risks. Issues like fraud, system downtime, and grievance redressal remain priorities.
- Tech Standardization: Ensuring interoperability and unified standards across platforms is essential.
Schengen Visa Cascade Regime
- 02 Aug 2025
In News:
Since 18 April 2024, the European Commission implemented a preferential “cascade” regime under the revised Schengen Visa Code (2020 reform), offering long-term, multiple-entry Schengen visas to Indian nationals with a clean travel history. Originally effective for India, Turkey, and Indonesia, this regime could expand to other countries based on diplomatic and readmission cooperation.
What Is the Schengen Area & Visa Basics
- The Schengen Area comprises 29 countries, including most EU members and four EFTA nations—allowing passport-free movement.
- A Schengen (short-stay) visa permits up to 90 days within any 180-day period. It is purpose-flexible (tourism, business, visiting family, etc.) but does not confer work rights.
The Cascade Regime – A Tiered System
Tier-Based Progression
The regime introduces a pyramid-like progression based on prior visa use:
|
Tier |
Requirement |
Visa Validity |
|
Entry-level |
First-time or minimal travel history |
Short-term, single-entry (probationary) |
|
Tier 1 |
Used three Schengen visas in the past 2 years |
1-year multiple-entry |
|
Tier 2 |
Held and lawfully used a 1-year multiple-entry visa in the past 2 years |
2-year multiple-entry |
|
Tier 3* |
Used a 2-year multiple-entry visa in the past 3 years |
5-year multiple-entry |
*Availability of the 5-year visa depends on passport validity.
Underlying Rule
Mexico’s 90/180 rule still applies: holders can stay only up to 90 days within any rolling 180-day period.
What's Special for Indian Nationals
- The cascade regime for Indians is more favorable than the general rule (which typically demands three prior visas within 2 years for progression). Indians now qualify for a 2-year visa with just two prior visas within 3 years, thanks to a special provision under Article 24(2c) of Regulation (EC) No 810/2009.
- The visa must not exceed passport validity—if the passport expires earlier, the visa has to be correspondingly shorter.
- The policy is discretionary—granting long-term visas (especially 5-year ones) depends on the visa officer’s judgement, even if eligibility criteria are technically met.
Strategic and Policy Significance
- People-to-people diplomacy: The cascade visa fosters cultural, business, and academic exchange, aligning with the EU's emphasis on soft power and deepening ties with India.
- Bilateral alignment: Reflects the EU-India Common Agenda on Migration and Mobility, and dovetails with negotiations around the India–EU Free Trade Agreement (FTA).
- Administrative efficiency: Long-term visas reduce repeat applications—beneficial for both visa applicants and consular resources.
- Reciprocity and expansion: Initially for India, Turkey, and Indonesia; the regime may expand to more countries based on cooperation levels.
SIMBEX-25

- 01 Aug 2025
In News:
- The 32nd edition of SIMBEX—India’s longest continuously conducted maritime bilateral exercise—was held from 28 July to 1 August 2025, hosted by Singapore. It included a Harbour Phase at Changi Naval Base and a Sea Phase in the southern South China Sea.
- Indian participation: INS Satpura, alongside INS Delhi, INS Kiltan, and the support vessel INS Shakti.
- Singapore Navy elements: RSN Vigilance and RSN Supreme, supported by MV Mentor and aerial units—S-70B Seahawk, Fokker-50 aircraft, and F-15SG fighters.
Objectives & Activities
Harbour Phase
- Featured Subject Matter Expert Exchanges (SMEEs), professional presentations, and strategic interactions.
- Conducted deck familiarisation visits aboard respective ships to foster doctrinal alignment
Sea Phase
- Encompassed advanced drill sequences, including:
- Air defence exercises, cross-deck helicopter operations
- Precision targeting, complex manoeuvres, and VBSS operations (Visit, Board, Search, and Seizure)
- Concluded with a ceremonial sail-past, symbolising professionalism and unity.
