Tensor Processing Units (TPUs)
- 07 Dec 2025
In News:
Recent reports indicate that Meta is in advanced discussions with Google to use its Tensor Processing Units (TPUs), highlighting growing competition in the global AI hardware ecosystem.
What is a TPU?
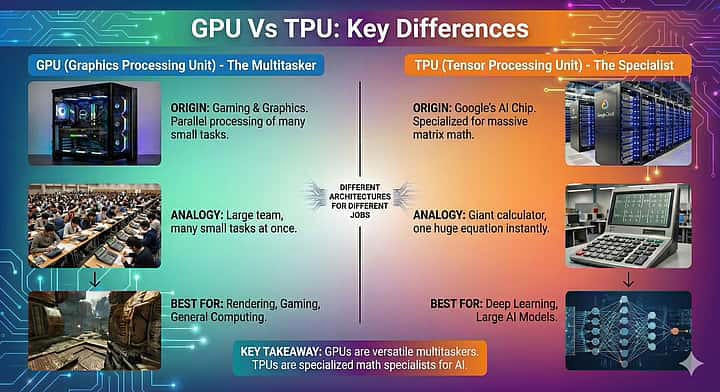
A Tensor Processing Unit (TPU) is a custom-designed semiconductor chip developed by Google to accelerate Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) workloads. Unlike Central Processing Units (CPUs), which handle general computing tasks, or Graphics Processing Units (GPUs), which are versatile and widely used for AI and graphics processing, TPUs are application-specific integrated circuits (ASICs) built specifically for deep learning operations.
Google began developing TPUs in the early 2010s to meet the growing computational demands of AI applications such as Google Search, Translate, Photos, and voice recognition systems. The first TPU was introduced around 2015–16, and multiple generations have since been deployed in Google’s data centres and cloud platforms.
How TPUs Work
AI models depend heavily on tensor operations—mathematical calculations involving multi-dimensional arrays of numbers. Deep neural networks process data through repeated matrix multiplications and tensor algebra, which are computationally intensive.
TPUs are optimised for these operations through:
- Massive Parallelism: They perform a very large number of calculations simultaneously.
- Specialised Architecture: Circuits are tailored for AI workloads, reducing unnecessary processing steps.
- Energy Efficiency: TPUs often deliver high performance with lower power consumption compared to traditional GPUs.
This makes them particularly efficient for training and inference in large-scale AI models.
TPUs vs CPUs vs GPUs
|
Feature |
CPU |
GPU |
TPU |
|
Primary Use |
General-purpose computing |
Graphics & parallel tasks |
AI/ML acceleration |
|
Flexibility |
Very high |
High |
Limited to AI tasks |
|
Optimised for |
Sequential tasks |
Parallel processing |
Tensor/matrix operations |
|
Energy Efficiency for AI |
Low |
Moderate |
High |
Strategic Importance
The reported interest of major AI firms in TPUs reflects a shift in the AI hardware landscape. For years, NVIDIA GPUs dominated AI training and deployment due to their performance and software ecosystem. However, large technology companies are increasingly investing in custom AI chips to reduce costs, improve efficiency, and reduce dependence on external suppliers.
Google has begun offering TPU access through its cloud infrastructure, enabling external firms to run AI workloads on TPU clusters. This signals the rise of merchant AI silicon, where companies design chips not only for internal use but also for commercial deployment.
CRIB Blood Group

- 31 Jul 2025
In News:
- In a landmark discovery in transfusion science, researchers from India and the UK have identified a new and ultra-rare human blood group named CRIB, with the first case detected at the Rotary Bangalore TTK Blood Centre.
- The CRIB group adds to India’s growing contribution to rare blood immunogenetics and has been officially recognised by the International Society of Blood Transfusion (ISBT) and the International Blood Group Reference Laboratory (IBGRL), UK.
What is the CRIB Blood Group?
- CRIB stands for Cromer India Bengaluru and also symbolically refers to its importance in newborn and fetal medicine.
- It is a new antigen within the Cromer blood group system, which is linked to the Decay-Accelerating Factor (DAF) protein on red blood cells.
- CRIB belongs to the broader INRA (Indian Rare Antigen) blood group system, officially recognised in 2022 by the ISBT.
