Gitchak nakana
- 02 Mar 2026
In News:
A new species of groundwater-dwelling fish, Gitchak nakana, has recently been discovered in Assam. The species was found in a dug-out well and represents the first aquifer-dwelling (phreatobitic) fish recorded from Northeast India. This discovery adds to India’s growing record of endemic and subterranean biodiversity.
About Gitchak nakana
- Type: Groundwater (aquifer-dwelling) fish
- Family: Cobitidae (Loaches)
- Genus: Newly described genus
- Size: Approximately 2 cm in length
- Habitat: Subterranean aquifers
- Location of Discovery: Assam
The species was discovered in a dug-out well, indicating its existence in underground water systems rather than surface water bodies such as rivers or ponds.
Etymology
The name reflects local linguistic heritage:
- “Gitchak” (Garo language) – means red, referring to its striking blood-red colour when alive.
- “Na-tok” / “kana” – refer to a blind fish.
The nomenclature highlights both the species’ morphology and its cultural-geographical context.
Unique Morphological Features
Gitchak nakana displays classic troglomorphic adaptations — traits evolved for life in complete darkness:
- Absence of externally visible eyes (blindness)
- Translucent, pigmentless body
- Extreme miniaturization (only 2 cm long)
- Complete absence of skull roof — the brain is covered dorsally only by skin
The lack of a skull roof is particularly unusual and makes it one of the most anatomically distinctive loach species recorded.
What are Phreatobitic Species?
- Phreatobitic organisms live in groundwater aquifers rather than surface water or caves.
- Aquifers are underground water-bearing geological formations.
- Such habitats are difficult to access and poorly studied, which explains why discoveries are rare.
Globally:
- More than 300 fish species are known from subterranean habitats.
- However, the vast majority inhabit caves.
- Less than 10% are known from groundwater aquifers, making this discovery scientifically significant.
Thus, Gitchak nakana represents a rare addition to the small global group of true aquifer-dwelling fishes.
Forest Owlet

- 02 Mar 2026
In News:
Recently, the Forest Owlet was sighted in Kuno National Park, Madhya Pradesh, marking its reappearance in the region 113 years after it was last recorded there. The species had not been seen in Kuno since the early 20th century, making this rediscovery ecologically significant. The development strengthens Kuno’s biodiversity profile, which has already gained prominence due to the cheetah reintroduction programme.
About the Forest Owlet
- Scientific Name: Athene (Heteroglaux) blewitti
- Family: Strigidae (typical owl family)
- First Described: 1873
- Presumed Extinct: After 1884 due to lack of sightings
- Rediscovered: 1997 in central India
The Forest Owlet was long considered extinct because it was not recorded for over a century after the late 19th century. Its rediscovery in 1997 was a landmark event in Indian ornithology, underscoring the importance of systematic biodiversity surveys.
Habitat and Ecology
Habitat
The species primarily inhabits:
- Tropical and subtropical moist lowland forests
- Dense deciduous woodlands
- Open dry deciduous teak forests
- Tropical and subtropical dry forests
It shows preference for dry deciduous forest ecosystems, especially those dominated by teak.
Distribution
The Forest Owlet is endemic to central India, meaning it is found nowhere else in the world.
Recorded populations exist in:
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra (notably Melghat Tiger Reserve)
- Odisha
- Chhattisgarh
- Gujarat
The recent sighting in Kuno National Park strengthens evidence of its fragmented but surviving populations across central Indian landscapes.
Physical Characteristics
The Forest Owlet has distinctive morphological features:
- Relatively unspotted crown
- Prominent white throat collar
- Thickly feathered legs
- Heavily banded wings and tail
Unlike many owls that are nocturnal, the Forest Owlet is diurnal (active during the day), which makes it relatively easier to observe compared to other owl species.
Diet and Behaviour
- Primarily feeds on rodents
- Also consumes lizards, skinks, and insects
- Hunts during daylight hours
- Typically seen perched on exposed branches while scanning for prey
Its diurnal nature and specific habitat requirements make it vulnerable to habitat degradation.
Conservation Status
- IUCN Red List: Endangered
- CITES: Appendix I (highest level of international trade protection)
The species faces threats from:
- Habitat loss due to deforestation
- Fragmentation of dry deciduous forests
- Agricultural expansion
- Developmental activities in central India
Given its limited distribution and small population size, conservation of intact forest patches in central India is critical for its survival.
State of India’s Environment (SOE) 2026
- 28 Feb 2026
In News:
The State of India’s Environment (SOE) 2026 report, released by the Centre for Science and Environment (CSE) and Down To Earth, highlights the accelerating ecological crisis at both global and national levels. The report warns that humanity has breached multiple planetary boundaries, pushing Earth’s life-support systems toward instability. It further links ecological degradation with intensifying human–tiger conflicts in India.
Planetary Boundaries Framework
The Planetary Boundaries framework, first proposed in 2009 by scientists led by Johan Rockström and updated in 2023, defines the safe operating limits within which humanity can function without destabilising Earth systems.
It identifies nine critical Earth system processes that regulate planetary stability. Crossing these limits increases the risk of abrupt, irreversible environmental changes. The boundaries are interconnected; transgression in one can trigger cascading impacts across others.
Status of the Nine Planetary Boundaries
According to SOE 2026, 7 out of 9 planetary boundaries have been breached:
1. Climate Change (Transgressed): Rising greenhouse gas concentrations are pushing the planet close to breaching the 1.5°C warming threshold, signalling potentially irreversible climate impacts.
2. Biosphere Integrity (Transgressed): Species extinction rates exceed 100 extinctions per million species years, nearly ten times the safe limit.
3. Land System Change (Transgressed): Global forest cover has declined to 59%, well below the 75% safe threshold, weakening carbon sinks and biodiversity resilience.
4. Freshwater Change (Transgressed): Over-extraction and climate variability are disrupting river systems, soil moisture cycles, and groundwater security.
5. Biogeochemical Flows (Transgressed): Excess nitrogen and phosphorus from fertilisers are causing eutrophication and ecosystem imbalance.
6. Novel Entities (Transgressed): Plastics, synthetic chemicals, and other pollutants are entering ecosystems without adequate safety assessment.
7. Ocean Acidification (Recently Transgressed): Ocean acidity has increased by 30–40% since the industrial era, threatening coral reefs and marine food webs.
Boundaries Within Limits (But Risky)
- Atmospheric Aerosol Loading – Currently within limits globally but regionally disruptive (e.g., monsoon variability).
- Stratospheric Ozone Depletion – Within safe limits due to the success of the Montreal Protocol, a major global environmental governance success.
Climate Crisis and Tipping Points
- The report warns that climate disruptions are occurring earlier than predicted. Critical ecosystems such as coral reefs and the Amazon rainforest are approaching tipping points, beyond which recovery may be impossible.
Biodiversity Loss and Forest Decline
- Habitat degradation, deforestation, and ecosystem imbalance are accelerating biodiversity loss. Declining forest cover and fragmented habitats are reducing ecological resilience and increasing human–wildlife interactions.
Rising Human–Tiger Conflict in India
The report highlights how ecological degradation is intensifying human–tiger conflicts:
- Habitat loss and prey depletion are altering tiger behaviour.
- Expansion of human settlements near forest areas increases encounters.
- The invasive species Lantana camara now occupies nearly 50% of forest and scrublands, suppressing native grasses.
- Reduced prey availability forces tigers to prey on cattle, escalating conflict with local communities.
This reflects how ecosystem imbalance directly affects conservation outcomes.
Pollution and Freshwater Stress
- Freshwater reserves face severe stress due to overuse and climate variability. Simultaneously, pollution from plastics and synthetic chemicals presents long-term ecological and health risks, reinforcing the urgency of regulating “novel entities.”
Key Recommendations
1. Institutional Strengthening
- Enhance the capacity and independence of the National Green Tribunal (NGT).
- Ensure environmental clearances prioritise ecological integrity over procedural compliance.
2. Sovereign Climate Action
- Integrate planetary boundaries into national accounting frameworks.
- Promote technology-led, full-stack decarbonisation strategies.
3. Community-Centric Conservation
- Adopt landscape-scale governance.
- Treat local communities as primary stakeholders in conservation rather than as obstacles.
Macaques
- 28 Feb 2026
In News:
A recent viral story from a Japanese zoo involving an abandoned baby Japanese macaque (“Punch”) brought global attention to the complex emotional bonds and strict social hierarchies within macaque societies. Beyond public curiosity, the episode highlights important aspects of primate behaviour, evolutionary biology, and conservation — areas relevant to biodiversity studies and wildlife management.
About Macaques
Macaques belong to the genus Macaca under the family Cercopithecidae (Old World monkeys). They are among the most widespread and adaptable primates in the world.
Distribution and Diversity
- Over 20 species
- Found mainly across Asia and parts of North Africa
- Highly adaptable to diverse ecological conditions, including forests, mountains, and urban environments
Their adaptability has enabled certain species to thrive even in human-dominated landscapes.
Important Species
1. Japanese Macaque (Macaca fuscata)
- Native to Japan
- Known as the “Snow Monkey”
- Famous for surviving in cold climates and bathing in natural hot springs
- Displays highly structured matrilineal social systems
2. Rhesus Macaque (Macaca mulatta)
- Widely distributed in North India and Southeast Asia
- Frequently found in urban and semi-urban areas
- Extensively used in medical and biomedical research, including vaccine development
3. Lion-tailed Macaque (Macaca silenus)
- Endangered species
- Endemic to the Western Ghats (India)
- Recognised by its distinctive silver-white mane
- Threatened by habitat fragmentation and deforestation
4. Crested Black Macaque (Macaca nigra)
- Native to Sulawesi (Indonesia)
- Characterised by a dark crest
- Classified as Critically Endangered
Social Behaviour and Hierarchy
Macaques are highly gregarious animals, living in troops governed by strict dominance hierarchies. Their social organisation is complex and deeply structured.
Female Hierarchy
- Rank is typically matrilineal (inherited from the mother).
- Daughters generally rank close to their mother’s position.
- In species such as the Japanese macaque, the “youngest sister rule” applies — the youngest daughter ranks above older sisters.
- Female bonds are stable and form the core of troop structure.
Male Hierarchy
- Determined by physical strength, alliances, and fighting ability.
- Males often migrate between troops.
- Rank can fluctuate over time.
The viral incident involving the abandoned baby macaque illustrates how social rank and maternal position significantly affect offspring survival and acceptance within the troop.
Ecological and Evolutionary Significance
Macaques provide valuable insights into:
- Evolution of primate social systems
- Behavioural ecology
- Conflict resolution and cooperation
- Human–wildlife interaction
Their structured dominance systems resemble early social organisation patterns in primates, offering important evolutionary parallels.
Conservation and Human Interface
While some species like the rhesus macaque thrive near human settlements, others such as the lion-tailed macaque face severe threats due to:
- Habitat fragmentation
- Deforestation
- Infrastructure expansion
- Human–wildlife conflict
Urban macaque populations often lead to conflict, necessitating balanced wildlife management policies.
International Climate Initiative (IKI)
- 27 Feb 2026
In News:
India and Germany have launched a €20 million (approximately ?180 crore) Large Grant project under Germany’s International Climate Initiative (IKI). The project focuses on strengthening climate resilience in India’s most vulnerable ecosystems through nature-based and sustainable adaptation strategies.
About the International Climate Initiative (IKI)
- Established in 2008, IKI is Germany’s principal funding instrument for international climate action.
- Supports projects in:
- Climate change mitigation
- Adaptation
- Biodiversity conservation
- Operates in over 150 partner countries, with 14 priority countries, including India, Brazil, China, South Africa, Indonesia, and Mexico.
- Aligns with global commitments under the Paris Agreement and the Convention on Biological Diversity (CBD).
IKI represents Germany’s climate diplomacy approach, combining financial assistance, technology cooperation, and capacity building.
Scope of the New India–Germany Project
The newly launched €20 million initiative targets high-risk and ecologically sensitive regions in India, promoting long-term resilience through ecosystem-based adaptation.
Priority Regions
- Himalayas
- Challenges: Glacier melt, glacial lake outburst floods (GLOFs), landslides.
- Significance: Water security for major river systems.
- Western Ghats
- Biodiversity hotspot facing deforestation and habitat fragmentation.
- Vulnerable to extreme rainfall events and ecological degradation.
- North-East India
- Fragile hill ecosystems prone to soil erosion and flooding.
- Rich in biodiversity but ecologically sensitive.
- Island Ecosystems (e.g., Andaman & Nicobar)
- Threatened by sea-level rise and coastal erosion.
- High vulnerability to cyclones and marine ecosystem disruption.
Focus Areas of Intervention
- Promotion of Nature-Based Solutions (NbS)
- Ecosystem restoration and conservation
- Climate-resilient livelihoods
- Capacity building at local and state levels
- Strengthening institutional frameworks for adaptation
Nature-based solutions integrate environmental restoration with socio-economic resilience, ensuring sustainability and community participation.
Strategic Significance
1. Strengthening India’s Climate Resilience
India faces:
- Rising temperatures
- Erratic monsoons
- Increased frequency of extreme weather events
- Biodiversity loss
This initiative enhances adaptive capacity in vulnerable geographies.
2. Alignment with India’s National Commitments
The project supports:
- India’s Nationally Determined Contributions (NDCs)
- Target of 50% cumulative electric power installed capacity from non-fossil fuel sources by 2030.
- Net-Zero Commitment (2070)
- National Action Plan on Climate Change (NAPCC) missions, particularly:
- National Mission for Sustaining the Himalayan Ecosystem
- National Mission on Sustainable Habitat
3. Global Climate Governance
- Reinforces North–South cooperation in climate finance.
- Demonstrates operationalisation of climate finance commitments under the Paris Agreement.
- Promotes biodiversity conservation alongside climate mitigation and adaptation.
4. Indo-German Strategic Partnership
Climate cooperation is a key pillar of the India–Germany Strategic Partnership, complementing collaboration in:
- Renewable energy
- Green hydrogen
- Sustainable urbanisation
- Technology and innovation
Carbon Capture and Utilisation (CCU)

- 27 Feb 2026
In News:
Recent discussions on India’s climate strategy have highlighted the growing importance of Carbon Capture and Utilisation (CCU) technologies, particularly for hard-to-abate sectors such as cement, steel, refineries, and chemicals. With India committing to net-zero emissions by 2070, CCU is emerging as a necessary complement to renewable energy expansion.
What is Carbon Capture and Utilisation (CCU)?
Carbon Capture and Utilisation (CCU) refers to a set of technologies that:
- Capture carbon dioxide (CO?) from industrial sources or directly from the atmosphere.
- Convert the captured CO? into useful products such as fuels, chemicals, building materials, or polymers.
Unlike Carbon Capture and Storage (CCS), where CO? is permanently stored underground, CCU reintegrates carbon into the economy, contributing to a circular carbon economy.
Why CCU is Necessary for India
1. High Emissions Profile
India is the world’s third-largest CO? emitter, with emissions primarily arising from:
- Power generation
- Cement production
- Steel manufacturing
- Chemicals and refineries
2. Hard-to-Abate Sectors
In industries like cement and steel:
- A significant portion of emissions comes from industrial processes themselves, not just fuel combustion.
- Renewable energy alone cannot fully eliminate these emissions.
3. Alignment with Net-Zero 2070
CCU supports:
- Deep industrial decarbonisation
- Circular economy goals
- Low-carbon industrial competitiveness
Thus, CCU acts as a bridge technology during the transition to a fully decarbonised economy.
Global Developments
- European Union: The EU Bioeconomy Strategy and Circular Economy Action Plan promote CCU for converting CO? into feedstocks for fuels and chemicals.
- Belgium: ArcelorMittal and Mitsubishi Heavy Industries are piloting technology to convert captured CO? into carbon monoxide for steel and chemical production.
- United States: Combines tax credits and public funding to scale CO?-derived fuels and chemicals.
- UAE: The Al Reyadah project integrates CCU with green hydrogen for CO?-to-chemicals hubs.
These initiatives indicate that CCU is becoming part of mainstream climate-industrial policy globally.
India’s Progress and Policy Push
1. Research and Roadmaps
- The Department of Science and Technology (DST) has prepared a dedicated R&D roadmap for CCU.
- The Ministry of Petroleum and Natural Gas has proposed a draft 2030 CCUS roadmap identifying potential projects.
2. Budgetary Support
- The Union Budget 2026–27 announced a ?20,000 crore scheme to scale up Carbon Capture, Utilisation and Storage (CCUS).
- Focus sectors: Power, Steel, Cement, Refineries, and Chemicals.
- Marks a shift from pilot projects to structured, policy-backed deployment.
3. Private Sector Initiatives
- Ambuja Cements (Adani Group) with IIT Bombay: Indo-Swedish CCU pilot converting CO? into fuels and materials.
- JK Cement: Developing CCU applications for lightweight concrete blocks and olefins.
- Organic Recycling Systems Limited (ORSL): Leading India’s first pilot-scale Bio-CCU platform, converting CO? from biogas into bio-alcohols and specialty chemicals.
Gentoo Penguin
- 21 Feb 2026
In News:
Gentoo penguins have been confirmed infected with H5 avian influenza (H5N1, clade 2.3.4.4b) on Heard Island, marking the first recorded bird infection in an Australian external territory. Earlier (November 2025), the virus had been detected in southern elephant seals. The strain has caused widespread mortality among seabirds and poultry globally.
About Gentoo Penguin
Taxonomy
- Scientific Name: Pygoscelis papua
- Genus: Pygoscelis
- Closely related to: Adélie penguin, and Chinstrap penguin
- Distribution: Antarctic Peninsula, Sub-Antarctic islands, Falkland Islands (South Atlantic Ocean), and Exclusively found in the Southern Hemisphere (45°–65° South latitude)
- Habitat: Prefer shoreline habitats, enabling quick access to marine food while nesting nearby.
- Characteristics
- Fastest underwater swimmers among penguins.
- Diurnal and highly social.
- Breed in colonies; remain in groups year-round.
- Diet: Carnivorous (mainly fish, krill, squid).
- Conservation Status: IUCN Red List: Least Concern
H5N1 Avian Influenza – Key Facts
- Highly pathogenic strain: H5N1 (clade 2.3.4.4b)
- Highly contagious and deadly among: Seabirds, Wild birds, Poultry, and Marine mammals (e.g., southern elephant seals, Antarctic fur seals)
Detection & Testing
- Preliminary tests conducted at the Commonwealth Scientific and Industrial Research Organisation (CSIRO)’s Australian Centre for Disease Preparedness.
- Samples collected during a scientific voyage (February 2026).
Observations
- No signs of large-scale mass mortality in surveyed areas.
- Australia’s national H5 bird flu–free status remains unchanged.
- Government has committed over A$100 million toward preparedness and biosecurity measures.
About Heard Island
- Australian external territory.
- Located:
- ~4,000 km south-west of Perth
- ~1,700 km north of Antarctica
- Situated in the Southern Ocean.
- Remote and ecologically sensitive sub-Antarctic ecosystem.
Red Sanders
- 23 Feb 2026
In News:
Busy Tirupati pilgrimage route makes Red Sanders smuggling easy in south Andhra Pradesh.
About Red Sanders
- Scientific Name: Pterocarpus santalinus
- Common Name: Red Sandalwood
- Type: Tropical dry deciduous tree
- Endemic to: Southern Andhra Pradesh
Geographic Distribution
- Restricted to three districts: Chittoor, Nellore, and YSR Kadapa
- Largest reserve located in the Seshachalam Biosphere Reserve, part of the Eastern Ghats
- Spread over 4,755 sq km
- Located about 35 km from Tirupati temple town
Ecological Characteristics
- Grows in rocky, degraded and red soil areas
- Requires hot and dry climate
- Fire-hardy and drought-resistant
- Slow-growing: 25–40 years to reach maturity
- Wood is relatively brittle compared to teak
Economic Importance
- Contains ‘Santalin’, a natural red dye
- Used in:
- Pharmaceutical preparations
- Textile and leather industries
- Food colouring
- Perfume and medicinal products
- Gained global attention in the 1960s when Japanese instrument makers used it for crafting the traditional shamisen due to superior tonal quality
Conservation Status
- IUCN Red List: Endangered
- CITES: Appendix II (International trade strictly regulated)
- Wildlife (Protection) Act, 1972: Schedule IV
Harvesting and felling inside reserve forests is prohibited. Legal trade permitted only under regulated plantation and CITES-controlled export mechanisms.
Red Sanders Smuggling: Key Issues
Role of Tirupati Pilgrimage Route
The proximity of the Tirupati pilgrimage corridor to Seshachalam forests facilitates smuggling due to:
- Heavy traffic movement
- Limited vehicle checking
- Multiple forest entry points
- Inter-state border with Tamil Nadu
Smugglers often:
- Enter from Tamil Nadu
- Disguise themselves as labourers or pilgrims
- Use small vehicles for transport
- Hide timber in containers or dump logs inside forests/water temporarily
- Use sea routes for international export
Organised Timber Mafia
- Operates in coordinated teams (felling transport units)
- Several trees cut within short duration
- Cross-firing incidents reported
- Forest officials issued arms after killings of personnel
- Andhra Pradesh Police–Forest Department task force formed in 2014
Recent Enforcement Action
- January 9, 2026: 75 Red Sanders logs seized in Kadapa division
Broader Issue: Illegal Timber and Deforestation
- India among top 10 forest-rich nations (area-wise)
- Since 1980, 1.5 million hectares of forest land diverted for development
- Majority diversion after 2000
- India is also one of the largest timber importers
- Illegal logging contributes to:
- Deforestation
- Carbon emissions
- Biodiversity loss
- Forest conflicts
Inter-state borders often act as transit hubs (e.g., timber movement in central India).
Conservation Efforts
- National Biodiversity Authority sanctioned ?82 lakh
- Andhra Pradesh State Biodiversity Board initiative
- Target: Raise 1 lakh (100,000) saplings
- Distribution to farmers for conservation and regulated cultivation
Malabar Pied Hornbill

- 19 Feb 2026
In News:
The Forest Department of Chhattisgarh has initiated the establishment of six “hornbill restaurants” in the Udanti Sitanadi Tiger Reserve (USTR) to support the rare Malabar Pied Hornbill and promote natural forest regeneration.
What are “Hornbill Restaurants”?
- Specially developed fruit-rich plantation zones inside forest areas.
- Designed to provide continuous food sources (especially native fruit-bearing trees).
- Aim to:
- Attract hornbills.
- Support breeding and nesting.
- Aid in natural seed dispersal and forest expansion.
The initiative uses hornbills’ natural seed-dispersal behaviour to promote forest regeneration while conserving a Near Threatened species.
Malabar Pied Hornbill
- Scientific Name: Anthracoceros coronatus
- Common Name: Lesser Pied Hornbill
- Medium-sized hornbill.
- Distinctive black and white plumage.
- Prominent curved bill with a casque on top.
- Habitat:
- Evergreen forests.
- Moist and dry deciduous forests.
- Often found near human settlements.
- Distribution:
- Western Ghats
- North-eastern Himalayan foothills (India and Nepal)
- Satpura Hills
- Sri Lanka
- Diet:
- Primarily frugivorous (fruit-eating).
- Becomes partly omnivorous during breeding season.
- Ecological Role:
- Acts as a key seed disperser.
- Indicator species of forest health and ecological stability.
Conservation Status
- IUCN Red List: Near Threatened
- Major Threats:
- Habitat loss
- Forest degradation
- Fragmentation
Udanti Sitanadi Tiger Reserve (USTR)
- Location: Located in Chhattisgarh.
- Formation: Created by merging Udanti Wildlife Sanctuary and Sitanadi Wildlife Sanctuary.
- Drainage System
- Major river: Mahanadi
- Tributaries: Udanti, Sitanadi, Indravan, Pairi
- Topography
- 19 named mountains.
- Deo Dongri – Highest peak.
- At?nga Dongar – Most prominent mountain.
- Vegetation: Predominantly tropical dry and moist deciduous forests.
Loggerhead Turtle

- 18 Feb 2026
In News:
Recent scientific observations indicate that rising ocean temperatures and declining food availability are significantly affecting the reproductive cycles, migratory behavior, and even body size of the loggerhead turtle. These developments underline the far-reaching ecological consequences of climate change on marine megafauna and highlight emerging conservation challenges.
About the Loggerhead Turtle
The loggerhead turtle (Caretta caretta) is an oceanic turtle belonging to the family Cheloniidae. It derives its name from its disproportionately large head, which houses powerful jaw muscles adapted for crushing hard-shelled prey.
Key Characteristics
- Size:
- World’s largest hard-shelled turtle
- Second-largest extant turtle after the leatherback sea turtle
- Lifespan: Can live for 80 years or more
- Navigation: Uses Earth’s geomagnetic field to navigate vast oceanic distances
- Diet: Omnivorous; primarily consumes bottom-dwelling invertebrates such as gastropods, bivalves, and decapods
- Habitat: Found both in open oceans and inshore ecosystems like bays, lagoons, salt marshes, and creeks
- Distribution: Atlantic, Indian, and Pacific Oceans, and the Mediterranean Sea
- Conservation Status: IUCN Red List – Vulnerable
Climate Change and Emerging Ecological Impacts
1. Altered Reproductive Patterns
- Loggerhead turtles exhibit temperature-dependent sex determination, where warmer sand temperatures produce more female hatchlings. Rising global temperatures are skewing sex ratios, potentially threatening long-term population stability.
- Additionally, warming seas are disrupting nesting timelines and hatchling survival rates, affecting recruitment into adult populations.
2. Changes in Migration Routes
- Loggerheads rely on geomagnetic cues to navigate across ocean basins. However, changing ocean currents and temperature gradients are altering traditional migratory pathways. Shifts in feeding grounds may force turtles to travel longer distances, increasing energy expenditure and exposure to threats such as fishing gear and marine pollution.
3. Impact on Body Size and Growth
- Studies suggest that declining prey availability linked to ocean warming and ecosystem shifts may be affecting growth rates and adult body size. Reduced food intake can influence reproductive success, as larger females generally produce more eggs.
Four-Pronged Threats
Climate change intensifies existing anthropogenic pressures:
- Rising Ocean Temperatures: Affect physiology, nesting, and food webs.
- Habitat Loss and Degradation: Coastal development and erosion reduce nesting beaches.
- Marine Pollution: Plastic debris and oil spills cause ingestion and entanglement.
- Bycatch in Fishing Gear: Accidental capture remains a major mortality factor.
Direct harvesting of turtles and eggs in some regions further compounds population decline.
Ecological Significance
- Loggerhead turtles play a crucial role in marine ecosystems by regulating populations of invertebrates and maintaining healthy benthic communities. Their decline can disrupt trophic balance and impact overall ocean biodiversity.
Conservation Imperatives
Addressing the challenges faced by loggerhead turtles requires:
- Strengthening marine protected areas
- Regulating coastal development
- Promoting climate mitigation strategies
- Reducing bycatch through turtle-excluder devices
- Enhancing global cooperation under marine conservation frameworks
Discovery of Two New Army Ant Species in the Eastern Ghats
- 17 Feb 2026
In News:
In a significant contribution to India’s biodiversity records, researchers from Karnataka and Odisha have discovered two new species of army ants - Aenictus chittoorensis and Aenictus lankamallensis - in the Eastern Ghats of Andhra Pradesh. The discovery highlights the rich yet underexplored biodiversity of peninsular India and underscores the ecological importance of invertebrate fauna in tropical ecosystems.
About Army Ants
Army ants belong to the subfamily Dorylinae and are known for their nomadic and highly predatory lifestyle. Unlike many other ant species, army ants do not construct permanent nests. Instead, they continuously move in search of food, making them one of the most dynamic components of tropical forest ecosystems.
They are predominantly found in tropical regions and are considered among the “big cats” of the insect world due to their aggressive and coordinated hunting behavior.
Distinctive Characteristics
- Nomadic Lifestyle: Army ants lack permanent nests. Instead, they form temporary living structures called bivouacs, created entirely from the interlocked bodies of worker ants.
- Massive Coordinated Raids: Colonies conduct synchronized raids, overwhelming insects and small invertebrates in their path. Their raids can drastically alter local arthropod populations.
- Morphological Features:
- Large, sharp mandibles
- Strong stinging ability
- Robust body structure adapted for predation
- Chemical Communication: Army ants are practically blind and rely heavily on chemical pheromones to navigate and communicate. They mark trails and follow scent paths laid by other workers.
- Colony Structure:
- A single queen lays all eggs.
- Female workers perform tasks such as foraging, protecting the colony, and tending to larvae.
This high degree of social organization reflects advanced eusocial behavior.
Ecological Role: Keystone Predators
Army ants are considered keystone predators in tropical ecosystems. Their ecological contributions include:
- Regulating arthropod populations by consuming large quantities of insects daily.
- Influencing forest biodiversity by reshaping prey communities.
- Supporting ecological networks — several bird species are known to follow army ant raids to capture fleeing insects.
By controlling invertebrate populations, they help maintain ecological balance and prevent outbreaks of certain insect species.
Significance of the Discovery
- Biodiversity Documentation: The identification of Aenictus chittoorensis and Aenictus lankamallensis adds to India’s documented insect diversity and strengthens taxonomic knowledge of the Eastern Ghats.
- Eastern Ghats as a Biodiversity Hotspot: Though less celebrated than the Western Ghats, the Eastern Ghats possess significant endemic diversity. Discoveries such as this underline the need for systematic biodiversity surveys in these fragmented hill ranges.
- Conservation Imperative: Habitat fragmentation, deforestation, mining, and climate change threaten forest ecosystems in the Eastern Ghats. The discovery reinforces the urgency of conserving lesser-known invertebrate fauna alongside charismatic megafauna.
- Scientific Relevance: Understanding army ant behavior and ecological dynamics can contribute to broader ecological research on predator-prey relationships and forest ecosystem functioning.
Black-Capped Capuchin Monkey

- 19 Dec 2025
In News:
The Bannerghatta Biological Park has imported eight black-capped capuchin monkeys from South Africa under an animal exchange programme.
About Black-Capped Capuchin Monkey
- Scientific Name:Sapajusapella
- Common Name: Tufted capuchin / Black-capped capuchin
- Native Range: Widespread across South America, especially the Amazon Basin
- Habitat: Black-capped capuchins are highly adaptable and inhabit:
- Tropical and subtropical forests
- Dry and submontane forests
- Savannah woodlands
- Mangroves
- Behaviour and Ecology
- Lifestyle: Arboreal (tree-dwelling) and diurnal (active during the day)
- Diet: Omnivorous - feeds on fruits, seeds, nuts, insects, lizards, eggs, and small crustaceans
- Communication: Uses vocal calls, body postures, touch, and scent cues
- Ecological Role: Acts as an important seed disperser, supporting forest regeneration
- Conservation Status
- IUCN Red List: Least Concern
Despite being widespread, habitat loss and illegal pet trade can pose local threats.
Bannerghatta Biological Park (BBP)
- Located about 22 km south of Bengaluru, Karnataka
- Was earlier part of Bannerghatta National Park and became an independent establishment in 2002
- Comprises multiple conservation and visitor facilities:
- Zoo
- Safari Park
- Butterfly Park
- Rescue & Rehabilitation Centre
- Special Feature: Houses India’s first fenced, forested elephant sanctuary within a biological park setting.
Carbon Capture, Usage and Storage
- 14 Feb 2026
In News:
The Prime Minister highlighted the importance of CCUS in decarbonising India’s heavy industries by sharing an article titled “Carbon capture can power India’s next steel revolution” authored by the Union Minister of Steel. Simultaneously, the Union Budget 2026–27 earmarked ?20,000 crore for a dedicated CCUS scheme, signalling a shift from pilot research to commercial deployment.
What is CCUS?
According to the International Energy Agency, Carbon Capture, Utilization and Storage (CCUS) refers to a set of technologies that capture carbon dioxide (CO?) from:
- Large industrial sources (power plants, steel, cement, refineries), or
- Directly from the atmosphere (Direct Air Capture).
The captured CO? is compressed and transported for either utilization or permanent geological storage.
The Three-Step Process
1. Capture: CO? is separated from other gases using:
- Chemical solvents
- Membranes
- Solid sorbents
2. Transport: Compressed CO? is transported through:
- Pipelines
- Ships
- Road tankers
3. Utilization or Storage
- Utilization (CCU): Conversion into urea, methanol, synthetic fuels, chemicals, building materials, or use in Enhanced Oil Recovery (EOR).
- Storage (CCS): Injection into deep geological formations such as depleted oil and gas fields or saline aquifers for long-term sequestration.
Why is CCUS crucial for India?
1. Decarbonising ‘Hard-to-Abate’ Sectors
Industries like steel and cement emit CO? due to chemical processes (e.g., calcination of limestone), not merely fuel combustion. CCUS is currently the only scalable solution to reduce such intrinsic emissions without shutting down production.
2. Powering India’s Steel Expansion
- India is the world’s second-largest crude steel producer (after China).
- Production: ~152 million tonnes (FY 2024–25).
- Under the National Steel Policy 2017, targets:
- 300 MT capacity by FY 2030–31
- 500 MT by 2047 (Viksit Bharat vision)
- Steel accounts for 10–12% of India’s total greenhouse gas emissions.
While hydrogen-based steelmaking is the long-term solution, CCUS acts as a bridge technology, enabling “Low-Carbon Steel” using existing plants.
3. Enhancing Energy Security
India derives 55–60% of its primary energy from coal. Immediate fossil fuel phase-out is economically disruptive. CCUS allows continued coal usage with reduced emissions during transition.
4. Circular Economy & Industrial Value Addition
Captured CO? can be:
- Converted to methanol (clean fuel)
- Used in Enhanced Oil Recovery (EOR)
- Converted into green urea or building materials
Thus, emissions become economic resources.
5. Safeguarding Exports from Carbon Taxes
Global trade is increasingly climate-regulated under mechanisms like the European Union Carbon Border Adjustment Mechanism (CBAM).
Low-carbon steel:
- Reduces export vulnerability
- Attracts climate-aligned investments
- Prevents “stranded assets” in India’s relatively young steel plants
6. Alignment with Global Commitments
CCUS supports:
- Paris Agreement (limit warming to 1.5–2°C)
- Sustainable Development Goals (Climate Action, Affordable & Clean Energy, Industry & Innovation)
India’s Key Initiatives on CCUS
1. Budgetary Push (2026–27)
- ?20,000 crore over five years
- Target sectors: Power, Steel, Cement, Refineries, Chemicals
2. NITI Aayog Policy Framework
- Proposed Viability Gap Funding (VGF)
- Development of CCUS hubs in industrial clusters (e.g., Gujarat, Odisha)
- Shared pipeline and storage infrastructure
3. Green Steel Taxonomy
Steel with emissions <2.2 tCO?e per tonne of crude steel qualifies as “Green Steel” (3–5 star ratings), incentivising adoption of CCUS and avoiding carbon taxes.
4. R&D and Institutional Support
National Centres of Excellence (NCoE-CCU)
- IIT Bombay
- Jawaharlal Nehru Centre for Advanced Scientific Research
DST Roadmap
- Pilot phase: 2025–30
- Commercial scale-up: 2035–45
Mission Innovation Challenge (2018)
- Joint initiative of DST & DBT
- Collaboration with 24 countries
- Focus on breakthrough capture and utilization technologies
Inhalable Microplastics

- 21 Dec 2025
In News:
A first-of-its-kind comprehensive study has detected inhalable microplastics in the ambient air of major Indian cities, uncovering a largely ignored dimension of urban air pollution. The research monitored air samples from densely populated market areas across Delhi, Mumbai, Kolkata, and Chennai, highlighting a regulatory blind spot in current air quality assessment systems.
What are Inhalable Microplastics?
- Definition: Tiny airborne plastic particles smaller than 10 micrometres (µm) that can remain suspended in air and be inhaled deep into the lungs.
- Unlike larger microplastics that settle quickly, these particles persist in the atmosphere due to low gravitational settling velocity.
- They are now emerging as airborne contaminants, alongside conventional pollutants such as PM?.? and PM??, sulphur dioxide (SO?), nitrogen dioxide (NO?), carbon monoxide (CO), ozone (O?), lead (Pb), and ammonia (NH?).
Sources of Inhalable Microplastics
- Tyre and brake wear from road transport
- Synthetic clothing fibres (polyester, nylon)
- Plastic packaging and urban waste mismanagement
- Paints, cosmetics, and open waste burning
Key Findings of the Study
- New Air Pollutant Identified: Inhalable microplastics are not adequately captured by existing Air Quality Index (AQI) frameworks.
- City-wise Variation: Levels were significantly higher in Delhi and Kolkata compared to Mumbai and Chennai, attributed to:
- Coastal dispersion of pollutants in Mumbai and Chennai
- Higher population density and poorer waste management in Delhi and Kolkata
- High Human Exposure: Urban residents inhale approximately 132 micrograms (µg) of microplastics daily, indicating chronic exposure at breathing height.
- Carrier of Toxins: These particles act as “Trojan horses,” transporting:
- Heavy metals (lead, cadmium)
- Endocrine-disrupting chemicals (phthalates)
- Health Risks:
- Deep lung penetration leading to respiratory disorders
- Increased risk of hormonal imbalance, cancer, and long-term lung damage
- Ability to carry microbes such as Aspergillus fumigatus, including antibiotic-resistance genes, raising concerns over drug-resistant respiratory infections
Microplastics: Background
- Definition: Plastic particles <5 mm in size; particles <100 nanometres are termed nanoplastics.
- Formation: Fragmentation of larger plastics due to UV radiation, heat, wind, waves, and mechanical abrasion.
- Types:
- Primary microplastics: Intentionally manufactured (microbeads in cosmetics, plastic pellets, synthetic fibres).
- Secondary microplastics: Formed from degradation of larger plastic items (bags, bottles, packaging, fishing nets).
Major Sources
- Synthetic textiles
- Road transport (tyre wear)
- Single-use plastics
- Personal care products
- Ineffective plastic waste management
Regulatory Measures in India
- Ban on single-use plastics
- India Plastics Pact
- Plastic Waste Management (Amendment) Rules, 2024
Dolphin Census in Odisha
- 13 Feb 2026
In News:
Odisha has registered its highest marine dolphin population in the past five years, with 765 dolphins recorded in the 2026 State-wide census. The estimation highlights stable to improving population trends and underscores the role of sustained conservation, habitat protection, and community participation.
About the Dolphin Census in Odisha
What is it?
- An annual scientific population estimation exercise assessing the abundance, distribution, and diversity of dolphins and other cetaceans in Odisha’s marine, estuarine, and lagoon ecosystems.
Conducting Authority
The census is conducted by the Wildlife Wing of the Forest, Environment and Climate Change Department, Government of Odisha. It involves:
- Forest officials and frontline staff
- Marine experts
- Boat-based and shore-based transect surveys
- Training in species identification and safety protocols
The exercise began in Chilika in 2008 and expanded to all coastal forest divisions since 2015.
Key Findings: Dolphin Census 2026
Total Population: 765 dolphins (An increase of 55 individuals compared to the previous year)
Species-wise Distribution
- Humpback Dolphins – 497
- Irrawaddy Dolphins – 208
- Bottlenose Dolphins – 55
- Spinner Dolphins – 3
- Finless Porpoise – 2
Key Conservation Zones
Chilika Lake
- Recorded 159 Irrawaddy dolphins.
- Hosts the largest single-area concentration of Irrawaddy dolphins globally.
- It is a Ramsar Site (wetland of international importance).
- Population has remained stagnant for two years due to:
- Slow breeding rate
- Habitat stress (prawn gheries, nylon fishing nets)
- Possible migration to other areas
Irrawaddy dolphins were also sighted in:
- Balasore
- Berhampur
- Puri Wildlife Division
- Rajnagar Mangrove Division
Gahirmatha Marine Sanctuary
- Emerged as a strong marine conservation zone.
- Recorded 474 Humpback dolphins, the highest among surveyed regions.
Conservation Significance
- Dolphins are protected under Schedule I of the Wildlife (Protection) Act, 1972 (highest level of legal protection).
- The Irrawaddy dolphin is classified as Endangered on the IUCN Red List.
- Dolphins serve as flagship and indicator species of marine ecosystem health.
Reasons for Population Improvement
- Habitat protection measures
- Regulation of fishing practices
- Community participation drives
- Scientific monitoring and inter-divisional coordination
- Capacity building of field staff
About Dolphins (General Features)
Dolphins are aquatic marine mammals belonging to the order Cetacea.
Key Characteristics:
- Highly intelligent; capable of complex communication.
- Use echolocation for navigation and hunting.
- Social animals living in pods.
- Slow breeding rate (especially Irrawaddy dolphins).
- Indicators of marine ecosystem health.
Species Found in Odisha
- Humpback Dolphin
- Irrawaddy Dolphin
- Bottlenose Dolphin
- Spinner Dolphin
- Finless Porpoise (closely related cetacean)
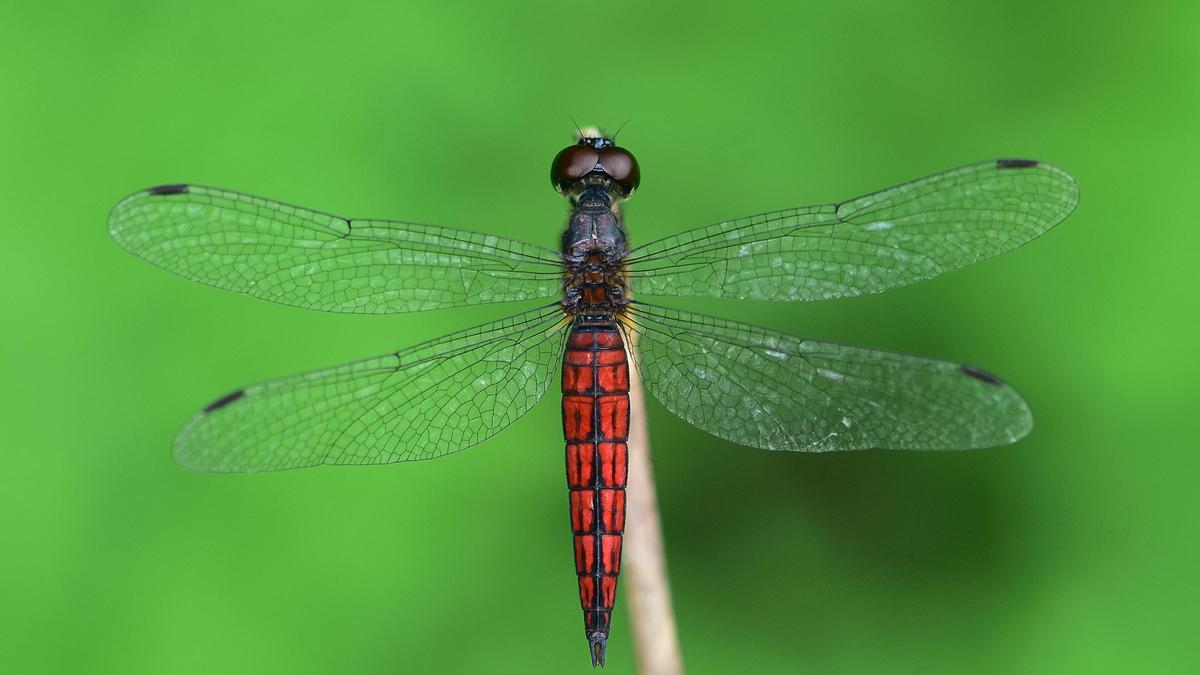
Discovery of Lyriothemis keralensis in Kerala

- 12 Feb 2026
In News:
Researchers have identified a new dragonfly species named Lyriothemis keralensis in Kerala, extending the known geographical range of the genus beyond northeast India. The discovery underscores the rich biodiversity of the Western Ghats and the importance of careful taxonomic studies.
Taxonomic Clarification
Although the species has been present in Kerala since 2013, it was misidentified for over a decade as Lyriothemis acigastra. Detailed morphological examination, including microscopic analysis and comparison with museum specimens, confirmed its distinct identity.
This highlights:
- The importance of systematic taxonomy
- The role of reference collections in biodiversity research
- Potential underestimation of species diversity in India
Key Features
The species exhibits pronounced sexual dimorphism:
- Males: Bright blood-red body with black markings
- Females: Yellow body with black markings
Such colour variation aids in species identification and reproductive behaviour studies.
Habitat and Ecology
Unlike many dragonflies associated with pristine forest ecosystems, Lyriothemis keralensis thrives in human-modified irrigation landscapes, including:
- Pineapple plantations
- Rubber plantations
- Shaded irrigation canals
Most recorded populations occur outside protected areas, indicating that biodiversity conservation must extend beyond national parks and wildlife sanctuaries.
Seasonality and Life Cycle
The species is:
- Seasonally visible during the Southwest Monsoon (late May to August)
- Present as aquatic larvae in water bodies for the remainder of the year
This seasonal emergence aligns with monsoon-driven ecological cycles in Kerala.
Conservation Concerns
The discovery raises important conservation issues:
- Plantation-dominated landscapes may act as secondary habitats
- Changes in irrigation patterns, pesticide use, and land conversion could threaten populations
- Lack of protection outside designated conservation zones may expose species to habitat loss
The finding reinforces the need for biodiversity-sensitive land-use planning, especially in agriculturally modified ecosystems.
Mangrove clam (Geloina erosa)
- 10 Feb 2026
The ICAR–Central Marine Fisheries Research Institute (CMFRI) has achieved a rare global scientific feat by successfully inducing captive breeding of the mangrove clam (Geloina erosa). This breakthrough enables controlled hatchery production of the species, offering a sustainable pathway for conservation, aquaculture, and ecosystem restoration.
About Mangrove Clam (Geloina erosa)
- Scientific name: Geloina erosa (also referred to in some literature as Polymesoda erosa)
- Common name: Mangrove clam / Mud clam
- Local name: “Kandal Kakka” (Northern Kerala)
- Type: Ecologically significant bivalve mollusc
Habitat and Distribution
- Found in organic-rich muddy substrates of intertidal mangrove and estuarine ecosystems
- Distributed across South and Southeast Asia
- Tolerates a wide salinity range, from brackish to near-freshwater conditions
- Deep-burrowing, semi-infaunal species; juveniles are more tide-independent
Key Ecological Characteristics
- Large Size:
- One of the world’s largest mangrove clams
- Reaches up to 10 cm shell width, making it valuable as a food resource
- Efficient Filter Feeder:
- Filters suspended particles and plankton
- Improves estuarine water quality through nutrient recycling
- Ecosystem Stabiliser:
- Burrowing behaviour stabilises sediments
- Enhances nutrient cycling
- Strengthens resilience of mangrove ecosystems
- Reproductive Biology:
- Sex differentiation based on gonad colour and structure (not external organs)
- Facilitates broodstock identification and reproductive studies
Scientific Breakthrough: Induced Breeding
CMFRI has achieved:
- Controlled spawning under captive conditions, reducing dependence on wild seed collection
- Complete life-cycle closure, successfully rearing the clam from embryo to larval stages and eventually to spat (around the 18th day)
- Hatchery-scale seed production feasibility
This represents a global first for this species and marks a major step in sustainable marine resource management.
Conservation and Aquaculture Applications
The hatchery-produced seeds can be utilised for:
- Grow-out farming:
- Suitable for estuarine aquaculture
- Requires minimal external feed and infrastructure
- Mangrove ranching:
- Release of juvenile clams into degraded mangrove habitats
- Aids ecological restoration
- Stock enhancement:
- Replenishes overexploited natural clam beds
- Reduces harvesting pressure on wild populations
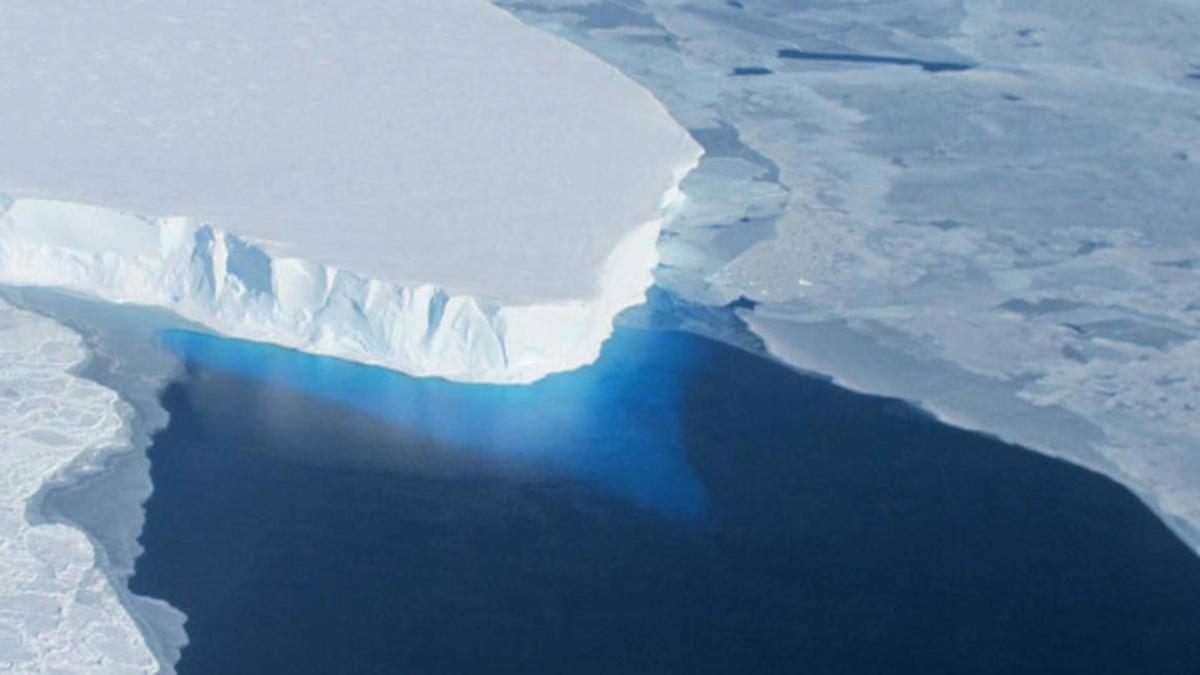
Thwaites Glacier

- 10 Feb 2026
In News:
The Thwaites Glacier, often referred to in popular media as the “Doomsday Glacier”, is one of the most crucial glaciers in the world for understanding future sea-level rise. Located in West Antarctica, it is an outflow glacier of the West Antarctic Ice Sheet (WAIS) and drains into the Amundsen Sea.
Why is Thwaites Glacier Important?
- Mass and Size: Thwaites is among the largest glaciers in Antarctica, covering an area comparable to a large country.
- Climate Sensitivity: The WAIS, of which Thwaites is a key component, is recognised as one of the planet’s climate tipping elements, meaning its destabilisation could trigger irreversible changes.
Unique Physical Characteristics
A defining feature of Thwaites Glacier is its retrograde bed slope, the land beneath it slopes downward as one moves inland and lies below sea level. This makes the glacier highly vulnerable to warm ocean water intrusion.
- Warm seawater flows beneath the glacier’s floating ice shelf, melting it from below.
- The ice shelf currently acts as a buttress or brace, slowing the flow of ice into the ocean.
- As the ice shelf thins or fractures, this restraining effect weakens, causing the glacier to accelerate and lose ice more rapidly.
Current Scientific Observations
Scientific studies have confirmed that Thwaites Glacier is:
- Thinning steadily
- Retreating inland
- Already contributing to global sea-level rise
The rapid melting is strongly linked to human-induced climate change, particularly rising ocean temperatures.
Potential Global Impacts
- Sea-Level Rise: A complete collapse of Thwaites over a long period could raise global sea levels by around 0.5 metres.
- Cascade Effect: Thwaites acts as a barrier holding back neighbouring glaciers in the WAIS. Its weakening could destabilise adjacent ice masses, further accelerating sea-level rise.
- Coastal Risks: Higher sea levels would increase coastal flooding, shoreline erosion, storm surges, and threaten:
- Coastal cities
- Low-lying islands
- Ports and critical infrastructure
Why It Matters for the World
Although Thwaites Glacier is geographically remote and far from human settlements, its evolution has global consequences. Changes in this single glacier have the potential to reshape coastlines worldwide, making it a key focus area for climate science, global risk assessment, and international climate policy.
Eurasian Otter

- 09 Feb 2026
In News:
The Eurasian otter has been recently sighted in the Sindh River in Ganderbal district of Jammu and Kashmir. This observation is ecologically significant as the species was earlier believed to have disappeared from the region, highlighting improving riverine ecosystem conditions and possible cross-border wildlife movement.
About Eurasian Otter
- Scientific Name: Lutra lutra
- Also known as: European otter, Common otter, Old World otter
- Type: Semi-aquatic, carnivorous mammal
- Behaviour: Elusive and largely solitary in nature
Distribution
- Global: Middle East, Europe, Northern Africa, Russia, China, and other parts of Asia
- India: Northern, North-Eastern, and Southern India
- In the Indian subcontinent, it is commonly associated with cold hill regions and mountain streams
Habitat
- Occupies a wide range of freshwater and coastal ecosystems such as:
- Rivers and streams
- Highland and lowland lakes
- Marshes, swamp forests, and coastal areas
- Habitat selection is independent of size, origin, or latitude of the water body
Key Adaptations and Features
- Webbed feet for efficient swimming
- Ability to close ears and nostrils underwater
- Dense, short fur that traps air for insulation
- Highly developed sense of sight, smell, and hearing, aiding hunting and survival
Ecological Significance
- Considered an indicator species for healthy freshwater ecosystems
- Presence reflects low pollution levels and good prey availability
Threats
- Water pollution
- Habitat degradation
- Illegal hunting for fur
Conservation Status
- IUCN Red List: Near Threatened
- CITES: Appendix I
- Wildlife (Protection) Act, 1972: Schedule II
Titanidiops Kolhapurensis

- 08 Feb 2026
In News:
A new species of trapdoor spider, Titanidiops kolhapurensis, has been discovered in the grasslands of Kolhapur district.
About Titanidiops kolhapurensis
- Habitat: Flat or gently sloping grassy meadows.
- Burrow structure: Constructs vertical or slanted burrows with entrances expertly camouflaged to blend with surrounding soil, making them nearly invisible.
- Distribution pattern: Found in native grasslands and natural forests, but absent in areas dominated by exotic plantations such as Gliricidia sepium (Undirmari).
- Conservation concern: On the verge of local extinction due to rapid habitat degradation and land-use change.
What are Trapdoor Spiders?
- A group of large-bodied, burrowing spiders found across several taxonomic families.
- Burrowing behaviour: Dig burrows up to 15 cm (6 inches) deep, sealed with a silken-hinged trapdoor.
- Feeding strategy: Ambush predators—rapidly open the door to seize passing insects or arthropods.
- Behaviour: Reclusive and timid; retreat quickly into burrows when disturbed.
- Human impact: Bite not medically significant to humans.
- Climate preference: Tropical, subtropical and warm regions.
- Size: Typically ~2.5 cm (1 inch) long; some species up to 4 cm (1.5 inches).
- Threats: Predation by spider-hunting wasps; low dispersal ability (juveniles remain close to maternal burrows), making populations highly vulnerable to habitat loss.
Why this discovery matters
- Highlights the ecological importance of native grasslands, often overlooked in conservation.
- Demonstrates the negative impact of exotic tree plantations on indigenous fauna.
- Strengthens the case for habitat-specific conservation planning in the Western India landscape.
Peregrine Falcon
- 08 Feb 2026
In News:
A wildlife researcher has recorded the first-ever sighting of the Siberian peregrine falcon in central Australia, a region where this subspecies had never been documented earlier. The observation expands the known range and movement patterns of this migratory raptor.
About the Peregrine Falcon
- A large cosmopolitan bird of prey belonging to the Falconidae family.
- Global distribution: Present on all continents except Antarctica, including several oceanic islands.
- Known for exceptional adaptability, occurring from Arctic tundra to temperate coastal regions.
Habitat & Nesting
- Preferred habitats: Open landscapes such as grasslands, tundra and meadows.
- Most abundant in tundra and coastal regions; relatively rare in tropical and sub-tropical zones.
- Nesting sites: Typically nests on cliff faces, rock ledges and crevices; in urban areas, may use tall buildings.
Key Characteristics
- Fastest bird in the world and the fastest animal during its hunting dive (stoop), reaching speeds over 300 km/h.
- Diurnal (active during the day).
- Behaviour: Solitary outside the breeding season; strongly territorial.
- Highly efficient aerial hunter, preying mainly on medium-sized birds.
Ecological Significance
- A top-level predator in avian food chains.
- Helps regulate populations of prey species such as pigeons and doves, contributing to ecological balance.
- Considered an important indicator species for ecosystem health due to its sensitivity to environmental changes.
Conservation Status
- IUCN Red List: Least Concern
- Earlier population declines due to pesticide use (notably DDT) were reversed through conservation measures, making it a global conservation success story.
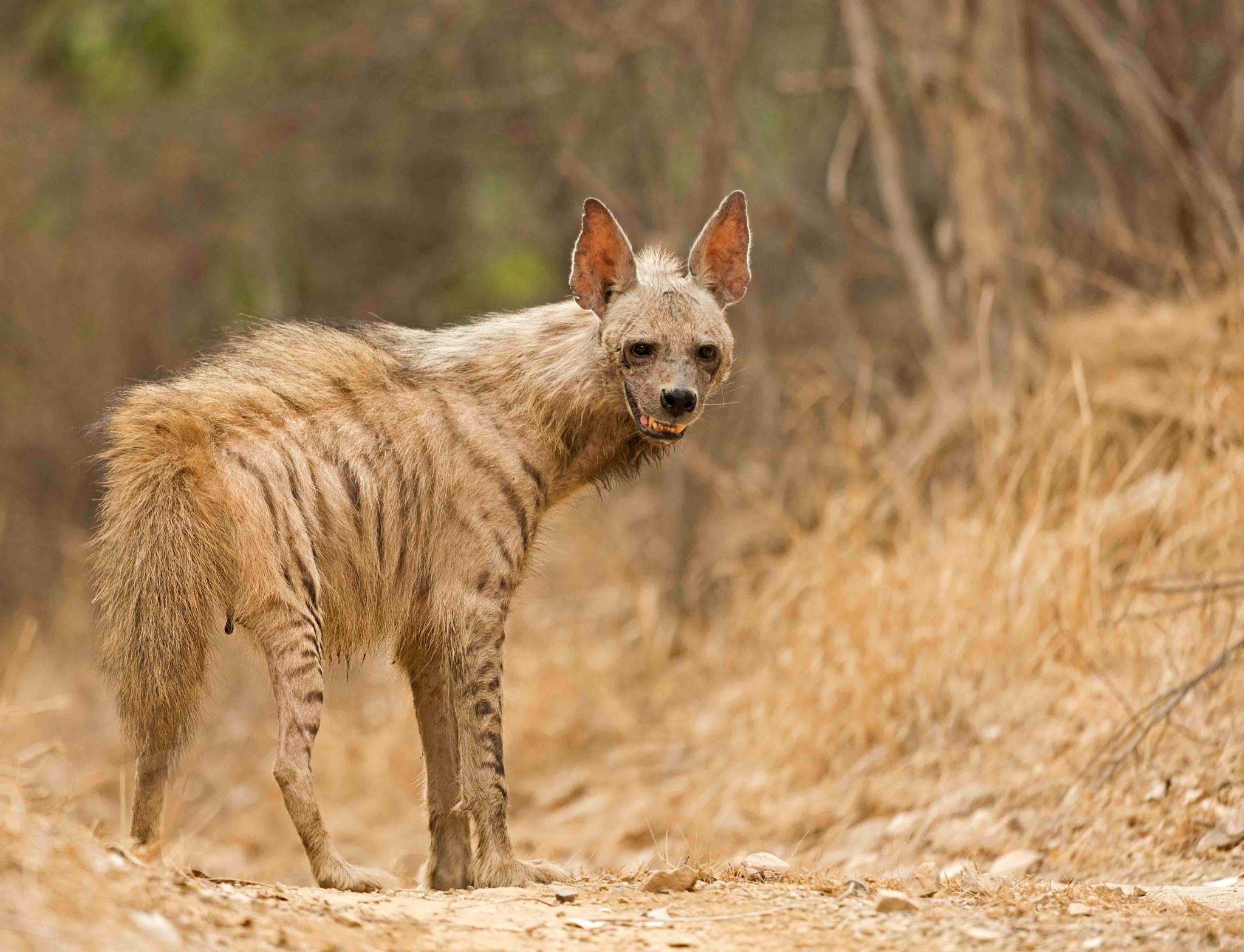
Rare Sighting of Striped Hyena in Kali Tiger Reserve

- 06 Feb 2026
In News:
A rare sighting of the striped hyena (Hyaena hyaena) has been reported from the Kali Tiger Reserve, located in the Uttara Kannada district of Karnataka. The sighting is ecologically significant as it highlights the presence of elusive carnivores beyond core forest habitats and reflects improving habitat connectivity within protected landscapes of the Western Ghats region.
About the Striped Hyena
The striped hyena is a medium-sized carnivorous mammal belonging to the Hyaenidae family, which comprises four extant species—striped hyena, spotted hyena, brown hyena, and aardwolf (the latter is insectivorous and not a true wolf).
Key characteristics:
- Appearance: Smaller than the spotted hyena, with a sloping back, erect mane, and distinctive dark vertical stripes along the body and legs.
- Distribution: Found across South Asia (India, Nepal, Afghanistan), North Africa, Sub-Saharan Africa, West Asia, and Central Asia.
- Habitat: Prefers open savannas, grasslands, scrub forests, and semi-arid landscapes, often living close to human settlements.
Behaviour and Ecology
- Feeding habit: Primarily a scavenger, feeding on carrion, animal remains, and occasionally human refuse, thereby playing a crucial role in ecosystem sanitation.
- Social structure: Generally solitary, though it exhibits limited social organisation.
- Territoriality: Uses scent marking to demarcate territories and deter rivals.
- Sexual hierarchy: Adult females dominate males and may display aggression toward other females.
Conservation Status
- IUCN Red List: Near Threatened
- Wildlife (Protection) Act, 1972: Schedule I, providing the highest level of legal protection in India
Despite its wide range, the species faces population decline due to habitat loss, persecution driven by myths, road mortality, and depletion of natural carrion.
Two New Ramsar Sites in India

- 17 Dec 2025
In News:
India has added two more wetlands to the list of Ramsar Sites of International Importance-Siliserh Lake in Rajasthan and Kopra Jalashay in Chhattisgarh. These designations highlight the ecological significance of inland water bodies in biodiversity conservation and water security.
Siliserh Lake
- Siliserh Lake is located in Rajasthan, within the buffer zone of the Sariska Tiger Reserve.
- It is a human-made lake constructed in 1845 by Maharaja Vinay Singh to provide drinking water to Alwar city.
- Situated in a semi-arid region, the lake serves as a crucial water source for wildlife and local communities. Its hydrological presence supports diverse habitats in an otherwise water-scarce landscape.
Biodiversity Significance
The wetland supports around 149 bird species and 17 mammal species. Notable fauna include:
- The vulnerable river tern
- The endangered tiger from the adjoining Sariska landscape
It also supports more than 1% of the biogeographic population of the black stork (Ciconia nigra), which is an important criterion under the Ramsar Convention.
Kopra Jalashay
- Kopra Jalashay is located in Chhattisgarh and is a reservoir situated in the upper catchment of the Mahanadi River.
- Its ecological importance arises from strong hydrological and habitat connectivity, which supports multiple wetland-dependent ecosystems.
Biodiversity Significance
The site supports over 60 migratory bird species, making it an important stopover, feeding, and nesting ground along avian migration routes.
Key species recorded here include:
- The vulnerable greater spotted eagle (Aquila clanga)
- The endangered Egyptian vulture (Neophron percnopterus)
Solid Waste Management (SWM) Rules, 2026

- 05 Feb 2026
In News:
The Ministry of Environment Forest and Climate Change has notified the Solid Waste Management Rules, 2026, replacing the 2016 rules under the Environment Protection Act. The new framework comes into force from 1 April 2026 and aims to strengthen segregation, accountability, and circular use of waste.
Key Objectives
The rules seek to reduce landfill dependence, promote scientific waste processing, operationalise the polluter pays principle, and align waste governance with circular economy goals under urban missions like Swachh Bharat Mission 2.0 and AMRUT 2.0.
Major Features
- Four-Stream Segregation at Source (Mandatory): Households, institutions, and establishments must segregate waste into:
- Wet waste: Kitchen and biodegradable waste; to be composted or bio-methanated
- Dry waste: Plastic, paper, metal, glass, etc.; to be sent to Material Recovery Facilities (MRFs)
- Sanitary waste: Diapers, sanitary pads, etc.; to be securely wrapped and separately stored
- Special care waste: Bulbs, medicines, paint containers, batteries; to be handed to authorised agencies
- Polluter Pays Principle: Environmental compensation will be imposed for violations such as non-registration, false reporting, and improper disposal. Guidelines will be framed by the Central Pollution Control Board, while enforcement will be done by State Pollution Control Boards and Pollution Control Committees.
- Bulk Waste Generators (BWGs) – Clear Definition: Entities are classified as BWGs if they meet any one of these thresholds:
- Floor area ≥ 20,000 sq m
- Water consumption ≥ 40,000 litres/day
- Waste generation ≥ 100 kg/day
This includes government offices, residential societies, institutions, universities, and commercial complexes—together accounting for nearly 30% of total waste.
- Extended Bulk Waste Generator Responsibility (EBWGR): BWGs must process wet waste on-site wherever feasible or obtain an EBWGR certificate. This reduces pressure on urban local bodies and enforces accountability at the source.
- Centralised Digital Monitoring: A national online portal will track registration, authorisation, waste processing, audits, and legacy waste remediation, replacing manual systems and improving transparency.
- Faster Land Allocation for Processing Facilities: Graded siting criteria and buffer norms for facilities handling over 5 tonnes/day will speed up infrastructure creation, guided by CPCB norms.
- Refuse Derived Fuel (RDF) Mandate: Industries such as cement kilns and waste-to-energy plants must increase RDF use from 5% to 15% over six years. RDF is high-calorific fuel made from non-recyclable dry waste, promoting resource recovery.
- Restrictions on Landfilling: Only inert, non-recyclable, and non-energy-recoverable waste can be landfilled. Higher landfill fees for unsegregated waste are intended to incentivise segregation.
- Legacy Waste Remediation: Mandatory biomining and bioremediation of old dumpsites with time-bound targets and quarterly reporting via the portal. District Collectors will oversee audits.
- Duties of Local Bodies and MRFs: Urban local bodies must ensure collection, segregation, and transportation. MRFs are formally recognised as key facilities for sorting and can also receive sanitary and other waste streams.
- Special Provisions for Hilly Areas and Islands: Local bodies can levy tourist user fees, regulate visitor numbers, and promote decentralised processing of biodegradable waste by hotels and institutions.
- Institutional Mechanism: State-level committees chaired by Chief Secretaries (or UT Administrators) will supervise implementation and advise CPCB.
Significance
India generates roughly 1.85 lakh tonnes of municipal solid waste per day (CPCB data). The 2026 rules emphasise prevention, segregation, recycling, and energy recovery before disposal, embedding circular economy principles in urban governance. Scientific waste handling reduces pollution, greenhouse gas emissions from landfills, and public health risks such as vector-borne diseases.
Challenges
Implementation gaps at municipal levels, inadequate processing infrastructure, weak segregation at household level, financial stress on smaller towns, and the need to formally integrate waste pickers remain major hurdles.
Way Forward
Success depends on strengthening urban local body capacity, behavioural change campaigns for segregation, private sector participation in recycling, technological tools for monitoring, and integration with climate, plastic, and renewable energy policies. If effectively executed, the SWM Rules, 2026 can transform India’s waste burden into an opportunity for sustainable and resource-efficient urban development.
Tapanuli Orangutan
- 16 Dec 2025
In News:
Scientists have warned that Cyclone Senyar-triggered floods and landslides in northern Sumatra may have killed 6–11% of the remaining Tapanuli orangutan population, pushing the species closer to extinction.
About the Tapanuli Orangutan
- The Tapanuli orangutan is the rarest great ape species in the world, formally identified as a distinct species in 2017. Fewer than 800 individuals are believed to survive in the wild.
- Habitat and Distribution
- Tapanuli orangutans are found only in the Batang Toru Ecosystem in North Sumatra, Indonesia.
- Their range is highly fragmented and restricted to upland and submontane rainforests south of Lake Toba, covering less than 3% of their historical range.
- Evidence suggests they were originally better adapted to lower-altitude forests but were pushed into higher terrain due to habitat loss.
- IUCN Status: The species is listed as Critically Endangered on the IUCN Red List due to its extremely small and declining population, restricted range, and ongoing threats.
Physical Characteristics
- Tapanuli orangutans resemble other orangutans in size but have distinct features. They possess smaller skulls, flatter faces, and thicker, frizzier orange fur. Adult flanged males have beards and moustaches, with flatter cheek pads covered in light-colored fuzz.
Behaviour and Ecology
- These orangutans are arboreal and largely solitary, spending most of their lives in the forest canopy.
- They are highly intelligent and known for tool use, using sticks and branches as hooks, scratchers, or to extract insects. Social learning and cultural transmission of behaviors have also been observed.
- Their life history is extremely slow, with one of the longest mother–offspring bonds in mammals (7–11 years). Males exhibit bimaturism, with two forms: unflanged males (smaller, no cheek pads) and dominant flanged males (large cheek pads and throat sacs).
- A unique ecological trait is their diet, which includes certain caterpillars and pinecones not known to be eaten by other orangutan species.
Why the Species is Extremely Vulnerable
The Tapanuli orangutan’s risk of extinction is amplified by:
- Extremely small total population
- Highly restricted and fragmented habitat
- Slow reproduction rate
- Increasing frequency of extreme weather events linked to climate change
- Ongoing habitat pressures from development and infrastructure
Even minor increases in mortality can have irreversible population-level consequences.
Conservation Significance
The Tapanuli orangutan represents the most ancient lineage of orangutans, despite being the most recently described. Its survival is crucial for preserving global great ape diversity and evolutionary history.
The recent cyclone highlights how climate-related disasters can become “extinction-level events” for species already on the brink.
NeophyteID App
- 04 Feb 2026
In News:
Kerala has taken a significant step in tech-enabled environmental governance with the launch of the NeophyteID mobile application by Chief Minister Pinarayi Vijayan. The app represents a convergence of artificial intelligence, citizen science, and biodiversity conservation, aimed at tackling the growing threat of invasive plant species in the state.
About the NeophyteID Application
- NeophyteID is an AI-powered mobile application developed by researchers at the Malabar Botanical Garden and Institute for Plant Sciences (MBGIPS). It is designed as a citizen-friendly digital tool to identify, report, and map invasive (neophyte) plant species across Kerala.
- The app enables local communities, students, researchers, and ecologists to collaboratively monitor plant invasions that threaten native biodiversity and ecosystem stability.
Key Features
1. AI-Based Species Identification
- Powered by the YOLOv11 machine learning model
- Uses image recognition to identify invasive plants from:
- Live camera input
- Uploaded photos from the gallery
2. Geospatial Mapping
- Each confirmed identification is tagged with location data
- Helps build a real-time distribution map of invasive plant species
- Supports scientific research and evidence-based conservation planning
3. Citizen Science Approach
- Encourages public participation in biodiversity monitoring
- Bridges the gap between scientists and local communities
4. Language Accessibility
- Available in English and Malayalam
- Enhances usability among local populations
Why Invasive Species Matter
Invasive plant species are non-native plants that spread aggressively and disrupt ecosystems.
Ecological Impacts
- Outcompete native flora for nutrients, sunlight, and space
- Reduce biodiversity
- Alter soil chemistry and hydrology
- Disrupt food chains and wildlife habitats
Economic & Social Impacts
- Damage agriculture and forestry
- Increase management costs
- Affect water bodies, fisheries, and tourism
SAKSHAM 2026
- 03 Feb 2026
In News:
In a bid to promote responsible energy consumption and reduce pressure on natural resources, the oil industry has launched SAKSHAM 2026, a nationwide fuel conservation awareness campaign. The initiative reflects India’s broader strategy of combining energy security, environmental sustainability, and public participation.
What is SAKSHAM?
SAKSHAM (Samrakshan Kshamatha Mahotsav) is an annual public awareness campaign initiated under the guidance of the Ministry of Petroleum and Natural Gas. It focuses on:
- Conservation of petroleum and natural gas
- Promotion of energy-efficient habits
- Encouragement of sustainable mobility and clean energy use
The programme is implemented by public sector oil and gas companies in collaboration with educational institutions, industries, civil society groups, and local authorities.
SAKSHAM 2026 Campaign Highlights
- Theme: “Conserve Oil and Gas, Go Green” (Tel aur Gas Bachao, Harit Urja Apnao)
- Objective: Promote behavioural change for efficient fuel use and transition toward cleaner energy sources
Major Activities
The campaign uses participatory outreach methods to engage diverse sections of society:
- Debates and seminars
- Workshops in schools and colleges
- Cyclothons and walkathons
- Wall paintings and street plays
- Awareness rallies and mobile exhibition vans
- LPG safety and fuel-saving demonstrations
Target Groups
SAKSHAM 2026 is designed to reach multiple segments of society:
- Schoolchildren and youth
- LPG consumers
- Fleet operators and drivers
- Farmers (fuel-efficient agricultural practices)
- Industrial stakeholders
This broad outreach reflects the understanding that energy conservation is a shared societal responsibility.
Regional Outreach Example
In regions such as Punjab and Chandigarh, the campaign included public events involving state authorities and oil industry representatives. Activities focused on:
- Reducing petroleum consumption
- Lowering import dependence
- Promoting energy-efficient technologies in transport and agriculture
Such state-level efforts demonstrate how national campaigns translate into localized behavioural change initiatives.
Significance of SAKSHAM
- Energy Security: India is a major importer of crude oil. Conservation reduces import bills and vulnerability to global price volatility.
- Environmental Sustainability: Efficient fuel use lowers carbon emissions and urban air pollution, supporting climate goals.
- Economic Savings: Fuel-efficient practices benefit households, industries, and transport operators through cost reduction.
- Behavioural Change: Unlike policy-only measures, SAKSHAM promotes citizen-led action, which is critical for long-term sustainability.
World Wetlands Day
- 03 Feb 2026
In News:
World Wetlands Day is observed every year on 2 February to raise global awareness about the importance of wetlands for ecological stability, climate resilience, and human well-being. The day commemorates the signing of the Ramsar Convention in Ramsar, Iran, in 1971, one of the oldest international environmental agreements and the only one dedicated to a single ecosystem.
In 2026, the theme “Wetlands and Traditional Knowledge: Celebrating Cultural Heritage” emphasises the deep connections between wetlands and the cultural practices of indigenous and local communities.
Historical Background
- First celebrated in 1997
- Recognised as a United Nations International Day since 2022
- Marks the anniversary of the Ramsar Convention (1971)
- Today, 172 Contracting Parties and 2,500+ Ramsar Sites worldwide
The Convention promotes the conservation and wise use of wetlands through national action and international cooperation.
Why Wetlands Matter
Wetlands are among the most productive ecosystems on Earth. They include peatlands, mangroves, rivers, lakes, floodplains, and marshes.
Ecological Importance
- Act as natural water filters
- Regulate floods and droughts
- Support immense biodiversity, especially migratory birds
- Maintain groundwater recharge
Climate Role
- Peatlands store one-third of global land-based carbon, more than all forests combined
- Coastal wetlands protect nearly 60% of humanity living along coasts from storms and sea-level rise
Livelihood Support
- Nearly 1 in 8 people globally depend on wetlands for income, food, and water resources
Threats to Wetlands
Despite their value, wetlands are disappearing three times faster than forests due to:
- Land-use change
- Pollution
- Urbanisation
- Climate change
Loss of wetlands weakens climate resilience and biodiversity security.
Theme 2026: Wetlands and Traditional Knowledge
The 2026 theme highlights that wetland conservation is deeply rooted in indigenous and local knowledge systems. Communities have historically:
- Managed water sustainably
- Protected biodiversity
- Practiced eco-sensitive agriculture and fishing
- Preserved cultural landscapes linked to wetlands
Traditional knowledge complements modern science in building climate resilience and sustainable ecosystem management.
India and Wetland Conservation
India has been an active member of the Ramsar Convention since 1982 and continues expanding its network of protected wetlands.
Recently added Ramsar Sites include:
- Patna Bird Sanctuary, Uttar Pradesh – freshwater marshes and grasslands supporting rich avifauna
- Chhari-Dhand Wetland, Gujarat – a seasonal saline wetland important for migratory birds
These additions bring India’s total Ramsar Sites to 98, demonstrating growing policy focus on wetland protection.
Community Role in Conservation
World Wetlands Day stresses citizen participation:
- Raising awareness about wetland values
- Reducing pollution and conserving water
- Supporting local restoration initiatives
- Promoting sustainable lifestyles
- Amplifying indigenous voices in environmental decision-making
Meghalaya’s Living Root Bridges

- 01 Feb 2026
In News:
India has formally submitted the Living Root Bridges of Meghalaya for inscription on the UNESCO World Heritage List under the title “Jingkieng Jri / Lyu Chrai Cultural Landscape” for the 2026–27 evaluation cycle. These bioengineered bridges, developed by indigenous communities, represent a rare example of living architecture, blending ecological knowledge, cultural traditions, and sustainable engineering.
What are Living Root Bridges?
Known locally as Jingkieng Jri (Khasi) or Lyu Chrai (Jaintia), these bridges are found across the southern slopes of the Khasi and Jaintia Hills in the state of Meghalaya.
They are:
- Living structures, grown rather than built
- Crafted using the aerial roots of the Ficus elastica (Indian rubber tree)
- Developed over 15–30 years
- Capable of spanning 15 to 250 feet
- Durable for several centuries with proper care
Construction Process: Indigenous Bioengineering
The bridges are a result of traditional tree-shaping techniques perfected over generations:
- Young aerial roots of Ficus trees are guided across streams using hollowed trunks of Areca catechu.
- These trunks protect the roots and direct their growth.
- A temporary bamboo scaffold supports the structure during early stages.
- Over time, roots thicken and undergo inosculation (natural fusion), forming a strong, self-supporting bridge.
- As the bridge matures, the support materials decay, leaving a resilient living structure.
This method reflects deep ecological understanding and sustainable resource use.
Cultural Landscape Significance
The nomination recognises not just the bridges but an entire cultural landscape shaped by the Khasi and Jaintia tribes. The bridges embody:
- Community-based land management
- Intergenerational knowledge transfer
- Spiritual reverence for Mei Ramew (Mother Earth)
- Harmony between human activity and fragile hill ecosystems
Thus, they represent intangible cultural heritage expressed through a tangible living form.
Why UNESCO Recognition Matters
Inclusion in the UNESCO World Heritage List would:
- Provide global recognition of indigenous ecological knowledge
- Strengthen conservation and sustainable tourism efforts
- Encourage preservation of traditional practices amid modernization
- Highlight nature-based solutions in climate-resilient infrastructure
Institutional Role in Nomination
The nomination dossier was submitted by India’s Permanent Representative to UNESCO with contributions from:
- Archaeological Survey of India
- Ministry of External Affairs
- Government of Meghalaya
- Local indigenous communities, who remain the primary custodians
India Adds Two New Ramsar Sites
- 01 Feb 2026
In News:
India has recently expanded its network of internationally recognised wetlands by designating two additional sites as Ramsar wetlands - the Patna Bird Sanctuary in Uttar Pradesh and Chhari-Dhand in Gujarat ahead of World Wetlands Day observed on 2 February. This brings the total number of Ramsar Sites in the country to 98, reflecting a significant increase from 26 sites in 2014 and underscoring India's growing commitment to wetland protection and biodiversity conservation.
Ramsar Convention: An Overview
The Ramsar Convention is an international treaty signed in 1971 in Ramsar, Iran, aimed at conserving wetlands and promoting their sustainable use. India became a signatory in 1982 and has progressively expanded its list of designated wetlands that meet criteria for ecological significance. Designation as a Ramsar Site recognises a wetland’s importance for biodiversity, water security, climate resilience, and ecosystem services.
Newly Designated Ramsar Sites
1. Patna Bird Sanctuary (Uttar Pradesh)
- Location & Ecosystem: Situated in eastern Uttar Pradesh, the sanctuary comprises freshwater marshes, grasslands, and woodland patches, embedded within an agricultural landscape.
- Biodiversity Value: The mosaic of habitats supports rich biodiversity and has been recognised as an Important Bird and Biodiversity Area (IBA) by BirdLife International.
- Flora and Fauna:
- Around 178 species of birds, including migratory and resident species
- Approximately 252 species of plants
- Ecological Significance: The wetland acts as a critical refuge for avifauna, contributing to regional ecological stability and supporting ecosystem services such as groundwater recharge.
2. Chhari-Dhand Wetland (Gujarat)
- Location & Nature: Located in the Kutch region of Gujarat, Chhari-Dhand is a seasonal saline wetland, positioned between the Banni grasslands and the salt flats of Kutch.
- Avifaunal Importance: It serves as an important wintering and stopover site for migratory waterfowl.
- Key Species Supported:
- Critically endangered sociable lapwing
- Vulnerable common pochard
- Annual congregation of common cranes (Grus grus)
- Ecological Role: The wetland sustains unique saline ecosystem biodiversity and supports pastoral and local livelihoods indirectly.
India’s First Indigenous Hydrogen Fuel Cell Vessel

- 15 Dec 2025
In News:
India has launched its first fully indigenous hydrogen fuel cell passenger vessel in Varanasi, marking a major milestone in the country’s transition to clean and sustainable inland water transport. The vessel was flagged off at Namo Ghat by the Union Minister for Ports, Shipping and Waterways, Sarbananda Sonowal, symbolising India’s commitment to green mobility and low-carbon infrastructure.
Technological Features of the Vessel
- The vessel has been designed and built indigenously by Cochin Shipyard Limited in collaboration with the Inland Waterways Authority of India (IWAI), which also owns the vessel.
- At its core is a Low-Temperature Proton Exchange Membrane (LT-PEM) fuel cell system. A Proton Exchange Membrane Fuel Cell (PEMFC) generates electricity through an electrochemical reaction between hydrogen and oxygen, without combustion. The only by-product of this process is water vapour, making it a near-zero emission technology.
- The vessel operates through a hybrid energy system, integrating:
- Hydrogen fuel cells
- Battery storage
- Solar power support
This design ensures energy efficiency, operational reliability, and reduced dependence on fossil fuels.
Strategic Policy Alignment
The launch aligns with India’s long-term maritime and climate strategies, including:
- Maritime India Vision 2030 (MIV 2030) – Focuses on sustainable port and waterways infrastructure, digitalisation, and alternative fuels.
- Maritime Amrit Kaal Vision 2047 (MAKV 2047) – Envisions India as a global maritime leader with green and smart transport systems.
It also contributes to India’s broader commitment to achieve net-zero emissions by 2070 by promoting clean energy in transport.
Significance for Inland Water Transport
The introduction of a hydrogen-powered vessel positions Varanasi at the forefront of India’s green waterways initiative. Inland waterways are being promoted as an energy-efficient and cost-effective mode of transport, and this step adds a sustainability dimension.
Key impacts include:
- Reduction in carbon emissions and air pollution in river cities
- Noise-free and pollution-free passenger travel
- Improved connectivity for pilgrims and tourists along the ghats
- Contribution to decongesting roads and lowering logistics costs
- Demonstration of indigenous clean technology leadership
Wider Environmental and Economic Implications
Hydrogen fuel cell technology is emerging as a critical pillar in India’s clean energy transition. Its use in inland waterways demonstrates sectoral decarbonisation beyond road and rail transport.
The project showcases:
- Growth of green shipbuilding capability in India
- Promotion of innovation-driven infrastructure
- Integration of renewable energy with mobility solutions
It also strengthens India’s position in the evolving global market for green maritime technology.
Champions of the Earth Award

- 15 Dec 2025
In News:
Environmental governance is increasingly central to global sustainable development discourse, particularly amid the escalating triple planetary crisis- climate change, biodiversity loss, and pollution. In this context, the Champions of the Earth Award by the United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP) stands as the world’s highest environmental honour. The 2025 award to Supriya Sahu, Additional Chief Secretary of Environment, Climate Change and Forests, Tamil Nadu, highlights India’s growing role in innovative and inclusive climate action.
About the Champions of the Earth Award
Instituted in 2005 by UNEP, the award recognises individuals and organisations demonstrating transformative environmental leadership. It honours trailblazers working on sustainable solutions to address global ecological challenges.
Award Categories include:
- Policy Leadership – Government leaders shaping environmental governance
- Inspiration and Action – Individuals mobilising people and driving behavioural change (Category of Supriya Sahu)
- Entrepreneurial Vision – Innovators creating sustainable systems and technologies
- Science and Innovation – Scientific and technological pioneers
- Lifetime Achievement – Long-term contribution to environmental protection
Why Supriya Sahu Was Honoured
UNEP recognised her under “Inspiration and Action” for demonstrating how integrated governance, nature-based solutions, and low-cost climate innovations can protect vulnerable communities while reducing greenhouse gas emissions.
Her work bridges climate mitigation, adaptation, biodiversity conservation, and livelihood creation — aligning local development with global climate goals.
Key Environmental Initiatives
1. Operation Blue Mountain (2000)
- Early campaign to eliminate single-use plastics in the Nilgiris
- One of India’s pioneering local anti-plastic movements
2. Cool Roof Project
- School rooftops painted white to reflect sunlight
- Reduced indoor temperatures and improved learning conditions
- A low-cost climate adaptation model now studied globally
3. Ecosystem Restoration
- Large-scale restoration of mangroves and wetlands
- Strengthens coastal resilience against cyclones and sea-level rise
- Enhances carbon sequestration and biodiversity
4. Expansion of Forest Cover
- Creation of 65 new reserve forests
- Combines conservation with community participation
5. Green Livelihoods
- Nature-based initiatives reportedly generated ~2.5 million green jobs
- Demonstrates how climate action can drive inclusive economic growth
Global and National Context
India has previously been recognised under this award, reflecting growing global acknowledgement of its environmental leadership. Notable past recipients include:
- Madhav Gadgil (2024)
- Narendra Modi (2018)
- Cochin International Airport (2018) – For solar-powered airport model
- Afroz Shah (2016) – For beach clean-up movement
This pattern indicates India’s expanding soft power in environmental diplomacy.
Western Tragopan
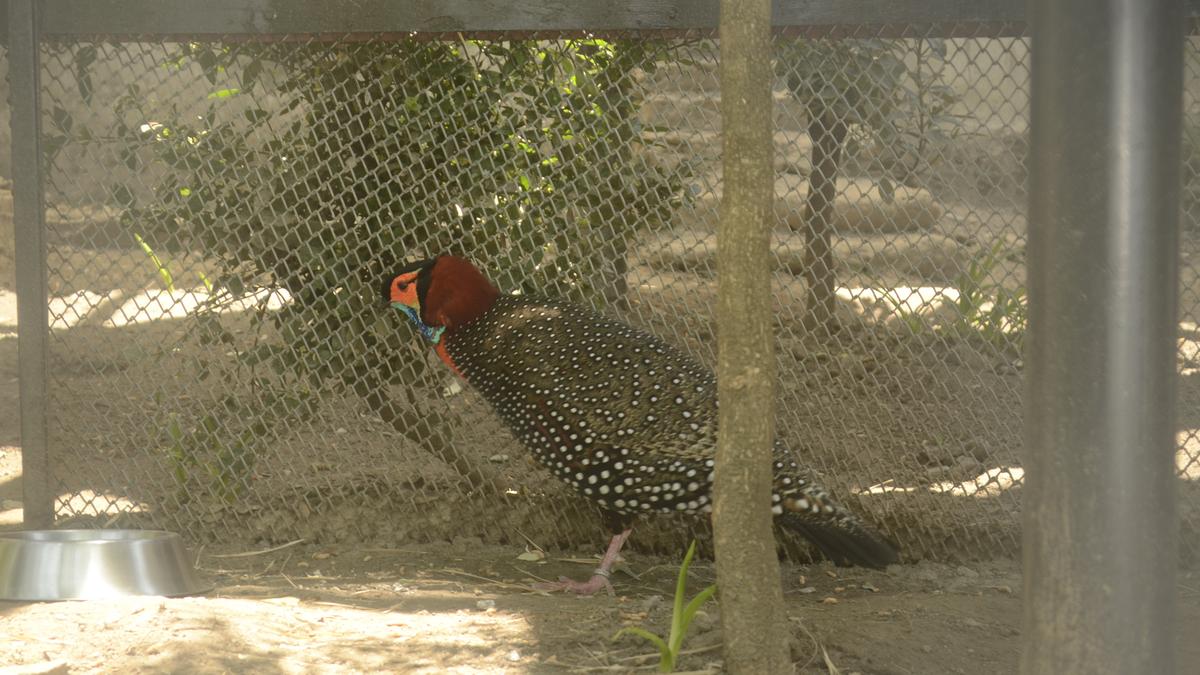

- 14 Dec 2025
In News:
Recent studies indicate that suitable habitats for the Western Tragopan exist in Jammu & Kashmir, but habitat fragmentation and human disturbance continue to threaten the species. Meanwhile, a captivebreeding programme at Sarahan Pheasantry (Himachal Pradesh) has helped stabilise its numbers.
About Western Tragopan
- Common Name: Western Tragopan
- Scientific Name:Tragopan melanocephalus
- Also known as Jujurana or “King of Birds”
- State Bird of Himachal Pradesh
- One of the world’s rarest pheasants
Habitat & Distribution
- Found in the Western Himalayas at elevations of 2,400–3,600 metres
- Prefers:
- Moist temperate forests
- Dense undergrowth
- Ringal bamboo thickets
- Rhododendron shrubs
- Conifer forests
Key Strongholds
- Great Himalayan National Park (Himachal Pradesh)
- Kazinag and Limber areas in Jammu & Kashmir
- Pockets in Uttarakhand and northern Pakistan
Populations now survive only in small, fragmented pockets.
Population Status
- IUCN estimates 3,000–9,500 mature individuals remain
- Entire global population forms a single fragile sub-population
- Around a quarter of the population occurs in the Western Himalayas and northern Pakistan
Key Characteristics
Male
- Velvet-black head
- Bright crimson breast
- White-spotted body
- Distinctive blue and orange facial wattles used in courtship displays
Female
- Smaller, brown and camouflaged
- Immature males resemble females
Behaviour
- Ground-dwelling and shy
- Most active at dawn and dusk
- Diet includes berries, seeds, buds, shoots, and insects
Breeding
- Breeding season: May–June
- Lays 3–5 eggs in well-hidden nests
Threats
- Habitat loss due to forest degradation
- Fragmentation of temperate forests
- Human disturbance (grazing, tourism, infrastructure)
- Hunting and poaching
These pressures reduce safe breeding areas and isolate populations.
Conservation Status
- Listed as Vulnerable on the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) Red List
- Recognised as a flagship and indicator species of high-altitude forest ecosystem health
Conservation Efforts
- Captive Breeding: The Sarahan Pheasantry in Himachal Pradesh has successfully bred 40+ Western Tragopans, creating an insurance population against extinction.
- Habitat Protection: Protected areas like Great Himalayan National Park and forest reserves in J&K are critical for wild populations.
However, reintroduction into natural habitats remains challenging due to ongoing habitat disturbance.
Global Environment Outlook–7 (GEO-7), 2025

- 13 Dec 2025
In News:
The 7th edition of the Global Environment Outlook (GEO-7) was released by the United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP) during its session in Nairobi, warning that the world is far off track in meeting climate and environmental goals.
About Global Environment Outlook (GEO)
- The Global Environment Outlook is UNEP’s flagship assessment of the state of the global environment, future risks, and policy solutions. It provides scientific evidence for international environmental decision-making.
Key Findings of GEO-7
Rising Greenhouse Gas Emissions
- Global GHG emissions have grown ~1.5% annually since 1990
- 2024 recorded temperatures around 1.55°C above pre-industrial levels
- Intensifying heatwaves, floods, droughts, and extreme events
Biodiversity Loss
- 1 million species (out of ~8 million) face extinction
- 20–40% of global land is degraded
- Over 3 billion people are affected by land degradation
Economic Costs of Environmental Damage
- Climate-related disasters cost ~USD 143 billion annually
- Air pollution caused USD 8.1 trillion in health damages in 2019 (≈6% of global GDP)
- 9 million deaths per year linked to pollution
Plastic Pollution Crisis
- About 8 billion tonnes of plastic waste pollute ecosystems
- Toxic chemical exposure leads to ~USD 1.5 trillion annual health losses
Projected Impacts if Current Trends Continue
- Temperature thresholds: Likely to exceed 1.5°C in early 2030s and 2°C by 2040s
- Economic decline: Global GDP may fall 4% by 2050 and 20% by 2100
- Loss of fertile land: Equivalent to losing a country-sized fertile area annually
- Food insecurity: Per capita food availability may drop 3.4% by 2050
- Rising hunger, poverty, displacement, and conflict risks
GEO-7 Recommended Transformative Actions
Economy & Finance
- Move beyond GDP to wealth-based indicators
- Price environmental externalities
- Invest in decarbonization, ecosystem restoration, sustainable agriculture
- USD 8 trillion/year investment needed till 2050
- Could generate USD 20 trillion annual benefits by 2070
Materials & Waste
- Promote circular economy models
- Transparent product design and recycling chains
- Shift from linear consumption to regenerative systems
Energy Transition
- Rapid decarbonization of energy
- Improve energy efficiency
- Secure sustainable critical mineral supply chains
- Reduce air pollution → 9 million premature deaths avoidable by 2050
Food Systems
- Promote sustainable diets
- Reduce food loss and waste
- Improve agricultural efficiency
- Could reduce undernourishment by ~200 million people
Ecosystem Protection
- Scale up ecosystem restoration
- Use Nature-based Solutions (NbS) for adaptation
- Stronger mitigation and biodiversity conservation policies
Collaborative & Integrated Governance
- Solutions must involve governments, private sector, civil society, academia, Indigenous communities
- Policies across sectors must be implemented together, not in isolation
About UNEP
- Established in 1972 after the Stockholm Conference
- Headquarters: Nairobi, Kenya
- Leading global authority on environmental issues
- Major reports include:
- Emissions Gap Report
- Adaptation Gap Report
- Global Environment Outlook
- Frontiers Report
African Penguin
- 13 Dec 2025
In News:
A recent scientific study reported that over 60,000 African penguins died of starvation between 2004 and 2011 after a sharp collapse in sardine stocks off southern Africa. The die-off was particularly severe around Dassen Island and Robben Island.
About the African Penguin
- Common Name: African Penguin
- Scientific Name:Spheniscus demersus
- One of the 18 penguin species globally
- Among the smallest penguins and strong swimmers
- Flightless, adapted to marine life
Distinctive Features
- Black facial mask and unique black chest-spot patterns (like fingerprints)
- Pink glands above the eyes help regulate body temperature (become pinker when hot)
Habitat & Distribution
- Found along the coasts of Namibia and South Africa
- Lives on sandy beaches and rocky shores, unlike Antarctic penguins
- Usually forages within 40 km of the shore
- Comes ashore for breeding, moulting, and resting
Breeding & Life Cycle
- Traditionally breeds in burrows dug into guano, which protect from heat
- Average lifespan: ~20 years in the wild
Annual Moult (Critical Survival Phase)
- Occurs once a year and lasts about 21 days
- Penguins remain on land and cannot enter the sea to feed
- They must build fat reserves before moulting
- During moult, they can lose nearly 50% of body mass
- After moulting, they need reliable food supply to regain strength
What Caused the Mass Starvation?
The study linked penguin deaths to collapse of sardine populations, their primary prey.
Key Findings
- Nearly 62,000 penguins died between 2004–2011
- Sardine stocks fell to ~25% below peak abundance
- Fishing pressure was extremely high, especially west of Cape Agulhas
- Exploitation rates peaked at 80% in 2006
- Large sardine catches occurred close to penguin colonies, reducing food access
Impact on Penguins
- Birds failed to build fat reserves before moult
- Post-moult weakened condition reduced their ability to catch prey
- Increased mortality due to starvation
Role of Climate Change
- Climate change is altering ocean temperatures and currents
- This affects distribution and availability of sardines
- Combined effect of overfishing + climate change intensifies food scarcity
Conservation Status
- Listed as Critically Endangered by the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN)
- Reclassified from Endangered to Critically Endangered in 2024
Conservation Concerns & Measures Needed
- Need for better fisheries management near penguin foraging areas
- Protection of key feeding grounds
- Long-term recovery of sardine biomass
- International conservation efforts under agreements like the African-Eurasian Migratory Waterbirds Agreement
Horn-Eyed Ghost Crab

- 10 Dec 2025
In News:
Researchers recently documented unusual predatory behaviour of a horn-eyed ghost crab at Rushikonda Beach, Visakhapatnam, drawing attention to the ecological role of ghost crabs in coastal ecosystems.
Taxonomy
- Belongs to the genus Ocypode
- Commonly known as ghost crabs due to their pale colour and rapid, almost “vanishing” movements on beaches
Habitat
- Found primarily in sandy intertidal zones
- Builds deep burrows above the high-tide line on beaches
- Most active during dawn, dusk, and night, avoiding daytime heat
Distribution
- Occurs widely across the Indo-Pacific region
- Range extends from the east coast of Africa to the Philippines, and from Japan to the Great Barrier Reef
- Absent in the Red Sea
- Six species of ghost crabs have been recorded along the Indian coastline
Physical and Behavioural Features
- Pale, sand-coloured body helps in camouflage against predators
- Possesses long legs adapted for fast sideways running
- The term “horn-eyed” refers to eye stalks that may appear elongated or horn-like
- Known for agile hunting and burrow-dwelling behaviour
Feeding Habits
Although traditionally considered scavengers, recent observations show active predation.
Diet includes:
- Clams
- Snails
- Marine worms
- Isopods
- Shrimps
- Insects
- Other crabs, including small hermit crabs
This highlights their role not just as scavengers but also as important predators in beach ecosystems.
Ecological Role
Horn-eyed ghost crabs are considered:
- Keystone species in sandy shore ecosystems
- Bio-indicators of coastal health
Why important?
- Their burrowing activity aerates sand and influences sediment structure
- Their feeding controls populations of smaller invertebrates
- Healthy ghost crab populations generally indicate less-disturbed beaches
Threats
Ghost crabs are sensitive to environmental disturbances. Major threats include:
- Coastal pollution
- Beach tourism and human trampling
- Changes in sediment patterns due to erosion or construction
- Rising sea temperatures
- Altered tidal cycles due to climate change
Such pressures may force them to shift habitats in search of food and suitable burrowing sites.
Dolomedes indicus
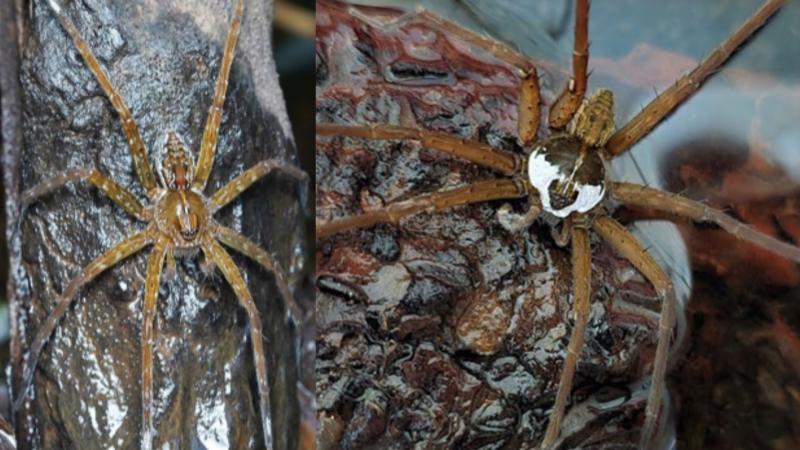

- 10 Dec 2025
In News:
Researchers have discovered a new spider species, Dolomedes indicus, in the evergreen rainforests of the Western Ghats, specifically in Wayanad district, Kerala.
What is Dolomedes indicus?
- Dolomedes indicus is a newly identified species of spider belonging to the genus Dolomedes, commonly known as raft spiders or fishing spiders.
- This discovery marks the first recorded member of the Dolomedes genus in India.
Genus Dolomedes (Raft/Fishing Spiders)
- Members of this genus are known for their semi-aquatic lifestyle.
- Unlike web-building spiders, they are active hunters.
- They are typically found near freshwater streams, ponds, and wetlands.
Habitat
- Found in evergreen forest streams of the Western Ghats, a global biodiversity hotspot.
- Prefers cool, clean, shaded freshwater habitats under dense forest canopies.
- Its presence indicates pristine stream ecosystems with minimal disturbance.
Behaviour and Hunting Strategy
Dolomedes indicus is a semi-aquatic predator that:
- Uses surface tension of water to stand and move on water surfaces
- Detects vibrations caused by insects or small aquatic animals struggling in water
- Swiftly lunges across the water to capture prey
- Is capable of swimming and diving to escape predators or catch prey
This makes it ecologically different from typical web-dependent house spiders.
Physical Characteristics
- Males: Identified by a distinctive snow-white marking extending from the face to the middle of the back
- Females: Larger in size and greenish-brown, helping them camouflage against mossy rocks and streamside vegetation
Sexual dimorphism (difference in appearance between males and females) is clearly visible.
Ecological Importance
- Being highly sensitive to environmental changes, Dolomedes indicus may serve as an indicator species
- Its survival depends on:
- Clean freshwater
- Stable forest canopy cover
- Undisturbed stream ecosystems
Thus, its presence can help scientists monitor freshwater ecosystem health and assess the impact of habitat degradation.
Significance of Discovery
- Highlights the rich but understudied biodiversity of the Western Ghats
- Expands the known geographical range of the Dolomedes genus
- Emphasizes the importance of conserving freshwater habitats within forest ecosystems
BNHS to Release Critically Endangered Vultures in Assam
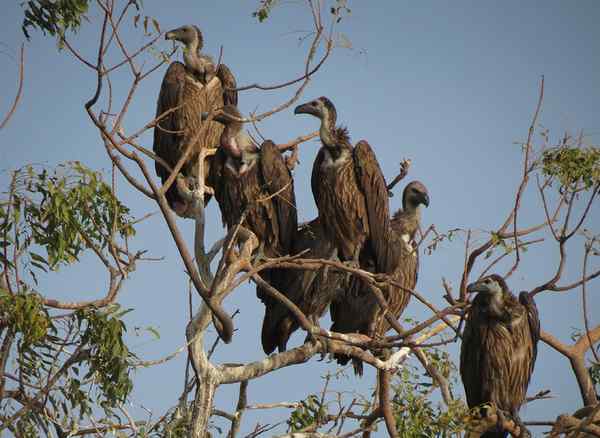

- 08 Dec 2025
In News:
The Bombay Natural History Society (BNHS) is set to release six captive-bred vultures-three males and three females-into the wild in Assam in January 2026. The birds belong to two critically endangered species: the Slender-billed Vulture and the White-rumped Vulture. The release will take place in Kamrup and Biswanath districts, areas within the natural range of these species and close to Kaziranga National Park.
This initiative is part of India’s long-term vulture recovery programme, supported by the Assam Forest Department and the Royal Society for the Protection of Birds (RSPB). BNHS has bred over 800 vulturesacross its conservation breeding centres and has worked for more than 15 years to prepare suitable habitats and community awareness for reintroduction.
Before release, the vultures will undergo a soft-release acclimatisation period of at least three months, allowing them to adapt to natural surroundings and observe other scavengers. Vultures are social birds, mature after about five years, and can live up to 50–60 years.
Slender-billed Vulture (Gyps tenuirostris)
- IUCN Status: Critically Endangered
- Distribution: Assam, Gangetic plains, Nepal, Bangladesh, Myanmar, Cambodia
- Habitat: Open landscapes, riverine areas, tall trees near human settlements
- Identification: Slender narrow bill, dark head, long bare neck, grey plumage
- Breeding: Slow breeder; lays one egg per clutch
- Diet: Carrion, often feeds with other vultures
- Threats: Veterinary drug poisoning (especially diclofenac), habitat loss
Population estimates suggest fewer than 1,000 mature individuals remain globally.
White-rumped Vulture (Gyps bengalensis)
- IUCN Status: Critically Endangered
- Distribution: Indian subcontinent, often near villages and towns
- Habitat: Plains, open country, nesting on tall trees
- Identification: Dark body, distinct white rump patch, white neck ruff
- Breeding: October–March season, one egg
- Diet: Carrion; commonly feeds in mixed-species groups
This species has suffered one of the fastest bird population crashes in history, primarily due to diclofenac, a veterinary anti-inflammatory drug toxic to vultures.
Vultures in India - Key Facts
India hosts 9 vulture species, including:
- Critically Endangered: White-rumped, Slender-billed, Indian (Long-billed), Red-headed Vulture
- Endangered: Egyptian Vulture, Himalayan Griffon (status often regionally assessed)
- Others: Griffon Vulture, Bearded Vulture, Cinereous Vulture
Why Vultures Matter
Vultures are vital scavengers that prevent the spread of diseases by rapidly disposing of carcasses. Their decline has led to ecological imbalance and increased feral dog populations, raising risks of rabies and other zoonotic diseases.
Conservation Measures in India
- Ban on veterinary diclofenac (2006)
- Vulture Safe Zones across several states
- Captive breeding programmes led by BNHS and state forest departments
- Community awareness and monitoring
The 2026 release in Assam marks an important step toward restoring these keystone scavengers to India’s ecosystems.
Antarctic Ozone Hole: Early Closure in 2025
- 07 Dec 2025
In News:
In 2025, the Antarctic ozone hole closed earlier than usual, with closure recorded on 1 December, marking one of the smallest ozone holes in the past five years. The early closure has been seen as a strong sign of long-term recovery of the ozone layer, despite the backdrop of record global temperatures.
What is the Antarctic Ozone Hole?
- The Antarctic ozone hole refers to the seasonal thinning of the stratospheric ozone layer over Antarctica during the austral spring (September–November). Scientists define the ozone hole as regions where ozone concentration falls below 220 Dobson Units (DU).
- It is not a literal hole but an area of severely reduced ozone levels in the stratosphere, first discovered in 1985.
Why Does the Ozone Hole Form Over Antarctica?
Several unique atmospheric conditions combine to intensify ozone depletion in the region:
1. Polar Vortex:During the Antarctic winter, a strong polar vortex traps cold air, preventing mixing with warmer air from lower latitudes.
2. Polar Stratospheric Clouds (PSCs):Extreme cold leads to PSC formation. These clouds facilitate chemical reactions that activate chlorine and bromine from human-made chemicals such as chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs) and halons.
3. Return of Sunlight:When sunlight returns in spring, it triggers rapid chemical reactions that destroy ozone molecules, producing the ozone hole.
2025 Ozone Hole Highlights
- The ozone hole reached a maximum area of just over 21 million sq km, significantly smaller than the record 29 million sq km in 2006.
- It closed earlier than usual, marking the second consecutive year of relatively small ozone holes.
- Scientists attribute this trend to declining levels of ozone-depleting substances (ODS) and favourable atmospheric conditions.
What is Ozone?
Ozone (O?) is a gas made of three oxygen atoms and exists in two layers:
|
Layer |
Type |
Role |
|
Stratosphere (15–30 km) |
Good ozone |
Absorbs harmful UV radiation |
|
Troposphere (near surface) |
Bad ozone |
Pollutant, contributes to smog |
Global average ozone concentration is about 300 DU.
Impacts of Ozone Depletion
- Increased UV-B radiation causes skin cancer, cataracts, and immune suppression
- Damages crops, forests, and marine phytoplankton
- Alters atmospheric circulation patterns in the Southern Hemisphere
Global Response
- Montreal Protocol (1987):A landmark global treaty phasing out ozone-depleting substances. It is the first UN treaty with universal ratification.
- Kigali Amendment (2016):Targets hydrofluorocarbons (HFCs)—not ozone-depleting but potent greenhouse gases.
These actions are estimated to prevent up to 0.5–1°C of global warming by 2050.
Outlook
If current trends continue, scientists estimate ozone levels could return to pre-1980 levels around:
- 2040 globally
- 2045 in the Arctic
- 2066 in Antarctica
World Soil Day (WSD)

- 07 Dec 2025
In News:
World Soil Day (WSD) is observed annually on 5 December to raise global awareness about the importance of healthy soils and to promote the sustainable management of soil resources. The observance is supported by the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) of the United Nations and endorsed by the UN General Assembly (UNGA).
History and Background
- The idea of a global day dedicated to soil conservation was first proposed in 2002 by the International Union of Soil Sciences (IUSS).
- FAO promoted the initiative, and in 2013 the FAO Conference endorsed the proposal and sought formal UN recognition.
- The UN General Assembly officially designated 5 December 2014 as the first World Soil Day.
Theme for 2025
“Healthy Soils for Healthy Cities”
The 2025 theme highlights the critical role of urban soils in supporting sustainable cities. It shifts attention from rural agriculture to the often-overlooked soils beneath urban environments.
Importance of Healthy Soils
Soils are a life-sustaining resource essential for:
- Food production
- Water filtration and groundwater recharge
- Carbon storage and climate regulation
- Biodiversity support
- Nutrient cycling
In urban areas, healthy soils help mitigate:
- Urban heat island effect
- Flooding by acting as natural water sponges
- Pollution through filtration of contaminants
- Food insecurity through urban agriculture
Extent of Soil Degradation
Despite their importance, soils are under severe stress:
- The FAO estimates that nearly one-third of the world’s soils are degraded.
- Urban soils face compaction, contamination, and sealing by concrete, reducing their ecological functions.
- Unsustainable agricultural practices, deforestation, and land misuse further worsen soil erosion and nutrient depletion.
Global Soil Conservation Efforts
1. Global Soil Partnership (GSP):An FAO-led initiative aimed at improving soil governance and promoting sustainable soil management worldwide.
2. United Nations Convention to Combat Desertification (UNCCD):Works to prevent land degradation and achieve Land Degradation Neutrality (LDN) by 2030.
India’s Soil Conservation Initiatives
India has launched multiple programmes to protect and restore soil health:
- Soil Health Card Scheme: Provides farmers with soil nutrient analysis to encourage balanced fertiliser use.
- Paramparagat Krishi Vikas Yojana (PKVY): Promotes organic farming to maintain soil fertility.
- Pradhan Mantri Krishi Sinchayee Yojana (PMKSY): Improves water management and reduces soil erosion.
- Watershed Development Programmes: Enhance soil moisture and prevent land degradation.
- MGNREGA land works: Support soil and water conservation at the local level.
- Smart Cities Mission: Encourages green infrastructure, open spaces, and soil-friendly urban planning.
Great Nicobar Crake

- 03 Dec 2025
In News:
Great Nicobar Island, the southernmost island of India in the Andaman & Nicobar archipelago, is emerging as a major hotspot of biological discoveries. Recent scientific studies from the area identified for a mega infrastructure development project have highlighted the island’s exceptional biodiversity and high endemism.
Since 2021, researchers have reported nearly 40 new species from Great Nicobar, with a significant number formally described only in the last few years. These findings underline the island’s ecological sensitivity.
Key Recent Discoveries
1. New Wolf Snake – Lycodonirwini
- Recently described species of wolf snake
- Known from only four records so far
- Named in honour of Steve Irwin
- Found in a very restricted range on Great Nicobar’s east coast
- Scientists recommend listing it as Endangered under IUCN Red List criteria due to:
- Rarity
- Limited distribution
- Habitat vulnerability
2. Great Nicobar Crake (Genus: Rallina)
A rare forest rail photographed only a handful of times over more than a decade.
Taxonomic Status
- Belongs to the genus Rallina (crakes/forest rails)
- May represent a new species to science based on distinct morphological traits
- Very little known about its distribution, population size, or ecology
Habitat
- Dense tropical rainforest undergrowth
- Associated with wet forest floors, streams, bamboo, cane, and vine thickets
Behaviour
- Ground-dwelling, shy and elusive
- Rarely flies; moves swiftly through vegetation
- Feeds on insects and small invertebrates
Conservation Note
- Not yet officially assessed by IUCN
- Likely to fall under Data Deficient or a threatened category if found to be endemic with a small range
Ecological & Conservation Significance
- Presence of range-restricted species indicates fragile ecosystems
- Frequent discoveries suggest large gaps in scientific knowledge
- Highlights the importance of:
- Long-term ecological monitoring
- Rigorous Environmental Impact Assessments (EIA)
- Habitat protection in the face of large infrastructure projects
Great Nicobar is considered one of the last extensive undisturbed tropical rainforest regions in India, making it critical for biodiversity conservation.
Bioremediation
- 03 Dec 2025
In News:
Human waste is leading to a world where access to clean air, water and soil is becoming increasingly difficult. The solution is two-pronged — reduce waste and clean up the waste already made.
What is bioremediation?
Bioremediation refers to the use of living organisms to clean up environmental pollution. The term literally means “restoring life through biology.” It involves harnessing microorganisms such as bacteria, fungi, algae, and plants to degrade, transform, or neutralise harmful contaminants in soil, water, and air.
These organisms use pollutants like oil, pesticides, plastics, and some heavy metals as sources of energy or nutrients. Through natural metabolic processes, they break down toxic substances into less harmful by-products such as water, carbon dioxide, and organic acids. In certain cases, microbes can also convert toxic metals into less mobile or less bioavailable forms, reducing their environmental impact.
Types of Bioremediation
Bioremediation is broadly classified into two types:
- In situ bioremediation involves treating contamination at the original site without removing soil or water. For example, oil-degrading bacteria may be applied directly to an oil spill.
- Ex situ bioremediation involves removing contaminated material to a controlled environment for treatment and returning it once cleaned. This is often used for heavily polluted soil or wastewater.
The effectiveness of bioremediation depends on factors such as temperature, pH, oxygen availability, and nutrient levels, which influence microbial growth and activity.
Modern Advances
Modern bioremediation combines traditional microbiology with advanced biotechnology. Scientists now use genetic and molecular tools to identify microbes with specific pollutant-degrading abilities. In some cases, genetically modified (GM) microorganisms are being designed to break down persistent pollutants like certain plastics or petroleum residues that natural microbes struggle to degrade.
Nanotechnology is also being explored, such as absorbent materials that help collect oil or pollutants before microbial treatment.
Why Bioremediation is important for India
India faces severe environmental challenges due to rapid industrialisation, urbanisation, and poor waste management. Many rivers receive untreated sewage and industrial effluents, while agricultural soils are affected by pesticide residues and heavy metals. Oil spills, landfill leachates, and industrial waste further degrade ecosystems and threaten public health.
Traditional remediation methods are often expensive, energy-intensive, and may generate secondary pollution. Bioremediation offers a cost-effective, scalable, and environmentally friendly alternative, especially for a country with vast contaminated areas and limited remediation resources.
India’s rich biodiversity provides an advantage, as indigenous microbes adapted to local climatic conditions can be more effective than imported strains.
Status of Bioremediation in India
Bioremediation is gradually gaining ground in India, though largely at pilot and project levels. Government-supported research institutions and universities are working on microbial solutions for treating sewage, industrial effluents, oil spills, and contaminated soils.
The Department of Biotechnology (DBT) has supported clean technology initiatives, and research organisations such as CSIR laboratories and IITs have developed microbial formulations and innovative materials for environmental cleanup. Start-ups are also entering the sector with products for wastewater and soil treatment.
Bioremediation aligns with national initiatives such as NamamiGange, Swachh Bharat Mission, and sustainable waste management efforts.
Advantages
Bioremediation is considered environmentally friendly because it relies on natural biological processes rather than harsh chemicals. It is generally cost-effective, requires less heavy infrastructure, and can offer a long-term solution, as pollutants are broken down rather than merely transferred elsewhere. It is particularly useful for treating oil contamination and organic pollutants.
Limitations and Risks
Bioremediation is not universally applicable. It works best for biodegradable pollutants, and some contaminants, particularly certain heavy metals and synthetic chemicals, may not be fully removed. The process can also be slow, sometimes taking months or years.
The use of genetically modified microorganisms raises biosafety concerns. If not properly regulated, their release into open environments could have unintended ecological impacts. There is also a need for site-specific knowledge, regulatory standards, and skilled personnel for large-scale adoption.
India’s Energy Policy in the Age of AI and Climate Change

- 02 Dec 2025
In News:
India’s energy policy is undergoing a structural transition as the rapid expansion of Artificial Intelligence (AI) and accelerating climate change reshape electricity demand, supply chains, and governance priorities. The traditional focus on access, affordability, and energy security is expanding to include decarbonisation, climate resilience, digital-era demand, and strategic autonomy, reflecting the changing contours of economic growth and technological transformation.
Key Trends Shaping India’s Energy Policy
- AI-Driven Electricity Demand: The rapid growth of AI and data centres is generating round-the-clock, gigawatt-scale electricity demand, compelling both Union and State governments to rethink renewable capacity addition, grid modernisation, and large-scale energy storage planning.
- Climate Change Pressures:Increasing heatwaves, floods, and extreme weather events are pushing policymakers to decouple GDP growth from carbon-intensive energy, aligning energy policy with India’s 2070 Net Zero commitment.
- Global Green Transition Dynamics:Rising dependence on critical minerals, concentration of renewable manufacturing, and friend-shoring strategies are influencing India’s industrial and strategic energy choices.
- Shift in Energy Governance:Energy governance is moving from a resource-centric approach to a systemic, multi-sectoral framework integrating climate policy, digital infrastructure, industrial strategy, and geopolitics.
Major Emerging Trade-offs
- Coal Economy vs Clean Energy Transition: Coal continues to support livelihoods of nearly 3.5 lakh workers, contributes significantly to state revenues in Jharkhand, Odisha, and Chhattisgarh, and underpins railway freight earnings. Simultaneously, India hosts six of the world’s ten most polluted cities (2024), creating a sharp tension between employment security and climate commitments.
- China-Dominated Green Supply Chains vs Strategic Autonomy:China controls around 80% of global solar module production, 95% of polysilicon and wafers, and 80% of lithium-ion battery processing. While imports from China enable rapid and low-cost renewable deployment, they increase strategic vulnerability, tariff exposure, and supply-chain risks.
- AI Data Centres vs Renewable Infrastructure Constraints:Proposed AI hubs by global and Indian firms demand 24×7 clean power. However, India’s grid-scale storage, pumped hydro capacity, and inter-state transmission networks remain inadequate, pushing some states to extend thermal power generation, thereby undermining decarbonisation goals.
Structural Governance Challenges
- Fragmented Institutional Framework:Energy governance is dispersed across multiple ministries—Power, New and Renewable Energy, Coal, Mines, and Commerce—with no single coordinating authority.
- Policy Incoherence:Industrial incentives promote data-centre expansion, while grid reforms and storage deployment lag behind, creating mismatches in policy objectives.
- Centre–State Divergences:Differences over coal phase-down, land acquisition, renewable corridors, and tariff structures slow capacity addition and infrastructure rollout.
- Inadequate Financing and R&D Models:Public sector–led approaches are insufficient for capital-intensive and R&D-driven sectors such as battery storage, offshore wind, and green hydrogen.
- Weak Policy Alignment:Poor alignment persists between climate commitments, PLI schemes, and technology missions related to AI and semiconductors.
Implications for India
India faces the risk of new energy insecurity if renewable and battery supply chains remain import-dependent. Rising AI-driven electricity demand may increase reliance on fossil fuels, undermining India’s Nationally Determined Contributions (NDCs). Slow expansion of grids and storage could deter investments in AI, electric vehicles, semiconductors, and aerospace, while a poorly managed coal transition may trigger regional unemployment, fiscal stress, and political resistance. Fragmented governance could delay India’s ambition to become a global AI and advanced-technology hub.
Sujalam Bharat Summit 2025

- 30 Nov 2025
In News:
The Ministry of Jal Shakti will host the Vision for Sujalam Bharat Summit 2025 at Bharat Mandapam, New Delhi, marking a major national initiative to build a coherent, practical and cooperative water security framework for India. The Summit forms part of NITI Aayog’s six thematic Departmental Summits, envisaged by the Prime Minister to bring together Central and State governments along with junior and field-level cadres for solution-oriented governance.
Objectives and Approach
The Summit aims to accelerate water sustainability through:
- Evidence-based policymaking
- Sectoral reforms
- Cooperative federalism in water governance
It adopts a whole-of-government approach, bridging the gap between policy formulation and on-ground implementation, and aligning national priorities with State- and community-level action.
Thematic Areas Covered
The Vision for Sujalam Bharat process encompasses six critical thematic areas:
- Rejuvenation of Rivers and Springs: Focus on Aviral (continuous) and Nirmal (clean) Dhara through spring-shed management, catchment protection, wetland restoration, riverfront development, and community-led river stewardship.
- Greywater Management and Reuse: Promotion of circular water use via pricing and financing models, nature-based solutions, septage management, and reuse in domestic, industrial and urban sectors.
- Technology-driven Water Management: Deployment of AI-based monitoring, micro-irrigation, leak detection, loss reduction, and precision agriculture to enhance demand-side efficiency.
- Water Conservation and Groundwater Recharge: Managed aquifer recharge, revival of traditional water systems, community-led groundwater governance, and behavioural change aligned with the LiFE (Lifestyle for Environment) initiative.
- Sustainable Drinking Water Supply: Emphasis on source sustainability planning, climate-resilient infrastructure, community-based operations and maintenance (O&M), and digital governance tools.
- Community & Institutional Engagement: Empowerment of Panchayati Raj Institutions (PRIs), Self-Help Groups (SHGs), frontline workers, and local bodies, alongside stronger inter-departmental convergence.
Consultative Process and Key Outcomes
Between September and October 2025, the Ministry conducted six thematic workshops, engaging over 2,800 participants from across States/UTs, Central ministries, technical institutions, PRIs, NGOs, SHGs and field-level officials.
Based on these consultations, five national priorities were identified:
- Strengthening source sustainability
- Scaling groundwater recharge
- Expanding modern and nature-based solutions
- Revitalising community institutions
- Enhancing inter-departmental convergence
Significance
- Provides a national roadmap for water-secure and climate-resilient India
- Integrates rural–urban water management, sanitation, irrigation efficiency and drinking water security
- Encourages community ownership of water assets for long-term sustainability
- Strengthens alignment between strategy and execution through cooperative federalism
Aravalli Hills
- 28 Nov 2025
In News:
The Supreme Court of India has accepted the recommendations of a Union Environment Ministry appointed committee on a uniform definition of the Aravalli Hills and Ranges, with the stated objective of restricting mining, prohibiting activity in core/inviolate areas, and enabling sustainable mining practices. The decision follows long-standing concerns over rampant legal and illegal mining in the Aravalli region.
Background
- The Aravalli Hills have faced decades of degradation due to mining and construction.
- In May 2024, the Supreme Court directed the Centre to evolve a uniform definition of the Aravallis, as the absence of clarity hindered effective regulation.
- Historically, the Forest Survey of India (FSI) used a 3-degree slope criterion (since 2010) to delineate Aravalli hills.
- A technical sub-committee (2024) later proposed identifying Aravalli hills as landforms with a minimum slope of 4.57 degrees (8%) and height of at least 30 m, which would have covered around 40% of the range.
New Definition Accepted by the Supreme Court
- Any landform with an elevation of 100 metres or more above local relief, along with its slopes and adjacent areas, will be considered part of the Aravalli Hills.
- As per internal FSI assessments:
- Only 1,048 hills (≈8.7%) out of over 12,000 hill features in Rajasthan meet the 100 m height criterion.
- Consequently, over 90% of the Aravalli landscape would fall outside the new definition.
Ecological Significance of the Aravalli Range
- The Aravalli Range stretches for about 692 km, from Gujarat to Delhi, via Rajasthan and Haryana; Rajasthan accounts for nearly two-thirds of its extent.
- It is the oldest mountain range in India and plays a vital role in:
- Acting as a barrier against desertification from the Thar Desert
- Regulating regional climate and air quality, especially in Delhi–NCR
- Serving as a watershed for rivers like Luni, Banas and Sabarmati
- Supporting biodiversity and wildlife corridors (e.g., Sariska–Ranthambhore)
Key Concerns with the New Definition
- Environmental impact: FSI cautioned that even low hills (10–30 m) function as crucial wind and dust barriers; their exclusion could worsen sand and dust transport toward the Indo-Gangetic plains and NCR.
- Methodological issues:
- Use of district-average slope and elevation masks the presence of local hill features.
- Comparing height above mean sea level with height above local relief leads to potential misclassification.
- Area exclusion: Several districts with known Aravalli features (e.g., Chittorgarh, Sawai Madhopur) were left out of the ministry’s Aravalli district list.
Way Forward
- While accepting the 100-m height definition, the Supreme Court has directed the Environment Ministry to prepare a Management Plan for Sustainable Mining, with technical support from the Indian Council of Forestry Research and Education (ICFRE).
- The plan aims to:
- Prevent illegal mining
- Regulate permitted mining sustainably
- Protect core/inviolate zones of the Aravalli ecosystem
African Grey Parrot

- 26 Nov 2025
In News:
RTI responses from 19 States and Union Territories reveal that State Forest Departments have no records of registered breeders or authorised pet shops dealing in the African grey parrot, despite the species being widely available in Indian pet markets. This has raised concerns about illegal and unreported exotic wildlife trade in India.
About the African Grey Parrot
- Common Name: African grey parrot
- Scientific Name: Psittacus erithacus
- Natural Range: West and Central Africa (savannas, mangroves, forest edges and clearings)
- Subspecies:
- Congo African Grey (CAG) – bright red tail
- Timneh African Grey (TAG) – maroon tail
- Distinctive Traits:
- Among the most intelligent parrots; exceptional mimicry and contextual speech
- Grey plumage, orange eyes; highly social and sensitive
- Ecological Role: Important seed disperser in African ecosystems
Conservation Status
- International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN): Endangered
- Convention on International Trade in Endangered Species of Wild Fauna and Flora (CITES): Appendix I
- Commercial international trade prohibited
- Requires individual CITES permits and strict documentation
Legal Framework for Trade in India
- Import & Breeding Requirements (for CITES Appendix I species):
- CITES import permit
- Directorate General of Foreign Trade (DGFT) import licence
- Prior approval / No-Objection Certificate from the Chief Wildlife Warden
- Breeding licence under Breeders of Species Licence Rules, 2023
- Obligation of States: Forest Departments are mandated to maintain registries of exotic species.
Humboldt Penguin
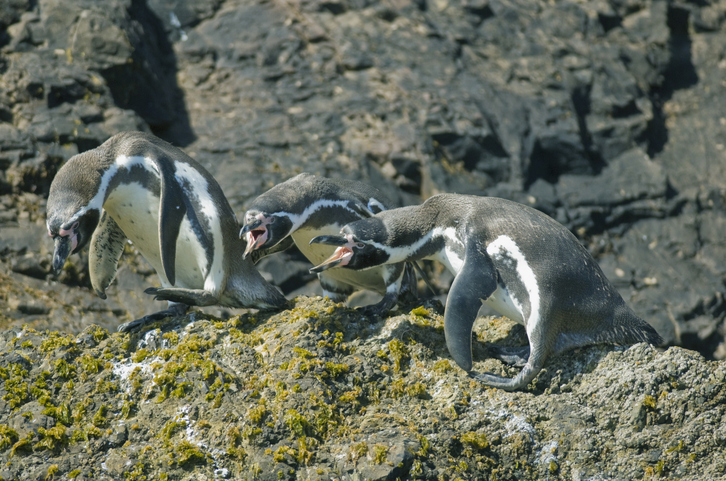

- 25 Nov 2025
In News:
Chile has reclassified the Humboldt penguin as Endangered, citing a sharp population decline along its Pacific coastline. Scientists warn that without stronger conservation measures, the species may face further decline.
About the Humboldt Penguin
- Scientific Name: Spheniscus humboldti
- Habitat Range: Coastal regions of Chile and Peru, closely associated with the Humboldt Current in the Pacific Ocean.
- Global Distribution: Nearly 80% of the world’s population is found along Chile’s coast.
- Population Trend: Declined from about 45,000 (late 1990s) to fewer than 20,000 at present.
Physical Features
- White C-shaped band extending from the eye around the head
- Distinct black breast band
- Pink fleshy patch around the eyes (thermoregulation)
Diet and Behaviour
- Diet: Carnivorous; feeds mainly on anchovies, sardines, herring, and small marine organisms.
- Nesting: Uses burrows, caves, and guano deposits; does not form large chick crèches, unlike many other penguin species.
Conservation Status
- Chile (National): Endangered
- IUCN: Vulnerable
- CITES: Appendix I (commercial trade prohibited)
Major Threats
- Overfishing & Bycatch: Competition with commercial fisheries; deaths in fishing nets
- Habitat Loss & Pollution: Coastal degradation and marine pollution
- Climate Change: Disruption of food availability and breeding cycles
- El Niño Events: Alter ocean productivity, reducing prey
- Disease: Outbreaks such as avian (bird) flu
Conservation Concerns
- Experts warn that continued pressures could push the species from Endangered to Critically Endangered.
- Reclassification highlights the need for:
- Stricter sustainable fishing regulations (industrial and small-scale)
- Protection of breeding and feeding habitats
- Integrated conservation measures beyond legal reclassification
COP30, Belém (Brazil)