Geopolitical Landscape
- Strategic Reach: Deployment of Indian vessels to Philippines and Vietnam — alongside participation in SIMBEX—demonstrates India’s extended operational posture in Southeast Asia amidst regional tensions, notably with China’s maritime assertiveness.
- Broader Continuity: The Indian Navy, operating via the Andaman and Nicobar Command, employs SIMBEX as part of a broader matrix of maritime outreach in the region, including CORPAT and MILAN exercises
Sawalkote Hydroelectric Project
- 01 Aug 2025
In News:
In a strategic shift, India has floated international tenders for constructing the long-stalled Sawalkote Hydroelectric Project (1,856 MW) on the Chenab River in Jammu & Kashmir, leveraging the fact that the Indus Waters Treaty (IWT) with Pakistan is currently in abeyance. This development marks a significant turn in India’s water diplomacy and infrastructure planning.
Background & Project Details
- Location & Nature: Sawalkote is a run-of-river hydropower project near Sidhu village in Ramban district, J&K.
- Conception & Delay: Originally conceived in the 1980s, handed to NHPC in 1985, then returned to JKSPDC in 1997. Despite Rs 430 crore spent on enabling infrastructure, the project remained unstarted until a 2021 MoU revived it under an BOOT (Build-Own-Operate-Transfer) model.
- Tender Process: In July 2025, NHPC invited international bids (design, planning, engineering) with bid submissions due by September 10, 2025.
- Scale & Costs: Estimated cost stands at Rs 22,704.8 crore, set to be executed in two phases.
- Environmental Clearances: Forest Advisory Committee granted in-principle approval for diversion of 847 hectares of forest land.
Indus Waters Treaty (IWT) & Its Suspension
- Treaty Overview: Signed in 1960 (brokered by the World Bank), IWT allocates the eastern rivers (Ravi, Beas, Sutlej) to India, and the western rivers (Indus, Chenab, Jhelum) to Pakistan. India retains limited non-consumptive usage rights for hydro-power on these western rivers.
- First Suspension: On 23 April 2025, following a terrorist attack in Pahalgam, India suspended the IWT, citing national security and the treaty’s exploitation by Pakistan for cross-border terrorism.
- Consequences: India ceased hydrological data sharing, blocked Pakistani access to project visits, and released annual joint-status reporting—effectively halting treaty obligations.
- Strategic Intent: This pause grants India freedom to launch projects like Sawalkote without Pakistan’s prior objections or IWT constraints.
Geopolitical Tensions & Ramifications
- Long-term Impact on Pakistan: The Indus system sustains ~80% of Pakistan’s agriculture and electricity. Disruption could severely undermine food security, hydropower production, and urban water supply.
- Symbolism of a Rift: The treaty had survived wars and conflicts. Its suspension is viewed as an overt break in regional cooperative norms, with potential for conflict escalation.
- Legal & Diplomatic Fallout: Pakistan views reduced water flows as “act of war”; it is exploring legal avenues and appealing for treaty revival.
- India’s Firm Stance: PM Modi has labeled the treaty “unjust,” declared “blood and water cannot flow together,” further hardening India's negotiating posture.
Strategic Evaluation
- Violation or Tactical Move? While the IWT allows limited usage by India, its suspension indicates a focus on infrastructure autonomy over the western river system.
- Regional Domino Effects: With rising global water disputes, actions like this may set precedent in viewing water as geopolitical leverage.
- Environmental & Social Risks: Dam construction and forest diversion raise ecological concerns; plus, local displacement and compensation need careful handling.
Skill Impact Bond (SIB)
- 01 Aug 2025
In News:
- India is at the cusp of a demographic transition, with a young workforce expected to drive its goal of becoming a $30 trillion economy by 2047.
- Yet, only ~4% of India’s workforce is formally skilled, and nearly 30% of trained individuals remain unemployed. Traditional skilling schemes have struggled, especially with job retention.
- Against this backdrop, Skill Impact Bond (SIB), launched in 2021, marks a paradigm shift in India’s skilling ecosystem by linking financing to actual outcomes.