Discovery and Identification:
- Detected in a 38-year-old South Indian woman undergoing cardiac surgery in Kolar, Karnataka.
- Her blood was pan-reactive, reacting with all samples including O+ blood.
- No match was found even among 20 family members, leading to further analysis.
- After 10 months of genetic study at IBGRL, UK, a novel antigen was confirmed and designated as CRIB.
Scientific and Medical Significance:
- Rare Antigen Profile: Individuals with CRIB blood type lack a high-prevalence antigen, making compatible transfusions highly complex.
- Hemolytic Disease Risk: The CRIB antigen is especially relevant in Hemolytic Disease of the Fetus and Newborn (HDFN), where maternal antibodies attack fetal red blood cells.
- Global First: It is the first discovery of its kind globally, expanding the total number of known human blood group systems.
Implications for India and the World:
- Transfusion Protocols: Requires specialised matching and CRIB-negative donor identification, necessitating rare donor registries.
- Prenatal Care: Early screening could prevent complications in pregnancies involving blood group incompatibilities.
- Healthcare Infrastructure: Highlights the need for investment in genetic screening, rare blood banks, and pan-India awareness among healthcare professionals.
- Research Opportunities: Opens new areas of study in genomics, population diversity, and immune response in transfusions.
Next Steps:
- Development of CRIB-specific antibody panels and diagnostic tests.
- Integration into global and national blood group databases.
- Promotion of international collaboration in transfusion science and rare donor management systems.
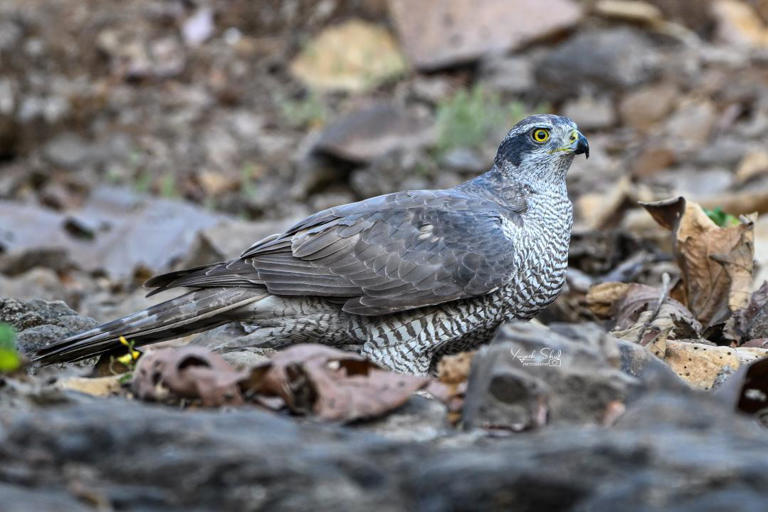
Eurasian Goshawk sighting at Tansa Wildlife Sanctuary

- 24 Mar 2025
In News:
A significant wildlife discovery has been made at Tansa Wildlife Sanctuary, Maharashtra, where the Eurasian goshawk, a large bird of prey, was spotted for the first time. This marks the first documented instance of the Eurasian goshawk in the sanctuary, although the species has been previously recorded in Maharashtra three times.
About the Eurasian Goshawk
- Scientific Name: Accipiter gentilis
- Description: A powerful raptor known for its short, broad wings and long tail.
- Habitat: Dense forests, particularly coniferous and mixed woodlands across Europe, Asia, and parts of North America.
- Winter Visitor: The Eurasian goshawk is a winter visitor to India, making this sighting at Tansa particularly noteworthy.
Tansa Wildlife Sanctuary
- Located in the foothills of the Western Ghats in Thane District, Maharashtra, Tansa Wildlife Sanctuary covers 320 sq. km.
- Positioned approximately 90 km northeast of Mumbai, it serves as a vital catchment area for Tansa Lake and is bordered by the Tansa and Vaitarna rivers.
Flora and Fauna
The sanctuary boasts a rich diversity of flora and fauna, including:
- 200 bird species
- 54 animal species, including endangered animals like:
- Panther
- Hyena
- Barking Deer
- Notable species include:
- Critically Endangered vultures
- Vulnerable Pallas’s fish-eagle
Vegetation and Landscape
- Southern Tropical Moist Deciduous Forest with patches of Evergreen Forest.