- 24 Nov 2025
In News:
The 30th Conference of the Parties (COP30) to the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC) concluded in Belém, Brazil, with the formal adoption of the Belém Package, marking a shift in global climate negotiations from ambition-setting to implementation and delivery.
Key Outcomes of COP30
1. Belém Package
- A set of 29 negotiated decisions focusing on implementation, not new binding targets.
- Emphasises climate finance, adaptation tracking, just transition, gender inclusion, and cooperative action to advance the Paris Agreement goals.
2. Global Mutirão Agreement & Platform
- Prioritises cooperation, collective action and deliverability over additional mandatory targets.
- Brazil launched the Global Mutirão Platform, a digital tool to narrow the gap between climate commitments and on-ground implementation, especially in energy, finance and trade.
3. Just Transition Mechanism (Belém Action Mechanism – BAM)
- Supports cooperation and capacity-building for workers and economies transitioning away from fossil fuels.
- Limitation: No assured or new financial commitments.
4. Tracking & Implementation Architecture
- Global Implementation Tracker and Belém Mission to 1.5°C launched to assess whether national actions and NDCs align with pathways limiting warming to 1.5°C.
- Signals a growing focus on monitoring delivery rather than announcing fresh pledges.
5. Adaptation-Focused Decisions
- National Adaptation Plan (NAP) Implementation Alliance launched to accelerate adaptation planning.
- Countries agreed to triple adaptation finance by 2030 (from 2025 levels), though sources and obligations remain unclear.
- Global Goal on Adaptation (GGA):Finalised the Baku Adaptation Roadmap with 59 voluntary indicators to track adaptation progress.
6. Sectoral & Thematic Initiatives
- Belém Health Action Plan: Strengthens climate-resilient health systems based on equity, climate justice and community participation.
- Tropical Forests Forever Facility (TFFF): A payment-for-performance mechanism using satellite monitoring to reward forest conservation; aims to mobiliseUSD 125 billion (Brazil committed USD 1 billion).
- Belém 4x Pledge: Quadrupling sustainable fuel use by 2035 (hydrogen, biofuels, biogas, e-fuels); progress to be monitored annually by the IEA.
- Belém Declaration on Hunger, Poverty & People-Centred Climate Action: Signed by 43 countries + EU, prioritising vulnerable communities, adaptation, and social protection.
- Belém Gender Action Plan (GAP): Strengthens gender-responsive climate governance and women’s participation.
India’s Position at COP30
Climate Finance as a Legal Obligation
- India, along with BASIC and LMDC groups, demanded predictable, grant-based climate finance under Article 9.1 of the Paris Agreement.
- Called for a universally accepted definition of climate finance and mobilisation of the USD 1.3 trillion goal under the Baku-to-Belém Roadmap (COP29).
- Highlighted the Adaptation Gap: Developing countries may need USD 310–365 billion annually by 2035, while current flows remain around USD 26 billion.
Equity & Climate Justice
- Reaffirmed CBDR–RC (Common But Differentiated Responsibilities and Respective Capabilities).
- Opposed trade-restrictive climate measures like the EU’s CBAM, calling them discriminatory.
Adaptation Priority
- Stressed that adaptation must receive equal priority with mitigation, especially for vulnerable countries.
Major Shortcomings of COP30
- No clear fossil fuel phase-out roadmap.
- Weak progress on climate finance, with no clarity on obligations or sources.
- Ambition gap persists due to delayed NDC submissions by major emitters.
- Implementation gap remains, with limited enforcement and accountability.
- Just Transition mechanism lacks dedicated funding.
COP30 (Belém) marked a transition from pledges to implementation, strengthened adaptation tracking and thematic actions, but fell short on finance clarity and fossil fuel transitionreinforcing India’s stance on equity, climate justice, and legally binding finance commitments.
Climate Change Performance Index
- 22 Nov 2025
In News:
India slipped 13 places to rank 23rd in the Climate Change Performance Index (CCPI) 2026, released on the sidelines of COP30 at Belém, Brazil.
About the Climate Change Performance Index (CCPI)
- Published by:Germanwatch, NewClimate Institute, and Climate Action Network
- First published: 2005
- Coverage: 63 countries + EU, accounting for >90% of global GHG emissions
- Purpose: Independent assessment of countries’ climate mitigation performance
Assessment Pillars (4):
- GHG Emissions
- Renewable Energy
- Energy Use
- Climate Policy
(Top three ranks are kept vacant if no country achieves a “very high” overall score.)
CCPI 2026: Global Highlights
- Top performers: Denmark, United Kingdom, Morocco
- Lowest-ranked G20 members: China (54th), Russia (64th), United States (65th), Saudi Arabia (67th)
India’s Performance – Key Facts
- Rank:23rd (down from 10th last year)
- Score: 61.31
- Category ratings:
- GHG Emissions: Medium
- Climate Policy: Medium
- Energy Use: Medium
- Renewable Energy: Low
Why the Decline?
- Rising GHG emission trends (ranked last on emission trend indicator)
- Increasing energy consumption
- Absence of a concrete coal phase-out plan
- Reclassification from “high” to “medium” performer, as India is also among the largest producers of oil, gas and coal
India’s Positives
- Renewables growth: Nearly 14% share in total energy mix (2015–2023)
- Installed capacity:>50% of electricity capacity from non-fossil sources (≈ 256 GW)
Ratanmahal Wildlife Sanctuary
- 22 Nov 2025
In News:
A wild tiger has established a sustained presence for about nine months in Ratanmahal Wildlife Sanctuary, marking the first long-term tiger residency in Gujarat in decades. The tiger, first sighted in February 2025, is believed to have naturally dispersed from Madhya Pradesh, highlighting improving habitat connectivity and ecosystem health along the inter-state border.
About Ratanmahal Wildlife Sanctuary
- Location:Gujarat; along the Gujarat–Madhya Pradesh border (major portion within Gujarat)
- Established: March 1982
- Also Known As:Ratanmahal Sloth Bear Sanctuary (hosts the highest sloth bear population in Gujarat)
- Hydrology: Forms the catchment of the Panam River, a key river of Central Gujarat
Habitat & Vegetation
- Forest Types:
- Dry teak forests at foothills
- Mixed deciduous forests with dry bamboo brakes on the periphery
- Plateau Vegetation: Dominance of Mahuda (Mahudo) with patches of Sadad and Timru
- Key Flora: Teak, bamboo, amla, dhavdo, kakadiyo, mahuda, tanach, charoli, ber, jamun, khakhro, dudhlo
Faunal Diversity
- Mammals: Leopard, Sloth bear, Palm civet, Indian civet, Four-horned antelope
- Birds:Loten’s sunbird, Large green barbet, Yellow-cheeked tit
- Recent Addition:Tiger (Panthera tigris)
Ecological Significance of the Tiger’s Return
- Indicator Species: Tigers are apex predators; their presence signals healthy prey base, water availability, and habitat quality.
- Natural Dispersal: The tiger was not translocated; it migrated naturally from MP, aided by landscape connectivity and population pressure there.
- Contrast with Past: A tiger that reached Mahisagar (2019) did not survive due to inadequate prey—underscoring the improved conditions now at Ratanmahal.
- Monitoring: Continuous surveillance via camera traps and field teams to track movement and behaviour.
Conservation Implications
- Unique Coexistence: Gujarat now hosts all three big cats—Asiatic lion, Indian leopard, and tiger—within the same broader landscape.
- Management Challenges: Overlapping ranges demand enhanced corridor management, conflict mitigation, and community safety measures.
- Policy Signal: Validates habitat restoration, prey augmentation, and inter-state ecological linkages.
Dugong

- 21 Nov 2025
In News:
A new global report released at the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) Conservation Congress in Abu Dhabi has warned that India’s dugong populations in the Gulf of Kutch, Gulf of Mannar–Palk Bay, and Andaman & Nicobar Islands face serious long-term survival risks due to habitat degradation and human pressures.
About Dugong
- Scientific Name:Dugong dugon
- Type: Large herbivorous marine mammal
- Evolutionary Links: Closely related to manatees; distantly related to elephants
- Common Name: Sea cow (inspired ancient “mermaid” myths due to gentle behaviour)
Distribution & Habitat
- Global: Warm, shallow coastal waters of the Indian and Pacific Oceans; largest stable population near north-western Australia
- India (Major Habitats):
- Gulf of Mannar–Palk Bay
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Gulf of Kutch
- Prefer calm, shallow (<10 m) coastal waters with abundant seagrass meadows
Key Biological Features
- Size: Up to 3 m long; 300–420 kg
- Morphology: Whale-like tail fluke; paddle-shaped flippers
- Diet:Exclusively herbivorous—feeds on seagrass
- Consumption: ~ 30–40 kg of seagrass/day
- Ecological Role:
- Act as “ecosystem engineers”—natural grazing maintains healthy seagrass
- Seagrass meadows function as blue carbon sinks, aiding climate regulation
- Life History: Long-lived (up to 70 years) but very low reproductive rate (calving once every 3–7 years)
Conservation Status
- IUCN Red List:Vulnerable (declining trend since 1982)
- India:Schedule I, Wild Life (Protection) Act, 1972 (highest legal protection)
Population Status in India (Indicative)
- Gulf of Mannar–Palk Bay: ~ 150–200 individuals (largest remaining group)
- Andaman & Nicobar Islands:<50 individuals
- Gulf of Kutch:<20 individuals(Exact estimates are difficult due to turbid waters and elusive behaviour.)
Major Threats
- Habitat Loss & Seagrass Degradation: Coastal pollution, sedimentation, dredging, port development
- Fisheries Bycatch: Accidental entanglement in fishing nets—primary cause of mortality
- Marine Pollution & Heavy Metals: Detection of arsenic, cadmium, chromium, mercury and lead in dugong tissues (linked to industrial discharge, agricultural runoff, untreated wastewater)
- Slow Reproduction: Limits population recovery
Conservation Measures in India
- MoEFCC Task Force (2010) on dugong conservation
- National Dugong Recovery Programme with Tamil Nadu, Gujarat, A&N
- Dugong Conservation Reserve, Palk Bay (2022)—448 sq km to protect seagrass and dugongs
- Ongoing need for stronger enforcement, bycatch reduction, and incentive-based fisheries management
Integrated Forum on Climate Change and Trade
- 20 Nov 2025
In News:
The 30th Conference of the Parties (COP30) to the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change formally launched the Integrated Forum on Climate Change and Trade (IFCCT) at Belém. The initiative responds to growing global concerns that climate policies and trade measures are increasingly intersectingand clashingwithout adequate coordination.
About the Integrated Forum on Climate Change and Trade
- Nature: A politically supported, non-negotiating forum
- Purpose: To provide a permanent space for countries to discuss the interface between climate action, trade policy, and development priorities
- Co-Chairing: Brazil and a developed-country partner
- Participation: Open to all Parties to the UNFCCC
- Institutional Status:
- Independent of both the WTO and the UNFCCC
- Does not negotiate binding outcomes, interpret agreements, adjudicate disputes, or assess specific national measures
Rationale
- Climate-related trade measures (e.g., tariffs, border carbon adjustments, industrial subsidies) are proliferating rapidly.
- Countries increasingly recognise that trade policy will shape their ability to meet climate goals.
- Uncoordinated actions risk fragmentation, trade disputes, and reduced trust, especially affecting developing countries.
Key Features
- Consultative Process:
- An open-ended consultation phase extending into 2026 to define discussion themes and the forum’s jurisdiction.
- First consultation round scheduled in Geneva, symbolically placing climate–trade dialogue close to the multilateral trading system.
- Interoperability Focus:Aims to promote coherence between climate and trade regimes, avoiding fragmented rule-making.
- Multi-Stakeholder Engagement:Involves civil society organisations, business associations, and international initiatives.
- Development-Oriented Approach:Seeks to amplify the voice of developing countries in shaping emerging trade rules linked to climate action.
Global Perspectives Highlighted at Launch
- Developing Countries: Emphasised concerns over unilateral trade measures and stressed principles like Common But Differentiated Responsibilities (CBDR).
- Developed Economies: Highlighted the need for open, rules-based trade to support clean technology transitions and emissions reduction.
- Institutional Concerns:The World Trade Organization warned that a patchwork of climate-related trade measures could undermine predictability unless better coordinated.
Significance
- Recognises that climate and trade can no longer be treated as separate policy domains.
- Attempts to prevent trade from becoming a fault line in global climate cooperation.
- Represents a strategic effort by the COP30 Presidency to align climate ambition with global economic governance.
Asiatic Caracal
- 20 Nov 2025
In News:
The elusive Asiatic Caracal was recently sighted at Ramgarh in Jaisalmer, marking a significant wildlife record for Rajasthan. Once widespread across India’s grasslands and semi-arid regions, the species had nearly disappeared from public consciousness due to its extremely low numbers and elusive behaviour.
About the Caracal
- Scientific Name:Caracal caracal
- Common Names: Desert lynx (misnomer); Siya gosh in India (Persian for “black ear”)
- Taxonomy: More closely related to the African golden cat and serval than to lynxes
- Type: Medium-sized wild cat, shy and predominantly nocturnal
Distribution
- Global: Africa, Central Asia, the Middle East, arid regions of Pakistan, and north-western India
- India: Extremely rare; estimated population of ~50 individuals, mainly confined to Rajasthan and Gujarat
Habitat
- Occupies semi-deserts, savannahs, shrublands, steppes, dry forests, and woodlands
- Strong preference for dry areas with low rainfall
Key Physical & Behavioural Features
- Solid build, long legs, short face, and distinctive black ear tufts
- Coat colour ranges from red-tan to sandy, with occasional black individuals
- Dark facial markings near eyes and nose; short, dense fur
- Back legs longer than front, aiding agility
- Exceptional leaper: can jump up to 3 metres (10 feet) to catch birds mid-air
- Speed: up to 80 km/h (50 mph) in short bursts
- Largely nocturnal and elusive, making sightings rare
Conservation Status
- IUCN Red List:Least Concern (globally)
- Indian Context: Despite global status, the species is locally threatened due to habitat loss, fragmentation, and very small population size
Foraminifera
- 19 Nov 2025
In News:
A recent global scientific review has identified 57 new living species of foraminifera, including newly recorded species from New Zealand waters. This research, published in Micropaleontology, used advanced DNA sequencing and morphological analysis to classify living species found in coastal and shallow seafloor sediments worldwide.
What are Foraminifera?
- Foraminifera (forams) are single-celled marine organisms found in:Open oceans, Coastal waters, and Estuaries
- They possess protective shells (tests) and exist as:Planktonic (free-floating), and Benthic (living on the sea floor)
Population Structure
- About 8,000–9,000 living species are known globally.
- Only ~40 species are planktonic; the majority are benthic.
- They generally measure less than 500 microns, though some tropical species can reach 20 cm.
Meaning of the Name
- “Foraminifera” comes from the presence of many tiny shell openings called foramina (“windows” in Latin).
- They extend pseudopodia (false feet) through these holes to move and capture food.
Feeding Habits
- Diet includes:Detritus on the sea floor, Diatoms, Algae, Bacteria, Tiny animals such as copepods
Shell Structure
- Forams build shells made of:
- Calcium carbonate (calcareous)or
- Aggregated sand grains (agglutinated)
- Shells range from single-chambered forms to complex multi-chambered coiling structures, despite their simple cellular structure.
Ecological and Scientific Importance
Foraminifera have existed for millions of years, making them valuable for:
- Paleoclimate reconstruction
- Sea-level change studies
- Pollution and sediment runoff assessment
- Understanding coastal earthquake and tsunami history
- Tracking marine ecosystem shifts
They are widely used in geology, paleoenvironmental studies, and environmental monitoring due to the long-term preservation of their shells in sediments.
Key Findings from the Latest Global Review
Diversity Distribution
- Highest diversity found in the Northwest Pacific (China–Japan coasts): 74 species
- Followed by Australia: 58 species
- No species recorded from Antarctica
- 24 species identified around the Arctic Ocean
New Zealand Findings
- Three new species were documented from:
- Stewart Island
- Tolaga Bay
- Waitemata Harbour
- These specimens are now stored in NZ museum collections.
Human-Driven Species Transport
- At least 33 non-native species were found far from their natural evolutionary origins.
- Likely transported across oceans unintentionally via:
- Ballast water from ships
- Sediment movement
This highlights the role of human activity in altering marine biodiversity patterns.
ARISE Program
- 16 Nov 2025
In News:
At the COP30 Climate Summit in Belém, Brazil, the Climate Investment Funds (CIF) launched a new climate-resilience initiative -ARISE (Accelerating Resilience Investments and Innovations for Sustainable Economies).Germany and Spain jointly committed USD 100 million as the program’s initial funding.
About ARISE Program
- ARISE is a next-generation climate resilience initiative aimed at enabling developing nations to withstand and adapt to increasing climate shocks such as floods, droughts, storms, and economic disruptions.
- Objectives
- Integrate climate resilience into national economic planning.
- Strengthen the adaptive capacity of vulnerable economies.
- Mobilisecatalytic finance for adaptation.
- Convert climate risks into opportunities for sustainable and inclusive growth.
- Facilitate investments from:
- Multilateral Development Banks (MDBs)
- Climate funds
- Private sector
- Key Functions
- Support countries in embedding resilience into development strategies.
- Unlock new financing channels and reduce investment risks.
- Enhance institutional and community-level preparedness.
About Climate Investment Funds (CIF)
- A $13 billion multilateral climate finance mechanism established in 2008, housed within the World Bank Group.
- Purpose: To provide concessional finance to developing countries for:
- Low-carbon development
- Climate resilience
- Clean technology deployment
- Nature-based solutions
- Coverage: Supports climate action in 70+ low- and middle-income countries.
- Institutional Framework: CIF is implemented through six Multilateral Development Banks (MDBs) including:
- World Bank
- IFC
- Asian Development Bank (ADB)
- African Development Bank (AfDB)
- European Bank for Reconstruction and Development (EBRD)
- Inter-American Development Bank (IDB)
This MDB-based structure ensures country-led implementation and strong international coordination.
Structure of CIF
CIF consists of two core funding windows:
1. Clean Technology Fund (CTF)
Focus:
- Renewable energy
- Clean transportation
- Energy efficiency
2. Strategic Climate Fund (SCF)
Focuses on innovative pilot initiatives such as:
- Pilot Program for Climate Resilience (PPCR)
- Forest Investment Program (FIP)
- Smart Cities Program
Finance Model
CIF operates on a blended finance approach:
- Combines concessional funding with MDB and private investments.
- Reduces financial risks to attract large-scale commercial capital.
- Catalyses transformational climate investments.
Global Cooling Watch 2025 Report
- 15 Nov 2025
In News:
United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP) released the Global Cooling Watch 2025 report at COP30 in Belém, Brazil, projecting that global cooling demand may triple by 2050 under current trends, resulting in a major rise in emissions and power system stress.
About Global Cooling Watch 2025 Report
- Nature: UNEP’s second global assessment on cooling and its environmental, economic, and equity dimensions.
- Purpose:
- Assess global cooling trends and future projections
- Present a Sustainable Cooling Pathway for near-zero emissions
- Support the Global Cooling Pledge framework
Key Findings and Trends
1. Rising Cooling Demand
- Cooling capacity expected to increase 2.6 times (from 22 TW to 58 TW) by 2050.
- Driven by urban expansion, rising incomes, and worsening heatwaves.
2. Emission Expansion
- Cooling-related emissions may reach 10.5 billion tonnes CO?e by 2050.
- Nearly double 2022 levels without stringent policy measures.
3. Developing Country Surge
- Cooling demand in Article 5 (developing) countries projected to grow fourfold, deepening infrastructure disparities.
4. Escalating Power Consumption
- Global cooling electricity use may rise from 5,000 TWh (2022) to 18,000 TWh (2050).
- Significant implications for peak load management, especially in tropical regions.
5. Heat Inequality
- Over 2 billion people lack access to affordable, efficient cooling systems.
- Heightened vulnerability to extreme heat stress.
6. Passive Cooling Potential
- Passive measures (reflective roofs, ventilation design, urban greening) can reduce indoor temperatures by up to 8°C.
- Potential to cut energy consumption by 15-55%.
7. Refrigerant Transition
- Switching from HFCs to low-GWP refrigerants may avert up to 0.4°C of warming this century.
8. Global Cooling Pledge Progress
- 72 countries + 80 organizations have joined.
- Target: 68% reduction in cooling-sector emissions by 2050.
Successes Highlighted
- Strengthened international cooperation via the Global Cooling Pledge.
- Wider adoption of passive cooling in building policies.
- Technological improvements boosting efficiency by around 50%.
- Enhanced private sector involvement in sustainable cooling solutions.
- Tiered access initiatives improving cooling equity.
Limitations and Challenges
- Persistent inequality in access to cooling in tropical developing nations.
- Global funding currently covers less than 20% of adaptation and resilience needs.
- Fragmented policy coordination across sectors.
- Delays in HFC phase-down and inadequate refrigerant disposal.
- Continued dependence on fossil-fuel-based electricity.
UNEP Recommendations
- Implement a Sustainable Cooling Pathway combining:
- Passive cooling design
- High-efficiency cooling appliances
- Rapid integration of renewable energy
- Strengthen Kigali Amendment implementation and ensure full refrigerant lifecycle recovery.
- Increase green finance through concessional loans, PPP models, and climate bonds.
- Make passive cooling standards mandatory in building codes and urban planning.
- Provide targeted subsidies and access programs for heat-vulnerable populations.
Methylocucumisoryzae
- 12 Nov 2025
In News:
India has identified a home-grown biological solution to methane mitigation, a major contributor to climate change, through the discovery of indigenous methanotrophic bacteria from rice fields and wetlands, particularly in western India. This discovery strengthens India’s climate response by leveraging natural microbial processes rather than energy-intensive technological interventions.
Methane and Climate Change
- Methane (CH?) is a colourless, odourless, flammable gas, also called marsh gas.
- It is the second most important greenhouse gas after carbon dioxide.
- Methane has ~26 times higher global warming potential than CO? over a 100-year period.
- Major sources include wetlands, rice paddies, ruminant livestock, and landfills, where methane is produced by methanogens under anaerobic conditions.
Methanotrophs: Natural Methane Mitigators
- Methanotrophs are methane-oxidising bacteria that consume methane as their energy source.
- They oxidise methane into CO? and water, while building their own biomass.
- Habitat: Wetlands, rice fields, ponds, quarry waters, and other oxygen–methane interface zones.
- Their ecological role is critical in preventing a sharp rise in atmospheric methane concentrations.
Discovery of Methylocucumisoryzae
Scientists at MACS Agharkar Research Institute, an autonomous institute under the Department of Science and Technology (DST), have isolated and characterisedIndia’s first indigenous methanotroph cultures.
- A novel genus and species named Methylocucumisoryzae was described.
- The bacterium has an oval, elongated, cucumber-like shape, earning it the nickname “methane-eating cucumber”.
- It remains phylogenetically unique and endemic, with no reports from outside India even after a decade of study.
Key Features of Methylocucumisoryzae
- Habitat: Rice fields, wetlands, and water-filled stone quarries (e.g., VetalTekdi–ARAI hill, Pune).
- Size: Unusually large for bacteria (3–6 µm), comparable to small yeast cells.
- Thermal behaviour: Strictly mesophilic; cannot grow above 37°C, unlike many methanotrophs.
- Colony colour: Light pale pink, linked to a carotenoid biosynthesis pathway.
- Ecological role: Indicates an active methane cycle in natural and semi-natural ecosystems.
Agricultural and Biotechnological Significance
- Experimental studies show that Methylocucumisoryzae can promote rice plant growth, inducing:
- Early flowering
- Increased grain yield
- Trials were conducted on the Indrayani rice variety, widely cultivated in Maharashtra.
- This highlights a dual benefit: climate mitigation and agricultural productivity.
Constraints and Way Forward
- A major limitation is the slow growth rate, restricting large-scale cultivation for direct application.
- However, its natural abundance in rice fields and wetlands suggests it already plays a silent but significant role in methane mitigation.
- Improving culture techniques could enable future use in climate-smart agriculture and biotechnological applications.
Rhesus Macaque

- 11 Nov 2025
In News:
Recently, the Standing Committee of the National Board for Wildlife (SC-NBWL) has recommended reinstating the Rhesus macaque (Macaca mulatta) under Schedule II of the Wildlife (Protection) Act, 1972. The move aims to restore statutory protection, regulate scientific management, and curb illegal capture, cruelty, and trade of the species.
Rationale Behind the Recommendation
The recommendation follows consultations with state governments and expert bodies amid rising human–wildlife conflict involving rhesus macaques. Senior officials highlighted that Section 11 of the Wildlife (Protection) Act empowers states to manage conflict situations even when a species is protected, allowing controlled interventions without removing legal safeguards.
The proposal was supported by the Chairman of the Animal Welfare Board of India, animal protection organisations, and backed by the Central Zoo Authority and the National Tiger Conservation Authority. States have been advised to prepare site-specific management, mitigation, rescue, and rehabilitation plans, supported by baseline studies from the Wildlife Institute of India.
About Rhesus Macaque
- Scientific name: Macaca mulatta
- Category: Old World monkey
- Distribution: India, South Asia, Southeast Asia, southern China
- Habitat: Forests, grasslands, mangroves, mountains; highly adaptable to human-dominated landscapes
- Diet: Omnivorous (fruits, seeds, roots, bark, cereals)
- Behaviour: Social, diurnal, terrestrial and arboreal; live in large troops with complex communication
Conservation Status
- IUCN Red List: Least Concern
- Wildlife (Protection) Act, 1972: Proposed Schedule II (restoration of protection)
UN Water Convention
- 10 Nov 2025
In News:
- Bangladesh became the first country in South Asia to accede to the UN Water Convention.
- Move highlights growing importance of transboundary water governance amid climate change and upstream interventions.
UN Water Convention
- Official Name: Convention on the Protection and Use of Transboundary Watercourses and International Lakes
- Adopted: 1992 (Helsinki)
- Entered into force: 1996
- Serviced by: United Nations Economic Commission for Europe (UNECE)
- Original scope: Pan-European region
- Global access: Open to all UN Member States since March 2016
Core Features of the Convention
- Legally binding international framework
- Promotes:
- Equitable and reasonable utilisation of shared watercourses
- Prevention, control, and reduction of transboundary impacts
- Sustainable management of international rivers and lakes
- Mandates:
- Cooperation among riparian states
- Formation of joint bodies and basin-level agreements
- Does not replace bilateral/multilateral treaties; rather supports and strengthens them
- Instrument for achieving SDGs, especially:
- SDG 6 (Clean Water and Sanitation)
- SDG 16 (Peace and Institutions)
- SDG 17 (Partnerships)
Why Bangladesh Joined – Key Drivers
- Downstream dependency:
- Shares the Ganges–Brahmaputra–Meghna (GBM) basin with India and China
- Only ~7% of GBM watershed lies within Bangladesh
- Water stress indicators:
- 60% population vulnerable to floods
- 20–25% land flooded annually
- 81 of 1,415 rivers dried up or near extinction
- Salinity intrusion and sea-level rise in delta regions
- Climate change impacts:Altered Himalayan River flows
- Legal step:
- Bangladesh High Court (2019) declared rivers as “legal persons”
Regional Context
- China:Motuo Hydropower Station on Yarlung Tsangpo (Tibet) – world’s largest proposed dam
- India:
- Existing treaties:
- Indus Waters Treaty (1960) – Pakistan
- Ganges Water Treaty (1996) – Bangladesh (renewal due 2026)
- Disputes:
- Teesta River
- Tipaimukh Dam (Barak River)
- River interlinking concerns
- Existing treaties:
India’s Concerns
- Convention may:
- Strengthen Bangladesh’s negotiation position
- Influence future Ganges Treaty renegotiation
- India traditionally prefers bilateral mechanisms over multilateral water frameworks
- Possibility of:
- Nepal & Bhutan following Bangladesh
- Bangladesh exploring trilateral cooperation with China and Pakistan
Black-Headed Ibis

- 10 Nov 2025
In News:
Recent sightings of a flock of Black-headed Ibis (Oriental White Ibis) in the salt pan regions of Thoothukudi district, Tamil Nadu, have drawn the attention of bird enthusiasts, ecologists, and conservationists. Such observations are significant not only for avifaunal studies but also as indicators of wetland health and ecological recovery, especially in coastal and human-modified landscapes.
About the Black-Headed Ibis
The Black-headed Ibis (Threskiornis melanocephalus), also known as the Oriental white ibis, Indian white ibis, or black-necked ibis, belongs to the family Threskiornithidae. It is a large wading bird, measuring about 65–76 cm in length, adapted to a wide variety of aquatic environments, which is why it is classified as a wader bird.
Morphologically, it is distinctive as the only native ibis species in its range with an overall white plumage combined with a black head and neck. Both males and females appear similar. Adults have greyish tail feathers, which turn jet black during the breeding season, adding to their ornamental appearance. The species is characterised by a long, curved bill, suited for probing mud and shallow water in search of food.
Habitat, Distribution and Ecology
The Black-headed Ibis is widely distributed across South and Southeast Asia, ranging from India westwards to Sri Lanka and eastwards up to Japan. It primarily inhabits wetlands, including lakes, marshes, riverbanks, and flooded agricultural fields. Notably, it is also found in coastal areas such as salt pans, as seen in Thoothukudi, and occasionally forages in dry fields and human-modified landscapes.
Its diet mainly consists of fish, insects, crustaceans, and other small aquatic organisms, making it an important component of wetland food webs. The presence of ibises, along with species such as flamingos, pelicans, and rosy starlings, reflects adequate food availability and suitable habitat conditions.
Conservation Status and Significance
At the global level, the Black-headed Ibis is classified as ‘Least Concern’ under the IUCN Red List. However, in parts of Asia, it is sometimes regarded as ‘Near Threatened’, owing to wetland degradation, pollution, altered hydrology, and habitat loss. This highlights the importance of regional conservation perspectives even when a species is not globally threatened.
The recent sightings in the salt pans of Thoothukudi are seen by experts as a positive ecological signal, suggesting improved habitat conditions following seasonal changes, particularly after the northeast monsoon (October–January), which replenishes wetlands and associated ecosystems.
Migratory Birds and Conservation Measures
The Thoothukudi observation also fits into a broader national context of avian conservation and migratory bird protection. Across India, wetlands and coastal regions act as crucial stopovers and wintering grounds for both resident and migratory birds. In this regard, proactive conservation measures, such as the declaration of a temporary ‘Silence Zone’ around Pangti village in Wokha district, Nagaland, to protect the globally significant congregation of Amur Falcons, demonstrate growing administrative and community awareness. Scientific studies have shown that excessive noise can disturb birds, disrupt breeding behaviour, and lead to habitat abandonment, underlining the need for habitat-sensitive governance.
Vedanthangal Bird Sanctuary

- 09 Nov 2025
In News:
Vedanthangal Bird Sanctuary in Tamil Nadu has witnessed the arrival of thousands of migratory birds, marking the beginning of the annual nesting and breeding season. More than 20 migratory bird species have already arrived, leading to increased ecological activity and tourist interest.
Location and Background
- Location: Chengalpattu district, Tamil Nadu
- Distance from Chennai: ~90 km south
- Type: Freshwater wetland and heronry
- Status: One of the oldest protected bird sanctuaries in India
Vedanthangal is a people-protected wetland, with a conservation history spanning centuries. Local communities traditionally protected nesting birds as the manure-rich water (Liquid Guano Effect) from the lake enhanced agricultural productivity in surrounding fields.
Ecological and International Importance
- Recognised as an Important Bird and Biodiversity Area (IBA)
- Lies in the Coromandel Coast biotic province
- Designated as a Ramsar Site in 2022, highlighting its global wetland importance
Avifaunal Diversity (Fauna)
The sanctuary currently hosts over 15,000 birds during peak season.
Early arrivals and breeding species:
- Open-billed stork (already completed breeding with visible chicks)
- Painted stork
- Black-headed ibis
- Eurasian spoonbill
- White ibis
Other prominent species:
- Grey heron, pond heron, night heron
- Little cormorant, darter
- Pelicans, egrets
- Lesser whistling duck, spot-billed duck
- Red-wattled lapwing, little grebe, common moorhen
Vegetation (Flora)
- Barringtonia trees – preferred nesting trees
- Alangium salviflorum
- Acacia nilotica
- Thorn forests and dry evergreen scrub
Forest authorities plan desilting operations and fresh plantation of barringtonia trees during summer when the tank dries, to support long-term nesting habitats.
Khangchendzonga National Park

- 08 Nov 2025
In News:
- The International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) has rated Khangchendzonga National Park as “Good” in its latest global review of Natural World Heritage Sites.
- It is the only Indian site to receive a positive “Good” conservation status, while sites like the Western Ghats and Sundarbans face concerns.
Location & Status
- Located in North Sikkim, along the India–Nepal border.
- Forms the core area of the Khangchendzonga Biosphere Reserve (KBR).
- India’s first “Mixed” UNESCO World Heritage Site (2016) – recognised for natural and cultural values.
- Part of the Himalaya Global Biodiversity Hotspot.
Geographical Features
- Area: ~ 1,784 sq. km
- Altitude Range: From 1,220 m to 8,586 m (vertical sweep of over 7 km).
- Home to Mount Khangchendzonga (8,586 m) - 3rd highest peak in the world.
- Landscape includes plains, deep valleys, alpine meadows, lakes, glaciers, and snow-clad mountains.
- Glaciers:
- 18 major glaciers (as per park records);
- Zemu Glacier - one of the largest glaciers in Asia.
Biodiversity
- Flora: Subtropical to alpine vegetation; oak, fir, birch, maple, rhododendron, alpine meadows.
- Fauna (Flagship species):
- Snow leopard
- Red panda
- Tibetan wolf
- Blue sheep
- Himalayan tahr
- Mainland serow
- Avifauna:
- Nearly half of India’s bird species recorded.
- Includes Impeyan pheasant (State bird of Sikkim) and Satyr tragopan.
Cultural & Community Significance
- One of the few regions with Lepcha tribal settlements.
- Known as “Mayel Lyang” (sacred land) by the Lepchas.
- Considered a sacred beyul (hidden valley) in Tibetan Buddhism.
- Ancient monasteries such as Tholung Monastery reflect cultural continuity.
Gravity Energy Storage
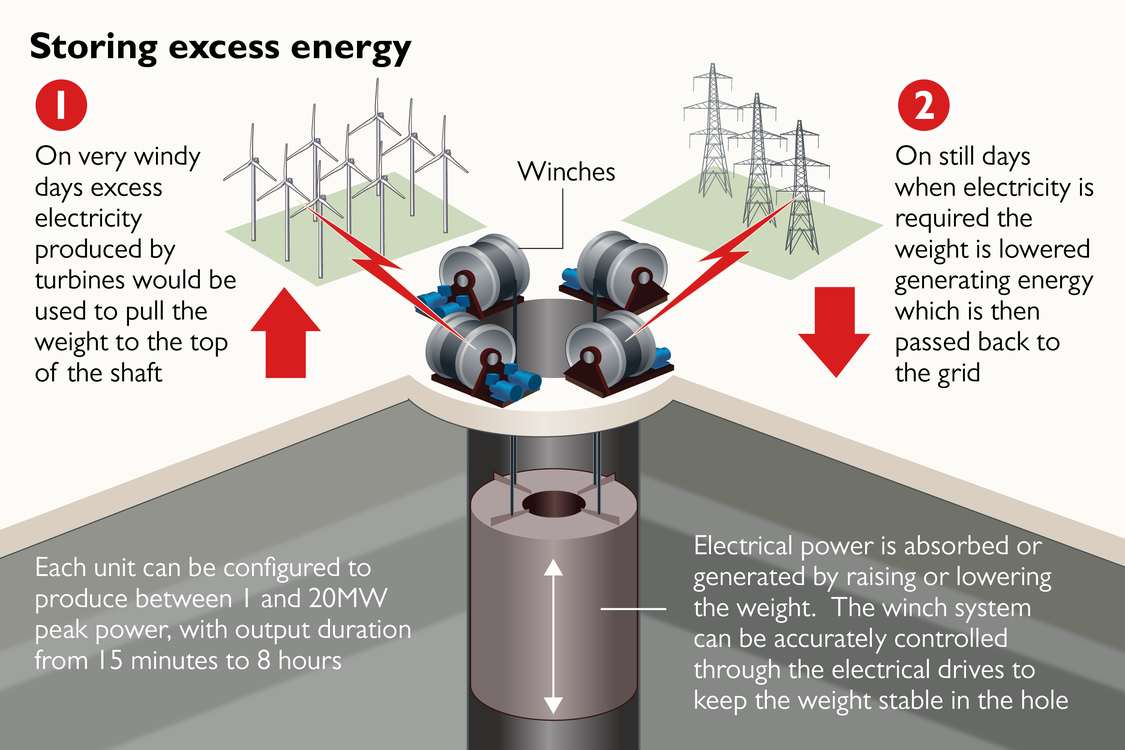
- 08 Nov 2025
In News:
As climate change intensifies and the global transition towards low-carbon energy accelerates, the integration of renewable energy into power grids has become a major policy and technological challenge. Solar and wind energy, though abundant and clean, are intermittent in nature, creating mismatches between electricity generation and demand. In this context, Gravity Energy Storage (GES) is emerging as a promising long-duration, grid-scale energy storage technology, offering a viable alternative to conventional battery-based systems.
What is Gravity Energy Storage?
Gravity Energy Storage is an innovative energy storage technology that harnesses gravitational potential energy to store and release electricity. It involves lifting a heavy mass during periods of surplus electricity generation and allowing it to descend when demand rises, thereby converting stored energy back into electricity. The technology is particularly suited for renewable-dominated power systems, where supply fluctuations are frequent.
Working Mechanism
The basic principle of gravity energy storage is simple yet effective:
- During periods of excess renewable energy generation, such as peak solar output, surplus electricity is used to lift a heavy mass—commonly water, concrete blocks, or compressed earth blocks.
- This process converts electrical energy into stored gravitational potential energy.
- When electricity demand exceeds supply or renewable generation falls, the mass is released to descend under gravity.
- The downward motion drives water or mechanical systems through a turbine, generating electricity that is fed back into the grid.
A typical configuration may involve a heavy piston within a fluid-filled cylindrical container, where the piston’s vertical movement enables controlled energy storage and release. Unlike pumped-hydro storage, gravity energy storage systems offer greater flexibility in site selection and do not require large reservoirs or specific topographical features.
Advantages of Gravity Energy Storage
Gravity energy storage offers several strategic advantages that make it attractive for long-term energy planning:
- Long operational life: These systems can operate for several decades with minimal maintenance, unlike batteries which degrade chemically over time.
- Environmentally benign: The absence of toxic chemicals eliminates risks related to pollution, recycling, and disposal, aligning with sustainability goals.
- Cost-effective at scale: Lower lifetime costs of energy and storage make it suitable for large-scale grid applications.
- Flexible deployment: Can be installed in urban, space-constrained, or environmentally sensitive areas where pumped-hydro or large battery systems are not feasible.
- Grid stability: Provides reliable energy during peak demand and enhances grid resilience in renewable-heavy energy systems.
Limitations and Challenges
Despite its potential, gravity energy storage faces certain constraints:
- Early stage of development: High initial capital costs and limited commercial deployment pose adoption challenges.
- Regulatory and infrastructure hurdles: Large-scale installations require regulatory approvals and long-term planning.
- Geographical constraints: Although more flexible than pumped hydro, suitable locations are still required for large infrastructure.
- Lower energy density: Compared to batteries, gravity energy storage is less suitable for compact or small-scale applications.
Significance for Energy Transition
Gravity energy storage represents an important step towards clean, reliable, and sustainable energy systems. By addressing the intermittency of renewable sources, it supports grid stability, energy security, and decarbonisation goals. For countries like India, which are rapidly expanding solar and wind capacity, such storage technologies can play a vital role in achieving energy transition targets, reducing dependence on fossil-fuel-based peaking power, and strengthening climate resilience.
Striped Hyena

- 08 Nov 2025
In News:
The recent sighting of a rare striped hyena (Hyaena hyaena) in the Kali Tiger Reserve near the Ganeshgudi bridge in Uttara Kannada district of Karnataka has drawn attention to changing wildlife movement patterns and the ecological importance of lesser-known carnivores. The observation, recorded on video by a local resident in early November 2025, marks the first documented presence of the species in this part of the Western Ghats, where it was previously unrecorded, particularly in the dense forests of the Dandeli region.
About the Striped Hyena
The striped hyena is a mammal belonging to the family Hyaenidae, which comprises four members: striped hyena, spotted hyena, brown hyena, and the aardwolf (the latter not being a true wolf). Compared to the spotted hyena, the striped hyena is smaller in size, with a distinctive coat marked by dark vertical stripes, giving it its name.
The species has a wide but fragmented distribution, extending across South Asia (India, Nepal, Afghanistan), North and Sub-Saharan Africa, West Asia, and parts of Central Asia. In India, it is typically associated with arid and semi-arid landscapes, inhabiting open savannas, grasslands, scrublands, and dry woodlands, rather than dense tropical forests.
Behaviour and Ecological Role
Striped hyenas are primarily nocturnal and solitary, though they display a limited social structure. They are territorial animals, marking boundaries through scent to deter rivals. An important behavioural trait is female dominance, with adult females generally more aggressive and dominant than males.
Ecologically, striped hyenas function mainly as scavengers, feeding on carrion and human refuse. By consuming animal remains, they play a critical role in ecosystem health, helping to prevent the spread of diseases and recycle nutrients. Forest officials have emphasised that the species poses no threat to humans, countering common misconceptions associated with hyenas.
Significance of the Kali Tiger Reserve Sighting
The appearance of a striped hyena in the lush, forested landscape of the Western Ghats is unusual and has generated scientific interest. Experts suggest that the animal may have dispersed from drier regions of northern Karnataka, such as Dharwad, possibly due to food scarcity, seasonal movement, climate-related habitat stress, or improved connectivity through wildlife corridors.
The sighting highlights the importance of landscape-level conservation, as wildlife movement increasingly transcends traditional habitat boundaries. In response, forest authorities have initiated non-invasive monitoring using camera traps to track the animal’s movement, ensure its safety, and assess the possibility of range expansion or previously undetected populations.
Conservation Status and Legal Protection
Despite its ecological importance, the striped hyena faces multiple threats, including habitat loss, road kills, persecution, and declining prey availability. Reflecting these pressures, the species is classified as Near Threatened on the IUCN Red List.
In India, it enjoys the highest level of legal protection under Schedule I of the Wildlife (Protection) Act, 1972, underscoring its conservation priority and the need for stringent safeguards.
Emissions Gap Report 2025
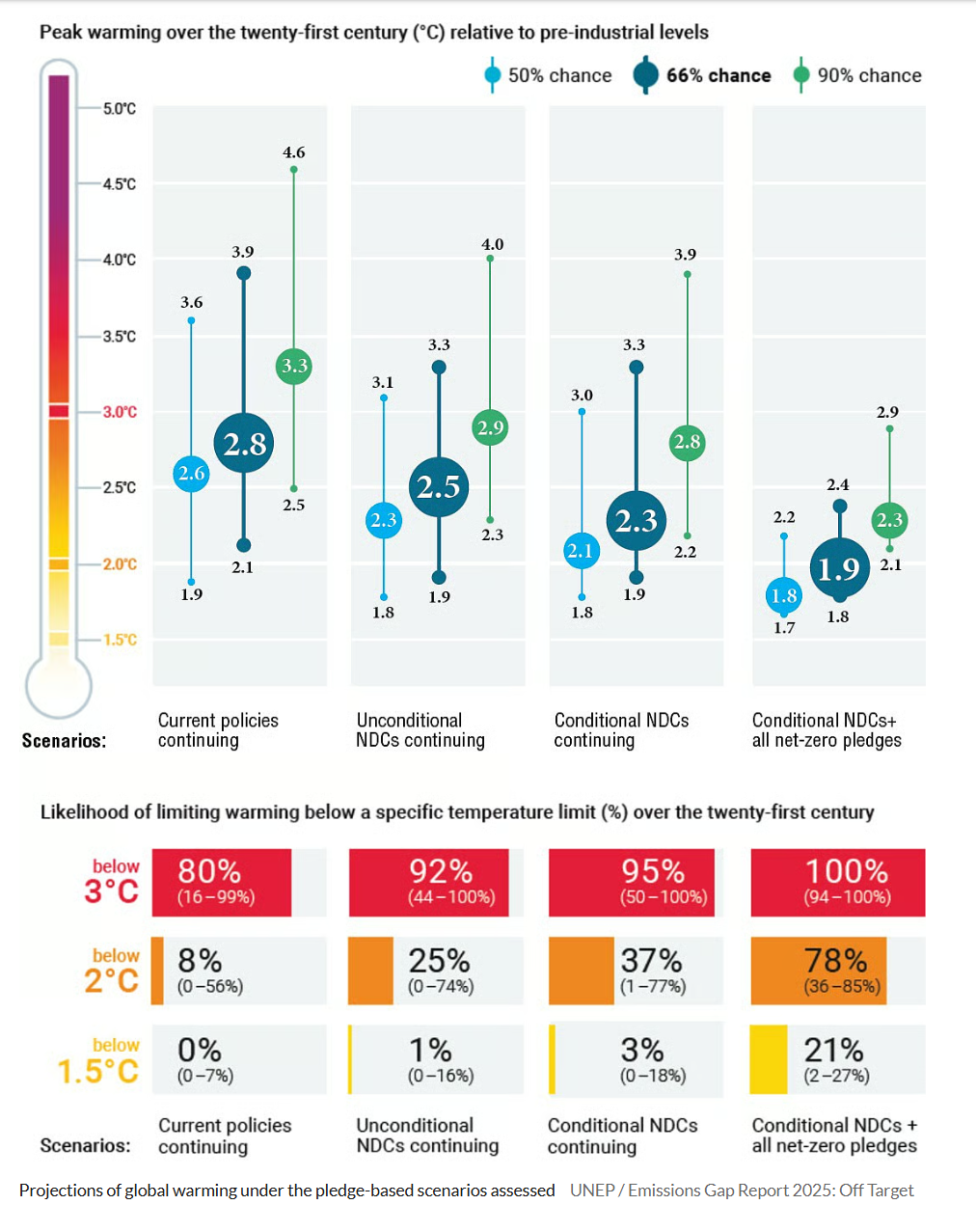
- 07 Nov 2025
In News:
The United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP), in its Emissions Gap Report (EGR) 2025 – “Off Target”, has warned that despite updated climate pledges by countries, the world remains dangerously off course to meet the Paris Agreement temperature goals. Current trajectories indicate that global warming will reach 2.3–2.5°C this century, far exceeding the ambition of limiting warming to well below 2°C, preferably 1.5°C.
About the Emissions Gap Report
The Emissions Gap Report is an annual flagship publication of UNEP, co-produced with the UNEP Copenhagen Climate Centre (UNEP-CCC). It assesses the gap between where global greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions are heading under current pledges and where they should be to meet Paris Agreement targets. The report is released every year ahead of the UN Climate Change Conference of Parties (COP).
Key Findings of Emissions Gap Report 2025
- Marginal Progress in Climate Pledges
- Even if all countries fully implement their latest Nationally Determined Contributions (NDCs), global temperature rise is projected at 2.3–2.5°C.
- This is only a modest improvement from last year’s estimate of 2.6–2.8°C, and UNEP notes that much of this improvement is due to accounting and methodological changes, not real emission reductions.
- Rising Global Emissions
- Global GHG emissions rose by 2.3% in 2024, reaching a record 57.7 gigatonnes of CO? equivalent.
- This growth rate is over four times the annual average of the 2010s, signalling a reversal of earlier decarbonisation trends.
- Low Participation and Weak Ambition
- As of September 30, 2025, only 60 Parties, representing 63% of global emissions, had submitted or announced new 2035 NDCs.
- Even full implementation of existing NDCs would reduce global emissions by only 15% by 2035 (from 2019 levels), whereas a 55% reduction is required to stay on the 1.5°C pathway.
- Implementation Gap
- Most countries are not on track to meet even their 2030 targets, revealing a “huge implementation gap” between commitments and action.
- Overshoot of 1.5°C is Now Likely
- UNEP warns that global temperatures are very likely to exceed 1.5°C within the next decade.
- The policy focus has shifted from prevention to ensuring that this overshoot is temporary and limited, as every fraction of warming avoided reduces climate damages, health risks, and dependence on uncertain carbon dioxide removal (CDR) technologies.
Role of the G20
The G20, responsible for about 77% of global emissions (excluding the African Union), holds the key to closing the emissions gap. Despite some members submitting new NDCs, the group as a whole remains off track for its 2030 goals, undermining global mitigation efforts.
Geopolitical and Structural Challenges
UNEP highlights that geopolitical uncertainties, including the proposed withdrawal of the United States from the Paris Agreement in 2026, could offset climate gains. According to the report, this alone could negate around 0.1°C of the projected improvement.
Opportunities and Way Forward
Despite the bleak outlook, UNEP notes that the world is technically well-positioned to accelerate climate action due to:
- Rapidly declining costs of renewable energy technologies such as solar and wind.
- Proven solutions that can deliver economic growth, jobs, energy security, and health benefits alongside emission reductions.
UNEP’s Key Recommendations
To close the emissions gap, UNEP calls for:
- Removal of policy, governance, institutional, and technical barriers.
- A massive scale-up of climate finance and technology transfer to developing countries.
- Redesign of the international financial architecture to unlock affordable and predictable climate finance.
Indian Mouse Deer
- 06 Nov 2025
In News:
A rare Indian mouse deer (Moschiola indica) was recently photographed at the Tungareshwar Wildlife Sanctuary (TWS) in Vasai by the Wildlife Research Division of the Vivek PARC Foundation. Sightings of this species are uncommon due to its nocturnal and secretive behaviour, highlighting the ecological value of the sanctuary as a refuge for elusive fauna.
About the Indian Mouse Deer
Taxonomy
- Common Name: Indian Mouse Deer / Indian Spotted Chevrotain
- Scientific Name: Moschiola indica
- Family: Tragulidae
- Order: Artiodactyla (even-toed ungulates)
- One of the smallest ungulates globally and the smallest deer-like species in India.
Key Characteristics
- Size:
- Shoulder height: 25–30 cm
- Body length: ~57.5 cm (23 inches)
- Weight: 2–4 kg
- Appearance:
- Dark brown fur with 4–5 rows of white dorsal spots
- White underparts
- Canines: Males possess tusk-like upper canines, used during territorial or mating conflicts.
- Stomach: Unique among ruminant-like species—has a three-chambered stomach instead of the typical four.
- Diet:
- Omnivorous tendencies: fruits, leaves, herbs, roots
- Occasionally eats insects, crustaceans, and small mammals
- Lifespan: 8–12 years
- Behaviour:
- Nocturnal, shy, and highly elusive, usually found in dense forest cover.
- Prefers habitats away from human settlements, making sightings rare.
Distribution
- Endemic to the Indian Subcontinent.
- India:
- Widespread in peninsular India.
- Common in Western Ghats, Eastern Ghats up to Odisha, and central Indian forests.
- Outside India:
- Old records from Nepal.
- Sri Lanka hosts a separate species: Spotted Chevrotain (Moschiola meminna).
Habitat
- Found in:
- Semi-evergreen forests
- Moist evergreen forests
- Tropical deciduous forests
Conservation Status
- IUCN Red List: Least Concern (LC)
- However, populations face threats from:
- Habitat loss and fragmentation
- Human disturbance
- Declining forest quality
- However, populations face threats from:
Pilia malenadu
- 05 Nov 2025
In News:
A biodiversity exploration team working in the Western Ghats has discovered a new spider species, Pilia malenadu, marking a major addition to India’s arachnid diversity. The finding is notable because species belonging to the genus Pilia were last reported more than 123 years ago (1902) from Kerala.
About Pilia malenadu
- Pilia malenadu is a newly identified jumping spider belonging to the genus Pilia (Family: Salticidae).
- Location of Discovery:
- Found at Madhugundi, in Mudigere taluk, Chikkamagaluru district, Karnataka.
- The site lies at the foothills of the Western Ghats, a global biodiversity hotspot.
- Etymology:
- The species is named “malenadu” to honour the local region (Malenadu/Malnad).
- Scientific Importance:
- First recorded species of Pilia since 1902.
- First time both male and female specimens of a Pilia species have been documented.
Habitat Specificity
- The species demonstrates high microhabitat specialization.
- Observed only on two plant species:
- Memecylon umbellatum
- Memecylon malabaricum
- Spiders were found concealed between the leaves of these plants, indicating a narrow ecological niche.
Conservation Implications
- The study highlights that Pilia malenadu is strictly habitat-specific.
- Loss or alteration of its host plant species or habitat could threaten the survival of this newly discovered spider.
- Underscores the need for habitat-level conservation in the Western Ghats, particularly in lesser-studied microhabitats.
Amphipod Species

- 05 Nov 2025
In News:
Researchers from Berhampur University (Odisha) and Hemchandracharya North Gujarat University (Gujarat) have identified two new species of marine amphipods from the Chilika Lagoon and the Gulf of Khambhat, underscoring India’s expanding marine biodiversity documentation.
What are Amphipods?
- Amphipods are small, shrimp-like crustaceans belonging to the subclass Amphipoda.
- They are related to crabs, lobsters, and shrimp.
- Occur in a wide range of habitats: marine, freshwater, subterranean caves, and even terrestrial zones (e.g., sandhoppers).
- The name Amphipoda means “different-footed”, referring to their anatomically varied appendages.
- Globally, 7,000+ species are known (majority under Gammaridea).
- Size range: 0.1 cm to 34 cm; deep-sea species tend to be the largest.
- Ecological role: mostly detritivorous or scavenging species that contribute to nutrient cycling and ecosystem cleaning.
Newly Discovered Species
1. Grandidierella geetanjalae
- Location: Chilika Lagoon, near Rambha (Ganjam district, Odisha).
- Size: ~5.5–6 mm.
- Naming: In honour of Geetanjali Dash, Vice-Chancellor of Berhampur University.
- Nature: Detritivorous; important for organic matter decomposition.
2. Grandidierella khambhatensis
- Location: Gulf of Khambhat, Gujarat.
- Size: ~5.5–6 mm.
- Naming: After its type locality (Khambhat).
- Ecological Role: Similar detritivorous function supporting ecosystem health.
Research Background and Previous Discoveries
- The research team has earlier discovered five amphipod species from eastern India, including:
- Quadrivisio chilikensis (Chilika, near Nalabana Bird Sanctuary)
- Demaorchestia alanensis (Barkul beach)
- Talorchestia buensis (West Bengal coast)
- These discoveries indicate that Indian coastal ecosystems remain under-explored and possess high micro-faunal diversity.
Ecological Importance
- Amphipods function as key components of benthic food webs, recycling detritus and supporting fish populations.
- Their presence is an indicator of habitat quality, especially in sensitive ecosystems such as lagoons, estuaries, and coastal wetlands.
- Discoveries from Chilika and Khambhat strengthen the case for monitoring anthropogenic pressures, salinity changes, and sediment dynamics in Indian coastal habitats.
Rowmari–Donduwa Wetland Complex

- 05 Nov 2025
In News:
The Rowmari–Donduwa Wetland Complex in Assam has recently emerged as a strong contender for Ramsar Site designation, driven by its exceptional biodiversity, critical ecological functions, and strategic location within the Kaziranga landscape.
Location and Ecological Setting
- The Rowmari–Donduwa Wetland Complex lies within the Laokhowa Wildlife Sanctuary, a buffer zone of the Kaziranga Tiger Reserve.
- It forms an interconnected floodplain–marsh system extending 2.5–3 sq km.
- Together with the adjoining Burhachapori WLS, it serves as an important wildlife corridor between the Kaziranga–Orang landscape, with the Brahmaputra River shaping its riverine and wetland ecosystems.
Biodiversity Significance
1. Exceptional Avifaunal Diversity
- The 6th Kaziranga Wetland Bird Census (2025) reported
- 20,653 birds from 75 species at Rowmari Beel
- 26,480 birds from 88 species at Donduwa Beel
- Total: 47,000+ birds
- This exceeds the bird counts of Northeast India’s existing Ramsar sites—Deepor Beel (Assam) and Loktak Lake (Manipur).
- More than 120 species of resident and migratory birds recorded, including threatened species such as:
- Knob-billed Duck
- Black-necked Stork
- Ferruginous Pochard
2. Habitat Diversity: The wetland complex contains marshes, floodplain lakes, grasslands, and riverine islands (chars), supporting high ecological productivity.
3. Presence of Rare & Endangered Species: Recent surveys by scholars from Tezpur, Gauhati, and Nagaon Universities have documented rare and critically endangered waterbirds, emphasizing the site's international ecological value.
The Ramsar Convention (1971)
- A global treaty for conservation and wise use of wetlands, signed at Ramsar, Iran (1971).
- India joined in 1982 and today hosts 94 Ramsar Sites (as of Nov 2025)—the highest in Asia.
- Chilika Lake (Odisha) was India’s first Ramsar Site (1981).
- Tamil Nadu has the highest number of Ramsar Sites among Indian states.
- About 10% of India’s wetland area is under the Ramsar framework.
Laokhowa–Burhachapori Wildlife Sanctuary
- Serves as a buffer and migration corridor between Kaziranga and Orang National Parks.
- Home to key species:
- Great Indian One-horned Rhinoceros
- Royal Bengal Tiger
- Asiatic Elephant
- Asiatic Water Buffalo
- Otters, pangolins
- The Brahmaputra River supports the Gangetic River Dolphin.
Kaziranga National Park
- Established: 1908, National Park (1974)
- UNESCO World Heritage Site: 1985
- Tiger Reserve: 2006
- Supports ~2,200 one-horned rhinos (≈ two-thirds of global population).
- Rich in large mammals, birds, and aquatic fauna, forming the ecological backbone of the region.
Laokhowa Wildlife Sanctuary & Roumari–Donduwa Wetland Complex
- 04 Nov 2025
In News:
Civil society groups and conservationists in Assam have urged the government to designate the Roumari–Donduwa Wetland Complex, located within the Laokhowa Wildlife Sanctuary, as a Ramsar Site. The demand is based on the wetland’s high ecological value, rich avifaunal diversity, and its fulfillment of multiple Ramsar criteria.
About Laokhowa Wildlife Sanctuary
- Location: Southern bank of the Brahmaputra River, in Nagaon District, Assam.
- Area: Approximately 70.13 sq. km.
- Ecological System: Part of the Laokhowa–Burachapori ecosystem and a notified buffer zone of Kaziranga Tiger Reserve (KTR).
- Landscape: Lies within the Brahmaputra Valley; surrounded by human-dominated areas except to the north.
- Flora: Habitat types include:
- Alluvial grasslands
- Alluvial forests
- Moist deciduous forests
- Tropical semi-evergreen forests
- Fauna: Home to key species such as:
- Indian One-Horned Rhinoceros
- Royal Bengal Tiger
- Asiatic Water Buffalo
- Elephants
Roumari–Donduwa Wetland Complex
- Situated within Laokhowa Wildlife Sanctuary; covers ~2.5–3 sq. km.
- Supports 120+ resident and migratory bird species.
- During the 6th Kaziranga Wetland Bird Census (2025):
- 47,000+ birds from 163 species were recorded—higher than counts from Assam’s only current Ramsar Site, Deepor Beel.
- Important species recorded include:
- Knob-billed Duck
- Lesser Adjutant Stork (EN)
- Black-necked Stork
- Ferruginous Pochard (NT)
- Common Pochard (VU)
Gogabeel Lake Added as a Ramsar Site
- 04 Nov 2025
In News:
India has added Gogabeel Lake in Katihar district, Bihar to the Ramsar List of Wetlands of International Importance, raising the country’s total Ramsar sites to 94. With this, Bihar now has six Ramsar sites, placing it third after Tamil Nadu and Uttar Pradesh.
About Gogabeel Lake
- Location: Katihar district, Bihar; part of the Trans-Gangetic Plains.
- Wetland Type: A classic oxbow lake, situated between:
- River Mahananda (North-East)
- River Ganga (South)
- Hydrology: During floods, the lake temporarily links the two rivers.
- Legal Status: Bihar’s first Community Reserve, managed with active involvement of local communities.
- Cultural Significance: Traditional festivals such as Sirva, Adra, and Chhath are observed in the wetland region.
Ecological Features
- Flora: Dominated by tropical dry deciduous vegetation typical of the region.
- Fauna: Important wintering site for migratory birds and species of global conservation significance. Key species:
- Smooth-Coated Otter (Lutrogale perspicillata) – Vulnerable.
- Helicopter Catfish (Wallago attu) – Vulnerable, with the lake serving as a breeding ground.
Supports diverse fish assemblages and contributes to local fisheries.
Significance of the New Ramsar Designation
- Strengthens India’s position as:
- 1st in Asia
- 3rd globally (after the UK and Mexico) in terms of number of Ramsar sites.
- India has added 67 new Ramsar sites in the past 11 years, covering 13.6 lakh hectares.
- Recent additions from Bihar also include Gokul Jalashay (Buxar) and Udaipur Jheel (West Champaran).
Why Wetlands Matter
- Wetlands are areas where water is present permanently or seasonally.
- Provide essential ecosystem services:
- Flood control and groundwater recharge
- Water purification
- Habitat for biodiversity
- Support to local livelihoods through food, fibre, and raw materials
Ramsar Convention
- Adopted: 1971, in Ramsar, Iran.
- Objective: Conservation and wise use of wetlands through national action and international cooperation.
- Members: 172 countries, including India.
- Global Count: 2,546 Ramsar sites worldwide.
AmazonFACE Project

- 02 Nov 2025
In News:
- The AmazonFACE Project, launched near Manaus, Brazil, is a pioneering climate research experiment designed to study how the Amazon rainforest—the world’s largest tropical forest—responds to future elevated CO? levels. The initiative is significant as Brazil prepares to host COP30 in Belém.
- It is the first experiment of its scale in a natural tropical forest, marking a major advancement in global climate science.
What is AmazonFACE?
- A long-term field experiment exposing mature tropical trees to projected future CO? concentrations.
- Located in an old-growth Amazon forest stand.
- Aims to understand how increased atmospheric carbon affects forest functioning, carbon cycling, water exchange and overall ecosystem resilience.
Technology Used: FACE
FACE (Free-Air CO? Enrichment) technology:
- Releases controlled amounts of CO? into open-air forest environments.
- Allows real-time assessment of how trees respond without disturbing natural forest structure.
- Previously used in temperate biomes, but AmazonFACE is the first large-scale FACE experiment in tropical forests.
Structure & Working
- The site contains six large steel-ring towers, each enclosing 50–70 mature trees.
- Three rings are fumigated with CO? at concentrations matching climate projections for 2050–2060.
- Three rings act as control plots.
- Sensors record data every 10 minutes, including:
- CO? absorption
- Oxygen and water vapour release
- Responses to rainfall, sunlight, and storms
- Later stages will simulate artificial microclimates with higher atmospheric CO?.
Institutional Support
- Led by INPA (National Institute for Amazon Research) and Universidade Estadual de Campinas.
- Supported by the Brazilian federal government and the United Kingdom.
Significance
- Helps model the future behaviour of the Amazon under climate stress.
- Provides insights into:
- Carbon sequestration capacity
- Forest growth patterns
- Water cycle feedbacks
- Potential ecosystem tipping points
- Critical for global climate policymaking, especially ahead of COP30, where adaptation and mitigation strategies for the Amazon biome will be central.
UNEP Adaptation Gap Report 2025
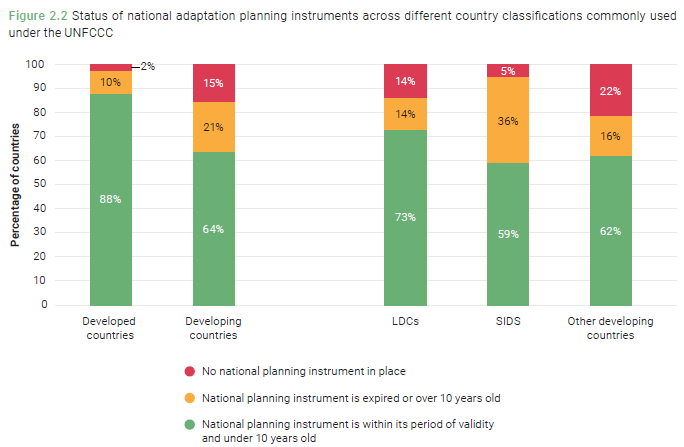
- 01 Nov 2025
In News:
The United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP) has released its flagship Adaptation Gap Report (AGR) 2025, titled “Running on Empty”.
The report warns that the global climate adaptation finance gap for developing countries has widened sharply, threatening progress toward climate resilience and the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs).
About the Adaptation Gap Report (AGR)
- Publisher: UNEP–Copenhagen Climate Centre, with global institutional contributions.
- Purpose: Tracks progress in climate adaptation planning, implementation, and finance, assessing global preparedness against climate impacts.
- Relevance: Supports policy negotiations under the UNFCCC and upcoming COP30 (Belém, Brazil).
Key Findings
1. Escalating Finance Needs
- Developing nations will require USD 310–365 billion annually by 2035, potentially rising to USD 440–520 billion when adjusted for inflation.
- The growing need reflects increasing risks from both rapid- and slow-onset climate events—heatwaves, floods, sea-level rise, and glacial melt.
2. Widening Adaptation Finance Gap
- Current adaptation finance (2023): Only USD 26 billion, covering just one-twelfth of total requirements.
- Finance gap: USD 284–339 billion annually.
- Falling trends: Funding fell from USD 28 billion (2022), meaning the Glasgow Climate Pact target of doubling adaptation finance by 2025 will likely be missed.
3. Debt-Heavy and Unequal Finance
- About 58% of adaptation finance is in the form of loans, many non-concessional—deepening debt vulnerabilities among developing nations.
- This creates a growing risk of “adaptation debt traps”, undermining the principle of climate justice.
4. Progress and Planning Gaps
- 172 countries have at least one National Adaptation Plan (NAP); however, 36 of them are outdated.
- 1,600+ adaptation actions have been reported globally, primarily in agriculture, water, biodiversity, and infrastructure, but few measure tangible resilience outcomes.
- Small Island Developing States (SIDS) show the highest integration of adaptation into national policies.
5. Limited Private Sector Role
- The private sector contributes only USD 5 billion annually, despite potential investment capacity up to USD 50 billion with supportive de-risking mechanisms.
- Low engagement is attributed to high risk perceptions and limited blended-finance instruments.
6. Multilateral Fund Support
- Disbursements through the Green Climate Fund (GCF), Global Environment Facility (GEF), and Adaptation Fund reached USD 920 million in 2024—an 86% rise over the previous five-year average, though UNEP warns this may be temporary.
Global Frameworks and Roadmaps
Baku–Belém Roadmap (COP29–COP30)
- Envisions USD 1.3 trillion per year by 2035 in total climate finance.
- Stresses the need for grant-based and concessional instruments rather than debt-heavy finance.
- Aims to align finance, transparency, and adaptation under a “global collective effort” (mutirão global) led by Brazil’s COP30 presidency.
New Collective Quantified Goal (NCQG)
- Proposed USD 300 billion by 2035, but UNEP cautions that it is insufficient and not inflation-adjusted, hence failing to meet real adaptation needs.
India and the Adaptation Gap Report 2025
1. National and Regional Context
- India’s climate strategy now prioritises adaptation-centric policies over mitigation, focusing on resilient agriculture, water systems, and disaster management.
- Frequent heatwaves, floods, and glacial retreats heighten India’s vulnerability, underscoring the need for adaptive investments.
2. Policy and Institutional Response
- India’s National Action Plan on Climate Change (NAPCC) and State Action Plans align with UNEP’s adaptation priorities.
- Initiatives like the International Solar Alliance (ISA), Coalition for Disaster Resilient Infrastructure (CDRI), and LiFE Mission showcase India’s global leadership in climate diplomacy.
3. Financial and Structural Constraints
- India continues to face adaptation investment gaps, relying heavily on concessional and multilateral finance.
- Domestic efforts like the National Adaptation Fund for Climate Change (NAFCC) are under fiscal strain due to limited international flow.
4. Developmental Balancing
- India maintains that development precedes decarbonisation, in line with the principle of Common But Differentiated Responsibilities and Respective Capabilities (CBDR–RC).
- The Economic Survey 2024–25 reiterates that achieving developed-nation status by 2047 is essential before aggressive deep decarbonisation.
- India remains committed to Net Zero by 2070, consistent with its Long-Term Low Emissions Development Strategy (LT-LEDS).
Cloud Seeding as a Pollution-Control Measure in Delhi
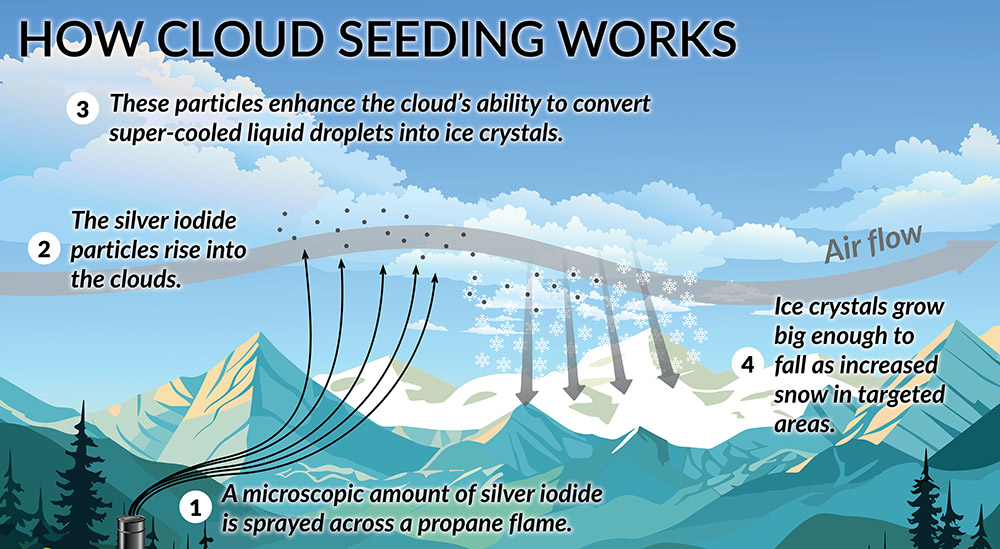
- 30 Oct 2025
In News:
With Delhi’s air quality plunging to severe levels each winter, the state government has renewed its call for cloud seeding as a potential intervention to reduce pollution. However, scientific assessments and governance experts warn that this approach offers limited, temporary relief and risks diverting attention from structural reforms required to address air pollution sustainably.
Why Delhi’s Air Quality Deteriorates in Winter
Delhi’s winter pollution is driven by a combination of meteorological and anthropogenic factors:
- Temperature Inversion: During winter, colder air remains trapped near the surface while warmer air lies above. This temperature inversion acts as a lid, preventing pollutants from rising and dispersing vertically.
- Low Wind Speeds: Weak winds limit horizontal movement of pollutants, causing particulate matter to accumulate in the lower atmosphere.
- Crop Residue Burning: Post-harvest stubble burning in Punjab, Haryana, and western Uttar Pradesh releases large quantities of smoke and suspended particles, which are carried to Delhi via prevailing winds.
- Dust and Urban Emissions: Vehicular emissions, construction dust, industrial exhaust, and waste burning remain trapped within the low boundary layer height, intensifying pollution.
- Post-Monsoon Stagnation: Stable high-pressure systems reduce atmospheric mixing, compounding North India’s chronic winter air quality problem.
What is Cloud Seeding?
Cloud seeding is a form of weather modification intended to enhance rainfall using chemical agents.
- Origin: First demonstrated in 1946 by Vincent J. Schaefer.
- Seeding Agents: Silver iodide, potassium iodide, sodium chloride, and dry ice are commonly used.
- Mechanism: The agents act as nuclei for condensation or ice-crystal formation, encouraging droplet growth. Once droplets become heavy, they fall as precipitation.
- Delivery Methods: Aircraft, rockets, or ground-based generators disperse particles into suitable moisture-laden clouds.
However, cloud seeding requires the presence of natural clouds with adequate moisture and cannot generate clouds on its own.
Scientific and Environmental Limitations
- Reliance on Existing Clouds: Delhi often lacks suitable cloud systems during peak pollution periods. Cloud seeding has no impact in the absence of adequate moisture.
- Weak Evidence of Effectiveness: Global scientific studies show inconsistent results. Even when rainfall occurs after seeding, establishing causality is difficult.
- Only Temporary Pollution Relief: Rain may wash away PM2.5 and PM10 temporarily, but pollution typically rebounds within 1–2 days. Secondary pollutants like ozone and sulphur dioxide remain unaffected.
- Environmental and Health Concerns: The use of silver iodide raises concerns regarding long-term ecological and health impacts due to chemical deposition. Evidence on safety is limited and inconclusive.
- Governance and Accountability Issues
- Unpredictable outcomes may lead to public criticism.
- Accountability becomes unclear if cloud seeding coincides with flooding or adverse weather events.
Ethical and Policy Concerns
- Misallocation of Resources: Investing in cloud seeding may divert funds from proven interventions.
- Distracting Public Attention: Temporary fixes risk undermining public trust and shifting focus away from systemic issues.
- Potential Misuse: Short-term optics may overshadow long-term environmental governance.
Real Solutions for Air Pollution Control
Experts emphasise that lasting improvement requires sustained structural action:
- Cleaner Transportation
- Strengthening public transport
- Transition to electric mobility
- Enforcing emission norms
- Sustainable Energy Transition
- Phasing down coal-based power
- Scaling up renewables
- Promoting clean industrial technologies
- Improved Waste Management
- Curbing open waste burning
- Efficient municipal systems
- Construction and Dust Control
- Enforcement of dust mitigation norms
- Use of green barriers and mechanised sweeping
- Agricultural Reforms
- Subsidising sustainable stubble management
- Promoting crop diversification in Punjab and Haryana
- Urban Planning Reforms
- Increasing green cover
- Reducing congestion through better mobility planning
UN’s Early Warnings for All (EW4All) Initiative
- 26 Oct 2025
In News:
The World Meteorological Organization (WMO), at its Extraordinary Congress in Geneva (October 2025), rallied its 193 Member States to commit to achieving universal early warning coverage by 2027 under the United Nations’ Early Warnings for All (EW4All) initiative. This global “Call to Action” seeks to ensure that no one dies for lack of warning in the face of intensifying weather, water, and climate-related disasters.
About Early Warning Systems (EWS)
An Early Warning System (EWS) is an integrated mechanism that combines:
- Hazard monitoring and forecasting,
- Disaster risk assessment,
- Communication of alerts, and
- Preparednessmeasures,to enable timely action that saves lives, livelihoods, and assets.
According to the WMO, a 24-hour advance warning can reduce disaster-related damage by up to 30%, underscoring the importance of predictive and community-based alert systems.
UN’s Early Warnings for All (EW4All) Initiative
- Launched: 2022 by UN Secretary-General António Guterres.
- Lead Agencies:
- World Meteorological Organization (WMO)
- UN Office for Disaster Risk Reduction (UNDRR)
- International Telecommunication Union (ITU)
- International Federation of Red Cross and Red Crescent Societies (IFRC)
- Goal: To ensure that every person on Earth is protected by life-saving early warnings for hazards such as cyclones, floods, droughts, and heatwaves by 2027.
- Philosophy: “Every dollar invested in early warnings saves up to fifteen dollars in avoided losses.”
The Early Warning “Value Chain”
The EW4All initiative emphasizes strengthening each link of the early warning value chain:
- Monitoring and Forecasting: Building accurate, real-time climate and hazard observation networks.
- Risk Assessment: Identifying vulnerable populations and areas through integrated risk mapping.
- Alert Dissemination: Delivering clear, trusted, and accessible alerts using multi-platform communication (digital, radio, community-based).
- Preparedness and Response: Ensuring communities understand warnings and act effectively.
Global Need and Rationale
- Over the past 50 years, climate, weather, and water-related disasters have claimed over 2 million lives, with 90% of deaths occurring in developing nations.
- Since 1970, economic losses from such disasters have exceeded US$4 trillion globally.
- Countries lacking multi-hazard early warning systems experience six times higher mortality and four times greater impacts than those equipped with such systems.
Current Global Status
- As of 2024, 108 countries have some capacity for multi-hazard early warning systems, up from 52 countries in 2014.
- However, Least Developed Countries (LDCs), Small Island Developing States (SIDS), and conflict-affected regions remain severely underprotected.
- A WMO assessment across 62 countries revealed:
- 50% have only basic hazard monitoring capacity.
- 16% have less than basic capacity.
- Technical barriers include:
- Weak observation networks,
- Limited data sharing,
- Inadequate financing, and
- Lack of community trust and awareness.
Progress Under EW4All
The WMO’s 2025 Congress marked a turning point as 193 nations endorsed a Call to Action for universal coverage by 2027.Key outcomes include:
- Country-led assessments and roadmaps for capacity building.
- Integration of EW4All targets with the Sendai Framework for Disaster Risk Reduction (2015–2030).
- Strengthened regional cooperation for hazard data sharing and early action.
- New partnerships between national meteorological services, private sector innovators, and humanitarian agencies.
Call to Action: Priority Measures
To meet the 2027 universal coverage target, WMO and the UN have urged governments to:
- Integrate EWS into national climate and disaster management policies.
- Secure long-term and predictable financing beyond short-term project aid.
- Empower National Meteorological and Hydrological Services (NMHSs) with clear mandates and authority.
- Ensure inclusivity by combining scientific data with indigenous knowledge to reach vulnerable and remote communities.
- Leverage innovation and AI to enhance the precision and speed of predictions.
- Promote open data sharing and capacity-building to close technological gaps.
Regional Implications for India
India, as one of the most climate-vulnerable nations facing monsoons, cyclones, and heatwaves, stands to benefit immensely from EW4All.
- India already operates a robust multi-hazard early warning system led by the India Meteorological Department (IMD), NDMA, and INCOIS.
- Integration under EW4All could help upgrade radar networks, enhance last-mile connectivity, and strengthen community-based disaster response.
- The initiative aligns with India’s National Disaster Management Plan (NDMP) and Sendai Framework priorities, reinforcing the “Zero Casualty” approach in disaster management.
FAO’s Global Forest Resources Assessment 2025
- 25 Oct 2025
In News:
India has moved up to the 9th position globally in total forest area, according to the Global Forest Resources Assessment (GFRA) 2025, released by the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) in Bali. The report reflects India’s steady progress in forest conservation, afforestation, and sustainable land management.
About the Global Forest Resources Assessment (GFRA)
- Published by: Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) of the United Nations
- Frequency: Every five years
- Objective: To provide comprehensive data on the world’s forests, covering their extent, condition, management, and use.
- 2025 Theme: Strengthening forest resilience for sustainable development.
Global Findings (GFRA 2025)
- Total global forest cover:4.14 billion hectares, accounting for 32% of the Earth’s land area, equivalent to 0.5 hectares per person.
- Top 10 countries by forest area:Russia, Brazil, Canada, USA, China, Democratic Republic of the Congo, Australia, Indonesia, India, and Peru.
- Deforestation trends:Global deforestation has slowed in the past decade, but the world continues to lose about 10.9 million hectares of forest annually (2015–2025)—a rate still considered alarming.
India’s Forest Status and Achievements
- Total forest cover:72.7 million hectares, accounting for about 2% of global forest area.
- Global ranking:
- 9th in total forest area (up from 10th position in the previous assessment).
- 3rd in annual forest area gain, after China and Russia, highlighting successful afforestation initiatives.
- Agroforestry Leadership:India and Indonesia together contribute over 70% of the world’s agroforestry areas, reflecting strong integration of trees in farmlands.
Significance of India’s Achievement
- Climate Change Mitigation:Expanding forest area enhances carbon sequestration, supporting India’s Nationally Determined Contributions (NDCs) under the Paris Agreement.
- Biodiversity Conservation:Forests serve as habitats for India’s rich flora and fauna, aiding ecosystem balance and wildlife protection.
- Livelihood and Socioeconomic Support:Around 275 million people in India depend on forests for subsistence, employment, and traditional livelihoods.
- Land and Water Security:Forests play a crucial role in soil conservation, groundwater recharge, and regulating hydrological cycles, particularly in fragile ecosystems.
- Global Commitments:Aligns with India’s obligations under the UN Decade on Ecosystem Restoration (2021–2030) and Sustainable Development Goal 15 (Life on Land).
Government Initiatives Driving Forest Growth
- Ek Ped MaaKe Naam Campaign:A nationwide movement encouraging citizens to plant trees in honor of their mothers, fostering personal and cultural ties to environmental conservation.
- National Mission for a Green India (GIM):A key component of the National Action Plan on Climate Change (NAPCC), targeting increased forest cover and improved forest quality to enhance carbon sinks.
- Compensatory Afforestation Fund Act, 2016 (CAMPA):Mandates compensatory levies for diversion of forest land for non-forest purposes and channels these funds into afforestation and eco-restoration activities.
- Eco-Sensitive Zones (ESZs):Buffer zones around Protected Areas, National Parks, and Wildlife Sanctuaries to limit harmful anthropogenic activities and protect ecological integrity.
- Joint Forest Management (JFM):Promotes community participation in forest conservation and regeneration by forming partnerships between local communities and forest departments.
Intrusion Detection System
- 25 Oct 2025
In News:
The Northeast Frontier Railway (NFR) has successfully completed trial works of the Intrusion Detection System (IDS) across four key railway sections in Assam and West Bengal to prevent elephant fatalities due to train collisions.
About the Intrusion Detection System (IDS)
The Intrusion Detection System (IDS) is a cutting-edge initiative of the Northeast Frontier Railway (NFR) under the Ministry of Railways, aimed at protecting wildlife—particularly elephants—while ensuring smooth and efficient railway operations through forested and ecologically sensitive zones.
Objective
- To minimize elephant deaths caused by train collisions along railway lines intersecting elephant corridors.
- To balance operational efficiency with ecological conservation, aligning with India’s broader goals of sustainable infrastructure and biodiversity protection.
Technology and Working
- Technology Used: IDS employsadvanced optical fibre sensing technology installed parallel to railway tracks at a distance of around 10 metres.
- Functioning:
- The system detects vibrations generated by elephant movement near railway tracks.
- These vibrations are captured by sensor cables, which relay the data to a central control room.
- The system then generates real-time alerts for train drivers and control rooms, enabling them to take immediate preventive actions, such as slowing down or halting trains.
This real-time detection mechanism ensures timely intervention and minimizes human-wildlife conflict along railway routes.
Implementation by NFR
The Intrusion Detection System has been successfully implemented in the following pilot sections:
- Madarihat–Nagrakata section (Alipurduar Division)
- Habaipur–Lamsakhang–Patharkhola–Lumding section (Lumding Division)
- Kamakhya–Azara–Mirza section (Rangiya Division)
- Titabar–Mariani–Nakachari section (Tinsukia Division)
- Coverage:The pilot installations collectively span 64.03 km of elephant corridors and 141 km of block sections, marking a significant step in NFR’s ongoing wildlife protection efforts.
Significance
- Wildlife Protection: Helps prevent accidental elephant deaths, promoting coexistence between rail infrastructure and biodiversity.
- Operational Efficiency: Enhances train safety by providing advance alerts, reducing service disruptions.
- Technological Advancement: Demonstrates the integration of AI and fibre-optic sensing in railway operations.
- Environmental Responsibility: Reflects the government’s commitment to sustainable development goals (SDGs), particularly those related to life on land (SDG-15) and industry, innovation and infrastructure (SDG-9).
Central Asian Mammals Initiative
- 24 Oct 2025
In News:
- Representatives from several Central Asian countries — including India — have endorsed a six-year work programme (2021–2026) under the Central Asian Mammals Initiative (CAMI) to identify and conserve priority transboundary regions crucial for the survival of 17 iconic mammal species across the region.
- The meeting was hosted by Uzbekistan, under its presidency of the 14th Conference of the Parties (COP14) to the Convention on the Conservation of Migratory Species of Wild Animals (CMS).
About the Central Asian Mammals Initiative (CAMI)
- Launched: 2014, during CMS COP11 (Quito, Ecuador).
- Objective: To halt and reverse the population decline of migratory mammals across 14 Central Asian countries, through coordinated conservation action.
- Framework: Provides a regional platform for cooperation among Range States to address shared threats such as habitat loss, poaching, migration barriers, and climate change.
Key Features
- Species Covered (17 total):Argali sheep, Asiatic cheetah, Asiatic wild ass, Bukhara deer, Eurasian lynx, Gobi bear, Goitered gazelle, Kiang, Mongolian gazelle, Pallas’s cat, Persian leopard, Przewalski’s horse, Saiga antelope, Snow leopard, Urial, Wild camel, and Wild yak.
- Range States Involved:Bhutan, China, India, Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Mongolia, Nepal, Pakistan, Tajikistan, Turkmenistan, and Uzbekistan; with Iran and the Russian Federation participating online.
- Collaborating Organizations: Over 15 conservation institutions, including IUCN, government agencies, and NGOs, are supporting the work programme’s implementation.
- Current Programme of Work: Adopted for 2021–2026, focuses on ecosystem-based conservation, improved connectivity, and data-sharing between range states.
Recent Meeting Outcomes
- Countries reaffirmed commitment to joint action for migratory mammal conservation, emphasizing that species conservation transcends national borders.
- Success stories shared included recovery trends in Saiga antelope, Bukhara deer, and Persian leopard populations.
- Delegates discussed persistent challenges such as fragmented habitats, climate change impacts, illegal hunting, and limited cross-border coordination.
- Uzbekistan’s Minister of Ecology Aziz Abdukhakimov highlighted the importance of a unified regional approach, stating that “these species know no borders, and neither should our conservation efforts.”
About the Convention on the Conservation of Migratory Species (CMS)
- Also known as: Bonn Convention.
- Established: 1979 in Bonn, Germany.
- Under the Aegis of: United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP).
- Mandate: To promote the conservation and sustainable use of migratory animals and their habitats worldwide.
- Nature: The only global and UN-based intergovernmental treaty exclusively focused on migratory species conservation.
- Instruments:
- Legally binding Agreements
- Non-binding Memoranda of Understanding (MoUs)
- Decision-making Body:Conference of the Parties (COP).
- Next Milestone:CMS COP15 will be held in Brazil (March 23–29, 2026), where the CAMI resolution will be reviewed and updated.
Indian Scops-Owl
- 24 Oct 2025
In News:
In a remarkable development, birdwatchers have reported the first-ever sighting of the Indian Scops-Owl (Otus bakkamoena) near the Daroji Sloth Bear Sanctuary in Vijayanagara district, Karnataka.
About the Indian Scops-Owl
- Scientific Name:Otus bakkamoena
- Family: Strigidae
- Distribution: Widely found across India, Nepal, Pakistan, Sri Lanka, and Iran.
- Habitat: Occupies forests, scrublands, and agricultural areas; it is non-migratory, remaining within a localized territory throughout the year.
Distinctive Features
- Size: Measures around 17–25 cm in height, with a wingspan of about 45 cm.
- Appearance: Characterized by ear-like tufts, a stocky body, short tail, and cryptic plumage of browns and greys that blend seamlessly with tree bark.
- Eyes: Large, bright yellow eyes (sometimes dark in appearance) with black pupils, providing enhanced nocturnal vision.
- Feathers: Soft and fluffy, aiding silent flight and insulation against cool night air.
- Behavior: A nocturnal predator, feeding mainly on insects and small invertebrates, playing an important role in natural pest control.
- Conservation Status:IUCN Red List:Least Concern
Ecological and Conservation Significance
- The sighting near Daroji Sloth Bear Sanctuary—a region primarily known for its sloth bear population and dry deciduous ecosystem—indicates a broader ecological range for the species than previously recorded.
- Experts suggest the observation could either represent an undocumented resident population or a rare dispersal event. Either case underscores the need for detailed ornithological surveys to assess the owl’s breeding and habitat patterns in the region.
- From a conservation perspective, the finding reinforces the importance of protecting lesser-known habitats within Karnataka, which continue to support undiscovered or rarely documented species.
Tetrataeniummanilalianum

- 23 Oct 2025
In News:
Researchers have recently discovered a new plant species named Tetrataeniummanilalianum in the Eravikulam National Park, Kerala, adding to the extraordinary biodiversity of the Western Ghats, one of the eight “hottest biodiversity hotspots” in the world. The finding has been published in the Nordic Journal of Botany (Sweden), underscoring India’s growing contributions to global botanical research.
About Tetrataeniummanilalianum
- The newly identified plant belongs to the carrot family (Apiaceae/Umbelliferae), which also includes species such as carrot, coriander, cumin, fennel, and ajwain.
- It was discovered in the high-altitude grasslands bordering the shola forests of the Eravikulam National Park in Idukki district, Kerala.
- The plant bears white flowers and possesses underground rhizomes. It sprouts and blooms only during the monsoon season, adapting to the region’s moist climatic conditions.
- This discovery marks the 48th identified species within the Tetrataenium genus and is the first of its kind recorded globally.
- The species has been named in honour of Prof. K.S. Manilal, a distinguished botanist, founder president of the Indian Association for Angiosperm Taxonomy (IAAT), and former Head of the Department of Botany at the University of Calicut.=
Ecological Context – Eravikulam National Park
- Location: Situated in the Idukki district of Kerala, the park spans 97 sq. km along the summit of the Western Ghats.
- Topography: Encompasses rolling grasslands interspersed with shola forests in the upper valleys.
- Climate: Receives heavy rainfall during both the southwest (June–July) and northeast (October–November) monsoons, making it one of the wettest regions in the world.
- Flora: Rich in endemic species such as Actinodaphnebourdilloni, Microtropisramiflora, Pittosporum tetraspermium, and the once-thought-extinct orchid Brachycorythiswightii.
- Fauna: Home to the endangered NilgiriTahr, with nearly half the world’s population residing here. Other species include the Gaur, Sloth Bear, Nilgiri Langur, Tiger, Leopard, Giant Squirrel, and Wild Dog.
- The park also hosts the Anamudi Peak (2,695 m), the highest mountain in South India, and is famous for the Neelakurinji flowers that bloom once every twelve years.
Carabid Beetle

- 22 Oct 2025
In News:
- Recent research has identified Carabid ground beetles (family: Carabidae) as potential bioindicators for tracking microplastic contamination in soil ecosystems.
- Given the increasing global concern over microplastic pollution, especially in terrestrial environments, this finding highlights the ecological significance of these beetles in environmental monitoring and sustainable agriculture.
About Carabid Beetles
- Taxonomy: Belong to the family Carabidae, a large and diverse group of insects commonly known as ground beetles.
- Distribution: Found globally across a range of habitats — from forests, grasslands, and wetlands to agricultural fields and urban landscapes.
- Adaptability: Thrive in temperate and tropical climates, indicating high ecological resilience.
Physical and Biological Features
- Appearance:Typically, dark, shiny, and robust-bodied insects with long legs and strong mandibles, enabling them to be agile hunters.
- Defence Mechanism: When threatened, they emit a pungent odour to deter predators.
- Diet: Predatory in nature; they feed on pests such as caterpillars, slugs, snails, and other small invertebrates, making them beneficial for biological pest control.
- Life Cycle: Undergo complete metamorphosis — progressing through four stages: egg, larva, pupa, and adult.
- Reproduction:Typically,sexual with internal fertilization.
Ecological Role and Importance
- Natural Pest Regulators: Their predatory behavior helps control pest populations, reducing dependence on chemical pesticides in agriculture.
- Key Role in Soil Ecology:
- Contribute to nutrient cycling by preying on decomposers and pest species.
- Influence soil food web structure, functioning both as predators and prey for higher trophic levels.
- Indicator Species: Their abundance and diversity reflect the overall health and fertility of soil ecosystems.
- Bioindicator Concept:Bioindicators are species or groups whose presence, absence, or physiological condition reflects the quality of the environment and ecological changes.
- In Agriculture:In India and other agrarian regions, farmers have traditionally used bioindicators—such as insects, birds, and soil invertebrates—to predict rainfall, assess soil fertility, and evaluate pest management success.
- Microplastic Tracking Role:
- Researchers have found that Carabid beetles accumulate microplastic particles in their bodies, particularly within their digestive tracts, after feeding in contaminated soil.
- Their wide distribution and soil-dwelling nature make them ideal sentinels for studying microplastic pollution in terrestrial habitats.
- By analysing beetle tissues and microplastic residues, scientists can map the extent and distribution of soil microplastics with greater accuracy.
Why Carabid Beetles Are Effective Bioindicators
- Widespread Occurrence: Present in nearly all terrestrial ecosystems, ensuring broad geographic monitoring coverage.
- Ecological Sensitivity: Rapidly respond to changes in soil composition, contamination, and habitat quality.
- Trophic Position: As mid-level predators, they integrate pollutants and environmental stresses from lower trophic levels.
- Ease of Sampling: Readily captured and monitored through standard ecological methods like pitfall traps.
- Non-destructive Monitoring: Studying beetle populations allows long-term soil health assessments without altering ecosystems.
Hygrocybe Pellucida
- 21 Oct 2025
In News:
In a significant biodiversity finding, Hygrocybe pellucida, a rare and recently identified fungus species, has been recorded for the first time in Telangana at the Kawal Tiger Reserve. The species, known for its vivid waxy appearance, was first described in Kerala in 2024 and belongs to the Hygrophoraceae family. This sighting expands its known range in southern India and highlights the ecological richness of the reserve.
About Hygrocybe pellucida
- Part of the Hygrocybe (waxcap) genus, containing ~350 species globally
- Distinguished by bright, translucent, waxy fruit bodies
- Prefers nutrient-poor, moss-rich forest floors and unimproved grasslands
- Indicator of undisturbed and pristine microhabitats
- Newly documented fungus species in India, reinforcing fungal diversity in tropical ecosystems
Ecological Significance
The discovery underscores the value of fungi as bioindicators of healthy ecosystems. It reflects the presence of intact microhabitats—moist, shaded forest floors with moss and low human interference—and complements ongoing biodiversity documentation in the region. Researchers have identified over 80 fungal species in Kawal, including several first records for Telangana, such as Marasmiushaematocephalus and Dacryopinaxspathularia.
Kawal Tiger Reserve: Key Facts
- Location: Telangana, along the Godavari River in the Deccan Peninsula–Central Highlands
- Declared Tiger Reserve: 2012 (originally a Wildlife Sanctuary)
- Landscape Linkages: Connects to Tadoba–Andhari (Maharashtra) and Indravati (Chhattisgarh) Tiger Reserves
- Topography: Part of the Sahyadri mountain ranges
- Rivers: Catchment area for Godavari and Kadam
- Vegetation:Southern Tropical Dry Deciduous Forests
- Flora: Teak, bamboo, Anogeissuslatifolia, Mitragyna parviflora, etc.
- Fauna: Tiger, leopard, sambar, blackbuck, nilgai, chinkara, chousingha, spotted deer
Conservation Perspective
While tiger conservation often takes center stage, this discovery emphasizes that forest floor biodiversity —including fungi and microfauna—plays a critical ecological role and requires equal attention. The finding strengthens the case for protecting microhabitats and maintaining minimal human disturbance in core forest areas.
Zombie Deer Disease
- 21 Oct 2025
In News:
Florida has recently confirmed new cases of Chronic Wasting Disease (CWD), commonly referred to as “Zombie Deer Disease,” heightening concerns among wildlife authorities in the United States. This marks the second confirmed case in wild deer in the state since the first detection in June 2023, triggering an emergency response and surveillance measures in affected regions.
What is Chronic Wasting Disease (CWD)?
CWD is a progressive, fatal neurodegenerative disease affecting deer, elk, moose, and reindeer. It damages the central nervous system, causing:
- Severe weight loss
- Disorientation and loss of awareness
- Abnormal behavior, including reduced fear of humans
- Excessive salivation, increased drinking and urination
- Progressive debilitation and death
The incubation period ranges from 18–24 months, during which animals may appear healthy before showing symptoms.
Cause
- CWD is caused by prions — infectious misfolded proteins that trigger abnormal protein folding in the brain.
- Unlike bacteria or viruses, prions contain no DNA or RNA.
- Prions create spongy holes in brain tissue, leading to neurological failure.
Transmission
CWD spreads through:
- Direct contact among animals
- Contaminated saliva, urine, blood, and feces
- Environmental persistence — prions survive for years in soil, plants, and water
- Movement of infected animals
- Scavengers dispersing prion material
- Use of natural deer urine lures by hunters
Prions are extremely resilient, making eradication difficult.
Threat to Humans
- No confirmed human cases have been reported so far.
- However, health experts advise caution due to similarities with Bovine Spongiform Encephalopathy (mad cow disease), a prion disorder linked to human deaths in the past.
- There is no cure or vaccine for CWD.
Tuvalu Island
- 21 Oct 2025
In News:
Tuvalu has formally become the 90th State Member of the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN), marking a major step in strengthening its global environmental engagement. This development aligns with the nation’s growing efforts to protect its fragile ecosystems and advocate for climate-vulnerable island states.
About Tuvalu
- Located in the west-central Pacific Ocean between Australia and Hawaii, Tuvalu (formerly the Ellice Islands) comprises nine low-lying atolls and coral islands spanning just 26 sq km—making it the fourth-smallest country in the world.
- With no point higher than 4.5 m above sea level, the country faces existential threats from sea-level rise, coastal erosion and climate change.
- It has an Exclusive Economic Zone (EEZ) of around 900,000 sq km, rich in marine biodiversity, coral reefs, fisheries and migratory seabirds.
- Tuvalu operates as a parliamentary democracy under a constitutional monarchy within the Commonwealth, recognizing King Charles III as head of state. Funafuti is the capital, and Tuvaluan and English are widely spoken. Its economy relies on subsistence activities, remittances, limited copra production, sale of postage stamps, and fisheries licensing revenues.
Significance of IUCN Membership
By joining IUCN, Tuvalu gains access to a global network of conservation experts, funding avenues and policy platforms. This membership strengthens its capacity to pursue:
- Climate change adaptation and resilience strategies
- Sustainable fisheries and marine resource management
- Community-driven conservation initiatives
- Partnerships with bodies such as the Green Climate Fund and Global Environment Facility
The move comes at a time when Pacific Island nations are pushing for stronger global action on climate change, adaptation financing and protection of ocean ecosystems.
Why It Matters
Tuvalu’s participation in IUCN brings heightened international focus on the plight of small island developing states (SIDS) facing climate-induced challenges. It enhances the country's voice in shaping global environmental governance and reinforces the need to safeguard vulnerable ecosystems and cultures deeply connected to the ocean.
SAIME Initiative

- 17 Oct 2025
In News:
A climate-adaptive aquaculture model from West Bengal’s Sundarbans — the Sustainable Aquaculture in Mangrove Ecosystems (SAIME) initiative — has recently received Global Technical Recognition from the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) of the United Nations. This recognition highlights a successful nature-based livelihood model that integrates aquaculture with mangrove restoration.
About the SAIME Initiative
The SAIME programme is a unique multi-stakeholder partnership aimed at promoting sustainable, mangrove-linked shrimp aquaculture while restoring fragile coastal ecosystems. By combining aquaculture practices with mangrove conservation, it seeks to build climate-resilient livelihoods in the vulnerable Sundarbans delta region.
- Focus: Climate-adaptive, ecosystem-based livelihood system
- Key Approach: Integrates brackish-water shrimp farming with mangrove plantation
- Objective:
- Protect mangrove forests
- Enhance biodiversity
- Provide sustainable income to coastal communities
- Implementation Partners:
- Nature Environment & Wildlife Society (NEWS)
- Global Nature Fund (GNF)
- Naturland (Germany-based standards organisation)
- Bangladesh Environment & Development Society (BEDS)
This model demonstrates how community-driven conservation can coexist with economic activity, reducing ecological pressure on mangrove ecosystems while supporting rural incomes.
Significance
Environmental Benefits
- Restores mangrove cover in cyclone-prone Sundarbans
- Enhances carbon sequestration, aiding climate mitigation
- Prevents coastal erosion and acts as a buffer against storm surges
- Supports rich biodiversity, including fish and crustacean populations
Socio-Economic Impact
- Offers a stable income source to local fishers and farmers
- Reduces dependency on destructive practices
- Strengthens climate resilience and livelihood security in vulnerable communities
Mangroves: Key Features
- Salt Tolerance:Specialised roots and salt-excreting mechanisms
- Aerial/Pneumatophore Roots: Enable respiration in waterlogged soils
- Prop Roots: Provide support against tides and cyclones
- Viviparous Seeds: Germinate on parent plant for survival in saline water
- Carbon Storage: Among the most carbon-rich ecosystems globally
Mangroves play a crucial role in mitigating climate change, protecting coasts, and supporting marine life — making their protection vital for ecological balance and disaster resilience.
Impatiens Rajibiana

- 16 Oct 2025
In News:
A team from the Botanical Survey of India (BSI) has identified a new species of balsam flower named Impatiens rajibiana in Arunachal Pradesh. The discovery was made in the natural forest areas of Shergaon, West Kameng district, highlighting the region’s rich floral biodiversity.
Key Details and Ecological Significance
- Impatiens rajibiana belongs to the Balsaminaceae family, commonly known as balsams.
- The species was located in moist, shaded habitats at an elevation of over 2,000 metres, indicating its preference for cool, humid, high-altitude forest ecosystems.
- Balsams are known for their delicate flowers and high levels of endemism, often restricted to narrow ecological zones.
- India currently hosts around 230 species of balsams, including the widely known Impatiens balsamina (garden balsam or touch-me-not).
- Arunachal Pradesh has emerged as a hotspot for balsam diversity. Between 2013 and 2017, more than 16 new species of Impatiens were documented from the state, such as Impatiens godfreyi and Impatiens sashinborthakurii, reinforcing the Eastern Himalayas’ status as a key centre of plant discovery.
Conservation Relevance
- The discovery of Impatiens rajibiana underlines the ecological value of the Eastern Himalayan region and the need for continued field surveys and conservation.
- As many balsam species have restricted distribution and small populations, they may be vulnerable to habitat disturbances, climate change, and anthropogenic pressures.
- Protecting fragile mountain ecosystems and promoting biodiversity research remain critical for safeguarding endemic plant species like Impatiens rajibiana.
Blue Flag Certification

- 15 Oct 2025
In News:
- Five beaches in Maharashtra have recently been awarded the prestigious Blue Flag certification, a global eco-label that recognises high standards in environmental management, cleanliness, and sustainable tourism.
- The certified beaches include Shrivardhan and Nagaon (Raigad district), Parnaka (Palghar), and Guhagar and Ladghar (Ratnagiri district). The announcement was made by the state government, marking a significant achievement in coastal conservation and eco-tourism promotion.
About Blue Flag Certification
The Blue Flag is an internationally recognised eco-label awarded by the Foundation for Environment Education (FEE), Denmark. Established in France in 1985 and expanded globally in 2001, it is regarded as one of the world's most prestigious voluntary awards for beaches, marinas, and sustainable tourism boats.
Criteria and Objectives
To receive the Blue Flag, sites must meet 33 stringent criteria across key focus areas:
- Water quality
- Environmental management
- Environmental education and awareness
- Safety and essential services
The certification aims to promote sustainable development in coastal and freshwater ecosystems by ensuring high cleanliness standards, protecting natural habitats, and encouraging responsible tourism practices. Its mission centers on environmental education, conservation, and sustainable tourism development.
Blue Flag Beaches in India
With the addition of the five Maharashtra beaches, India continues to expand its presence on the global sustainable tourism map. Previously recognised Indian Blue Flag beaches include:
- Shivrajpur (Gujarat)
- Ghoghla (Diu)
- Kasarkod and Padubidri (Karnataka)
- Kappad (Kerala)
- Rushikonda (Andhra Pradesh)
- Golden Beach (Odisha)
- Radhanagar (Andaman & Nicobar)
- Kovalam (Tamil Nadu)
- Eden (Puducherry)
- Minicoy Thundi and Kadmat (Lakshadweep)
Significance
This recognition underscores India's ongoing efforts to align coastal tourism with global environmental standards, enhance beach amenities, and promote eco-friendly tourism models. It also strengthens India's initiative to improve coastal governance under programmes like the Integrated Coastal Zone Management Project and the government's broader sustainability mission.
Armenia Joins IUCN

- 15 Oct 2025
In News:
Armenia has recently become the newest State Member of the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN), marking a key milestone in its environmental policy direction. The announcement was made at the IUCN World Conservation Congress in Abu Dhabi, reflecting Armenia’s growing commitment to global biodiversity protection, sustainable development, and alignment with international conservation frameworks.
Significance of Membership
By joining IUCN, Armenia gains access to global research, conservation tools, and international collaborations. This step also supports its preparations to host COP17 of the Convention on Biological Diversity in 2026, signalling its intent to play a leadership role in global biodiversity discussions.
IUCN leadership has welcomed Armenia’s membership, noting that it aligns with the country’s efforts to expand protected areas, restore degraded ecosystems, and bring its environmental laws in line with international standards.
Armenia’s Biodiversity and Conservation Efforts
Situated at the crossroads of Europe and Asia, Armenia hosts varied ecosystems—from alpine meadows and mountain forests to semi-deserts and freshwater bodies. These habitats support several threatened and endemic species, including:
- Caucasian leopard (Critically Endangered)
- Bezoar goat
- Sevan trout, native to Lake Sevan
The country has made progress in environmental governance through initiatives such as its National Biodiversity Strategy and Action Plan and the Red Book of Armenia. Its conservation agenda includes forest restoration across 12.9% of its territory by 2030, strengthening biodiversity monitoring, and expanding protected areas.
Geographical and Environmental Profile of Armenia
- Location: Southern Caucasus; landlocked
- Borders: Georgia (north), Azerbaijan (east), Iran (southeast), Turkey (west)
- Terrain: Dominated by the Lesser Caucasus Mountains; volcanic soils rich in nitrogen, potash, phosphates
- Highest Peak:Mount Aragats (4,090 m)
- Climate: Highland continental — hot summers, cold winters
- Rivers: Aras, Hrazdan, Arpa, Vorotan — key for irrigation and hydropower
- Major Lake:Lake Sevan, Armenia’s largest freshwater body
- Resources: Small deposits of copper, gold, molybdenum, zinc, bauxite
- Capital & Language: Yerevan; Armenian
IUCN Kenton Miller Award 2025

- 14 Oct 2025
In News:
India has achieved a landmark moment in global conservation as Dr. Sonali Ghosh, Field Director of Kaziranga National Park and Tiger Reserve (Assam), became the first Indian to receive the prestigious IUCN WCPA Kenton Miller Award 2025. The honour was announced at the IUCN World Conservation Congress in Abu Dhabi, highlighting India’s rising leadership in biodiversity governance and protected-area innovation.
About the IUCN Kenton Miller Award
- Instituted: 1999
- Presented by:IUCN World Commission on Protected Areas (WCPA)
- Named after: Dr. Kenton R. Miller, eminent conservationist & former IUCN Director-General
- Purpose:Recognisesoutstanding innovation and excellence in the sustainability and governance of protected areas
- Eligibility: Protected-area managers, researchers, community/indigenous conservation practitioners
- Award Components:
- USD 5,000 grant
- Global citation
- Sponsored participation at the IUCN Congress
Significance of Dr. Ghosh’s Contribution
Dr. Ghosh has been awarded for pioneering inclusive and sustainable protected-area management across the Kaziranga-Orang-Manas landscape. Key initiatives include:
- Community-centric conservation: Empowering local and indigenous communities as co-stewards
- Eco-tourism models: Ensuring livelihood security while safeguarding biodiversity
- Anti-poaching and habitat security: Strengthening surveillance and ecological connectivity
- Gender inclusion: Promoting women’s participation in frontline conservation forces
Her leadership reflects India’s approach to biodiversity protection through grassroots participation, science-based governance, and livelihood integration.
Broader Context: India at the IUCN Congress
At the Congress, India reiterated its commitment to global environmental cooperation. Union Minister Kirti Vardhan Singh engaged with international delegates and IUCN leadership on advancing shared conservation goals, reinforcing India's stance as a proactive global environmental actor.
About IUCN and the World Conservation Congress
- Founded: 1948
- HQ: Switzerland
- Global network of governments, NGOs, and experts from 160+ countries
- World Conservation Congress: Held every four years to set global biodiversity priorities
Previous Winner (2023)
- Maria del Carmen Garcia Rivas (Mexico) – Honoured for community-led management of marine protected areas.
IUCN World Heritage Outlook 2025
- 14 Oct 2025
In News:
- The IUCN World Heritage Outlook 4, to be launched at the IUCN World Conservation Congress 2025 in Abu Dhabi, represents the world’s most comprehensive periodic evaluation of the conservation status of UNESCO natural and mixed World Heritage Sites.
- Conducted every 3–5 years by the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) and the World Commission on Protected Areas (WCPA), it provides an independent, transparent assessment of protection efforts, threats, and future prospects for these globally significant ecosystems.
Purpose and Significance
The Outlook functions as a global conservation barometer designed to:
- Monitor the state of conservation of natural World Heritage Sites
- Highlight exemplary site management and transfer of best practices
- Provide early warnings for ecological degradation and governance failures
- Bridge data gaps through expert-led evaluation and advanced monitoring tools
- Showcase the societal and ecological benefits of natural heritage, including livelihoods, disaster resilience, and carbon storage
This mechanism complements UNESCO’s statutory monitoring under the 1972 World Heritage Convention, strengthening global efforts to realize the Kunming–Montreal Global Biodiversity Framework (KM-GBF) targets by 2030.
Global Conservation Outlook: Key Findings (2025)
- ~65% of sites show stable or improving health since 2020, reflecting enhanced governance and restoration actions. Example: Galápagos Islands, Yellowstone National Park
- Over 80% of sites face direct climate threats—coral bleaching, glacier retreat, wildfires. Example: Great Barrier Reef
- ≈60% experience pressures from invasive species, habitat loss, and unsustainable resource use
- Marine sites like Komodo National Park (Indonesia) and Aldabra Atoll (Seychelles) show progress through sustainable tourism and science-based management
- Technology integration (AI, satellite mapping, eDNA) is improving real-time monitoring. Example: AI-enabled wildlife tracking in Okavango Delta
- Around 15 sites have moved into the Danger List due to conflict, pollution, and climate impacts
- Natural World Heritage sites hold ~10% of global terrestrial carbon, underlining their climate role
Natural World Heritage: Global Profile (2024)
- 271 sites with natural Outstanding Universal Value
- 231 natural, 40 mixed
- 22% of all World Heritage properties (1,223 total)
- Over 470 million hectares protected across land and sea
- Represent ~8% of global protected area coverage
- Spread across 115 countries
- Africa: 47
- Asia-Pacific: 85
- Europe & North America: 83
- Latin America & Caribbean: 47
- Arab region: 9
- 18 transboundary sites; 15 in Danger List
India: Trends and Insights
India hosts 7 natural and mixed World Heritage Sites, spanning the Himalayas to coastal wetlands, constituting ~1.5% of global natural WH coverage.
Positive developments
- Kaziranga&Manas: Improved biodiversity and anti-poaching success through community stewardship and regulated ecotourism
Sites of concern
- Sundarbans: Declining mangroves due to salinity rise, cyclones, and sea-level change
- Western Ghats: Pressures from mining, infrastructure, and land-use conflicts
- Nanda Devi & Great Himalayan National Park: Glacial melt and invasive species affecting Himalayan watersheds
Policy support
- Wildlife (Protection) Amendment Act, 2022
- LiFE Mission for sustainable lifestyles aligned with KM-GBF
- Funding gaps: ~30–40% higher financial allocation needed, especially for marine and transboundary sites
Major Challenges
|
Challenge |
Impact |
|
Climate change |
Coral bleaching, glacial retreat, desertification |
|
Unsustainable development |
Habitat fragmentation, tourism pressure |
|
Funding shortfalls |
Inadequate staffing, weak surveillance |
|
Governance issues |
Overlapping mandates, weak enforcement |
|
Biodiversity data gaps |
Limits adaptive and real-time conservation |
Recommendations
- Climate-resilient planning: Integrate heritage into national climate strategies. Example: Aligning LiFE and National Adaptation Fund with site targets
- Green financing: Carbon credits, biodiversity funds, CSR, eco-investment
UNDP–GEF BIOFIN as model - Local and Indigenous partnership: Community co-management and benefit-sharing. Example: Eco-Development Committees in Manas and Periyar
- Tech-enabled conservation: AI surveillance, remote sensing, eDNA, drones. Example: IUCN Global Ecosystem Atlas initiative
- Transboundary cooperation: Joint research and ecological corridors. Example: India–Nepal Terai Arc Landscape
India’s National Red List Roadmap

- 12 Oct 2025
In News:
At the IUCN World Conservation Congress 2025 in Abu Dhabi, India launched its National Red List Roadmap and Vision 2025–2030, marking a significant milestone in national biodiversity documentation and conservation policy. The initiativerepresents India’s commitment to establishing a comprehensive, science-based framework for assessing species and shaping long-term conservation priorities.
The National Red List Roadmap: Overview and Objectives
The National Red List Roadmap is India’s first integrated national initiative to identify, classify, and conserve threatened species across ecosystems — terrestrial, freshwater, and marine — in alignment with IUCN global standards.
It seeks to:
- Develop a nationally coordinated and inclusive red-listing system for flora and fauna.
- Generate baseline data and threat assessments to guide evidence-based policymaking.
- Strengthen India’s obligations under the Convention on Biological Diversity (CBD) and the Kunming–Montreal Global Biodiversity Framework (KMGBF).
- Foster collaboration among scientists, conservationists, and local communities to ensure equitable biodiversity protection.
The programme will culminate in the publication of India’s National Red Data Books for flora and fauna by 2030, creating an authoritative reference for conservation planning.
Institutional Collaboration
The roadmap is jointly prepared by:
- Zoological Survey of India (ZSI)
- Botanical Survey of India (BSI)
- IUCN-India, and
- Centre for Species Survival (CSS), India
This inter-agency collaboration ensures a unified system that combines scientific taxonomy, digital technology, and local knowledge systems to monitor and protect India’s biological diversity.
Vision 2025–2030: India’s Strategic Conservation Blueprint
The Vision 2025–2030 document provides a forward-looking framework to guide biodiversity governance over the next decade. It focuses on data-driven conservation, institutional synergy, and community participation, aligning with the UN Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) and KMGBF targets.
Key Objectives:
- Establish a centralised biodiversity database for national-level coordination.
- Enhance species identification and taxonomy through expert collaboration.
- Integrate digital tools, GIS mapping, and field surveys for real-time species monitoring.
- Build a network connecting scientific institutions, local communities, and policymakers.
- Promote inclusive and equitable participation of indigenous and local communities in conservation processes.
By 2030, India aims to complete comprehensive species assessments, update threat categories, and integrate the results into national wildlife action plans and climate strategies.
India’s Biodiversity Profile
India is recognised as one of the 17 megadiverse countries in the world and hosts four of the 36 global biodiversity hotspots — the Himalayas, Western Ghats, Indo-Burma, and Sundaland.
Key Statistics:
- Covers 2.4% of global land area but supports nearly 8% of global flora and 7.5% of global fauna.
- Houses over 104,000 faunal species, 18,000 species of flowering plants, and around 20,000 marine species.
- Approximately 28% of plant species and 30% of animal species are endemic to India.
These figures underscore India’s ecological richness and the urgency for systematic monitoring and protection.
Legal and Policy Backing
- The initiative aligns with India’s robust legal framework for biodiversity conservation, anchored in the Wild Life (Protection) Act, 1972, which was amended in 2022 to extend protection to species listed under the CITES Appendices.
- The National Red List Roadmap will complement existing programmes like the National Biodiversity Mission, National Wildlife Action Plan, and Integrated Development of Wildlife Habitats, ensuring that conservation decisions are guided by scientific evidence and threat analysis.
Significance for Conservation Policy
- Evidence-Based Decision-Making: The roadmap institutionalises data-backed conservation planning.
- National Accountability: Regular species assessments will help monitor progress under national and global biodiversity targets.
- Scientific Collaboration: Encourages coordination among researchers, policymakers, and conservation agencies.
- Public Engagement: Integrates traditional ecological knowledge and community-driven documentation.
- Global Alignment: Reinforces India’s commitment to the Kunming–Montreal Global Biodiversity Framework and CBD Aichi Targets.
Tigers Outside Tiger Reserves (TOTR) Project
- 10 Oct 2025
In News:
During Wildlife Week 2025 (October 2–8), the Union Minister for Environment, Forest and Climate Change, Bhupender Yadav, launched five major species conservation and conflict management initiatives at the Forest Research Institute (FRI), Dehradun. The initiatives aim to reinforce India’s commitment to biodiversity conservation while addressing the growing challenge of human–wildlife conflict amid rapid development.
The Five Initiatives
- Project Dolphin (Phase II)
- Project Sloth Bear
- Project Gharial
- Centre of Excellence for Human–Wildlife Conflict Management (CoE–HWC)
- Tigers Outside Tiger Reserves (TOTR)
In addition, four national-level action plans and field guides were unveiled to support species monitoring and population assessment of river dolphins, tigers, snow leopards, Great Indian Bustard, and Lesser Florican.
1. Tigers Outside Tiger Reserves (TOTR) Project
Overview
- A new national-level initiative by the MoEFCC and National Tiger Conservation Authority (NTCA).
- Implementation period: 2025–2028
- Budget: ?88.7 crore
- Coordination: Centrally by NTCA; executed by State Forest Departments.
Objectives
- Reduce human–tiger conflict in non-reserve areas.
- Ensure safe coexistence between communities and tigers dispersing beyond reserves due to population recovery and habitat fragmentation.
- Promote a landscape-level conservation approach integrating ecological, social, and livelihood priorities.
Geographical Coverage
- Encompasses 80 forest divisions across 17 tiger-range states, including Madhya Pradesh, Maharashtra, Karnataka, Uttarakhand, Assam, Kerala, Tamil Nadu, West Bengal, andArunachal Pradesh.
- Focuses on corridors and buffer areas adjoining major tiger reserves.
Key Features
- Technology & Monitoring:Use of AI-based early warning systems, drones, camera traps, GPS-enabled patrolling, andMSTrIPES app for real-time tracking.
- Community Participation:
- Establishment of Rapid Response Teams (RRTs) equipped with tranquilization gear, rescue tools, and vehicles.
- Launch of “Bagh Mitra” (Tiger Friends)programmes and student jungle camps to foster coexistence.
- Institutional Framework:
- NTCA to oversee implementation; Chief Wildlife Wardens and State CAMPA authorities to manage funds and on-ground execution.
Significance
- India hosts 70% of the global tiger population — 3,682 as of 2022.
- Around 35–40% (1,325 tigers) now live outside protected areas, increasing the frequency of human–tiger encounters.
- The TOTR project seeks to balance conservation with human safety through modern technology, community outreach, and continuous monitoring.
Project Dolphin (Phase II)
- Focuses on conserving river and marine cetaceans, including the endangered Ganga River Dolphin and Indus Dolphin.
- Aims to enhance habitat protection, improve water quality in river ecosystems, and strengthen anti-poaching measures.
- Encourages local community participation and awareness through riverine eco-tourism and citizen science initiatives.
Project Sloth Bear
- India’s first national framework for the conservation of sloth bears, a species threatened by habitat loss, poaching, and human conflict.
- Focus areas include:
- Habitat restoration and connectivity,
- Mitigation of bear–human conflict,
- Establishment of rescue and rehabilitation centres, and
- Awareness campaigns for community coexistence.
Project Gharial
- Aims to revive populations of the critically endangered gharial in Indian rivers like the Chambal and Gandak.
- Measures include nest protection, captive breeding, river habitat restoration, and monitoring through telemetry.
- Seeks to strengthen coordination among state wildlife departments, river authorities, andlocal communities.
Centre of Excellence for Human–Wildlife Conflict Management (CoE–HWC)
- Location:Sálim Ali Centre for Ornithology and Natural History (SACON), Coimbatore.
- Purpose:
- To serve as a national research and policy hub for addressing human–wildlife conflicts.
- Develop AI-based conflict prediction models, design field-level mitigation tools, and train forest officials and local communities.
Coral Larvae Cryobank

- 09 Oct 2025
In News:
In a significant step toward marine conservation, the Philippines has established Southeast Asia’s first coral larvae cryobank, aimed at safeguarding coral genetic diversity and restoring threatened reef ecosystems. The initiative marks a pioneering regional collaboration among research institutions in the Philippines, Taiwan, Indonesia, Malaysia, and Thailand.
About the Coral Cryobank Initiative
- The Coral Larvae Cryobank is designed to freeze and store coral larvae at ultra-low temperatures, thereby preserving their genetic material for future reef restoration.
- It is part of a regional conservation programme supported by the Coral Research & Development Accelerator Platform, with technical guidance from Dr. Chiahsin Lin and the University of the Philippines Marine Science Institute.
- The cryobank acts as a “genetic insurance policy” to protect coral biodiversity in the face of rising ocean temperatures, pollution, and habitat destruction.
Cryopreservation: The Science Behind It
Cryopreservation is a process of preserving living cells or tissues at –196°C using liquid nitrogen, which halts all biological activity.
- Cryoprotectant solutions (such as glycerol, DMSO, and ethylene glycol) are used to prevent ice crystal formation that can damage cells.
- The process of vitrification converts the larvae into a glass-like state, allowing them to remain intact indefinitely.
- Laser-assisted thawing enables rapid revival of viable coral larvae, which can later be used for reef restoration and rehabilitation.
This technique ensures that coral genetic material remains preserved even if wild populations are damaged by bleaching events or ocean warming.
The Coral Triangle: The ‘Amazon of the Seas’
- The Coral Triangle, often termed the “Amazon of the Seas”, spans about 6 million sq. km across Indonesia, Malaysia, Papua New Guinea, the Philippines, Solomon Islands, and Timor-Leste.
- It covers two major biogeographic regions — the Indonesian–Philippines Region and the Far Southwestern Pacific Region — and represents the richest marine biodiversity hotspot on Earth.
Key Features
- Home to over 75% of global coral species and one-third of all reef fish.
- Supports six of the world’s seven marine turtle species.
- Sustains the livelihoods and food security of over 120 million people.
- Hosts vast mangrove forests and seagrass ecosystems, critical for carbon sequestration and coastal protection.
Threats to Coral Ecosystems
The Coral Triangle faces escalating threats due to climate change and anthropogenic pressures.
- Rising sea temperatures trigger coral bleaching, where corals expel symbiotic algae (zooxanthellae), turning white and losing energy sources.
- The Status of Coral Reefs of the World 2020 report found that 14% of the world’s corals were lost between 2009 and 2018.
- Projections indicate that 70–90% of live corals could vanish by 2050 without effective conservation.
- Destructive fishing, coastal pollution, and unregulated tourism further degrade reef habitats.
Understanding Corals
- Corals are marine invertebrates belonging to the Cnidaria phylum.
- They consist of tiny organisms called polyps, which secrete calcium carbonate skeletons that form coral reefs.
- The color of corals arises from symbiotic algae within their tissues, essential for nutrient exchange.
- Types of coral reefs:
- Fringing reefs – develop along shorelines
- Barrier reefs – found in open water separated from land by lagoons
- Atolls – circular reefs surrounding submerged volcanoes
- Coral reefs act as nurseries for one-fourth of all marine life, providing food, shelter, and breeding grounds.
Significance of Coral Cryobanking
The cryobank serves as a long-term safeguard for coral biodiversity by ensuring viable genetic material remains preserved even in the event of large-scale reef degradation.
Key benefits include:
- Conservation of genetic diversity for future breeding and research.
- Restoration of degraded reefs through reintroduction of cryopreserved larvae.
- Strengthening regional resilience against climate-induced coral loss.
- Promotion of scientific cooperation across Southeast Asian nations.
Ortolan Bunting

- 08 Oct 2025
In News:
A rare European migratory bird, the Ortolan Bunting (Emberizahortulana), was recently spotted in Baruipur, on the southern outskirts of Kolkata, West Bengal. This marks only the second recorded sighting of the species in the state, with the last being in the Sundarbans in 2014.
About Ortolan Bunting:
- Scientific Name:Emberizahortulana
- Type: Small Palearctic migratory songbird
- Distribution: Native to Europe and parts of Central Asia, extending east to Mongolia and north to the Arctic Circle.
- Migration: The species typically migrates to sub-Saharan Africa during the winter months.
Habitat and Characteristics:
- Preferred Habitat: Open or semi-open agricultural lands, slopes, and grasslands with scattered shrubs; generally avoids dense forests and oceanic climates.
- Altitude Range: Found up to 2,500 metres in suitable habitats.
- Physical Features:
- Length: 16–17 cm; Wingspan: about 25 cm.
- Males have a greenish-grey head, yellow throat, and brown-streaked body.
- Females and juveniles are smaller and duller, with spotted underparts.
- Possess a conical beak suited for cracking seeds.
Conservation Status:
- IUCN Red List: Least Concern
Despite its status, the Ortolan Bunting faces population decline in parts of Europe due to habitat loss and illegal hunting — particularly in France, where it was once considered a delicacy.
Significance of the Sighting:
- Highlights the importance of citizen-led biodiversity monitoring through platforms like eBird and BirdForum.
- Suggests potential changes in migratory routes, possibly influenced by climatic shifts.
- Reinforces West Bengal’s ecological diversity, which continues to attract rare and migratory bird species.
Snow Leopard
- 07 Oct 2025
In News:
- A recent survey by the Wildlife Wing of the Himachal Pradesh Forest Department has revealed that the state now hosts 83 adult snow leopards, a notable increase from the 51 recorded in 2021.
- Conducted over one year with strong community participation, the assessment marks Himachal Pradesh as the first state in India to carry out a second state-wide snow leopard survey, providing a robust baseline for future conservation efforts.
About Snow Leopards (Panthera uncia):
- Known as the “ghost of the mountains”, snow leopards are large, elusive wild cats and serve as important indicator species for fragile high-altitude ecosystems.
- State Animal: Himachal Pradesh
- Distribution: Native to high mountains across 12 countries in Central and South Asia, including Afghanistan, China, India, Nepal, and Mongolia. In India, found in Western Himalayas (J&K, Ladakh, Himachal Pradesh, Uttarakhand) and Eastern Himalayas (Sikkim, Arunachal Pradesh).
- IUCN Status: Vulnerable (VU)
Key Characteristics:
- Physical Traits: Thick white-grey fur with dark rosettes for camouflage; powerful hind legs for leaping across rugged terrain.
- Diet: Carnivorous—feeds on blue sheep, Himalayan ibex, marmots, pikas, hares, and other high-altitude prey.
- Habitat & Territory: Prefers cold deserts and rocky slopes above 3,000 m, sometimes reaching 5,500 m; requires large territories (5–190 sq miles) due to low prey density.
- Behavior: Solitary and territorial, mostly nocturnal and elusive.
Survey Highlights:
- Conducted across six sites covering Himachal’s 26,000 sq km snow leopard habitat using camera traps.
- Snow leopards recorded in core areas such as Lahaul-Spiti, Kinnaur, and Pangi Valley, and also beyond protected areas like Kibber Wildlife Sanctuary, Great Himalayan National Park, Sechu Tuan Nala, and Asrang Wildlife Sanctuary.
- Prey and Biodiversity: Updated distribution maps for blue sheep, Himalayan ibex, musk deer, Himalayan wolves, brown bears, red foxes, leopards, and martens. First official sighting of Pallas’s cat in Kinnaur and rediscovery of the woolly flying squirrel in Lahaul.
Two New Ramsar Sites in Bihar
- 05 Oct 2025
In News:
India has recently added two wetlands from Bihar — Gokul Jalashay (Buxar district) and Udaipur Jheel (West Champaran district) — to the List of Wetlands of International Importance under the Ramsar Convention.
With these inclusions, India now has 93 Ramsar sites, covering a total area of 13,60,719 hectares, consolidating its position as Asia’s leading country in terms of Ramsar designations and third globally, after the United Kingdom (176) and Mexico (144).
About the New Ramsar Sites
1. Gokul Jalashay (Buxar District)
- Type: Oxbow lake, situated on the southern edge of the River Ganga.
- Ecological Role: Acts as a natural flood buffer, reducing inundation risk for nearby settlements.
- Biodiversity: Supports over 50 species of resident and migratory birds and provides fish breeding grounds.
- Socio-economic Importance: Local communities depend on the lake for fishing, agriculture, and irrigation, integrating ecological sustainability with livelihoods.
- Cultural Practice: Villagers collectively clean and restore the wetland annually during a traditional festival, reflecting community-led conservation.
2. Udaipur Jheel (West Champaran District)
- Type: Oxbow lake located within the Udaipur Wildlife Sanctuary.
- Biodiversity: Hosts 280 plant species, including Alysicarpus roxburghianus, an Indian endemic.
- Avifauna: Serves as a key wintering habitat for over 35 migratory bird species, notably the vulnerable Common Pochard (Aythya ferina).
- Ecological Significance: Functions as a biodiversity hotspot and climate buffer, maintaining the hydrological balance in the region.
Understanding Oxbow Lakes
- An oxbow lake is a crescent-shaped waterbody formed when a meandering river is cut off from its main channel due to erosion and deposition processes. These lakes often evolve into rich wetland ecosystems, supporting diverse aquatic flora and fauna.
About Wetlands
- Wetlands are areas where water saturation—either permanent or seasonal—creates conditions that sustain distinctive plant and animal communities.
- They include marshes, fens, peatlands, floodplains, estuaries, and even shallow marine areas (up to 6 metres deep).
- They serve as ecological ecotones, forming transitions between terrestrial and aquatic systems and offering critical ecosystem services like flood control, groundwater recharge, carbon sequestration, and biodiversity support.
The Ramsar Convention
- Adopted: 1971 at Ramsar, Iran; came into force in 1975.
- Nature: An intergovernmental treaty under the auspices of UNESCO.
- Objective: To promote the conservation and wise use of wetlands and their resources.
- Criteria: A site must meet at least one of nine criteria, such as supporting 20,000 or more waterbirds, or hosting endangered species.
- India’s Participation: Ratified in 1982; currently one of the most active contracting parties.
Montreux Record
The Montreux Record is a register of threatened Ramsar sites where ecological character has degraded due to human interference or pollution.
- Indian sites listed:
- Keoladeo National Park (Rajasthan)– 1990
- Loktak Lake (Manipur) – 1993
- Chilika Lake (Odisha) was earlier listed in 1993 but successfully removed in 2002, becoming Asia’s first site to be delisted after restoration efforts.
Red Sanders

- 04 Oct 2025
In News:
- Recently, the National Biodiversity Authority (NBA) sanctioned ?82 lakh to the Andhra Pradesh Biodiversity Board for the conservation of Red Sanders (Pterocarpus santalinus), an endemic and endangered tree species of India.
- The initiative, undertaken under the Access and Benefit Sharing (ABS) mechanism of the Biological Diversity Act, 2002 (amended in 2023), marks a crucial step towards community-based biodiversity conservation.
About Red Sanders
- Red Sanders, also known as Red Sandalwood, is native to the Southern Eastern Ghats, particularly in the Anantapur, Chittoor, Kadapa, and Kurnool districts of Andhra Pradesh.
- The species thrives in rocky, red soil regions with a hot and dry climate, often in degraded or fallow lands.
- Renowned for its deep red wood, which commands high demand in international markets for musical instruments, furniture, and medicinal purposes, Red Sanders faces serious threats from illegal felling and smuggling. Due to its restricted distribution and exploitation, it is listed as:
- IUCN: Endangered
- CITES: Appendix II (regulated international trade)
- Wildlife (Protection) Act, 1972: Schedule IV
Conservation Initiative
- The ?82 lakh grant aims to raise one lakh saplings of Red Sanders, which will be distributed among farmers under the Trees Outside Forests (ToF)programme. This aligns with India’s broader goal of enhancing green cover beyond traditional forest areas.
- The funds are sourced from benefit-sharing amounts collected from users of Red Sanders, ensuring that economic benefits are returned to local stakeholders such as farmers, tribal communities, and Biodiversity Management Committees (BMCs). The initiative exemplifies how the Access and Benefit Sharing mechanism promotes equitable sharing of biological resources and converts conservation into a community-driven effort.
- In addition, the NBA has previously released ?31.55 crore to the Andhra Pradesh Forest Department for similar conservation and protection activities related to Red Sanders. The present funding will further strengthen grassroots conservation, generating local employment, fostering skill development, and enhancing community stewardship of biodiversity resources.
National Biodiversity Authority (NBA)
The National Biodiversity Authority, headquartered in Chennai, is a statutory body established under the Biological Diversity Act, 2002, and became operational in 2003. It works in coordination with:
- State Biodiversity Boards (SBBs): Regulate access to biological resources at the state level.
- Biodiversity Management Committees (BMCs): Function at the local level to document and conserve biodiversity through People’s Biodiversity Registers (PBRs).
Composition:
- Chairperson: An eminent expert in biodiversity conservation and sustainable resource use.
- 10 Ex-officio Members: Senior representatives from various ministries.
- 5 Non-official Members: Experts from relevant fields of biodiversity management.
Pallid Fish Eagle
- 03 Oct 2025
In News:
- The Corbett Tiger Reserve (CTR) in Uttarakhand, famed globally for its tigers, has recently emerged as a crucial sanctuary for raptors, with a preliminary survey confirming the presence of 30 species of birds of prey.
- Conducted jointly by the State Forest Department and the World Wide Fund for Nature (WWF), the survey has documented several rare and threatened species, including the Pallid Fish Eagle, whose nesting in the region is extremely rare.
Corbett Tiger Reserve: Overview
- Location: Foothills of the Himalayas, Uttarakhand.
- Established: Originally as Hailey National Park in 1936; first national park in India and the first to be included under Project Tiger.
- Terrain: Undulating with valleys; rivers Ramganga, Pallaen, and Sonanadi traverse the reserve.
- Vegetation: North Indian tropical moist and dry deciduous forests, with sal and mixed forests, interspersed with grasslands and riparian vegetation.
- Ecological Significance: A vital ecological corridor supporting both tiger populations and diverse avian species.
Pallid Fish Eagle (Haliaeetus leucoryphus)
- Common Names: Pallas’s Sea Eagle, Band-Tailed Fish Eagle.
- Size & Appearance: Large, brownish sea eagle.
- Habitat: Near lakes, rivers, and marshes, ranging from lowlands to 5,000 metres elevation.
- Diet: Primarily fish, but also opportunistically hunts other prey.
- Breeding: Builds large nests in tall trees, usually near water bodies.
- Distribution: East Palearctic regions — Kazakhstan, Russia, Tajikistan, Turkmenistan, Uzbekistan, Mongolia, China, India, Nepal, Bangladesh, and Myanmar.
- Conservation Status: Endangered (IUCN Red List).
- Threats: Habitat degradation, pollution, overfishing, and human disturbances.
- Significance in CTR: The discovery of a nesting site indicates active breeding, highlighting the reserve as a safe habitat for this threatened raptor.
Raptor Diversity in CTR
- Total Species Documented: 30 species of raptors, including both resident and migratory birds.
- Nesting Species: Evidence of nests from nine raptor species, including:
- Crested Serpent Eagle
- Hawk Eagle
- Red-Headed Vulture
- Indian Spotted Eagle
- White-Rumped Vulture
- Egyptian Vulture
- Indian Vulture
- Significance: The presence of nests indicates active breeding, confirming CTR as a protected and thriving habitat for raptors.
Conservation and Ecological Implications
- The discovery emphasizes CTR’s dual role as a tiger reserve and a key sanctuary for avian predators.
- Historical declines in vulture populations due to habitat disruption and veterinary drug use underscore the importance of protected habitats like CTR.
- CTR provides a superior ecological corridor, allowing threatened and migratory species to breed and sustain populations.
- Ongoing surveys aim to collect species profiles, population counts, and nesting specifics, forming the basis for targeted conservation strategies.
Ophiorrhizaechinate
- 03 Oct 2025
In News:
In a remarkable botanical discovery, researchers have identified a new species of coffee plant, Ophiorrhizaechinata, in the biodiversity-rich shola forests of Devikulam, located in the Idukki district of Kerala. The finding underscores the ecological richness of the Western Ghats, a UNESCO World Heritage Site and one of the world’s eight “hottest hotspots” of biological diversity.
About Ophiorrhizaechinata
- Ophiorrhizaechinata is a newly discovered species belonging to the Rubiaceae family, which also includes the well-known coffee plant (Coffea species).
- The discovery was made by botanists from Sacred Heart College, Thevara, St. Teresa’s College, Ernakulam, and St. Thomas College, Thrissur, and has been published in the Nordic Journal of Botany.
- The plant grows in the ecotone region — the transitional zone between evergreen forests and grasslands — at an altitude of about 1,630 metres above sea level.
- So far, the species has been recorded only from its type locality in Devikulam, with an area of occupancy less than 4 sq. km and a population of around 35 plants, indicating its extremely limited distribution.
Biological Characteristics and Significance
- The species is closely related to Ophiorrhizamungos, commonly known as Indian Snake Root, which has long been used in traditional medicine for its anticancer and anti-venom properties.
- Given this close genetic relationship, researchers believe O. echinata may possess valuable medicinal potential, warranting further phytochemical and pharmacological studies.
- Its presence in the shola ecosystem—a habitat known for high endemism and speciation—highlights the ecological uniqueness and evolutionary importance of such forest environments.
Ecological and Conservation Importance
- The discovery reinforces the Western Ghats’ status as a centre of endemism, particularly for the Rubiaceae family, to which over ten coffee-related species are native in India.
- The limited distribution and small population make O. echinatavulnerable to habitat loss and anthropogenic pressures such as deforestation, tourism, and climate change.
- Scientists emphasize the need for urgent habitat conservation measures and in-situ protection to ensure the species’ survival, along with further research on its chemical composition and ecological interactions.
Coffee Diversity in India
- India produced approximately 3.63 lakh metric tonnes of coffee in 2024–25, mainly of Arabica and Robusta varieties.
- However, the discovery of Ophiorrhizaechinata adds to the botanical richness of native coffee-related plants found in the Western Ghats. According to the Coffee Board of India, over 100 coffee plant species are known globally, of which more than ten occur naturally in the Western Ghats region.
UNESCO’s World Network of Biosphere Reserves
- 02 Oct 2025
In News:
UNESCO has included India’s Cold Desert Biosphere Reserve, located in Lahaul-Spiti district of Himachal Pradesh, in its World Network of Biosphere Reserves (WNBR) during the 37th ICC–MAB session (2025). This recognition makes it India’s first high-altitude cold desert biosphere reserve to join the global network, highlighting the country’s commitment to sustainable mountain ecosystem management.
About the Cold Desert Biosphere Reserve
- Established: 2009
- Location: Western Himalayas, Trans-Himalayan region of Himachal Pradesh
- Area: 7,770 sq. km
- Altitude: 3,300–6,600 m
- Constituent Areas:Pin Valley National Park, Kibber Wildlife Sanctuary, Chandratal Wetland, and adjoining regions.
- Terrain: Windswept plateaus, glacial valleys, alpine lakes, and high-altitude deserts.
- Zonation:
- Core Zone – 2,665 sq. km
- Buffer Zone – 3,977 sq. km
- Transition Zone – 1,128 sq. km
Biodiversity and Communities
- Flora: 655 herbs, 41 shrubs, and 17 tree species, including 14 endemic and 47 medicinal plants vital for the Sowa Rigpa (Amchi) traditional healing system.
- Fauna: 17 mammal and 119 bird species, including Snow Leopard, Tibetan Antelope, Himalayan Wolf, and Himalayan Ibex.
- Communities: Around 12,000 residents dependent on pastoralism, yak/goat herding, and high-altitude farming (barley and peas).
Lachipora Wildlife Sanctuary