What is the Skill Impact Bond (SIB)?
- Launched: November 2021.
- Implementing Agency: National Skill Development Corporation (NSDC) under Ministry of Skill Development & Entrepreneurship.
- Partners: British Asian Trust, Children’s Investment Fund Foundation (CIFF), HSBC India, JSW Foundation, Dubai Cares.
- Target: Train 50,000 youth (60% women), ensure sustained employment.
It is India’s first development impact bond focused on employment, not just certification.
How Does SIB Work?
- Risk Investors (Private/Philanthropic): Provide upfront funds to service providers (training institutes).
- Service Providers: Deliver skill training, placement support, and post-placement mentoring.
- Outcome Funders (Govt/Donors): Repay investors if measurable outcomes are achieved (job placement + retention).
- Third-Party Evaluator: Verifies outcomes.
Key Distinction: Funding is tied to placement and retention, not mere enrolment/certification.
Progress So Far
- 23,700 youth trained across 13 sectors & 30 job roles.
- 72% women participation – one of the highest in any skilling programme.
- 75% placed in jobs, and 60% retained beyond 3 months, exceeding national averages (<10% under older schemes).
- Jharkhand, UP, Delhi are leading states in enrolment.
Significance
- Women-led Growth:
- 72% women trainees; many first-generation formal workers (tribal, rural, conservative households).
- Skilling gives women not just jobs but also agency, confidence, and identity.
- Outcome-Based Financing:
- Ensures accountability of training providers.
- Attracts private/philanthropic capital into public welfare.
- Addresses Retention Challenge:
- Traditional skilling: 84% complete training, but <10% stay in jobs beyond 3 months.
- SIB model pushes for long-term impact.
- Replicable Model:
- Can be scaled to health, education, social welfare.
- Example: Project AMBER (apprenticeship-based skilling) also uses this financing.
Challenges Ahead
- Scale vs Depth: Training 50,000 is significant, but India needs millions of skilled youth annually.
- Social Barriers: Women face mobility, safety, and cultural challenges in sustaining employment.
- Monitoring & Evaluation: Requires robust third-party systems to measure outcomes fairly.
- Private Participation: Sustaining investor confidence demands continuous success stories.
Way Forward
- Expand outcome-based financing to more sectors.
- Strengthen ecosystem for women (hostels, childcare, safe mobility).
- Continuous mentoring & alumni networks to ensure retention.
- Use digital platforms for scalable skilling and tracking.
Barbados Threadsnake (Tetracheilostoma carlae)
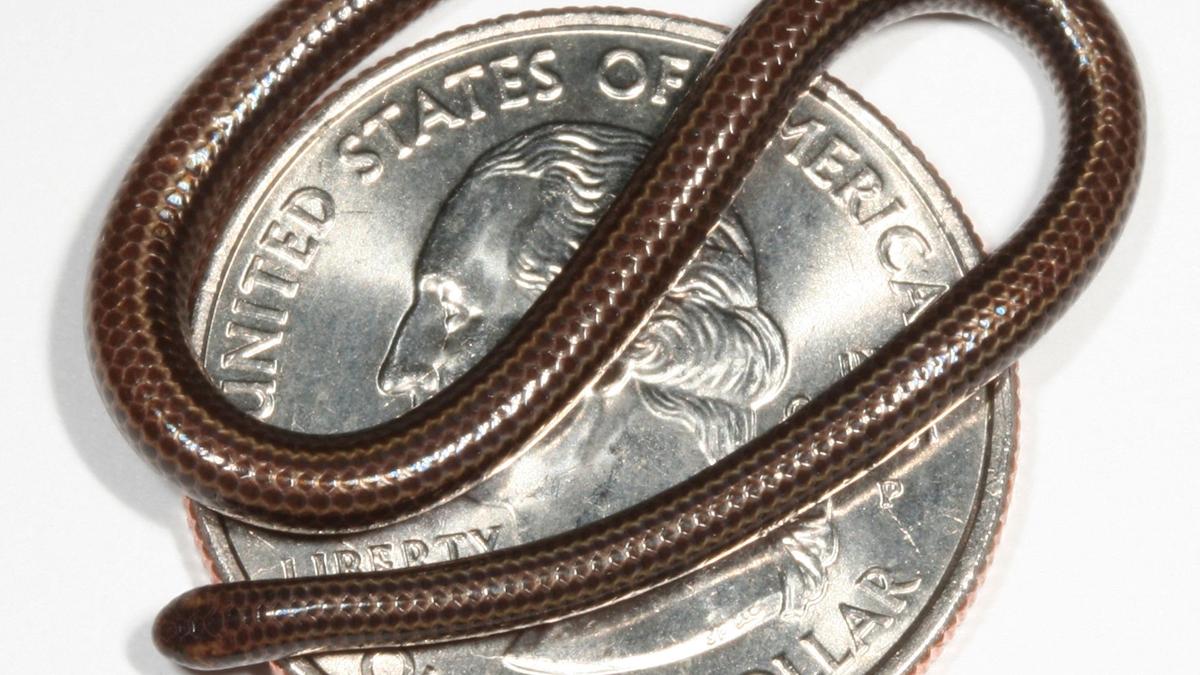

- 01 Aug 2025
In News:
The Barbados threadsnake, long considered lost to science, has made a startling comeback. This diminutive reptile—no longer than a coin—was rediscovered in Barbados in March 2025, nearly two decades after its last documented sighting. Its reappearance has reignited global interest in its conservation and the fragile ecosystems it inhabits.
Key Attributes & Taxonomy
- Scientific Classification: Tetracheilostoma carlae, family Leptotyphlopida.
- Size & Weight: Adults reach approximately 9–10 cm (3–4 in) in length and weigh ~0.6 g (~0.02 oz)—making it the world’s smallest known snake
- Physical Traits: Extremely slender—about as thick as a spaghetti noodle. Distinguished by pale orange dorsal stripes and a small scale on the snout
- Vision & Behavior: A blind, fossorial snake that burrows underground, especially hiding under rocks during the day.
- Diet: Feeds on termite and ant larvae—its petite jaws prevent it from consuming larger prey.
- Reproduction: Oviparous, laying only one large egg at a time, with hatchlings already about half the size of adults.
Rediscovery: A Significant Scientific Moment
- Context: The species had not been observed since 2006, and earlier specimens were often misidentified in museum collections.
- 2025 Rediscovery: During a March ecological survey in central Barbados by the Ministry of Environment and Re:wild, the snake was found under a rock near a jack-in-the-box tree. It was confirmed after microscopic and morphological assessment at the University of the West Indies.
- Reactions: This turn of events is hailed as a conservation triumph and a poignant reminder of Barbados’s biodiversity despite its heavily altered landscape.
Conservation Context & Implications
- Habitat Loss: Over 98% of Barbados’s primary forests have been cleared, leaving threadsnake habitats limited to a few square kilometers of secondary forests, particularly in the Scotland District.
- Threats: Loss of habitat and competition from the invasive Brahminy blind snake (Ramphotyphlops braminus), which reproduces asexually and may outcompete the threadsnake.
- Conservation Action: The rediscovery falls under the broader Conserving Barbados’ Endemic Reptiles (CBER) project. Future plans focus on mapping its range, safeguarding habitats, and preserving biodiversity as part of Barbados's compliance with the Kunming-Montreal Global Biodiversity Framework.
Dorjilung Hydropower Project

- 01 Aug 2025
In News:
India and Bhutan share one of the most successful models of hydropower cooperation in South Asia. The launch of the 1125 MW Dorjilung Hydropower Project in Bhutan, with Tata Power’s equity participation alongside Bhutan’s Druk Green Power Corporation (DGPC), marks a turning point in cross-border energy diplomacy. Unlike earlier projects dominated by Indian government financing, Dorjilung reflects a shift towards Public–Private Partnership (PPP), multilateral funding, and private sector involvement.