- Flora includes trees like Kalamb, Bibla, Khair, Hed, Teak, and Bamboo.
Avian Discoveries
Tansa Wildlife Sanctuary is also renowned for its avian discoveries, such as the critically endangered Forest Owlet, which was first documented here in 2014. This discovery highlighted the sanctuary’s significance for bird conservation.
Conservation Efforts and Ecological Role
The sighting of the Eurasian goshawk further emphasizes the critical need for ongoing conservation efforts at Tansa Wildlife Sanctuary.
Role of the Eurasian Goshawk in Ecosystem
As a bird of prey, the Eurasian goshawk plays a vital role in maintaining ecological balance by controlling populations of smaller mammals and birds.
Though listed as "Least Concern" on the IUCN Red List, the Eurasian goshawk’s presence underscores the sanctuary’s importance in the region’s biodiversity.
WEST Tokamak Reactor

- 23 Feb 2025
In News:
The WEST Tokamak reactor in southern France has set a new world record by sustaining a nuclear fusion plasma for 1,337 seconds (22 minutes and 17 seconds), surpassing the previous record of 1,066 seconds held by China’s EAST reactor by 25%. This achievement is a major milestone in the global quest for clean, limitless energy through nuclear fusion.
About Nuclear Fusion
- Nuclear Fusion is the process of combining two light atomic nuclei (typically deuterium and tritium) to form a heavier nucleus, releasing vast amounts of energy.
- The mass defect (loss of mass) in the fusion process converts into energy, as per Einstein’s equation E=mc2E = mc^2E=mc2.
- This reaction occurs in the plasma state—a hot, ionized gas consisting of free electrons and atomic nuclei.
How Tokamak Reactors Work
- A Tokamak is a doughnut-shaped (toroidal) magnetic confinement device that replicates the Sun’s fusion process.
- It uses superconducting magnetic coils to confine and heat the plasma to temperatures exceeding 50 million°C, about three times hotter than the Sun's core.
- Fusion reactors inject external power (WEST used 2 MW) to maintain the plasma and prevent it from touching reactor walls.
WEST Reactor: Key Highlights
- Operated by the French Alternative Energies and Atomic Energy Commission (CEA).
- Aims to simulate long-duration, high-temperature plasma conditions.
- Reached a plasma state sustained for over 22 minutes at 50 million°C.
- Contributes critical insights and validation to the ongoing ITER project, the world’s largest nuclear fusion experiment also based in southern France.
Significance of the Achievement
To make fusion viable for electricity generation, three key conditions must be met:
- High temperature – to overcome electrostatic repulsion between nuclei.
- Sustained confinement time – achieved by WEST.
- Sufficient plasma density – to ensure high collision rates.
Maintaining plasma for extended durations is crucial for transitioning from experimental reactors to commercial fusion energy systems.
Advantages of Nuclear Fusion
- High Energy Output: Produces 4x more energy per kg of fuel than fission, and nearly 4 million times more than fossil fuels.
- Environmentally Clean: Emits no greenhouse gases or long-lived radioactive waste. Only byproducts are inert helium and neutrons.
- Abundant Fuel Supply: Fusion uses deuterium (from seawater) and tritium, eliminating the need for uranium mining.
- Inherent Safety: Fusion reactions are inherently safe as they cannot trigger uncontrolled chain reactions, unlike fission.
Fusion vs. Fission: A Comparison
Aspect Nuclear Fusion Nuclear Fission
Process Combines light nuclei Splits heavy nuclei
Fuel Deuterium and Tritium Uranium or Plutonium
Energy Output Extremely high Moderate
Waste Minimal and short-lived Long-lived radioactive waste
Emissions No greenhouse gases Potential radiation hazards
Safety No risk of meltdown Risk of runaway reactions/meltdowns
Global Perspective
- Over 200 tokamaks are operational globally.
- The ITER project is set to become the centerpiece of global fusion research.
- Recent breakthroughs like those at WEST provide a technical roadmap for future commercial reactors.