- 01 Oct 2025
In News:
The District Magistrate of Baramulla has ordered the immediate closure of 14 gypsum mining units operating within the prohibited 1-km radius of the Lachipora Wildlife Sanctuary in north Kashmir’s Uri subdivision, following directives from the Supreme Court of India.
Background and Legal Context
- The decision is based on the Supreme Court judgment in State of Uttarakhand & Others vs. Nandan Singh Bora & Others, which mandates that no mining or quarrying activity is permissible within 1 km of any protected forest or wildlife sanctuary.
- Furthermore, if the Eco-Sensitive Zone (ESZ) of a sanctuary extends beyond 1 km, the restriction applies to the entire notified ESZ area.
- Subsequent surveys conducted by the Wildlife Warden, North Kashmir Division (Sopore), confirmed that several gypsum mining units were functioning within the restricted buffer zone of Lachipora. Acting on this report, the district authorities ordered the immediate suspension of all mining operations to prevent further ecological degradation.
- Officials emphasized that the move aims to preserve the fragile ecology of the region, which forms a vital part of the North Kashmir forest belt and supports diverse wildlife species. The crackdown also aligns with the Geology and Mining Department’s intensified efforts to curb illegal quarrying across Baramulla district.
About Lachipora Wildlife Sanctuary
- Location: Situated in Baramulla district, Jammu & Kashmir, near the village of Lachipora, on the northern banks of the Jhelum River.
- Established: 1987
- Area: 141 sq. km
- Altitude Range: 1,630–3,300 metres
- Topography: Comprises a varied landscape of alpine meadows, gentle to steep slopes, and rocky cliffs, supporting rich biodiversity.
Ecological Significance
- Flora:The sanctuary hosts extensive coniferous forests of deodar, Himalayan white pine, and blue pine, along with broadleaf species such as birch, horse chestnut, West Himalayan fir, and Persian walnut.
- Fauna:
- Habitat for endangered species like the Hangul (Kashmir stag) and Markhor, a wild goat known for its spiral horns.
- Home to Himalayan black bear, snow leopard, musk deer, and several small mammals.
- Recognized as an Important Bird Area (IBA) for harboring the vulnerable Western Tragopan and other high-altitude avifauna.
UNEP Young Champions of the Earth Award 2025
- 30 Sep 2025
In News:
The United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP) has announced the winners of the 2025 Young Champions of the Earth Award, recognising three outstanding entrepreneurs from India, Kenya, and the United States for their innovative solutions addressing pressing environmental challenges.
About the Award
- Launched: 2017
- Relaunched: 2025, in partnership with Planet A, an environmental awareness initiative co-founded by U.S. cleantech executive Chris Kemper.
- Organised by:United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP)
- Objective: To empower and celebrate young innovators (below 30 years of age) offering scalable solutions to the triple planetary crisis — climate change, biodiversity loss, and pollution & waste.
Each winner receives USD 20,000 in seed funding, mentorship, and access to a global platform to expand their innovations. They also participate in the Planet A Pitch Competition, with opportunities to win an additional USD 100,000 growth grant and a potential USD 1 million seed investment.
2025 Award Winners
- JinaliMody (India) – Founder, Banofi Leather
- Innovation: Produces sustainable, leather-like material from banana crop waste.
- Impact: Reduces water consumption, chemical pollution, and carbon emissions associated with traditional leather production.
- Significance: A women-led initiative tackling the fast fashion industry’s environmental footprint while promoting circular economy principles.
- Joseph Nguthiru (Kenya) – Founder, HyaPak
- Innovation: Converts the invasive water hyacinth from Lake Naivasha into biodegradable packaging and seedling wrappers.
- Impact: Provides a sustainable alternative to single-use plastics while addressing invasive species management.
- Noemi Florea (United States) – Founder, Cycleau
- Innovation: Developed a compact greywater reuse system that can retrofit household sinks, showers, and laundry units.
- Impact: Converts wastewater into potable water using low energy, offering a scalable model for water conservation and reuse.
Significance
- The award exemplifies youth-driven environmental innovation, aligning with UNEP’s broader mission to foster sustainable solutions.
- It highlights global South participation, with India and Kenya demonstrating leadership in low-cost, eco-friendly technologies.
- The 2025 relaunch underscores growing private sector and media collaboration in advancing environmental entrepreneurship through platforms like Planet A.
Global Forest Fund

- 29 Sep 2025
In News:
- Brazil is set to become the first country to invest in the Tropical Forests Forever Facility (TFFF) — a multilateral fund designed to support long-term tropical forest conservation.
- The announcement is expected to be made at the United Nations headquarters in New York, marking a major step toward reshaping global climate finance ahead of COP30, which Brazil will host in Belém, Amazon region, in November.
About the Tropical Forests Forever Facility (TFFF)
- Origin: Proposed by Brazil during COP28 (UAE, 2023), the TFFF aims to create a permanent, self-sustaining financial mechanism to conserve tropical forests across the globe.
- Nature: It is a global, multilateral, and endowment-style fund—the first of its kind—dedicated exclusively to protecting tropical forests and ensuring steady, performance-based payments to countries maintaining their forest cover.
- Goal: To mobilize USD 125 billion through a blended finance structure, combining sovereign and private-sector contributions.
Financial Structure and Mechanism
- Funding Model:The fund will function as a permanent endowment, investing its corpus in diversified financial portfolios that generate sustainable returns.
- The returns will finance annual stipends to participating tropical forest countries (TFCs), based on the extent of their standing forests.
- Composition of Funds:
- Sponsors (20%) – High-income countries (as per World Bank classification) and global philanthropies.
- Market Investors (80%) – Institutional investors, sovereign wealth funds, and endowments participating via debt instruments (such as green bonds).
- Fund Management: Likely to be handled by a Multilateral Development Bank (MDB) such as the World Bank, ensuring transparency and credibility.
- Initial Target:To reach the full USD 125 billion goal, Brazil plans to secure an initial USD 25 billion from governments and philanthropies, which would serve as an anchor to attract an additional USD 100 billion from private investors.
Brazil’s Role and Strategic Intent
- Brazil’s upcoming investment will make it the first contributor to the fund — signaling its confidence in the mechanism and encouraging other nations to follow suit.
- According to official sources, the investment amount will be “considerable,” intended to set a benchmark and demonstrate Brazil’s commitment to global forest conservation.
- As home to the world’s largest tropical rainforest, Brazil stands to receive significant future payouts under the TFFF, reinforcing its dual role as a beneficiary and a leader in climate stewardship.
Global Participation and Support
- Several countries have already expressed interest in joining the initiative, including China, the United Kingdom, France, Germany, Norway, Singapore, and the United Arab Emirates.
- Notably, China has conveyed its intention to contribute among the first investors — a move seen as a potential turning point in global climate finance, traditionally dominated by Western donors.
Significance
- Bridging Climate Finance Gaps:The TFFF introduces a results-based, long-term funding model for forest conservation, shifting away from short-term grants toward permanent, scalable financing.
- Shared Global Responsibility:The participation of both developed and developing nations underscores a more equitable climate finance architecture, aligning with the principle of common but differentiated responsibilities (CBDR).
- Boost to COP30 and Viksit Bharat 2047 Goals:Brazil’s leadership strengthens its position ahead of COP30 and aligns with India’s own emphasis on sustainable development and green finance under Mission LiFE and Viksit Bharat 2047 frameworks.
- Preserving Global Carbon Sinks:By rewarding countries for maintaining forests, the fund provides a direct economic incentive for protecting vital ecosystems that regulate global climate patterns.
Impatiens Selvasinghii
- 28 Sep 2025
In News:
- In a significant botanical discovery, researchers from Madura College, Madurai, have identified a new species of flowering plant belonging to the genus Impatiens in the Kudremukh range of the Western Ghats, Karnataka.
- The species has been named Impatiens selvasinghii in honour of Dr. P. Selva Singh Richard, Associate Professor of Botany at Madras Christian College (MCC), for his pioneering contributions to the study of reproductive biology of endemic and endangered plants of the Western Ghats.
Key Details of the Discovery
- Location:Kudremukh Peak, Chikkamagaluru district, Karnataka
- Altitude: Approximately 1,630 metres above sea level
- Published in:Taiwania, an international peer-reviewed botanical journal
- Unique Features: The species is distinguished by its exceptionally small flowers—the smallest among known balsams of the Western Ghats—and prominently lobed wing petals.
- Ecological Role: Small insects are dependent on this species for survival, underscoring its role in the local micro-ecosystem.
The Genus Impatiens in India
- India hosts over 280 taxa of Impatiens, widely distributed across the Eastern Himalayas and the Western Ghats.
- About 210 taxa are endemic to India, with 130 species unique to the Western Ghats.
- Notably, around 80% of the Impatiens species in the Western Ghats are categorized as endangered, highlighting the region’s ecological vulnerability.
Conservation Concerns
Researchers have cautioned that Impatiens selvasinghii is located along a popular trekking route in Kudremukh, where over-tourism and habitat disturbance could threaten its survival. Given the fragile mountain ecosystem and high endemicity of balsam species, measures for habitat protection and responsible ecotourism are vital.
AI-enabled Centre at Betla National Park
- 27 Sep 2025
In News:
Betla National Park, located in Latehar district, Jharkhand, will soon host India’s first AI-enabled nature experience centre. Part of the Palamu Tiger Reserve (PTR), the park is known for its rich biodiversity, including tigers, elephants, and diverse flora and fauna. PTR is one of the first nine tiger reserves established under Project Tiger (1973), covering a total area of 1,129.93 sq. km, and was notified as a National Park in 1986.
About the AI-Enabled Centre
The centre, developed by Palamu Tiger Reserve authorities under Deputy Director Prajesh Kant Jena, aims to provide visitors with an immersive, high-tech wildlife experience. Unlike conventional nature interpretation centres, it will use cutting-edge technologies to recreate the dynamics of the jungle ecosystem, including:
- AI assistants for guided learning.
- 3D holographic projections to display lifelike animal behaviour.
- Augmented Reality (AR) and immersive sound effects to simulate waterfalls, bird calls, predator-prey interactions, and herd movements.
- Ecosystem simulation, portraying animal movement, food-sharing activities, and other natural behaviours in a realistic manner.
Purpose and Significance
The centre, themed “Threads of Nature,” is designed to convey the interconnection between humans and nature. Key objectives include:
- Enhancing eco-tourism by offering a realistic jungle experience, including sightings of tiger hunts, elephant herds, and lions.
- Promoting conservation awareness through interactive learning and observation tools.
- Supporting researchers and nature enthusiasts with virtual wildlife monitoring capabilities.
Unique Features
While nature interpretation centres have existed in Betla since the 1970s, this facility represents the first high-tech effort in India to integrate AI, AR/VR, holograms, and immersive sound for wildlife education. Visitors will not just see static models or photographs but will experience the sights, sounds, and atmosphere of a living jungle, providing a deeper understanding of ecosystem dynamics.
By merging technology with conservation education, the Betla AI-enabled centre is poised to become a pioneering hub for tourism, research, and ecological awareness in Jharkhand and across India.
Striped Dolphin
- 27 Sep 2025
In News:
- In a rare observation, a pod of striped dolphins (Stenella coeruleoalba) was recently sighted off the Visakhapatnam coast in Andhra Pradesh.
- The sighting, captured on video by a local fisherman from Muthyalammapalem, has drawn attention to the rich but under-documented marine biodiversity of India’s eastern coastline.
- The species was identified by the East Coast Conservation Team (ECCT) with assistance from the Marine Mammal Research and Conservation Network of India — marking one of the few verified records of striped dolphins in Andhra waters.
About Striped Dolphins (Stenella coeruleoalba)
|
Aspect |
Details |
|
Family |
Delphinidae (Oceanic dolphins) |
|
IUCN Status |
Least Concern |
|
Distribution |
Found in tropical and temperate waters of all major oceans — including the Mediterranean Sea, Japan, South Africa, Western Australia, New Zealand, and occasionally, Indian waters. |
|
Habitat |
Prefer deep offshore waters and upwelling zones where nutrient-rich cold water supports abundant marine life. Often found near continental shelf edges. |
|
Physical Features |
Length: ~2.2–2.6 m; streamlined body; long beak (rostrum); tall, curved dorsal fin. Notable dark stripes run from the beak through the eye and down the sides, giving the species its name. |
|
Behaviour |
Found in tight pods of 25–100 individuals. Known for acrobatics such as breaching, leaping, and the characteristic “roto-tailing” — a spinning motion of the tail while airborne. |
|
Lifespan |
Up to 58 years. |
|
Diet |
Primarily small fish, squid, and crustaceans. |
Ecological and Conservation Significance
The recent sighting highlights the ecological richness of the Bay of Bengal, especially the Visakhapatnam coast, which supports diverse marine fauna but remains scientifically under-surveyed.
Such sightings are crucial for:
- Enhancing knowledge about the migratory patterns and population structure of marine mammals in Indian waters.
- Assessing ecosystem health, since dolphins are indicator species reflecting the condition of marine food chains.
- Formulating regional conservation policies for marine biodiversity and sustainable fisheries.
The ECCT’s collaboration with fishermen exemplifies a community-based conservation model, where local knowledge complements formal scientific documentation — essential for protecting fragile marine ecosystems.
Recent Discoveries Indicating Biodiversity Potential
During recent coastal surveys, researchers even rediscovered a sea slug species in Visakhapatnam that had not been recorded in nearly 180 years, further proving the hidden biodiversity of India’s east coast and the urgent need for systematic monitoring.
High Seas Treaty of UN Reaches Entry into Force Threshold
- 26 Sep 2025
In News:
- The Biodiversity Beyond National Jurisdiction (BBNJ) Treaty, also known as the UN High Seas Treaty, has crossed the crucial threshold of 60 ratifications, enabling it to enter into force on January 17, 2026. With Morocco and Sierra Leone becoming the 60th and 61st ratifying nations, this milestone marks a historic step in the global conservation of marine biodiversity in international waters.
- So far, 143 countries, including India, have signed the treaty, reflecting strong international consensus on protecting marine ecosystems that lie beyond national boundaries.
About the BBNJ Treaty
- Full Name:Agreement under the United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea on the Conservation and Sustainable Use of Marine Biological Diversity of Areas Beyond National Jurisdiction (BBNJ).
- Parent Framework: Builds upon the UN Convention on the Law of the Sea (UNCLOS), adopted in 1982 and effective since 1994 — often called the “Constitution for the Oceans”.
- Geographical Scope: Applies to areas beyond 200 nautical miles from the Exclusive Economic Zones (EEZs) of coastal nations, commonly referred to as the high seas.
- Coverage: These high seas account for nearly two-thirds of the global ocean and cover over 70% of the Earth’s surface, yet currently, only 1.44% are under any form of protection.
Objectives and Key Provisions
The BBNJ Treaty seeks to conserve and sustainably use marine biodiversity in areas beyond national jurisdiction through legally binding measures. Its major provisions include:
- Creation of Marine Protected Areas (MPAs):
- Aims to designate and manage MPAs in international waters.
- Currently, 6.35% of the ocean is protected, with only 1.89% designated as no-take MPAs, where all extractive activities such as fishing, mining, and drilling are prohibited.
- This aligns with the Kunming-Montreal Global Biodiversity Framework target of protecting 30% of global land and sea areas by 2030 (30x30 goal).
- Equitable Sharing of Marine Genetic Resources (MGRs):
- Establishes mechanisms to ensure fair and equitable distribution of benefits derived from marine genetic resources — biological materials such as microorganisms, plants, and animals with applications in pharmaceuticals and biotechnology.
- Mandatory Environmental Impact Assessments (EIAs):Mandates EIAs for high-impact activities like deep-sea mining, carbon sequestration, and bioprospecting in international waters to mitigate potential ecological harm.
- Scientific Cooperation and Technology Transfer:Encourages capacity building, data sharing, and technology transfer to support developing nations in ocean research and sustainable marine resource management.
Process for the Treaty’s Entry into Force
- Condition: The BBNJ Treaty enters into force 120 days after the deposit of the 60th instrument of ratification, approval, or accession.
- Implementation Date: Given the 60th ratification milestone was achieved in September 2025, the treaty will legally come into effect on January 17, 2026.
- Next Steps:
- Preparatory Commission (PrepCom): Tasked with operationalizing the treaty by establishing scientific and technical bodies, expert qualifications, and procedural frameworks for reviewing MPA proposals.
- First Conference of Parties (COP1): Will convene post-entry into force to initiate formal implementation. Key agenda items include governance mechanisms, financial arrangements, and the Clearing-House Mechanism for information exchange.
India’s Role and Strategic Interests
- India’s Involvement:
- The Union Cabinet approved India’s signing of the BBNJ Treaty in July 2024.
- India is among the 143 signatories, signaling commitment to sustainable ocean governance.
- Strategic Significance for India:
- Enhanced Oceanic Presence: Expands India’s strategic and scientific footprint beyond its Exclusive Economic Zone (EEZ).
- Scientific Research: Facilitates participation in global marine research, access to marine genetic resources, and technological collaboration.
- Alignment with SDG-14: Advances India’s commitment to Sustainable Development Goal 14 – “Life Below Water”, which seeks to conserve and sustainably use ocean resources.
- Diplomatic and Environmental Leadership: Positions India as a responsible stakeholder in global commons management and strengthens its environmental diplomacy credentials.
Papikonda National Park
- 25 Sep 2025
In News:
A recent study published in the Records of the Zoological Survey of India has documented 51 species of herpetofauna — including amphibians and reptiles — in Papikonda National Park, located in the northern part of the Eastern Ghats, Andhra Pradesh. This comprehensive survey marks a significant step in understanding the region’s biodiversity, which has remained largely underexplored.
Key Findings of the Study
Researchers recorded 18 amphibians, 21 lizards, 10 snakes, and 2 turtles through extensive fieldwork conducted between September 2021 and February 2023. The study revealed three species — Minervaryakalinga, Sphaerothecamaskeyi, and Hemidactylus kangerensis — reported for the first time in Andhra Pradesh.
According to the IUCN Red List (2024):
- 46 species are listed as Least Concern,
- 3 species are Not Yet Assessed,
- Hemidactylus kangerensis is Endangered, and
- Lissemyspunctata is Vulnerable.
Under the Wildlife (Protection) Act, 2022, several species enjoy legal protection:
- Schedule I:Chamaeleozeylanicus, Calodactylodes aureus, Pangshura tentoria, Lissemyspunctata
- Schedule II:Hoplobatrachustigerinus, Euphlyctiscyanophlyctis
The study also highlighted rare species such as Psammodynastespulverulentus and Argyrophisdiardii, the latter recorded for the first time in the Eastern Ghats. Two Eastern Ghats endemics — the Indian golden gecko (Calodactylodes aureus) and Dutta’s Mahendragiri gecko (Hemidactylus sushilduttai) — were also documented.
About Papikonda National Park
- Location: East and West Godavari districts, Andhra Pradesh
- Area: Approximately 1,012.86 sq km
- Established: Declared a Reserved Forest (1882), Wildlife Sanctuary (1978), and upgraded to National Park (2008)
- Landscape: Rugged terrain of the Eastern Ghats, divided by the Godavari River, with elevation ranging from 20–850 metres
- Geographical Features: Contains 62 named mountains, including Devara Konda (highest point) and Verala Konda (most prominent peak)
- Recognition: Identified as an Important Bird and Biodiversity Area (IBA) by BirdLife International
Flora and Fauna
- Vegetation: Tropical moist deciduous, semi-evergreen, and dry deciduous forests.
- Flora: Teak, rosewood, sandalwood, bamboo, sal, mahua, pterocarpus, terminalia, cassia, and eucalyptus.
- Fauna: Bengal tiger, Indian leopard, sloth bear, dhole (wild dog), sambar, and spotted deer.
- Unique Feature: Home to the “KanchuMekha”, a rare dwarf goat breed native to the region.
Conservation Significance
- The study provides baseline data crucial for biodiversity conservation and monitoring in the Eastern Ghats. Researchers warned that herpetofaunal populations face multiple threats — including habitat loss, fragmentation, emerging diseases, and climate change.
- Rare and threatened species like the Jeypore Hill Gecko (Geckoellajeyporensis), Barkud Spotted Skink (Barkudiainsularis), and King Cobra (Ophiophagus hannah) emphasize the need for targeted conservation strategies.
- The authors advocated for systematic surveys and integrated taxonomic approaches across the Eastern Ghats to enhance understanding of species distribution and to strengthen regional conservation planning.
Red-Necked Phalarope

- 24 Sep 2025
In News:
In a notable development for ornithology and biodiversity conservation, the Red-necked Phalarope (Phalaropuslobatus), a rare migratory shorebird, has been sighted for the first time at the Nanjarayan Bird Sanctuary near Tiruppur, Tamil Nadu.
About the Red-Necked Phalarope
The Red-necked Phalarope is a small, migratory wader renowned for its unique feeding behavior and striking breeding plumage.
- Distinctive Feeding Behavior:It is known for its characteristic habit of spinning rapidly in circles on the water surface to stir up small invertebrates and plankton, which it then feeds upon.
- Physical Features:During the breeding season, the bird exhibits chestnut-red plumage extending from behind the ear to the sides of the neck — a feature that gives it its name.
Unusually among birds, the female is more brightly coloured than the male, and the species displays polyandrous behaviour (females mate with multiple males), with males incubating the eggs and caring for the chicks.
Distribution and Habitat
The Red-necked Phalarope has a circumpolar distribution, breeding in boreal and tundra zones between 60° and 70° latitude, across regions such as the Arctic coasts, Aleutian Islands, and northern Britain.
- During migration and the non-breeding season, it spends much of its time at sea, especially across:
- The Arabian Sea,
- Waters off central-west South America, and
- The central Indonesian to western Melanesian regions.
The recent sighting at Nanjarayan Bird Sanctuary — a vital inland wetland ecosystem — highlights the site’s growing importance as a stopover for migratory shorebirds along the Central Asian Flyway.
Conservation Status
- IUCN Red List:Least Concern
Despite being widespread globally, localized population declines have been observed due to habitat degradation, pollution, and climate-induced changes in migratory routes.
Iridogorgia Chewbacca
- 22 Sep 2025
In News:
Marine scientists have identified a new species of deep-sea coral, named Iridogorgiachewbacca, after the iconic Star Wars character Chewbacca. The name was inspired by the coral’s long, curly, and “hairy” branches resembling the furry appearance of the Wookiee warrior from the franchise.
Discovery and Habitat
- The coral was first observed in 2006 off the coast of Moloka?i (Hawaii) and later near the Mariana Trench in 2016, within the tropical western Pacific Ocean.
- It has now been officially described and classified as a new species in the genus Iridogorgia, following extensive research and genetic testing conducted by an international team of scientists, including Professor Les Watling from the University of Hawai?i at M?noa.
- The discovery was formally published in the scientific journal Zootaxa, highlighting its contribution to deep-sea biodiversity research.
About Iridogorgiachewbacca
- Taxonomy: Belongs to the genus Iridogorgia under the class Anthozoa, a group of deep-sea soft corals.
- Physical Features:Characterised by long, flexible, spiral-like branches with a shiny surface that reflects light in unique ways. These hair-like branches give it a distinct “furry” appearance.
- Growth Pattern: The coral grows upright and solitary on deep-sea rocky substrates, often hundreds to thousands of metres below sea level.
- Colony Structure: Each coral colony is made up of thousands of small polyps working together as a single organism.
Scientific Significance
The identification of Iridogorgiachewbacca underscores the vast biodiversity of the deep ocean, much of which remains unexplored. Even in relatively well-studied regions such as the western Pacific, new species continue to be discovered, highlighting the importance of deep-sea research and conservation.
Understanding Corals
- Biological Nature: Corals are marine animals, not plants, and remain sessile (attached to the seabed).
- Symbiotic Relationship: They coexist with microscopic algae called zooxanthellae, which provide nutrients through photosynthesis.
- Feeding: Corals also use their tiny, tentacle-like structures to capture food particles from the surrounding water.
- Ecological Role: Coral ecosystems support immense marine biodiversity, acting as habitats, breeding grounds, and protection zones for numerous marine species.
Why It Matters
- Expands scientific understanding of deep-sea ecosystems and their unique biodiversity.
- Reinforces the need for marine conservation amid increasing threats from deep-sea mining, climate change, and ocean acidification.
- Demonstrates how popular culture references can enhance public engagement with scientific discoveries, making marine science more accessible.
Yellow-Crested Cockatoos

- 21 Sep 2025
In News:
Critically endangered yellow-crested cockatoos (Cacatuasulphurea) have established an unexpected refuge among Hong Kong’s urban landscape, including its parks and university campuses. Once native to Indonesia and East Timor, these snow-white birds with striking yellow crests now face multiple survival challenges, both globally and locally.
Population and Distribution
- The global wild population of yellow-crested cockatoos is estimated at up to 2,000 mature individuals, with around 10% residing in Hong Kong, largely as descendants of released or escaped caged birds.
- Historically, the species was widespread across central and eastern Indonesia and East Timor, but habitat loss has led to dramatic declines on many islands.
- In Hong Kong, they have adapted to urban life but depend on tree cavities for nesting, similar to their natural habitats.
Ecology and Behavior
- Appearance: Medium-sized cockatoo, predominantly white plumage, with a yellow or orange retractable crest.
- Habitat: Forests, forest edges, scrublands, and cultivated areas from sea level up to 1,500 meters.
- Diet: Omnivorous—seeds, fruits, nuts, berries, occasionally insects, small reptiles, and roots.
- Social Behavior: Monogamous, gregarious, and capable of mimicking sounds.
- Breeding Season: September to May.
Threats to Survival
- Habitat Loss: Typhoons, deforestation, and government-led tree trimming in urban areas reduce natural nesting sites.
- Illegal Pet Trade: Poaching continues to threaten wild populations in native habitats.
- Climate Change: Rising temperatures dry out forests, increasing susceptibility to fires and other environmental stresses.
Conservation Initiatives
To counter declining nesting opportunities, Hong Kong conservationists have implemented a practical solution: artificial nest boxes that replicate natural tree cavities.
Eustoma

- 20 Sep 2025
In News:
The National Botanical Research Institute (NBRI), under the Council of Scientific and Industrial Research (CSIR), has achieved a remarkable breakthrough by successfully cultivating the Eustoma flower in Odisha. This marks the first instance of the exotic ornamental species blooming locally in the state, which until now depended solely on imports for its availability.
About Eustoma
- Scientifically known as Eustoma grandiflorum and commonly referred to as Lisianthus, Prairie Gentian, or Texas Bluebell, the flower is a perennial herbaceous ornamental species native to the grasslands of North America — including Mexico, the southern United States, the Caribbean, and northern South America. Globally, it ranks among the top ten popular cut flowers due to its elegance and commercial appeal.
Distinctive Features
- Eustoma is renowned for its rose-like blossoms, vibrant color range, long stems, and extended vase life, which have earned it the title of the “next rose” in the international flower trade. Its blooms exhibit a rich palette of colors — from pure white to shades of pink, purple, and blue — making it highly desirable for cut flower arrangements and potted ornamental use.
Growth Conditions and Habitat
- The plant thrives in warm, sunny climates and prefers well-drained yet moisture-retentive soil, enriched with garden compost or well-rotted manure. In its natural habitat, it grows in grasslands and disturbed areas, making it adaptable to varied environmental conditions when cultivated with appropriate care.
Significance of the Odisha Breakthrough
- The successful cultivation of Eustoma in Odisha represents a scientific and economic milestone. Previously, the flower had to be imported, which limited access for local floriculturists and increased costs. With NBRI’s intervention, local propagation techniques have now been developed, enabling indigenous production of this high-value ornamental crop.
- By adopting Eustoma cultivation, farmers in Odisha and other states with similar climatic conditions can benefit from higher income potential due to the flower’s global demand and premium market value.
Broader Implications
- The success underscores India’s growing capabilities in plant biotechnology, floriculture innovation, and agro-based entrepreneurship. It aligns with the government’s broader objectives of Atmanirbhar Bharat (self-reliant India) by reducing dependency on imports and promoting sustainable rural livelihoods through scientific advancements.
Brown Trout

- 17 Sep 2025
In News:
- Kashmir is embarking on a significant initiative to revive its brown trout (Salmo trutta) population, a species first introduced to the Valley by the British in 1900.
- Once a hallmark of Kashmir’s cold-water streams and a popular game fish, the brown trout population had declined over decades due to unregulated angling, habitat degradation, and ecological disturbances.
- The Fisheries Department of Jammu & Kashmir plans to reintroduce the species into streams and lakes, aiming to combine conservation with tourism promotion.
About Brown Trout
- The brown trout is a cold-water, salmonid fish native to Europe, northern Africa, and parts of Asia. It prefers cool, well-oxygenated freshwater streams, often residing in crevices between boulders. Typically, individuals grow 15–22 inches in length and weigh 1–5 pounds.
- Brown trout are renowned as a game fish due to their aggressive and elusive nature, which makes angling challenging and rewarding.
- Globally, brown trout have been introduced widely as a game fish, but outside their native range, they are considered one of the world’s worst invasive species.
- In India, their introduction to Kashmir was facilitated by Frank J Mitchel, a British entrepreneur, and earlier attempts during Maharaja Pratap Singh’s era. The fish initially thrived in streams such as Panzagam, Lidder, Bringhi, and Ferozpora, eventually supporting recreational fishing and angling tourism.
Revival Initiative
The current revival project is supported under Pradhan Mantri Matsya Sampada Yojana (PMMSY) and J&K’s Holistic Agricultural Development Programme, enabling the import of 3 lakh pure brown trout eggs from Denmark. These were hatched at the Tchansar Hatchery in Kulgam, marking a milestone as previous efforts primarily focused on rainbow trout for food production rather than wild trout restoration.
Rearing brown trout posed unique challenges:
- They refuse artificial feed, requiring specially formulated diets of crustaceans mixed with cod liver oil.
- They feed in darkness, prompting hatchery modifications to simulate natural conditions and monitor feeding.
The October–November period, coinciding with their breeding season, was chosen for release as brown trout exhibit lower aggression and reduced cannibalism, increasing survival rates. Streams and lakes targeted for reintroduction include Veshav River and Kounsarnag Lake in Kulgam.
Ecological and Socioeconomic Significance
Reintroduction serves multiple purposes:
- Biodiversity restoration: Revives native aquatic fauna and strengthens freshwater ecosystems.
- Tourism enhancement: Brown trout are a draw for anglers, boosting local tourism and allied services.
- Heritage and culture: The initiative reconnects the Valley with a century-old ecological and recreational tradition.
Experts, however, caution that habitat preservation is crucial, emphasizing the need to control illegal riverbed mining and maintain clean, oxygen-rich streams for the trout’s survival.
Conservation Status and Global Context
According to the IUCN Red List, the brown trout is listed as Least Concern, reflecting its wide distribution and adaptability in native ranges. However, localized conservation efforts, such as this reintroduction in Kashmir, are essential to sustain ecologically and economically significant populations in specific regions.
Amrit Sarovar Mission

- 17 Sep 2025
In News:
- The Amrit Sarovar Mission, launched by Prime Minister Narendra Modi in April 2022, is a flagship initiative aimed at addressing water scarcity and promoting sustainable rural development across India.
- The mission seeks to construct or rejuvenate 75 Amrit Sarovars (ponds) in each district, as part of the celebrations of Azadi ka Amrit Mahotsav.
- As of 2025, the government has reported the creation of over 68,000 Amrit Sarovars nationwide, marking a significant milestone in water conservation and community engagement.
Objectives and Significance
The mission’s primary objectives include:
- Water conservation and management in rural areas.
- Enhancement of local livelihoods through irrigation, fisheries, duckery, cultivation of water chestnut, and water-based tourism.
- Promotion of social cohesion by establishing Amrit Sarovars as community gathering points.
- Integration of government initiatives through a “Whole of Government” approach, ensuring convergence of resources and expertise.
Each Amrit Sarovar is designed to have a minimum pondage area of one acre with a water-holding capacity of about 10,000 cubic metres. Surrounding vegetation typically includes trees such as Neem, Peepal, and Banyan, contributing to ecological sustainability and enhancing biodiversity.
Participatory and Institutional Framework
The site selection and supervision of Amrit Sarovars are conducted by Gram Sabhas, with Panchayat representatives overseeing the development. This participatory approach ensures that local communities have ownership and accountability for the maintenance and sustainable use of water resources.
The mission operates on convergence principles, utilizing funds and resources from multiple sources including:
- Mahatma Gandhi NREGS
- 15th Finance Commission Grants
- Pradhan Mantri Krishi Sinchai Yojana (PMKSY) sub-schemes, such as Watershed Development and Har Khet Ko Pani
- State government schemes
There is no separate financial allocation for the mission; rather, it leverages ongoing programs for maximum impact.
Technology and Monitoring
To ensure efficient implementation and progress tracking, the Bhaskaracharya National Institute for Space Applications and Geo-informatics (BISAG-N) has been engaged as a technical partner. The institute has developed the Amrit Sarovar Portal and Mobile App, which enables real-time monitoring, reporting, and evaluation of district-level activities.
Workshops and Capacity Building
The Ministry of Rural Development organized a national workshop in New Delhi to reinforce the mission’s technical foundations and promote community-driven sustainable practices. Officials from states and Union Territories discussed strategies to enhance technical capacity, innovation, and inter-departmental collaboration, paving the way for the next phase of the mission.
Impact and Prospects
The Amrit Sarovar Mission exemplifies integrated rural development, linking water security, ecological sustainability, and livelihood generation. By reviving traditional water bodies and creating new ponds, it contributes to groundwater recharge, climate resilience, and rural prosperity. The initiative also strengthens people’s participation in natural resource management, ensuring that water resources are used efficiently and sustainably.
As the mission progresses, it is expected to play a critical role in mitigating rural water crises, enhancing agricultural productivity, and fostering inclusive growth in India’s villages.
Cicadas
- 16 Sep 2025
In News:
The recent reappearance of cicadas in Kerala’s Silent Valley National Park — after decades of absence — has intrigued ecologists. It is being seen both as a possible indicator of ecosystem recovery and as a warning signal of ecological disruption caused by climate change and habitat alteration.
About Silent Valley
Located in the Nilgiri Hills of Kerala’s Western Ghats, Silent Valley National Park spans about 90 sq. km and represents one of India’s most pristine tropical rainforests. The forest’s name owes itself to the striking absence of cicada calls, which are ubiquitous in most tropical forests. The absence of these insects — known for their high-decibel songs — was noted as early as the 1840s by British botanist Robert Wight, making it an ecological enigma.
Understanding Cicadas
Cicadas are hemipteran insects recognized for their loud, species-specific acoustic signals. They spend most of their lives underground as nymphs, feeding on tree root sap, before emerging for a short adult phase primarily to mate.
- Habitat: Mostly canopy dwellers in natural forests with mature trees.
- Types:
- Annual cicadas – emerge every year in summer, often camouflaged among trees.
- Periodical cicadas – emerge collectively after 13 or 17 years of dormancy.
- Ecological Roles:
- Aerate soil and enhance nutrient cycling.
- Serve as prey for birds, reptiles, and mammals.
- After death, their bodies enrich soil nitrogen, aiding forest regeneration.
The Mystery of Silence
Unlike most tropical forests, Silent Valley lacked the characteristic cicada chorus. Scientists have proposed several hypotheses for this anomaly:
- Microclimate Conditions: The valley’s bowl-shaped topography, constant mist, and moisture-rich soils may hinder nymph development that prefers drier soil.
- Vegetation Composition: Unique tree species and leaf litter dynamics may not support cicada life cycles.
- Historical Climatic Shifts: Subtle long-term climate variations might have altered habitat suitability.
- Natural Absence Hypothesis: Cicadas may never have colonized this particular ecosystem in significant numbers.
Return of the Cicadas
Recent field surveys and local observations indicate a gradual resurgence of cicada populations in certain forest patches.
- Possible Causes:
- Shifts in vegetation structure and canopy composition.
- Rising temperatures and erratic rainfall patterns altering habitat conditions.
- Natural dispersal from adjoining forest landscapes.
Ecological and Conservation Implications
The reappearance of cicadas serves as a bioindicator — revealing subtle ecological shifts often invisible to human monitoring.
- It may represent resilience and natural regeneration following decades of conservation success since the 1984 ban on the Silent Valley hydroelectric project.
- Alternatively, it might indicate climate instability and biodiversity imbalance, as species distributions shift in response to anthropogenic pressures.
Silent Valley’s surrounding areas now face deforestation, plantation expansion, and tourism pressure, threatening its delicate ecological balance. Continuous long-term monitoring of insect diversity, vegetation, and microclimate is essential to interpret whether this trend marks recovery or disruption.
Biodiversity Heritage Site

- 14 Sep 2025
In News:
Bengaluru has recently witnessed the declaration of 8.6 acres of green cover at Cantonment Railway Colony as a Biodiversity Heritage Site (BHS)—the second in the city after the Gandhi Krishi Vigyan Kendra (GKVK). This decision marks a crucial step in safeguarding urban green spaces under increasing developmental pressures.
Citizen-led Conservation Movement
- The site was earlier earmarked for commercial development by the Rail Land Development Authority in collaboration with private real estate players. However, strong resistance emerged from citizens and environmental groups, particularly the ParisarakkagiNaavu organization. A large-scale campaign saw the participation of over 15,000 residents, of whom only two opposed the proposal, reflecting strong public consensus in favor of conservation.
- This site houses 371 trees across nearly 50 species, highlighting its ecological diversity. The move demonstrates how community activism and participatory governance can effectively influence environmental decision-making.
About Biodiversity Heritage Sites
Biodiversity Heritage Sites are unique ecosystems identified for their ecological, cultural, and evolutionary significance. They may encompass terrestrial, aquatic, coastal, or marine ecosystems. Key features include:
- High species richness (wild and domesticated), including endemic and threatened species.
- Presence of keystone species, wild ancestors of cultivated plants, or species of evolutionary importance.
- Historical or cultural relevance, such as fossil beds or sites linked with traditional practices.
The first BHS in India was the Nallur Tamarind Grove (2007, Karnataka), and since then, several others have been declared across states.
Legal Framework
The Biological Diversity Act, 2002 (Section 37) empowers state governments to notify areas of biodiversity importance as BHS, in consultation with local bodies. Key provisions include:
- State autonomy in management, conservation, and framing rehabilitation schemes for affected communities.
- Community participation, with no restrictions on prevailing traditional practices unless voluntarily adopted.
- Purpose: Enhancing quality of life and ensuring sustainable use of biodiversity resources.
Thus, the Cantonment Colony green cover’s recognition aligns with both ecological imperatives and community welfare.
Significance for Bengaluru and Urban India
- Urban ecological security: Protecting 8.6 acres of dense green cover helps counteract urban heat islands, air pollution, and biodiversity loss in one of India’s most rapidly expanding cities.
- Community stewardship: The initiative illustrates how local involvement strengthens environmental governance.
- Policy relevance: The case highlights the role of public consultation in environmental decision-making, setting a precedent for other urban centers facing similar challenges.
National Forest Martyrs Day 2025

- 13 Sep 2025
In News:
- National Forest Martyrs Day is observed annually on September 11 to pay tribute to forest officials, personnel, and community members who have sacrificed their lives while protecting India’s forests and wildlife.
- The day recognizes the risks undertaken in the line of duty against threats like illegal logging, poaching, encroachment, and forest fires.
Historical Background
- The observance is rooted in the Khejarli Massacre of 1730 in present-day Rajasthan. When Maharaja Abhai Singh of Marwar ordered the felling of Khejri trees for palace construction, the Bishnoi community, led by Amrita Devi Bishnoi, resisted by embracing the trees. In the brutal crackdown, 363 villagers lost their lives to protect their sacred groves.
- This legacy later inspired environmental movements such as the Chipko Movement (1970s), reinforcing India’s tradition of community-led conservation. Recognizing this historic sacrifice, the Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change (MoEFCC) officially declared September 11 as National Forest Martyrs Day in 2013.
Significance
- Commemoration of Sacrifice: The day honours not only the Bishnoi martyrs but also countless forest personnel who have died in the line of duty.
- Environmental Awareness: Highlights the critical role of forests in climate regulation, biodiversity conservation, and ecosystem services like air and water purification.
- Community Involvement: Encourages local communities to uphold traditions of eco-conscious living.
- Policy Emphasis: Reinforces the need for stronger laws and protection mechanisms for natural resources and frontline forest staff.
Observance
The day is marked through:
- Memorial ceremonies in forest departments.
- Tree plantation drives to promote ecological restoration.
- Awareness campaigns and educational programmes in schools and communities.
- Community participation to spread the message of sustainable living and conservation.
Vulture Network Portal

- 12 Sep 2025
In News:
- Vultures, once abundant across India, have faced catastrophic population declines over the past three decades due to carcass poisoning, harmful veterinary drugs (notably diclofenac), and negative social perceptions.
- Recognizing the urgency of conservation, an Assam-based foundation has launched India’s first dedicated vulture conservation portal to create a knowledge-sharing and awareness-driven network for their protection.
The Vulture Network Portal
- Nature: A cloud-based, first-of-its-kind portal in India dedicated to vulture conservation.
- Developer: We Foundation India, in collaboration with partners like the Assam Bird Monitoring Network and other organizations.
- Functions:
- Compiles scientific information on vultures.
- Provides freely downloadable outreach materials for awareness campaigns.
- Disseminates conservation material in local languages (beginning with Assamese) to ensure community participation.
- Focuses on addressing key threats to vultures, including:
- Carcass poisoning.
- Harmful veterinary drugs such as diclofenac.
- Myths and negative social perceptions around scavenger birds.
Significance
- Community Engagement: Builds a network of individuals and organizations working for vulture conservation.
- Policy & Awareness: Offers a centralized platform to support awareness drives, education, and grassroots campaigns.
- Localized Impact: By promoting information in regional languages, it enhances outreach among rural communities, where interaction with vultures is most direct.
Vultures of India
India hosts several species of vultures, many of which are critically endangered:
- Slender-billed vulture – ~800 mature individuals left.
- White-rumped vulture.
- Red-headed vulture.
- Himalayan griffon.
- Indian vulture.
- Cinereous vulture.
- Eurasian griffon.
- Egyptian vulture.
- Bearded vulture.
Conservation Context
- India has already banned the veterinary use of diclofenac (a major cause of vulture deaths) and promoted safer alternatives like meloxicam.
- Initiatives such as Vulture Safe Zones, breeding centres, and now this digital portal strengthen the country’s commitment to vulture conservation.
- As vultures play a critical ecological role as scavengers, their survival is linked to disease control and overall ecosystem health.
Environment Auditors

- 11 Sep 2025
In News:
The Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change (MoEFCC) has notified the Environment Audit Rules, 2025, authorising the creation of a new, independent cadre of environment auditors. This marks a significant reform in India’s environmental governance framework, aiming to strengthen compliance, accountability, and transparency in monitoring ecological regulations.
Background and Rationale
Environmental monitoring in India is primarily overseen by the Central Pollution Control Board (CPCB), Regional Offices of MoEFCC, and State Pollution Control Boards (SPCBs)/Pollution Control Committees (PCCs). However, these bodies face persistent challenges of manpower shortage, limited resources, and infrastructural constraints, which hinder effective enforcement across the vast number of industries and projects.
To address this gap, the government has introduced environment auditors—certified professionals or accredited private agencies—who can supplement regulatory agencies in compliance verification. This is expected to enhance the implementation of environmental laws while promoting self-regulation by industries.
Key Features of Environment Auditors
- Legal Basis: Established under the Environment Audit Rules, 2025.
- Nature: Independent class of licensed professionals/agencies accredited to inspect, verify, and audit industrial and infrastructure projects.
- Functions:
- Conduct systematic environmental audits of projects under existing environmental laws.
- Sample and analyse emissions, effluents, and waste.
- Report non-compliance and compute environmental compensation.
- Act as verifiers under multiple regulatory frameworks, including the Green Credit Rules, E-Waste Rules, and Plastic Waste Rules.
- Provide independent data for climate action planning, ESG ratings, and sustainable development initiatives.
Linkage with Green Credit Rules
Audits by these accredited agencies will also support compliance with the Green Credit Rules, 2023, which incentivise activities like afforestation, water management, waste reduction, and pollution control through tradable “green credits.” Environment auditors will thus act as third-party verifiers, ensuring credibility in the crediting process.
Significance of the Reform
- Bridges Institutional Deficits: Addresses manpower and infrastructure shortages in SPCBs and CPCB.
- Promotes Accountability: Encourages industries to adopt self-compliance mechanisms rather than relying solely on regulatory enforcement.
- Enhances Transparency: Independent, third-party verification fosters stakeholder trust in environmental governance.
- Strengthens Climate Commitments: Provides robust compliance data for India’s climate action goals and sustainability reporting.
- Reduces Regulatory Burden: Eases the monitoring load on overstretched government agencies.
Acanthamoeba

- 10 Sep 2025
In News:
Recent studies have revealed that Acanthamoeba, a free-living amoeba, is more widespread in Kerala’s waterbodies than previously believed. This raises significant public health concerns, especially due to its ability to cause severe and often fatal infections.
About Acanthamoeba
- Nature: A single-celled, free-living amoeba found in water, soil, and dust.
- Habitats: Frequently detected in swimming pools, hot tubs, household wells, drinking water systems, humidifiers, and HVAC (heating, ventilation, and air conditioning) systems.
- Mode of Transmission: Enters the human body through skin wounds, inhalation via lungs/nasal cavity, or eye exposure (notably among contact lens users).
Types of Infections
- Granulomatous Amebic Encephalitis (GAE): Affects the brain; almost always fatal.
- Cutaneous Acanthamoebiasis: Skin infection through wounds.
- Acanthamoeba Rhinosinusitis: Infection of the nasal cavity and sinuses.
- Acanthamoeba Keratitis: Serious eye infection, often in healthy individuals and contact lens users; may lead to permanent vision loss.
Kerala Case Study
- In 2013, research from the Regional Institute of Ophthalmology (Kerala) identified that several cases of non-healing corneal ulcers were due to Acanthamoeba keratitis, traced back to household wells as the infection source.
- Current findings indicate that Acanthamoeba is more widespread in Kerala’s natural and man-made waterbodies than earlier thought, heightening risks of waterborne and eye-related infections.
Significance
- The rise of Acanthamoeba-related keratitis underlines the need for safe water practices, improved eye hygiene among contact lens users, and awareness of rare pathogens.
- Its resilience across diverse environments makes it a public health challenge, especially in regions dependent on household wells and untreated water sources.
Debrigarh Wildlife Sanctuary
- 10 Sep 2025
In News:
Odisha’s Debrigarh Wildlife Sanctuary has recently been approved by the National Tiger Conservation Authority (NTCA) to become India’s newest tiger reserve. This marks a significant ecological achievement rooted in community participation, innovative eco-tourism, and conservation success.
Location and Geography
- Situated in western Odisha, near Sambalpur and Bargarh district, Debrigarh is bordered by the Hirakud Reservoir—a Ramsar-tagged wetland and part of the Mahanadi River system.
- The Hirakud Dam, the world’s longest earthen dam, lies adjacent to the sanctuary.
- Spread over 804 sq km, it includes around 347 sq km of core area, encompassing forests, grasslands, and wetlands, making it a unique amphi-terrestrial ecosystem.
Historical Significance
- The rugged terrain of Debrigarh was a strategic base for freedom fighter Veer Surendra Sai during his armed resistance against British colonial rule.
- Sites like Bara Bakra/Barapathara remain important heritage landmarks within the sanctuary.
Flora and Fauna
- Vegetation: Dominated by mixed and dry deciduous forests, with species such as Sal, Asana, Bija, Aanla, and Dhaura.
- Mammals: Indian bison (gaur), sambar deer, wild boar, chousingha (four-horned antelope), leopards, sloth bears, and wild dogs.
- Avifauna: Over 300 bird species, including 120 migratory species such as crested serpent eagle, drongo, tree pie, flower peckers, and white-eye oriental.
Eco-Tourism and Innovation
- Debrigarh is home to India’s first dark sky tourism hub, offering stargazing facilities.
- Adventure tourism includes safaris (53 vehicles), kayaking, cycling, and birding trails, designed with minimal ecological footprint.
Conservation and Community Model
- Declared a sanctuary in 1985 and upgraded to a tiger reserve in 2025.
- A community-led model: Over 400 families voluntarily relocated with rehabilitation packages; 155 villages actively participate in conservation and eco-tourism activities.
- Wildlife success: Expansion of prey base, increase in gaur population, and nearly 40% of herds comprising newborns, reflecting ecosystem recovery.
Significance
Debrigarh exemplifies a national model of integrated conservation, blending:
- Biodiversity protection (tiger reserve status, prey base recovery).
- Cultural heritage (legacy of Veer Surendra Sai).
- Sustainable eco-tourism (dark sky hub, water- and land-based safaris).
- Community participation (relocation and livelihood integration).
Its success offers a replicable blueprint for wildlife conservation across India, highlighting how ecological protection, heritage, and rural livelihoods can be balanced under one framework.
Senna spectabilis
- 09 Sep 2025
In News:
Invasive alien species are among the biggest threats to global biodiversity, ecosystem balance, and local livelihoods. In South India, Senna spectabilis, introduced in the 1980s for ornamental and fuelwood purposes, has emerged as a serious ecological challenge. Its unchecked spread across the Nilgiri Biosphere Reserve (NBR) has disrupted native ecosystems, escalated human-wildlife conflicts, and triggered large-scale forest degradation.
AboutSenna spectabilis
- Origin: Native to tropical America.
- Common Names: Popcorn Bush Cedar, Archibald's Cassia, Golden Shower, Fetid Cassia, etc.
- Characteristics: Grows 7–18 metres tall, forms dense sterile thickets, alters soil chemistry, suppresses native vegetation, and deprives herbivores of food.
- Confusion: Resembles Kerala’s state flower Cassia fistula (Kanikkonna), aiding its popularity in afforestation drives.
- IUCN Status: Classified as Least Concern.
- Challenge: Prolific seed production (up to 6,000 seeds annually), viability for nearly a decade, and quick regrowth even after cutting.
Ecological and Social Impacts
- Biodiversity Loss – Chokes out native species, prevents natural regeneration, and alters ecosystem dynamics.
- Food Chain Disruption – Loss of grasses and shrubs reduces prey availability for carnivores.
- Human-Wildlife Conflict – Decline in herbivore populations forces elephants, tigers, and deer to enter human settlements.
- Forest Degradation – Spread across Wayanad, Bandipur, and Mudumalai wildlife regions, threatening one of Asia’s most critical wildlife corridors.
- Spread Beyond South India – Reports of infestation in Andhra Pradesh, Goa, and Maharashtra.
A 2021 Rufford Foundation study showed Senna had spread over 23% of Wayanad Wildlife Sanctuary, now estimated at 40%.
Kerala’s “Wayanad Model” of Restoration
Kerala pioneered India’s first science-based, community-led eradication program at Tholpetty range, Wayanad Wildlife Sanctuary:
- Scale: 383 acres cleared; 46,450 trees uprooted; total eco-restoration covers 560 acres.
- Innovation: A lightweight hand-held uprooting tool designed by a marine engineer enabled complete root removal.
- Community Participation: Tribal youth (Kurichiya, Kattunaikka) trained as forest restoration guardians.
- Biodiversity Revival:
- 80 native tree species replanted.
- 15 indigenous grasses naturally regenerated.
- 184 bird species recorded in post-restoration zones.
- Return of elephants and deer to reclaimed patches.
This approach of “un-planting mistakes” emphasizes uprooting rather than cutting, ensuring long-term ecological recovery.
Policy and Replication
- Cross-border Extension: Karnataka adopted the Wayanad model in Nagarhole Tiger Reserve (DB Kuppe range). Tamil Nadu is exploring similar interventions.
- Utilisation of Biomass: Pilot projects have converted Senna wood into 6,000 tonnes of paper pulp; however, experts caution that biomass use alone will not halt invasion unless roots are fully removed.
- Other Invasives: The Senna challenge mirrors broader issues with Lantana, Eupatorium, and Acacia, which silently erode ecosystems across India.
Invasive Species
- Definition: An invasive species is a non-native organism that causes ecological, economic, or health harm in a new environment.
- Introduction Pathways: Ballast water of ships, aquaculture, ornamental planting, and accidental releases.
- Impacts: Extinction of native species, biodiversity loss, ecosystem degradation, and livelihood disruptions.
Gastrochiluspechei
- 07 Sep 2025
In News:
Researchers have discovered a new orchid species, Gastrochiluspechei, in Vijoynagar, Arunachal Pradesh, one of India’s remotest administrative circles bordering Myanmar. Until now, this orchid was known to bloom only in Myanmar, highlighting the floristic link between Arunachal Pradesh and Southeast Asia.
Key Features of Gastrochiluspechei
- Genus: Belongs to the Gastrochilus genus, first recorded in 1825, comprising 77 species spread across tropical, subtropical, and temperate Asia.
- Identification: Distinguished by short axillary inflorescence, brightly coloured flowers, a distinct epichile on the hypochile, and two porate, globose pollinia on a slender stipe.
- Habitat: Thrives in moist, evergreen rainforests, growing on small trees near riverbanks.
- Flowering Season: Blooms between September and October.
Floristic Significance
- With this finding, India now records 23 species of the Gastrochilus genus, of which 15 are from Arunachal Pradesh.
- The discovery reinforces Arunachal Pradesh’s title as the “Orchid State of India,” which harbours about 60% of the country’s orchid diversity.
- It also provides scientific evidence of the biogeographical continuity between Arunachal Pradesh and Myanmar, where the species was earlier recorded in Kachin’s Putao County.
Broader Context
Orchids are not only indicators of ecological richness but also hold significance for conservation, floriculture, and sustainable livelihoods. The discovery of Gastrochiluspechei adds to India’s botanical wealth and underscores the need to preserve fragile Himalayan ecosystems where such rare species thrive.
Indian Rosewood
- 06 Sep 2025
In News:
- Indian rosewood (Dalbergialatifolia in the south and Dalbergia sissoo in the north), often referred to as the “ivory of the forests”, is prized globally for its rich grain, deep colour, and durability.
- It serves as both a premium timber resource for furniture, handicrafts, and musical instruments, and an ecologically significant species that enhances soil fertility through nitrogen fixation, supports bird and insect diversity, and acts as a long-term carbon sink.
Distribution and Habitat
- Dalbergialatifolia: Native to the Nilgiris, Anamalai, and Parambikulam ranges in Tamil Nadu, with significant habitats in Karnataka and Kerala.
- Dalbergia sissoo (North Indian rosewood): Found along the Himalayan foothills, from Afghanistan to Bihar, typically growing along riverbanks between 200–1,400 m elevation.
- Recent habitat modelling by the Institute of Wood Science and Technology (IWST), Bengaluru, using 3,224 geo-referenced points and 19 bioclimatic variables, found that only 17.2% of India’s suitable habitat lies within protected areas.
Current Status in Tamil Nadu
- Field surveys (2019–2025) by IWST and the Indian Council of Forestry Research and Education revealed that Tamil Nadu has the lowest density of rosewood in South India, with just 2.85 trees per 0.1 hectare, compared to 6.19 in Karnataka and 5.38 in Kerala.
- The populations are dominated by mature, ageing trees with little or no natural regeneration, and seedlings are rare or absent in many areas.
- The situation has worsened after the lapse of the Tamil Nadu Rosewood (Conservation) Act, 1995, which had regulated felling of rosewood for nearly three decades.
- With no renewal after February 2025, privately owned rosewood, especially in tea plantations of the Nilgiris, faces heightened risk of exploitation.
Threats
- Weak Legal Safeguards – With the lapse of State legislation, most rosewood outside protected areas is exposed to felling and land-use change.
- Climate Change – IWST modelling projects shrinking suitable habitats in coming decades, further compounding the species’ vulnerability.
- International Demand – Luxury furniture and musical instruments drive high global demand.
- Regeneration Crisis – Ageing tree populations without sufficient seedlings threaten long-term survival.
Conservation Status
- IUCN Red List: Vulnerable (since 2018).
- CITES: Appendix II (regulated trade).
- India’s Last National Assessment (2011–12): Near Threatened.
Blue Sea Dragons
- 06 Sep 2025
In News:
Recently, several beaches in Guardamar del Segura, Spain, were closed after an unusual invasion of blue sea dragons (Glaucus atlanticus), a rare but strikingly beautiful species of sea slug. Authorities imposed the ban as a precautionary measure to protect residents and tourists from potential stings.
About Blue Sea Dragons
- Taxonomy: A type of mollusk belonging to the nudibranch family.
- Other Names: Also called blue sea slugs, sea swallows, and blue angels.
- Appearance: Known for their ethereal blue and silver coloration and small size (1–3 cm), often floating upside down on the ocean surface.
- Distribution: Found across Atlantic, Pacific, and Indian Oceans in tropical and temperate waters.
- Reproduction: They are hermaphrodites, possessing both male and female reproductive organs.
Feeding and Venom Storage
- Diet consists mainly of venomous siphonophores such as the Portuguese man-o’-war and bluebottle jellyfish.
- Instead of digesting their prey’s stinging cells (nematocysts), they store and concentrate them in finger-like structures on their backs called cerata.
- This makes their sting more potent than that of the original prey, giving them a powerful defence mechanism despite their fragile appearance.
Impact on Humans
- Though not venomous on their own, their stored nematocysts can deliver extremely painful stings.
- Reported symptoms include nausea, vomiting, pain, dermatitis, allergic reactions, and post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation.
- Children and elderly individuals are especially vulnerable.
Air Quality Life Index
- 04 Sep 2025
In News:
Air pollution has emerged as India’s gravest public health challenge, surpassing traditional concerns like malnutrition, unsafe water, and tobacco use. The Air Quality Life Index (AQLI) 2025 Report, prepared by the Energy Policy Institute at the University of Chicago (EPIC), highlights how toxic air substantially reduces life expectancy across the country, with disproportionate impacts in the northern belt.
About Air Quality Life Index (AQLI)
- Developed by Michael Greenstone and EPIC, University of Chicago.
- Quantifies the impact of long-term exposure to PM2.5 on life expectancy.
- Combines research evidence with global particulate pollution data to estimate the loss in healthy years of life.
Key Findings of AQLI 2025 Report
National Impact
- Average life expectancy loss in India: 3.5 years.
- All 1.4 billion Indians live in areas exceeding the WHO’s safe limit of 5 µg/m³ for PM2.5.
- Comparative impact:
- Malnutrition: 1.6 years lost
- Tobacco use: 1.5 years lost
- Unsafe water & sanitation: 8.4 months lost
Regional Disparities
- Northern India is the world’s most polluted region, with 544.4 million people (38.9% of population) exposed to severe pollution.
- Delhi-NCR: Worst affected, with residents losing 8.2 years of life expectancy (WHO standards).
- By India’s weaker PM2.5 norm (40 µg/m³): 4.74 years lost.
- Other states:
- Bihar: 5.6 years lost
- Haryana: 5.3 years lost
- Uttar Pradesh: 5 years lost
South Asian Context
- South Asia remains the most polluted region globally.
- PM2.5 levels rose by 2.8% in 2023 after a brief decline in 2022.
- Regional impact:
- 3 years cut from average life expectancy.
- Over 8 years lost in most affected zones.
Standards and Gains from Pollution Reduction
- 46% of Indians live in areas exceeding even India’s own PM2.5 limit of 40 µg/m³.
- Meeting national standards could add 1.5 years to life expectancy.
- Meeting WHO standards could add up to 9.4 months even in relatively cleaner regions.
Ethanol Blending in India

- 02 Sep 2025
In News:
India has been steadily advancing towards ethanol blending in petrol to reduce dependence on fossil fuels, cut carbon emissions, and boost the agricultural economy. Recently, debates have intensified after the nationwide rollout of E20 fuel (20% ethanol + 80% petrol) in July 2025—five years ahead of its initial 2030 target. Concerns were raised about its impact on older vehicles and consumer safety.
What is Ethanol Blending?
- Ethanol (C?H?OH): A renewable, biodegradable, and clean-burning fuel derived from biomass such as sugarcane molasses, rice, maize, barley, and wheat.
- Ethanol Blending: Mixing ethanol with petrol to increase oxygen content, leading to cleaner combustion, reduced greenhouse gas emissions, and lower crude oil imports.
- India’s Ethanol Blended Petrol (EBP) Programme began in 2003.
- Progress:
- 10% blending target achieved in 2021-22
- 12.06% in 2022-23
- 14.06% in 2023-24
- 20% blending achieved in July 2025, ahead of the 2030 deadline.
E20 Fuel and Automobile Industry Response
- E20 fuel is now being offered at petrol pumps, replacing earlier E5/E10 options.
- The Society of Indian Automobile Manufacturers (SIAM) confirmed that warranties will remain valid for older cars even if they were not originally designed for E20.
- Automakers are issuing dealer advisories on E20 usage in pre-2023 vehicles, when flex-fuel-compatible models began rolling out.
- The government has also announced guidelines for 27% ethanol blending, further deepening the transition.
Concerns and Challenges
- Fuel Efficiency & Engine Issues: Some vehicle owners have reported lower mileage and performance issues with E20.
- Warranty and Consumer Trust: Initial confusion over automaker responsibility raised fears of invalidated warranties.
- Agricultural Dependence: Heavy reliance on sugarcane and food crops raises concerns about the food vs. fuel debate and water stress.
- Supply Chain & Technology: Ethanol storage, transport, and blending infrastructure must scale up nationwide.
- Legal Challenge: A public interest litigation (PIL) on the impact of E20 is pending before the Supreme Court.
Benefits of Ethanol Blending
- Environmental: Cuts CO? emissions, improves urban air quality, and reduces vehicular pollution.
- Economic: Reduces crude oil imports (India imports ~85% of crude requirements), saving forex reserves.
- Agricultural: Provides a stable market for farmers through ethanol demand from crops like sugarcane, maize, and rice.
- Strategic: Contributes to India’s energy security and climate commitments under Paris Agreement & Net Zero 2070 goals.
Government Push and Future Roadmap
- Union Minister Nitin Gadkari has reiterated that higher ethanol blending is central to India’s green mobility transition.
- India is also exploring flex-fuel vehicles and second-generation (2G) ethanol derived from agricultural residues to address food security concerns.
- Targets:
- 27% blending roadmap under preparation.
- Expansion of ethanol production capacity through distilleries and 2G ethanol plants.
- Incentives for biofuel research, hybrid engines, and flex-fuel adoption.
International Centre for Integrated Mountain Development
- 02 Sep 2025
In News:
The Hindu Kush Himalaya (HKH), spanning about 3,500 km across eight countries—Afghanistan, Bangladesh, Bhutan, China, India, Myanmar, Nepal, and Pakistan—is a global ecological and hydrological powerhouse.
Often termed the “Third Pole”, it holds the largest area of permanent ice cover outside the Arctic and Antarctic, feeding 10 major Asian river systems including the Indus, Ganga, and Brahmaputra. Despite its significance, a new report by the International Centre for Integrated Mountain Development (ICIMOD) warns that the region is tapping only 6.1% of its vast renewable energy potential, exposing vulnerabilities in the face of climate change.
About ICIMOD
- Established in 1983, headquartered in Kathmandu, Nepal.
- Intergovernmental body representing eight member countries of the HKH.
- Mission: Build and share knowledge to drive regional policy, investments, and climate-resilient development.
- Functions:
- Knowledge generation and sharing.
- Bridging science, policy, and practice.
- Providing a regional platform for sustainable mountain development.
Renewable Energy Potential in HKH
- Total hydropower potential: 882 GW.
- Of this, 635 GW lies in the trans-boundary rivers of HKH.
- Only 49% of hydropower potential is currently harnessed.
- Non-hydro potential: Nearly 3 Terawatts (solar & wind).
- Combined renewable energy potential in the region: >3.5 Terawatts.
- Current share in Total Primary Energy Supply (TPES): just 6.1%.
Country-wise Renewable Scenario
- Bhutan & Nepal: Generate 100% of electricity from renewables.
- India: Renewables contribute 23% of electricity generation.
- Others: Reliance on fossil fuels remains very high (Bangladesh 98%, Pakistan 76%, China 67%, Myanmar 51%).
- Traditional biomass use: Alarmingly high in rural areas—two-thirds of Nepal’s TPES, half of Myanmar’s, one-fourth of Bhutan’s and Pakistan’s—leading to severe air quality and health issues.
Climate Change & Energy Risks
The report highlights that climate variability is destabilising energy systems:
- Increased water variability and changing hydrological regimes reduce hydropower reliability.
- Glacial Lake Outburst Floods (GLOFs) and extreme weather events threaten nearly two-thirds of existing and planned hydropower projects.
- Infrastructure damage due to landslides, floods, and mega-floods is rising.
Policy Recommendations
- Integrate disaster risk reduction into hydropower and renewable energy projects.
- Explore “dams equivalents” like:
- Climate-resilient irrigation systems.
- On-farm water-efficient practices.
- Urban water storage solutions.
- Scaling up solar and wind power.
- Promote regional cooperation through platforms like SAARC Energy Centre and BIMSTEC Energy Ministers’ Conference.
- Attract international finance and private investment to overcome capital constraints.
- Encourage south-south collaboration, technology exchange, and joint research.
Significance for India
- India, a major HKH country, has both high renewable potential and high fossil fuel dependence.
- Regional clean energy cooperation can:
- Enhance energy security.
- Reduce import dependence.
- Create green jobs.
- Help achieve India’s Nationally Determined Contributions (NDCs) under the Paris Agreement.
Vaquita Porpoise
- 01 Sep 2025
In News:
- The vaquita porpoise (Phocoena sinus), the world’s rarest marine mammal, is on the brink of extinction with only about 10 individuals remaining in the northern Gulf of California (Sea of Cortez), Mexico.
- Despite global attention, weak enforcement of wildlife protection laws in Mexico and the persistence of illegal fishing practices have accelerated the species’ decline.
- A recent report by the North American Environmental Commission under the United States-Mexico-Canada Agreement (USMCA) has held Mexico accountable for failing to safeguard the vaquita.
The Vaquita: An Overview
- Discovery: Identified in 1958.
- Classification: Smallest member of the cetacean family (whales, dolphins, porpoises), diverged from dolphins ~15 million years ago.
- Habitat: Restricted to shallow waters (up to 50 m deep) in the Upper Gulf of California.
- Appearance: Distinct dark eye rings, lip patches, and a large dorsal fin aiding heat release.
- Behavior: Solitary or small-group species, shy, avoids boats.
- Status:
- IUCN Red List: Critically Endangered.
- CITES: Appendix I (strict trade regulation).
Causes of Decline
- Gillnet Bycatch:
- The primary threat is entanglement in illegal gillnets set for totoaba fish, whose swim bladder fetches high prices in East Asia.
- Despite Mexico’s ban on gillnets since 2020, on-ground reports reveal continued use.
- Weak Enforcement:
- Only 10 of the 850 promised satellite trackers fitted on fishing vessels.
- Fishermen bypass restrictions by sending illegal catch to other regions.
- Institutional Failures:
- Lack of adequate vessel inspections, monitoring, and promotion of alternative fishing gear.
- Mexico’s enforcement claims contradicted by eyewitness accounts and NGO reports.
International Pressure and USMCA Mechanisms
- The USMCA Environmental Commission report has urged the United States to hold Mexico accountable.
- Under USMCA, the US can:
- Press for stricter compliance through consultations.
- Escalate disputes to a panel stage.
- Impose import penalties if Mexico fails to enforce the ban in vaquita habitats.
Sundarbans Tiger Reserve
- 31 Aug 2025
In News:
The Sundarbans Tiger Reserve (STR) in West Bengal has become India’s second-largest tiger reserve after the National Board for Wildlife (NBWL) approved the state government’s proposal to expand its area by 1,044.68 sq km. With this addition, STR now spans 3,629.57 sq km, moving up from the seventh to the second position among the country’s 58 tiger reserves, next only to Andhra Pradesh’s Nagarjunasagar-Srisailam Tiger Reserve (3,727.82 sq km).
Expansion Details
- The newly added area includes three tiger-bearing forest ranges of South 24 Parganas district: Matla, Raidighi, and Ramganga.
- The expansion brings all tiger-bearing mangrove forests under the unified management of STR, ensuring uniform application of National Tiger Conservation Authority (NTCA) guidelines.
- The proposal was first conceived nearly two decades ago, revived in 2022–23, and formally cleared by NBWL in August 2025 after approvals from the State Wildlife Board and NTCA.
Location and Ecological Importance
- STR is located in the coastal districts of West Bengal, at the southernmost tip of the Gangetic delta, bordering the Bay of Bengal.
- It is part of the world’s largest delta, formed by the Ganga and Brahmaputra rivers.
- STR is unique as it is the only mangrove habitat in the world (shared with Bangladesh) that supports a significant tiger population.
- It also holds the status of a National Park and a Biosphere Reserve.
Boundaries
- East: International boundary with Bangladesh (rivers Harinbhanga, Raimangal, Kalindi).
- South: Bay of Bengal.
- West: River Matla (boundary with South 24-Parganas Forest Division).
- North-West: Rivers Bidya and Gomdi.
Biodiversity
- Flora: True mangroves, mangrove associates, halophytic herbs, shrubs, weeds, epiphytes, and parasitic plants.
- Fauna: Bengal tiger, estuarine crocodile, fishing cat, Gangetic and Irrawaddy dolphins, king cobra, water monitor lizard, and numerous bird and fish species.
Conservation and Development Implications
- Estimated tiger population: ~101 (80 within STR, 21 in adjoining forests). The number is expected to increase with better management.
- Expansion is expected to enhance:
- Central funding for tiger conservation.
- Tourism potential and local economic benefits.
- Infrastructure and staff capacity within the reserve.
- Conservationists welcome the move as long overdue, while some forest officials caution about manpower shortages (currently only 40% of sanctioned strength).
Blue Carbon

- 30 Aug 2025
In News:
Seaweed farming has emerged as a potential Blue Carbon strategy, yet empirical estimates of carbon burial from such farms remain lacking in the literature.
What is Blue Carbon?
- Blue Carbon refers to organic carbon captured and stored by ocean-based vegetated ecosystems such as mangroves, saltmarshes, and seagrass meadows.
- The term “blue” highlights its association with aquatic ecosystems.
- Most blue carbon comes from carbon dioxide dissolved directly into the ocean. Smaller amounts are stored in:
- Underwater sediments and soils
- Coastal vegetation
- Organic molecules (DNA, proteins, etc.)
- Marine organisms (phytoplankton, whales, etc.)
- Despite covering just 2% of the ocean surface, these ecosystems account for 50% of total oceanic carbon absorption, making them vital in global climate mitigation efforts.
Seaweed Farming as a Blue Carbon Strategy
- Emerging Role: Seaweed cultivation has been identified as a potential Blue Carbon pathway, though empirical evidence of its carbon burial capacity has been limited until recently.
- Global Study: An analysis of 20 seaweed farms worldwide, aged between 2 and 300 years and ranging from 1 to 15,000 hectares, provides new insights.
- Findings:
- Sediment organic carbon stocks increased with farm age, reaching 140 tC ha?¹ in the oldest farm.
- Average burial rates: 1.87 ± 0.73 tCO?e ha?¹ yr?¹ in farm sediments, nearly double that of nearby reference sediments.
- Excess CO?e burial attributable to seaweed farming: 1.06 ± 0.74 tCO?e ha?¹ yr?¹.
- Conclusion: Seaweed farms in depositional environments act as effective carbon sinks, with burial rates at the lower end of traditional Blue Carbon habitats but increasing significantly with farm maturity.
Significance
- Reinforces the role of marine ecosystems in carbon sequestration.
- Highlights seaweed farming as a scalable, nature-based climate solution alongside mangroves, saltmarshes, and seagrasses.
- Provides a scientific basis for integrating seaweed aquaculture into Blue Carbon policies and climate strategies.
India’s Push for 27% Ethanol Blending
- 28 Aug 2025
In News:
India has announced its ambitious plan to increase ethanol blending in petrol to 27% (E27) by 2030, building upon the successful Ethanol Blended Petrol (EBP) Programme launched in 2003. This move aligns with India’s goals of energy security, environmental sustainability, and rural development.
Background and Progress
- EBP Programme: Started with 5% blending, it has grown from less than 2% a decade ago to 10% (E10) by 2022, with 20% blending (E20) projected for 2025, five years ahead of schedule.
- Ethanol Feedstocks: Primarily derived from sugarcane, maize, and surplus food grains, with an increasing push for second-generation ethanol from crop residues and agricultural waste under PM-JI-VAN Yojana.
- Energy Security: India imports nearly 88% of crude oil, spending over $120 billion annually. Ethanol blending reduces crude imports, conserves foreign exchange, and mitigates vulnerability to global price shocks.
- Environmental Goals: Ethanol blends reduce carbon monoxide and hydrocarbon emissions, supporting the National Green Mobility Strategy and India’s Net Zero 2070 commitment.
Economic and Social Benefits
- Farmer Welfare: The programme has channeled over ?1.2 lakh crore to farmers and nearly ?2 lakh crore to distilleries, providing stable markets for sugarcane, maize, and other crops.
- Rural Development: Ethanol distilleries generate employment, promote agro-industries, and reduce distress migration.
- Circular Economy Link: Second-generation ethanol initiatives convert crop residues and waste into energy, addressing stubble burning and enhancing sustainability.
Challenges and Risks
- Food Security: Rising ethanol demand strains maize and grain supplies. In 2023, a 5-million-tonne maize shortfall forced imports, affecting poultry, starch industries, and food prices.
- Water Use: Sugarcane requires 1,500–2,000 litres of water per kg of sugar, risking groundwater depletion in states like Maharashtra and Uttar Pradesh.
- Technological Issues: Higher blends can reduce fuel efficiency by 6–7% in vehicles not designed for ethanol. Adoption of Flex Fuel Vehicles is slow and more costly.
- Supply-Side Constraints: India produced 7 billion litres of ethanol in 2023 but will require over 12 billion litres by 2030. Financially stressed sugar mills and limited investment in grain-based or second-generation plants challenge scaling.
- Infrastructure Needs: Storage, transport, and fuel dispensing networks must expand nationwide to meet E27 targets.
Policy Recommendations
- Feedstock Diversification: Rapid development of second-generation ethanol from crop residues, forestry waste, and municipal solid waste.
- Consumer Incentives: Subsidies for Flex Fuel Vehicles, retrofitting existing engines, and awareness campaigns to ensure adoption.
- Public–Private Partnerships: Investment and collaboration to scale production, distribution, and technology adoption.
- Integration with Clean Energy Transition: Ethanol should complement electric mobility and green hydrogen, serving as a bridge solution for decarbonisation while more transformative technologies mature.
Climate Change and Workplace Heat Stress
- 28 Aug 2025
In News:
The WHO–WMO joint report (2025), Climate Change and Workplace Heat Stress, warns that rising global temperatures are creating an unprecedented occupational health and productivity crisis. The year 2024 was the warmest on record, with global average temperatures 1.45°C above pre-industrial levels, and the decade 2015–2024 being the hottest ever recorded.
Key Findings
- Productivity Losses: Each 1°C rise in Wet-Bulb Globe Temperature (WBGT) above 20°C reduces global worker productivity by 2–3%. Sun exposure further raises WBGT by 2–3°C, amplifying risk.
- Scale of Exposure: Over 2.4 billion workers are directly exposed; annually, 22.85 million injuries, 18,970 deaths, and 2.09 million disability-adjusted life years (DALYs) are linked to workplace heat stress (ILO estimates).
- Geographical Hotspots: South Asia, Sub-Saharan Africa, and the Middle East face the highest risks. Heat stress now affects 30% of the global population seasonally or daily.
- Health Impacts: More than one-third of workers in hot conditions report physiological heat strain (hyperthermia, kidney dysfunction, dehydration, neurological problems). WHO safety guidance (1969) recommends that core body temperature during an 8-hour shift not exceed 38°C, a threshold increasingly breached.
- Climate Change Dimension: Daytime peaks of 40–50°C are becoming frequent even outside the tropics. Europe’s 2023 heatwave saw worker fatalities, showing that occupational heat stress is no longer limited to equatorial regions.
India’s Experience
In India, informal workers in brick kilns, construction, agriculture, and power looms are the most affected. Many begin work before sunrise to avoid peak heat, yet still suffer dehydration, dizziness, and lost wages as work hours shrink. Indoor workplaces with poor ventilation often become “furnaces,” leading to chronic fatigue, kidney strain, and even fatalities. By 2030, the ILO projects India could lose 34 million full-time equivalent jobs, particularly in agriculture and construction, due to heat stress.
Wider Implications
- Public Health Burden – Rising cases of heat stroke, cardiovascular collapse, and chronic kidney disease (26.2 million cases in 2020 alone) strain already weak health systems.
- Economic Losses – Developing economies face shrinking GDP as productivity drops; agriculture and construction are most vulnerable.
- Social Inequality – The poor, migrant labourers, and women are disproportionately at risk due to unsafe working conditions and lack of social protection.
- Climate Justice – Regions contributing least to emissions, like Bangladesh and Sub-Saharan Africa, suffer the harshest effects, deepening global inequities.
- Food Security – Agricultural labour productivity loss disrupts crop cycles and threatens farmer incomes, worsening hunger and malnutrition.
- Legal Burden – Rising occupational illness cases risk overwhelming compensation systems and highlight gaps in labour safety laws.
Adaptation Strategies
- Occupational Heat Action Plans: Early warning systems, rescheduling work timings, shaded shelters, and worker training.Example: The Ahmedabad Heat Action Plan (India) has reduced heatwave mortality through alerts, shelters, and training.
- Infrastructure & Technology: Cooling shelters, hydration points, and mechanisation to reduce manual strain.Example: Bangladesh’s garment sector has piloted low-cost ventilation and cooling fans, lowering worker fatigue.
- Labour Policy Reforms: Enforcing heat-index-based work-hour rules, mandatory rest breaks, and compensation for heat-linked illnesses.Example: Qatar bans outdoor work between 10 am–3:30 pm during peak summer.
- Public Health Measures: Hydration protocols, health screenings, and recognition of heat stress as an occupational disease.Example: US OSHA’s “Water–Rest–Shade” campaigninstitutionalises hydration and rest breaks.
- Global & National Coordination: Mainstreaming heat stress into ILO conventions, COP climate talks, and SDG frameworks, with climate finance support for vulnerable economies.Example: Australia integrates climate projections into mining and agriculture workplace safety standards.
National Tiger Conservation Authority’s Corridor Restriction
- 27 Aug 2025
In News:
The National Tiger Conservation Authority (NTCA), the apex statutory body under the Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change (MoEFCC), has recently issued a clarification restricting the definition of tiger corridors to only the 32 “least cost pathways” identified in 2014 and those recorded in Tiger Conservation Plans (TCPs) of individual reserves. This excludes later studies by the Wildlife Institute of India (WII) (2016, 2021) and data from the All-India Tiger Estimation (AITE) exercises.
What are Tiger Corridors?
Tiger corridors are natural pathways that connect fragmented tiger habitats, allowing for:
- Genetic flow and long-term survival of populations.
- Migration and dispersal between reserves.
- Minimisation of human-wildlife conflict through guided movement.
Projects that require land in or around these corridors or reserves need statutory clearance from the Standing Committee of the National Board for Wildlife (SC-NBWL) under the Wildlife Protection Act, 1972.
About NTCA
- Established: 2005 (through 2006 amendment of Wildlife Protection Act, 1972).
- Chairperson: Union Minister of Environment, Forest and Climate Change.
- Functions:
- Approves TCPs of states.
- Provides financial and technical support for tiger conservation.
- Oversees Project Tiger implementation.
- Conducts All-India Tiger Estimation (AITE) every 4 years.
- Ensures ecological connectivity through corridor protection.
The Recent Controversy
- NTCA had earlier told the Bombay High Court (July 2025) that multiple benchmarks would be used to identify corridors, including:
- Protected areas with tiger occupancy.
- 2014 least-cost pathways.
- WII studies (2016, 2021).
- AITE distribution data.
- However, in its latest clarification, NTCA restricted corridors only to 2014 least-cost pathways and TCP records, ignoring updated scientific models.
Potential Beneficiaries
Industrial projects, particularly in Maharashtra, such as:
- Western Coalfields Limited’s Durgapur open cast mines.
- Lloyds Metals & Energy’s Surajgarh iron ore mines in Gadchiroli.
Scientific Concerns
- 2014 NTCA Report itself noted that its corridors were “minimal requirement” and alternative connectivities also needed conservation.
- Newer studies (e.g., Circuitscape modelling, 2025) suggest at least 192 corridors across 10 central Indian states, far beyond the restricted 32.
- Narrowing protection risks fragmentation of habitats, reducing gene flow and increasing chances of local extinctions.
India’s Draft Climate Finance Taxonomy

- 27 Aug 2025
In News:
In May 2025, the Ministry of Finance (Department of Economic Affairs) released India’s draft Climate Finance Taxonomy (CFT) for public consultation. This initiative is timely, as it coincides with India’s expanding climate finance ecosystem, including green bonds, carbon credit trading, and global commitments under the Paris Agreement and net-zero targets by 2070.
What is a Climate Finance Taxonomy?
- A classification framework that defines which sectors, technologies, and activities qualify as climate-aligned investments.
- It is described as a “living document”, evolving with India’s domestic priorities and international climate obligations.
- Core purpose: To mobilise public and private finance, ensure transparency, and prevent greenwashing.
Key Features of India’s Draft CFT
- Scope: Covers activities contributing to mitigation, adaptation, and low-carbon transition.
- Review Mechanism
- Annual reviews for course correction.
- Five-year reviews aligned with India’s Nationally Determined Contributions (NDCs) and the UNFCCC global stocktake.
- Legal Coherence
- Designed to be consistent with Indian laws (Energy Conservation Act, SEBI regulations, Carbon Credit Trading Scheme).
- Harmonised with international standards for credibility.
- Substantive Clarity: Provides clear, precise, and updated definitions that are accessible to both experts and non-experts.
- Inclusivity
- Simplified compliance for MSMEs, informal sector actors, and vulnerable communities.
- Staggered timelines for smaller entities to avoid exclusion.
- Institutional Accountability
- Proposal for a standing review unit/expert committee.
- Public dashboards to ensure transparency and investor confidence.
Significance
- Boosts Investor Confidence: Provides clarity for domestic and global investors in India’s green economy.
- Ensures Transparency: Prevents mislabeling of projects as “green,” tackling greenwashing risks.
- Mobilises Finance: Unlocks predictable, science-based finance flows for mitigation and adaptation.
- Supports Net-Zero Goals: Complements instruments like green bonds and carbon credit markets.
- Global Positioning: Strengthens India’s role in shaping international norms on climate finance.
National Policy to Promote Globally Important Agricultural Heritage Systems (GIAHS) in India
- 26 Aug 2025
In News:
- The Globally Important Agricultural Heritage Systems (GIAHS) programme, launched by the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) in 2002 at the World Summit on Sustainable Development, aims to conserve unique agricultural systems that sustain biodiversity, traditional knowledge, and rural livelihoods while adapting to modern challenges such as climate change, biodiversity loss, and community displacement.
- GIAHS adopts a multi-stakeholder approach by offering technical assistance, enhancing the value of traditional agricultural knowledge, and stimulating markets through agrotourism, product branding, and sustainable value chains.
India’s Recognised GIAHS Sites
Currently, India hosts three GIAHS sites, each reflecting diverse agro-ecological and cultural traditions:
- Koraput Region (Odisha):
- Known for subsistence paddy cultivation on highland slopes.
- Conserves a wide range of paddy landraces and farmer-developed varieties.
- Rich in medicinal plant genetic resources, closely linked with indigenous tribal knowledge.
- Supported by community seed banks, organic farming practices, and branding initiatives under state biodiversity programmes.
- Kuttanad Farming System (Kerala):
- A rare below-sea-level farming landscape.
- Comprises wetlands for paddy, garden lands for coconut and food crops, and inland water bodies for fishing and shell collection.
- Infrastructure development works under RKVY-DPR projects, such as HaritamHarippad in Alappuzha, and research on ecological utilization of water hyacinth are underway.
- Saffron Heritage of Kashmir:
- Represents a traditional agro-pastoral system of saffron cultivation.
- Characterized by organic farming practices, intercropping, and soil conservation.
- Supported through Rashtriya Krishi Vikas Yojana (RKVY) and the Mission for Integrated Development of Horticulture (MIDH) for revival and economic sustainability.
National Support Mechanisms
- Government Schemes: RKVY, MIDH, and other sectoral interventions promote conservation, branding, and livelihood opportunities.
- Biodiversity Revival: Emphasis on neglected crops and forgotten foods to ensure resilience.
- Integration with Research: State-supported projects in Kerala and Odisha enhance scientific validation and infrastructure.
Significance
- Ensures balance between conservation and socioeconomic development.
- Protects traditional knowledge systems and cultural landscapes.
- Enhances climate resilience and strengthens India’s commitment to sustainable agriculture.
- Promotes rural development, agrotourism, and niche product markets, thereby contributing to farmer incomes.
Sliteye Shark
- 25 Aug 2025
In News:
For the first time, scientists have recorded the sliteye shark (Loxodonmacrorhinus) in the Great Chagos Bank, the world’s largest coral atoll in the Indian Ocean. The discovery underscores the hidden biodiversity of the Chagos Archipelago and its Marine Protected Area (MPA), highlighting the ecological importance of deepwater habitats.
About the Sliteye Shark
The sliteye shark is a small-bodied requiem shark in the family Carcharhinidae and is the only species in the genus Loxodon. Named for its distinctive slit-like eyes, the species is adapted to low-light, deepwater environments, though it can also inhabit clear, shallow seas.
- Scientific Name:Loxodonmacrorhinus
- Size: Up to 95 cm in length
- Features: Slender body, long narrow face, large eyes, short furrows at mouth corners, small teeth with protruding tips, absent or rudimentary ridge between dorsal fins, gray coloration with white belly, dark-edged caudal and first dorsal fins
- Distribution: Tropical waters of the Indian and western Pacific Oceans, including countries such as India, Indonesia, Sri Lanka, Japan, Australia, China, Kenya, South Africa, and others between 34°N and 30°S
Discovery in Chagos
- Researchers observed two sliteye sharks at depths of 23–29 metres, just 11 km apart, using Baited Remote Underwater Video systems in deep seagrass habitats on the southern rim of the Great Chagos Bank. These meadows, first mapped in 2016 using satellite tracking of green turtles, support more than 110 fish species and are now confirmed as important for sliteye sharks as well.
Conservation Concerns
- The sliteye shark is classified as Near Threatened by the IUCN Red List, with populations projected to decline by approximately 30% over the next 15 years due to heavy fishing pressure.
- The Chagos discovery raises critical questions regarding the species’ abundance, habitat use, and conservation needs.
- The study forms part of a project led by Swansea University in collaboration with international partners, funded by the Bertarelli Foundation, with full findings expected in 2026. The results strengthen the case for protecting deepwater seagrass habitats in the Indian Ocean.
Water-Scarce Districts in India
- 22 Aug 2025
In News:
Water, being a State subject, places the responsibility for augmentation, conservation, and efficient management primarily on State Governments. However, the Central Government supplements efforts through technical and financial support. Recent assessments by the Central Ground Water Board (CGWB) highlight the growing challenge of water scarcity in India.
Water-Scarce Districts in India
- The “National Compilation of Dynamic Ground Water Resources of India, 2024” jointly prepared by CGWB and State Governments, categorises districts based on groundwater status.
- Classification:
- Over-exploited: 102 districts
- Critical: 22 districts
- Semi-critical: 69 districts
- Total water-stressed districts:193
- Causes of Stress: Over-extraction for agriculture, rapid urbanisation, industrial demand, erratic monsoons, and climate variability.
- Geographic Spread: Punjab, Haryana, Rajasthan, Tamil Nadu, and Karnataka are among the most affected.
Government Initiatives
1. Jal Shakti Abhiyan (JSA) – 2019 onwards
- A mission-mode campaign for water conservation in 256 water-stressed districts.
- Scaled up nationwide with the tagline: “Catch the Rain – Where it Falls, When it Falls.”
2. Thematic Focus under JSA: Catch the Rain (CTR)
- 2023 – Source Sustainability for Drinking Water: Focused on 150 districts identified by Jal Jeevan Mission.
- 2024 – Nari Shakti se Jal Shakti: Focused on 151 districts identified by CGWB, highlighting women’s role in water management.
- 2025 – Jal Sanchay Jan Bhagidari: Focused on 148 districts, emphasising community participation, inter-sectoral convergence, and innovative financing.
3. Institutional Mechanism
- Central Teams: Comprising Central Nodal Officers (Additional Secretary/Joint Secretary level) and Technical Officers from agencies like CWC, CGWB, NIH, CSMRS, CWPRS, etc., for field monitoring and technical support.
- State Nodal Officers: Oversee campaign execution at state level.
- 148 Central Nodal Officers appointed for high-focus districts in JSA: CTR 2025–26.
Significance of Water Scarcity Data
- Drinking Water Security: Ensures reliable access in rural and urban areas.
- Climate Adaptation: Builds resilience against droughts and erratic rainfall.
- Policy Planning: Provides evidence for programmes such as Jal Jeevan Mission, Atal Bhujal Yojana, and achieving SDG 6 (Clean Water and Sanitation).
- Public Awareness & Participation: Encourages community-led water conservation for sustainable outcomes.
Antitrisuloides catocalina
- 21 Aug 2025
In News:
Scientists have recently recorded the presence of the rare moth species Antitrisuloides catocalina at the Choolannur Peafowl Sanctuary in Palakkad district, Kerala, marking its first documented occurrence in the Western Ghats.
About Antitrisuloides catocalina
- Belongs to the Noctuidae family and genus Antitrisuloides, which has only two known species worldwide.
- It is a rare nocturnal moth, earlier reported only from Northeast India.
- The specimen identified in Kerala has been confirmed as the subspecies Antitrisuloides catocalina cyclica.
- Its discovery extends the known range of the species and highlights the hidden diversity of moth fauna in the Western Ghats.
About Choolannur Peafowl Sanctuary
- Popularly known as Mayiladumpara.
- Located in Palakkad district, Kerala.
- Established in 1996, it is the only peacock sanctuary in Kerala and the first of its kind in India.
- Dedicated exclusively to the breeding and conservation of peafowls.
- Named in memory of K.K. Neelakantan (Induchoodan), renowned ornithologist and nature writer, who hailed from the nearby village of Kavassery.
Significance of the Discovery
- Expands the documented geographical distribution of A. catocalina.
- Reinforces the role of the Western Ghats as a biodiversity hotspot with high levels of endemism and undocumented species.
- Highlights the importance of systematic surveys in lesser-studied taxa like moths, which can act as indicators of ecosystem health.
Damselfly Species
- 21 Aug 2025
In News:
Researchers have discovered two new species of damselflies in the Western Ghats—Konkan Shadowdamsel from Maharashtra’s Sindhudurg district and Crimson Shadowdamsel (Protosticta sanguinithorax) from Kerala’s Thiruvananthapuram district. The findings were published in the international journal Zootaxa.
About the New Species
- Group: Both belong to the genus Protosticta, commonly called Shadowdamsels, which prefer shaded forest habitats and pristine streams.
- Physical Traits:
- Crimson Shadowdamsel → reddish body.
- Konkan Shadowdamsel → coffee-brown ground colouration.
- Previously, these were mistaken for the Red-spot Shadowdamsel (Protosticta sanguinostigma), described over a century ago from the Nilgiris, which is jet black in colour.
- Identification: Differentiation was confirmed using high-resolution microscopy and molecular analysis of the COI gene, a standard marker for species classification.
- Distribution: Both species are endemics with very restricted microhabitats in the Western Ghats, often outside protected areas.
Ecological Importance
- Shadowdamsels are considered bioindicators:
- Found only in pristine forests with good canopy cover and unpolluted streams.
- Their presence reflects the ecological health of habitats.
- Many species are microendemics, restricted to small hill ranges, making them highly vulnerable to habitat disturbance.
- Current threats include expansion of plantations, deforestation of shade trees, and loss of natural streams.
Damselflies: A Brief Overview
- Belong to the order Odonata, along with dragonflies.
- Characteristics: slender body, delicate net-veined wings, weak flight.
- Habitat: shallow freshwater ecosystems.
- Difference from dragonflies: generally smaller, more fragile, and weaker fliers.
Gaur
- 20 Aug 2025
In News:
The Palamau Tiger Reserve (PTR), the last stronghold of the Gaur (Bos gaurus) in Jharkhand, has reported an alarming decline in population. Once spread across Saranda, Dalma, Hazaribagh, Gumla, and other forests of the state, Gaurs are now restricted to small and isolated groups in PTR’s northern range.
About Gaur
- Common name: Indian Bison
- Family: Bovidae; largest species of wild cattle.
- Distribution: Native to South and Southeast Asia.
- Preferred habitat:
- Evergreen, semi-evergreen, and moist deciduous forests with grasslands.
- Hilly terrains below 1,500–1,800 m with large, undisturbed forests and reliable water sources.
Conservation Status
- IUCN Red List: Vulnerable
- CITES: Appendix I
- Wildlife Protection Act, 1972: Schedule I
Population Trends in PTR
- 1970s population: ~150
- Recent study: Only 68 individuals remain.
- Demography: Slightly female-biased sex ratio (1:1.32), but very low numbers of juveniles and calves indicate poor recovery.
Ecological Significance
- Important prey species for large predators such as tigers and leopards.
- Herbivory: Helps regulate vegetation dynamics.
- Seed dispersal: Contributes to forest regeneration and ecosystem balance.
Causes of Decline
- Habitat degradation & fragmentation due to human activity.
- Anthropogenic pressures: Rising livestock populations (approx. 1.5 lakh around Betla region).
- Disease transmission from domestic cattle (e.g., foot-and-mouth disease, rinderpest).
- Genetic bottlenecks due to small and isolated herds.
Recovery Efforts in PTR
- Action Plan: “Ecology and Recovery Plan of Gaur in PTR” prepared after two years of research.
- Habitat improvement: Grassland expanded from 190 ha to 400 ha; waterholes secured.
- Security: 40 anti-poaching camps with round-the-clock staff.
- Technology: Use of GPS and modern monitoring systems.
- Disease control: Large-scale livestock vaccination programmes to reduce risks.
- Genetic infusion: Proposal to introduce Gaurs from Kanha Tiger Reserve (Madhya Pradesh) to improve genetic diversity.
About Palamau Tiger Reserve
- Location: Chota Nagpur Plateau, Jharkhand.
- Established: One of the first nine tiger reserves (1973 Project Tiger).
- Area: 1,129 sq km (Core: 414 sq km; Buffer: 715 sq km).
- Protected areas within PTR:
- Palamau Wildlife Sanctuary
- Betla National Park
Smooth-Coated Otters
- 17 Aug 2025
In News:
In a significant conservation development, the National Zoological Park (NZP), Delhi, has welcomed a pair of smooth-coated otters from the Shyamaprasad Mukherji Zoological Garden, Surat, marking the first such arrival in two decades. The last otter at the Delhi Zoo died in 2004. The transfer took place under a Central Zoo Authority (CZA)-approved exchange programme.
About Smooth-Coated Otters (Lutrogaleperspicillata)
- Taxonomy: The only extant member of the genus Lutrogale.
- Distribution: Found across India, southern and Southeast Asia, China, and Iraq (small population).
- Habitat: Freshwater wetlands, mangroves, peat swamps, forested rivers, lakes, rice paddies; capable of long overland movements.
- Features:
- Largest otter species in Southeast Asia.
- Smooth, short fur (brown dorsally, lighter ventrally) with water-repellent guard hairs.
- Social animals, hunt in groups, often using V-formations while fishing upstream.
- Threats:
- Habitat loss due to urbanization, agriculture, and pollution (fertilizers, pesticides).
- Poaching for fur and pet trade.
- Conservation Status: IUCN – Vulnerable.
Operation Falcon and Rhino Conservation in Assam
- 14 Aug 2025
In News:
The Assam government has achieved major success in protecting the greater one-horned rhinoceros through Operation Falcon, a joint initiative of the Assam Police and Forest Department launched in 2024. The operation was initiated after the killing of two rhinos prompted a shift in anti-poaching strategy.
Key Outcomes
- 42 poachers arrested across districts including Biswanath (18), Darrang (8), Nagaon (6), Karbi Anglong (5), Sonitpur (2), and one each in Udalguri, Dibrugarh, and Cachar.
- Six major poaching gangs with links to illegal trade through Myanmar dismantled.
- Nine poaching attempts foiled using digital and on-ground intelligence.
- Zero rhino killings reported in 2025 so far.
Conservation Impact
- Rhino poaching in Assam has dropped by 86% since 2016, when the BJP came to power.
- Annual data shows steady decline: one rhino killed in 2021, none in 2022, one in 2023, two in 2024, and none so far in 2025.
- Enhanced coordination, intelligence-driven operations, and rapid response mechanisms have been key factors.
About Assam’s Rhinos (Census 2022)
- Total Rhinos: 2,895 in Assam.
- Distribution:
- Kaziranga National Park & Tiger Reserve – 2,613 (largest habitat, ~1,300 sq km).
- Orang National Park & Tiger Reserve – 125.
- Pobitora Wildlife Sanctuary – 107.
- Manas National Park & Tiger Reserve – 50.
Significance of Operation Falcon
- Biodiversity Protection: Safeguards the greater one-horned rhino, listed as Vulnerable on the IUCN Red List.
- International Recognition: Strengthens India’s image in global wildlife conservation.
- Eco-Tourism Boost: Ensures safety in parks like Kaziranga, enhancing Assam’s tourism appeal.
World Elephant Day 2025

- 13 Aug 2025
In News:
World Elephant Day 2025 was celebrated on August 12 in Coimbatore, Tamil Nadu, organised by the Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change (MoEF&CC) in collaboration with the Tamil Nadu Forest Department. The event focused on human–elephant conflict (HEC) mitigation and reaffirmed global commitment to elephant conservation.
About World Elephant Day
- Launched in 2012 by Patricia Sims (Canada) and the Elephant Reintroduction Foundation of Thailand.
- Aims to promote conservation of elephants, raise awareness on threats like habitat loss, poaching, and HEC, and encourage human–elephant coexistence.
Elephants in India
- India holds 60% of the global wild elephant population.
- 33 Elephant Reserves and 150 Elephant Corridors (as per 2023 Report).
- Elephants are recognised as National Heritage Animal of India.
- Legal and institutional backing provided through Project Elephant (1992), Wildlife Protection Act, and corridor conservation measures.
Human–Elephant Conflict (HEC)
- Rising incidents of elephants entering human settlements due to habitat loss, fragmentation, and search for food/water.
- The Coimbatore workshop under World Elephant Day 2025 brought together policymakers, foresters, conservationists, and civil society to share best practices.
- Measures discussed: habitat management, corridor maintenance, awareness campaigns, and capacity building in high-conflict areas.
- Focus on balancing wildlife conservation with human safety through community participation and scientific approaches.
Public Participation
- 12 lakh students from 5,000 schools across India joined awareness programmes.
- Citizen outreach emphasised coexistence, youth engagement, and long-term behavioural change in society.
Conservation Status (IUCN Red List)
- Asian Elephant (Elephas maximus): Endangered.
- African Savanna Elephant (Loxodonta africana): Endangered.
- African Forest Elephant (Loxodonta cyclotis): Critically Endangered.
Ecological Importance of Elephants
- Keystone species: maintain grasslands, disperse seeds, create water holes, and support biodiversity.
- Social structure: Matriarch-led herds with strong communal care for calves; males often solitary or in small groups.
- Long gestation (22 months) and slow reproduction make them vulnerable to population decline.
Global Risk of Zoonotic Diseases and India’s Preparedness
- 12 Aug 2025
In News:
A recent study published in Science Advances has highlighted that over 9.3% of the world’s land surface is at high (6.3%) or very high (3%) risk of zoonotic outbreaks — diseases transmitted between animals and humans. About 3% of the global population lives in extremely high-risk areas, while nearly 20% live in medium-risk zones.
The study introduced a Global Epidemic Risk Index, combining country-specific zoonotic risk factors with national preparedness capacities, to help policymakers strengthen health systems, allocate resources effectively, and enhance global cooperation.
Disease Burden and Examples
- Zoonotic diseases account for 60% of all known infectious diseases and up to 75% of emerging infectious diseases (EIDs).
- Globally, they cause 2.5 billion cases and 2.7 million deaths annually.
- Examples: Rabies, anthrax, influenza (H1N1, H5N1), Nipah virus, brucellosis, tuberculosis, Ebola, SARS, MERS, and Covid-19.
Drivers of Spillover Events
- Climate Change: Rising temperatures, erratic rainfall, and water scarcity heighten risks by altering habitats and vector distribution.
- Land Use Change: Deforestation, urban expansion, and agricultural intensification increase human–animal contact.
- Transmission Routes:
- Direct (e.g., avian influenza)
- Food-borne (e.g., salmonella)
- Vector-borne (e.g., West Nile virus)
- Water-borne (e.g., cryptosporidiosis)
Regional Vulnerabilities
- Latin America: 27% of land at high risk
- Oceania: 18.6%
- Asia: 7%
- Africa: 5%
India’s Vulnerability
- An ICMR study (2018–23) found that 8.3% of all reported outbreaks (583 of 6,948) were zoonotic.
- Outbreaks peaked during June–August, linked to monsoon-driven ecological changes.
- The Northeast region accounted for 35.8% of reported zoonotic outbreaks.
India’s Initiatives
- National Animal Disease Control Programme (NADCP): Mass vaccination to eliminate Foot & Mouth Disease (FMD) and Brucellosis.
- Target: Control FMD by 2025 and eradicate by 2030.
- National One Health Programme for Prevention and Control of Zoonoses (2013): Integrated surveillance and inter-sectoral coordination.
- Animal Birth Control (Dogs) Rules, 2023: Rabies vaccination and sterilisation of stray dogs.
- Rabies Vaccination under ASCAD (Livestock Health & Disease Control Programme).
Global Initiatives
- Zoonotic Disease Integrated Action (ZODIAC): Launched by IAEA (2020) for early detection and rapid response.
- World Zoonoses Day (6 July): Marks Louis Pasteur’s rabies vaccine in 1885.
- G20 Pandemic Fund: Financial support for strengthening preparedness and response.
- Global Early Warning System (GLEWS): A WHO–FAO–WOAH collaboration for coordinated zoonotic disease surveillance.
One Health Approach
The One Health framework recognizes the interconnectedness of human, animal, and environmental health. It promotes collaborative, multisectoral strategies for sustainable disease prevention and response.
Rhisotope Project

- 12 Aug 2025
In News:
South Africa, which shelters the world’s largest rhino population, has lost over 10,000 rhinos in the last decade to poaching driven by the illegal horn trade in Asian markets. To counter this crisis, the University of the Witwatersrand, in collaboration with the International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA), has launched the Rhisotope Project (2024) — a novel initiative using radioactive isotopes to protect rhinos.
What is the Rhisotope Project?
- A non-invasive procedure where rhino horns are injected with low doses of radioisotopes.
- The process is harmless to rhinos but makes horns:
- Detectable through Radiation Portal Monitors (RPMs) and scanners at borders, ports, and airports — even in sealed shipping containers.
- Toxic and unfit for human use, reducing demand in illegal trade.
- Pilot studies (2024–25):
- 20 rhinos in the Waterberg Biosphere Reserve were treated.
- Tests by Ghent University (Belgium) showed no cellular damage or health impact.
- 3D-printed horns used in trials confirmed detectability in container loads.
Why Radioisotopes?
- Radioisotopes are unstable forms of elements that emit ionising radiation (alpha, beta, gamma) to achieve stability.
- They are easily traceable with nuclear detection systems.
- Already widely used in medicine (I-131 for thyroid, Tc-99m for imaging), archaeology (C-14 dating), and industry.
The Scale of the Crisis
- Global rhino numbers: Declined from ~5,00,000 in the early 20th century to ~27,000 today (IUCN).
- South Africa: Lost 103 rhinos to poaching in the first quarter of 2025 alone.
- Conventional measures like dehorning reduce poaching but disrupt rhino social behaviour and habitat use. The Rhisotope Project offers a less disruptive alternative.
Broader Conservation Significance
- If successful, the method could be extended to other endangered species like elephants and pangolins.
- It represents an international collaboration that combines nuclear science with wildlife conservation, redefining the role of technology in biodiversity protection.
Threats Beyond Poaching
- Invasive species: Plants like Parthenium threaten habitats (e.g., Assam’s Pobitora Wildlife Sanctuary, home to the densest one-horned rhino population).
- Climate change: Intensified droughts and monsoons push rhinos into human-dominated landscapes, increasing conflicts.
- Habitat loss due to agricultural expansion and human settlement.
Rhino Conservation Initiatives
- Global/Regional:
- New Delhi Declaration on Asian Rhinos (2019)
- DNA Profiling of all Rhinos for tracking and protection
- India-specific:
- National Rhino Conservation Strategy
- Indian Rhino Vision 2020 (for Assam’s one-horned rhinos)
About the IAEA
- Established in 1957 as the UN’s “Atoms for Peace”organisation.
- Promotes peaceful applications of nuclear technology while preventing misuse for weapons.
- 178 member states; India is a founding member.
- Awarded the 2005 Nobel Peace Prize for contributions to nuclear safety and disarmament.
- HQ: Vienna, Austria. Reports to both UNGA and UNSC.
World Lion Day 2025
- 11 Aug 2025
In News:
India celebrated World Lion Day 2025 at Barda Wildlife Sanctuary, Gujarat, marking a milestone in wildlife conservation. The event highlighted the success of Project Lion, launched by Prime Minister Narendra Modi on 15th August 2020, and underscored India’s global leadership in protecting the endangered Asiatic Lion (Panthera leopersica).
Status of Asiatic Lions
- Population Growth: Numbers rose from 284 in 1990 to 674 in 2020, and further to 891 in 2025(16th Lion Census). This reflects a 32% increase since 2020 and 70% rise over the last decade.
- Distribution: The lions roam across ~35,000 sq. km in 11 districts of Saurashtra, with Gir National Park as the core habitat. In recent years, Barda Wildlife Sanctuary (192 sq. km) has emerged as a second home, hosting 17 lions including 11 cubs.
- Global Significance: If Asiatic lions survive anywhere today, it is solely in India—making their conservation a matter of both ecological and national pride.
Ecological and Cultural Importance
- Apex Predators: Regulate herbivore populations, prevent overgrazing, and maintain ecosystem balance.
- Cultural Symbolism: Depicted on the National Emblem and Indian currency, symbolizing strength and heritage.
- Unique Traits: Asiatic lions are smaller than African lions, with a distinct belly fold and less prominent mane (ears remain visible).
Conservation Measures
1. Project Lion (2020–2030)
- Budget: ?2,927 crore sanctioned.
- Focus Areas:
- Habitat improvement and prey base augmentation.
- Scientific monitoring using GPS, GIS-based real-time surveillance, and automated sensor grids.
- Veterinary healthcare (National Referral Centre at Junagadh).
- Human–wildlife conflict mitigation.
- Community participation and eco-tourism.
2. Greater Gir Concept: Expands protected landscapes toGirnar, Pania, Mitiyala, and Bardasanctuaries to reduce habitat pressure.
3. Recent Developments
- ?180 crore wildlife and ecotourism initiative launched in 2025 for new habitats, safari park, and veterinary facilities.
- Barda Safari Park & Zoo approved to boost ecotourism and conservation.
- Return of lions to Barda after 143 years, enhancing biodiversity and eco-tourism potential.
4. Global Cooperation
- International Big Cats Alliance (IBCA, 2023): A platform of 97 countries for sharing knowledge and resources on big cat conservation.
Conservation Status
- Panthera leo (Lion)IUCN Red List: Vulnerable (Green Status: Largely Depleted).
- CITES: Appendix I.
- Wildlife (Protection) Act, 1972: Schedule I species.
- Part of India’s Species Recovery Programme under the Centrally Sponsored Scheme – Development of Wildlife Habitat.
Tuvalu’s Planned Climate Migration to Australia

- 10 Aug 2025
In News:
Tuvalu, a small Pacific island nation, is undertaking the world’s first planned national migration due to the existential threat posed by climate change and rising sea levels. The initiative stems from the Falepili Union Treaty (2023) signed between Tuvalu and Australia, marking a landmark case in global climate governance and migration policy.
Why Migration is Needed
- Geography & Vulnerability: Tuvalu consists of nine coral atolls with a total land area of just 25.14 sq. km and a population of ~11,000 (2022 census). Its average elevation is only 2 metres, making it highly vulnerable to flooding, storm surges, and coastal erosion.
- Climate Impact:
- NASA’s Sea Level Change Team reported that sea levels in Tuvalu were already 15 cm higher in 2023 compared to the previous 30 years.
- At this rate, most of Tuvalu could be submerged by 2050.
- Two of its nine atolls are already largely underwater.
- Scientists warn the islands may become uninhabitable within 80 years.
The Falepili Union Treaty (2023)
- Migration Provision: Australia will grant 280 Tuvaluans permanent residency annually, with access to healthcare, education, housing, and employment.
- Selection Mechanism: Migration is ballot-based. The first phase (June–July 2025) saw 8,750 registrations. The first group of 280 migrants was selected on 25 July 2025.
- Scale: Along with other pathways to Australia and New Zealand, up to 4% of Tuvalu’s population could migrate annually. Within a decade, nearly 40% of the population may relocate, although some may return periodically.
- Objective: To ensure “mobility with dignity”, preventing Tuvaluans from becoming stateless climate refugees.
International Significance
- Precedent for Climate Migration: This is the first-ever state-backed relocation of an entire population due to climate change, setting a model for other vulnerable island nations.
- Global Climate Justice: Tuvalu’s case highlights the plight of Small Island Developing States (SIDS) and the urgent need for stronger international climate agreements.
- Diplomatic Signalling: Tuvalu’s Prime Minister Feleti Teo has called for a new global treaty safeguarding nations at risk from rising seas.
About Tuvalu
- Location: Polynesian island nation in the Pacific Ocean, midway between Australia and Hawaii.
- Capital: Funafuti.
- Population: ~11,000 (second least populous UN member after Vatican City).
- Economy: Relies on fishing licenses, foreign aid, and remittances from Tuvaluan seafarers.
- UN Membership: Since 2000; actively champions the rights of climate-vulnerable states.
Clouded Leopard
- 10 Aug 2025
In News:
A rare video recently shared by Indian Forest Service officer Susanta Nanda offered a rare glimpse into the secretive life of the clouded leopard (Neofelisnebulosa), showcasing a mother with her cubs in the rainforests of Northeast India. The sighting highlights the critical conservation importance of this elusive and endangered species.
About the Clouded Leopard
- Scientific name:Neofelisnebulosa (mainland Asia); Neofelisdiardi (Sunda clouded leopard, Sumatra & Borneo).
- Classification: Among the most ancient cat species; neither a true “great cat” nor a small cat — cannot roar or purr.
- Size: Medium-sized (60–110 cm long; 11–20 kg); lifespan ~13–17 years.
- Distinctive features:
- Named for large “cloud-like” coat patterns (ellipses with dark edges).
- Exceptionally long tail (often body-length) for balance.
- Long canine teeth, proportionally the same size as those of a tiger.
- Broad paws and short legs, making it an agile climber; one of the only cats that can climb down trees headfirst, hang upside down, and hunt arboreally.
- Behaviour: Solitary, shy, and nocturnal.
Distribution and Habitat
- Found across Nepal, Bangladesh, India, Indochina, Sumatra, Borneo, and southern China (historically also Taiwan).
- In India: Present in Sikkim, northern West Bengal, Meghalaya, Tripura, Mizoram, Manipur, Assam, Nagaland, and Arunachal Pradesh.
- Declared the State Animal of Meghalaya.
- Habitat preference: Lowland tropical rainforests, but also found in dry woodlands, secondary forests, high altitudes in the Himalayas, and even mangrove swamps (Borneo).
Conservation Status
- IUCN Red List:Vulnerable.
- Global wild population:fewer than 10,000 individuals.
- Threats:
- Habitat loss (deforestation, infrastructure expansion).
- Poachingfor pelts and body parts.
- Human-wildlife conflict.
Conservation Significance
- Rare sightings, such as the video from Northeast India, underscore the species’ ecological and cultural importance.
- Conservationists stress the need for:
- Habitat protection through transboundary wildlife corridors.
- Strengthening protected areas across Northeast India.
- Community participation to reduce conflict and safeguard prey base.
Great Barrier Reef
- 10 Aug 2025
In News:
The Great Barrier Reef (GBR), the world’s largest living structure and a UNESCO World Heritage Site (1981), has recorded its steepest decline in hard coral cover in nearly four decades, according to the Australian Institute of Marine Science (AIMS) 2025 survey. The reef, spread over 2,000 km along Australia’s northeast coast and covering ~350,000 sq. km, accounts for nearly 10% of global coral reef ecosystems and hosts extraordinary biodiversity, including 400 coral species, 1,500 fish species, 4,000 mollusk species, six of seven turtle species, dugongs, and numerous seabirds.
The 2024–25 Mass Bleaching Event
- The 2024 bleaching, the fifth since 2016, coincided with record ocean heat stress, cyclones, flooding, and crown-of-thorns starfish outbreaks.
- AIMS’ long-term monitoring across 124 reefs (Aug 2024–May 2025) revealed:
- 48% reefs showed a decline in coral cover,
- 42% reefs showed no change,
- Only 10% reefs recorded recovery.
- Some areas, especially in the northern GBR (around Lizard Island), lost over 70% of hard coral cover, the sharpest decline since monitoring began in 1986.
Regional Breakdown of Coral Loss (2024–25)
- Northern GBR: Coral cover dropped from 39.8% to 30% (–24.8%), driven by record heat stress, cyclones, and freshwater inundation.
- Central GBR: Cover fell by 13.9% to 28.6%, with Cairns sector reefs losing 6–60% due to Cyclone Jasper (2023) and flooding.
- Southern GBR: Sharpest relative loss, down from 38.9% to 26.9% (–30.6%), largely due to extreme heat stress in the Capricorn-Bunker sector, storm damage, and coral disease.
Drivers of Decline
- Climate change-induced heat stress – primary driver of bleaching.
- Cyclones & floods – physical damage and sedimentation.
- Crown-of-thorns starfish – venomous predators that feed on corals.
- Coral disease – post-bleaching infections weaken recovery.
Oscillating Ecosystem Under Stress
- Acropora corals, fast-growing and heat-resilient species that helped reef recovery (2017–24), were worst hit.
- Scientists warn of increasing volatility in coral cover, shifting between record highs and lows within short periods.
- Before the 1990s, mass bleaching was rare (first major event: 1998). Since 2020, GBR has faced bleaching in 2020, 2022, 2024, and 2025, with two consecutive years of mass bleaching for the second time in a decade.
Global Perspective
According to the US NOAA, between Jan 2023 and May 2025, 83.9% of global coral reef area experienced bleaching-level heat stress, with mass bleaching reported in at least 83 countries and territories.
Conservation & Outlook
The GBR, managed largely under the Great Barrier Reef Marine Park Authority, remains one of the most studied ecosystems. However, repeated bleaching events are leaving insufficient recovery time, pushing the ecosystem toward collapse. Scientists warn the window to save the GBR is rapidly closing without urgent global climate action.
France’s Largest Wildfire in Decades
- 09 Aug 2025
In News:
Recently, southern France witnessed its worst wildfire since 1949, scorching nearly 16,000 hectares (39,500+ acres) of forests and villages—an area 1.5 times the size of Paris. Though the blaze has now been contained, firefighters remain deployed to prevent flare-ups and secure the affected zone.
Causes and Challenges
- Climatic Drivers: Officials and France’s Environment Minister attributed the fire’s intensity to climate change, prolonged drought, strong winds, and extremely dry vegetation.
- Geographic Factors: Proximity to the Pyrenees mountains and the Mediterranean coast made the terrain vulnerable to rapid fire spread. Loss of traditional vineyards and land-use changes further accelerated the blaze.
- Future Risks: France’s weather office has warned of fresh heatwaves, increasing wildfire vulnerability across southern Europe.
Geographic Overview of France
- Location: Northern & Eastern Hemispheres; bordered by Belgium, Luxembourg, Germany, Switzerland, Italy, Spain, Andorra.
- Water Bodies: Bounded by the Bay of Biscay (west), English Channel (northwest), and Mediterranean Sea (south).
- Major Rivers:Loire (into Atlantic), Seine (into English Channel).
- Mountain Ranges:Alps, Jura, and Pyrenees (natural border with Spain).
- Resources: Coal, iron ore, bauxite, zinc, uranium, potash, gypsum, etc.
- Overseas Regions: Guadeloupe, French Guiana, Réunion, Martinique, Mayotte.
- Capital: Paris.
Asian Giant Tortoise

- 08 Aug 2025
In News:
The Asian Giant Tortoise, the largest tortoise in mainland Asia, has been reintroduced into the Zeliang Community Reserve in Peren district, Nagaland. Local youth groups have been engaged as “tortoise guardians” to ensure protection.
About Asian Giant Tortoise
- Scientific name:Manouriaemysphayrei
- Common name: Asian Giant Tortoise / “Small elephants of the forests” (due to their role in forest ecology).
- Lineage: Among the oldest tortoise lineages in the world; display unique nesting behaviour similar to crocodilians, where they protect eggs and regulate incubation temperatures.
- Appearance: Hatchlings are greyish-brown, becoming charcoal-colored in adulthood.
- Diet: Bamboo shoots, tubers, soft vegetation, some invertebrates, and frogs.
Habitat & Distribution
- Habitat: Tropical and subtropical evergreen hill forests.
- Range in India: Northeastern states – Arunachal Pradesh, Nagaland, Assam.
- Global distribution: Bangladesh, Myanmar, Thailand, Malaysia, Indonesia.
Ecological Role
- Seed Dispersal: Helps regenerate forests by dispersing seeds.
- Scavenging: Cleans forest floor by feeding on decomposed organic matter.
Threats
- Hunting and collection for consumption.
- Illegal trade (pets and exotic meat).
- Habitat destruction due to shifting cultivation, deforestation, and infrastructure projects.
Conservation Status
- IUCN Red List: Critically Endangered
- CITES: Appendix II
Conservation Efforts
- Captive Breeding & Assurance Colonies for population recovery.
- Reintroduction Programmes like the recent one in Nagaland.
- Community-based conservation with active participation of locals as guardians.
- Field Surveys to monitor population health and habitat conditions.
Nahargarh Wildlife Sanctuary
- 04 Aug 2025
In News:
The Rajasthan Forest Department has recently redrawn the boundaries of the Nahargarh Wildlife Sanctuary (NWS), located near Jaipur, sparking controversy among conservationists and legal experts. The move, alleged to benefit luxury hotels and commercial establishments within the sanctuary and its Eco-Sensitive Zone (ESZ), has raised questions about legality, ecological safeguards, and governance.
About Nahargarh Wildlife Sanctuary
- Location: ~20 km from Jaipur, under the Aravalli range.
- Size: Originally ~720 hectares; currently notified as 6,025.74 hectares across 16 villages.
- History: Named after Nahargarh Fort, built by Maharaja Sawai Jai Singh II in the 18th century.
- Nahargarh Biological Park: Part of the sanctuary, noted for its lion safari.
- Flora: Dry deciduous forests, scrublands, grasslands.
- Fauna: Leopards, deer, sloth bears, wild boars, lions, tigers, reptiles like pythons and monitor lizards, and diverse birdlife including owls, eagles, and peacocks.
The Controversy
- Procedural Lapses
- Under Section 26A of the Wildlife Protection Act, 1972, any change in sanctuary boundaries requires approval from the National Board for Wildlife (NBWL).
- Experts cite the 2013 Supreme Court judgment (Centre for Environmental Law, WWF-India vs Union of India), which mandated NBWL clearance for altering protected area limits.
- However, Rajasthan submitted revised maps to the National Green Tribunal (NGT) in July 2025 without NBWL’s recommendation.
- Alleged Motivations
- Activists claim the revised map excludes “Described Areas” (revenue lands held by public and private bodies) while retaining only Reserved Forest patches.
- This adjustment allegedly protects existing luxury hotels and other constructions in the ESZ, some of which earlier faced demolition orders for violations.
- Government’s Justification
- Officials argue the 1980 notification used “grossly approximate” boundary descriptions.
- Over four decades, urbanisation and topographical changes blurred the original limits.
- A GIS-based remapping exercise using high-resolution satellite imagery and land records was undertaken, and state approval was granted in July 2025.
Indo-Burma Ramsar Regional Initiative (IBRRI)
- 03 Aug 2025
In News:
The 15th Conference of the Parties (COP15) to the Ramsar Convention concluded with a significant side event of the Indo-Burma Ramsar Regional Initiative (IBRRI), highlighting collaborative efforts for wetland conservation and restoration across Southeast Asia.
About IBRRI
- Origin: Jointly developed by the Ramsar National Focal Points of Cambodia, Lao PDR, Myanmar, Thailand, and Viet Nam, with technical support from the IUCN Asia Regional Office.
- Aim: To coordinate and support the implementation of the Strategic Plan of the Ramsar Convention, particularly in addressing wetland degradation.
- Support: Backed by IUCN’s BRIDGE (Building River Dialogue and Governance) project, which promotes sustainable water management, biodiversity conservation, and cross-border cooperation.
Governance Structure
To ensure oversight, transparency, and inclusivity, IBRRI has developed a multi-tiered governance framework:
- Steering Committee: Comprising Ramsar Administrative Authorities from the five member countries.
- Secretariat: Hosted by the IUCN Asia Regional Office, Bangkok.
- Stakeholder Committee: Provides technical and strategic guidance, ensuring multi-stakeholder participation including governments, NGOs, and civil society.
Strategic Plan 2025–2030
- Launch: Officially unveiled during COP15 as a transboundary framework for wetland management.
- Objective: To halt and reverse wetland loss across member states through restoration, sustainable use, and regional cooperation.
- Approach: Promotes knowledge exchange, policy coordination, and joint action for wetland conservation.
About BRIDGE Project
- Aim: To strengthen transboundary water governance by catalysingsustainable management of shared rivers, ensuring water security, conserving biodiversity, and fostering peaceful cooperation across borders.
Significance
- Provides a regional mechanism for Ramsar Convention implementation.
- Enhances transboundary cooperation in the Indo-Burma region, which hosts critical wetland ecosystems.
- Contributes to biodiversity conservation, climate resilience, and sustainable development goals (SDGs).
OECD Report on Plastic Pollution in Southeast & East Asia
- 03 Aug 2025
In News:
The Organisation for Economic Cooperation and Development (OECD) has warned that plastic use and waste in Southeast and East Asia could nearly double by 2050 unless countries adopt urgent and stringent policy measures. The findings are particularly significant as they coincide with the final round of UN negotiations on a global plastics treaty scheduled in August 2025 in Geneva.
Key Findings of the OECD Report
1. Surge in Plastic Use and Waste
- Plastic consumption in the ASEAN Plus Three (APT) region – which includes ASEAN-10 (Brunei, Cambodia, Indonesia, Laos, Malaysia, Myanmar, Philippines, Singapore, Thailand, Vietnam) plus China, Japan, and South Korea – is projected to rise from 152 million tonnes (2022) to 280 million tonnes (2050).
- Plastic waste will increase from 113 million tonnes (2022) to 242 million tonnes (2050).
- Packaging waste alone will almost double, from 49 million tonnes to 91 million tonnes.
2. Regional Disparities
- China will see the largest absolute rise, from 76 million tonnes (2022) to 160 million tonnes (2050).
- Lower-middle-income ASEAN nations such as Indonesia, Vietnam, and the Philippines will see the sharpest relative increase, with plastic waste nearly quadrupling from 7.5 million tonnes to 28 million tonnes.
3. Mismanaged Waste and Leakage
- Share of mismanaged plastic waste may fall (29% → 23% between 2022–2050), but total mismanaged waste will grow from 33 million tonnes to 56 million tonnes.
- The region is already the largest contributor to global plastic leakage – 8.4 million tonnes in 2022 (one-third of global leakage), projected to rise to 14.1 million tonnes by 2050.
- Plastic build-up:
- Freshwater systems: from 57 million tonnes (2022) → 126 million tonnes (2050).
- Oceans: from 17 million tonnes (2022) → 55 million tonnes (2050).
4. Climate Implications
- Greenhouse gas emissions from the plastic lifecycle (production + waste management) in the APT region are expected to nearly double from 0.6 GtCO?e (2022) to over 1 GtCO?e (2050).
Global High Stringency Scenario: Pathway to Solutions
OECD outlines a Global High Stringency (GHS) policy scenario that can reverse the trajectory:
- Plastic use: Could drop by 28% by 2050.
- Plastic waste: Could fall by 23%.
- Recycling: Average recycling rate could reach 54%, with secondary plastics meeting all future demand growth.
- Mismanaged waste: Could decline by 97%, drastically reducing environmental leakage.
Key recommended measures:
- Phase out single-use plastics.
- Strengthen waste collection systems and invest in recycling infrastructure.
- Promote circular economy approaches and regional cooperation.
Regional and Global Implications
- Cross-border challenge: Plastics persist for decades and move across boundaries. Poorer ASEAN nations like Indonesia often receive waste leakage from wealthier neighbours and China, with spillover impacts reaching the Indian Ocean and African coasts.
- Climate risks: Rising plastic demand intensifies emissions, undermining climate action goals.
- Global treaty negotiations: The report’s timing strengthens the case for an ambitious legally binding plastics treaty.
ICJ Ruling on the Kyoto Protocol
- 03 Aug 2025
In News:
In a landmark advisory opinion, the International Court of Justice (ICJ) has clarified that the Kyoto Protocol (1997) remains legally valid and binding, even after the Paris Agreement (2015) came into effect. This ruling has revived the Protocol’s legal relevance and has far-reaching implications for international climate law and global climate governance.
Background: The Kyoto Protocol
- Adopted: 1997; Entered into force: 2005 under the UN Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC).
- Nature: First binding international treaty mandating emission reductions by industrialised nations (Annex-I countries).
- Principle: Based on Common but Differentiated Responsibilities and Respective Capabilities (CBDR–RC), recognising that developed nations bear greater responsibility due to their historical emissions.
- Commitment Periods:
- First: 2008–2012
- Second: 2012–2020
- Obligations:
- Quantified emission reduction targets (from 1990 baseline).
- Provision of finance and technology transfer to developing nations.
- Market-based mechanisms such as the Clean Development Mechanism (CDM).
Why was Kyoto Considered Obsolete?
- US Non-Ratification: The largest historical emitter never joined the Protocol.
- Withdrawals: Countries like Canada and Japan later exited or refused binding targets.
- Rise of New Emitters: China overtook the US as the largest emitter by mid-2000s but, as a “developing country,” had no binding obligations.
- Shift to Paris Agreement (2015):
- Kyoto: Top-down, binding targets for developed countries.
- Paris: Bottom-up, voluntary Nationally Determined Contributions (NDCs) for all states.
- With no third commitment period defined after 2020, Kyoto was widely seen as defunct though never formally repealed.
ICJ’s Key Rulings
- Kyoto Still in Force: The absence of a new commitment period does not terminate the Protocol; it remains part of applicable international law.
- Legal Accountability: Non-compliance with emission reduction targets can constitute an “internationally wrongful act.”
- Retroactive Review: Past obligations (e.g., unfulfilled first commitment period targets) remain open for assessment.
- Advisory but Influential: Though not legally binding, the ruling strengthens grounds for climate litigation and accountability mechanisms.
Significance of the Ruling
- Legal Continuity: Confirms coexistence of Kyoto and Paris, rather than substitution.
- Revival of CBDR–RC: Re-emphasises differentiated responsibilities of developed nations, which Paris had diluted.
- Climate Justice: Opens the door for renewed scrutiny of historical emitters and their unfulfilled obligations.
- Litigation Pathways: Strengthens civil society and state efforts to seek compensation or stronger climate actions through international and domestic courts.
Implications for Global Climate Governance
- Developed countries face renewed legal and moral pressure to honour past commitments and extend finance and technology support.
- Developing nations gain a stronger footing to demand accountability for historical emissions.
- The ruling highlights the layered nature of international climate treaties, with Kyoto, UNFCCC, and Paris coexisting rather than replacing each other.
- It may reshape climate negotiations by reviving unfinished obligations under Kyoto while reinforcing Paris as the ongoing framework.
Barbados Threadsnake (Tetracheilostoma carlae)
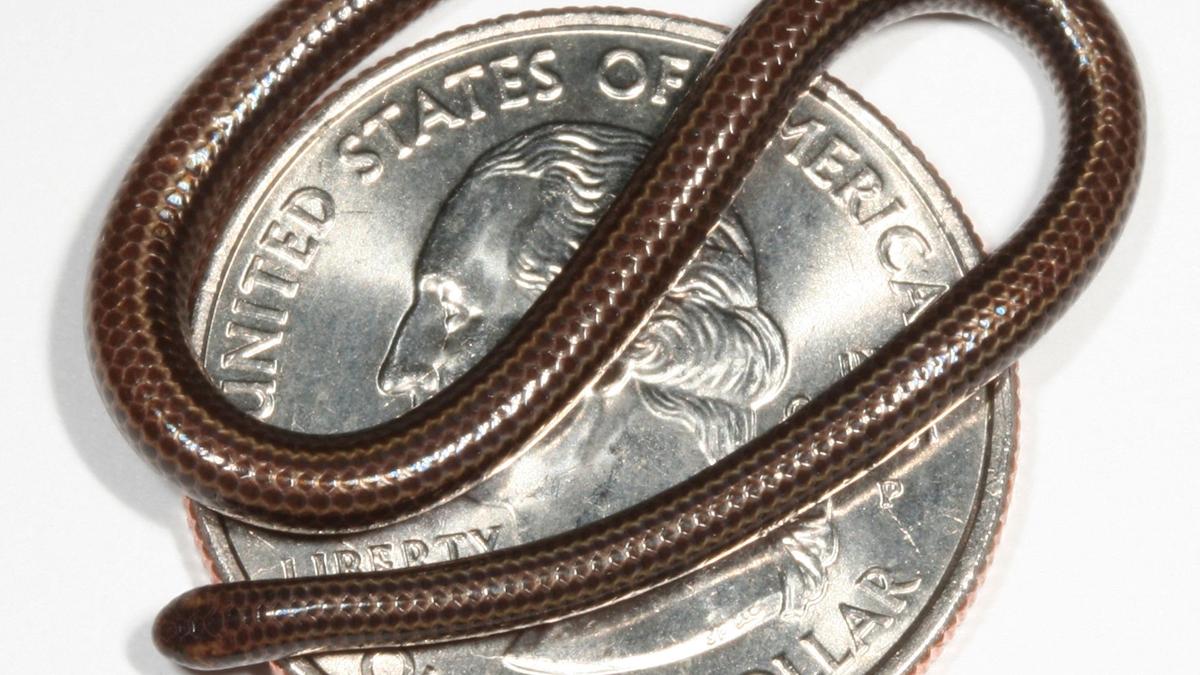