Key Features of the Project
- Type: Run-of-the-river scheme on the Kurichhu River (tributary of Drangmechhu, flows into India).
- Location: Mongar and Lhuentse districts, eastern Bhutan.
- Technical Specs:
- Dam height: ~139.5 m (concrete-gravity).
- Headrace tunnel: 15 km.
- Powerhouse: 6 Francis turbines.
- Annual generation: ~4.5 TWh.
- Cost: USD 1.7 billion (~?150 billion).
- Funding: World Bank.
- Equity Structure: DGPC (60%) + Tata Power (40%).
- Timeline: Commissioning expected by 2032.
India–Bhutan Energy Ties
- Existing Cooperation:
- Governed by the 2006 Bilateral Agreement on Hydropower Cooperation (protocol revised 2009).
- 4 operational projects supplying power to India: Chhukha (336 MW), Kurichhu (60 MW), Tala (1020 MW), Mangdechhu (720 MW).
- Punatsangchhu I (1200 MW) and Punatsangchhu II (1020 MW) under construction.
- Economic Importance for Bhutan:
- Hydropower exports = 40% of govt revenue and 25% of GDP.
- India buys surplus electricity, ensuring stable market access.
- India’s Strategic Interest:
- Ensures clean energy imports.
- Strengthens regional energy security.
- Counters Chinese presence in the Himalayan hydropower sector.
What Makes Dorjilung Different?
- PPP & Private Sector Role: First large-scale project with an Indian private company (Tata Power) holding major equity.
- Diversified Financing: World Bank funding reduces Bhutan’s dependence on Indian grants and credit lines.
- B2B Model: Moves from a government-to-government (G2G) model to business-to-business (B2B), granting Bhutan greater autonomy and bargaining parity.
- Integrated Renewable Plan: Tata Power–DGPC partnership envisions 5000 MW clean energy capacity, including:
- Dorjilung (1125 MW)
- Gongri (740 MW)
- Jeri Pumped Storage (1800 MW)
- Chamkharchhu IV (364 MW)
- Solar projects (500 MW).
Strategic & Geopolitical Significance
- For Bhutan:
- Reduces financial vulnerability by avoiding overdependence on Indian government aid.
- Attracts global institutions (World Bank), raising international credibility.
- Boosts local development in eastern districts (infrastructure, jobs).
- For India:
- Enhances energy security via long-term clean energy imports.
- Strengthens economic diplomacy with a trusted neighbour.
- Counters China’s Belt and Road Initiative (BRI) push in Himalayan hydropower (e.g., Nepal’s tilt towards Chinese funding).
- Supports Paris Agreement & renewable targets.
- For the Region:
- Creates scope for regional energy grids under BIMSTEC and BBIN (Bangladesh, Bhutan, India, Nepal).
- Encourages private-sector led cross-border energy trade.
Challenges Ahead
- Delayed Timelines: Past Bhutanese projects (e.g., Punatsangchhu I & II) suffered huge delays and cost overruns.
- Debt Burden: Large projects raise Bhutan’s external debt, though hydropower revenue offsets this risk.
- Environmental Concerns: Dam construction in fragile Himalayan ecosystems risks landslides, habitat loss, and displacement.
- Domestic Politics: Growing debate within Bhutan on overdependence on India; balancing autonomy with partnership is key.
- Regional Rivalries: India’s refusal to import power from Chinese-funded projects in Nepal shows how geopolitics can complicate energy trade.
Way Forward
- Diversify Financing: Blend of multilateral, private, and bilateral sources to reduce dependency risks.
- Strengthen Grid Connectivity: Expand India–Bhutan–Bangladesh power corridors.
- Sustainable Practices: Ensure climate-resilient dam design, environmental safeguards, and local community participation.
- Expand Solar–Hydro Synergy: Hybrid models (hydropower + solar) to ensure round-the-clock renewable supply.
- Institutional Mechanisms: Strengthen the India–Bhutan Joint Group on Hydropower Projects for dispute resolution and faster approvals.