- 01 Aug 2025
In News:
The Barbados threadsnake, long considered lost to science, has made a startling comeback. This diminutive reptile—no longer than a coin—was rediscovered in Barbados in March 2025, nearly two decades after its last documented sighting. Its reappearance has reignited global interest in its conservation and the fragile ecosystems it inhabits.
Key Attributes & Taxonomy
- Scientific Classification: Tetracheilostoma carlae, family Leptotyphlopida.
- Size & Weight: Adults reach approximately 9–10 cm (3–4 in) in length and weigh ~0.6 g (~0.02 oz)—making it the world’s smallest known snake
- Physical Traits: Extremely slender—about as thick as a spaghetti noodle. Distinguished by pale orange dorsal stripes and a small scale on the snout
- Vision & Behavior: A blind, fossorial snake that burrows underground, especially hiding under rocks during the day.
- Diet: Feeds on termite and ant larvae—its petite jaws prevent it from consuming larger prey.
- Reproduction: Oviparous, laying only one large egg at a time, with hatchlings already about half the size of adults.
Rediscovery: A Significant Scientific Moment
- Context: The species had not been observed since 2006, and earlier specimens were often misidentified in museum collections.
- 2025 Rediscovery: During a March ecological survey in central Barbados by the Ministry of Environment and Re:wild, the snake was found under a rock near a jack-in-the-box tree. It was confirmed after microscopic and morphological assessment at the University of the West Indies.
- Reactions: This turn of events is hailed as a conservation triumph and a poignant reminder of Barbados’s biodiversity despite its heavily altered landscape.
Conservation Context & Implications
- Habitat Loss: Over 98% of Barbados’s primary forests have been cleared, leaving threadsnake habitats limited to a few square kilometers of secondary forests, particularly in the Scotland District.
- Threats: Loss of habitat and competition from the invasive Brahminy blind snake (Ramphotyphlops braminus), which reproduces asexually and may outcompete the threadsnake.
- Conservation Action: The rediscovery falls under the broader Conserving Barbados’ Endemic Reptiles (CBER) project. Future plans focus on mapping its range, safeguarding habitats, and preserving biodiversity as part of Barbados's compliance with the Kunming-Montreal Global Biodiversity Framework.
First-Ever Grassland Bird Census in Kaziranga National Park
- 31 Jul 2025
In News:
The first dedicated Grassland Bird Census was conducted in Kaziranga National Park, Assam, marking a significant step in avian biodiversity monitoring in India. The initiative was widely acknowledged, including by Prime Minister Narendra Modi in his Mann Ki Baat broadcast, for its innovative use of Artificial Intelligence (AI) and acoustic monitoring.
Objective and Significance
- Purpose: To systematically monitor the population, breeding patterns, and habitat health of grassland-dwelling bird species, many of which are rare or threatened.
- Conservation Value: Grassland birds serve as ecological indicators of habitat quality, akin to how BMI reflects human health.
- Highlight Species:
- Documented 43 bird species
- Included 1 Critically Endangered, 2 Endangered, and 6 Vulnerable species (IUCN Red List)
- Notably, over 85 nests of the endangered Finn’s Weaver, endemic to the Brahmaputra floodplains, were discovered.
Methodology & Technological Innovations
- Conducted By: Joint effort of forest officials, Kaziranga National Park authorities, conservationists, and researchers including INSPIRE fellow Chiranjib Bora.
- Sites Covered: 185 grassland locations across the national park.
- Tools Used:
- Passive Acoustic Monitoring: Audio recorders placed atop trees to capture bird calls during the breeding season.
- AI Integration:
- BirdNET Software used to automatically identify bird species by analyzing vocalizations.
- Spectrograms enabled visual analysis of sound frequencies for accurate classification.
Key Innovations and Impact
- First of its Kind: India’s first census focused exclusively on grassland bird species, often overlooked in standard bird surveys.
- Non-Intrusive Monitoring: AI-powered audio analysis allowed species identification without disturbing natural behavior.
- Awareness & Biodiversity Education: The census is a powerful example of how technology and sensitivity can together enhance biodiversity understanding and conservation awareness.
Golden Jackal

- 30 Jul 2025
In News:
A recent citizen science study conducted by the Aranyakam Nature Foundation estimates that Kerala is home to approximately 20,000 to 30,000 golden jackals (Canis aureus naria), highlighting the species' wide distribution and adaptability across the state’s diverse landscapes.
Key Ecological Facts
- Scientific Name: Canis aureus
- Common Names: Golden Jackal, Common Jackal
- Physical Appearance: Medium-sized canid, smaller than a wolf and larger than a fox; coat ranges from golden to pale brown, varying seasonally.
- Behaviour: Primarily nocturnal in human-dominated areas; lives in monogamous pairs, often uses burrows or rock crevices for shelter.
- Diet: Omnivorous; consumes small mammals, birds, fish, insects, hares, fruits, and is known to scavenge near human settlements.
Habitat and Distribution
- Found in South, Southeast, and Central Asia, extending into Southeastern Europe and North-East Africa.
- In India, widespread from the Himalayan foothills to the Western Ghats, including Kerala, Maharashtra, Rajasthan, and Haryana.
- Preferred Habitats: Open lowland regions, especially below 200m elevation. In Kerala:
- Coconut groves (24%)
- Rural settlements (10%)
- Urban areas (5.6%)
- Rare in protected forest areas (only 2% of sightings)
Key Findings from Kerala Study
- Over 5,000 sightings were recorded across 874 villages, involving 2,200+ participants.
- High adaptability to human-modified landscapes such as peri-urban zones and coastal belts.
- Ecological Concerns:
- Rising cases of poultry predation
- Risk of rabies transmission
- Increasing dependence on organic waste, especially near coastlines
- Threat of hybridisation with stray dogs, posing genetic risks
Conservation Status
- IUCN Red List: Least Concern
- CITES: Appendix III
- Wildlife Protection Act, 1972 (India): Schedule I (highest protection under Indian law)
Glacial Lake Outburst Floods (GLOFs)
- 29 Jul 2025
In News:
- In recent years, Glacial Lake Outburst Floods (GLOFs) have emerged as a critical concern in the Himalayan region, particularly affecting countries like India, Nepal, Bhutan, and China.
- The July 8, 2025, GLOF in Nepal—which washed away a China-built bridge and crippled hydropower plants supplying 8% of Nepal’s electricity—has drawn urgent attention to the increasing frequency and severity of such events.
- For India, especially in the Indian Himalayan Region (IHR), GLOFs pose an escalating risk to lives, infrastructure, and ecological systems due to climate change and unregulated development.
What is a Glacial Lake Outburst Flood (GLOF)?
A GLOF is the sudden, catastrophic release of water from a glacial lake—typically dammed by ice or moraine (glacial debris). The floodwaters often cause massive downstream destruction, marked by:
- Extremely high discharge volumes
- Destructive debris flows
- Short warning times
Types of Glacial Lakes in the Himalayas
- Supraglacial Lakes: Form on the surface of glaciers due to meltwater accumulation. Highly unstable during summer.
- Example: Cirenma Co in Tibet (1981), July 2024 Nepal GLOF.
- Moraine-Dammed Lakes: Form at glacier snouts, blocked by weak debris. Most vulnerable to outbursts.
- Example: South Lhonak (Sikkim), Tsho Rolpa (Nepal), Shako Cho (Sikkim)
Causes of GLOFs
Natural Triggers
- Glacial Retreat: Rising temperatures accelerate glacial melt, enlarging lakes.
- Ice or Rock Avalanches: Sudden falls into lakes displace water and rupture dams.
- Cloudbursts & Heavy Rainfall: Rapid rise in water levels increases pressure on dams.
- Seismic Activity: Earthquakes can destabilize moraine dams.
- Internal Piping: Seepage within dams weakens structural integrity over time.
Anthropogenic Factors
- Climate Change: Human-induced warming accelerates glacial melt.
- Unregulated Development: Construction near glacial zones—e.g., hydropower—exacerbates risk.
- Example: Teesta-III dam destruction in 2023.
Impacts of GLOFs
On Human Life and Infrastructure
- Casualties: Kedarnath (2013) and Sikkim (2023) GLOFs caused hundreds of deaths.
- Hydropower & Transport Damage: Washed-out roads, bridges, and dams; loss of electricity and connectivity.
- Displacement & Livelihood Loss: Long-term socio-economic disruption in affected regions.
On Environment
- River Course Changes & Silting: Raised riverbeds and reduced flood-carrying capacity.
- Teesta river rose several meters post-2023 flood.
- Habitat Loss & Biodiversity Decline: Ecological imbalance in alpine and riparian zones.
- Long-Term Ecosystem Stress: Sedimentation affects water quality and ecosystem resilience.
The Situation in India
India’s Himalayan arc—covering J&K, Ladakh, Himachal Pradesh, Uttarakhand, Sikkim, and Arunachal Pradesh—houses:
- 28,000 glacial lakes
- 7,500 lakes above 4,500 m altitude
- 11 major river basins
Yet, the region lacks sufficient monitoring infrastructure and early warning systems, primarily due to remoteness and hostile terrain.
Notable GLOF events:
- Kedarnath (2013): Triggered by cloudburst and glacial melt.
- South Lhonak (2023): Avalanche-triggered breach, damaging a $2 billion hydro project.
India’s Institutional Response to GLOF Risks
1. National Disaster Management Authority (NDMA) Initiatives
India has transitioned from reactive relief to proactive risk mitigation, through:
- National GLOF Programme: A ?150 crore initiative targeting 195 high-risk lakes.
- Committee on Disaster Risk Reduction (CoDRR): Coordinates central and state agencies, scientific institutions, and communities.
2. Five-Pronged Strategy
- Hazard Assessment: Classification of lakes by size, dam type, and downstream threat.
- Automated Weather & Water Stations (AWWS): Real-time monitoring (e.g., in Sikkim).
- Early Warning Systems (EWS): ITBP-led manual alerts; multilingual digital alerts in pilot stages.
- Engineering Interventions:
- Bathymetry and ERT scans
- Artificial channels and retention structures
- Community Engagement:
- Sensitization on religious and ecological concerns.
- Involving locals in scientific expeditions for credibility and access.
Technological Interventions
- SAR Interferometry: Satellite-based technique to detect micro-slope changes.
- Electrical Resistivity Tomography (ERT): Detects ice-cores under moraine dams.
- Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAVs): High-resolution terrain mapping.
- Remote Sensing: Tracks surface area growth of glacial lakes (but is post-facto).
Status of Mitigation Efforts
- Expeditions to 40 high-risk lakes in 2024 across J&K, Ladakh, HP, UK, Sikkim, and Arunachal Pradesh yielded positive outcomes.
- Installation of AWWS at lakes in Sikkim providing 10-minute interval data and daily lake imagery.
- ITBP trained for early alerts in absence of automated systems.
- More stations and expeditions are planned post-monsoon 2025.
Transboundary Challenges
- Many GLOF-prone lakes lie in Tibet, with rivers flowing into Nepal, Bhutan, and India.
- Nepal has faced multiple transboundary GLOFs recently (2024–25), with little to no warning from China.
- Example: July 8, 2025 GLOF from Tibet triggered floods in Nepal, destroying infrastructure.
- Past major GLOFs: Cirenma Co (1981), Dig Tsho (1985), Tama Pokhari (1998).
Policy Recommendations
- Strengthen Early Warning Systems: Expand AWWS and EWS coverage, integrate with mobile alerts.
- Transboundary Collaboration: Create shared protocols for upstream monitoring and data exchange with China, Nepal, and Bhutan.
- Integrate Climate Adaptation in Planning: Include GLOF risk in disaster risk reduction and infrastructure resilience planning.
- Ban Critical Infrastructure: Avoid siting major installations near vulnerable glacial zones.
- Promote Indigenous Technology: Invest in SAR, ERT, and AI-based modelling to predict GLOF risks.
- Community-Led Risk Reduction: Involve local populations in monitoring, response planning, and implementation.
Environmental Flow (E-Flow) in Indian Rivers
- 28 Jul 2025
In News:
Union Jal Shakti Minister Shri C.R. Patil recently chaired a crucial meeting focused on the Environmental Flow (E-Flow) of the Ganga River and its tributaries, with particular attention to the Yamuna River. This initiative is a part of the broader effort to ensure the ecological sustainability of India’s river systems.
What is Environmental Flow (E-Flow)?
Environmental Flow refers to the quantity, timing, and quality of water flow necessary to sustain freshwater ecosystems and the livelihoods dependent on them. It ensures that rivers maintain their ecological integrity, supporting aquatic life, estuarine health, and human usage in a sustainable manner.
Why is E-Flow Important?
- Maintains ecological balance in rivers and estuaries.
- Supports aquatic biodiversity, especially key fish species.
- Provides long-term ecological and economic benefits.
- Balances human needs and environmental sustainability, especially in overexploited river basins.
Challenges in Maintaining E-Flow:
- Construction of dams and barrages.
- Pollution and urban encroachments.
- Over-extraction of water for agriculture and industry.
These interventions disrupt natural flow patterns, threatening riverine ecosystems and dependent communities.
Government Initiatives and Studies:
Environmental Flow Notification (2018):
- Introduced by the government to regulate minimum required flows in the Ganga. However, a review of its impact is now being undertaken to determine its effectiveness and the need for improvements.
Recent Meeting Outcomes:
- Emphasis on strengthening the e-flow framework, especially for the Yamuna River, which faces severe pollution and over-extraction issues.
- Need for a robust, inclusive, and scientific approach to water management.
Studies Approved Under National Mission for Clean Ganga (NMCG):
|
Institution |
Rivers/Sub-Basins Assigned |
|
NIH Roorkee |
Chambal, Son, Damodar |
|
IIT Roorkee |
Ghaghara, Gomti |
|
IIT Kanpur |
Kosi, Gandak, Mahananda |
These studies aim to assess current flow conditions and recommend sustainable flow levels.
Way Forward:
- Expedite assessments under NMCG and ensure multi-stakeholder participation.
- Develop comprehensive water flow strategies for heavily impacted rivers like the Yamuna.
- Strengthen decision-making frameworks to balance ecological and human needs.
Decline of Coral Reefs in Lakshadweep: A 24-Year Study

- 27 Jul 2025
In News:
A recent 24-year study (1998–2022) of coral reefs in the Lakshadweep Archipelago revealed that live coral cover has declined by nearly 50%, from about 37.2% to 19.1%. The research, conducted across three atolls—Agatti, Kadmat, and Kavaratti—highlights the severe impact of repeated marine heatwaves linked to climate change.
What are Corals?
Corals are small, soft-bodied marine invertebrates belonging to the Cnidaria group. Individual corals, called polyps, secrete a calcium carbonate exoskeleton, forming vast reef structures. Coral reefs provide crucial habitats for about 25% of marine life and support over 1 billion people worldwide with food, livelihoods, and coastal protection.
Types and Distribution:
India’s coral reefs are mainly found in the Gulf of Kutch, Gulf of Mannar, Andaman & Nicobar Islands, Lakshadweep Islands, and Malvan.
Causes of Coral Decline:
- Marine Heatwaves & Climate Change: Rising sea surface temperatures disrupt the symbiotic relationship between corals and their algae (zooxanthellae), causing bleaching and mortality.
- Ocean Acidification: Increased CO? lowers ocean pH, hampering coral skeleton formation.
- Pollution: Land runoff with fertilizers, pesticides, and heavy metals harms coral health.
- Physical Damage: Coastal development, sedimentation, and unsustainable fishing.
- Overfishing: Imbalance in reef ecosystems due to loss of algae-eating fish.
Key Findings from the Lakshadweep Study:
- Coral mortality from bleaching has decreased over time but so has the reefs’ recovery rate.
- Heat-sensitive coral species have largely disappeared, leaving more stress-tolerant species like Porites dominant.
- Recovery accelerates only if reefs are given at least a six-year gap between bleaching events.
- The 2010 marine heatwave was the most severe, with a Degree Heating Week (DHW) value of 6.7, indicating significant heat stress.
- The study emphasizes the need for longer recovery periods between bleaching for coral regeneration.
Implications for Conservation:
- The study provides a predictive framework to identify reefs vulnerable to bleaching and prioritize restoration.
- Local conservation must be combined with urgent global climate action to reduce the frequency of heatwaves.
- Without global intervention, even resilient coral species may not survive repeated disturbances.
This study underscores the vulnerability of India’s coral reefs, especially in Lakshadweep, to climate change and highlights the urgent need for integrated local and global conservation efforts.
ICJ Declares Clean Environment a Human Right
- 27 Jul 2025
In News:
In a historic advisory opinion delivered on 23rd July 2025, the International Court of Justice (ICJ) recognized the right to a clean, healthy, and sustainable environment as a fundamental human right. The opinion was issued at the request of the UN General Assembly (2023) following lobbying by Vanuatu and supported by over 130 countries, mainly small island developing states (SIDS) vulnerable to climate change.
Key Legal Questions Addressed:
- What are states’ obligations under international law to mitigate climate change?
- What are the legal consequences of failing to act on climate commitments?
Major Highlights of the ICJ Advisory Opinion:
1. Environment as a Human Right
- The Court affirmed that access to a clean, healthy, and sustainable environment is inherent to the enjoyment of other human rights.
- Based on customary international law, UNGA Resolution 76/300 (2022), and international human rights treaties.
2. Binding Legal Duties
- States are bound under UNFCCC, Kyoto Protocol, and Paris Agreement to:
- Implement mitigation and adaptation policies.
- Submit and update Nationally Determined Contributions (NDCs).
- Facilitate technology transfer and climate finance.
3. Due Diligence and Liability
- States must prevent significant transboundary environmental harm and regulate both public and private actors (e.g., fossil fuel companies).
- Failure to act amounts to an internationally wrongful act, triggering:
- Cessation,
- Guarantees of non-repetition,
- Compensation or restitution.
4. Historical Emissions & Responsibility
- The ICJ accepted that cumulative emissions can be legally attributed to specific states.
- Supports legal claims for reparations and accountability based on historic contributions to climate change.
5. Climate Obligations as Erga Omnes
- These duties are owed to the entire international community.
- Any state can seek enforcement, regardless of direct injury.
6. Scientific Attribution Accepted
- Climate science was admitted as legal evidence.
- Allows courts to establish causal links between emissions and environmental harm.
Geopolitical & Legal Implications:
- Empowers SIDS and developing nations in climate negotiations.
- Opens doors to domestic and international litigation based on environmental rights.
- Highlights inadequacy of current global agreements in ensuring timely climate action.
- Major emitters like USA and Russia have resisted legally binding obligations through courts.
Relevance for India:
- Reinforces Article 21 (Right to Life) and Article 48A (Protection of Environment) of the Indian Constitution.
- Can influence Indian courts and tribunals (e.g., NGT, Supreme Court) in:
- Air and water pollution cases,
- Waste management,
- Climate adaptation litigation.
This ruling marks a critical shift in international environmental law, signaling greater legal accountability for climate action and strengthening the legal foundation for future climate justice claims.
Long-Billed Bush Warbler
- 25 Jul 2025
In News:
In a significant ornithological event, a team of birders has confirmed the first Indian sighting in 46 years of the elusive Long-billed Bush Warbler (Locustella major). The bird was observed in dense willow thickets at an altitude of over 3,200 metres in Suru Valley, Ladakh.
About Long-Billed Bush Warbler
- Scientific Name: Locustella major
- Common Name: Long-Billed Bush Warbler (formerly Long-billed Grasshopper Warbler)
- Type: Medium-sized, skulking songbird of the bush warbler group
- Size: Approximately 15–17 cm in length
- Plumage:
- Brownish-olive upperparts with fine streaking
- Pale underparts (whitish or buff)
- Both sexes appear similar
- Call: Produces an insect-like clicking sound used for territory marking and mate attraction
Distribution and Habitat
- Global Range:
- Limited distribution in the mountains of Central Asia
- Documented in India, Pakistan, China, and Tajikistan
- Preferred Habitat:
- Altitude: 2,400–3,600 metres
- Found on grassy slopes with bushes and weeds
- Upland terraced cultivation and forest edge clearings
- Often observed among Rumex, sea buckthorn, and Ribes gooseberry shrubs near spruce forests
Conservation Status
- IUCN Red List: Near Threatened (NT)
- Reasons for decline include habitat loss, especially due to conversion of bushland into agricultural fields.
Significance of the 2025 Sighting
- The last confirmed Indian record was in 1979 near Sankoo in Kargil, by researchers from Southampton University.
- Historically, the species was relatively common in Dras and Suru valleys until the early 20th century.
- The recent sighting aligns with records from nearby Gilgit-Baltistan (2022–2025), where the species has been increasingly documented at similar altitudes (3,000–3,100 m).
Ambrosia Beetle

- 23 Jul 2025
In News:
Rubber plantations in Kerala, the heart of India’s natural rubber production, are under significant threat due to an invasive insect-fungal association. A mutualistic relationship between the ambrosia beetle (Euplatypus parallelus) and two fungal species (Fusarium ambrosia and Fusarium solani) has caused widespread tree damage, including leaf fall, trunk drying, and reduction in latex yield. This development poses a serious risk to India's rubber economy, biodiversity, and public health.
Key Highlights:
Ambrosia Beetle
- Origin: Native to Central and South America.
- First reported in India: In 2012, from cashew trees in Ponda, Goa.
- Current host: Rubber trees in Kerala, especially in Irrity-Kannur region.
Fungal Partners
- Fusarium ambrosia
- Fusarium solani — first time reported in association with adult ambrosia beetles in India.
Mutualistic Relationship
- The beetles do not feed on wood, but carry fungi into tunnels (galleries) bored into the tree bark.
- The fungi feed on wood, releasing enzymes that degrade plant tissue.
- Beetles and their larvae then feed on the nutrient-rich fungal mycelia.
- This association causes systemic infections in trees, often leading to their death.
Impact on Rubber Trees
- Weakens wood structure
- Causes severe leaf fall and drying of trunks
- Blocks xylem vessels, reducing water transport
- Leads to reduced latex production
- Long recovery time and high tree mortality
- The infection is hard to treat, as fungi lodge deep in plant tissues where fungicides and insecticides are ineffective.
Wider Implications
Scientific Concerns
- Fungi like Fusarium solani can evolve to associate with other beetles, expanding the range of infection to cashew, coconut, coffee, mango, and teak.
- These fungi can spread through soil or be carried by insect vectors, making containment difficult.
Health Hazards
- Fusarium species are opportunistic pathogens in humans.
- Workers in plantations may be exposed to these fungi, especially those with compromised immunity.
India’s Rubber Sector at Risk
- India is the 6th largest producer of rubber globally.
- Kerala accounts for 90% of national production and 72% of cultivation area.
- The economic stakes are high, as the beetle-fungi threat endangers not only latex yields but also the livelihoods of thousands of smallholder farmers.
Response Measures and Strategies
Current Management Practices
- Use of antifungal agents
- Pruning or burning infected parts
- Installation of ambrosia beetle traps
- Chipping infected wood to prevent spread
Challenges
- No mycangia (fungal sacs) found in beetles in India — raises questions on fungal transmission mechanisms.
- Soil- and insect-mediated spread of fungi makes conventional phytosanitary measures ineffective for broadleaf trees like rubber.
Suggested Solutions
- Genetically modified (GM) rubber plants to resist fungal infection (debated).
- Use of antagonistic fungi or microbial consortia inside plants to outcompete pathogens.
- Location-specific strategies based on geography and host tree characteristics.
- Greater collaboration between researchers and policymakers to monitor and contain the threat.
Allographa effusosoredica
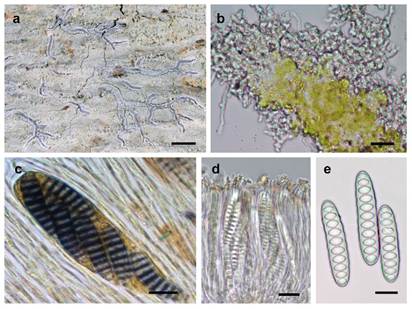
- 20 Jul 2025
In News:
A team of Indian scientists from MACS-Agharkar Research Institute, Pune (under the Department of Science & Technology) has discovered a new species of lichen named Allographa effusosoredica in the Western Ghats, a UNESCO World Heritage Site and biodiversity hotspot. This crustose lichen exhibits effuse soredia and contains norstictic acid, a rare secondary metabolite within its genus.
Scientific and Molecular Significance
- The species was examined through polyphasic taxonomy, integrating:
- Morphological traits
- Chemical profiling
- Molecular sequencing using genetic markers:
- Fungal DNA markers: mtSSU, LSU, RPB2
- Algal symbiont marker: ITS
- The lichen’s photobiont was identified as a species of Trentepohlia, advancing the understanding of tropical algal diversity in lichens.
- Though morphologically similar to Graphis glaucescens, it is phylogenetically closest to Allographa xanthospora.
Symbiosis in Lichens
- Lichens are composite organisms, formed by a symbiotic association between:
- A fungal partner (mycobiont) — provides structure and protection.
- A photosynthetic partner (photobiont), such as green algae or cyanobacteria — produces nutrients via photosynthesis.
- This discovery supports the concept of locally adapted symbiosis, emphasizing co-evolution in tropical ecosystems.
Ecological Importance of Lichens
- Lichens are vital for:
- Soil formation
- Feeding insect populations
- Acting as bioindicators of air quality and ecosystem health.
Conservation and Biodiversity Impact
- Allographa effusosoredica is:
- The 53rd Allographa species reported from India.
- The 22nd species of this genus documented in the Western Ghats.
- The first Indian Allographa species validated using molecular tools.
- The study was supported by the Anusandhan National Research Foundation (ANRF) and contributes to the growing inventory of India’s cryptic biodiversity.
Global Wetland Outlook 2025
- 20 Jul 2025
In News:
The Global Wetland Outlook (GWO) 2025, released by the Ramsar Convention on Wetlands, highlights alarming degradation trends in global wetlands—especially in Africa, Latin America, and the Caribbean—with implications for climate resilience, biodiversity, and socio-economic wellbeing.
What are Wetlands?
A wetland is a land area saturated with water—either permanently or seasonally—and functions as a distinct ecosystem. Wetlands include:
- Inland: Lakes, rivers, swamps, peatlands
- Coastal: Mangroves, tidal flats, coral reefs, estuaries
- Human-made: Rice paddies, reservoirs, wastewater ponds
Key Findings:
- Produced by: Scientific and Technical Review Panel (STRP) of the Ramsar Convention
- Global Wetland Loss: Since 1970, the world has lost 411 million hectares of wetlands—a 22% decline in extent.
- Current loss rate: ~0.52% annually
- Regional Degradation:
- Most severe in Africa, Latin America, and the Caribbean
- Africa’s wetlands are deteriorating faster than they can be restored, especially in South Africa
- Drivers of degradation:
- Africa, Latin America & Caribbean: Urbanisation, industrialisation, infrastructure development
- Europe: Drought
- North America & Oceania: Invasive species
- Economic Valuation:
- Global value of wetlands: $7.98 to $39.01 trillion/year
- Africa’s wetlands (2023): $825.7 billion, vs Asia’s $10.58 trillion
- Restoration Costs vs Conservation:
- Restoration: $1,000 to $70,000 per hectare/year
- Conservation is cheaper and more effective long-term
- Policy Insight: Most wetlands in Least Developed Countries (LDCs) are in poor condition, while those in high-income countries are in better health.
Africa’s Wetlands: A Deepening Crisis
- Millions depend on wetlands for food, water, disaster protection, and climate resilience.
- The Kafue Flats (Zambia) restoration example shows:
- $300,000 investment revived flooding
- Supported biodiversity and over a million people
- Boosted artisanal fisheries worth $30 million annually
- Warning from Ramsar Secretariat: Loss of wetlands is a major barrier to achieving global climate, biodiversity, food, and poverty targets.
India and Wetlands
- India has ~4.6% of its land as wetlands
- Hosts 91 Ramsar Sites – largest in South Asia and third in Asia
- Wetland types: Himalayan high-altitude lakes, Gangetic floodplains, mangroves (e.g., Sundarbans), coastal lagoons
Importance of Wetlands:
|
Function |
Explanation |
|
Biodiversity Hotspots |
Support endangered and endemic species |
|
Water Purification |
Trap pollutants and sediments |
|
Flood Regulation |
Act as natural buffers |
|
Carbon Sequestration |
Slow decomposition stores carbon |
|
Livelihoods |
Sustain agriculture, fisheries, tourism |
Ramsar Convention on Wetlands
- Adopted: 1971, Ramsar, Iran | Came into force: 1975
- India joined: 1982
- Goal: Conservation and wise use of wetlands globally
- Ramsar Site Criteria: Supports endangered species, ≥20,000 waterbirds, or critical fish spawning grounds
Key Framework: Kunming-Montreal Global Biodiversity Framework (GBF)
- Adopted in 2022 (COP15 to Convention on Biological Diversity)
- Dubbed “Paris Agreement for Nature”
- Targets:
- Halve invasive species spread
- Cut harmful subsidies by $500 billion/year
- 30x30 Target: Protect 30% of land + marine areas by 2030
- Restore 30% of degraded ecosystems by 2030
Recommendations from GWO 2025
- Increase Wetland Financing:
- Incorporate wetlands in KM-GBF finance targets
- Mobilise private-public funding
- Cross-Border Collaboration: Enhance regional conservation partnerships, especially in Africa
- Value Nature in National Accounts: Recognise GDP contributions from wetlands, forests, biodiversity
- Invest in Nature-Based Solutions: Wetlands can buffer climate shocks and reduce disaster response costs
Sierra Leone’s First UNESCO World Heritage Site
- 17 Jul 2025
In News:
In a landmark achievement for global environmental conservation, Sierra Leone has secured its first UNESCO World Heritage Site with the inscription of the Gola-Tiwai Complex, comprising the Tiwai Island Wildlife Sanctuary and the Gola Rainforest National Park (GRNP). This milestone is the result of over three decades of environmental activism led by Tommy Garnett, founder of the Environmental Foundation for Africa (EFA).
About the Gola-Tiwai World Heritage Site
Location
- Southern Sierra Leone, along the Moa River, near the Liberia border.
Components
- Tiwai Island Wildlife Sanctuary
- Area: Only 12 sq. km
- Biodiversity: Home to 11 primate species, including:
- Western Chimpanzee (endangered)
- Diana Monkey
- *King Colobus Monkey
- Serves as a biodiversity research hub and ecotourism destination in West Africa.
- Gola Rainforest National Park
- Sierra Leone’s largest tropical rainforest
- Biodiversity Highlights:
- Pygmy Hippopotamus
- Critically Endangered African Forest Elephant
- Numerous bird, insect, and plant species
- Provides critical services such as:
- Carbon sequestration
- Climate regulation
- Genetic biodiversity conservation
Ecological and Global Significance
- Biodiversity Hotspot: The Gola-Tiwai complex is one of the most biologically diverse areas in West Africa.
- Sustainable Development Model:
- Combines community engagement, scientific research, and eco-tourism.
- Sets a precedent for post-conflict environmental restoration.
- Global Climate Importance: The rainforest acts as a carbon sink, playing a role in mitigating climate change.
- Cultural-Ecological Linkages: Local communities depend on forests for livelihoods, traditions, and spiritual practices.
Geographical Context: Sierra Leone
Capital: Freetown
- Located on a peninsula with one of the world’s largest natural harbours.
Neighbouring Countries: Guinea (North and East), Liberia (Southeast), Atlantic Ocean (Southwest)
Key Geographical Features:
- Mountains:
- Mount Bintimani (Loma Mansa) – Highest peak at 1,948 m (6,391 ft)
- Tingi Hills, Sula Plateau, Kambui Schists
- Rivers:
- Major rivers: Moa, Sewa, Mano, Rokel
- Originate in Fouta Djallon highlands in Guinea
- Coastal Plains: Include mangrove swamps, lateritic soils, and seasonally flooded Bolilands
- Climate: Tropical with high rainfall and Harmattan winds in dry seasons
Natural Resources:
- Rich in diamonds, gold, rutile, and bauxite
- Economy based on mining and agriculture
RhoDIS India

- 16 Jul 2025
In News:
A specialised team has begun the genetic analysis of 2,573 rhino horn samples in India, with the goal of enhancing rhino conservation and curbing wildlife crimes. This is part of the RhoDIS India (Rhino DNA Index System) initiative.
About RhoDIS India Programme:
- Launched in 2016 by the Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change (MoEFCC) in collaboration with:
- Wildlife Institute of India (WII), Dehradun
- State forest departments of Assam, West Bengal, and Uttar Pradesh
- WWF India
- Objective:
To create a DNA database of individual rhinos for:- Aiding wildlife crime investigations
- Supporting scientific management of the rhino population
- Implementation:
The genetic lab at WII Dehradun handles DNA profiling using a standardised protocol approved by the MoEFCC. It involves short tandem repeat (STR) allele analysis for generating unique genetic signatures for each rhino.
Recent Developments in Assam:
- In September 2021, the Assam Forest Department verified and destroyed 2,479 rhino horns stored in state treasuries, excluding horns under court cases or of special scientific interest.
- Prior to destruction, tiny samples from 2,573 horns were preserved for DNA and chemical analysis. These samples have now been repackaged and transported to WII for genetic sequencing.
- This analysis will help track temporal genetic changes and improve understanding of the rhino population’s genetic health across Assam.
- The entire repackaging process was recorded and monitored by independent experts to ensure transparency.
Significance of RhoDIS:
- Provides individual identification of rhinos from horn samples, helping track poaching incidents and illegal wildlife trade.
- Strengthens forensic evidence in courts related to wildlife crime.
- Assists in population management through genetic diversity assessments.
What is a Rhino Horn?
- Composed of keratin, the same protein found in human nails and horse hooves.
- Contains sulphur-rich amino acids like cysteine, and minerals such as calcium carbonate and phosphate.
- Greater one-horned rhinos (found in India) have a single horn, unlike African species with two.
Great Hornbill Sighting
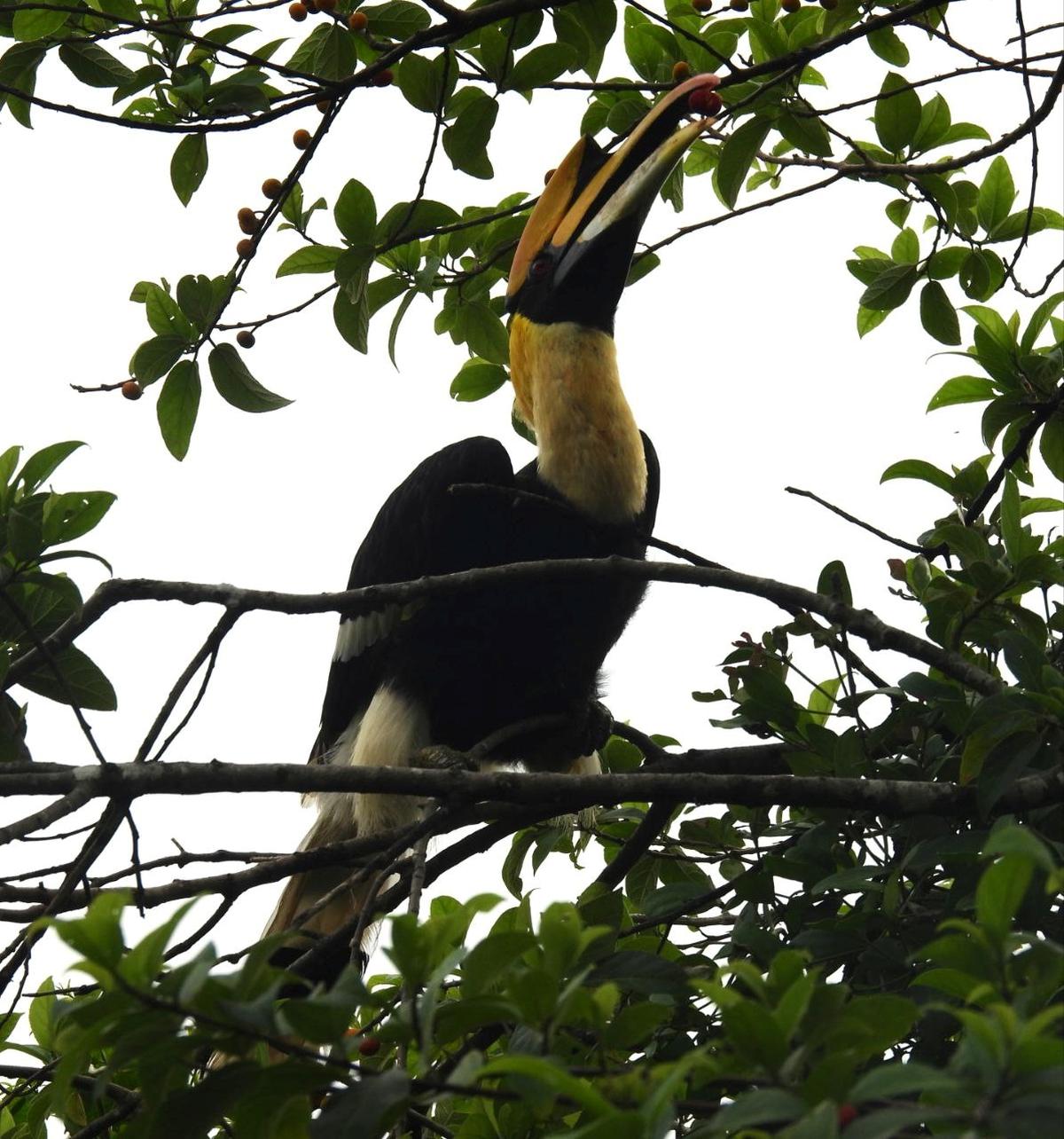

- 11 Jul 2025
In News:
In a rare and ecologically significant event, the Great Hornbill (Buceros bicornis), Kerala’s State Bird, was recently spotted in the coastal belt of Kakkampara, near Ezhimala in Kannur district. This area lies well outside the species’ typical forested habitats, making the sighting both unusual and important for biodiversity assessments.
About the Great Hornbill
- The Great Hornbill, also known as the great Indian hornbill or great pied hornbill, is one of the largest members of the hornbill family.
- It is primarily found in the Western Ghats, forests along the Himalayas, and parts of Southeast Asia.
- Its preferred habitat includes wet evergreen and moist deciduous forests at elevations between 600 to 2000 meters.
- This large, vividly colored bird measures between 95 to 120 cm in length with a wingspan of 151 to 178 cm, and typically weighs around 3 kilograms.
- The hornbill is easily identifiable by its prominent casque, a hollow structure on top of its large yellow bill. Males and females look similar, although males can be distinguished by their red irises and slightly larger casques, whereas females have white irises.
- Hornbills are primarily frugivorous, feeding on a variety of forest fruits, especially figs. However, they are opportunistic and may also consume small reptiles, birds, and mammals.
- A distinctive feature of the Great Hornbill is the tinted oil secreted by its preen gland, which gives its feathers, bill, and casque a yellow to reddish hue during grooming.
Conservation Status and Legal Protection
- The Great Hornbill is listed as ‘Vulnerable’ on the IUCN Red List due to habitat loss, hunting, and fragmented populations.
- In India, it is provided the highest level of protection under Schedule I of the Wildlife (Protection) Act, 1972, making it illegal to hunt or trade the species.
Ecological Importance of the Ezhimala Sighting
The occurrence of the Great Hornbill in a coastal region far from its usual forest range is considered a valuable ecological indicator. Experts believe such sightings could hint at changing habitat patterns, microhabitat availability, or even displacement due to habitat disturbance in core forest areas. The area around Ezhimala, despite human habitation, appears to sustain enough ecological richness to attract such a rare forest species.
Pethia dibrugarhensis
- 08 Jul 2025
In News:
A team of Indian researchers has identified a new species of freshwater fish in the Brahmaputra River near Maijan, Dibrugarh (Assam). The species has been named Pethia dibrugarhensis, in reference to its place of discovery.
Discovery Details:
- The discovery was made during a freshwater biodiversity survey conducted by:
- ICAR–Central Inland Fisheries Research Institute (CIFRI) – Barrackpore & Guwahati centres
- Manipur University
- The findings were published in the international journal National Academy Science Letters (Springer Nature).
About the Species:
- Family: Cyprinidae (the carp family)
- Genus: Pethia
- Common Group: Barbs (small indigenous freshwater fish)
- Habitat: Found in moderately fast-flowing stretches of the Brahmaputra, with a mud-sand-stone substrate. It shares its habitat with other small indigenous fish species native to northeastern India.
Distinctive Characteristics:
- Incomplete lateral line
- A prominent black blotch on both dorsal and ventral sides of the caudal peduncle
- Absence of humeral marks and barbels
- These unique morphological traits set it apart from other known species in the genus Pethia.
Significance:
- The discovery highlights the rich and underexplored aquatic biodiversity of the Brahmaputra river system.
- It underscores the importance of systematic ichthyofaunal surveys for biodiversity conservation, especially in ecologically sensitive regions like the Northeast.
- According to the researchers, documenting such species is critical before they are impacted by environmental degradation and habitat loss.
Green Climate Fund

- 07 Jul 2025
In News:
- The Green Climate Fund (GCF) has approved over USD 120 million to support climate adaptation initiatives in Ghana, the Maldives, and Mauritania, with technical development by the UN Environment Programme (UNEP).
- The projects aim to build climate resilience among vulnerable populations through nature-based solutions, climate-resilient agriculture, early warning systems, and water security enhancements.
- These initiatives are critical in delivering adaptation finance to regions like Small Island Developing States (SIDS) and the Sahel, addressing some of the most urgent climate vulnerabilities and are expected to benefit over 3.5 million people.
Project Highlights by Country:
Ghana: Agroecological Resilience in Northern Regions
- Total funding: USD 70 million (USD 63 million GCF grant).
- Objective: Strengthen climate resilience in eight districts across North East, Upper East, and Upper West Ghana.
- Key Interventions:
- Improve access to climate data and early warnings.
- Enable dry-season farming via water storage.
- Restore 28,000 hectares of degraded land to improve water retention and soil health.
- Impact:
- Direct benefits for 619,000 people.
- Early warning systems to reach 2.9 million.
- Improved food security for 120,000 individuals.
- Implementing agencies: Ghana EPA and Ghana Meteorological Agency.
Maldives: Early Warning and Risk Reduction in a SIDS
- Total funding: USD 25 million.
- Project Name: Toward Risk-Aware and Climate-Resilient Communities (TRACT).
- Focus: Expand multi-hazard early warning systems and build national capacity under the Early Warnings for All (EW4All) initiative.
- Risks Addressed: Rising sea levels, storm surges, heatwaves, and coastal erosion threatening agriculture, fisheries, and tourism.
- Impact:
- Coverage for over 500,000 people.
- Special emphasis on remote and marginalized communities, including women and children.
Mauritania: Ecosystem Restoration in the Sahel
- Total funding: USD 33 million (USD 30 million GCF grant).
- Objective: Address desertification, drought, and water scarcity across four vulnerable regions.
- Key Activities:
- Build green-grey infrastructure to stabilize sand dunes.
- Improve water access for farming and land rehabilitation.
- Promote climate-resilient agriculture to reduce food imports.
- Impact:
- 85,000 people to benefit directly; 145,000 indirectly.
- 2,100 hectares of land to be protected.
- Supports the Great Green Wall Initiative—Africa’s flagship response to desertification.
Institutional Roles and Significance:
- The UNEP, as a global leader in environmental governance, has played a key role in contextualizing science-based, locally led climate solutions.
- The GCF, under the Paris Agreement framework, remains the largest international climate fund, supporting countries in implementing their Nationally Determined Contributions (NDCs).
Hong Kong International Convention (HKC)

- 03 Jul 2025
In News:
The Hong Kong International Convention (HKC) for the safe and environmentally sound recycling of ships officially came into force on June 26, 2025.
About HKC:
- The HKC is a global treaty adopted under the aegis of the International Maritime Organization (IMO) to regulate the safe and environmentally sustainable recycling of ships that have reached the end of their operational life.
Objectives:
- Protect human health, especially that of shipbreaking workers.
- Prevent environmental pollution during ship dismantling.
- Control and manage hazardous materials such as asbestos, heavy metals, and hydrocarbons.
- Ensure safe waste handling and disposal practices in recycling yards.
Key Provisions:
- Inventory of Hazardous Materials (IHM):Ships must maintain an IHM listing all hazardous substances on board.
- Ship Recycling Plan (SRP):A certified SRP must be approved before the ship is sent for dismantling.
- Recycling Completion Certificate:Recycling facilities must issue this certificate within 14 days of dismantling completion.
- Third-Party Audits and Certification:Classification societies recognized by the IMO will conduct compliance audits and issue relevant certifications.
- Authorized Recycling Yards:The convention promotes the use of regulated and approved facilities for ship recycling to ensure compliance with international safety and environmental norms.
Significance:
- Strengthens global maritime safety and sustainable shipbreaking practices.
- Encourages modernization and regulation of recycling yards, especially in developing countries like India and Bangladesh.
- Aligns ship recycling with UN Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), particularly those on health, environment, and decent work.
Candida tropicalis
- 29 Jun 2025
In News:
A recent study published in PLoS Biology by researchers from Fudan University, China, has uncovered a disturbing link between the agricultural use of a common fungicide and the emergence of azole-resistant Candida tropicalis, a fungal pathogen responsible for high-mortality infections, especially in India and other tropical regions.
Candida tropicalis and Public Health Risk
- Candida tropicalis is a major fungal pathogen, particularly prevalent in India, associated with mortality rates of 55–60%.
- Azole-class antifungal drugs, such as fluconazole and voriconazole, are frontline treatments.
- Growing drug resistance is being reported in clinics globally, raising serious concerns for treatment efficacy and public health.
Fungicide Link to Drug Resistance
- Tebuconazole, a triazole-based fungicide, widely used in agriculture and gardening, has been found to be the primary driver of cross-resistance to clinical azoles in C. tropicalis.
- Tebuconazole accumulates and persists in the environment, exerting selective pressure on fungal strains.
- Clinical strains exposed to tebuconazole showed cross-resistance to both fluconazole and voriconazole.
Mechanism of Resistance: Ploidy Plasticity and Aneuploidy
- Resistant strains exhibit aneuploidy – a deviation in chromosome number, often with duplications or deletions of chromosome segments.
- This phenomenon, termed ploidy plasticity, is rare in most organisms due to its detrimental effects, but in C. tropicalis, it enables adaptive resistance.
Genetic Changes Observed:
- Duplication of TAC1 gene segment led to overexpression of ABC-transporters, proteins that pump out azoles and reduce their effectiveness.
- Deletion of HMG1 gene segment increased the synthesis of ergosterol, a compound crucial to fungal membranes, thus enhancing azole resistance.
- These adaptations allowed the resistant strains to trade growth rate for survival under antifungal pressure.
Emergence of Stable Haploid Strains
- The study unexpectedly identified haploid strains of C. tropicalis among resistant isolates.
- These haploids were found to be mating-competent, raising concerns over the genetic transfer of resistance traits.
- Further genomic analysis confirmed that naturally occurring haploid strains also exist, such as two clinical isolates from Spain.
Virulence and Resistance in Animal Models
- In mouse models, strains with altered ploidy exhibited greater virulence than their progenitor strains when treated with fluconazole.
- This finding suggests a dual threat: enhanced resistance and increased disease severity.
Implications and Concerns
- The unregulated and widespread use of triazole fungicides like tebuconazole in agriculture is unintentionally selecting for clinically significant drug resistance.
- These resistant fungal strains pose a direct threat to human health, particularly in immunocompromised patients and in settings with limited alternative antifungal therapies.
- Resistant strains can potentially spread and recombine through mating, complicating containment efforts.
State of the Climate in Asia 2024 Report

- 29 Jun 2025
In News:
The World Meteorological Organization (WMO) has released its annual State of the Climate in Asia 2024report, highlighting alarming trends in climate change impacts across the Asian continent. The report confirms that Asia is warming at nearly twice the global average, causing severe socio-economic and environmental consequences.
Key Climate Trends and Indicators in Asia (2024)
- Record Heat:The year 2024 was the warmest year in Asia’s history, marked by prolonged and widespread heatwaves across land and oceanic areas.
- Global Comparison:The global mean temperature in 2024 was the highest on record (1850–2024), surpassing the previous record of 1.45°C set in 2023. Each year between 2015 and 2024 ranks among the 10 warmest globally.
- Sea Surface Temperatures & Marine Heatwaves:Sea surface temperatures reached record highs,with Asian waters warming nearly twice as fast as the global average. Most Asian ocean areas experienced strong to extreme marine heatwaves, especially in the northern Indian Ocean, East China Sea, Yellow Sea, and waters near Japan.
- Sea Level Rise:Sea levels rose faster than the global average on both Pacific and Indian Ocean coasts of Asia, exacerbating risks for low-lying coastal areas.
Cryospheric Changes and Glacier Loss
- In Central Himalayas and Tian Shan ranges, 23 out of 24 monitored glaciers experienced mass loss in 2024.
- Consequences included increased risk of glacial lake outburst floods (GLOFs), landslides, and long-term threats to water security.
Scientific Warnings and Observations
The report highlights that the warming trend from 1991 to 2024 in Asia is nearly twice as fast as that between 1961 and 1990, underlining the acceleration of climate risks.
Implications for Asia
- Environmental:Rapid glacier melt, rising sea levels, and extreme weather are disrupting ecosystems, causing habitat loss and biodiversity decline.
- Economic:Agriculture, fisheries, and coastal infrastructure are suffering massive losses due to droughts, floods, and storms.
- Social:Heatwaves, displacements, and disaster-related fatalities are disproportionately affecting vulnerable populations, including the poor and elderly.
Enhanced Rock Weathering (ERW)

- 29 Jun 2025
In News:
Enhanced Rock Weathering (ERW) is emerging as a novel nature-based carbon removal strategy, gaining global traction from Brazil’s sugar plantations to tea estates in India. It is being explored as a scalable solution to climate change through natural carbon capture mechanisms.
What is Enhanced Rock Weathering (ERW)?
- Definition: ERW is a geoengineering technique that accelerates the natural chemical process of rock weathering to capture and store atmospheric carbon dioxide (CO?).
- Scientific Basis:
- Natural weathering involves the breakdown of silicate rocks through carbonic acid, formed when CO? dissolves in water, eventually locking the carbon in stable forms like bicarbonate or limestone.
- ERW accelerates this process using fast-weathering rocks like basalt, ground into fine particles to maximize surface area and reactivity.
Effectiveness and Challenges
- Potential Carbon Removal:
- A US-based study found that 50 tonnes of basalt/hectare/year could potentially remove up to 10.5 tonnes of CO?/hectare over four years.
- However, field trials in Malaysia (oil palm) and Australia (sugarcane) have shown lower than expected carbon capture rates.
- Key Variables Affecting Effectiveness:
- Rock type and mineralogy
- Soil characteristics
- Temperature and rainfall patterns
- Land management practices
- Measurement Difficulties:
- Current techniques often overestimate CO? capture due to detection of cations that form even in the absence of carbonic acid reactions.
- Risk: This can lead to inaccurate carbon credit claims, undermining offset integrity.
Co-Benefits of ERW
- Soil Health Improvement:
- Increases soil alkalinity → Improves nutrient availability and crop productivity.
- Contributes to soil formation and resilience.
- Resource Efficiency:Basalt is abundant and often a quarrying by-product, lowering costs and emissions associated with mining.
- Ocean Acidification Mitigation:Even if CO? isn't sequestered directly, rock in the soil can neutralize acidic runoff, preventing CO? release from aquatic systems downstream.
Risks and Concerns
- Health & Safety:
- Finely crushed rock may contain toxic heavy metals (depending on composition).
- Protective equipment is necessary during application.
- Carbon Credit Integrity:Overestimated CO? removal may allow companies to offset emissions inaccurately, leading to net increase in atmospheric carbon.
Global Adoption and Projects
- Countries Involved:Brazil, India, USA, Europe, and Latin America are trialing or implementing ERW.
- India Focus:Trials underway in Darjeeling tea plantations and other agricultural regions through startups like Mati Carbon.
- Global Milestones:
- First verified ERW carbon removal credits issued from a Brazilian project.
- Google signed the largest ERW deal for 200,000 tonnes of CO? removal credits (to be delivered by early 2030s).
- Terradot, an ERW company, sold 90,000 tonnes of carbon credits for $27 million, backed by firms like H&M.
Investor Interest and Innovation Push
- Private Sector Engagement:ERW has attracted big tech, fast fashion, and aviation sectors seeking nature-based offset solutions.
- Prize Recognition:Mati Carbon won the $50 million X Prize for carbon removal, recognizing the potential scalability and innovation of ERW.
SDG Index 2025

- 27 Jun 2025
In News:
India has ranked 99th out of 193 countries in the Sustainable Development Goals (SDG) Index 2025, marking the first time it has entered the top 100. India scored 67 in the index, as per the Sustainable Development Report 2025 released by the U.N. Sustainable Development Solutions Network.
About the Sustainable Development Report 2025
- Publisher: U.N. Sustainable Development Solutions Network.
- Objective: Tracks annual progress on the 17 Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) adopted by all UN member states in 2015.
- Coverage: 193 countries.
- Relevance: Assesses national performance across economic, social, and environmental dimensions of sustainability.
Key Highlights of the 2025 Report
Global Trends
- SDG Progress Stalled Globally: Only 17% of the SDG targets are projected to be met by 2030.
- Barriers to Progress: Conflicts, structural vulnerabilities, and constrained fiscal space are key impediments.
- Top Performers:
- Finland ranks 1st, followed by Sweden (2nd) and Denmark (3rd).
- However, many European nations face serious challenges related to climate change and biodiversity loss, due to unsustainable consumption patterns.
Regional Insights
- East and South Asia have shown the fastest progress since 2015, attributed to rapid socioeconomic development.
- India’s Achievement: Ranked 99th, entering the top 100 for the first time.
Sectoral Progress and Setbacks
- Areas of Strong Progress Globally:
- Access to electricity (SDG 7)
- Use of mobile broadband and internet (SDG 9)
- Reduction in child and neonatal mortality (SDG 3)
- Areas of Reversal Since 2015:
- Rising obesity rates (SDG 2)
- Decline in press freedom (SDG 16)
- Poor sustainable nitrogen management (SDG 2)
- Worsening Red List Index (biodiversity loss – SDG 15)
- Weakening Corruption Perceptions Index (SDG 16)
Commitment to Multilateralism
- Top 3 Countries Committed to UN Multilateralism:
- Barbados
- Jamaica
- Trinidad and Tobago
Notable National Rankings
- Brazil (25): Highest among G20 nations.
- Chile (7): Highest among OECD countries.
Rising Evaporative Demand and Thirstwaves

- 26 Jun 2025
In News:
The rising evaporative demand—a measure of how thirsty the atmosphere is—is spotlighting India’s significant data and research gaps related to climate extremes, water stress, and agricultural vulnerability. While global studies are increasingly focusing on "thirstwaves", India lacks adequate research and monitoring frameworks on this critical issue.
What is Evaporative Demand?
- Evaporative demand indicates the near-maximum amount of water that would evaporate from land or vegetation if enough water is available.
- It is not equivalent to actual evaporation, which also depends on water availability.
- Driven by atmospheric factors:
- Temperature
- Wind speed
- Solar radiation
- Humidity
- Cloud cover
High evaporative demand leads to quicker drying of soil and vegetation, increasing drought risk, crop stress, and wildfire susceptibility.
What is a Thirstwave?
- Coined by MeetpalKukal (University of Idaho) and Mike Hobbins (NOAA/University of Colorado).
- Definition: Three or more consecutive days of abnormally high evaporative demand.
- Drivers: Combination of high temperature, low humidity, high solar radiation, and wind speed.
- Impacts:
- Reduces water availability for crops.
- Stresses vegetation.
- Increases fire danger.
- Accelerates drought onset and intensification.
Unlike heatwaves driven by temperature alone, thirstwaves are multi-dimensional and can be more damaging to crops and ecosystems.
Scientific Findings & India-Specific Observations
Global Evidence:
- Kukal& Hobbins’ study (published in Earth’s Future) noted:
- Increased frequency, intensity, and duration of thirstwaves in the U.S.
- Reduced likelihood of zero-thirstwave periods during growing seasons.
India’s Research Gap:
- Chronic shortage of real-time data on evaporative demand and extreme events.
- 1997 Study (Chattopadhyay &Hulme):
- Analyzed 30 years of IMD data.
- Found declining evaporation and potential evapotranspiration, likely due to increased humidity, despite warming.
- Projected future temperature rise would eventually override humidity effects, increasing evaporative demand.
Recent Developments in India:
- IIT Roorkee, NIH & European collaborators (2022):
- Studied 100 river sub-basins.
- Found highest rise in actual evapotranspiration in Northern India, Western Himalayas, and Eastern Himalayan regions.
- Interpreted as signs of increased vegetation or agricultural expansion.
Measurement Techniques:
- Standardised Short-Crop Evapotranspiration:
- A simplified metric to measure water demand of a 12 cm tall, healthy grass under ideal moisture conditions.
- Recommended for crop irrigation planning.
- Rising values signal increasing atmospheric demand and need for adaptive water management.
Implications for India:
- Agriculture and Food Security:
- India’s irrigated crops, especially rice and wheat, are vulnerable to atmospheric water demand.
- Rising thirstwaves threaten to decrease productivity even in well-irrigated regions.
- Water Resource Management:
- Increases soil moisture stress and reduces groundwater recharge.
- Calls for real-time tracking systems for evaporative stress.
- Disaster Preparedness:
- Thirstwaves may precede or exacerbate droughts and wildfires.
- Regions not traditionally drought-prone may still suffer from evaporative shocks.
- Research and Monitoring Needs:
- Lack of indigenous data on thirstwaves.
- Current efforts:Ongoing Indo-U.S. collaboration (University of Idaho & NIT Jalandhar) aims to map South Asian thirstwaves under the Water Advanced Research and Innovation Program.
Way Forward:
- Integrate evaporative demand and thirstwave parameters into IMD's early warning systems.
- Promote region-specific studies on crop sensitivity to evaporative demand.
- Develop adaptive irrigation protocols based on short-crop evapotranspiration trends.
- Sensitise farmers, water managers, and policymakers on atmospheric water demand risks.
- Invest in climate-resilient agriculture and data-driven water governance.
UNEP’s NDC Cooling Guidelines 2025

- 26 Jun 2025
In News:
The United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP) has released the NDC Cooling Guidelines 2025, aimed at supporting countries in integrating sustainable cooling strategies into their Nationally Determined Contributions (NDCs) under the Paris Agreement. The initiative addresses both climate mitigation and adaptation challenges posed by rising global temperatures and energy demand.
About the NDC Cooling Guidelines 2025
- Purpose:Provides a structured global framework for countries to incorporate sustainable cooling into national climate action plans, balancing mitigation, adaptation, and developmental needs.
- Developed by:UNEP’s Cool Coalition NDC Working Group, in collaboration with partners like UNDP.
- Primary Objectives:
- Mainstream sustainable cooling in national NDCs.
- Reduce sectoral emissions by 60% by 2050.
- Improve access to cooling for 1.1 billion vulnerable people.
- Establish robust Monitoring, Reporting, and Verification (MRV) mechanisms.
- Align with the Kigali Amendment to the Montreal Protocol and the Global Cooling Pledge.
Global Cooling Landscape: Key Data Points
- Current Impact:
- Cooling accounts for nearly 7% of global GHG emissions, projected to exceed 10% by 2050.
- Cooling consumes 20% of global building electricity, and up to 50% in countries like UAE.
- Access Challenges:1.1 billion people worldwide lack access to efficient and affordable cooling, threatening lives, food security, and healthcare.
- Efficiency Potential:By doubling appliance efficiency, access can expand sixfold without proportionate emission growth.
Challenges in the Cooling Sector
- Rising Emissions:Without immediate policy interventions, emissions from cooling are expected to double by mid-century, increasing climate and energy pressures.
- Access Inequality:Many low-income and rural populations remain exposed to extreme heat due to lack of sustainable cooling.
- Policy Gaps:Only 27% of updated NDCs currently include specific energy efficiency targets related to cooling.
- Gendered Impacts:Women, especially in vulnerable communities, face greater health risks from inadequate cooling and heat stress.
- Reinforcing Heat-Cooling Loop:Increasing temperatures escalate cooling demand, which if met with inefficient systems, leads to more emissions, exacerbating global warming—a vicious cycle.
Six-Step Framework in the Guidelines
- Baseline Assessment:Measure current energy use and refrigerant emissions in the cooling sector.
- Target Setting:Define clear, time-bound targets aligned with national climate priorities.
- Monitoring, Reporting, Verification (MRV):Develop transparent systems to track and report progress.
- Policy Tools:
- Introduce Minimum Energy Performance Standards (MEPS)
- Phase down high-GWP refrigerants
- Promote urban greening and passive cooling techniques
- Governance & Institutional Support:Establish cross-sectoral coordination, incorporating gender-sensitive planning.
- Financing & Equity:Mobilize investments and develop policies to enable equitable access to sustainable cooling technologies.
Country-Level Initiatives
- Nigeria:Integrated National Cooling Action Plan (NCAP) into its NDC, with a focus on heat-resilient rural infrastructure.
- United Arab Emirates (UAE):Adopted district cooling systems and high-efficiency air conditioning in its updated climate roadmap (NDC 3.0).
- Grenada:Committed to becoming the first HFC-free nation, aiming for complete refrigerant phase-down.
Himalayan Brown Bear
- 25 Jun 2025
In News:
In a significant development for Himalayan biodiversity, a rare sighting of a Himalayan Brown Bear with its family has been reported for the first time in the Dumka region between Nelang and Bhairon Ghati, within Gangotri National Park, Uttarakhand. The sighting has enthused wildlife experts and is viewed as a positive indicator of range expansion and ecosystem resilience in this fragile high-altitude region.
Significance of the Sighting
- This marks the first recorded presence of a brown bear in this specific stretch of the park.
- Previously, sightings were limited to Gomukh (6 bears) and Kedartal (3 bears), both located above 3,000 m.
About the Himalayan Brown Bear
- Scientific Name: Ursus arctos isabellinus
- Common Names: Himalayan Red Bear, Isabelline Bear; known as Denmo in Ladakhi.
- It is believed to be one of the most ancient brown bear lineages and may have inspired the Yeti legend due to its upright gait.
Distribution and Habitat
- Found in the northwestern and central Himalayas: India, Pakistan, Nepal, Bhutan, and China (Tibet).
- In India: Exists in fragmented populations in Jammu & Kashmir, Himachal Pradesh, and Uttarakhand.
- Inhabits elevations between 3,000 and 5,500 meters, usually above the timberline in alpine meadows and snow-clad regions.
Ecological Features
- Size: Males average 1.9 m and 135 kg; females 1.6 m and 70 kg.
- Fur: Sandy or reddish-brown; thick to endure high-altitude cold.
- Diet: Omnivorous – consumes roots, berries, nuts, small mammals, fish, and insects.
- Behavior: Solitary, except during mating or a mother with cubs; hibernates during winter in dens.
- Lifespan: 20–30 years in the wild.
Conservation Status
- IUCN Red List: Critically Endangered
- Wildlife (Protection) Act, 1972 (India): Schedule I
- CITES: Appendix I
Revised Green India Mission (GIM)
- 22 Jun 2025
In News:
Recently, the Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change released the revised roadmap for the National Mission for a Green India (GIM). The updated strategy focuses on restoring degraded ecosystems, enhancing forest cover, and addressing climate impacts, especially in vulnerable landscapes like the Aravallis, Western Ghats, Himalayas, and mangroves.
About Green India Mission (GIM)
- Launched in: 2014
- Under: National Action Plan on Climate Change (NAPCC)
- Nodal Ministry: Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change (MoEFCC)
- Core Objectives:
- Increase forest/tree cover by 5 million hectares.
- Improve the quality of forest cover on another 5 million hectares.
- Restore degraded ecosystems and enhance biodiversity.
- Improve the livelihoods of forest-dependent communities.
Achievements So Far
- Afforestation Activities: 11.22 million hectares covered (2015–16 to 2020–21) through central and state schemes.
- Funding: ?624.71 crore released (2019–24) to 18 states; ?575.55 crore utilized.
- Target Areas: Selected based on ecological vulnerability, sequestration potential, and restoration needs.
Key Features of the Revised Roadmap
- Landscape-Specific Restoration:
- Prioritizes Aravalli ranges, Western Ghats, Himalayas, and mangrove ecosystems.
- Emphasizes regionally adapted best practices for ecosystem restoration.
- Integration with Aravalli Green Wall Project:
- Aims to combat desertification and sandstorm risks in northern India.
- Initial restoration planned across 8 lakh hectares in 29 districts of 4 states.
- Estimated cost: ?16,053 crore.
- Aims to develop a 5 km buffer zone covering 6.45 million hectares around the Aravallis.
- Western Ghats Focus:
- Tackling deforestation, illegal mining, and degradation.
- Measures include afforestation, groundwater recharge, and mining site restoration.
Combating Land Degradation and Climate Change
- Land Degradation (2018–19): Affected 97.85 million hectares (~1/3rd of India’s land), per ISRO data.
- India’s Climate Targets (2030):
- Create an additional carbon sink of 2.5–3 billion tonnes of CO? equivalent via forest/tree cover.
- Restore 26 million hectares of degraded land.
- Carbon Sequestration Potential (FSI Estimates):
- Restoration of open forests can sequester 1.89 billion tonnes of CO? over 15 million hectares.
- With intensified afforestation and aligned schemes, forest cover could reach 24.7 million hectares—achieving a carbon sink of 3.39 billion tonnes CO? equivalent by 2030.
Significance of the Revised Mission
- Aligns with India’s NDCs under the Paris Agreement.
- Supports goals under UNCCD and UNFCCC.
- Helps mitigate climate change impacts by creating natural buffers and carbon sinks.
- Promotes ecological sustainability, biodiversity conservation, and community livelihood enhancement.
UN Oceans Conference 2025

- 21 Jun 2025
In News:
The third United Nations Oceans Conference (UNOC) was recently held in France, witnessing major developments in international marine conservation. One of the most significant outcomes was the near-finalisation of the Biodiversity Beyond National Jurisdiction (BBNJ) agreement, also referred to as the High Seas Treaty.
As of now, 56 countries have ratified the treaty out of the required 60, bringing it close to the threshold for becoming legally binding. Notably, India and the United States have not yet ratified the agreement, although India has officially stated it is in the process of doing so.
About the BBNJ Treaty
- The BBNJ Treaty is a legally binding agreement developed under the framework of the United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea (UNCLOS).
- Its aim is to regulate the use and protection of biodiversity in areas of the ocean that lie beyond national jurisdictions, also known as the high seas.
- The core objectives of the BBNJ Treaty include the creation of marine protected areas (MPAs) in international waters, regulation of marine genetic resources, enforcement of environmental impact assessments (EIAs) for activities in these regions, and capacity-building and technology transfer to support developing countries.
- The treaty is crucial because the high seas cover about 64% of the ocean’s surface and are largely unregulated.
- The BBNJ aligns with the Convention on Biological Diversity (CBD) target of conserving 30% of marine and coastal areas by 2030. Once the treaty secures the required number of 60 ratifications, it will enter into force after a 120-day waiting period. This will pave the way for the first Conference of Parties (COP) under the BBNJ to be held by late 2026.
Challenges to Implementation
- A major hurdle to the implementation of the BBNJ is the equitable sharing of benefits from marine genetic resources found in the high seas. These resources include unique life forms from deep-sea ecosystems that could have commercial applications in fields like pharmaceuticals and biotechnology.
- Since the high seas are global commons and not owned by any single nation, there is no clear consensus on how benefits should be shared.
- Environmental groups have also raised concerns that without a strong ban on resource extraction, the treaty may fall short of its conservation goals and could lead to unchecked exploitation of oceanic biodiversity.
Key Outcomes and Commitments from UNOC 2025
While the treaty itself is still awaiting full ratification, the conference saw a number of voluntary national and institutional commitments toward marine protection and sustainable ocean governance:
- The European Commission pledged €1 billion to support ocean conservation, marine science, and sustainable fisheries.
- French Polynesia committed to creating the world’s largest marine protected area, covering approximately five million square kilometres, equivalent to its entire exclusive economic zone (EEZ).
- New Zealand announced a contribution of $52 million to enhance ocean governance, science, and management in the Pacific Islands region.
- Germany launched an immediate action programme worth €100 million for the recovery and clearance of legacy munitions in the Baltic and North Seas.
- A coalition of 37 countries, led by Panama and Canada, initiated the High Ambition Coalition for a Quiet Ocean, the first global initiative to address ocean noise pollution.
- Italy committed €6.5 million to strengthen surveillance by the Coast Guard in marine protected areas and around oil platforms.
- Canada contributed $9 million to the Ocean Risk and Resilience Action Alliance, aiming to help Small Island Developing States (SIDS) and coastal countries build resilience against climate change using nature-based solutions.
- Spain pledged to establish five new marine protected areas, increasing its protected marine territory to 25%.
- A group of UN agencies introduced the One Ocean Finance initiative, which aims to mobilize investment from blue economy sectors to fund ocean sustainability.
Gharial Conservation

- 20 Jun 2025
In News:
On World Crocodile Day (June 17, 2025), Etawah district in Uttar Pradesh marked the 50th anniversary of India’s pioneering Gharial Conservation Programme, commemorating five decades of sustained efforts to protect the endangered gharial (Gavialis gangeticus) along the Chambal River.
About the Gharial Conservation Programme
- Launched in: 1975
- Initiated by: Forest Department of Uttar Pradesh and Society for Conservation of Nature (SCON)
- Supported by: UNDP, FAO, and Government of India
- Location: Primarily focused on Chambal River in Etawah district, Uttar Pradesh
- Breeding Facility: Kukrail Gharial Rehabilitation Centre, Lucknow
Why Gharial Conservation Matters
- Species: Gharial (Gavialis gangeticus) — endemic, freshwater crocodilian
- Status: Critically Endangered (IUCN Red List)
- Habitat: Prefers deep, fast-flowing rivers with sandy banks and minimal human interference
- Threats: Habitat destruction, sand mining, illegal fishing, entanglement in nets, and declining fish stocks
Programme Objectives
- Protect wild gharial populations in natural river habitats.
- Enhance population through captive breeding and release.
- Study habitat biology and gharial behaviour to inform scientific conservation.
- Promote coexistence between gharials and local fishing communities.
- Create awareness and engage local populations in conservation.
Key Features of the Programme
- Egg Collection: Gharial eggs are safely collected from natural nests on riverbanks.
- Artificial Incubation: Maintained under controlled temperature and humidity to improve hatching success.
- Captive Rearing: Hatchlings are reared for 3–5 years at Kukrail Centre until they are strong enough for survival in the wild.
- Release Strategy: Tagged juveniles are released in protected stretches of the Chambal River.
- Community Involvement: Local fishermen and villagers are involved in conservation-linked livelihoods to reduce human-wildlife conflict.
Impact and Legacy (1975–2025)
- One of India’s earliest species-specific conservation programmes.
- Created a successful model of “rear-and-release” conservation.
- Helped stabilize the gharial population in Chambal, now one of the last strongholds for the species.
- Promoted community-based conservation and scientific habitat management.
Global Drought Outlook 2025
- 20 Jun 2025
In News:
- The Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD) has released the “Global Drought Outlook 2025”, presenting a stark warning about the increasing frequency, severity, and impact of droughts worldwide.
- The report, titled “Global Drought Outlook: Trends, Impacts and Policies to Adapt to a Drier World”, offers a comprehensive assessment of drought patterns, consequences, and adaptation strategies, making it crucial for policymakers and global environmental governance.
Understanding Drought:
Drought is defined as a hydrological imbalance, characterised by prolonged periods of “drier-than-normal” conditions that deplete soil moisture, surface water, and groundwater. The report identifies three main types:
- Meteorological Drought: Caused by significantly below-average rainfall over an extended period.
- Agricultural Drought: Occurs when soil moisture becomes insufficient for crops and vegetation.
- Hydrological Drought: Involves declining water levels in rivers, lakes, and aquifers, affecting supply for human and ecological needs.
Global Trends and Projections
- Drought-Affected Land: The share of global land experiencing drought has doubled since 1900, driven by climate change and unsustainable land use.
- Current Impact (2023): Nearly 48% of the world’s land experienced at least one month of extreme drought.
- Regional Hotspots: Western USA, South America, Europe, Africa, and Australia are increasingly vulnerable.
- Groundwater Stress: Around 62% of monitored aquifers show declining trends.
- Future Risk: At +4°C global warming, droughts could become 7 times more frequent and severe by 2100, posing systemic global threats to food, water, and economic security.
Multidimensional Impacts of Drought
Ecological:
- 37% of global soils have dried significantly since 1980.
- River and groundwater depletion are threatening biodiversity and ecosystem services.
Economic:
- Drought-related losses are increasing by 3–7.5% annually.
- Modern droughts are twice as costly as in 2000; costs may rise 35% by 2035.
- Agriculture is most affected: crop yields drop up to 22% in drought years.
- Drought causes a 40% drop in river-based trade and a 25% decline in hydropower output.
Social:
- Droughts account for 34% of disaster-related deaths, though only 6% of disasters are droughts.
- It is a major driver of food insecurity, internal displacement, and climate migration, especially in Sub-Saharan Africa.
- Political instability and conflict often correlate with drought-induced resource scarcity.
Adaptation and Mitigation Strategies
The OECD emphasizes a multi-sectoral approach to manage drought risks:
- Integrated Water Resource Management (IWRM):
- Balancing water use and renewal.
- Promoting efficient and equitable water allocation.
- Nature-based Solutions (NbS):
- Urban de-sealing to enhance groundwater recharge.
- Landscape restoration to improve water retention and ecosystem resilience.
- Sustainable Agriculture:
- Adoption of drought-resistant crops and micro-irrigation systems.
- Can reduce water use by up to 76%.
- Urban Planning: Permeable infrastructure restores aquifers (e.g., US examples show 780 million m³/year recovery).
- Early Warning Systems: Enhanced drought monitoring, forecasting, and risk mapping.
- Policy Integration: Embedding climate resilience into national water and land-use policies.
- Cross-Sector Coordination: Engaging sectors like agriculture, energy, transport, construction, and health.
- Economic Benefits: Every $1 invested in drought resilience yields $2–$10 in benefits.
International Big Cat Alliance (IBCA)
- 18 Jun 2025
In News:
The first General Assembly of the International Big Cat Alliance (IBCA) was held in New Delhi, marking a significant moment in global biodiversity governance. Chaired by Union Environment Minister Bhupender Yadav, who was unanimously elected President of the IBCA, the event underscored India’s leadership in international wildlife conservation diplomacy.
What is IBCA?
- The International Big Cat Alliance (IBCA) is a multinational initiative launched by India in March 2024 to conserve the world’s seven major big cat species—Tiger, Lion, Leopard, Snow Leopard, Cheetah, Jaguar, and Puma—through collective action, knowledge exchange, and capacity building.
- It is coordinated by the National Tiger Conservation Authority (NTCA) under the Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change (MoEFCC).
- The Alliance was conceptualized following Prime Minister Narendra Modi’s announcement during the 50th anniversary of Project Tiger in April 2023.
Objectives of IBCA
- Promote global collaboration for the protection and conservation of big cats.
- Replicate successful conservation practices across member nations.
- Create a common pool of financial, technical, and institutional resources.
- Address gaps in capacity building, financing, and data sharing.
- Link conservation efforts with livelihood enhancement and climate resilience in big cat habitats.
- Strengthen efforts against poaching and illegal wildlife trade through joint surveillance and data exchange.
Membership
- 95 Range Countries (where the species naturally occur) are eligible to join.
- By September 2024, 25 countries including Bangladesh, Nigeria, Peru, and Ecuador had joined.
- Membership is open to all UN member states through a Note Verbale.
- The IBCA attained legal status after five countries—Nicaragua, Eswatini, India, Somalia, and Liberia—signed the Framework Agreement.
Key Functions of IBCA
- Shared Repository: Compilation of proven conservation strategies for scalable, science-based solutions.
- Training and Capacity Building: Organizes technical workshops and institutional exchanges.
- Scientific and Policy Support: Funds research, drives policy reforms, and raises awareness.
- Technological Innovation: Introduces advanced tools to tackle habitat degradation and prey base decline.
- Sustainable Livelihoods: Integrates conservation with community-based development models.
- Anti-Poaching Collaboration: Facilitates real-time data sharing and joint actions against wildlife trafficking.
Highlights from the 2025 General Assembly
- Venue: New Delhi, India
- Participating Nations: Ministerial delegations from nine countries including Bhutan, Cambodia, Kazakhstan, Liberia, Suriname, Somalia, Republic of Guinea, Eswatini, and India.
- Institutional Milestones:
- India ratified as the permanent headquarters of IBCA.
- The Headquarters Agreement was formally ratified, enabling the establishment of IBCA offices in India.
- Leadership: Bhupender Yadav, India’s Environment Minister, was elected as the first President of IBCA.
- Funding Commitment: India pledged ?150 crore (2023–28) to support IBCA’s establishment, coordination, and conservation activities.
Significance for India and the Global South
- Reinforces India’s role as a conservation leader and soft power in environmental diplomacy.
- Positions India as the epicentre for global big cat conservation, akin to its leadership in tiger conservation under Project Tiger.
- Encourages South-South cooperation in biodiversity preservation.
- Aligns with global commitments like CBD, CITES, and SDG 15 (Life on Land).
Bonn Climate Change Conference 2025
- 18 Jun 2025
In News:
The Bonn Climate Change Conference 2025 began in Bonn, Germany, with over 5,000 delegates from governments, international organisations, civil society, and scientific bodies. It serves as a crucial platform for setting the technical and political groundwork ahead of COP29.
What is the Bonn Climate Conference?
- A mid-year climate summit held annually under the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC).
- Also referred to as the Sessions of the UNFCCC Subsidiary Bodies (SBs).
- First held in 1995, after the UNFCCC was signed in 1992.
- Hosted in: Bonn, Germany (home of the UNFCCC headquarters).
- Organised by: The UNFCCC Secretariat.
Main Objectives
- Prepare for COP Summits: Provides a platform for technical discussions that shape the COP agenda (COP29 in this case).
- Review of Commitments: Tracks implementation of earlier climate agreements like the Paris Agreement.
- Science–Policy Integration: Connects IPCC research with policymaking processes.
- Support for Developing Nations: Discusses climate finance and technology transfer mechanisms.
- Inclusive Participation: Engages Indigenous communities, NGOs, experts, and private stakeholders.
Subsidiary Bodies of the UNFCCC
- SBI (Subsidiary Body for Implementation):
- Reviews how climate commitments are implemented.
- Facilitates support for developing countries.
- SBSTA (Subsidiary Body for Scientific and Technological Advice):
- Provides scientific guidance.
- Bridges IPCC reports with UNFCCC decision-making.
Key Focus in 2025
Global Goal on Adaptation (GGA)
- Originally mentioned in the Paris Agreement (2015).
- Received major progress only during COP28 (Dubai).
- Aim: Establish a global, measurable, and equitable adaptation framework, similar to the 1.5°C target for mitigation.
- Bonn 2025 focuses on operationalising this goal, especially for climate-vulnerable nations.
Importance of the Bonn Conference
- Pre-COP Platform: Decisions taken here set the tone and agenda for COP summits.
- Technical + Political Dialogue: Encourages cooperation between scientists, policymakers, and climate negotiators.
- Influences Global Climate Action: Outcomes impact the direction of global climate governance.
AviList
- 17 Jun 2025
In News:
Recently, the global ornithological and conservation community witnessed a landmark development with the launch of AviList, the first-ever unified global checklist of bird species. This effort is the culmination of four years of work by the Working Group on Avian Checklists, representing leading ornithological and conservation institutions.
About AviList:
- What is it? AviList is a comprehensive, standardized, and freely accessible global bird species checklist.
- Total Entries (2025 Edition):
- Species: 11,131
- Subspecies: 19,879
- Genera: 2,376
- Families: 252
- Orders: 46
- Replacing Previous Lists:
- International Ornithological Committee (IOC) List
- Clements Checklist
- Update Mechanism: To be updated annually
- Access and Formats:
- Available freely at www.avilist.org
- Downloadable in full or short versions in .xlsx and .csv formats.
Developed By:
Working Group on Avian Checklists, comprising representatives from:
- BirdLife International
- Cornell Lab of Ornithology
- American Ornithologists' Society
- International Ornithologists’ Union
- Avibase (Global Bird Database)
Significance and Benefits:
- Conservation and Research Clarity:
- A unified taxonomy helps prioritize conservation efforts by eliminating taxonomic inconsistencies.
- Scientists can now communicate uniformly on species classification and distribution.
- Global Standardization: Replaces multiple competing checklists, reducing confusion and ensuring consistency across countries and platforms.
- Interdisciplinary Use: Supports birdwatchers, scientists, policymakers, and conservationists in sharing data, linking platforms, and enhancing global collaborations.
- Improved Policy and Decision-Making: Aids in aligning biodiversity policies across nations by ensuring a standardized species concept.
- Technological Integration: Enables harmonization of databases and online tools like eBird, Avibase, and global biodiversity monitoring platforms.
Spartaeus karigiri
- 15 Jun 2025
In News:
A team of researchers has identified a new species of jumping spiders of the Spartaeinae subfamily in southern India, known for their intelligent hunting skills and web-invasion tactics.
Source: European Journal of Taxonomy (June 2025)
Key Facts:
- Species Name: Spartaeus karigiri
- Taxonomy:
- Family: Salticidae (Jumping Spiders)
- Subfamily: Spartaeinae
- Genus: Spartaeus
- Named After: Karigiri (Elephant Hill) in Devarayanadurga, Karnataka.
Significance:
- First recorded presence of Spartaeus and Sonoita genera in India.
- These genera were previously known only from Southeast Asia and Africa.
- Discovery expands India’s Spartaeinae spider fauna to 15 species across 10 genera.
Features of Spartaeus karigiri:
- Noted for intelligent hunting and web-invasion tactics.
- Possesses keen eyesight and mimics prey to deceive other spiders.
- Males were found in rocky crevices; females guarding egg clutches.
- Found in Karnataka and Villupuram, Tamil Nadu.
Other Findings:
- Sonoita cf. lightfooti, previously known from Africa, was also found in Karnataka.
- A taxonomic correction: Marpissa gangasagarensis (2005) is the same as Phaeacius fimbriatus (1900).
Conservation and Research Insight:
- India's arachnid diversity remains under-studied.
- New discoveries indicate rich but undocumented biodiversity in Indian terrains.
Ocean Darkening
- 16 Jun 2025
In News:
A recent study titled "Darkening of the Global Ocean", led by researchers from the University of Plymouth, has revealed that over 21% of the global ocean has darkened between 2003 and 2022, marking a significant environmental concern. The phenomenon, known as ocean darkening, is increasingly disrupting marine ecosystems and global climate regulation.
What is Ocean Darkening?
Ocean darkening refers to the reduction in the photic zone — the upper layer of the ocean (up to ~200 meters deep) where sunlight penetrates to support photosynthesis. This zone is foundational to:
- ~90% of marine biodiversity
- Climate regulation
- Ocean productivity
- Global fisheries
The study used satellite data and modeling based on the Diffuse Attenuation Coefficient (Kd 490), which measures how rapidly light fades through seawater. It found:
- 21% of global oceans experienced darkening in two decades.
- 9% saw photic depth decline by over 50 meters.
- 2.6% saw a reduction exceeding 100 meters — an area roughly equal to the size of Africa.
Geographic Distribution
- High darkening: Arctic, Antarctic, Gulf Stream, North Sea, eastern UK coast.
- Lesser darkening or even brightening: Some parts of the English Channel.
- The open ocean and climate-sensitive zones have witnessed the most pronounced declines.
Causes of Ocean Darkening
- Coastal Zones:
- Runoff of agricultural nutrients, organic matter, and sediments.
- Leads to algal blooms that block sunlight.
- Open Ocean:
- Shifts in plankton dynamics
- Rising sea surface temperatures
- Altered ocean circulation patterns
These changes may be linked to climate change, land-use modifications, and increased rainfall-driven erosion.
Impact on Marine Ecosystems
Ocean darkening leads to:
- Shrinking habitats for light-sensitive species like Calanus copepods (key zooplankton and food web base).
- Disrupted feeding, migration, and reproduction cycles due to reduced solar and lunar light cues.
- Increased crowding in shallower waters, intensifying competition and predation.
- Collapse of marine food chains, even in areas with minimal fishing pressure.
Experts warn that this could represent one of the largest habitat losses in recent history, with implications for:
- Biodiversity
- Carbon cycling
- Oxygen production
- Ocean buffering against climate change
State of World Marine Fishery Resources 2025

- 14 Jun 2025
In News:
The Food and Agriculture Organization’s (FAO) 2025 Report on the State of World Marine Fishery Resources, released during the UN Ocean Conference (UNOC3) in Nice, France, offers a comprehensive assessment of global fish stock sustainability, regional disparities, and governance challenges.
Key Findings:
- Global Sustainability: 64.5% of marine fishery stocks are fished within biologically sustainable levels, indicating modest improvement. However, 35.5% remain overexploited.
- Deep-Sea Species Vulnerability: Only 29% of deep-sea species are sustainably harvested, largely due to biological traits like slow growth, delayed maturity, and low reproductive rates. These characteristics impair recovery from overfishing.
- Migratory Shark Concerns: Of the 23 shark stocks assessed, 43.5% are overfished, especially in the tropical Indo-Pacific where they frequently become bycatch in tuna fisheries.
- Tuna Success Story: 87% of evaluated tuna and tuna-like species are sustainably fished, a result of effective regulation by Regional Fisheries Management Organizations (RFMOs).
- Regional Disparities: The northeast and southwest Pacific show high sustainability levels, while areas such as the Mediterranean and Black Sea lag, with only 35.1% of stocks sustainably managed.
- Data Gaps: Despite high reported sustainability (72.7%) in the eastern Indian Ocean, concerns remain due to insufficient species-specific stock assessments.
Governance and Policy Challenges:
- Illegal, Unreported and Unregulated (IUU) Fishing: Continues to threaten stock sustainability. IUU encompasses:
- Illegal: Breaches of domestic or international laws.
- Unreported: Failure to report or misreport catches.
- Unregulated: Conducted by vessels operating beyond jurisdictional authority, undermining conservation efforts.
- Subsidy Prohibitions (WTO Agreement):
- Bans financial support to vessels engaging in IUU fishing.
- Restricts subsidies for overfished stocks unless recovery measures are implemented.
- Prohibits aid for fishing in unregulated high seas zones.
Critical Analysis:
Positives:
- The rise in sustainable stocks signifies improved management awareness, particularly in regulated regions like the Pacific.
- Tuna fisheries demonstrate successful use of scientific tools—catch reporting and onboard observers—under RFMOs.
- The global survey included over 600 experts across 90 nations, lending credibility and robustness.
Negatives:
- Deep-sea stocks remain acutely overfished and biologically vulnerable.
- Shark species, integral to marine food webs, continue to suffer from bycatch and poor regulatory coverage.
- Monitoring shortfalls in Southeast Asia and African coasts prevent precise biomass estimation and conservation action.
- Weaker implementation and unregulated artisanal practices challenge sustainability in Mediterranean and Black Sea regions.
Recommendations for Sustainable Fisheries Governance:
- Empower RFMOs with real-time monitoring systems, electronic catch reporting, and observer programs.
- Adopt Ecosystem-Based Approaches that integrate climate resilience and biodiversity objectives.
- Strengthen Data Infrastructure in data-deficient regions with support from international bodies like the FAO and World Bank.
- Curtail Harmful Subsidies as per WTO protocols to reduce economic incentives driving overfishing.
- Promote Community Participation through co-management strategies and the development of Marine Protected Areas (MPAs).
Rediscovery of the Eurasian Otter in Kashmir
- 12 Jun 2025
In News:
After being presumed extinct in the Kashmir Valley for nearly three decades, the Eurasian otter (Lutra lutra) has been spotted again in the Lidder River in Srigufwara, South Kashmir. This rare sighting rekindles hope for the revival of the Valley’s aquatic biodiversity.
About Eurasian Otter:
- Common Names: Eurasian otter, European otter, Common otter, Old-World otter
- Local Name in Kashmir: Vuder
- Type: Semi-aquatic carnivorous mammal
- Distribution:
- Widely spread across Europe, the Middle East, Northern Africa, and Asia (from Eastern Russia to China).
- In India, found in northern, northeastern, and southern regions.
- In Kashmir, historically abundant in Dal Lake, Dachigam streams, Rambiara stream, and the Lidder River.
Habitat & Features:
- Habitat:
- Occupies diverse freshwater and coastal ecosystems—lakes, rivers, marshes, swamp forests, and mountain streams.
- In the Indian subcontinent, prefers cold hill and mountain waters.
- Physical Traits & Adaptations:
- Sleek brown fur (lighter underneath), long streamlined body, short legs, and thick tail.
- Aquatic adaptations:
- Webbed feet
- Ability to close ears and nostrils underwater
- Dense fur trapping air for insulation
- Excellent vision, hearing, and olfactory senses.
- Behavior: Elusive, solitary, and primarily nocturnal.
Conservation Concerns:
- Primary Threats:
- Water pollution degrading habitats
- Hunting for fur, historically significant in Kashmir
- Conservation Status:
- IUCN Red List: Near Threatened
- Wildlife Protection Act, 1972 (India): Schedule II
- CITES: Appendix I
Blue NDC Challenge
- 12 Jun 2025
In News:
At the Third United Nations Ocean Conference (UNOC3) held in Nice, France (June 9–13, 2025), Brazil and France launched the Blue NDC Challenge — a major international initiative to integrate ocean-based climate solutions into Nationally Determined Contributions (NDCs) under the Paris Agreement, in the lead-up to UNFCCC COP30, to be held in Belem, Brazil.
What is the Blue NDC Challenge?
The Blue NDC Challenge is a multilateral climate action initiative urging countries to incorporate ocean-centric measures into their updated NDCs. It aims to enhance climate mitigation and adaptation by recognizing the vital role of oceans and coastal ecosystems in addressing the climate crisis.
- Launched by: Brazil and France
- Platform: UNOC3 (June 2025)
- Target: Updated NDCs due for 2035 (deadline: February 10, 2025)
Participating Countries (as of June 2025):
- Founding: Brazil, France
- Joined: Australia, Fiji, Kenya, Mexico, Palau, Seychelles
Objectives and Key Features:
- Ocean-Integrated NDCs
- Include marine ecosystems, coastal zones, mangroves, coral reefs, and salt marshes in national climate plans.
- Integrate Marine Spatial Planning (MSP) and Integrated Coastal Zone Management (ICZM).
- Sustainable Blue Economy
- Promote climate-resilient fisheries and carbon-smart aquaculture.
- Expand clean ocean energy: offshore wind, wave, and tidal power.
- Decarbonization and Adaptation
- Phase out offshore oil and gas projects.
- Reduce emissions in shipping, seafood value chains, and coastal infrastructure.
- Boost resilience in maritime sectors vulnerable to climate risks.
- Restoration and Conservation
- Focus on the restoration of mangroves, salt marshes, and coral reefs—which are effective carbon sinks and natural buffers against sea-level rise.
- Global Partnerships and Support Mechanisms
- Supported by:
- Global Mangrove Alliance
- UN High-Level Climate Champions
- World Resources Institute (WRI)
- Ocean Breakthroughs (Marrakech Partnership for Global Climate Action)
- Supported by:
Significance and Leadership:
- Brazil’s Climate Leadership
- Brazil’s 2035 NDC (submitted in November 2024) includes, for the first time, a dedicated Ocean and Coastal Zones component.
- Brazil is also investing in marine conservation, supported by a $6.8 million fund from Bloomberg Philanthropies (June 8, 2025).
- Expert Insights:
- Mangroves sequester carbon 10 times faster than terrestrial forests.
- Including oceans in NDCs can unlock greater political and financial support, according to Conservation International and WRI.
- Emission Reduction Potential:
- According to WRI, ocean-based solutions can contribute up to 35% of the global emissions reduction needed to stay within the 1.5°C limit.
Relevance for India and the World:
- With India’s vast coastline and diverse marine ecosystems, incorporating ocean-based climate actions into its NDCs could enhance climate resilience, especially for coastal communities.
- Global focus on oceans marks a shift towards holistic climate policy, integrating land, sea, and people-centric approaches.
Discovery of Spathaspina noohi
- 11 Jun 2025
In News:
A significant addition to India's rich biodiversity has emerged from the forests of Meghalaya with the discovery of a new beetle species, Spathaspina noohi. This unique species not only adds to the biological inventory of the region but also necessitated the creation of an entirely new genus, highlighting the ecological and taxonomic uniqueness of the organism.
Location of Discovery
- The beetle was found in the Umran area of Ri Bhoi district, Meghalaya.
- Elevation: 781 metres above sea level.
- The discovery was made by S. S. Anooj, entomologist from Kerala Agricultural University, and formally described by B. Ramesha in the international journal Zootaxa.
Taxonomic Significance
- Spathaspina noohi belongs to the Curculionidae family, commonly known as weevils, which includes over 60,000 species globally.
- Due to a highly distinctive sword-like spine on its back, it was classified under a new genus—Spathaspina, a name derived from Latin:
- Spatha = sword
- Spina = spine
Subfamily and Tribe Characteristics
- The beetle falls under the Ceutorhynchinae subfamily, which includes about 1,300 species worldwide.
- The subfamily is characterized by:
- Compact, robust body
- Ability to tuck their snout (rostrum) between the front legs when resting
- A visible back structure (mesanepimera)
- Within this subfamily, the beetle is linked to the tribe Mecysmoderini, comprising 8 genera and 107 species. This tribe is noted for its thoracic spines and specialized antenna structures, mostly found in South and Southeast Asia.
Ecological Role of Weevils
While many weevils are considered agricultural pests, others, including Spathaspina noohi, play vital ecological roles such as:
- Controlling invasive plant species
- Maintaining ecosystem balance
Geographical Distribution of Ceutorhynchinae
- These beetles are present across most continents except:
- New Zealand
- Oceania
- Antarctica
- Southern parts of South America
- Their highest diversity is noted in the Palaearctic Region (Europe, North Africa, parts of Asia), followed by the Oriental Region (South and Southeast Asia).
Commemorative Naming
The species is named in honour of P. B. Nooh, IAS, Director of Tourism, Government of Kerala. This acknowledges his contribution to eco-tourism and sustainable development, symbolizing the interconnection between biodiversity conservation and responsible tourism.
Myotis himalaicus

- 10 Jun 2025
In News:
A new bat species, the Himalayan Long-Tailed Myotis (Myotis himalaicus), has been described based on fieldwork in Uttarakhand and historical specimens from Pakistan. Published in Zootaxa journal by a team of Indian and international scientists.
Key Findings of the Study
- Study Area: Western Himalayas – Himachal Pradesh & Uttarakhand (2017–2021).
- Total Bat Species Documented: 29, including new records and confirmations.
- Raises India's bat species count to 135.
About Himalayan Long-Tailed Myotis (Myotis himalaicus)
Feature Description
Family/Genus Belongs to the Myotis frater complex
Habitat Deodar, pine, and cedar forests on southern Himalayan slopes
Distribution Found in Uttarakhand (India) and Khyber Pakhtunkhwa (Pakistan)
Size Medium-sized (~3.5 inches, <1 oz)
Morphology Delicate feet, long thumbs with short claws, short ears, fine teeth
Conservation Status Recently described; appears rare
Other Major Additions/Clarifications
- East Asian Free-Tailed Bat (Tadarida insignis):
- First confirmed record in India.
- Extends known range eastward by 2,500 km.
- Earlier misidentified as Tadarida teniotis.
- Babu’s Pipistrelle (Pipistrellus babu):
- Revalidated as a distinct species, not a synonym of Javan pipistrelle.
- Distribution: Pakistan, India, Nepal.
- First specimen-based confirmations in India for:
- Savi’s pipistrelle (Hypsugo savii)
- Japanese greater horseshoe bat (Rhinolophus nippon)
Ecological Importance of Bats
- Insect Control: Consume pests and mosquitoes.
- Pollination & Seed Dispersal: Important for forest regeneration.
- Fertilizer Contribution: Bat guano rich in Nitrogen & Phosphorous; boosts crop yield.
Stratospheric Aerosol Injection (SAI)
- 10 Jun 2025
In News:
A study recently published in the journal Earth’s Future offered an innovative approach to SAI technique that could reduce its costs but also bring it closer to fruition despite the opposition to it.
What is Stratospheric Aerosol Injection (SAI)?
- SAI is a proposed solar geoengineering technique to cool the Earth by injecting reflective aerosols (e.g. sulphur dioxide) into the stratosphere to reflect sunlight and reduce surface temperatures.
- Inspired by volcanic eruptions, like Mount Pinatubo (1991), which naturally cooled the Earth by emitting aerosols.
Recent Study Highlights (June 2025)
- Published in Earth’s Future journal.
- Led by Alistair Duffey, University College London.
- Used UK Earth System Model 1 (UKESM1) for climate simulations.
Key Findings
- Injecting 12 million tonnes of sulphur dioxide annually at 13 km altitude (spring/summer in each hemisphere) could cool the Earth by ~0.6°C.
- To cool by 1°C, ~21 million tonnes/year are needed at that altitude.
- Only 7.6 million tonnes/year are needed at higher altitudes (subtropics) for the same cooling.
Innovative Proposal
- Low-altitude SAI using modified existing aircraft (e.g. Boeing 777F) instead of specially designed high-altitude aircraft:
- Stratosphere is lower near poles (12–13 km), so current aircraft can reach it.
- Cost-effective and faster to deploy than high-altitude (~20 km) methods.
- Could begin within years, rather than a decade-long wait for new aircraft.
Risks and Concerns
- Tripling aerosol quantity (in low-altitude strategy) raises:
- Ozone depletion
- Acid rain
- Altered weather patterns
- Uneven global effects (benefits poles more, tropics less)
- Moral hazard: may reduce incentives to cut emissions.
- Governance challenge: One country’s action impacts all nations → risk of geopolitical conflict.
Why it matters
- Global GHG emissions are still rising.
- Climate mitigation through decarbonisation is slow and politically vulnerable.
- Technologies like SAI offer a stopgap, but not a substitute for emission cuts.
Tamhini Wildlife Sanctuary

- 10 Jun 2025
In News:
The Maharashtra Forest Department partnered with Microsoft and Pune-based CYDA (Centre for Youth Development and Activities) to address the eco-restoration project in the Tamhini Wildlife Sanctuary.
Location & Geography:
- Situated in the Western Ghats, about 70 km from Pune, Maharashtra.
- Notified as a Wildlife Sanctuary in January 2013.
- Spread over 49.62 sq. km, comprising:
- 12 forest compartments from Paund and Sinhgad ranges (Pune forest division).
- 8 compartments from Mangaon range (Roha division, Thane).
Vegetation Types:
- Dominated by evergreen, semi-evergreen, and moist deciduous forests.
- Rich floral diversity including teak, bamboo, Ain, Shisham, mango, and jamun.
Biodiversity Highlights:
- Mammals (28 species):
- Includes the Indian Giant Squirrel (Shekaru) – state animal of Maharashtra.
- Also hosts Indian pangolin, barking deer, Indian civet, and wild boar.
- Home to the Kondana Soft-furred Rat (Millardia kondana) – an endangered species.
- Birds (150 species):
- Notable species: Malabar whistling thrush, golden oriole, crested serpent eagle, Indian pitta, grey junglefowl.
- Includes 12 species endemic to India.
- Insects & Others:
- 72 species of butterflies, 18 reptile species, and 33 invertebrate species.
Ecological Importance:
- Part of the Western Ghats, a globally recognized biodiversity hotspot.
- Habitat for rare, endemic, and threatened species.
- Supports vital ecosystem services, aiding in climate regulation, water conservation, and pollination.
Recent Conservation Initiative:
- A collaborative eco-restoration project was launched by the Maharashtra Forest Department, Microsoft, and CYDA (Centre for Youth Development and Activities), Pune.
- Aim: Address socio-ecological challenges, promote community engagement, and leverage technology in conservation.
Eco-tourism Potential:
- Features popular trekking and nature spots like Andharban forest, Plus Valley, and Devkund.
- Attracts high tourist footfall, especially during monsoon, including bird watchers and nature enthusiasts.
Ranthambore Tiger Reserve
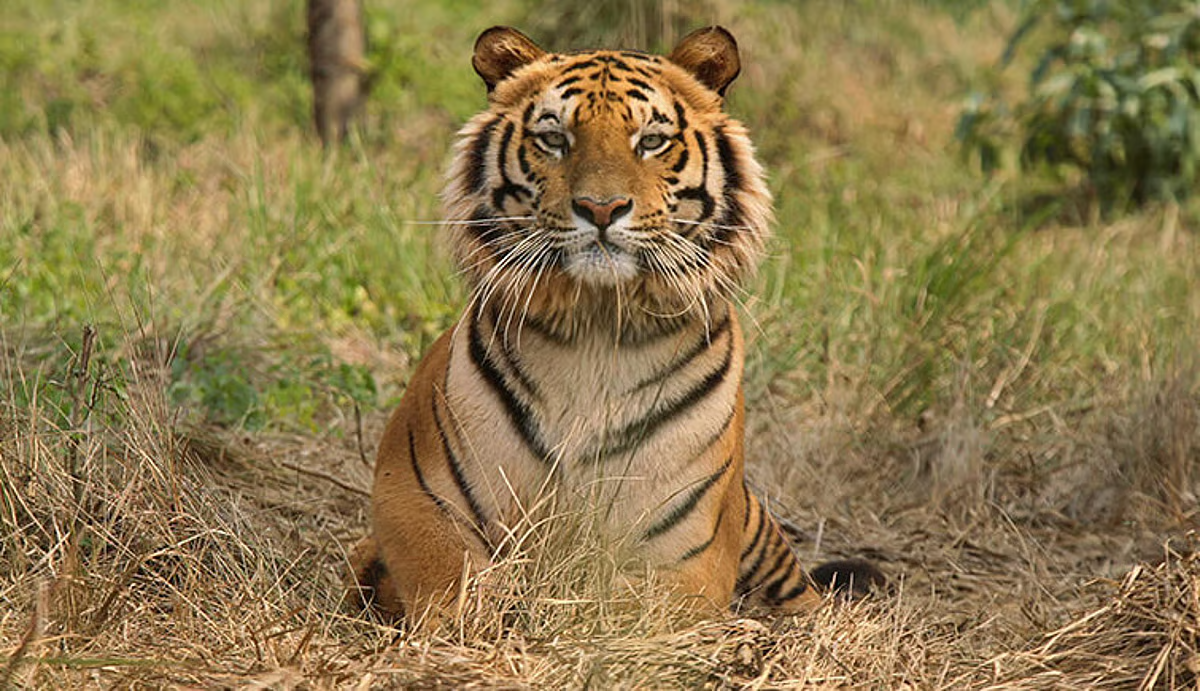

- 09 Jun 2025
In News:
The Supreme Court of India has recently ordered the Rajasthan government to impose an immediate ban on all mining activities within the core area of the Ranthambore Tiger Reserve, citing concerns over wildlife protection and habitat preservation.
About Ranthambore Tiger Reserve
- Location: Sawai Madhopur district, southeastern Rajasthan.
- Named After: Ranthambore Fort, a UNESCO World Heritage Site, located within the reserve.
- Geographical Boundaries:
- North: Bounded by the Banas River
- South: Bounded by the Chambal River
- Terrain: High rocky plateaus, valleys, rivers, lakes, and historic ruins including forts and mosques.
- Total Area: ~1,411 sq.km, making it one of the largest tiger reserves in northern India.
- Surrounding Ranges: Located at the confluence of the Aravalli and Vindhya hill ranges.
Ecology and Biodiversity
Vegetation: Dominated by dry deciduous forests and open grassy meadows.
- Flora:
- Predominantly Dhok tree (Anogeissus pendula).
- Other species: Acacia, Capparis, Zizyphus, Prosopis, etc.
Water Bodies:
- Important lakes include:
- Padam Talab
- Raj Bagh Talab
- Malik Talab
Fauna:
- Apex predator: Royal Bengal Tiger
- Other mammals:
- Leopard, Caracal, Jungle Cat
- Sambar, Chital, Chinkara, Wild Boar
Historical Significance: Previously served as the royal hunting grounds of the Maharajas of Jaipur.
Rediscovery of Losgna Genus in India
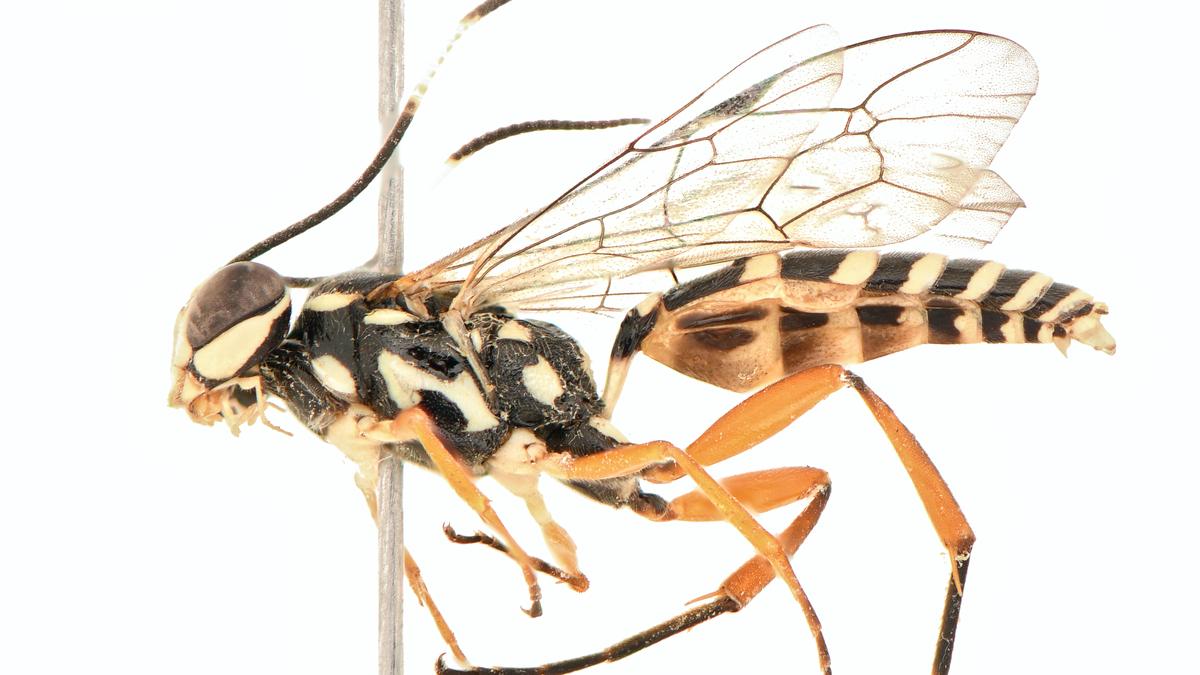

- 08 Jun 2025
In News:
At a time when habitat loss and climate change threaten countless species, the discovery of a new species of parasitic wasp - named ‘Losgna Occidentalis’ from Chandigarh has drawn attention to the unexplored richness of India’s biodiversity.
Location of Discovery
- Place: Chandigarh, Union Territory of India
- Habitat: Urban dry scrub forest
- Time: Winter of 2023–24
- Significance: First formal description of any insect species from Chandigarh
Species Description
- Name: Losgna occidentalis
- Genus: Losgna (Ichneumonidae family – Parasitic wasps)
- Group Role: Parasitic wasps known for laying eggs inside/on arthropod hosts
- Ecological Role: Pollinators and biological control agents (important in ecosystems)
Historical Context
- Losgna genus was last recorded in India in 1965, in Heinrich’s monograph
- No Indian records or specimens existed post-1965 in any institution
- Only known specimens (of other Losgna species) are preserved in:
- Natural History Museum, London
- The Hope Collection, Oxford University
- Zoologische Staatssammlung München, Germany
Naming Rationale
- "Occidentalis" (Latin for "Western")
- Signifies the westernmost known range of the genus
- Earlier Losgna records were only from:
- Northeast India
- Southeast Asia (tropical forests)
- Published in Zootaxa (peer-reviewed journal for animal taxonomy)
Importance & Implications
- Rediscovery highlights India’s hidden and threatened biodiversity
- Emphasizes the critical role of taxonomy in conservation
- Shows potential for citizen-led discoveries and backyard biodiversity
- Demonstrates the need for:
- Responsible specimen collection
- International scientific collaboration
- Support for underfunded taxonomy sectors
Indian Giant Flying Squirrel
- 13 Apr 2025
In News:
A rare sighting of the Indian Giant Flying Squirrel (Petauristaphilippensis) has been reported in Ranikhet, a hill station in Uttarakhand, highlighting the ecological richness of the region.
About Indian Giant Flying Squirrel
Feature Description
Scientific Name Petauristaphilippensis
Size Body length: 30–45 cm; Tail length: up to 60 cm
Appearance Rufous coat, grey underparts, large eyes, and a gliding membrane from wrist
to ankle
Locomotion Glides up to 60 meters between trees using patagium (gliding membrane)
Habitat and Distribution
- Found in tropical and subtropical forests across central and southern India
- Inhabits evergreen, semi-evergreen, and deciduous forests, especially near forest edges
- Recent sighting in Uttarakhand indicates possible range expansion or overlooked presence
Ecological Role
- Diet: Fruits, nuts, leaves, and bark
- Acts as a seed disperser, supporting forest regeneration
- Considered a keystone species due to its ecological significance
Behavioural Traits
- Nocturnal and arboreal
- Emits alarm calls upon detecting predators like owls
- Active at night, gliding from tree to tree in search of food
Conservation Status
Category Status
IUCN Red List (Global) Least Concern
IUCN Status (India) Near Threatened (due to habitat loss)
Wildlife Protection Act, 1972 Schedule II
Threats
- Habitat loss and fragmentation
- Deforestation and degradation of forest corridors
- Increasing human encroachment in forested landscapes
Kerala Researchers win International Grant for Hornbill Conservation
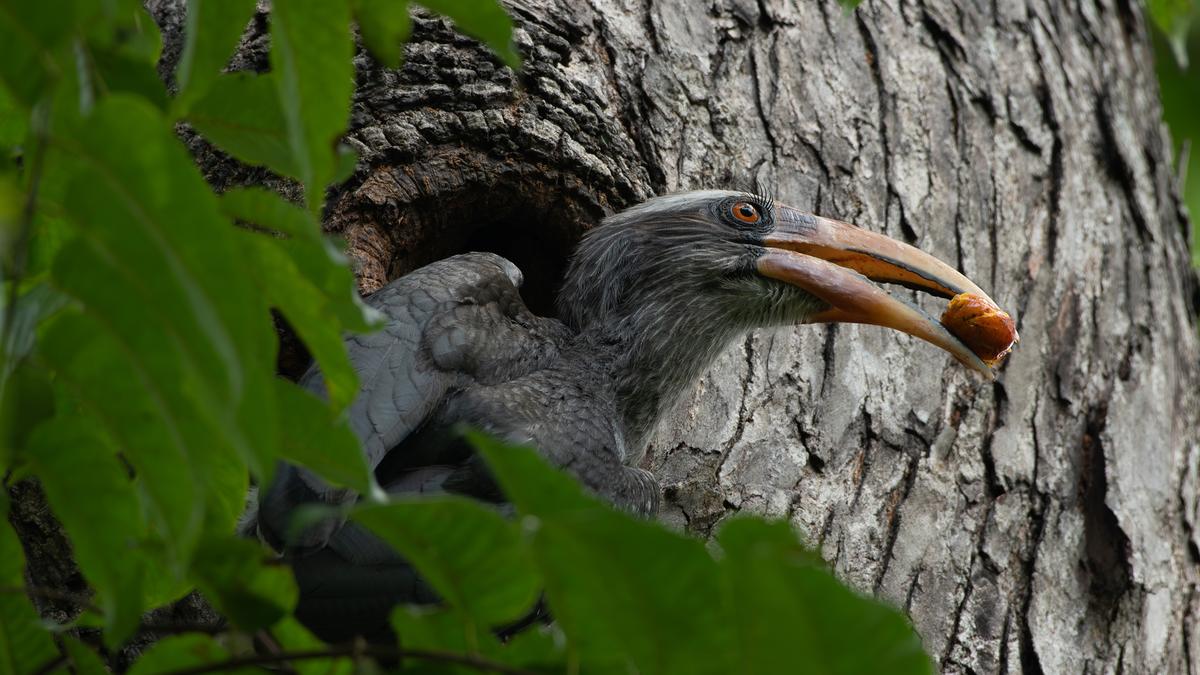

- 13 Apr 2025
In News:
A team of young researchers from Kerala has won the prestigious Future Conservationist Award by the Conservation Leadership Programme (CLP) for their community-driven project on conserving the Malabar Grey Hornbill in Wayanad.
About Malabar Grey Hornbill (Ocyceros griseus)
- Status: Vulnerable (IUCN Red List)
- Legal Protection: Schedule IV of the Wildlife Protection Act, 1972
- Endemic to: Western Ghatsand parts of the Nilgiris, Wayanad, and Anamalai Hills in Southern India.
- Habitat: Evergreen forests, plantations, and agricultural landscapes
- Ecological Importance: Cavity-nesting frugivore, plays a key role in seed dispersal
- Nesting Behavior:
- Nests in secondary cavities (e.g., old woodpecker hollows)
- Reuses the same nesting cavity for years
- Dependent on cavity-bearing trees, often outside protected areas
About the Future Conservationist Award (CLP)
- Awarded By:
- Fauna & Flora International
- BirdLife International
- Wildlife Conservation Society
- Purpose: Supports early-career conservationists with funding and mentorship
- Focus Areas: Field conservation, community engagement, biodiversity monitoring
Indian Star Tortoise
- 12 Apr 2025
In News:
In a significant conservation achievement under the Turtle Rehabilitation Project (TRP), 340 Indian Star Tortoises were successfully released into the wild at Jogapur Reserve Forest, located in Chandrapur district, Maharashtra.
Indian Star Tortoise (Geochelone elegans)
- IUCN Status:Vulnerable
- CITES Listing:Appendix I
- Protection under Indian Law:Schedule I, Wildlife (Protection) Act, 1972
Habitat & Range:
- Native to Northwest India, Southern India, and Sri Lanka
- Prefers arid and semi-arid ecosystems including scrublands, dry forests, grasslands, and semi-deserts
Key Characteristics:
- Recognizable by the radiating star-like patterns on its domed shell
- Faces high poaching pressure due to demand in the illegal exotic pet trade
- Exhibits crepuscular behavior (most active during dawn and dusk)
- Primarily herbivorous, consuming grasses, flowers, and leafy vegetation
Turtle Rehabilitation Project (TRP): A Conservation Initiative
- Launched: Late 2024; witnessed a major release event in April 2025
- Implemented By: Maharashtra Forest Department in collaboration with RESQ Charitable Trust
Objectives:
- Rescue and rehabilitate illegally trafficked tortoises and turtles
- Facilitate safe reintroduction into natural habitats through:
- Medical treatment
- Acclimatization to wild conditions
- Biometric tracking for post-release monitoring
- Raise public awareness via community engagement and school outreach
Blue Washing of Polluting Industries
- 12 Apr 2025
In News:
- The Central Pollution Control Board (CPCB) has recently introduced a new ‘Blue Category’ for industries under its Essential Environmental Services (EES) framework.
- Notably, Waste-to-Energy (WTE) incineration plants, previously classified as highly polluting ‘Red Category’ industries, have now been controversially reclassified under this new category.
Background: Pollution Index (PI) and Industry Categorisation
- The Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change (MoEFCC) classifies industries into categories — White, Green, Orange, and Red — based on a Pollution Index (PI) (0–100 scale).
- White (0–20): Least polluting
- Green (21–40)
- Orange (41–59)
- Red (60–100): Most polluting
- WTE plants, with a PI of 97.6, were originally in the Red Category.
What is the new Blue Category?
- Created under Essential Environmental Services (EES) classification.
- Grants 2 additional years of “Consent to Operate” (essentially, consent to pollute).
- Aims to support infrastructure like composting units, biogas plants, material recovery facilities, etc
Controversy: WTE Incineration in the Blue Category
- WTE plants burn unsegregated municipal solid waste (MSW) to generate electricity by producing steam to drive turbines.
- Unlike claimed benefits, WTE plants emit more CO? per unit of electricity than coal-fired plants, contributing to climate change.
- CPCB’s inspection reports found that Delhi’s WTE plants exceeded emission norms, releasing carcinogens and other pollutants such as:
- SOx, NOx, HCL, PM, Dioxins, and Furans
- In FY 2022–23, Delhi’s WTE plants incinerated ~735,840 tons of plastic, contributing significantly to Delhi’s poor air quality.
- These plants also generate hazardous ash, requiring secure landfill disposal.
Issues with Reclassification
- The CPCB’s own guidelines state that:
- Only projects that do not emit hazardous waste or
- Projects that promote the circular economy can be blue-listed.
- However, leading government institute CSIR-NEERI has observed that WTE plants violate the principles of the circular economy and contravene Solid Waste Management Rules, 2016.
- Reclassification undermines environmental safeguards, harms waste pickers’ livelihoods, and imposes financial burdens on Urban Local Bodies (ULBs).
Arctic Biome: From Carbon Sink to Carbon Source

- 11 Apr 2025
Context:
- The Arctic biome, primarily a treeless tundra, spans approximately 11.5 million km² and includes regions in Canada, Greenland, Iceland, and Eurasia.
- It is characterized by permafrost (permanently frozen ground) close to the surface, limiting plant root growth.
- Vegetation consists of grasses, lichens, mosses, and low shrubs, while fauna includes polar bears, arctic foxes, caribou, musk ox, and migratory birds like snow geese.
- Climatic conditions are harsh, with temperatures ranging from -60°C in winter to 15.5°C in summer, and annual precipitation between 150–250 mm, mostly as snow.
- Despite nutrient-poor soils, the biome has functioned as a major carbon sink by storing carbon in peat and humus.
The Arctic Boreal Zone (ABZ) and Carbon Dynamics
The Arctic Boreal Zone (ABZ), which includes tundra, coniferous forests, and wetlands, has historically played a crucial role in global carbon sequestration. Its coniferous forests form the largest land-based biome on Earth.
However, recent studies, including one in Nature Climate Change (2025), indicate that over 30% of the ABZ has shifted from being a carbon sink to a carbon source. This reversal is primarily driven by:
- Permafrost thawing: Warmer topsoil temperatures lead to decomposition of organic matter, releasing CO? and methane.
- Frequent and intense wildfires: These burn organic-rich soils, releasing large volumes of carbon.
This transition creates a positive feedback loop: Wildfires release carbon → global temperatures rise → permafrost thaws → more emissions → more fires.
Fire Trends and Global Impact
Data from the Copernicus Atmosphere Monitoring Service (CAMS) reveal that wildfires released 800,000 tonnes of carbon in January 2025 alone, nearly 4 times more than in the same period a decade ago.
Key wildfire incidents include:
- Texas and Oklahoma (USA): Destroyed 14,000+ structures, burned 16,000 hectares, and displaced thousands.
- Ofunato City (Japan): One of the country’s largest fires in 50 years, affecting nearly 2,900 hectares.
According to the India State of Forest Report (Dec 2024):
- Uttarakhand recorded the highest number of forest fires (5,315 fires) between Nov 2022–June 2023.
- However, fire hotspots are declining: 2.23 lakh (2021–22) → 2.12 lakh (2022–23) → 2.03 lakh (2023–24).
India’s Changing Fire and Climate Profile
Research by IIT Kharagpur and the Indian Institute of Tropical Meteorology shows that land temperatures in northwest, northeast, and central India are rising by:
- 0.1–0.3°C/decade (pre-monsoon)
- 0.2–0.4°C/decade (post-monsoon)
This trend has led to earlier, longer, and slower-moving heatwaves, increasing wildfire vulnerability. India emits an estimated 69 million tonnes of CO? annually from forest fires.
Key Findings from the 2024 Arctic Report Card (NOAA)
The U.S. National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) confirms that the Arctic tundra is becoming a carbon source, exacerbated by fossil fuel pollution and recurrent wildfires. According to NOAA, this shift reflects persistent, long-term climate trends, not mere variability.
A global study of 200 monitoring sites (1990–2020) found:
- Alaska contributed 44% of the ABZ’s new carbon emissions.
- Northern Europe and Siberia added 25% and 13%, respectively.
- Non-summer months now emit more carbon than the entire summer absorption.
Historical fire events like the 2003 Siberian fires and the 2012 Timmins fire (Canada) significantly accelerated this trend.
Greater Flamingo Sanctuary

- 07 Jun 2025
In News:
On the occasion of World Environment Day 2025, the Tamil Nadu government officially declared the Greater Flamingo Sanctuary at Dhanushkodi, Ramanathapuram district, aiming to protect a vital stopover site for migratory birds along the Central Asian Flyway.
Key Highlights
What is it?
A newly notified wildlife sanctuary dedicated to safeguarding migratory wetland birds, especially the greater flamingo (Phoenicopterus roseus), in their natural resting and breeding habitat.
Location and Area:
- Located in Rameshwaram taluk, Ramanathapuram district, Tamil Nadu.
- Covers approximately 524.7 hectares of revenue and forest land.
- Lies within the Gulf of Mannar Biosphere Reserve, a globally recognized marine ecosystem.
Ecological Significance
- Functions as a critical site along the Central Asian Flyway, one of the key migratory bird routes.
- As per the 2023–24 Wetland Bird Survey, the region hosts 10,700+ wetland birds representing 128 species, including:
- Flamingos (greater and lesser)
- Herons, egrets, sandpipers, etc.
- The sanctuary harbours diverse ecosystems, such as:
- Mangroves (Avicennia, Rhizophora)
- Mudflats, marshes, sand dunes, and lagoons
- Nesting grounds for sea turtles and marine biodiversity
Conservation and Socioeconomic Benefits
- Strengthens coastal resilience by preventing erosion through natural mangrove buffers.
- Promotes responsible ecotourism, raising awareness of wetland and avian conservation.
- Supports local livelihoods via employment in conservation and tourism activities.
About the Greater Flamingo (Phoenicopterus roseus)
Attribute Details
Size 90–150 cm tall, long necks and legs
Coloration Pink hue from carotenoid-rich diet
Feeding Uses specialized downward-curved bill for filter feeding in shallow waters
Reproduction Builds cone-shaped mud nests, lays 1–2 eggs, both parents incubate
Chick Rearing Chicks are white and fed through regurgitation
Social Traits Highly gregarious, breeds in large colonies and flies in V-formations
Behavioral Note Often seen standing on one leg, possibly to conserve body heat
EnviStats India 2025
- 06 Jun 2025
In News:
India's annual mean temperature rise up from 25.05°C in 2001 to 25.74°C in 2024, Electricity generation from renewable sources increased more than three times in 10 years.
- Released by: Ministry of Statistics and Programme Implementation (MoSPI) on June 5, 2025, on the occasion of World Environment Day
- Framework Used: UN's Framework for the Development of Environment Statistics (FDES 2013)
Key Highlights:
Climate Trends
- Annual Mean Temperature rose from 25.05°C (2001) to 25.74°C (2024).
- 2024 recorded as India’s hottest year since 1901; also, globally the hottest year in 175 years.
- Annual Minimum and Maximum Temperatures (2021–24):
- Minimum: 19.32°C → 20.24°C
- Maximum: 30.78°C → 31.25°C
Rainfall Patterns
- Rainfall shows seasonal concentration between June–September, with signs of shifting patterns such as late onset or extended rains into October.
- No clear long-term trend, reflecting erratic monsoonal behaviour.
Energy Generation
Thermal & Renewable Power (2013–14 to 2023–24)
- Thermal: 7.92 lakh GWh → 13.26 lakh GWh
- Renewable: 65,520 GWh → 2.25 lakh GWh, over 3x increase in renewable energy output in a decade.
Biodiversity and Faunal Statistics
Faunal Diversity
- Global Faunal Species: 16,73,627
- India's Share: 1,04,561 species
- Habitat-specific Species in India:
- Soil Ecosystem: 22,404
- Freshwater Ecosystem: 9,436
- Mangrove System: 5,023
- Estuarine Ecosystem: 3,383
- Marine Fauna (India): 20,613 out of global 2,47,605
Fisheries Production
Inland vs. Marine Fish (2013–14 to 2023–24)
- Inland Fish Production: 61 lakh tonnes → 139 lakh tonnes
- Marine Fish Production: 34 lakh tonnes → 45 lakh tonnes
Public Expenditure (2021–22)
- Environment Sustainability Sector: ?2,433 crore (highest among sectors)
- Conservation of Natural Resources: Increasing trend
- Agro-Forestry: Lowest allocation
New Data indicators introduced
- Ramsar sites
- Access to sanitation
- Transport infrastructure
- Electricity access
Kichan and Menar Wetlands
- 05 Jun 2025
In News:
Recently, the Union Ministry of Environment announced that Kichan (Phalodi) and Menar (Udaipur) wetlands in Rajasthan have been recognized as Ramsar Sites, bringing India’s total to 91 Ramsar-designated wetlands—the highest in Asia.
About Menar Wetland:
- A freshwater monsoon wetland complex in Udaipur district, Rajasthan.
- Formed by three primary ponds: Braham Talab, Dhand Talab, and Kheroda Talab; the latter two are connected by flooded agricultural land during the monsoon.
- Habitat for endangered and migratory birds such as:
- Critically Endangered: White-rumped vulture (Gyps bengalensis), Long-billed vulture (Gyps indicus)
- Other species: Himalayan griffon, Egyptian vulture, Dalmatian pelican, Ferruginous pochard, Black-tailed godwit
- Home to over 70 plant species, including mango trees (Mangifera indica) that host colonies of Indian flying foxes (Pteropus giganteus).
- Community-led conservation: Menar village residents prevent poaching and fishing, earning it the title "Bird Village".
About Kichan Wetland:
- Located in Phalodi, Jodhpur, in the northern Thar Desert of Rajasthan.
- Comprises:
- Ratri Nadi (river)
- Vijaysagar Talab (pond)
- Riparian and scrub habitats
- Notable for supporting drought-resistant flora and over 150 bird species.
- Globally known for hosting over 22,000 migratory demoiselle cranes (Anthropoides virgo) each winter.
- A hub for birdwatchers, tourists, scientists, and students.
Ramsar Convention Overview:
- An intergovernmental treaty for the conservation of wetlands, signed in 1971 in Ramsar, Iran.
- Headquartered in Gland, Switzerland.
- Wetlands listed under the convention are known as Ramsar Sites—of international importance.
- Member countries (Contracting Parties) commit to identifying and protecting these wetlands.
World Environment Day 2025
- 05 Jun 2025
In News:
Every year on June 5, people across the globe unite to celebrate World Environment Day, an initiative led by the United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP).
Key Highlights:
- Observed on: June 5 annually
- Initiated by: United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP)
- First celebrated: 1973 (following the 1972 Stockholm Conference on the Human Environment)
- Objective: Promote global awareness and action for environmental protection
Theme for 2025: "Beat Plastic Pollution"
- Focuses on the escalating crisis of plastic pollution and its adverse impact on ecosystems, wildlife, and human health.
- Highlights the need to transition away from single-use plastics, promote sustainable consumption, and adopt eco-friendly alternatives.
Key Statistics:
- Plastic production: Increased from 2 million tonnes (1950) to 430 million tonnes (2025)
- Marine pollution:19–23 million tonnes of plastic enter aquatic ecosystems annually
- Microplastics detected in oceans, mountains, and the human body
Host Country for 2025: Republic of Korea
- Chosen for its leadership in green innovation and sustainable practices.
- Initiatives include:
- Advanced waste segregation and recycling systems
- Bans on single-use plastics in major outlets
- Promotion of tech-driven eco-solutions
By hosting, South Korea aims to showcase scalable models for combating plastic pollution globally.
Historical Background
- Stockholm Conference 1972 laid the foundation for modern environmental governance.
- UNEP assigns a theme and host country annually to align global action.
- Over 150 countries now participate through:
- Clean-up drives
- Tree plantation campaigns
- Policy forums
- Environmental education programs
Significance
World Environment Day plays a vital role in:
- Raising awareness on climate change, pollution, deforestation, and sustainability
- Encouraging individual and community-level action
- Facilitating policy dialogue and regulatory reform
- Mobilizing youth leadership in environmental movements
Caspian Gull (Laruscachinnans)
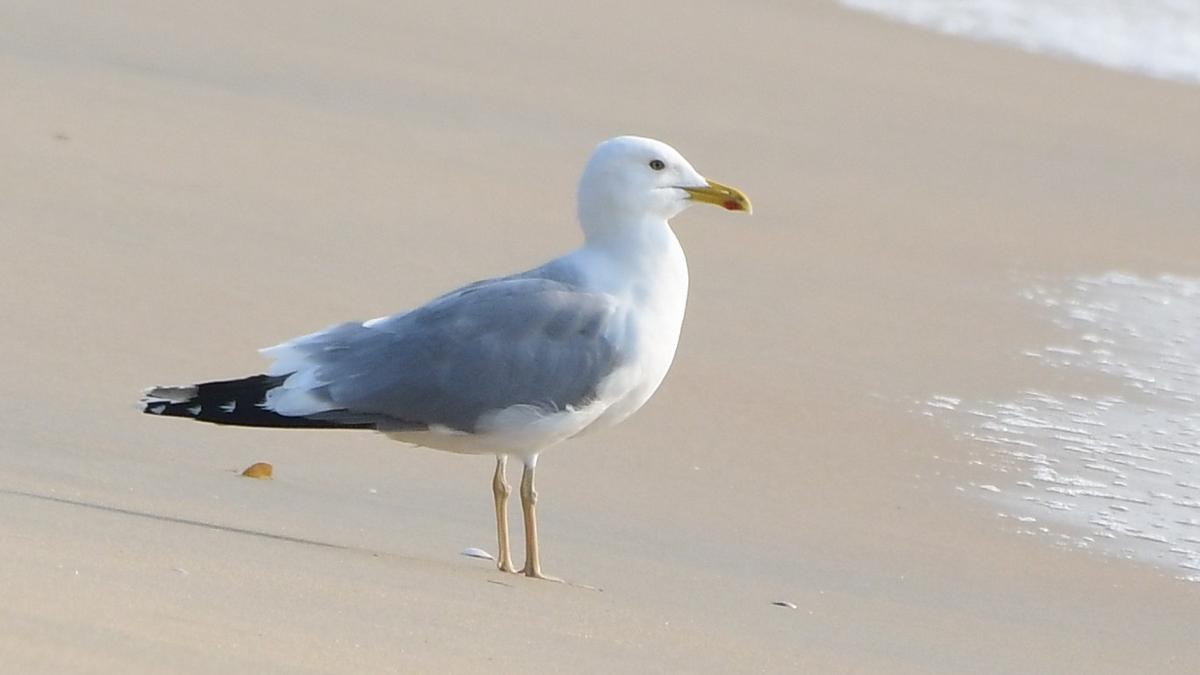

- 04 Jun 2025
In News:
In a significant ornithological development, the Caspian Gull, one of the rarest gull species to be recorded in India, was positively identified five years after being sighted at Kappad Beach, Kozhikode, Kerala. This marks the first confirmed sighting of the species in Kerala, and only the second in southern India.
Discovery and Identification:
- Ornithologist Abdulla Paleri first spotted the bird in February 2020 but took five years to confirm its identity due to its close resemblance to the more commonly seen Steppe Gull.
- The Caspian Gull differs subtly in features such as head and beak shape, posture, wing pattern, and leg morphology.
- Images were shared with international experts and on the eBird platform, where ornithologists Oscar Campbell and Hans Larsson confirmed the identification. The sighting has remained unchallenged since.
About Caspian Gull (Laruscachinnans):
- A monotypic, large, white-headed gull species, considered rare in India.
- Regularly breeds in Central Asia, particularly in steppe and semi-desert habitats with lakes, rivers, and reservoirs.
- Nesting usually occurs on flat, low-lying areas near water bodies, often surrounded by reedbeds.
- The species feeds on fish, insects, molluscs, and other invertebrates.
Migration Pattern:
- It migrates from the Black Sea and Caspian Sea region to southern and eastern Kazakhstan, western China, and parts of South Asia during winter.
- Traditionally winters in the eastern Mediterranean, Persian Gulf, and western India (like Gujarat).
- Increasingly, small populations are dispersing into Europe, including Sweden, Norway, and Denmark.
- The Kozhikode gull is believed to be a straggler—a bird that deviates from its usual migratory route.
Conservation Status:
- IUCN Red List:Least Concern, Despite its rarity in India, the species is not globally threatened.
Jharkhand’s First Tiger Safari
- 03 Jun 2025
In News:
The Jharkhand government has proposed setting up its first-ever tiger safari in the fringe area of the Palamau Tiger Reserve (PTR), located in Latehar district. This initiative aims to promote wildlife education, conservation awareness, and eco-tourism, while also creating employment opportunities.
What is a Tiger Safari?
A tiger safari refers to a tourism model where rescued, conflict-prone, or orphaned tigers are housed in naturalistic enclosures, ensuring sightings for visitors. It differs from traditional wild safaris, where sightings are not guaranteed. The concept was first proposed in the NTCA's 2012 tourism guidelines, refined in 2016, and later aligned with the Supreme Court’s 2024 directive, which mandates that such safaris be located outside core and buffer zones of tiger reserves.
Legal and Regulatory Framework
- Governed by:
- Wildlife (Protection) Act, 1972
- National Tiger Conservation Authority (NTCA) Guidelines (2012, 2016)
- Central Zoo Authority (CZA) for animal welfare, enclosure design, and project compliance
- Supreme Court Ruling (March 2024):
- Tiger safaris must not be located inside core or buffer zones.
- Intended to protect natural habitats and uphold conservation goals.
About Palamau Tiger Reserve (PTR)
- Established: 1974 under Project Tiger
- Location: Chhotanagpur Plateau, Jharkhand
- Rivers: North Koel, Burha (perennial), Auranga
- Vegetation: Northern Tropical Dry Deciduous forest (Sal-dominated)
- Key Fauna: Bengal Tiger, Asiatic Elephant, Sloth Bear, Leopard, Indian Pangolin, Otter
- Historical Note: Site of the world’s first pugmark-based tiger census (1932)
Project Details
- Location: Barwadih Western Forest Range (fringe of PTR, outside core/buffer zones)
- Size: Approx. 150 hectares
- Animals Housed: Only rescued, conflict-prone, or orphaned tigers from reserves/zoos (not wild or zoo-bred tigers unless approved)
- Objectives:
- Promote tourism and conservation education
- Create an experiential learning space for visitors
- Generate employment (~200 local jobs)
The Central Zoo Authority (CZA) will assess the site and species selection. Post Forest Department clearance, the Detailed Project Report (DPR) will be submitted to NTCA and CZA. Approvals may take 5–6 months, followed by a construction period of ~18 months.
Concerns and Challenges
- Tribal and Community Rights:Activists caution that such projects may marginalize forest-dwelling communities and restrict access to traditional forest-based livelihoods (grazing, NTFP collection).
- Consent of Local Communities:As per the Forest Rights Act, projects on forest land must involve Gram Sabha consultation. Activists argue this has yet to be fully addressed.
- State's Clarification:Officials maintain that the site lies on forest land under state management, with no expected displacement.
Sabine’s Gull Spotted at Nalsarovar
- 03 Jun 2025
In News:
In a remarkable ornithological event, the Sabine’s Gull — a rare Arctic seabird — has been observed at Nalsarovar Bird Sanctuary in Gujarat. This marks the species’ first recorded appearance in India since 2013, when it was last sighted in Kerala, underlining the dynamic migratory patterns affecting India’s wetland ecosystems.
About Nalsarovar Bird Sanctuary
- Located nearly 64 km west of Ahmedabad, Nalsarovar Bird Sanctuary is one of Gujarat’s most prominent wetland ecosystems. Encompassing an area of 120.82 sq km, it comprises a shallow, seasonal lake interspersed with around 360 islets, creating a rich mosaic of aquatic habitats.
- This natural lake traces its origin to the 15th century, following the construction of a check dam on the Sabarmati River. Initially designed to serve irrigation and drinking water needs of nearby villages, the lake gradually evolved into a crucial habitat for avifauna. Recognition of its ecological significance grew over time, prompting colonial authorities in the early 20th century to take protective measures.
- Eventually, in 1969, the Government of Gujarat declared Nalsarovar a bird sanctuary, and it was further accorded the status of a Ramsar wetland site in 2012, signifying its global importance under the Ramsar Convention.
- Flora: The sanctuary supports a wide variety of aquatic and wetland plant life, with 48 algae species and 72 flowering plant species recorded. Common plant species include Cyperus, Scirpus, Typha ungustata, Eleocharis palustris, Ruppia, Potamogeton, Vallisneria, Naias, and Chara.
- Fauna:Nalsarovar is home to nearly 250 bird species, making it a haven for bird watchers. Regular sightings include both greater and lesser flamingos, pelicans, ducks, geese, coots, rails, cranes, and a variety of wading and aquatic birds like herons, egrets, storks, spoonbills, and sarus cranes.
- Beyond birds, the sanctuary also supports mammalian fauna. On its southern and southwestern peripheries, species such as the Indian wild ass, mongoose, jungle cat, Indian fox, jackal, wolf, and striped hyena are found.
Sabine’s Gull: Profile
- The Sabine’s Gull (Xemasabini), also known as the fork-tailed gull or xeme, is a small gull species notable for its elegant flight and distinctive wing markings. Adults can be recognized by their pale grey backs, black wingtips, white secondary feathers, and forked white tails.
- This gull breeds in high Arctic and subarctic zones across North America, Russia, Greenland, and Svalbard, and is a rare migrant in South Asia.
- According to the IUCN Red List, it is currently categorized as a species of Least Concern, although sightings in India are extremely uncommon.
Kawal Tiger Reserve and KumramBheem Conservation Reserve
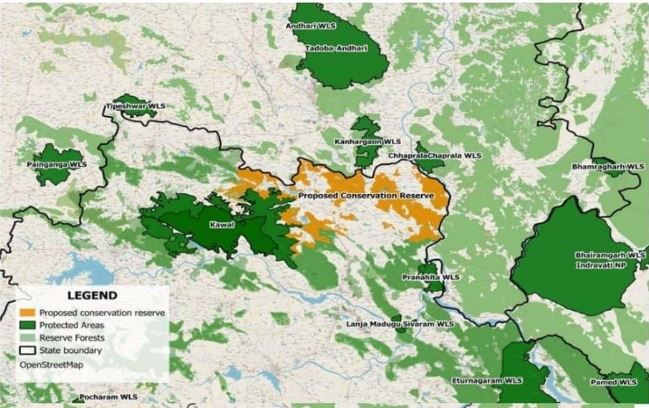
- 02 Jun 2025
In News:
In a recent development, the Telangana government has designated the tiger corridor connecting the Kawal Tiger Reserve (Telangana) with the Tadoba-Andhari Tiger Reserve (Maharashtra) as the KumramBheem Conservation Reserve, under Section 36(A) of the Wildlife Protection Act, 1972. This move is aimed at preserving critical wildlife corridors in the Central Indian Landscape.
Kawal Tiger Reserve:
- Location: Situated in Telangana, along the Godavari River, forming part of the Deccan Peninsula – Central Highlands.
- Biogeographic Zone: Lies at the southern tip of the Central Indian Tiger Landscape.
- Connectivity: Links with Tadoba-Andhari (Maharashtra), Indravati (Chhattisgarh), and other reserves like Tipeshwar, Chaprala, and Kanhargaon.
- Vegetation Type: Southern Tropical Dry Deciduous Forests.
- Flora: Dominated by teak, bamboo, and species like Anogeissuslatifolia, Terminalia arjuna, Boswellia serrata, etc.
- Fauna: Hosts tiger, leopard, nilgai, chinkara, sambar, blackbuck, wild dog, wolf, and jungle cat.
KumramBheem Conservation Reserve: Newly Notified Area
- Legal Basis: Declared under Section 36(A), Wildlife Protection Act, 1972, which allows states to notify government-owned land adjacent to or connecting protected areas as conservation reserves.
- Total Area: 1,492.88 sq km (149,288.48 hectares)
- District &Mandals Covered: Spread across KumramBheemAsifabad district, covering parts of Kerameri, Wankidi, Asifabad, Sirpur, Koutala, Bejjur, Kagaznagar, Rebbana, Dahegaon, and Tiryanimandals.
- Forest Blocks Included: 78 blocks including Garlapet, Ada, Manikgarh East & West, Danora, Gudem, Bejjur, Kadamba, and Girali.
Ecological Significance
- Tiger Movement: Over the last decade, more than 45 unique tigers (mostly transient) have been documented in this corridor through camera trapping and surveys.
- Breeding Evidence: Since 2015, 17 tiger cubs born from 3 tigresses have been recorded. The 2022 Tiger Census confirmed 4 adult tigers and 3 cubs in the area.
- Leopard Presence: 8 leopards were recorded during the All India Leopard Estimation, 2022.
- Other Carnivores: Includes sloth bear, hyena, wild dog, wolf, honey badger, and jungle cat.
- Herbivore Diversity: Rich prey base such as gaur, sambar, nilgai, chital, muntjac, four-horned antelope, and Indian gazelle.
- Avifauna: Home to 240+ bird species, including rare species like the Malabar Pied Hornbill and Long-billed Vulture, the latter using the reserve as a nesting site.
- Elephant Movement: Occasional elephant presence has also been reported.
Governance
A Conservation Reserve Management Committee has been established. Members include:
- District Forest Officer (DFO) of KumramBheemAsifabad (Convenor)
- Sarpanches of local panchayats (e.g., Karji, Motlaguda, Murliguda)
- Representatives from NGOs like Hyderabad Tiger Conservation Society, WWF-India, and Wildlife Conservation Trust
- Officials from Veterinary, Agriculture, and Forest Divisions
Perito Moreno Glacier

- 01 Jun 2025
In News:
- The Perito Moreno Glacier, often referred to as the ‘White Giant’, is Argentina’s most iconic glacier, located in the Los Glaciares National Park, a UNESCO World Heritage Site.
- Situated in the Andes Mountains, near El Calafate in Santa Cruz province, this glacier spans approximately 250 sq km—about the size of Patna, Bihar—and stretches 30 km in length, with ice walls rising 60 meters above water.
- Formed during the last Ice Age (~18,000 years ago), Perito Moreno has historically remained unusually stable, defying the global trend of rapid glacier retreat. However, this stability changed around 2020, raising alarms among scientists.
Recent Developments and Ice Calving Events
- Perito Moreno is globally renowned for its ice calving events, where massive blocks of ice break off into the lake with thunderous crashes. These events, though natural due to the glacier’s forward motion, have recently become more intense.
- On April 21, 2025, a colossal ice chunk the size of a 20-story building plunged 70 meters into the water—an increasingly frequent occurrence in the past 4–6 years.
- According to local experts and a 2024 government-backed report, the glacier has been retreating steadily since 2015, with an average mass loss of 0.85 meters annually—the fastest in nearly five decades.
- Between 2020 and 2023, the glacier lost over 700 meters of mass, equivalent to around seven large ice blocks.
Causes: Global Warming & Climate Impact
- The primary cause behind this dramatic retreat is climate change. Scientists from IANIGLA (Argentine Institute of Glaciology and Environmental Sciences) and CONICET state that the region has experienced an air temperature rise of 0.06°C per decade and reduced precipitation, leading to less snow accumulation and thinning of the glacier.
Global Perspective on Glacier Retreat
Perito Moreno is now part of a larger, alarming global trend.
- A 2024 study in Nature estimates that glaciers worldwide are losing 273 billion tonnes of ice annually, contributing to a 2 cm rise in global sea levels this century alone.
- A UNESCO report (March 2025) highlighted that glaciers (excluding Greenland and Antarctica) have shed over 9,000 billion tonnes of ice since 1975—comparable to an ice block the size of Germany with 25 meters thickness.
Environmental Significance
- Freshwater Source: Perito Moreno is a major reservoir of freshwater in Argentina.
- Tourism: The glacier attracts global tourists, boosting the local economy.
- Climate Indicator: Its recent retreat reflects the delayed but accelerating impact of global warming, making it a critical environmental bellwether.
Theobaldius konkanensis
- 09 Apr 2025
In News:
A new species of land snail, Theobaldius konkanensis, has been discovered by a collaborative team of Indian and UK researchers from the Konkan region of Maharashtra. This species adds to the growing biodiversity records of the northern Western Ghats, a globally recognized but under-explored biodiversity hotspot.
Key Facts at a Glance
- Scientific Name: Theobaldius konkanensis
- Discovered in: Ratnagiri and Raigad districts, Maharashtra (Dev Gireshwar Temple, Uttamrao Patil Biodiversity Garden, Kesharnath Vishnu Temple, and Phansad Sanctuary)
- Elevation: 80–240 metres above sea level
- Habitat: Tropical evergreen and semi-evergreen forests
- Active Months: June to September (monsoon); only shells visible in other months
- Habits: Active both day and night, often under forest canopy in shaded, moist leaf litter
Morphological Features
- Shell Characteristics:
- Slightly flattened with a raised centre and deep triangular notch near the aperture
- Operculum (protective cover) has raised whorl edges and short spines
- Corneous yellow with brown striations
- Thick, conoidally depressed, and widely umbilicated
- Body: Stout and rounded
Taxonomic Context
- Family: Cyclophoridae (Caenogastropoda)
- Genus: Theobaldius
- Now includes 20 species: 9 in India, 11 in Sri Lanka, and 1 in Sumatra (Indonesia)
- In India, 6 species are endemic to the Western Ghats
- Only T. annulatus is found in both Sri Lanka and the Western Ghats
Ecological and Conservation Significance
- Bioindicators: Land snails are sensitive to climatic changes and environmental disturbances
- Endemism: T. konkanensis is restricted to specific forest patches in the Konkan, highlighting the ecological uniqueness of the region
- Threats: Increasing anthropogenic pressures and habitat degradation threaten snail species with restricted distribution
Reproductive Biology (General Traits of Land Snails)
- Breeding mainly in monsoon
- Reproduce through both cross- and self-fertilisation
- Courtship includes dart-shooting behavior; mating may last hours
- Eggs laid in moist soil or leaf litter; hatch in 2–4 weeks
- Lifespan: 2 to 7 years
Woolly Flying Squirrel
- 08 Apr 2025
In News:
The Wildlife Wing of the Himachal Pradesh Forest Department (HPFD) has recently documented the first-ever photographic evidence of the Woolly Flying Squirrel in Miyar Valley, located in the Lahaul and Spiti district. This marks a significant discovery, as the species is extremely elusive and rarely sighted.
About Woolly Flying Squirrel
- Common Name: Woolly Flying Squirrel / Western Woolly Flying Squirrel
- Scientific Name: Eupetaurus cinereus
- Taxonomy: The only known species under the genus Eupetaurus
- Conservation Status: Listed as Endangered on the IUCN Red List
Habitat and Distribution
- Endemism: Confined to the northwestern Himalayas
- Countries Found: Northern Pakistan and northwestern India
- Habitat Type: Inhabits a narrow elevational range within dry coniferous forests, typically in fragmented habitats
- Historical Records:
- Rediscovered in 1994, nearly 70 years after it was presumed extinct
- Since then, reported from Sai Valley, Gorabad, and Balti Gali in northern Pakistan
Key Characteristics
- Equipped with patagium (elastic skin membrane) that connects the forelimbs and hind limbs, enabling gliding—typical of flying squirrels
- Fur: Dense, straight, and silky
- Dorsal side: Blue-gray
- Ventral side: Pale gray
- Throat and ears: Covered in creamy white hairs
- Feet soles: Dense black fur, except for bare pinkish-brown toe pads
Calotes zolaiking
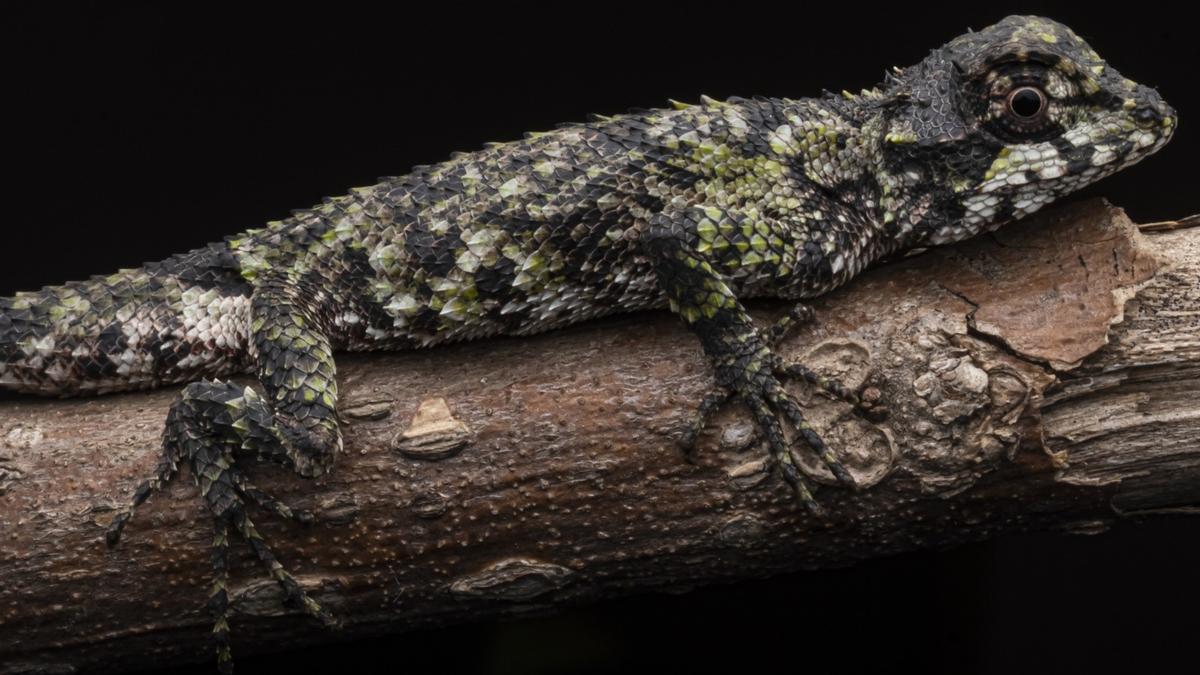

- 31 May 2025
In News:
The rare lizard species Calotes zolaiking has been recorded for the first time in Meghalaya, marking a significant extension of its known habitat and triggering grassroots conservation efforts.
About Calotes zolaiking
- Scientific Classification: Belongs to the Calotes genus under the Agamidae family.
- First Described: In 2019 from Aizawl district, Mizoram.
- Appearance: About 5 inches in length; green body with dark patches and strongly keeled scales (scales with a raised ridge).
- Behaviour: Arboreal (tree-dwelling), diurnal, fast runners, and capable swimmers.
- Diet: Insectivorous—feeds on insects and small invertebrates.
Distribution and Habitat
- New Sighting: Mawmluh village, East Khasi Hills, Meghalaya, April 2024.
- Range Extension: Approx. 172 km aerially from the original Mizoram locality.
- Genus Distribution: Found across India, Sri Lanka, Southeast Asia, and parts of Oceania.
- India's Richness: 14 known Calotes species in India; 9 recorded in the Northeast region.
Conservation Significance
- Community Role: Local residents Goldenstar Thongni and Banyllashisha Wankhar played a key role in identifying and collecting specimens.
- Catalyst for Conservation: The species' discovery has motivated the local community in Mawmluh and Sohra (Cherrapunji) to strengthen forest protection amidst threats from limestone mining and industrial activities.
- Sacred Groves: Traditional conservation spaces like sacred groves are being revitalized in light of the new biodiversity significance.
- Scientific Impact: The find was featured in Zootaxa, a peer-reviewed taxonomy journal, adding global recognition.
Broader Ecological Relevance
- Biodiversity Surveys: The discovery underscores the need for continuous herpetofaunal surveys in the Khasi Hills due to forest degradation.
- Historical Context: Cited alongside Stoliczkia khasiensis, a snake species last seen in 1870, highlighting the risk of species being lost without systematic documentation.
Pedicularis rajeshiana

- 30 May 2025
In News:
Researchers from the Botanical Survey of India (BSI), under the Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change (MoEF&CC), have discovered a new plant species — Pedicularis rajeshiana — in the high-altitude regions of Rohtang Pass, Himachal Pradesh.
Key Facts:
Taxonomy and Classification
- Scientific Name: Pedicularis rajeshiana
- Family: Orobanchaceae
- Common Group: Louseworts (Hemiparasitic plants – partially dependent on host plants for nutrients, but also photosynthetic)
- Named by: Botanist Dr. Arti Garg, formerly of BSI Prayagraj, now with BSI Dehradun
- Publication: Officially recorded in the international journal Phytotaxa (Mongolia)
Habitat and Discovery
- Location: Rohtang Pass, Pir Panjal range, Western Himalayas
- Altitude: ~4,390 metres (14,400 feet)
- Habitat: Shaded rocky slopes in scattered patches
- Discovery Project: "Flora of India" initiative by MoEF&CC and BSI
Unique Botanical Characteristics
- Size: Smaller than related species like P. porrecta and P. heydei
- Floral Features:
- Deeply cut lower labium (lip)
- Stamens positioned at three distinct levels inside the flower
- Rare pollen morphology with croton-like surface texture
- Two flowers observed with twin galea (hood-like structures) — a first in the genus, possibly an evolutionary trait to enhance pollination
Ecological Significance
- Endemicity: Many Pedicularis species are habitat-specific and endemic to certain Himalayan regions
- India's Diversity: Home to 83 known species of Pedicularis, with 36 in the western Himalayas
- Conservation Value: The specificity of habitat and rarity suggest potential threat status; conservation is crucial.
WMO Climate Forecast 2025–2029
- 30 May 2025
In News:
The World Meteorological Organization (WMO) has released its latest decadal climate forecast (2025–2029), warning of a continued trend of record-breaking global temperatures. This projection raises serious concerns about climate risks, sustainable development, and international climate commitments under the Paris Agreement.
Key Projections:
- Annual Global Temperature Rise: Each year from 2025–2029 is projected to be 1.2°C to 1.9°C above pre-industrial levels (1850–1900).
- Record Heat Likelihood:
- 80% chance that at least one year will surpass 2024, currently the warmest year on record.
- 86% probability that one year will exceed the 1.5°C threshold.
- Five-Year Mean Warming: 70% chance that the 2025–2029 average will be above 1.5°C, a sharp rise from 47% (2024–2028) and 32% (2023–2027).
Note: The Paris Agreement’s 1.5°C limit refers to long-term (20-year) averages, but short-term overshoots are now increasingly probable.
Regional and Thematic Insights:
1. Arctic Amplification: Arctic winters (Nov–Mar) are projected to be 2.4°C warmer than the 1991–2020 average—3.5× faster than the global rate.
2. Sea Ice Decline: Continued sea ice reduction is expected in the Barents Sea, Bering Sea, and Sea of Okhotsk, impacting marine biodiversity and indigenous livelihoods.
3. Precipitation Variability:
- Wetter-than-average conditions likely in:
- Sahel region
- Northern Europe
- Alaska and Northern Siberia
- Drier conditions expected over:
- Amazon Basin
- Parts of South Asia
South Asia may witness generally wet years, though seasonal variability will persist.
Impact and Implications:
- Extreme Weather Events: Increased warming will fuel more intense heatwaves, extreme rainfall, droughts, and floods, stressing both urban systems and agriculture.
- Cryosphere and Ocean Changes:
- Accelerated glacier and sea ice melt will raise sea levels.
- Ocean heating contributes to acidification and marine biodiversity loss.
- Threat to Sustainable Development: Progress on SDGs, particularly food security, water availability, and health, is at risk in vulnerable regions.
Way Forward:
- Revise NDCs at COP30: Strengthen and align Nationally Determined Contributions (NDCs) with the 1.5°C goal.
- Accelerate Clean Energy Transition: Promote renewables, energy efficiency, and net-zero strategies to reduce GHG emissions.
- Adaptation and Resilience: Invest in climate-resilient infrastructure and early warning systems.
- Climate Monitoring & Forecasting: Enhance WMO-led regional forecasts and risk assessment tools.
- Preserve Natural Carbon Sinks: Protect forests, wetlands, and oceans to mitigate atmospheric CO?.
Alicella gigantea
- 27 May 2025
In News:
Rare giant shrimp is more widespread than previously believed; new findings reveal.
About the Species:
- Alicella gigantea is a giant deep-sea amphipod crustacean, growing up to 34 cm in length, making it one of the largest known amphipods.
- Amphipods are shrimp-like organisms; over 10,000 species are known globally, inhabiting a wide range of aquatic environments.
Habitat and Depth Range:
- Inhabits the abyssal (3,000–6,000 m) and hadal zones (>6,000 m) of the ocean.
- Notable sightings include:
- A 28 cm specimen observed at 5,304 m in the North Pacific.
- Captures from 6,746 m depth in the Murray Fracture Zone (North Pacific).
Global Distribution:
- Contrary to earlier beliefs, A. gigantea is not rare but is among the most widely distributed deep-sea species.
- Recent analysis compiled 195 records from 75 locations across the Pacific, Atlantic, and Indian Oceans, covering 15 different seafloor features.
- Found in 59% of the world’s oceans.
- The Pacific Ocean is its most significant habitat, with 75% of the seafloor in its suitable depth range.
Genetic Insights:
- Genetic analyses (16S, COI, 28S genes) show low genetic divergence across populations.
- This suggests A. gigantea represents a single, globally distributed species with strong genetic conservation.
- A shared haplotype network across regions indicates minimal genetic differentiation, supporting global connectivity among populations.
Conservation and Research Significance:
- Despite its wide range, A. gigantea remains poorly understood, particularly in terms of population size, ecology, and evolutionary history.
- Only seven studies have sequenced its DNA to date.
- The findings are a significant step toward understanding deep-sea biodiversity, biogeography, and conservation priorities in abyssal ecosystems.
Sagarmatha Sambaad 2025

- 27 May 2025
In News:
Union Environment Minister Shri Bhupender Yadav represented India at the 1st Sagarmatha Sambaad in Kathmandu, Nepal, a high-level biennial global dialogue convened under the theme “Climate Change, Mountains, and the Future of Humanity.”
The forum, held during the International Year of Glaciers’ Preservation 2025, focused on mountain ecosystems, climate resilience, and transboundary conservation.
India’s Key Proposals and Commitments
Reaffirmed India’s climate leadership and proposed a five-point call for global action to protect mountain ecosystems:
- Enhanced Scientific Cooperation: Promote joint research on cryospheric changes, biodiversity, and hydrological cycles.
- Building Climate Resilience: Develop early warning systems for Glacial Lake Outburst Floods (GLOFs) and invest in climate-resilient infrastructure in mountainous areas.
- Empowering Mountain Communities: Center policies on local welfare, integrate traditional ecological knowledge, and promote green livelihoods such as eco-tourism.
- Providing Green Finance: Ensure adequate and predictable climate finance for adaptation and mitigation in mountain nations, in line with the Paris Agreement.
- Recognizing Mountain Perspectives: Integrate mountain-specific issues into global climate negotiations and sustainable development agendas.
India’s Initiatives and Regional Cooperation
India highlighted the ecological value of the Himalayas and called for enhanced transboundary conservation among Himalayan nations under the International Big Cats Alliance. This alliance promotes joint protection of species like snow leopards, tigers, and leopards.
- Under Project Snow Leopard, India conducted its first comprehensive snow leopard assessment (2019–2023), recording 718 snow leopards, comprising 10–15% of the global population.
Significance of the Himalayan Ecosystem
- Hydrological Role: The Himalayas are the "Water Towers of Asia", feeding rivers like the Ganga, Brahmaputra, and Indus, and supplying around 1.2 trillion cubic meters of freshwater annually.
- Ecological Richness: A biodiversity hotspot, home to over 10,000 vascular plant species, 979 bird species, and 300 mammals such as the red panda and Himalayan tahr.
- Cultural Importance: Sacred in Hinduism and Buddhism, the Himalayas house pilgrimage sites like Kedarnath, Badrinath, and Mount Kailash.
- Economic Value: Support tourism, agriculture, forestry, and renewable energy. States like Uttarakhand, Assam, and West Bengal derive over 10% of state GDP from tourism.
The Lohit Basin project in Arunachal Pradesh (13,000 MW) exemplifies hydropower potential. - Climate Regulation: The range blocks cold Central Asian winds and influences monsoon patterns, ensuring rainfall for agriculture. Himalayan forests are major carbon sinks, mitigating global warming.
Key Challenges in the Himalayan Region
- Climate Disasters: Rising temperatures and glacier melt cause avalanches, landslides, and cloudbursts. E.g., 2025 Uttarakhand avalanche; 2023 Sikkim GLOF.
- Unsustainable Development: Slope cutting, deforestation, and seismic vulnerability threaten settlements (e.g., Joshimath subsidence linked to infrastructure projects).
- Glacier Retreat:
- Gangotri glacier has retreated over 850 meters in 25 years.
- Hindu Kush glaciers may lose 75% of volume by 2100.
- Biodiversity Loss: Invasive species and habitat loss displace native flora and fauna; 90% of endemic species in Sikkim Himalayas displaced.
- Unregulated Tourism: Littering and plastic waste—92.7% of Himalayan waste is plastic, 72% non-recyclable (2022 audit).
Recommendations for Sustainable Development
- Eco-sensitive Infrastructure: Mandatory Environmental Impact Assessments (EIAs), bioengineering, and electric mobility in high-altitude towns.
- Regulated Tourism: Introduce carrying capacity limits, permit-based entry, and promote low-impact tourism models.
- Glacier Monitoring & Water Management: Use remote sensing and GIS for glacier health; adopt ice stupas, rainwater harvesting, and efficient irrigation.
- Afforestation & Forest Conservation: Launch community-driven forestry projects (e.g., Van Andolan in Uttarakhand) to restore degraded ecosystems.
- Climate Adaptation Strategies: Expand early warning systems for GLOFs; promote climate-resilient crops and agricultural practices.
- Sustainable Livelihoods: Encourage organic farming, herbal industries, and eco-handicrafts to diversify mountain economies.
Turtle Conservation in Assam’s Temple Ponds
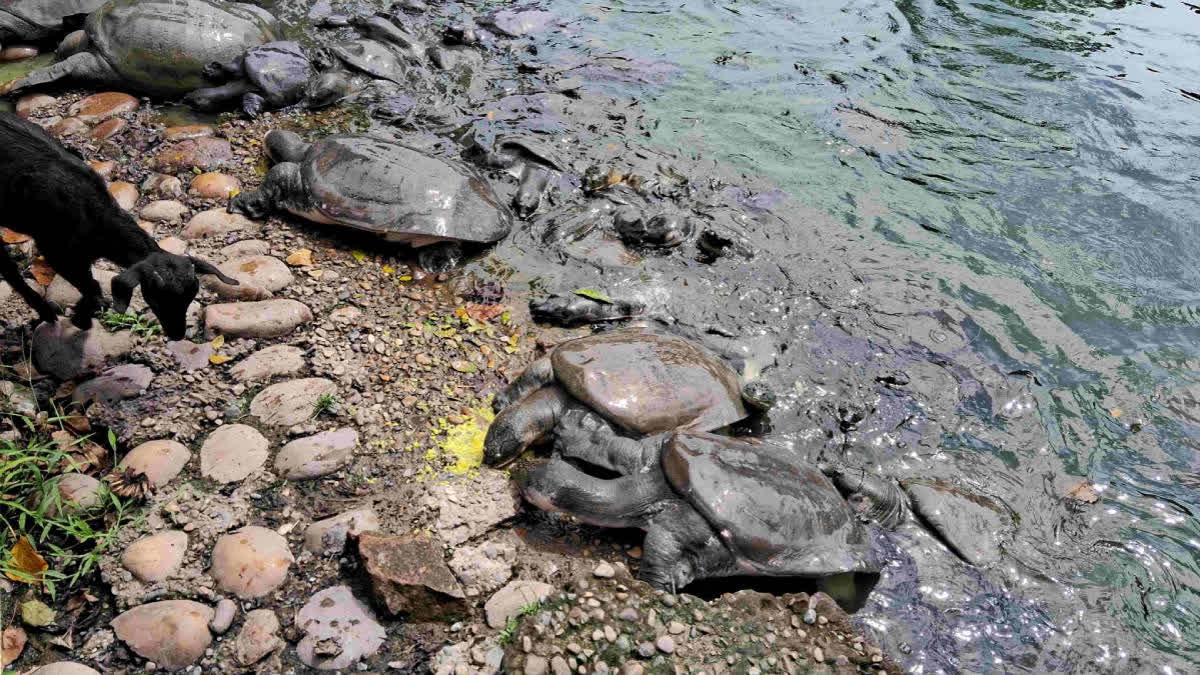

- 26 May 2025
In News:
On World Turtle Day (May 23, 2025), Assam’s Nagshankar Temple was officially declared a model temple for turtle conservation, highlighting the ecological role of temple ponds in preserving India’s turtle biodiversity.
Key Highlights
Nagshankar Temple – A Model for Turtle Conservation
- Location: Sootea town, Biswanath district, ~70 km from Tezpur, Assam.
- Established: Believed to be built in the 4th century AD by King Nagashankar of the Nagakha dynasty.
- Religious Importance: Dedicated to Lord Shiva, but turtles are revered as incarnations of Lord Vishnu.
- Ecological Value: Functions as a micro-wildlife sanctuary — home to 250–300 turtles, along with peacocks, pythons, and deer.
Turtle Conservation Initiatives
Species Conserved:
- Black Softshell Turtle (Nilssonia nigricans) – Critically Endangered
- Indian Softshell Turtle (Nilssonia gangetica)
- Malayan Softshell Turtle
These species thrive in the temple pond, which is fed by the Brahmaputra River basin, offering a suitable natural habitat.
Community & Scientific Collaboration:
- Key Stakeholders:
- Nagshankar Temple Committee
- Turtle Survival Alliance (TSA) India
- Help Earth (NGO)
- Kaziranga National Park & Tiger Reserve
- Assam Forest Department
- Conservation Methods:
- Artificial egg incubation and wild release of hatchlings.
- Dried-fish diet introduced for temple turtles, replacing harmful offerings (e.g., biscuits, puffed rice).
- Capacity-building workshops for forest staff and students to aid in turtle surveys.
Result: 486 hatchlings of the black softshell turtle have been released into the wild from the Nagshankar Temple pond.
Statewide Turtle Conservation Model
- Assam houses ~25 temple ponds actively involved in turtle conservation.
- Notable site: Hayagriva Madhav Temple in Hajo (Kamrup district).
- State Zoo in Guwahati has a dedicated breeding facility (established 2010) for the Assam Roofed Turtle (Pangshura sylhetensis, "Asomi Dura").
Schistura densiclava
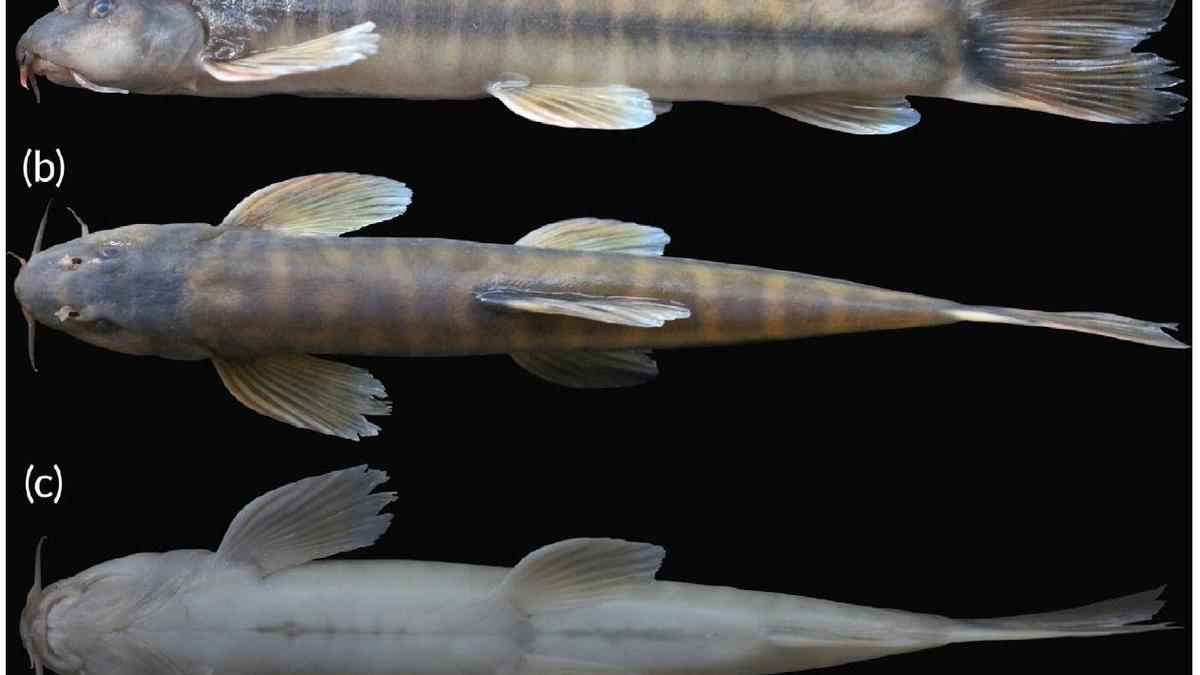

- 26 May 2025
In News:
A newly discovered species of cave-dwelling loach, Schistura densiclava, has been recorded from the Krem Mawjymbuin cave in the East Khasi Hills district of Meghalaya, India. This species becomes the sixth known cave-dwelling fish from the state, emphasizing Meghalaya’s rich subterranean biodiversity.
Taxonomy and Classification
- Family: Nemacheilidae (bottom-dwelling freshwater fishes)
- Type: Troglophile — adapted to live in caves but can survive and reproduce in surface (epigean) waters.
- Distinct Feature: Unlike typical cave fishes, S. densiclava retains pigmentation and functional eyes, indicating adaptability to both subterranean and overground aquatic environments.
Habitat and Environment
- Found 60 meters inside the Krem Mawjymbuin, a limestone cave with a surveyed length of 1.6 km and an altitude of 206 meters.
- The species inhabits a cool, fast-flowing stream with a temperature of 18°C and low oxygen levels.
- The cave is ecologically sensitive and was previously in the news due to a local ban on worship at a Shivalinga-like formation within it.
Morphological Characteristics
- Coloration: Pale yellow-green body with 14–20 greyish to faint black vertical bars.
- Named densiclava due to the thick dark stripe near the dorsal fin ("densiclava" = Latin for "thick stripe").
- Sexual Dimorphism:
- Males: Slimmer with irregular patterns and puffier cheeks.
- Females: Sturdier with more consistent markings.
Scientific Significance
- Genetic testing confirmed Schistura densiclava as a distinct and previously unrecorded species.
- Its endemic distribution, limited to a single cave system, marks it as a species of high conservation concern.
- The discovery was published in the Journal of Fish Biology by a team led by Kangkan Sarma from Gauhati University, along with other Indian ichthyologists.
Artificial Rain to combat Delhi’s Air Pollution
- 06 Apr 2025
In News:
With the national capital grappling with chronic air pollution every winter, the Delhi Government is exploring artificial rain (cloud seeding) as a potential mitigation strategy. In a recent high-level meeting chaired by Environment Minister Manjinder Singh Sirsa, experts and representatives from key institutions brainstormed the feasibility and logistics of implementing cloud seeding in Delhi's airspace.
What is Artificial Rain (Cloud Seeding)?
- Cloud seeding is a form of weather modification aimed at inducing rainfall.
- It involves spraying chemical agents such as silver iodide or salt particles into clouds to stimulate condensation and precipitation.
- Requires favourable meteorological conditions, especially adequate moisture and cloud density.
- Usually conducted using aircraft or ground-based dispersal systems.
Significance for Delhi:
- Rainfall helps settle airborne particulate matter (PM2.5 and PM10), thereby reducing pollution levels.
- Delhi’s air quality worsens in winter due to a combination of low wind speeds, crop residue burning, vehicular and industrial emissions, and construction dust.
- Artificial rain could serve as an emergency intervention to improve air quality during severe pollution episodes.
Key Highlights of the Meeting:
- Convened by Delhi Environment Department with participation from:
- CPCB, DPCC
- Ministry of Defence, MoEFCC
- IIT-Kanpur, India Meteorological Department (IMD)
- Directorate General of Civil Aviation (DGCA), AAI
- IIT-Kanpur scientists shared results from previous successful cloud seeding trials in Kanpur (2023), demonstrating its potential under ideal conditions.
- Past trials in 2018 also showed partial success, with rainfall occurring in 5 out of 6 attempts during pre-monsoon months.
Challenges Identified:
- Weather-dependence: Effectiveness relies heavily on cloud presence and moisture levels, which are limited in Delhi during winters.
- Airspace clearance and coordination among multiple agencies (civil aviation, defence).
- High costs and uncertain outcomes make it a supplementary, not primary, solution.
Complementary Measures Underway:
- Delhi’s 14-point action plan to curb dust pollution includes:
- Anti-smog guns, covering construction sites, cleaning of construction vehicles, andregulated debris disposal.
- Exploring static ionisation systems as an alternative to cloud seeding for artificial precipitation.
Euphaeawayanadensis
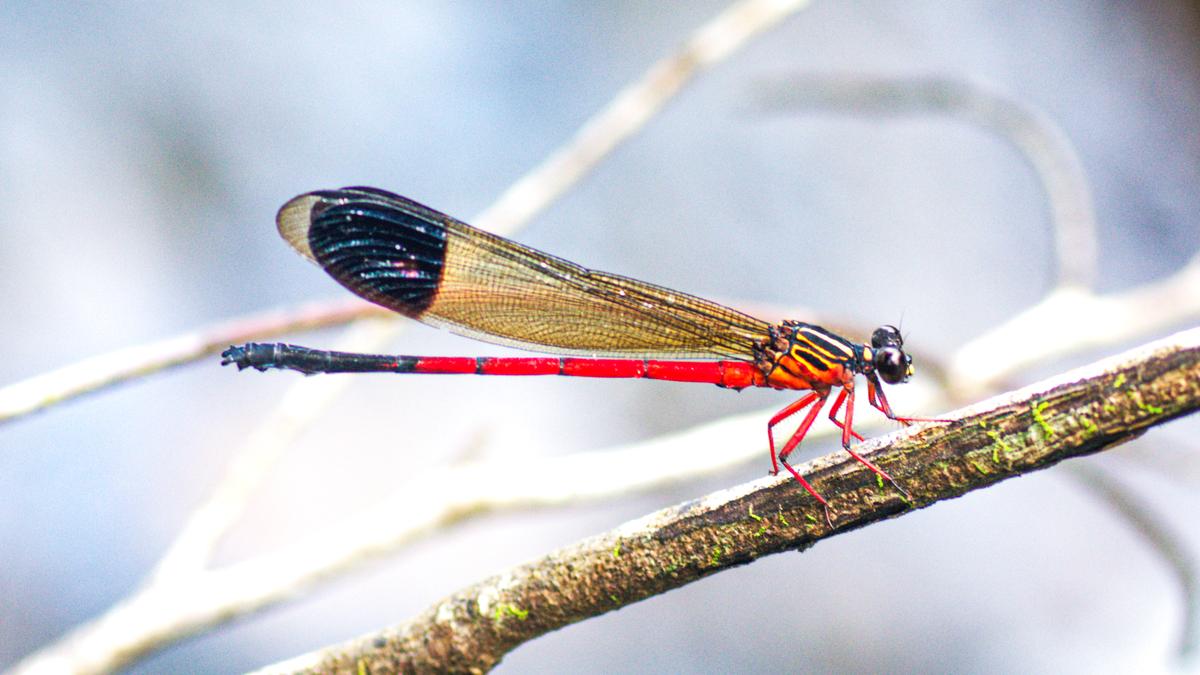

- 05 Apr 2025
In News:
A new species of damselfly, Euphaeawayanadensis, has been discovered in the Wayanad region of Kerala, marking a significant addition to India’s odonate diversity.
Key Details:
- Taxonomy:
- Belongs to the family Euphaeidae.
- Officially recognized as Kerala’s 191stodonate species (including damselflies and dragonflies).
- 223rd species recorded from the Western Ghats.
- Discovery and Research:
- First observed in 2013 at Kalindi River, Thirunelli, Wayanad.
- Confirmed after field studies conducted until 2023 across Wayanad, Aralam (Kannur), and western Coorg slopes (Karnataka).
- Discovery published in the peer-reviewed journal ENTOMON.
- Research Contributors:Collaborative effort involving scientists from Kerala Agricultural University, Alphonsa College, and conservation groups like Warblers and Waders, Travancore Nature History Society.
- Identification Process:
- Initially mistaken for Euphaeapseudodispar (from Maharashtra).
- Declared a distinct species based on morphological traits and genetic analysis.
Distinct Morphological Features
- Hind wing: Longer black patch compared to similar species.
- Stripes: Broader, uninterrupted humeral and antehumeral stripes in males.
- Male genital vesicle: Structurally unique from related species.
Habitat & Distribution
- Inhabits fast-flowing rocky streams with aquatic vegetation.
- Found in evergreen and semi-evergreen forests along stream banks.
- Active throughout the year except March–April (dry season).
- Shows restricted distribution, making it ecologically vulnerable.
Conservation Importance
- The discovery underlines the biodiversity richness of the Western Ghats.
- Highlights the need for targeted conservation of aquatic invertebrates in fragile ecosystems like Wayanad.
- Emphasised by experts from the IUCN Dragonfly Specialist Group.
State of the World’s Animal Health Report 2025

- 25 May 2025
In News:
Infectious animal diseases are spreading to previously unaffected regions and species, with nearly half (47 per cent) capable of zoonotic transmission or spreading between animals, according to the inaugural State of the World’s Animal Health report released by the World Organisation for Animal Health (WOAH).
Key Details:
Published by:
- World Organisation for Animal Health (WOAH), formerly OIE (Office International des Epizooties), founded in 1924, headquartered in Paris.
- Recognized by the WTO for setting global standards on animal health and zoonotic disease control.
Objective of the Report:
- To provide a comprehensive global assessment of animal health trends, risks, and disease outbreaks.
- To promote a One Health approach, linking animal health with human health and environmental sustainability.
Major Findings:
1. Rising Zoonotic Threats:
- 47% of animal diseases reported between 2005–2023 have zoonotic potential (can spread from animals to humans).
- These include avian influenza, African swine fever (ASF), foot-and-mouth disease (FMD), and Peste des Petits Ruminants (PPR).
2. Geographic Expansion of Diseases:
- Diseases are emerging in new regions and species due to climate change, global trade, and ecosystem disruptions.
- Example: ASF jumped over 1,800 km to reach Sri Lanka in 2024, marking the year's most significant disease leap.
- PPR re-emerged in Europe, traditionally limited to developing regions.
3. Avian Influenza Evolution:
- Over 630 million birds culled or lost in 20 years.
- In 2024, more outbreaks were reported in non-poultry species (55 countries) than poultry (42 countries).
- Mammal infections doubled, raising concerns of cross-species transmission.
4. Other Notable Disease Events:
- Germany faced its first FMD outbreak since 1988.
- New World Screwworm, a parasitic fly, re-emerged in Mexico and Nicaragua.
- Bluetongue virus reported in 23 countries with over 3,500 cases in 2024.
Antimicrobial Resistance (AMR): A Global Threat
Key Data:
- By 2050, AMR may cause:
- Loss of livestock threatening food security for 2 billion people.
- $100 trillion global economic loss.
Drivers:
- Indiscriminate use of antibiotics in livestock, aquaculture, and agriculture.
- Around 20% of countries still use antimicrobials as growth promoters, including high-priority drugs like colistin and enrofloxacin.
Trends:
- Global antibiotic use in animals fell by 5% (2020–2022).
- Europe: 23% decline.
- Africa: 20% decline.
Recommendations by WOAH:
- Enhance vaccine access and distribution, especially in low-income countries.
- Strengthen Veterinary Services, surveillance, and biosecurity.
- Improve hygiene and disease prevention to reduce antibiotic dependence.
- Promote international cooperation under the One Health framework.
- Ban or regulate the use of antibiotics as growth promoters.
About WOAH:
- Intergovernmental organization with 183 member countries, including India.
- Monitors, controls, and reports on animal diseases to ensure safe trade, public health, and food security.
- Partner in Global Action Plan on AMR with WHO and FAO.
Indian Initiatives on AMR & Animal Health:
- National Action Plan on AMR (2017–2021) – Focus on awareness, surveillance, infection control, and R&D.
- FSSAI guidelines to regulate antibiotic residues in food of animal origin.
- National Animal Disease Control Programme (NADCP) – Focus on vaccination against FMD and Brucellosis.
India’s Climate Physical Risk (CPR)

- 21 May 2025
In News:
Amid rising climate-induced disasters—floods, heatwaves, droughts—the Union Home Minister recently called for proactive climate risk assessments. India, however, lacks a comprehensive and standardised system to assess Climate Physical Risks (CPR), exposing critical gaps in preparedness.
What is Climate Physical Risk (CPR)?
Definition: CPR refers to the potential damage from:
- Acute events: Floods, cyclones, heatwaves.
- Chronic stresses: Changing monsoon patterns, droughts.
IPCC Formula:
CPR = Hazard × Exposure × Vulnerability
- Hazard: Climate threats like floods or wildfires.
- Exposure: Presence of people/assets in risk-prone areas.
- Vulnerability: System's capacity to withstand and recover.
Why CPR Assessment Matters for India
- High Risk: Over 80% of Indians reside in districts exposed to climate disasters (World Bank).
- Systemic Threat: Affects not just the environment, but public health, agriculture, economy, and national security.
- Future-proofing Development: Long-term planning must consider CPR for sustainable infrastructure and financial stability.
Challenges in India’s CPR Management
- Fragmented Efforts: Multiple agencies (IMD, IITs, NIDM) conduct isolated studies with no integration.
- Lack of Standardised Data: No central repository for CPR metrics at the district or panchayat level.
- Modelling Limitations: Global models like RCPs and SSPs fail to capture India's hyper-local climate variations.
- Private Sector Constraints: Businesses lack tools to evaluate climate risks across supply chains.
Global Best Practices
- Mandatory Climate Disclosures: Global frameworks like ISSB S2 and EU Taxonomy require companies to report CPRs.
- Adaptation as Priority: Nations, including the Global North, are investing in adaptation infrastructure, recognizing its economic returns.
- UNEP estimates: $1 in adaptation = $4 saved in disaster recovery.
Initiatives by India
- Adaptation Communication (2023): India’s first report to the UNFCCC under Article 7 of the Paris Agreement.
- National Adaptation Plan (NAP): In progress; covers 9 thematic sectors with district-level focus.
- RBI Framework: Climate risk integrated into financial supervision and regulatory assessments.
Supreme Court Strikes Down Retrospective Environmental Clearances

- 20 May 2025
In News:
In a significant verdict for environmental governance, the Supreme Court of India, in the case Vanashakti v. Union of India (May 2025), struck down the 2017 notification and 2021 Standard Operating Procedure (SOP) issued by the Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change (MoEF&CC). These instruments allowed retrospective (ex-post facto) environmental clearances—i.e., granting environmental approval to industries after they had begun operations without prior clearance.
What are Retrospective Environmental Clearances?
- Definition: Ex-post facto clearances permit projects to start operations without prior Environmental Impact Assessment (EIA) approval and seek clearance later.
- Contradiction: These violate the EIA Notification, 2006, issued under the Environment (Protection) Act, 1986, which mandates prior approval before beginning any project impacting the environment.
Details of the 2017 Notification & 2021 SOP
- 2017 Notification:
- Provided a one-time 6-month window for industries that violated clearance norms to regularize operations.
- Central-level appraisal for all cases, regardless of project size or category.
- Violators remained subject to action by State Pollution Control Boards.
- Intended to bring violators under regulatory oversight and ensure remediation costs.
- 2021 SOP:
- Issued to standardize processing of violation cases following an NGT directive.
- Did not use the term “ex-post facto”, but allowed project appraisals after operations began—effectively regularising violations.
- Appraisal Committee: A committee led by NEERI’s former director S.R. Wate appraised such cases over 47 meetings between 2017–2021.
Supreme Court’s Rationale
- Violation of Fundamental Rights:
- Held the 2017 Notification and 2021 SOP unconstitutional as they violate:
- Article 21 – Right to a clean and pollution-free environment.
- Article 14 – Equality before law; violators were unjustly protected.
- Held the 2017 Notification and 2021 SOP unconstitutional as they violate:
- Against Environmental Jurisprudence:
- Reaffirmed past rulings:
- Common Cause v. Union of India (2017)
- Alembic Pharmaceuticals v. Rohit Prajapati (2020)
- These had declared ex-post facto clearances illegal and anathema to environmental law.
- Reaffirmed past rulings:
- On “One-Time” Justification:
- Rejected the Centre’s argument that the 2017 measure was a one-time exception.
- Even a one-time relaxation, the Court said, undermines environmental protections and encourages illegal practices.
- Criticized Centre's Intent:
- Noted that the SOP was a disguised attempt to bring back ex-post facto clearances.
- Warned against such “clever drafting” to bypass the law.
Implications of the Verdict
- Reinforces EIA Norms: Upholds the mandatory prior environmental clearance process under EIA 2006.
- Strengthens Environmental Rule of Law: Emphasizes precautionary principle and polluter pays principle.
- Curtails Regulatory Evasion: Sends a clear message that industries cannot bypass environmental safeguards.
- Protects Public Health: Highlights link between environmental damage and issues like pollution in Delhi.
- Judicial Oversight: Asserts constitutional checks on executive actions that dilute environmental protections.
Operation Olivia

- 20 May 2025
In News:
Operation Olivia is an annual conservation initiative launched by the Indian Coast Guard (ICG) in collaboration with the Odisha Forest Department, aimed at protecting the nesting habitats of Olive Ridley turtles along the Odisha coastline. It is conducted from November to May, aligning with the turtles’ mass nesting (Arribada) season.
Key Features of Operation Olivia (as of 2025)
- In February 2025, a record 6.98 lakh Olive Ridley turtles nested at the Rushikulya river mouth.
- Since inception, the ICG has conducted:
- 5,387 surface patrol sorties
- 1,768 aerial surveillance missions
- 366 boats involved in illegal fishing were detained, ensuring effective protection of the turtles' breeding grounds.
- 225 ship days and 388 aircraft hours were dedicated to Operation Olivia during a recent season.
- Focus areas include Gahirmatha Beach, Rushikulya, and Dhamra river mouths in Odisha—home to over 8 lakh nesting turtles annually.
Conservation Measures
- Fishing ban within 20 km of nesting coasts (Devi, Dhamra, and Rushikulya rivers), enforced under:
- Orissa Marine Fishing Regulation Act, 1982
- Wildlife Protection Act, 1972
- Promotion of Turtle Excluder Devices (TEDs) to reduce accidental bycatch.
- Community awareness campaigns and MoUs with NGOs to ensure local participation and education on marine conservation.
About Olive Ridley Turtles
- Scientific Name:Lepidochelysolivacea
- IUCN Status: Vulnerable
- Legal Protection:
- Schedule I, Wildlife Protection Act, 1972
- Appendix I, CITES
- Habitat: Warm tropical waters of the Pacific, Atlantic, and Indian Oceans
- India’s Nesting Sites:
- Gahirmatha Marine Sanctuary – world’s largest rookery
- Rushikulya and Devi river mouths in Odisha
- Unique Feature: Mass nesting behavior known as Arribada, where thousands of females lay eggs on the same beach.
- Behavior: Omnivorous and solitary; migrate thousands of kilometers annually between feeding and breeding grounds.
Coral Reefs

- 19 May 2025
In News:
In a paper published in the Cell Press journal Trends in Biotechnology, researchers demonstrate that the ink could boost coral settlement by more than 20 times, which they hope could contribute to rebuilding coral reefs around the world.
Recent Development in Coral Restoration
- Institution: University of California, San Diego
- Innovation: Development of SNAP-X, a specialized bio-ink.
- Significance: SNAP-X boosts coral larvae settlement by 20 times, marking a major advancement in coral reef restoration, especially vital in the context of climate change-induced reef degradation.
What are Coral Reefs?
- Coral reefs are diverse marine ecosystems formed by colonies of coral polyps, which secrete calcium carbonate to create hard exoskeletons.
- These ecosystems thrive in warm, shallow, and clear tropical waters and are among the most productive on Earth.
Examples of Coral Reefs
- Global: Great Barrier Reef (Australia)
- India: Gulf of Mannar, Lakshadweep Islands
Importance of Coral Reefs
- Biodiversity Hotspots: Support thousands of marine species.
- Coastal Protection: Act as natural barriers against storms and erosion.
- Livelihoods: Sustain tourism and fisheries industries.
- Food Security: Provide fish and other resources to coastal communities.
Types of Coral Reefs
- Fringing Reefs
- Found close to coastlines
- Separated from land by shallow lagoons
- Most widespread type
- Barrier Reefs
- Located farther from shore
- Separated by deeper, wider lagoons
- Example: Great Barrier Reef
- Atolls
- Ring-shaped reefs surrounding a central lagoon
- Often form around subsiding volcanic islands
- Found in the Indian and Pacific Oceans
Favorable Conditions for Coral Reef Growth
Factor Requirement
Water Temperature Around 20°C; typically in tropical zones (30°N to 30°S)
Sunlight Shallow depths (up to ~55 meters) allow photosynthesis
Water Clarity Low nutrient and sediment levels for light penetration
Salinity Stable marine salinity levels
Pollution Minimal; corals are sensitive to chemical/sediment pollutants
Food Supply Plankton-rich water sustains coral polyp
Mosurafentoni
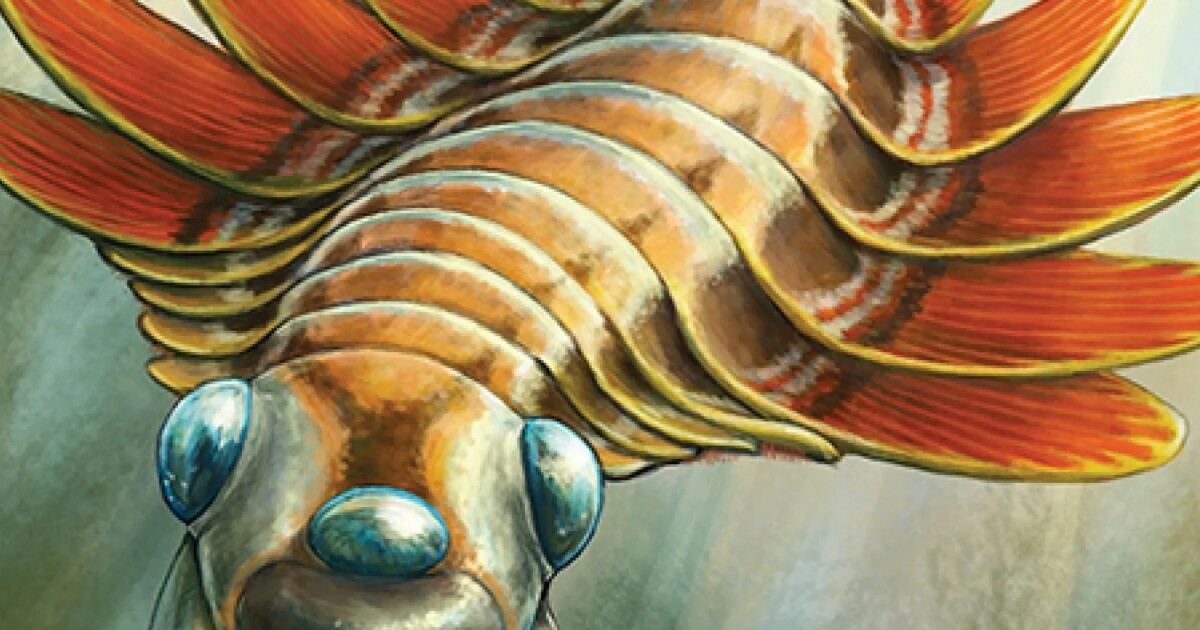

- 19 May 2025
In News:
A new species named Mosurafentoni—a small, three-eyed sea predator—has been discovered in fossils dating back 506 million years. The findings were published in Royal Society Open Science.
Key Highlights:
- Time Period: Cambrian Period (approx. 506 million years ago)
- Classification: Belonged to Radiodonts, an extinct group related to modern-day arthropods like insects, spiders, and crustaceans.
- Unique Traits:
- Three eyes – with a large third eye on the head.
- Jointed claws – similar to crabs or insects, possibly used for capturing prey.
- Swimming style – moved like a stingray using multiple undulating flaps; referred to as “flying underwater”.
- Body structure – featured a trunk-like segment with 16 parts and gills, aiding respiration.
- Mouth – circular, resembling a pencil sharpener lined with serrated plates for slicing prey.
- Size – around the length of a human finger.
- Nickname: Dubbed the "Sea Moth" due to its flapping motion and size.
Ecological Role
- Likely fed on smaller marine organisms like worms and crustaceans.
- Possibly preyed upon by larger predators such as ancient jellyfish.
Evolutionary Significance
- Shows early arthropod diversity and evolutionary complexity.
- Body structure similarities with modern species like horseshoe crabs and woodlice suggest parallel evolutionary adaptations.
- Helps understand the transition from simple worm-like organisms to complex body plans in early marine ecosystems.
Tsarap Chu Conservation Reserve
- 17 May 2025
In News:
Recently, the Himachal Pradesh Government notified the Tsarap Chu Conservation Reserve, making it India’s largest conservation reserve, spanning 1,585 sq km. It is located in the Spiti Valley of Lahaul-Spiti district, a high-altitude, cold desert ecosystem.
Legal Status:
- Declared under Section 36A(1) of the Wildlife (Protection) Act, 1972
- It is Himachal Pradesh’s fifth conservation reserve after Darlaghat, Naina Devi, Potter Hill, and Shilli
Geographical Significance:
- Boundaries:
- North: Union Territory of Ladakh
- East: Kibber Wildlife Sanctuary (up to Malang Nala and LungarLungpa)
- South: KabjimaNala
- West: Chandratal Wildlife Sanctuary
- Encompasses the confluence of Unam River and CharapNala
- Serves as the catchment area of Charap Nallah and a critical wildlife corridor linking Kibber and Chandratal sanctuaries
Ecological Importance:
- Identified as a high-density snow leopard habitat
- Other key species:
- Tibetan wolf, bharal (blue sheep), Himalayan ibex
- Kiang (Tibetan wild ass), Tibetan argali
- Rich in avian biodiversity: Rose Finch, Tibetan Raven, Yellow-billed Chough
Management and Community Involvement:
- To be managed by a Conservation Reserve Management Committee including local Panchayat representatives
- Emphasizes community-based conservation, balancing ecological goals with local livelihoods
- Promotes eco-tourism, wildlife research, and nature-based livelihood opportunities
Indian Grey Wolf
- 15 May 2025
In News:
The Indian grey wolf, a keystone predator crucial to maintaining the ecological balance of India’s grasslands, is facing a sharp population decline. The primary threat stems from increasing encounters with feral (free-ranging) dogs, which pose risks of disease transmission, competition, and hybridization.
Profile:
- Scientific Classification:A subspecies of the grey wolf (Canis lupus), native to the Indian subcontinent and parts of Southwest Asia.
- Habitat:Inhabits scrublands, semi-arid grasslands, and pastoral agro-ecosystems, often overlapping with human-dominated landscapes.
- Physical Traits:Intermediate in size between the Tibetan and Arabian wolves, the Indian grey wolf is adapted to warmer climates and lacks the dense winter coat of its colder-climate relatives.
- Behavioral Characteristics:
- Primarily nocturnal
- Hunts in small packs
- Less vocal than other wolf subspecies
- Geographical Range:Extends from Israel in the west to the Indian subcontinent in the east.
Legal and Conservation Status
- IUCN Red List:Least Concern globally, but considered locally endangered in India due to habitat loss and increasing threats.
- CITES Listing:Appendix I – Species facing extinction, with trade subject to strict regulation.
- Wildlife (Protection) Act, 1972: Listed under Schedule I, ensuring maximum legal protection within India.
Conservation Dilemma: Feral Dogs
- The Maharashtra Forest Rules, 2014 permit the removal of non-wild species, like dogs, from protected forest areas if they pose a threat to native wildlife.
- Despite this provision, forest officials often refrain from culling dogs due to ethical and animal rights concerns.
- Vaccination programs are proposed as alternatives to mitigate disease risks like canine distemper virus (CDV), but implementation remains logistically challenging.
Key Threats
- Disease Transmission: Feral dogs carry zoonotic diseases such as CDV, which can infect and decimate wolf populations.
- Hybridization: Interbreeding with dogs leads to genetic dilution, threatening the purity and survival of the species.
- Competition: Feral dogs compete with wolves for food and territory.
Case Study: Kadbanwadi Grassland, Maharashtra
- Location: Situated in Indapur tehsil, Pune district, this grassland spans over 2,000 hectares.
- Biodiversity Hotspot: Home to species like the Bengal fox, striped hyena, Brahminy kite, and the Indian grey wolf.
- Cultural Coexistence: The local shepherd communities have shared a mutually respectful relationship with wolves over generations, reflecting a model of harmonious coexistence.
Geotubing

- 14 May 2025
In News:
A joint study conducted by the National Institute of Ocean Technology (NIOT) and the Kerala State Coastal Area Development Corporation (KSCADC) has confirmed the effectiveness of geotubing-based offshore breakwaters in managing coastal erosion at Poonthura, Kerala. The installation not only mitigated shoreline erosion but also contributed to sustainable beach formation—highlighting the method's potential for broader coastal protection strategies.
What is Geotubing?
Geotubing involves the use of large geotextile tubes, filled with sand or slurry, which are strategically placed underwater to reduce wave energy and prevent shoreline erosion. At Poonthura, three vertical layers of 15-meter circumference geotubes were installed perpendicular to the coast, forming submerged breakwaters that trap sediment and promote natural sand deposition.
Materials and Construction
- Geotubes Composition:Constructed from high-performance woven geotextiles, typically made of polypropylene (PP) or polyester (PET).
- Material Properties:These fabrics are designed to be permeable, durable, and resistant to UV radiation, chemical exposure, and microbial degradation, making them well-suited for long-term marine use.
Key Functional Features
- Wave Energy Dissipation:Submerged geotubes act as barriers that absorb and deflect wave energy before it reaches the shoreline.
- Beach Nourishment Support:By slowing wave action, the geotubes encourage natural sand accumulation, supporting beach regeneration.
Advantages of Geotubing
- High Durability:Withstands tensile stress and harsh environmental conditions, including chemical and biological exposure.
- Environmentally Friendly:Geotubing is non-toxic and contributes to coastal and wetland restoration without polluting ecosystems.
- Cost-Effective:More economical than traditional concrete or steel structures and easier to install, particularly in remote or variable terrains.
- Customizable Design:Geotubes can be tailored in size and configuration to suit specific project requirements and geographical conditions.
- Multi-Functional Utility:Beyond coastal defense, geotubes are effective in flood management, riverbank stabilization, sludge dewatering, and landfill containment.
Broader Applications of Geotubing
- Coastal Protection:Used in breakwaters, seawalls, and dune reinforcement projects.
- River and Lake Management:Effective for stabilizing riverbanks and controlling sedimentation.
- Wastewater Treatment:Applied in industrial and municipal dewatering processes.
- Infrastructure Support:Utilized in the construction of roads, railways, ports, and reservoirs.
- Environmental Remediation:Useful for site isolation, pollution control, and ecosystem restoration.
20th Session of the United Nations Forum on Forests (UNFF20)

- 13 May 2025
In News:
India actively participated in the 20th session of the United Nations Forum on Forests (UNFF20) held from May 5 to 9, 2025, at the United Nations Headquarters, New York. UNFF, established in 2000 by the UN Economic and Social Council (ECOSOC), is the sole intergovernmental platform dedicated to global forest policy dialogue and coordination, aiming to promote sustainable forest management (SFM) and strengthen political commitment worldwide.
Key Objectives and Functions of UNFF
- Promotes conservation, management, and sustainable development of all forest types.
- Supports the implementation of Agenda 21, Rio Forest Principles, and the UN Strategic Plan for Forests 2017–2030.
- Oversees six voluntary Global Forest Goals (GFGs) and 26 targets, including reversing deforestation and enhancing forest governance.
- Facilitates cooperation through technical exchanges, policy development, financing mechanisms like the Global Forest Financing Facilitation Network, and advocacy linking forests with climate, biodiversity, and sustainable development.
India’s Highlights at UNFF20
India reaffirmed its commitment to the Voluntary National Contributions (VNCs) under the UN Strategic Plan for Forests 2017–2030, reporting progress in increasing its forest and tree cover, which now constitutes 25.17% of the country’s geographical area, as per the latest India State of Forest Report. Major achievements include:
- Restoration efforts under the Aravalli Green Wall project.
- A 7.86% increase in mangrove cover over the past decade.
- Afforestation of over 1.55 lakh hectares through the Green India Mission.
- Plantation of 1.4 billion seedlings under the “Ek Ped MaaKe Naam” (Plant4Mother) campaign.
Global Contributions and Initiatives
India extended an invitation to all UN member states to join the International Big Cat Alliance (IBCA)—a global platform launched by India to conserve seven big cat species through collaborative research, knowledge exchange, and capacity-building.
India also emphasized the importance of incorporating the outcomes of the Country-Led Initiative (CLI) on forest fire management and forest certification—hosted by India in Dehradun in October 2023—into formal global mechanisms. It acknowledged contributions from other countries such as the Republic of Congo, Democratic People’s Republic of Korea, and Austria in this initiative.
Policy and Technical Engagements
India hosted a side event titled “Restoring Degraded Forest Landscapes: India’s Approach to Sustainable Forest Management and Climate Resilience”, showcasing integrated forest restoration strategies combining policy innovation, resource convergence, community participation, and technology.
In a high-level panel on “Valuing Forest Ecosystems in National Policy and Strategy,” India shared pilot study findings from Uttarakhand, Rajasthan, and tiger reserves that quantified ecosystem services like carbon sequestration, water provisioning, and biodiversity conservation. India stressed the need to incorporate ecosystem valuation into national planning to enhance forest governance and ecological sustainability.
Significance of UNFF20
The session focused on advancing three Global Forest Goals:
- Reversing forest cover loss.
- Increasing protected and sustainably managed forests.
- Promoting forest governance and legal frameworks.
UNFF20 aimed to strengthen global dialogue following the 2024 midterm review of the international arrangement on forests and set the agenda for future policy deliberations in 2026. It underscored the critical role forests play in climate resilience, biodiversity, livelihoods, and sustainable development.
Carbon Border Adjustment Mechanism (CBAM)
- 11 May 2025
In News:
India has warned it will retaliate if the United Kingdom implements its proposed Carbon Border Adjustment Mechanism (CBAM) from January 1, 2027, calling it a violation of the Common But Differentiated Responsibilities (CBDR) principle of international climate agreements.
What is Carbon Border Adjustment Mechanism (CBAM)?
- It is a carbon tax on imports based on their carbon intensity of production.
- Aim: Prevent carbon leakage by aligning the cost of carbon between domestic and foreign producers.
- Sectors likely to be initially targeted include steel, cement, aluminium, and energy-intensive products.
- The UK is expected to implement its version of CBAM in 2027, following a similar approach by the European Union.
India’s Concerns
- Violation of CBDR Principle
- CBAM undermines the UNFCCC and Paris Agreement, which recognize that developing countries require flexibility and support for decarbonization.
- India’s per capita emissions are low, but its carbon intensity is higher due to developmental needs.
- Unfair Trade Practice
- CBAM could nullify tariff concessions negotiated under the India–UK Free Trade Agreement (FTA).
- Finance Minister Nirmala Sitharaman and Commerce Minister Piyush Goyal have labelled CBAM “unfair” and discriminatory.
- Double Taxation and Export Losses
- Indian exporters may face double taxation—domestic environmental levies and UK’s border tax.
- India proposed a ‘rebalancing mechanism’ and MSME carve-out, both of which the UK declined.
- Export-heavy sectors like textiles, leather, ceramics, engineering goods, and steel may be hit hard due to sustainability compliance burdens.
- MSME Vulnerability
- Labour-intensive MSMEs lack the capacity to meet expensive ESG norms and carbon tracking requirements.
- India's request for exemption or compensation for MSMEs was not accepted.
India’s Response Strategy
- India reserves the right to retaliate if CBAM is imposed.
- Potential responses include:
- Domestic carbon taxation to offset UK’s CBAM and use revenue for green transition.
- Invoking a rebalancing clause under the FTA’s “general exceptions” (similar to GATT), allowing trade countermeasures for environmental or public interest.
Strategic Implications for India
- Non-tariff barriers like CBAM can undermine market access gained through FTAs.
- India must stay alert to evolving trade conditions involving environment, labour, IPR, and gender standards, which often require policy adjustments.
- Calls for India to strengthen its carbon tracking, ESG frameworks, and climate-compliant production systems to remain globally competitive.
Saola Genome Mapping
- 11 May 2025
In News:
An international team of scientists has successfully mapped the genome of the saola (Pseudoryxnghetinhensis), the world’s rarest large land mammal, providing critical insights for conservation through genetic rescue and captive breeding.
About Saola
- Common Name: Asian Unicorn
- Scientific Name: Pseudoryxnghetinhensis
- First Described: 1993 (based on a skull found in Vietnam in 1992)
- Classification: Bovine species, closely related to cattle but resembling an antelope
- Habitat: Endemic to the Annamite Mountains along the Laos–Vietnam border; prefers humid evergreen forests
- IUCN Status: Critically Endangered
- Estimated Population (2015): 50–300 individuals
- Physical Traits:
- Height: ~33 inches at shoulder
- Both sexes possess straight, parallel horns (~20 inches)
- Distinct white facial markings and muzzle scent glands
Major Threats
- Habitat loss, primarily due to agricultural expansion and forest degradation
- Poaching and indiscriminate snaring, including by-catch in traps set for other animals
- Lack of successful captive care: Over 20 captured saolas died in the 1990s due to inadequate professional care
Genome Mapping and Key Findings
- Sample Base: Genomes of 26 individuals sequenced using remains sourced from hunter households
- Population Divergence: Two genetically distinct populations emerged 5,000–20,000 years ago, likely due to:
- Forest fragmentation during/after the Last Glacial Maximum
- Expansion of human activities such as agriculture, burning, and hunting around 4,000 years ago
- Genetic Complementarity: Each population retains different genetic variants, offering potential for enhanced genetic diversity if combined
- Scientific Importance:
- Confirms historical population isolation and genetic loss
- Provides a genetic foundation for targeted conservation efforts
Conservation Implications
- Captive Breeding Program: Plans underway in Vietnam to establish a well-equipped breeding center
- Goal: Capture at least a dozen individuals from both genetic lineages to create a genetically resilient population
- Long-term Vision: Reintroduction into protected forest areas with strict anti-poaching measures
IMO’s Draft Net-Zero Framework for Shipping
- 09 May 2025
In News:
The International Maritime Organization (IMO) has approved a draft Net-Zero Framework aimed at achieving net-zero greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions from global shipping by around 2050. This is a major milestone in aligning the maritime sector with global climate goals.
Overview of the Draft Net-Zero Framework
What is it?
The framework proposes a legally binding global mechanism to reduce GHG emissions in the maritime industry. It is the first international effort to combine sector-wide emissions caps with a carbon pricing model, setting a precedent for other global industries.
Key Features
- Legal Foundation: Introduced under Chapter 5 of MARPOL Annex VI, focusing on the prevention of air pollution from ships.
- Global Fuel Standard (GFI): Requires ships to reduce GHG intensity of fuel on a “well-to-wake” basis (i.e., accounting for emissions from fuel production to usage).
- Carbon Pricing Mechanism:
- Ships that exceed GFI thresholds must purchase remedial credits.
- Ships using low-GHG fuels can earn and trade surplus credits.
- IMO Net-Zero Fund:
- Redistributes carbon revenues to support:
- Zero-emission vessels
- R&D and capacity building
- Climate resilience initiatives in Small Island Developing States (SIDS) and Least Developed Countries (LDCs).
- Redistributes carbon revenues to support:
- Scope: Applies to ships over 5,000 gross tonnage (GT), covering approximately 85% of global maritime CO? emissions.
- Compliance Tools:
- Credit trading among ships.
- Purchase of credits through the IMO fund.
- Credit banking for future compliance.
Significance of the Framework
- First Global Regulation of Its Kind: Introduces a unified emissions and pricing system for international shipping, transcending national boundaries.
- Promotes Technological Shift: Encourages the adoption of green fuels, carbon capture systems, and hybrid propulsion technologies.
- Supports Climate Goals: Aligns with the Paris Agreement and the IMO’s 2023 Strategy for emissions reduction.
- Equity and Justice-Based Approach: Prioritises financial and technological support to vulnerable maritime nations.
- Catalyst for Green Shipping: Expected to boost demand for ammonia, green methanol, and hydrogen-based marine fuels.
India’s First Inter-State Cheetah Conservation Corridor
- 04 May 2025
In News:
Rajasthan has joined hands with Madhya Pradesh to develop India’s first inter-state cheetah conservation corridor, a landmark initiative under the Cheetah Reintroduction Project. The corridor will facilitate the safe movement of cheetahs across a 17,000 sq. km protected landscape, enhancing conservation and habitat connectivity.
Key Features of the Cheetah Conservation Corridor
Aspect Details
Total Area 17,000 sq. km (MP: 10,500 sq. km; Rajasthan: 6,500 sq. km)
States Involved Madhya Pradesh and Rajasthan
Supported by National Tiger Conservation Authority (NTCA), Wildlife Institute of India (WII)
MoU Status In progress between Chief Ministers of MP and Rajasthan
Geographical Scope and Key Sites
- PalpurKuno National Park (MP):Core site for cheetah reintroduction; located in Sheopur district.
- Gandhi Sagar Sanctuary (MP):Being developed as a second habitat for cheetahs; located in Mandsaur district along the Chambal River.
- Mukundara Hills Tiger Reserve (Rajasthan):Proposed extension site; comprises parts of Darrah, Jawahar Sagar, and Chambal sanctuaries in Kota division.
- Rajasthan Districts Involved:Kota, Bundi, Baran, Jhalawar, Sawai Madhopur, Karauli, Chittorgarh
- Proposed Future Expansion:Forest regions of Jhansi and Lalitpur in Uttar Pradesh
Objectives and Benefits
- Inter-State Wildlife Connectivity:India’s first corridor linking cheetah habitats across state borders.
- Seamless Migration:Enables cheetahs to roam freely between reserves, mimicking natural ecological patterns.
- Ecological Restoration:Aims to revive and conserve India’s arid grassland ecosystems, which are essential habitats for cheetahs.
- Federal Conservation Model:Demonstrates cooperative federalism in wildlife management and biodiversity conservation.
- Global Recognition:Touted as a unique conservation model in Asia, aligning with Convention on Biological Diversity (CBD) targets.
Global push for complete ban on Chlorpyrifos
- 04 May 2025
In News:
At the ongoing 2025 Conference of the Parties (COP) to the Basel, Rotterdam, and Stockholm (BRS) Conventions in Geneva, there has been a renewed global call to list chlorpyrifos under Annex A of the Stockholm Convention, which would mandate a complete global ban without exemptions.
About Chlorpyrifos
- Type: Organophosphate insecticide.
- Usage: Widely used in agriculture and public health to control pests like mosquitoes, termites, and roundworms.
- Mechanism: Inhibits the acetylcholinesterase enzyme, disrupting nerve functions in pests and non-target species including humans.
- Introduced in India: Registered under the Insecticides Act, 1968 since 1977.
- Consumption in India: Accounted for 9.4% of total insecticide use in 2016–17 (IPEN Report).
Health and Environmental Concerns
- Human Impact: Exposure via skin, inhalation, or ingestion can cause headache, nausea, dizziness, muscle cramps, and in severe cases, paralysis and respiratory distress. Forms a toxic byproduct (chlorpyrifos oxon) in the body.
- Environmental Impact:
- Persistence: Remains in soil for weeks to years; degrades slowly in acidic conditions.
- Water Contamination: Reaches water bodies through erosion.
- Toxicity: Highly toxic to birds, fish, bees, and earthworms.
- Bioaccumulation and Biomagnification: Accumulates in organisms and magnifies through the food chain.
- Detection in India: Residues found in agricultural produce, water, human blood, and breast milk.
- A 2003 Indian study recorded levels 41 times higher than WHO safety limits.
Stockholm Convention on POPs (2001; in force since 2004)
- Objective: Eliminate or restrict Persistent Organic Pollutants (POPs).
- Annex A: Complete elimination of listed chemicals (e.g., aldrin, chlordane).
- Annex B: Restricted use.
- Annex C: Minimize unintentional emissions.
- Financial Mechanism: Supported by Global Environment Facility (GEF).
- India’s Status: Ratified in 2006.
- Enacted "Regulation of POPs Rules, 2018" under the Environment (Protection) Act, 1986.
Persistent Organic Pollutants (POPs): Overview
- Definition: Toxic, long-lasting, bioaccumulative chemicals resistant to degradation.
- Health Effects: Cause cancer, endocrine disruption, immune suppression, neurotoxicity, and reproductive harm.
- Examples: DDT, Endosulfan, Aldrin, Dieldrin, PCBs.
Debate at Geneva Meeting (2025)
- Proposal: Listing chlorpyrifos in Annex A without exemptions.
- Supporting Arguments:
- Recommended by the POPs Review Committee (POPRC).
- Detected even in remote areas like the Arctic.
- Long-term harm to child brain development (as per PAN International).
- Disproportionate impact on vulnerable and developing nations.
- Safe alternatives (e.g., agroecological and organic practices) are available.
- India’s Opposition: Cited lack of viable alternatives and threat to food security.
AI-Based Real-Time Forest Alert System
- 04 May 2025
In News:
Madhya Pradesh has become the first state in India to implement an AI-based Real-Time Forest Alert System (RTFAS), marking a significant leap in leveraging technology for sustainable forest management.
Key Highlights
- The AI-based Real-Time Forest Alert System integrates satellite imagery, machine learning, and mobile app feedback for proactive forest monitoring.
- The system is currently being piloted in five forest divisions: Shivpuri, Guna, Vidisha, Burhanpur, and Khandwa—regions with high incidences of encroachment and deforestation.
- Developed using the Google Earth Engine, the system analyses multi-temporal satellite data to detect land use changes, such as:
- Encroachment
- Tree felling
- Construction
- Agricultural expansion
Features of the AI System (RTFAS)
- Custom AI Model: Detects forest degradation by comparing satellite images from three different dates.
- Real-Time Alerts: Sent to forest staff via a mobile application, enabling instant field verification with:
- GPS-tagged photographs
- Voice notes
- Geo-fencing tools
- Interactive Dashboard: Displays live alerts categorized by beat and region with filters for area, density, and time.
- Data Enrichment: Includes indices such as:
- NDVI (Normalized Difference Vegetation Index)
- SAVI (Soil Adjusted Vegetation Index)
- EVI (Enhanced Vegetation Index)
- SAR (Synthetic Aperture Radar)
Forest Status in Madhya Pradesh & India
- Madhya Pradesh:
- Has the largest forest cover in India: 85,724 sq. km (India State of Forest Report 2023)
- Also reported the highest deforestation: 612.41 sq. km lost in 2023
- India:
- Forest and tree cover: 25.17% of total geographical area
- Below the 33% target set by the National Forest Policy, 1988
Role of Technology in Forest Conservation
Application Technology Used
Forest Monitoring AI + Satellite imaging (e.g., RTFAS)
Forest Fires AI cameras, thermal sensors, satellite constellations (e.g., FireSat), drones
Encroachment Detection Satellite alerts with 2–3 day response time
Human-Wildlife Conflict AI camera traps, GPS tracking, RFID tags, geofencing
Afforestation Green bots for planting and monitoring tree growth
Biodiversity Monitoring Acoustic AI (e.g., Rainforest Connection), Environmental DNA (eDNA)
India’s Initiatives for Sustainable Forest Management
Government Initiatives:
- Green India Mission: Increased forest cover by 0.56% (2017–2021)
- National Agroforestry Policy (2014): Promotes tree farming on private lands
- CAMPA (Compensatory Afforestation Fund): Reforestation of diverted forest lands
- Trees Outside Forests in India (TOFI): Involves private stakeholders in increasing green cover
Community & Corporate Involvement:
- CSR-driven plantations by auto, cement, and energy sectors
- Agroforestry: Integrates timber, fruit, and medicinal plants with crops
- Carbon Credit-linked Afforestation
Red-Crowned Roofed Turtle

- 02 May 2025
In News:
After nearly 30 years of absence, the Red-Crowned Roofed Turtle (Batagurkachuga) has been rediscovered in the Ganga River — a significant success for conservation efforts aimed at reviving endangered freshwater species.
Overview
- Commonly known as the Bengal Roof Turtle, it is a rare species of freshwater turtle found only in South Asia.
- Scientific Name: Batagurkachuga
Geographical Distribution
- Native Range: India, Nepal, and Bangladesh.
- Historical Presence: Widely distributed across the Ganga River system in India and Bangladesh, with additional presence in the Brahmaputra River basin.
- Current Habitat in India: The most viable population is now confined to the National Chambal Sanctuary, a protected riverine stretch for species like gharials and turtles.
Distinctive Features
- Size: Medium-sized species, females can grow up to 56 cm in length and weigh up to 25 kg, while males are significantly smaller.
- Coloration: Notable for their reddish-orange head marked with a black crown, and a greenish-brown carapace patterned with yellow streaks.
- Plastron (under-shell): Yellow with distinctive black markings.
- Adaptations: Possess a broad head, strong jaws, and webbed feet, suited for an aquatic lifestyle.
- Diet: Omnivorous — consumes both plant material and small aquatic organisms.
Conservation Status
- IUCN Red List: Critically Endangered
- Wildlife (Protection) Act, 1972: Listed under Schedule I – providing the highest level of legal protection in India.
- CITES: Included in Appendix II, regulating international trade.
Urban Heat Island (UHI) Effect
- 01 May 2025
In News:
With accelerating urbanization and climate change, the Urban Heat Island (UHI) phenomenon has emerged as a significant public health and environmental concern. Recent studies, including one published in Nature Climate Change, highlight that while UHIs elevate heat-related mortality, they simultaneously reduce cold-related deaths, especially in colder regions. This dual impact has major implications for urban planning and climate adaptation strategies.
What is Urban Heat Island (UHI)?
- Definition: UHI refers to the phenomenon where urban areas experience higher temperatures than surrounding rural regions due to human activities and urban infrastructure.
- Cities Affected: Notable examples include New Delhi, Moscow, New York, Paris, and London, where dense infrastructure and limited vegetation intensify urban heat.
Key Causes of UHI
- Impervious Surfaces: Materials like asphalt and concrete absorb heat during the day and release it slowly at night due to low albedo.
- Lack of Vegetation: Reduced greenery limits evapotranspiration, curbing natural cooling.
- Anthropogenic Heat: Heat from vehicles, air conditioners, and industries raises ambient temperatures.
- Air Pollution: Black carbon and particulates absorb solar radiation, compounding heat effects.
- Urban Morphology: Dense construction and narrow streets create a canyon effect, trapping heat and reducing airflow.
Dual Impact on Mortality
A 2025 study led by Dr. Wenfeng Zhan analyzed temperature-related mortality across 3,000+ cities globally using remote sensing and socioeconomic data:
- Cold-related Deaths Reduced: In 2018, the decline in cold-related fatalities was 4.4 times higher than the rise in heat-related deaths due to UHI.
- High-Latitude Cities: In cities like Moscow, cold-related deaths decreased 11.5 times more than heat-related deaths increased.
- Key Insight: The UHI effect's net mortality impact can vary significantly by region and season.
Consequences of UHI
- Increased Energy Demand: Higher temperatures raise demand for air conditioning, increasing fossil fuel use and emissions.
- Health Risks: Elevated risks of heat stroke, dehydration, and cardiovascular stress, especially among the elderly and urban poor.
- Deterioration of Air Quality: Heat-induced formation of ground-level ozone exacerbates respiratory ailments.
- Water Stress: Faster evaporation and increased demand for cooling water pressure urban water resources.
- Biodiversity Decline: Excessive heat and lack of green spaces threaten urban flora and fauna.
Mitigation Strategies
- Cool Roofs (Los Angeles):Mandates reflective roofing in new buildings and renovations to reduce heat absorption.
- Smart Cooling Systems (Dubai):Centralized chilled water systems reduce cooling energy by 30–50% compared to individual AC units.
- Cool Streets Initiative (Paris):Converts streets to pedestrian zones, replaces asphalt with vegetation, and expands urban greenery.
Great White Sharks

- 30 Mar 2025
In News:
A 20-year study in South Africa reveals that the decline of Great White Sharks disrupted marine ecosystems, causing cascading food web imbalances.
Key Highlights:
- Scientific Name:Carcharodon carcharias
- IUCN Red List Status:Vulnerable
- Habitat and Distribution:
- Commonly found in temperate coastal waters, including regions off the USA, South Africa, Australia, and Japan.
- Highly migratory, often venturing into tropical waters but returning to temperate zones for feeding.
- Key Biological Features:
- Endothermic Adaptation: Capable of maintaining body temperature higher than surrounding waters (regional endothermy).
- Body Structure: Streamlined, torpedo-shaped body with serrated teeth for efficient hunting.
- Feeding Behavior: Ambush predator – uses a "bite-and-wait" strategy to hunt seals, dolphins, and large fish.
- Reproduction:
- Viviparous: Gives birth to live young.
- Gestation Period: Around 12 months.
- Maturity:
- Females: Mature at 15–16 feet, around 12–18 years of age.
- Males: Mature at 11–13 feet, around 10 years of age.
- Ecological Importance:
- Apex Predator: Plays a crucial role in maintaining the balance of marine ecosystems by regulating populations of prey such as seals and mid-level predators.
- Indicator Species: Their presence signals the health and stability of marine ecosystems.
- Ecological Disruption in South Africa – Key Findings:
- A 20-year study in False Bay, South Africa, revealed a significant decline in Great White Shark numbers.
- This led to:
- A surge in seal populations and sevengill sharks.
- A corresponding collapse in populations of smaller sharks and fish, showcasing a trophic cascade and food web imbalance.
Bhadra Wildlife Sanctuary

- 29 Mar 2025
In News:
Karnataka Forest Department has initiated a "soft release" strategy to address the escalating human-elephant conflict in the districts of Hassan, Chikkamagaluru, and Kodagu. The strategy involves the phased rehabilitation of captured elephants into the Bhadra Wildlife Sanctuary (BWS).
Soft Release Strategy – Key Highlights
- Objective: To rehabilitate conflict-prone wild elephants and reduce human-elephant encounters.
- Implementation Site:Bhadra Wildlife Sanctuary (BWS), Chikkamagaluru district.
- Initial Step: Captured elephants will be placed in a 20 sq. km enclosure within the sanctuary.
- Purpose of Enclosure:
- Acclimatisation to the wild.
- Health monitoring and behavioural assessment.
- Final Release: Once deemed fit, elephants will be released into one of four pre-identified zones in BWS, chosen based on:
- Availability of water and forage.
- Absence of human activity.
- Road connectivity.
Monitoring & Management
- The enclosure will be fenced using railway barricades.
- A dedicated team of veterinarians will supervise the elephants from a nearby veterinary centre.
- Minimal human interaction will be ensured during the acclimatisation period.
- Expert guidance is being provided by Prof. R. Sukumar (Indian Institute of Science) and senior forest officials.
About Bhadra Wildlife Sanctuary (BWS)
- Location: Western Ghats, Karnataka.
- Area: 492.30 sq. km.
- Also Known As:Muthodi Wildlife Sanctuary.
- Named After: Bhadra River.
- Status: A designated Project Tiger Reserve.
Ecological Significance
- Forest Types:
- Southern Moist Mixed Deciduous Forests.
- Dry Deciduous Forests.
- Shola Forests.
- Wildlife Diversity:
- Mammals: Tigers, leopards, elephants, gaurs, dholes, and deer.
- Birds: ~250 species, including endemic birds like Hornbills, Malabar Trogon, and Hill Myna.
Significance of the Initiative
- Biodiversity Conservation: Enhances protection of endangered species and habitats in the Western Ghats.
- Conflict Mitigation: Aims to provide a sustainable solution to frequent elephant incursions, crop damage, and human casualties.
- Model Strategy: Draws upon similar practices implemented in West Bengal and tailors them to Karnataka’s ecological conditions.
Accelerated Glacier Loss in Hindu Kush Himalayas
- 28 Mar 2025
In News:
On World Day for Glaciers (March 21, 2025), the United Nations World Water Development Report 2025 revealed that glaciers globally are retreating at an alarming rate, with the Hindu Kush Himalaya (HKH) region witnessing the most severe impact — glacier loss accelerated by 65% between 2011–2020 compared to the previous decade.
Key Facts about Hindu Kush Himalaya (HKH) Region
- Geographical Spread: Extends over 3,500 km across 8 countries — Afghanistan, Bangladesh, Bhutan, China, India, Myanmar, Nepal, and Pakistan.
- Population Impact:
- 240 million people live in the HKH region.
- An additional 1.65 billion people downstream depend on its waters for drinking, agriculture, hydropower, and sanitation.
- Glacial Reservoir: Known as the “Third Pole” or “Water Tower of Asia”, the HKH stores more ice than anywhere outside the Arctic and Antarctic.
- River Systems: Source of 10 major river basins, including the Ganges, Indus, Brahmaputra, and Mekong.
Projected Glacier Loss (HKH and Global)
Temperature Rise (°C) HKH Glacier Volume Loss by 2100
1.5°C to 2°C 30%–50%
Above 2°C ~45% (from 2020 baseline)
- Global Glacier Loss: Mountain glaciers may lose 26%–41% of total mass globally by 2100, affecting 1.1 billion people in mountain regions.
Disaster Risks from Glacier Melt
- Glacial Lake Outburst Floods (GLOFs):
- Trigger flash floods and landslides.
- Have caused over 12,000 deaths globally in the past 200 years.
- In the HKH region alone, GLOFs are linked to over 7,000 deaths in the last 190 years.
- Risk of GLOFs may triple by 2100.
- Glacial Lakes: Rapid warming is expanding the number and area of glacier-fed lakes, increasing hazard potential.
Cryosphere and Climate Change
- Hydrological Changes: Melting glaciers alter water runoff patterns, with varied impacts across river basins — increasing monsoon runoff in some while reducing dry-season flows in others.
- Hydropower Challenges:
- Glacial melt initially boosts hydropower potential but may be offset by increased evaporation and reduced glacier mass over time.
- Many hydropower and cryptocurrency mining projects are unregulated and stress fragile mountain ecosystems.
- Mountain-Based Industries: Lithium mining in the Andes, for instance, uses up to 2,000 m³ of water per tonne, intensifying water stress.
Governance and Cooperation Gaps
- Weak Water Governance: Mountain regions, including the HKH, lack effective transboundary cooperation due to mutual distrust and poor data sharing.
- Transboundary Action Plan (HKH):
- Enhance cooperation at all levels.
- Prioritize rights and knowledge of mountain people.
- Limit global warming to 1.5°C.
- Fast-track SDG implementation in mountain areas.
- Strengthen ecosystem resilience and biodiversity.
- Promote regional data sharing and scientific collaboration.
UN Actions and Global Recognition
- International Year of Glacier Preservation (IYGP): 2025
- Decade of Action on Cryospheric Science: 2025–2034 — to advance global efforts in glacier conservation, data collection, and sustainable development in cryosphere-dependent regions.
Rushikonda Beach Regains prestigious Blue Flag Certification

- 27 Mar 2025
In News:
Rushikonda Beach, located in Visakhapatnam, Andhra Pradesh, has successfully regained its Blue Flag certification after a temporary withdrawal due to non-compliance issues. It remains the only Blue Flag-certified beach in Andhra Pradesh and one of 13 such beaches in India.
What is the Blue Flag Certification?
- Administered by: Foundation for Environmental Education (FEE), Denmark.
- National Operator in India: Blue Flag India under the Society of Integrated Coastal Management (SICOM).
- Purpose: Recognizes beaches meeting strict standards of environmental management, safety, cleanliness, and facilities.
- Criteria: Beaches must comply with 33 environmental and safety criteria, including water quality, waste management, safety measures, and environmental education.
- Control Visits: National Operator conducts scheduled and surprise inspections.
Reasons for Temporary Withdrawal
- The Blue Flag tag was withdrawn after complaints of poor maintenance and non-compliance with amenities.
- Non-compliance types:
- Minor issues require rectification within 10 days.
- Multiple or major issues can lead to temporary or season-long withdrawal.
- Rushikonda Beach lost the tag for about two weeks before corrective measures were implemented.
Measures Taken for Regaining the Blue Flag
- Repair and upgrade of beach amenities.
- Plans to install bamboo fencing around the premises to protect the area.
- Public appeals to avoid littering and misuse.
- Education drives for local fisherfolk on beach cleanliness.
- Plans to promote tourism with new beach shacks and regulated alcohol sales, awaiting government approval.
- Identification of 10 other beaches in Andhra Pradesh for upgradation and Blue Flag certification.
Importance of the Blue Flag Tag for Rushikonda Beach
- Tourism Impact: The Blue Flag is internationally recognized by tourists as a mark of safety, cleanliness, and eco-friendliness.
- Environmental Awareness: Promotes responsible tourism and protects coastal ecosystems.
- Local Economy: Supports livelihoods of petty vendors and fisherfolk by attracting visitors.
Key Facts About Rushikonda Beach
- Location: Visakhapatnam, Andhra Pradesh.
- Awarded Blue Flag: First awarded in 2020.
- Features: Golden sands, clear waters, and well-maintained recreational amenities.
- Significance: The only Blue Flag beach in Andhra Pradesh and among 13 in India.
Permafrost Degradation in the Kashmir Himalayas

- 26 Mar 2025
In News:
Permafrost, the ground that remains frozen for at least two years, has long been a critical feature in high-altitude regions like the Kashmir Himalayas. Recent studies have highlighted that melting permafrost is emerging as a significant environmental threat, with the potential to disrupt both ecological systems and infrastructure in the region.
Key Findings of Recent Studies
- Extent of Permafrost: Permafrost covers 64.8% of Jammu & Kashmir (J&K) and Ladakh, with 26.7% being continuous, 23.8% discontinuous, and 14.3% sporadic.
- Regional Distribution: Ladakh has the highest concentration of permafrost (87%), while areas like the Shigar Valley and Siwaliks have no permafrost.
- Impact on Infrastructure: Permafrost degradation threatens key infrastructure, including roads, settlements, and hydropower projects. Approximately 193 km of roads, 2,415 households, and eight hydropower projects are at risk due to thawing permafrost.
- Glacial Lake Outburst Floods (GLOFs): Permafrost thaw increases the likelihood of GLOFs, as seen in recent events like the 2021 Chamoli disaster and the 2023 South Lhonak GLOF. These floods, triggered by the instability of glacial lakes formed by melting ice, can cause significant destruction.
Environmental Impacts of Permafrost Thawing
- Carbon Release: As permafrost melts, it releases stored organic carbon, including methane, a potent greenhouse gas that exacerbates climate change.
- Hydrological Changes: Thawing permafrost can alter river flow and groundwater availability, impacting water resources for local communities and ecosystems.
- Geological Instability: The breakdown of permafrost leads to landslides and slope instability, posing risks to both natural landscapes and human settlements.
Factors Contributing to Permafrost Degradation
- Global Warming: Rising surface temperatures are the primary driver of permafrost thaw.
- Human Activities: Construction activities, including road-building, dam construction, and real estate development, disturb the stability of permafrost. Additionally, deforestation and land-use changes increase the exposure of permafrost to solar radiation, accelerating its degradation.
- Natural Events: Earthquakes and natural processes, like rock-ice avalanches, also contribute to the destabilization of permafrost.
Risks to Local Communities and Infrastructure
- Vulnerable Regions: Thousands of households and critical infrastructure in permafrost-rich areas, such as Ladakh, are at risk due to permafrost thawing. Military and strategic infrastructure, including roads vital for connectivity, may face serious disruptions, compromising national security.
- Glacial Lake Outburst Floods (GLOFs): The melting of glaciers can lead to the formation of proglacial lakes, increasing the risk of GLOFs. In J&K, 332 such lakes have been identified, with 65 showing significant flood risks. GLOFs are a major threat to downstream communities and infrastructure.
Way Forward: Mitigating Risks
- Integrated Planning: Future infrastructure development, especially roads and hydropower projects, should incorporate data on permafrost zones. Risk-sensitive land-use planning and construction methods must be adopted to minimize environmental damage.
- Enhanced Monitoring: Remote sensing technologies, including satellite-based monitoring and ground-based LiDAR systems, should be employed to track permafrost degradation and associated environmental changes more effectively.
- Comprehensive Environmental Assessments: Environmental Impact Assessments (EIAs) must be strengthened to include the risks of permafrost thawing, particularly in relation to GLOFs, landslides, and groundwater depletion. This is crucial for ensuring that development projects in these regions do not exacerbate the environmental risks posed by permafrost degradation.
Targeted Species Conservation
- 26 Mar 2025
In News:
A major global study published in PLOS Biology (March 2025) has reaffirmed that targeted species-specific conservation measures are critical in reversing biodiversity loss and preventing extinctions. Despite the ongoing biodiversity crisis, where six times more species are declining than improving, the study found that where conservation efforts were applied, results were overwhelmingly positive.
Analyzing over 67,000 animal species from the IUCN Red List, researchers from institutions including the University of Cambridge, IUCN, and BirdLife International discovered that 99.3% of species that improved in threat status since 1980 had benefitted from conservation interventions, such as habitat protection, reintroduction, breeding programmes, and legal protections. Of the 969 species with globally increasing populations, 78.3% were under active conservation.
Notable global success stories include:
- Iberian Lynx: Rebounded from a few hundred to several thousand through breeding and habitat restoration.
- K?k?p? (New Zealand parrot): Revived via intensive monitoring and predator control.
- European Bison: Successfully reintroduced in Eastern Europe after extinction in the wild.
- Marine species such as humpback and blue whales also recovered after international moratoriums on whaling.
Island ecosystems like New Zealand, Mauritius, and the Seychelles showed the highest concentration of species recovery, while decline hotspots included the Tropical Andes, Sumatra, Malaysia, and Borneo.
Despite these successes, the study cautions that since 1980, 1,220 species of birds, mammals, and amphibians have deteriorated in Red List status compared to only 201 species that improved.
Causes include habitat loss, pollution, overexploitation, climate change, invasive species, and disease.The study called for landscape-scale conservation and ambitious implementation of Goal A of the Kunming-Montreal Global Biodiversity Framework to halt extinction risk and restore resilient populations.
India’s Species-Specific Conservation Efforts
India has adopted a multi-pronged species-specific conservation approach, primarily under the Integrated Development of Wildlife Habitats (IDWH), 2008, which continues under the 15th Finance Commission (2021–26). The scheme focuses on critically endangered species through captive breeding, habitat restoration, and community participation.
Key initiatives include:
- Species Recovery Programme: Prioritizes 22 species (16 terrestrial and 6 aquatic) for focused conservation.
- Project Tiger (1973) and Project Elephant (1992): Flagship conservation efforts for apex species.
- Project Crocodile: Initiated post-Wildlife (Protection) Act, 1972, supported by the UN. Saltwater crocodiles in Bhitarkanika increased from 95 (1975) to 1,811.
- Sea Turtle Conservation Project (1999): Focuses on Olive Ridley Turtles, listed as Vulnerable (IUCN), Schedule I (WLPA), and Appendix I (CITES).
- Vulture Action Plan 2020–25: Aims to eliminate diclofenac use and protect food sources for vultures. India's first Vulture Conservation and Breeding Centre (VCBC) was set up in Pinjore, Haryana.
- Indian Rhino Vision 2020: Increased the Greater One-Horned Rhinoceros population in Kaziranga National Park to over 2,600 (2022).
- Project Cheetah (2022): Reintroduces cheetahs extinct in India since 1952, with cheetahs from Namibia and South Africa released in Kuno National Park. India saw its first wild cheetah birth in 2023 after 75 years.
- Maharashtra’s Pangolin Action Plan: The first dedicated plan for pangolin conservation. Pangolins are listed under Schedule I of the WLPA, receiving the highest level of protection.
Global Environmental Data Strategy (GEDS)
- 25 Mar 2025
In News:
- The Global Environmental Data Strategy (GEDS), spearheaded by the United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP), is a comprehensive framework designed to address the triple planetary crises of climate change, pollution, and biodiversity loss.
- GEDS aims to leverage high-quality, accessible environmental data to support informed decision-making, foster innovative digital solutions, and promote sustainable development.
- The strategy is currently under development, with UNEP working to finalize it by December 2025. It emphasizes overcoming barriers such as data fragmentation, lack of interoperability, and limited access, which hinder the effective use of environmental data.
Key Focus Areas of GEDS
The GEDS framework is built around five key pillars that focus on overcoming challenges and unlocking the potential of environmental data:
- Data Quality and Provenance:
- Establishing standardized frameworks and mechanisms to classify and ensure the accuracy of environmental data.
- Focusing on data quality and developing systems to trace its origin (provenance).
- Data Governance:
- Promoting ethical and sustainable methodologies for managing environmental data.
- Developing governance models to ensure data is managed in a transparent and responsible way.
- Data Interoperability:
- Federating global and thematic data standards to allow seamless data sharing and integration.
- Ensuring that data across different platforms and systems can communicate with each other, facilitating better collaboration.
- Inclusive Data Access:
- Ensuring open, affordable, and machine-readable access to environmental data for all stakeholders.
- Addressing issues related to data discoverability and making data AI-ready to foster innovative solutions.
- Capacity-Building:
- Enhancing the skills and knowledge needed for effective data collection, governance, and use.
- Focusing on strengthening global initiatives, particularly in the Global South, to improve data management capabilities and foster inclusive participation.
Significance of GEDS
- Tackling Environmental Crises: GEDS provides a data-driven approach to addressing the challenges of climate change, pollution, and biodiversity loss, aligning with global efforts to achieve the UN Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs).
- Supporting Informed Decision-Making: By ensuring the availability of high-quality environmental data, GEDS helps governments, organizations, and communities make evidence-based decisions that are crucial for environmental sustainability.
- Fostering Innovation: The strategy facilitates the development of AI and data analytics tools to create innovative solutions for environmental management and protection.
- Global Collaboration: By promoting international cooperation and sharing of environmental data, GEDS aims to improve global collaboration to combat environmental challenges.
World Water Day 2025

- 25 Mar 2025
In News:
Marking World Water Day, the Ministry of Jal Shakti, in collaboration with the Ministry of Environment, Forest & Climate Change and the Government of Haryana, launched the much-anticipated sixth edition of Jal Shakti Abhiyan: Catch the Rain - 2025 in Panchkula, Haryana.
World Water Day 2025
- Observed On: 22nd March 2025
- 2025 Theme: ‘Glacier Preservation’
- Global Context: Declared by the United Nations General Assembly in 1993, conceptualized at the 1992 Rio Earth Summit.
- Linked SDG: Sustainable Development Goal 6 (SDG-6) – Clean Water and Sanitation for All by 2030.
- Purpose: To raise global awareness on water conservation and promote sustainable water use.
India's Observance: Launch of Jal Shakti Abhiyan – Catch the Rain 2025
- Launched by: Ministry of Jal Shakti, in collaboration with Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change (MoEFCC) and Government of Haryana.
- Launch Venue: Panchkula, Haryana (first time outside Delhi).
- Theme: “????????????????: ??????????????” (People’s Action for Water Conservation – Towards Intensified Community Connect).
- Focus Areas:
- Rainwater harvesting
- Groundwater recharge
- Community-led water conservation
- Ecological restoration (forests, rivers, springs)
Key Campaigns & Initiatives
Jal Shakti Abhiyan: Catch the Rain 2025 (JSA:CTR)
- Targeted Districts: 148 water-stressed districts across India.
- Tagline: “Catch the Rain where it falls, when it falls.”
- Objective: Promote localized water conservation through people’s participation and decentralized planning.
“Jal-Jangal-Jan” Abhiyan
- Aim: Restore ecological connectivity between water, forests, and communities.
- Collaborators: MoEFCC and Jal Shakti Ministry.
- Tools Used: Awareness videos, AV content, best practice compilations.
State-Level Innovations: Haryana Model
- Launched:
- Mukhyamantri Jal Sanchay Yojana – Enhancing water harvesting through community participation.
- Water Resources Atlas – Scientific mapping of water availability.
- Online Canal Water Management System – Real-time irrigation data for efficiency.
- E-booklet on Integrated Water Resources Management.
- Infrastructure Projects under SBM-G & JSA:
- Community Sanitary Complexes
- Solid & Liquid Waste Management
- Gobardhan (Biogas) Projects
- Borewell Recharge Systems
- Micro-irrigation and Rainwater Harvesting Projects
Key Government Schemes Related to Water
- Jal Shakti Abhiyan (JSA) – Time-bound, mission-mode campaign for water conservation.
- Atal Bhujal Yojana – Participatory groundwater management in critical areas.
- AMRUT 2.0 – Urban water supply and sewerage services improvement.
Eurasian Goshawk sighting at Tansa Wildlife Sanctuary

- 24 Mar 2025
In News:
A significant wildlife discovery has been made at Tansa Wildlife Sanctuary, Maharashtra, where the Eurasian goshawk, a large bird of prey, was spotted for the first time. This marks the first documented instance of the Eurasian goshawk in the sanctuary, although the species has been previously recorded in Maharashtra three times.
About the Eurasian Goshawk
- Scientific Name: Accipiter gentilis
- Description: A powerful raptor known for its short, broad wings and long tail.
- Habitat: Dense forests, particularly coniferous and mixed woodlands across Europe, Asia, and parts of North America.
- Winter Visitor: The Eurasian goshawk is a winter visitor to India, making this sighting at Tansa particularly noteworthy.
Tansa Wildlife Sanctuary
- Located in the foothills of the Western Ghats in Thane District, Maharashtra, Tansa Wildlife Sanctuary covers 320 sq. km.
- Positioned approximately 90 km northeast of Mumbai, it serves as a vital catchment area for Tansa Lake and is bordered by the Tansa and Vaitarna rivers.
Flora and Fauna
The sanctuary boasts a rich diversity of flora and fauna, including:
- 200 bird species
- 54 animal species, including endangered animals like:
- Panther
- Hyena
- Barking Deer
- Notable species include:
- Critically Endangered vultures
- Vulnerable Pallas’s fish-eagle
Vegetation and Landscape
- Southern Tropical Moist Deciduous Forest with patches of Evergreen Forest.
- Flora includes trees like Kalamb, Bibla, Khair, Hed, Teak, and Bamboo.
Avian Discoveries
Tansa Wildlife Sanctuary is also renowned for its avian discoveries, such as the critically endangered Forest Owlet, which was first documented here in 2014. This discovery highlighted the sanctuary’s significance for bird conservation.
Conservation Efforts and Ecological Role
The sighting of the Eurasian goshawk further emphasizes the critical need for ongoing conservation efforts at Tansa Wildlife Sanctuary.
Role of the Eurasian Goshawk in Ecosystem
As a bird of prey, the Eurasian goshawk plays a vital role in maintaining ecological balance by controlling populations of smaller mammals and birds.
Though listed as "Least Concern" on the IUCN Red List, the Eurasian goshawk’s presence underscores the sanctuary’s importance in the region’s biodiversity.
2030 Global Forest Vision (GFV)
- 23 Mar 2025
In News:
The 2030 Global Forest Vision (GFV), released in March 2025 by the Forest Declaration Assessment (FDA), outlines priority actions for governments to reverse forest loss and align environmental and trade policies ahead of UNFCCC COP30 (November 2025).
Background:
- The Forest Declaration Assessment (FDA) was established in 2015 to monitor progress on the New York Declaration on Forests (NYDF), a voluntary pact launched in 2014.
- NYDF includes 10 goals aimed at halting deforestation by 2030 and is supported by governments, corporations, indigenous groups, and civil society.
- India is not a signatory to the NYDF as of 2025.
Current State of Forests (Key Data):
- Despite commitments from 140 countries, 6.37 million hectares of forests were lost in 2023.
- Major drivers of deforestation:
- Agricultural demand for palm oil, soy, beef, and timber.
- 80% of Amazon deforestation is due to cattle ranching.
- 800+ million trees lost between 2017–2022 to meet Brazilian beef exports.
- In Indonesia and Malaysia, palm oil expansion threatens orangutans and Sumatran tigers.
Eight Priority Actions for Governments (GFV 2025):
- Ambition:Integrate forest conservation into national climate and biodiversity plans and COP30 commitments.
- Trade:Ensure legal, deforestation-free, and degradation-free trade through international partnerships.
- Finance:Scale up results-based payments and forest carbon credit systems, as agreed in the 2024 Forest & Climate Leaders’ Statement.
- Rights:Secure land rights of Indigenous Peoples (IPs) and Local Communities (LCs) to protect traditional forest stewardship.
- Supervision:Mandate financial institutions to assess and manage forest-related risks.
- Subsidies:Repurpose harmful subsidies to support sustainable food systems, bioeconomy, and forest management.
- Governance:Align land-use sector governance with global forest and climate commitments.
- Debt Flexibility:Recognize forests as natural capital in debt management to enhance fiscal space for forest-rich countries.
Global and Regional Efforts:
- EU Deforestation Regulation (2026):Bans imports linked to deforestation; companies must ensure supply chain transparency.
- U.S. Initiatives:Stricter laws against illegal logging and deforestation-linked imports.
- Challenges:
- China and India have not implemented deforestation-free trade regulations.
- Smallholder farmers lack the resources to certify products as deforestation-free.
- Developing nations (Brazil, Indonesia, African countries) express concerns over economic impacts of stricter trade rules.
Recommendations by GFV 2025:
- Tighten Global Trade Policies:Prevent companies from rerouting products to markets with weak regulations.
- Adopt Deforestation-Free Trade Laws:India, China, and other major economies urged to enact such policies.
- Support Local Economies:Provide technical and financial support to farmers for sustainable practices.
- Enhance Global Monitoring:Improve tracking systems for forest-linked commodities and promote global cooperation.
WEF UpLink Annual Impact Report 2025

- 21 Mar 2025
In News:
The World Economic Forum’s (WEF) UpLink Annual Impact Report 2025 underscores the significant contributions of early-stage start-ups in tackling climate and sustainability challenges globally.
About UpLink:
- Launched: 2020 at Davos by WEF in collaboration with Deloitte and Salesforce.
- Objective: Open innovation platform to support the UN Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) by connecting entrepreneurs with experts, investors, and stakeholders.
Key Environmental and Social Impacts (2023–2024):
Category Impact
Carbon Emissions 142,400 tonnes of CO? prevented (equal to emissions
of ~30,000 cars)
Ecosystem Protection 140 million hectares of land and water safeguarded
Water Management 2.5 billion litres of hazardous wastewater treated
Waste Management 28 million tonnes of waste tracked
Water, Sanitation & Hygiene (WASH) 2.7 million people gained improved access
Job Creation 30,000+ new jobs generated
Livelihood Support ~500,000 smallholder farmers and fishers experienced
income growth
Waste Collector Empowerment 18,000 collectors integrated into formal markets
Notable Indian Contributions:
- Indra Water: Processed 1.2 billion litres of wastewater in 2024 (243% rise from 2022).
- S4S Technologies: Reduced 60,000 tonnes of food waste — enough to feed 2.7 million people for a month.
Global Innovations Highlighted:
- EnviCore (Canada): Uses mining waste in construction to cut emissions.
- Umgrauemeio (Brazil): AI-based wildfire monitoring across 6.7 million hectares of forests.
- SHAYP: Saved 7 billion litres of water in 2024 using leakage detection; aims for 100 billion litres by 2027.
- GreenPlat (Brazil): Tracked 12.3 million tonnes more waste in 2024 than the previous year.
Investment and Innovation Trends:
- Total Funds Raised by UpLink Ventures in 2024: $633 million (up by $196 million from 2023).
- Customer Base Growth: Nearly 50% of ventures reported over 40% increase in customers.
- Circular Economy Focus: 13 ventures supported under the Traceability for Circularity Challenge to promote ethical and waste-reducing value chains.
Future Focus Areas (Planned by UpLink):
- Sustainable mining
- Carbon capture technologies
- AI-driven environmental monitoring
State of the Global Climate 2024 Report
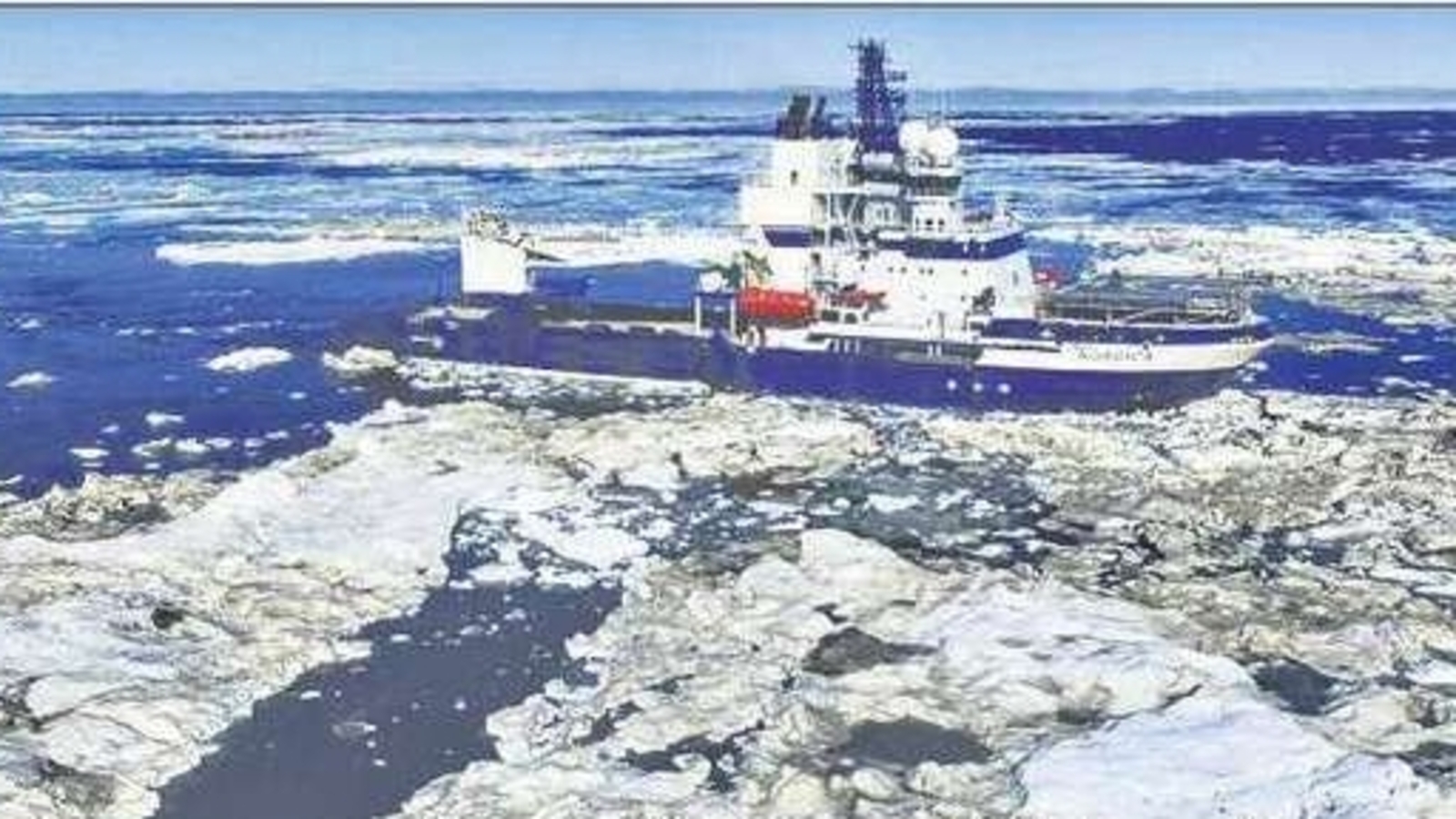

- 21 Mar 2025
In News:
The World Meteorological Organization (WMO) released its State of the Global Climate 2024 Report at COP29 (Baku), warning that global warming is dangerously close to breaching the 1.5°C threshold set by the Paris Agreement.
About WMO
- Type: UN Specialized Agency
- Established: 1950
- Headquarters: Geneva, Switzerland
- Membership: 193 (187 Member States + 6 Territories)
- Mandate: Meteorology, operational hydrology, and geophysical sciences.
- Reports Released:
- State of the Global Climate Report
- Greenhouse Gas Bulletin
- Global Water Resources Report
- State of Climate Services Report
- United in Science Report
Key Findings – State of Global Climate 2024
Global Temperature Rise
- Current warming: 1.34°C–1.41°C above pre-industrial levels.
- 19 of the last 20 months crossed the 1.5°C threshold temporarily.
- 2024: Warmest year in the 175-year observational record.
- Projected crossing of the 1.5°C threshold: by September 2029.
Greenhouse Gases (2023)
- CO?: 420 ppm – 151% of pre-industrial levels (highest in 800,000 years)
- CH? (Methane): 1923 ppb – 266% of pre-industrial levels
- N?O (Nitrous Oxide): 335.8 ppb – 124% of pre-industrial levels
Ocean & Cryosphere
- Ocean Heat Content: Highest in 65 years – oceans absorb 90% of global heat
- Sea Level Rise:
- 1993–2002: 2.1 mm/year
- 2015–2024: 4.7 mm/year (rate doubled)
- Glacier Melt:
- 2022–2024: Largest 3-year negative mass balance on record
- Severe loss in Norway, Sweden, Svalbard, and Andes
- Arctic Sea Ice: Record lows for 18 consecutive years
- Antarctic Sea Ice: 2nd-lowest extent ever
- Ocean Acidification:
- Surface pH falling fastest in Indian Ocean, Southern Ocean, and Pacific
- Effects irreversible for centuries
Extreme Weather Events & Displacement
- 2024: Record-high displacements from climate disasters
- Cyclones, floods, and droughts worsened food and humanitarian crises
- Worst-hit regions: East Asia, Southeast Europe, West Asia, Mediterranean
Reasons Behind These Trends
- GHG Emissions: Fossil fuel combustion, industrial emissions, agriculture, and deforestation.
- El Niño Effect: Warm Pacific currents intensified 2024’s global heat.
- Urban Heat Islands: Dense cities retain heat, increasing local warming.
- Ocean Absorption: Excess atmospheric CO? and heat absorbed by oceans.
Global Climate Governance
- UNFCCC (1992): Multilateral treaty for climate action.
- Paris Agreement (2015):
- Goal: Limit warming to below 2°C, aim for 1.5°C.
- Nationally Determined Contributions (NDCs)
- $100 billion/year climate finance pledge
- Global Methane Pledge (2021): Cut methane emissions by 30% by 2030.
- Global Ocean Treaty (2023): Protect 30% of oceans by 2030.
- UN Decade on Ecosystem Restoration (2021–2030): Forest and marine recovery.
- IPCC: UN scientific body for climate assessments (doesn’t conduct research).
India’s Climate Initiatives
Targets & Strategies
- Net Zero by 2070 (COP26)
- LT-LEDS (2022): Long-term low emissions strategy
- Updated NDC (2022):
- Reduce GDP emissions intensity by 45% by 2030 (vs. 2005)
- 50% electricity capacity from non-fossil sources by 2030
Renewable Energy & Alliances
- International Solar Alliance (ISA):
- Launched with France in 2015 (COP21)
- Aim: Mobilize $1 trillion in solar investments by 2030
Afforestation & Ecosystem Protection
- Green Credit Program (2023) – incentivizes afforestation
- Ek Ped MaaKe Naam (2024) – tree plantation campaign
- NAP, CAMPA, Forest Act 1980 – promote forest restoration
- MISHTI (2023) – Mangrove restoration (?12.55 cr in 2024–25)
Behavioral Change
- LiFE (Lifestyle for Environment) – promotes sustainable consumption
Challenges to Climate Action
Sector Key Challenges
Energy High coal dependence (>50%), renewable intermittency, grid gaps, foreign tech reliance
Urbanization Rising energy/waste demand, land use conflicts
Industry Hard-to-abate emissions in cement, steel, transport
Agriculture Fossil fuel inputs, livestock methane, fertilizer N?O
Finance Climate finance disparities; India criticized COP29’s $300 bn/year goal as insufficient
Equity Developed nations emit more, but developing nations suffer more
Greenwashing Misleading climate claims by corporates/governments
National Wildlife Health Policy (NWHP)

- 20 Mar 2025
In News:
In the aftermath of the COVID-19 pandemic, the Government of India is formulating the National Wildlife Health Policy (NWHP) to address the growing threat of zoonotic diseases through integrated wildlife health management. Over 60% of emerging infectious diseases in humans originate from animals, underscoring the importance of a "One Health" approach—integrating human, animal, and environmental health.
Key Objectives of NWHP
- Establish a comprehensive wildlife disease surveillance system.
- Strengthen diagnostic infrastructure and research capacity.
- Facilitate cross-sectoral collaboration among environment, agriculture, and animal husbandry ministries.
- Integrate existing animal and human health data systems with wildlife health information.
Institutional Framework & Implementation
- National Referral Centre for Wildlife (NRC-W):
- Inaugurated in Junagadh, Gujarat (March 2024).
- India’s first wildlife disease diagnostic and research centre.
- Will serve as a referral hub for investigating wildlife mortality and outbreak events.
- Wildlife Health Information System (WHIS):
- Proposed digital system for real-time disease data collection, reporting, and analysis.
- Will integrate with National Animal Disease Reporting System (NADRS) and National Animal Disease Referral Expert System (NADRES).
- Satellite Diagnostic Labs:To be established near important forest zones for timely wildlife disease detection and diagnosis.
- Community Engagement:Involves measures like cattle vaccination near national parks to reduce disease transmission risks.
Key Agencies Involved
- Central Zoo Authority (CZA): Nodal agency under the Wildlife Protection Act, 1972; responsible for policy coordination and implementation.
- Office of the Principal Scientific Adviser and IIT-Bombay: Supporting technical and policy formulation.
- Ernst & Young: Consultancy support.
- Ministry of Environment, Forest & Climate Change (MoEF&CC): Policy oversight.
Alignment with Existing Conservation Frameworks
- National Wildlife Action Plan (2017–31):
- Provides for 103 actions and 250 projects.
- Includes protocols for disease surveillance in protected areas and tiger reserves.
- Wildlife Protection Act, 1972: Provides legal basis for wildlife health regulation and zoonotic disease control.
Chhareda Panchayat Water Conservation Model

- 19 Mar 2025
In News:
Rajasthan’s Chhareda Panchayat in Dausa district has emerged as a leading example of effective water conservation, driven by a community-driven initiative that has significantly transformed agricultural practices and farmer livelihoods. The project, led by Vipra Goyal, an alumnus of IIT-Kharagpur, has revolutionized water usage in the region through the construction of 250 farm ponds.
Key Aspects:
- Objective:The model aims to address water scarcity and groundwater depletion through rainwater harvesting and the construction of farm ponds, reducing dependence on overexploited groundwater sources.
How Farm Ponds are Contributing to Water Conservation in Rajasthan
- Rainwater Harvesting:Farm ponds serve as storage systems for rainwater, minimizing reliance on deep, contaminated groundwater sources. This helps prevent the further depletion of underground water reserves.
- Year-Round Water Availability:The ponds provide consistent water supply for both kharif and rabi crops, ensuring that farmers can grow crops throughout the year without facing water shortages.
- Groundwater Conservation:By reducing the need to extract groundwater, this initiative has helped conserve approximately 30 crore litres of water annually, easing the pressure on local aquifers.
- Boosting Agricultural Productivity and Income:With reliable water sources, farmers have shifted from subsistence farming to growing cash crops, which has resulted in a collective increase of about ?5 crore in household incomes.
- Reduced Water Pollution:The initiative avoids the use of groundwater contaminated with harmful substances like arsenic and fluoride, which are prevalent in many areas of Rajasthan.
- Sustainability and Climate Resilience:The farm ponds offer a climate-resilient solution, ensuring that agriculture in water-scarce regions is sustainable even in the face of erratic rainfall patterns.
- Cost-Free Construction:The construction of the ponds has been facilitated through CSR funds and government schemes, making the project cost-free for farmers.
International Big Cat Alliance (IBCA)
- 19 Mar 2025
In News:
The International Big Cat Alliance (IBCA), a treaty-based intergovernmental organisation dedicated to the conservation of seven major big cat species, has officially signed an agreement with the Government of India, establishing India as the permanent host of its headquarters and secretariat.
Background and Launch
- Launched: April 2023 by Prime Minister Narendra Modi during the 50th anniversary celebrations of Project Tiger.
- Objective: To facilitate global cooperation for the conservation of seven big cats:Tiger, Lion, Leopard, Snow Leopard, Cheetah, Puma, andJaguar.
- The IBCA is implemented through the National Tiger Conservation Authority (NTCA) under the Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change (MoEFCC).
International Status and Membership
- The IBCA became a treaty-based intergovernmental alliance after five countries ratified the framework agreement:India, Liberia, Eswatini, Somalia, andNicaragua.
- India formally joined the IBCA in September 2023.
- The alliance is open to all UN Member States, including:
- Range countries (where big cats are native), and
- Non-range countries that wish to support conservation efforts globally.
Headquarters and Agreement
- On March 28, 2024, the Union Cabinet approved the establishment of the IBCA headquarters in India.
- An agreement was signed in May 2024 between the IBCA and the Indian government, outlining:
- Privileges and immunities for IBCA personnel,
- Visa facilitation, and
- Operational and legal provisions for the headquarters.
Funding and Support
- India has committed a total of ?150 crore (2023–2028) for:
- Creating a corpus fund,
- Building infrastructure, and
- Meeting recurring expenditures over five years.
Colossal Squid

- 19 Mar 2025
In News:
In a landmark moment for marine biology, scientists have captured the first-ever footage of a colossal squid in its natural deep-sea habitat. The sighting was made by an international research team using a remotely operated submersible in the South Atlantic Ocean, near the South Sandwich Islands, and was announced by the Schmidt Ocean Institute in April 2025.
About the Colossal Squid
- Scientific Name:Mesonychoteuthishamiltoni
- Distribution: Found in the cold, deep waters of the Southern Ocean near Antarctica
- IUCN Status:Least Concern
The colossal squid is among the largest and most elusive invertebrates on Earth. The filmed specimen was a juvenile about 30 cm (1 foot) long, observed at a depth of 600 meters. However, fully grown adults can reach up to 7 meters (23 feet) in length and weigh around 500 kg.
Key Features
- Body: Tube-shaped and soft-bodied, similar to octopuses but far more massive
- Arms & Tentacles: Equipped with suckers and sharp, swivelling hooks — a feature unique to the species
- Eyes: Possess the largest eyes known in the animal kingdom, aiding visibility in the pitch-dark ocean depths
- Coloration:
- Juveniles are nearly transparent, giving them a glassy, ghost-like appearance
- Adults become opaque, with dark red or purple hues and muscular limbs
Scientific Importance & Recent Discovery
- This deep-sea sighting comes almost a century after the species was first identified, and confirms long-standing hypotheses based on carcasses found in the stomachs of whales and seabirds.
- The team is now testing improved camera systems to attempt capturing footage of an adult colossal squid in action.
India’s Carbon Credit Trading Scheme (CCTS)
- 16 Mar 2025
In News:
To meet its climate commitments under the Paris Agreement, India is moving towards a market-based mechanism for emissions reduction through the Carbon Credit Trading Scheme (CCTS), 2023. The scheme was made possible by amending the Energy Conservation Act, 2021 and replaces the Perform, Achieve, and Trade (PAT) scheme operational since 2012.
What is the Carbon Credit Trading Scheme (CCTS)?
- CCTS is India’s version of an emissions trading system (ETS) designed to reduce greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions intensity — emissions per unit of output — rather than absolute emissions.
- It introduces Carbon Credit Certificates (CCC), each representing one tonne of CO? equivalent (tCO?e) reduction.
- Managed by the Bureau of Energy Efficiency (BEE) and coordinated by a National Steering Committee, the scheme involves various regulatory bodies including electricity exchanges, MoEFCC, and the Central Electricity Regulatory Commission.
Key Features of the CCTS
Aspect Description
Transition from PAT - Shifts focus from energy efficiency (PAT) to emission intensity (CCTS).
Coverage - Initially targets energy-intensive sectors: Iron & Steel, Cement, Aluminium,
Fertilisers, Refineries, Pulp & Paper, and Textiles (~16% of national
GHG emissions). Power sector (~40%) may be included later.
Dual Mechanisms - 1. Compliance: Mandates targets for large emitters. 2. Offset:
Voluntary participants earn credits by reducing emissions.
Implementation Timeline - Expected to launch fully by mid-2026, in a phased manner.
Global Context of Carbon Pricing
- As of June 2024, 89 countries operate carbon pricing mechanisms, covering 12.8 Gt CO?e (25% of global emissions).
- Carbon pricing methods:
- ETS (Cap-and-Trade / Baseline-and-Credit): Companies trade allowances or credits based on performance.
- Carbon Tax: Fixed price on emissions; provides cost certainty but not emissions certainty.
- Crediting Mechanism: Projects generating verified emission reductions earn tradable carbon credits.
Challenges in Implementing CCTS
- Target Setting: Overly lenient targets may cause credit oversupply, reducing prices; overly strict ones risk high compliance costs.
- Compliance Gaps: Under PAT, over half the required energy certificates were never purchased, with no penalties imposed.
- Delays: Credit issuance under PAT (Phase IV onwards) has been delayed since 2021, affecting market confidence.
- Transparency: Lack of public access to data on actual performance undermines accountability.
- Monitoring and Verification (MRV): Requires robust systems to prevent double counting and ensure credible reporting.
Steps to Strengthen India’s Carbon Market
- Align with global practices: Learn from the EU ETS — implement strict monitoring, gradual tightening of caps, and price stability mechanisms.
- Robust MRV Framework: Ensure accuracy in emission data to boost trust.
- Digital Trading Platform: Track and authenticate credit transactions; avoid fraud.
- Industry Incentives: Encourage early compliance via tax benefits and access to green finance.
- Trade Compatibility: Prepare for global measures like the EU’s Carbon Border Adjustment Mechanism (CBAM) by ensuring transparency and comparability.
India’s CCTS represents a significant shift in climate governance by institutionalizing carbon pricing. While it brings India in line with evolving global practices, the success of the Indian carbon market will depend on credible enforcement, transparent functioning, and strong regulatory architecture. If implemented effectively, it can drive low-carbon growth and support India’s target of reducing emissions intensity by 45% by 2030.
Pobitora Wildlife Sanctuary

- 15 Mar 2025
In News:
Pobitora Wildlife Sanctuary, located in Assam, is renowned for its high density of the Great Indian One-Horned Rhinoceros and diverse biodiversity. The sanctuary, covering 38.85 km², is facing a growing concern as one of its major wetlands, TamulidobaBeel, is drying up. This situation underscores the urgent need for habitat management to protect the sanctuary's wildlife.
About Pobitora Wildlife Sanctuary:
- Location: Located within 30 km of Guwahati, Assam, it was established in 1998 and spans 48.81 km².
- Fauna: Famous for its rhino population, the sanctuary also houses leopards, wild boars, barking deer, wild buffaloes, and over 2,000 migratory birds.
- Flora: The sanctuary is dominated by wet savannah and marshland, though the invasive water hyacinth is a significant problem, especially for waterfowl.
TamulidobaBeel: A Crucial Wetland
- Role: A key water body within the sanctuary, TamulidobaBeel is vital for rhinos, water buffaloes, and migratory birds.
- Drying Concern: Experts and locals have observed the early drying up of the Beel, a trend that has worsened over the past few years. Migratory birds have already abandoned the wetland earlier than expected, signaling a broader ecological imbalance.
Factors Contributing to Drying of the Wetland:
- Siltation: The deposition of silt has significantly reduced water retention in the Beel.
- Climate Change: Predictions of a hotter weather season (March-May 2025) by the India Meteorological Department suggest further strain on the sanctuary's water resources, affecting biodiversity.
Ecological Implications:
- Rhino Habitat Impact: About 20-25 rhinos are regularly found near TamulidobaBeel. The drying of this wetland increases water scarcity in their core habitat, risking human-animal conflicts as rhinos may stray outside the sanctuary.
- Bird Migration: The Beel also serves as a migratory bird hub, particularly in winter. Early drying may disrupt migration patterns, affecting bird populations.
Government Response and Measures:
- Desilting Efforts: The Forest Department has taken proactive measures, including desilting the Beel to restore water levels and maintain its ecological functions.
- Expert Consultations: Collaborations with institutions like IIT Guwahati are underway to assess and manage the wetland restoration scientifically.
- Long-term Plans: Restoration efforts are focused on improving water retention and managing silt deposition, alongside broader habitat management initiatives.
Expert Recommendations:
- Experts emphasized the critical need for scientific habitat management and stressed the importance of restoring wetlands to ensure the sanctuary's long-term ecological balance.
- The government must focus on sustainable habitat conservation and water management strategies to protect species, especially the rhinos.
World Air Quality Report 2024
- 15 Mar 2025
In News:
India remains among the world’s most polluted countries despite slight improvements in air quality.
Published by: IQAir (Swiss Air Quality Technology Firm)
Key Findings:
- India’s Global Rank: 5th most polluted country in 2024 (improved from 3rd in 2023).
- Average PM2.5 Level (India): 50.6 µg/m³ in 2024 — 10 times higher than the WHO guideline of 5 µg/m³.
- Top Polluted Cities:
- Byrnihat (Assam-Meghalaya border) — most polluted city globally with PM2.5 at 128.2 µg/m³.
- Delhi — most polluted capital city globally with PM2.5 at 91.6 µg/m³.
- 13 of the world’s 20 most polluted cities are in India, including Mullanpur, Faridabad, Gurugram, Bhiwadi, Noida, and Ganganagar.
- Northern India: Faces severe pollution due to crop stubble burning (contributes ~60% of PM2.5 levels).
- Global Air Quality: 91% of countries exceeded WHO PM2.5 safe limits; only 12 countries met the recommended levels.
Major Sources of PM2.5 Pollution:
- Vehicular emissions
- Industrial discharges
- Biomass burning (e.g., firewood, crop residue)
Health & Environmental Impact:
- Health: Linked to respiratory and cardiovascular diseases, cancers; reduces life expectancy by ~5.2 years in India.
- Annual Death Toll: ~1.5 million deaths in India linked to PM2.5 exposure (2009–2019, Lancet Study).
- WHO: 99% of the world’s population breathes polluted air.
India’s Measures to Combat Air Pollution:
Initiative Description
NCAP (2019) - Aims to reduce PM levels by 20–30% in non-attainment cities by
2026. Focuses on monitoring, emissions control, public awareness.
BS-VI Emission Standards - Implemented in 2020 for vehicles to reduce vehicular pollution.
FAME Scheme - Promotes electric and hybrid vehicles to cut down transport-related emissions.
PM Ujjwala Yojana - Provides LPG connections to reduce indoor air pollution from biomass.
GRIHA - Encourages eco-friendly construction practices.
GRAP - Emergency action plan in Delhi-NCR during high pollution episodes.
Commission for Air Quality Management - Coordinates air quality actions across NCR and
nearby areas.
Public Transport & Regulation - Expanding metro/bus networks, penalising high-emission vehicles.
Way Forward:
- Strengthen enforcement of emission norms for vehicles and industries.
- Promote LPG usage over biomass for cooking, especially among rural poor.
- Increase public transport options and incentivise clean technologies.
- Raise awareness and improve inter-state coordination on stubble burning.
Uniyalakeralensis
- 15 Mar 2025
In News:
Researchers have confirmed the discovery of a new flowering plant species named Uniyalakeralensis (family: Asteraceae) in the Agasthyamala Biosphere Reserve (ABR), located in the southern Western Ghats of Kerala. Endemic to southwest India, the species is named in honour of the state of Kerala.
Key Features:
- Plant Type: Dense shrub with light purple flowers, growing 1–3 metres tall.
- Distinctive Traits: Larger leaves, longer petioles (leaf stalks), and fewer lateral veins compared to related species like U. comorinensis and U. salviifolia.
- Flowering & Fruiting Period: August to April.
- Habitat: Open areas on western mountain slopes of ABR, at elevations between 700–1,400 metres.
- Distribution: Around 5,000 individuals across four subpopulations, covering an estimated area of 250 km².
- IUCN Status (2024): Data Deficient (DD) due to limited information on long-term population trends.
The plant was first collected in 1998 and initially misidentified as Vernonia multibracteata. Later taxonomic revisions led to the recognition of Uniyala as a separate genus, named after botanist B.P. Uniyal, with this species formally described as new.
About Agasthyamala Biosphere Reserve (ABR):
- Location: Spans parts of Kerala and Tamil Nadu in the southern Western Ghats.
- UNESCO Status: Recognized under the Man and the Biosphere (MAB) Programme in 2016.
- Biodiversity Highlights: Home to over 2,254 higher plant species, including 405 endemics; key fauna includesNilgiriTahr, Lion-tailed Macaque, Bengal Tiger, and Indian Elephant.
- Indigenous Communities: Inhabited by the Kani tribes in both states.
Madhav National Park
- 13 Mar 2025
In News:
Madhav National Park in Madhya Pradesh has been declared India’s 58th Tiger Reserve and the 9th in Madhya Pradesh, strengthening the state's status as a leader in tiger conservation.
About Madhav National Park
- Location: Shivpuri district, Madhya Pradesh; part of the Chambal region and the Upper Vindhyan Hills on the northern fringe of the Central Highlands.
- Established: As Madhya Bharat National Park in 1955; renamed Madhav National Park in 1959.
- National Park Status: Since 1958.
- Area: Approx. 354 sq km (expanded from 165 sq km).
- Historical Significance: Former hunting ground of Mughal emperors and Maharaja of Gwalior; named after Maharaja Madhav Rao Scindia.
Ecological Profile
- Vegetation:
- Northern Tropical Dry Deciduous Forests
- Dry Thorn Forests typical of North-Western Madhya Pradesh
- Fauna:
- Large Mammals: Tigers, leopards, wolves, jackals, foxes, wild dogs
- Antelopes: Nilgai, Chinkara, Chowsinga
- Deer Species: Chital, Sambar, Barking Deer
- Others: Crocodiles, porcupines, wild pigs, pythons
- Aquatic Ecosystems:
- Two major lakes: Sakhya Sagar and Madhav Sagar support aquatic biodiversity
Tiger Conservation Highlights
- Declared a Tiger Reserve: In 2024, becoming India’s 58th and Madhya Pradesh’s 9th.
- Tiger Reintroduction: Began in 2023; currently home to five tigers, including two cubs.
- Core and Buffer Zones:
- Core Zone: Strictly protected, no human activity
- Buffer Zone: Allows limited, regulated human use to support coexistence
Governance and Protection Framework
- Tiger Reserve Status:
- Notified under Section 38V of the Wildlife Protection Act, 1972
- Falls under Project Tiger (1973), monitored by the National Tiger Conservation Authority (NTCA)
- Approval Process:
- State Government Proposal
- NTCA Evaluation
- MoEFCC Final Notification
- Monitoring System: M-STrIPES (Monitoring System for Tigers – Intensive Protection and Ecological Status) used for surveillance and conservation.
Antarctic Circumpolar Current (ACC) Slowing Down
- 12 Mar 2025
In News:
Recent scientific studies have revealed that the Antarctic Circumpolar Current (ACC)—the strongest and most powerful ocean current on Earth—is slowing down due to accelerated melting of Antarctic ice sheets caused by global warming.
What is ACC?
- The ACC flows clockwise around Antarctica and is the only ocean current that connects the Atlantic, Pacific, and Indian Oceans.
- It is five times stronger than the Gulf Stream and over 100 times more powerful than the Amazon River.
- Driven by strong westerly winds, it is the largest wind-driven ocean current and plays a vital role in regulating the Earth’s climate.
Key Functions and Significance
- Climate Regulation: Distributes heat, nutrients, and water across ocean basins.
- Carbon Sink: Aids in oceanic absorption of atmospheric carbon dioxide, mitigating global warming.
- Marine Barrier: Acts as a natural wall preventing invasive species (e.g., bull kelp, mollusks, shrimp) from reaching Antarctica.
- Prevents Warm Water Intrusion: Helps keep warm ocean currents away from the fragile Antarctic ice shelves.
Findings from Recent Research
- A study by the University of Melbourne and NORCE Norwegian Research Centre, published in Environmental Research Letters, warns that the ACC could slow down by 20% by 2050 under high emissions scenarios.
- Researchers used high-resolution ocean and sea ice simulations on Australia’s GADI supercomputer to project these changes.
- The weakening is largely attributed to the freshwater input from melting ice, which alters ocean salinity and disrupts the formation of Antarctic Bottom Water (AABW)—a crucial component of global ocean circulation.
Reasons for ACC Weakening
- Freshwater Dilution: Melting ice reduces salinity, weakening the density-driven AABW circulation.
- Altered Wind Patterns: Climate change may shift westerly wind patterns that drive the ACC.
- Positive Feedback Loop: Reduced sea ice further warms oceans, accelerating ice melt and weakening the current further.
Potential Global Impacts
- Climate Extremes: Disruption in global heat distribution may lead to increased climate variability and extreme weather events.
- Accelerated Global Warming: Slower circulation reduces the ocean’s carbon sequestration capacity.
- Biodiversity Threats: Invasive species could reach Antarctica, disrupting native ecosystems and food chains (e.g., penguins and krill).
- Global Ocean Circulation Impact: AABW weakening may disrupt the thermohaline circulation affecting global ocean systems.
Japan’s Largest Wildfire in Decades
- 11 Mar 2025
In News:
Japan is currently battling its most extensive wildfire in over three decades, with flames spreading across approximately 1,200 hectares of forest in Ofunato, a coastal city in Iwate Prefecture, located in northern Honshu Island. This is Japan's largest wildfire since the 1992 Kushiro fire in Hokkaido, which burned 1,030 hectares.
The cause remains unknown, and the situation is worsened by record-low rainfall (2.5 mm in February) and the hottest year on record in 2023, highlighting the growing impact of climate change. The region is also vulnerable due to its dense forests, dry winter winds, and limited precipitation during February–April, a peak season for wildfires in Japan.
About Ofunato and Iwate Prefecture
- Location: Ofunato is in Iwate Prefecture, northern Japan, along the Pacific coast.
- Ecological Importance: It features mountainous terrain, coastal forests, and is known for fisheries, tourism, and biodiversity.
Japan – Geographical Context
- Location: East Asia, surrounded by the Pacific Ocean.
- Capital: Tokyo.
- Neighbouring Countries (via maritime boundaries): China, South Korea, North Korea, Russia, Taiwan.
- Geological Features:
- Over 80% mountainous terrain; part of the Pacific Ring of Fire (earthquake and volcanic activity-prone).
- Major Islands: Honshu (location of Ofunato), Hokkaido, Kyushu, Shikoku.
- Climate: Ranges from humid subtropical (south) to cold continental (north).
- Major Rivers: Shinano, Tone, Kiso.
Rare Civet Cat
- 10 Mar 2025
In News:
Recently, a rare civet cat, typically native to the Seshachalam forests near Tirumala, was unexpectedly sighted near Tadepalli in Guntur district, Andhra Pradesh. The animal entered a residential area, startling locals, and was later safely rescued and examined by forest officials.
About Civet Cats
- Taxonomy:Civets belong to the Viverridae family, which includes civets, genets, oyans, and linsangs. There are 15–20 species across 10–12 genera.
- Distribution:Found in Africa, southern Europe, and Asia, including eight wild species in India.
- Common Palm Civet and Small Indian Civet are widely distributed.
- The Malabar Large-spotted Civet (Viverracivettina) is critically endangered and endemic to the Western Ghats.
- Conservation Status:The Malabar Civet is listed as Critically Endangered under the IUCN Red List.
Physical Characteristics:
- Appearance: Cat-like, with thickly furred tail, pointed snout, and small ears.
- Size: Body length: 40–85 cm; Tail: 13–66 cm; Weight: 1.5–11 kg.
- Coloration: Usually buff or grayish, with black spots, stripes, or both.
Behavior and Habitat:
- Nocturnal and Solitary: Typically dwell in tree hollows, rocks, or similar secluded areas.
- Diet: Primarily frugivorous and insectivorous, occasionally feeding on small animals.
- Habitat Range: Though mostly forest-dwelling, rare sightings in urban zones have occurred, as seen in the Tadepalli incident.
Significance of Recent Sighting:
- The civet descended from Tadepalli hills and entered a home, prompting forest department intervention.
- Identified as a rare species similar to African civets.
- Medically examined, found healthy, and is to be rehabilitated into the wild.
- The incident highlights growing human-wildlife interactions and the need for urban wildlife awareness.
Lake Tanganyika

- 09 Mar 2025
In News:
- The countries bordering Lake Tanganyika—Burundi, Democratic Republic of Congo (DRC), Tanzania, and Zambia—have launched a five-year biodiversity conservation project.
- The initiative, led by the United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP) and funded by the Global Environment Facility (GEF), aims to tackle transboundary threats to the lake’s biodiversity.
About Lake Tanganyika:
Feature Details
Location East Africa
Bordering Countries Burundi, DRC, Tanzania, Zambia
Length Over 400 miles (Longest freshwater lake in the world by length)
Depth One of the world’s deepest lakes
Geological Setting Located in the Western Rift Valley
Major Inflows Malagarasi, Ruzizi, Kalambo Rivers
Outflow Lukuga River (into the Lualaba River)
Flora Located at the floral transition zone of eastern and western Africa; oil palms found along shores
Livelihood Agriculture (rice, subsistence crops) and fishing are common
Key Features of the Conservation Project:
- Project Title:Biodiversity Conservation, Sustainable Land Management and Enhanced Water Security in Lake Tanganyika Basin
- Budget: USD 14.5 million
- Implementing Agency: UNOPS
- Strategic Partner: Lake Tanganyika Authority
- Framework Basis: Convention on the Sustainable Management of Lake Tanganyika (2003)
Project Objectives:
- Transboundary Cooperation: Foster collaboration among the four bordering nations
- Sustainable Fisheries: Establish fishing standards, including gear type, mesh sizes, and quotas
- Critical Habitat Protection: Secure core conservation zones in three protected areas and ensure sustainable use in buffer zones
- Community Involvement: Promote local participation in fisheries management and livelihood alternatives
- Land Restoration: Rehabilitate degraded landscapes and reduce environmental stressors
- Biodiversity Protection: Align with the Kunming-Montreal Global Biodiversity Framework goals
Why It Matters:
- Biodiversity Hotspot: The basin supports over 10 million people and is home to rich and unique freshwater biodiversity
- Threats: Habitat destruction, overfishing, pollution, invasive species, climate change, and uncoordinated lake management
- Alarming Trend: Global freshwater biodiversity has declined by 84% in the last century, faster than terrestrial or marine biomes
- Economic Risk: The global value of lake ecosystem services (~USD 3 trillion) could drop by 20% by 2050 if degradation continues
Marbled Cat
- 09 Mar 2025
In News:
- Rare marbled cats (Pardofelis marmorata) were recently captured on camera traps in DehingPatkai National Park, located in Assam's Tinsukia district.
- This was part of a two-month biodiversity monitoring initiative launched in November 2024 by the Assam Forest Department in collaboration with the Wildlife Institute of India (WII).
Significance of the Sighting:
- 2–3 individuals were recorded, marking a significant discovery for biodiversity documentation in Northeast India.
- Assam's Forest Minister and conservationists hailed the event as a testament to successful conservation efforts and the rich biodiversity of DehingPatkai.
About the Marbled Cat:
- Scientific Name: Pardofelis marmorata
- IUCN Status: Near Threatened (NT)
- Habitat: Dense tropical and subtropical forests; found at elevations up to 2,500 metres
- Distribution:
- Countries: India, Nepal, Bhutan, Bangladesh, Myanmar, Thailand, Laos
- In India: Found primarily in Arunachal Pradesh, Assam, Meghalaya, and Nagaland
Physical Features:
- Small wild cat with distinctive marbled-patterned fur (brown/grey with black stripes and spots)
- Excellent arboreal climber, capable of leaping between trees
- Males weigh 4.5–9 kg; females weigh 2.5–5 kg
- Solitary and territorial; marks territory with scent
Conservation Implications:
- The sighting underscores the ecological value of DehingPatkai, a critical habitat for many rare and threatened species.
- Experts stress the need for continued research, habitat preservation, and protection of Eastern Himalayan forests to ensure the survival of elusive species like the marbled cat.
Colossal A23a Iceberg
- 08 Mar 2025
In News:
The colossal iceberg A23a -- which is more than twice the size of Greater London and weighs nearly one trillion tonnes -- has been drifting north from Antarctica towards South Georgia island since 2020.
What is A23a?
A23a is currently the world’s largest iceberg, covering an area of approximately 3,672 sq. km—more than twice the size of Greater London—and weighing nearly one trillion tonnes. It calved from the Filchner Ice Shelf (Antarctica) in 1986 and remained grounded in the Weddell Sea for over 30 years before breaking free in 2020 and drifting northward.
Current Status:
As of March 2025, A23a appears to have run aground about 70–73 km from South Georgia Island in the South Atlantic Ocean. This grounding may spare the island’s rich wildlife, particularly penguins and seals, from disruption in feeding routes and breeding patterns.
Ecological Implications:
- If it had drifted closer, it could have blocked access to feeding grounds, leading to increased mortality of chicks and pups.
- In its current position, nutrients released by its melting and grounding may enhance marine food availability, supporting the local ecosystem.
- This comes as a relief after a difficult season caused by an avian flu outbreak among local wildlife.
Geopolitical Context:
- South Georgia Island is a British Overseas Territory administered by the UK but also claimed by Argentina.
- There is no permanent human population on the island, minimizing direct human impact.
Iceberg Dynamics & Climate Change Link:
- Icebergs such as A23a are natural parts of the Antarctic ice sheet lifecycle, calving from glaciers or ice shelves.
- They are made of freshwater ice, with around 90% submerged below the surface.
- While large icebergs are not new, the rate of calving and ice loss has accelerated, with Antarctic ice shelves losing ~6,000 billion tonnes of mass since 2000.
- Scientists warn that a global temperature rise of 1.5–2°C above pre-industrial levels may trigger irreversible melting, potentially causing sea-level rise of several metres.
Navigation and Fishing Impact:
- The iceberg currently poses no danger to shipping due to its visibility and size.
- However, as it breaks into smaller fragments (bergy bits), it may pose navigation hazards and force commercial fishing vessels to avoid the area.
Colossal A23a Iceberg
- 08 Mar 2025
In News:
The colossal iceberg A23a -- which is more than twice the size of Greater London and weighs nearly one trillion tonnes -- has been drifting north from Antarctica towards South Georgia island since 2020.
What is A23a?
A23a is currently the world’s largest iceberg, covering an area of approximately 3,672 sq. km—more than twice the size of Greater London—and weighing nearly one trillion tonnes. It calved from the Filchner Ice Shelf (Antarctica) in 1986 and remained grounded in the Weddell Sea for over 30 years before breaking free in 2020 and drifting northward.
Current Status:
As of March 2025, A23a appears to have run aground about 70–73 km from South Georgia Island in the South Atlantic Ocean. This grounding may spare the island’s rich wildlife, particularly penguins and seals, from disruption in feeding routes and breeding patterns.
Ecological Implications:
- If it had drifted closer, it could have blocked access to feeding grounds, leading to increased mortality of chicks and pups.
- In its current position, nutrients released by its melting and grounding may enhance marine food availability, supporting the local ecosystem.
- This comes as a relief after a difficult season caused by an avian flu outbreak among local wildlife.
Geopolitical Context:
- South Georgia Island is a British Overseas Territory administered by the UK but also claimed by Argentina.
- There is no permanent human population on the island, minimizing direct human impact.
Iceberg Dynamics & Climate Change Link:
- Icebergs such as A23a are natural parts of the Antarctic ice sheet lifecycle, calving from glaciers or ice shelves.
- They are made of freshwater ice, with around 90% submerged below the surface.
- While large icebergs are not new, the rate of calving and ice loss has accelerated, with Antarctic ice shelves losing ~6,000 billion tonnes of mass since 2000.
- Scientists warn that a global temperature rise of 1.5–2°C above pre-industrial levels may trigger irreversible melting, potentially causing sea-level rise of several metres.
Navigation and Fishing Impact:
- The iceberg currently poses no danger to shipping due to its visibility and size.
- However, as it breaks into smaller fragments (bergy bits), it may pose navigation hazards and force commercial fishing vessels to avoid the area.
Carbon Intensity

- 08 Mar 2025
What is Carbon Intensity?
Carbon intensity refers to the amount of carbon dioxide (CO?) emitted per unit of output in a particular sector or economy. It integrates environmental accountability into performance metrics across industries and nations.
- Sectoral Carbon Intensity: For example, in the steel sector, it is measured as tonnes of steel produced per tonne of CO? emitted.
- National Carbon Intensity: At the country level, it is calculated by dividing GDP per capita by CO? emissions, offering insights into how efficiently a nation grows economically while managing emissions.
Why is Carbon Intensity Important?
- It allows for the tracking of emissions relative to economic or production output, highlighting whether growth is becoming cleaner over time.
- It enables comparison across sectors and geographies by normalizing emissions data.
Relevance for India and Global Commitments:
- Under the Paris Agreement (2015), India has committed to reducing the emissions intensity of its GDP by 45% by 2030 from 2005 levels.
- Monitoring carbon intensity helps India evaluate progress toward this Nationally Determined Contribution (NDC) goal while ensuring sustainable development.
Global Context:
- China recently reported a 3.4% reduction in carbon intensity in 2024, although it fell short of its 3.9% target.
- Such data underscores the challenge of balancing economic growth with climate responsibility, especially for large emitters.
New Species of Jumping Spiders Discovered in Western Ghats
- 08 Mar 2025
In News:
Two new species of jumping spiders belonging to the genus Epidelaxia have been discovered from the Shendurney Wildlife Sanctuary in Kollam, Kerala, marking the first recorded presence of this genus in India. Previously, Epidelaxia was considered endemic to Sri Lanka.
Details of the Discovery
- Species: Epidelaxiafalciformis sp. nov. and Epidelaxiapalustris sp. nov.
- Discovered during field studies in December 2022 and April 2023.
- Conducted by researchers from:
- University of Kerala
- Saveetha Medical College, Chennai
- Bharata Mata College, Kochi
- Published in Zootaxa (Feb 2025), a peer-reviewed journal.
Physical Features
- Females: Yellow triangular mark on the prosoma (front body) and white orbital setae around the eyes.
- Males of E. falciformis: Brown carapace with a yellow-brown stripe.
- Males of E. palustris: Pale brown band along the side of the body.
- Size:
- E. falciformis: 4.39 mm
- E. palustris: 4.57 mm (males), 3.69 mm (females)
Ecological Context
- These species are highly adapted to dense foliage in the Western Ghats, a recognized global biodiversity hotspot.
- The discovery extends the known geographical range of the genus and highlights the rich, yet underexplored, arachnid diversity of the Western Ghats.
World Wildlife Day 2025

- 05 Mar 2025
In News:
World Wildlife Day is observed on March 3 every year, and in 2025, it will be observed under the theme of “Wildlife Conservation Finance: Investing in People and Planet.”
Key Details:
- Declared by: United Nations General Assembly (UNGA)
- First Observed: 2014
- Occasion: Commemorates the signing of CITES (Convention on International Trade in Endangered Species of Wild Fauna and Flora) in 1973.
- Theme 2025:“Wildlife Conservation Finance: Investing in People and Planet”
Purpose and Significance
World Wildlife Day is an annual UN-recognized global event aimed at:
- Raising awareness about wild fauna and flora.
- Highlighting threats such as climate change, poaching, habitat destruction, and illegal wildlife trade.
- Encouraging global cooperation for wildlife protection.
- Promoting innovative financing models to bridge the estimated $824 billion global biodiversity funding gap.
2025 Theme Focus: Conservation Finance
The 2025 theme calls for sustainable financial strategies, emphasizing:
- Wildlife Conservation Bonds
- Debt-for-Nature Swaps
- Green Bonds and Carbon Credits
- Payments for Ecosystem Services (PES)
- Public-Private Partnerships
These mechanisms aim to support conservation while fostering economic opportunities for local communities.
Timeline of Key Events
- 1973: CITES adopted.
- 2013: UNGA designates March 3 as World Wildlife Day.
- 2014: First official celebration.
- 2021: Theme – Forests and Livelihoods.
- 2025: Theme – Finance for Conservation.
Wildlife Status in India
- Protected Areas: 1,014 total (as of 2024), including:
- 106 National Parks
- 573 Wildlife Sanctuaries
- 115 Conservation Reserves
- 220 Community Reserves
(Covers ~5.32% of India’s total area)
- Tiger Population (2022): 3,682 – ~75% of global wild tigers
- Asiatic Lion Population (2020): ~674 (only in Gujarat's Gir Forest)
- India's Biodiversity Share:
- 7.6% of global mammal species
- 14.7% of amphibians
- 6% of birds and reptiles
- 6% of flowering plants
Major Causes of Wildlife Decline
- Habitat loss & fragmentation
- Illegal wildlife trade and poaching
- Climate change and pollution
- Invasive species
- Industrialization & urban expansion
Conservation Measures in India
- Project Tiger (1973): Boosted tiger numbers significantly.
- Project Elephant (1992): Focuses on elephant corridors and human-wildlife conflict mitigation.
- Wildlife Protection Act (1972): Key legal framework to safeguard endangered species.
- Eco-Sensitive Zones (ESZs): Buffer areas around protected habitats.
- Community Initiatives: Ecotourism, local participation in conservation.
MISHTI Scheme

- 03 Mar 2025
In News:
Gujarat has emerged as the national leader in mangrove afforestation, covering 19,020 hectares in just two years under the Centre’s ‘MISHTI’ scheme.
Key Highlights:
- The Mangrove Initiative for Shoreline Habitats and Tangible Incomes (MISHTI) scheme was launched in 2023 under the Union Budget for 2023-24.
- The scheme aims to restore degraded mangrove ecosystems and increase India’s mangrove cover, enhancing coastal resilience while fostering sustainable livelihoods for coastal communities.
- Implemented from 2023 to 2028, the scheme is funded through various channels, including the CAMPA Fund (Compensatory Afforestation Fund Management and Planning Authority), MGNREGS (Mahatma Gandhi National Rural Employment Guarantee Scheme), and other governmental and private funding sources.
- The initiative also supports India’s participation in the global Mangrove Alliance for Climate (MAC) launched at COP27.
Key Objectives of MISHTI
- Ecological Restoration: To restore degraded mangrove ecosystems and expand mangrove cover across coastal areas.
- Coastal Resilience: To strengthen coastal resilience against climate change, such as coastal erosion and rising sea levels.
- Livelihood Generation: To promote ecotourism, sustainable livelihoods, and fishing opportunities for coastal communities.
- Climate Change Mitigation: The scheme plays a crucial role in protecting shorelines from storms, supporting India's commitments under the Paris Agreement and the UN Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs).
Gujarat’s Role in MISHTI Scheme
- Gujarat has emerged as the national leader in mangrove afforestation under the MISHTI scheme, planting over 19,000 hectares of mangroves in just two years.
- The state is spearheading the mangrove expansion efforts, with its coastline covering diverse ecosystems such as mangroves, coral reefs, and seagrasses.
- Gujarat has surpassed the Central Government’s target of planting 540 sq. km of mangroves in five years, completing plantation across 190 sq. km in the initial two years of the scheme.
Mangrove Distribution in Gujarat
- Gujarat's mangrove cover is distributed strategically across different coastal regions:
- Kutch: 799 sq. km, including the Gulf of Kutch, home to the Marine National Park and Wildlife Sanctuary.
- Other Coastal Districts: Jamnagar, Rajkot (Morbi), Porbandar, DevbhoomiDwarka (236 sq. km).
- Central and Southern Belt: Includes Bhavnagar, Ahmedabad, Anand, Bharuch, Surat, Navsari, and Valsad, covering 134 sq. km, with important areas like the Gulf of Khambhat and Dumas-Ubhrat.
- Saurashtra Region: Amreli, Junagadh, and Gir-Somnath maintain 6 sq. km of mangrove cover.
Significance of Mangroves
- Erosion Prevention: Mangroves act as a natural barrier, protecting coastal regions from erosion caused by waves and storms.
- Biodiversity Support: They provide vital breeding grounds for fish and other marine species, supporting coastal livelihoods.
- Climate Resilience: Mangroves help mitigate the effects of climate change by shielding vulnerable coastal communities from cyclones, reducing salinity, and preserving agricultural lands.
Global and National Mangrove Status
- Global Mangrove Distribution: Mangroves are found in tropical and subtropical regions worldwide, providing critical ecosystem services.
- India’s Mangrove Cover: According to the India State of Forest Report 2023, India has a total mangrove cover of 4,991.68 km², which accounts for 15% of the country’s total geographical area. The MISHTI scheme plays a pivotal role in further expanding this cover.
Cali Fund
- 01 Mar 2025
In News:
‘Cali Fund’ launched at CBD COP16 in Rome to boost biodiversity finance.
Key Details:
- Launched at: COP16 to the UN Convention on Biological Diversity (CBD), held in Rome in 2025.
- Purpose: The Cali Fund aims to promote the fair and equitable sharing of benefits arising from the use of Digital Sequence Information (DSI) on genetic resources, marking a major step towards fulfilling Goal C and Target 13 of the Kunming-Montreal Global Biodiversity Framework (KMGBF)—which targets halting and reversing biodiversity loss by 2030.
Key Features of the Cali Fund:
- Origin: It builds on the multilateral mechanism adopted during COP15 (2022) and was operationalised at COP16 (2025).
- Objective:Mobilise financial contributions from the private sector to support biodiversity conservation and implementation of National Biodiversity Strategies and Action Plans (NBSAPs).
- Hosted By: Multi-Partner Trust Fund Office (MPTFO).
- Managed By: United Nations Development Programme (UNDP) and United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP).
- Secretariat: Hosted by the Convention on Biological Diversity (CBD).
Funding Mechanism:
- Source of Contributions: Companies commercially utilisingDSI—genetic data from plants, animals, and microorganisms—especially in sectors like:
- Pharmaceuticals
- Cosmetics
- Agriculture and biotechnology
- Industrial biotech and AI-assisted research
- Exemptions: Academic institutions, public research bodies, and entities not reliant on DSI are exempt.
- Allocation:
- 50% of resources are earmarked for indigenous peoples and local communities, especially women and youth, recognising their key role in biodiversity protection.
Significance:
- Global First: First UN biodiversity fund to receive direct contributions from private companies.
- Support for Biodiversity Action Plans: Assists developing countries in implementing their KMGBF targets and NBSAPs.
- Boosts Scientific Research: Enhances capabilities for storing, using, and analysing DSI.
- Promotes Collective Action: Encourages industries benefiting from biodiversity to reinvest in its protection—ushering in a new era of biodiversity finance.
About Digital Sequence Information (DSI):
- Definition: Digitally stored genetic data from DNA, RNA, and proteins.
- Use Cases: Vital for research in health, food security, climate change, conservation, and bioeconomy.
- Governance: Discussed under CBD, WHO PIP Framework, UN Law of the Sea, and others.
PRAKRITI 2025

- 28 Feb 2025
In News:
- The International Conference on Carbon Markets – PRAKRITI 2025 was inaugurated by the Minister of Power and Housing and Urban Affairs.
- Organized by the Bureau of Energy Efficiency (BEE) under the Ministry of Power, the event served as a major platform for global dialogue on carbon markets, climate finance, and sustainability strategies.
Key Highlights:
PRAKRITI 2025 (Promoting Resilience, Awareness, Knowledge, and Resources for Integrating Transformational Initiatives) aimed to:
- Understand the functioning of Indian and global carbon markets.
- Discuss challenges, dynamics, and opportunities in carbon trading.
- Strengthen carbon credits, offset mechanisms, and compliance systems.
- Promote renewable energy, green innovations, and ecosystem-based interventions.
- Foster collaboration between governments, industries, and citizens.
Insights from PRAKRITI 2025
- Global Linkages:India’s carbon market will increasingly be influenced by global policies such as the European Union’s Carbon Border Adjustment Mechanism (CBAM), which imposes carbon pricing on imports like steel and aluminium. Indian industries must prepare to maintain competitiveness.
- Carbon Market Mechanisms:
- Under Article 6 of the Paris Agreement, carbon trading allows entities to buy carbon credits to offset emissions.
- Carbon credit = reduction of 1 metric ton of CO? or equivalent GHGs.
- India’s Progress:
- India ranks second globally in Clean Development Mechanism (CDM) project registrations.
- The Perform, Achieve and Trade (PAT) scheme, regulated by BEE, has saved over 106 million tonnes of CO? since 2015.
- Development of a domestic carbon market is a priority to align with global standards and leverage international finance.
- Challenges Highlighted:
- Need for robust Monitoring, Reporting, and Verification (MRV) frameworks.
- Ensuring fair benefit distribution among stakeholders.
- Developing policies tailored to India’s economic and social realities.
- Increasing private sector engagement and incentivizing renewable energy developers.
Bureau of Energy Efficiency (BEE)
- Established: 1 March 2002 under the Energy Conservation Act, 2001.
- Mandate: Develop policies and programmes to promote energy efficiency, coordinate with stakeholders, and promote self-regulation within market principles to reduce India's energy intensity.
- Role in Carbon Market: BEE is the nodal agency regulating India’s carbon trading schemes and energy conservation initiatives.
Northern Pintail Duck

- 26 Feb 2025
In News:
A flock of Northern Pintail ducks was recently sighted at an unprecedented altitude of 13,500 feet in Tawang, Arunachal Pradesh—far above their typical wintering habitats. This rare event has sparked interest in their migration behavior and adaptability to high altitudes.
About Northern Pintail Duck
- Scientific Name:Anas acuta
- Type: Migratory waterfowl known for elegance and long-range migration
- Common Nickname: Northern nomads
Distribution & Migration
- Found across every continent except Antarctica
- Breed in northern regions of Europe, Asia, and North America
- Migrate southward in winter to regions including the Indian subcontinent
- Typically observed in low-lying wetlands; rarely at high altitudes
- Do not breed or reside south of the equator
- Seen in the high-altitude region of Arunachal Pradesh during winter, raising questions about changing migration patterns and climate adaptability
Key Features
- Size: Around 60 cm in length, over 1 kg in weight
- Wingspan: Up to 91 cm
- Speed: Capable of flying at 48 miles per hour due to aerodynamic build
- Male Appearance: Buff-gray body, chocolate-brown head, broad white stripe on chest, black back patterns
- Female Appearance: Mottled brown body, lighter chest and neck
Conservation Status
- Listed as “Least Concern” under the IUCN Red List
- Despite being widespread, their migratory nature warrants regular monitoring to track habitat changes and population health
Soliga Tribe and Tiger Conservation

- 26 Feb 2025
In News:
In the 119th edition of Mann Ki Baat, Prime Minister Narendra Modi lauded the Soliga tribe of the BiligiriRanganathaswamy Temple (BRT) Tiger Reserve in Karnataka for their significant role in tiger conservation and sustainable forest practices.
Who are the Soligas?
- Location: Indigenous, forest-dwelling tribe residing primarily in Chamarajanagar district, Karnataka, and parts of Tamil Nadu, especially around Biligiri Rangana Hills and Male Mahadeshwara Hills.
- Meaning of the Name: "Soliga" translates to “children of bamboo”, symbolizing their deep ecological ties.
- Language: They speak Sholaga (a Dravidian language), along with Kannada and Tamil.
- Lifestyle:Soligas live in bamboo-and-mud huts, practice shifting cultivation, and depend on non-timber forest produce (NTFP) for sustenance.
- Diet & Livelihood:Honey is a staple in their diet; they extensively forage and harvest forest produce like amla, gooseberries, and medicinal herbs, leaving a portion for wildlife—a reflection of their conservation ethos.
Religious and Cultural Practices:
- Soligasworship wildlife, especially the tiger, locally called “DoddaNayi” (Great Dog). They have even built temples dedicated to tigers.
- Their belief system includes Hindu customs, animism, and naturism, highlighting their spiritual connection with nature.
- They produce eco-friendly artifacts like ‘jottai’ (leaf cups), showcasing sustainable craftsmanship.
Recognition of Forest Rights:
- In 2011, Soligas became the first tribal community in India to receive legal recognition of their forest rights within a tiger reserve, under the Forest Rights Act (FRA).
- This ruling allowed them to reside within the BRT Tiger Reserve and sustainably collect forest produce without displacing wildlife.
Role in Tiger Conservation:
- Soligas’ traditional knowledge of forest ecology helps them coexist peacefully with wildlife, minimizing human-animal conflict.
- They assist the Forest Department in fire prevention, wildlife tracking, and ecological management.
- Their cultural practices ensure minimal disturbance to wildlife. For instance, during harvest, they intentionally leave 25–33% of the produce in the forest for animals.
BiligiriRanganathaswamy Temple (BRT) Tiger Reserve:
- Location: Chamarajanagar district, Karnataka; lies at the confluence of the Western and Eastern Ghats, forming a critical wildlife corridor.
- Ecosystem: Rich in biodiversity with forest types including:
- Southern Tropical Evergreen
- Semi-Evergreen
- Moist Deciduous
- Flora:Axlewood, Rosewood, Terminalia spp., Indian Gooseberry, Ceylon Oak, Golden Shower Tree.
- Fauna: Tigers, Wild Dogs, Sloth Bears, Sambars, Bison, and endangered species like the Icthyophisghytinosus (Caecilian).
- Cultural Site: Named after Lord Rangaswamy, the reserve houses the Biligiri Temple atop mist-covered hills.
Northern White Rhino
- 25 Feb 2025
In News:
The Northern White Rhino (NWR) is on the brink of extinction, with only two females—Najin and Fatu—remaining at the Ol Pejeta Conservancy in Kenya. However, a breakthrough in In-Vitro Fertilization (IVF) has rekindled hope for reviving this subspecies, with 36 lab-created embryos ready for implantation. This effort is part of an international project named BioRescue.
About the White Rhino
- Scientific Name: Ceratotherium simum
- Common Name: Square-lipped rhinoceros (due to broad upper lip)
- Subspecies:
- Northern White Rhino (Ceratotherium simum cottoni)
- Southern White Rhino (Ceratotherium simum simum)
- Habitat:
- Southern White Rhino: South Africa, Namibia, Zimbabwe, Kenya
- Northern White Rhino: Historically central and eastern Africa; now only in captivity
- IUCN Status:
- White Rhino (overall): Near Threatened
- Northern White Rhino: Critically Endangered
- Southern White Rhino: Near Threatened
Biological Features
- Second-largest land mammal after elephants
- Square upper lip adapted for grazing on short grasses
- Two horns, with the front horn being larger
- No actual color difference between black and white rhinos
Social & Dietary Behavior
- Diet: Pure herbivores; feed almost exclusively on short grasses
- Behavior:
- Semi-social and territorial
- Males mark territories with dung
- SWRs form larger social herds; NWRs were found in smaller groups
Threats to Survival
- Poaching for horns
- Habitat loss due to human encroachment
- Civil unrest, particularly in their native range
- Low genetic diversity, especially critical in the NWR
- Climate change, affecting habitat and water sources
Conservation Through Reproductive Technology
BioRescue Initiative
- An international scientific effort launched in 2015 to save the NWR using advanced reproductive technologies.
- Uses frozen sperm from deceased males and eggs from Najin and Fatu to create embryos in the lab.
- 36 embryos have been successfully created and are stored for future implantation.
IVF and Surrogacy
- First-ever rhino pregnancy via lab-made embryo announced recently.
- Southern white rhinos are used as surrogate mothers due to genetic similarity and higher population.
- IVF and embryo transfers are the only options since the last male NWR, Sudan, died in 2018, and both remaining females are non-reproductive due to age and health.
Challenges & Concerns
- Limited gene pool restricts genetic variability.
- Loss of unique traits if crossbred with southern white rhinos.
- Behavioral imprinting: IVF calves must learn from remaining NWR females before they pass away.
- Ethical and ecological concerns: Critics argue conservation must also address root causes like poaching, habitat destruction, and lack of genetic diversity, not just focus on “test-tube” solutions.
Indian Rhinoceros
- Scientific Name: Rhinoceros unicornis (Greater One-Horned Rhino)
- IUCN Status: Vulnerable
- Habitat: Indian subcontinent (Assam, West Bengal, UP, Nepal)
- It is distinct from African rhinos, both genetically and ecologically.
Dr. Purnima Devi Barman

- 24 Feb 2025
In News:
Indian wildlife biologist Dr. Purnima Devi Barman has been named among TIME Magazine’s Women of the Year 2025, recognizing her as one of 13 global leaders working toward a more equitable and sustainable world. She is the only Indian woman on the list.
Key Contributions:
- Known for her pioneering conservation work with the greater adjutant stork (locally called Hargila), once critically endangered and culturally stigmatized in Assam.
- Founded the Hargila Army, a women-led grassroots movement focused on protecting the stork’s habitat and changing negative local perceptions.
- Her model uniquely blends wildlife conservation with women’s empowerment, engaging thousands of rural women in ecological and livelihood activities.
Impact:
- Due to her efforts, the greater adjutant stork’s population in Assam has significantly recovered, leading to its status being upgraded from “endangered” to “near threatened” by IUCN.
- The Hargila Army, with over 10,000 members, participates in bird rescue, awareness campaigns, tree planting, and embroidery-based income generation.
- Her approach has become a global model for community-based conservation.
Background:
- Hails from the Kamrup region of Assam.
- Holds a Master’s degree in Zoology from Gauhati University.
- Inspired by her early life near the Brahmaputra and her grandmother’s teachings on biodiversity.
Awards & Recognition:
- Nari Shakti Puraskar (2017) – India’s highest civilian award for women.
- UN Champions of the Earth Award (2022) – For entrepreneurial vision in conservation.
- Whitley Gold Award (2017, 2024) – Often called the "Green Oscar".
Other Roles:
- Director of Women in Nature Network (YNN) – India chapter.
- Member of IUCN’s Stork, Ibis, and Spoonbill Specialist Group.
About TIME Magazine:
- Founded in 1923, USA.
- Known for its global recognitions like Person of the Year and Women of the Year.
- Now operates as a multimedia platform covering politics, science, and culture.
Mass Stranding of False Killer Whales in Tasmania

- 23 Feb 2025
In News:
Recently, over 150 false killer whales were found stranded on a remote beach near Arthur River on the northwest coast of Tasmania, Australia. The incident is one of several mass strandings reported in the region in recent years.
The event echoes earlier mass strandings:
- In 2022, 230 pilot whales stranded at Macquarie Harbor.
- In 2020, 470 long-finned pilot whales were stranded at the same site—the largest mass stranding in Australian history.
Possible Causes of Whale Strandings
Although the precise cause remains uncertain, potential factors include:
- Disorientation from loud underwater noises (e.g., naval exercises, seismic surveys)
- Illness, old age, injury
- Fleeing predators
- Severe weather events
- Geomagnetic anomalies
About False Killer Whales
- False killer whales (Pseudorca crassidens) are not true killer whales but belong to the Delphinidae family, which also includes dolphins and pilot whales.
- They are large, social cetaceans, often found in warm, deep oceanic waters.
- These whales are highly vocal and social, forming strong social bonds within pods.
- Like other cetaceans, they rely on echolocation (underwater sound) for communication, hunting, and navigation.
About Killer Whales (Orcas)
- Although not involved in the stranding, killer whales (Orcinus orca) are relevant as close relatives within the same family (Delphinidae).
- Known for their distinct black and white markings, orcas are the largest members of the dolphin family.
- They are globally distributed in both open oceans and coastal waters.
- Killer whales live in stable matrilineal pods and use complex vocalizations.
Conservation Status
- The IUCN Red List classifies false killer whales and killer whales as Data Deficient, indicating that there is insufficient information to assess their risk of extinction.
AI-Powered Surveillance in Similipal Tiger Reserve

- 21 Feb 2025
In News:
The Similipal Tiger Reserve in Odisha has seen a significant drop in poaching activities following the deployment of TrailGuard AI-enabled surveillance cameras. These advanced systems are helping protect both forest personnel and wildlife by providing real-time alerts and enhancing enforcement actions.
About TrailGuard AI System
- Developed by: Nightjar Technologies, Gurgaon.
- Design:
- Two-part system: a pen-sized camera unit and a notepad-sized battery/communication unit connected via a 2-metre cable.
- Camouflaged and compact, reducing chances of being detected or stolen.
- Operation:
- Operates in low-power mode by default, switches to high-power mode upon sensing movement.
- Uses on-device AI inference to identify object classes (e.g., humans, animals, vehicles).
- Sends alerts via cellular network within 30–40 seconds to a central control room.
- Battery life: 6 months to 1 year.
- Cost: ?50,000–53,000 per unit.
Impact and Achievements
- Installed: 100–150 AI-enabled cameras in Similipal.
- In 10 months, led to:
- 96 poachers arrested
- 86+ country-made guns seized
- 40+ arrests in December 2024 alone
- Enabled quick house raids and identifications using photographic evidence.
- Enabled one conviction within six months, with more expected.
Integrated Enforcement System
- Real-time alerts displayed on a central control room screen.
- Information shared swiftly via WhatsApp groups and VHF radio.
- Ground teams rely on human intelligence sources (including undercover staff) to identify suspects.
- Raids and arrests are executed only after 100% identity confirmation, ensuring due process.
Advantages of the System
- Enhances forest ranger safety.
- Enables targeted and proactive patrolling.
- Effective in challenging terrains with minimal maintenance.
- Also used to monitor wildlife, including profiling of tuskers.
- Functions as an anti-poaching as well as human-wildlife conflict mitigation tool.
Wider Adoption and Future Plans
- Apart from Similipal, TrailGuard AI has been deployed at:
- Kanha Tiger Reserve, Madhya Pradesh (20 cameras)
- Dudhwa National Park, Uttar Pradesh (10 cameras)
- Total: Active in 14+ sites across five states
- Planned expansion to other protected areas in Odisha.
Community Sensitivity and Tribal Engagement
- Similipal is surrounded by tribal communities, where hunting has traditional roots.
- Increased surveillance has caused concerns over restricted forest access for collecting firewood and non-timber forest products.
- The forest department is:
- Holding awareness meetings in local languages.
- Exploring safe and non-intrusive access solutions for villagers.
- Ensuring that enforcement doesn’t indiscriminately impact local livelihoods.
Conservation Significance
- Demonstrates the fusion of technology with conservation.
- Aligns with India’s broader environmental goals under:
- Project Tiger
- National Wildlife Action Plan
- Digital India initiatives in conservation.
Climate Risk Index 2025
- 19 Feb 2025
In News:
- The Climate Risk Index (CRI) 2025, published by the international environmental think tank Germanwatch, ranks countries based on their vulnerability to extreme weather events, assessing both human and economic losses due to climate-induced disasters.
- The index, which has been released annually since 2006, covers a 30-year period, evaluating the impact of extreme weather events in terms of economic losses, fatalities, and the number of affected people.
Key Findings:
- Global Impact: From 1993 to 2022, more than 9,400 extreme weather events occurred globally, resulting in 765,000 fatalities and USD 4.2 trillion in economic losses. Heatwaves, droughts, and floods were the leading causes of fatalities and displacement, with heatwaves alone claiming 61,778 lives (83% of fatalities) in 2022. Droughts affected the largest number of people, with 59% of the global population impacted during the past three decades.
- India's Position: India ranks as the 6th most affected country in the world by climate change between 1993 and 2022, suffering significant losses. During this period, the country experienced over 400 extreme weather events, including floods, heatwaves, cyclones, and droughts, causing a loss of USD 180 billion in economic damages and leading to at least 80,000 fatalities (10% of global deaths).
Some notable extreme weather events include:
-
- Cyclones: Gujarat (1998), Odisha (1999), Hudhud (2014), and Amphan (2020).
- Floods: Uttarakhand (2013), Jammu and Kashmir (2014), and Kerala (2018).
- Heatwaves: Intense temperatures exceeding 50°C in 1998, 2002, 2003, and 2015.
Methodology of the Climate Risk Index
The CRI assesses the impact of extreme weather events across three hazard categories:
- Hydrological (floods, landslides),
- Meteorological (storms, cyclones),
- Climatological (heatwaves, droughts).
The six key indicators used for the ranking are:
- Economic loss
- Fatalities
- Affecting population, assessed in both absolute and relative terms.
Climate Risk and Its Implications for India
India’s vulnerability to climate change is highlighted by frequent and intense extreme weather events. The country faces risks from:
- Floods: Regular heavy monsoons lead to significant displacement and damage to infrastructure and agriculture.
- Cyclones: Rising sea levels and warming oceans increase the frequency and intensity of cyclones.
- Heatwaves: India experiences rising temperatures, with heatwaves becoming more intense, contributing to health crises.
- Droughts: A growing concern, affecting agriculture and water resources.
Additionally, the Asia-Pacific Climate Report 2024 projects that India may face a 24.7% GDP loss by 2070 due to climate change impacts, driven by rising sea levels and decreasing labor productivity.
Global Challenges in Climate Change Mitigation
- Historical Responsibility vs. Future Emissions: Developed nations, despite having contributed more to global emissions historically, are pressuring emerging economies like India to take greater responsibility for climate action. This has led to tensions over burden-sharing and the need for climate finance.
- Global Temperature Breach: In 2024, the world breached the 1.5°C threshold for a full year, highlighting the inadequacy of current mitigation efforts. Projections indicate a global temperature increase of 2.6-3.1°C by 2100 if current trends continue.
- Weak Commitments and Insufficient Finance: Many countries have not updated their Nationally Determined Contributions (NDCs), and the USD 300 billion annual funding promised for developing nations is insufficient to meet climate adaptation and mitigation needs.
India's Climate Adaptation Challenges and Suggestions
India faces several climate adaptation challenges, including inadequate infrastructure, insufficient funding, and a lack of robust policy frameworks for disaster risk management. To enhance adaptation efforts, the following measures are suggested:
- Enhanced Climate Finance: Developing countries need greater financial and technical support to manage and adapt to climate-induced losses.
- Strengthening Mitigation Efforts: Nations, including India, must scale up their NDCs to restrict global warming to 1.5°C or lower.
- Accountability of High-Income Countries: Developed nations must expedite mitigation actions and increase financial contributions to support climate-vulnerable countries like India.
Gulf of Eilat
- 19 Feb 2025
In News:
A new study has revealed that the coral reefs in the Gulf of Eilat (also known as the Gulf of Aqaba) faced a 3,000-year growth shutdown due to global cooling. However, these reefs later recovered naturally from deeper waters, demonstrating resilience in the face of environmental changes.
About the Gulf of Eilat (Gulf of Aqaba)
- Location: The Gulf of Eilat is a northern extension of the Red Sea, positioned east of the Sinai Peninsula and west of the Arabian Peninsula. It is strategically significant and is also known as the Gulf of Aqaba.
- Neighbouring Nations: The Gulf shares its coastline with four countries: Egypt, Israel, Jordan, and Saudi Arabia.
- Geographical Features:
- The Gulf includes important cities like Taba (Egypt), Eilat (Israel), and Aqaba (Jordan), all located at the Gulf’s northernmost point.
- It has a maximum depth of 1,850 meters, making it much deeper than the adjacent Gulf of Suez.
- The Gulf forms the southern end of the Dead Sea Transform, a significant tectonic fault zone, contributing to its unique geological and environmental features.
- Coral Ecosystem: The Gulf of Eilat is home to the world’s northernmost coral reefs. Despite facing various environmental challenges, these reefs have shown remarkable resilience over the years, highlighting their ability to adapt to changing conditions.
Environmental Challenges and Recovery
- The 3,000-year growth shutdown of the coral reefs in the Gulf of Eilat was primarily driven by global cooling. This climatic phenomenon significantly impacted the growth of the reefs, causing a temporary halt in their development. However, the coral ecosystems in the Gulf have since recovered naturally, drawing from deeper waters to rebuild and thrive once again.
- This recovery underscores the resilience of coral ecosystems despite adverse environmental conditions. It also provides valuable insights into how these ecosystems can recover when given the opportunity, even after significant disruptions caused by global climate changes.
Implications for Coral Reef Conservation
- The study's findings emphasize the importance of understanding the adaptive capacity of coral reefs, which are among the most vulnerable ecosystems to climate change.
- The ability of coral reefs in the Gulf of Eilat to recover after a prolonged period of cooling demonstrates that marine ecosystems can endure long-term environmental stress if they are allowed to regenerate naturally.
- This has significant implications for global coral conservation efforts, which must focus on creating conditions that allow reefs to adapt and recover from environmental stresses, including global warming, ocean acidification, and pollution.
- The Gulf of Eilat’s coral reefs provide an important case study for understanding ecological resilience and the potential for natural recovery in marine ecosystems.
Crocodile Catfish

- 17 Feb 2025
In News:
The recent discovery of the Crocodile Catfish (Bagariussuchus) in the Bahini River near Basistha, Guwahati, Assam, has garnered attention from conservationists and ecologists alike. As one of the largest freshwater catfish species in Asia, its presence in Indian waters raises both scientific interest and ecological concerns.
Taxonomy and Distribution
- Scientific Name: Bagariussuchus
- Family: Sisoridae – the largest family of Asian catfishes, widely distributed across South and Southeast Asia.
- Common Names: Asian Giant River Catfish, Crocodile Goonch Catfish, Giant Devil Catfish
- Geographical Range: Native to countries including India, Nepal, Bangladesh, Myanmar, and Thailand.
Habitat and Morphological Features
- Natural Habitat: Prefers fast-flowing rivers, deep pools, turbulent rapids, and areas with rocky or gravelly substrates.
- Often found among boulders, submerged roots, and debris, thriving in cool, oxygen-rich waters.
- Physical Description:
- Long, cylindrical body with a broad head and wide mouth.
- Typicallydark brown to black, with irregular patches or spots for camouflage.
- Dorsal fin is elongated, stretching along most of the back.
- Size: Can grow up to 1.5 meters in length and weigh over 50 kilograms, though smaller specimens (~70 cm) are also observed.
Behaviour and Ecology
- Feeding Habits: A carnivorous predator, feeding on smaller fish, crustaceans, and aquatic invertebrates.
- Known for its voracious appetite, capable of consuming prey nearly its own size.
- Most active during evening or nighttime, making it a nocturnal feeder.
- Sexual Dimorphism: Males are generally slimmer and may exhibit slightly brighter coloration than females.
Ecological Concerns
- The discovery of the Crocodile Catfish in a non-native region like the Bahini River raises concerns about its invasive potential.
- It can threaten native aquatic biodiversity by preying on indigenous species and disturbing the ecological balance.
- Overfeeding and rapid proliferation can degrade water quality and disrupt food chains.
Conservation Status
- IUCN Red List: Near Threatened (NT): This status reflects concerns about habitat degradation, overfishing, and ecological displacement, which may impact population stability across its range.
Rising Heatwaves in India
- 16 Feb 2025
In News:
India is increasingly facing more frequent, intense, and prolonged heatwaves, posing a significant threat to public health, economic productivity, agricultural stability, andenvironmental sustainability. This trend underscores the broader implications of climate change, particularly for developing economies with large vulnerable populations.
Understanding Heatwaves
A heatwave is defined as a prolonged period of abnormally high temperatures, often accompanied by high humidity. As per the India Meteorological Department (IMD):
- A heatwave is declared when the maximum temperature reaches at least 40°C in plains and 30°C in hilly regions.
- The severity is determined by how much the temperature exceeds the normal.
Impacts of Heatwaves
- Public Health:
- Prolonged heat exposure increases the risk of heatstroke, dehydration, and worsens cardiovascular and respiratory illnesses.
- Vulnerable groups include the elderly, outdoor workers, and those without access to cooling.
- Livelihoods and Employment:
- According to the World Bank, India could lose 34 million jobs by 2030 due to heat-stress-related productivity declines.
- The informal sector and outdoor labourers are especially at risk.
- Agriculture and Food Security:
- Heat stress leads to reduced crop yields, livestock deaths, and increased irrigation demand.
- It threatens the food supply chain and rural incomes.
- Water Scarcity:
- 54% of India’s land is under high to extremely high water stress, as per the World Resources Institute (WRI).
- Heatwaves exacerbate droughts and deplete groundwater sources.
- Environmental Degradation:
- Higher temperatures increase the risk of wildfires, especially in forested and arid zones.
- Ecosystem services and biodiversity are under stress.
- Infrastructure and Energy:
- Rising temperatures lead to increased energy demand for cooling, straining power grids.
- Urban infrastructure suffers due to heat-induced wear and tear.
Gangasagar Mela

- 16 Feb 2025
In News:
Recently, several Ministers of the West Bengal government gathered at a conference room on Sagar Island, situated at the mouth of the Bay of Bengal — the southernmost tip of the State — to brief mediapersons on the arrangements for the Gangasagar Mela 2025.
Gangasagar Mela: Overview
- Second-largest human congregation in the world, after the Kumbh Mela.
- Held annually on Makar Sankranti (January 14) at the confluence of River Ganga and Bay of Bengal.
- Pilgrims take a holy dip at the confluence; site houses the Kapil Muni Temple.
- In 2025, the West Bengal government claimed over 1.10 crore pilgrims visited.
Location & Geography
- Sagar Island (Sagardwip/Ganga Sagar):
- Located ~120 km from Kolkata.
- Largest island in the Sundarbans archipelago.
- Population: ~2 lakh (2011 Census).
- Classified under the sand group category.
- Accessed by crossing the Muriganga River via ferry.
Climate Change Impact
- Rising sea levels and erosion are threatening Sagar Island:
- Sea has advanced from 1,500 m to 470 m from the Kapil Muni Temple in ~10 years.
- Tidal surge rises from 4.6 m to 7.6 m during high tides.
- Erosion worsened by:
- Mangrove destruction for construction during mela.
- Flattening of sand dunes and vegetation, removing natural barriers.
Environmental Challenges
- Constructions often violate Coastal Regulation Zone (CRZ) norms (no construction within 500 m of high tide line).
- Beaches have turned muddy, unfit for bathing; pilgrims walk through marshes.
- Concrete embankments, built after removing mangroves, washed away during cyclones.
- Geotextiles used for erosion control are ineffective near the temple due to strong wave action.
Cyclones & Vulnerability
- Recent major cyclones: Yaas (2021), Remal (May 2024), Dana (Oct 2024).
- Local communities frequently displaced; loss of livestock and property reported.
- Rising salinity impacting fish farming and livelihoods.
Socio-Economic Impact
- Youth migration due to lack of job opportunities.
- Local economy disrupted by environmental stress.
- Many locals say the mela offers little direct benefit to them.
Governance and Policy Issues
- West Bengal government spent ~?250 crore in 2024 for mela arrangements.
- Proposed ?4,100 crore World Bank-funded embankment project:
- World Bank: 70% cost; State: 30%.
- Aimed at protecting 52 inhabited islands in Sundarbans.
- Centre-State conflict:
- WB government alleges non-cooperation from the Centre.
- No Central funds provided for the mela, unlike the Kumbh Mela.
- Demand for national mela status for Gangasagar.
Cultural and Political Dimensions
- Religious significance emphasized by Shankaracharya of Puri.
- Soft Hindutva strategy attributed to West Bengal’s ruling party (TMC).
- Political undertones visible in temple construction and event promotion.
S?janam

- 14 Feb 2025
In News:
In a significant stride toward sustainable healthcare and waste management, India launched its first indigenous Automated Biomedical Waste Treatment Plant, named S?janam, on April 13, 2025, at AIIMS, New Delhi.
Developed by the CSIR-National Institute for Interdisciplinary Science and Technology (CSIR-NIIST), Thiruvananthapuram, under the Ministry of Science & Technology, this innovative rig marks a paradigm shift in handling biomedical waste, moving away from conventional, polluting incineration techniques.
Why this matter?
India generates approximately 743 tonnes of biomedical waste daily (CPCB, 2023). Safe disposal has been a persistent challenge due to limited infrastructure, high costs, and environmental concerns. The launch of S?janam aligns with the government’s push for “Waste to Wealth” and environmentally responsible healthcare infrastructure, as part of the Atmanirbhar Bharat and Swachh Bharat initiatives.
What is S?janam?
- An automated, eco-friendly biomedical waste treatment rig.
- Designed to disinfect pathogenic waste like blood, urine, sputum, and lab disposables.
- Does not use incinerators, which release toxic emissions such as dioxins and furans.
Key Features & Capacity
Feature Details
Disinfection Process Non-incineration, antimicrobial treatment
Daily Treatment Capacity 400 kg of total biomedical waste
Organic Waste Handling Initially handles 10 kg/day of degradable medical waste
Environmental Safety Neutralizes foul odor; releases pleasant fragrance
Health Safety Minimizes human exposure and risk of contamination
Validation Third-party tested; treated material safer than organic vermicompost
Significance for Public Health and Environment
- Reduces dependency on expensive, energy-intensive incinerators.
- Eco-friendly solution that prevents toxic emissions and groundwater contamination.
- Aligns with Bio-Medical Waste Management Rules, 2016, which mandate safe segregation, treatment, and disposal.
- Enhances India’s capability to respond to health crises (e.g., pandemics), where waste generation spikes.
Strategic Implications
- Promotes indigenous technological innovation under “Make in India.”
- Offers a scalable solution for both urban and rural healthcare setups.
- Contributes to India’s climate commitments by cutting healthcare-related emissions.
Pong Dam Lake Wildlife Sanctuary
- 11 Feb 2025
In News:
Pong Dam Lake Wildlife Sanctuary, located in the Kangra district of Himachal Pradesh, has witnessed a record-breaking influx of migratory birds in 2025, according to the latest annual bird census conducted on February 1, 2025.
The sanctuary, a designated Ramsar Site (since 2002) and a Wetland of National Importance (1994), recorded a total of 1,53,719 birds across 97 species, indicating a sharp rise in avifaunal population and reaffirming its ecological significance.
Key Highlights from the 2025 Census
- Migratory birds recorded: 1,44,371 individuals from 55 species.
- Total bird count: 1,53,719 birds from 97 species.
- Increase from 2024: 83,555 more birds.
- Bar-headed Goose population: 90,959 (up from 37,501 in 2024) — highest ever recorded since the census began in 2004.
Other dominant waterfowl included:
- Eurasian Coots – 10,785
- Common Pochards – 9,692
- Common Teals – 8,497
- Northern Pintails – 8,053
Lesser-spotted species included the Greater and Lesser White-fronted Goose, Red Crested Pochard, and Northern Lapwing.
Reasons Behind the Surge
- Experts attribute the significant increase in bird numbers to a decline in the water level of Pong Dam Lake, which exposed additional lakebed areas, creating new feeding grounds. This has made the sanctuary increasingly attractive to birds migrating from Tibet, Central Asia, Russia, Siberia, and the Trans-Himalayan region.
Survey and Conservation Collaboration
- The census was conducted by over 100 participants, including officials from the Himachal Pradesh Forest Department, experts from the Bombay Natural History Society, Wildlife Institute of India, and local birdwatchers. The sanctuary was divided into 25 zones for comprehensive coverage.
- To further conservation efforts, a new Interpretation Centre was inaugurated on January 18, 2025, aimed at promoting awareness about the wetland's role in sustaining biodiversity and supporting migratory birds.
Ecological and Geographical Profile
Pong Dam Lake (Maharana Pratap Sagar)
- Type: Manmade reservoir formed by construction of Pong Dam on the Beas River.
- Location: Wetland zone of the Shivalik hills, Kangra district, Himachal Pradesh.
- Area: Approx. 307 sq. km — among the largest man-made wetlands in northern India.
- Importance: Key stopover on the Trans-Himalayan flyway for migratory birds.
Flora
- Vegetation types: Submerged aquatic vegetation, grasslands, forests.
- Dominant species:Eucalyptus, Acacia, Shisham.
Fauna
- Avifauna: Over 220 bird species recorded; 54 waterfowl species.
- Notable birds: Bar-headed Geese, Pintails, Pochards, Coots, Grebes, Cormorants, Herons, Storks, Grey Partridge, Peafowl.
- Mammals: Sambar, Barking Deer, Nilgai, Wild Boar, Clawless Otter, Leopard.
Rhododendron wattii

- 10 Feb 2025
In News:
A recent study has highlighted the alarming decline of the rare Rhododendron wattii, a species endemic to Nagaland and Manipur, especially in the Dzukou Valley, Nagaland. The species is now on the brink of extinction due to severe threats to its survival, raising serious conservation concerns.
Botanical Profile
- Taxonomy and Discovery:
- First collected by Sir George Watt during his 1882–85 survey in the Japfu Hill range, Nagaland.
- Belongs to the Rhododendron genus, which has over 1,000 species worldwide.
- India hosts 132 taxa, of which 129 are found in the northeastern region.
- Growth and Habitat:
- Grows as a small tree or shrub in the temperate biome.
- Attains a maximum height of 25 feet.
- Endemic to Manipur and Nagaland, predominantly in the Dzukou Valley at ~2,600 metres altitude.
- Phenological Features:
- Evergreen plant with year-round leaf renewal.
- Flowering: Late February to April.
- Fruiting:April to December.
- Produces trusses of 18–25 pink flowers with dark flecks and purplish basal blotches.
- Pollinated by the Fire-tailed Sunbird (Aethopygaignicauda) and bumble bees.
Conservation Concerns:
- Conservation Status:
- Listed as Vulnerable by the IUCN Red List due to:
- Severe population fragmentation.
- Area of occupancy less than 500 sq. km.
- Botanists at the Botanical Survey of India consider it Critically Endangered in its natural habitat.
- Listed as Vulnerable by the IUCN Red List due to:
- Threats to Survival:
- Poor seedling survivability despite abundant seed production.
- Anthropogenic pressures such as:
- Deforestation
- Habitat destruction
- Use of trees for firewood by local communities.
- Wildfires: A major fire incident in 2020–21 severely impacted the Dzukou Valley.
- The lone surviving Rhododendron wattii tree was recorded far from human trails during a recent field study.
Recent Study Highlights:
- Conducted by Imtilila Jing and S.K. Chaturvedi of Nagaland University.
- Published in the Journal of Threatened Taxa.
- Found only one living tree in the surveyed area of 27 sq. km of Dzukou Valley.
- The last previously reported tree in Nagaland (2012–13) was cut down.
Additional Botanical Development in the Region:
While the situation of Rhododendron wattii is grim, the region also witnessed a positive botanical development:
- Discovery of Phalaenopsis wilsonii, a new orchid species in Manipur’s Senapati district.
- Identified by researchers from the Institute of Bioresources and Sustainable Development (IBSD), Imphal.
- It is the ninth species of the Phalaenopsis genus recorded in Manipur.
Bryospilus Bharaticus

- 08 Feb 2025
In News:
A new species of water flea, Bryospilus (Indobryospilus) bharaticus n. sp., was recently discovered from moss growth on the walls of the Korigad Fort near Pune, Maharashtra.
This marks the first recorded discovery of the genus Bryospilus in Tropical Asia, underscoring the ecological uniqueness of the Western Ghats, a UNESCO World Heritage biodiversity hotspot.
Taxonomic and Morphological Highlights
- It belongs to the genus Bryospilus, a group of tiny crustaceans known as water fleas, which typically inhabit rivers, ponds, and pools.
- The species displays adaptations for semi-terrestrial life, notably using its antennae with large spines for crawling through thick, debris-laden water films on moss surfaces.
- It lacks a main eye—an evolutionary adaptation to low-light habitats where color vision is unnecessary for foraging.
Ecological and Evolutionary Significance
- The genus Bryospilus includes species found in semi-terrestrial habitats in rainforests of West Africa, South and Central America, and New Zealand, making this Indian discovery a significant biogeographical addition.
- The organism’s relatives are typically found in littoral (vegetated) zones of water bodies, whereas some occur in open waters.
- The researchers suggest that ancestors of this species existed on the Indian subcontinent prior to the breakup of Gondwanaland, around 200 million years ago, hinting at Bryospilus bharaticus as a potential Gondwanan relict species.
- Each known Bryospilus species has been isolated to a specific former Gondwanan continent, reinforcing the evolutionary legacy of this find.
Research and Conservation Implications
- The discovery was part of an ongoing survey of underexplored crustacean taxa in the Western Ghats, led by Sameer Padhye and Kan Van Damme, and published in the Journal of Crustacean Biology (Oxford Academic, Sept 2024).
- The species was found in pristine, undisturbed moss habitats on Deccan Plateau hill forts, highlighting the importance of conserving such microhabitats.
- Zooplankton like water fleas are highly sensitive to environmental changes and serve as bioindicators of ecological health. The presence of B. bharaticus indicates low human disturbance in its habitat.
- The authors warn that air pollution and habitat disturbance could threaten these fragile ecosystems and stress the urgency of habitat protection, especially for organisms invisible to the naked eye.
Kolleru Lake
- 06 Feb 2025
In News:
The Southern Zonal Bench of the National Green Tribunal (NGT) has recently restrained the Andhra Pradesh government from proceeding with six proposed infrastructure projects in the Kolleru wetland area, citing violations of environmental protocols and lack of statutory clearances.
About Kolleru Lake
- Location: Northeastern Andhra Pradesh, between the Krishna and Godavari river deltas, near Eluru city.
- Type: One of Asia’s largest shallow freshwater lakes, covering an area of 308 sq. km.
- Hydrology:
- Fed by Budameru and Tammileru rivers.
- Drains into the Bay of Bengal via Upputeru river (a tidal water channel).
- Acts as a natural flood-balancing reservoir for the Krishna and Godavari river systems.
- Ecological Importance:
- Declared a Wildlife Sanctuary in 1999 and a Ramsar Site in 2002.
- Designated as an Important Bird Area (IBA) due to the presence of over 50,000 waterfowl annually.
- Lies on the Central Asian Flyway (CAF), a major migratory bird route.
- Key Avian Species:
- Grey Pelican (indicator species), Siberian Cranes, Glossy Ibis, Open-billed Stork, Purple Moorhen, Painted Storks.
Kolleru Bird Sanctuary
- A protected wetland marsh habitat within the Kolleru Lake region.
- Supports diverse aquatic flora and fauna, serving as a crucial ecosystem for migratory and resident bird species.
Infrastructure Projects and Legal Challenges
- The projects were proposed under the entity "A.P. Krishna – Kolleru Salinity Mitigation Projects Corporation Limited" with a total capital outlay of approximately ?2,952 crore.
- The plans included construction of three regulators-cum-roads across the Upputeru river and other barrages, regulators, and sluices, falling within the Coastal Regulation Zone (CRZ).
- The Andhra Pradesh Water Resources Department (WRD) issued G.O. Ms. No. 63 (dated 2nd December 2020) authorizing the project.
Grounds for NGT Intervention
- Key objections included:
- Absence of scientific or ecological studies.
- Lack of consultations with wetland experts, wildlife conservationists, and hydrologists.
- No clearances obtained from:
- Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change (MoEF&CC)
- A.P. Coastal Zone Management Authority (CZMA)
- A.P. Pollution Control Board (PCB)
- National Board for Wildlife (NBWL)
NGT Observations and Ruling
- The tribunal emphasized the need for comprehensive evaluation of ecological and hydrological impacts before proceeding.
- It cited potential threats to the lake’s ecosystem, including:
- Disruption to natural hydrology.
- Loss of biodiversity and eco-sensitive habitats.
- The NGT ruled that the projects should not proceed unless fully compliant with environmental laws and backed by appropriate expert assessments.
- The ruling reinforced India's obligations under the Ramsar Convention and domestic environmental legislation, stressing the urgent need to protect the integrity of the Kolleru ecosystem.
Golden-headed Cisticola

- 05 Feb 2025
In News:
In a remarkable ornithological development, the Golden-headed Cisticola (Cisticola exilis) has been sighted in the Mathikettan Shola National Park, Idukki district, Kerala, marking its first recorded presence in the southern Western Ghats after a significant gap.
The finding underscores the ecological richness of the region and highlights the need for intensified avian research in the Western Ghats.
About Golden-headed Cisticola (Cisticola exilis)
- Also known as the bright-capped cisticola, it is a small warbler belonging to the family Cisticolidae.
- It is an omnivorous bird, feeding primarily on invertebrates such as insects and small slugs, along with grass seeds.
- The species is typically found in grassland habitats within mountain ranges, and has been previously recorded in parts of Karnataka, Tamil Nadu, and northern Kerala, notably in Banasura Hills, Wayanad. However, this is the first confirmed sighting in the southern part of the Palakkad Gap.
Physical features of breeding males include:
- Golden-orange plumage on the head, neck, and chest
- Pinkish beaks
- Black streaks on the back
- A distinctive call that aids identification
Habitat and Distribution
- It is widely distributed across Australia and several Asian countries.
- In India, its presence had been limited to select regions of the Western Ghats, making its recent sighting in Mathikettan Shola both rare and ecologically significant.
Conservation Status
- According to the IUCN Red List, the Golden-headed Cisticola is classified as Least Concern. Despite this, the new finding calls for further research into its habitat preferences and conservation needs within India.
About Mathikettan Shola National Park
Located in the southern part of the Palakkad Gap in the Western Ghats of Kerala, Mathikettan Shola is a vital biodiversity hotspot.
- It comprises evergreen forests, moist deciduous forests, shola grasslands, and semi-evergreen vegetation.
- The park hosts three major streams: Uchillkuthi Puzha, Mathikettan Puzha, and Njandar, which are tributaries of the Panniyar River.
- Its highest point is Kattumala, located at the eastern border adjoining Tamil Nadu.
- The Muthavan tribal community resides near the park’s northeastern boundary, reflecting the intricate human-nature interface in the region.
Scientific and Conservation Importance
The rediscovery has been documented in the journal Malabar Trogon by the Malabar Natural History Society, bringing attention to the importance of long-term monitoring and baseline studies in underexplored ecosystems.
It emphasizes:
- The ecological richness of the Western Ghats, a UNESCO World Heritage site.
- The importance of citizen science, as local birdwatchers played a key role in the finding.
- The need for enhanced habitat protection and ornithological research in grassland ecosystems of high-altitude regions.
World Wetlands Day 2025

- 04 Feb 2025
In News:
World Wetlands Day is observed every year on 2nd February to commemorate the adoption of the Ramsar Convention on Wetlands in 1971 in Ramsar, Iran.
India has been a signatory to the Convention since 1982 and has actively worked towards the conservation and sustainable management of wetlands—critical ecosystems that serve as biodiversity hotspots, natural flood buffers, and carbon sinks.
Theme 2025: "Protecting Wetlands for Our Common Future"
The 2025 theme emphasizes collaborative efforts to protect wetlands to ensure ecological sustainability, biodiversity preservation, and long-term human well-being. It highlights the need for integrated management and foresight in conservation strategies.
Key Event: Parvati Arga Ramsar Site, Gonda, Uttar Pradesh
The Union Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change (MoEFCC) organized the national-level celebrations of World Wetlands Day 2025 at the Parvati Arga Ramsar Site in Gonda district, Uttar Pradesh.
Significance of the Site
- Comprises two rain-fed oxbow lakes—Parvati and Arga—located in the terai region of the Gangetic plains.
- Supports endangered and critically endangered species like the white-rumped vulture, Indian vulture, and Egyptian vulture.
- Attracts migratory birds such as Eurasian coots, greylag geese, northern pintails, and red-crested pochards.
- Threatened by invasive species, notably the common water hyacinth.
- The nearby Tikri Forest is being developed as an eco-tourism site, and a nature-culture tourism corridor is planned between Ayodhya and Devi Patan.
Cultural and Economic Value
- The area includes heritage sites such as the birthplaces of Maharishi Patanjali and Goswami Tulsidas, enhancing its potential as a religious and cultural tourism hub.
- A MoU between Amazon and ARGA (UP Government initiative) aims to empower women entrepreneurs through digital training and market access under Amazon’s Saheli programme.
India's Wetland Landscape and New Ramsar Sites (2025 Update)
India’s tally of Ramsar Sites has risen to 89, with four new additions:
- Udhwa Lake – Jharkhand (first Ramsar site for the state)
- Theerthangal – Tamil Nadu
- Sakkarakottai – Tamil Nadu
- Khecheopalri – Sikkim (first Ramsar site for the state)
- Tamil Nadu leads with 20 Ramsar Sites, followed by Uttar Pradesh with 10 sites.
- Total area under Ramsar protection in India is now approximately 1.358 million hectares.
Amrit Dharohar Initiative
Launched in June 2023, the Amrit Dharohar initiative promotes conservation and sustainable use of Ramsar Sites over three years. It aligns with Budget 2023–24 announcements and focuses on:
- Species and Habitat Conservation
- Nature Tourism
- Wetlands-based Livelihoods
- Wetlands and Carbon Mitigation
The initiative encourages convergence among central ministries, state authorities, and community stakeholders.
Workshops and Public Engagement
A regional workshop for Northern States was organized on 1st February 2025, with participants from nine states and UTs, highlighting collaborative models in wetland management. The main event also included:
- Exhibitions on eco-friendly products, wetland conservation, and green skills.
- Launch of publications like the Integrated Management Plan for Parvati Arga, Factbook of India’s 85 Ramsar Sites, and Development of Van Taungya Villages.
- Felicitation of painting, quiz, and Nukkad Natak competition winners, promoting grassroots awareness.
Significance of Wetlands in India
Wetlands are water-covered ecosystems, either permanently or seasonally flooded. They:
- Support rich biodiversity, including migratory birds and aquatic species.
- Recharge groundwater and regulate floods.
- Provide livelihoods through fisheries and tourism.
- Act as natural carbon sinks, aiding in climate change mitigation.
Major Threats
- Pollution from industrial and domestic effluents
- Encroachment and urbanization
- Invasive species
Guneri Inland Mangrove

- 03 Feb 2025
In News:
In 2024, the Gujarat government declared the Inland Mangrove of Guneri, located in Kutch district, as the first Biodiversity Heritage Site (BHS) of the state under the Biological Diversity Act, 2002. The declaration followed a recommendation by the Gujarat Biodiversity Board.
Key Features of Guneri Inland Mangroves:
- Location: Guneri village, Lakhtar tehsil, Kutch district, Gujarat.
- Area: 32.78 hectares.
- Distance from Sea: ~45 km from the Arabian Sea; ~4 km from Kori Creek.
- Nature: Inland (non-coastal) mangrove ecosystem — one of only eight such sites globally and the last remaining in India.
- Terrain: Flat land resembling a forest; no tidal influence or sludge typically seen in coastal mangroves.
- Water Source: Sustained by groundwater retained in limestone deposits; no direct contact with seawater.
Ecological and Geological Significance:
- Possibly originated from:
- Miocene marine transgression, or
- Along the ancient Saraswati River, believed to have flowed in the Great Rann of Kutch around 3000–4000 BCE.
- Limestone formations in western Kutch provide continuous subsurface water flow, enabling survival of this unique mangrove system.
Biodiversity:
- Habitat to:
- 20 migratory bird species
- 25 resident migratory avifaunal species
- Acts as a vital ecosystem for local and seasonal wildlife.
Mangroves in India – 2024 Snapshot:
- As per the “Red List of Mangrove Ecosystems” (May 22, 2024):
- India has 3% of South Asia’s mangrove cover.
- Total mangrove area: 4,975 sq km (0.15% of India's land area).
- Increase: 54 sq km (1.10%) since last assessment.
- State-wise share:
- West Bengal: 42.45% (notably South 24 Parganas & Sundarbans)
- Gujarat: 23.66% (with highest increase: 37 sq km)
- Andaman & Nicobar Islands: 12.39%
Legal Framework:
- Declared under the Biological Diversity Act, 2002, which empowers state governments to notify BHS after consulting local self-government bodies.
- A local Biodiversity Management Committee (BMC), including representatives from self-governance institutions, will oversee protection and conservation.
- This provides a formal structure for site management, previously absent.
Conservation Measures:
- Training programs for local and tribal communities along with forest officials.
- A management plan will be implemented to preserve the unique flora and fauna.
Microplastics detected in Delhi’s Groundwater

- 02 Feb 2025
In News:
A first-of-its-kind study, commissioned by the Delhi government and conducted by The Energy and Resources Institute (TERI), has revealed the presence of microplastics in groundwater across all 11 districts of Delhi. The interim findings, submitted in November 2024, also reported microplastics in Yamuna River water and soil samples along its banks.
Key Findings:
- Widespread Contamination: Microplastics were found in groundwater samples across Delhi, indicating potential contamination due to leaching from the Yamuna River.
- Additional Contamination: Microplastics were also detected in the Yamuna's water and riverbank soil, suggesting environmental pervasiveness.
- Water Usage Impact: Since Delhi relies on borewells and treated groundwater for drinking and domestic purposes, this contamination raises serious public health concerns.
- No Objection by Authorities: The Delhi government has not disputed the study’s interim findings; further post-monsoon analysis is underway, and a final report is expected later in 2025.
What Are Microplastics?
According to the UN Environment Programme (UNEP):
- Definition: Plastic particles less than 5 mm in size
- Types:
- Primary Microplastics: Manufactured for use in cosmetics (e.g., microbeads) and textiles (e.g., microfibers from clothing, nets)
- Secondary Microplastics: Result from breakdown of larger plastics (e.g., bottles) due to sunlight, abrasion, and ocean waves
Environmental & Health Impacts:
- Persistence: Microplastics are non-biodegradable, mobile, and difficult to eliminate from natural ecosystems.
- Toxicity:
- Can adsorb harmful chemicals, making them more toxic
- Known to bioaccumulate in aquatic food chains
- Human Exposure: Microplastics can enter the human body via:
- Inhalation (air)
- Ingestion (water and seafood)
- Dermal absorption (through skin)
- Health Risks (UNEP Report – From Pollution to Solution, 2021):
- Potential effects on genetics, brain development, respiration, and placental health in newborns
- No global standard exists for safe microplastic limits in drinking water
Saffron Reedtail Damselfly
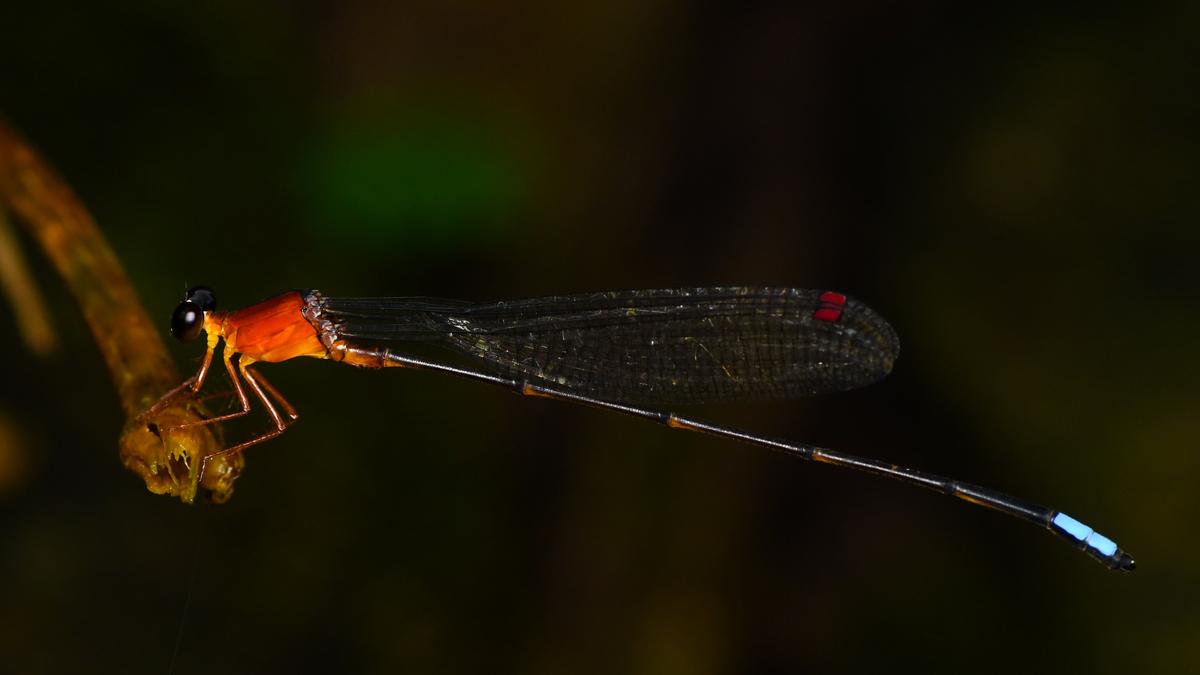

- 02 Feb 2025
In News:
For the first time, the Saffron Reedtail Damselfly, a rare and endemic species of the Western Ghats, has been recorded in Karnataka.
This significant discovery was made in Madhugundi village, Chikkamagaluru district, along the Nethravati River. The findings were published in the journal Entomon.
Key Facts:
- Scientific Name: Indosticta deccanensis
- Common Name: Saffron Reedtail
- Family: Platystictidae (commonly known as shadow damselflies)
- Appearance: Slender, delicate body with a characteristic saffron coloration
- Habitat: Prefers slow-moving forest streams surrounded by thick vegetation; requires pristine water quality
Ecological Significance:
- Indicator Species: Highly sensitive to environmental changes and pollution, indicating a healthy, undisturbed ecosystem.
- Biodiversity Implication:
- Previously recorded only in Tamil Nadu and Kerala.
- The first sighting in Karnataka (northern Western Ghats) extends the known range of the species, suggesting it may be more widely distributed than earlier believed.
Conservation Relevance:
- The discovery underscores the ecological richness of the Madhugundi forests, which were severely affected by floods and landslides in 2019.
- Highlights the urgency to protect fragile ecosystems from deforestation, water pollution, and climate change, especially in biodiversity hotspots like the Western Ghats.
About Damselflies (Order: Odonata):
- General Features:
- Predatory, aerial insects
- Slender bodies with net-veined wings
- Fly weakly compared to dragonflies
- Mostly inhabit freshwater habitats
Rusty-Spotted Cat

- 01 Feb 2025
In News:
For the first time, the Rusty-Spotted Cat (Prionailurus rubiginosus) has been spotted in the forests of Purulia district, West Bengal, captured on a camera trap set up by the NGO HEAL during pangolin poaching surveillance. This marks a significant range extension and has excited conservationists and forest officials.
Key Features
- World’s smallest and lightest wild cat: Weighs between 900 grams to 1.5 kg
- Length: Approx. 1.5 feet, with a 1-foot-long tail
- Appearance:
- Fawn-grey coat with rusty red spots on back and flanks
- Short, rounded head with two white facial streaks
- Large eyes with greyish-brown to amber irises – an adaptation to nocturnal behavior
- Short legs, black-soled feet, and an unmarked rusty tail
- Behavior:
- Nocturnal and elusive
- Uses scent marking to establish territory
- Gestation period: 66–70 days
Habitat and Distribution
- Found in dry deciduous and semi-deciduous forests, including:
- Northern & Central India, Western Ghats, Rajasthan, Kachchh, and Peninsular India
- Also present in Sri Lanka and Nepal
- India hosts 80% of the global population
Conservation Status
- IUCN Red List: Near Threatened, due to habitat loss, fragmentation, and human-wildlife conflict
- Wildlife Protection Act, 1972: Schedule I species (highest protection)
Significance of Purulia Sighting
- Located on the eastern edge of the Chota Nagpur Plateau
- Forests are interconnected with neighboring regions like Jharkhand and Odisha
- Notified as reserved forests, not protected forests
- Threats: Hunting by local communities, habitat degradation
Impact of Conservation Efforts
- Post-COVID, the forest ecosystem in Purulia has improved due to reduced human disturbance
- Past sightings of leopards, bears, jackals, and foxes indicate a thriving ecosystem
- HEAL and the Forest Department have launched livestock compensation programs to reduce retaliatory killings of carnivores
India adds 4 new Ramsar Sites

- 01 Feb 2025
In News:
The Government of India has added four new Ramsar sites, increasing the total to 89, the highest in Asia and third globally. The newly designated wetlands include:
- Sakkarakottai Bird Sanctuary (Tamil Nadu)
- Therthangal Bird Sanctuary (Tamil Nadu)
- Khecheopalri Wetland (Sikkim)
- Udhwa Lake (Jharkhand)
This marks a significant milestone as Sikkim and Jharkhand have received their first Ramsar recognitions, while Tamil Nadu strengthens its lead with 20 Ramsar sites, the most among Indian states.
About the Ramsar Convention
- Adopted: 1971 in Ramsar, Iran
- Objective: Conservation and wise use of wetlands through local, national, and international cooperation.
- World Wetlands Day: Celebrated on 2nd February to promote awareness.
Key Highlights:
Therthangal Bird Sanctuary – Tamil Nadu
- Notified in 2010; covers 29.29 ha.
- Crucial breeding and foraging site for waterbirds like Spot-billed Pelican, Black-headed Ibis, and Oriental Darter.
- Aids groundwater recharge and climate regulation.
- Part of the Central Asian Flyway.
Sakkarakottai Bird Sanctuary – Tamil Nadu
- Notified in 2012; spans 230.49 ha.
- Located near Gulf of Mannar; significant stopover for migratory birds.
- Hosts endemic species and near-threatened fauna like Lion-tailed Macaque and Giant Squirrel.
Khecheopalri Wetland – Sikkim
- Sacred lake revered by Buddhists and Hindus; called Sho Dzo Sho locally.
- Known as a wish-fulfilling lake.
- Birds prevent leaves from settling on the surface.
- Rich in avifauna: fishing eagles, Brahminy kites.
- Integral to ecotourism and biodiversity conservation.
Udhwa Lake – Jharkhand
- Comprises Pataura Jheel (155 ha) and Brahma Jamalpur Jheel (410 ha).
- First Ramsar site of Jharkhand; near Ganga River.
- Declared a bird sanctuary in 1991; attracts migratory birds from September onwards.
Falls under the Gangetic Plains biogeographic zone.
Environment Protection (End-of-Life Vehicles) Rules, 2025
- 31 Jan 2025
In News:
MoEFCC Notifies Rules for End-of-Life Vehicles to Minimize Waste and Pollution.
Key Highlights:
Notified by: Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change (MoEF&CC)
Effective from: April 1, 2025
Legal Basis: Environment Protection Act, 1986
Objective: To promote environmentally sound management of end-of-life vehicles (ELVs), enable recycling and reuse of vehicle components, and reduce resource extraction, pollution, and waste generation.
Key Features of the ELV Rules, 2025
1. Scope and Coverage
- Applicable to all vehicle categories including electric vehicles (EVs), e-rickshaws, and e-carts.
- Exempted vehicles: Agricultural tractors, trailers, combine harvesters, and power tillers.
- Exempted waste types: Batteries, plastics, tyres, used oil, and e-waste (governed under separate waste management rules).
2. Extended Producer Responsibility (EPR)
- Vehicle producers are mandated to meet annual scrapping targets based on the age of vehicles:
- Transport vehicles: 15 years
- Non-transport vehicles: 20 years
- Producers must fulfill their EPR obligations for all vehicles introduced into the domestic market, including those used internally.
- Annual EPR declarations must be submitted to the Central Pollution Control Board (CPCB) by April 30 each year.
- Producers must promote ELV deposition at designated collection centres or Registered Vehicle Scrapping Facilities (RVSFs).
3. Responsibilities of Stakeholders
- Registered Owners & Bulk Consumers: Required to deposit ELVs at designated centres or RVSFs within 180 days of becoming unfit.
- Collection Centres:
- Handle ELVs in an environmentally responsible manner.
- Maintain records and ensure safe storage and transfer to RVSFs.
- Registered Vehicle Scrapping Facilities (RVSFs):
- Undertake depollution, dismantling, segregation, and recycling.
- Ensure environmentally sound disposal of non-recyclables via authorized TSDFs.
- Issue EPR certificates based on the volume of steel processed; valid for 5 years.
4. Monitoring, Compliance, and Penalties
- CPCB and State Pollution Control Boards (SPCBs) are responsible for:
- Registration, inspection, and audit of producers, RVSFs, and bulk consumers.
- Taking action against non-compliance, including suspension or cancellation of registration.
- Levying environmental compensation for violations that cause harm to public health or the environment.
5. Registration & Certification
- Producers register with CPCB; RVSFs and bulk consumers with respective SPCBs.
- Registration certificates are issued within 15 days of application via a centralized online portal.
- EPR certificates are non-transferable and allow adjustment of both current and backlog obligations.
Related Policy and Incentives by MoRTH
The Ministry of Road Transport and Highways (MoRTH) supports the ELV Rules through:
- Vehicle Scrapping Policy: Targets voluntary phasing out of unfit and polluting vehicles.
- Motor Vehicles (Registration and Functions of Vehicle Scrapping Facility) Rules, 2021: Provides operational criteria for RVSFs.
- Central Motor Vehicles (Amendment) Rules, 2021:
- Waiver of registration fee for buyers submitting ELV Certificates of Deposit.
- Concession in motor vehicle tax: 25% for non-transport, 15% for transport vehicles.
Electric Mobility Push
- MoRTH has issued several notifications promoting EVs, including:
- Permit exemptions for battery-operated and ethanol/methanol-fueled vehicles.
- Fee exemptions for registration and renewals.
- Tourist permit benefits for EVs and distinct registration marks for visibility.
PM E-DRIVE Scheme
- Launched by Ministry of Heavy Industries on 29th September 2024 with a ?10,900 crore outlay.
- Aims to support electric 2-wheelers, 3-wheelers, ambulances, trucks, and buses with ?3,679 crore in demand incentives.
- Targets subsidization of over 28 lakh EVs.
Olive Ridley Turtles
- 30 Jan 2025
In News:
The Rushikulya river mouth in Odisha is witnessing the anticipated mass nesting of Olive Ridley turtles — a critical event for the survival of this vulnerable marine species. This phenomenon, known as arribada, highlights the ecological significance of India’s coastal biodiversity and the urgent need for marine conservation.
About Olive Ridley Turtles (Lepidochelys olivacea)
- Taxonomy:
- Scientific Name: Lepidochelys olivacea
- Class: Reptilia
- Family: Cheloniidae
- Physical Features: These turtles are the smallest and most abundant of all sea turtle species. They are recognized by their olive or grayish-green heart-shaped carapace. Males and females are similar in size, though females have slightly rounder shells.
- Habitat and Distribution: Olive Ridleys are found in warm, tropical waters of the Pacific, Atlantic, and Indian Oceans, inhabiting both open ocean (pelagic) and coastal waters.
Mass Nesting: The Arribada Phenomenon
- Arribada (Spanish for "arrival") refers to the synchronized mass nesting behavior where thousands of females gather on a single beach to lay eggs.
- Nesting occurs annually between December and March, after long migrations of up to 9,000 km. Each female may lay 90–120 eggs, 1 to 3 times per season.
- Temperature-dependent sex determination influences hatchling sex ratios.
- After nesting, females return to the sea, leaving eggs buried in sand.
Major Nesting Sites in India
- Odisha Coast is the most significant nesting ground in India and globally:
- Gahirmatha Marine Sanctuary: World’s largest mass nesting site.
- Rushikulya River Mouth: Second-largest nesting beach in India.
- Devi River Mouth: Another key nesting site in Odisha.
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands have recently emerged as a new mass nesting area, with over 5,000 nests reported in one season.
Ecological Role and Behavior
- Diet: Omnivorous — they feed on jellyfish, crabs, snails, prawns, molluscs, algae, and small fish.
- Behavior: These turtles undertake long migrations annually between feeding and breeding grounds, spending most of their lives at sea.
Protection Status
- IUCN Red List: Vulnerable
- CITES: Appendix I
- Wildlife (Protection) Act, 1972 (India): Schedule I (highest protection)
Threats to Survival
- Bycatch in Fishing Gear: Accidental entanglement in trawls, gillnets, and longlines.
- Habitat Loss: Coastal development for ports, tourism, and industry disrupts nesting beaches.
- Poaching: Turtles and their eggs are harvested for meat, shell, and leather.
- Pollution: Plastic ingestion and marine debris pose severe health risks.
- Climate Change: Rising sea levels and increased sand temperatures impact nesting and hatchling sex ratios.
Conservation Initiatives
- Operation Olivia: Initiated by the Indian Coast Guard in the 1980s to protect turtles during nesting and prevent illegal fishing.
- Turtle Excluder Devices (TEDs): Mandated by the Odisha government in trawl nets; allow turtles to escape while retaining fish catch.
- Tagging Programs: Use of non-corrosive metal tags to study migration patterns and inform conservation strategies.
Asian Waterbird Census 2025

- 29 Jan 2025
In News:
As per the Asian Waterbird Census-2025, a record number of 39,725 birds belonging to 106 species have been sighted in the Coringa Wildlife Sanctuary and adjoining wetlands.
Asian Waterbird Census (AWC): An Overview
- AWC is an annual citizen-science programme that supports the conservation of wetlands and waterbirds across Asia.
- Initiated in 1987 in the Indian subcontinent, it now covers extensive regions of East and Southeast Asia, Japan, Australasia, and parts of the Central Asian and East Asian–Australasian Flyways.
- AWC is the Asian chapter of the global International Waterbird Census (IWC).
- In India, it is coordinated by the Bombay Natural History Society (BNHS) and the Wildlife Institute of India (WII) every January.
About BNHS (Bombay Natural History Society)
- An Indian NGO engaged in biodiversity research and conservation.
- Recognized as a Scientific and Industrial Research Organisation (SIRO) by the Department of Science and Technology.
- Official partner of BirdLife International in India.
Coringa Wildlife Sanctuary (Andhra Pradesh): Census Findings 2025
- The Asian Waterbird Census 2025 recorded a record 39,725 birds representing 106 species in the Coringa Wildlife Sanctuary (CWS) and adjoining Godavari estuary wetlands.
- Of these, nearly 70 species are migratory, using the site as a key winter feeding ground.
Species of Conservation Concern
- Endangered species sighted:
- Indian Skimmer (Rynchops albicollis) – ~450 individuals sighted
- Black-bellied Tern (Sterna acuticauda)
- Great Knot (Calidris tenuirostris)
- Vulnerable species: Common Pochard (Aythya ferina)
- Near Threatened species: 11 species identified
Migratory Pathways and Monitoring
- Migrants such as the Great Knot travel from Russia, Siberia, China, and Mongolia to the Godavari estuary.
- A tagged Great Knot, tracked from Russia, was recorded after a 7,500 km journey, seen in Bhairavapalem mudflat and Etimoga wetland in successive winters (2024 and 2025).
- Data sharing with global avian research groups aids in tracking migratory patterns and supports conservation of endangered species.
Ecological and Ramsar Significance
- The Godavari estuary supports feeding grounds for nearly 90,000 birds, as observed by CWS authorities.
- Avian diversity is a key criterion for Ramsar Site designation, and experts advocate for Coringa Wildlife Sanctuary and its surroundings to be recognized as a wetland of international importance under the Ramsar Convention.
Indian Squid

- 29 Jan 2025
In News:
Researchers at the Central Marine Fisheries Research Institute (CMFRI), Kochi, have successfully decoded the gene expression pattern of the Indian squid (Uroteuthis duvaucelii), marking a major scientific advancement with wide-ranging implications for neuroscience, environmental studies, and sustainable marine resource management.
About Indian Squid
- Common Name: Indian Calamari
- Scientific Classification: Cephalopod
- Size: Typically 20–30 cm; can grow up to 50 cm
- Appearance: Light pinkish-grey body with two large fins, eight arms, and two longer tentacles used for capturing prey
- Key Abilities:
- Camouflage
- Jet propulsion for rapid movement
- Advanced nervous system
- Problem-solving skills and behavioral intelligence
Habitat & Distribution
- Preferred Habitat: Coastal and open sea regions of the Indian Ocean
- Found at depths ranging from 100 to 500 meters, some even up to 1,500 meters
- Requires high dissolved oxygen levels for respiration
- Geographic Distribution:
- Widely distributed in the Indo-West Pacific
- Found in Indian Ocean, Red Sea, Arabian Sea, from Mozambique to the South China Sea, Philippine Sea, and northward to Taiwan
- Conservation Status: IUCN Red List: Least Concern
Scientific Significance of Genetic Research
- Key Findings:
- Revealed genetic similarities with higher vertebrates like fish and humans, suggesting deep evolutionary links
- Indicates that Indian squid could serve as a model organism to study brain evolution, intelligence, and neurobiological functions
- Potential to inform research in neural circuits, memory, learning, and even neurological diseases
- Findings may also explain squid's adaptive success, such as evading predators and fishing pressures due to high cognitive ability
Institutional Background: CMFRI
- Established: 1947
- Affiliation: Part of the Indian Council of Agricultural Research (ICAR) since 1967
- Headquarters: Kochi, Kerala
- Mandate: Research on sustainable marine fisheries and ecosystem conservation
CMFRI’s Broader Recommendations for Sustainable Marine Management
- Enactment of Sea Fishing Act to regulate fishing beyond territorial waters
- Institutionalization of ecological stock assessments for sustainable exploitation
- Simplification and promotion of open mariculture with focus on environmental sustainability
- Use of AI-based systems to estimate landings and monitor fishing vessels
- Deep-sea resource exploration and alternative fishing methods
- Institutional mechanism for supervising deep-sea fishing
- Strengthening insurance coverage for marine fishers
Chinar Trees

- 22 Jan 2025
In News:
The J&K Forest Department, in collaboration with the J&K Forest Research Institute (JKFRI), has launched a pioneering conservation initiative to digitally preserve the iconic Chinar trees (Platanus orientalis)—a vital part of Kashmir’s ecological and cultural heritage.
Significance of Chinar Trees:
- Locally known as Boonyi or Boueen, Chinar trees are deeply embedded in Kashmir’s cultural identity.
- These deciduous trees can grow up to 30 meters tall with a girth of 10–15 meters, and can live for over 600 years.
- They are known for their seasonal leaf color transformation—from green in summer to red, amber, and yellow in autumn.
- Notable specimens include Asia’s largest Chinar in Ganderbal and the oldest known Chinar (647 years) in Chattergam, Budgam.
Challenges to Chinar Survival:
- Urban expansion and habitat encroachment.
- Climate change, altering precipitation and temperature patterns.
- Illegal felling and timber exploitation.
- Increased susceptibility to pests and diseases.
Tree Aadhaar & Geo-Tagging Initiative:
- Over 28,500 Chinar trees have been geo-tagged and assigned unique Tree Aadhaar numbers from 2021 to 2023.
- Each tree is fitted with a QR-coded digital plate, enabling real-time access to:
- Tree location, height, girth, canopy dimensions
- Health status, ecological threats, and pest presence
- These plates are spring-mounted metal tags to prevent damage to the trees.
Conservation Goals & Future Plans:
- Digital Protection: Enables proactive monitoring and protection through a centralized database.
- Chinar Atlas: A comprehensive mapping of all Chinar trees in the region.
- Public Access Website: A dedicated digital portal is planned for broader access to Chinar data.
- Risk Assessment: Use of USG-based, non-invasive surveys to identify trees at risk without human interference.
- Emphasis on covering remote and restricted areas in future phases to ensure inclusivity in conservation.
Konkan Region’s Sada and Biodiversity

- 14 Jan 2025
In News:
A Konkan secret, the flat-top sada is a freshwater paradise.
Key Highlights:
Geography of Sada:
- The Konkan region lies between the Arabian Sea and the Western Ghats.
- Sada refers to flat-topped hills, formed by centuries of erosion, and is a prominent feature in the Ratnagiri district.
- These areas are typically barren except during the monsoon season when they come alive with flora and fauna.
Biodiversity and Ecosystem Services:
- A biodiversity survey between 2022-2024 recorded 459 plant species, with 105 being endemic to the Konkan region.
- The survey also identified 31 species of reptiles, 13 species of amphibians, 169 species of birds, and 41 species of mammals.
- These ecosystems play a vital role in water conservation. The lateritic soil layer atop the Sada acts as a catchment for rainwater, recharging the groundwater and providing freshwater to local communities year-round.
Traditional Land Use and Agriculture:
- Local Farming: During monsoons, the Sada is used by locals for growing traditional crops like rice and millets (e.g., nanchani), using sustainable farming practices without pesticides or chemical fertilizers.
- Water Management: The locals rely on open wells, springs, and perennial streams for freshwater, which are carefully maintained through cultural rituals and community hygiene practices.
Conservation and Cultural Importance:
- The region is home to geoglyphs, ancient artworks estimated to be 10,000 years old, adding to its cultural and historical significance.
- Waterbodies on the Sada serve as habitats for species like the Indian flapshell turtle (Lissemys punctata) and provide water for other wildlife, including leopards, jackals, hyenas, barking deer, and migratory birds.
Environmental Threats:
- Land-use Change: Increasing conversion of open land and croplands into orchards and residential areas, along with various developmental projects, threatens the region's biodiversity.
- Mining: Extraction of laterite stones for construction purposes is another environmental risk.
- Wasteland Classification: The region is often classified as a ‘wasteland’ in the Wasteland Atlas, further complicating conservation efforts.
World’s First Cryo-Born Baby Corals

- 13 Jan 2025
In News:
World’s First Cryo-Born Baby Corals Successfully Settled on the Great Barrier Reef.
Introduction to Cryo-Born Corals
- Cryo-born corals are created using cryopreservation techniques, which involve freezing coral cells and tissues at very low temperatures.
- The process preserves coral cells by preventing the formation of ice crystals that would otherwise damage them.
- Cryopreservation involves adding cryoprotectants to remove water from cells, enabling their survival during freezing and thawing.
Significance of the Breakthrough
- Climate Change Resilience: The initiative aims to create heat-tolerant corals, which are crucial in combating the impact of rising ocean temperatures due to climate change.
- Selective Breeding Advantage: Cryopreservation allows for controlled breeding and bypasses the limitations of natural coral spawning, which occurs only once a year. This enables multiple reproduction cycles without disturbing wild populations.
The Process of Cryo-Born Coral Production
- Sperm Collection: During coral spawning events, sperm from various coral species is collected and frozen at -196°C using liquid nitrogen, halting metabolic processes.
- Coral Egg Fertilization: Cryopreserved sperm is used to fertilize fresh coral eggs, which are grown in a specialized research facility called the National Sea Simulator.
- Coral Cradles: After growth, the cryo-born corals are carefully transported and settled into specially designed "coral cradles" placed in the Great Barrier Reef, where their growth is monitored during their critical first year.
Importance of Cryo-Born Corals in Reef Restoration
- The primary aim is to introduce millions of heat-tolerant corals annually to restore reefs affected by climate change.
- The Taronga CryoDiversity Bank houses the world’s largest frozen coral sperm collection from 32 coral species, collected annually since 2011, providing a resource for future restoration efforts.
Coral Reefs: An Overview
- Corals are marine invertebrates from the class Anthozoa, phylum Cnidaria.
- Reefs are built by colonies of coral polyps that secrete limestone skeletons and rely on symbiotic algae (zooxanthellae) for nutrition.
- Coral reefs are typically found in shallow, sunlit waters with a temperature range of 16-32°C and depths less than 50 meters.
Global and Indian Coral Conservation Efforts
- India:
- The National Committee on Wetlands, Mangroves, and Coral Reefs (1986) advises on conservation measures.
- The Environment (Protection) Act (1986) prohibits the use of coral and sand in construction.
- Zoological Survey of India (ZSI) uses Biorock technology for coral restoration.
- Global Efforts:
- CITES lists coral species in Appendix II, regulating coral trade.
- The World Heritage Convention designates coral reefs as protected sites.
Global Impact and Future Directions
- The innovative work by Australian scientists opens the door for large-scale restoration efforts by allowing more controlled breeding and genetic diversity, making corals more resilient to climate change.
- This breakthrough could revolutionize coral restoration, scaling up efforts to introduce millions of resilient corals to reefs worldwide, building long-term resilience against climate change.
Miyawaki Technique
- 09 Jan 2025
In News:
- Prayagraj Municipal Corporation has successfully transformed over 56,000 square meters of garbage dumps and barren lands into lush green forests using the Miyawaki Technique over the past two years, as part of environmental conservation efforts in preparation for Mahakumbh 2025.
About Miyawaki Technique:
- Origin: Developed by Akira Miyawaki, a Japanese botanist, in the 1970s to create dense and fast-growing forests.
- Key Features:
- Dense Planting: Trees and shrubs are planted close together, often using native species.
- Accelerated Growth: Trees grow 10 times faster than in traditional forests.
- Soil Restoration: Improves soil fertility and promotes natural regeneration.
- Biodiversity Boost: Supports a variety of flora and fauna by mimicking natural ecosystems.
- Significance:
- Urban Reforestation: Converts barren or polluted lands into green spaces.
- Environmental Benefits:
- Reduces air and water pollution.
- Absorbs carbon and helps combat climate change.
- Lowers temperatures by 4-7°C.
- Sustainability: Prevents soil erosion and promotes long-term ecological balance.
Miyawaki Forests in Prayagraj:
- Achievements:
- Over 56,000 square meters of land converted into dense forests using the Miyawaki technique over the last two years.
- The project aims to create oxygen banks in preparation for the Mahakumbh 2025 and enhance air quality for millions of expected visitors.
- Plantations:
- 55,800 square meters of area developed across 10+ locations in Prayagraj.
- Largest plantation: 1.2 lakh trees in Naini industrial area.
- 27,000 trees planted in Baswar after cleaning the city's largest garbage dump.
- Environmental Impact:
- The plantations are helping to reduce dust, dirt, and foul odors, thus improving air quality.
- Temperature regulation: The dense forests can lower temperatures by 4 to 7 degrees Celsius.
- Biodiversity and Soil Fertility: Accelerated growth of trees boosts biodiversity and improves soil fertility.
- Tree Species Planted:
- Mango, Mahua, Neem, Peepal, Tamarind, Arjuna, Teak, Amla.
- Ornamental and medicinal plants like Hibiscus, Kadamba, Gulmohar, etc.
- Other species include Sheesham, Bamboo, Lemon, Drumstick (Sahjan), and Tecoma.
Benefits of Miyawaki Forests:
- Air and Water Pollution Reduction: Trees absorb carbon, purify air, and improve water quality.
- Temperature Control: The forests help in reducing urban heat islands, lowering the temperature during hot months.
- Soil Conservation: The dense forests prevent soil erosion and promote the regeneration of the natural ecosystem.
- Enhanced Biodiversity: The technique supports a rich variety of species, improving ecological balance.
Chhattisgarh’s Link between Forest Ecosystem and Green GDP

- 06 Jan 2025
In News:
In a first, the Chhattisgarh state has introduced an innovative plan that connects the ecosystem services of its forests with the Green Gross Domestic Product (Green GDP).
Key Highlights:
Chhattisgarh's Green GDP Initiative:
- First State in India to link forest ecosystem services with Green GDP.
- Forests cover 44% of Chhattisgarh's land area, playing a vital role in climate change mitigation.
- Key forest products (tendu leaves, lac, honey, medicinal plants) contribute significantly to the rural economy.
Green GDP:
- Definition: An adjustment of traditional GDP that accounts for environmental costs like resource depletion and ecosystem degradation.
- Formula:
- Green GDP = Net Domestic Product (NDP) − (Cost of Resource Depletion + Ecosystem Degradation)
- NDP = GDP − Depreciation of Produced Assets.
Importance of Green GDP:
- Traditional GDP overlooks the environmental cost, treating activities like deforestation as economic gains.
- Green GDP adjusts for sustainability, ensuring long-term economic growth aligns with environmental preservation.
Global Context & Initiatives:
- SEEA (System of Environmental-Economic Accounting): Developed by the UN to track economic-environment relationships.
- WAVES: World Bank initiative integrating natural capital into national economic accounts.
- Bhutan’s GNH: Emphasizes ecological sustainability in development.
Benefits of Green GDP for Chhattisgarh:
- Promotes sustainable development by integrating economic and environmental goals.
- Climate Change Mitigation: Forests help absorb CO2, playing a key role in carbon sequestration.
- Biodiversity Conservation: Supports sustainable use of resources, preserving ecosystems.
- Cultural Integration: Acknowledges forests' cultural and spiritual importance to local tribal communities (e.g., sacred groves).
Key Features of the Initiative:
- Valuing Ecosystem Services: Includes clean air (CO? absorption), water conservation, and biodiversity.
- Eco-tourism Promotion: Developing jungle safaris and national parks, boosting local employment.
- Scientific Assessments: Employing experts to quantify forest contributions to the economy.
Challenges of Green GDP Framework:
- Valuation Complexity: Difficult to assign monetary value to non-market environmental benefits like biodiversity.
- Data Gaps: Lack of comprehensive data on environmental degradation and resource usage.
- Implementation: Requires significant changes in accounting systems and policymaking.
- Forest Definition: Plantations like oil palm may be counted as forests, misleading environmental assessments.
- Political Resistance: States may manipulate data to secure funding, prioritizing plantations over natural forests.
- Local Integration: Difficulties in involving local bodies like Panchayats due to literacy and awareness gaps.
Future of Green GDP:
- Sustainable Resource Use: Encourages responsible consumption and production, aligning with SDG 12.
- Climate Action: Contributes to the reduction of fossil fuel reliance and promotes renewable energy, aligning with SDG 13.
- Green Investments: Stimulates green technologies and industries, fostering sustainable economic growth (SDG 8).
Translocation of Tigers from Madhya Pradesh
- 05 Jan 2025
In News:
Madhya Pradesh to translocate 15 Tigers to Rajasthan, Odisha and Chhattisgarh.
Key Highlights of the Translocation:
- Scale of Translocation: Largest relocation of big cats from a single state in India.
- Approval: NTCA has approved the translocation of 15 tigers from Madhya Pradesh to Rajasthan, Chhattisgarh, and Odisha.
- Source Reserves:
- Bandhavgarh, Panna, Kanha, and Pench Tiger Reserves in Madhya Pradesh.
- Distribution Plan:
- Rajasthan: 4 tigresses.
- Chhattisgarh: 2 male tigers and 6 tigresses.
- Odisha: 1 male tiger and 2 tigresses.
- Funding: States receiving tigers will bear all expenses related to translocation.
Objectives of the Translocation:
- Enhance Tiger Conservation: Reintroduce and bolster tiger populations in recipient states.
- Population Management: Relocate tigers to areas with suitable habitats to alleviate territorial disputes in overpopulated reserves.
- Genetic Diversity: Introduce new individuals to isolated tiger groups to prevent inbreeding and support long-term species survival.
About Kanha, Bandhavgarh, and Pench Tiger Reserves:
- Kanha Tiger Reserve:
- Location: Maikal range of the Satpura Mountains.
- Significance: Largest national park in Madhya Pradesh.
- Distinct Feature: First tiger reserve in India with an official mascot, ‘Bhoorsingh the Barasingha’.
- Flora and Fauna: Rich biodiversity with Royal Bengal Tigers, leopards, and the IUCN Vulnerable species, Barasingha.
- Bandhavgarh Tiger Reserve:
- Location: Between Vindhyan and Satpura ranges in Umaria district, Madhya Pradesh.
- Significance: Known for one of the highest densities of Royal Bengal Tigers in India.
- Historical Link: The ancient Bandhavgarh Fort, linked to the legend of Lord Rama and Lakshmana.
- Pench Tiger Reserve:
- Location: Spans Seoni and Chhindwara districts in Madhya Pradesh, extends into Maharashtra.
- Significance: Inspiration for Rudyard Kipling’s The Jungle Book.
- Flora and Fauna: Includes teak, saag, mahua forests; tigers, leopards, wild dogs, and gaur are key species.
Tiger Translocation Project Overview:
- First Project:
- Initiated in 2018, two tigers relocated from Kanha and Bandhavgarh to Satkosia Tiger Reserve in Odisha.
- Main Objectives:
- Reintroduce Tigers: In areas where they have been extirpated or extinct.
- Alleviate Territorial Disputes: Overpopulated reserves need additional tigers to reduce human-animal conflict.
Benefits of Translocation:
- Ecological Balance: Restores predator-prey dynamics in underpopulated reserves.
- Human-Animal Conflict Mitigation: Reduces conflict in overcrowded reserves.
- Rewilding Landscapes: Revives areas where tigers were locally extinct.
Concerns Associated with Translocation:
- Local Community Protests: Villagers fear tigers will pose a threat to their safety.
- Territorial Disputes: New tigers may face conflict with resident tigers.
- Poor Forest Management: Inadequate prey augmentation and habitat management may hinder success.
Madhya Pradesh’s Role in Tiger Conservation:
- Largest Tiger Population: Madhya Pradesh hosts the largest number of tigers in India, with 785 tigers as per NTCA’s 2022 report.
- Tiger Reserves: The state is home to nine tiger reserves, including the newly notified Madhav Tiger Reserve in Shivpuri.
- Translocation Strategy: Madhya Pradesh’s involvement helps reduce local tiger population pressure and contributes to broader conservation efforts across India.
Inter-State Tiger Translocation Goals:
- Reinforcement and Reintroduction: Introduce tigers into areas historically part of their range but from which they have been extirpated or extinct.
- Genetic Diversity: Introduce new tigers to isolated populations to maintain long-term population health.
CGWB Report on Groundwater Contamination
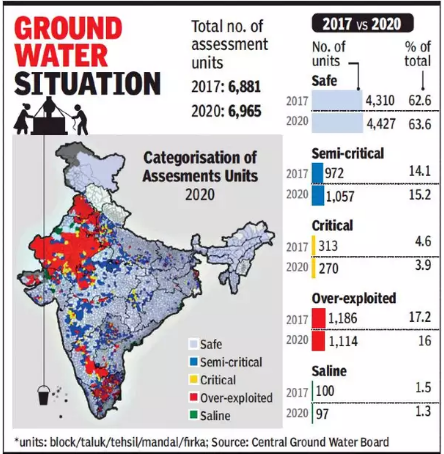
- 03 Jan 2025
In News:
The Central Ground Water Board (CGWB) report on groundwater quality reveals alarming levels of contamination in India's groundwater, with a focus on nitrate, fluoride, arsenic, and uranium. The report highlights the impact of agricultural practices, poor waste management, and urbanisation on water quality.
Key Highlights:
Nitrate Contamination:
- 440 districts in India report excessive nitrate levels in groundwater, with 20% of samples exceeding the permissible nitrate limit of 45 mg/L (WHO and BIS standards).
- High-risk regions: Rajasthan (49%), Karnataka (48%), and Tamil Nadu (37%) are the top states with high nitrate levels. Other affected states include Maharashtra, Telangana, Andhra Pradesh, and Madhya Pradesh.
- Causes: Nitrate contamination is mainly due to excessive use of nitrogen-based fertilizers, over-irrigation, and poor management of animal waste. Urbanisation and improper sewage systems exacerbate the problem.
Other Groundwater Contaminants:
- Fluoride contamination: A significant concern in Rajasthan, Haryana, Karnataka, Andhra Pradesh, and Telangana.
- Arsenic contamination: Elevated arsenic levels found in several states, especially in floodplains of the Ganga and Brahmaputra rivers (West Bengal, Jharkhand, Bihar, Uttar Pradesh, Assam, and Manipur).
- Uranium contamination: 42% of uranium-contaminated samples are from Rajasthan, and 30% from Punjab. Chronic exposure to uranium leads to kidney damage.
Groundwater Extraction and Availability:
- 60.4% of groundwater is being extracted across India.
- 73% of groundwater blocks are classified as in the ‘safe’ zone, an improvement from 67.4% in 2022.
Monsoon Impact:
- Nitrate contamination increases post-monsoon, with 32.66% of samples exceeding safe limits during the rainy season.
Health Implications:
- High nitrate levels, particularly dangerous for infants, can cause blue baby syndrome (methemoglobinemia).
- Long-term exposure to contaminants like fluoride and arsenic can lead to fluorosis and increase the risk of cancers and skin lesions.
Sources of Contamination:
- Agricultural practices: Excessive use of fertilizers, pesticides, and improper irrigation.
- Waste disposal: Leaking septic systems, sewage, and hazardous waste sites contribute to contamination.
- Urbanisation: Increased wastewater and sewage, along with poor waste management, worsen the issue.
Measures to Address Contamination:
- Jal Shakti Abhiyan (JSA) and Atal Bhujal Yojana (ABHY) aim to conserve and manage groundwater resources.
- National Aquifer Mapping and Management Program (NAQUIM) to assess and map aquifer systems.
- Pollution control programs: Under the Water (Prevention & Control) Act, 1974, and initiatives like sewage treatment plants and effluent treatment plants to manage wastewater.
- Public awareness: Campaigns like Swachh Bharat Mission and Catch the Rain educate communities on the importance of groundwater conservation.
Key Statistics:
- 56% of districts in India report groundwater nitrate levels exceeding the safe limit of 45 mg/L.
- Monsoon effects: Post-monsoon data shows a significant increase in contamination levels (32.66% vs. 30.77% pre-monsoon).
Stellaria bengalensis

- 02 Jan 2025
In News:
After a plant species of the genus Stellaria (family Caryophyllaceae) was reported from Kerala earlier this year, researchers have identified another member of the same genus at Kalimpong district in West Bengal.
Key Highlights:
Discovery and Identification:
- Published: The discovery was published in Phytotaxa.
- Location: Found in Kalimpong district, West Bengal, at altitudes of 2,245-2,450 metres in the Sangser forest.
- Named: The species is named Stellaria bengalensis after the state of West Bengal.
Taxonomy and Characteristics:
- Family: Caryophyllaceae.
- Type: Annual herb.
- Size: Grows to a height of 8 to 10.5 cm.
- Flowers: White in color, with shorter petals, often included within the sepal, and absence of bracts.
- Seeds: Sharp and pointed.
- Flowering and Fruiting: Occurs from May to September.
Distribution:
- Region: Primarily found in the Himalayan region.
- Similar Species: Stellaria mcclintockiae, identified earlier in Kerala (Nelliyampathy Hills).
- Both species grow in muddy soil slopes and are annuals.
Conservation Status:
- Under IUCN (International Union for Conservation of Nature) criteria, the species is assessed as "data deficient", pending further studies.
- Potential Habitat: There is a possibility of finding more populations in the western Himalayas.
Significance:
- Stellaria bengalensis is the second Stellaria species reported in India in 2025.
- India is home to about 22 Stellaria species, predominantly found in the Himalayan region.
- The discovery adds to biodiversity knowledge in India and underscores the importance of studying plant species in the region.
Sambar Deer

- 29 Dec 2024
In News:
Three poachers were arrested for killing a sambar deer in the Daying Ering Memorial Wildlife Sanctuary (DEMWS), East Siang district, Arunachal Pradesh.
Action Taken:
- Poachers Arrested: The poachers were booked under the Wildlife Protection Act 1972 and Arms Act 1959. The seized articles were handed over to the police, and a FIR was registered.
- Sanctuary Protection Efforts: The Divisional Forest Officer (DFO) emphasized the need for intensified surveillance to prevent further hunting incidents. Public cooperation was urged to report such incidents for prompt action.
About Sambar Deer:
- Scientific Name: Rusa unicolor.
- Native Regions: Found across the Indian subcontinent and Southeast Asia.
- Other Names: Known as Jarao in Nepal and Four-eyed deer in China.
- IUCN Red List: Listed as Vulnerable.
Key Features:
- Size: Stands between 1.2–1.4 meters at the shoulder.
- Weight: Can reach up to 550 kg, making it the largest oriental deer.
- Coat: Dark brown with a ruff around the neck, and unspotted.
- Antlers: Male sambar bears long, rugged antlers with three points (tines).
- Behavior: Elusive, most active at dusk and night.
Habitat:
- Water Dependency: Always found near water sources.
- Habitat Range: Dry deciduous forests, rainforests, and mixed forests.
- Social Structure: Often found alone or in small groups.
About Daying Ering Memorial Wildlife Sanctuary (DEMWS):
- Location: Situated in East Siang district, Arunachal Pradesh.
- Established: Originally established as Lali Wildlife Sanctuary in 1976, renamed Daying Ering Memorial in 1986.
- Climate: Tropical, receiving both north-east and south-west monsoons.
- Waterways: Home to the Siang River, one of Arunachal's major rivers.
Flora:
- Vegetation: Composed mainly of riverine plains with a variety of thatch and grasses.
- Trees: Includes scattered patches of trees such as Termenelia myriocarpa, Dillenia indica, Albizia spp., and Bombax ceiba.
Fauna:
- Mammals: Includes Hog Deer, Wild Pig, Tiger, and Elephant.
- Birds: Over 150 species of birds, including endangered species like the White-Winged Wood Duck and Bengal Florican.
Cephalopods

- 26 Dec 2024
In News:
Octopuses and their relatives are a new animal welfare frontier
- Cephalopods are highly intelligent, marine invertebrates that include species such as octopuses, squids, and cuttlefish.
- They are members of the class Cephalopoda in the phylum Mollusca, which is known for its diversity and complex morphology.
- Cephalopods are often considered one of the most behaviorally and morphologically complex classes within this phylum.
Key Features and Anatomy
Cephalopods exhibit several distinctive features:
- Body Structure: They have a head-foot structure, where the head is merged with the foot, and arms/tentacles surround the head. The arms and tentacles are derivatives of the foot, with some species possessing additional appendages for grasping or movement.
- Tentacles and Beak: Cephalopods possess tentacles, often with suction cups or hooks for capturing prey. They also have beak-like jaws, which are used to break down food.
- Eyes and Vision: Their unique W-shaped pupils enhance their vision. Most cephalopods are believed to be colorblind, but they exhibit remarkable visual camouflage through chromatophores (pigment cells) and reflectors beneath their skin, which can produce a wide range of colors and patterns.
- Movement: Cephalopods use jet propulsion to move. By expelling water from their mantle cavity, they can quickly travel through the water. Some species, like octopuses, also "walk" using their arms, while squids and cuttlefish employ fins for propulsion.
- Circulatory System: They have three hearts. Two hearts pump deoxygenated blood, while the third pumps oxygenated blood. Their blood is blue due to the presence of copper-based hemocyanin, which is effective in cold, low-oxygen environments.
- Neural Systems: Cephalopods are known for their advanced nervous systems. A significant portion of the neurons, especially in octopuses, are not located in the central brain but are distributed across the arms in “mini-brains” or ganglia, which helps coordinate movement and sensory functions independently.
Cognitive Abilities
Cephalopods have garnered significant attention due to their impressive cognitive abilities. Their intelligence is demonstrated in several areas:
- Problem-Solving: They are capable of using tools and strategies to solve complex tasks, such as escaping enclosures or catching prey.
- Learning and Memory: Cephalopods exhibit sophisticated learning behaviors, including associative learning and memory. Some species are known to delay gratification, choosing more preferred food items over immediate but less desirable ones. They also show evidence of "reversal learning," where they can adjust their behavior in response to changing environmental cues.
- Camouflage and Communication: Cephalopods can manipulate their skin's color and texture for camouflage, aiding in hunting and predator avoidance. For example, the Australian giant cuttlefish uses its chromatophores to communicate with potential mates or warn off competitors.
Species Diversity
Cephalopods are classified into three primary superorders:
- Octopodiforms: Includes octopuses (e.g., Octopus vulgaris), which are known for their intelligence and ability to solve problems.
- Decapodiforms: Includes squids and cuttlefish (e.g., Sepia officinalis, Architeuthis dux), which possess unique locomotion and hunting strategies.
- Nautiloids: Includes the chambered nautilus, the only cephalopod with an external shell, which is considered more primitive compared to other cephalopods.
Ethical and Conservation Concerns
Due to their intelligence and advanced nervous systems, cephalopods are becoming a focus of ethical debates regarding their treatment. Recently, California and Washington have enacted bans on octopus farming, and Hawaii is considering similar measures. These decisions are driven by the growing understanding of cephalopods' cognitive abilities and their capacity for suffering. As a result, there are increasing calls for humane treatment regulations similar to those for vertebrates.
Environmental and Ecological Role
Cephalopods play crucial roles in marine ecosystems. As carnivorous predators, they help maintain the balance of marine food chains by hunting smaller prey. Some species, such as the cuttlefish, also play important roles in communicating and signaling within their species through visual displays.
IPBES Nexus Report

- 22 Dec 2024
In News:
The IPBES Nexus Report, formally titled The Assessment Report on the Interlinkages Among Biodiversity, Water, Food, and Health, was released to address the interconnected global challenges of climate change, biodiversity loss, food insecurity, water scarcity, and health risks. The report stresses that these challenges are deeply intertwined and cannot be solved separately; doing so would lead to ineffective or even counterproductive results.
Key Highlights of the Nexus Report
- Interconnections Between Global Challenges: The report emphasizes the strong interlinkages between the five major global challenges:
- Biodiversity Loss
- Water Scarcity
- Food Insecurity
- Health Risks
- Climate Change
It argues that efforts to address these challenges independently are ineffective and often exacerbate the problems. For example, scaling up food production to combat hunger can put more pressure on land, water, and biodiversity.
- Economic Cost of Biodiversity Loss:
- Global GDP Dependency: Over half of the global GDP (approximately $58 trillion annually) depends on nature. Biodiversity degradation significantly undermines productivity and economic output.
- Unaccounted Costs: The neglect of biodiversity in economic activities contributes to a loss of $10-25 trillion annually.
- Delayed Action: Delaying action on biodiversity conservation could double the costs within the next decade, potentially incurring $500 billion per year in additional costs.
- Synergistic Approach: The report identifies over 70 response options that promote synergistic outcomes across the five challenges. These include:
- Restoring Carbon-Rich Ecosystems: Such as forests, soils, and mangroves to address climate change and biodiversity loss.
- Managing Biodiversity to Prevent Disease Transmission: Effective biodiversity management reduces risks of diseases passing from animals to humans (zoonotic diseases).
- Sustainable Diets: Promoting diets that are both healthy and environmentally sustainable.
- Nature-Based Solutions: Implementing solutions that rely on natural processes to mitigate challenges like water scarcity and climate change.
- Inequality and Vulnerability: The report highlights how inequality exacerbates the challenges. Vulnerable populations, especially those living in areas where biodiversity has sharply declined, face increased health risks, malnutrition, and economic instability. 41% of people live in regions where biodiversity loss has been particularly severe, and 9% face high health burdens due to these declines.
- Principles for Transformative Change: The report outlines principles for achieving transformative change:
- Equity and Justice: Ensuring fair distribution of resources and opportunities for all.
- Pluralism and Inclusion: Embracing diverse perspectives and voices in policy-making.
- Respectful Human-Nature Relationships: Recognizing and nurturing reciprocal relationships between humans and nature.
- Adaptive Learning and Action: Continuously evolving policies and strategies based on feedback and new evidence.
- Urgency for Immediate Action: The report stresses that immediate action is critical. If the world continues to neglect biodiversity, it will face not only environmental collapse but also a missed opportunity for economic growth. Immediate implementation of nature-positive strategies could unlock $10 trillion in business opportunities and create 400 million jobs by 2030.
The IPBES Transformative Change Assessment Report
- This report builds upon the 2019 IPBES Global Assessment Report and advocates for transformative change to halt biodiversity loss and achieve global development goals. It defines transformative change as a system-wide shift in:
- Views: Changing how we think about nature and its value.
- Structures: Reforming systems of governance and organization.
- Practices: Changing behaviors and practices that harm nature.
Key Challenges to Transformative Change:
- Disconnection from Nature: Human societies' disconnection from nature, often rooted in historical domination, is a major cause of biodiversity loss.
- Economic Inequality: The concentration of power and wealth exacerbates environmental degradation.
- Unsustainable Consumption: Unsustainable patterns of consumption and production are significant drivers of environmental harm.
Synergistic Strategies for Transformation:
- Conserve and Regenerate: Restore ecosystems that have both ecological and cultural value.
- Mainstream Biodiversity: Integrate biodiversity considerations into sectors like agriculture, forestry, and infrastructure development.
- Transform Economic Systems: Adopt policies such as true cost accounting and sustainability-based tax principles to internalize the environmental costs of economic activities.
- Inclusive Governance: Promote governance systems that involve all stakeholders, especially local communities, in decision-making.
India State of Forest Report 2023

- 22 Dec 2024
In News:
The India State of Forest Report 2023 (ISFR 2023) was released by the Union Minister for Environment, Forest, and Climate Change at the Forest Research Institute in Dehradun. This biennial report, published by the Forest Survey of India (FSI), assesses the forest and tree resources of the country based on satellite data and field-based inventories. The ISFR 2023 is the 18th edition of this report, with the first published in 1987.
Key Findings
- Total Forest and Tree Cover:
- Area: 827,357 sq km (25.17% of India's geographical area)
- Breakdown:
- Forest cover: 715,343 sq km (21.76%)
- Tree cover: 112,014 sq km (3.41%)
- Increase from 2021: An increase of 1,445 sq km, including:
- Forest cover: +156 sq km
- Tree cover: +1,289 sq km
- State-wise Forest and Tree Cover:
- Top 3 States by Total Forest and Tree Cover Area:
- Madhya Pradesh (85,724 sq km)
- Arunachal Pradesh (67,083 sq km)
- Maharashtra (65,383 sq km)
- Top 3 States by Forest Cover:
- Madhya Pradesh (77,073 sq km)
- Arunachal Pradesh (65,882 sq km)
- Chhattisgarh (55,812 sq km)
- States with Maximum Increase in Forest and Tree Cover:
- Chhattisgarh, Uttar Pradesh, Odisha, and Rajasthan
- Mizoram, Gujarat, and Odisha showed the most significant increase in forest cover.
- Top 3 States by Total Forest and Tree Cover Area:
- Forest Cover Percentage (as a proportion of total geographical area):
- Lakshadweep: 91.33% (Highest)
- Mizoram: 85.34%
- Andaman & Nicobar Islands: 81.62%
- 19 States/UTs have over 33% forest cover, with 8 states having more than 75%.
- Mangrove Cover:
- Total Mangrove Cover: 4,992 sq km (a decrease of 7.43 sq km from 2021).
- Notable Changes: Gujarat saw the largest loss of mangroves, whereas Andhra Pradesh and Maharashtra reported increases.
- Carbon Stock and Climate Targets:
- Total Carbon Stock: 7,285.5 million tonnes (an increase of 81.5 million tonnes from the previous assessment).
- Nationally Determined Contributions (NDC):
- India’s carbon stock has reached 30.43 billion tonnes of CO2 equivalent.
- Achieved an additional 2.29 billion tonnes of carbon sink compared to the 2005 baseline, towards the 2030 target of 2.5-3.0 billion tonnes.
- Bamboo and Timber Production:
- Bamboo Bearing Area: Estimated at 154,670 sq km, an increase of 5,227 sq km since 2021.
- Timber Potential: Estimated annual potential production of 91.51 million cubic meters from trees outside forests.
Achievements:
- There has been a notable increase in the forest and tree cover, particularly in states like Chhattisgarh, Uttar Pradesh, Odisha, and Rajasthan.
- The carbon stock in forests has increased, helping India make significant progress in its climate change mitigation goals.
- The bamboo bearing area has also expanded, promoting biodiversity and economic benefits through bamboo cultivation.
Concerns:
- Mangrove Loss: Gujarat experienced a notable decrease in mangrove area, highlighting the need for focused conservation efforts in coastal regions.
Forest Survey of India (FSI) Overview
- Established: 1981, under the Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change (MoEFCC).
- Mission: To assess, monitor, and research forest resources across India, providing data for sustainable management, national planning, and conservation.
- Headquarters: Dehradun, Uttarakhand.
72% Decline in Bird Species at Bordoibam-Bilmukh Bird Sanctuary, Assam

- 21 Dec 2024
In News:
A recent study has revealed a dramatic decline in the number of bird species at Assam's Bordoibam-Bilmukh Bird Sanctuary (BBBS). The sanctuary, once home to a rich diversity of avian species, has experienced a 72% decline in bird species over the past 27 years. The study, published in the Journal of Threatened Taxa, highlights the severe biodiversity crisis facing the sanctuary.
Key Findings:
- Bird Species Count Decline:
- In 1997, the sanctuary recorded 167 bird species.
- Recent surveys (2022-2024) have only recorded 47 species, marking a 71.85% decline in species count.
- Surveys:
- 2011 Survey: Recorded 133 species (86 resident, 23 migratory, 24 local migrants).
- 2017-2018 Survey: Found 120 species, along with a variety of other biodiversity, including macrophytes, fish, and aquatic ferns.
- Impact on Migratory Birds:
- Migratory species like Brown Shrike, Citrine Wagtail, and White Wagtail (winter migrants), and the Lesser Kestrel (summer migrant) were recorded recently.
- Main Causes of Decline:
- Anthropogenic Activities: Overfishing, poaching, excessive harvesting of aquatic plants, and egg collection.
- Land Use Changes: Habitat degradation due to agriculture, machinery noise, and land being used as pasture areas.
- Disruption of Food Chain: Habitat loss and changes in foraging and breeding grounds for both migratory and resident birds.
- Species of Concern:
- Poached Birds: Lesser whistling duck, Fulvous whistling duck, White-breasted waterhen, Indian pond heron, Eastern spotted dove, and Yellow-footed green pigeon.
- Threatened Species: The sanctuary is home to globally threatened species like the Spot-billed Pelican and Lesser Adjutant.
About Bordoibam-Bilmukh Bird Sanctuary:
- Location: Situated between Dhemaji and Lakhimpur districts in Assam, the sanctuary spans 11.25 sq. km at an altitude of 90-95 meters above sea level.
- History: Declared a wildlife sanctuary in 1996, it was originally part of the Subansiri River which has now shifted 7 km from the wetland.
- Climate & Vegetation:
- Moist tropical climate with an average annual rainfall of around 2,000 mm.
- The vegetation includes flooded valley grasslands and wetland plants, providing crucial habitat for migratory birds.
- Significance for Avian Species:
- Hosts a variety of migratory waterfowl, especially during the winter.
- Home to globally threatened bird species like the Spot-billed Pelican and Lesser Adjutant, along with resident birds such as the Indian Pond Heron and Fulvous Whistling Duck.
Conservation Efforts:
- The decline in bird species at the sanctuary has raised alarm about the degradation of wetland habitats.
- The study emphasizes that habitat loss can disrupt the food chain, water table, and nutrient cycle, which in turn harms both the ecosystem and human communities.
- The authors of the study advocate for intense conservation efforts to restore and protect the sanctuary’s biodiversity.
Assam's Biodiversity:
- Assam is one of India's most biodiverse states, with around 950 bird species, including 17 endemic species.
- The state also hosts 55 Important Bird and Biodiversity Areas (IBA), which are vital hotspots for avian species.
India's First-Ever Ganges River Dolphin Tagging in Assam
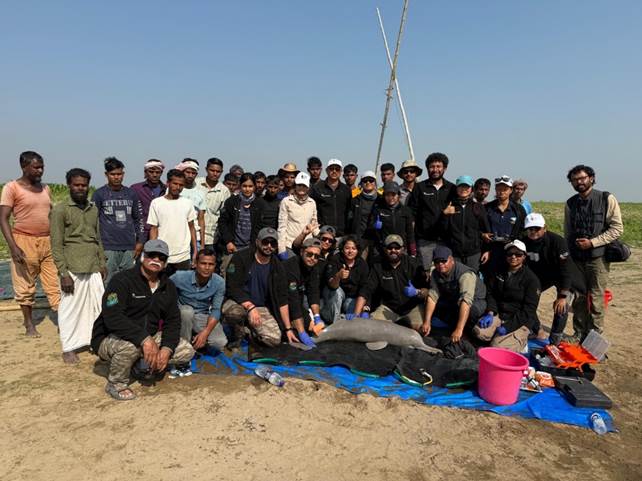

- 19 Dec 2024
In News:
India conducts the first-ever satellite tagging of the Ganges River Dolphin (Platanista gangetica) in Assam, a key step in wildlife conservation.
Key Highlights:
Objective of Tagging: The tagging aims to understand:
- Migratory patterns
- Range and distribution
- Habitat utilization, especially in fragmented river systems.
Key Participants:
- Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change (MoEFCC)
- Wildlife Institute of India (WII)
- Assam Forest Department
- Aaranyak (NGO)
- Funded by the National CAMPA Authority.
Significance of the Tagging:
- Technology Used: Lightweight satellite tags compatible with Argos systems were employed, minimizing interference with the dolphin’s movement despite its limited surfacing time (5-30 seconds).
- Insight into Dolphin Ecology: Helps fill knowledge gaps regarding habitat needs and seasonal migration, especially in disturbed river ecosystems.
Ganges River Dolphin – India's National Aquatic Animal:
- Endemic to India with around 90% of the population in India.
- Known for being nearly blind and using echolocation for navigation and hunting.
- Plays a crucial role as an apex predator and indicator species for river ecosystem health.
Project Dolphin:
- Launched by PM Narendra Modi in 2020, modeled after Project Tiger.
- Focuses on conservation of riverine and marine dolphins.
- A 10-year initiative funded by MoEFCC to safeguard dolphin populations and address ecosystem challenges.
Conservation Status:
- IUCN: Endangered.
- Protection: Included in Schedule I of the Wildlife Protection Act (1972) and CITES Appendix I.
- Major Threats: Habitat degradation, pollution, bycatch, and water abstraction, compounded by damming and sand mining.
Broader Impact:
- The tagging initiative contributes to evidence-based conservation strategies for Ganges River Dolphins.
- Will aid in the development of a comprehensive conservation action plan for the species.
- Expands the understanding of critical habitats within river ecosystems, benefiting both biodiversity and the communities dependent on these resources.
National Wildlife Health Policy (NWHP)

- 19 Dec 2024
In News:
The Central Zoo Authority, under the aegis of the Ministry of Environment Forest and Climate Change (MoEF&CC) has taken up the development of the ‘National Wildlife Health Policy in consultative workshop held in Indira Prayavaran Bhawan, New Delhi.
Key Highlights:
- Organized by: Central Zoo Authority (CZA), under the Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change (MoEF&CC).
- Event: Consultative workshop held at Indira Prayavaran Bhawan, New Delhi, on the development of the National Wildlife Health Policy (NWHP).
- Purpose: To address health threats to wildlife and integrate wildlife health management with public and animal health.
Goals of the National Wildlife Health Policy (NWHP):
- One Health Approach: Integrates human, animal, and environmental health, recognizing their interdependence.
- Focus Areas:
- Prevent and control zoonotic diseases.
- Improve disease surveillance and early detection, especially in protected areas.
- Promote biosecurity measures and epidemic preparedness.
- Enhance research and development in wildlife health management.
- Advocate for community awareness on wildlife health and conservation.
Key Features of the Policy:
- Wildlife Health Management Unit (WHMU): Proposed unit to oversee the policy's implementation.
- Collaboration: Involves coordination with various stakeholders including government ministries, NGOs, academic institutions, and veterinary universities.
- Disease Surveillance: Establish protocols for monitoring and controlling wildlife diseases, especially in protected areas.
- Capacity Building: Training programs for professionals involved in wildlife conservation and health management.
- Biosecurity Protocols: Strengthen measures to reduce disease transmission risks.
Supporting Institutions:
- GISE Hub, IIT Bombay and Office of the Principal Scientific Adviser to the Government of India are providing support in policy development.
Challenges Addressed:
- Wildlife in India faces various health challenges including:
- Infectious diseases (e.g., Canine Distemper Virus).
- Habitat loss and climate change impacts.
- Illegal wildlife trade and other anthropogenic pressures.
- India has over 91,000 wildlife species and more than 1,000 protected areas, making comprehensive health management crucial.
Expected Outcomes:
- Comprehensive Framework: A science-based framework for wildlife health, integrating ecological, human, and animal health.
- Disease Outbreak Response: Structured mechanisms for disease management, surveillance, and legal frameworks.
- Public Health Integration: Safeguard wildlife health, which directly impacts balanced ecosystems and biodiversity.
Policy’s Strategic Alignment:
- National Wildlife Action Plan (2017-31): The policy complements the action plan’s 103 conservation actions and 250 projects, including disease surveillance protocols in tiger reserves and other protected areas.
- Research & Development: Encourages the development of strategies to manage wildlife health and prevent disease outbreaks.
Wroughton’s Free-Tailed Bat

- 19 Dec 2024
In News:
Wroughton’s free-tailed bat, a highly rare species of molossus bat, has been spotted at the Delhi Development Authority (DDA)’s Yamuna Biodiversity Park, marking a unique sighting.
Key Highlights:
- Species Overview: Wroughton’s free-tailed bat (Otomops wroughtoni) is a rare species of molossus bat, notable for its powerful flight and ecological importance in controlling insect populations and assisting in pollination.
- Conservation Status:
- IUCN: Listed as "Data Deficient".
- Protection: Listed under Schedule I of the Wildlife (Protection) Act, 1972.
- Geographical Distribution:
- Primarily found in the Western Ghats, with a single known breeding colony.
- Small colonies in Jaintia Hills, Meghalaya, and a solitary individual sighted in Cambodia.
- Physical Characteristics:
- Large in size, with huge ears extending beyond the muzzle.
- Bicoloured velvet fur.
- Noted for powerful flying capabilities, enabling long-distance foraging.
- Ecological Role:
- Regulates insect populations.
- Known for assisting in pollination.
- Habitat:
- Roosts in caves, or dark, damp, and slightly warm places, typically in moderate-sized colonies.
- Significance of the Delhi Sighting:
- The sighting at Yamuna Biodiversity Park is significant for Delhi, marking a rare occurrence in the region.
- Delhi's bat species: The city is home to about 14 bat species, with four species, including the Indian false vampire and Egyptian free-tailed bat, considered locally extinct.
- Conservation Efforts:
- Two decades of ecological restoration have created specialized niches in the area, aiding species rewilding and ecological balance.
- The Aravalli Biodiversity Park in Gurugram now serves as the only known roosting site for the Blyth’s horseshoe bat in Delhi NCR.
- Additional Notes:
- Wroughton’s free-tailed bat was considered critically endangered until 2000 due to its limited known population. However, the discovery of populations in other regions has led to a reclassification to "Data Deficient".
- Despite being discovered over a century ago, much about the bat's feeding ecology remains unknown.
Little Bunting

- 16 Dec 2024
In News:
Little Bunting recently spotted in Mount Abu, Rajasthan, a sighting previously unseen in the region.
About the Little Bunting:
- Scientific Name: Emberiza pusilla
- Family: Bunting family (Emberizidae)
- IUCN Red List Status: Least Concern
Distribution:
- Breeding Range: Far northeast Europe and northern Eurosiberia to the Russian Far East (taiga region).
- Migratory Pattern: Migrates to the subtropics during winter, with sightings in northern India, southern China, and northern Southeast Asia.
Physical Features:
- Size: Small bird, measuring 12–14 cm (4.7–5.5 inches).
- Coloration:
- White underparts with dark streaking on the breast and sides.
- Chestnut face with a white malar stripe, black crown stripes, and a white eye-ring.
- Fine dark border behind chestnut cheeks.
- Similarity: Resembles a small female reed bunting but with distinct black crown stripes.
Call and Song:
- Call: Distinctive "zik".
- Song: A rolling "siroo-sir-sir-siroo".
Habitat and Behavior:
- Typically found in agricultural areas, feeding on grains.
- Migration: Avoids extreme cold conditions, possibly due to climate change influencing its movement into Rajasthan.
Recent Sightings in India: Spotted in Gurugram, Chandigarh, northern Punjab, and now Rajasthan.
Conservation Significance: The sighting underscores the need to preserve forest areas and wetlands for migratory species like the Little Bunting.
Santa Ana Winds

- 15 Dec 2024
In News:
The ongoing Franklin Fire in Malibu, California, has burned over 4,000 acres and affected around 22,000 people. Although the exact cause of the fire is still under investigation, experts point to two key factors contributing to the intensity of the blaze: Santa Ana winds and climate change.
Santa Ana Winds
- Santa Ana winds are powerful, dry winds that typically occur in Southern California from October to January.
- They are caused when high-pressure systems over the Great Basin (the area between the Rocky Mountains and Sierra Nevada) push air toward low-pressure areas over California’s coast.
- As the air moves downhill through mountain passes, it compresses and heats up, which significantly lowers the humidity—sometimes to levels below 10%—creating dry conditions. This extremely low moisture content dehydrates vegetation, making it highly susceptible to combustion.
- These winds have been a natural feature of California's weather, contributing to wildfires for years. However, when combined with other factors like climate change, their impact has become more severe.
The Role of Climate Change
While Santa Ana winds have long played a role in California's wildfires, climate change has exacerbated the situation in recent years. The state's wildfire season has lengthened due to rising global temperatures, which have led to:
- Warmer springs and summers.
- Earlier snowmelt in spring, which leaves vegetation drier for longer periods.
- Longer and more intense dry seasons, which cause increased moisture stress on vegetation.
As a result, forests and brushlands are now more vulnerable to fires. Climate change has also contributed to more extreme weather events, including heatwaves, which further dry out vegetation and create favorable conditions for wildfires.
Intensification of Wildfire Seasons
Recent studies have shown that California's wildfire season has grown longer over the past two decades. For example, a 2021 study in Nature Scientific Reports found that the state's annual burn season has shifted, with the peak fire season now occurring earlier in the year, from August to July. Additionally, research published in PNAS (Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences) in 2023 indicated that the largest wildfires in California history have occurred in the past 20 years, with five of the top 10 largest fires taking place in 2020 alone.
Looking Ahead
The situation is expected to worsen as climate change continues. If global temperatures rise by more than 3°C by the end of the century, as predicted by the United Nations, California’s wildfire risk will likely intensify. The combination of Santa Ana winds and increasingly dry conditions will continue to make areas like Malibu, and much of California, more prone to destructive wildfires.
In conclusion, while Santa Ana winds remain a natural contributor to California's wildfires, the influence of climate change has significantly lengthened the wildfire season, making wildfires more frequent, intense, and harder to control. The continued rise in global temperatures only accelerates these trends, posing a growing challenge for fire management and public safety in California.
International Mountain Day 2024
- 13 Dec 2024
In News:
On 11th December 2024, the Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change, in collaboration with the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) and G.B. Pant National Institute of Himalayan Environment (NIHE), hosted an event titled ‘Youth for the Himalaya: Innovate, Inspire, Impact’ to mark International Mountain Day.
Event Overview:
- The event was themed “Mountain Solutions for a Sustainable Future – Innovation, Adaptation, and Youth.”
- It emphasized the critical role of young people in addressing the environmental challenges faced by the Indian Himalayan Region (IHR).
- The aim was to showcase youth-driven innovations contributing to the region's sustainability, catalyzing active youth participation in environmental actions. This initiative aligns with the Mission LiFE (Lifestyle for Environment), launched by Prime Minister Narendra Modi, which encourages sustainable practices and collective environmental responsibility.
Key Highlights:
- Young changemakers, innovators, and stakeholders from across the country participated, including students, youth representatives, and members of the private sector, civil society, and government.
- The event highlighted discussions on sustainable solutions for the Himalayan region, integrating traditional knowledge with modern technological advancements in areas like eco-tourism, biodiversity conservation, and climate resilience.
- Short films and videos produced by NIHE and IUCN, such as "Promoting Conservation of Threatened Plant Species in the Western Himalayas" and "Himalayan Futures: Voices from the Ground," were also showcased.
International Mountain Day
- International Mountain Day, observed every year on December 11th since 2003, was established by the United Nations to raise awareness about the sustainable development of mountain regions.
- Mountains cover about one-fifth of the Earth's surface and provide essential freshwater to half of humanity, supporting agriculture, clean energy, and health.
Indian Himalayan Region (IHR)
- The IHR spans 13 Indian states and union territories, stretching approximately 2,500 kilometers from west to east. It is a biodiversity hotspot with significant ecological and cultural value. However, it faces challenges such as unsustainable development, climate change impacts, cultural erosion, and rising tourism.
Key Concerns for IHR:
- Unsustainable Development: Infrastructure projects and deforestation disrupt ecosystems.
- Climate Change: Glacial melting and rising temperatures affect water resources and increase flood risks.
- Cultural Erosion: Modernization threatens traditional practices of indigenous communities.
- Tourism Pressure: Waste generation due to growing tourism puts immense pressure on the region's fragile ecology.
Measures for Protection:
- Sustainable Tourism: Promoting eco-tourism and enforcing capacity limits to minimize environmental impact.
- Water Management: Capturing glacial meltwater for agriculture and ecosystem support.
- Disaster Preparedness: Developing disaster management strategies and early warning systems for events like landslides and floods.
- Bio-Cultural Conservation: Protecting both natural biodiversity and indigenous cultural practices through designated zones.
- Integrated Development: Establishing a "Himalayan Authority" for coordinated development in line with Sustainable Development Goals.
Champions of the Earth Award

- 11 Dec 2024
In News:
- Madhav Gadgil, an Indian ecologist, received the UN Environment Programme (UNEP)'s Champions of the Earth Award in 2024.
- The Champions of the Earth Award is UNEP’s highest environmental honor, recognizing individuals, organizations, and governments for significant contributions to environmental protection and sustainable development.
Contributions of Madhav Gadgil:
- Work in Western Ghats:
- Gadgil is recognized for his seminal work in the Western Ghats, an ecologically sensitive region in India, which is a global biodiversity hotspot.
- He chaired the Western Ghats Ecology Expert Panel (WGEEP), formed by the Indian government to assess the impacts of population pressure, climate change, and development on the region.
- Recommendations by WGEEP:
- Ecologically Sensitive Area (ESA): Recommended declaring the entire Western Ghats range as an ESA.
- The WGEEP suggested dividing the Western Ghats into three Ecologically Sensitive Zones (ESZ) based on environmental sensitivity.
- Development Restrictions: Proposed a ban on activities like mining, quarrying, thermal power plants, and large-scale hydropower projects in the most sensitive zones (ESZ-1).
- Governance Recommendations: Suggested a bottom-to-top governance approach, beginning with Gram Sabhas, and the creation of a Western Ghats Ecology Authority (WGEA) for effective management.
- Impact of Gadgil’s Work:
- His research and recommendations have played a crucial role in shaping environmental policy and public opinion in India.
- The UNESCO World Heritage status for the Western Ghats in 2012 was a significant step in global recognition of the region’s ecological importance.
About the Champions of the Earth Award:
- History & Significance:
- Established in 2005, the award recognizes trailblazers working towards addressing the triple planetary crisis: climate change, biodiversity loss, and pollution.
- Since its inception, it has honored 122 laureates who have shown outstanding leadership in environmental conservation.
- 2024 Awardees:
- Madhav Gadgil (India) – for his work on the Western Ghats.
- Sonia Guajajara (Brazil) – for advocacy for Indigenous rights and environmental protection.
- Amy Bowers Cordalis (USA) – for her work in Indigenous rights and ecosystem restoration.
- Gabriel Paun (Romania) – for defending Europe’s old growth forests from illegal logging.
- Lu Qi (China) – for contributions to afforestation and combating desertification.
- SEKEM (Egypt) – for advancing sustainable agriculture.
Key Facts about UNEP:
- UN Environment Programme (UNEP):
- Established in 1972, UNEP is a leading global authority on environmental issues.
- UNEP aims to address climate change, nature and biodiversity loss, and pollution through scientific research, policy support, and public advocacy.
- UNEP is headquartered in Nairobi, Kenya and works closely with 193 Member States to tackle the planet’s most pressing environmental challenges.
Moths' Reproductive Choices Based on Plant Acoustic Emissions

- 09 Dec 2024
In News:
A new study, "Female Moths Incorporate Plant Acoustic Emissions into Their Oviposition Decision-Making Process," published last month, explores how female moths use sounds emitted by plants to choose where to lay their eggs.
Key Highlights:
Significance of Plant Emitted Sounds:
- Background: Last year, it was discovered that plants emit ultrasonic clicks or pops when stressed (e.g., dehydration). These sounds, although inaudible to humans, can be detected by animals, including insects.
- Moths’ Sensitivity: Moths, particularly the Egyptian cotton leafworm, are shown to be sensitive to these plant sounds, which they use as cues for laying eggs on plants.
Methodology:
- Experimental Setup: Researchers placed a hydrated tomato plant in an experimental arena with another hydrated plant that emitted distress sounds. They observed the behavior of female Egyptian cotton leafworms to understand how these sounds influenced their oviposition choices.
- Initial Finding: Moths typically choose healthy, thriving plants to lay eggs, as they provide better food sources for the larvae.
Study Findings:
- Moths’ Response to Sounds: The moths preferred to lay eggs on the “silent” plant rather than the one emitting distress sounds. This indicates that moths can not only detect the presence of a plant but also interpret acoustic signals to inform their egg-laying decisions.
- Implications: This behavior suggests that moths use a complex set of sensory inputs, including plant-emitted sounds, to select the most suitable plant for offspring development.
Broader Ecological Context:
- Moths as Insects: Moths belong to the order Lepidoptera and are found in diverse environments globally, except polar regions. With around 160,000 species, they are highly adapted and often nocturnal, though some species are diurnal.
- Impact on Agriculture: Certain moth species, especially during their caterpillar stage, are major agricultural pests (e.g., corn borers, bollworms), making understanding their behavior crucial for pest management strategies.
- Climate Change Considerations: Moths, like other species, are impacted by climate change, which can alter the timing and growth of plants they depend on, potentially influencing their reproductive strategies.
Conclusion:
- Innovative Findings: The study reveals a previously unknown aspect of moth behavior, showing that they incorporate plant acoustic emissions into their oviposition decisions.
- Future Implications: This discovery opens avenues for further studies on how environmental signals, like sound, affect the behavior of insects, and how these behaviors could be impacted by changing environmental conditions.
Markhor Spotted in North Kashmir's Baramulla

- 08 Dec 2024
In News:
Recently, a Markhor, a rare wild goat with spiral-shaped horns, was spotted in Noorkha village of Boniyar in Baramulla district, North Kashmir.The animal was seen near a waterfall in Noorkha, prompting locals to alert the authorities.
Key Highlights:
- The Markhor (Capra falconeri) is a large, wild goat species native to mountainous regions in Central and South Asia, including countries such as Pakistan, Afghanistan, India, and others.
- The species is considered endangered and is listed under Schedule I of the Wildlife Protection Act, 1972.
- The Markhor population in India is concentrated in areas like Shopian, Banihal Pass, Shamsbari, and Kazinag in Jammu and Kashmir.An estimated 300 Markhors live in Kashmir's dense pine and birch forests.
- Threats and Conservation Status:
- The Markhor faces threats due to human activities and natural factors, leading to a decline in its population.
- It is classified as 'Near Threatened' on the IUCN Red List and protected under the Indian Wildlife Protection Act and the Jammu and Kashmir Wildlife Protection Act.
- Significance of the Sighting:The sighting of the Markhor has excited both villagers and wildlife enthusiasts, as these animals are not typically found outside their natural habitats, particularly near human settlements.
Community and Individual Forest Rights in Anamalai Tiger Reserve (ATR)

- 08 Dec 2024
In News:
- The Coimbatore District Collector, granted community and individual forest rights under the Forest Rights Act, 2006, to tribal settlements in the Anamalai Tiger Reserve (ATR) on December 6, 2024.These rights were handed over to three tribal settlements and 14 families at a function in Coimbatore.
Key Highlights:
- Community Forest Rights:
- Three tribal settlements in ATR—Nagaroothu I, Nagaroothu II, and Chinnarpathi—were granted community rights.
- These rights allow the settlements to collect forest produce excluding timber, such as mango, amla, honey, tamarind, and grass for making brooms.
- Individual Forest Rights:
- Individual rights were granted to 14 families from the Old Sarkarpathy tribal settlement.
- The families had requested these rights for traditional cultivation practices passed down by their ancestors.
- The individual rights were approved after the recommendation of a sub-divisional committee and scrutiny by a district-level committee.
- About the Forest Rights Act (FRA), 2006:
- Purpose: The FRA was enacted to address historical injustices faced by forest-dwelling communities and ensure their livelihood and food security.
- Key Provisions:
- Individual Rights: Self-cultivation, habitation, and in-situ rehabilitation.
- Community Rights: Access to grazing, fishing, water bodies in forests, and protection of traditional knowledge and customary rights.
- Eligibility: Rights can be claimed by any community or individual who has lived in the forest for at least three generations (75 years) before December 13, 2005.
- Critical Wildlife Habitats: The Act mandates that critical wildlife habitats in national parks and sanctuaries remain inviolate for wildlife conservation.
- Authorities Involved in Vesting Forest Rights:
- Gram Sabha: Initiates the process for determining the nature and extent of rights.
- Sub-Divisional Level Committee: Examines resolutions passed by the Gram Sabha.
- District Level Committee: Grants final approval for forest rights.
- Challenges with Forest Rights Implementation:
- The Xaxa Committee pointed out several challenges in the implementation of the FRA, such as:
- Arbitrary rejection of claims.
- Lack of deadlines for claims processing.
- Unaddressed rights of communities displaced by development projects.
- The Xaxa Committee pointed out several challenges in the implementation of the FRA, such as:
- About Anamalai Tiger Reserve:
- Located in the Anamalai Hills of Pollachi and Coimbatore District, Tamil Nadu, at an altitude of 1,400 meters.
- Established as a tiger reserve in 2007, it is surrounded by multiple protected areas like the Parambikulam Tiger Reserve, Chinnar Wildlife Sanctuary, and Eravikulam National Park.
- Biodiversity in Anamalai Tiger Reserve:
- Habitats: The reserve contains wet evergreen forests, semi-evergreen forests, moist deciduous forests, dry deciduous forests, and unique habitats like montane grasslands and marshy grasslands.
- Flora: The reserve is home to around 2,500 species of angiosperms, including species like balsam, orchids, and wild relatives of cultivated crops such as mango, jackfruit, cardamom, and pepper.
- Fauna: It supports various wildlife species, including tigers, Asiatic elephants, sambars, spotted deer, leopards, jackals, and jungle cats.
Sacred Groves

- 08 Dec 2024
In News:
Preserving India’s sacred groves can help country achieve its conservation & climate goals.
Sacred Groves in India:
- Sacred groves are forest patches that are culturally and spiritually important for various communities.
- They are known by different names across India: sarnas in Jharkhand, devgudis in Chhattisgarh, and orans in Rajasthan.
- Groves vary in size from small clusters of trees to expansive forests covering several acres.
Threats to Sacred Groves:
- Sacred groves are increasingly under threat due to deforestation, mining, and development activities.
- Many sacred groves are being displaced or degraded, putting biodiversity and cultural practices at risk.
Ecological and Cultural Importance:
- Sacred groves are rich in biodiversity and serve as important carbon sinks, contributing to climate change mitigation.
- They have been maintained by indigenous communities for centuries, creating a deep connection between people and nature.
- Sacred groves also play a crucial role in preserving indigenous spiritual practices and cultural heritage.
Contribution to Climate and Conservation Goals:
- India’s climate commitment of achieving net-zero emissions by 2070 requires the protection of forests, including sacred groves.
- Sacred groves, when properly managed, can help in carbon sequestration and climate change mitigation.
- Preserving these groves can support forest conservation and foster coexistence with wildlife, ensuring a balance between development and environmental preservation.
Role of Indigenous Communities:
- Indigenous communities have long used sacred groves to regulate the use of forest resources and ensure environmental sustainability.
- Before modern ecological concepts, sacred groves were seen as natural conservation practices guided by spiritual beliefs.
- This traditional wisdom can be leveraged to enhance conservation efforts in India.
Examples of Successful Sacred Grove Conservation:
- Waghoba Grove in Maharashtra:
- Located in Chinchwadi village, the Taata chi Vanrai grove is dedicated to Waghoba, the tiger deity, and covers eight acres.
- Local communities, including the Thakars, have successfully resisted illegal timber extraction and helped conserve the grove, witnessing the return of wildlife like leopards.
- Worship of Waghoba has played a significant role in preserving forest patches and fostering human-animal coexistence.
- Tadoba-Andhari Tiger Reserve:
- Sacred groves around the Tadoba Reserve, dedicated to Waghoba, are important in reducing human-wildlife conflicts by promoting spiritual ties with the forest.
Government and Community Efforts:
- The Jharkhand government introduced the concept of gherabandi (boundary walls) in 2019 to conserve sacred groves.
- In Chhattisgarh, the renovation of sacred groves has been undertaken to protect and restore these areas.
- Despite these efforts, challenges remain in involving local communities and integrating sacred groves into broader conservation policies.
The Role of OECMs in Sacred Grove Conservation:
- Sacred groves are considered part of Other Effective Area-Based Conservation Measures (OECMs), which are areas conserved for biodiversity outside protected regions.
- OECMs recognize the cultural, spiritual, and socio-economic value of these areas and promote sustainable conservation practices that benefit both biodiversity and local communities.
- Sacred groves play an essential role in achieving long-term biodiversity conservation and ecosystem services.
World’s Oldest Wild Bird Lays Egg at 74 in Hawaii

- 08 Dec 2024
In News:
Wisdom, the world’s oldest known wild bird, a Laysan albatross, has laid her estimated 60th egg at the age of 74. This remarkable event occurred at the Midway Atoll National Wildlife Refuge in the Pacific Ocean, part of the Hawaiian Archipelago.
Background on Wisdom and Laysan Albatrosses
Wisdom, first banded as an adult in 1956, has been a part of the albatross population in the Pacific for decades. Laysan albatrosses are known for their strong migratory habits and lifelong pair bonding.
The Life Cycle of the Laysan Albatross
The egg incubation process for Laysan albatrosses is shared between both parents and lasts around seven months. Once the chick hatches, it takes five to six months to develop before it is ready to take its first flight over the ocean. These seabirds, which predominantly feed on squid and fish eggs, spend the majority of their lives soaring across the open seas.
Wisdom’s longevity and success in raising up to 30 chicks over her lifetime have been notable achievements. While Laysan albatrosses typically live up to 68 years, Wisdom’s age surpasses this average by several years.
About the Laysan Albatross
The Laysan albatross (Phoebastriaimmutabilis) is a large seabird found across the North Pacific. The Northwestern Hawaiian Islands host nearly the entire population of Laysan albatrosses, with most breeding pairs found on islands like Laysan and Midway Atoll. These birds are known for their long-distance soaring capabilities, with some covering hundreds of miles a day without flapping their wings.
Laysan albatrosses have blackish-brown upper wings and backs, with flashes of white in their primary feathers. They are monogamous, forming lifelong bonds with a single mate. Despite their impressive flying ability and vast range, their population is currently listed as "Near Threatened" by the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN).
Overview of Global Plastic Treaty Negotiations

- 05 Dec 2024
In News:
The recent negotiations for a global treaty aimed at curbing plastic pollution, held in Busan, South Korea, concluded without reaching a legally binding agreement. This marked the fifth round of discussions since the United Nations Environment Assembly (UNEA) initiated the process in March 2022, with the goal of finalizing a treaty by the end of 2024. The failure to adopt a treaty was primarily due to disagreements over production cap goals and the elimination of specific plastic chemicals and products.
Key Points of Dispute
- Production Cap Goals: A coalition of over 100 countries, including many from Africa, Latin America, and the European Union, pushed for clear production cap goals in the treaty. They argued that such measures are essential for effective regulation of plastic pollution.
- Opposition from Oil-Producing Nations: Conversely, a group of “like-minded countries” such as Saudi Arabia, Kuwait, Russia, and Iran opposed these provisions. They contended that regulating production cuts exceeded the original mandate set by UNEA and could lead to trade restrictions disguised as environmental measures. India and China aligned with this coalition, emphasizing their concerns regarding economic impacts.
Draft Treaty Highlights
Despite the failure to finalize an agreement, discussions produced a draft text that included both consensus points and contentious issues:
- Consensus Points:
- Proposals for banning open dumping and burning of plastics.
- Definitions for various plastic types were suggested but lacked clarity on contentious terms like microplastics.
- Contentious Issues:
-
- The draft did not adequately address definitions for microplastics or recycling standards.
- References to single-use plastics were included but faced pushback from certain nations.
India’s Position
India articulated its stance focusing on several key areas:
- Development Rights: Emphasized the need for recognizing varying responsibilities among countries in managing plastic pollution while considering their developmental rights.
- Technical and Financial Support: Advocated for provisions ensuring technical assistance and financial support for developing nations to manage plastic waste effectively.
- Opposition to Production Caps: India opposed any articles that would impose caps on polymer production, arguing that such measures were not directly linked to reducing plastic pollution.
Future Steps
The negotiations will continue with plans to reconvene in 2025. In the meantime, global plastic production is projected to rise significantly, potentially tripling by 2050 if no urgent action is taken. The ongoing dialogue will need to address both environmental concerns and developmental needs to create a balanced approach toward managing plastic pollution globally.
Global Context and Initiatives
The need for a global treaty is underscored by alarming statistics:
- Over 462 million tons of plastic are produced annually, with a significant portion contributing to pollution.
- Microplastics have infiltrated ecosystems worldwide, affecting biodiversity and human health.
Countries like Rwanda and Austria have implemented successful measures to reduce plastic waste, serving as models for global efforts. Initiatives such as the UNDP Plastic Waste Management Program in India aim to enhance waste management practices while addressing environmental impacts.
ICJ Hearing on Landmark Climate Change Case

- 04 Dec 2024
In News:
- The International Court of Justice (ICJ) has begun hearings on a landmark climate change case, seeking an advisory opinion on the obligations of countries under international law regarding climate change.
- The case stems from a UN General Assembly (UNGA) resolution initiated by Vanuatu in March 2023, co-sponsored by 132 countries.
Background:
- Vanuatu, a small island nation, faces existential threats from rising sea levels.
- The resolution was passed to clarify climate obligations in light of international laws, including the UNFCCC, Paris Agreement, and other legal instruments like the UN Convention on the Law of the Seas, and the Universal Declaration on Human Rights.
Global Impact of the Case:
- The outcome of the case could influence global climate governance, particularly in the context of climate negotiations.
- It may broaden the legal basis for climate obligations and underscore the legal consequences for non-compliance.
India’s Position:
- India has voiced concerns about the judicial process being the best approach to tackle climate issues, advocating for diplomatic efforts.
- India is scheduled to make its submission on December 5, highlighting its preference for a collaborative, non-top-down approach in climate discussions.
Implications for Developed and Developing Countries:
- The case highlights the historical responsibility of developed countries for climate change due to their higher emissions.
- The ICJ's advisory opinion could reinforce the argument that developed countries' obligations extend beyond the UNFCCC and Paris Agreement, incorporating broader international legal frameworks.
Climate Litigation and Precedent:
- The ICJ ruling could set a precedent for climate litigation, potentially influencing over 2,600 ongoing climate lawsuits globally.
- Notable rulings include the European Court of Human Rights, which held Switzerland accountable for failing to meet emissions targets, and India's Supreme Court recognizing the right to be free from adverse climate impacts in 2023.
Record Participation and Importance of the Case:
- The ICJ has received over 90 written submissions, with 97 countries and 12 international organizations participating in the hearings.
- The case is significant for the growing number of climate-related lawsuits and the evolving nature of international climate law.
Future Prospects:
- The ICJ’s advisory opinion, though non-binding, could significantly impact future climate negotiations, particularly in terms of responsibility sharing and climate finance.
- The outcome could also influence calls for compensation for climate damages, especially from vulnerable states like small island nations.
Madhya Pradesh’s 8th Tiger Reserve: Ratapani

- 03 Dec 2024
In News:
Recently, the Ratapani Wildlife Sanctuary in Madhya Pradesh was officially declared a Tiger Reserve, making it the 8th such reserve in the state. This declaration follows approval from the Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change through the National Tiger Conservation Authority (NTCA).
Key Details:
- Core Area: 763.8 sq. km
- Buffer Area: 507.6 sq. km
- Total Area: 1,271.4 sq. km
- Ratapani Tiger Reserve is located in the Raisen and Sehore districts, within the Vindhya hills, and is home to approximately 90 tigers.
- It also forms a crucial part of Madhya Pradesh’s tiger habitat and serves as a migration corridor from the Satpura ranges.
Economic and Ecotourism Benefits:
- The designation will boost ecotourism, generating employment and improving livelihoods for local communities.
- Eco-development programs will support residents, providing new opportunities and addressing the balance between conservation and human interests.
Wildlife Conservation and Management:
- The reserve will focus on habitat management, wildlife protection, and community engagement.
- The core area has been recognized as a critical tiger habitat under the Wildlife Protection Act, 1972.
- Efforts will include strengthening anti-poaching measures, improving surveillance, and enhancing prey base restoration.
Significance for Madhya Pradesh:
- This move places Madhya Pradesh as the "Tiger State of India", with significant conservation focus on the Ratapani and Madhav National Park (also in the process of becoming a tiger reserve).
- Madhya Pradesh now hosts 8 tiger reserves, contributing significantly to the country's overall tiger conservation efforts.
Global Matchmaking Platform (GMP)
- 28 Nov 2024
In News:
- GMP was launched at COP29, on Energy Day, by the United Nations Industrial Development Organization (UNIDO) and the Climate Club.
- Aimed at accelerating industrial decarbonisation in heavy-emitting industries of emerging and developing economies (EMDEs).
- The platform addresses the annual funding gap of US$125 billion required to achieve net-zero emissions goals.
Key Highlights:
Support Mechanism:
- GMP operates as a support mechanism for the Climate Club, with the secretariat hosted by UNIDO.
- Activities are supported by the interim secretariat of the OECD and the International Energy Agency (IEA).
Key Objectives:
- Match country-specific decarbonisation needs with global technical and financial resources.
- Facilitate the decarbonisation of energy and emissions-intensive industrial sectors, such as steel, cement, chemicals, and aluminium.
- Offer assistance in policy development, technology transfer, and investment facilitation to promote low-carbon industrial practices.
Global Participation:
- Countries like Germany, Chile, Uruguay, Turkey, Bangladesh, and Indonesia are actively involved.
- Non-state actors include UNIDO, World Bank, Climate Investment Funds (CIF), and GIZ, supporting the platform’s initiatives.
Funding Gap:
- Industrial decarbonisation requires an increase in investments from US$15 billion (current) to US$70 billion by 2030, and US$125 billion by 2050, especially for sectors like steel and cement.
Climate Club Work Programme (2025-26):
- The GMP is part of the Climate Club's new work programme for 2025-26, focusing on:
- Advancing ambitious climate change mitigation policies.
- Transforming industries through decarbonisation.
- Boosting international climate cooperation.
Industrial Decarbonisation:
- Decarbonisation refers to reducing carbon dioxide (CO2) and greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions from industrial activities.
- Key sectors for decarbonisation include petroleum refining, chemical manufacturing, iron and steel, cement production, and the food and beverage sector.
Support for EMDEs:
- The platform focuses on helping emerging and developing economies overcome challenges such as lack of resources, technology, and capacity to adopt cleaner industrial methods.
- Climate finance is crucial to pilot and scale low-carbon technologies in these regions.
Future Role of GMP:
- The GMP will play a critical role in incorporating industrial decarbonisation into countries’ Nationally Determined Contributions (NDCs) for COP30.
- The platform aims to accelerate progress by connecting developing countries with finance, technology, and expertise to transition to low-emission industries.
Palparescontrarius

- 25 Nov 2024
In News:
Palparescontrarius is a species of antlion that was recently spotted for the first time in Tamil Nadu, on the Madras Christian College (MCC) campus. It is notable for being a large-sized adult antlion that resembles a dragonfly but has distinct characteristics that separate it from dragonflies, such as its clubbed antennae and fluttering flight.
Key Features of Palparescontrarius:
- Appearance:
- The adult Palparescontrarius is large and resembles a dragonfly in its general body structure.
- It has lacy wings, long clubbed antennae, and a slender, grayish body.
- Its wings are typically clear, although some species of antlions have spots on their wings.
- Flight and Behavior:
- Unlike dragonflies, Palparescontrarius has a distinct fluttering flight.
- It is a weak flier and can often be spotted at night near illuminated spots.
- Habitat and Lifestyle:
- Like other antlions, Palparescontrarius is found in dry, sandy regions and is mostly active at night.
- The larvae of this species are particularly known for their predatory behavior, as they trap ants and other small insects in cone-shaped pits they dig into the sand.
- Ecological Importance:
- Antlions, including Palparescontrarius, are harmless to humans and beneficial to the environment because they feed on ants and other insects, thus helping to control pest populations.
Imperial Eagle(Aquila heliaca)

- 24 Nov 2024
In News:
- A rare Imperial Eagle (Aquila heliaca) was spotted in the PulluzhiKole wetlands. This marks a significant event as the species was last reported in Kannur in 2003.
Key Highlights:
- Habitat and Migration:
- The Imperial Eagle primarily breeds in southeastern Europe, west, and central Asia.
- During the winter months, it migrates to regions including northeastern Africa, West Asia, and parts of Southeast Asia.
- Conservation Status:The IUCN Red List lists the Imperial Eagle as a vulnerable species, indicating its potential risk of extinction, underscoring the need for its conservation efforts.
- Importance of Conservation:
- The Kole fields are a Ramsar-protected area, emphasizing their critical role in preserving migratory bird habitats.
- Ongoing conservation and observation efforts in these wetlands are essential for protecting the diverse bird species that use the area.
Features of the Imperial Eagle:
- Scientific Name: Aquila heliaca
- Physical Characteristics:
- Size: Length ranges from 68 to 90 cm, with a wingspan between 1.76 to 2.2 meters.
- Color: It has a pale golden crown and nape, with a grey base extending to the tail. Its wings feature prominent white "braces" on the scapulars.
- Sexual Dimorphism: Males are typically smaller than females.
- Habitat: Prefers old forests, mountainous regions, and riverside forests.
- Feeding: It has strong legs and curved talons for capturing and killing prey, and exceptional eyesight to spot prey from high altitudes.
- Conservation Efforts: Continued monitoring and protection of the Kole wetlands and other vital habitats are crucial for the survival of this vulnerable species and other at-risk birds.
Minke Whale

- 24 Nov 2024
In News:
Scientists have directly measured the hearing range of minke whales for the first time, finding that they can detect high-frequency sounds up to 90 kHz.
Key Highlights:
- Implication for Ocean Noise: The study suggests that baleen whales, including minke whales, may be more affected by anthropogenic ocean noise (e.g., naval sonar) than previously recognized, as their hearing range had been underestimated.
- Research Method: A novel catch-and-release technique was used to temporarily hold adolescent minke whales in Norway for auditory evoked potential (AEP) tests to measure their hearing sensitivity.
- Findings: Contrary to the belief that baleen whales are low-frequency specialists, minke whales can detect frequencies between 45 kHz to 90 kHz.
- Impact of Findings: The results could affect future regulations on ocean noise and its impact on marine mammals, as better hearing data is now available for baleen whales.
Minke Whale Overview:
- Family: Minke whales are members of the baleen or "great" whale family and are the smallest of the rorquals.
- Species: There are two recognized species:
- Common minke whale (Balaenoptera acutorostrata), found in various ocean basins.
- Antarctic minke whale (B. bonaerensis), found in the Southern Hemisphere.
- Subspecies:
- Dwarf minke whale: An unnamed subspecies of the common minke whale, mostly in the Southern Hemisphere.
- North Atlantic (B. a. acutorostrata) and North Pacific (B. a. scammoni) subspecies of common minke whales.
- Distribution: Minke whales are widely spread across tropical, temperate, and polar regions (65°S to 80°N), with common minke whales in all ocean basins and dwarf minke whales mostly in the Southern Hemisphere.
- Feeding Areas: They feed in cooler waters at higher latitudes and can be found both inshore and offshore.
- Conservation Status (IUCN):
- Common minke whale: Least Concern.
- Antarctic minke whale: Data Deficient.
Cicada

- 23 Nov 2024
In News:
North American cicadas have life cycles that last for prime numbers of years, putting pressure on the idea that humans created mathematics.
What are Cicadas?
- Classification: Cicadas are insects that belong to the order Hemiptera and the superfamily Cicadoidea.
- Physical Features: Hemipteran insects (also known as true bugs) have piercing-sucking mouthparts and two pairs of wings.
- Life Span: Cicadas spend the majority of their life underground, feeding on plant sap. Once they emerge from the soil, they have a short adult life span of about 2 to 4 weeks.
Habitat:
- Preferred Environment: Cicadas are typically found in natural forests with large trees and are considered canopy dwellers.
- Global Distribution: Cicadas are found on every continent except Antarctica. The highest genetic diversity of cicadas is found in India and Bangladesh, followed by China.
Cicada Emergence and Life Cycle:
- Life Cycle: Cicadas have a complex life cycle, involving long periods of underground development followed by brief adult emergence.
- Periodical Cicadas: There are species of cicadas that emerge in 13-year and 17-year cycles.
- Broods: Initially, 30 broods were categorized based on geography and emergence times, but currently, only about 15 broods remain active due to some broods becoming extinct.
- Unique Phenomenon: In April 2024, a rare event is expected where a trillion cicadas from two different broods will emerge simultaneously in the Midwest and Southeast regions of the United States.
Cicada's underground Development:
- Feeding on Sap: During their underground phase, cicadas feed on the sap of plants.
- Purpose of Long Development: Researchers believe the long development period helps cicadas evade above-ground predators by keeping them hidden in the soil.
Vulnerability after Emergence:
- Emergence Behavior: Once cicadas emerge, they construct a "cicada hut" to shed their nymphal skins, then climb onto nearby trees or vegetation.
- Predator Vulnerability: Adult cicadas are vulnerable to predators such as turtles and other forest creatures because they are clumsy and defenseless, making them easy prey for predators.
Significance of the 2024 Emergence:
- The coinciding emergence of cicadas from different broods (13-year and 17-year cycles) is a rare event that highlights the complexity and mathematical precision behind the cicada life cycle.
Rare Leucistic Peacock

- 22 Nov 2024
In News:
Tamil Nadu Forest Department staff and members of a non-governmental organisation rescued a rare peacock with white feathers, caused by a genetic condition called leucism, in Coimbatore.
Key Highlights:
Incident Details:
- Species: Indian peacock (Pavocristatus), known for its beautiful plumage.
- Condition: The peacock was rescued due to a leg injury and its rare white plumage.
- Cause of White Plumage: The bird's white feathers are caused by leucism, a genetic condition that reduces pigmentation in feathers while leaving eye color unaffected.
Expert Insights:
- Leucism: It causes partial loss of pigmentation in animals. A leucistic animal retains normal eye color but has pale or white coloration.
- Distinction from Albinism: Unlike albinism, which results in a complete lack of melanin and often causes red or pink eyes, leucistic animals retain normal eye pigmentation.
- Identification of Leucism in Peacock: The bird’s dark eyes and pink bill and feet confirmed it as fully leucistic.
Peacock Species:
- Indian Peacock (Pavocristatus): The National Bird of India, native to India and Sri Lanka. It belongs to the Phasianidae family, which also includes pheasants, quails, and jungle fowl.
- Green Peacock (Pavomuticus): Found from Myanmar to Java.
Conservation Status:
- IUCN Status: Listed as Least Concern.
- Wildlife Protection Act, 1972: The Indian peacock is listed under Schedule I, offering it the highest level of legal protection in India.
Climate Change Performance (CCPI 2025)
- 22 Nov 2024
In News:
Recently, the Climate Change Performance Index (CCPI 2025) report was released at the annual UN climate conference in Baku.
Key Highlights:
- It is published by think tanks German watch, New Climate Institute, and Climate Action Network International.It was first published in 2005.
- It tracks the progress of the world’s largest emitters in terms of emissions, renewables, and climate policy.
India's Ranking in Climate Change Performance (CCPI 2025)
- India's Rank: 10th (Dropped two places from the previous year).
- Key Factors for India's High Rank:
- Low per capita emissions: 2.9 tons of CO2 equivalent (global average: 6.6 tons).
- Rapid deployment of renewables: India is a leader in solar energy projects, including large-scale solar and rooftop solar schemes.
- Renewable energy targets: Aims for 500 GW of renewable energy capacity by 2030.
- Energy efficiency standards: Introduced, but coverage remains inadequate.
- Electric vehicle (EV) deployment: Significant progress, especially in two-wheelers.
- Challenges for India:
- Heavy reliance on coal: India remains one of the top 10 countries with the largest developed coal reserves.
- Growth-oriented approach: Economic growth and energy demand continue to drive climate action, with limited change in climate policy expected.
- Future Pledges:
- Net-zero emissions by 2070.
- Global leadership in green energy.
CCPI 2025 Rankings Overview
Rank
Country
Key Points
1-3
Empty
No country performed well enough to achieve a "very high" rating.
4
Denmark
Leading climate actions but ranks 4th technically.
5
Netherlands
Strong climate performance, follows Denmark.
6
U.K.
Notable improvement due to coal phase-out and halting new fossil fuel licenses.
10
India
High performer, despite challenges like reliance on coal.
55
China
Largest emitter, heavily reliant on coal, ranks 55th despite promising plans.
57
U.S.
Second-largest emitter, ranks 57th with insufficient climate targets.
59
Argentina
Major climate policy setbacks, including potential exit from Paris Agreement.
64-67
Iran, Saudi Arabia, UAE, Russia
Lowest-ranked, major oil and gas producers with weak climate policies.
General Findings of the Report
- CCPI Methodology: Assesses 63 countries (plus the EU) responsible for 90% of global emissions based on their emissions, renewable energy efforts, and climate policies.
- Global Trends:
- No country has been able to secure a "very high" rating across all categories.
- Denmark and Netherlands are among the top performers.
- The U.K. shows significant progress with its coal phase-out and fossil fuel policies.
Graded Response Action Plan (GRAP-IV)

- 19 Nov 2024
In News:
As Delhi’s AQI worsened, the Commission for Air Quality Management issued the order to activate Stage-IV of the Graded Response Action Plan.
Restrictions Under GRAP-IV in Delhi-NCR
- Truck Movement:
- Banned except for essential goods and trucks using clean fuels (LNG, CNG, BS-VI diesel, or electric).
- Non-essential light commercial vehicles registered outside Delhi are also banned unless they are CNG or BS-VI diesel or electric vehicles (EVs).
- Delhi-registered BS-IV or older diesel vehicles (medium and heavy goods vehicles) are banned, except for those in essential services.
- Construction Activities:Suspension of all construction work, including public projects like highways, roads, flyovers, power lines, pipelines, etc.
- Schools and Work:
- Online classes for students of Classes 6 to 9 and Class 11.
- Work from home (WFH) recommendations for 50% office capacity in NCR.
- Central government employees may also be asked to work from home.
- Offline classes for Classes 10 and 12 continue, but schools for other classes must shift to online mode.
- Other Measures:
- State governments may impose additional measures such as:
- Closure of colleges.
- Odd-even vehicle scheme.
- Restrictions on non-essential commercial activities.
- State governments may impose additional measures such as:
About GRAP (Graded Response Action Plan)
- Purpose: A plan to reduce air pollution in the Delhi-NCR region based on AQI levels.
- Approved By: Supreme Court in 2016 (M.C. Mehta v. Union of India).
- Notified by MoEFCC: 2017.
- Implementation Authority: CAQM (Commission for Air Quality Management).
Stages of GRAP
GRAP is an incremental system, with measures activated as air quality deteriorates:
- Stage 1: Poor AQI (201-300) – Basic pollution control measures.
- Stage 2: Very Poor AQI (301-400) – Enhanced measures.
- Stage 3: Severe AQI (401-450) – Stricter actions like shutting down industries.
- Stage 4: Severe Plus AQI (Above 450) – Most stringent restrictions, as activated on November 18, 2024.
Air Quality Index (AQI)
- Introduced: 2014, by Central Pollution Control Board (CPCB).
- Categories:
- Good: 0-50
- Satisfactory: 51-100
- Moderately Polluted: 101-200
- Poor: 201-300
- Very Poor: 301-400
- Severe: 401-450
- Severe Plus: 451 and above (current status in Delhi).
- Pollutants Considered: PM10, PM2.5, NO?, SO?, CO, O?, NH?, and Pb.
- Measurement: 24-hour average values for PMs, and 8-hour averages for CO and O?.
Commission for Air Quality Management (CAQM)
- Established: Under the Commission for Air Quality Management in National Capital Region (NCR) Act, 2021.
- Mandate: To coordinate, research, and manage air quality issues in the NCR and adjoining areas.
- Composition: Includes government officials, technical experts, and NGO representatives.
- Jurisdiction: Covers Delhi and parts of Haryana, Uttar Pradesh, and Rajasthan.
Guru Ghasidas-TamorPingla Tiger Reserve

- 19 Nov 2024
In News:
The Guru Ghasidas-TamorPingla Tiger Reserve in Chhattisgarh has been officially notified as India's 56th tiger reserve, marking a significant milestone in the country's conservation efforts. Here's an overview of this new reserve:
Key Details:
- Location: The tiger reserve is located across the Manendragarh-Chirmiri-Bharatpur, Korea, Surajpur, and Balrampur districts of Chhattisgarh.
- Area: The reserve spans 2,829.38 square kilometers and includes both core and buffer zones.
- Core/critical habitat: 2,049.2 sq. km (includes the Guru Ghasidas National Park and TamorPingla Wildlife Sanctuary).
- Buffer zone: 780.15 sq. km.
- Rank: It is the third largest tiger reserve in India, after the Nagarjunasagar-Srisailam Tiger Reserve (Andhra Pradesh) and Manas Tiger Reserve (Assam).
Connectivity:
The reserve forms part of a landscape complex that extends over nearly 4,500 sq. km and is interconnected with other major tiger reserves:
- Sanjay Dubri Tiger Reserve (Madhya Pradesh) to the north.
- Bandhavgarh Tiger Reserve (Madhya Pradesh) to the west.
- Palamau Tiger Reserve (Jharkhand) to the east.
This connectivity supports greater wildlife movement, reducing the risk of inbreeding and strengthening the overall conservation efforts for the tiger population.
Biodiversity:
The Guru Ghasidas-TamorPingla Tiger Reserve is ecologically rich, harboring a wide array of species:
- 753 species have been documented, including:
- 230 bird species.
- 55 mammal species, including several threatened species such as tigers, leopards, sloth bears, and wolves.
- A variety of invertebrates, especially insects.
- The reserve's terrain includes dense forests, streams, rivers, and varied elevations, making it an ideal habitat for tigers and other wildlife.
Ecological Importance:
- Situated in the Chota Nagpur and Baghelkhand plateaus, the reserve has varied landscapes that contribute to its ecological diversity. The region's tropical climate and dense forests make it a critical habitat for tigers and other wildlife.
- The reserve's core area forms an important critical tiger habitat, providing a sanctuary for tigers to thrive with minimal human disturbance.
Conservation Impact:
With the addition of this tiger reserve, Chhattisgarh now boasts four tiger reserves, complementing the existing Udanti-Sitanadi, Achanakmar, and Indravati reserves. This bolsters the state's and the country's ongoing efforts to protect and conserve tigers, which are a keystone species in maintaining ecological balance.
Procedural Steps for Notification:
- Identification: The state government identifies a significant ecological area with potential for tiger conservation.
- NTCA Approval: After a thorough assessment, the National Tiger Conservation Authority (NTCA) evaluates and approves the proposal.
- State Notification: The state government officially notifies the area as a tiger reserve under the Wildlife Protection Act of 1972.
- Implementation: The state, with NTCA support, begins implementing conservation and management strategies.
Mystery mollusk
- 18 Nov 2024
In News:
- In a groundbreaking discovery, researchers have identified a new species of sea slug deep within the ocean’s midnight zone—a place that lies between 3,300 to 13,100 feet (1,000 to 4,000 meters) below the ocean's surface.
- The species, named Bathydeviuscaudactylus, is a glowing, swimming sea slug that exhibits several unique adaptations to survive in the extreme conditions of the deep ocean.
Key Features of BathydeviusCaudactylus
- Glowing Bioluminescence: One of the most striking features of this newly discovered mollusk is its ability to glow with bioluminescence. Bathydevius emits a soft, starry glow, an adaptation seen in only a few deep-sea species. The glowing feature plays a role in distracting predators and even includes the ability to detach glowing projections from its tail as a decoy.
- Unique Body Structure: Unlike most sea slugs that typically live on the seafloor, Bathydevius has evolved to thrive in the open water. It has a gelatinous, paddle-like tail and a large, bowl-shaped hood that covers its internal organs, making it appear somewhat like a “megaphone with a feathered tail.” This structure helps it capture prey, such as mysid shrimp, which it traps using its hood.
- Adaptations for Deep Sea Life: Bathydevius' transparent body, along with its ability to drift with ocean currents and flex its body to move vertically in the water column, allow it to navigate the depths of the midnight zone. Its hermaphroditic nature means it carries both male and female reproductive organs, allowing it to reproduce by attaching to the seafloor and laying eggs when needed.
Discovery and Exploration
- The unusual species was first encountered by researchers from the Monterey Bay Aquarium Research Institute (MBARI) during a deep-sea dive in February 2000 using a remotely operated vehicle (ROV) called Tiburon. Since then, more than 150 sightings have been made of the creature in the waters off the Pacific Coast of North America, ranging from Oregon to Southern California.
- Interestingly, similar creatures have been observed by the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) in the Mariana Trench, suggesting that Bathydevius may have a wider range than initially thought. A specimen was eventually collected for further study, revealing its identity as a nudibranch, a type of soft-bodied marine mollusk.
Survival Tactics and Behavior
- Prey Capture: Unlike typical sea slugs that scrape food from the seafloor, Bathydevius uses its large hood to trap crustaceans like mysid shrimp. This allows it to thrive in the open ocean where food can be harder to obtain.
- Defensive Mechanisms: When threatened, Bathydevius can glow with bioluminescence to distract predators. This glow, which creates a starry appearance across its back, has been seen in other deep-sea species but is rare in nudibranchs. Additionally, it can detach part of its tail (a glowing projection) to confuse attackers, similar to how lizards shed their tails as a defense mechanism.
- Reproduction and Movement: As a hermaphrodite, Bathydevius has the ability to self-fertilize or mate with other individuals. During reproduction, it descends to the seafloor and uses its foot to temporarily attach, releasing eggs before returning to its swimming lifestyle. It also relies on its flexible, transparent body to blend in with the surroundings and evade predators.
Red-Headed Vulture

- 17 Nov 2024
In News:
- The Red-Headed Vulture, a critically endangered species, has been sighted for the first time in Kasaragod, Kerala, marking an important addition to the region’s avian biodiversity. This rare sighting occurred at Manhampothikunnu near Mavungal. Prior to this, the species was predominantly seen in the Wayanad region of Kerala.
- This discovery brings the total number of bird species recorded in Kasaragod to 407, showcasing the district's growing avian diversity.
About the Red-Headed Vulture:
- The Red-Headed Vulture (also known as the Asian King Vulture or Pondicherry Vulture) is one of the rarest and most critically endangered species of vultures in India. It is known for its distinctive scarlet red head and black body with a white patch on the abdomen.
- Physical Features: The bird is medium-sized, weighing around 5 kg, with a wingspan of up to 2.5 meters and a length of 80 cm. It is typically solitary, often found alone or with a mate.
- Distribution: Historically found in Central India, Nepal, Myanmar, Thailand, Vietnam, and parts of Kerala, Karnataka, and Tamil Nadu, the Red-Headed Vulture’s numbers have drastically declined in recent decades.
Conservation Status:
- IUCN Red List: The Red-Headed Vulture is classified as Critically Endangered.
- Wildlife Protection Act, 1972: It is listed under Schedule 1, offering it the highest level of legal protection.
- CITES: The species is also listed in Appendix II, indicating that it requires international conservation efforts to prevent it from becoming endangered.
Threats to Vultures:
- Diclofenac Poisoning: The significant decline in vulture populations in India, including the Red-Headed Vulture, is primarily due to the widespread use of diclofenac (a veterinary drug) to treat livestock. When vultures consume the carcasses of treated animals, they ingest the toxic drug, leading to kidney failure and death.
- Other threats include pesticide contamination, lead poisoning, habitat loss, and collisions with man-made structures like power lines and wind turbines.
Conservation Efforts in India:
- India has undertaken various efforts to protect vultures, including banning diclofenac in 2006 and expanding the ban to other harmful drugs like ketoprofen and aceclofenac in 2023.
- Vulture Conservation Breeding Centres (VCBCs): These centers are focused on captive breeding and reintroduction programs for vultures, helping to increase their populations. The Jatayu Conservation and Breeding Centre in Uttar Pradesh is one of the latest initiatives, set up to protect and rehabilitate vultures.
- Vulture Safe Zones have been created across India, providing safe habitats for vulture species to recover.
- Vulture Restaurant Initiative: In some regions, safe feeding centers (such as in Jharkhand) have been established, where vultures are provided uncontaminated carcasses, reducing their exposure to toxic substances.
- Legal Protection: Several species of vultures, including the Red-Headed Vulture, are protected under Schedule I of the Wildlife Protection Act, 1972, ensuring stringent legal measures against poaching and habitat destruction.
Global Conservation Efforts:
- India’s vulture conservation initiatives are part of a broader international effort under the SAVE (Saving Asia’s Vultures from Extinction) programme, which involves multiple regional and global organizations working to protect vulture species in South Asia.
Decline in African Elephant Population

- 14 Nov 2024
In News:
- The population of African elephants has been declining rapidly, with data showing alarming drops across the African continent.
- Survey Period: The study covers population data from 475 sites in 37 countries over 52 years (1964-2016).
- Population Decrease:
- Savannah Elephants: A 70% decline on average across surveyed sites.
- Forest Elephants: A 90% decline on average across surveyed sites.
- Overall Impact: The study indicates a 77% average decline in elephant populations across both species.
Main Drivers of Decline
- Poaching: Illegal hunting for ivory and other body parts remains a major threat.
- Habitat Loss: Urbanization, agricultural expansion, and climate change are encroaching on the elephant’s natural habitats.
- Human-Elephant Conflict: Increased human settlements near elephant habitats lead to conflicts, further endangering elephant populations.
Species Overview
- Two Subspecies:
- Savannah Elephant (Loxodonta africana): Larger and more common, found in open savannas.
- Forest Elephant (Loxodonta cyclotis): Smaller and more elusive, found in dense rainforests.
- Conservation Status:
- Savannah Elephant: Endangered (IUCN).
- Forest Elephant: Critically Endangered (IUCN).
- CITES Listing: Both species are listed under CITES Appendix I, which bans international trade in endangered species.
Regional Impact
- Northern and Eastern Africa: These regions have seen drastic declines, particularly in the Sahel (Mali, Chad, Nigeria), where elephants have been extirpated (locally extinct) due to poaching and insufficient protection.
- Southern Africa: Positive Growth in some areas, particularly in Botswana, Zimbabwe, and Namibia, where elephant populations are growing due to strong conservation efforts.
Conservation Success
- Southern Africa: 42% of the surveyed sites showed increasing elephant populations, a testament to successful conservation strategies.
- Government and NGO Efforts: Successful population growth is often attributed to active management, including anti-poaching laws, protected areas, and conservation funding.
Elephant Behavior and Reproduction
- Social Structure: Elephants live in family units led by mature females, with strong social bonds.
- Low Sleep Time: Elephants sleep only 2 hours per day on average.
- Reproduction: They have a long gestation period of up to 2 years, and calves are cared for by mothers and allomothers (non-mother females).
Conservation Challenges
- Sustainability: Continued poaching and habitat destruction threaten to undo gains made in conservation.
- Fragmentation of Populations: With many elephants in isolated pockets, genetic diversity is declining, which could lead to long-term problems for species survival.
Global Nature Conservation Index (NCI) 2024
- 13 Nov 2024
In News:
India with an abysmal score of 45.5 (out of 100) has been ranked 176th in the Global Nature Conservation Index, 2024.
Key Highlights:
- India's Ranking:
- Ranked 176th out of 180 countries in the 2024 Global Nature Conservation Index (NCI).
- India is listed among the five worst performers, along with Kiribati (180), Turkey (179), Iraq (178), and Micronesia (177).
- Score: 45.5 out of 100, indicating significant conservation challenges.
- Key Factors Contributing to Low Rank:
- Inefficient land management practices.
- Rising threats to biodiversity, exacerbated by unsustainable development and climate change.
- Four Key Markers Assessed by the NCI:
- Land Management: Ineffective management leading to significant land conversion.
- Threats to Biodiversity: Habitat loss, fragmentation, and deforestation.
- Capacity and Governance: Need for stronger political will and better enforcement of conservation laws.
- Future Trends: Growing pressure from population density, climate change, and illegal wildlife trade.
- Sustainable Land Use Concerns:
- 53% of land has been converted for urban, industrial, and agricultural purposes.
- High use of pesticides and concerns over soil pollution.
- Sustainable nitrogen index of 0.77 indicates significant risks to soil health.
- Marine Conservation Issues:
- Only 0.2% of India’s national waterways are under protected areas, with no protected areas within its Exclusive Economic Zone (EEZ).
- Significant improvements needed in marine conservation despite 7.5% of terrestrial areas being protected.
- Deforestation and Habitat Loss:
- 23,300 sq. km of tree cover lost between 2001-2019 due to deforestation.
- Habitat fragmentation from agriculture, urbanization, and infrastructure development.
- Impact of climate change on sensitive ecosystems like alpine regions and coral reefs.
- Biodiversity Decline:
- Despite 40% of marine species and 65% of terrestrial species being within Protected Areas (PAs), many species continue to face population decline.
- 67.5% of marine species and 46.9% of terrestrial species are still experiencing population declines.
- Illegal Wildlife Trade:
- India is the fourth-largest illegal wildlife trading nation globally, with an estimated annual trade value of £15 billion.
- The NCI emphasizes the need for stronger enforcement and international cooperation to combat wildlife trafficking.
- Ecological Wealth Under Threat:
- India’s high population density (with a population that has doubled since the late 1970s) continues to put pressure on its ecological wealth.
- The country faces significant biodiversity challenges due to overpopulation and unsustainable development.
- Recommendations and Optimism:
- The NCI stresses the need for strong political will and commitment to sustainable development.
- India can improve its rank by strengthening conservation laws, improving governance, and securing funding for environmental initiatives.
- The NCI remains optimistic about India’s potential to address its conservation challenges and achieve more sustainable outcomes in the future.
- About the Nature Conservation Index (NCI):
- Developed by: Goldman Sonnenfeldt School of Sustainability and Climate Change (Ben-Gurion University) and BioDB.com (a biodiversity database).
- Purpose: Evaluates the conservation efforts of countries, using a data-driven approach to balance conservation and development.
- Key Focus Areas: Land management, biodiversity threats, governance, and future sustainability trends.
Diclipterapolymorpha

- 12 Nov 2024
In News:
A new species of Dicliptera, named Diclipterapolymorpha, has been discovered in the Northern Western Ghats of India.
Habitat and Location:
- Diclipterapolymorpha was found in the grasslands of Talegaon-Dabhade, a region known for its grasslands and fodder markets.
- The species thrives in the harsh climatic conditions of the Northern Western Ghats, an area vulnerable to summer droughts and frequent human-induced fires.
Unique Characteristics:
- The species is fire-resilient (pyrophytic), exhibiting a rare dual-blooming pattern:
- First Blooming: Occurs post-monsoon, typically from November to March/April.
- Second Blooming: Triggered by grassland fires in May and June, during which the plant produces dwarf flowering shoots.
- The inflorescence structure is unique in India, with its cymules developing into spicate inflorescences, a feature more commonly found in African species.
Taxonomy:
- The species is named Diclipterapolymorpha to reflect its diverse morphological traits.
- It is taxonomically distinct within the Dicliptera genus, with no known Indian species exhibiting similar characteristics.
Conservation Implications:
- The discovery highlights the need to carefully manage grassland ecosystems, as the species is adapted to fire but still vulnerable to habitat degradation.
- Human-induced fires are essential for the species' blooming cycle but must be managed to avoid overuse and degradation of habitat.
- The species' limited habitat range underscores the need for conservation efforts to protect the delicate ecosystems of the Western Ghats.
Publication:
- A research paper detailing the discovery of Diclipterapolymorpha has been published in the prestigious Kew Bulletin.
Arpactophiluspulawskii
- 11 Nov 2024
In News:
- Arpactophiluspulawskii, a new species of aphid wasp, was discovered in Nagaland (Khuzama district), marking the first record of the genus Arpactophilus outside Australasia.
- This significant discovery highlights the biodiversity of Northeastern India, a region known for its rich and unexplored fauna.
Importance of Discovery:
- The Zoological Survey of India (ZSI) researchers cataloged the species, marking a major range expansion for the genus Arpactophilus, previously only found in Australasia, including regions like New Caledonia.
- The discovery expands the genus’s known distribution by thousands of kilometers, suggesting ecological connections between Nagaland and the Australasian region.
Species Characteristics:
- Arpactophiluspulawskii is distinguished by its square-shaped head, an inverted V-shaped uplifted clypeus, and rust-colored body markings.
- It features a uniquely textured thorax, setting it apart from other species in the genus.
- The wasp was collected from an altitude of over 1,800 meters, indicating Nagaland’s ecological diversity at high altitudes.
Ecological Significance:
- The Arpactophilus genus is known for its unique nesting behavior: females use silk from their abdomen to create protective cells in old termite galleries or mud nests.
- The discovery suggests that Nagaland’s ecological conditions (e.g., high altitude, diverse habitat) support the presence of such specialized fauna, making the region an important site for entomological research.
Taxonomic Contribution:
- The species is named Arpactophiluspulawskii in honor of Dr. Wojciech J. Pulawski, a distinguished expert in wasp taxonomy.
Scientific and Research Implications:
- The discovery is expected to stimulate further entomological research in Northeastern India, especially in areas like Nagaland, which are often overlooked in global biodiversity studies.
- Researchers believe that this discovery could lead to the identification of other unknown species in the region, expanding our understanding of species distribution and the ecological connectivity between regions.
Adaptation Gap Report 2024
- 08 Nov 2024
In News:
The Adaptation Gap Report 2024, published by the United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP), underscores the urgent need for enhanced climate adaptation efforts, particularly through increased financial support for developing countries. The report, titled Come Hell and High Water, provides an annual assessment of global adaptation progress in planning, implementation, and financing.
Key Findings
- Adaptation Gap:
- The adaptation finance gap is estimated at $187–359 billion per year.
- Current adaptation finance falls short, with only $28 billion provided in 2022, meeting just 5% of projected needs.
- Adaptation Progress:
- International public adaptation finance to developing countries rose to $27.5 billion in 2022, up from $19 billion in 2019, reflecting progress toward the Glasgow Climate Pact's goal of doubling finance by 2025.
- Significance of Adaptation:
- Ambitious adaptation measures could reduce global climate risk by 50%.
- For instance, $16 billion annually in agriculture could prevent climate-induced hunger for 78 million people.
- Impact of Global Warming:
- According to UNEP's Emissions Gap Report 2024, global temperatures may increase by 2.6°C–3.1°C above pre-industrial levels by 2100.
- Developing countries face severe vulnerabilities, evidenced by recent floods in Nepal, Nigeria, and Chad.
- National Adaptation Plans (NAPs):
- While 171 countries have at least one adaptation policy, progress in implementation remains slow.
- 10 countries have shown no interest in developing adaptation policies.
Challenges in Adaptation Financing
- Financial Burden: Adaptation projects such as seawalls and resilient infrastructure are costly for developing nations.
- Funding Shortfalls:
- Developed nations have failed to meet financial commitments like the $100 billion goal set for 2020.
- The adaptation finance gap remains significant in non-private sector-funded areas, such as ecosystem preservation.
- High-Interest Loans: Much current funding relies on high-interest loans, increasing the debt burden for recipient countries.
Recommendations
- Adopt New Financing Goals: Establish an ambitious New Collective Quantified Goal for climate finance at COP29.
- Strategic Adaptation Financing:
- Shift from project-based to anticipatory and transformational financing.
- Invest in harder-to-finance areas like ecosystem preservation and cultural heritage.
- Alternative Financing Models: Encourage risk finance, resilience bonds, debt-for-adaptation swaps, and payments for ecosystem services.
Global and Indian Initiatives
Global Initiatives:
- Paris Agreement: Sets a global adaptation goal to enhance resilience.
- UAE Framework for Global Climate Resilience: Introduced at COP28, focusing on agriculture, water, and health adaptation targets.
- Adaptation Fund: Provides project funding for developing nations under the Kyoto Protocol.
Indian Initiatives:
- National Action Plan on Climate Change (NAPCC): Includes eight missions, such as the National Adaptation Fund for Climate Change (NAFCC).
- Sectoral Schemes:
- MISHTI: Mangrove initiative for shoreline protection.
- Amrit Dharohar: Enhances wetland ecosystems.
- India's adaptation spending accounted for 5.6% of GDP in 2021–2022.
Protected Planet Report 2024

- 08 Nov 2024
In News:
The Protected Planet Report 2024, released by UNEP-WCMC and IUCN, evaluates global progress toward achieving Target 3 of the Kunming-Montreal Global Biodiversity Framework (KM-GBF). This target aims to conserve 30% of Earth's terrestrial, inland water, coastal, and marine areas by 2030.
Key Highlights of the Report
- Current Global Coverage
- Land and Inland Waters: 17.6% protected.
- Oceans and Coastal Areas: 8.4% protected.
- Progress since 2020: Minimal increase (<0.5% for both realms), equivalent to an area twice the size of Colombia.
- Remaining Challenges to Achieve Target 3 by 2030
- Land: An additional 12.4% of land area must be protected (equivalent to Brazil + Australia).
- Ocean: 21.6% more marine areas must be safeguarded (larger than the Indian Ocean).
- Key Gaps:
- Only 8.5% of protected areas on land are well-connected.
- Only one-fifth of the areas critical for biodiversity are fully protected.
- Biodiversity representation remains uneven, with some ecological regions having no protection at all.
- Governance and Effectiveness Issues
- Less than 5% of protected land and 1.3% of marine areas have management effectiveness assessments.
- Only 0.2% of protected land and 0.01% of marine areas have undergone equitable governance assessments.
- Indigenous governance covers less than 4% of protected areas despite Indigenous and traditional territories covering 13.6% of the terrestrial areas.
- Ocean Conservation Progress: Most progress is in national waters; however, areas beyond national jurisdiction (the high seas) remain underrepresented (<11% coverage).
- Data Deficiency: Insufficient data to measure biodiversity outcomes, equity, and governance in protected areas.
Importance of Target 3
- Biodiversity Benefits: Protected areas play a critical role in halting and reversing biodiversity loss.
- Ecosystem Services: These areas contribute to clean air, water, climate regulation, and food security.
- Cultural and Economic Significance: They uphold the rights of Indigenous Peoples and local communities, ensuring equitable governance and sustainable resource use.
Key Recommendations
- Accelerate Conservation Efforts:
- Expand protected and conserved areas with a focus on biodiversity hotspots.
- Ensure areas are ecologically connected and effectively managed.
- Strengthen Indigenous and Local Contributions:
- Recognize and support the stewardship of Indigenous Peoples and local communities.
- Ensure their voices and knowledge systems are integrated into conservation planning.
- Improve Governance and Equity:
- Address gaps in equitable governance and include rights-based approaches.
- Global Cooperation:
- Increase international financing to developing nations for biodiversity conservation.
- Foster cross-border partnerships and support data-sharing initiatives.
- Enhance Data Availability:
- Collect and disseminate data on the effectiveness of protected areas and their biodiversity outcomes.
India’s Role and Strategy
- Commitment to KM-GBF: India updated its National Biodiversity Strategy and Action Plan (NBSAP) to align with the KM-GBF goals, aiming to protect 30% of natural areas by 2030.
- Focus on Restoration: Prioritizes the restoration of forests, rivers, and other ecosystems to maintain essential resources like clean air and water.
- Indigenous Participation: India emphasizes integrating Indigenous territories into its conservation framework.
Okinawicius tekdi
- 07 Nov 2024
In News:
Researchers have recently discovered a new species of jumping spider in the Baner Hill area, underscoring the region's rich biodiversity and the growing need to preserve the natural landscapes around Pune.
About Okinawicius tekdi:
- The newly identified species, named Okinawicius tekdi, is a jumping spider that contributes to the growing diversity of India's spider population, now numbering 326 species of jumping spiders.
- The name "tekdi" comes from the Marathi word for "hill," reflecting the spider's habitat.
- The last time a spider species was identified in Pune was over three decades ago.
About Jumping Spiders:
- Jumping spiders belong to the family Salticidae and are known for their distinctive eight legs and remarkable jumping ability.
- These spiders possess a segmented body, a tough exoskeleton, and jointed legs.
- In addition to their agility, they are famous for spinning webs that they use to capture their prey.
World Cities Report 2024
- 07 Nov 2024
In News:
The World Cities Report 2024, released by UN-Habitat, highlights the urgent need for cities to address climate change, both as victims and major contributors.
Key Findings of the Report
- Temperature Increases by 2040: Nearly 2 billion people living in urban areas are projected to face at least a 0.5°C rise in temperature by 2040, exposing them to heatwaves and other climate-related risks.
- Urban Vulnerability and Climate Risk:
- Cities are disproportionately affected by climate change while being major contributors to greenhouse gas emissions, which exacerbates their vulnerability to events like floods, cyclones, and heatwaves.
- The urban population is facing a dual challenge: increased heat and extreme weather events such as flooding, cyclones, and erratic rainfall.
- Sea-Level Rise and Coastal Risks: Over 2,000 cities in low coastal areas, many located under 5 meters above sea level, are at heightened risk from sea-level rise and storm surges, potentially affecting more than 1.4 billion people by 2040.
- Riverine Flooding: Flood exposure in cities is growing 3.5 times faster than in rural areas, with 517 million people in urban areas projected to be exposed to riverine flooding by 2030.
- Investment Gap: Cities require between USD 4.5 trillion and USD 5.4 trillion annually to build and maintain climate-resilient systems, but current investments stand at only USD 831 billion, highlighting a massive funding shortfall.
- Decline in Urban Green Spaces: The average share of urban green spaces has dropped from 19.5% in 1990 to 13.9% in 2020, reducing cities' ability to absorb carbon, manage heat, and provide essential ecosystem services.
- Vulnerable Communities: Informal settlements and slums, often situated in environmentally sensitive areas, are disproportionately affected by climate impacts. These communities lack adequate infrastructure and are often unable to invest in necessary upgrades due to eviction fears or lack of legal recognition.
- Green Gentrification: While climate interventions like park creation can provide environmental benefits, they can also lead to green gentrification—displacing low-income households or increasing property values and rents, thus pricing vulnerable communities out.
Contributing Factors to Urban Global Warming
- Energy Consumption: Urban areas account for 71-76% of global CO? emissions from energy use, driven by dense populations, industrial activities, transportation, and high-energy demand for buildings.
- Industrial Activities: Urban industries and power plants release a variety of greenhouse gases (GHGs), including CO?, methane (CH?), and nitrous oxide (N?O).
- Land Use Changes: Urban expansion leads to deforestation and reduced carbon absorption, contributing to global warming. Urban land areas are expected to more than triple by 2050, accelerating environmental degradation.
- Waste Generation: Decomposing waste in landfills releases methane, a potent GHG, exacerbating the greenhouse effect.
- Urban Heat Island Effect: Urban Heat Islands (UHIs) occur when cities absorb and retain more heat due to their dense infrastructure (asphalt, concrete, and buildings), increasing local temperatures and energy consumption.
Impacts of Global Warming on Cities
- Heatwaves: Cities, especially in warmer regions like India, are experiencing more severe heatwaves and rising temperatures.
- Urban Heat Island Effect: UHIs increase the intensity of heatwaves, particularly in high-density cities, where buildings and roads trap heat, exacerbating energy demands and public health risks.
- Coastal Flooding: Rising sea levels threaten coastal cities with flooding and storm surges, displacing communities and disrupting economies.
- Wildfire Seasons: Warming temperatures and prolonged droughts increase the risk of wildfires in urban areas, particularly in forest-adjacent cities.
India's Climate Initiatives for Urban Areas
- Smart Cities Mission: Focuses on developing sustainable urban infrastructure, promoting smart technologies, and enhancing resilience to climate impacts.
- AMRUT Mission: Aims to provide basic infrastructure and sustainable urban development in cities, including water supply, sewage, and green spaces.
- Swachh Bharat Mission-Urban: Focuses on improving waste management and reducing pollution in urban areas.
- FAME India Scheme (Faster Adoption and Manufacturing of Hybrid and Electric Vehicles): Promotes electric vehicles to reduce urban air pollution and carbon emissions.
- Green Energy Corridor (GEC): Facilitates the integration of renewable energy sources into the national grid, encouraging clean energy use in urban centers.
IUCN’s First Global Tree Assessment

- 05 Nov 2024
In News:
More than one in three tree species threatened with extinction, finds IUCN’s first Global Tree Assessment
Key Highlights:
Global Tree Extinction Risk:
- 38% of the world’s tree species are now facing the risk of extinction — over one in three tree species is at risk.
- This means 16,425 out of 47,282 tree speciesanalyzed by the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) are under threat.
- Threatened tree species outnumber all threatened birds, mammals, reptiles, and amphibians combined, highlighting the urgent need for conservation action.
Key Drivers of Threat:
- Deforestation: The primary threat to trees is deforestation, driven by agriculture, livestock rearing, and urban development, especially in tropical regions.
- Climate Change: Rising sea levels and increasingly frequent storms exacerbate the threats, particularly in tropical regions and islands.
- Invasive Species & Pests: Non-native species, pests, and diseases are adding pressure to vulnerable tree populations.
Geographic Vulnerabilities:
- Islands are particularly vulnerable, with a high proportion of threatened species due to habitat destruction and urbanization.
- South America, which boasts the highest tree diversity, faces significant threats, with 3,356 out of 13,668 species at risk, mainly due to deforestation for agriculture.
Ecological and Economic Importance of Trees:
- Trees play a fundamental role in carbon, water, and nutrient cycles, and are critical for soil formation and climate regulation.
- The loss of trees poses a growing threat to thousands of other species of plants, fungi, and animals.
- Trees are essential for local communities, providing resources such as timber, medicines, food, and fuel. Over 5,000 species of trees are used for timber and construction, while more than 2,000 species are vital for food, fuel, and medicine.
Conservation Status:
- Tree species are threatened across 192 countries.
- The assessment is the first global analysis of the conservation status of trees, enabling better-informed conservation decisions.
Positive Actions and Strategies:
- Successful community-driven conservation efforts have had positive outcomes in places like the Juan Fernández Islands, Cuba, Madagascar, and Fiji.
- Some countries, including Ghana, Colombia, Chile, and Kenya, already have national strategies for tree conservation.
- Ex-situ conservation, such as seed banks and botanical gardens, is also crucial to safeguard species that may not survive in the wild.
Urgent Call for Action:
The IUCN Global Tree Assessment underlines the urgent need for enhanced conservation efforts, including:
- Habitat protection and restoration.
- Ex-situ conservation through seed banks and botanical gardens.
- Diversified and species-focused reforestation strategies.
- Supporting community-led conservation initiatives to safeguard vulnerable tree species.
Asia-Pacific Climate Report 2024

- 05 Nov 2024
In News:
Climate change to put APAC GDP on thin ice with 41% melt by 2100.
Key Highlights:
- Economic Losses Due to Climate Change:
- APAC Region: High-end greenhouse gas emissions could reduce GDP by 17% by 2070 and 41% by 2100.
- India: Projected to experience a 24.7% GDP loss by 2070, with neighboring countries like Bangladesh (30.5%), Vietnam (30.2%), and Indonesia (26.8%) facing even steeper declines.
- Major Drivers of Economic Losses:
- Sea-Level Rise: Up to 300 million people at risk of coastal flooding by 2070. Annual damages could reach $3 trillion by 2070.
- Labour Productivity: The APAC region could lose 4.9% of GDP from reduced labour productivity, with India facing a sharper 11.6% loss.
- Cooling Demand: Rising temperatures could reduce regional GDP by 3.3%, but India's cooling demands could cut its GDP by 5.1%.
- Flooding and Storms: Increased rainfall and storm intensity will exacerbate flooding and landslides, particularly in mountainous regions like the India-China border, where landslides could rise by 30-70% under severe warming.
- Impact on Key Sectors:
- River Flooding: By 2070, annual riverine flooding could cause $1.3 trillion in damages across the APAC, affecting over 110 million people. India could face over $1,100 billion in flood-related damages annually.
- Forest Productivity: Climate change could reduce forest productivity by 10-30% by 2070 across APAC. India could see losses over 25%, making it one of the hardest-hit countries, alongside Vietnam and Southeast Asia.
- Climate Risks and Vulnerabilities:
- Coastal Flooding: Coastal flooding could lead to widespread economic damage, with India expected to suffer significant losses, particularly in coastal areas.
- Ecosystem Threats: Intensified storms, rainfall, and landslides will affect ecosystems, forests, and agriculture across the region.
- Climate Change and Adaptation Needs:
- Investment Requirements: Developing Asia requires $102–431 billion annually for climate adaptation, far exceeding the $34 billion tracked from 2021 to 2022.
- Private Investment: The report highlights the need for greater private climate investment and regulatory reforms to attract capital for adaptation initiatives.
- Renewable Energy: APAC is well-positioned to embrace renewable energy for a net-zero transition, and the use of carbon markets could help achieve climate goals cost-effectively.
- Regional Net-Zero Goals and Progress:
- Net-Zero Targets: 36 out of 44 Asian economies have set net-zero emissions targets, but only 4 have legally committed to these goals. India and China target 2070 and 2060, respectively, while many OECD countries aim for 2050 targets.
- Policy Gaps: Developing Asia needs clearer policies and increased financing to meet climate ambitions. Institutions like ADB are crucial in supporting these efforts.
- Action Plan for the Future:
- Urgent Climate Action: The report stresses the importance of coordinated action to address escalating climate risks.
- Enhanced Adaptation Finance: There is a need to scale up adaptation-focused finance to tackle the growing climate challenges facing the region.
India's Vulnerability and Climate Challenges:
- Labour Impact: India is expected to experience a 11.6% GDP loss due to declining labour productivity, the highest among APAC countries.
- Cooling Demands: A 5.1% reduction in GDP due to increased cooling demand.
- Flood Damage: India’s flood-related losses could surpass $1.1 trillion annually by 2070, with damages to residential and commercial properties.
Kodo Millet

- 03 Nov 2024
In News:
Kodo millet is a staple food for many tribal and economically weaker sections in India. It is one of the 'hardiest crops, drought tolerant with high yield potential and excellent storage properties,' according to researchers
Background on Kodo Millet:
- Kodo millet (Paspalum scrobiculatum), also known as Kodra or Varagu, is a hardy, drought-tolerant crop widely grown in India, especially in Madhya Pradesh.
- It is a staple food for many tribal and economically weaker sections of India and is used to make various dishes like idli, dosa, and rotis.
- Kodo millet is valued for its high yield, nutritional benefits (rich in vitamins, minerals, antioxidants), and storage properties.
Incident in Bandhavgarh Tiger Reserve:
- 10 elephants from a herd of 13 died over three days in Madhya Pradesh’s Bandhavgarh Tiger Reserve.
- The cause of death was suspected to be mycotoxins associated with kodo millet, particularly Cyclopiazonic Acid (CPA), which is toxic to animals.
Historical Cases of Kodo Poisoning:
- The first human cases of kodo poisoning were reported in 1922 in the Indian Medical Gazette.
- Animals, including elephants, have also been affected by kodo millet consumption, with documented deaths as early as 1983.
- Cyclopiazonic Acid (CPA), a mycotoxin, was identified as the cause of kodo poisoning in the 1980s.
Why Does Kodo Millet Become Poisonous?
- Kodo millet is grown in dry and semi-arid regions and is vulnerable to fungal infections, particularly Ergot fungus, which produces CPA.
- When the crop encounters rainfall during maturing and harvesting, fungal infection can lead to "poisoned kodo," known locally as 'Matawna Kodoo' or 'Matona Kodo'.
- The mycotoxins in the infected millet are stable and resistant to standard food processing techniques.
Impact of Mycotoxins on Animals:
- Symptoms of poisoning: Vomiting, giddiness, unconsciousness, rapid pulse, cold extremities, limb tremors.
- Nervous and cardiovascular systems are primarily affected, causing liver dysfunction, heart damage, and gastrointestinal issues.
- In severe cases, consumption of infected kodo millet can cause death due to cardiovascular collapse and organ failure.
- Similar symptoms of depression and loss of mobility were observed in animal studies, including in mice.
Solution to Kodo Toxicity:
- Biocontrol agents (organisms that fight harmful pathogens) can help reduce fungal growth and mycotoxin production in kodo millet.
- Good agricultural practices: Sorting, proper storage in airtight containers, and avoiding moisture exposure during threshing can minimize contamination.
- Post-harvest management: Removing infected grains is crucial to preventing the spread of the disease.
Detection of Mycotoxins in Kodo Millet:
- Challenges: Mycotoxins are often undetectable by sight, and traditional methods like chromatography are time-consuming.
- Rapid detection tools: Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays (ELISA), lateral flow assays (LFAs), and biosensors offer faster, on-site methods for detecting mycotoxins in kodo millet.
Centre for Science and Environment

- 03 Nov 2024
In News:
Centre for Science and Environment release a report on Extended Producer Responsibility (EPR) for Plastic Packaging
Key Findings:
- EPR Guidelines (2022) were a step towards enforcing the "polluter pays" principle, but the system faces significant issues in its implementation and registration processes.
- Centre for Science and Environment (CSE) report, released on October 29, 2024, highlights gaps in the EPR system for plastic packaging and suggests corrective actions.
EPR Guidelines Overview:
- Issued by: Union Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change (MoEFCC).
- Objective: Hold producers, importers, brand owners (PIBOs), and plastic waste processors (PWPs) responsible for managing plastic packaging waste.
- Key Requirements:
- PIBOs must register on a centralized portal and set targets for collection, recycling, and reuse of plastic packaging.
- Registration involves compliance with targets on end-of-life recycling and recycled content usage.
Problems Identified in the Current EPR System:
- Low Registration and Enrollment:
- 41,577 registrations on the EPR portal, but a significant discrepancy in the type of stakeholders registered.
- 83% of registered entities are importers, 11% are producers, and only 6% are brand owners.
- Producers contribute 65% of the plastic packaging in the market but have low registration.
- Absence of Key Polluters:
- Manufacturers of virgin plastics are notably absent from the portal, despite being required to register.
- Fraudulent Practices:
- 700,000 fake certificates were generated by plastic recyclers, far exceeding the actual certificate generation capacity.
- The Central Pollution Control Board (CPCB) found that such fraudulent activities are undermining the integrity of the system.
- For example, end-of-life co-processing units (e.g., cement plants) claimed to have processed 335.4 million tonnes per annum of plastic waste, while their actual capacity is just 11.4 million tonnes per annum.
- Underreporting and Mismanagement:
- Despite 23.9 million tonnes of plastic packaging being introduced into the market, the CPCB’s estimation of plastic waste generation (4.1 MT annually) is underestimated.
- Lack of Stakeholder Representation:
- Urban local bodies and informal waste collectors—key contributors to plastic waste management—are not included in the EPR framework, which limits their incentives and support.
Recommendations for Improvement:
- Incorporate the Informal Sector:
- Recognize informal waste collectors and waste management agencies in the EPR framework to improve traceability and ensure better waste management.
- Eliminate Fraudulent Practices:
- Strict actions need to be taken against fraudulent recyclers and fake certificate issuers to restore credibility to the EPR system.
- Establish Fair Pricing for EPR Certificates:
- Undertake baseline cost studies to determine the true costs of plastic waste management, ensuring fair pricing for recycling certificates and preventing undervaluation.
- Standardize Packaging:
- Focus on product standardization to ensure that packaging materials are uniform and easily recyclable.
- Strengthen Monitoring:
- Improve oversight on the registration process and ensure that all polluters (producers, importers, brand owners) comply with the system’s guidelines.
EPR and Plastic Waste Management: Context and Importance
- Extended Producer Responsibility (EPR) is a policy approach where the responsibility of managing the entire lifecycle of plastic products (from production to disposal) lies with the producer.
- It is an essential part of India’s Plastic Waste Management Rules (2016), which mandate the recycling and proper disposal of plastic packaging waste.
Key Elements of EPR:
- Producer Accountability: Producers are responsible for the take-back, recycling, and final disposal of plastic packaging.
- Waste Minimization: Encourages reducing waste at the source by promoting sustainable packaging designs.
- Lifecycle Approach: Considers the entire lifecycle of the product, focusing on sustainability from production to disposal.
- Polluter Pays Principle: Ensures that the cost of waste management is borne by those responsible for generating the waste.
National Biodiversity Strategy and Action Plan (NBSAP) 2024-2030

- 03 Nov 2024
In News:
The updated NBSAP was released by India at the 16th Conference of Parties (COP16) to the Convention on Biological Diversity (CBD).
Overview of the NBSAP (2024-30):
- Title:Updated National Biodiversity Strategies and Action Plan: A Roadmap for Conservation of India’s Biodiversity.
- Objective: To provide a comprehensive roadmap for biodiversity conservation, aligning with global frameworks like the Kunming-Montreal Global Biodiversity Framework (KMGBF).
Key Features of the Updated NBSAP:
- Alignment with Global Frameworks:
- The Kunming-Montreal Global Biodiversity Framework (KMGBF) adopted in 2022 aims to halt and reverse biodiversity loss by 2030.
- India’s updated NBSAP aligns with KMGBF’s goals, focusing on biodiversity conservation, sustainable resource use, and ensuring fair benefit-sharing.
- 23 National Biodiversity Targets:
- The targets are focused on three key themes:
- Reducing threats to biodiversity
- Ensuring sustainable use of biodiversity
- Enhancing tools for biodiversity implementation
- The targets are focused on three key themes:
- Key Domains of Focus:
- Area-based conservation: Protecting ecosystems and habitats.
- Ecosystem resilience: Enhancing the ability of ecosystems to withstand environmental stressors.
- Recovery and conservation of threatened species.
- Conservation of agrobiodiversity: Ensuring the sustainability of agricultural biodiversity.
- Sustainable management of biodiversity.
- Enabling tools and solutions: Including financial and technical support for implementation.
- Financial Plan and Expenditure:
- Biodiversity Expenditure Review (BER) estimated an average annual expenditure of Rs 32,20,713 crore (FY 2017-2022) for biodiversity conservation.
- Future funding requirements (FY 2024-2030) estimated at Rs 81,664.88 crore annually at the central government level.
- Biodiversity Finance Plan suggests financing solutions, including public finance, corporate social responsibility (CSR), Ecological Fiscal Transfer (EFT), and Access and Benefit Sharing (ABS) mechanisms.
- Capacity Building:
- The NBSAP stresses the need for capacity building across various levels—national, state, and local.
- Focus on skills acquisition for biodiversity management and enhancing knowledge to implement conservation strategies.
Implementation Framework:
- Multi-Level Governance:
- At the national level, the Ministry of Environment, Forest, and Climate Change (MoEFCC) will oversee implementation with involvement from 22 other ministries.
- State-level: Involves State Biodiversity Boards and Union Territory Biodiversity Councils.
- Local level: Community-driven efforts through Biodiversity Management Committees.
- BIOFIN and Resource Mobilization:
- India is recognized as a leading country in the implementation of the Biodiversity Finance Initiative (BIOFIN).
- Encouragement for private entrepreneurs, businesses, and international donors to invest in biodiversity through innovative financial instruments like:
- Green Bonds
- Green Funds
- Payment for Ecosystem Services (PES)
- Incentives for Financial Solutions:
- India aims to explore funding from corporate social responsibility (CSR), ecological fiscal transfers, and access and benefit sharing mechanisms to meet the financial needs for biodiversity conservation.
Challenges and Strategies:
- Challenges India Faces:
- Habitat fragmentation
- Pollution
- Illegal wildlife trade
- Adverse effects of climate change
- Strategic Responses:
- The updated NBSAP provides strategies to address these challenges, ensuring comprehensive conservation and sustainable use of biodiversity.
Wildlife Crime Control Bureau (WCCB)
- 03 Nov 2024
In News:
The Wildlife Crime Control Bureau (WCCB) of the Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate change has constituted a team to enquire into the death of ten elephants in Bandhavgarh Tiger Reserve of Madhya Pradesh. The team is conducting an independent enquiry in the matter.
- Incident Overview:
- Ten elephants found dead in Bandhavgarh Tiger Reserve, Madhya Pradesh, between October 29-31, 2024.
- Preliminary cause of death suspected to be poisoning; final cause pending postmortem and toxicological analysis.
- Government Actions:
- Union Government:
- The Wildlife Crime Control Bureau (WCCB) has set up a team to conduct an independent investigation into the deaths.
- Madhya Pradesh Government:
- Constituted a five-member State-level inquiry committee, headed by the Additional Principal Chief Conservator of Forests (APCCF, Wildlife).
- Committee includes members from civil society, scientists, and veterinarians.
- The State Tiger Strike Force (STSF) is conducting field investigations, combing surrounding areas for further clues.
- Other Involved Authorities:
- The Principal Chief Conservator of Forests (PCCF) and Chief Wildlife Warden of Madhya Pradesh are directly supervising the inquiry in Bandhavgarh.
- Senior officials from the National Tiger Conservation Authority (NTCA) have visited the site for discussions and investigation.
- Union Government:
About Wildlife Crime Control Bureau (WCCB):
- Mandate:
- Combats organized wildlife crime through intelligence gathering and coordination with enforcement agencies.
- Develops wildlife crime data and assists in prosecutions.
- Provides capacity building for wildlife crime enforcement agencies.
- Operations & Initiatives:
- Conducts operations like SAVE KURMA, THUNDERBIRD, WILDNET, and more to counter wildlife crimes.
- Nodal Ministry: Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change.
- Headquarters: New Delhi.
Melanistic Tigers
- 01 Nov 2024
In News:
- Odisha government relocated a tigress from Maharashtra’s Tadoba-Andhari Tiger Reserve to Similipal Tiger Reserve, Odisha, to address inbreeding issues among the tiger population.
- The tigress is part of a genetic diversification plan to remedy the increasing number of pseudo-melanistic tigers in the region.
Pseudo-melanistic Tigers:
- Pseudo-melanistic tigers, often referred to as "black tigers," exhibit a darker coat with broader, more prominent stripes.
- The mutation leads to the appearance of a mostly black fur, with occasional white-orange stripes.
Genetic Basis:
- This coloration is due to a mutation in the Taqpep gene, which causes the widening and darkening of stripes on the tiger's coat.
- The mutation is linked to genetic drift and inbreeding within the isolated Similipal population.
Historical Context:
- These tigers were once considered mythical until the 1700s, with sightings only being documented in the 1990s and 2017-18.
- The first confirmed genetic evidence of the black tiger appeared when a cub was born in captivity at Oklahoma City Zoo in the 1970s.
Distribution and Prevalence:
- Pseudo-melanistic tigers are predominantly found in Similipal Tiger Reserve, with 27 out of 30 tigers in Odisha exhibiting the trait.
- Other instances of such tigers exist in captivity, such as in Nandankanan Zoological Park (Bhubaneswar) and Arignar Anna Zoological Park (Chennai), both tracing ancestry to Similipal.
Genetic Studies:
- A 2021 study by the National Centre for Biological Sciences (NCBS) linked the Taqpep gene mutation to the unique appearance of these tigers.
- The mutation causes a missense change in the gene, replacing Cytosine with Thymine (C1360T), altering the tiger’s coat pattern.
High Frequency of Mutation in Similipal:
- Genetic analyses indicate a high frequency of the Taqpep gene mutation in Similipal tigers, with a 60% chance that a tiger born there will carry the mutated gene.
- Inbreeding and genetic isolation have contributed to this phenomenon, as Similipal’s tiger population is geographically cut off from other populations.
MhadeiWildlife Sanctuary
- 01 Nov 2024
In News:
An adult tigress and three cubs have been spotted in the Mhadei wildlife sanctuary in Goa marking the first time evidence of the species has been recorded in the forests bordering the states of Maharashtra and Karnataka since 2020.
Key Highlights:
Location and Geography:
- It is located near Chorla Ghat, between North Goa and Belgavi, and borders Maharashtra and Karnataka.
- The sanctuary is traversed by the Mhadei River, which meets the sea at Panaji, Goa.
Ecological Significance:
- It is part of the Western Ghats, a UNESCO World Heritage site, and shares this ecosystem with Mollem National Park and other protected areas in Goa.
- The sanctuary is integral to wildlife corridors connecting the Sahyadri Tiger Reserve (Maharashtra) and Kali Tiger Reserve (Karnataka), critical for tiger conservation.
Flora and Fauna:
- It is home to diverse wildlife, including the critically endangered Long-billed vultures that nest at Vazra Falls.
- The region supports a variety of flora and fauna due to its biodiversity-rich Western Ghats ecosystem.
Conservation Status and Recommendations:
- Goa is the only state in India to have its entire portion of the Western Ghats under state protection, with Mhadei WLS being a key area.
- The National Tiger Conservation Authority (NTCA) has recommended that Mhadei WLS be designated as a tiger reserve to enhance protection efforts.
- The sanctuary is a potential candidate for inclusion under Project Tiger.
- In 2020, a Royal Bengal tigress and her cubs were tragically poisoned due to human-animal conflict.
Mahadayi Water Dispute:
- The Mahadayi (Madei, Mandovi) River is a source of dispute between Karnataka and Goa regarding water sharing.
- Karnataka seeks to divert water from the river to the Malaprabha River basin for drinking water supply in several districts, through the Kalasa-Banduri Nala project.
- The matter is currently being heard in the Supreme Court.
Report of The Lancet Countdown on Health and Climate Change, 2024

- 30 Oct 2024
In News:
The 2024 edition of The Lancet Countdown on Health and Climate Change presents critical insights into the intersection of health and climate change.
Key Findings from the 2024 Report
- Air Pollution and Mortality in India:
- In 2021, air pollution was responsible for 1.6 million deaths in India.
- Fossil fuels (coal and liquid gas) were identified as major contributors, accounting for 38% of these deaths.
- India was ranked as the second-highest emitter of PM2.5 globally in 2022, contributing 15.8% of consumption-based and 16.9% of production-based PM2.5 emissions.
- Impact of Heat Stress:
- In 2023, India experienced 2400 hours (or 100 days) of moderate to high heat stress, particularly during light outdoor activities like walking.
- Heatwaves have become more frequent, with adults over 65 years experiencing 8.4 heatwave days per year, a 58% increase from 1990-1999.
- This increased heat exposure has led to a loss of 181 billion labor hours globally, translating into an economic loss of approximately $141 billion.
- Global and National Trends in Air Pollution:
- PM2.5 is particularly hazardous because it is fine enough to enter the lungs and bloodstream, leading to severe health risks like respiratory and cardiovascular diseases.
- Nitrogen Dioxide (NO?), Sulphur Dioxide (SO?), Carbon Monoxide (CO), and Ozone (O?) were identified as other pollutants contributing to poor air quality in India.
- Health Impact of Extreme Weather:
- The 2023 heatwave was one of the hottest years on record, exacerbating health risks worldwide, especially for the elderly.
- Droughts and heatwaves also contributed to a rise in food insecurity, affecting millions globally.
- Disease Transmission and Climate Change:
- Dengue transmission potential rose by 85% from 1951-1960 to 2014-2023.
- Coastal areas suitable for the spread of Vibrio pathogens, which cause cholera, expanded by 23%, affecting over 210 million people.
- Health Effects of Fossil Fuel Pollution:
- Continued reliance on fossil fuels worsens air quality, leading to health problems such as respiratory diseases, cardiovascular issues, and adverse pregnancy outcomes.
Government Efforts to Tackle Air Pollution in India
- National Clean Air Programme (NCAP):
- NCAP is a national strategy to reduce air pollution across India, with specific action plans for 131 non-attainment cities. The initiative is supported through various central government schemes such as:
- Swachh Bharat Mission (Urban)
- Atal Mission for Rejuvenation and Urban Transformation (AMRUT)
- Smart City Mission
- Faster Adoption and Manufacturing of Hybrid and Electric Vehicles (FAME-II)
- NCAP is a national strategy to reduce air pollution across India, with specific action plans for 131 non-attainment cities. The initiative is supported through various central government schemes such as:
- Bharat Stage VI (BS-VI) Emission Norms:
- BS-VI standards aim to significantly reduce vehicular pollution, lowering permissible limits for NOx and particulate matter (PM) emissions from vehicles.
- System of Air Quality and Weather Forecasting and Research (SAFAR):
- SAFAR measures air quality and provides forecasts for metropolitan cities based on real-time data, helping authorities take preventive actions.
- Promotion of Renewable Energy:
- India achieved a record 11% of electricity from renewable energy in 2022. However, 71% of India’s electricity still comes from coal, underscoring the need for a faster transition to cleaner energy sources.
Greenhouse Gas Levels Hit Record High in 2023: World Meteorological Organization (WMO)

- 29 Oct 2024
In News:
According to the WMO, the last time the earth had a similar CO2 concentration was 3-5 million years ago, when temperatures were 2-3°C higher and sea levels were 10-20 metres higher than they are now
Key Highlights:
- Record High Greenhouse Gas (GHG) Levels:
- In 2023, annual mean carbon dioxide (CO2) levels rose by 2.3 parts per million (ppm), reaching a new record of 420 ppm.
- This marks the 12th consecutive year with an increase of over 2 ppm in CO2 levels.
- Historical Context:
- CO2 levels not seen in 3-5 million years, when temperatures were 2-3°C higher, and sea levels were 10-20 meters higher than they are today.
- Key GHGs at Record Highs:
- The globally averaged surface concentrations of CO2, methane, and nitrous oxide all reached new highs in 2023.
- Contributors to the Increase in CO2:
- Natural Variability: Natural factors such as large vegetation fires and reduced carbon absorption by forests contributed to higher CO2 levels.
- Human Activity: High fossil fuel emissions from human and industrial activities also played a major role.
- El Niño Phenomenon: The El Niño event led to higher temperatures and drier conditions, exacerbating the rise in GHG levels through increased wildfires and reduced carbon absorption by land sinks.
- Climate Feedback Loop Concerns:
- The WMO warned of a vicious cycle:
- Climate change could cause ecosystems to become larger sources of GHGs.
- Wildfires could release more carbon, and warmer oceans may absorb less CO2, leading to more CO2 remaining in the atmosphere, accelerating global warming.
- The WMO warned of a vicious cycle:
- Radiative Forcing:
- Radiative forcing (the warming effect on climate) from long-lived GHGs has increased by 51.5% from 1990 to 2023, with CO2 contributing 81% of this increase.
- Methane Concerns:
- Methane saw its largest three-year increase between 2020 and 2022.
- This increase was linked to warmer temperatures and wetter land conditions during the 2020-2022 La Niña conditions, which caused an uptick in methane emissions from natural wetlands.
- Long-Term Impact of CO2:
- Given CO2's long atmospheric lifetime, even with rapid emissions reductions, the warming effect will persist for several decades.
Emissions Gap Report 2024

- 28 Oct 2024
In News:
The United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP) recently published the Emissions Gap Report 2024, in anticipation of the COP29 meeting of the UNFCCC to be held in Baku, Azerbaijan.
Key Highlights:
- Current Trajectory of Global Warming:
- If countries continue with current environmental policies, global temperatures are expected to rise by 3.1°C above pre-industrial levels.
- This is significantly higher than the Paris Agreement target of limiting global warming to well below 2°C, with an effort to cap it at 1.5°C.
- Paris Agreement at Risk:
- Even if all Nationally Determined Contributions (NDCs) are fully implemented (including both unconditional and conditional emissions reduction targets), the world would still experience 2.6°C of warming by 2030.
- This presents a major challenge to achieving the Paris Agreement’s climate goals.
- Urgent Need for Action:
- To limit global warming to 1.5°C, greenhouse gas emissions must peak before 2025 and decline by 43% by 2030.
- The report highlights the emission gap between current pledges and what is required to meet the 1.5°C goal.
- Record High Emissions:
- Global greenhouse gas emissions hit a record 57.1 gigatons of CO? equivalent in 2023.
- This represents an increase of 1.3% compared to 2022, continuing the upward trend from the previous decade.
- India’s Emissions:
- India’s greenhouse gas emissions grew by 6.1% between 2022 and 2023.
- Per capita emissions in India were 2.9 tCO?e in 2022, significantly lower than China (11 tCO?e) and the U.S. (18 tCO?e).
- G20 Countries’ Contribution:
- G20 countries, excluding the African Union, contributed 77% of global emissions in 2023.
- The six largest emitters (including China, U.S., and India) were responsible for 63% of global emissions.
- This shows a significant imbalance in emissions, with developed countries having much higher per capita emissions compared to developing nations like India and Africa.
- Necessary Emissions Cuts:
- To keep the 1.5°C target within reach, global emissions need to be cut by at least 7.5% annually until 2035.
- Cost of bridging the emissions gap: Achieving net-zero by 2050 will require USD 900 billion to USD 2.1 trillion annually, approximately 1% of global GDP.
- Emission Reduction Pathways:
- Renewable Energy: Scaling up solar and wind energy technologies could contribute up to 27% of the required emissions reductions by 2030.
- Forest Conservation: Protecting and restoring forests could provide 20% of the required emissions reductions by 2030.
- Other crucial measures include improving energy efficiency, transitioning to electric vehicles, and focusing on fuel switching in key sectors like transport, industry, and buildings.
- Disparities in Emissions:
- Despite changes over the past two decades, large disparities remain between emissions across regions.
- Developed countries have three times higher per capita emissions compared to the global average, while India, the African Union, and least developed countries continue to have much lower emissions.
- Call to Action:
- UNEP Executive Director Inger Andersen urged countries to act now, stating: “No more hot air, please.” The urgency is to ramp up climate pledges and ensure stronger actions in the upcoming COP29 talks in Baku, Azerbaijan (November 2024), where nations must work to get on a 1.5°C pathway.
United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP)
- Established: 1972, following the United Nations Conference on the Human Environment in Stockholm.
- Headquarters: Nairobi, Kenya.
- Governing Body: The United Nations Environment Assembly (UNEA), which is the world’s highest-level decision-making body on environmental matters, with 193 Member States.
- Programs & Initiatives: UNEP leads global efforts on climate action, ecosystem restoration, clean seas, and supports the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs).
- Reports: UNEP publishes crucial assessments like the Emissions Gap Report, Global Environment Outlook, and Adaptation Gap Report, influencing global environmental policies.
Hong Kong Discovers Dinosaur Fossils

- 28 Oct 2024
In News:
Hong Kong discovers dinosaur fossils for the first time
Key Details:
-
- Significance: This marks the first-ever discovery of dinosaur fossils in Hong Kong.
- Time Period:The fossils date back to the Cretaceous Period, approximately 145 million to 66 million years ago.
- Fossil Details:The fossils belong to a large dinosaur, but further studies are required to determine the exact species.Initial analysis suggests the dinosaur may have been buried by sand and gravel after death, later being washed to the surface by a flood before being buried again.
- Site and Protection:Port Island, part of a geopark, is closed to the public to facilitate ongoing fossil investigations and excavation work.
- Geological and Archaeological Importance:The discovery underscores the significance of Hong Kong's geoparks and its role in preserving and showcasing natural history.This finding contributes to global understanding of prehistoric life, especially in the Cretaceous period.
2024 Global Nature Conservation Index (NCI)

- 28 Oct 2024
In News:
India with an abysmal score of 45.5 (out of 100) has been ranked 176th in the Global Nature Conservation Index, 2024.
India's Ranking and Score:
- Rank: India ranks 176th out of 180 countries.
- Score: 45.5 out of 100.
- Context: India is listed among the five "worst performers," alongside Kiribati (180), Turkey (179), Iraq (178), and Micronesia (177).
Key Factors Affecting India’s Ranking:
- Inefficient Land Management: The main contributing factor to India's low ranking.
- Threats to Biodiversity: Rising threats due to habitat loss, deforestation, climate change, and pollution.
- Deforestation: Between 2001 and 2019, India lost 23,300 sq. km of tree cover, exacerbating biodiversity loss.
Focus Areas of the Nature Conservation Index (NCI):
- Land Management: Inefficient land use practices, with 53% of land converted for urban, industrial, and agricultural purposes.
- Biodiversity Threats: Habitat loss, fragmentation, and declining populations of marine and terrestrial species.
- Governance and Capacity: Challenges in enforcement of laws and governance structures that support conservation.
- Future Trends: India faces both opportunities and challenges, given its high population density and rapid development.
Key Findings:
- Land Conversion and Urbanization: High rates of land conversion (53%) for development purposes, contributing to habitat loss.
- Soil Pollution: Issues with pesticide use and soil pollution (low nitrogen index of 0.77), affecting soil health.
- Marine Conservation: Only 0.2% of national waterways and none within the Exclusive Economic Zone (EEZ) are protected.
- Deforestation Impact: Loss of 23,300 sq. km of forest between 2001-2019.
- Biodiversity Decline: Despite 40% of marine species and 65% of terrestrial species in protected areas, biodiversity continues to decline—67.5% of marine species and 46.9% of terrestrial species face population decreases.
Marine and Terrestrial Conservation:
- Marine Areas: Need for greater investment in marine conservation, as India's marine protected areas (MPAs) are limited.
- Protected Areas: While 7.5% of India’s terrestrial area is protected, significant threats like climate change and habitat fragmentation persist.
Biodiversity and Climate Change:
- Climate Change Risks: Impacts on vulnerable ecosystems, including coral reefs and alpine regions, further threaten biodiversity.
- Population Growth: India’s rapidly growing population (one of the highest in the world) places constant pressure on natural resources and ecosystems.
Illegal Wildlife Trade:
- Global Ranking: India is the fourth-largest illegal wildlife trader globally, with an annual trade worth approximately £15 billion.
- Call for Action: Stronger enforcement of wildlife protection laws and international cooperation are crucial to combat illegal wildlife trade.
SDGs and India’s Conservation Challenges:
- SDG 14 (Life Below Water) and SDG 15 (Life on Land): India faces significant challenges in meeting these Sustainable Development Goals, particularly in protecting marine life and terrestrial ecosystems.
Recommendations for Improvement:
- Stronger Political Will: Political commitment is essential for passing laws that promote sustainable development and biodiversity conservation.
- Enforcement and Funding: Increased funding for environmental initiatives and better enforcement of conservation policies are necessary to address the conservation challenges.
- Sustainable Development: Integrating sustainable land use practices and improving governance structures for conservation are key areas for focus.
Pandemic Fund Project

- 27 Oct 2024
In News:
Recently, the Union Minister Shri Rajiv Ranjan Singh, Ministry of Fisheries, Animal Husbandry and Dairying launched the Pandemic Fund Project on "Animal Health Security Strengthening in India for Pandemic Preparedness and Response"in New Delhi.
Key Highlights:
Launch of Pandemic Fund Project
- Objective: Strengthening animal health security in India to enhance pandemic preparedness and response.
- Funding: $25 million initiative funded by the G20 Pandemic Fund.
- Location: New Delhi, Ministry of Fisheries, Animal Husbandry, and Dairying.
Context and Importance
- Livestock Sector: Crucial for socio-economic upliftment, contributing to employment and rural development.
- Growth in Livestock Sector: Significant progress in the last 9 years through schemes like the National Animal Disease Control Program (NADCP).
- Key Diseases Targeted:
- Foot and Mouth Disease (FMD): Aimed at eradication, with over 90.87 crore vaccines administered.
- Brucellosis: Over 4.23 crore vaccines administered.
Objectives of the Pandemic Fund Project
- Enhanced Disease Surveillance: Includes genomic and environmental monitoring for early warning systems.
- Laboratory Infrastructure Development: Upgradation for better diagnosis and disease management.
- Cross-Border Collaboration: Strengthening partnerships for global monitoring of zoonotic diseases.
- Integrated Monitoring System: Creation of a robust system for managing zoonotic diseases, with a focus on early detection and containment.
Documents Released for Strengthening Animal Health
- Standard Veterinary Treatment Guidelines (SVTG):
- Best practices for veterinary care to improve livestock health and productivity.
- Supports national action plans, especially for combating antimicrobial resistance.
- Crisis Management Plan (CMP) for Animal Diseases:
- Framework for effective response and containment during animal disease outbreaks.
- Ensures timely mitigation of animal disease crises.
One Health Approach
- Integration of Human, Animal, and Environmental Health: Key to preventing and managing future health crises.
- Zoonotic Risks: The project emphasizes reducing zoonotic disease transmission from animals to humans, crucial given the origins of many recent public health emergencies.
Implementation and Collaboration
- The project will be executed in collaboration with global institutions:
- Asian Development Bank (ADB)
- Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO)
- World Bank
Great Indian Bustard (GIB)
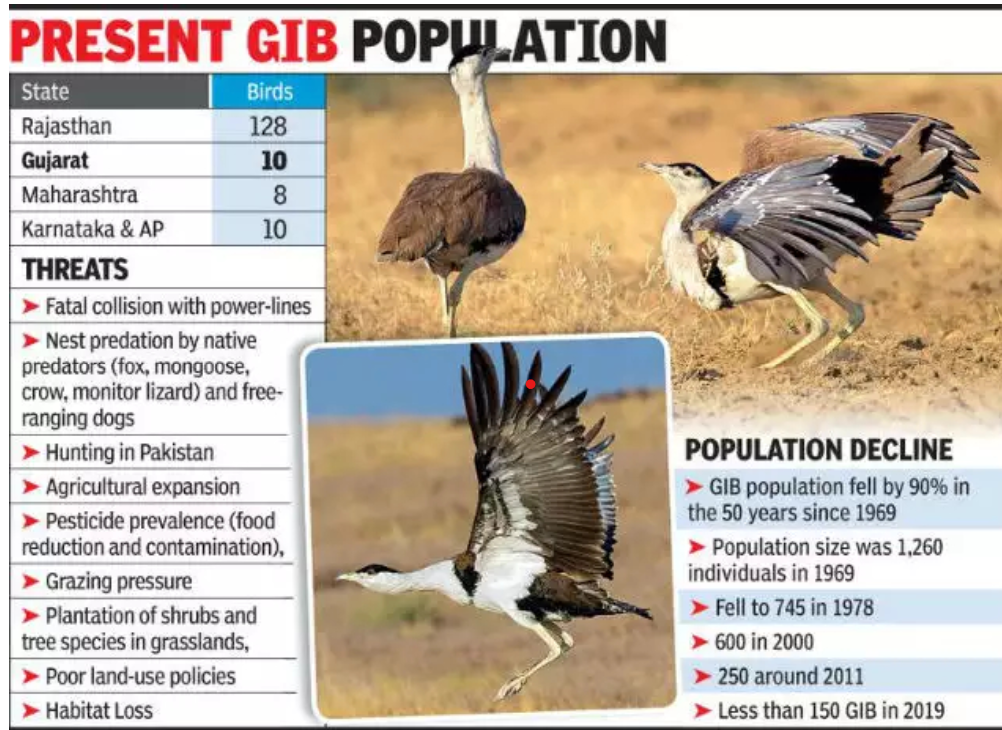
- 25 Oct 2024
A critically endangered Great Indian Bustard (GIB) chick was successfully born through artificial insemination (AI) at a breeding center in Jaisalmer, Rajasthan, marking a crucial step in efforts to save the species.
Endangered Status:
- The Great Indian Bustard is classified as critically endangered with fewer than 150 individuals left in the wild in India.
- About 90% of these birds are found in the desert areas of Rajasthan, with smaller populations in Gujarat, Maharashtra, Andhra Pradesh, and Karnataka.
Main Threats to the Species:
- Habitat Loss: The primary threat is the loss of habitat, which is often perceived as wasteland and is diverted for infrastructure projects like roads and development.
- Slow Reproductive Rate: The bustard’s low reproductive rate exacerbates its risk of extinction.
Conservation Efforts: Bustard Recovery Program
- In 2016, the Union Ministry of Environment, Forests and Climate Change launched the Bustard Recovery Program to focus on captive breeding and creating a sustainable environment for the reintroduction of GIBs into the wild.
- A dedicated GIB breeding center was set up at the Desert National Park in Jaisalmer, Rajasthan, as part of this initiative.
- Protection Status of GIB:
- IUCN: Critically Endangered
- CITES: Appendix 1
- Convention on Migratory Species (CMS): Appendix I
- Wildlife (Protection) Act, 1972: Schedule I
- It is also the state bird of Rajasthan, emphasizing its importance in the region’s biodiversity.
Tenkana

- 23 Oct 2024
In News:
- A team of arachnologists has discovered a new genus of jumping spiders, Tenkana, found across southern India and northern Sri Lanka.
- The discovery includes two previously known species, Tenkanamanu and Tenkanaarkavathi, and introduces a new species, Tenkanajayamangali, from Karnataka.
Name and Origin:
- The name Tenkana comes from the Kannada word for "south," reflecting the geographical region where all known species of this genus are found—southern India and northern Sri Lanka.
- The genus belongs to the Plexippina subtribe of jumping spiders, which is distinct from related genera like Hyllus and Telamonia.
Key Findings:
- Tenkanajayamangali was first discovered in Devarayanadurga reserve forest, Tumakuru district, Karnataka, at the origin of the Jayamangali river.
- The new species was identified through genetic analysis and physical examination, showing it did not match any known species.
Physical Characteristics:
- The male and female Tenkanajayamangali exhibit distinct physical differences.
- The male has pale hairs covering most of its carapace, while the female is grey with a pattern.
- The ocular area of T. jayamangali is uniformly covered with white hairs, in contrast to T. arkavathi and T. manu, which have distinctive markings.
Habitat and Distribution:
- Tenkana spiders are typically ground-dwelling and prefer dry, open habitats like short grasses, leaf litter, and rocky outcrops.
- These spiders have been observed in Tamil Nadu, Puducherry, Karnataka, Telangana, Andhra Pradesh, and some areas in Sri Lanka.
- The male and female spiders of T. jayamangali were discovered in different regions, 2 km apart, at the hilltop and foothills of the same forest.
Ecological and Behavioral Insights:
- The Tenkana genus is considered endemic to India, with species observed in diverse regions such as Bengaluru, Yercaud (Tamil Nadu), and Bannerghatta (Karnataka).
- These spiders are found in complex microhabitats, like shaded short grasses with dry leaf litter or rocky outcrops in relatively dry habitats.
- The movement of Tenkana spiders resembles that of Stenaelurillus, another ground-dwelling spider species.
The case for a nature restoration law in India

- 22 Oct 2024
In News:
The Nature Restoration Law (NRL), which was enacted by the European Union (EU), is an inspiring model from which India can draw points to tackle its growing environmental crises.
Background of the NRL in the EU
- The Nature Restoration Law (NRL) was enacted by the European Union (EU) to restore ecosystems and combat biodiversity loss.
- Adopted on June 17, 2024, by the EU’s Environmental Council.
- Key objectives:
- Restore 20% of EU’s land and sea areas by 2030.
- Achieve full restoration of all ecosystems by 2050.
- Part of the EU’s Biodiversity Strategy for 2030 and European Green Deal.
- Target Areas:
- Forests, agricultural lands, rivers, urban spaces.
- Restoration measures include:
- 25,000 km of free-flowing rivers.
- Planting 3 billion trees by 2030.
- Global Impact: NRL is a critical tool in reversing Europe’s biodiversity loss, where 80% of habitats are in poor condition.
Environmental Crisis in India
- Land Degradation:
- 29.7% of India’s total geographical area is affected by land degradation (as per ISRO’s Desertification and Land Degradation Atlas, 2018-19).
- 97.85 million hectares of land degraded, with a significant increase since 2003-05.
- Major desertification hotspots in Gujarat, Karnataka, Maharashtra, and Rajasthan.
- Desertification: A growing concern, affecting 83.69 million hectares in 2018-19.
- Ongoing Efforts:
- Green India Mission, Pradhan Mantri Krishi Sinchayee Yojana, and National Afforestation Programme have had positive effects.
- Integrated Watershed Management Programme is the second-largest watershed programme globally.
Need for a Comprehensive Nature Restoration Law in India
- The scale of India’s environmental challenges requires a comprehensive nature restoration law similar to the EU’s NRL.
- The law should have legally binding targets to restore degraded landscapes and ensure ecosystem sustainability.
Key Features of an Indian Nature Restoration Law
- Restoration Targets:
- 20% of degraded land to be restored by 2030.
- Full restoration of ecosystems (forests, wetlands, rivers, agricultural lands, urban spaces) by 2050.
- Wetland Restoration:
- Target restoring 30% of degraded wetlands by 2030.
- Priority wetlands like Sundarbans and Chilika Lake play critical roles in biodiversity and carbon sequestration.
- Biodiversity in Agriculture:
- Promote agroforestry and sustainable agriculture practices.
- Use biodiversity indicators (e.g., butterfly or bird index) to monitor progress.
- River Restoration:
- Focus on free-flowing rivers such as the Ganga and Yamuna.
- Address pollution, obstructions, and ecosystem damage in major rivers.
- Urban Green Spaces:
- Ensure no net loss of urban green spaces.
- Promote urban forests in cities like Bengaluru and Delhi, where urban heat islands and air quality degradation are prominent.
Economic and Social Benefits of Ecosystem Restoration
- Global Economic Impact:
- Nature restoration could generate $10 trillion annually by 2030 (World Economic Forum estimate).
- Benefits for India:
- Agricultural Productivity: Restoring degraded land will enhance farm productivity.
- Water Security: Improved land restoration will contribute to better water availability.
- Job Creation: Millions of rural jobs could be created through ecosystem restoration efforts.
- Contributing to SDGs:
- The law would help India meet SDG 15 (sustainable management of forests, combating desertification).
- Climate Change Mitigation:
- Restoring ecosystems can help India enhance its carbon sinks, which is crucial for meeting Paris Agreement targets.
- Degraded lands lose their capacity to absorb carbon dioxide, contributing to global warming.
IAEA’s 2024 Climate Change and Nuclear Power Report

- 22 Oct 2024
In News:
- The 2024 edition of the IAEA’s Climate Change and Nuclear Power report has been released, highlighting the need for a significant increase in investment to achieve goals for expanding nuclear power.
- The new report was launched last week on the margins of the Clean Energy Ministerial (CEM) in Brazil.
Key Highlights:
- Nuclear Power's Role in Climate Change Mitigation:
- Nuclear energy is gaining global interest as nations seek to enhance energy security and decarbonize economies.
- To meet net-zero emissions by 2050, nuclear power is projected to play a pivotal role, with a projected capacity increase of 2.5 times the current level by mid-century in the IAEA's high case scenario.
- Investment Needs for Nuclear Expansion:
- Annual investment required to meet the IAEA's high case scenario (2050 nuclear capacity) is USD 125 billion, a significant increase from USD 50 billion annually from 2017-2023.
- If the aspirational goal to triple nuclear capacity (as pledged by over 20 countries at COP28) is to be met, USD 150 billion annually would be necessary.
- Challenges in Financing: Upfront capital for nuclear power plants is expensive, posing challenges, especially in market-driven economies and developing countries.
- Private Sector and Multilateral Support:
- The private sector will need to play a larger role in financing nuclear projects.
- The IAEA is engaging with multilateral development banks to improve financing options for developing countries to invest in nuclear energy.
- Private finance initiatives: In September 2024, 14 major financial institutions signaled readiness to help fund nuclear newbuild projects.
- Nuclear Financing at Clean Energy Ministerial (CEM):
- The IAEA report was launched during the 15th CEM in Brazil, a high-level forum for advancing clean energy technologies.
- Key stakeholders from Brazil, the IAEA, the International Energy Agency (IEA), and the U.S. discussed strategies for securing nuclear power financing, especially in the context of COP29 (2024) where clean energy financing will be a key focus.
- Nuclear Energy in the EU’s Sustainable Financing:
- The EU taxonomy for sustainable activities now includes nuclear power, facilitating the issuance of green bonds for nuclear projects in Finland and France (2023).
- EDF received €4 billion in green bonds and around €7 billion in green loans (2022-2024).
- Investment in Nuclear Power:
- To meet global climate goals, nuclear power capacity must increase by 1.8 times by 2035.
- Effective financing mechanisms are crucial to scale up nuclear power and develop the workforce and supply chains needed for the energy transition.
- Policy Reform and International Partnerships:
- The report advocates for policy reforms and international partnerships to bridge the financing gap and accelerate nuclear power deployment, particularly in emerging markets and developing economies.
- Focus on technologies such as small modular reactors (SMRs), which could play a role in the energy transition.
- Key Areas to Support Nuclear Growth:
- Robust regulatory frameworks and new delivery models are essential to unlock investments.
- Development of skilled labor and effective stakeholder engagement is crucial for the expansion of nuclear energy.
- Energy System Modelling and Planning:
- The IAEA’s energy system modelling tools assist countries like Brazil in planning nuclear power projects, including cost analyses for electricity generation and financing strategies.
Role of the International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA):
- Mandate: The IAEA is the leading international body for promoting the safe, secure, and peaceful use of nuclear energy and technologies.
- Functions:
- Nuclear safeguards: Ensuring nuclear activities remain peaceful and preventing the diversion of nuclear materials for weapons purposes.
- Assisting member states with technical support, knowledge sharing, and strengthening nuclear safety and security.
- The IAEA also supports capacity-building and emergency response in case of nuclear or radiological incidents.
- Structure:
- The IAEA General Conference is made up of all 178 member states, meeting annually to approve budgets and policies.
- The Board of Governors (35 members) meets several times a year to oversee the agency's activities and appointments.
- Headquarters: Vienna, Austria
- The IAEA is part of the United Nations family, reporting to both the UN General Assembly and the Security Council.
Funga Taxonomic Kingdom

- 21 Oct 2024
In News:
- Chile and the United Kingdom have prepared a proposal to recognize fungi as an independent kingdom, termed "Funga", alongside flora (plants) and fauna (animals).
- This will be presented at the 16th Conference of Parties (COP16) of the UN Convention on Biological Diversity (CBD), to be held in Cali, Colombia in October 2024.
- Why Funga?
- Fungi (e.g., mushrooms, moulds, yeast, lichen) play crucial ecological roles, but have historically been overlooked in conservation strategies.
- Fungi contribute significantly to decomposition, forest regeneration, carbon sequestration, and the global nutrient cycle.
- The recognition aims to strengthen fungal conservation by integrating fungi into global legislation and policies.
- Ecological Importance of Fungi:
- Decomposition: Fungi break down organic matter, facilitating nutrient recycling in ecosystems.
- Symbiotic Relationships: Many fungi form crucial symbiotic relationships with plants (e.g., mycorrhizal associations) and animals.
- Climate Mitigation: Boreal forest fungi absorb large amounts of carbon through symbiosis with plants, playing a role in mitigating climate change.
- Pollution Remediation: Fungi can help clean polluted soils by breaking down toxins.
- Food Production: Fungi are essential for producing common foods like bread, cheese, wine, beer, and chocolate.
- Health: Fungi produce antibiotics (e.g., penicillin) and aid in mammalian digestion.
- Scientific Recognition:
- In August 2021, the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) recognized fungi as one of the three kingdoms of life, alongside plants and animals.
- The 3F initiative (Flora, Fauna, and Funga), led by Giuliana Furci, aims to promote the international recognition and protection of fungi.
- Diversity and Research Gaps:
- Only 8% of the estimated 2.2 to 3.8 million fungal species have been formally described.
- Approximately 2,000 new fungal species are discovered annually, indicating the vast underexplored diversity of fungi.
- Threats to Fungi:
- Fungi face significant threats from deforestation, climate change, pollution, overharvesting, and fungicide use.
- These threats disrupt the symbiotic relationships fungi share with plants and animals, leading to ecosystem instability.
- Nitrogen enrichment in soils and habitat loss further exacerbate these risks.
Key Facts About Fungi
- Biological Characteristics:
- Fungi are eukaryotic organisms with rigid cell walls made of chitin (distinct from the cellulose found in plant cell walls).
- They are heterotrophic, meaning they absorb nutrients from their environment through external digestion (secreting enzymes to break down organic material before absorption).
- Reproductive Strategies:
- Fungi reproduce both asexually (via spores) and sexually, ensuring their proliferation across ecosystems.
- Growth Form:
- Fungi grow primarily as mycelium, a network of hyphae (filamentous structures) that helps in nutrient absorption and environmental interaction.
- Symbiotic Relationships:
- Fungi form mycorrhizal relationships with plants, enhancing nutrient exchange, and lichen associations with algae, providing mutual benefits in extreme environments.
COP16 to the Convention on Biological Diversity (CBD)

- 20 Oct 2024
In News:
The 16th Conference of the Parties (COP16) to the Convention on Biological Diversity (CBD) will take place in Cali, Colombia, from October 21, 2024. This marks the first gathering since the adoption of the Kunming-Montreal Global Biodiversity Framework (KMGBF) in 2022.
About Convention on Biological Diversity (CBD)
- Adopted in 1992, the CBD is the most comprehensive international treaty focused on biodiversity conservation, the sustainable use of natural resources, and the fair sharing of benefits derived from genetic resources. It has been ratified by 196 countries, making it a key global instrument for biodiversity governance.
Key Objectives of the CBD
- Conservation of Biodiversity: Protecting genetic, species, and ecosystem diversity.
- Sustainable Use of Resources: Ensuring resources are used in a way that does not deplete or degrade biodiversity.
- Fair Sharing of Benefits: Ensuring that benefits from genetic resources are shared equitably with countries of origin.
Notable Frameworks within CBD
- Nagoya Protocol (2010): Establishes a framework for the fair and equitable sharing of benefits from the utilization of genetic resources.
- Cartagena Protocol (2000): Regulates the transboundary movement of living modified organisms (LMOs) resulting from modern biotechnology.
The Kunming-Montreal Global Biodiversity Framework (KMGBF)
- Adoption: The KMGBF was adopted at COP15 in 2022, following the Kunming Declaration.
- Targets: The framework includes 23 targets for 2030 and 4 global goals for 2050, aimed at reversing biodiversity loss and promoting sustainability.
- Notably, the 30x30 Target aims for 30% of the world’s land and oceans to be conserved by 2030. This is a key agenda item at COP16.
- The framework also emphasizes equitable access to genetic resources and the sharing of benefits from their use (Target 13).
Challenges and Issues at COP16
- Benefit-Sharing from Digital Sequence Information (DSI):
- A key issue is the fair sharing of benefits from digital sequence information (DSI) on genetic resources. The adoption of a global mechanism for this issue is still pending, as negotiations between developed and developing countries remain unresolved.
- Developed nations advocate for unrestricted access to genetic materials in exchange for voluntary contributions to a global fund.
- Developing nations seek a more equitable system, aligned with the CBD's principles of fair benefit-sharing.
- A key issue is the fair sharing of benefits from digital sequence information (DSI) on genetic resources. The adoption of a global mechanism for this issue is still pending, as negotiations between developed and developing countries remain unresolved.
- 30x30 Target Progress:
- The 30x30 target, which aims to conserve 30% of land and oceans by 2030, is far from being met:
- 17.5% of land and 8.4% of oceans are currently under protection.
- Concerns persist about the effectiveness of these protected areas, as studies suggest they may not be sufficient for long-term biodiversity conservation.
- The 30x30 target, which aims to conserve 30% of land and oceans by 2030, is far from being met:
- Financial Commitments (Target 19):
- Developed countries have pledged $20 billion annually for biodiversity financing by 2025. However, progress is slow:
- By September 2024, only $8.2 billion (41% of the target) had been committed.
- COP16 will assess whether this target can be met, with further announcements expected.
- Developed countries have pledged $20 billion annually for biodiversity financing by 2025. However, progress is slow:
- Implementation Gaps:
- Countries are required to set national targets aligned with the KMGBF. As of COP16, only 100 parties have submitted their targets, and 30 countries have updated their National Biodiversity Strategies and Action Plans (NBSAPs).
- A significant implementation gap remains in translating these targets into concrete actions.
Focus Areas for COP16
- Strengthening the 30x30 Target:
- COP16 will push for enhanced efforts to meet the 30x30 conservation goal. There is a need for better management and monitoring of protected areas to ensure they contribute to biodiversity preservation.
- Finalizing Benefit-Sharing Mechanism:
- Countries will focus on finalizing the multilateral benefit-sharing mechanism for genetic resources and DSI. The goal is to ensure that countries benefiting from genetic resources share those benefits with the countries of origin, addressing the issue of biopiracy and ensuring equitable access.
- Financial Commitment and Tracking:
- The financial shortfall for biodiversity conservation will be a critical discussion point. Effective monitoring of the biodiversity finance tracker will be needed to ensure that developed countries meet their $20 billion/year commitment.
- Addressing Implementation Gaps:
- There is a need to enhance monitoring and reporting mechanisms, improve national strategies, and align financial support with on-ground conservation efforts.
National Green Hydrogen Mission

- 19 Oct 2024
In News:
- The Union Government has sanctioned three pilot projects under the National Green Hydrogen Mission to explore the use of green hydrogen in steel production.
- The initiative aims to demonstrate safe and efficient hydrogen-based steelmaking processes, validate their technical feasibility, and evaluate economic viability for low-carbon steel production.
- Objectives of the Scheme:
- Identify and test advanced technologies for utilizing green hydrogen in the steel sector.
- Demonstrate safe and secure operation of hydrogen-based steel production.
- Validate technical and economic feasibility, contributing to decarbonization of iron and steel manufacturing.
- Pilot Project Components:
-
- 100% Hydrogen-based Direct Reduced Iron (DRI) using vertical shaft furnaces.
- Hydrogen use in Blast Furnace to reduce coal/coke consumption.
- Hydrogen injection in vertical shaft-based DRI units.
-
- Sanctioned Pilot Projects:
- Matrix Gas and Renewables Ltd
- Capacity: 50 tons per day (TPD).
- Consortium Partners: Gensol Engineering Ltd, IIT Bhubaneswar, Metsol AB (Sweden).
- Simplex Castings Ltd
- Capacity: 40 TPD.
- Consortium Partners: BSBK Pvt. Ltd., Ten Eight Investment, IIT Bhilai.
- Steel Authority of India Ltd (SAIL)
- Capacity: 3,200 TPD (Ranchi).
- Financial Support:
- Total Government Funding: ?347 crore for the three projects.
- These pilot projects are expected to be commissioned within the next three years and may serve as a blueprint for scaling up such technologies in India.
- About the National Green Hydrogen Mission:
- Launched: January 4, 2023.
- Total Budget: ?19,744 crore (up to FY 2029-30).
- Primary Goal: Establish India as a global hub for green hydrogen production and export while fostering decarbonization in sectors like steel, mobility, and energy.
- Key Features of the Mission:
- SIGHT (Strategic Interventions for Green Hydrogen Transition):
- Supports domestic manufacturing of electrolysers and promotes the production and use of green hydrogen.
- Expected Outcomes by 2030:
- Green Hydrogen Production: At least 5 million metric tons (MMT) annually.
- Renewable Energy: Addition of 125 GW in renewable energy capacity.
- Investment: Over ?8 lakh crore in green hydrogen technologies.
- Employment: Creation of 6 lakh jobs.
- Reduction in Fossil Fuel Imports: Savings of over ?1 lakh crore.
- GHG Emissions Reduction: Avoidance of nearly 50 MMT of annual greenhouse gas emissions.
- SIGHT (Strategic Interventions for Green Hydrogen Transition):
- Phase-wise Implementation:
- Phase I (2022-26): Focus on demand creation and initial deployment in existing hydrogen-using sectors (like steel and mobility).
- Phase II (2026-30): Expansion to new sectors with a push toward commercialization of green hydrogen.
The National Green Hydrogen Mission aims to significantly decarbonize India’s steel sector and other industries by leveraging hydrogen technology. With ?347 crore allocated for pilot projects in steelmaking, the initiative sets the stage for scalable, low-carbon steel production, contributing to India's clean energy transition and supporting its goal to become a global leader in green hydrogen.
Haber-Bosch process
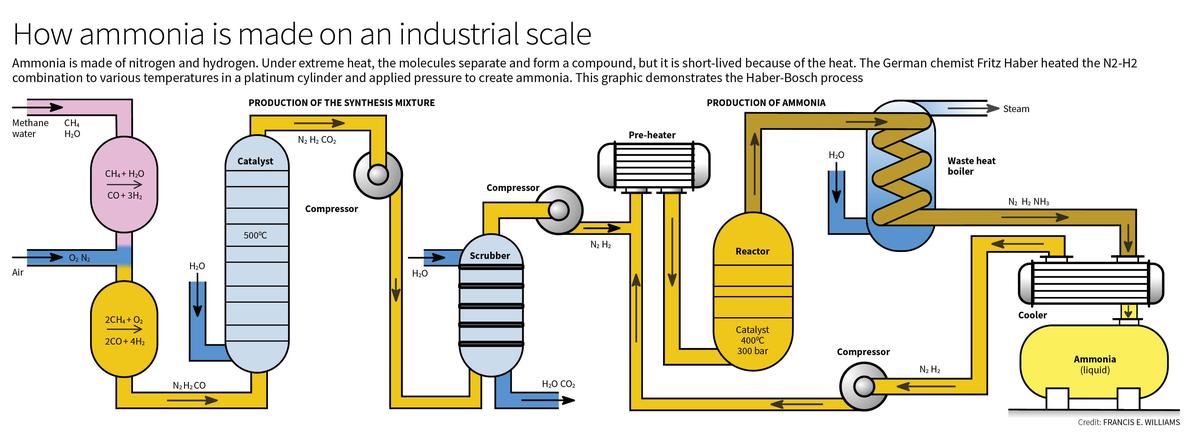
- 15 Oct 2024
In News:
The Haber-Bosch process has fundamentally transformed agricultural practices and global food production, enabling the conversion of atmospheric nitrogen into ammonia, which is essential for fertilizers.
The Nitrogen Molecule
- Composition: Nitrogen primarily exists as molecular nitrogen (N?) in the atmosphere, where two nitrogen atoms are bonded with a strong triple bond. This bond is very stable and requires significant energy (946 kJ/mol) to break, rendering N? largely inert and unavailable for direct use by plants.
Nitrogen in Nature
- Natural Fixation: In nature, the energy required to break the N? bond is typically provided by phenomena like lightning, which converts nitrogen to reactive forms such as nitrogen oxides (NO and NO?). These can subsequently form nitric acid when they react with water, depositing reactive nitrogen through rainfall.
- Microbial Processes: Certain bacteria, including Azotobacter and Rhizobia, can fix atmospheric nitrogen into reactive forms, supporting plant growth. Azolla, a fern with a symbiotic cyanobacterium, also helps in nitrogen fixation.
The Nitrogen Cycle
- Plant Uptake: Plants absorb reactive nitrogen in the form of ammonium (NH??) and nitrate (NO??) from the soil, essential for synthesizing proteins and other vital compounds. Humans and animals rely on plants for their nitrogen intake.
- Cycle Completeness: While nitrogen is returned to the soil through excretion and decomposition, some is lost back to the atmosphere as N?. This loss contributes to the depletion of soil nitrogen, especially in crops that do not fix their own nitrogen.
Ammonia Production
- Haber-Bosch Process: This process synthesizes ammonia from nitrogen and hydrogen under high pressure and temperature, using a catalyst to enhance efficiency. Initially developed by Fritz Haber and scaled by Carl Bosch, this method became the backbone of modern fertilizer production.
Benefits and Downsides of Fertilizers
- Food Security: The Haber-Bosch process has significantly increased food production, contributing to a remarkable rise in global food supply and preventing widespread hunger. It is estimated that one-third of the world’s population relies on fertilizers produced via this process for their food.
- Environmental Impact: The widespread use of nitrogen fertilizers can lead to environmental issues:
- Excess Nutrients: Over-application can result in nutrient runoff into water bodies, causing eutrophication, which depletes oxygen and harms aquatic life.
- Acid Rain: Reactive nitrogen can contribute to acid rain, affecting soil health and biodiversity.
- Soil Degradation: Continuous fertilizer use without adequate replenishment of nutrients can degrade soil quality over time.
While the Haber-Bosch process is crucial for modern agriculture and food security, it also presents significant environmental challenges. The balance between using fertilizers effectively and sustainably is essential to ensure that technological advancements do not come at the cost of ecological health. As such, addressing food security requires not just technological innovation, but also thoughtful political and social engagement to manage resources responsibly.
Unexpected Transformation of the Sahara Desert
- 10 Oct 2024
In News:
The Sahara Desert, one of the driest regions globally, is undergoing a surprising transformation due to an extratropical cyclone that impacted northwestern Africa on September 7-8, leading to patches of green across Morocco, Algeria, Tunisia, and Libya.
Key Details:
- Satellite Observations: NASA's satellite images reveal extensive greenery sprouting in areas typically known for drought conditions, as reported by NASA’s Earth Observatory.
- Flourishing Vegetation: Climate researcher Sylwia Trzaska noted that shrubs and trees are thriving in low-lying regions like riverbeds. Peter de Menocal, president of the Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution, highlighted that plant life can quickly respond to significant rainfall, transforming dunes into vibrant landscapes.
- Historical Context: Research indicates that the Sahara was once a lush environment with lakes and vegetation between 11,000 and 5,000 years ago. Recent heavy rains have replenished normally dry lakes.
- Rainfall Dynamics: The unusual rainfall event is attributed to the northward shift of the Intertropical Convergence Zone (ITCZ), which has moved further north than usual, resulting in equatorial-like downpours in the Sahara. Some areas experienced over half a foot of rain, surpassing typical annual precipitation levels.
- Impact of Rain Patterns: While the rains primarily affected less populated regions, severe flooding has resulted in over 1,000 fatalities and impacted around four million people across 14 African nations, according to reports from the World Food Programme and Associated Press.
- Climate Change Factors: Experts suggest that the repositioning of the ITCZ may be connected to record-high ocean temperatures and climate change, potentially altering rainfall patterns across Africa.
- Future Projections: As global ocean temperatures stabilize, de Menocal predicts that the rain belt may revert to a more southerly position, potentially crossing the equator.
- Sahara Desert Facts:
o The Sahara is the world's largest hot desert, spanning approximately 4,800 km in length and 1,800 km in width.
o It covers about 31% of the African continent, extending across 11 North African nations, including Algeria, Egypt, Mali, Morocco, Western Sahara, Tunisia, Chad, Libya, Mauritania, Niger, and Sudan
Caracal

- 10 Oct 2024
In News:
The Gujarat government has recently announced plans to establish a Caracal Breeding and Conservation Center in the Chadva Rakhal area of Kutch, with a budget of ?10 crore.
About the Caracal
- The caracal, known locally as "siya gosh" (meaning "black ear" in Persian), is a reclusive and primarily nocturnal feline celebrated for its agility and remarkable skill in catching birds mid-flight.
- In terms of nesting, caracals typically utilize abandoned porcupine burrows or rock crevices for denning and are often found with their young hidden among dense vegetation. They tend to live in small groups, and their elusive behavior makes them hard to spot in the wild.
Habitat and Distribution
Caracals inhabit various environments, including woodlands, savannahs, and scrub forests. In India, suitable habitats are found in regions such as Kutch, the Malwa Plateau, the Aravalli hills, and Bundelkhand. This species is also present in numerous countries across Africa, the Middle East, Central Asia, and South Asia.
Threats to Survival
The caracal faces significant threats from extensive hunting, illegal wildlife trade, and the destruction of its natural habitats.
Conservation Status
According to the IUCN, the caracal is classified as "Least Concern." In India, it is protected under Schedule I of the Wildlife (Protection) Act, 1972.
Increasing Frequency of Typhoons in Southeast Asia
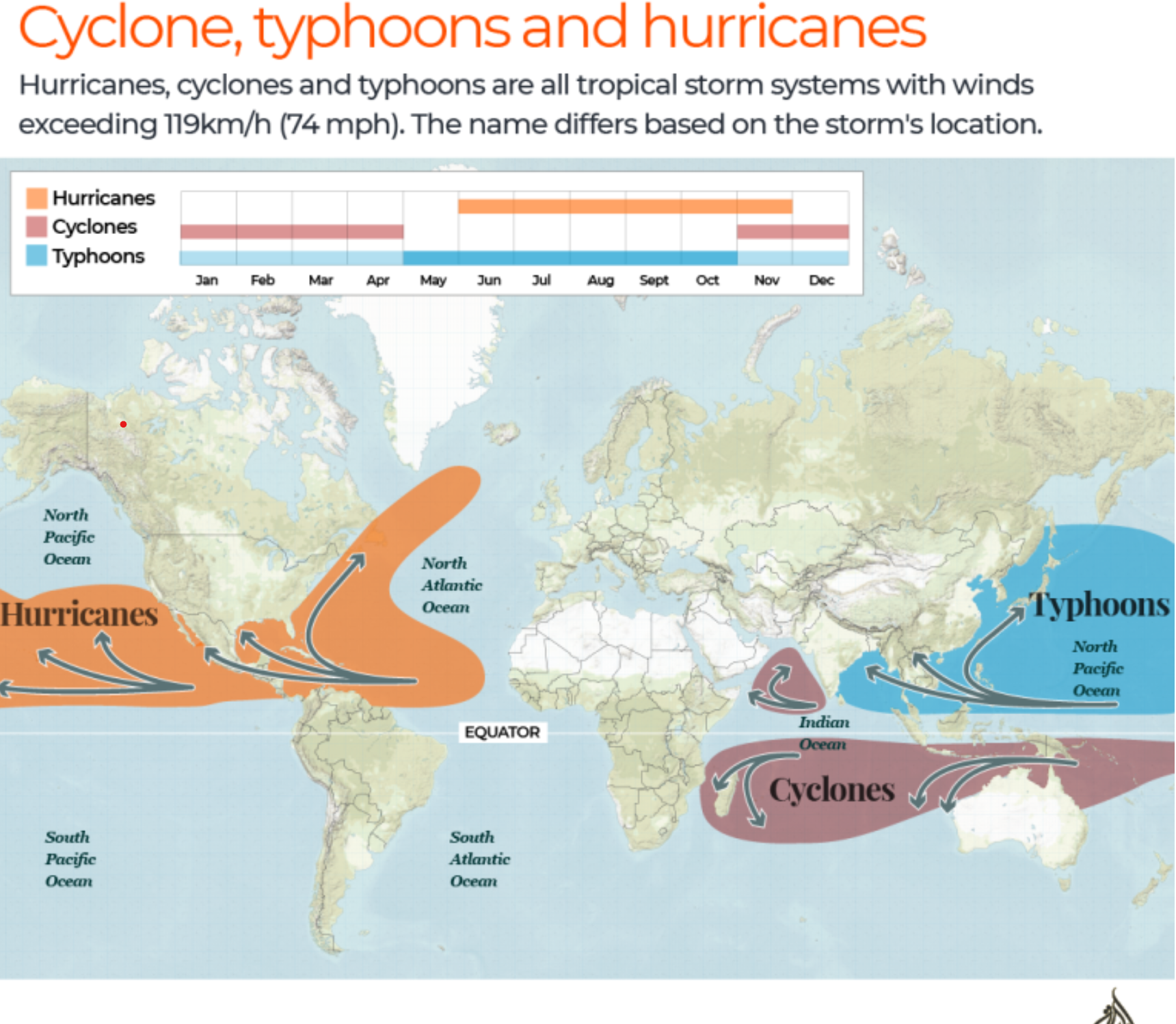
- 07 Oct 2024
In News:
Overview of Typhoons
- Definition: A typhoon is a type of cyclone with wind speeds of 119 km/h or more, forming over warm ocean waters near the equator.
- Mechanism: As warm, moist air rises from the ocean, it creates a low-pressure system, leading to the characteristic circular wind patterns: anticlockwise in the Northern Hemisphere and clockwise in the Southern Hemisphere.
Recent Typhoon Events
- Typhoon Yagi: The most powerful tropical cyclone in Asia in 2024, with peak winds of 260 km/h. It caused significant destruction across Myanmar, Vietnam, Laos, and Thailand, displacing around 631,000 people and resulting in over 500 fatalities.
- Typhoon Bebinca: Reached wind speeds of 151 km/h, classified as a Category 1 storm, impacting eastern China with heavy rainfall and forcing evacuations for over 414,000 residents.
- Typhoon Shanshan: Affected Japan, bringing severe weather conditions.
Why are Typhoons more frequent?
- Rising Sea Surface Temperatures:
- Global warming has raised ocean temperatures, providing more energy for typhoon formation and intensification.
- Atmospheric Circulation Changes:
- Alterations in patterns, such as the weakening of the Walker Circulation, affect the frequency and paths of typhoons.
- El Niño and La Niña Effects:
- The El Niño-Southern Oscillation significantly influences typhoon activity. El Niño years often lead to increased typhoon occurrences in Southeast Asia, while La Niña can enhance cyclone activity in the Western Pacific.
- Increased Atmospheric Moisture:
- Higher global temperatures result in more evaporation, adding moisture to the atmosphere, which fuels stronger storms and increases rainfall intensity.
- Geographical Vulnerability:
- Southeast Asia’s location near warm ocean currents makes it a hotspot for typhoon activity, particularly along its extensive coastlines.
- Marine Heat Waves:
- Climate change has led to more frequent marine heat waves, causing extreme ocean warming, which contributes to intensified storms.
- Weaker Land-Sea Temperature Gradients:
- Changes in temperature differences between land and sea can prolong storm duration and severity.
- Urbanization and Environmental Degradation:
- Rapid urban development and the destruction of coastal ecosystems, like mangroves, diminish natural barriers against storm impacts.
Humanitarian Impact and Response
- The increasing intensity and frequency of typhoons have precipitated severe humanitarian crises in affected regions. The need for international cooperation in disaster response has become critical, involving collaboration among governments, civil societies, and humanitarian organizations to provide aid and support for those affected.
- Understanding the multifaceted reasons behind the rising frequency of typhoons is crucial for developing effective strategies to mitigate their impacts and enhance community resilience in Southeast Asia.
Discovery of New Hammerhead Shark Species

- 06 Oct 2024
In News:
A team of marine biologists led by a Florida International University researcher has described a new species of the shark genus Sphyrna from the Caribbean and the Southwest Atlantic.
- New Species: Named Sphyrna alleni (common name: shovelbill shark).
- Habitat: Found in coastal waters, estuaries, coral reefs, and seagrass beds from Belize to Brazil, with confirmed presence in:
- Caribbean: Belize, Panama, Colombia, Trinidad and Tobago.
- Southwestern Atlantic: Brazil.
- Characteristics:
- Small species, less than 1.5 m in length.
- Distinctive flat, shovel-shaped head lacking indentations on the anterior edge.
- Different from Sphyrna tiburo:
- More rounded anterior margin.
- Absence of lobules on the posterior margin.
- Higher precaudal vertebral count (80-83 vs. ~73 in Sphyrna tiburo).
- Evolutionary Insight: Possible sister lineage to Sphyrna vespertina, suggesting Sphyrna tiburo diverged later.
- Conservation Status:
- Hammerhead sharks are highly threatened, primarily due to overfishing.
- Most species, except Sphyrna gilberti, are listed as Vulnerable, Endangered, or Critically Endangered by the IUCN.
- Current IUCN assessment of Sphyrna tiburo as Globally Endangered may need reevaluation considering the new findings.
- Management Recommendations:
- Increased management efforts needed for Sphyrna alleni, particularly restrictions on gillnets and trawls, which significantly impact this species.
- Publication: Findings reported in the journal Zootaxa.
Status of Elephant in India 2022-23

- 05 Oct 2024
In News:
- Shelved Census Report: The Environment Ministry has delayed the release of the elephant census report, “Status of Elephant in India 2022-23,” due to a lag in the Northeast census, with publication on hold until at least June 2025.
- Population Decline: Preliminary data from the report indicates significant drops in elephant populations across several regions:
- Southern West Bengal: 84% decline
- Jharkhand: 64% decline
- Odisha: 54% decline
- Kerala: 51% decline
- Developmental Threats: The report cites “mushrooming developmental projects,” including unregulated mining and infrastructure development, as major threats to elephant populations.
- Methodological Concerns: The Environment Ministry noted that refined counting methods could explain some discrepancies, suggesting new data may not be directly comparable to previous censuses conducted every five years since the 1990s.
- Old Counting Methods:
- Pre-2002: Elephants were counted using the “total direct count” method, which involved simple head counts but lacked scientific rigor for larger populations.
- 2002: Introduction of the “indirect dung count” method, where dung samples were used to estimate density based on decay rates.
- Sample Block Counts: Modified methods involved surveying limited areas (5 sq km) to improve detection accuracy.
- Elephants vs. Tigers: In 2021, a harmonized approach for estimating elephant and tiger populations was proposed, utilizing a similar block and co-variate methodology for both species.
- Genetic Mark-Recapture: The 2022-23 elephant census employed a genetic mark-recapture model using dung samples to identify individual elephants.
- Impact of Delay: Experts argue that withholding the available data hinders conservation efforts and governance. Delays could exacerbate the plight of elephant populations, particularly in regions facing specific threats, such as mining in Odisha.
Key Findings of the Unreleased Report:
- Overall Decline: The overall elephant population has decreased by 20% since 2017, with some areas reporting reductions of up to 41%.
- Regional Impact:
- Southern West Bengal, Jharkhand, and Odisha have seen losses of nearly 1,700 elephants.
- The Western Ghats region indicates an 18% decline.
- Northeast Region: The census for this area relies on extrapolated data from 2017, with approximately one-third of India's elephants located there.
- Contributing Factors: Habitat fragmentation, poaching, and human-elephant conflicts due to developmental activities are major threats.
- Conservation Recommendations: Strategies to strengthen elephant corridors, restore habitats, and enhance community involvement in conservation are vital.
- Challenges in the Northeast: Urban development, mining, and agriculture significantly threaten elephant movement and survival, underscoring the need for targeted conservation strategies.
- Conservation Status of Elephants in India:
- Leading States: Karnataka, Assam, and Kerala have the highest elephant populations.
- Conservation Status: Elephants are classified as Endangered on the IUCN Red List and are protected under multiple international conventions.
- Threats to Elephants:
- Habitat Loss: Rapid human population growth is diminishing elephant habitats.
- Fragmentation: Habitat disruption from construction and development projects is prevalent.
- Unlawful Killing: Human-elephant conflict often leads to retaliatory killings.
- Poaching: Targeting of male elephants for tusks continues to threaten genetic diversity.
- Conservation Measures:
- Financial support under various government schemes for habitat conservation and human-elephant conflict resolution.
- Establishment of 33 Elephant Reserves across 14 states.
- Collaborative efforts with railways and power departments to mitigate risks.
- Regular elephant census every five years by the Wildlife Institute of India (WII) for monitoring populations.
ETURNAGARAM WILDLIFE SANCTUARY

- 29 Sep 2024
In News:
A rare collision of two cyclones has led to significant environmental impact, including the flattening of thousands of trees within the sanctuary.
Key Details:
- Location: Situated in the Mulugu district of Telangana, near the borders of Maharashtra and Chhattisgarh. Approximately 100 km from Warangal and 250 km from Hyderabad.
- Establishment: Declared a wildlife sanctuary in 1952 by the Nizam government of Hyderabad.
- Area: Covers around 806 square kilometers.
Geographic Features
Rivers:
- Dayyam Vagu: A significant water source that divides the sanctuary into two parts.
- Godavari River: Flows through the sanctuary, contributing to its rich biodiversity.
Flora
- Vegetation: Dense tropical dry deciduous forest.
- Key Species: Includes teak, bamboo, madhuca, and terminalia trees, creating a lush habitat.
Fauna
- Wildlife: Home to diverse species such as:
- Mammals: Tiger, leopard, panther, wolf, wild dogs, jackals, sloth bear, chousingha, blackbuck, nilgai, sambar, spotted deer, and four-horned antelope.
- Reptiles: Notable for its population of mugger crocodiles and snakes, including cobras, pythons, and kraits.
Cultural Significance
- Temple: The famous Sammakka-Saralamma Temple is located within the sanctuary.
PLANETARY BOUNDARIES AND OCEAN ACIDIFICATION
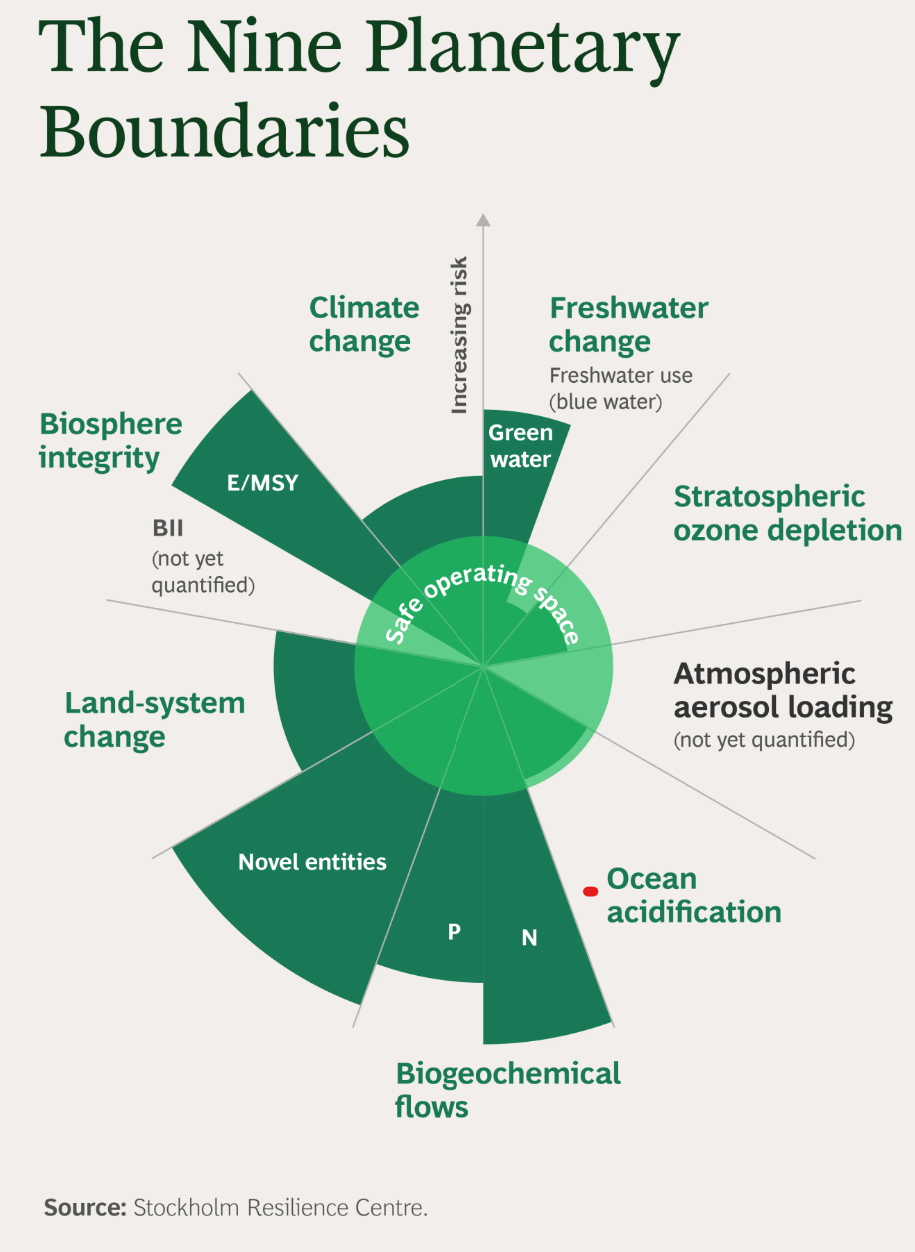
- 27 Sep 2024
In News:
A new report from the Potsdam Institute for Climate Impact Research (PIK) indicates that the world's oceans are nearing critical acidity levels.
- Key Findings:
- Nine Crucial Factors: The report identifies nine essential elements for sustaining life on Earth.
- Exceeded Limits: Six of these factors have already surpassed safe limits due to human activities.
- Ocean Acidification: This is poised to become the seventh boundary breached.
- Crossed Boundaries:
- Factors Affected:
- Climate change
- Loss of natural species and habitats
- Depletion of freshwater resources
- Increase in pollutants, including plastics and agricultural chemicals
- Factors Affected:
- Causes of Ocean Acidification:
- Primarily driven by rising carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions from burning fossil fuels (oil, coal, gas).
- Implications of Acidification:
- Damage to corals, shellfish, and phytoplankton, disrupting marine ecosystems.
- Threats to food supplies for billions of people.
- Reduced capacity of oceans to absorb CO2, exacerbating global warming.
- Ozone Layer Status:
- Currently not close to being breached; showing recovery since the banning of harmful chemicals in 1987.
- Air Quality Concerns:
- A ninth boundary related to particulate matter is near danger limits.
- Improvements in air quality are noted, but industrializing nations still face pollution risks.
- Tipping Points:
- Crossing these boundaries could lead to irreversible and catastrophic consequences for humanity and future generations.
- All boundaries are interconnected; breaching one can destabilize the entire system.
- Opportunities for Solutions:
- Addressing critical issues, such as limiting temperature rise to 1.5 degrees Celsius above pre-industrial levels, can have widespread benefits across multiple environmental challenges.
Planetary boundaries
- The planetary boundaries were introduced in 2009 to define the global environmental limits within which humans can safely live.
- Johan Rockström, former director of the Stockholm Resilience Centre, led a group of 28 renowned scientists to identify the nine processes that regulate the stability and resilience of the Earth system.
- Climate Change: Greenhouse gas concentrations, primarily CO2, are the primary metric here. Exceeding the recommended levels risks amplifying global warming.
- Ocean Acidification: Oceans absorb CO2, leading to decreased pH levels. This boundary measures the carbonate ion concentration, vital for marine life like corals.
- Stratospheric Ozone Depletion: The ozone layer protects life from harmful ultraviolet radiation. This boundary emphasizes the ozone concentration in the stratosphere.
- Nitrogen and Phosphorus Cycles: Excess nitrogen and phosphorus, often from fertilizers, can disrupt ecosystems. Here, the focus is on their flow into the environment.
- Freshwater Use: Freshwater is vital for life. This boundary pinpoints the annual consumption of freshwater resources.
- Land-System Change: As we modify landscapes, particularly through deforestation, we alter habitats and carbon storage capabilities. This threshold concerns the amount of forested land remaining.
- Biodiversity Loss: Biodiversity underpins ecosystem resilience. This metric observes the extinction rate of species.
- Atmospheric Aerosol Loading: Aerosols influence climate and human health. This boundary examines their density in the atmosphere.
- Chemical Pollution: Synthetic chemicals can harm ecosystems and human health. This boundary reviews their concentration and spread.
NAGAR VAN YOJANA (NVY)

- 25 Sep 2024
In News:
Recently, the Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change, Government of India achieved a 100-Day Target of 100 Nagar Vans under Nagar Van Yojana (NVY) with the objective to Enhance Urban Greenery.
Key Details:
- Launch: Initiated in 2020 to enhance urban greenery, improve quality of life, and foster social cohesion.
- Financial Support: Offers ?4 lakh per hectare for creation and maintenance of urban forests.
- Area Specification: Nagar Van areas range from 10 to 50 hectares.
- Coverage: Applicable to all cities with Municipal Corporations, Municipalities, and Urban Local Bodies (ULBs).
Achievements
- 100-Day Target: The Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change achieved a target of 100 Nagar Vans, surpassing it with the approval of 111 Nagar Vans in just 100 days.
- Geographic Spread: These 111 Nagar Vans are distributed across six states and one Union Territory.
Features of Nagar Vans
- Biodiversity Focus: Emphasis on planting fruit-bearing, medicinal, and native species to attract wildlife and maintain ecological balance.
- Community Involvement: Engages citizens, students, and stakeholders through tree planting, educational programs, and sustainable management.
- Design Elements: Each Nagar Van includes two-thirds tree cover and features components like Biodiversity Parks, Smriti Vans, Butterfly Conservatories, Herbal Gardens, and Matri Vans.
Future Goals
- Expansion Plans: Target to develop 1,000 Nagar Vans by 2027, supported by the National Compensatory Afforestation Management and Planning Authority (National CAMPA).
- Environmental Impact: Aims to protect forest land from degradation and address urban environmental issues such as air pollution and habitat loss.
Ek Ped Maa Ke Naam Campaign
- Launch Date: Introduced on June 5, 2024, during World Environment Day.
- Purpose: Encourages tree planting as a tribute to mothers, fostering a culture of environmental stewardship.
- Tree Planting Goals: Aims to plant 80 crore trees by September 2024 and 140 crore by March 2025.
- Tracking Efforts: Participants can document their planting through the MeriLiFE portal, where over 75 crore saplings have been recorded.
Recent Initiatives
- Tree Plantation Drive: A recent drive on September 17, 2024, aimed at creating Matri Vans in newly approved Nagar Vans, highlighting community and governmental collaboration for sustainable urban development.
Ideas4LiFE Initiative

- 25 Sep 2024
In News:
The Ideas4LiFE portal was launched by Union Minister for Environment, Forest and Climate Change, at IIT Delhi.
- Purpose: Designed to invite innovative ideas related to products and services that promote environmentally friendly lifestyles.
- Development Partner: Created in collaboration with UNICEF YuWaah.
Key Features of the Ideas4LiFE Portal
- Themes: Aligned with Mission LiFE, focusing on:
- Water Conservation
- Energy Efficiency
- Waste Reduction
- E-Waste Management
- Minimizing Single-Use Plastics
- Embracing Sustainable Food Practices
- Fostering Healthy Lifestyles
- Recognition: Winning ideas will be awarded attractive prizes for both individuals and institutions.
Engagement and Outreach
- Submissions: As of now, the portal has received approximately 3,300 registrations and over 1,000 ideas.
- Social Media Impact: The initiative has garnered 46.5 million impressions and a reach of 13.5 million through social media under the hashtag #Ideas4LiFE.
Collaboration with Educational Institutions
- Partnerships: Collaborations with the University Grants Commission (UGC), All-India Council for Technical Education (AICTE), and various educational institutions to promote the Ideathon among students and researchers.
- Objective: Encourage the academic community to contribute innovative, citizen-focused ideas that support sustainable living.
Future Plans
- Evaluation Process: Submitted ideas will be evaluated by a jury, leading to the announcement of shortlisted and winning ideas.
- Implementation: Winning ideas will be included in a national repository, allowing stakeholders, including government bodies and private entities, to nurture and scale these innovations.
Mission LiFE Context
- Definition: Mission LiFE (Lifestyle For Environment) is a campaign initiated at UN Climate Change Conference COP26 in 2021.
- Goals:
- Mobilize at least one billion people for environmental protection.
- Make 80% of villages and urban local bodies environment-friendly by 2028.
- Promote small, everyday actions to combat climate change.
- Philosophy: Emphasizes the P3 model—Pro Planet People—uniting individuals in the commitment to environmental stewardship.
GREENLAND LANDSLIDE AND GLOBAL SEISMIC WAVES

- 24 Sep 2024
In News:
Massive Greenland landslide sent seismic waves around earth for 9 days. One year ago, roughly 25 million cubic metres of ice and rock splashed into the Dickson Fjord in Greenland and displaced the water enough to give rise to a 200-metre high mega-tsunami; in this way, a melting glacier led to a planet-wide tremor, and researchers warn that it may not be the last
Seismic Observations
- Detection: Unusual seismic signals recorded by stations worldwide, characterized by a single frequency, unlike typical earthquake vibrations.
- Classification: Initially termed a "USO" (unidentified seismic object) due to its atypical properties.
- Duration: Waves persisted for nine days, unlike typical aftershock patterns.
Investigation Efforts
- Collaboration: Involved over 68 researchers from 40 universities across 15 countries.
- Data Sources: Combined seismic data, satellite imagery, water level monitors, and a classified bathymetric map from the Danish Navy.
- Conclusion: The seismic waves resulted from a massive landslide caused by the collapse of Hvide Støvhorn peak, which triggered a series of events leading to the tsunami.
Mega-Tsunami and Seiche
- Tsunami Details:
- Created by the avalanche crashing into the fjord, displacing water significantly.
- Resulted in waves that reflected off fjord walls, reaching heights of nearly 110 meters due to the fjord's unique shape.
- Seiche Phenomenon:
- Oscillations in the fjord persisted for over nine days, reflecting the energy from the landslide.
- Maximum amplitude of the seiche recorded at 7.4 meters, with a frequency of 11.45 MHz.
Climate Context
- Global Warming Impact: Thinning glaciers contributed to instability in the region, making such landslides more likely.
- Future Predictions: Researchers warn of increased frequency and scale of similar events as climate change continues to affect Arctic and subarctic regions.
Key Takeaways
- The Greenland landslide serves as a reminder of the unpredictable consequences of climate change, including massive geological events.
- The incident highlights the interconnectedness of natural systems and the potential for localized events to have global repercussions.
COP 29 AT BAKU

- 23 Sep 2024
In News:
Azerbaijan is making a significant move in the global climate finance landscape by proposing the Climate Finance Action Fund (CFAF) at the upcoming COP29 conference. This fund aims to gather voluntary contributions from fossil-fuel-producing nations and companies, with Azerbaijan itself making the initial investment. The fund’s goal is to support climate action in developing countries, which often struggle to finance their environmental initiatives.
Key Aspects of the CFAF:
- Voluntary Contributions: The fund seeks donations from fossil fuel entities, allowing them to contribute based on a fixed amount or production volumes.
- Bipartite Allocation: Proposed funds will be split equally—half for climate projects in developing nations and half for supporting those countries in executing their national climate action plans.
- Operational Threshold: The CFAF will only commence operations once it secures a minimum of $1 billion and commitments from at least ten countries to participate.
Context of COP29:
COP29, hosted in Baku from November 11 to 22, centers on finalizing a climate finance agreement, particularly the obligations of developed nations post-2025. This follows the ongoing struggle to meet the $100 billion annual financing target established in the Paris Agreement.
Additional Proposals:
Azerbaijan has also introduced several other initiatives as part of its agenda, including:
- Expanding Global Energy Storage: Aiming to increase capacity sixfold by 2030.
- Green Hydrogen Market: Fostering a global marketplace for green hydrogen.
- Minimizing Emissions from Digital Growth: Ensuring that the environmental impact of increasing digitalization and data centers is mitigated.
Challenges Ahead:
Despite the ambitious plans, there are significant hurdles to overcome, including establishing a robust framework for the CFAF, garnering international support, and ensuring compliance from contributors. As the conference approaches, ongoing negotiations will be crucial to achieving substantial agreements on climate finance that can lead to meaningful progress in combating climate change.
AMUR FALCONS

- 22 Sep 2024
In News:
An order issued by the District Magistrate directed the owners of air guns to deposit their hunting weapons at the offices of respective village authorities.
Amur Falcons: An Overview
Scientific Classification:
- Common Name: Amur Falcon
- Scientific Name: Falco amurensis
- Family: Falconidae
Physical Characteristics:
- Size: Small raptors, approximately 28-30 cm in length.
- Distinctive Features: Dark plumage with white wing linings; reddish-orange eyes and feet.
Migration Patterns:
- Breeding Grounds: Southeastern Russia and northern China.
- Migratory Route: They leave their breeding areas in autumn, traveling south to round the Himalayas, stopping in Nagaland, and then heading towards the Western Ghats before crossing the Indian Ocean to reach South Africa.
- Distance: These falcons undertake an incredible journey of around 22,000 kilometers annually, making them one of the most remarkable long-distance migrants among raptors.
Diet:
- Primarily insectivorous, they also consume small vertebrates when available.
Conservation Status:
- IUCN Status: Least Concern
- Legal Protection:
- Wildlife Protection Act, 1972: Schedule IV
- Convention on Migratory Species (CMS): Appendix II
Recent Conservation Efforts:
- Ban in Manipur: The Tamenglong district administration has imposed a ban on hunting, catching, killing, and selling Amur falcons in preparation for their migratory arrival.
- Tagging Program: In 2016, radio transmitters were used to monitor their migration routes.
- Awareness Initiatives: An annual ‘Amur Falcon Festival’ in Tamenglong district promotes awareness and celebrates these migratory birds.
Threats:
- Amur falcons face various threats including habitat loss, hunting, and illegal trapping.
Cultural Significance:
- Locally known as ‘Kahuaipuina’ in Manipur and ‘Molulem’ in Nagaland, these birds hold ecological and cultural significance, particularly in regions that serve as critical stopover points during migration.
Summary
The Amur falcon is a small but remarkable migratory raptor known for its long-distance travels from its breeding grounds in Asia to Africa. Conservation efforts in India, particularly in the Tamenglong district of Manipur, aim to protect these birds from hunting and habitat loss, ensuring their continued survival and highlighting their importance in the ecosystem.
WORLD RHINO DAY

- 22 Sep 2024
In News:
Celebrated annually on September 22, World Rhino Day raises awareness about the critical conservation status of rhinoceroses and the myriad threats they face, such as poaching and habitat loss. This day, first initiated by the World Wildlife Fund South Africa in 2010, aims to highlight the need for the conservation of all five species of rhinos: the Javan, Sumatran, Black, Greater One-Horned, and White rhinos.
The Current Status of Rhino Species
- Among the five rhino species, three are classified as
- Critically Endangered: the Black, Javan, and Sumatran rhinos.
- The White Rhino is considered Near Threatened, with the Northern White Rhino itself critically endangered.
- The Greater One-Horned Rhino, primarily found in India, is listed as Vulnerable.
Notably, Kaziranga National Park in Assam is home to the largest population of Greater One-Horned Rhinos, boasting approximately 3,700 individuals.
Conservation Efforts
In India, initiatives like Project Rhino play a crucial role in safeguarding rhino populations. This project focuses on preventing poaching, enhancing habitat management, and increasing public awareness. It collaborates with various conservation groups and government agencies to strengthen law enforcement against poaching and to relocate rhinos to safer areas.
Another significant program is the Indian Rhino Vision 2020 (IRV 2020), aimed at boosting the population of Greater One-Horned Rhinos in Assam, particularly in regions where they had previously become extinct.
Surprising Facts About Rhinos
- Despite their thick skin, rhinos can get sunburned.
- Rhinos are related to zebras, horses, and tapirs.
- All five species are considered endangered.
- A group of rhinos is called a "crash."
- Rhinos' horns are made of keratin, the same protein found in human hair and nails.
- The term "rhinoceros" comes from two Greek words meaning "nose" and "horn."
- Rhinos and elephants are not natural enemies.
- One of the most famous depictions of a rhino is Albrecht Dürer's woodcut from 1515.
- The gestation period for rhinos can last up to 16 months.
- Rhinos have historically been used in traditional Asian medicine.
INDIA JOINS THE INTERNATIONAL BIG CAT ALLIANCE (IBCA)
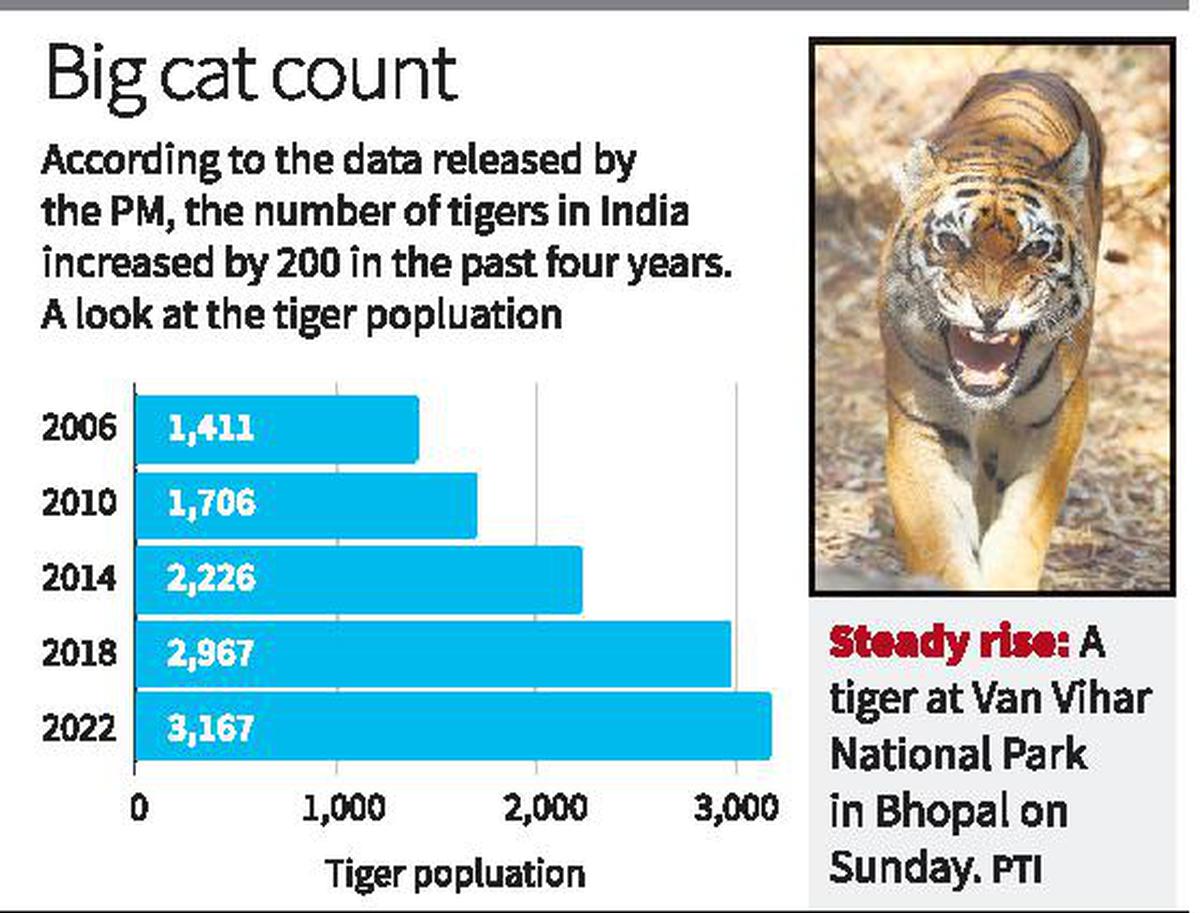
- 21 Sep 2024
In News:
India formally joined the International Big Cat Alliance (IBCA), launched by Prime Minister Narendra Modi on April 9, 2023, during the 50th anniversary of Project Tiger.
- Objective: The IBCA aims to conserve the world's seven big cat species: tiger, lion, leopard, snow leopard, cheetah, jaguar, and puma, focusing on their protection and natural habitats.
- Founding Members: India joins Nicaragua, Eswatini, and Somalia as founding members of the IBCA, which will collaborate with 24 countries and nine organizations.
- Headquarters: The IBCA will be headquartered in India, facilitating efforts to protect big cats and their ecosystems.
Purpose and Goals of IBCA
- Conservation Focus: The alliance addresses common challenges in the protection of the seven big cats, promoting sustainable resource use and tackling climate change.
- Collaboration and Support: The IBCA will provide a platform for member nations to share knowledge, expertise, and support recovery efforts in potential habitats.
- Mobilization of Resources: The alliance aims to mobilize financial and technical resources for effective conservation strategies based on global experiences.
Background and Evolution
- Inception: PM Modi proposed an international initiative against poaching and illegal wildlife trade in 2019, advocating for collaboration among tiger range countries.
- Extension of Project Tiger: The IBCA serves as an extension of India's long-standing commitment to wildlife protection, initially exemplified by the launch of Project Tiger in 1973.
Big Cat Species Overview
- Tiger (Endangered)
- Population: Approx. 3,167 in India, accounting for over 75% of the global population.
- Threats: Habitat loss, poaching, and climate change impacting their territory.
- Lion (Vulnerable)
- Population: Estimated 700 in India.
- Threats: Habitat reduction and targeted poaching.
- Leopard (Near Threatened)
- Population: Around 13,000 in India, with approximately 250,000 globally.
- Threats: Habitat loss and human-wildlife conflict.
- Snow Leopard (Vulnerable)
- Population: 400-700 in India, with global estimates of 4,000-6,500.
- Threats: Poaching, habitat loss, and human disturbances.
- Cheetah (Vulnerable)
- Population: Declined to less than 7,000 globally; declared extinct in India in 1952.
- Threats: Habitat loss, climate change, and illegal trafficking.
- Jaguar (Near Threatened)
- Population: Approximately 173,000 globally, primarily in South America.
- Threats: Deforestation, illegal hunting, and habitat fragmentation.
- Puma (Near Threatened)
- Population: Estimated 50,000, experiencing a decline.
- Threats: Habitat loss and human-wildlife conflict.
Future Initiatives
- Translocation Efforts: Following successful cheetah translocations from Namibia and South Africa, India plans to explore similar initiatives for other big cats.
- Global Cooperation: The IBCA will strengthen conservation efforts by working with a broader network of range countries to combat poaching and promote habitat preservation.
What is the current status of the introduction of African cheetahs?

- 17 Sep 2024
In News:
Project Cheetah has encountered significant setbacks, including prolonged captivity and cheetah fatalities; with long-term success hinging on finding sufficient habitat, scientific management, and community support, the project’s future depends on overcoming these enormous challenges.
Overview of Project Cheetah:
- Cheetah Action Plan (CAP): India’s initiative to reintroduce African cheetahs, aimed at species conservation and ecosystem restoration.
- Long-term Commitment: Requires a minimum of 25 years of financial, technical, and administrative support from various governmental bodies.
Challenges Faced:
- Extended Captivity:
- Cheetahs have been held in captivity longer than planned, with only 12 of the original 20 surviving.
- Delays in the release process raise concerns about the cheetahs' fitness for survival in the wild.
- Health Issues and Fatalities:
- Several cheetahs have died due to pre-existing health conditions or management failures before being released.
- Captivity duration exceeds guidelines set by Namibian policy, rendering the cheetahs unfit for release.
- Environmental Adaptation Problems:
- Some deaths attributed to environmental stressors, such as heat stroke and improper management of conditions leading to health complications.
Location for Introduction:
- Kuno National Park: Chosen for its suitable habitat and prey base. However, many cheetahs remain confined, with release dates now pushed to late 2024 or early 2025.
- Additional Sites: Plans for a captive breeding facility in Gujarat and potential releases in Nauradehi Wildlife Sanctuary.
Management and Oversight:
- An expert committee, led by the National Tiger Conservation Authority (NTCA), oversees the project. Responsibilities include negotiating with African countries for cheetah procurement and implementing field activities.
Goals and Measurable Outcomes:
- Short-term Objectives: Achieve a 50% survival rate in the first year, establish home ranges, and generate eco-tourism revenue.
- Long-term Success: Establish a stable cheetah population, improve habitat quality, and support local economies.
Future Considerations:
- The project lacks a definitive sunset clause but will require ongoing management for decades.
- The key question remains whether India has sufficient habitat (4,000 to 8,000 sq. km) to support a viable population of free-ranging cheetahs.
Conclusion: Project Cheetah faces significant challenges in achieving its ambitious conservation goals, raising questions about its long-term viability and management practices.
Trilobite fossils from upstate New York reveal extra set of legs
- 15 Sep 2024
In News:
A new study finds that a trilobite species with exceptionally well-preserved fossils from upstate New York has an additional set of legs underneath its head.
Key details:
- The research, led by the American Museum of Natural History and Nanjing University in China, suggests that having a fifth pair of head appendages might be more widespread among trilobites than once thought.
- Published in the journal Palaeontology, the study helps researchers better understand how trilobite heads are segmented.
Trilobites
- Trilobites are a group of extinct arthropods whose living relatives include lobsters and spiders.
- Like other arthropods, the bodies of trilobites are made up of many segments, with the head region comprised of several fused segments.
- As with other parts of the trilobite body (the thorax and tail), these segments were associated with appendages, which ranged in function from sensing to feeding to locomotion.
- Trilobites are a group of extinct marine arthropods that first appeared around 521 million years ago, shortly after the beginning of the Cambrian period, living through the majority of the Palaeozoic Era, for nearly 300 million years. They died out at the end of the Permian, 251 million years ago, killed by the end Permian mass extinction event that removed over 90% of all species on Earth. They were very diverse for much of the Palaeozoic, and today trilobite fossils are found all over the world.
- The name 'trilobite' comes from the distinctive three-fold longitudinal division of the dorsal exoskeleton into a central axis, flanked on either side by lateral (pleural) areas.
Two ways
The segments in the trilobite head can be counted in two different ways: by looking at the grooves (called furrows) on the upper side of the trilobite fossil’s hard exoskeleton, or by counting the pairs of preserved antennae and legs on the underside of the fossil. The soft appendages of trilobites are rarely preserved, though, and when looking at the segments in the trilobite head, researchers regularly find a mismatch between these two methods.
In the new study, researchers examined newly recovered specimens of the exceptionally preserved trilobite Triarthrus eatoni from upstate New York. These fossils, known for the gold shine of the pyrite replacement preserving them, show an additional, previously undescribed leg underneath the head.
Resolving mismatch
By making comparisons with another trilobite species, the exceptionally preserved Olenoides serratusfrom the Burgess Shale in British Columbia, the researchers propose a model for how appendages were attached to the head in relation to the grooves in the exoskeleton.
This model resolves the apparent mismatch and indicates that the trilobite head included six segments: an anterior segment associated with the developmental origin of the eyes and five additional segments, associated with one pair of antennae and four pairs of walking legs, respectively.
40% Amazon rainforest unprotected: why is this significant for climate change?

- 12 Sep 2024
In News
- Scientists agree that preserving the Amazon rainforest is critical to combating global warming, but new data published recently, indicate huge swathes of the jungles that are vital to the world’s climate remain unprotected.
- Nearly 40% of the areas of the Amazon rainforest most critical to curbing climate change have not been granted special government protection, as either nature or indigenous reserves, according to an analysis by nonprofit Amazon Conservation.
- The areas lie in the far southwest of the Amazon in Peru and the far northeast in Brazil, French Guiana, and Suriname, the data show.
- Those parts of the Amazon have the biggest, densest trees and the most continuous canopy cover. That means these areas hold the most carbon, which would be released into the atmosphere as climate-warming greenhouse gas if the jungle is destroyed by fire or logging.
What satellite data show
- Amazon Conservation analysed new data from the satellite imaging company Planet that used lasers to get a three-dimensional picture of the forest and combined it with machine-learning models.
- Only aboveground vegetation was considered, and not underground carbon in roots and soils.
- Amazon Conservation’s Monitoring of the Andean Amazon Project (MAAP)’s analysis shows that 61% of the peak carbon areas in the Amazon are protected as indigenous reserves or other protected lands, but the rest generally has no official designation.
- In Brazil, Suriname and French Guiana, only 51% of peak carbon areas are labeled for preservation. Peru protects a higher proportion of its critical areas, but some of the areas that have been left unprotected have been earmarked for logging.
Why the Amazon matters
- MAAP published an analysis last month showing that the Amazon contained 71.5 billion tonnes of carbon, roughly double the global carbon dioxide emissions for 2022. That analysis showed that the Amazon just barely absorbed more carbon than it released in the decade leading up to 2022, a positive signal for the world’s climate.
- But that remains an area of intense debate, with other studies showing the Amazon has flipped to become an emissions source.
- As the effects of anthropogenic climate change become more stark with each passing day, the Amazon becomes one of the most valuable assets for the planet’s health. Scientists say that if the Amazon becomes an emission source instead of a carbon sink — which absorbs carbon from the atmosphere — the impact on the planet may be cataclysmic.
Controversy over Mumbai's salt pans: why do these lands matter?

- 12 Sep 2024
In News:
Earlier this month, the Centre approved the transfer of 256 acres of salt pan land in Mumbai to the Dharavi Redevelopment Project Pvt Ltd (DRPPL), a joint venture between Adani Realty Group and the Maharashtra government, for building rental housing for slum dwellers.
What are salt pan lands?
- They comprise parcels of low-lying lands where seawater flows in at certain times, and leaves behind salt and other minerals. Along with Mumbai’s mangroves (also at risk due to development), this ecosystem is instrumental in protecting the city from flooding.
- According to the Coastal Regulation Zone (CRZ) notification of 2011, the ecologically sensitive salt pans fall under CRZ-1B category, where no economic activity is allowed with the exception of salt extraction and natural gas exploration.
- In all, 5,378 acres of land in Mumbai have been designated as salt pan lands, approximately nine times the size of the Dharavi slum. About 31% of this land is located in residential and commercial belts, and roughly 480 acres are encroached upon, a 2014 study by the state government found. The same study found that about 1,672 acres of Mumbai’s more than 5,000 acres of salt pan lands are “developable”.
- Nationally, some 60,000 acres have been demarcated as salt pan lands, spread across Maharashtra, Andhra Pradesh, Tamil Nadu, Odisha, Gujarat, and Karnataka. Andhra Pradesh (20,716 acres) boasts the largest expanse of such land, followed by Tamil Nadu (17,095 acres) and Maharashtra (12,662 acres).
Why are Mumbai’s salt pan lands at risk?
Development Pressure
- Land Scarcity: Mumbai faces severe land scarcity, with its burgeoning population and high demand for space. Salt pans, being some of the last undeveloped areas, are increasingly targeted for various projects.
- Development Plans: Multiple state governments have eyed salt pan lands for different uses.
Environmental Significance
- Flood Prevention: Salt pans are situated in low-lying areas that naturally collect rainwater and tidal flows, helping to mitigate flooding in Mumbai’s eastern suburbs. They act as natural buffers, absorbing excess water during heavy rains and high tides.
- Historical Context: During the July 2005 deluge, salt pans helped reduce the impact of flooding compared to other areas of Mumbai, highlighting their role in flood management.
- Ecosystems: Salt pans are home to various species of birds and insects and contribute to local biodiversity. The destruction of these lands could lead to loss of habitat and disruption of local ecosystems.
Risks of Development
- Flooding Concerns: Environmentalists argue that constructing on these low-lying areas will lead to increased flooding in areas like Vikhroli, Kanjurmarg, and Bhandup. This is because the land’s natural ability to absorb and manage water will be compromised.
- Quality of Life Issues: Relocating slum-dwellers to these areas raises concerns about their living conditions. Salt pans are prone to flooding, which could undermine the quality of life for new residents. The cost of making these lands habitable, including extensive land filling and waterproofing measures, could negate the benefits of affordable housing.
- Conflict with Climate Goals: There is a contradiction between Mumbai’s Climate Action Plan, which recognizes climate threats, and the push to develop areas critical for flood management.
Jal Sanchay Jan Bhagidari Initiative

- 09 Sep 2024
In News:
Prime Minister Shri Narendra Modi recently launched the ‘Jal Sanchay Jan Bhagidari’ initiative via video conferencing from Surat, Gujarat.
Key Points:
- Campaign and Objectives:
- Objective: The initiative seeks to bolster water conservation through extensive public and governmental collaboration.
- Scope: About 24,800 rainwater harvesting structures will be constructed across Gujarat.
- Approach: Emphasizes a Whole-of-Society and Whole-of-Government approach to water management.
- Significance:
- Cultural Significance: PM Modi highlighted that water conservation is deeply embedded in Indian culture, with water revered as a divine entity and rivers considered Goddesses.
- Policy and Virtue: He stated that water conservation transcends policy and is both an effort and a virtue, reflecting social commitment and cultural consciousness.
- Future Challenges: The Prime Minister acknowledged the exacerbating impact of water scarcity due to climate change, urging a shift to the ‘Reduce, Reuse, Recharge, and Recycle’ mantra for sustainable water management.
- Impact of Drought and Water Scarcity:
- Recent Challenges: The drought affecting the Amazon region and other parts of India has highlighted the urgent need for effective water conservation strategies.
- Water Table Decline: Significant declines in river levels, such as the Rio Negro reaching its lowest minimum (12.7 meters) on record, and the death of endangered species due to low water levels underscore the crisis.
- Government Initiatives:
- Jal Jeevan Mission: Aims to provide piped water to every home, with significant progress noted from 3 crore households to over 15 crore.
- Jal Shakti Abhiyan: Focuses on renovation and construction of water sources with widespread public participation.
- Amrit Sarovar: Over 60,000 Amrit Sarovars have been constructed under this campaign, which began during the Azadi Ka Amrit Mahotsav.
- Innovative Solutions and Technological Integration:
- Drip Irrigation: Promotion of water-efficient farming techniques like drip irrigation to ensure sustainable agriculture.
- Support for Farmers: Encouragement for cultivating less water-intensive crops such as pulses and millets.
- Role of Industries:
- CSR Contributions: Industries have played a significant role in water conservation through initiatives like Net Zero Liquid Discharge Standards and the completion of 10,000 borewell recharge structures in Gujarat.
- Future Plans: The ‘Jal Sanchay-Jan Bhagidari Abhiyan’ aims to create an additional 24,000 recharge structures.
- Conclusion and Vision:
- Global Leadership: PM Modi expressed his belief that India can become a global leader in water conservation.
- Public Movement: Stressed the importance of continuing public participation in water conservation to make India a model for global sustainability.
Background: The ‘Jal Sanchay Jan Bhagidari’ initiative builds on the success of the earlier Jal Sanchay program by involving citizens, local bodies, and industries in water conservation efforts. The initiative aligns with the vision of water security and aims to mobilize collective action for long-term sustainability.
Key Data:
- Construction of 24,800 rainwater harvesting structures.
- Significant increase in tap water connections from 3 crore to over 15 crore households.
- Creation of more than 60,000 Amrit Sarovars across the country.
- Completion of 10,000 borewell recharge structures in Gujarat.
Climate change drives Amazon rainforest's record drought, study finds
- 09 Sep 2024
In News:
The drought that hit all nine Amazon rainforest countries - including Brazil, Colombia, Venezuela and Peru - is expected to worsen in 2024
Role of Climate Change:
- Likelihood Increase: Climate change made the drought 30 times more likely.
- Temperature and Rainfall: It drove extreme high temperatures and contributed to lower rainfall.
Future Projections:
- Expected Worsening: The drought is predicted to worsen in 2024, with the rainy season expected to recede in May.
Impact on Ecosystems:
- River Levels: Rivers have reached their lowest levels on record, with the Rio Negro river falling to its lowest minimum (12.7 meters) since records began in 1902.
- Dolphin Deaths: At least 178 endangered pink and gray Amazon river dolphins died due to low water levels and high temperatures.
- Fish Deaths: Thousands of fish died from low oxygen levels in Amazon tributaries.
Impact on Human Life:
- Disruptions: Waterways dried up rapidly, forcing people to undertake long journeys across dried river sections to access essential goods like food and medicine.
Contributing Factors:
- El Niño Influence: Periodic warming in the Eastern Pacific Ocean (El Niño) contributed to decreased rainfall but not to higher temperatures.
Potential Consequences:
- Forest Fires and Biome Health: The drought could exacerbate forest fires, combined with climate change and deforestation, potentially pushing the Amazon toward a point of no return where it ceases to be a lush rainforest.
- Previous Droughts: While the region has experienced at least three intense droughts in the past 20 years, this one’s impact on the entire Amazon basin is unprecedented.
In a first, critically endangered elongated tortoise spotted in Aravallis

- 10 Sep 2024
In News:
- A critically endangered species, the elongated tortoise (Indotestudo elongata), was spotted in Haryana’s Damdama area during a research survey in the Aravallis.
Key Features:
- The tortoise is medium-sized with a yellowish brown or olive shell and distinct black blotches at the centre of each scute.
- The tortoise has on its nostril a pink ring, which appears in the breeding season.
- Mature individuals of both sexes develop a distinct pinkish colouration surrounding the nostrils and eyes during the season.
- Habitat:
- The tortoise, found in the Sal deciduous and hilly evergreen forests, is distributed across Southeast Asia from northern India, Nepal, Bhutan, and Bangladesh in the west, eastward through Myanmar, Thailand, and all of Indochina, north to Guangxi Province of China and south to Peninsular Malaysia.
- A disjunct tortoise population exists in the Chota Nagpur plateau in eastern India. It also inhabits lowlands and foothills of up to 1,000 m above sea level.
- There have not been enough surveys to ascertain its presence in Aravallis, but the tortoise is found in the foothills of the Himalayas.
- It inhabits wetter areas and discovering it here is an aberration than a norm, adding it cannot be ruled out that the tortoise was brought by trade.
Conservation Status:
- International Union for Conservation of Nature’s (IUCN) Status: Critically Endangered, under criteria A2cd.
Threats:
- Currently, I. elongata is heavily exploited for food and traditional medicine throughout its range.
- Local people often opportunistically capture tortoises while farming or extracting other forest resources. However, deliberate hunting also occurs and dogs continue to be widely used for finding tortoises.
Global Species Action Plan (GSAP) SKILLS Platform

- 24 May 2024
Why is it in the News?
In response to the escalating biodiversity crisis, the Global Species Action Plan (GSAP) is designed to support the implementation of the Kunming-Montreal Global Biodiversity Framework (GBF).
About GSAP SKILLS Platform:
- The Global Species Action Plan (GSAP) SKILLS platform, standing for (Species Conservation Knowledge, Information, Learning, Leverage, and Sharing), brings the GSAP’s content online and enables real-time updates of technical tools and resources.
- This platform aims to facilitate global collaboration and partnership by connecting decision-makers, species conservation practitioners, and experts at all levels.
- It ensures accessibility and relevance by providing real-time updates on technical tools and resources.
- Each target within the Global Biodiversity Framework is accompanied by a summary and rationale for species conservation interventions, actions, and sub-actions, along with the actors involved and the technical tools and resources required, facilitating the scaling-up of implementation efforts.
- Managed proactively by the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN), the platform meets the needs of governments and stakeholders to take decisive action for species conservation.
- The development of the GSAP SKILLS platform has been principally supported by the Ministry of Environment, Republic of Korea, with additional resources from the Tech4Nature Initiative, launched by IUCN and Huawei in 2020.
What is the Global Species Action Plan?
- It has been developed to support the implementation of the Kunming-Montreal Global Biodiversity Framework (GBF) and to address the increasing biodiversity loss worldwide.
- It outlines strategic interventions and actions to conserve and sustainably manage species while ensuring equitable benefits.
About Kunming-Montreal Global Biodiversity Framework:
- The Kunming-Montreal Global Biodiversity Framework (GBF) is an outcome of the 2022 United Nations Biodiversity Conference.
- Its tentative title had been the "Post-2020 Global Biodiversity Framework".
- The GBF was adopted by the 15th Conference of Parties (COP15) to the Convention on Biological Diversity (CBD) on 19 December 2022.
- It has been promoted as a "Paris Agreement for Nature".
- It is one of a handful of agreements under the auspices of the CBD, and it is the most significant to date.
- It has been hailed as a "huge, historic moment" and a "major win for our planet and for all of humanity."
- UN Secretary-General António Guterres speaking at the 2022 biodiversity conference in Montreal which led to this treaty
- The Framework is named after two cities, Kunming, which was scheduled to be the host city for COP15 in October 2020 but postponed and subsequently relinquished the hosting duties due to China's COVID policy, and Montreal, which is the seat of the Convention on Biological Diversity Secretariat and stepped in to host COP15 after Kunming's cancellation.
Baobab Tree

- 17 May 2024
Why is it in the News?
A new study has uncovered the origins of baobabs, the tall and uniquely shaped deciduous trees that are famously spotted on the island of Madagascar.
What are Baobab Trees?
- Baobabs are known for their great heights, with some extending up to 50 metres, and exceptionally long lifespans going up to 2,000 years.
- In India too, a few baobab trees exist, including one near the Golconda Fort in Andhra Pradesh that is believed to be more than 400 years old.
- The trees have trunks with large circumferences and thin, spindly branches.
- In local cultures, the trees are also revered because of the multiple uses their parts have, with the fruits and seeds being edible, the seed oil used for cooking and the bark fibre for clothing.
- They are also called “upside down” trees because of their tops resembling an uprooted plant turned upside down.
Essential for the ecosystem:
- Baobab trees are fundamental to the entire dry African savanna ecosystem.
- They help keep soil conditions humid, aid nutrient recycling, and slow soil erosion with their massive root systems.
- As a succulent, the tree absorbs and stores water from the rainy season in its massive trunk, producing a nutrient-dense fruit in the dry season, which can grow up to a foot long.
- The fruit contains tartaric acid and Vitamin C, serving as a vital nutrient and food source for many species.
- They are also an essential source of water and shelter for hundreds of animals, including birds, lizards, monkeys, and even elephants – which can eat their bark for moisture when there is no water nearby.
In human culture:
- For humans, the baobab’s fruit pulp can be eaten, soaked in water to make a refreshing drink, preserved into a jam, or roasted and ground to make a coffee-like substance.
- The bark can be pounded to make everything from rope, mats, and baskets to paper and cloth.
- Leaves are also used, they can be boiled and eaten, or glue can be made from their flower’s pollen.
What Did the Study Find?
- The study highlighted the threats facing baobab trees and examined their genetic makeup.
- It reported that three Madagascar species of baobab trees are threatened with extinction, according to the IUCN Red List of Threatened Species.
- The study identified various threats, including residential and commercial development and livestock farming, which require land clearing.
- However, even species not currently endangered show declining populations, suggesting that more rigorous conservation strategies are needed to ensure their long-term survival.
- This necessitates a detailed understanding of the baobabs' genetics.
- Genomic sequencing revealed a consensus on the monophyly of the Malagasy lineage from Madagascar.
- According to DNA studies, baobab trees first arose in Madagascar 21 million years ago, with their seeds later carried by ocean currents to Australia and mainland Africa, where they evolved into distinct species.
- The study also warned that climate change poses severe threats to Adansonia suarezensis from Madagascar, predicting its possible extinction by 2080.
- Due to their unique ecological roles and low genetic diversity, these species are likely to have reduced resilience to environmental changes and habitat fragmentation.
Leopard Cat

- 17 May 2024
Why is it in the News?
The leopard cat (Prionailurus bengalensis), a small wild cat native to South, Southeast and East Asia, was recently spotted in Maharashtra’s Pench, in what is being billed as Central India’s first sighting of the species.
About Leopard Cat:
- The Leopard cat (Prionailurus bengalensis) is a small wild cat native to continental South, Southeast, and East Asia.
- With its distinctive leopard-like colouring, this small wildcat is known for its remarkable adaptability and extensive distribution across Asia.
Habitat and Distribution:
- Leopard cats can be found in a variety of environments, ranging from the Amur region in Russia to the Korean Peninsula, China, Indochina, the Indian Subcontinent, northern Pakistan, and as far south as the Philippines and the Sunda Islands of Indonesia.
- Although they can inhabit agriculturally used areas, leopard cats prefer forested habitats, including tropical evergreen rainforests, subtropical deciduous and coniferous forests, and plantations at various altitudes.
Physical Characteristics:
- Size and appearance vary considerably across their range, with a length of 45 to 75 cm (18 to 30 inches), excluding their 23-35 cm (9-13.8 inches) tail.
- Their colouration ranges from pale tawny to yellow, red, or grey, with white underparts and distinctive spots.
- Most leopard cats have four black stripes running from their forehead to the nape, breaking into short bands and elongated spots on their shoulders.
Behaviour and Diet:
- As solitary and nocturnal carnivores, leopard cats primarily feed on rodents, tree shrews, and hares, playing a crucial role in maintaining the balance of their ecosystems.
Conservation Status:
- Listed as "Least Concern" on the IUCN Red List, leopard cats face threats from habitat loss, poaching, and human-wildlife conflict. Continued monitoring and conservation efforts are essential to protect this species and its vital role in Asia's diverse ecosystems.
Facts about Pench Tiger Reserve:
- Location: Situated in the southern reaches of the Satpura hills, the Pench Tiger Reserve spans Seoni and Chhindwara districts in Madhya Pradesh and extends into Nagpur district in Maharashtra as a separate Sanctuary.
- It derives its name from the Pench River, which flows from north to south through the Reserve.
- The reserve encompasses the Indira Priyadarshini Pench National Park, the Pench Mowgli Sanctuary, and a buffer zone.
- The area served as the inspiration for Rudyard Kipling's renowned work, "The Jungle Book."
- Vegetation: The undulating topography supports a diverse range of vegetation, from moist, sheltered valleys to open, dry deciduous forests.
- Flora: Pench Tiger Reserve boasts a rich variety of flora, including teak, saag, mahua, and various grasses and shrubs.
- Fauna: Renowned for its wildlife diversity, the reserve is home to large herds of Chital, Sambar, Nilgai, Gaur (Indian Bison), and wild boar.
- Key predators include the tiger, leopard, wild dogs, and wolf. Additionally, the reserve supports over 325 species of resident and migratory birds, including the Malabar Pied Hornbill, Indian Pitta, Osprey, Grey Headed Fishing Eagle, and White Eyed Buzzard.
Fukushima Water Issue

- 01 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
Recently, Japan announced that its experts have engaged in discussions with their Chinese counterparts to address Beijing's concerns regarding the release of treated radioactive wastewater from the damaged Fukushima Daiichi nuclear power plant into the sea.
What is the Fukushima Water Issue?
- In 2021, the Japanese government unveiled plans to gradually discharge over one million tonnes of contaminated water from the Fukushima nuclear plant into the ocean over the next three decades.
- The contaminated water is a residual product of the devastating 2011 earthquake and tsunami that incapacitated the Fukushima Daiichi nuclear power plant, resulting in the release of radioactive materials.
- After more than ten years of storing this wastewater, Japan asserts that they are facing storage space limitations and contends that the treated water is now safe for release.
Concerns Surrounding the Fukushima Water Discharge:
- Tritium and Carbon-14: The water from Fukushima undergoes filtration via the Advanced Liquid Processing System (ALPS), effectively reducing most radioactive contaminants to acceptable safety levels, except tritium and carbon-14.
- While both emit low levels of radiation, consumption in large quantities could potentially pose risks.
- Insufficient Research: Scientists emphasize the need for further investigation into the potential impact of the water discharge on the ocean bed and marine ecosystems.
- The Pacific Islands Forum regional group has labeled the proposed plan as "another significant nuclear contamination disaster," citing ongoing challenges faced by its member nations due to past US nuclear testing.
Pacific Islands Forum (PIF):
- The Pacific Islands Forum (PIF) is an inter-governmental organization that aims to enhance cooperation among countries and territories of Oceania, including the formation of a trade bloc and regional peacekeeping operations.
- It was founded in 1971 as the South Pacific Forum (SPF), and changed its name in 1999 to "Pacific Islands Forum", to be more inclusive of the Forum's Oceania-spanning membership of both north and south Pacific island countries, including Australia.
- It is a United Nations General Assembly observer.
- The PIF secretariat is located in Suva, the capital of Fiji.
Nuclear Incidents:
- A nuclear and radiation incident denotes an occurrence that has resulted in significant repercussions for individuals, the environment, or the facility involved.
- These may entail fatal consequences for individuals, substantial releases of radioactivity into the environment, or reactor core meltdowns.
- Globally, there have been a total of 99 incidents at nuclear power plants.
- Fifty-seven of these incidents have transpired since the Chornobyl disaster, with the United States accounting for 57% of all nuclear-related incidents.
- Noteworthy nuclear power plant mishaps encompass:
- Fukushima Daiichi nuclear disaster (2011)
- Chernobyl disaster (1986)
- Three Mile Island accident (1979), and
- The SL-1 accident (1961).
Black Carbon

- 27 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
As per a study, the residential sector is responsible for 47% of India's overall black carbon emissions.
What is Black Carbon?
- Black carbon is the dark, sooty material emitted alongside other pollutants when biomass and fossil fuels are not fully combusted.
- It contributes to global warming and poses severe risks.
- Studies have found a direct link between exposure to black carbon and a higher risk of heart disease, birth complications, and premature death.
- Most black carbon emissions in India arise from burning biomass, such as cow dung or straw, in traditional cookstoves.
- According to a 2016 study, the residential sector contributes 47% of India’s total black carbon emissions.
- Industries contribute a further 22%, diesel vehicles 17%, open burning 12%, and other sources 2%.
- Decarbonization efforts in the industry and transport sectors in the past decade have yielded reductions in black carbon emissions, but the residential sector remains a challenge.
- Black carbon is a potent contributor to global warming due to its efficient absorption of light and subsequent heating of its surroundings.
- This process leads to the conversion of incoming solar radiation into heat.
- Moreover, black carbon influences cloud formation and affects regional circulation and precipitation patterns.
- When deposited on ice and snow, it diminishes surface albedo, reducing their ability to reflect sunlight and causing surface warming.
Impacts:
- Black carbon significantly contributes to global warming and poses substantial risks to human health.
- Exposure to black carbon has been linked to increased incidences of heart disease, birth complications, and premature mortality.
- Its warming effect on climate is estimated to be 460-1,500 times more potent than that of CO2.
Netravati River

- 23 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
The principal bench of the National Green Tribunal (NGT) in New Delhi has initiated action on the Netravati Waterfront Promenade Development Project in Mangaluru.
About the Netravati River:
- The Netravati River, also known as Netravathi Nadi, originates from the Bangrabalige valley, Yelaneeru Ghat in Kudremukh, Chikkamagaluru district, Karnataka, India.
- It passes through the revered pilgrimage site Dharmasthala, earning recognition as one of India's sacred rivers.
- Converging with the Kumaradhara River at Uppinangadi, it eventually flows into the Arabian Sea, south of Mangalore city, serving as the primary water source for Bantwal and Mangalore.
- The Netravati railway bridge, a prominent structure, acts as the gateway to Mangalore.
- Historically known as the Bantwal River, it was documented as unfordable during the South-West Monsoon in the 1855 Gazetteer of Southern India.
- The river's navigability by small country craft and its influence on local geography and transport, including the naming of the Netravati Express train, underscores its significance in the region's history.
- Instances of flooding, notably in 1928 and 1974, have shaped the lives of residents, prompting relocations and resilience
About the National Green Tribunal:
- The National Green Tribunal (NGT) was established under the National Green Tribunal Act of 2010.
- While its principal seat is located in New Delhi, it also holds sessions in Bhopal, Pune, Kolkata, and Chennai.
- The NGT is entrusted with the responsibility of adjudicating applications or appeals, ensuring their final disposition within six months of filing.
Composition:
- The tribunal comprises a Chairperson, Judicial Members, and Expert Members, each serving a non-renewable term of five years.
- The appointment of the Chairperson is made by the Central Government in consultation with the Chief Justice of India (CJI).
- A Selection Committee, constituted by the Central Government, is responsible for appointing both Judicial and Expert Members.
- The tribunal can accommodate a minimum of 10 and a maximum of 20 full-time Judicial and Expert Members.
Powers & Jurisdiction:
- Established to efficiently handle cases concerning environmental protection and conservation of natural resources, including forests.
- It possesses appellate jurisdiction akin to a court.
- While not bound by the procedural formalities outlined in the Code of Civil Procedure, 1908, the NGT operates based on the principles of natural justice.
Pusa Basmati Rice

- 21 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
Even as basmati rice exports from the country are poised to scale a new high, scientists at the Indian Agricultural Research Institute (IARI) have red-flagged the “illegal” cultivation of its blockbuster varieties in Pakistan.
Unauthorized Cultivation and Export of Pusa Basmati Rice Varieties in Pakistan:
- Despite being officially registered and protected Indian varieties, several IARI-bred Basmati rice varieties, such as Pusa Basmati 1121, Pusa Basmati-6, and Pusa Basmati 1509, are being illegally cultivated and marketed in Pakistan.
- Recent YouTube videos even feature newer IARI varieties like Pusa Basmati-1847, PB-1885, and PB-1886, released in late 2021.
- Pakistan's unauthorized Basmati exports have been substantial, with 7.58 lt ($694.55 million) in 2021-22 and 5.95 lt ($650.42 million) in 2022-23 (July-June).
- This growth is partly due to the depreciation of the Pakistani rupee, allowing the country to offer lower export prices than India.
- The proliferation of these protected varieties in Pakistan can be attributed to the ease of seed multiplication.
- With just a small quantity of seeds, large-scale cultivation can be established within two years of the variety's release in India.
- This unauthorized cultivation not only undermines India's intellectual property rights but also impacts the competitiveness of India's Basmati rice exports in the global market.
What is the Basmati Crop Improvement Program?
- The Basmati Crop Improvement Program focuses on refining the unique qualities of Basmati rice, such as its distinct grain characteristics, cooking properties, and pleasing aroma.
- IARI has played a crucial role in the genetic enhancement, leading to the development of high-yielding, semi-dwarf, and photo-insensitive Basmati varieties like Pusa Basmati 1.
- These improvements have significantly reduced the crop duration from 160 to 120 days and increased productivity from 2.5 to 6-8 tons per hectare.
- As a result, these advanced Basmati varieties account for approximately 90% of India's projected $5.5 billion exports in 2023-24.
- This achievement contributes to substantial foreign exchange earnings and economic growth for the country.
Key Features of IARI-Developed Basmati Rice Varieties:
- IARI has cultivated various Basmati rice varieties with distinct characteristics, including:
- Pusa Basmati 1121: Known as the world's longest Basmati rice, it matures in 145 days with an average yield of 45 q/ha.
- Pusa Basmati 1509: Derived from Pusa 1121 x Pusa 1301, this variety addresses Pusa Basmati 1121's weaknesses, matures in 115 days, and yields 5 tons/ha.
- Improved Pusa Basmati 1 (Pusa 1460): This variety, the first product of molecular breeding in Indian rice, is an enhanced Pusa Basmati 1 with bacterial leaf blight resistance.
- Pusa Basmati 6 (Pusa 1401): Offering superior grain quality, this variety improves upon Pusa 1121's yielding ability, agronomy, and cooking quality.
- Pusa RH10: The world's first superfine grain aromatic rice hybrid, it was released in 2001 for commercial cultivation in specific irrigated ecosystems.
Registration and Cultivation Areas of Pusa Basmati Rice in India:
- All Pusa Basmati rice varieties are officially recognized under the Seeds Act 1966 and can be cultivated within the designated Geographical Indication (GI) area of Basmati rice in India, encompassing seven northern states.
- These varieties are further registered under the Protection of Plant Varieties and Farmers' Rights Act 2001, which permits only Indian farmers to sow, save, re-sow, exchange, or share the seeds of protected/registered varieties.
State of Global Climate Report 2023

- 20 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
In line with a host of observations by climate agencies in the preceding three months, the World Meteorological Organisation (WMO) has officially confirmed 2023 to be the hottest year on record.
About the State of Global Climate Report 2023:
- Published annually by the World Meteorological Organization (WMO), the State of Global Climate Report provides a detailed analysis of the Earth's climate system.
- Contributors to the report include various UN organizations, National Meteorological and Hydrological Services, Global Data and Analysis Centers, Regional Climate Centres, the World Climate Research Programme (WCRP), and more.
Highlights of the 2023 Report:
- Record-Breaking Global Temperatures: 2023 was the hottest year on record, with a global average near-surface temperature of 1.45°Celsius (±0.12°C) above the pre-industrial baseline.
- The past ten years were also the warmest decade recorded.
- Extensive Marine Heatwaves: Nearly one-third of the global ocean experienced a marine heatwave on an average day in 2023.
- Over 90% of the ocean had faced heatwave conditions at some point during the year, negatively impacting ecosystems and food systems.
- Unprecedented Glacier Ice Loss: Preliminary data reveals the largest loss of ice since 1950 for the global set of reference glaciers, driven by extreme melt in western North America and Europe.
- Surge in Renewable Energy Capacity: Renewable capacity additions in 2023 increased by almost 50% from 2022, totaling 510 gigawatts (GW) and marking the highest rate in the past two decades.
- These findings emphasize the pressing need to address climate change through effective international cooperation, policymaking, and sustainable practices.
About the World Meteorological Organisation (WMO):
- The World Meteorological Organization (WMO) is a specialized agency of the United Nations that fosters international cooperation in atmospheric science, climatology, hydrology, and geophysics.
- Founded in 1950, WMO originated from the International Meteorological Organization established in 1873 to facilitate the exchange of weather data and research.
- Today, WMO comprises 193 member countries and territories and promotes the free exchange of meteorological and hydrological data, information, and research.
- By collaborating with various partners, WMO contributes to environmental protection, climate change mitigation, and sustainable development efforts worldwide.
- Headquarters: Geneva, Switzerland.
Equity Issues in IPCC Reports

- 18 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
In a study published recently, researchers analyzed more than 500 future emissions scenarios the UN Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) assessed in its latest reports.
About the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC):
- The IPCC was created in 1988 by the World Meteorological Organization (WMO) and the United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP).
- It is the leading international body for the assessment of climate change.
- It is a key source of scientific information and technical guidance to the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC) and the Paris Agreement.
- The IPCC provides governments with scientific information for use in developing climate policies.
- The IPCC currently has 195 members.
- The IPCC does not undertake new research. Instead, it synthesizes published and peer-reviewed literature to develop a comprehensive assessment of scientific understanding.
- These assessments are published in IPCC reports.
- They are subject to multiple drafting and review processes to promote an objective, comprehensive, and transparent assessment of current knowledge.
- The IPCC’s work is guided by principles and procedures that govern all main activities of the organization.
- IPCC member governments and observer organizations nominate experts and the IPCC's scientific governing body, the IPCC Bureau, selects authors and editors with expertise in a range of scientific, technical, and socio-economic fields.
What are IPCC Assessment Reports?
- Typically, IPCC reports comprise three Working Group reports:
- One on physical science
- One on climate adaptation, and
- One on mitigation action.
- One synthesis report consolidates findings from the three Working Group reports.
- Then there are thematic special reports.
- Each report assesses climate-related scientific literature to capture the state of scientific, technical, and socio-economic knowledge on climate change.
- The IPCC is currently in its Seventh Assessment cycle (AR7).
How Does it Assess Future Scenarios?
- The IPCC uses ‘modelled pathways’ to estimate what it will take to limit the warming of the earth’s surface.
- These pathways are drawn using Integrated Assessment Models (IAMs) that describe human and earth systems.
- IAMs are complex models that examine possible futures of the energy and climate systems and economies.
- Its macroeconomic models can point to future growth levels in terms of GDP;
- Its energy models can project future consumption
- Vegetation models can examine land-use changes; and
- Earth-system models use the laws of physics to understand how climate evolves.
- With such integration across disciplines, IAMs are meant to provide policy-relevant guidelines on climate action.
- However, these models also have shortcomings. They prioritize least-cost assessments — for example, the absolute cost of setting up a solar plant or undertaking afforestation in India is lower than in the U.S.
- However, experts have said they could exercise the option of enabling countries to equitably share the burden of action, where the richest undertake more drastic mitigation action more immediately.
About the Latest Study:
- Conducted by a team of specialists from Bengaluru and Chennai, the study scrutinized 556 scenarios outlined in the IPCC's AR6 report.
- Their findings indicate that by 2050, per-capita GDP in Sub-Saharan Africa, South Asia, West Asia, and other parts of Asia will remain below the global average.
- Collectively, these regions account for 60% of the global population.
- Additionally, the study highlighted disparities in the consumption of goods and services, as well as energy and fossil fuel consumption, between the Global North and the Global South.
Why Does Equity Matter?
- Equity is crucial in climate action as per the UNFCCC, which mandates developed nations to lead in combating climate change.
- However, current modeling approaches often overlook equity, burdening poorer nations disproportionately.
- Researchers highlight the need for modeling techniques that prioritize climate justice and equitable distribution of responsibilities.
- They argue that mitigation pathways should ensure developed regions accelerate towards net negative emissions and allocate carbon budgets to less developed regions.
- Addressing this gap requires a paradigm shift in scenario building, emphasizing both equity and environmental sustainability.
- This approach is vital for fostering global cooperation and achieving meaningful climate action.
Kerala declares man-animal conflict a state-specific disaster

- 08 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
Amid repeated deaths from animal attacks and rising anger over them, Kerala recently declared man-animal conflict as a state-specific disaster, becoming the first state in the country to do so.
What is Man-animal Conflict?
- Man-animal conflict refers to the interaction between wild animals and humans, resulting in adverse outcomes for both people and wildlife, as well as their habitats.
- Escalating Conflict: In states across India, human-wildlife conflict has intensified, leading to a significant rise in human casualties.
- For instance, in Maharashtra, the conflict resulted in 86 in 2021 and 105 deaths in 2022, marking a sharp increase compared to previous decades.
Causes:
- Factors contributing to this conflict include the encroachment of grodeathswing human and animal populations into each other's territories, habitat fragmentation due to legal and illegal land use changes, alterations in cropping patterns attracting wildlife to agriculture, and habitat destruction from invasive alien species.
- Despite having over 700 protected areas, a substantial portion of elephant, lion, and tiger ranges lie outside these protected zones, exacerbating the conflict.
Ecologist Perspective:
- Ecologist Madhav Gadgil highlights that the Wildlife Protection Act of 1972 has inadvertently facilitated an environment where wild animals can invade human habitats with impunity.
- He cites the optimal foraging theory in ecology, which underscores animals' efforts to maximize nutrient intake while minimizing time, effort, and risks.
Solutions:
- Addressing the issue requires robust enforcement and pragmatic policies to mitigate conflict incidences.
- Engaging local communities, as suggested by the Future for All Report 2021 (by WWF and UNEP), fosters coexistence between humans and wildlife, acknowledging that complete elimination of conflicts is impractical.
- Additionally, awareness campaigns aimed at educating the public about man-animal conflict and skill development initiatives for communities living near forests can alleviate pressures on agricultural and forest lands.
Kerala's Decision to Declare Man-Animal Conflict as a State-Specific Disaster:
- Implications of the Decision: Currently, the management of man-animal conflict falls under the jurisdiction of the forest department, operating in accordance with the Wildlife Protection Act.
- By designating man-animal conflict as a state-specific disaster, the responsibility for addressing it shifts to the state disaster management authority, empowered by the Disaster Management Act, enabling swifter and more decisive action.
- Rationale for the Decision: Instances of loss of life due to man-animal conflict have prompted calls to tranquilize, capture, or eliminate the responsible animals.
- Presently, the chief wildlife warden, holding the sole authority in the state, makes decisions regarding wild animals causing disturbances in human settlements.
- Past decisions to tranquilize aggressive animals, like wild elephants, have faced legal challenges.
- Under the disaster management authority, actions can be taken that supersede other regulations, including those outlined in the Wildlife Protection Act.
- According to the Disaster Management Act, except for the Supreme Court or a High Court, no court has jurisdiction to entertain suits or proceedings regarding actions taken by relevant authorities in line with the Act.
- Additionally, the Act stipulates that its provisions hold precedence over any other law during the specific period of a declared disaster.
Kerala's Success in Managing Man-Animal Conflict:
- Kerala, with approximately 5,700 wild elephants in 2017, comprising 19% of the nationwide population of 30,000, witnessed a significantly lower incidence of human fatalities caused by elephants, accounting for only 81 (4%) of the 2,036 deaths recorded in India between 2018 and 2021.
- Factors Contributing to Kerala's Effective Management of Man-Animal Conflict:
- Maintenance of Unchanged Wilderness Boundaries: Kerala has largely preserved the boundaries between wilderness and civilization in recent years, contributing to the mitigation of man-animal conflicts.
- Evolution of Agricultural Practices: Changes in agricultural practices, such as the cultivation of crops like coffee, pepper, and tea, which hold less appeal for elephants, have helped reduce conflicts between humans and elephants.
- Unique Elephant Characteristics: Individual elephants are identified and named based on their distinct characteristics, such as Kabali, an elephant residing in the Athirapally jungle in Thrissur district, known for its tendency to attack or chase automobiles.
- These factors collectively contribute to Kerala's successful management of man-animal conflict, resulting in relatively fewer human fatalities caused by elephants compared to other regions in India.
Trees in Corbett fell prey to greedy nexus, says Supreme Court

- 07 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
The Supreme Court on Wednesday condemned the illegal felling of over 6,000 trees to construct buildings, ostensibly for “eco-tourism” at the Jim Corbett National Park in Uttarakhand, as a “classic case” of nexus between politicians and officials working to ransack the environment for short-term commercial ends.
News Summary:
- In 2023, a series of applications brought attention to the creation of alleged illegal buildings and encroachment on water bodies, prompting court intervention.
- Petitioners highlighted violations of environmental norms and encroachment into core wildlife habitats.
- Evidence presented during proceedings revealed unauthorized constructions within the national park, including concrete and iron enclosures purportedly intended for a 'safari' experience.
- Moreover, it was disclosed that over 6,000 trees had been felled in the national park under the pretext of safari development.
Supreme Court’s Observations:
- The Court has raised concerns regarding the necessity of developing facilities within natural forest environments, particularly in areas designated for the protection of endangered species like tigers.
- Directing the Government to establish a committee, the Supreme Court seeks recommendations on whether tiger safaris should be permitted in buffer or fringe areas and what guidelines should govern their establishment if allowed.
- Additionally, the Court has strongly criticized the illegal constructions and extensive tree felling in Uttarakhand's Corbett National Park.
What are the Core and Buffer Areas in Tiger Reserves?
- As per the Wild Life (Protection) Amendment Act of 2006, a Tiger Reserve comprises core or critical habitat and a buffer zone surrounding it.
- Core areas hold the legal status of a National Park or a Sanctuary.
- Buffer zones consist of a mix of forest and non-forest land, managed as a multiple-use area.
- The buffer area acts as a protective barrier, absorbing the impact of poaching pressure on tiger and other wildlife populations.
About Jim Corbett National Park:
- Location: Situated in the Nainital district of Uttarakhand, Jim Corbett National Park is renowned for its rich biodiversity.
Key Facts:
- Established in 1935, it is India’s oldest national park.
- Initially named Hailey National Park after its founder Sir Malcolm Hailey, it was renamed Corbett National Park in 1956 to honor Jim Corbett's contributions to wildlife preservation in India.
- Corbett National Park boasts the highest population of tigers in India, highlighting its importance for tiger conservation efforts.
- Flora: Dominated by Sal, Semal, Kharpat, Sissoo, Khair, Dhak, Khingan, Bakli, Bel, Ber, Bamboo, Khingam, Jamun, Kanju, Rohini, and Pula trees.
- Sal, Khair, and Sissoo are prominently featured throughout the park.
- Fauna: Home to diverse wildlife including Tiger, Leopard, Elephant, Chital Deer, Sambar Deer, Hogg Deer, Barking Deer, Wild Boar, Langur, Wild pig, Rhesus Monkey, Jackal, Rabbit, Yellow Throated Martin, and Otters.
- Various reptiles such as Crocodile, Gharial, King Cobra, Common Krait, Cobra, Russell's Viper, Rock Python, and Monitor Lizard inhabit the park.
- The Kosi River feeds the eastern periphery of Corbett National Park.
- The Ramganga River (West) and its tributaries Sonanadi, Palain, and Mandal serve as significant hydrological resources for the park.
Exclusive-World on brink of fourth mass coral reef bleaching event- NOAA

- 06 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
The world stands on the brink of witnessing its fourth mass coral bleaching event, a phenomenon that threatens to hit vast expanses of tropical reefs, including significant portions of Australia's iconic Great Barrier Reef.
Key Findings from the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA):
- Impending Fourth Mass Coral Bleaching Event: The world is on the brink of a fourth mass coral bleaching event, following those in 1998, 2010, and 2014.
- To classify as global, widespread bleaching must occur across three ocean basins: the Atlantic, Pacific, and Indian.
- Impact of Previous Events: The last global mass coral bleaching event occurred from 2014 to 2017, resulting in the loss of nearly a third of the Great Barrier Reef's corals.
- Preliminary data indicates that approximately 15% of the world's reefs experienced significant coral die-offs during this event.
- Current Situation: This year is witnessing even more severe bleaching events, with the Caribbean experiencing its worst coral bleaching on record following the Northern Hemisphere summer last year.
- Link to Climate Phenomena: Coral bleaching is often associated with the naturally occurring El Niño climate phenomenon, which leads to warmer ocean waters.
- Climate Change Impact: The world recently experienced its first 12-month period with an average temperature exceeding 1.5 degrees Celsius (2.7 degrees Fahrenheit) above pre-industrial levels.
- A temperature rise of 1.5°C is considered the tipping point for mass coral die-offs, with scientists estimating that 90% of the world's corals could be lost as a result.
About the Corals and Coral Reefs:
- Corals: Corals are animals known as polyps, which engage in a symbiotic relationship with tiny algae called zooxanthellae.
- These algae provide corals with food and oxygen, while corals offer them a safe habitat.
- Coral Reefs: Coral reefs are limestone structures formed by thousands of tiny coral animals and are predominantly found in tropical climates.
Coral Bleaching and Its Concerns:
- Coral bleaching occurs when corals are exposed to stressful conditions like high temperatures, pollution, or changes in water chemistry, leading them to expel the zooxanthellae.
- Without these algae, corals lose their color and turn white, hence the term 'bleaching,' and cannot survive for long in this state.
- Recovery Potential: Despite its severity, coral bleaching doesn't necessarily mean the end of the reef; timely removal of stressors can facilitate the return of zooxanthellae and coral recovery.
- Ecological Importance: Coral reefs serve as habitats and food sources for numerous fish and marine species.
- They also offer coastal protection from erosion and storms and play a critical role in regulating the Earth's climate by absorbing and storing carbon dioxide.
- Cultural and Aesthetic Value: Beyond their ecological functions, coral reefs represent stunning biodiversity and natural beauty, making their loss a tragic prospect for future generations.
- Impacts: When coral reefs suffer, so do the ecosystems and communities reliant on them, underscoring the far-reaching consequences of coral degradation.
Google-backed satellite to track global oil industry methane emissions
- 06 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
MethaneSAT — a satellite which will track and measure methane emissions at a global scale — was launched aboard a SpaceX Falcon9 rocket from California recently.
What is MethaneSAT?
- MethaneSAT will orbit the Earth 15 times a day, monitoring the oil and gas sector.
- It will create a large amount of data, which will tell “how much methane is coming from where, who’s responsible, and are those emissions going up or down over time”.
- The data collected by MethaneSAT will be made public for free in near real-time.
- This will allow stakeholders and regulators to take action to reduce methane emissions.
Institutions involved in the development:
- The entity behind MethaneSAT is the Environmental Defense Fund (EDF) — a US-based nonprofit environmental advocacy group.
- To develop the satellite, EDF partnered with Harvard University, the Smithsonian Astrophysical Observatory, and the New Zealand Space Agency.
Features of MethaneSAT:
- Historically, tracking the source of methane emissions and measuring them has been quite challenging.
- ?While some satellites can provide high-resolution data, they can only scan specific, pre-targeted sites.
- Others can examine larger areas and detect large emitting events, but cannot scan “smaller sources that account for the majority of emissions in many, if not most, regions,” the EDF statement added.
- Due to this discrepancy, according to an International Energy Agency (IEA) report, global methane emissions are about 70 per cent higher than levels reported by national governments.
- MethaneSAT is expected to fix the issue.
- Equipped with a high-resolution infrared sensor and a spectrometer, the satellite will fill critical data gaps.
- It can track differences in methane concentrations as small as three parts per billion in the atmosphere, which enables it to pick up smaller emissions sources than the previous satellites.
- MethaneSAT also has a wide-camera view — of about 200 km by 200 km — allowing it to identify larger emitters so-called “super emitters”.
Significance of MethaneSAT:
- Advancing the Goals of the Global Methane Pledge 2021: The Global Methane Pledge, signed by over 150 countries in 2021, aims to reduce collective methane emissions by at least 30% from 2020 levels by 2030.
- During the previous year's COP, over 50 companies pledged to significantly reduce methane emissions and routine flaring.
- MethaneSAT will play a crucial role in helping these entities achieve their targets.
- Enhancing Transparency: The satellite will usher in a new era of transparency by providing publicly available data accessible to anyone worldwide.
- This data will enable monitoring of methane commitments made by governments and corporations, promoting accountability and transparency in emission reduction efforts."
Why Do We Need to Track and Measure Methane Emission?
- Methane is an invisible but strong greenhouse gas, and the second largest contributor to global warming after carbon dioxide, responsible for 30 percent of global heating since the Industrial Revolution.
- According to the United Nations Environment Programme, over a period of 20 years, methane is 80 times more potent at warming than carbon dioxide.
- The gas also contributes to the formation of ground-level ozone — a colorless and highly irritating gas that forms just above the Earth’s surface.
- According to a 2022 report, exposure to ground-level ozone could be contributing to one million premature deaths every year.
- Therefore, it is crucial to cut methane emissions and the main culprit, fossil fuel operations, which account for about 40 percent of all human-caused methane emissions.
- The objective of MethaneSAT is to help achieve this goal.
Carbon Capture and How it Can Help Save the Planet

- 05 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
Germany has recently declared its approval for carbon capture and offshore storage for specific industrial sectors.
What is Carbon Capture and Storage?
- CCS refers to a host of different technologies that capture CO2 emissions from large point sources like refineries or power plants and trap them beneath the Earth.
- Notably, CCS is different from carbon dioxide removal (CDR), where CO2 is removed from the atmosphere.
- CCS involves three different techniques of capturing carbon, including: Post-combustion, Pre-combustion, and Oxyfuel combustion.
- In post-combustion, CO2 is removed after the fossil fuel has been burnt. By using a chemical solvent, CO2 is separated from the exhaust or ‘flue’ gasses and then captured.
- Pre-combustion involves removing CO2 before burning the fossil fuel. “First, the fossil fuel is partially burned in a ‘gasifier’ to form synthetic gas. CO2 can be captured from this relatively pure exhaust stream,” according to a report by the British Geological Survey. The method also generates hydrogen, which is separated and can be used as fuel.
- In oxyfuel combustion, the fossil fuel is burnt with almost pure oxygen, which produces CO2 and water vapor. The water is condensed through cooling and CO2 is separated and captured. Out of the three methods, oxyfuel combustion is the most efficient but the oxygen burning process needs a lot of energy.
- Post-combustion and oxyfuel combustion equipment can be retro-fitted in existing plants that were originally built without them. Pre-combustion equipment, however, needs “larger modifications to the operation of the facility and are therefore more suitable to new plants.
- After capture, CO2 is compressed into a liquid state and transported to suitable storage sites.
- Although CO2 can be transported through ship, rail, or road tanker, pipeline is the cheapest and most reliable method.
Can Carbon Capture Help Save the world?
- Operational CCS projects generally claim to be 90 percent efficient, meaning they can capture 90 per cent of carbon and store it.
- Studies, however, have shown that a number of these projects are not as efficient as they claim to be.
- For example, a 2022 study by the Institute for Energy Economics and Financial Analysis (IEEFA) found most of the 13 flagship CCS projects worldwide that it analyzed have either underperformed or failed entirely.
- Moreover, CCS technologies are quite expensive.
- When CCS is attached to coal and gas power stations it is likely to be at least six times more expensive than electricity generated from wind power backed by battery storage.
- It is far cheaper and more efficient to avoid CO2 emissions in the first place.
- There are also only a few operational CCS projects across the world even though the technology has been pushed for decades.
- According to the International Energy Agency (IEA), there were 40 operational CCS projects in 2023, which captured more than 45 metric tonnes (Mt) of CO2 annually.
- To ensure the planet doesn’t breach the 1.5 degree Celsius temperature increase limit, it would take an “inconceivable” amount of carbon capture “if oil and natural gas consumption were to evolve as projected under today’s policy settings.
- It added that the electricity required to capture that level of carbon as of 2050 would be more than the entire planet’s use of electricity in 2022.
- Therefore, there couldn’t be an overreliance on carbon capture as a solution to tackle climate change.
PM Modi hails those supporting wildlife conservation efforts on World Wildlife Day

- 04 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
On the occasion of World Wildlife Day on March 3, Prime Minister Narendra Modi lauded those at the forefront of sustainable practices and supporting wildlife conservation efforts.
About the World Wildlife Day:
- World Wildlife Day is observed to advocate for sustainable practices that contribute to biodiversity conservation and to enhance public consciousness about the importance of safeguarding and nurturing animals.
- It endeavors to underscore the interconnectedness of all life forms on Earth and to foster harmonious coexistence between humans and animals through activism, advocacy, and education.
Origins:
- Initially proposed by Thailand to the UN General Assembly in 2013, World Wildlife Day aimed to dedicate a day to spotlight the significance of wild animals and plants worldwide.
- On December 20, 2013, the General Assembly adopted a resolution, designating March 3 as World Wildlife Day from 2014 onwards.
- Coinciding with the day, the Convention on International Trade in Endangered Species of Wild Fauna and Flora (CITES) was signed in 1973, emphasizing the importance of safeguarding species from the threats of international trade.
The theme of WWD 2024:
- The theme, "Connecting People and Planet: Exploring Digital Innovation in Wildlife Conservation," underscores the potential of technological advancements to revolutionize conservation efforts.
- In today's digital era, technological breakthroughs offer novel solutions to persistent conservation challenges, making this theme particularly relevant.
Significance:
- World Wildlife Day serves as a vital global awareness platform for animal protection and conservation.
- It reinforces the intrinsic value of animals and advocates for treating them with compassion, integrity, and reverence.
About the Convention on International Trade in Endangered Species of Wild Fauna and Flora (CITES):
- CITES is an international treaty that aims to regulate and monitor the trade of endangered plants and animals, including their parts and derivatives, to ensure their survival in the wild.
- Under CITES, member countries are required to regulate and monitor the trade of endangered species through a system of permits and quotas.
- They must also report regularly on their implementation of the treaty and collaborate with other countries to ensure its effectiveness.
- Currently, CITES has 184 parties.
Doomsday Glacier has lost 50 billion tons of ice, melting began 80 years ago
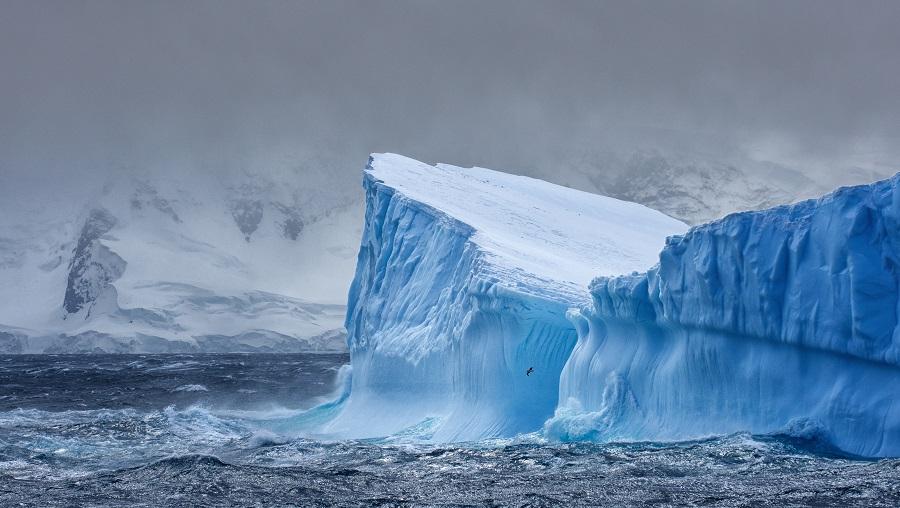

- 01 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
Antarctica's Doomsday Glacier, the world's widest glacier, has lost over 50 billion tons of ice and the melting rate is on the rise as the continent gets warmer.
What is Doomsday Glacier?
- The Thwaites Glacier (also known as Doomsday Glacier), a massive and world’s widest glacier is located in West Antarctica.
- The Doomsday nickname reflects the potential for catastrophic flooding if the glacier were to collapse completely.
- Scientists are particularly concerned about Thwaites Glacier because of its size and location.
- If it were to collapse or significantly retreat, it could lead to a more rapid flow of ice from the interior of West Antarctica into the ocean, contributing to rising sea levels.
- The collapse could lead to a 65 cm rise in global sea level.
- The ice loss in the region has been observed to be accelerating since the 1970s, however, so far it remained unclear as to when this retreat began.
- The significant glacial retreat began in the 1940s and the findings coincide with previous work that studied retreat on Pine Island Glacier and found glacial retreat began in the ‘40s as well.
- This change is not random nor specific to one glacier but It is part of a larger context of a changing climate.
Why Did the Melting Begin?
- The meeting was kicked off by an extreme El Nino climate pattern that warmed the west Antarctic, and since then the glacier has not been able to recover from the damage.
- It is significant that El Niño only lasted a couple of years, but the two glaciers, Thwaites and Pine Island remain in significant retreat.
- Once the system is kicked out of balance, the retreat is ongoing.
- The Doomsday Glacier's melting remains one of the most crucial events triggered and accelerated by climate change and could lead to the submergence of several coastal regions of the world.
India to set up International Big Cat Alliance

- 01 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
The Union Environment Ministry plans to set up and coordinate an International Big Cat Alliance (IBCA), along the lines of the International Solar Alliance, an India-headquartered initiative to promote solar installations globally.
About the International Big Cat Alliance (IBCA):
- The idea of the International Big Cat Alliance (IBCA) was first given by Prime Minister Modi during his speech on the occasion of Global Tiger Day in 2019.
- He called for developing an alliance of global leaders to curb poaching in Asia.
- The alliance was formally announced on April 9, 202, in Mysuru, as India commemorated the completion of 50 years of Project Tiger.
- The alliance will focus on the conservation of seven big cats, which include Tiger, Lion, Leopard, Snow Leopard, Puma, Jaguar, and Cheetah. Out of these, five are found in India.
- Membership to the IBCA is open to 97 'range' countries, encompassing the natural habitats of these big cats, as well as other interested nations and international organizations.
- The alliance aims to facilitate cooperation among countries to advance the conservation agenda for mutual benefit.
- Operating with a multifaceted approach, the IBCA endeavours to establish robust linkages across various domains, including knowledge sharing, capacity building, networking, advocacy, financial and resource support, research, technical assistance, education, and awareness.
- Governance of the alliance consists of a General Assembly comprising all member countries, a Council comprised of seven to fifteen member countries elected by the General Assembly for a five-year term, and a Secretariat.
- The IBCA Secretary General, appointed by the General Assembly upon the Council's recommendation, serves a specific term.
- To support its initiatives, the IBCA has secured initial funding of Rs. 150 crore from the Government of India for the period spanning from 2023-24 to 2027-28.
European Parliament adopts nature restoration law

- 29 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
The European Parliament recently adopted the first European Union (EU) law to restore degraded ecosystems across the 27-nation political and economic bloc.
About the Nature Restoration Law:
- The Nature Restoration Law is hailed as a significant stride toward rejuvenating Europe’s natural habitats, with a staggering 81% currently classified as being in poor health.
- It sets a pioneering example for global emulation, emphasizing the criticality of safeguarding and revitalizing our natural environment for the welfare of forthcoming generations.
Objectives:
- This legislation aims to rejuvenate ecosystems, habitats, and species across the European Union's (EU) terrestrial and marine domains, fostering the enduring recuperation of diverse and robust nature.
- Additionally, it endeavors to contribute to the EU's climate mitigation and adaptation objectives while fulfilling international commitments.
- These directives aspire to encompass a minimum of 20% of the EU's land and marine territories by 2030, with the ultimate goal of restoring all ecosystems in need by 2050.
Specific Targets:
- Wetlands, forests, grasslands, rivers, lakes, heath & scrub, rocky habitats, and dunes: The objective is to enhance and restore biodiverse habitats on a large scale, fostering the recovery of species populations through habitat improvement and expansion.
- Pollinating Insects: The target is to reverse the decline of pollinator populations by 2030, aiming for a positive trajectory in pollinator numbers.
- Forest Ecosystems: The aim is to promote an upward trend in standing and fallen deadwood, varied aged forests, forest connectivity, common forest bird populations, and organic carbon reserves.
- Urban Ecosystems: The objective is to achieve zero net loss of green urban spaces by 2030 and expand the total area covered by green urban spaces by 2040 and 2050.
- Agricultural Ecosystems: The goal is to bolster grassland butterfly and farmland bird populations, increase organic carbon reserves in cropland mineral soils, and augment the proportion of agricultural land featuring diverse landscape characteristics.
About the European Union (EU):
- The European Union (EU) is a political and economic union of 27 European countries that collaborate on various issues, including trade, security, and environmental protection.
- Founded after World War II to promote peace and economic cooperation, the EU has evolved into a complex organization with its own institutions, laws, and currency (the euro).
- It operates on the principles of democracy, human rights, and the rule of law, with the European Commission, European Parliament, and European Council among its key decision-making bodies.
- The EU's single market allows for the free movement of goods, services, capital, and people across member states, fostering economic growth and prosperity.
- Additionally, the EU plays a prominent role in global affairs, advocating for multilateralism, sustainable development, and climate action.
Malta becomes the 119th member of the International Solar Alliance

- 21 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
Malta became the 119th country to join the International Solar Alliance recently.
About the International Solar Alliance (ISA):
- The International Solar Alliance (ISA) is an alliance of more than 120 signatory countries that aims to reduce the dependence on non-renewable sources of energy like fossil fuels.
- Currently, 118 countries are signatories to the ISA Framework Agreement.
- The ISA is an action-oriented, member-driven, collaborative platform for increased deployment of solar energy technologies as a means for bringing energy access, ensuring energy security, and driving energy transition in its member countries.
- The platform strives to develop and deploy cost-effective and transformational energy solutions powered by the sun to help member countries develop low-carbon growth trajectories, with a particular focus on delivering impact in countries categorised as Least Developed Countries (LDCs) and the Small Island Developing States (SIDS).
- The ISA was conceived as a joint effort by India and France to mobilise efforts against climate change through the deployment of solar energy solutions.
- It was conceptualised on the sidelines of the 21st Conference of Parties (COP21) to the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC) held in Paris in 2015.
Role of India:
- As a founding member, India holds a pivotal position within the alliance, serving both as a host nation and a major contributor to achieving its objectives.
- The ISA marks a historic milestone as the first international organisation to establish its secretariat in India.
- With a target of generating 100 GW of solar energy by 2022, India's commitment represents a significant portion of the ISA's overall goal.
Recent Developments:
- The ISA was granted Observer Status by the UN General Assembly, fostering closer collaboration between the alliance and the United Nations to advance global energy growth and development.
- The approval of the 'Solar Facility' by the ISA introduces a payment guarantee mechanism aimed at incentivizing investments in solar projects, further driving progress towards sustainable energy initiatives.
Resource Efficiency and Circular Economy Industry Coalition (RECEIC) (Indian Express)

- 27 Jul 2023
Why in the News?
Union Environment, Forest and Climate Change Minister Bhupender Yadav on Thursday launched a Resource Efficiency Circular Economy Industry Coalition (RECEIC), conceptualised under India’s G20 Presidency, to promote the practices of resource efficiency and circular economy globally.
About Resource Efficiency and Circular Economy Industry Coalition (RECEIC):
- RECEIC was launched in 2023 at Chennai, Tamil Nadu, with the honorable presence of Shri Bhupender Yadav, Minister for Environment, Forest, and Climate Change.
- The launch event witnessed the participation of distinguished guests, including the Commissioner on Environment from the European Union and esteemed Ministers from Canada, France, Italy, Denmark, Mauritius, and the United Arab Emirates.
- Industry-Driven Initiative:
- RECEIC is an industry-led initiative with a primary goal of fostering global resource efficiency and circular economy practices.
- Embracing the circular economy model, RECEIC promotes production and consumption practices involving sharing, leasing, reusing, repairing, refurbishing, and recycling materials and products to maximize their utility.
- Sustainable Impact:
- The coalition is envisioned to be a self-sustaining entity, committed to lasting environmental sustainability, beyond India's G20 Presidency.
- Founding Members:
- With 39 companies headquartered in 11 different countries, the coalition boasts a diverse group of founding members.
- As a collaborative platform, RECEIC fosters knowledge-sharing, best practice exchange, and the adoption of sustainable approaches among participating industries.
7th Global Environment Facility (GEF) Assembly (Down to Earth)
- 26 Aug 2023
What is the News ?
As per the chief executive of the Global Environment Facility (GEF) in a plenary session, it will likely to work more closely with civil society organisations in the future.
Facts About:
About: Environmental leaders from 185 countries will gather in Vancouver, Canada for the Seventh Assembly of the Global Environment Facility from August 22-26, 2023.
Global Environment Facility (GEF): The GEF Assembly, which meets every 4 years, is the global body that coordinates financing for international efforts to address climate change, biodiversity loss, pollution, and factors inhibiting land and ocean health.
Points of discussion:
- Building on recent diplomatic breakthroughs on biodiversity loss, toxic chemicals, and the high seas, the GEF Assembly will be a critical stocktaking for 2030 goals to end pollution and nature loss, combat climate change, and propel inclusive, locally-led conservation.
- GEF would work directly with non-governmental organisations that work at the convention level.
- It is set to include the launch of the Global Biodiversity Framework Fund, a new source of funding for protecting species and ecosystems globally.
- The fund will open new avenues for private sector and philanthropic support to enable rapid implementation of the historic Global Biodiversity Framework agreed at COP15 in Montreal, December 2022, and of the high seas treaty adopted in New York City, in June 2023.
Need of such an initiative:
- Biodiversity funding needs differ between recipient countries, for example between countries with key areas for biodiversity (often large emerging countries such as Brazil and Indonesia) and the least developed countries (LDCs) or Small Island Developing States (SIDS), for which it is more difficult to access funds.
Global Biodiversity Framework:
- It contains goals to be achieved by 2050 focus on ecosystem and specieshealth including;
- To halt human-induced species extinction,
- The sustainable use of biodiversity,
- Equitable sharing of benefits, and
- On implementation and finance to include closing the biodiversity finance gap of $700 billion per year.
Source: https://update-mac.com/?tid=103&tag_id=1528a5df-4f9e-4046-9232-3361bc5f2c12&cnv_id=e891de8lpg6sc0b4c&placement=20427977&sub1=726006&clickcost=0
